High-resolution scanning microscopy distinguishing between at least two spectral ranges
A scanning microscopy, high-resolution technique used in the field of fluorescence radiation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
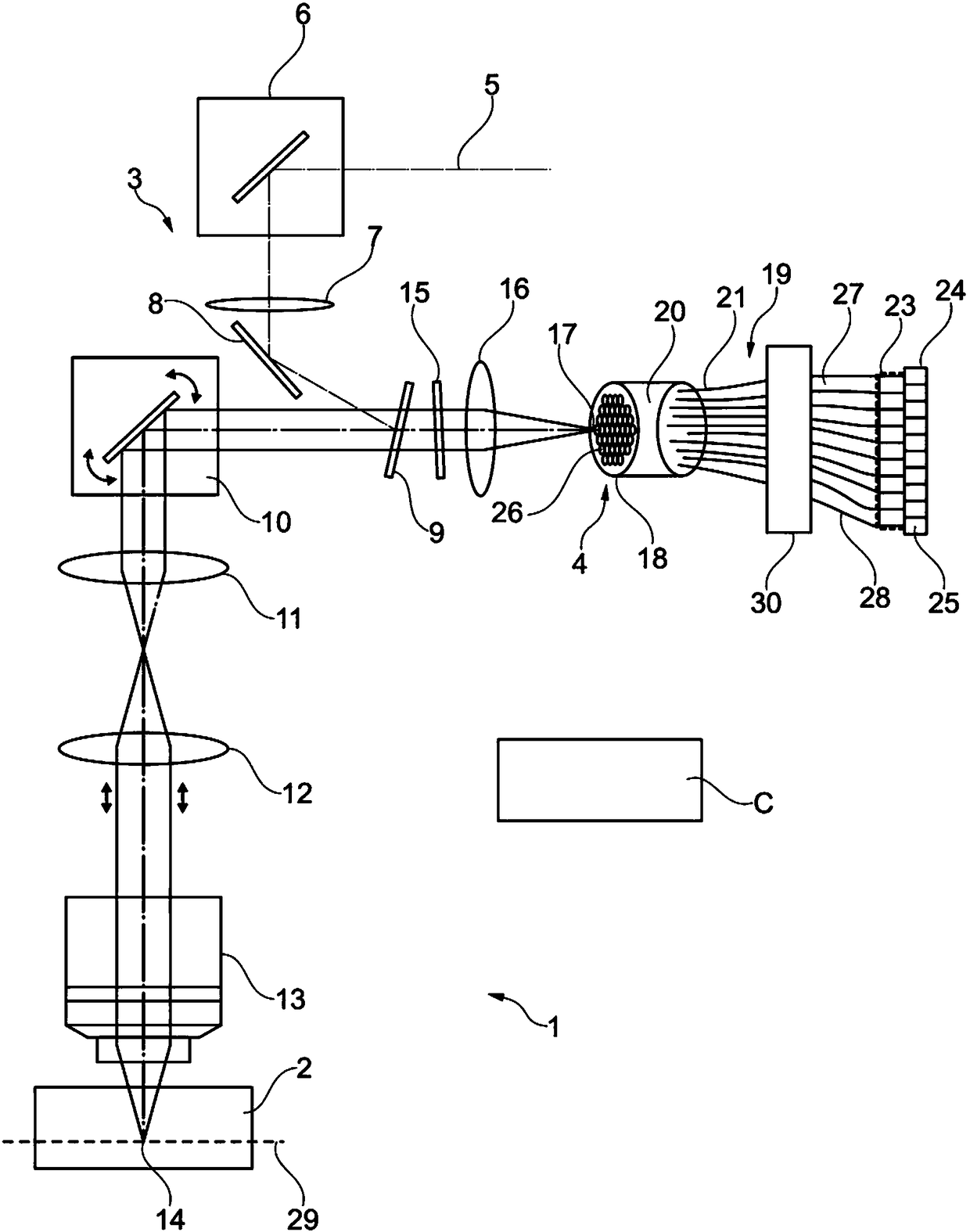
[0044] figure 1 A laser scanning microscope 1 configured for microscopy of a sample 2 is schematically shown. A laser scanning microscope (hereinafter referred to as LSM) 1 is controlled by a control device C and includes an illumination beam path 3 and an imaging beam path 4 . The illuminating beam path illuminates the spot on the sample 2 and the imaging beam path 4 images the spot in a diffraction-limited manner for detection. The illumination beam path 3 and the imaging beam path 4 share an optical unit.
[0045] The sample 2 is illuminated in the LSM 1 with the provided laser beam 5 , which is coupled to a mirror 8 via a deflecting mirror 6 (which would otherwise not be functionally necessary) and a lens 7 . The mirror 8 ensures that the laser beam 5 is incident on the incoupling element (for example the transmission filter 9 ) at a reflection angle. For the sake of clarity, only the main axis is depicted for the laser beam 5 .
[0046] After the laser beam 5 has bee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com