Patents
Literature
129 results about "Gangliocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gangliocyte [gang´gle-o-sīt] a ganglion cell. gan·gli·on cell originally, any nerve cell (neuron); in current usage, a neuron the cell body of which is located outside the limits of the brain and spinal cord, hence forming part of the peripheral nervous system; ganglion cells are either 1) the pseudounipolar cells of the sensory spinal and cranial ...
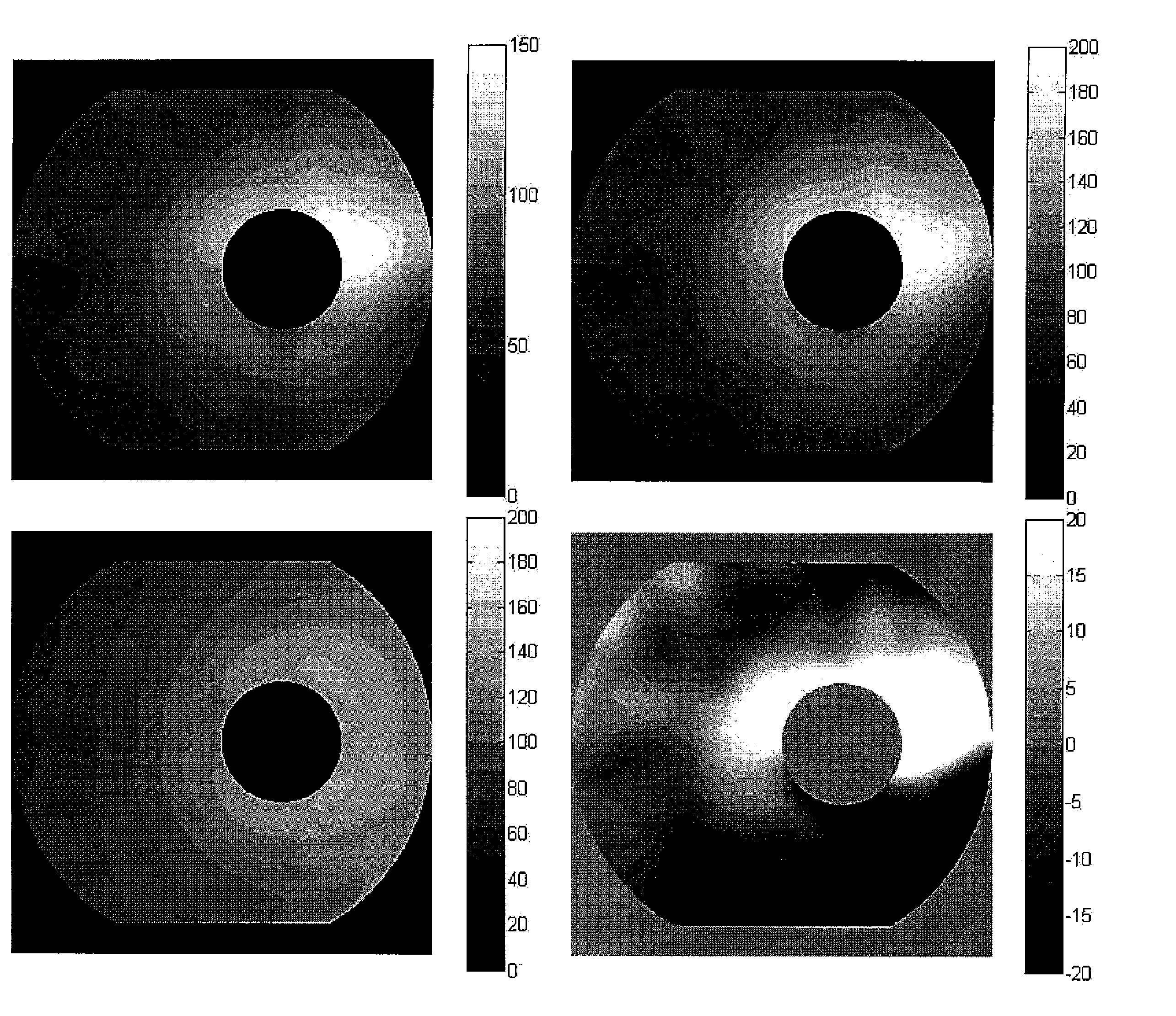
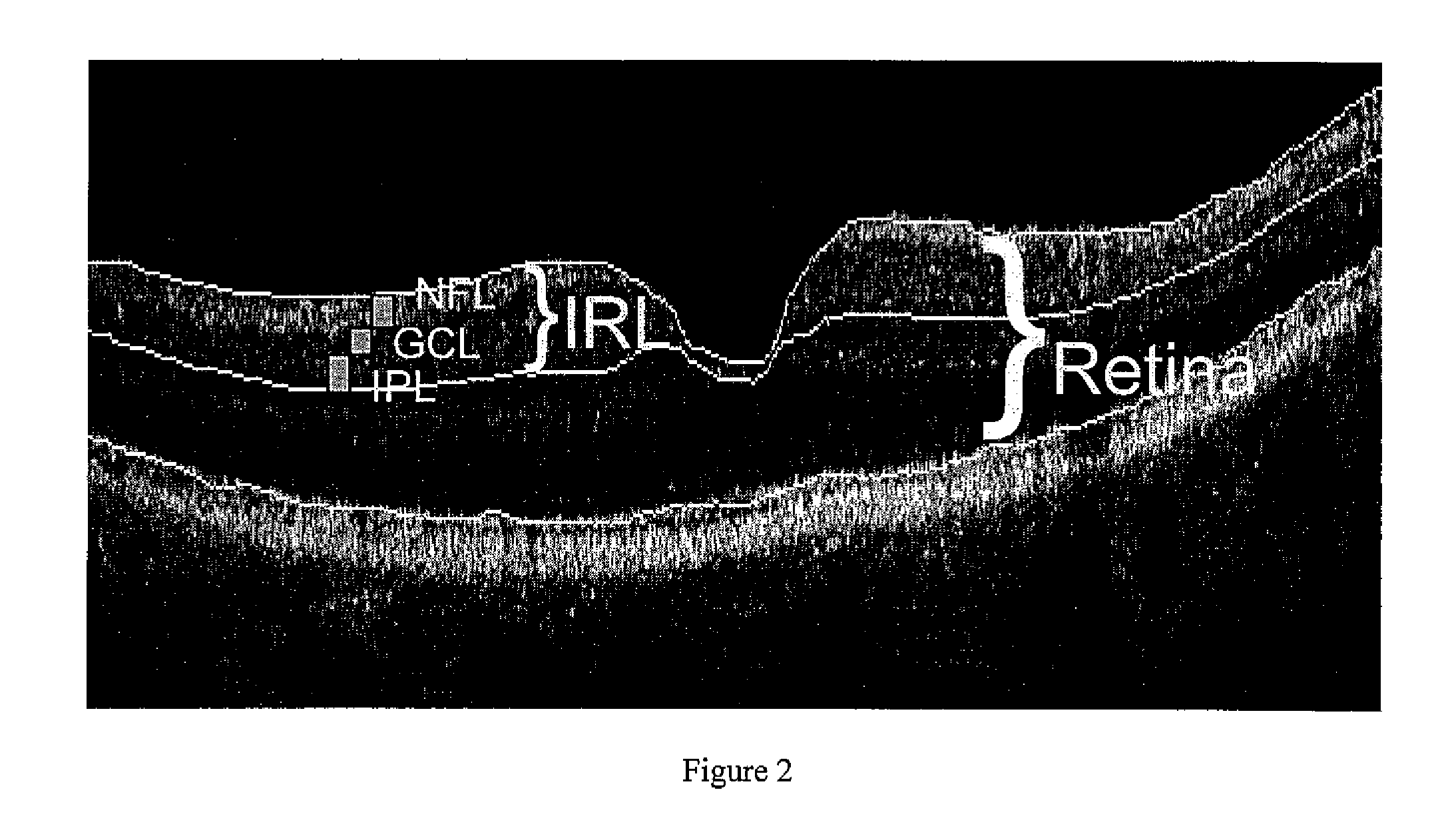
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Mimicking neural coding in retinal ganglion cells with short pulse electrical stimulation
A method, device and system for stimulating visual tissue, typically in the retina or visual cortex, to achieve an artificial percept of light or image. The method includes providing stimulating electrodes suitable for placement in proximity to the visual tissue and generating a series of short-duration stimulation signals having a duration of less than about 0.5 milliseconds each. The short-duration stimulation signals are applied through the stimulating electrodes with varying frequencies that are substantially matched to a spiking range of frequencies of at least one ganglion cell for perceiving brightness or image.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
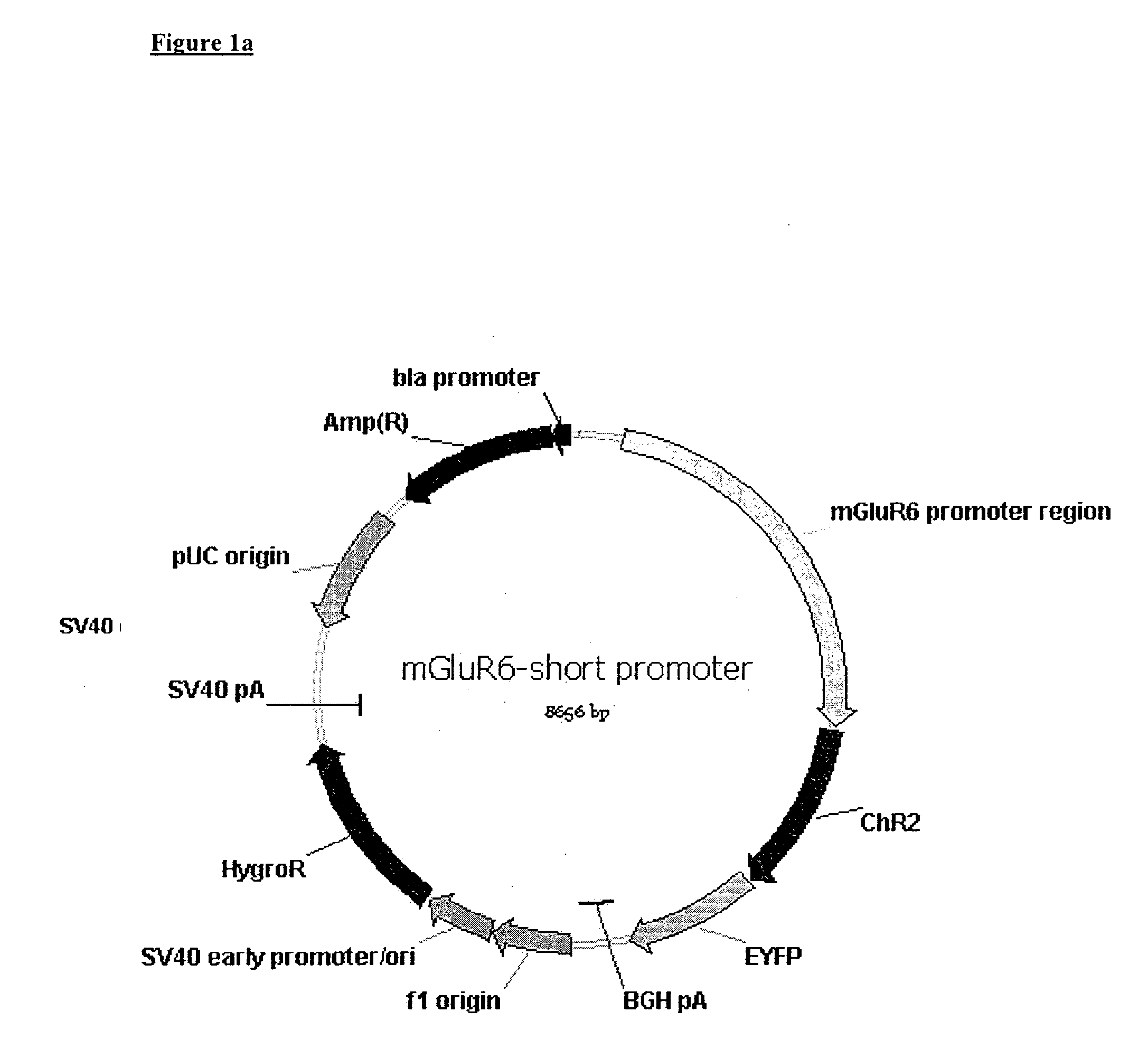
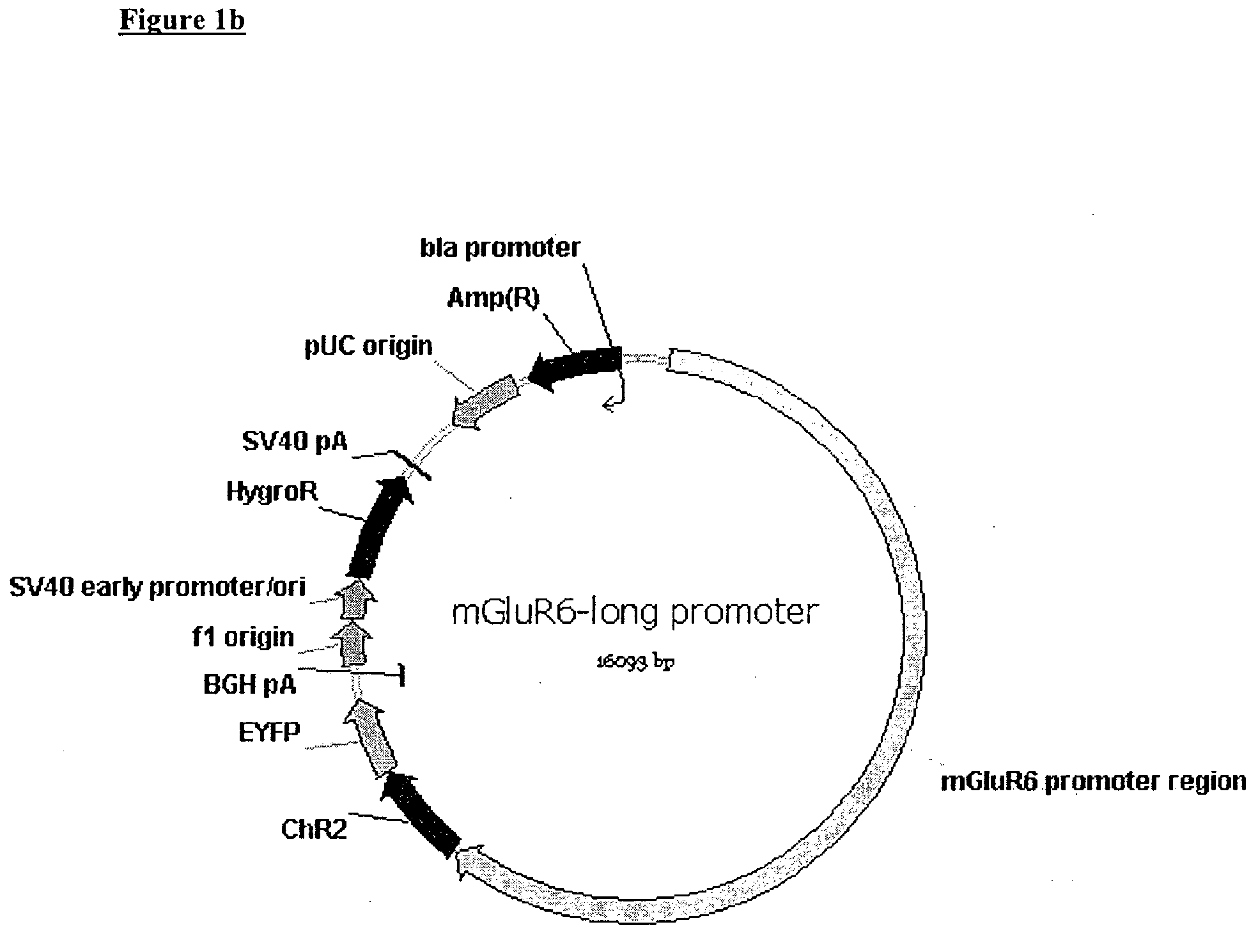
Use of Light Sensitive Genes
InactiveUS20090088399A1Prevent and show degenerationImprove eyesightOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell specificLight-gated ion channel
The invention relates to the use of a light-gated ion channel for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of blindness and a method for expressing said cell specific fashion, e.g. in ON-bipolar cells, ON-ganglion cells, or AII amacrine cells.
Owner:NOVARTIS FORSCHUNGSSTIFTUNG ZWEIGNIEDERLASSUNG FRIEDRICH MIESCHER INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES FMI
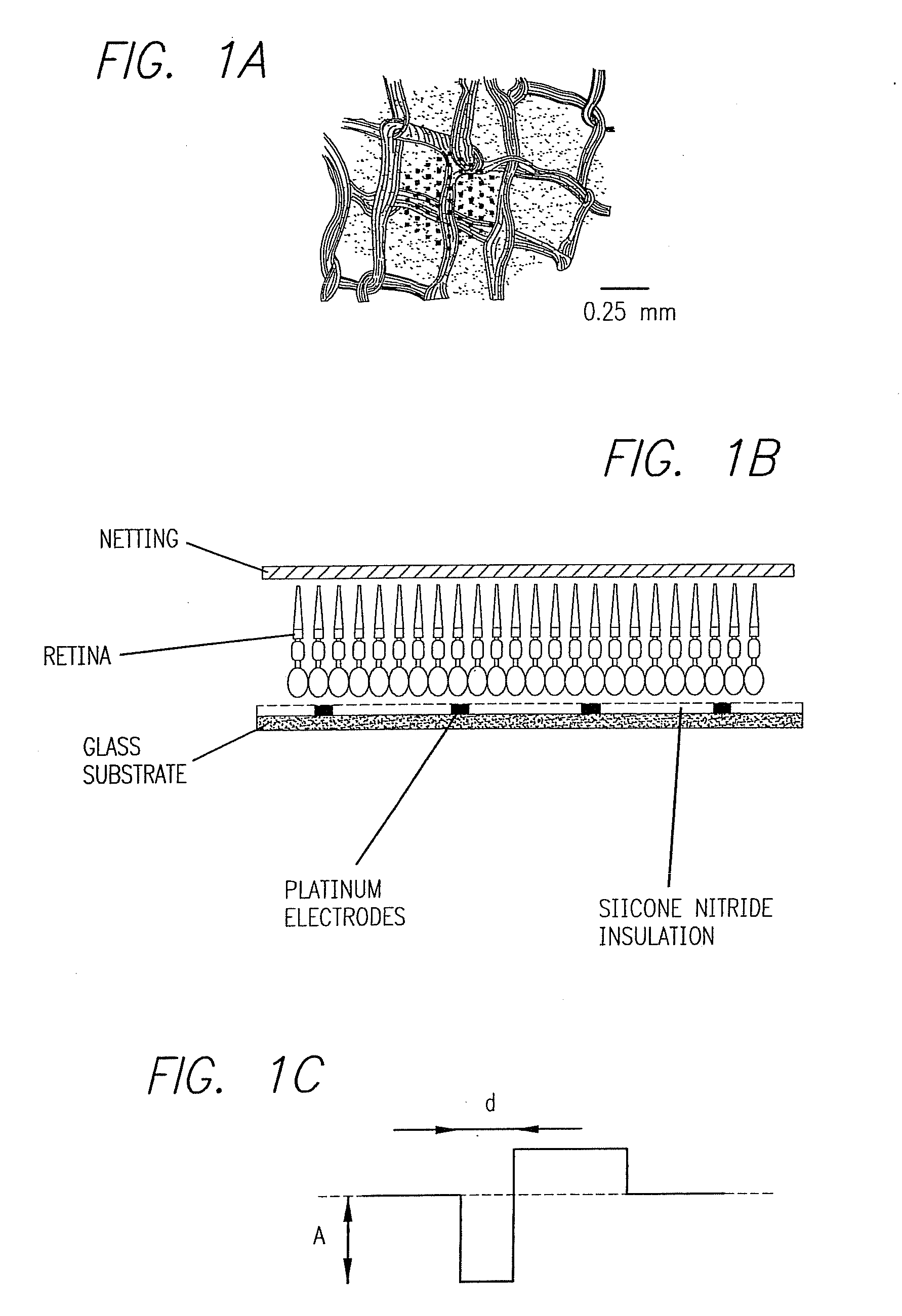
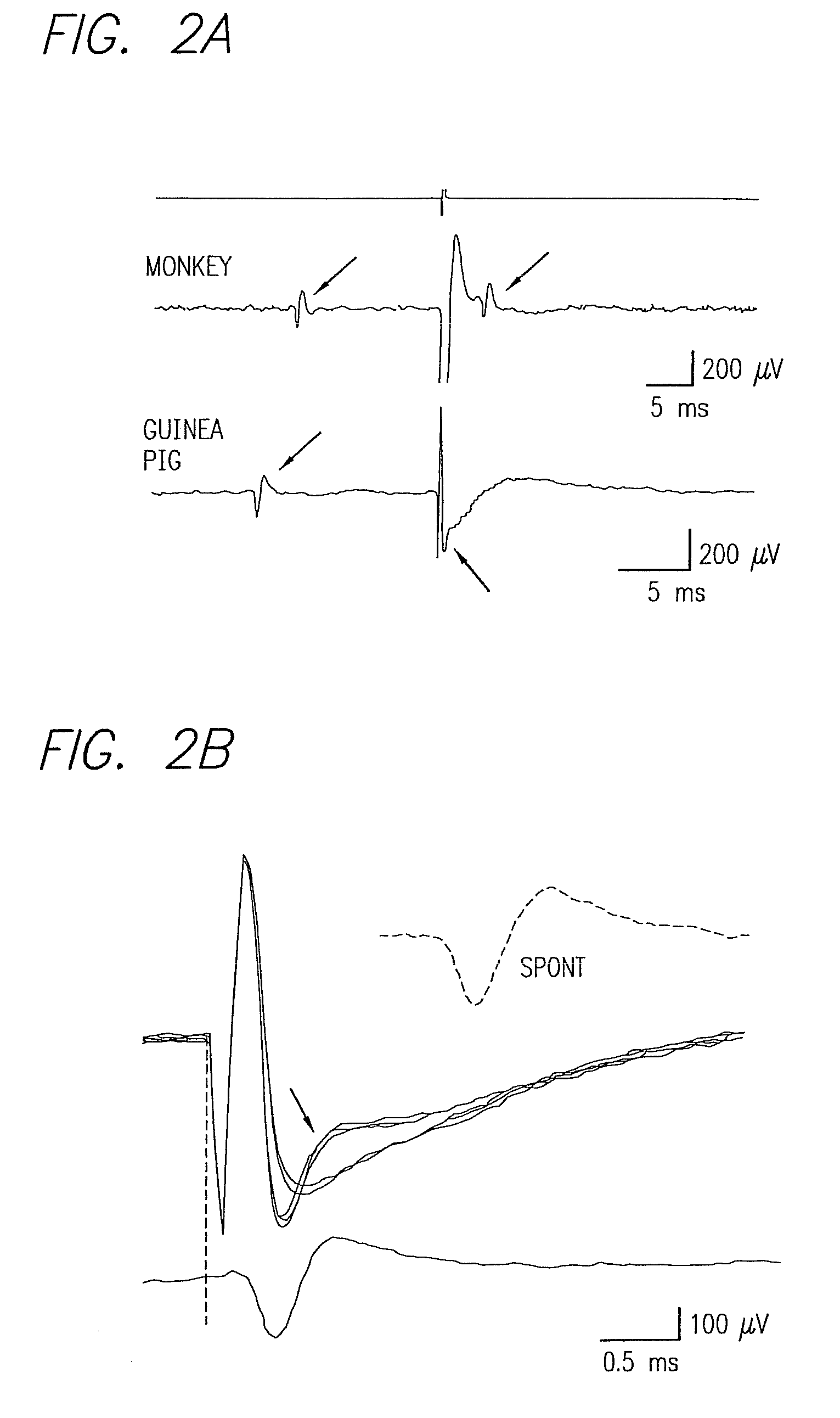
Method and apparatus for visual neural stimulation
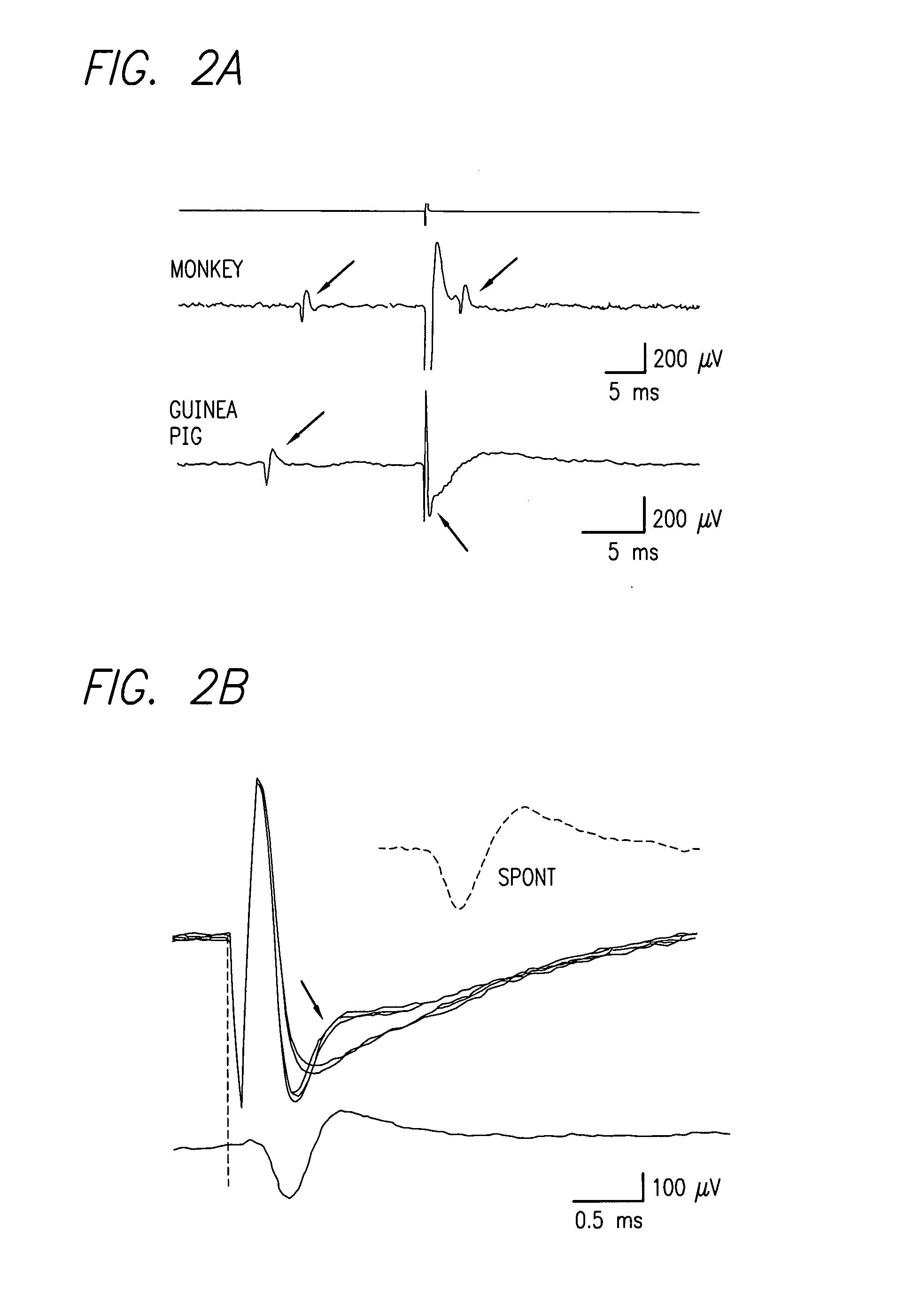
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
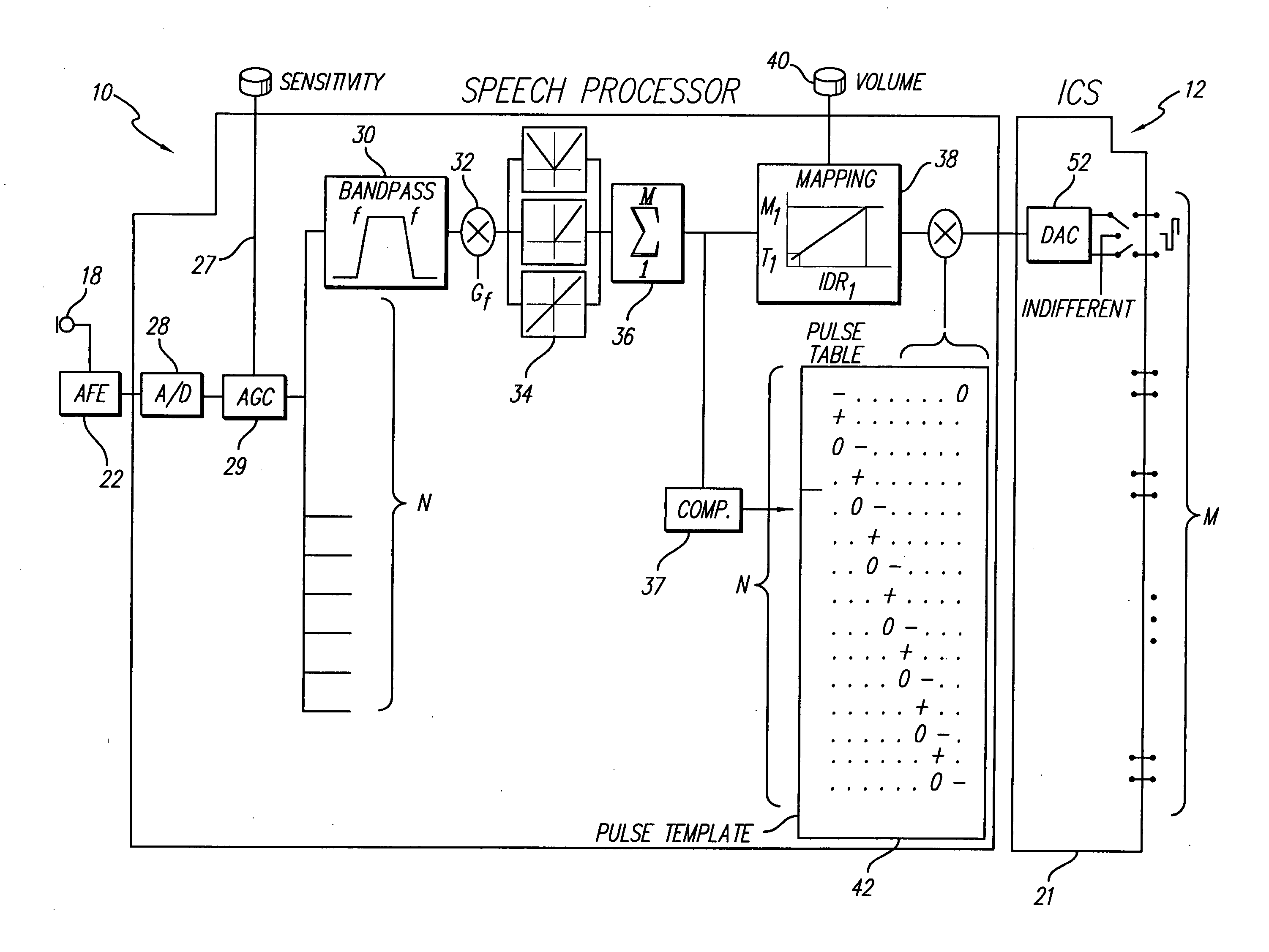
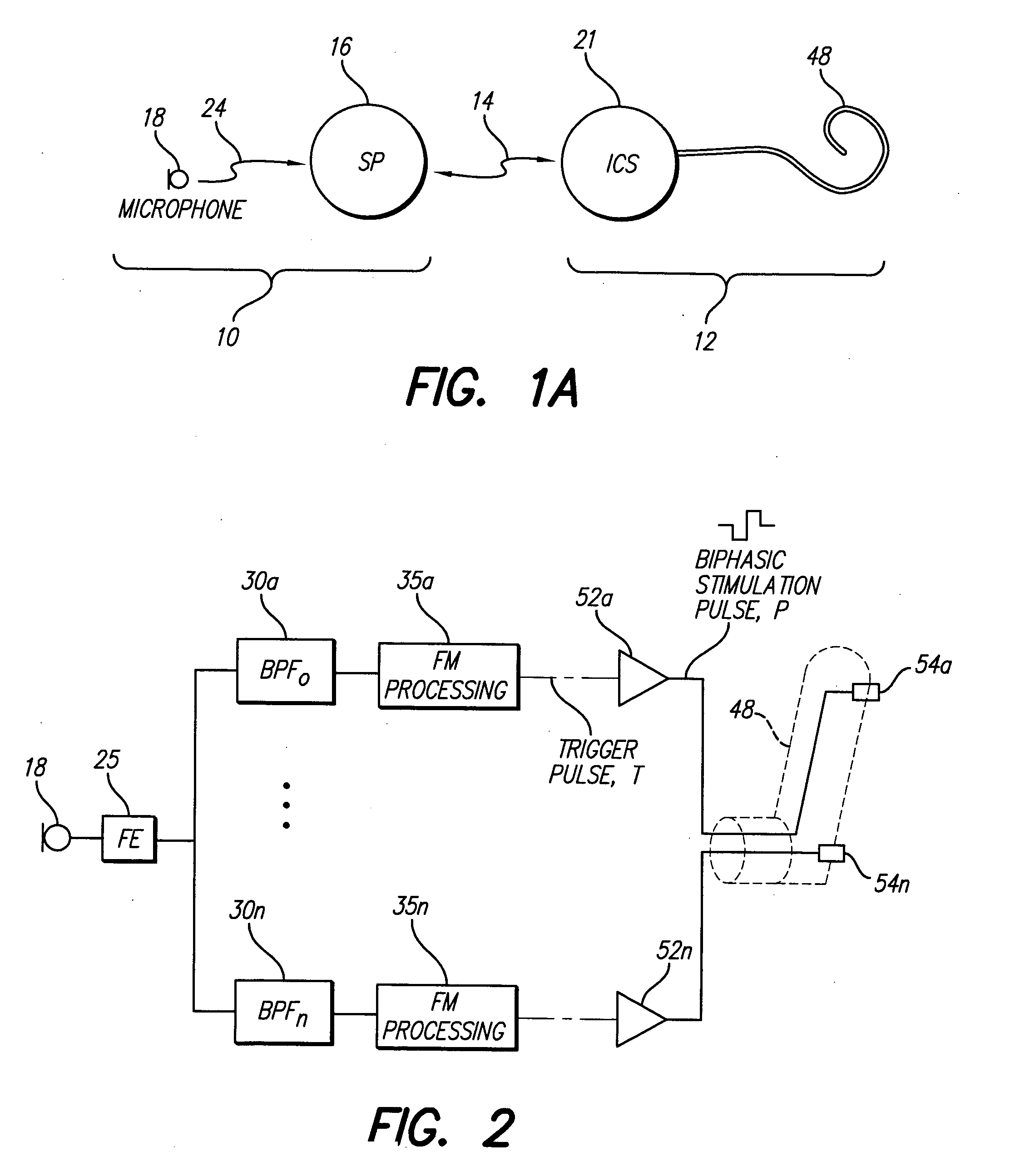
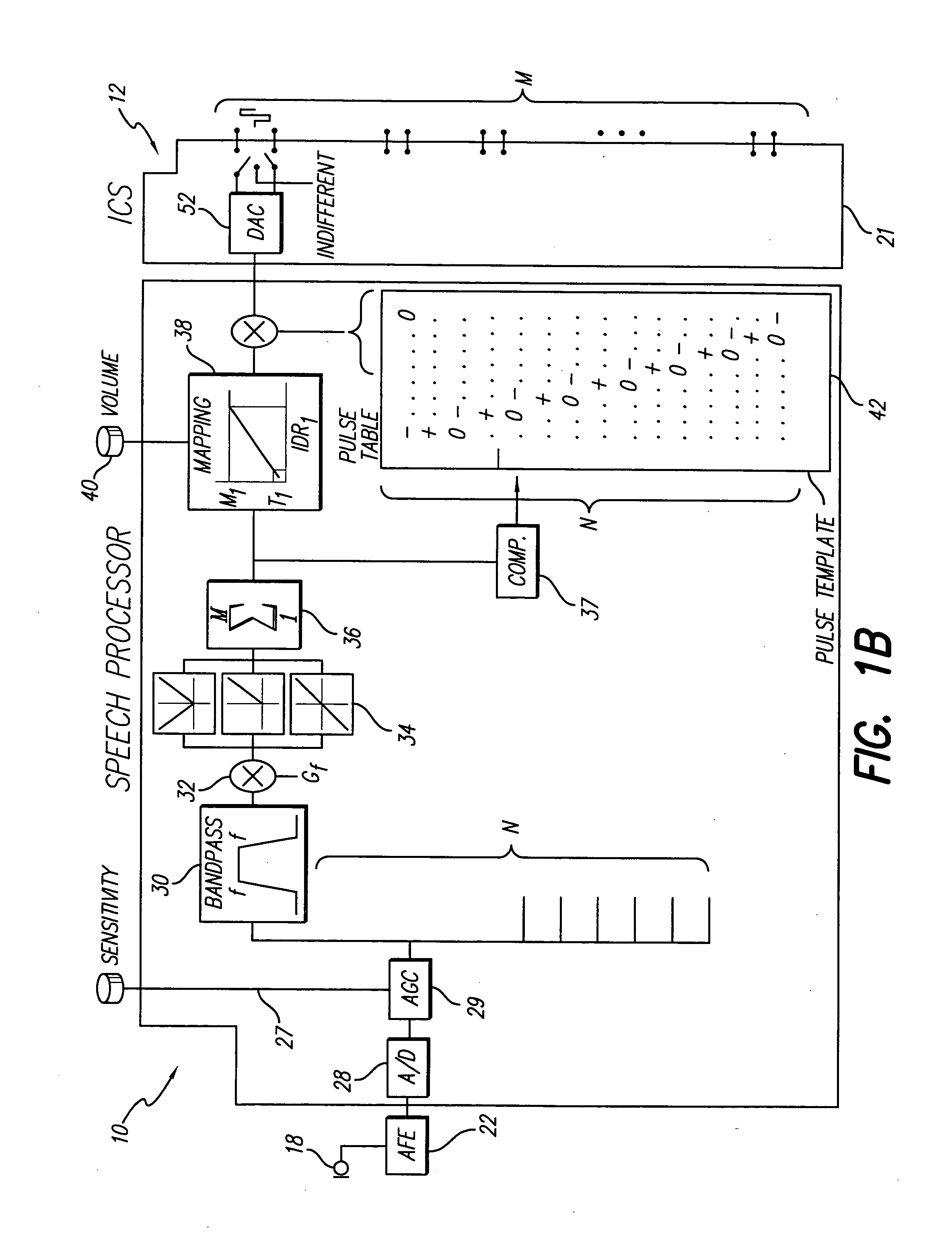
Frequency modulated stimulation strategy for cochlear implant system
InactiveUS20070239227A1Provide temporal informationReduce power consumptionElectrotherapyTectorial membraneBand-pass filter
A new speech processing strategy, termed Frequency Modulated Stimulation (FMS), is provided for use with a cochlear prosthetic. The FMS strategy advantageously mimics the neural firing patterns of the healthy cochlea by controlling when and where stimulation pulses are presented in the cochlea. The benefits of this approach are its simplicity and its ability to provide temporal information at relatively low power consumption. The stimulation that results has high temporal precision and a low pulse presentation rate. The power efficiency of the FMS strategy is three to six times greater than that of a CIS strategy with comparable thresholds. The FMS strategy depends on the probability that at any point along the basilar membrane the ganglion cells are most likely to respond during the upward motion of the basilar membrane, when the hair cells are pushed toward the tectorial membrane. At low frequencies, this probability accounts for phase locking of the neurons to each peak of the motion. At high frequency locations, phase locking occurs at integer multiples of the vibration cycles because the vibration of the membrane is faster than the refractory period of the neurons. The FMS strategy provided by the invention takes advantage of the natural behavior of the ganglion cells by outputting a biphasic pulse at the preset integer multiples of the vibration cycles. Integer multiples are determined by counting the positive-to-negative zero crossings, or equivalent frequency counting, at the output of the band pass filters that decompose the incoming audio signal(s).
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Method and Apparatus for Visual Neural Stimulation
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
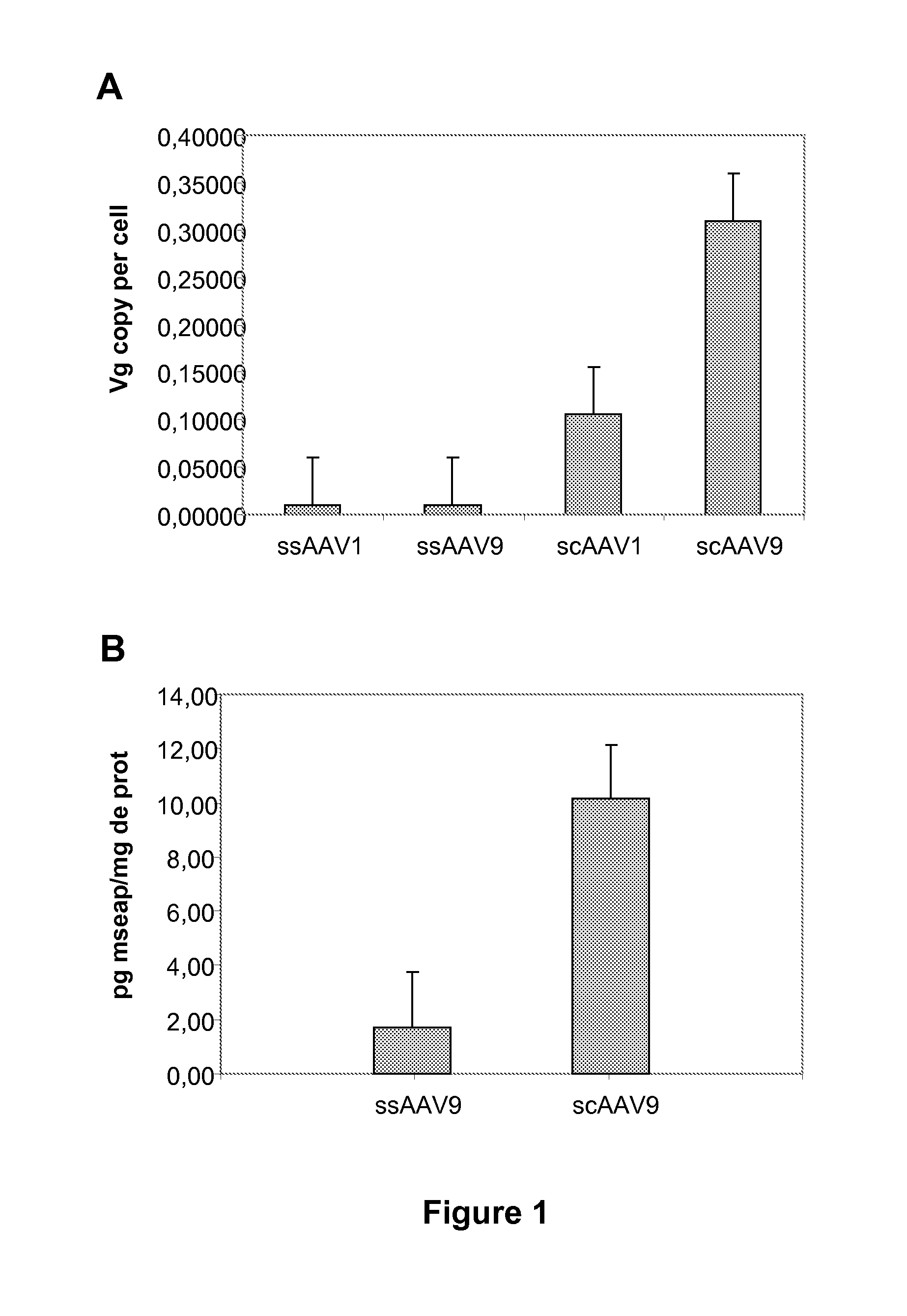
Widespread gene delivery to the retina using systemic administration of aav vectors
InactiveUS20120141422A1Efficient transductionImprove the level ofBiocideSenses disorderGene deliveryMammal
The present invention relates to compositions and methods, in particular to methods based on systemic administration of scAAV, for delivering genes to cells of the retina of mammals, and in particular to photoreceptor cells, ganglion cells, glial cells, inner nuclear layer cells or cells of the retinal pigmented epithelium.
Owner:ASSOC INST DE MYOLOGIE +4
Method for augmenting vision in persons suffering from photoreceptor cell degeneration
The invention provides compositions and methods of treating subjects afflicted with a photoreceptor disorder. Methods for treating a subject suffering from a disorder characterized by photoreceptor cell degeneration are provided, wherein a gene encoding a photosensitive protein is introduced into a retinal cell of a subject. In one aspect of the invention, the retinal cells which receive the photosensitive protein include non-photoreceptor cells such as horizontal cells, amacrine cells, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
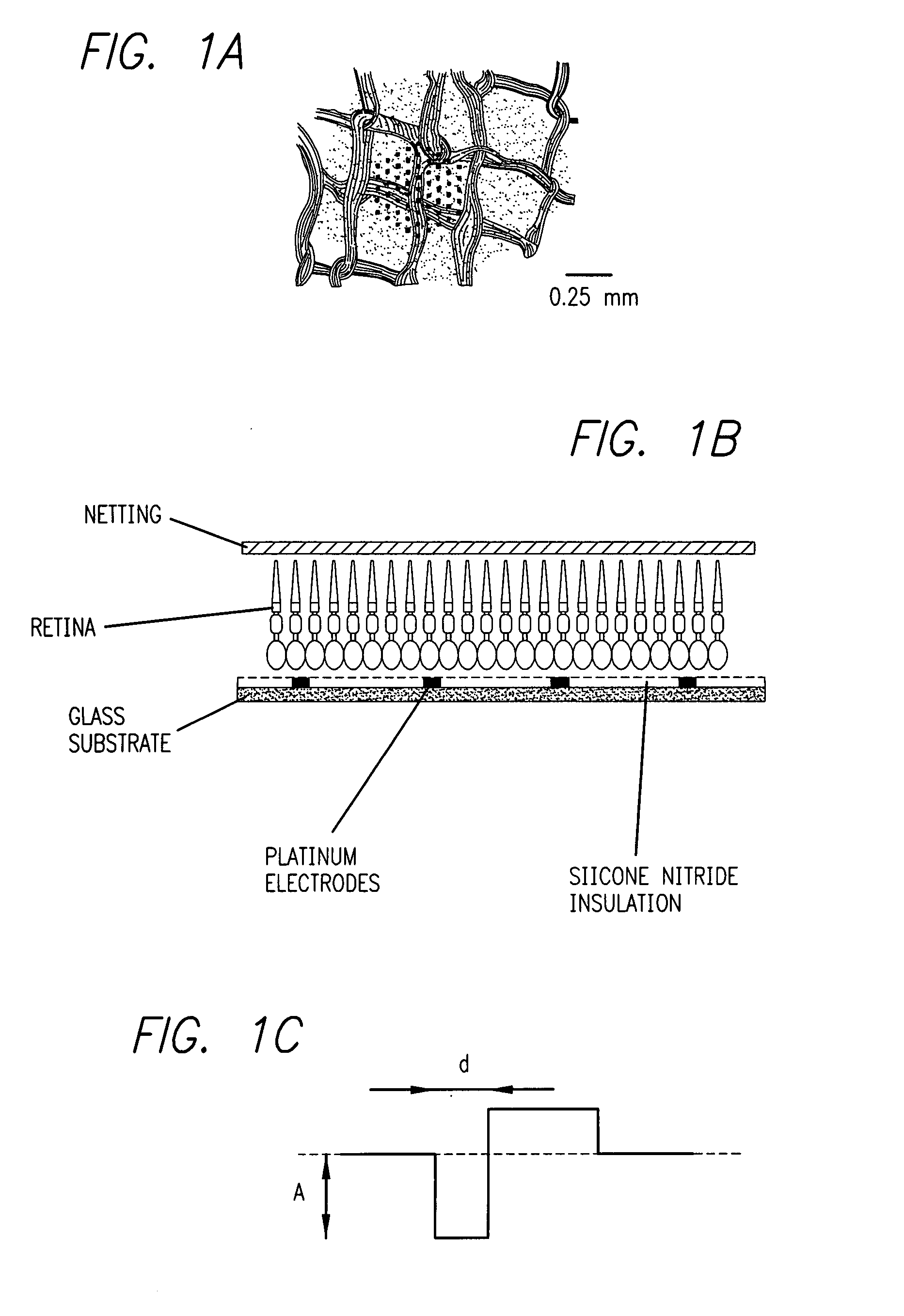
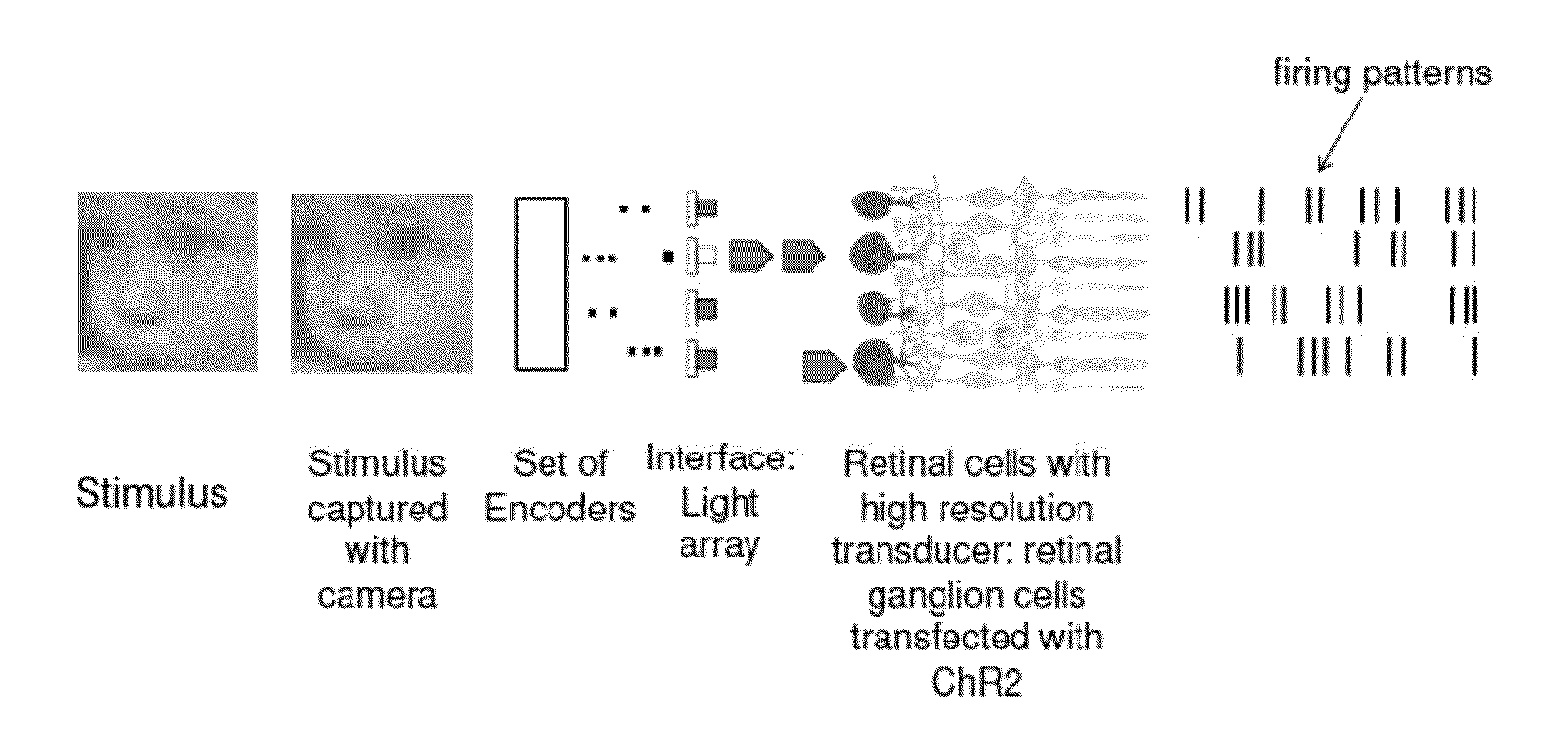
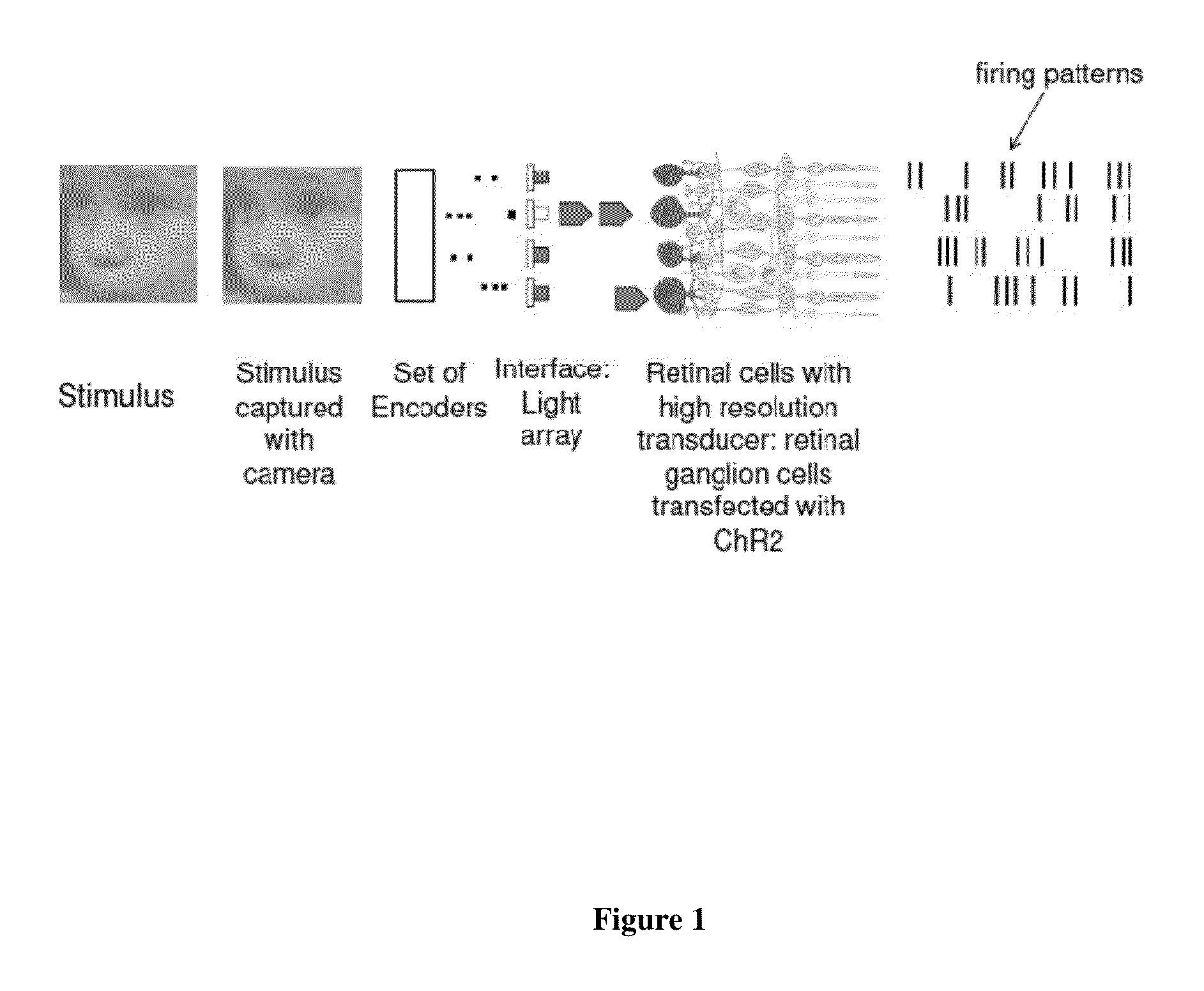
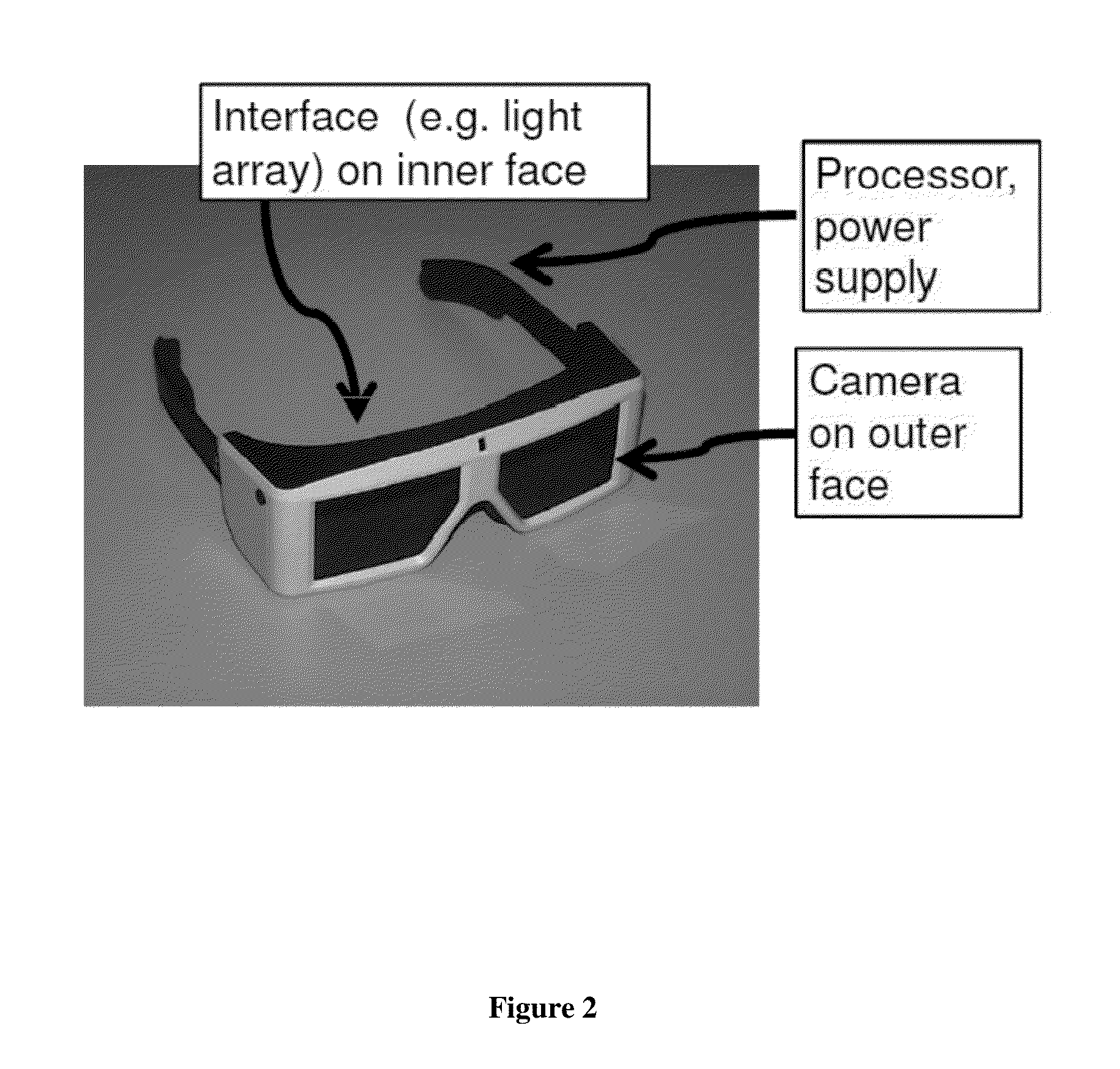
Retina prosthesis
ActiveUS20130110236A1Maximize likelihoodEasy to set upHead electrodesEye treatmentDiseaseRetinal Prosthesis
The invention provides a retinal prosthetic method and device that mimics the responses of the retina to a broad range of stimuli, including natural stimuli. Ganglion cell firing patterns are generated in response to a stimulus using a set of encoders, interfaces, and transducers, where each transducer targets a single cell or a small number of cells. The conversion occurs on the same time scale as that carried out by the normal retina. In addition, aspects of the invention may be used with robotic or other mechanical devices, where processing of visual information is required. The encoders may be adjusted over time with aging or the progression of a disease.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
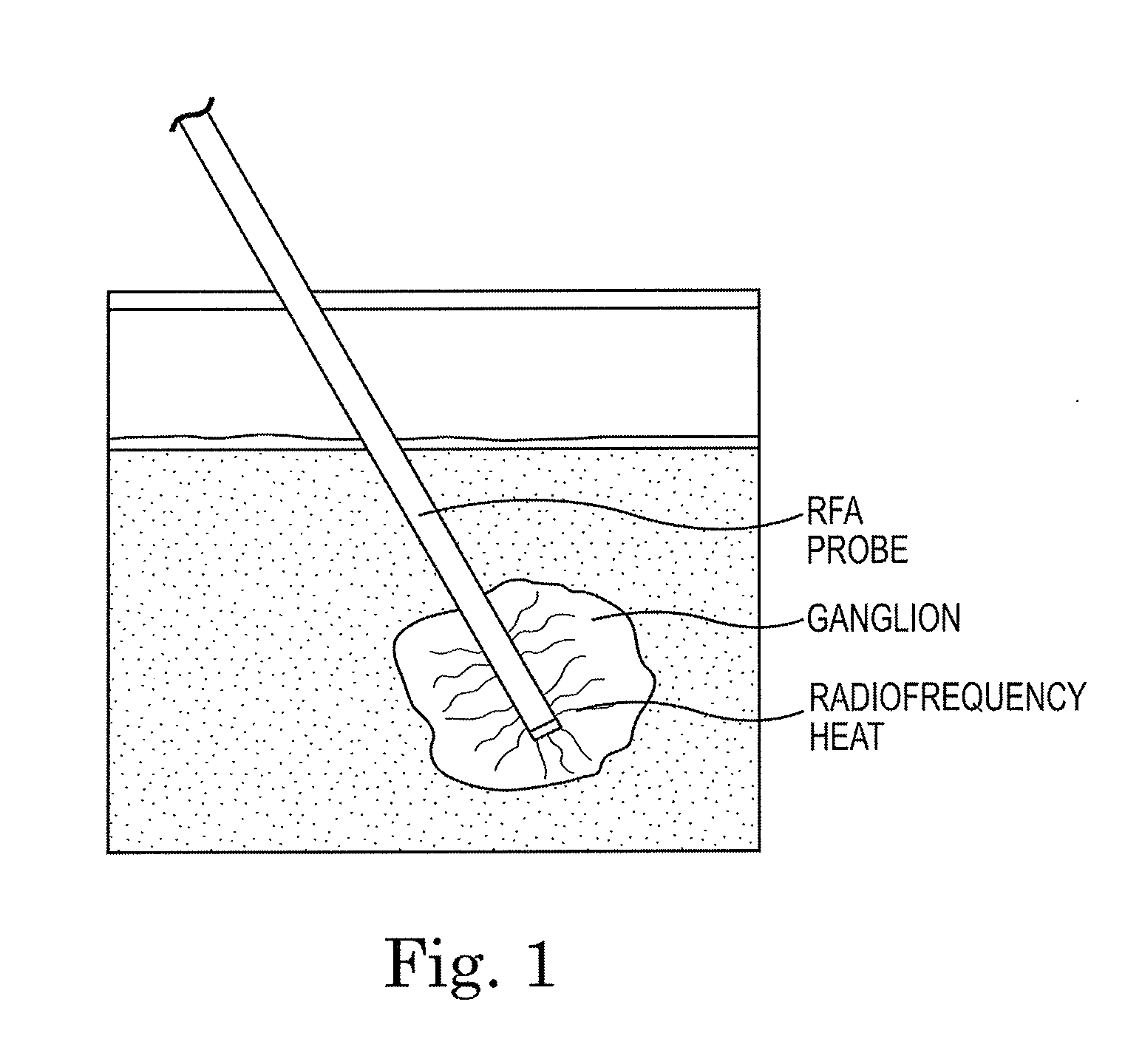
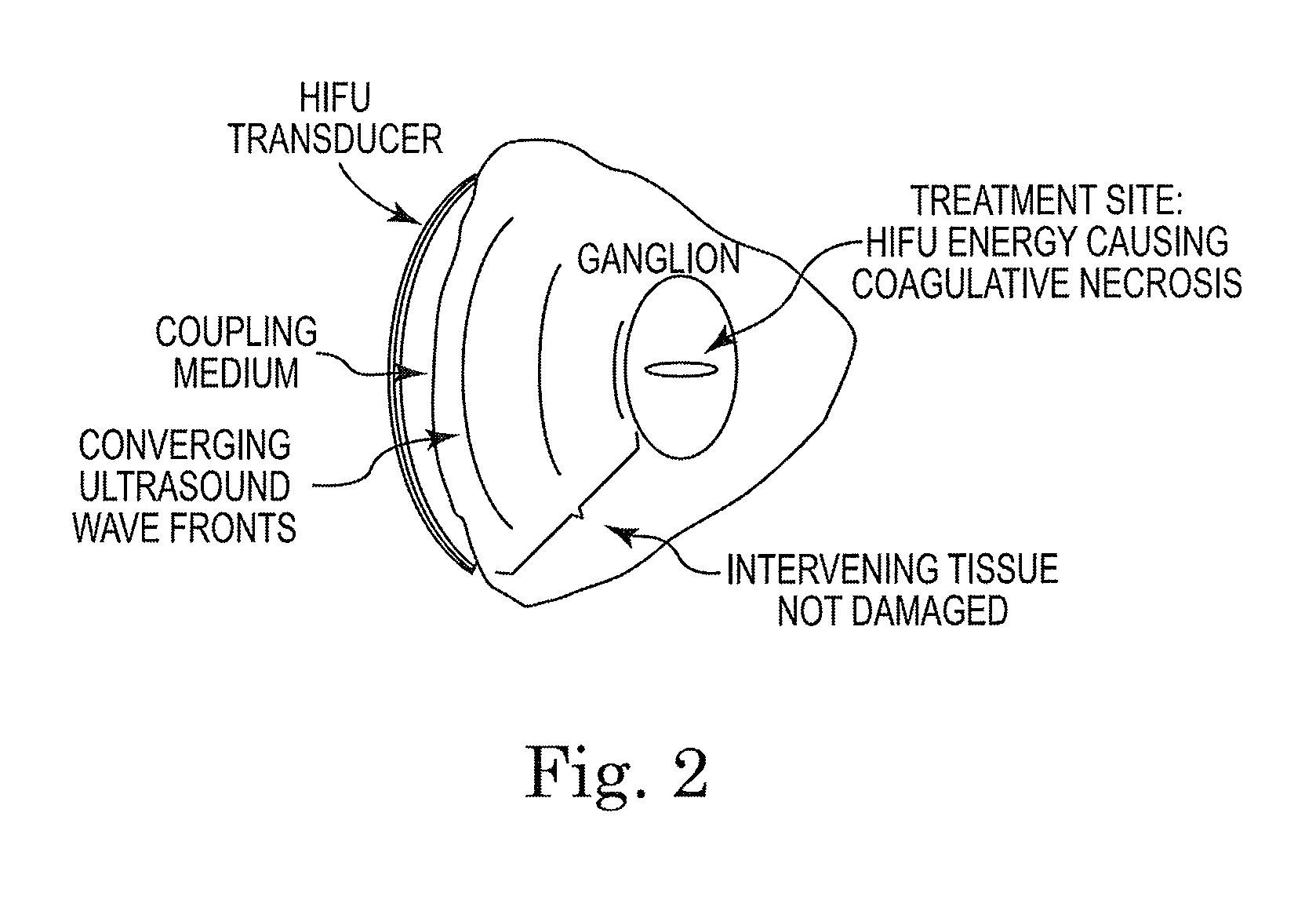
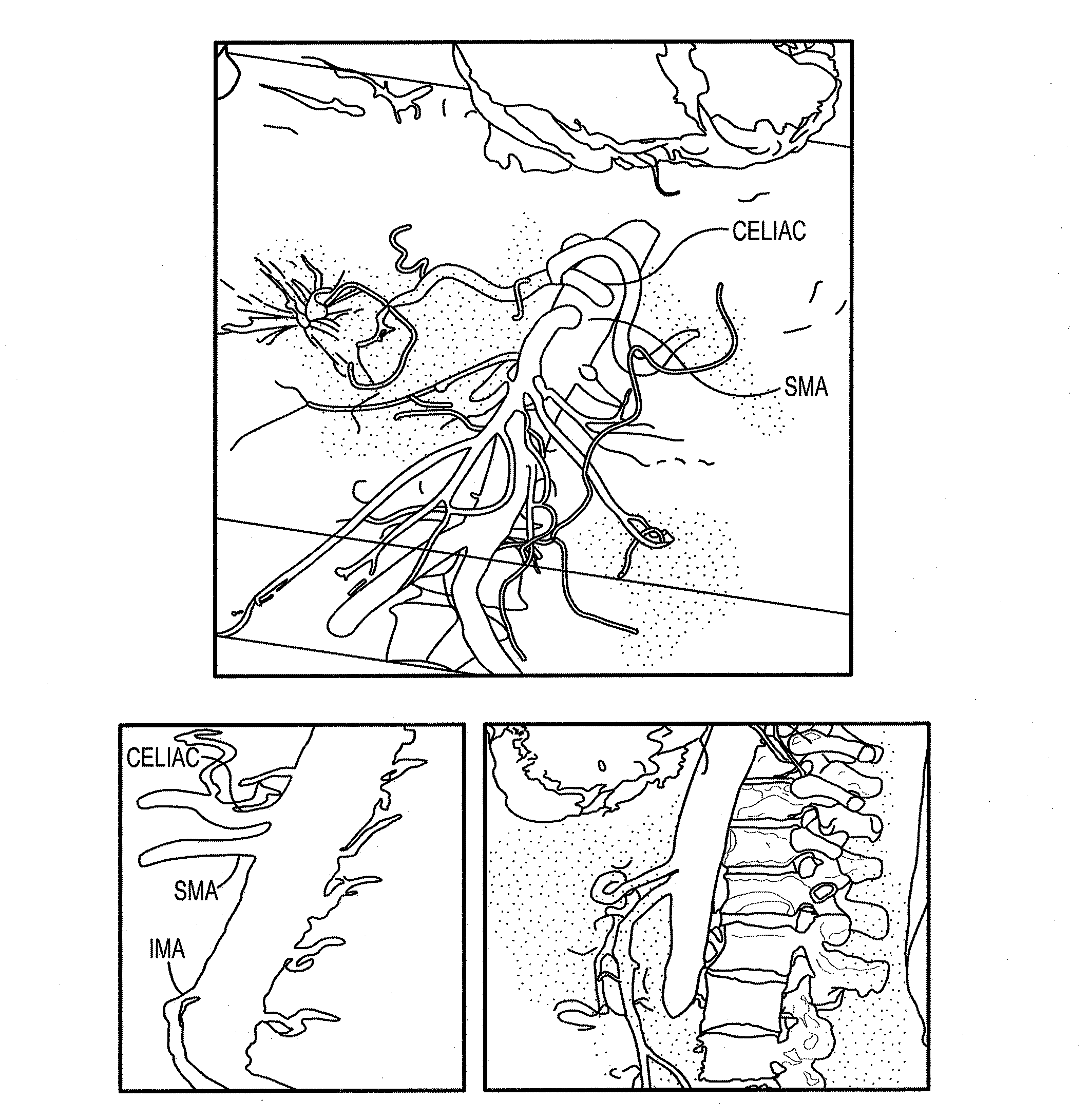
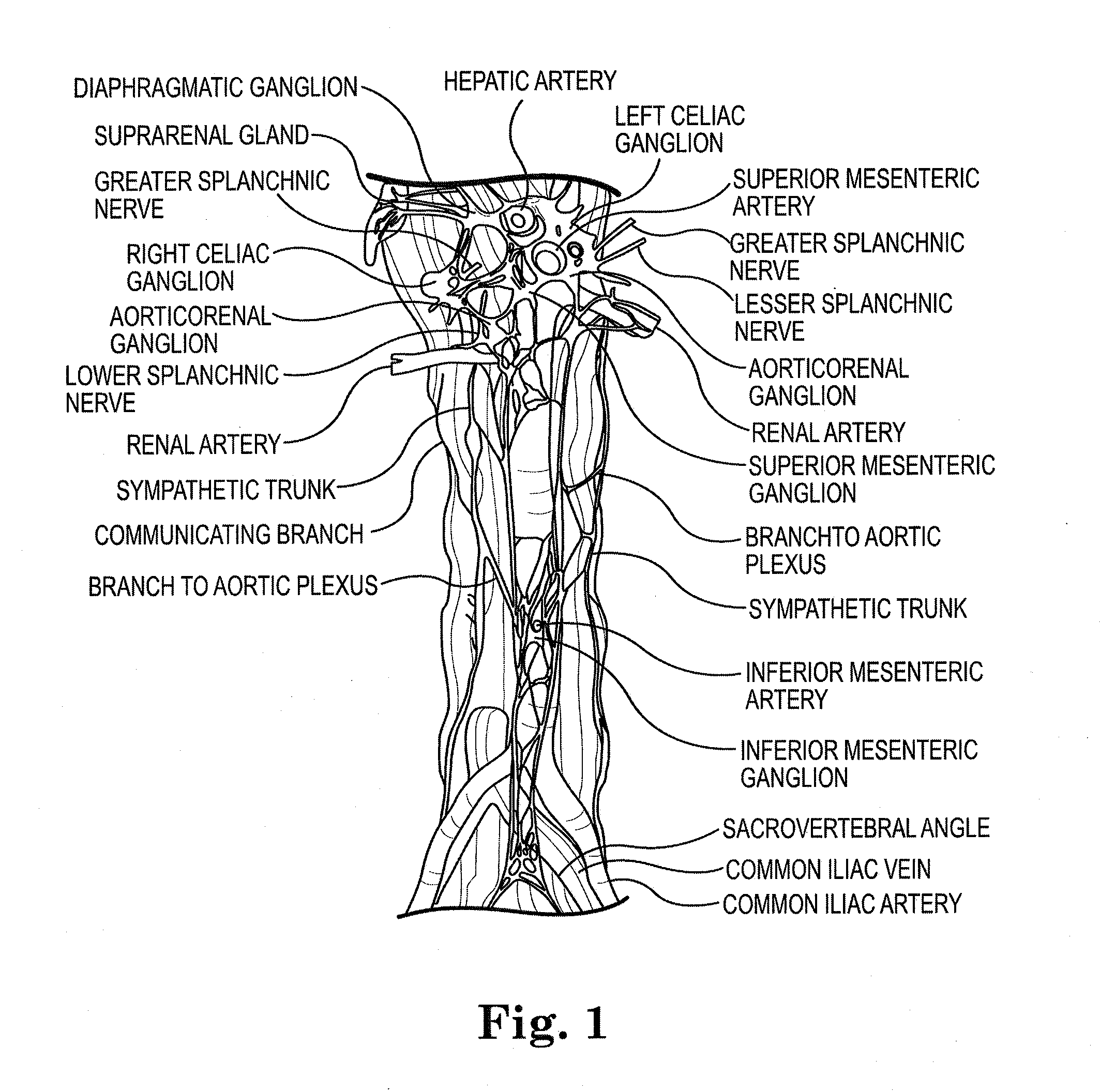
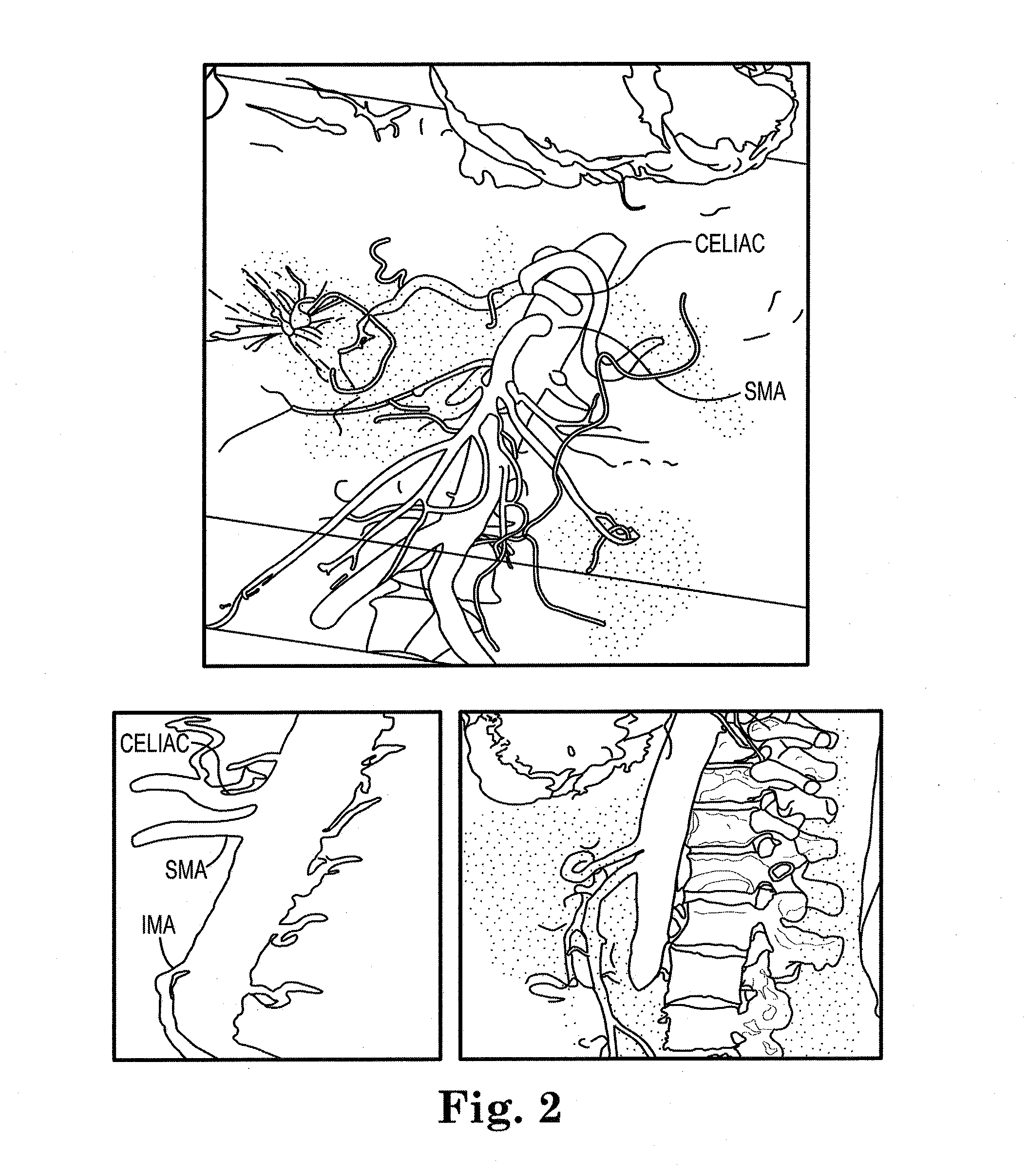
System and method of trans-abdominal pre-aortic ganglion ablation
InactiveUS20130331813A1Overcomes shortcomingEffectiveUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsAbdominal wallHigh intensity
A method of modulating a physiological parameter of a patient by percutaneously or transcutaneously disabling one or more pre-aortic ganglion cells within a pre-aortic ganglion via the anterior abdominal wall and improving the physiological parameter is provided. The pre-aortic ganglion cells may be disabled by applying radiofrequency, high intensity or low intensity focused ultrasound.
Owner:ENIGMA MEDICAL
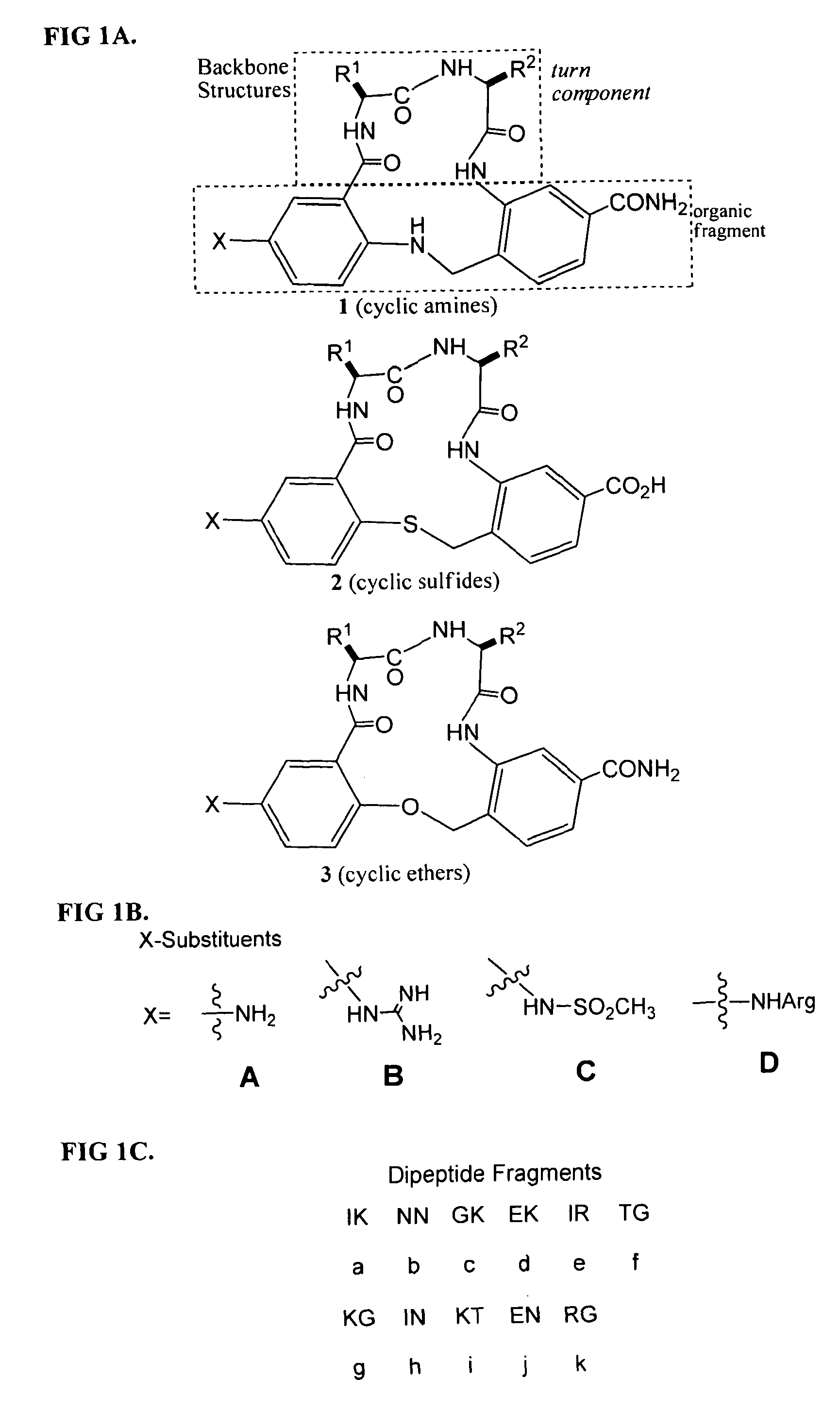
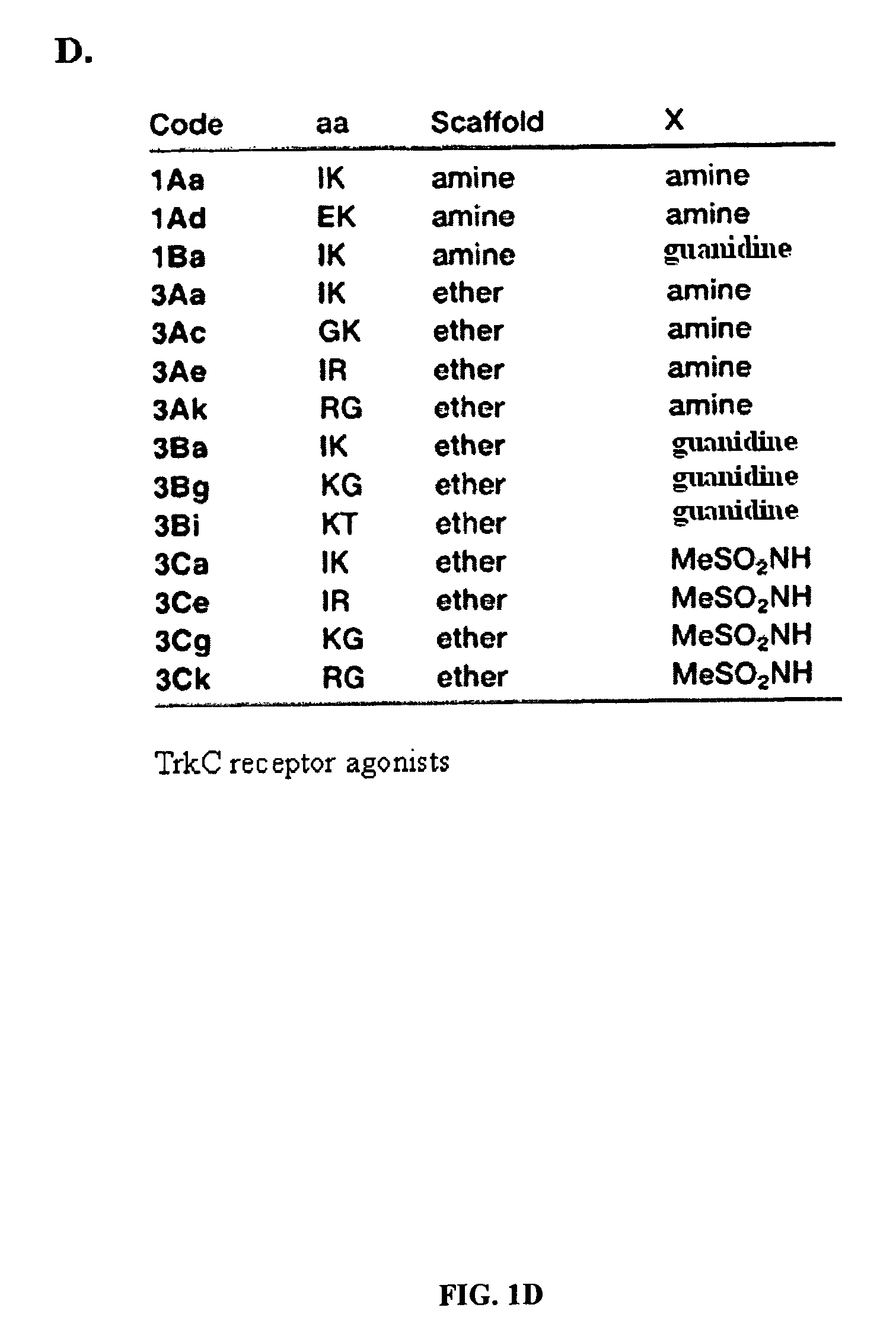
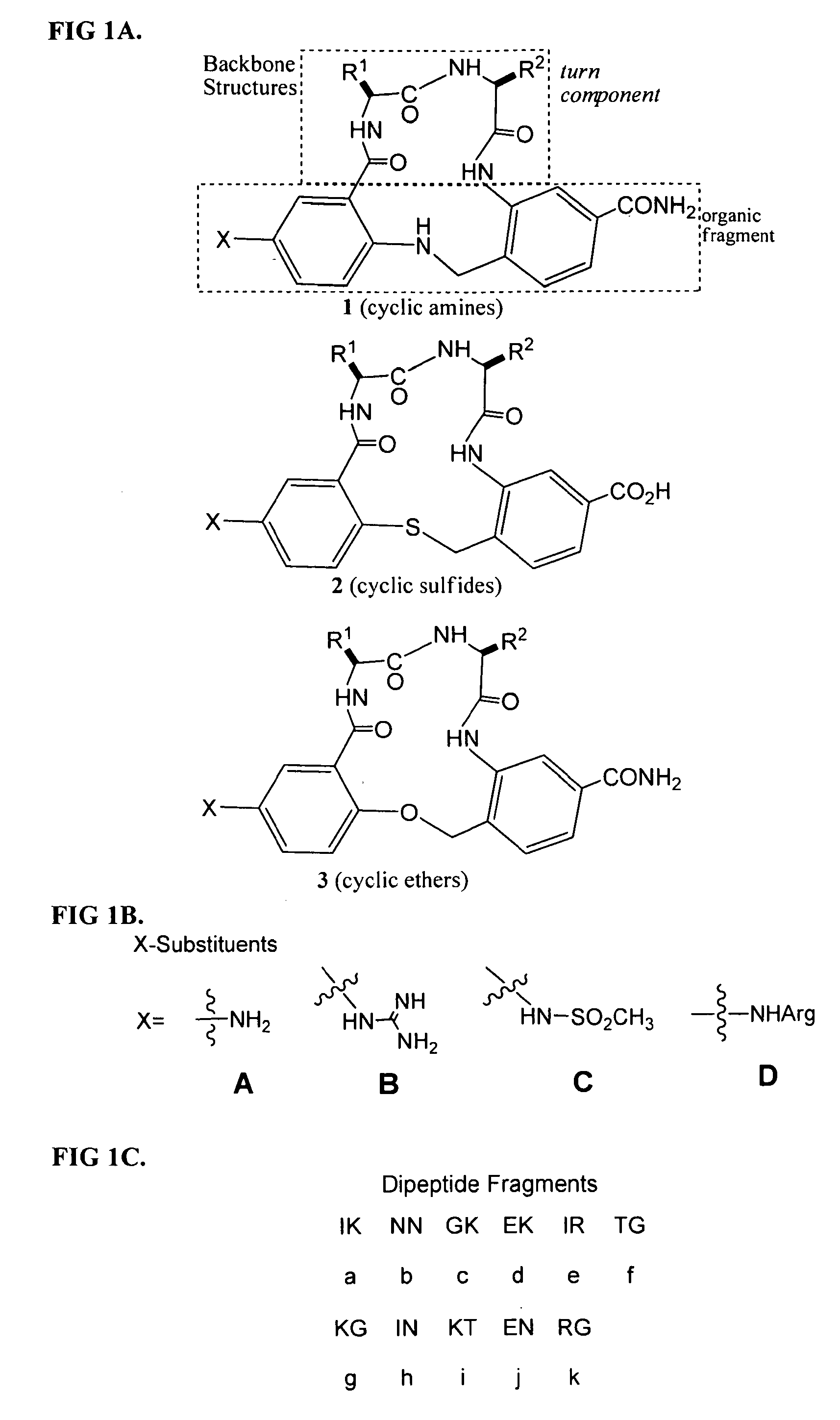
Methods of use of trk receptor modulators
ActiveUS20100048461A1Stable and easy to administerEasy to manageOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCyclic compoundTrk receptor
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death and / or glaucoma using modulators of neurotrophic receptors that comprise β-turn peptidomimetic cyclic compounds or derivatives thereof. The neurotrophic receptor modulators can be used alone, in combination and / or in conjunction with one or more other compounds, molecules or drugs that treat or prevent ocular hypertension, RGC death and / or glaucoma.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
hNT-neuron human neuronal cells to replace ganglion cells
Disclosed herein is the treatment of vision loss in a mammal by transplanting an effective amount of hNT-Neuron cells. The treatment can be accomplished by injecting the cells into the retinal area of the eye. Additionally, the cells can be injected into the visual cortex of the brain. Conditions to be treated are vision loss due to optic nerve damage, including glaucoma, optic nerve sheath meningioma and glioma, Graves' ophthalmopathy, benign or malignant orbital tumors, metastatic lesions, tumors arising from the adjacent paranasal sinuses or middle cranial fossa, giant pituitary adenomas, brain tumors or abscesses, cerebral trauma or hemorrhage, meningitis, arachnoidal adhesions, pseudotumor cerebri, cavernous sinus thrombosis, dural sinus thrombosis, encephalitis, space-occupying brain lesions, severe hypertensive disease or pulmonary emphysema.
Owner:LAYTON BIOSCI
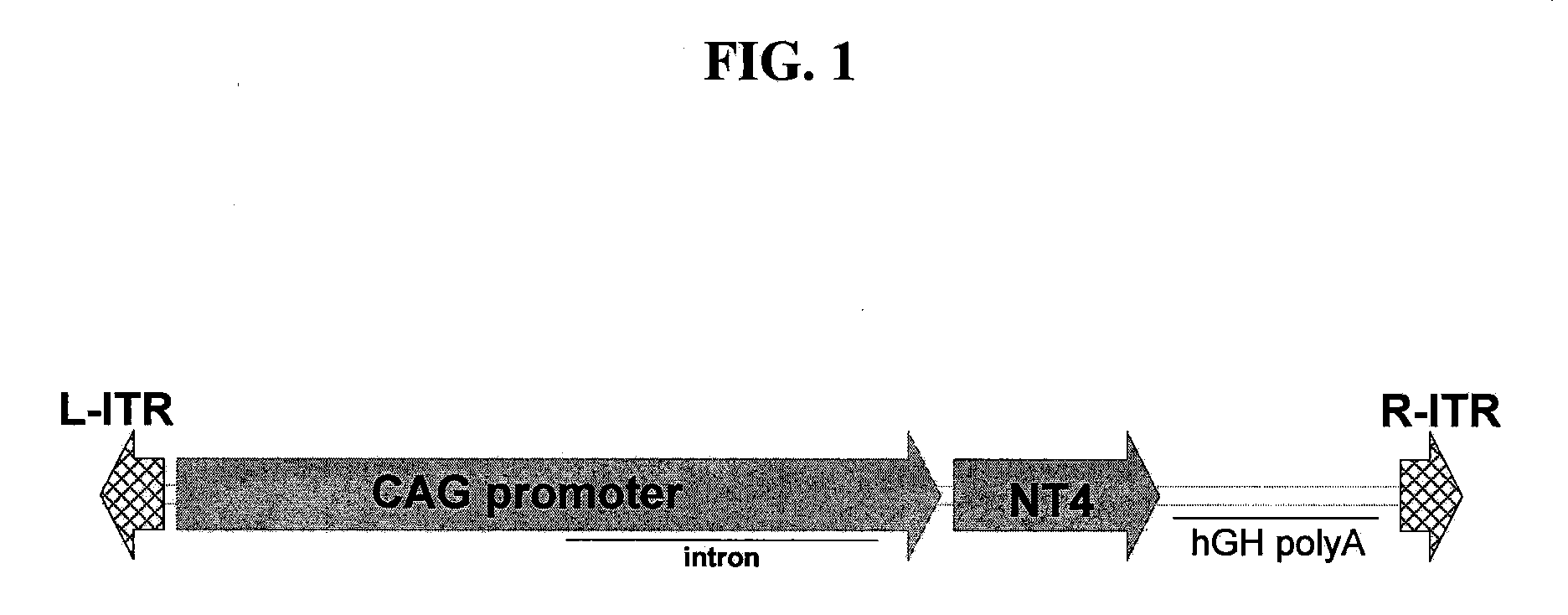
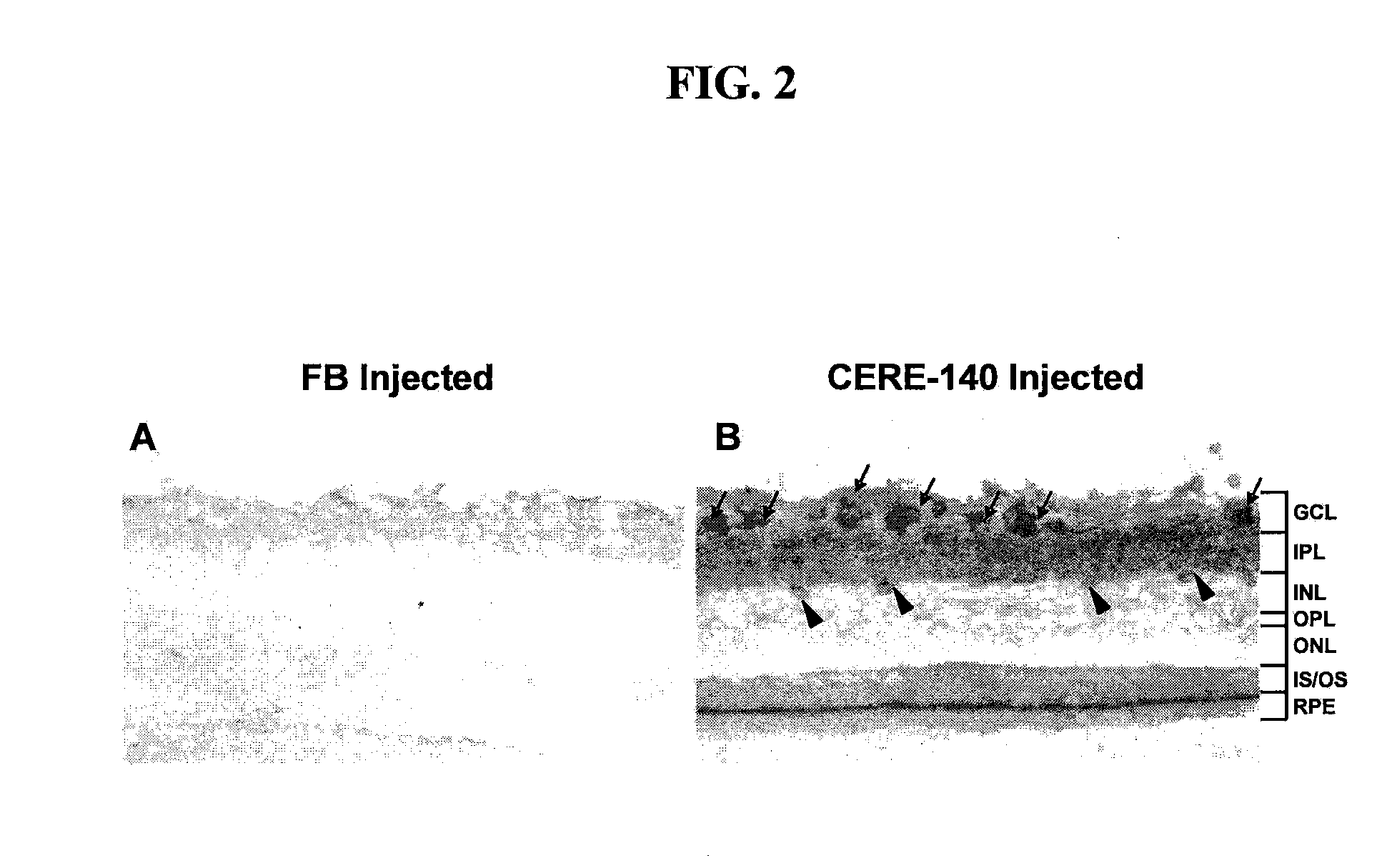
Rescue of Photoreceptors by Intravitreal Administration of an Expression Vector Encoding a Therapeutic Protein
InactiveUS20090202505A1Increase amplitudeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseTherapeutic protein
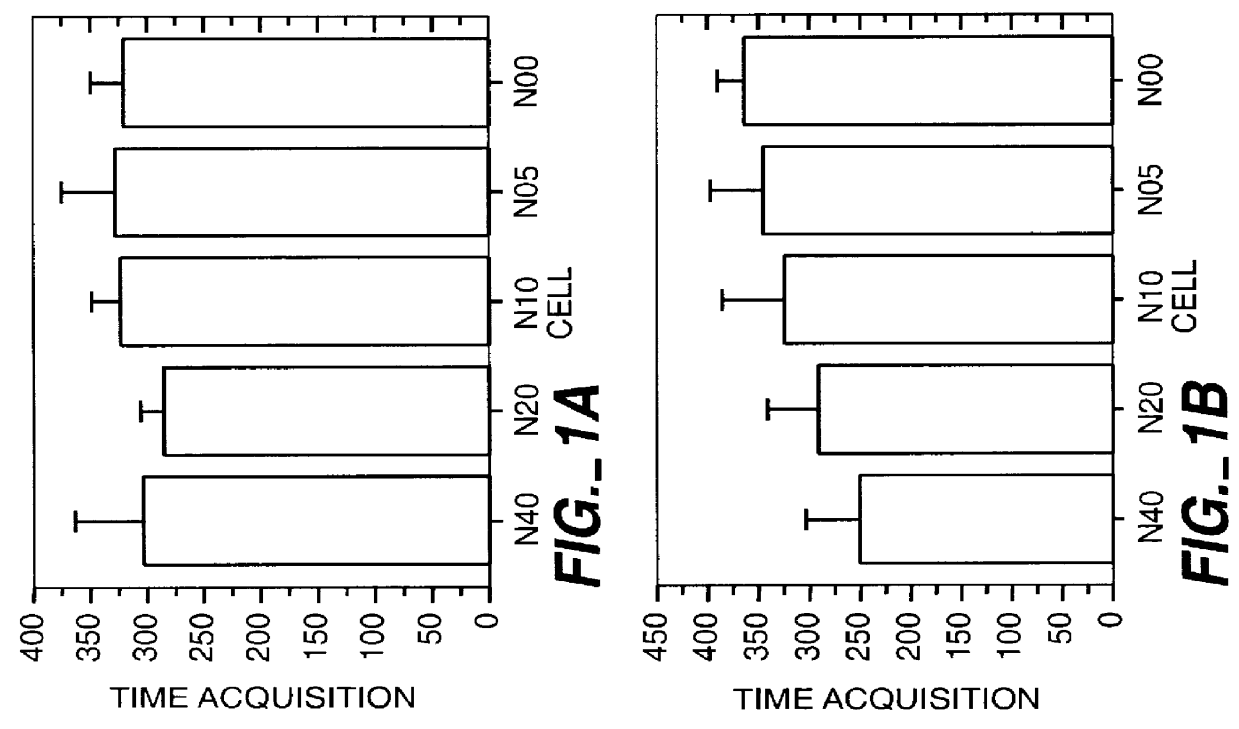
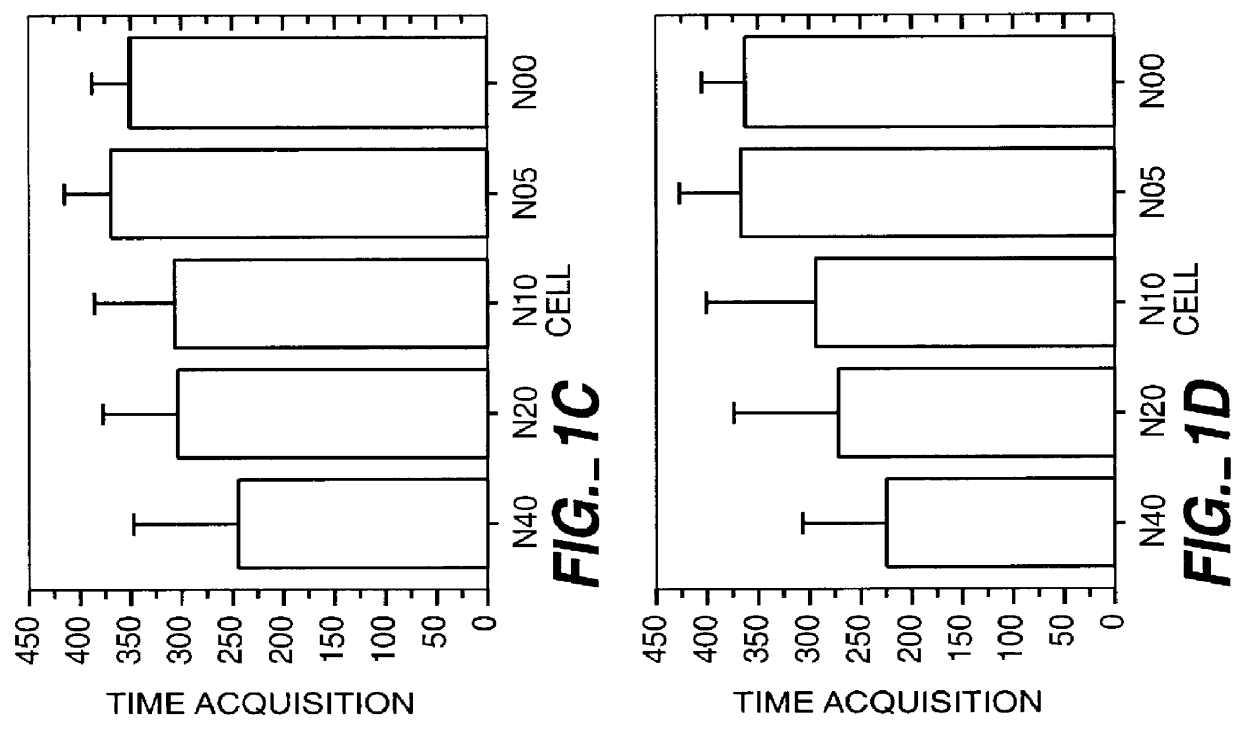
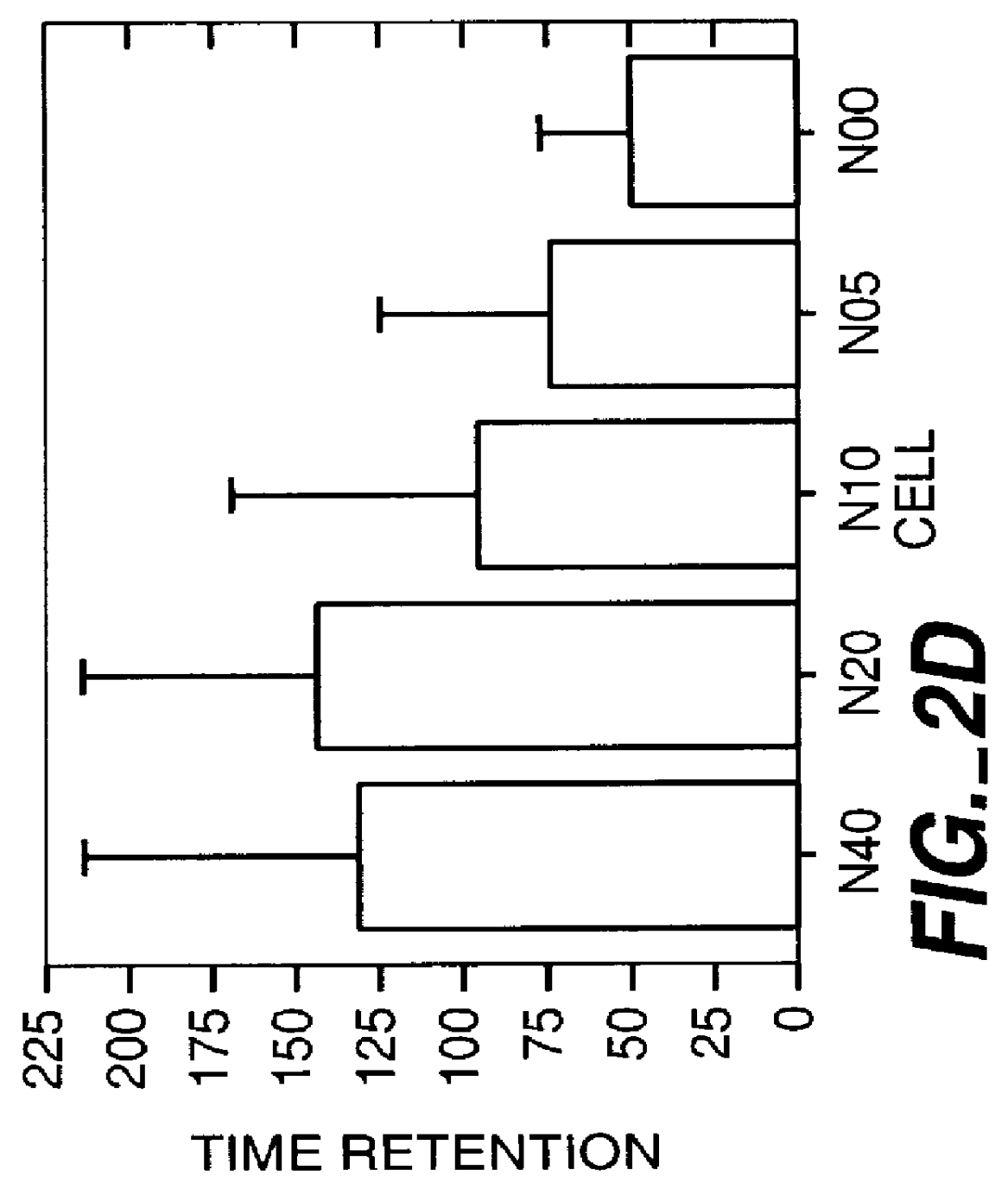
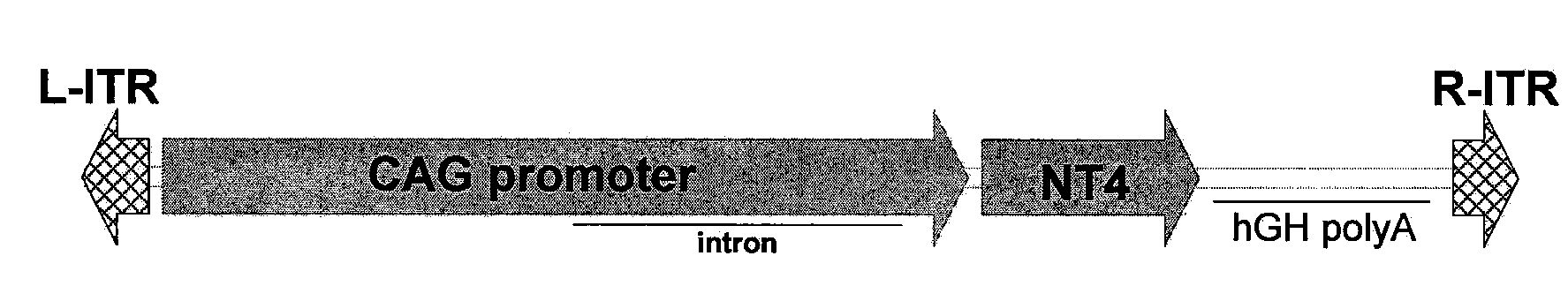
The invention provides methods for treating ocular diseases using a recombinant vehicle to express a protein useful in the treatment of ocular disease, with particular preference for use of neurotrophin-4 (NT4) for targeting subpopulations of cells in the retina. A genetically engineered gene transfer vector containing sequences encoding a growth factor such as neurotrophin-4 (NT4) is used to transduce cells of the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer, in situ, via administration of the vector intravitreally. Accordingly, methods are disclosed for treating subjects in need thereof by therapeutic protein delivery via a recombinant expression vector, including rescue of photoreceptors by targeting the RGC layer subpopulation of retinal cells.
Owner:CEREGENE
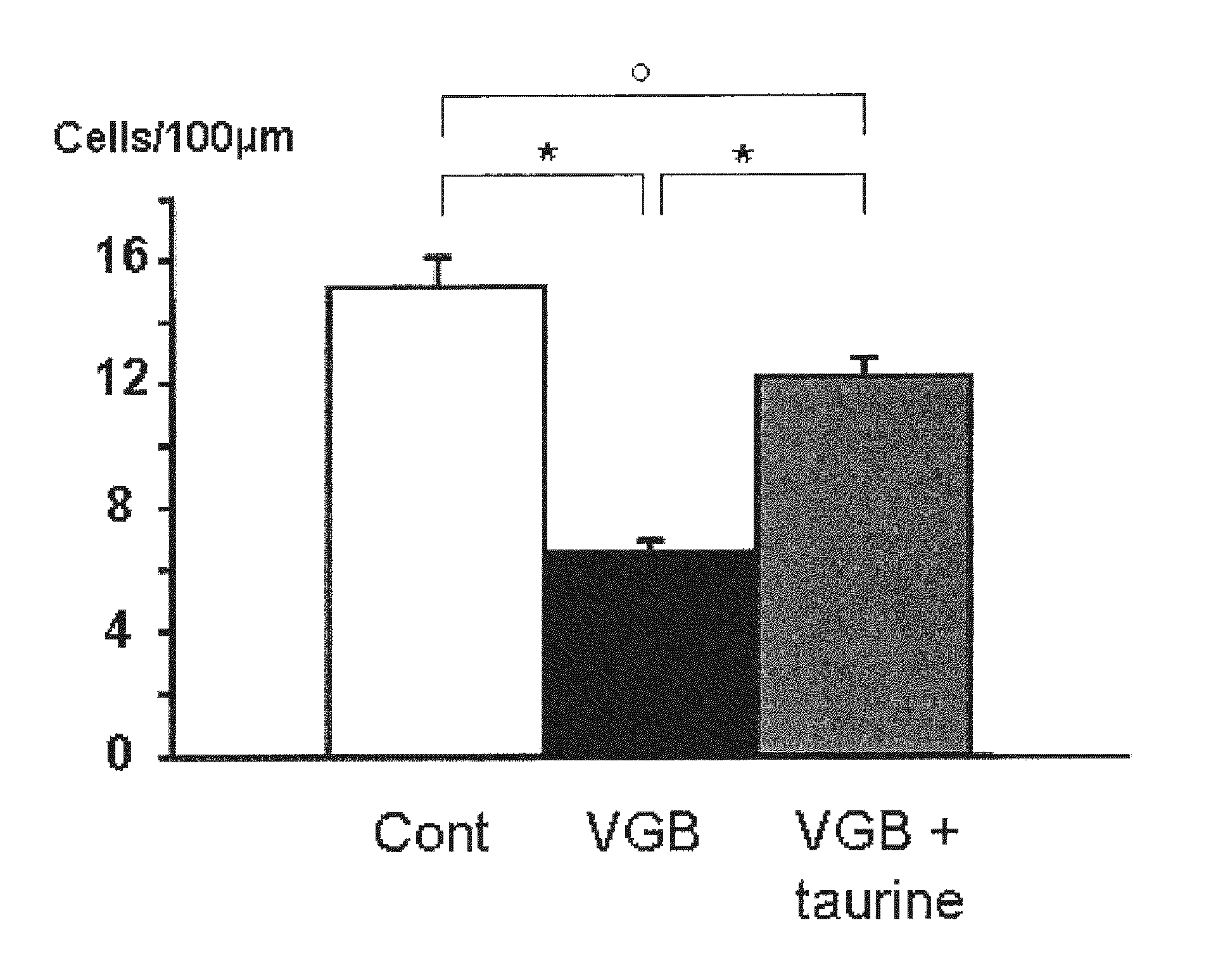
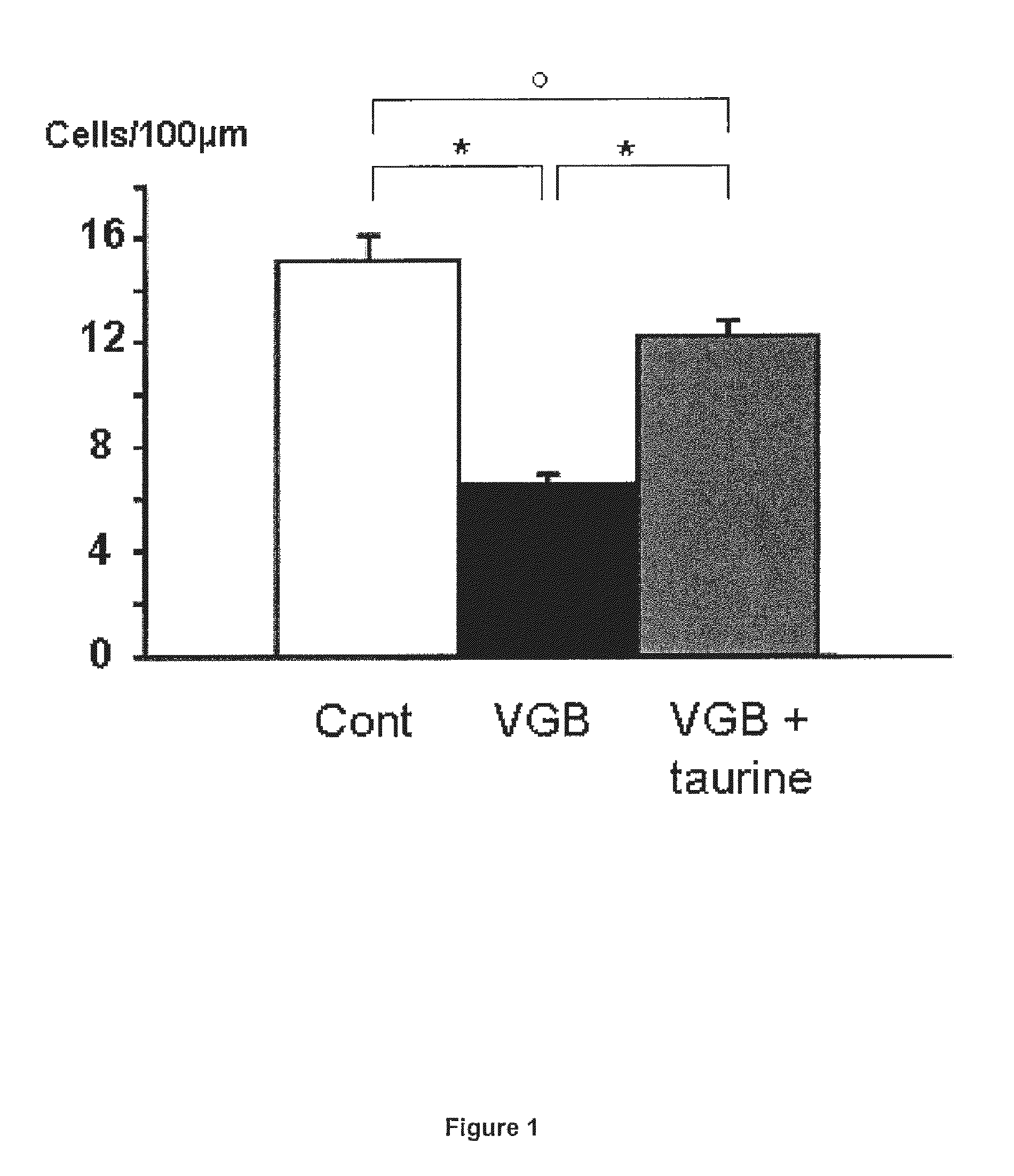
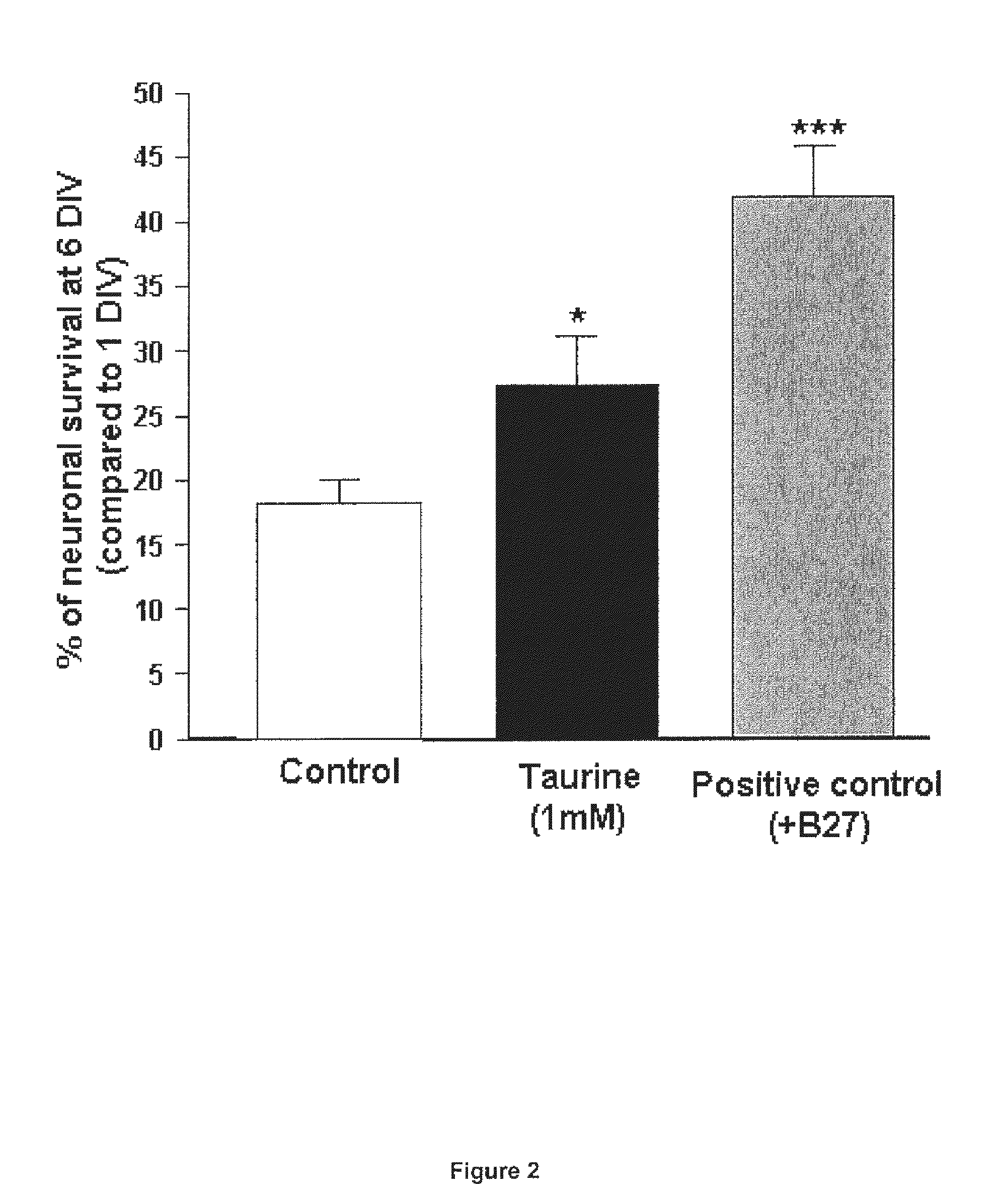
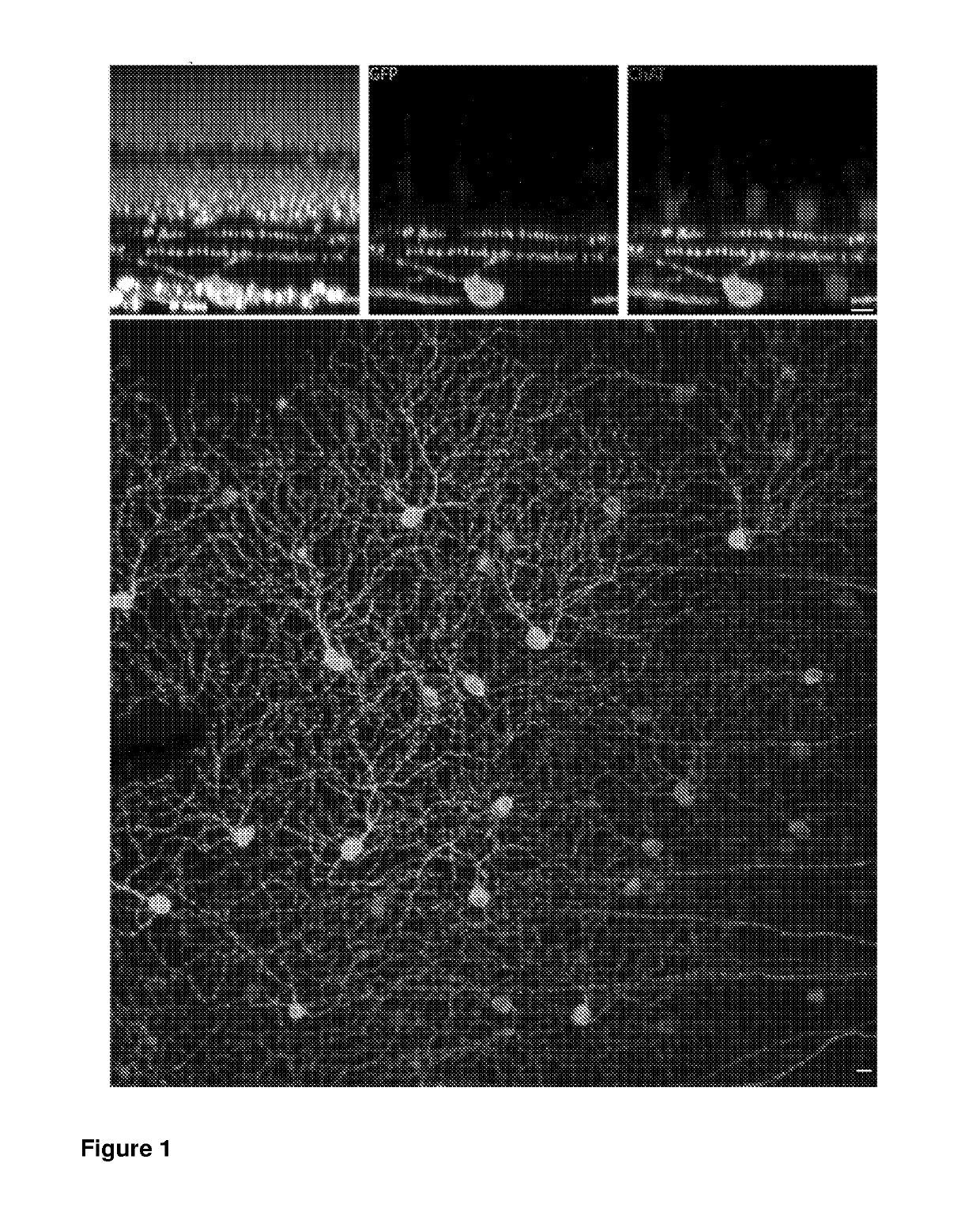
Taurine or taurine-like substances for the prevention and treatment of a disease associated with retinal ganglion cell degeneration
InactiveUS20120027723A1Prevent degradationPrevention and treatment of a diseaseHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseTaurine biosynthesis
The present invention relates to taurine or taurine-like substances for the prevention and treatment of a disease associated with retinal ganglion cell degeneration. More particularly the invention relates to a substance selected from the group consisting of taurine, a taurine precursor, a taurine metabolite, a taurine derivative, a taurine analog and a substance required for the taurine biosynthesis for the prevention and treatment of a disease associated with retinal ganglion cell degeneration.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
SynP198, a promoter for the specific expression of genes in direction selective retinal ganglion cells
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid molecule comprising, or consisting of, the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 or a nucleic acid sequence of at least 400 bp having at least 80% identity to said sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, wherein said isolated nucleic acid molecule specifically leads to the expression in direction selective retinal ganglion cells of a gene when operatively linked to a nucleic acid sequence coding for said gene.
Owner:FRIEDRICH MIESCHER INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Method and apparatus for optogenetic treatment of blindness including retinitis pigmentosa
ActiveUS20100268150A1Efficient activationBehavioral improvementElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsOptogeneticsRetinitis pigmentosa
An apparatus for in vivo electroporating a plasmid into a retina of any eye includes a first electrode with a first polarity of voltage placed in contact with a cornea of the eye, a second electrode with an opposite second voltage at least in part behind the retina, and a pulsed voltage source for providing a pulsed DC voltage with an optimized field strength amplitude, frequency, number of pulses, group repetition rate and duration of pulse and group repetition, which are optimized for transfection of the channelrhodospsin-2 (ChR2) gene into the retinal ganglion cells. An in vivo method for treating retinal ganglion cells in an eye without use of viral transfection includes the steps of nonviral in vivo delivering a channelrhodospsin-2 (ChR2) gene to target the specific (retinal ganglion) cells of a retina by intravitreous injection of plasmid DNA, electroporating the plasmid into the retina and use of image intensification device for stimulating the retinal ganglion cells with ambient lighting conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lighting apparatus
ActiveUS20180153018A1Improve readabilityLight source combinationsElectrical apparatusLight equipmentRetinal ganglion cell
A lighting apparatus includes a light emitter that emits a first illumination light as a display illumination light. The optical characteristics of the first illumination light are: a correlated color temperature in a range from 3800 K to 6500 K, inclusive; chromaticity deviation Duv in a range from −9 to 0, inclusive; and an intrinsic photosensitive retinal ganglion cell (ipRGC) stimulus level of at least 0.6, the ipRGC stimulus level being a value standardized by setting an ipRGC stimulus level of light emitted from a D65 light source to 1.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109055428AImprove survival rateInfection effect is goodSenses disorderGenetic material ingredientsBeta globinIntraocular pressure
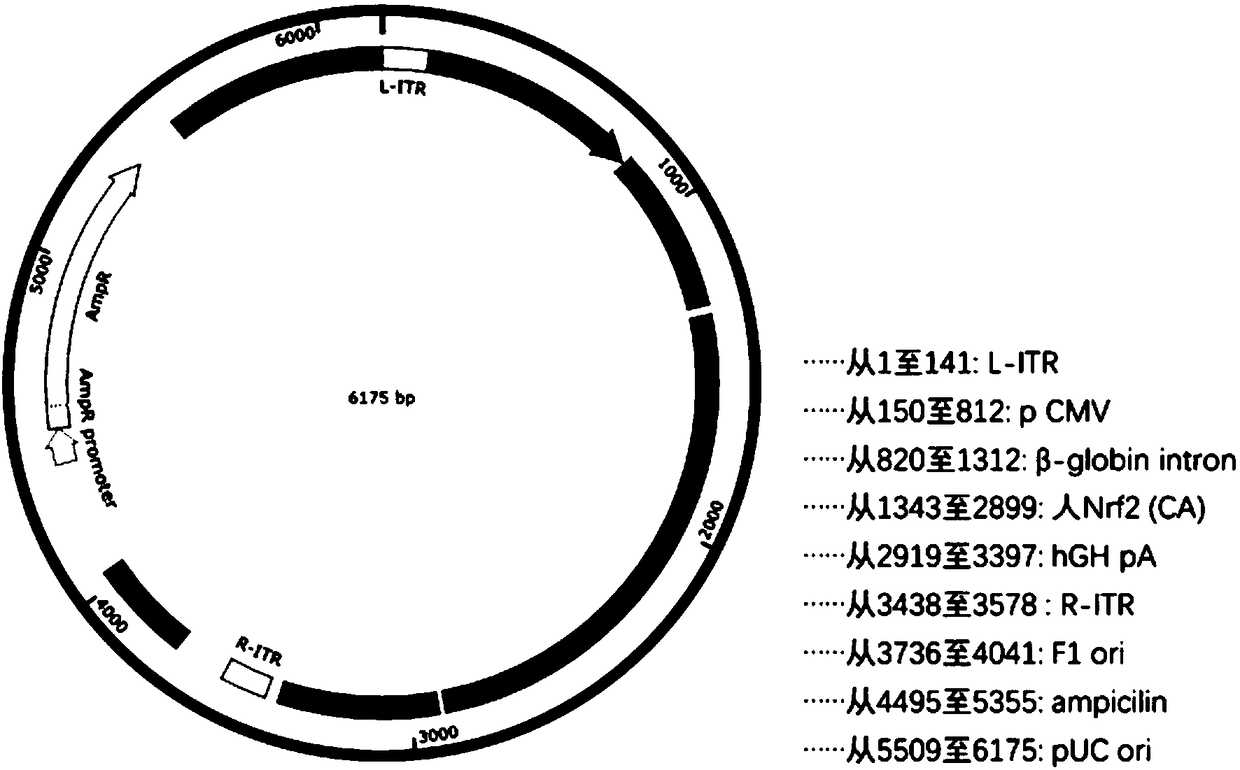
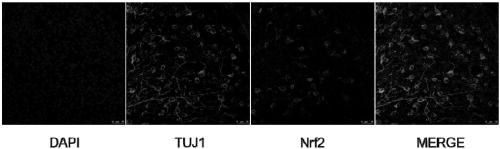
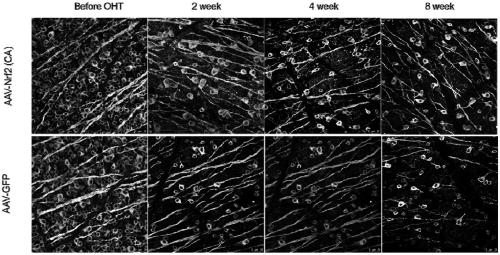
The invention relates to a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector. The recombinant adeno-associated virus vector comprises constitutively active human Nrf2 (Nrf2 (CA)), a CMV promoter / enhancer, beta-globin intron for increasing gene expression, human growth hormone poly (A) tail sequence, etc. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector and the application of the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector or a composition containing the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector in preparing a medicine for treating glaucoma retinal ganglion cell denaturation. The recombinant adeno-associated virus vector provided by the invention can obviously reduce the intraocular pressure of a mouse, increase the survival rate of RGCs of the mouse, and effectively treat glaucoma retinal ganglion cell pathological changes.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method of providing ocular neuroprotection
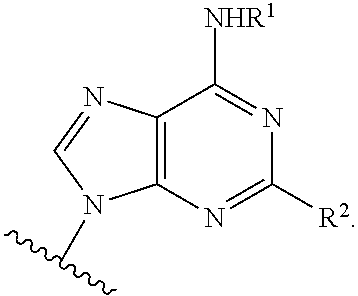
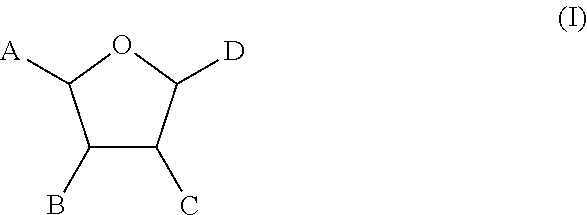
InactiveUS20140275128A1Preventing and reducing and treating damageReduce cell damageBiocideSenses disorderMedicinePurine derivative
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
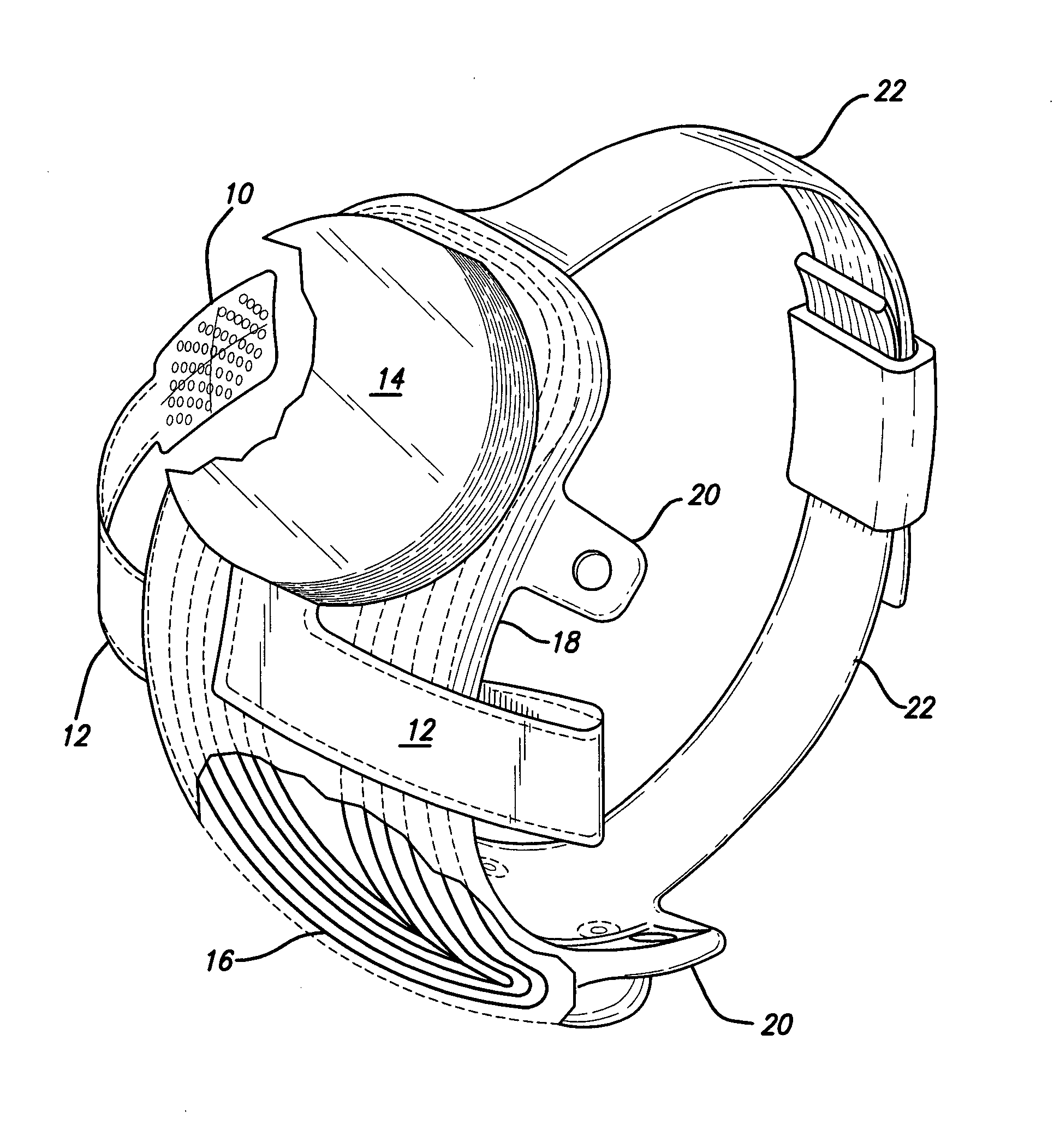
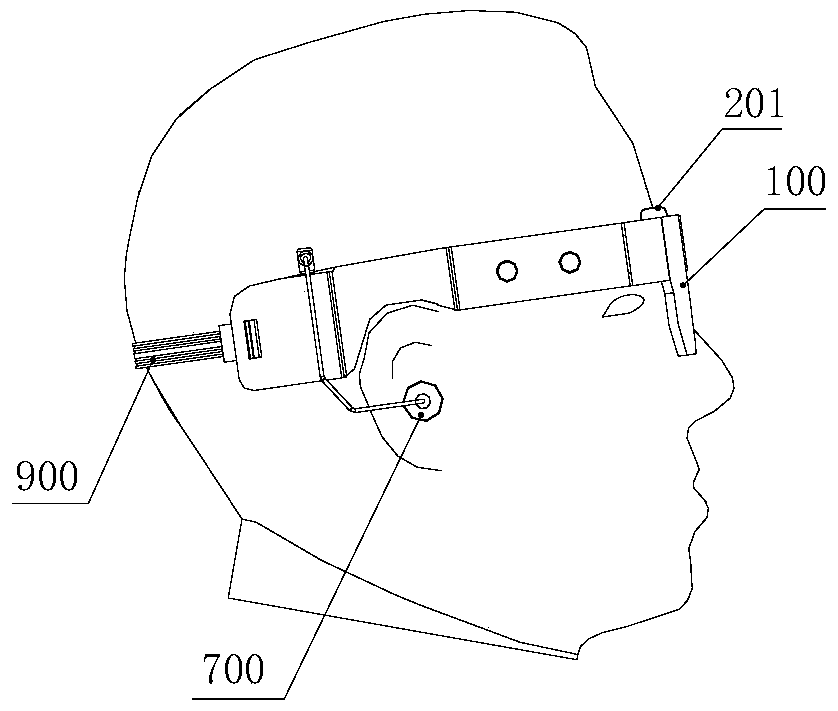
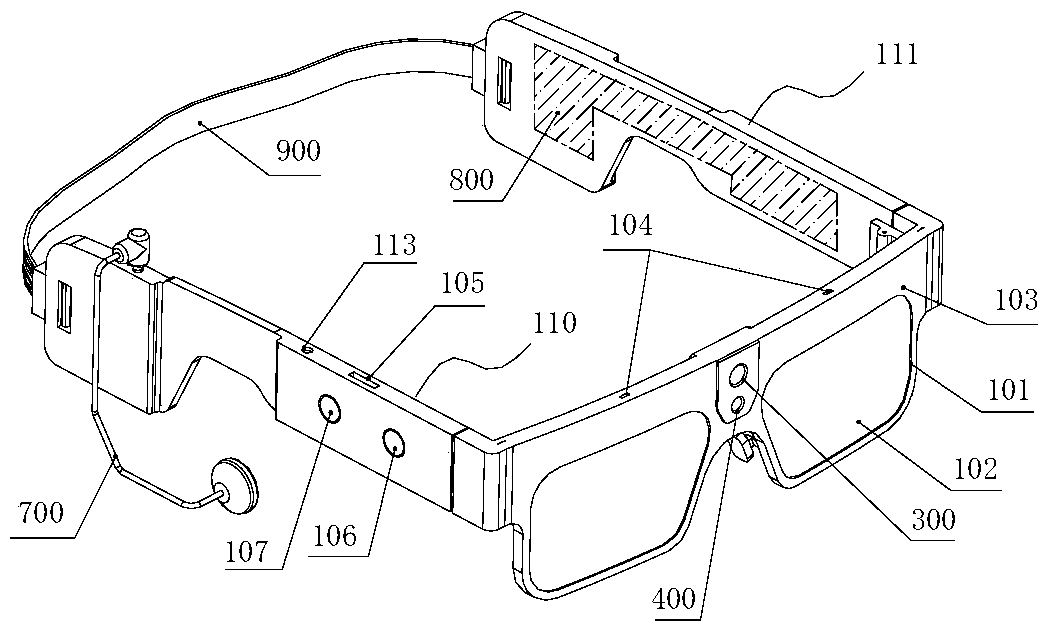
Intelligent wearing device for vision recovery of patient with posteriority blindness and making method thereof
The invention discloses an intelligent wearing device for vision recovery of a patient with posteriority blindness and a making method thereof. The device comprises microelectrode arrays, a pair of intelligent glasses, earphones, elastic belt buckles and stimulating signal guide soft belts, wherein the microelectrode arrays are arranged in the eyes of the patient; the intelligent glasses, the earphones and the elastic belt buckles are arranged outside the eyes of the patient; the stimulating signal guide soft belts are arranged between the microelectrode arrays and the intelligent glasses. An outside image is shot by a microcamera arranged in front of the intelligent glasses and processed by a control system into a bidirectional electronic impulse signal, and the signal is transmitted by the stimulating signal guide soft belts to the microelectrode arrays arranged between the outermost layers of retinas and choroids to electrically stimulate ganglion cells; optic nerves transmit a biological signal generated by stimulation to a visual area of the cerebral cortex, are recognized by the brain and then make the blind patient restore part of visual performance to an outside object. The intelligent wearing device has the advantages of being good in stimulation effect, safe in use, attractive in appearance and convenient to wear.
Owner:戴国群
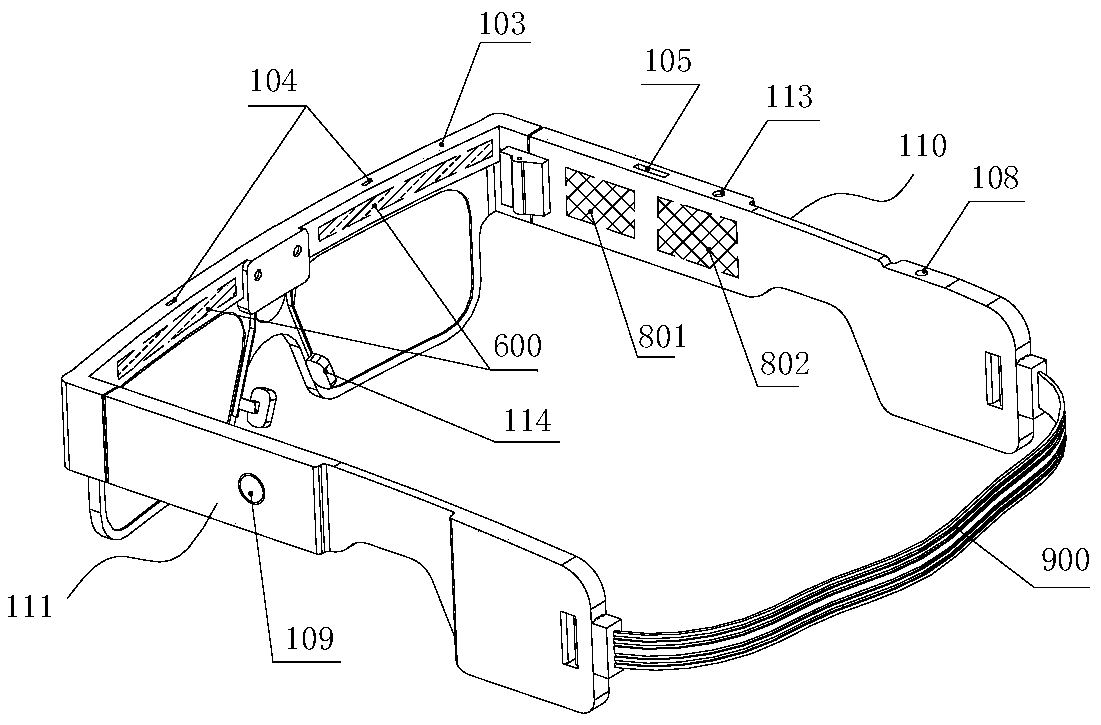
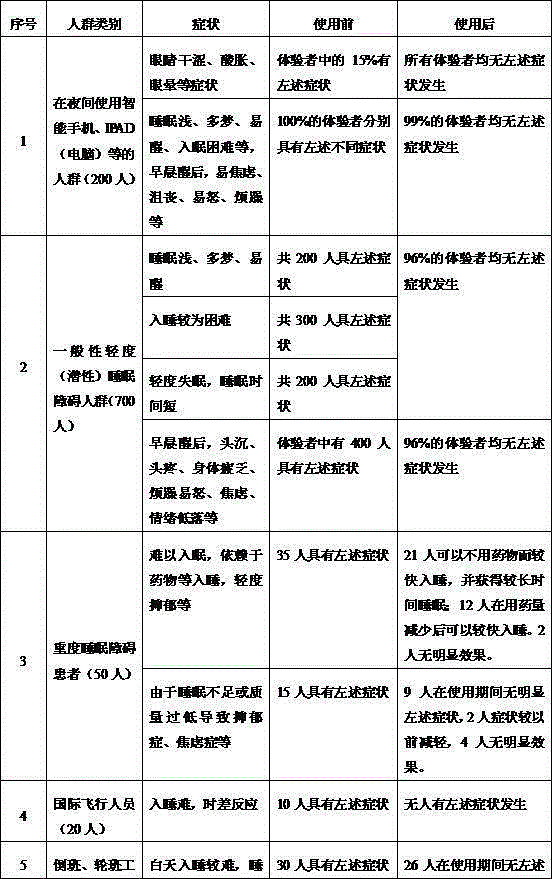
Eye-protecting and sleep-facilitating healthy glasses
InactiveCN105204179AImprove sleep qualityPrevent macular degenerationOptical partsOptical elementsEye protectingInsomnia
The invention relates to eye-protecting and sleep-facilitating healthy glasses. The glasses are characterized in that according to the light transmittance of lenses, the transmittance of a 400-520 nm spectral interval is 10-35%, the transmittance of a 540-569 nm spectral interval is 35-96%, the transmittance of a 570-600 nm spectral interval is 92-97%, and the transmittance of a 600-700 nm spectral interval is 88-93%. The eye-protecting and sleep-facilitating healthy glasses can stop and optimize a spectrum waveband which is sensed by SCN ganglion cells and can stop melatonin secretion or reduce the secretion amount and will not affect normal work and life of people after being worn, wherein the work and life do not contain work and life needing accurate colors; the glasses serve as a means for improving sleep quality of modern human beings and treating or assisting in treating insomnia of patients with sleep disorder and other symptoms.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAOBORUI HEALTH TECH
Mimicking neural coding in retinal ganglion cells with short pulse electrical stimulation
A method, device and system for stimulating visual tissue, typically in the retina or visual cortex, to achieve an artificial percept of light or image. The method includes providing stimulating electrodes suitable for placement in proximity to the visual tissue and generating a series of short-duration stimulation signals having a duration of less than about 0.5 milliseconds each. The short-duration stimulation signals are applied through the stimulating electrodes with varying frequencies that are substantially matched to a spiking range of frequencies of at least one ganglion cell for perceiving brightness or image.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Methods and compositions for preserving retinal ganglion cells
ActiveUS20160367619A1Reduce lossSenses disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismVisual functionGlaucoma
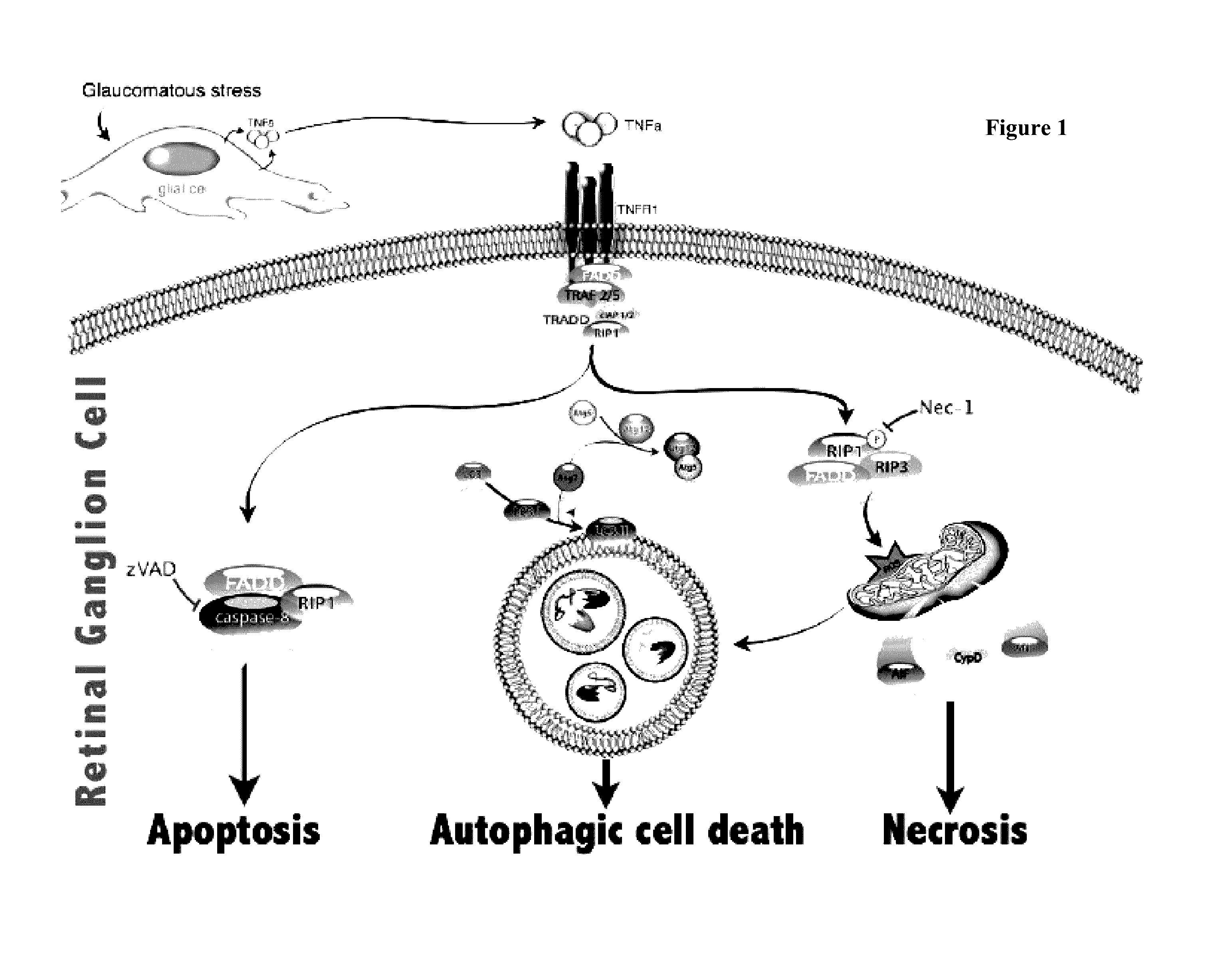
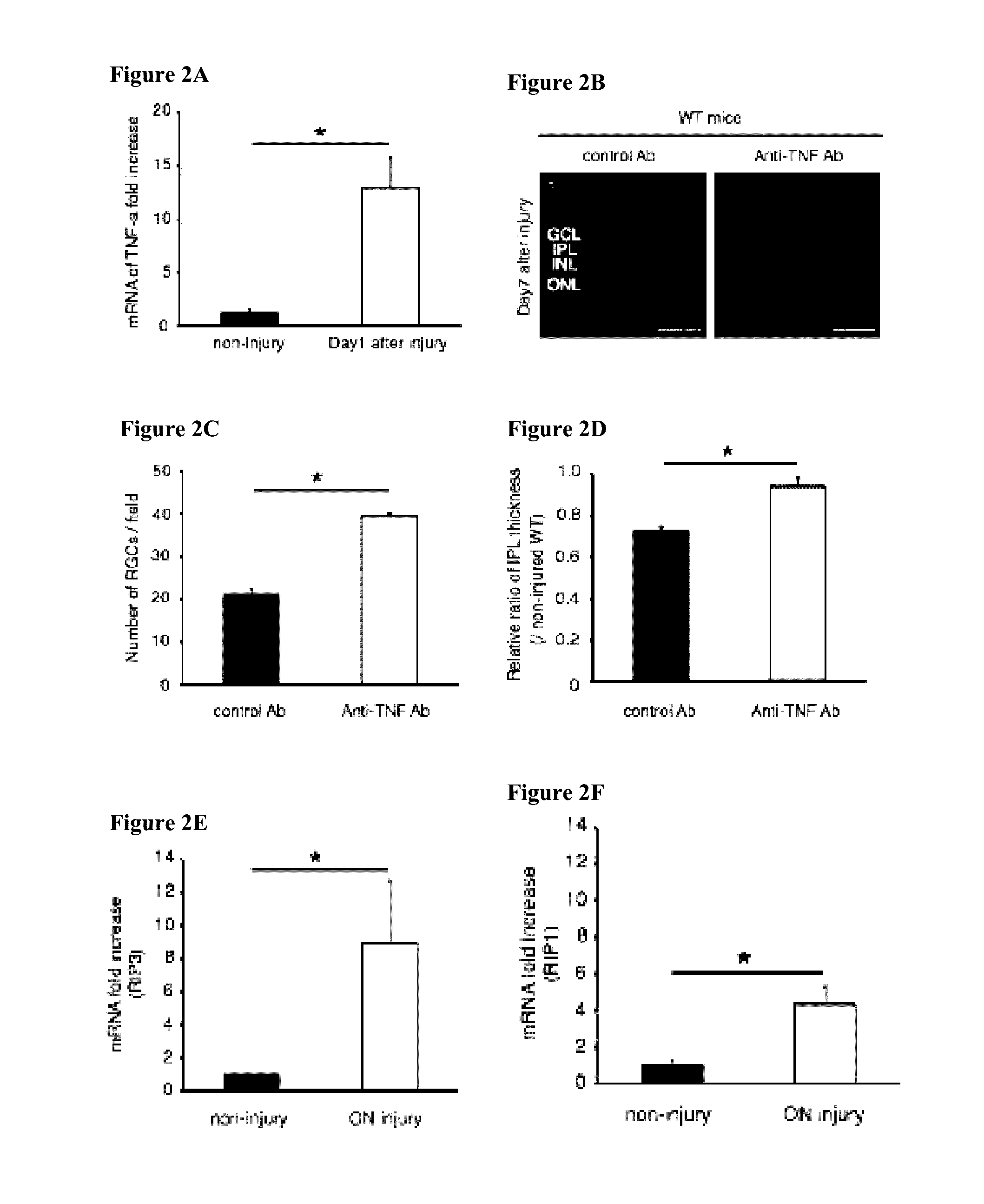
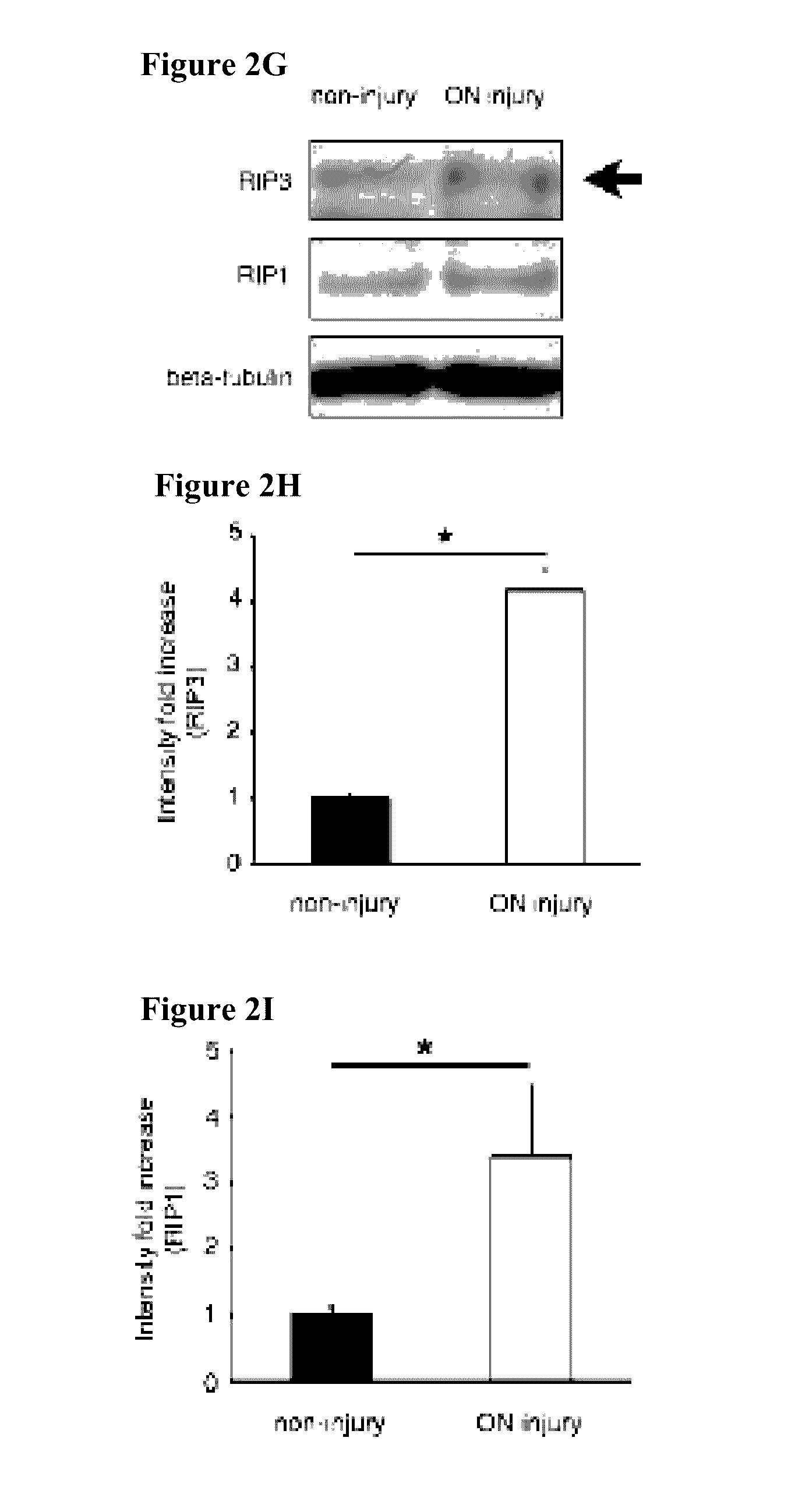
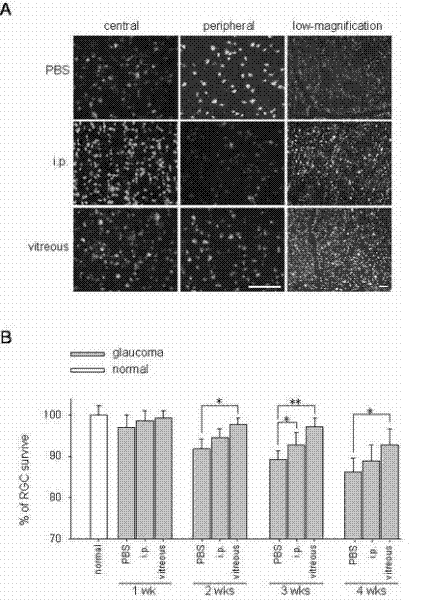
Provided are methods and compositions for maintaining the viability of retinal ganglion cells in a subject with an ocular disorder including, for example, glaucoma and optic nerve injury. The viability of the retinal ganglion cells can be preserved by administering a necrosis inhibitor either alone or in combination with an apoptosis inhibitor to a subject having an eye with the ocular condition. The compositions, when administered, maintain the viability of the cells and / or promote axon regeneration, thereby minimizing the loss of vision or visual function associated with the ocular disorder.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS EYE & EAR INFARY
Application of sodium valproate in preparation of medicament for treating or improving optic nerve pathological changes of glaucoma
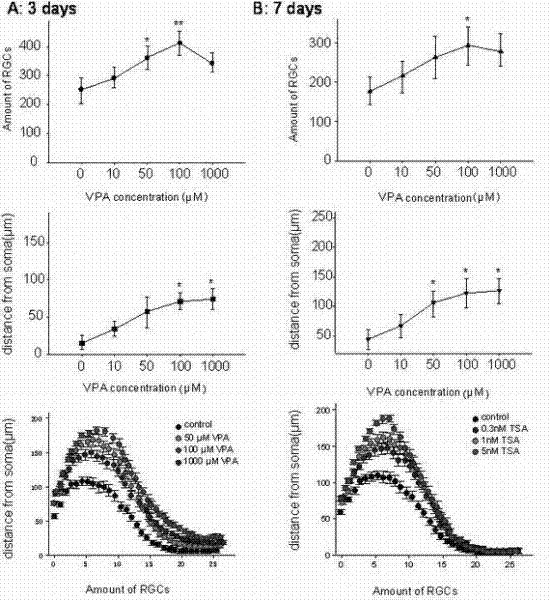
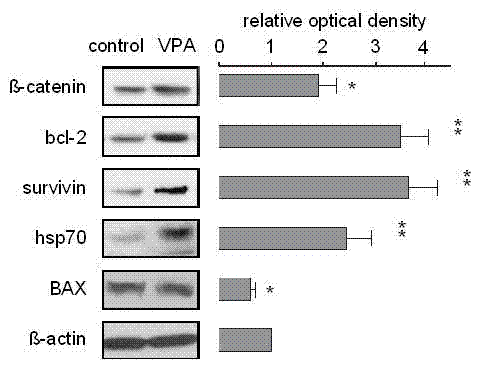
InactiveCN102218051AThrough highEasy to degradeSenses disorderAntinoxious agentsRetinal ganglionHigh intraocular pressure
The invention belongs to the field of pharmacy, and relates to application of sodium valproate in preparation of medicaments for treating or improving optic nerve pathological changes of glaucoma. The in-vitro cell culture experiment and in-vivo animal experiment indicate that sodium valproate with certain concentration can promote retina ganglionic cells (RGCs) cultured in vitro to survive and enhance the extension capacity of the axon, and can lower the expression of proapoptotic gene BAX and promote the RGCs to survive under the conditions of chronic high intraocular pressure, thereby relieving the damage of RGCs. The experiments prove that the sodium valproate can protect the RGCs in the aspects of multiple pathogeneses of glaucoma optic nerve pathological changes, and further more, can be used as an active ingredient for preaprating medicaments for treating glaucoma optic nerve pathological changes, especially medicaments for protecting RGCs. The invention has important application value and favorable social and economic benefits in clinical treatment of glaucoma.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
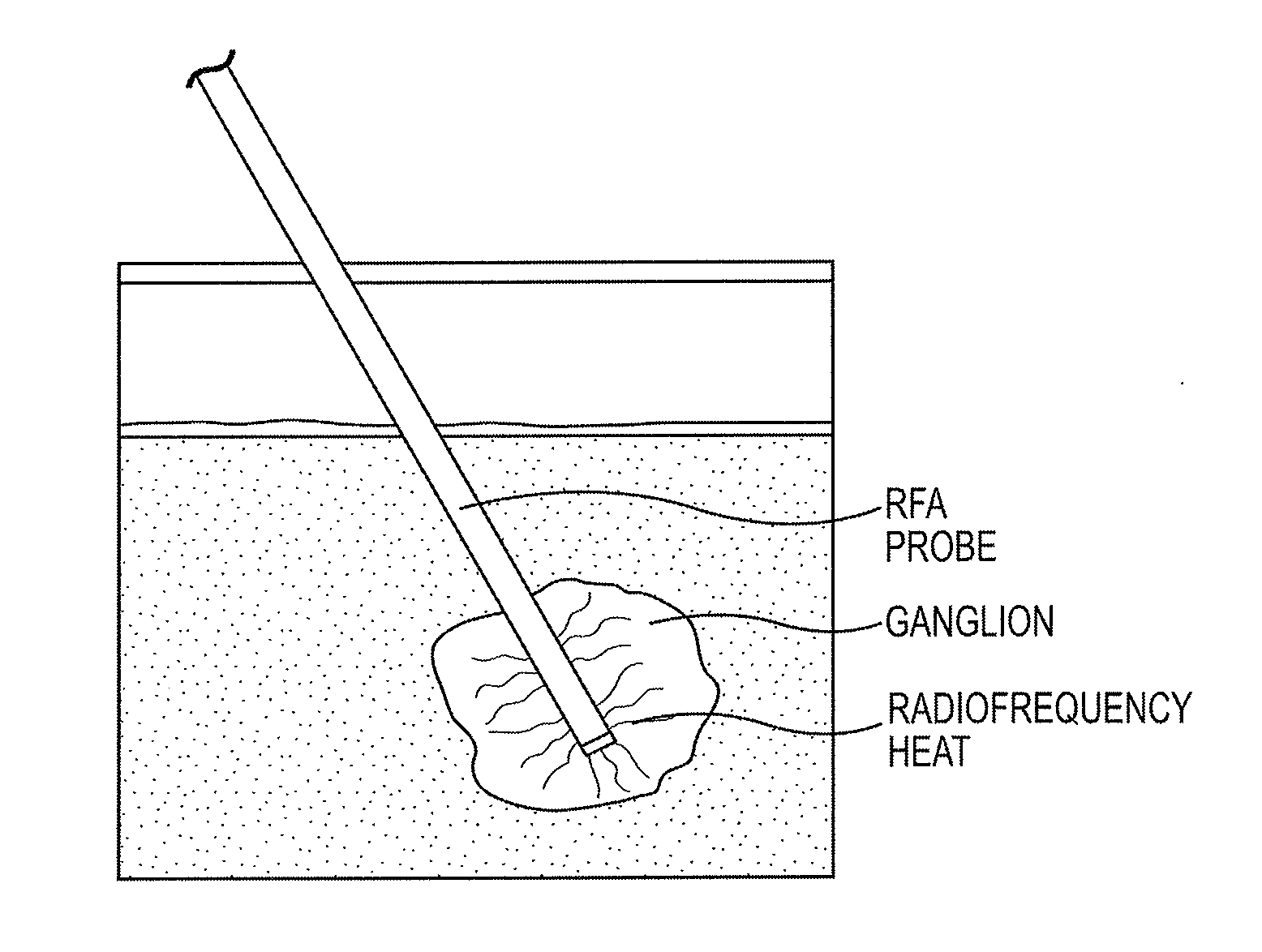
System and method of pre-aortic ganglion ablation
InactiveUS20130296836A1Avoid dissectionWorsening renal functionUltrasound therapyHydroxy compound active ingredientsGanglion-Like CellAorta
A method of modulating a physiological parameter of a patient is provided. The method includes disabling one or more pre-aortic ganglion cells within a pre-aortic ganglion and improving the physiological parameter. The method further includes destroying a pre-aortic ganglion cell to prevent regeneration.
Owner:ENIGMA MEDICAL
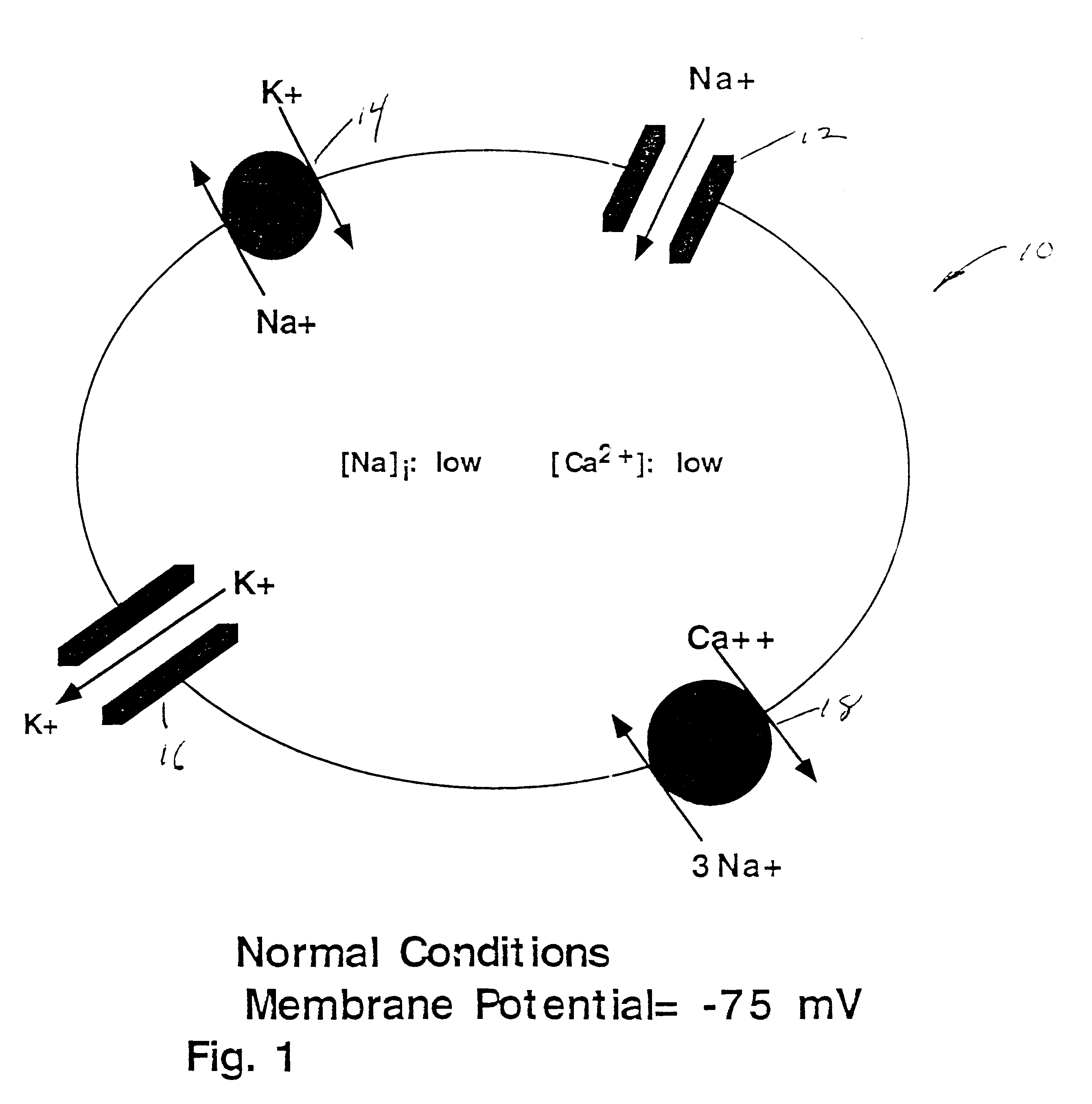
Inhibition of noninactivating Na channels of mammalian optic nerve as a means of preventing optic nerve degeneration associated with glaucoma
InactiveUS6326389B1Avoid cell deathBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRetinal ganglionGanglion-Like Cell
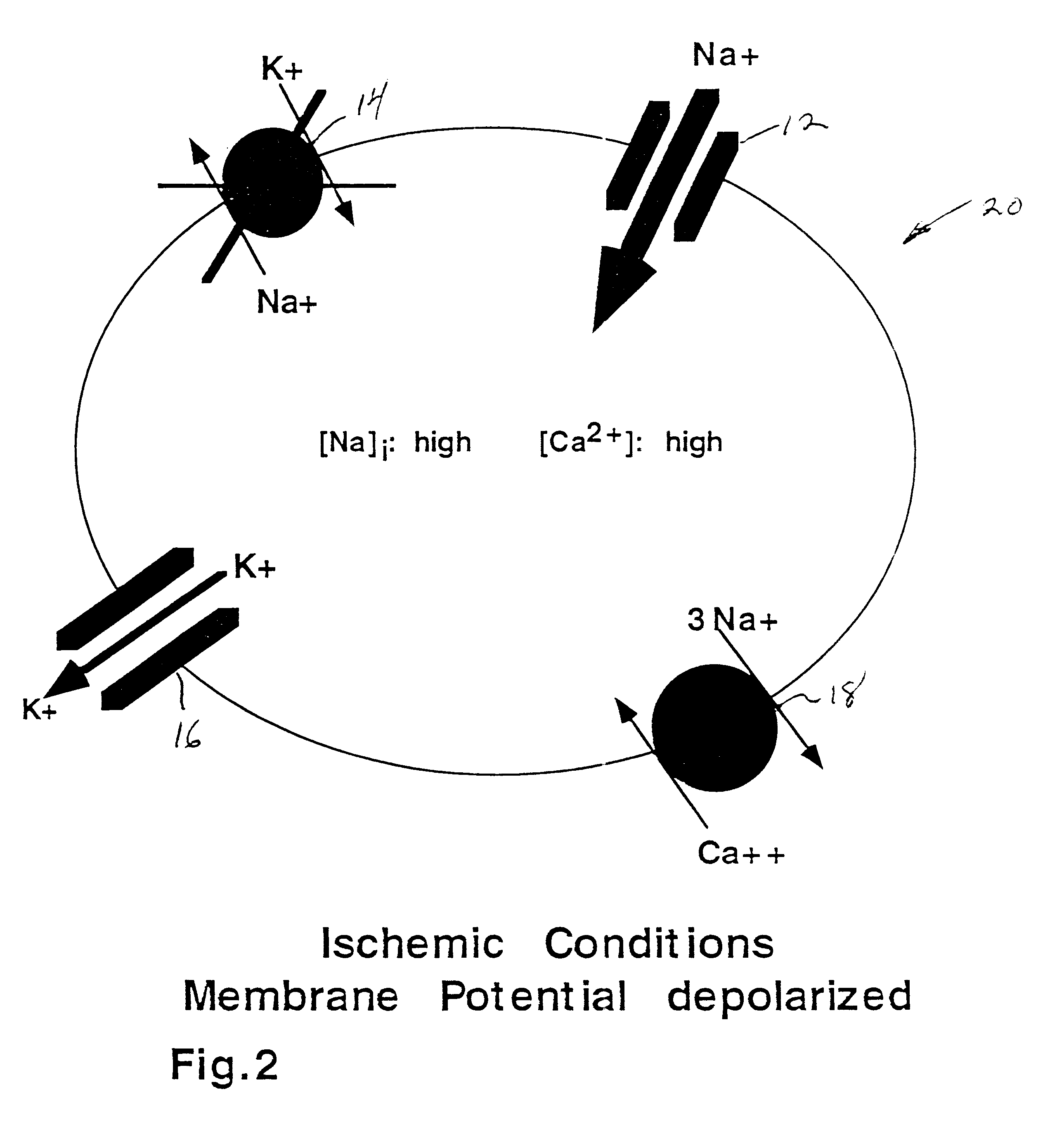
A method an composition for altering a plausible sequence of pathological events in retinal ganglion cells associated with glaucoma, the sequence including membrane depolarization, influx of millimolar amounts of Na+ via non-inactivating Na+ channels, and the lethal elevation of cell Ca2+ due to reversal of the Na+ / Ca2+ exchanger. The method includes blocking, by administration of a selected composition, of associated, non-inactivating Na+ channels in retinal ganglion cells in order to limit Na+ / Ca30 exchange in the retinal ganglion cells and prevent buildup of the Ca2+ level in the retinal ganglion cells to a lethal level. The results in a method of preventing retinal ganglion cell death, associated with glaucoma, by administering to the optic nerve of a mammal, a compound which blocks the non-inactivating sodium ion channels of the optic nerve. Alternately, said invention relates to a method of preventing optic retinal ganglion cell death in a human by administering to the retinal ganglion cells of said human a compound which blocks the non-inactivating sodium ion channel of the retinal ganglion cells.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
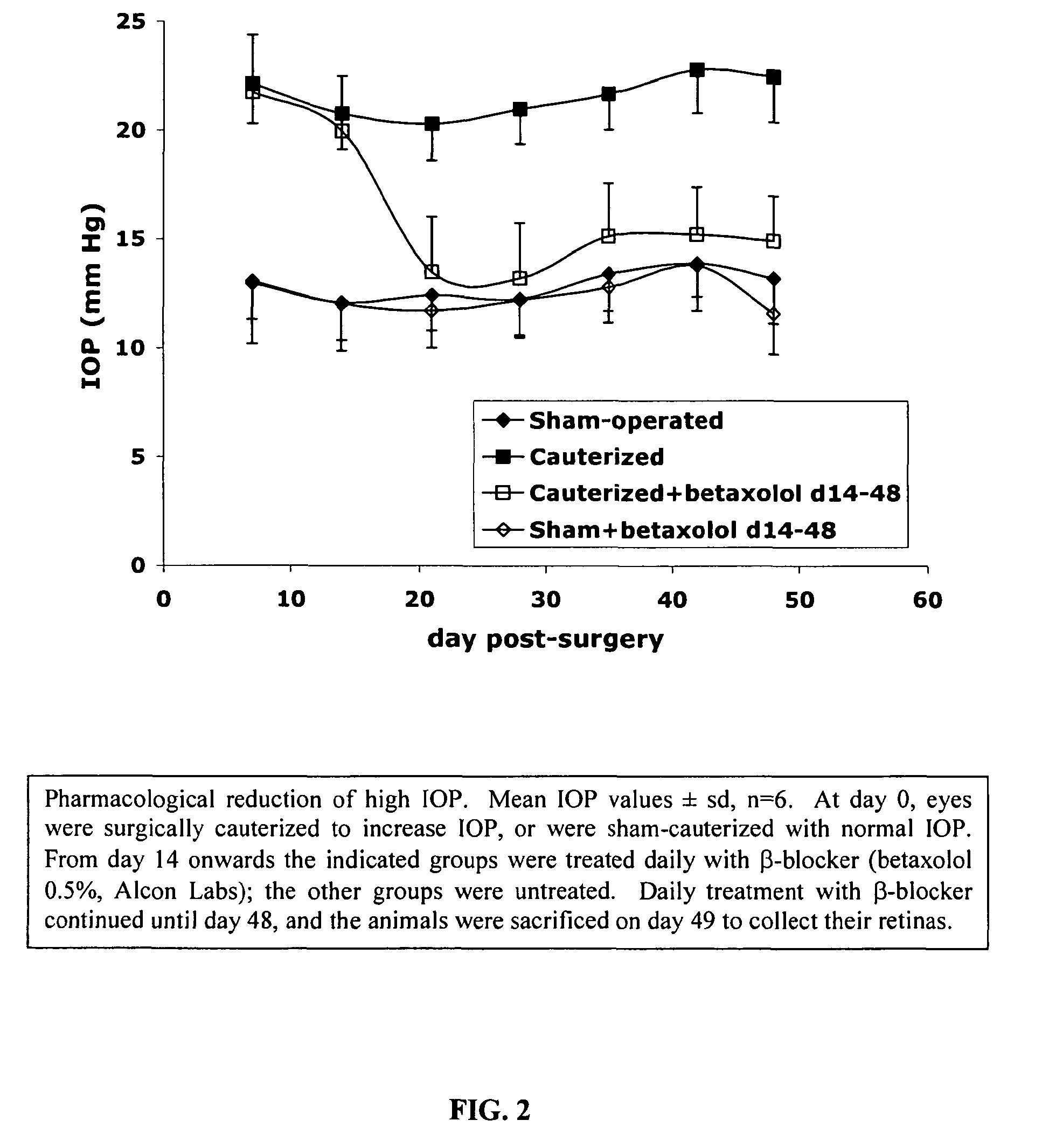
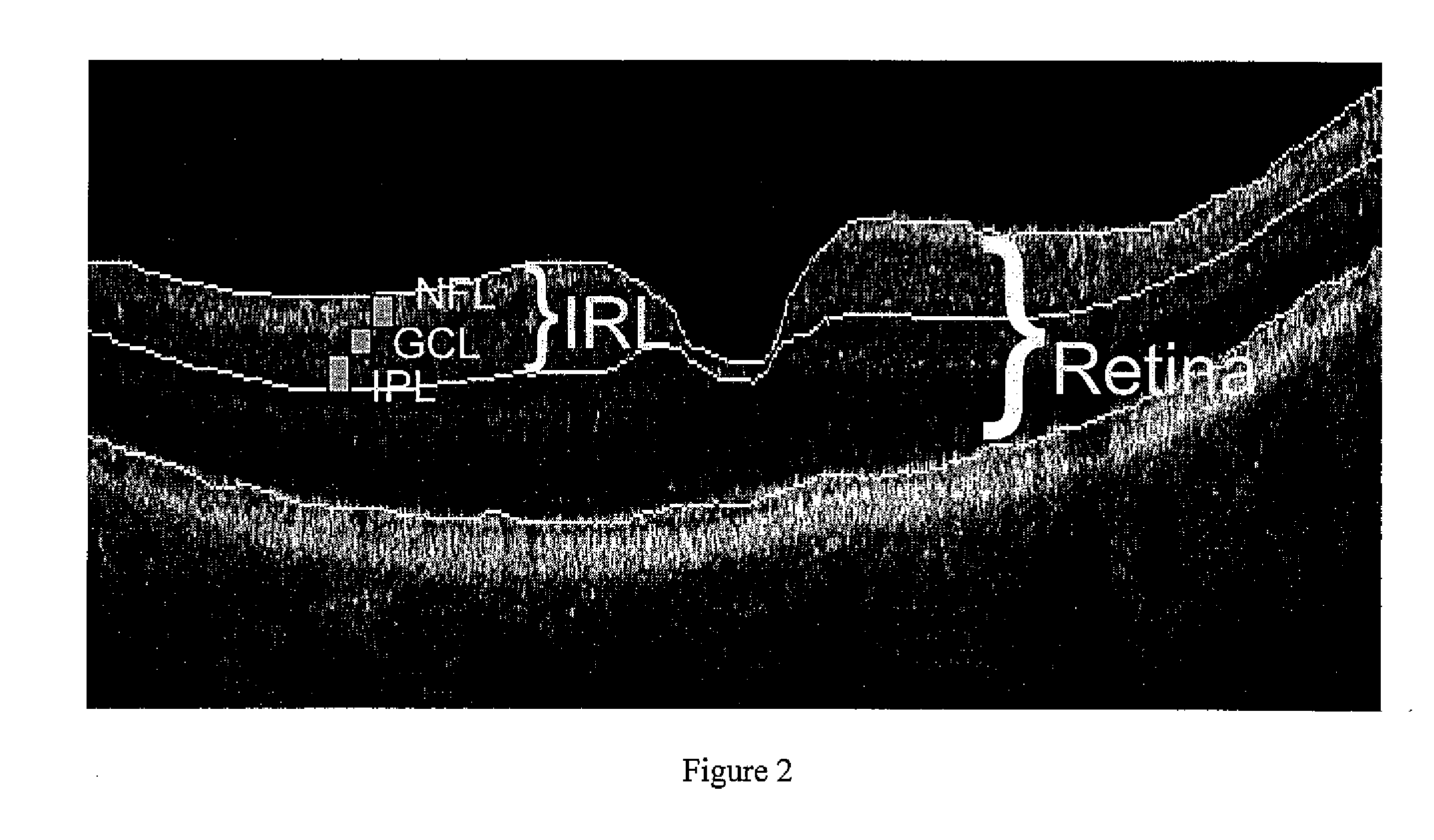
Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma
InactiveCN101879161ALower eye pressure is goodOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderBenzeneRetinal ganglion
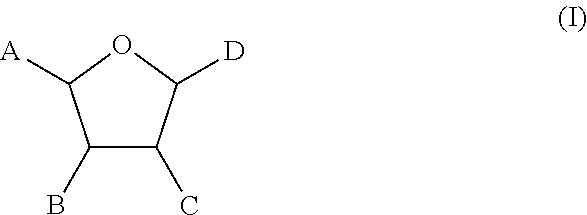
The invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis and medicines, in particular to application of an N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing a drug for treating glaucoma. In the invention, experiments prove that the N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative shown by a formula I has better action of lowering intraocular pressure and protecting ganglion cells, can take the dual effects of protecting optic nerves and RGC (Retinal Ganglion Cells) while lowering the intraocular pressure and provides a new selection for preparing the drug for treating the glaucoma.
Owner:四川爱森生物科技有限公司
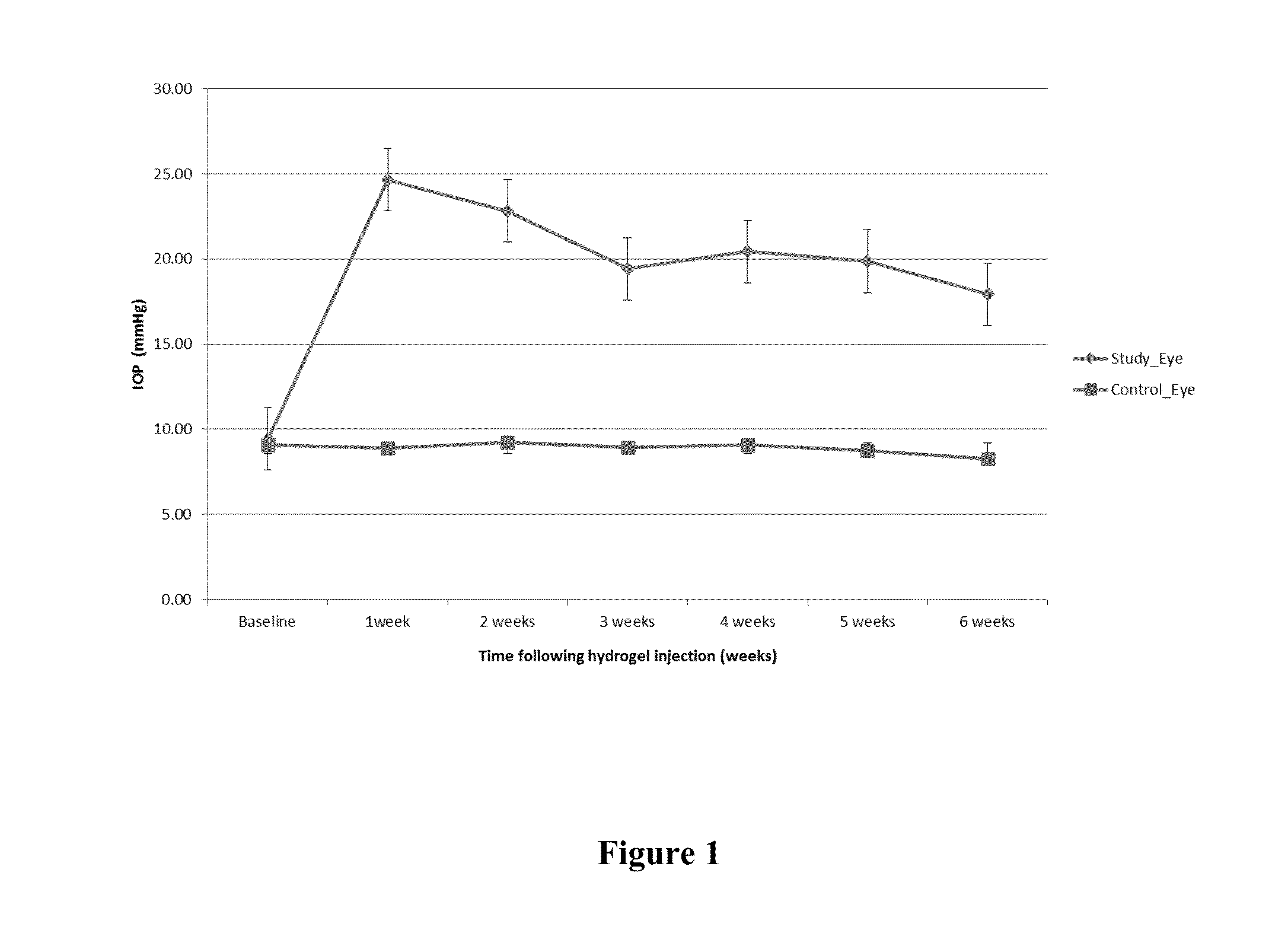
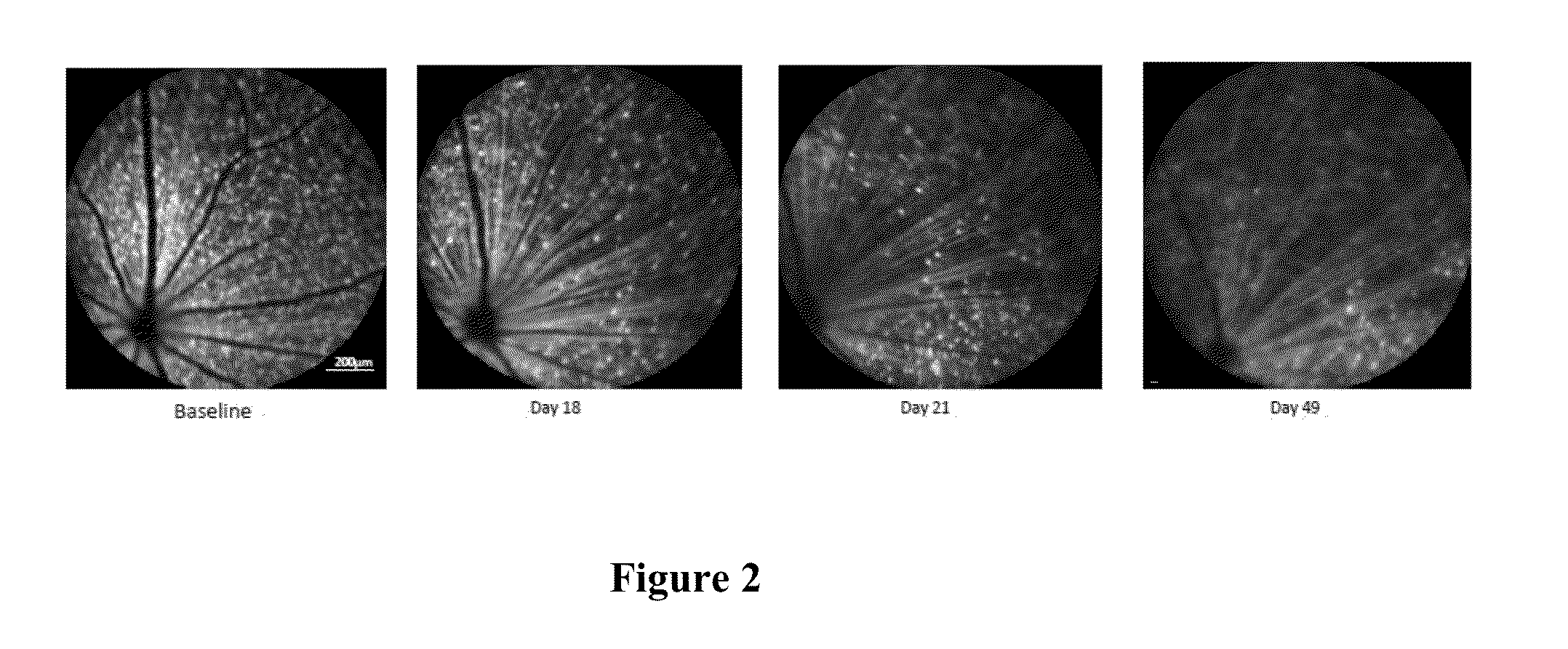
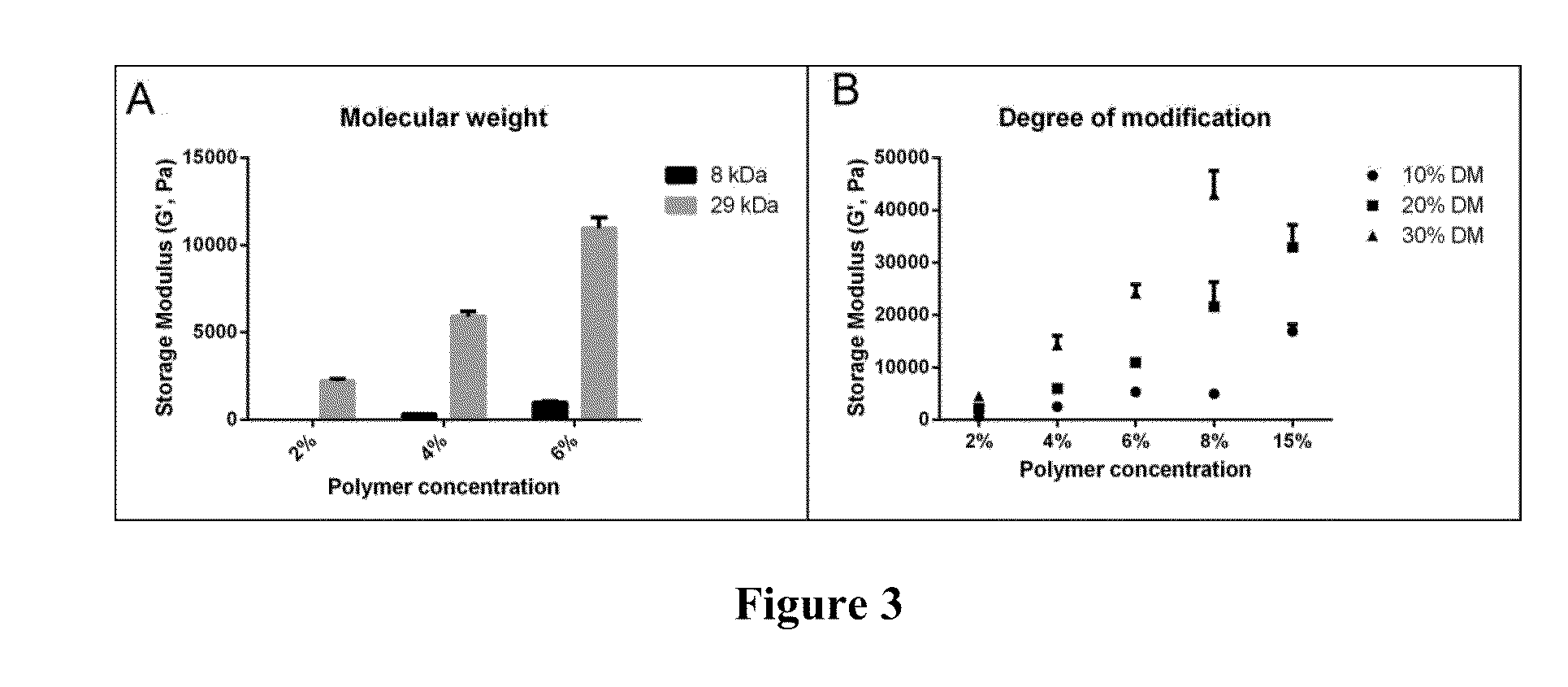
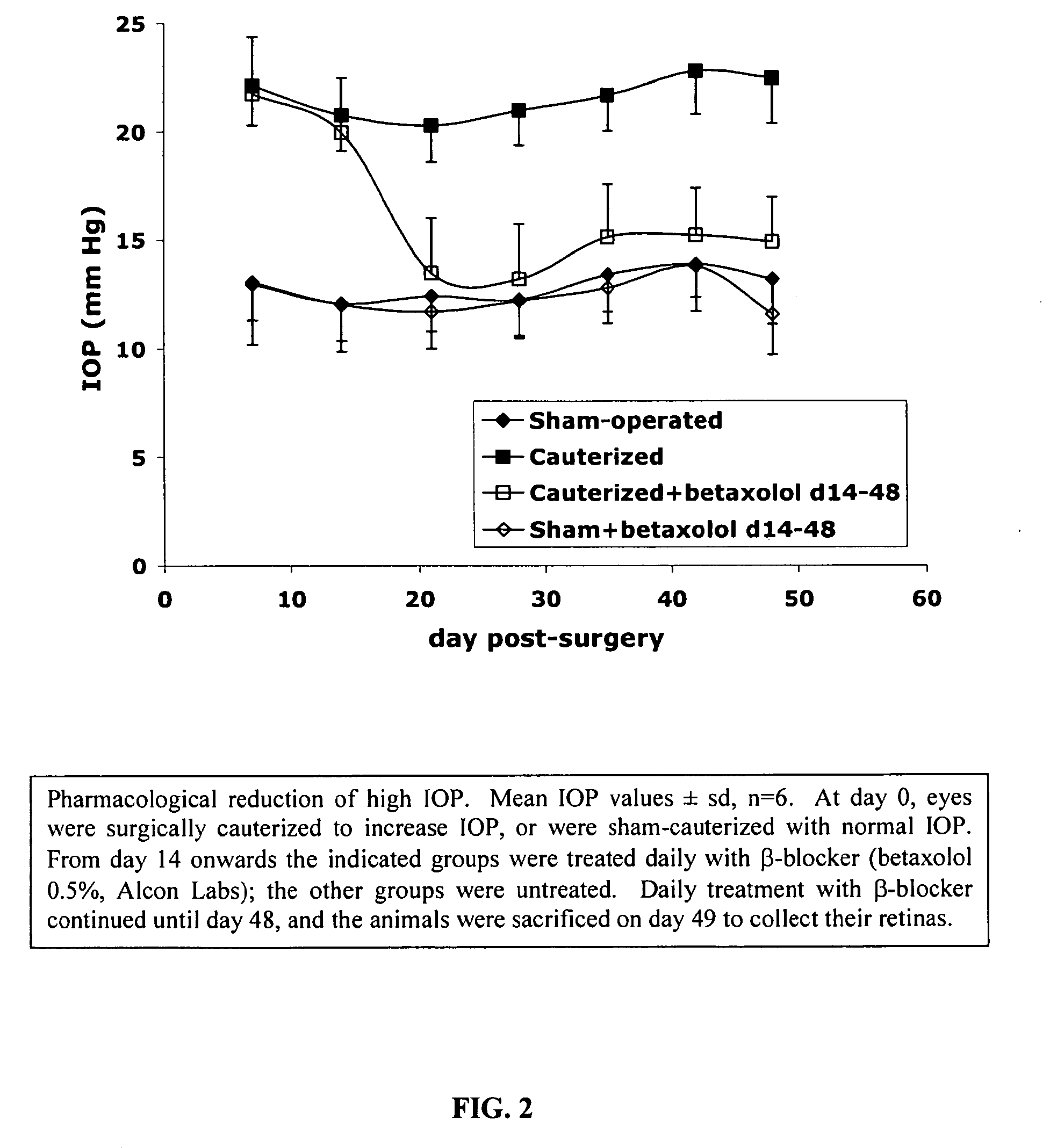
Induction of chronic elevation of intraocular pressure with intracameral cross-linking hydrogel
The present invention provides a method for inducing chronic elevation of intraocular pressure in the eyes of an animal by introducing into the eyes a cross-linking hydrogel, an animal produced by this method, as well as a screening method useful for identifying compounds capable of modulating intraocular pressure as well as for identifying compounds capable of modulating retinal ganglion cell survival and / or regeneration.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods of use of Trk receptor modulators
ActiveUS8648169B2Stable and easy to administerOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCyclic compoundTrk receptor
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death and / or glaucoma using modulators of neurotrophic receptors that comprise β-turn peptidomimetic cyclic compounds or derivatives thereof. The neurotrophic receptor modulators can be used alone, in combination and / or in conjunction with one or more other compounds, molecules or drugs that treat or prevent ocular hypertension, RGC death and / or glaucoma.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/0b0c9c9f-e7b9-48dd-aec3-ad654b220e39/HDA0000023355830000011.PNG)
![Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/0b0c9c9f-e7b9-48dd-aec3-ad654b220e39/HDA0000023355830000012.PNG)
![Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma Application of N-[4-(monohydro-pyrazol-4-) phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzdioxan-2-amide derivative in preparing drug for treating glaucoma](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/0b0c9c9f-e7b9-48dd-aec3-ad654b220e39/HDA0000023355830000021.PNG)