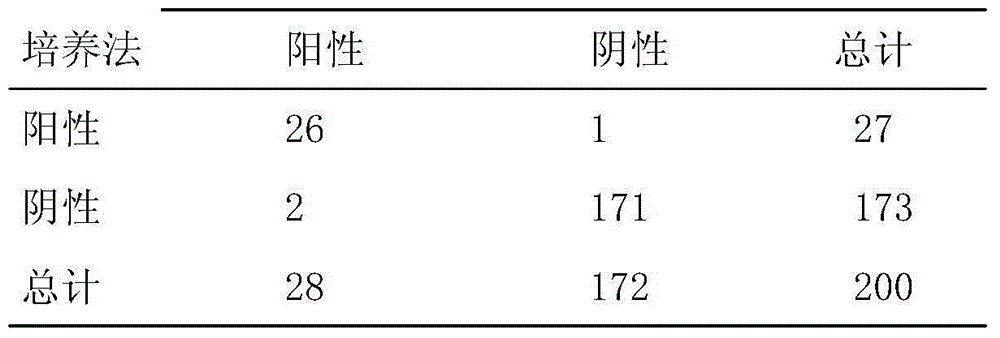
Patents
Literature
520 results about "Microplate Reader" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
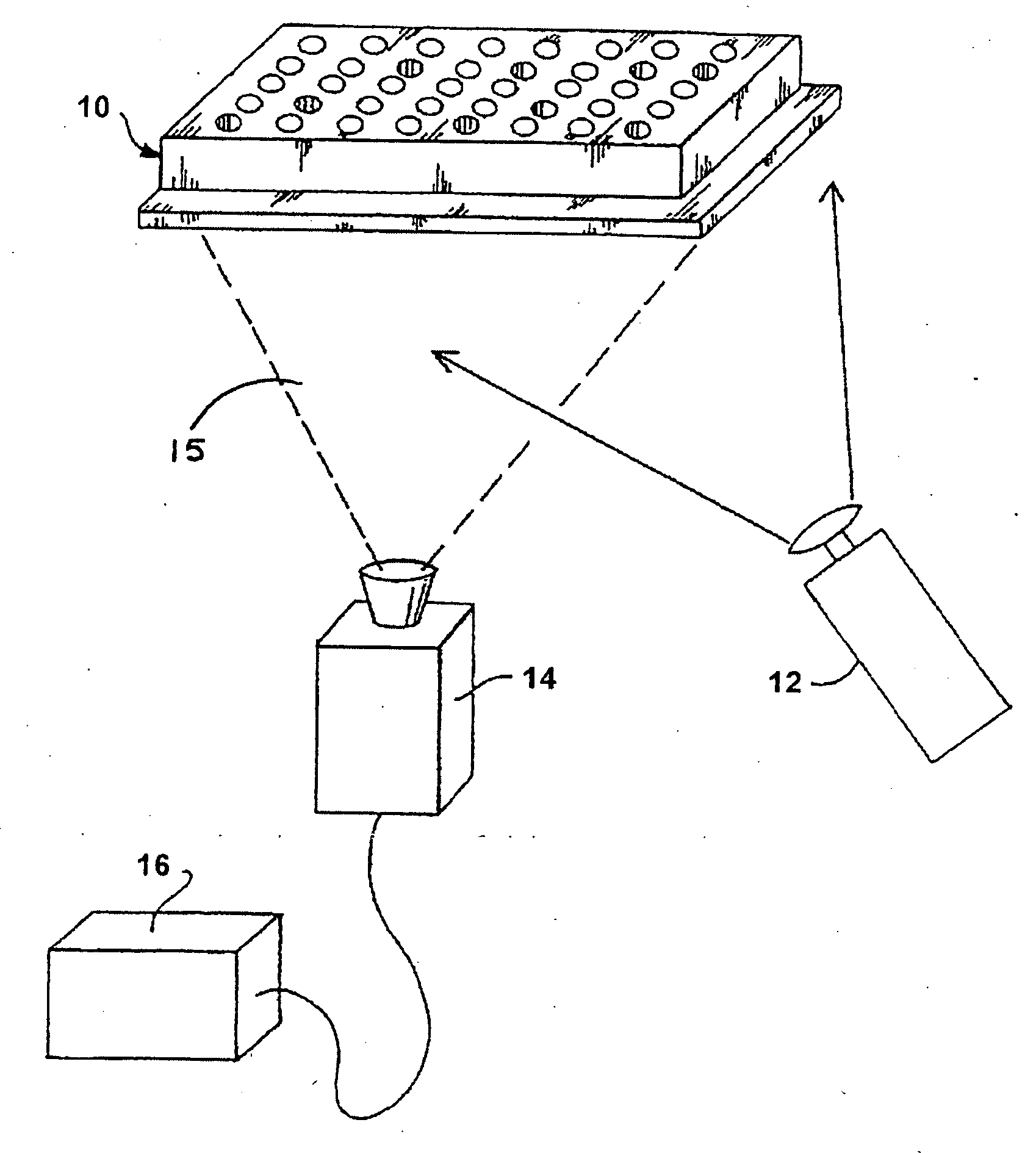
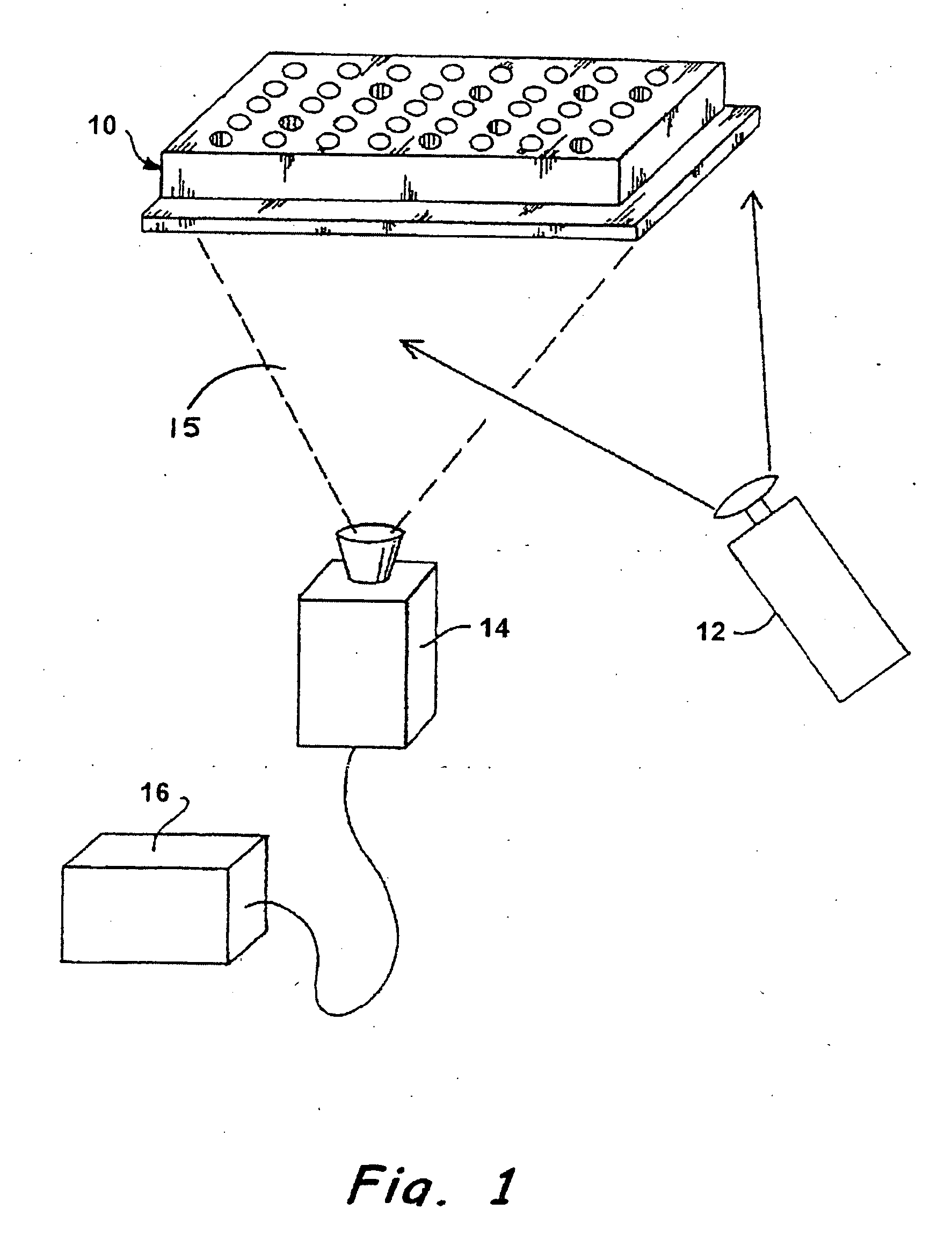
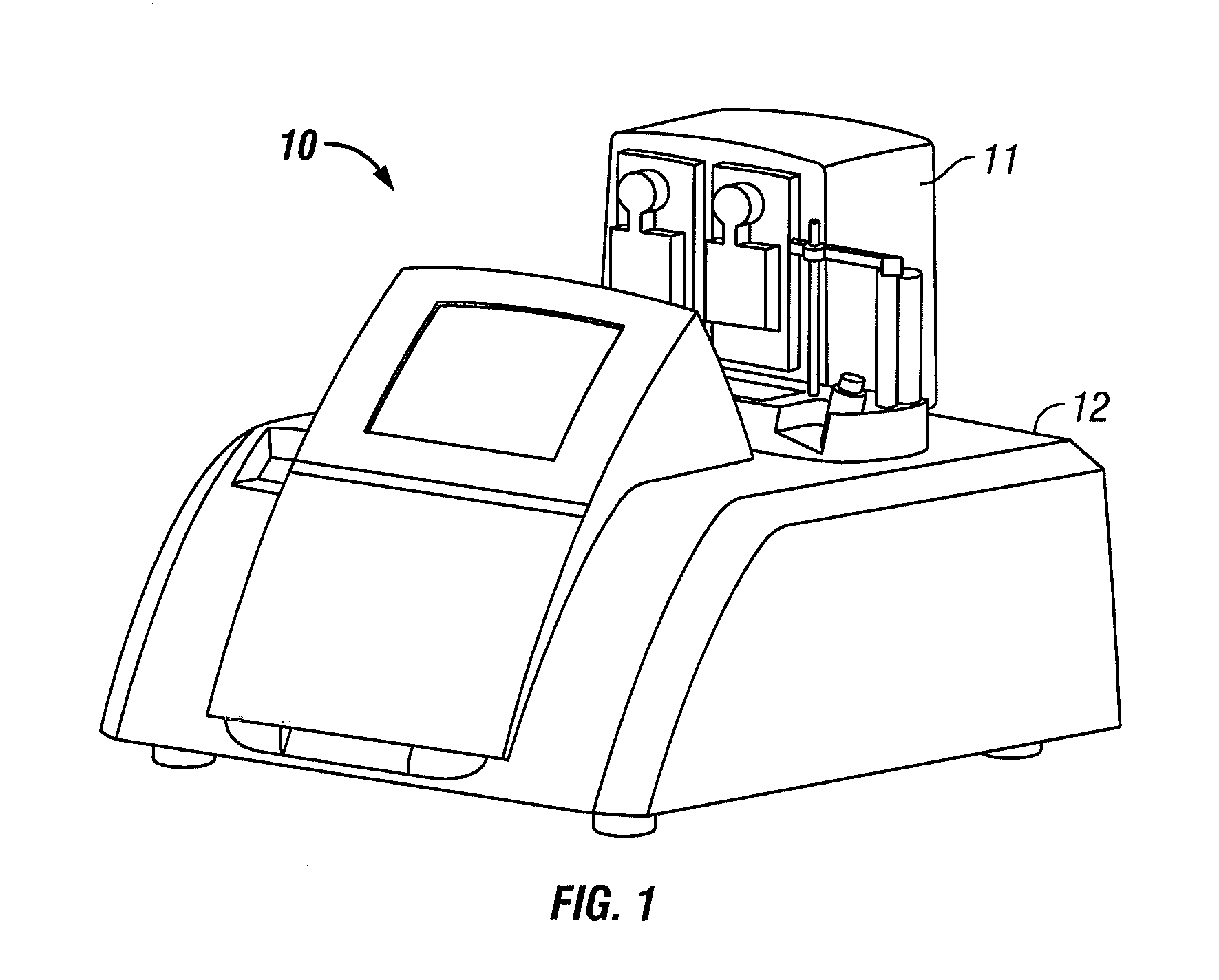
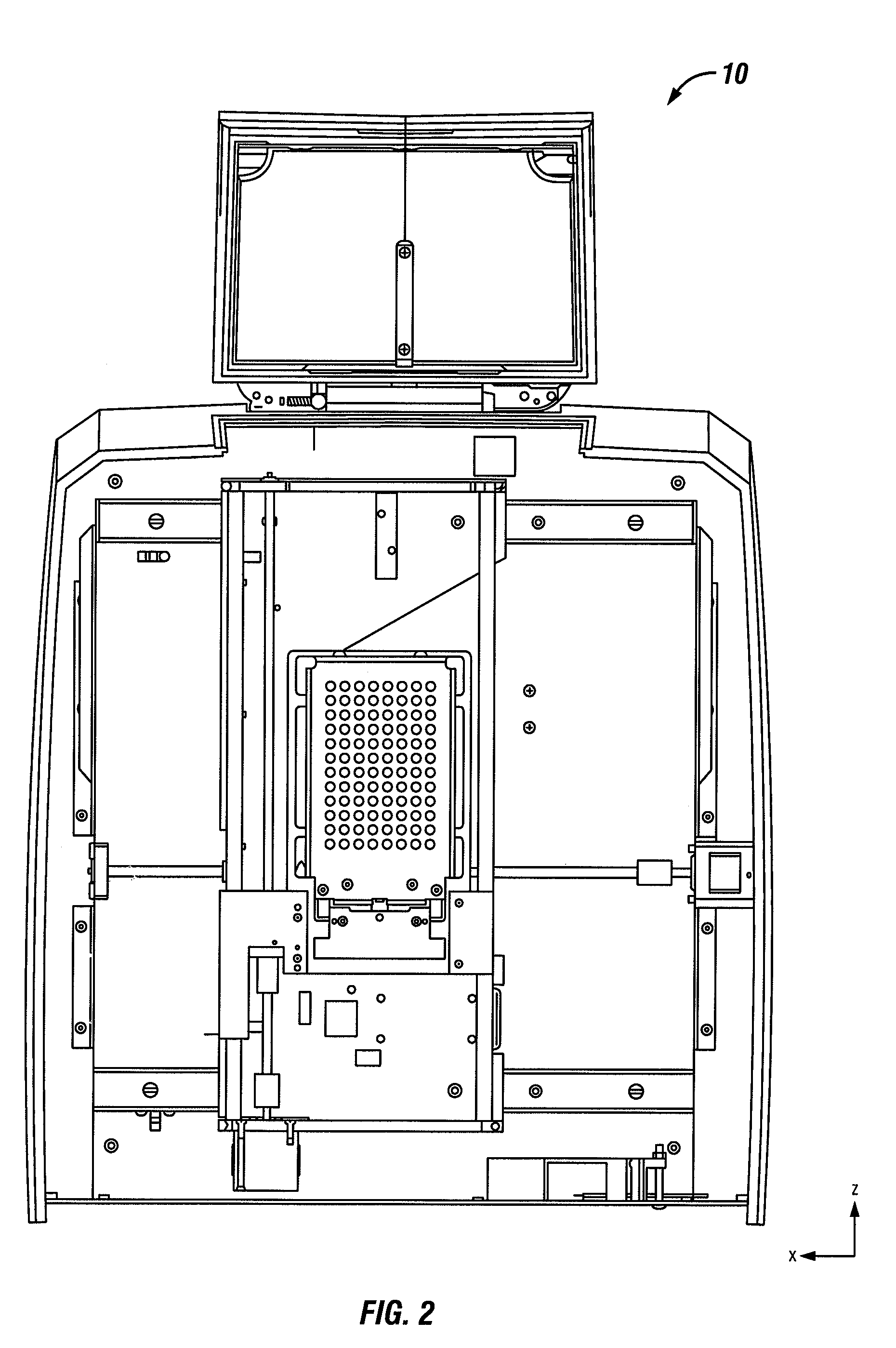
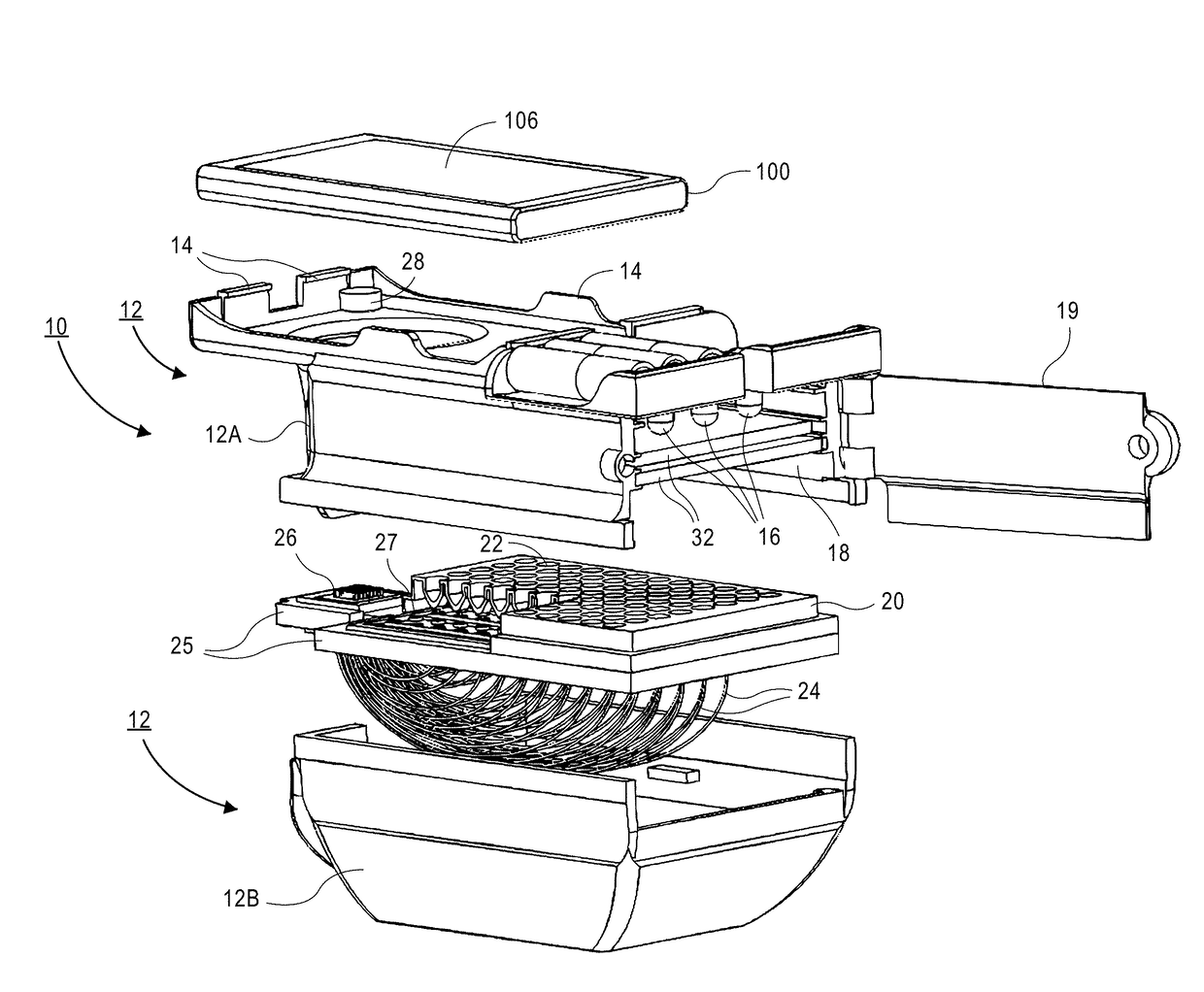
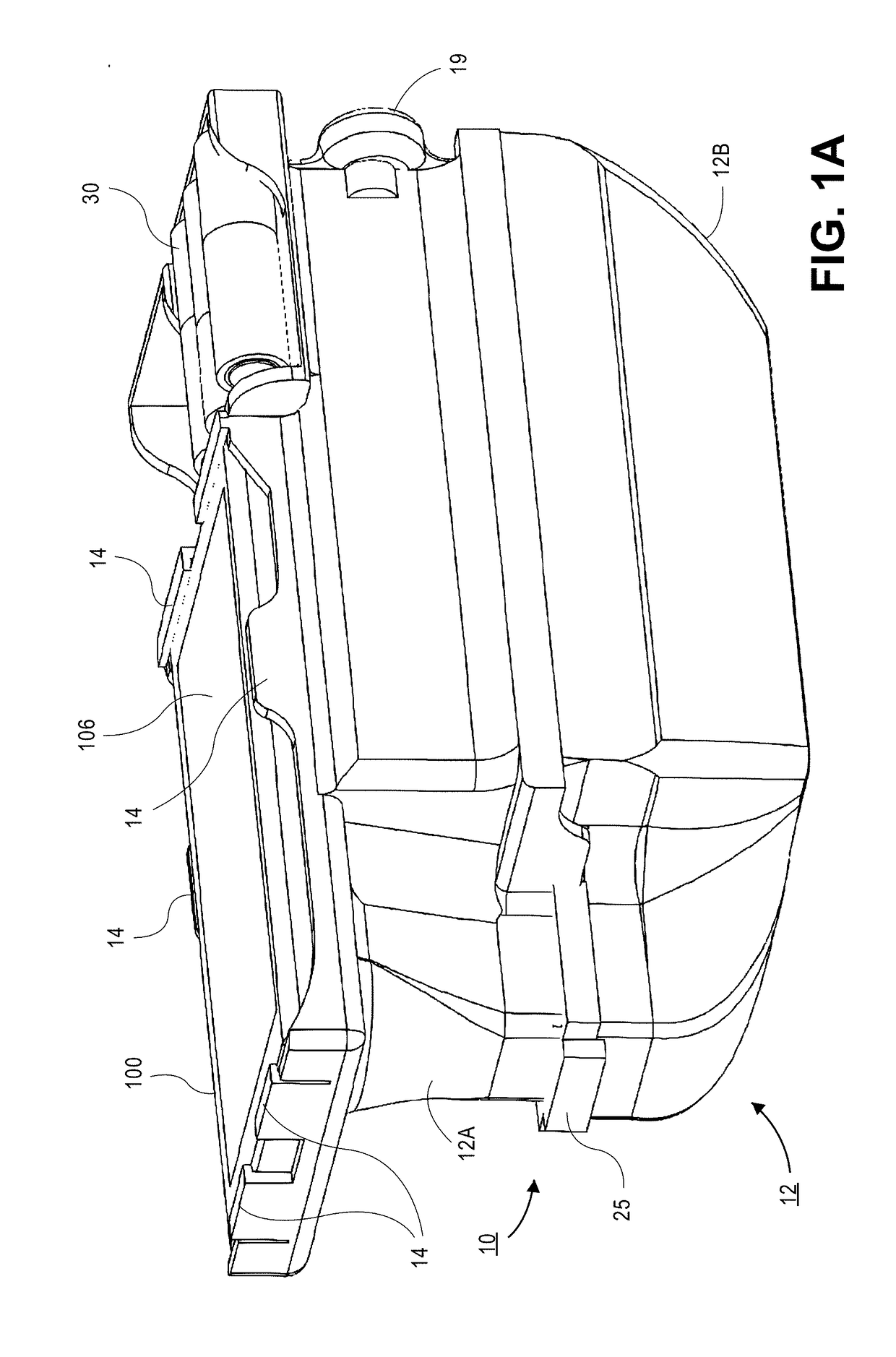
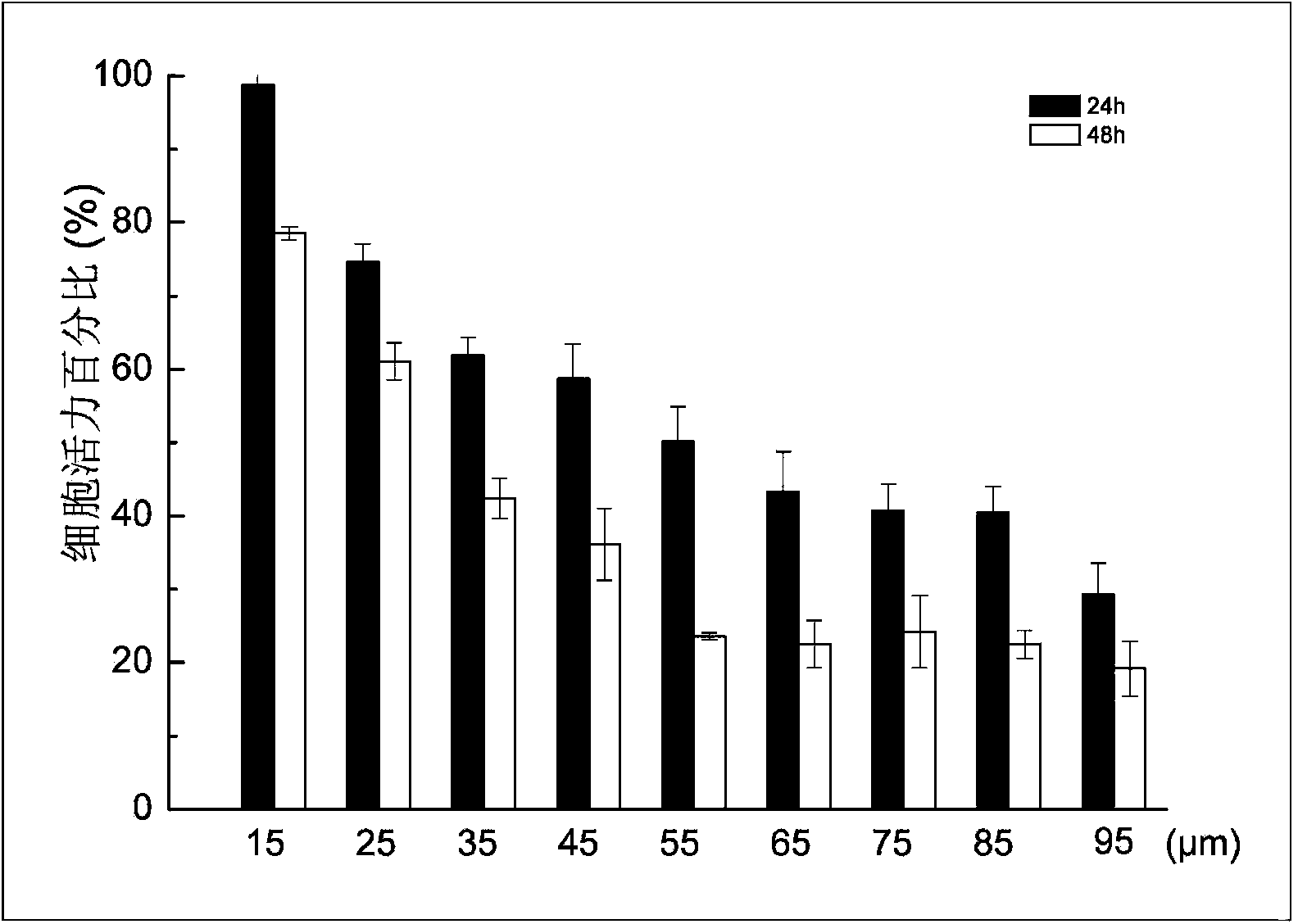
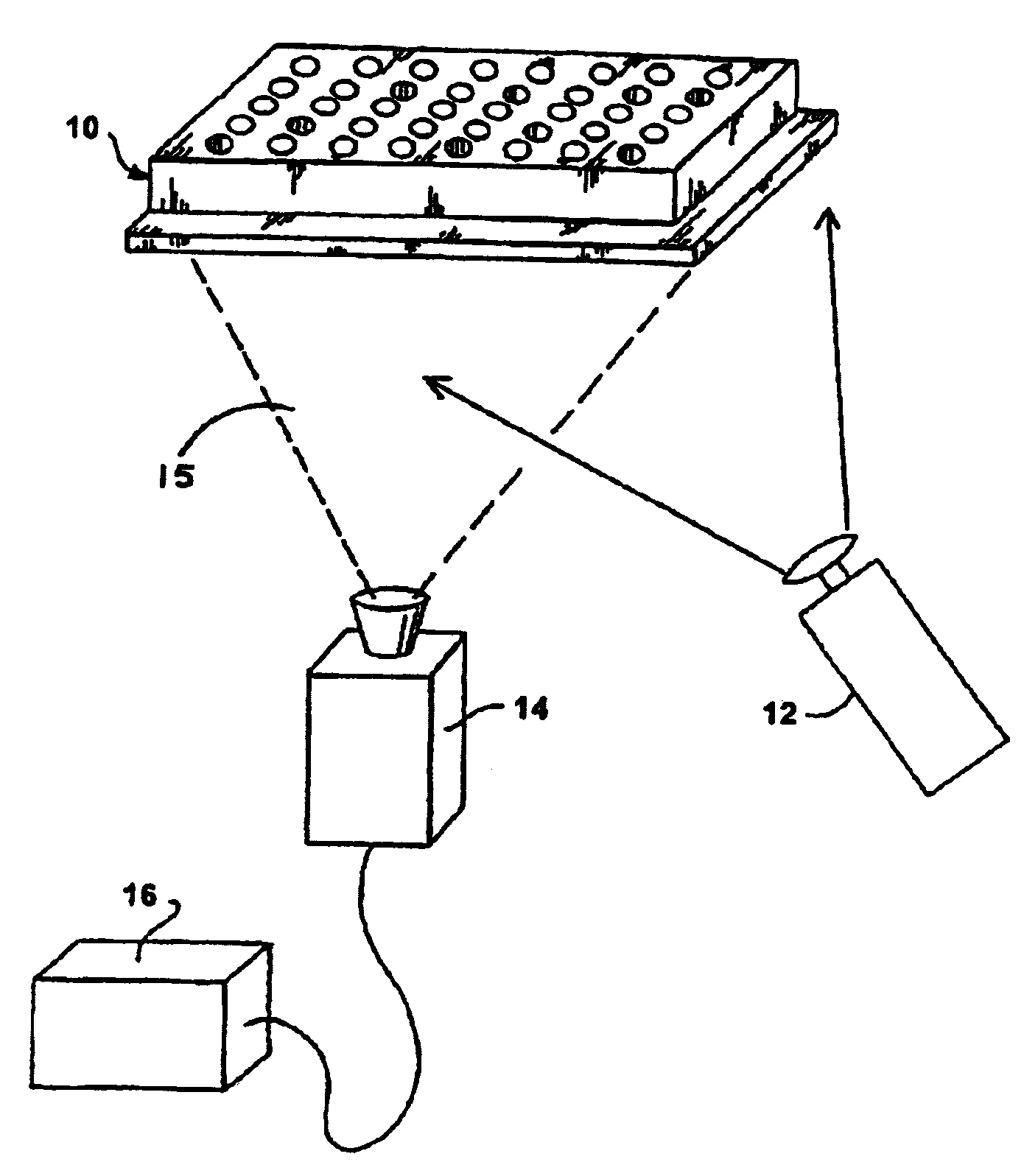
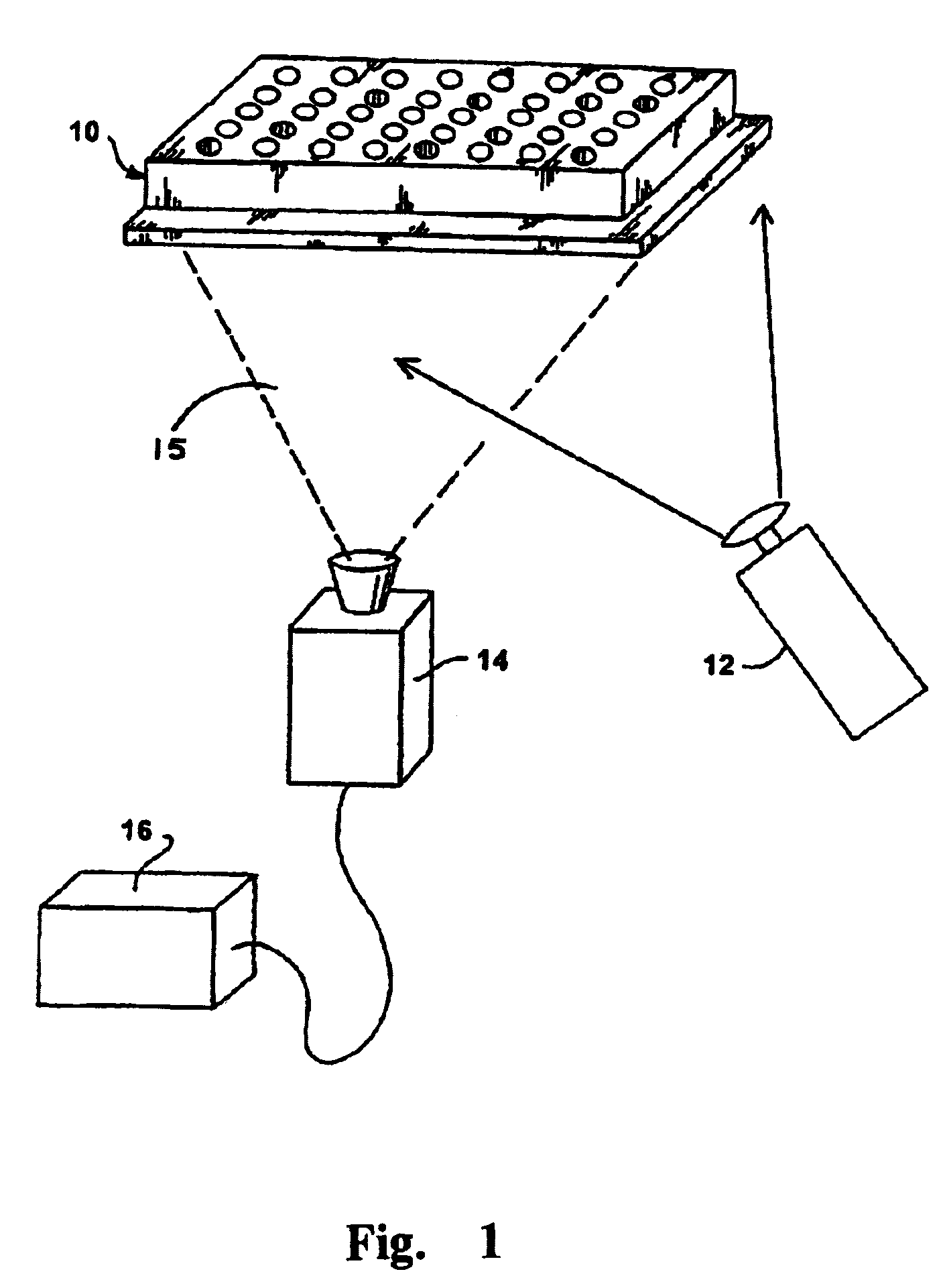
An instrument for the automated determination of absorbance data from multiple samples contained in a microplate.
Reflective optic system for imaging microplate readers
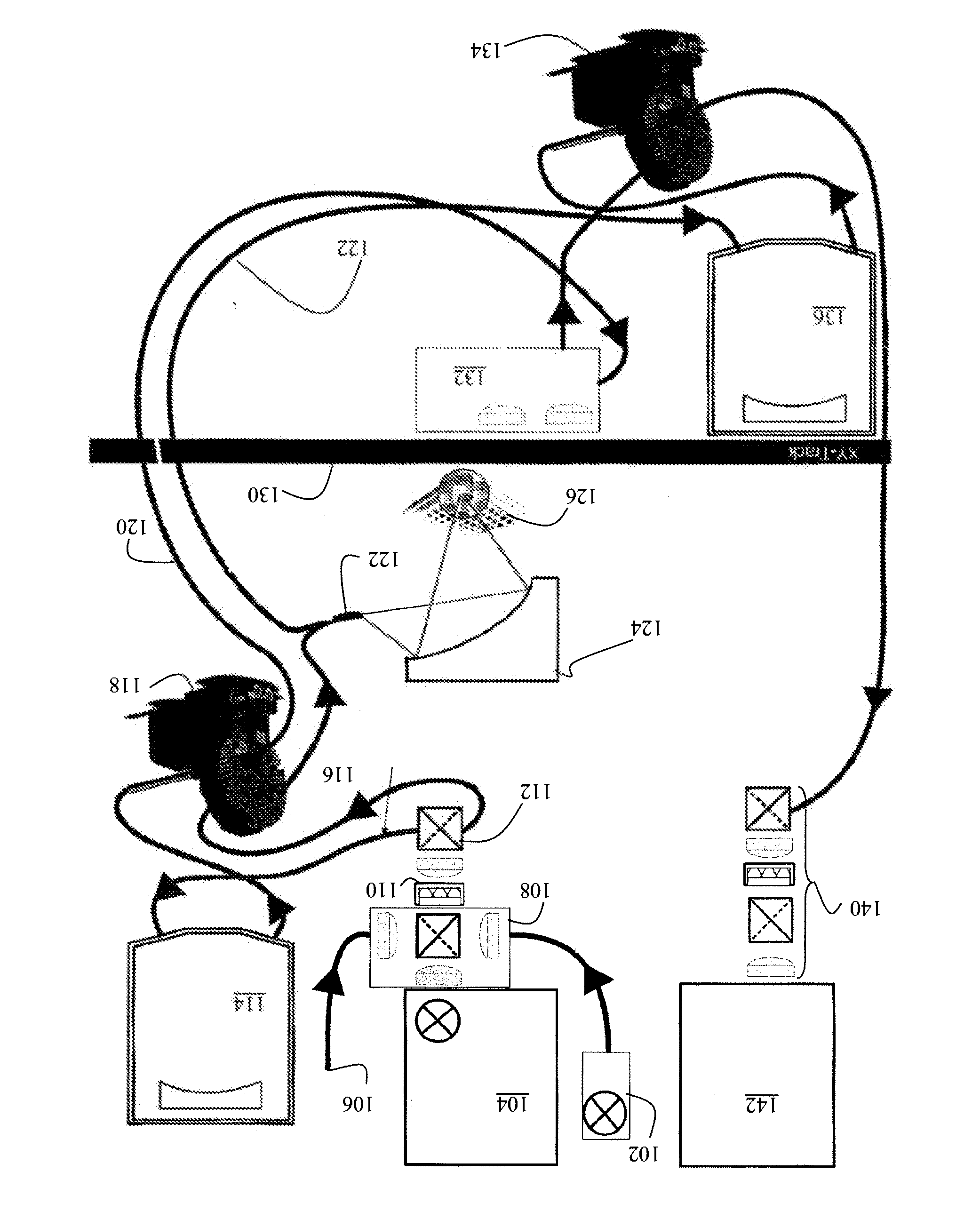
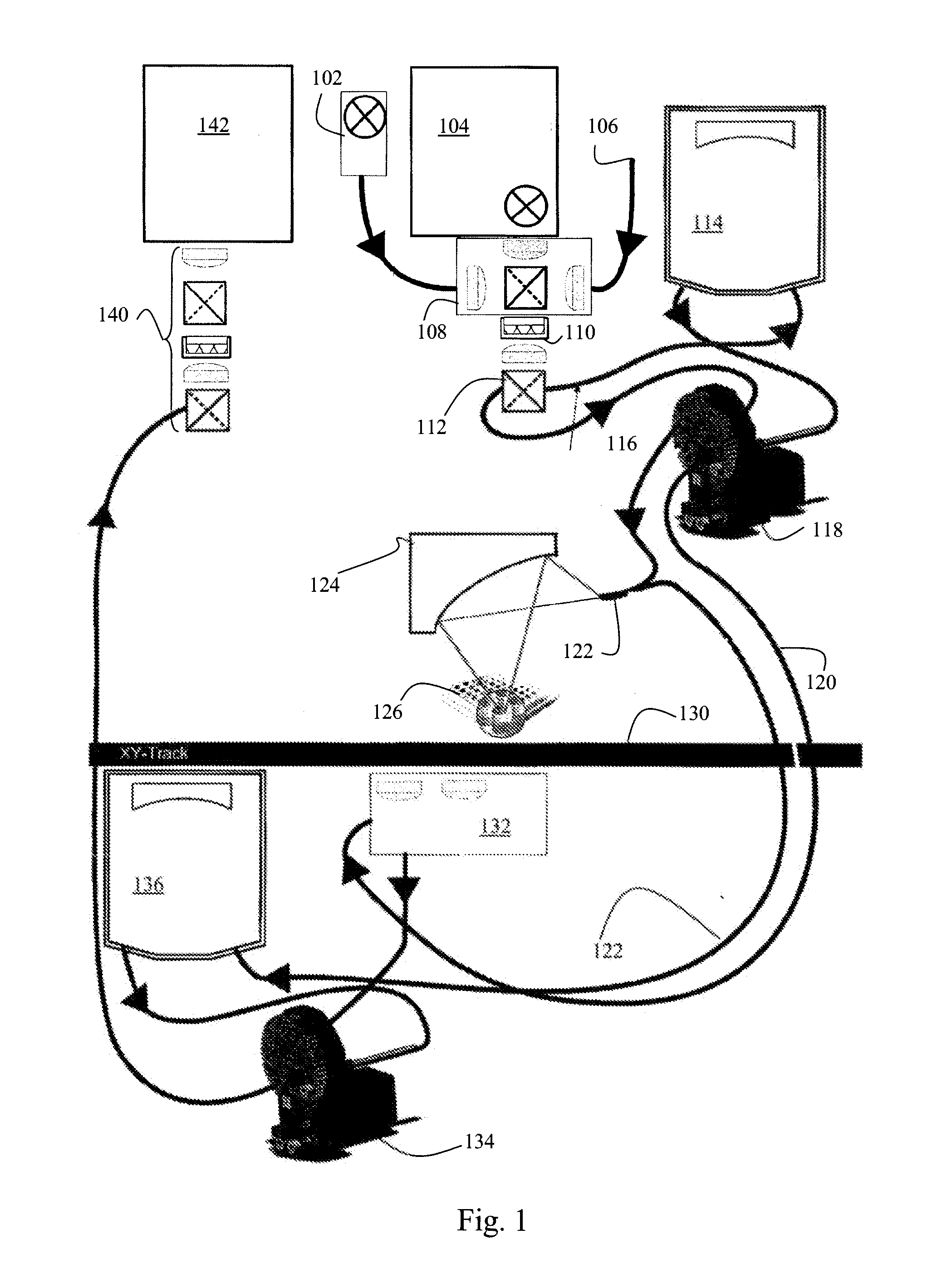
A reflective light imaging system for use in high-throughput screening of samples disposed in multiple-well plates. The system can include a set of mirrors and lenses. The first mirror has a central aperture through which light from the object passes. The first mirror has a concave reflective surface that faces the image plane. The next element is a second mirror with a convex reflective surface. The system can include an aberration corrective system positioned between the second mirror and the image plane, and an optical sensor near the image plane. Light from an object passes through the central aperture of the first mirror and is reflected off the convex surface of the second mirror. The light then strikes the reflective surface of the first mirror. The light from the first mirror is then collected by the aberration correction system and transmitted toward the image plane.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
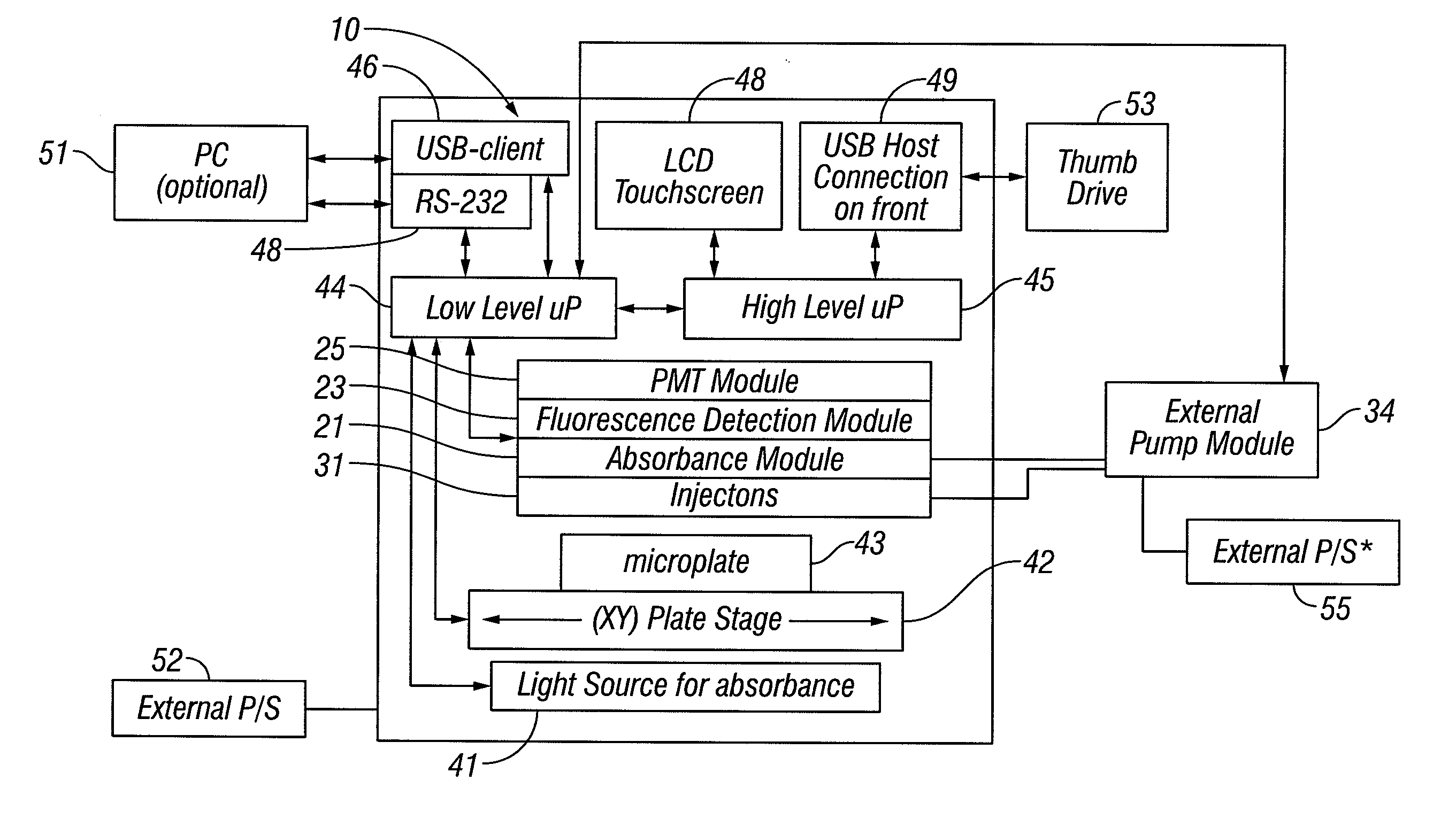
Multi-Mode Modular Method and Apparatus for Micro-titer Plate Analysis
InactiveUS20070248494A1Inexpensively and simply upgraded and reconfiguredDifferent setBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific detectionAbsorbance
A reconfigurable microplate reader comprises a plurality of user installable detection modules. Each module comprises a self-contained detector for a microplate reader. Each module reconfigures the microplate reader to implement at least one specific detection scheme for detecting any of luminescence, fluorescence, and absorbance and / or reconfiguring said microplate reader to implement any of a fluorometer and a luminometer. A microplate reader platform has a port for coupling at least one user installable detection module thereto. The platform also comprises a user interface from the platform to the module, a machine interface from the platform to the module, and a platform configuration mechanism for recognizing a specific detection scheme for an installed detection module and for configuring the platform to support the specific detection scheme.
Owner:TURNER BIOSYST
Micro-plate reader for elisa testing
ActiveUS20180196193A1More compactMore denseTelevision system detailsDigital computer detailsFiberReduced size
A micro-plate reader for use with a portable electronic device having a camera includes an opto-mechanical attachment configured to attach / detach to the portable electronic device and includes an array of illumination sources. A slot in the opto-mechanical attachment is dimensioned to receive an optically transparent plate containing an array of wells. Optical fibers are located in the opto-mechanical attachment and transmit light from each well to a reduced size header having, wherein the fiber array in the header has a cross-sectional area that is ≤10× the cross-sectional area of the wells in the plate. A lens located in the opto-mechanical attachment transmits light from the header fibers to the camera. Software executed on the portable electronic device or other computer is used to process the images to generate qualitative clinical determinations and / or quantitative index values for the separate wells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cpf1 reagent kit and detection method for quickly detecting nucleic acid of African swine fever virus
ActiveCN110551846AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAfrican swine feverFluorescence
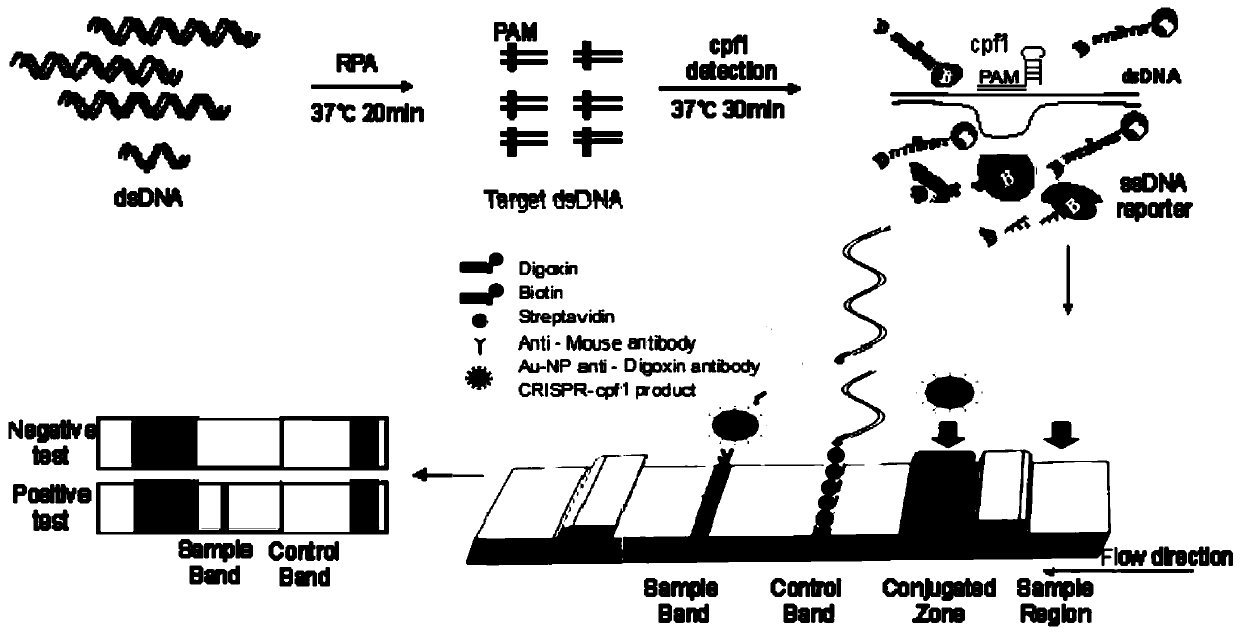
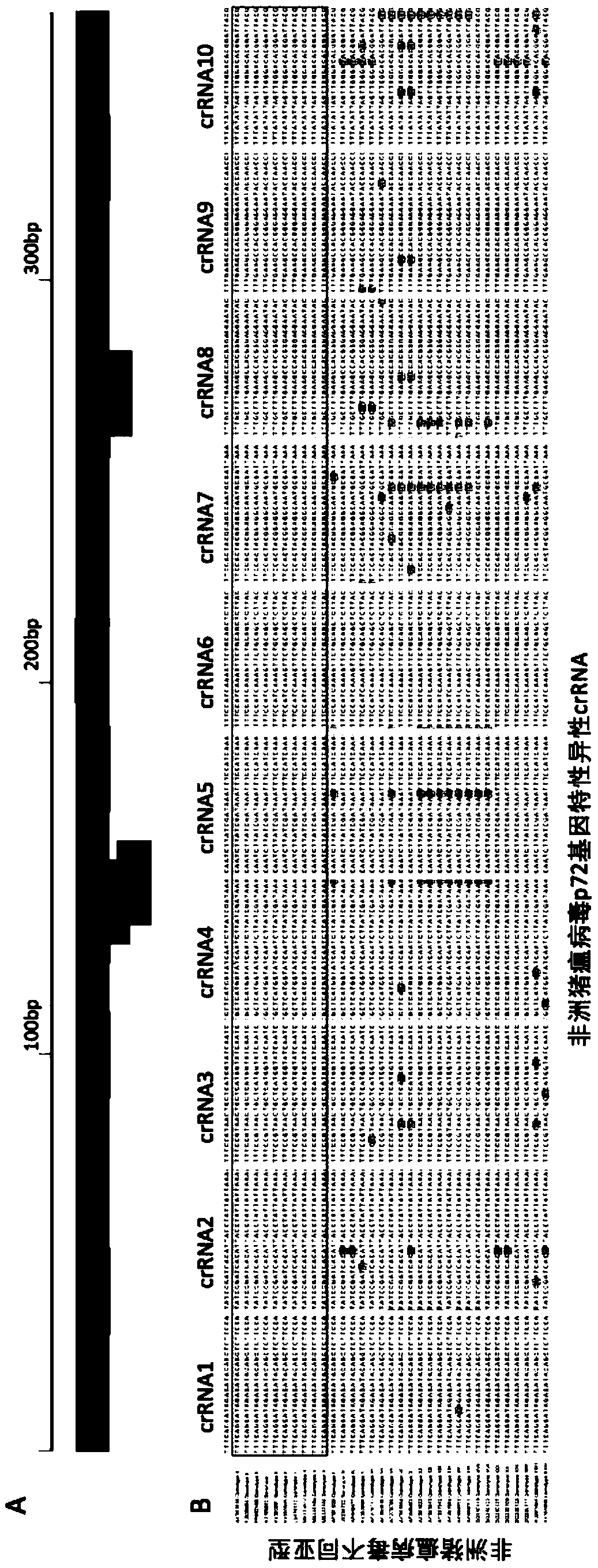
The invention discloses a Cpf1 reagent kit for quickly detecting nucleic acid of an African swine fever virus. The Cpf1 reagent kit comprises a Cpf1 detection system suitable for quickly detecting theAfrican swine fever virus, and an immune colloidal gold test strip, wherein the Cpf1 detection system comprises specific crRNA protein, specific Cpf1 protein and a single-chain DNA(ssDNA) reporting system in accordance with a p72 gene of the African swine fever virus, the specific crRNA is one or more of crRNAs from ASFV P72 crRNA1 to ASFV P72 crRNA10, and the sequence of the specific crRNA is SEQ NO.4 to SEQ NO.13; and the single-chain DNA(ssDNA) reporting system comprises ssDNA FQreporter for fluorescence detection of a microplate reader and / or ssDNA DB reporter for detecting the immune colloidal gold test strip. According to the Cpf1 reagent kit disclosed by the invention, for the first time, the Cpf1 is used for detecting the African swine fever virus, and has the advantages of beinghigh in sensitivity, high in specificity, short in time consumption, high in flux, independent of large-scale experiment equipment and the like. The advantages enable a detection method based on the immune colloidal gold test strip developed by the invention to be conveniently used in basic laboratories and breeding enterprises to be used for performing detection, identification and diagnosis on basic quick detection of the African swine fever.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Method for detecting tetracycline residues in milk and drinking water
InactiveCN103149167AQuick checkThe results are highly reliableColor/spectral properties measurementsCow milkElectrolyte
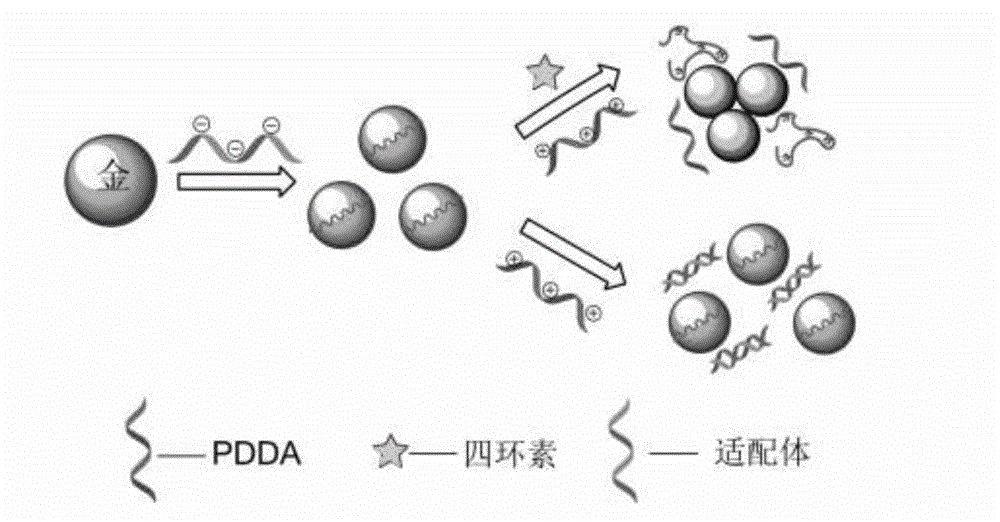
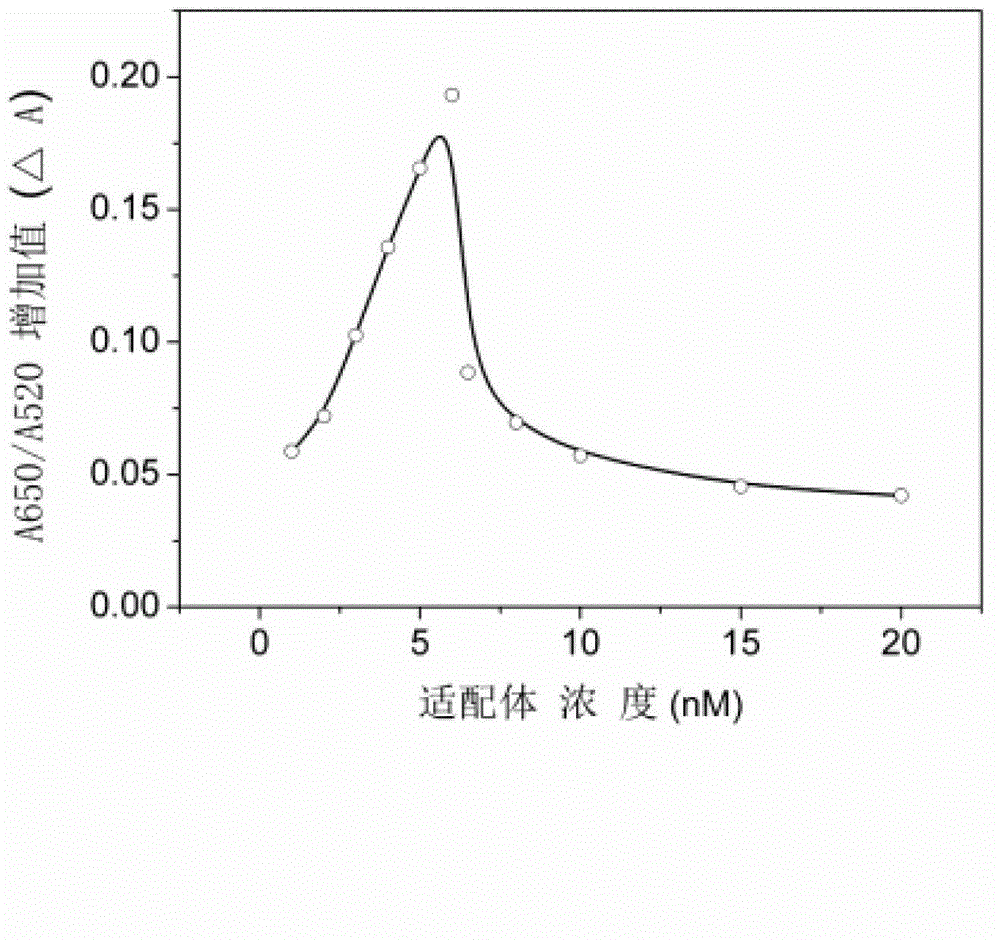
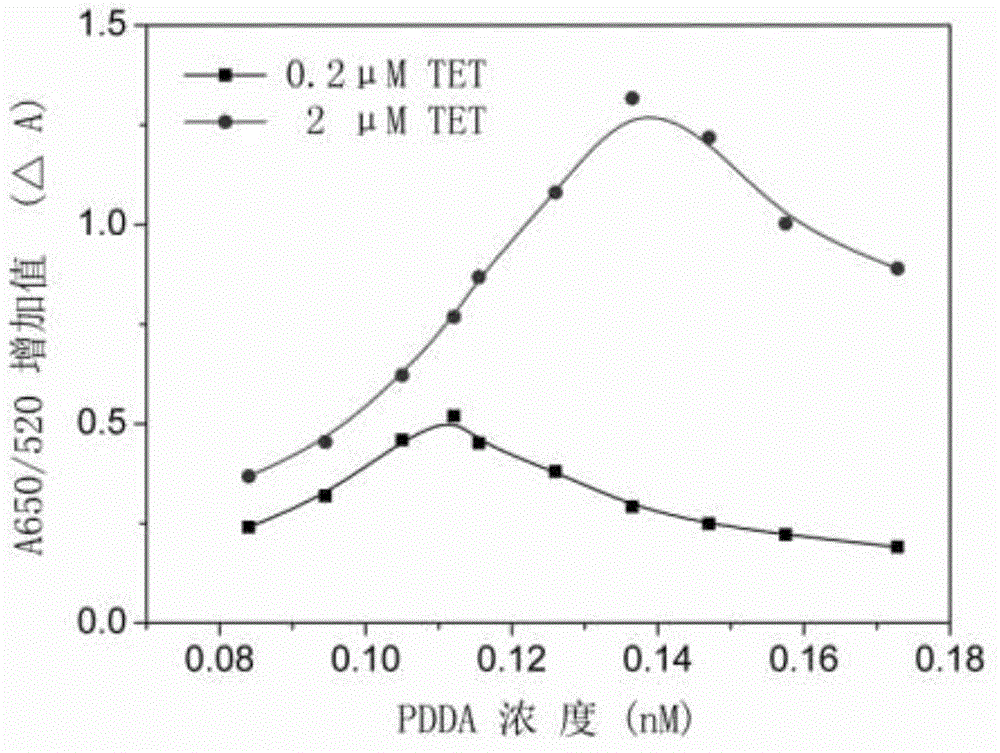
The invention discloses a method for detecting tetracycline residues in milk and drinking water and belongs to the technical field of food safety. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a detection system with known tetracycline concentration to obtain a light absorption difference standard curve, fitting the curve to obtain a regression equation, mixing milk or drinking water to be detected with an acetic acid solution to obtain a mixed solution, centrifuging and layering the mixed solution to obtain a supernatant liquid, adding a tetracycline aptamer solution, adding a nanogold solution after incubation, finally adding positive ion electrolyte, determining the difference of the light adsorption rates at the 650nm part and the 520nm part of an electrolyte standard solution and a blank control solution by a microplate reader, and calculating the content of the tetracycline in milk and drinking water to be detected under the control of the equation obtained by fitting the standard curve. The method is high in speed, low in cost, high in sensitivity, good in selectivity, and convenient to operate without depending on large-sized instruments or equipment, the lowest detection limit is 45.8nM, the defects that the existing aptamer is time-wasting due to marking and high in cost are overcome and the method has the advantages of high speed, sensitivity and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
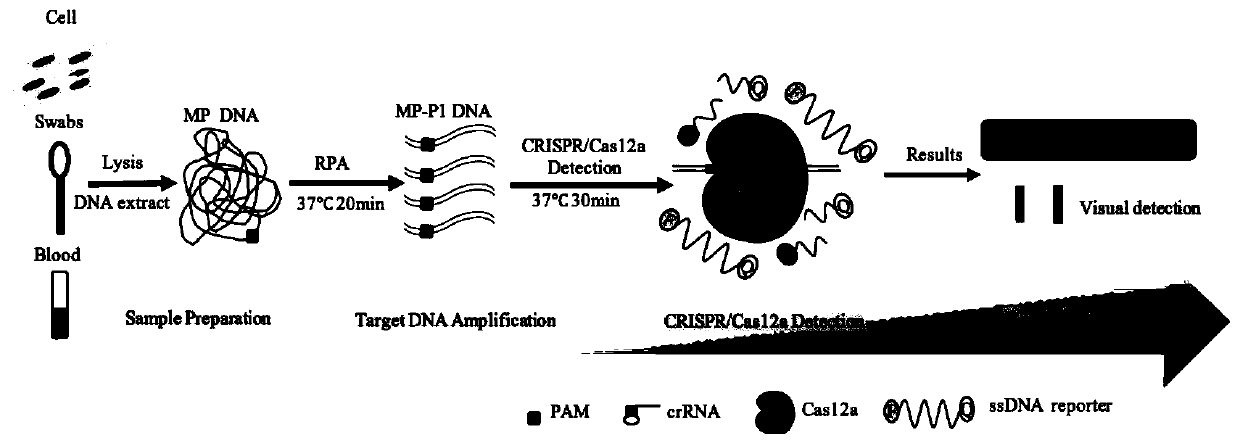
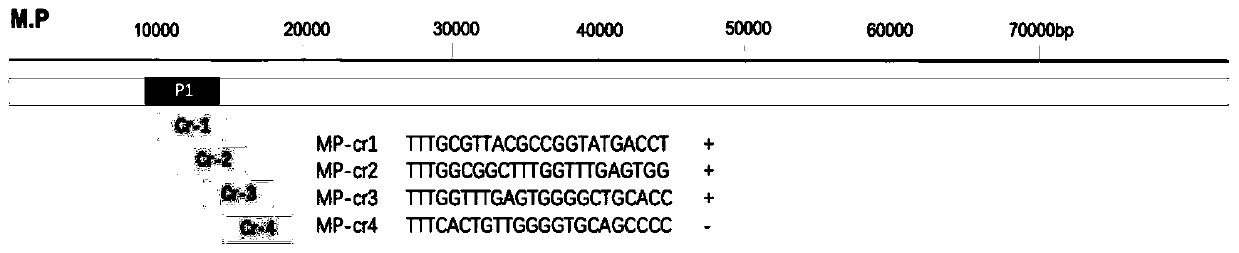
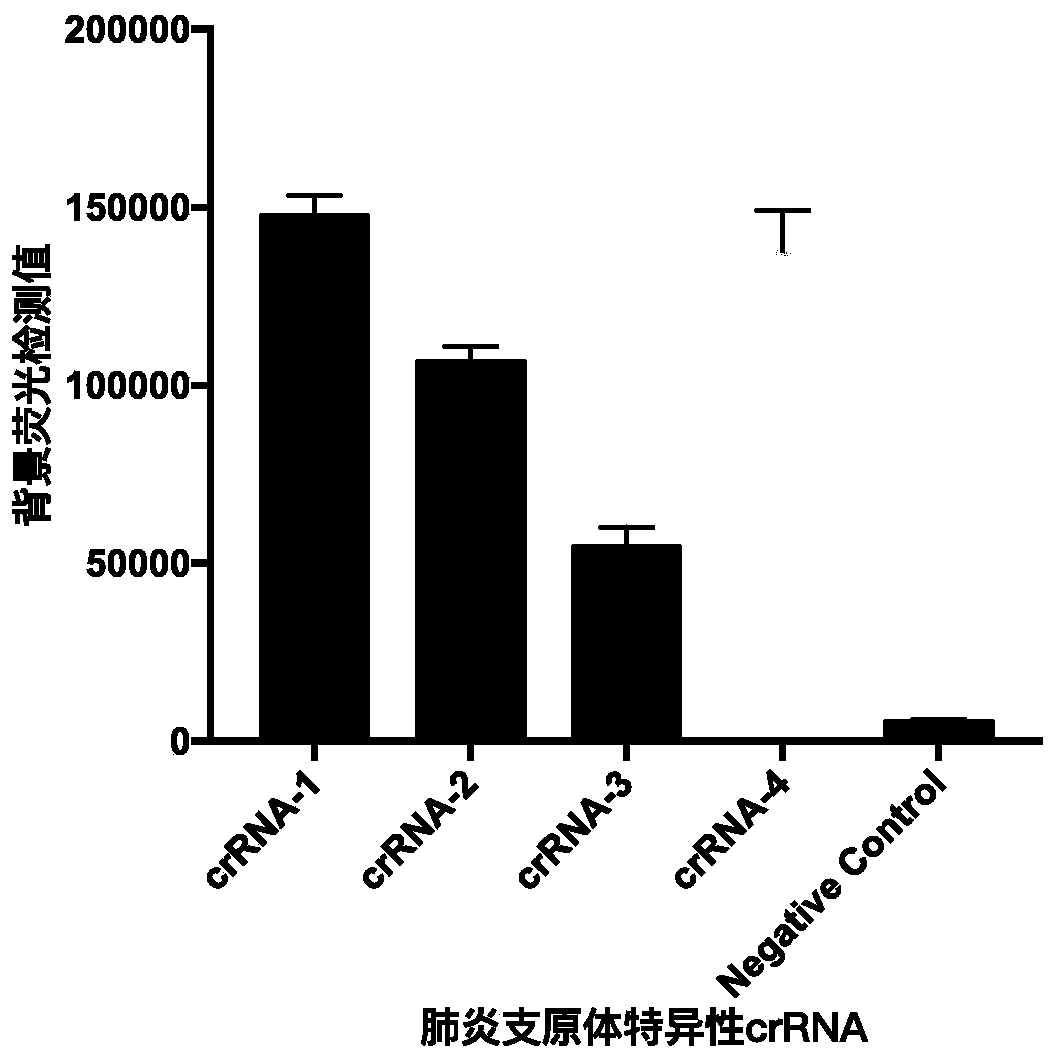
Kit and detection method for rapid detection of nucleic acid of mycoplasma pneumonia on basis of CRISPR/Cas12a
InactiveCN111187804AHigh sensitivityHighly conservativeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
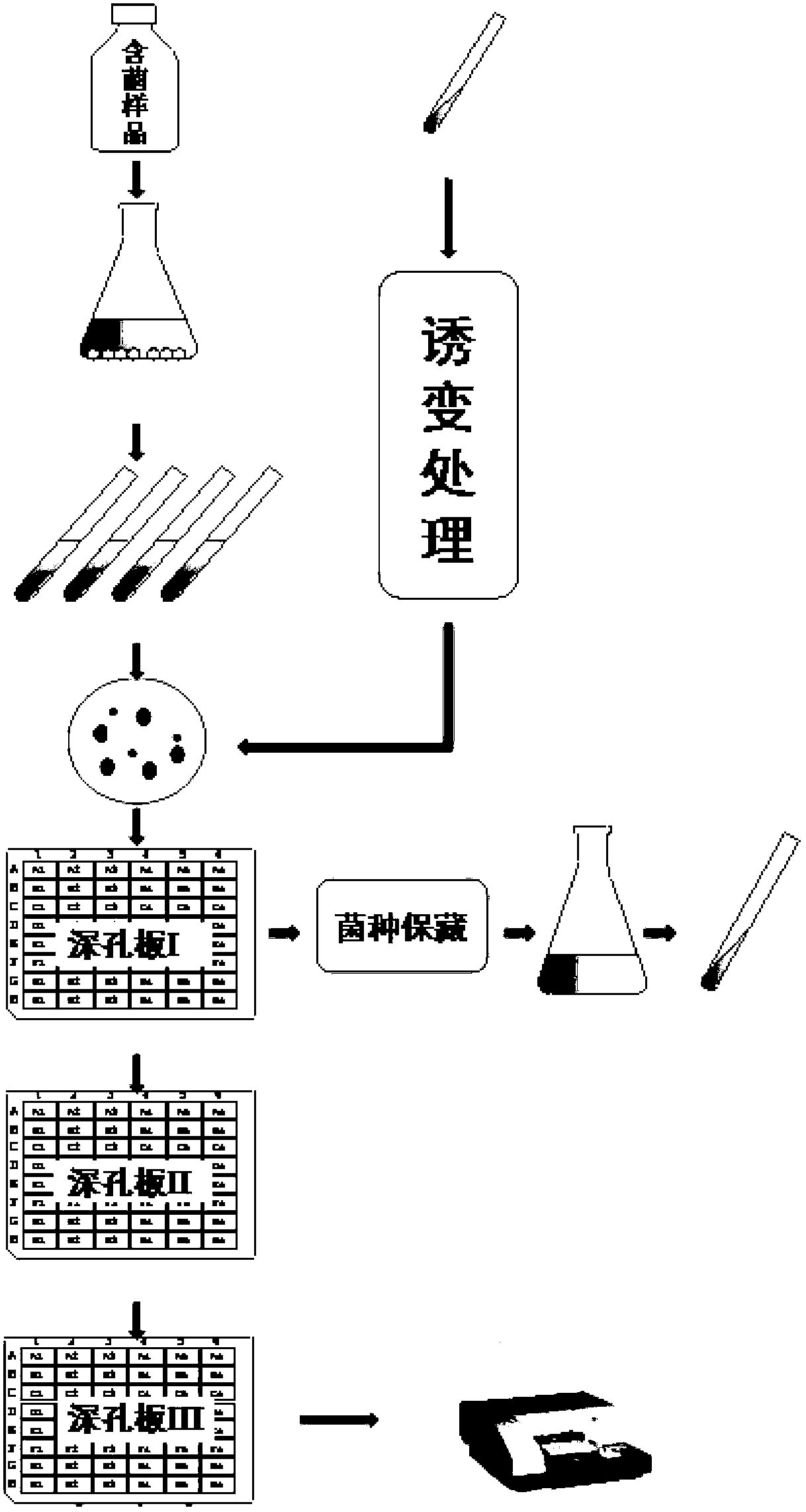
High-throughput screening method for high-yield monascus pigment strain
InactiveCN103725669AMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsBiology
The invention relates to a high-throughput screening method for a high-yield monascus pigment strain. The method comprises the following steps of all mutated monascus suspensions to a deep-well plate for mixed culturing, performing high-throughput detection to obtain a mixture with the highest yield, performing plate separation and purification, and performing shake flask fermentation and detection to obtain a pure high-yield strain. The complete high-throughput screening method integrating a deep-well plate culturing technology and microplate reader detection is convenient, rapid, accurate and efficient.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel coronavirus rapid detection test paper and detection method
PendingCN111337669ASuitable for on-site screeningReduce the risk of infectionImmunoassaysReceptorHorse radish peroxidase
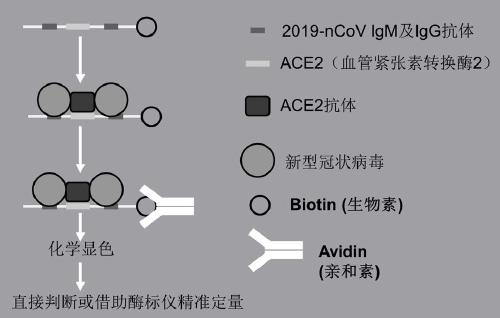
The invention discloses novel coronavirus rapid detection test paper and a detection method. The novel coronavirus rapid detection test paper is composed of a sample pad, a colloidal gold pad, a reaction color development area, a water absorption area and a supporting plate; the sample pad and the water absorption pad are arranged on the supporting plate and located on the two opposite sides of the supporting plate respectively, and the sample pad is suction filter paper or a glass fiber membrane and used for bearing an object to be detected; a nitrocellulose membrane is fixed on the supporting plate, and the absorbent pad is absorbent paper; through double binding of a novel coronavirus antibody and a receptor ACE2 protein of a virus, a coronavirus protein antigen is specifically capturedand bound by adopting double enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; the ACE2 antibody in the test paper reaction color development area is combined with biotin, avidin is connected with horse radish peroxidase, and through a biotin-avidin system, rapid judgment can be achieved through chemical color development, and the virus content can also be accurately detected through a microplate reader.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Method for detecting glucose by ferroferric oxide nano particle catalytic chemiluminescence
InactiveCN102053085AEasy to operateLow costChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminolBiocompatibility Testing
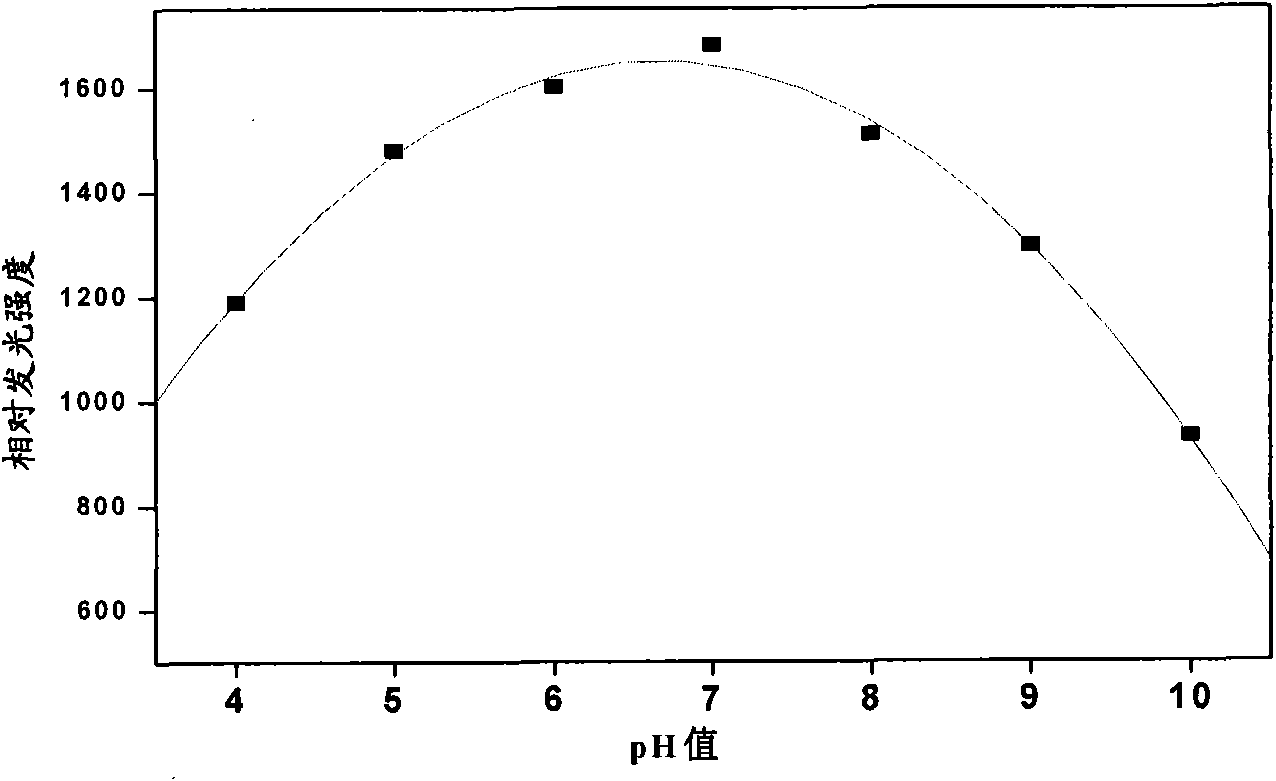
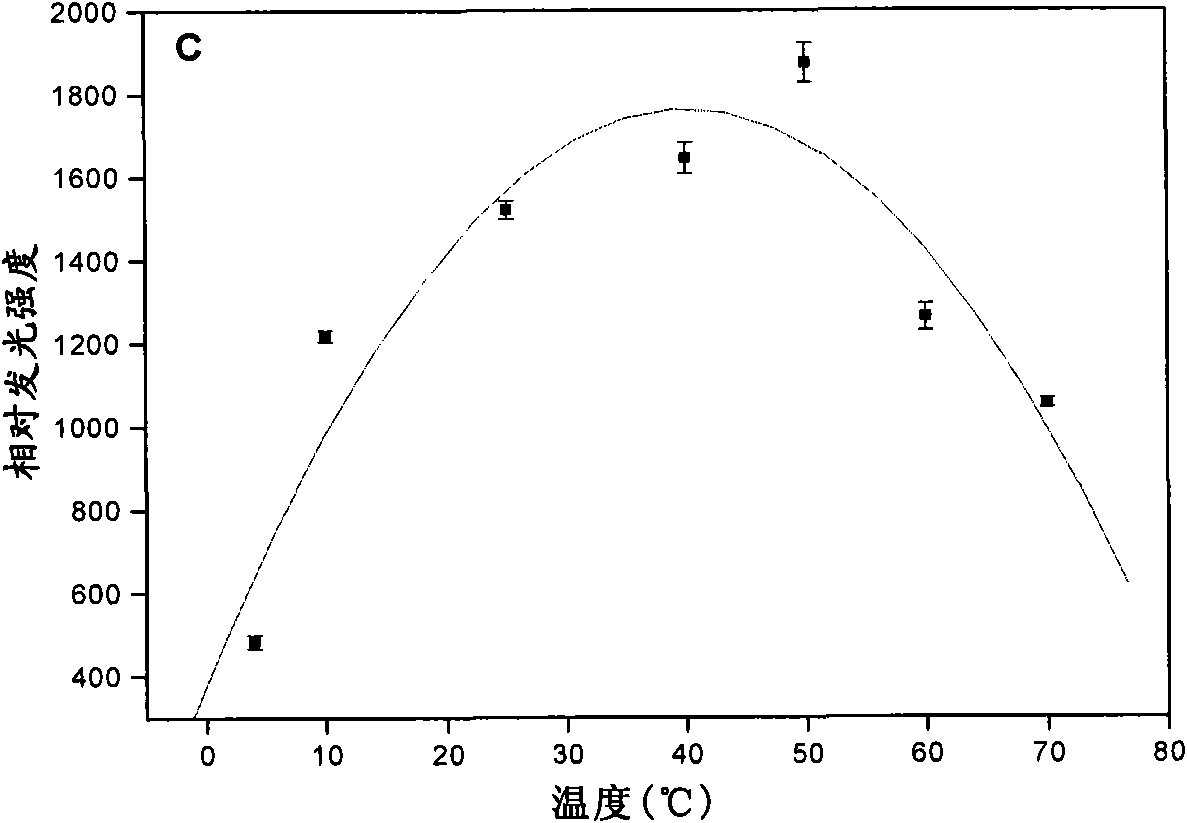
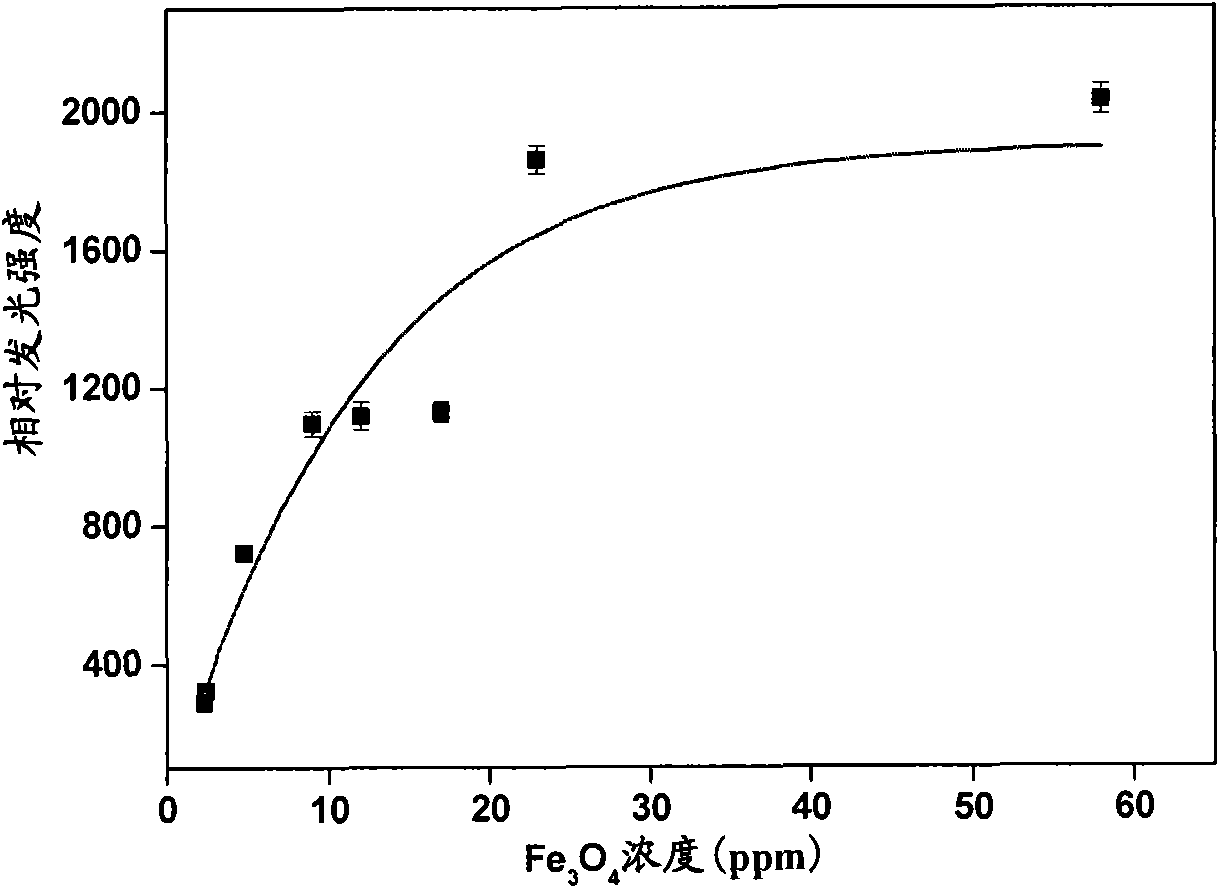
The invention discloses a method for detecting glucose by ferroferric oxide nano particle catalytic chemiluminescence, which comprises the following steps of: at the temperature of between 10 DEG C and 60 DEG C, adding a glucose solution into a ferroferric oxide nano granule-luminol-H2O2 solution system, the pH of which is 4.0 to 9.0; and detecting the concentration of the glucose by using a SpectraMaxM2 microplate reader, wherein the concentration of the ferroferric oxide nano particles is more than or equal to 10ppm. The average granule diameter of the ferroferric oxide nano particles is 25nanometers. By using the characteristics of high adsorption, biocompatibility, zymoid catalytic property and reuse of the ferroferric oxide nano particles, the glucose chemiluminescence detection method with simple operation, low cost, wide linear range and low detection limit is established to realize simple, convenient and high-sensitivity detection of the glucose content in the fields of clinic and food.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid and high-flux acute toxicity test method for luminous bacteria
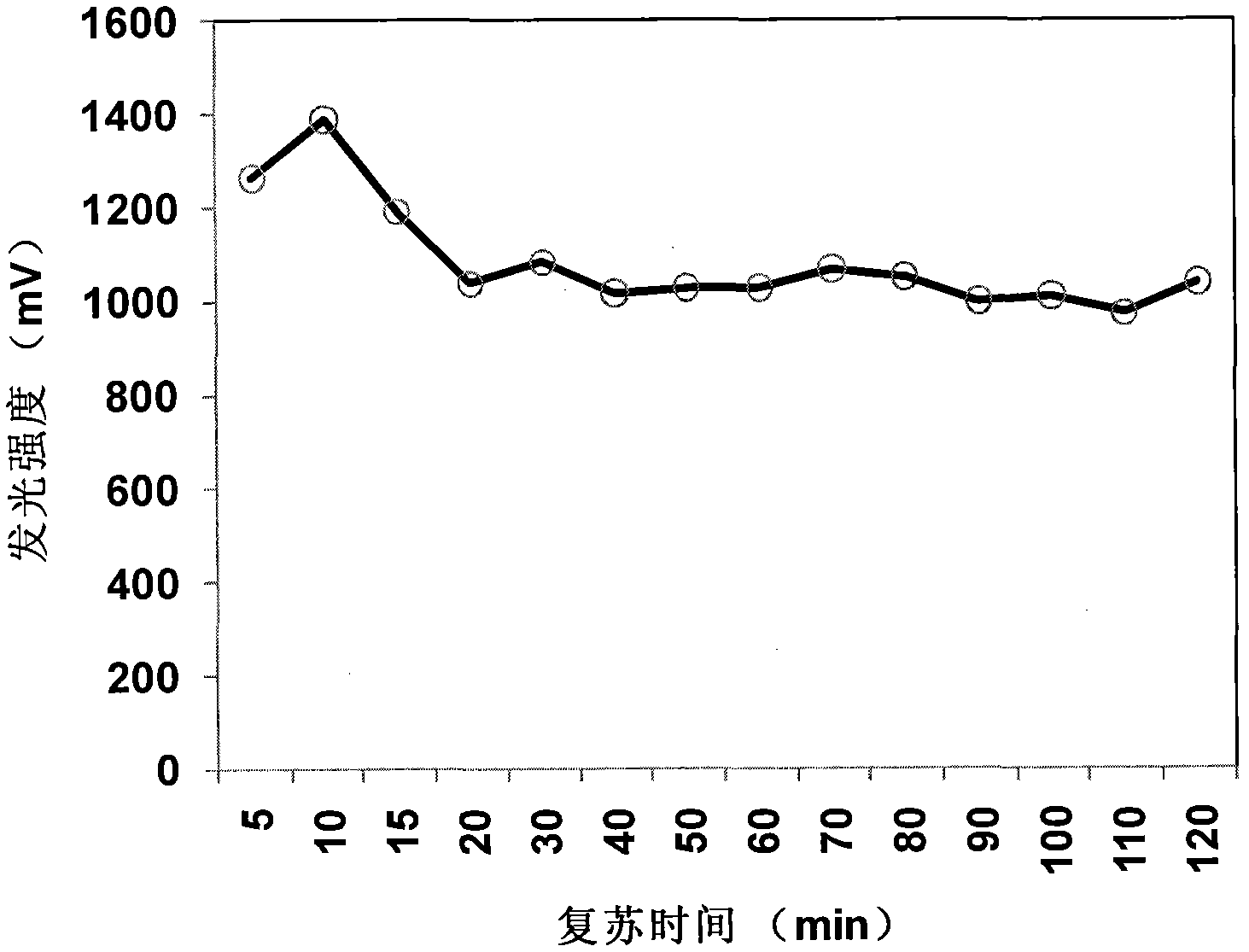
InactiveCN102465167AAchieve high-throughput quantizationReduce volumeMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute toxicity testingLuminous intensity
The invention relates to a rapid and high-flux acute toxicity test method for luminous bacteria, belonging to technical fields of analysis and detection. A luminous bacteria reviving solution is developed and can be used for rapidly reviving lyophilized luminous bacteria powder and cryopreserved strains within 30min, and the revived bacterium liquid can be directly used for a toxicity test as a working bacterium liquid without pre-culture after being stirred for a certain time. Meanwhile, a microporous plate is selected to serve as an exposing container and a detection tank for the toxicity test, a sample to be tested and the working bacterium liquid are added into pores and exposed for 15min, and then can be subjected to a luminous intensity test by adopting a chemiluminescence ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) reader. By adoption of the method, not only is a tedious and time-consuming working bacterium liquid pre-culture procedure omitted, but also the detection time is saved, the cost is reduced, the accuracy of a test result is increased, the high flux of the toxicity test is realized, and a wide popularization and application prospect is achieved.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
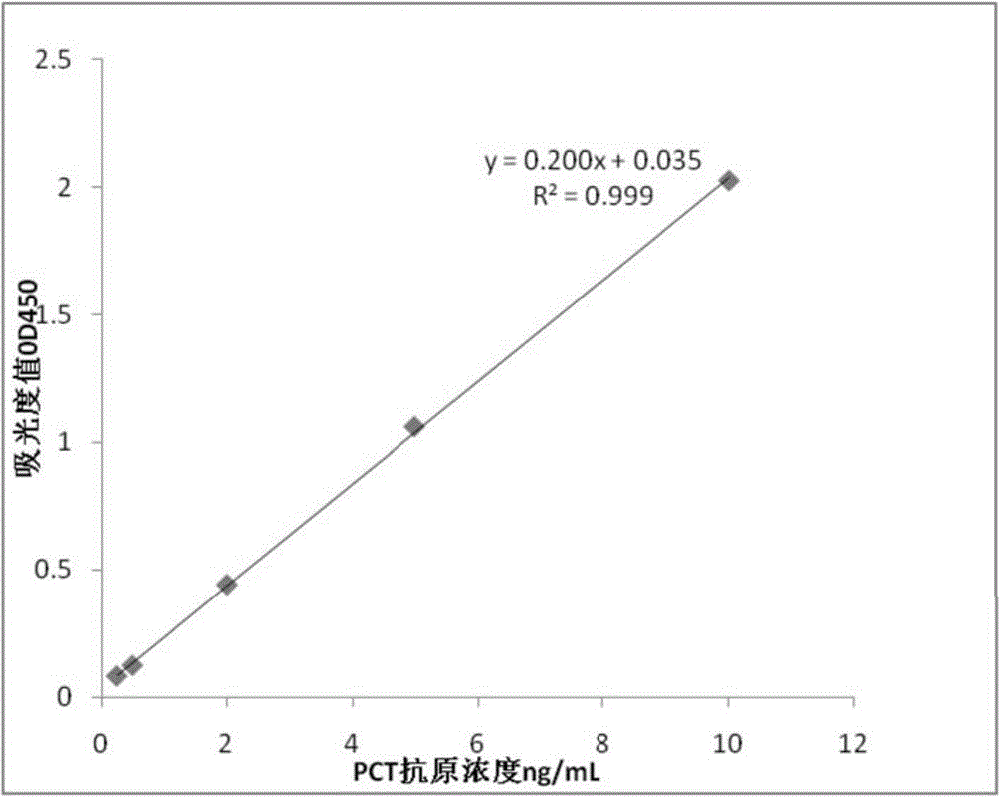
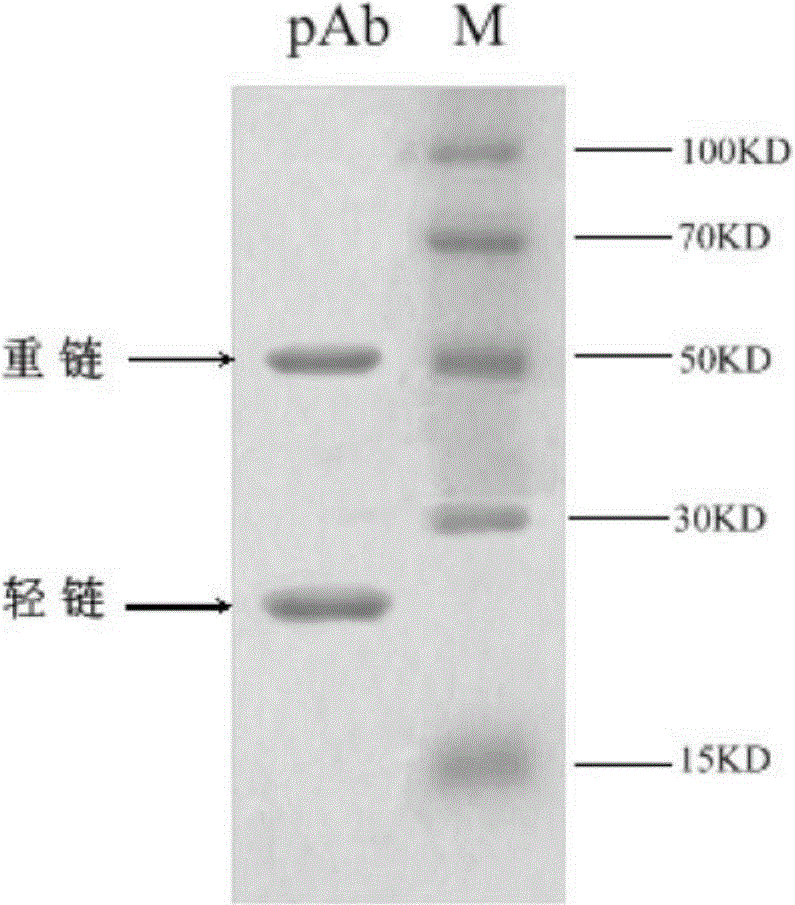
Human procalcitonin immunodetection kit, and preparation method and application thereof
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Rapid human respiratory syncytial virus detection method and kit based on magnetic separating and quantum dot labeling
ActiveCN105319373AIt has the effect of synergistic amplification of multiple signalsFast separationBiological testingEtiologyFluorescence
The invention provides a human respiratory syncytial virus antigen detection method based on magnetic separating and quantum dot labeling. The method comprises the steps that 1, immune nano magnetic beads resisting a human respiratory syncytial virus are prepared; 2, quantum-dot-labeled nano-probes resisting the human respiratory syncytial virus are prepared; 3, after a sample to be detected is dissolved with a sample processing solution, the immune nano magnetic beads resisting the human respiratory syncytial virus are added in a dissolved solution, magnetic separating is performed after full mixing and reacting are performed, washing is performed with a PBST buffer solution, the quantum-dot-labeled nano-probes resisting the human respiratory syncytial virus are added in obtained precipitates, magnetic separating is performed after reacting is performed, and after washing is performed with the PBST buffer solution, a fluorescence value is detected with a fluorescence microplate reader. Accordingly, the accurate, rapid and high-sensitivity method for detecting the human respiratory syncytial virus is established, and the very high practical value in the aspects such as clinical diagnosis, etiology identification and epidemiological investigation of the human respiratory syncytial virus is achieved.
Owner:湖北诺美华抗体药物技术有限公司
High throughput screening method of aminopeptidase and high-yield strain thereof
InactiveCN102994387AImprove efficiencyHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationWater bathsHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a high throughput screening method of aminopeptidase and a high-yield strain thereof, relates to a high throughput screening method of aminopeptidase and a high-yield microorganism bacterial strain thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: vaccinating a single colony in the hole of a deep-hole plate I on a medium containing a seed liquid, performing shaking cultivation, vaccinating the seed liquid in the hole of the deep-hole plate I correspondingly into the hole of a deep-hole plate II equipped with a fermentation medium, performing shaking cultivation, and centrifuging the deep-hole plate II to obtain the supernatant crude enzyme; adding a buffer solution and a chromogenic substrate solution or fluorogenic substrate solution in the micropore of an elisa plate, adding the dilute crude enzyme to be tested, carrying out water-bath reaction for 10-30 minutes at 30-70 DEG C, adding a 30-50% acetic acid solution immediately after the water-bath reaction and terminating the reaction; and measuring the absorbance or fluorescence intensity of the reaction liquid by a microplate reader, and calculating the enzyme activity according the standard curve and the dilution ratio of the crude enzyme. According to the invention, the goals of high throughput cultivation, high throughput preparation of crude enzyme and the high throughput test of the enzyme activity are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Quick counting method for microcystis aeruginosa
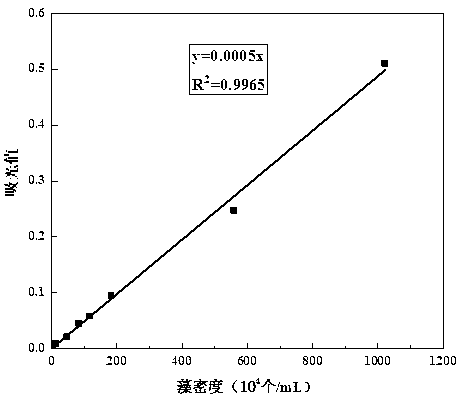
InactiveCN103276045ASignificant correlation coefficientThe pre-processing process is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPhysical chemistryMicrobiology
The invention discloses a quick counting method for microcystis aeruginosa. The quick counting method comprises the following steps of: measuring the absorbancy of microcystis aeruginosa with different concentrations at wavelength of 680nm through a microplate reader, accurately counting frustules through a microscope at the same time, creating a good linear relation between the absorbancy and cell density, and quickly counting the microcystis aeruginosa in a sample to be measured through an obtained correction curve or regression equation. The simple, safe, effective and quick quantifying method for microcystis aeruginosa provided by the invention overcomes the defects of lack of algae monitoring and counting measures and low monitoring and counting efficiency in China.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Method for detecting nitrite in blood
ActiveCN103760121AThe amount required for detection is smallImprove detection efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMatrix solutionHematological test
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting nitrite in blood. A porous plate and a microplate reader are used to measure the absorbancy of a colored complex formed by the nitrite and Griess, and the blood containing no nitrite is taken as a matrix solution for making a working curve, so that the interference of a blood matrix is eliminated, and the sensitivity and the accuracy of the detection are improved. The method has the characteristics of high accuracy, large detection sample capacity, small detected sample amount, high detection efficiency and the like.
Owner:云南健牛环境监测有限公司
Aspergillus galactomannan (GM) antigen immunodetection kit as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105866407ASensitive detectionIncreased sensitivityBiological material analysisColor depthCoincidence
The invention provides an Aspergillus galactomannan (GM) antigen immunoassay kit, comprising a solid phase carrier coated with GM antigen, an anti-GM antigen polyclonal antibody and a GM antigen standard product, the kit first GM antigen is coated on a solid phase carrier. During detection, the sample to be tested or GM antigen standard competes with the coated antigen for limited antibody binding sites, and then a color reaction occurs between the enzyme and the substrate, and the color depth of the measurement result It is negatively correlated with the concentration of the antigen to be tested. A standard curve can be drawn according to the GM antigen standard, and the concentration of the antigen to be tested can be calculated according to the standard curve equation. The kit has good sensitivity and specificity, the result coincides with the reference reagent in a high rate, and can provide more accurate and reliable test results. Its operation is simple and easy, and the detection is fast and sensitive. Inexpensive, the detection kit provides an effective tool for the quantitative detection of GM antigen.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Preparation and detection method of aflatoxin G1 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit
The invention discloses an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting aflatoxin G1 in peanuts, cereals and milk products. In the kit, based on a competitive ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method, ELISA plate micropores are coated with the aflatoxin G1 antigen. The detection comprises the following steps: adding a standard product or sample solution, an aflatoxin G1 antibody and an enzyme marker; competitively combining the coating antigen and the aflatoxin G1 added into the sample with the aflatoxin G1 antibody; washing off the uncombined antigen and antibody; further combining the combined antigen-antibody compound with the enzyme marker; washing off the uncombined antigen and antibody, and developing color through a TMB substrate; adding a reaction stop solution, and detecting with a 450 / 630nm dual-wavelength microplate reader, wherein the aflatoxin G1 concentration in the sample is inversely proportional to the absorption light intensity; and comparing with the standard curve and multiplying with corresponding dilution ratio to obtain the content of aflatoxin G1 in the sample.
Owner:JIANGSU WISE SCI & TECH DEV
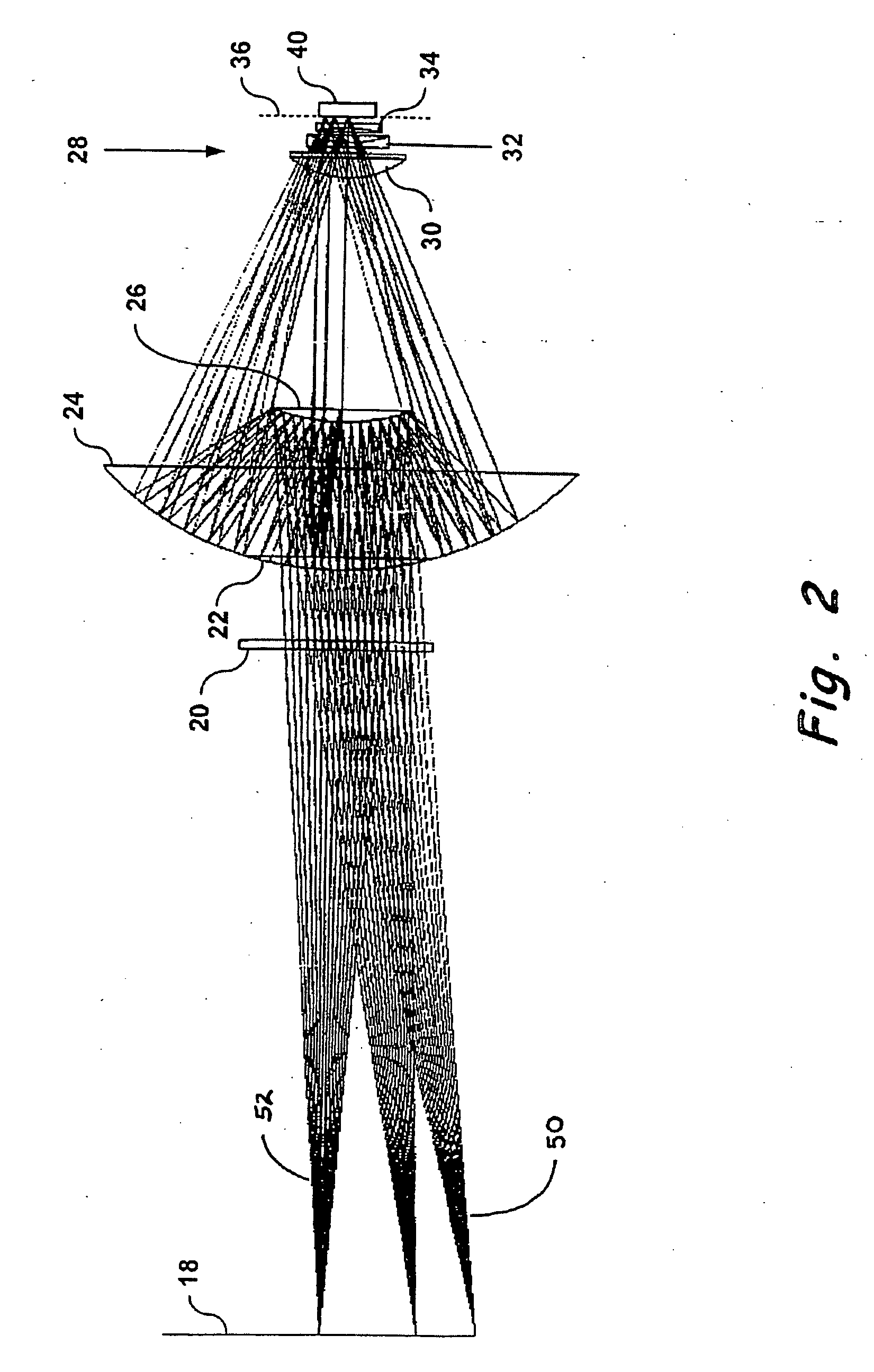
Optical system
InactiveUS20060119845A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce the numberRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFiberExcitation beam
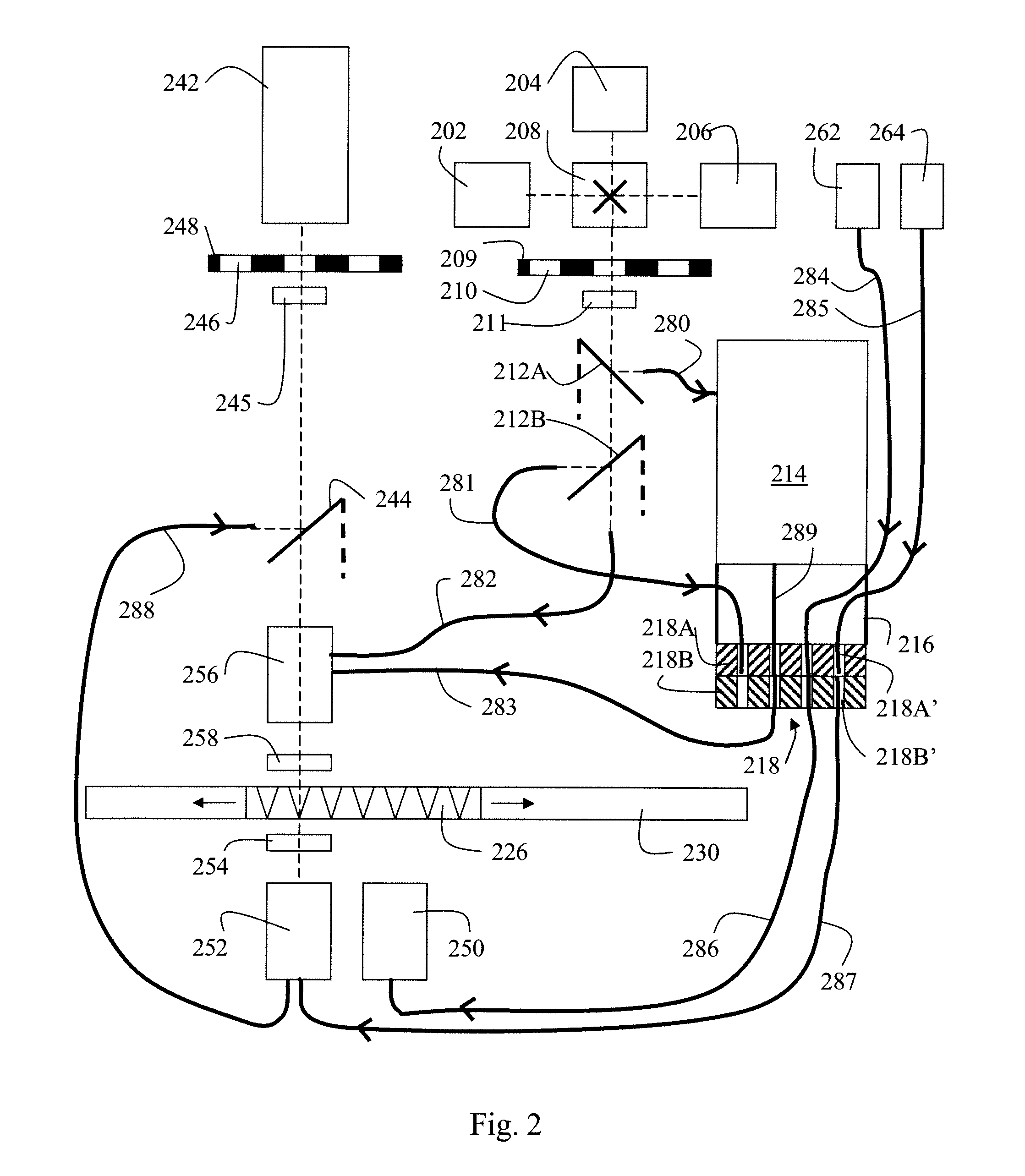
An optical system is provided for achieving enhanced rejection of scattered excitation light and superior signal-to-noise performance when reading microplate wells. The optical system uses an axial configuration in which the excitation beam incident upon the sample propagates along the axis of the microplate well. Excitation light from a light source, such as a lamp or fiber optic bundle, is collimated into a beam using a lens. A reflective pick-off mirror is then used to reflect the collimated excitation beam upward along the well axis. A focusing lens, with a diameter exceeding the diameter of the collimated excitation beam, is used to focus the excitation beam in the well. The same broad lens is used to collimate the emitted fluorescent light, of which a large percentage propagates axially past the pick-off mirror towards a second focusing lens that focuses the emission beam onto the face of a fiber optic bundle. The emitted light is later filtered and detected using at a position that is optically shielded from the aforementioned optical system. The optical system is incorporated into a microplate reader or automated assay instrument in order to provide a compact assembly for sensitive fluorescence measurements either above or below the microplate. The optical system further enables the simultaneous measurement of absorbance and fluorescence in a compact optical configuration.
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
Urease michaelis constant determination method
InactiveCN104697990ASimple test methodFast test methodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorEnzyme catalysisAbsorbance
The invention relates to a urease michaelis constant determination method, namely a urease-phenol red method, belonging to the technical field of biochemistry and application enzymology. The determination method provided by the invention is characterized in that a series of urea solutions with different concentrations act as a substrate, and phenol red acts as an indicating agent, urea is decomposed to generate ammonia under the action of urease michaelis, and pH value is increased; the color of a system becomes dark under the action of the phenol red indicating agent, the absorbancy is increased, and is determined by a spectrophotometer or a microplate reader. The enzymatic reaction velocity is in direct proportion to the increase of the absorbancy value, so that the reciprocal 1 / delta A of the absorbancy increase value can replace 1 / V in a linewaver-Burk equation 1 / V=Km / (Vmax[S])+1 / Vmax, and the reciprocal 1 / [S] of the concentration of the substrate urea is plotted; the intercept -1 / Km of a straight line on the X axis can be obtained via the linewaver-Burk equation, and the Km value is resolved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Validation plate for fluorescence polarization microplate readers
A polarization validation microplate for validating fluorescence polarization readers includes a microplate housing and one or more sealed fluorescence polarization samples in the housing positioned for reading by a fluorescence polarization reader.
Owner:HUDSON GORDON S
Application of echinacoside in anti-tumor medicaments
ActiveCN104288170AInhibitory activityBlock scavenging oxidationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMalachite greenCancer cell
The invention relates to application of echinacoside in anti-tumor medicaments. The application provided by the invention is as follows: firstly adding MTH1, inorganic pyrophosphatase and dGTP into a reaction solution (100mM pH 8.0 Tris-acetic acid, 40mM NaCl, 10mM magnesium acetate, 0.005% Tween 20 and 1mM DTT), incubating an enzyme and a substrate at room temperature for 1h, then adding 25 mu l of malachite green solution to terminate reaction and performing absorbance detection at 630nm by using an iMark microplate reader, wherein results show that echinacoside has a significant effect of inhibiting enzyme activity of MTH1; and secondly detecting the effects of echinacoside against tumor cells at the cellular level by an MTT experiment, wherein the results show that echinacoside can obviously inhibit the growth of SW480 colon cancer cells and U2OS human osteosarcoma cells. According to the application provided by the invention, echinacoside is used for inhibiting specific enzyme MTH1 for maintaining survival in the tumor cells, and oxidized nucleotide is mixed into DNA, thereby resulting in fatal DNA double-strand break in the cancer cells, producing an anti-tumor effect, finding a new medical use of echinacoside and laying a foundation for future development of the new anti-tumor medicaments.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for detecting SPA FC fragment bound mammalian blood serum total IgG by dolloidal gold marker protein A
A method for detecting total IgG combined with Fc fragment of Staphylococci protein A (SPA) in mammalian serum with colloidal gold-labeled protein A comprises the following steps of: 1) construction of a standard curve and calculation of regression equation for each batch of colloidal gold-labeled probe and micro-reaction by (1) setting 8 standard holes, adding 50MuL 0.01M TBS solution (pH 7.4, containing 0.1% calf serum) to each hole; (2) adding 50MuL standard IgG solution from the first hole to the sixth hole by doubling dilution, sucking out 50MuL TBS solution from the seventh hole, adding 50MuL standard IgG solution, and leaving the eighth hole as a blank control; (3) adding 50MuL colloidal gold-labeled probe diluted by 2-6 times in the reaction holes; (4) completely mixing the reaction plate, and reacting at room temperature for 20-40min; (5) detecting absorbance at 620nm with a microplate-reader for ELISA; and (6) calculating common logarithm of the absorbance associated with the standard IgG; and 2) sample detection by (1) adding 50MuL sample solution in the sample holes; (2) adding 50MuL diluted colloidal gold-labeled probe in the sample holes; (3) completely mixing the reaction plate, and reacting at room temperature for 20-40min; and (4) detecting absorbance of each hole at 620nm with the microplate-reader for ELISA, and calculating corresponding IgG values according to the regression equation of the standard curve.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sample Measurement System
ActiveUS20110049385A1Good optical performanceLow costRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFluorescenceMonochromator
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for optically analysing samples contained in sample sites of a sample holder by means of fluorescence. The apparatus comprises a first light source comprising a plurality of individual light sources having narrow wavelength bands, means for further limiting wavelength bands of the light emitted by the individual light sources, means for guiding the reduced-wavelength light to the sample sites of the sample holder, and a detector for detecting light from the sample sites. According to the invention said means for further reducing the wavelength bands emitted by the individual light sources comprise a wavelength-tunable single monochromator. The invention allows manufacturing of a microplate reader having the capability for fluorescence measurements at a continuous wavelength range, while maintaining the cost of the device at a reasonable level.
Owner:PEKINELMER SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Halomonas sp. capable of degrading phenols and high-throughput screening method and application thereof
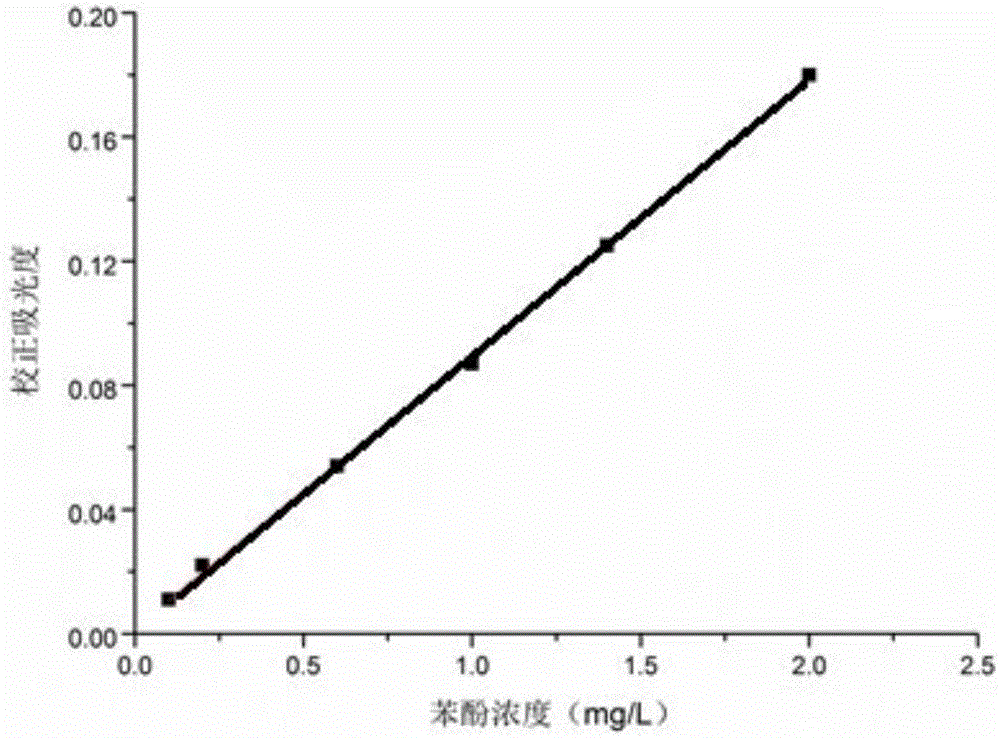
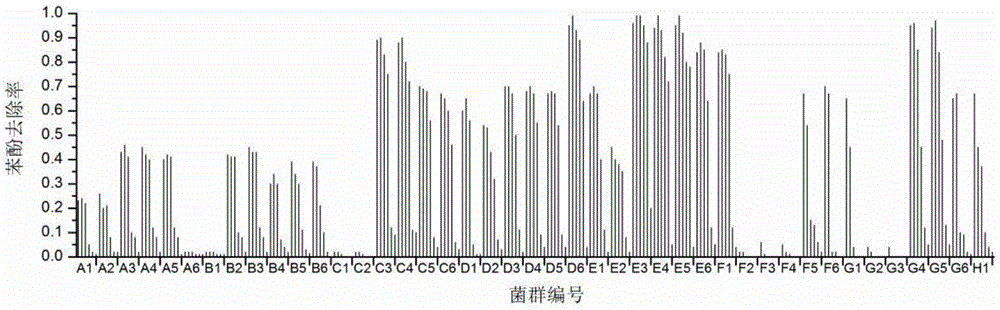
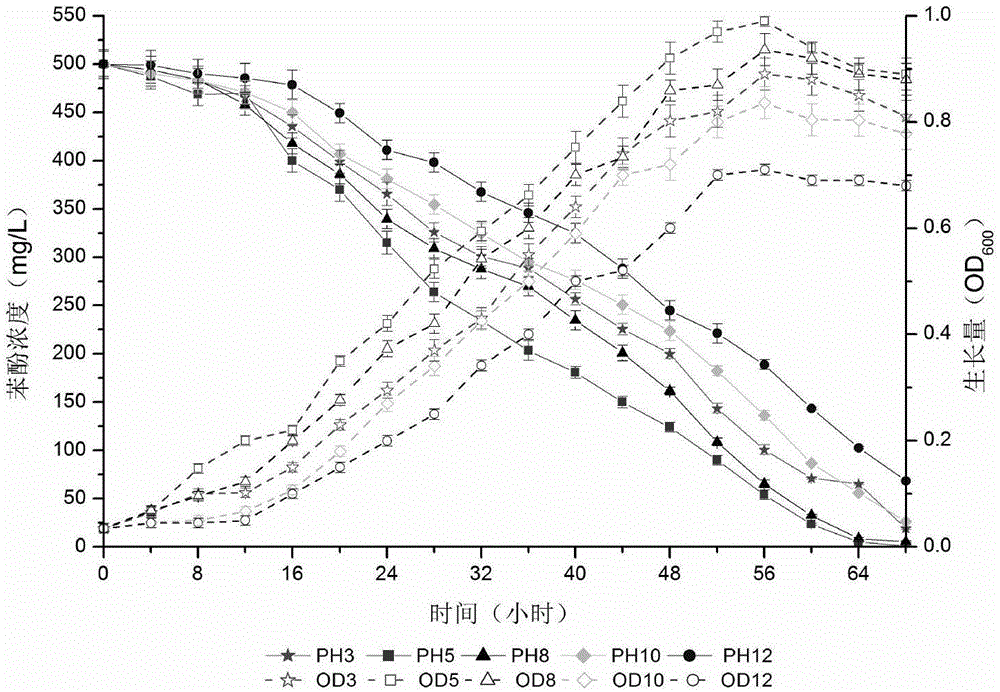
InactiveCN105087425ABacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhenol
The invention discloses Halomonas sp. capable of degrading phenols and a high-throughput screening method and application thereof. The Halomonas sp. PH4-5 is preserved under CGMCC 10666. A bacterial liquid is cultured with a 48-pore deep-pore board, phenol concentration is measured by 96-pore microplate reader plate spectrophotometry based on 4-amino antipyrine colorimetry, moderately halophilic bacteria efficient in degrading phenols are screened from 43 environmental samples contaminated by high salinity and organics, the Halomonas sp. is separated and verified from an optimal flora E3, and a salt tolerant degrading mechanism of the Halomonas sp. is studied. Studying results show that quick screening of environmental degrading bacteria provides methodological basis and also provides technical support for the treatment of high-salinity phenolic wastewater.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase
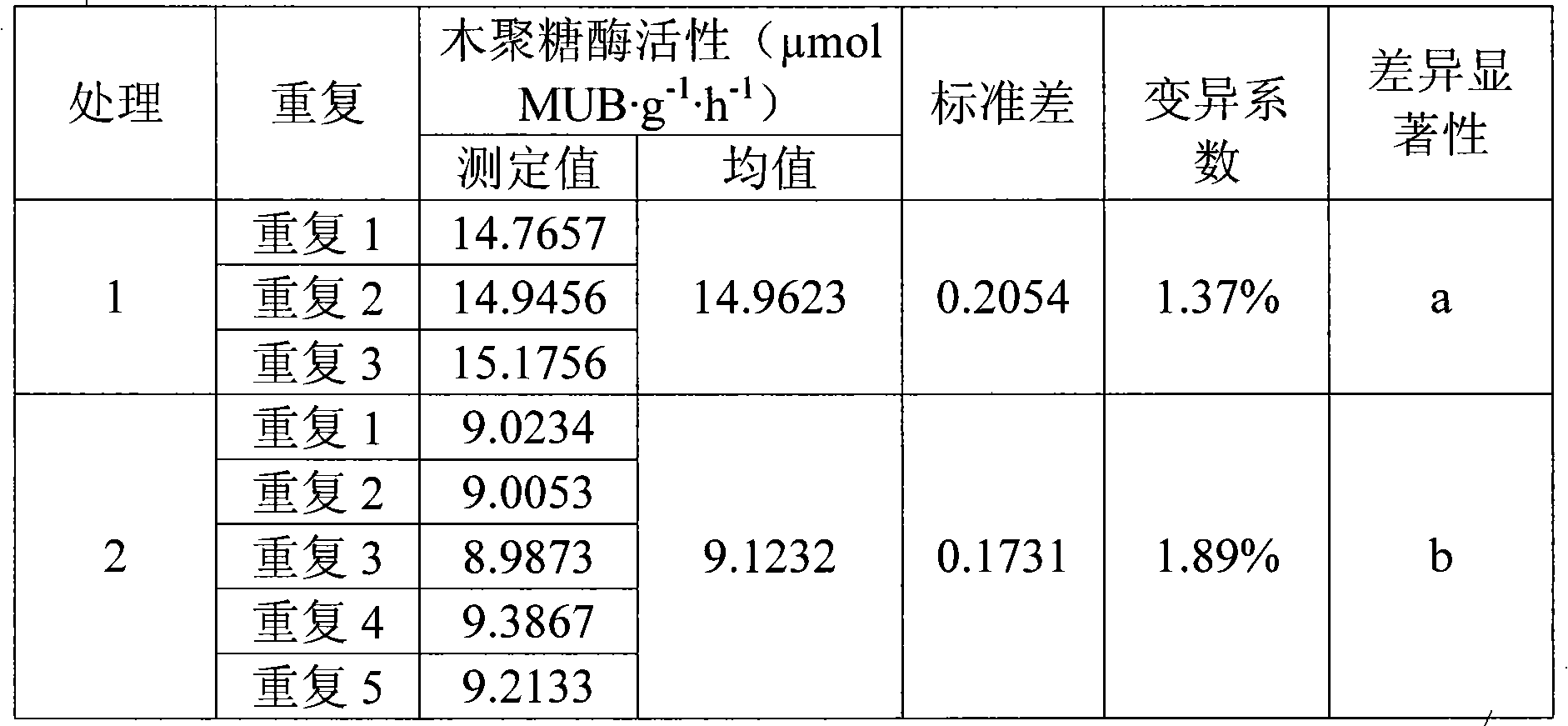
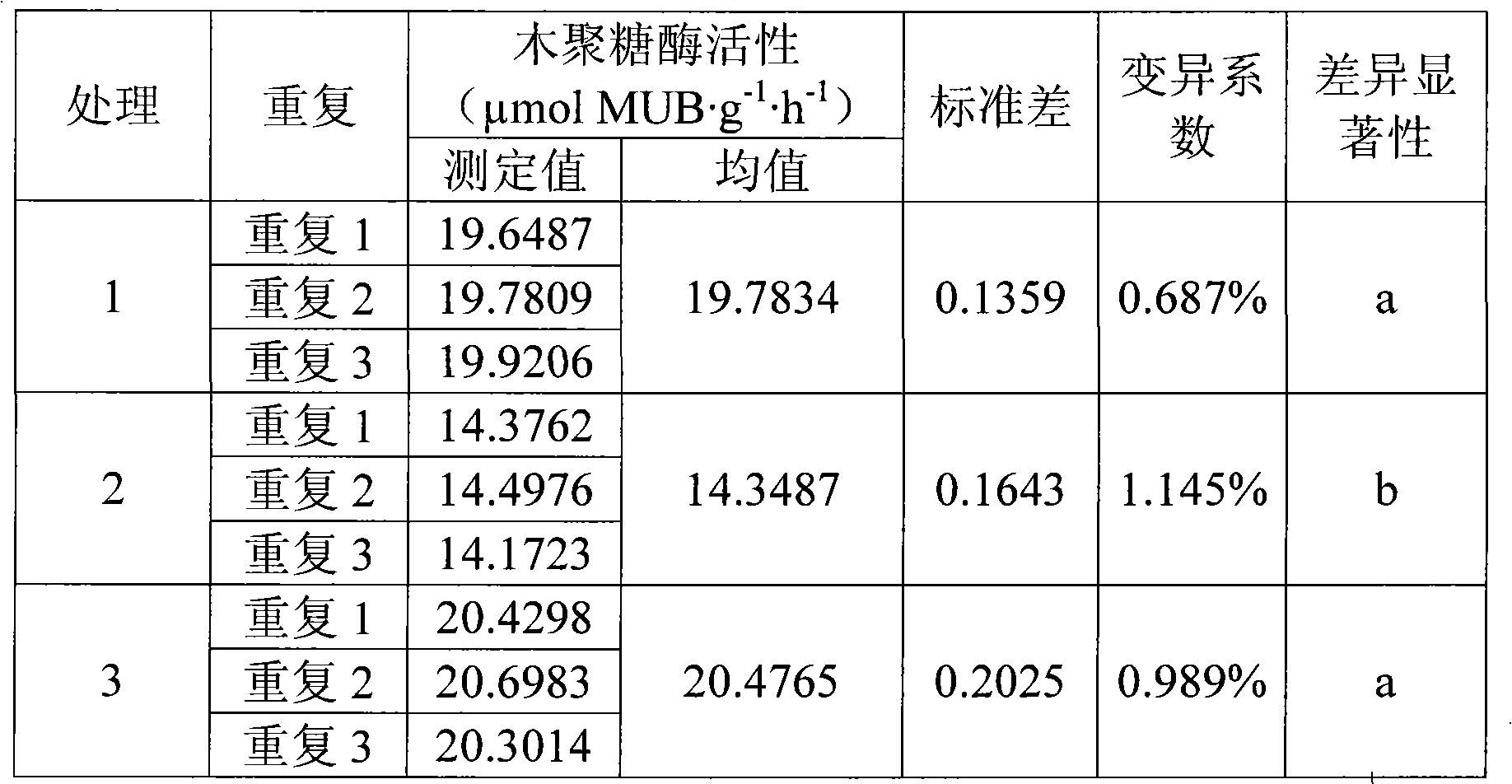
InactiveCN101586145AReduce incubation timeShort training timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationExoxylanase activity
The invention relates to an analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase, which comprises the following steps: firstly, weighting n sieved air dry soil samples into n thick test tubes, adding acetic acid buffer solution into each test tube, oscillating by a vortex oscillator, getting soil suspension into 96 micropore plates under the oscillation condition, adding 4-MUB-7-Beta-D-xyloside substrate solution into n-1 holes, and adding water with equal quantity into the other one hole so as to be used as non-substrate contrast, adding substrate solution with equal quantity and water with equal quantity into the (n+1)th hole so as to be used as soli-free contrast, oscillating and culturing under constant temperature; secondly, adding NaOH into the micropore plates to terminate the reaction after the culture is finished; thirdly, performing the fluorimetric determination to resultant of reaction by a multifunctional microplate reader; and fourthly, calculating the activity of the xylanase. Compared with the traditional method, the invention shortens the culture time, omits the operation procedures of filtration, and the like, and simplifies the operation steps; meanwhile, the determination data of fluorescent materials in the micropore plate can be obtained within 15s through the multifunctional microplate reader, huge samples are allowed to be simultaneously determined; and moreover, the invention has high accuracy and easy operation, stable and reliable result and good reproduction quality.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Drugs
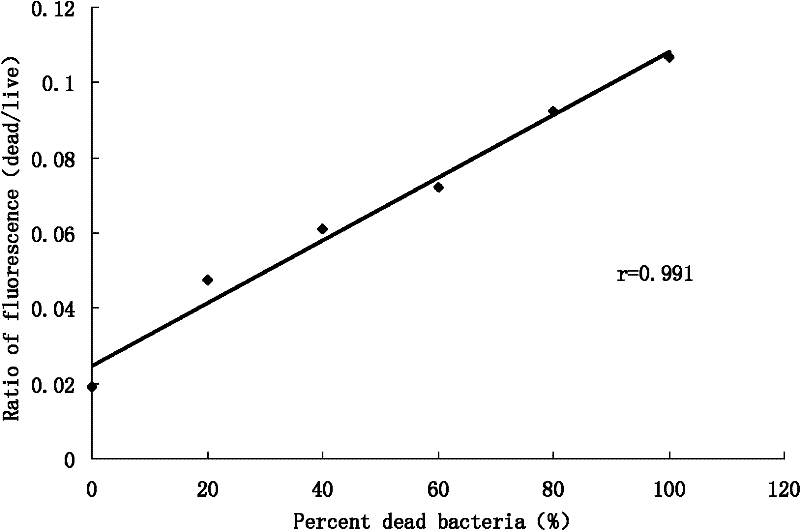
ActiveCN102288586AMIC value is accurateLow costFluorescence/phosphorescenceMinimum inhibitory concentrationConcentration gradient
The invention discloses a method capable of rapidly, simply, conveniently and quantitatively detecting minimal inhibitory concentration, and the method comprises the following steps of: in accordance with the standard of CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) (Version 2010), adding a fresh enterococcus suspension of a certain concentration into a sterile 96-well plate containing concentration gradient antibacterials for co-incubation; upon the ending of the 4-hour incubation, adding a fixed amount of fluorescent dyes SYTOX Green and DAPI (4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole) to all the wells, protecting the wells from light for 15 minutes at room temperature, reading the fluorescent intensity of the two dyes in the wells by use of a fluorescent microplate reader respectively; after relevant background fluorescence is deducted, drawing a corresponding curve between bacterial fluorescence intensity ratio (Pdead / livel) and concentration of drug (CDrug), and determining the minimal concentration of drug corresponding to the moment the Pdead / livel is no longer fluctuated as the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) of the antibiotic to the bacterium. The detection method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being simple, convenient, rapid and objective and being capable of performing mathematic statistics and analysis directly on detected data, becomes a new detection method for determining the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibacterials, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
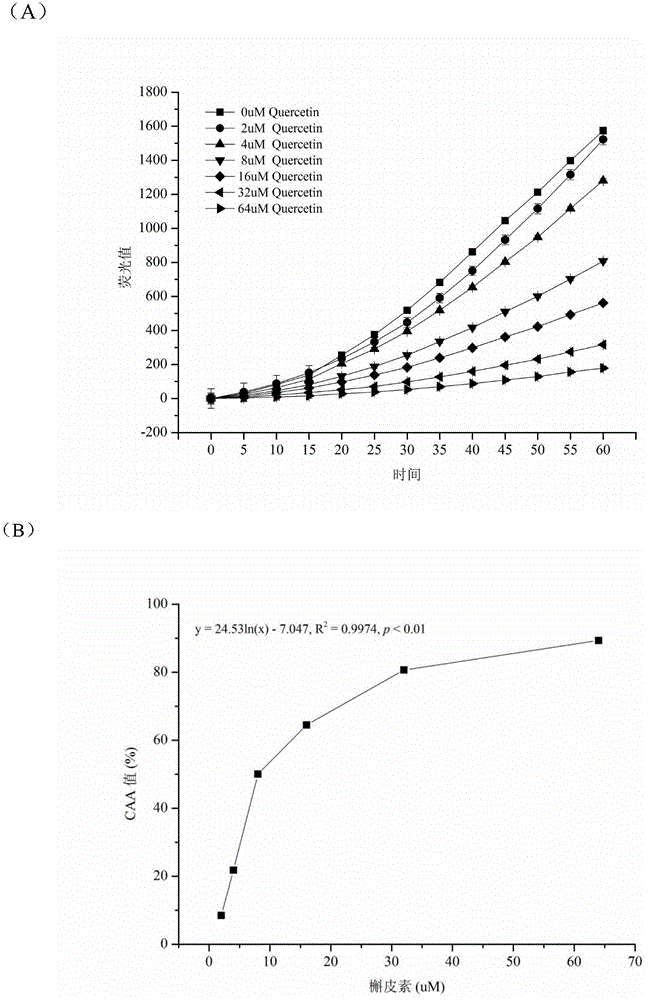
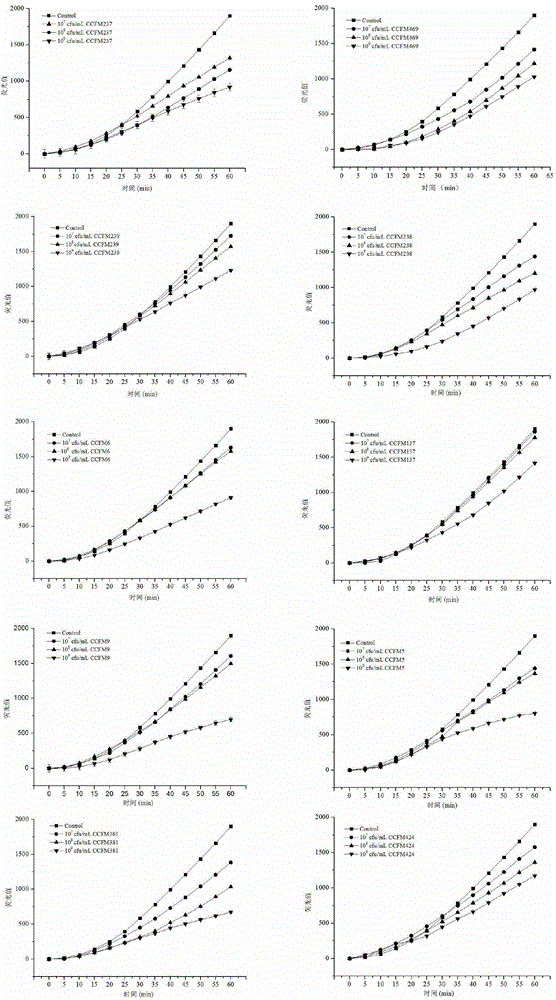
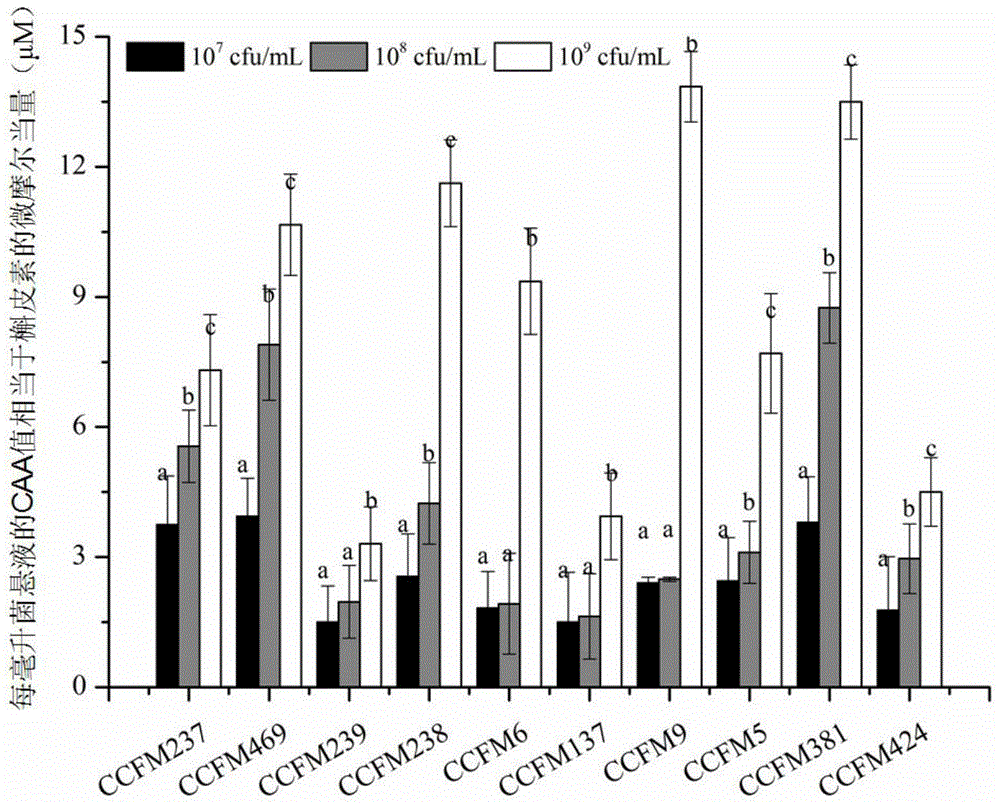
Method for measuring antioxidant activity of lactic acid bacteria based on cellular level
The invention discloses a method for measuring the antioxidant activity of lactic acid bacteria based on a cellular level and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. According to the method, a full-wave fluorescent scanning type microplate reader with a 96-hole ferment plate based on the cellular level is utilized to replace a conventional spectrophotometer so as to measure the antioxidant capability of a treated sample; a fluorescent probe and a free-radical initiator are utilized to perform batched rapid and accurate measurement on lactic acid bacteria within 1 hour, so that a rapid detection method is provided for researching the antioxidant activity of the lactic acid bacteria at the cellular level; by utilizing the method, the antioxidant activity of the different strains of lactic acid bacteria can be measured within ultrashort time, and the antioxidant level of the lactic acid bacteria can be rapidly and accurately reflected.
Owner:YANGZHOU YANGDA KANGYUAN DAIRY +1
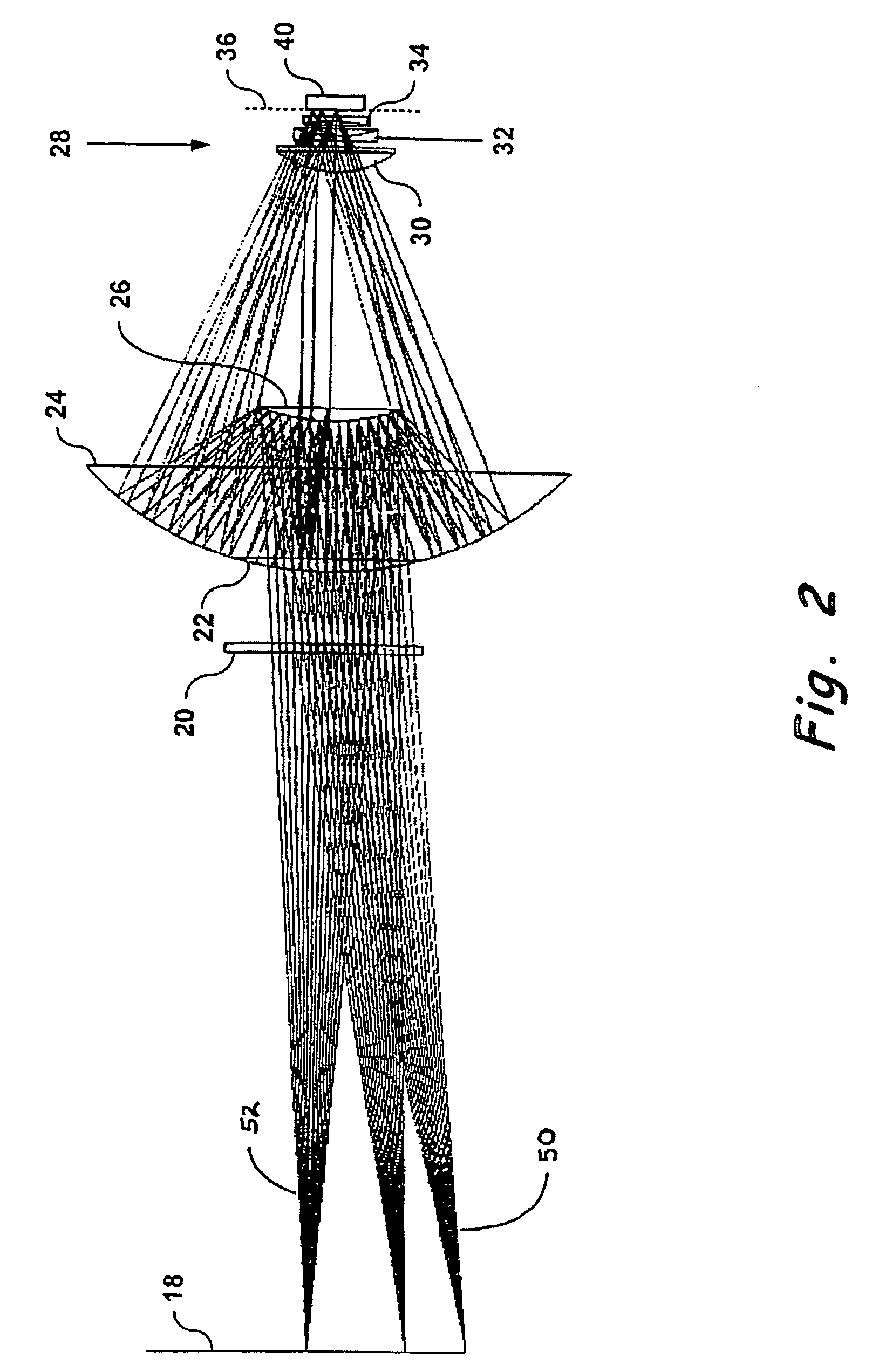
Reflective optic system for imaging microplate readers
InactiveUS7265829B2Wide field of viewRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationCamera lensOptoelectronics
A reflective light imaging system for use in high-throughput screening of samples disposed in multiple-well plates. The system can include a set of mirrors and lenses. The first mirror has a central aperture through which light from the object passes. The first mirror has a concave reflective surface that faces the image plane. The next element is a second mirror with a convex reflective surface. The system can include an aberration corrective system positioned between the second mirror and the image plane, and an optical sensor near the image plane. Light from an object passes through the central aperture of the first mirror and is reflected off the convex surface of the second mirror. The light then strikes the reflective surface of the first mirror. The light from the first mirror is then collected by the aberration correction system and transmitted toward the image plane.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
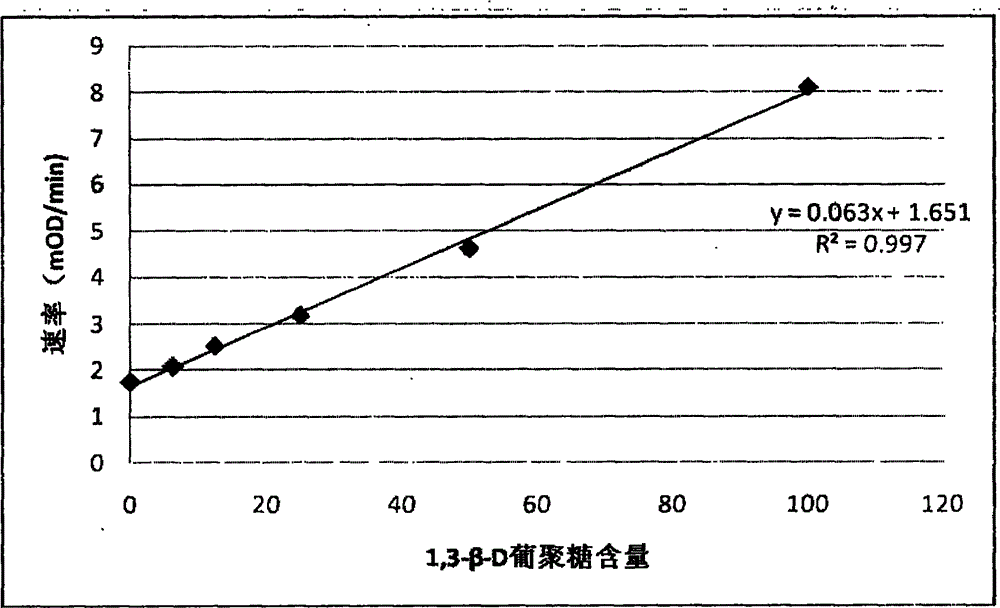
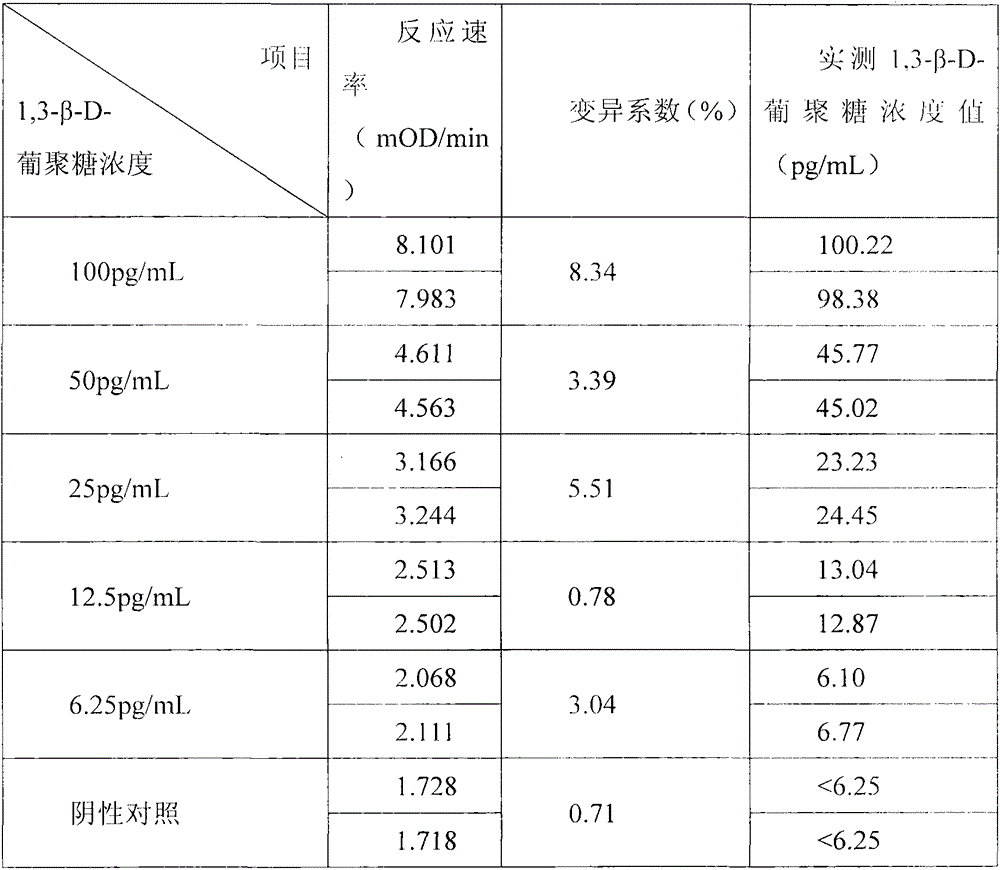
Developing-process fungus 1,3-beta-D-glucan detection kit for human body fluid
ActiveCN105021817AReduce false positive rateLess susceptible to interferenceColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingZymogenEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a developing-process fungus 1,3-beta-D-glucan detection kit for human body fluid. The developing-process fungus 1,3-beta-D-glucan detection kit comprises a reaction main agent, a main agent compound solution, a sample treatment solution, heat-source-free water, a standard product and a quality control product, wherein the reaction main agent takes horseshoe crab blood cells as a main raw material and contains G factors, coagulase, coagulase zymogen and a polypeptide developing substrate; the polypeptide developing substrate is synthesized tripeptide or tetrapeptide with a Gly-Arg tail end connected with a PNA; the polypeptide developing substrate is subjected to enzyme digestion by adopting the coagulase; after the free paranitroaniline (PNA) is generated, a microplate reader is used for directly detecting so that a detection route is shortened and the cost is reduced; the microplate reader is used for carrying out a velocity-method enzyme kinetics detection method so that the sensitivity is relatively high when being compared with a nephelometry detection method; and the reaction main agent is not easily interfered by protein in a body fluid sample and medicines to generate non-specific turbidity, so that the probability of a false positive detection result is reduced and the detection accuracy is relatively high.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Method for detecting enzymatic activity of phospholipid-depending factor X activator
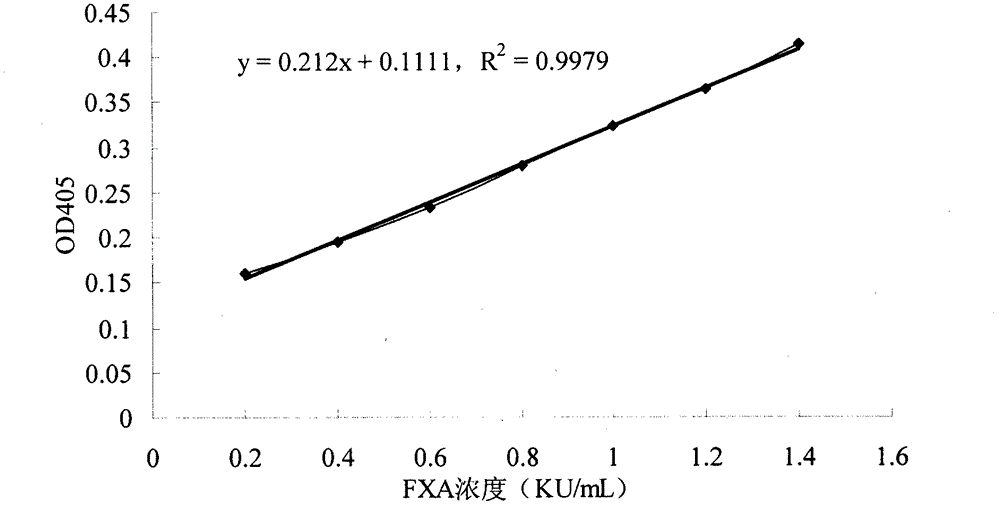
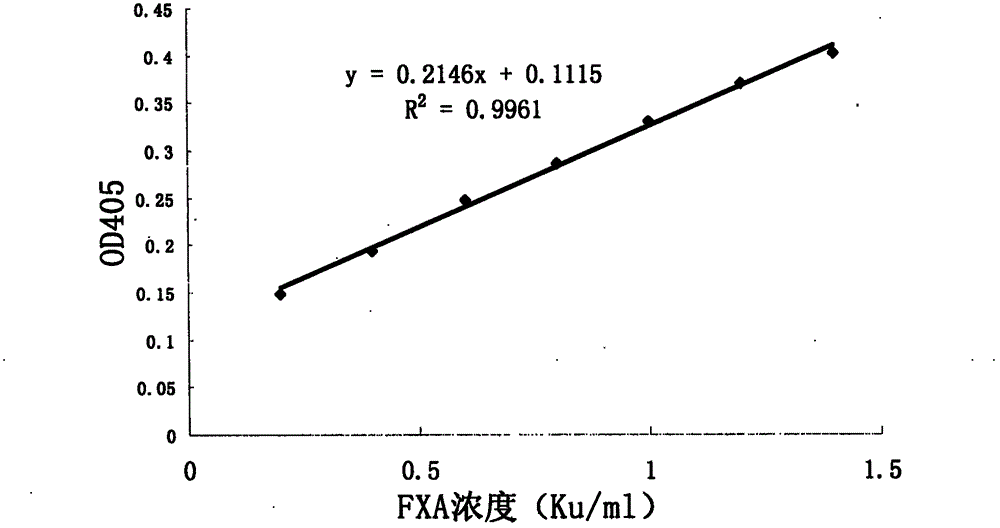
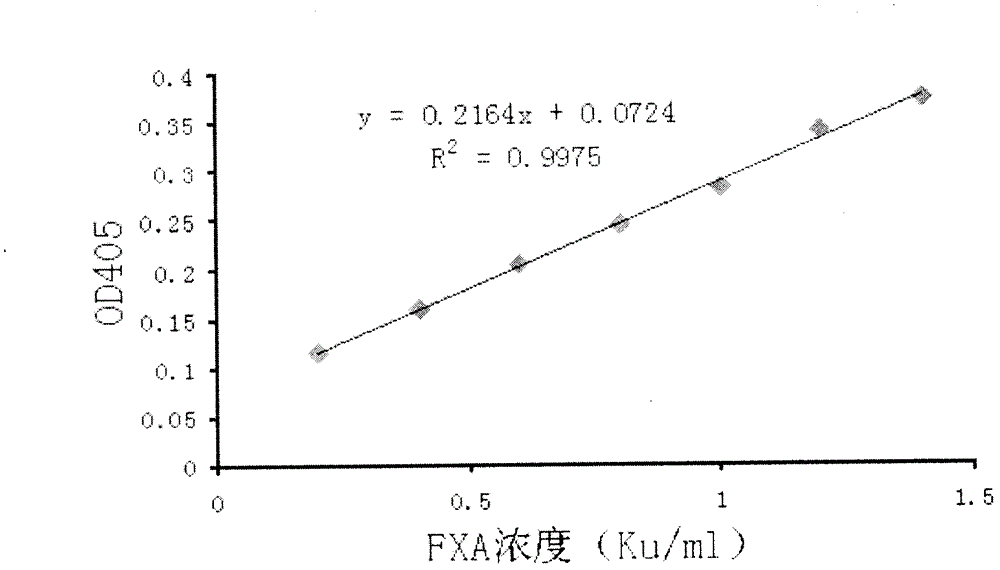
InactiveCN102798598AShorten read timeSmall system volumeMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsQuality controlChromogenic substrate assay
The invention discloses a method for quickly and specifically detecting the enzymatic activity of a phospholipid-depending factor X activator. A chromogenic substrate assay is adopted, a microplate reader is used, a linear reaction curve is obtained in a certain reaction time and a certain-activity standard substance range, a linear relation between a light absorption value of a product and the concentration of the phospholipid-depending factor X activator is established, and the corresponding enzymatic activity of a sample is calculated. In addition, the recovery rate and accuracy of the standard curve are carefully researched. The method is high in accuracy, simple in steps and convenient to impellent in a laboratory, and is suitable for quality control of X activator raw materials and hemocoagulase preparations.
Owner:ZHAOKE PHARMA HEFEI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com