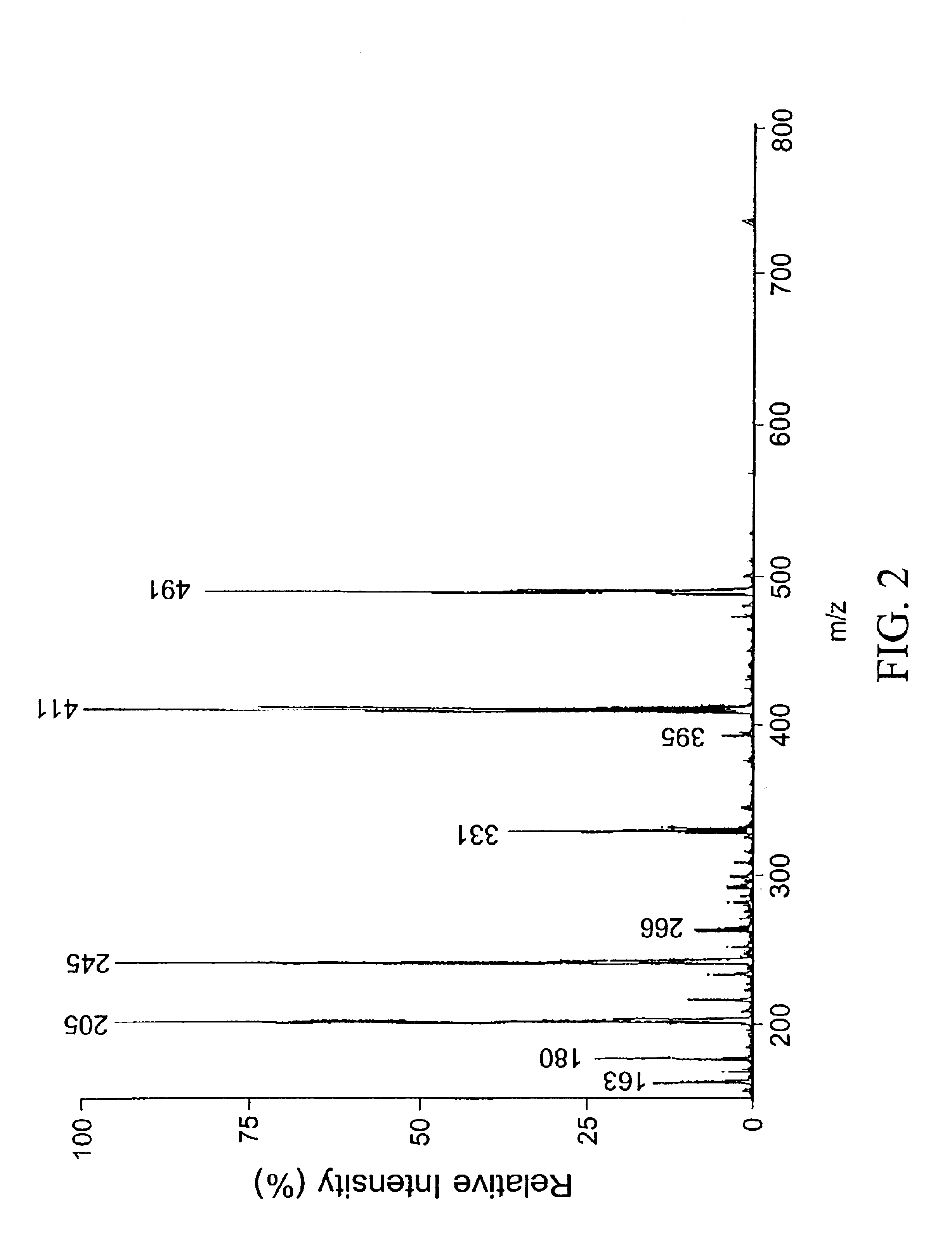
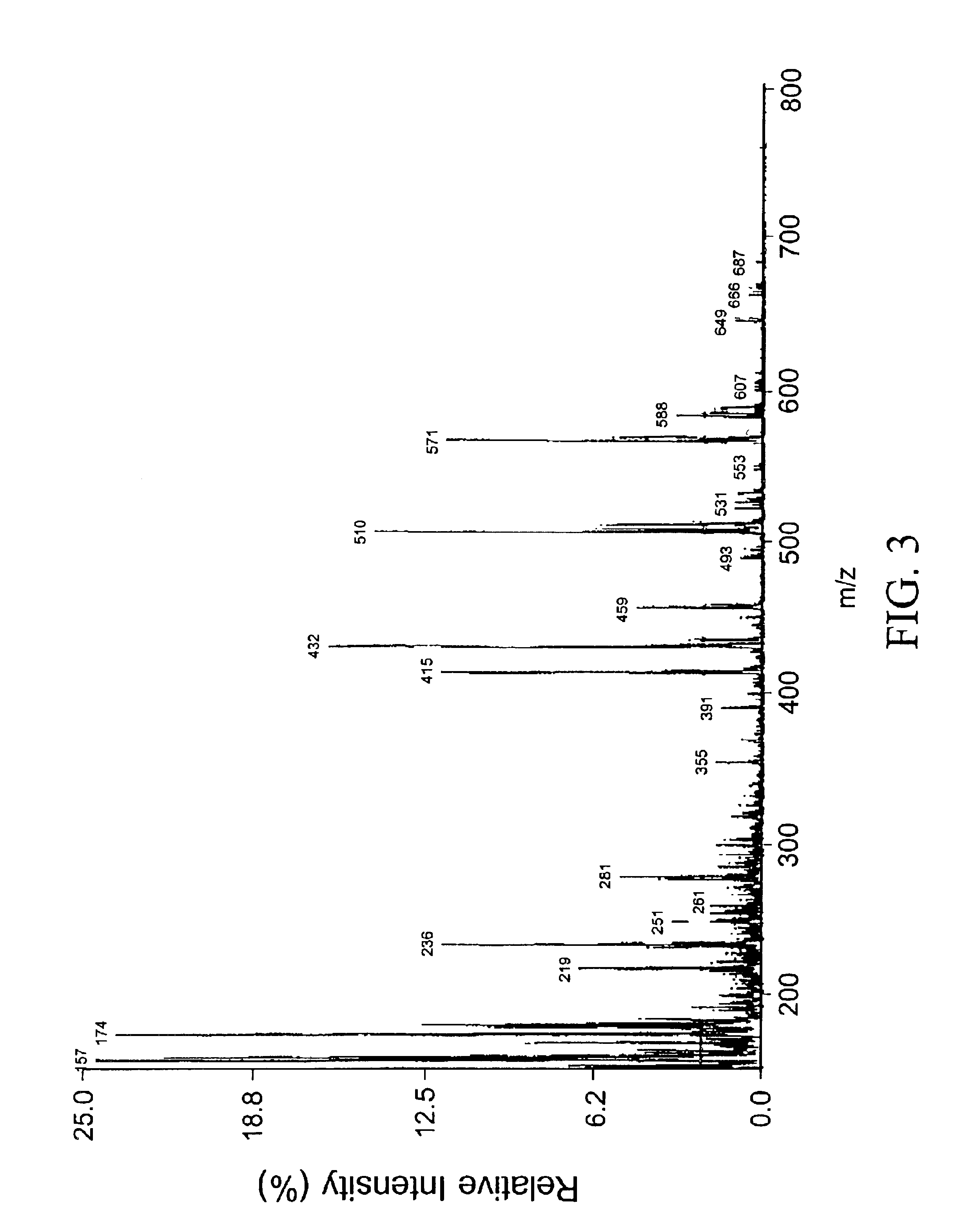
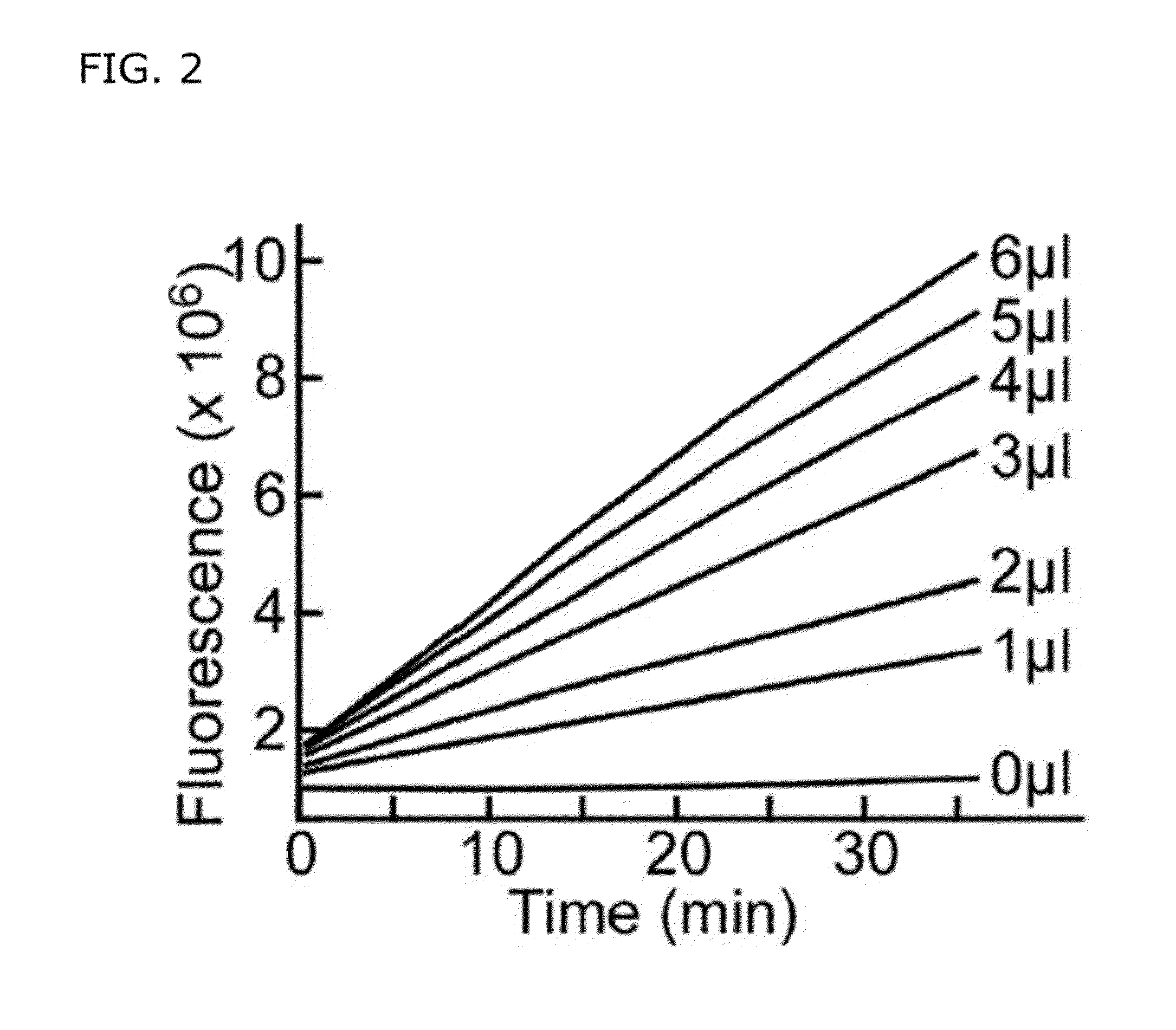
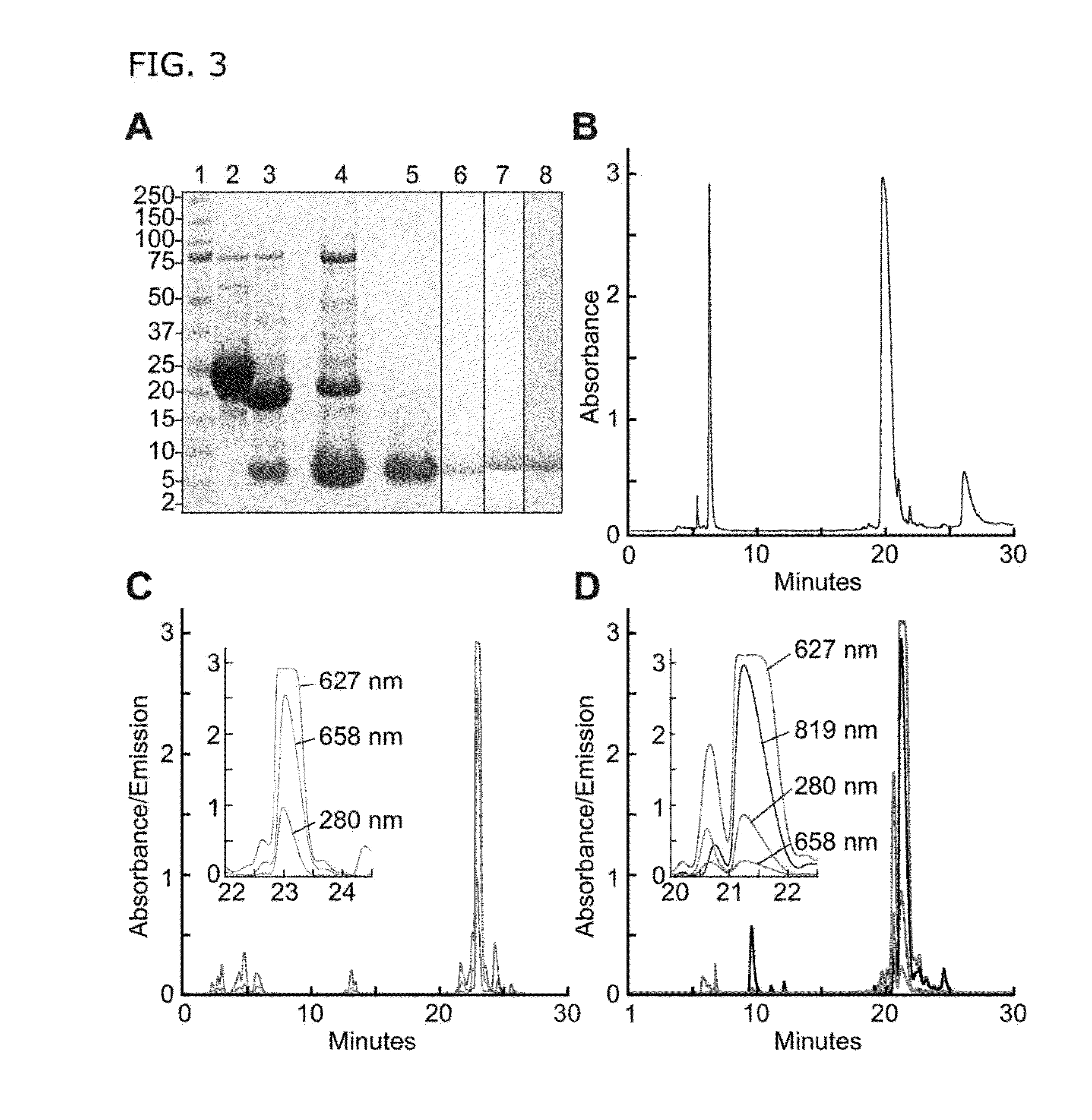
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Fluorogenic Substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorogenic substrate. [′flu̇r·ə‚jen·ik ′səb‚strāt] (chemistry) A nonfluorescent material that is acted upon by an enzyme to produce a fluorescent compound.
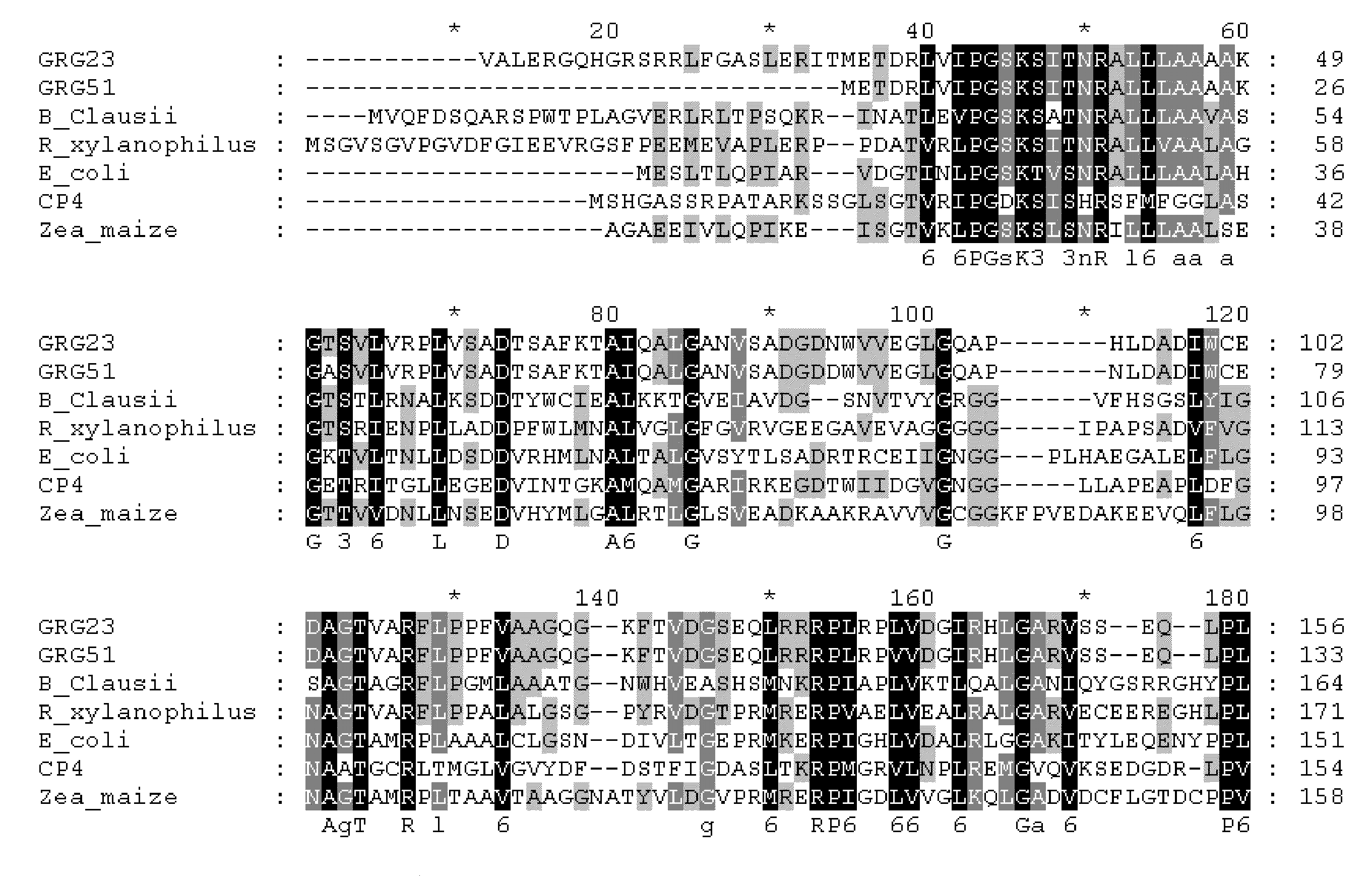
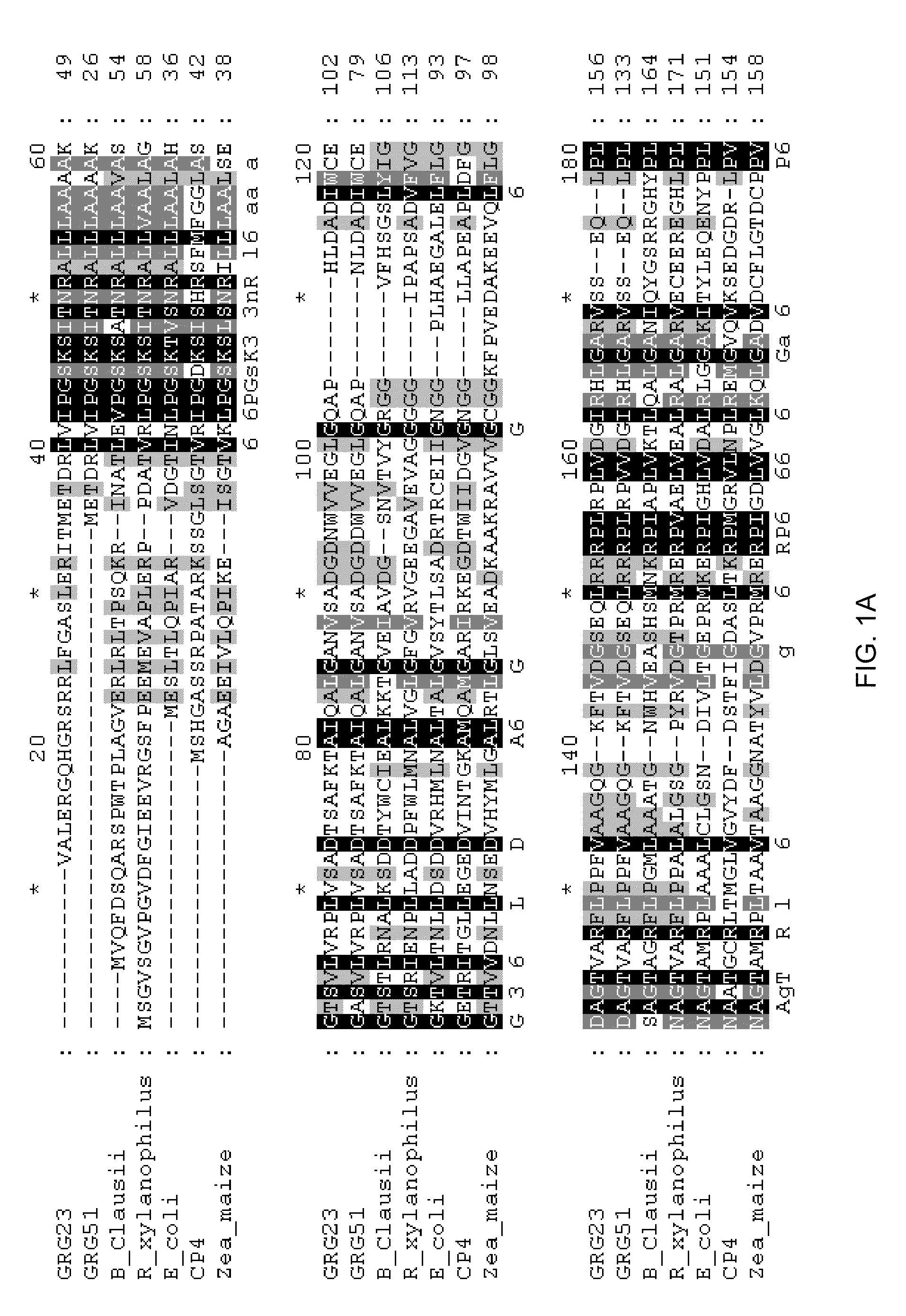
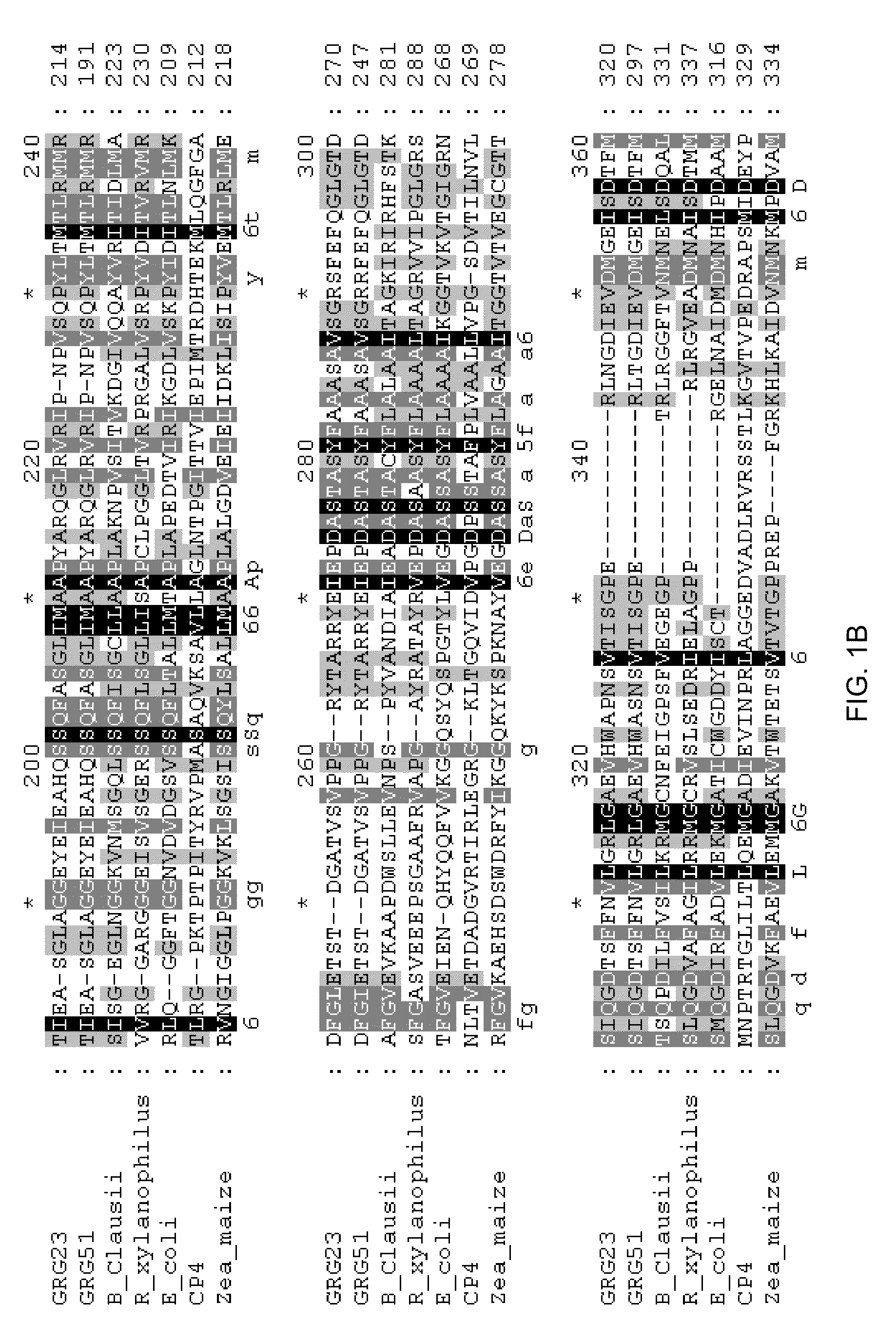
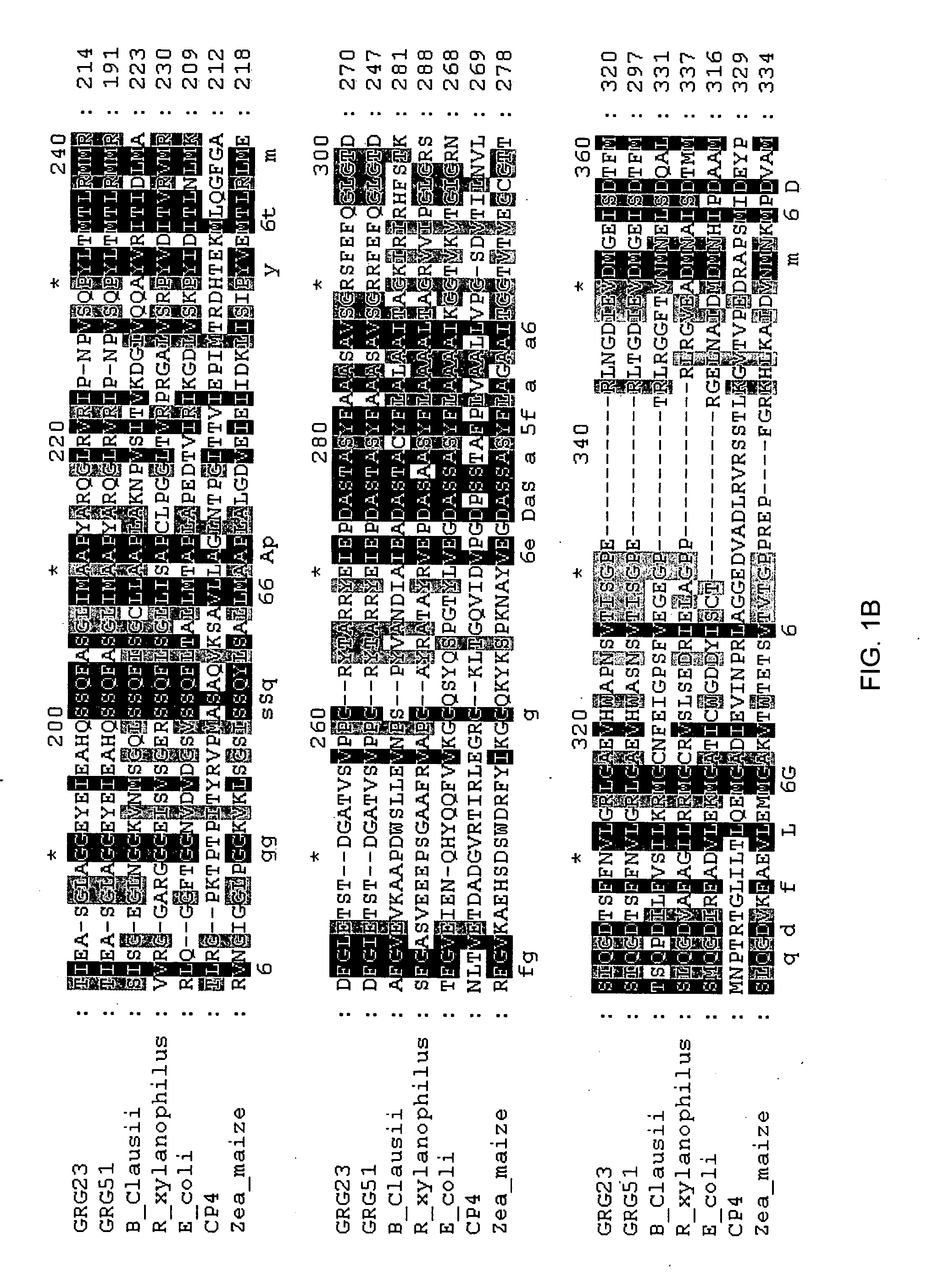
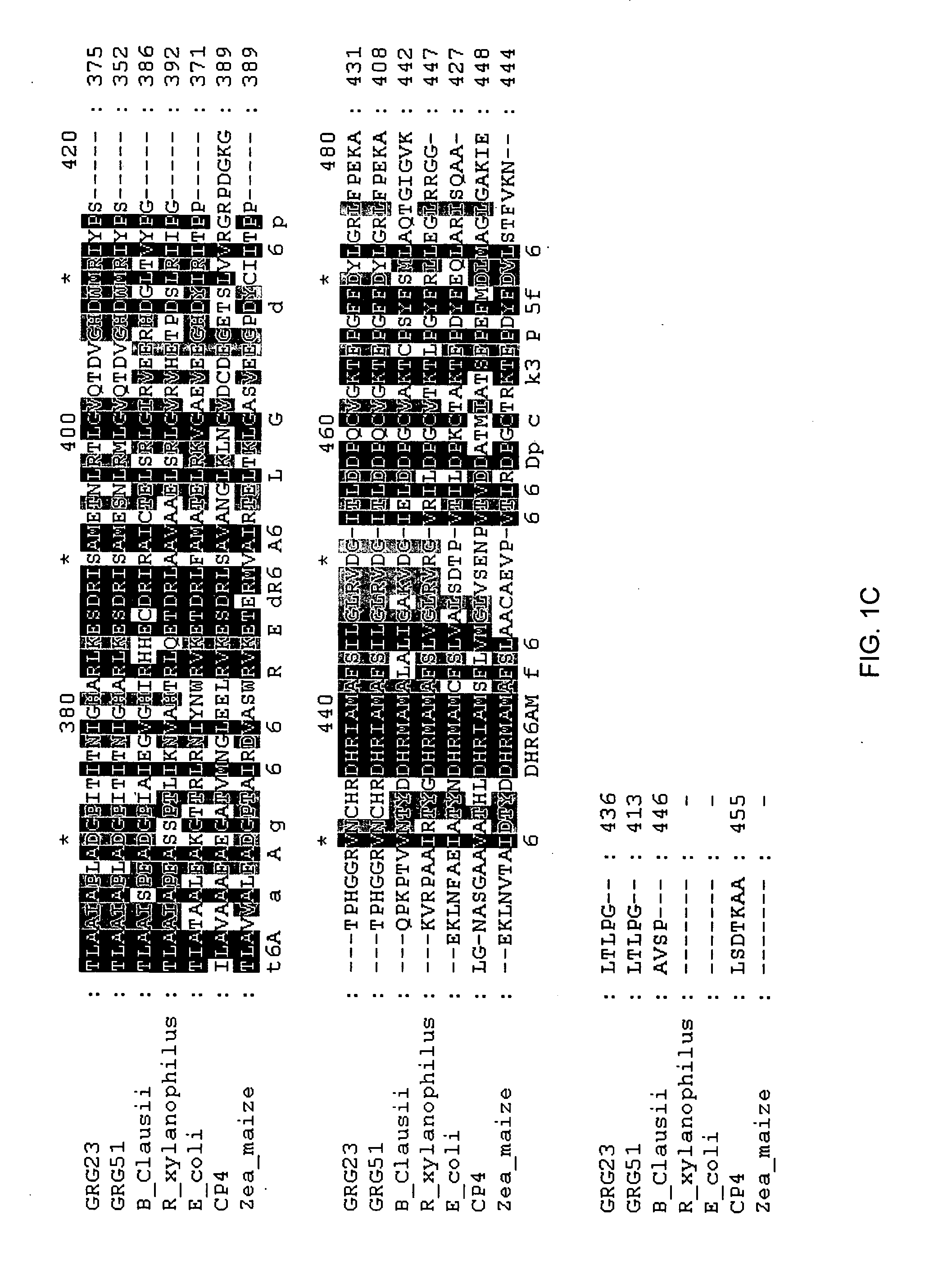
Grg23 and grg51 genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, or 6, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, or 5. The present invention additionally provides a method to measure enzyme kinetic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
GRG23 and GRG 51 genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, or 6, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, or 5. The present invention additionally provides a method to measure enzyme kinetic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
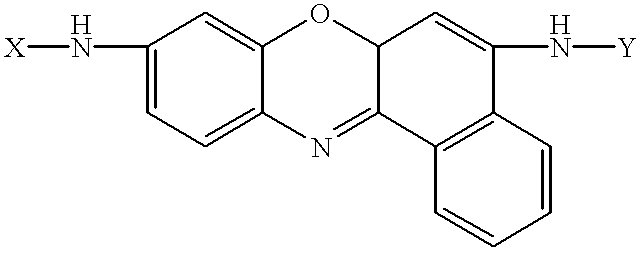
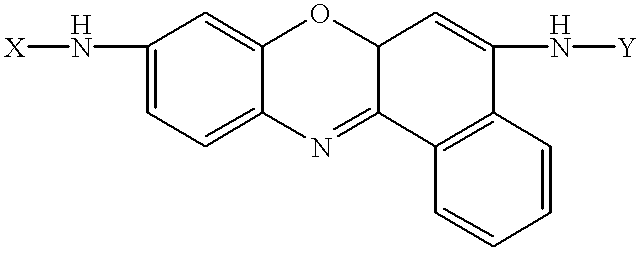
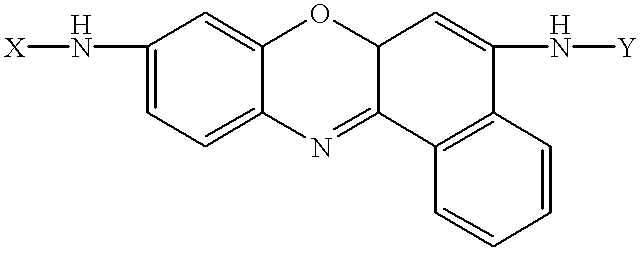
Amino acid substituted-cresyl violet, synthetic fluorogenic substrates for the analysis of agents in individual in vivo cells or tissue
InactiveUS6235493B1Organic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAmino acid substitutionTissue sample
The present invention concerns a method to detect the presence of an enzyme in in vivo or in vitro tissue or cell, which method comprises:(a) obtaining a tissue or cell sample to be analyzed;(b) contacting the tissue or cell sample with a substrate of the structure selected from the group consisting of:X=H or one or more natural or synthetic amino acids with or without amino blocking groups,Y=H or one or more natural or synthetic amino acids with or without amino blocking groups,wherein X and Y are the same or different and are amino acid sequences of between about 1 to 1,000,000 amino acids wherein each amino acid is the same or a different amino acid, with the proviso that at least one of X or Y is at least one amino acid;(c) when an enzyme is present in the tissue or cell sample which degrades X, Y and combinations thereof, fluorescent cresyl violet is released in the tissue sample producing a color change;(d) detecting the presence and amount of the enzyme present by the detection and quantification of the fluorescence produced; and(e) optionally comparing the fluorescence to a pre-calibrated fluorescence scale to quantify the fluorescence present. A diagnostic kit for use and a method to prepare amino acid cresyl violet derivatives are described.
Owner:MP BIOMEDICALS
Automated hybridization/imaging device for fluorescent multiplex DNA sequencing
InactiveUS20020012910A1Easy to disassembleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSludge treatmentHybridization probeSize fractionated
A method is disclosed for automated multiplex sequencing of DNA with an integrated automated imaging hybridization chamber system. This system comprises an hybridization chamber device for mounting a membrane containing size-fractionated multiplex sequencing reaction products, apparatus for fluid delivery to the chamber device, imaging apparatus for light delivery to the membrane and image recording of fluorescence emanating from the membrane while in the chamber device, and programmable controller apparatus for controlling operation of the system. The multiplex reaction products are hybridized with a probe, then an enzyme (such as alkaline phosphatase) is bound to a binding moiety on the probe, and a fluorogenic substrate (such as a benzothiazole derivative) is introduced into the chamber device by the fluid delivery apparatus. The enzyme converts the fluorogenic substrate into a fluorescent product which, when illuminated in the chamber device with a beam of light from the imaging apparatus, excites fluorescence of the fluorescent product to produce a pattern of hybridization. The pattern of hybridization is imaged by a CCD camera component of the imaging apparatus to obtain a series of digital signals. These signals are converted by the controller apparatus into a string of nucleotides corresponding to the nucleotide sequence an automated sequence reader. The method and apparatus are also applicable to other membrane-based applications such as colony and plaque hybridization and Southern, Northern, and Western blots.
Owner:WEISS ROBERT B +6
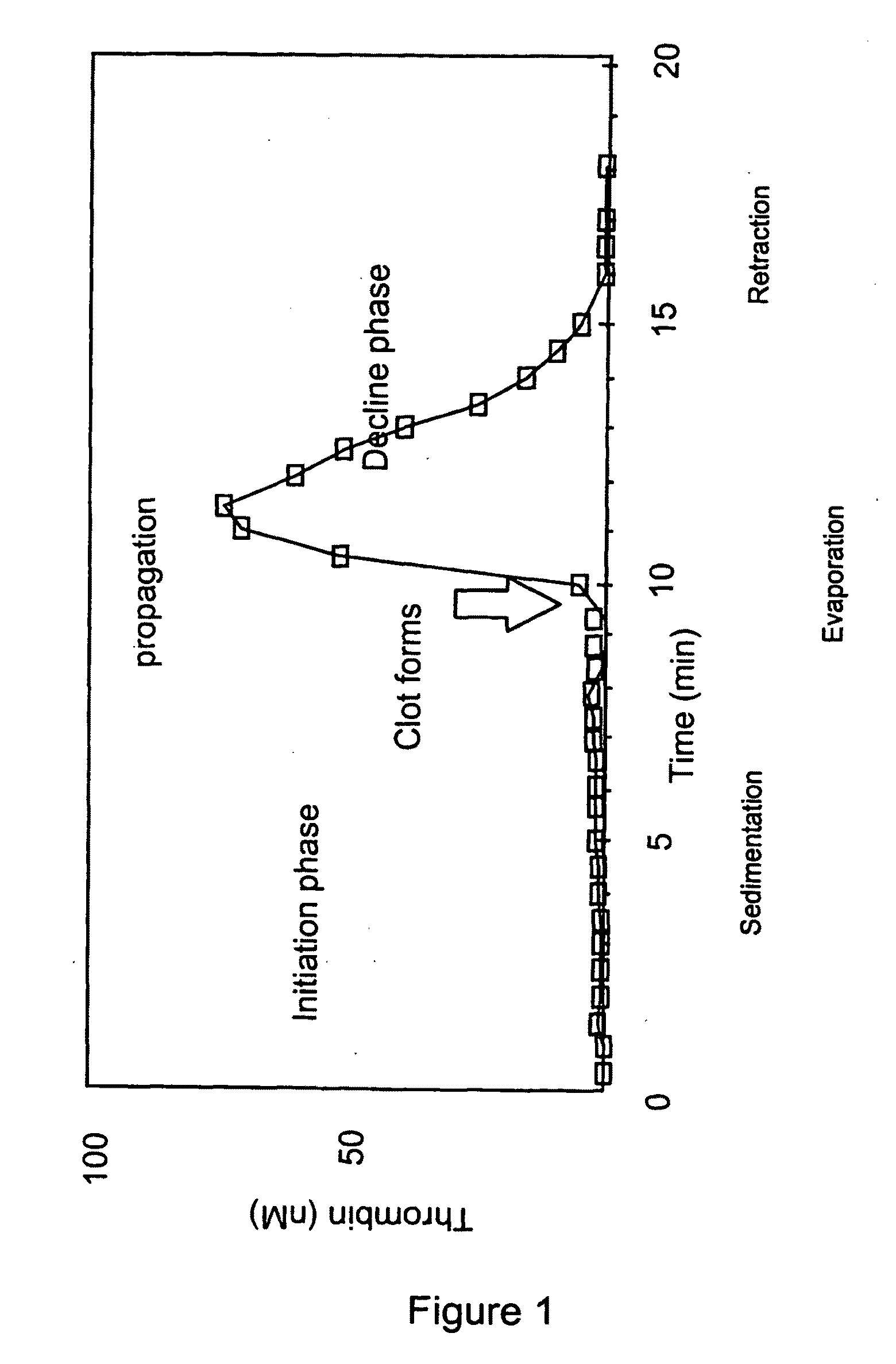
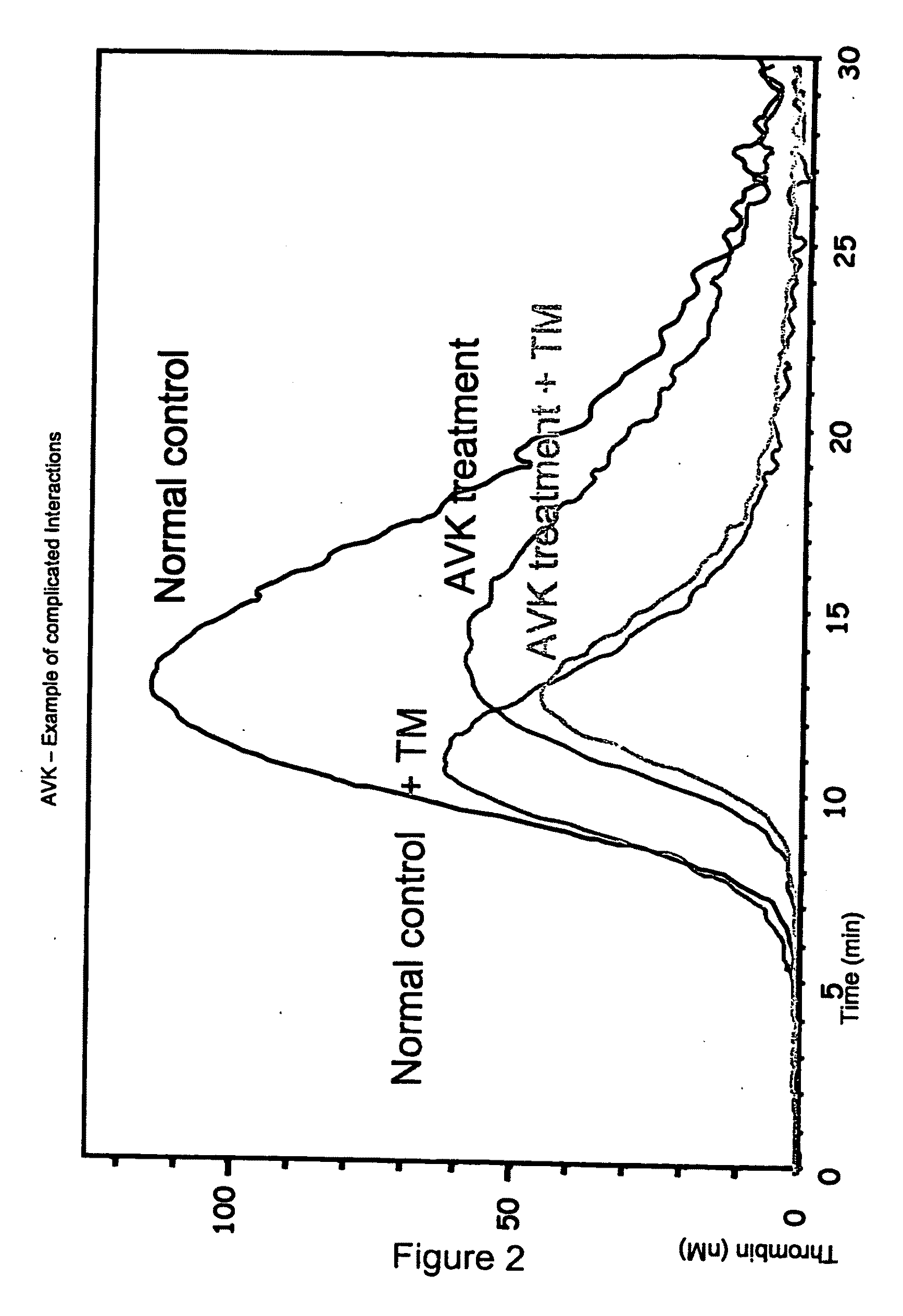
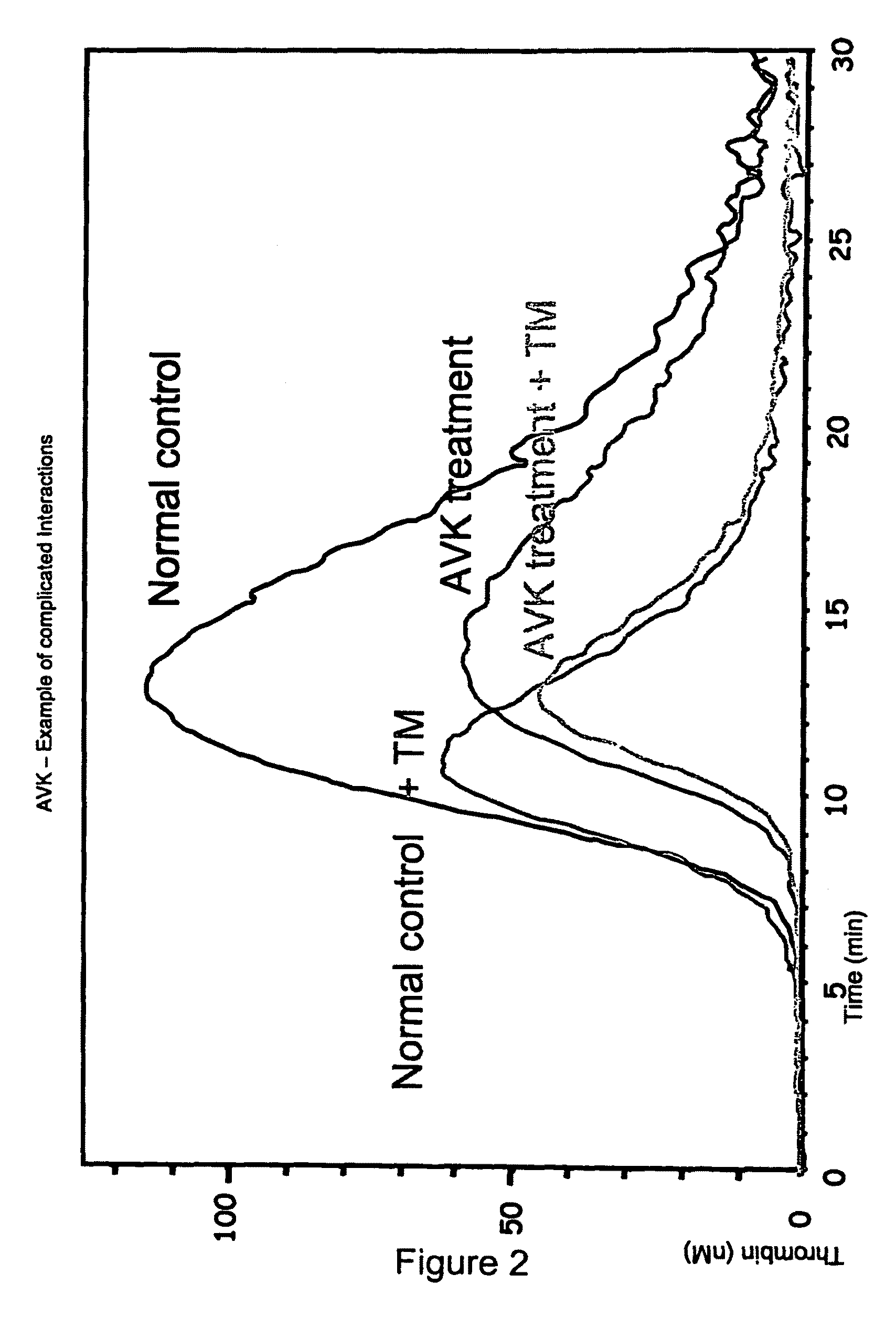
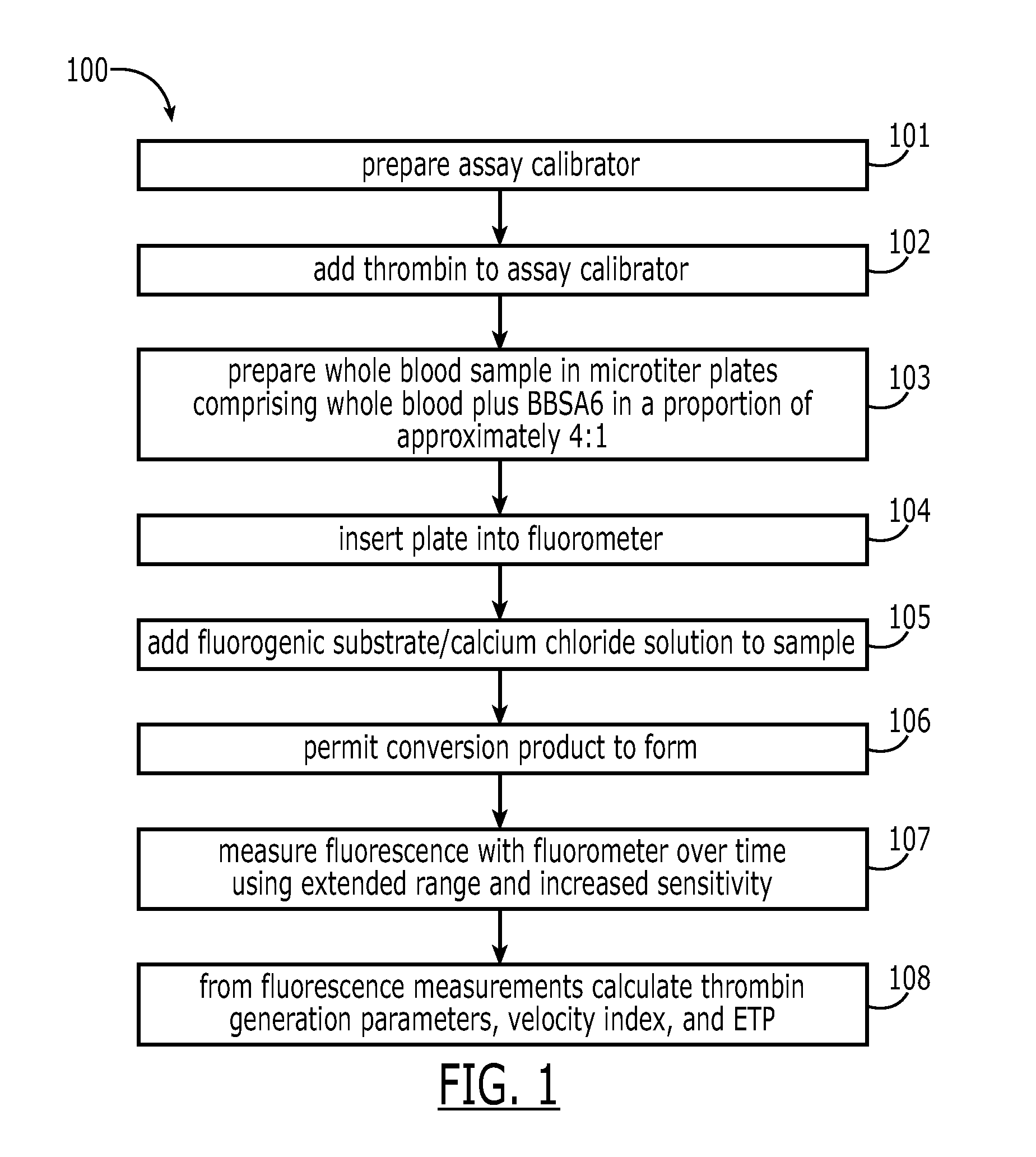
Measuring thrombin activity in whole blood
ActiveUS20090311730A1Increase the areaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisThrombin activityThrombin generation
The invention relates to a method for in vitro determining thrombin activity in a sample wherein the sample is a blood sample and thrombin generation is measured by the steps of: —contacting a layer of said sample with a fluorogenic substrate of thrombin, wherein said layer has a thickness within a range of 0.05 to 5 mm and a surface within a range of 10 to 500 mm2; —allowing thrombin to generate in said sample; —measuring the fluorescence emitted from the surface of the layer, by the fluorescent group released from the fluorogenic substrate as a result of enzymatic action of generated thrombin on said fluorogenic substrate.
Owner:SYNAPSE INC
Device and Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Multiple Groups of Microorganisms
ActiveUS20080113404A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsUltravioletFluorogenic Substrate
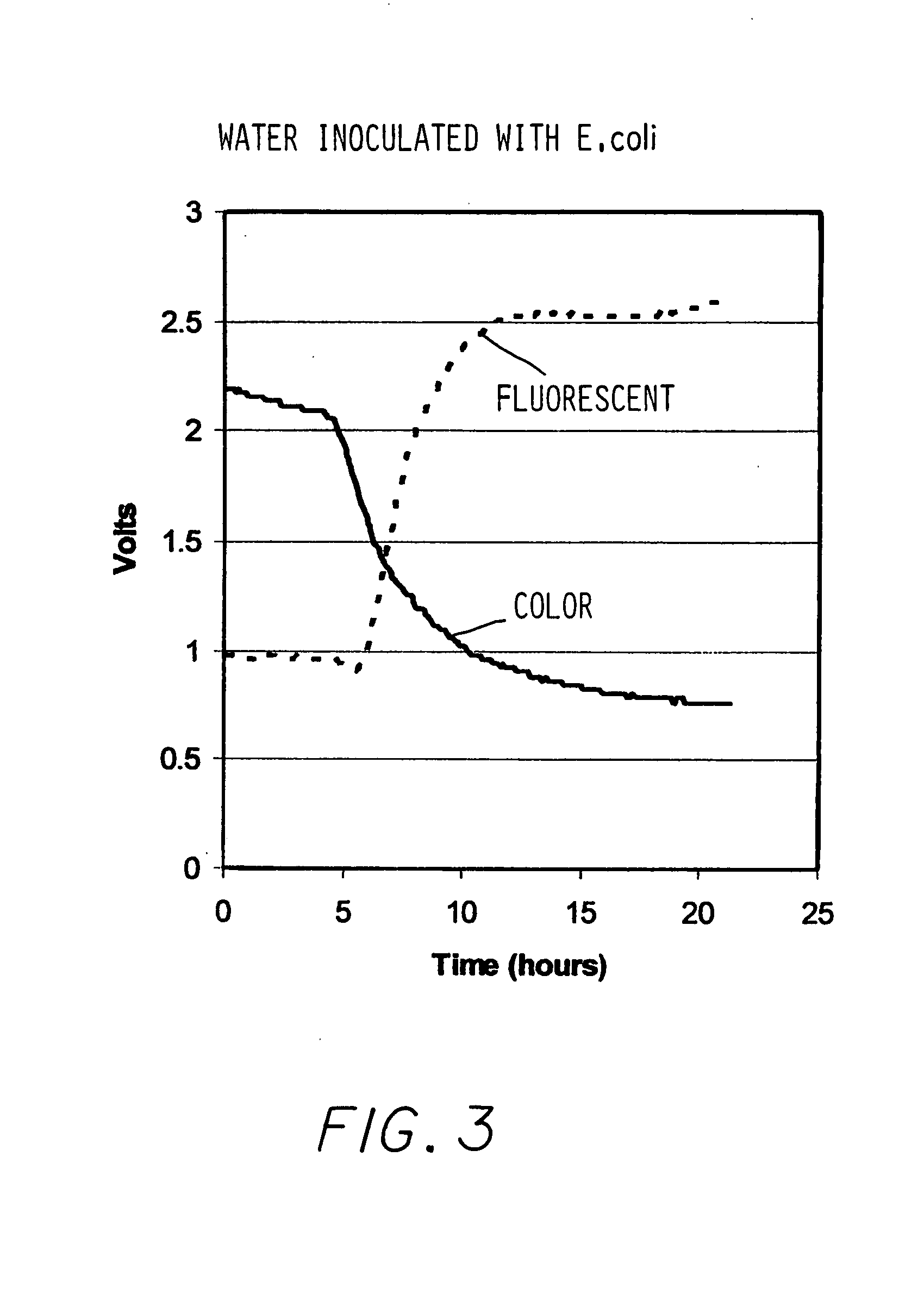
A device and method simultaneously detects and enumerates two groups of microorganisms in a test sample, utilizing a single test container. In the container liquid growth media, a chromogenic substrate and a fluorogenic substrate are mixed with the test sample. The test container is incubated to allow bacterial growth and metabolism. Spectral changes of the substrates are dynamically detected using two external light sources aimed at a transparent section of the test container, and a single external photo detector. One light source operates in the visible band and the second in the long ultraviolet band. The two dynamic time patterns generated by the two substrates are analyzed in real time to determine the presence or absence of each microorganisms group and to enumerate their original concentrations in the test sample.
Owner:NEOGEN CORP
Method for building BCRP (breast cancer resistance proteins) mediated medicine transport models for research on 3D (three-dimensional) organs of small intestines and application
InactiveCN107012116ASimple and fast operationEfficient detectionGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMatrigelFluorescence
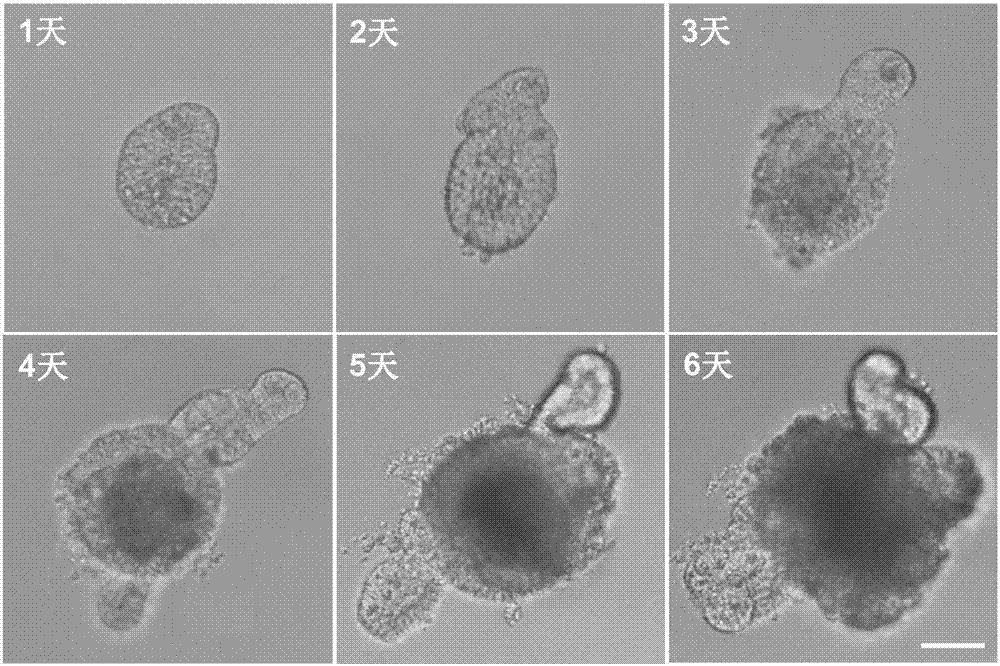
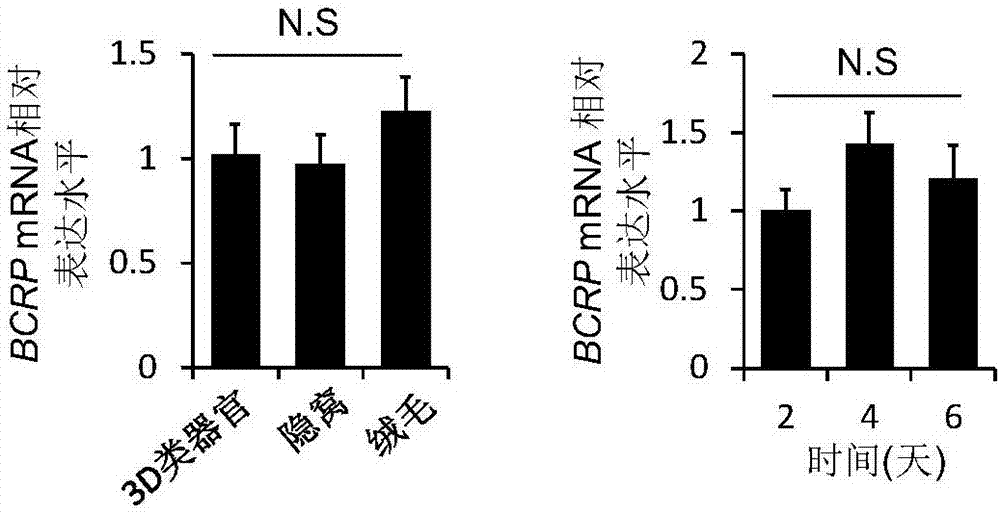
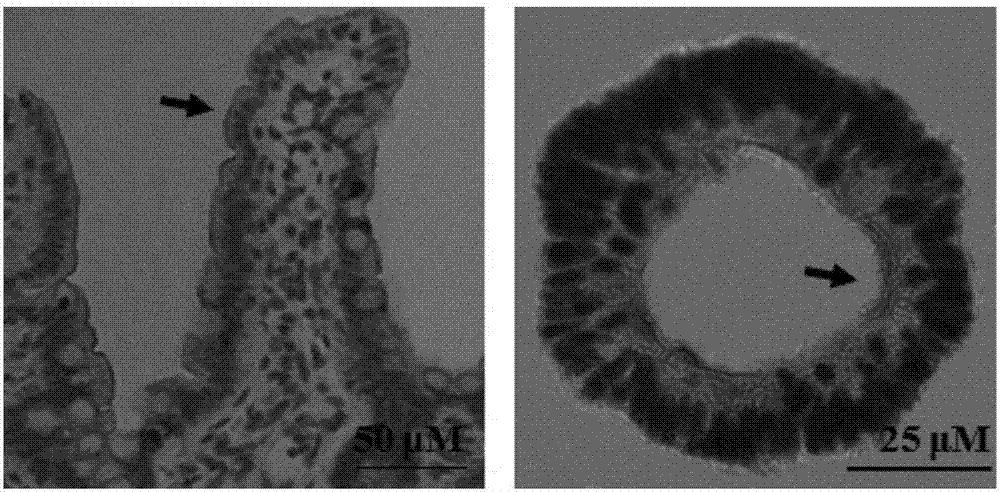
The invention discloses a method for building medicine transport models for research on BCRP (breast cancer resistance proteins) mediation for 3D (three-dimensional) organs of the small intestines of mice. The method includes separating crypts from the small intestines of the mice by means of digestion, suspending the crypts in matrigel and then joining the crypts with cell culture plates and promoting differentiation of the crypts by the aid of ADMEM / F12 media with Respondin-1, m-noggin and m-EGF cell differentiation growth factors to form the 3D organs; carrying out morphologic observation and detecting the expression level of BCRP genes and proteins to verify the feasibility of model theories; carrying out research on the trans-membrane transport activity of BCRP in the 3D organs by the aid of fluorescent substrates Hoechst 33342 of the BCRP and inhibitors Ko143 or YHO-13177 of the fluorescent substrates by co-incubation processes. The method has the advantages that the medicine trans-cell-membrane transport in-vitro models for the research on the BCRP mediation for the 3D organs of the small intestines of the mice are built for the first time, and the method for building the models is easy and convenient to implement and high in detection efficiency and speed and can be widely applied to screening BCRP substrates and inhibitors in an in-vitro manner.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
High throughput screening method of aminopeptidase and high-yield strain thereof
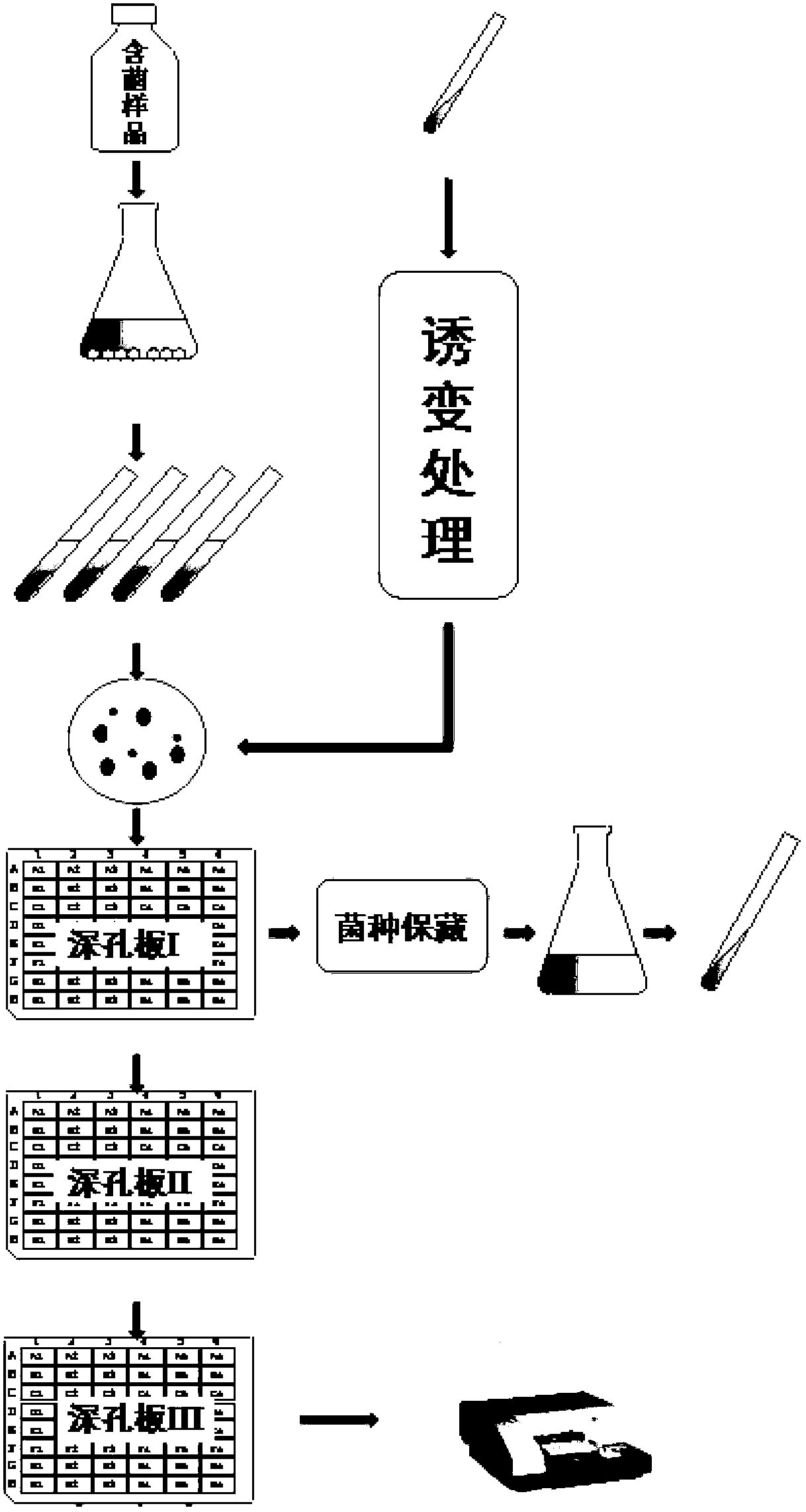
InactiveCN102994387AImprove efficiencyHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationWater bathsHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a high throughput screening method of aminopeptidase and a high-yield strain thereof, relates to a high throughput screening method of aminopeptidase and a high-yield microorganism bacterial strain thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: vaccinating a single colony in the hole of a deep-hole plate I on a medium containing a seed liquid, performing shaking cultivation, vaccinating the seed liquid in the hole of the deep-hole plate I correspondingly into the hole of a deep-hole plate II equipped with a fermentation medium, performing shaking cultivation, and centrifuging the deep-hole plate II to obtain the supernatant crude enzyme; adding a buffer solution and a chromogenic substrate solution or fluorogenic substrate solution in the micropore of an elisa plate, adding the dilute crude enzyme to be tested, carrying out water-bath reaction for 10-30 minutes at 30-70 DEG C, adding a 30-50% acetic acid solution immediately after the water-bath reaction and terminating the reaction; and measuring the absorbance or fluorescence intensity of the reaction liquid by a microplate reader, and calculating the enzyme activity according the standard curve and the dilution ratio of the crude enzyme. According to the invention, the goals of high throughput cultivation, high throughput preparation of crude enzyme and the high throughput test of the enzyme activity are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Measuring thrombin activity in whole blood
ActiveUS8916356B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisThrombin activityThrombin generation
Owner:SYNAPSE INC
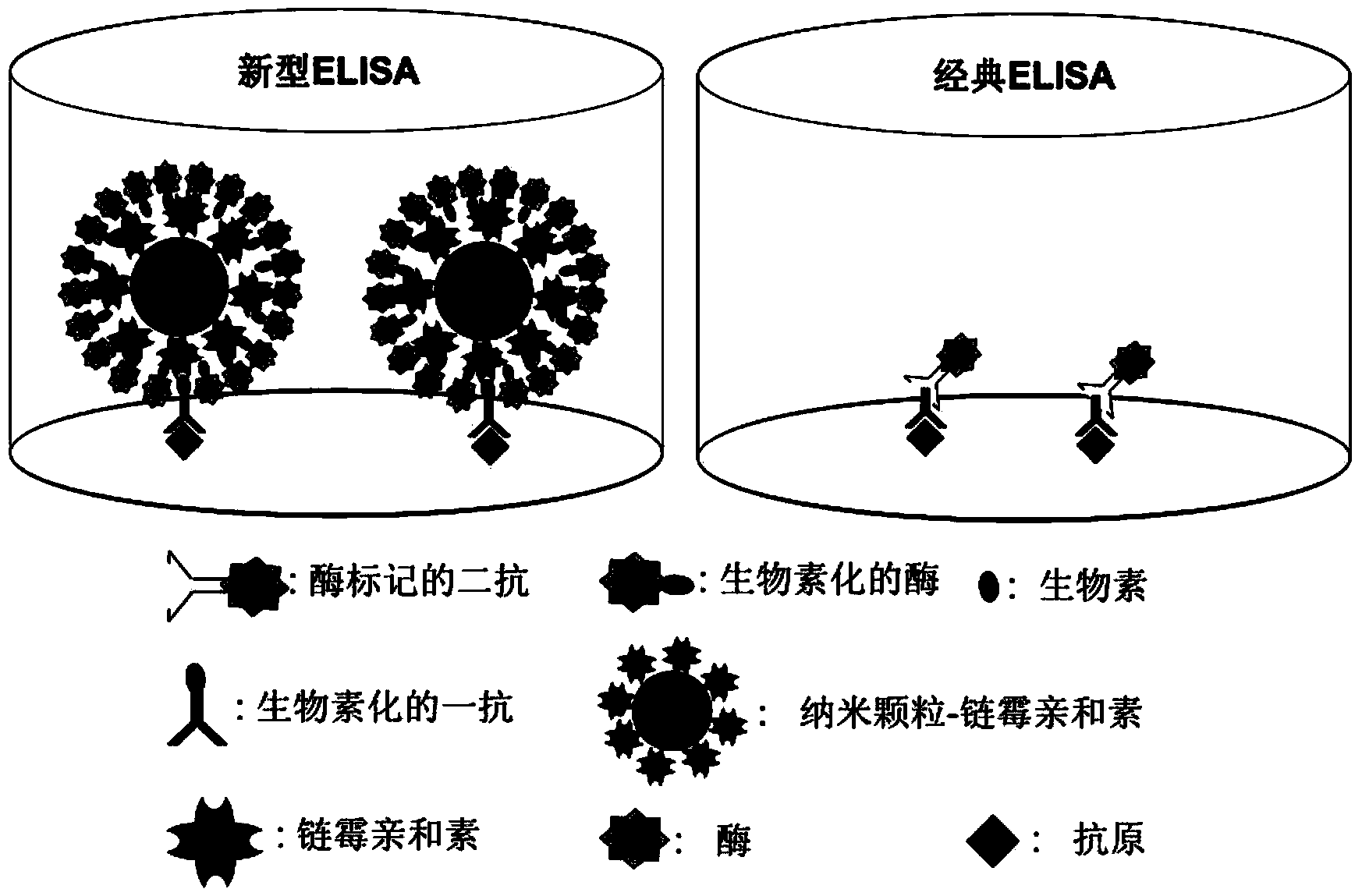
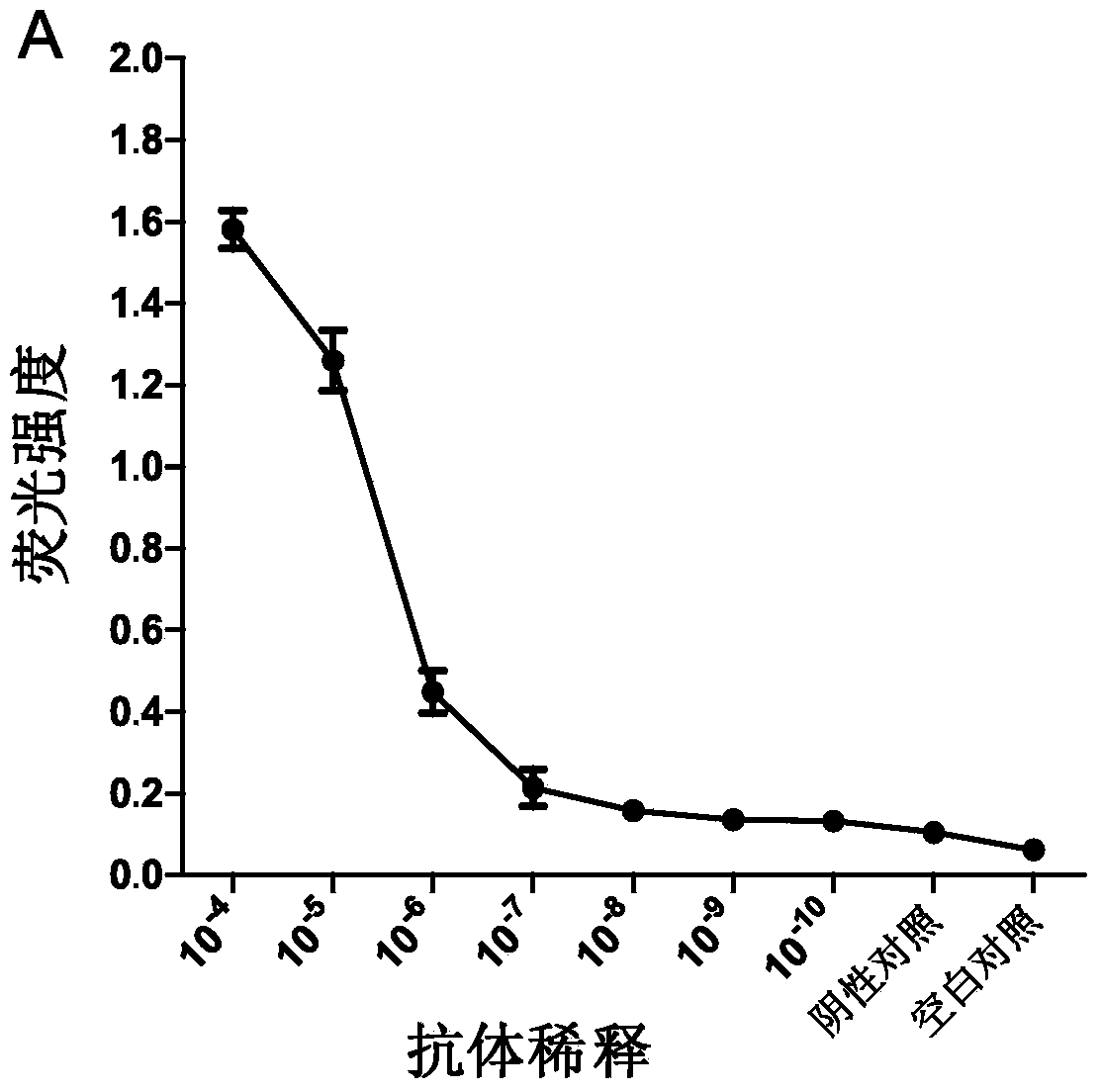
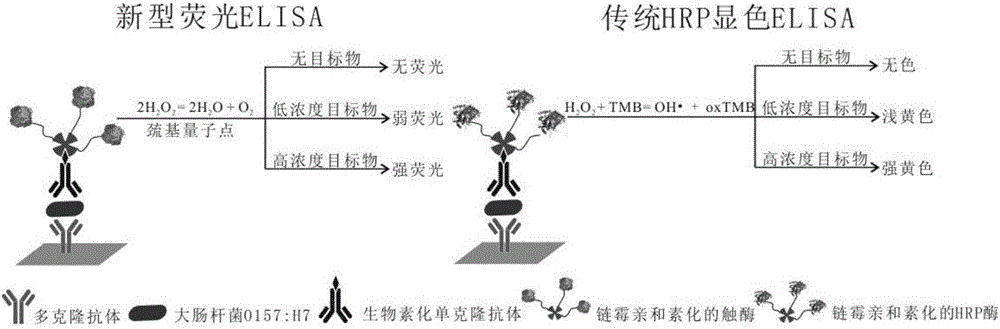
Establishment of novel ultrasensitiveness ELISA method
ActiveCN103513027AHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexChromogenic Substrates
The invention provides a novel ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method with high detection sensitivity. The detection sensitivity of the novel ELISA method can reach 100 times of that of an existing ELISA method. In the novel ELISA method, a more sensitive novel fluorogenic substrate is used for replacing a chemical chromogenic substrate in the conventional ELISA method; moreover, a high-efficiency stable enzyme capable of catalyzing the fluorogenic substrate to generate a luminescent effect is used as a marker enzyme so as to realize that the luminescent effect of the substrate reaches the minimum enzyme quantity required for the detectable level; the novel ELISA method also uses a gold nanoparticle coupling streptavidin system with excellent biocompatibility for realizing an amplification effect of an enzymatic reaction; integration of improvement measures on the three aspects finally implements great improvement on the detection sensitivity of the ELISA method.
Owner:CHANGCHUN BCHT BIOTECH
Fluorescent substrates for determining lysine modifying enzyme activity
ActiveUS20140335550A1Reduce usageProfiling their selectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymeMedicinal chemistry
Owner:BROAD INSTITUTE
Cloned enzyme-donor immunoassay (CEDIA) ImmunoChip drug detecting kit
Rapid drug detection is a regular detection item for public security departments, drug control organizations, sports events, enlistment and entry departments. At present, colloidal gold test paper is a basic choice for rapid drug detection, but the sensitivity of the colloidal gold test paper is low, the possibility of fake positive and fake negative results is high, the repeatability is low and the quantification is impossible. The invention discloses a cloned enzyme-donor immunoassay (CEDIA) ImmunoChip drug detecting kit. The kit comprises an immuno chip on which the combination of an enzyme donor and an enzyme receptor is immobilized, wherein the enzyme donor can be coupled with a drug micromolecule by a chemical bond to form an enzyme-donor-labeled exogenous antigen so as to be used for detecting whether a specific anti-drug antibody which can be competitively combined with the enzyme-donor-labeled exogenous antigen exists in a sample to be detected by a CEDIA ImmunoChip drug detecting method and calibration is carried out by using a novel fluorogenic substrate. The kit has the advantages of sensitive reaction, high accuracy, no cross reaction and high repeatability, and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIHANG BIOTECH
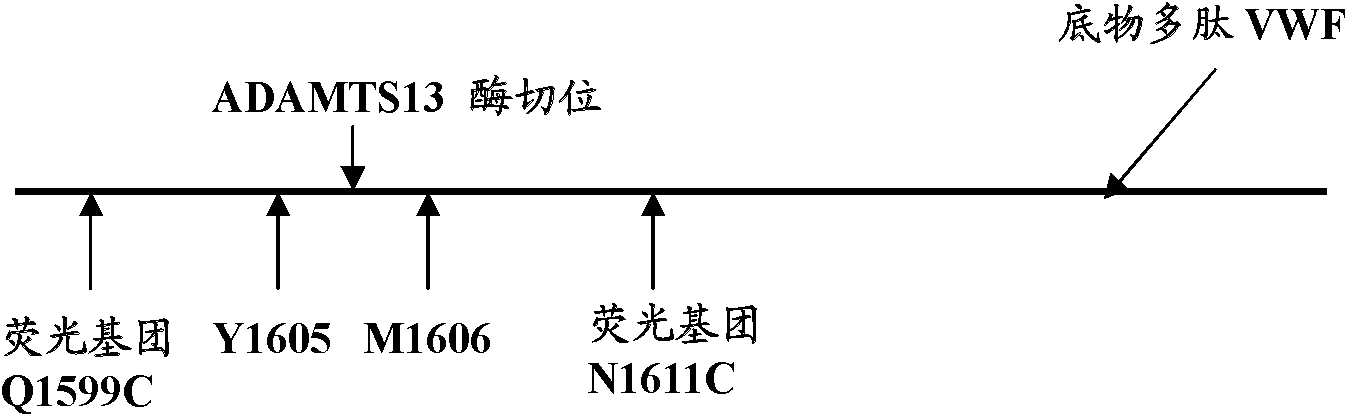
Fluorogenic substrate for detecting ADAMTS13 enzymatic activity and detection method
InactiveCN102533937ASimple and fast operationThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsFluoresceinBlood plasma
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, in particular to a fluorogenic substrate for detecting ADAMTS13 enzymatic activity and a detection method. The fluorogenic substrate for detecting the ADAMTS13 enzymatic activity comprises an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and sulfydryl of cysteine at the 4 position and the 15 position at the N end of the amino acid sequence is combined with fluorescein-5- maleimide. Q1599C of the fluorogenic substrate is closer to N1611C modified site, simultaneously the N-end sequence of the fluorogenic substrate does not contain extra amino acid GS, and enzymolysis can be conducted on the fluorogenic substrate through ADAMTS13 more effectively. Therefore, sensitivity for detecting ADAMTS13 enzymatic activity can be improved. The method for detecting the ADAMTS13 enzymatic activity is convenient to operate, accurate in detection result, high in sensitivity and suitable for quick detection of the ADAMTS13 enzymatic activity in blood plasma in hospitals, health departments and medical research and development institutions at different levels.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
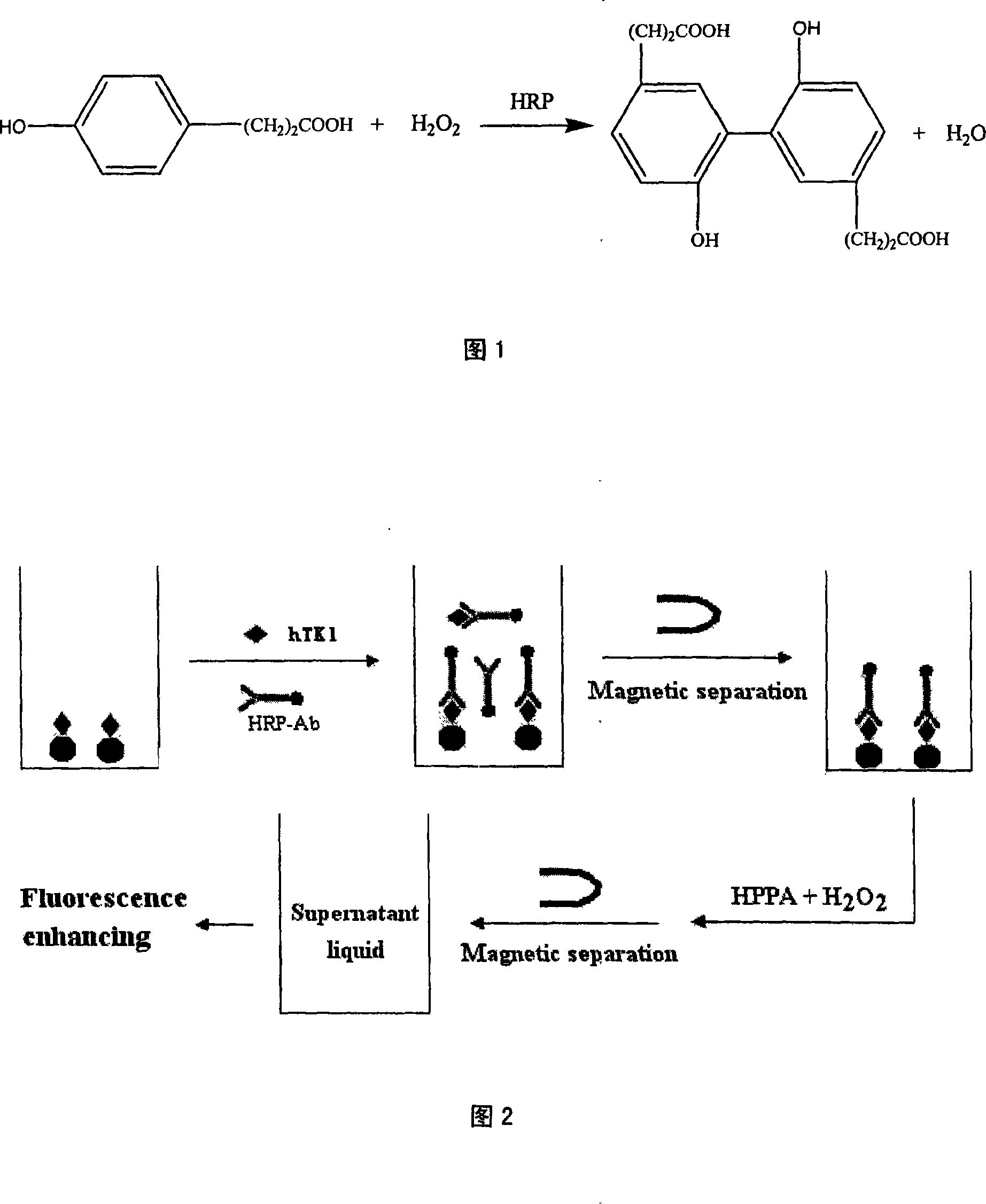
Novel method for analyzing human thymidine kinase fluorescence immune based on magnetic nanometer particular
InactiveCN101231288ALow costEasy to operateMaterial analysisImmune complex depositionMagnetite Nanoparticles
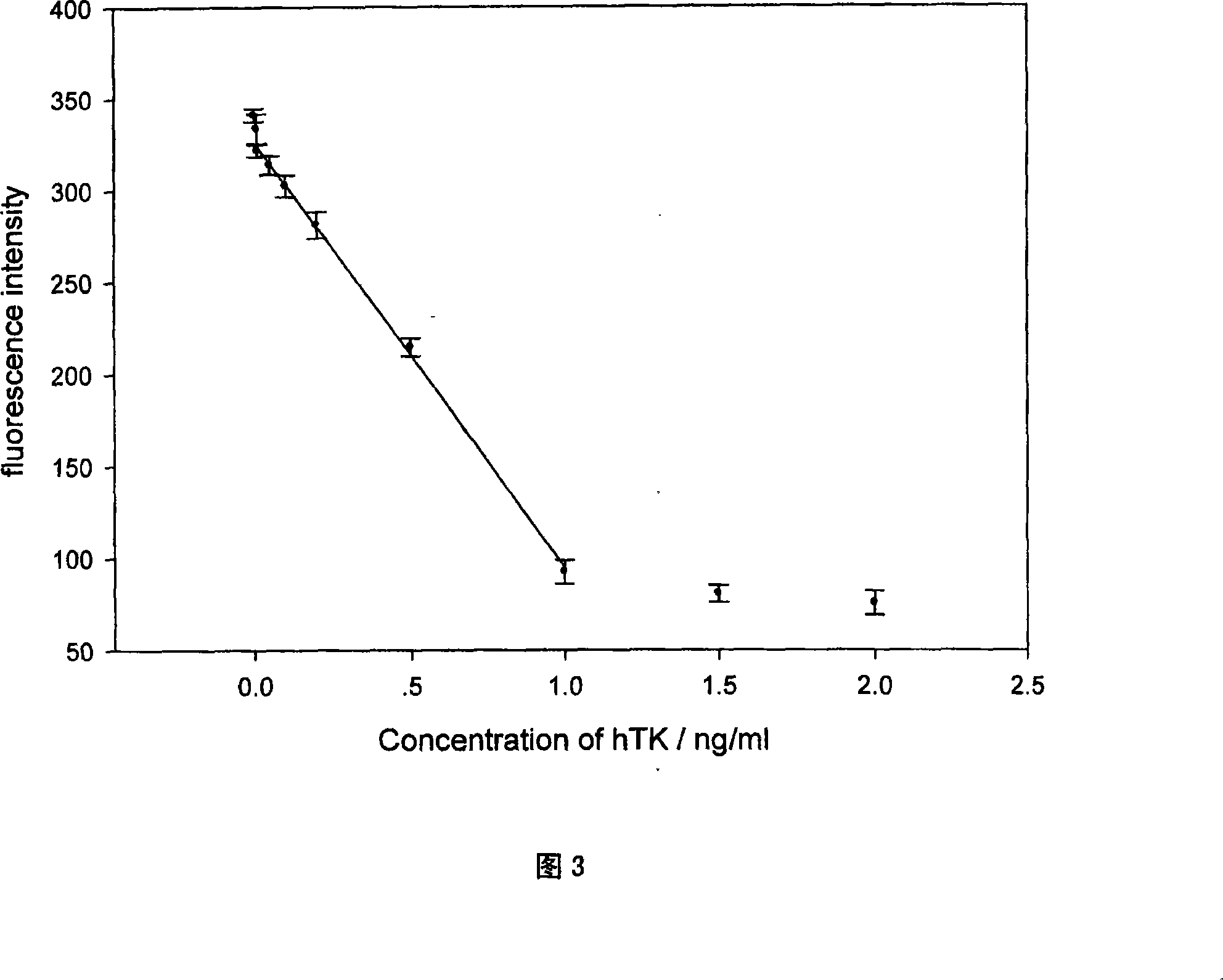
The invention relates to a new fluoroimmunoassay method for human thymidine kinase fluoroimmunoassay based on magnetic nanometer grains. The invention sets up a quick and simple immunological detecting technology for the high flux human thymidine kinase (hTK1), and the technology is used for the hTK1 clinical examination. The hTK1 is fixed with covalence on the surface of an amido silanization superparamagnetism nanometer grain immobilized carrier through glutaric dialdehyde, a competitive immunoassay method is adopted, horse radish peroxidase is used as an enzyme labeling, ethyl-para-hydroxyphenyl acid is used as a fluorogenic substrate, thereby realizing the detecting for the hTK1. The amido silanization nucleocapsid-shaped magnetic nanometer grains are evenly dispersed in liquidoid, thereby having the advantages of fixation and uniformity, high specificity, good repeatability, quick reaction velocity, etc., under the action of an adscititious magnetic field, the invention can effectively realize the separation and enrichment of the immune complex and the reaction liquid of the nucleocapsid-shaped magnetic nanometer grains, the operation of the analytical method is simple, accurate, sensitive and fast, automatic detection is easy to be realized, and large batch of test task can be completed.
Owner:丁克祥
Method and apparatus for rapidly analyzing microorganisms using petri plates
InactiveUS20120295299A1Avoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismStaining
A growth plate or Petri plate and a method for detection and identification of microorganisms by specific or non-specific staining of colonies or microcolonies is described. Analytical substances (chromogenic or fluorogenic substrates, biochemical dyes, dyes indicators of pH, antibiotics and other biological active substances) are applied to the lower surface of a nutrient agar layer. The substances diffuse in the agar, reach cells and react with them. Because colonies or microcolonies are not removed from the media, they retain their shape, color, size and other useful characteristics for analytical purposes.
Owner:SPECTROFERM
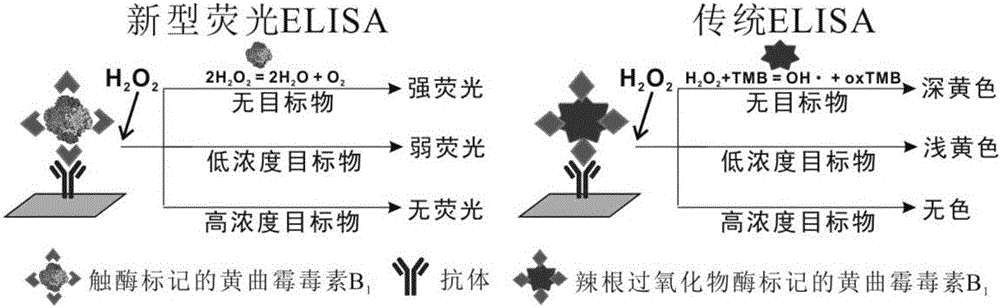
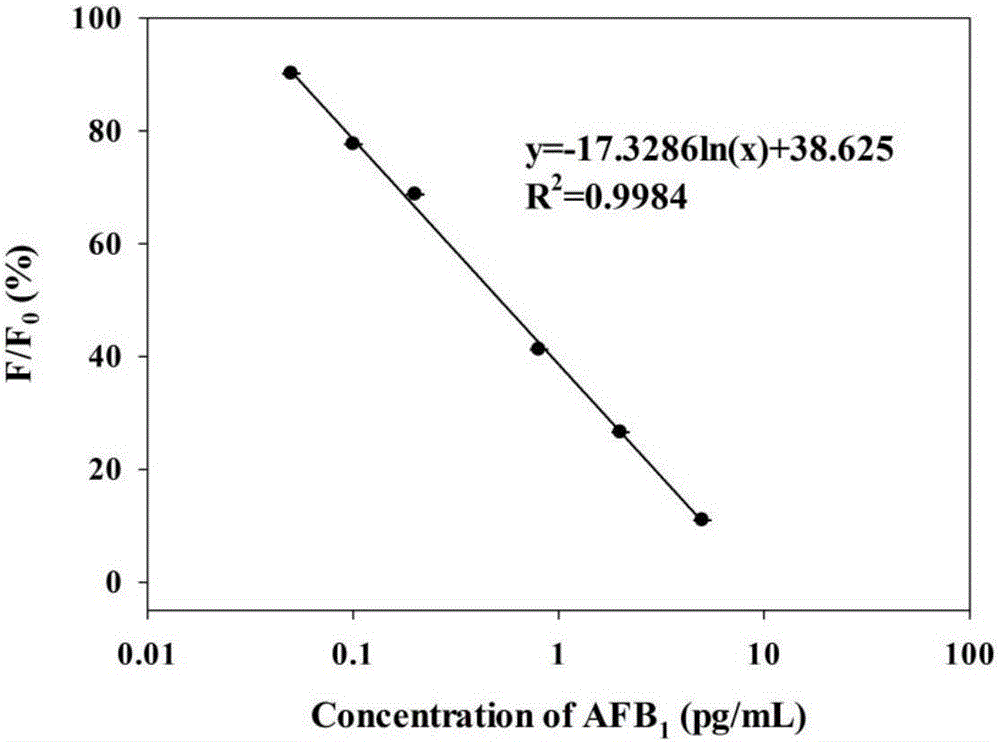
Method for detecting aflatoxin B1
ActiveCN105759045ALow costHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysisDecompositionCatalytic function
The invention provides a method for detecting aflatoxin B1. The method is based on a direct competitive ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) technique, firstly, monoclonal antibodies are coated, a to-be-detected sample and aflatoxin B1 labeled with catalase C100 are added, aflatoxin B1 in the sample and the aflatoxin B1 labeled with catalase C100 are competitively combined with the monoclonal antibodies fixed on an ELISA plate, fluorescence quenching of cadmium telluride quantum dots modified with mercaptopropionic acid is reduced through decomposition of hydrogen peroxide under the catalytic function of catalase, and the content of aflatoxin B1 in the sample is judged according to the fluorescence intensity. According to the method, new catalase is introduced innovatively, and the reaction precision is improved while the cost is reduced; meanwhile, a more sensitive novel fluorogenic substrate, namely, the cadmium telluride quantum dots modified with mercaptopropionic acid, is adopted, and the lighting sensitivity is remarkably improved by comparison with traditional TMB (tetramethylbenzidine) substrates.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Methods and reagents for improved cell-based assays
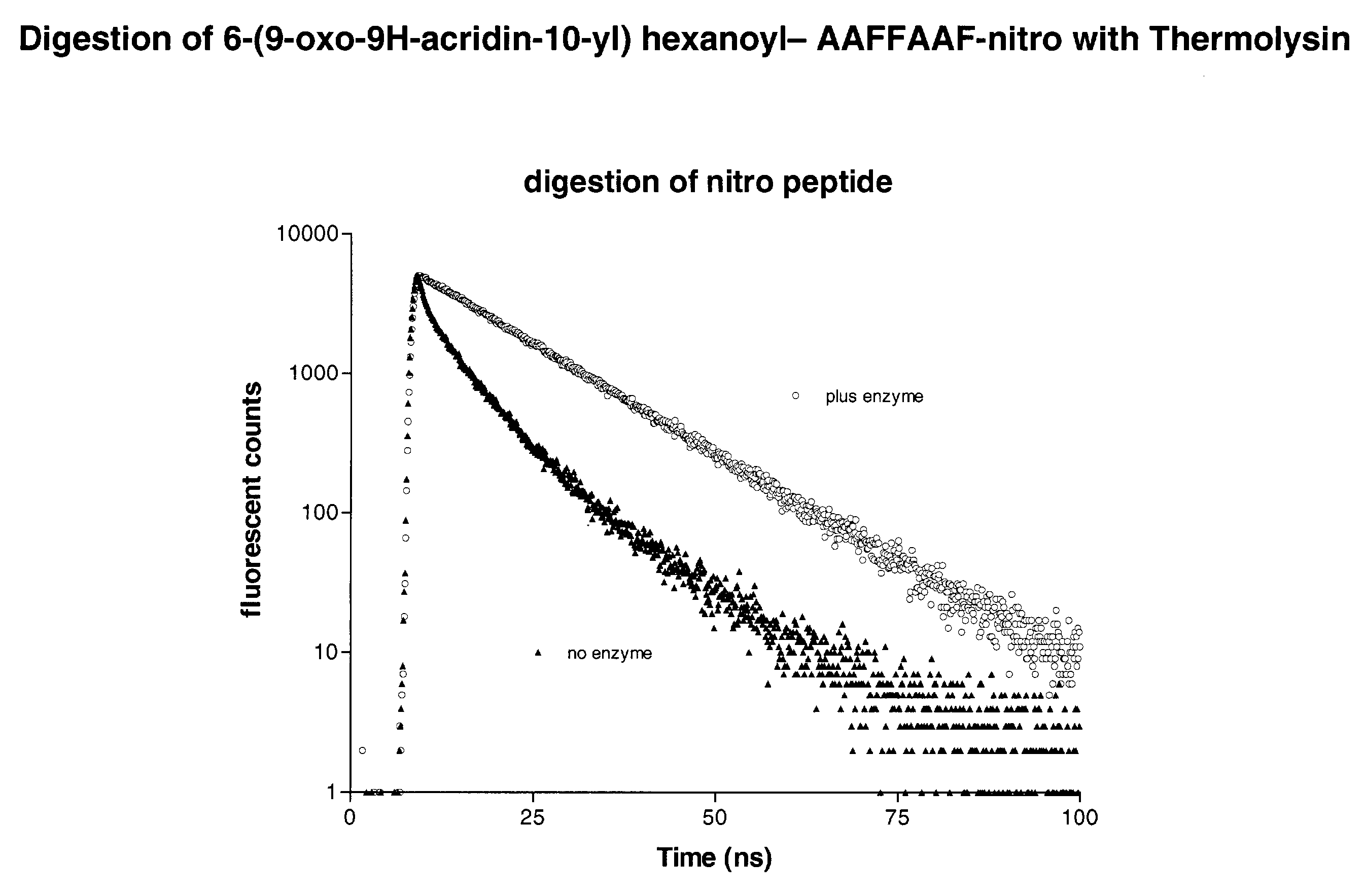
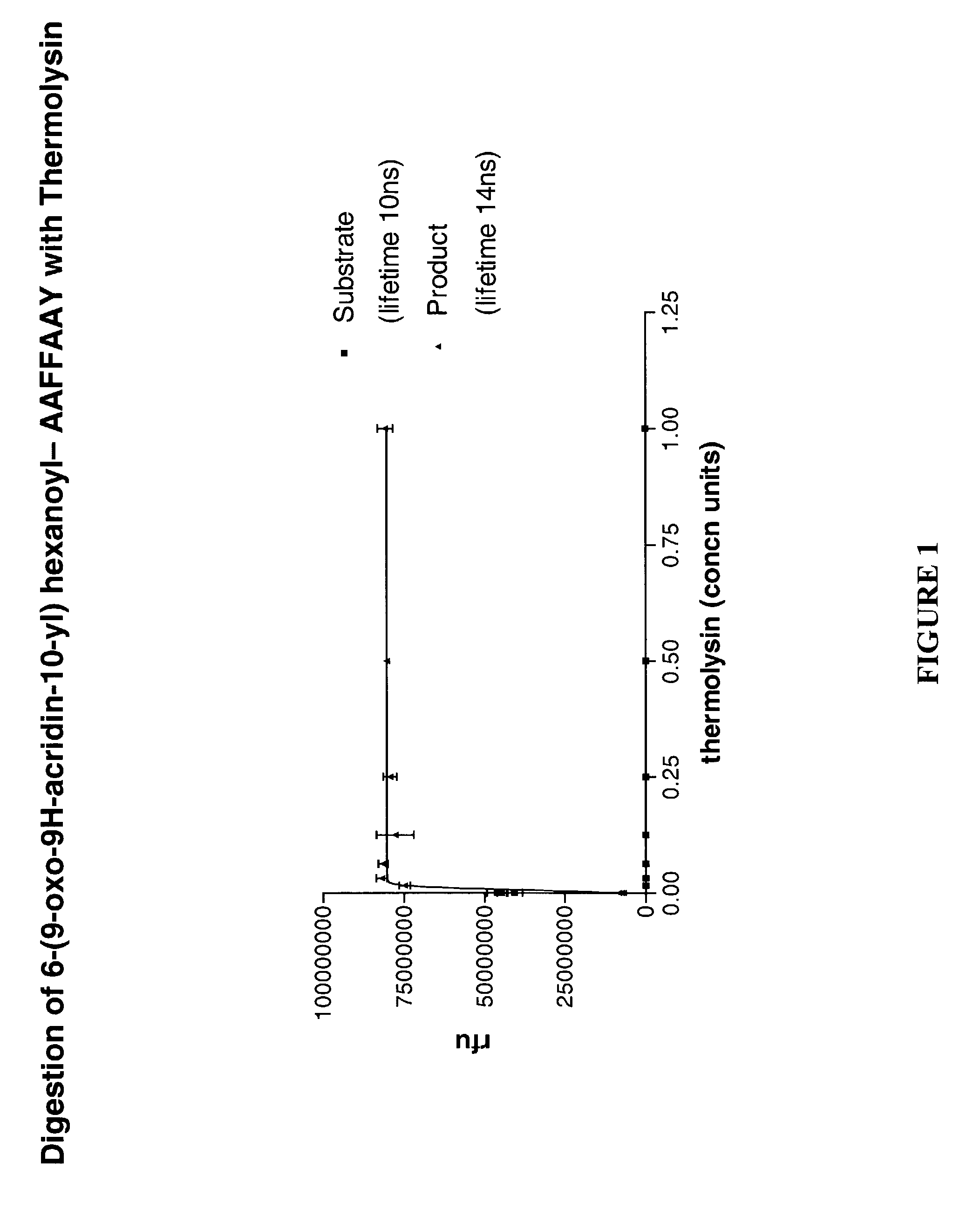
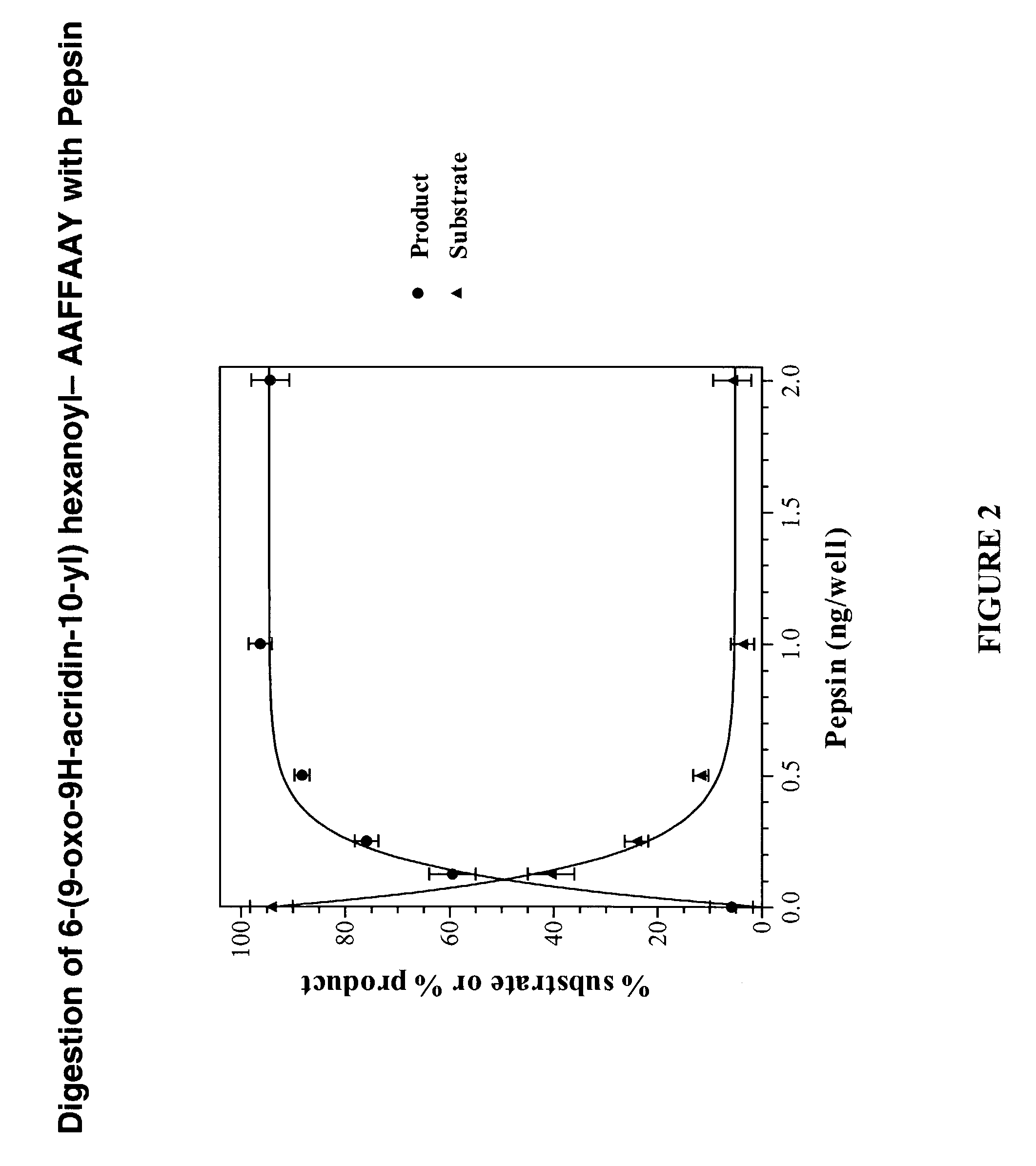
InactiveUS7026111B2HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell based assaysFluorogenic Substrate
The ability to efficiently determine the state of enzyme expression in cells has long been desired as material to the diagnosis of disease. This invention relates to cytoenzymology, and more particularly to improved reagents for use in cell-based assays, especially those using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Use of bacterial beta-lactamase for in vitro diagnostics and in vivo imaging, diagnostics and therapeutics
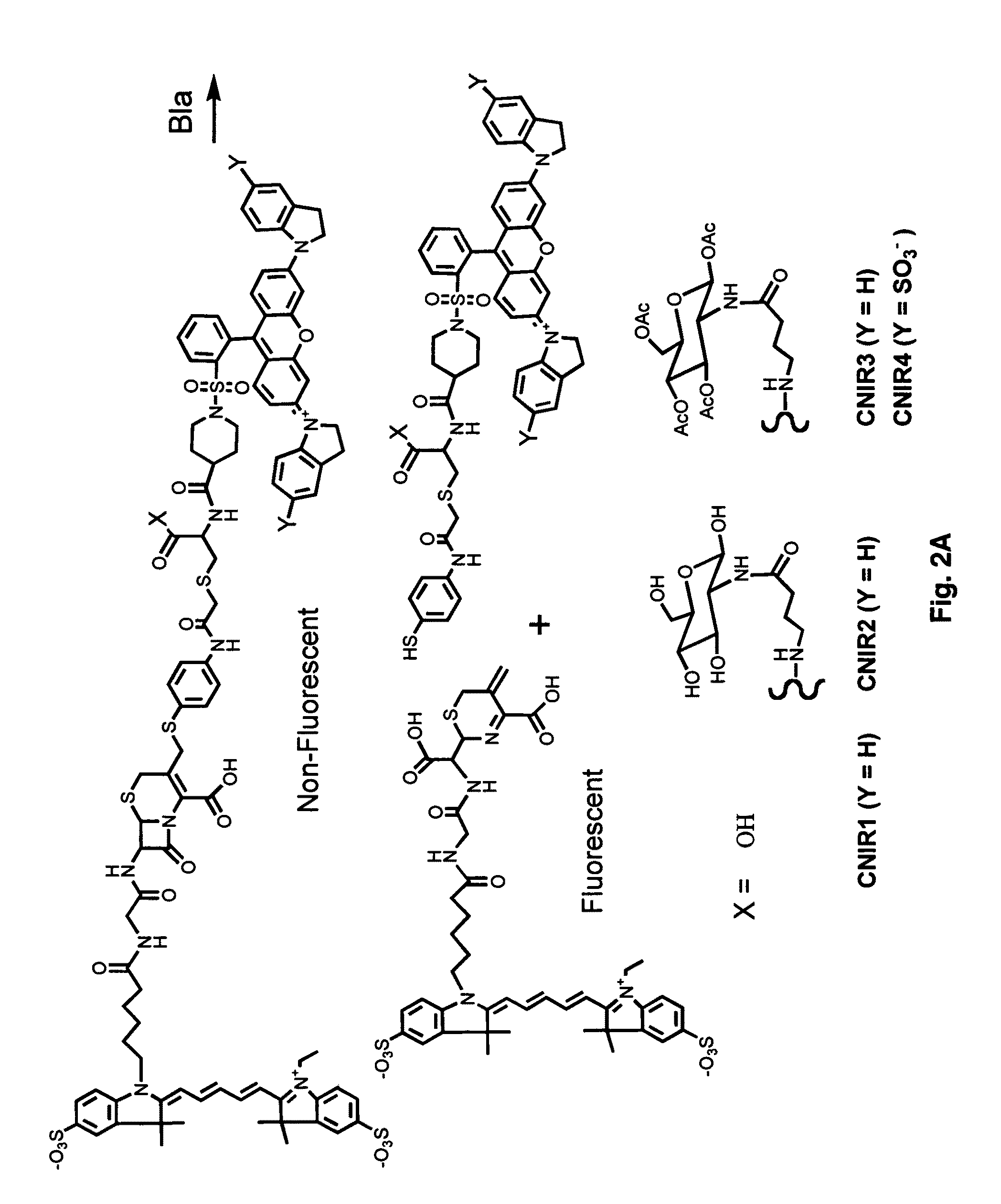
Provided herein are imaging methods for detecting, diagnosing and imaging pathogenic bacteria or a pathophysiological condition associated therewith using fluorescent, luminescent or colorimetric detection agents, e.g., fluorogenic substrates for bacterial enzymes, caged luciferins and fluorescent proteins, luciferases and enzymes expressed by recombinant bacteria. Signals emitted by the fluorescent, luminescent or colorimetric detection agents in the presence of the bacteria are compared to controls to detect and locate the pathogenic bacteria. Also provided is a method for screening therapeutic agents to treat the pathophysiological conditions by measuring fluorescence or luminescence emitted from the detection agents in the presence and absence of the potential therapeutic agent. In addition, a method for detecting a pathogenic bacteria via PET or SPECT imaging using a positron-emitting or gamma-emitting substrate for a beta-lactamase or other enzyme or protein of the pathogenic bacteria. Further provided are the fluorogenic substrates CNIR-7 or CNIR7-TAT or the radiolabeled substrates.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Methods for measuring enzyme activity
InactiveUS7727739B2High fluorescence intensityIncrease enzyme activityCompound screeningPeptide librariesIn vivoFluorogenic Substrate
Owner:TTP LABTECH
Use of bacterial beta-lactamase for in vitro diagnostics and in vivo imaging, diagnostics and therapeutics
InactiveUS20110020240A1Decrease in gamma emissionEffective conditioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic chemistryMycobacterium InfectionsIn vivo
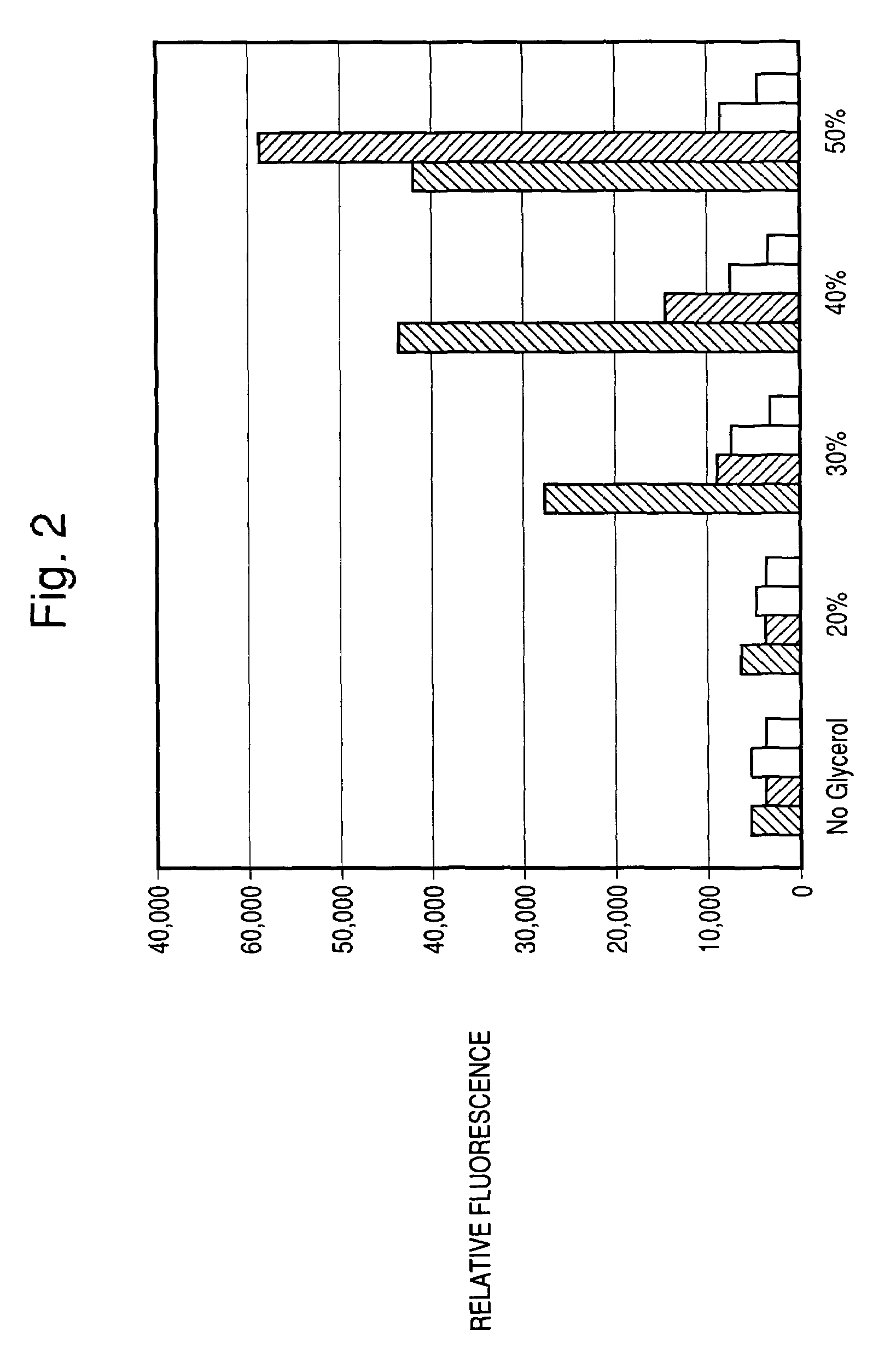
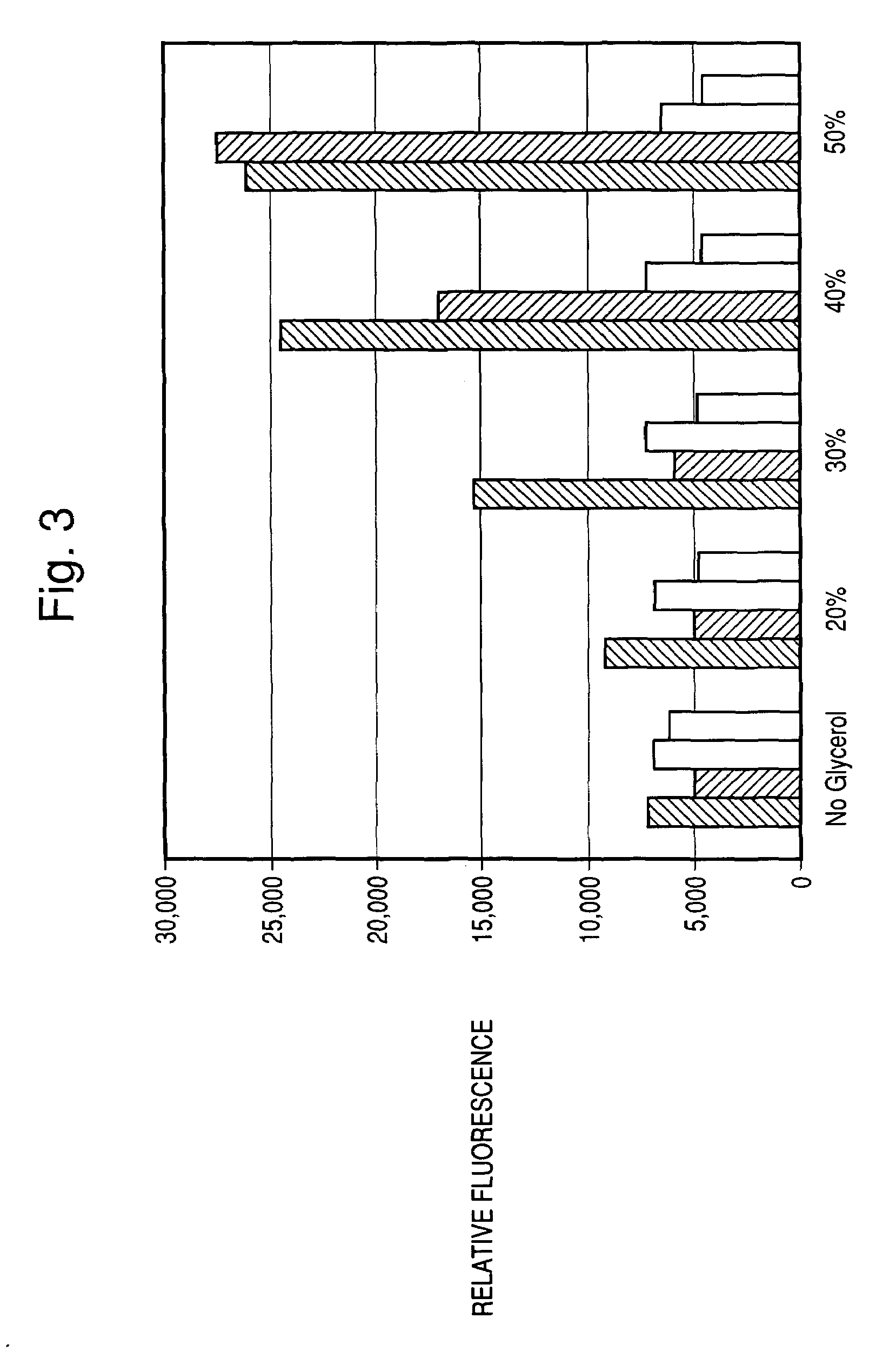
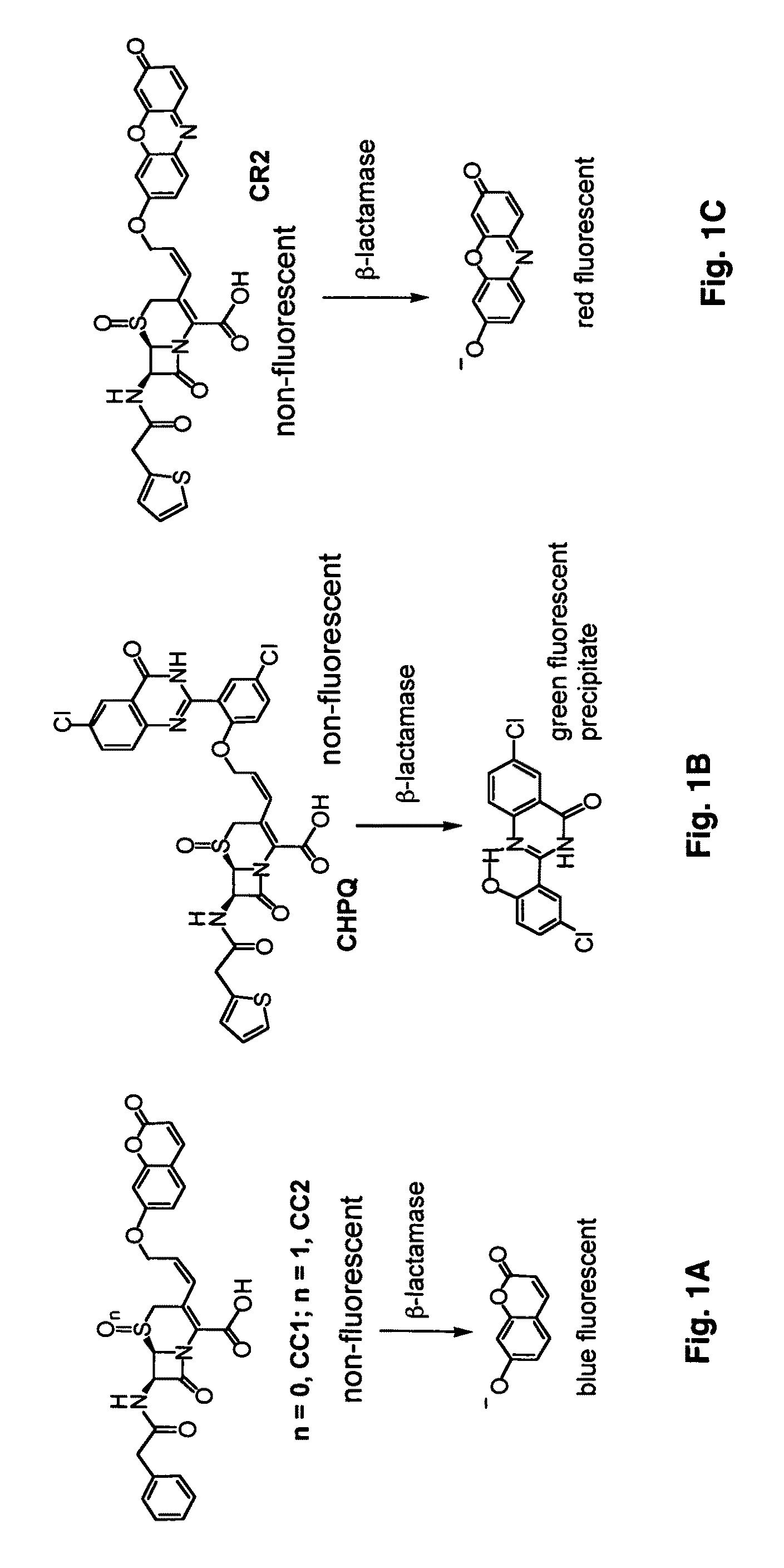
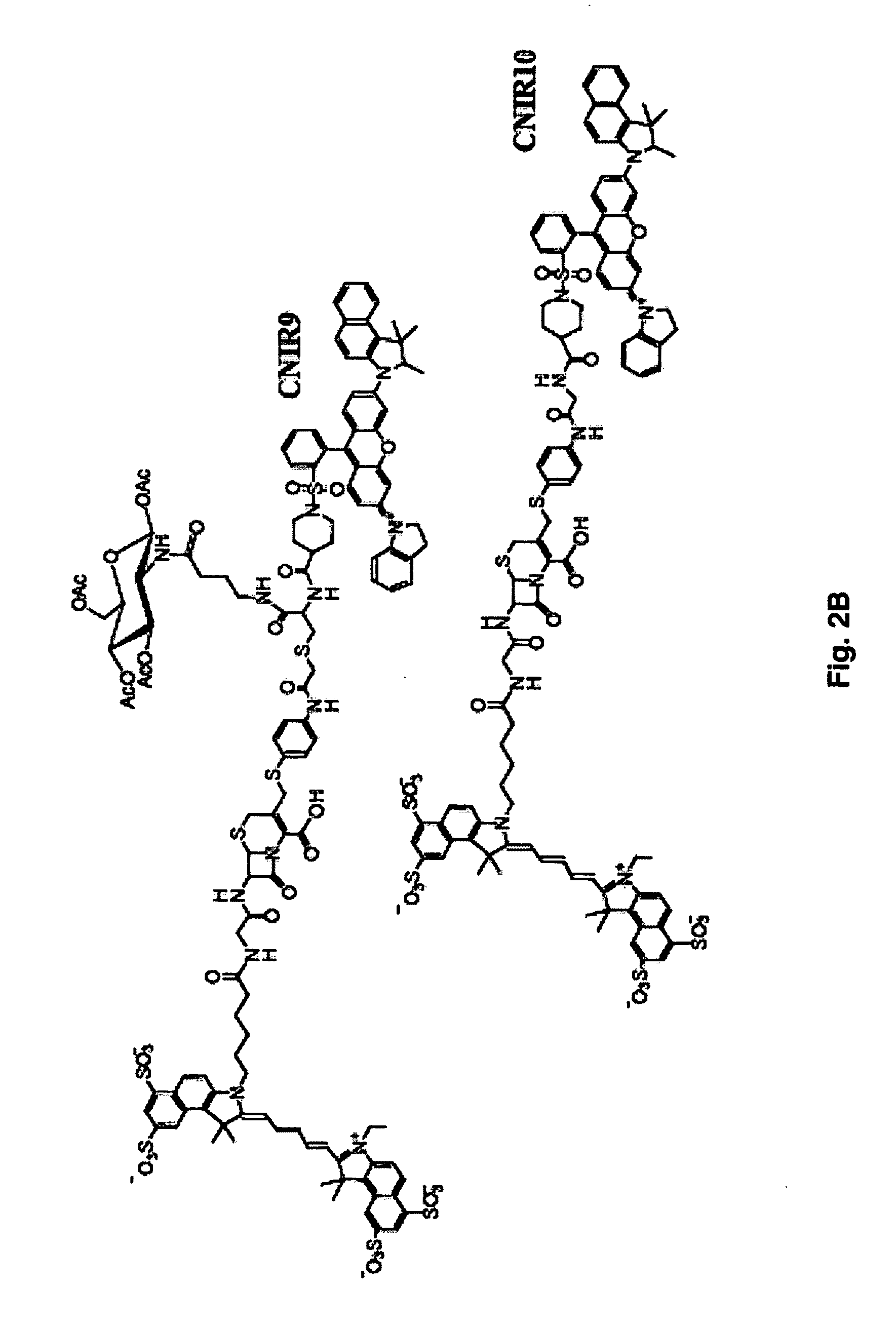
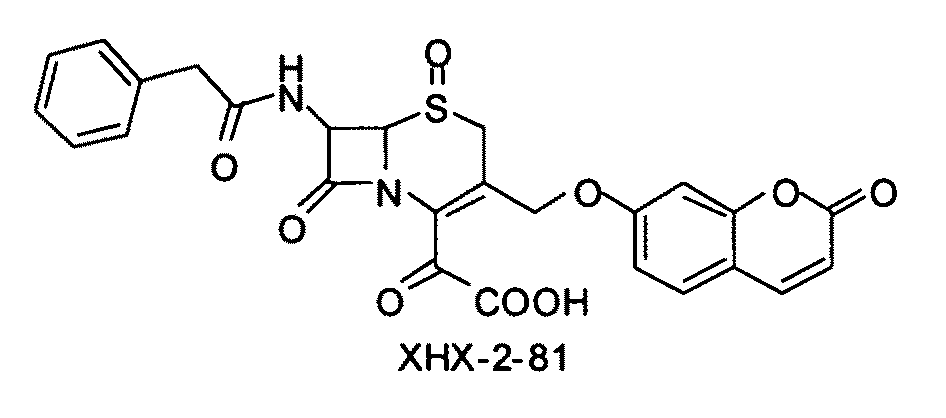
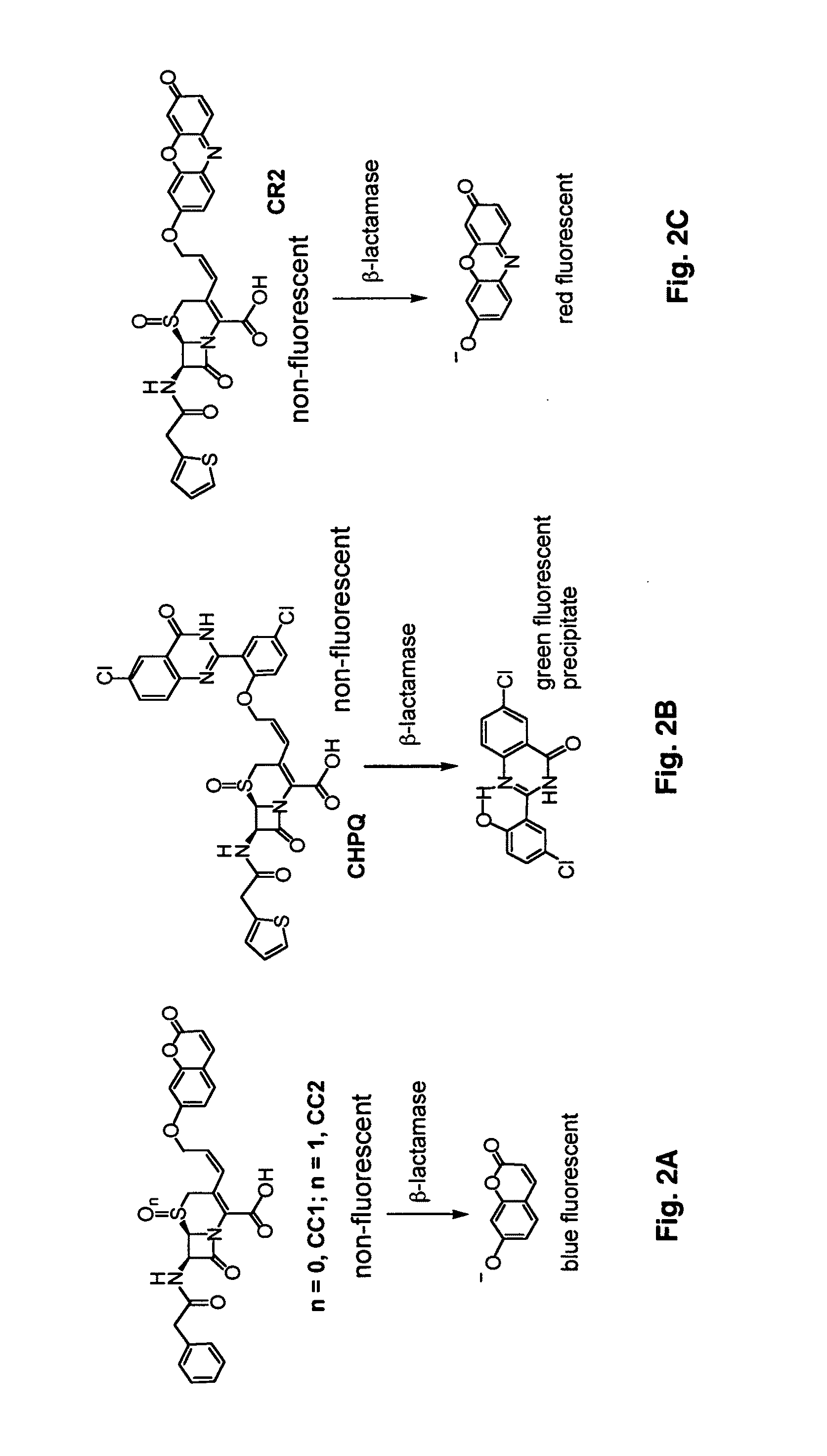
Provided herein are imaging methods for detecting, diagnosing and imaging pathogenic bacteria or a pathophysiological condition associated therewith using fluorogenic substrates for bacterial enzymes. Fluorescent, luminescent or colorimetric signals emitted by substrates or enzyme products in the presence of the bacteria are compared to controls to detect and locate the pathogenic bacteria. Provided is a method for screening therapeutic agents to treat the pathophysiological conditions by measuring a signal emitted from the fluorogenic substrates or products in the presence and absence of the potential therapeutic agent. In addition, a diagnostic method for detecting a mycobacterial infection in a subject by contacting biological samples with a fluorogenic substrate and imaging for signals emitted from a mycobacterial beta-lactamase product. Provided are fluorogenic substrates CC1, CC2, CHPQ, CR2, CNIR1, CNIR2, CNIR3, CNIR4, CNIR5, CNIR5-QSY22, CNIR7, CNIR9, CNIR10, CNIR-TAT, CDC-1, CDC-2, CDC-3, CDC-4, CDC-5, XHX2-81, XHX2-91, XHX3-26, or XHX3-32 or a derivative thereof.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Measuring The Activity Of Proteases
InactiveUS20100267054A1Sensitive measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActivity measurementFluorogenic Substrate
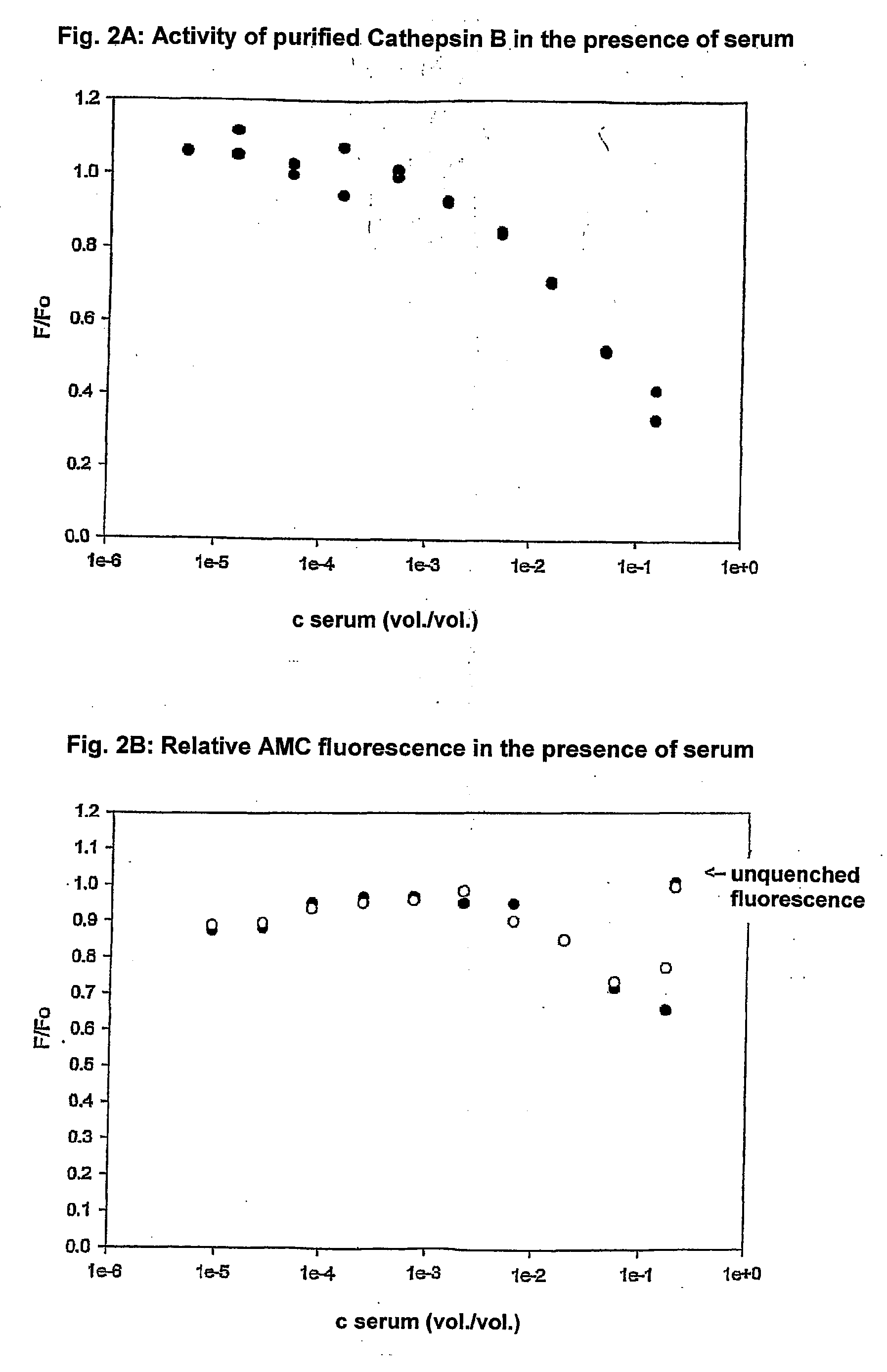
A method and apparatuses for determining the total content of proteases by means of measuring their enzyme activity after previous deinhibition is disclosed. In biological samples, lysosomal proteases are completely (e.g. in blood serum) or partly (e.g. in tissue homogenates) inhibited. A method proposed for the deinhibition entails immersing a solid support material (e.g. nylon or nitrocellulose) as plastic strip to which is linked, covalently or by adsorption, an inhibitor-binding substance which binds the inhibitor corresponding to the protease more strongly than the protease in the sample for measurement. After the deinhibition has taken place, the plastic strip is removed from the liquid sample for measurement, and the sample for measurement is passed on for measurement of the enzyme activity. Fluorogenic substrates from which the fluorogen 7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin is eliminated proved to be particularly advantageous for the activity measurement. These substrates make it possible for the sensitivity on measurement in microtitre plates with a fluorescence reader to be at least 10 times higher compared with conventional AMC substrates in blood serum, and thus for the fluorimetric determination of such enzyme activities in blood serum to be efficient with this measuring arrangement which is widely used in clinical laboratories.
Owner:PAPST MOTOREN GMBH & CO KG
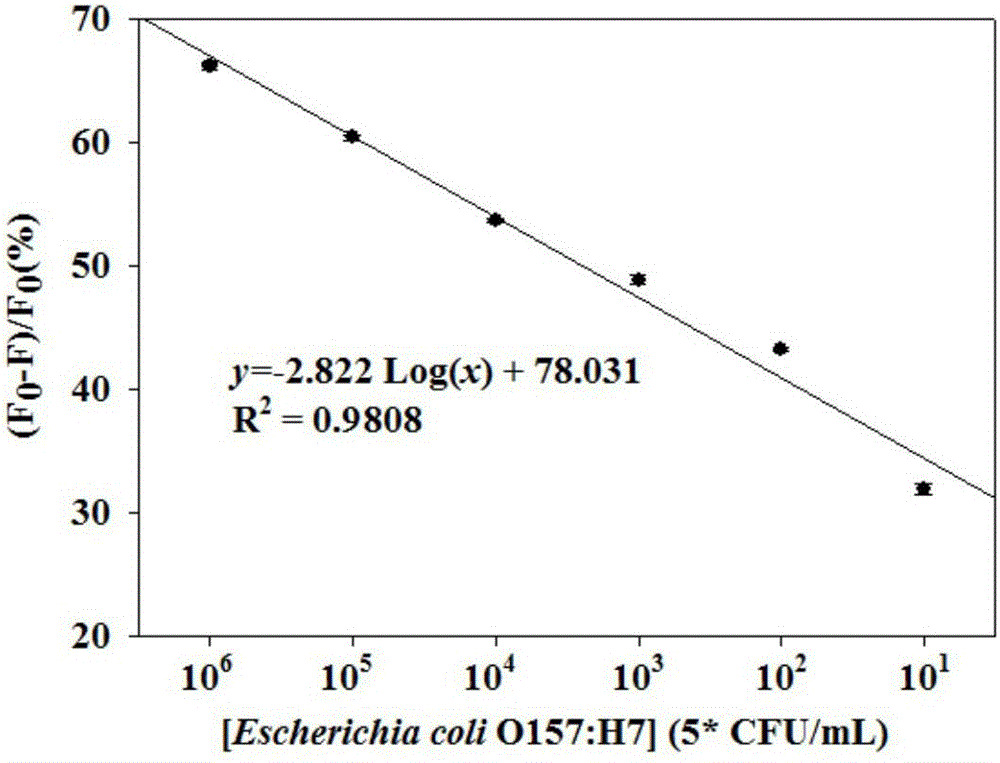
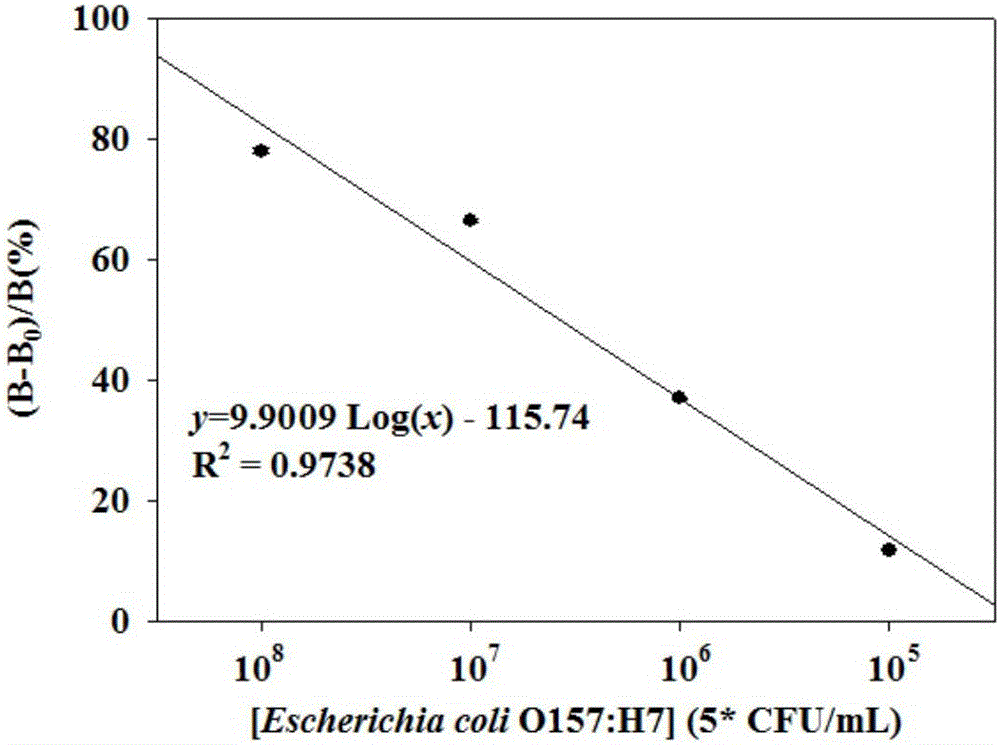
Method for detecting escherichia coli O157:H7
InactiveCN105759032ALow costHigh detection sensitivityBiological material analysisBiotin-streptavidin complexEscherichia coli
The invention provides a method for detecting escherichia coli O157:H7. According to the method, firstly, escherichia coli O157:H7 and coated polyclonal antibodies are combined, then connected with biotinylated monoclonal antibodies and connected with catalase C100 labeled with streptavidin, fluorescence quenching of cadmium telluride quantum dots modified with mercaptopropionic acid is reduced through decomposition of hydrogen peroxide under the catalytic function of catalase, and the concentration of escherichia coli O157:H7 in a sample is judged according to the fluorescence intensity. The method is based on a double-antibody sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and adopts a biotin-avidin system for amplifying a reaction. More importantly, a novel antibody labeling enzyme (catalase C100) and a more sensitive fluorogenic substrate (cadmium telluride quantum dots) are adopted and matched with an effective reaction condition, accordingly, the detection sensitivity is remarkably improved, the cost is reduced, the detection efficiency is improved, and the method has good popularization prospect.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method for detecting beta-lactamase in dairy produce
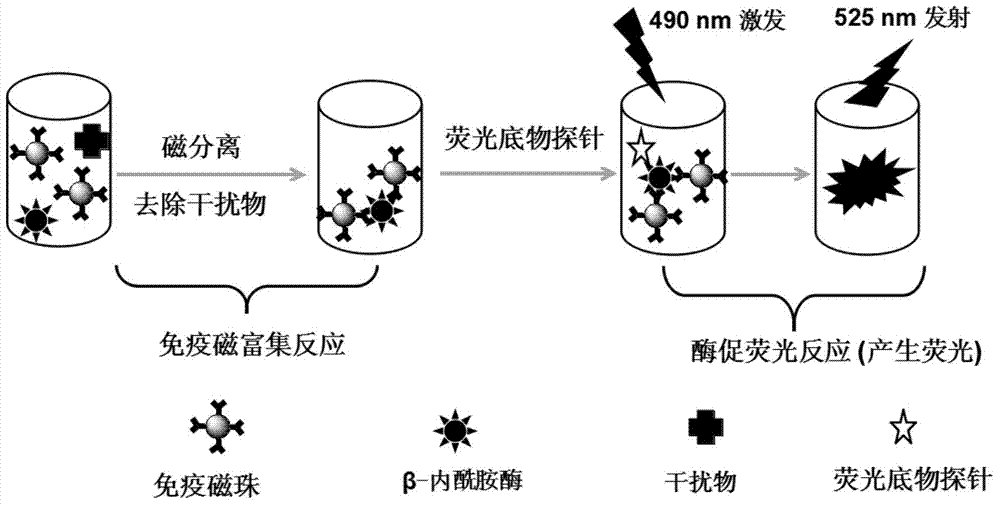
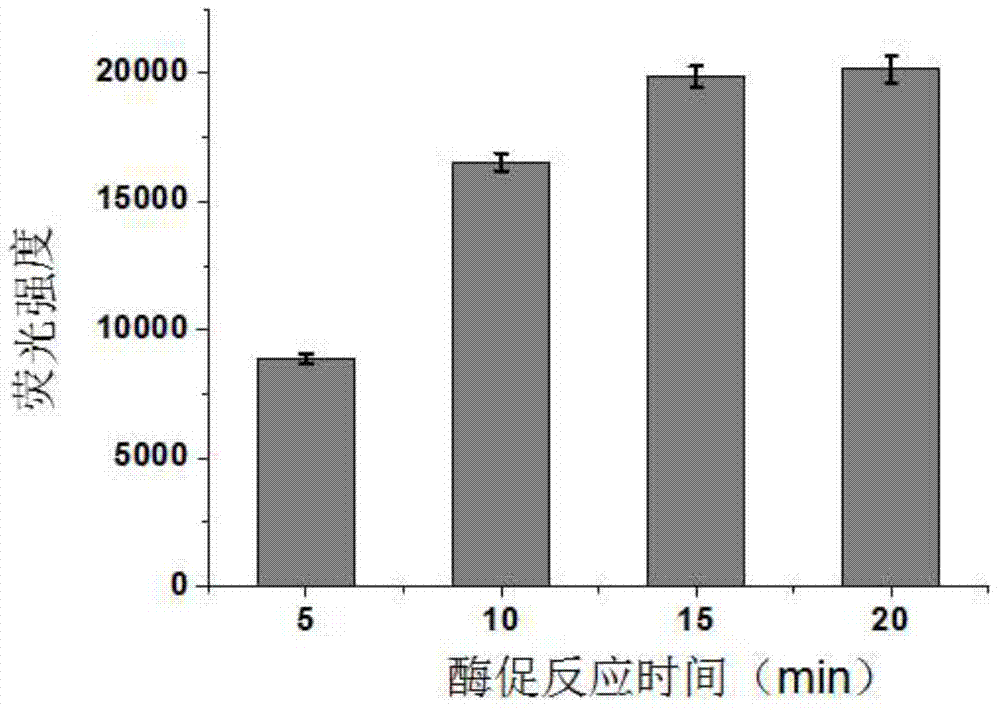
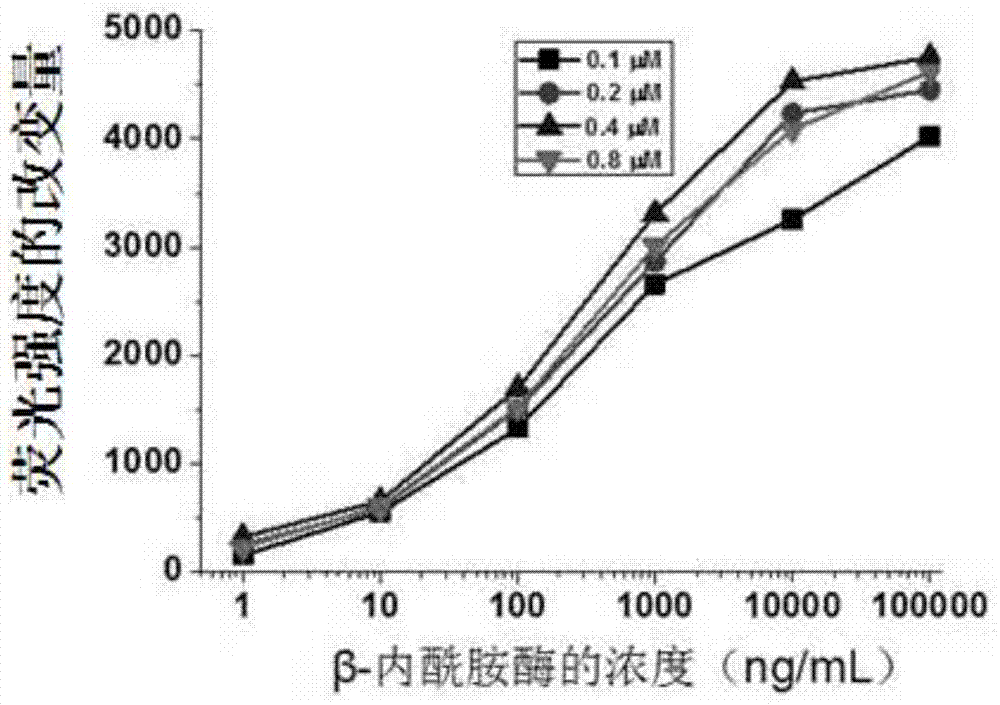
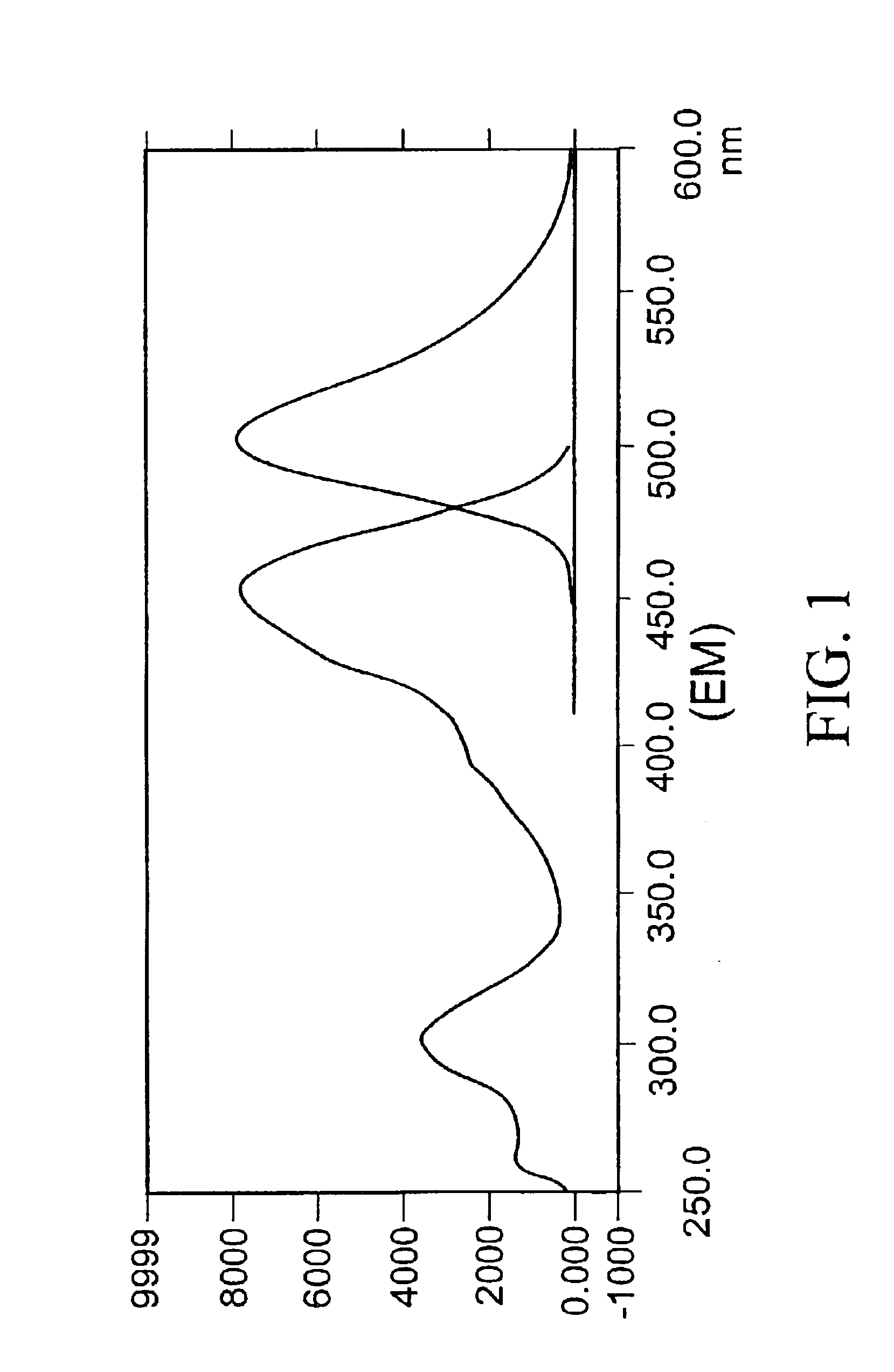
ActiveCN104714006AHigh sensitivityShorten detection timeBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisFluorescein
The invention relates to a method for detecting beta-lactamase in a dairy produce. The method is characterized in that a fluorescence substrate probe which can be specifically catalyzed by beta-lactamase is designed, and the main structure of the fluorescence substrate probe is chemically synthesized through using the mother ring of fluorescein and beta-lactam antibiotic. The beta-lactamase can catalyze the fluorescence substrate probe to emit strong fluorescence, and the content of beta-lactamase is calculated according to the fluorescence intensity obtained through a reaction. 0.1ng / mL of Beta-lactamase can be detected through the method, the sensitivity of the method is two orders of magnitude higher than that of traditional ELISA methods, the detection time is shortened to 45min, and the method also has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity, rapid detection, and great reduction of the detection cost.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Fluorogenic substrates
InactiveUS6949632B2Increase conversion rateHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesAntibioticsWater solubleHydrolysis
The subject invention provides compounds useful as fluorogenic substrates for the hydrolytic enzymes. Upon hydrolysis of the hydrolyzable group, a halo-pyrene substituted molecule is developed which is highly fluorescent, water soluble and exhibits several desirable characteristics, including a large Stokes' shift.
Owner:CHROMAGEN
Fluorogenic substrate for adamts13
InactiveUS20130023004A1High detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFluorophoreAmino acid composition
Disclosed are fluorogenic substrates for measuring ADAMTS13 activity or ADAMTS13 inhibitor activity. Substrates can comprise an oligopeptide which can consist of up to 80 amino acids of sequence of von Willebrand Factor (VWF). The oligopeptide can include modifications of sequence of VWF, including an amino-terminal glycine, a scissile Y-M peptide, and a cysteine substitution located from 1 to 12 amino acids from the scissile Y-M in the carboxy terminal direction. A substrate can further comprise a fluorophore and a fluorescence quencher bound to the oligopeptide on opposite sides of the scissile Y-M peptide, wherein the fluorescence quencher is not identical to the fluorophore. An oligopeptide can be encoded by a nucleic acid sequence which can also encode a His tag. An oligopeptide can be expressed in a cell or microorganism. Also disclosed are methods of using a fluorogenic substrate to measure ADAMTS13 activity or ADAMTS13 inhibitor activity.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Reagent for detecting lipase and method for rapidly detecting lipase
ActiveCN103983626AImprove stabilityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceDairy foodsPreservative
The invention discloses a reagent for rapidly detecting lipase in a dairy food. The reagent comprises a solution A, a solution B and a standard substance, wherein the standard substance is methoxyl resorufin, the solution A is a PBS, and the solution B contains a fluorogenic substrate, a buffer solution, an emulsifying agent and a preservative. The invention further discloses a method for rapidly detecting lipase in the dairy food by using the reagent. The method comprises the steps: drawing a standard curve, reading a sample fluorescence value and calculating the lipase enzyme. According to the method, the sensitivity is high, the operation is simple, the workload is small, the system errors are small, multiple test repeatability is good, rapidness and convenience are achieved, and a detection result can be obtained within 20-60min.
Owner:淮安安福科技有限公司
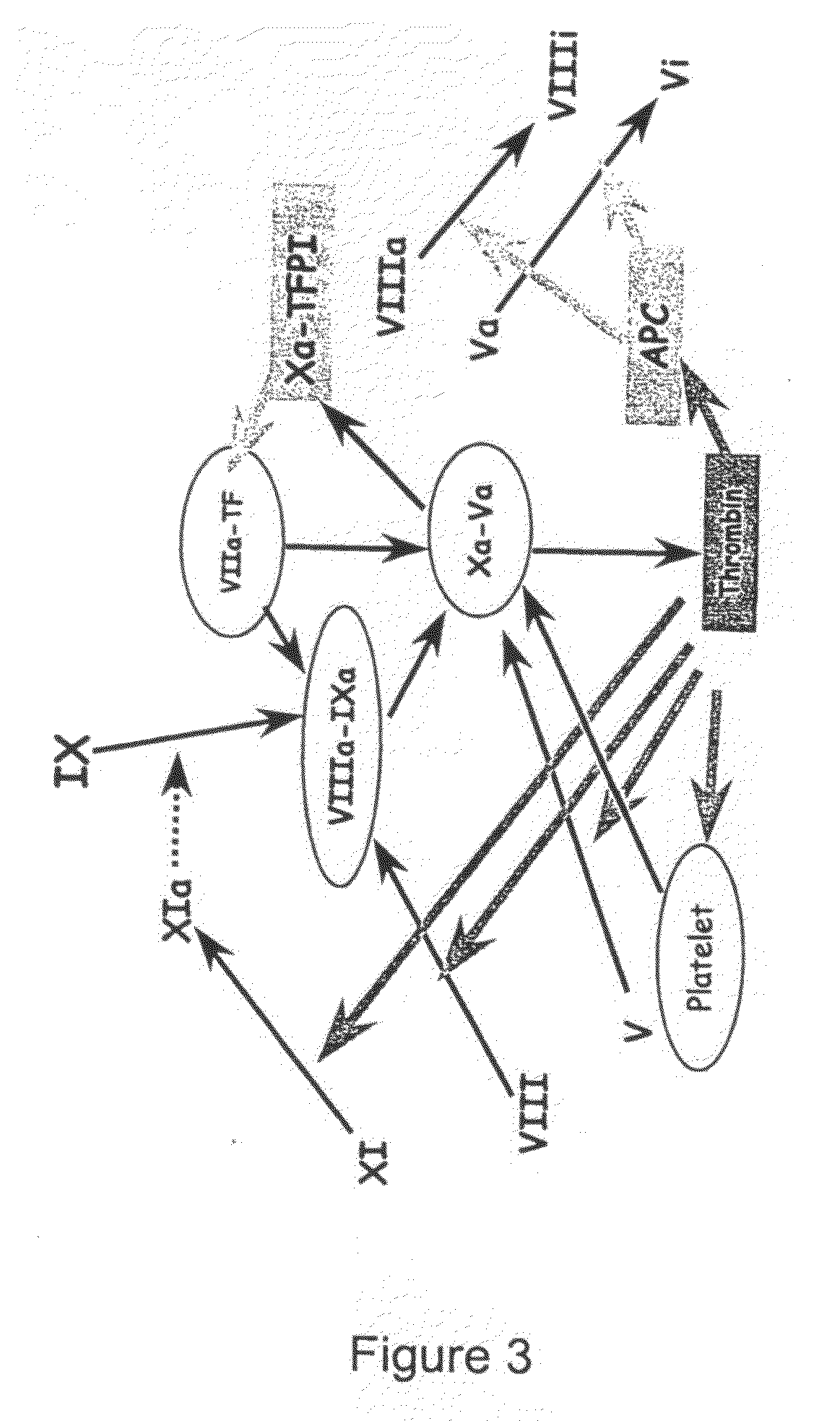
Method for detecting activated blood coagulation factor XI in human intravenous immunoglobulin
ActiveCN103185710AAvoid preactivationIndirectly reflect changes in production contentFluorescence/phosphorescenceInitiation factorFactor ii
The invention discloses a method for detecting an activated blood coagulation factor XI in human intravenous immunoglobulin. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) mixing an IVIG (intravenous immunoglobulin) sample with specially-preprocessed platelet-poor plasma (PPP); (2) adding a thrombin specific fluorogenic substrate with a phospholipid agent into a reaction system; (3) adding an initiation factor for starting a TGT (thrombin generation test), wherein the initiation factor comprises a calcium ion source and the phospholipid agent; (4) obtaining a thrombin generation curve providing parameters by the optimized reaction system; and (5) negatively correlating the peak time of thrombin (TTP) of the detected sample with the FXIa (activated blood coagulation factor XI) level in the sample. The FXIa level in the detected sample can be indirectly obtained by comparing the TTP of the detected sample with that of an FXIa standard sample. The method is suitable for detecting residual micro FXIa in human intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) products and is used for extracorporal evaluation of thrombosis risk of related products.
Owner:BLOOD TRASFUSION INST CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Preparation method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting ovarian cancer tumor marker CA125 based on trypsin fluorogenic substrate
InactiveCN106442993AExcellent optical propertiesHigh detection sensitivityDisease diagnosisAntigenProtein markers
The invention relates to a preparation method of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting an ovarian cancer tumor marker CA125 based on a trypsin fluorogenic substrate. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology and a fluorescent detection technology are combined to prepare a detection probe through trypsin and a tumor marker corresponding antibody Ab2; the probe, the tumor marker and another tumor marker antibody Ab1 embedded into the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit can form a structure similar to a sandwich through the action between antigens of the antibodies; finally fluorescence is generated through the action between enzyme and the fluorescent substrate to qualitatively and quantitatively detect the ovarian cancer related tumor marker CA125, and a novel method for detecting protein markers is established. The preparation method has the characteristics that the whole preparation process is simple and suitable for industrial production; the protein markers can be qualitatively and quantitatively detected according to the fluorescent characteristics of the fluorogenic substrate and the action of the fluorogenic substrate with the enzyme, and the specificity is good; the whole detection process is low in cost and very convenient to operate; the novel method for detecting the protein markers is established.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and Apparatus for Rapid Detection and Identification of Live Microorganisms Immobilized On Permeable Membrane by Antibodies
InactiveUS20100227338A1Quick checkQuick identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismImmobilized Antibodies
An apparatus and method is provided for the rapid detection, identification and / or enumeration of one or more live target microorganisms growing on solid nutrient media or filtration membrane. Microcolonies or colonies attach to a porous transfer permeable membrane loaded with immobilized antibodies specific for target microorganisms. Non-specific cells are washed out of the permeable membrane and the membrane then is placed on a container containing a chromogenic and / or a fluorogenic substrate and incubated to allow coloration and subsequent identification and enumeration of color spots of targeted microorganisms and patterns of microcolonies or colonies.
Owner:NANOLOGIX INC
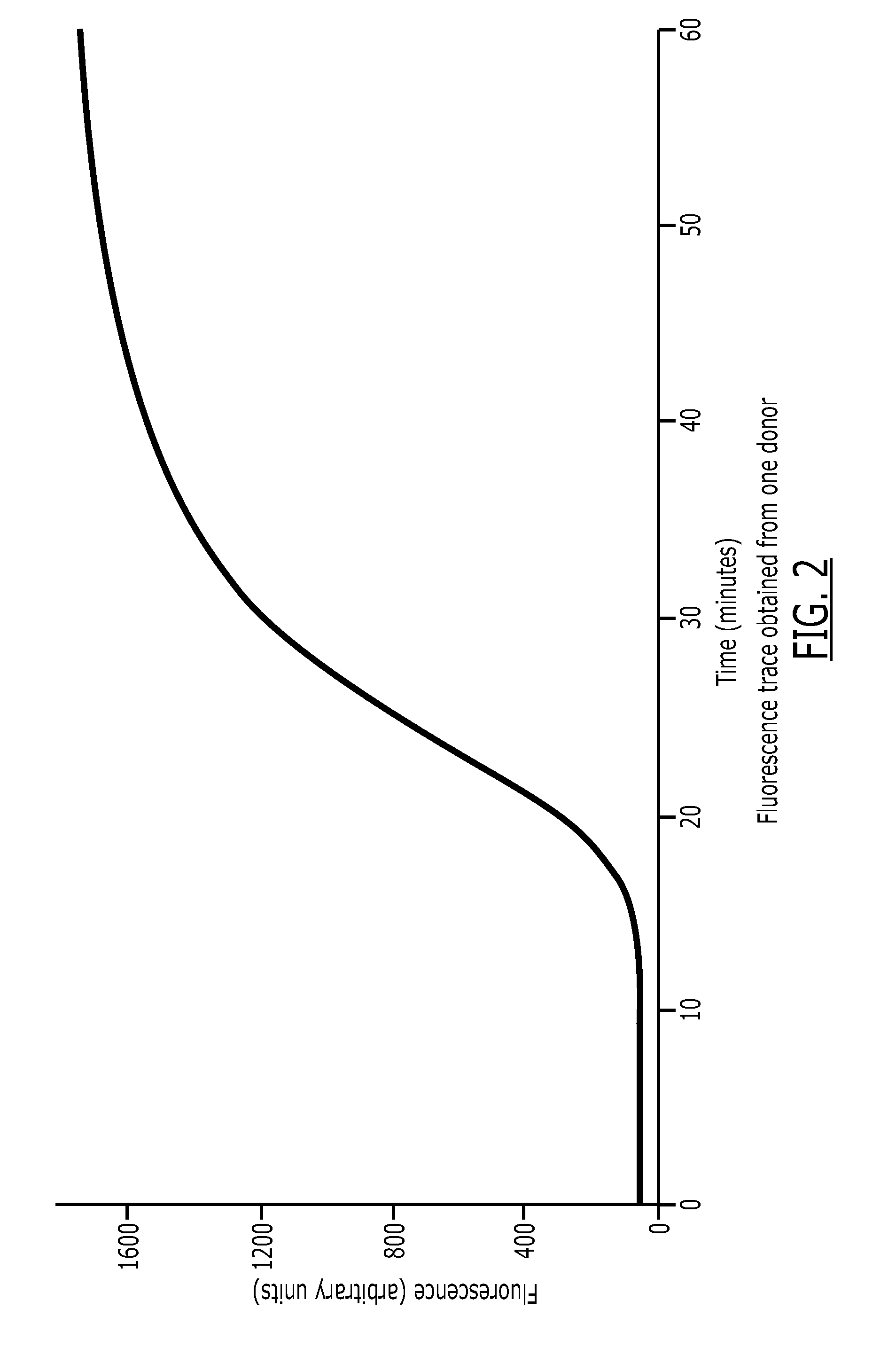
Thrombin Generation Determination Method
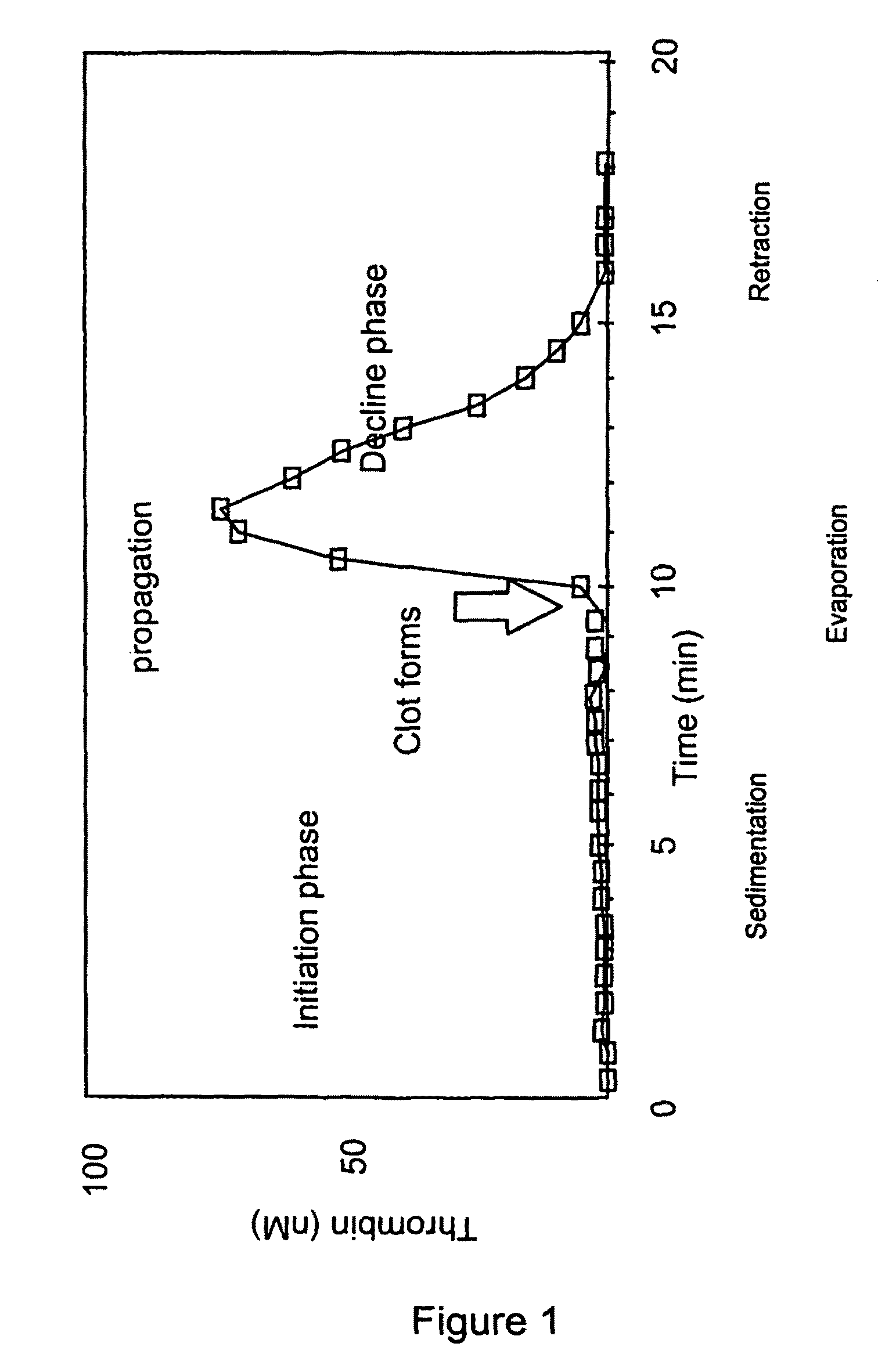
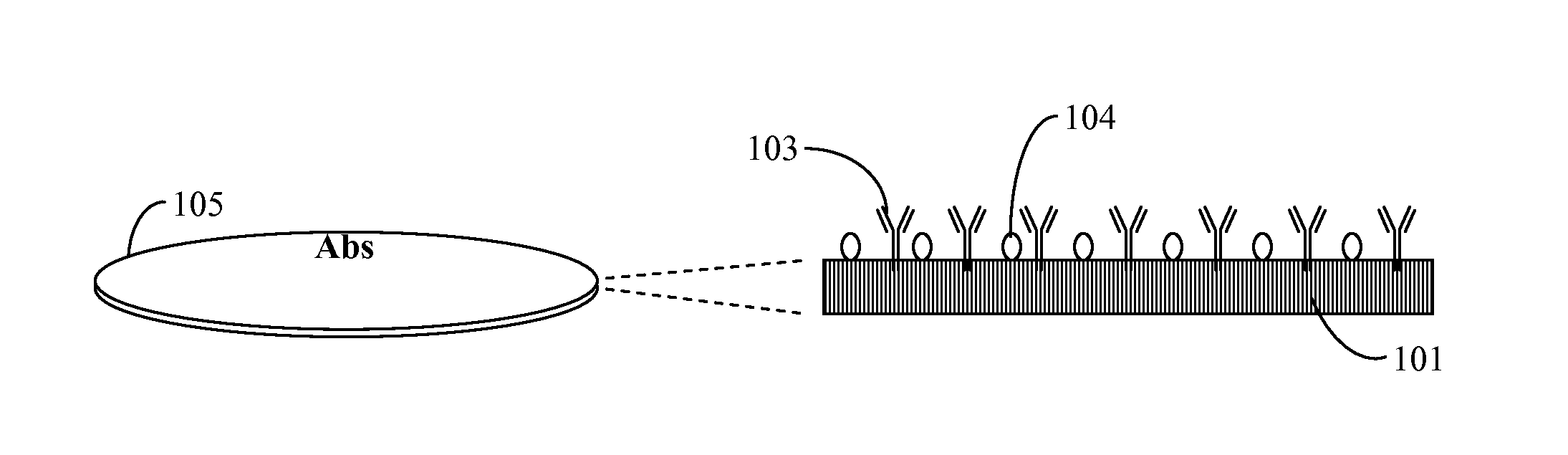
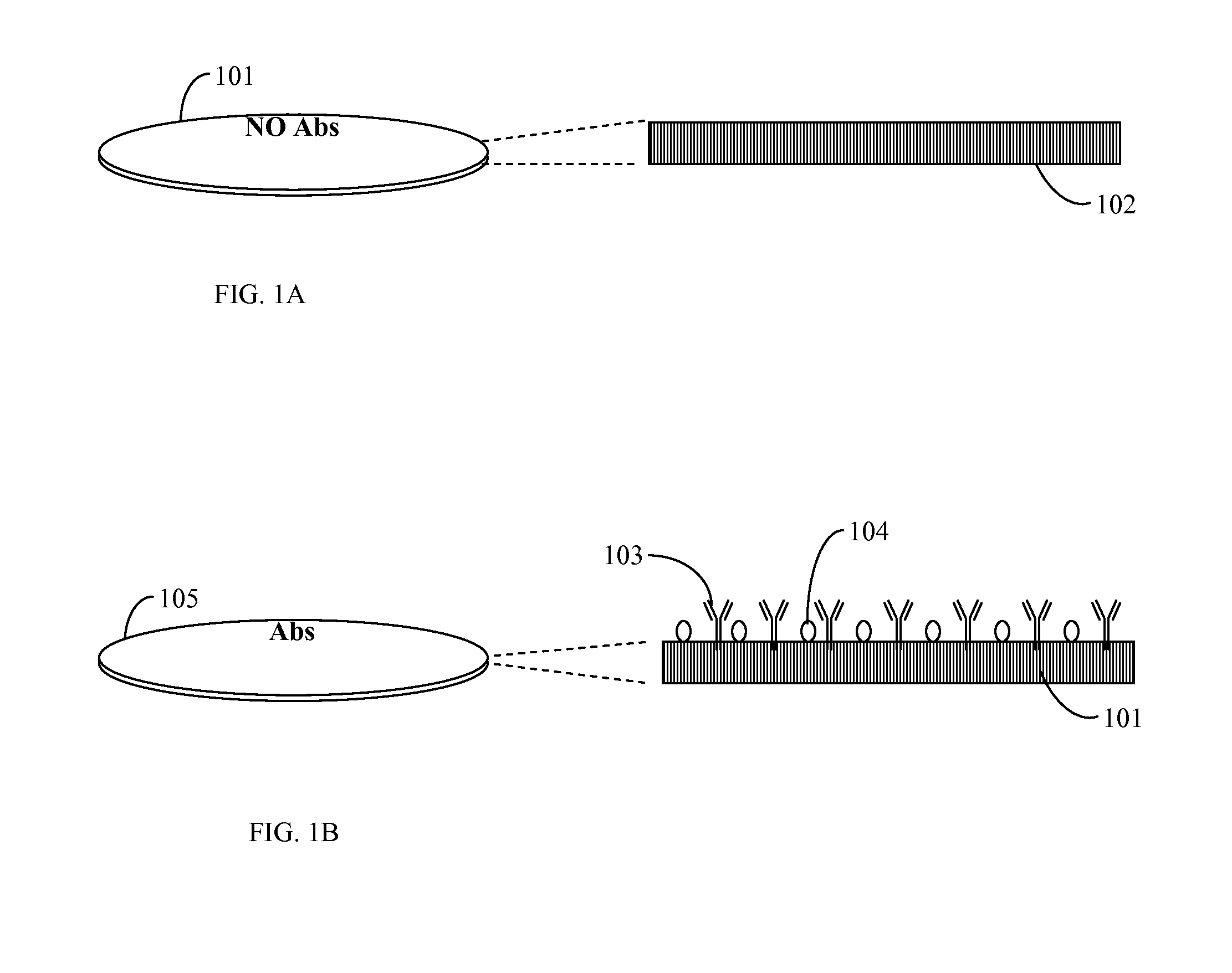
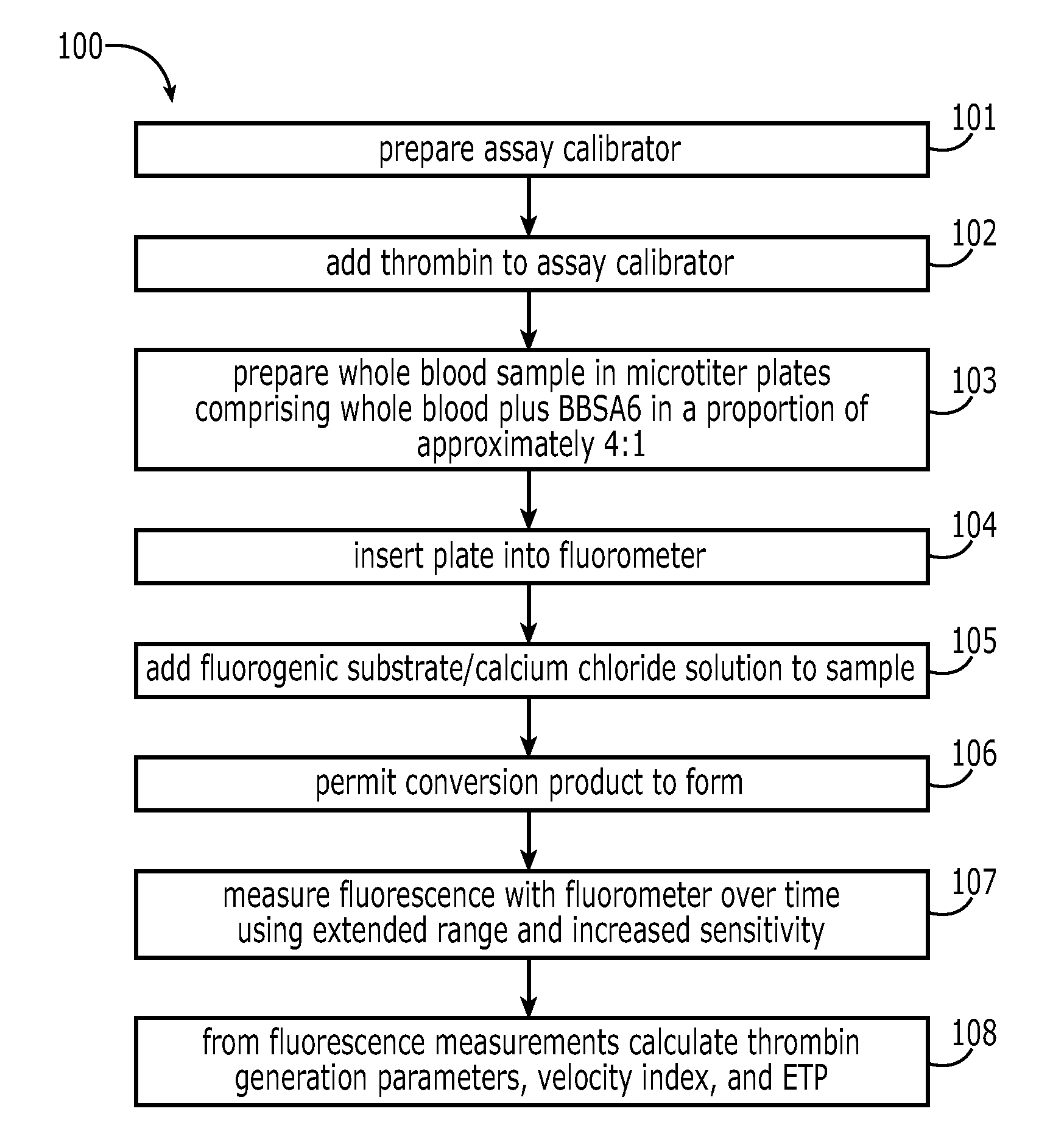
InactiveUS20110183365A1Reliable measurement methodMinimally dilutedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTemporal changeThrombin generation
A method for measuring a generation of thrombin in a sample of whole blood as a function of time includes adding to a sample of whole blood a fluorogenic substrate and a thrombin activator to form an activated sample. A conversion product is permitted to form in the activated sample. Fluorescence is measured as a function of time from a fluorescent group that is released during the formation of the conversion product with the use of a fluorescence detector. The fluorescence detector operates in an extended range mode and has an increased sensitivity. Thrombin generation as a function of time can then be calculated from the measured fluorescence as a function of time.
Owner:ADVENTIST HEALTH SYSTSUNBELT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com