Patents
Literature
130 results about "Fractography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fractography is the study of the fracture surfaces of materials. Fractographic methods are routinely used to determine the cause of failure in engineering structures, especially in product failure and the practice of forensic engineering or failure analysis. In material science research, fractography is used to develop and evaluate theoretical models of crack growth behavior.
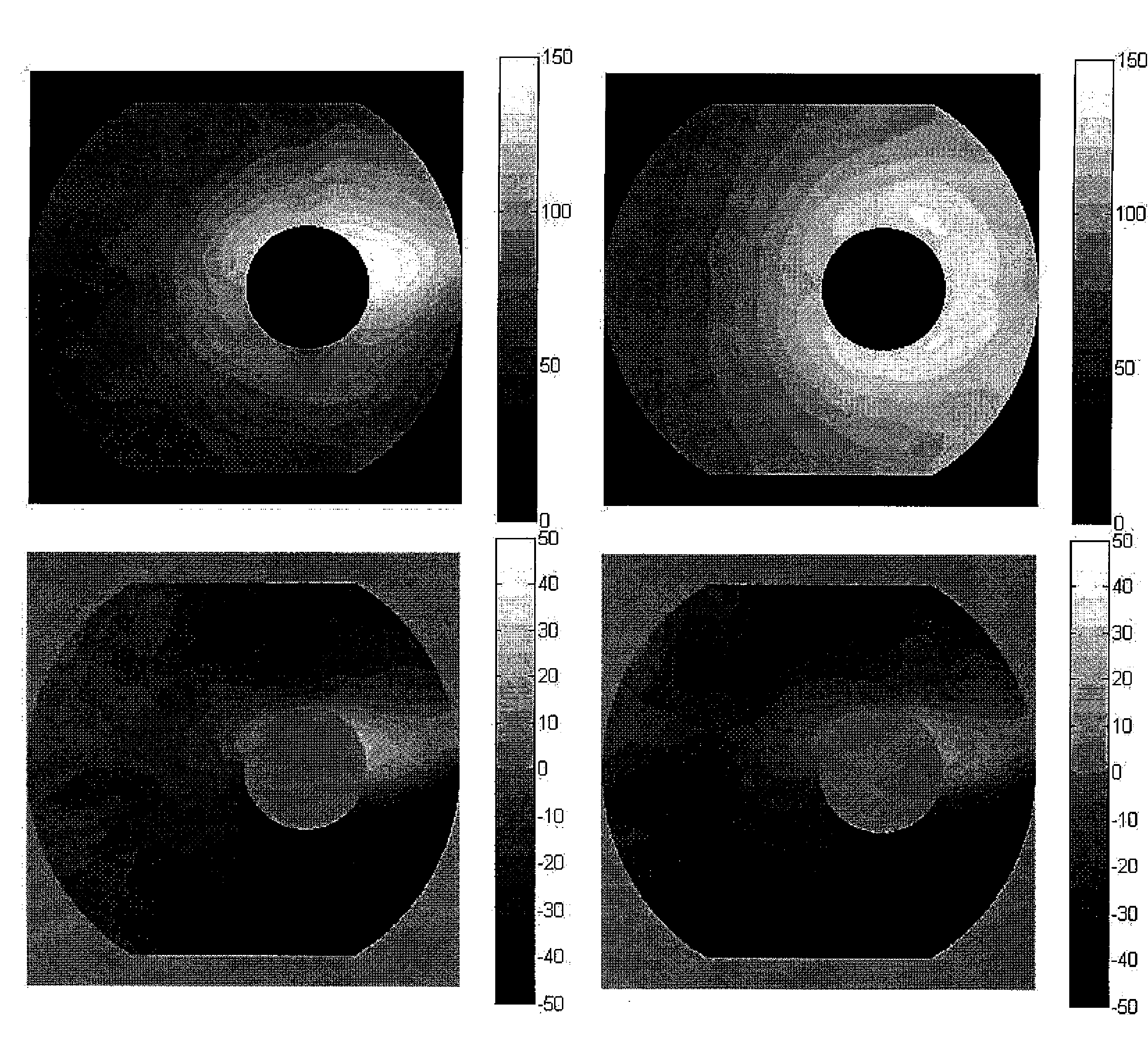
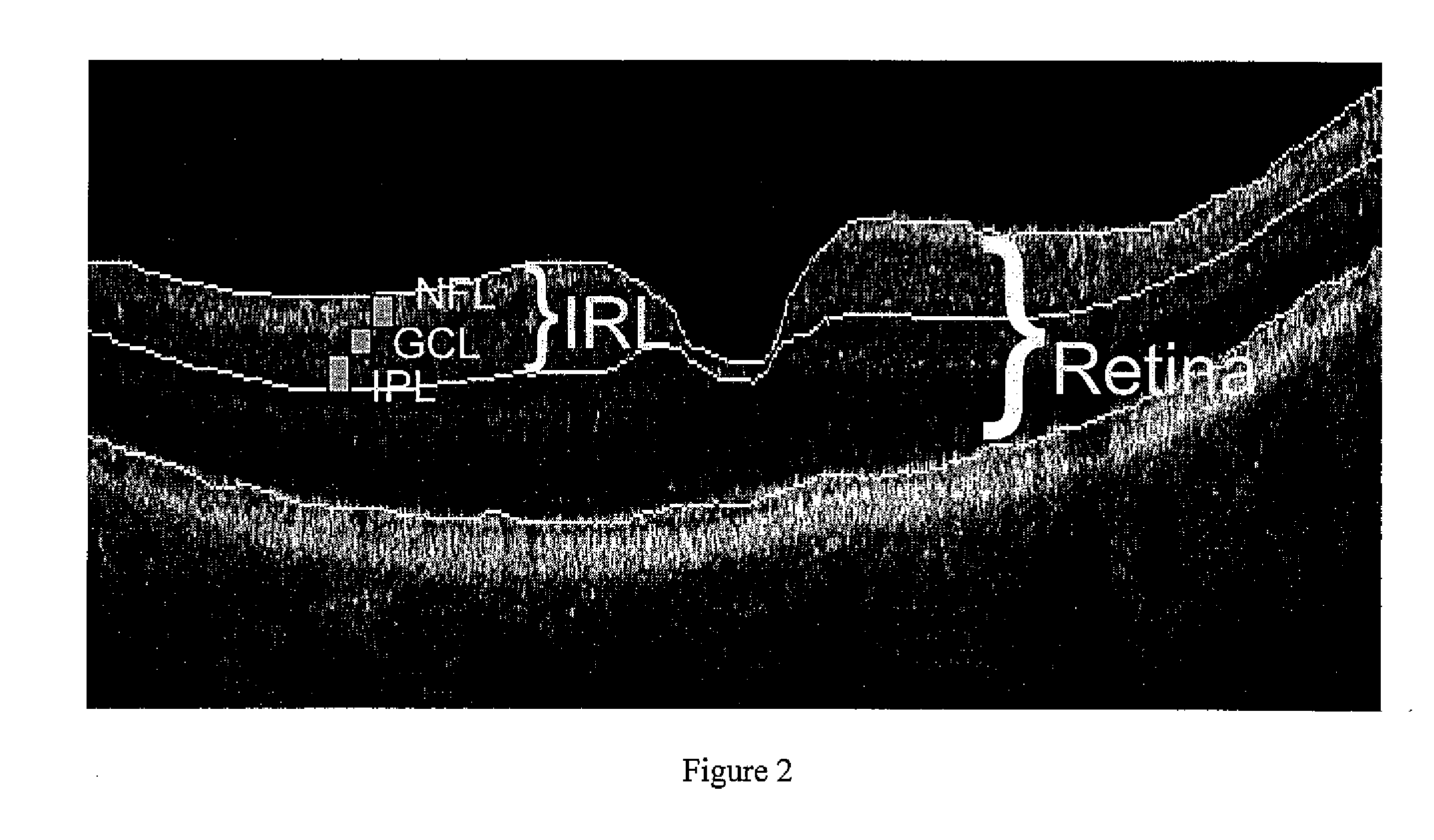
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
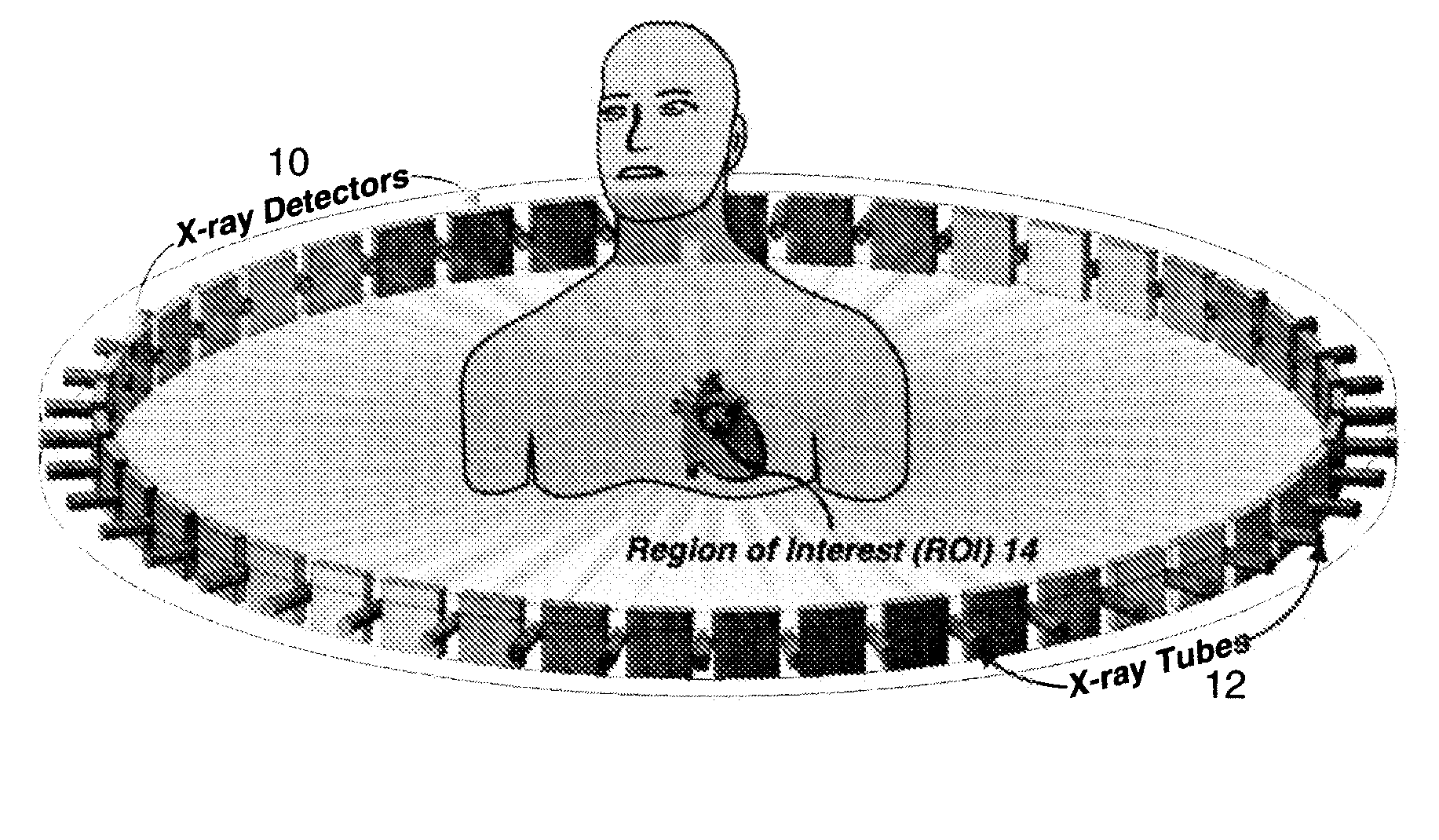
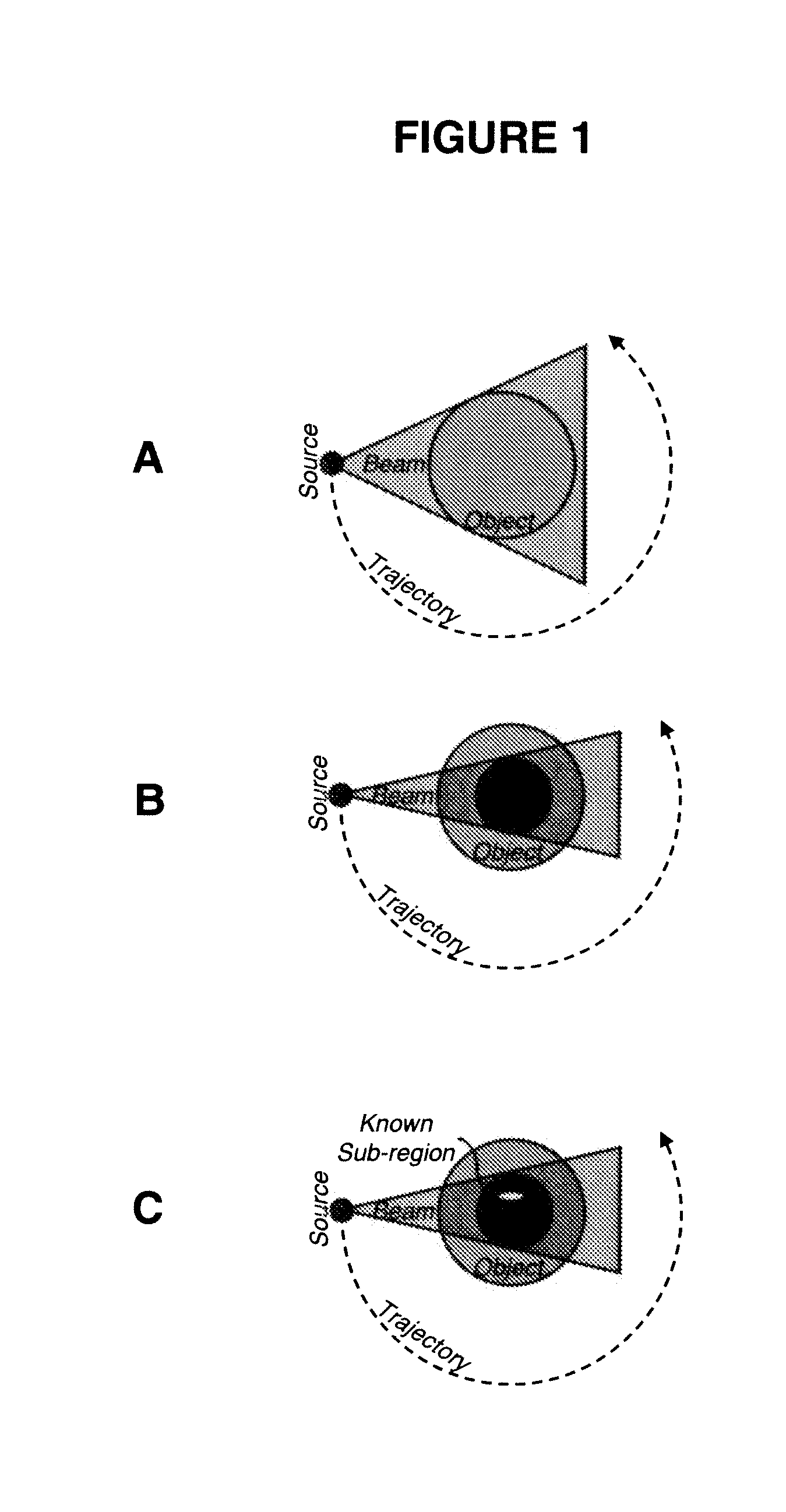
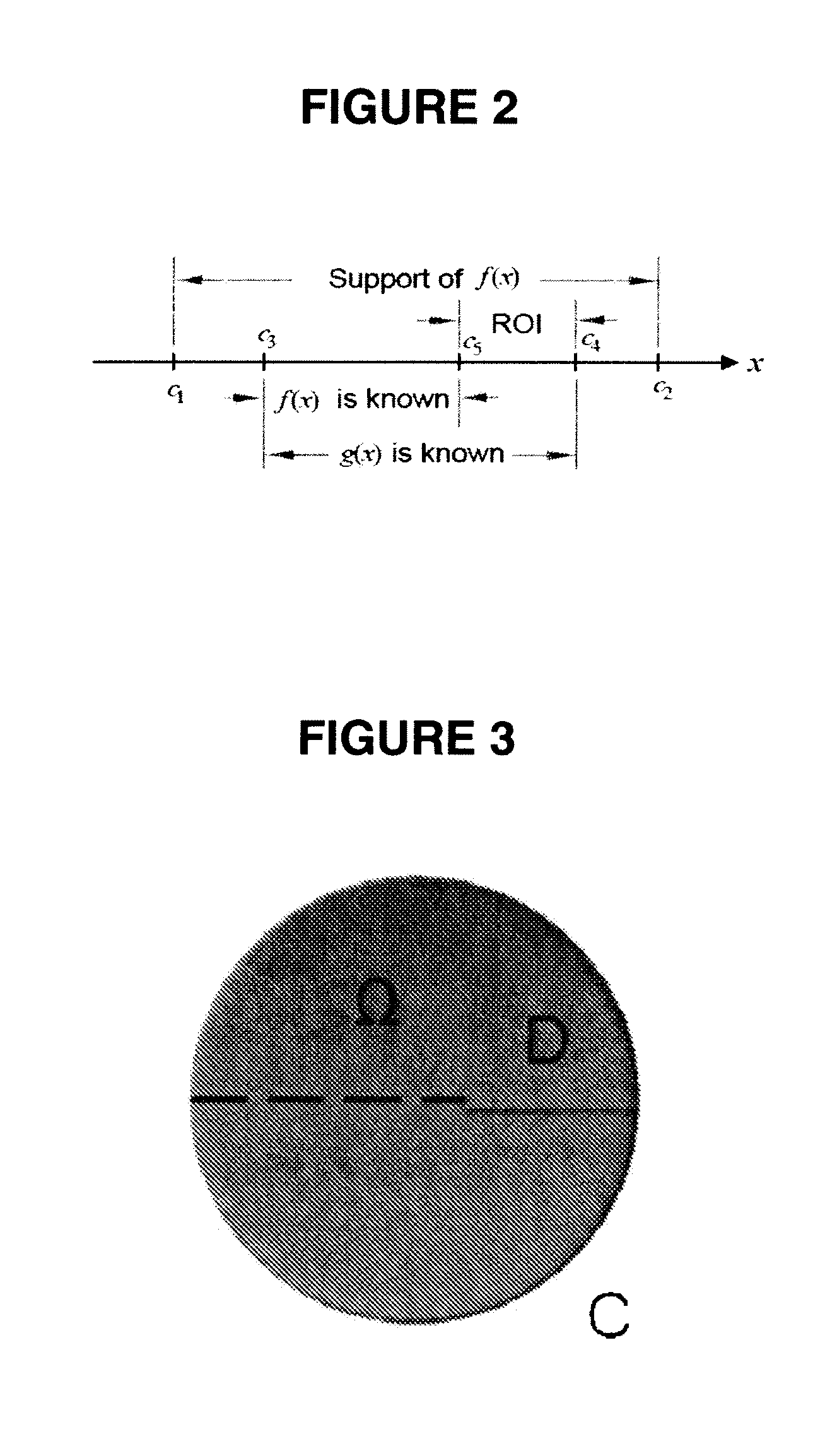
Interior Tomography and Instant Tomography by Reconstruction from Truncated Limited-Angle Projection Data
InactiveUS20090196393A1Faithful resolution of featureHigh spatial contrastReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAttenuation coefficientFractography
A system and method for tomographic image reconstruction using truncated limited-angle projection data that allows exact interior reconstruction (interior tomography) of a region of interest (ROI) based on the linear attenuation coefficient distribution of a subregion within the ROI, thereby improving image quality while reducing radiation dosage. In addition, the method includes parallel interior tomography using multiple sources beamed at multiple angles through an ROI and that enables higher temporal resolution.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Tomography by Emission of Positrons (Pet) System
InactiveUS20080103391A1Easy to integrateHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHuman bodyFractography
Tomography by emission of positrons (pet) system dedicated to examinations of human body parts such as the breast, axilla, head, neck, liver, heart, lungs, prostate region and other body extremities which is composed of at least two detecting plates (detector heads) with dimensions that are optimized for the breast, axilla region, brain and prostrate region or other extremities; motorized mechanical means to allow the movement of the plates under manual or computer control, making it possible to collect data in several orientations as needed for tomographic image reconstruction; an electronics system composed by a front-end electronics system, located physically on the detector heads, and a trigger and data acquisition system located off-detector in an electronic crate; a data acquisition and control software; and an image reconstruction and analysis software that allows reconstructing, visualizing and analyzing the data produced during the examination.
Owner:FFCUL BEB FUNDACAO DA FACULDADE DE CIENCIAS DA UNIV DE LISBOA INST +6
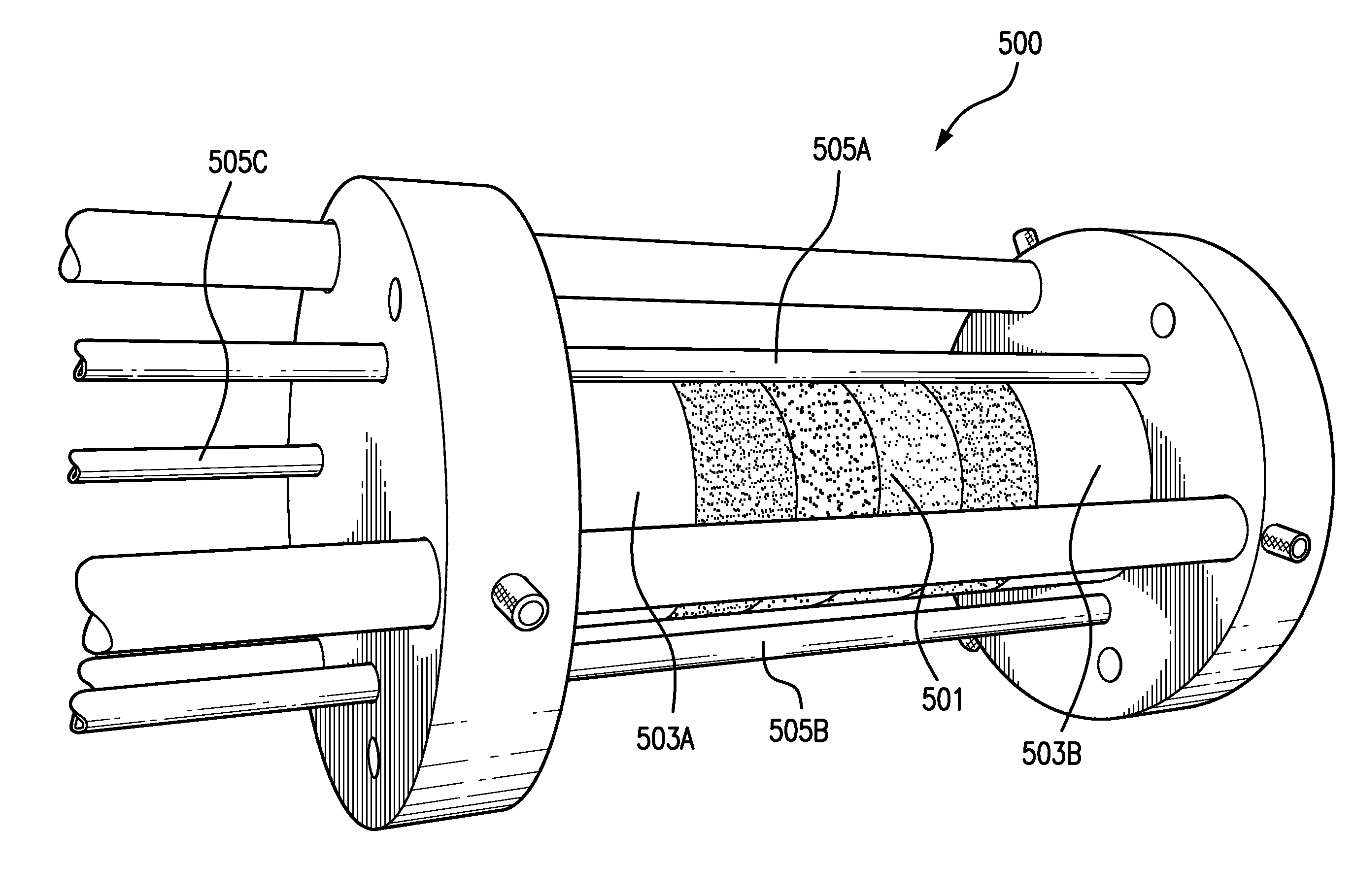
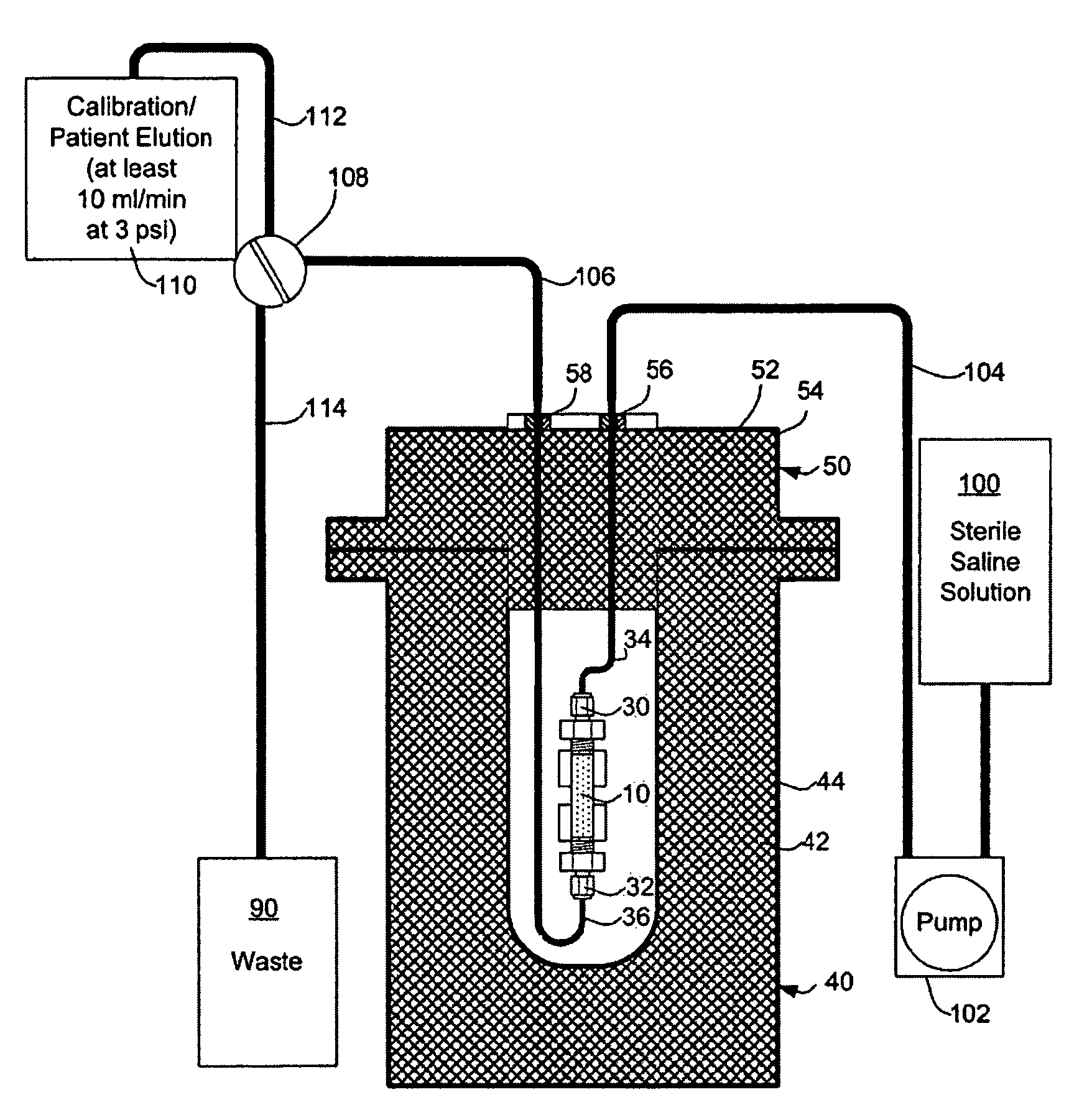
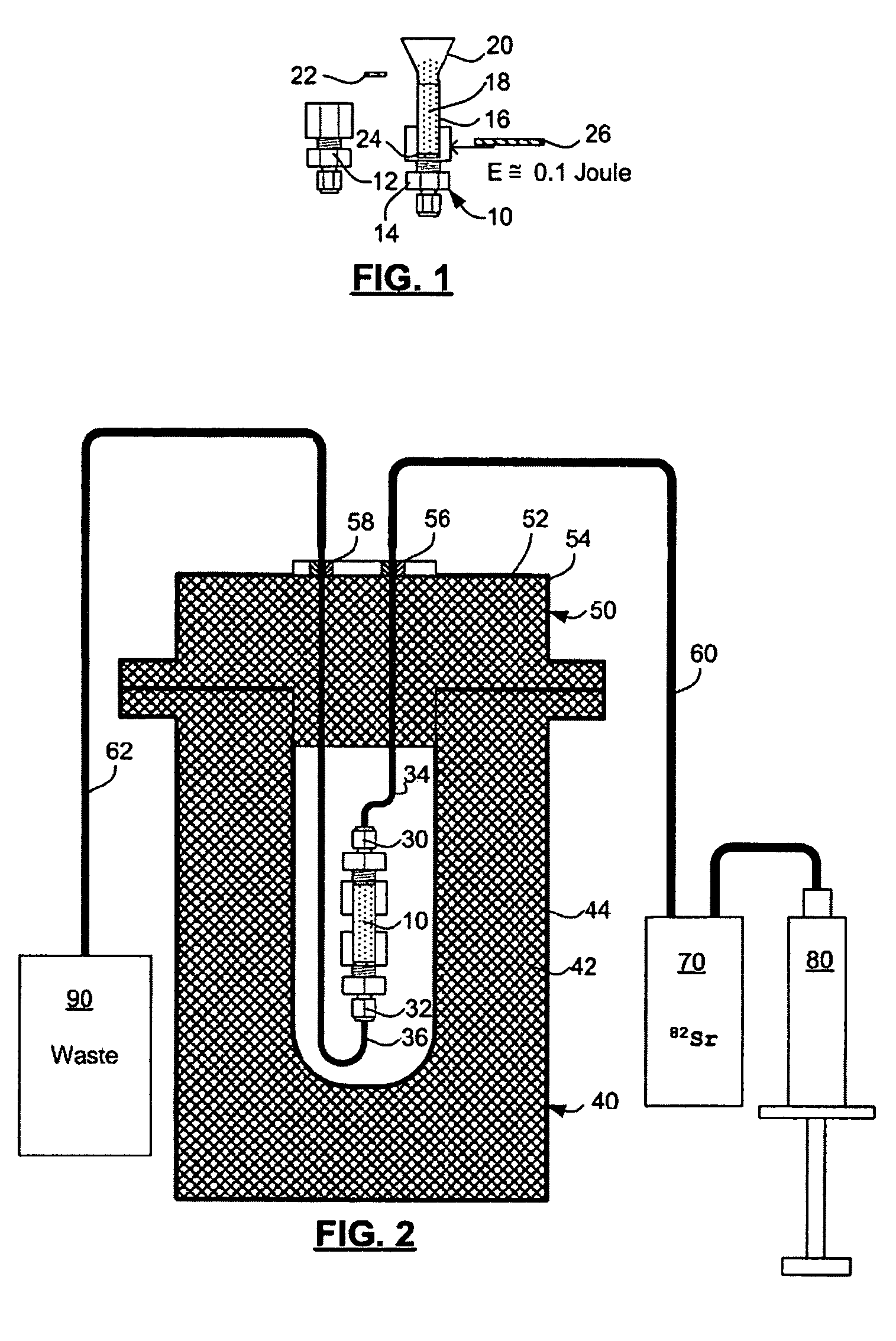
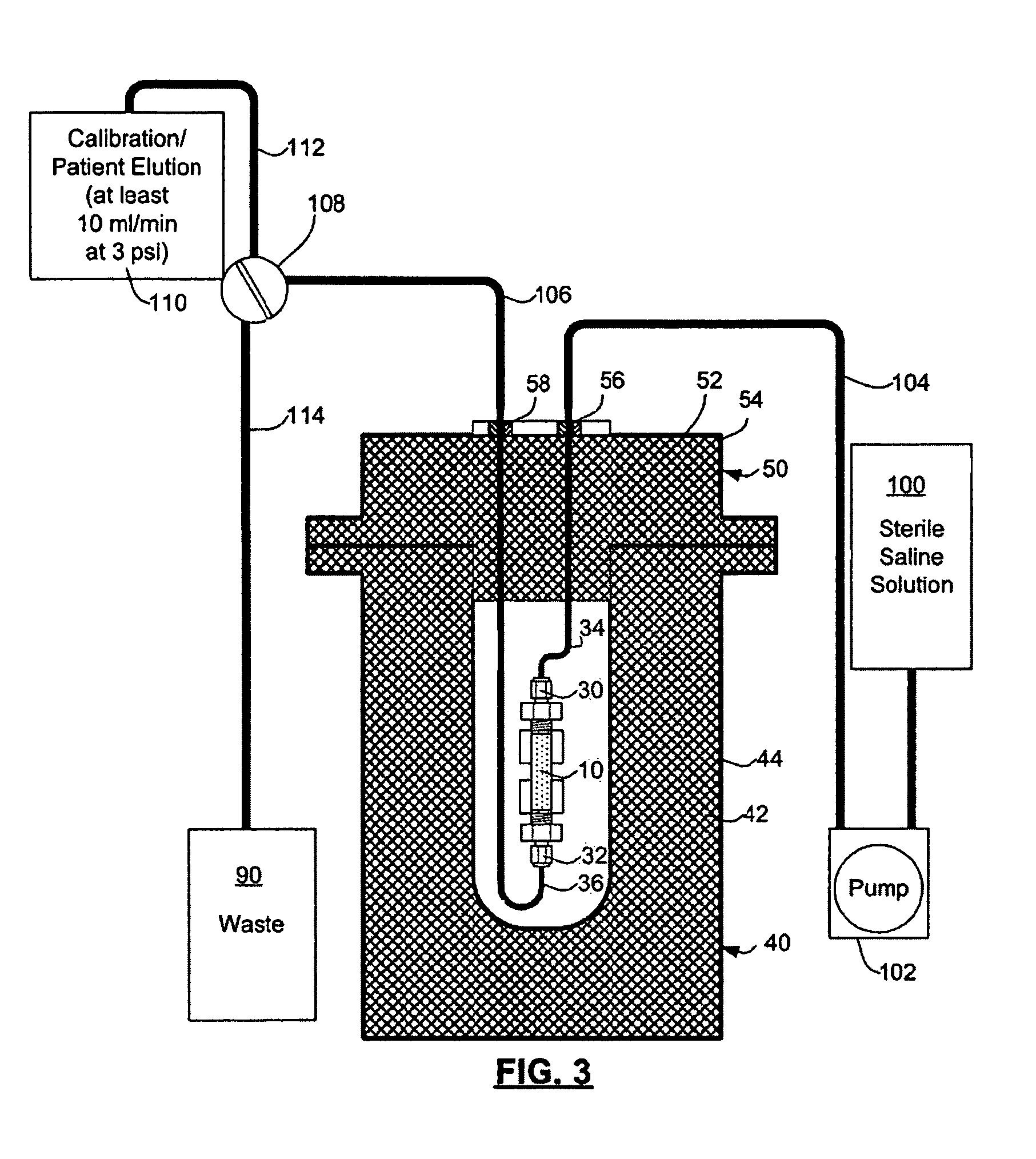
Rubidium generator for cardiac perfusion imaging and method of making and maintaining same
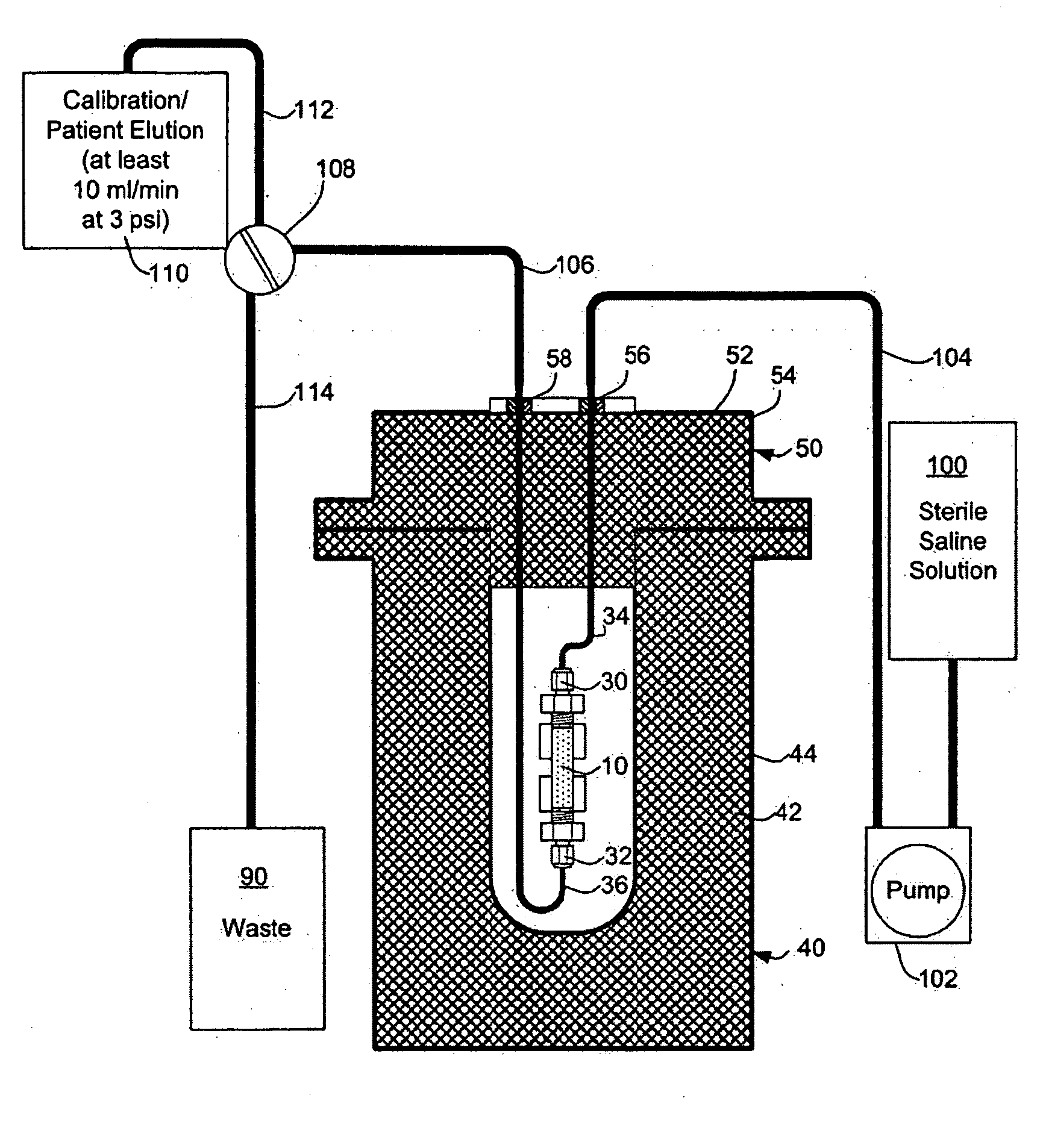
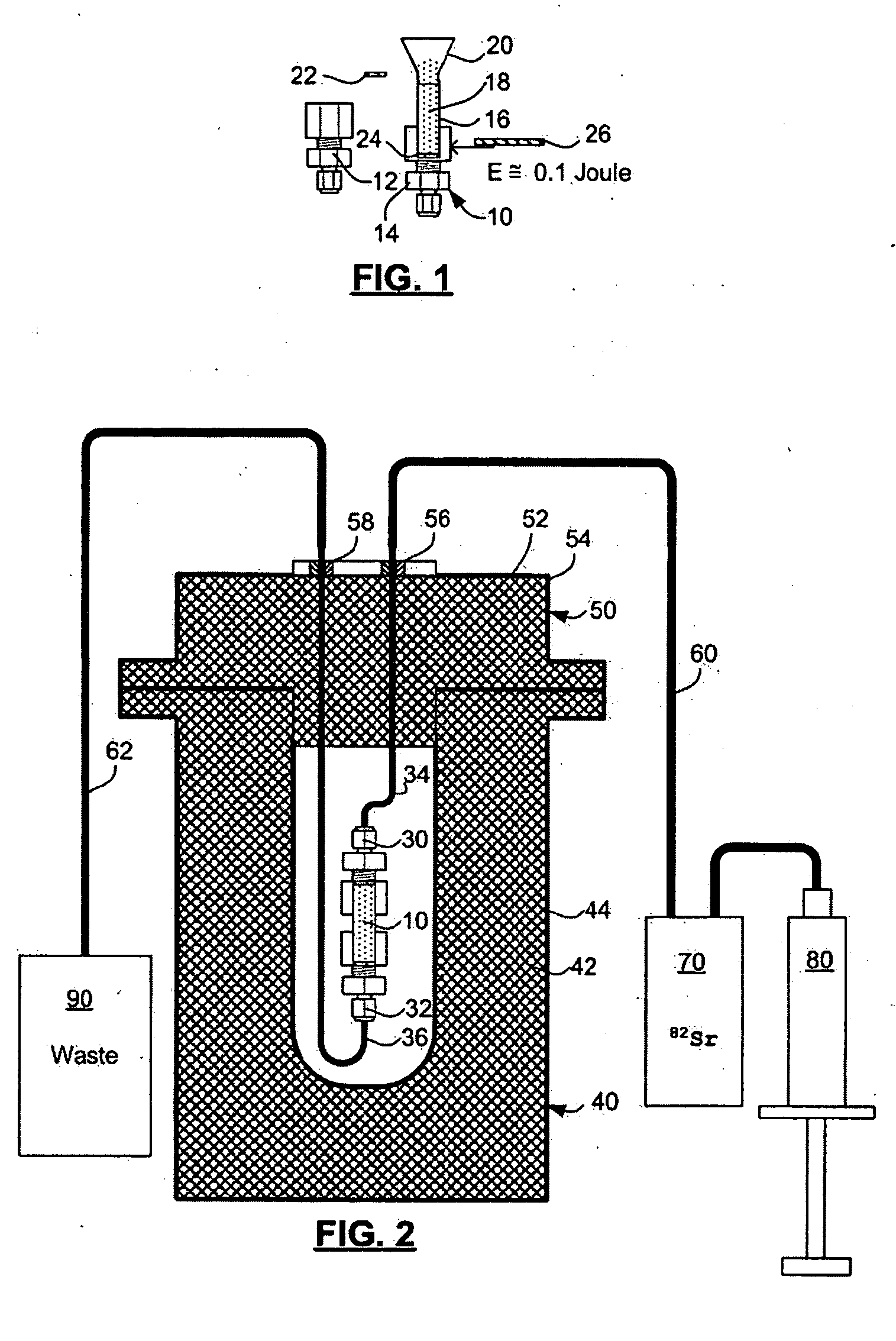
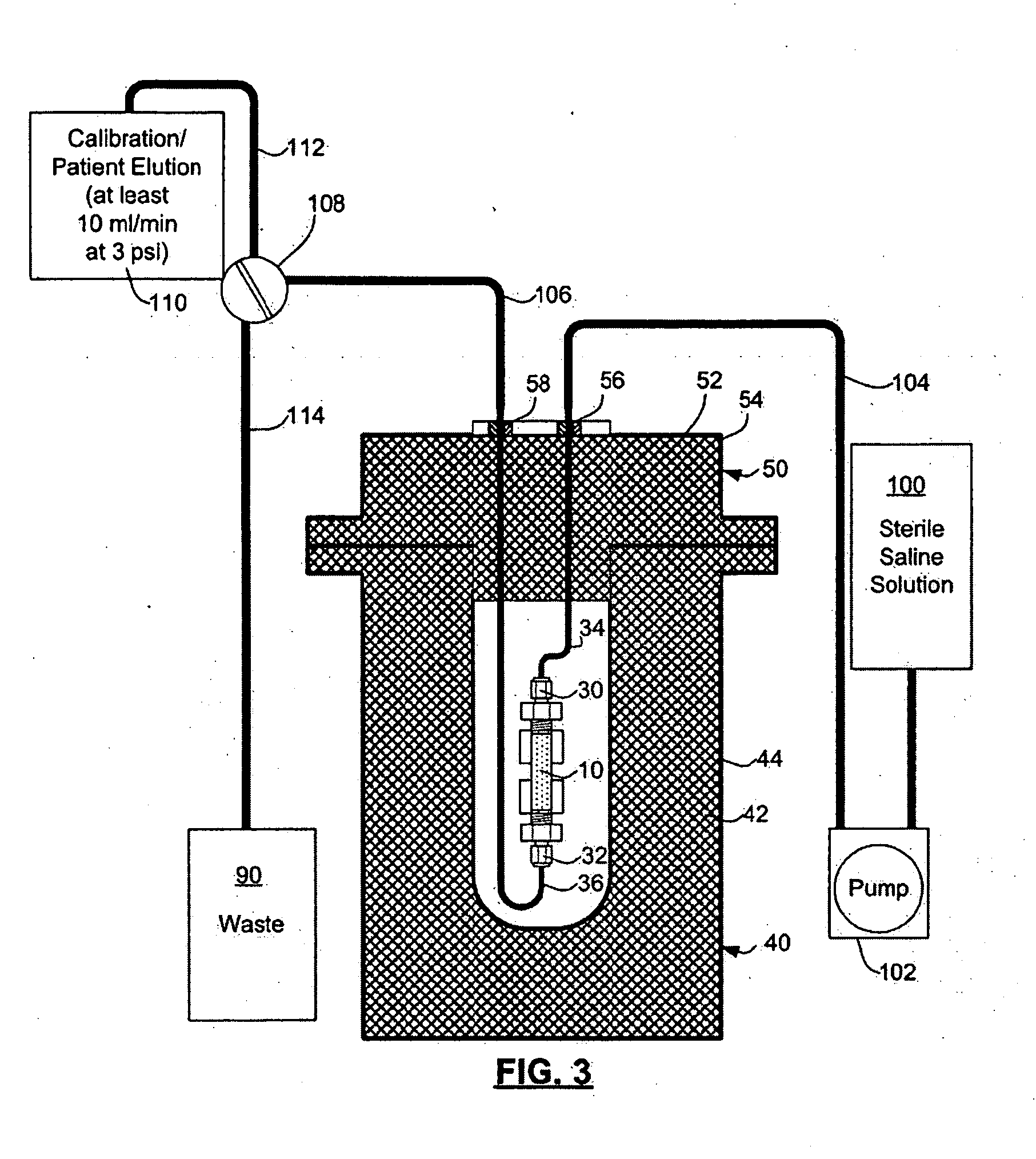
ActiveUS20070140958A1Low pressure elutionFacilitates precision flow controlIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsFractographyRubidium
An 82Sr / 82Rb generator column is made using a fluid impervious cylindrical container having a cover for closing the container in a fluid tight seal, and further having an inlet for connection of a conduit for delivering a fluid into the container and an outlet for connection of a conduit for conducting the fluid from the container. An ion exchange material fills the container, the ion exchange material being compacted within the container to a density that permits, the ion exchange material to be eluted at a rate of at least 5 ml / min at a fluid pressure of 1.5 pounds per square inch (10 kPa). The generator column can be repeatedly recharged with 82Sr. The generator column is compatible with either three-dimensional or two-dimensional positron emission tomography systems.
Owner:OTTAWA HEART INST RES
Scintillation substances (variants)
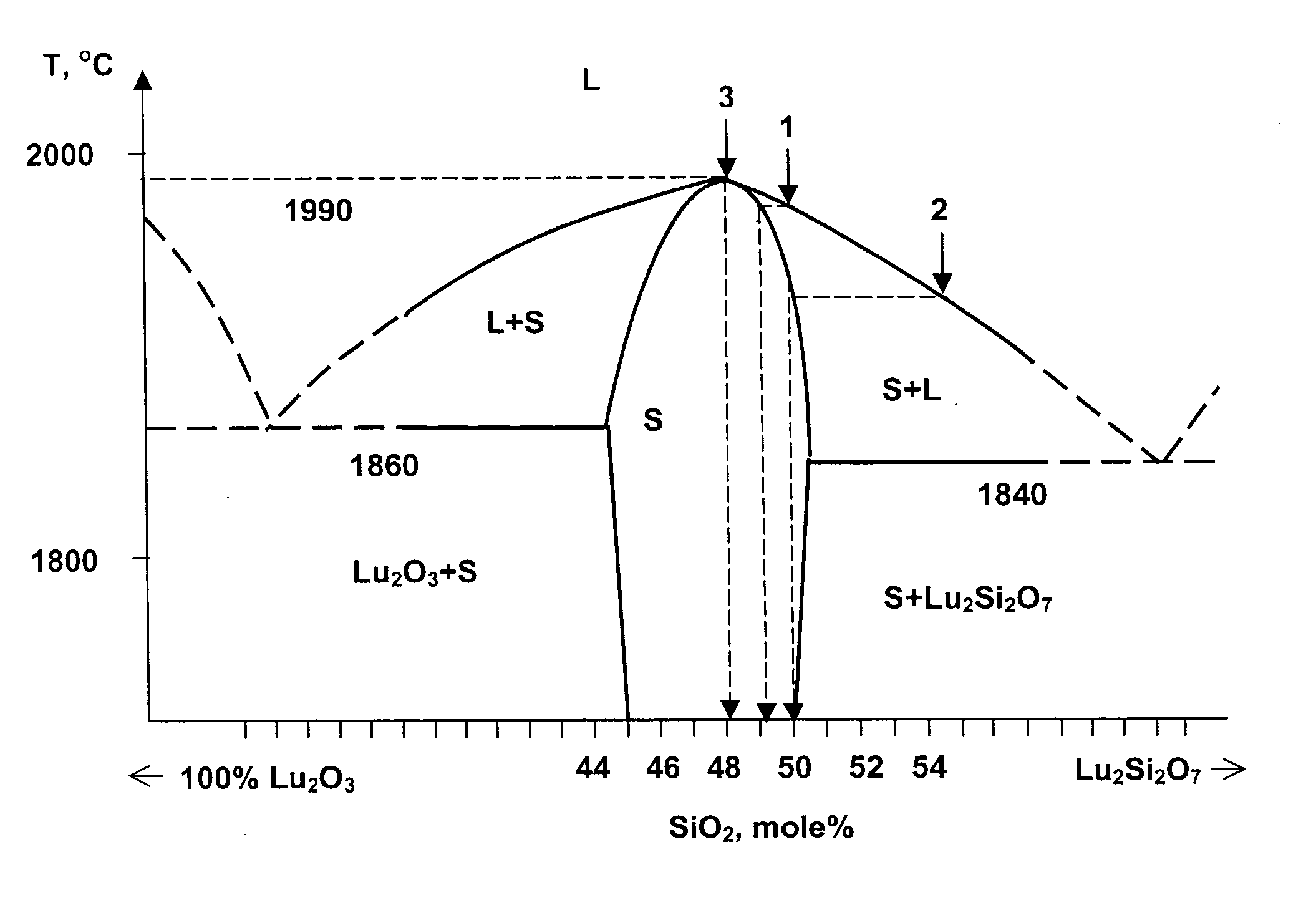
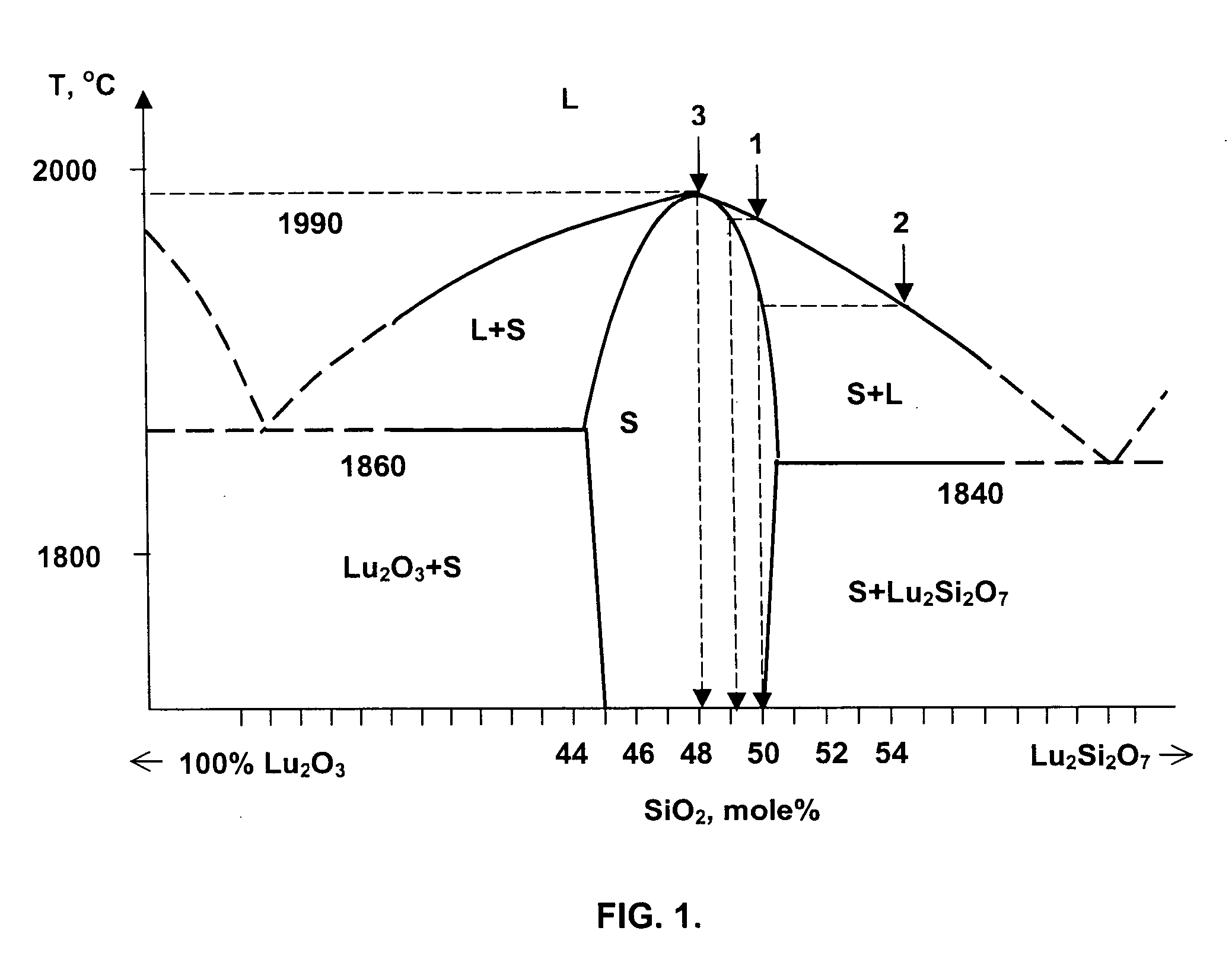
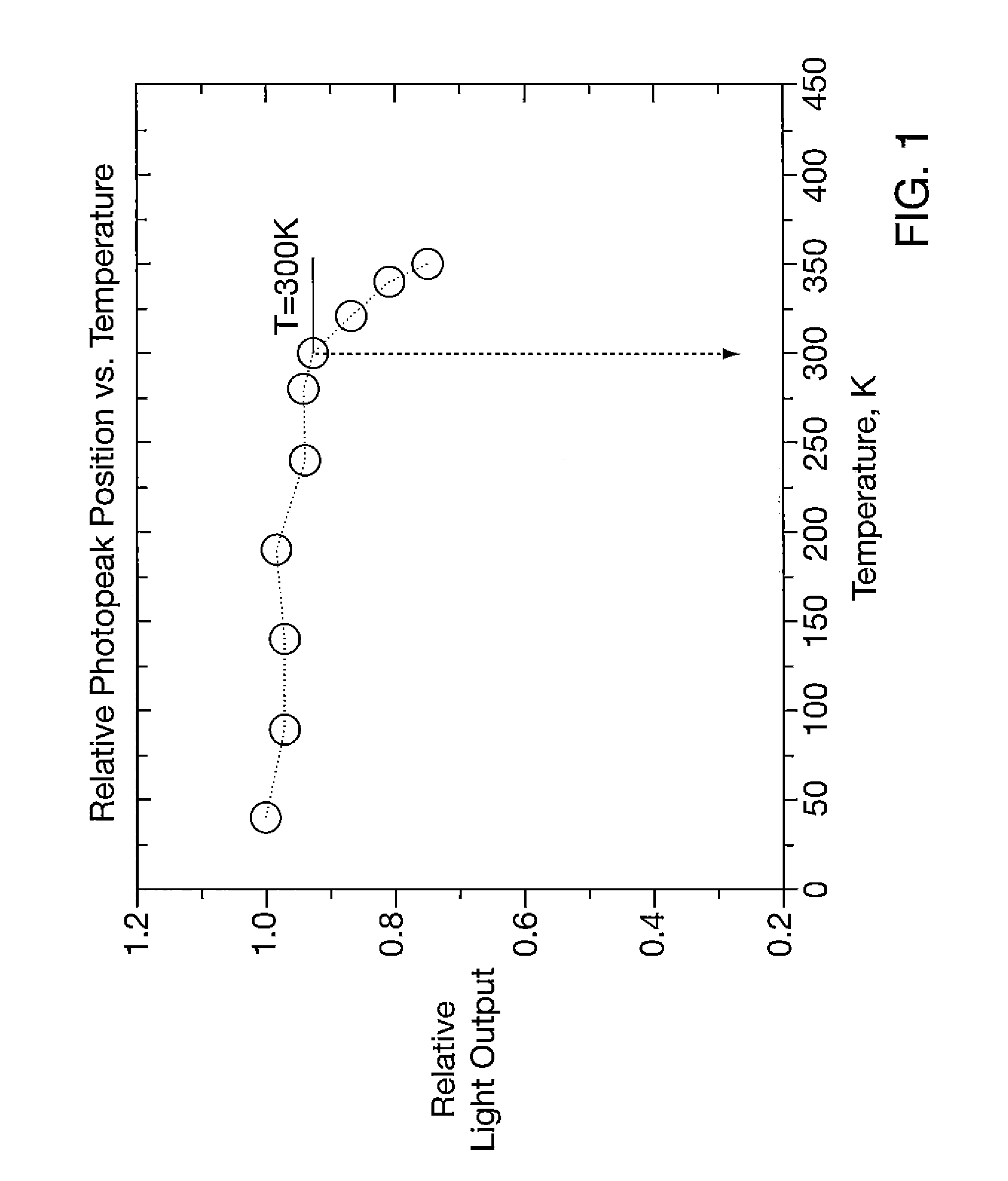
ActiveUS20060086311A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh light yieldPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltFractographyLutetium
Inventions relate to scintillation substances and they may be utilized in nuclear physics, medicine and oil industry for recording and measurements of X-ray, gamma-ray and alpha-ray, nondestructive testing of solid states structure, three-dimensional positron-emission tomography and X-ray computer tomography and fluorography. Substances based on silicate comprising lutetium and cerium characterised in that compositions of substances are represented by chemical formulae CexLu2+2y−xSi1−yO5+y, CexLiq+pLu2−p+2y−x−zAzSi1−yO5+y−p, CexLiq+pLu9.33−x−p−z□0.67AzSi6O26−p, where A is at least one element selected from group consisting of Gd, Sc, Y, La, Eu, Tb, x is value between 1×10−4 f.units and 0.02 f.units., y is value between 0.024 f.units and 0.09 f.units, z is value does not exceeding 0.05 f.units, q is value does not exceeding 0.2 f.units, p is value does not exceeding 0.05 f.units. Achievable technical result is the scintillating substance having high density, high light yield, low afterglow, and low percentage loss during fabrication of scintillating elements.
Owner:ZECOTEK HLDG INC
Transmission mode terahertz computed tomography
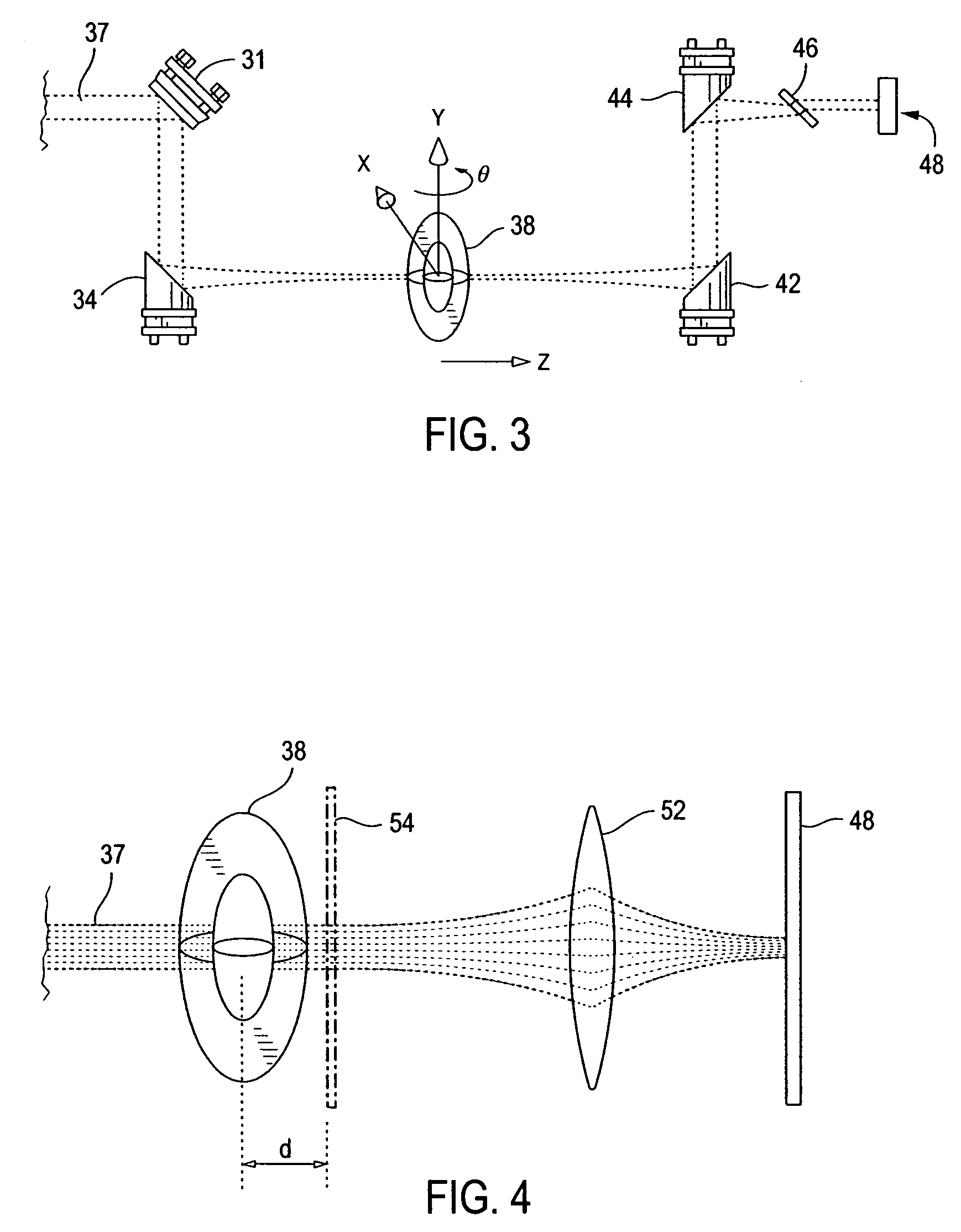
A method of obtaining a series of images of a three-dimensional object by transmitting pulsed terahertz (THz) radiation through the entire object from a plurality of angles, optically detecting changes in the transmitted THz radiation using pulsed laser radiation, and constructing a plurality of imaged slices of the three-dimensional object using the detected changes in the transmitted THz radiation. The THz radiation is transmitted through the object as a scanning spot. The object is placed within the Rayleigh range of the focused THz beam and a focusing system is used to transfer the imaging plane from adjacent the object to a desired distance away from the object. A related system is also disclosed.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
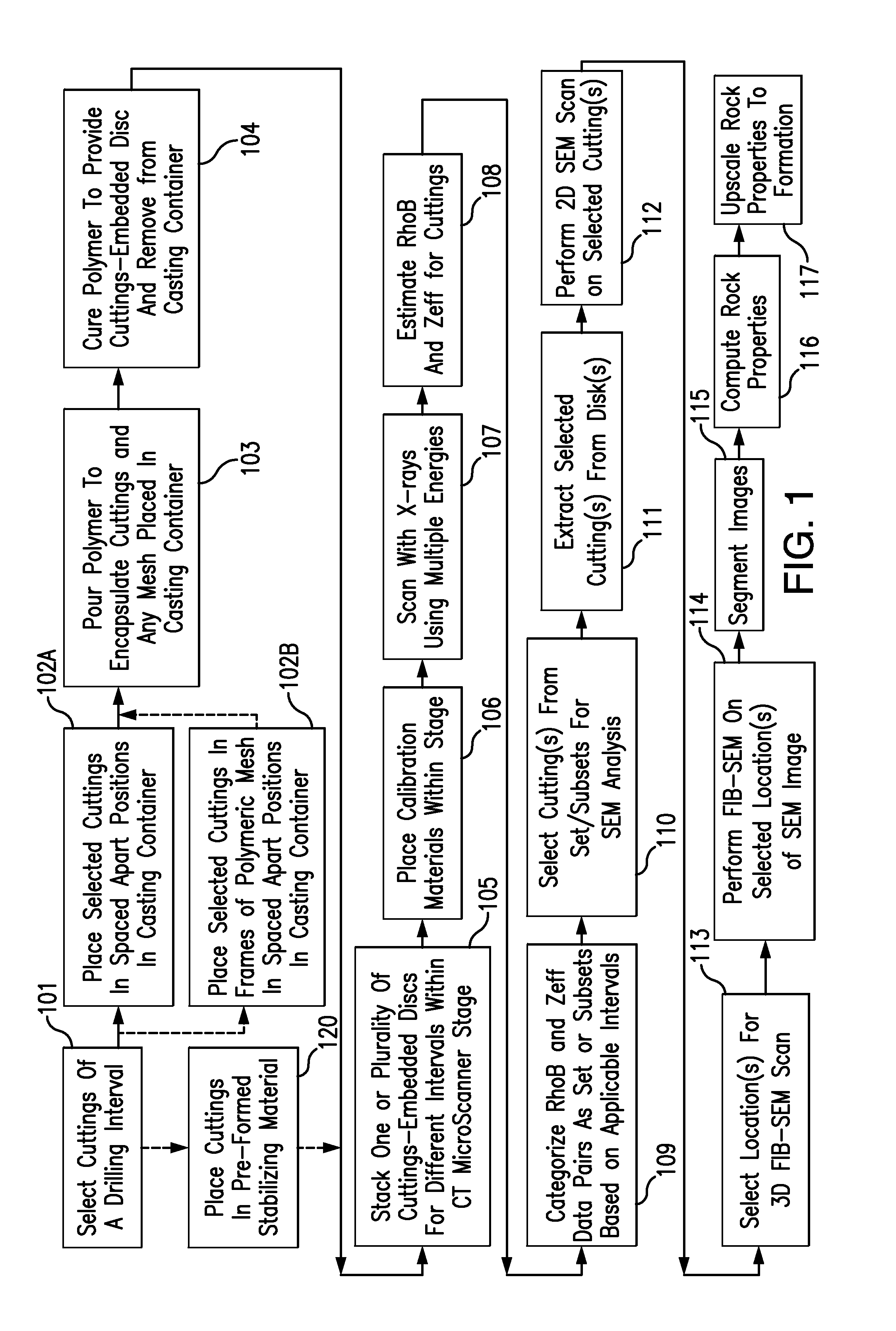
Method And System For Multi-Energy Computer Tomographic Cuttings Analysis
ActiveUS20130301794A1Simple processImprove analysisRadiation/particle handlingPreparing sample for investigationFractographyPorous medium
A method and a system are provided to prepare a plurality of cuttings or other rock fragments or other porous media, such as cuttings from a drilling interval or multiple intervals, for computer tomographic scanning at the same time. A method and system also are provided to allow organization of mass quantities of cuttings or other rock fragments obtained from intervals of a well to more accurately categorize the cuttings to assist selections thereof for more detailed digital rock analysis, such as using SEM and FIB-SEM systems, are provided. A method and system also are provided to allow characterization of facies occurrence frequency of a depth interval using drill cuttings or other rock fragments. Computerized systems, computer readable media, and programs for performing the methods are also provided.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
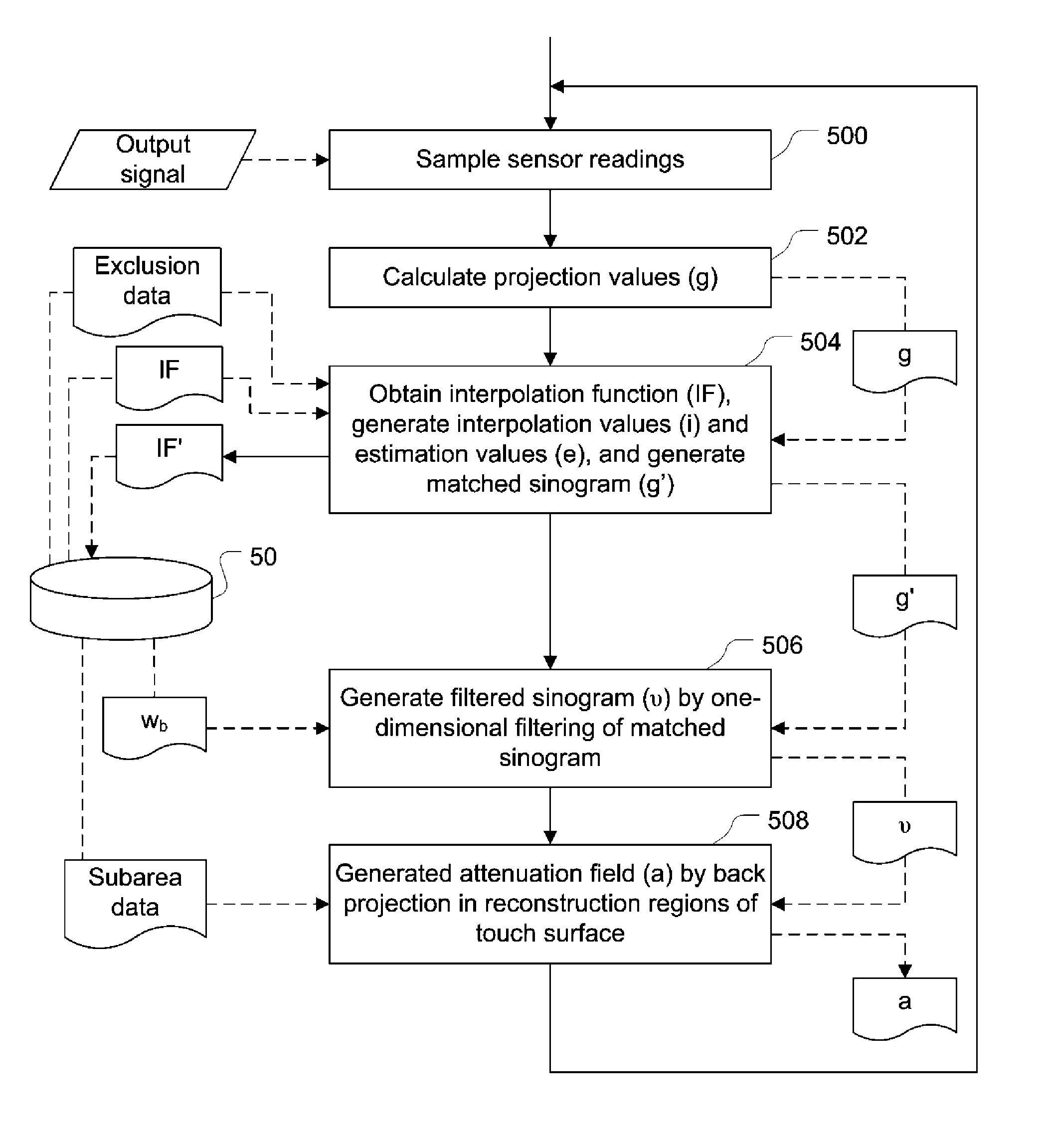
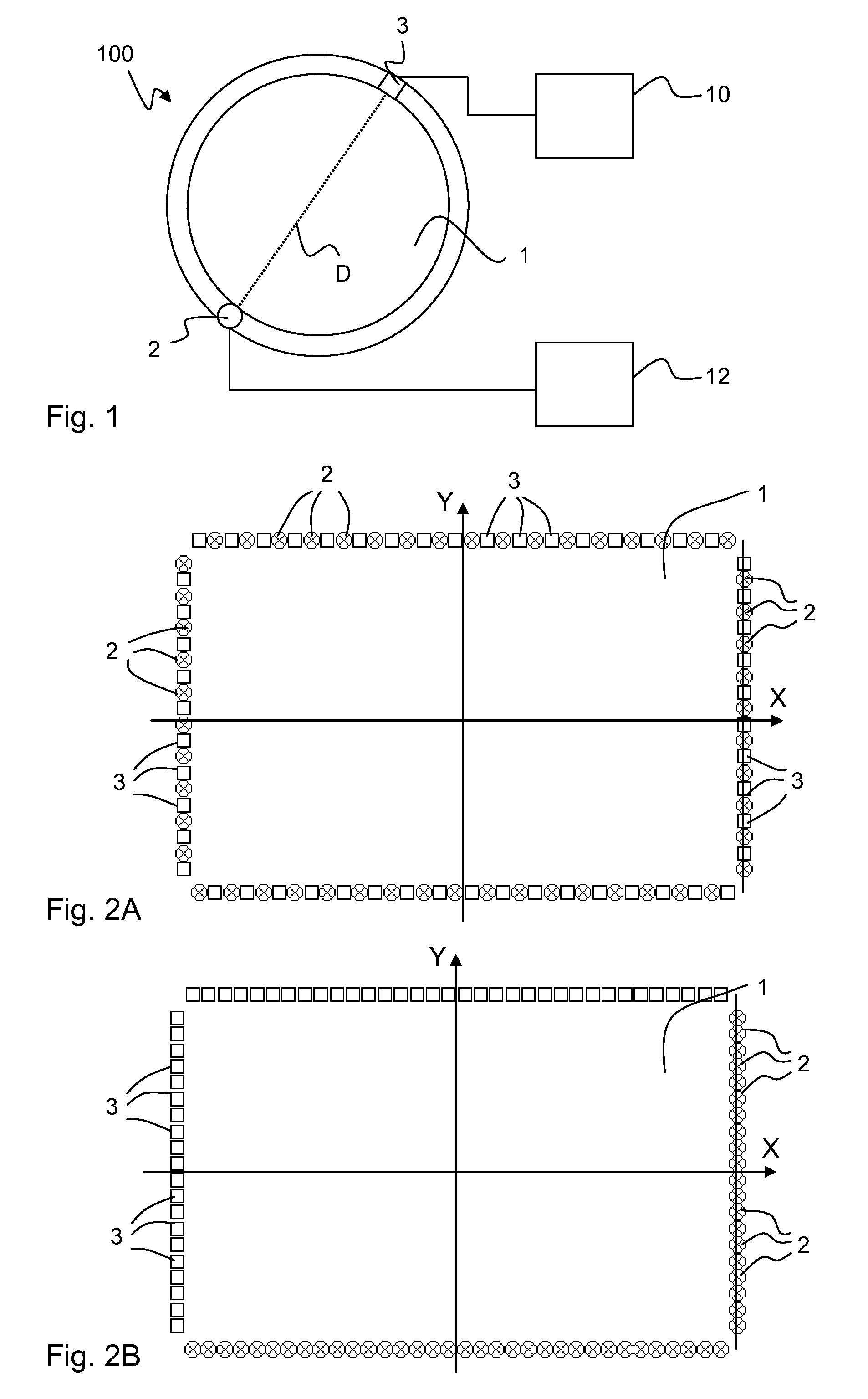
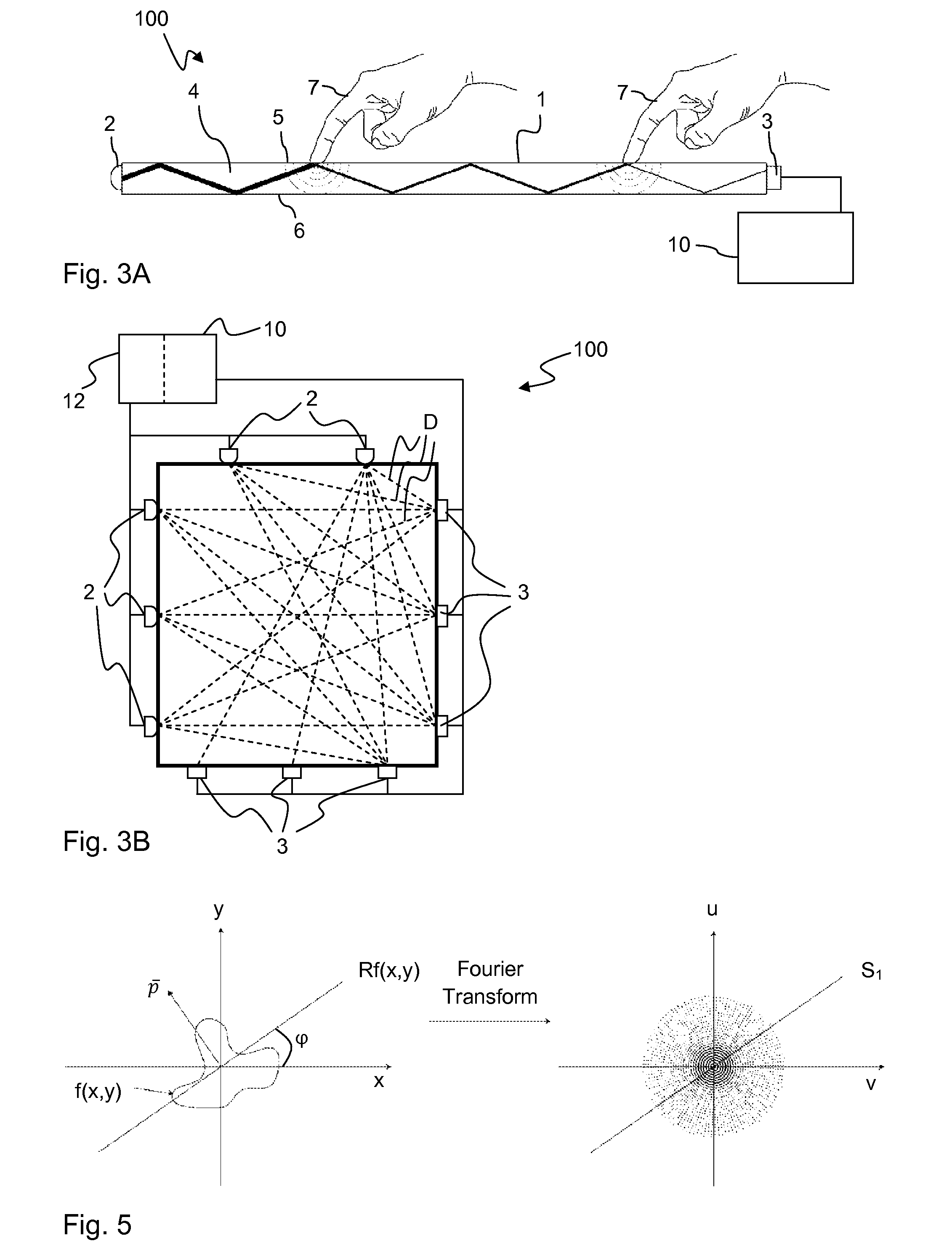
Touch determination by tomographic reconstruction
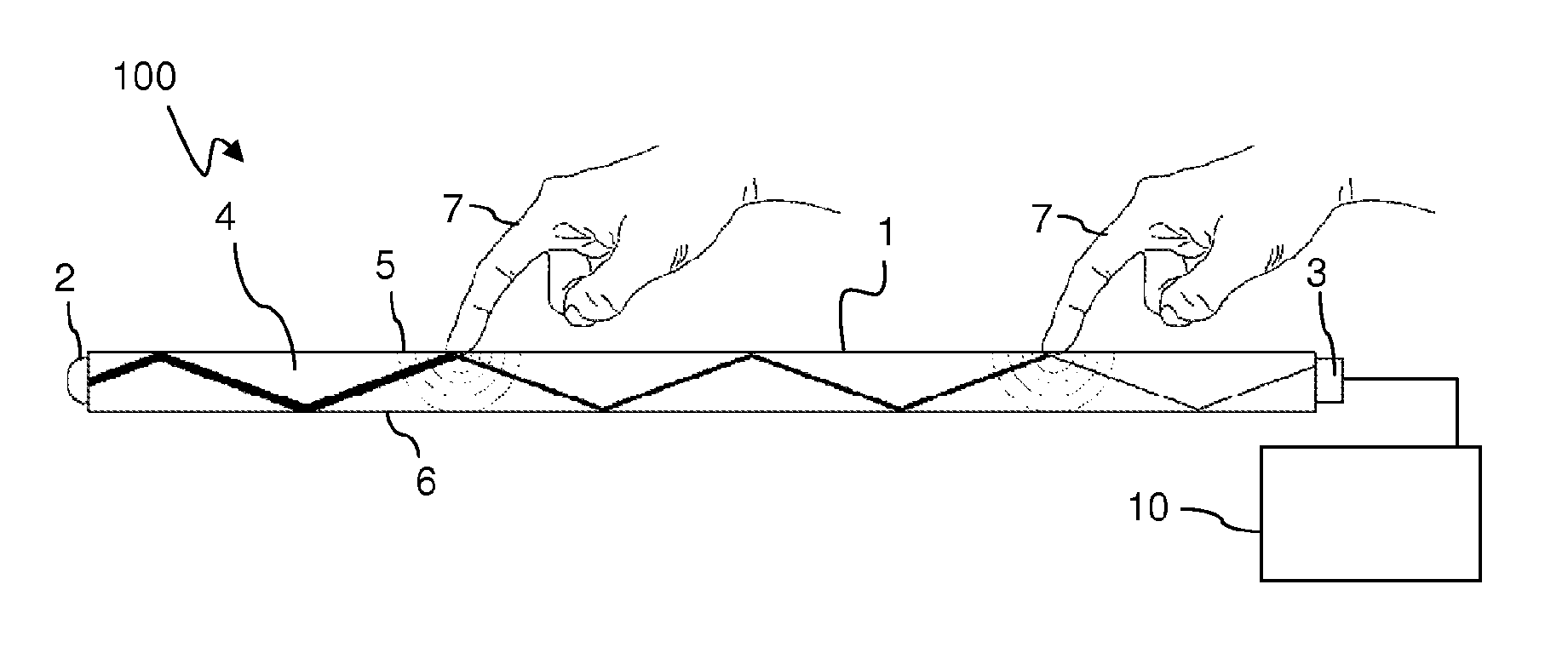
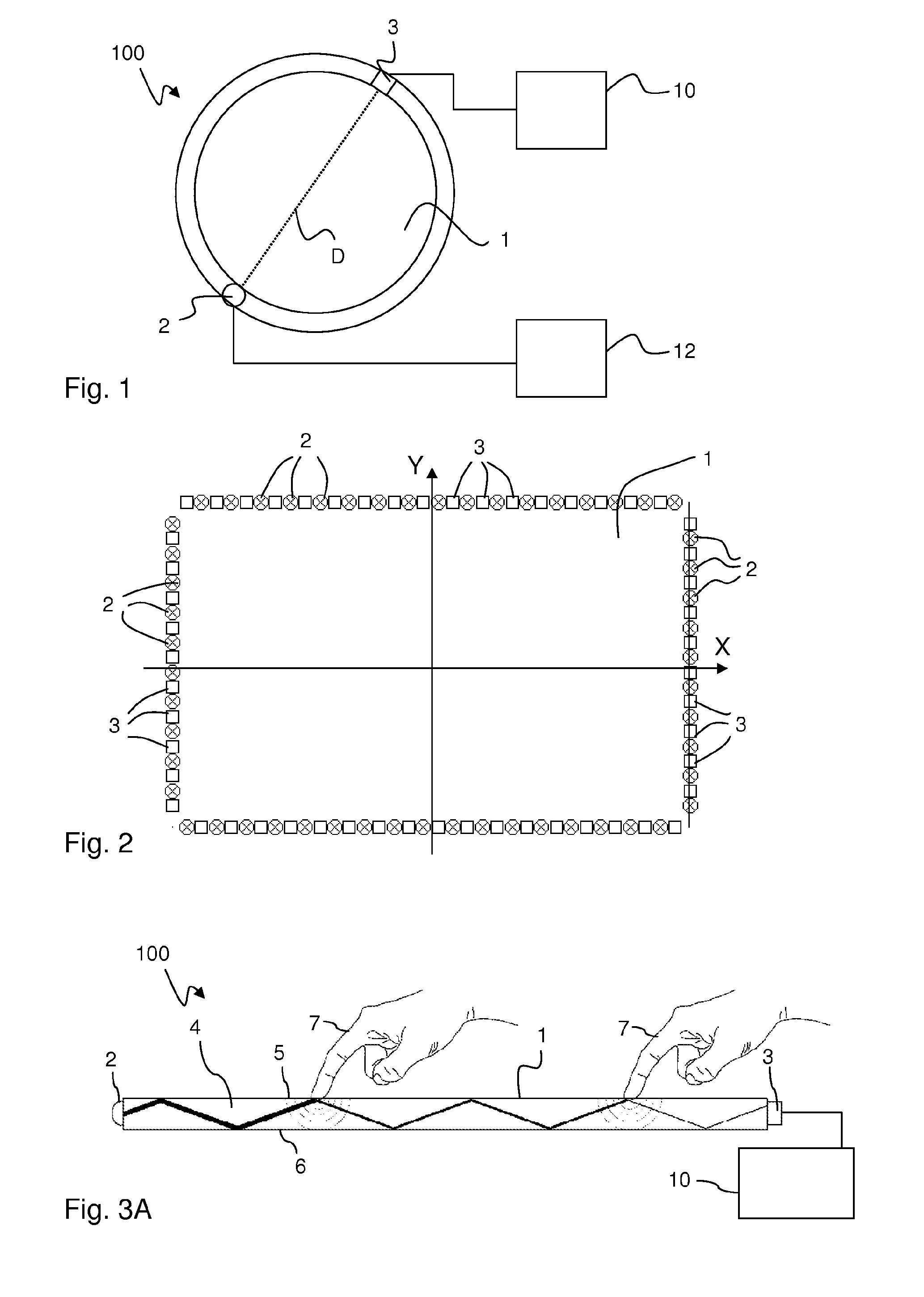
InactiveUS8780066B2Solve the lack of precisionTransmission systemsGraph readingTotal internal reflectionFractography
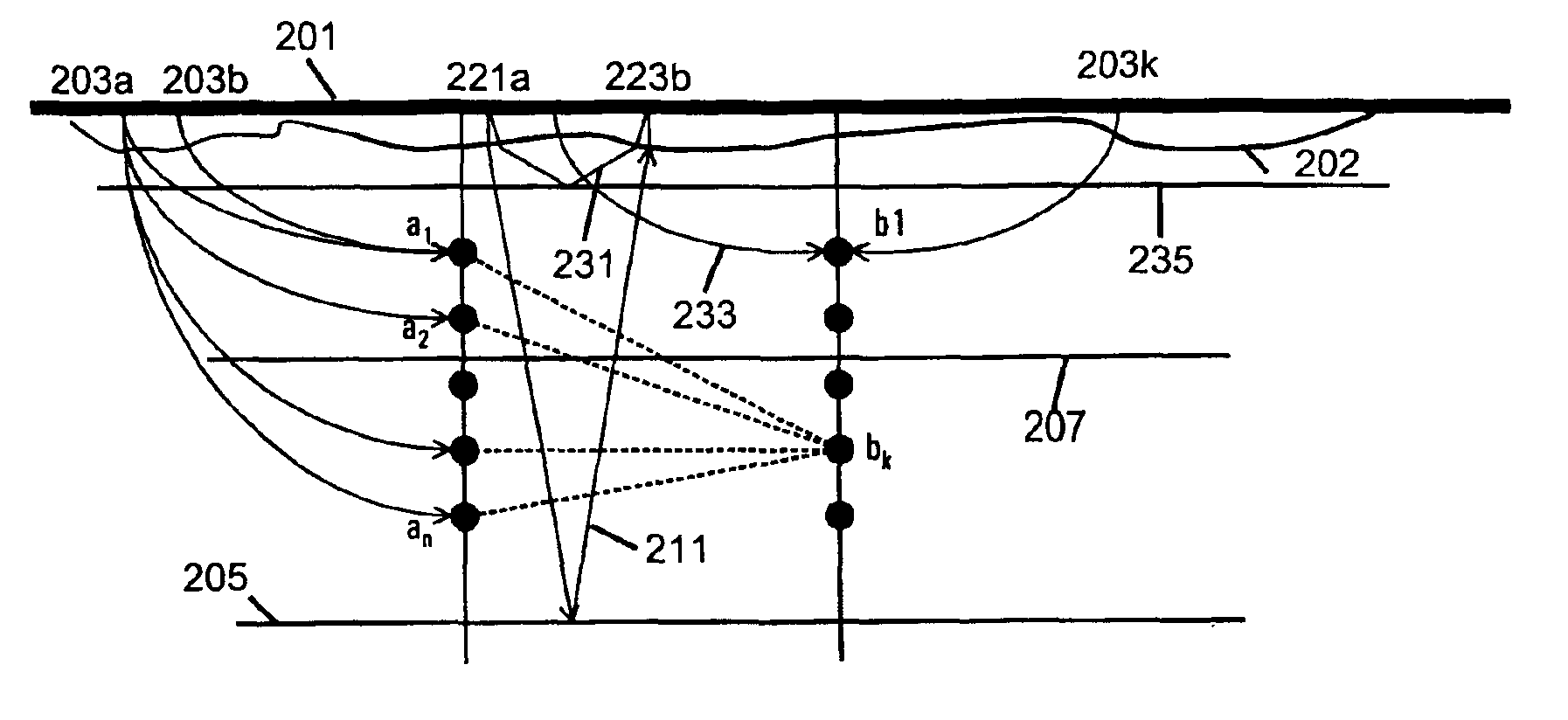
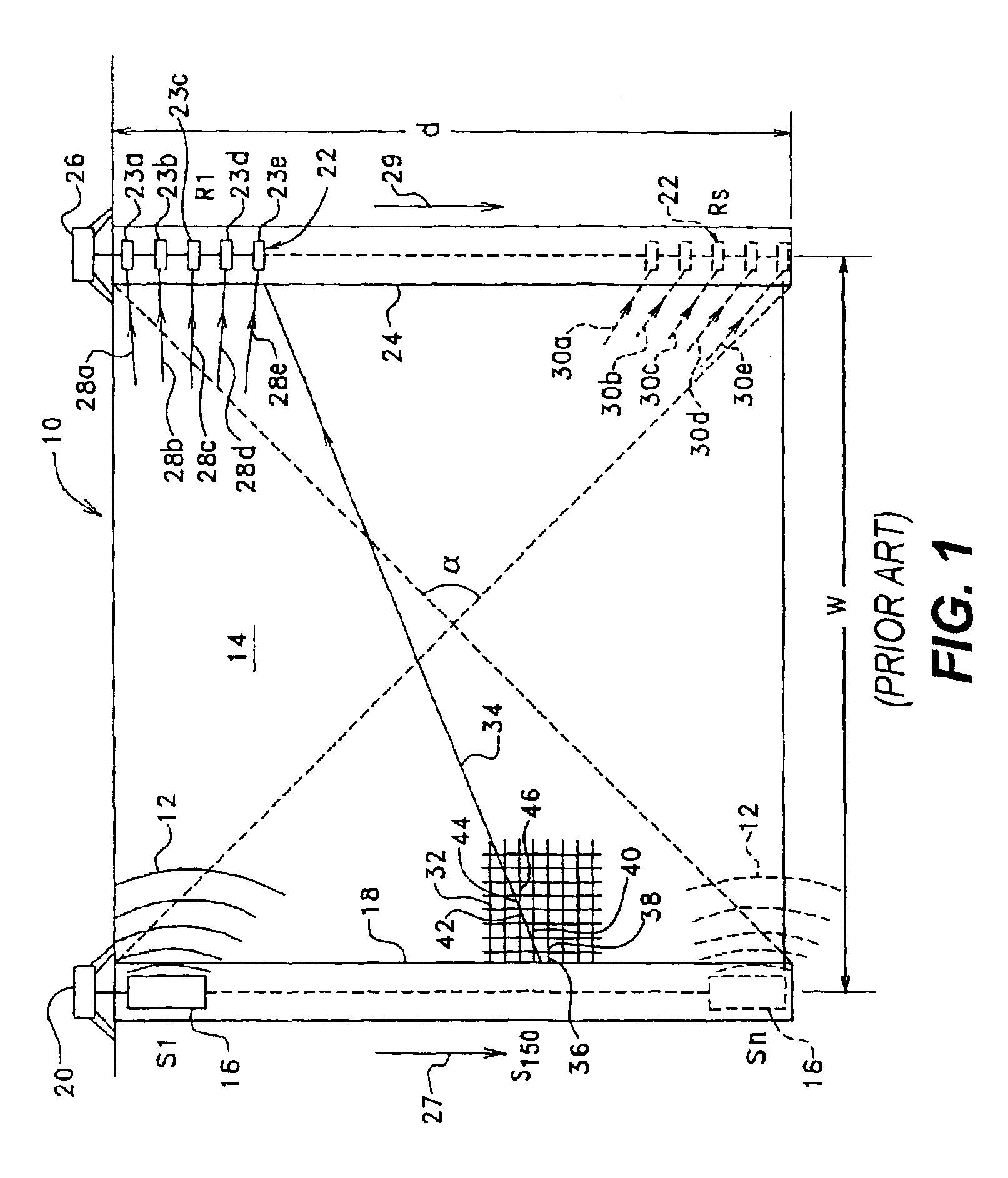
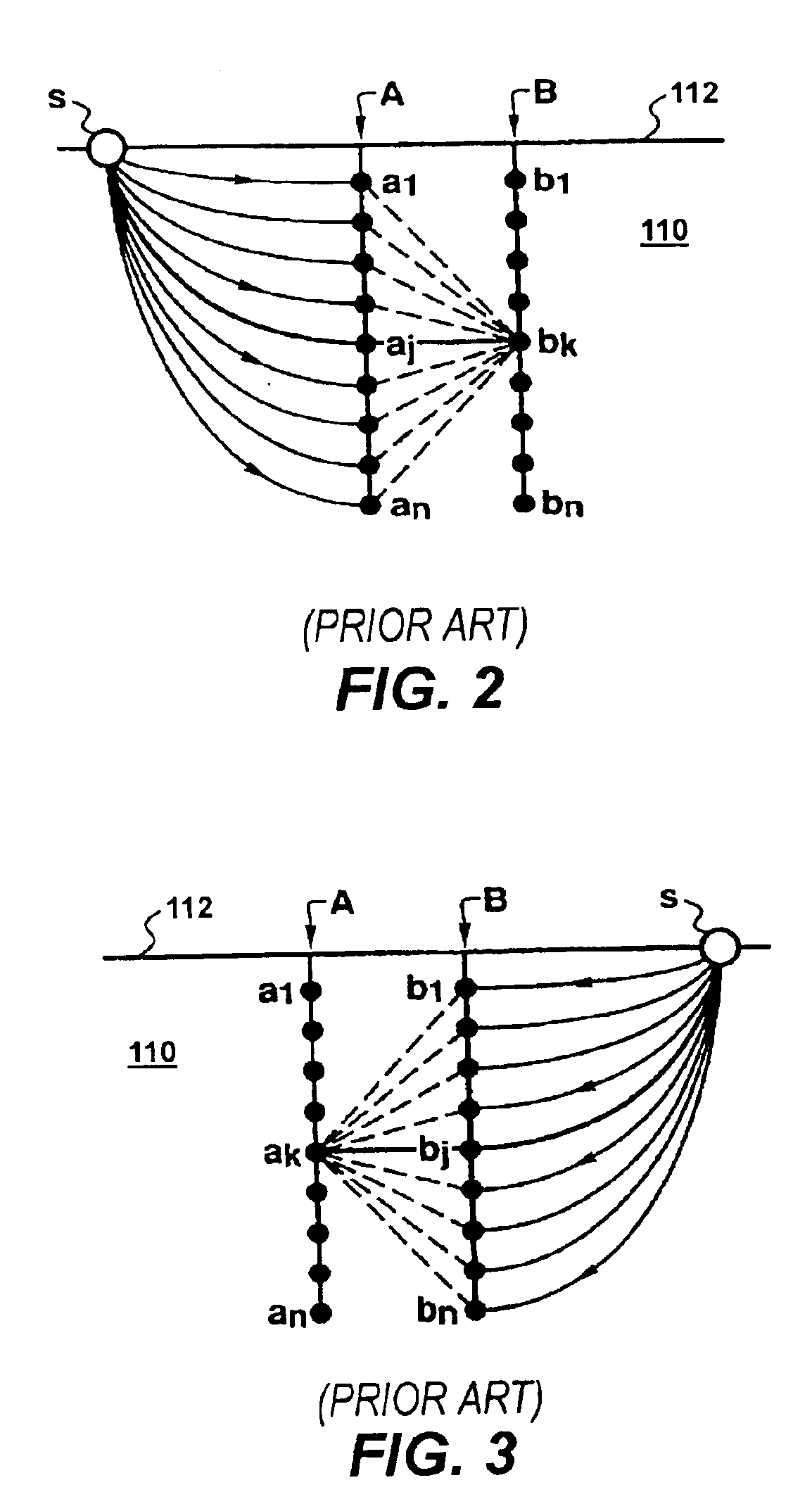
A touch-sensitive apparatus comprises a panel configured to conduct signals from a plurality of peripheral incoupling points to a plurality of peripheral outcoupling points. Actual detection lines are defined between pairs of incoupling and outcoupling points to extend across a surface portion of the panel. The signals may be in the form of light, and objects touching the surface portion may affect the light via frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR). A signal generator is coupled to the incoupling points to generate the signals, and a signal detector is coupled to the outcoupling points to generate an output signal. A data processor operates on the output signal to enable identification of touching objects. The output signal is processed (40) to generate a set of data samples, which are indicative of detected energy for at least a subset of the actual detection lines. The set of data samples is processed (42) to generate a set of matched samples, which are indicative of estimated detected energy for fictitious detection lines that have a location on the surface portion that matches a standard geometry for tomographic reconstruction. The set of matched samples is processed (44, 46) by tomographic reconstruction to generate data indicative of a distribution of an energy-related parameter within at least part of the surface portion.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Rubidium generator for cardiac perfusion imaging and method of making and maintaining same
ActiveUS8071959B2Low pressure elutionFacilitates precision flow controlIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsFractographyRubidium
An 82Sr / 82Rb generator column is made using a fluid impervious cylindrical container having a cover for closing the container in a fluid tight seal, and further having an inlet for connection of a conduit for delivering a fluid into the container and an outlet for connection of a conduit for conducting the fluid from the container. An ion exchange material fills the container, the ion exchange material being compacted within the container to a density that permits the ion exchange material to be eluted at a rate of at least 5 ml / min at a fluid pressure of 1.5 pounds per square inch (10 kPa). The generator column can be repeatedly recharged with 82Sr. The generator column is compatible with either three-dimensional or two-dimensional positron emission tomography systems.
Owner:OTTAWA HEART INST RES CORP
System and method for specificity-based multimodality three- dimensional optical tomography imaging
InactiveUS20120302880A1Accurate imaging effectImprove robustnessReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsFractographyOptical tomography
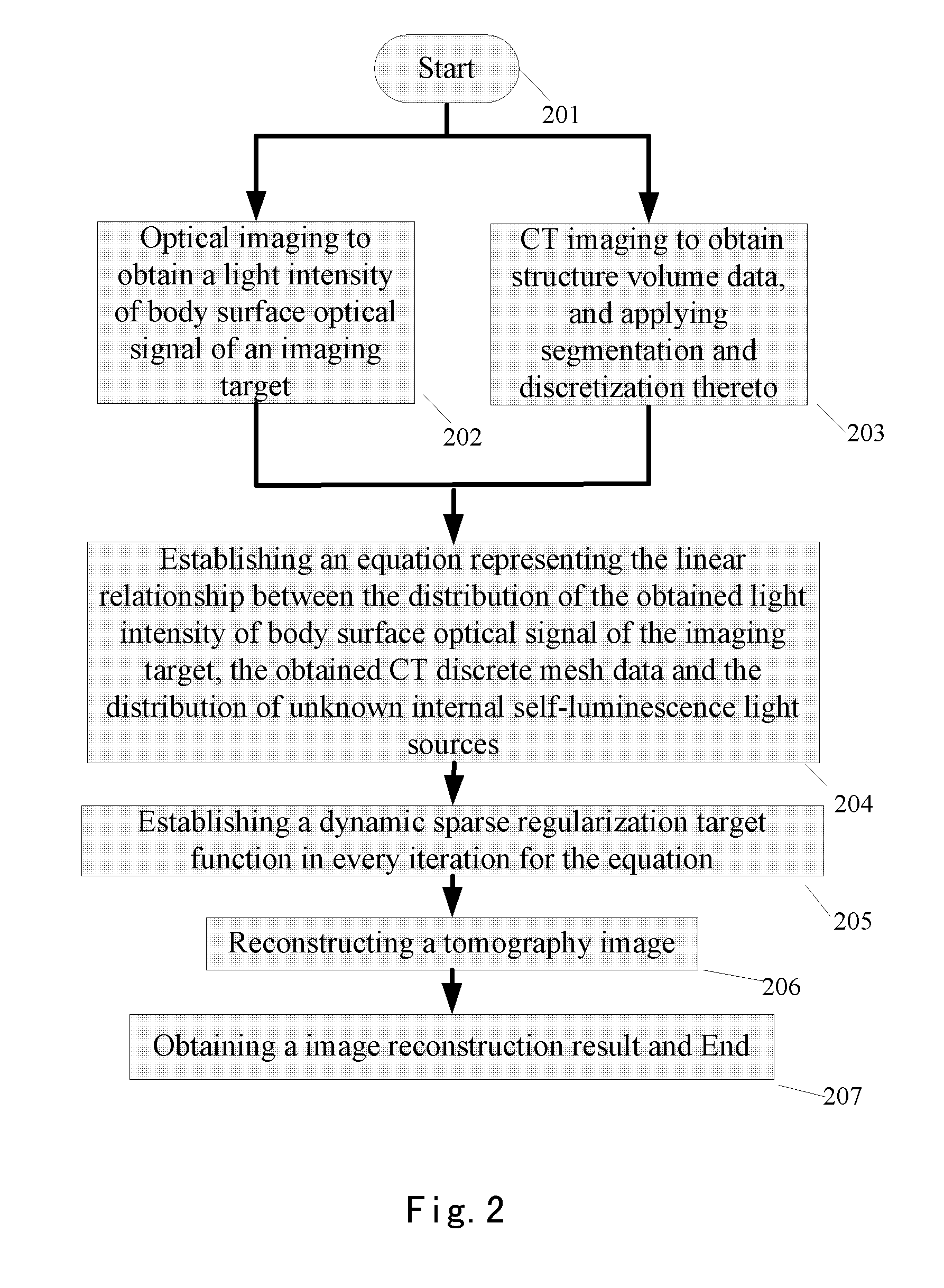
A system and method for specificity-based multimodality three-dimensional optical tomography imaging comprises steps of: optical imaging to obtain a light intensity of body surface optical signal of an imaging target; CT imaging to obtain structure volume data; establishing an equation representing a linear relationship between the distribution of the obtained light intensity of body surface optical signal of the imaging target, the obtained CT discrete mesh data and the distribution of unknown internal self-luminescence light sources; establishing a dynamic sparse regularization target function in every iteration for the equation; and reconstructing a tomography image. The present invention well considers the optical specificity of tissue, in which there is a non-uniform optical characteristic parameter distribution within the same tissue when finite element modeling is used, which is closer to the real situation, so that an accurate imaging effect is achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional reconstruction method for concrete CT (computed tomography) image
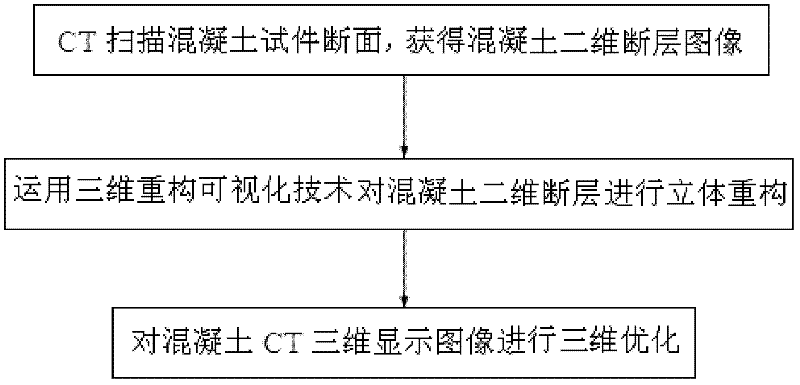
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method for a concrete CT (computed tomography) image, comprising the following steps of: firstly, performing tomography on a concrete test sample by a CT machine; secondly, performing three-dimensional reconstruction on the concrete CT image by using a ray-casting algorithm, so as to obtain real images of aggregates, mortar and holes; and finally, performing three-dimensional stereo reconstruction on the concrete CT image by using a visualization tool VTK (visualization tool kit). The three-dimensional reconstruction method for the concrete CT (computed tomography) image, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of being strong in real-time performance, high in operation efficiency, and capable of clearly and reliably distinguishing the aggregates, the mortar and the holes. A real meso-structure model of concrete can be obtained through a three-dimensional reconstruction result, the three-dimensional reconstruction result can be subjected to a test comparison with a concrete mesoscopic numerical simulation result, and a numerical analysis model is corrected.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Touch determination by tomographic reconstruction
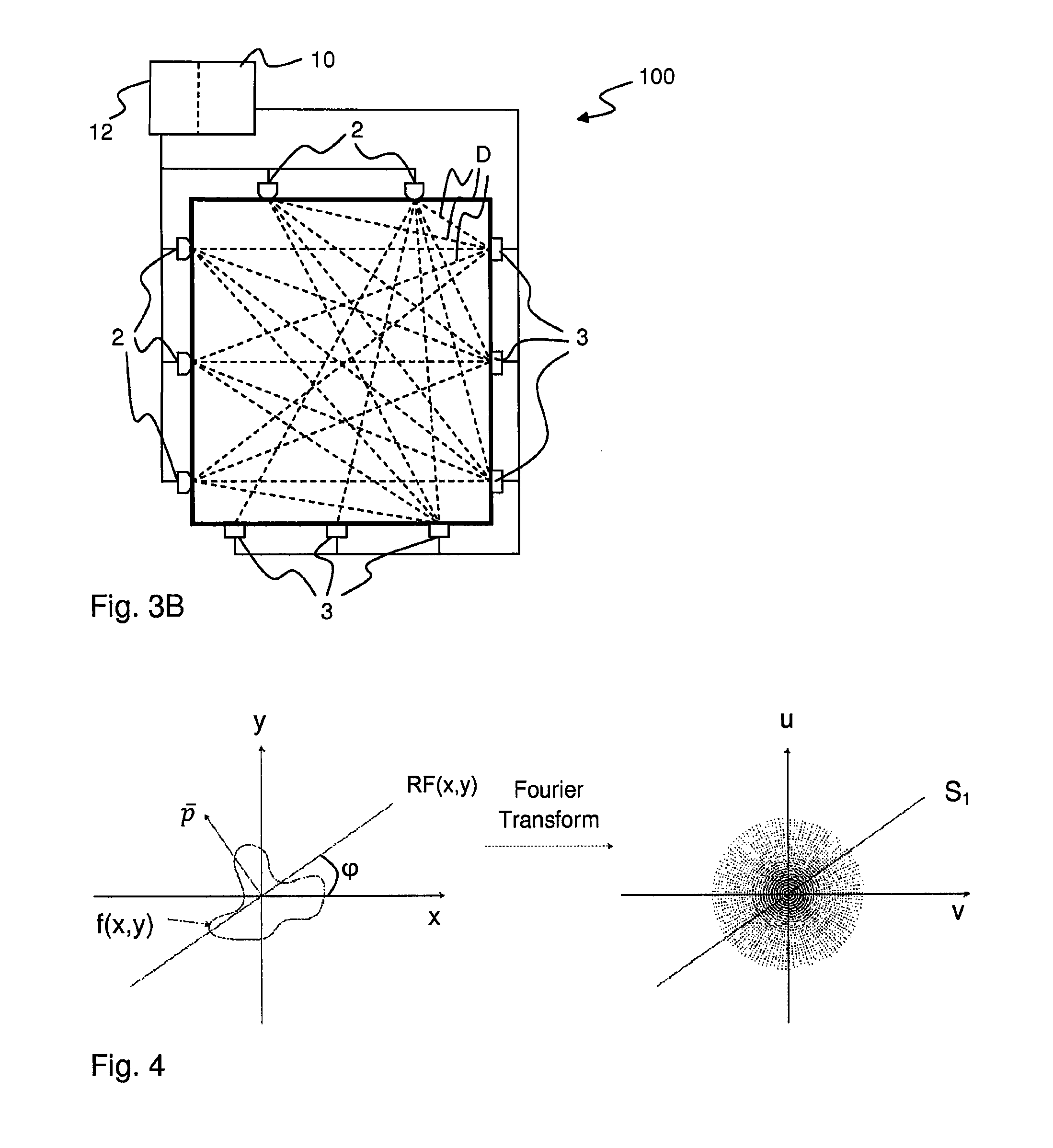
InactiveUS9411444B2Solve the lack of precisionInput/output processes for data processingFractographyTomographic reconstruction
A touch-sensitive apparatus comprises a panel for conducting signals from incoupling points to outcoupling points. Detection lines are defined between pairs of incoupling and outcoupling points. A signal generator is coupled to the incoupling points to generate the signals. A data processor processes the output signal to generate a set of data samples, which are non-uniformly arranged in a two-dimensional sample space. Each data sample is indicative of detected energy on a detection line and is defined by a signal value and first and second dimension values defining the location of the detection line on the surface portion. Adjustment factors are obtained for the data samples, each adjustment factor being representative of the local density of data samples in the sample space. The data samples are processed by tomographic reconstruction, while applying the adjustment factors, to generate a reconstructed distribution of an energy-related parameter within the surface portion.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
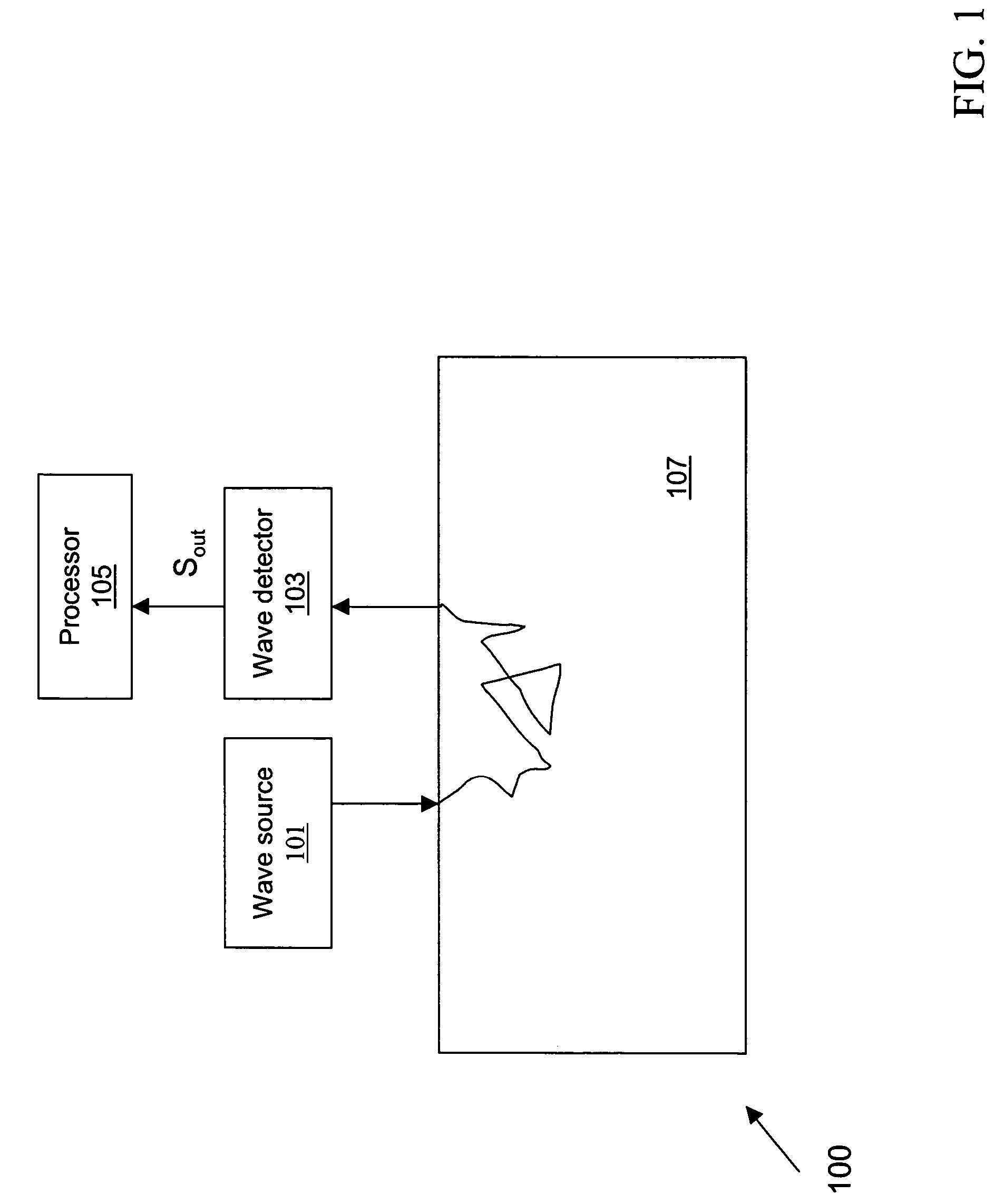
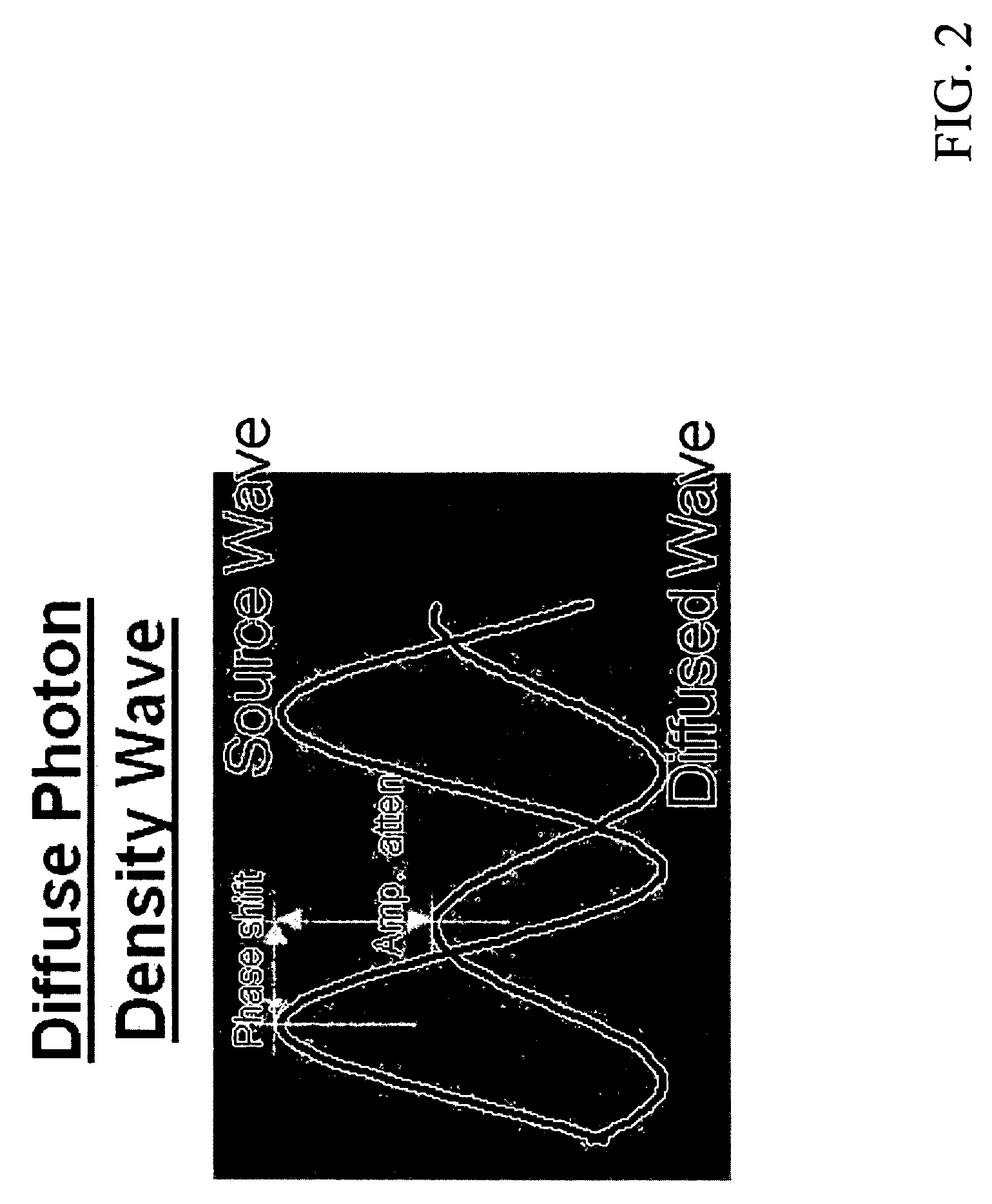
Optical apparatus and method of use for non-invasive tomographic scan of biological tissues
The present invention relates to a non-invasive optical system equipped with optical tomographic scanning method and algorithm for quantifying scattering and absorption properties and chromophore concentrations of highly scattering medium such as biological tissues, for 3D mapping and imaging reconstruction of the spatial and temporal variations in such properties. The invention further relates to a method and an apparatus for simultaneous measurement of concentrations of biochemical substances and blood oxygen saturation inside a biological tissue and arterial blood.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH +1
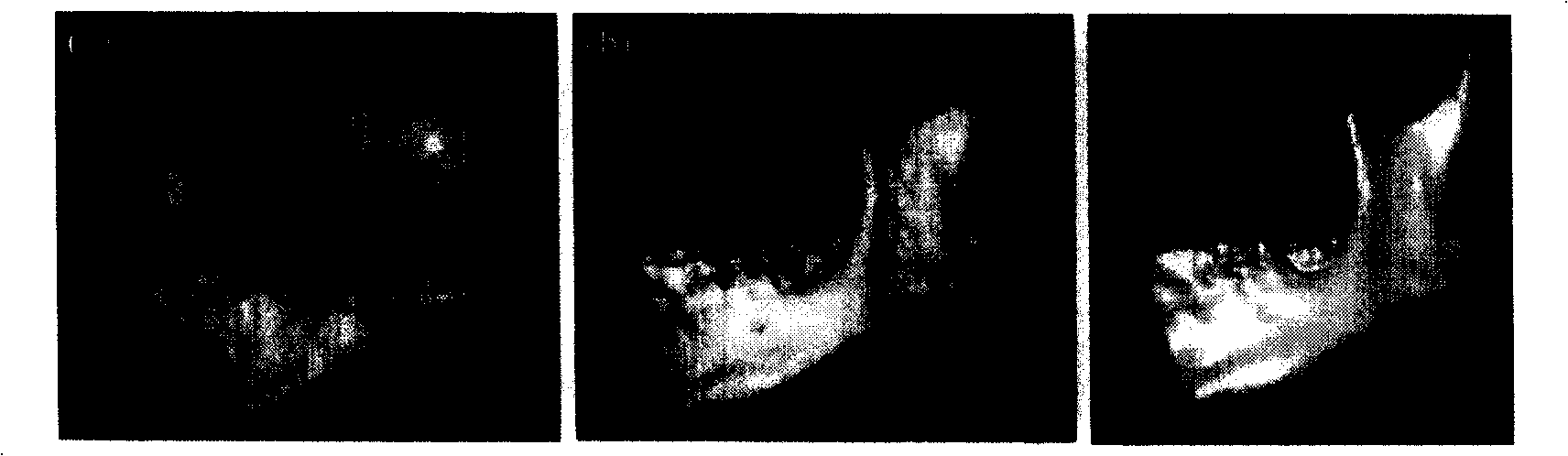
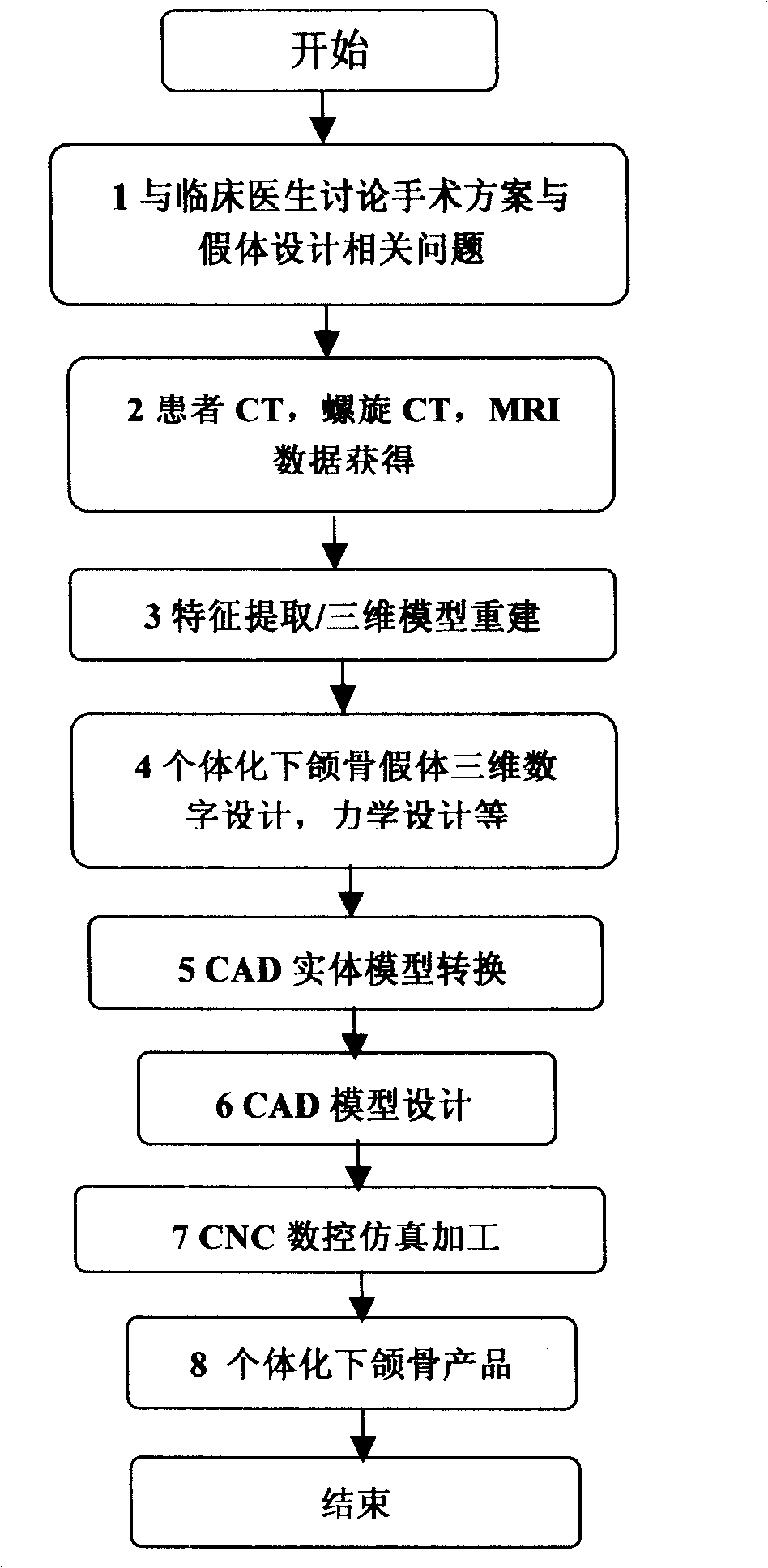
Titanium individuation mandibula prosthesis and preparation
InactiveCN101259046AConform to biomechanical characteristicsGood for postoperative recoveryBone implantFractographyBiomechanics
The invention relates to individualized mandible prosthesis of titanium alloy and a preparation method, which is applicable to a field of coaptation and repairing after a defect and loss of the mandible caused by injuries or tumors, etc. The individualized mandible prosthesis essentially consists of a substitute of a defected or lost part and connecting and positioning wing spans. The prosthesis is characterized in that the whole mandible of a patient is scanned by a CT or MRI fault scan; after processing the graph and image, soft tissues and hard tissues are separated according to the fault scan graph, thus a three-dimensional reconstruction of the mandible of the patient is realized; according to biological symmetry principle, a model of the unimpaired side of the mandible of the patient is used for a mirror image processing so as to obtain a mandible prosthesis model of the lost side of the mandible of the patient; the data of the prosthesis model are transformed and the connecting and fixing wing spans are designed on the model; a processing order of the model is input into a CNC processing center and the substitute prosthesis of the mandible of the patient is directly cut out. The mandible prosthesis produced by the invention has a good dynamic capacity and biological dynamic characteristics; the problem of an individualized match is directly solved; and the prosthesis is excellently matched with the mandible of the patient.
Owner:上海双申医疗器械股份有限公司
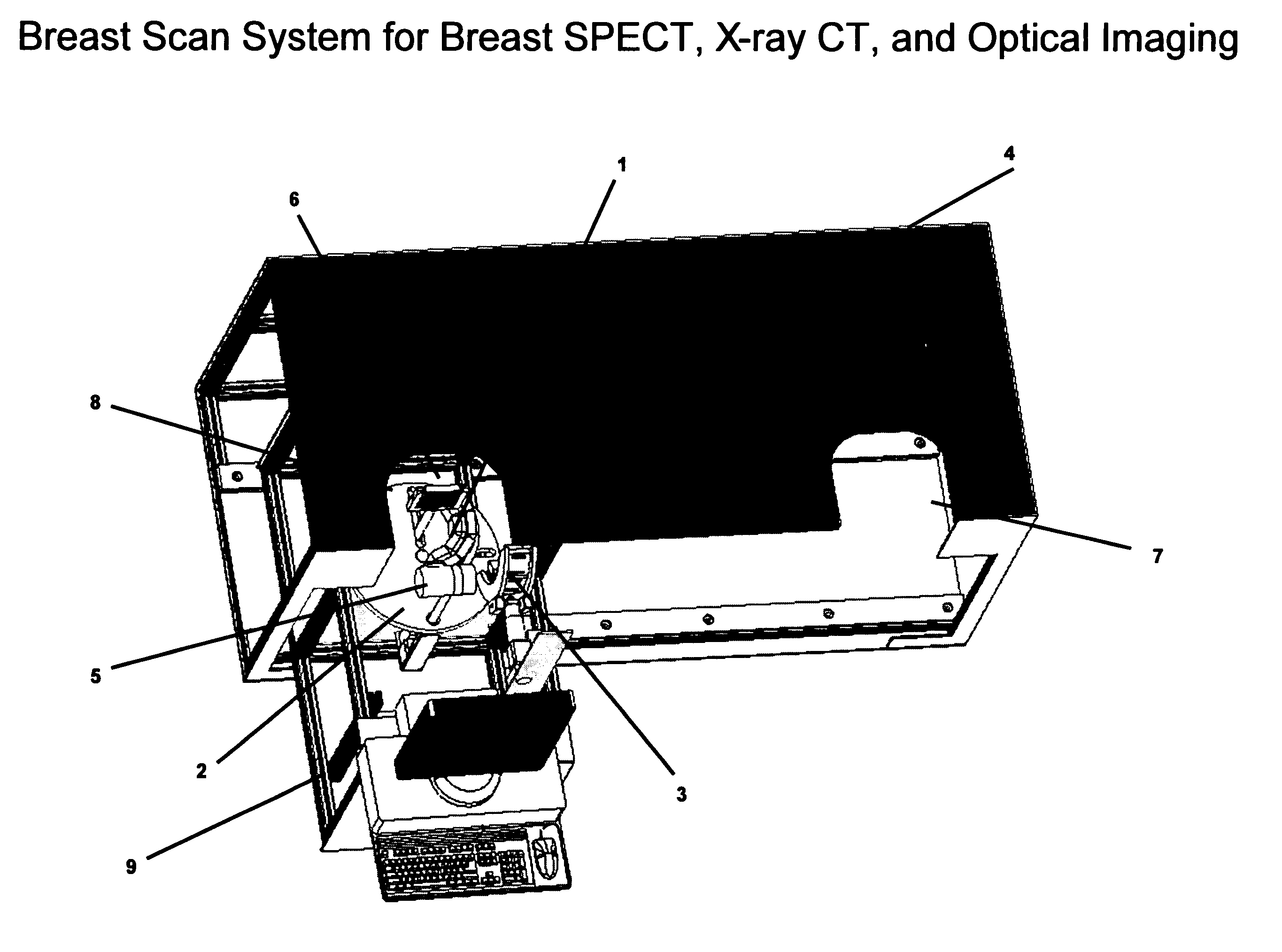
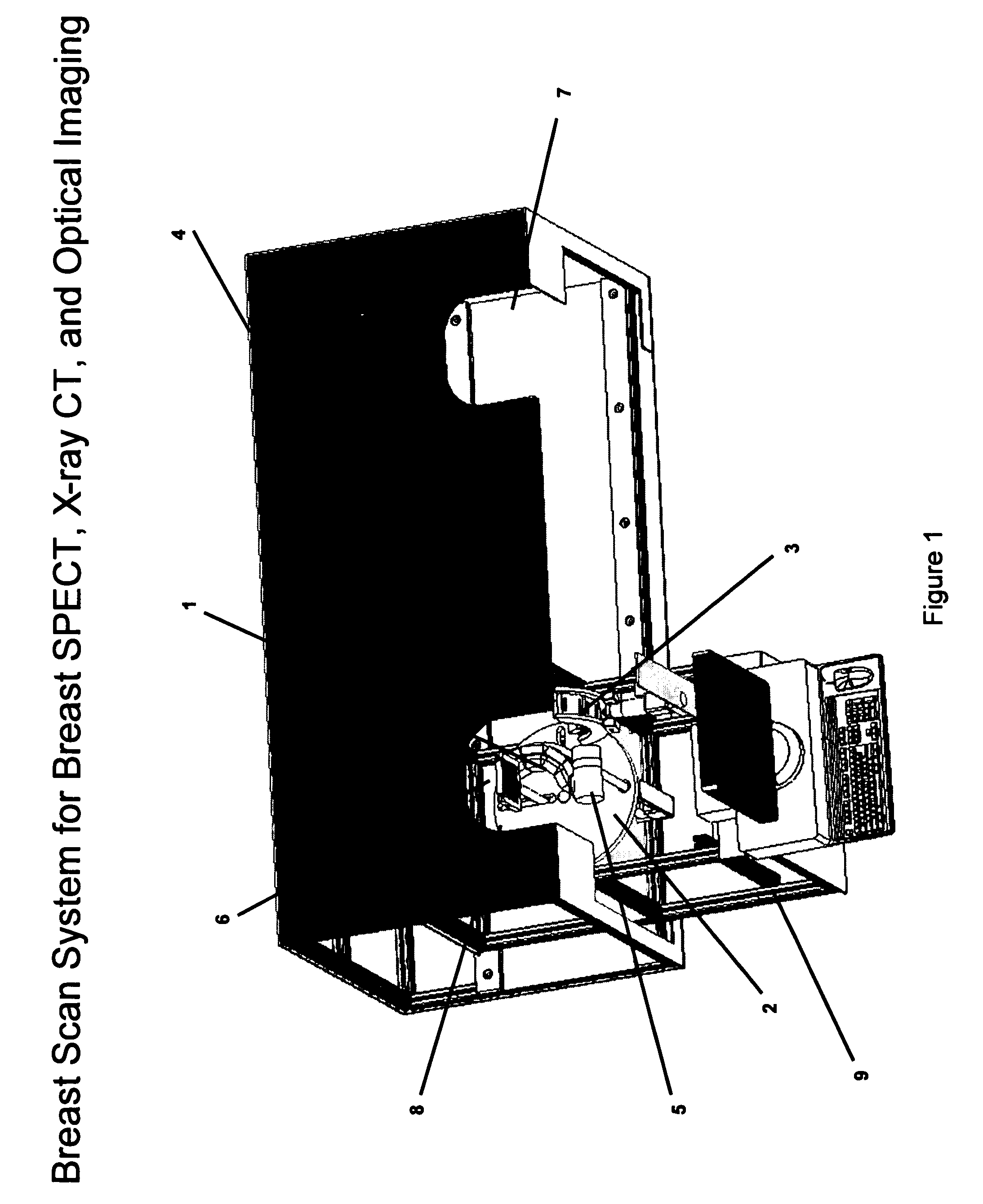
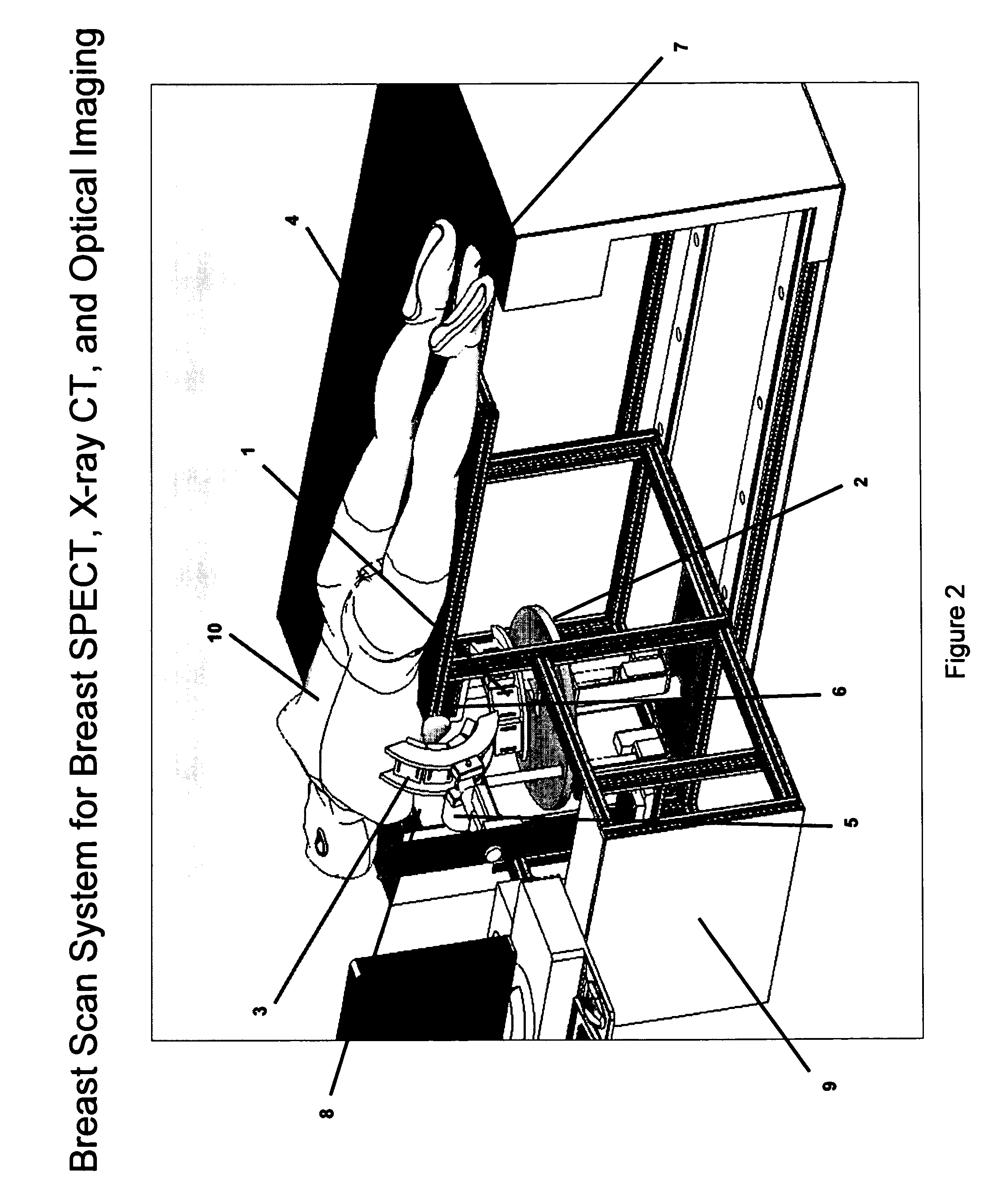
Breast diagnostic apparatus for fused SPECT, PET, x-ray CT, and optical surface imaging of breast cancer
InactiveUS20060239398A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove system capabilitiesDiagnostics using lightPatient positioning for diagnosticsOptical reflectionImage-Guided Therapy
A new method of breast imaging to improve the detection of cancer during early stages of development is disclosed. The system combines molecular images of radioisotope uptake in cancerous cells with three dimensional high resolution single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), x-ray computed tomography (CT) and optical reflectance and emission (ORE) images of the breast. The system acquires data from nuclear isotopes within the breast and processes the data into three dimensional molecular tomographic images of cancerous cellular activity, morphological three dimensional x-ray density tomographic images and three dimensional optical surface images. These three sets of images or data are then combined to provide information as to the sensitivity and specificity as to the type of cancer present, three dimensional information as to the physical location of the cancer and reference information for radiologists, surgeons, oncologists and patients in order to plan stereo-tactic biopsy, minimally invasive surgery and image guided therapy, if necessary.
Owner:FUSED MULTIMODALITY IMAGING
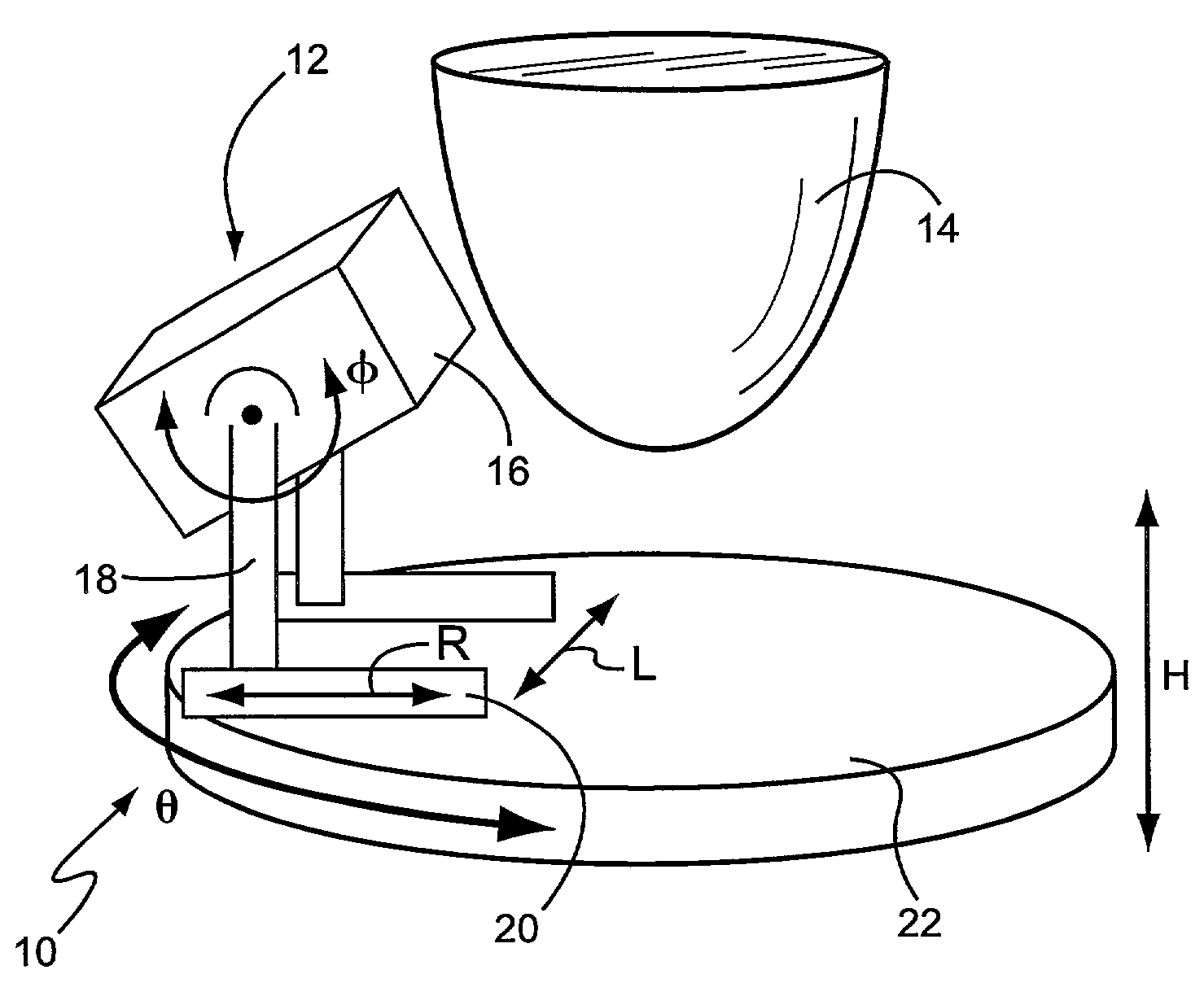
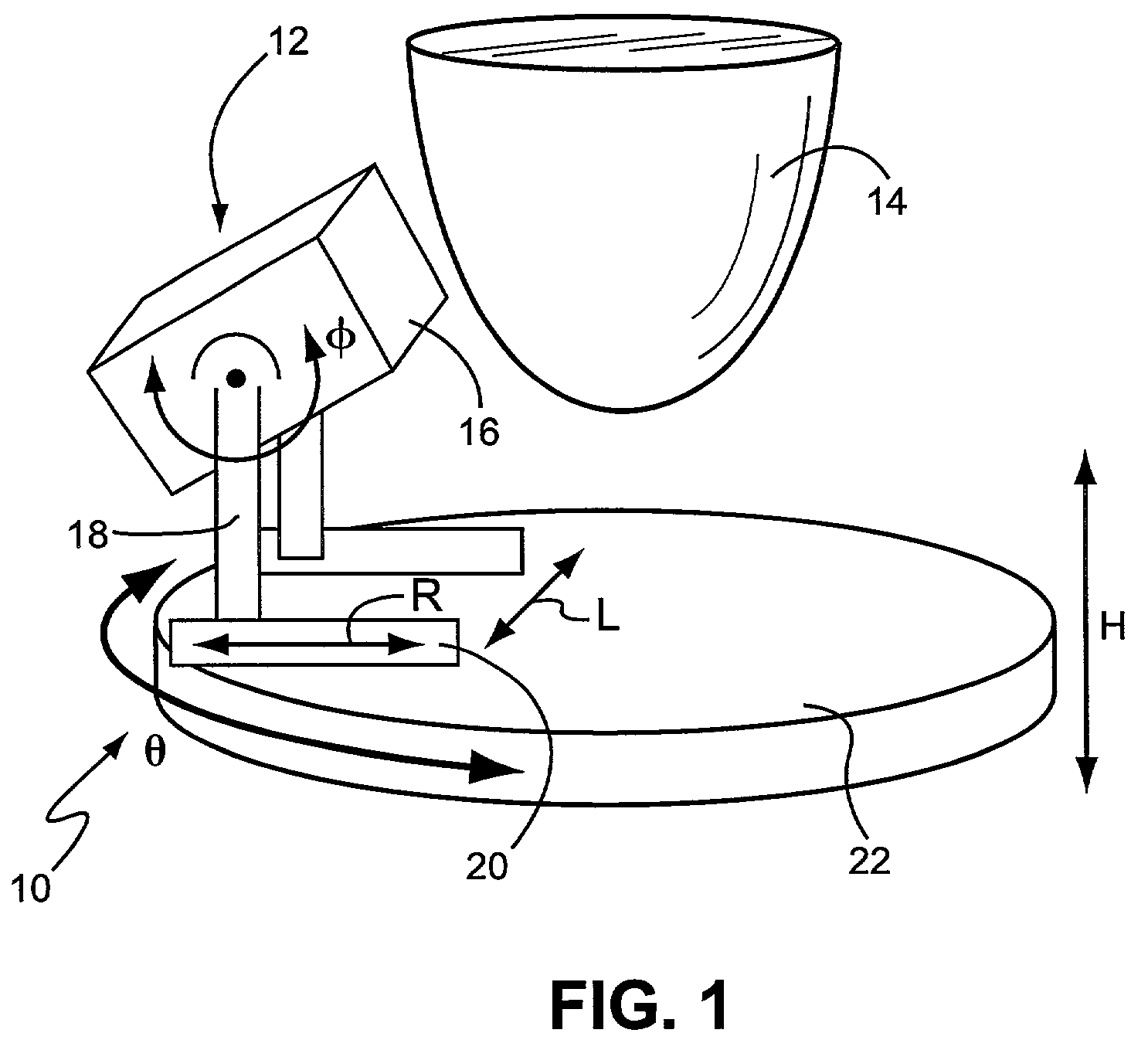
Application specific emission and transmission tomography
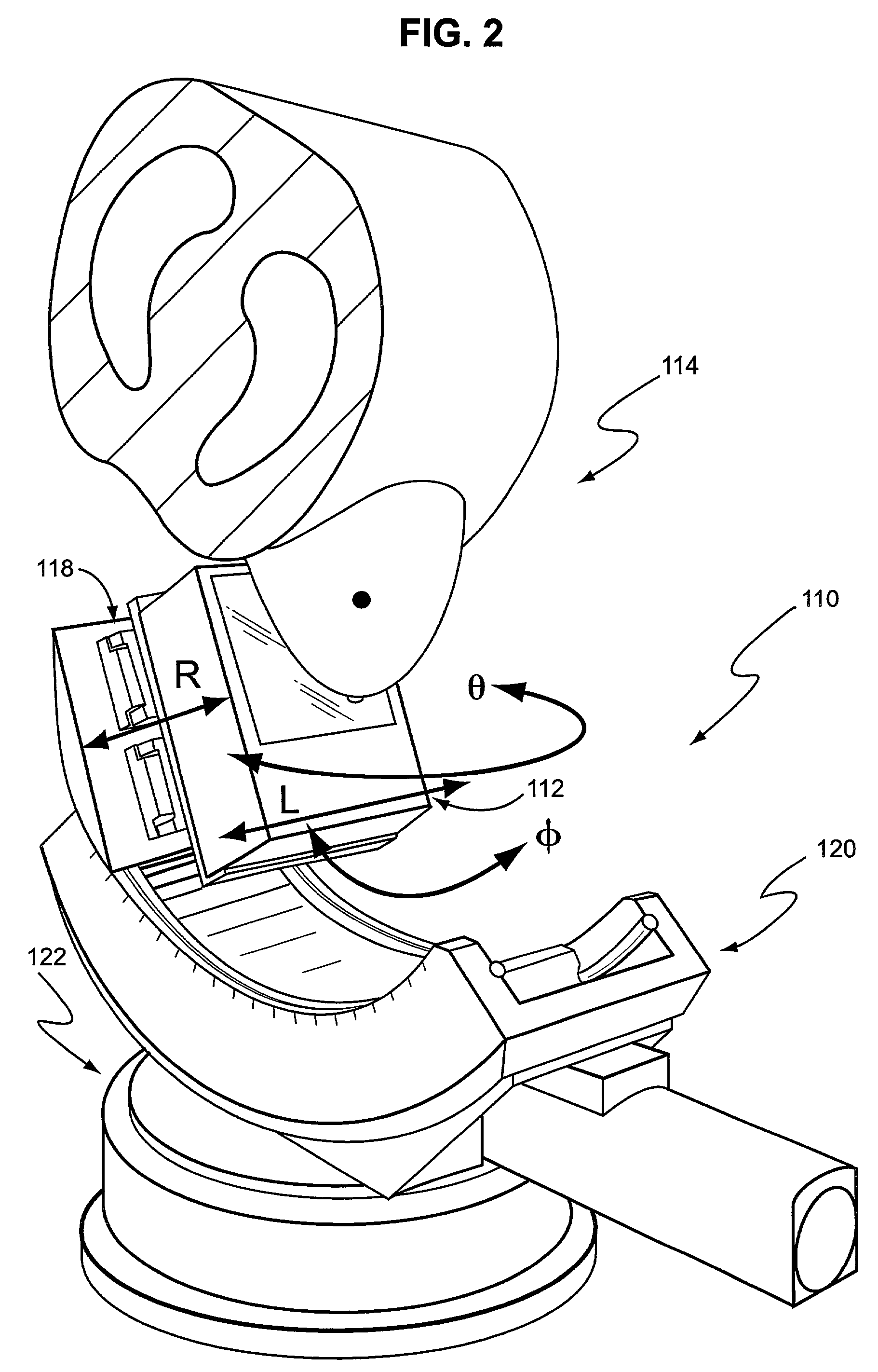
ActiveUS7609808B2Minimize scatter contaminationImprove performancePatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringFractographyX-ray
A compact and mobile gantry for 3-dimensional Application Specific Emission and / or Transmission Tomography (ASETT) imaging of the breast in single photon or coincidence emission modes, and single photon, or coincidence, or x-ray transmission modes. While the ASETT gantry was designed, built and evaluated for imaging metabolically active lesions in the pendant breast, it can also be used to image other organs and objects. This system overcomes physical constraints associated with imaging a pendulous breast in prone patients, while simultaneously satisfying sampling criteria for sufficient data collection in the pendulous breast reference frame. When combined with an offset cone-beam tomographic x-ray transmission imaging system, this dual modality ASETT system could provide simultaneous and coregistered structural and functional information about large or dense breasts, breasts with indeterminate x-ray mammography, and could also be used to accurately 3-dimensionally guide biopsy or surgical resection. Moreover, with the offset beam orientation, the transmission system is designed to have a variable FOV and minimize overall absorbed breast dose.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Walkaway tomographic monitoring
Surface seismic sources are used to simulate crosswell data between the two wells, and, using surface receivers, reflection seismic data are obtained over the region between the two wells. Reflection data are preferably obtained from reflectors both above and below the reservoir. Tomographic analysis of the simulated crosswell and reflection data gives a model of the reservoir. Changes in the model are indicative of reservoir fluid changes, pressure changes, or compaction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
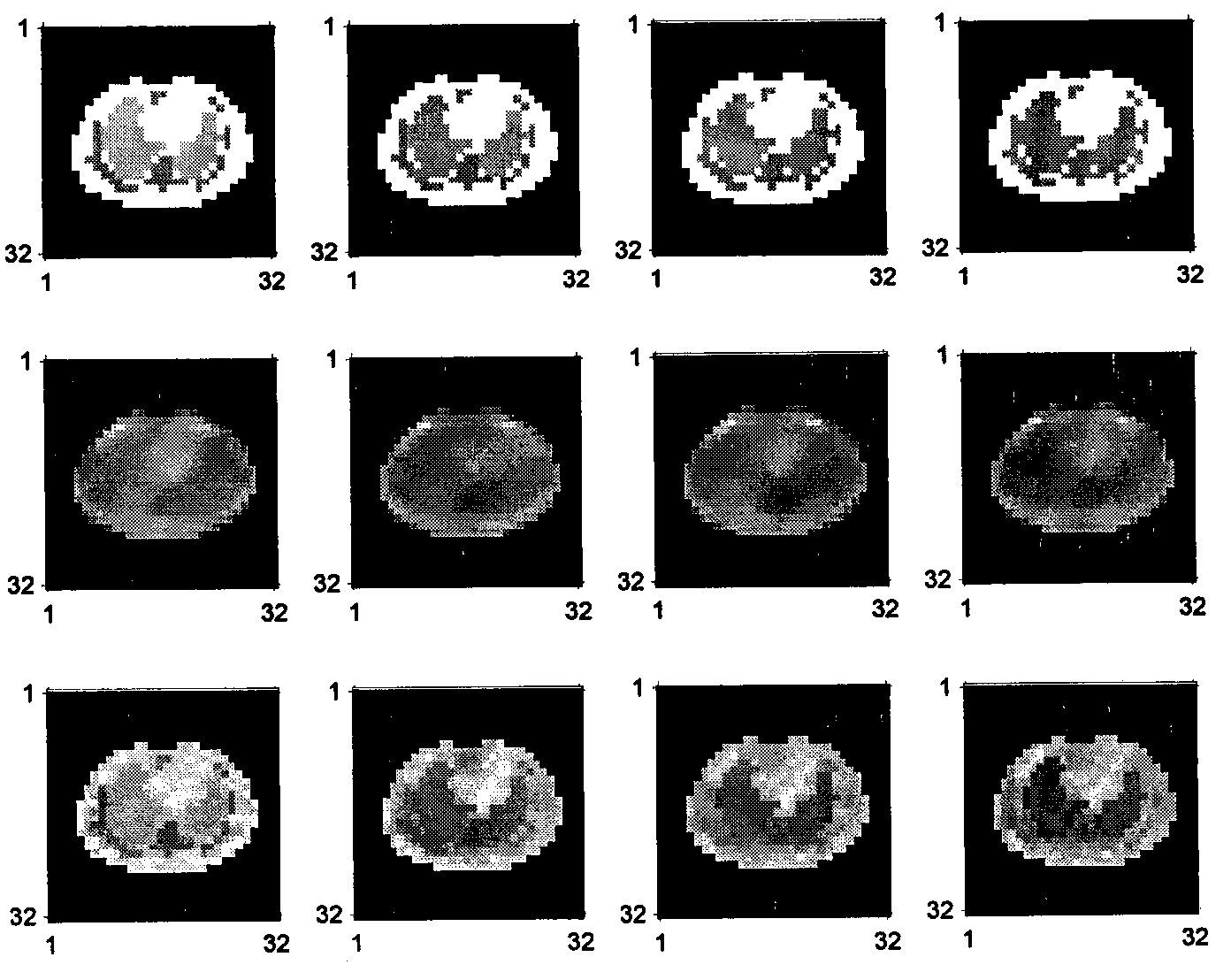
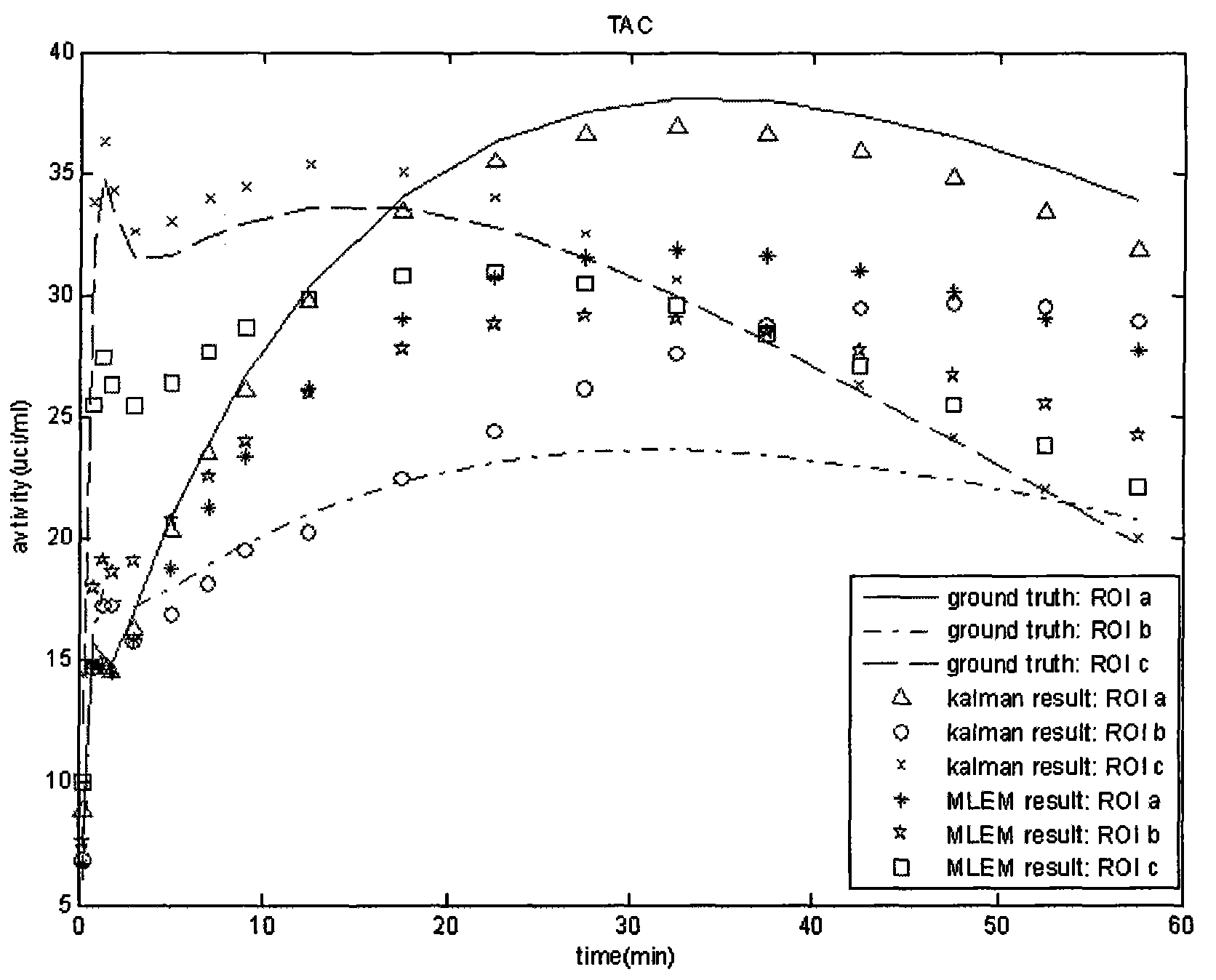
Kalman filtering image reconstruction method in PET imaging
ActiveCN101499173AQuality improvementRaise the bias2D-image generationComputerised tomographsFractographyImaging quality
The invention provides a method for rebuilding Kallman filtering image in PET imaging. The method includes steps as follows: obtaining a sinusoidal chart of an original projective line through PET positron emission faultage scanner, establishing a state space system, getting radioactivity activity distribution through the Kallman filtering method based on the state space and rebuilding image. The method rebuild PET image by using the Kallman filtering method based on the state space system which can increase the rebuild image quality efficiently; compared with the prior rebuild method, declination and dispersion of the rebuild result are increased greatly.
Owner:刘华锋
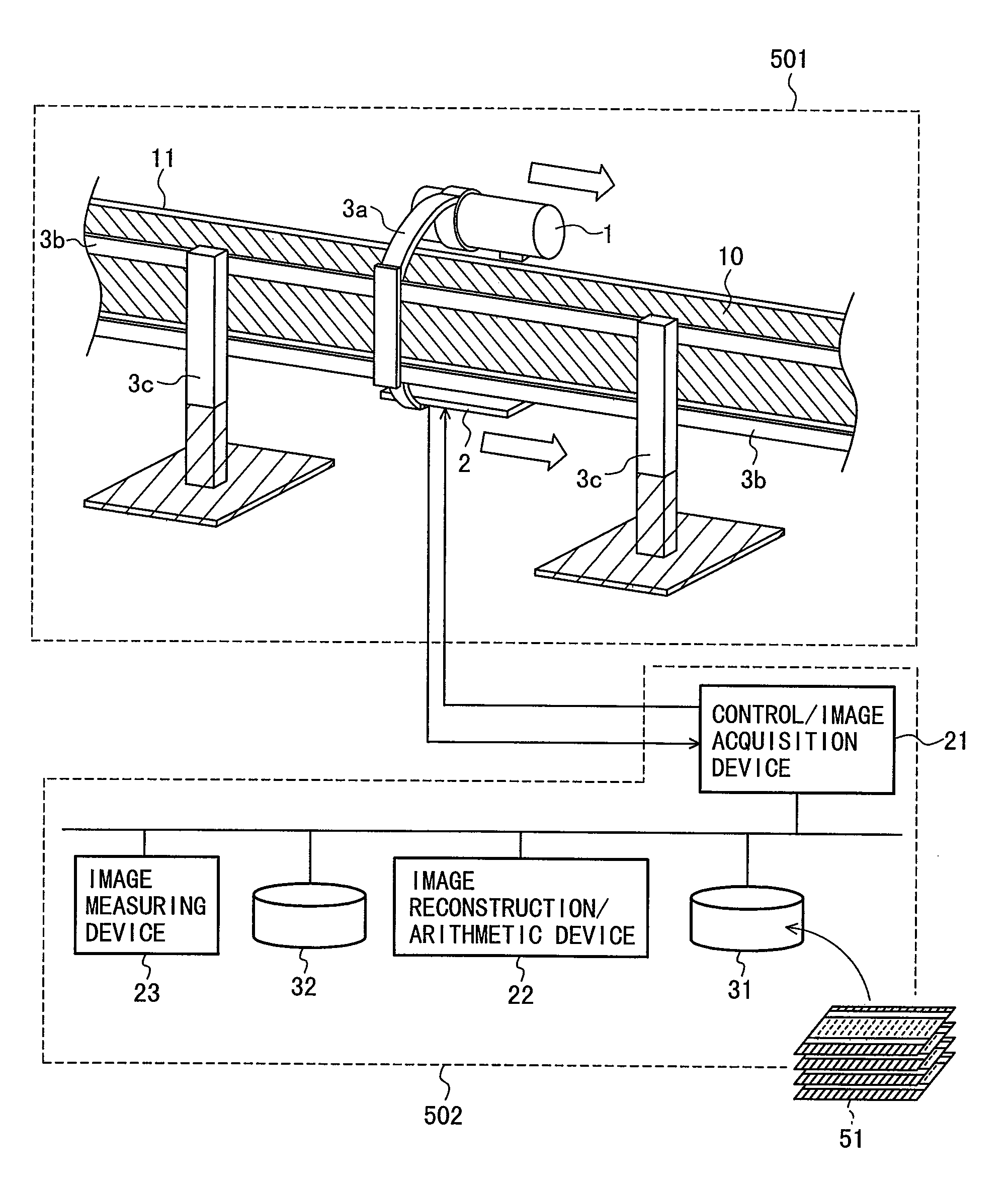
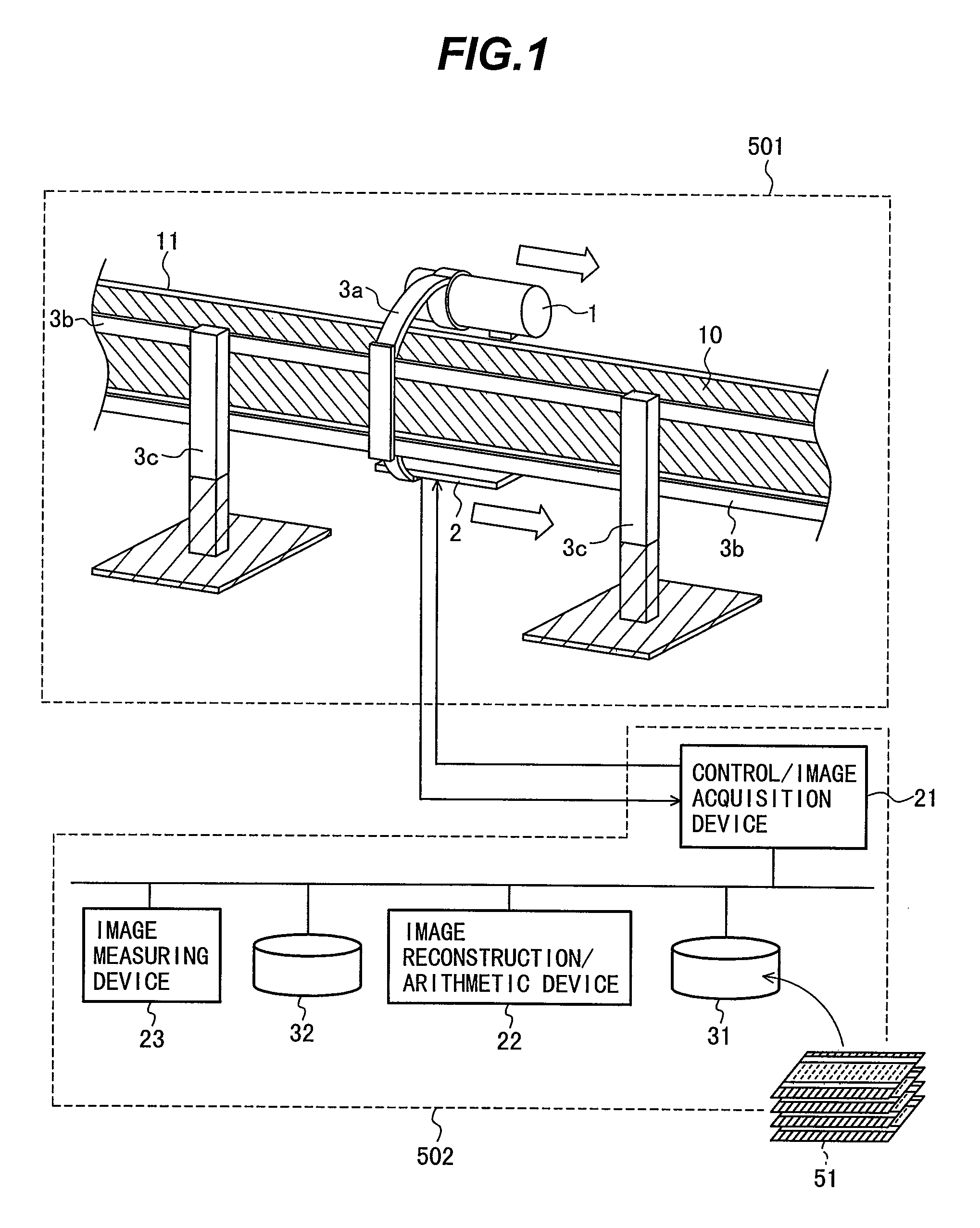
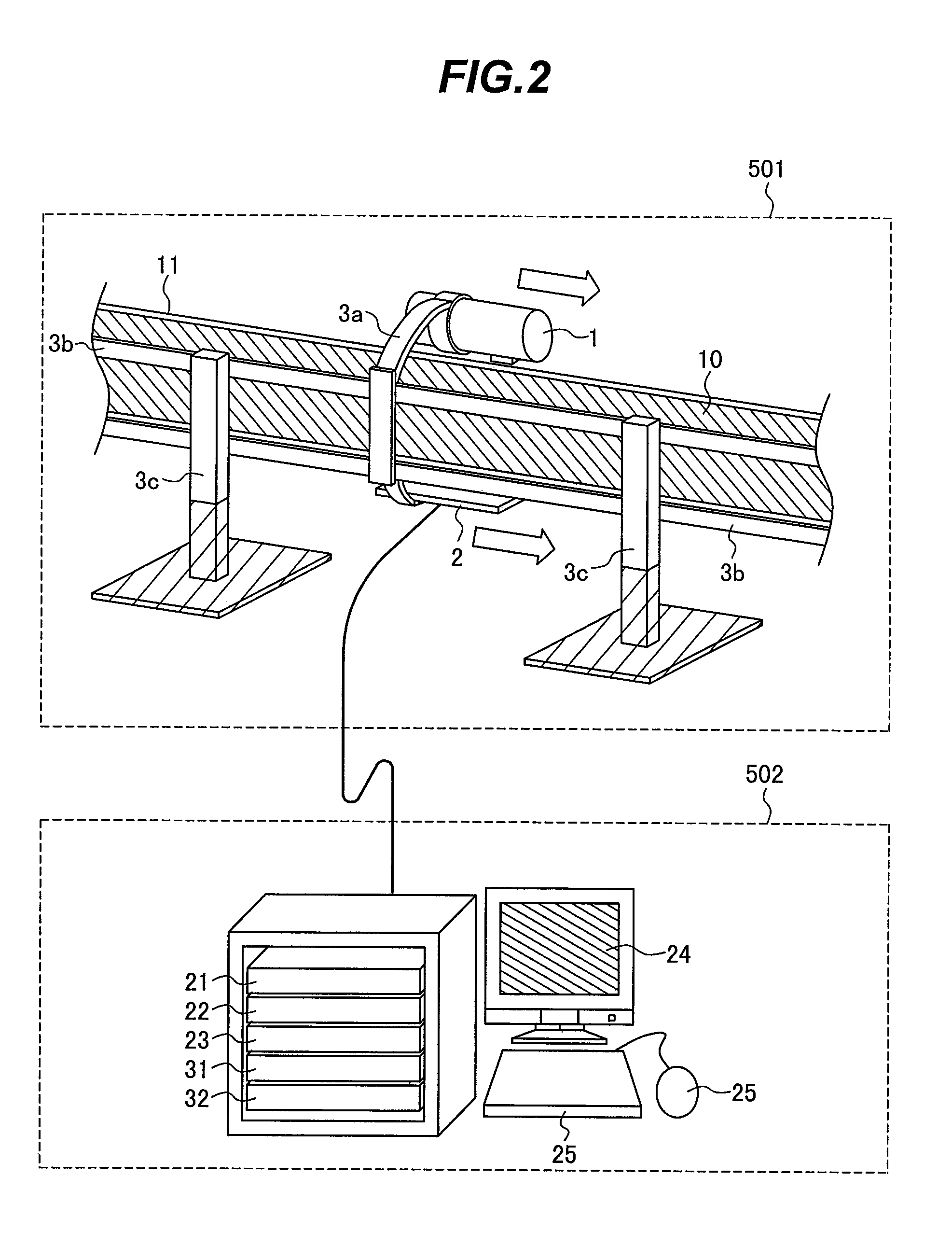
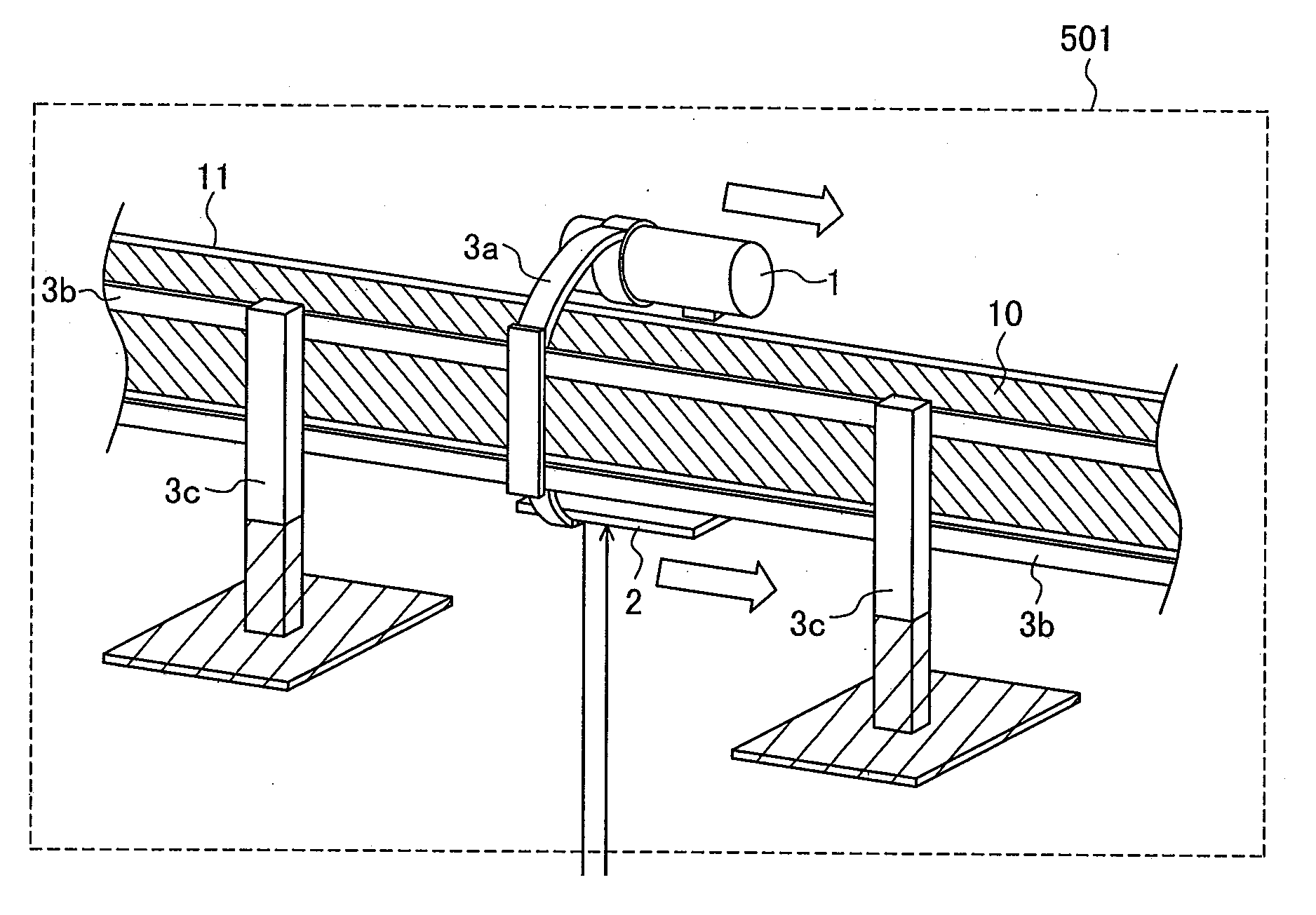
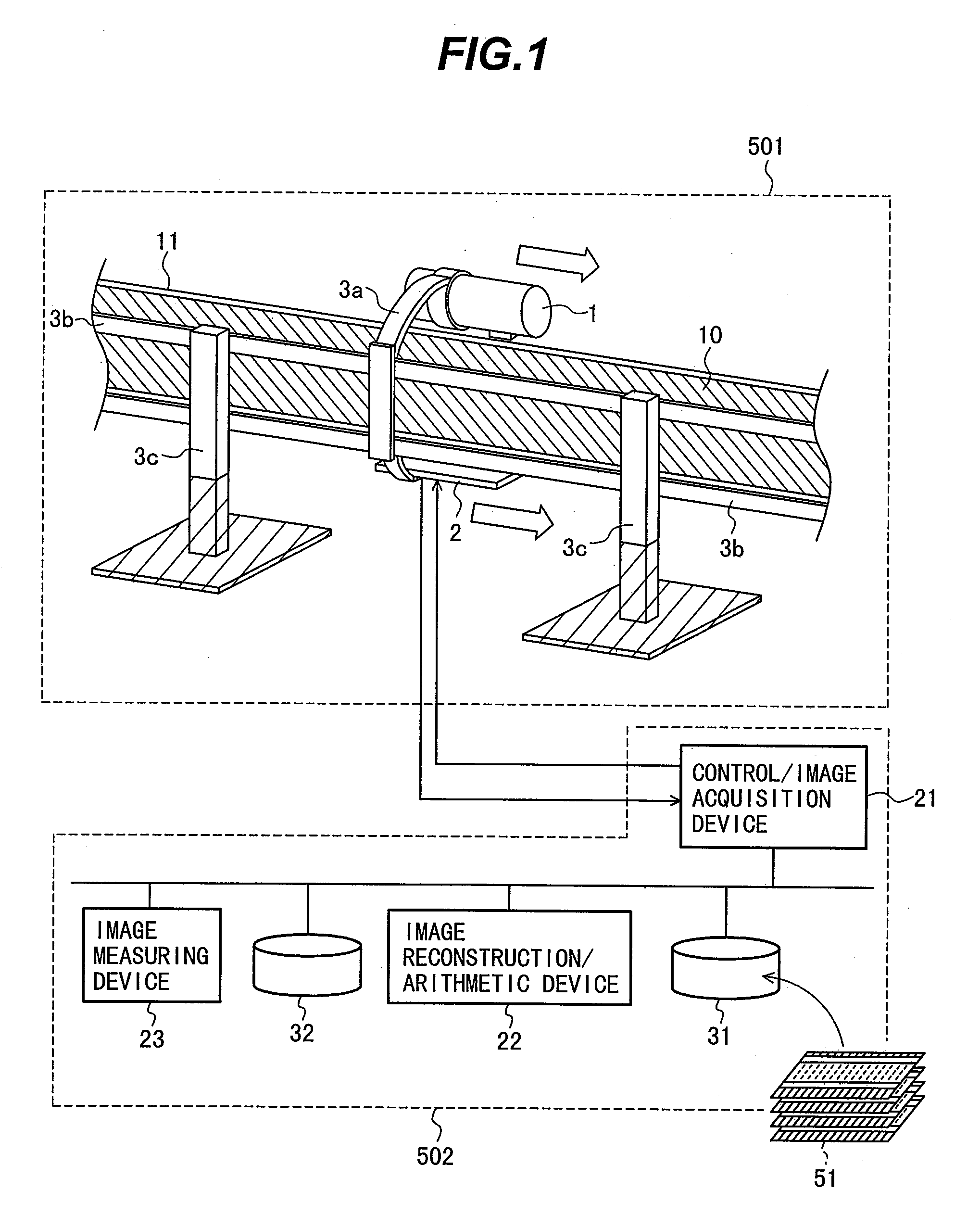
Method for inspecting pipes, and radiographic non-destructive inspection apparatus
ActiveUS7885381B2Improve inspection efficiencyX-ray/infra-red processesRadiation/particle handlingNon destructiveFractography
The pipe inspection method and apparatus can be used to implement rapid, tomographic inspection of a pipe set up at a narrow location. The pipe inspection method includes: a first step for scanning the pipe by translating a radiation source and radiation detector arranged opposedly to the pipe; a second step for the radiation detector to detect radiation that the radiation source has emitted, at given scanning distance intervals; a third step for creating a transmission image of the pipe, based on a radiation dose that the radiation detector has detected; and a fourth step for constructing a tomogram or stereoscopic image of the pipe, based on the transmission image. Thus, it is possible to provide the pipe inspection method and apparatus that can be used to implement rapid, tomographic inspection of the pipe set up at a narrow location.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Method for inspecting pipes, and radiographic non-destructive inspection apparatus
ActiveUS20080267345A1Improve inspection efficiencyX-ray/infra-red processesRadiation/particle handlingNon destructiveFractography
The pipe inspection method and apparatus can be used to implement rapid, tomographic inspection of a pipe set up at a narrow location. The pipe inspection method of the present invention includes: a first step for scanning the pipe by translating a radiation source and radiation detector arranged opposedly to the pipe; a second step for the radiation detector to detect radiation that the radiation source has emitted, at given scanning distance intervals; a third step for creating a transmission image of the pipe, based on a radiation dose that the radiation detector has detected; and a fourth step for constructing a tomogram or stereoscopic image of the pipe, based on the transmission image. According to this invention, it is possible to provide the pipe inspection method and apparatus that can be used to implement rapid, tomographic inspection of the pipe set up at a narrow location.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Micro-CT technology-based reservoir core three-dimensional entity model reconstruction method
ActiveCN105261068AValid descriptionEffective Digital Management3D modellingFractographyReconstruction method
The invention relates to a micro-CT technology-based reservoir core three-dimensional entity model reconstruction method. The method includes the following steps that: a micro-CT technology is utilized to scan a reservoir core, so that a sectional scanning image of the reservoir core can be obtained, so that a CT image of a real reservoir core can be obtained, and a watershed algorithm is adopted to perform image segmentation on the CT image, so that the three-dimensional data of the image can be obtained; a Marching Cubes algorithm is adopted to generate a three-dimensional surface model of the reservoir core; and with the three-dimensional surface model of the reservoir core adopted as constraints, a constrained Delaunay tetrahedralization algorithm is utilized to generate the three-dimensional entity model of the reservoir core. According to the method of the invention, the three-dimensional entity model of the real reservoir core is established based on the sectional scanning image of the reservoir core, so that the obtained three-dimensional entity model of the reservoir core is more approximate to the structure of a real reservoir core. The method of the invention has the advantages of high accuracy and high efficiency. With the method adopted, defects of poor accuracy and low efficiency in the reconstruction of the three-dimensional entity model of a reservoir core in the prior art can be eliminated, and an effective guarantee can be provided for reservoir core simulation characteristic research.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Visual uniaxial penetrating test-based bituminous mixture homogeneity evaluation method
InactiveCN105806861AThe evaluation result is accurateHigh industrial applicabilityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFractographyTomography
The invention discloses a visual uniaxial penetrating test-based bituminous mixture homogeneity evaluation method, which comprises the following steps: carrying out indoor molding or drilling a cylindrical core sample on site, acquiring two-dimensional horizontal section images of a plurality of bituminous mixture test pieces through tomoscan of an industrial CT machine, and then preprocessing and intensifying the two-dimensional horizontal section images acquired by the CT machine to generate gray images; recognizing and segmenting the processed bituminous mixture section gray images to obtain a boundary coordinate of each aggregate and gap in the bituminous mixture section images, establishing a three-dimensional discrete element model of the bituminous mixture and carrying out a virtual uniaxial penetration test, and evaluating the bituminous mixture homogeneity by using the uniaxial penetration strength index variable coefficient obtained by the test. The bituminous mixture homogeneity evaluation method is based on the visual uniaxial penetrating test, and the bituminous mixture homogeneity is quantitatively evaluated by using the uniaxial penetration strength index variable coefficient, so the industrial practicability and maneuverability are very strong.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
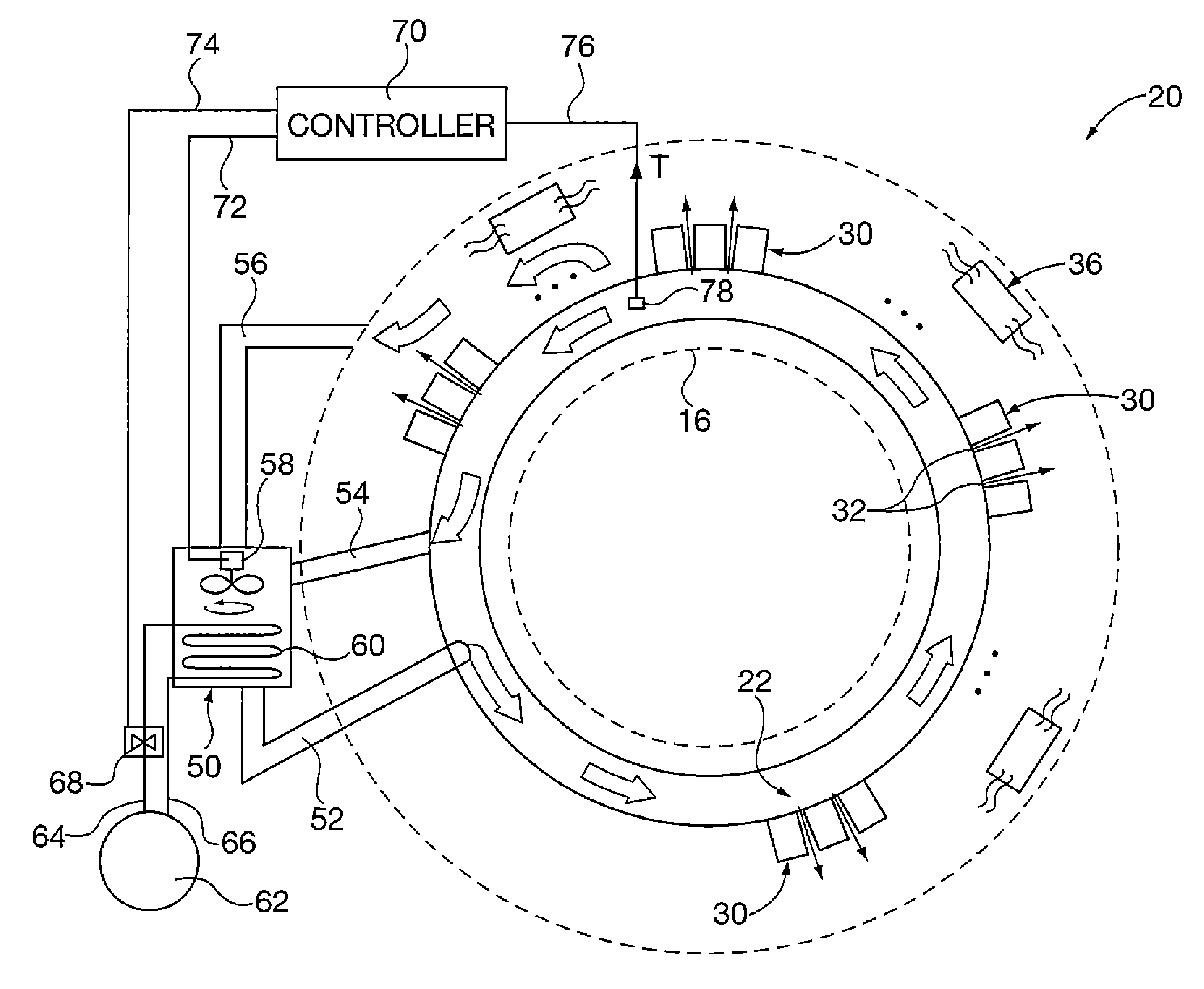
Apparatus and methods for cooling positron emission tomography scanner detector crystals
InactiveUS20130119259A1Sensitivity is increased and stabilizedWeaken energyMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyFractographyCompanion animal
Detector crystals in a positron emission tomography (PET) apparatus gantry are cooled by directing cooling gas flow into a cooling duct bounded by the crystals and a cover defining the patient scanning field within the gantry. The cooling gas cools the crystals. Cooling gas may also be directed radially outwardly from the cooling duct into spatial gaps defined between detector enclosures that include the crystals, further isolating heat generated by other components within gantry from the detector crystals. Cooling gas is provided by a cooling system that may be incorporated within the gantry, external the gantry or a combination of both. Cooling gas can be provided by directing air within the gantry in contact with internal gantry cooling tubes and routing cooled air directly into the cooling duct with a powered fan.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
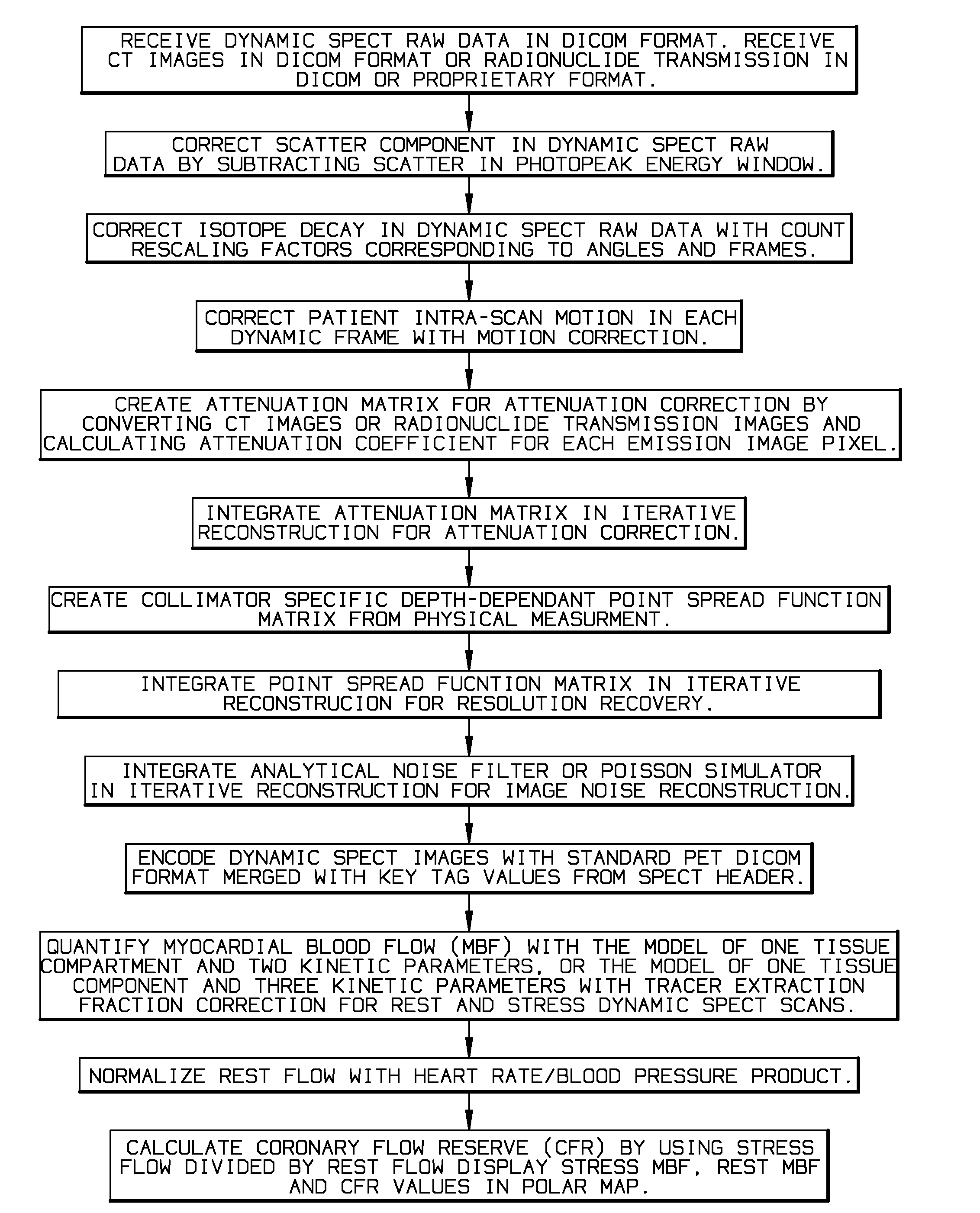
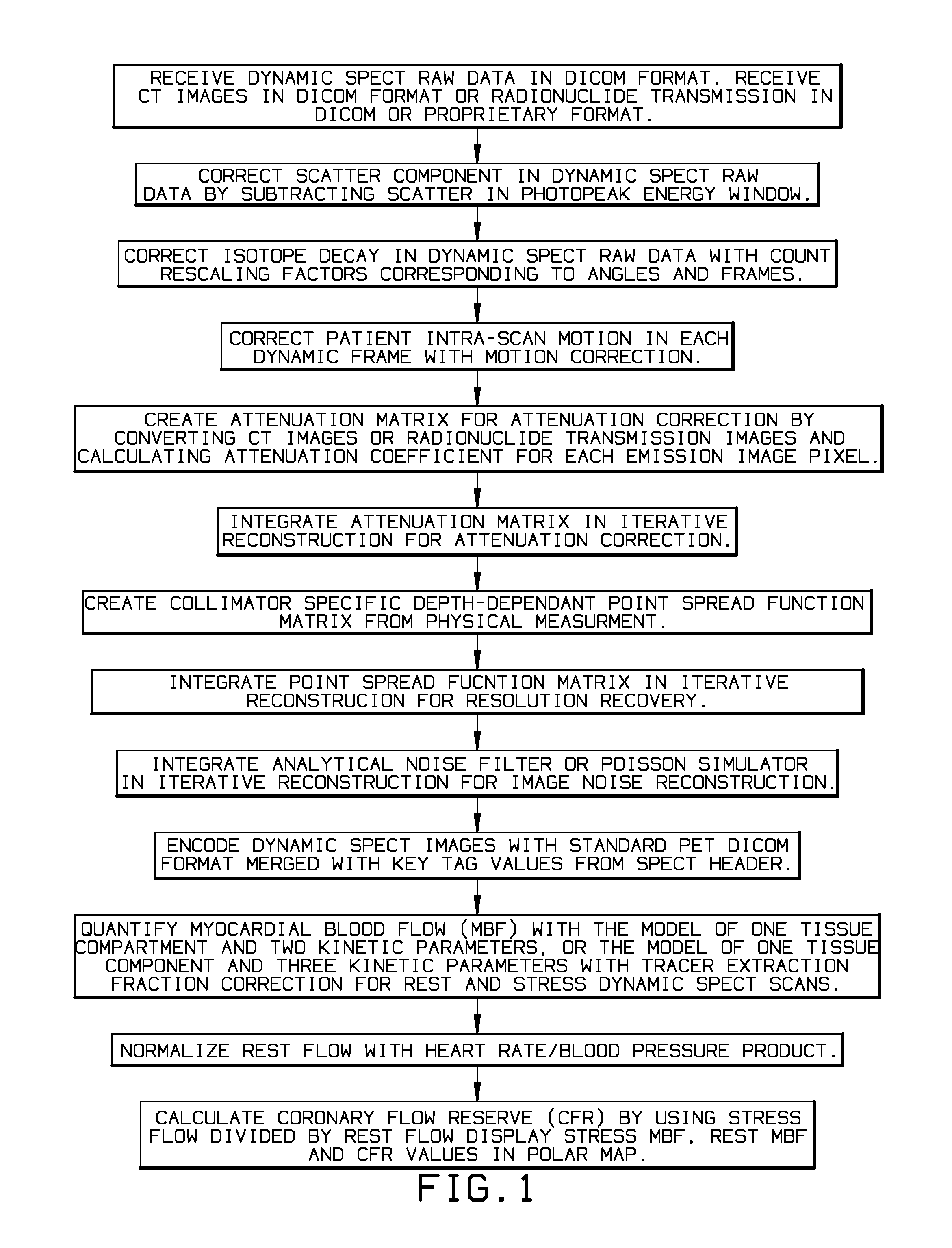
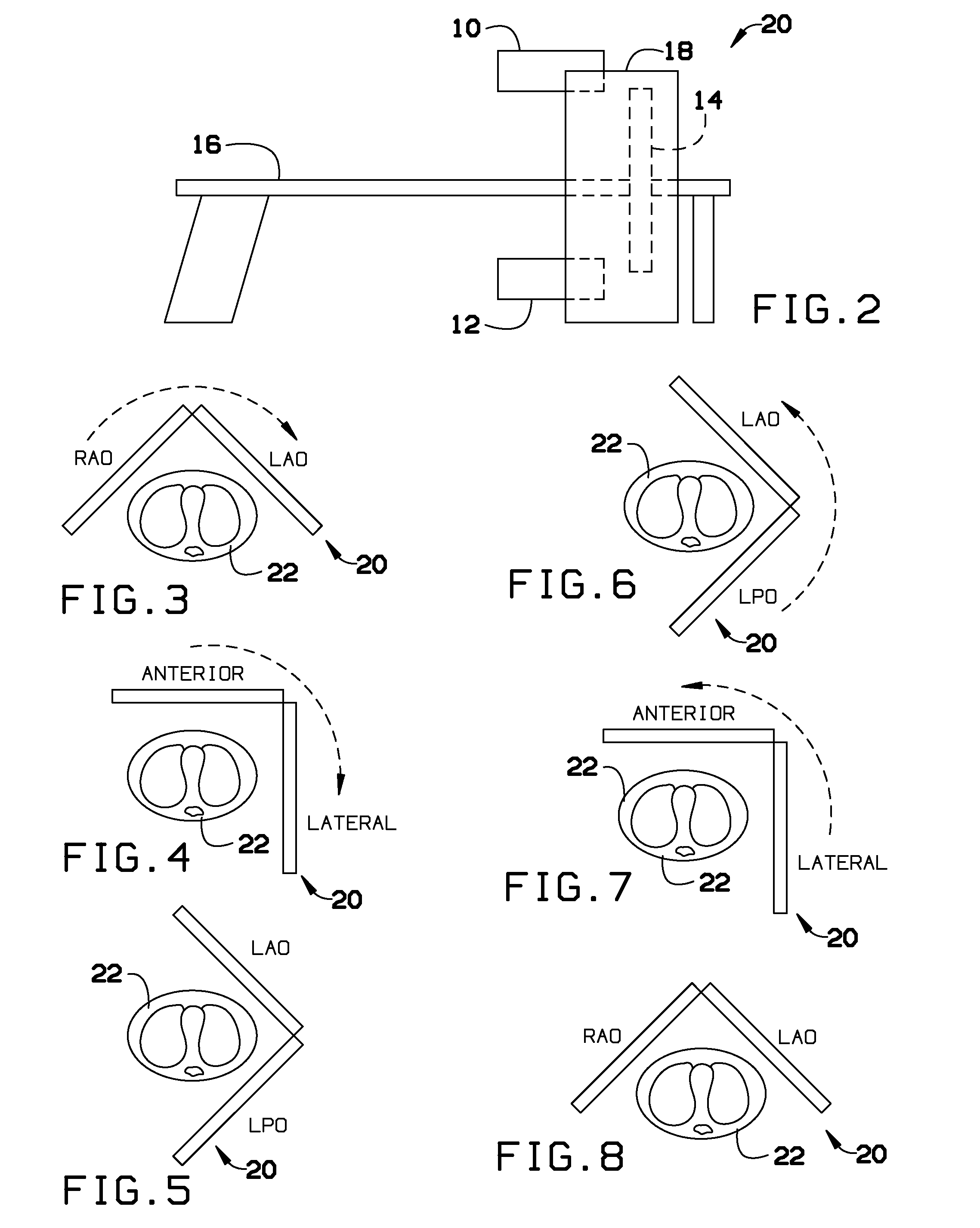
Myocardial blood flow quantitation with dynamic spect or spect/ct imaging
InactiveUS20140341453A1Remove image noiseReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFractographySpect imaging
A quantitative Single Photon Computed Emission Tomography (SPECT) reconstruction system for myocardial blood flow quantitation with SPECT or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography / Computed Tomography (SPECT / CT) dynamic imaging. The present invention solves the problems of physical interference and patient motions in dynamic SPECT imaging to enable the quantitative ability for myocardial blood flow (MBF) and coronary flow reserve (CFR) quantification.
Owner:HSU BAILING +1
Interior uniformity recognition method based on relative density of all components of bituminous mixture
InactiveCN104931515AEigenvalue avoidanceImprove computing efficiencyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPattern recognitionFractography
The invention discloses an interior uniformity recognition method based on the relative density of all components of a bituminous mixture. The interior uniformity recognition method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing tomography in the axial direction of a bituminous mixture test piece to form a plurality of sections of which the effective areas are the same; secondly, dividing each section into a plurality of regular small areas, and establishing a digital image set of the interior structure of the bituminous mixture test piece; thirdly, performing compiled image segmentation and threshold selection; meanwhile, calculating the relative density of all the components in an image according to actual density values and the area ratio of coarse aggregates, gaps and mortar in each small area of the digital image, directly evaluating the interior structure uniformity of the bituminous mixture according to data, and quantitatively judging the damage position of the interior structure of the bituminous mixture.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Templates for assessing bone quality and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080119719A1Realistic and accurate depictionConvenient medical treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisFractographyVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to the preparation and use of novel bone templates that can be prepared using a comprehensive approach to observing microstructural features of bone, including trabecular thickness and trabecular density. These features are assessed in regions of interest in a bone (e.g., proximal femur, distal femur, wrist, spine, etc.) as observed using digital radiographic techniques or clinical imaging, such as Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) and computed tomography (CT) scanners. The microstructural features are presented in the form of data based on scanning results and are also assessed and / or organized in terms of age, gender, race, pathology, clinical history, and other patient population parameters. The template can be used to assess bone quality, predict the likelihood of bone fracture, and evaluate prosthesis design and placement, based on an image of a corresponding subject bone, e.g. the bone of a patient.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Finite element modeling method for human head for researching collision damage of automobile
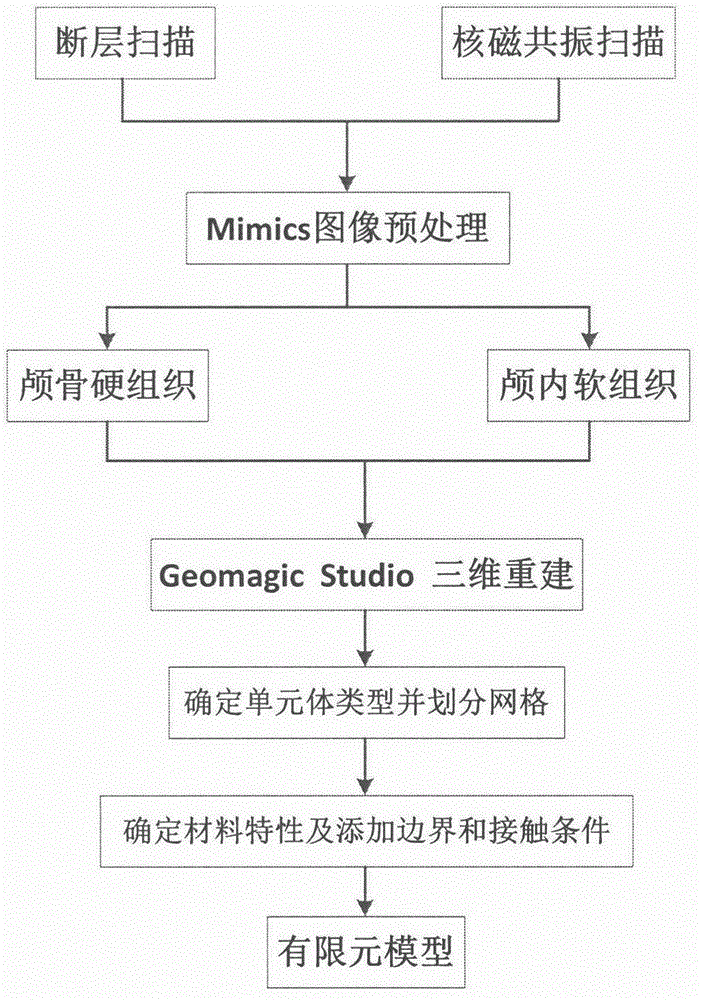
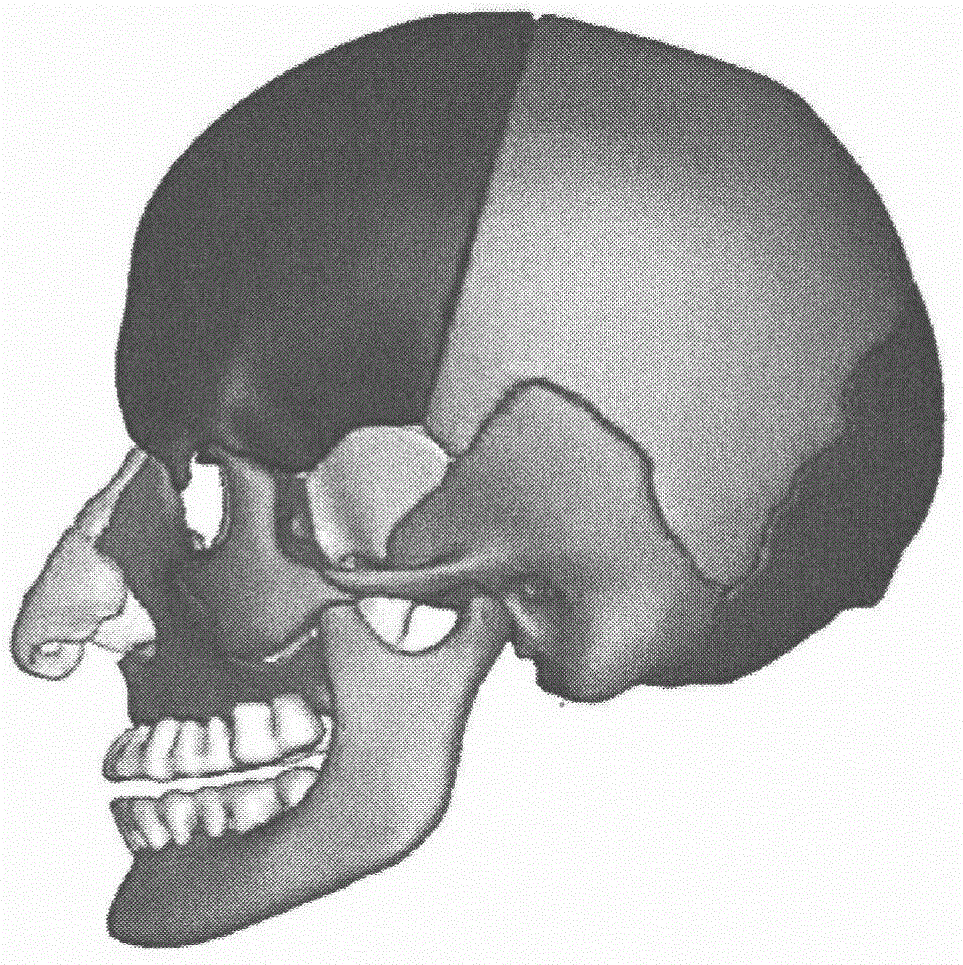
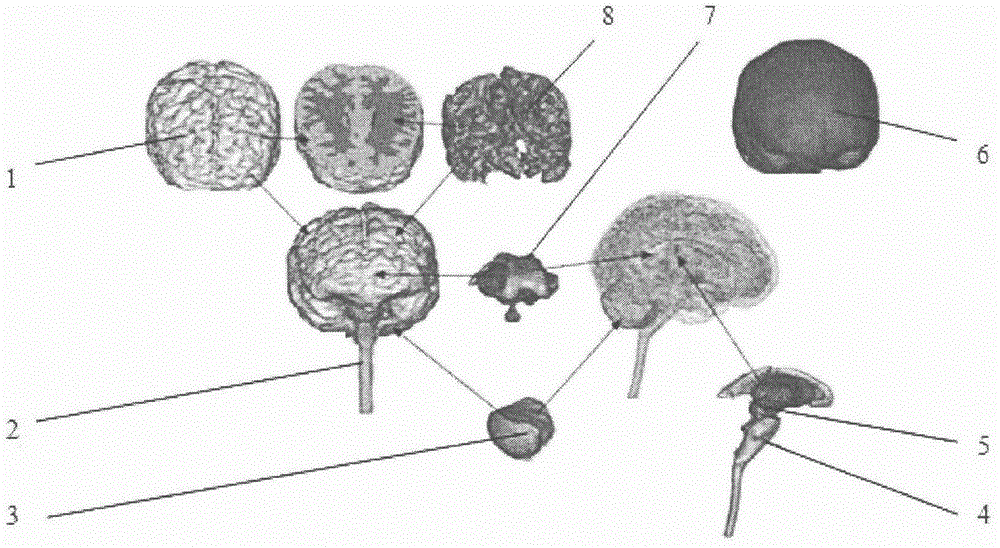
InactiveCN106777473ADetailed head anatomyImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFractography
The invention provides a finite element modeling method for a human head for researching collision damage of an automobile. The finite element modeling method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance scanning on the human head to obtain a tomography scanning image; secondly, importing the tomography scanning image into Mimics, and preprocessing the tomography scanning image to obtain point cloud data; thirdly, importing the point cloud data obtained in the second step into Geomagic Studio, and carrying out parameterized processing on the point cloud data to generate curved surfaces; detecting the generated curved surfaces, and fitting all the curved surfaces by using cubic Bezeir curves to obtain a three-dimensional geometrical model; fourthly, importing the three-dimensional geometrical model into HyperMesh for dividing meshes, setting the type of a unit body into a linear tetrahedral unit and optimizing local grids to obtain a three-dimensional solid model; fifthly, importing the three-dimensional solid model into Abaqus, defining characteristic parameters of tissue materials, and adding boundary and contact conditions for tissues to obtain a finite element model of the human head.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
PET concentration reestablishing method based on Kalman filtration in limited sampling angle
ActiveCN101627919AImprove adaptabilityThe result is obviousComputerised tomographsTomographyFractographyFiltration
The invention discloses a PET concentration reestablishing method based on Kalman filtration in a limited sampling angle, comprising the following steps: obtaining incomplete sine figure data of an original projection line by a PET positive electron emission faultage scanner; establishing a state space system by combining a house model theory; and finally solving by a Kalman filtering method based on the state space theory to obtain radioactivity distribution, namely realizing image reestablishment. Because of the transcendental guide of a house model and the high adaptability of the Kalman filtering method on the incomplete data, the quality of a reestablished PET image is not influenced by data loss. Compared with an MLEM experiment of the prior reestablishing method, both the qualitative analyzing result and the quantitative analyzing result indicate that the method has certain superiority.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
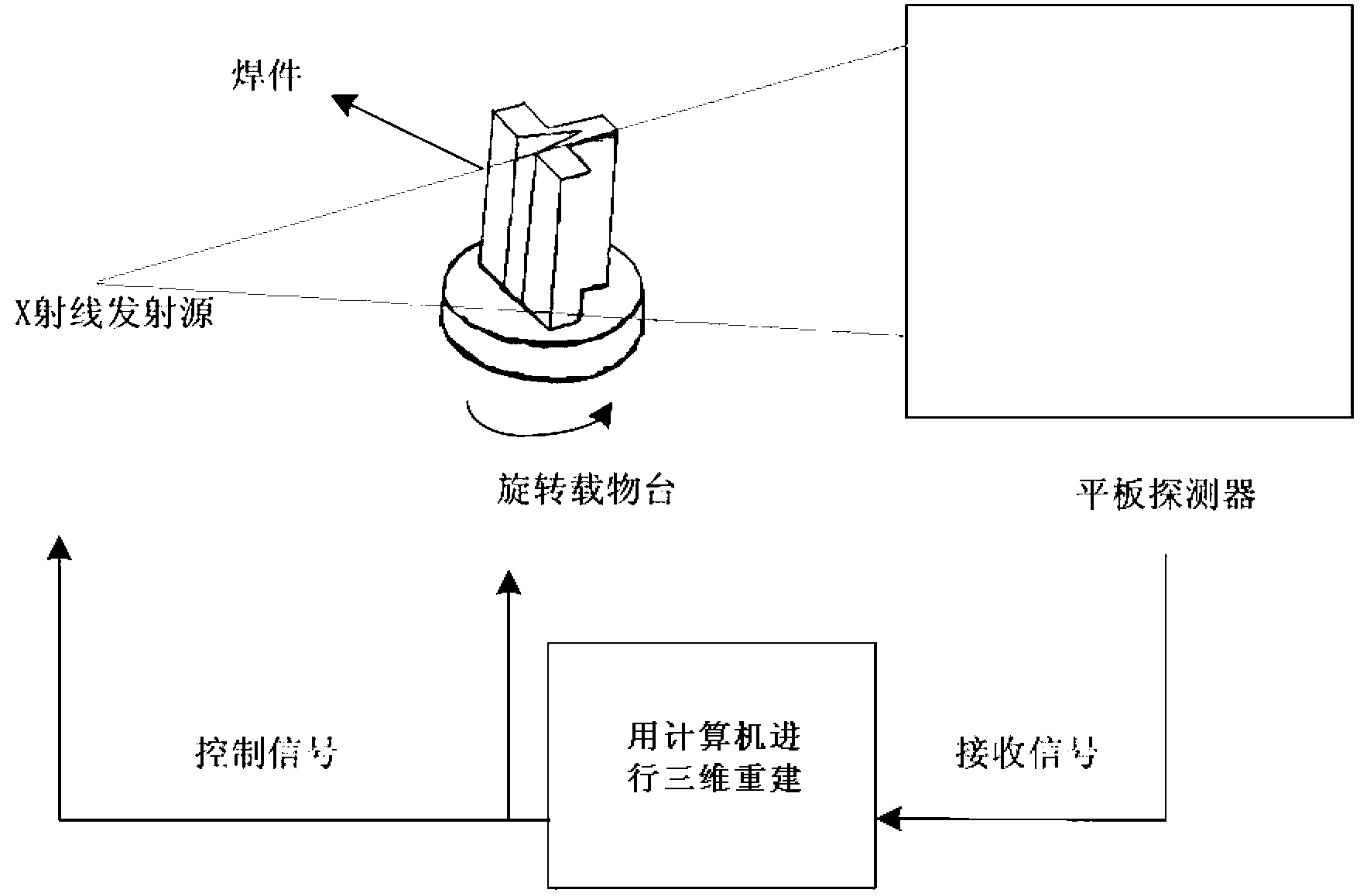
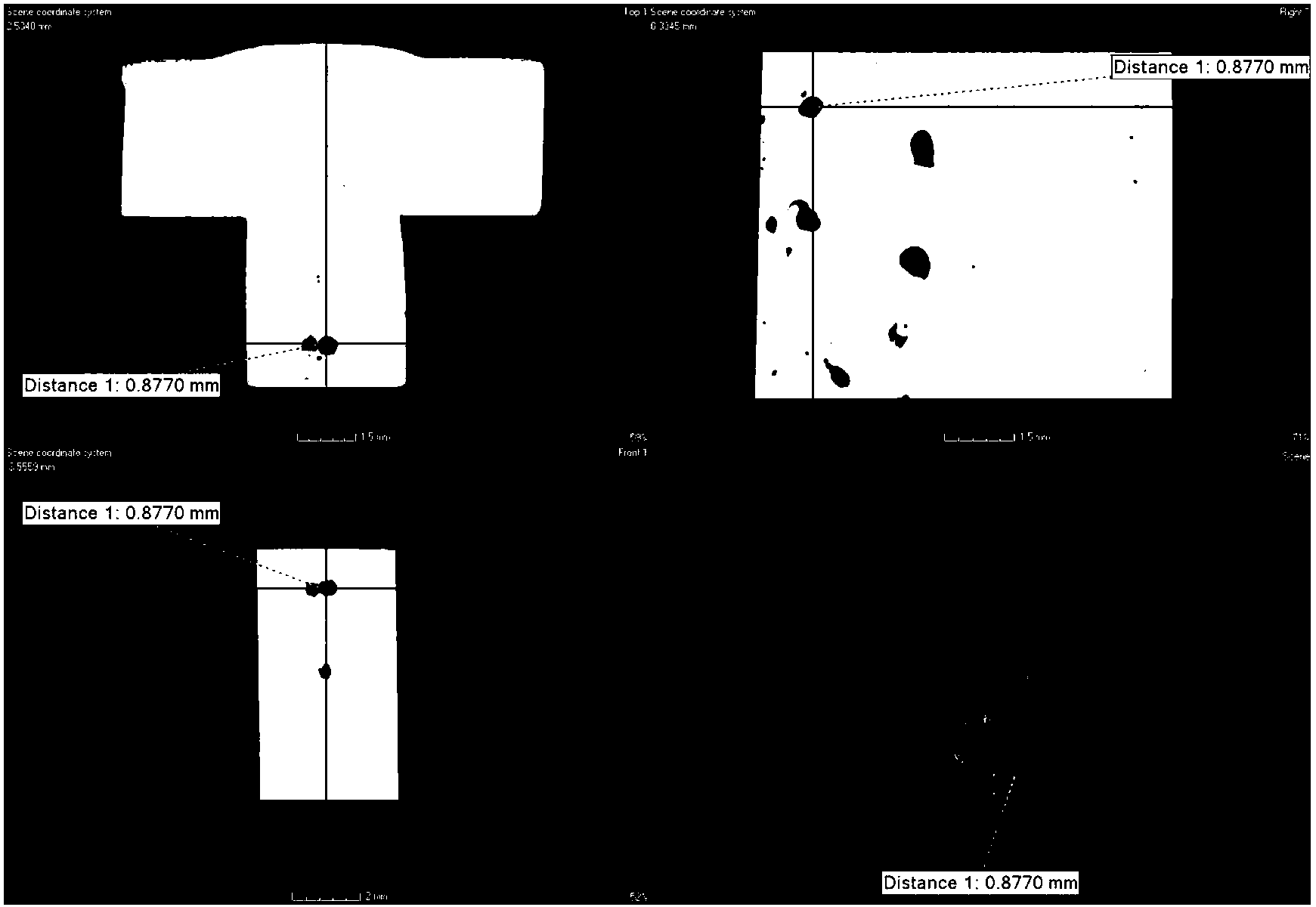
New non-destructive detection method for morphology and distribution of pores in welding seam
InactiveCN103234990AReduce sensitivityPrecise positioningMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFractographyX-ray
The present invention discloses a new non-destructive detection method for morphology and distribution of pores in welding seam. According to the method, a novel Nano-CT tomography system is adopted to detect a weldment, an X-ray source is adopted to carry out 360 DEG scanning on the welding component, a certain degree of attenuation can be generated when X rays penetrate through the weldment, energy attenuation of the X rays passing through the pores in a welding seam can be significantly lower than energy attenuation of the surrounding rays, a flat panel detector is adopted to receive transmission energies of different degrees of the attenuations so as to obtain multiple groups of tomography scanning images, and three-dimensional reconstruction is performed on the multiple groups of the tomography data to obtain a three-dimensional detection image of pore defect in the welding seam. The detection method has the following characteristics that: resolution is high, imaging is intuitive, the method is not affected by a weldment material type, a shape, a structure and other factors, important information such as a three-dimensional morphology, a pore size, a spatial distribution characteristic and the like of the pores in the welding seam can be obtained, and important significance is provided for pore classification, defect assessment and other aspects, wherein the important information such as a three-dimensional morphology, a pore size, a spatial distribution characteristic and the like is difficult obtained by using the conventional method.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
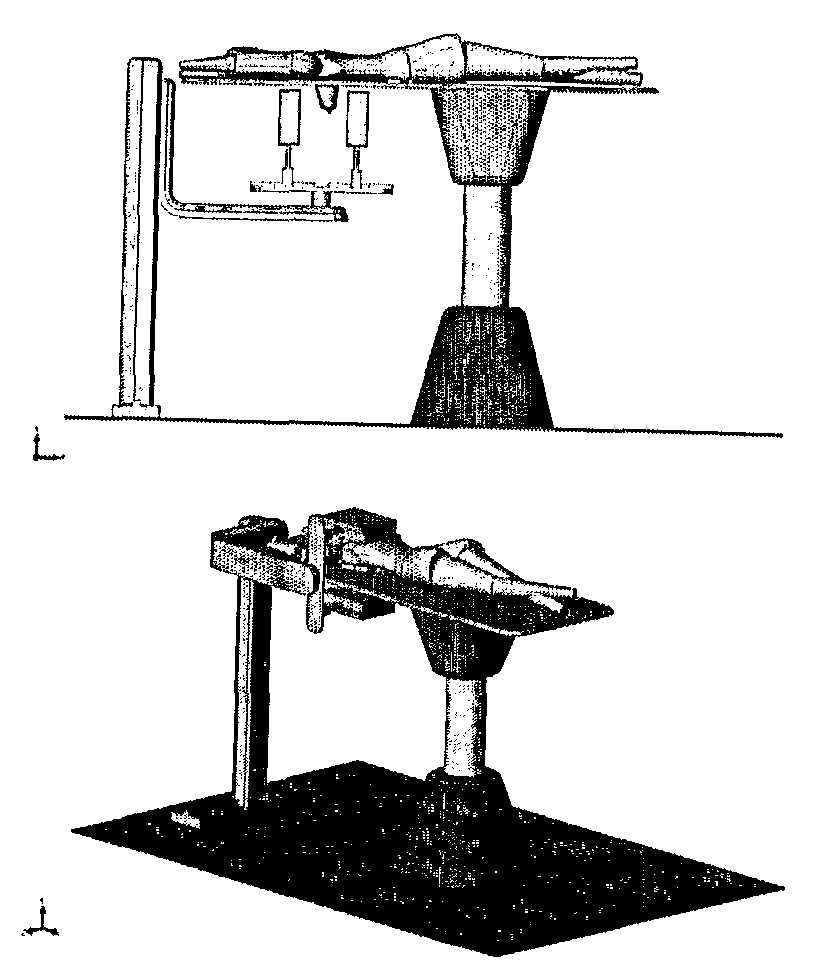
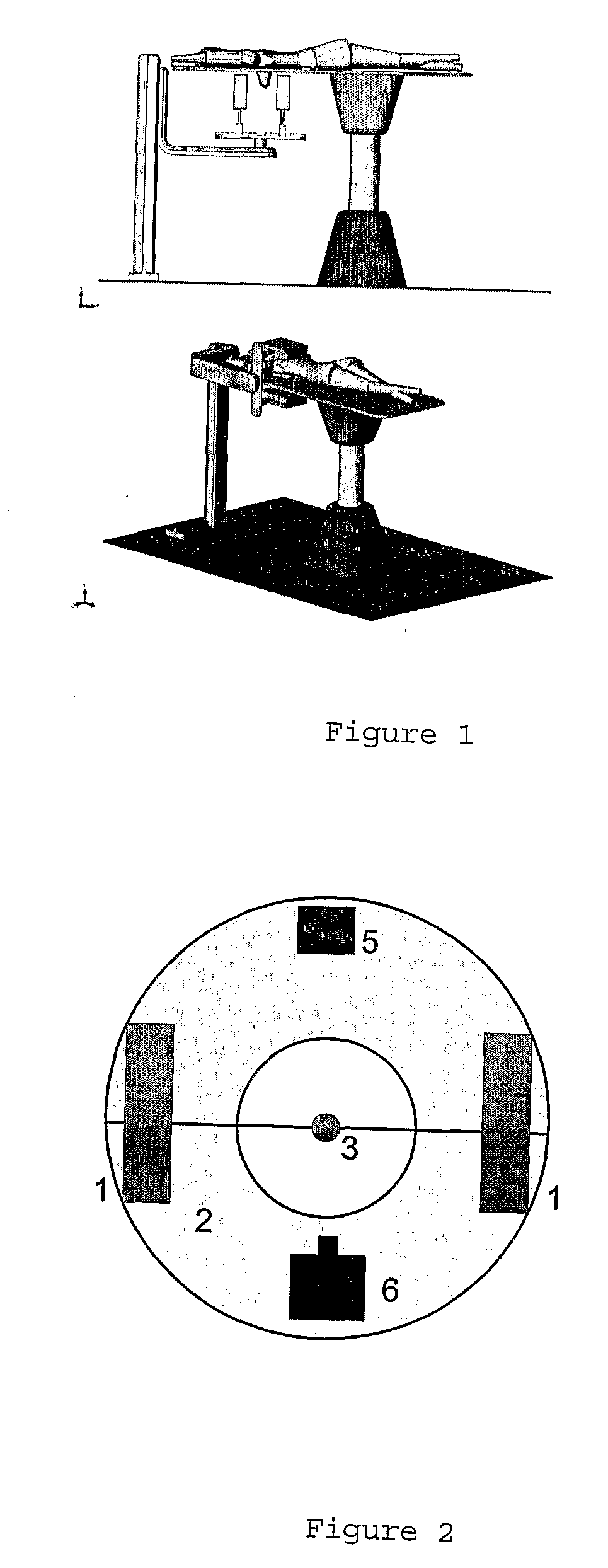
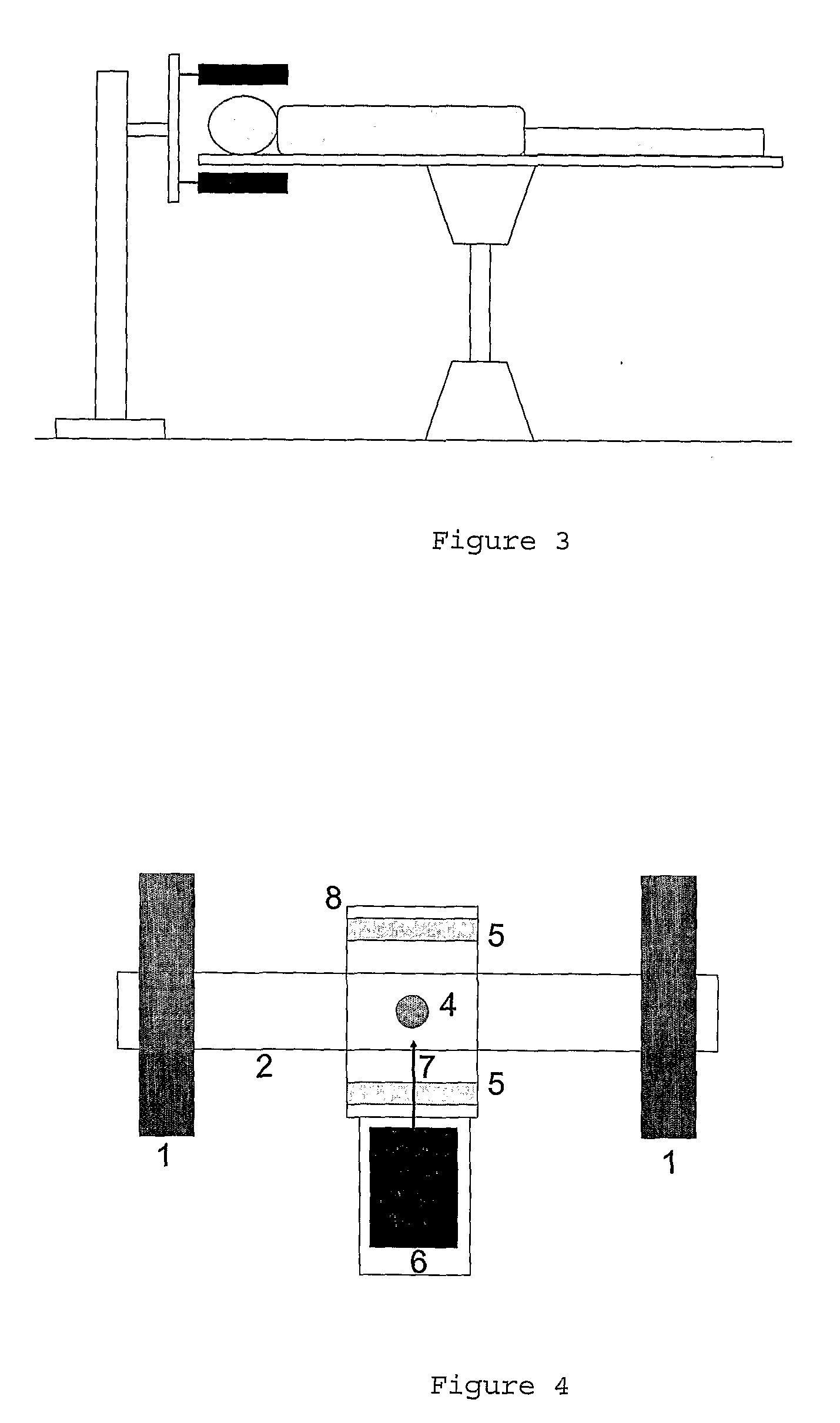
Automatic limb fracture reduction method and automatic limb fracture reduction system
InactiveCN103750888AReduce difficultyEasy to adjustSurgeryComputerised tomographsFeature extractionFractography
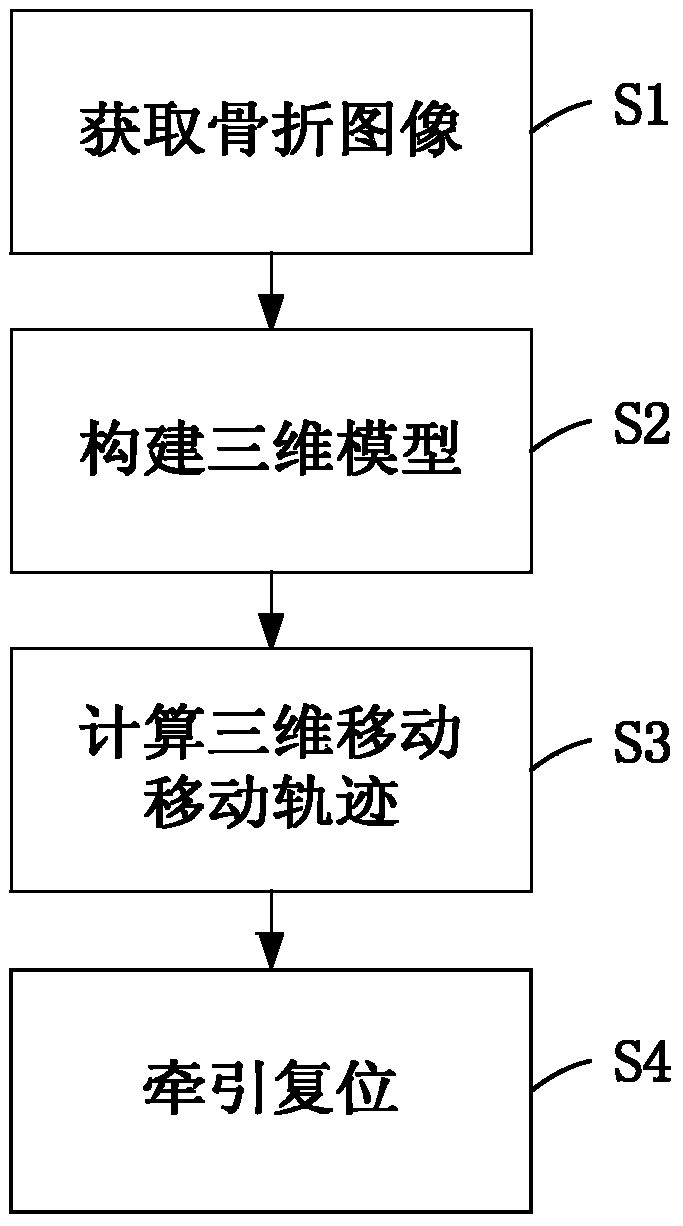
The invention discloses an automatic limb fracture reduction method and an automatic limb fracture reduction system. The automatic limb fracture reduction method comprises the steps that tomoscan is conducted on the fractured part of a patient through X rays, fracture information is obtained through a detector matched with the X rays, a digital-to-analog converter is used for converting the fracture information into digital quantity, and the digital quantity is made to form an image matrix through a computer; denoising, enhancement, restoration, segmentation and feature extraction are conducted on the image matrix, so that a second-level image is formed; binaryzation and edge extraction are conducted on the second-level image, so that approximation of a contour line is realized, and a third-level image is formed; the third-level image is vectorized, and a three-dimensional model is reconstructed; fitting is conducted according to the edge curve of the fractured part in the three-dimensional model, and a three-dimensional movement trajectory required by fracture reduction is determined through the computer; traction reduction is conducted on the fractured part through a traction machine under the control of the computer. By means of the automatic limb fracture reduction method and the automatic limb fracture reduction system, the fracture reduction difficulty is lowered to a great extent, and mechanical reduction accuracy is improved.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com