Method and device for detecting and separating HP (helicobacter pylori) ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay)
A Helicobacter pylori, fully mixed technology, applied in the field of microelectronic medical detection, to achieve the effect of portability, high degree of automation, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
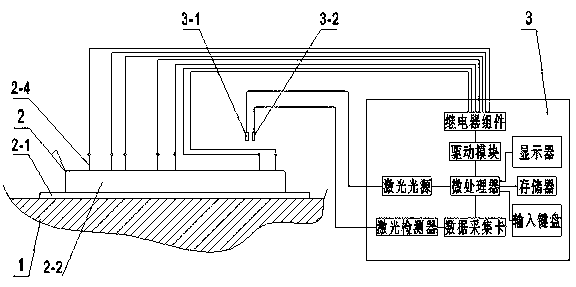
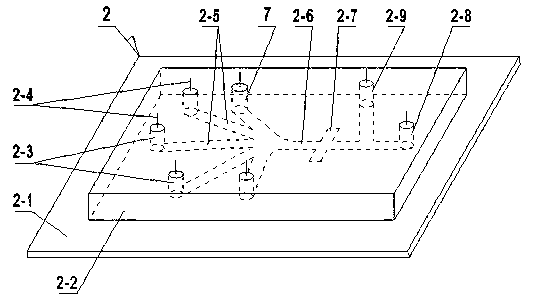
[0022] See figure 1 , figure 2 , A method for detecting and separating Helicobacter pylori by ELISA, including the following steps:
[0023] (A) Prepare magnetic beads with HP antibodies on the surface, enzyme-labeled antibodies that can react with HP, and enzyme reaction substrates that can react with enzymes;
[0024] (B) Put the prepared magnetic beads, enzyme-labeled antibody, enzyme reaction substrate, gastric juice sample, and cleaning solution into different sample reservoirs on the microfluidic chip, and control the different reservoirs through electric control Liquid flow in
[0025] (C) Mix the magnetic bead antibody and the gastric juice sample thoroughly in the microchannel, and HP will bind to the magnetic bead to form a magnetic bead antigen-antibody complex;
[0026] (D) Fix the magnetic beads in the microchannel, and clean and remove other unbound substances with electric control cleaning liquid;
[0027] (E) Mix the magnetic bead antigen-antibody complex and enzyme-l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com