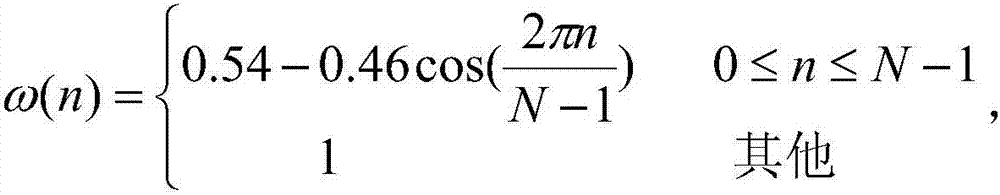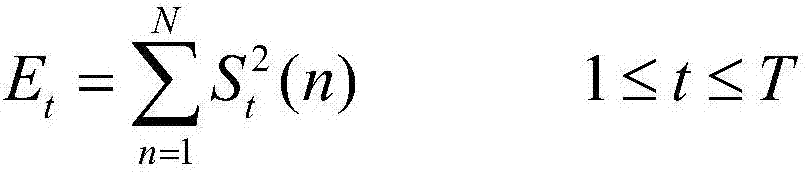Patents
Literature
75 results about "Vocal folds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
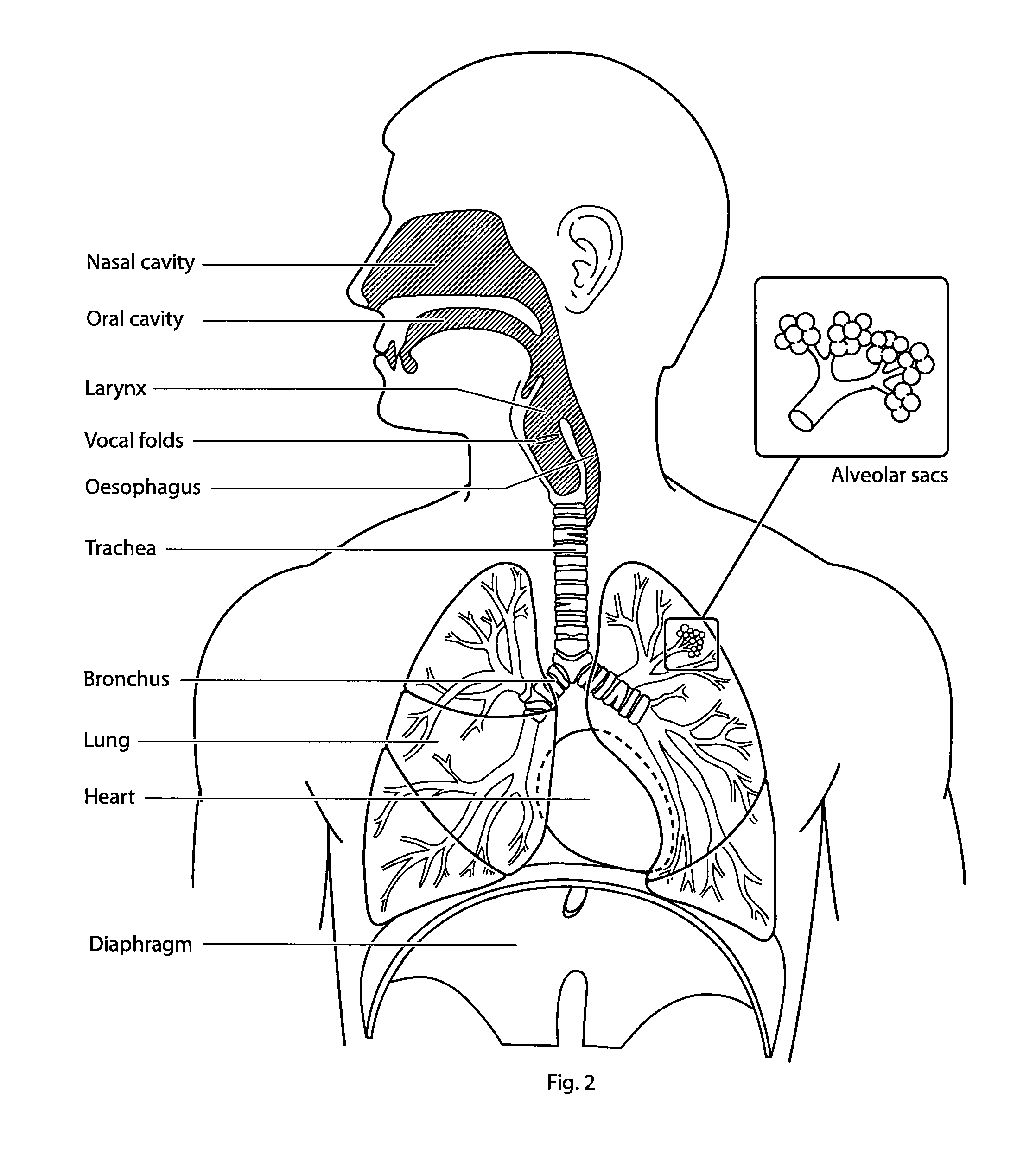
The vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of tissue in the throat that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve.
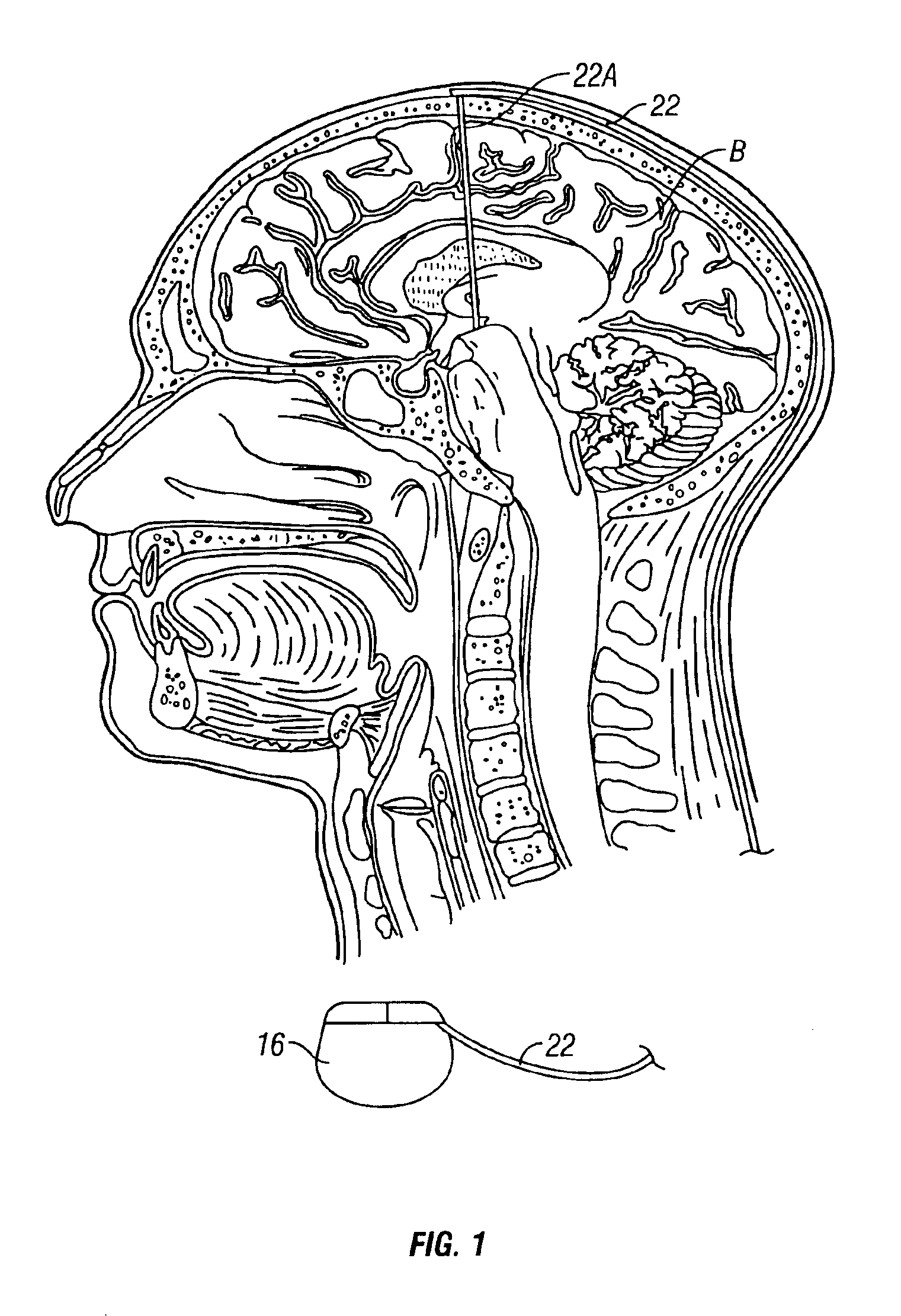
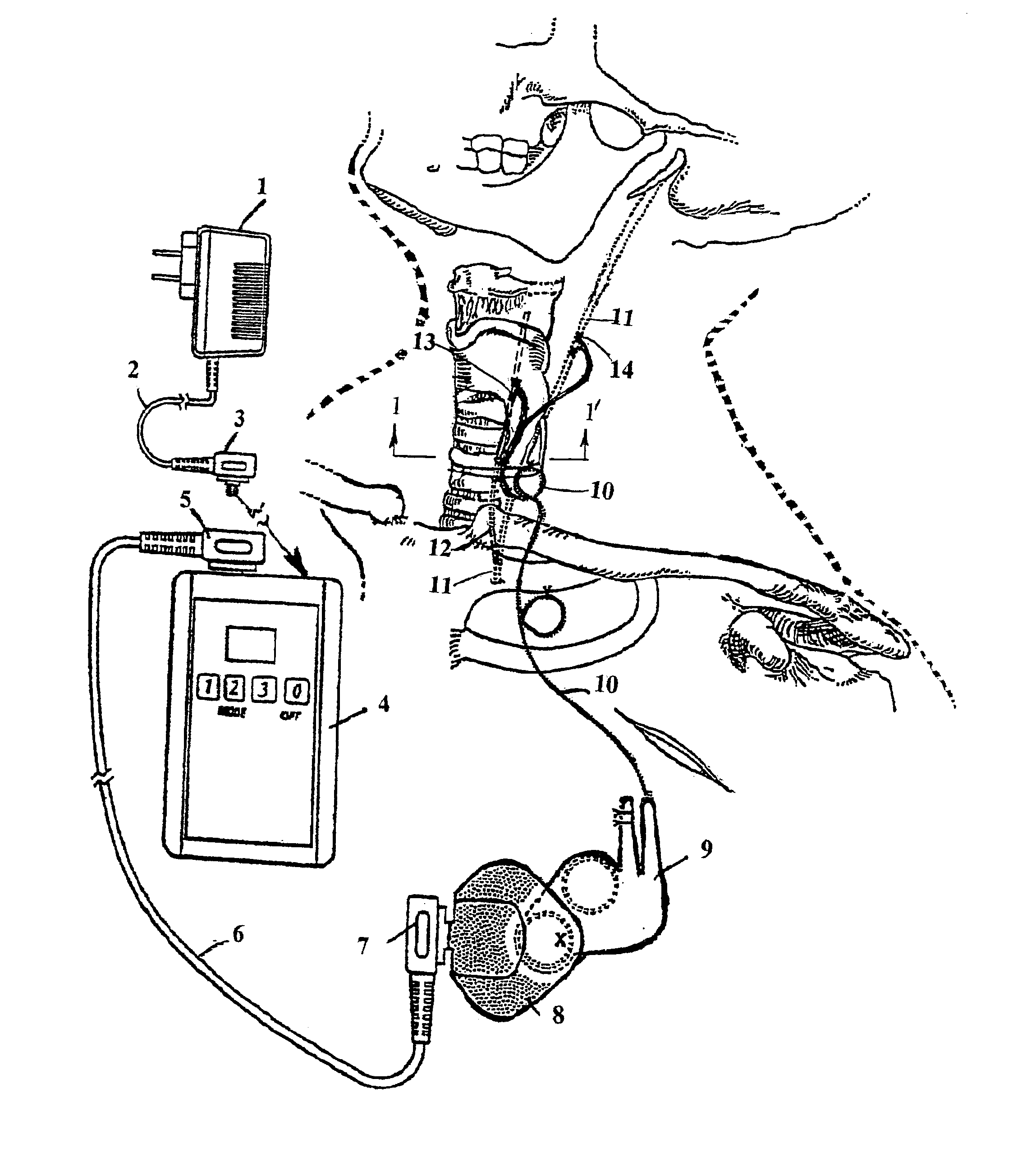
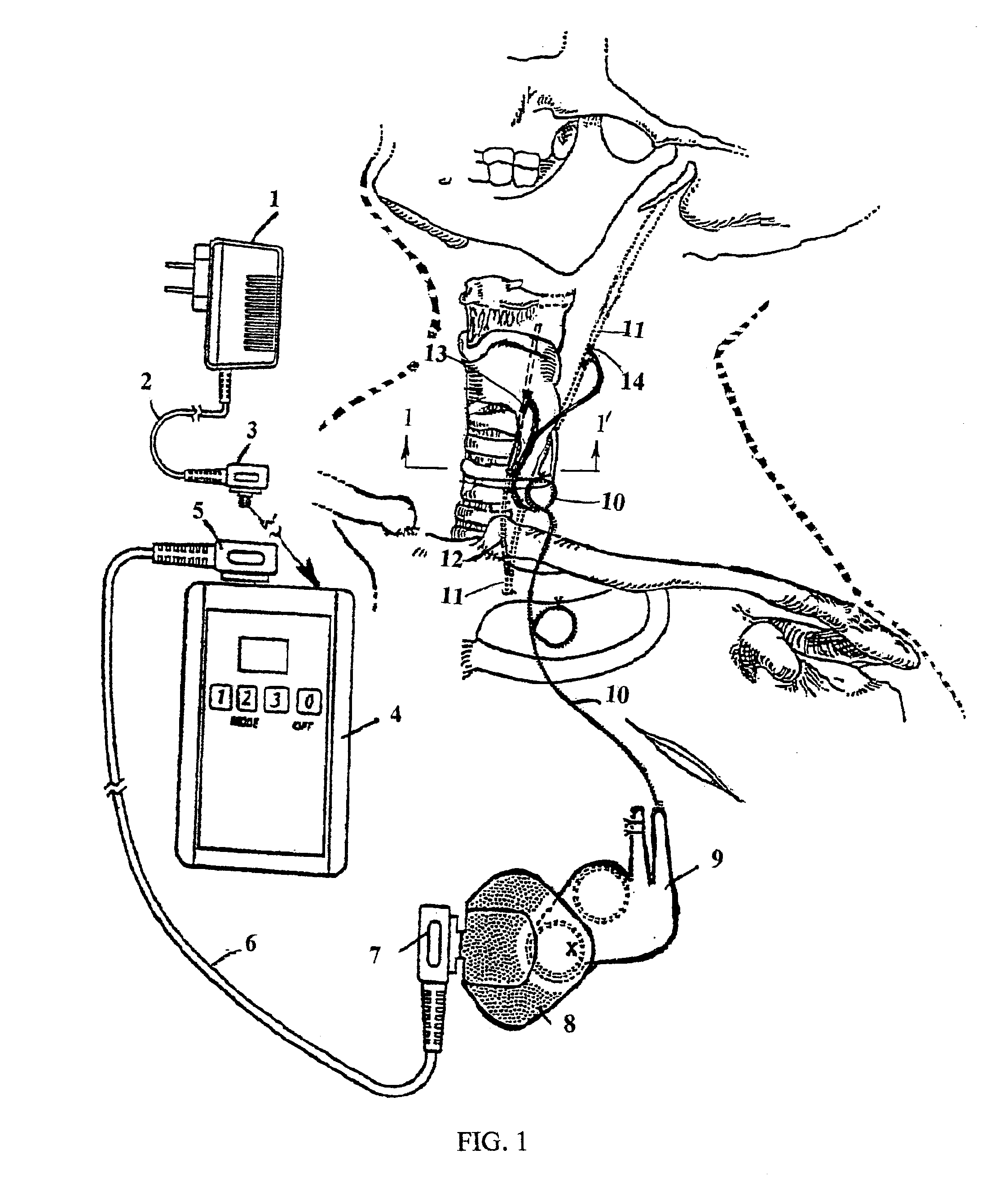
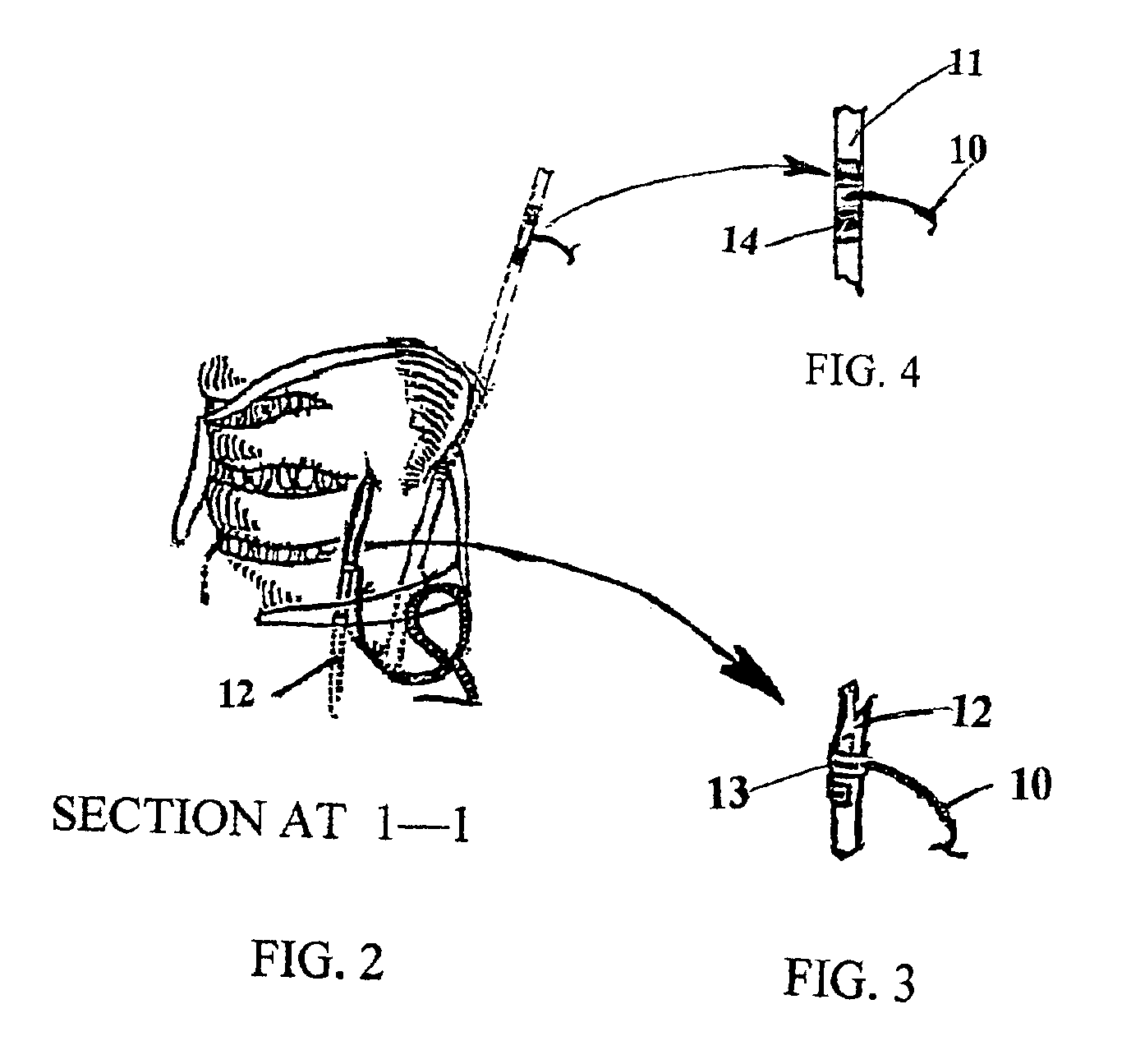
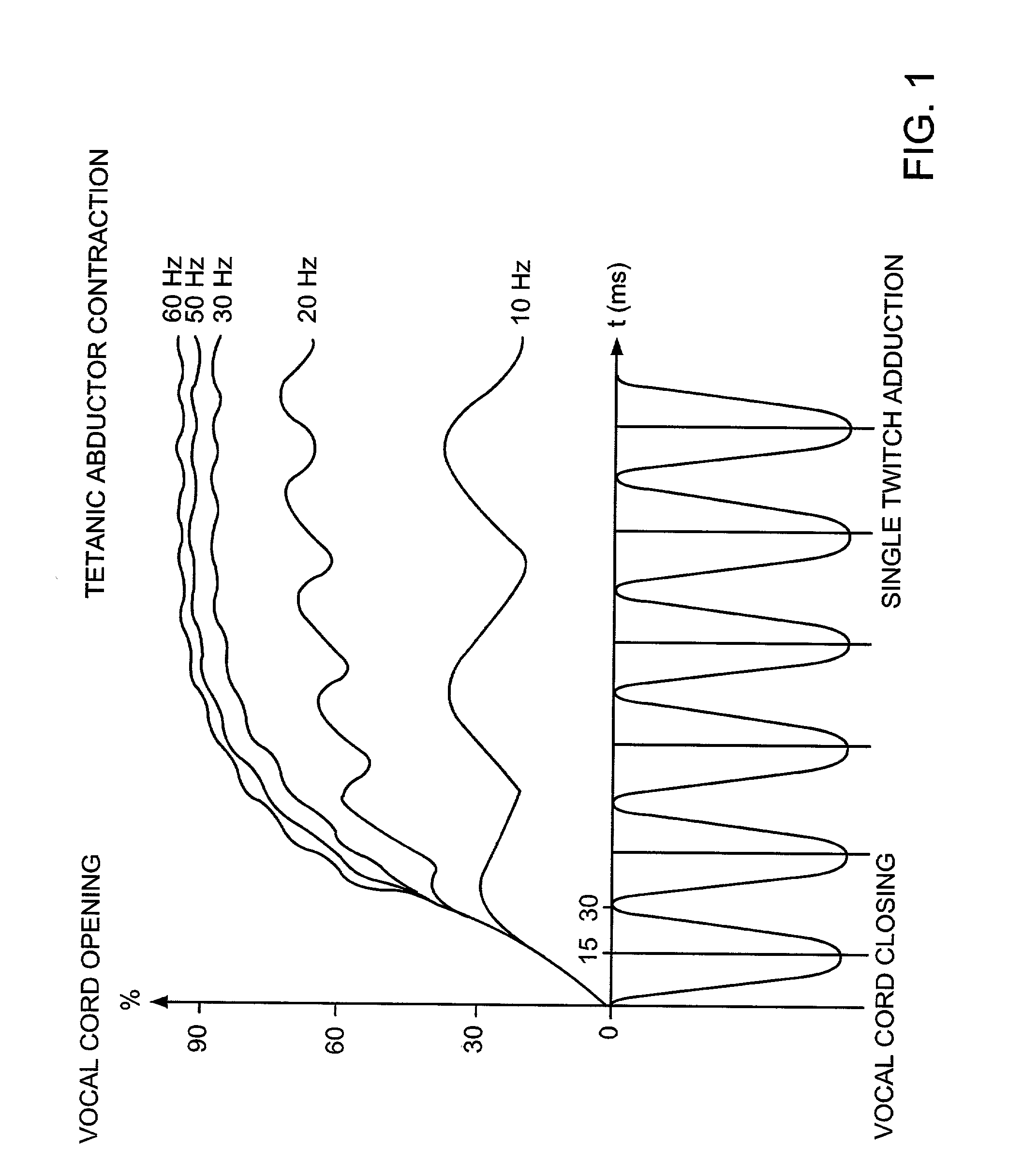
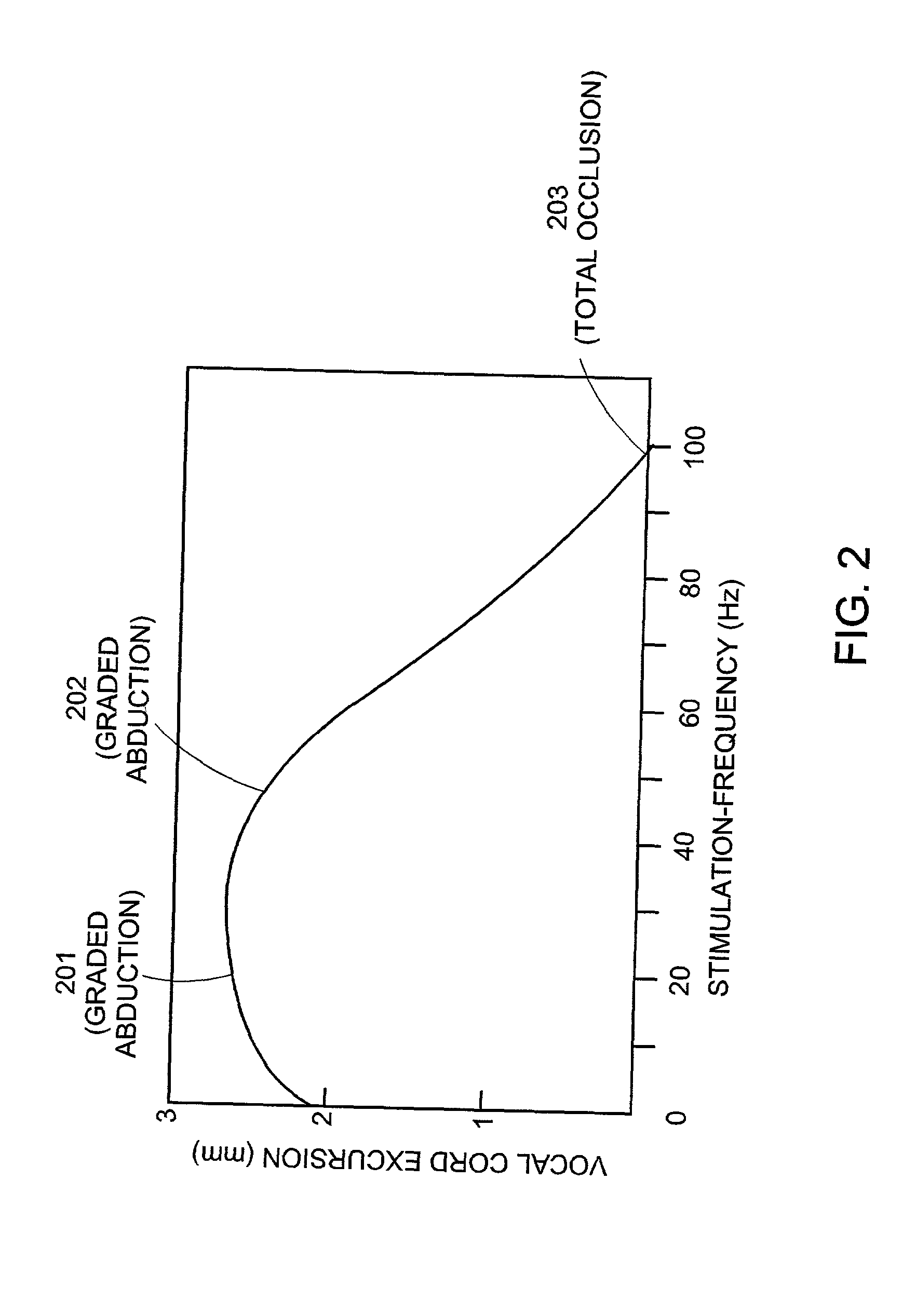
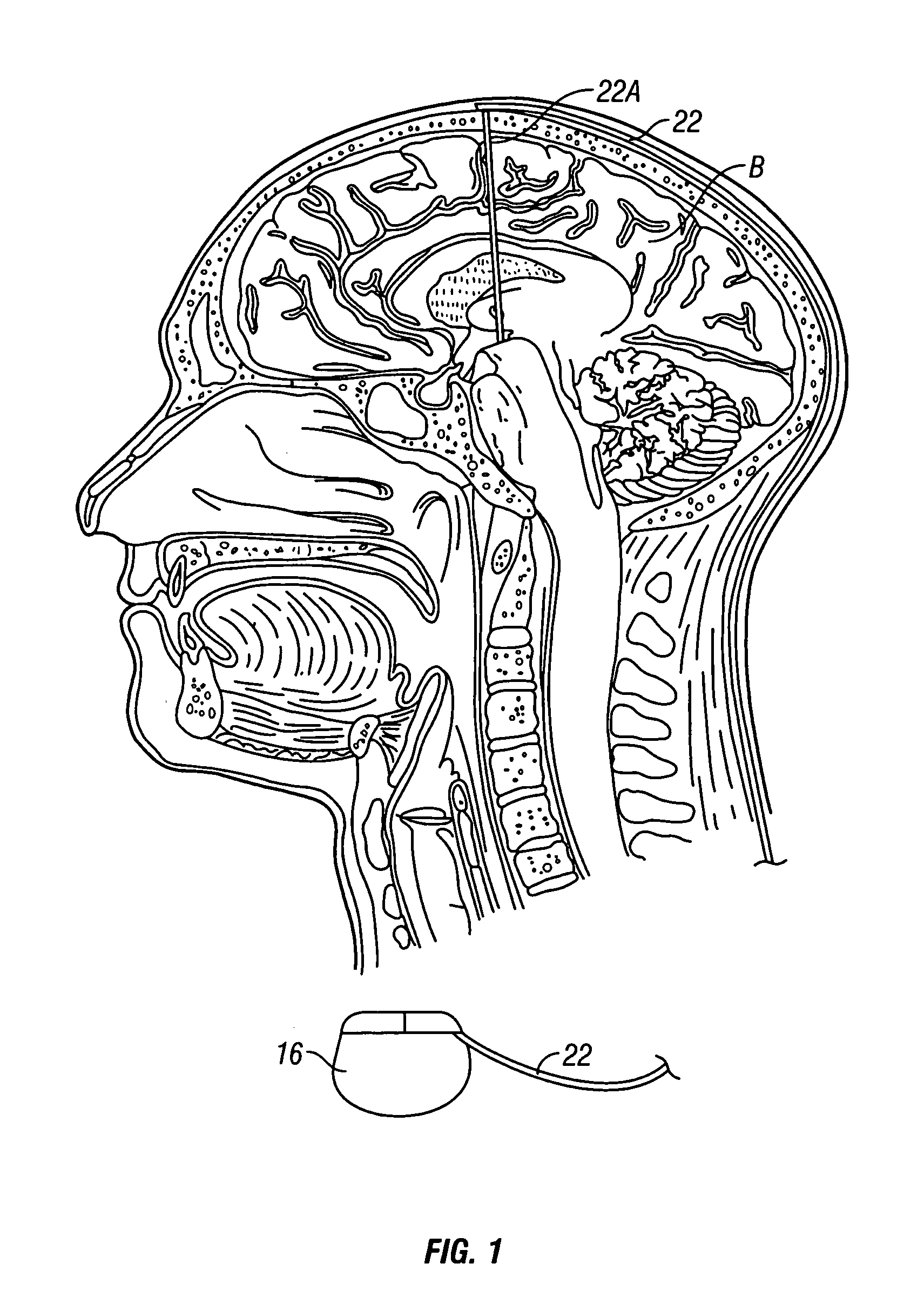
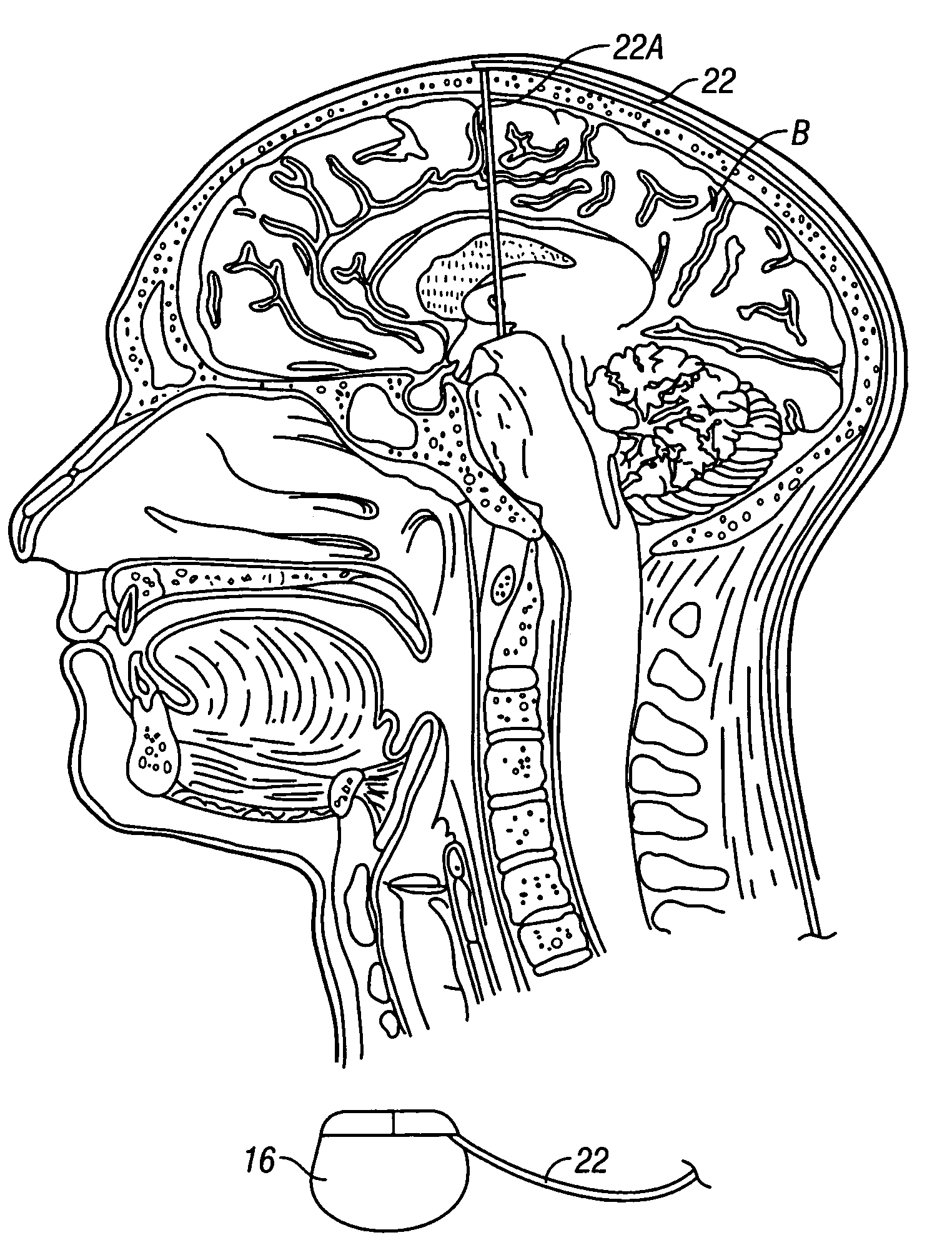
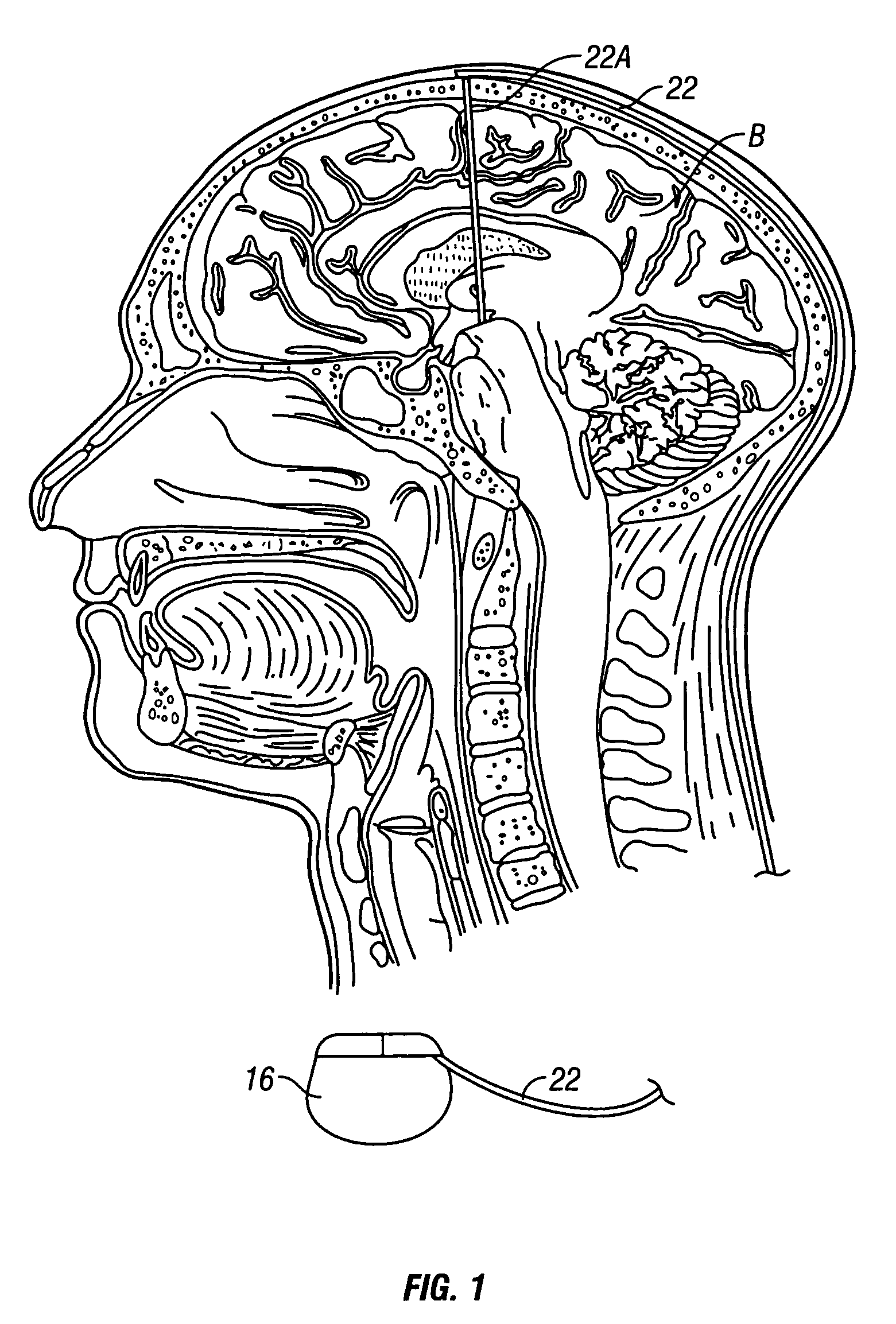
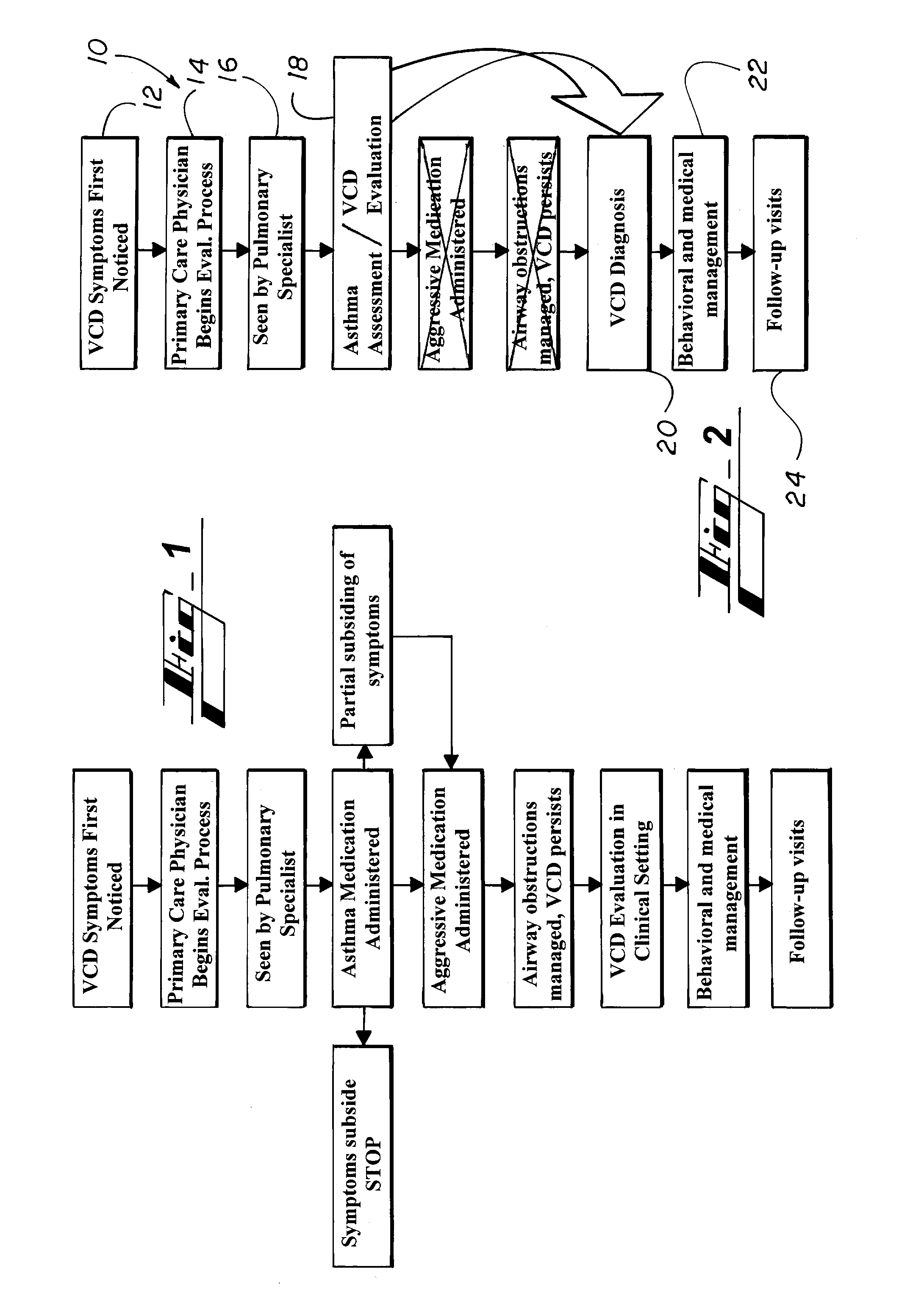
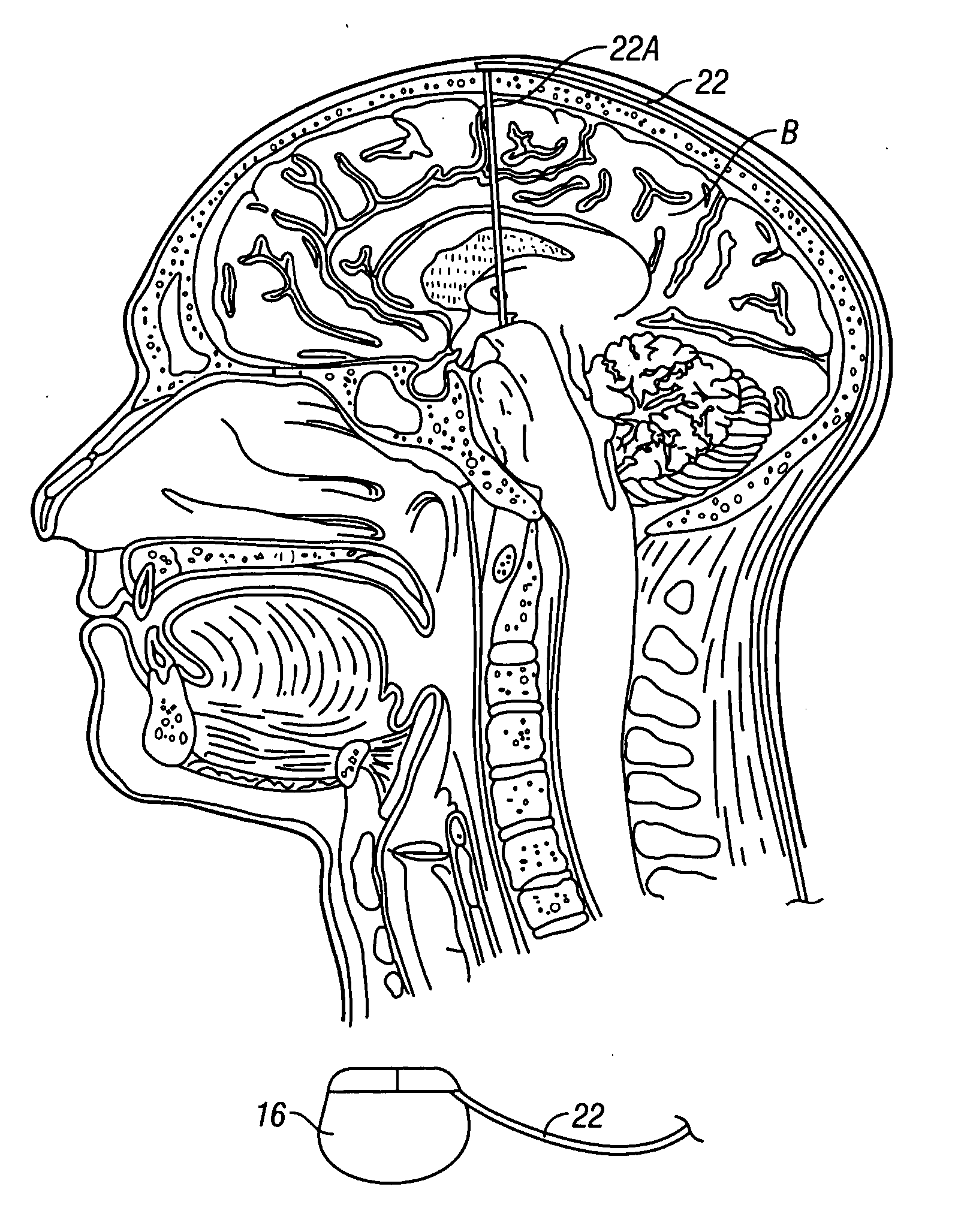
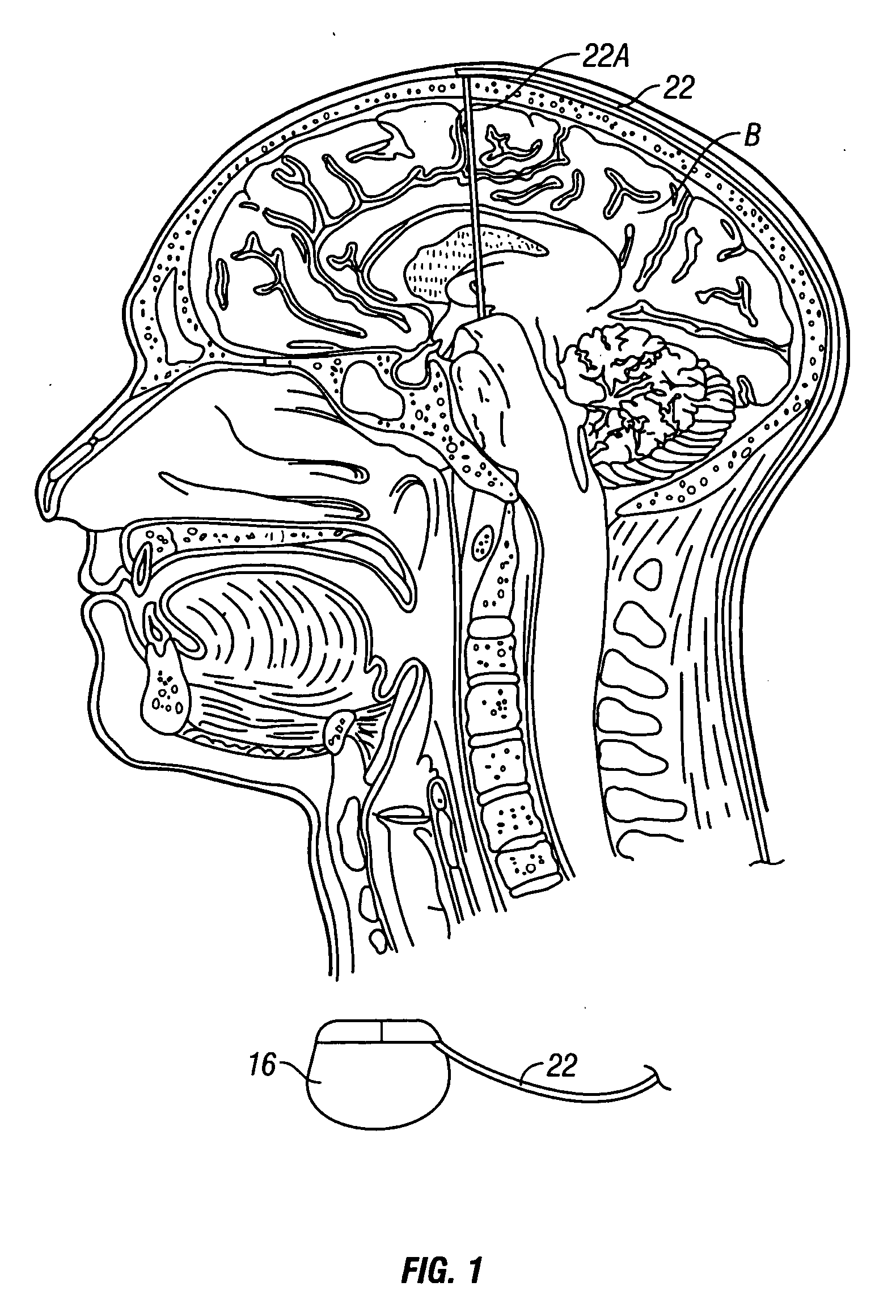
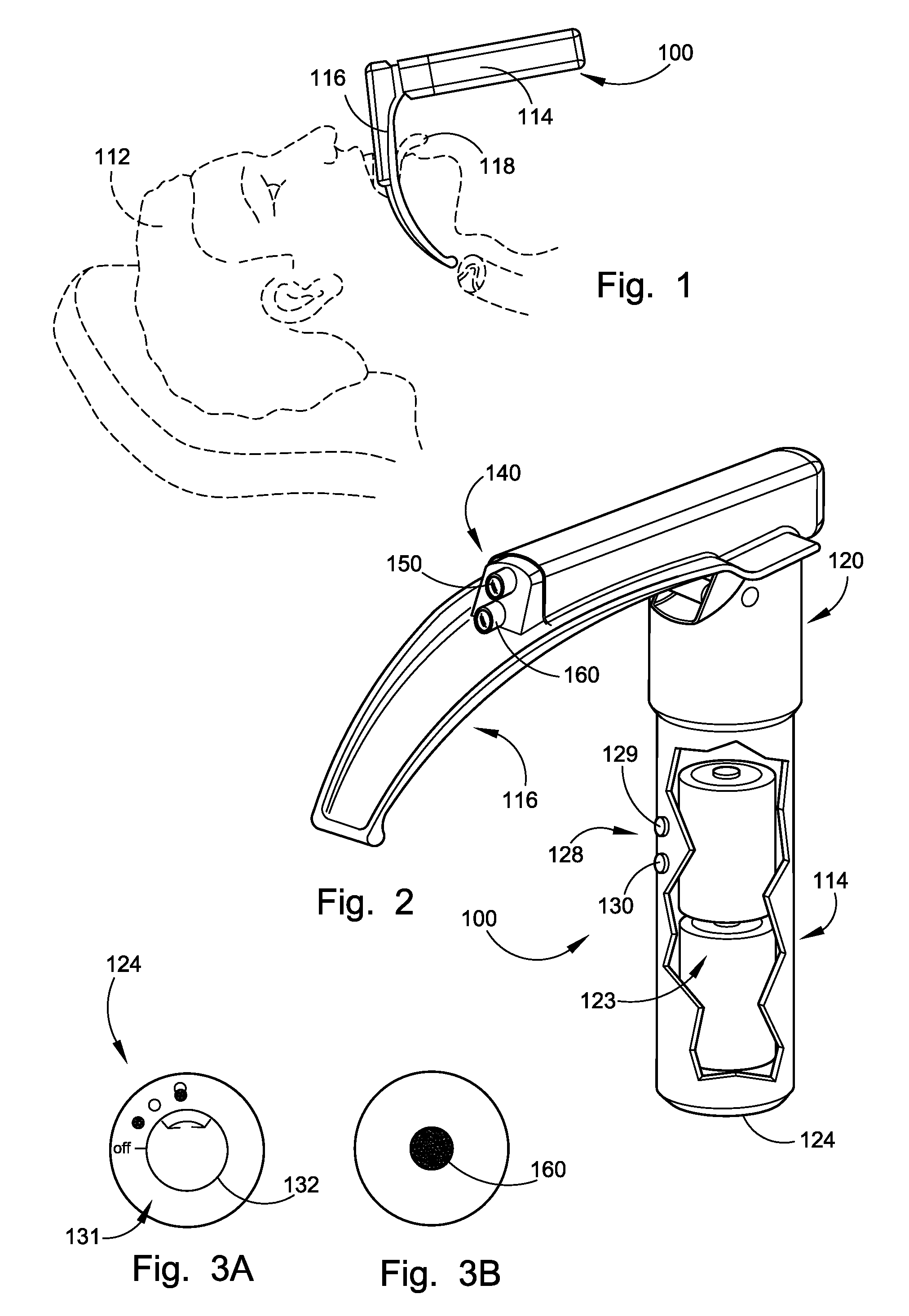
Cranial nerve stimulation to treat a vocal cord disorder
Disclosed is a method of treating a patient having a vocal cord disorder, comprising coupling at least one electrode to at least one cranial nerve of the patient, wherein the cranial nerve is selected from the group consisting of a vagus nerve, a trigeminal nerve, and a glossopharyngeal nerve, and applying an electrical signal to the cranial nerve using the electrode to treat the vocal cord disorder. The electrode may be coupled to a branch of the vagus nerve selected from the group consisting of a recurrent laryngeal nerve, the external branch of a superior laryngeal nerve, the internal branch of a superior laryngeal nerve, and a pharyngeal plexus. Also disclosed is a computer readable program storage device encoded with instructions that, when executed by a computer, perform the method, and a medical device and a vocal cord disorder treatment system that may be used in performance of the method.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
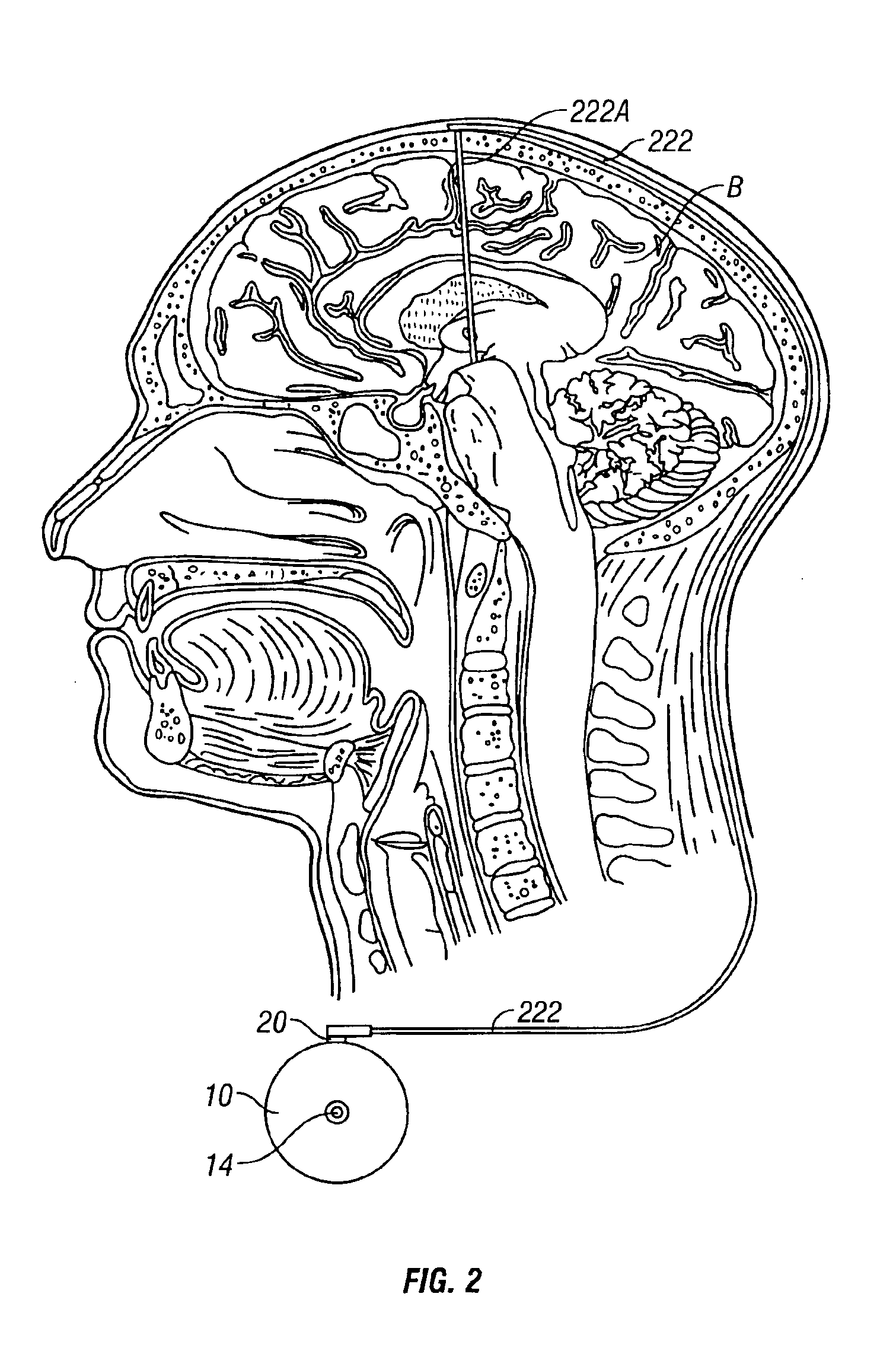
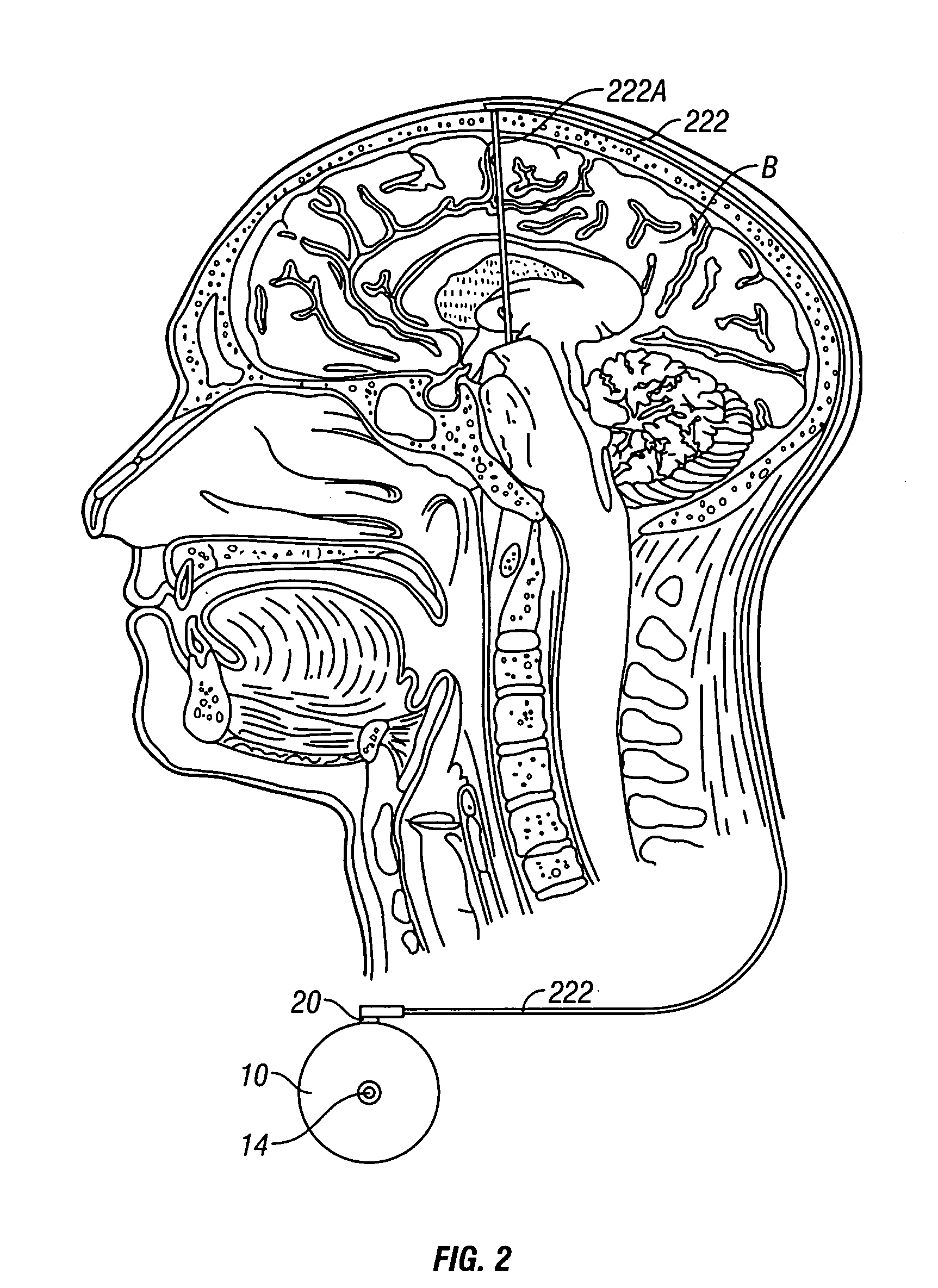
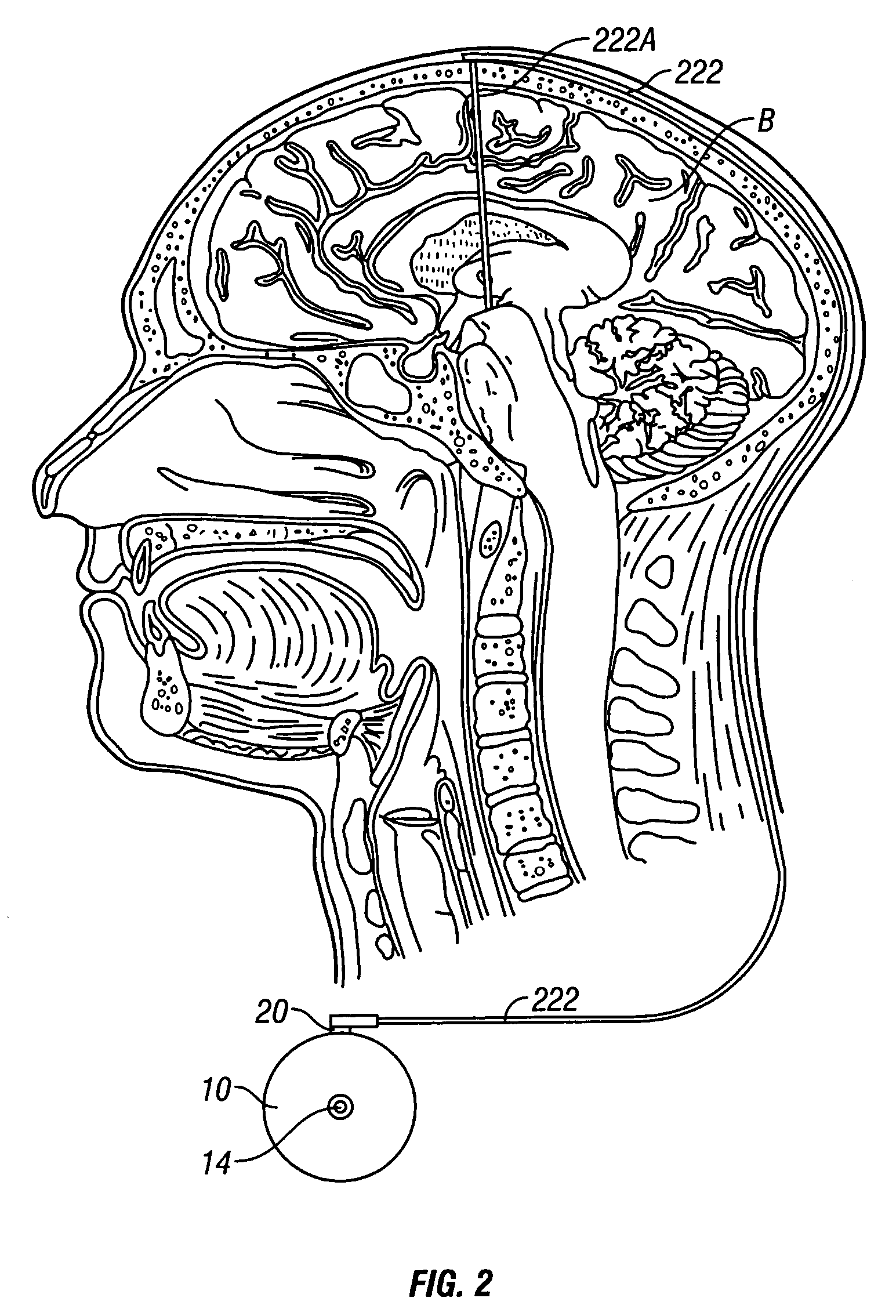
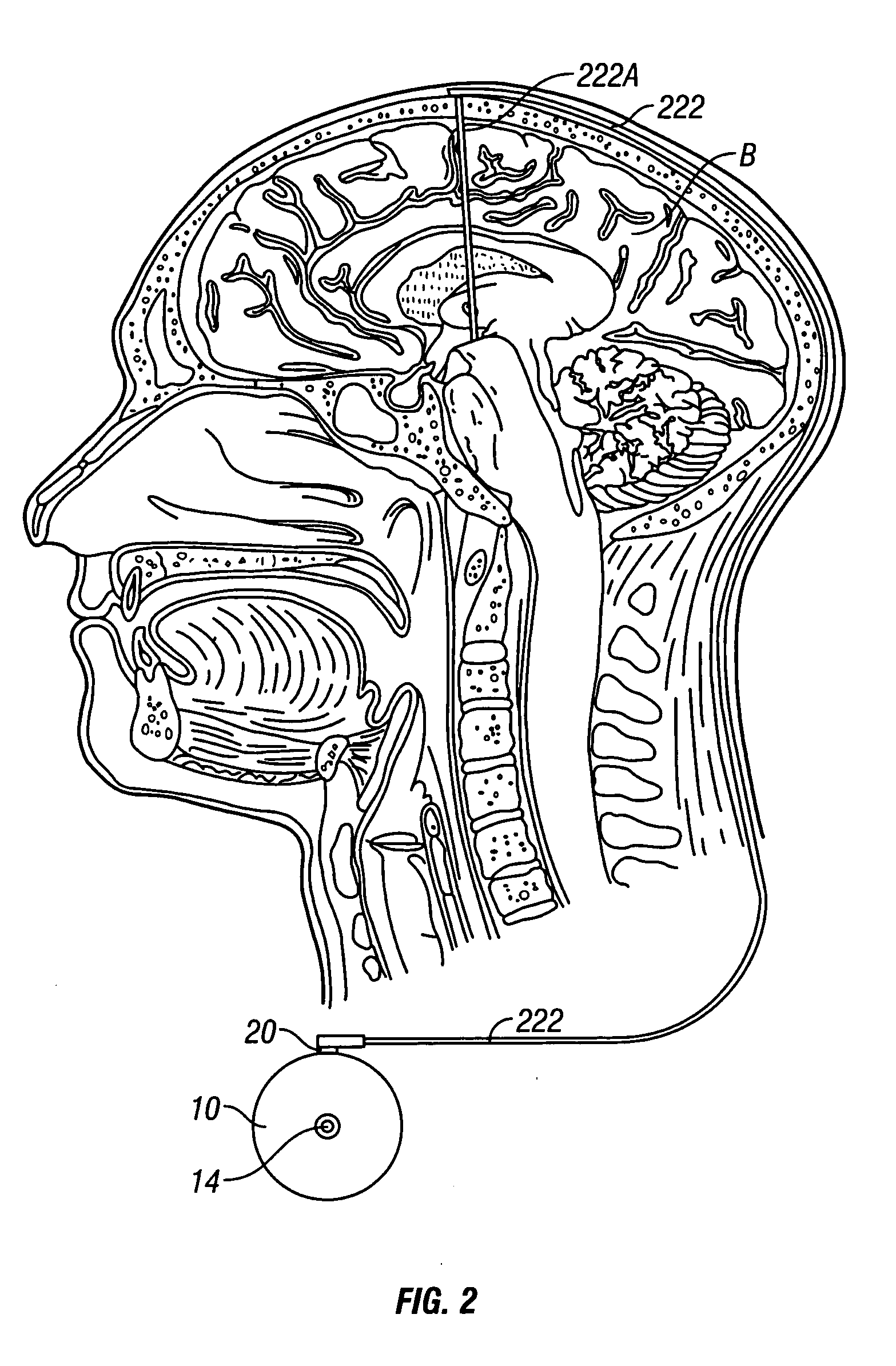
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
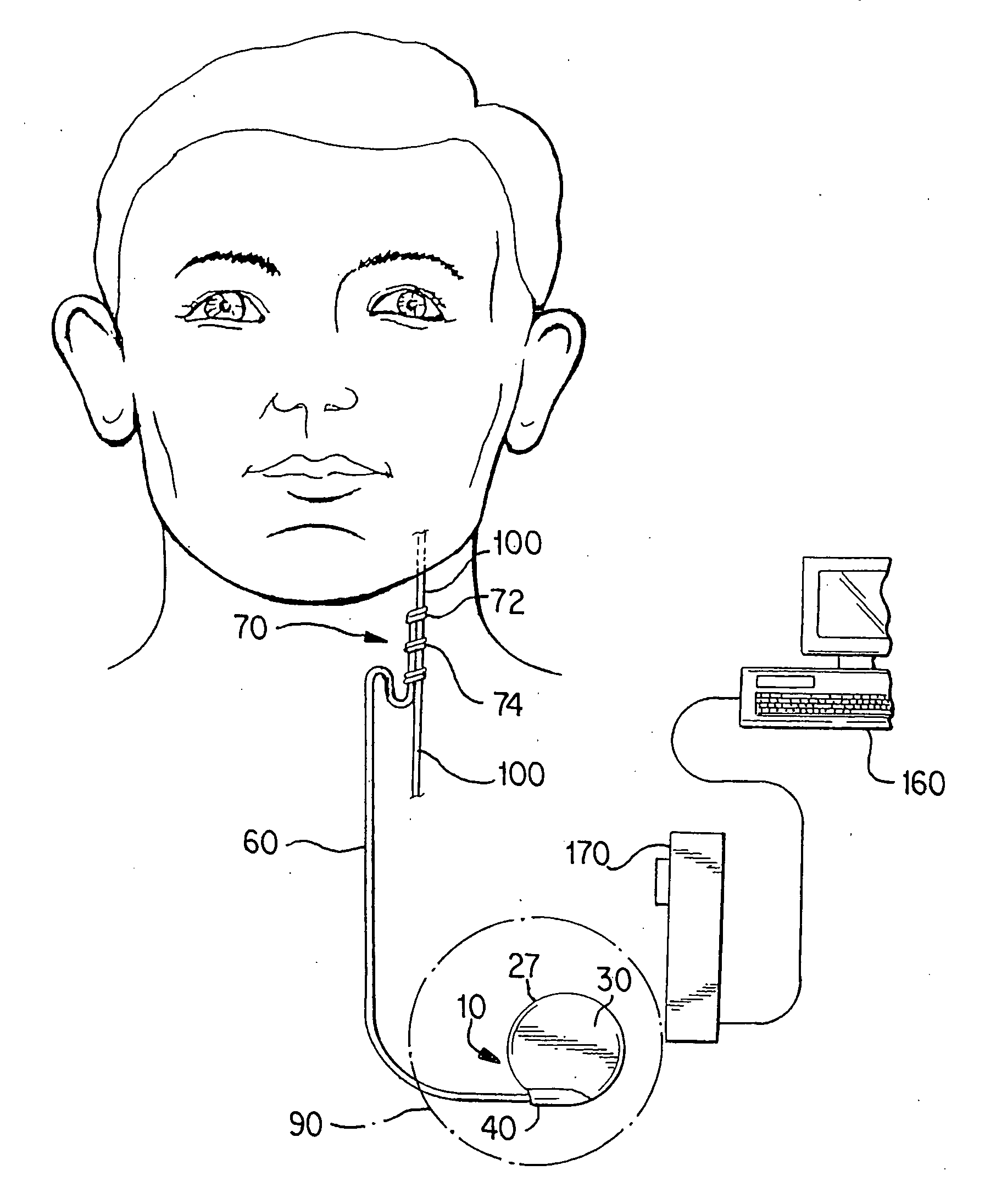
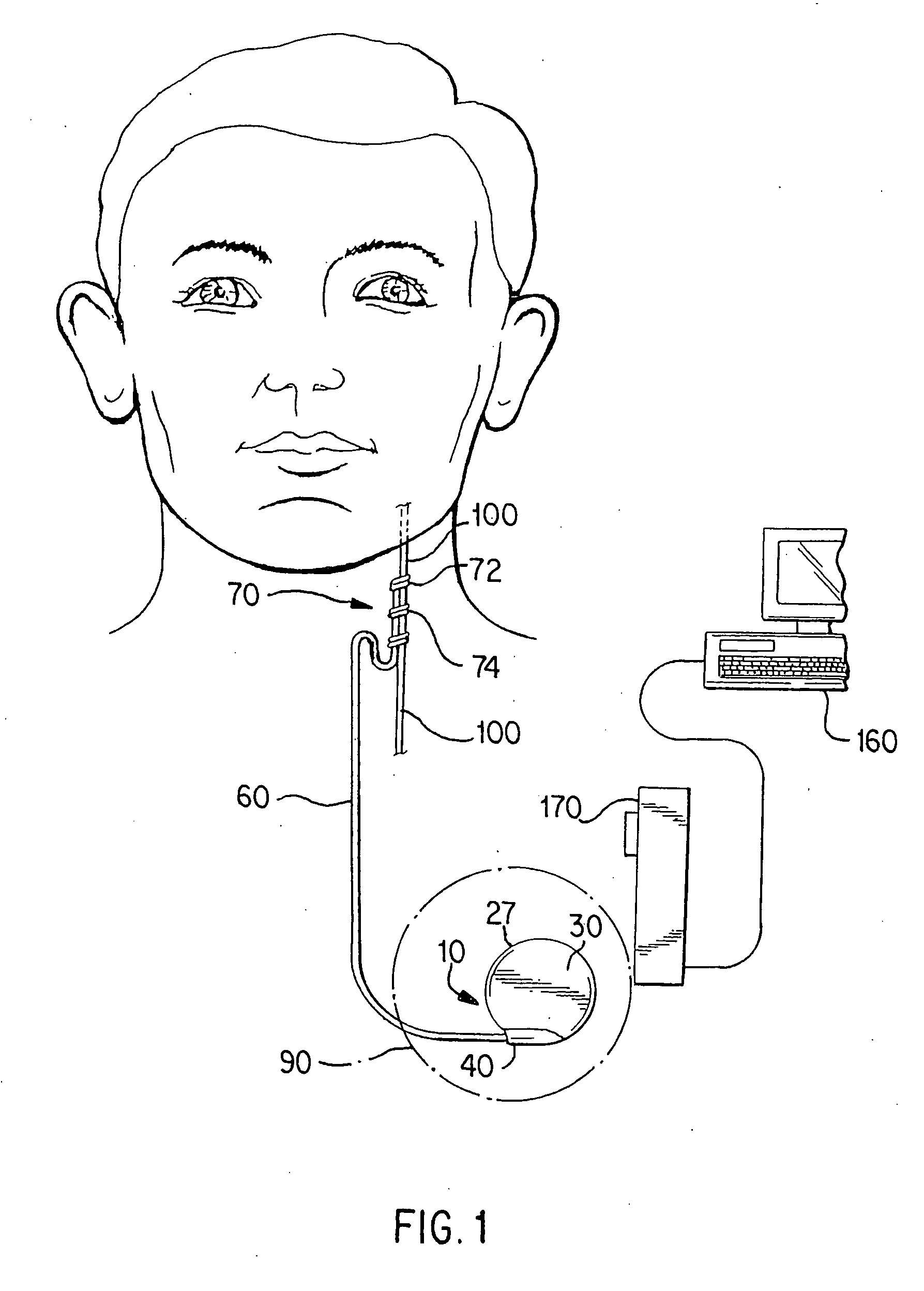
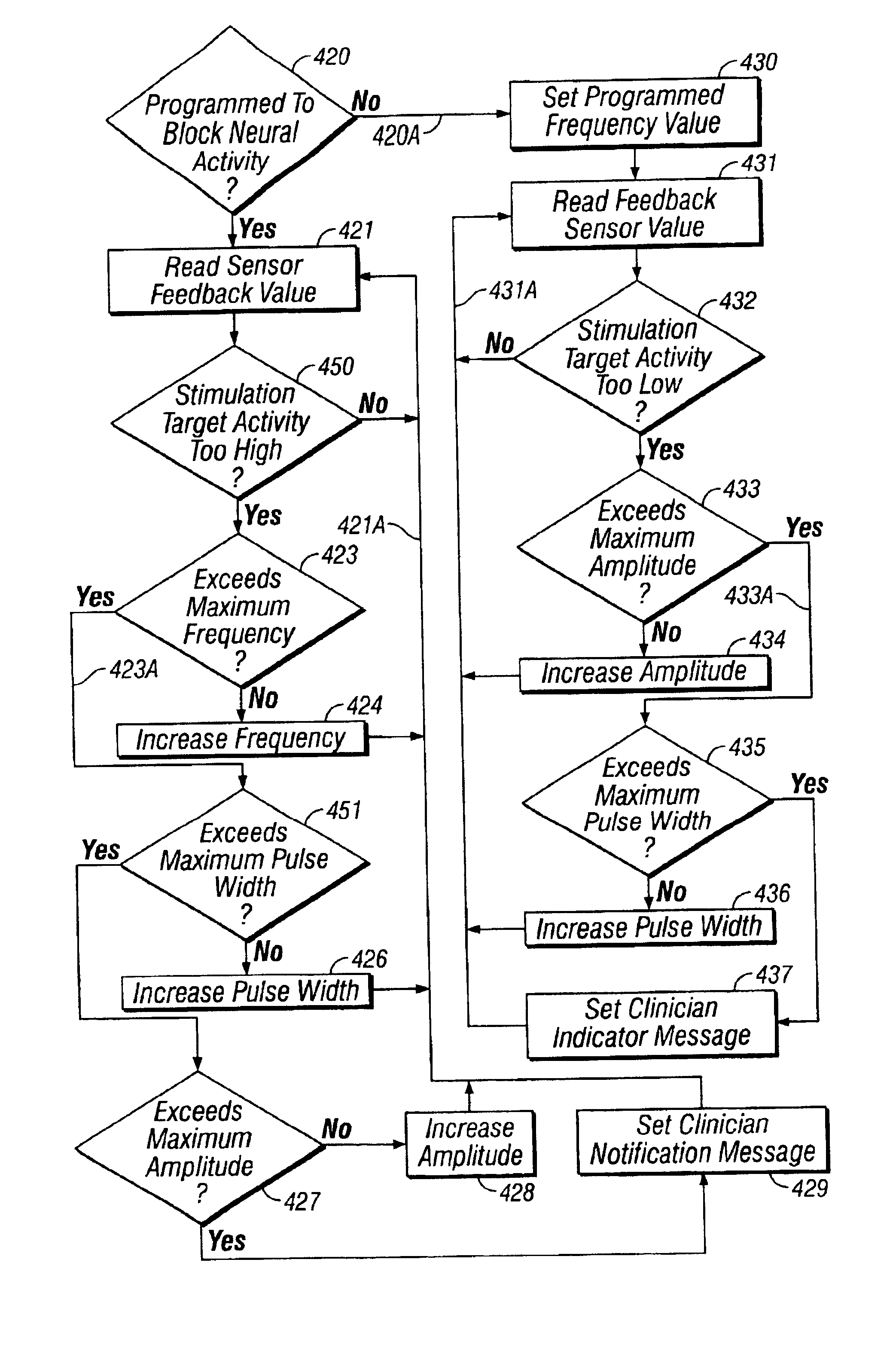
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
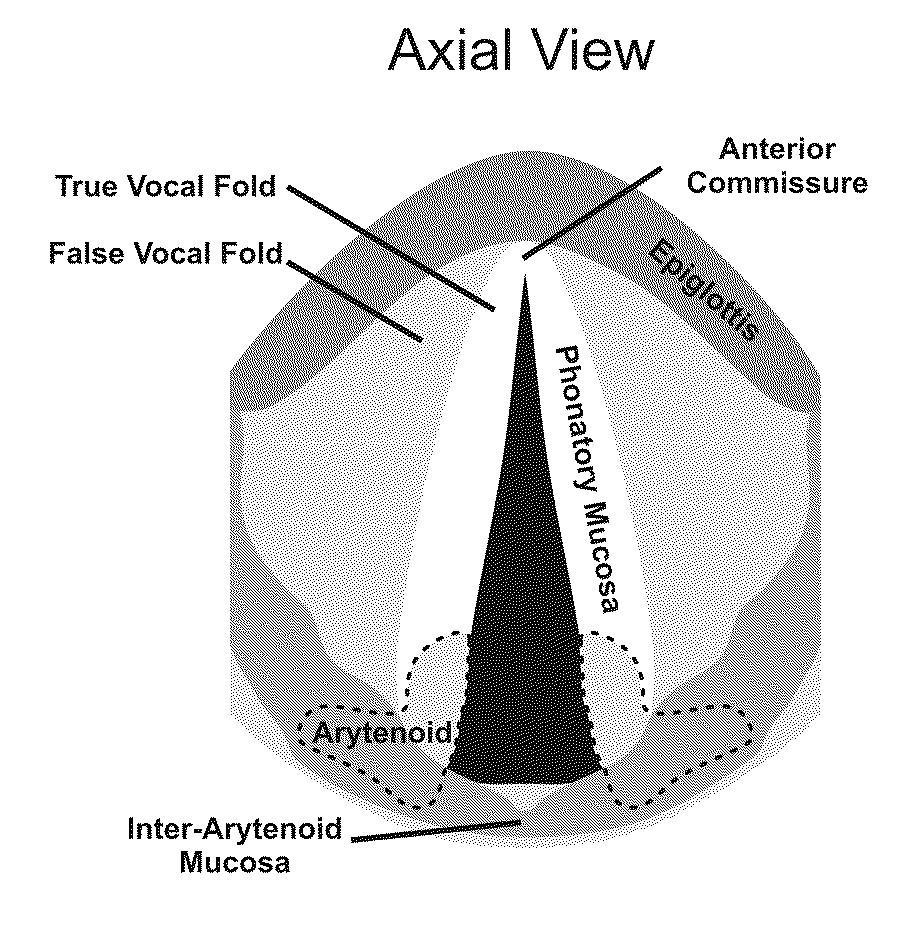
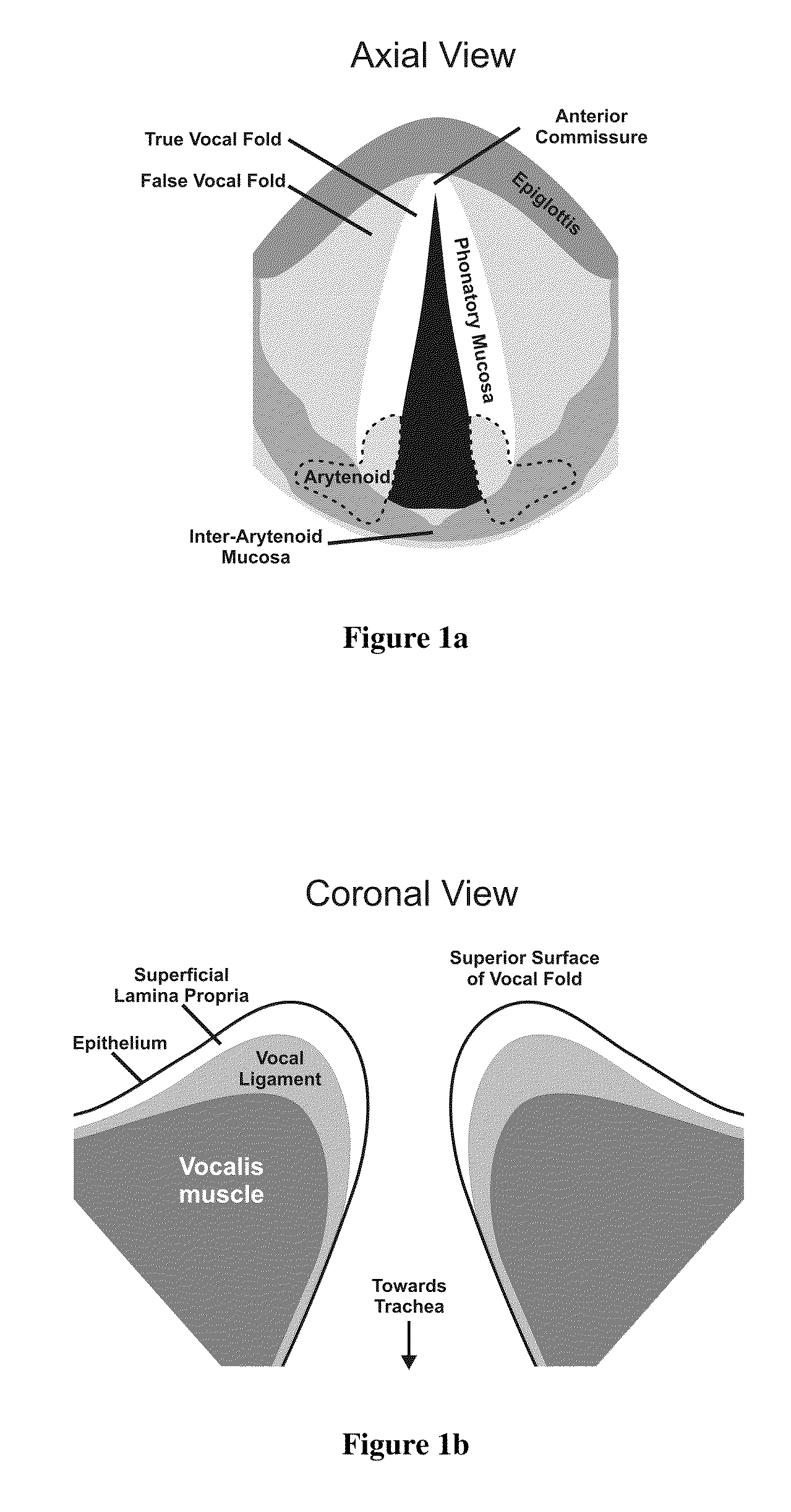
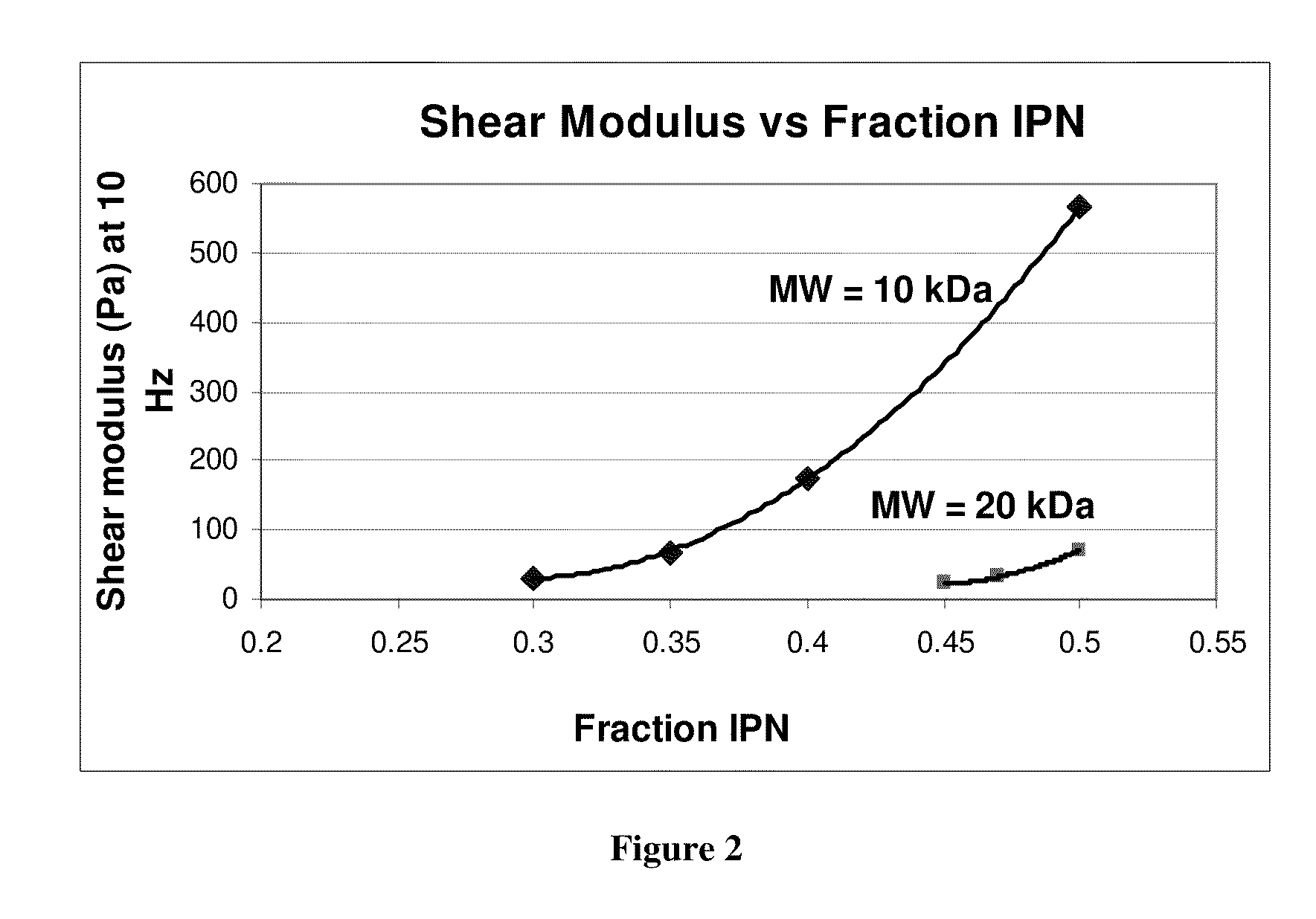
Hydrogels for vocal cord and soft tissue augmentation and repair
ActiveUS20100055184A1Repairing pliabilityDiminished functional vibratory capacityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEpitheliumBreast implant
The present invention provides hydrogels and compositions thereof for vocal cord repair or augmentation, as well as other soft tissue repair or augmentation (e.g., bladder neck augmentation, dermal fillers, breast implants, intervertebral disks, muscle-mass). The hydrogels or compositions thereof are injected into the superficial lamina propria or phonatory epithelium to restore the phonatory mucosa of the vocal cords, thereby restoring a patient's voice. In particular, it has been discovered that hydrogels with an elastic shear modulus of approximately 25 Pa are useful in restoring the pliability of the phonatory mucosa. The invention also provides methods of preparing and using the inventive hydrogels.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system for dynamic vocal fold closure with neuro-electrical stimulation
InactiveUS6978787B1Reduce inhalationAssisting swallowingElectrotherapyDiagnosticsElectricityTreatment duration
A method and system for treating dysphagia using electrical stimulation of a human's or animals's vagus nerve, or recurrent laryngeal nerve, or both to cause glottic or vocal fold motion in humans or animals. Stimulation is caused by utilizing a power source; an external controller for generating and providing an output signal having a given intensity, frequency, and pulse duration; an output protector circuit for limiting the intensity of the output signal; a treatment duration circuit for controlling the duration of operation of the external controller, a ramp control circuit for controlling the intensity of the output signal; and a monitor portion for displaying operating parameters of the device. The external controller regulates the intensity, the frequency, and the pulse duration of the output signal in accordance with a procedure for treating dysphagia.
Owner:BRONIATOWSKI MICHAEL
Pacemaker for bilateral vocal cord autoparalysis
InactiveUS7069082B2ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationBilateral vocal cord paralysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
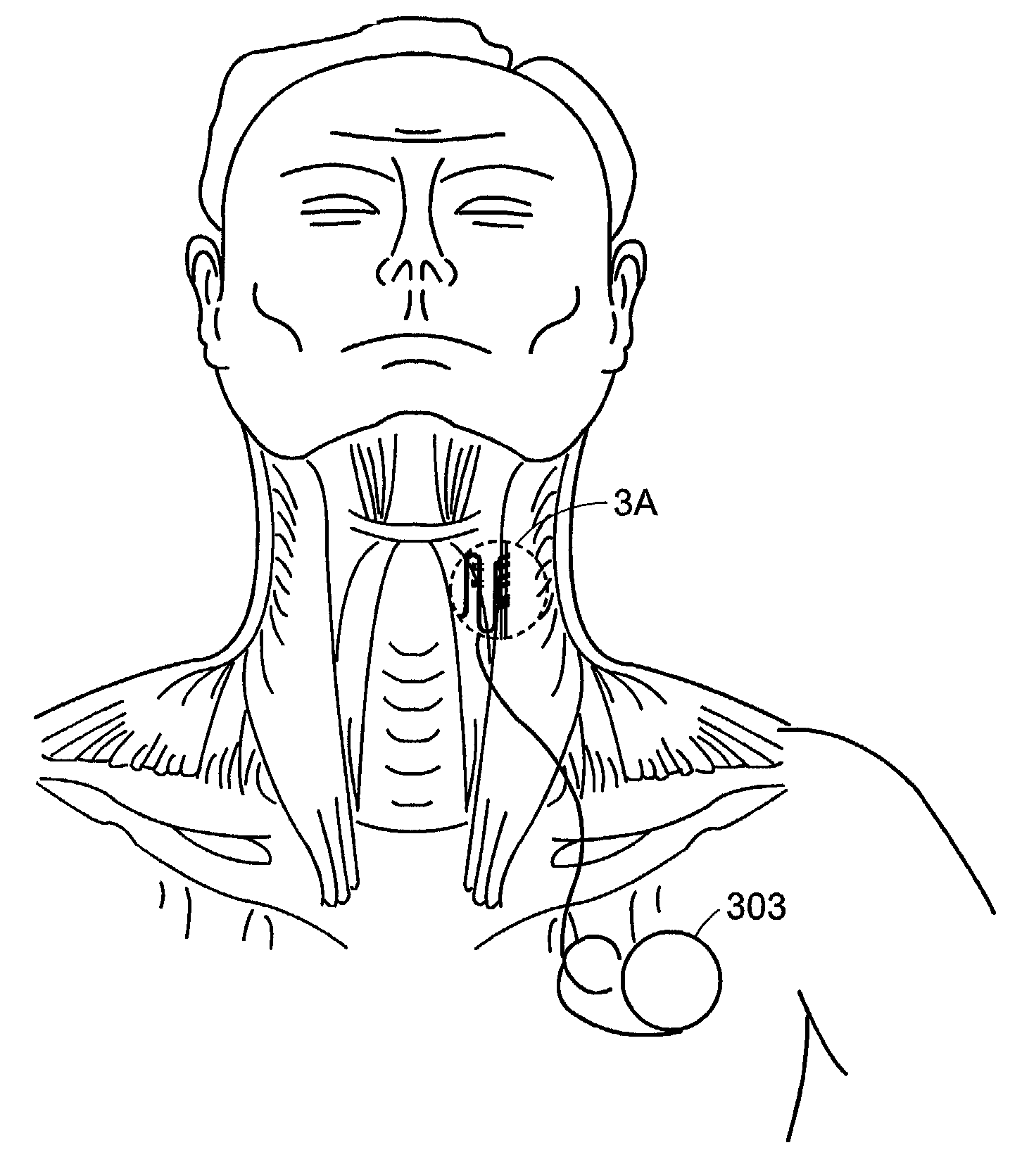
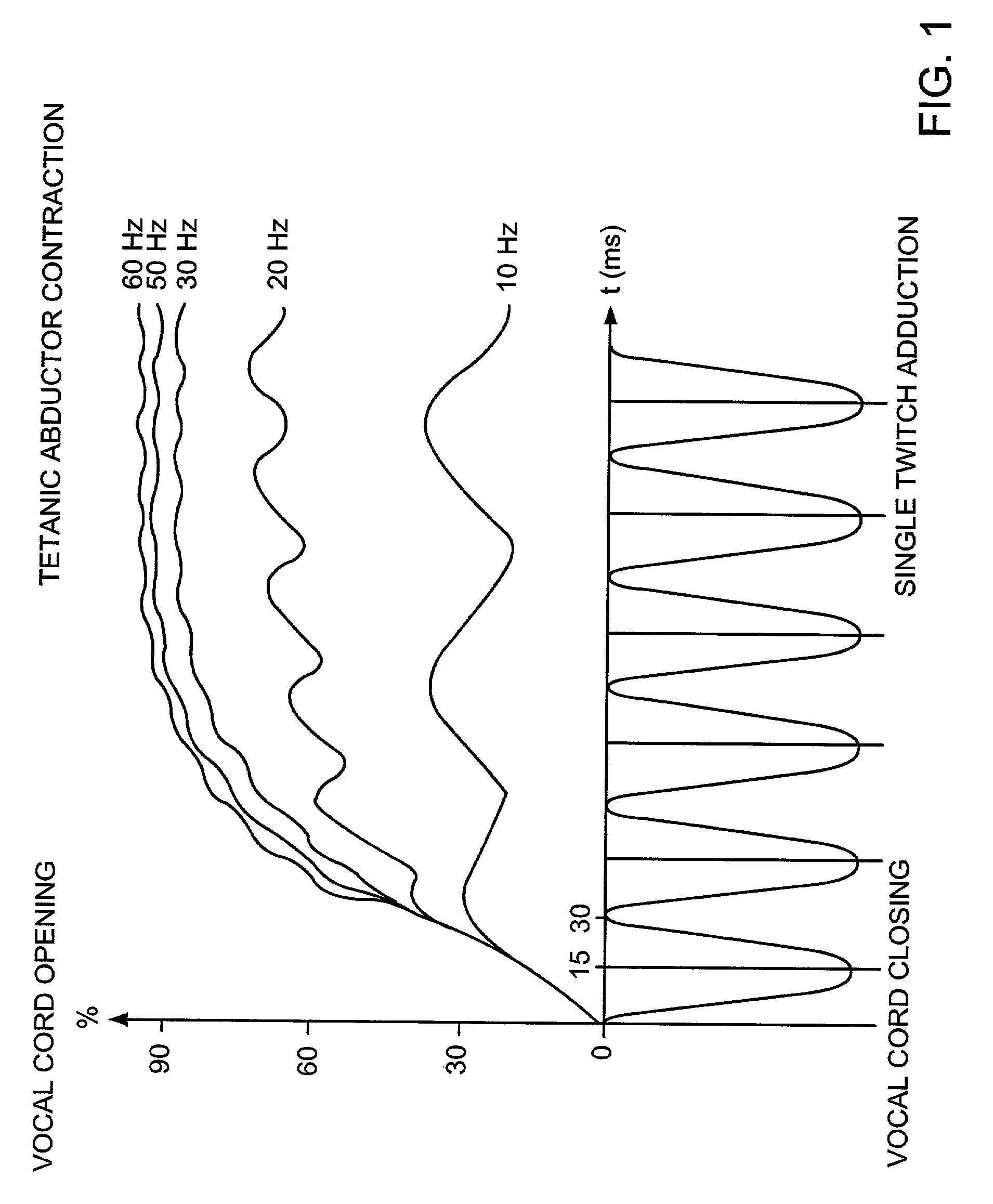
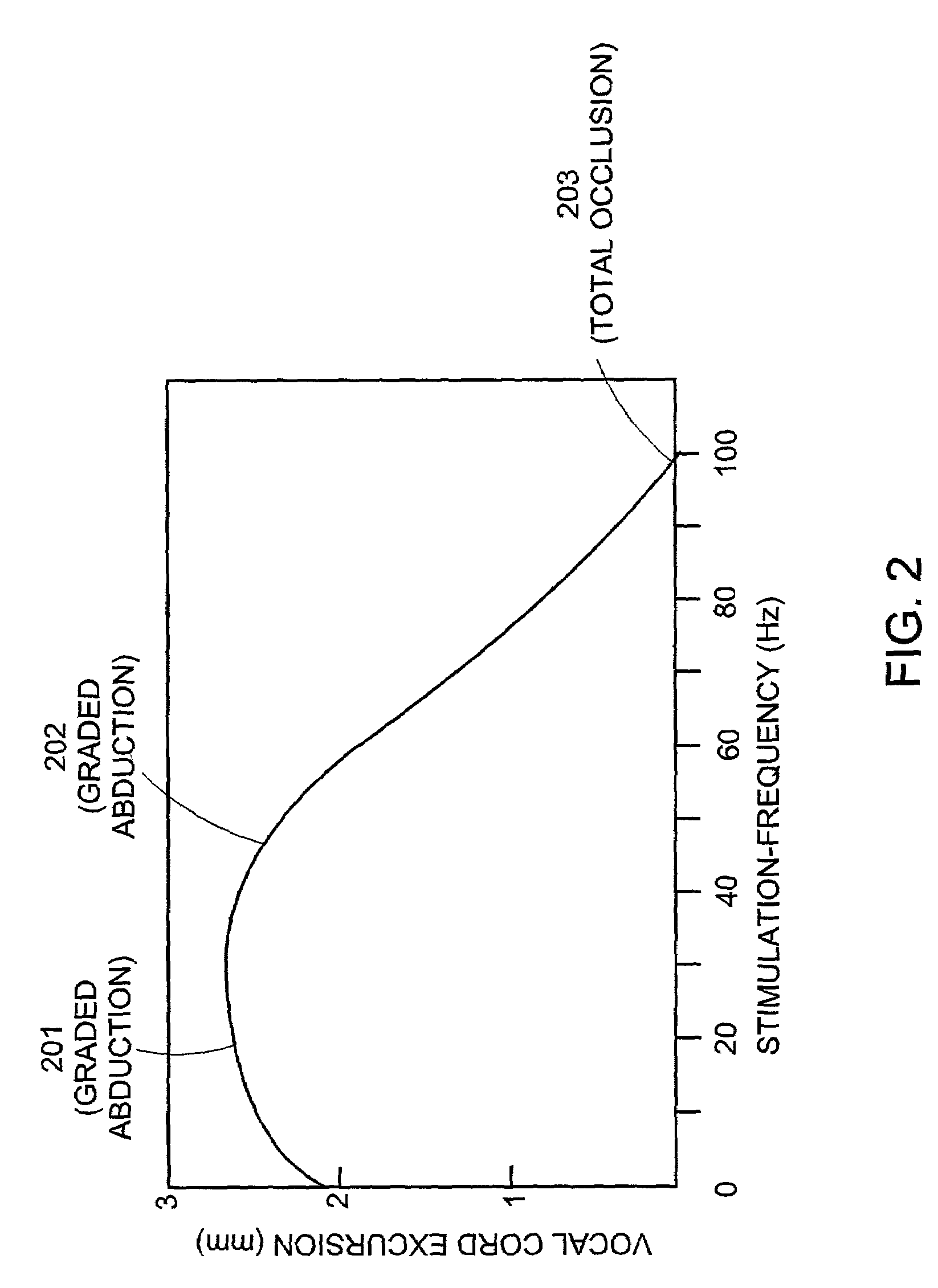
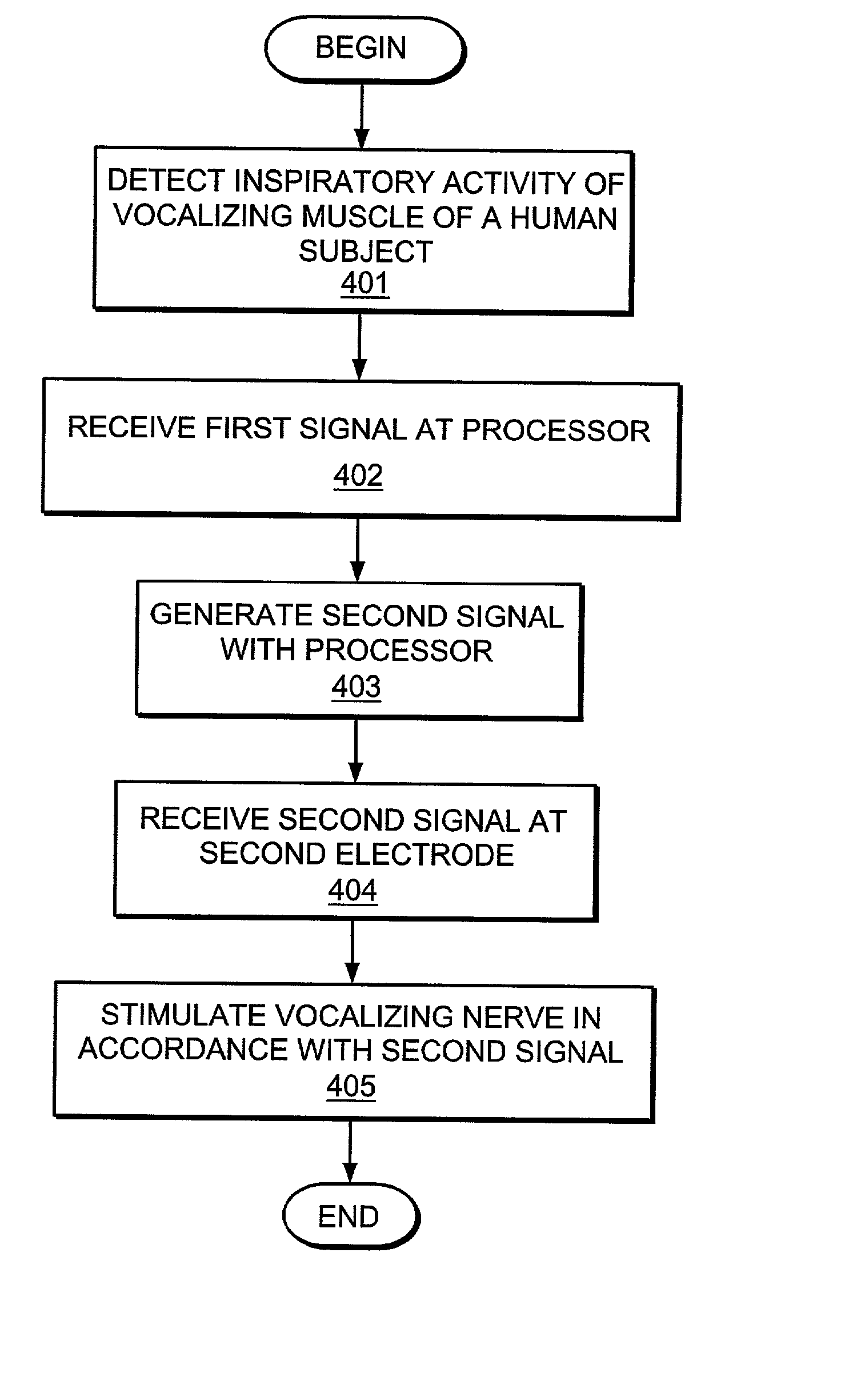
A pacemaker system for a human subject having bilateral vocal cord paralysis includes a sensing electrode for detecting inspiratory activity of a vocalizing muscle of the subject and generating a first signal, and a processor for receiving the first signal from the sensing electrode and generating a second signal. The second signal is substantially synchronous with the first signal. A stimulating electrode receives the second signal from the pulse generator and stimulating a vocalizing nerve of the subject.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Pacemaker for bilateral vocal cord autoparalysis
InactiveUS20020156507A1Heart stimulatorsArtificial respirationBilateral vocal cord paralysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
A pacemaker system for a human subject having bilateral vocal cord paralysis includes a sensing electrode for detecting inspiratory activity of a vocalizing muscle of the subject and generating a first signal, and a processor for receiving the first signal from the sensing electrode and generating a second signal. The second signal is substantially synchronous with the first signal. A stimulating electrode receives the second signal from the pulse generator and stimulating a vocalizing nerve of the subject.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
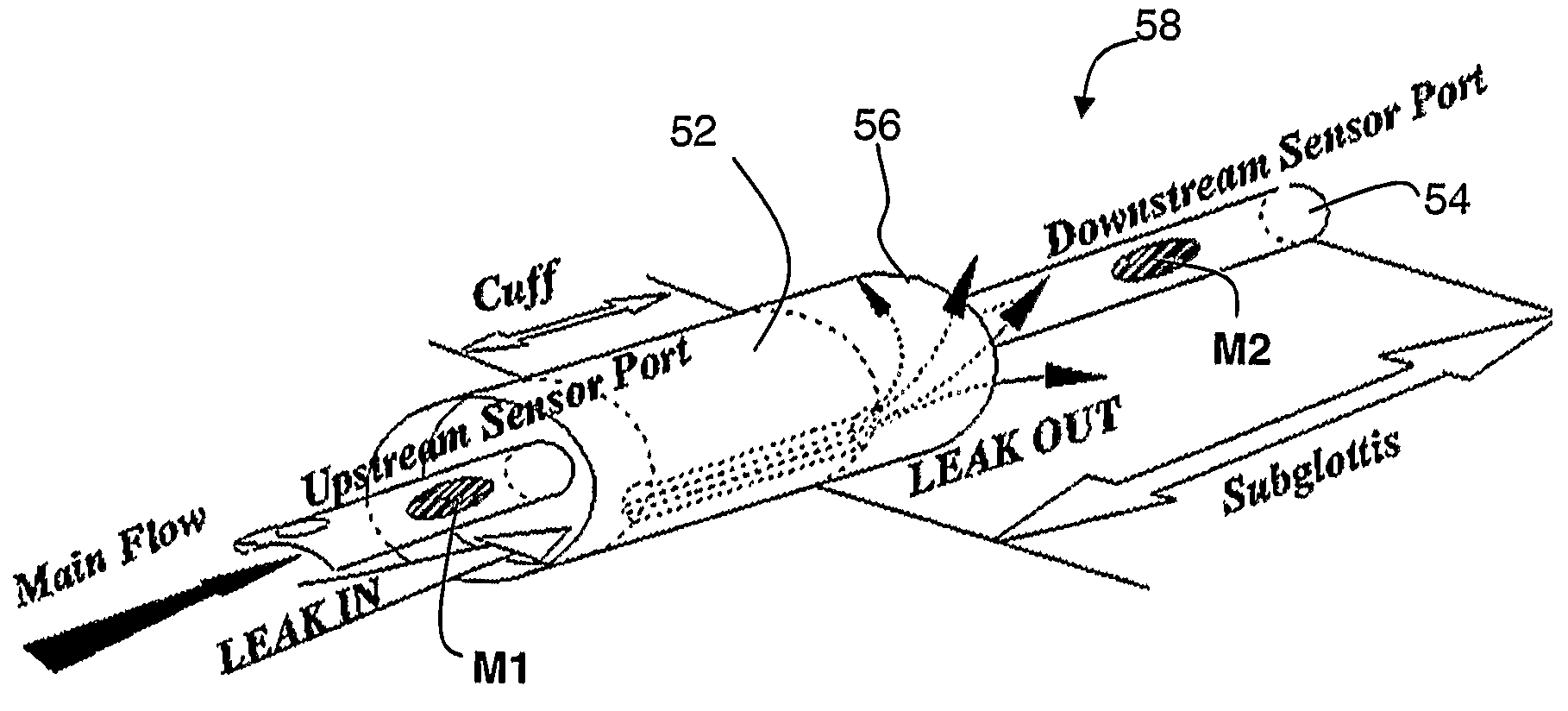
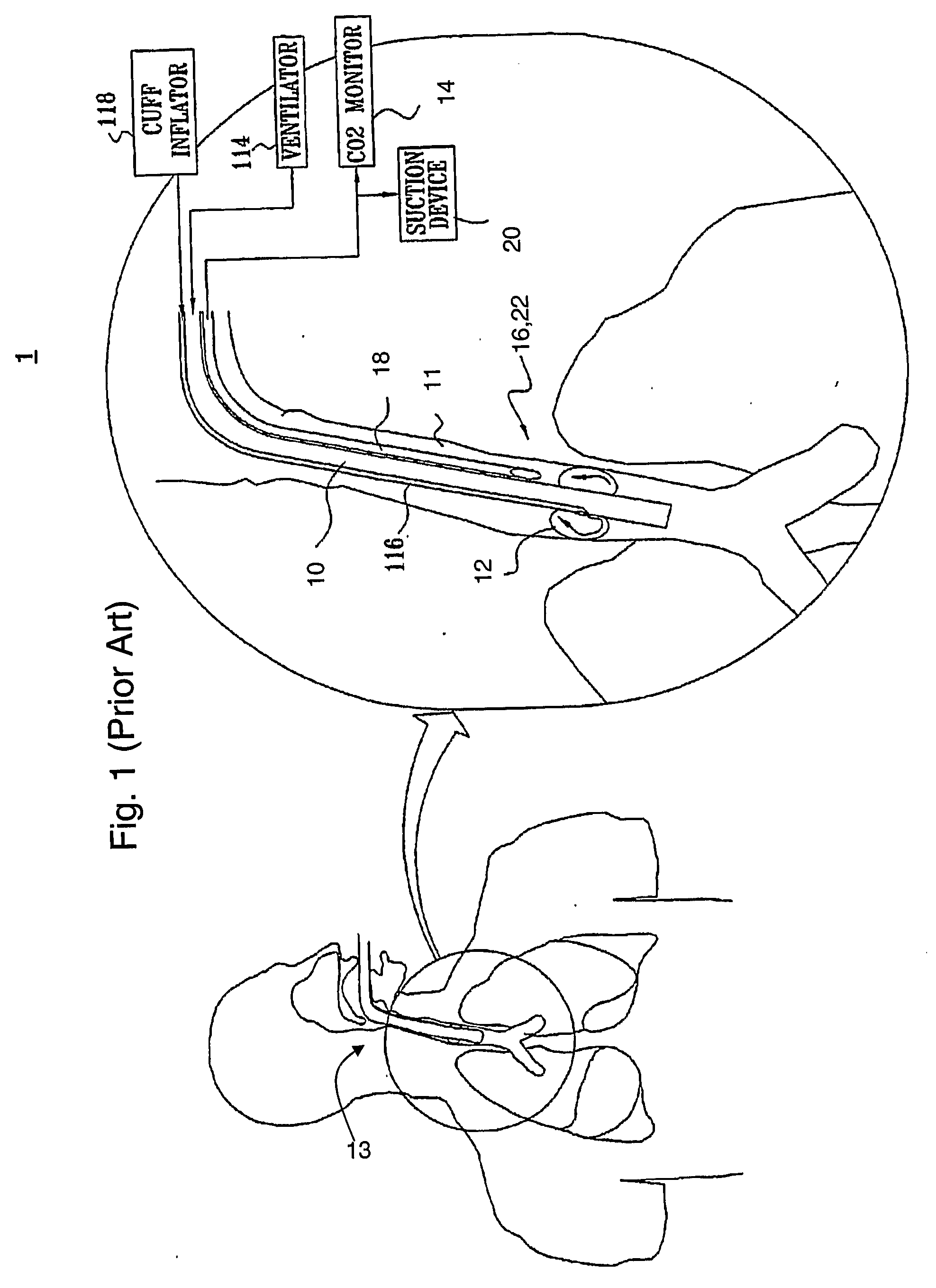
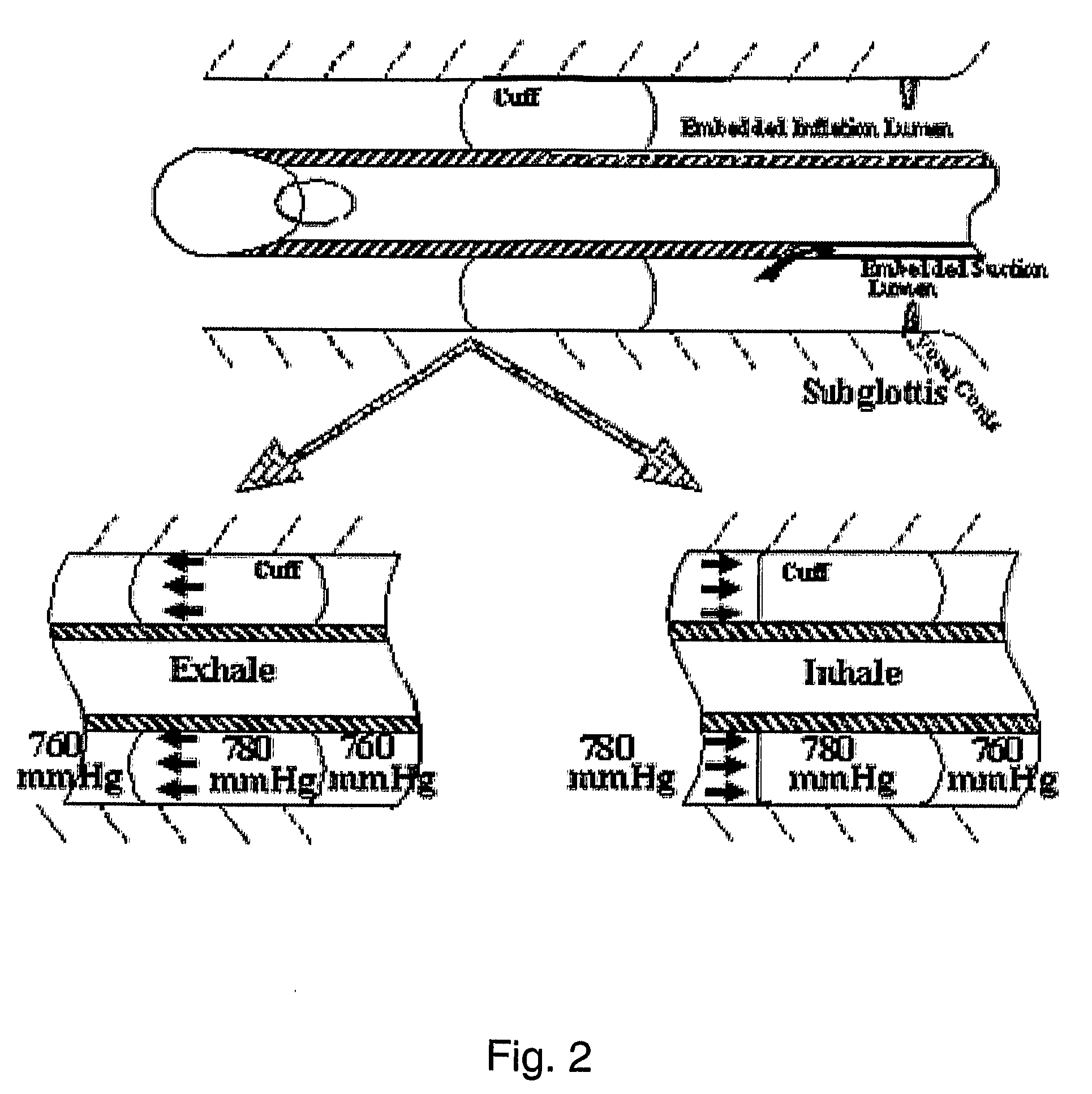
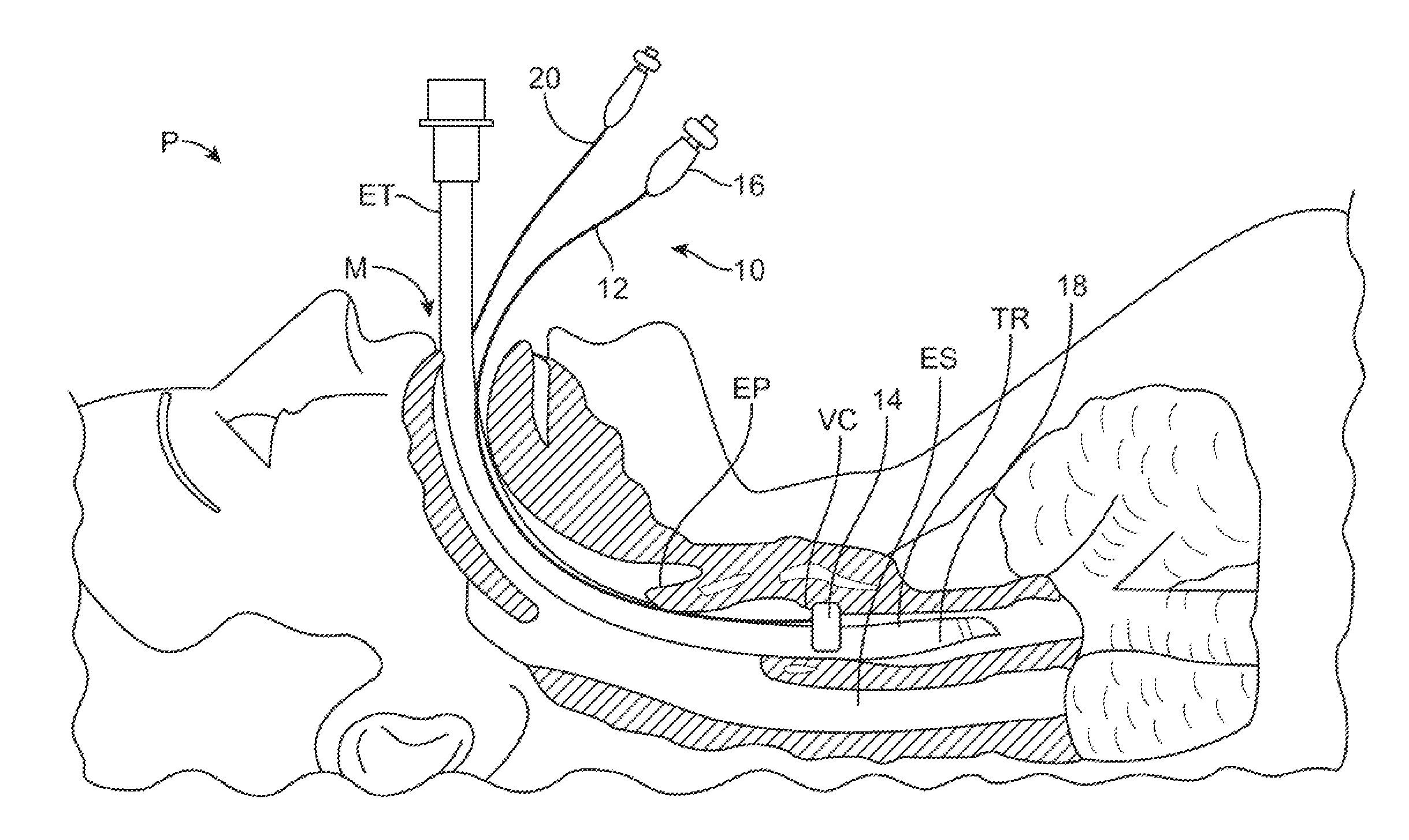
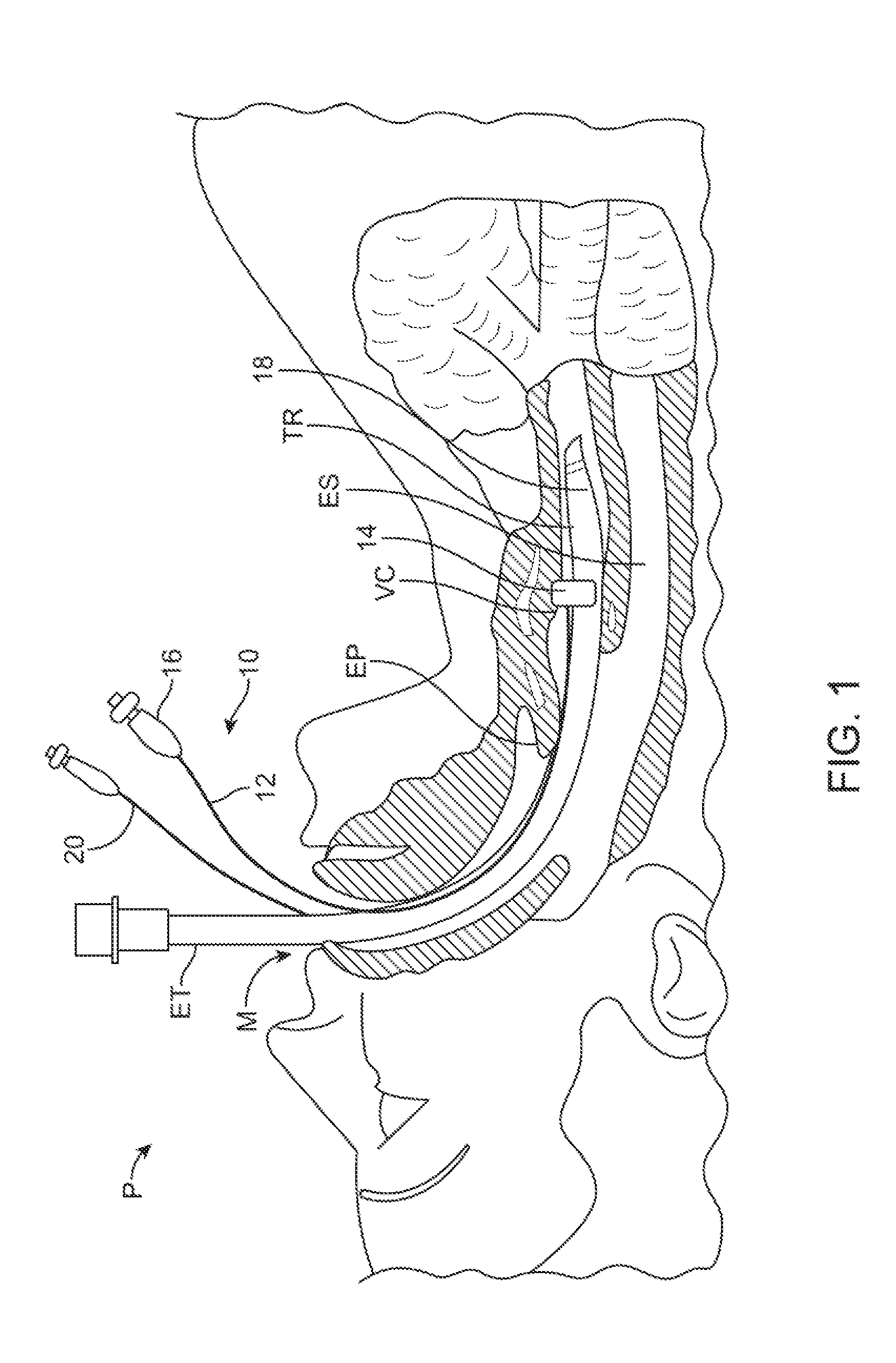
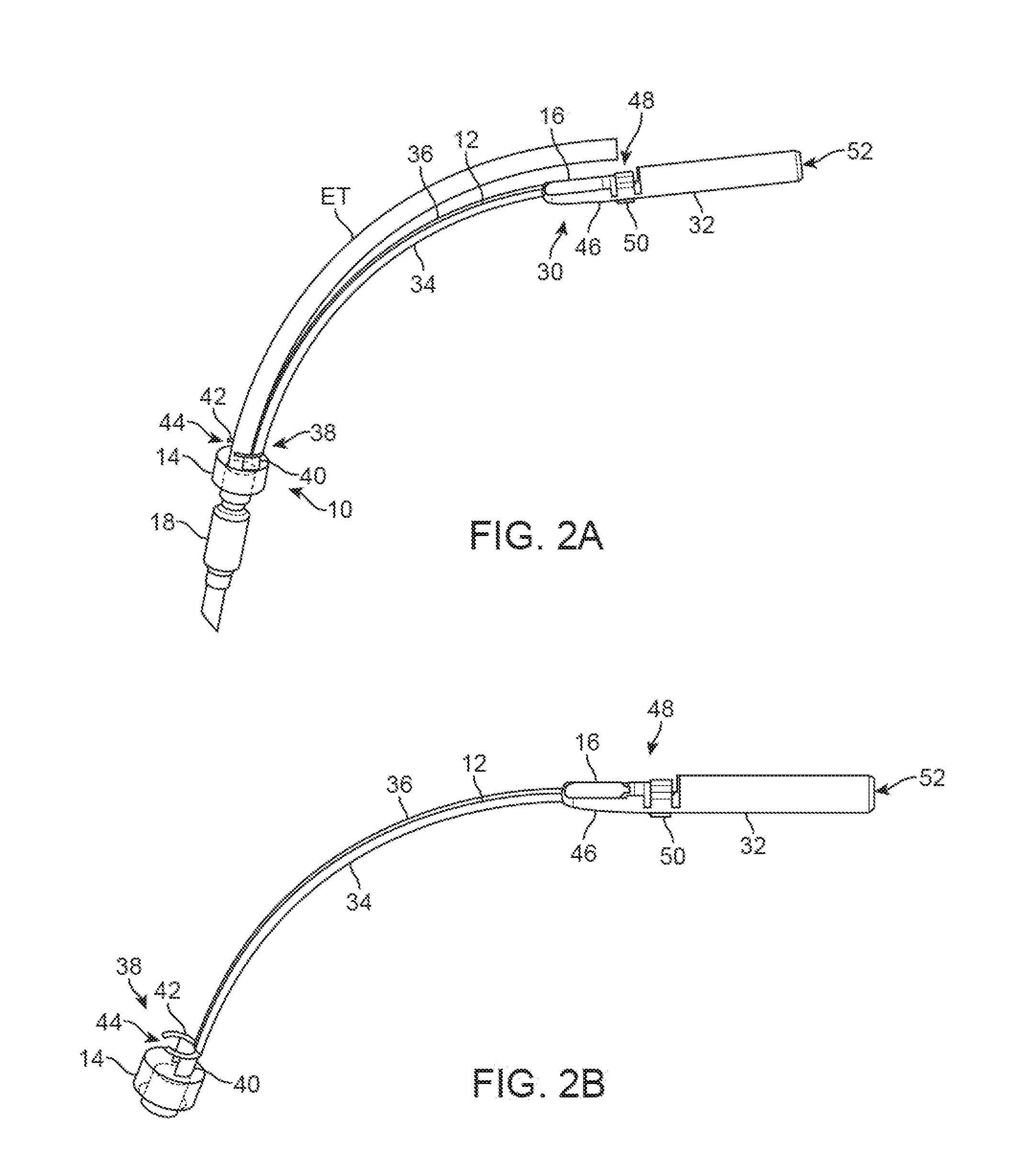
Ajustment of endotracheal tube cuff filling
A method of intubating a subject is disclosed. The method comprises inserting an endotracheal tube into the tracheal airway of the subject; inflating a cuff associated with the endotracheal tube within the airway below the vocal cords; measuring a level of at least one measure being indicative of leakage of secretion past the cuff to the lungs; comparing the level of the measure with an optimal level of the measure; and adjusting inflation of the cuff based on the comparison so as to generally minimize leakage of secretion from above the cuff to the lungs, while minimizing pressure associated damages to the airway. The measure(s) can be carbon dioxide concentration, a proxy measure from which such concentration can be inferred, or the level of one or more additives delivered to a subject during intubation.
Owner:HOSPITECH RESPIRATION
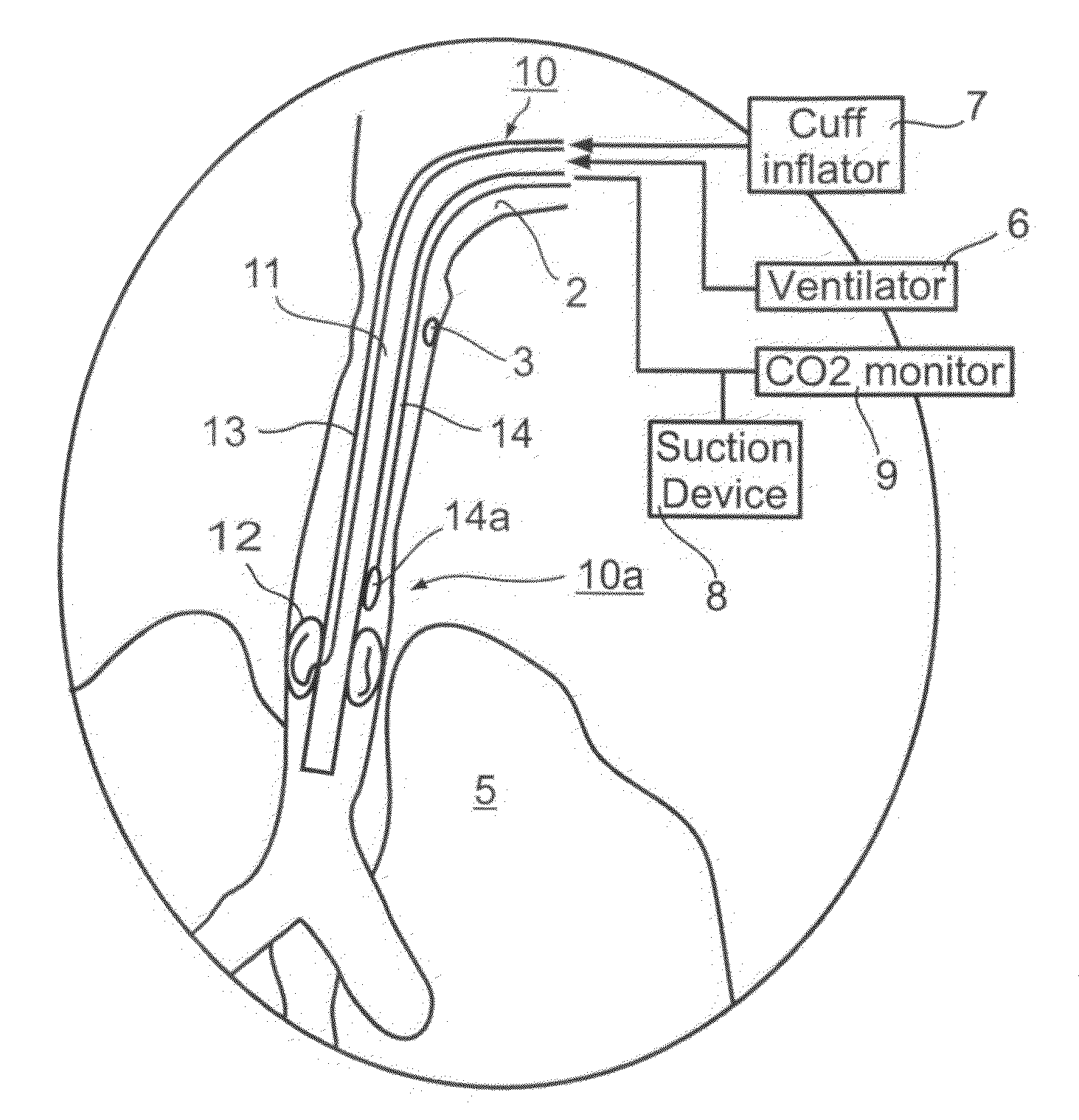
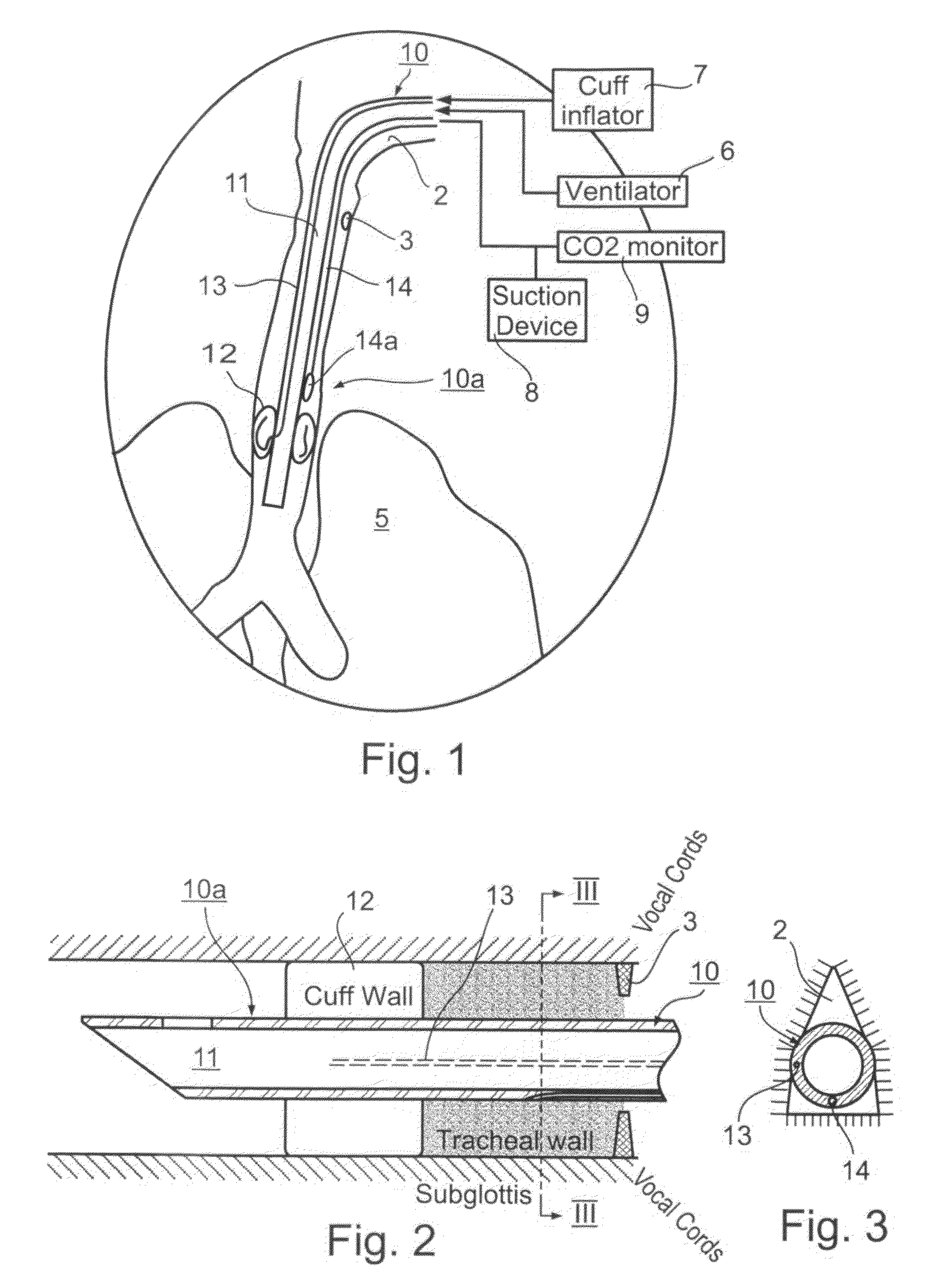
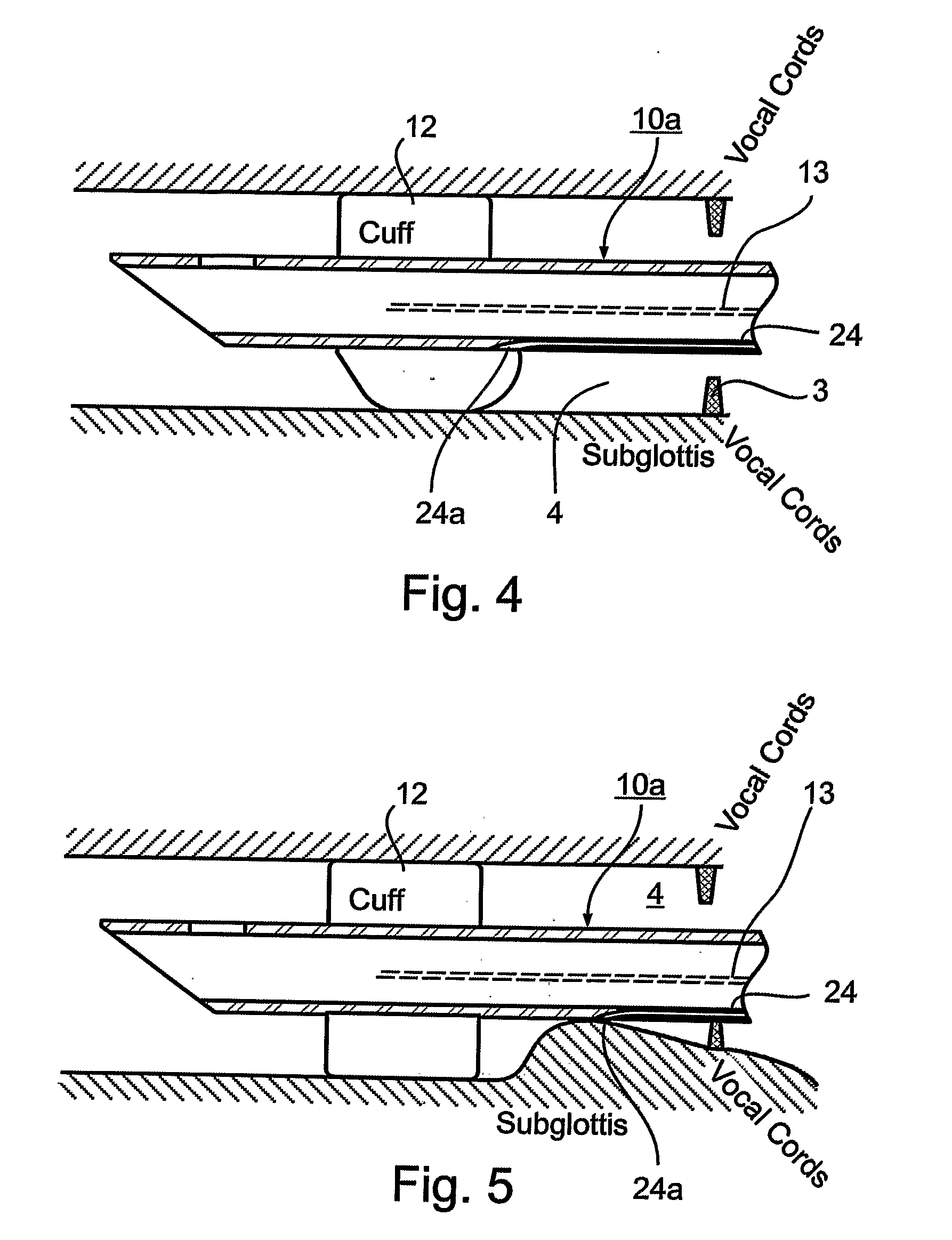
Endotracheal Tube and Intubation System Including Same
ActiveUS20090038620A1Reduce chanceEfficient evacuationTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheal tubeSubglottic area
An endotracheal tube for mechanically ventilating patients is disclosed. The endotracheal tube comprises a distal end for insertion into the patient's airway, past the vocal chords, through the subglottal region, and into the patient's lung; and a proximal end for connection to a mechanical ventilator. The endotracheal tube further comprises a cuff at the distal end of the endotracheal tube to be located in the subglottal region of the patient below the vocal chords, an inflating lumen for inflating the cuff, and a suction lumen having a suction inlet port leading from the outer surface of the endotracheal tube, and to be located in the subglottal region, for evacuating secretions and / or rinsing fluid from the subglottal region during the mechanical ventilation of the patient. The distal end of the endotracheal tube is formed with an outer surface configuration effective to prevent blockage of the suction inlet port by the cuff or by tracheal mucosal tissue of the patient during a negative pressure condition in the suction lumen.
Owner:HOSPITECH RESPIRATION
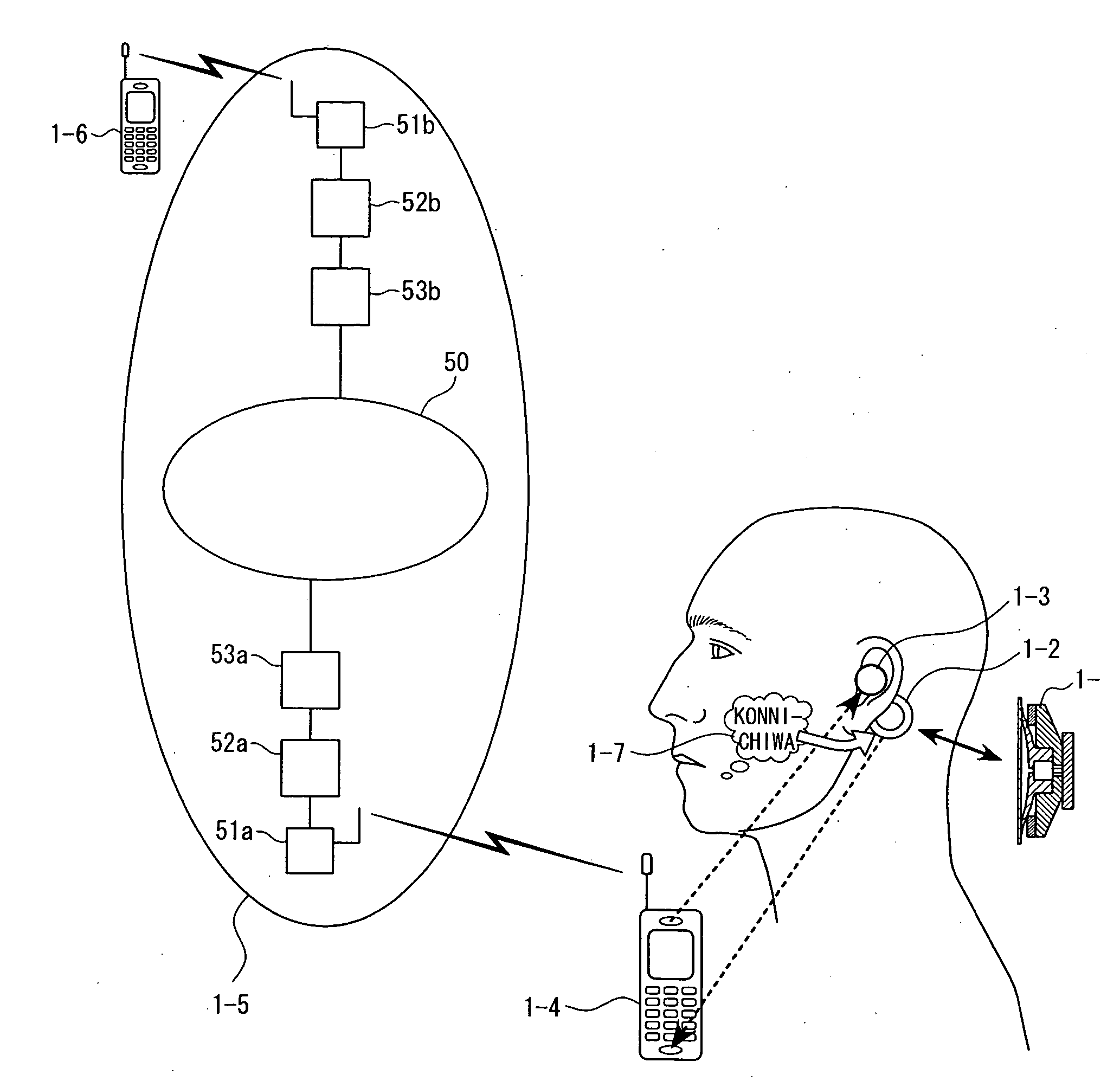
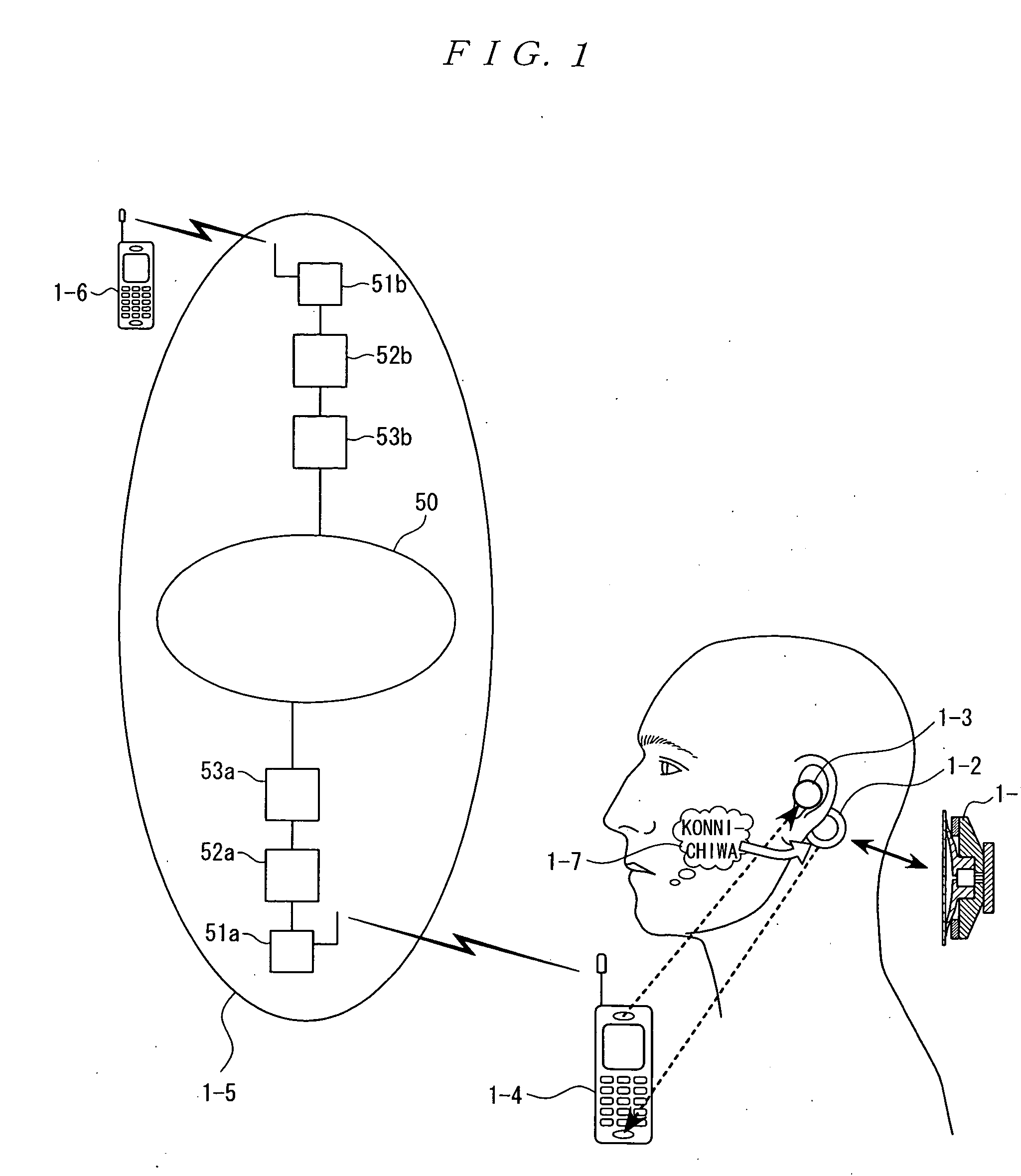
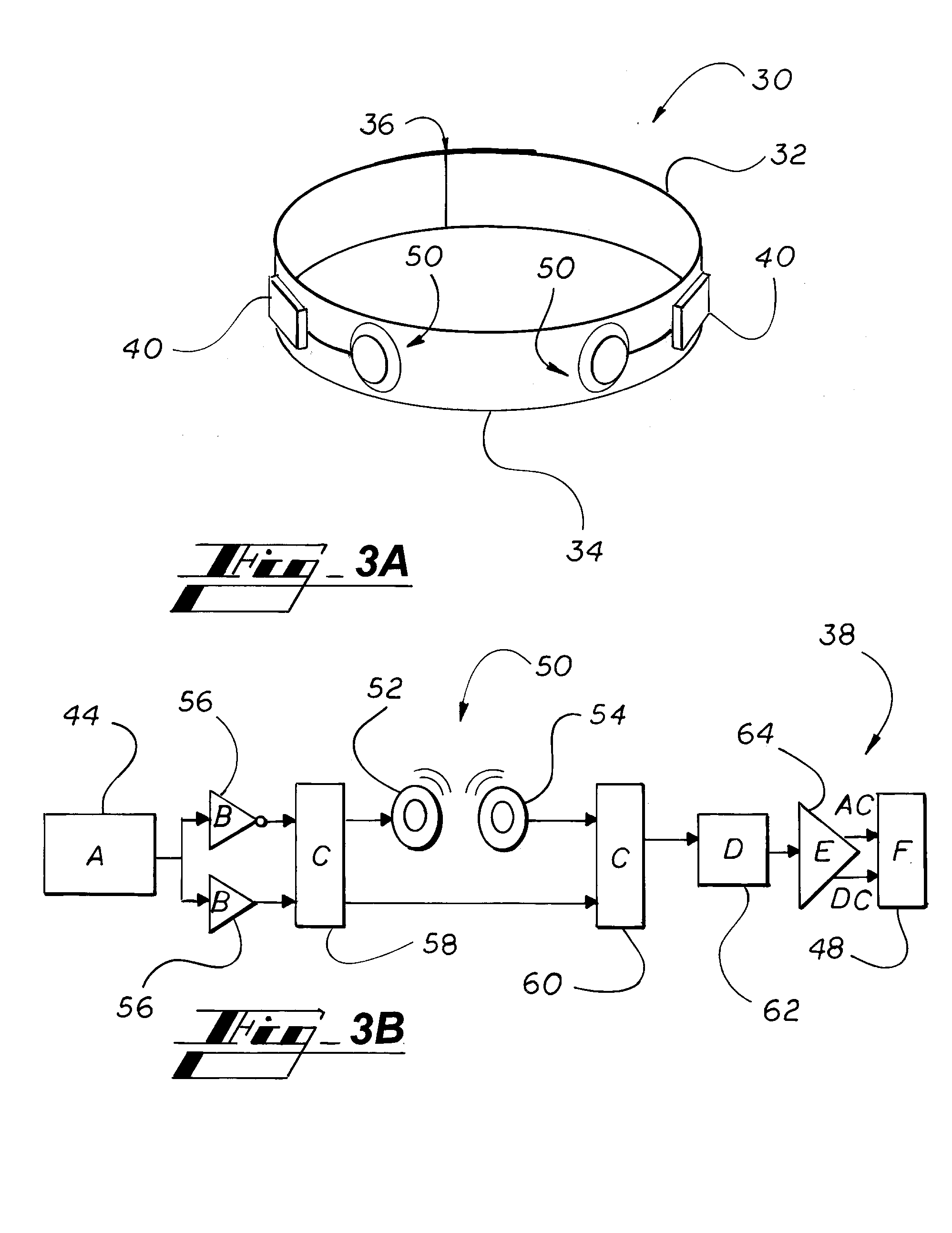
Microphone and communication interface system
InactiveUS20050244020A1Avoid damaging the environmentHigh expiratoryMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsSpeech recognitionCultural practiceHuman body
The present invention eliminates the disadvantages of an analysis target used by a cellular phone and speech recognition, that is, a normal sound which is transmitted through the air and which is externally sampled through a microphone, and improves the disadvantages that noise may be mixed or occur in the target, that information may leak, and that corrections are difficult. The present invention also provides a personal portable information terminal realizing new portable terminal communications which do not require training and which conform to the cultural practice of human beings. In the present invention, no apparatus that obtains an analysis target is put off human body, and a normal sound is not an analysis target. A stethoscope-type microphone is installed on the surface of the human skin. Then, a vibration sound is sampled which is obtained when a non-audible murmur articulated in association with speech action (the motion of the mouth) not using the regular vibration of the vocal cords is transmitted through the flesh. A vibration sound obtained when a non-audible murmur amplified is transmitted through the flesh is similar to a whisper. The vibration sound can thus be heard and understood by human beings. Accordingly, the vibration sound can be used for a speech over the cellular phone as it is. Further, when the vibration sound obtained when the non-audible murmur is transmitted through the flesh is analyzed and converted into parameters, a kind of soundless recognition is realized. The present invention replaces the HMM model, conventionally used for speech recognition by an acoustic model created on the basis of a vibration sound obtained when a non-audible murmur is transmitted through the flesh. Therefore, the present invention provides a new method of inputting data to the personal portable information terminal.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for vocal cord reconstruction
A method for surgical repair of damaged or diseased head and neck tissues is described. In one aspect of the invention tissue graft constructs comprising vertebrate submucosa or vertebrate basement membrane materials are used to repair and promote growth of endogenous vocal cord tissue.
Owner:CLARIAN HEALTH PARTNERS
Augmentation and repair of vocal cord tissue defects
InactiveUS7412978B1Reduce the possibilityLower potentialBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCorrective surgeryTissue defect
A method for corrective surgery in a human subject of a vocal cord defect amenable to rectification by the augmentation of tissue subadjacent to the vocal cord defect, the method comprising: placing an effective amount of autologous in vitro cultured cells into a vocal cord tissue of the subject in a position subadjacent to the vocal cord defect, wherein the vocal cord tissue is selected from the group consisting of a scar, Reinke's space, a muscle of the vocal cord, and the lamina propria, wherein the in vitro cultured cells are obtained by culturing a plurality of viable cells retrieved from the subject, and wherein the cultured cells are suspended in a collagen or modified collagen solution prior to injection of the cultured cells. The in vitro cultured cells can be fibroblasts, e.g., fibroblasts derived from dermis, fascia, connective tissue, or lamina propria.
Owner:CASTLE CREEK BIOSCIENCES LLC
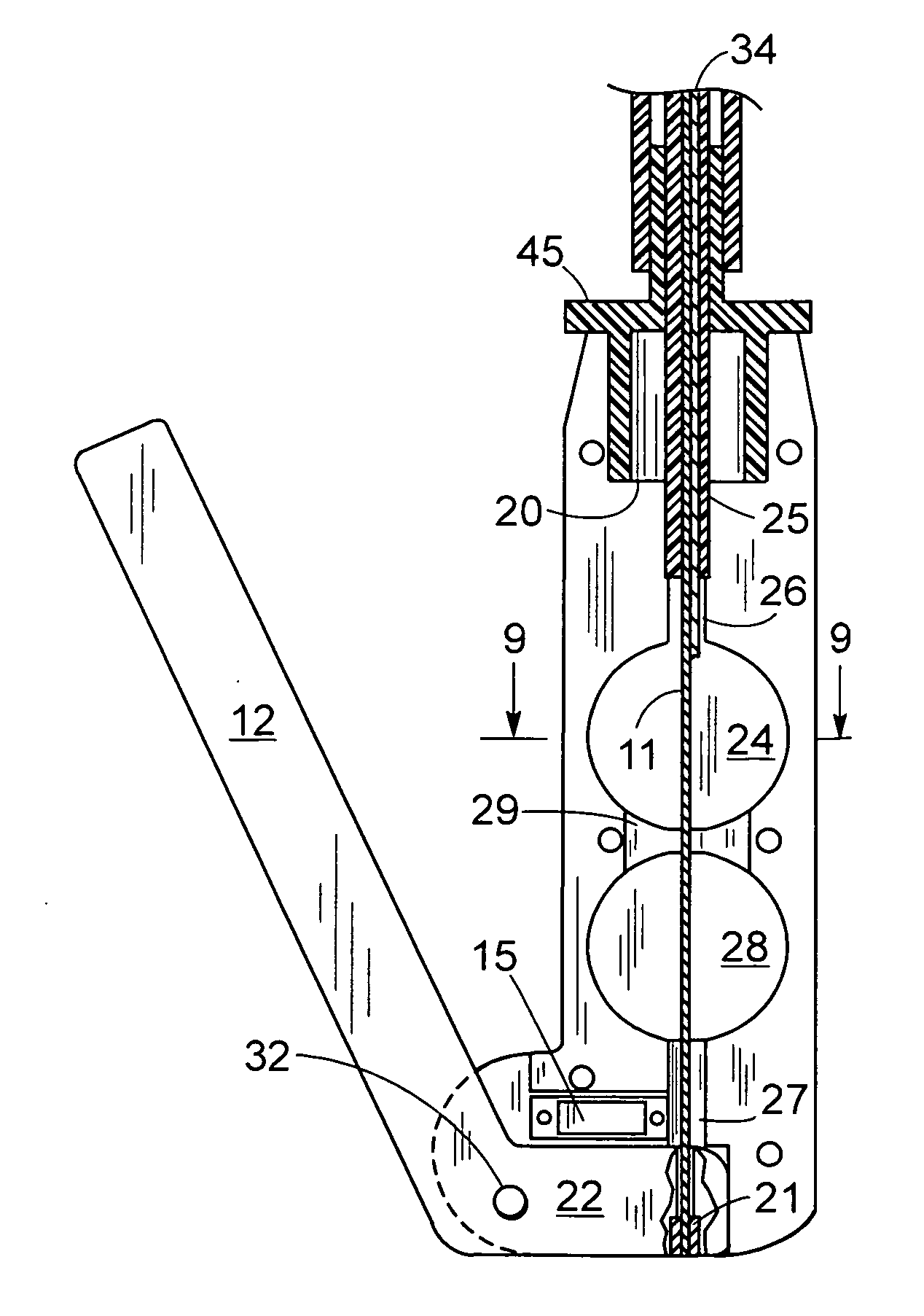
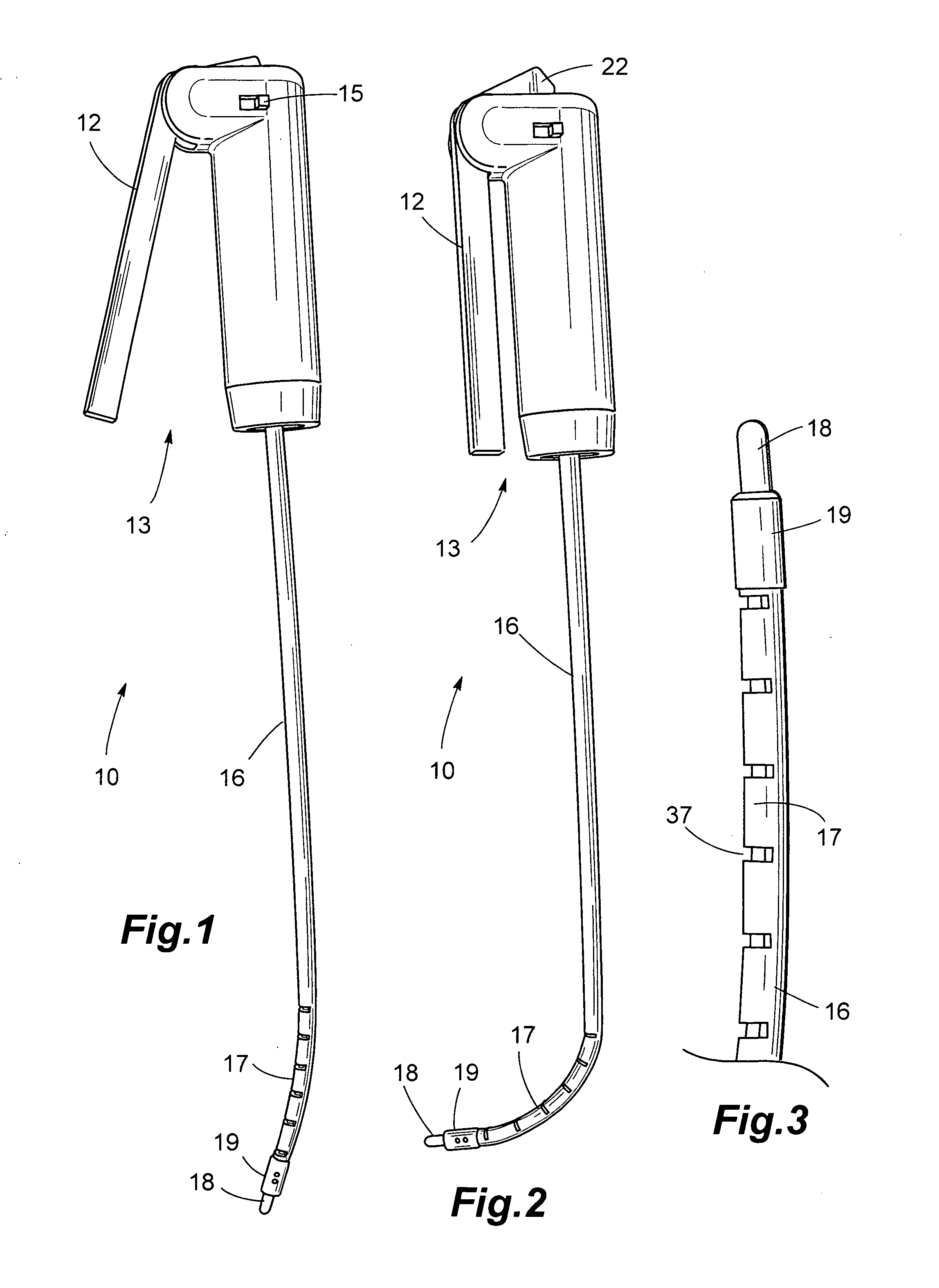
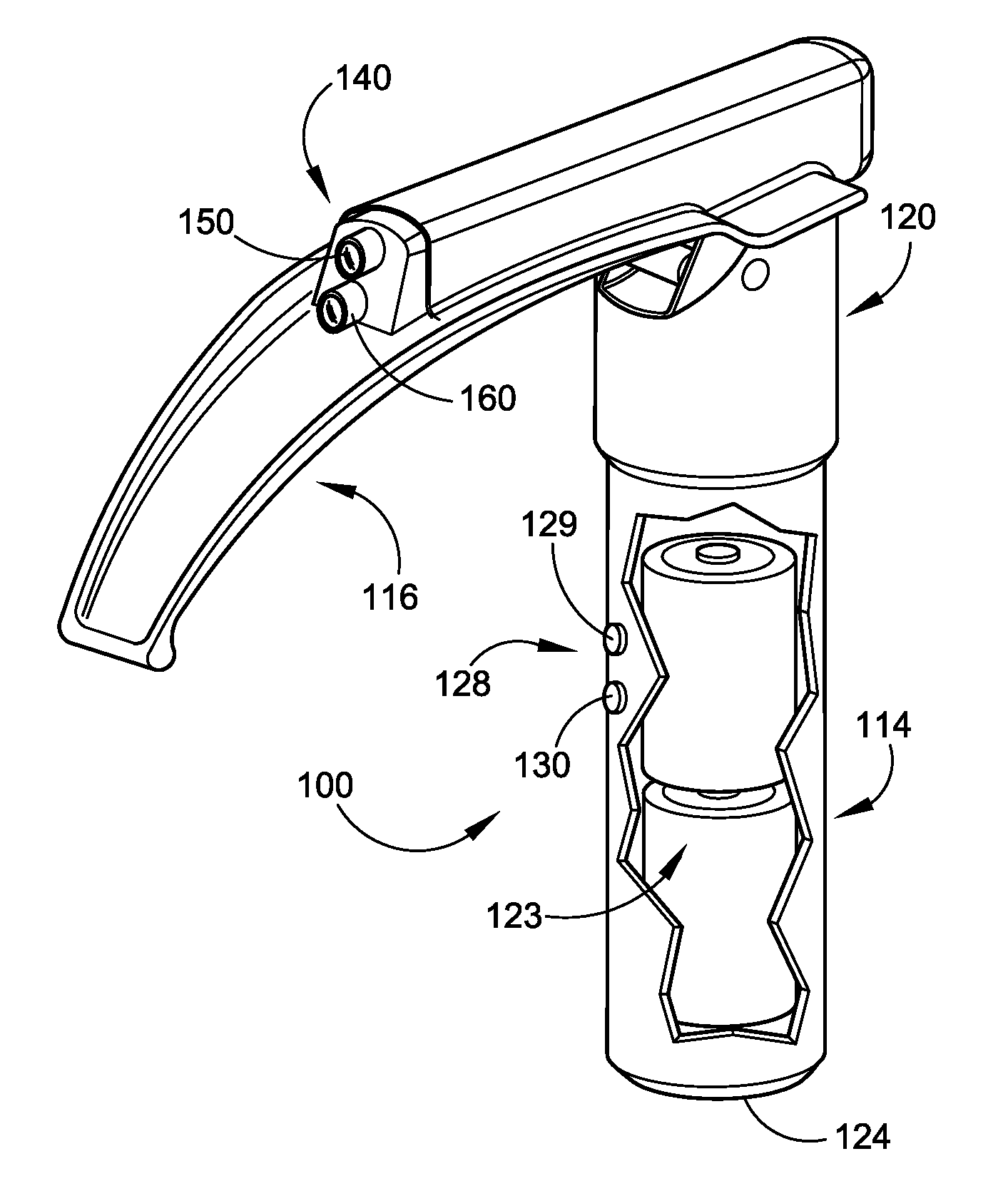
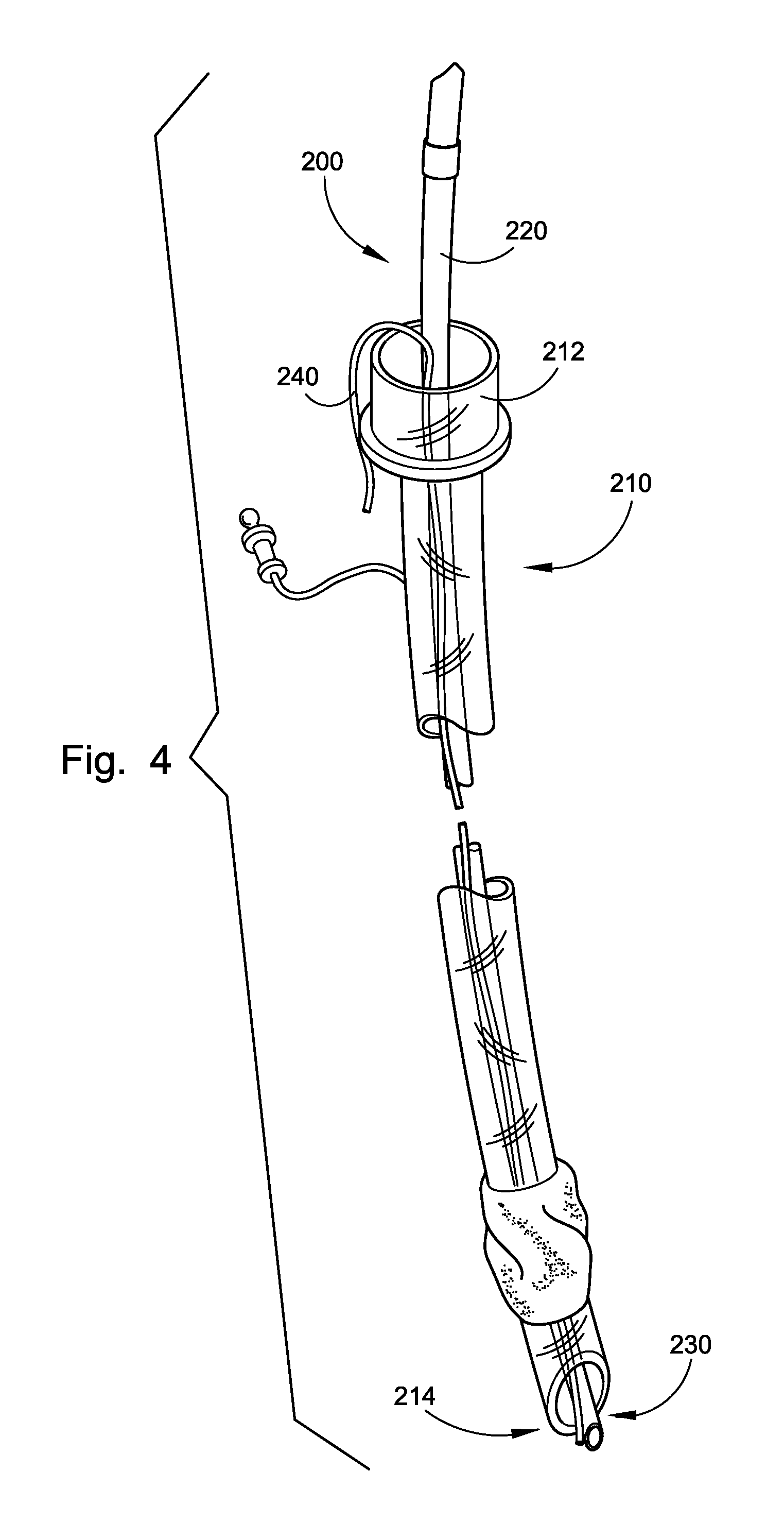
Endo-tracheal intubation device with adjustably bendable stylet
ActiveUS20110265789A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useTracheal tubesBronchoscopesControl mannerTracheal intubation
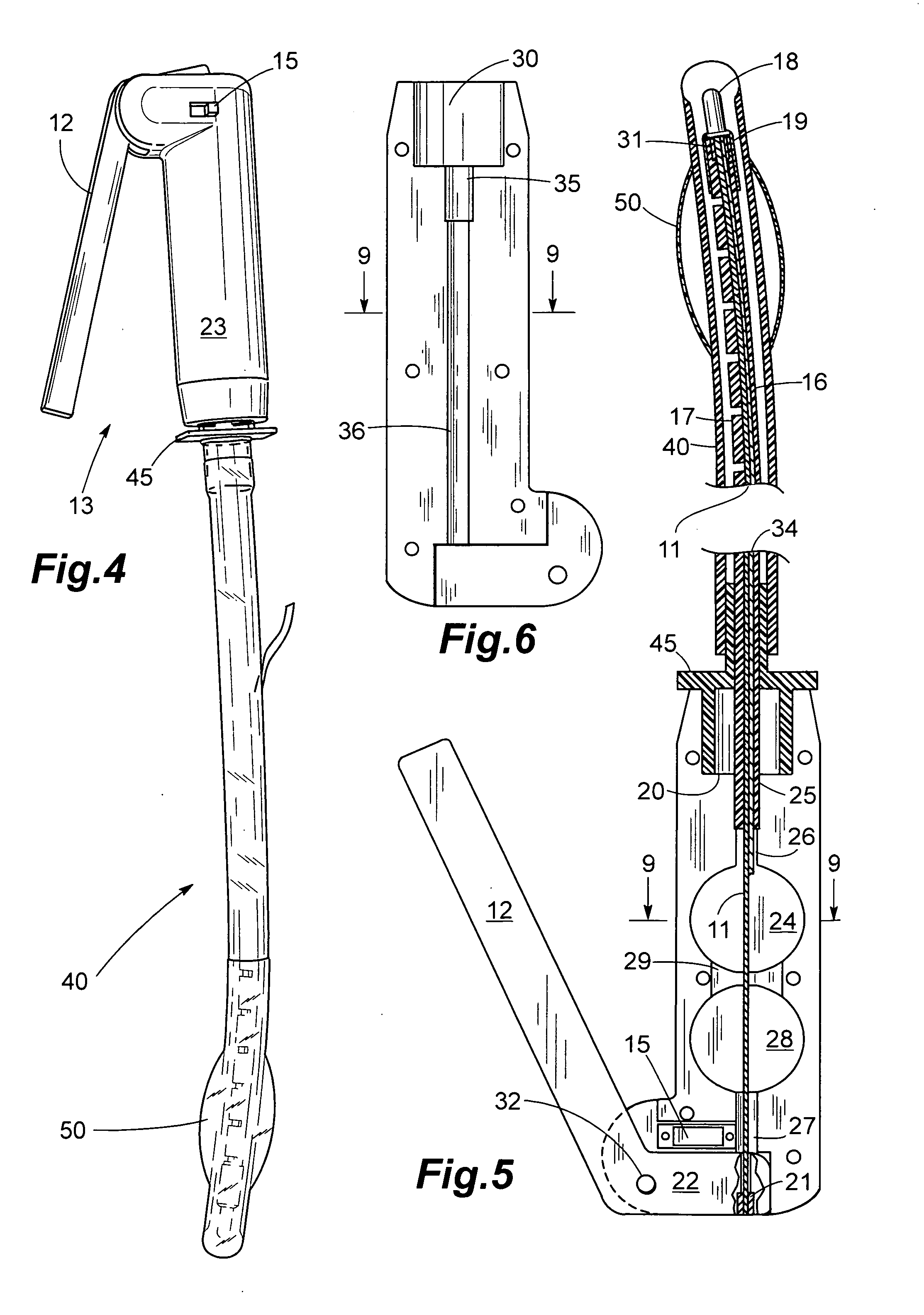
An inexpensive, endo-tracheal intubation device suitable for single patient use by emergency health care workers, which comprises a stylet having a tube which is scored in such a way that it can be bent using a wire encased in the tube. The wire is attached to both the stylet's end distal from a stylet-holder and to the short arm of a bell crank pivotally mounted in the holder. Grasping the stylet holder in one hand, the operator can move the bell crank's trigger arm with his finger(s), thereby causing the stylet to bend in a controlled manner. In use, a conventional airway tube is mounted on the stylet holder so as to encase the portion of the stylet which protrudes outwardly therefrom. A light on the stylet's tip allows visualization of the patient's vocal cords. After the user gently pushes the airway tube / stylet combination between them, the stylet is then removed for ventilation.
Owner:SYNCRO MEDICAL INNOVATIONS
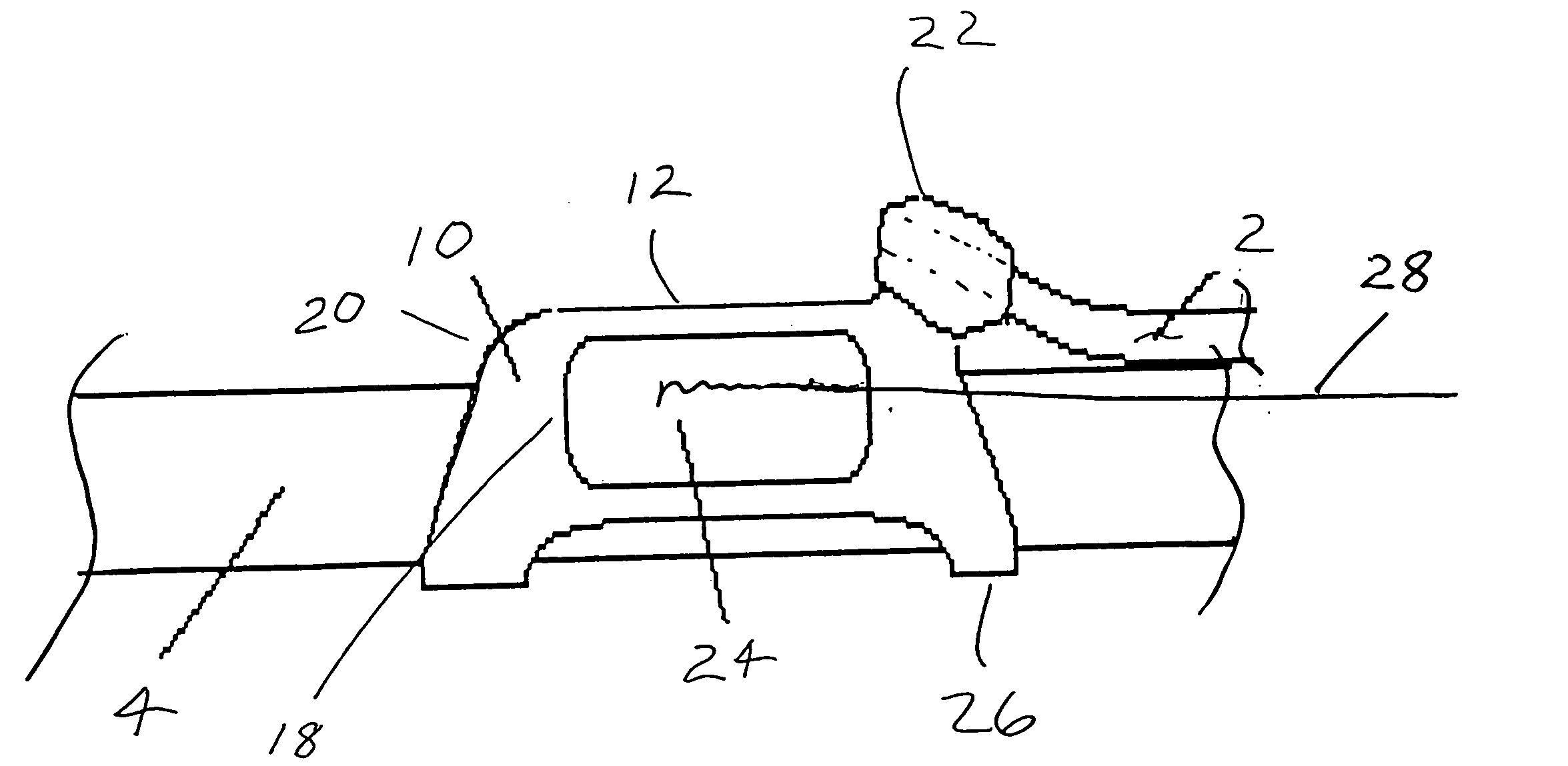
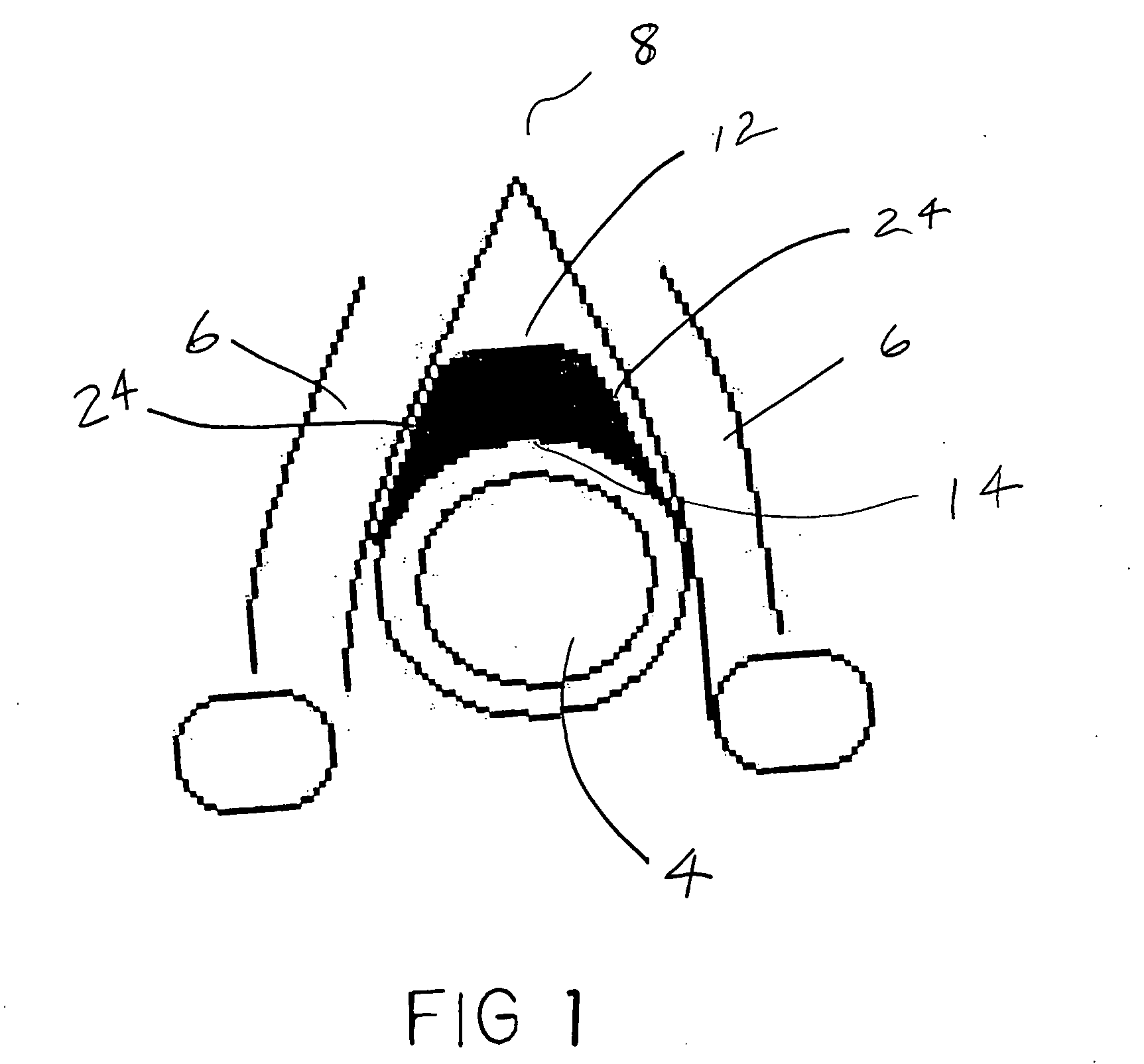
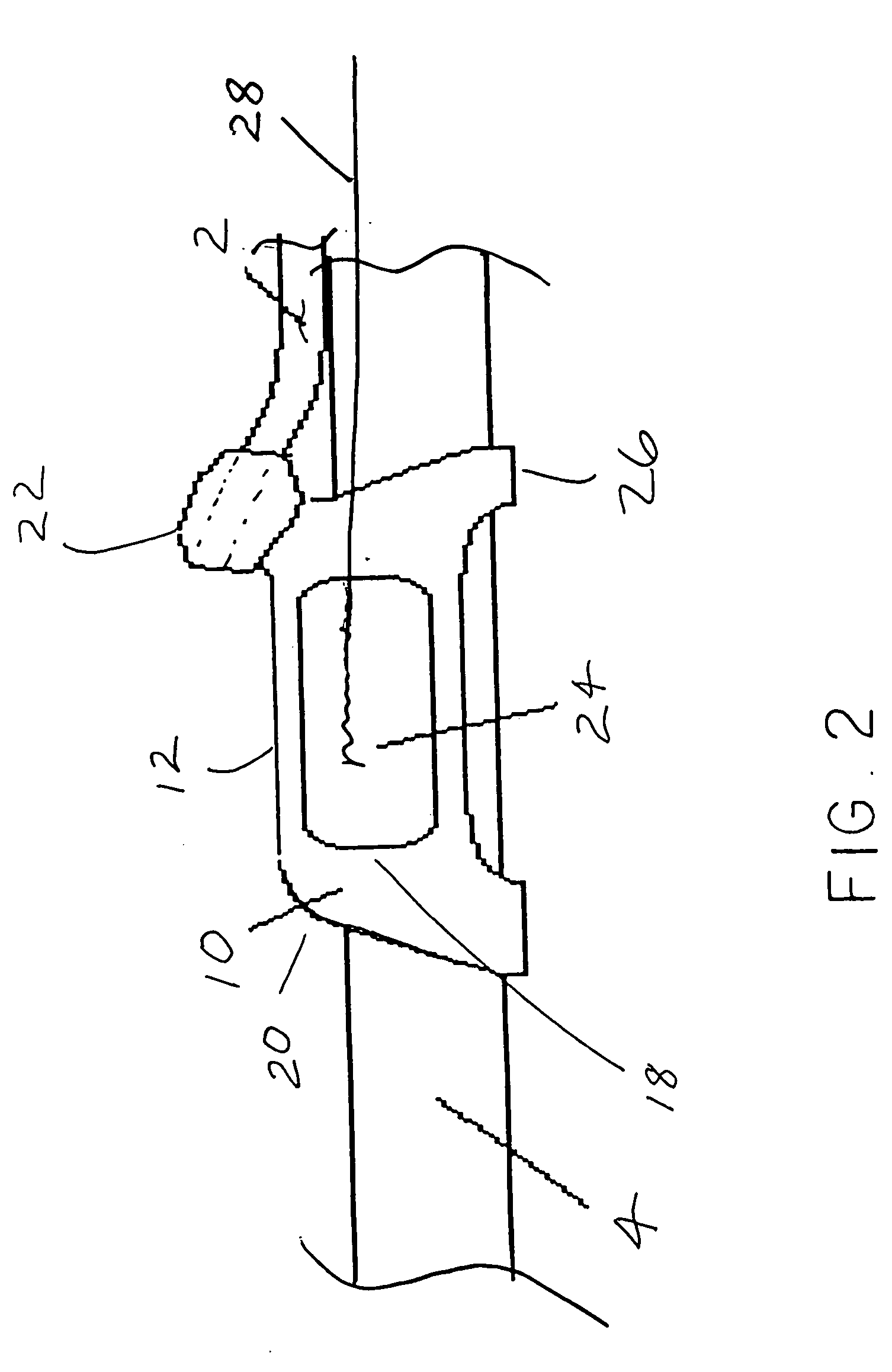
Endotracheal positioning device
An endotracheal positioning device having an elongated triangular shape with a superior surface that projects towards the junction of the vocal cords, a posterior surface that projects towards the endotracheal tube or the posterior-interior surface of the cricoid cartilage, and generally straight right and left lateral surfaces that project anterior lateral on either side toward the vocal cords. The lateral surface are of appropriate dimensions for attachment of laryngeal surface electrodes. The device has a center opening or channel that may wrap around, slide over, or may otherwise be attached to an endotracheal tube or to a high pressure ventilatory apparatus of any type. The device has an attachment or docking recess on its proximal aspect for an actuating rod or a fiber optic laryngoscope. This allows continuous viewing of the larynx for positioning, insertion, and continuous monitoring of the vocal cords during surgical procedures.
Owner:REA JAMES LEE
Devices and methods for preventing tracheal aspiration
Devices and methods for preventing tracheal aspiration as described where a cuff assembly having an inflatable member with an inflation tube fluidly coupled may be placed over a proximal end of an endotracheal tube or laryngeal mask and inserted into the patient trachea with the endotracheal tube or separately after the endotracheal tube has already been positioned. In either case, the inflatable member may be positioned distal (or inferior) to the vocal cords and proximal to the endotracheal balloon via a delivery instrument which automatically positions the balloon in proximity to the vocal cords.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Tissue augmentation material and method
InactiveUS7968110B2Reduce deliveryAnti-incontinence devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCelluloseCarrageenan
Owner:MERZ NORTH AMERICA
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Breathing assistance system with speech detection
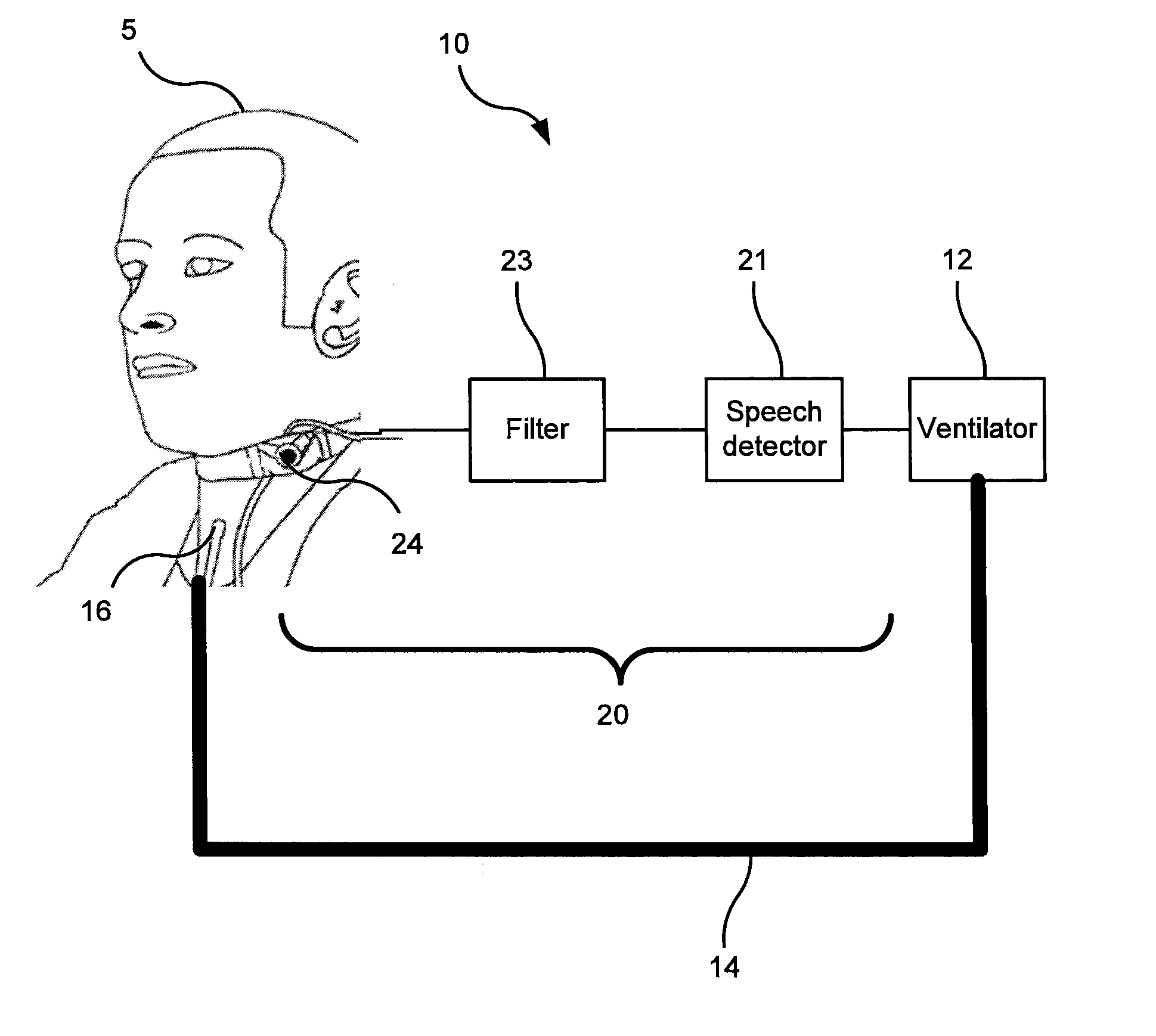
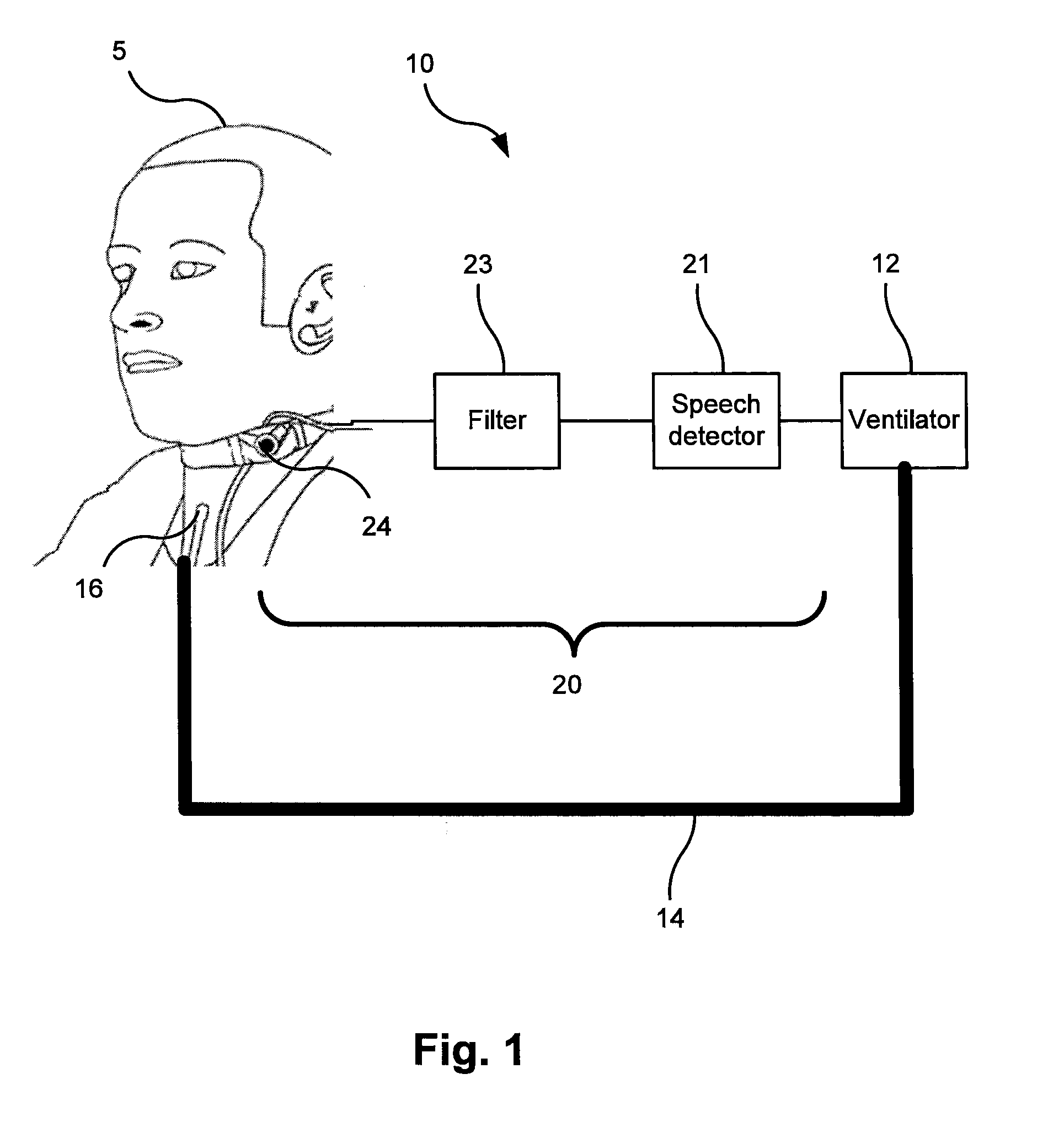
ActiveUS20150202395A1Improve comfortIncrease costTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheostomy tubesIntensive care medicine
Disclosed is a breathing assistance system (10) comprising: a ventilator (12), a breathing lumen (14) arranged to communicate a flow of air between the ventilator and a tracheostomy tube (16) in the trachea of a patient, and a sensor (24) configured to generate a vibration signal representing vocal cord vibrations of the patient. The system is configured to facilitate the flow of exhaled air to the atmosphere via the upper airway of the patient in response to detection in the vibration signal of speech or attempted speech by the patient.
Owner:RESMED PARIS
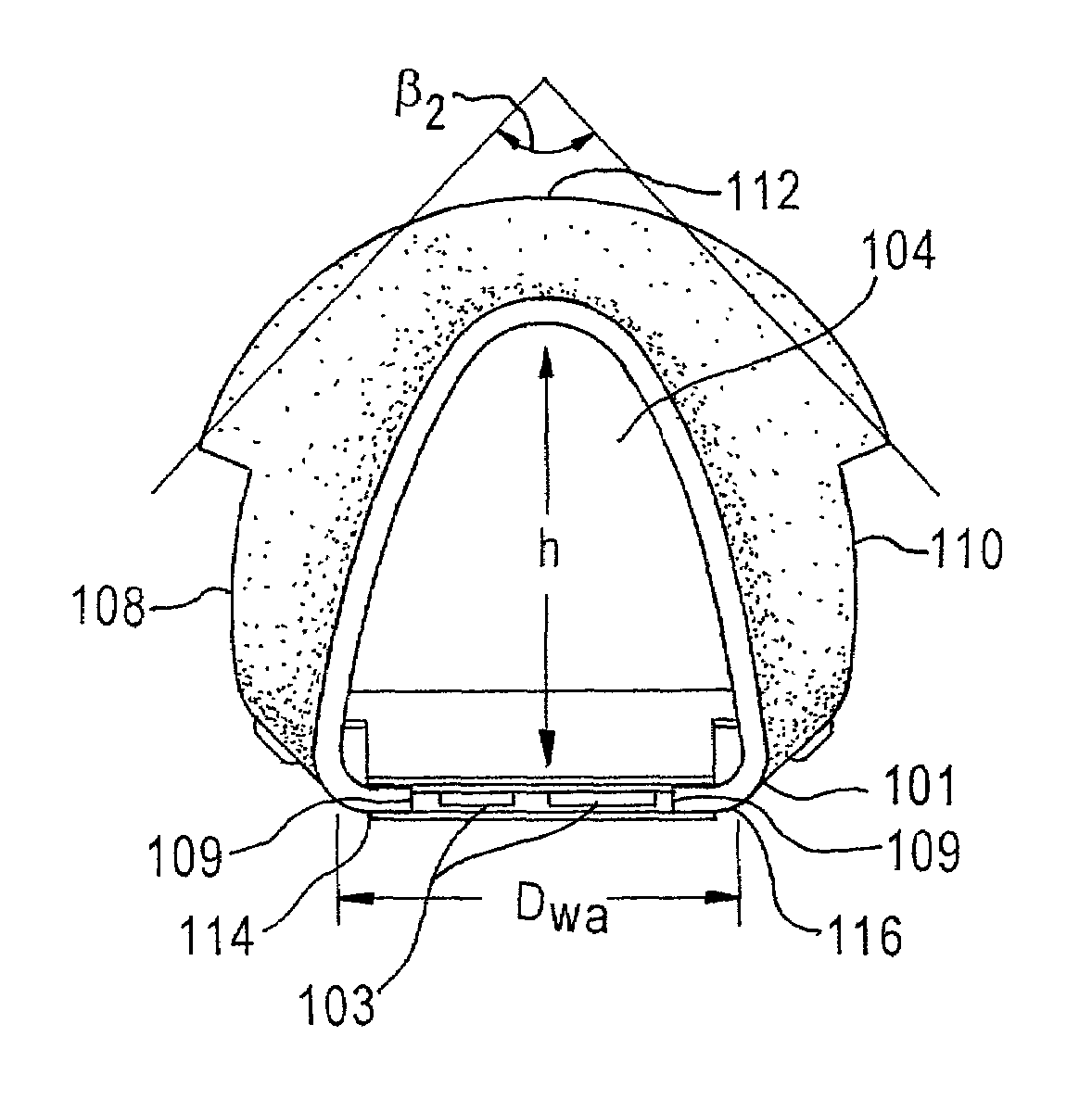
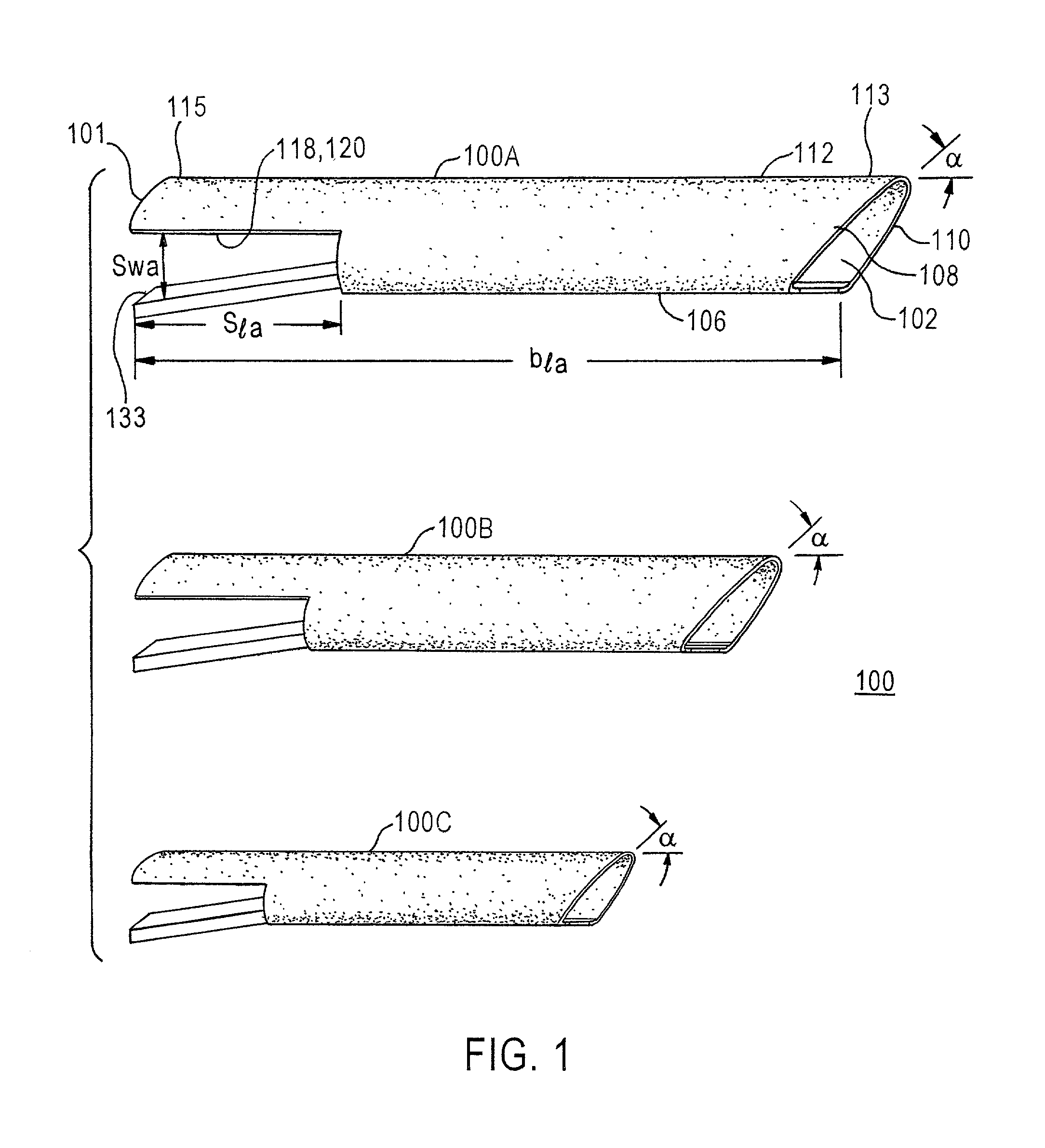
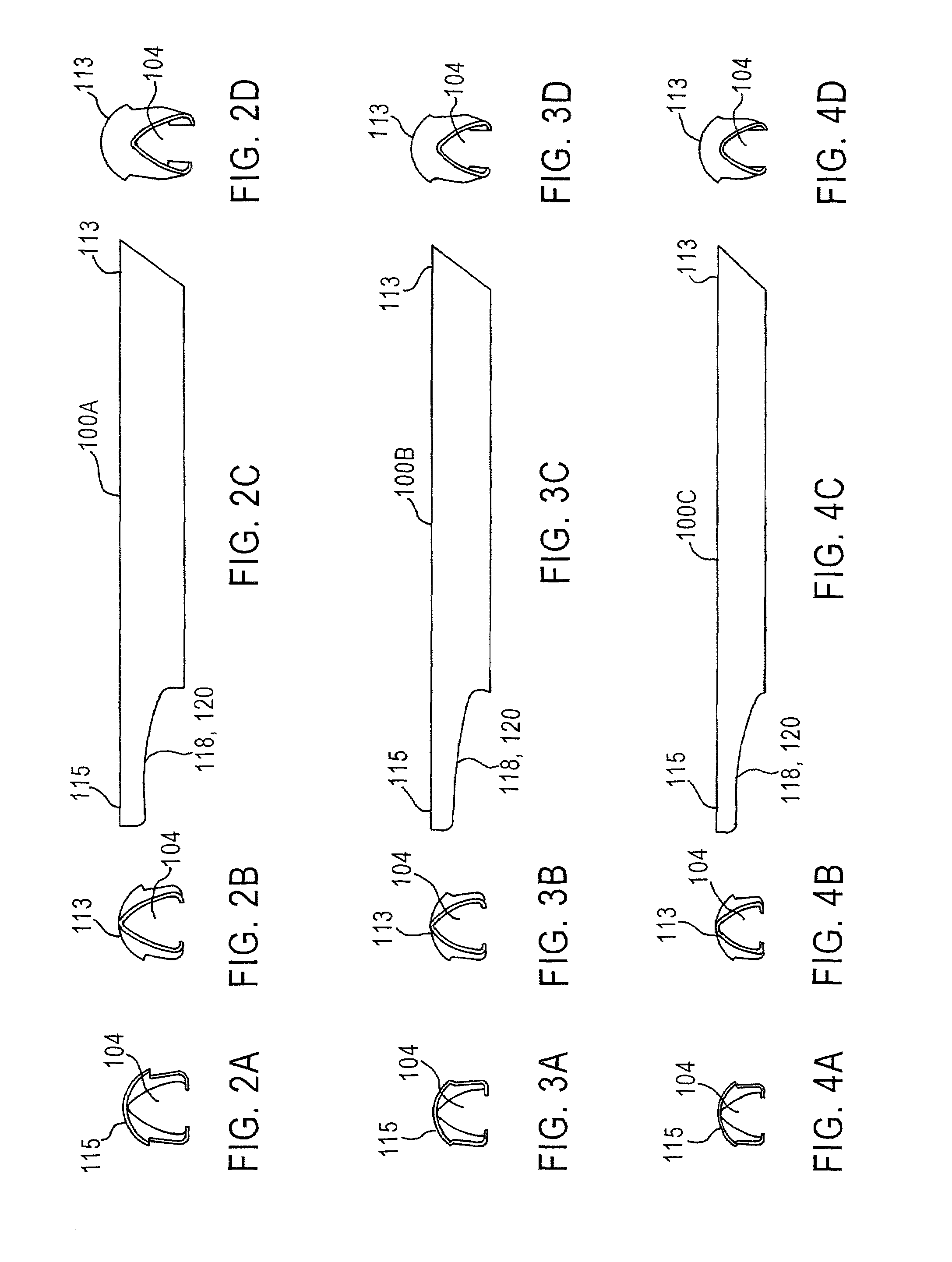
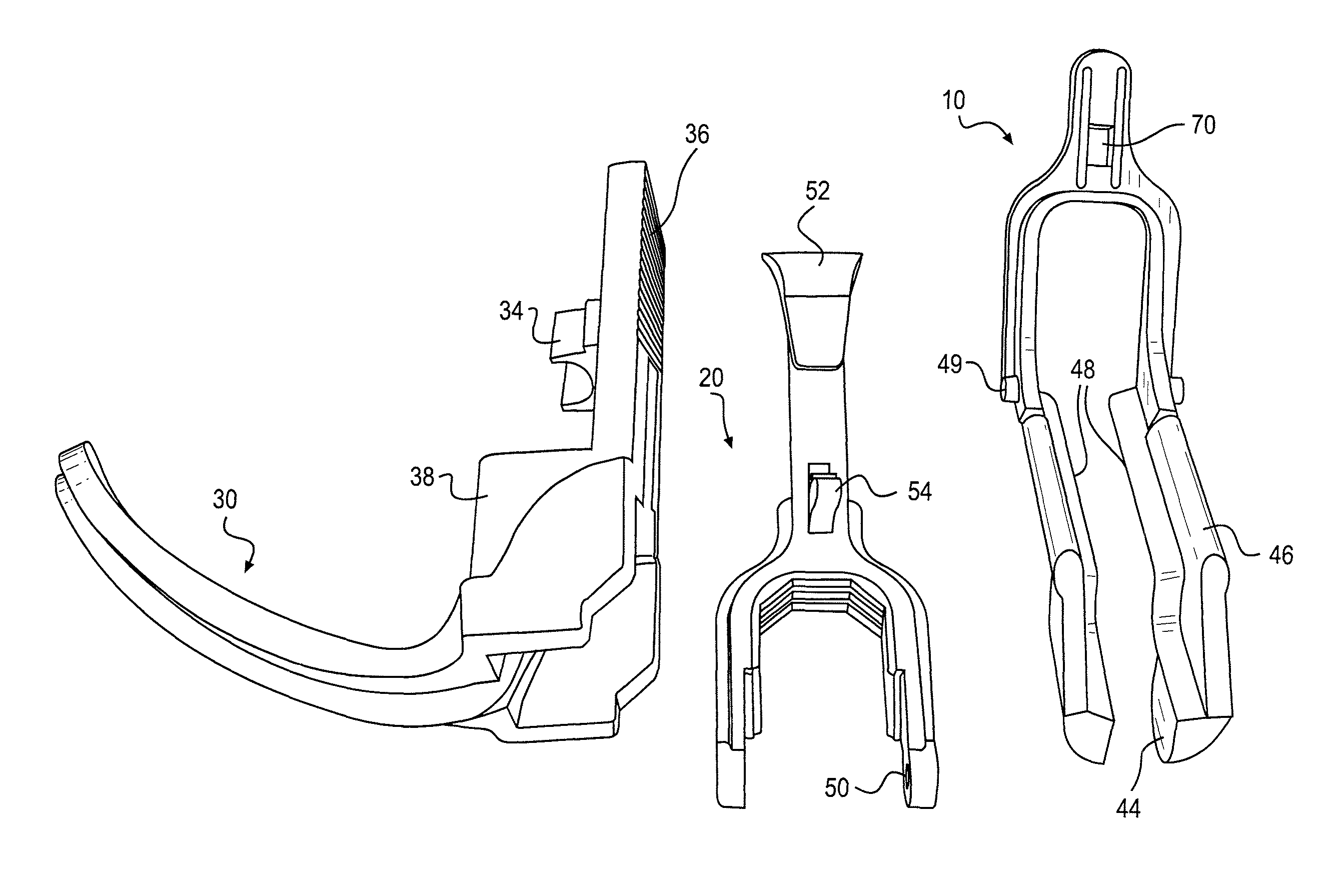
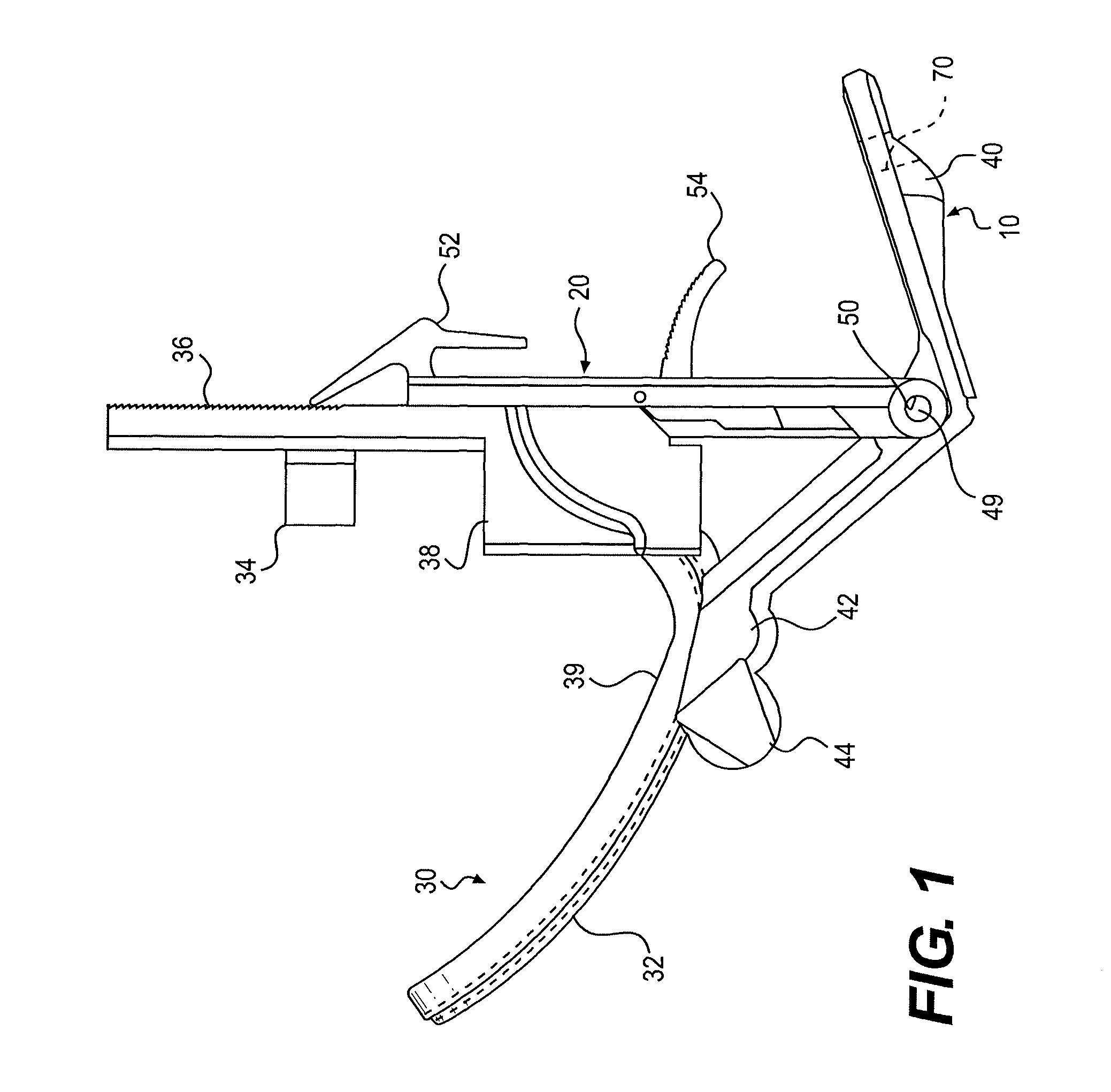
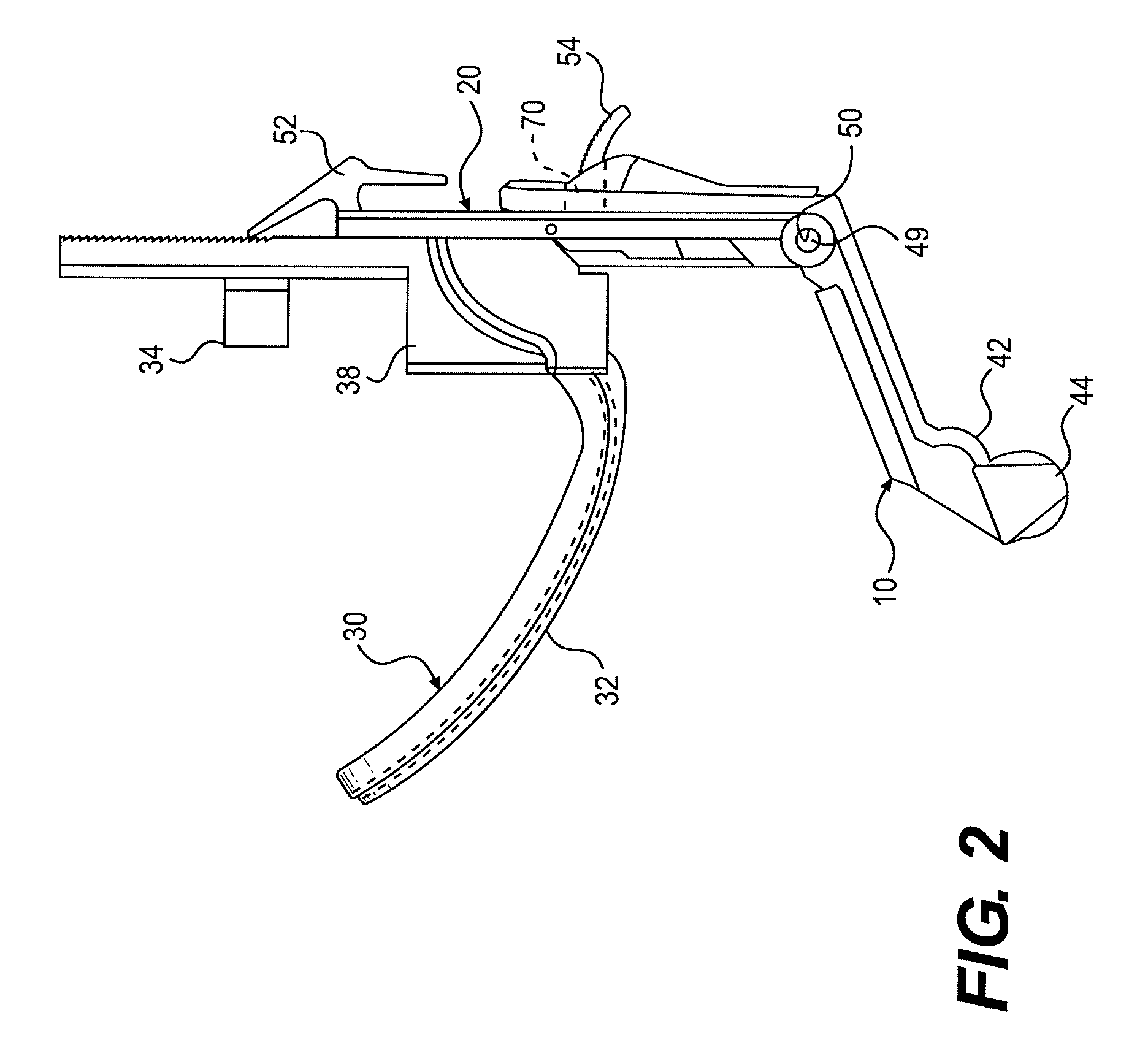
Universal modular glottiscope system having intra-wall channels for vocal fold microsurgery or orotracheal intubation
An element for a phonomicrosurgical modular glottiscope system comprises a proximal end; a distal end; a pair of opposing curved sides intersecting at an apex line; a substantially planar base, and internal channels disposed within the base. The base plate is removably attached to the pair of curved sides, and the base and curved sides define a lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. The internal channels include a first internal channel that provides illumination to the distal end and a second internal channel that provides aspiration to the distal end. In operation, the distal end of the element is inserted into a body cavity and the lumen provides visualization of the distal end and access to the distal end for tools inserted into the lumen from the proximal end. A method of manufacturing the element is also disclosed.
Owner:ZEITELS STEVEN M
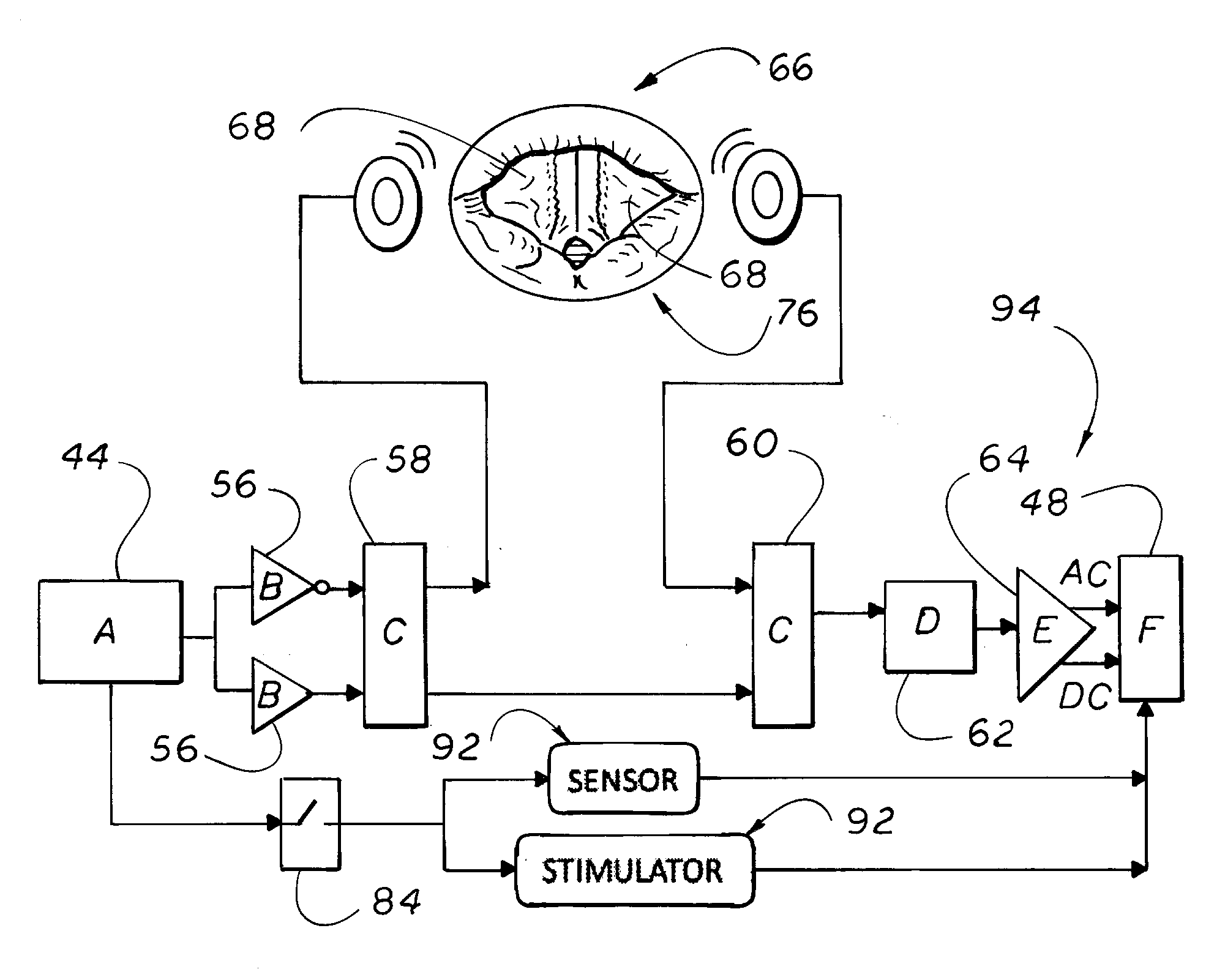
Methods and devices for diagnosing and treating vocal cord dysfunction
Methods for diagnosing and treating vocal cord dysfunction by recording the position of the vocal cords of a subject during a monitoring period are disclosed. Portable devices are disclosed using electronic signals to provide diagnostic data indicating a subject's closed or open vocal cords to diagnose and treat vocal cord dysfunction. Corresponding software and circuitry are also disclosed.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Dynamic vibrational method and device for vocal fold tissue growth
InactiveUS20100291045A1Induced differentiationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideCultured cellBiology
Dynamic vibrational methods and devices for inducing differentiation of stem cells into vocal fold fibroblast-like cells or for generating vocal fold-like tissue from cultured cells. Also provided are matrices providing sustained release of growth factors, and bioreactors generating and delivering a high frequency vibration with in-plane shear stress to cultured cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Laryngoscope and Method of Use
InactiveUS20090318769A1Improve visualizationGood colorBronchoscopesTracheal tubesEndotracheal intubationCatheter
A laryngoscope for use in viewing the vocal cords of a patient in performance of an endotracheal intubation. The laryngoscope includes a handle to be gripped by a medical professional in performing the endotracheal intubation; a blade portion extending from the handle to lift the patient's tongue and mandible for viewing the vocal cords and aid in the insertion of an endotracheal tube; a power source; and a black light source powered by the power source and carried by the blade portion to prompt the visible effects of fluorescence and phosphorescence with respect to the patient's vocal cords for viewing the vocal cords and passing of the endotracheal tube there between during endotracheal intubation.
Owner:SALTER LABS
Method for treating autism spectrum disorders
InactiveUS20100233662A1Increase range and complexityImproving production and perceptionTeaching apparatusOral pharyngealArticulatory gestures
A therapeutic method for developing the ability of subjects with autism spectrum disorders to produce and perceive spoken language, including sequentially modeling a set of words, the speaking of which involves making a first and a second articulatory gesture, as pictures corresponding to such words are displayed, in order to induce the subject to attempt to say the modeled words, until the subject is able to produce the constrictions of the oral-pharyngeal cavity associated with both of said articulatory gestures of the words together with vibration of the vocal folds, and the subject is able to produce such words intelligibly. The subject's ability is incrementally expanded using sets of words involving the making of other articulatory gestures until the subject is able to intelligibly produce words involving substantially all of the articulatory gestures used in the language of interest. Positive visual reinforcement is given to the subject for each word that the subject is able to produce intelligibly. For subjects having a level of intelligibility, the ability to produce generative speech is developed, first by displaying a set of pictures depicting actions corresponding to verbs, the speaking of which involves making a first articulatory gesture and modeling or phonetically facilitating the verb corresponding to each of said pictures until the subject is able to produce the verbs. Positive feedback is provided to the subject each time the subject says verb corresponding to one of said displayed pictures by animating said picture to produce the action corresponding to the verb. The subject's ability is expanded using sets of verbs involving the making of other articulatory gestures and further expanded using phrases containing such verbs with the display of corresponding pictures. In the next stage of the method the subject's ability to produce generative language is further expanded with the use of stories. The subject's progress is monitored by uploading and analyzing data including speech samples.
Owner:THE SPEECH INST
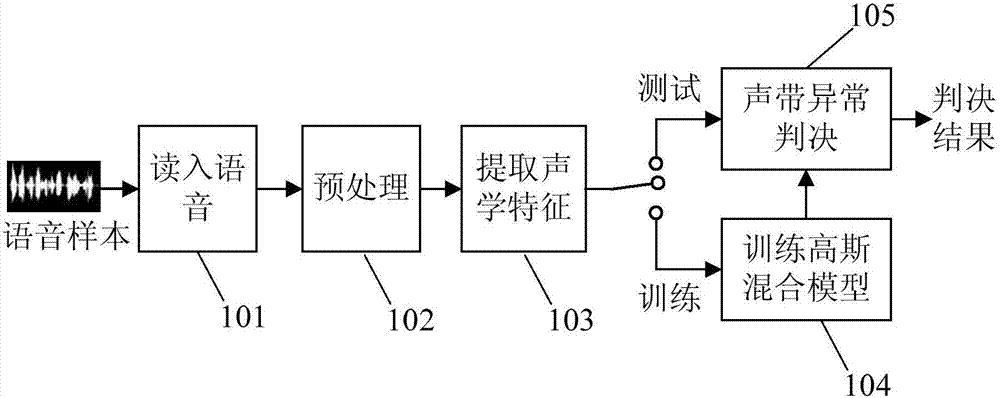
Vocal cord anomaly detection method based on acoustic phonetic features
The invention discloses a vocal cord anomaly detection method based on acoustic phonetic features. The method comprises the steps of firstly, extracting mel frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC), the fundamental frequency F0, the fundamental frequency perturbation Jitter, the amplitude perturbation Shimmer and the harmonics to noise ratio HNR for each frame of voices; adopting acoustic features as an input, and respectively training a Gaussian mixture model theta A and a Gaussian mixture model theta N based on the expectation-maximization EM algorithm, wherein the Gaussian mixture model theta A and the Gaussian mixture model theta N respectively represents the vocal cord abnormal state and the vocal cord normal state; finally, respectively inputting the feature matrix F of the test voice into the Gaussian mixture model theta A and the Gaussian mixture model theta N so as to obtain a corresponding output probability P (F|theta A) and a corresponding output probability P (F|theta N). If the P (F|theta A) is larger than the P (F|theta N), the vocal cord of the speaker of the test voice is abnormal. Otherwise, the vocal cord of the speaker of the test voice is normal. According to the technical scheme of the invention, multiple sets of acoustic features, adopted as the inputs of Gaussian mixture models, are extracted from the test voice, wherein the acoustic features can effectively reflect the state of the vocal cord. Therefore, voices in the vocal cord abnormal state and in the vocal cord normal state can be effectively distinguished. As a result, whether the vocal cord of the speaker of the test voice is abnormal or not can be judged. The method has the advantages of non-intrusion, convenience, low cost and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
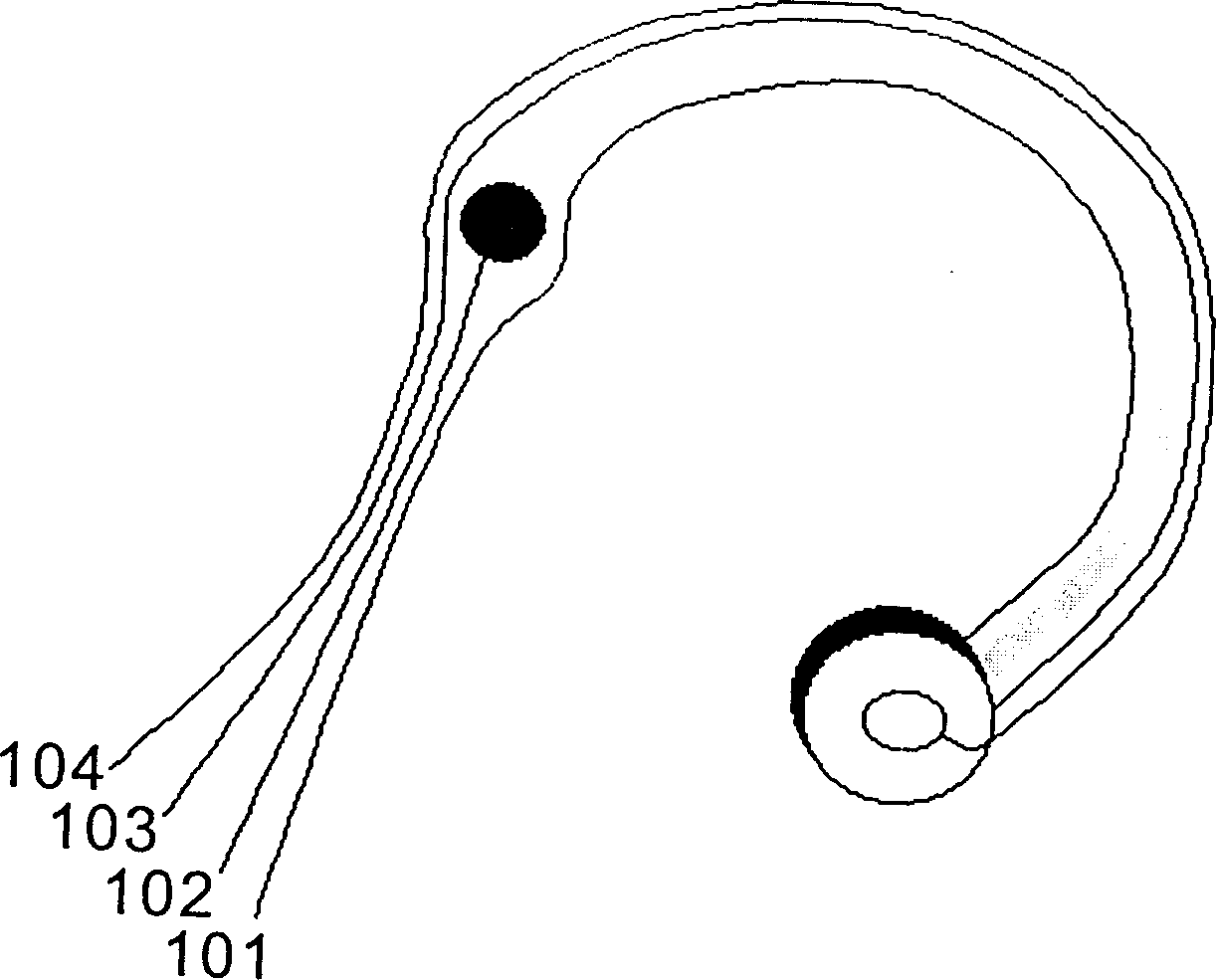
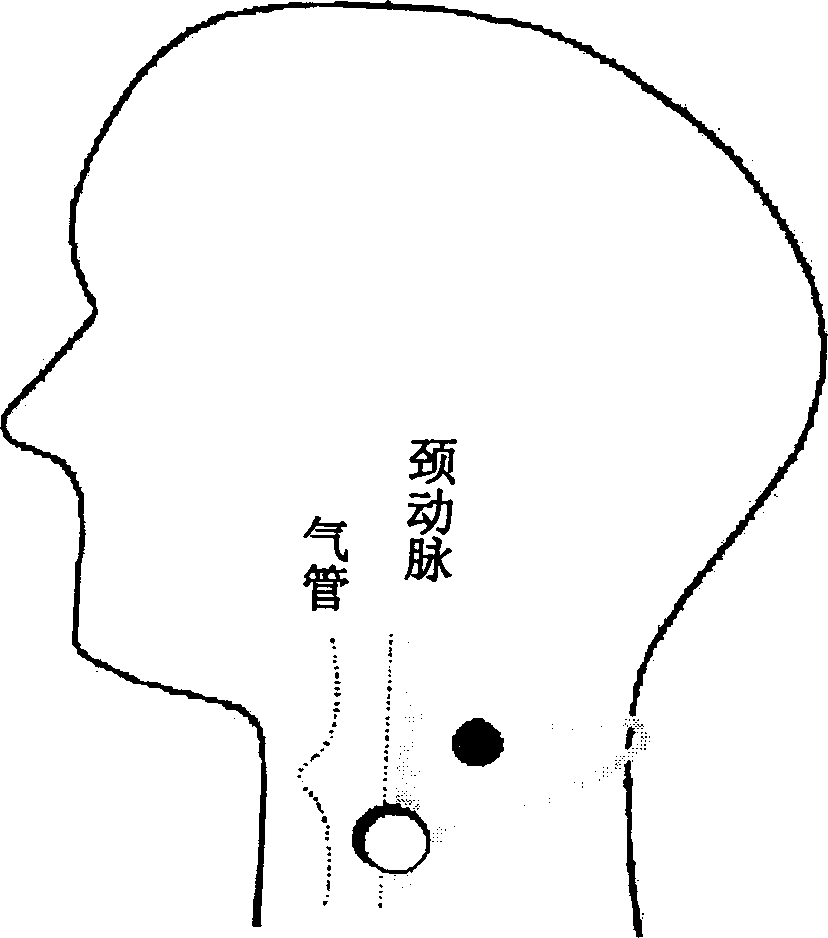
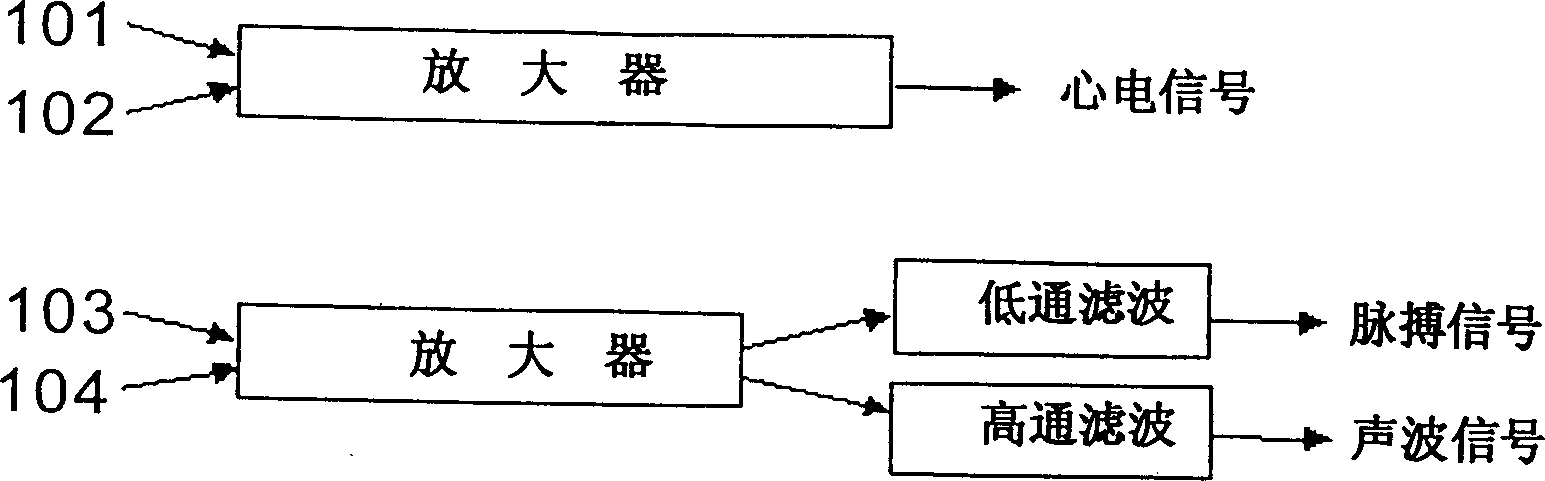
Sensor capable of synchronously measuring electrocardio, pulse and sound-wave signals from neck
The present invention discloses a kind of sensor and an analysis system capable of simultaneously measuring three kinds of basic physiological signals of electrocardiosignal, pulse and sound wave to make computer digital diagnosis to obtain the physiological indexes of cardiac function, automatic nervous function, vocal fold function and respiratory tract function. Its measured physiological signal can be processed by on-line analysis mode or off-line analysis mode after it is stored, it can utilize digital communication to make on-line or off-line analysis to attain the goal of communication diagnosis, curing or heat-care.
Owner:LEADTEK
Device for self-monitoring of vocal intensity
InactiveUS20060183964A1Improve speech clarityImprove intelligibilityStammering correctionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesVocal intensityVisual perception
A device to monitor vocal information such as vocal volume and frequency and provide such information in a plurality of forms, such as tactile, audible, temporal, and visual; and to induce altered vocal volume and / or frequency by altering how the user hears his or her voice, such as by shifting the frequency at which the user hears his or her own voice; for the treatment of vocal nodules, Parkinson's disease, or stuttering.
Owner:KEHOE THOMAS DAVID
Laryngoscope
ActiveUS8083672B2Strong and reliable and inexpensive and simple to useBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesTracheal tubeCatheter
Owner:MINSON MATTHEW
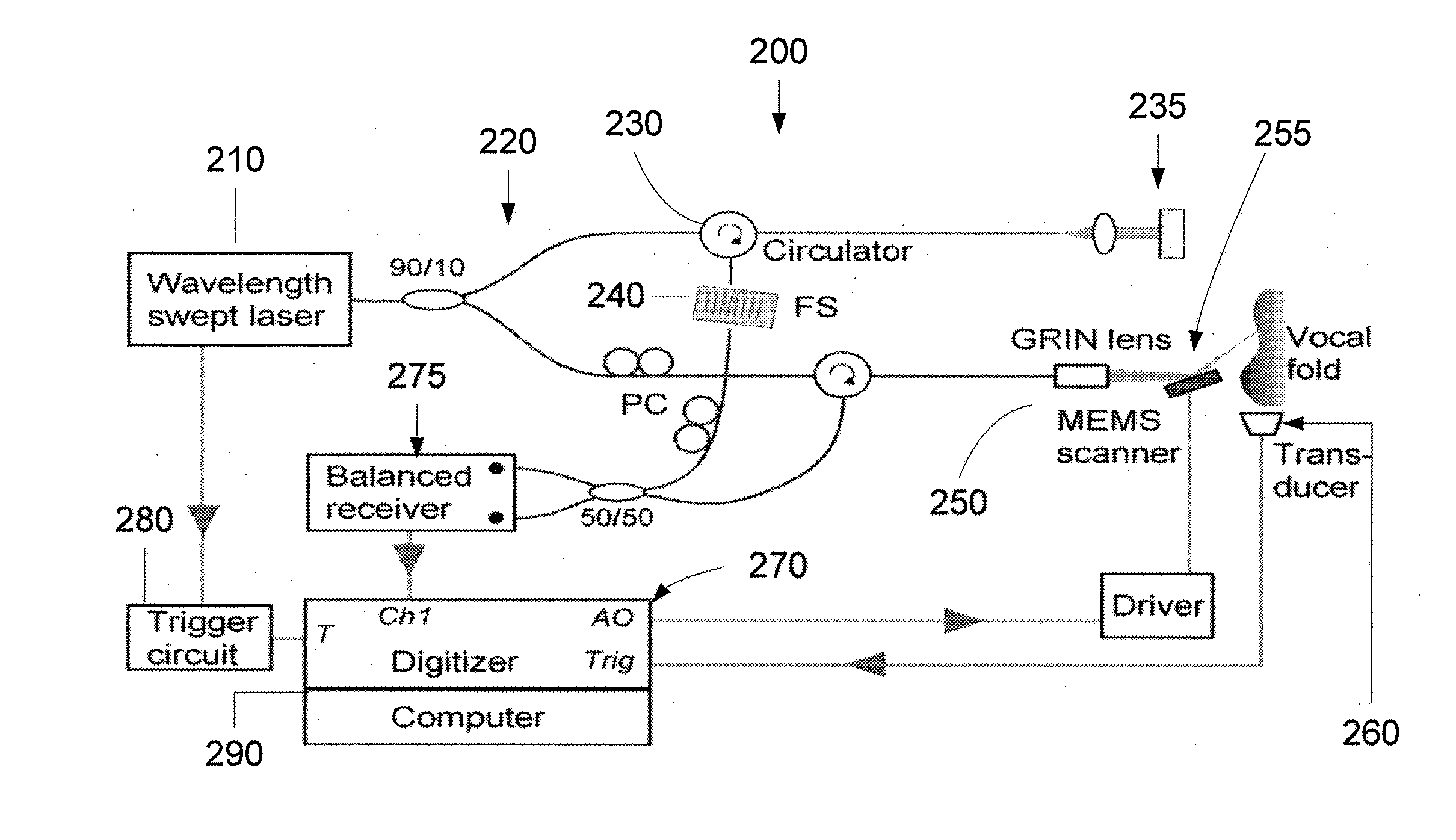
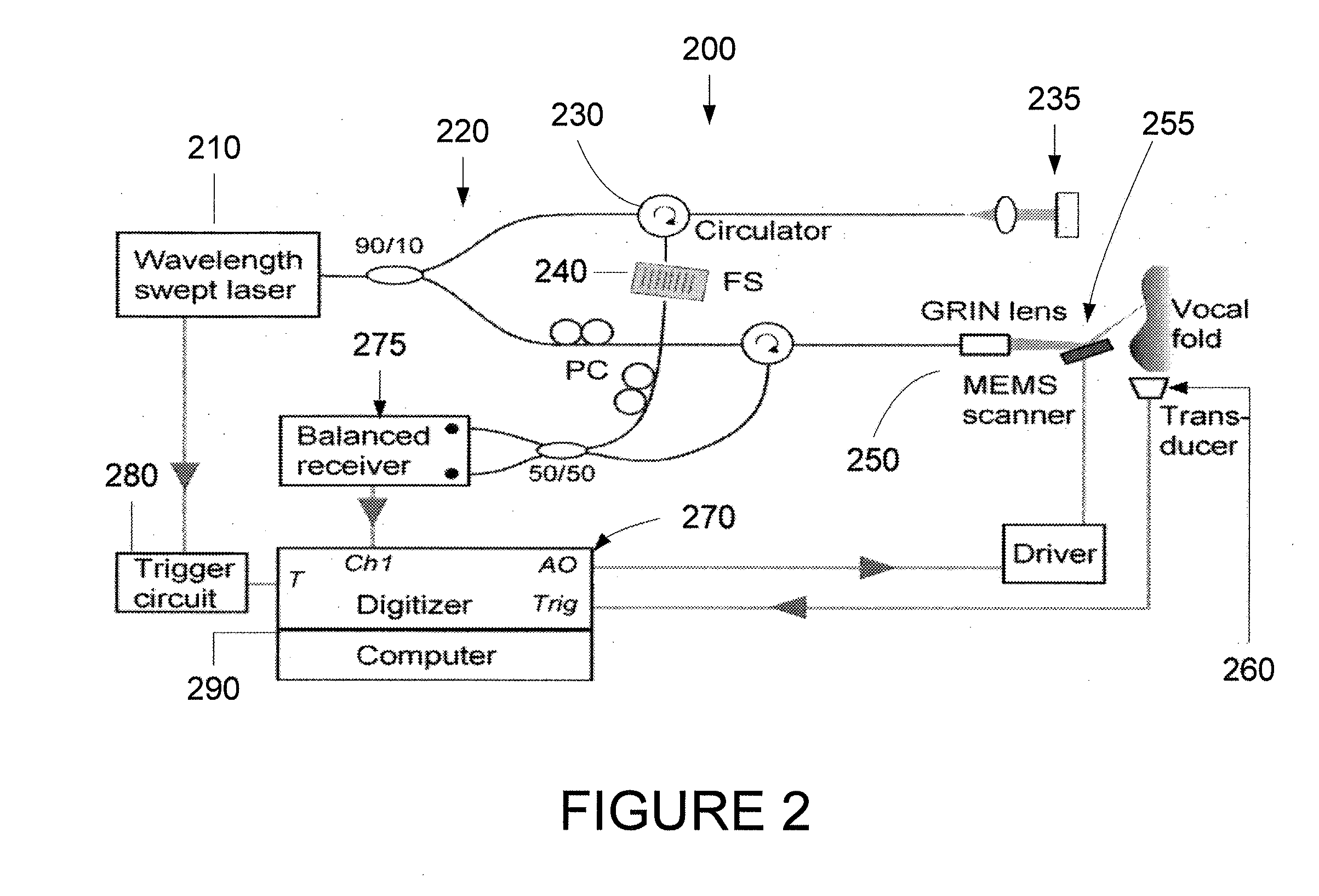
Methods and arrangements for analysis, diagnosis, and treatment monitoring of vocal folds by optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20110224541A1Enhance the imageStable phonationBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesSingle cycleComputer science
Exemplary embodiments of an apparatus and a method can be provided. For example, a first information can be obtained for at least one signal that is (i) at least partially periodic and (ii) associated with at least one structure. In addition, a second information associated with the structure can be generated at multiple time points within a single cycle of the at least one signal. The second information can include information for the structure below a surface thereof. Further, it is possible to generate a third information based on the first information and the second information, where the third information is associated with at least one characteristic of the structure.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
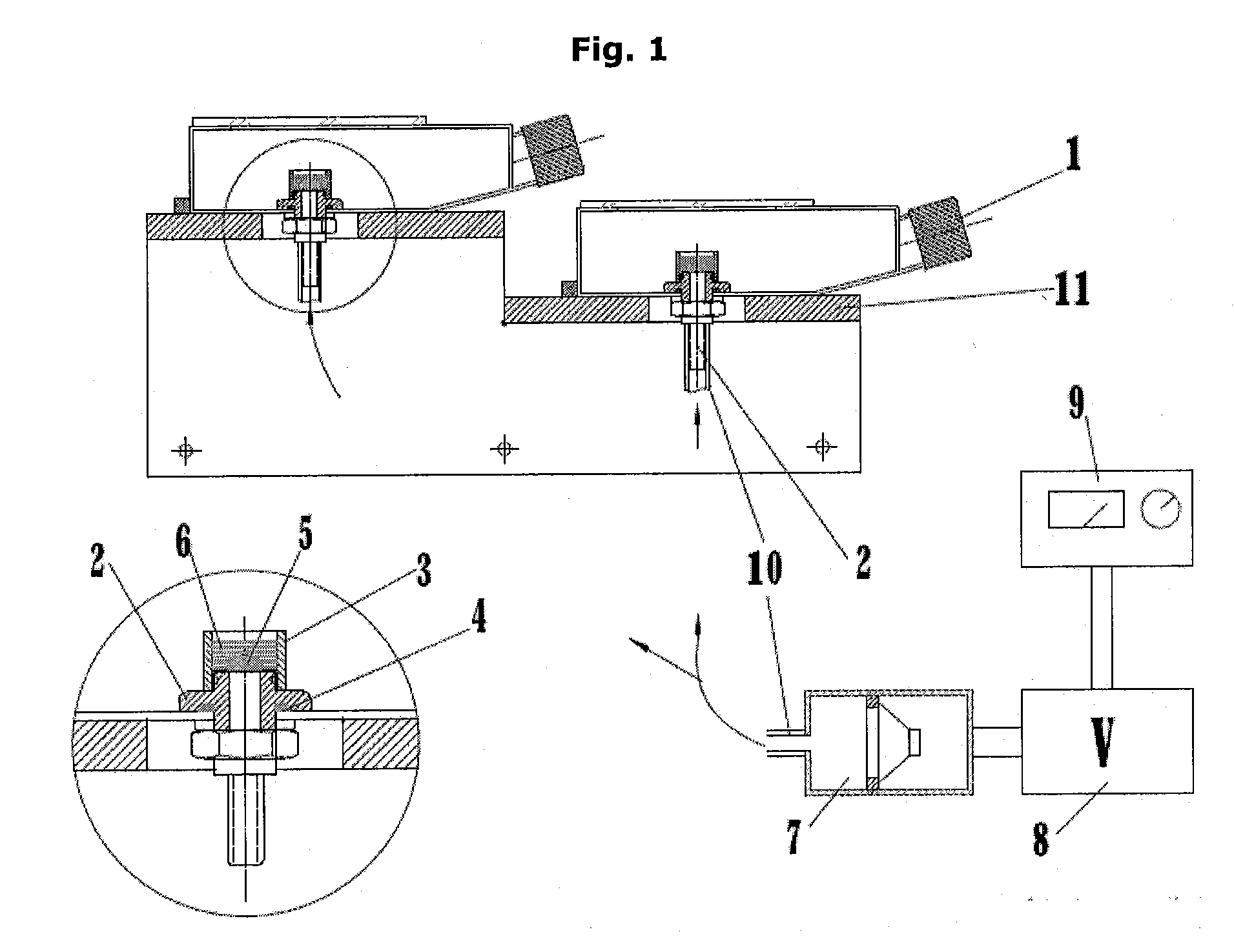
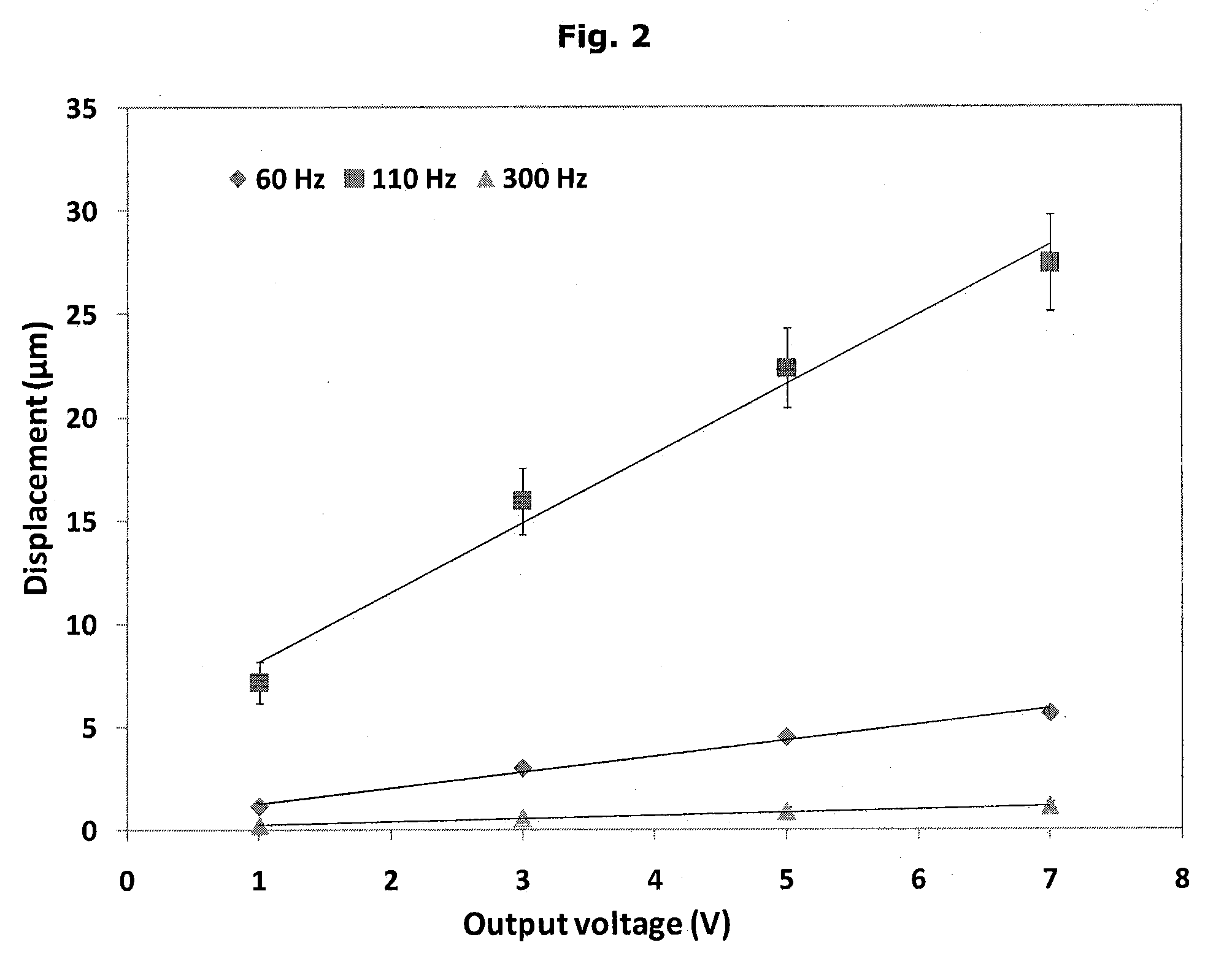
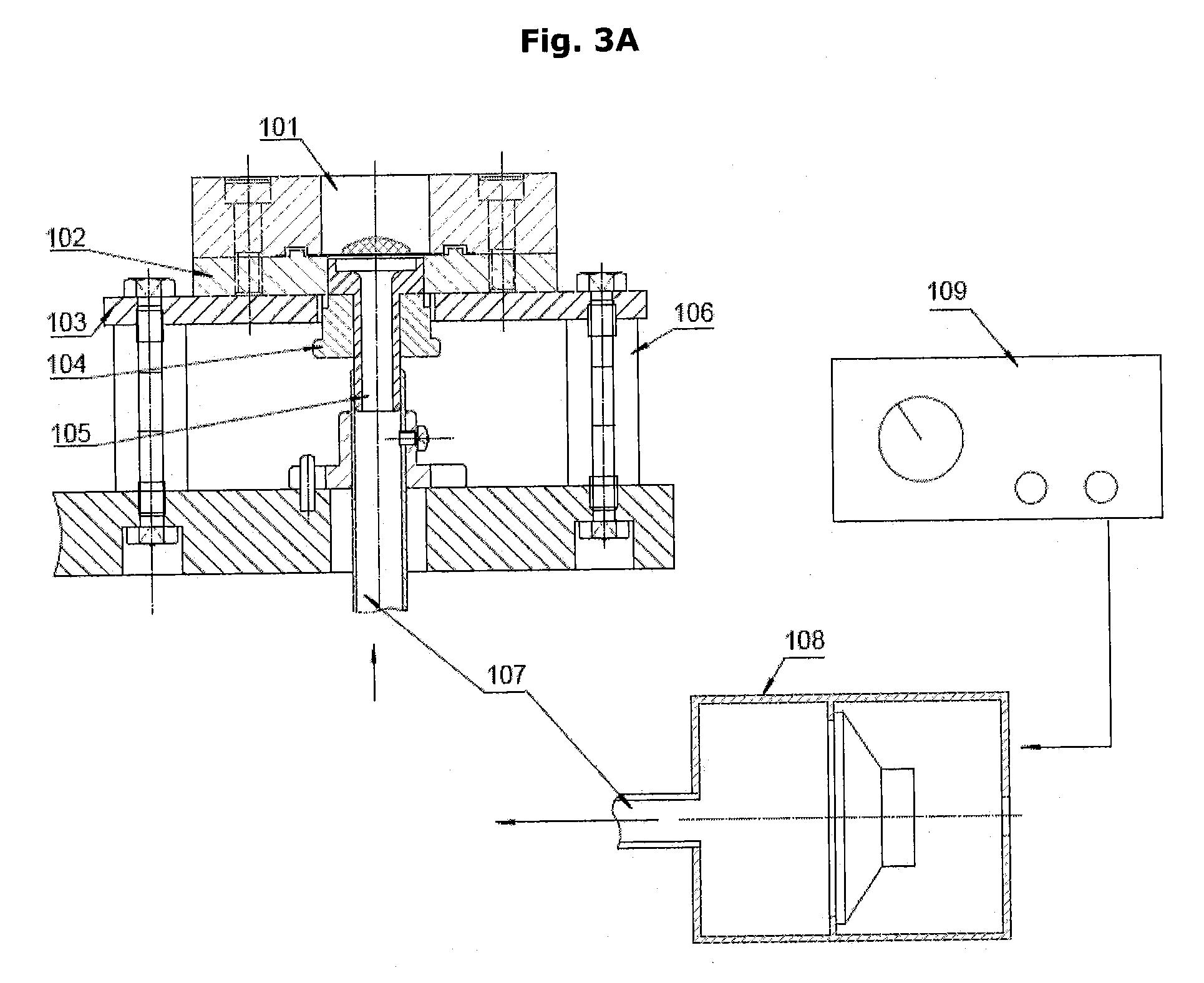
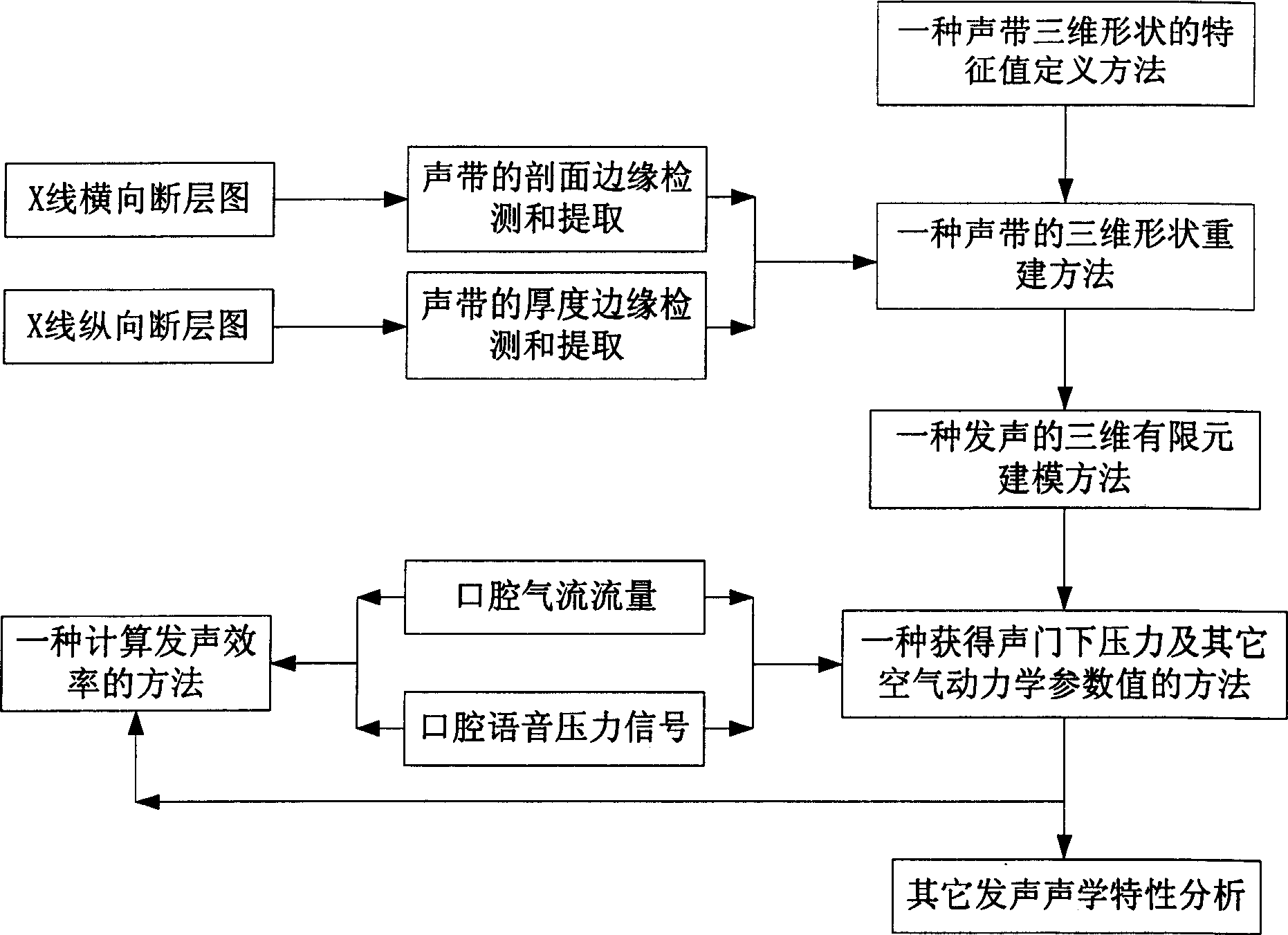
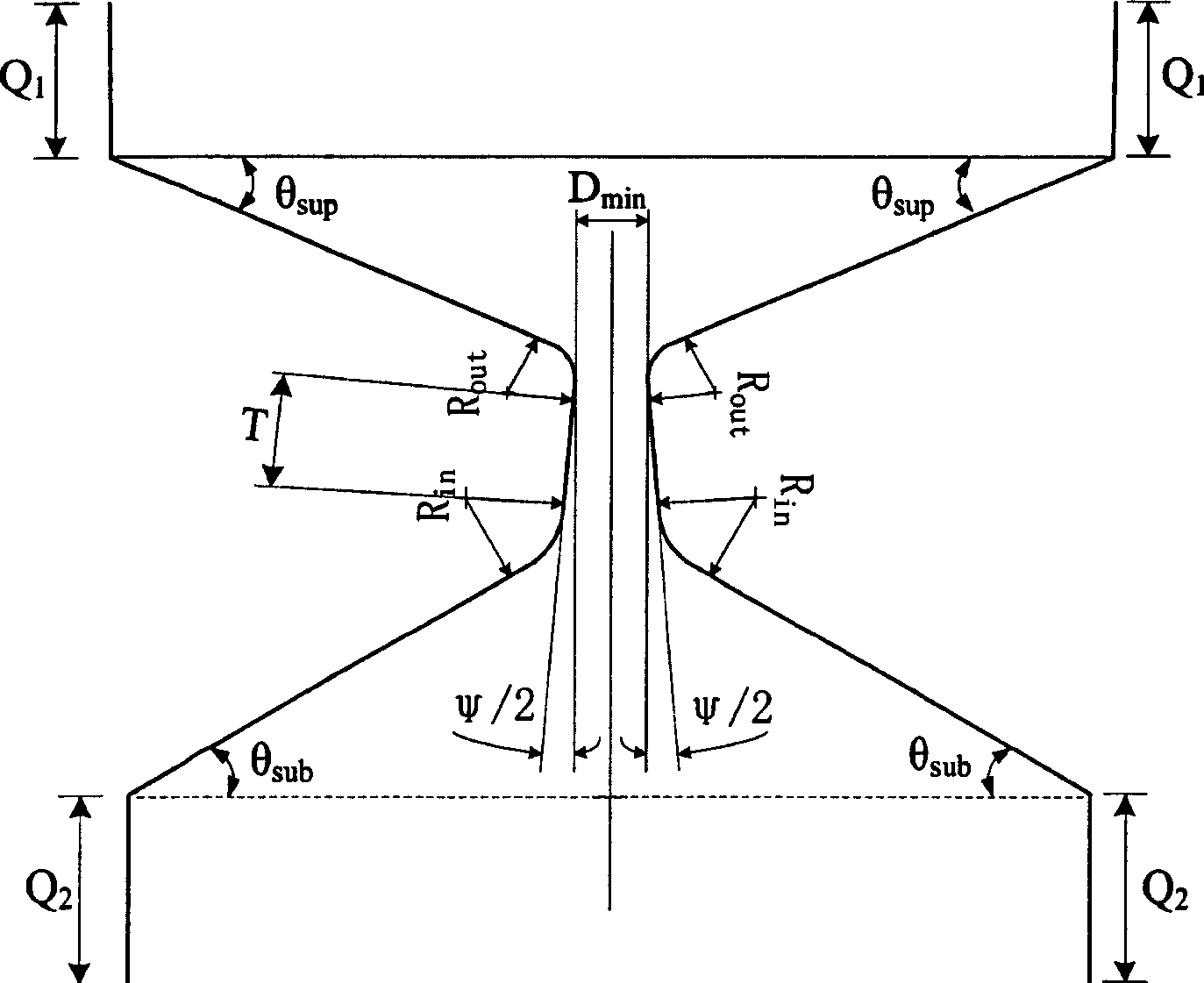
A method for obtaining subglottic pressure value and calculating phonation efficiency
The invention discloses the glottal pressure and computational sounding efficiency and aerodynamics parameter value on the base of aerodynamics modeling technology. The method comprises as follows: providing the method of defining vocal fold three-dimensional geometrical form characteristic value; offering the vocal fold surface three-dimensional reconstruction method; providing the aerodynamics modeling method which is based on three-dimensional finite element algorithm; providing the method of getting glottal pressure and computational sounding efficiency. The method is used to auxiliary diagnose throat, and has significant meaning in sounding function evaluation, sounding physiology, basic research, artistic noise, phonetic science, speech signal processing and linguistic science.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com