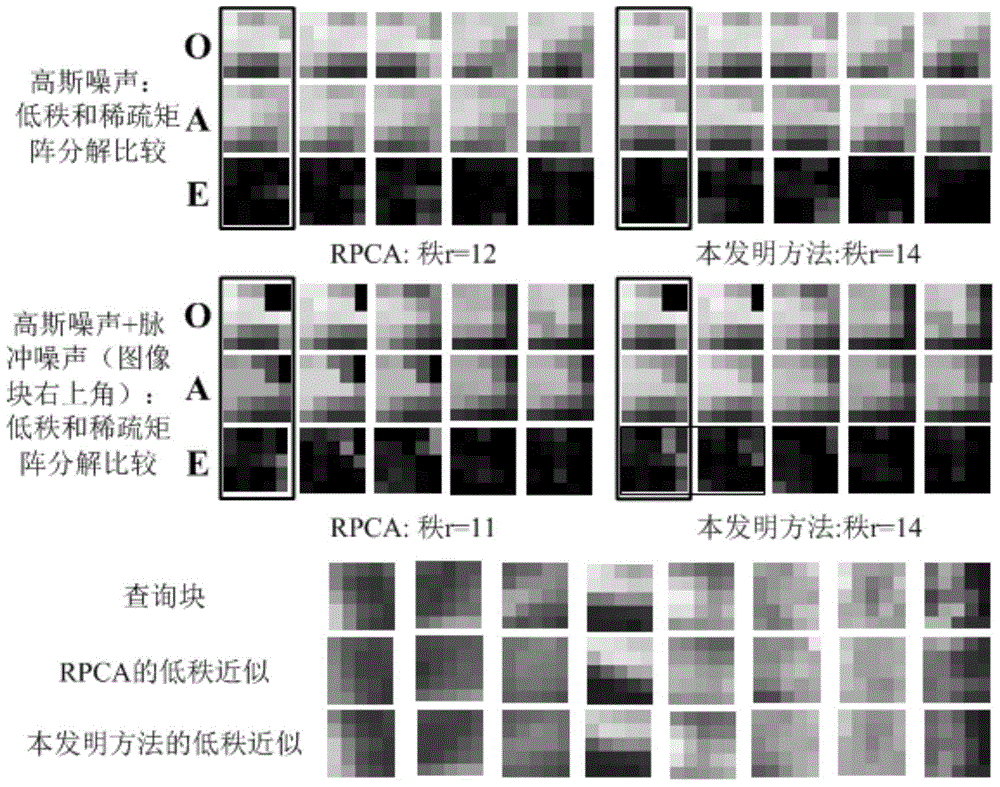
Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Remove image noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Super-resolution method based on single image
ActiveCN104008538AImprove realismImprove accuracyImage enhancementGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionWeight coefficient
The invention relates to a super-resolution method based on a single image. The super-resolution method includes the steps that S1, bicubic interpolation is carried out on the input low-resolution image to obtain an initial high-resolution image; S2, the initial high-resolution image is divided into a plurality of image blocks overlapped mutually, then a similar image block grouping is obtained, and image noise of the similar image block grouping is removed; S3, the multiple denoised image blocks are fused into a whole high-resolution image, a non-local similar image block and a weighting coefficient of each image block are solved, and the redundancy weight of a non-local similar image block grouping is calculated; S4, an on-line dictionary is updated according to the similar image block grouping and fused with an off-line dictionary; S5, the sparse representation coefficient, about a fused dictionary, of each image block is solved; S6, all the image blocks and the whole high-resolution image are reconstructed, if iterations do not converge and the number of the iterations is smaller than a preset threshold value, the previous steps are executed again, and otherwise the high-resolution image is output. The reality sense and accuracy of super-resolution reconstruction are promoted, and the super-resolution method has the advantage of removing the image noise at the same time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for generating high iso image
ActiveUS20110096201A1Remove image noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Computer science
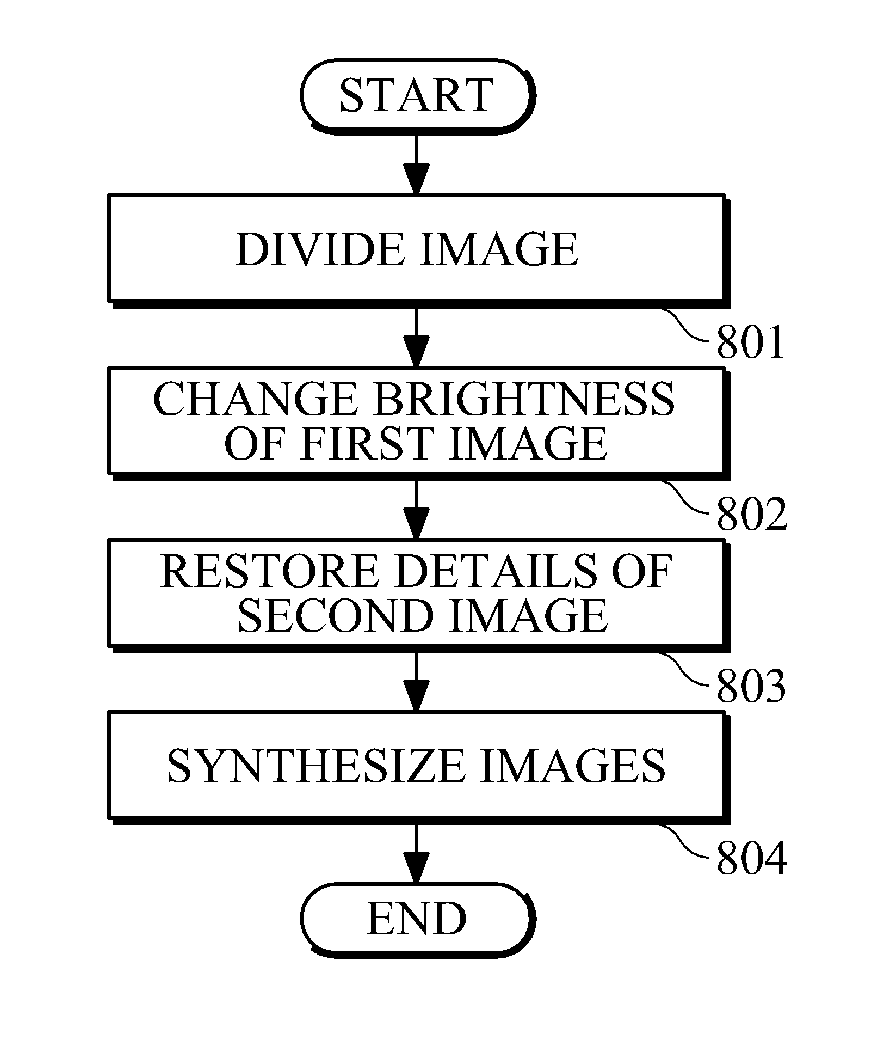
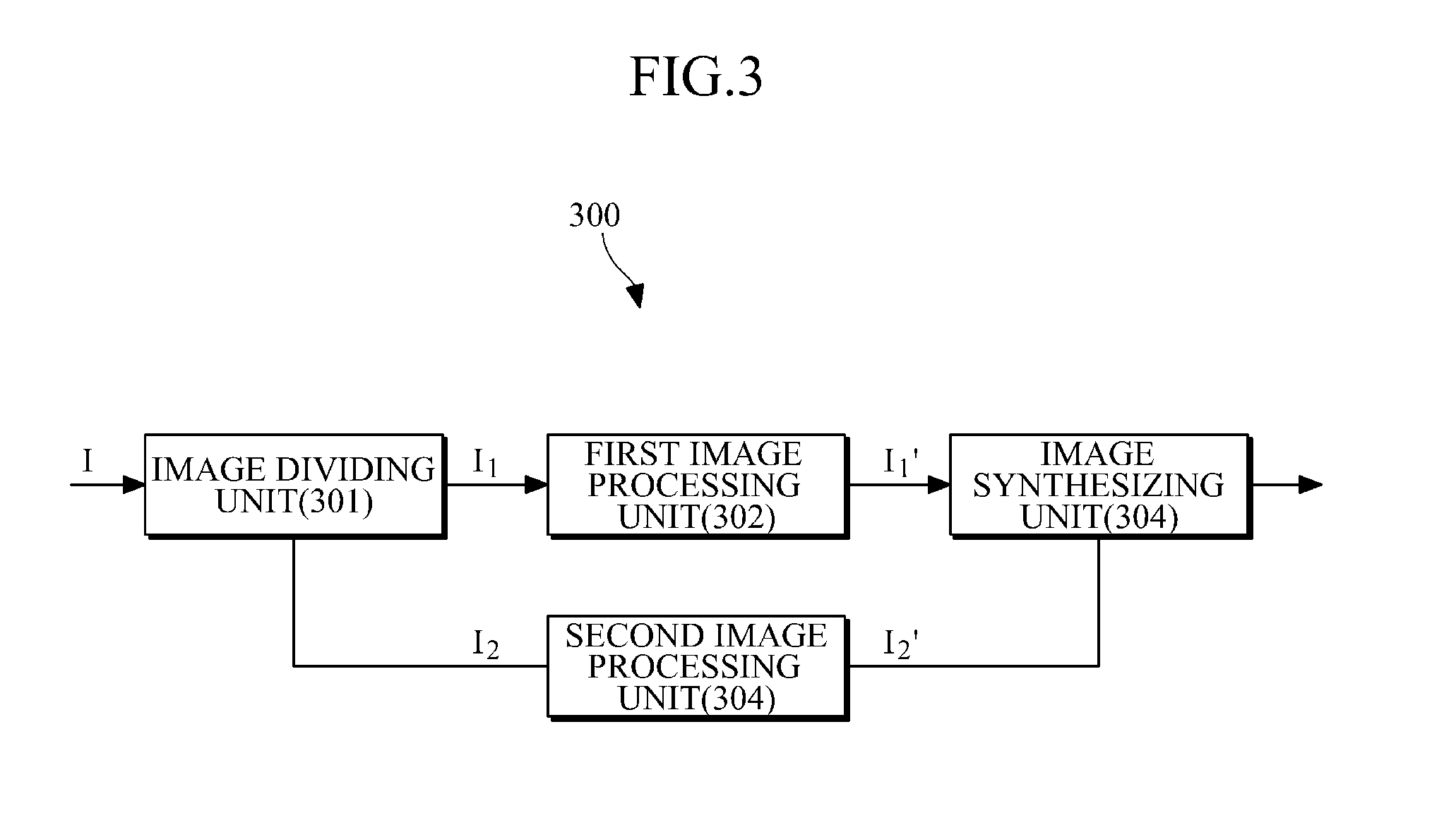
An apparatus and method for generating a high ISO image are provided. To this end, an image may be divided into a first image having a low frequency component and a second image having a high frequency component. A brightness of the first image may be changed, and details of the second image may be restored. The first image having the changed brightness and the second image having the restored details may be synthesized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Noise reduction system, noise reduction method, recording medium, and electronic camera
ActiveUS7382406B2Noise to be removedHinder resolutionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionNoise reduction
A noise reduction system comprises an inputting unit inputting image data, and a noise reduction unit performing a process for removing noise of the image data input by the inputting unit. The noise reduction unit includes a representative value calculating unit calculating a representative value from the level values of a plurality of pixels in a predetermined direction, which include an observed pixel of the input image data, a representative value selecting unit selecting one representative value according to a predetermined condition from among a plurality of representative values which are calculated by the representative value calculating unit and correspond to a plurality of directions, and a replacing unit replacing the level value of the observed pixel with the representative value selected by the representative value selecting unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
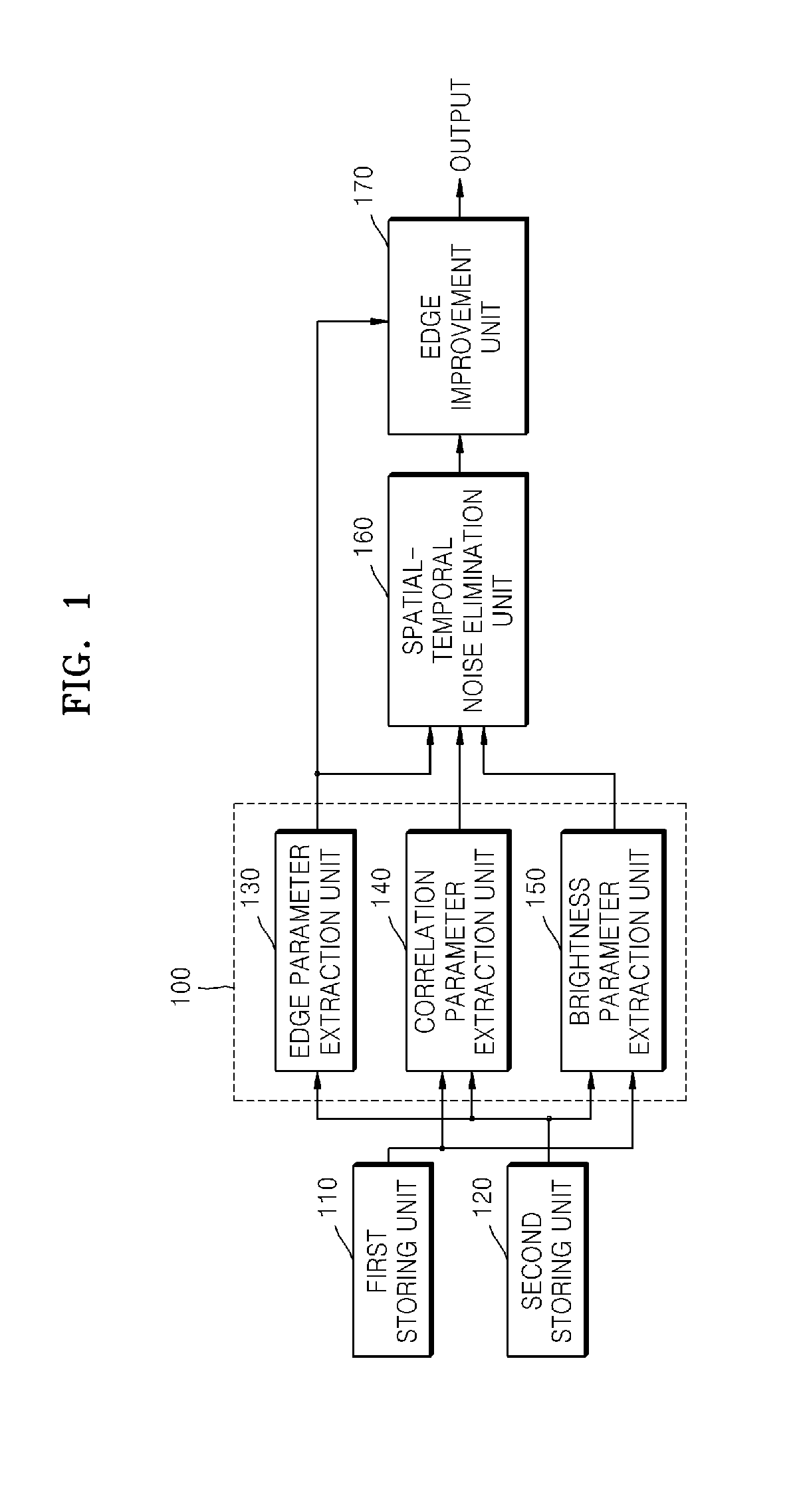
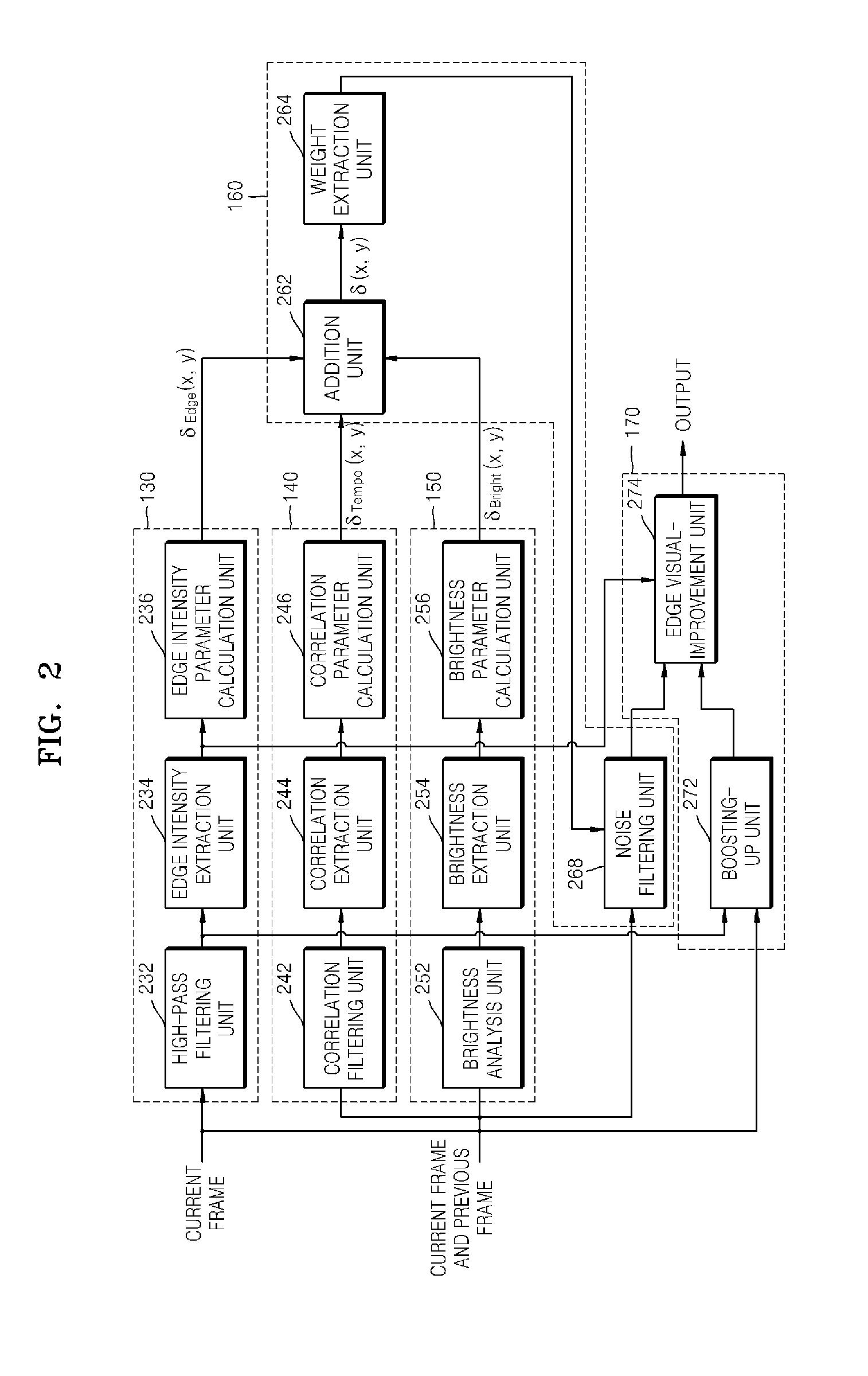
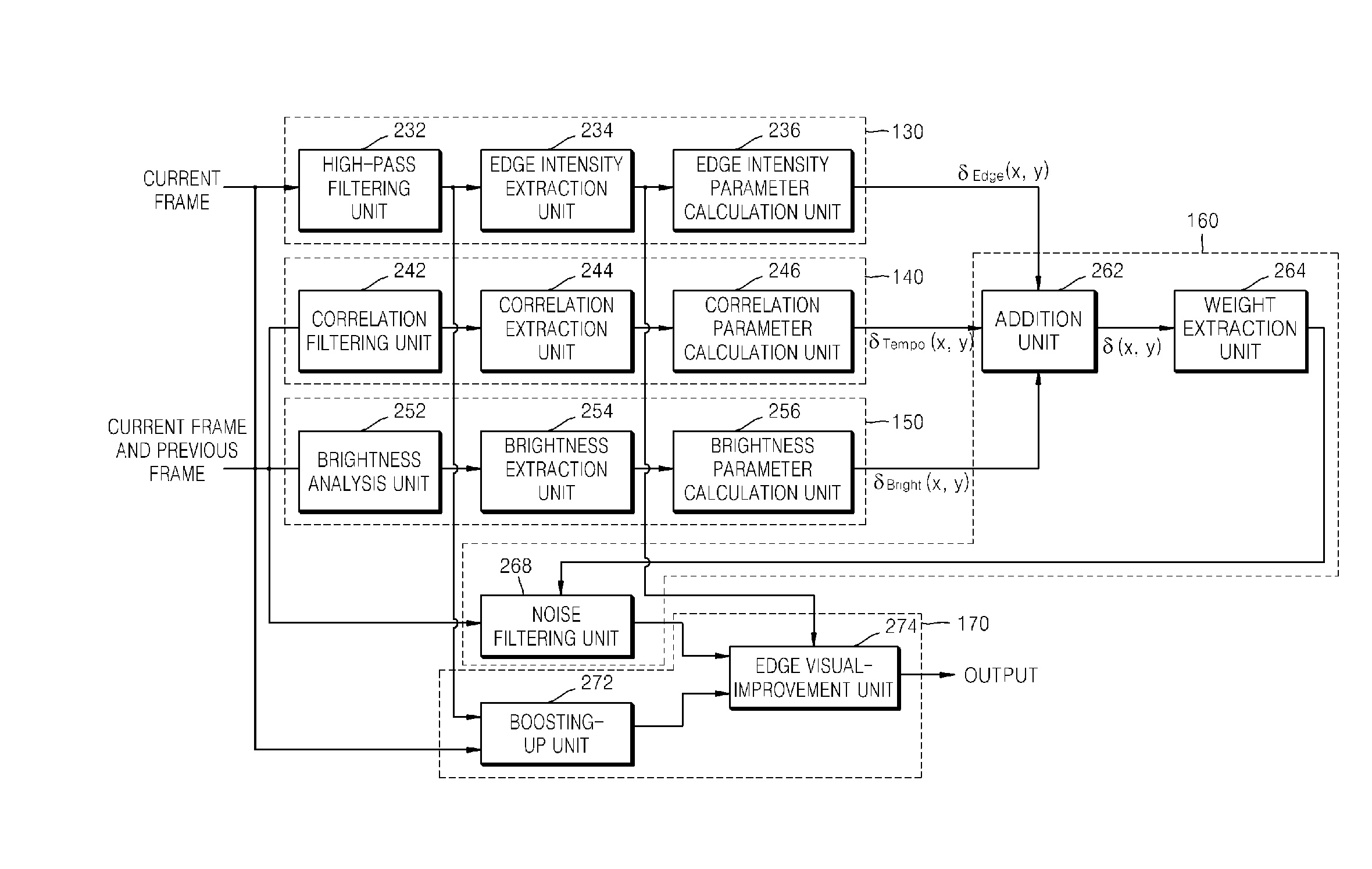
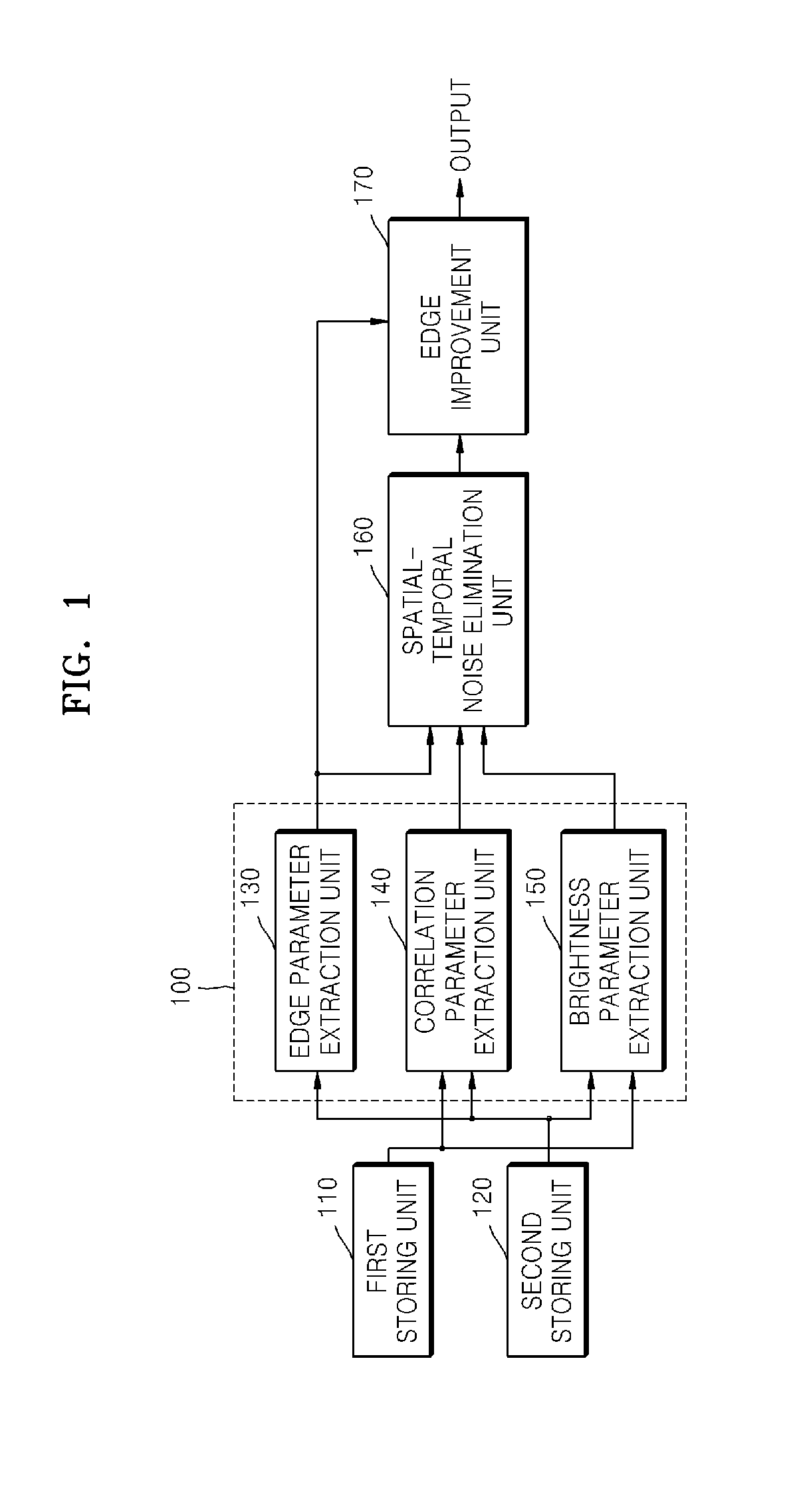
Method of and apparatus for eliminating image noise
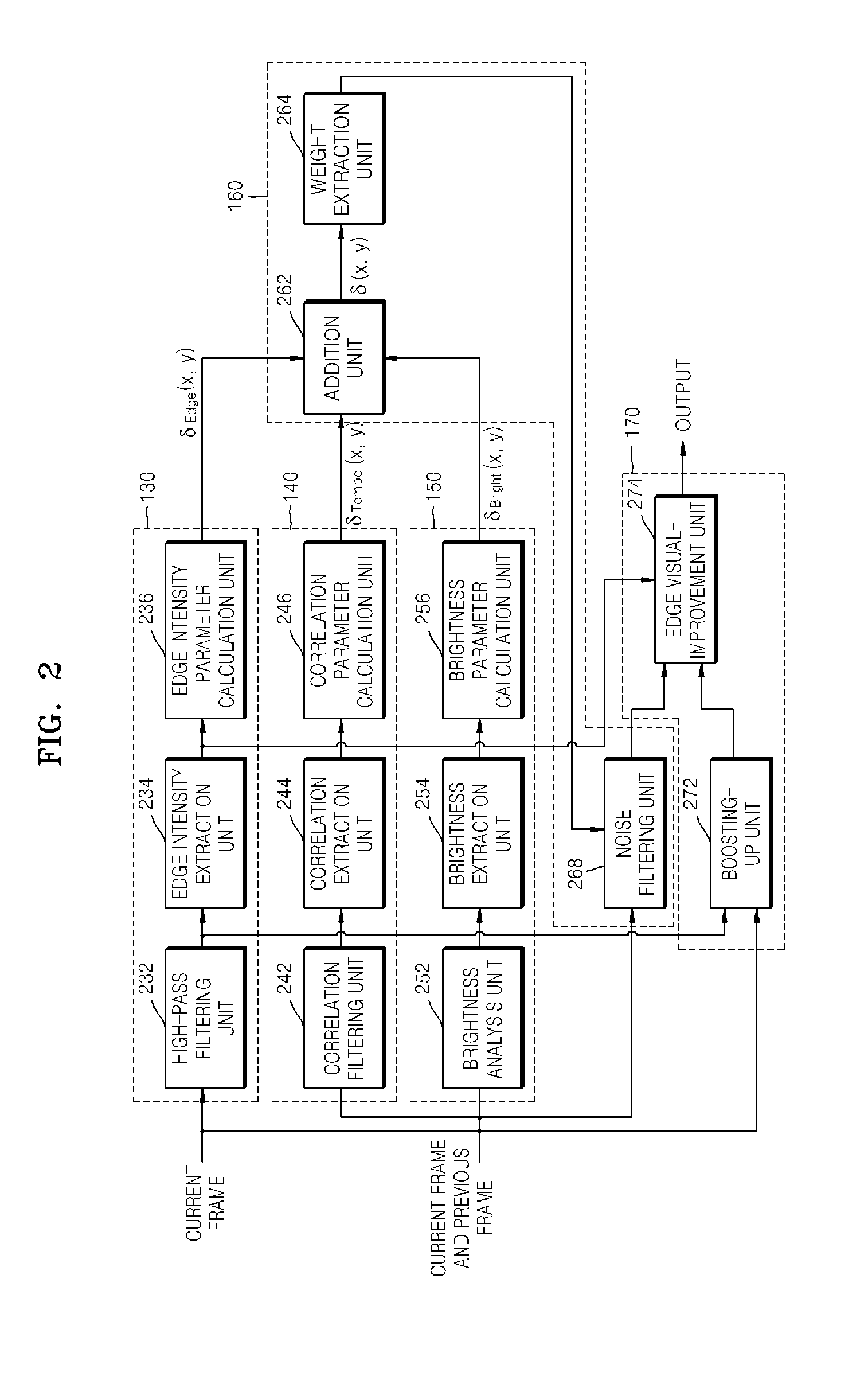
InactiveUS20080118179A1Improve visibilityEliminate image noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSpacetimeTemporal noise
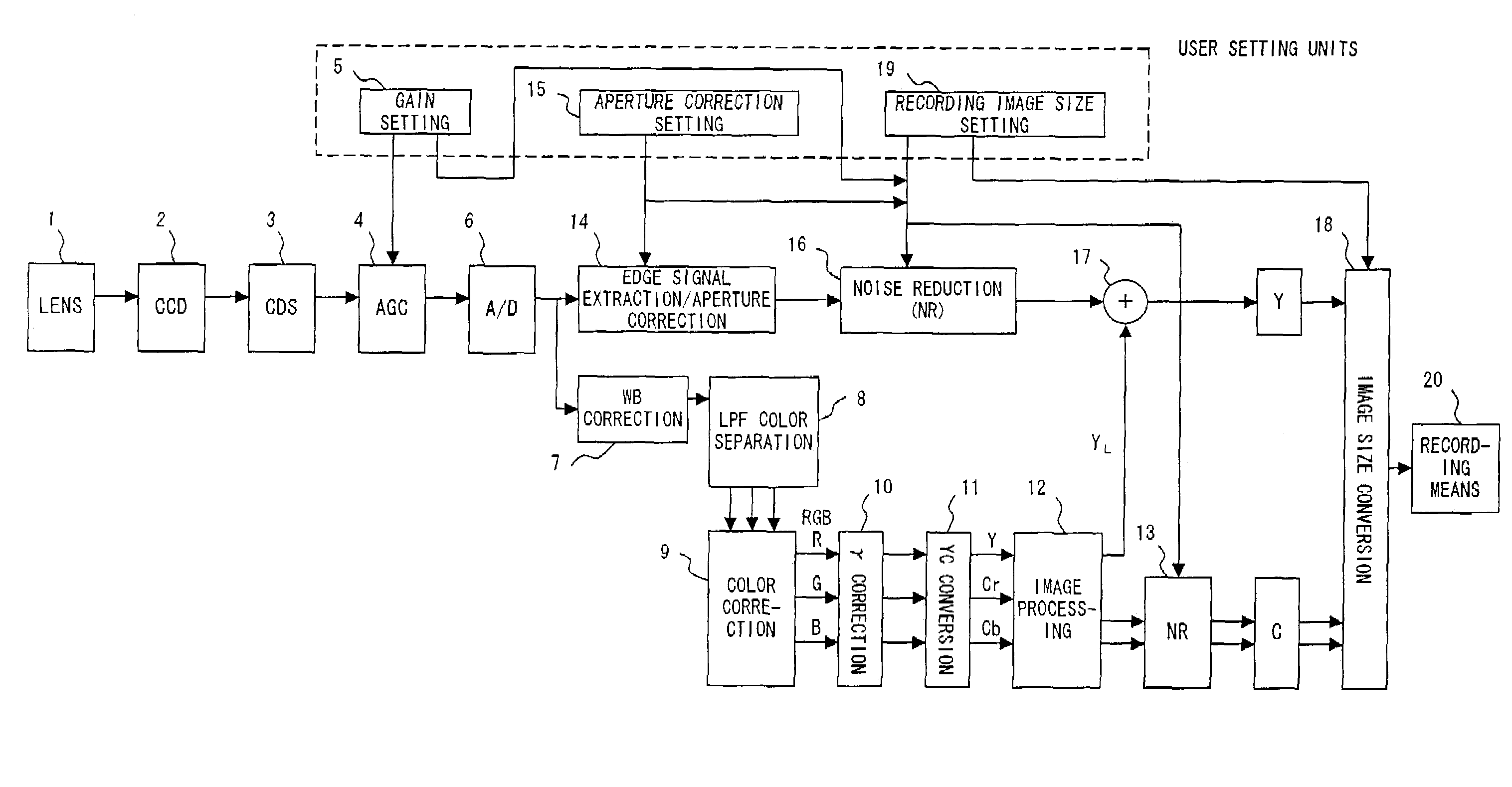
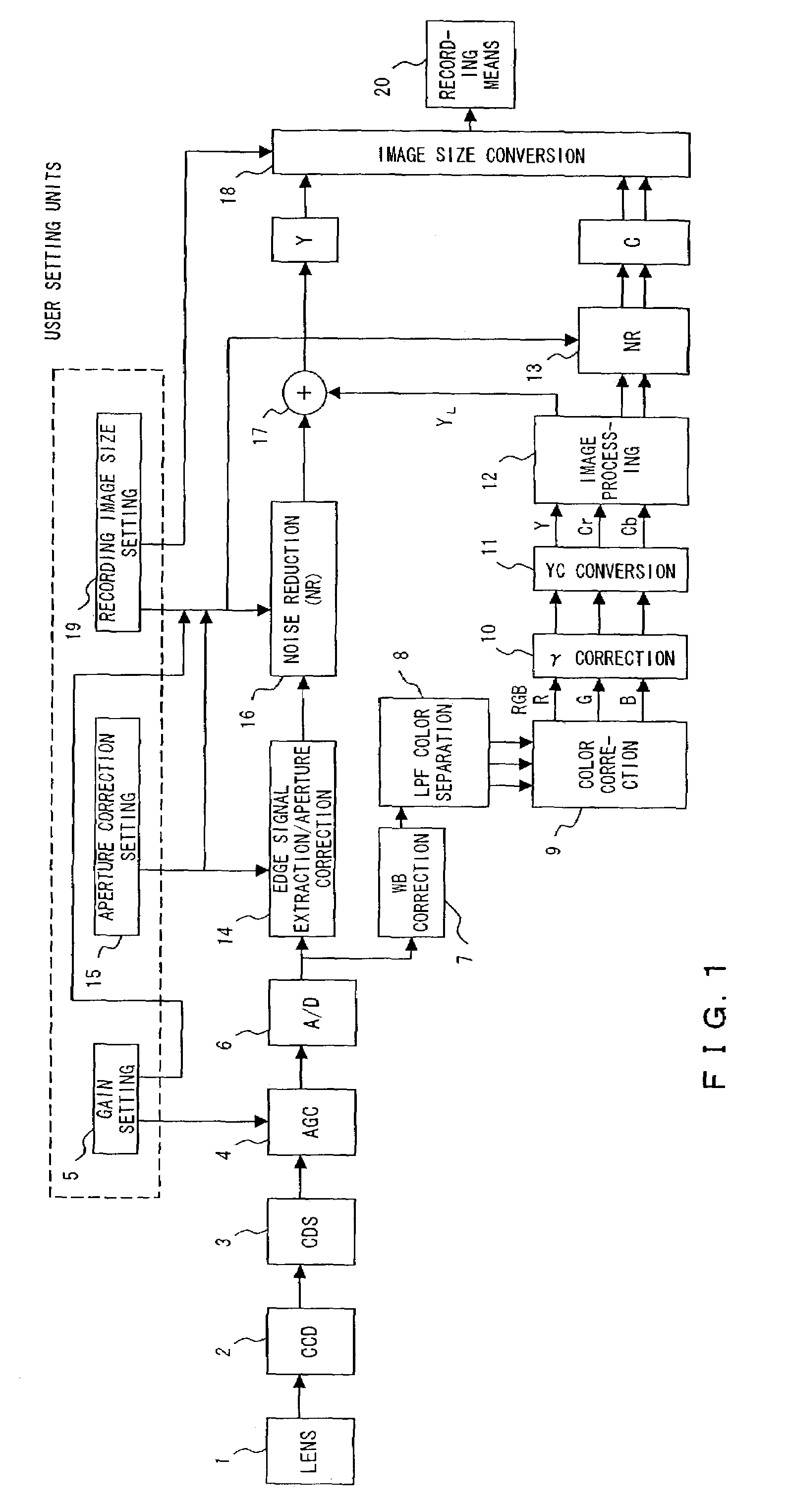
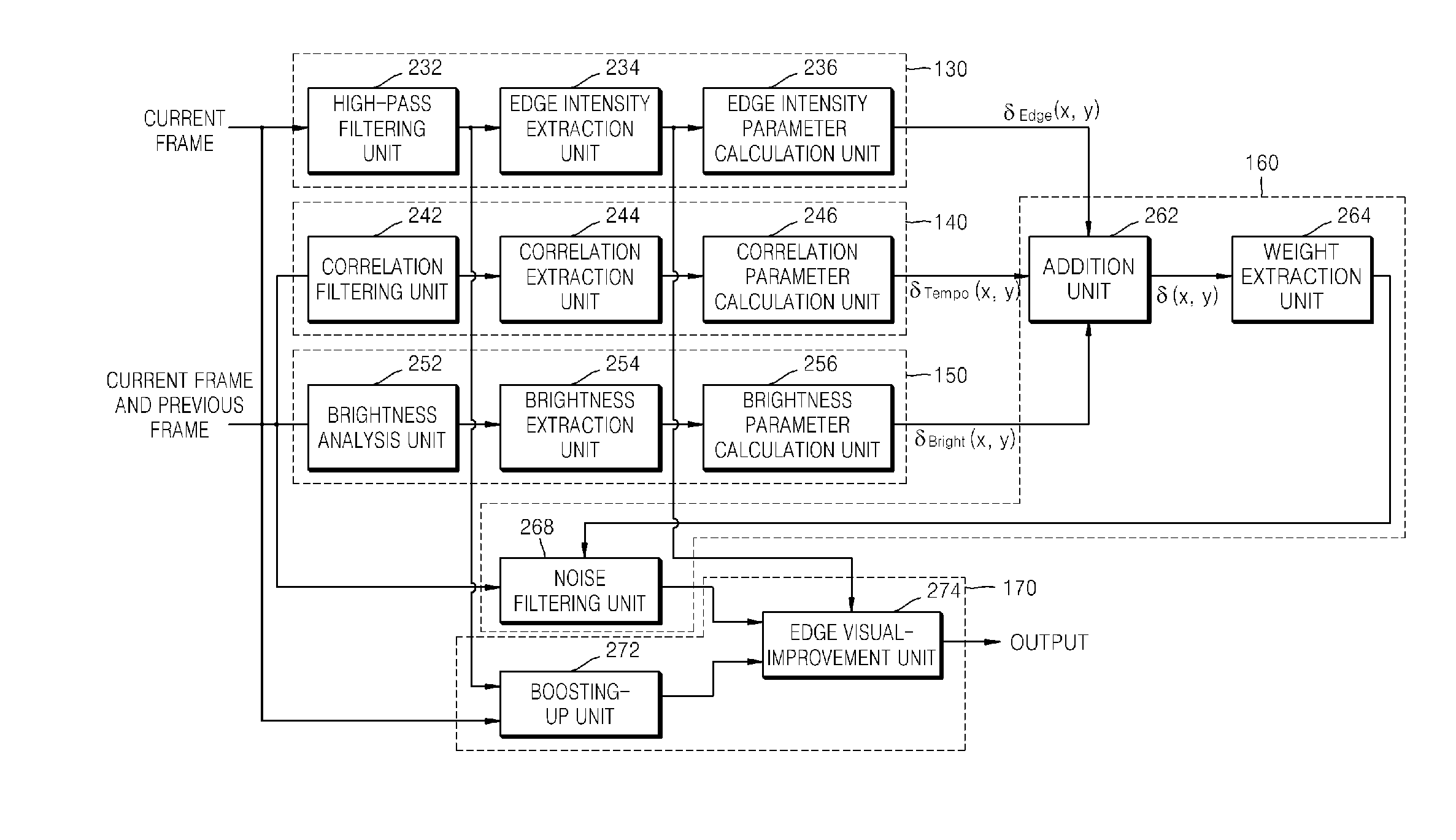
A method and apparatus are provided for eliminating image noise to remove spatial-temporal noise and improve visibility. The method includes extracting a spatial-temporal noise level of neighbor pixels around a current pixel, filtering noise of the current pixel by applying a weight to spatial-temporal pixels around the current pixel based on the extracted spatial-temporal noise level, and applying a weight to the noise-filtered pixel and a boosted-up pixel based on an edge intensity and summing the weight-applied pixels. The spatial-temporal noise level is extracted based on spatial-temporal information of neighbor pixels around a current pixel in a current frame and spatial-temporal information of neighbor pixels around a current pixel in a previous frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for quantifying soil macropore spatial network structure based on CT scanning technology
ActiveCN106546521AData augmentationImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial structureCt scanners
The invention discloses a method for quantifying a soil macropore spatial network structure based on the CT scanning technology. The method comprises the following steps of sample collection, CT scanning, threshold value selection, data enhancement, image cutting and binarization, three-dimensional visualization and three-dimensional quantization analysis. The method has the advantages that a professional undistributed soil sampling instrument is used for sampling, and disturbance in the undistributed soil collecting process is reduced; a CT scanner and professional three-dimensional analysis software are combined, the most proper threshold value cutting method is adopted, and three-dimensional quantifying analysis of the soil macropore spatial structure is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for enhancing image acquired by radiographic system
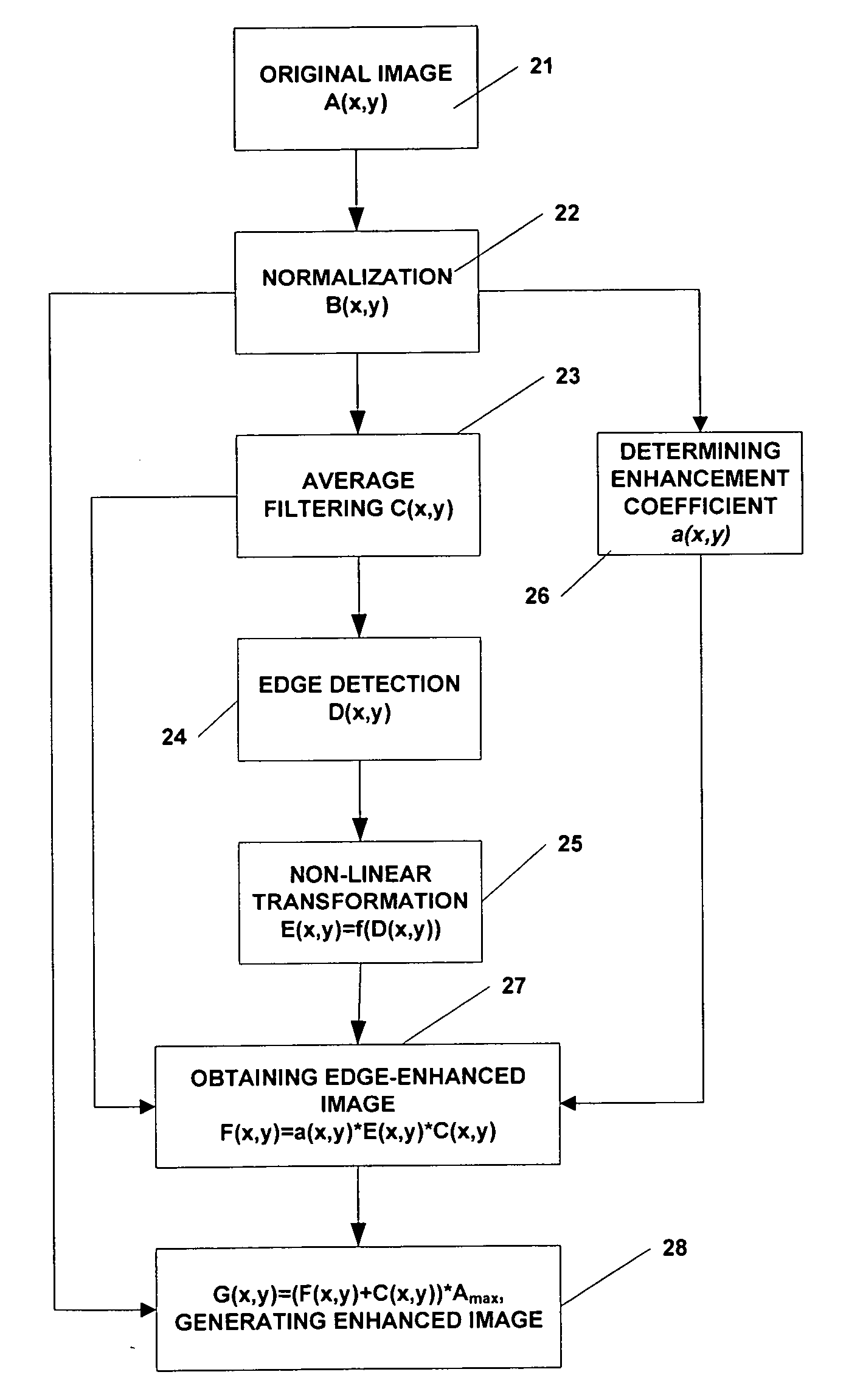
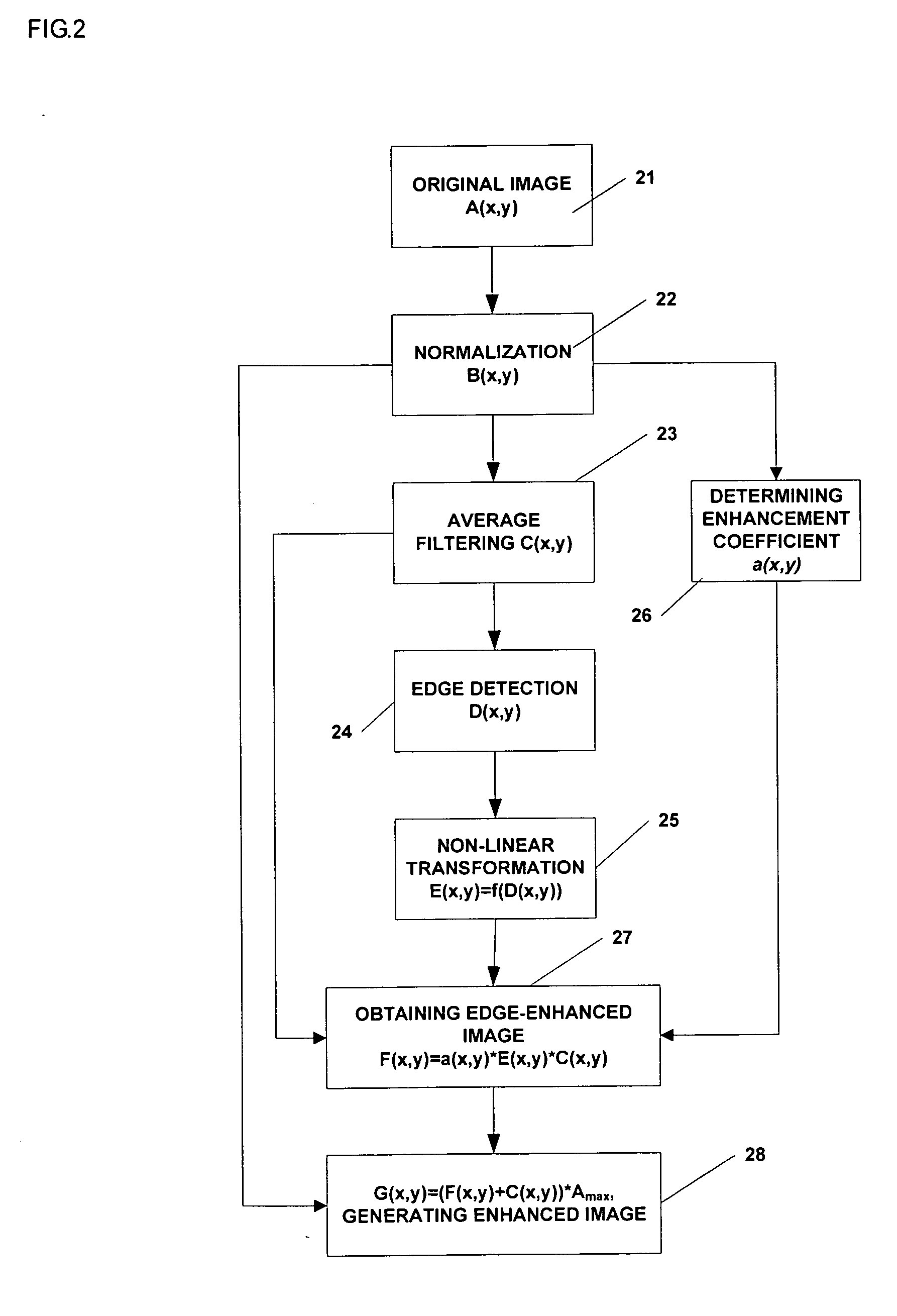
ActiveUS7689055B2Enhanced informationRemove image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingLow-pass filter
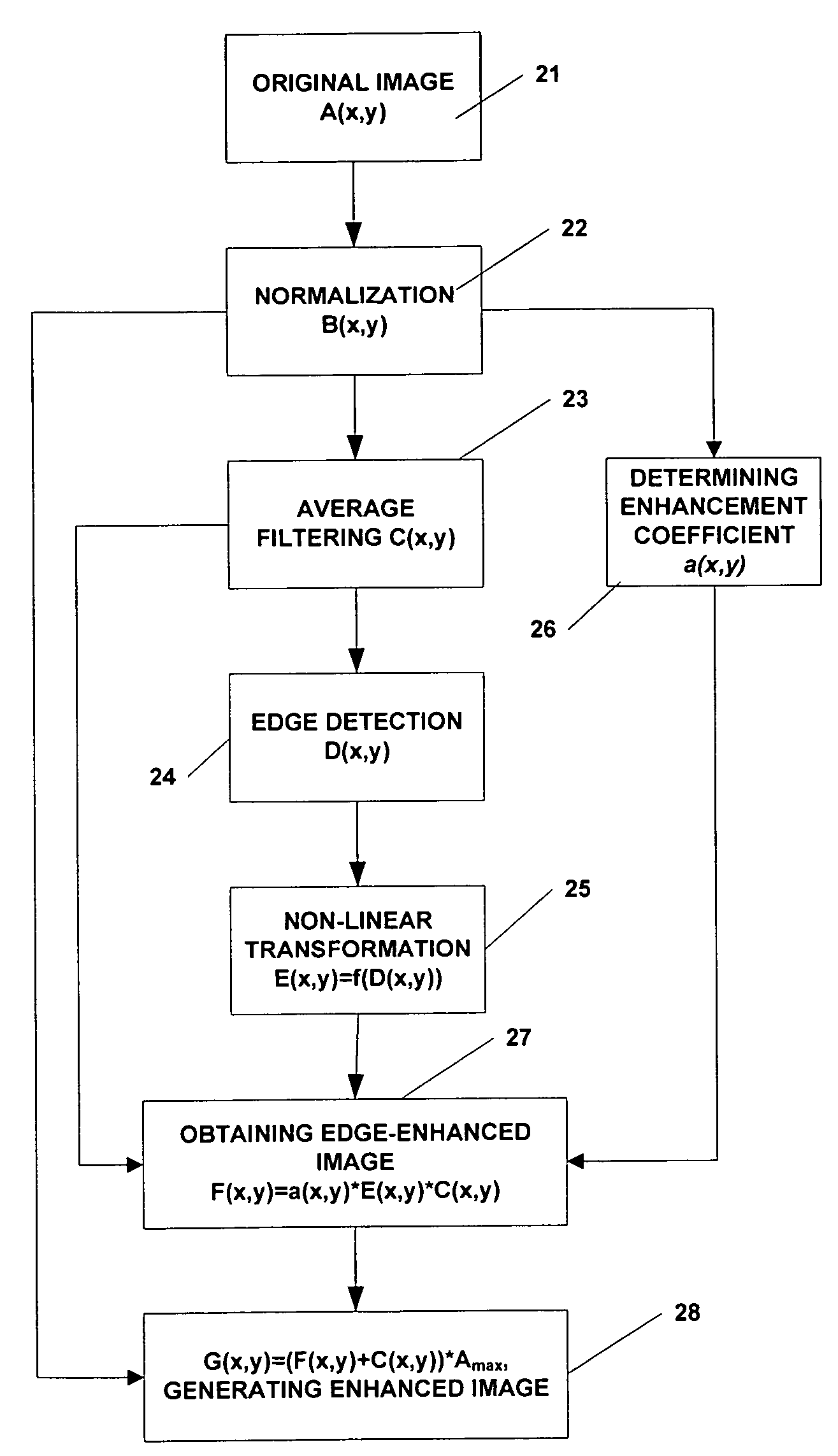
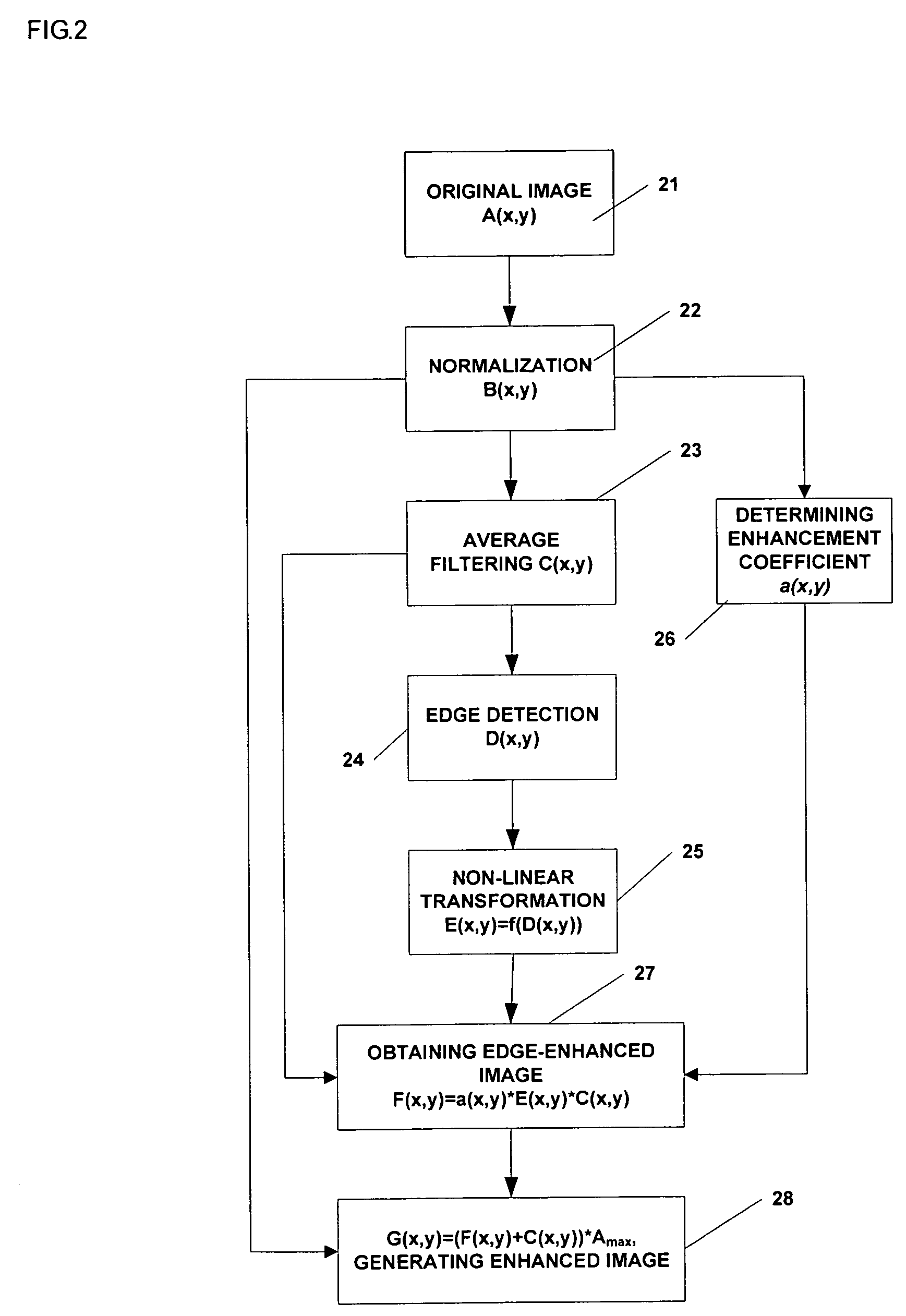
A method of image information enhancement in radiography relates to image information processing techniques in radiography. The method comprising steps of: normalizing an acquired image A(x,y) to form a normalized image B(x,y); filtering the normalized image B(x,y) by a low-pass filter to obtain an filtered image C(x,y); calculating a relative standard deviation for each pixel in the image A(x,y), three times the relative standard deviation being an edge threshold for each pixel; thresholding a difference image obtained by subtracting the filtered image C(x,y) from the normalized image B(x,y) by using the edge threshold for each pixel to form a threshold-processed image D(x,y); enhancing a contrast of the threshold-processed image D(x,y) by using a non-linear function to form a contrast-enhanced image E(x,y); determining a enhancement coefficient a(x,y); obtaining a edge-enhanced image F(x,y) by multiplying the enhancement coefficient a(x,y), the contrast-enhanced image E(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y); and generating a resulting image by multiplying a sum of the edge-enhanced image F(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y) with the maximum value Amax As compared with the prior arts, the inventive method has a fast processing speed for image information enhancement and a simple algorithm, images clearly, eliminates noises in the images, and satisfies the requirements of relatively more enhancement to the contrast of the dark regions in the scanned images.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
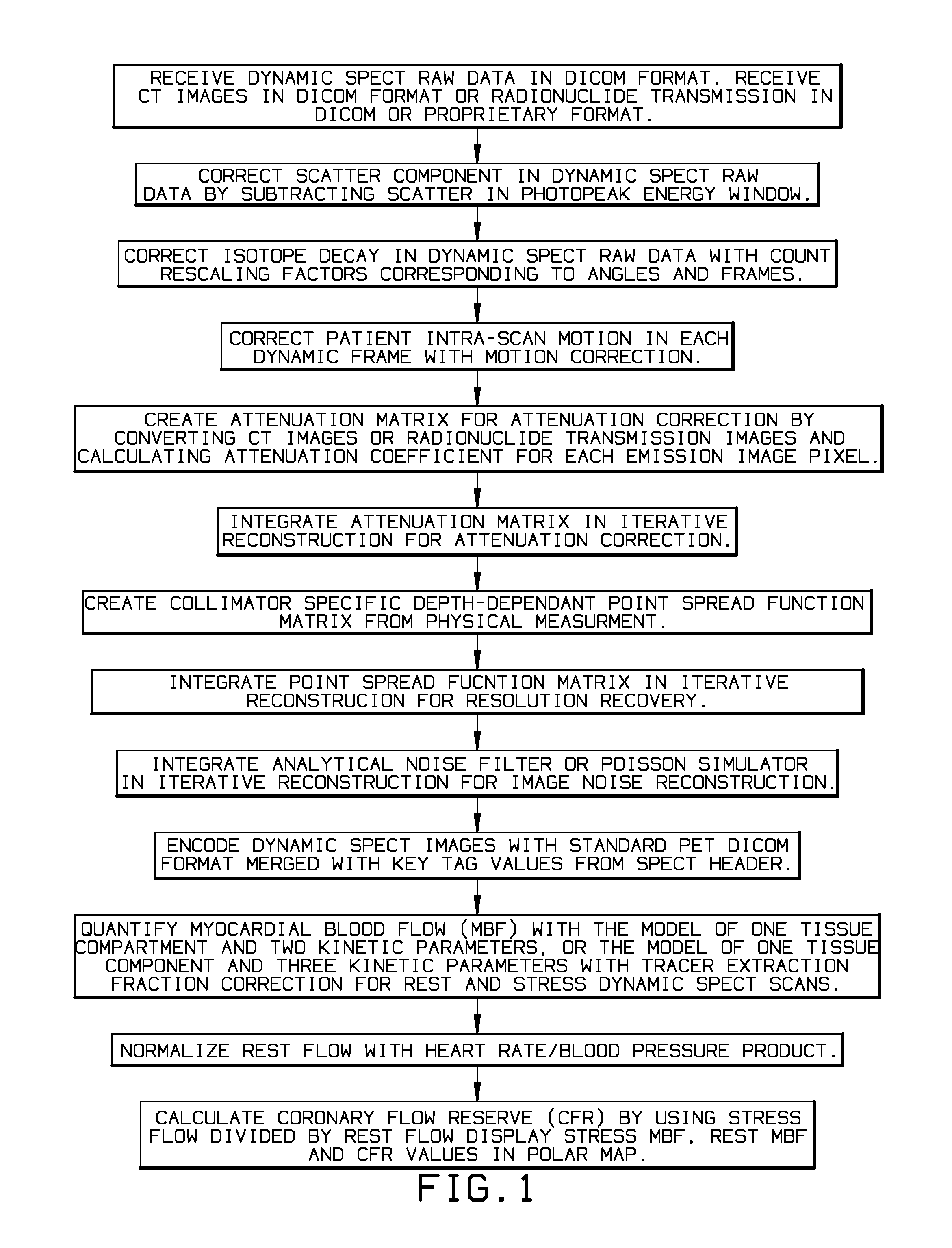
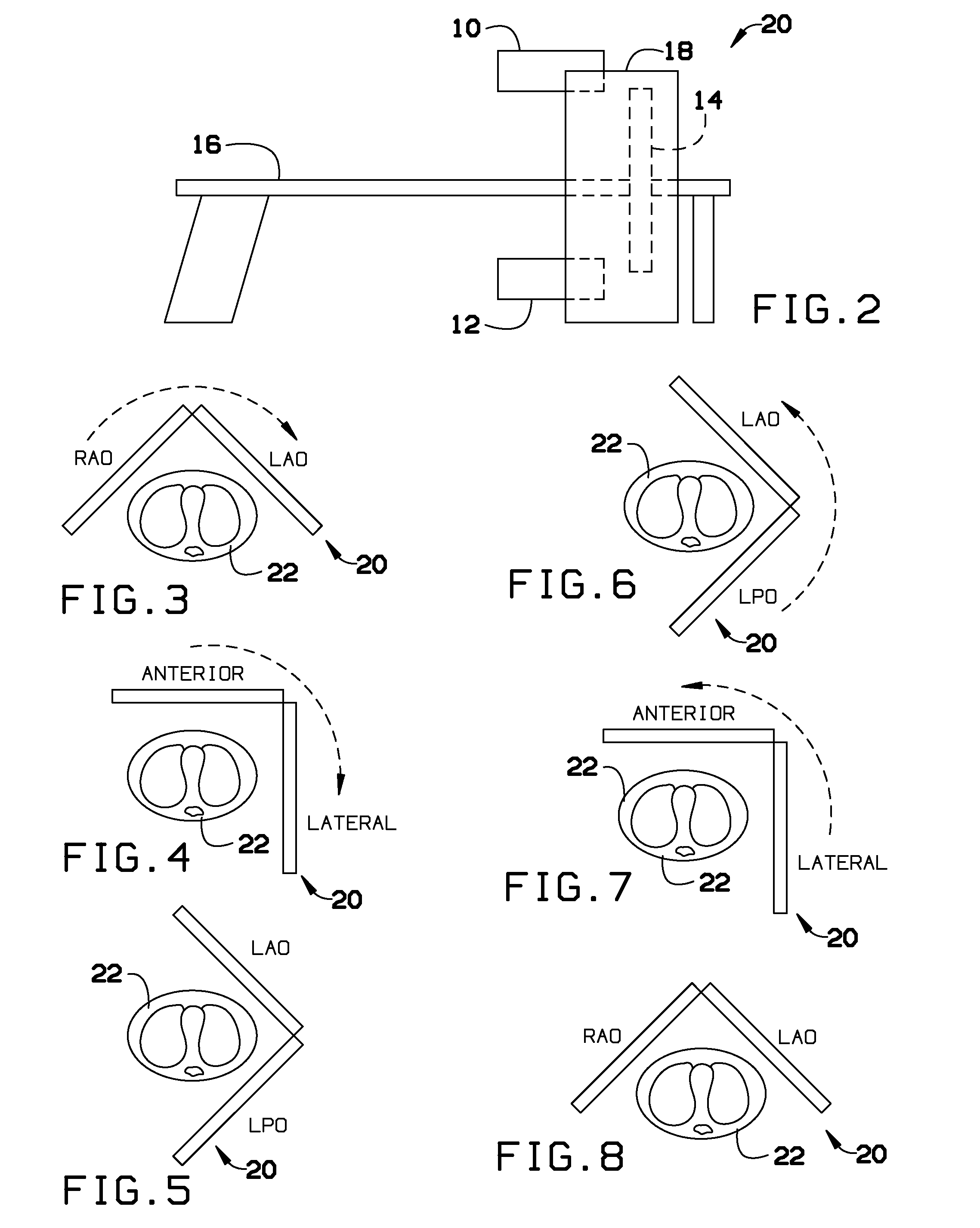
Myocardial blood flow quantitation with dynamic spect or spect/ct imaging
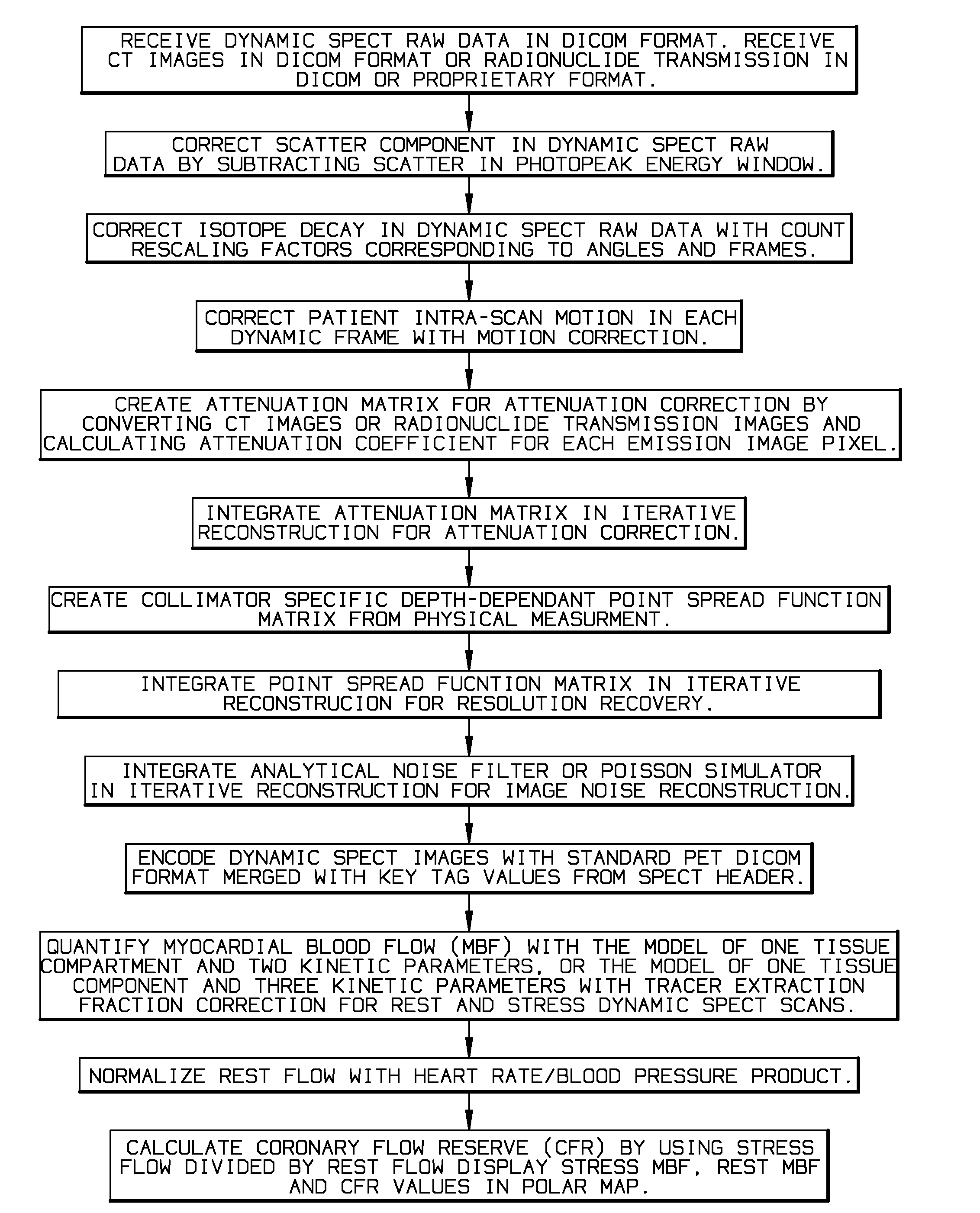
InactiveUS20140341453A1Remove image noiseReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFractographySpect imaging
A quantitative Single Photon Computed Emission Tomography (SPECT) reconstruction system for myocardial blood flow quantitation with SPECT or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography / Computed Tomography (SPECT / CT) dynamic imaging. The present invention solves the problems of physical interference and patient motions in dynamic SPECT imaging to enable the quantitative ability for myocardial blood flow (MBF) and coronary flow reserve (CFR) quantification.
Owner:HSU BAILING +1
Method of and apparatus for eliminating image noise
InactiveUS8050509B2Remove image noiseIncrease awarenessImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionTemporal information
A method and apparatus are provided for eliminating image noise to remove spatial-temporal noise and improve visibility. The method includes extracting a spatial-temporal noise level of neighbor pixels around a current pixel, filtering noise of the current pixel by applying a weight to spatial-temporal pixels around the current pixel based on the extracted spatial-temporal noise level, and applying a weight to the noise-filtered pixel and a boosted-up pixel based on an edge intensity and summing the weight-applied pixels. The spatial-temporal noise level is extracted based on spatial-temporal information of neighbor pixels around a current pixel in a current frame and spatial-temporal information of neighbor pixels around a current pixel in a previous frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for enhancing image acquired by radiographic system
ActiveUS20060291742A1Advanced image informationClear scanned imageImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingRelative standard deviation
A method of image information enhancement in radiography relates to image information processing techniques in radiography. The method comprising steps of: normalizing an acquired image A(x,y) to form a normalized image B(x,y); filtering the normalized image B(x,y) by a low-pass filter to obtain an filtered image C(x,y); calculating a relative standard deviation for each pixel in the image A(x,y), three times the relative standard deviation being an edge threshold for each pixel; thresholding a difference image obtained by subtracting the filtered image C(x,y) from the normalized image B(x,y) by using the edge threshold for each pixel to form a threshold-processed image D(x,y); enhancing a contrast of the threshold-processed image D(x,y) by using a non-linear function to form a contrast-enhanced image E(x,y); determining a enhancement coefficient a(x,y); obtaining a edge-enhanced image F(x,y) by multiplying the enhancement coefficient a(x,y), the contrast-enhanced image E(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y); and generating a resulting image by multiplying a sum of the edge-enhanced image F(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y) with the maximum value Amax As compared with the prior arts, the inventive method has a fast processing speed for image information enhancement and a simple algorithm, images clearly, eliminates noises in the images, and satisfies the requirements of relatively more enhancement to the contrast of the dark regions in the scanned images.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
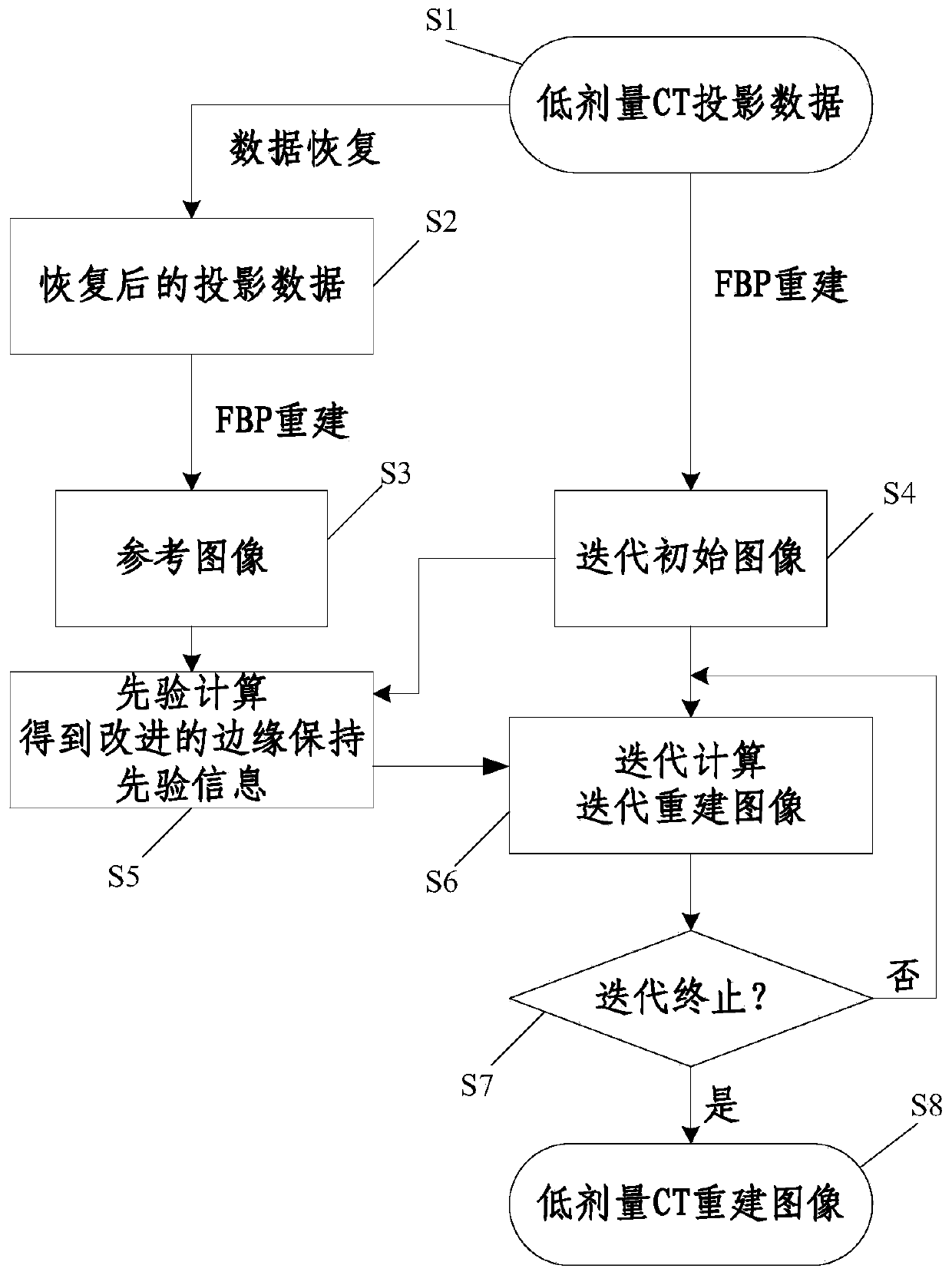
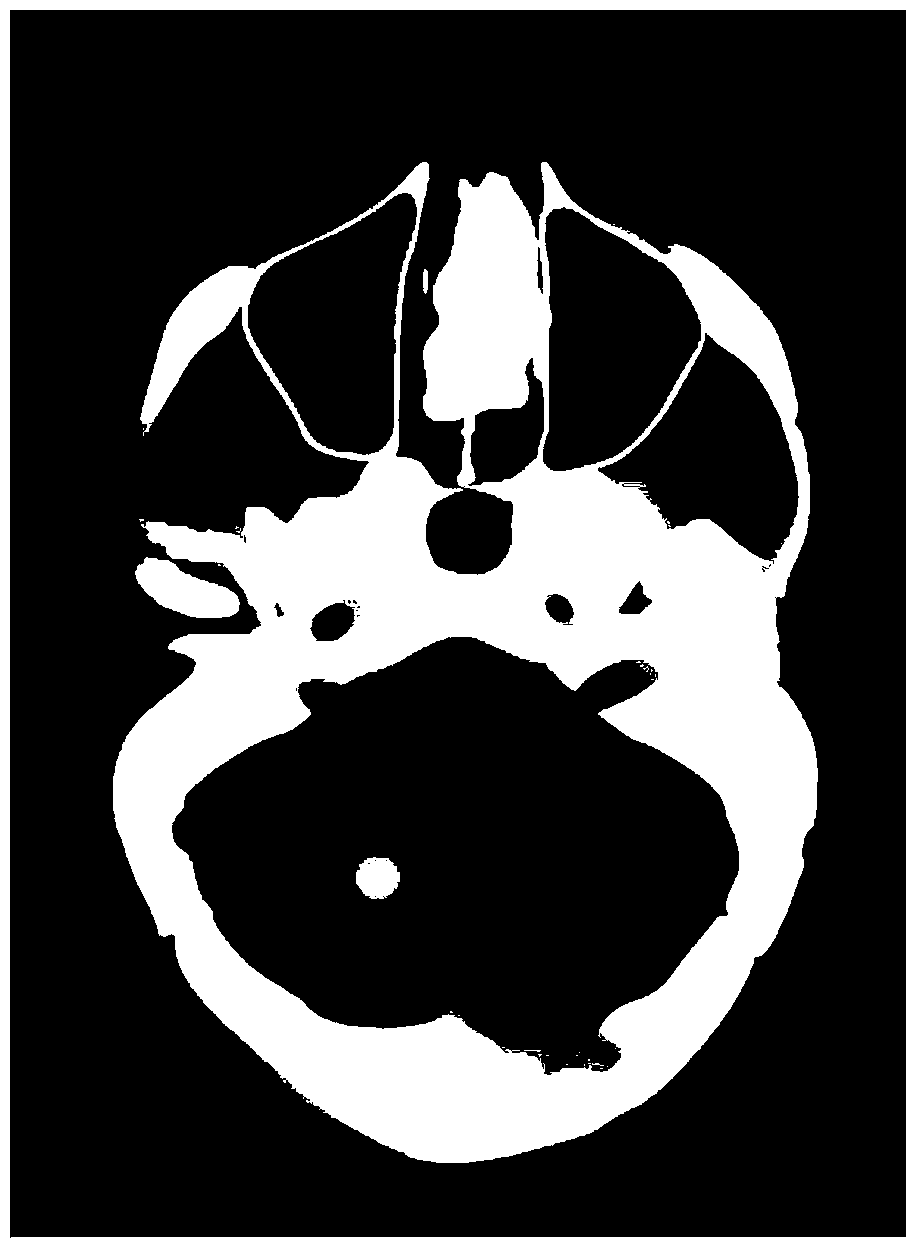
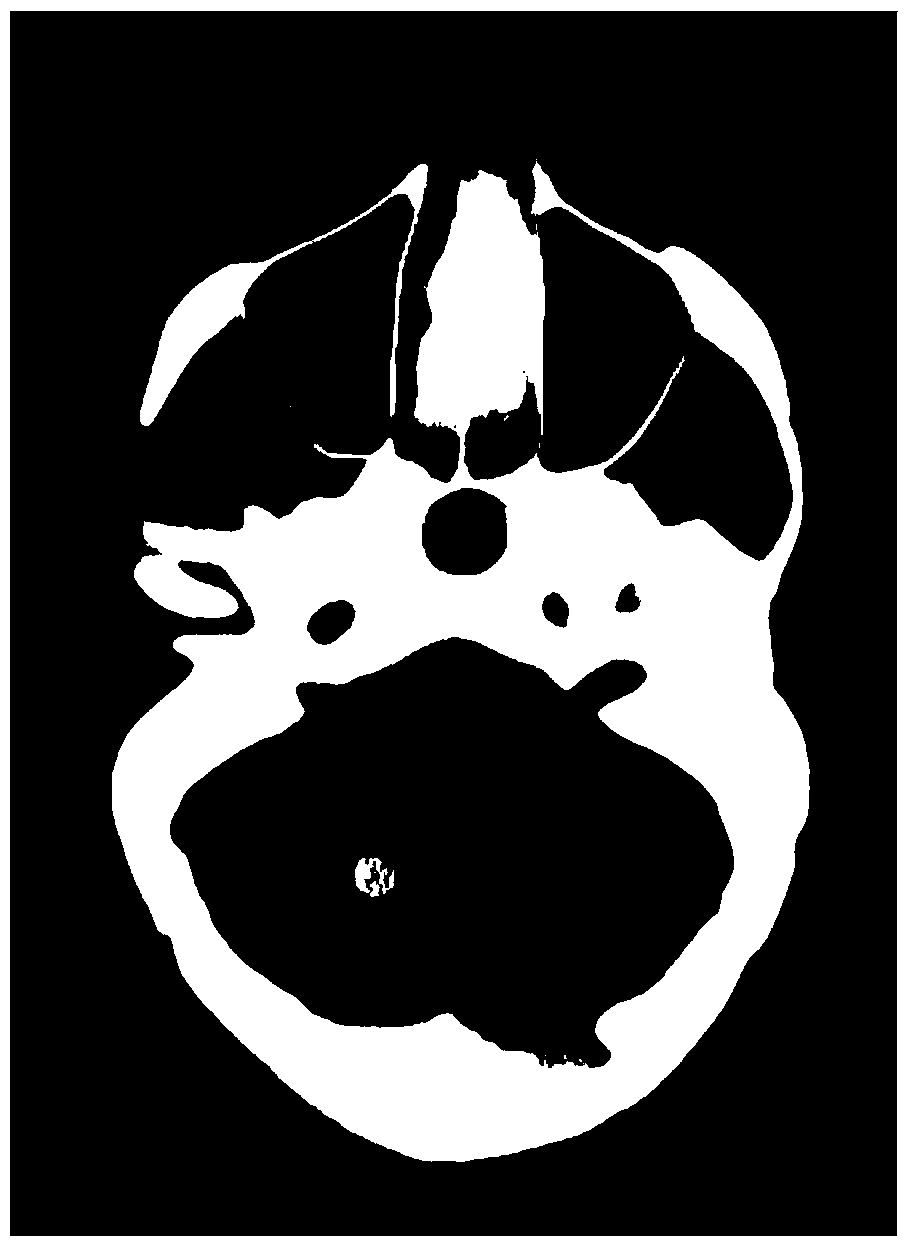
Statistical iterative reconstructing method for low-dose X-ray CT image
InactiveCN103810735ARemove image noiseStreak suppressionImage enhancement2D-image generationReference imageX-ray
The invention discloses a statistical iterative reconstructing method for a low-dose X-ray CT image. The statistical iterative reconstructing method includes reconstructing an image for projection data y<raw> of the low-dose X-ray image of CT equipment to obtain an initial iterative image mu<init>; restoring the projection data y<raw> to obtain the restored projection data y<restored>, reconstructing an image for the restored projection data y<restored> to obtain a reference image mu<ref>; based on the reference image mu<ref> and the initial iterative image mu<init>, constructing an edge-preserving prior R (mu<init>) according to FORMULA (shown in the description), wherein phi () is an energy potential function, and SRNLM (mu<init>) is non-local mean filtering led by the reference image mu<ref>; performing iterative computation according to the edge-preserving prior R (mu<init>) of the initial iterative image mu<init> by means of a statistical iterative formula to obtain an iterative reconstructed image mu<iter>; when the iterative result of the reconstructed image mu<iter> satisfies the iteration stopping condition, stopping iterating, and obtaining the final reconstructed image of the low-dose X-ray CT image. The statistical iterative reconstructing method for the low-dose X-ray CT image is capable of effectively eliminating the image noise, inhibiting the streak artifact and well keeping the detail information of the image.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
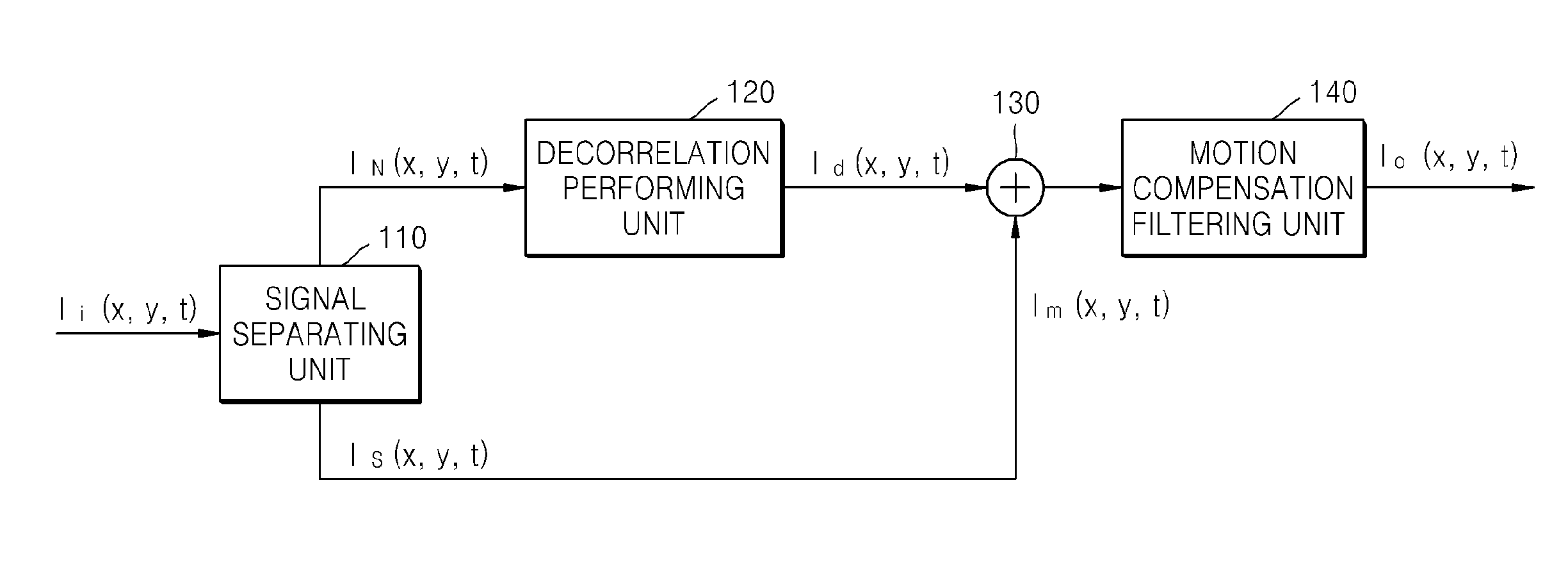
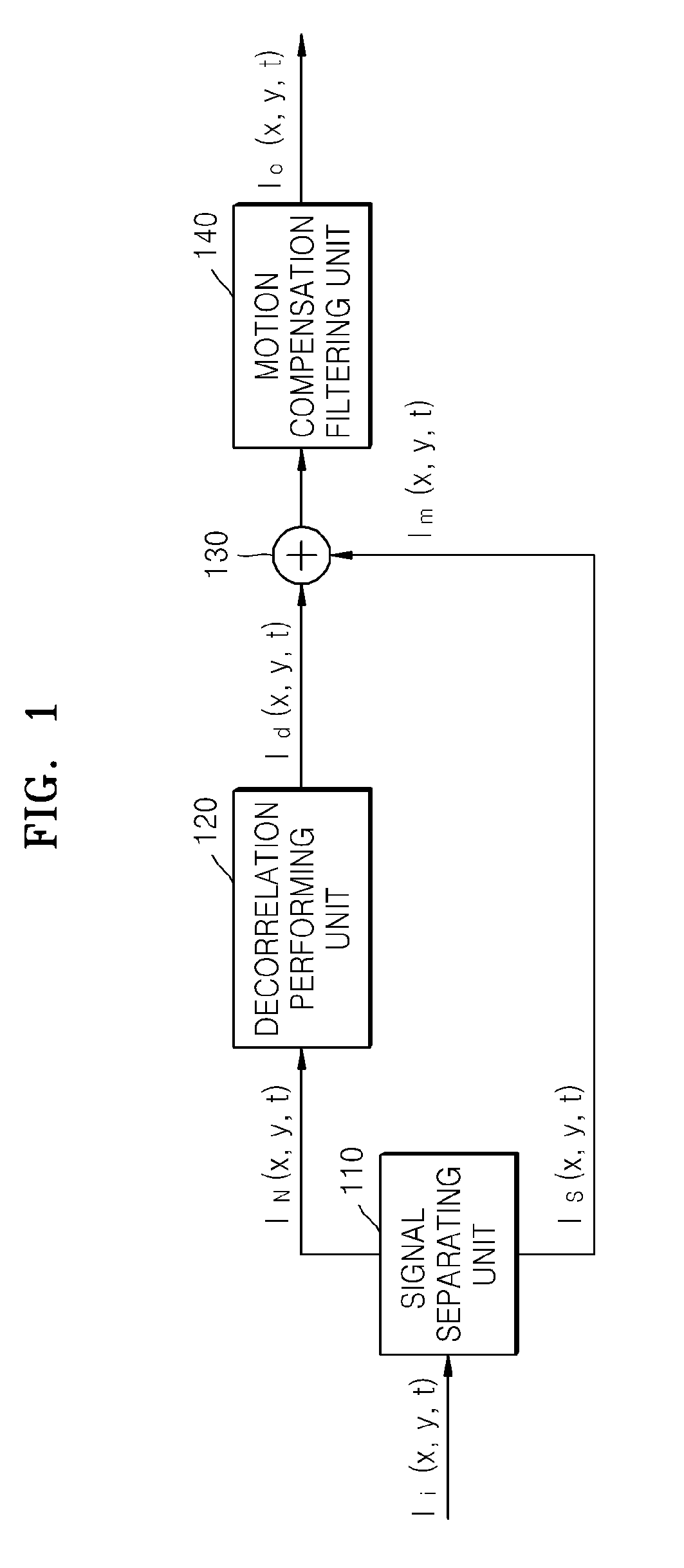
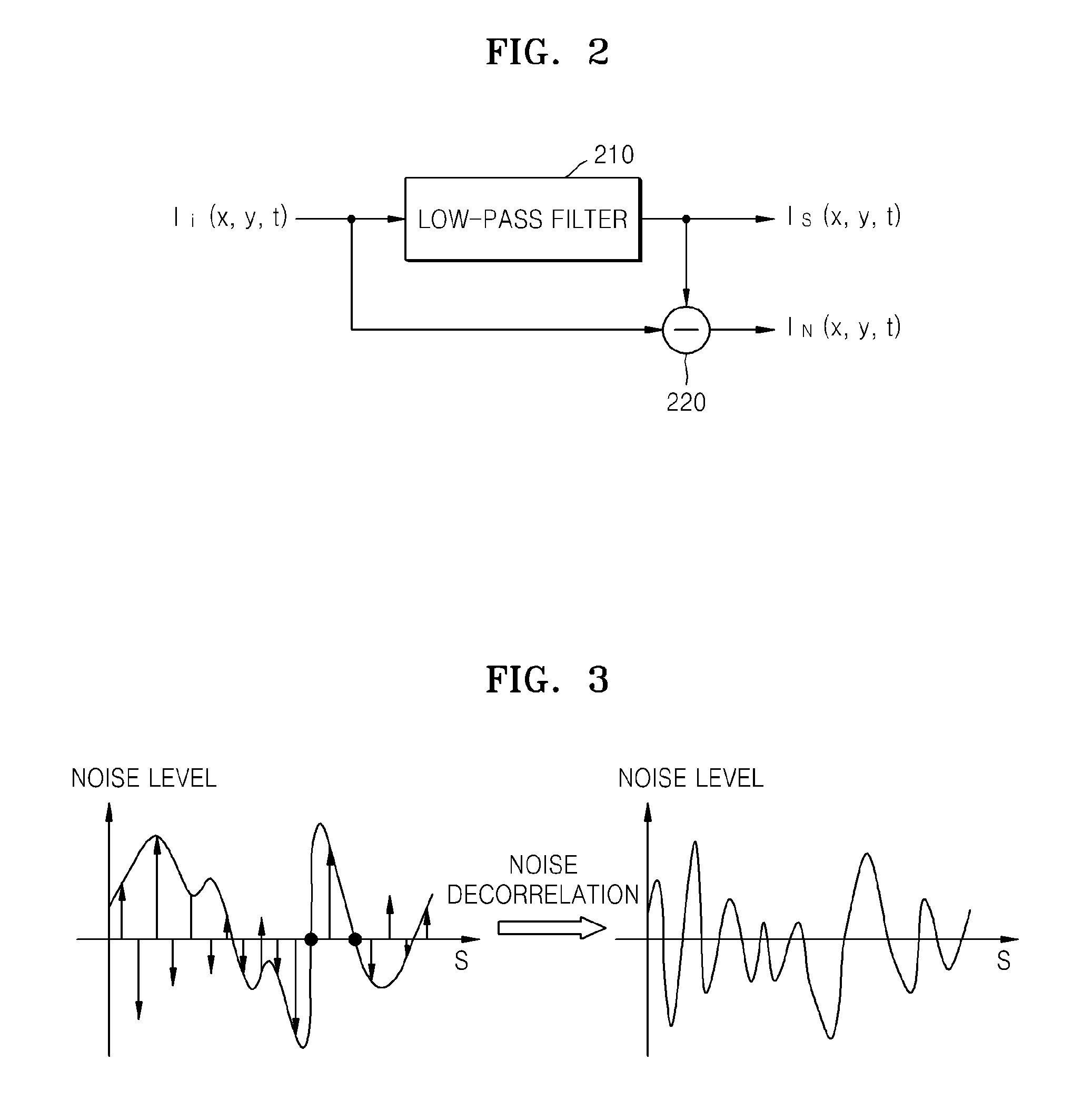
Method and apparatus for removing image noise
ActiveUS20100150465A1Remove image noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionImage signal
Provided are a method and apparatus for removing image noise. The method includes: separating an input image signal into a signal component and a noise component; converting the noise component into a decorrelated noise component that is spatiotemporally decorrelated from neighboring pixels; and generating an image signal by adding the decorrelated noise component to the signal component.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
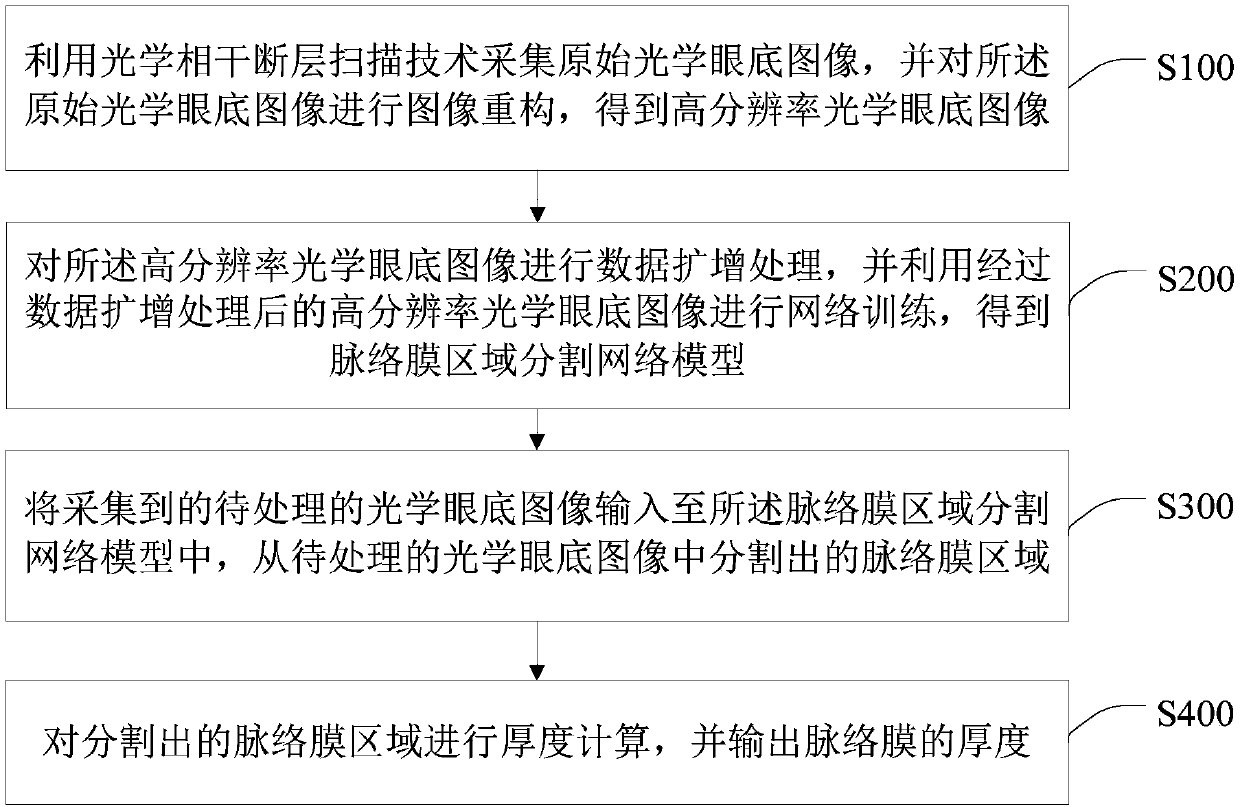
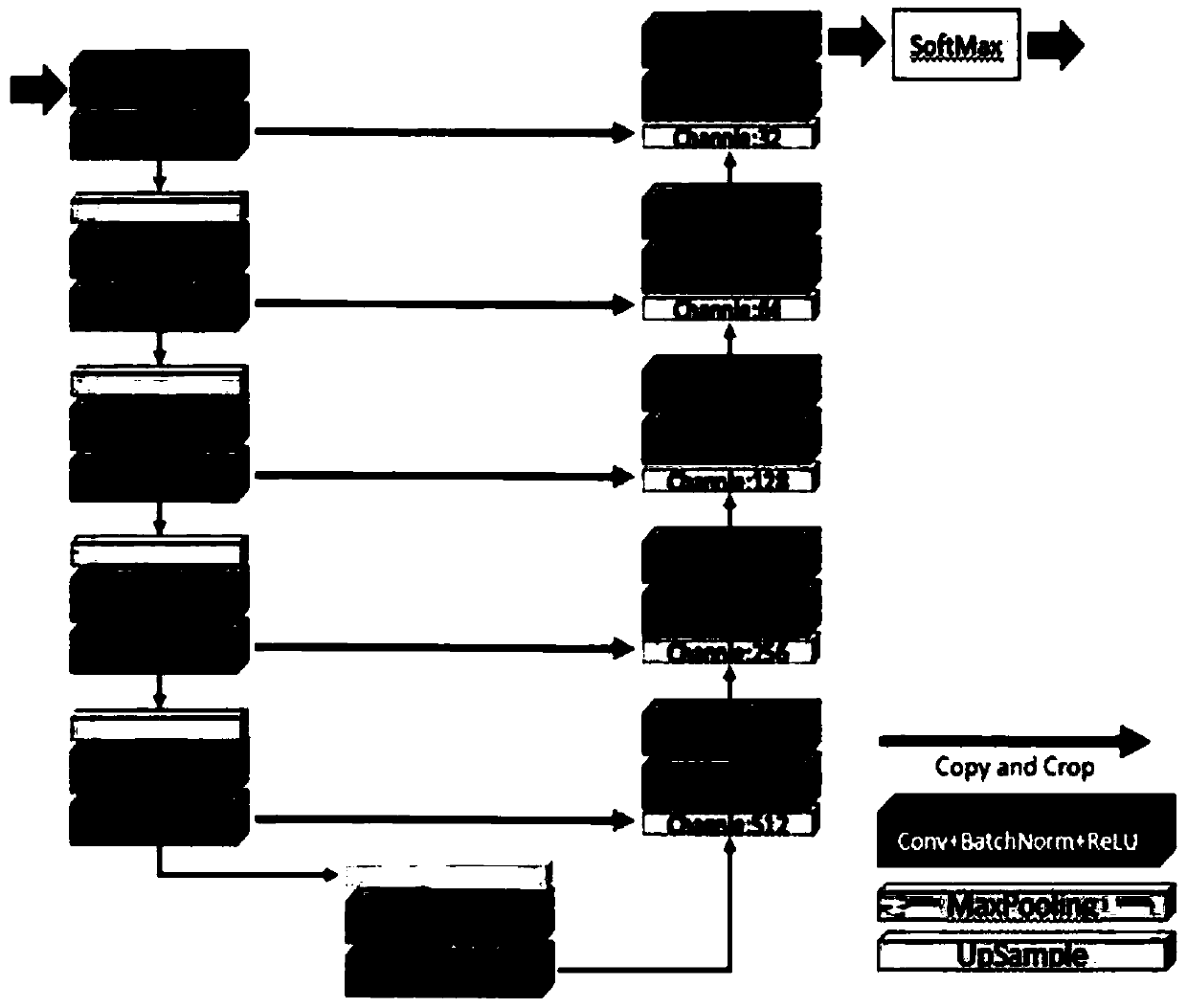
Optical fundus image segmentation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN109615634AHigh measurement accuracyRemove image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork modelComputer science
The invention discloses an optical fundus image segmentation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: employing an optical coherence tomography technology to collect an original optical fundus image, carrying out the image reconstruction of the original optical fundus image, and obtaining a high-resolution optical fundus image; performing dataamplification on the high-resolution optical fundus image, and performing network training by using the high-resolution optical fundus image subjected to data amplification processing to obtain a choroid region segmentation network model; and inputting the collected to-be-processed optical fundus image into the choroid region segmentation network model, and segmenting a choroid region from the to-be-processed optical fundus image. By constructing the choroid segmentation network model, the choroid region can be automatically segmented from the optical fundus image, and the thickness of the segmented choroid can be automatically calculated, so that the image noise in the optical fundus image can be eliminated, the measurement precision of the choroid can be improved, and the subjective deviation can be eliminated.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
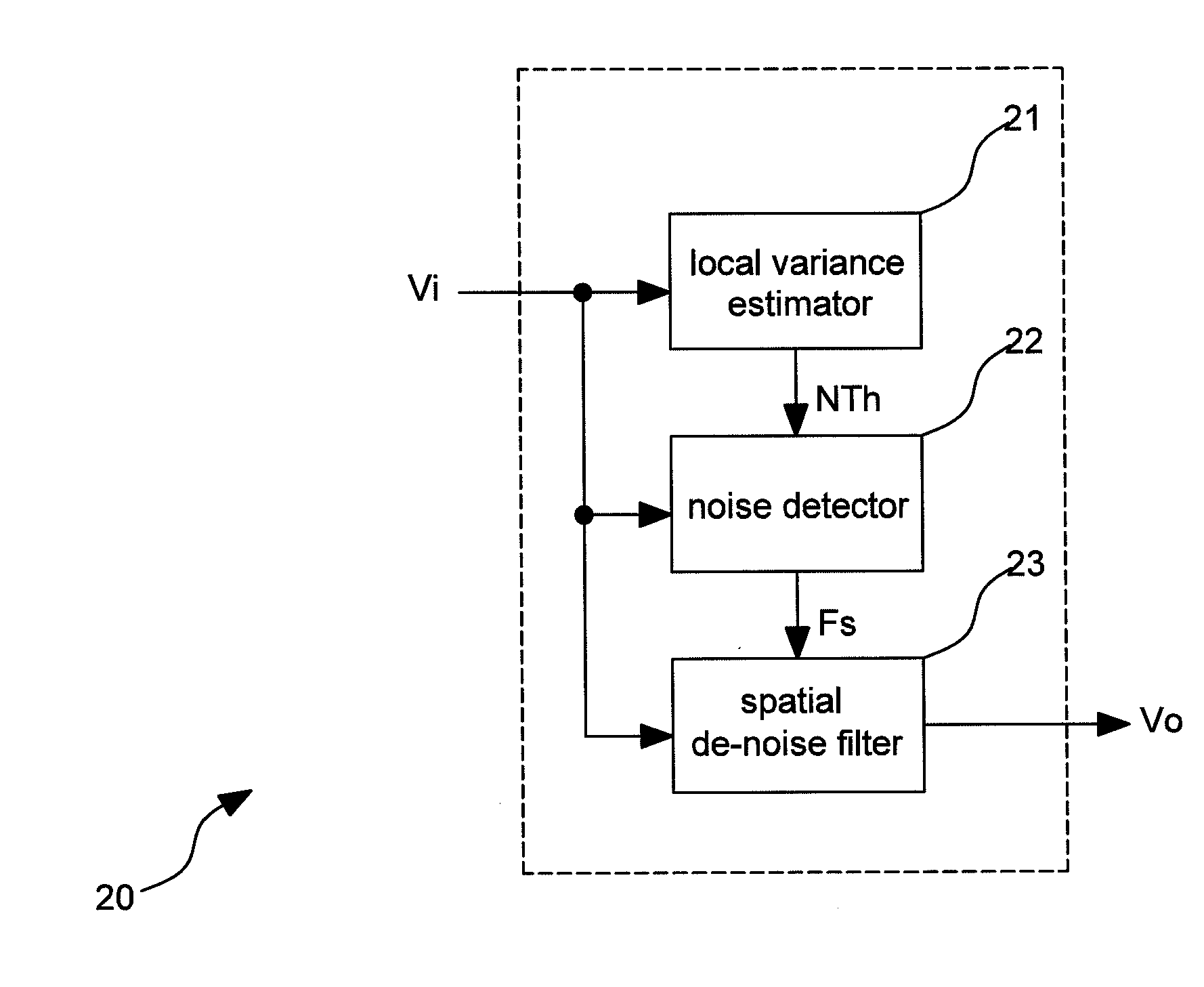
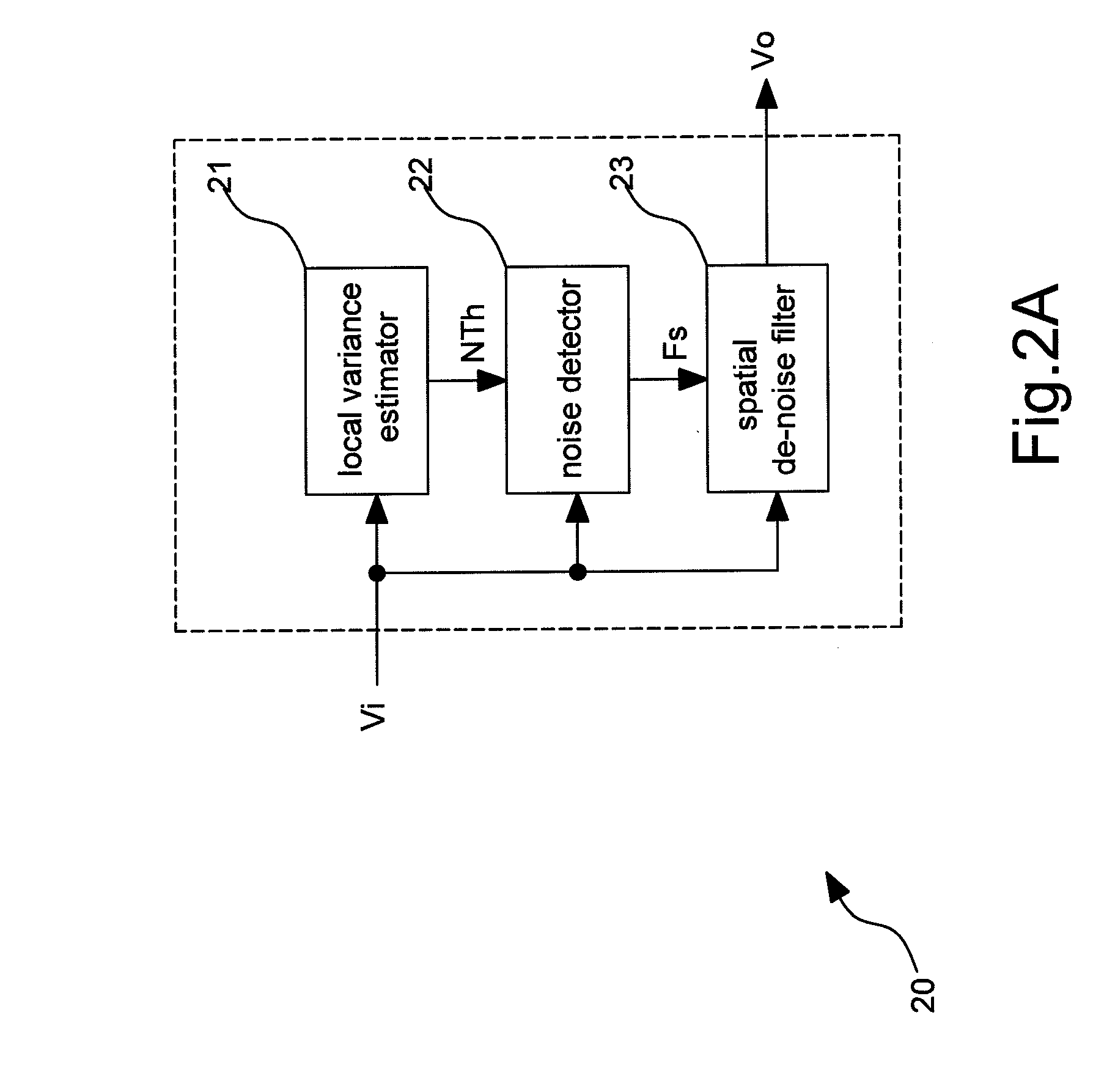
Image processing device and spatial noise reducing method
ActiveUS20110243472A1Cancel noiseExpand the borderImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial noiseImaging processing
The invention discloses an image processing device and method thereof. The image processing device includes an local variance estimator, a noise detector, a spatial de-noise filter. The local variance estimator estimates each pixel of an input image signal to separately output a local variance value of each pixel, and generates a noise threshold according to the local variance values. The noise detector determines which pixel indicates noise or image according to the noise threshold. The spatial de-noise filter filers the pixel indicating noise to generate an output image signal.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
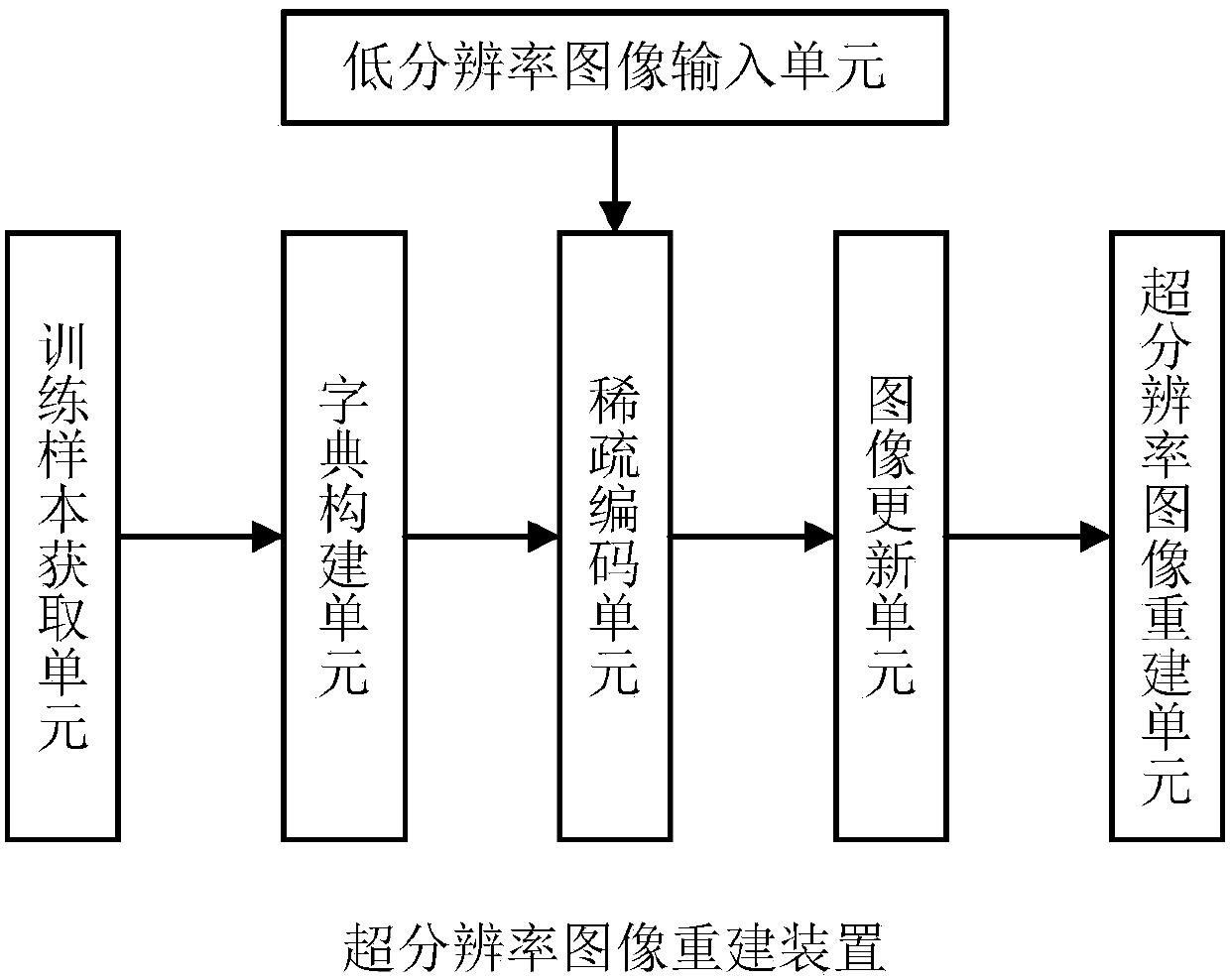
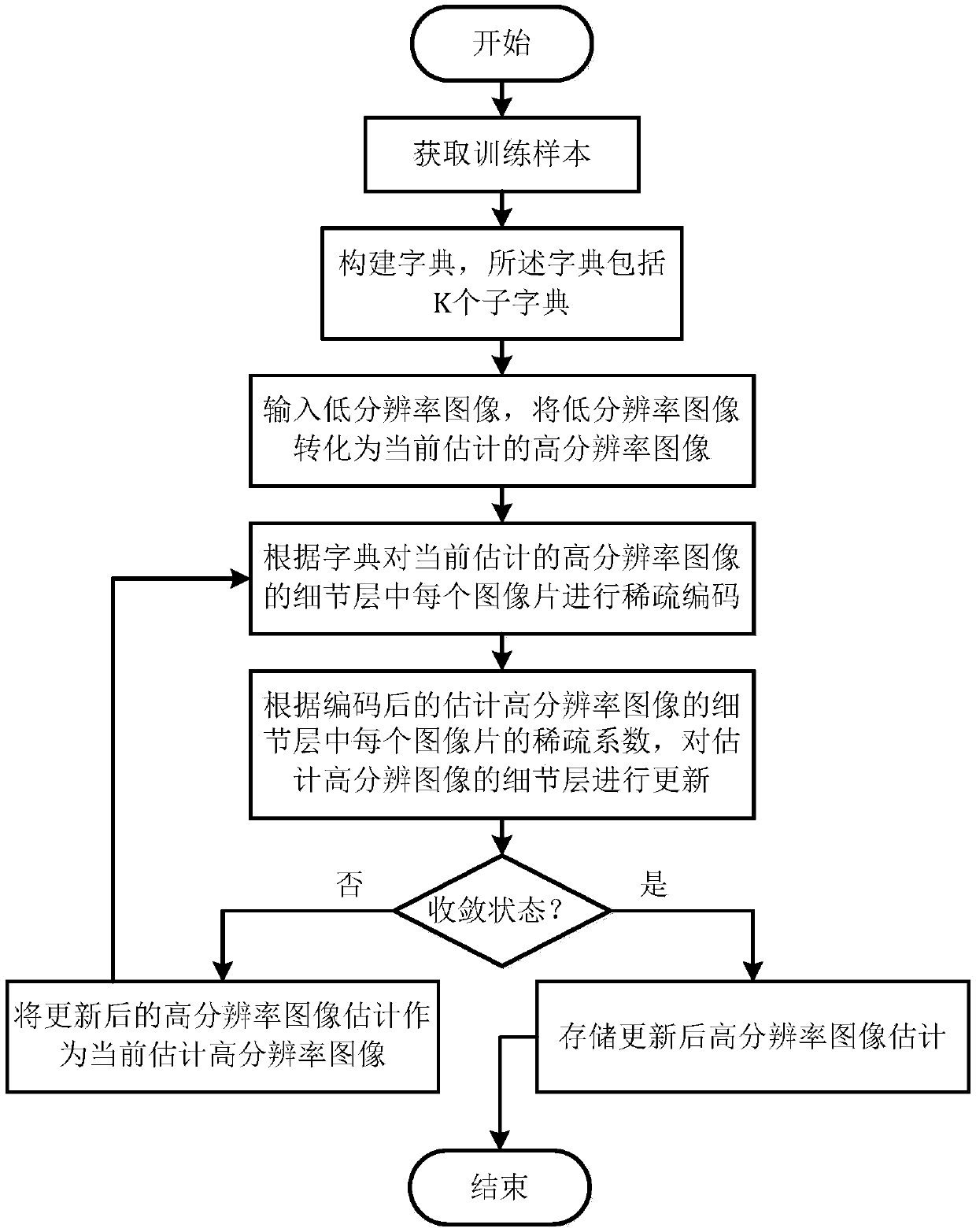
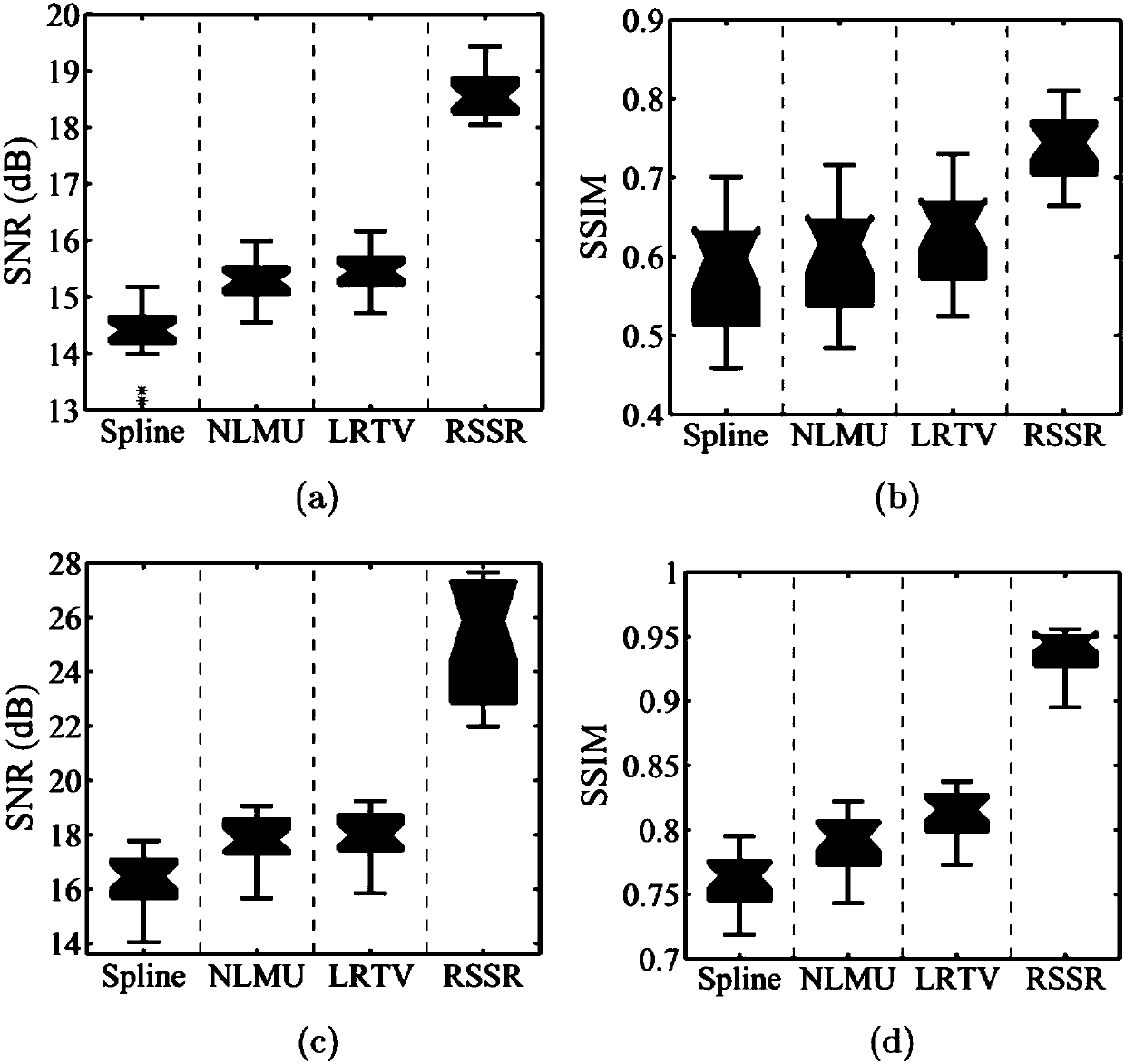
Super-resolution image reconstruction method and device
InactiveCN107845065ARemove image noiseGood subjective and objective effectImage enhancementImage analysisDistortionMri image
The invention provides a super-resolution image reconstruction device. The device comprises a training sample obtaining unit, a dictionary construction unit, a low-resolution image input unit, a sparse encoding unit, an image updating unit and a super-resolution image reconstruction unit, wherein the training sample obtaining unit is used for obtaining training samples; the dictionary constructionunit is used for constructing a dictionary; the low-resolution image input unit is used for converting low-resolution images into high-resolution images to carry out initial estimation; the sparse encoding unit is used for carrying out sparse encoding on each image patch in a detail layer of the currently estimated high-resolution image according to the dictionary; the image updating unit is usedfor updating the detail layer of the currently estimated high-resolution image; and the super-resolution image reconstruction unit is used for storing the updated high-resolution image to carry out estimation when iterative solution is in a convergence state, and otherwise, circularly and iteratively carrying out sparse encoding on each image patch in the detail layer in high-resolution image estimation. The invention furthermore discloses a corresponding super-resolution image reconstruction method. Through the super-resolution image reconstruction method and device, magnetic resonance imageresolution can be remarkably improved, distortions such as image noise and blurring can be effectively removed, complicated fine structures can be recovered and better subjective and objective effects can be provided.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV +1
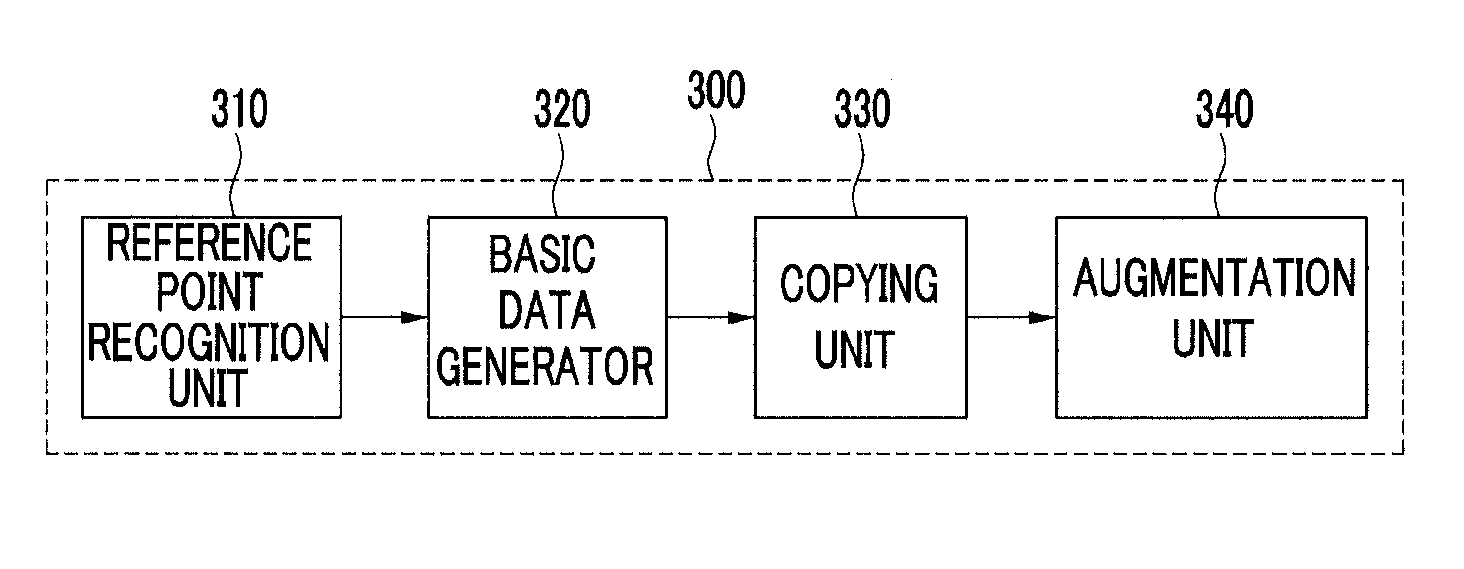
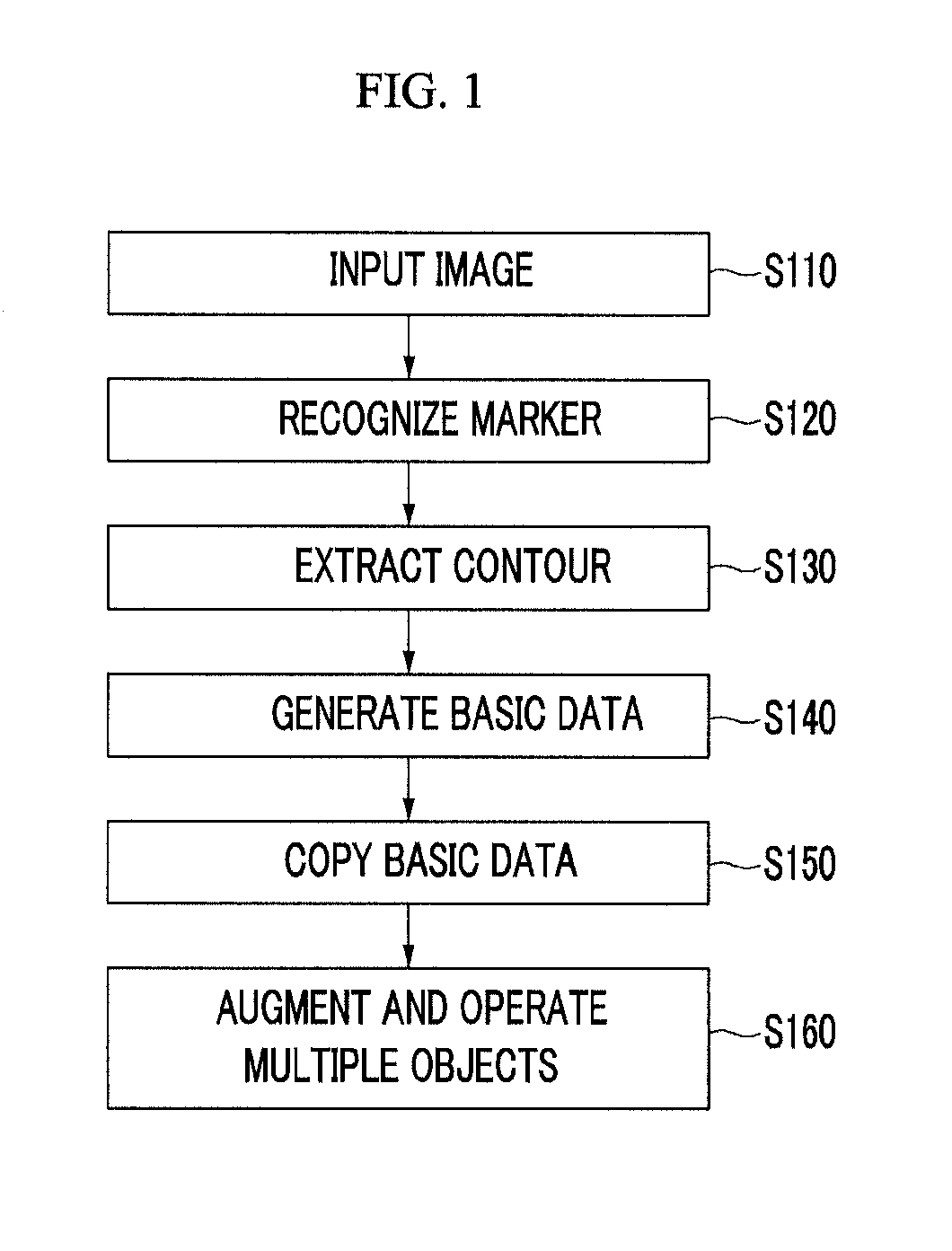
Apparatus and method for operating multiple object of augmented reality system
InactiveUS20120154439A1Improve performanceReduce inconvenienceCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processingComputer graphics (images)Operating system
An apparatus for operating multiple objects in an augmented reality system converts a reference point recognized in an input image into copyable basic data, then copies the basic data to each position of a screen where the image is to be output, and then augments an object by using a copy of the basic data as the reference point.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
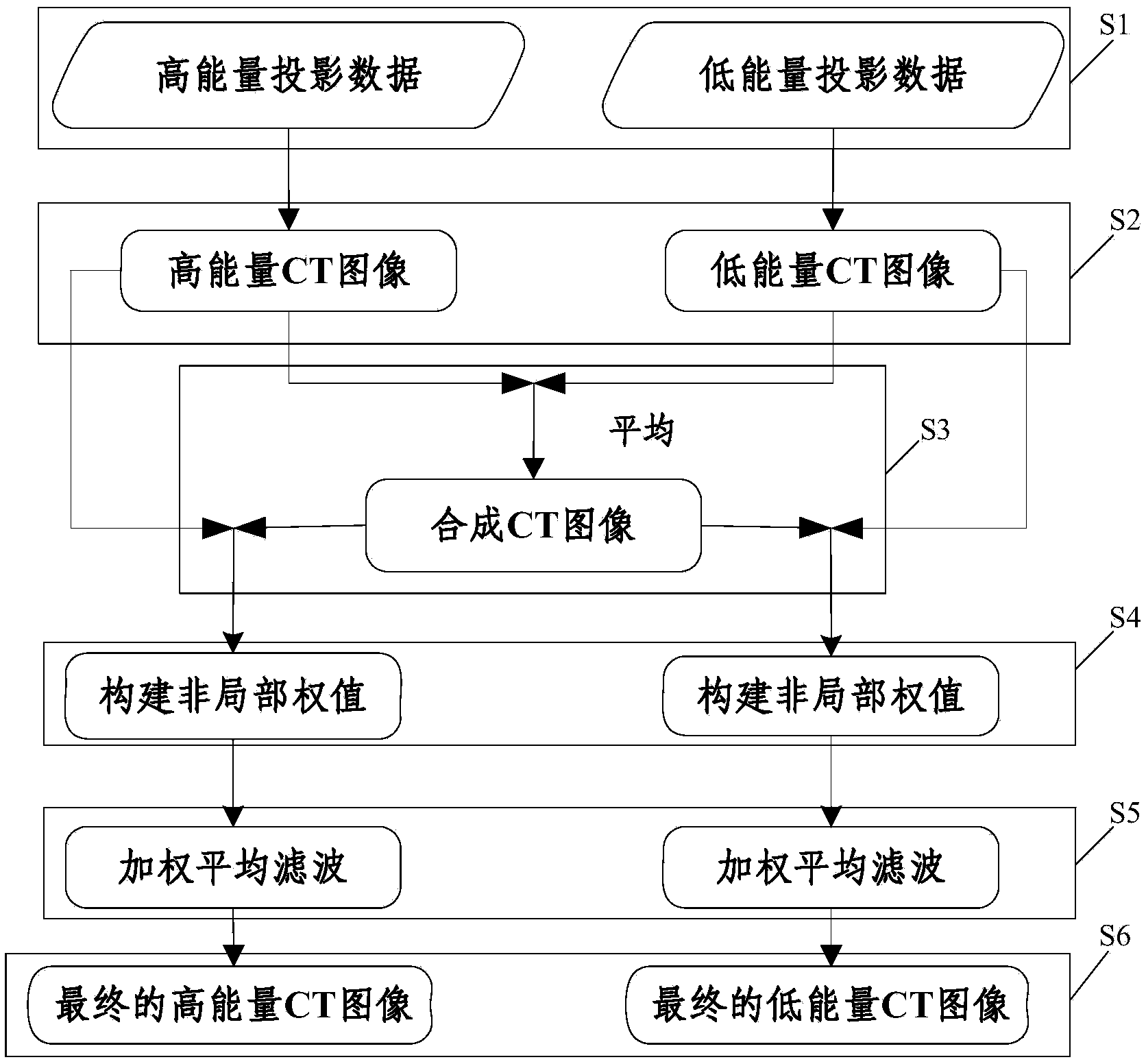
Method for recovering and processing energy spectrum CT images
InactiveCN103793890AQuality improvementEfficient acquisitionImage enhancementAverage filterHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for recovering and processing energy spectrum CT images. The method comprises the steps that low-energy CT projection data ylow and high-energy CT projection data yhigh are obtained, CT image reconstruction is respectively conducted on the low-energy CT projection data ylow and the high-energy CT projection data yhigh, and a low-energy CT image mulow and a high-energy CT image muhigh are obtained; synthesis is conducted on the low-energy CT image mulow and the high-energy CT image muhigh, so that a synthesized CT image mucom is obtained; a weighted average filter is arranged and combined with the synthesized CT image mucom to conduct weighted average filtering processing on the low-energy CT image mulow and the high-energy CT image muhigh respectively, so that a final high-energy CT image mulow (restored) and a final low-energy CT image muhigh (restored) after restoration are respectively obtained. The method can rapidly and efficiently obtain the energy spectrum CT images with high quality, low-dose sending is applied, generation of the high-quality CT images is guaranteed, and therefore the robustness is good and image noise and restraining image artifacts can be effectively eliminated.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
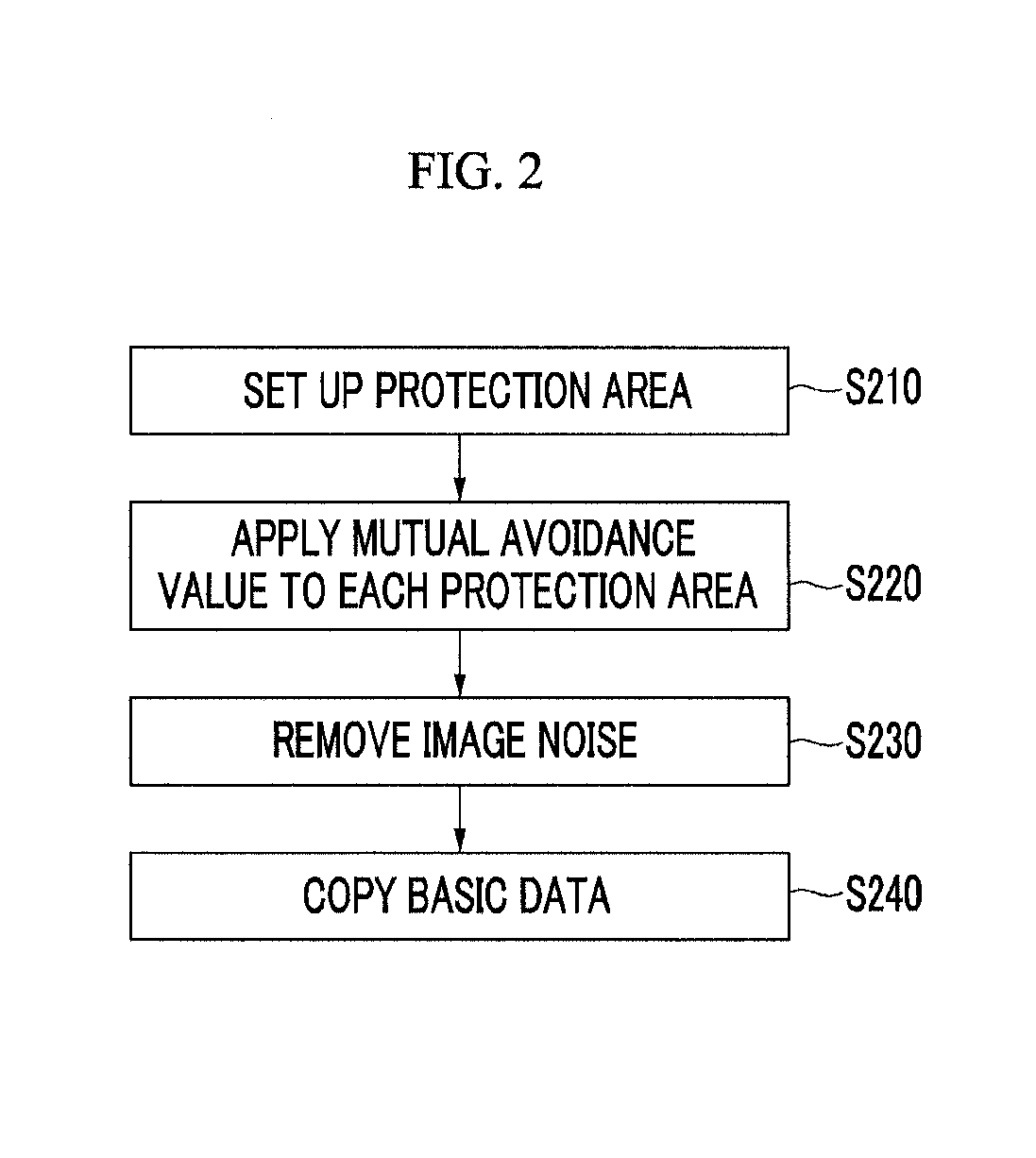
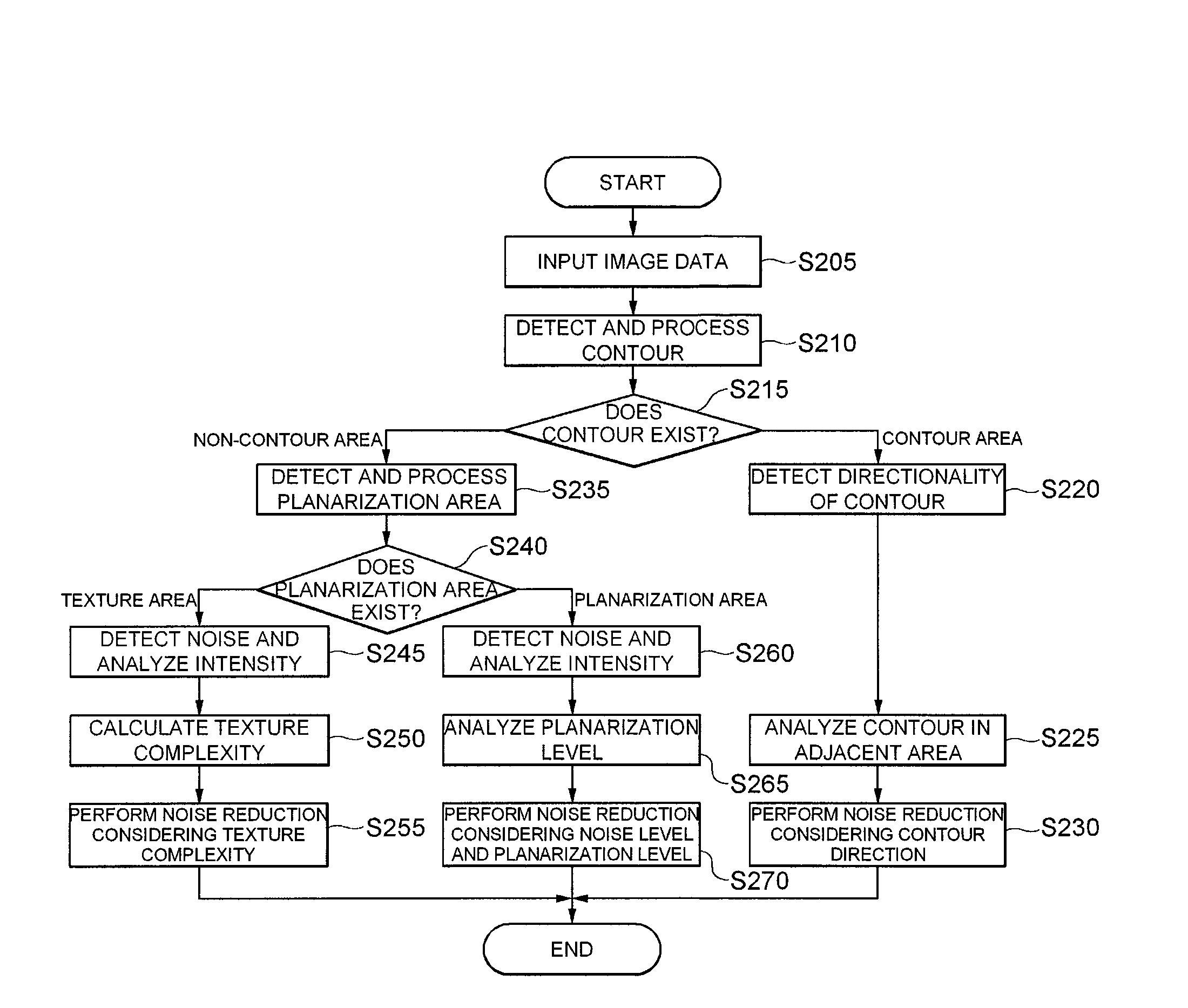
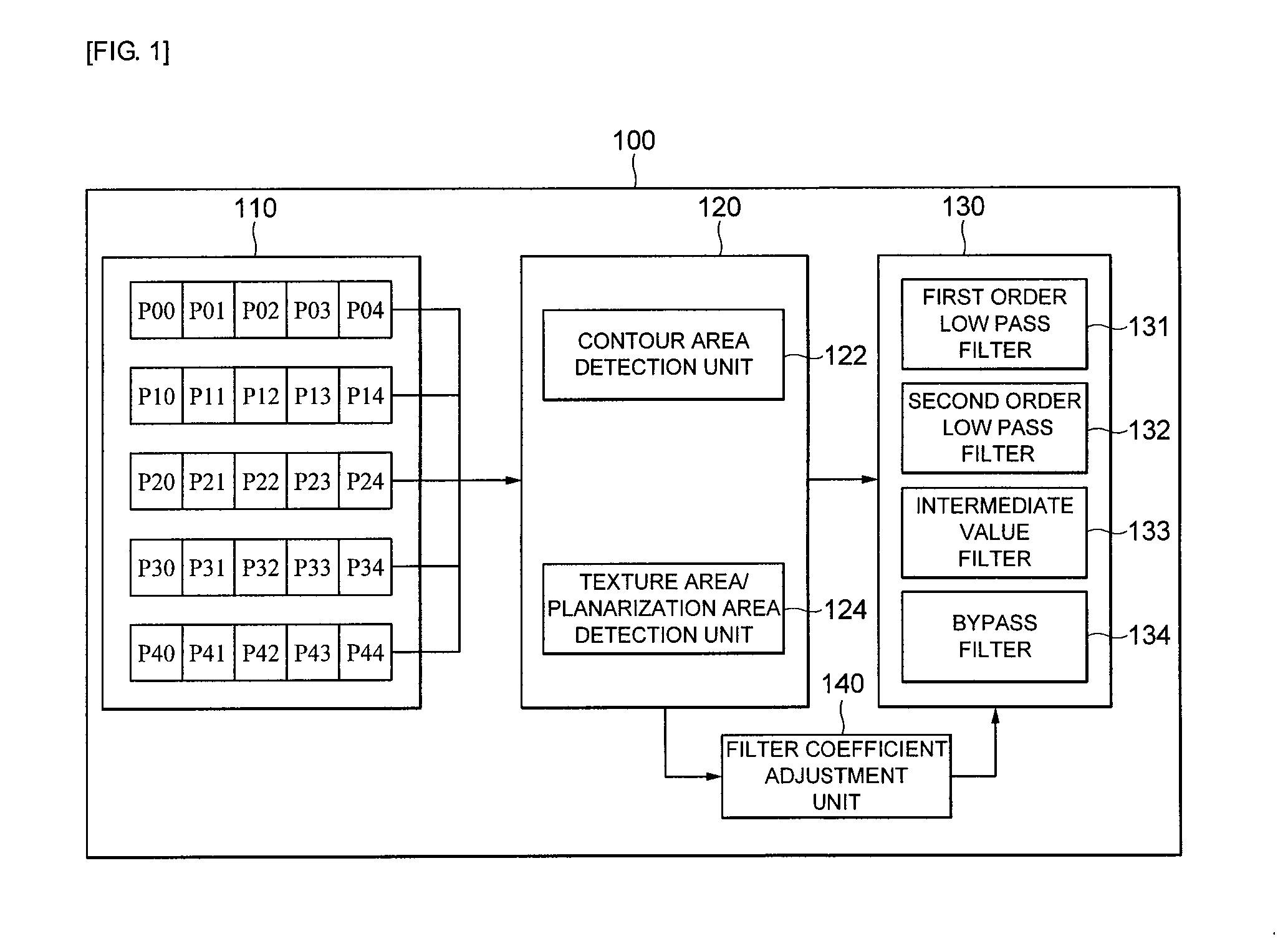
Apparatus for removing image noise and method thereof
InactiveUS20110007973A1Remove image noiseReduce image noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsNoise removalNoise reduction
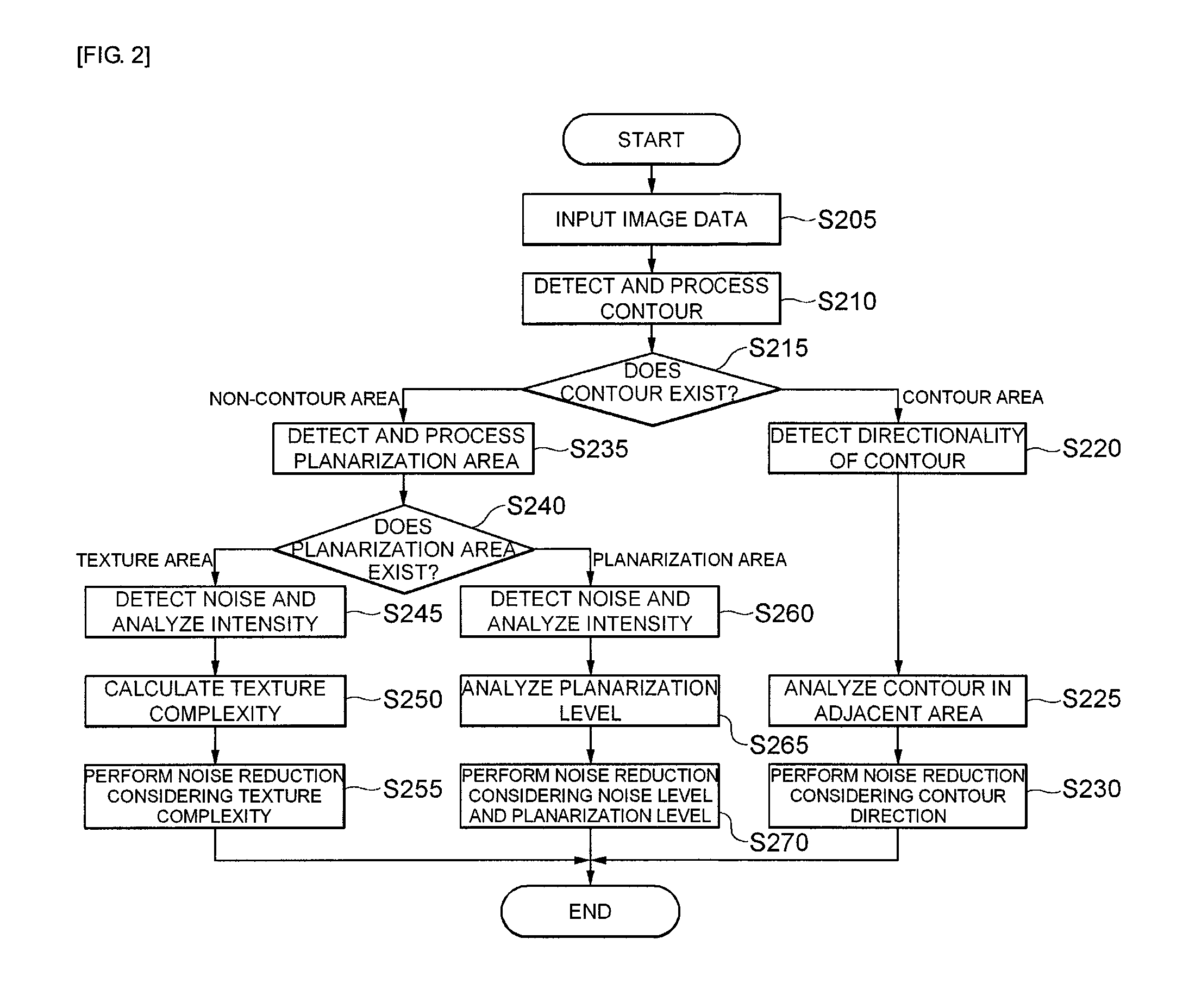
The present invention relates to an apparatus for removing image noise and a method thereof. There is provided with an apparatus for removing image noise including a buffer register that divides image signals in an n*n area obtained from an image sensor into brightness components and chroma components to store them as pixel values; an image analyzing unit that classifies the n*n area stored in the buffer register into a contour area, a texture area, and a planarization area; and a noise reduction unit that designs noise removal filters according to the features of the classified areas to reduce image noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
External parameter calibration method and system for single-line laser radar and visible light camera
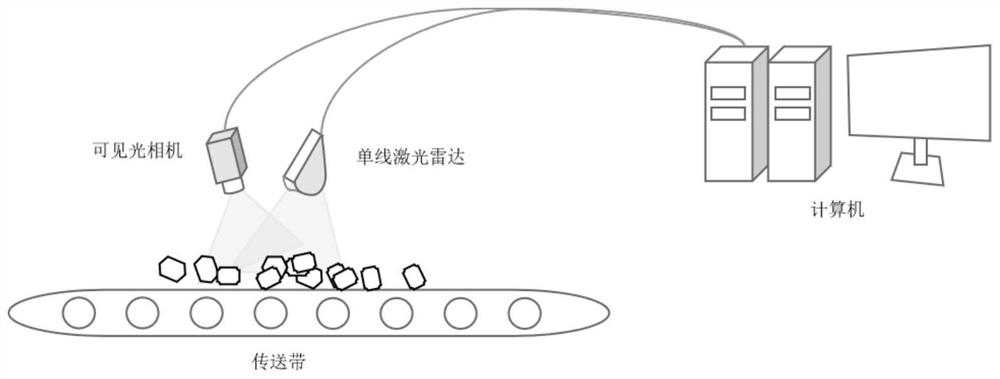
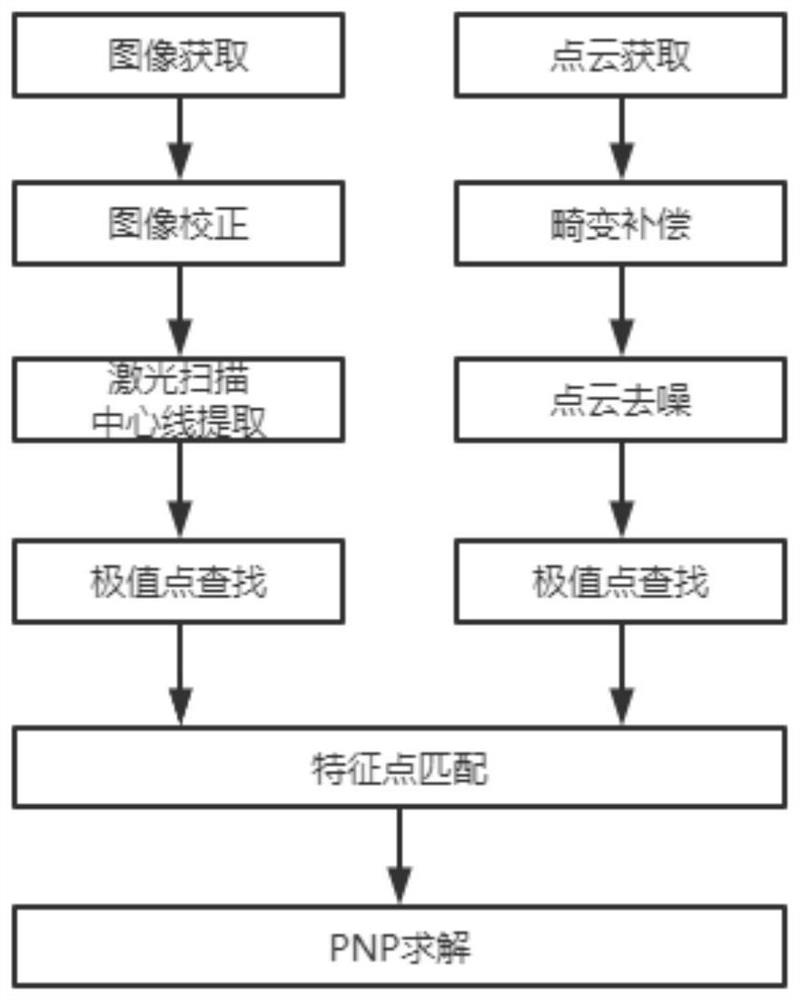
PendingCN113838141ASolve technical problems with low accuracySimplify the calibration processImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudLaser scanning
The invention discloses an external parameter calibration method and system for a single-line laser radar and a visible light camera, and the method comprises the steps: collecting time and space synchronous furnace charge image data and point cloud data, correcting a furnace charge image according to a camera distortion model, and further extracting a laser scanning center line; determining a two-dimensional coordinate corresponding to a local extreme value of a laser scanning center line in an image coordinate system, and performing interpolation on the sparse point cloud data to obtain a three-dimensional coordinate of the local extreme value of the point cloud data in a radar coordinate system; according to the feature point pairs of the two-dimensional coordinate corresponding to the local extreme value of the laser scanning center line in the image coordinate system and the three-dimensional coordinate of the local extreme value of the point cloud data in the radar coordinate system, utilizing a linear least square method to obtain an external parameter matrix of the camera and the single-line laser radar; the technical problem that the existing laser radar and camera external parameter calibration precision is low is solved, the single-line laser radar and the visible light camera can be calibrated online in real time, and the external parameter matrix is corrected.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
System and method for determining solute concentration in a colored liquid sample
ActiveUS20170074783A1Remove image noiseColor/spectral properties measurementsMobile deviceEnvironmental geology
The present invention relates to a method and system, particularly a mobile device, configured for determining the solute concentrations in a colored liquid sample, which is based on imaging of the sample and standards of known concentrations of solute, and determining the concentration of the sample on the basis of processing the images and the color values that they provide.
Owner:LAB4U INC
Non-linear image enhancement method, and edge detection method using the same
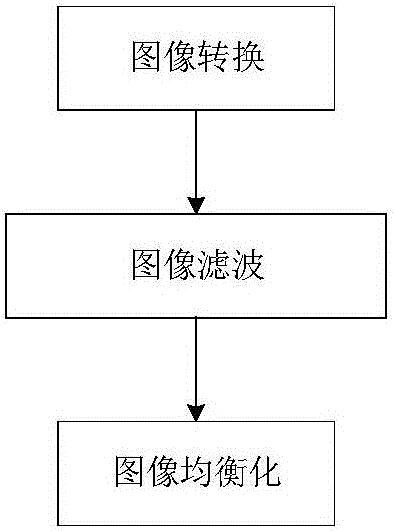
InactiveCN105894474AOvercome limitationsEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingEdge extraction
The invention discloses a non-linear image enhancement method, and an edge detection method using the same. The non-linear image enhancement method includes the following steps: image conversion, image filtering and image equalization. The edge detection method also includes the steps: image denoising, gradient calculating, marking of non-edge pixels, and fine edge treatment. The non-linear image enhancement method, and the edge detection method using the same utilize the non-linear image filtering and equalization method to effectively eliminate image noises and enhance image effect, can overcome the limitation of a linear method, are higher in practicality, and can perform edge extraction after image enhancement, wherein the employed edge extraction algorithm has better detection capability and positioning capability and has minimum response so that the image contour can be extracted more clearly.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Face recognition intelligent monitoring system
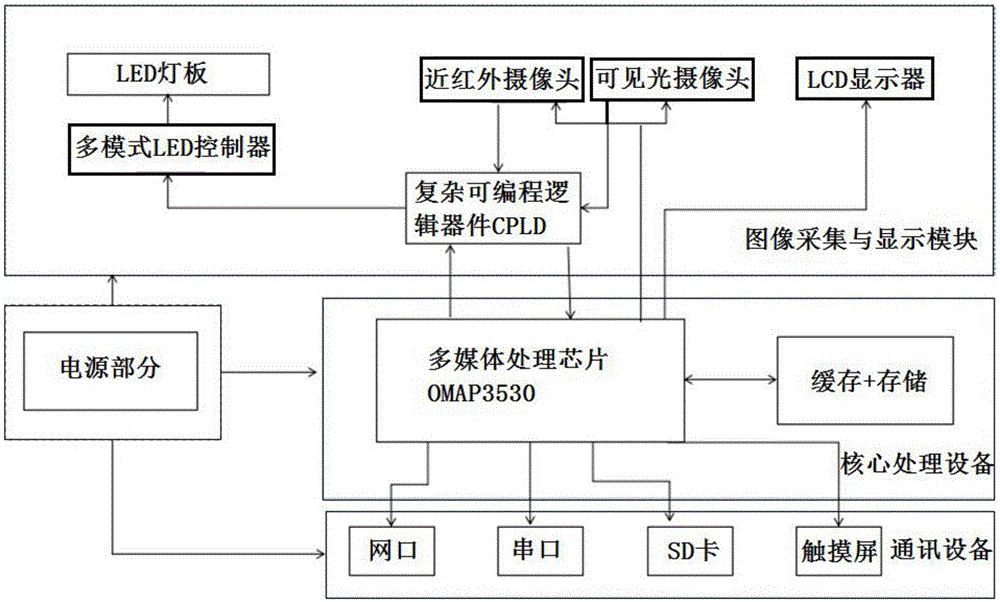
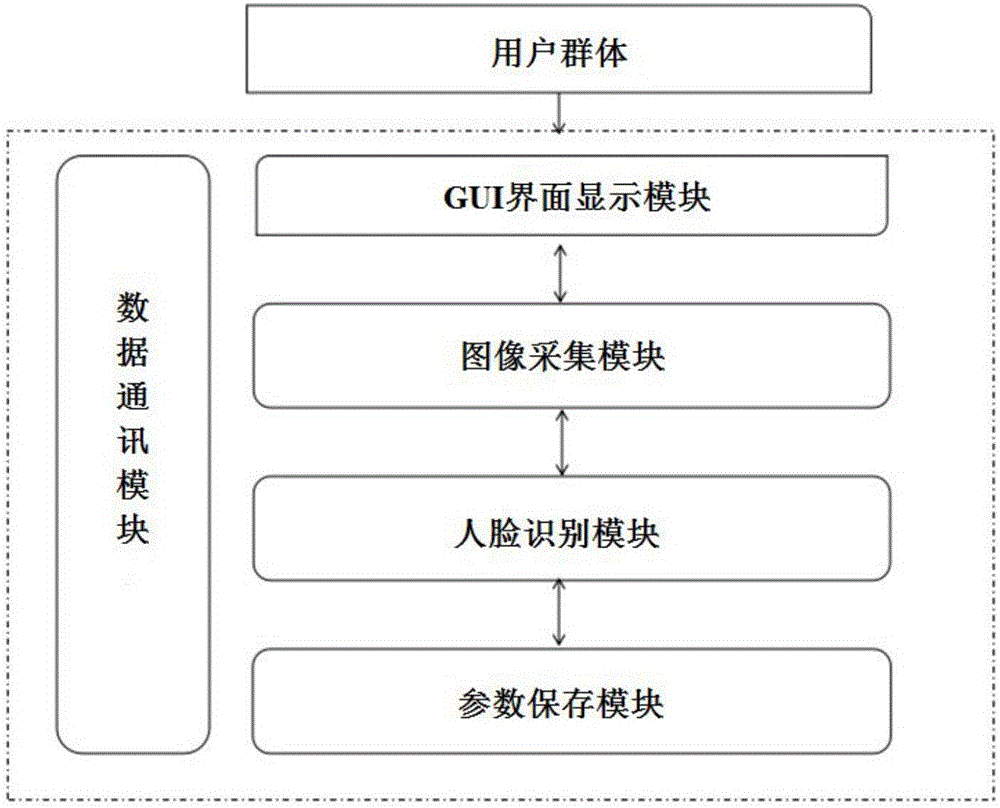
InactiveCN107527025AIncrease contrastRemove image noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionLED displayProgrammable logic device
The invention discloses a face recognition intelligent monitoring system which comprises an image acquisition and display device, a core processing device, a communication device and a power supply part. The image acquisition and display device comprises a near infrared camera, a visible light camera and an LED display, and a complex programmable logic device (CPLD) connected with the near infrared camera and the visible light camera. The CPLD is connected with an LED light board through a multi-mode LED controller. The core processing device is a multimedia processing chip OMAP3530 connected with the image acquisition and display device. The communication device comprises a network port, a serial port, an SD card and a touch screen. The power supply part provides power support for the device. The face recognition intelligent monitoring system can automatically recognize a human face without being limited by light conditions, and performs analysis and comparison, and provides technical support for security work.
Owner:青岛萨纳斯新能源科技有限公司
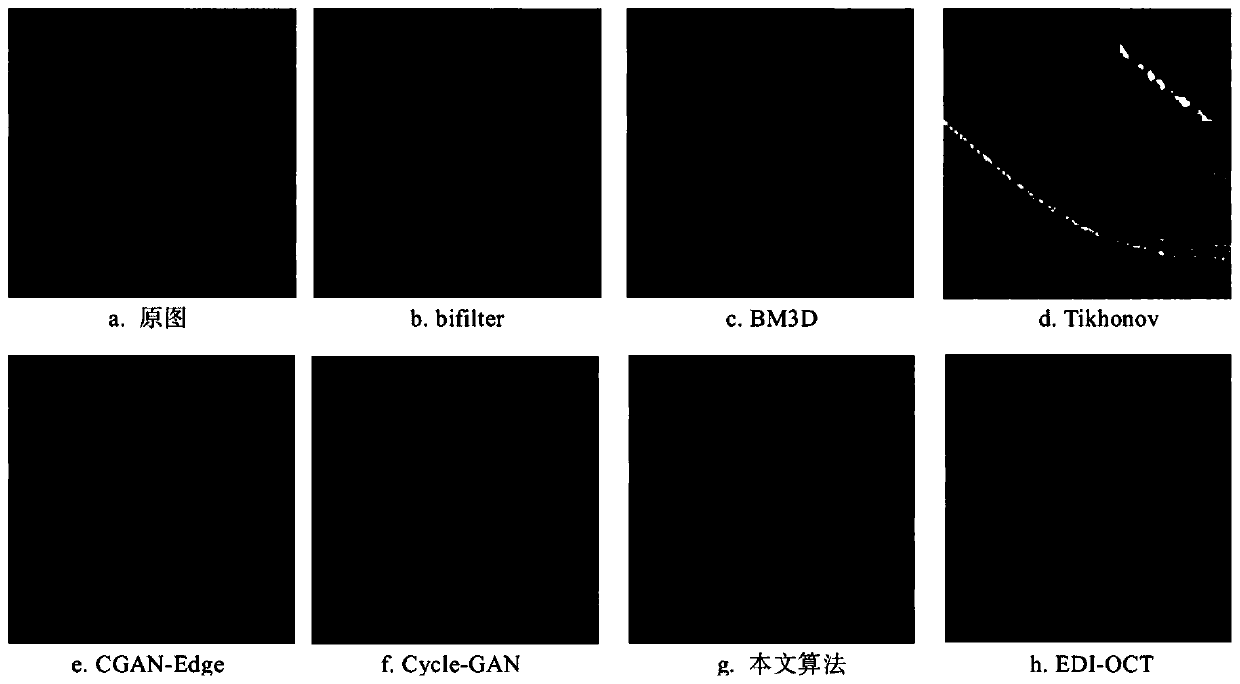
SD-OCT denoising method based on unsupervised adversarial neural network
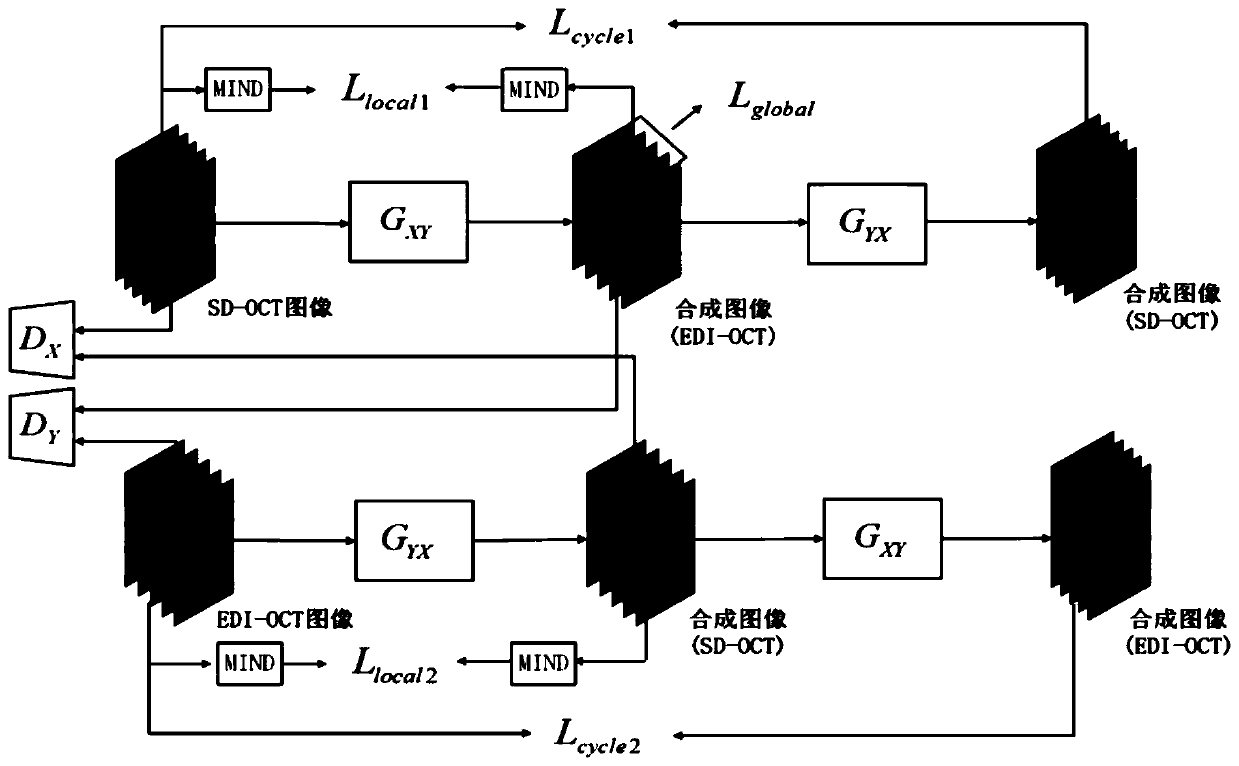
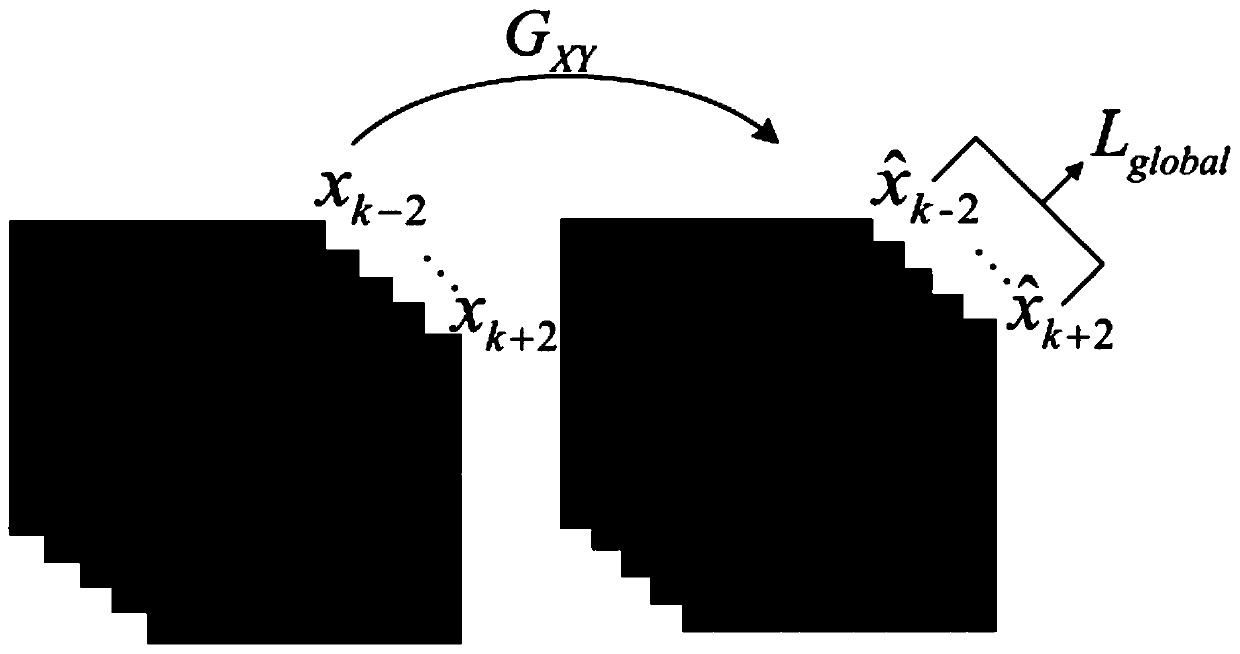
PendingCN110428385AMaintain structureKeep local detailsImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingObjective quality
The invention provides an SD-OCT denoising method based on an unsupervised adversarial neural network, and the method achieves the generation of an image with EDI-OCT quality from SD-OCT through the unsupervised learning of the migration from an SD-OCT image domain to an EDI-OCT image domain, thereby achieving the purpose of denoising. The global structure loss and the local structure loss are added to the model, so that the structure information and the local details of the image can be effectively maintained. Compared with an existing image noise reduction algorithm, the method has the advantages that image noise and strip artifacts are effectively removed from the processed image of the model, local details of the image are well reserved, and the processed image is closer to the original image. Meanwhile, the parameter index of the model prediction image is higher than other algorithm processing results. Therefore, no matter from subjective visual effect or objective quality evaluation, the processing result of the model provided by the invention is superior to the processing results of other algorithms, which indicates that the model provided by the invention is feasible and effective in the aspect of SD-OCT image denoising.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Anisotropic Gradient Regularization for Image Denoising, Compression, and Interpolation
InactiveUS20140140636A1Minimize anisotropic gradient normRemove image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingDe noise
De-noising an image by Anisotropic Gradient Regulation commences by first choosing edge directions for the image. Thereafter, an anisotropic gradient norm is established for the image from anisotropic gradient norms along the selected edge directions. The image pixels undergo adjustment to minimize the anisotropic gradient norm for the image, thereby removing image noise.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
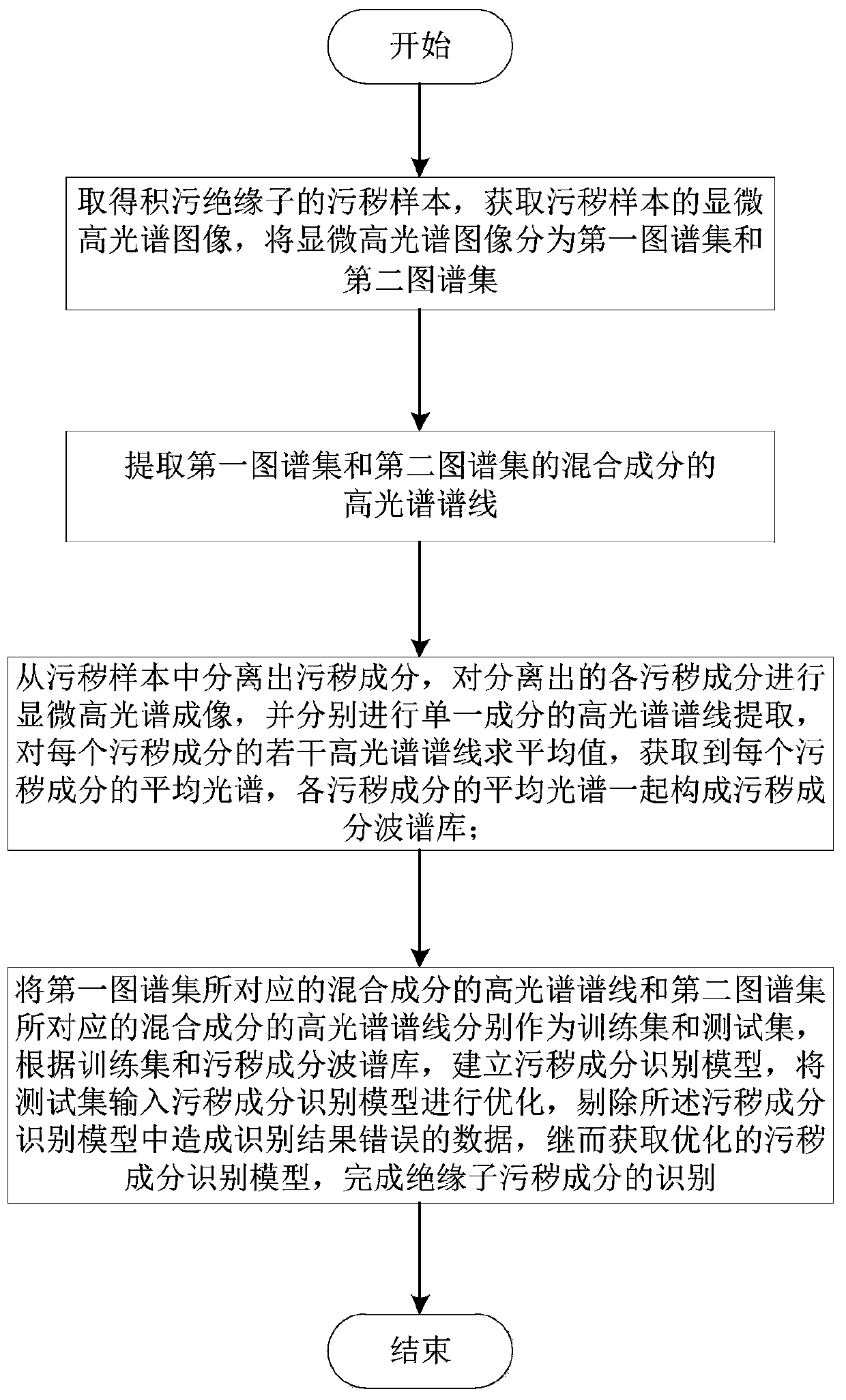
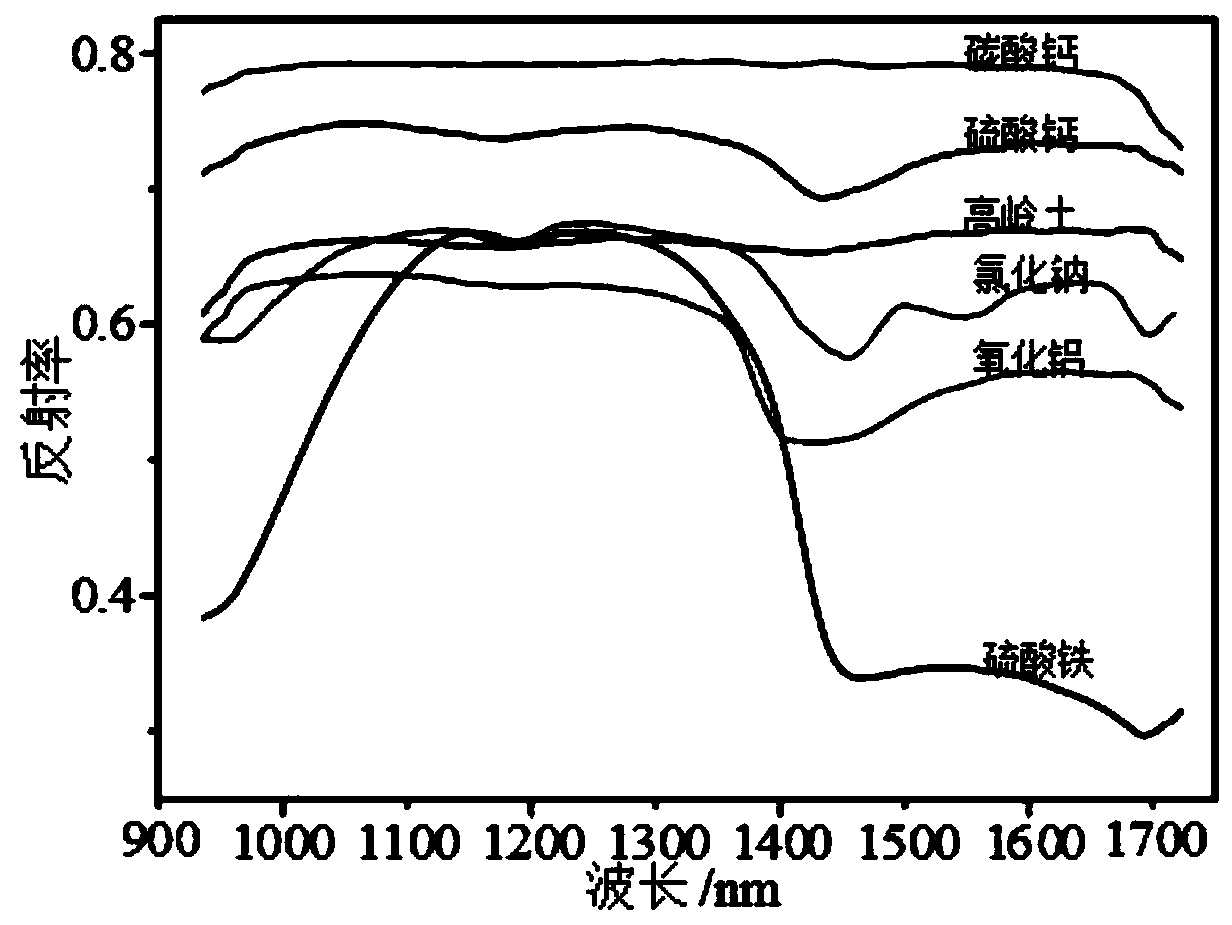
Insulator pollution component identification method based on microscopic hyperspectral technology
ActiveCN110261405AOvercome the Difficulties of UnmixingImprove accuracyImage enhancementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationComputer scienceTest set
The invention discloses an insulator pollution component identification method based on a microscopic hyperspectral technology, and belongs to the technical field of power transmission and transformation equipment operation state maintenance. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a microscopic hyperspectral image of pollution samples of a pollution accumulation insulator, and dividing the microscopic hyperspectral image into a first map set and a second map set; respectively extracting hyperspectral spectral lines of mixed components of the pollution samples in the first map set and the second map set; separating the pollution components of the pollution samples, performing microscopic hyperspectral imaging on each pollution component, and establishing a pollution component spectrum library; establishing a pollution component identification model based on the pollution component spectrum library and the hyperspectral spectral lines of the pollution sample mixed components corresponding to the first map set, taking the hyperspectral spectral lines of the pollution sample mixed components corresponding to the second map set as a test set, and inputting the test set into the pollution component identification model for optimization. The method achieves microscopic detection of the insulator pollution components, is simple in operation process, is beneficial to identification of the pollution components, and can observe the distribution of the pollution components on the surface of the insulator.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV +1
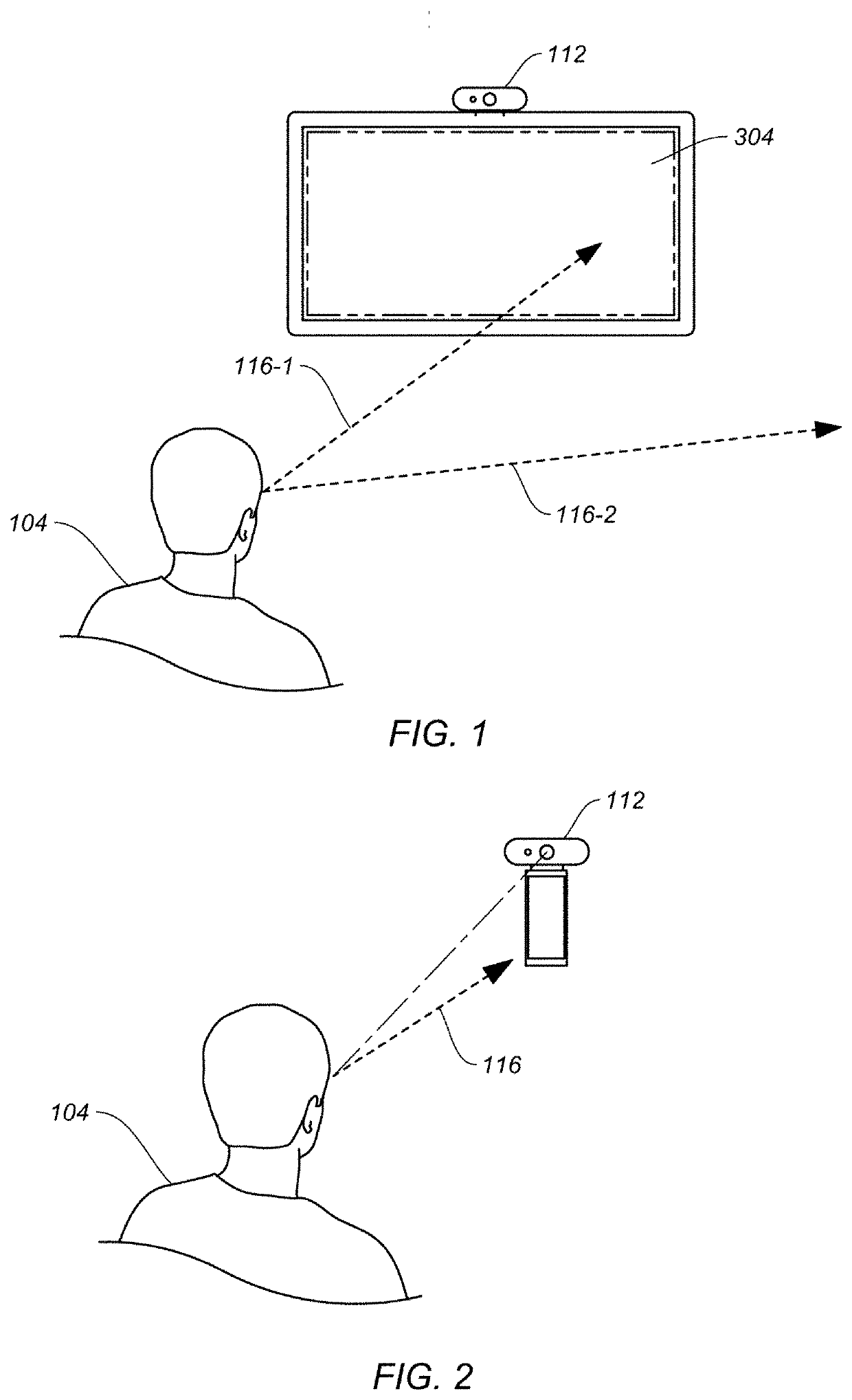
User recognition and gaze tracking in a video system
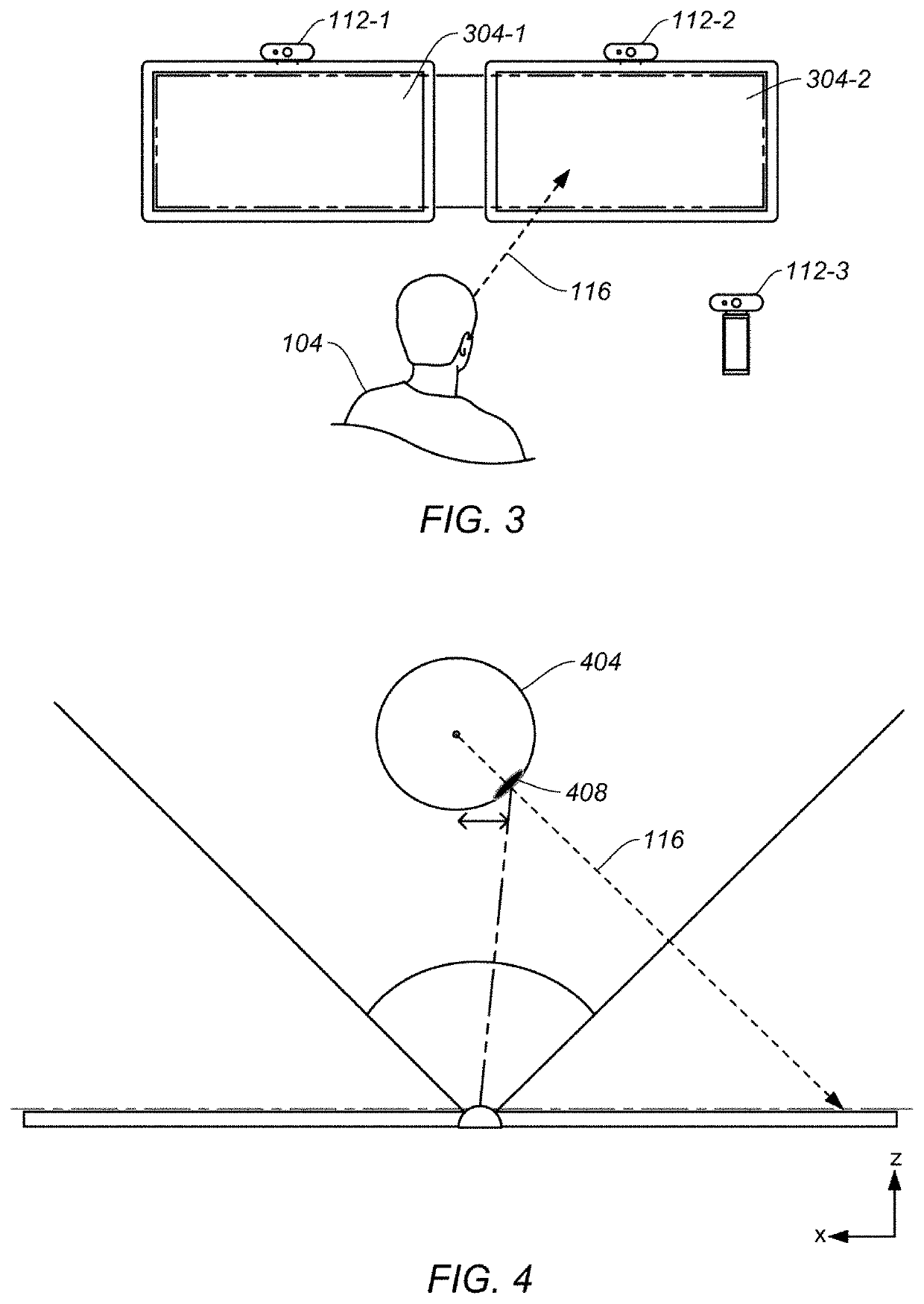
ActiveUS20210201021A1Remove image noiseInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisGaze directionsComputer graphics (images)
Some embodiments include a computer-implemented method for tracking a gaze of a user that can include receiving image data that includes a plurality of eye landmarks that identify a perimeter of a user's eye, applying dynamic thresholding to the image data, determining a convex hull based on the dynamically thresholded and image data, computing and fitting an ellipse along a boundary of the convex hull, the ellipse corresponding to an iris of the user's eye, updating the image data with the computed ellipse, computing a refined ellipse by reapplying the dynamic thresholding and determining the convex hull using the updated image data, and determining a gaze direction of the user based in part on a position of the refined ellipse relative to the perimeter of the user's eye.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
System and method for enhancement processing of video images
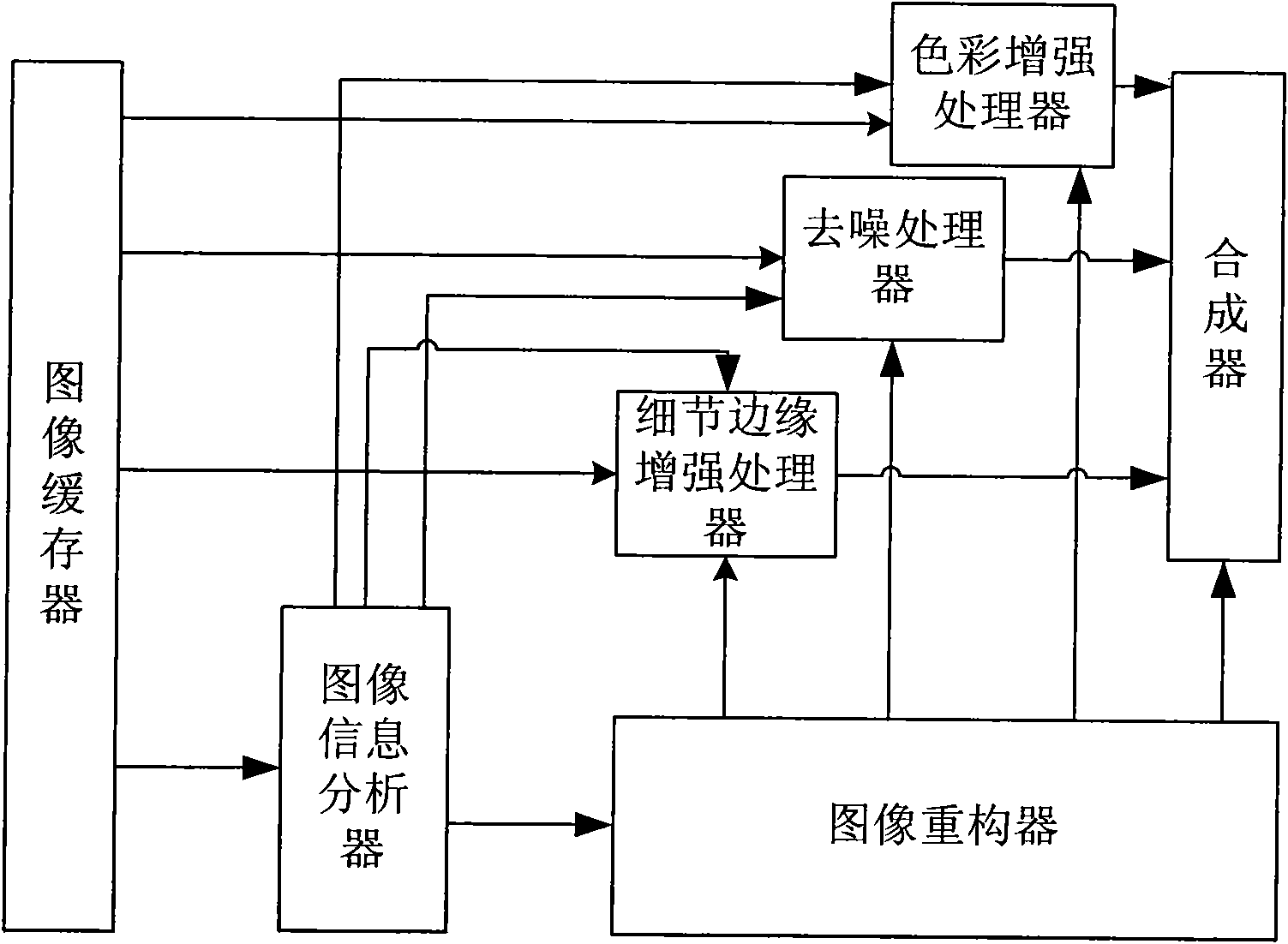
InactiveCN101610347ARecover image detailsRecovery DetailsTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMotion vectorHandling system
The invention relates to an image processing system and a processing method. The system comprises an image buffer, an image information analyzer, an image reconstruction device, a detail edge enhancement processor, a de-noising processor, a color processor and a synthesizer. The method comprises: extracting motion vector information, color region information and noise distribution information of images according to the sequence data of read original images; restructuring images according to the motion vector information of the original images and transmitting new image data together with the motion vector information, color region information and noise distribution information of the images into a color processor; using the detail edge enhancement processor; using the de-noising processor; and obtaining final processed data according to the image data subjected to edge enhancement, the de-noised image data and the data after color enhancement. The invention utilizes motion estimation and motion compensation to effectively restore image details, enhance colors and remove image noise.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANYUN NETWORK TECH
Radio frequency high-Q value band-pass filter
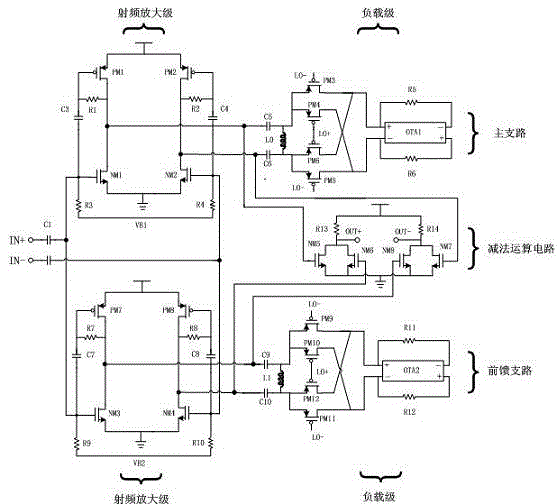
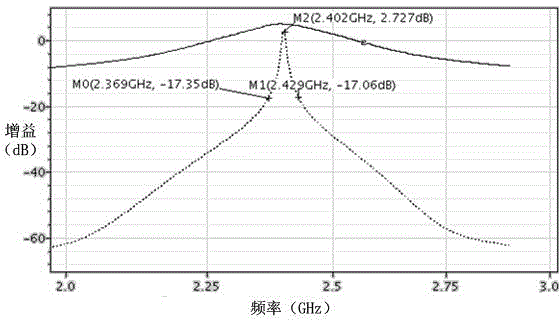
ActiveCN104617913ADecrease the stop-band rejection ratioRemove image noiseMultiple-port active networksFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
The invention discloses a radio frequency high-Q value band-pass filter. The radio frequency high-Q value band-pass filter is a feed-forward structure. The radio frequency high-Q value band-pass filter comprises a main branch circuit, a feed-forward branch circuit and a subtraction circuit. The main branch circuit and feed-forward branch circuit are the same in structure, each of the main branch circuit and feed-forward branch circuit comprises a radio frequency amplification stage and a load stage, wherein the load stage is composed of a switch mixing stage of a passive mixer and a trans-impedance stage. The input impedance characteristic of a trans-impedance amplifier is moved to a radio frequency local oscillator by means of the impedance move characteristic of the passive mixer on the frequency so as to enable the main branch to turn into a radio frequency high-Q value band elimination filter. In order to guarantee the phase matching between the output ends of the feed-forward branch and main branch, the feed-forward branch uses the same structure with that of the main branch, and the in-band rejection ratio and stop band width of the band elimination filter of the branch are reduced through changing the feedback resistance value of the trans-impedance stage in the feed-forward branch. A radio-frequency band pass effect is realized through subtracting the output signal of the main branch from the output signal of the feed-forward branch through the subtraction circuit.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for processing impeller flow field images of centrifugal pump
ActiveCN104156920ARemove image noiseStable and reliable speedImage enhancementImage pairComputer science
The invention discloses a method for processing impeller flow field images of a centrifugal pump. The method is mainly used for processing impeller images with complex rotating boundaries, which are shot in a PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) test of the centrifugal pump to obtain a real flow field velocity and relates to the field of fluid experiment. The method comprises the following steps: testing the flow field by using the PIV and shooting a group of flow field image pairs; diving the boundaries of the flow fields in PIV flow field images and using the boundaries of the flow fields to generate mask images; performing mask calibration on the mask images and the PIV flow field images to obtain masked images; performing cross-correlation processing on the masked images and calculating to obtain the velocity of the flow field. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good simplicity, good convenience for operation, easiness for realization and higher generality; the impeller flow field with the complex rotating boundaries in the PIV of the centrifugal pump can be effectively processed.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
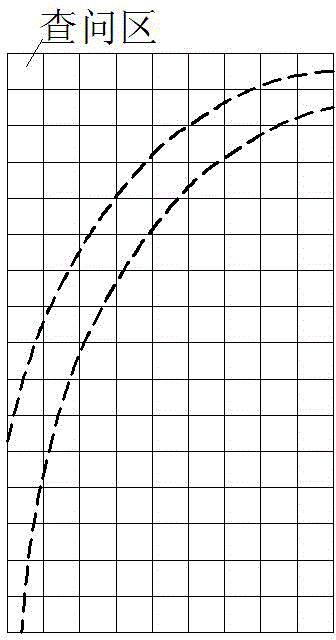
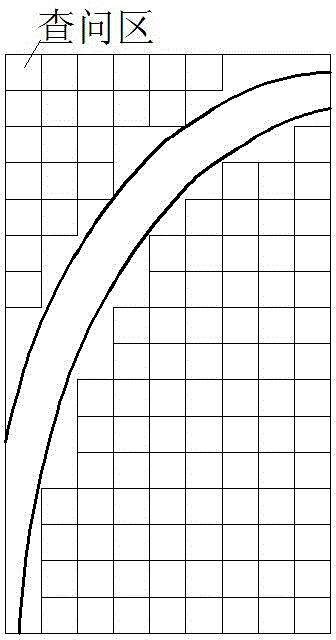
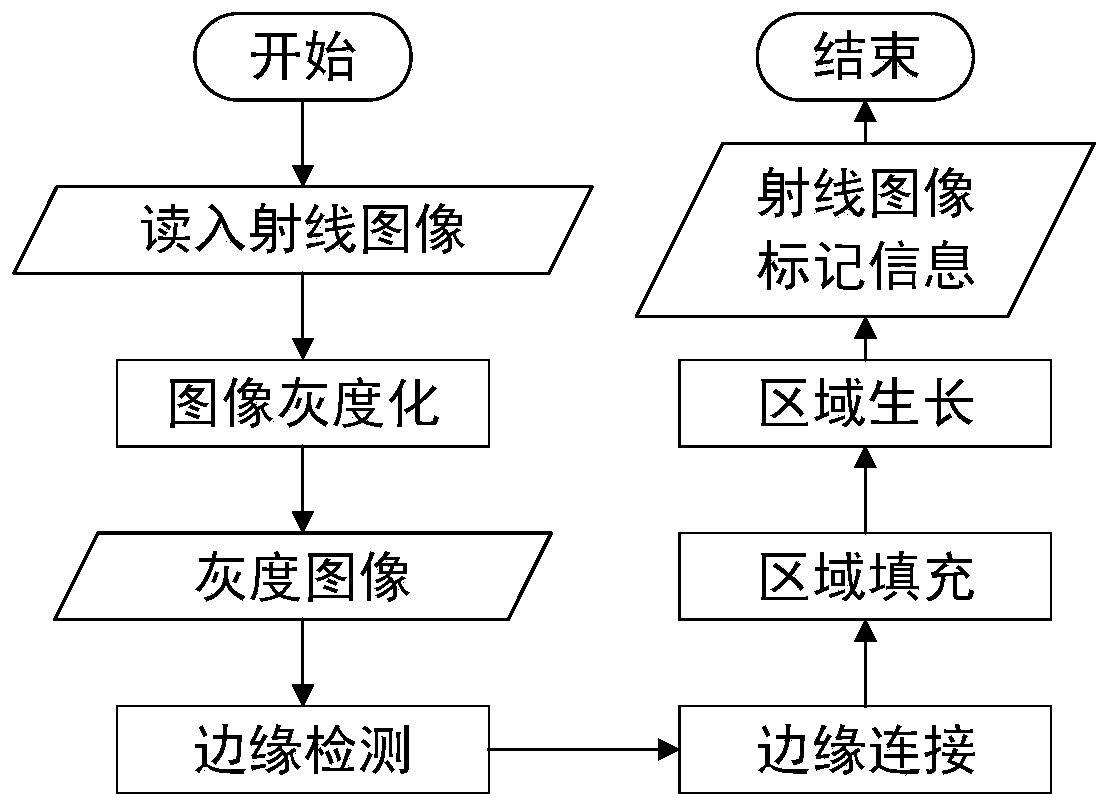
A ray detection image mark information character segmentation method based on edge detection
InactiveCN109766892ARemove image noiseFix image blurCharacter and pattern recognitionEdge basedRegion growing
The invention discloses a ray detection image mark information character segmentation method based on edge detection, and the method comprises the steps of reading a ray image, and carrying out the graying of the ray image, and obtaining a gray image; secondly, carrying out edge detection on the gray level image by utilizing an improved LOG edge detection operator to obtain a binary image containing edge information of the gray level image; performing edge connection on discontinuous breakpoints in the binary image to obtain a binary image containing continuous edge information; carrying out region filling operation on the binary image to obtain a filled image; and finally, extracting all connected regions in the image by adopting a region growing method, and comparing different areas between the connected regions of the mark information and the non-mark information so as to complete character segmentation of the mark information of the ray image. According to the present invention, the characters of the ray image marking information can be rapidly and effectively segmented, and a good foundation is laid for subsequent ray image marking information recognition.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of adopting spatial light modulators to improve computational holographic reconstruction image quality
The invention discloses a method of adopting spatial light modulators to improve the computational holographic reconstruction image quality. The method is realized by a system formed by a laser, a filter, a collimating lens, a first spatial light modulator, a second spatial light modulator, a first computer, a second computer and a receiving screen. In the method, a shaping hologram generated by the computer is loaded on the first spatial light modulator through a driving panel, a Gaussian beam with non-uniform light intensity distribution generated after a laser source passes through a filterunit becomes a round beam with uniform light intensity distribution, the round beam after shaping is used as a reconstruction light source and shines on the second spatial light modulator loaded withthe reconstruction hologram, and high-quality computational holographic reconstruction is realized.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com