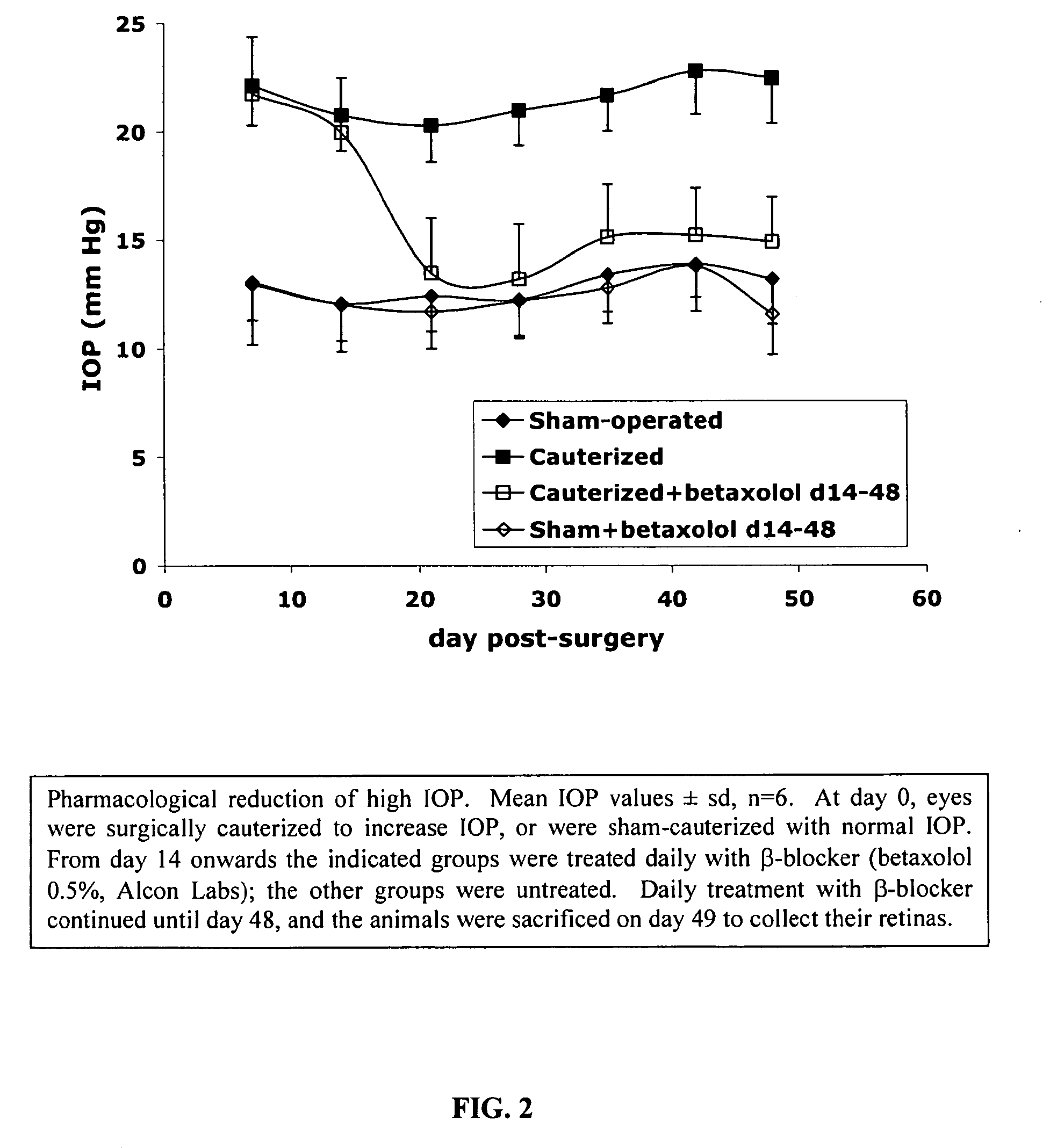
Patents
Literature
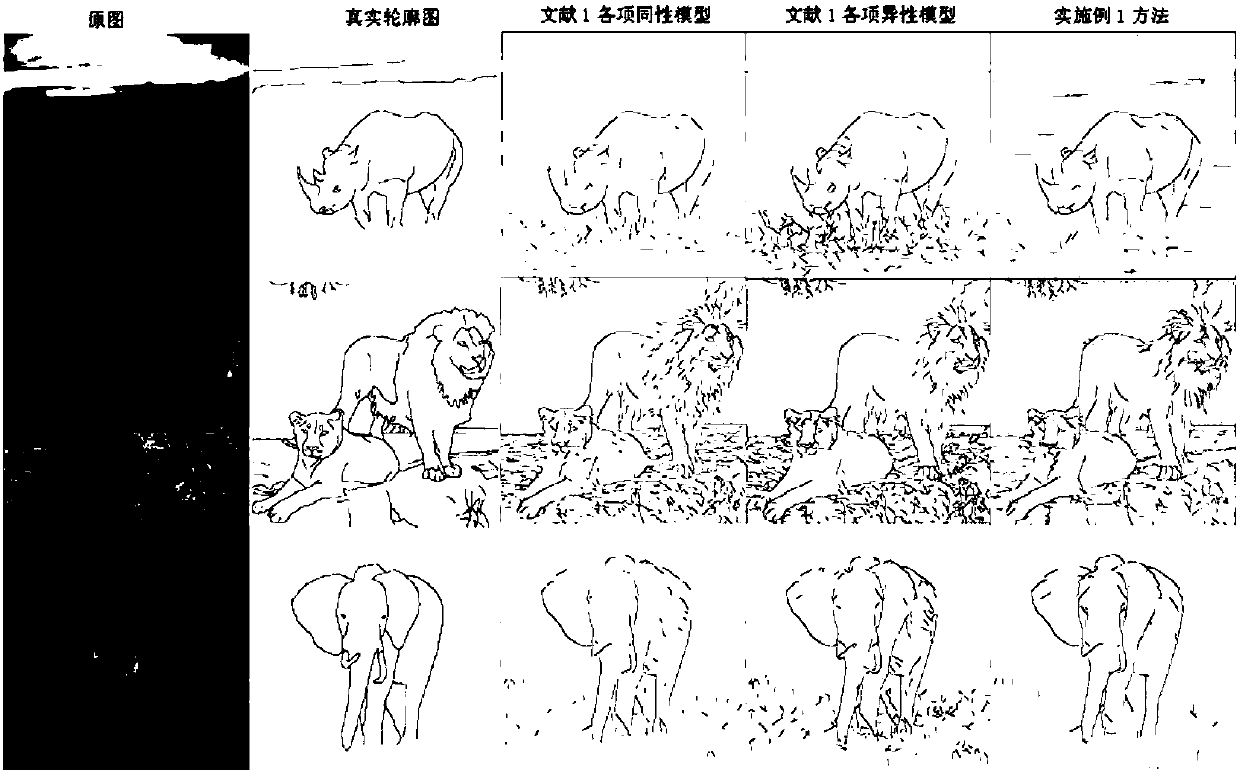
194 results about "Retinal ganglion cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
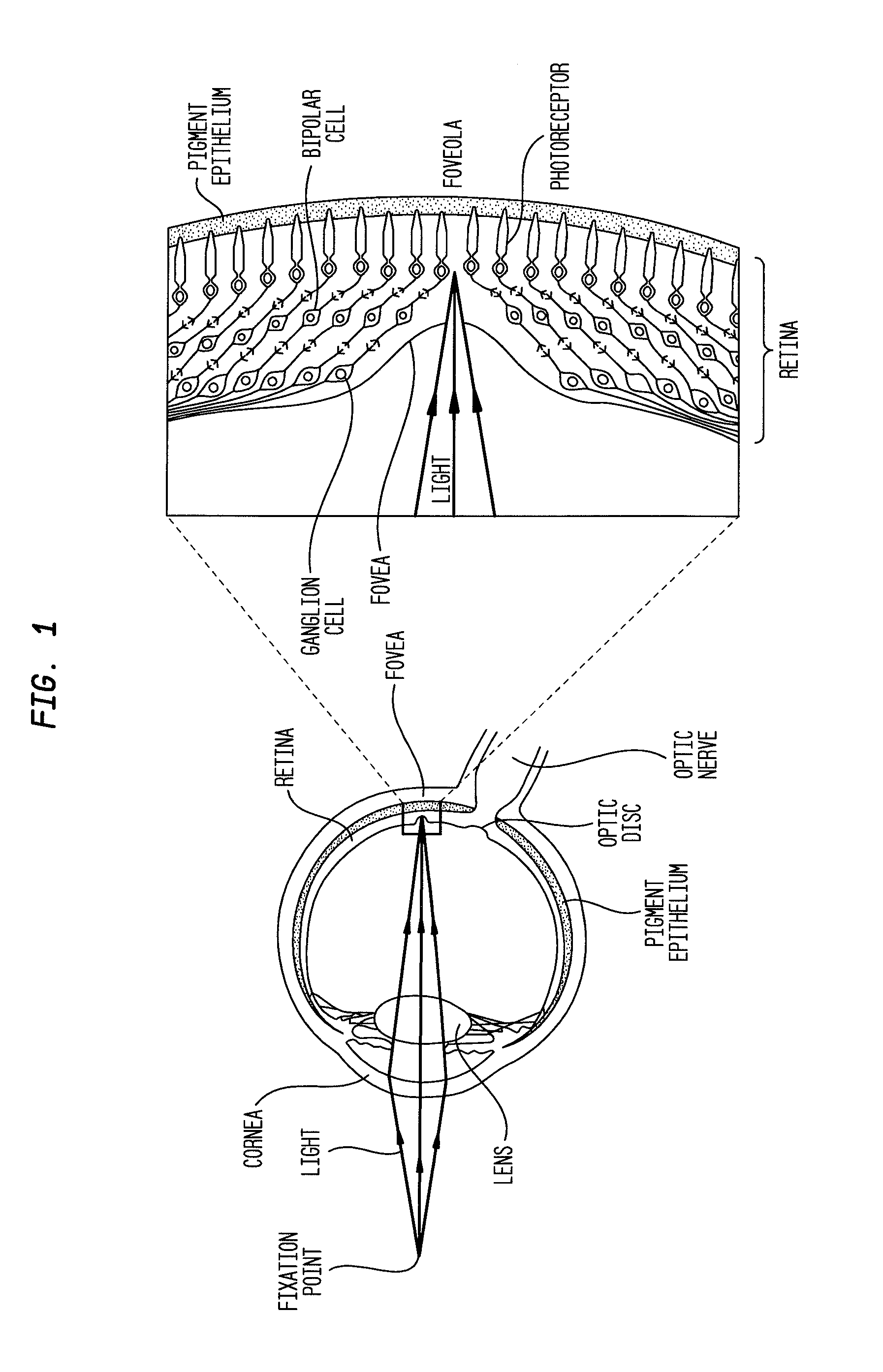
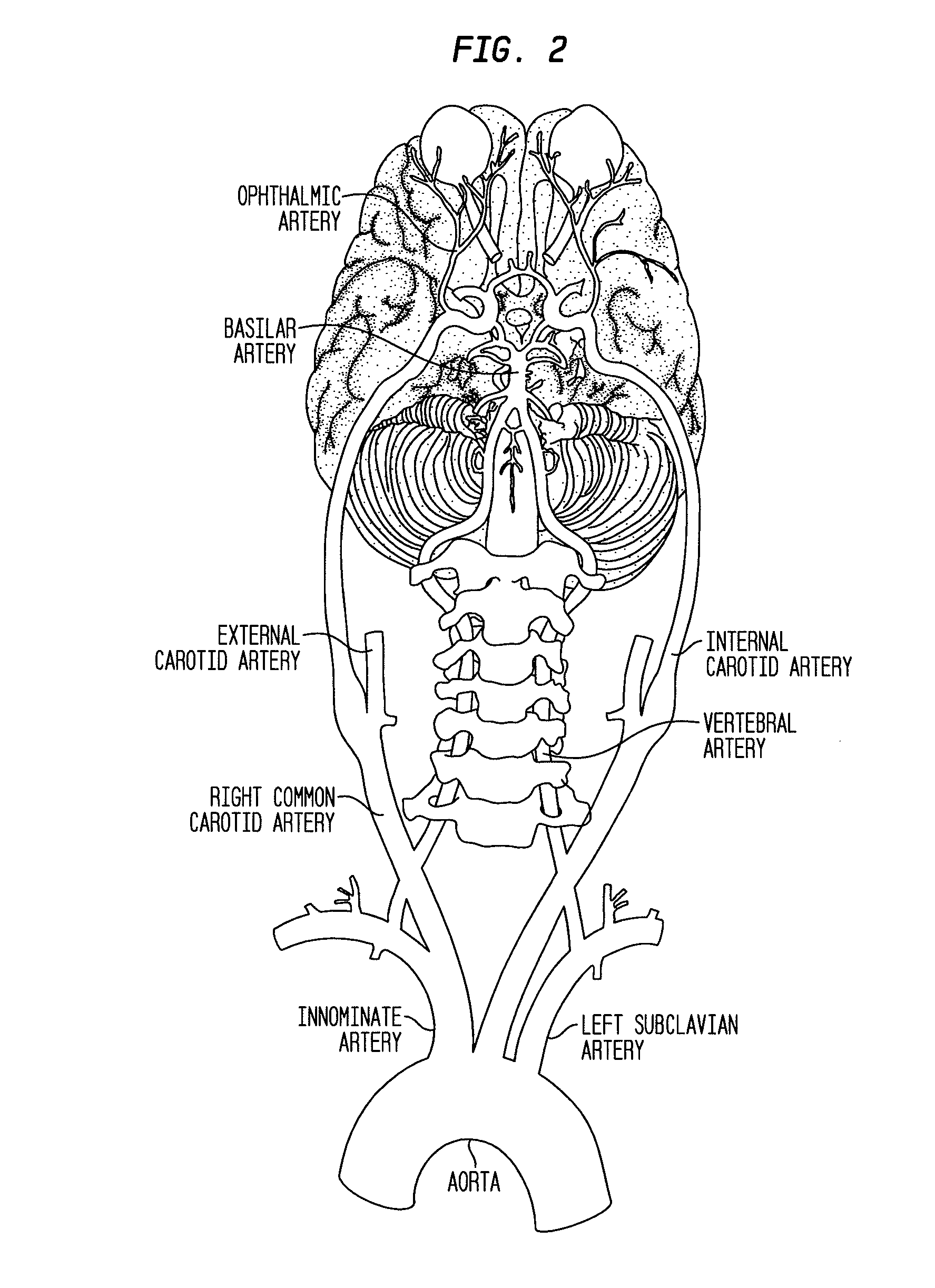
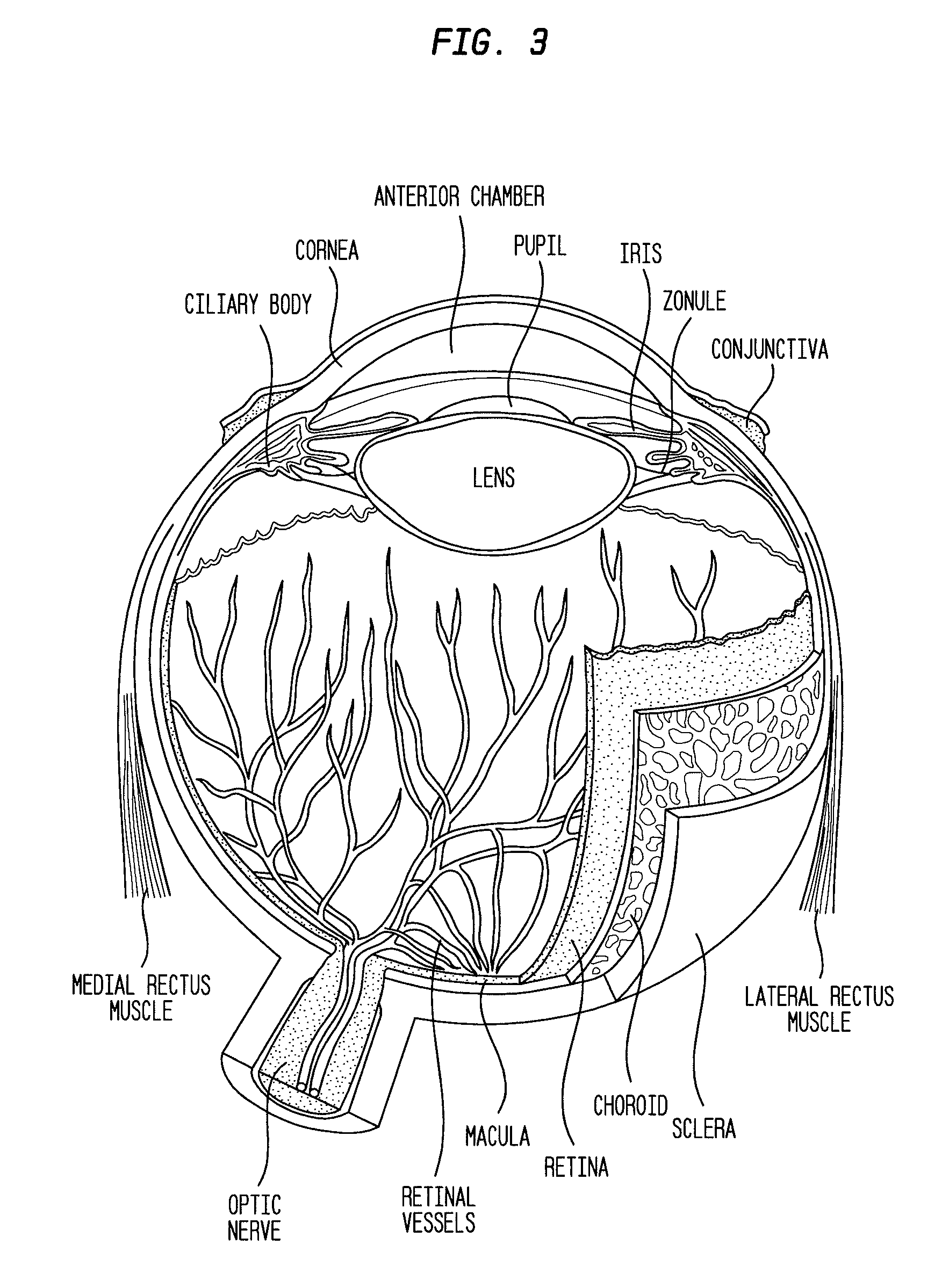
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain.
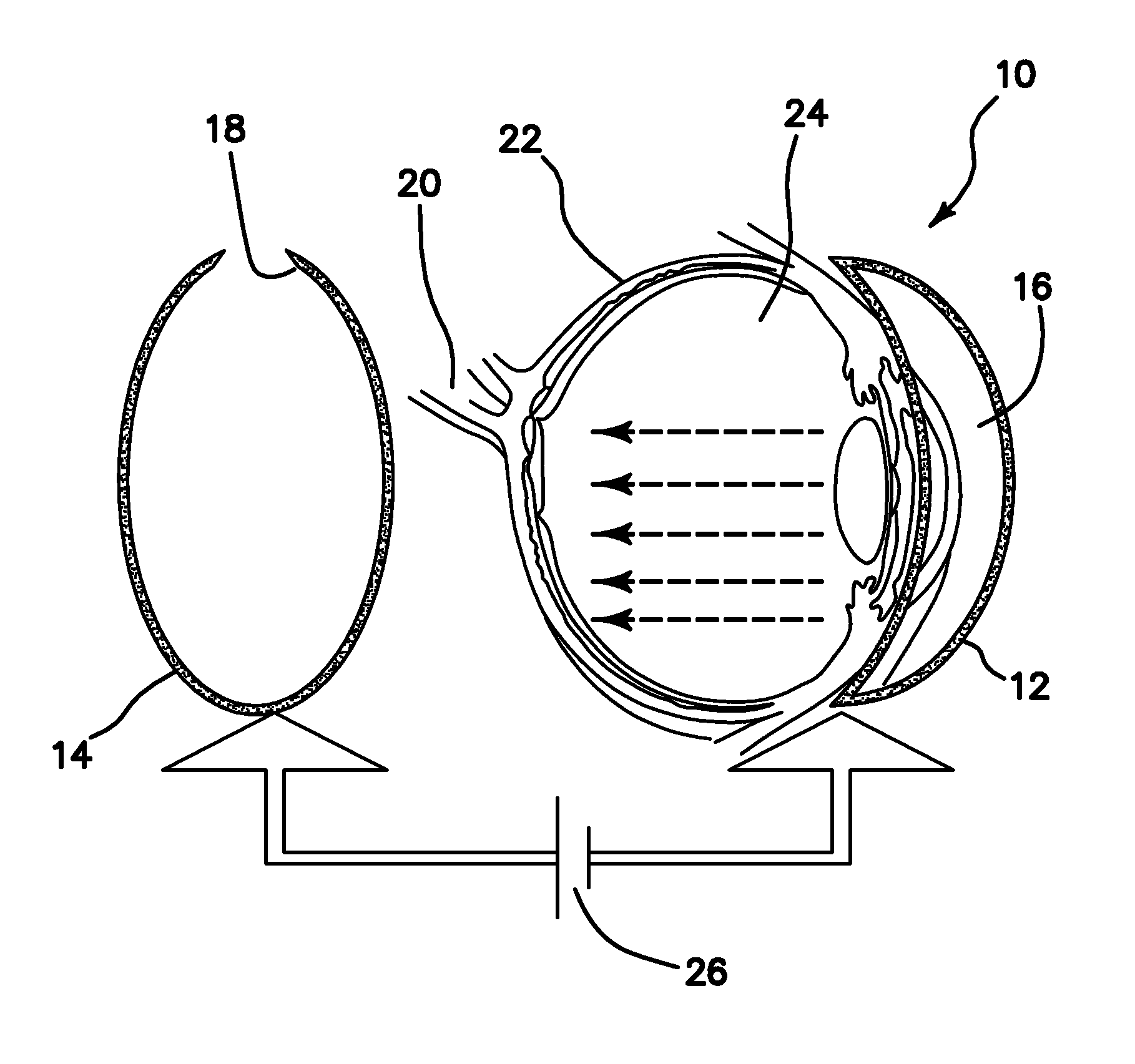
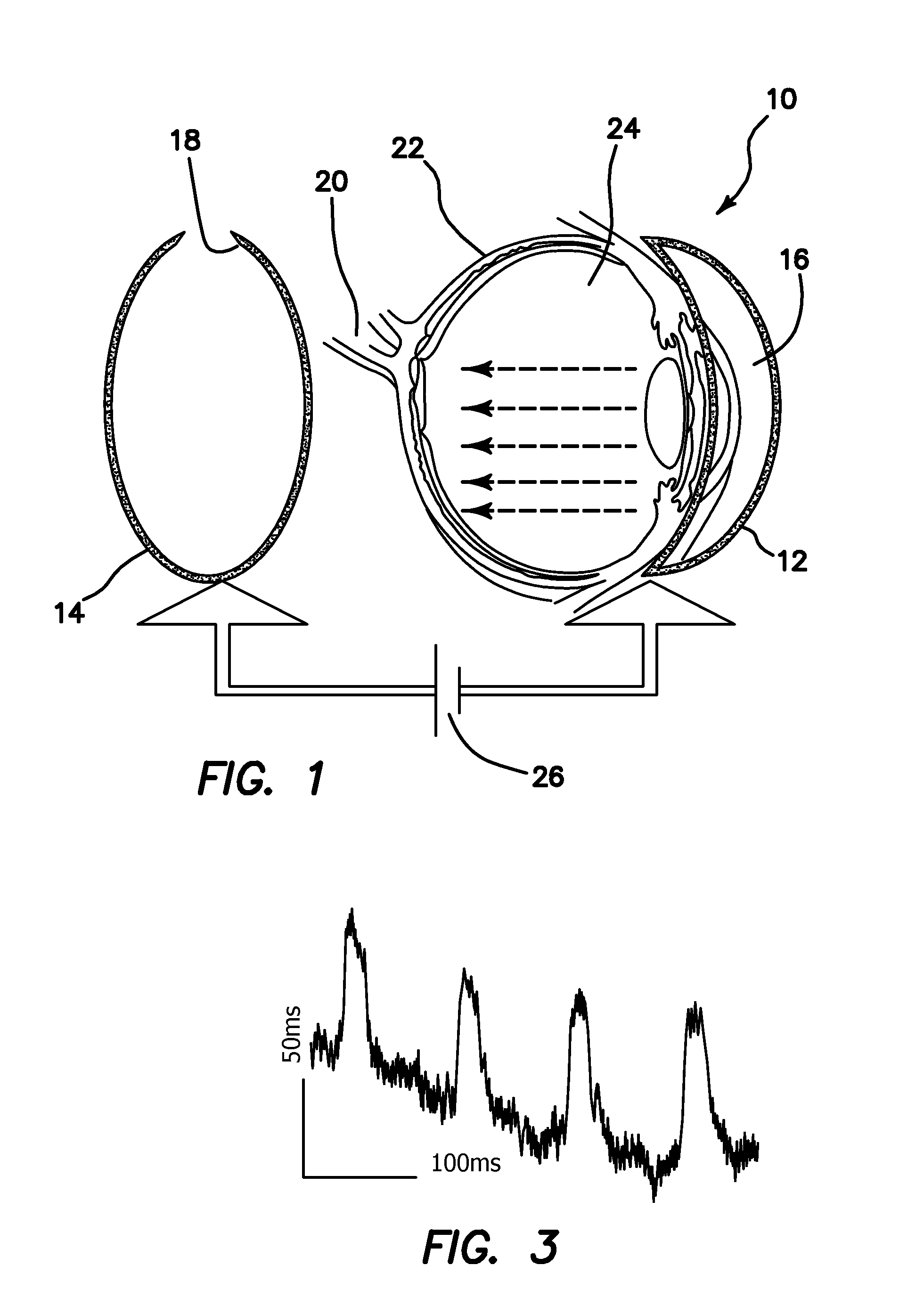
Mimicking neural coding in retinal ganglion cells with short pulse electrical stimulation
A method, device and system for stimulating visual tissue, typically in the retina or visual cortex, to achieve an artificial percept of light or image. The method includes providing stimulating electrodes suitable for placement in proximity to the visual tissue and generating a series of short-duration stimulation signals having a duration of less than about 0.5 milliseconds each. The short-duration stimulation signals are applied through the stimulating electrodes with varying frequencies that are substantially matched to a spiking range of frequencies of at least one ganglion cell for perceiving brightness or image.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Methods and formulations for treating glaucoma
InactiveUS20050163873A1Inhibit progressReduce riskBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsNerve cellsRetinal ganglion cell
Embodiments of the invention are directed toward neuroprotective formulations that may prevent the progression of glaucoma by strengthening the resistance of nerve cells to damage. Some embodiments of the invention are directed toward neuroprotective formulations that may limit and prevent glaucomatous damage by blocking the mechanisms that lead to retinal ganglion cell death. Other embodiments of the invention involve specific component formulations and methods of using the formulations.
Owner:RITCH ROBERT
System and process for neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma
ActiveUS20160346126A1Good conditionFunction increaseLaser surgeryDiagnosticsGlaucomaRetinal ganglion
Providing neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma includes generating a micropulsed laser light beam having parameters and characteristics, including pulse length, power, and duty cycle, selected to create a therapeutic effect with no visible laser lesions or tissue damage to the retina. The laser light beam is applied to retinal and / or foveal tissue of an eye having glaucoma or a risk of glaucoma to create a therapeutic effect to the retinal and / or foveal tissue exposed to the laser light beam without destroying or permanently damaging the retinal and / or foveal tissue and improve function or condition of an optic nerve and / or retinal ganglion cells of the eye.
Owner:OJAI RETINAL TECH
Suppression of eIF5A1 expression to prevent retinal ganglion cell death in the glaucomatous eye
InactiveUS20030225022A1Avoid deathInhibit expressionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsApoptosisGanglion-Like Cell
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
In vivo imaging of amyloid plaques in glaucoma using intravenous injectable dyes
InactiveUS20050214222A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLuminescence/biological staining preparationNervous systemFluorescence
In vivo imaging may be used to assess a condition (e.g., a state of glaucoma or a state of ocular hypertension) of an eye of a living animal. A dye may be intravenously injected into the living animal. The dye may bind to amyloid in the nervous system of the animal. Images may be taken of a retina, an optic nerve head, an optic nerve, the lateral geniculate nucleus, and / or the visual cortex. Images may be taken using methods such as fluorescent angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, positron emission tomography, and / or single photon emission computed tomography. The condition of the eye and / or retinal ganglion cells in the eye may be assessed from one or more of the images. The condition of the eye may be assessed based on the presence of amyloid in one or more of the images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Composition and method for the treatment or prevention of glaucoma and ocular hypertension
InactiveUS20100310637A1Increase successLower eye pressureSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsRetinal ganglionFhit gene
This invention relates to compositions and methods for lowering intraocular pressure and treatment and / or prevention of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. The invention provides insulin, isoforms of insulin, analoges of insulin, fragments of insulin peptide and other products of protein / gene engineered modifications of insulin for the lowering of intraocular pressure. The invention also provides insulin, isoforms of insulin, analoges of insulin, fragments of insulin and other products of protein / gene engineered modifications of insulin for increasing the success of glaucoma surgical procedures. The invention further provides insulin, isoforms of insulin, analoges of insulin, fragments of insulin and other products of protein / gene engineered modifications of insulin for neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells.
Owner:ABDULRAZIK MUHAMMAD
Artificial retina implant
ActiveCN104873330AVascular effects are smallEasy to observeEye treatmentArtificial respirationRetinal ganglionEngineering
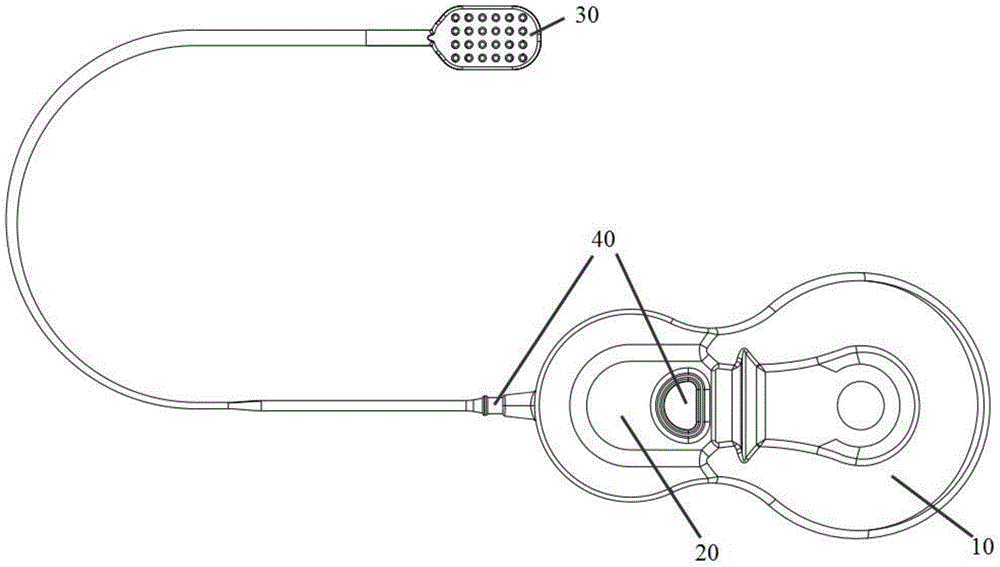
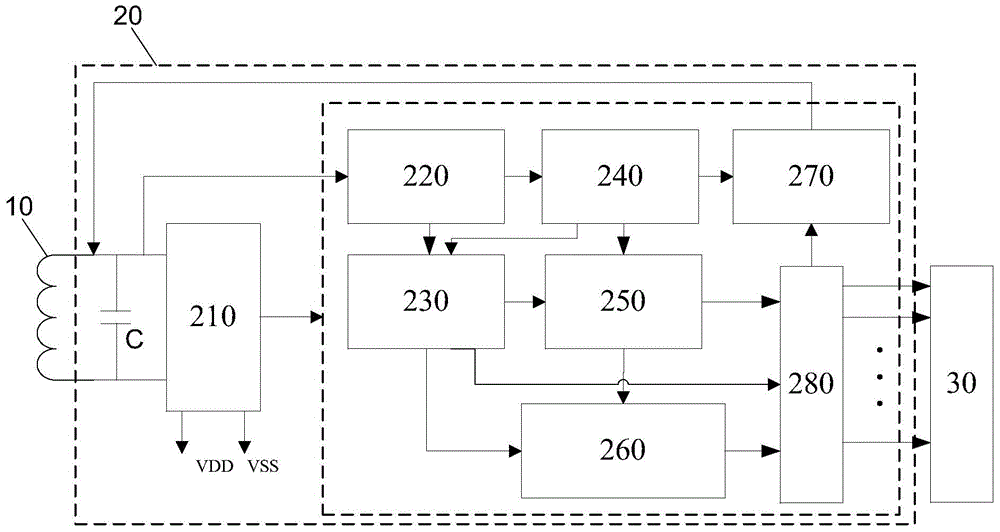
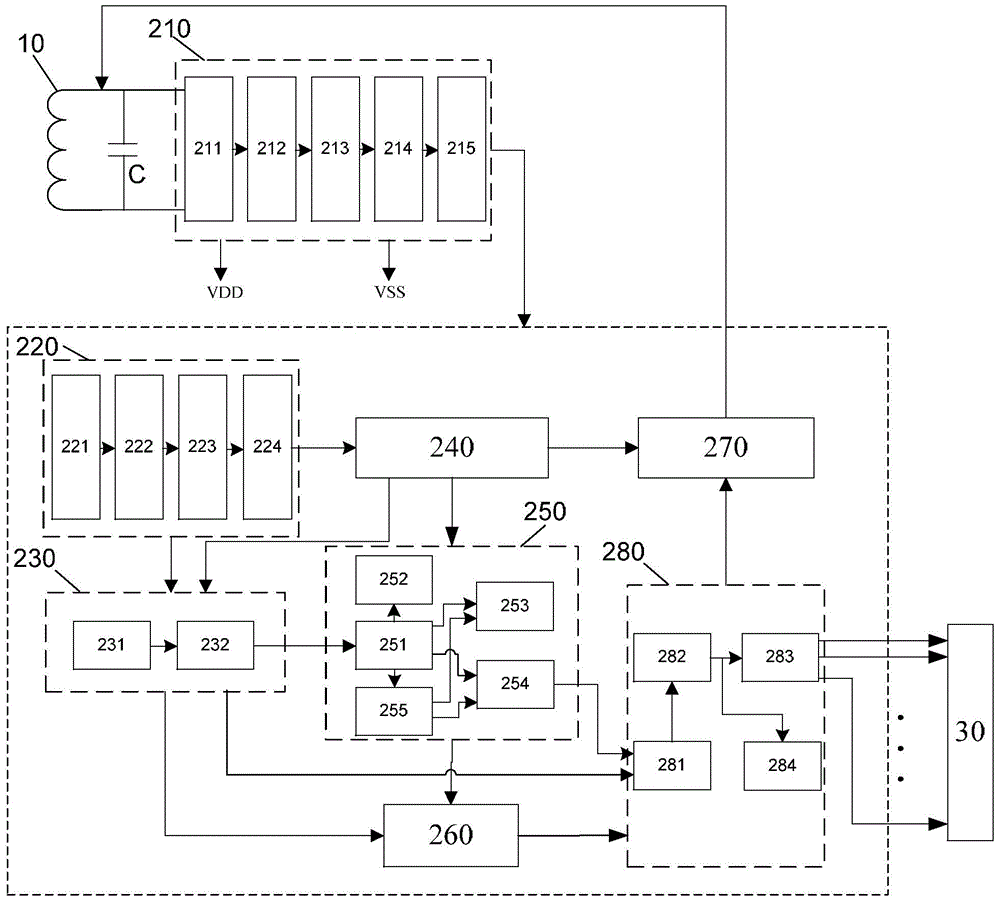
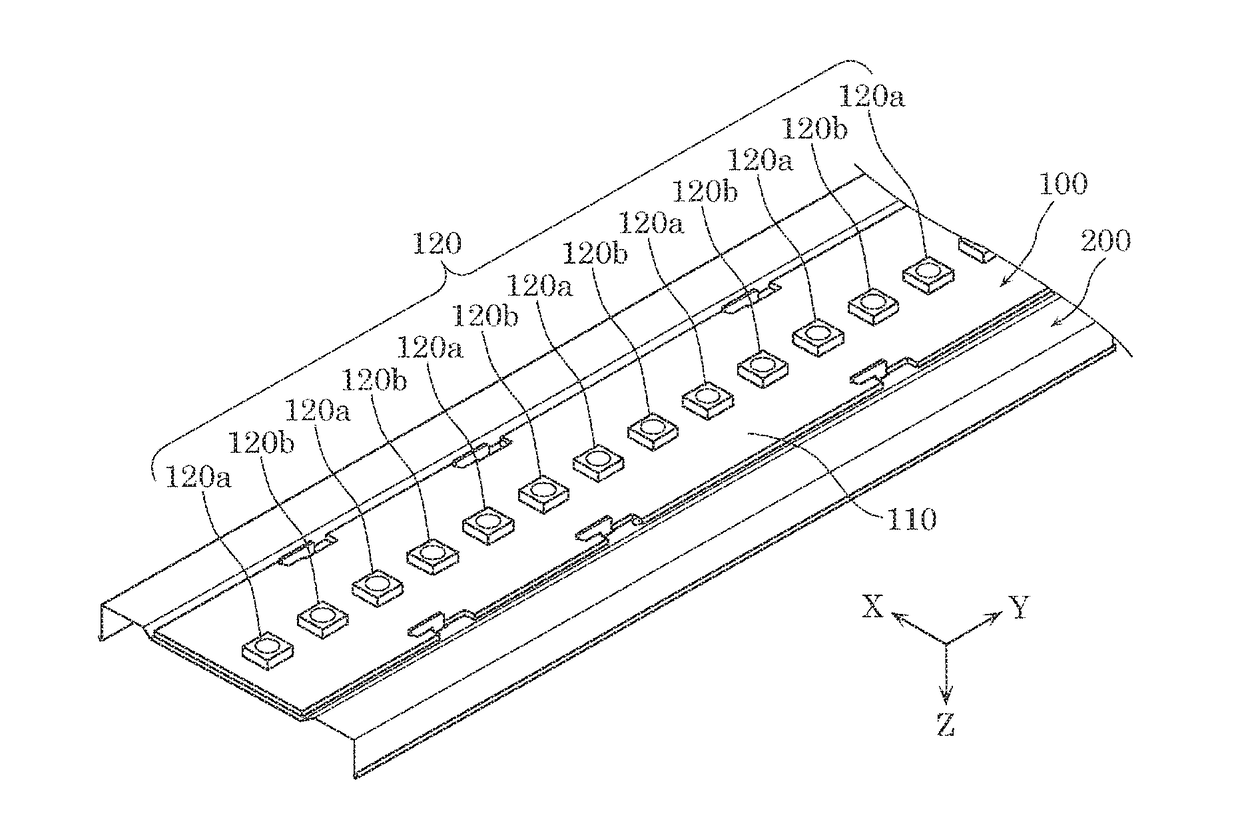
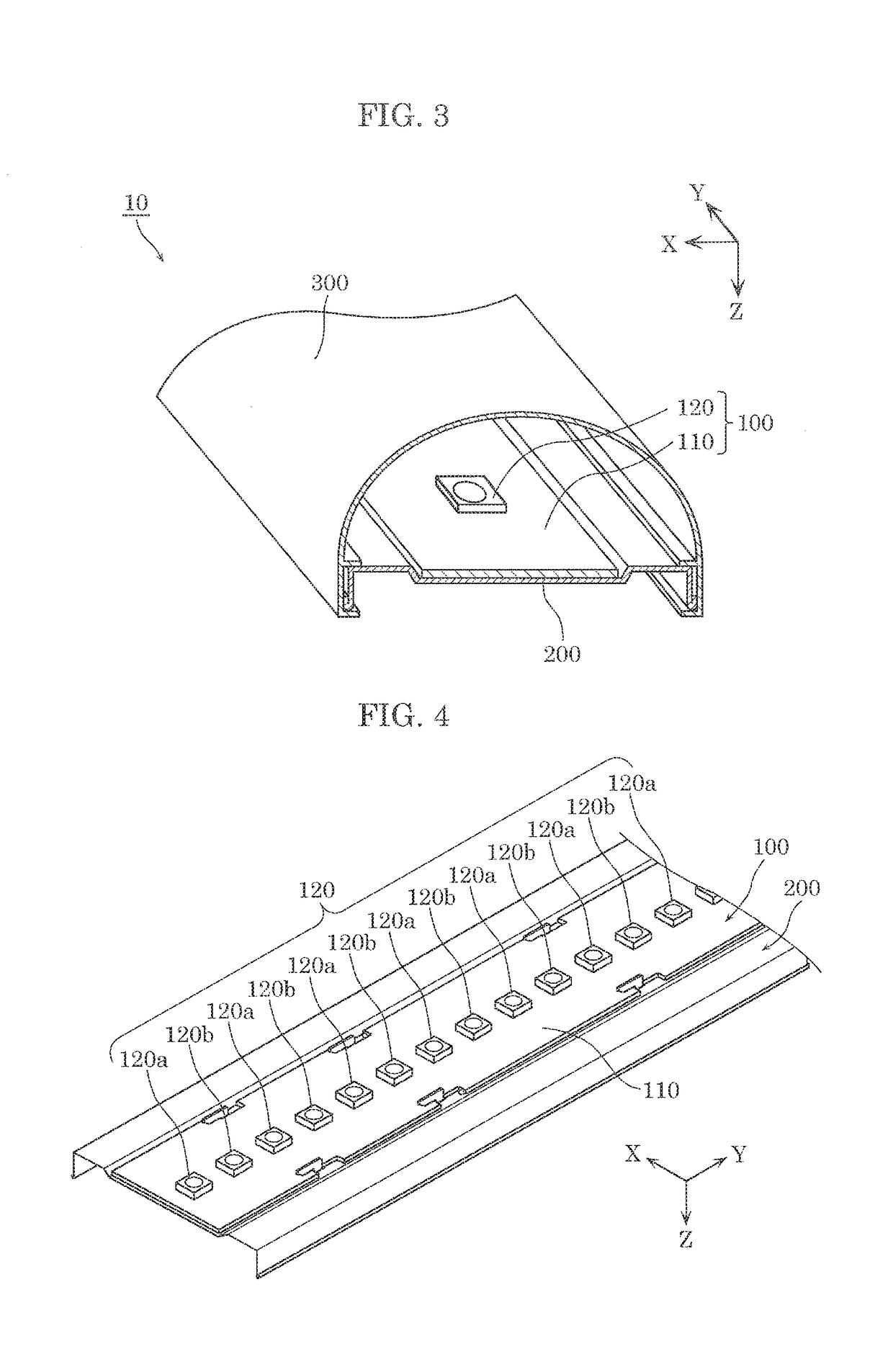
The invention discloses an artificial retina implant. The artificial retina implant comprises a receiving coil, a demodulation stimulation module, an electrode array and a loop electrode. The receiving coil is in alignment connection with a transmission coil of an artificial retina in-vitro device and receives image coding signals and energy emitted by the in-vitro device, the demodulation stimulation module is connected with the receiving coil and decodes the image coding signals received by the receiving coil, converts the received image coding signals into electrical signals and transmits the electrical signals to the electrode array, and the received energy is converted. The artificial retina implant can achieve the visual effect only by stimulating retinal ganglion cells of the inner layer, and is easy to implant, safe and reliable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NUROTRON BIOTECH
Long-acting sustained release preparation for preventing or treating retinal damage, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102233129ARelieve painSolve the problem of long-term frequent injectionsSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrosphereRetinal ganglion
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations, and relates to a long-acting sustained release preparation for preventing or treating retinal damage, and a preparation method thereof. The long-acting sustained release preparation takes erythropoietin (EPO) as an active component, takes dextran as a protective agent for the active component, and takes poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), polylactic acid or polycaprolactone as a coating component to prepare sustained release microspheres, wherein the erythropoietin is coated by the poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), polylactic acid or polycaprolactone. Proven by animal experiments, the sustained release microspheres of the long-acting sustained release preparation provided by the invention have the same protective actions on the ganglionic cells of damaged retinas by single vitreous chamber injection and repeated EPO protein vitreous chamber injection, and the sustained release microspheres are capable of avoiding a series of complications caused by many times of injection and overcoming the defects of repeated intraocular injection administration and gene therapy. The long-acting sustained release preparation provided by the invention adopts intraocular local administration, can reduce the dosage and treatment cost, and can not generate adverse effects on other organs or tissues in vivo.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
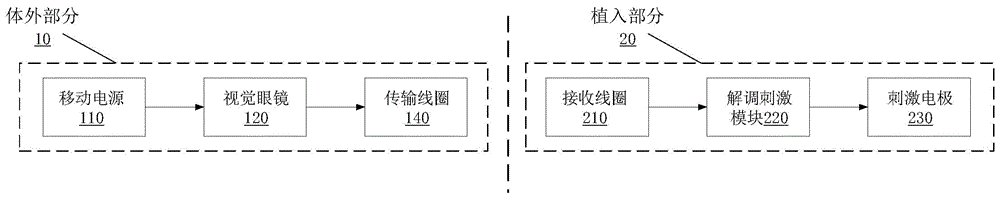
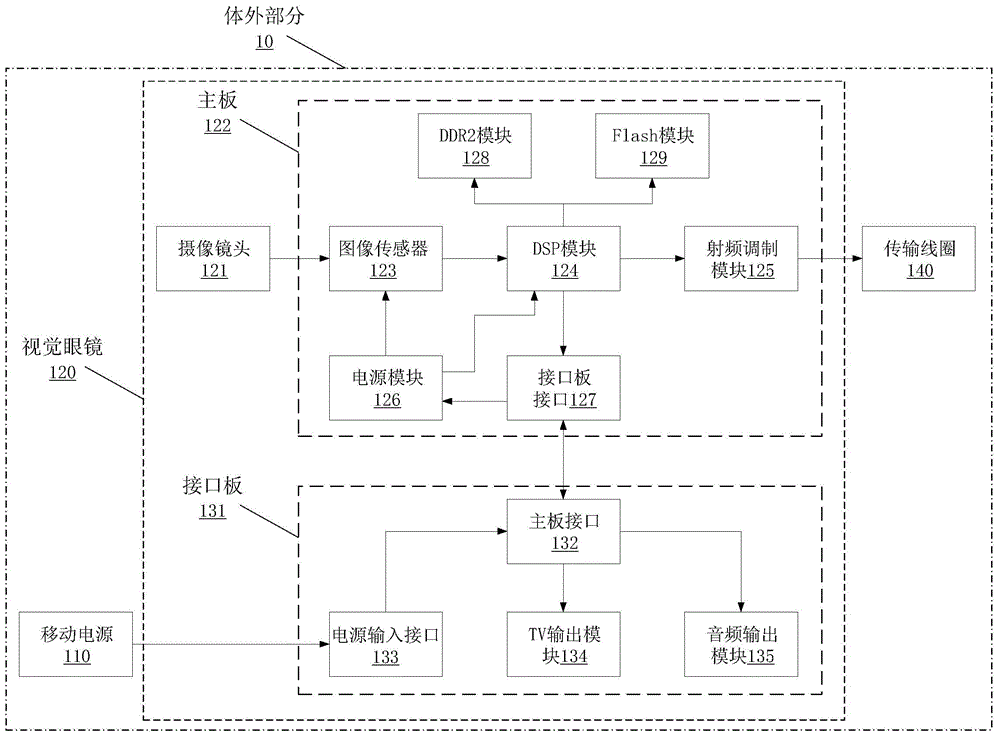
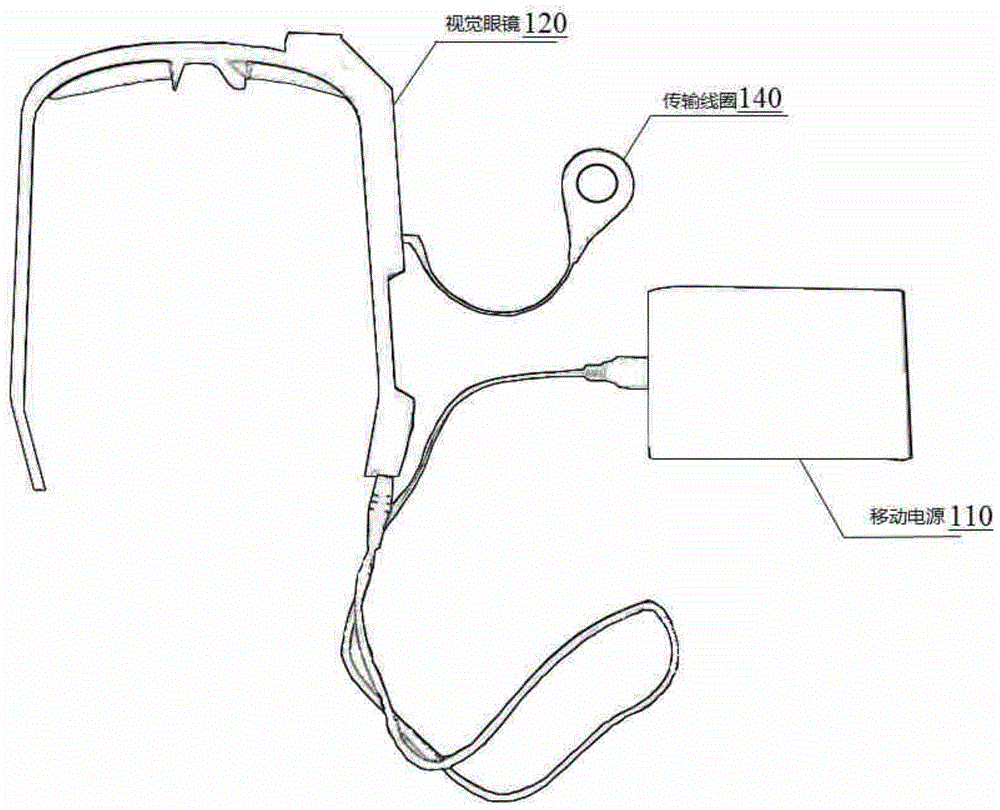
Artificial retina system
ActiveCN104825248ALittle effect on blood supplyEasy to observeEye implantsClosed circuit television systemsCamera lensRetinal ganglion
The invention discloses an artificial retina system which comprises an in-vitro part and an implantation part. The in-vitro part comprises a portable power source, vision glasses and a transmission coil. The portable power source is connected with the vision glasses to provide external power supply for the whole artificial retina system. The vision glasses comprise a camera lens, a main board and an interface board. The transmission coil is connected with a radio frequency modulation module and used for receiving an image coded signal. The implantation part comprises a receiving coil, a demodulation stimulating module and a stimulating electrode. The receiving coil is in alignment connection with the transmission coil. The demodulation stimulating module is connected with the receiving coil, decodes the image coded signal received by the receiving coil and converts the image coded signal into an electric signal to be transmitted to the stimulating electrode. The stimulating electrode comprises a plurality of contact electrodes and electrode wires connected with the contact electrodes one to one. The artificial retina system can directly stimulate retinal ganglion cells on the innermost layer, most electronic devices are arranged on the in-vitro part, and therefore images are updated and processed easily.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NUROTRON BIOTECH
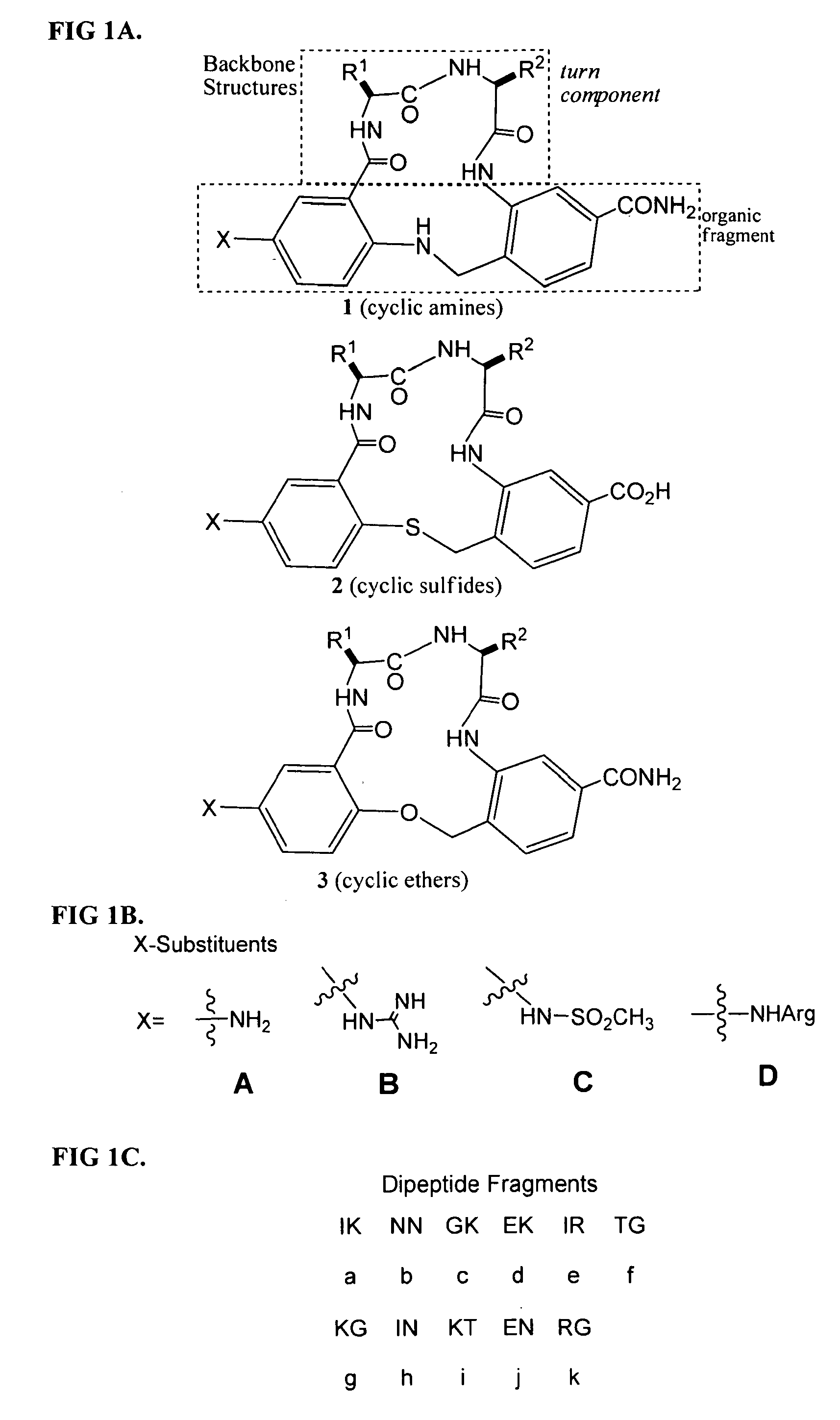
Methods of use of trk receptor modulators
ActiveUS20100048461A1Stable and easy to administerEasy to manageOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCyclic compoundTrk receptor
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death and / or glaucoma using modulators of neurotrophic receptors that comprise β-turn peptidomimetic cyclic compounds or derivatives thereof. The neurotrophic receptor modulators can be used alone, in combination and / or in conjunction with one or more other compounds, molecules or drugs that treat or prevent ocular hypertension, RGC death and / or glaucoma.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
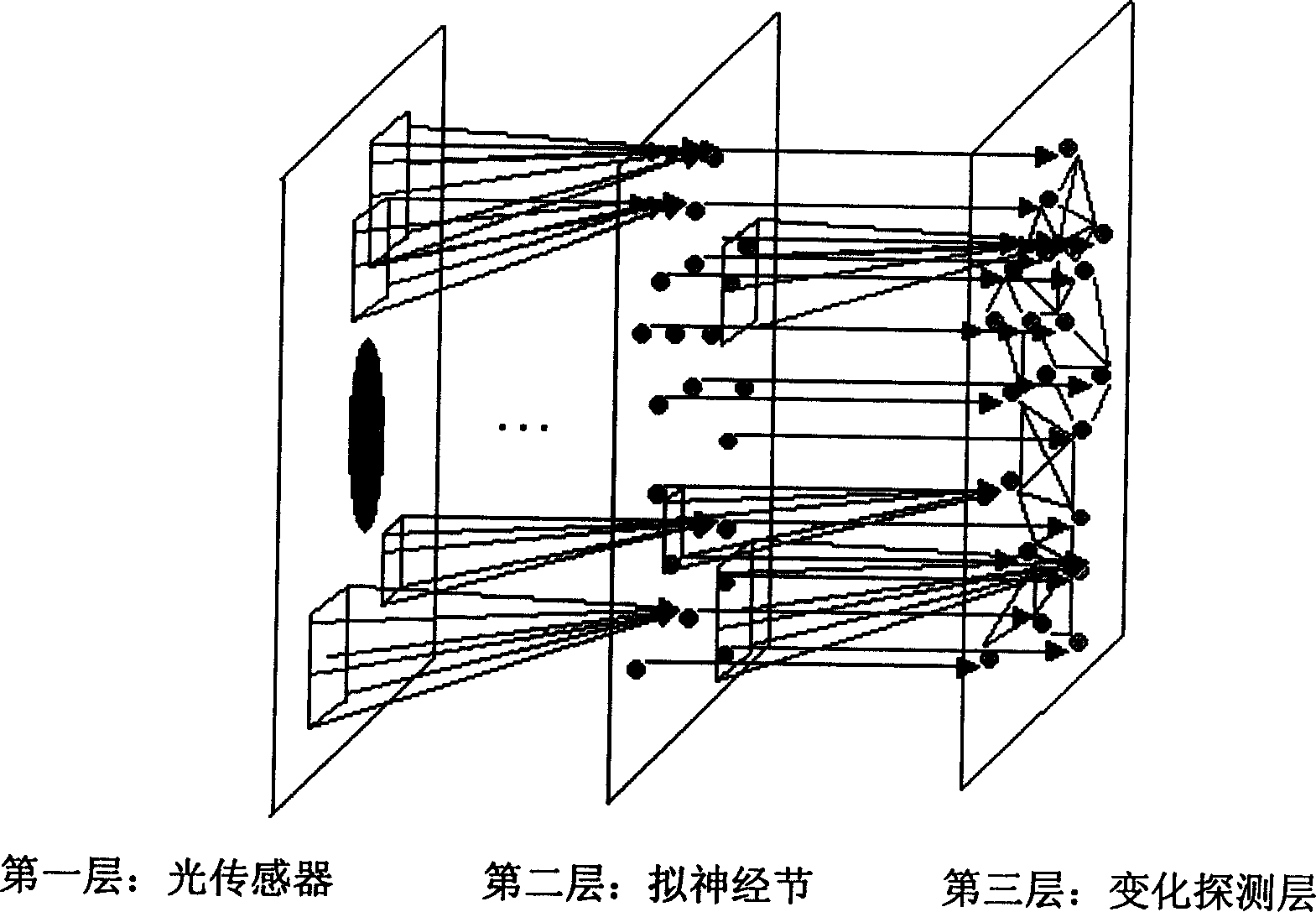
Wild size variable hierarchical network model of retina ganglion cell sensing and its algorithm
InactiveCN1564195ASimplify complexityUniform sizeBiological neural network modelsInformation processingNetwork model
Basic ideas of the invention are that through simulating information processing flow of early vision of biologic optic nerve system, designing following items solves certain issues. The said items designed in the invention are: layered network structure of simulating layered information processing mode in biologic optic nerve system; computing unit of imitating nerve ganglion, and its variable distribution of sensing field on sensor layer; computing unit for detecting moving orientation in third layer possessing local stage by stage computing mechanism; alertness algorithm for detecting moving event. The invention makes the designed parts release conflict between computing efficiency, precision and computation resources, as well as makes machine vision system pay attention to first important information, meanwhile keep alertness around.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Long-acting sustained release preparation for preventing or treating retinal damage, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102233129BImprove survival rateLong-term protectionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrosphereRetinal ganglion
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Rescue of Photoreceptors by Intravitreal Administration of an Expression Vector Encoding a Therapeutic Protein
InactiveUS20090202505A1Increase amplitudeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseTherapeutic protein
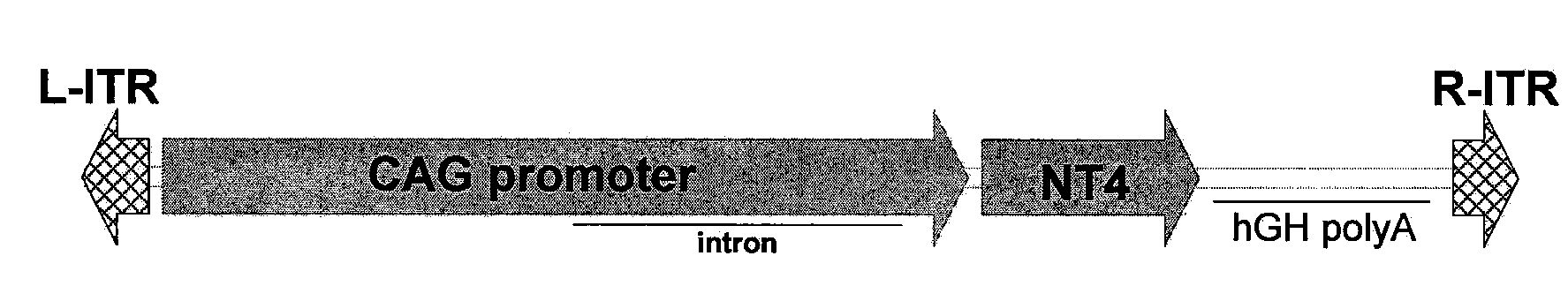
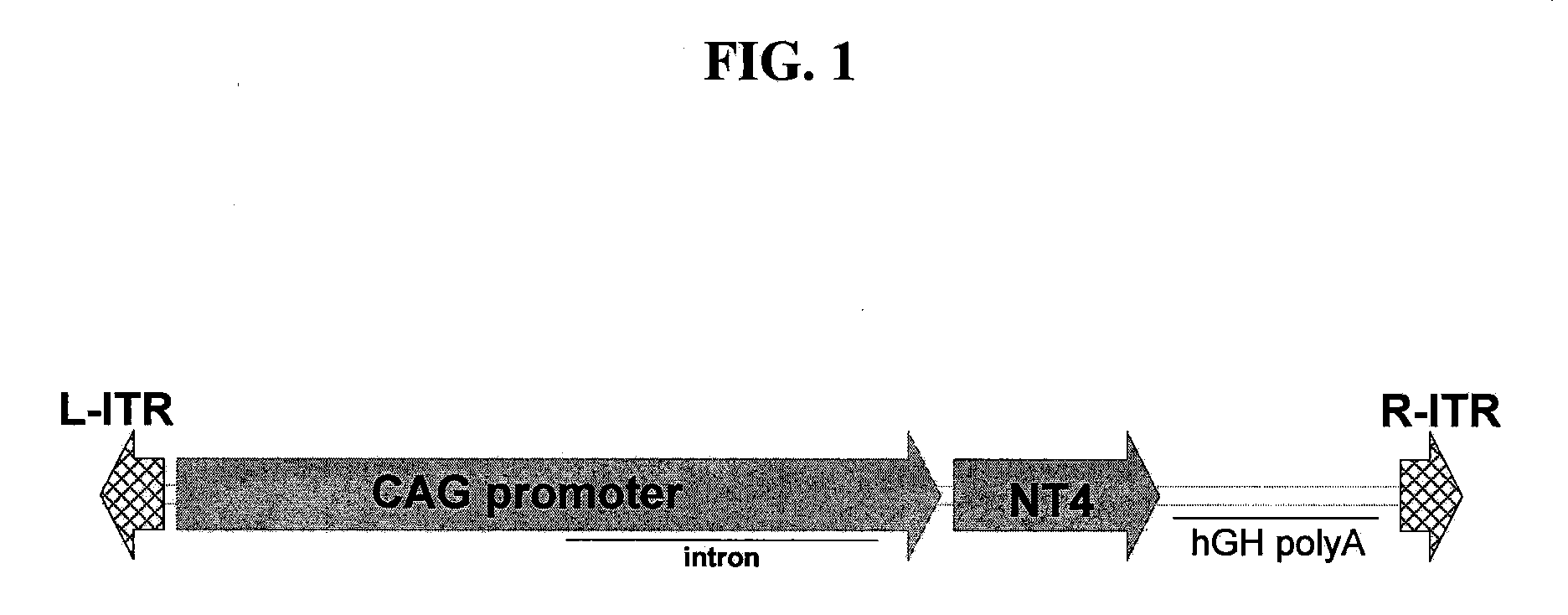
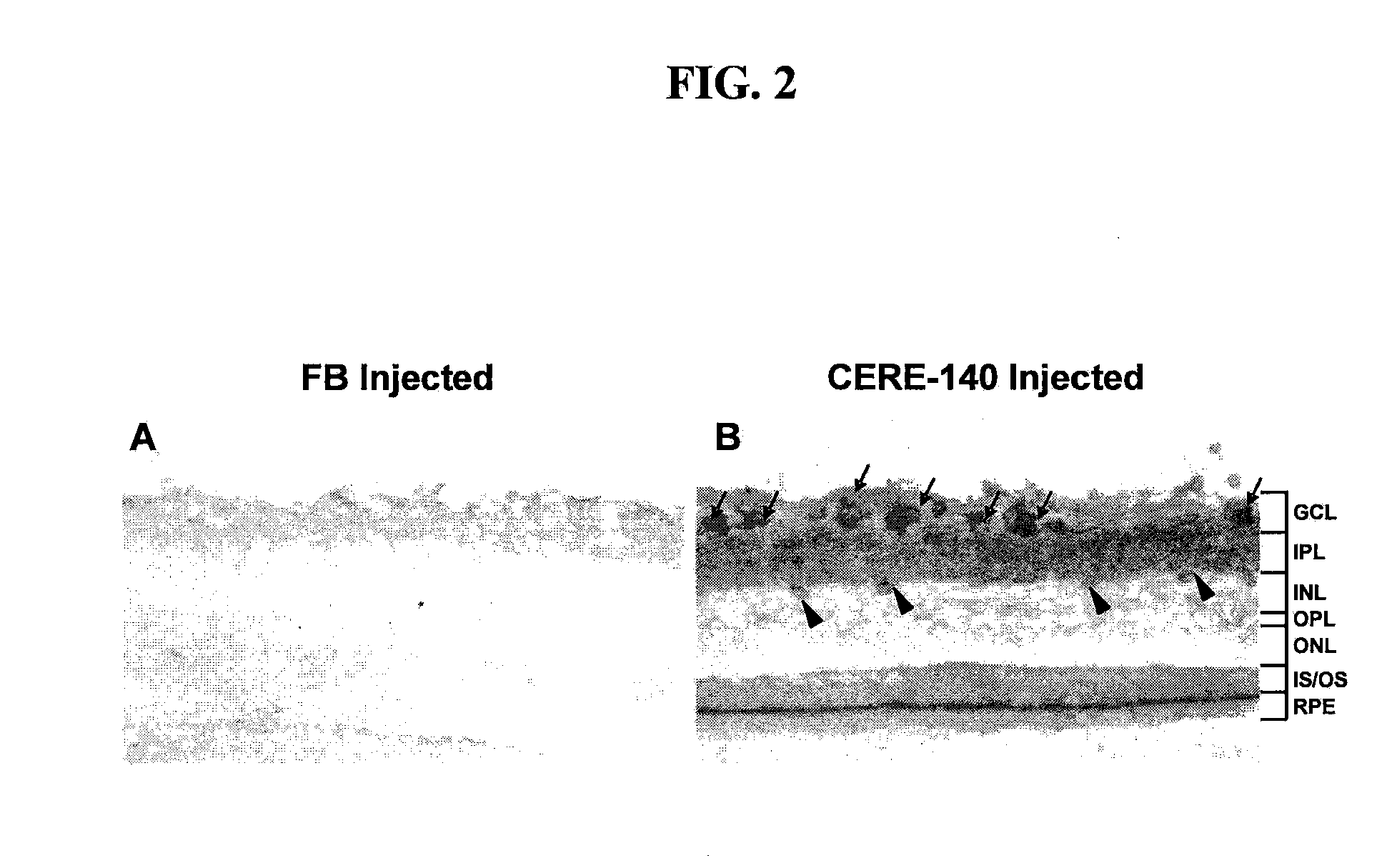
The invention provides methods for treating ocular diseases using a recombinant vehicle to express a protein useful in the treatment of ocular disease, with particular preference for use of neurotrophin-4 (NT4) for targeting subpopulations of cells in the retina. A genetically engineered gene transfer vector containing sequences encoding a growth factor such as neurotrophin-4 (NT4) is used to transduce cells of the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer, in situ, via administration of the vector intravitreally. Accordingly, methods are disclosed for treating subjects in need thereof by therapeutic protein delivery via a recombinant expression vector, including rescue of photoreceptors by targeting the RGC layer subpopulation of retinal cells.
Owner:CEREGENE
Neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells
InactiveUS20090220516A1Increase pressureReduce releaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsExtracellularGlaucoma
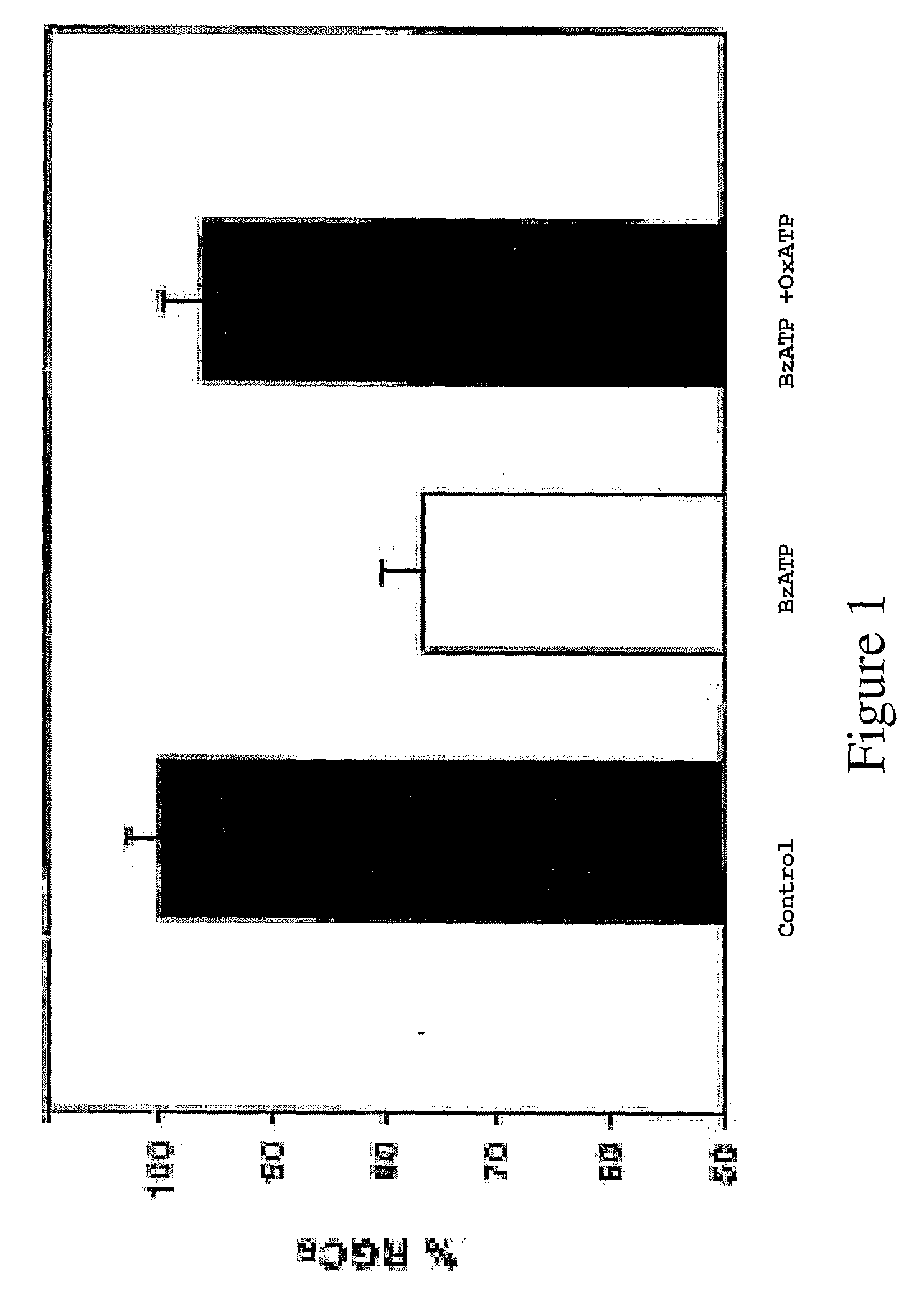
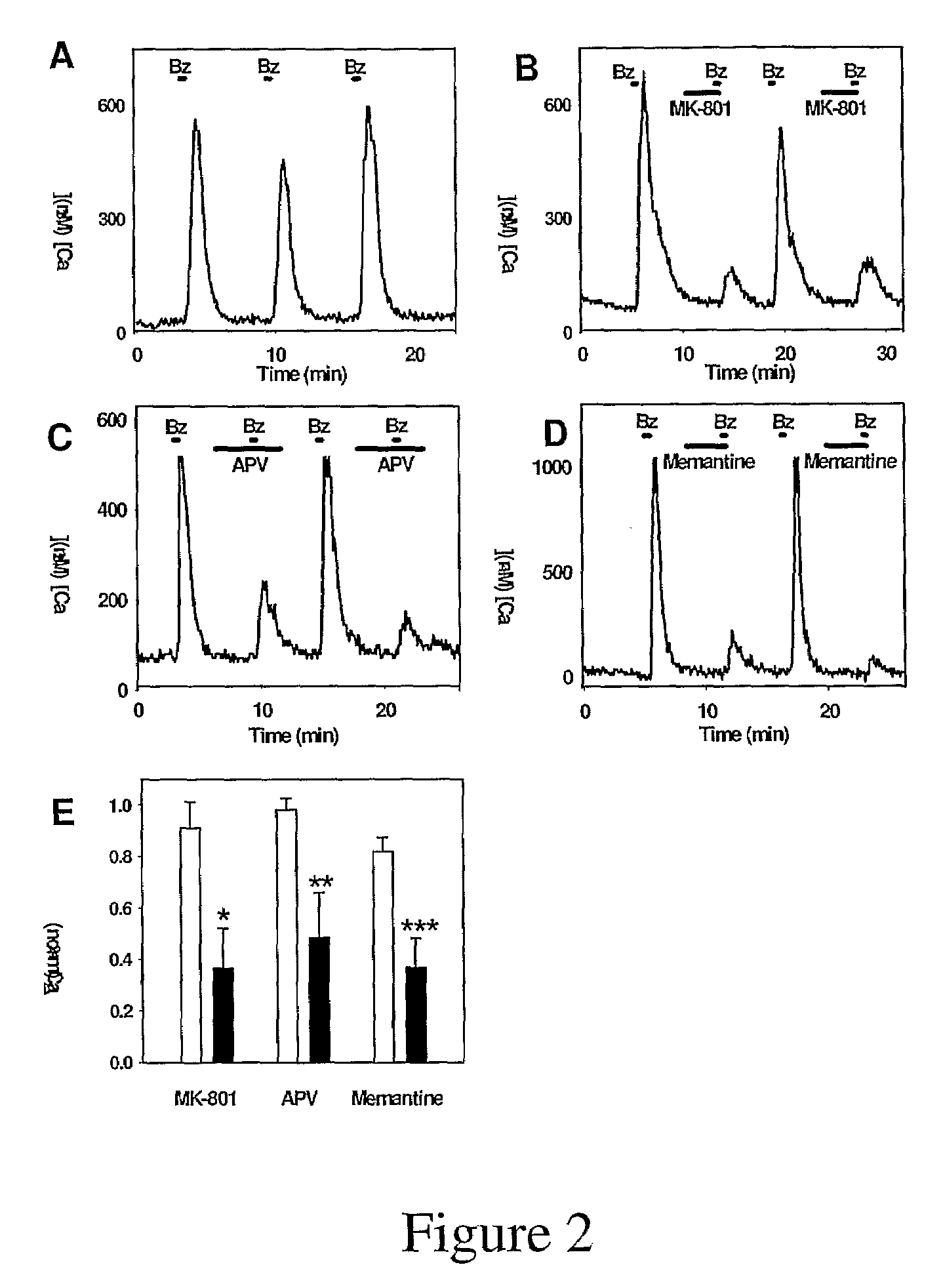
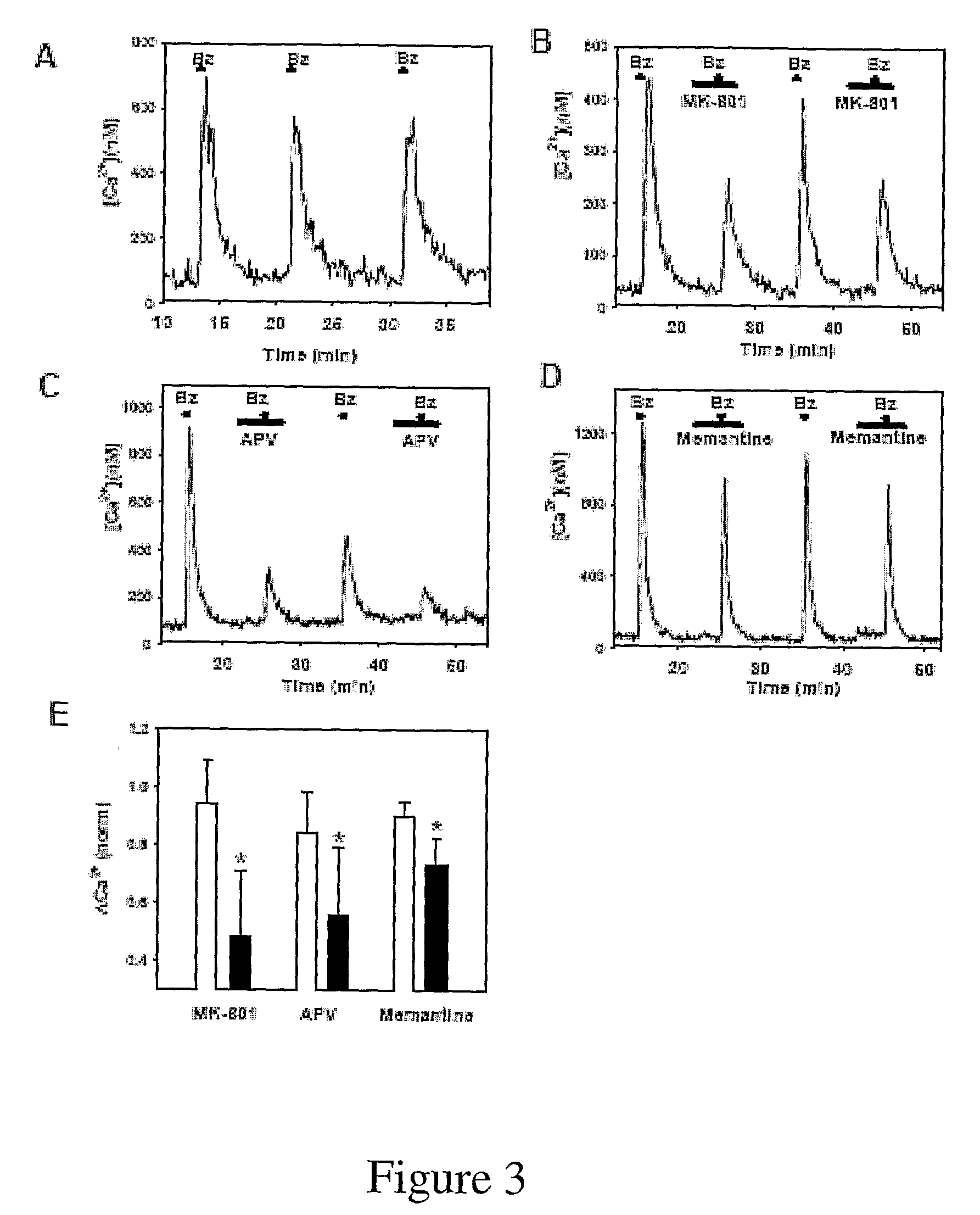
This invention relates to the neuroprotection of the optic nerve and the treatment of glaucoma, more specifically, the invention is directed to a method of preventing, inhibiting, decreasing incidence and suppressing death in ganglion cells by manipulating the P2X7 and A3 receptors on ganglion cells, by reducing levels of ATP released into the extracellular space of the retina and enhancing the conversion of released extracellular ATP into adenosine.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
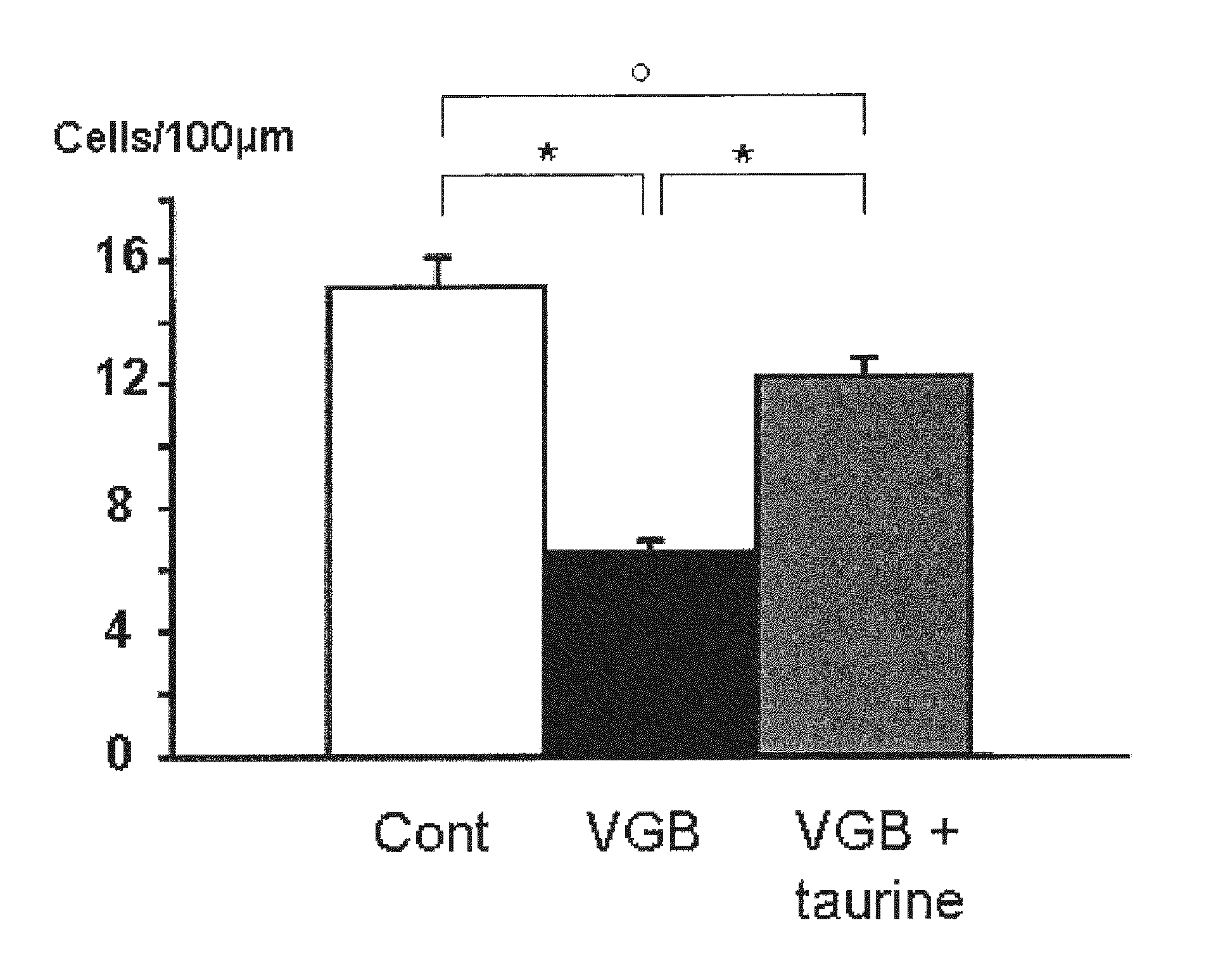
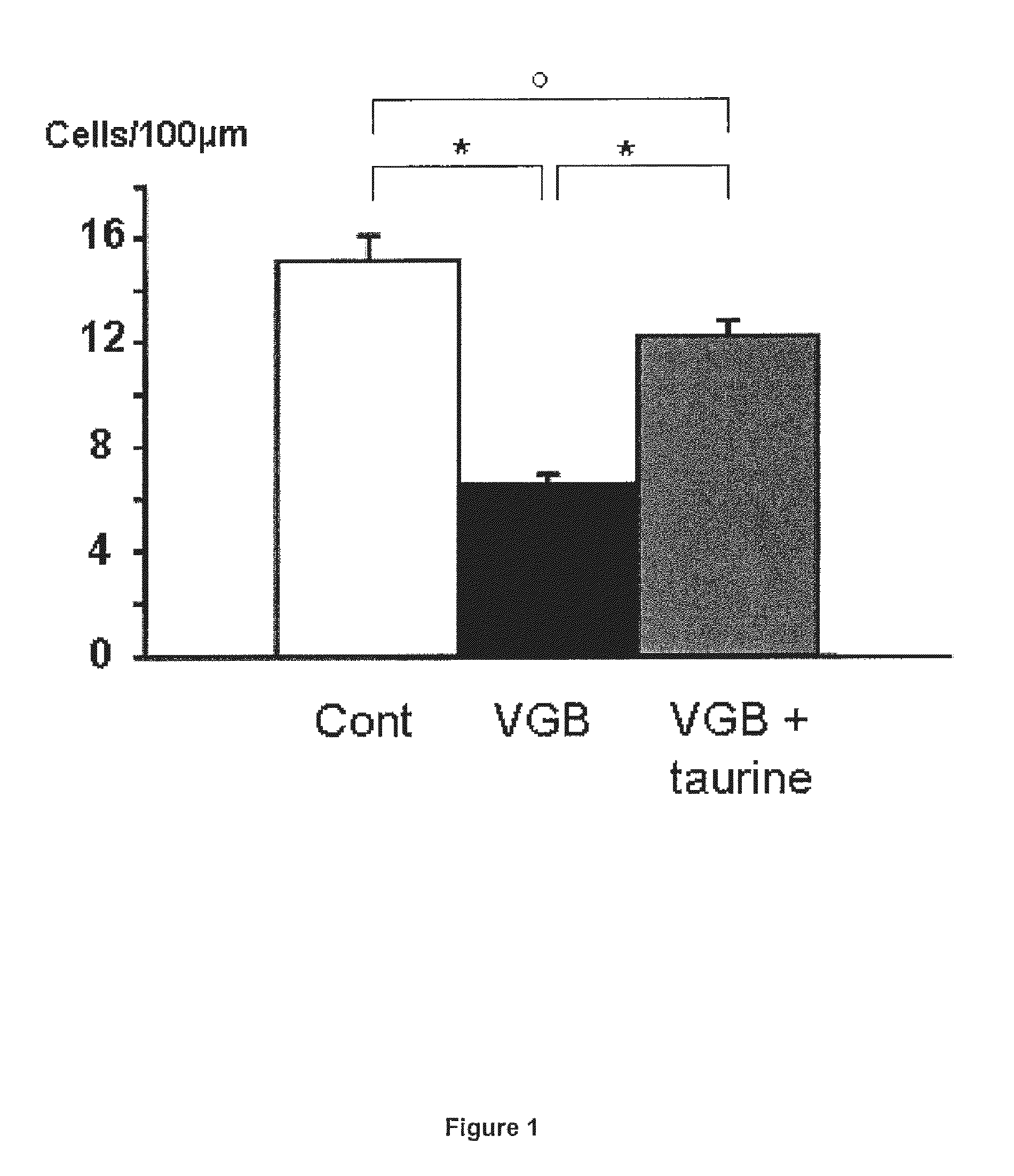
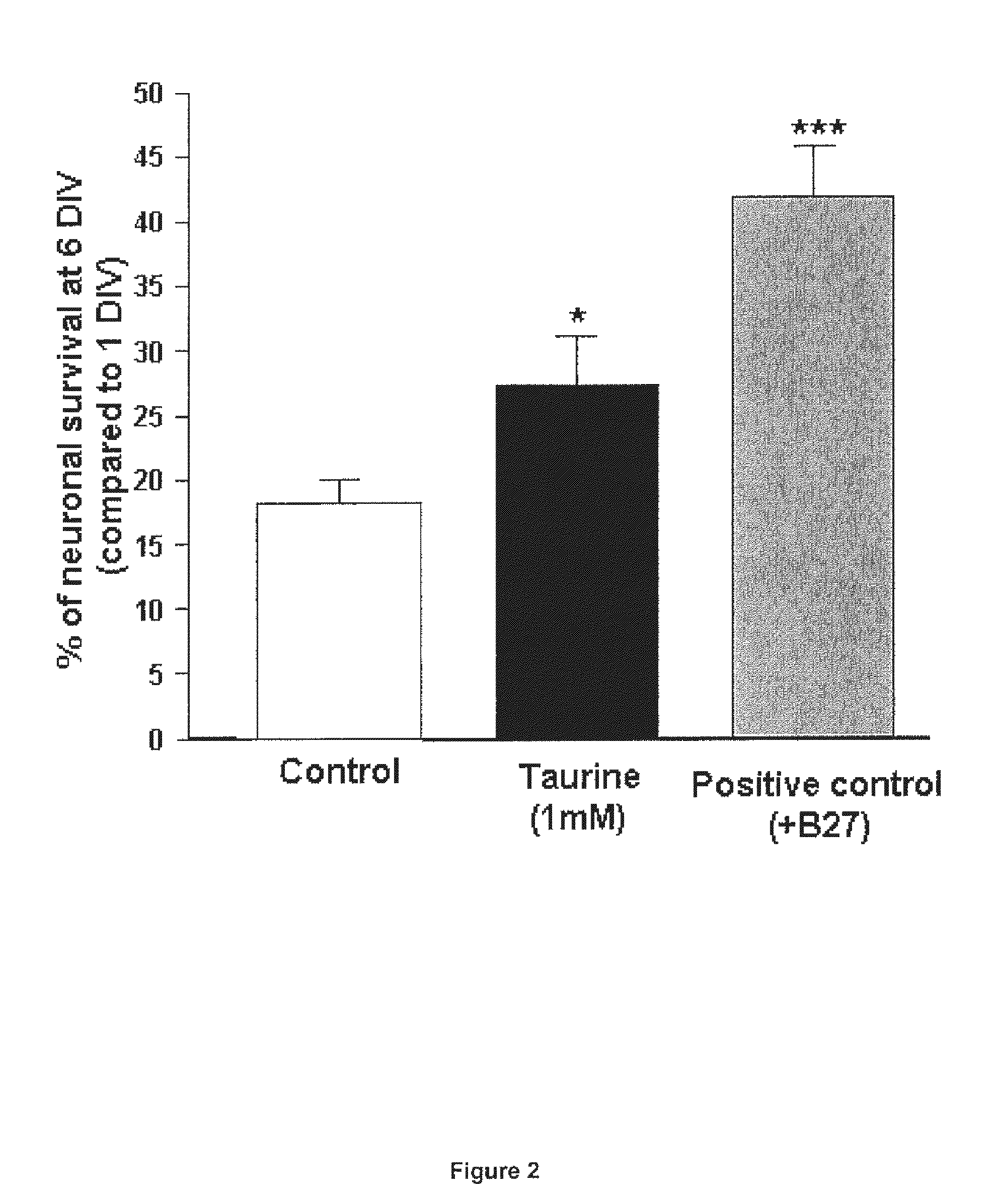
Taurine or taurine-like substances for the prevention and treatment of a disease associated with retinal ganglion cell degeneration
InactiveUS20120027723A1Prevent degradationPrevention and treatment of a diseaseHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseTaurine biosynthesis
The present invention relates to taurine or taurine-like substances for the prevention and treatment of a disease associated with retinal ganglion cell degeneration. More particularly the invention relates to a substance selected from the group consisting of taurine, a taurine precursor, a taurine metabolite, a taurine derivative, a taurine analog and a substance required for the taurine biosynthesis for the prevention and treatment of a disease associated with retinal ganglion cell degeneration.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
SynP198, a promoter for the specific expression of genes in direction selective retinal ganglion cells
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid molecule comprising, or consisting of, the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 or a nucleic acid sequence of at least 400 bp having at least 80% identity to said sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, wherein said isolated nucleic acid molecule specifically leads to the expression in direction selective retinal ganglion cells of a gene when operatively linked to a nucleic acid sequence coding for said gene.
Owner:FRIEDRICH MIESCHER INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Visual function disorder improving agents
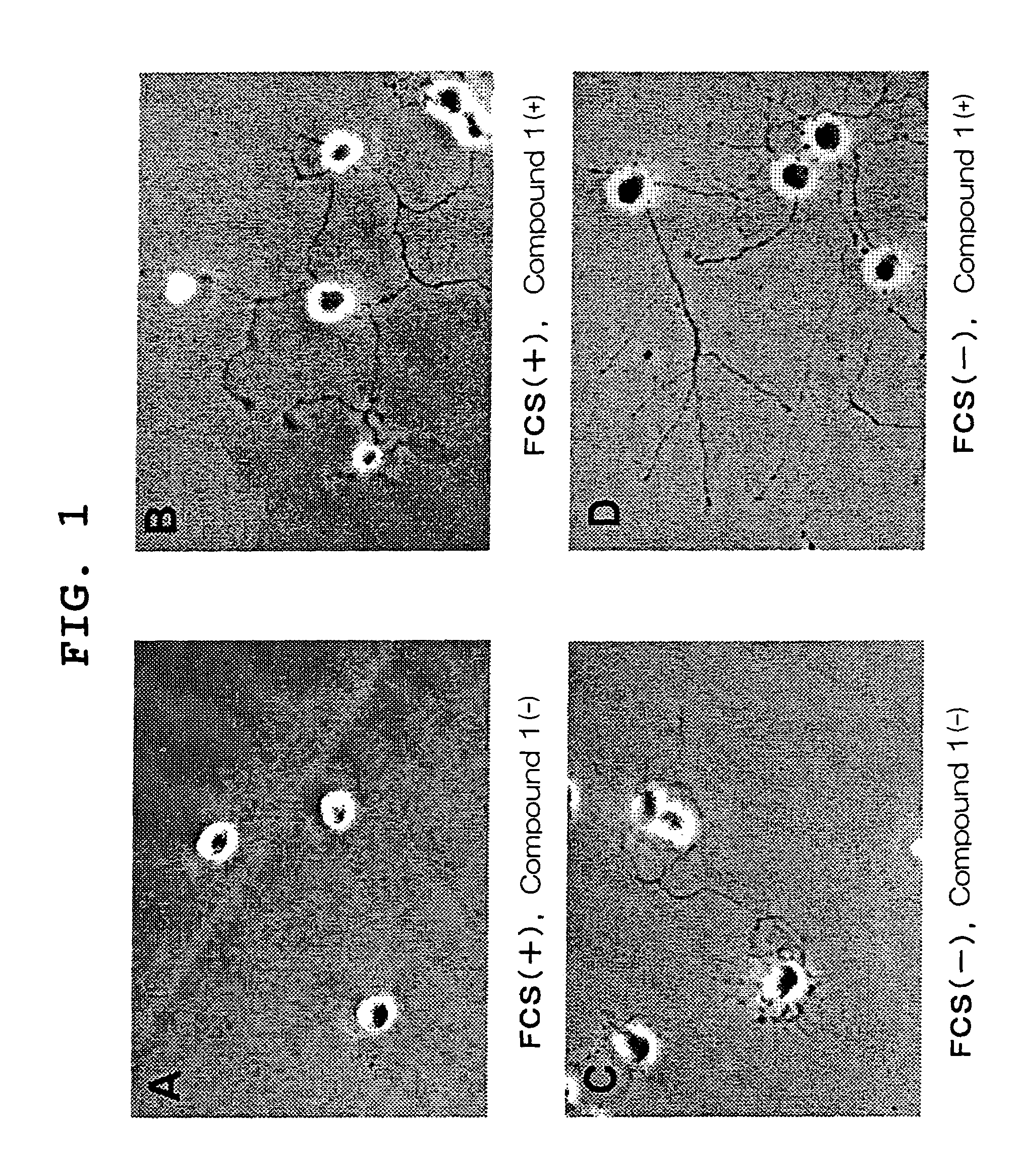
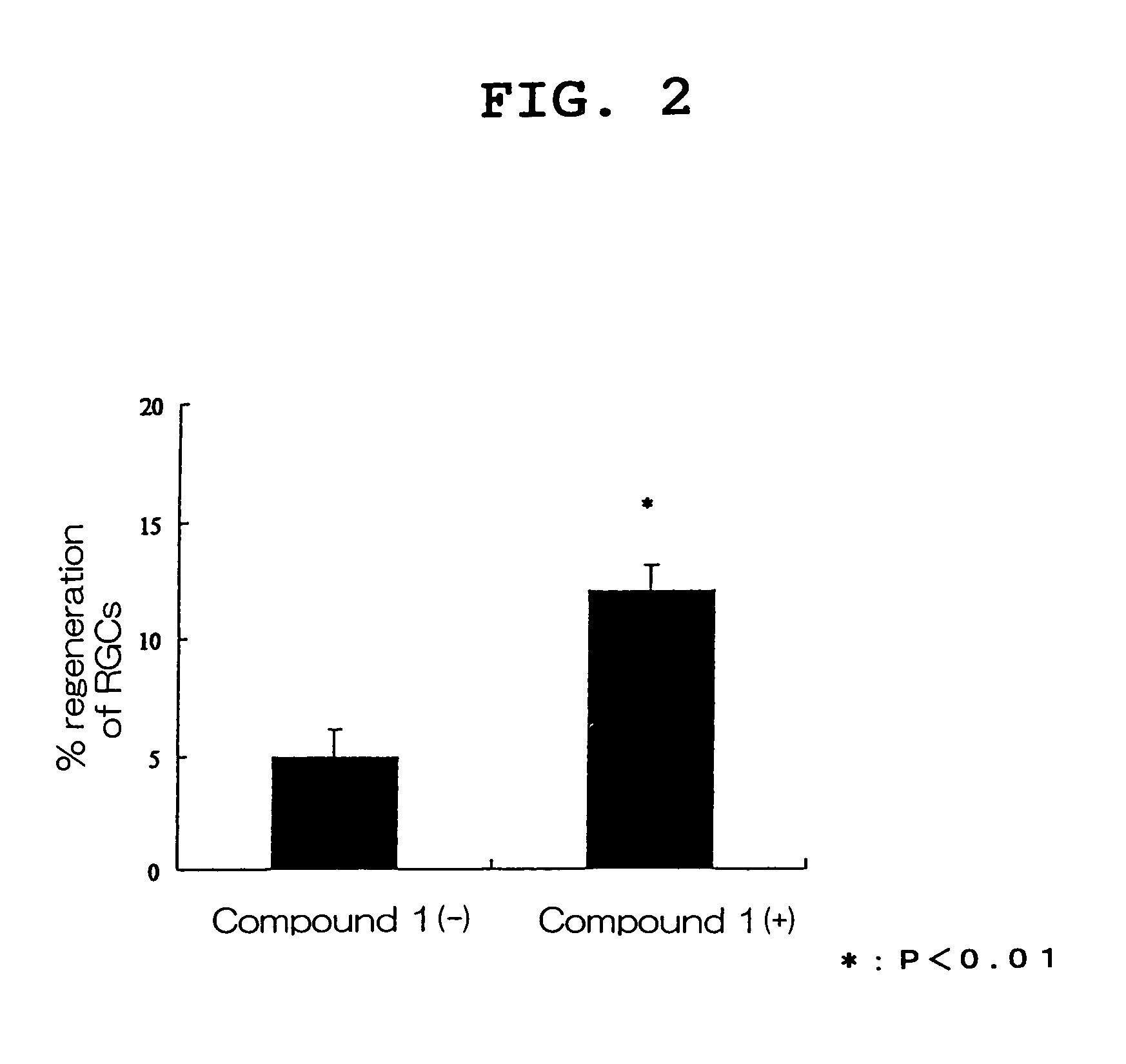
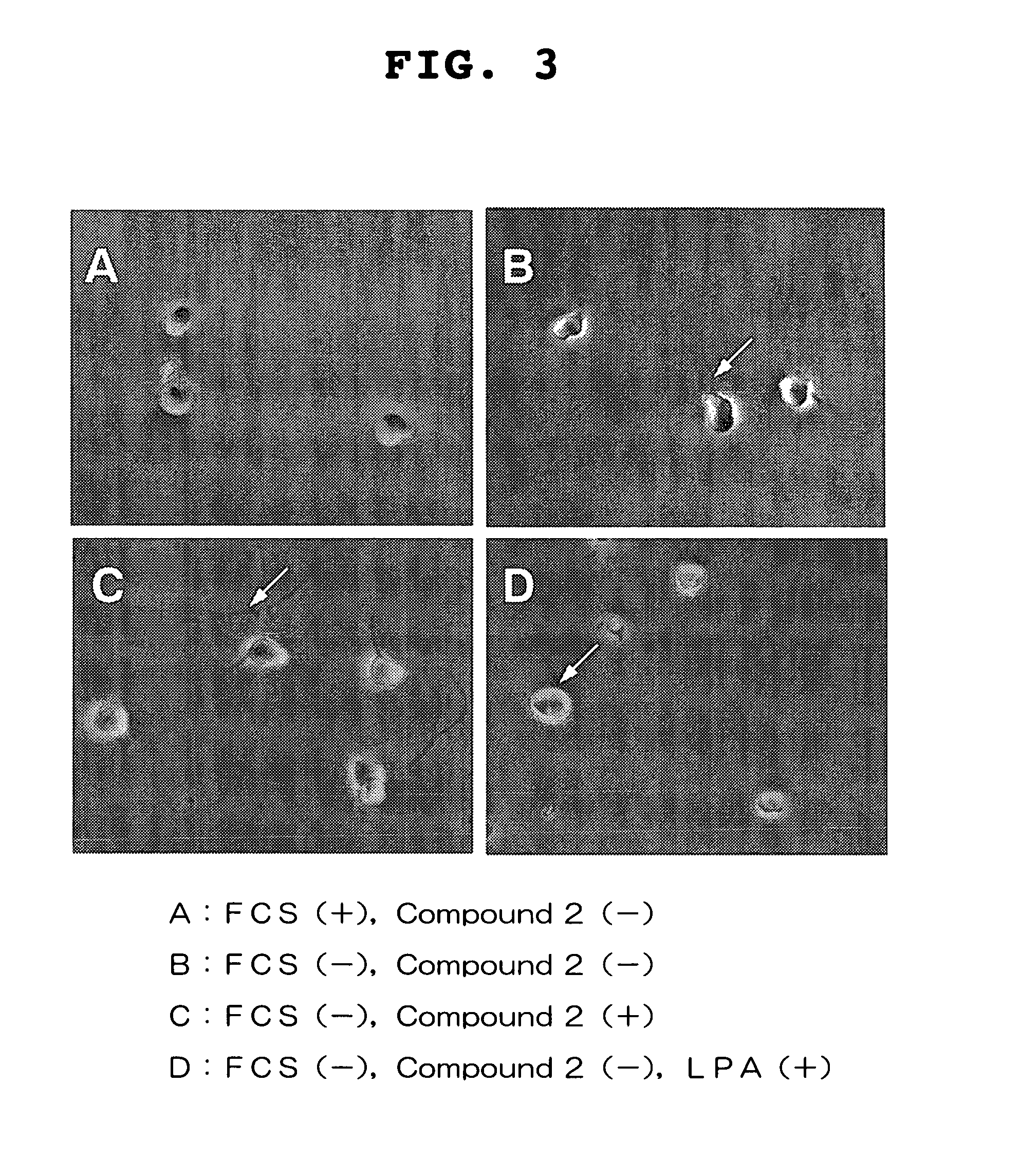
The present invention provides a visual function disorder improving agent containing a compound having Rho kinase inhibitory activity, particularly (R)-(+)-N-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)-4-(1-aminoethyl)benzamide, as an effective component. This agent has axon of the retinal ganglion cellal extension promoting action and optic nerve cell regeneration promoting action, and is useful for the treatment of a visual function disorder associated with various eye diseases caused by damage, defects, degeneration and the like in the retinal or optic nerve.
Owner:SENJU PHARMA CO LTD +1
Compositions And Methods For Treatment of Neural Disorders Using Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Superfamily Proteins And Their Antagonists
InactiveUS20090215671A1Enabling modulationEfficient modulationSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProgenitorDisease
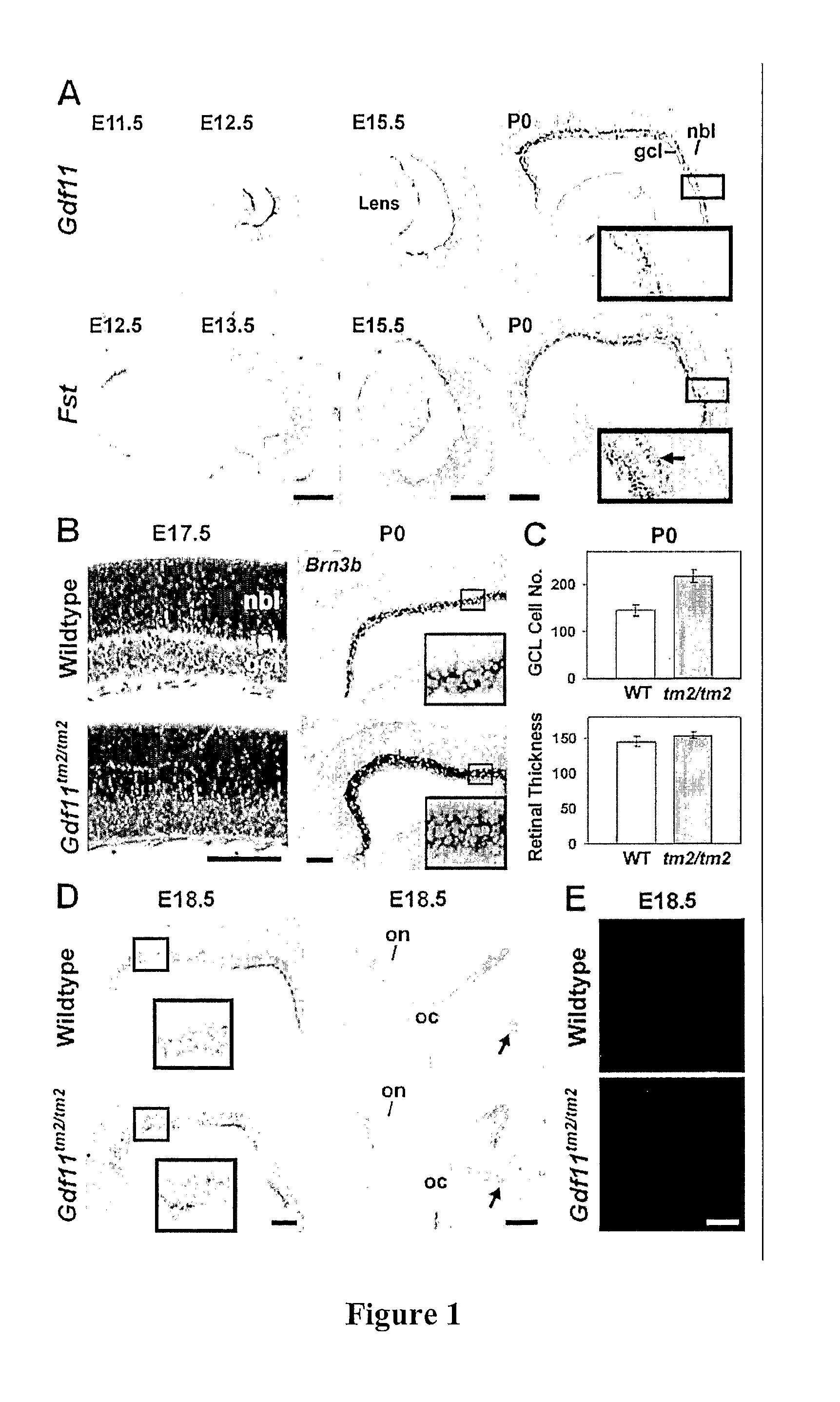
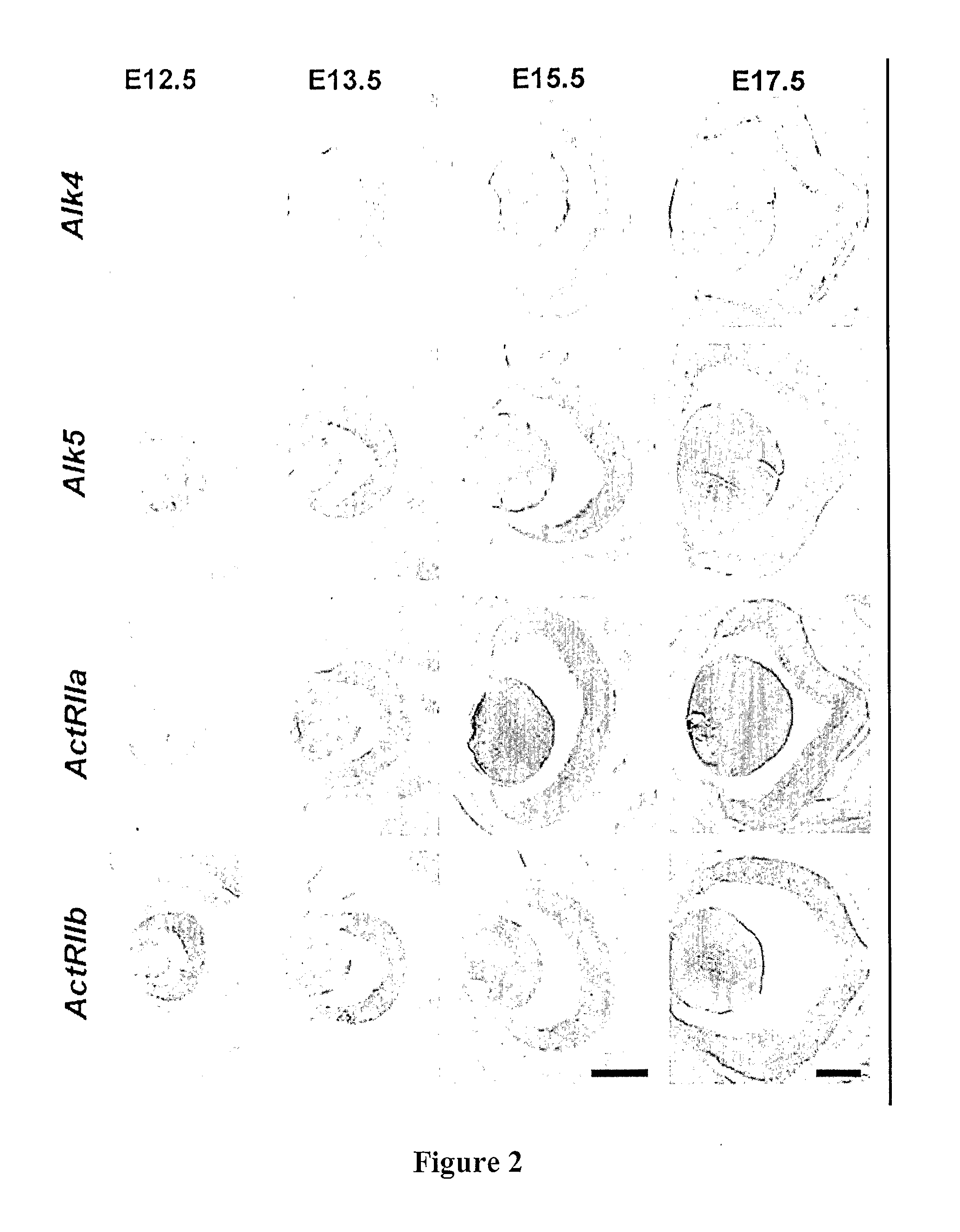
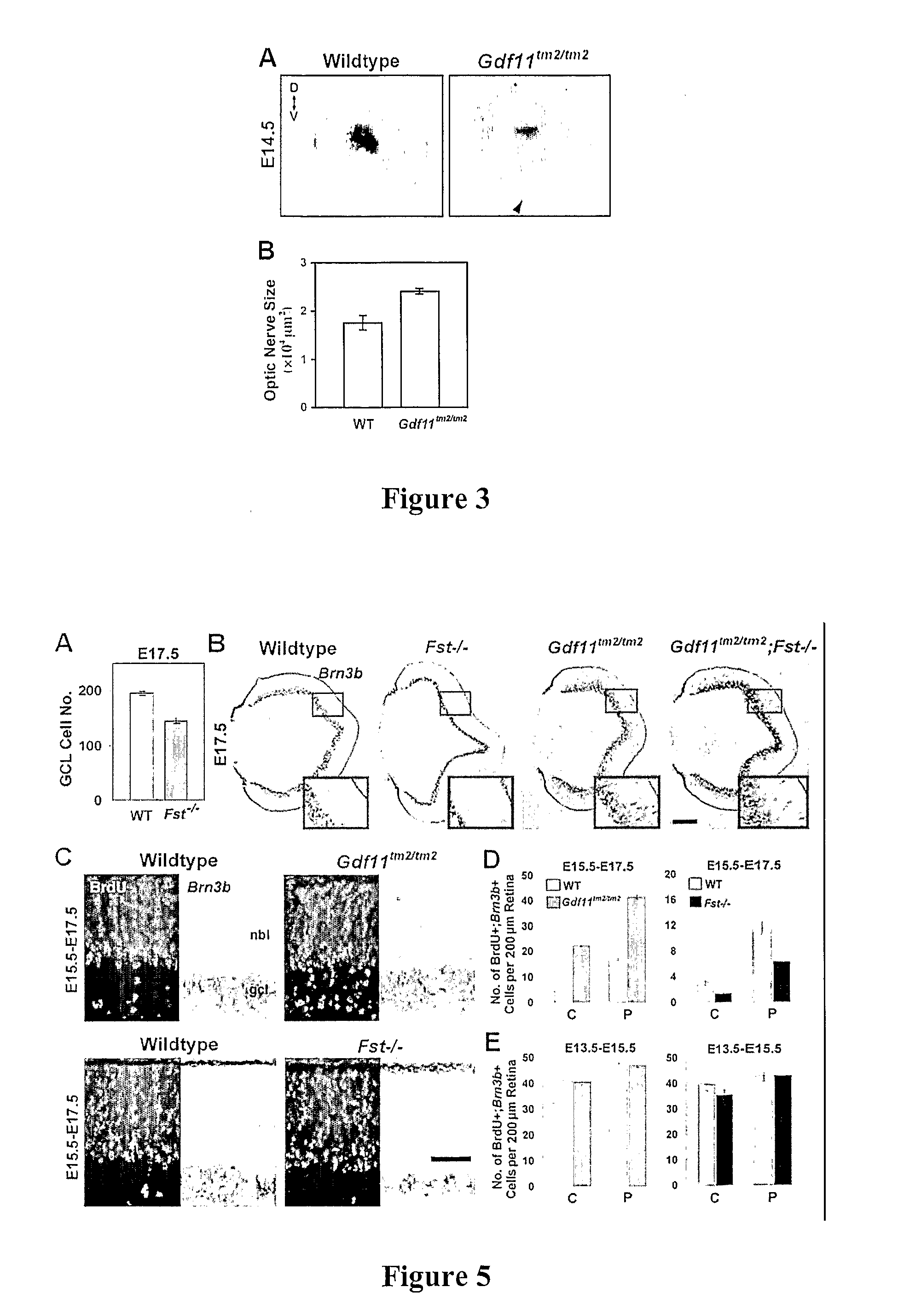
Contemplated compositions and methods employ a TGF-beta superfamily protein or antagonist thereof to treat a neural disorder characterized by an imbalance in differentiated functional sensory and neural cells derived from a sensory / neural progenitor cell. Preferably, GDF-11 and / or antagonists thereof are employed in the treatment of diseases in which visual and / or auditory progenitor cells will provide for a repair mechanism to the disease. Most preferably, GDF-11 is employed as a modulator of competency to increase production of retinal ganglion cells, retinal photoreceptors, retinal amacrine cells, sensory hair and supporting cells of the vestibulocochlear epithelium, and / or neurons and supporting cells of the spiral acoustic ganglion and vestibulo-cochlear (auditory) nerve to which it gives rise.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for optogenetic treatment of blindness including retinitis pigmentosa
ActiveUS20100268150A1Efficient activationBehavioral improvementElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsOptogeneticsRetinitis pigmentosa
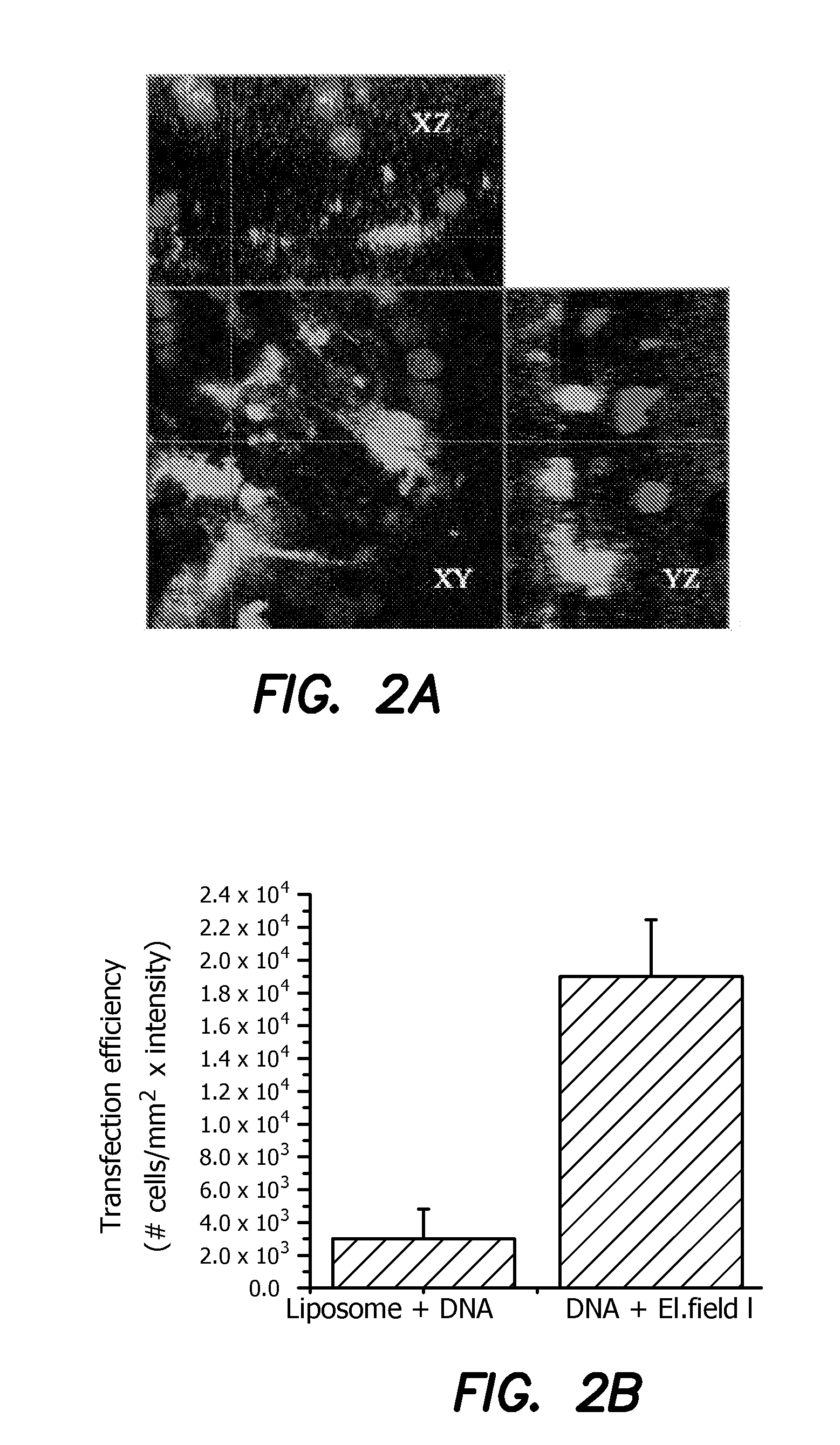
An apparatus for in vivo electroporating a plasmid into a retina of any eye includes a first electrode with a first polarity of voltage placed in contact with a cornea of the eye, a second electrode with an opposite second voltage at least in part behind the retina, and a pulsed voltage source for providing a pulsed DC voltage with an optimized field strength amplitude, frequency, number of pulses, group repetition rate and duration of pulse and group repetition, which are optimized for transfection of the channelrhodospsin-2 (ChR2) gene into the retinal ganglion cells. An in vivo method for treating retinal ganglion cells in an eye without use of viral transfection includes the steps of nonviral in vivo delivering a channelrhodospsin-2 (ChR2) gene to target the specific (retinal ganglion) cells of a retina by intravitreous injection of plasmid DNA, electroporating the plasmid into the retina and use of image intensification device for stimulating the retinal ganglion cells with ambient lighting conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micro-electrode array chip before retina in field of artificial vision
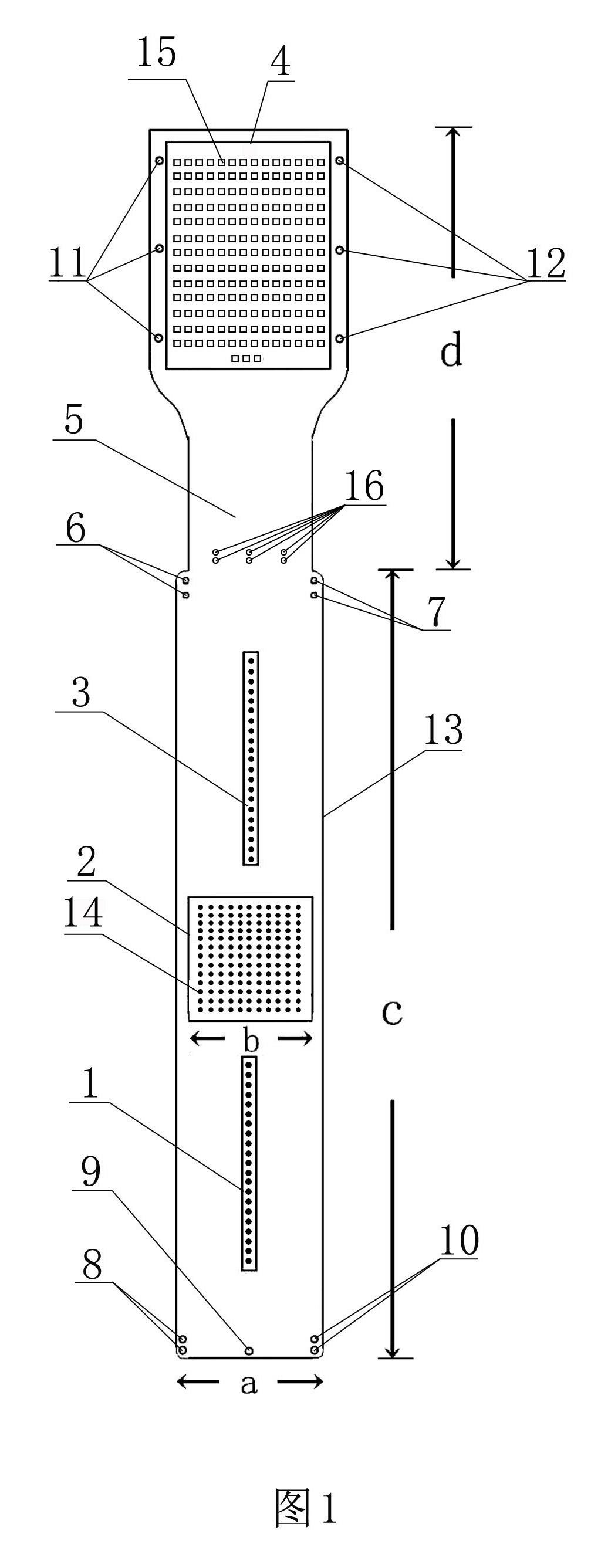
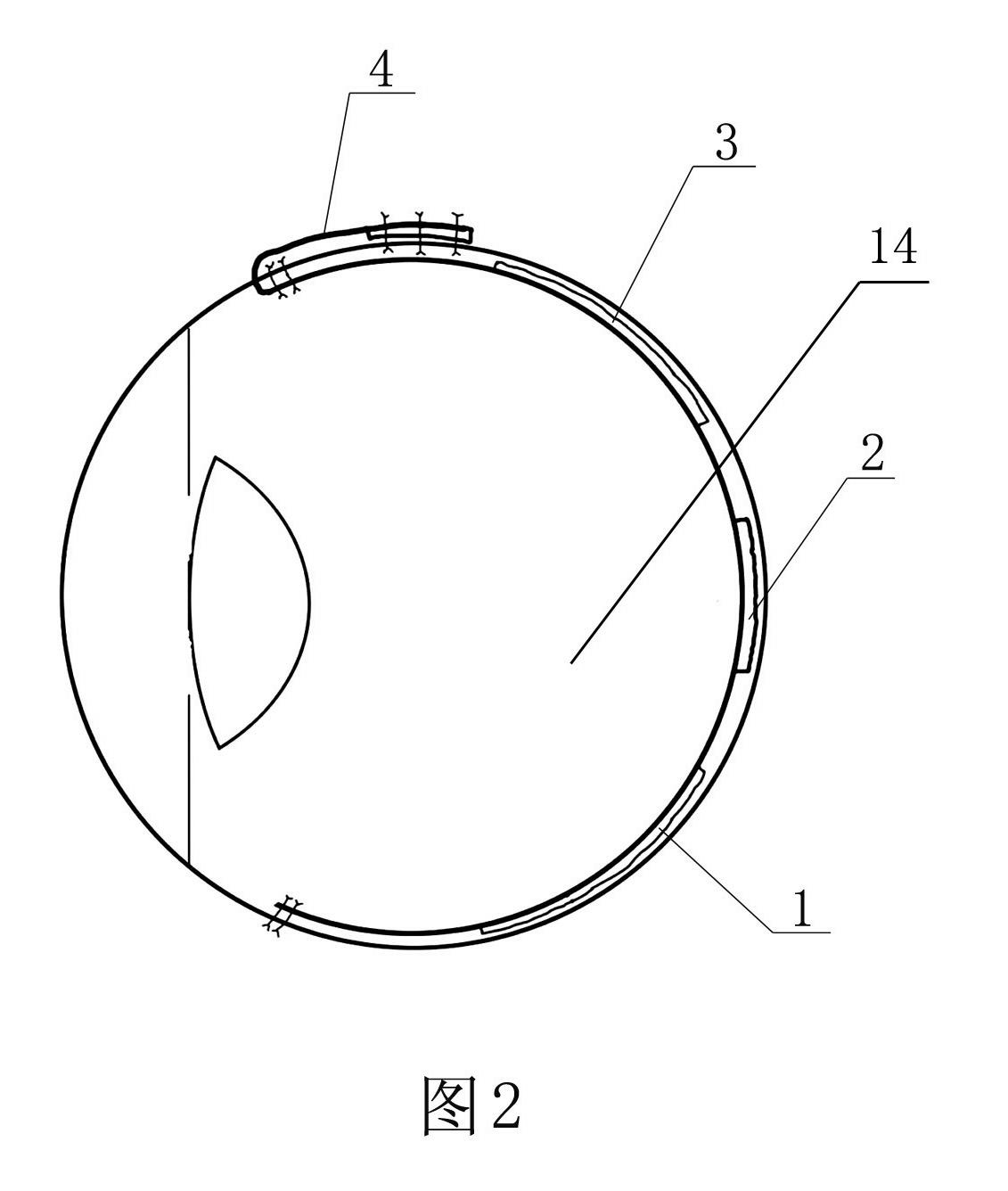
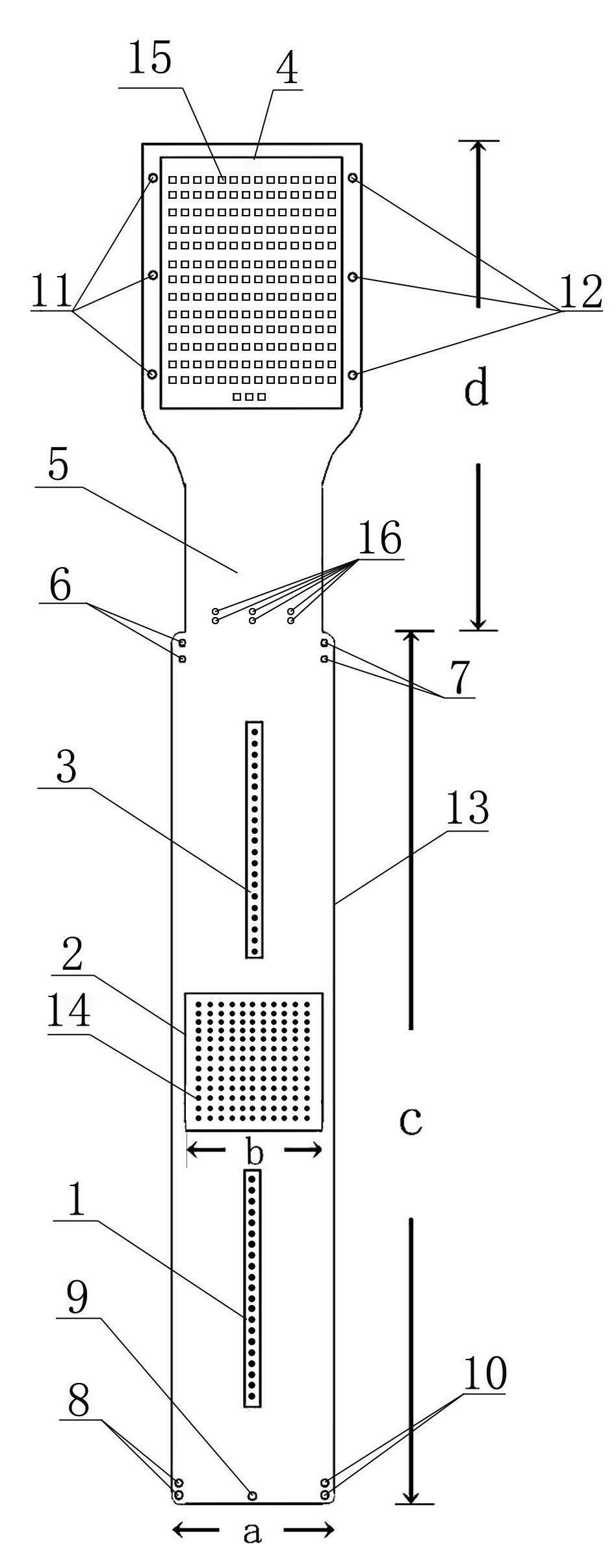
The invention discloses a micro-electrode array chip before retina in the field of artificial vision. The micro-electrode array chip comprises a chip substrate, a lead buried in the chip substrate and micro-electrodes protruding the surface of the substrate and forming an array. The edge of the lower end of the chip substrate is provided with at least two lower suture line preformed holes; a micro-electrode arrangement lower area, a micro-electrode arrangement middle area, a micro-electrode arrangement upper area, a substrate reduction area and a substrate expansion area are sequentially arranged on the chip substrate from bottom to top; the substrate expansion area contains contacts corresponding to the electrode arrangement areas, and are connected with the micro-electrodes through the lead buried in the chip substrate; the chip substrate close to the lower end of the substrate reduction area is provided with at least three groups of two sclera cut suture line preformed holes, and two edges are respectively provided with at least two upper suture line preformed holes; and two sides of the substrate expansion area are provided with eye external suture line preformed holes. The micro-electrode array chip can stimulate retinal ganlion cells of the blind to recover partial vision of the blind, and avoids rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, choroidal hemorrhage and sympathetic ophthalmia caused by iatrogenic retinal breaks.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Lighting apparatus
ActiveUS20180153018A1Improve readabilityLight source combinationsElectrical apparatusLight equipmentRetinal ganglion cell
A lighting apparatus includes a light emitter that emits a first illumination light as a display illumination light. The optical characteristics of the first illumination light are: a correlated color temperature in a range from 3800 K to 6500 K, inclusive; chromaticity deviation Duv in a range from −9 to 0, inclusive; and an intrinsic photosensitive retinal ganglion cell (ipRGC) stimulus level of at least 0.6, the ipRGC stimulus level being a value standardized by setting an ipRGC stimulus level of light emitted from a D65 light source to 1.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Systems and methods for determining retinal ganglion cell populations and associated treatments
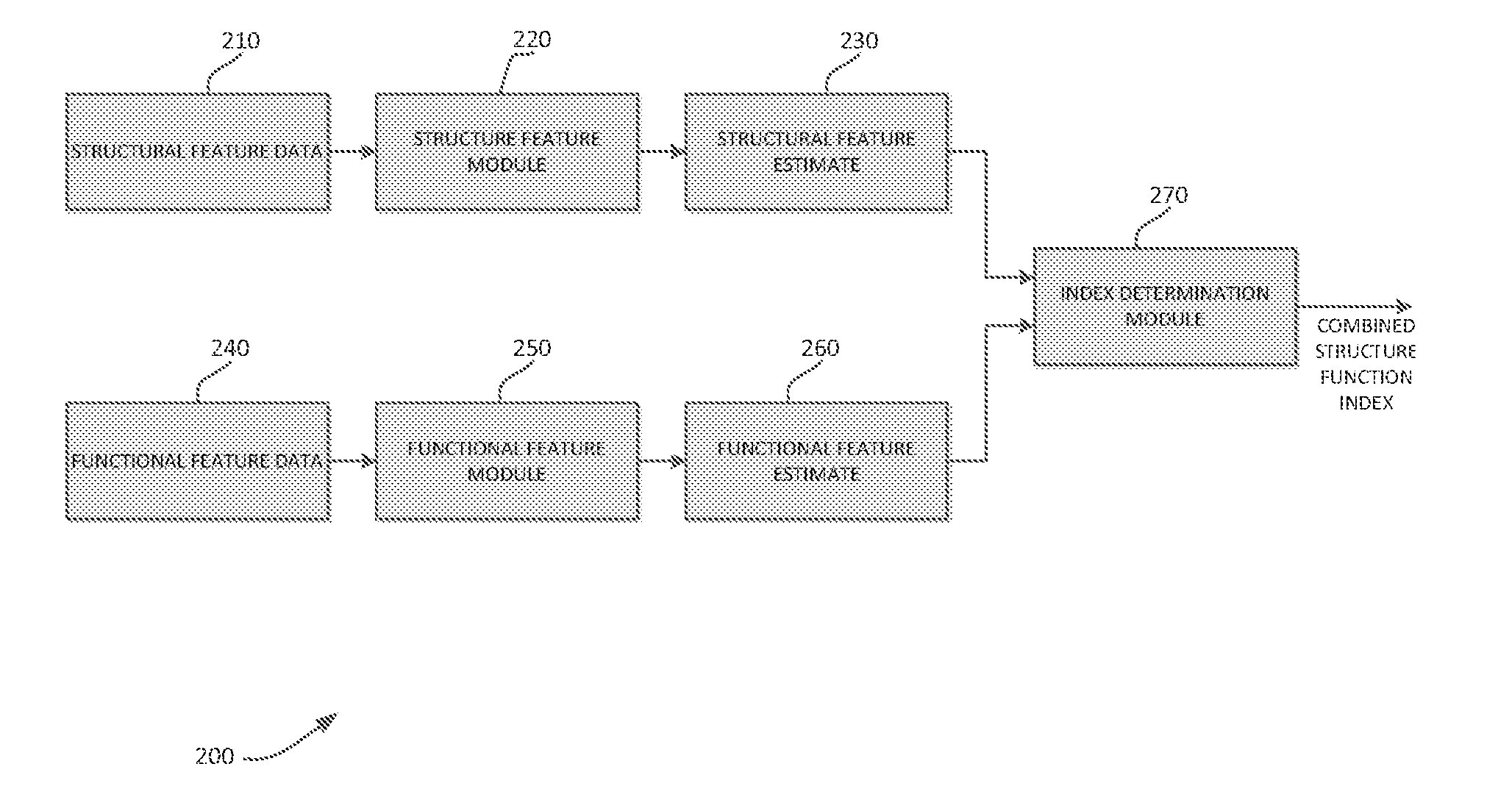
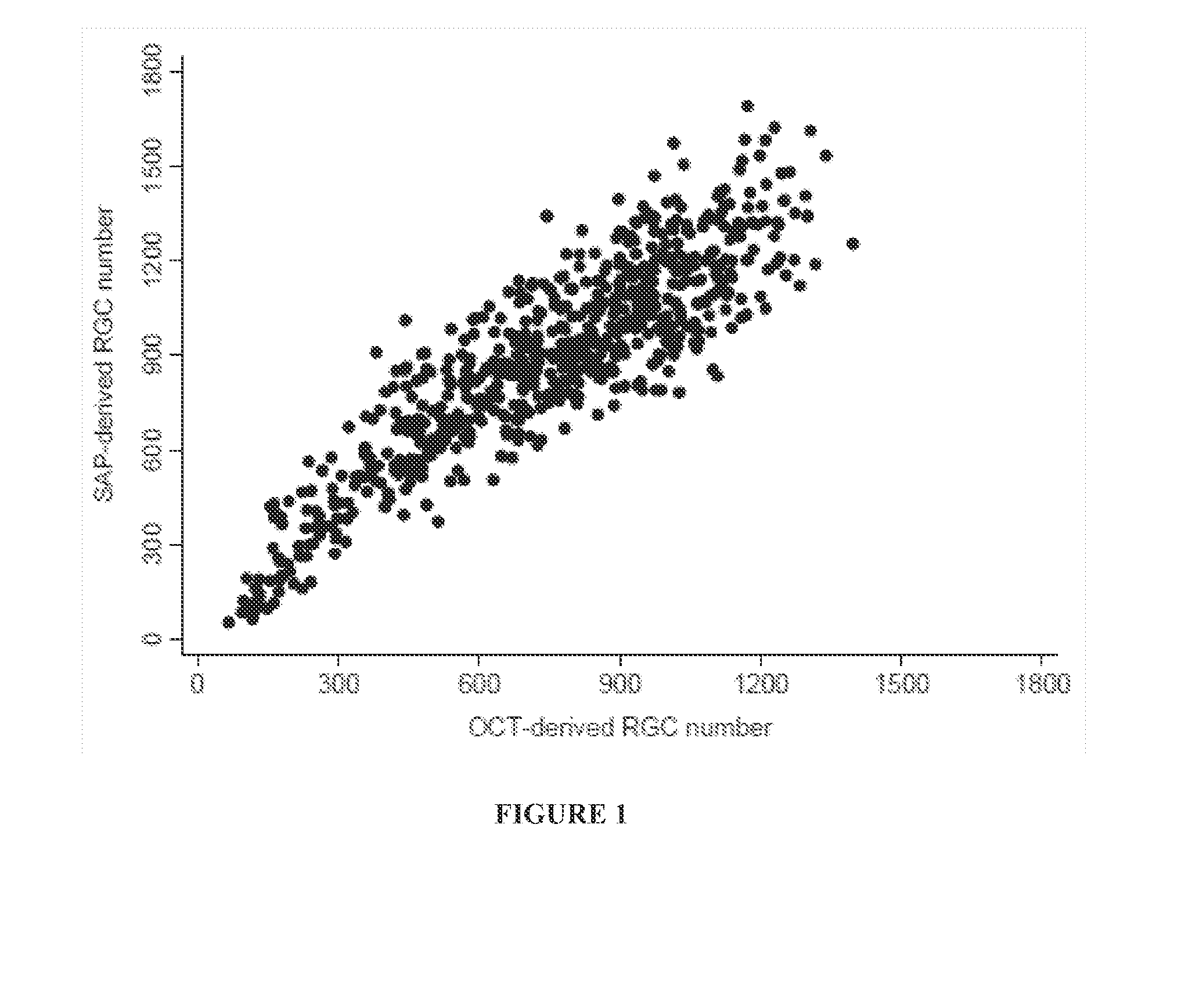
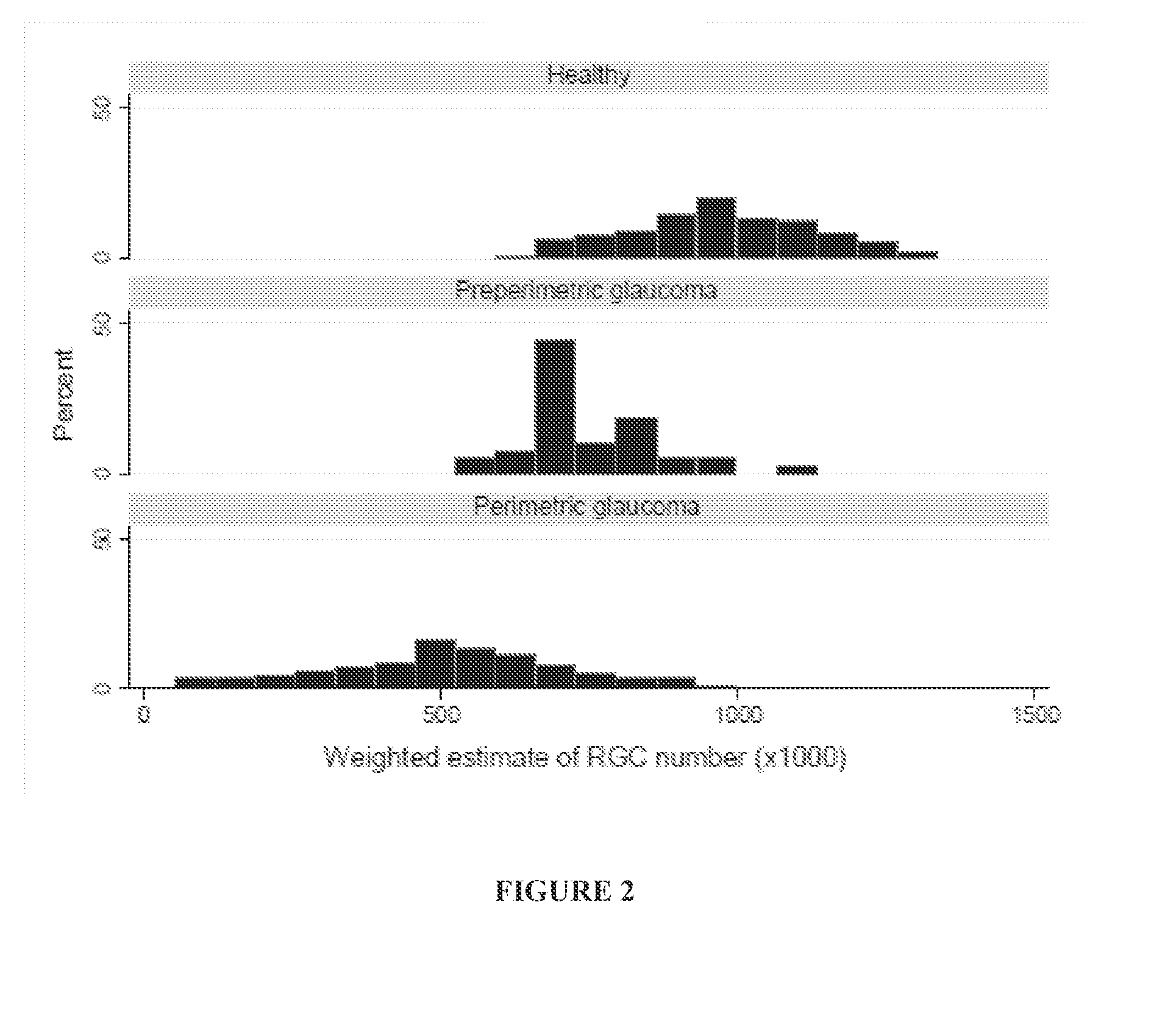
A new combined index of structure and function (CSFI) for staging and detecting glaucomatous damage is provided. An observational study including 333 glaucomatous eyes (295 with perimetric glaucoma and 38 with preperimetric glaucoma) and 330 eyes of healthy subjects is described. All eyes were tested with standard automated perimetry (SAP) and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SDOCT) within 6 months. Estimates of the number of retinal ganglion cells (RGC) were obtained from SAP and SDOCT and a weighted averaging scheme was used to obtain a final estimate of the number of RGCs for each eye. The CSFI was calculated as the percent loss of RGCs obtained by subtracting estimated from expected RGC numbers. The performance of the CSFI for discriminating glaucoma from normal eyes and the different stages of disease was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The mean CSFI, representing the mean estimated percent loss of RGCs, was 41% and 17% in the perimetric and pre-perimetric groups, respectively (P<0.001). They were both significantly higher than the mean CSFI in the normal group (P<Q.0( )1). The CSFI had larger ROC curve areas than isolated indexes of structure and function for detecting perimetric and preperimetric glaucoma and differentiating among early, moderate and advanced stages of visual field loss. An index combining structure and function performed better than isolated structural and functional measures for detection of perimetric and preperimetric glaucoma as well as for discriminating different stages of the disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
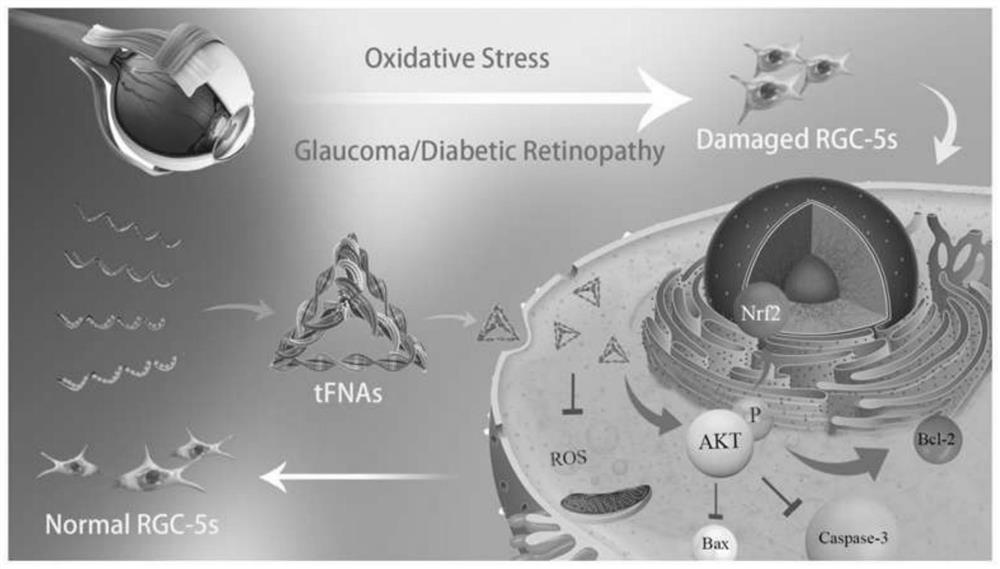
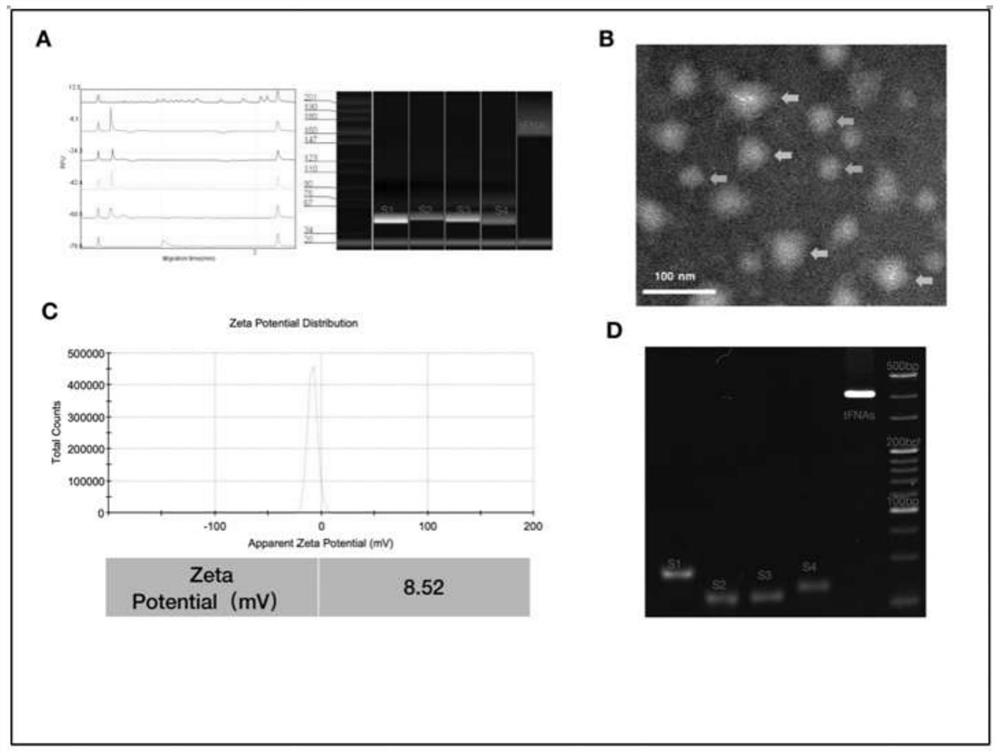
Medicine for preventing oxidative stress of retinal ganglion cells and wet macular degeneration
ActiveCN112007044AInhibit apoptosisImprove protectionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseRetinal ganglion
The invention provides a medicine for preventing retinal ganglion oxidative stress. The medicine is a preparation prepared by taking a DNA tetrahedron as an active component and adding pharmaceutically acceptable auxiliary materials or auxiliary components. The invention also provides application of the DNA tetrahedron in preparation of the medicine for preventing oxidative stress of retinal ganglion cells and apoptosis. The tFNA is used for preparing the medicine for preventing oxidative stress of the retinal ganglion cells, is helpful for treating diseases caused by oxidative stress of the retinal ganglion cells such as glaucoma, and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU GENREZE GENE TECH CO LTD
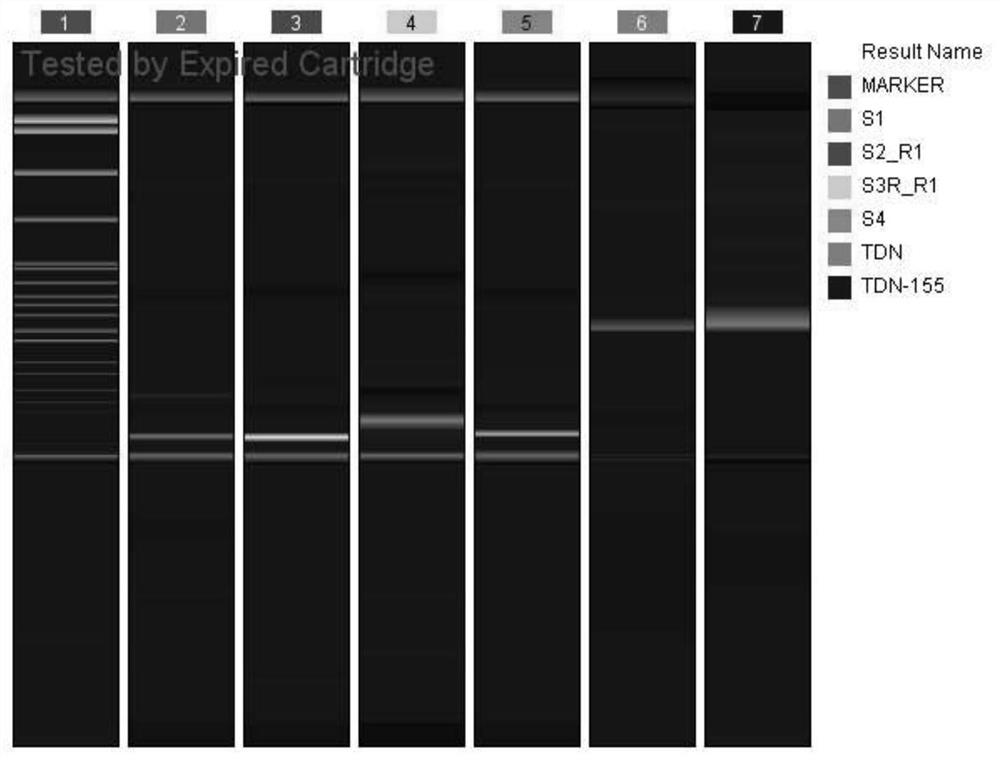
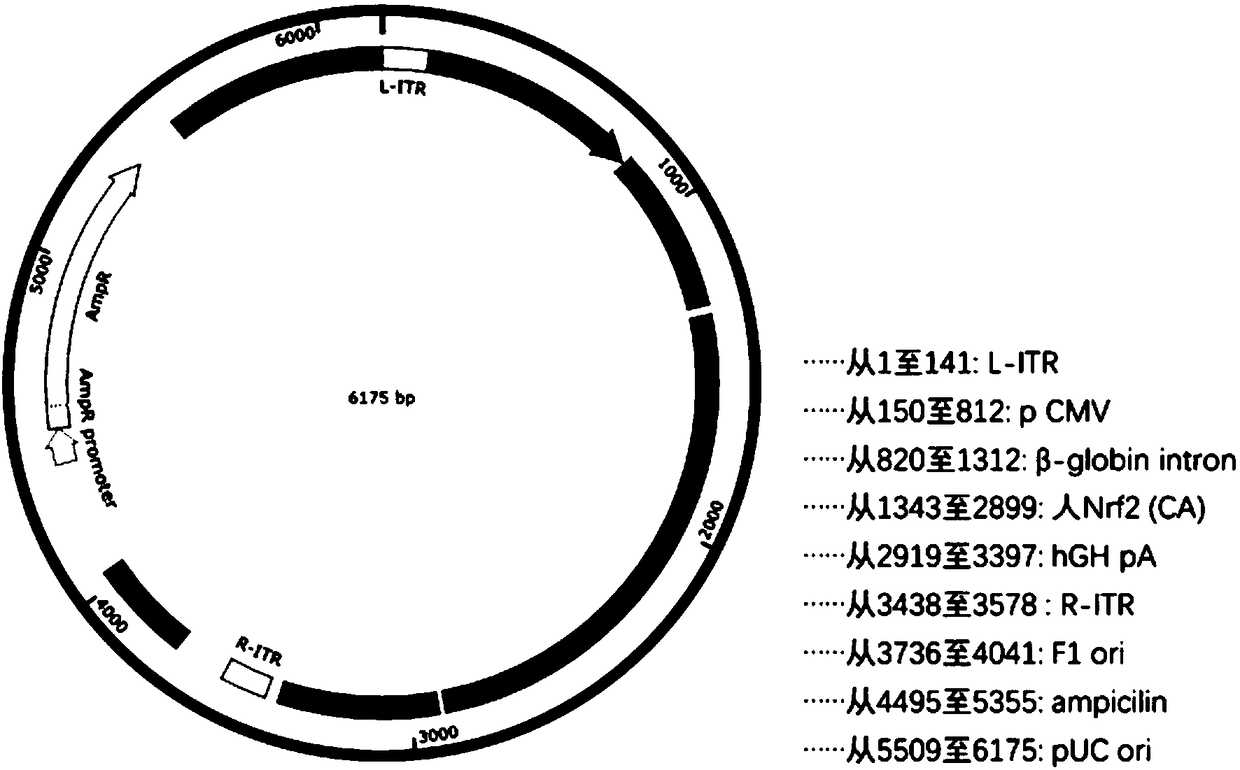
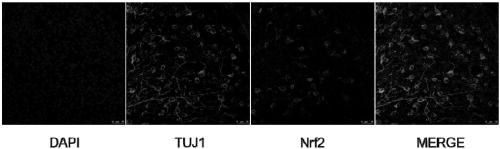
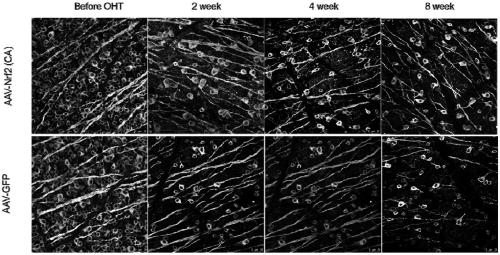
Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109055428AImprove survival rateInfection effect is goodSenses disorderGenetic material ingredientsBeta globinIntraocular pressure
The invention relates to a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector. The recombinant adeno-associated virus vector comprises constitutively active human Nrf2 (Nrf2 (CA)), a CMV promoter / enhancer, beta-globin intron for increasing gene expression, human growth hormone poly (A) tail sequence, etc. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector and the application of the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector or a composition containing the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector in preparing a medicine for treating glaucoma retinal ganglion cell denaturation. The recombinant adeno-associated virus vector provided by the invention can obviously reduce the intraocular pressure of a mouse, increase the survival rate of RGCs of the mouse, and effectively treat glaucoma retinal ganglion cell pathological changes.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
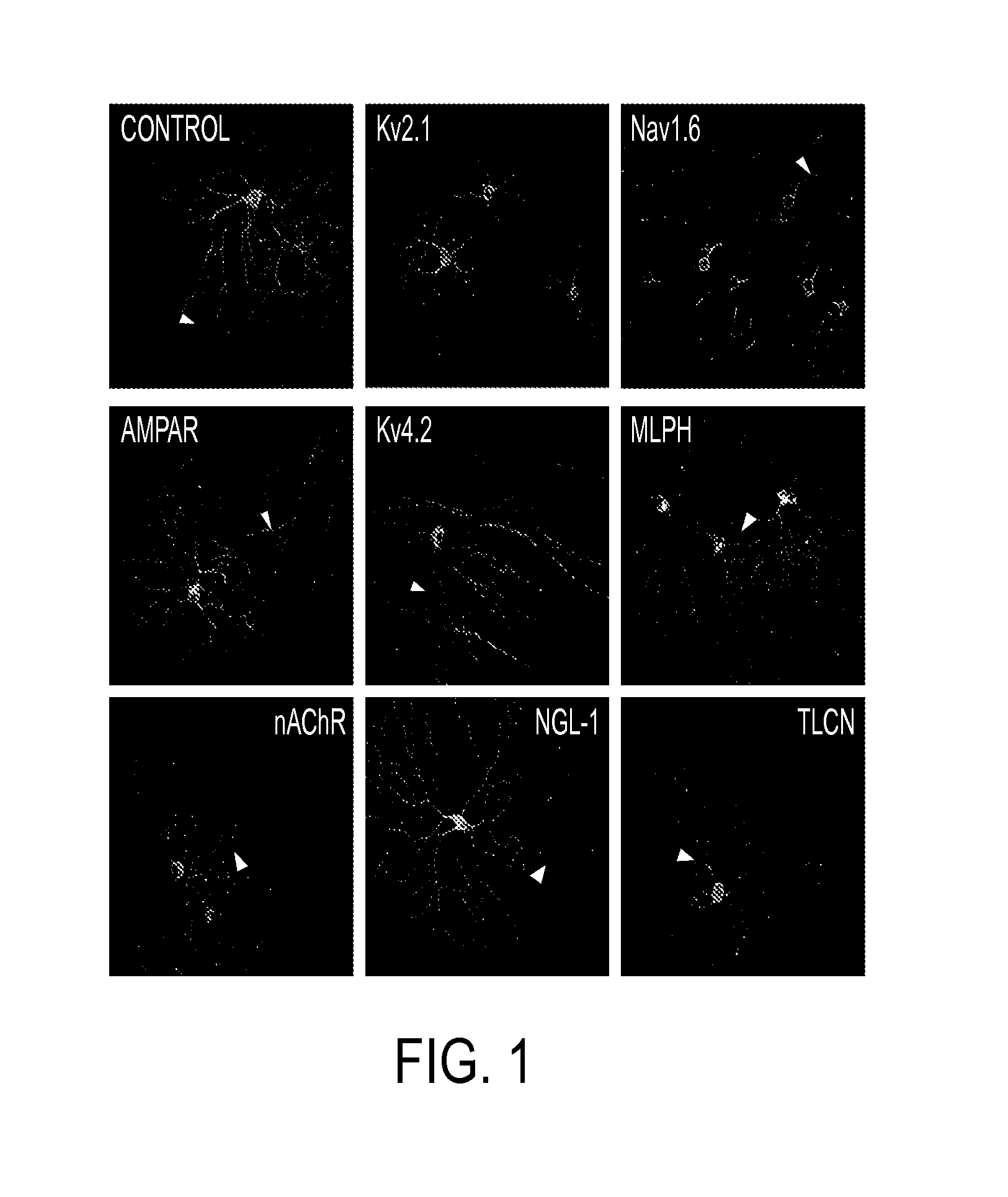
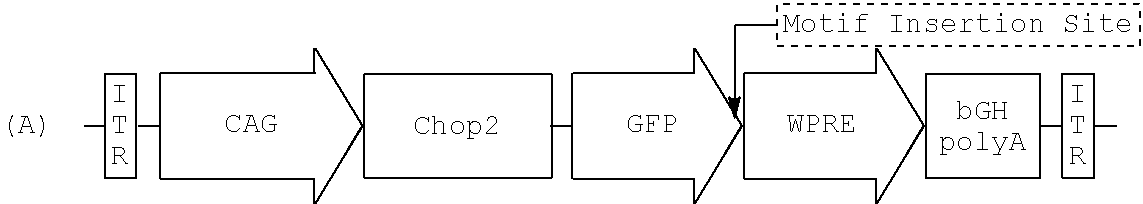
AAV-Mediated Subcellular Targeting of Heterologous Rhodopsins in Retinal Ganglion Cells
ActiveUS20130259833A1Enhanced spatial controlStrong specificityBiocideSenses disorderHeterologousDisease
Microbial type rhodopsins, such as the light-gated cation-selective membrane channel, channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2 / ChR2) or the ion pump halorhodopsin (HaloR) are expressed in retinal ganglion cells upon transduction using recombinant AAV vectors. Selective targeting of these transgenes for expression in discrete subcellular regions or sites is achieved by including a sorting motif in the vector that can target either the central area or surround (off-center) area of these cells. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding such rhodopsins and sorting motifs and their use in methods of differential expression of the transgene are disclosed. These compositions and methods provide significant improvements for restoring visual perception and various aspects of vision, particular in patients with retinal disease.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
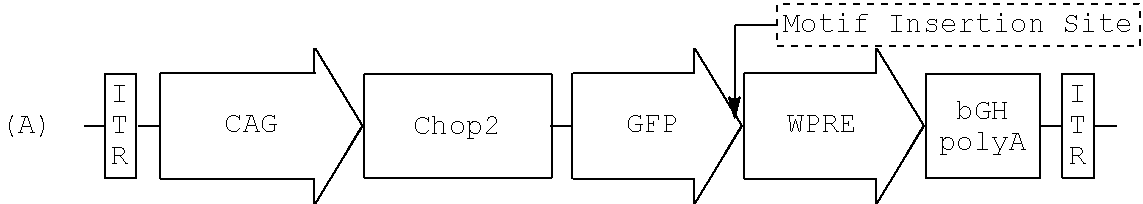
AAV-mediated subcellular targeting of heterologous rhodopsins in retinal ganglion cells
Microbial type rhodopsins, such as the light-gated cation-selective membrane channel, channel-rhodopsin-2 (Chop2 / ChR2) or the ion pump halorhodopsin (HaloR) are expressed in retinal ganglion cells upon transduction using recombinant AAV vectors. Selective targeting of these transgenes for expression in discrete subcellular regions or sites is achieved by including a sorting motif in the vector that can target either the central area or surround (off-center) area of these cells. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding such rhodopsins and sorting motifs and their use in methods of differential expression of the transgene are disclosed. These compositions and methods provide significant improvements for restoring visual perception and various aspects of vision, particular in patients with retinal disease.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Contour detection method based on non-classical receptive field and linear nonlinear modulation
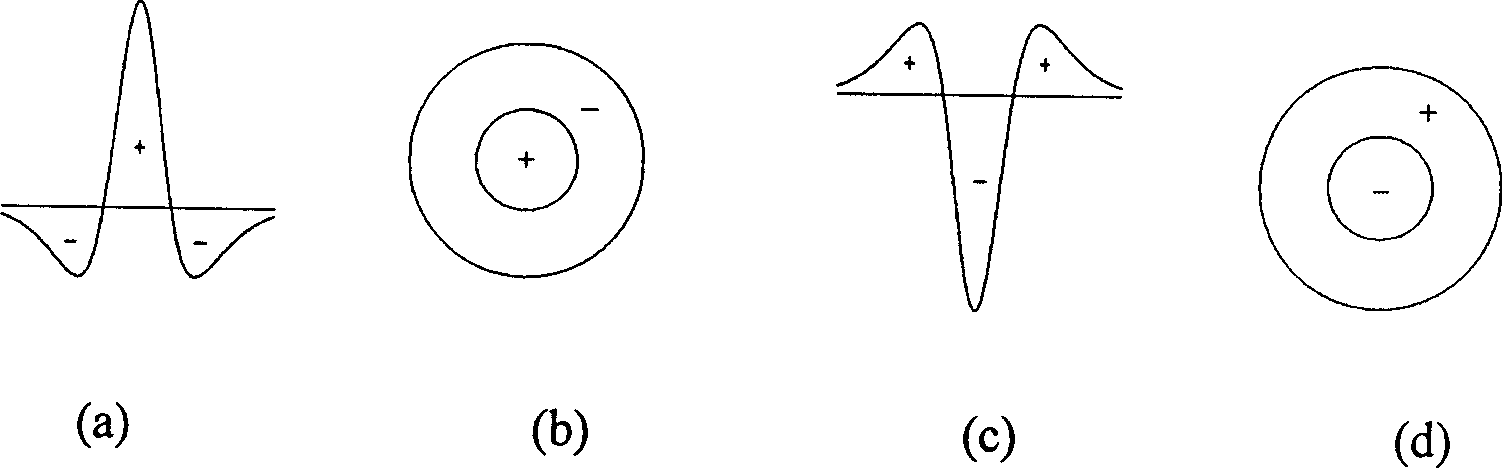
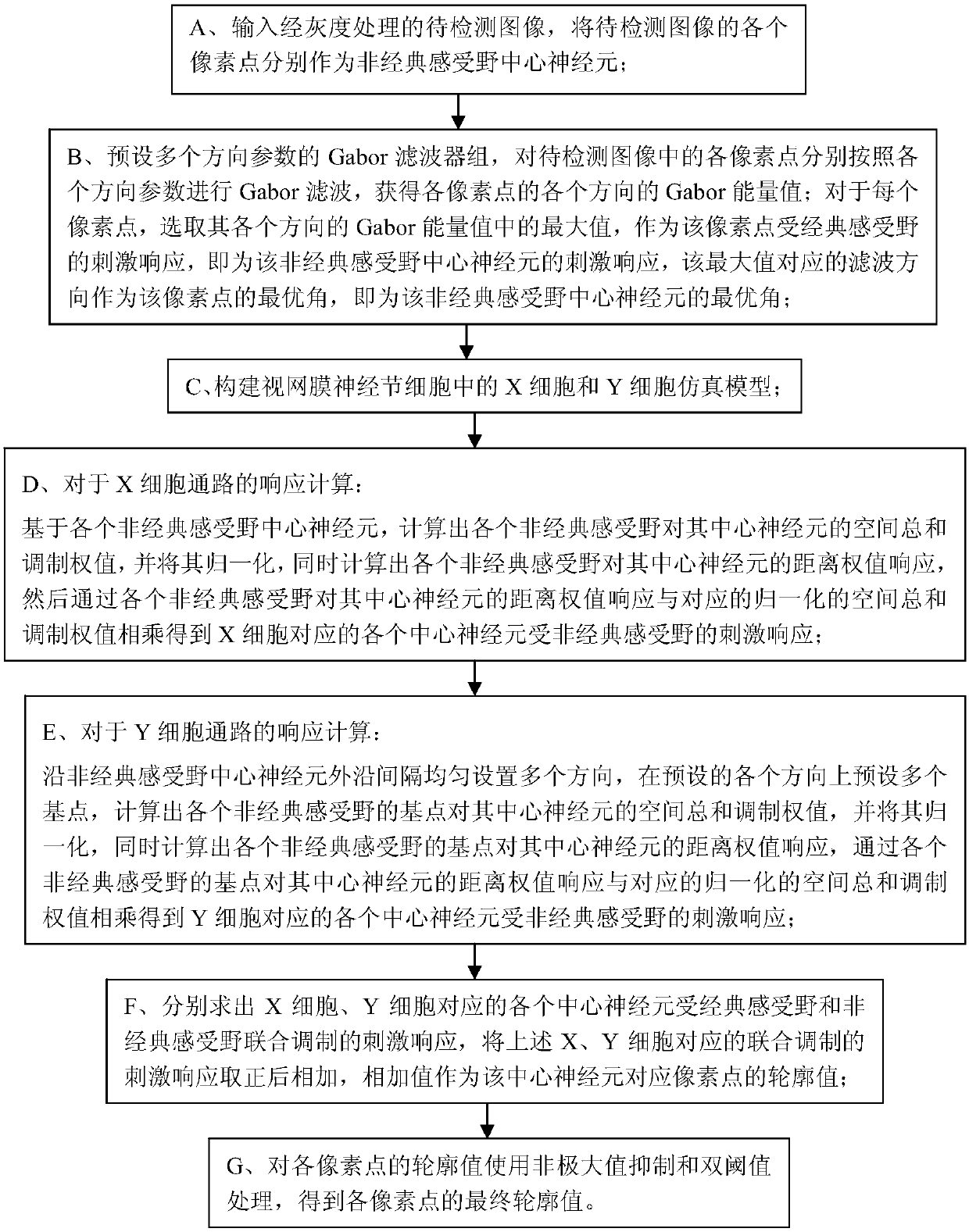
ActiveCN107067407ARealize simulationStable contour informationImage enhancementImage analysisCentral neuronNonlinear modulation
The present invention provides a contour detection method based on a non-classical receptive field and linear nonlinear modulation. The method comprises: A, inputting an image to be detected through gray processing; B, performing Gabor filtering of the image to be detected to obtain the Gabor energy value of each direction of each pixel point; C, constructing X-cell and Y-cell simulation models in a retina ganglion cell; D, calculating and obtaining stimulating response of each central neuron through the non-classical receptive field corresponding to the X cell; E, calculating and obtaining the stimulating response of each central neuron through the non-classical receptive field corresponding to the Y cell; F, respectively calculating the stimulating response of central neurons of the X cell and the Y cell through the combined modulation of the classical receptive field and the non-classical receptive field, and performing addition of the stimulating response of central neurons of the X cell and the Y cell to take as a corresponding contour value; and G performing processing of the contour values of each pixel point to obtain a final contour value. The contour detection method based on the non-classical receptive field and the linear nonlinear modulation overcomes the defect that the contour recognition rate is low in the prior art, and has good simulation effect and high contour recognition rate.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Compositions and methods for reducing visual loss
InactiveUS20160346224A1Reduce visual lossOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderParticulatesSide effect
The described invention provides a method for reducing visual loss and for treating one or more of adverse consequence of an eye disease, including abnormal intraocular pressure, retinal vascular disease, retinal ganglion cell death, or a combination thereof in order to reduce visual loss. The method entails providing a flowable particulate composition that contains a particulate formulation comprising a plurality of particles of uniform size distribution, a therapeutic amount of a therapeutic agent selected from a voltage-gated calcium channel antagonist, an endothelin receptor antagonist, or a combination thereof, and optionally an additional therapeutic agent, wherein the particles are of uniform size distribution, and wherein each particle comprises a matrix; and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical composition is characterized by: dispersal of the therapeutic agent throughout each particle, adsorption of the therapeutic agent onto the particles, or placement of the therapeutic agent in a core surrounded by a coating, sustained release of the therapeutic agent and optionally the additional therapeutic agent from the composition, and a local therapeutic effect that is effective to reduce signs or symptoms of the adverse consequence without entering systemic circulation in an amount to cause unwanted side effects. The method further entails administering a therapeutic amount of the pharmaceutical composition by a means for administration at a site of administration. The administering includes topically, parenterally, or by implantation. Sites of administration include intraocularly, intraorbitally, or into subconjunctival space.
Owner:EDGE THERAPEUTICS
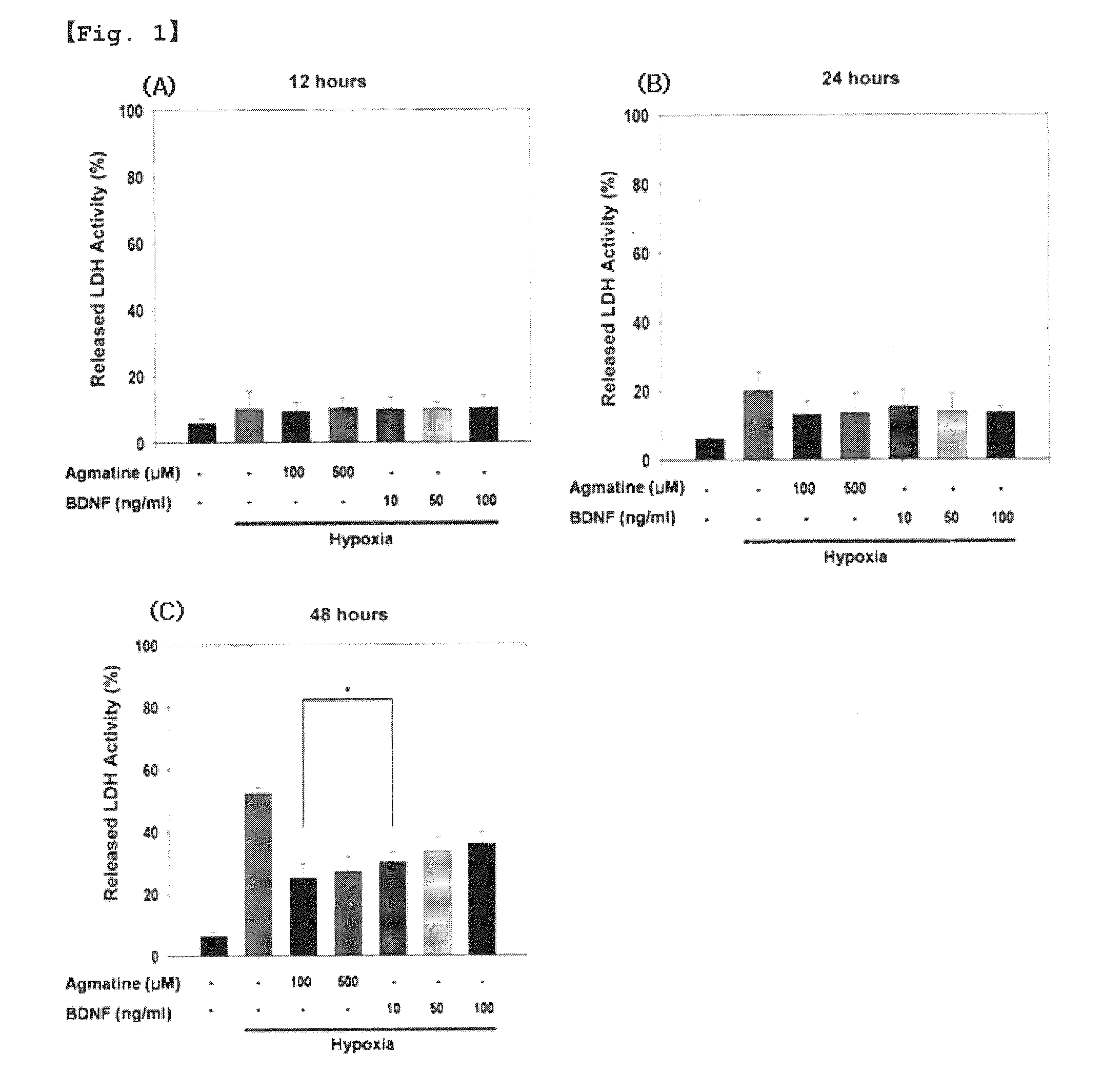
Use of agmatine for protection of retinal ganglion cells
ActiveUS20100130783A1Curing and preventing eye diseaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsApoptosisFactor ii
A use method of agmatine or a pharmaceutically allowable salt thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same are disclosed. The method and pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can effectively cure or prevent eye diseases preferably including glaucoma, retinopathy, and optic neuropathy associated with apoptosis in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), particularly hypoxia-induced or tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced apoptosis.
Owner:SEONG GONG JE +3
Method of providing ocular neuroprotection
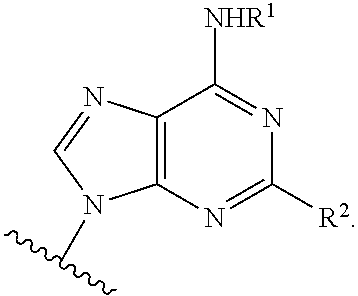
InactiveUS20140275128A1Preventing and reducing and treating damageReduce cell damageBiocideSenses disorderMedicinePurine derivative
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com