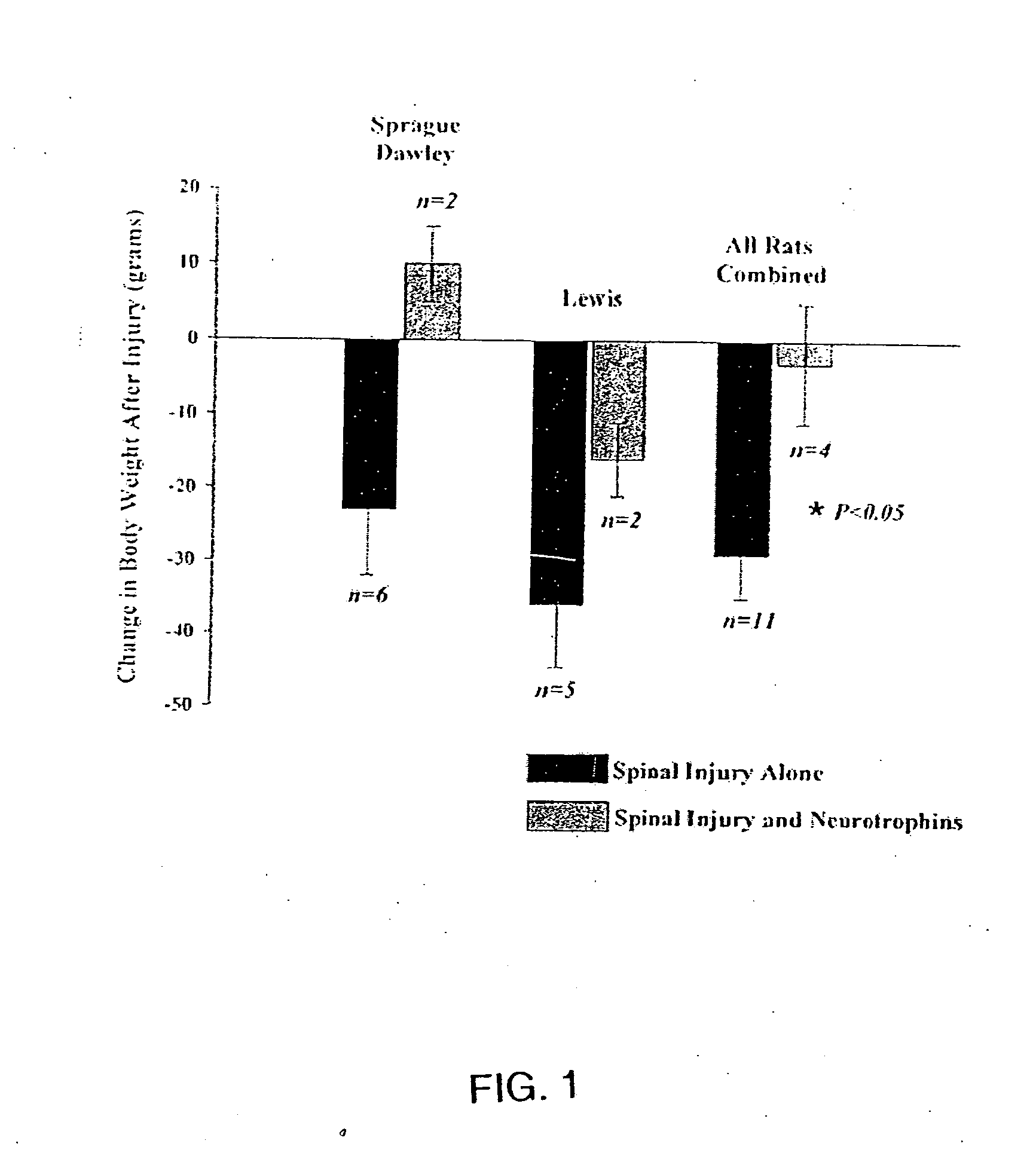
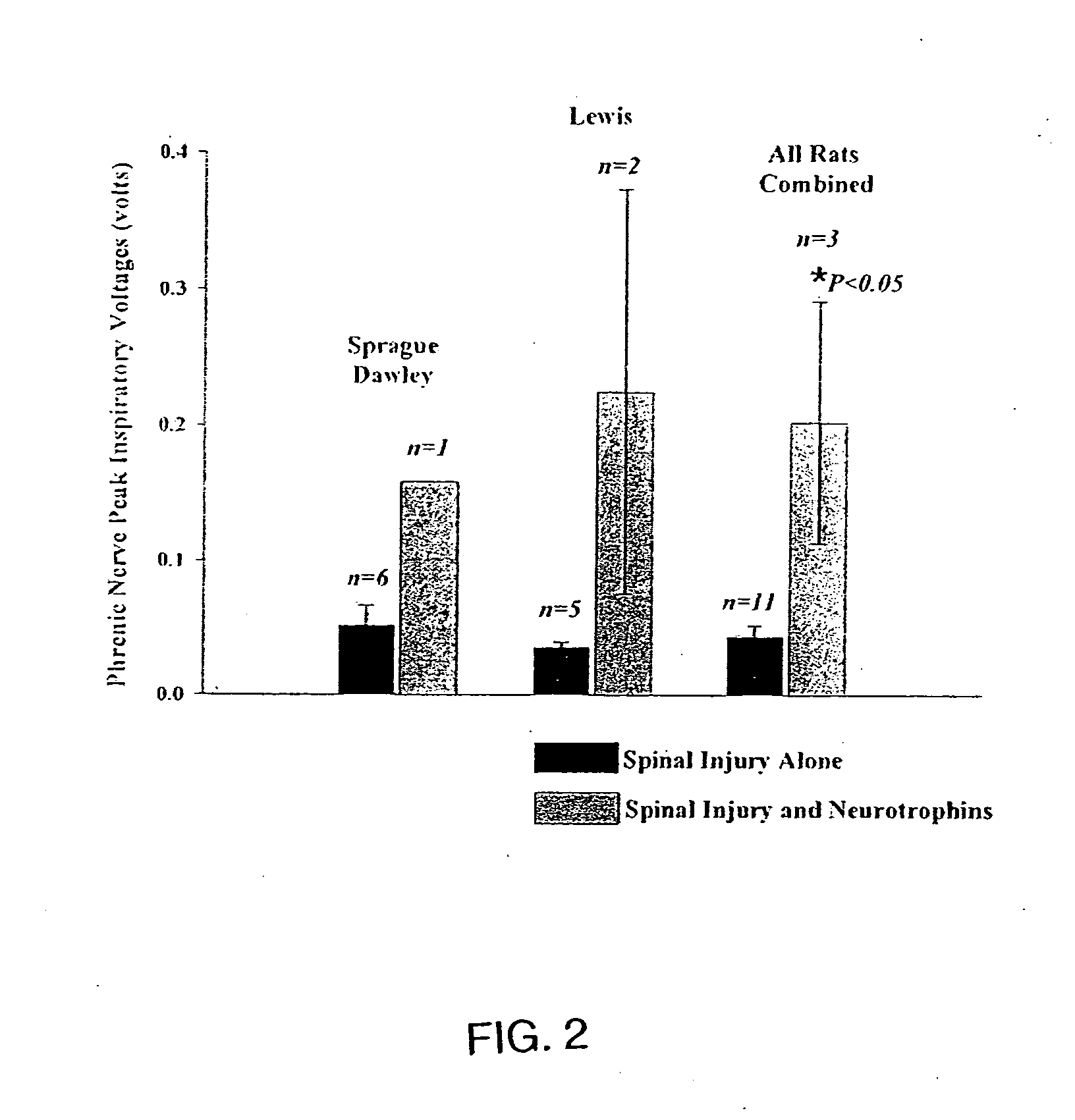
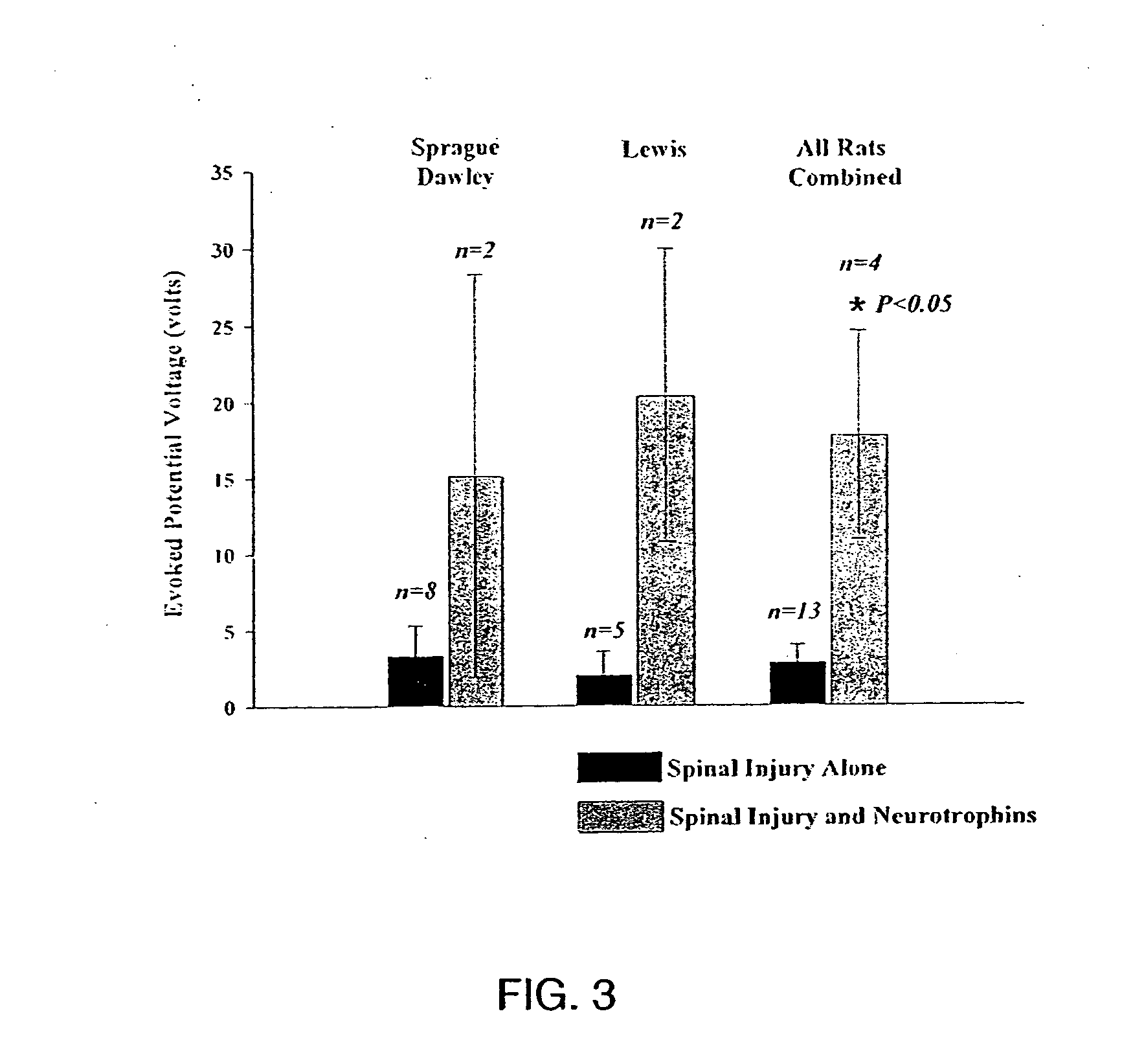
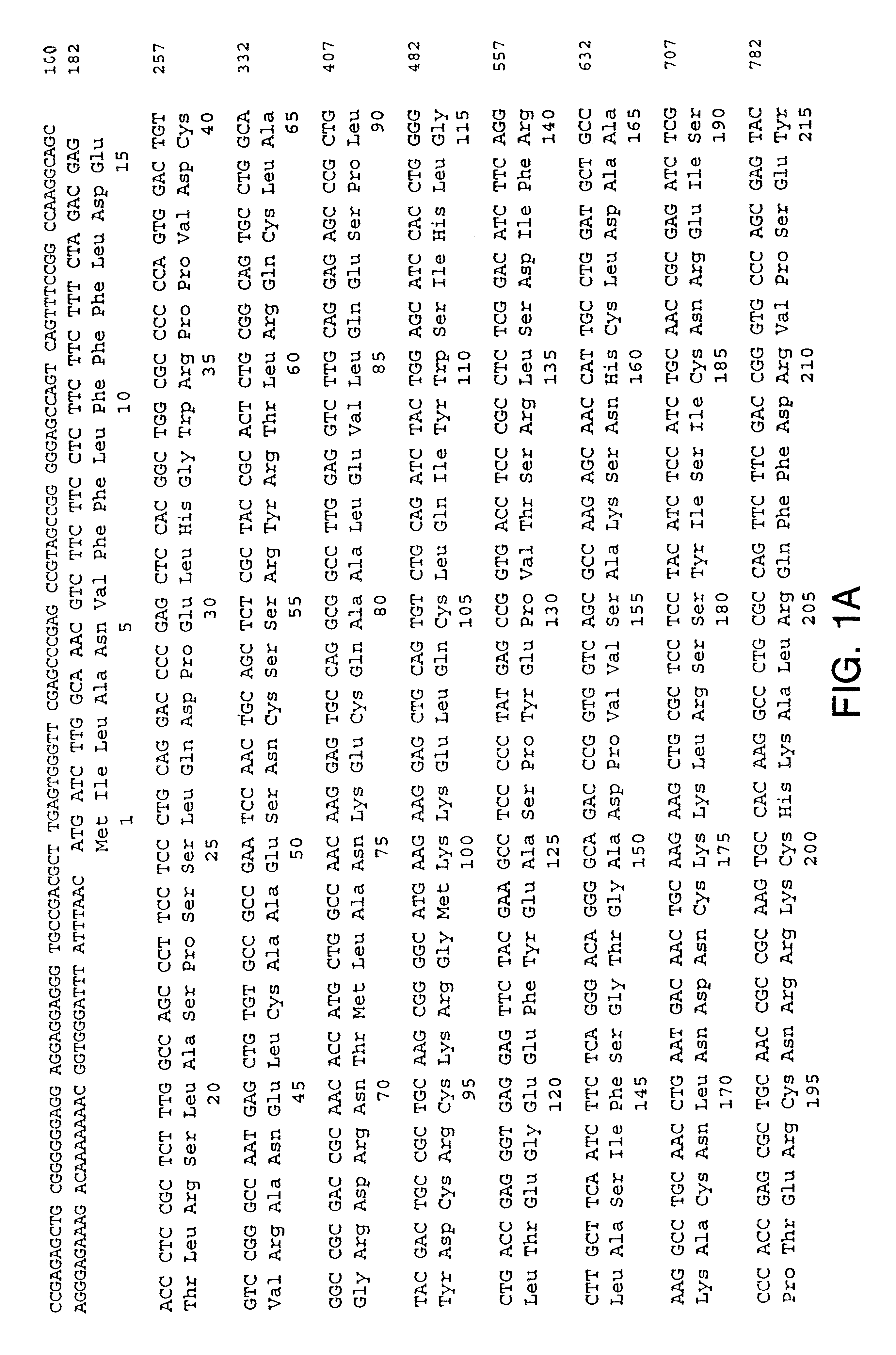
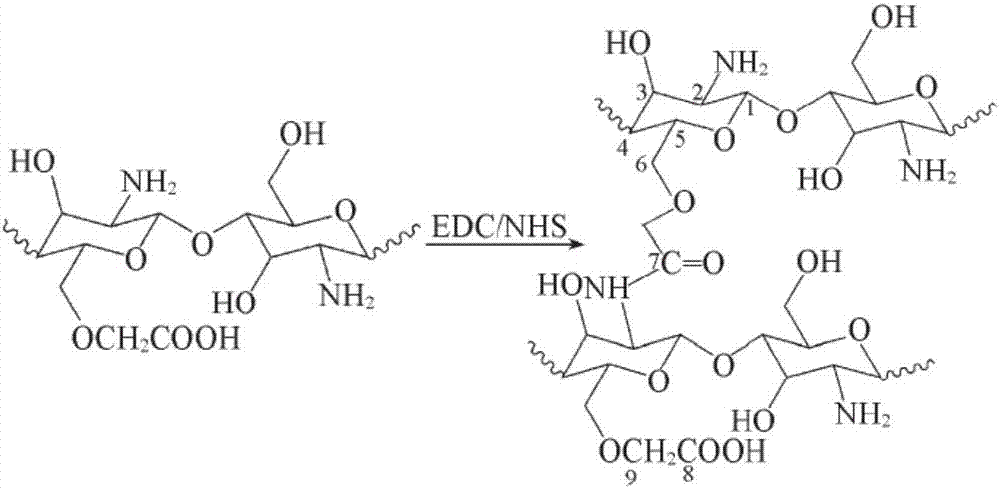
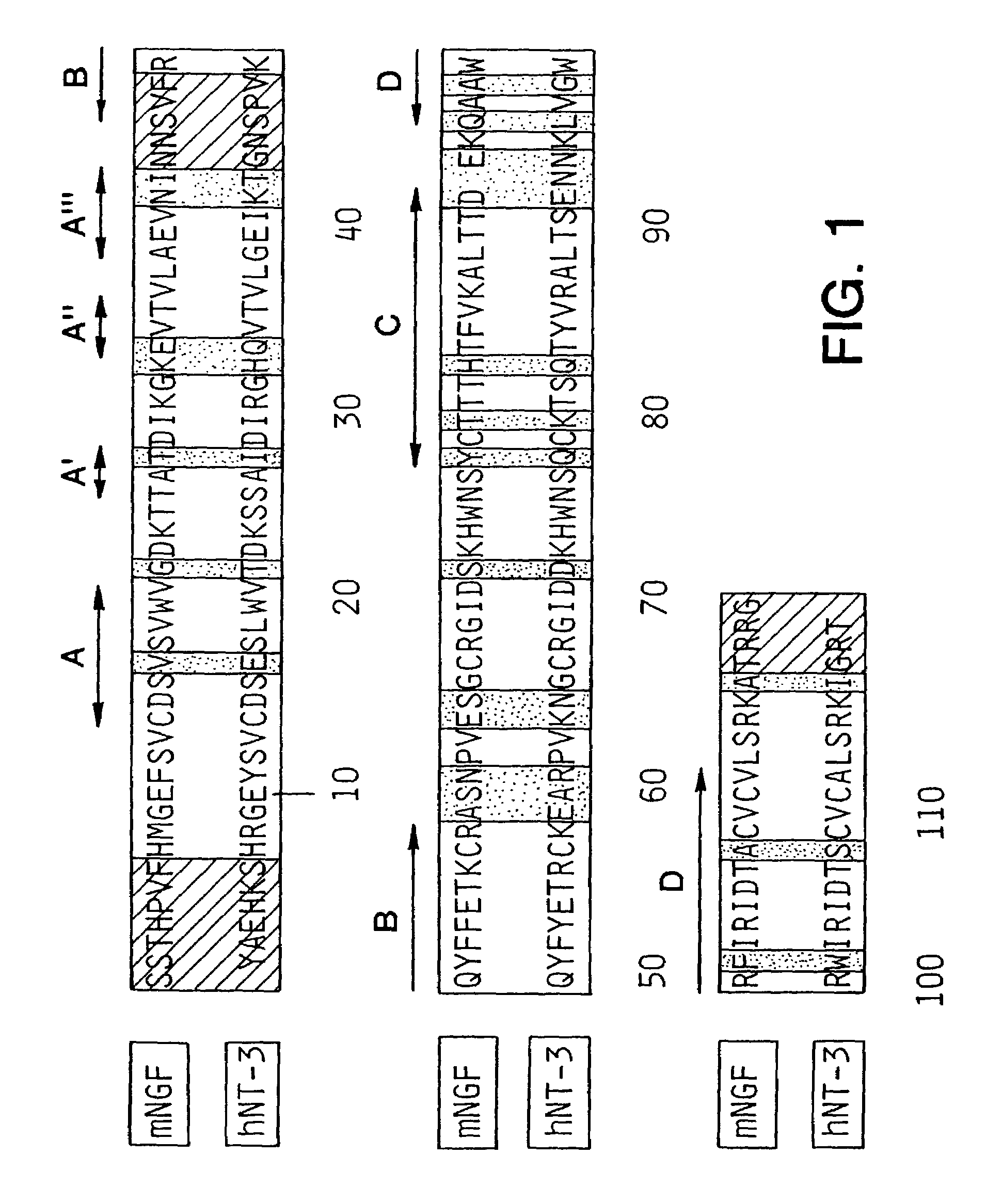
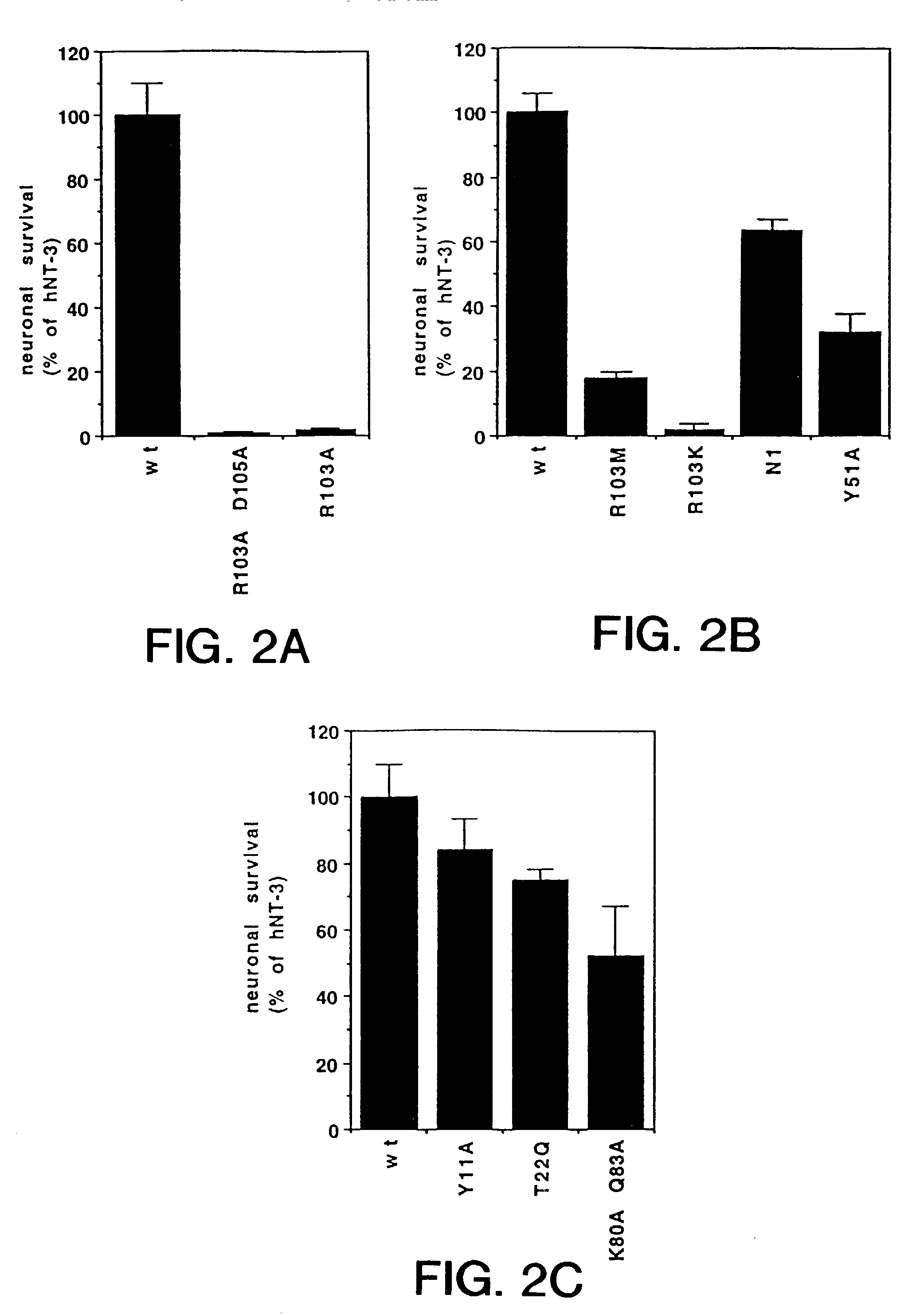
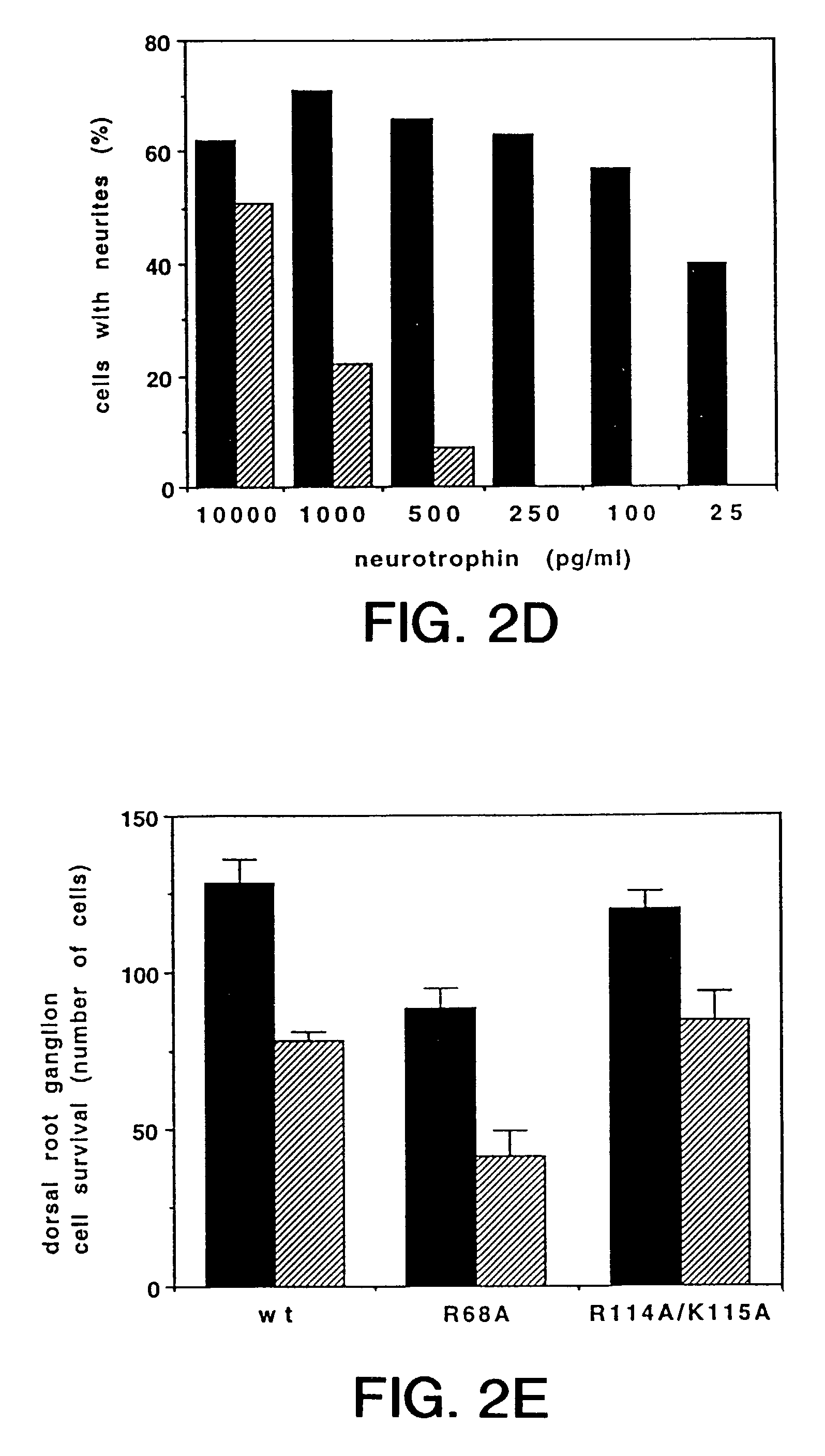
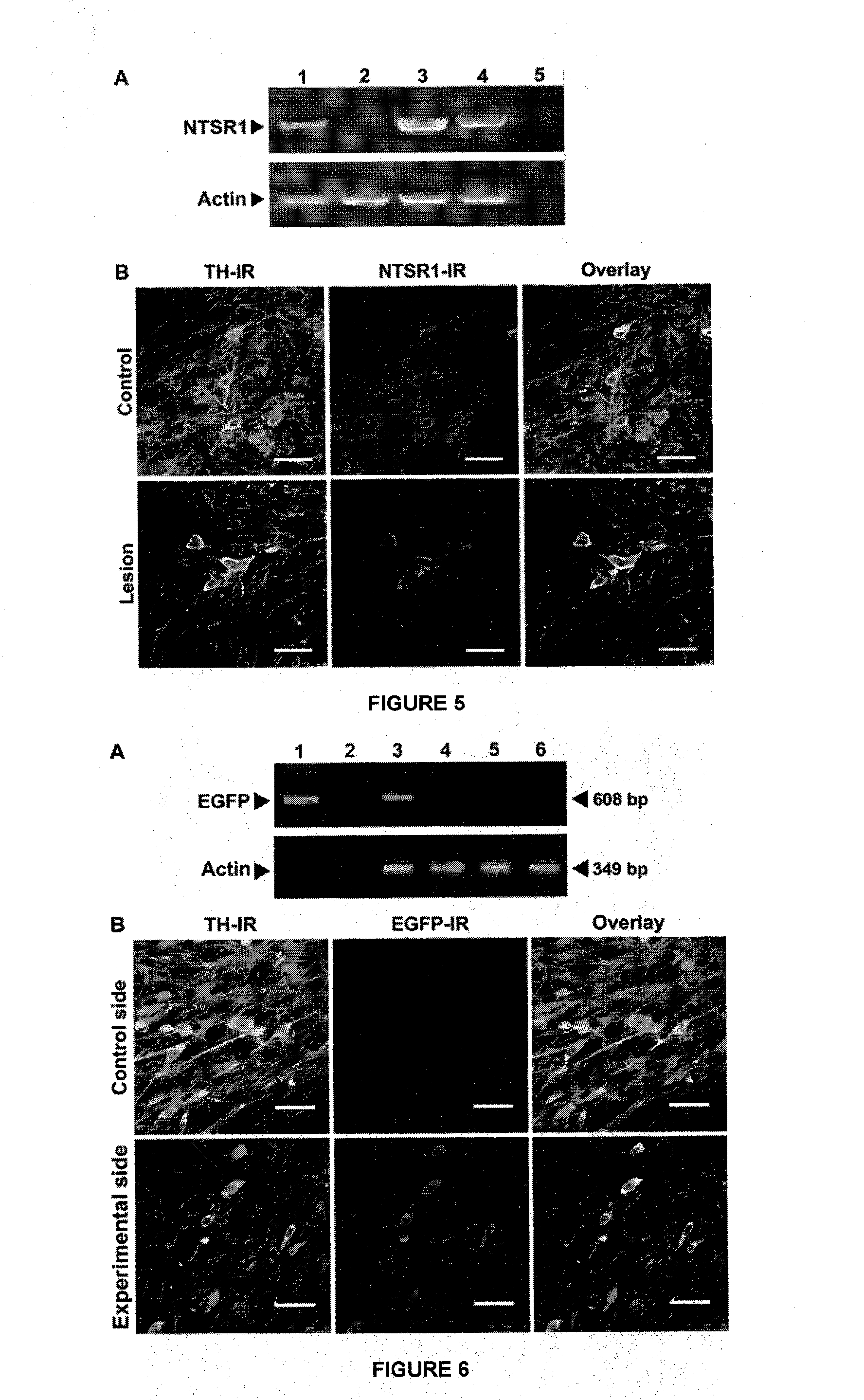
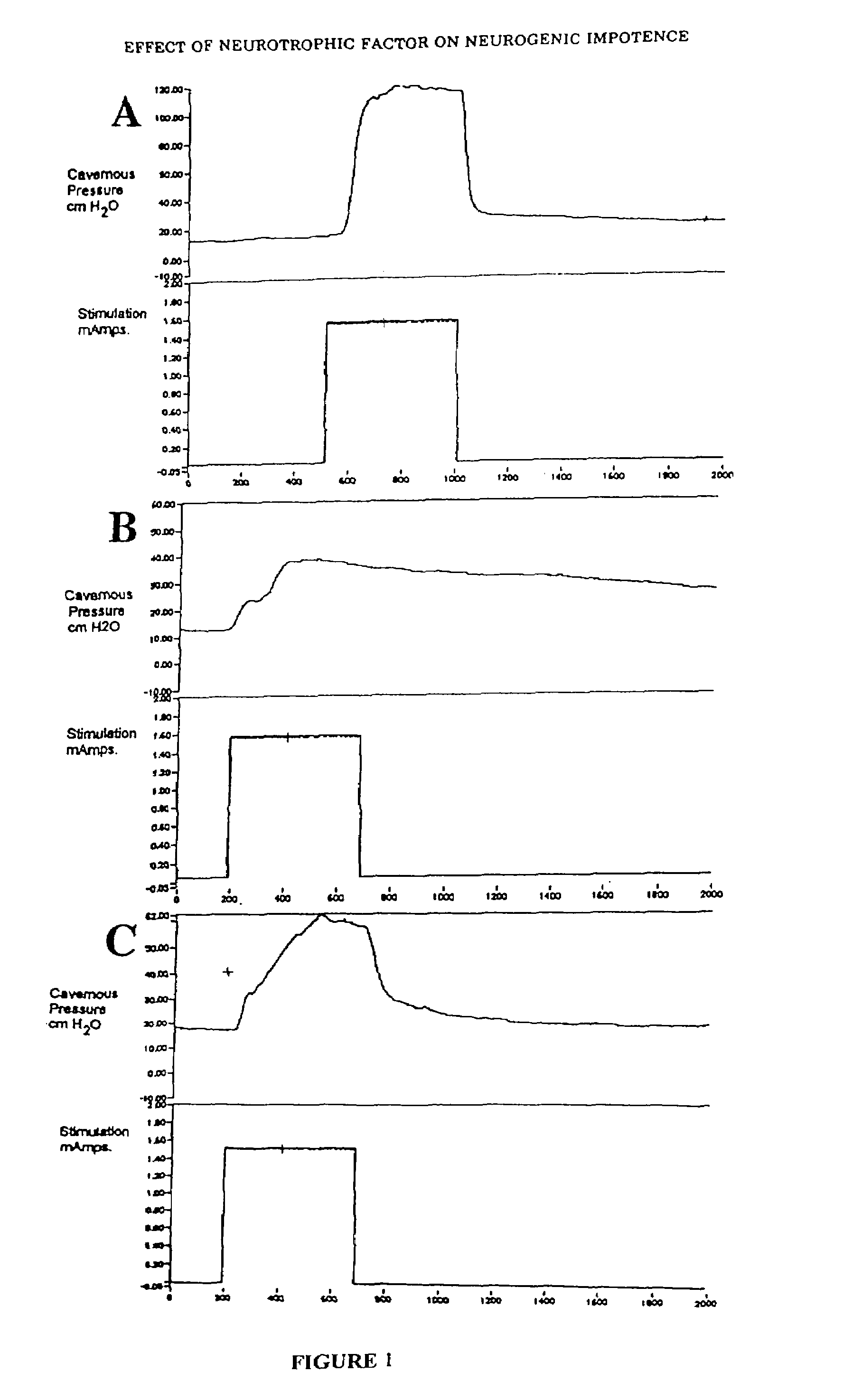
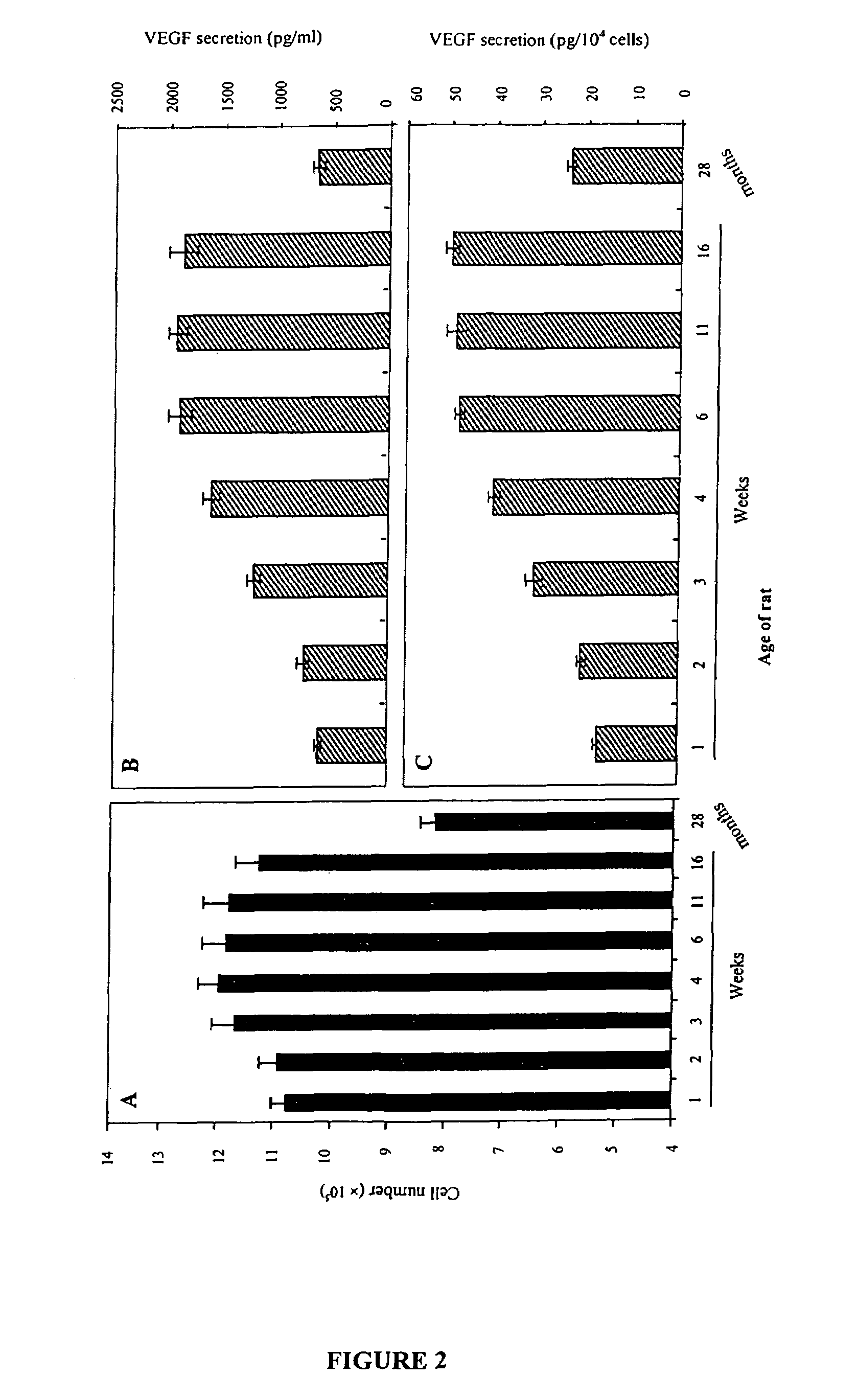
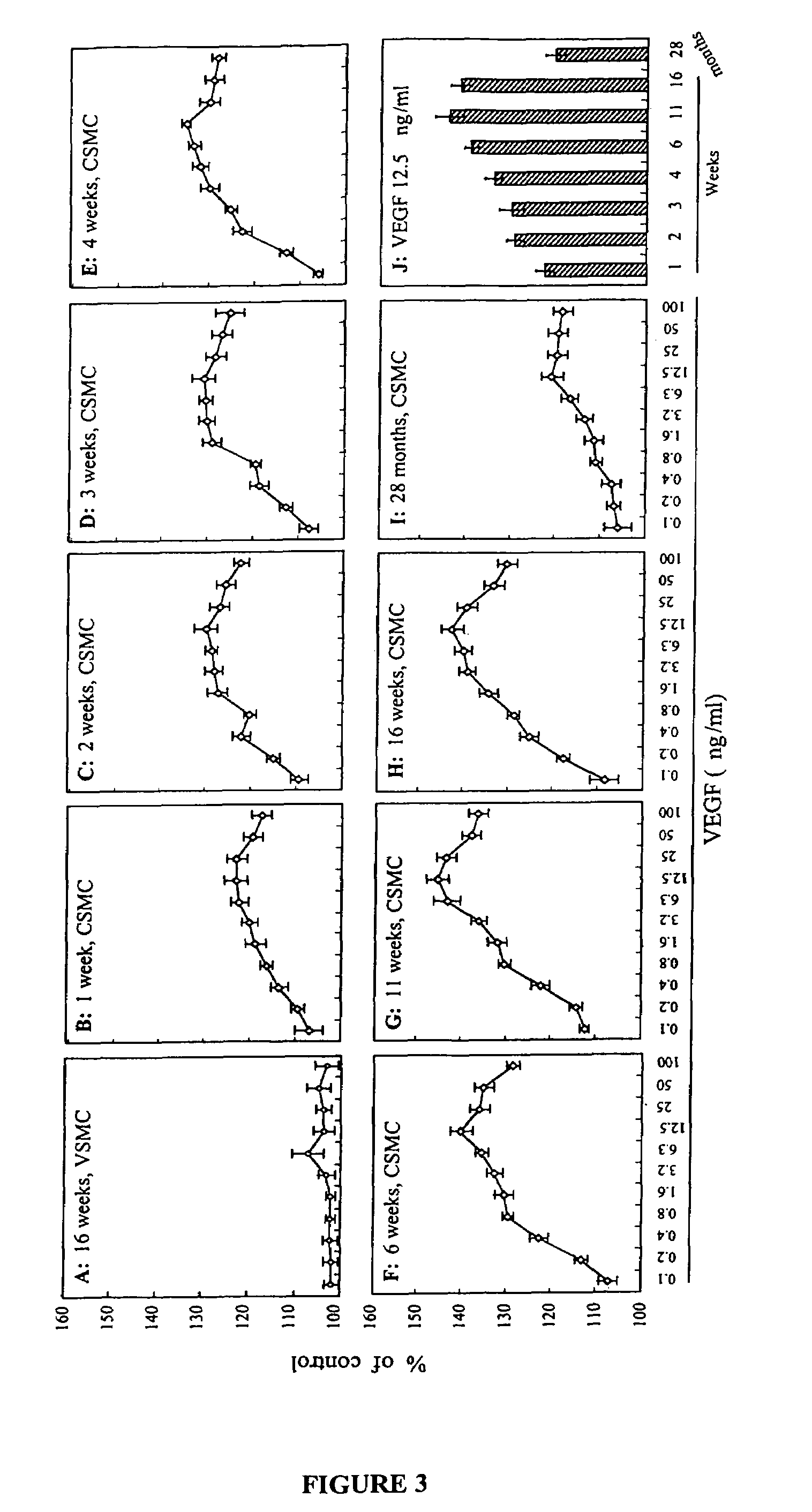
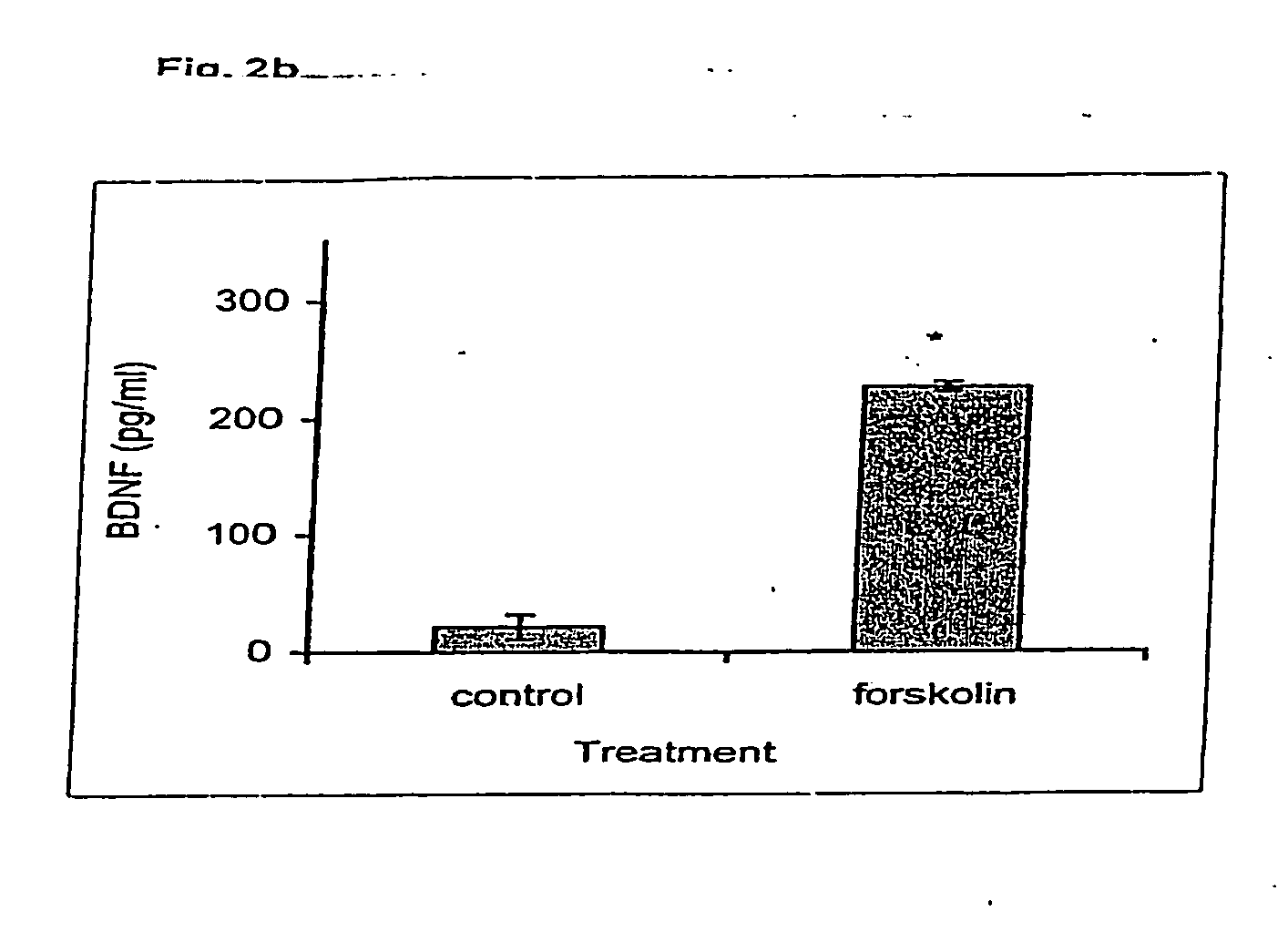
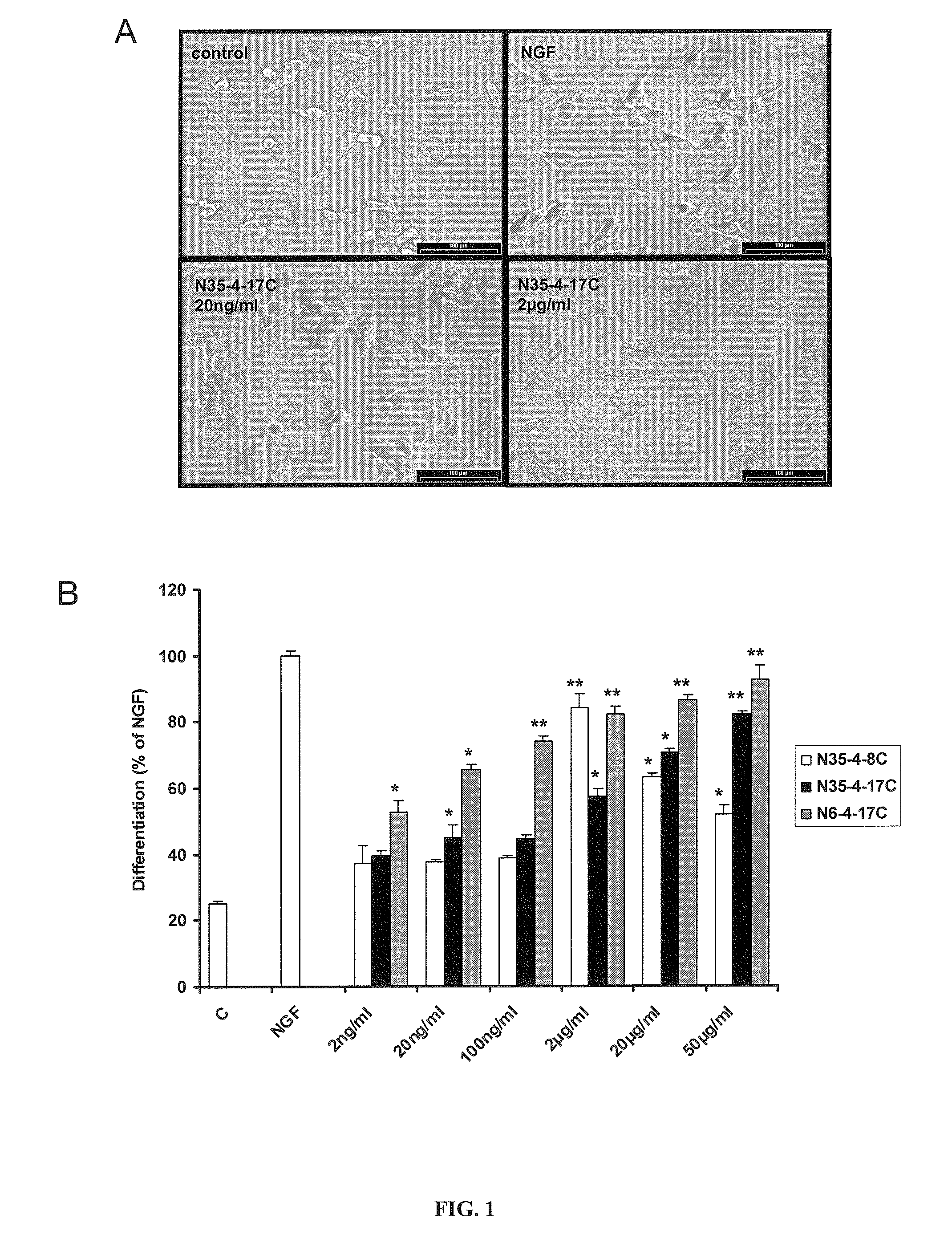
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Neurotrophin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neurotrophins are a family of proteins that induce the survival, development, and function of neurons. They belong to a class of growth factors, secreted proteins that are capable of signaling particular cells to survive, differentiate, or grow. Growth factors such as neurotrophins that promote the survival of neurons are known as neurotrophic factors. Neurotrophic factors are secreted by target tissue and act by preventing the associated neuron from initiating programmed cell death – thus allowing the neurons to survive. Neurotrophins also induce differentiation of progenitor cells, to form neurons.
Trophic factor combinations for nervous system treatment
The present invention relates to a composition including an effective amount of at least one of an antimicrobial peptide and a substance having an antimicrobial peptide effect and an effective amount of a neurotrophin. The composition can also include an effective amount of at least one of a growth factor and a neuropeptide. The present invention also relates a method of treating an injury to a nervous system of an animal that includes the steps of identifying the injury to the nervous system and applying to the injury an effective amount of at least one of antimicrobial peptide and a substance having an antimicrobial peptide effect. The method can also include applying an effective amount of one or more trophic factors selected from the group consisting of a growth factor, a neurotrophin, and a neuropeptide to the injury.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Neurturin receptor
InactiveUS6777196B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsExtracellularCell activity
NTNRalpha, NTNRalpha extracellular domain (ECD), NTNRalpha variants, chimeric NTNRalpha (e.g., NTNRalpha immunoadhesion), and antibodies which bind thereto (including agonist and neutralizing antibodies) are disclosed. Various uses for these molecules are described, including methods to modulate cell activity and survival by response to NTNRalpha-ligands, for example NTN, by providing NTNRalpha to the cell.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
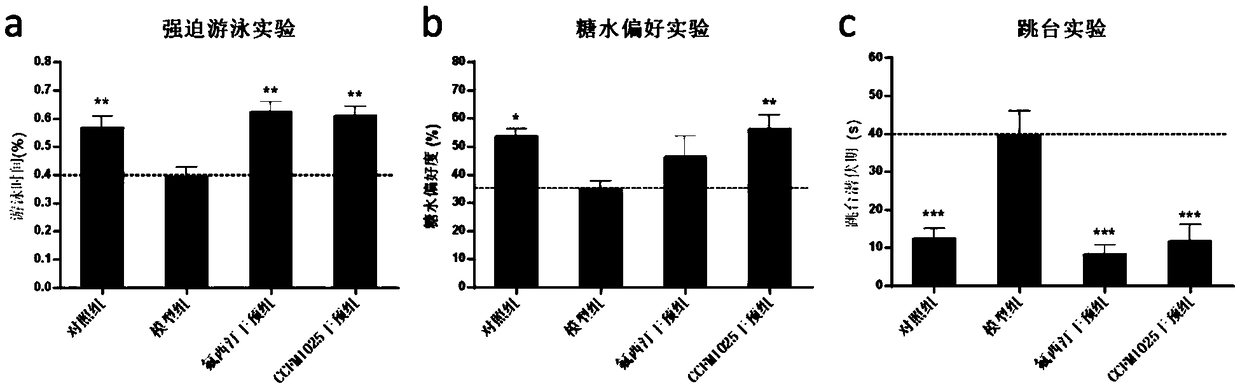
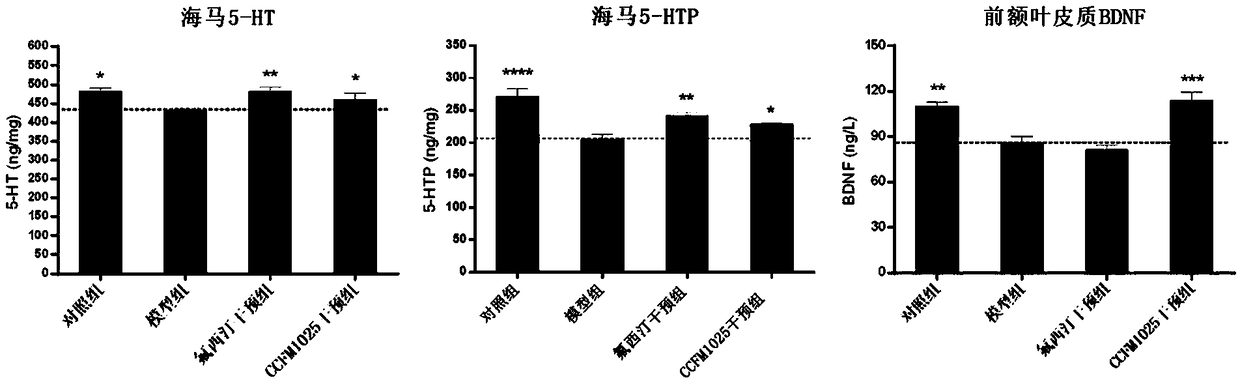
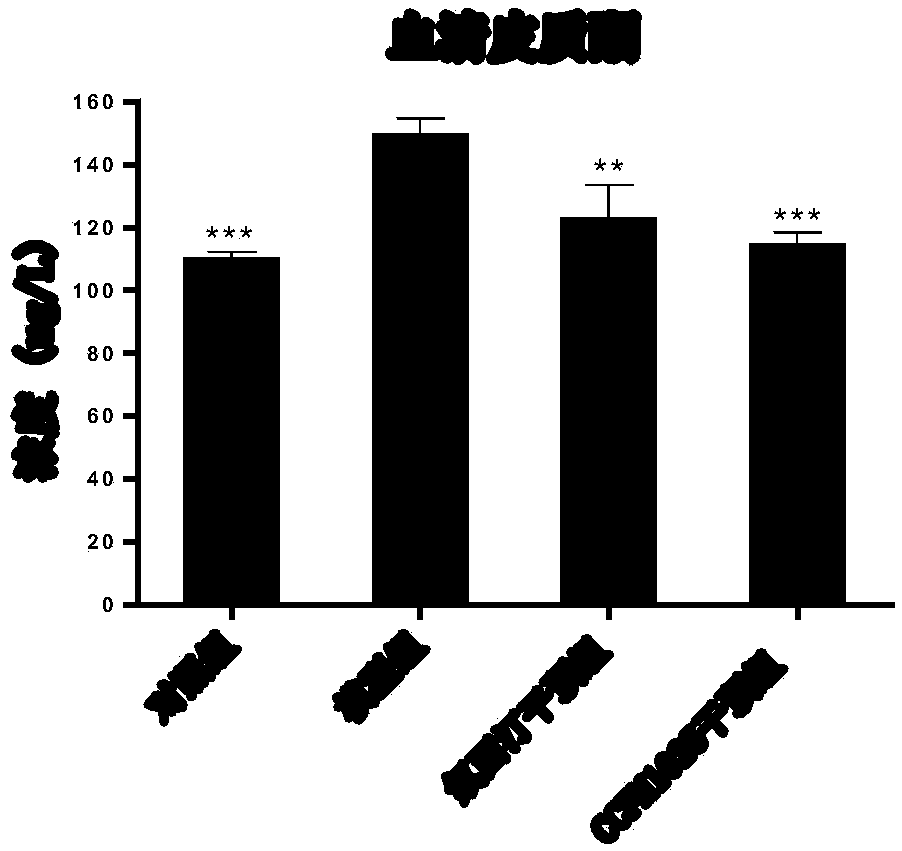
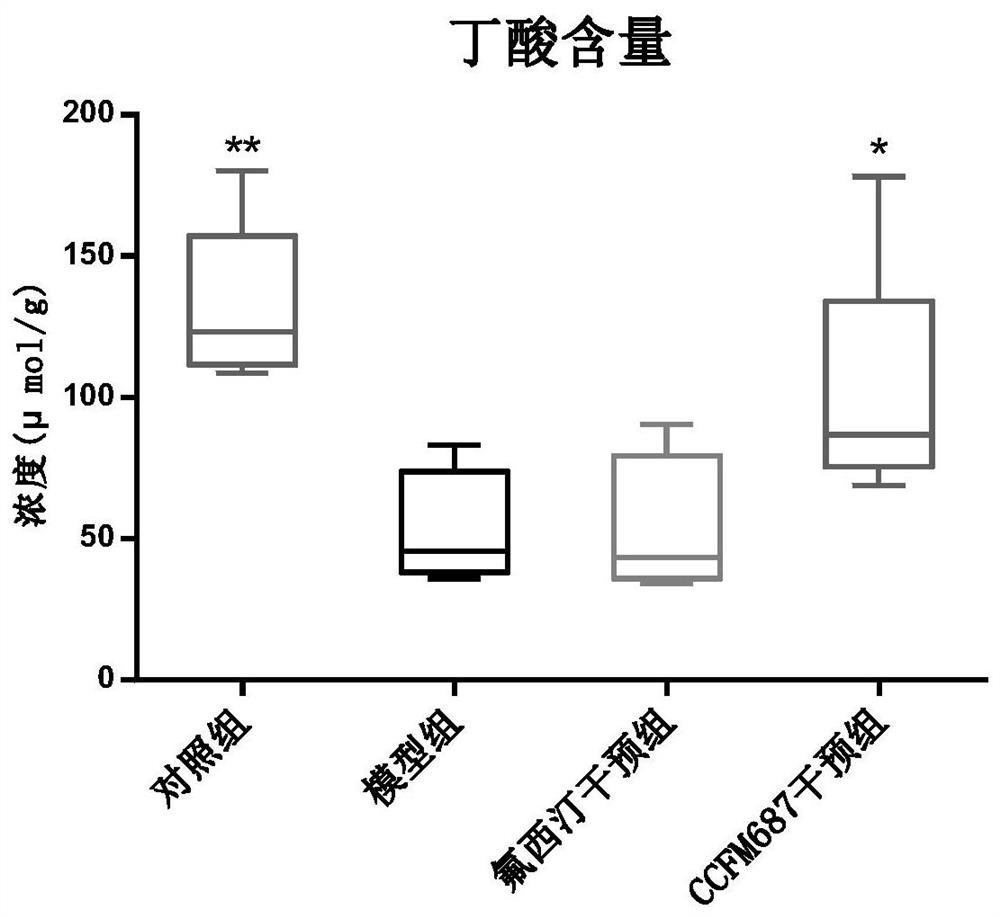
Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025, fermented food and application thereof
ActiveCN108949640ARelieve depression-like behaviorImprove the level ofNervous disorderBacteriaGut floraEnteropathy
The invention relates to bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025, a fermented food and application thereof. The bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 can be used for improving the depression-like behavior of a depression mouse, improving 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain of the depression mouse, improving the level of 5-hydroxytryptamine and a brain-derived neurotrophic factor, reducing the level of corticosteronein serum of the depression mouse, improving the level of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the serum of the depression mouse, improving intestinal flora disturbance of the depression mouse, reducing the abundance of intestinal veillonella, improving the abundance of bifidobacterium and mycoplasmataceae, improving alpha-diversity of intestinal flora and reducing occurrence of inflammatory bowel disease and obesity. By adopting the bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025, the mRNA level of tryptophan hydroxylase in a simulated entero-chromaffin cell can be improved, the secretion volume of 5-hydroxytryptophane ofthe cell can be improved, and a precursor substance is specifically provided to synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain. The bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 has a wide application prospect.
Owner:无锡食生臻选生物科技有限公司
Polypyrrole biological conductive hydrogel, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107137765APromote proliferation and differentiationGuide growthAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryPolypyrroleFreeze-drying
The invention relates to polypyrrole biological conductive hydrogel, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps; preparing carboxymethylchitosan hydrogel from carboxymethyl chitosan by using a crosslinking agent under a certain condition, and performing freeze-drying treatment; performing electrochemical synthesis on a pyrrole monomer to obtain polypyrrole, adding a dopant into the polypyrrole to perform modification and performing ball-milling and crushing to enable the particle size to be matched with the pore diameter of pores of the carboxymethylchitosan hydrogel; blending nerve growth factors into water, adding modified polypyrrole particles, stirring and dispersing uniformly, putting the carboxymethylchitosan hydrogel to enable the solution to be completely absorbed, adding water, vibrating, and completely swelling and balancing to obtain the polypyrrole biological conductive hydrogel. When the polypyrrole biological conductive hydrogel is applied to neural restoration, sustained release of neurotrophic factors can be completed, nerve cells can be subjected to certain electrical stimulation through bioelectrical or external electrical stimulation, proliferation and differentiation of the nerve cells are promoted through double effects of electric stimulation and neurotrophic factor induction, and nerve axon growth is guided.
Owner:深圳南泥湾科技有限公司
Pantropic neurotrophic factors
Pantropic neurotrophic factors which have multiple neurotrophic specificities are provided. The pantropic neurotrophic factors of the present invention are useful in the treatment of neuronal disorders. Nucleic acids and expression vectors encoding the pantropic neurotrophins are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Polynucleotides encoding a neurotrophic factor receptor
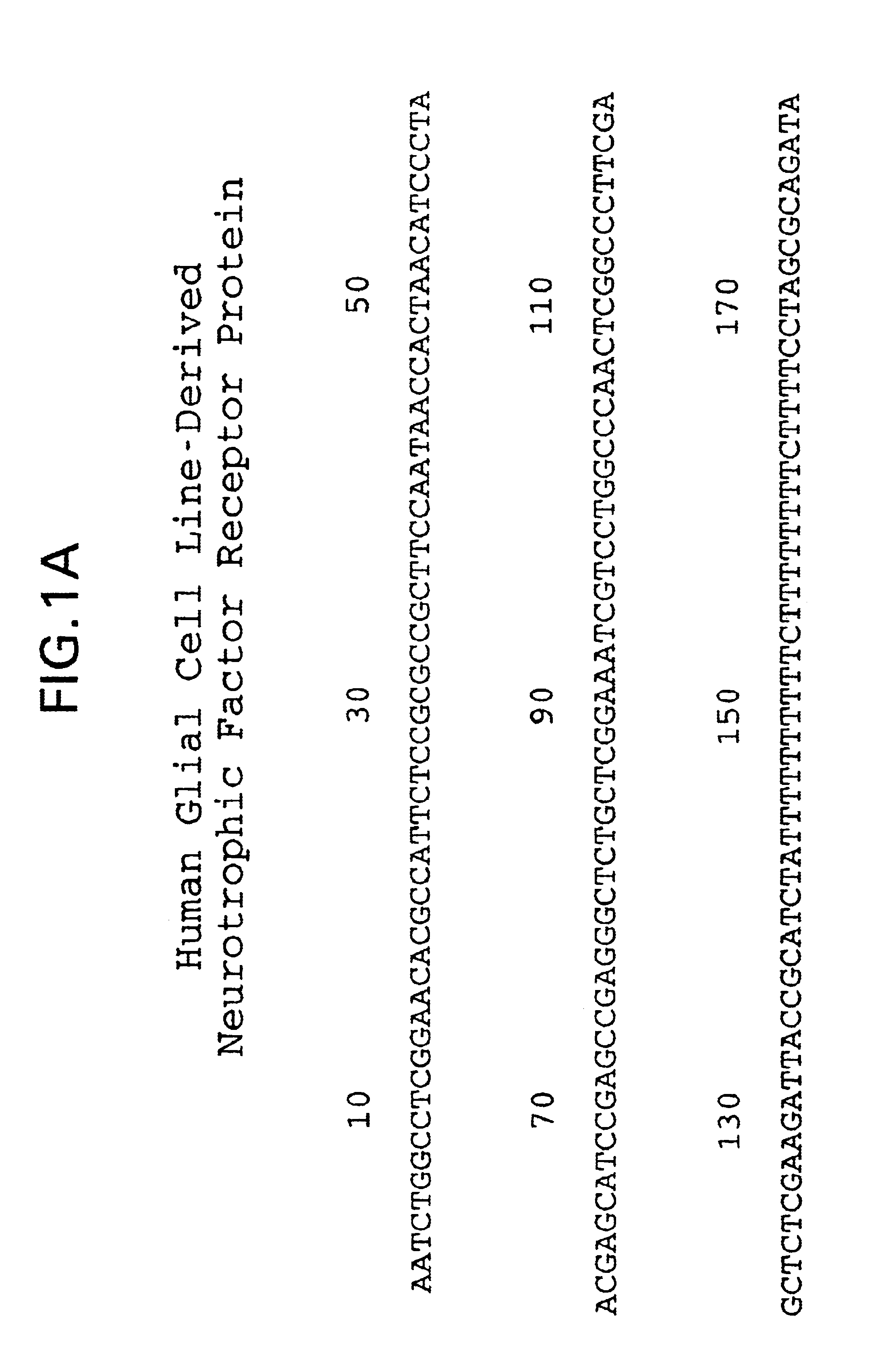
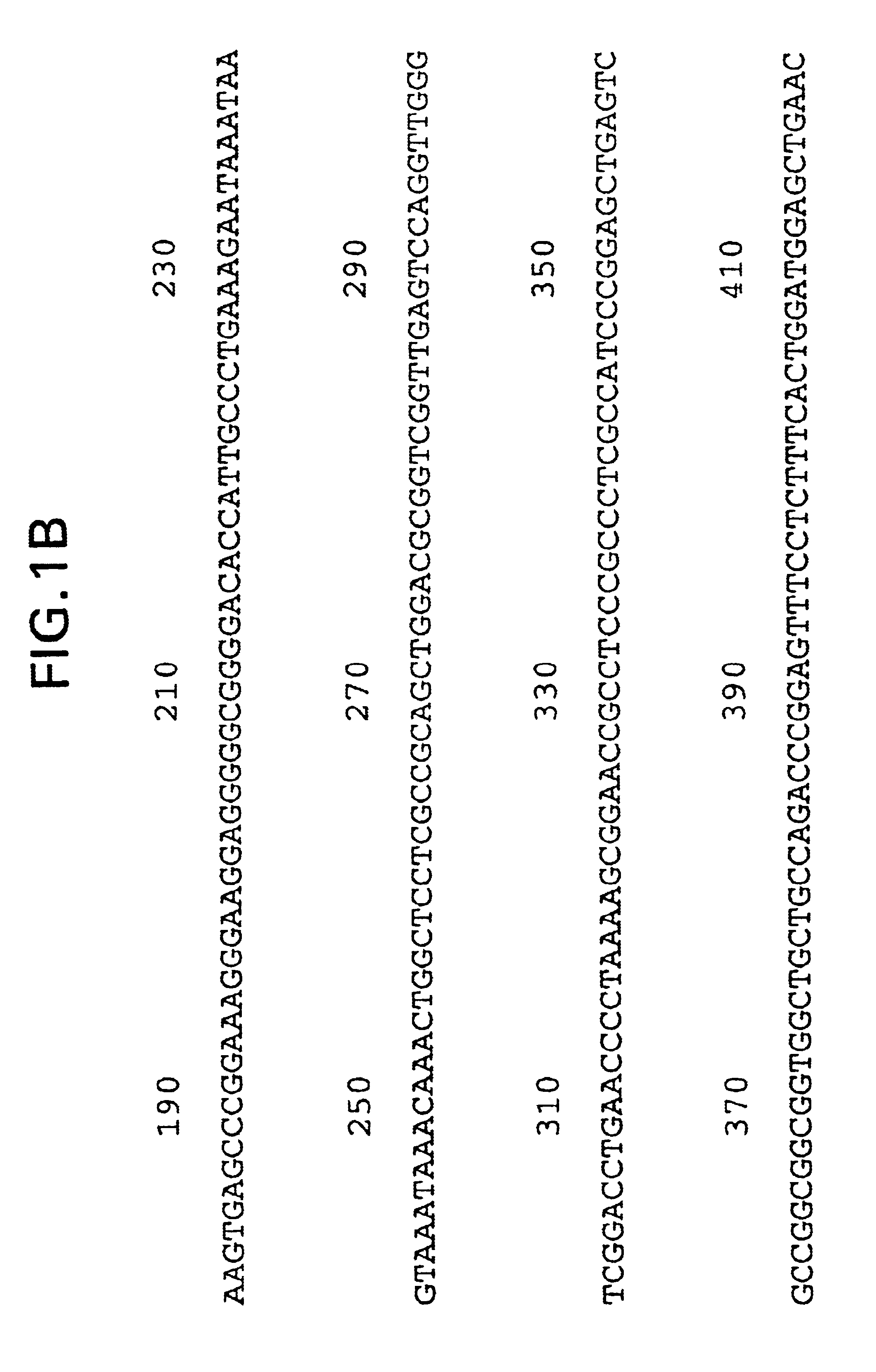
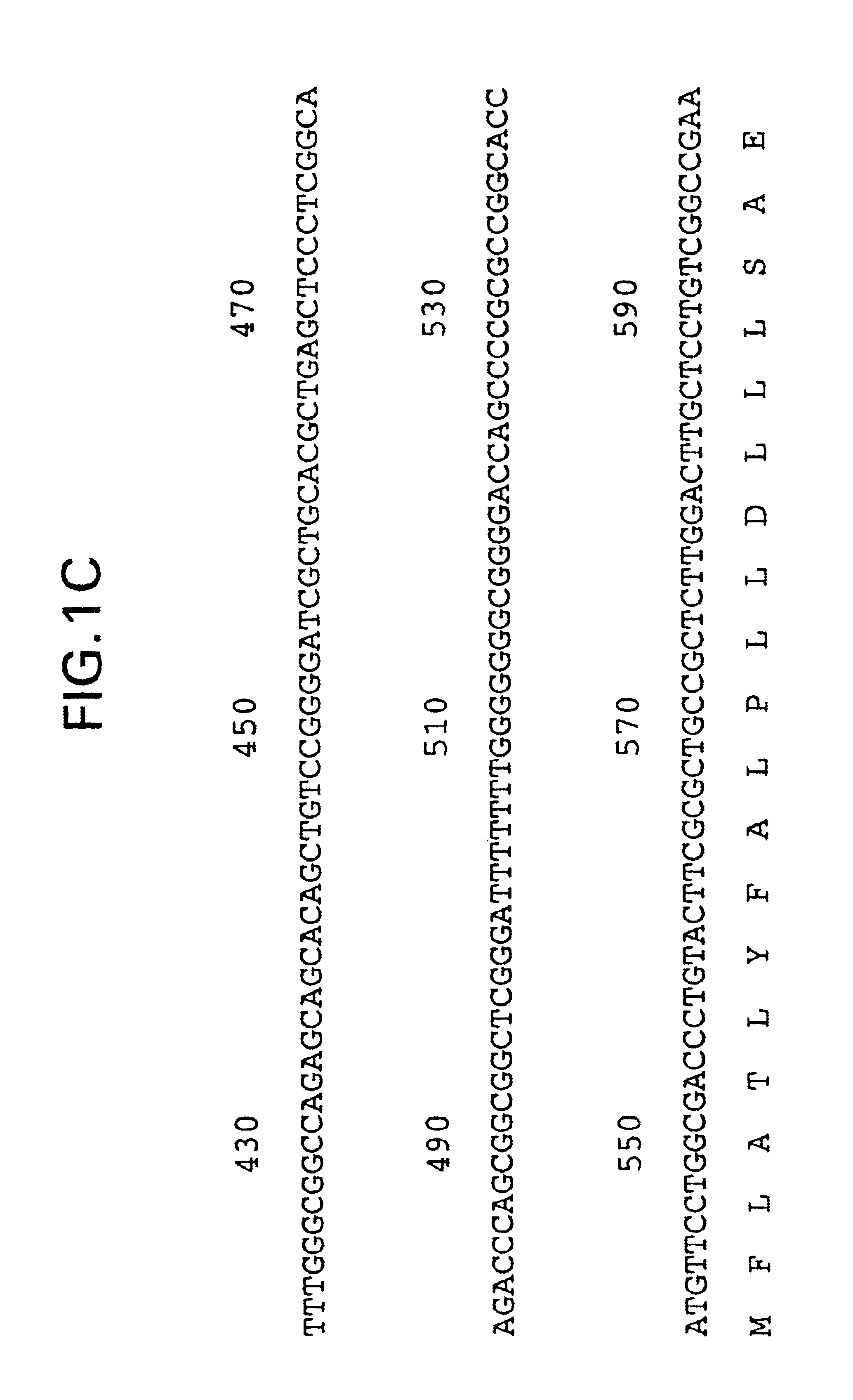
The present invention relates to glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), a potent neurotrophin that exhibits a broad spectrum of biological activities on a variety of cell types from both the central and peripheral nervous systems. The present invention involves the cloning and characterization of receptors for GDNF. Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences are described for GDNFR protein products. A hydrophobic domain with the features of a signal peptide is found at the amino terminus, while a second hydrophobic domain at the carboxy terminus is involved in the linkage of the receptor to the cell membrane. The lack of a transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic region indicates that GDNFR requires one or more accessory molecules in order to mediate transmembrane signaling. GDNFR mRNA is widely distributed in both nervous system and non-neural tissues, consistent with the similar distribution found for GDNF.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Modulation of activity of proneurotrophins
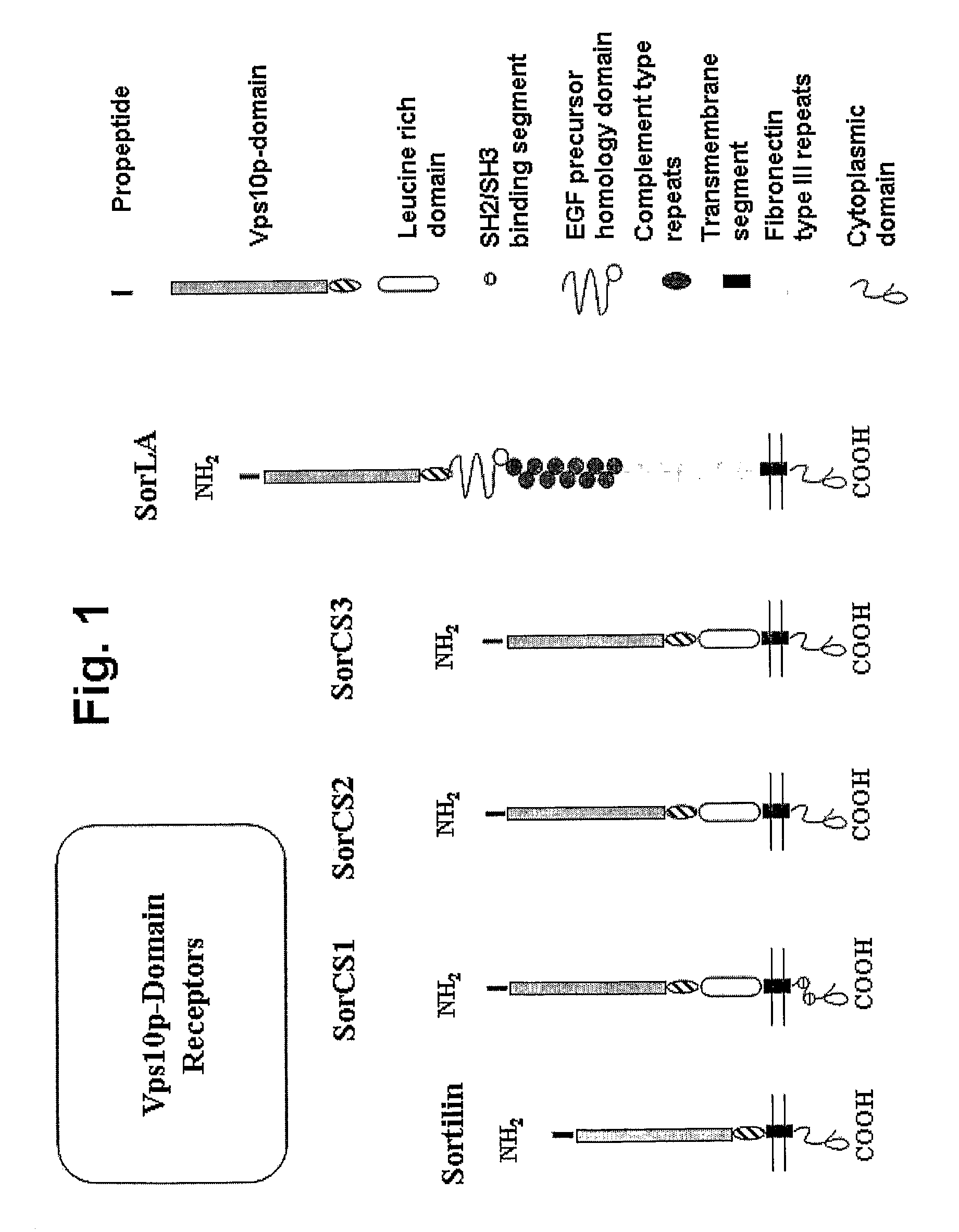
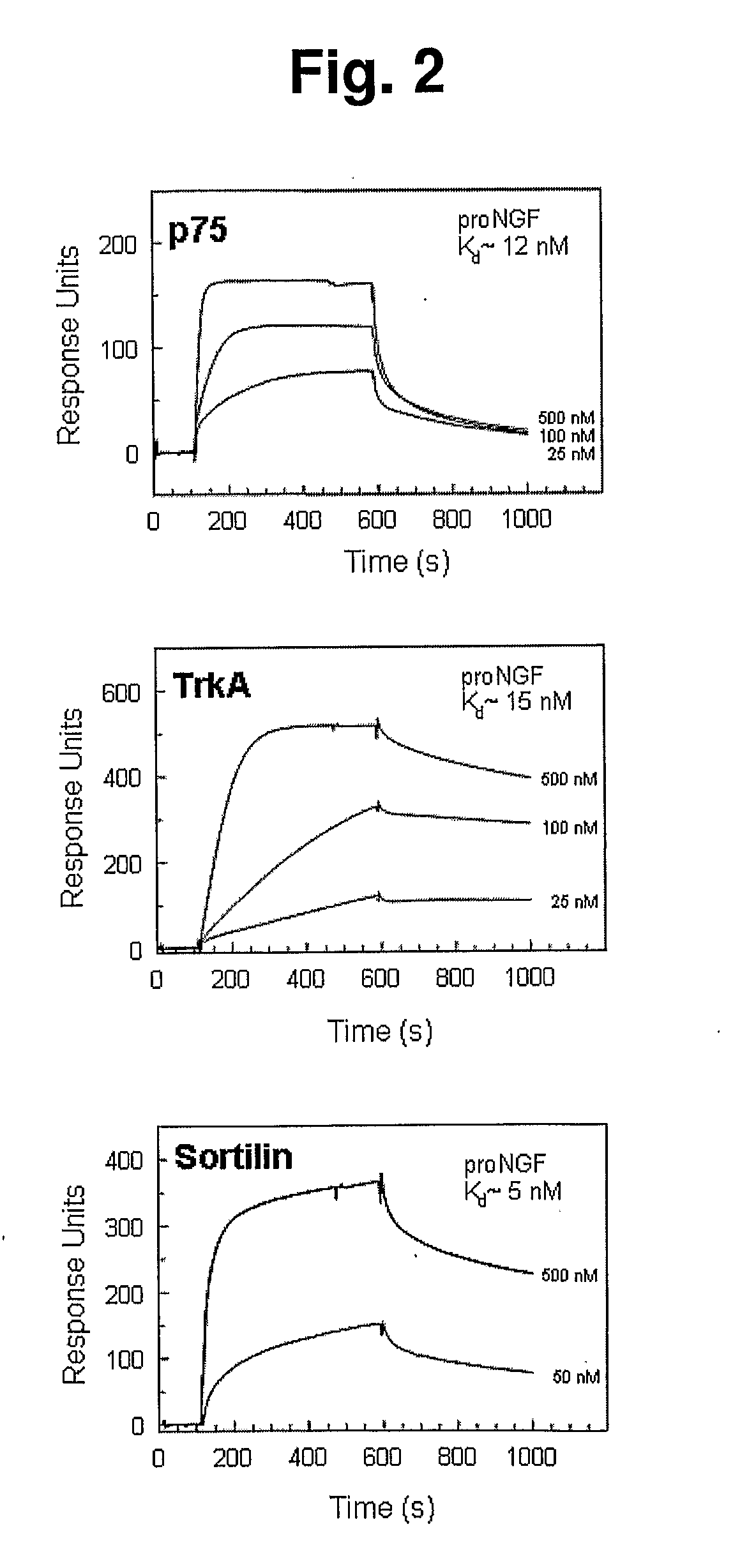
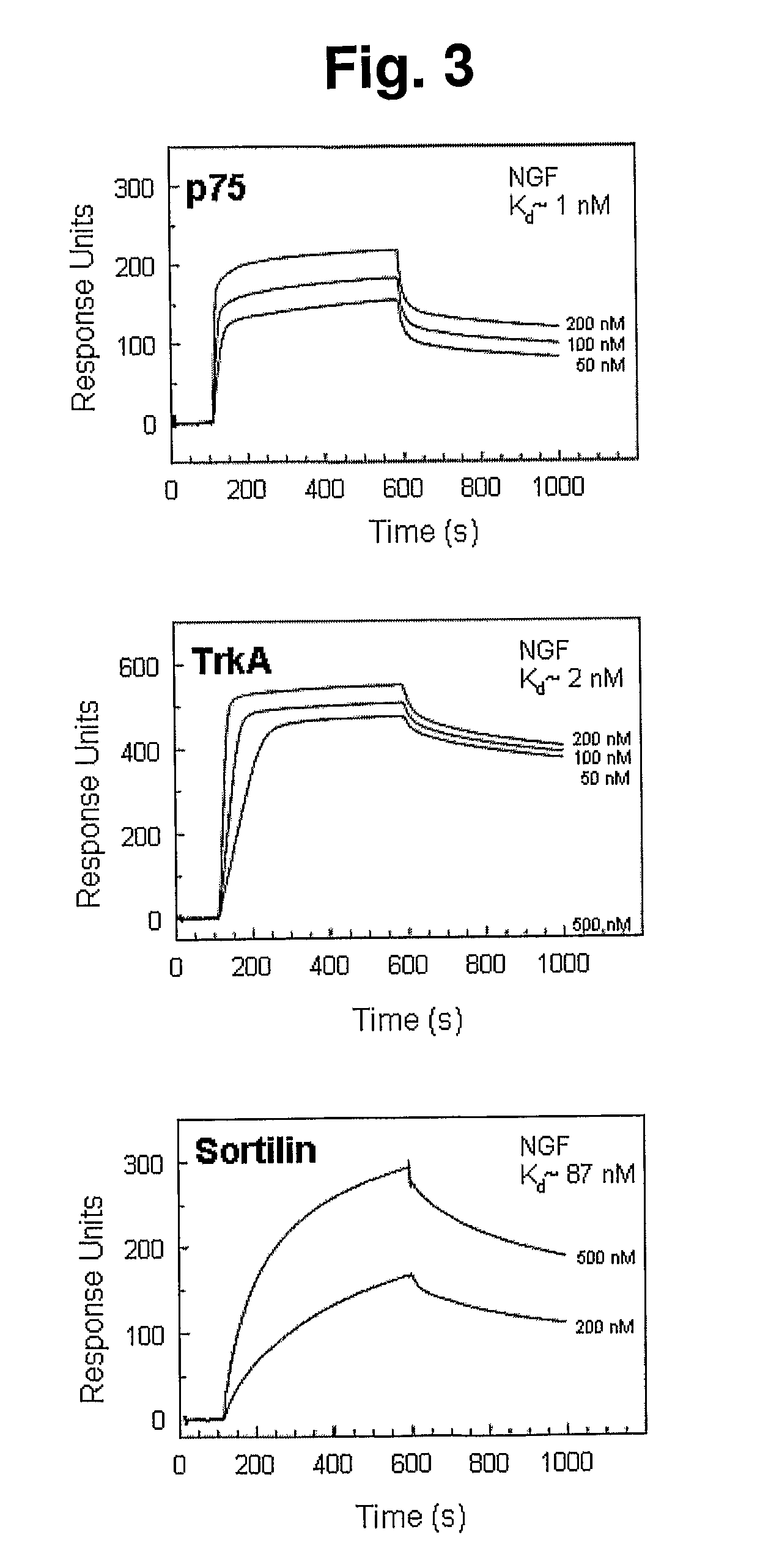
The present invention provides agents for inhibiting binding of a pro-neurotrophin to a Vps10p-domain receptor, in particular the binding of a pro-NGF or a pro-BDNF to a Sortilin receptor. The invention thus provides agents for the manufacture of a medicament, for treating and / or preventing disease or disorders such as but not limited to neurological, neuropsychiatric and ocular diseases, disorders, and degeneration as well as obesity, diabetes, pain and / or nociception in an individual.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Compositions and Methods for Parkinson's Disease Treatment by BDNF-flag Gene Transfer through Neurotensin Polyplex to Nigral Dopamine Neuro
InactiveUS20150335764A1Increase in BDNF levelReduced amphetamine-induced rotational behaviorCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderGenomicsExpression gene
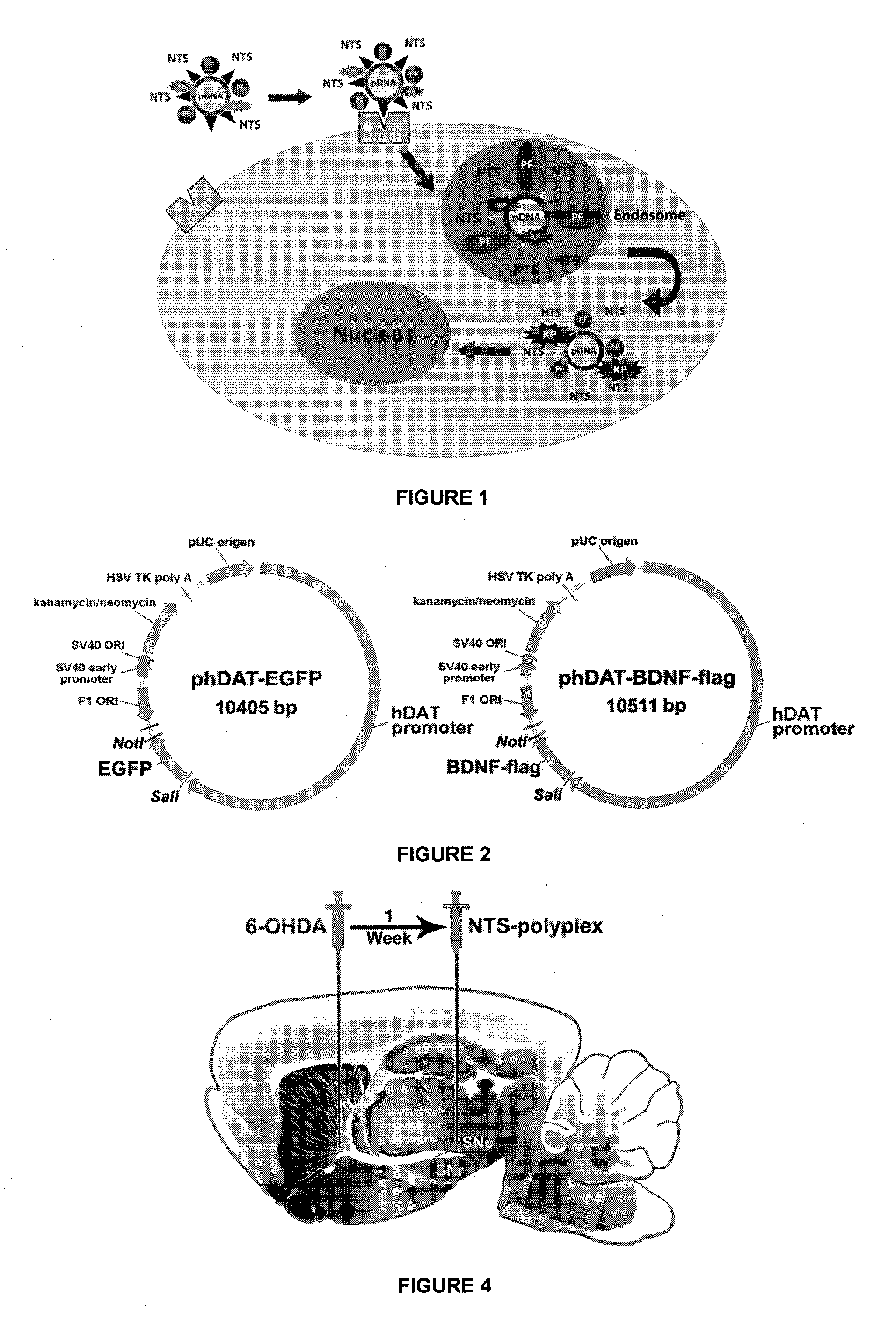
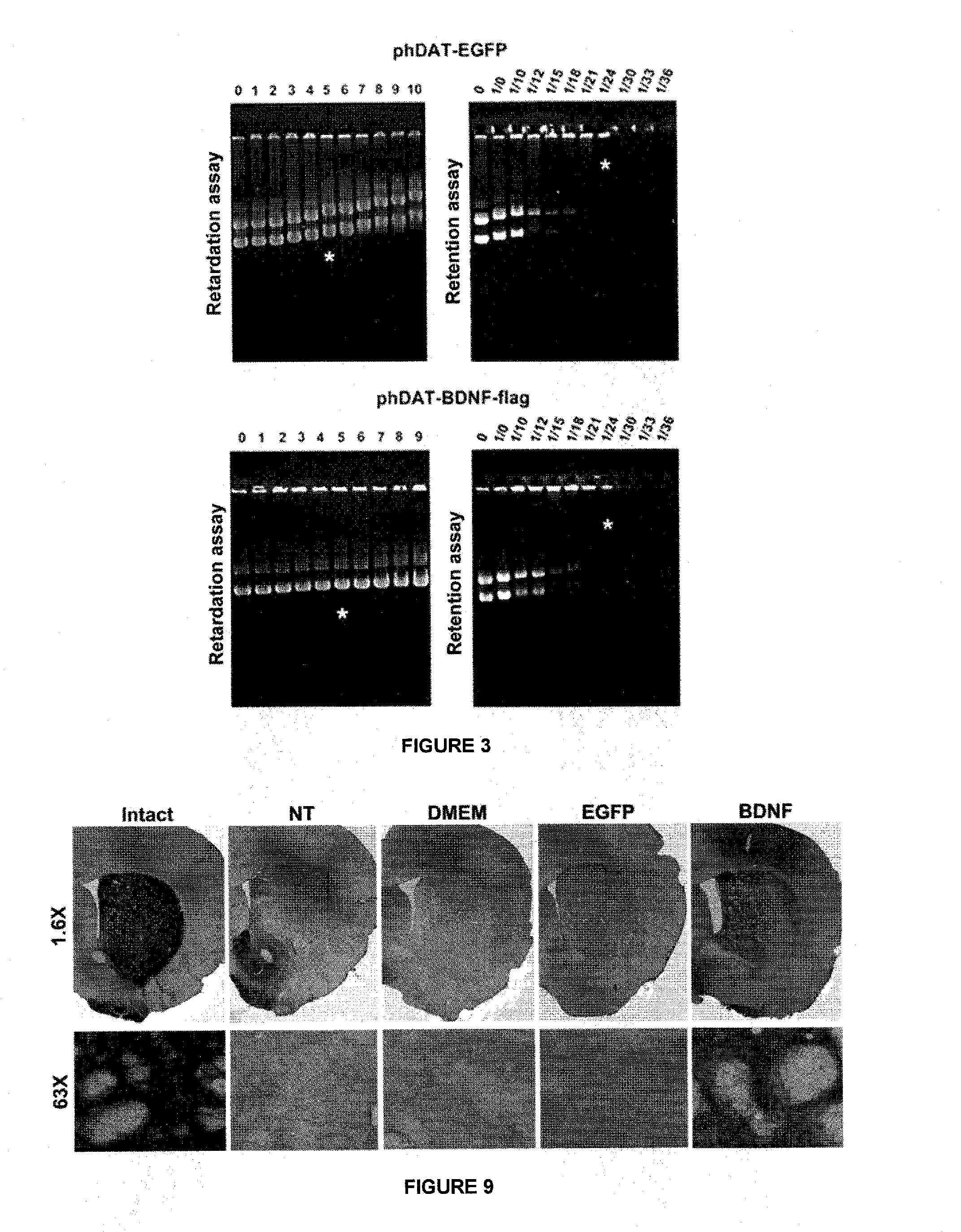
The present invention pertains to the field of genomics and nanotechnology, specifically to the in vivo gene expression technologies and their application in gene therapy. It consists of the performance of the NTS-polyplex nanocomplex, which can carry nucleic acids to the neurons, involving neurotrophic therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, the present invention addresses the treatment of Parkinson's disease by the regulated expression of the BDNF neurotrophin.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION & DE ESTUDIOS AVANZADOS DEL INST POLITECNICO NACIONAL
Methods and compositions for treating male erectile dysfunction
InactiveUS7265091B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsFemale Sexual Arousal DisorderNeurotrophin-3
The invention provides a method for preventing or treating male erectile dysfunction or female sexual arousal disorder by administering an effective amount of one or more factors from a group of factors including vascular endothelial growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, neurotrophin-3, neurotrophin-4, or angiopoietin-1, wherein the factor is a full length protein or a nucleic acid encoding the factor, or a functional derivative or fragment thereof, or an agent that enhances production and / or male erection or female sexual arousal stimulating function of the factor(s). Combinations, kits, and combinatorial methods are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mitigating symptoms and behaviors of substance abuse by modulating GDNF or BDNF pathway activity
InactiveUS20050203011A1Reduces behavioral effect of ethanolDecrease in BDNF levelHormone peptidesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubstance abuserMammal
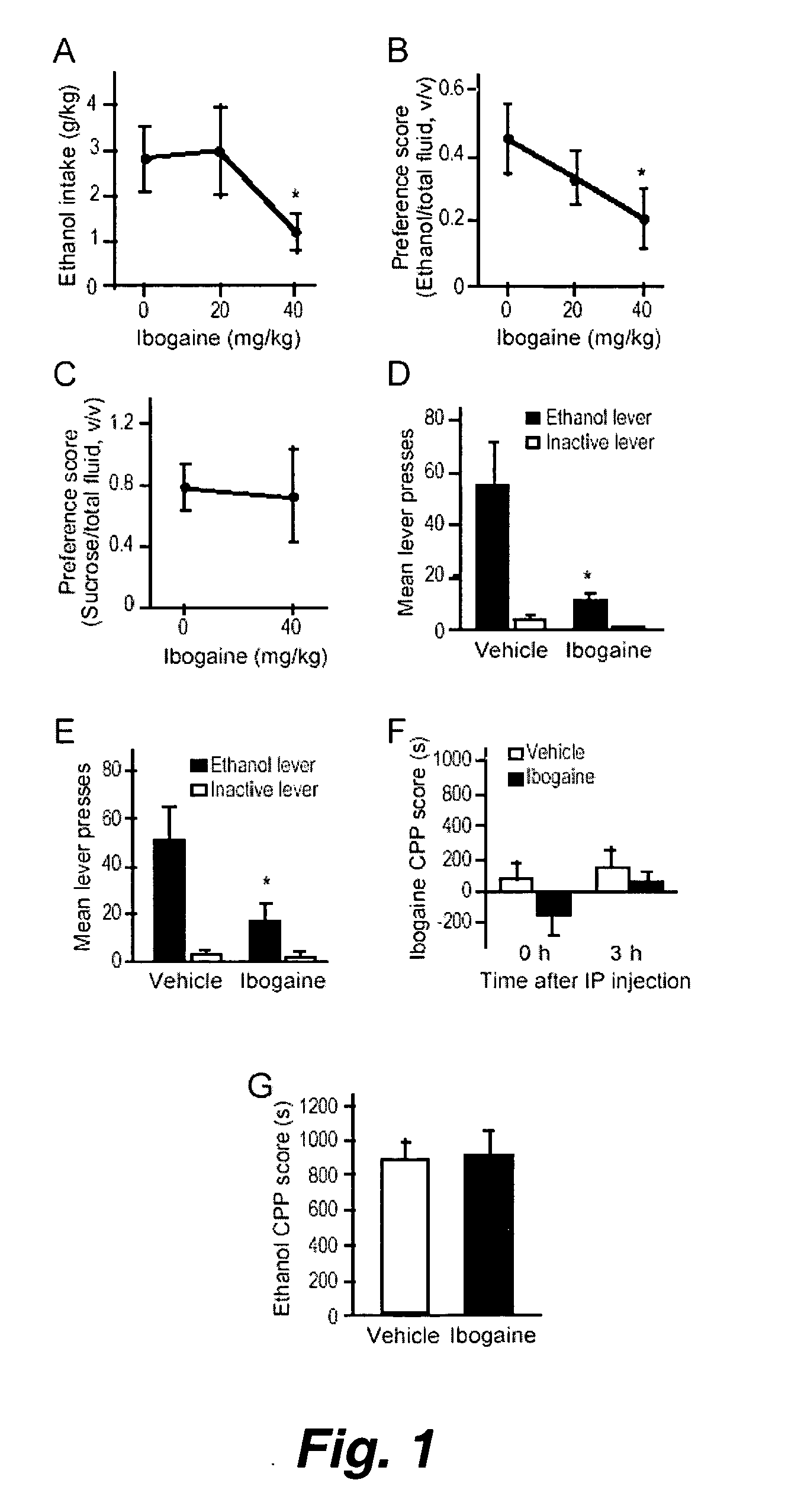
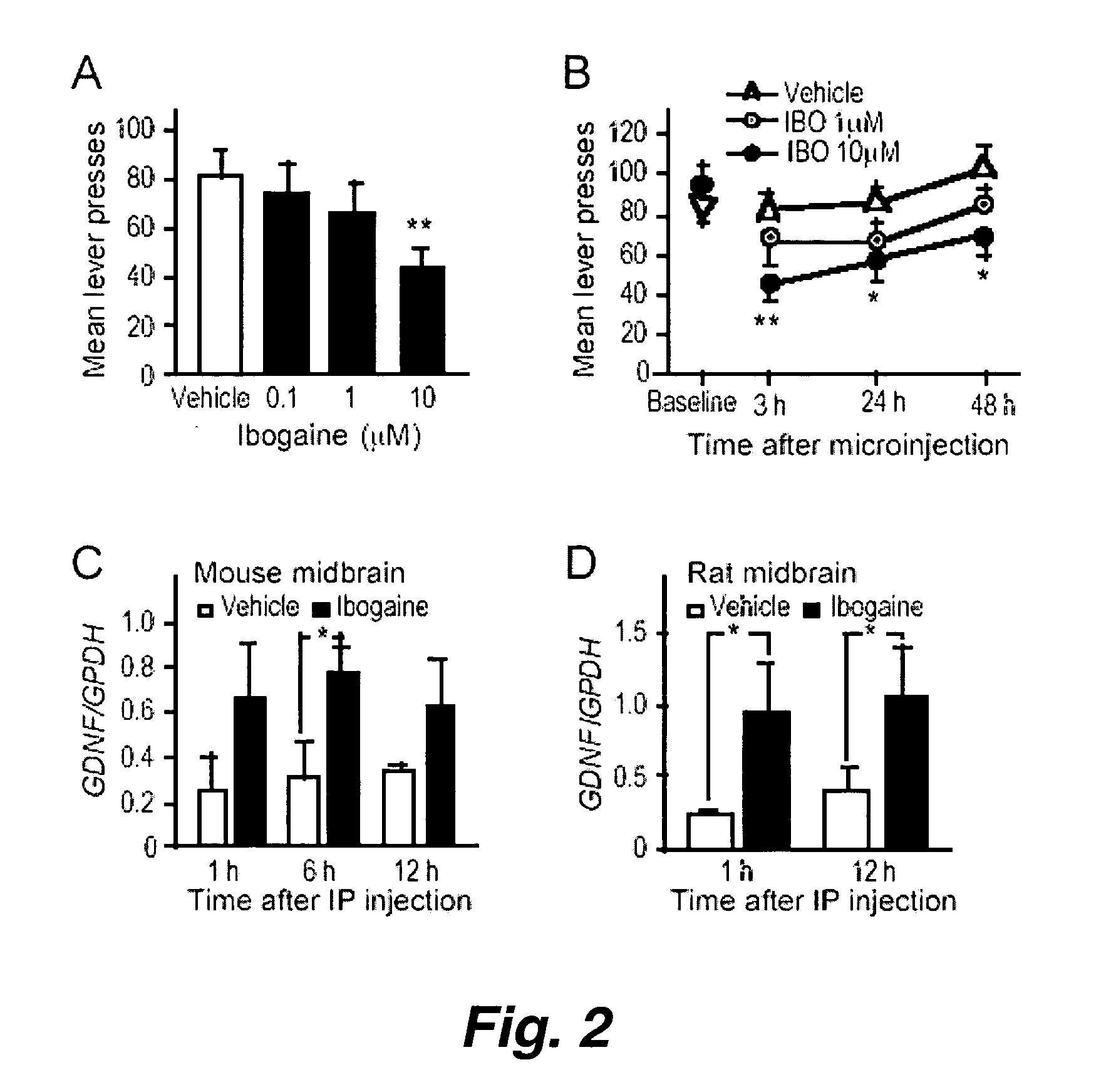
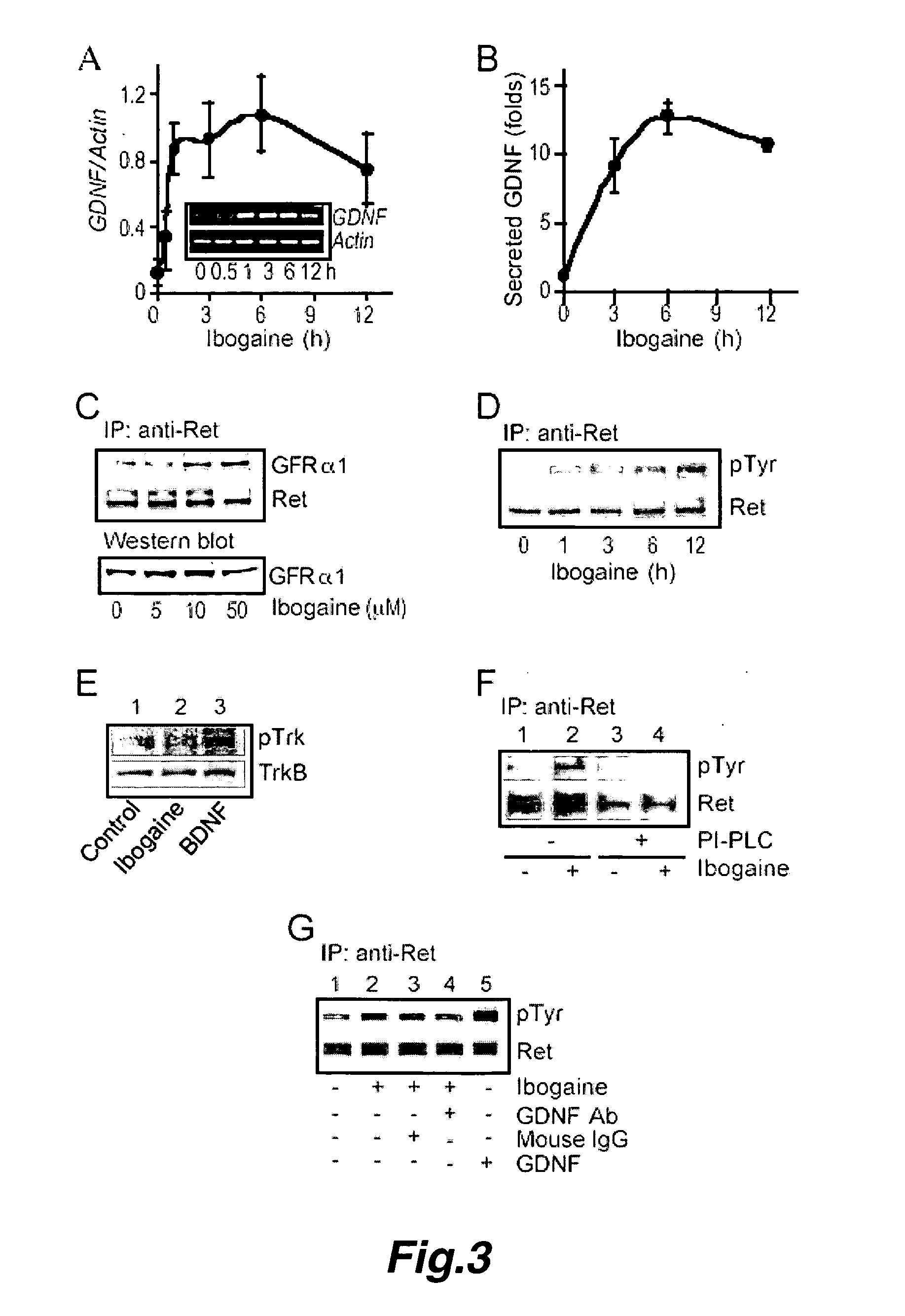
This invention pertains to the discovery that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its associated signaling pathway is involved in reversing and / or counteracting neuroadaptations within the mesolimbic system that contribute to the development and / or maintenance of addiction (e.g. alcohol addiction). This invention also pertains to the discovery that ibogaine activity is mediated by changes in mRNA expression of GDNF. Thus, in certain embodiments, this inventioni provides a method of mitigating one or more symptoms of substance abuse in a mammal by increasing the expression or activity of GDNF, BDNF, RACK1, and / or the dopamine D3 receptor (D3R) in said mammal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for selectively inhibiting reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine using yeast extract
InactiveUS20060140974A1Reduce premenstrual syndromes (PMSSlow downBiocideMicroorganismsAnti-Anxiety AgentsAnti stress
A yeast extract or yeast-derived bioactive peptide having an activity of selectively inhibiting reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, which can be effectively used in preventing or treating various diseases related to reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, especially depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue and obesity are provided. Also, a yeast extract or yeast-derived bioactive peptide having activities as an anti-stress agent, an anti-fatigue agent, premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menstrual pain relaxants, and a brain-neurotrophic factor, and a method for preparing the bioactive peptide are provided. The yeast extract or yeast-derived bioactive peptide is effective in relieving stress, nervousness, anxiety, tension, insomnia, fatigue, and imbalance in the autonomic nerve regulation. Therefore, the yeast extract or yeast-derived bioactive peptide is vailable as an anti-depression agent, an anti-anxiety agent, an anti-stress agent, an anti-fatigue agent, an anti-obesity agent, premenstrual syndrome and menstrual pain relaxants, a bain-neurotrophin, and a source of active foods having these activities.
Owner:LEE MOON SUP +1
Treatment of behavioral disorders
InactiveUS20050192290A1Ameliorate behavioral disorderSufficient amountBiocideNervous disorderTherapeutic ACTHFexofenadine
The present invention relates to a method for treating a behavior disorder comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of antihistamine, such as ceterizine, fexofenadine; loratadine, and desloratadine. The behavioral disorders may include ADHD, anxieity, depression, and autism. The method may include the administration of the antihistamine in combination with a stimulant medication, such as methylphenidate, thereby to achieve a synergistic effect. In any event, the amount of antihistamine and / or stimulant is effective to downregulate neurotrophic factors such as nerve growth factor or CD40. The invention is also directed to a method of preventing the onset of behavior disorders in patients presenting with symptoms of allergic rhinitis.
Owner:MELAMED ISAAC
Mesenchymal stem cell for expressing related gene of neurotrophin family and application thereof
The invention relates to a mesenchymal stem cell of marrow, umbilical cord or bleeding of the umbilicus and purpose in the field of cell transplantation, stem cell culture, expansion and oriented differentiation. The mesenchymal stem cell for expressing a related gene of a neurotrophin family is prepared by the following steps of extracting a mesenchymal stem cell from the marrow, the umbilical cord or the bleeding of the umbilicus; recombining the related gene of the neurotrophin family to an AAV (Adeno-Associated Virus) used as a carrier; preparing the AAV expressing the related gene of the neurotrophin family; and infecting separated and purified mesenchymal stem cell through AAV particles to obtain the mesenchymal stem cell expressing the related gene of the neurotrophin family. The invention is used as a culture layer cell to provide a manually controlled microenvironment for stem cell culture, expansion and oriented differentiation and promote the proliferation and the oriented differentiation of the stem cells so as to provide a new curing measure for human diseases.
Owner:广州吉帝生物科技有限公司
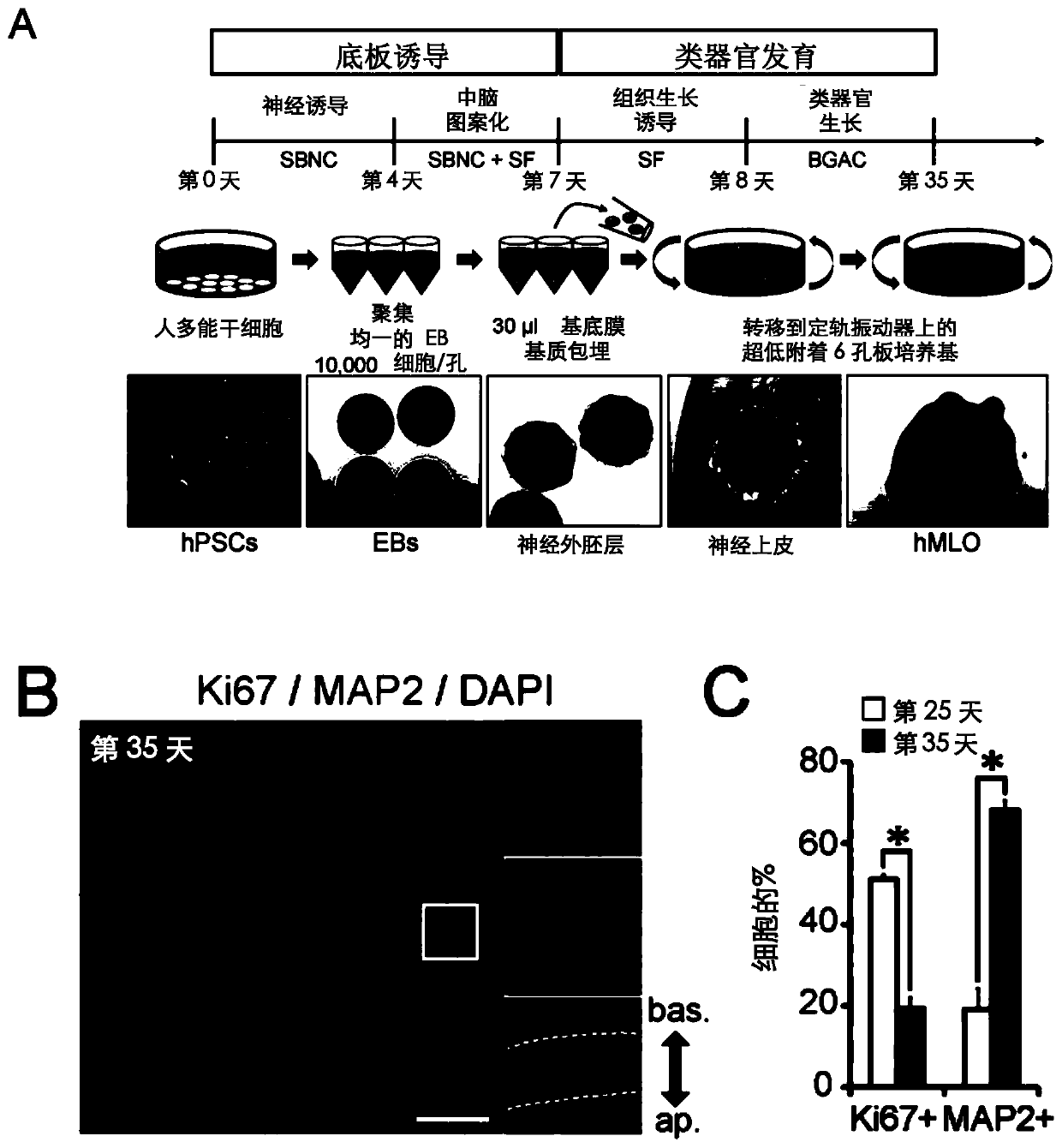
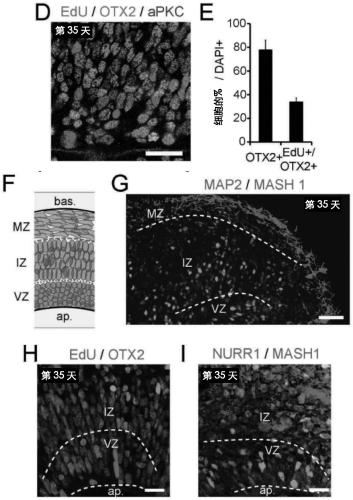
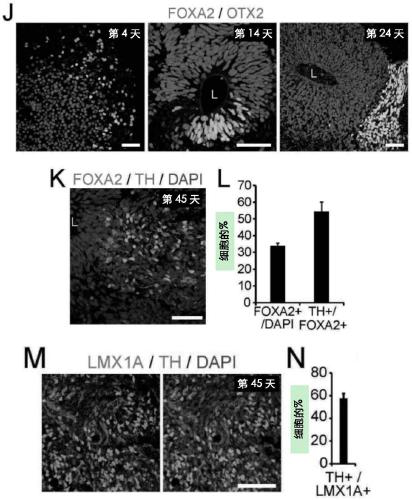
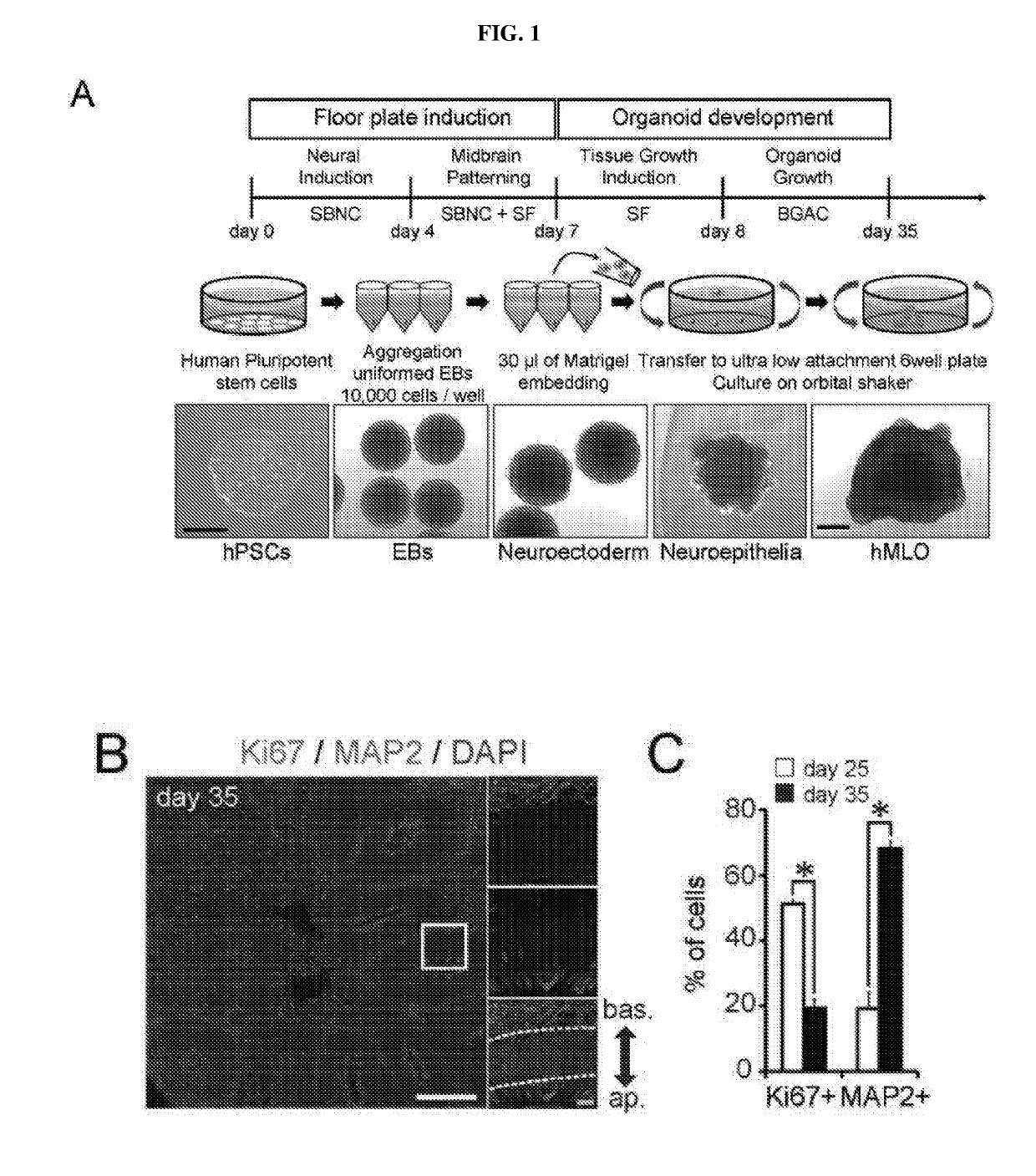
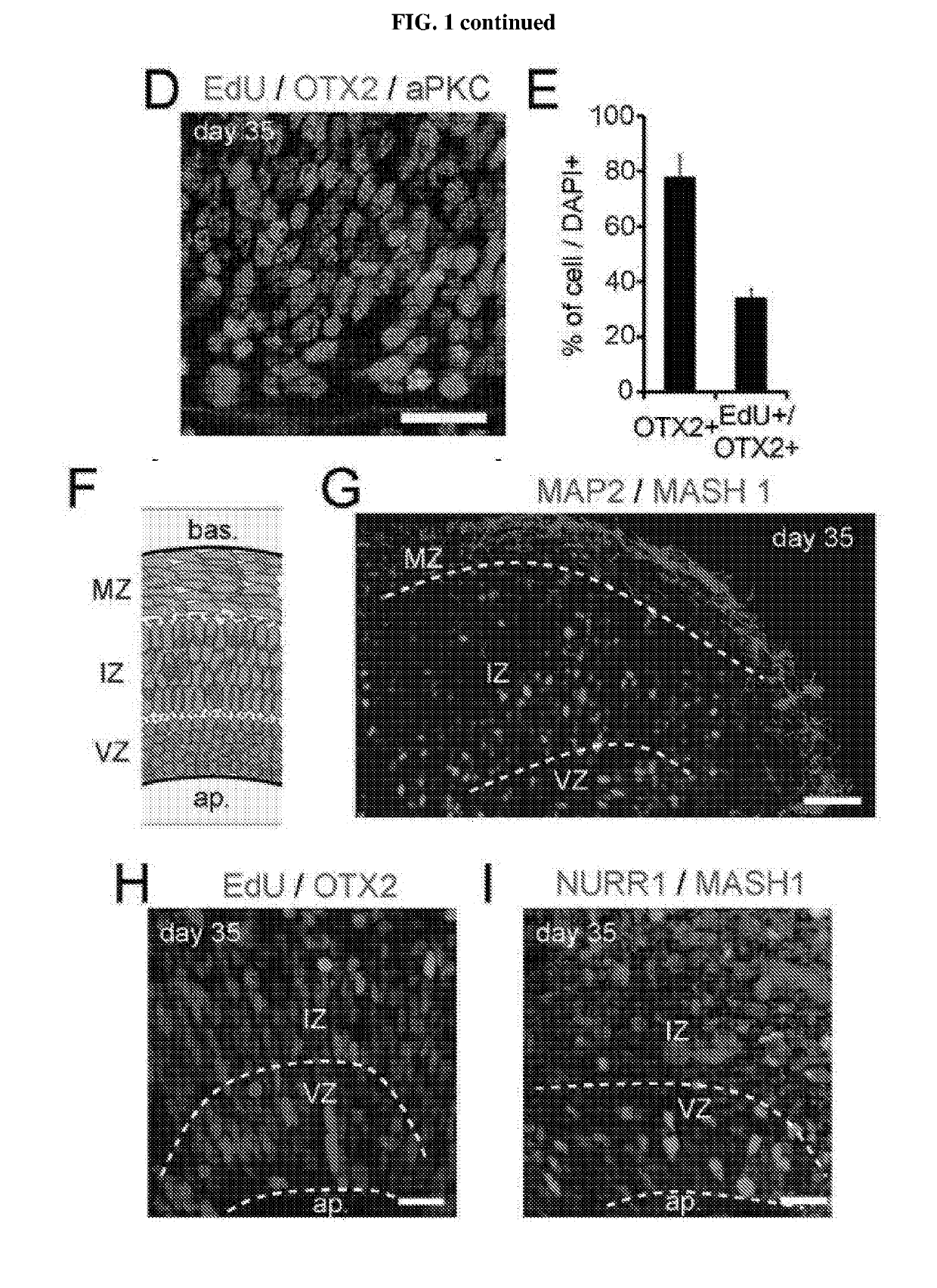
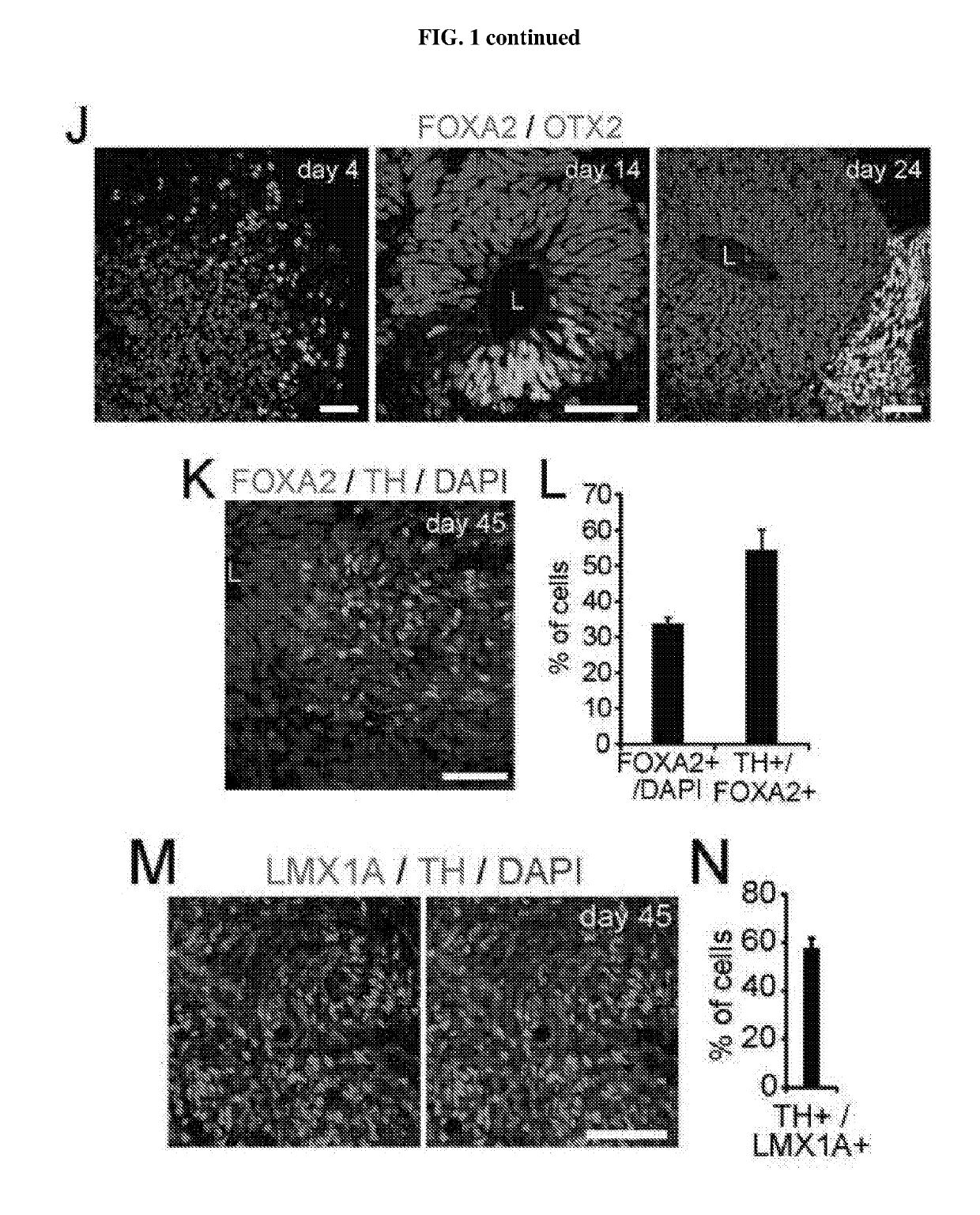
Generation of midbrain-specific organoids from human pluripotent stem cells
PendingCN109996870ACell culture mediaNervous system cellsPluripotential stem cellCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present invention provides a method of deriving and maintaining a midbrain-like organoid in culture, comprising (a) culturing pluripotent stem cells to obtain neuronal lineage embryoid bodies; (b)culturing the neuronal lineage embryoid bodies from (a) to obtain midbrain regionalized tissues; (c) embedding and culturing the midbrain regionalized tissues from (b) in an extracellular matrix to obtain neuroepithelial tissues; and (c) culturing the neuroepithelial tissues from (c) to obtain a midbrain-like organoid. Also disclosed herein are culture media suitable for deriving and maintainingneuronal lineage embryoid bodies comprising (a) TGF-beta inhibitor and / or SMAD2 / 3 inhibitors; and (b) WNT-signaling activator; culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining midbrain regionalizedtissues comprising (a) TGF-beta inhibitor and / or SMAD2 / 3 inhibitors; (b) WNT-signaling activator; (c) hedgehog signaling protein; and (d) a fibroblast growth factor; culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining neuroepithelial tissues comprising (a) hedgehog signaling protein; and (b) a fibroblast growth factor and culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining a midbrain-like organoid comprising (a) neurotrophin factor; (b) ascorbic acid; and (c) an activator of cAMP-dependent pathway.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
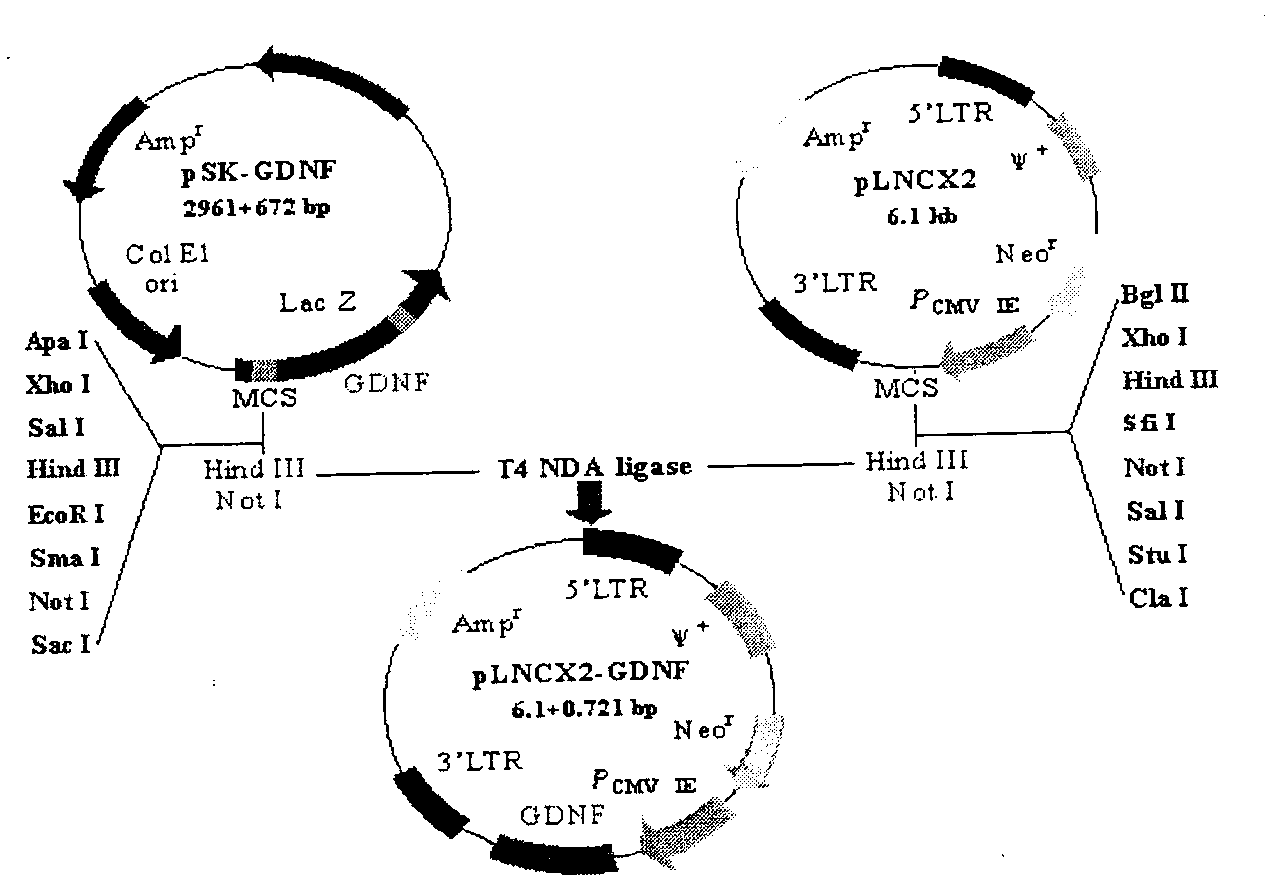
Construction method of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified embryo neural stem cell
InactiveCN103215225AViruses/bacteriophagesBiological testingGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factorNeuronal degeneration
The invention relates to a biotechnology and especially relates to a construction method of a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified embryo neural stem cell. The construction method comprises the following steps of 1, plasmid transformation, 2, plasmid digestion purification, 3, target gene and vector cloning, 4, recombinant plasmid packaging, 5, recombinant plasmid identification, 6, virus titer determination, 7, stem cell culture, 8, virus infection of the stem cells, 9, transgenic stem cell identification, 10, transgenic stem cell target-protein content determination, and 11, transgenic stem cell biological-activity detection. The glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified embryo neural stem cell has strong effects of promoting survival of dopaminergic neurons and retains characteristics of the original neural stem cell. The glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified embryo neural stem cell has good effects of treating motor neuron damage diseases and neuronal degeneration diseases.
Owner:孙勇
Methods for therapy of neurodegenerative disease of the brain
InactiveUS20070249554A1Avoid restrictionsReduce adverse effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCholinergic cellsMammalian brain
A specific clinical protocol for use toward therapy of defective, diseased and damaged cholinergic neurons in the mammalian brain, of particular usefulness for treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. The protocol is practiced by delivering a definite concentration of recombinant neurotrophin into, or within close proximity of, identified defective, diseased or damaged brain cells. Using a viral vector, the concentration of neurotrophin delivered as part of a neurotrophic composition varies from 1010 to 1015 neurotrophin encoding viral particles / ml of composition fluid. Each delivery site receives form 2.5 μl to 25 μl of neurotrophic composition delivered slowly, as in over a period of time ranging upward of 10 minutes / delivery site. Each delivery site is at, or within 500 μm of, a targeted cell, and no more than about 10 mm from another delivery site. Stable in situ neurotrophin expression can be achieved for 12 months, or longer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biological load indicator and method of measuring biological load
Disclosed are techniques capable of objectively and specifically evaluating various mental or physical conditions, of which evaluation was conventionally possible only by subjective symptom-dependent methods, such as stress and fatigue. Specifically disclosed are a stress or fatigue indicating agent including at least two factors selected from the group consisting of IL-1, IL-1ra, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-9, IL-10, IL-11, IL-12, IL-13, IL-15, IL-17, IL-18, Eotaxin, FGF basic, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFN- , IFN-+-, IP-10, MCP-1, MIP-1+-, MIP-1, PDGF-BB, RANTES, TNF-+-, VEGF, CSF-2, TGF-, neurotrophin 5, MCP-3, -2-microglobulin, angiotensin II, CSF-3, CXC chemokine ligand 1, CXC chemokine ligand 5 and HGF; an agent for testing stress or fatigue including at least two molecules selected from the group consisting of molecules specifically recognizing the factors, respectively; a method of measuring stress or fatigue with the test agent; and an indicating agent for evaluating the intensity of mental conditions or disorders, including at least two factors selected from the factor group, wherein each of the factors is weighted.
Owner:关山敦生
Nanoparticles loaded with neurotrophic factors, and preparation and applications thereof
InactiveCN103656623AStrong drug release functionGood biocompatibilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEpsilon-PolylysineMicrosphere
The invention discloses nanoparticles loaded with therapeutic factors or neurotrophic factors. The nanoparticles are made of a high molecular material; the high molecular material is composed of biocompatible positively charged epsilon-polylysine and negatively charged heparin; the mass ratio of epsilon-polylysine to heparin ranges from 1:20 to 1:1; and average particle size grain diameter of the nanoparticles ranges from 100 to 400nm. The epsilon-polylysine-heparin nanoparticles are taken as carriers for loading of neurotrophic factors, and are high in biocompatibility, and stable in biochemical properties. The nanoparticles loaded with neurotrophic factors are capable of promoting cell axon growth effectively via sustained release.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
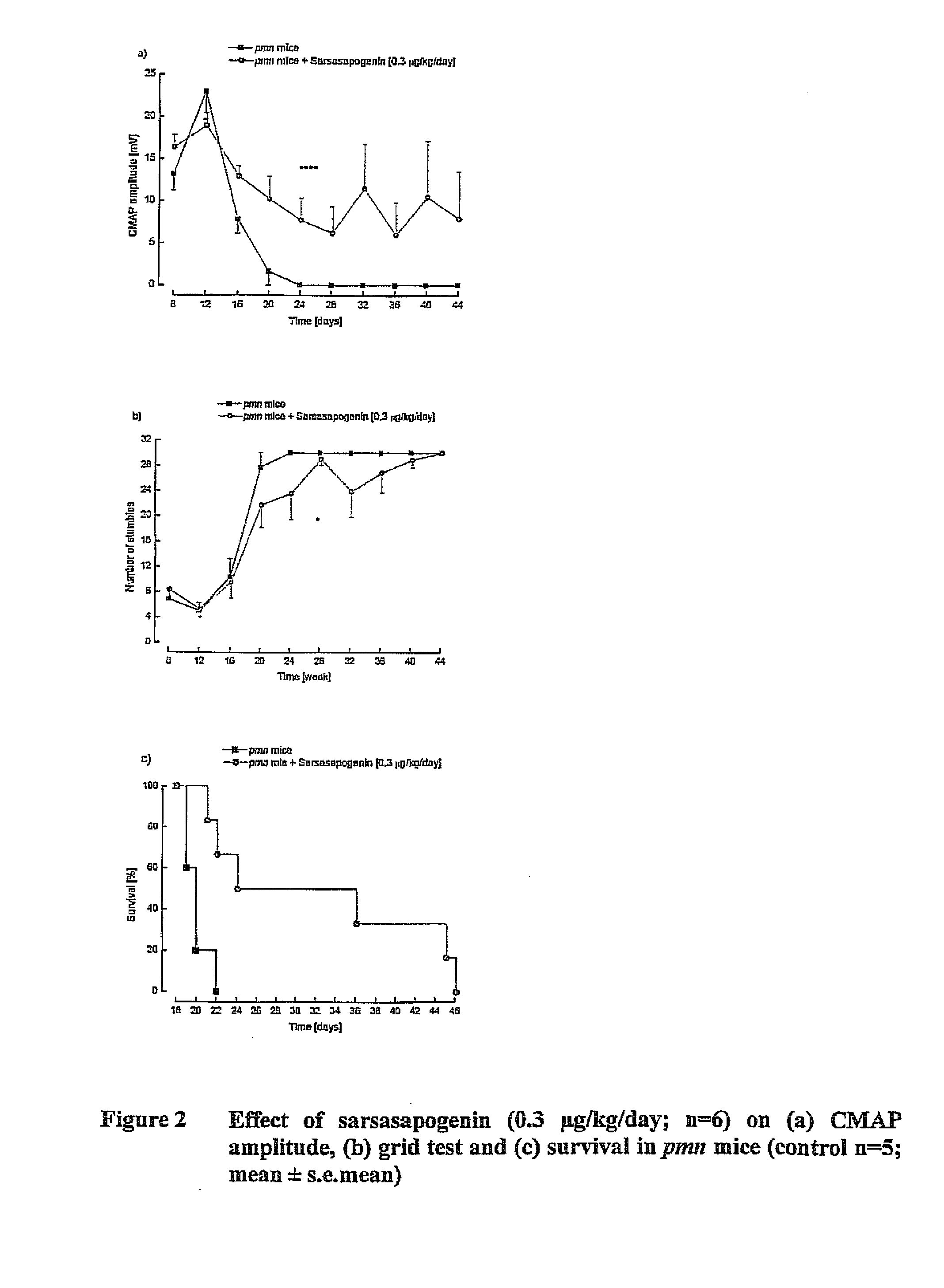
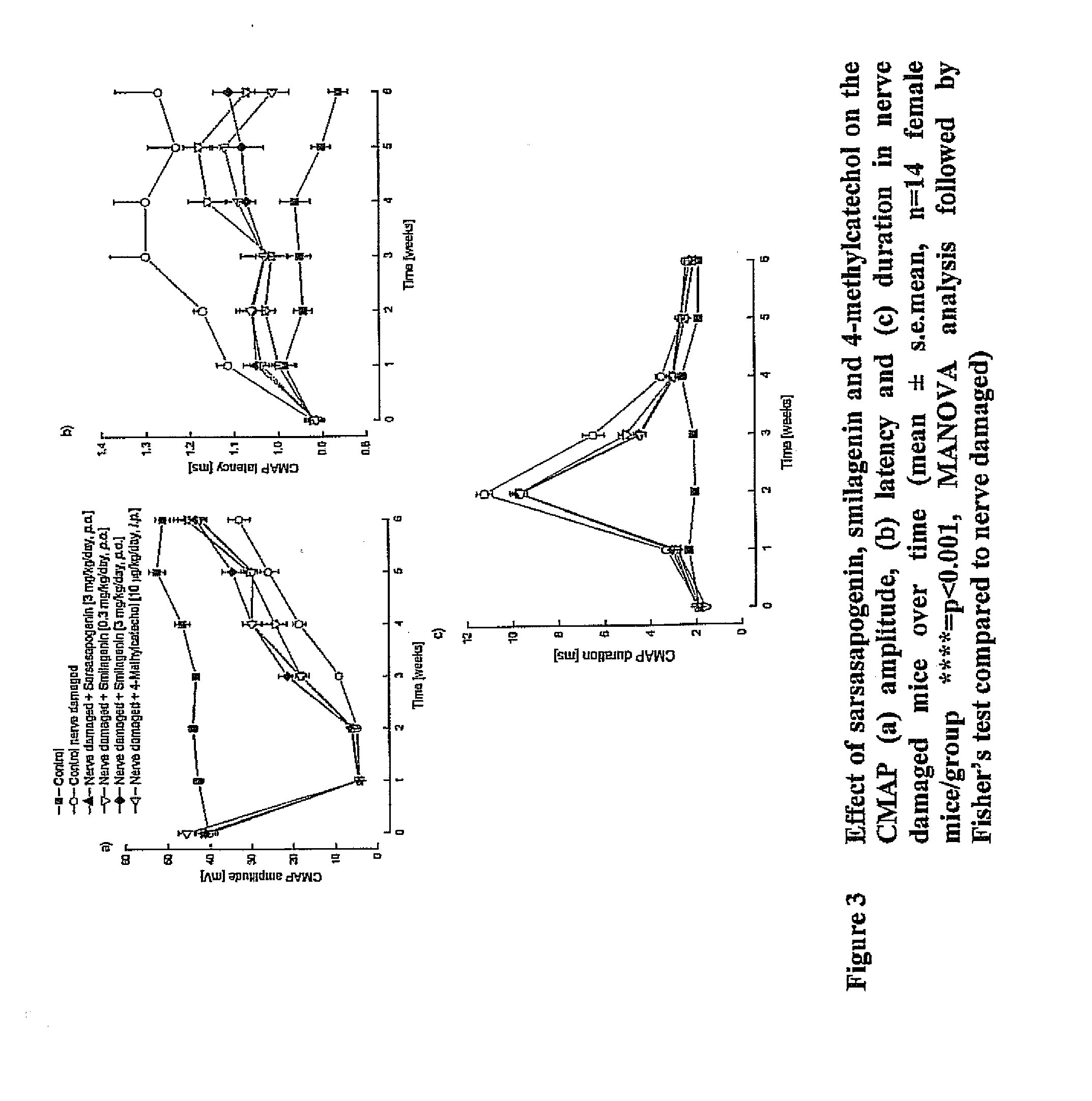
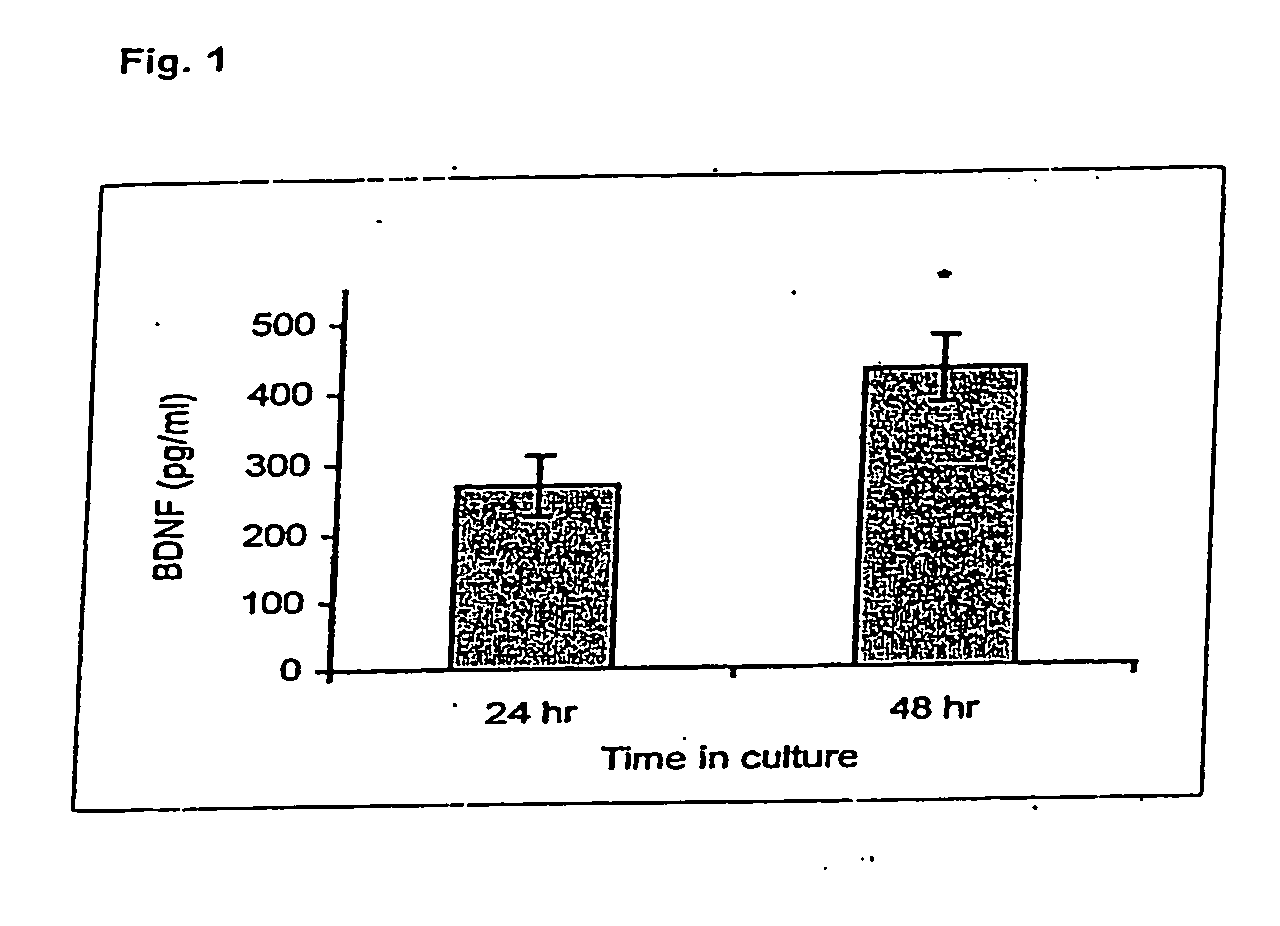
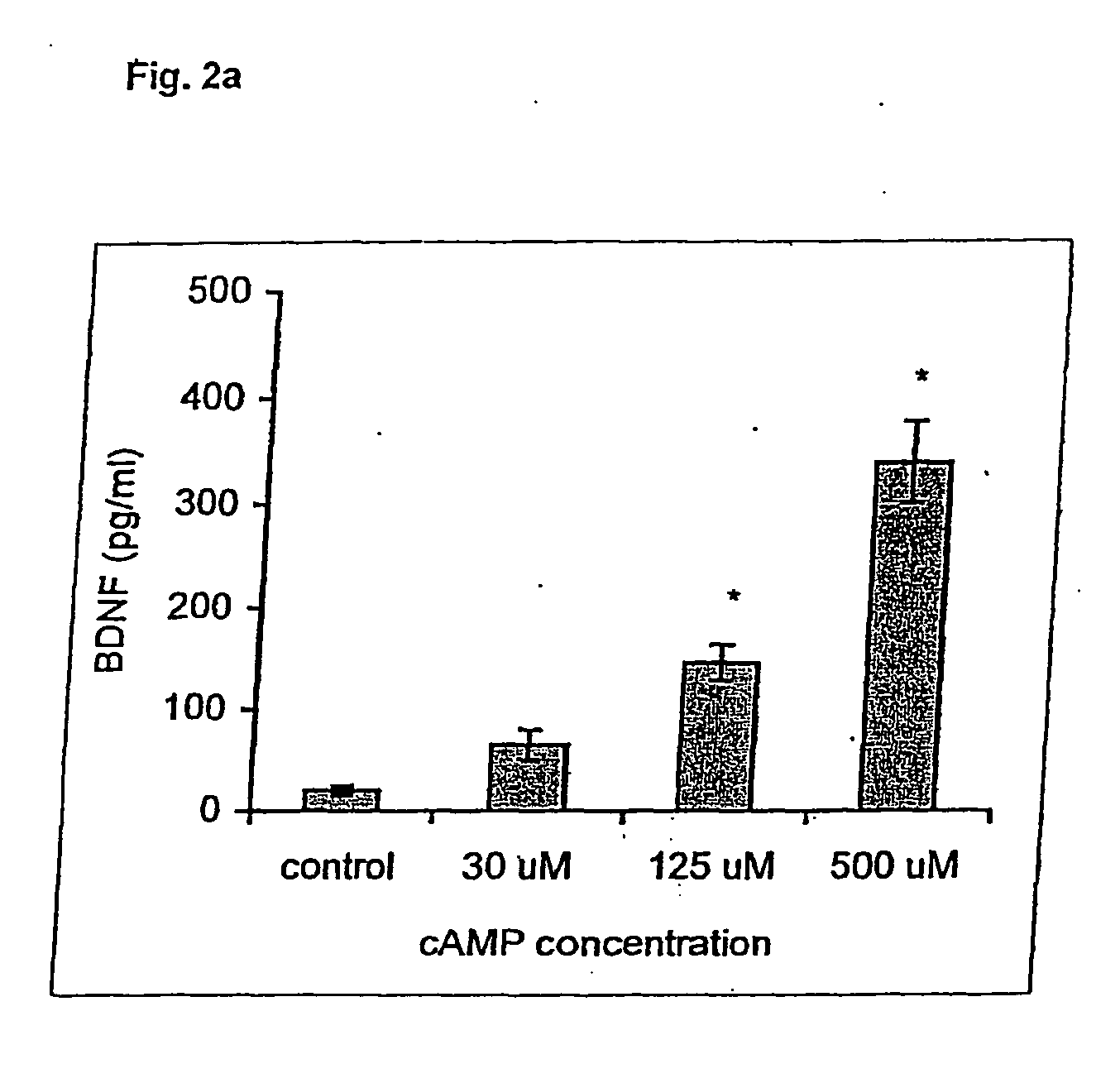
Treatment of neurotrophic factor mediated disorders
InactiveUS20120034193A1Increase speedQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseSide effect
An agent selected from A / B-cis furostane, furostene, spirostane and spirostene steroidal sapogenins and ester, ether, ketone and glycosylated forms thereof is used to induce self-regulated homeostasis of neurotrophic factors (NFs), for example BDNF and / or GDNF, NFs with limited and manageable side effects in a subject, by modulating NFs in a non-toxic manner under homeostatic control. An effective amount of at least one such agent is administered to the subject, particularly in the treatment or prevention of a range of NF-mediated disorders, particularly neurological, psychiatric, inflammatory, allergic, immune and neoplastic disorders, and in the restoration or normalisation of neuronal and other function in or in relation to any damaged or abnormal tissue, including when assisting tissue (for example, skin, bone, eye and muscle) healing and general skin, bone, eye and muscle health.
Owner:PHYTOPHARM LTD
Method of utilizing neurotrophins to manipulate reproductive capacity
InactiveUS20060088884A1Stimulate oocyte productionStimulate maturationOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningReproductive capacityBiology
Methods and kits are provided for manipulating and predicting the reproductive capacity of a female subject. The presence of endogenous neurotrophins and addition of exogenous neurotrophins, particularly BDNF, NT-4 / 5, and NGF, increase the reproductive capacity of a female patient by binding to receptors on the oocytes and stimulating maturation of the oocytes. Administration of antagonists act as a contraceptive because the antagonists prevent the neurotrophins from binding to oocyte receptors. Neurotrophins may also be used to stimulate the maturation of oocyte in vitro.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method of inducing differentiation of neural stem cell into dopaminergic neuron by using recombinant slow virus
ActiveCN103865956AMultiple differentiation potentialHigh expressionNervous system cellsFermentationSingle cell suspensionApoptosis
The invention relates to bioengineering technologies, and particularly relates a method of inducing differentiation of neural stem cells into dopaminergic neurons by using recombinant slow virus. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant slow virus vector; separating, culturing and identifying the neural stem cells; transfecting the recombinant slow virus into NSCs; identifying the NSCs transfected by the recombinant slow virus, wherein the process of transfecting the recombinant slow virus into the NSCs comprises the following steps: digesting NSCs after being subjected to three times of passages to prepare a single-cell suspension, and inoculating into a culture plate; transfecting the TH+Brn4 gene recombinant slow virus; adding the slow virus and ploybrene, uniformly shaking, putting the culture plate into an incubator to culture for 1-2 hours, and replacing fresh differential culture medium; meanwhile, screening by using puromycin to obtain stable transfected cells. The method has the advantages as follows: by constructing the slow virus vectors of target genes TH and Brn4, exogenous genes after transfecting the NSCs can be stably expressed in cells; high proportion of TH positive dopaminergic neuron is generated after differentiation; the Brn4 can promote high expression of neurotrophic factors and has the function of inhibiting apoptosis.
Owner:HELP STEM CELL INNOVATIONS CO LTD
Peptoid Agonists of Nerve Growth Factor and Their Use as Medicaments
InactiveUS20120237552A1Preventing and treating nerve cell deathPreventing and treating and damageSenses disorderNervous disorderSide effectHalf-life
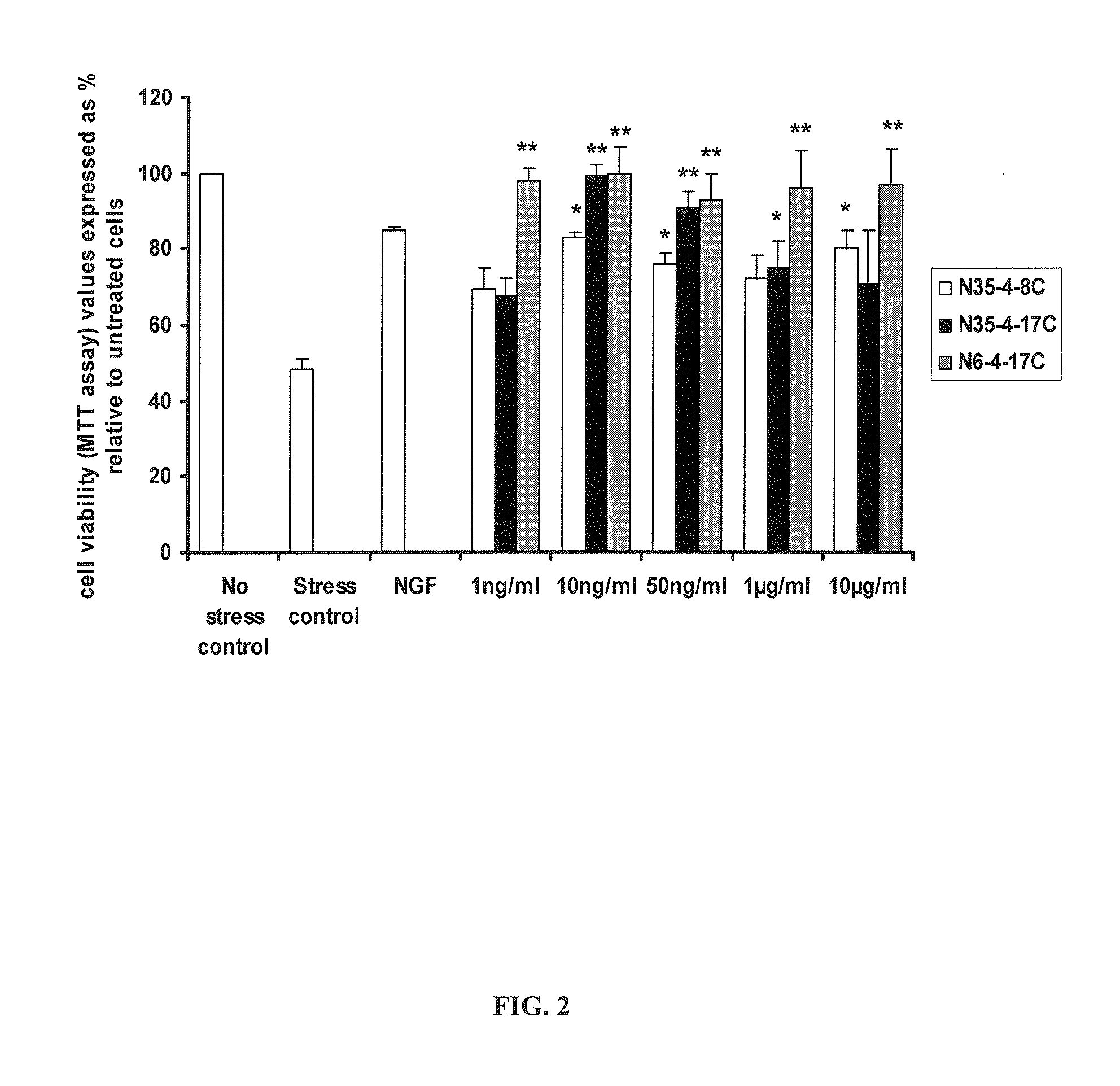
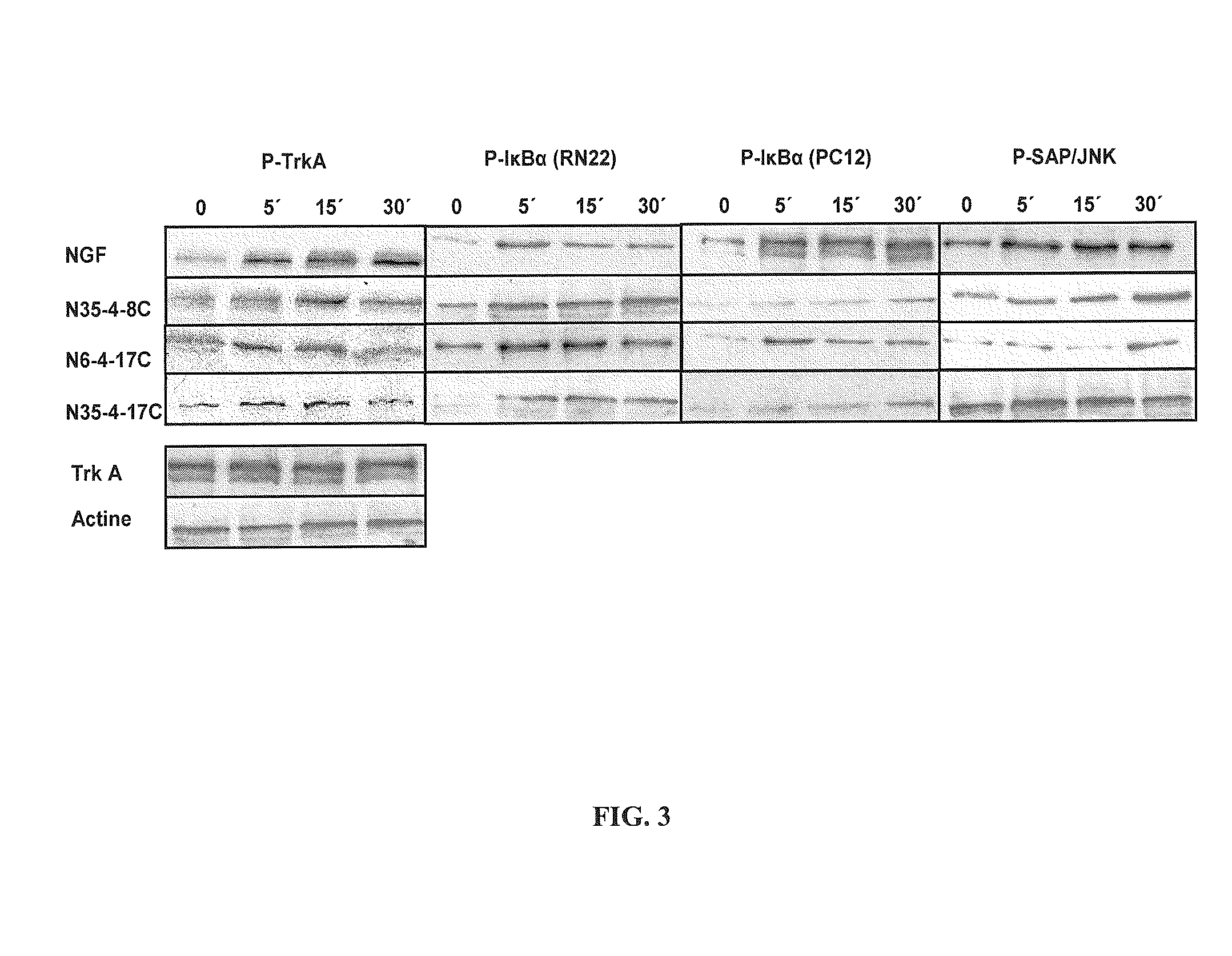
Neurotrophin binding to its specific receptors Trk A and p75 leads to the activation of multiple signalling cascades, culminating in neuroprotective and regenerative effects, including neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth. Neurotrophic factors have been used for the treatment of several neurodegenerative diseases. However, their use is limited by their inability to cross the blood-brain barrier, their short half life and their side effects. Small molecule neurotrophin mimetics may be beneficial in treating a number of neurodegenerative disorders. The present invention shows the capacity of nerve growth factor agonist molecules of Formulae I-IV, as defined in the specification, to induce differentiation in PC 12 cells, promote survival in RN22 cells and activate Trk A, IkBa and SAPK / JNK phosphorylation to various extents in both cell lines. In addition these molecules were able to ameliorate acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a multiple sclerosis (MS) animal model, inhibiting brain inflammation and reducing brain damage. We also observed suppression in the production of pro-inflammatory genes like the inducible nitric oxide synthase. These small molecules with NGF agonist activity may be beneficial for MS and other neurodegenerative diseases due to its neuroprotective and immunomodulatory properties.
Owner:MORENO BEATRIZ +4
Fusion protein penetrating blood-brain barrier with nerve nourishment gene and encoding gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101157730AExert biological activityCorrect N-terminal conformationPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesNervous systemCell membrane
The present invention discloses a clone of a neurotrophic factor fusion protein gene containing a protein transduction domain, the expression and the purification of the protein, the biological activity of the fusion protein, and the effect for penetrating a cell membrane, particularly for the blood-brain barrier in vivo. The fusion protein comprises a first area which has at least 75 percent of a homologous sequence with a neurotrophic factor and a second area which has at least 75 percent of a homologous sequence with an amino acid sequence of the protein transduction domain, and the second area is positioned at a carboxyl-terminal of the first area; the present invention can carry out the replacement, deletion or addition of the amino acid residues under the premise of not changing the characteristics of the fusion protein. The fusion protein can be used as a drug for the treatment of a plurality of neurodegenerative disorders in central nervous system and the peripheral neuropathies by peripheral routes for drug delivery.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for producing dopamine-producing neural precursor cells
ActiveCN109072198AGet efficientlyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCell-Extracellular MatrixCulture fluid
Dopamine-producing neural precursor cells are produced by: producing a cell population containing Corin and / or Lrtm1 positive cells via steps (1) and (2) as will be shown below; collecting the Corin and / or Lrtm1 positive cells from the cell population thus obtained by using a substance that binds to Corin and / or a substance that binds to Lrtm1; and suspension-culturing the Corin and / or Lrtm1 positive cells in a liquid culture medium that contains one or more neurotrophic factors: (1) a step for adhesion-culturing pluripotent stem cells in the absence of any feeder cells in an undifferentiatedstate-maintaining culture medium that contains a sonic hedgehog (SHH) signal stimulant and an undifferentiated state-maintaining factor in the presence of an extracellular matrix; and (2) a step for culturing the cell population obtained in step (1) in a liquid culture medium that contains one or more differentiation inducing factors.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Methods of treating peripheral neuropathies using neurotrophin-3
InactiveUS6933276B1Supports survivalNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeurotrophin-3Neurotrophic factors
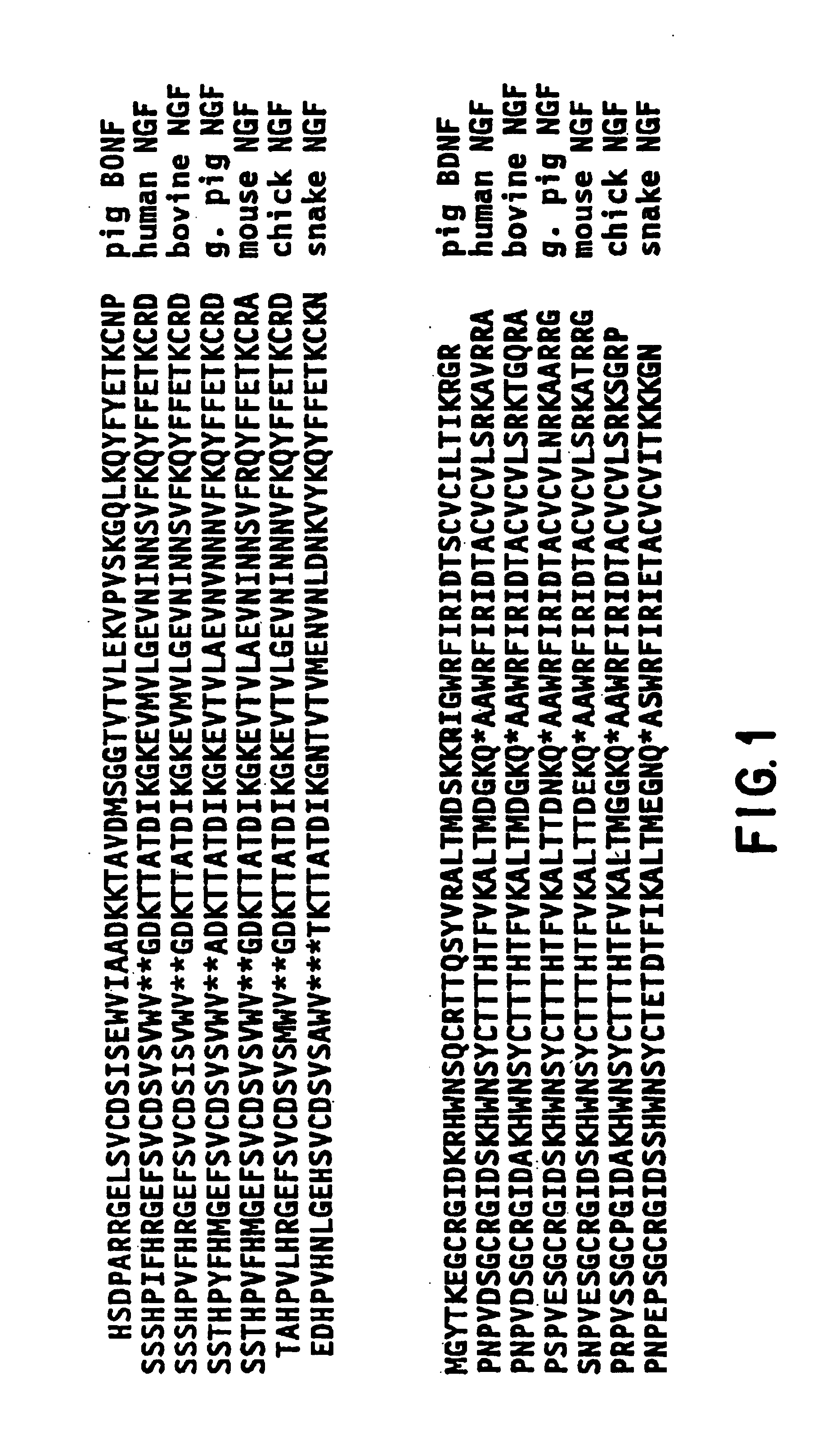
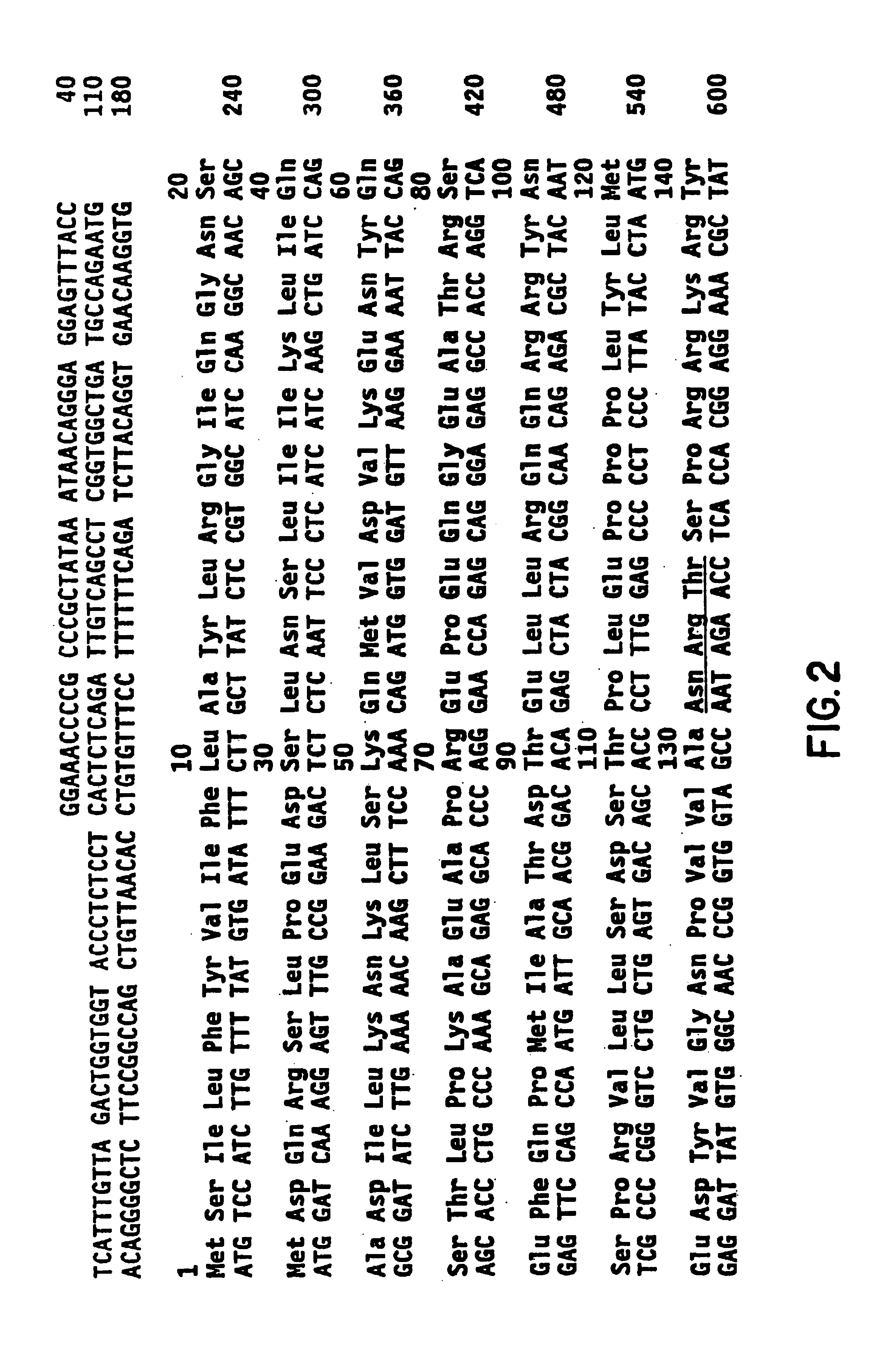
The present invention relates to neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), a newly discovered member of the BDNF gene family. It is based, in part, on the identification of regions of nucleic acid sequence homology shared by BDNF and NGF (U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07 / 400,591, filed Aug. 30, 1989, incorporated by reference herein). According to the present invention, these regions of homology may be used to identify new members of the BDNF / NGF gene family; such methodology was used to identify NT-3. The present invention provides for the genes and gene products of new BDNF / NGF related neurotrophic factors identified by these methods. According to the invention, NT-3 may be used in the diagnosis and / or treatment of neurologic disorders, including, but not limited to, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Because NT-3 has been observed to exhibit a spectrum of activity different from the spcificities of BDNF or NGF, NT-3 provides new and valuable options for enducing regrowth and repair in the central nervous system.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
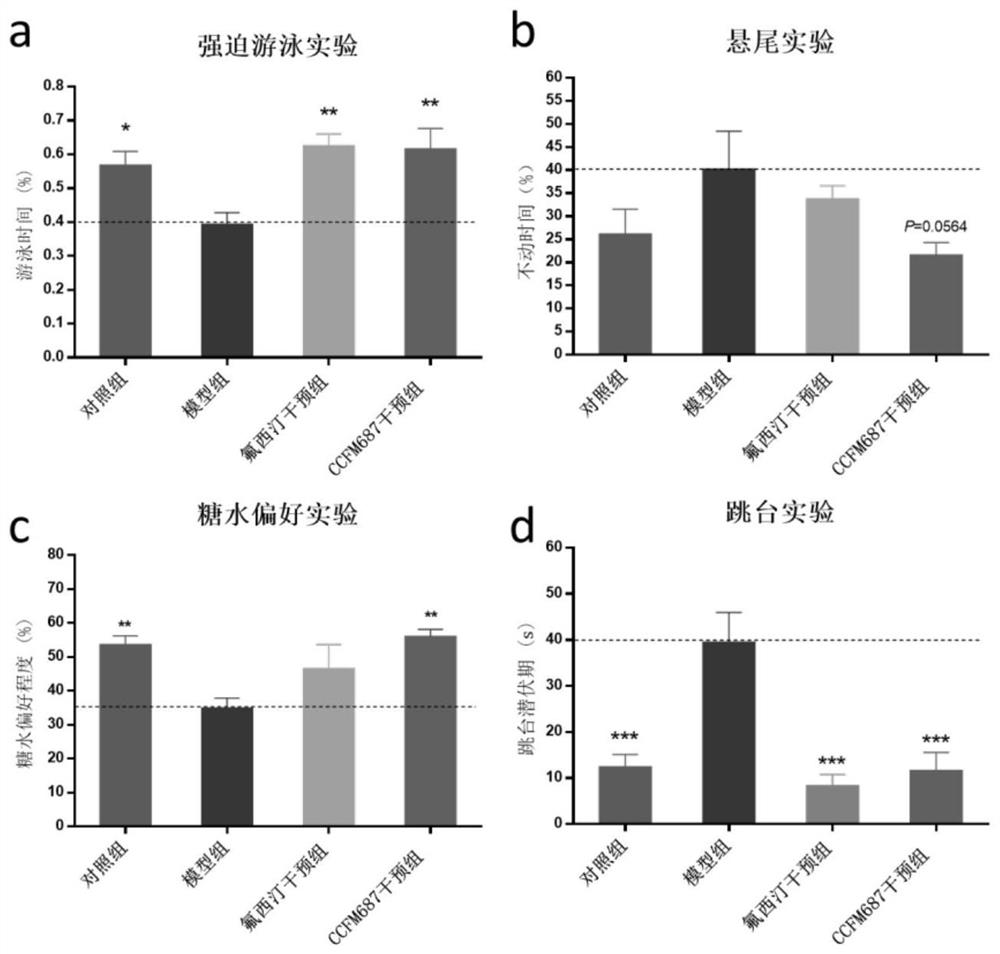
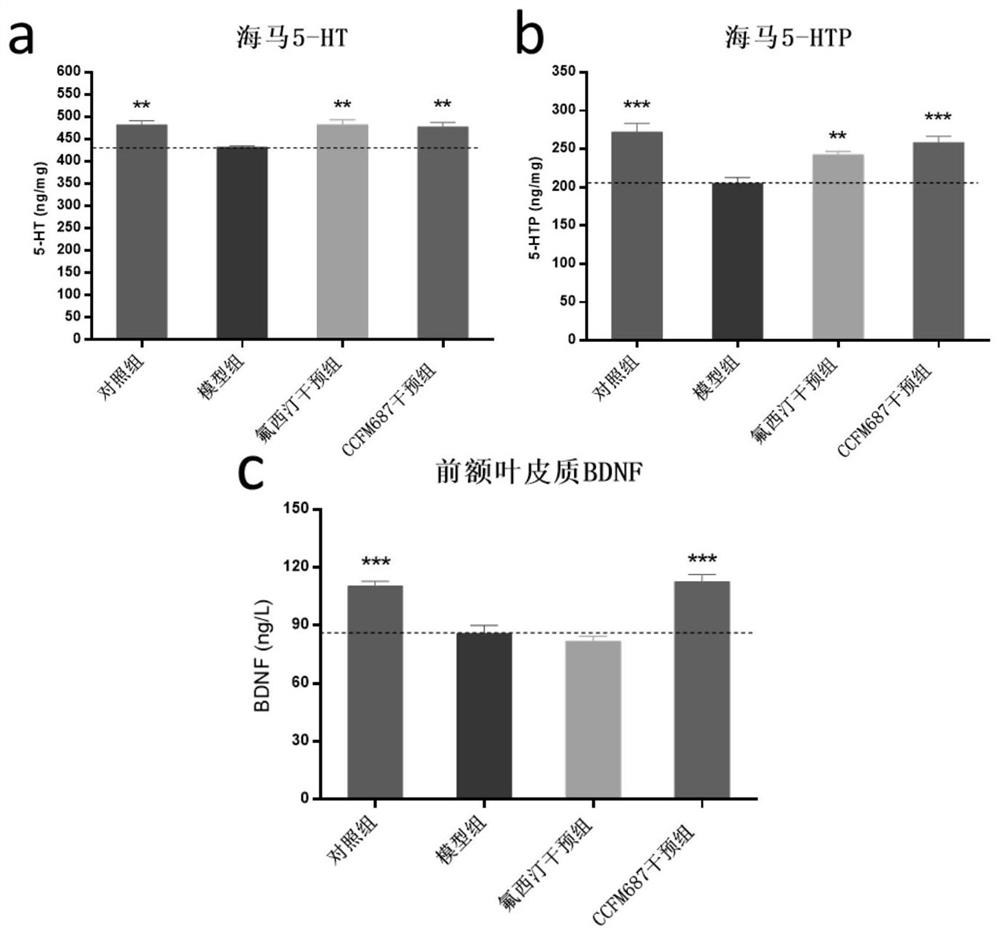
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis ccfm687, its fermented food and its application
ActiveCN109055269BRelieve depression-like behaviorImprove the level ofNervous disorderBacteriaBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention relates to bifidobacterium longum subspecies CCFM687, fermented food and application thereof. Bifidobacterium longum infantile subspecies CCFM687 of the present invention can improve the depression-like behavior of depressed mice, improve the levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-hydroxytryptophan and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the brain of depressed mice; improve depression Butyric acid content in the gut of mice; lower intestinal abundance of Desulfovibrio spp., increased abundance of Bifidobacterium and S24‑7 families, increased gut microbiota α‑diversity, and improved intestinal Intestinal flora disorder, reduce the occurrence of autism, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity and type I diabetes; increase the mRNA level of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 in simulated enterochromaffin cells, and increase the 5-hydroxychromatin level of the cells The secretion of amino acid provides precursor substances for the synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain. Therefore, it has broad application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
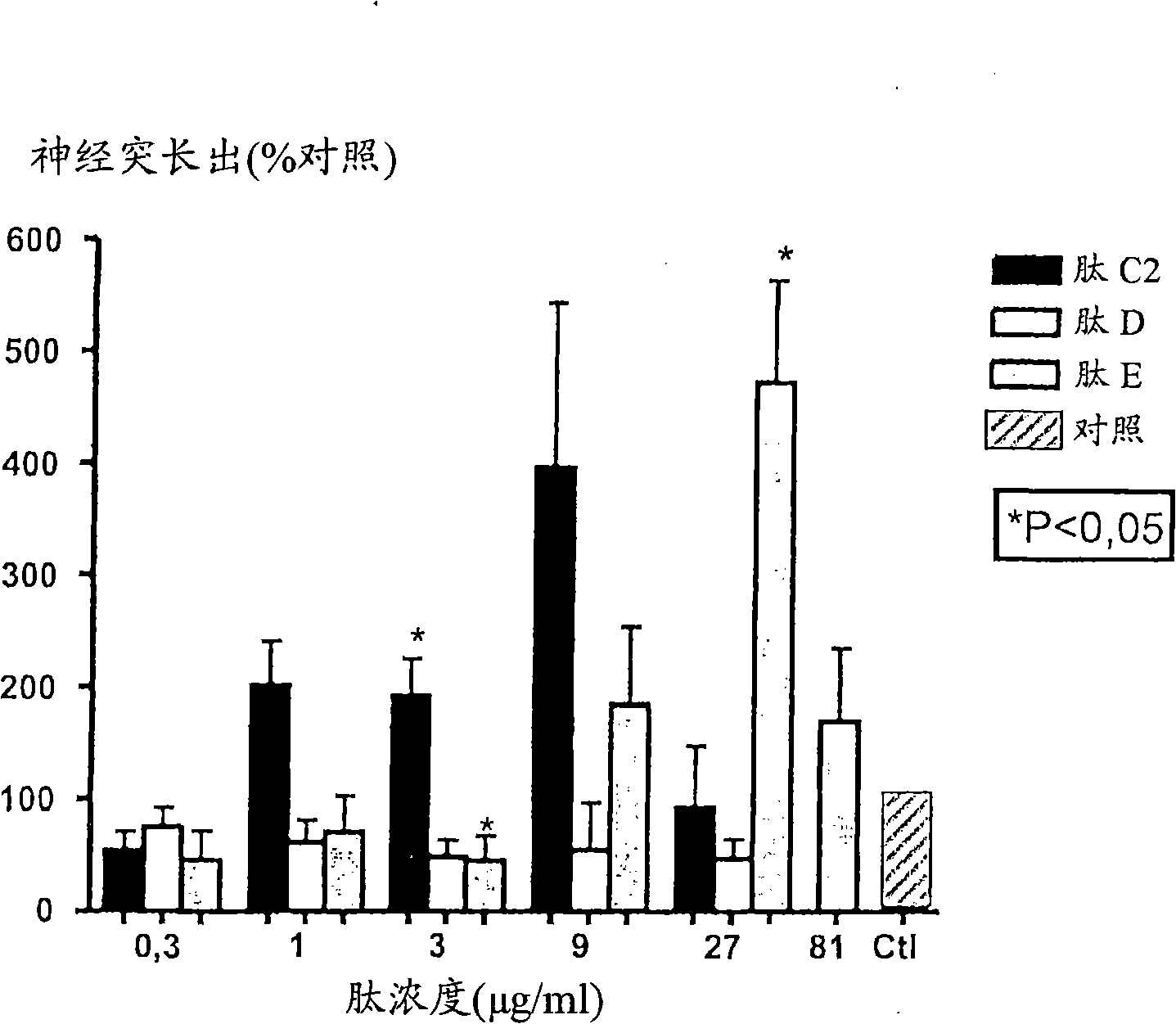
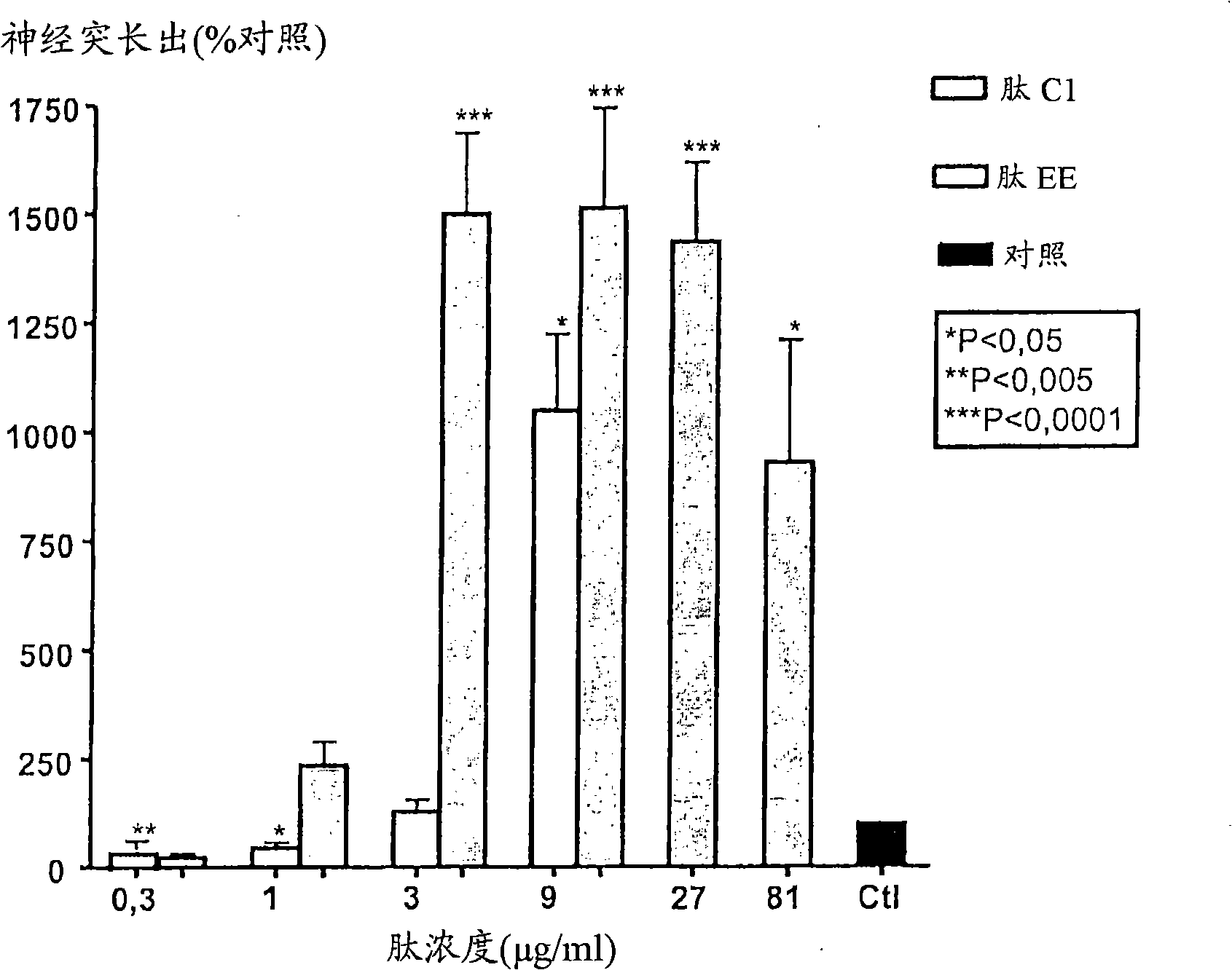
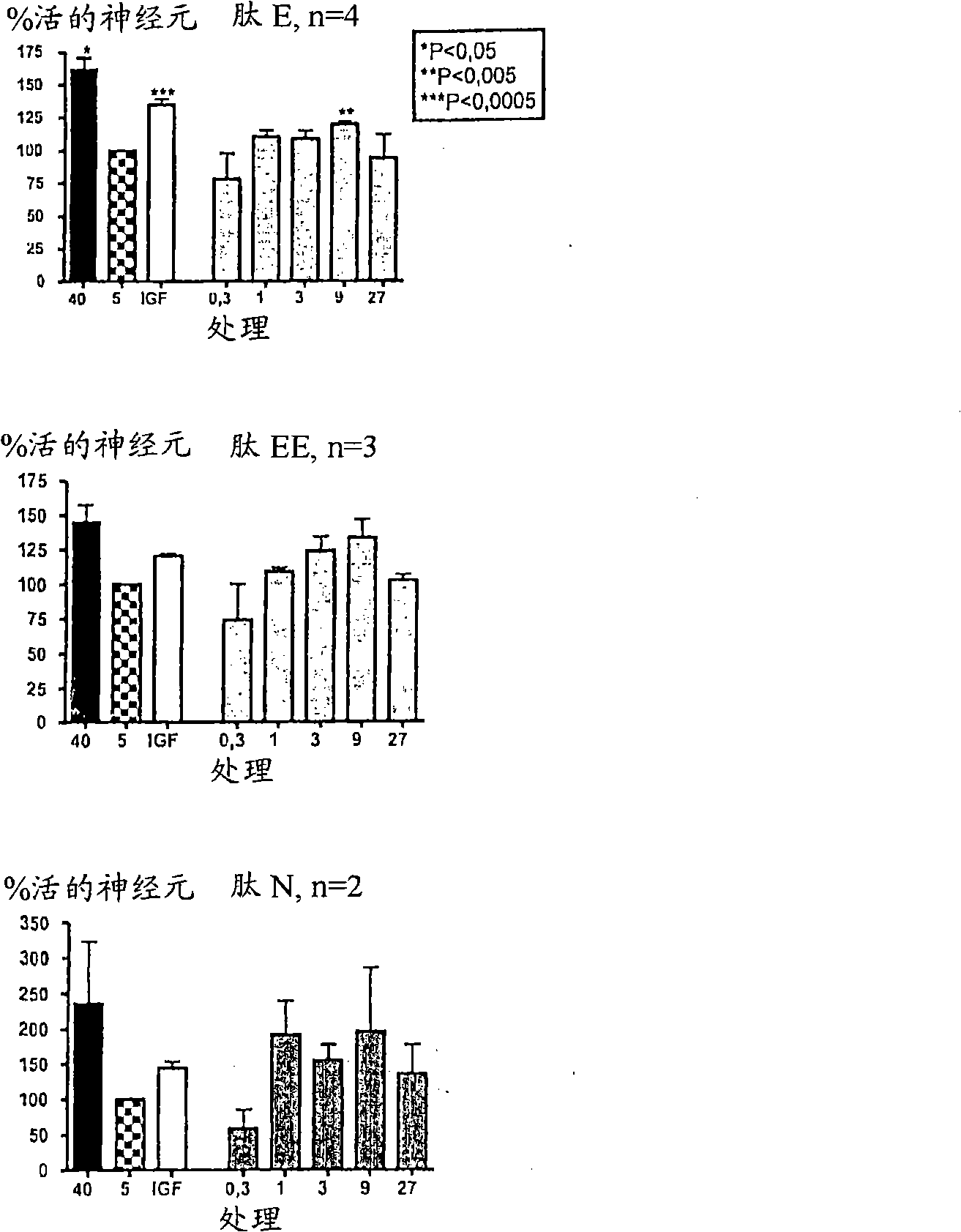
Neurotrophin-derived peptide sequences
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
Method for therapy of neurodegenerative disease of the brain
InactiveUS20060051322A1Reduce adverse effectsAvoid restrictionsBiocideNervous disorderCholinergic cellsNeuro-degenerative disease
A specific clinical protocol for use toward therapy of defective, diseased and damaged cholinergic neurons in the mammalian brain, of particular usefulness for treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. The protocol is practiced by delivering a definite concentration of recombinant neurotrophin into, or within close proximity of, identified defective, diseased or damaged brain cells. Using a viral vector, the concentration of neurotrophin delivered as part of a neurotrophic composition varies from 1010 to 1015 neurotrophin encoding viral particles / ml of composition fluid. Each delivery site receives form 2.5 μl to 25 μl of neurotrophic composition, delivered slowly, as in over a period of time ranging upwards of 10 minutes / delivery site. Each delivery site is at, or within 500 μm of, a targeted cell, and no more than about 10 mm from another delivery site. Stable in situ neurotrophin expression can be achieved for 12 months, or longer.
Owner:TUSZYNSKI MARK H
Treatment of neurotrophic factor mediated disorders
InactiveCN102355902AManageable side effectsManageable Adverse Side EffectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNeurophysinsSide effect
An agent selected from A / B-cis furostane, furostene, spirostane and spirostene steroidal sapogenins and ester, ether, ketone and glycosylated forms thereof is used to induce self- regulated homeostasis of neurotrophic factors(NFs), for example BDNF and / or GDNF, NFs with limited and manageable side effects in a subject, by modulating NFs in a non- toxic manner under homeostatic control. An effective amount of at least one such agent is administered to the subject, particularly in the treatment or prevention of a range of NF- mediated disorders, particularly neurological, psychiatric, inflammatory,allergic,immune and neoplastic disorders, and in the restoration or normalisation of neuronal and other function in or in relation to any damaged or abnormal tissue, including when assisting tissue (for example, skin, bone, eye and muscle) healing and general skin, bone, eye and muscle health.
Owner:PHYTOPHARM LTD
Generation of midbrain-specific organoids from human pluripotent stem cells
The present disclosure provides a method of deriving and maintaining a midbrain-like organoid in culture, comprising (a) culturing pluripotent stem cells to obtain neuronal lineage embryoid bodies; (b) culturing the neuronal lineage embryoid bodies from (a) to obtain midbrain regionalized tissues; (c) embedding and culturing the midbrain regionalized tissues from (b) in an extracellular matrix to obtain neuroepithelial tissues; and (c) culturing the neuroepithelial tissues from (c) to obtain a midbrain-like organoid. Also disclosed herein are culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining neuronal lineage embryoid bodies comprising (a) TGF-β Inhibitor and / or SMAD2 / 3 inhibitors; and (b) WNT-signaling activator; culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining midbrain regionalized tissues comprising (a) TGF-β Inhibitor and / or SMAD2 / 3 inhibitors; (b) WNT-signaling activator; (c) hedgehog signaling protein; and (d) fibroblast growth factor; culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining neuroepithelial tissues comprising (a) hedgehog signaling protein; and (b) fibroblast growth factor and culture media suitable for deriving and maintaining a midbrain-like organoid comprising (a) neurotrophin factor; (b) ascorbic acid; and (c) activator of cAMP-dependent pathway.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com