Patents
Literature
203 results about "Spect imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
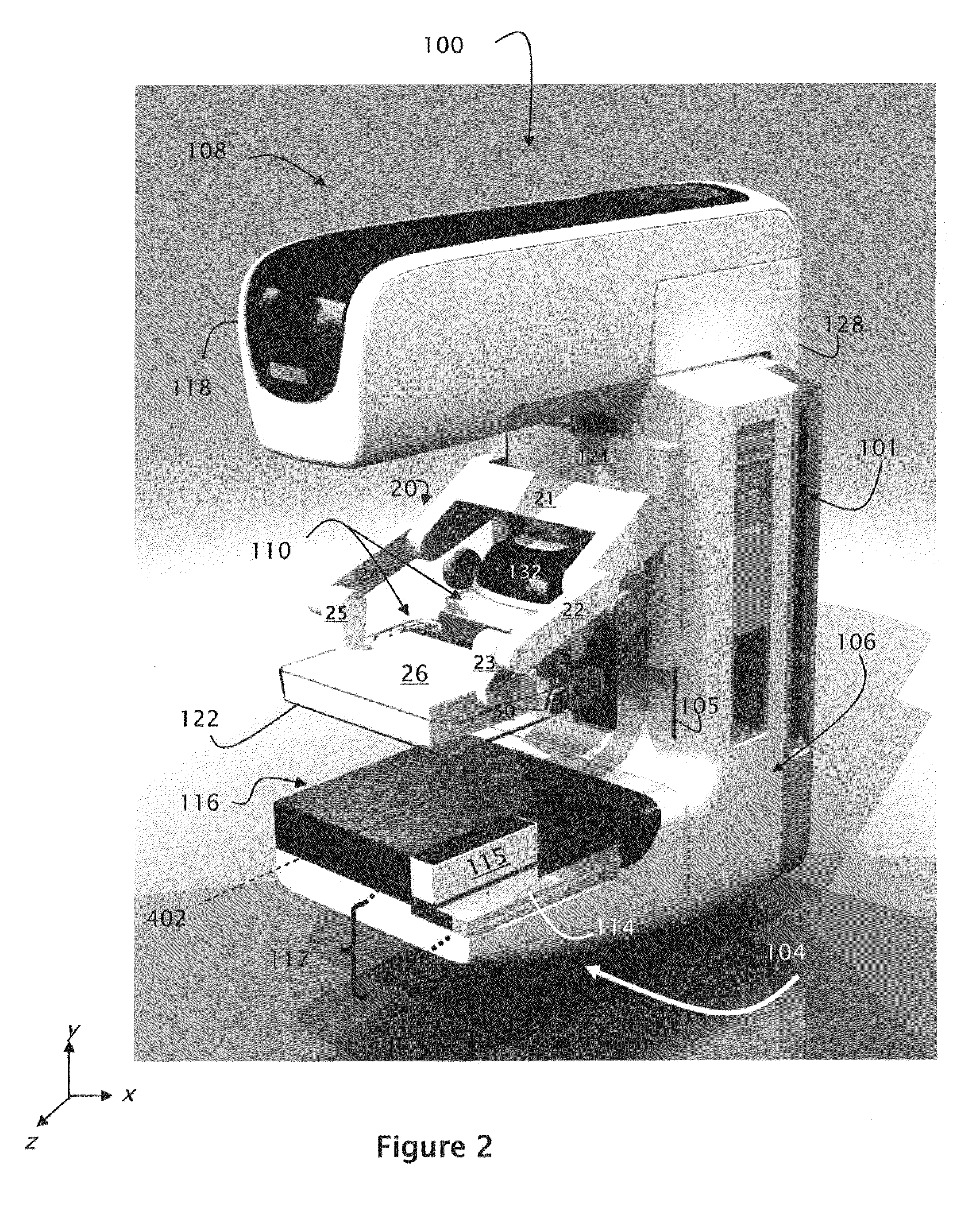
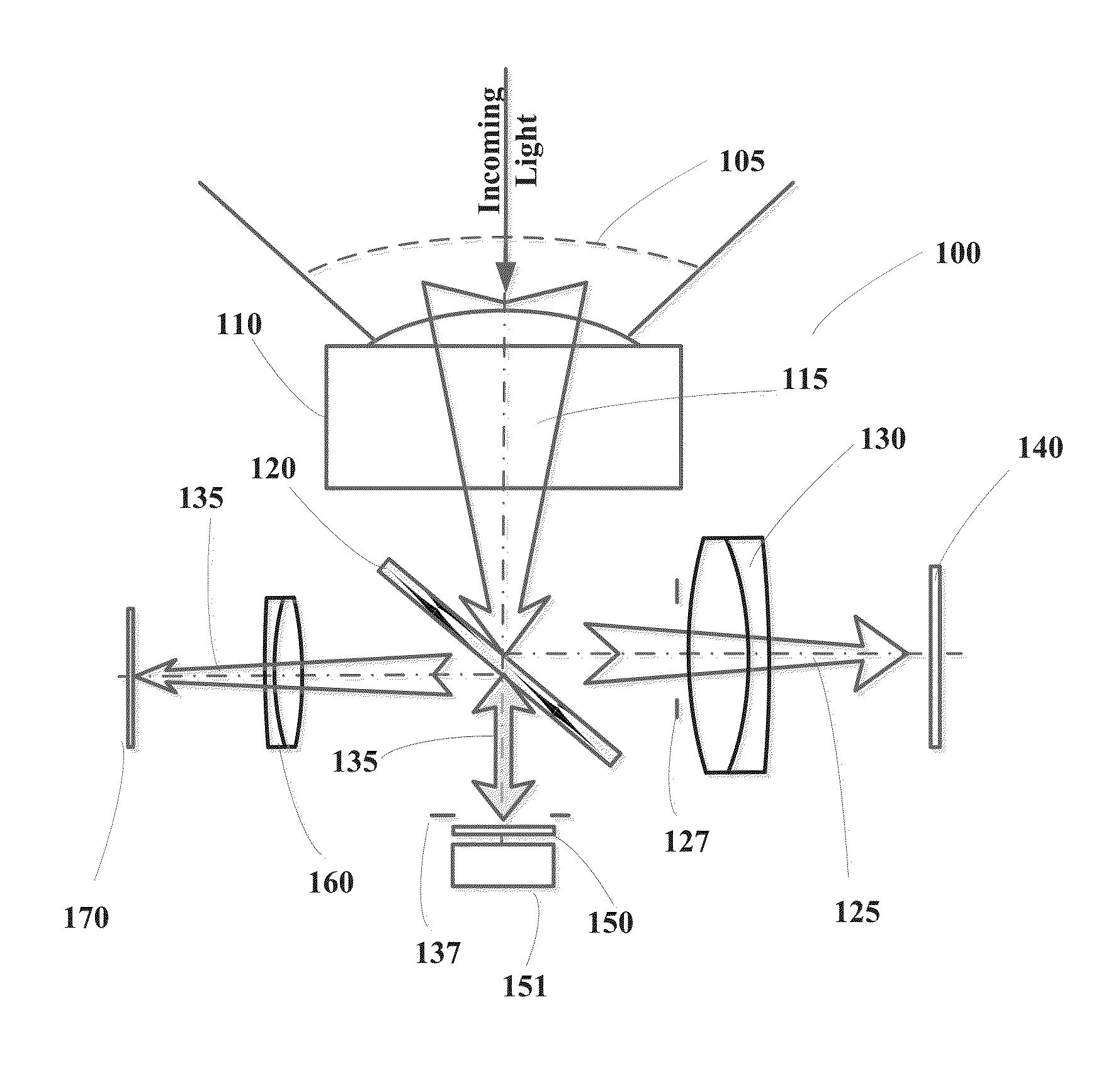
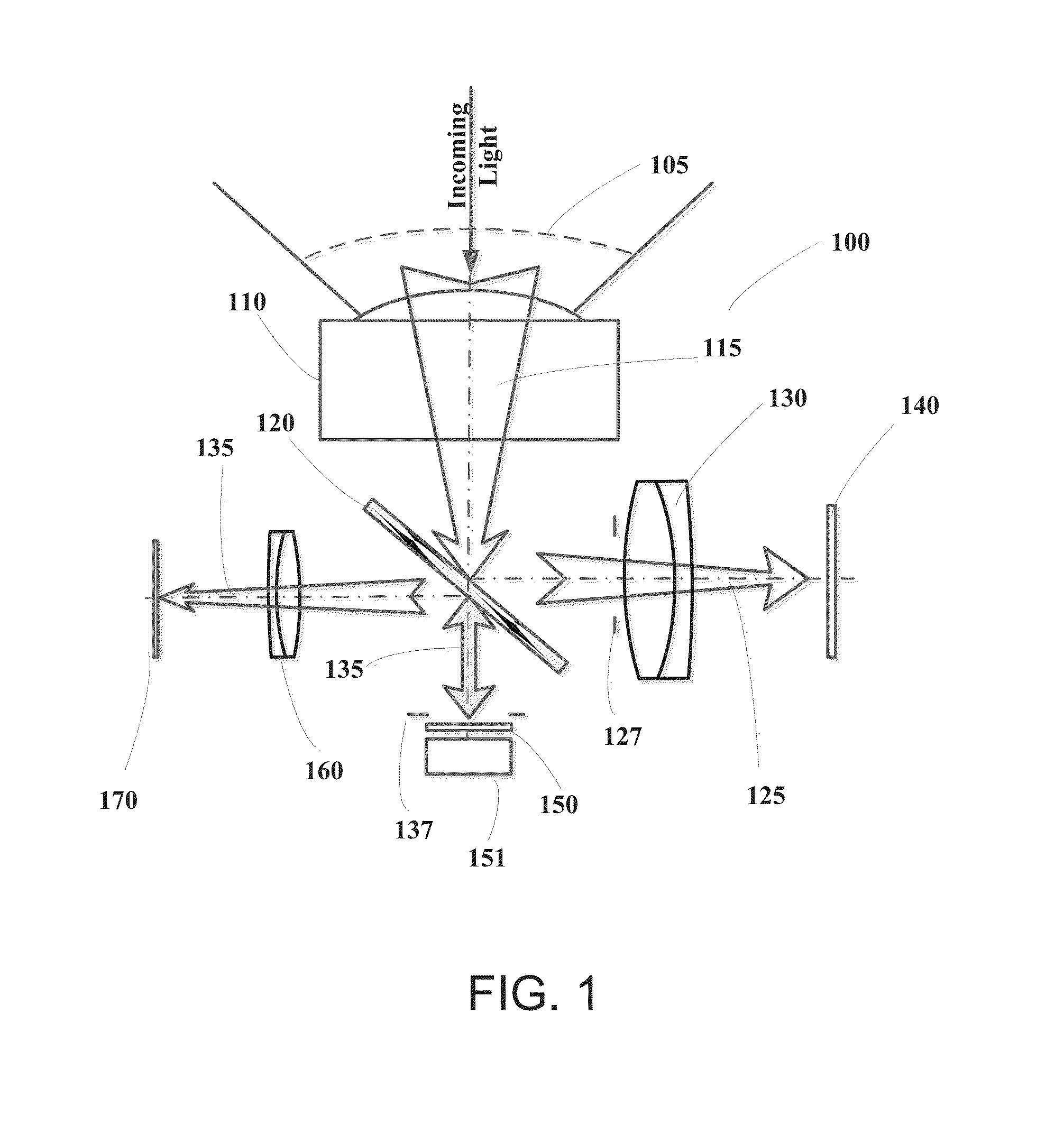
Wide-field of view (FOV) imaging devices with active foveation capability
ActiveUS20140218468A1High resolutionIncrease frame rateTelevision system detailsPrismsWide fieldFoveated imaging
The present invention comprises a foveated imaging system capable of capturing a wide field of view image and a foveated image, where the foveated image is a controllable region of interest of the wide field of view image.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Nuclear medicine tomography systems, detectors and methods
ActiveUS20150119704A1Reduce spatial resolutionAvoid interferenceRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImage resolution
An N-M tomography system comprising: a carrier for the subject of an examination procedure; a plurality of detector heads; a carrier for the detector heads; and a detector positioning arrangement operable to position the detector heads during performance of a scan without interference or collision between adjacent detector heads to establish a variable bore size and configuration for the examination. Additionally, collimated detectors providing variable spatial resolution for SPECT imaging and which can also be used for PET imaging, whereby one set of detectors can be selectably used for either modality, or for both simultaneously.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Integrated Breast X-Ray and Molecular Imaging System
ActiveUS20100260316A1Increase speedImprove accuracyTomosynthesisMaterial analysis by optical meansTomosynthesisMolecular imaging
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Radioimaging applications of and novel formulations of teboroxime
ActiveUS20100140483A1Material analysis by optical meansRadioactive preparation carriersCardiac imagingSpect imaging
A method for cardiac imaging is provided, including administering to an adult human subject an amount of a teboroxime species having a radioactivity of less than 5 mCi at a time of administration, and performing a SPECT imaging procedure of a cardiac region of interest (ROI) of the subject. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
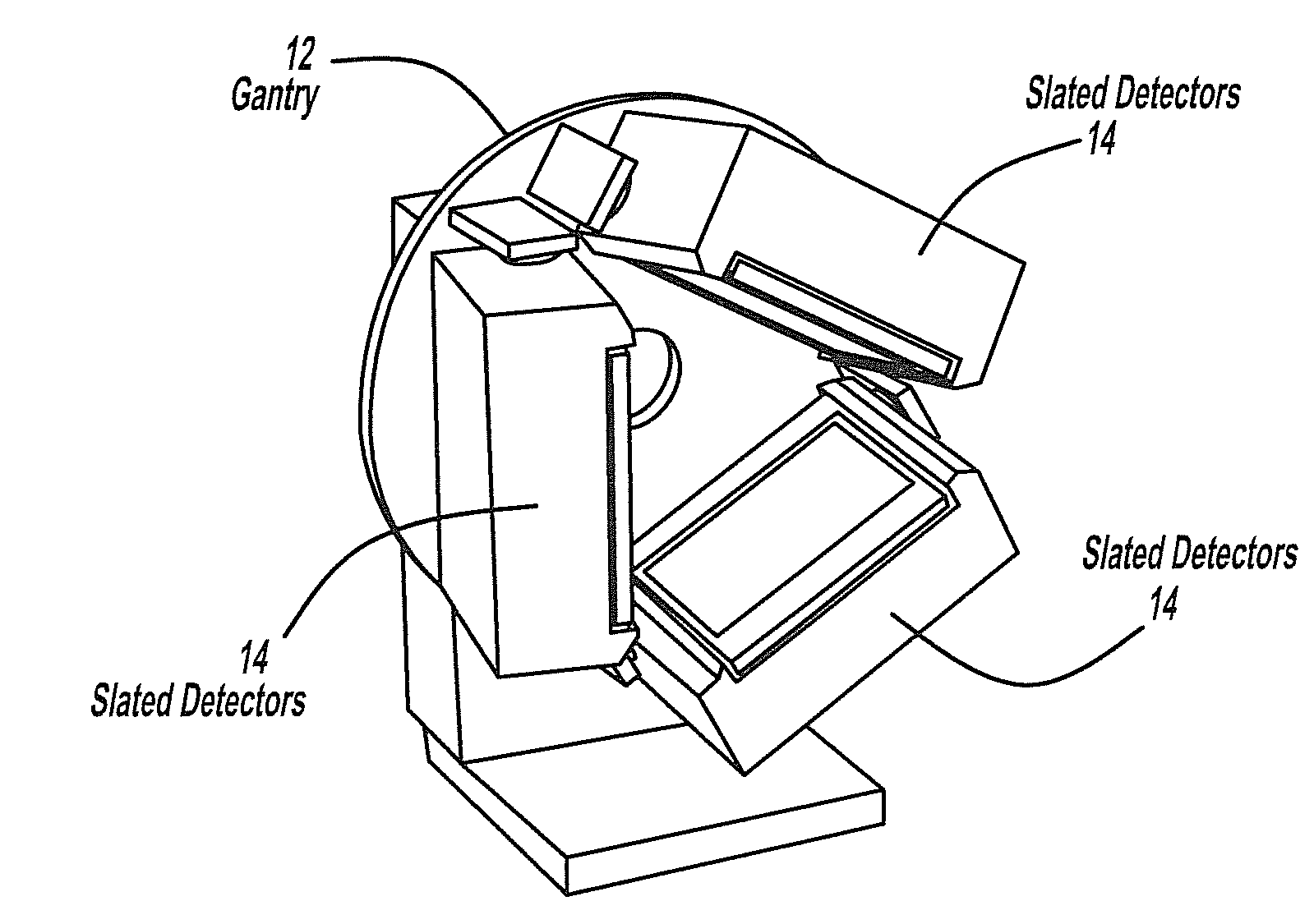
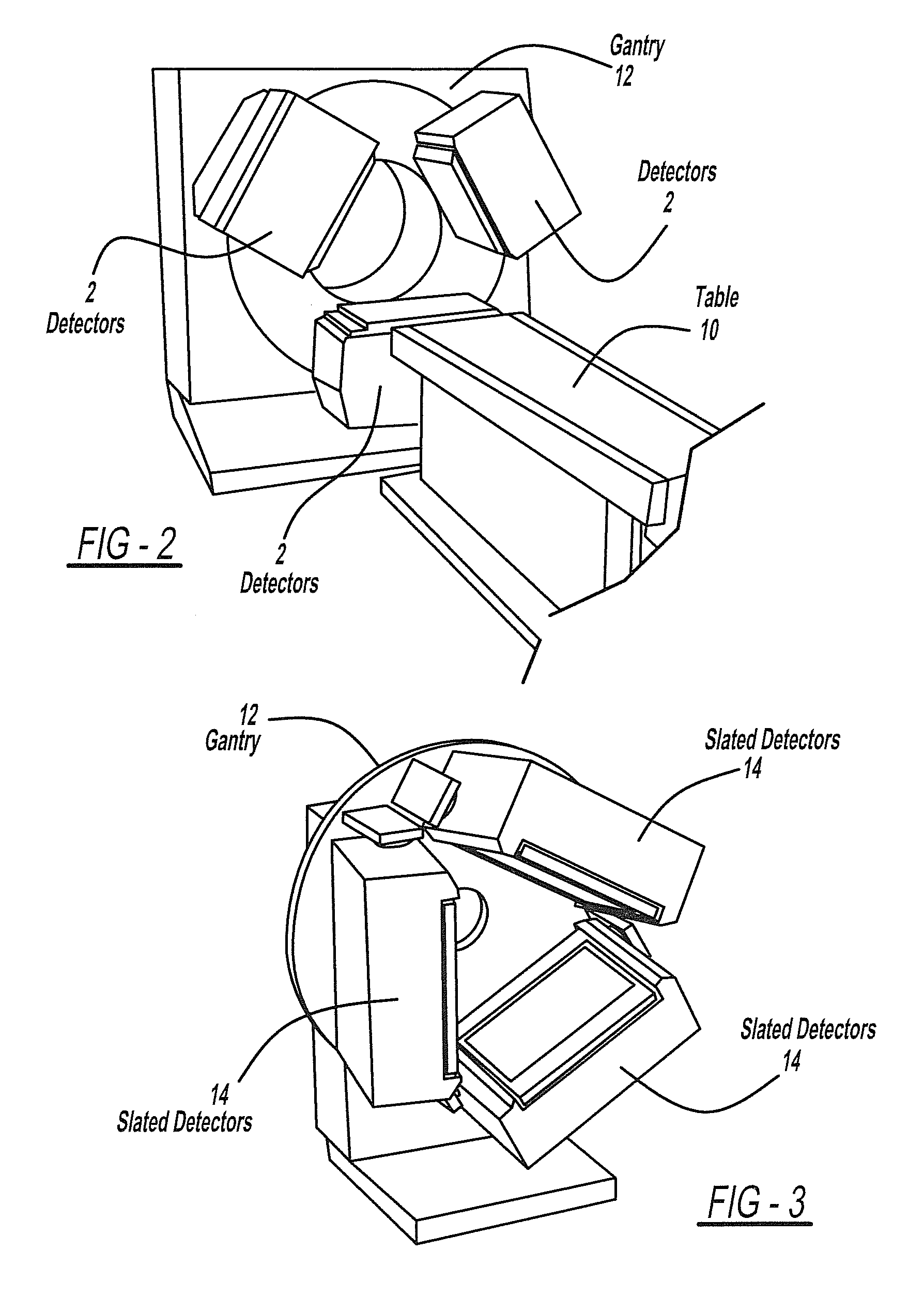
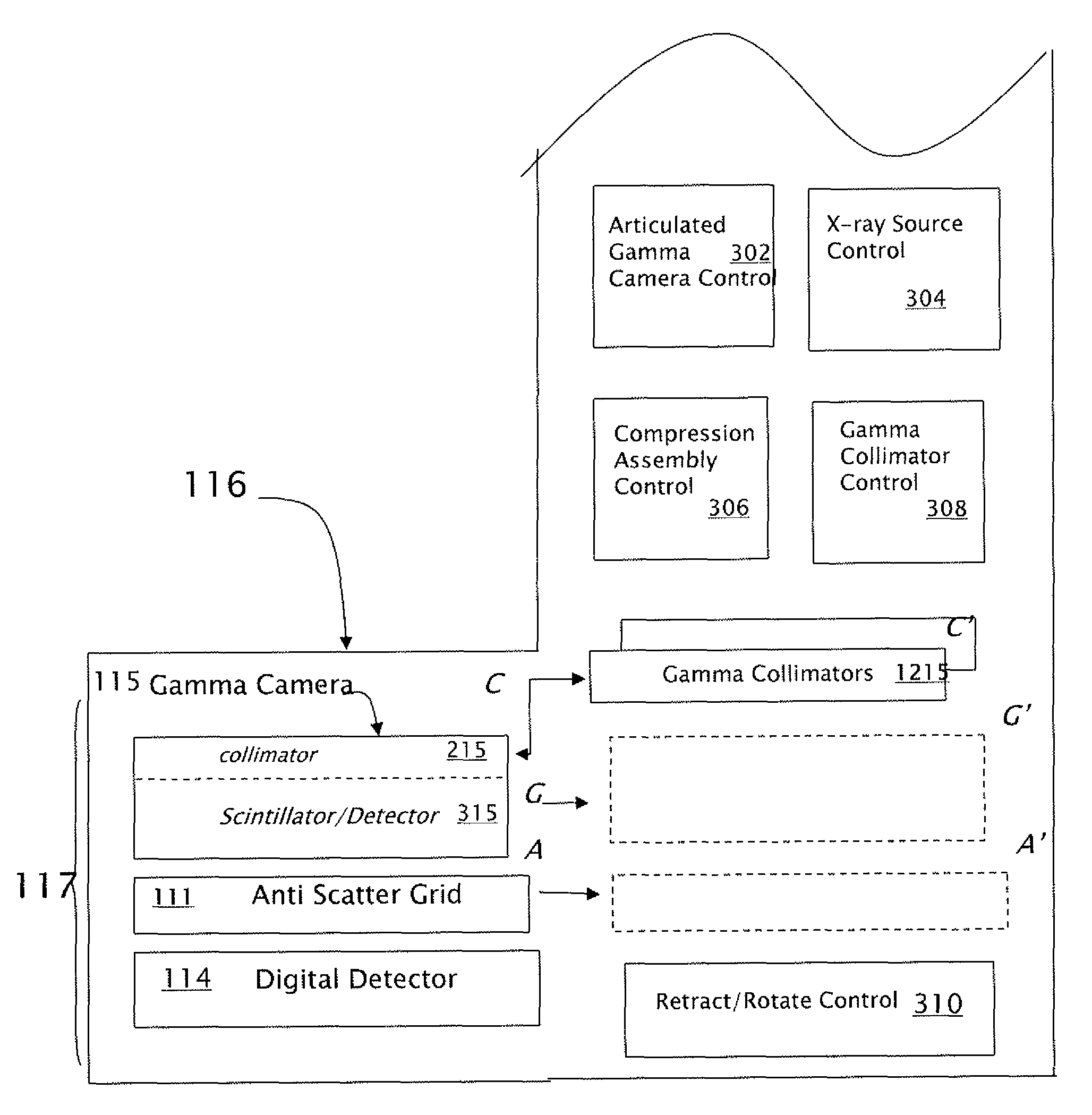
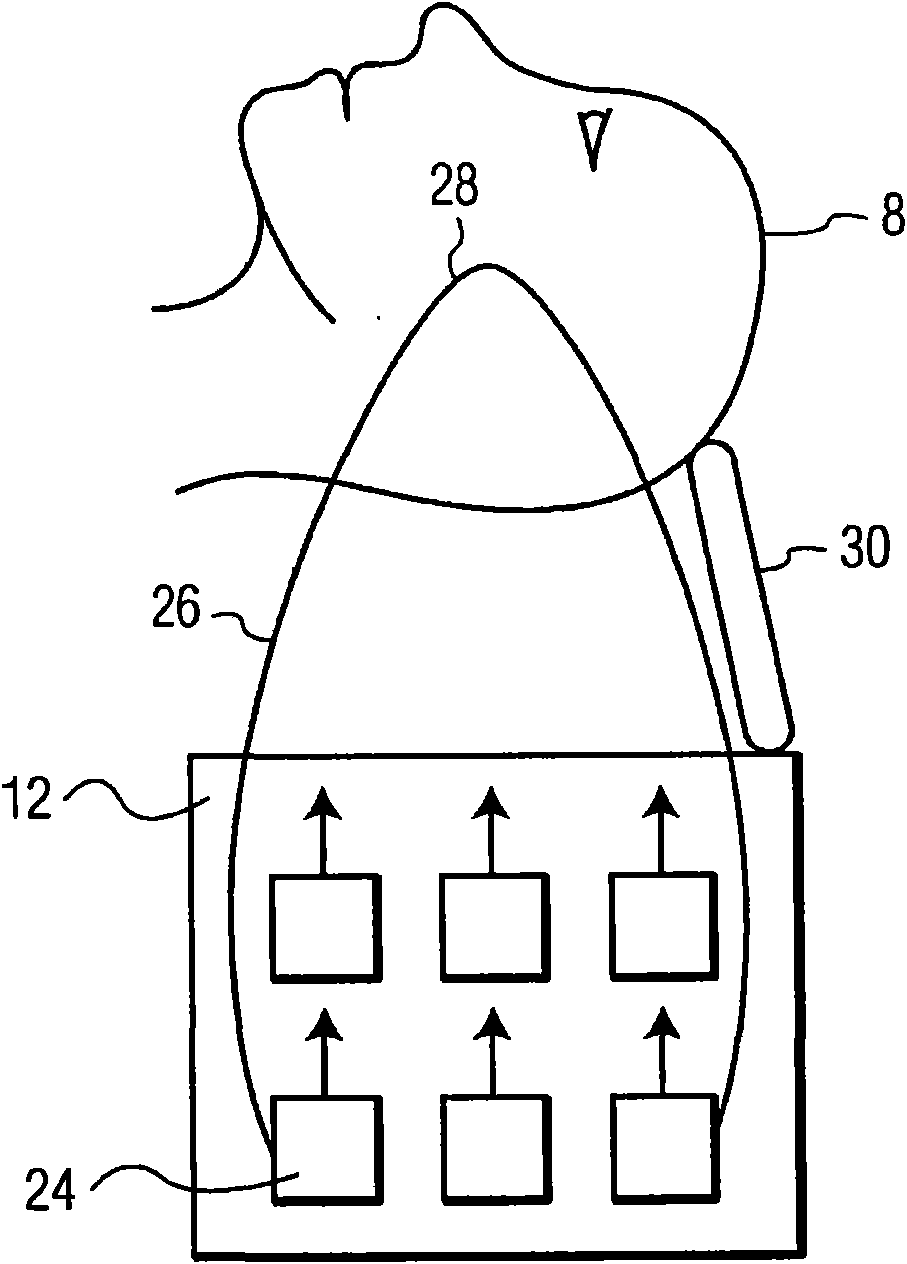
Gamma camera system with slanted detectors, slanted collimators, and a support hood
InactiveUS20100001192A1Improving camera workflowHigh outputHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPatient positioning for diagnosticsImaging qualityEngineering
According to the present invention, there is provided a gamma camera system for brain SPECT imaging including slanted detectors with slanted hole collimators and a special hood-shaped head support device. The present invention eliminates the need for radial detector motion and therefore for collision sensing devices and safety related circuitry as required in prior art gamma cameras. Furthermore, the design and shape of the present invention reduces the necessary camera setup procedure, thereby improving camera workflow and output. The present invention's hood-shaped head support encapsulates the patient's head, preventing long hair from being entangled with the detectors while providing increased patient safety and comfort. Furthermore, the hood gently restrains the patients head, leading to less patient movement and improved image quality. In addition the hood enables very close detector proximity to the patient's head leading to further improvements in image quality.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
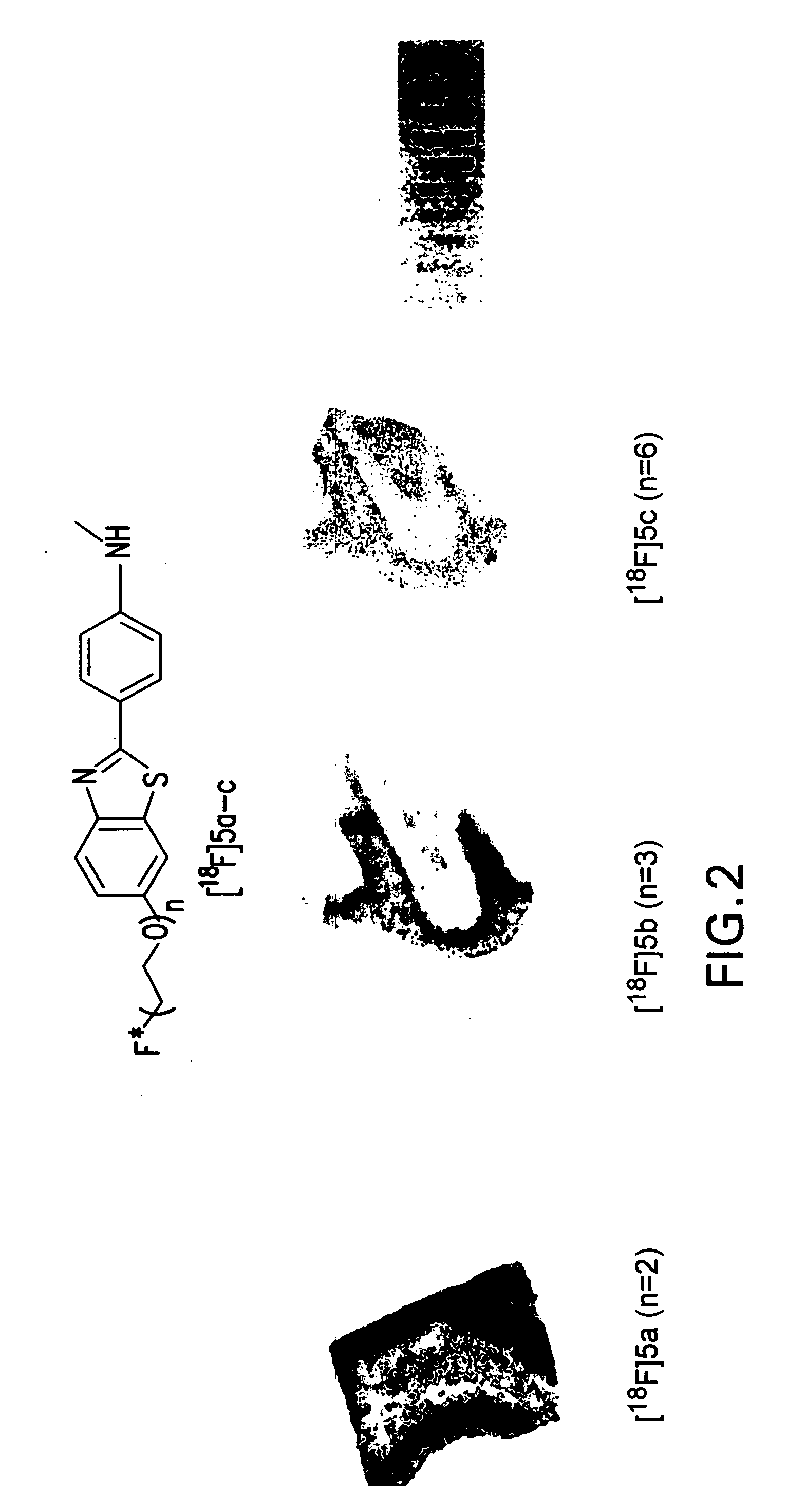
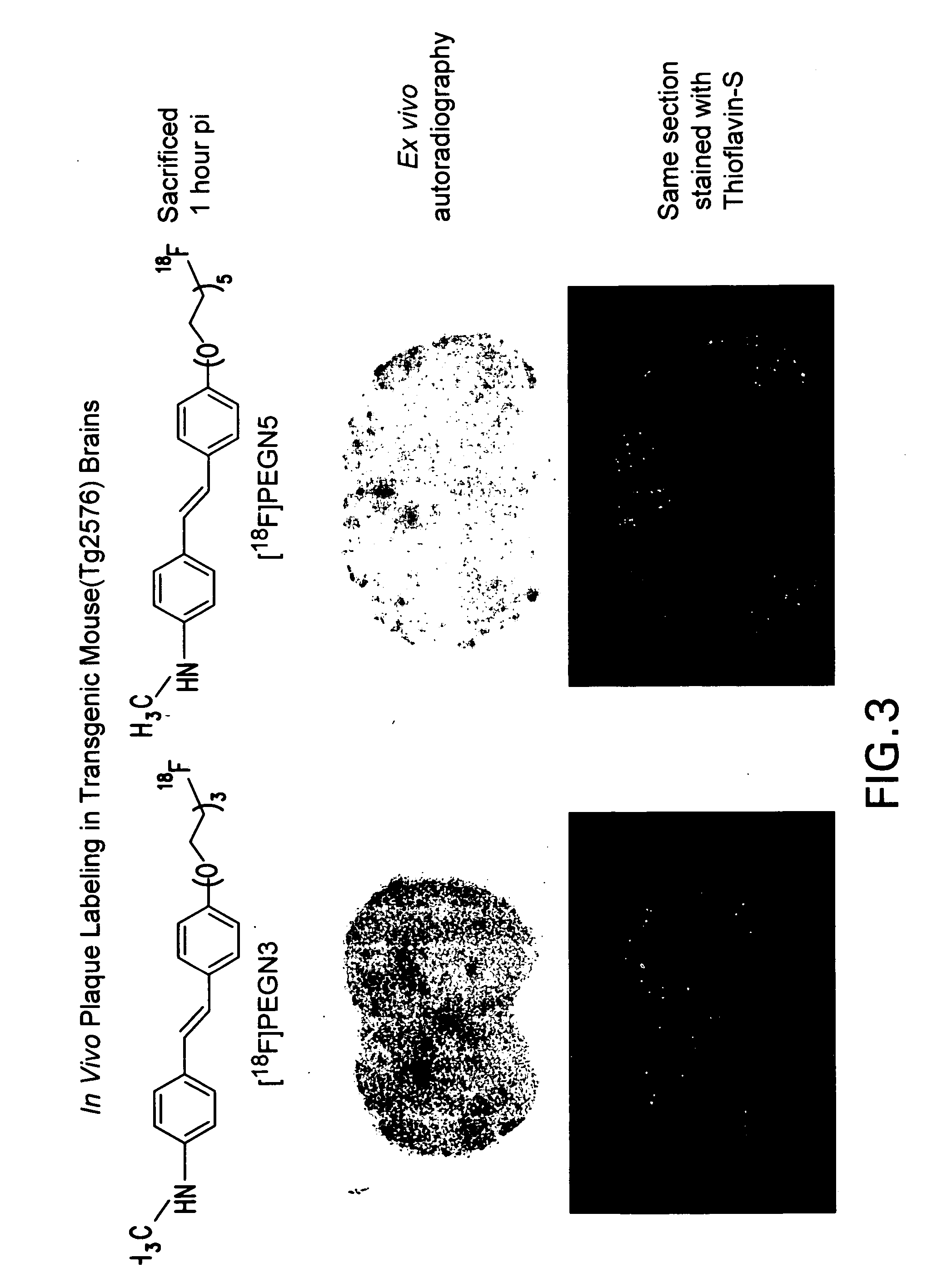
Radiolabeled-pegylation of ligands for use as imaging agents
InactiveUS20070031328A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCompound (substance)Imaging agent
The present invention is directed to a method of using radiolabeled ethylene glycol (n=1) (EG) or polyethylene glycol (n=from 2 to 10) (PEG) as a labeling group moiety on compounds that can be useful for imaging tissues. Specifically, the EG or PEG moiety preferably contains a radiofluorine (18F), and is covalently bonded to a ligand (L). The L portion of the molecule can be any molecule appropriate for covalently bonding with the radiolabeled EG or PEG moiety and subsequent use as an imaging agent. In particular, the imaging agent is preferably an agent suitable for administering to a mammal and detecting by PET or SPECT imaging.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
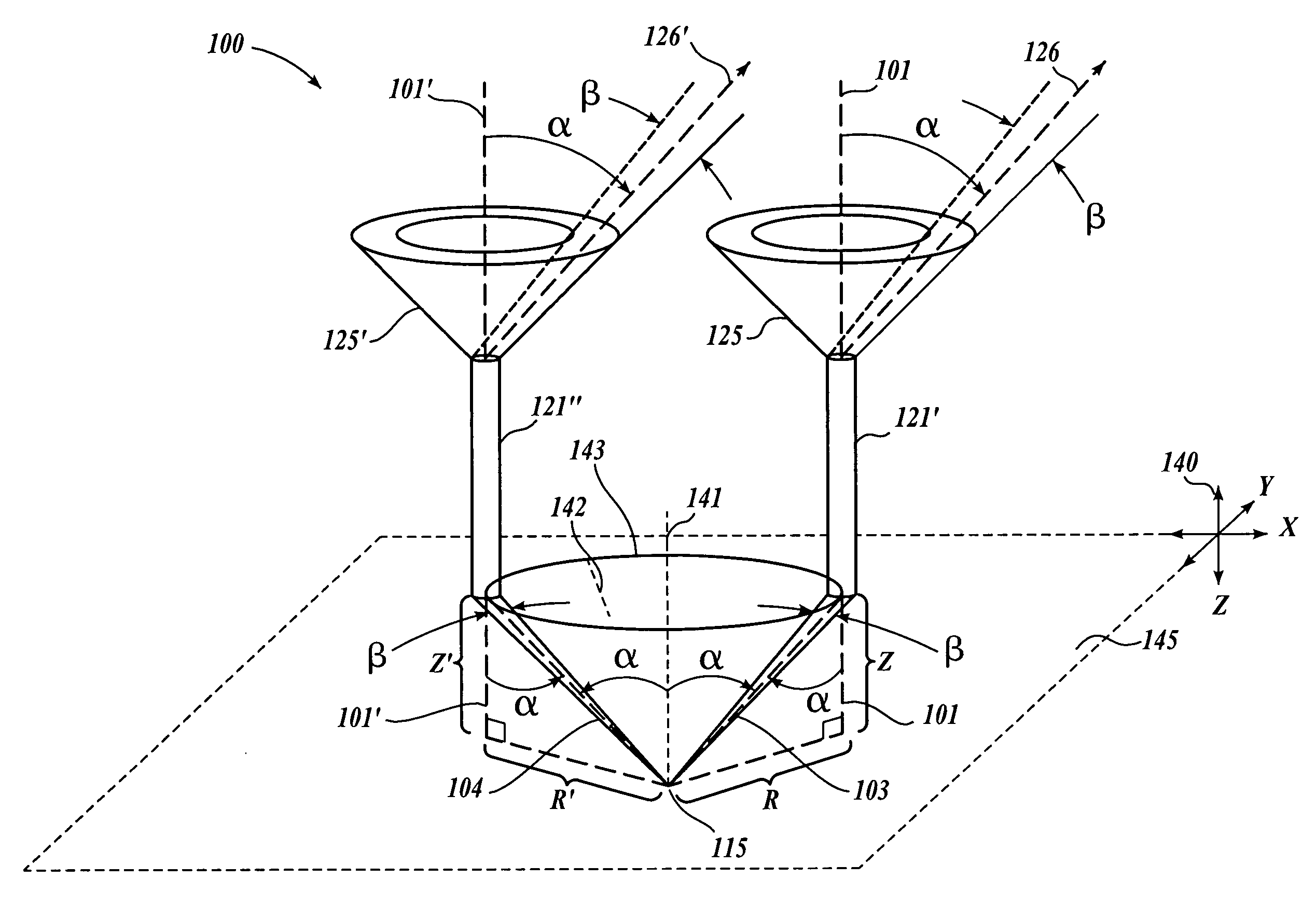
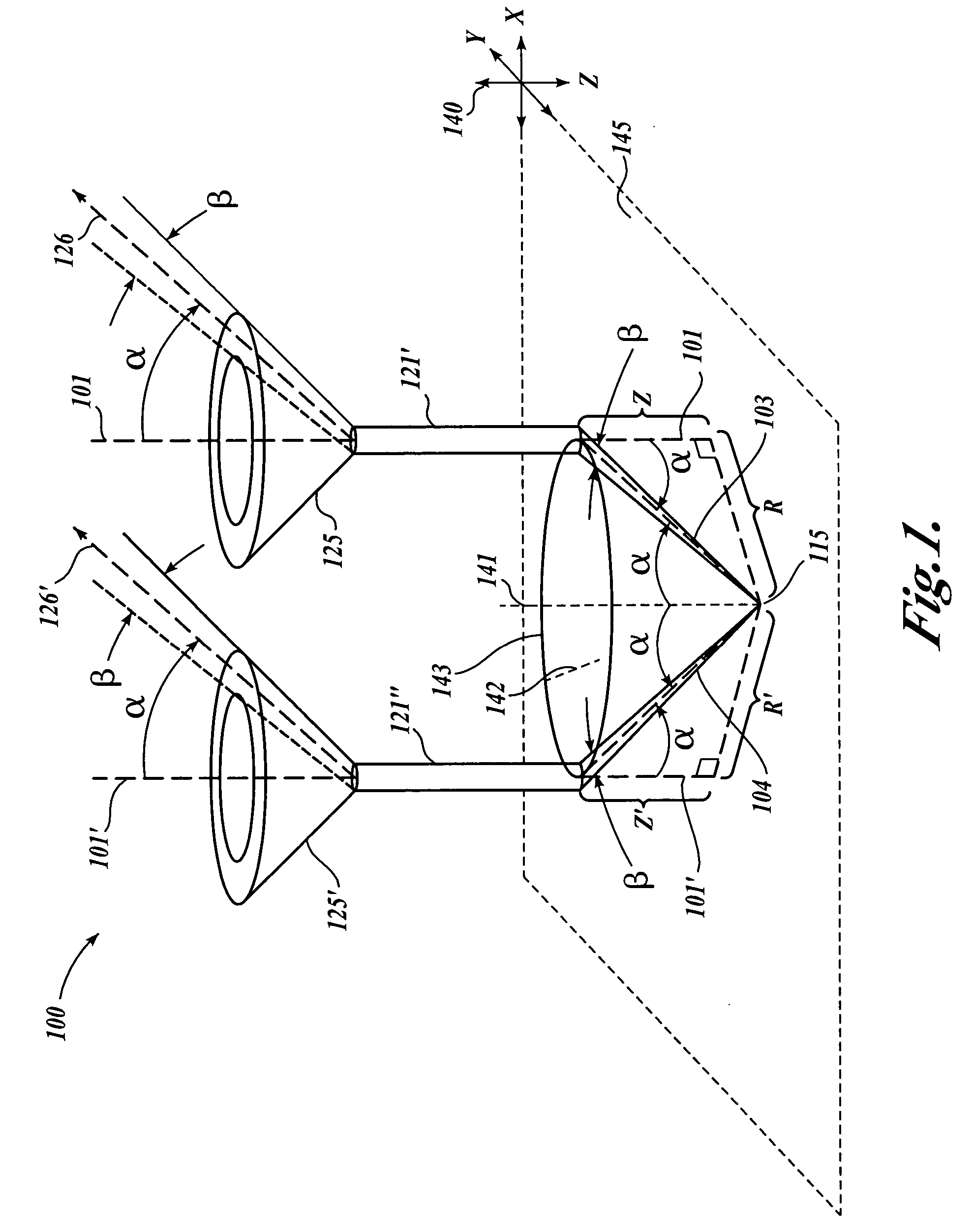
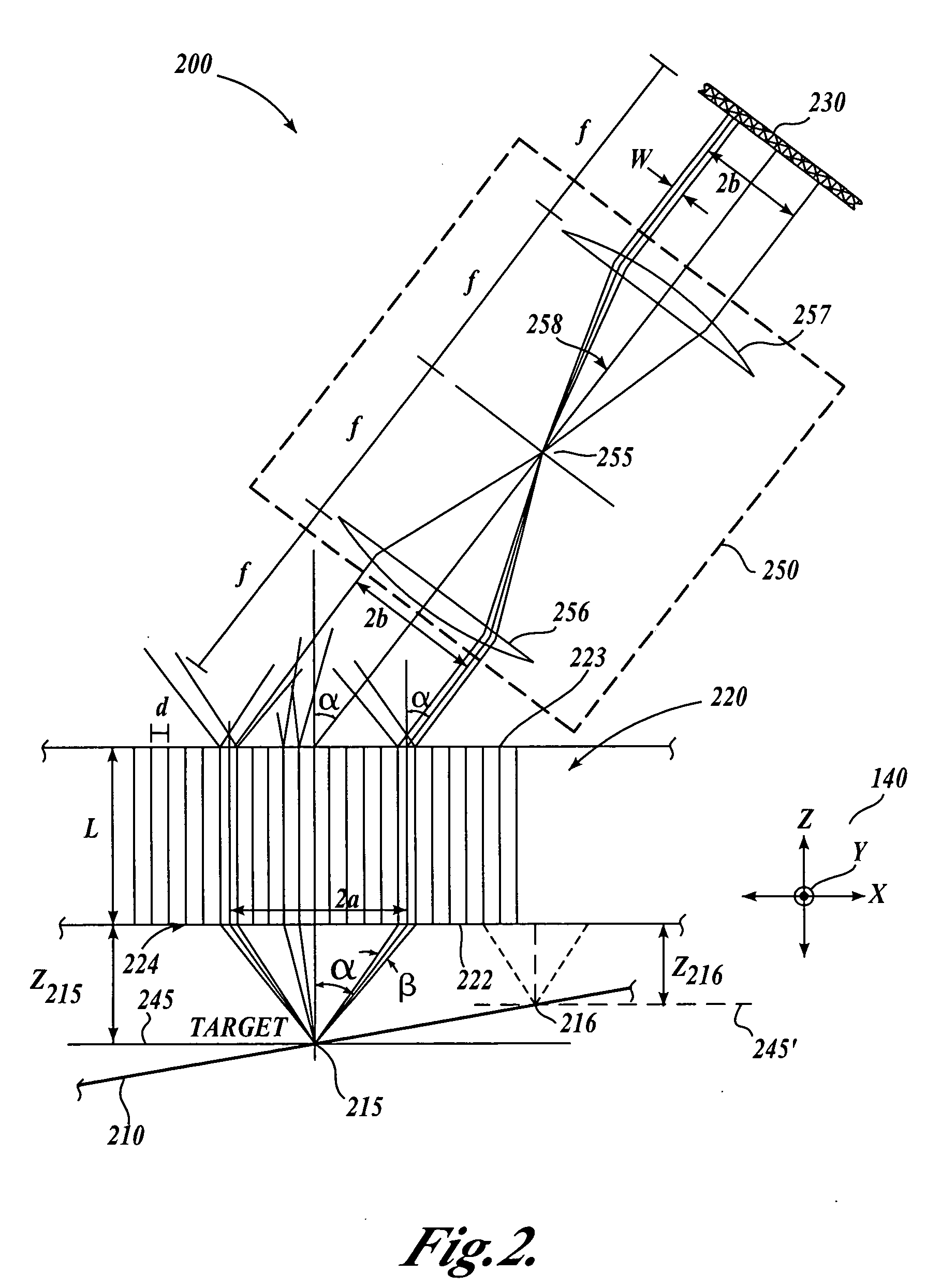
Optical path array and angular filter for translation and orientation sensing
ActiveUS20050211885A1Improve accuracyOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAbsolute measurementOrientation sensing
A position sensor using a novel optical path array (OPA) element, an angle-selective spatial filter, and an imaging array is capable of measuring the translation and orientation relative to a target member in X, Y, Z, yaw, pitch, and roll (“6D”) simultaneously, and with high precision. A target member includes an array of target points surrounded by a contrasting surface. The position sensor uses the OPA element in combination with the angle-selective spatial filter in a target point imaging arrangement such that the imaging array of the position sensor only receives light rays that enter the OPA element according to an operable cone angle α. Accordingly, each target point generally produces a ring-shaped image having a size on the imaging array that varies with the Z position of each target point. The X-Y position of each target point image on the imaging array varies with the X-Y position of each target point. Accordingly, three or more target point images analyzed in the same image are usable to determine a 6D measurement relative to the target member. X and Y displacement of the target member can be accumulated by known methods and the other 6D measurement components are absolute measurements at any position.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
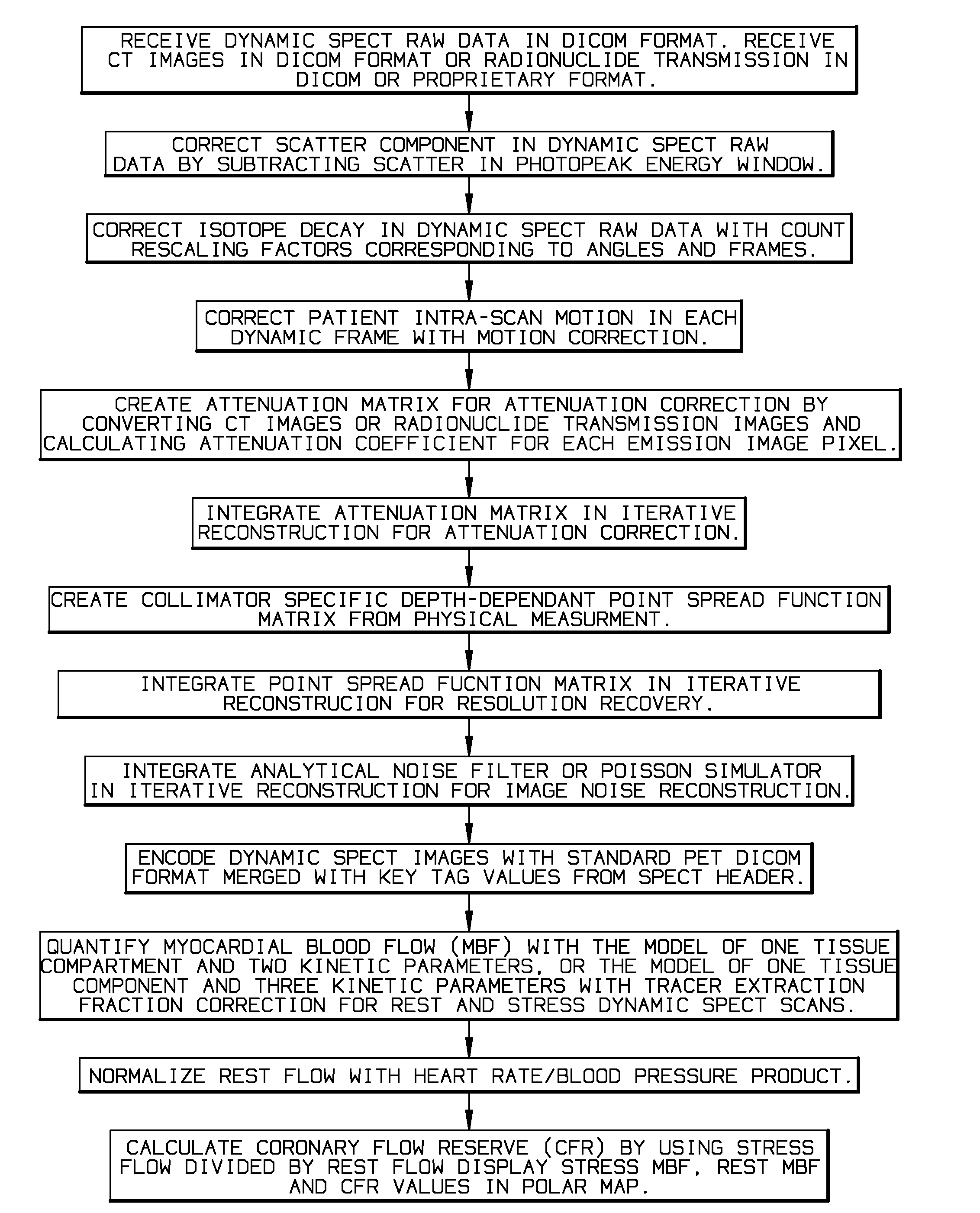
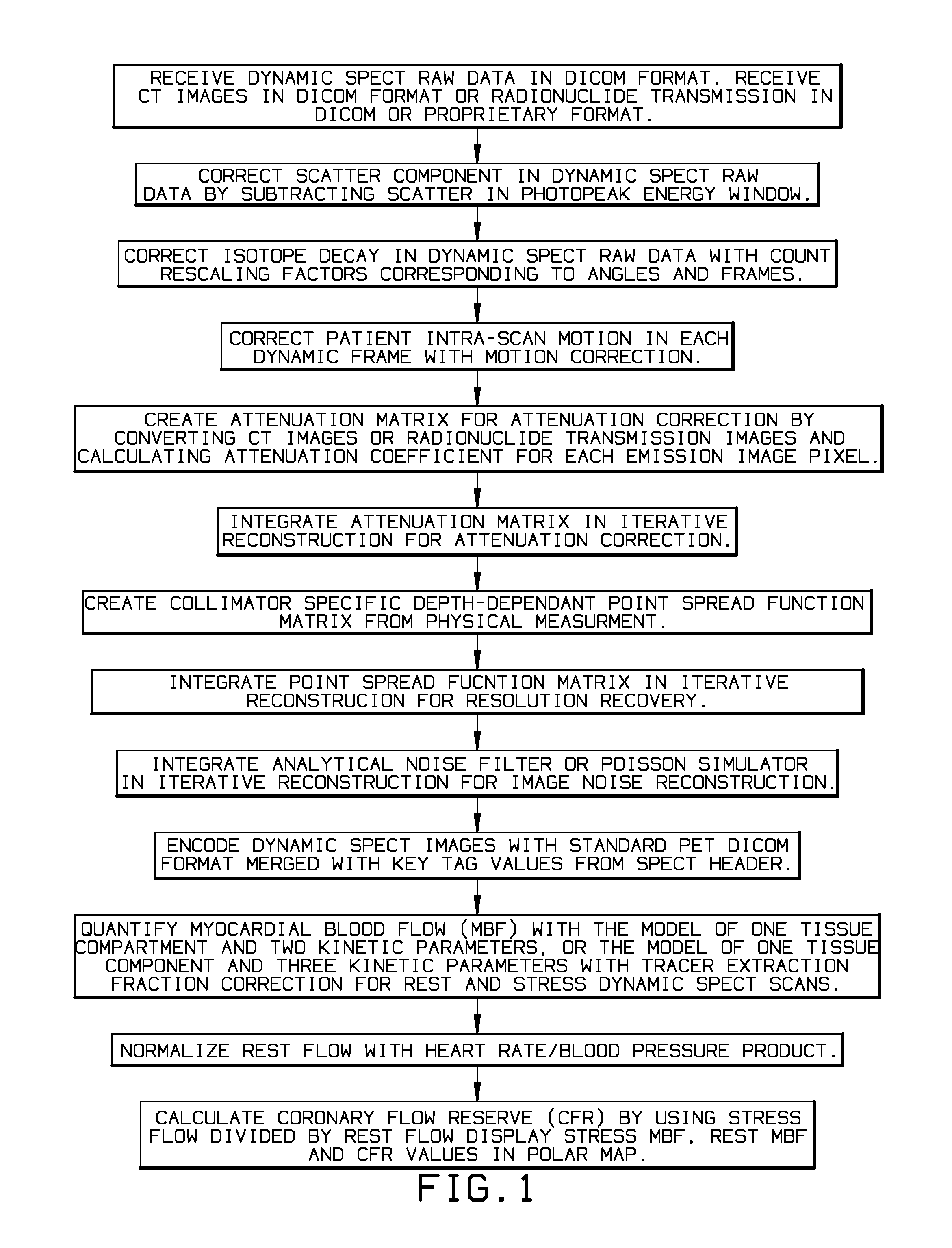
Myocardial blood flow quantitation with dynamic spect or spect/ct imaging
InactiveUS20140341453A1Remove image noiseReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFractographySpect imaging
A quantitative Single Photon Computed Emission Tomography (SPECT) reconstruction system for myocardial blood flow quantitation with SPECT or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography / Computed Tomography (SPECT / CT) dynamic imaging. The present invention solves the problems of physical interference and patient motions in dynamic SPECT imaging to enable the quantitative ability for myocardial blood flow (MBF) and coronary flow reserve (CFR) quantification.
Owner:HSU BAILING +1
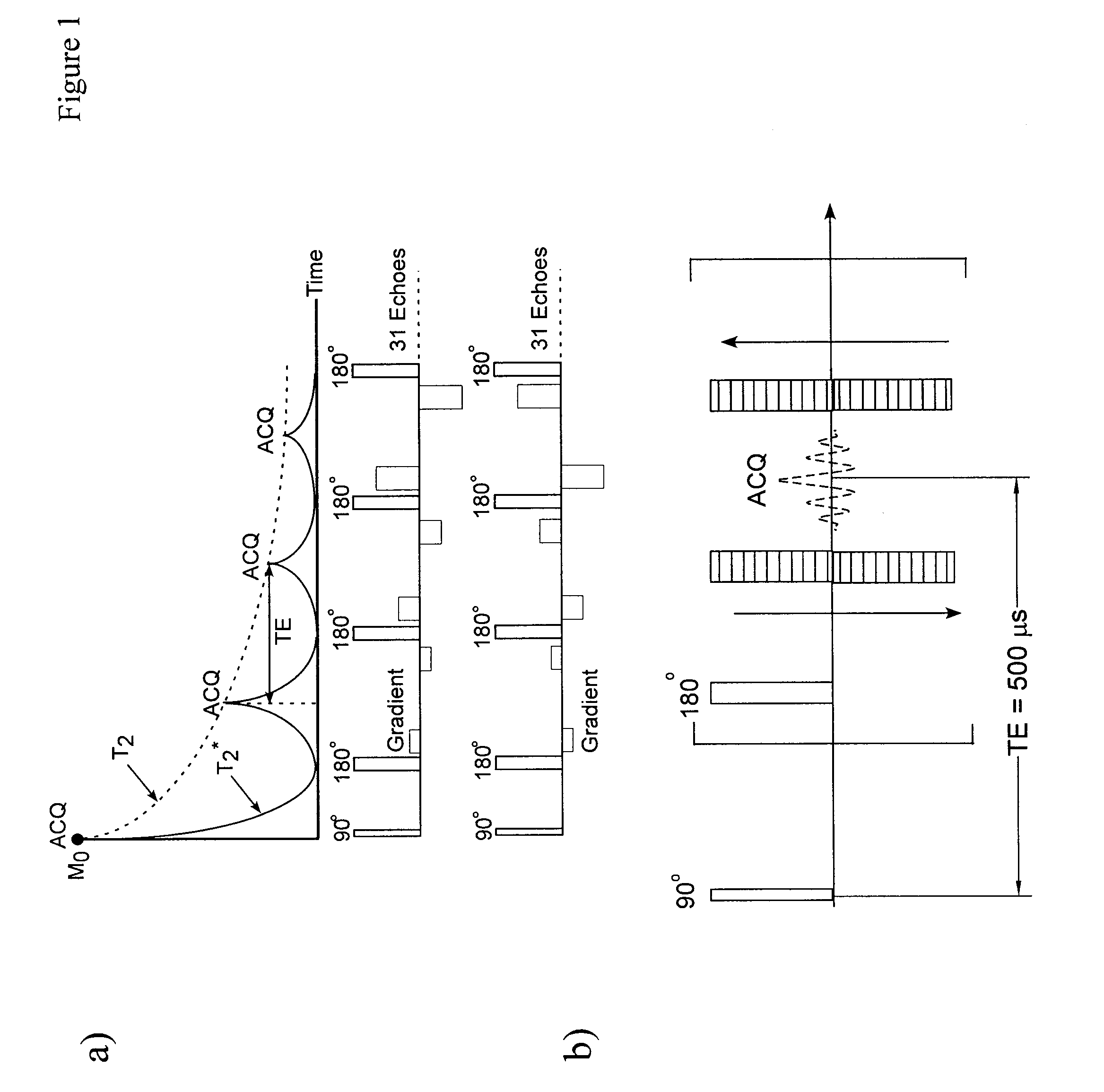
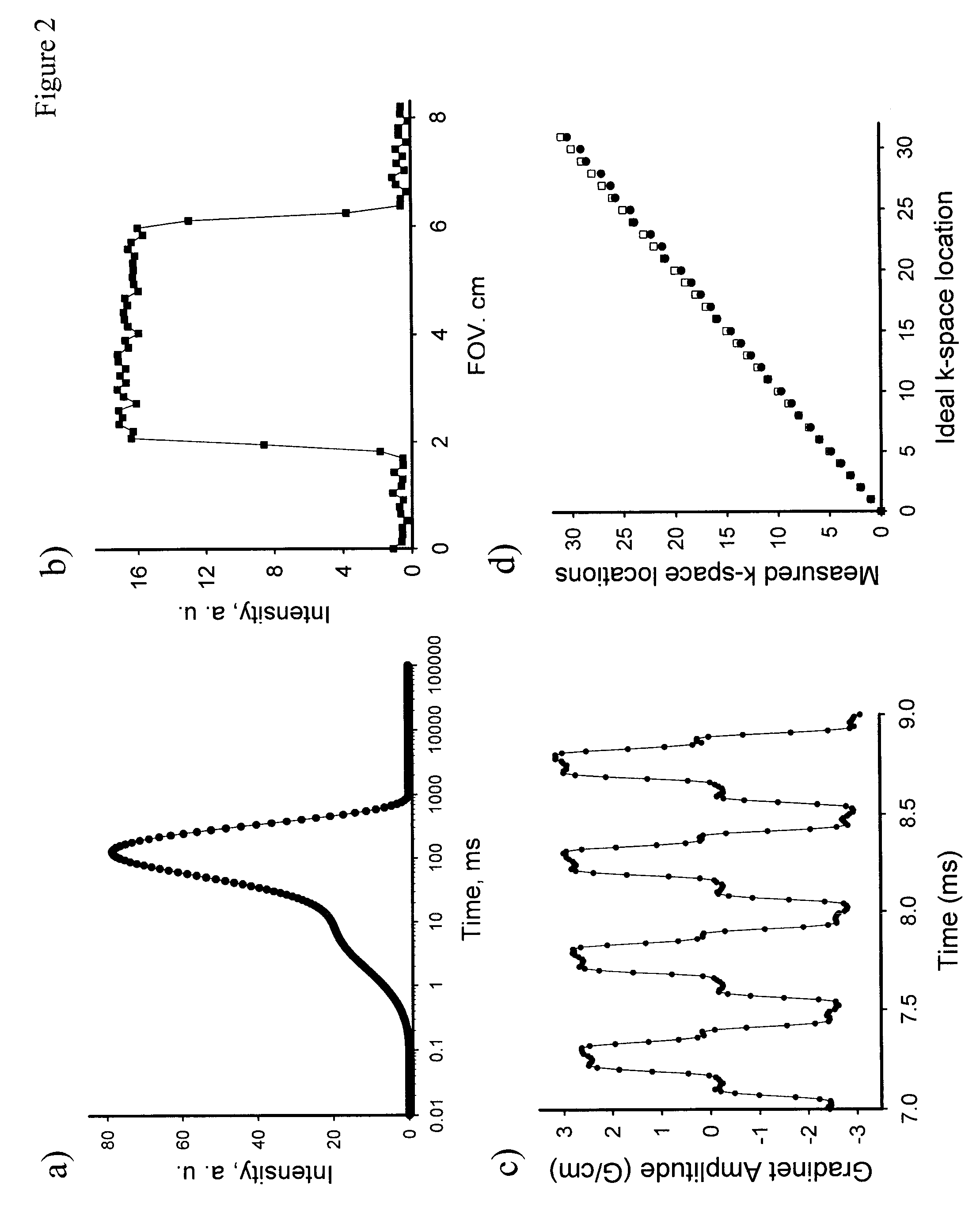
Spin echo SPI methods for quantitative analysis of fluids in porous media
ActiveUS9018950B2Rapid determinationSimple methodElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpatially resolvedCapillary pressure
A method of measuring a parameter in a sample by imaging at least a portion of the sample using a spin-echo single-point imaging (SE-SPI) pulse sequence. This method involves applying a pure phase encoding to the SE-SPI pulse sequence, acquiring a multiplicity of echoes, and determining the spatially resolved T2 distribution. In another embodiment, individual echoes are separately phase encoded in a multi-echo acquisition and the SE-SPI pulse sequence is a hybrid SE-SPI sequence. In another embodiment, an external force can be used to build up a distribution of saturations in the sample, and a T2 distribution can be measured for the sample, which is then used to determine a parameter of the sample. A spatially resolved T2 distribution can also be measured and a resulting spatially resolved T2 distribution used to determine the T2 distribution as a function of capillary pressure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
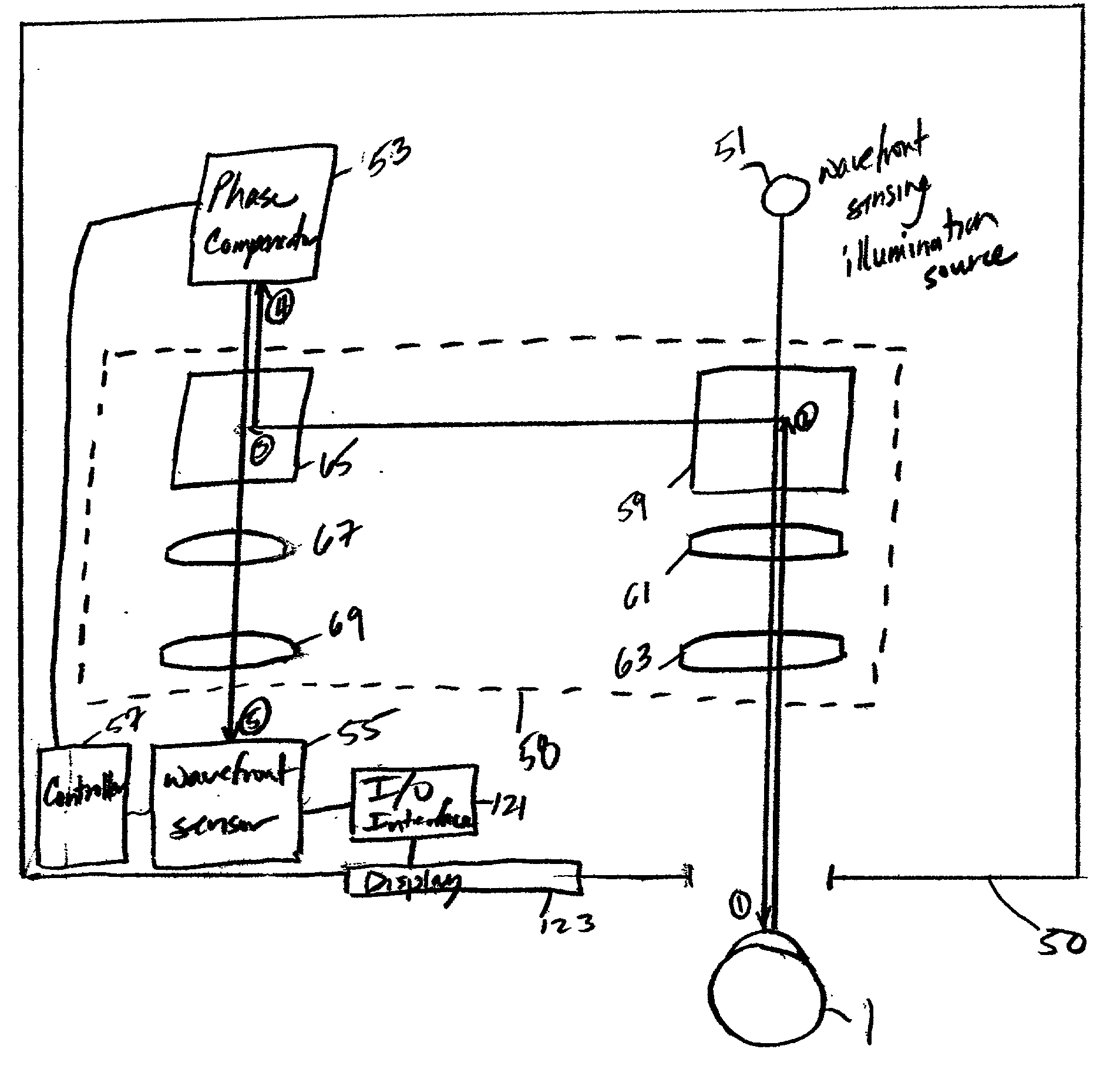
Opthalmic instrument having wavefront sensor with multiple imaging devices that simultaneously capture multiple images of an array of spots produced by a lenslet array
An improved ophthalmic instrument including a wavefront sensor that estimates aberrations in reflections of the light formed as a spot image on the retina of the human eye. The wavefront sensor includes a beam splitter operably disposed between a lenslet array and multiple imaging devices. The lenslet array forms a first array of spots, and the multiple imaging devices capture multiple images of the first array of spots for use in estimating the aberrations of the eye in a manner that minimizes the adverse effects of eye movement on the accuracy of such estimates. The beam splitter preferably comprises a prismatic beam splitter that splits light incident thereto into multiple arms. The multiple image devices may capture at least a first image of the first array of spots at best focus and a second image of the first array of spots near best focus for use in dynamically identifying sub-arrays (pixel areas) of the Hartmann spot imaging device (e.g., the imaging device that will be used for the determination of Hartmann spot positions) that avoid dot crossover for a particular wavefront measurement. An additional imaging device may be operably coupled to the beam splitter to capture at least one image of the pupil image plane of the lenslet array for use in identifying fiducial points therein (or for automatically identifying lenslet centers therein), thereby minimizing the adverse effects of eye movement on the accuracy of such measurements.
Owner:ADAPTIVE OPTICS ASSOC +1
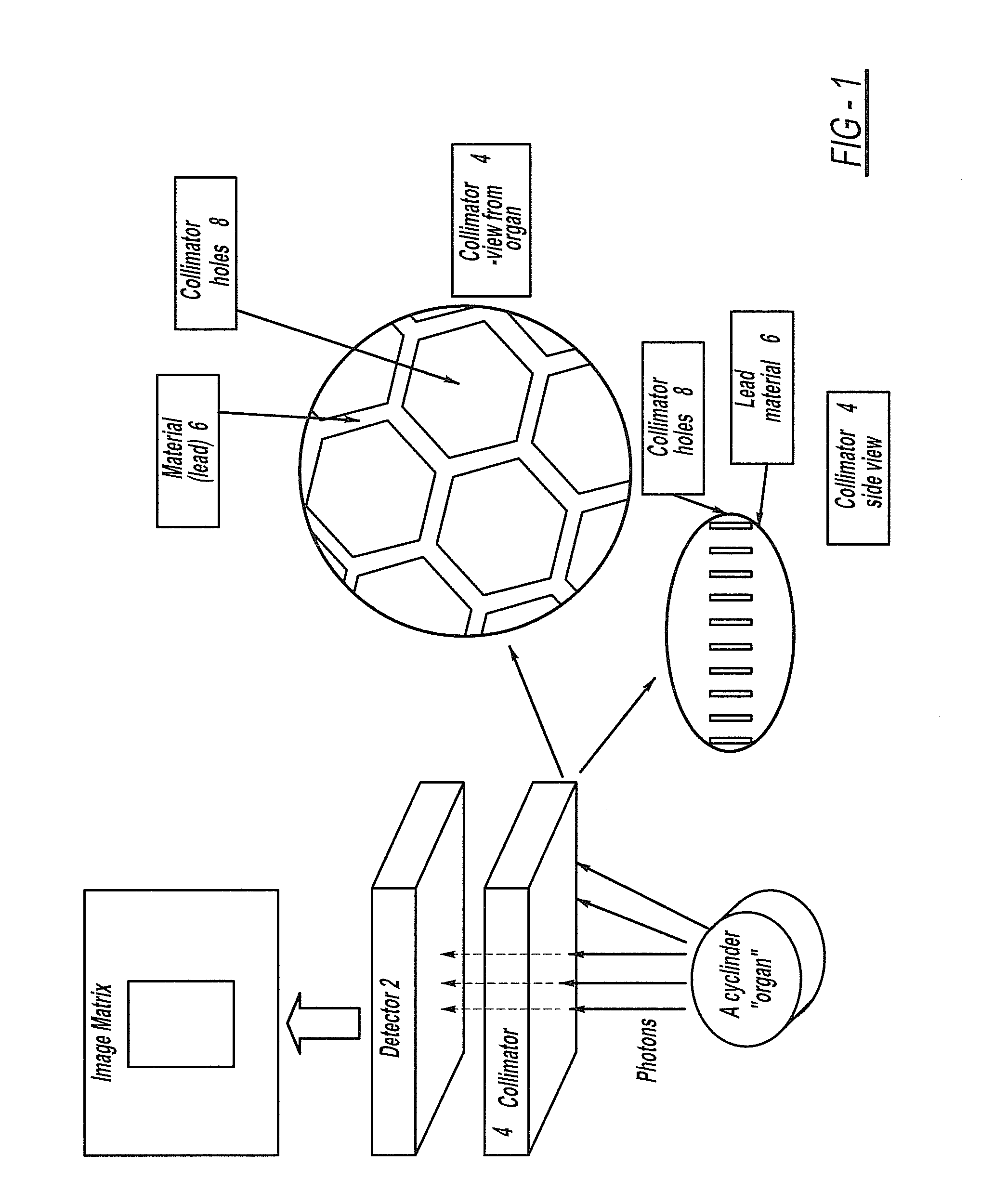
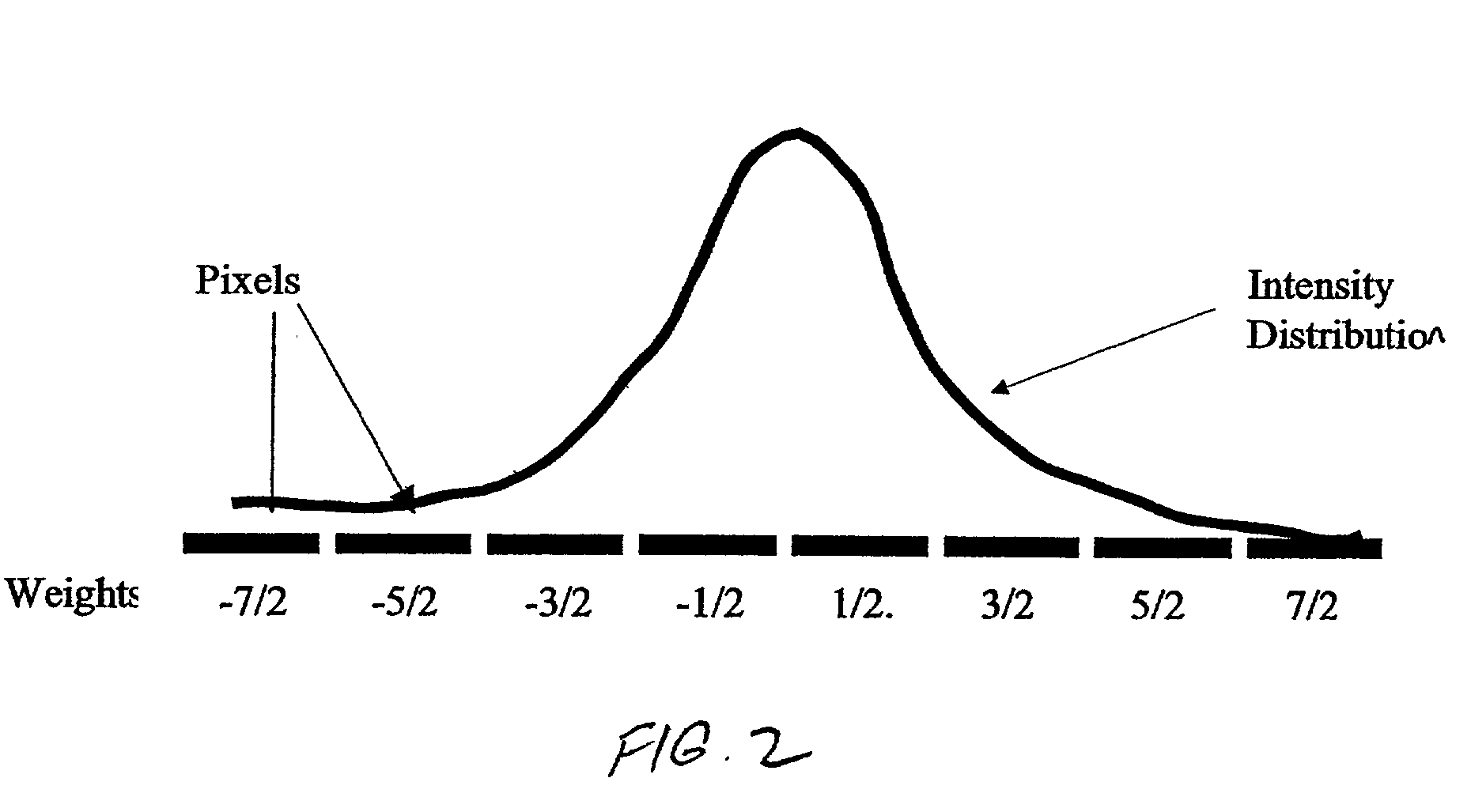
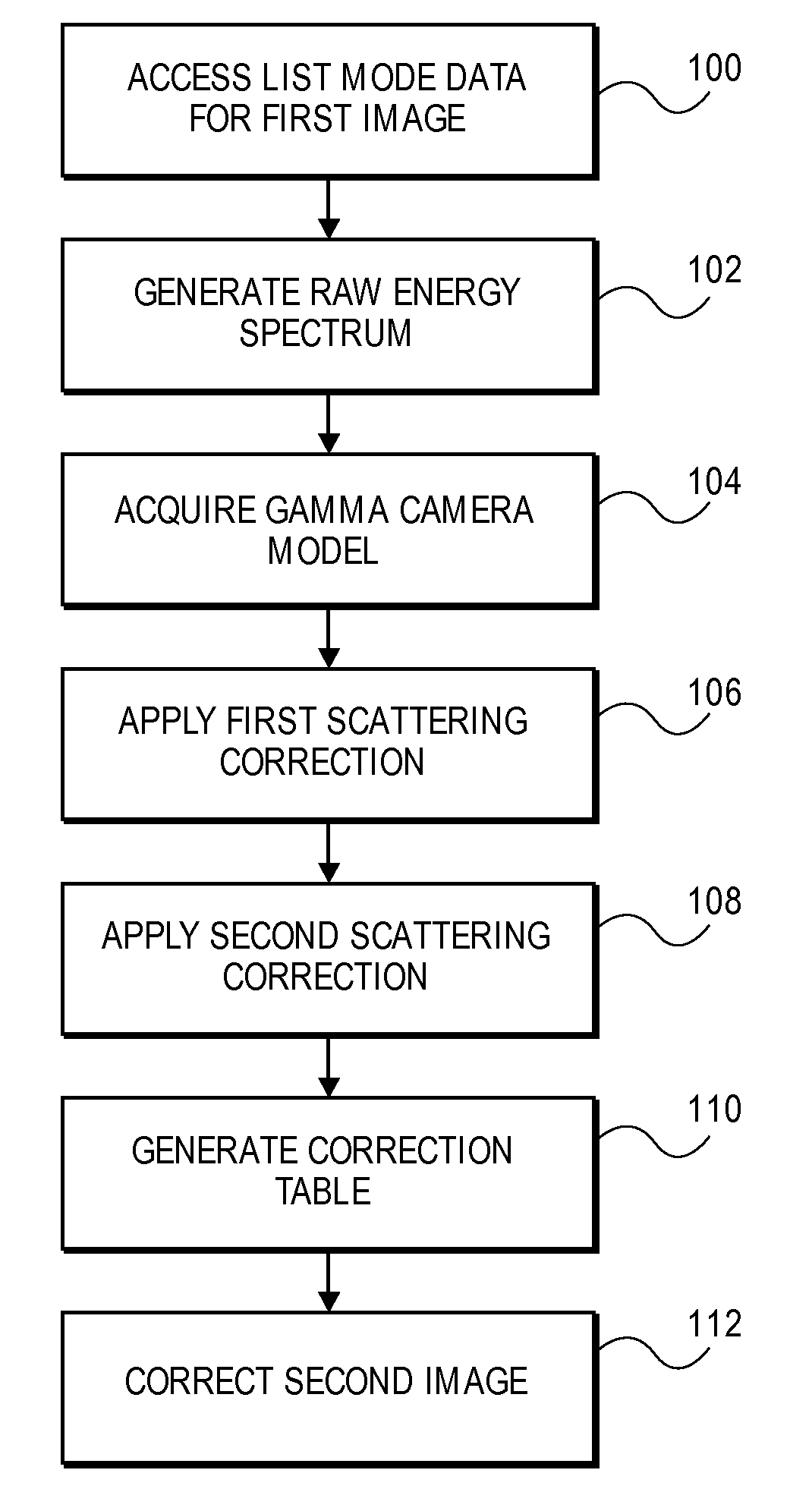
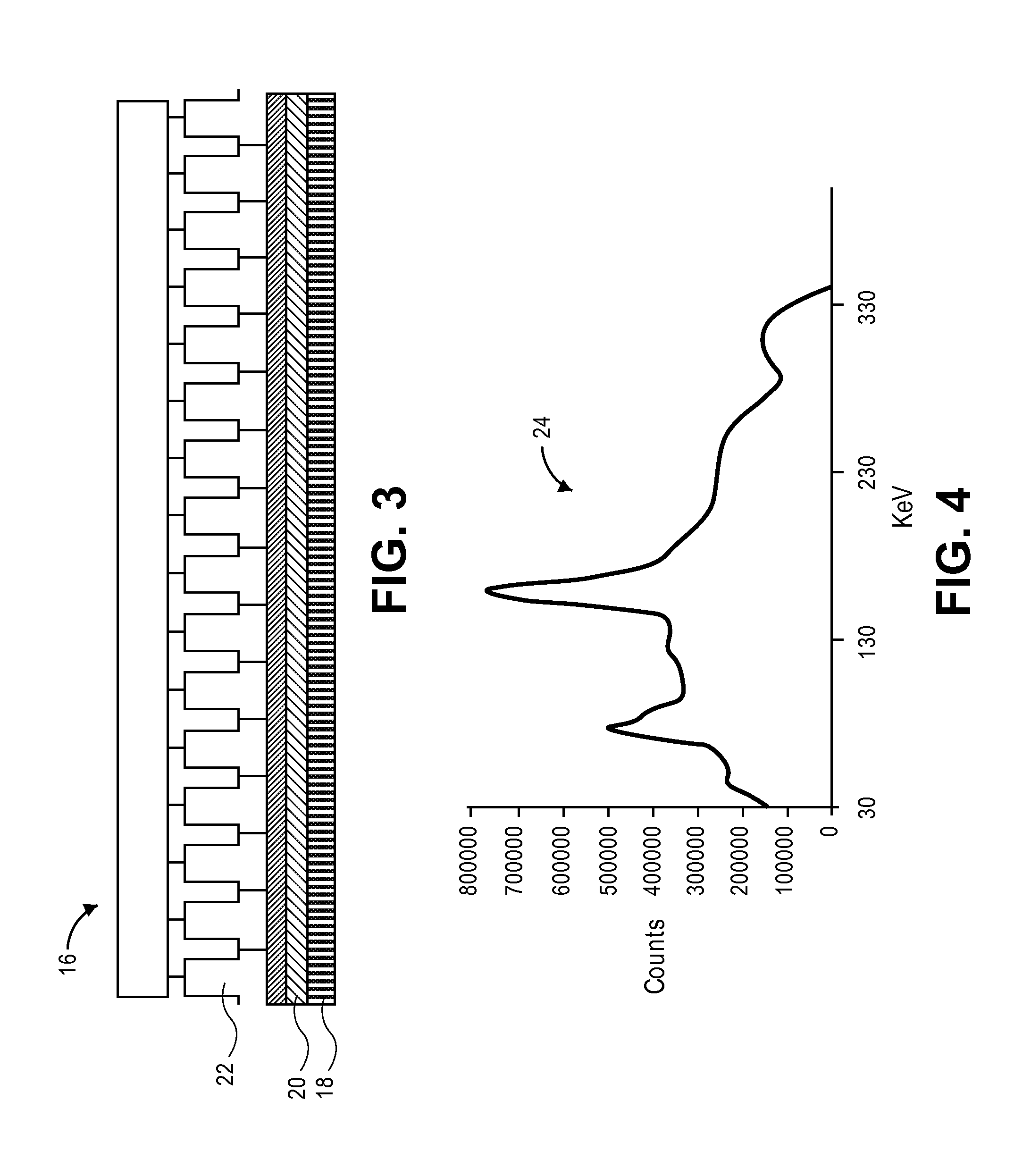
Method and apparatus for correcting scattering in spect imaging
A method and apparatus for correcting scattering in SPECT I-123 imaging. The method generally includes: accessing list mode data for a plurality of pixels corresponding to a first SPECT I-123 image generated using a gamma camera; generating a raw energy spectrum for at least some of the pixels utilizing the acquired list mode data; acquiring a gamma camera model corresponding to the gamma camera; utilizing the gamma camera model and an iterative algorithm to apply a first scattering correction to the raw energy spectrum; utilizing a Compton window to apply a second scattering correction to the raw energy spectrum; and generating a correction table with the corrected raw energy spectrum.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING TECH
Integrated breast X-ray and molecular imaging system
ActiveUS8217357B2Increase speedImprove accuracyTomosynthesisSolid-state devicesTomosynthesisMolecular imaging
An integrated tomosynthesis / molecular breast imaging device having improved sensitivity includes tomosynthesis imaging components and molecular breast imaging components. The imaging components may be used individually or in combination to provide a system with improved sensitivity and specificity. Molecular imaging components may be smoothly advanced or withdrawn depending upon the desired imaging mode. The system supports both PET and SPECT imaging and enables SPECT collimation to be modified in accordance with image capture requirements.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
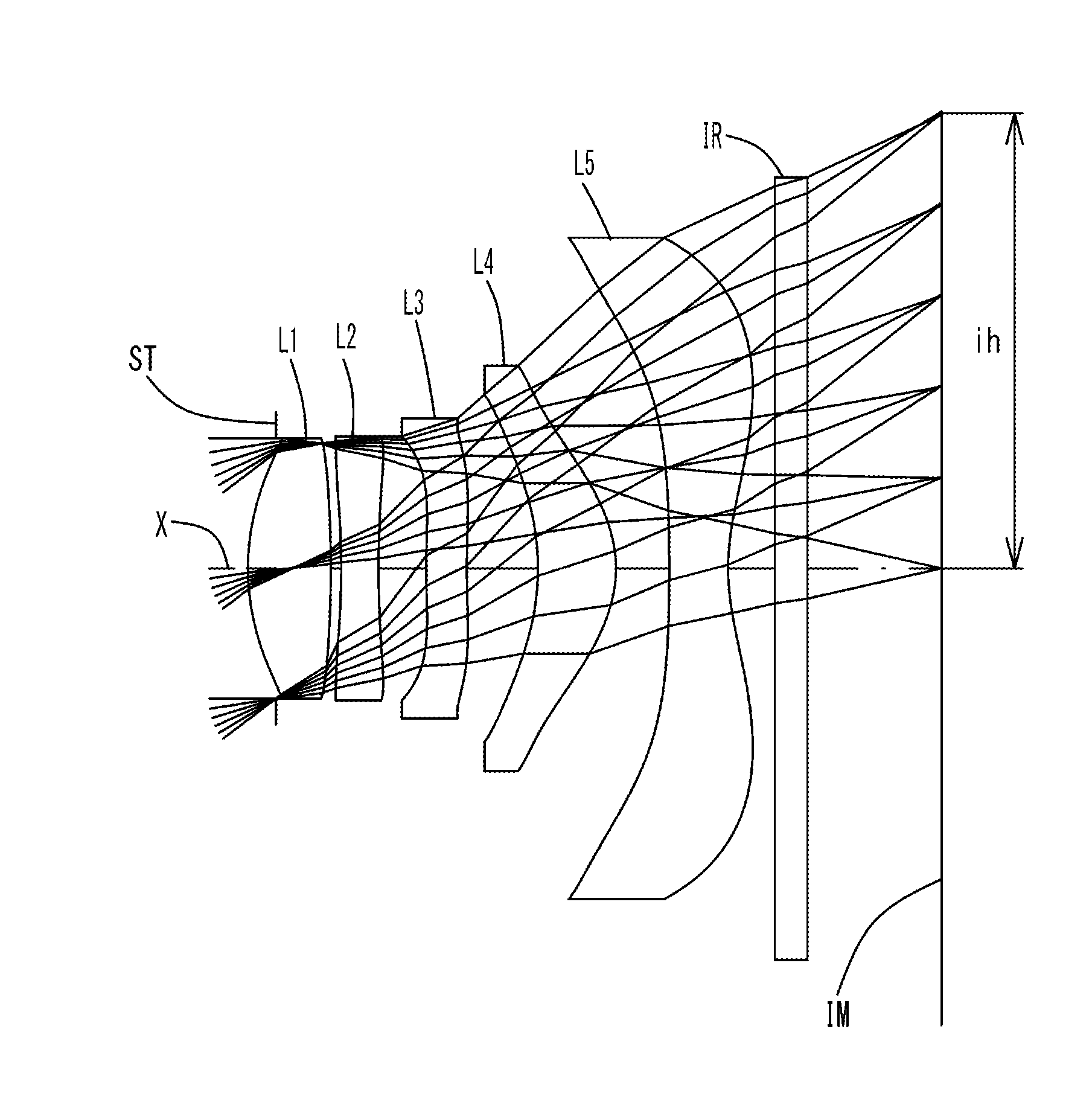
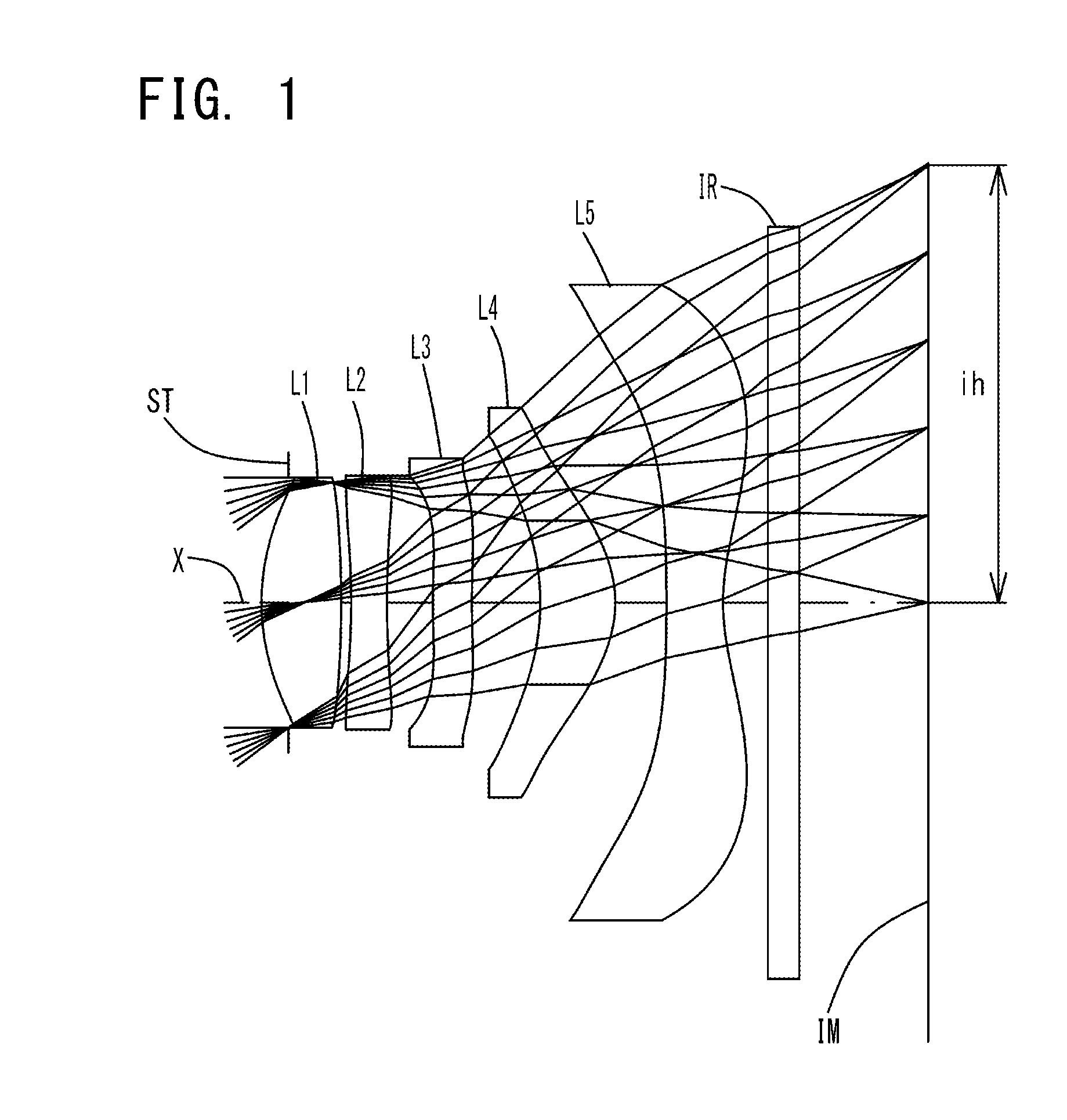
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20160011399A1Correct chromatic aberrationSuppress ghost phenomenonLensWide fieldOphthalmology
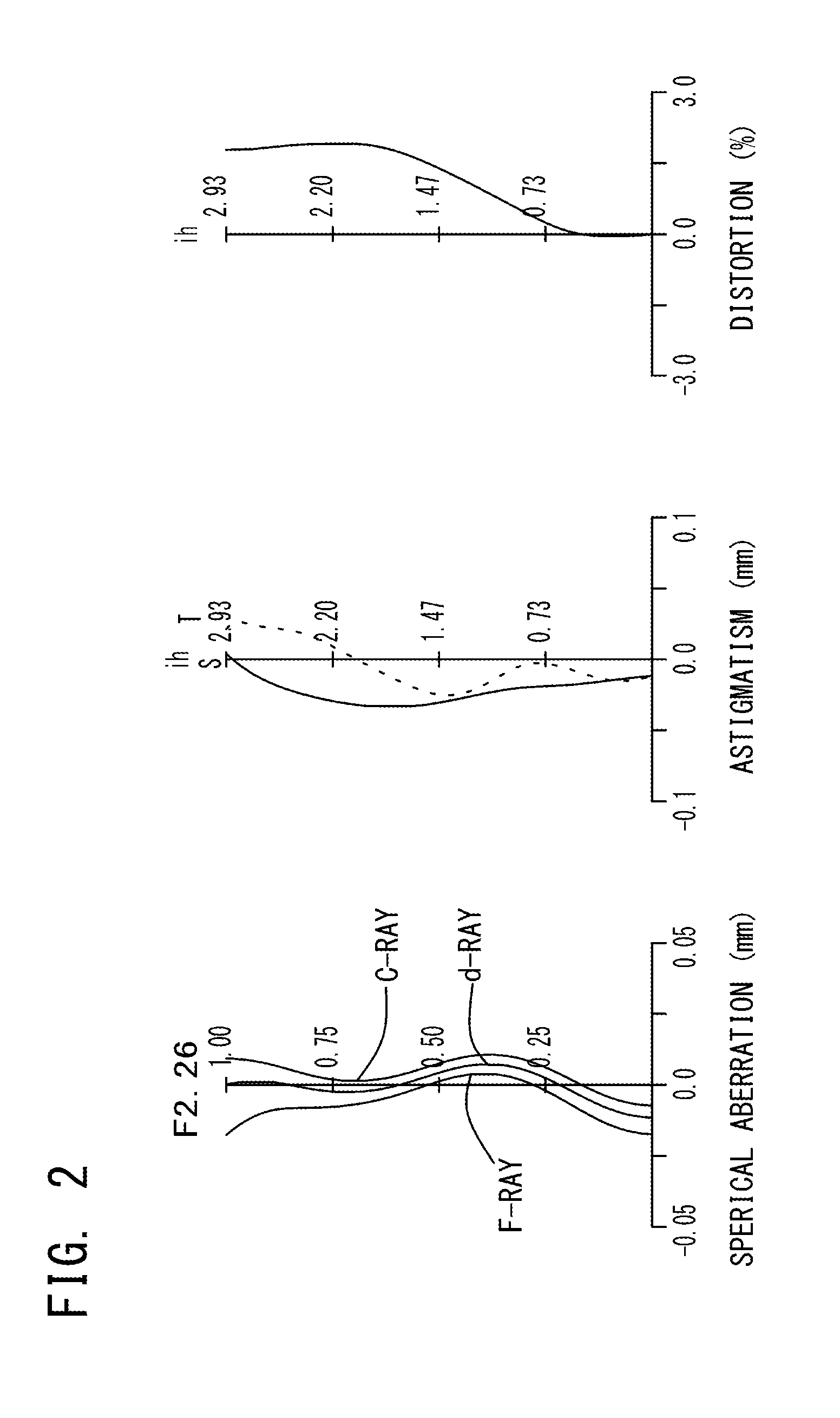
A compact, low-profile, low-cost imaging lens with brightness of F-value 2.5 or less and a wide field of view, which corrects aberrations properly. Elements are arranged from an object side: an aperture stop, positive first lens having a convex object-side surface, negative biconcave second lens having concave object-side and image-side surfaces, positive or negative third lens having a convex object-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; positive meniscus double-sided aspheric fourth lens having a convex image-side surface; and negative double-sided aspheric fifth lens having a concave image-side surface. The fifth lens' aspheric image-side surface has a pole-change point off an optical axis, and the imaging lens satisfies the following conditional expressions:TTL / 2ih≦0.8 (1)1.60<Nd3<1.70 (2)4.0<|r9 / r10|<14.0 (3)whereTTL: total track lengthih: maximum image heightNd3: third lens refractive index at d-rayr9: curvature radius of the fifth lens object-side surfacer10: curvature radius of the fifth lens image-side surface.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Wheel tread extraction and splicing method based on image processing
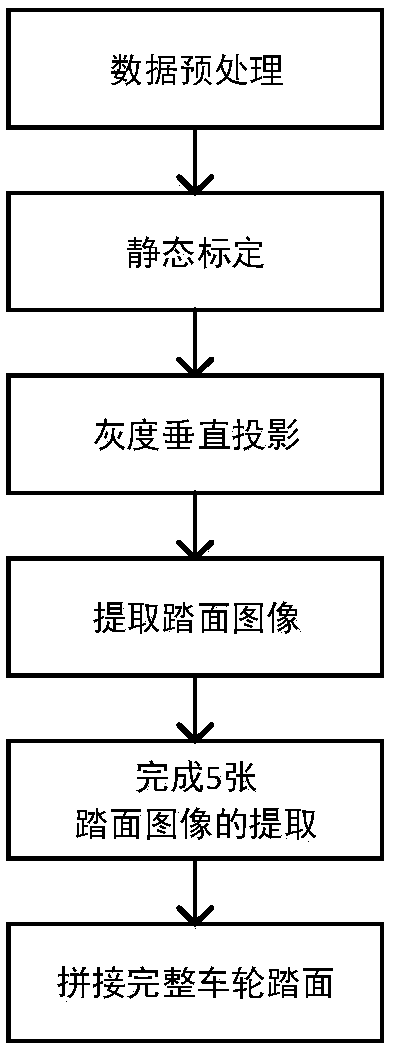
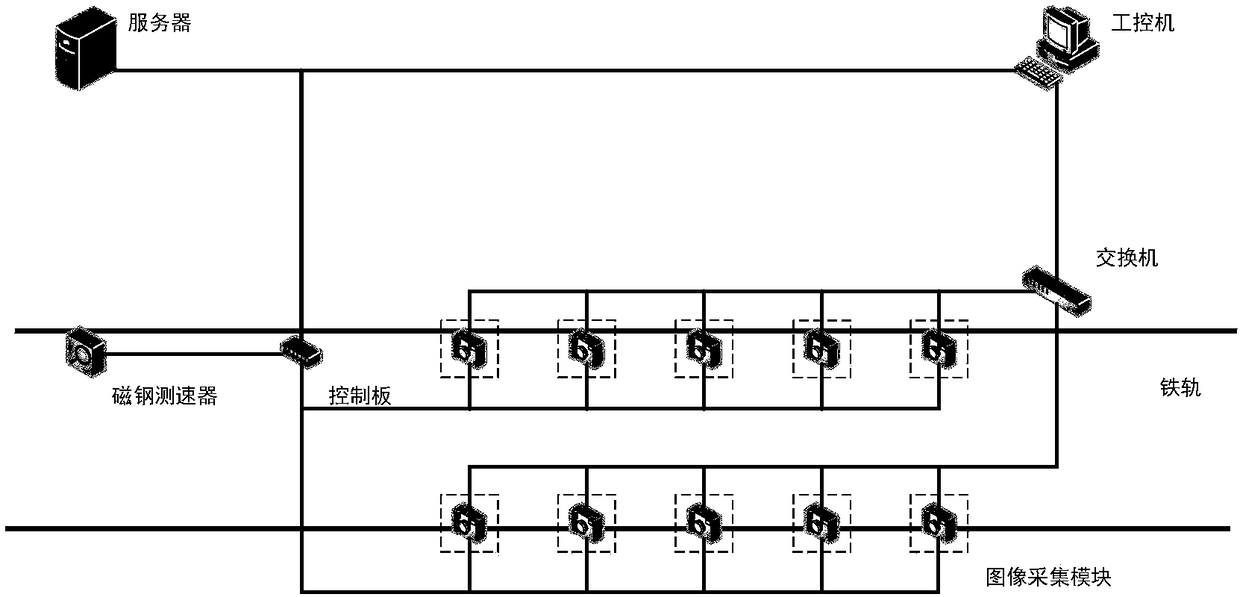
InactiveCN108520521AImprove robustnessImplement extractionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The present invention discloses a train wheel tread extraction and splicing method based on image segmentation and image fusion. The method comprises the steps of: dividing a wheel tread primary areaaccording to the feature of wheel image collection device fixed point imaging, employing a gray-scale projection technology, further locating a tread area according to the size of the gray projectionvalue and the variation rate, on this basis, employing an edge detection method to detect a wheel flange wire, completing wheel tread extraction, and finally, calculating the minimum smooth width according to the gray difference of a wheel tread overlapping area, splicing the wheel tread through a pixel matching method based on a space, and generating a 360-degree wheel tread panoramic image. Thewheel tread extraction and splicing method based on image processing belongs to the pre-processing technology of a locomotive damaging detection system, can effectively and rapidly extract the locomotive tread area, can improve the preprocessing speed of the locomotive damaging detection system, and has high practicability and wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
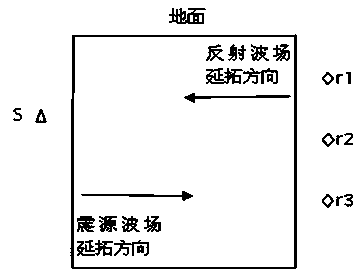
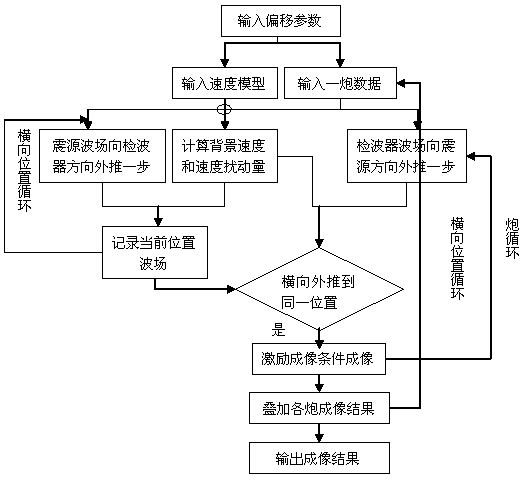
Continuation imaging method suitable for cross-well seismic large-angle reflection conditions
ActiveCN104570124AAdapt to lateral changesImprove imaging effectSeismology for water-loggingTemporal informationContinuation
The invention discloses a continuation imaging method suitable for cross-well seismic large-angle reflection conditions. The continuation imaging method comprises the following steps: when a direct wave is removed, a wave field of a seismic source transversely extend towards a wave detector, and a receiving wave field of the wave detector transversely extends towards the seismic source; when the wave field of the seismic source and the receiving wave field of the wave detector extend to the same position, related imaging conditions are utilized for transverse continuation imaging; after images of all shot points are formed, the images are overlapped to obtain an imaging profile for cross-well seismic depth domain migration. The continuation imaging method has the advantages that a large angle of information dissemination is converted into a small angle in the direction of transverse continuation, so that the imaging effect of a vertical large-angle region is improved; separating an uplink reflected wave from a downlink reflected wave is not needed, so that the impact of the poor separating effect on an imaging result is avoided; not only the kinematic characteristics (such as temporal information) of cross-well seismic reflected wave data, but also the dynamic characteristics (such as amplitude information) of the cross-well seismic reflected wave data and the particularity of a cross-well seismic observation method are considered, so that the continuation imaging method is accurate in imaging and high in precision.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
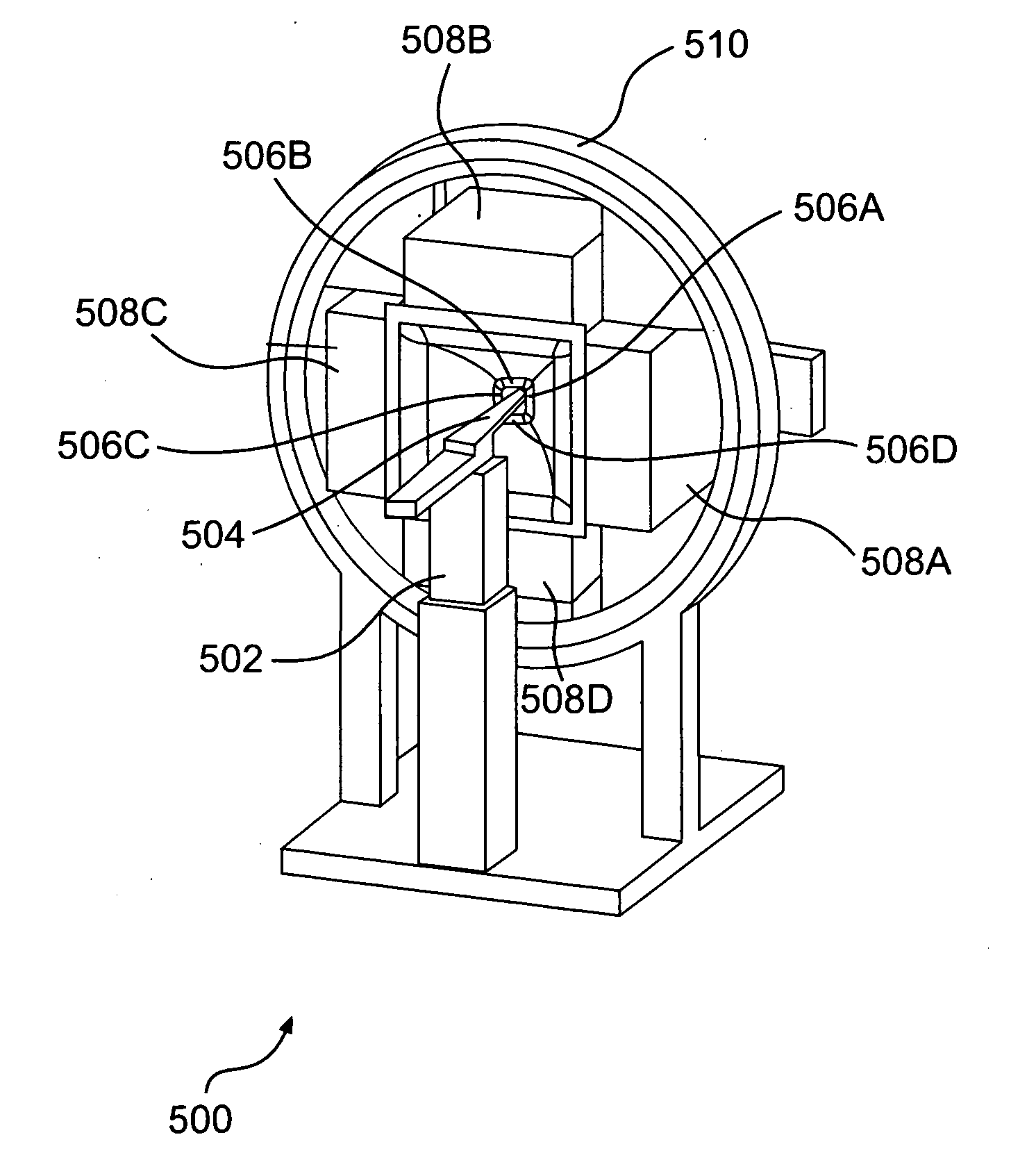
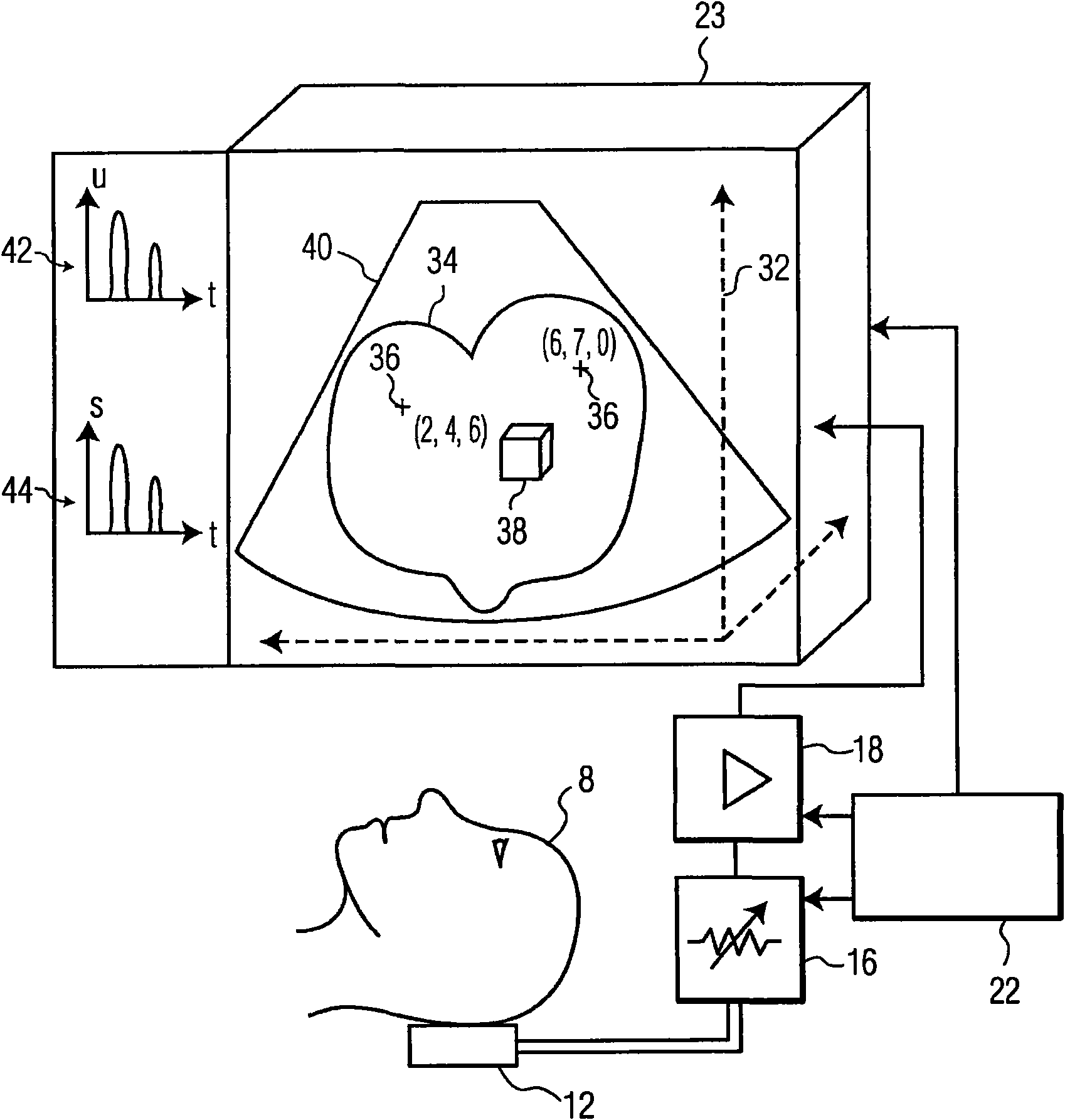
Detector head position calibration and correction for SPECT imaging apparatus using virtual CT
ActiveUS20070290125A1Precise alignmentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMedical imagingMultiple point
A multiple point source test phantom is used for calibration of detector positioning of a nuclear medical imaging apparatus. An absolute coordinate system for the detectors is aligned to an image reconstruction space coordinate system by fitting a Gaussian surface to a peak of a center point source of said test phantom, and using displacement parameters as obtained from the fitted Gaussian surface to calculate a displacement correction parameter, which is used to move a patient bed of the imaging apparatus such that the image reconstruction space is aligned with the absolute coordinate system.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
TDI-CCD-based large-aperture long-focal length remote sensing camera distortion measurement device and measurement method
ActiveCN105758623AHigh precisionImprove Distortion Testing EfficiencyTesting optical propertiesMeasurement deviceBroom
The invention relates to a large-aperture long-focal length remote sensing camera distortion measurement device and a measurement method. The device comprises a collimator, a two-dimensional turntable, a mechanical shutter, an integrating sphere, a star point target, and a TDI-CCD long-focal length large-aperture remote sensing camera, wherein the TDI-CCD long-focal length large-aperture remote sensing camera is arranged on the two-dimensional turntable; the collimator is arranged at the entrance pupil place of the TDI-CCD long-focal length large-aperture remote sensing camera; and the light input end of the collimator is sequentially provided with the mechanical shutter, the star point target and the integrating sphere. The TDI-CCD long-focal length large-aperture remote sensing camera works in a planer array imaging mode, the mechanical shutter and the camera are exposed synchronously, the star point target serves as a camera imaging target via the collimator, and for completing each time of star point imaging, the turntable is rotated for an angle in a vertical integrating direction along the TDI sensor. Thus, the whole sensor is traversed, images of multiple of star point images at different positions are acquired, and through carrying out matching calculation between precise positions of the star point images and rotation angles of the turntable, distortion coefficients of the TDI-CCD linear array remote sensing camera in vertical and parallel push-broom directions can be acquired at the same time.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Collimator
ActiveUS20180000431A1Avoid interferenceIncrease and decrease spatial resolutionPatient positioning for diagnosticsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImage resolution
An N-M tomography system comprising: a carrier for the subject of an examination procedure; a plurality of detector heads; a carrier for the detector heads; and a detector positioning arrangement operable to position the detector heads during performance of a scan without interference or collision between adjacent detector heads to establish a variable bore size and configuration for the examination. Additionally, collimated detectors providing variable spatial resolution for SPECT imaging and which can also be used for PET imaging, whereby one set of detectors can be selectably used for either modality, or for both simultaneously.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Multiple modality cardiac imaging
InactiveCN103458790AEasy diagnosisReduce inspection costsReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsFlat panel detectorUltrasound attenuation
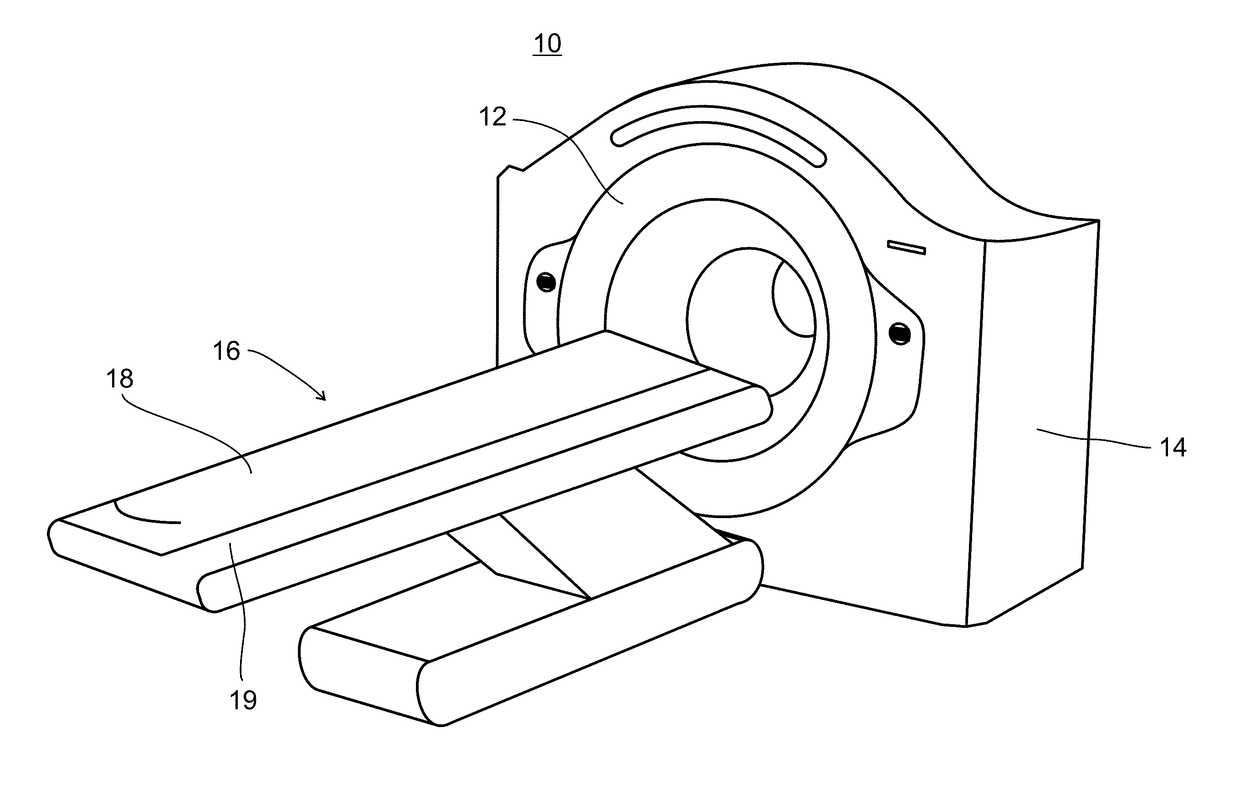
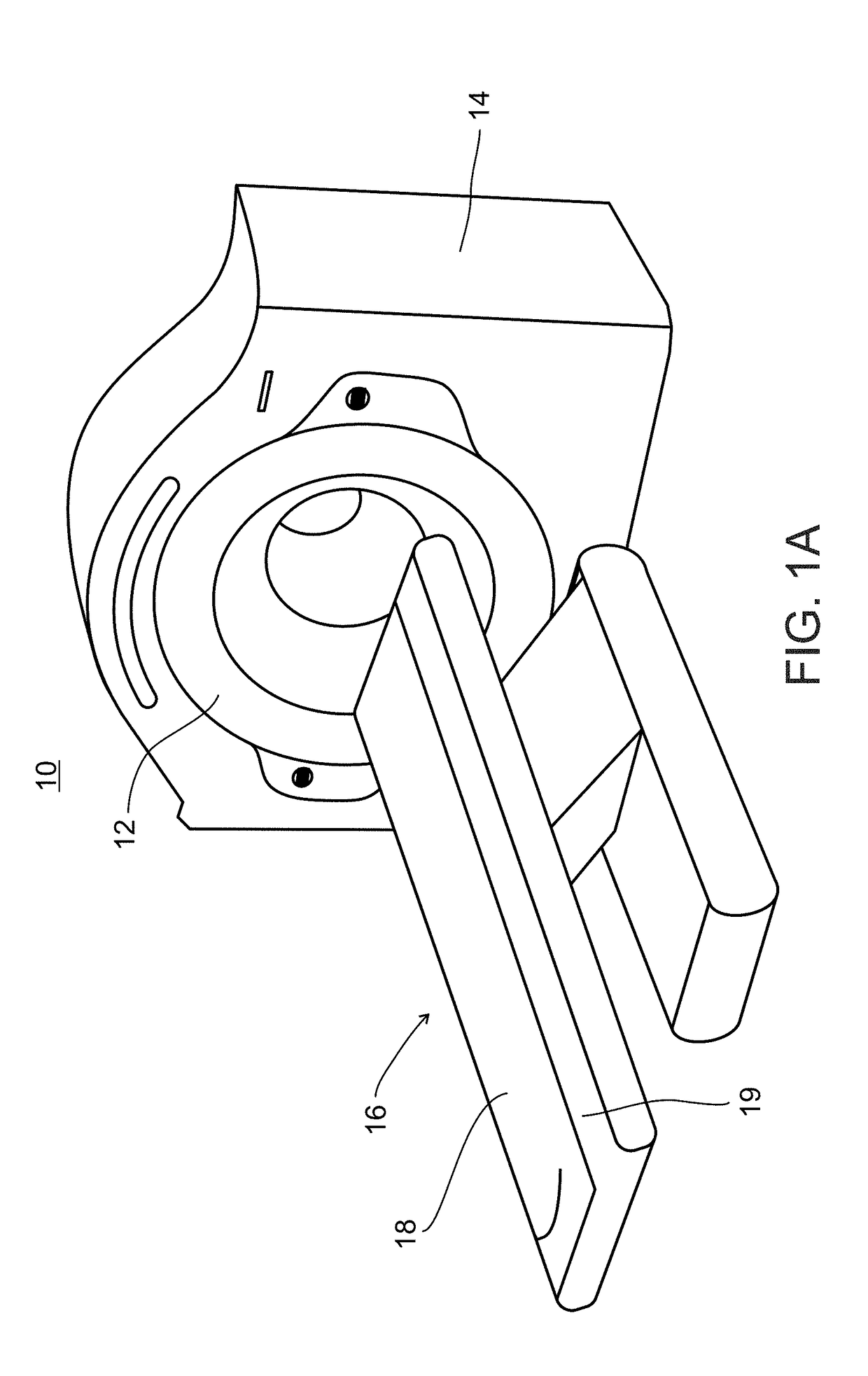
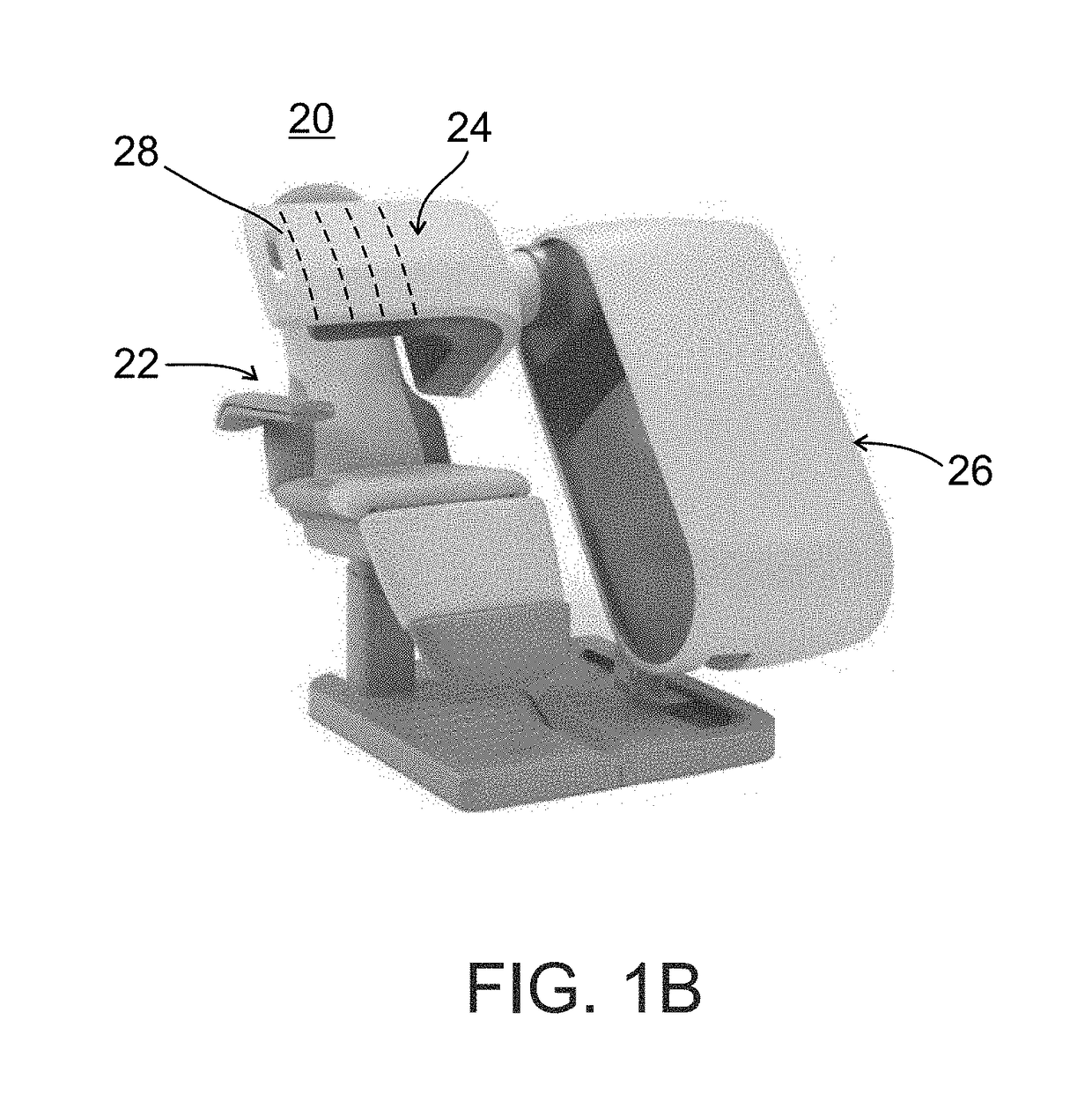
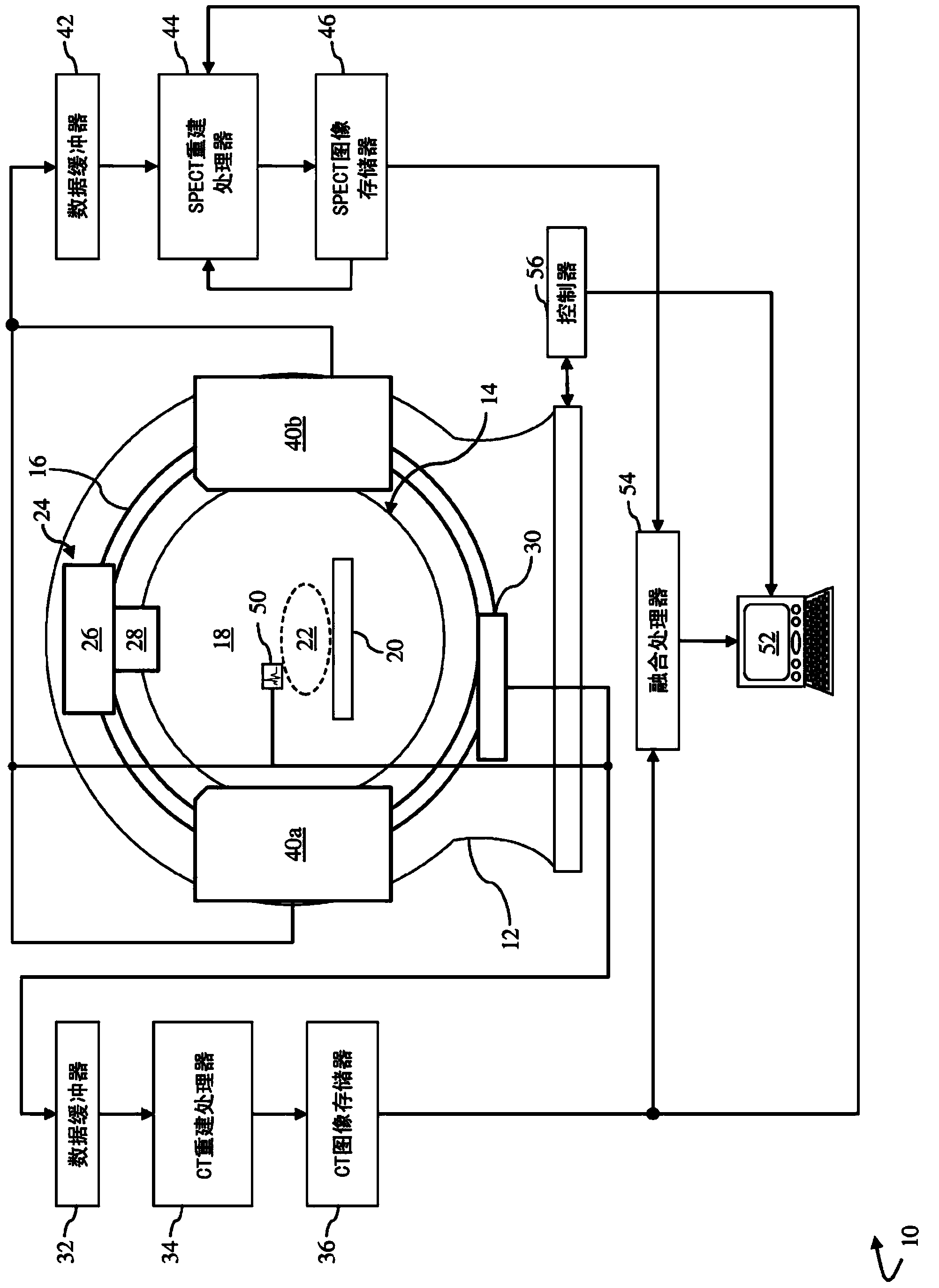
A multiple modality imaging system 10 for cardiac imaging includes x-ray scanners 24,30 which acquires contrast enhanced CT projection data of coronary arteries with a laterally offset flat panel detector and SPECT imaging scanners 40a,40b, which share the same examination region and gantry as the x-ray scanners, acquires nuclear projection data of the coronary arteries. A CT reconstruction processor 34 generates a 3D coronary artery image representation, at least one planar coronary artery angiogram, and a 3D attenuation correction map from the acquired CT projection data. A SPECT reconstruction processor 44 corrects the acquired nuclear projection data based on the generated attenuation correction map and generates a SPECT image representation of the coronary arteries from the corrected nuclear projection data. A fusion processor 54 combines the nuclear image representation, the 3D vessel image representation, and the at least one planar vessel angiogram into a composite image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
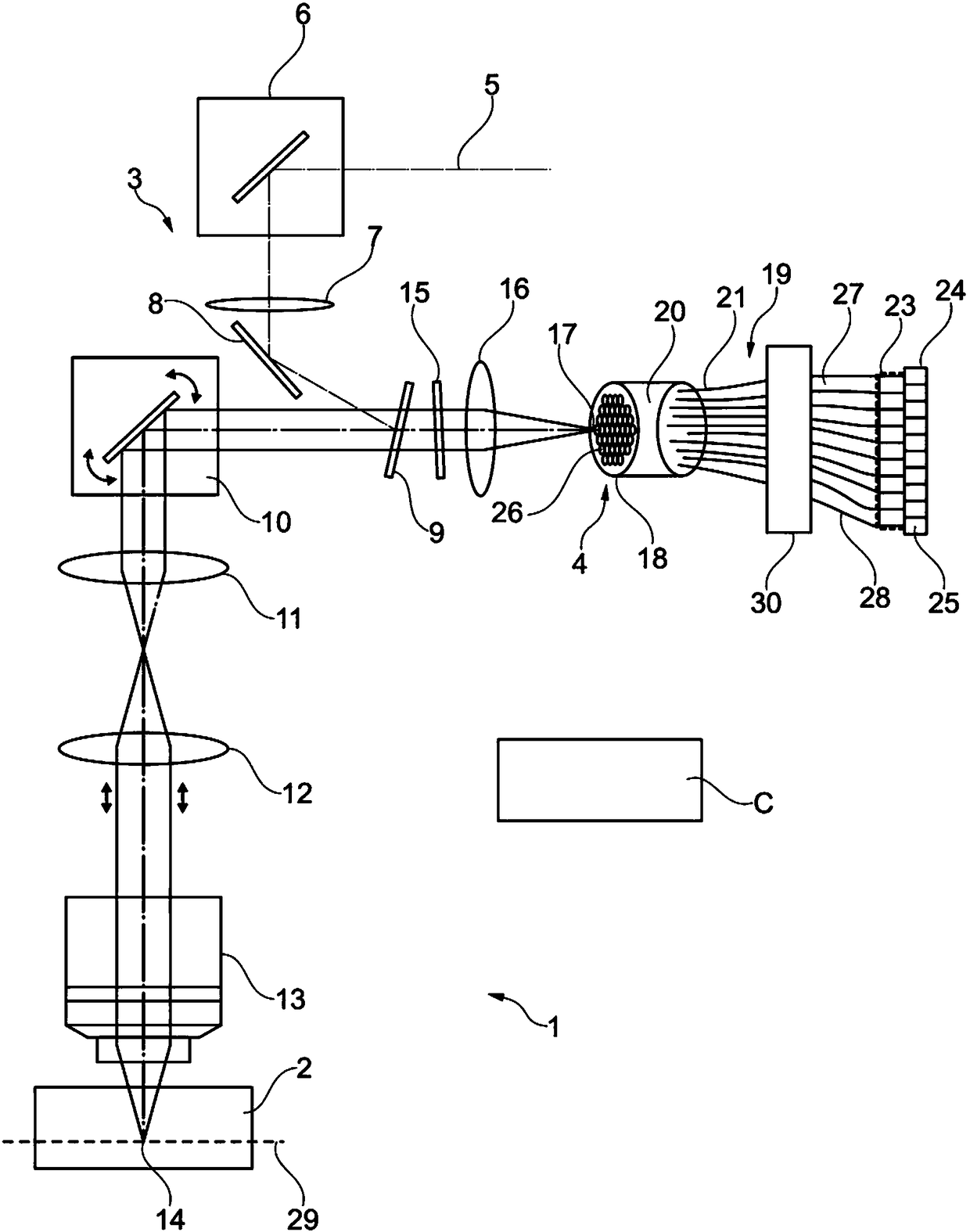
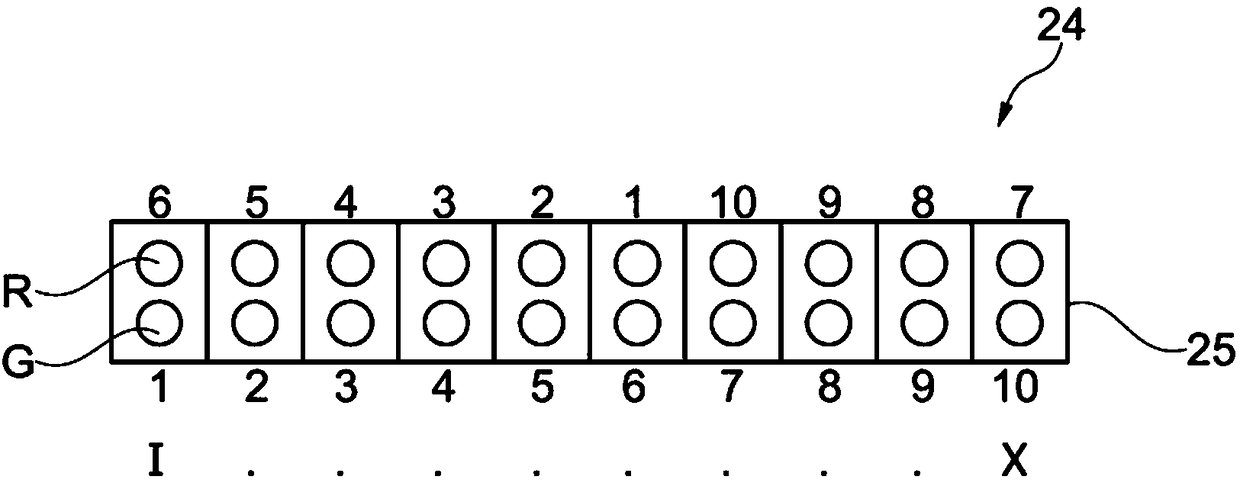
High-resolution scanning microscopy distinguishing between at least two spectral ranges
For the purposes of high-resolution scanning microscopy, a sample (2) is excited by illumination radiation (5) to emit fluorescent radiation in such a way that the illumination radiation (5) is focused at a point in or on the sample (2), so as to form a diffraction-limited illumination spot (14). The point is imaged in a diffraction image (17) on a detector (19) in a diffraction-limited manner, wherein the detector (19) has detector elements (25) and a plurality of location channels (21) which resolve a diffraction structure of the diffraction image (17). The sample (2) is scanned with variousscanning positions with an increment smaller than half the diameter of the illumination spot (14). An image of the sample (2) with a resolution that is increased beyond a resolution limit of the image is generated from the data of the detector (19) and from the scanning positions associated with these data. In order to distinguish between at least two predetermined spectral channels (R, G) in thefluorescent radiation of the sample (2), for each location channel (21) there is an independent beam path leading to a separating element (30) that spectrally divides these beam paths into the spectral channels (R, G) and then remixes the spectral channels (R, G) of the different location channels into the same number, on additional independent beam paths (28), such that a plurality of the additional independent beam paths (28) receive the radiation in different spectral channels (R, G) and from different location channels (21), and each of these additional independent beam paths (28) leads to one of the detector elements (25).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method for non-invasive quantitative assessment of radioactive tracer levels in the blood stream
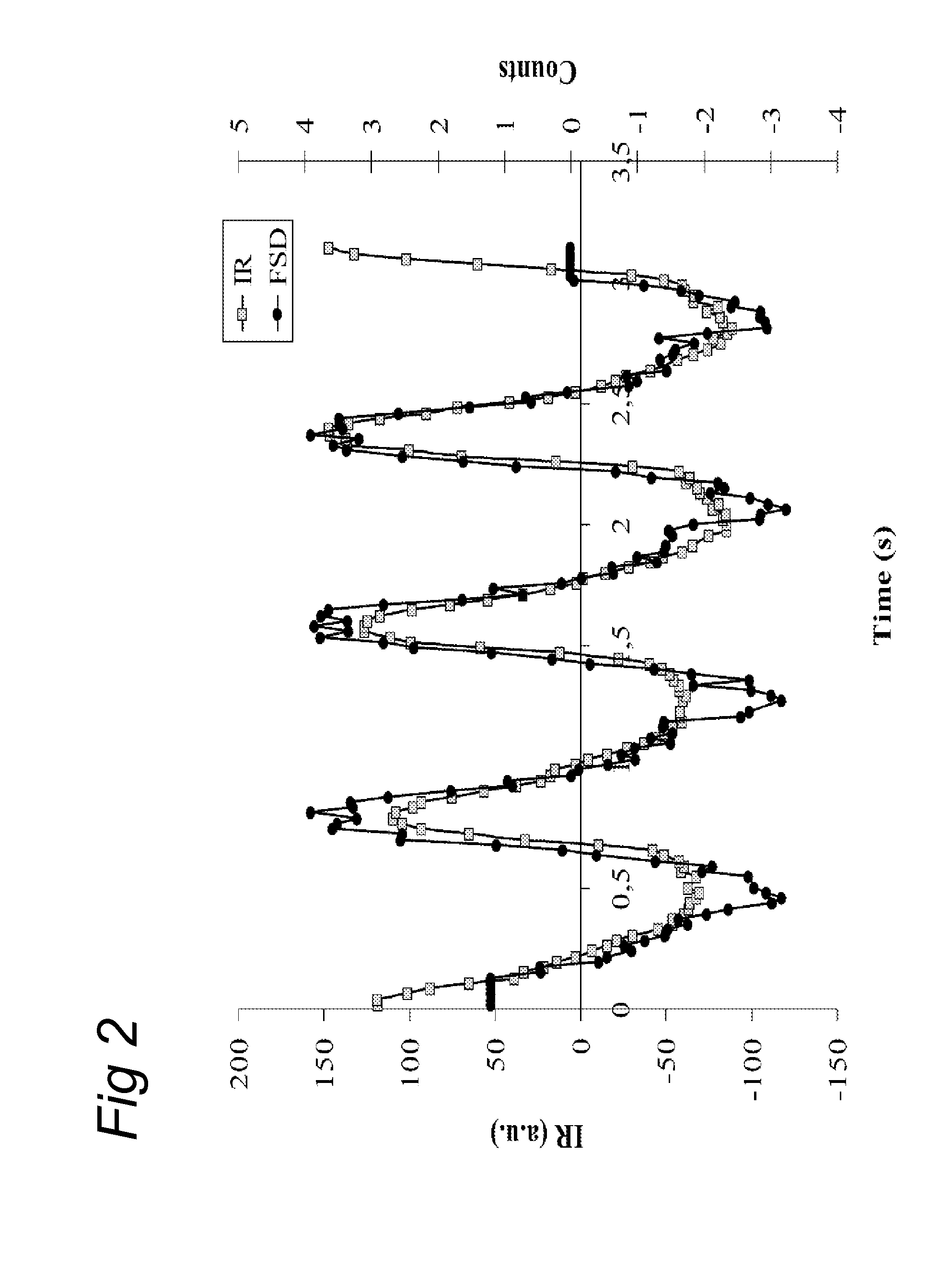
A method and system for non-invasive quantitative assessment of radionuclide tracer levels in the blood stream. The method relies on the finding that the gamma-radiation signal acquired using a gamma scintillation probe, is the resultant from a wave-component with changing amplitude, resulting from the radiotracer in the bloodstream and a non-wave background component resulting from radiotracer distributed throughout the tissue surrounding the arterial vessel. The method involves phase-sensitive conversion of the ‘input signal’, extracting there from an output signal representing the signal component originating from the bloodstream, using the changes in arterial blood volume as the reference wave-form. A particular aspect of the invention concerns methods of quantitative PET or SPECT imaging wherein the concentration of radionuclides in the blood stream as a function of time after injection is assessed using the method of the invention.
Owner:NETHERLANDS CANCER INST
Myocardial blood flow quantitation system and method with dynamic SPECT or SPECT/CT imaging
ActiveCN104161534AResolve interferenceHave the ability to quantifyReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsDynamic imagingTomography
A quantitative Single Photon Computed Emission Tomography (SPECT) reconstruction system for myocardial blood flow quantitation with SPECT or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography / Computed Tomography (SPECT / CT) dynamic imaging. The present invention solves the problems of physical interference and patient motions in dynamic SPECT imaging to enable the quantitative ability for myocardial blood flow (MBF) and coronary flow reserve (CFR) quantification.
Owner:北京百灵云生物医学科技有限公司
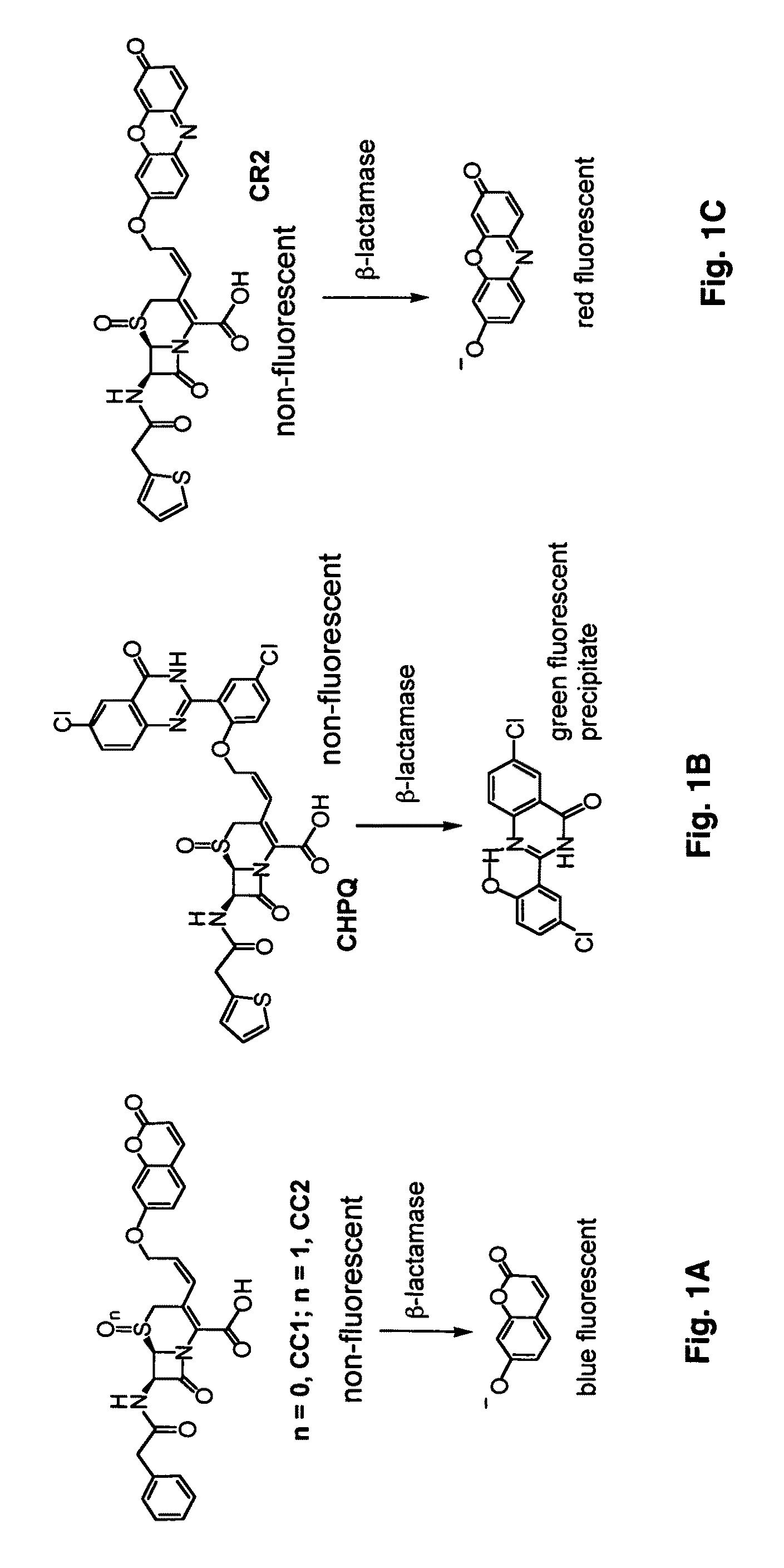
Use of bacterial beta-lactamase for in vitro diagnostics and in vivo imaging, diagnostics and therapeutics
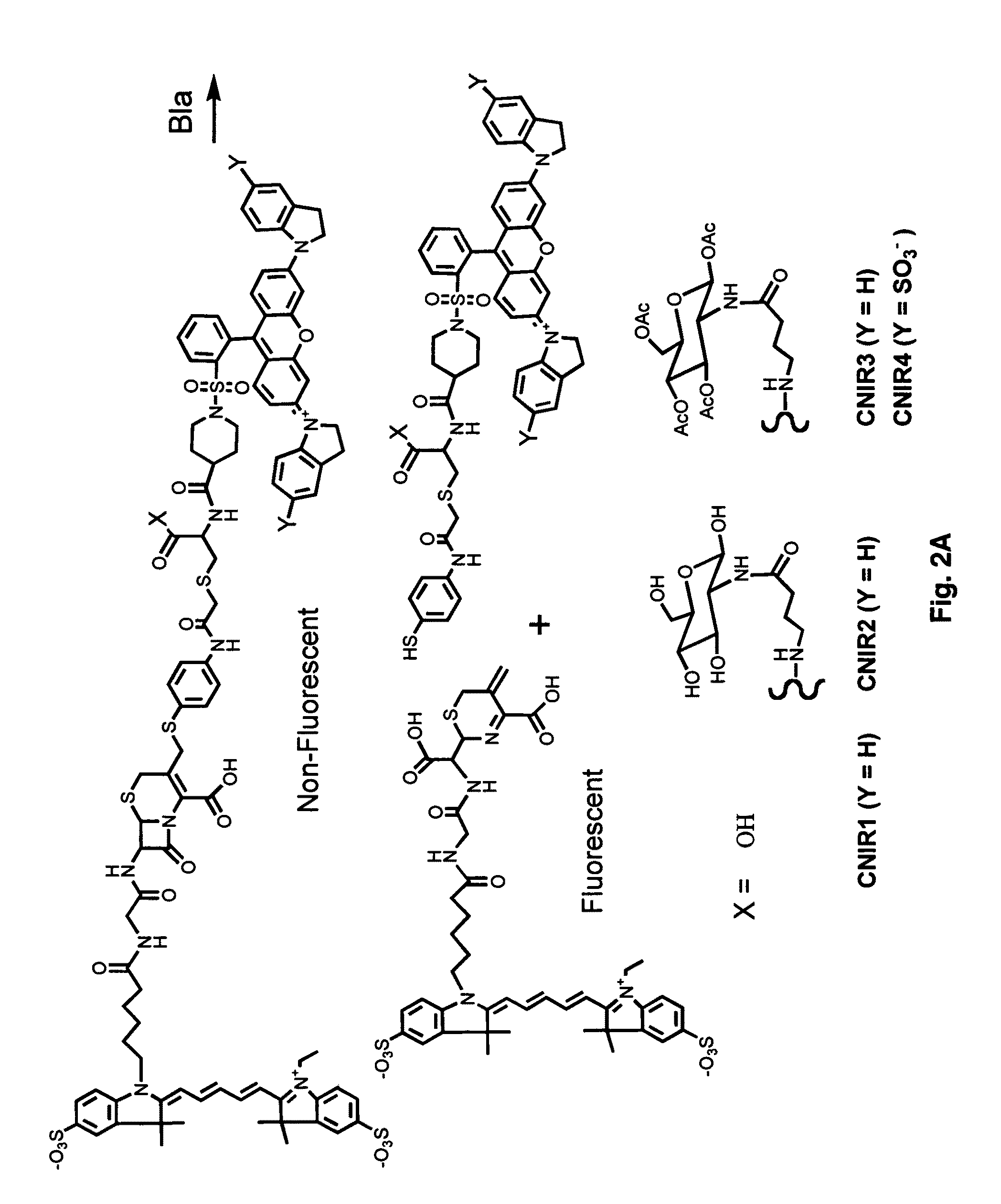
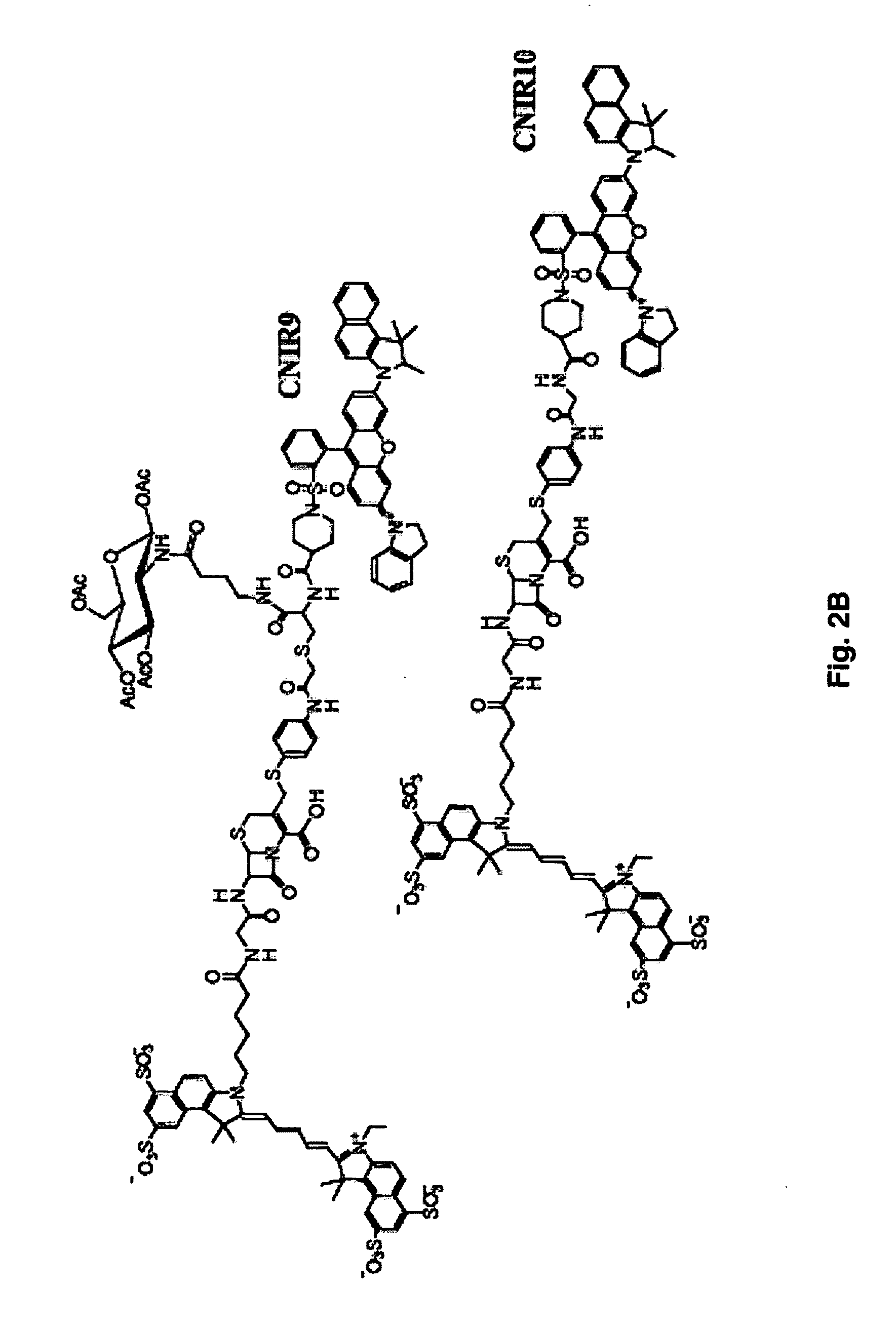
Provided herein are imaging methods for detecting, diagnosing and imaging pathogenic bacteria or a pathophysiological condition associated therewith using fluorescent, luminescent or colorimetric detection agents, e.g., fluorogenic substrates for bacterial enzymes, caged luciferins and fluorescent proteins, luciferases and enzymes expressed by recombinant bacteria. Signals emitted by the fluorescent, luminescent or colorimetric detection agents in the presence of the bacteria are compared to controls to detect and locate the pathogenic bacteria. Also provided is a method for screening therapeutic agents to treat the pathophysiological conditions by measuring fluorescence or luminescence emitted from the detection agents in the presence and absence of the potential therapeutic agent. In addition, a method for detecting a pathogenic bacteria via PET or SPECT imaging using a positron-emitting or gamma-emitting substrate for a beta-lactamase or other enzyme or protein of the pathogenic bacteria. Further provided are the fluorogenic substrates CNIR-7 or CNIR7-TAT or the radiolabeled substrates.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
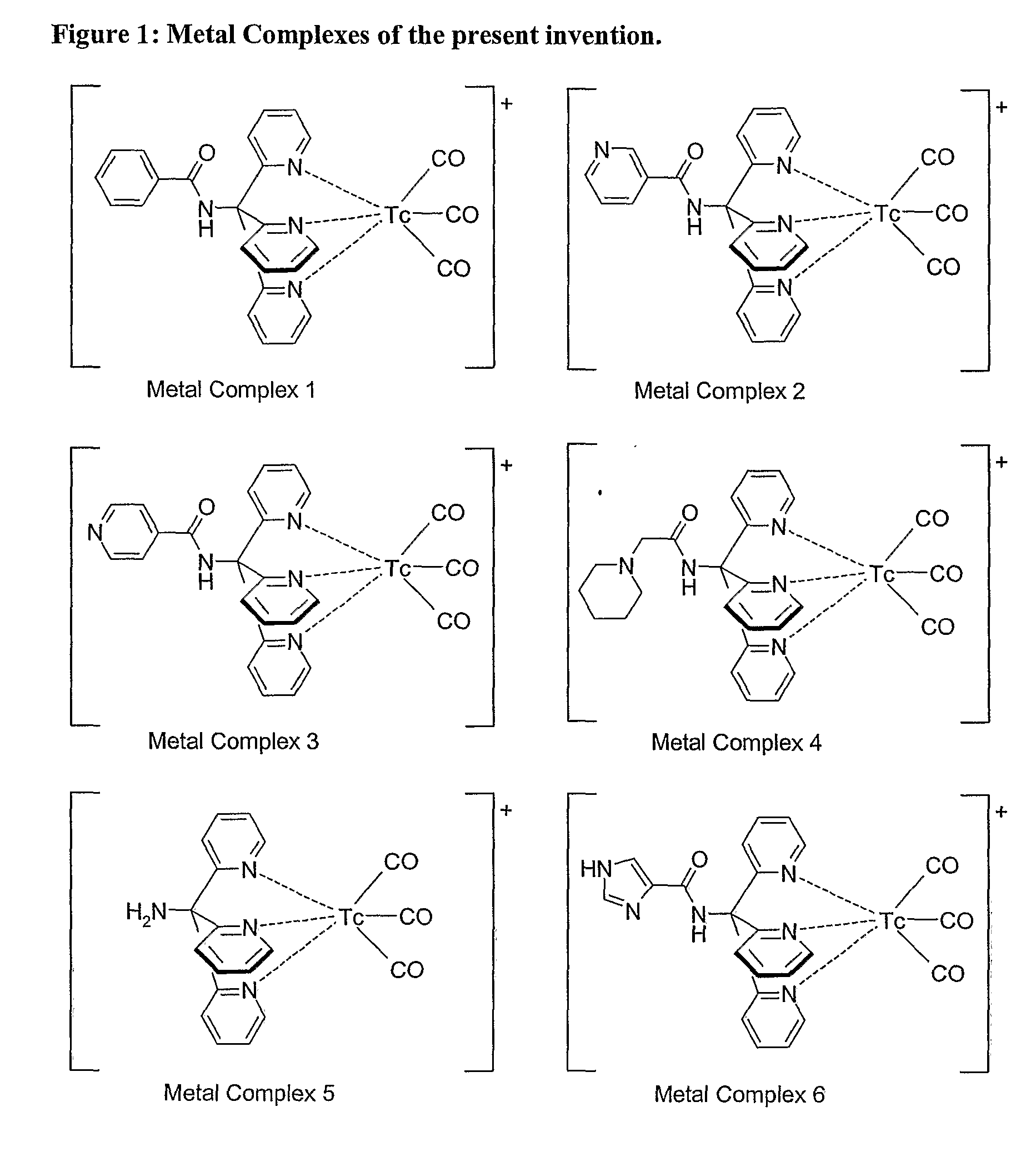
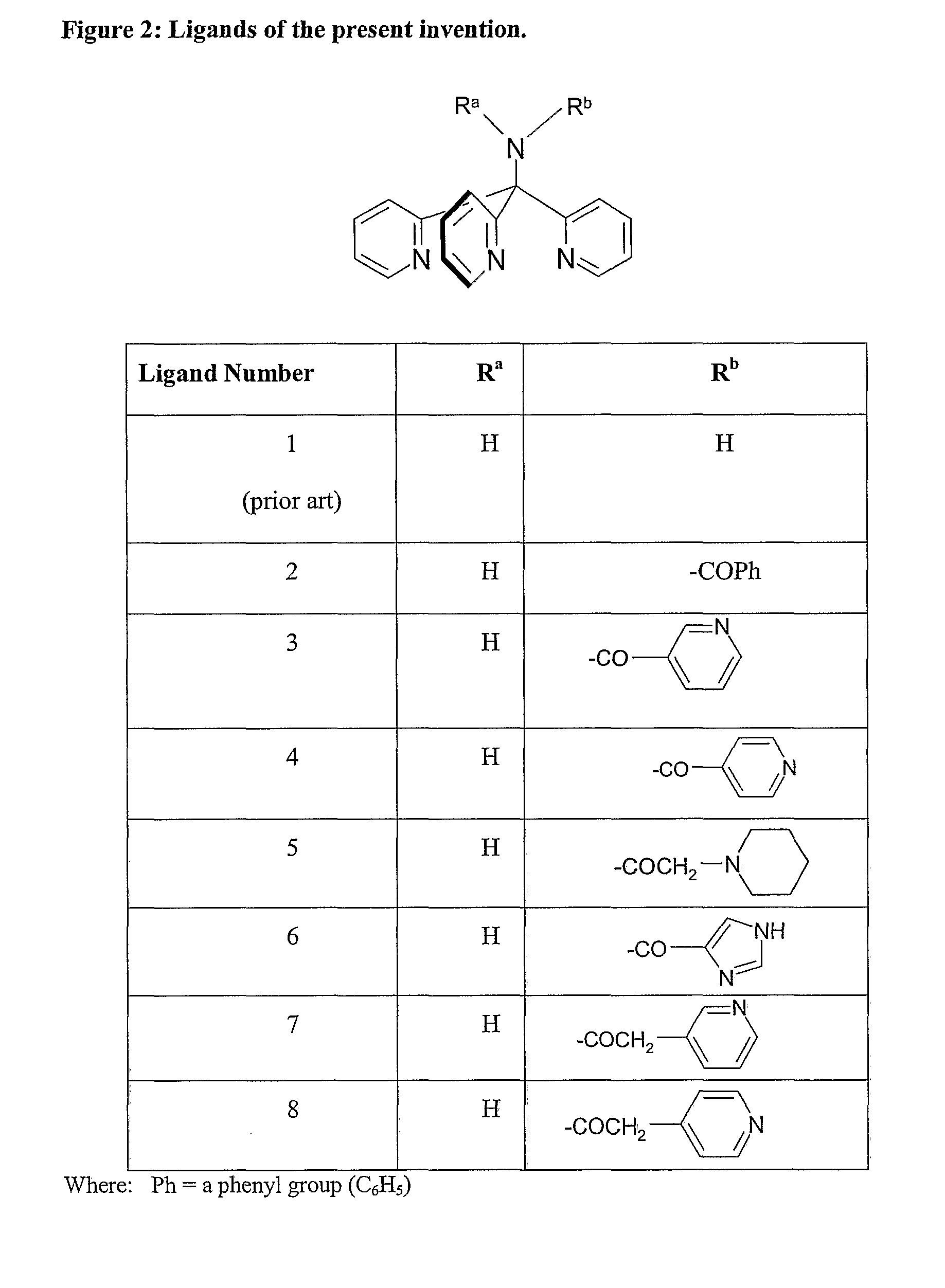
Novel Technetium and Rhenium Complexes.
InactiveUS20080219921A1Reduce impurityManufacture be controlledGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersRheniumTechnetium
Novel radioactive technetium and rhenium complexes comprising tripodal ligands are provided by the present invention. In particular, Tc(I) complexes are provided by the present invention. Novel ligands suitable for the formation of the technetium and rhenium complexes of the invention are also provided, as well as radiopharmaceutical compositions comprising said complexes, kits for their preparation. The invention also relates to the us of 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals of the invention for SPECT imaging.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
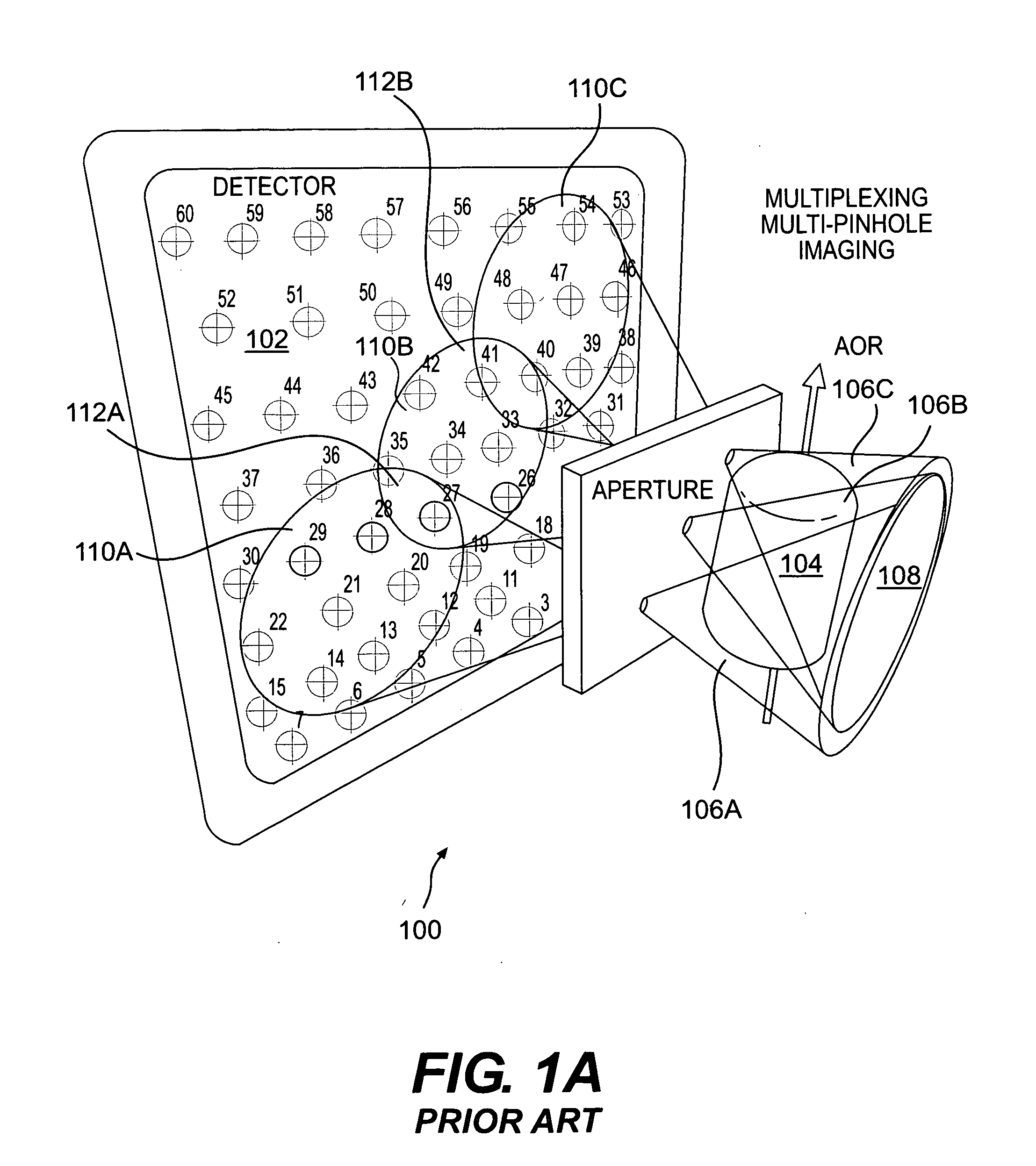
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) using helical scanning with multiplexing multi-pinhole apertures
InactiveUS20080087829A1Improve sensitivity and resolutionEasy to castMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMultiplexingImaging equipment
The reconstruction of artifact free images is made possible by the implementation of a SPECT imaging device that employs helical scanning. The SPECT imaging device includes a detector configured to detect photons, such as photons, that are projected onto it. A collimator is axially aligned with the detector and includes a plurality of pinholes configured to create overlapping projections of the photons. An object support structure is configured to move in a direction that is axially aligned with the detector and collimator. The detector and collimator are configured to rotate around the object support structure in a transaxial plane to the object support structure while the object support structure moves in an axial direct to the collimator and detector.
Owner:BIOSCAN
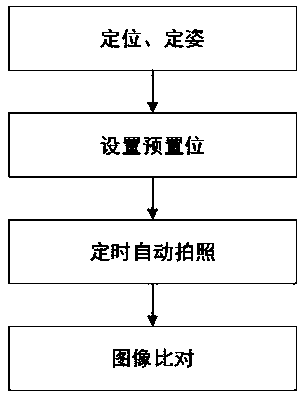
Fixed-point imaging monitoring method
InactiveCN108965808AReduce inspection workloadRealize traceabilityClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringImage contrast
The invention discloses a fixed-point imaging monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) moving visual angles of cameras to a place needing to be intensively monitored, adjustingthe angles and the focal distances, and performing positioning and attitude determining; (2) correcting azimuth numerical values of all cameras to correspond to visual angle numerical values in a video monitoring system in one-to-one way, and setting a preset location of each camera; (3) setting the photographing time, and automatically photographing the preset locations; and (4) checking a preset location photo, performing the retrospective and image contrast with the historic static data for the doubtful photo, thereby helping inspection staff monitor suspected illegal land use informationpreferably. Through the fixed point imaging monitoring method disclosed by the invention, the retrospective and image contrast of the real-time dynamic data and the historic static data are realized,the environment and land utilization statuses at various monitoring points and the surrounding thereof are provided, thereby helping the inspection personnel monitor the suspected illegal land use condition preferably.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE SURVEYING & MAPPING ENG INST
High-precision diagnostic equipment collimation method and device thereof
InactiveCN102038552AHigh precision aimingSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement pointMonitoring system
The invention provides a high-precision diagnostic equipment collimation method and a device thereof, and aims to solve the problems of low collimation precision, complex collimation device and limited space in the traditional collimation method. The method comprises the following steps: imaging a target point on two sets of CCDs (Charge Coupled Devices) in an optical imaging convergence measurement mode; interpreting the two sets of CCD images to obtain CCD convergence measuring point coordinates; when the CCD convergence measuring point coordinates coincide with the initialization-given target point coordinates, indicating that the diagnostic equipment strictly points to the target point, which means collimated; and when the CCD convergence measuring point coordinates do not coincide with the initialization-given target point coordinates, adjusting the degree of freedom of the diagnostic equipment collimation structure in three directions according to the CCD convergence measurement model established during initialization until the CCD convergence measuring point coincides with the target point. The invention has high collimation precision up to 5-10 mu m; and the system can judge whether the diagnostic equipment is collimated without a target monitoring system for observing the collimation condition of the collimated target point, so that the invention is convenient for use.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrated SPECT imaging and ultrasound therapy system
InactiveCN101573076AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorDevice form
A method and apparatus for the integration of an ultrasound transducer with a SPECT imaging system is disclosed. The ultrasound transducer allows the delivery of particle-born drug therapies or thermally active therapies at the same site detected with SPECT imaging. The system includes a SPECT imaging subsystem; an ultrasound transducer for producing a signal representative of applied ultrasound and signally coupled to the SPECT imaging subsystem; and co-registering means for co-registering the signal representative of applied ultrasound in a coordinate system of SPECT imaging subsystem. The SPECT subsystem may be replaced with a SPECT / CT combined system to provide morphology that allows for treatment planning. In another embodiment, the ultrasound transducer can be used intermittently with the sequential gathering of SPECT images for tracking time-varying properties of the binding of specific SPECT contrast agents to biomarkers of disease. In this way, the ultrasound and SPECT imaging devices form a novel combination to improve patient care through improved spatial registration, therapy planning, and workflow.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Microscope device for detecting printed circuit board (PCB)
InactiveCN102866164AConvenient fixed-point imaging shootingGuaranteed detection effectOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a microscope device for detecting a printed circuit board (PCB), which comprises a working platform, a support which is fixed on the working platform, a charge coupled device (CCD) microscopic imaging lens which is installed on the support and a PCB carrying platform which is arranged below the CCD microscopic imaging lens; and the microscope device is characterized in that the working platform is provided with a movable seat through an X-axis electric-control lead screw transmission pair, the movable seat is provided with the PCB carrying platform through a Y-axis electric-control lead screw transmission pair, the CCD microscopic imaging lens is installed on the support through a Z-axis electric-control lead screw transmission pair, the Z axis is vertical to the working platform, and the X axis, the Y axis and the Z axis form a spatial right-angled coordinate system. The microscope device has high adaptability aiming at the PCB size specification and is convenient for the CCD microscopic imaging lens to carry out the fixed-point imaging photography on a detect part on the PCB, so that the detection effect is guaranteed.
Owner:SUZHOU SUNSHINE LASER & ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
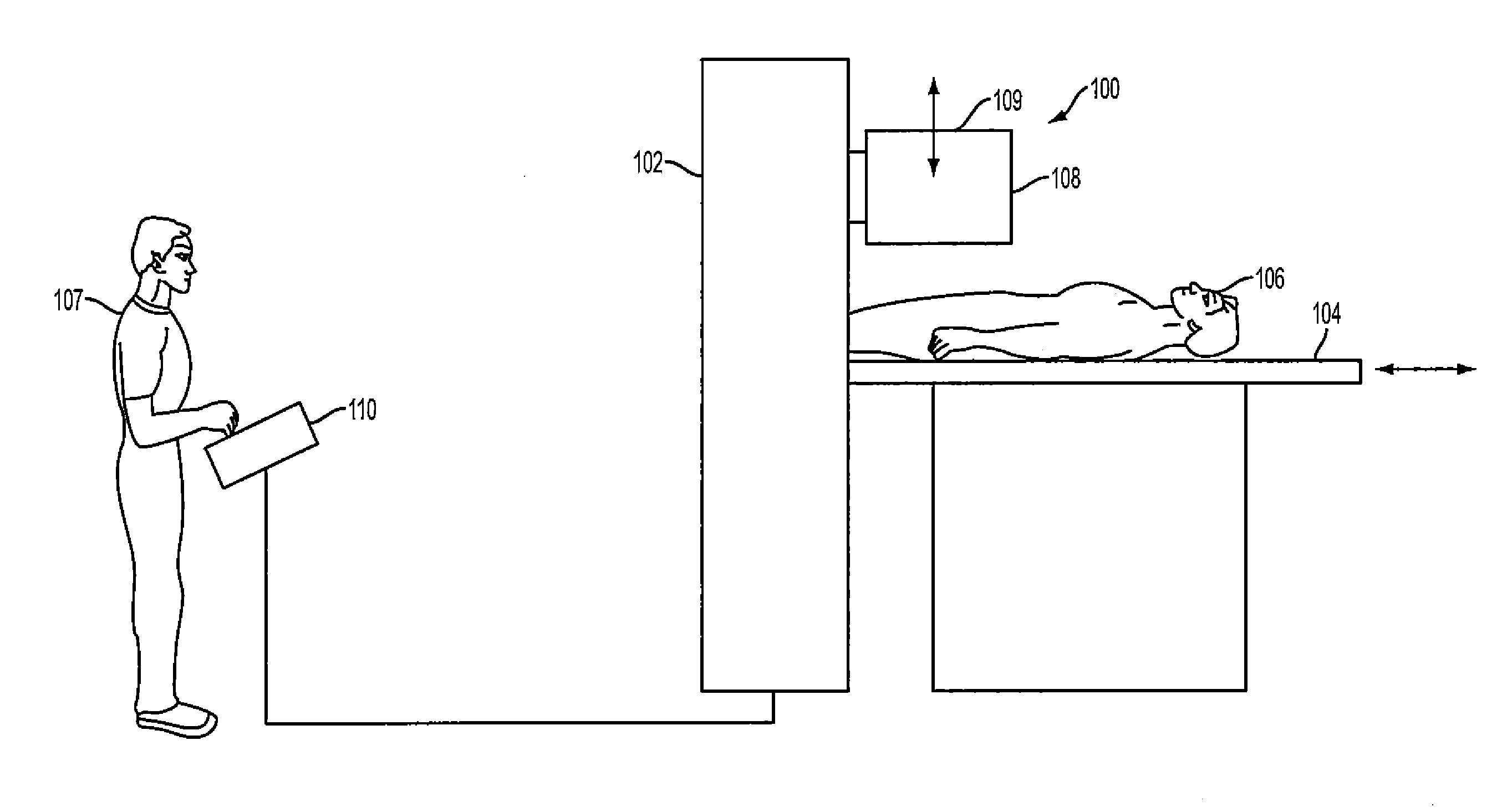
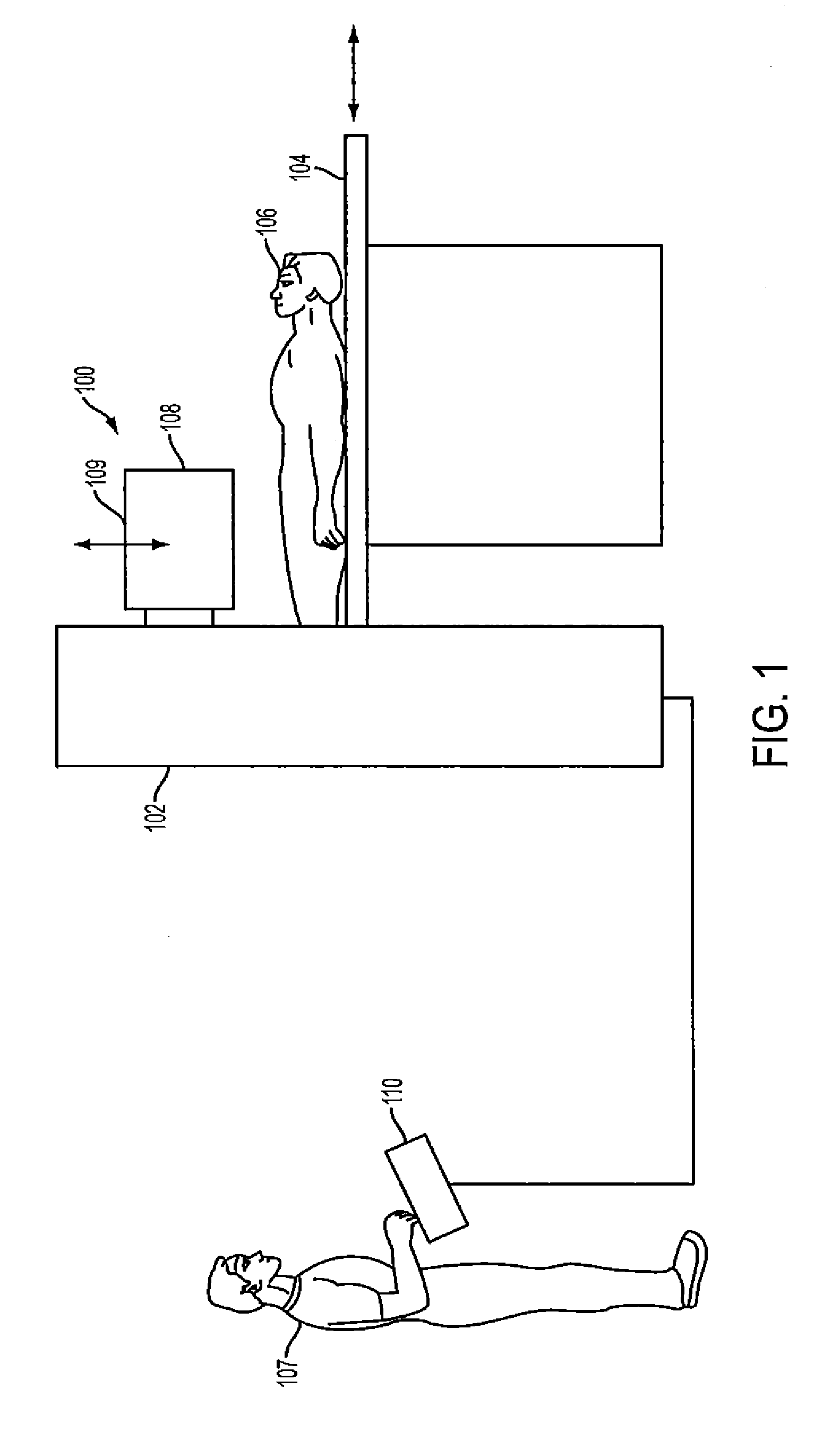
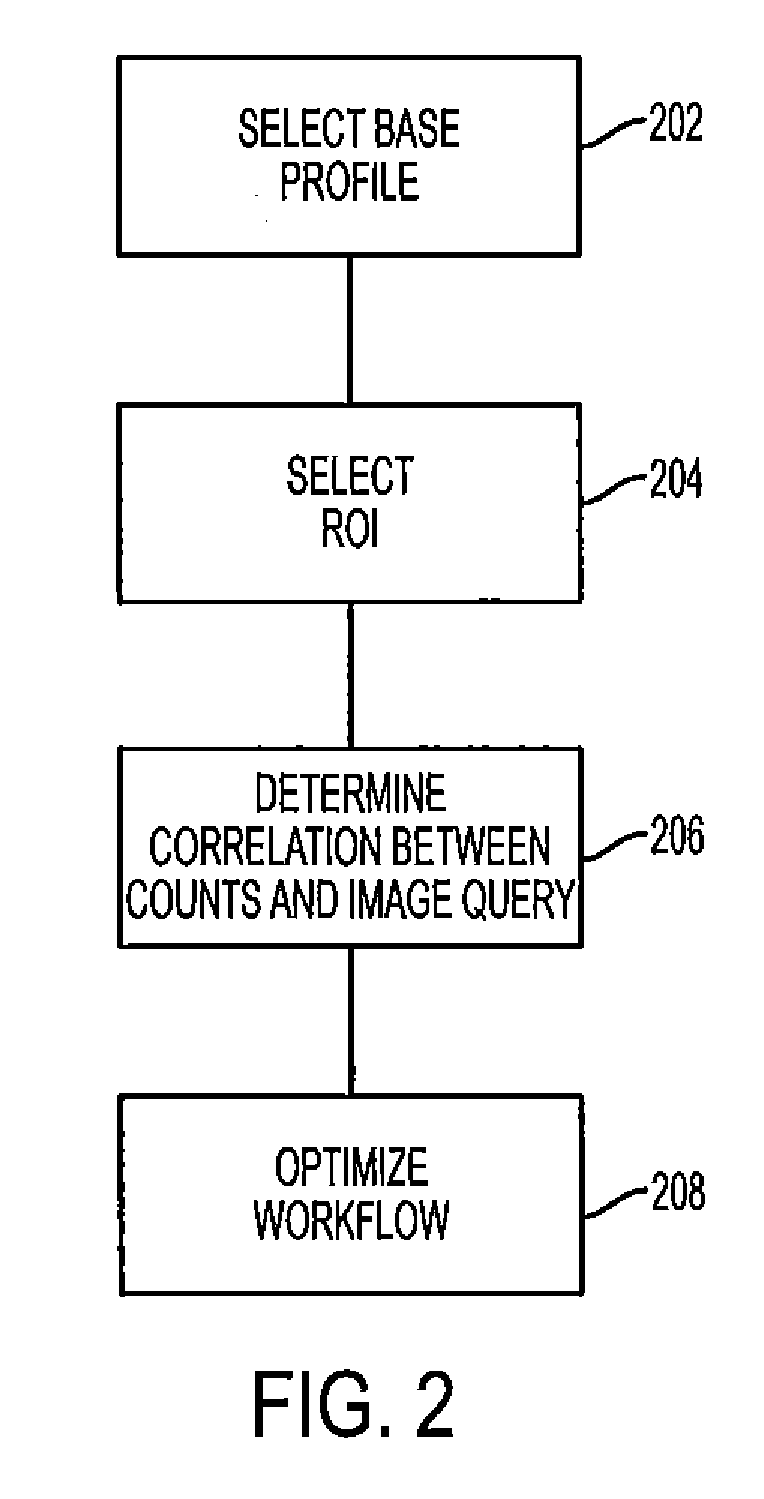
Method and Apparatus to Optimize Injected Dose and Scan Time in SPECT Imaging
ActiveUS20120018645A1Simple stepsQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyImaging qualitySpect imaging
An apparatus and method are provided for optimizing an amount of radiation dose and acquisition time in cardiac Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) imaging. The apparatus and method include providing an organ, acquiring images of the organ at projected views. Then a projected view that projects the organ as an annulus is selected; a region of interest (ROI) is also selected in the projected view, wherein the ROI is in a lateral wall of the organ. An average count in the ROI is determined; and an image quality of a reconstructed image based on the average count is predicted.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com