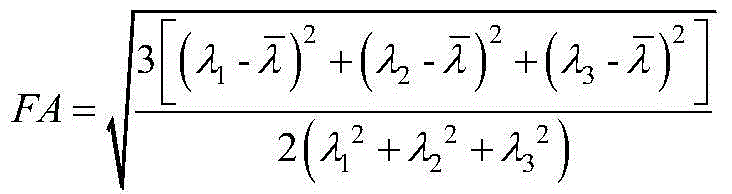Patents
Literature
127 results about "Midbrain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The midbrain or mesencephalon (UK: /ˌmɛsɛnˈsɛfəlɒn, -kɛf-/, US: /ˌmɛzənˈsɛfələn/; from Greek mesos 'middle', and enkephalos 'brain') is a portion of the central nervous system associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.
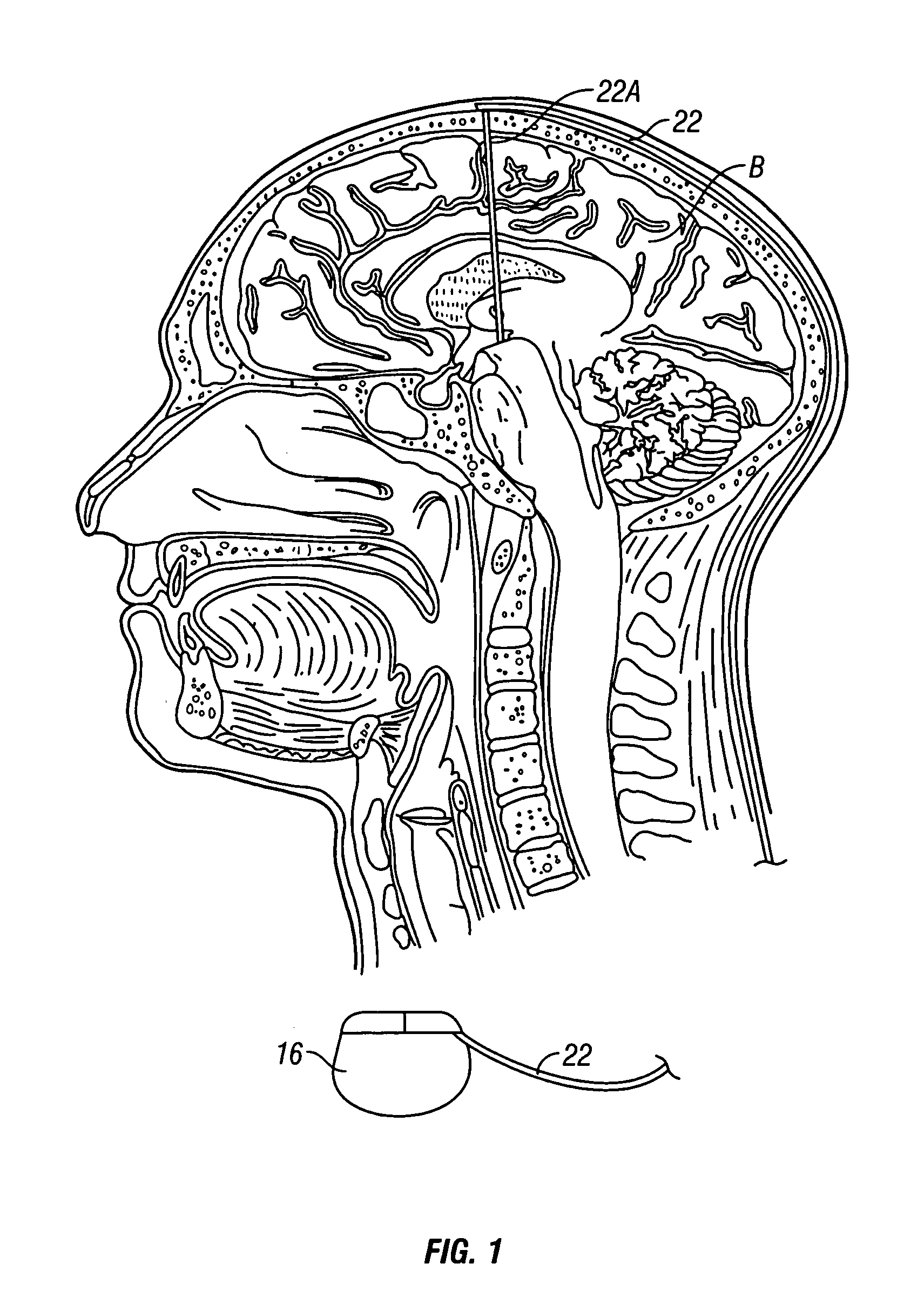
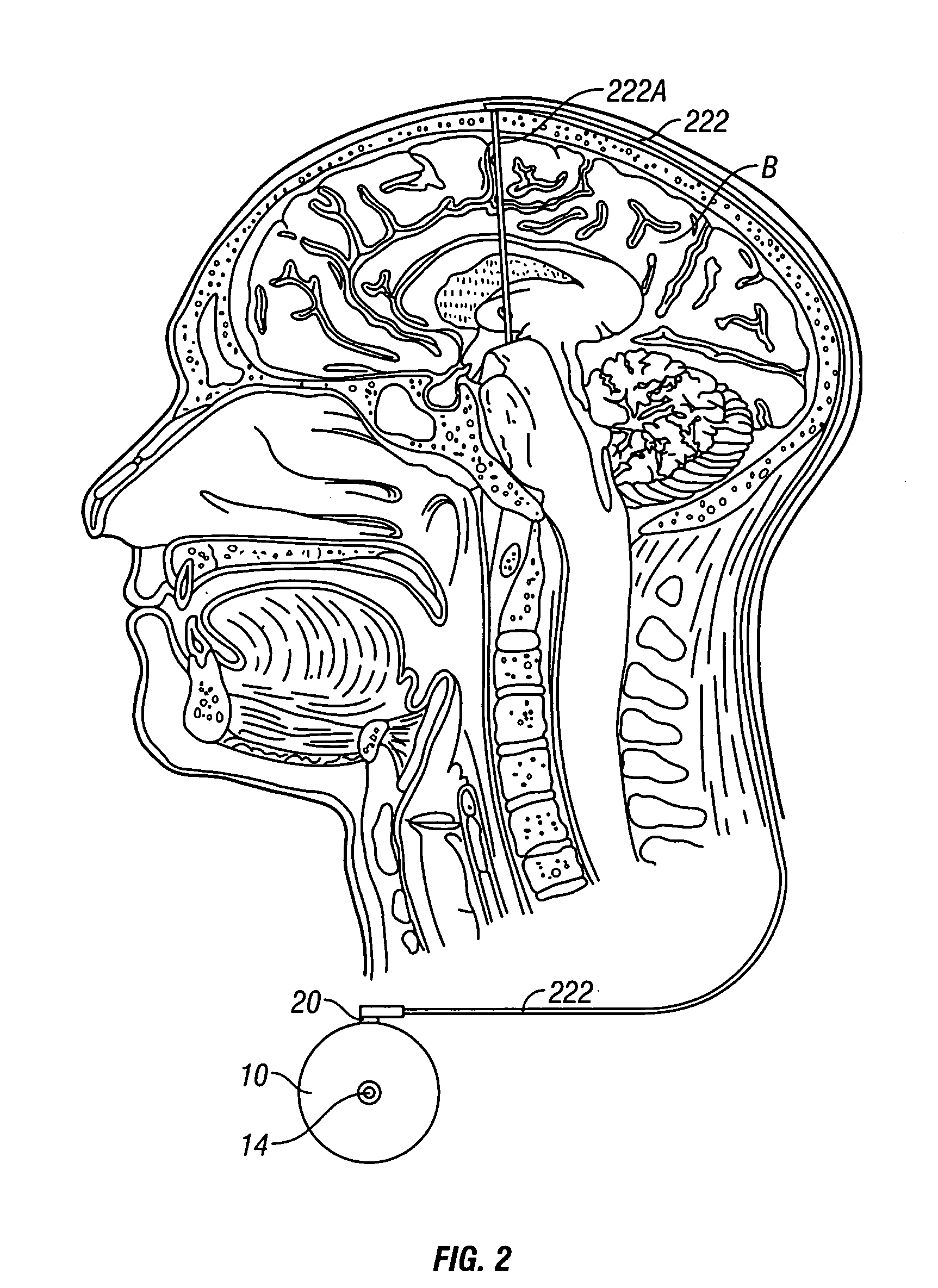
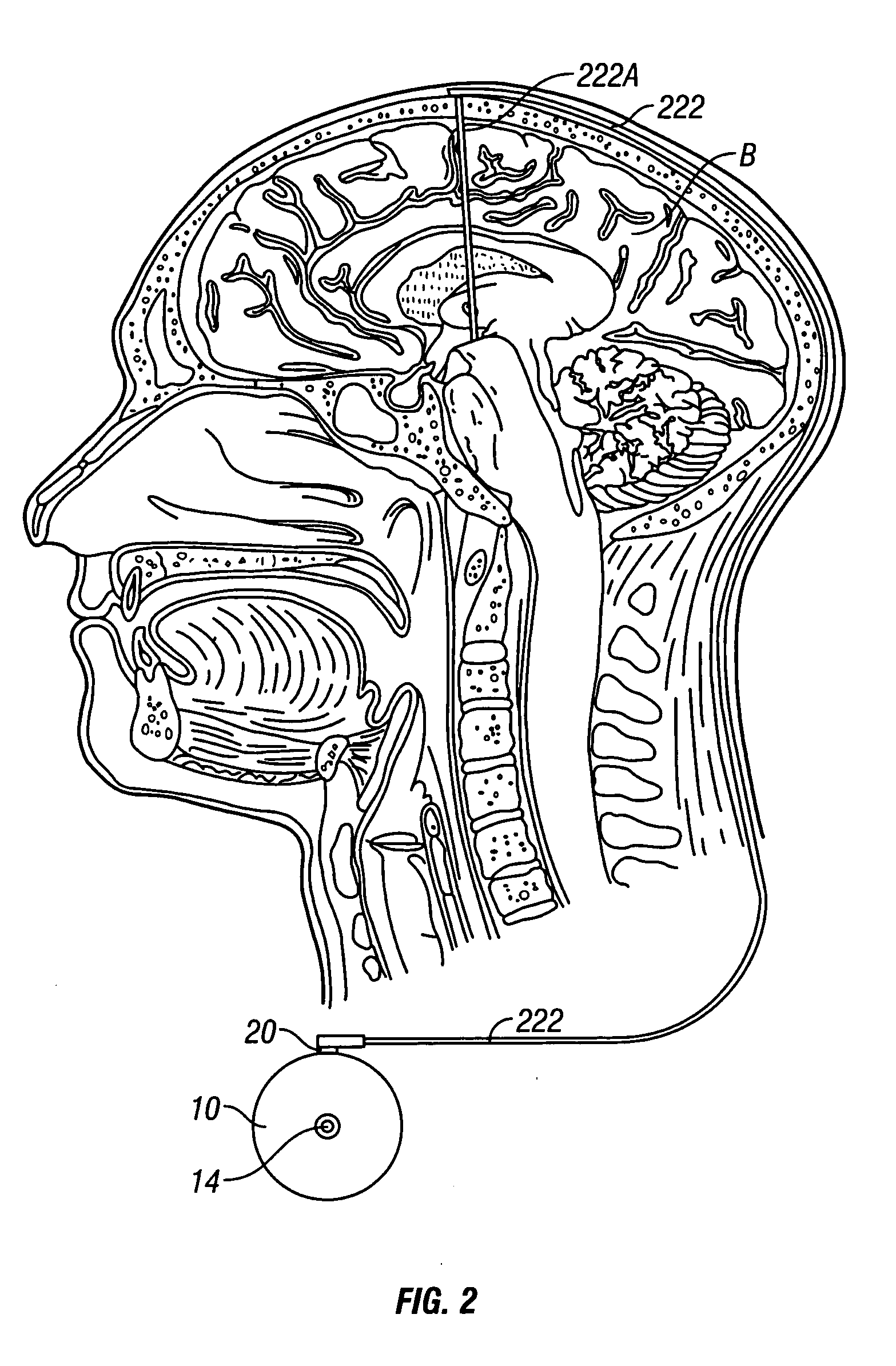
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
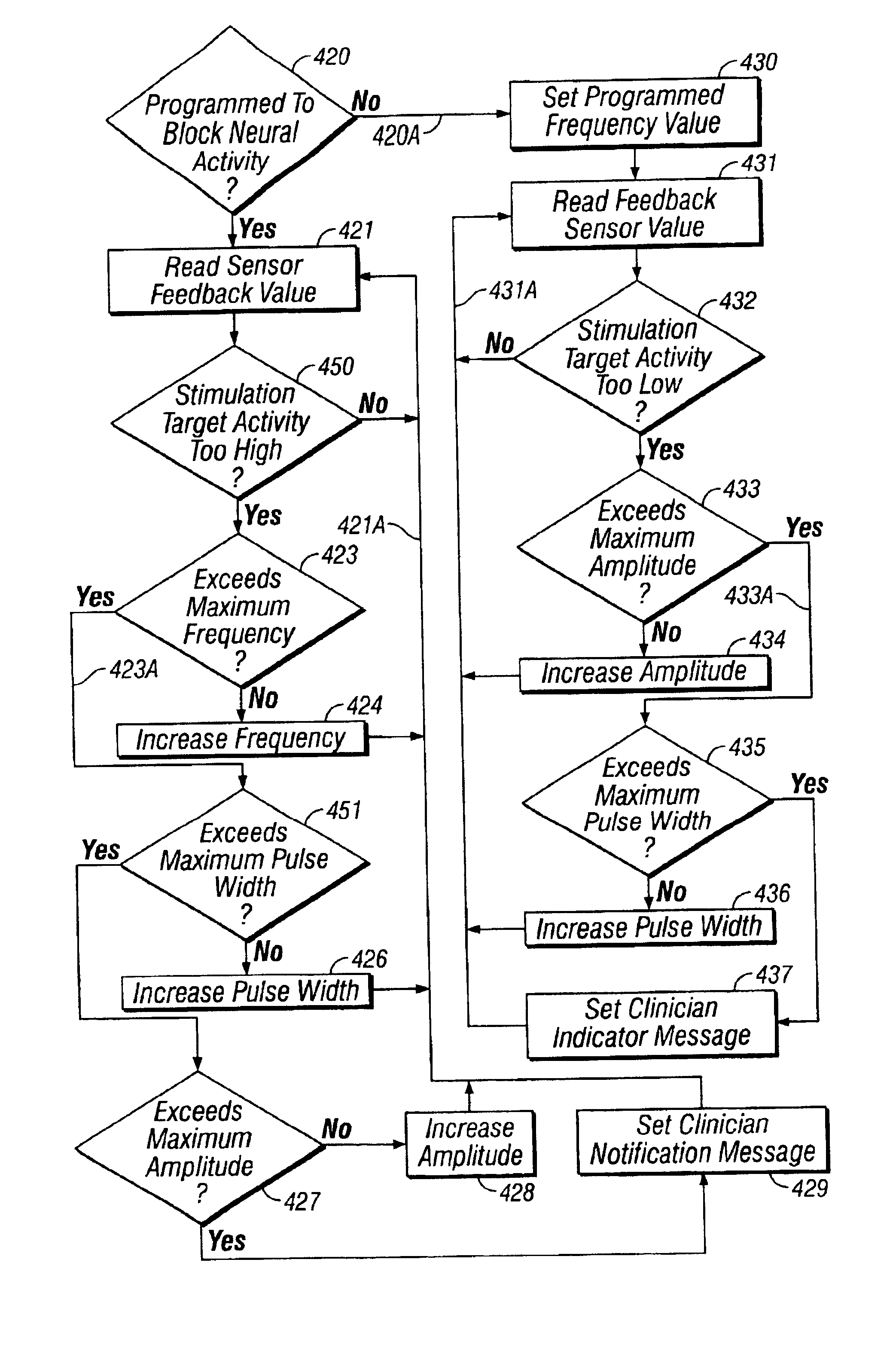
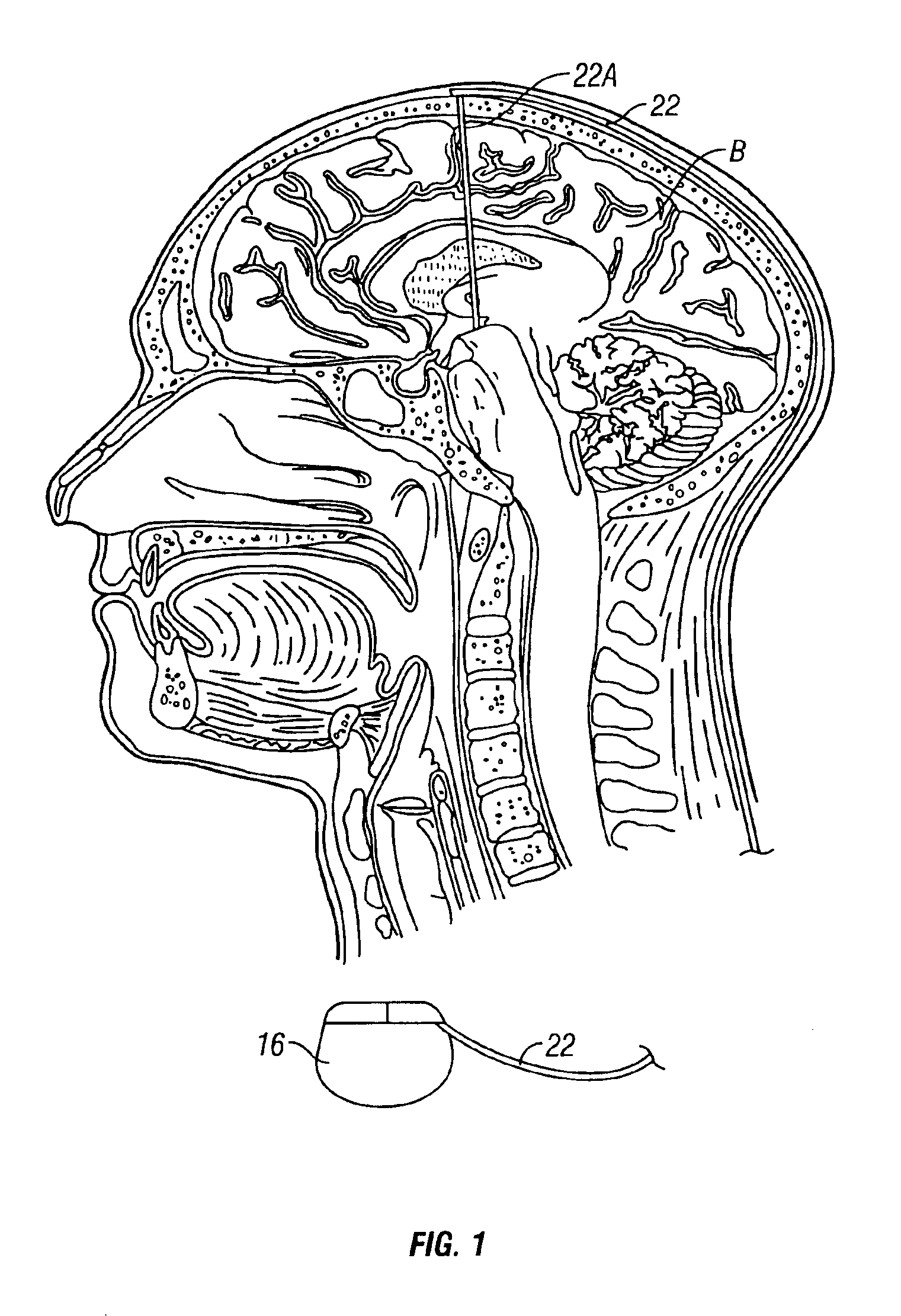
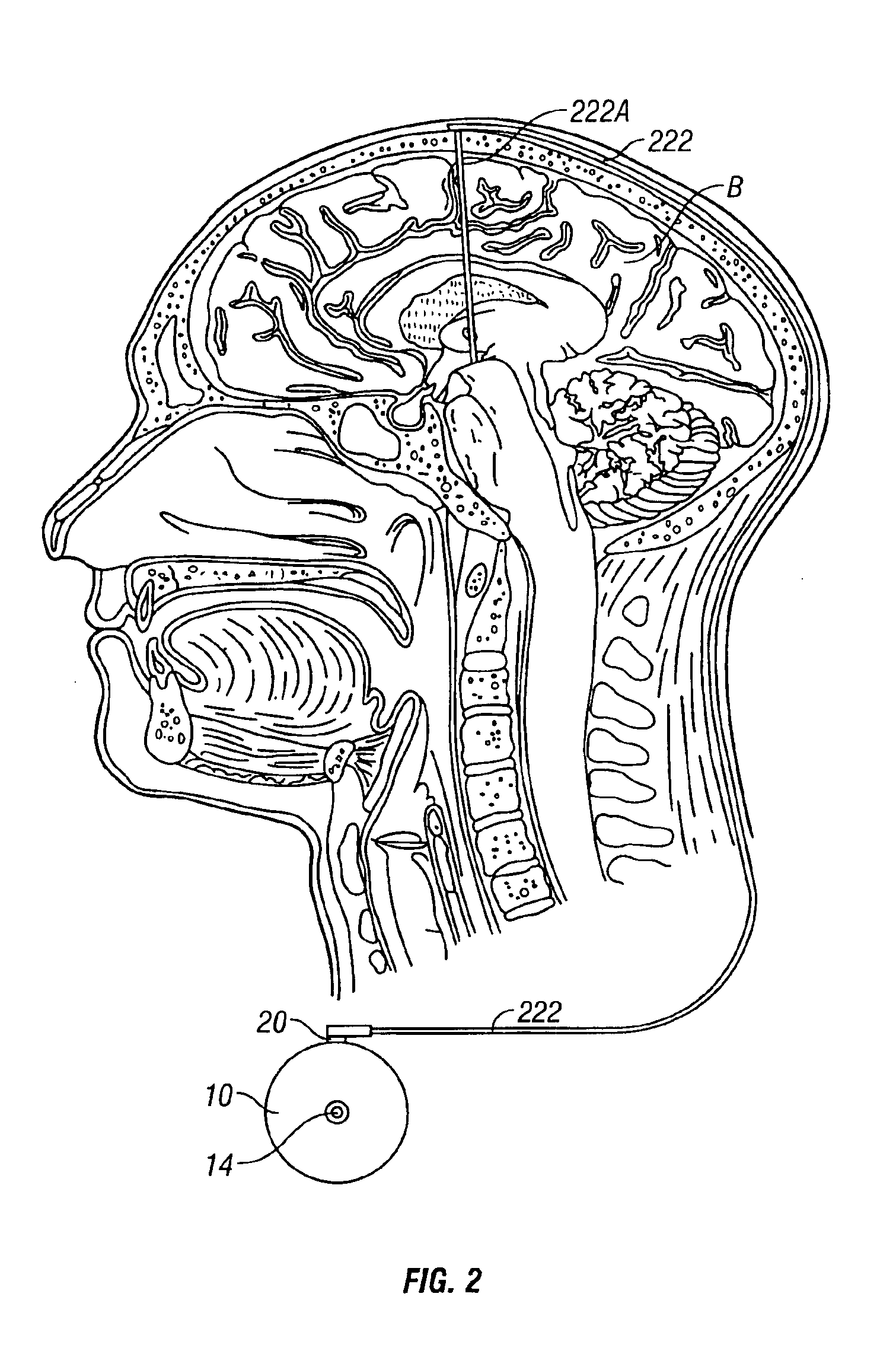
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Auditory midbrain implant
InactiveUS20050004627A1Rigidity can be alteredThinnerHead electrodesEar treatmentMidbrainEngineering
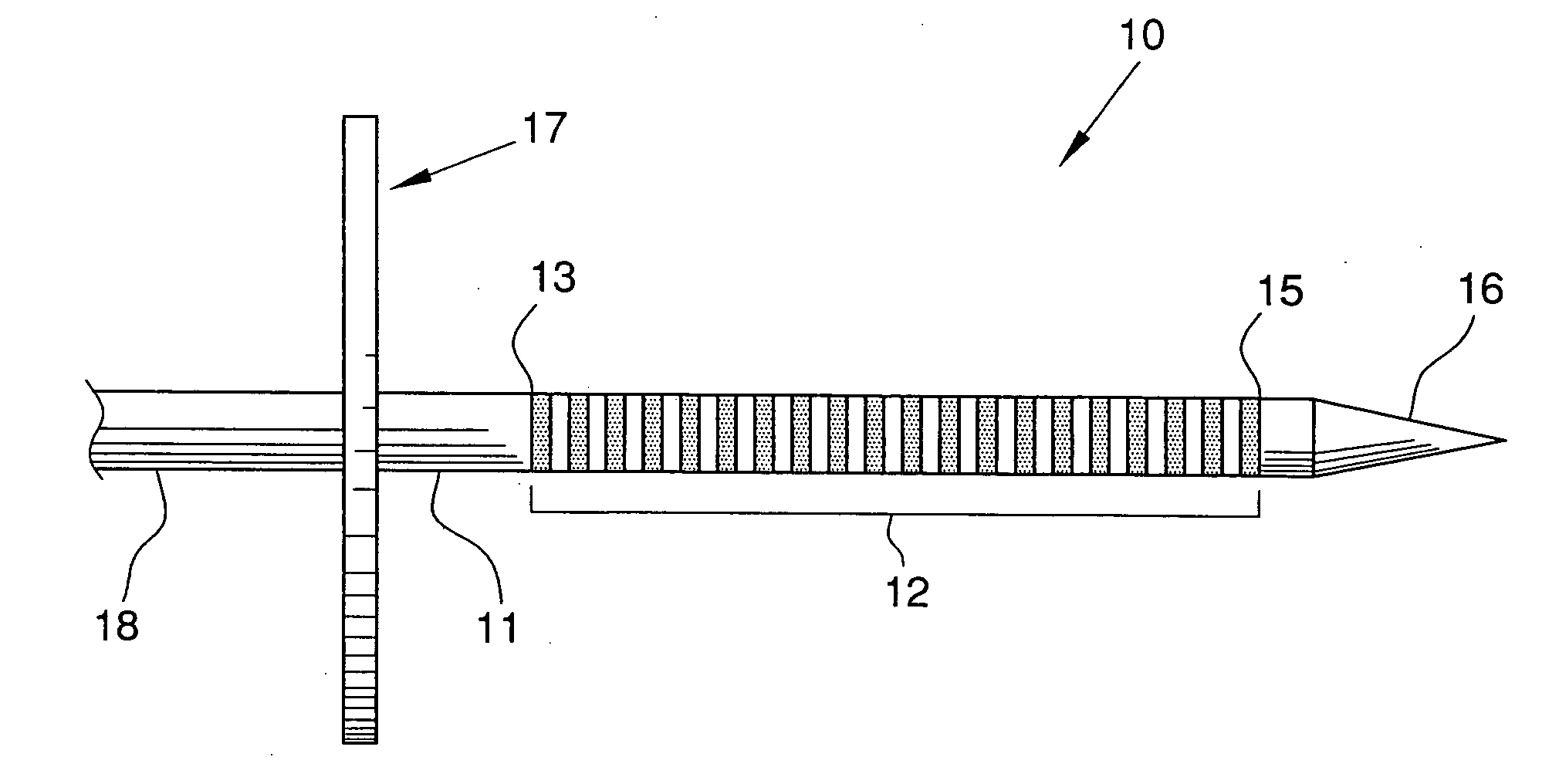
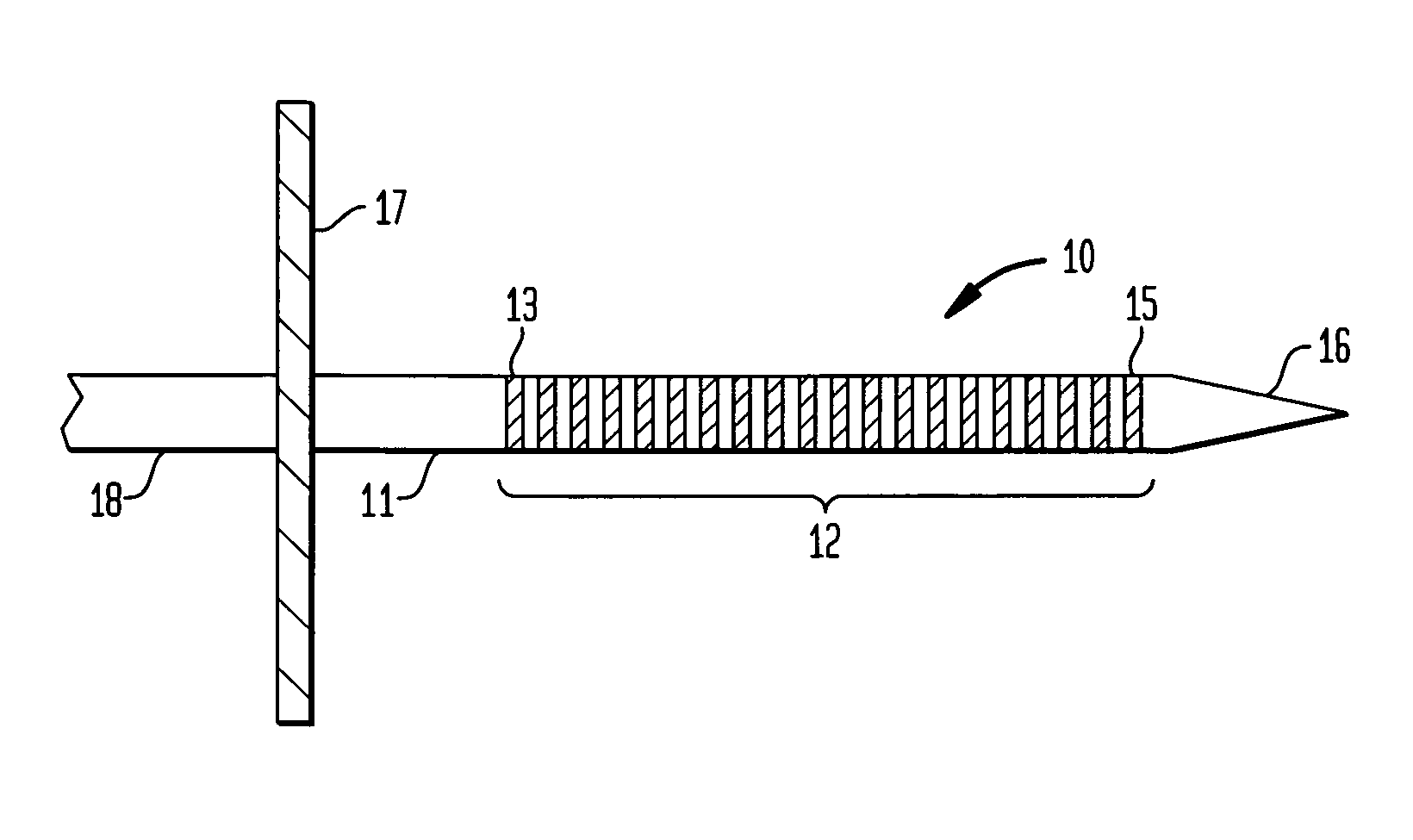
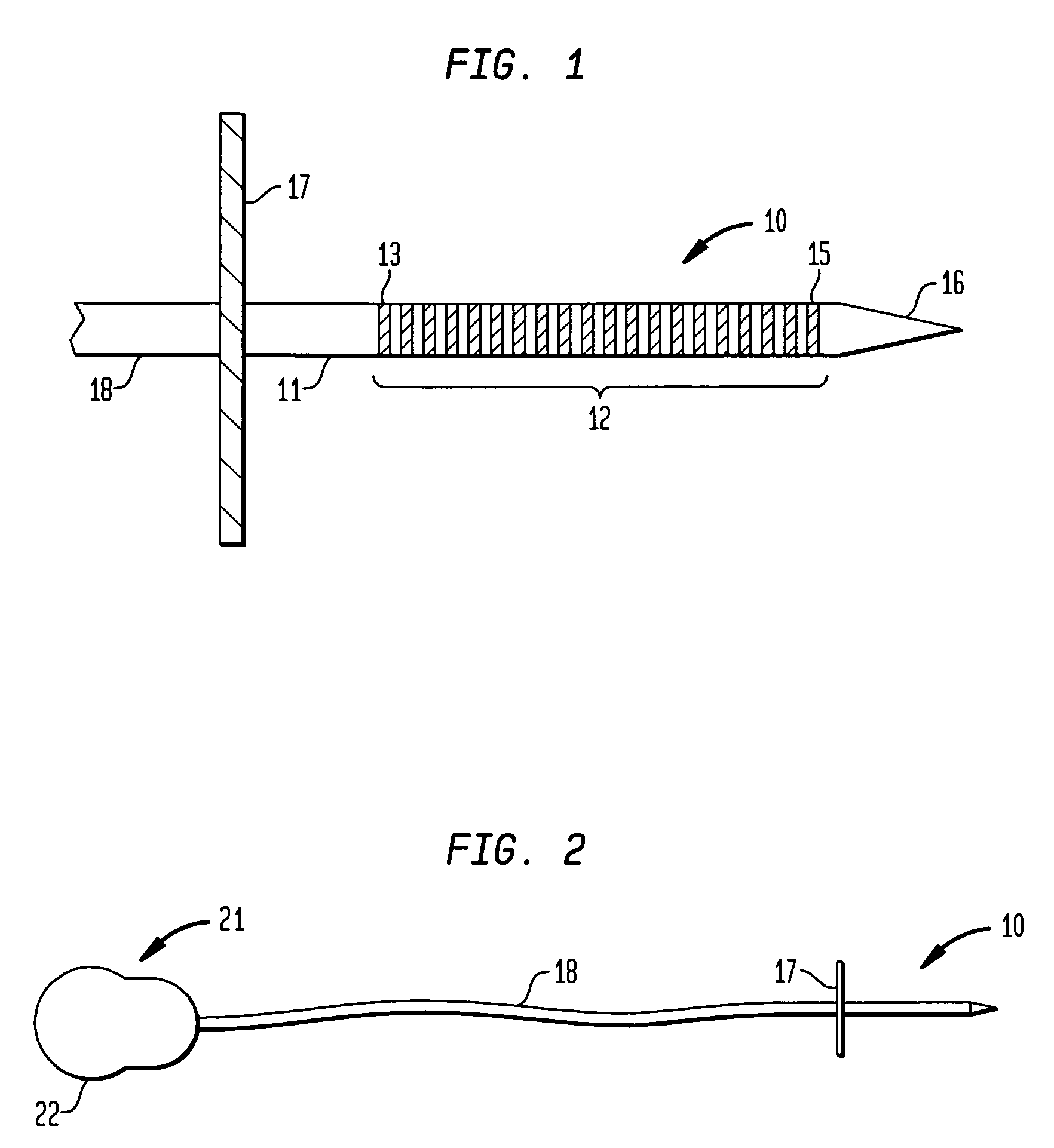
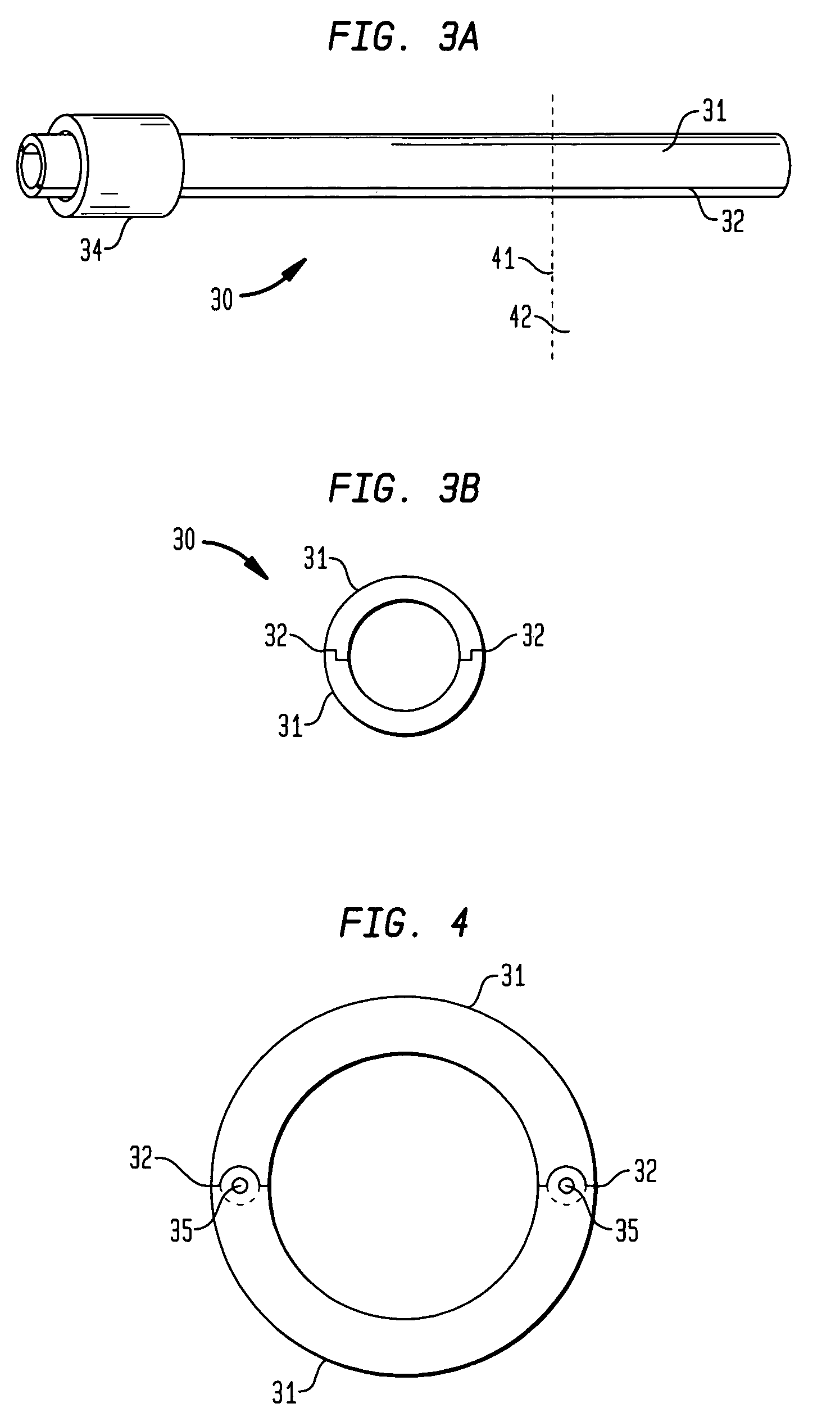
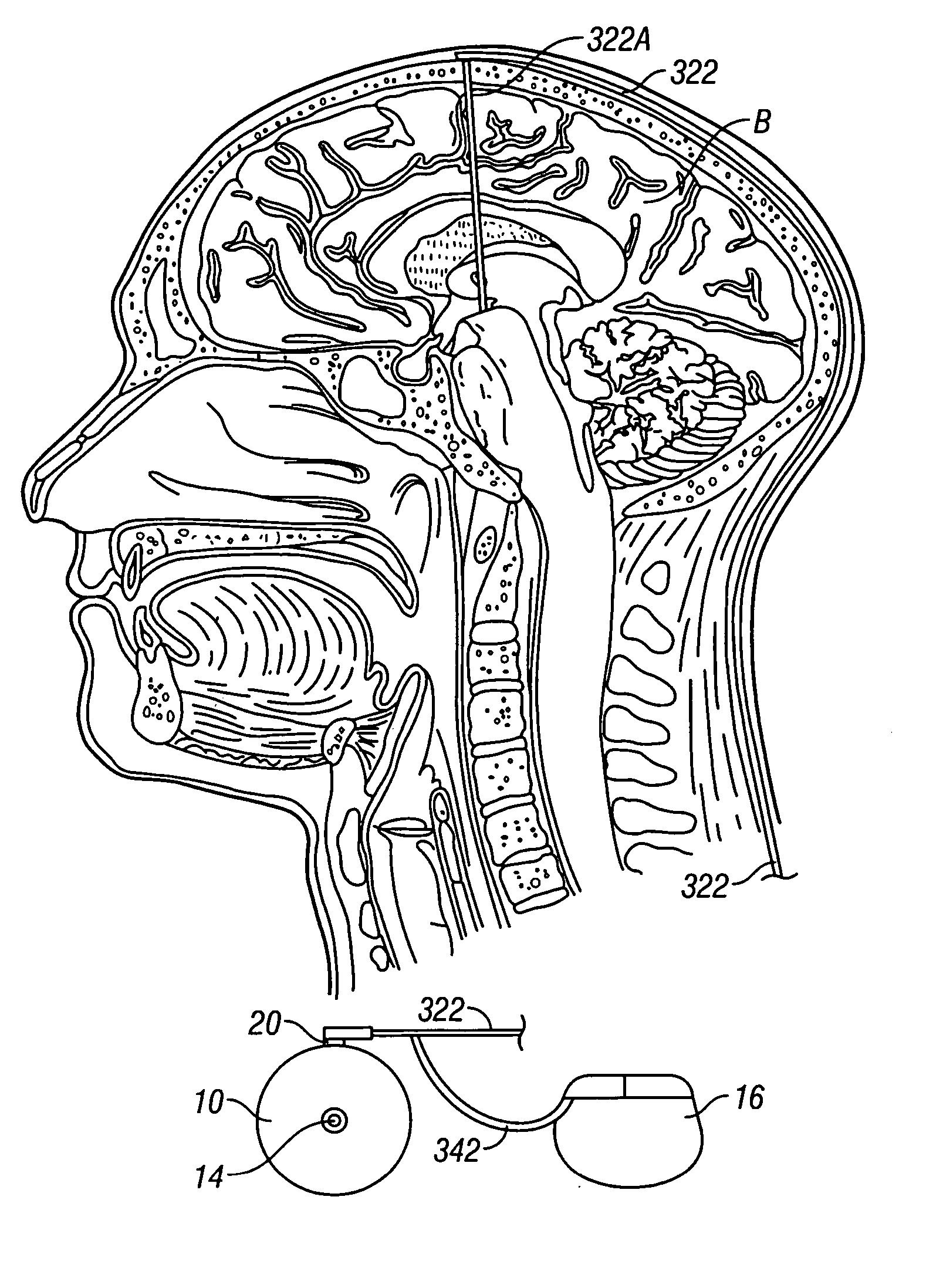
An electrode array (10) that is implantable within the inferior colliculus of the midbrain and / or other appropriate regions of the brain of an implantee and adapted to provide electrical stimulation thereto. The electrode array (10) an elongate member (11) having a plurality of electrodes (12) mounted thereon in a longitudinal array. A delivery cannula (30) for delivering the electrode array (10) comprised of two half-pipes (31) is also described.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
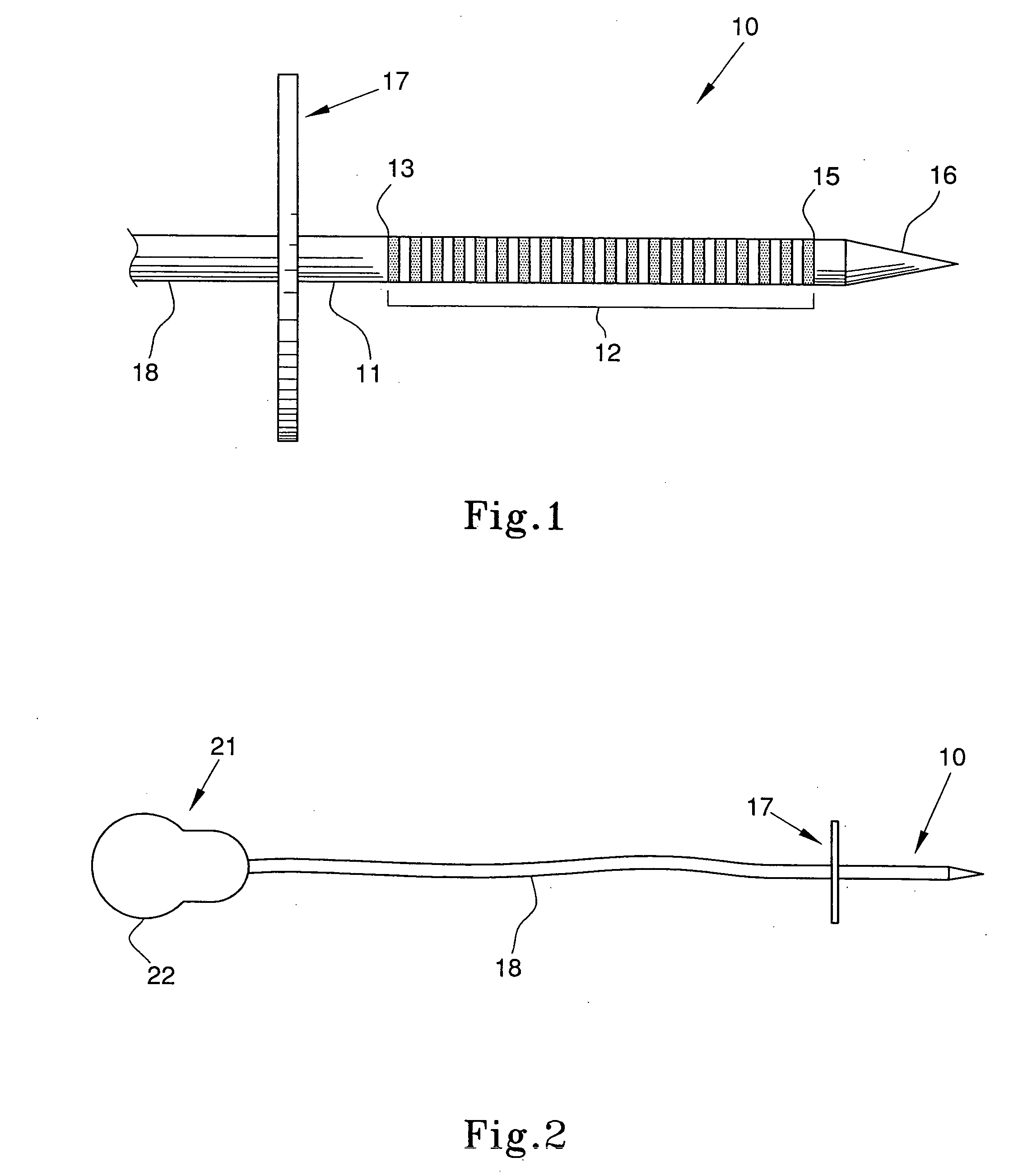
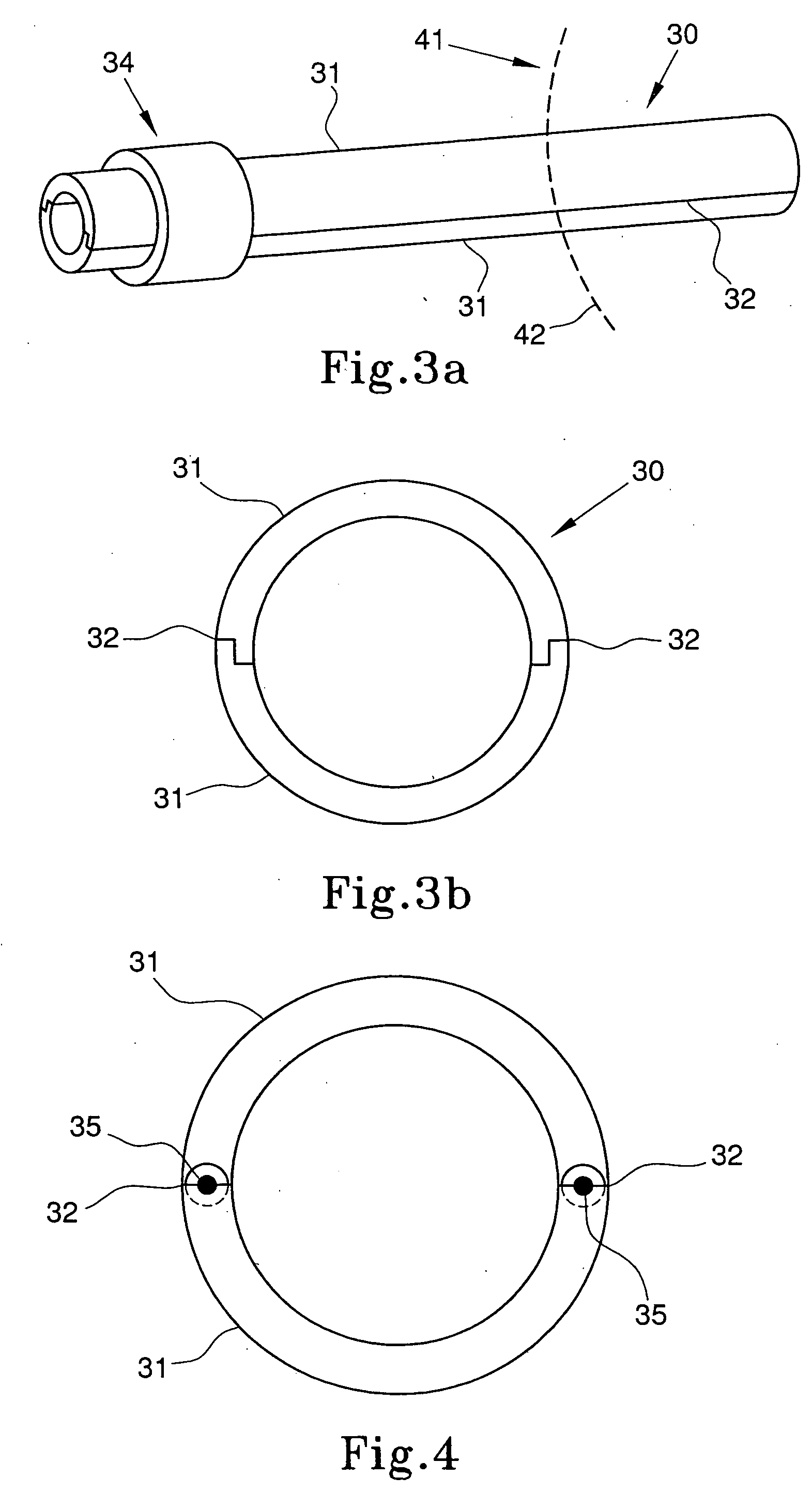
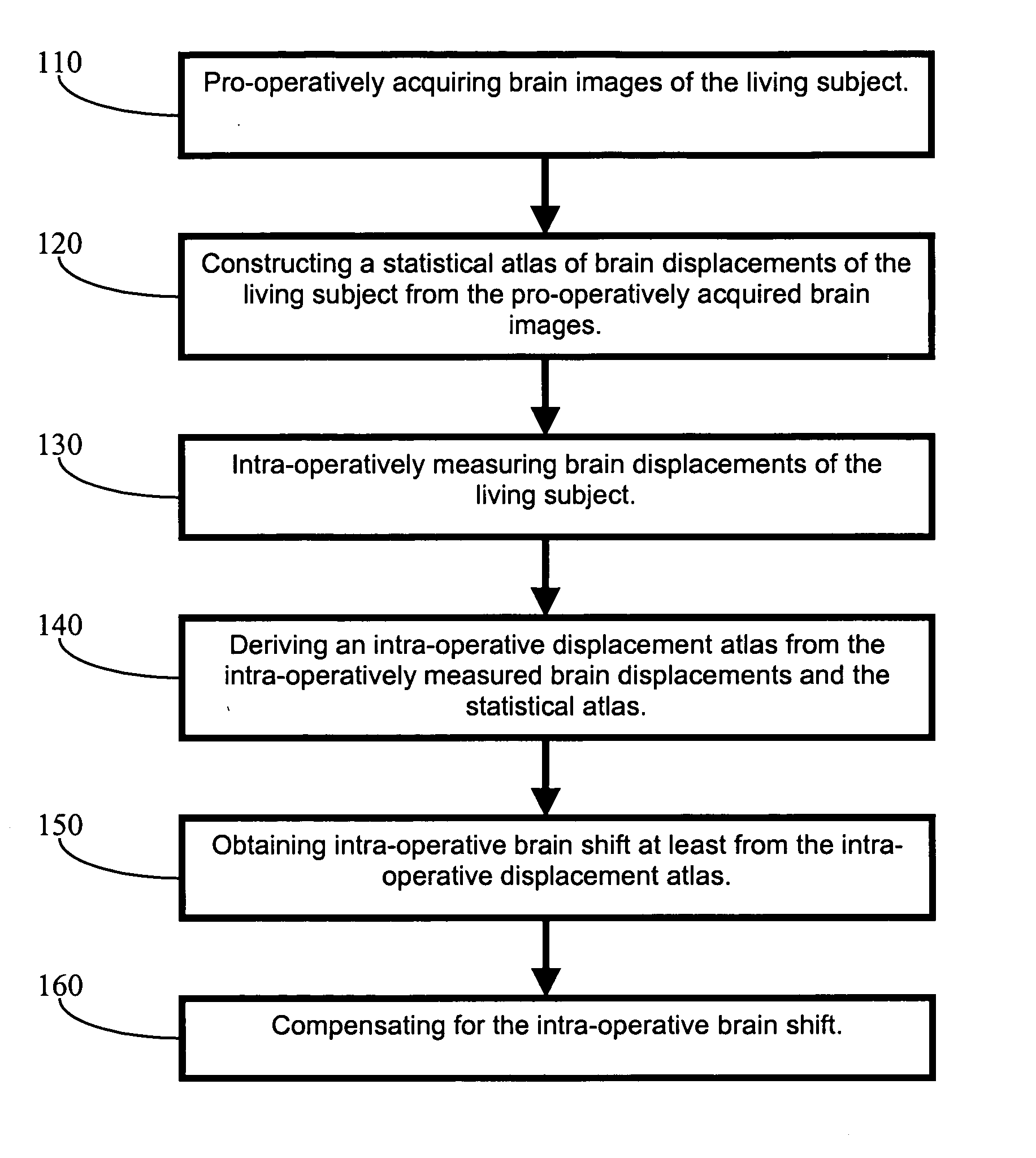
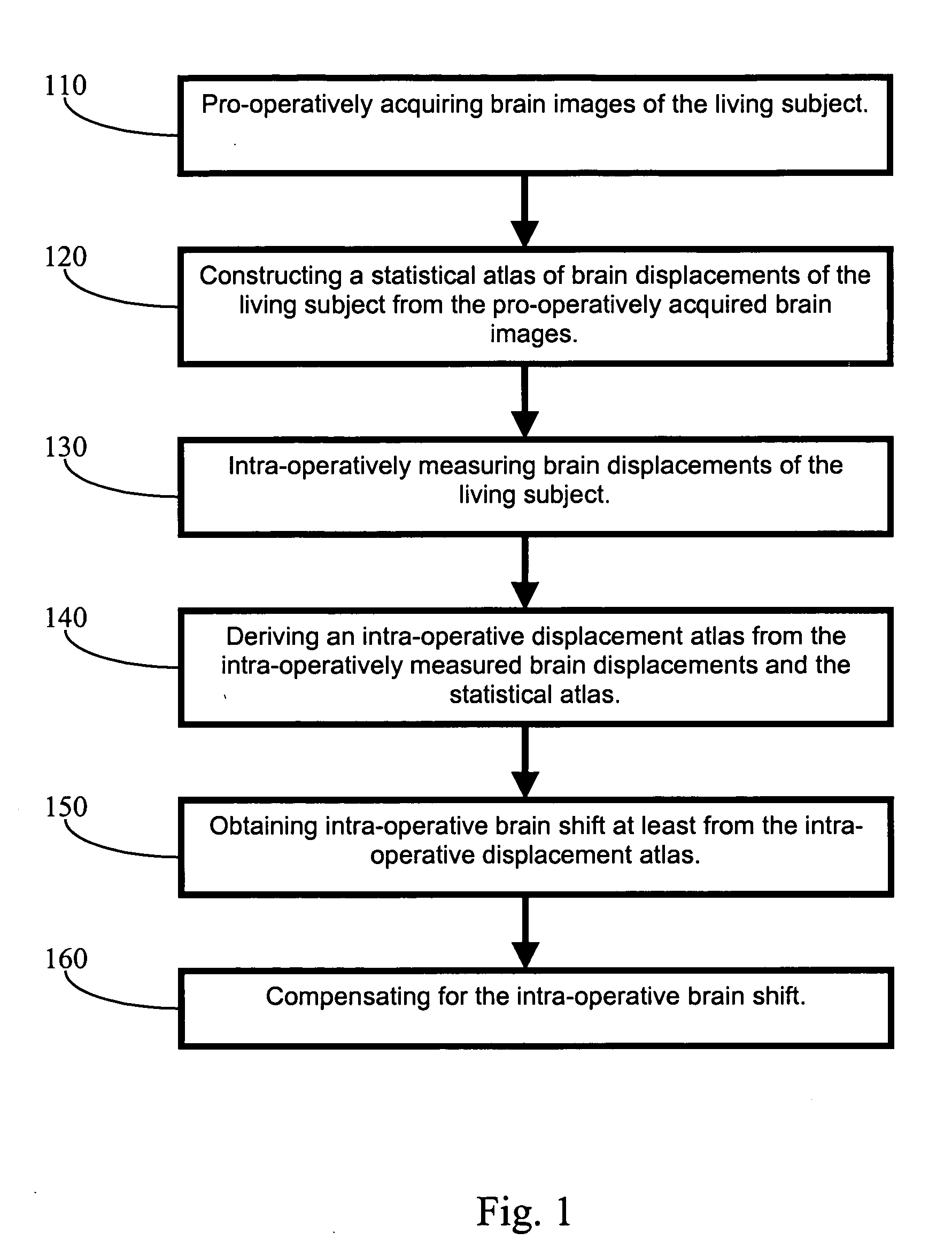
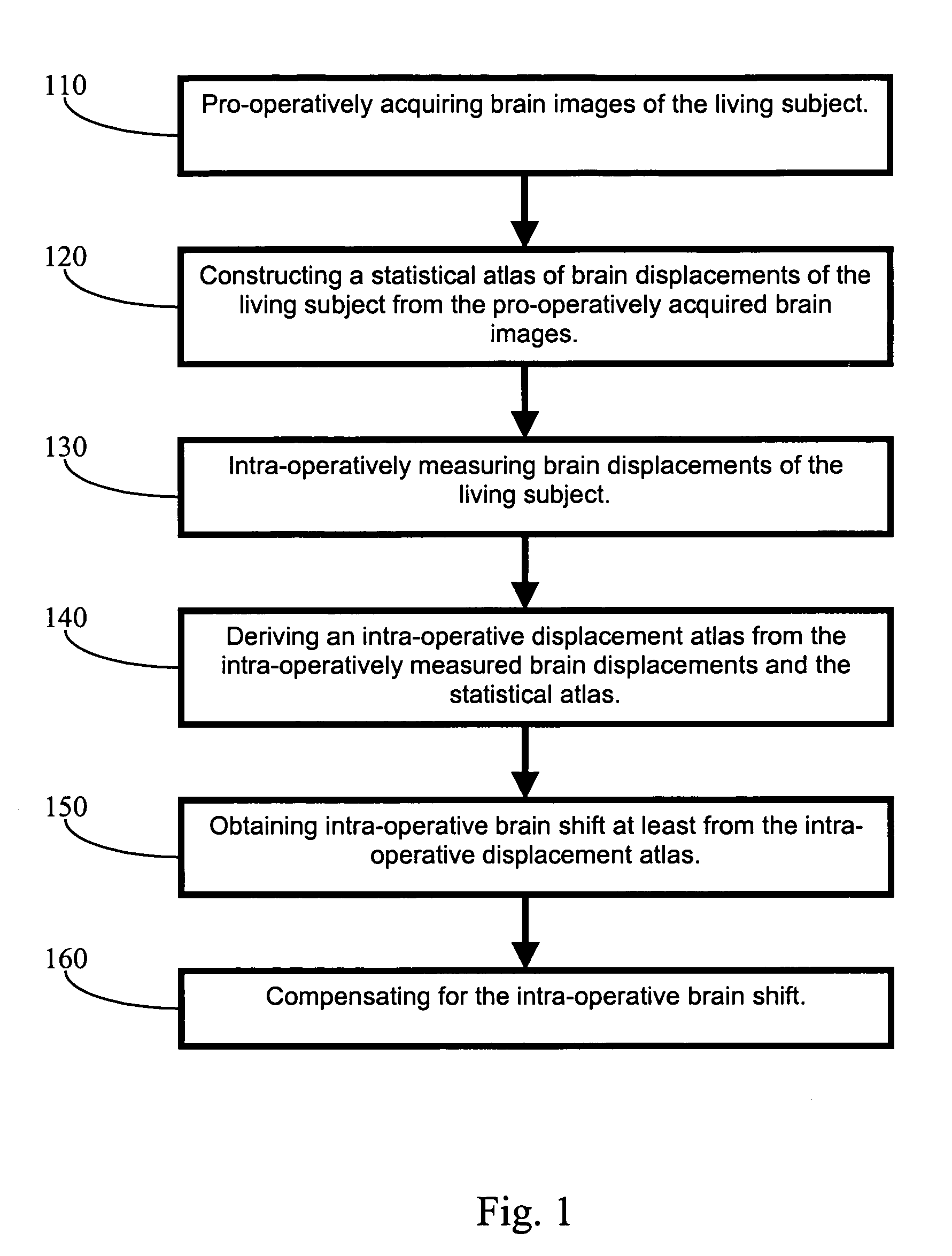
Apparatus and methods of brain shift compensation and applications of the same
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Neurostimulation device for treating mood disorders
A device and method for treating a mood and / or anxiety disorder are disclosed which provide for stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of mood disorders. In certain embodiments, brain stimulation is combined with cranial nerve stimulation for enhancing symptomatic relief of the disorder. Certain embodiments also employ a sensing capability for optimizing the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Auditory midbrain implant
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
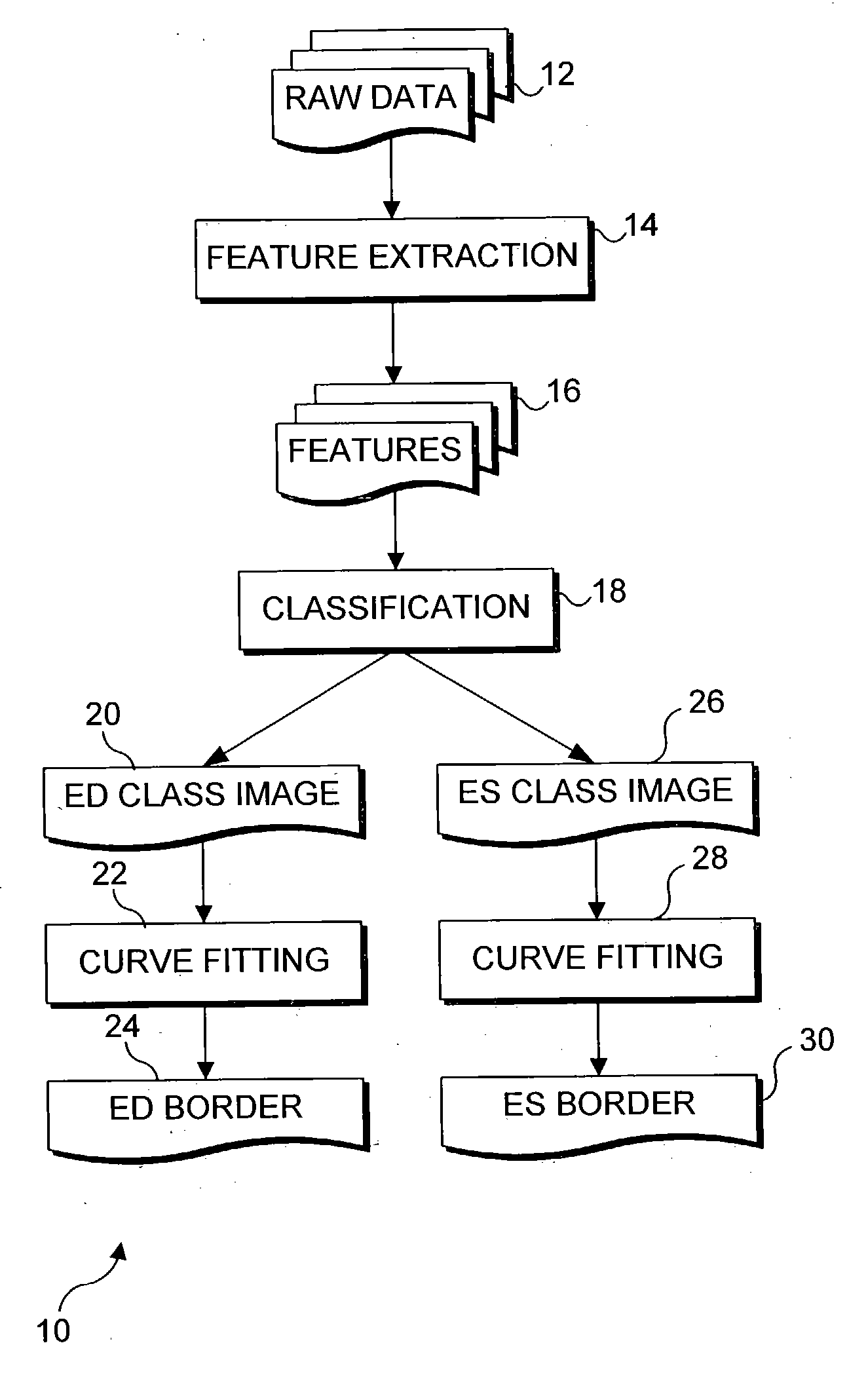
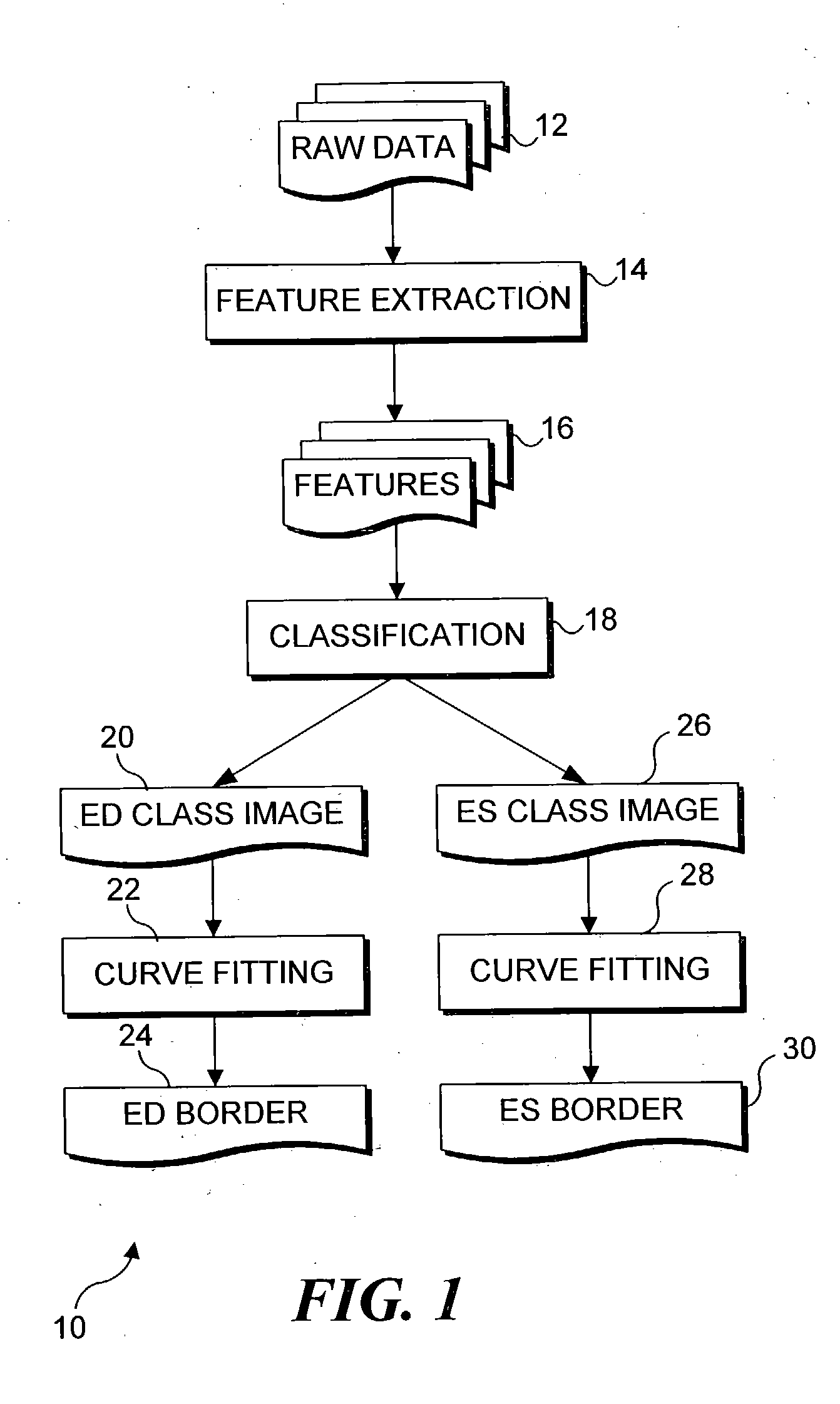
Segmentation of left ventriculograms using boosted decision trees
An automated method for determining the location of the left ventricle at user-selected end diastole (ED) and end systole (ES) frames in a contrast-enhanced left ventriculogram. Locations of a small number of anatomic landmarks are specified in the ED and ES frames. A set of feature images is computed from the raw ventriculogram gray-level images and the anatomic landmarks. Variations in image intensity caused by the imaging device used to produce the images are eliminated by de-flickering the image frames of interest. Boosted decision-tree classifiers, trained on manually segmented ventriculograms, are used to determine the pixels that are inside the ventricle in the ED and ES frames. Border pixels are then determined by applying dilation and erosion to the classifier output. Smooth curves are fit to the border pixels. Display of the resulting contours of each image frame enables a physician to more readily diagnose physiological defects of the heart.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
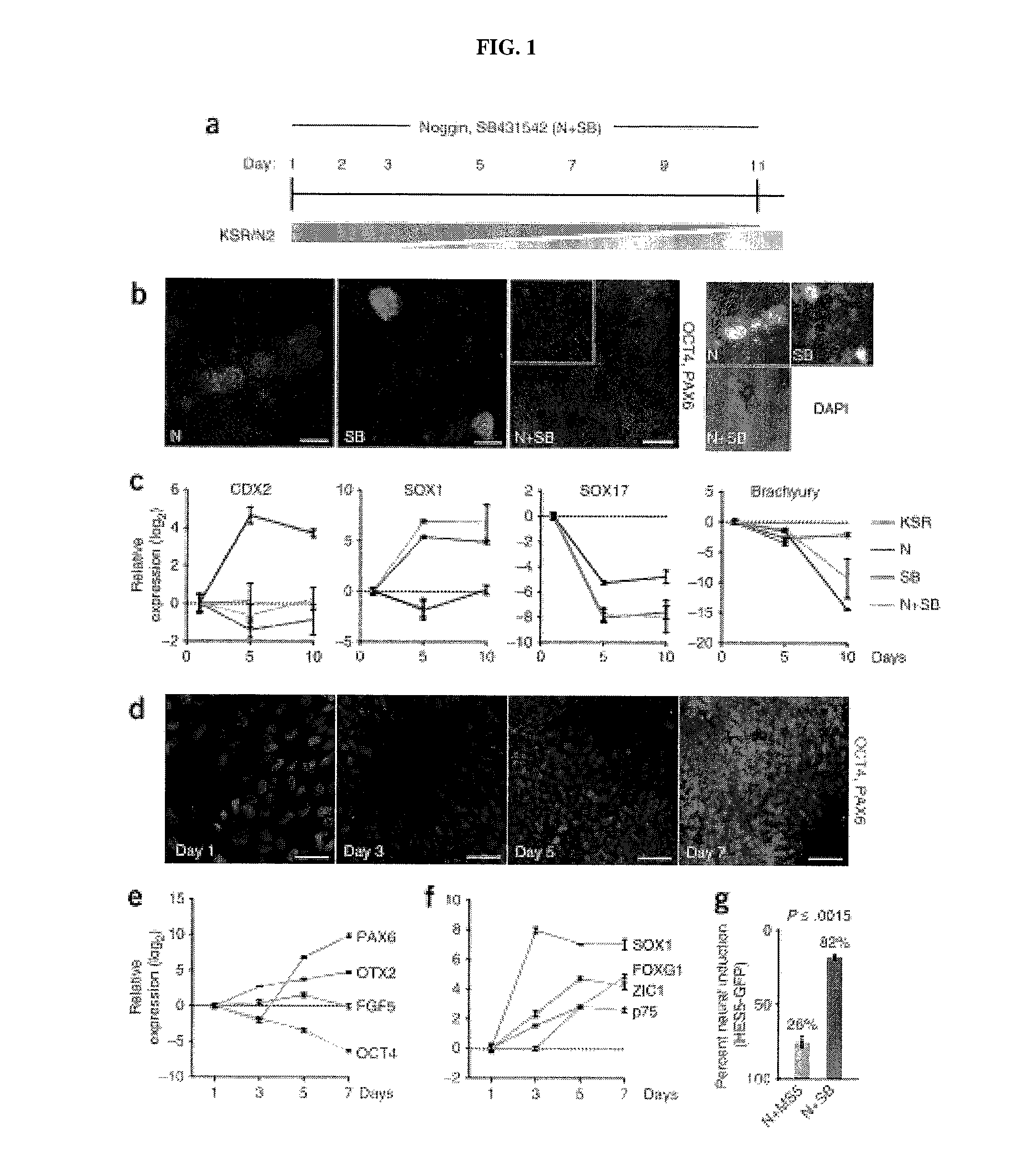
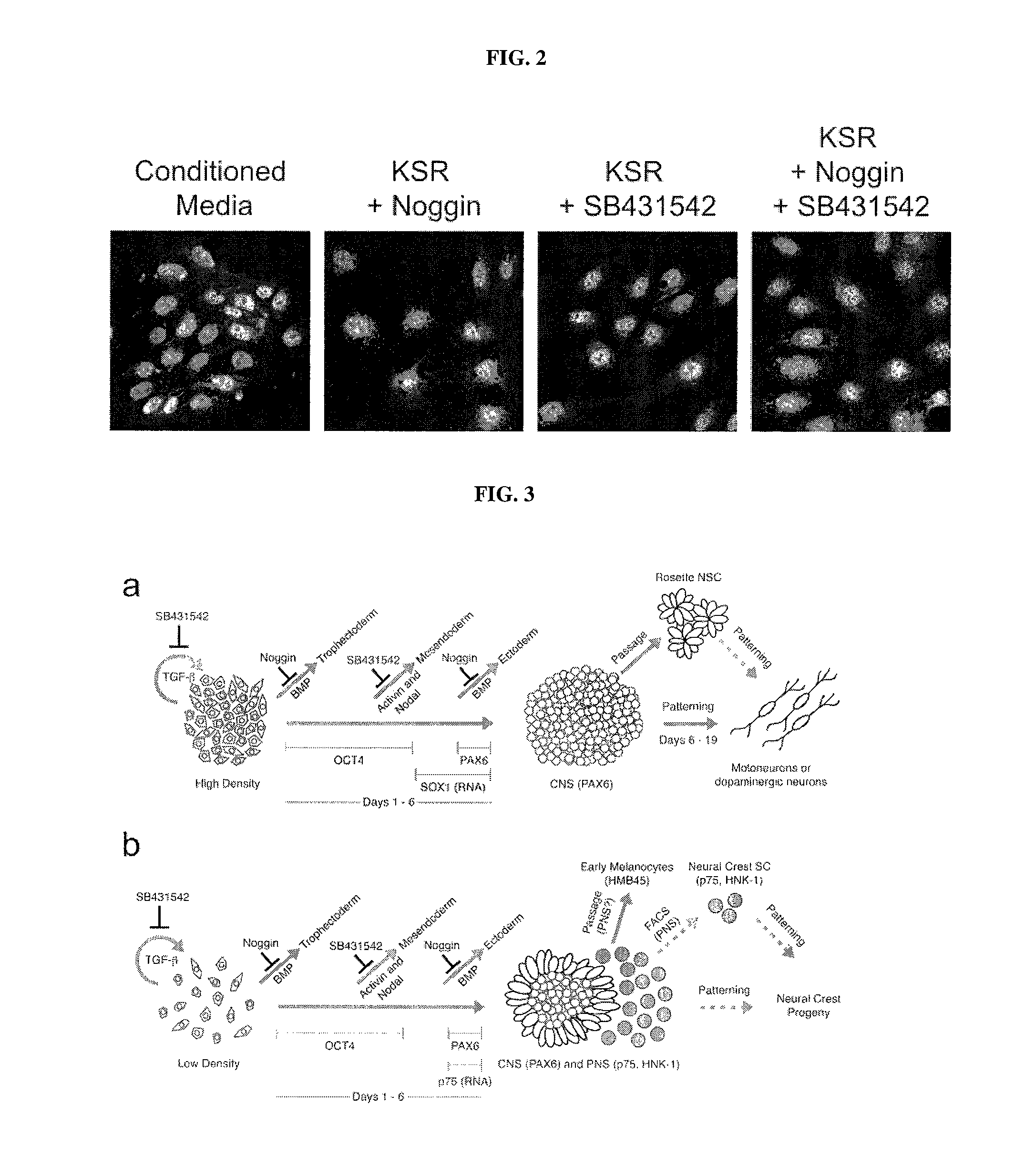
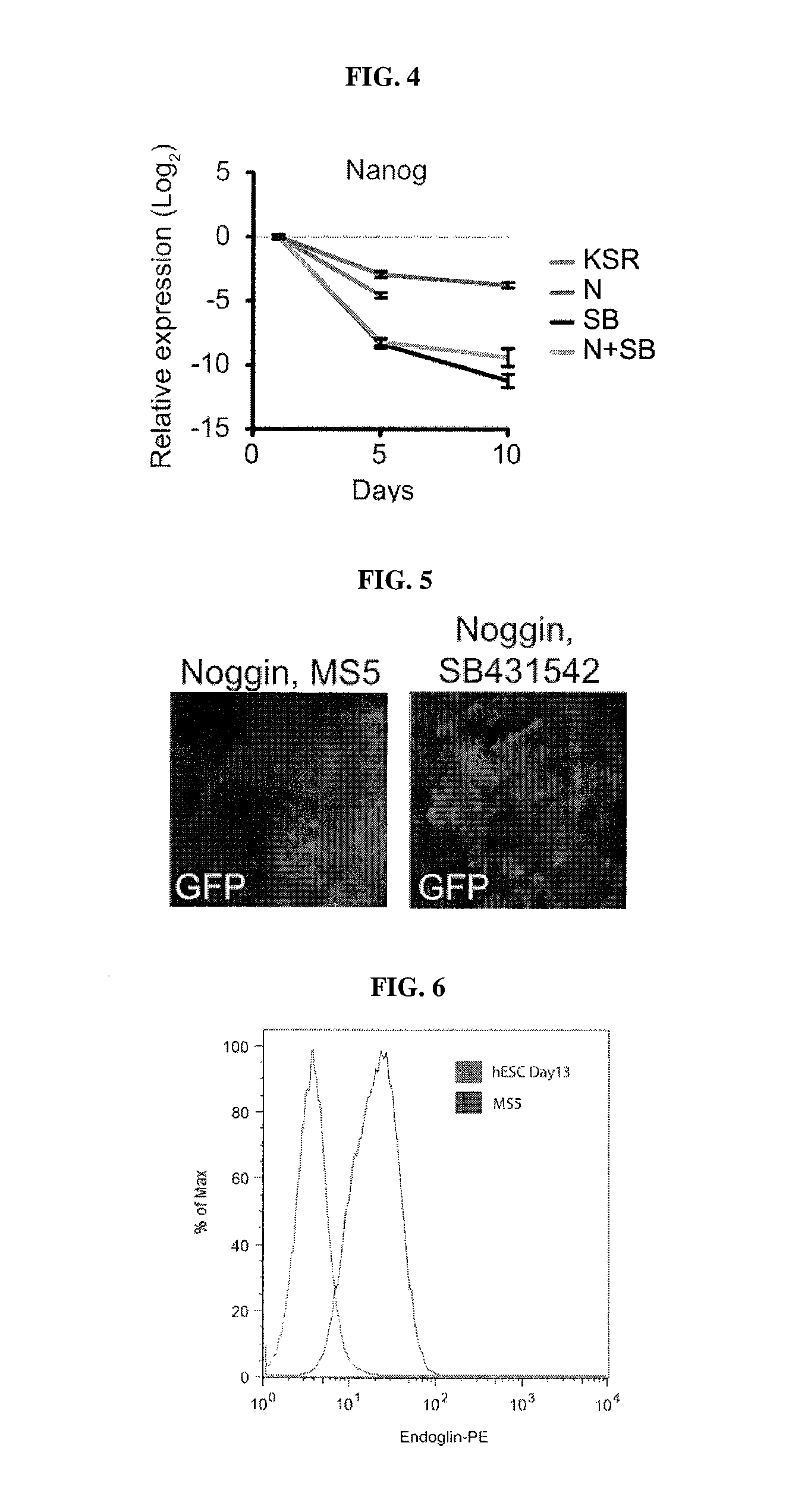
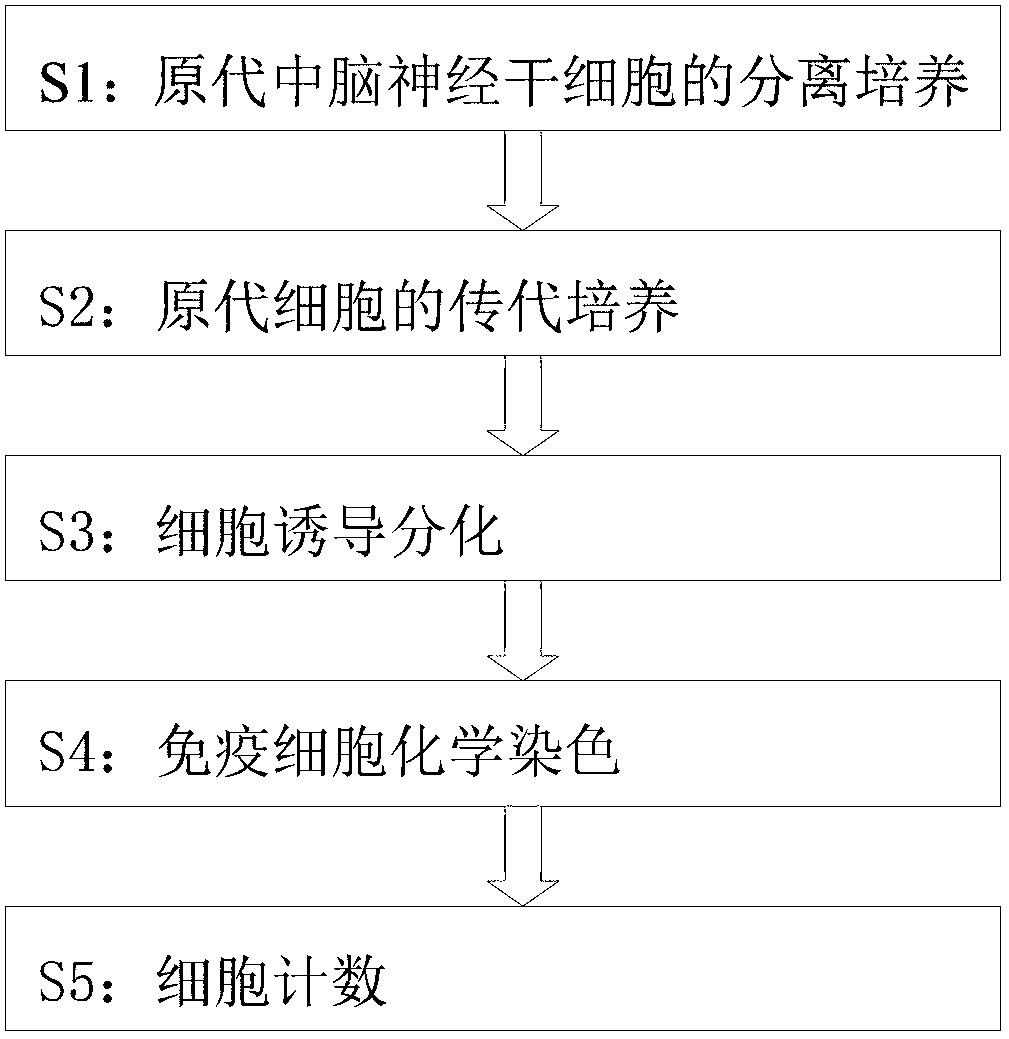
Methods of neural conversion of human embryonic stem cells
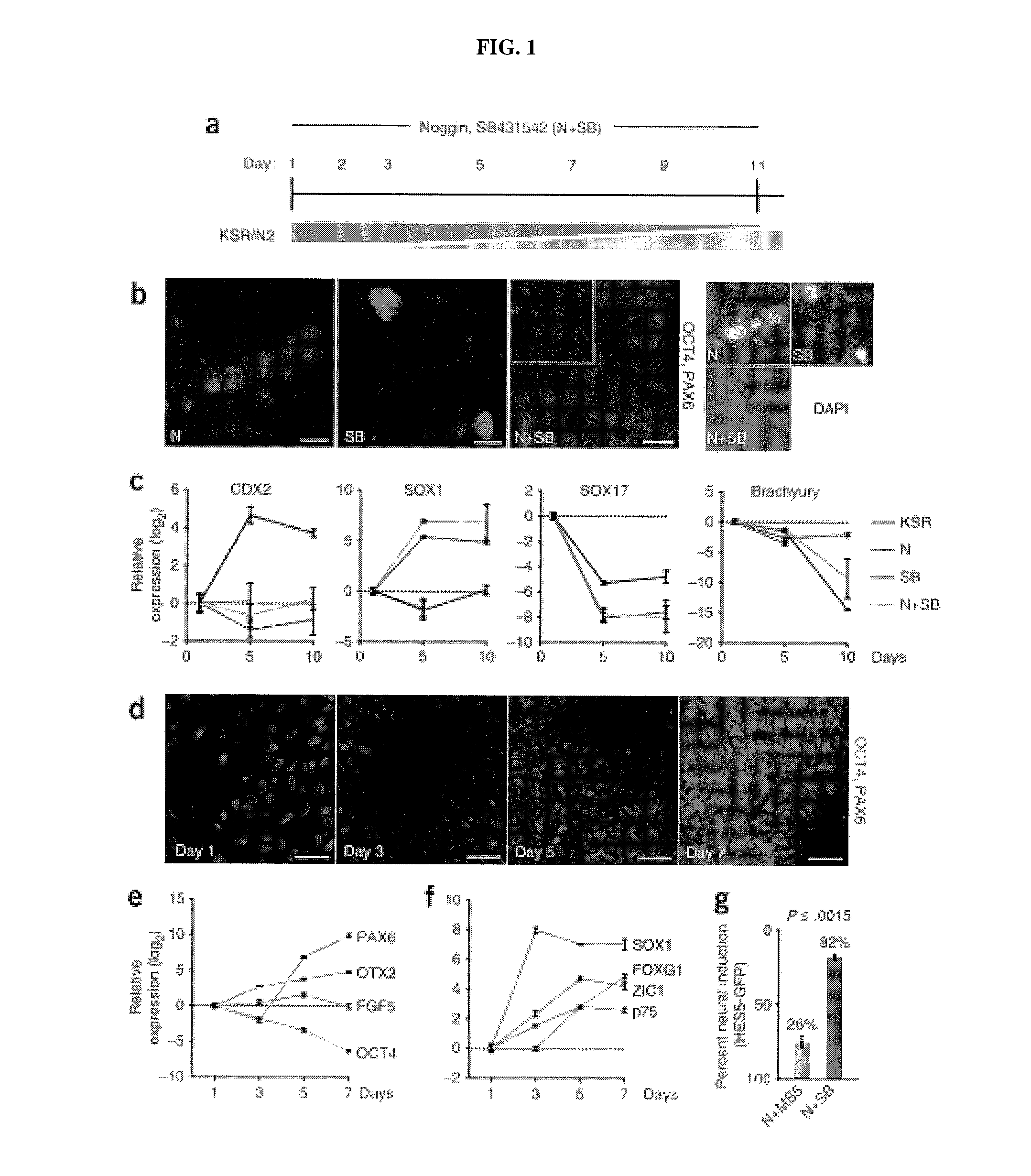
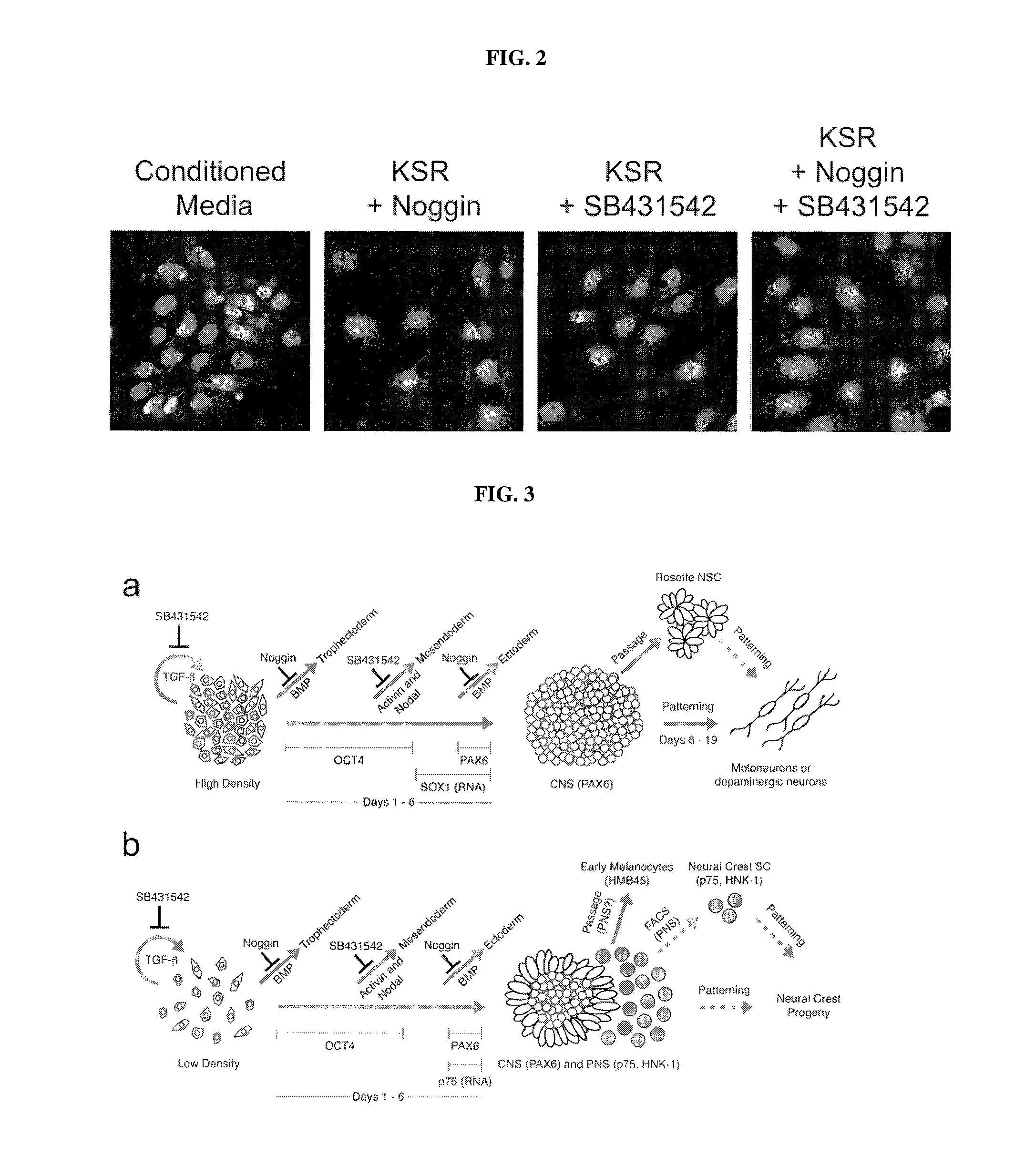
ActiveUS20120094381A1Reducing DKK- protein functionImprove featuresCulture processNervous system cellsNeural plateDirected differentiation
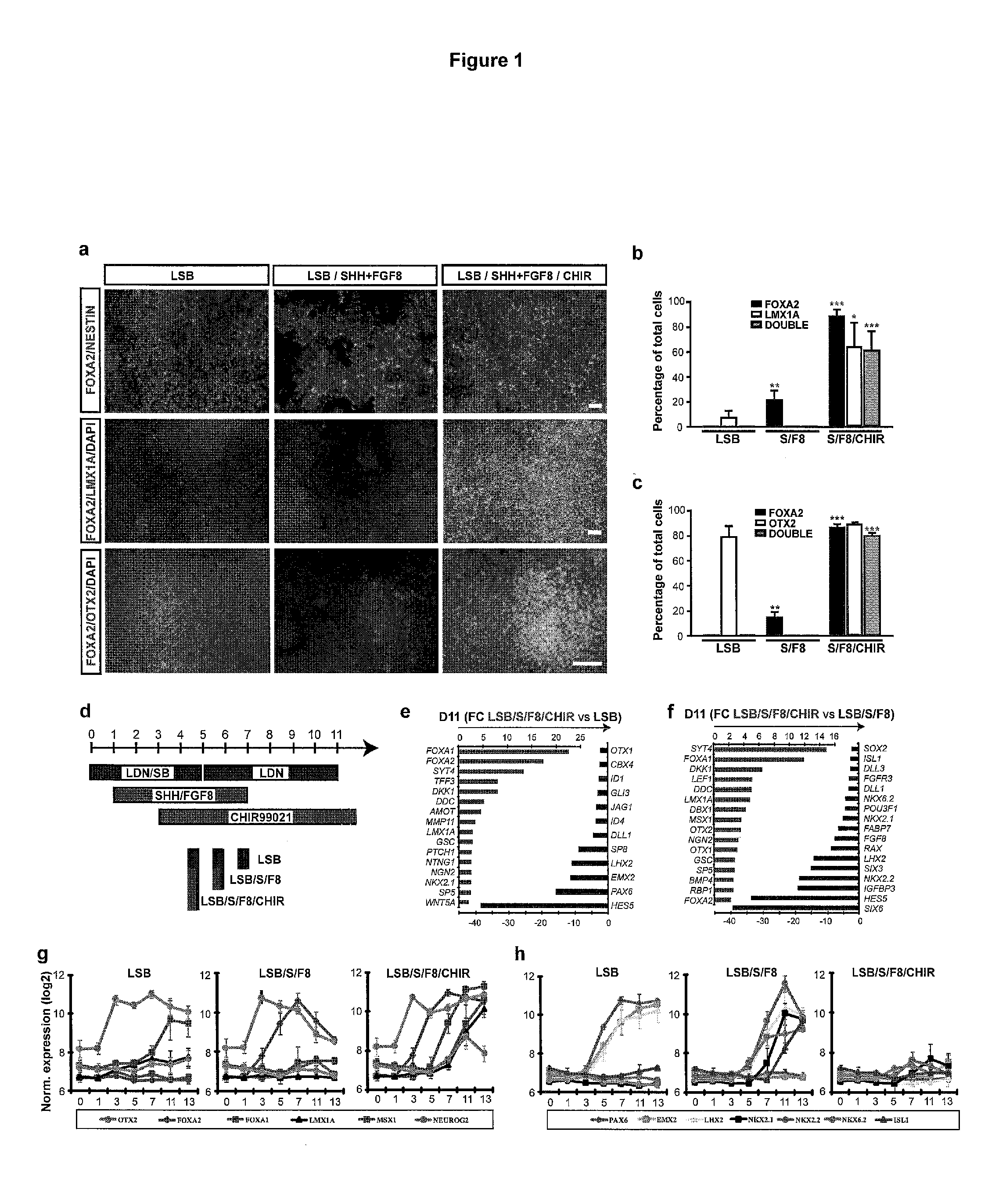
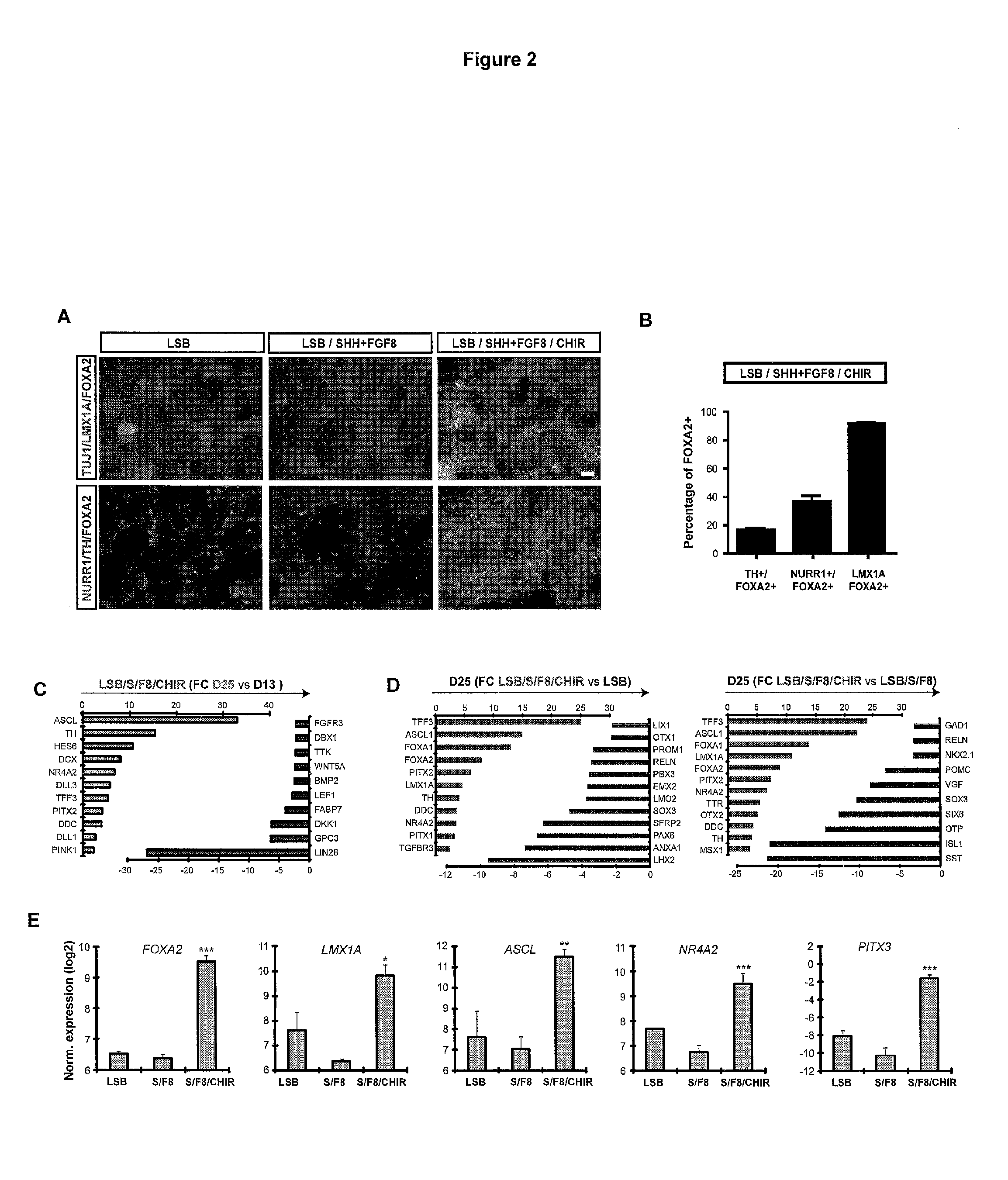
The present invention relates generally to the field of cell biology of stem cells, more specifically the directed differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, including human embryonic stem cells (hESC), somatic stem cells, and induced human pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) using novel culture conditions. Specifically, methods are provided for obtaining neural tissue, floor plate cells, and placode including induction of neural plate development in hESCs for obtaining midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons, motorneurons, and sensory neurons. Further, neural plate tissue obtained using methods of the present inventions are contemplated for use in co-cultures with other tissues as inducers for shifting differentiation pathways, i.e. patterning.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
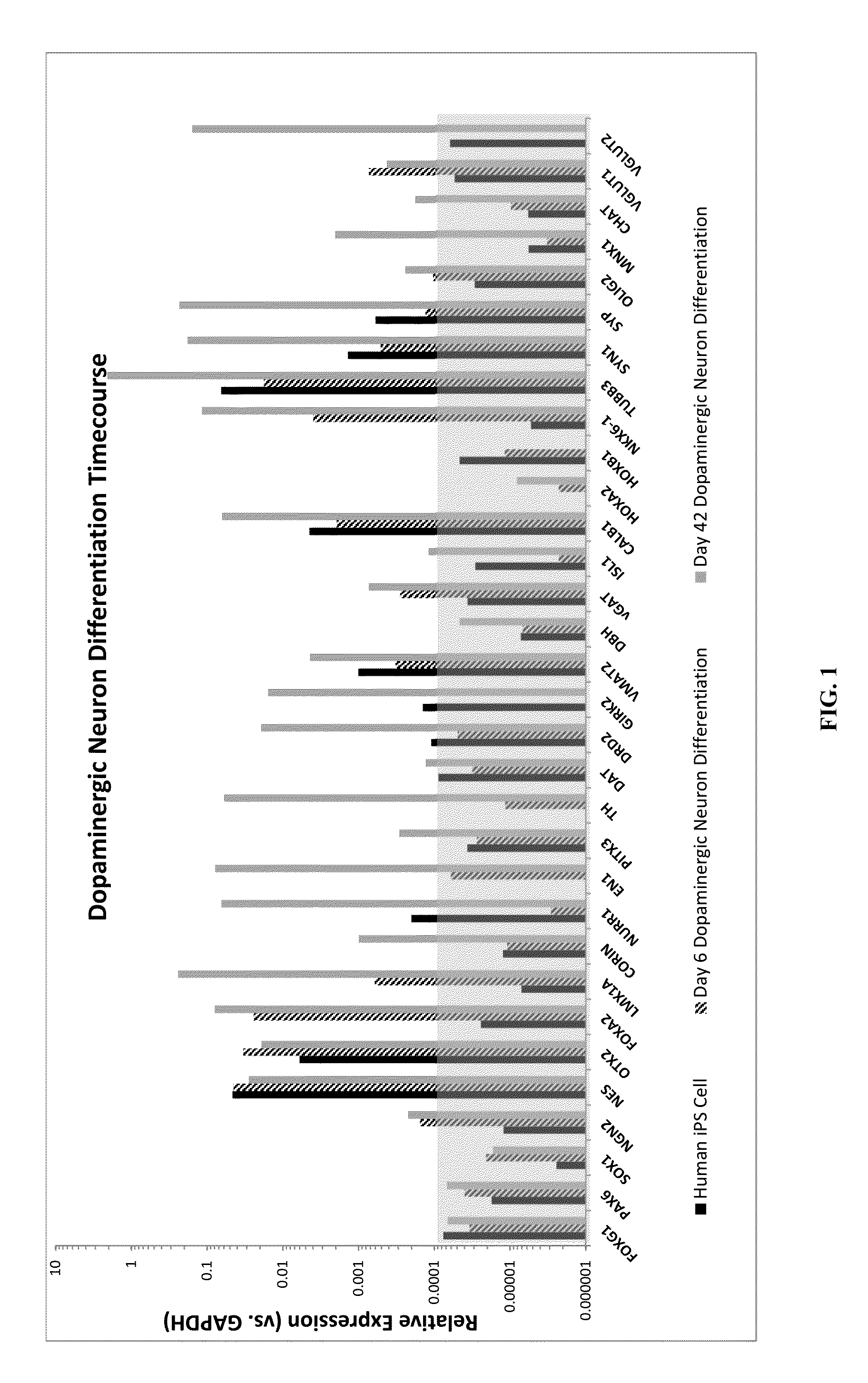
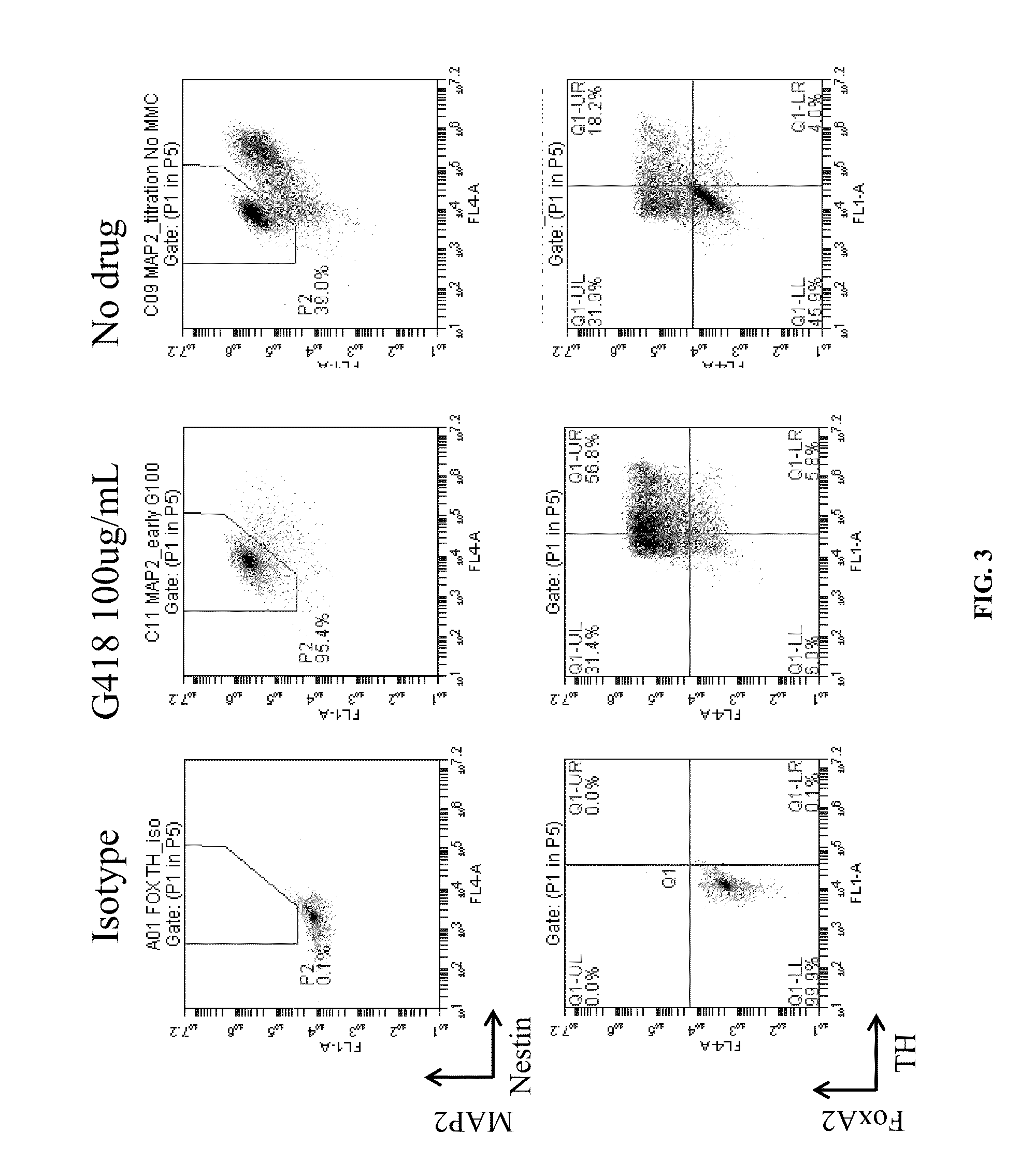
Production of midbrain dopaminergic neurons and methods for the use thereof
Methods are provided for efficient production of midbrain dopaminergic (DA) neurons. In some aspects, methods involve differentiation and selection of DA neurons for a transgenic pluripotent cell population (e.g., cells comprising a selectable marker gene). Cell populations produced by the instant methods and methods of their use are likewise provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Apparatus and methods of brain shift compensation and applications of the same
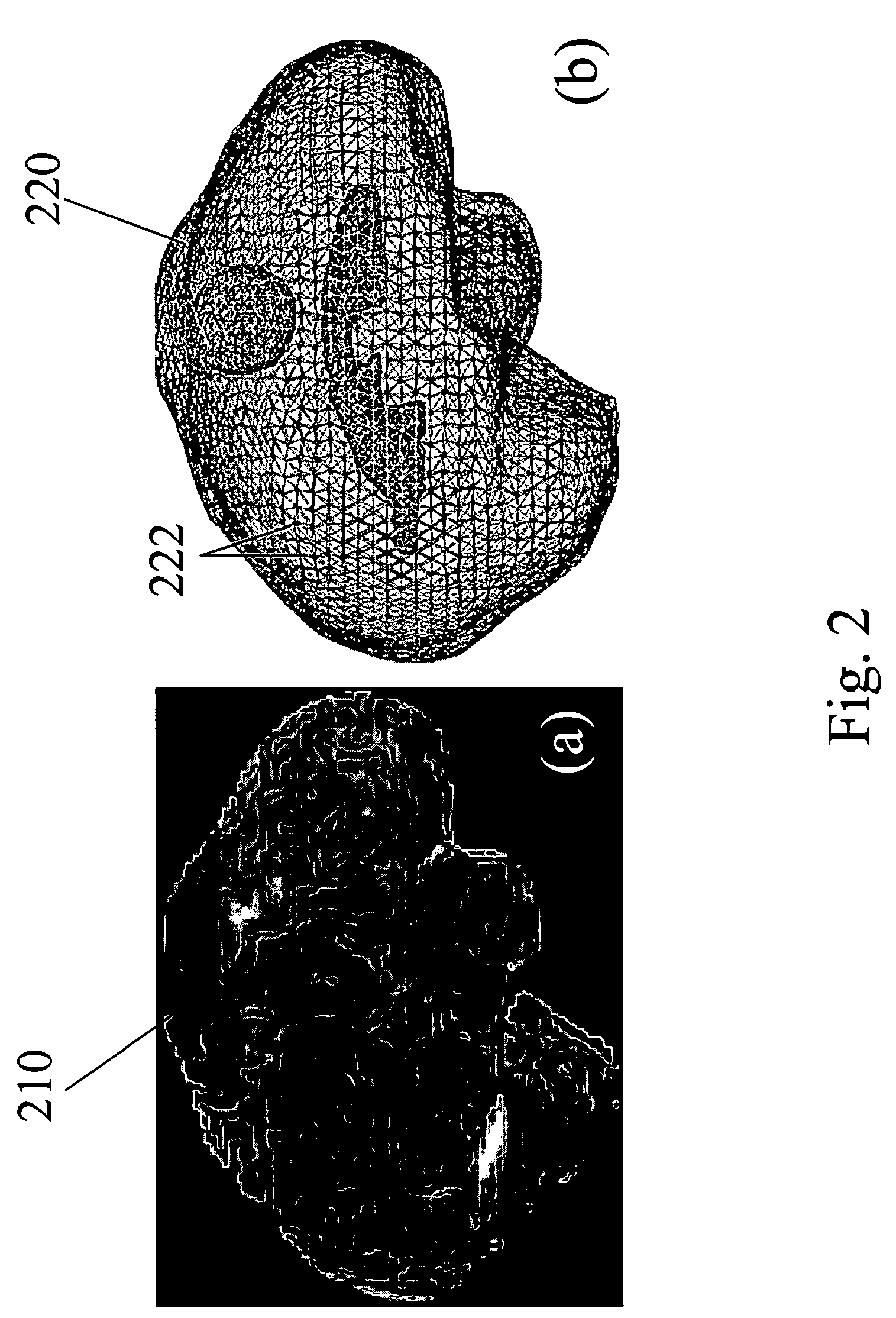
ActiveUS7072705B2Image analysisSurgical navigation systemsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMidbrain
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons for engraftment
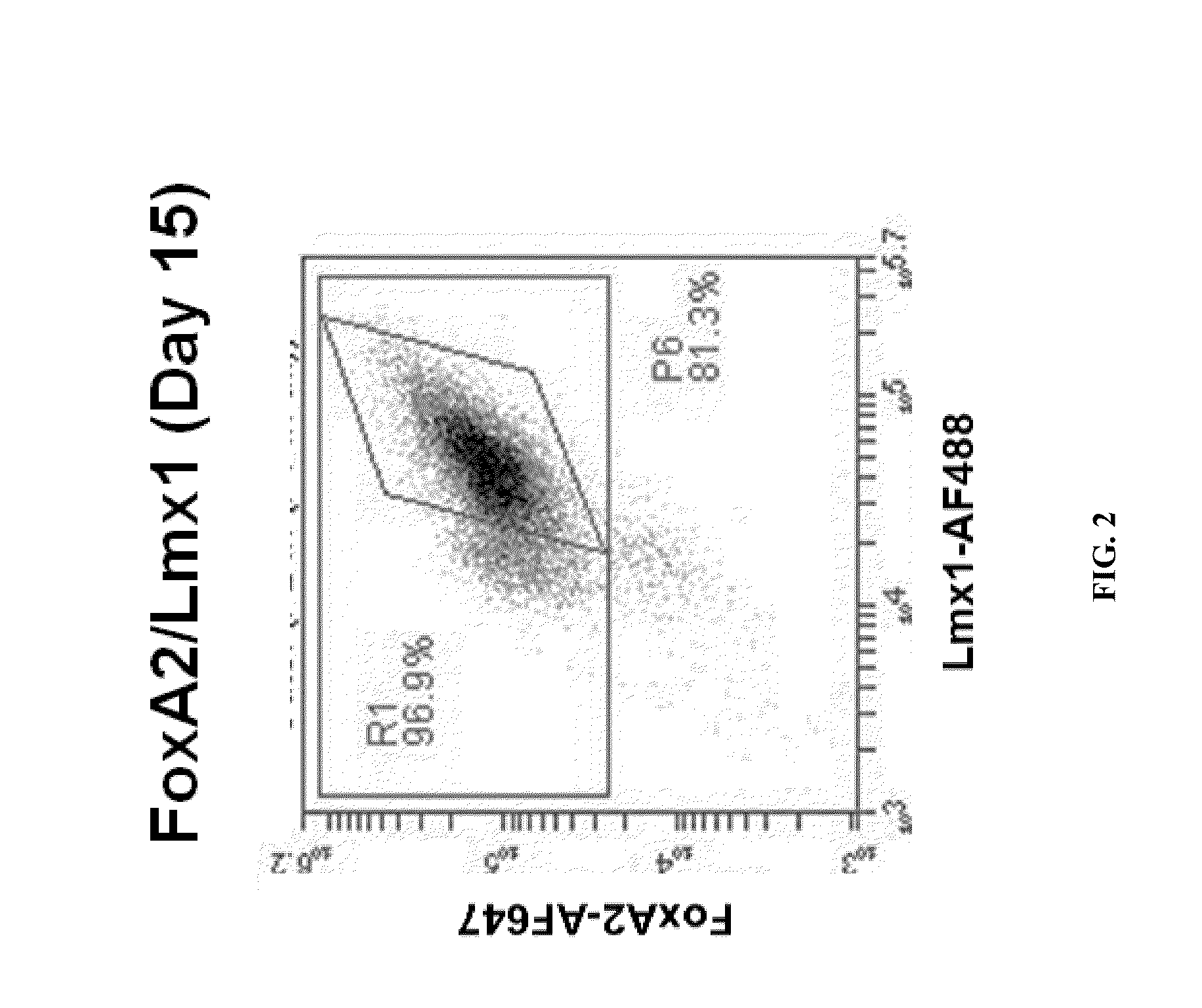
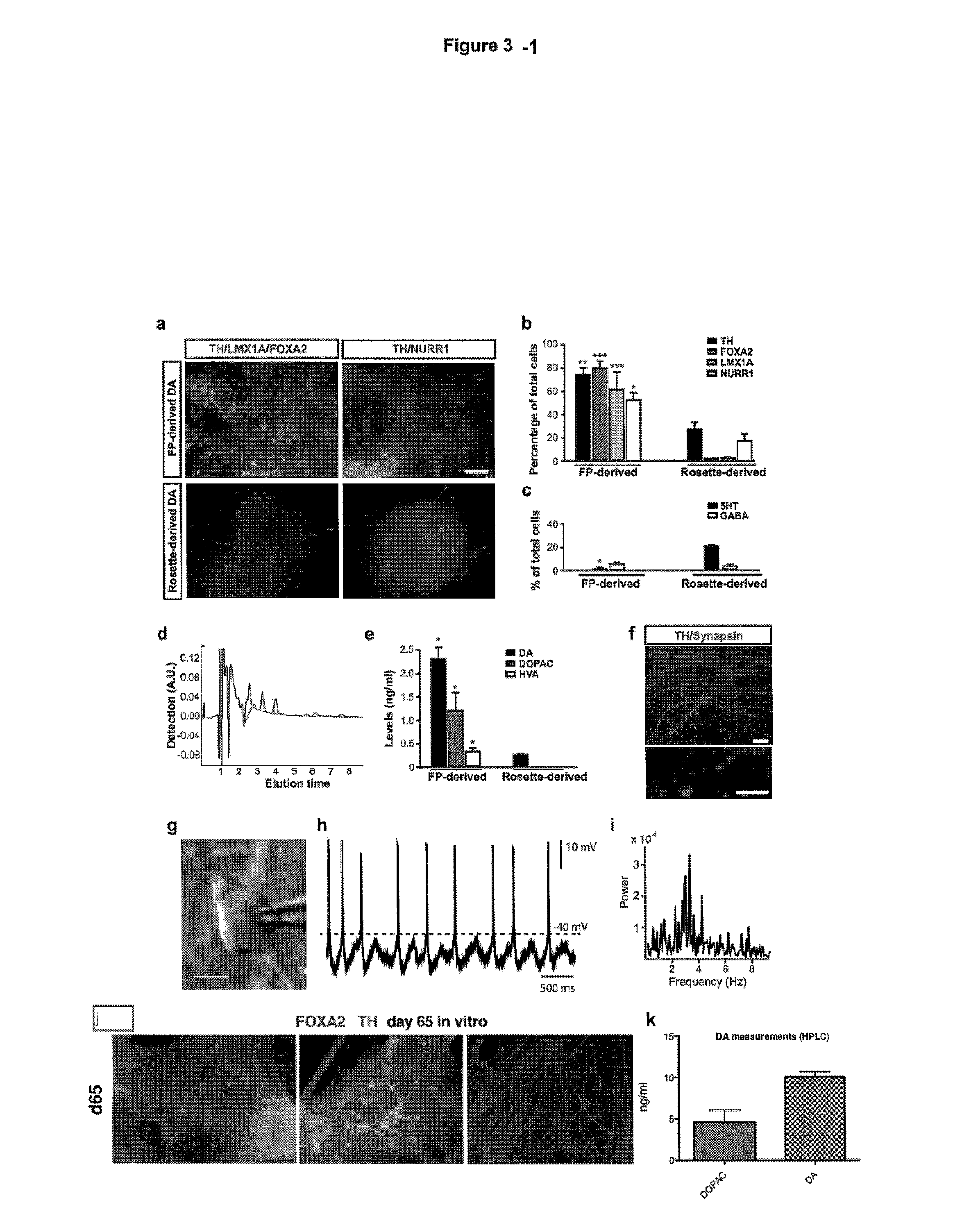
The present invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular the lineage specific differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, which can include, but is not limited to, human embryonic stem cells (hESC) in addition to nonembryonic human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), somatic stem cells, stem cells from patients with a disease, or any other cell capable of lineage specific differentiation. Specifically described are methods to direct the lineage specific differentiation of hESC and / or hiPSC into floor plate midbrain progenitor cells and then further into large populations of midbrain fate FOXA2+LMX1A+TH+ dopamine (DA) neurons using novel culture conditions. The midbrain fate FOXA2+LMX1A+TH+ dopamine (DA) neurons made using the methods of the present invention are further contemplated for various uses including, but not limited to, use in in vitro drug discovery assays, neurology research, and as a therapeutic to reverse disease of, or damage to, a lack of dopamine neurons in a patient. Further, compositions and methods are provided for differentiating midbrain fate FOXA2+LMX1A+TH+ dopamine (DA) neurons from human pluripotent stem cells for use in disease modeling, in particular Parkinson's disease. Additionally, authentic DA neurons are enriched for markers, such as CD142, and A9 type neuronal cells.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
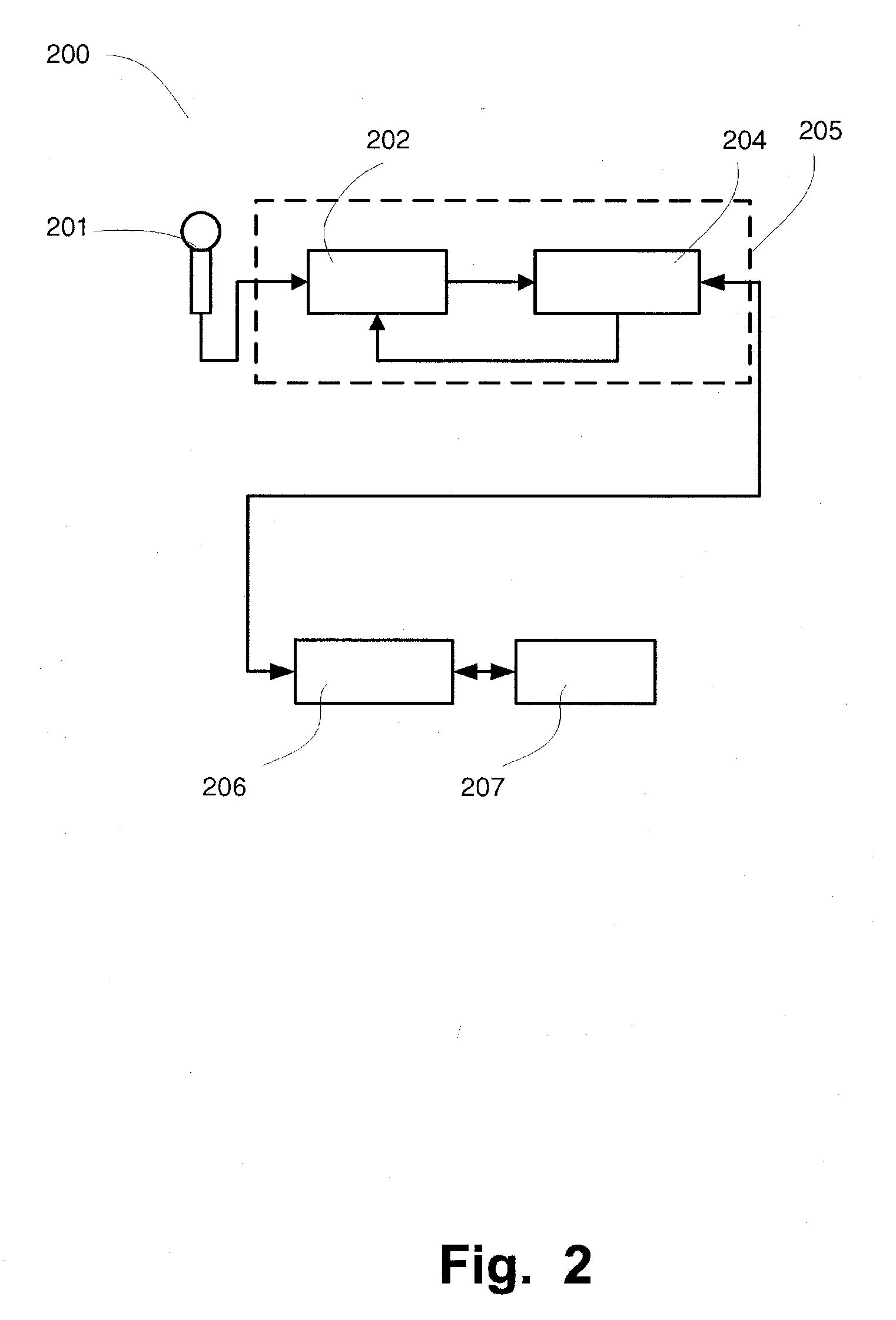
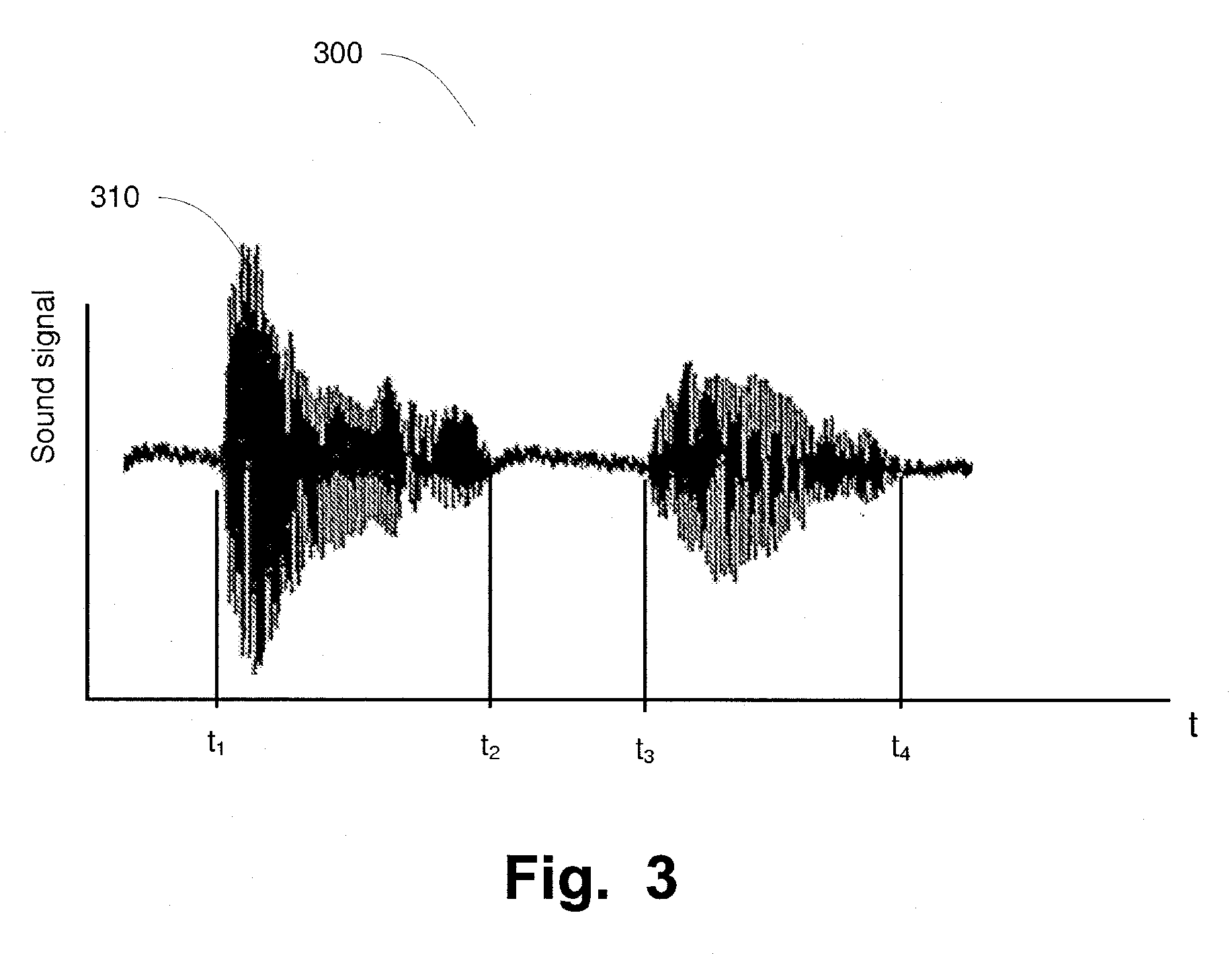
System and methods for assessment of the aging brain and its brain disease induced brain dysfunctions by speech analysis
InactiveUS20100298649A1Reduce financial costsEasily decideSpeech analysisTelemedicineDiseaseMidbrain
A system and method for assessment of a brain status of a subject are disclosed. The brain status comprises a brain disease induced brain dysfunction. An occurrence and / or stage of the brain disease induced brain dysfunction in the subject is determined. The system comprises an apparatus that is adapted to determine the occurrence and / or stage of the brain disease induced brain dysfunction in the subject from random speech of the subject. The apparatus (200) comprises units that are operatively connected to each other, which comprises a unit (205) for registering the speech of the subject over a period of time; a unit (206) devised for analyzing the registered speech and configured to determine a pause component of the speech; and a unit that is adapted to determine the occurrence and / or stage of the brain disease induced brain dysfunction from the pause component, wherein said pause component is an accumulated pause time of a total time of said speech correlated to said occurrence and / or stage of said brain dysfunction.
Owner:PHIBIO SCI
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods of neural conversion of human embryonic stem cells
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
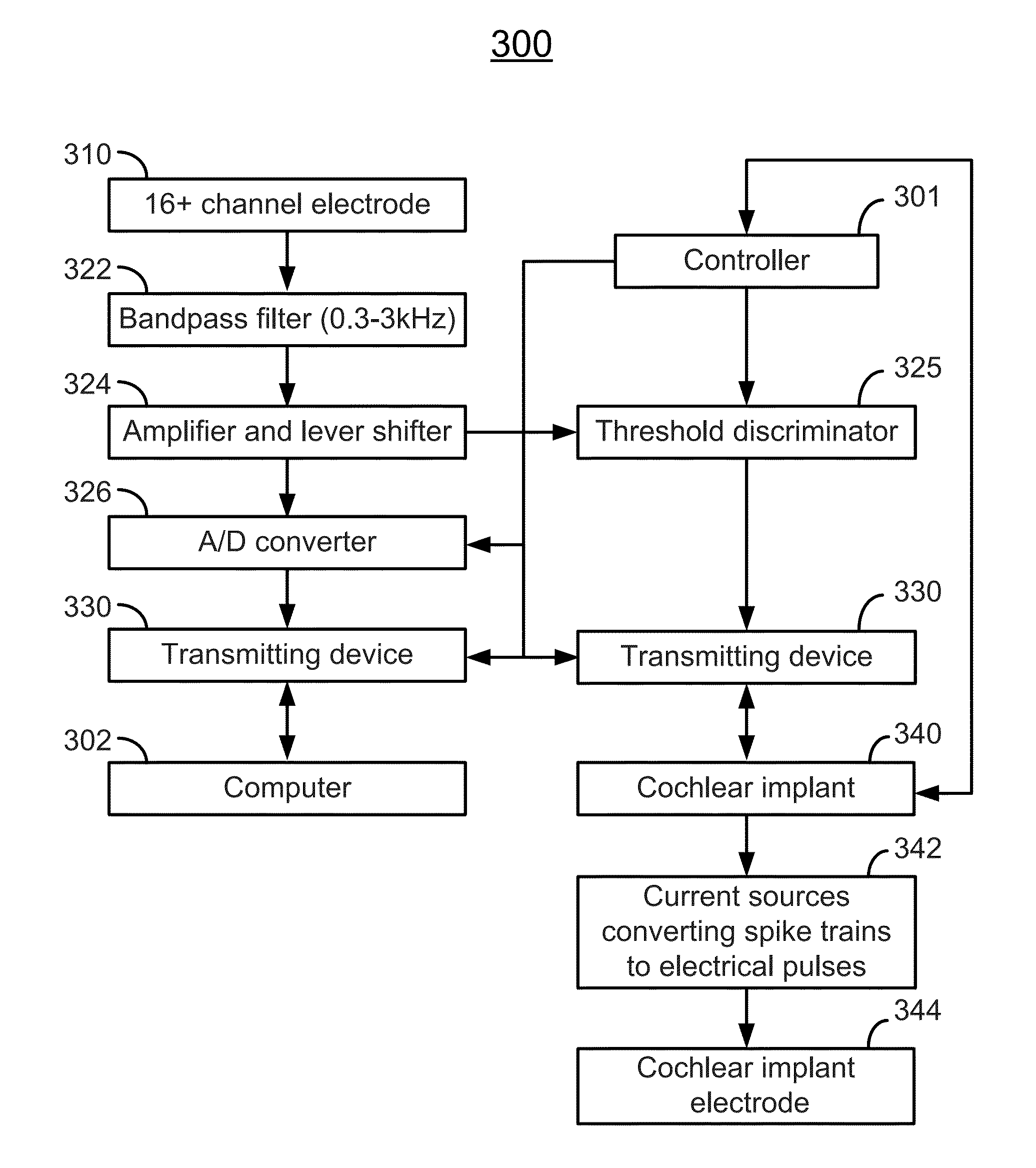
System and method for animal-human neural interface
Aspects of the invention include system and method for transmitting neural data extracted from an electrical signal of a non-human mammal to a human. The system includes an electrode implantable into the animal auditory nerve, brainstem, or midbrain of the non-human mammal, configured to record the electrical signal of the non-human mammal, the electrical signal being in the form of sequences of pulses or pulse trains encoding frequency information of the non-human mammal, a processing device electrically coupled with the electrode, configured to process the electrical signal and convert the processed electrical signal into a digital signal, a transmitting device electrically coupled with the processing device, configured to transmit the digital signal, and a receiving device electrically coupled with the transmitting device, configured to receive the transmitted digital signal, convert the received digital signal into a sensory output perceptible to the human, and apply the sensory output to the human.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Human mesencephalon cell lines and methods of use therefor
Conditionally-immortalized human mesencephalon cell lines are provided. Such cell lines, which may be clonal, may be used to generate neurons, including dopaminergic neurons. The cell lines and / or differentiated cells may be used for the development of therapeutic agents to prevent and treat a variety of neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease. The cell lines and / or differentiated cells may also be used in assays and for the general study of mesencephalon cell development and differentiation.
Owner:SIGNAL PHARM INC
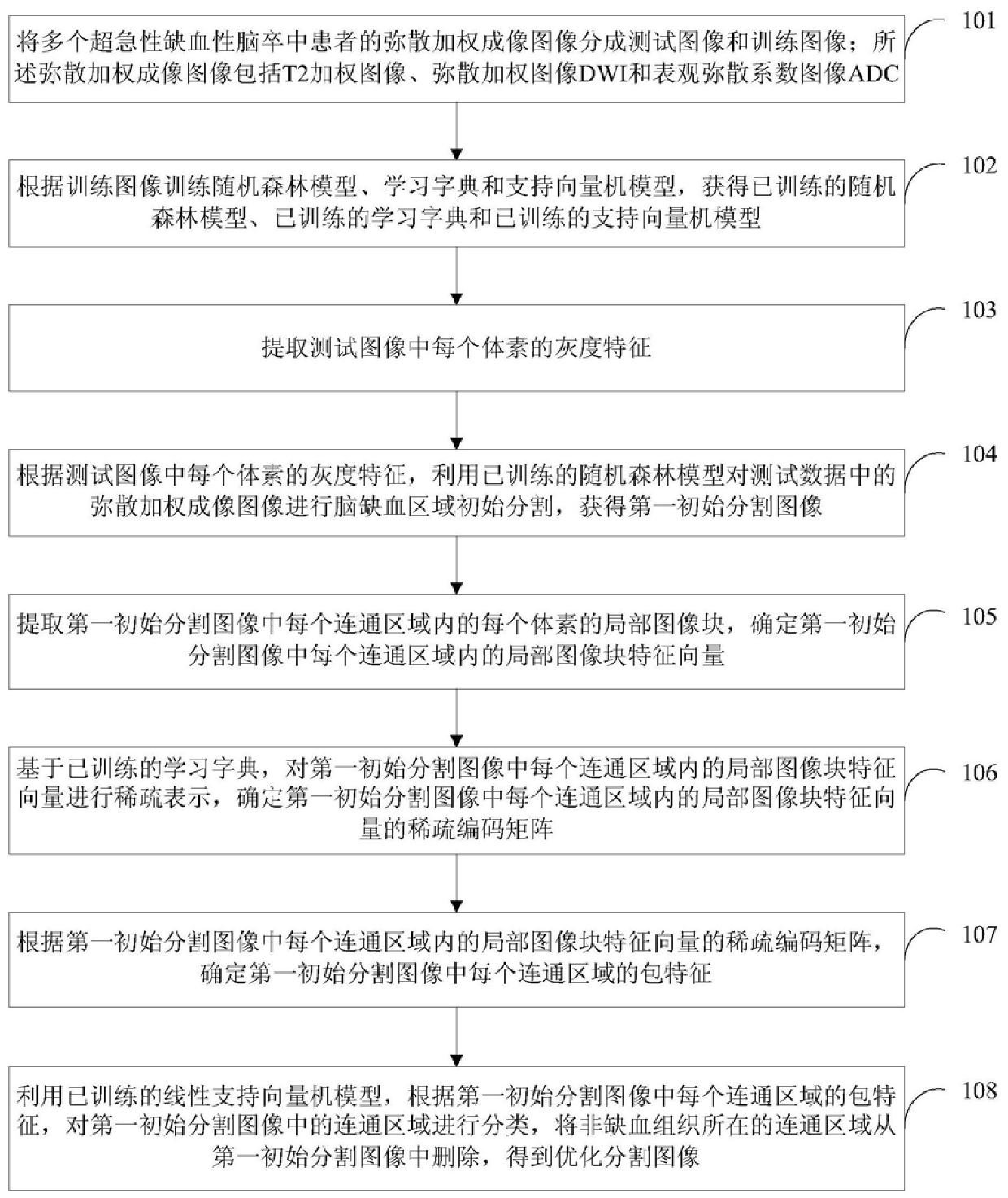
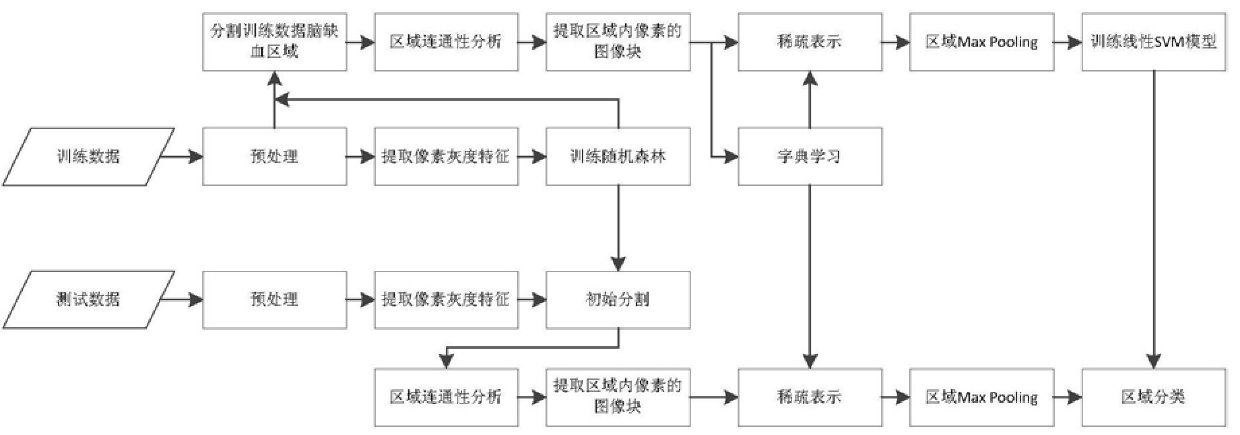
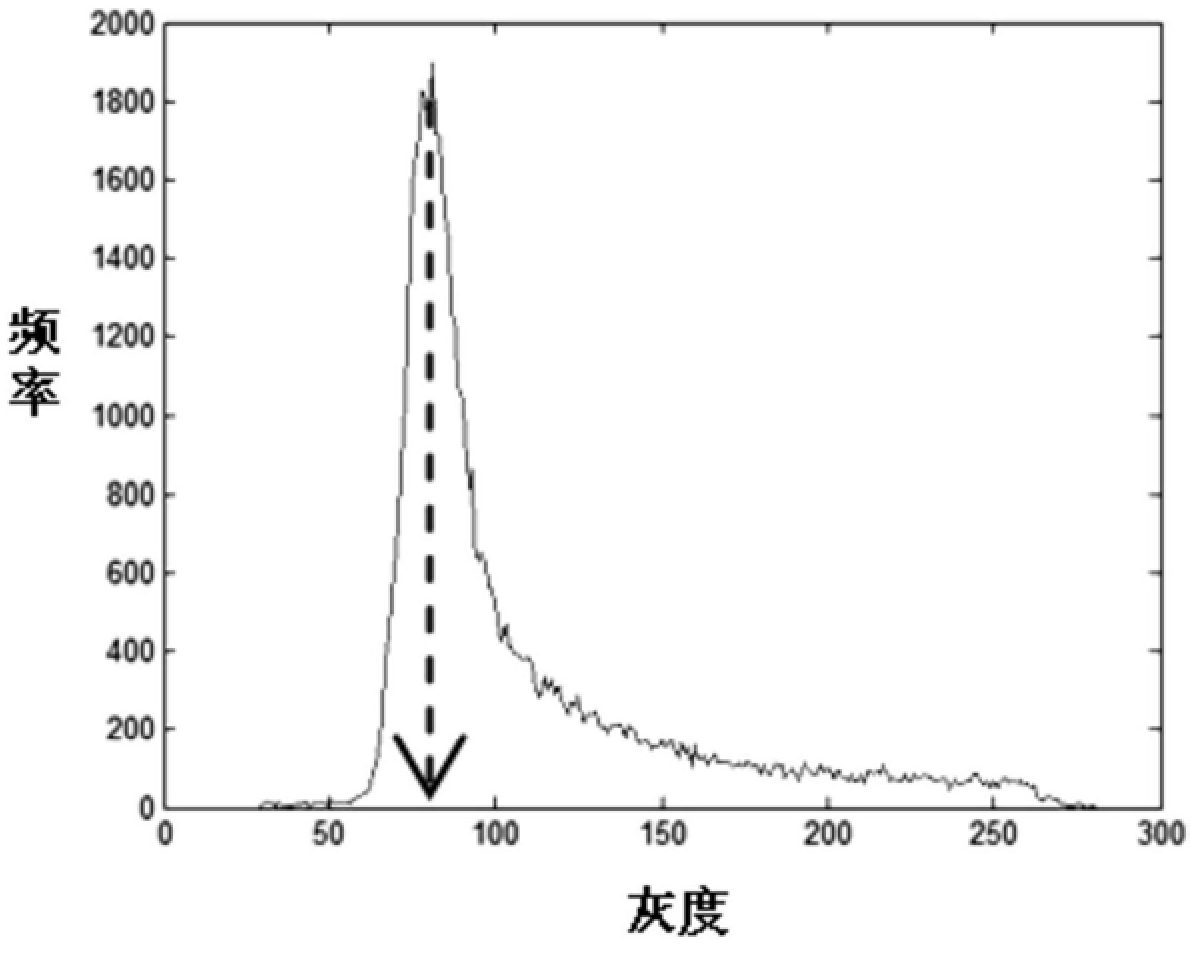
Method and device for segmenting cerebral ischemia areas in diffusion-weighted images
ActiveCN108122221AImprove Segmentation AccuracyResolve identifiabilityImage enhancementImage analysisSupport vector machineFeature vector
The invention provides a method and device for segmenting cerebral ischemia areas in diffusion-weighted images. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing diffusion-weighted images of a plurality of super-acute ischemic stroke patients into test images and training images; training a random forest model, a learning dictionary and a support vector machine model according to the trainingimages; carrying out initial cerebral ischemia area segmentation by utilizing the trained random forest model according to grey features of voxels in the test images; determining a sparse encoding matrix of a local image block feature vector of each voxel in connected regions on the basis of the trained learning dictionary; and classifying each connected area by utilizing the trained linear support vector machine model according to a package feature of each connected area, and deleting the connected areas, in which non-ischemic tissues are located, from a first initially segmented image so asto obtain an optimal segmented image. According to the method and device, automatic recognition and segmentation of super-acute cerebral ischemia areas can be solved, and the ischemia area segmentation precision is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vector-mediated gene regulation in midbrain dopamine neurons
InactiveUS20060153807A1Protection in vitroBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCarrier mediatedMidbrain
The present invention provides compositions and methods for vector mediated gene regulation in neurons. Specifically, the present invention provides therapeutic compositions comprising viral vectors that allow for the over-expression and RNAi mediated knockdown of genes in vivo. The present invention further provides methods for treating or preventing neurodegeneration in a subject, and for protecting neurons from damage in the context of neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, the present invention provides a composition, and use of the composition in improving animal models of neurodegeneration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Memantine For The Treatment Of Mild And Mild To Moderate Alzheimer's Disease
InactiveUS20100048726A1Preventing decrease in glucose metabolismBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseMidbrain
Owner:FOREST LAB HLDG LTD
Skull endosseous module for ultrasound penetration
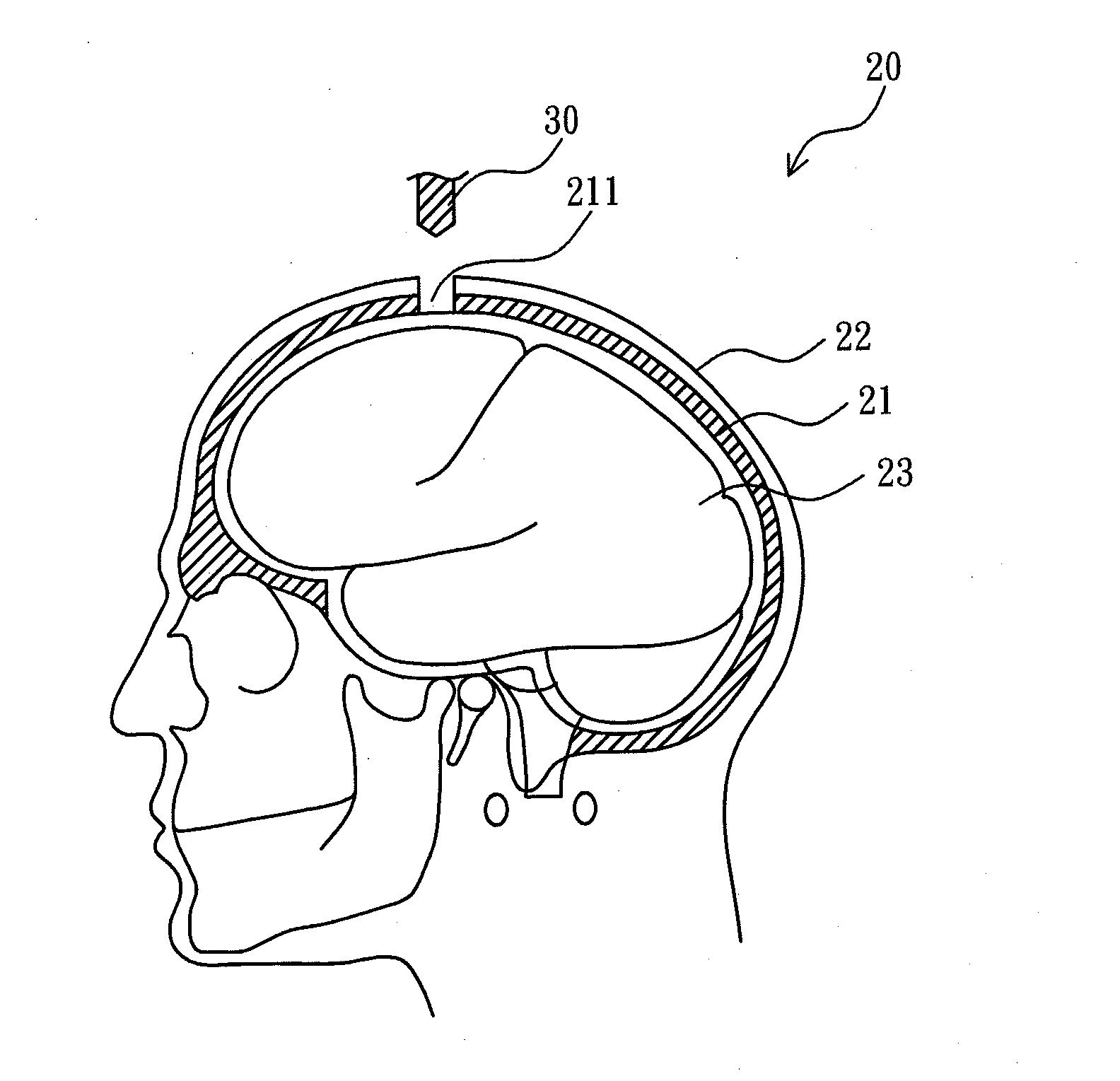
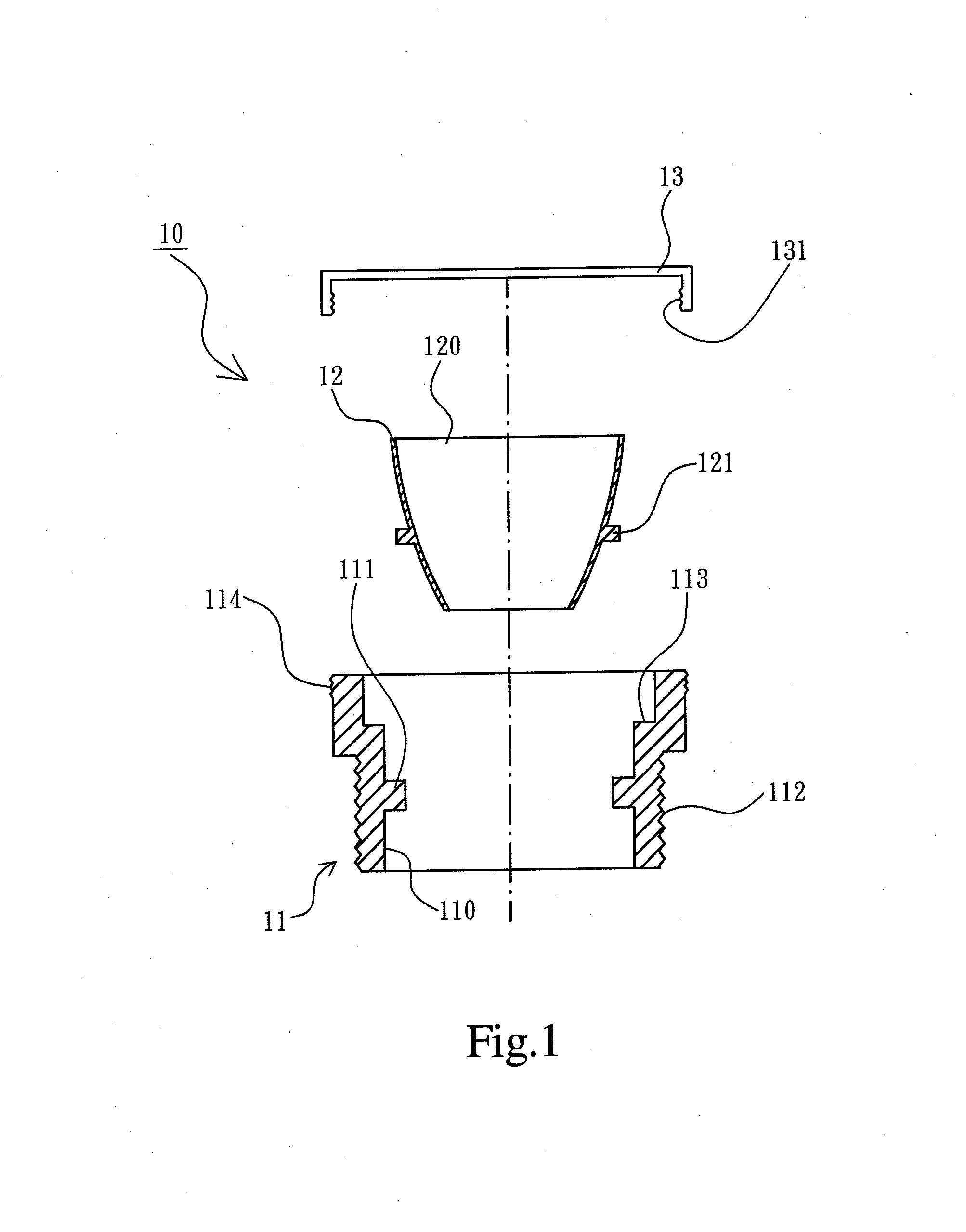
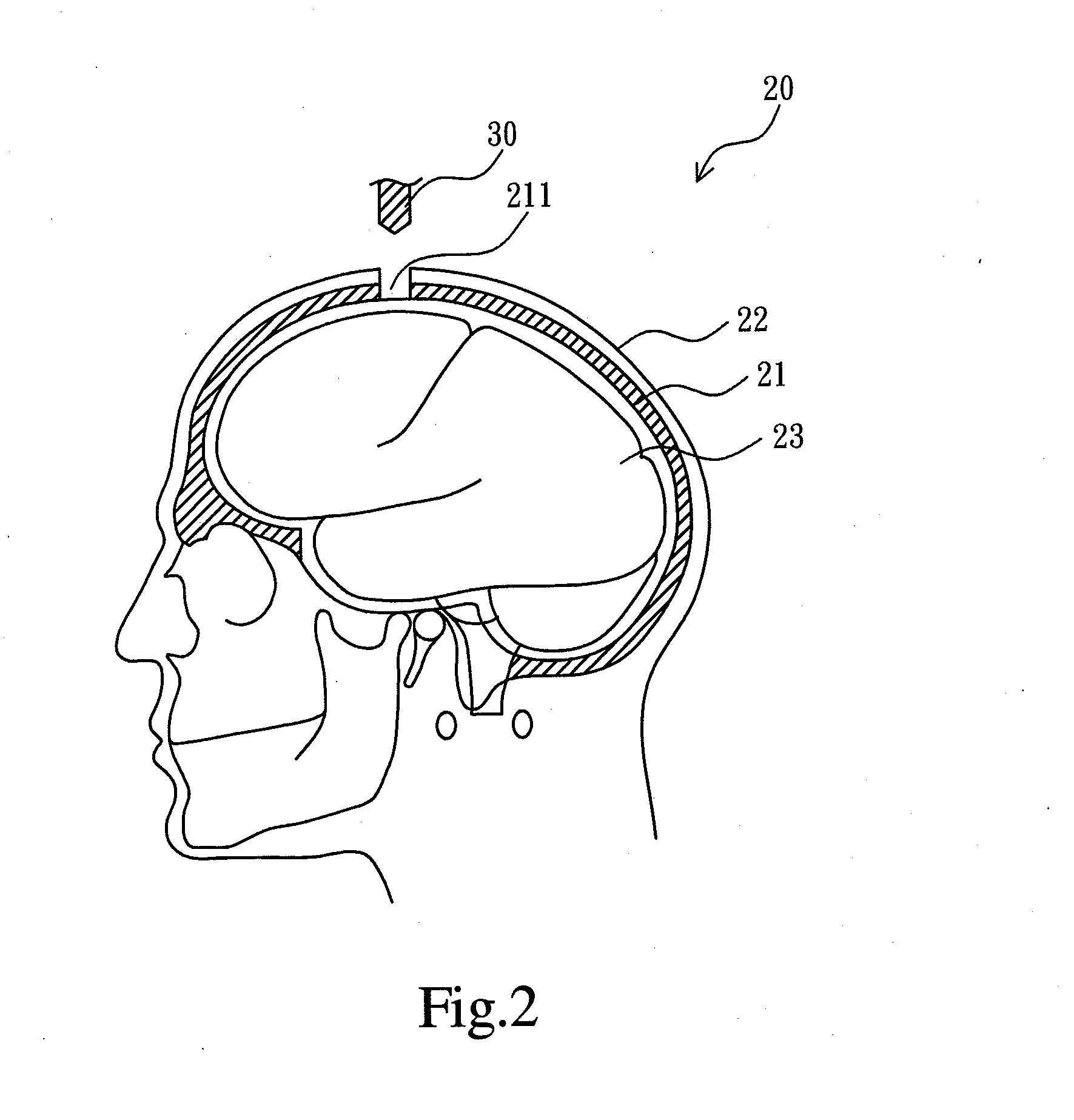
ActiveUS20130345599A1Simple structureImprove convenienceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceMidbrain
A skull endosseous module for ultrasound penetration is provided and includes a fixation sleeve permanently inserted and positioned in a drilled hole of a skull, a movable sleeve movably inserted in the fixation sleeve for providing a hollow ultrasound guiding channel; and an outer cover mounted on an outer opening of the fixation sleeve and covered by a scalp tissue. Thus, an ultrasound device outside the scalp tissue can generate ultrasounds to pass through the outer cover and the ultrasound guiding channel for affecting a target region of a brain tissue in the skull.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Cerebrum functional zone specificity electroencephalogram detecting method based on vector multi-classification
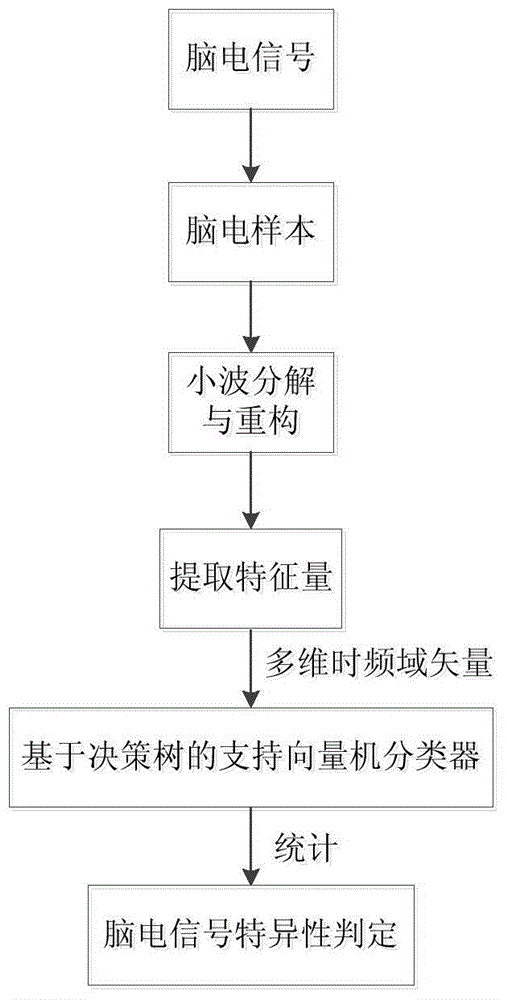
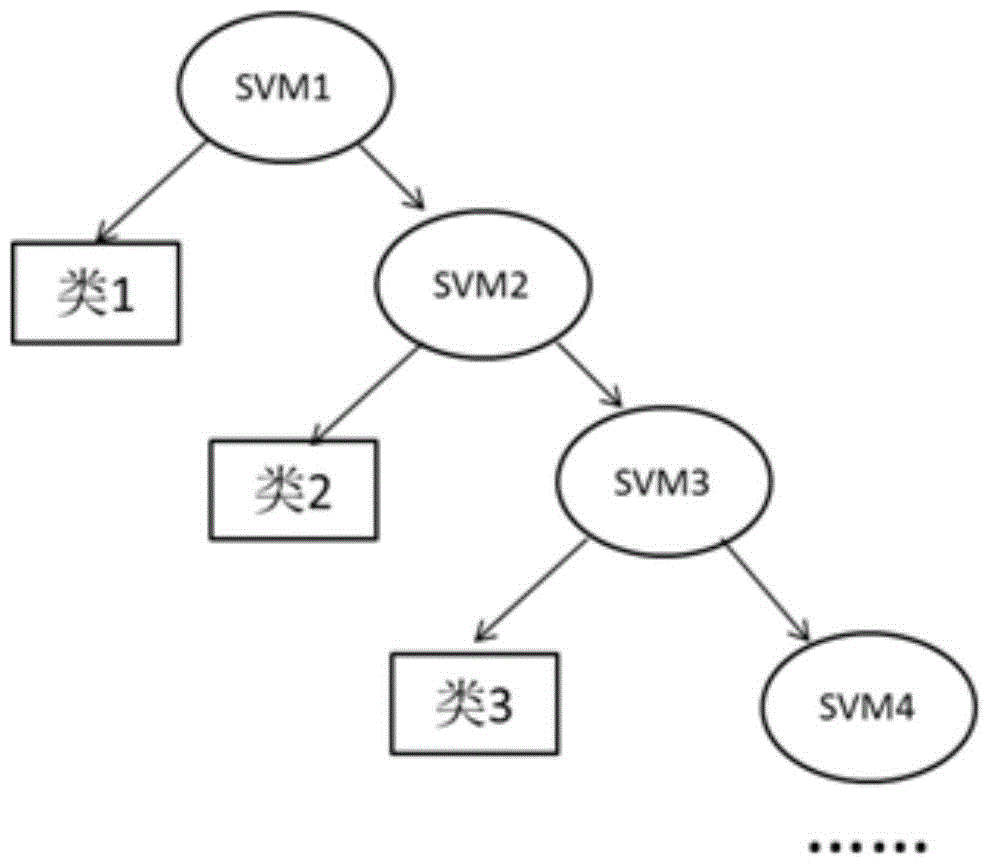
ActiveCN104958072AAccurate identificationImprove detection accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsClassification methodsMulti dimensional
The invention relates to a cerebrum functional zone specificity electroencephalogram detecting method based on vector multi-classification. The cerebrum functional zone specificity electroencephalogram detecting method is characterized by including the following steps: firstly, in the state that a detected person executes or receives a specificity task, electroencephalogram signals are collected; then a vector multi-classification method is adopted, wavelet decomposition is carried out on the electroencephalogram signals, all single sub-frequency-band signals are reconstituted, the energy differences of the single sub-frequency-band signals before and after a task event is executed serve as characteristic quantities, and multi-dimensional time-frequency domain vectors are constructed; and finally, a support vector machine multi-classification algorithm based on a decision-making tree is adopted for classifying the multi-dimensional time-frequency domain vectors, so that the specificities of electrodes when the electroencephalogram signals are led to the electrodes are identified, and cerebral cortex functional zone specificity detection can be completed. By means of the cerebrum functional zone specificity electroencephalogram detecting method, the electroencephalogram specificities of the cerebral cortex functional zone can be scientifically and accurately detected; and the method can be widely applied to studying and clinic application of neurosciences such as intra-operation cerebrum function positioning, cognitive function evaluation and cerebrum-computer interfaces based on electroencephalogram analysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
SiRNA targeting to synaptotagmin-11 (Syt11), expression vector, virions and pharmaceutical applications of SiRNA, expression vector and virions
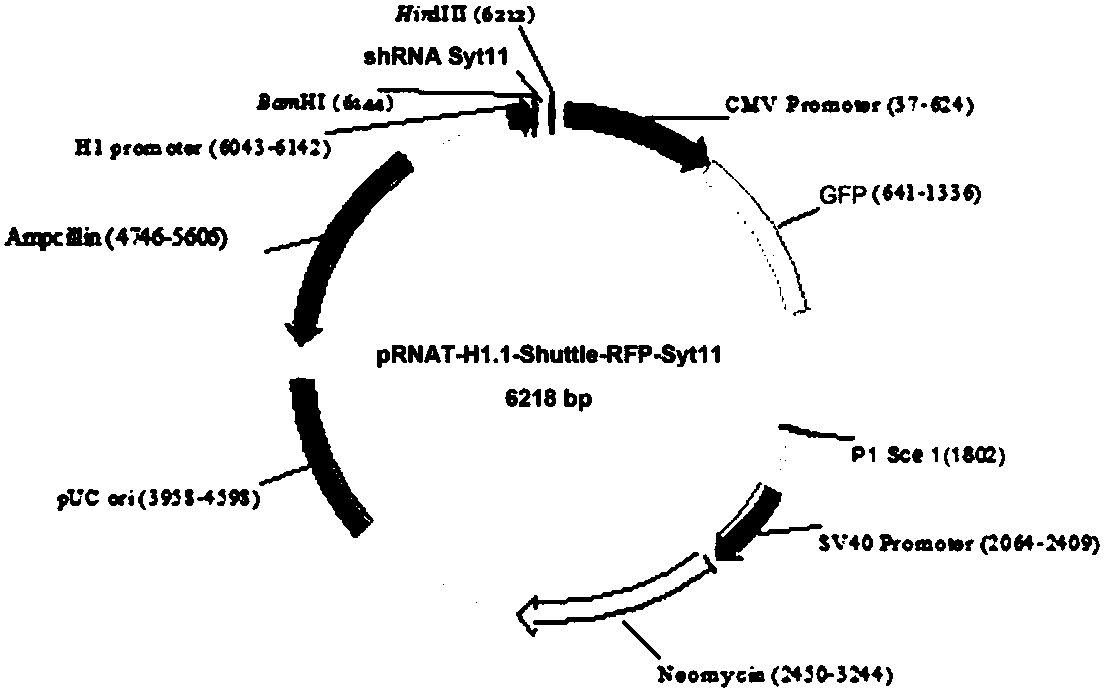
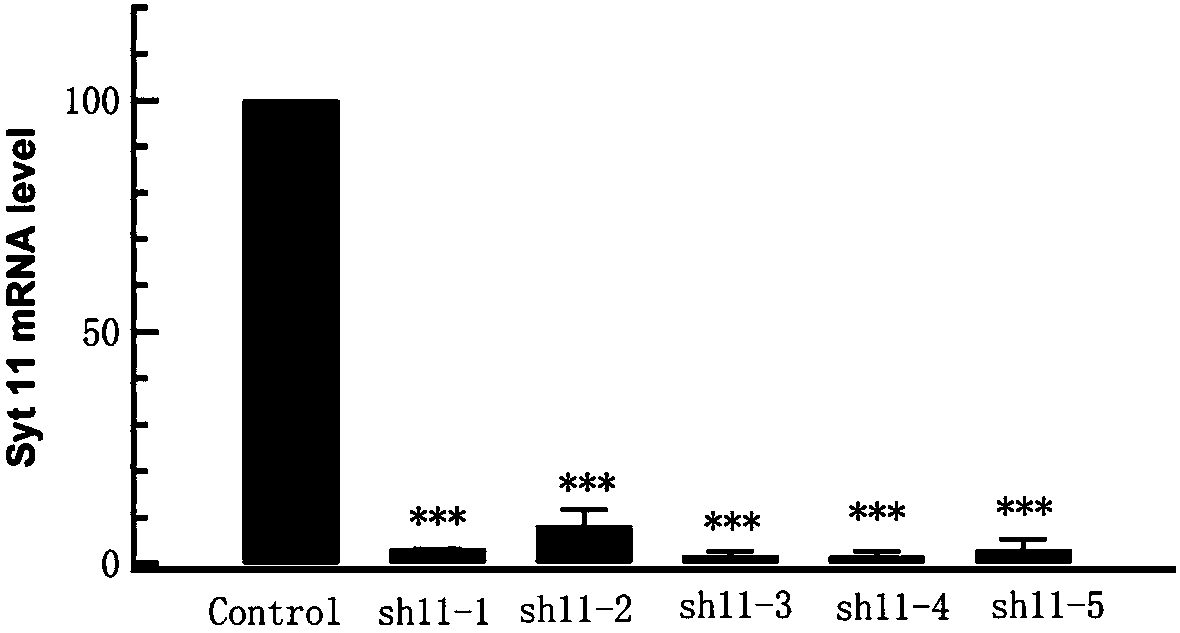
ActiveCN107893078AReverse the pathological processInhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNucleotide
The invention provides siRNA targeting to synaptotagmin-11 (Syt11), an expression vector, virions and pharmaceutical applications of the SiRNA, the expression vector and the virions, belongs to the technical field of biological medicines, and in particular relates to siRNA for inhibiting the gene expression of synaptotagmin-11 (Syt11), a medicinal composition adopting the siRNA as the active ingredient, a recombinant vector expressing the siRNA, an expression virus, and applications of the siRNA, the medicinal composition, the recombinant vector and the expression virus in Parkinson diseases and other diseases relevant to the expression of the Syt 11. According to the technical scheme, aiming at the nucleotide sequence of the synaptotagmin-11 (Syt11) gene, the small interfering RNA is designed and synthesized, the shRNA expression vector and expression virus aiming at the target sequence are constructed, and the siRNA specifically targets to the Syt11 gene in the mRNA level, can effectively inhibit the expression of the Syt11, and is used for treating Parkinson syndrome and other diseases related to the expression of the Syt11. After being transferred into midbrain substantia nigranerve cells, the siRNA can effectively silence the expression of the Syt11 and reverse the pathological process of the Parkinson syndrome.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Application of chlorogenic acid in preparation of medicines for treating parkinson disease
InactiveCN104644624AHas a therapeutic effectSymptoms improvedOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderChlorogenic acidMidbrain
The invention discloses an application of chlorogenic acid in preparation of medicines for treating a parkinson disease. The chlorogenic acid is beneficial to reduction of the toxicity of substantia nigra and striatum neurons and activation of the autophagy activity of substantia nigra and striatum neurons in a midbrain, beneficial to adjustment of blood ketone content of a parkinson disease mice model, and beneficial to inhibition of apoptosis of substantia nigra cells in the parkinson disease mice model, and plays positive improvement and treatment roles in symptoms, pathology and the like of the parkinson disease.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHANG BIO TECH CO LTD
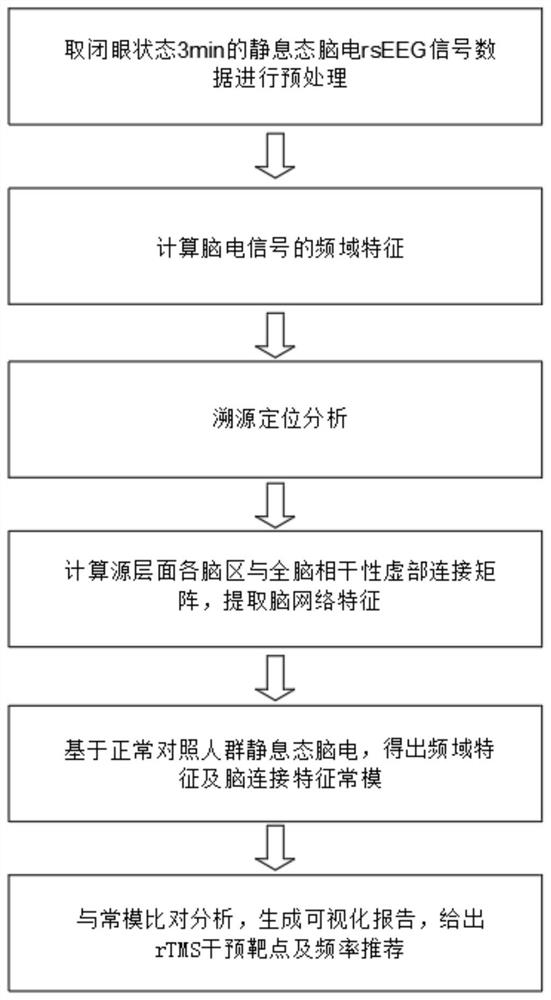
Automatic analysis method and system based on resting-state EEG frequency domain characteristics and brain network
PendingCN113576491AFacilitates automated batch processingImprove work efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNetwork connectionMATLAB
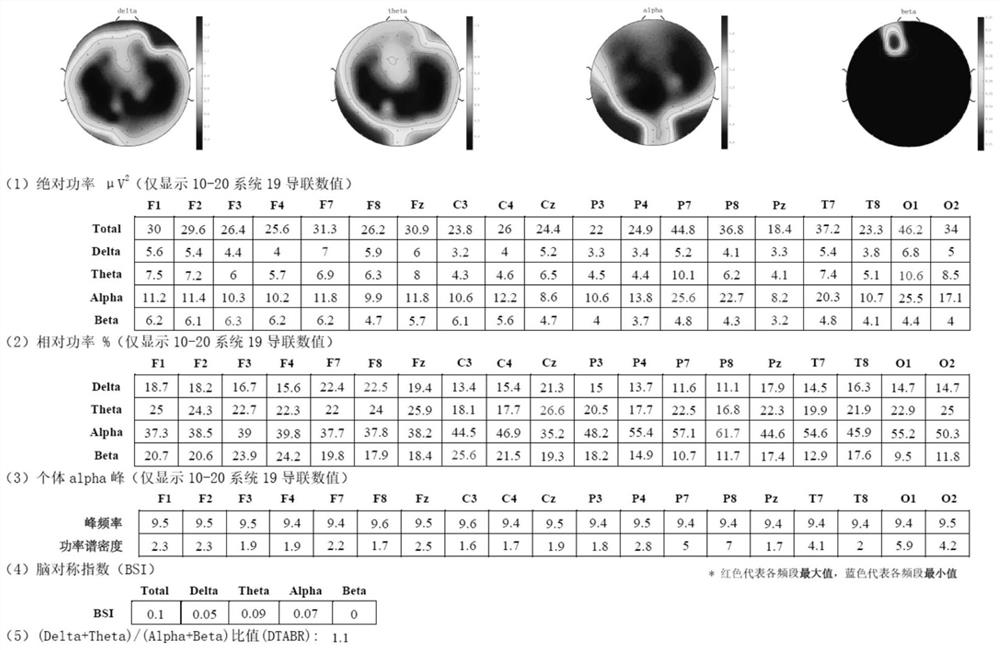
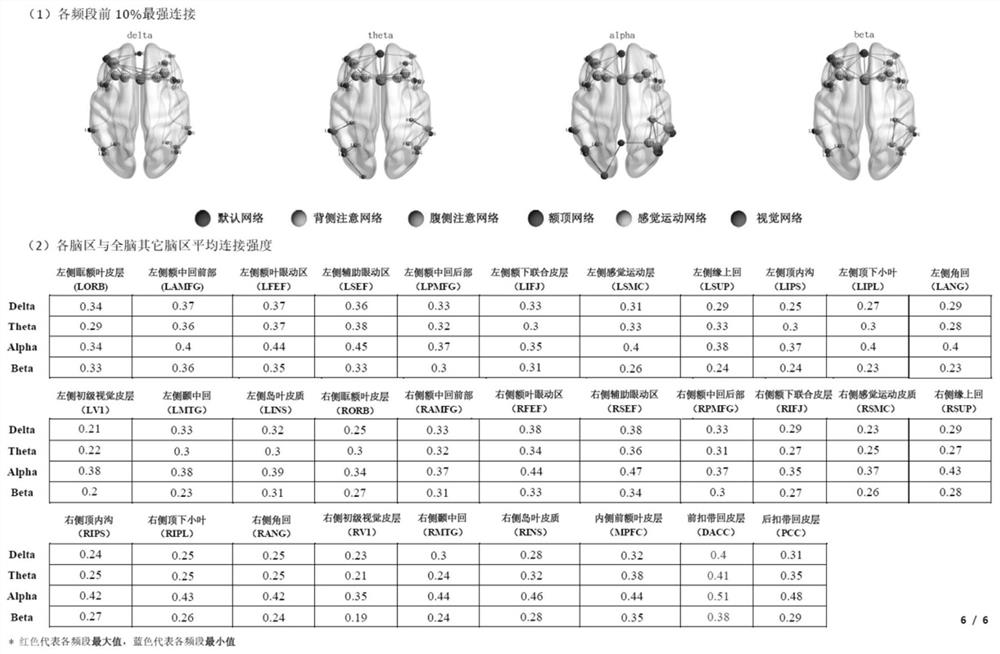
The invention discloses an automatic analysis method and system based on resting-state EEG frequency domain characteristics and a brain network, and the method comprises the steps: calling a Matlab data processing script, carrying out the preprocessing of the resting-state EEG of a patient in an eye-closed state for 3 minutes, calculating the frequency domain characteristics of the EEG, and further calculating and extracting the average brain network connection strength of different brain regions and the whole brain through the traceability positioning analysis. According to the method, the first 10% of strongest connections are visualized, and the two-dimensional electroencephalogram is quickly converted into high-readability digital and image information, so that automatic batch processing of electroencephalogram frequency domain characteristics and brain network analysis in scientific research work is facilitated, the working efficiency is improved, and the labor cost is saved. And on the other hand, the abnormal frequency domain and the brain region of the patient are accurately identified by comparing and identifying with a standardized reference value of a health contrast norm, and a powerful technical means is provided for realizing individualized and precise non-invasive nerve regulation and control.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Regulation of differentiation into dopaminergic neurons by metalloprotease
InactiveUS20160040126A1Reduce expressionReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderProgenitorDisease
The present invention relates to a method for regulating the differentiation of neural stem cells or neural progenitor cells into dopaminergic neural cells, the method comprising increasing or inhibiting the activity of ADAM17 and / or ADAM10 in neural stem cells or neural progenitor cells, and to the use of an activator or inhibitor of ADMA17 and / or ADAM10.The method and composition according to the invention can regulate the activity of ADAM17 and / or ADAM10 in neural stem cells or neural progenitor cells to increase dopaminergic neural cells in the midbrain area, and thereby providing the effect of treating diseases induced by the death of dopaminergic neural cells such as Parkinson's disease. In addition, the method and composition according to the invention can inhibit the activity of ADAM17 and / or ADAM10, and thereby improving effect of treating diseases such as tumor. Thus, the present invention is very useful.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
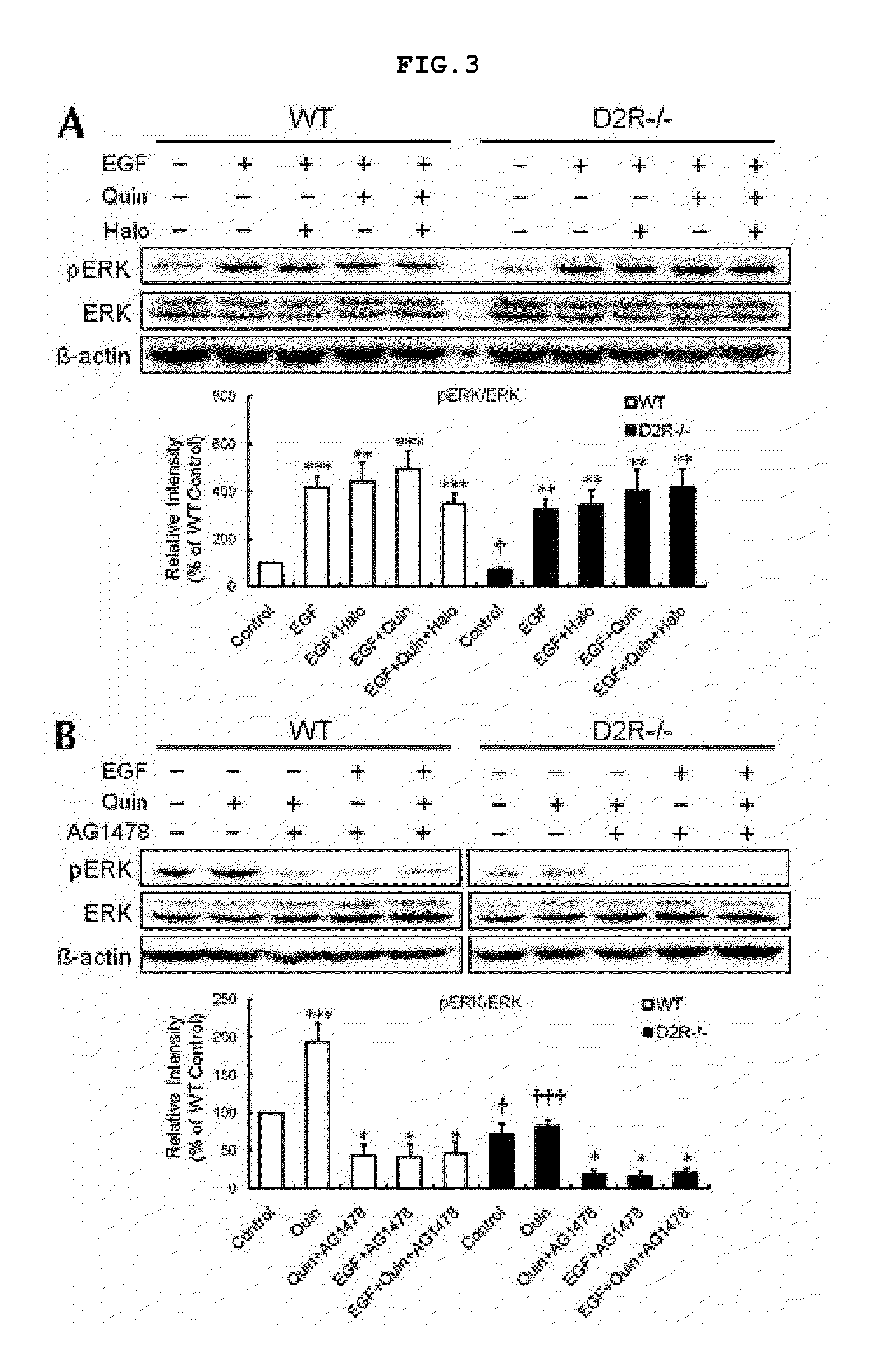
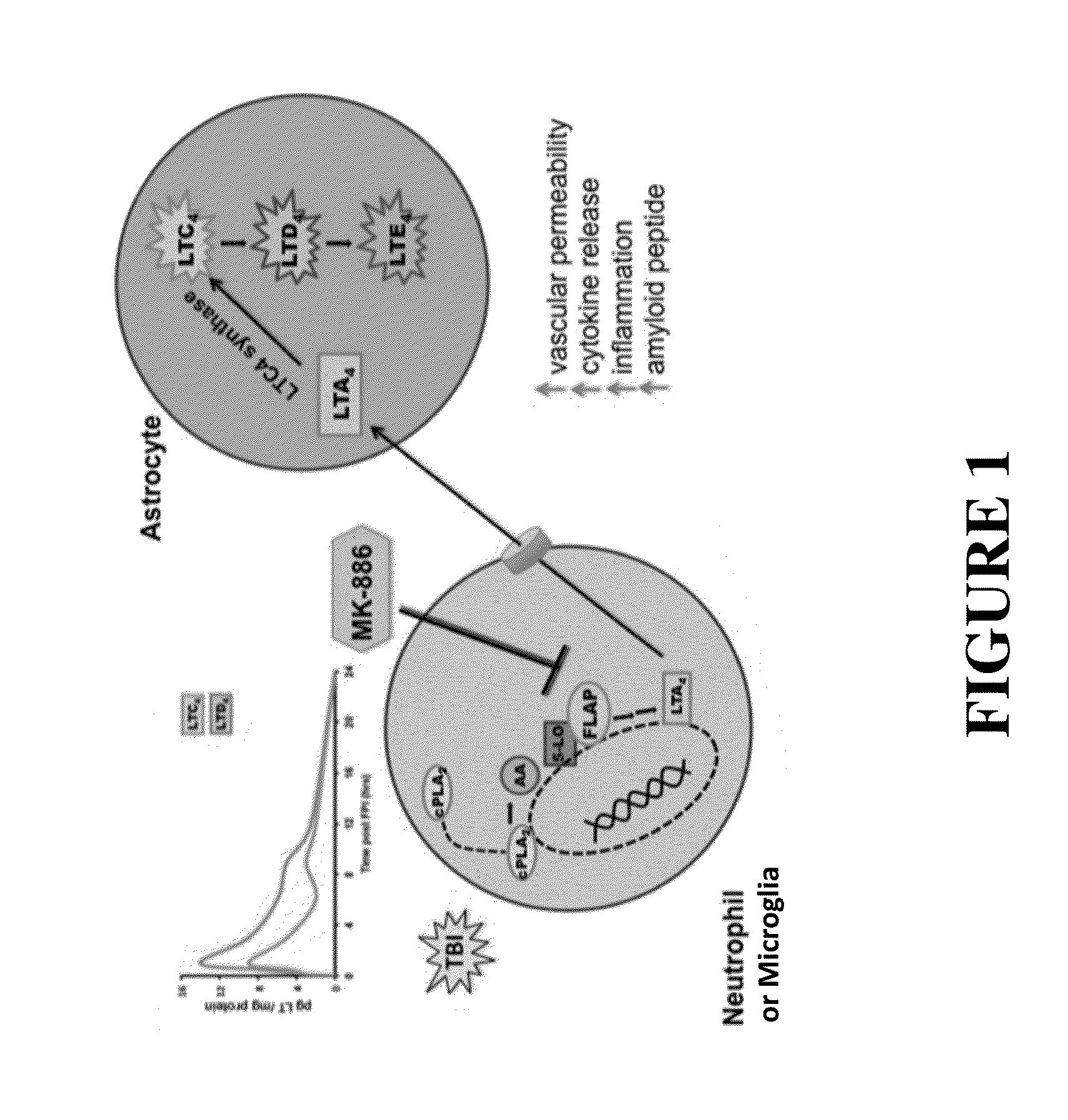
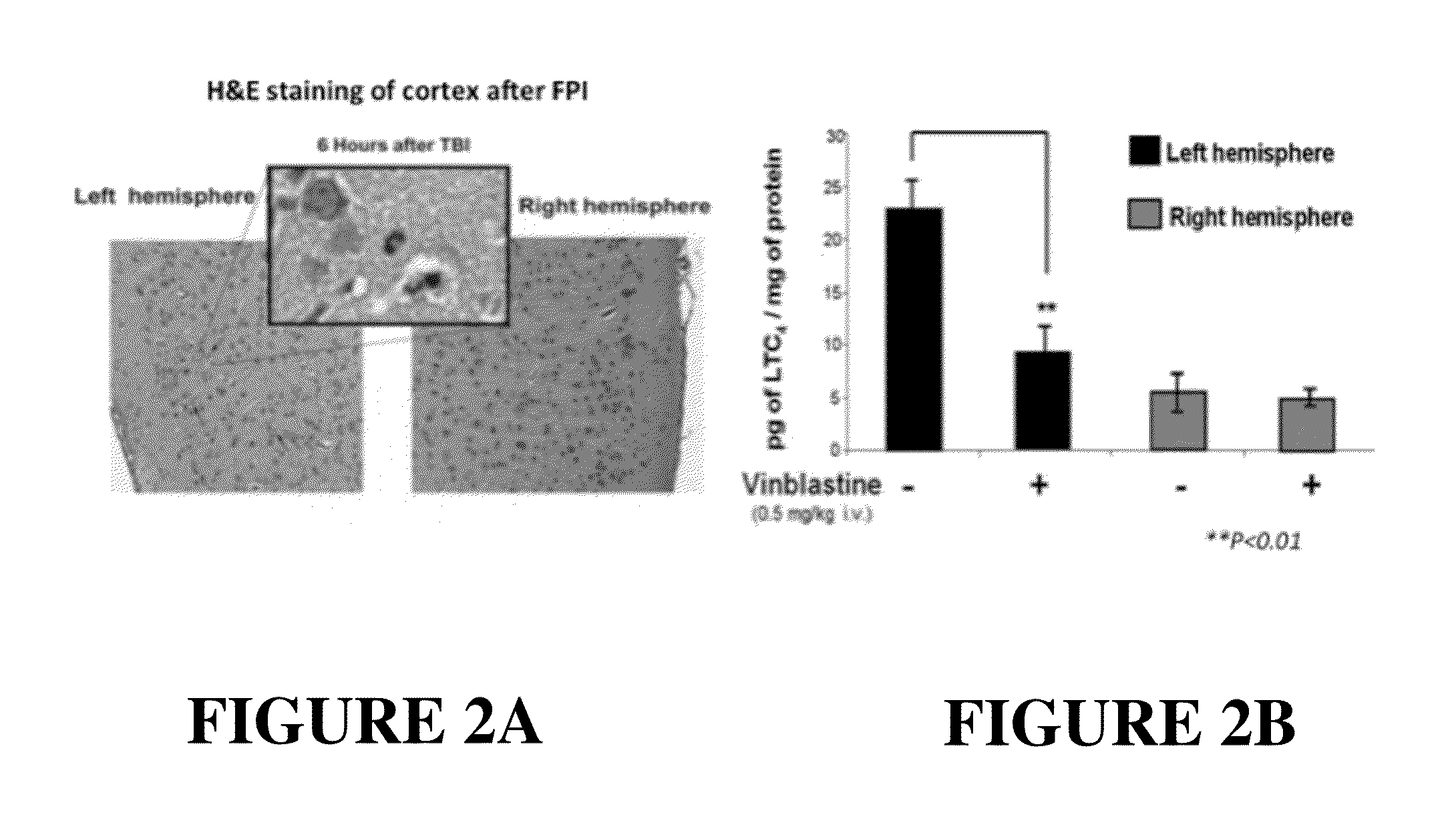
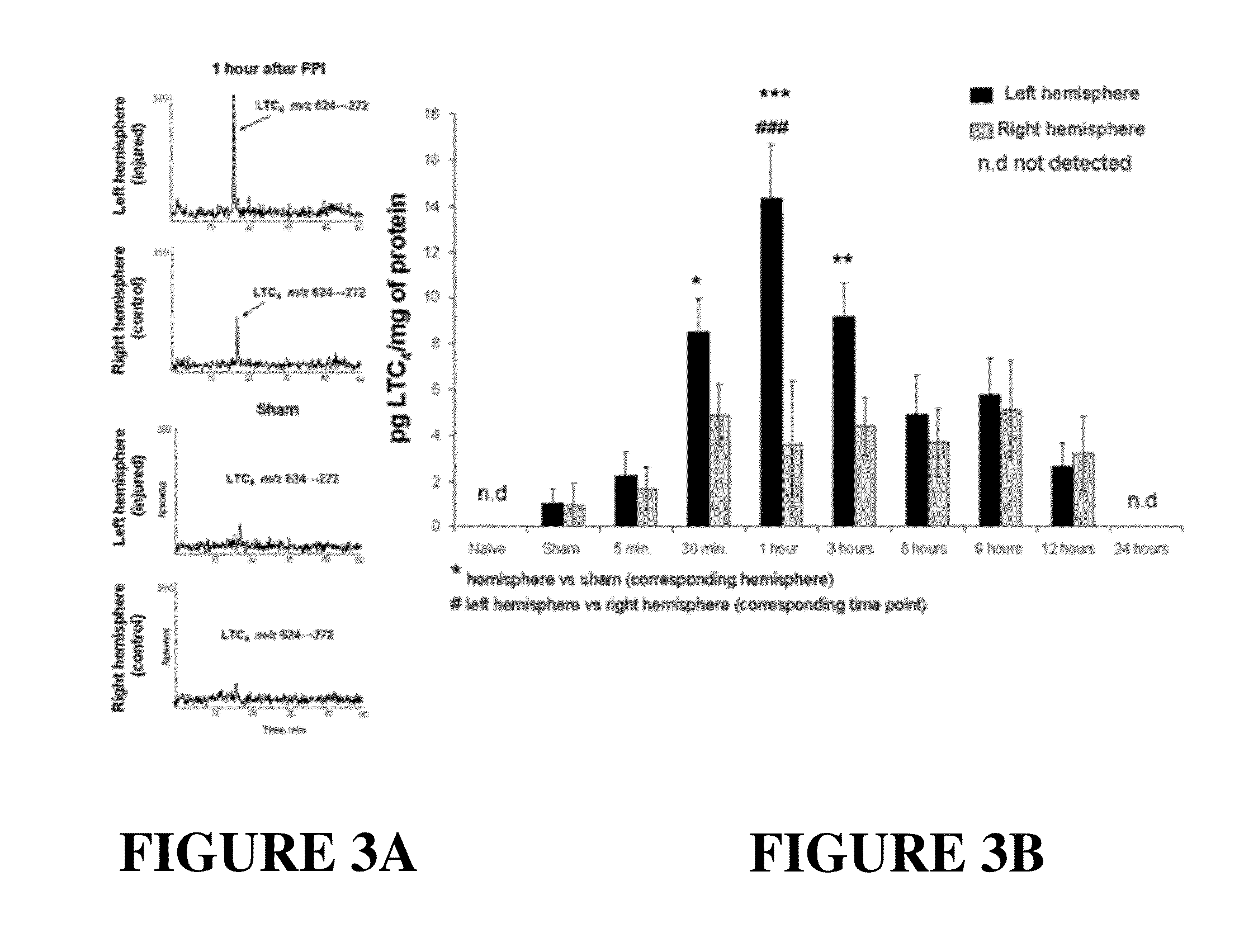
Use Of Flap Inhibitors To Reduce Neuroinflammation Mediated Injury In The Central Nervous System
The present invention provides methods of attenuating or preventing brain injury mediated damage in the central nervous system by attenuating or preventing leukotriene-mediated events following a brain injury or long-term neuroinflammation after brain injury, in Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and post-traumatic stress disorder. The methods comprise administering at least one 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) inhibitor either before or after the brain injury. The method finds use in the treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, post-traumatic stress disorder and other brain injuries associated with production of leukotrienes in the central nervous system. Preferably the FLAP inhibitor is administered intranasally and preferably for certain high risk individuals prophylactically prior to any potential brain injury event.
Owner:BIOSCI PHARMA PARTNERS
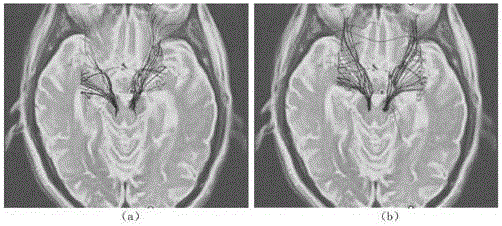
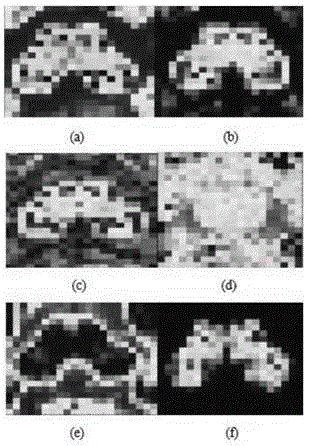
Comprehensive analytical method for predicting early-stage Parkinson's disease
A comprehensive analytical method for predicting early-stage Parkinson's disease comprises the following steps: S1, reading diffusion weighted magnetic resonance data DW-MRI, carrying out noise reduction and pre-smoothing processing on all the data, carrying out modeling and imaging and fiber tracking by applying diffusion tensor imaging and high angular resolution diffusion imaging technologies to acquire voxel fiber direction information, and calculating six types of brain fiber variation analysis index data; S2, extracting and marking special brain region voxel information, selecting a continuous region as a midbrain substantia nigra region by virtue of setting a threshold value of an anisotropic fraction, and then screening and extracting the index data in interested regions; and S3, carrying out comprehensive analysis by applying a SPSS analytical tool according to the six types of brain fiber variation analysis index data obtained by the step S2 to obtain a fiber variation result on the midbrain substantia nigra regions of a testee and a normal person so as to predict the sickness status of the testee. The method provided by the invention is high in resolution and accurate and reliable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
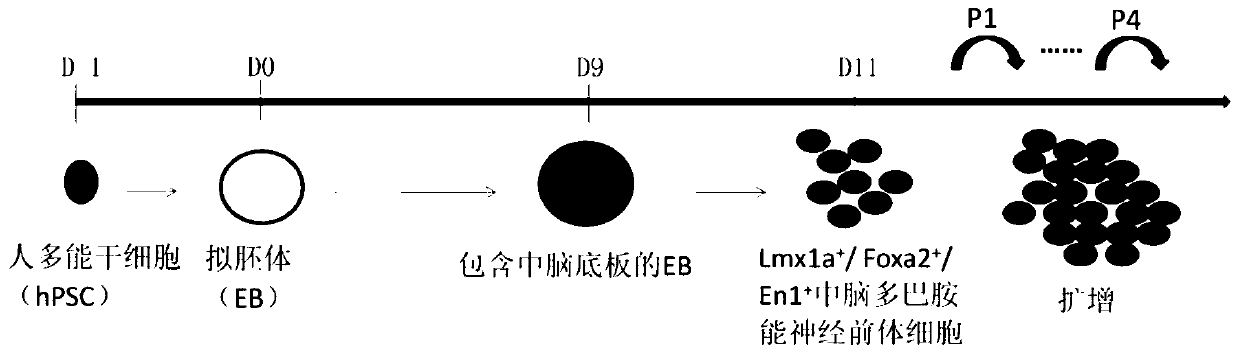
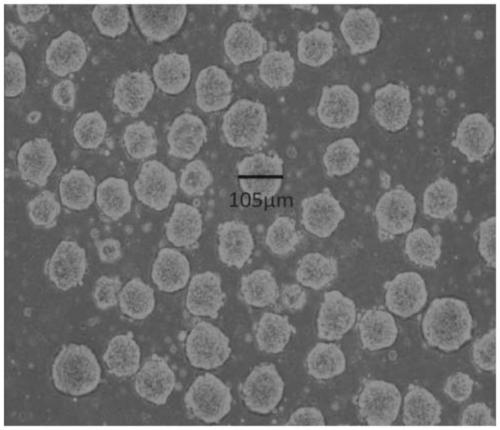
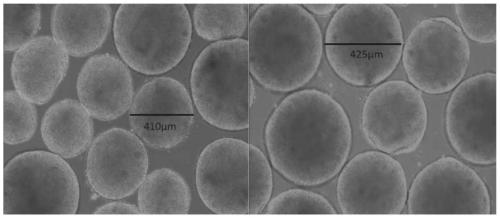
Midbrain dopaminergic nerve precursor cells and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109880800AFunctionalClinical majorNervous disorderNervous system cellsClinical gradeMidbrain
The invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular to midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cell expresses Lmx1a+, Foxa2+, En1+ and Otx2+, wherein the midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cell does not express one or more of Nkx2.1, DBX1 and GBX2. The method for preparing the mesencephalic dopaminergic neural precursor cell comprises the following steps: embryoid bodies are formed, midbrain floor cells are obtained, and midbrain dopaminergic neural precursor cells are obtained. By adopting the preparation method, the mesencephalic dopaminergic nerve cells can be rapidly and efficiently differentiated from the human pluripotent stem cells, and the problems are solved that an existing differentiation method is long in time, unstable in effect and low in efficiency, the culture system containing serum or the trophoblast cells are not conducive to the production of subsequent clinical-grade cell preparations and the like.
Owner:安徽中盛溯源生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com