Patents
Literature
730 results about "Treatment glaucoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
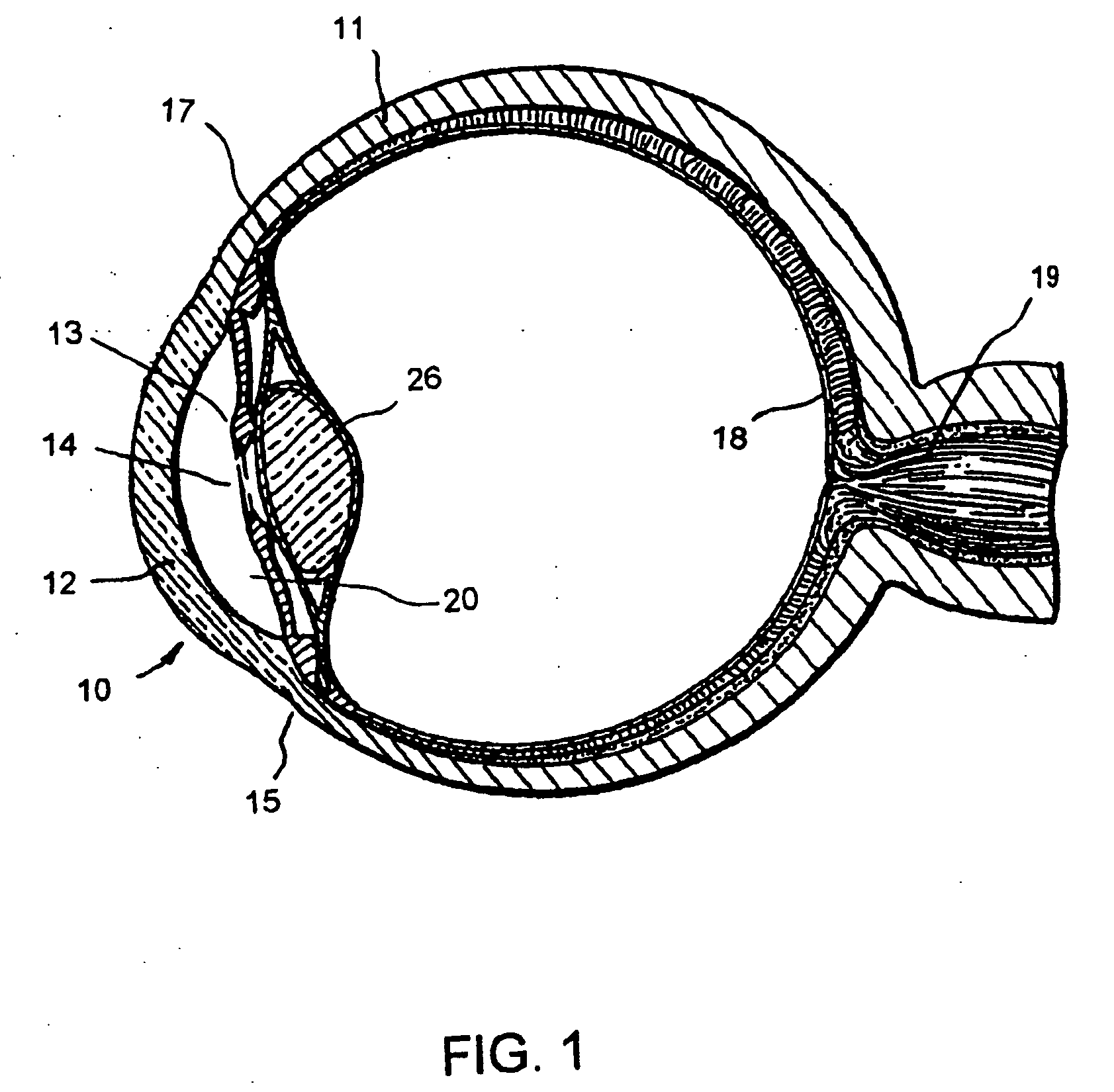
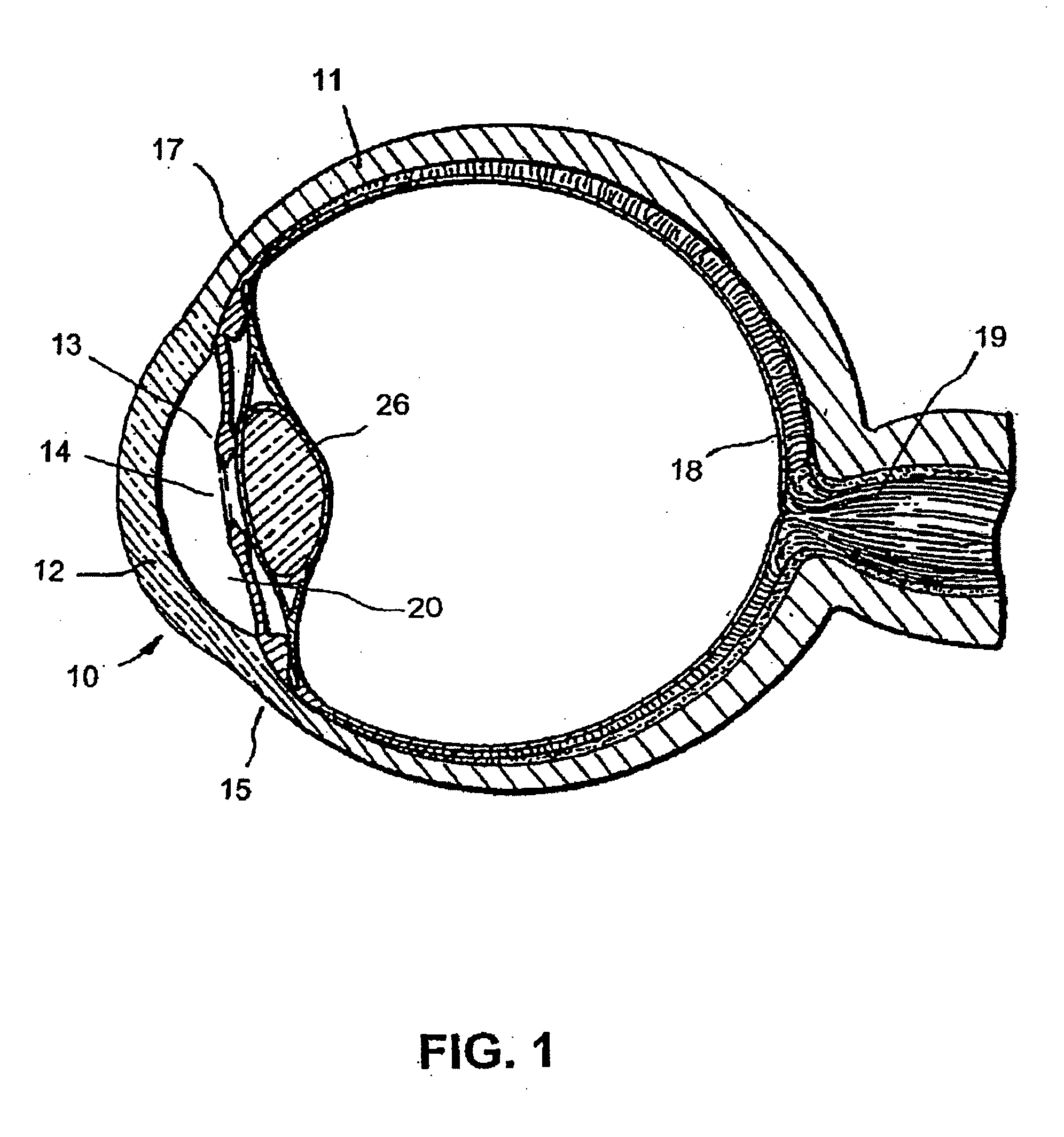
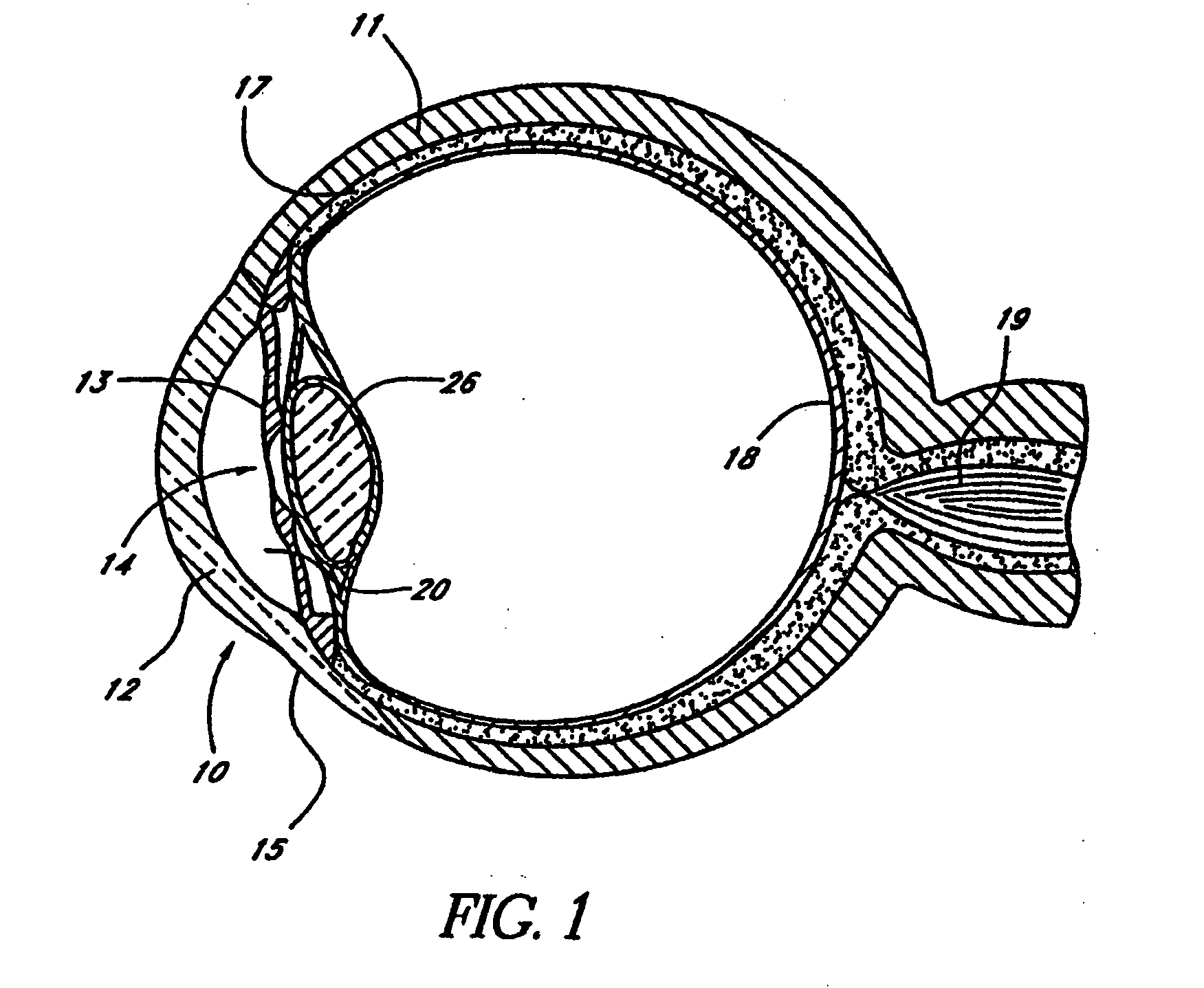
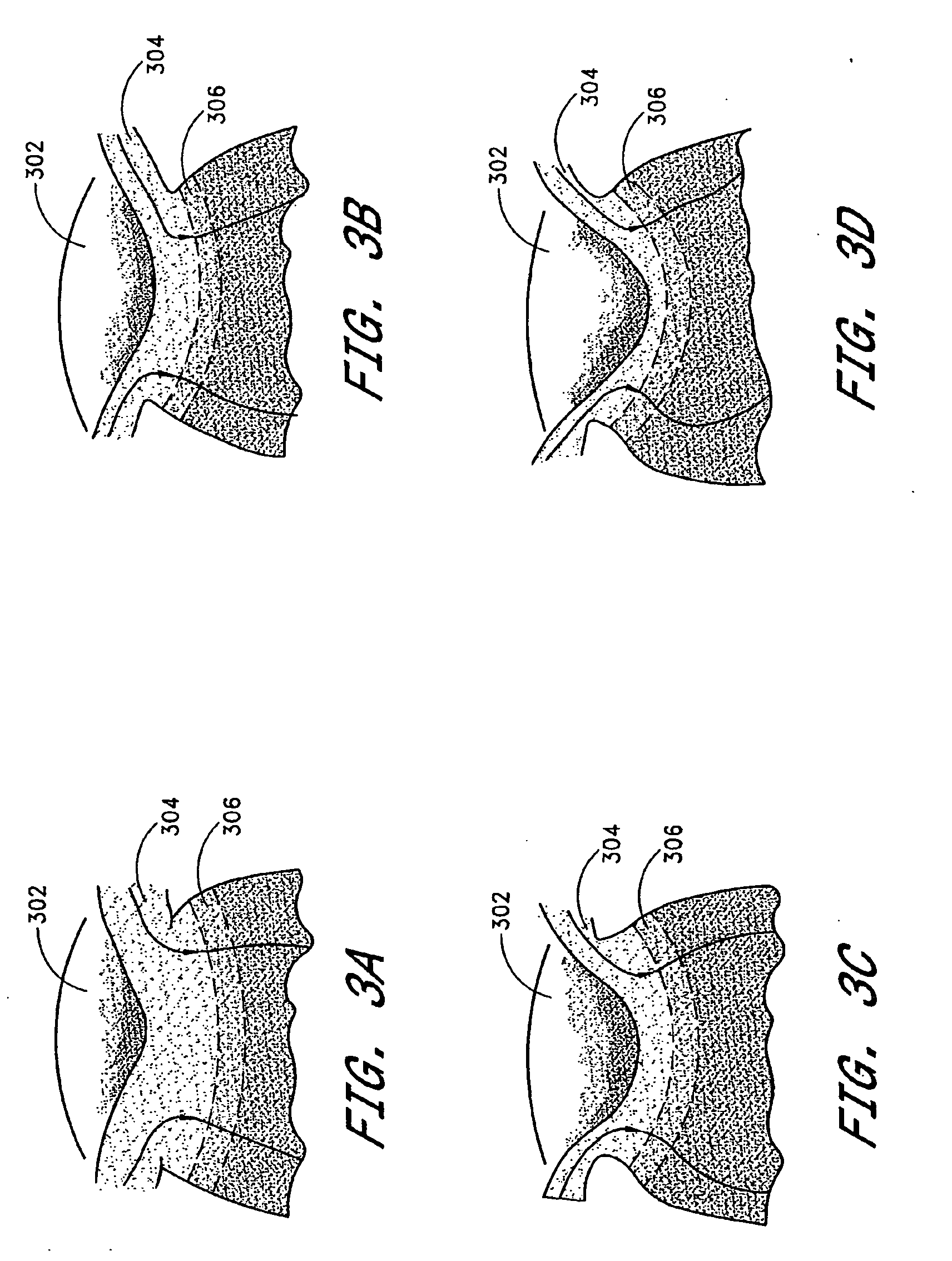
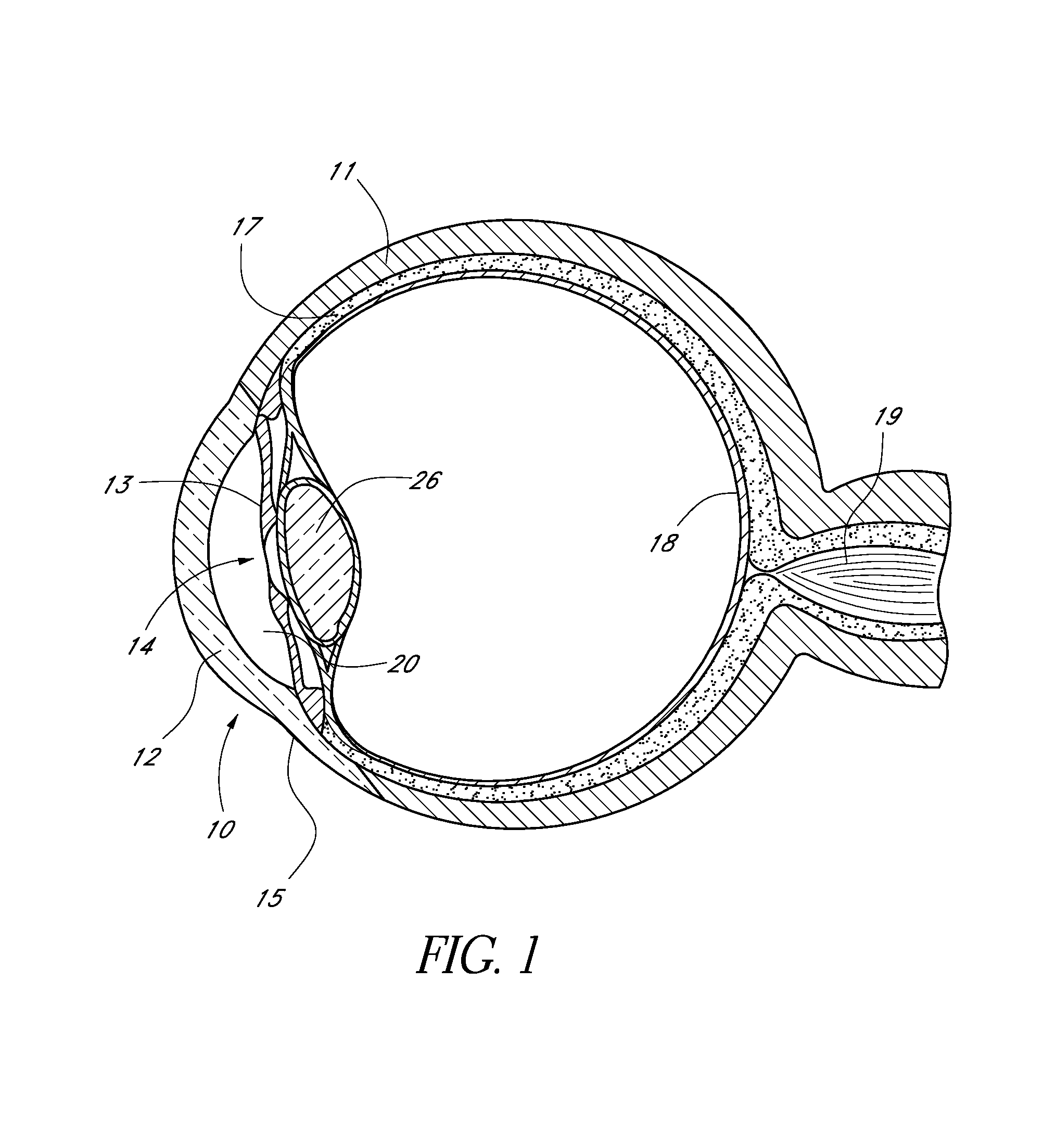
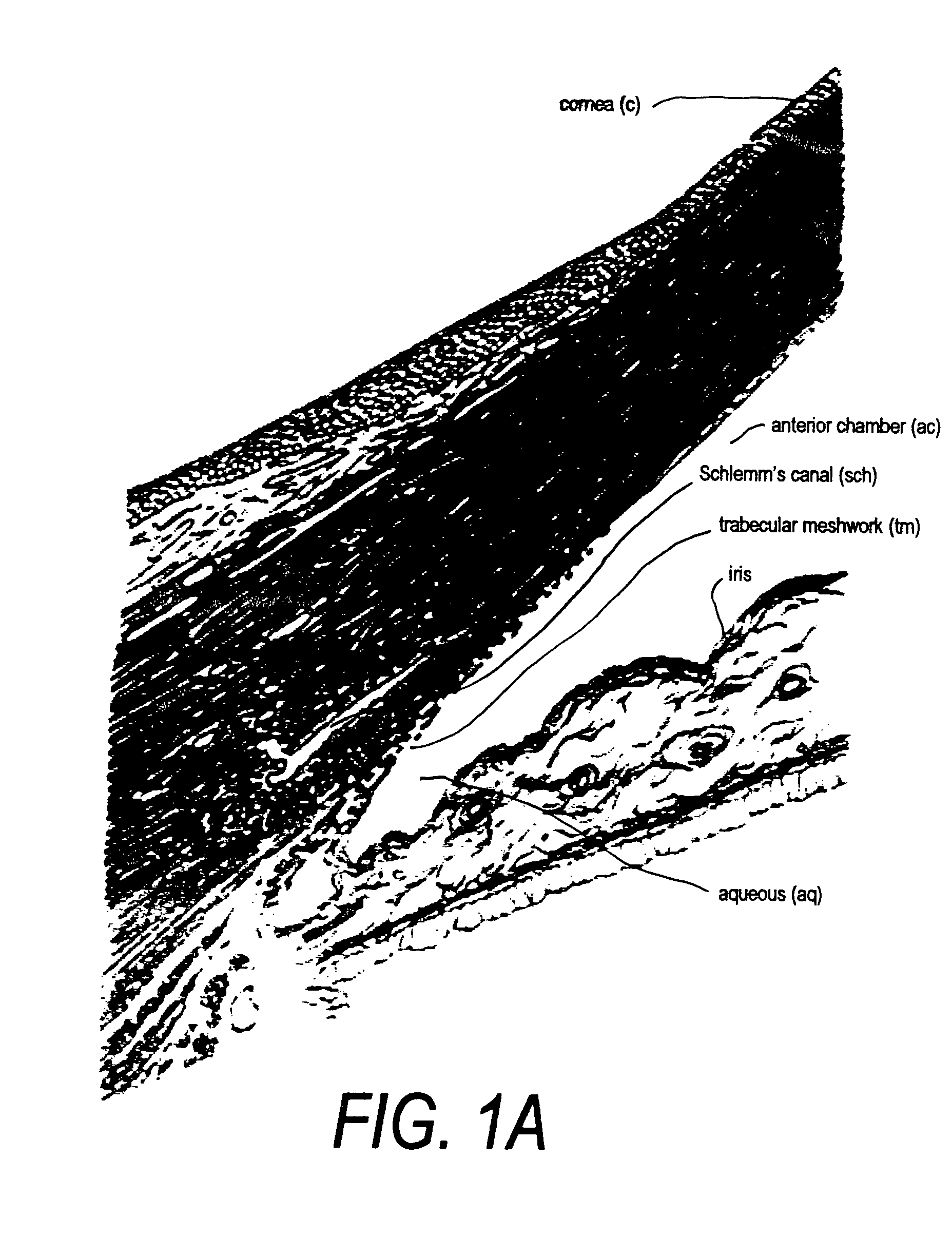
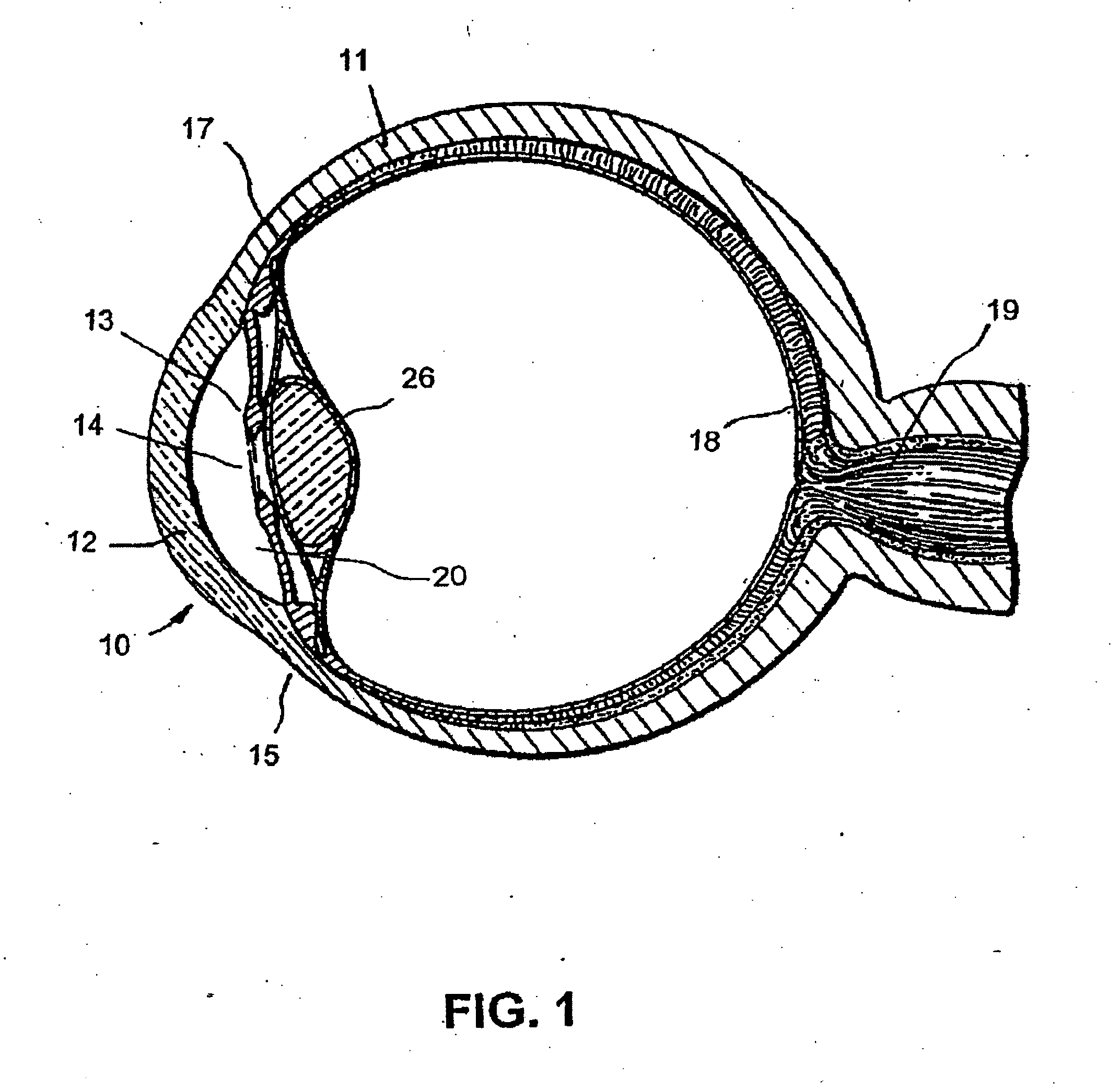
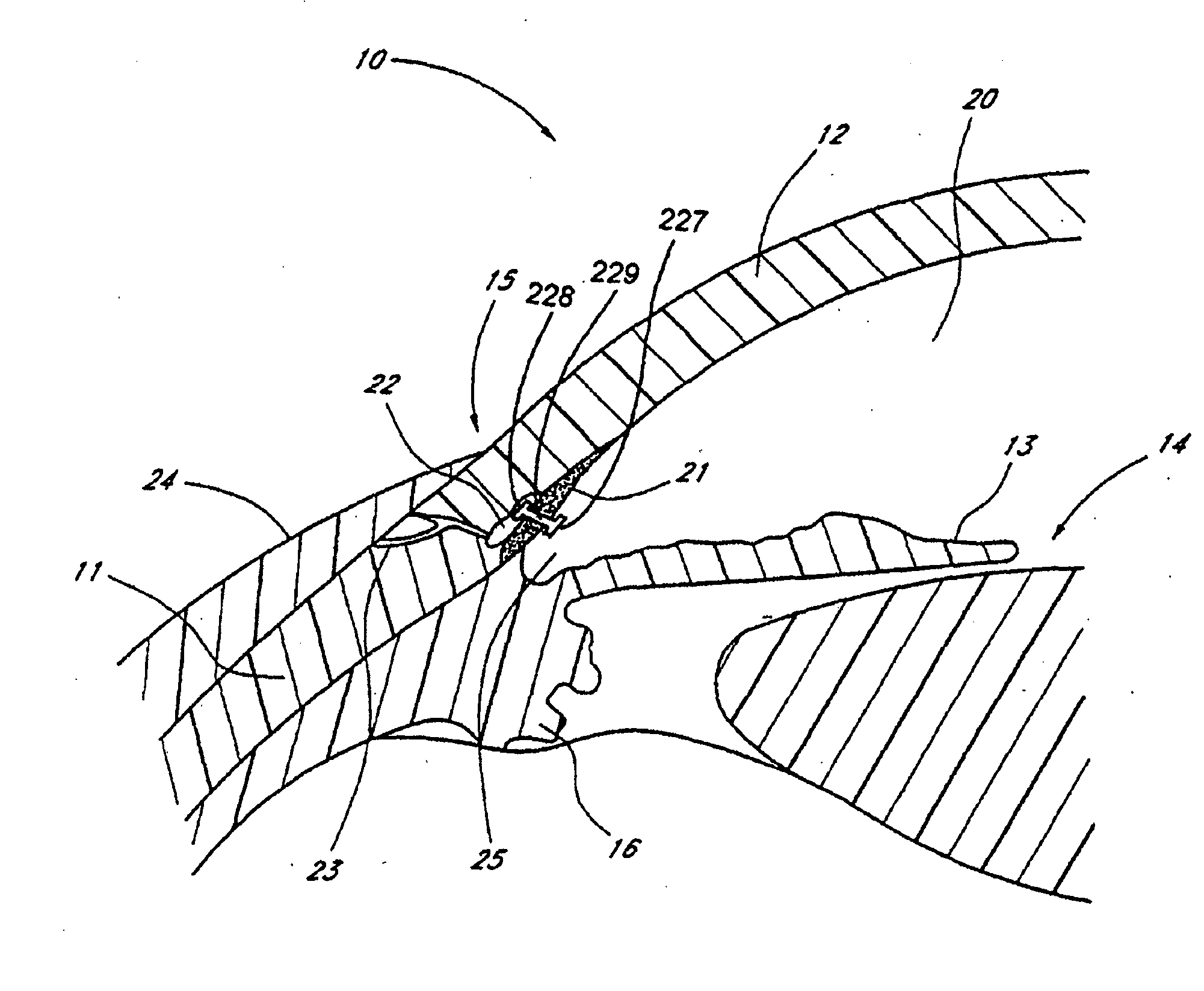
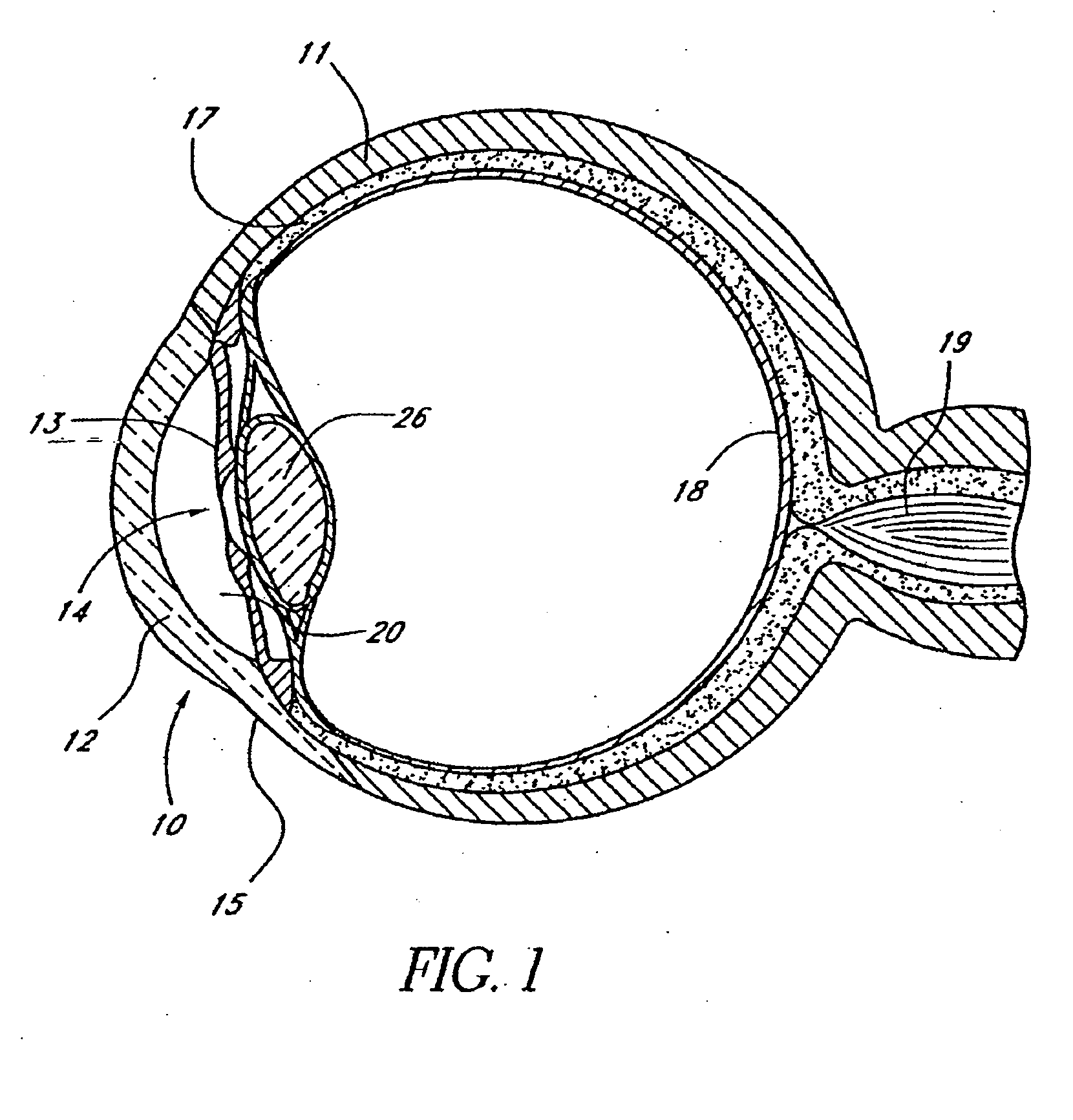
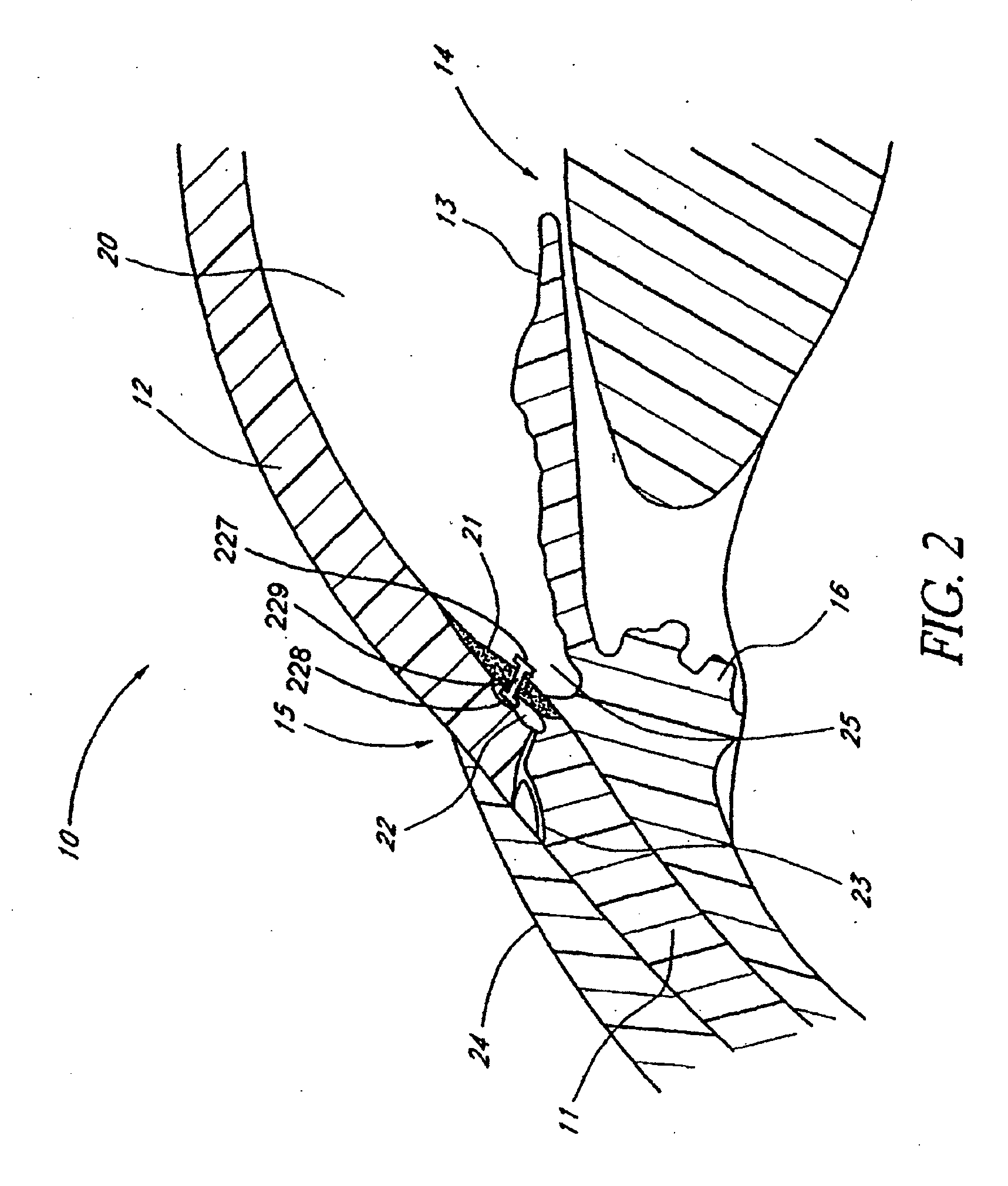
Glaucoma is usually treated with eyedrops, although laser treatment and surgery can also be used. Most cases can be controlled well with these treatments, thereby preventing further loss of vision. Much research into the causes and treatment of glaucoma is being carried out throughout the world.
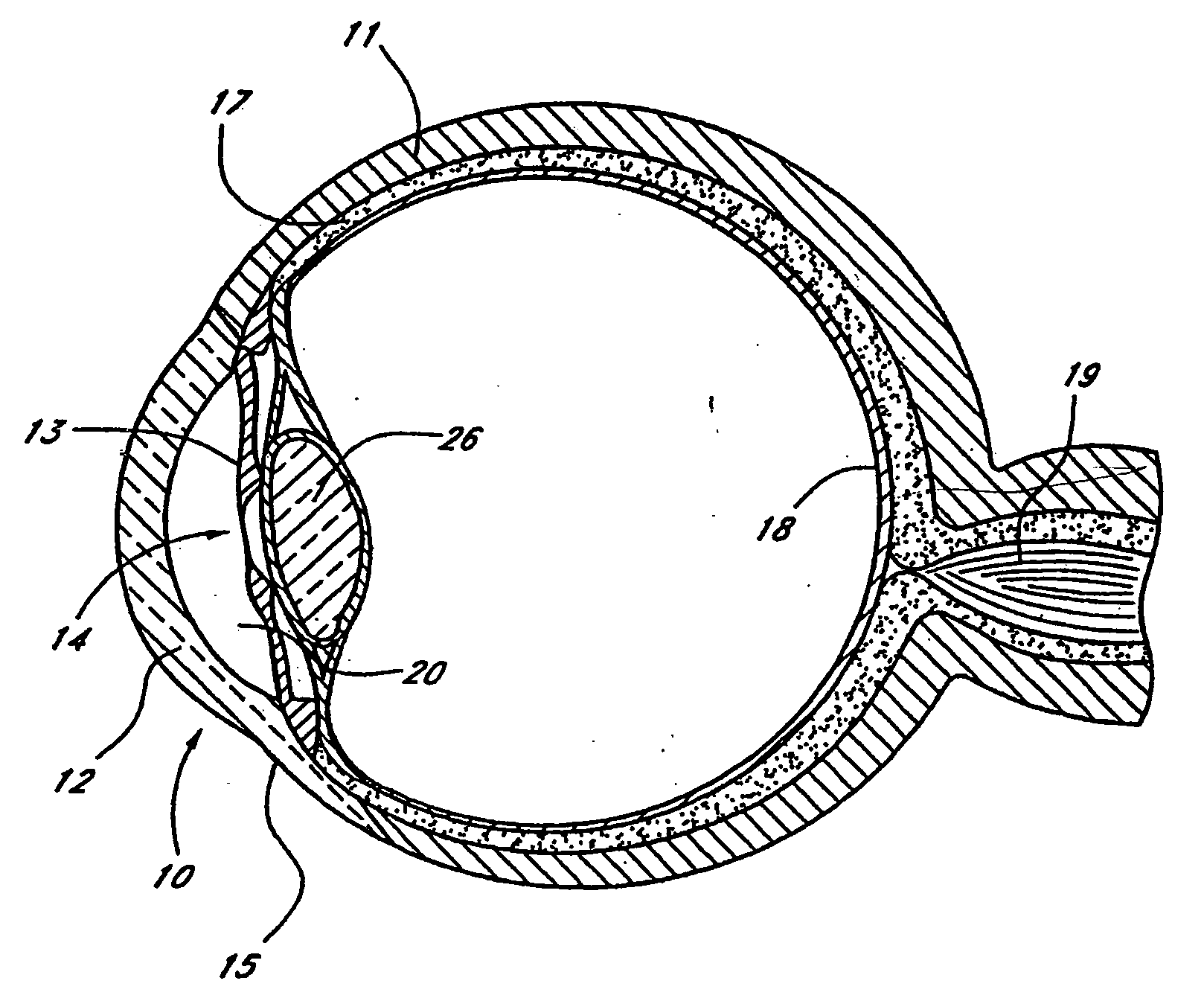
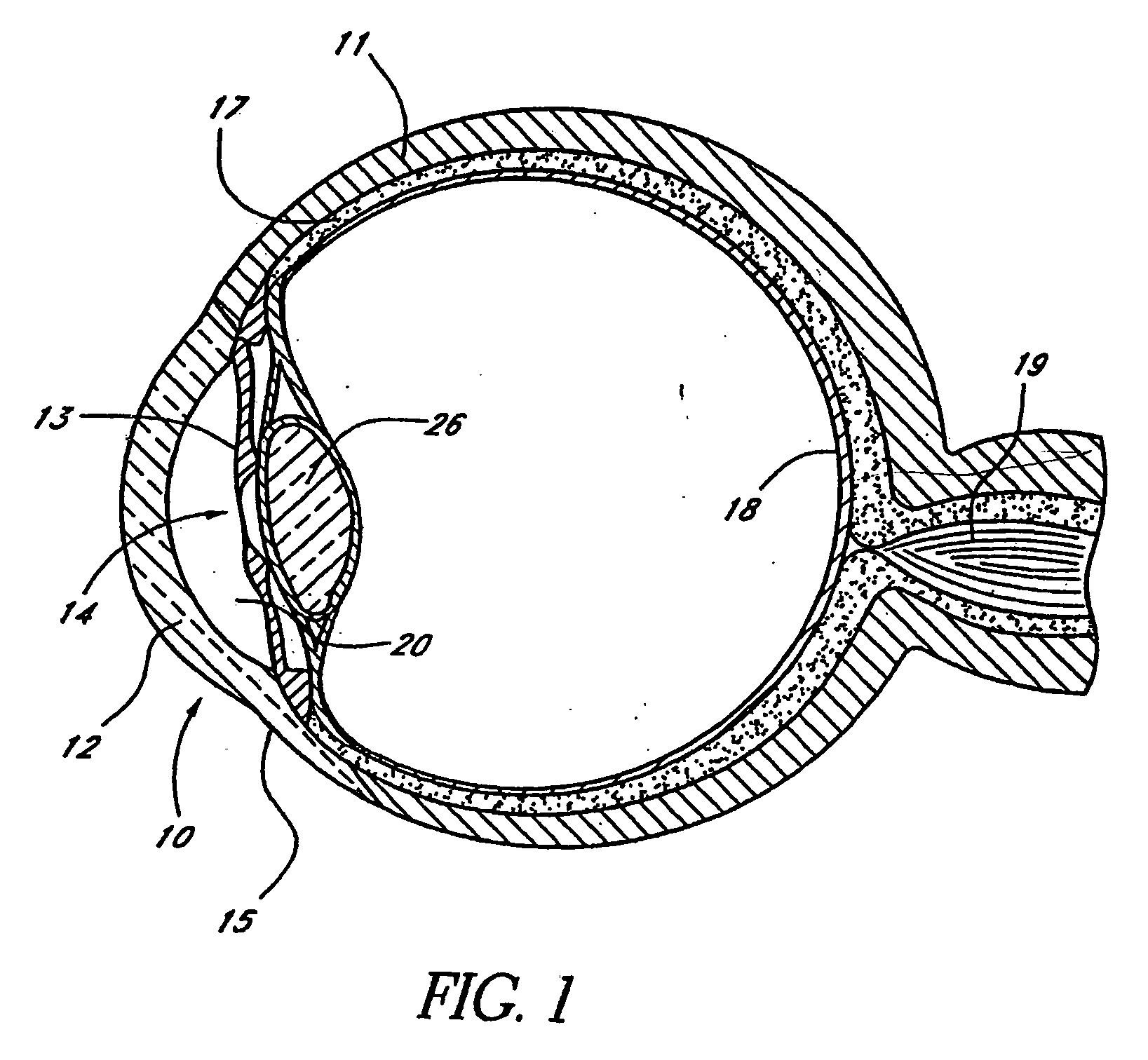
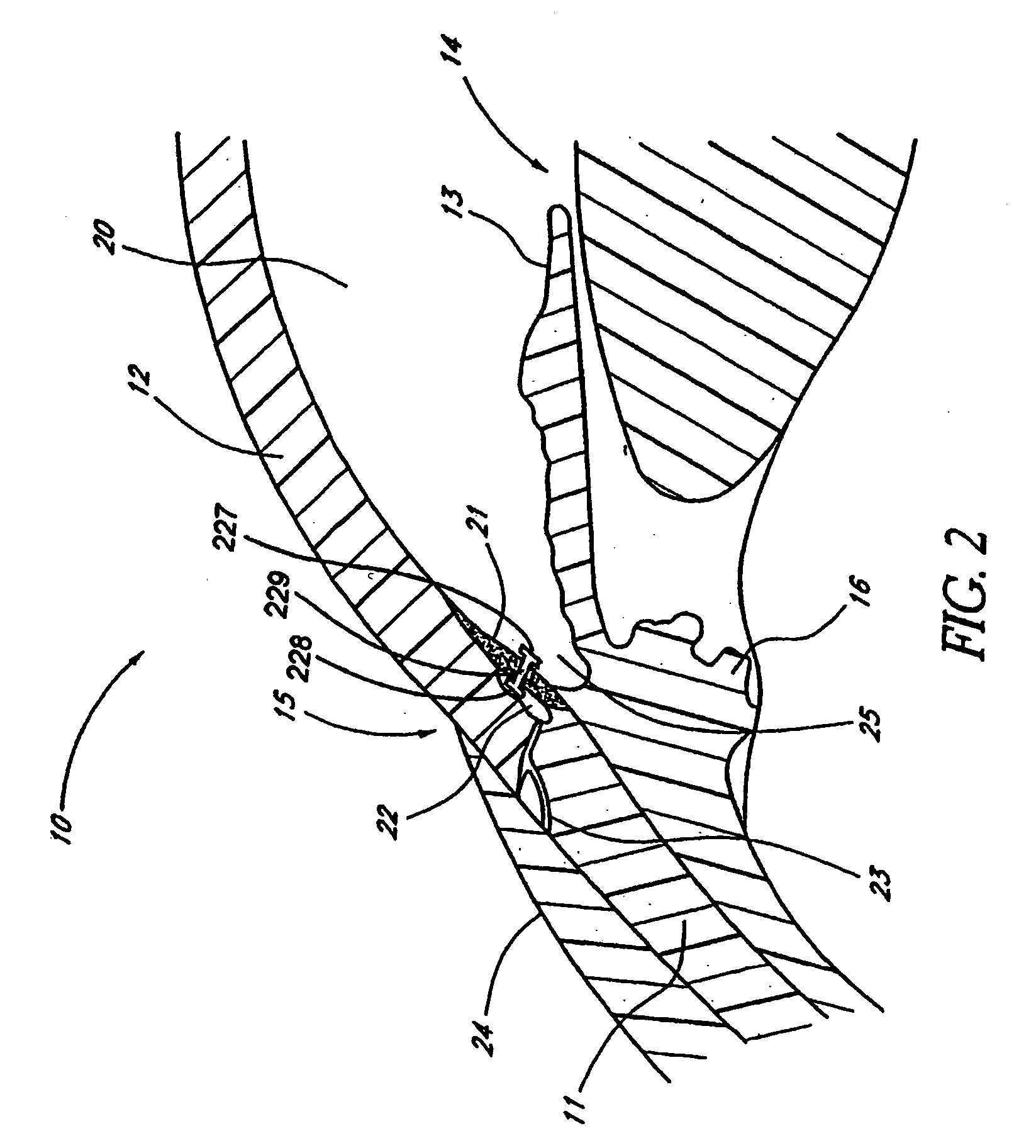
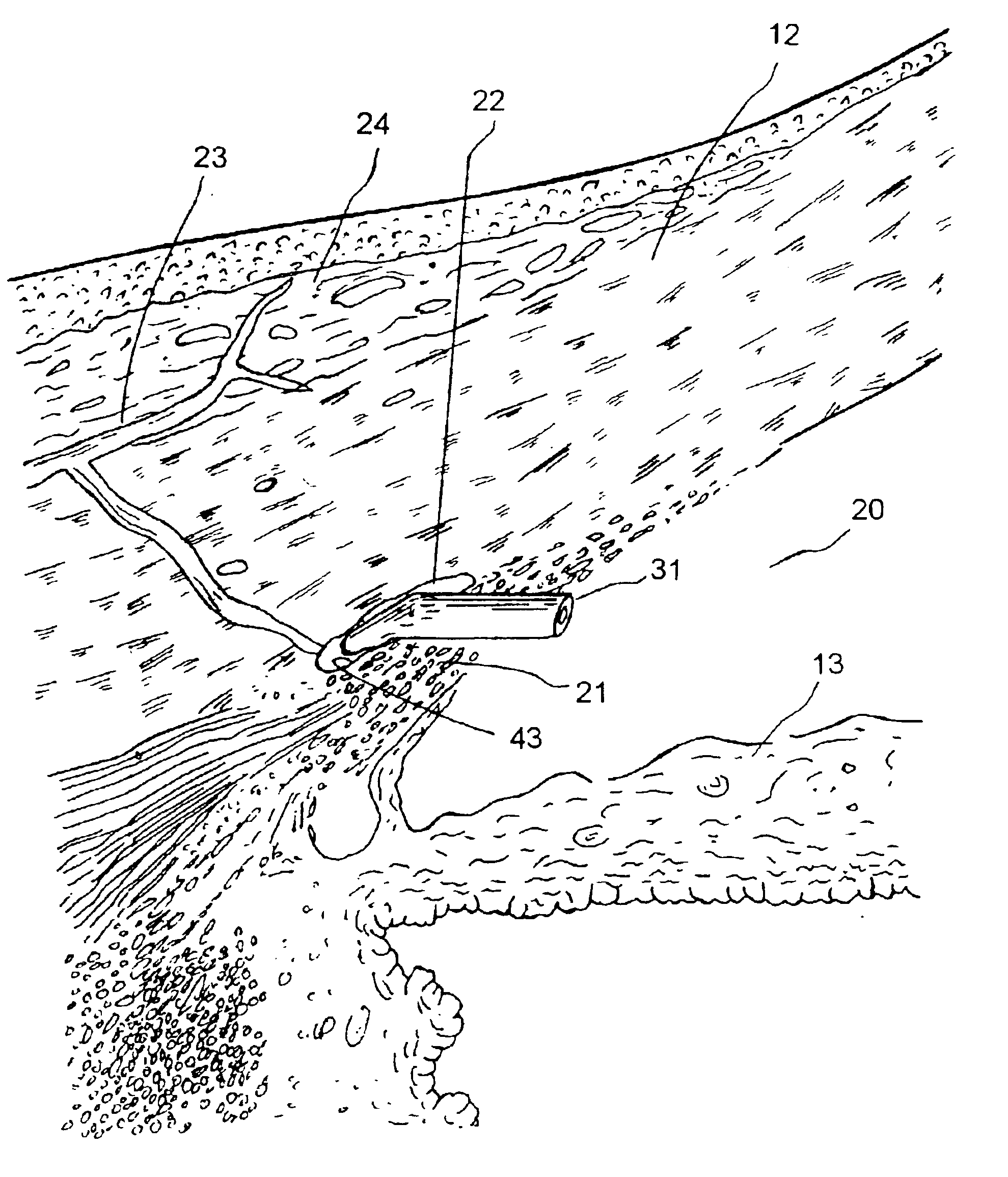
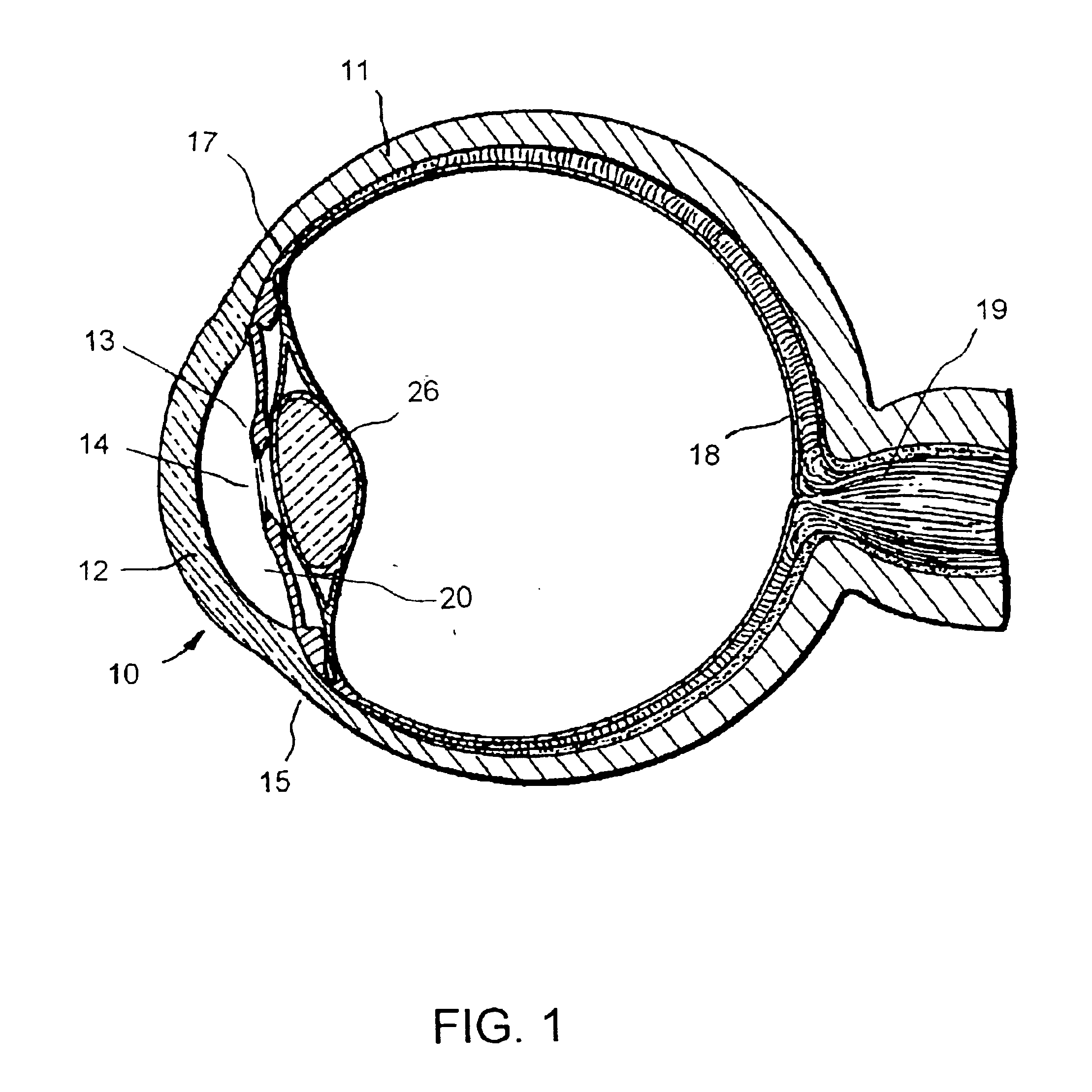
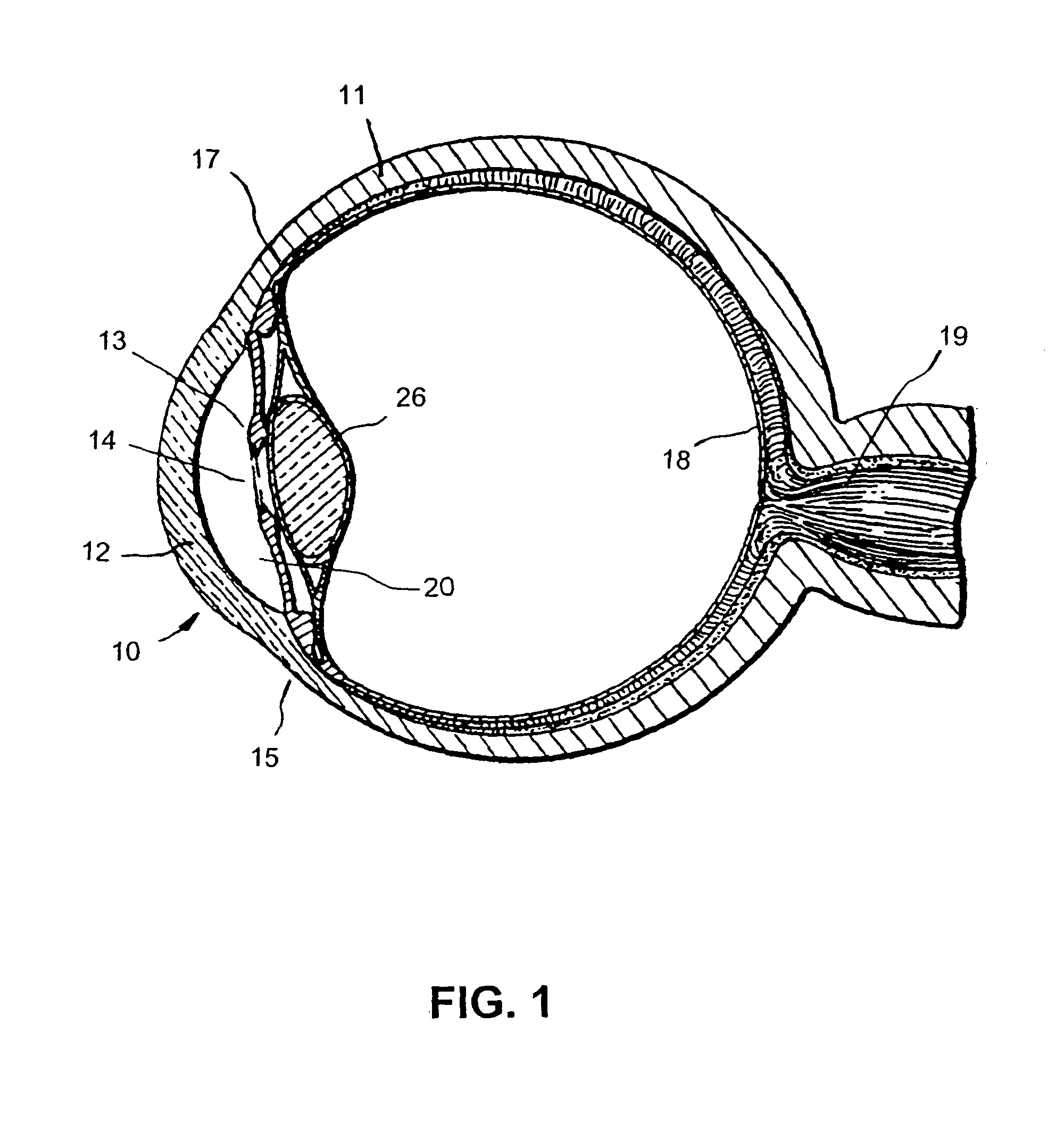
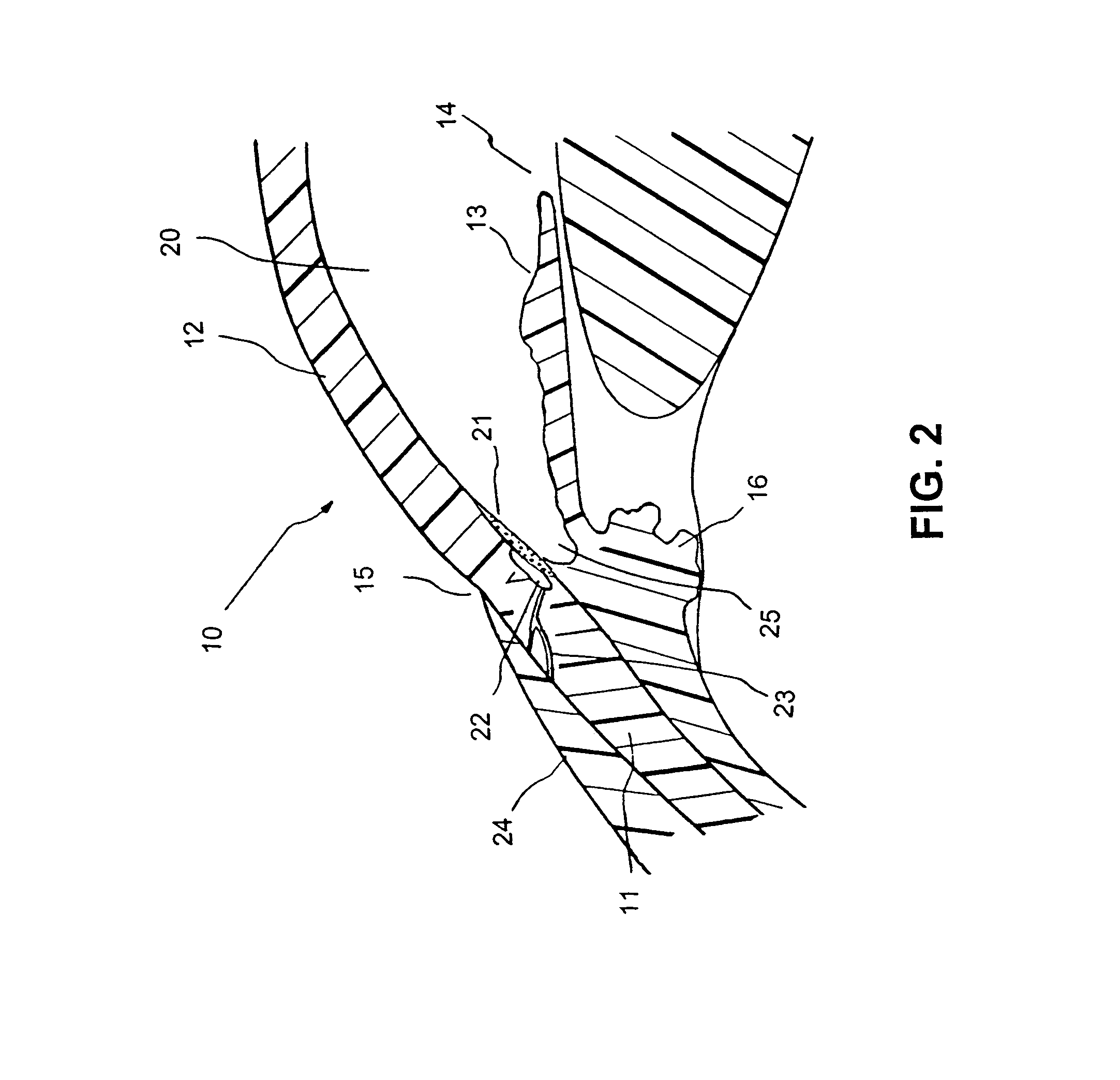
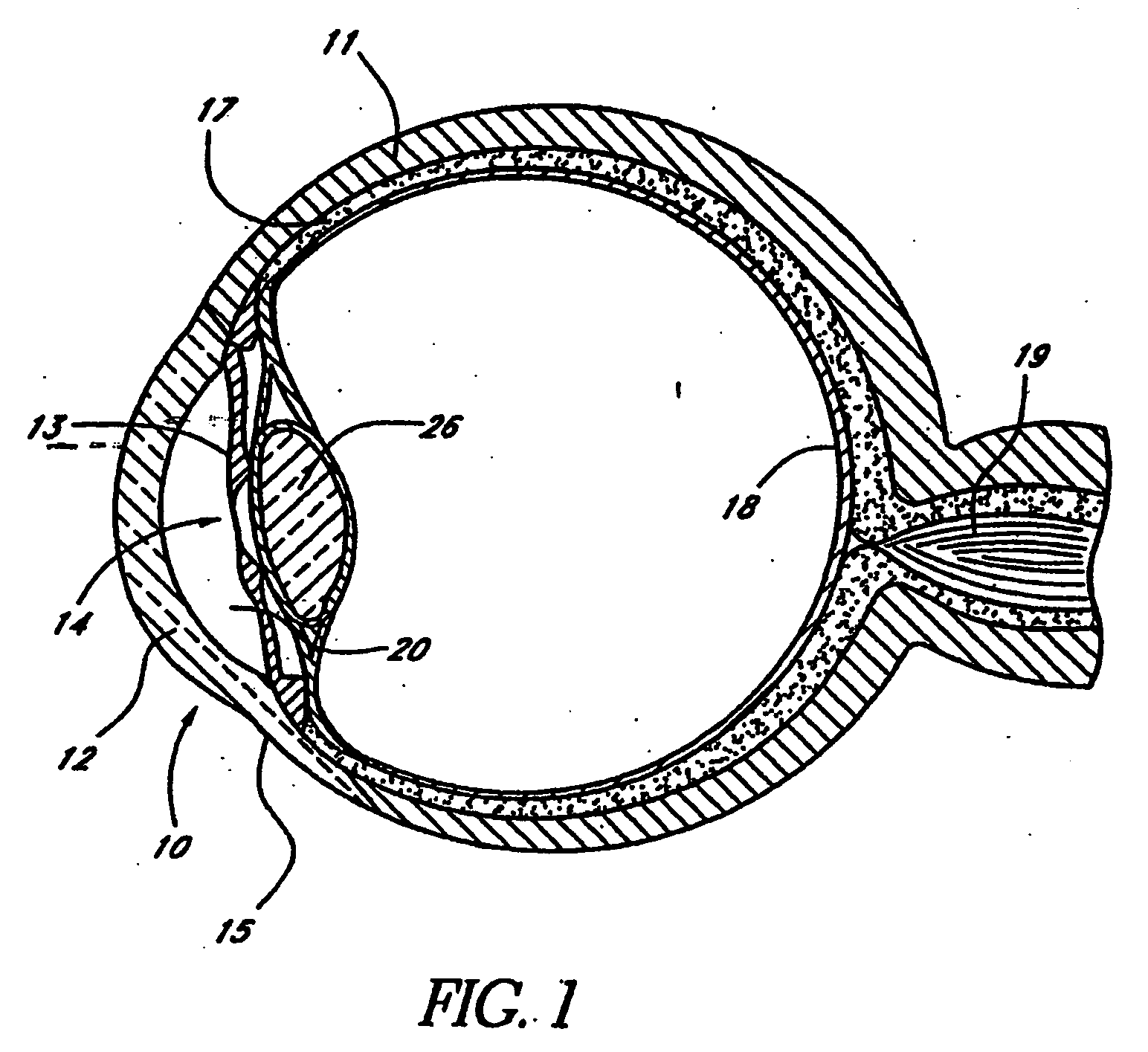
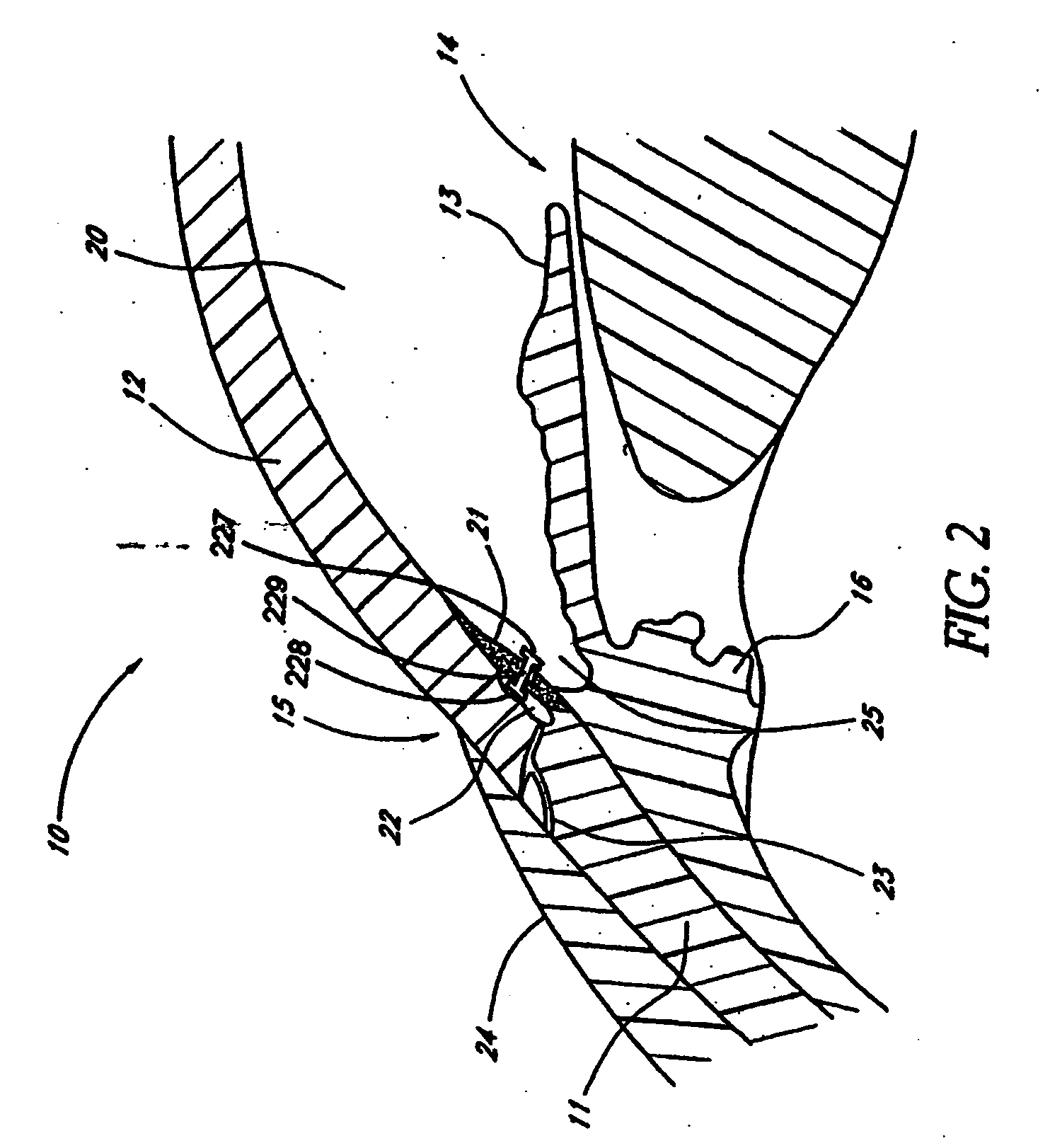
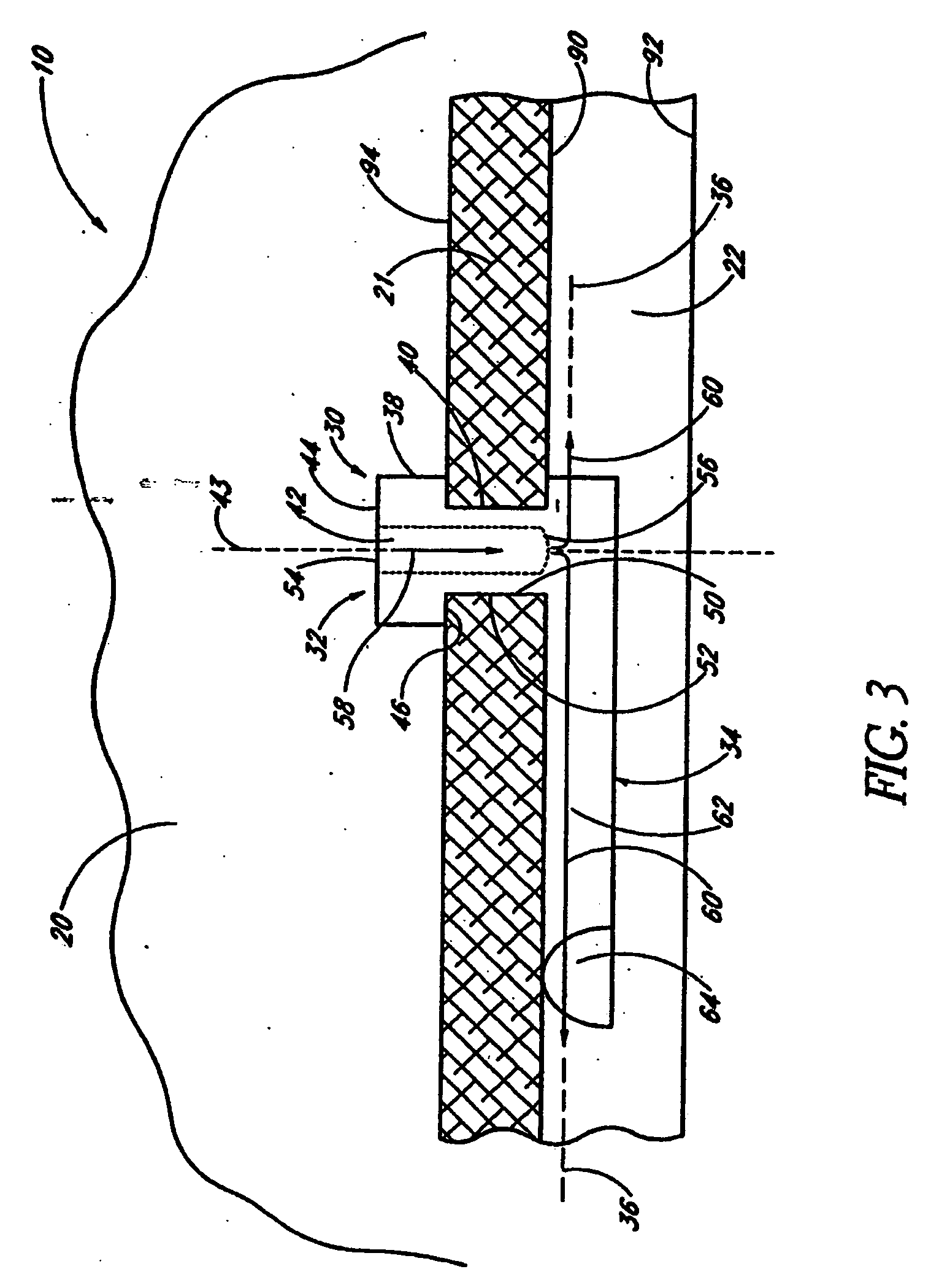
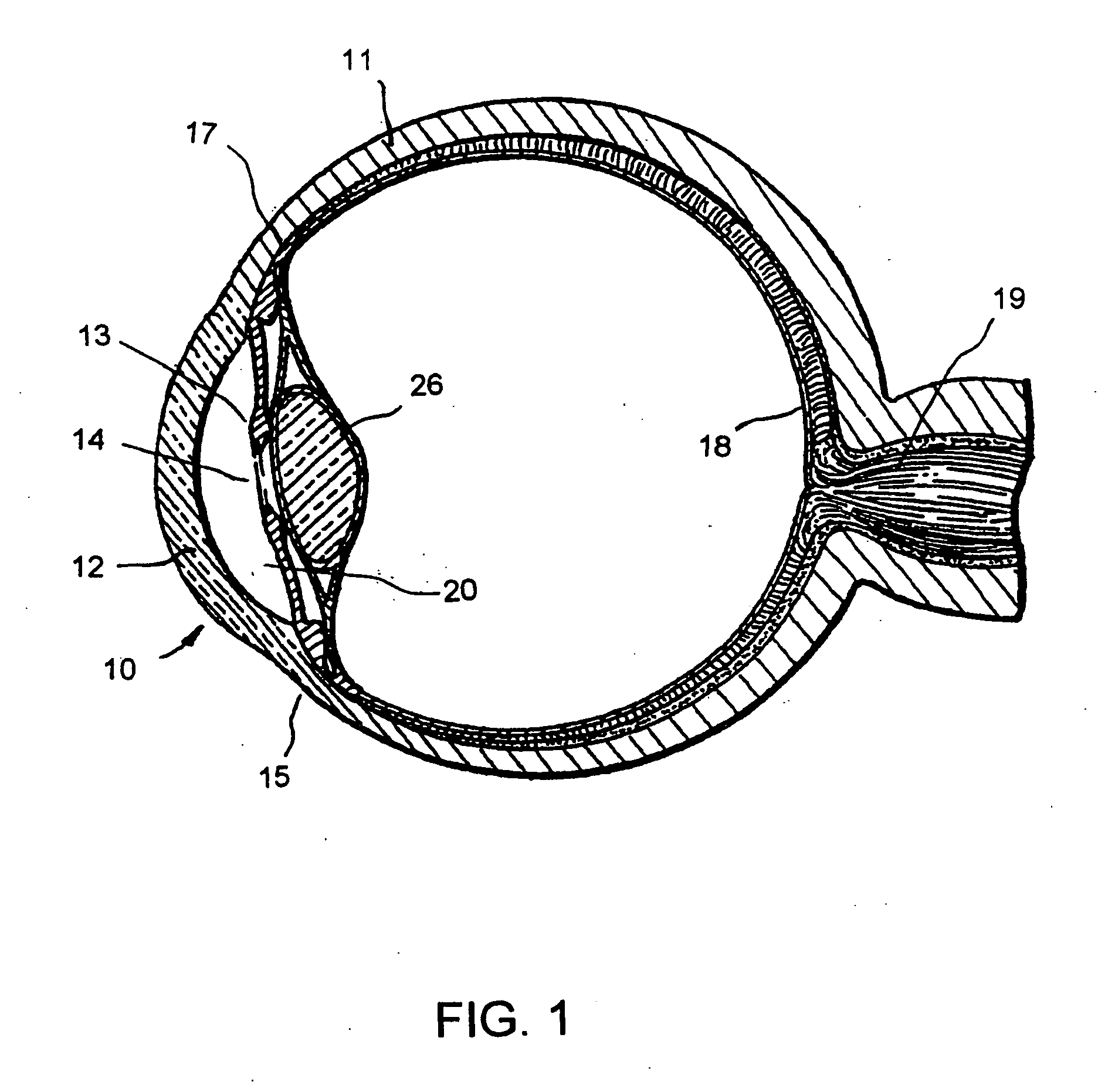
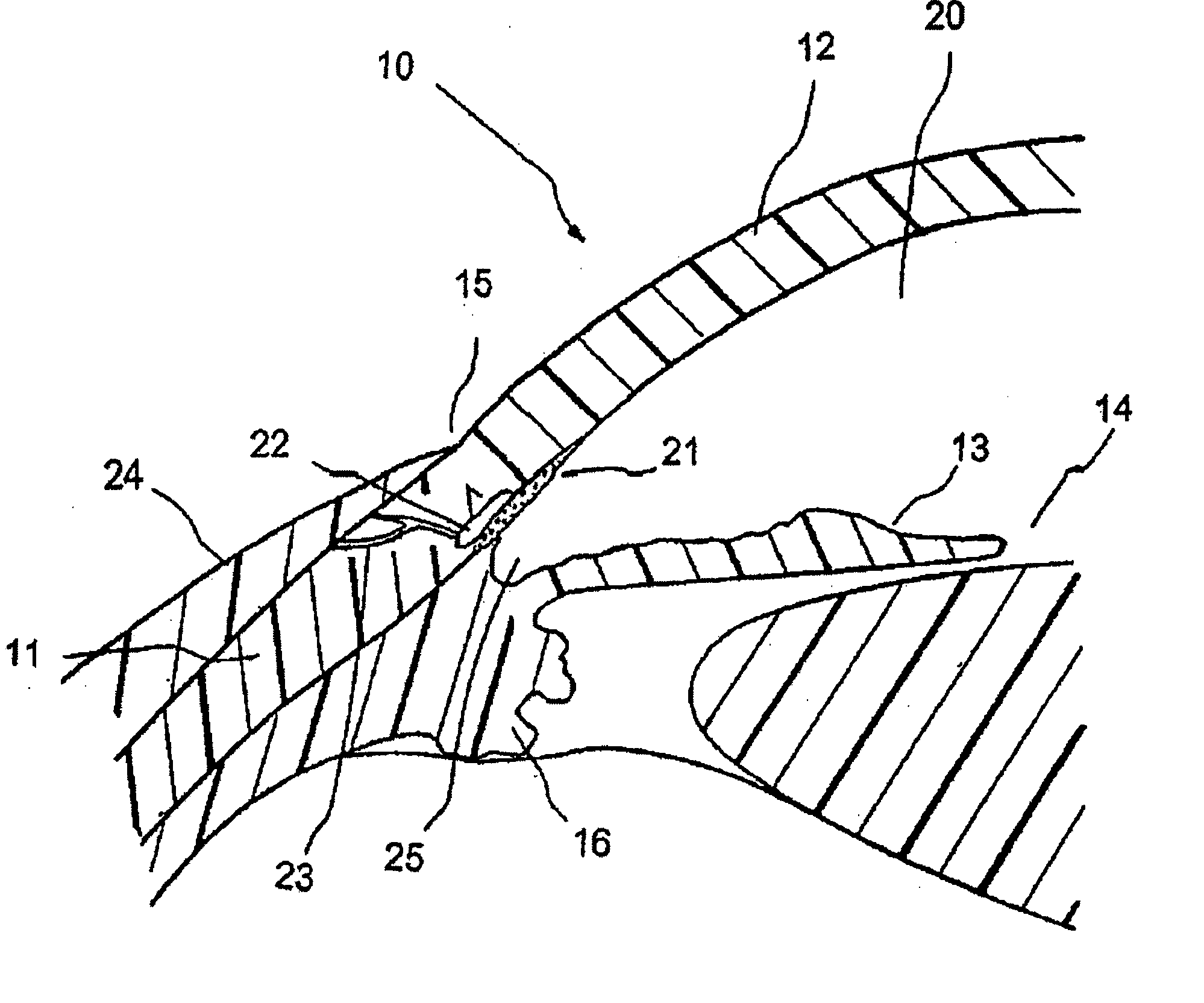
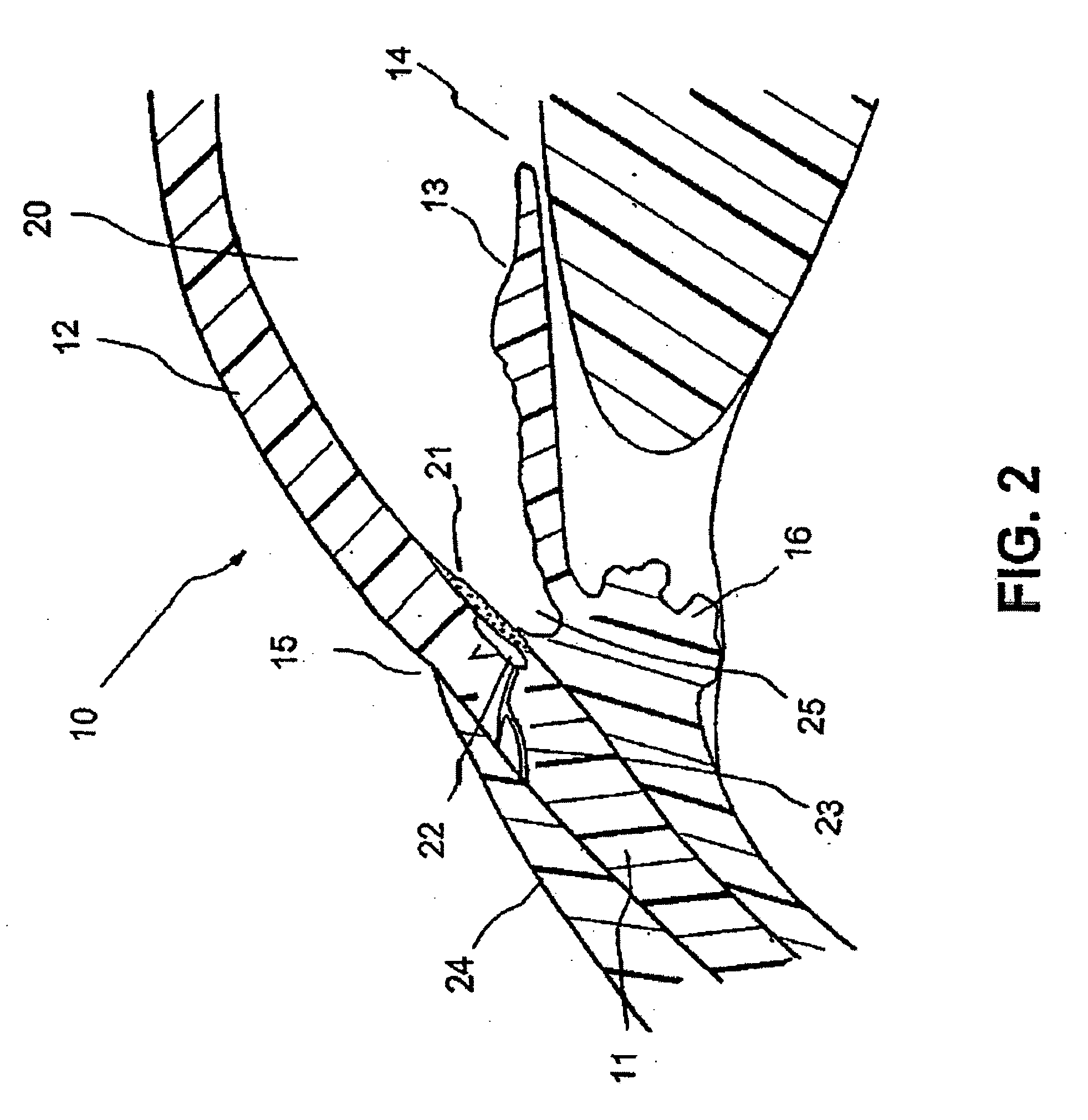
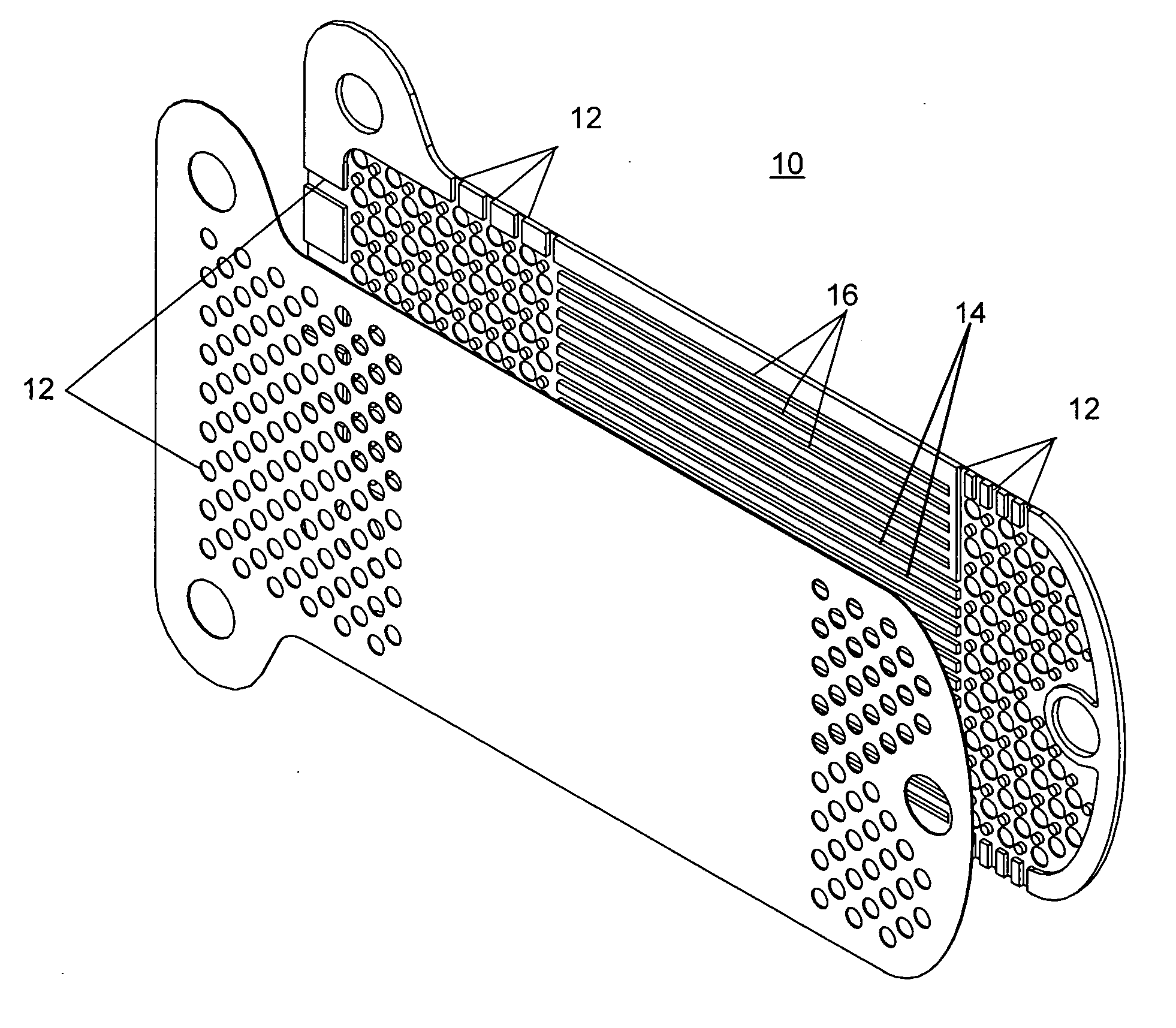
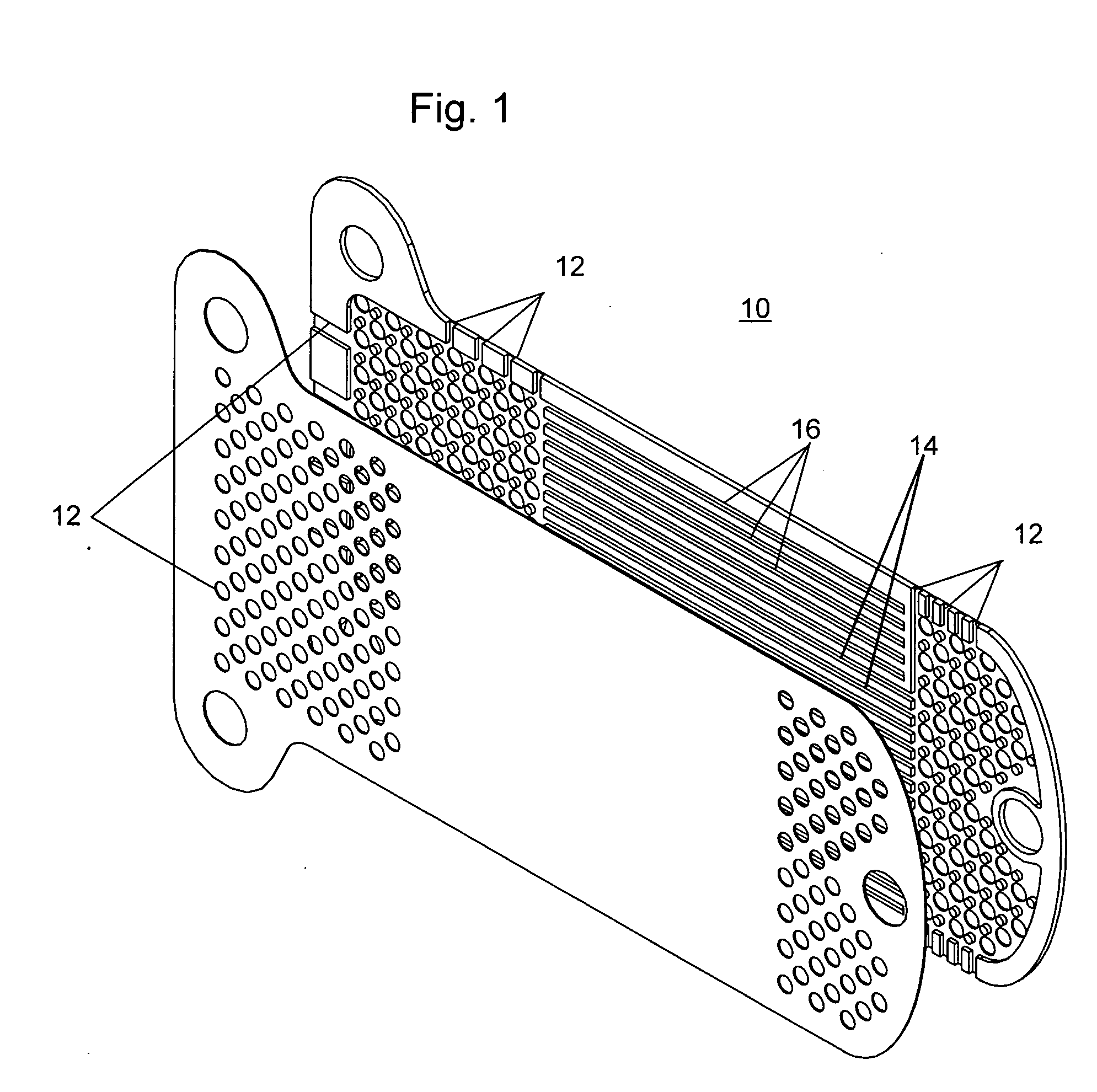
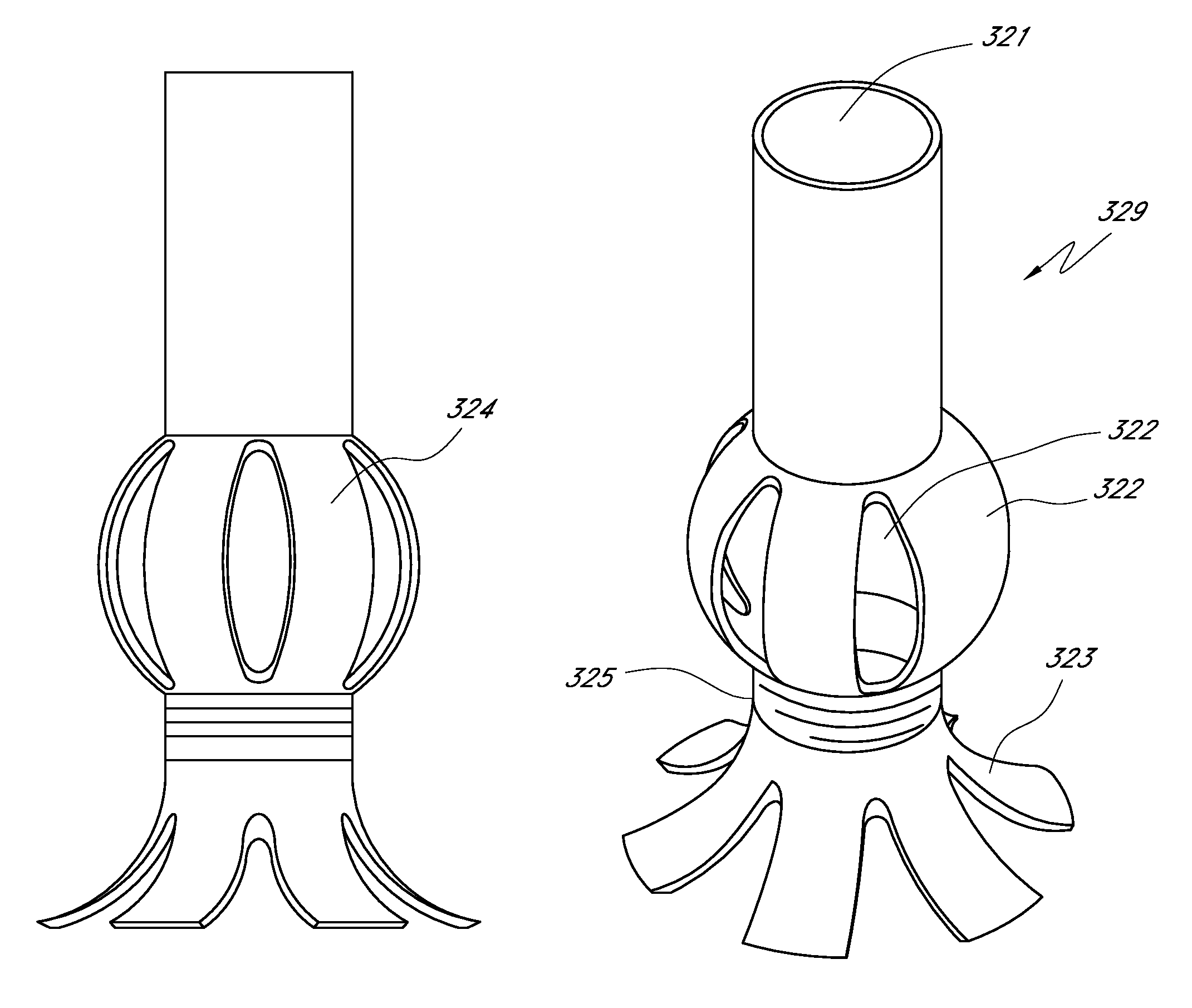
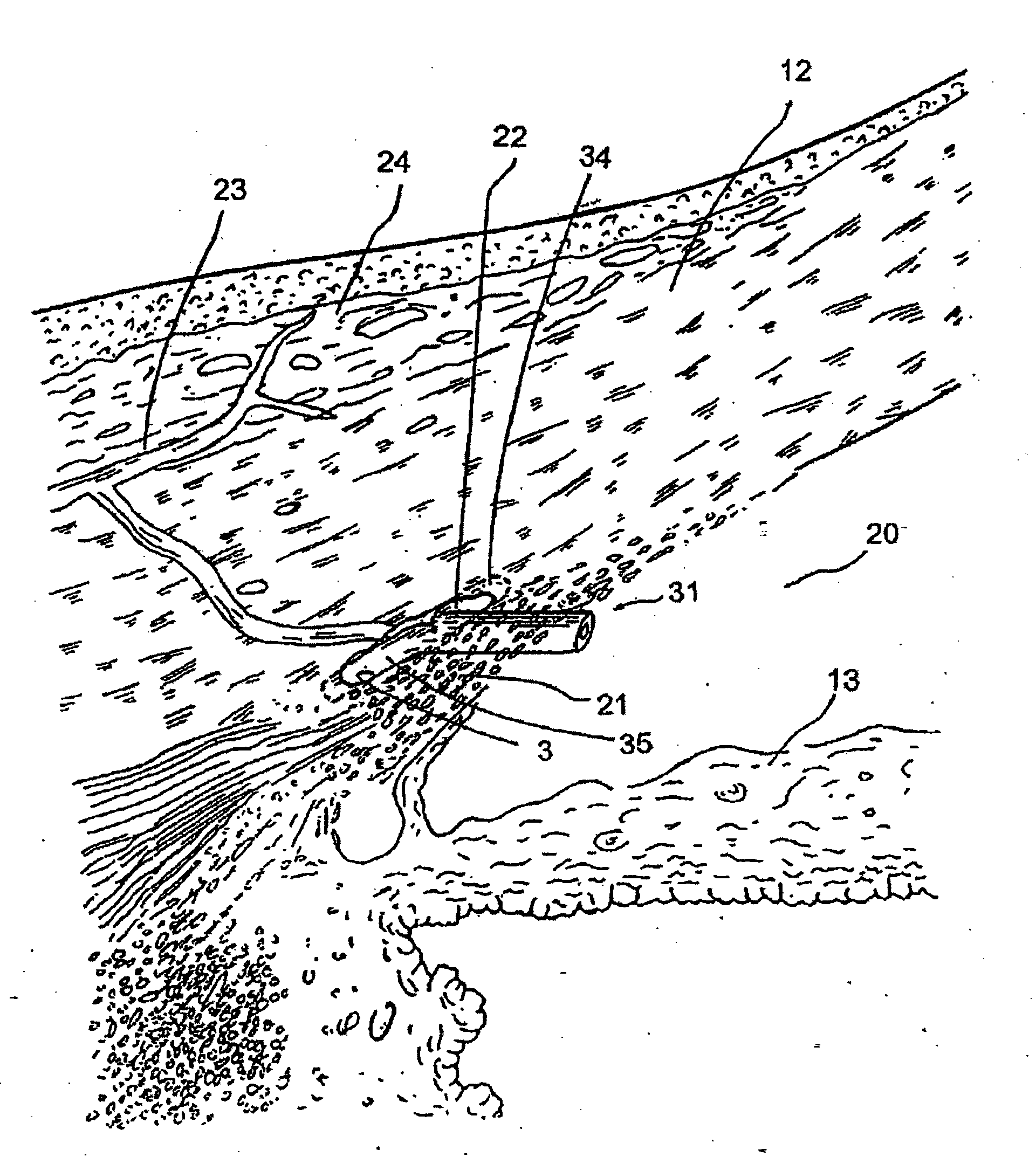
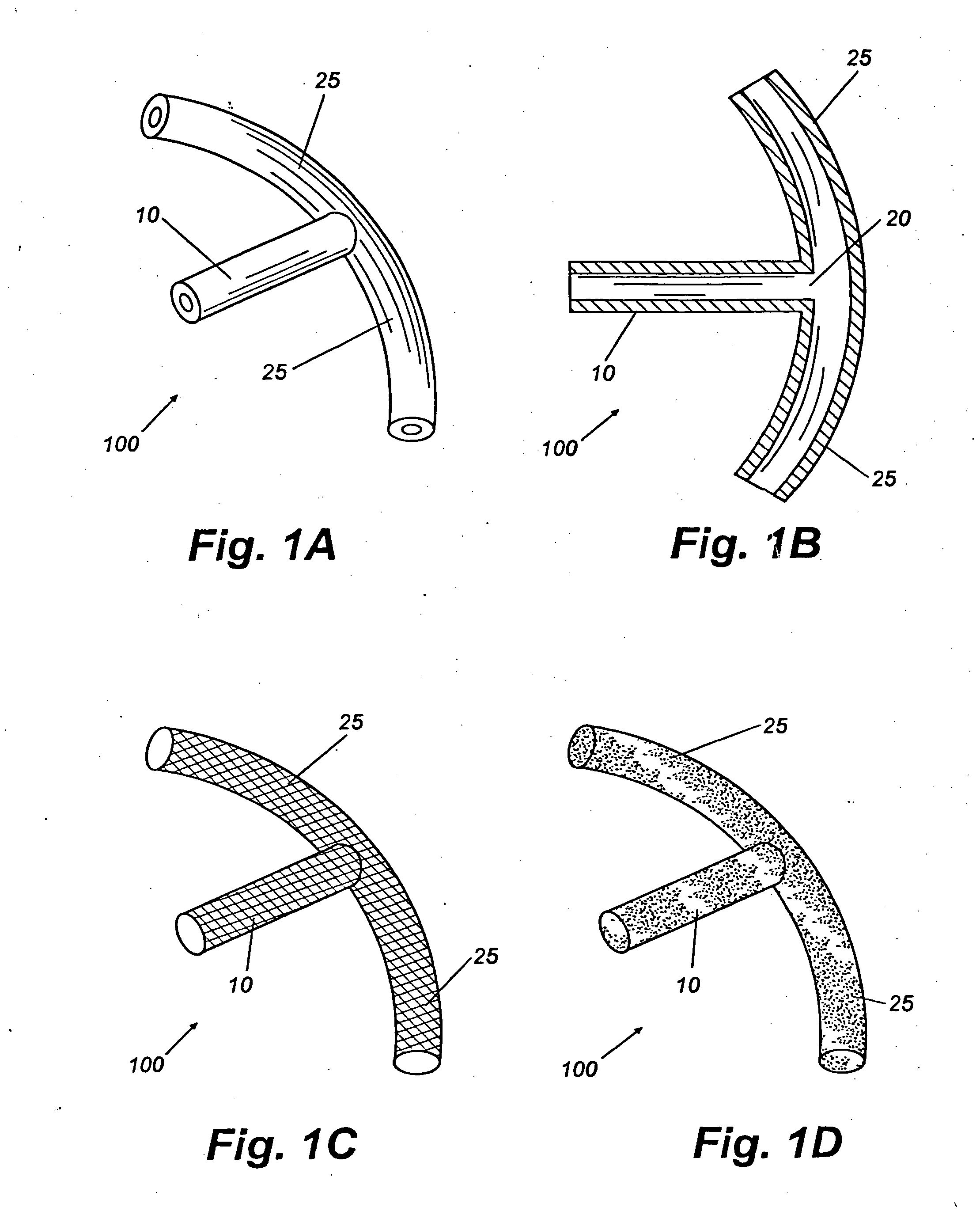
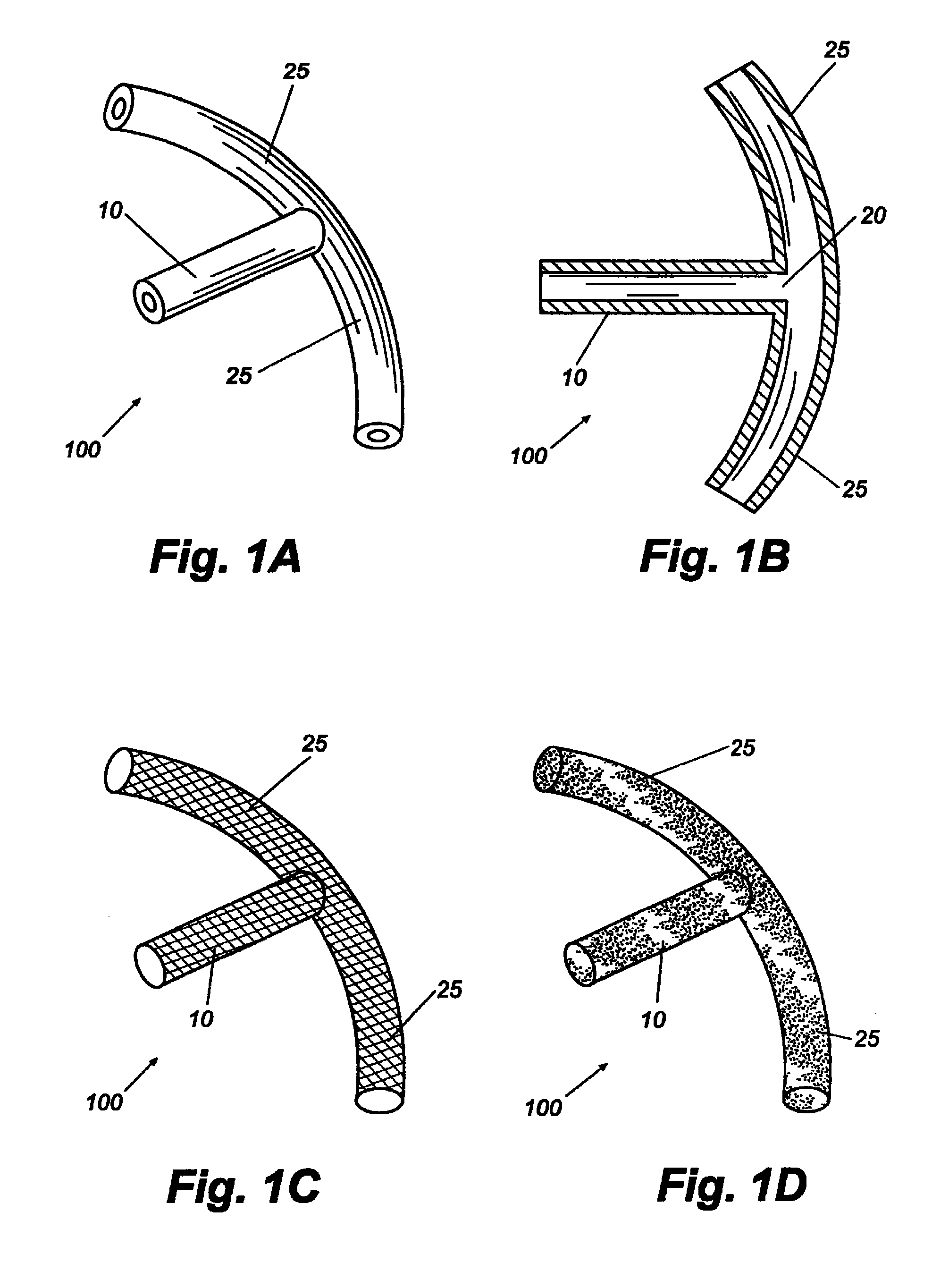
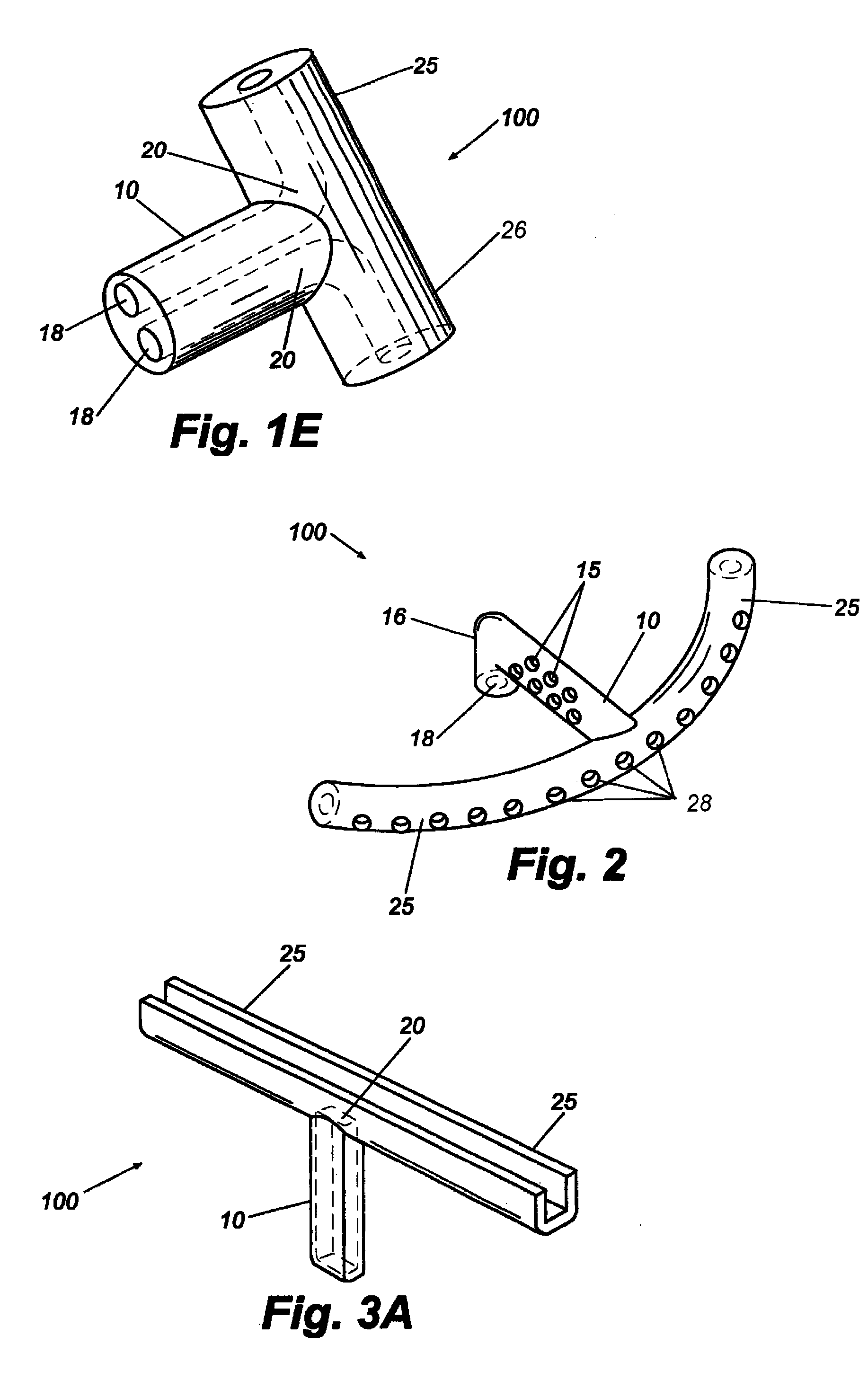
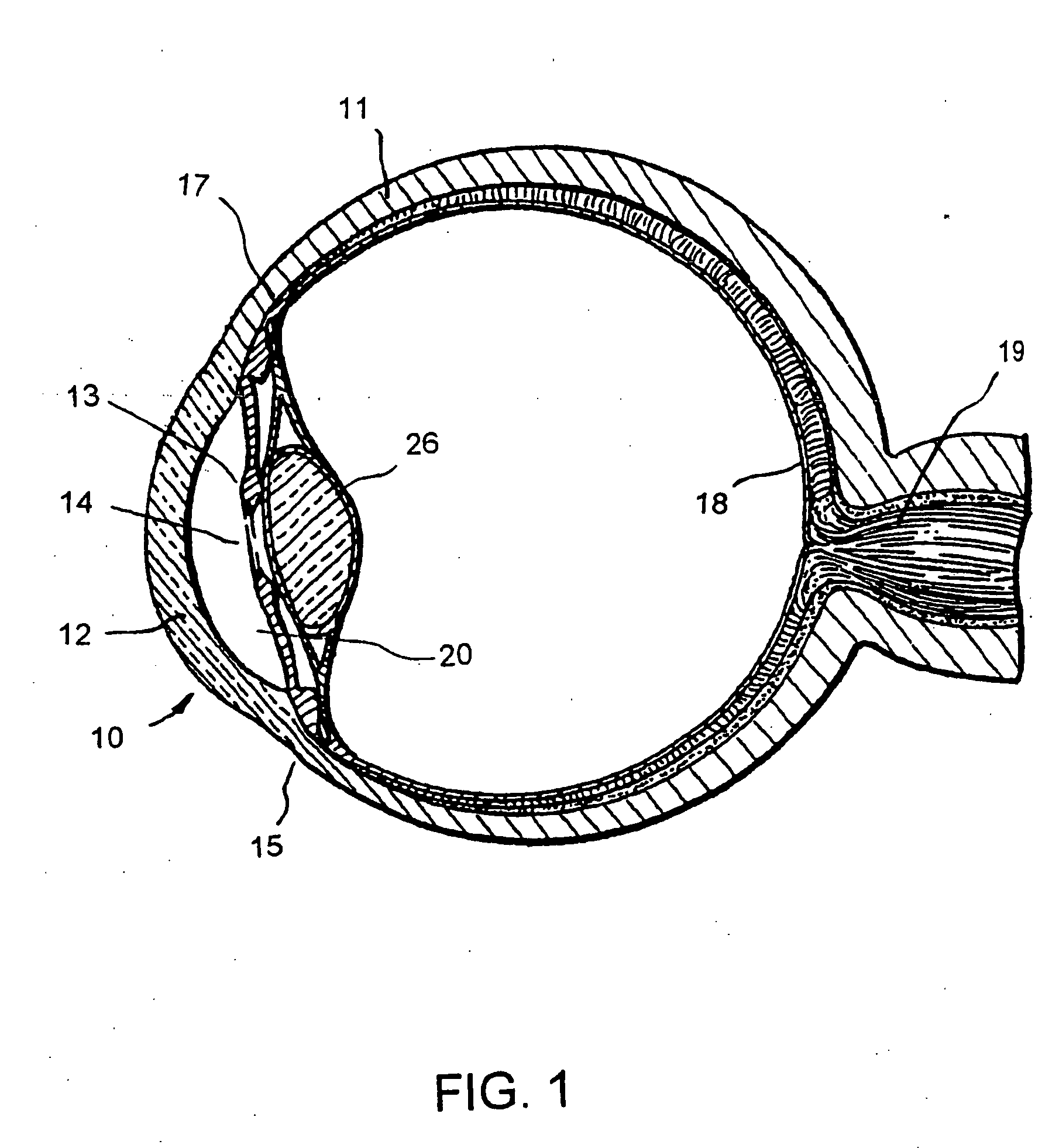
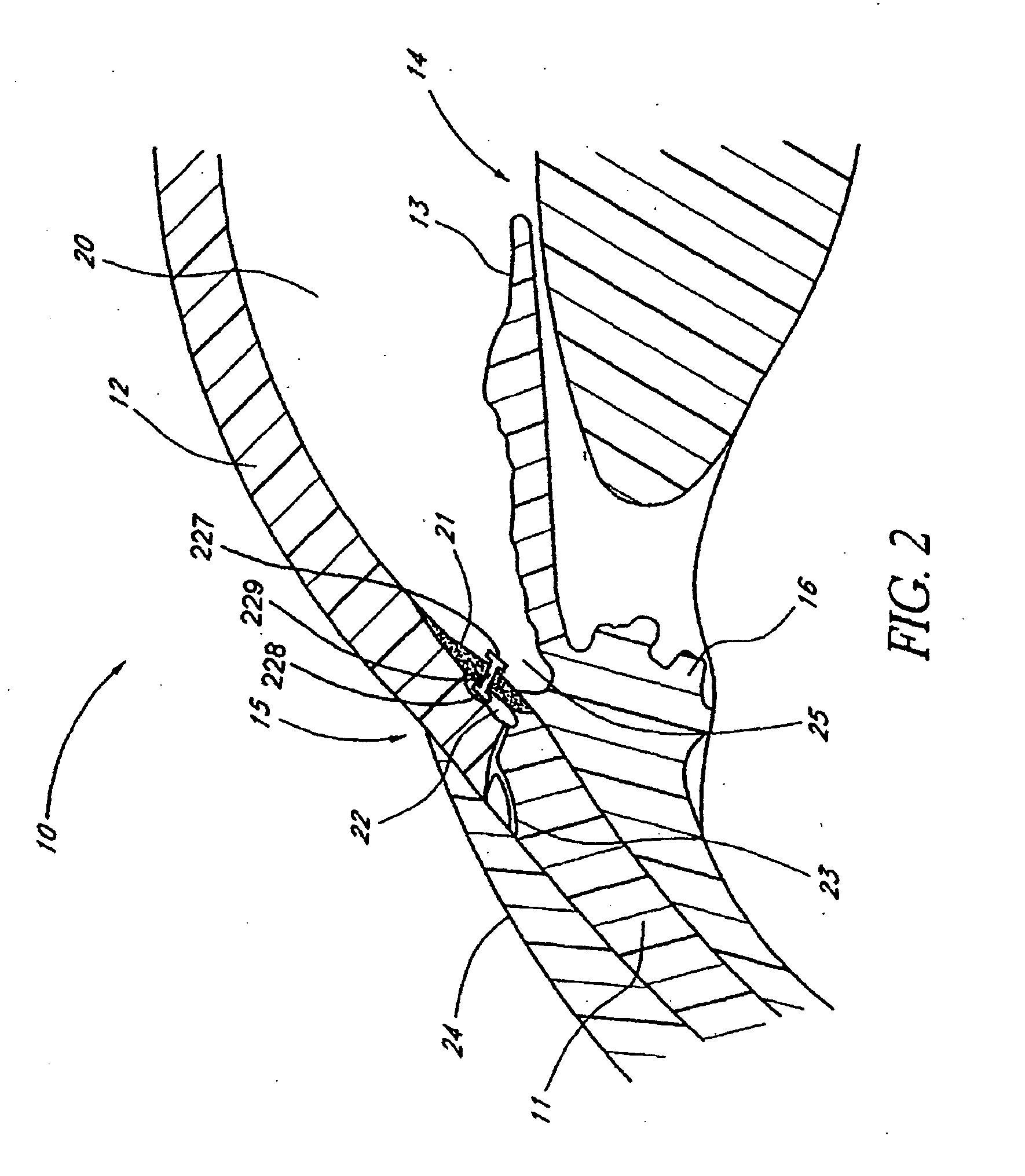
Glaucoma implant with therapeutic agents
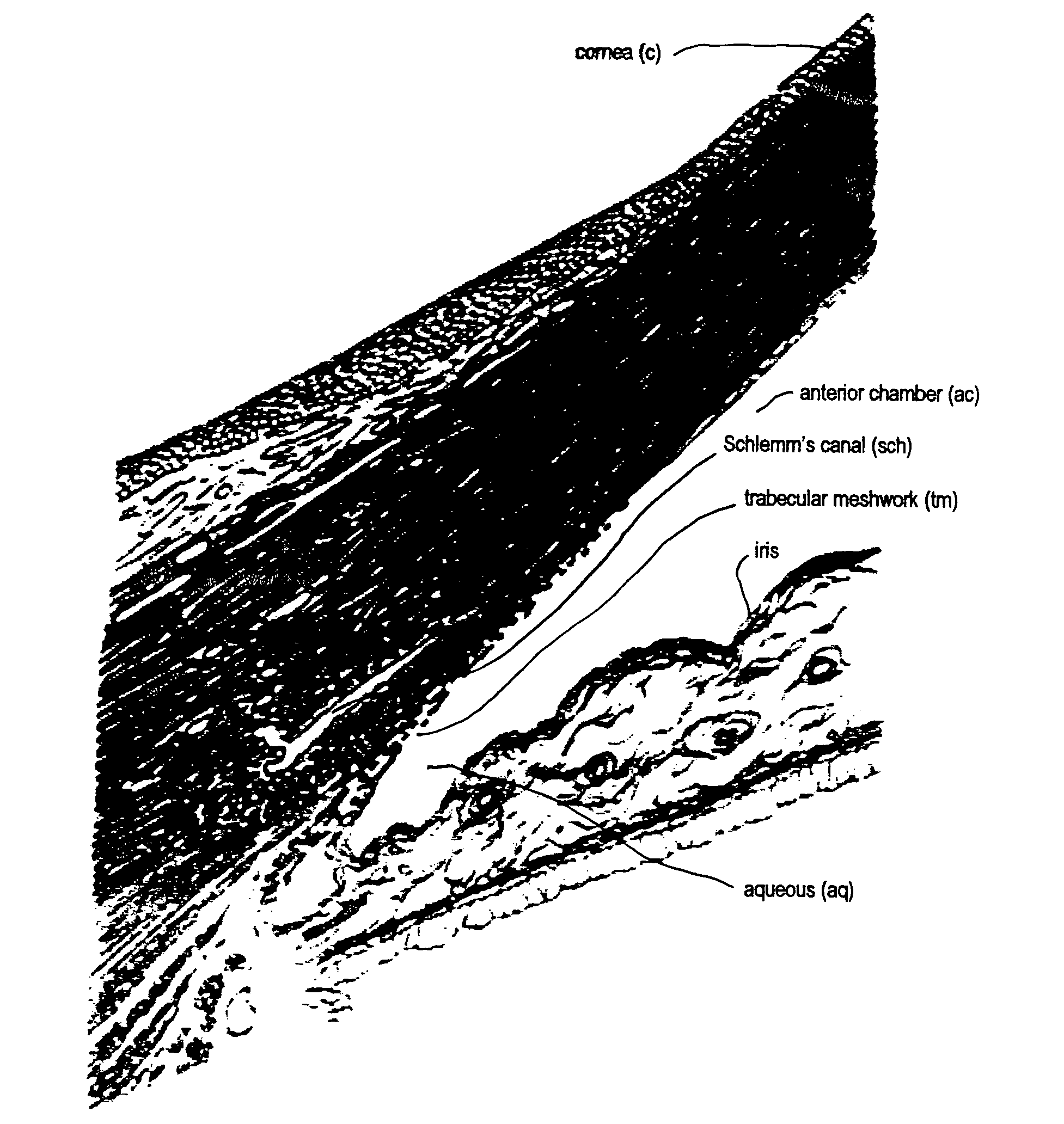
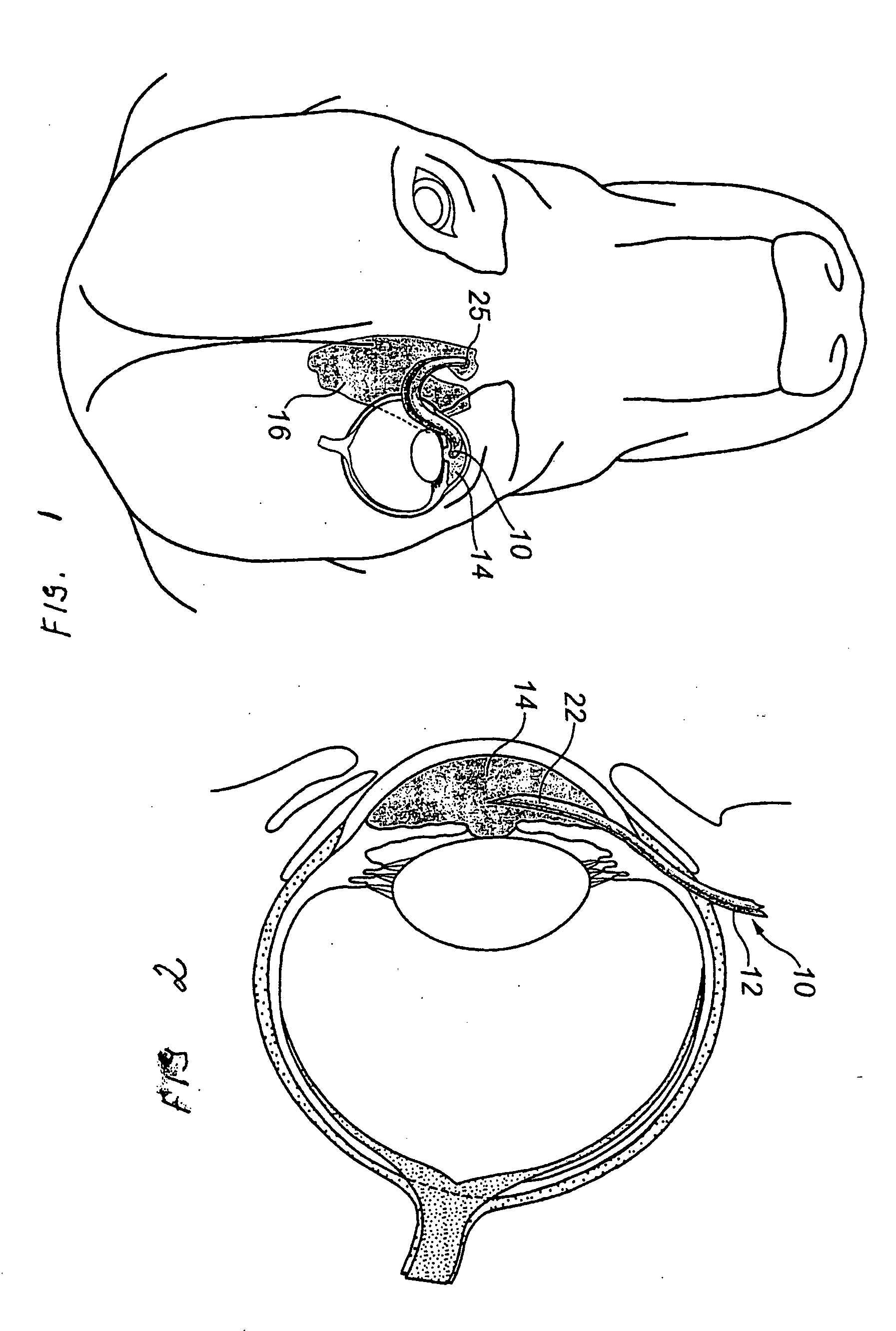
InactiveUS20040127843A1Convenient treatmentReduce and inhibit and slow effectEye surgeryWound drainsAqueous humorSchlemm's canal
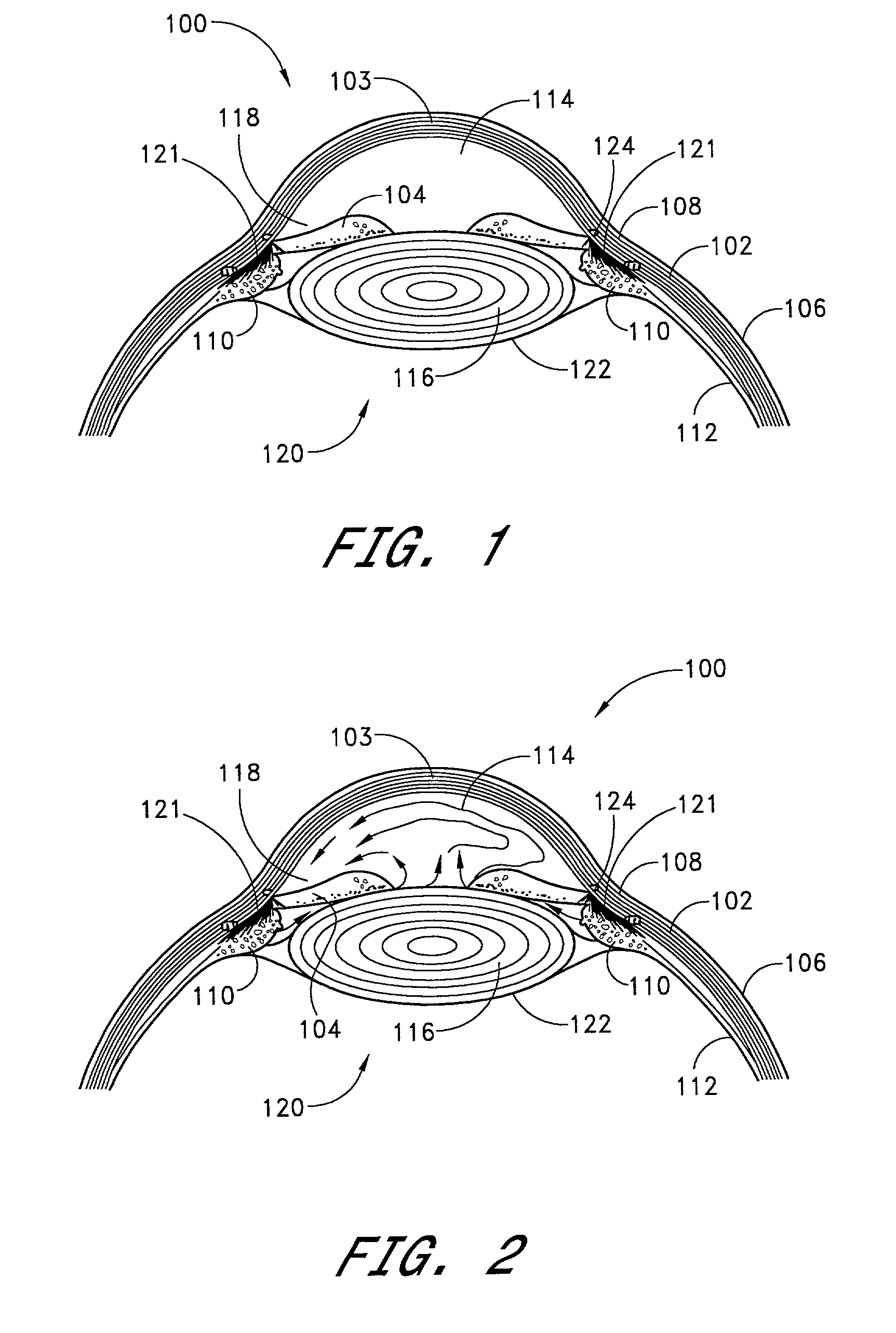
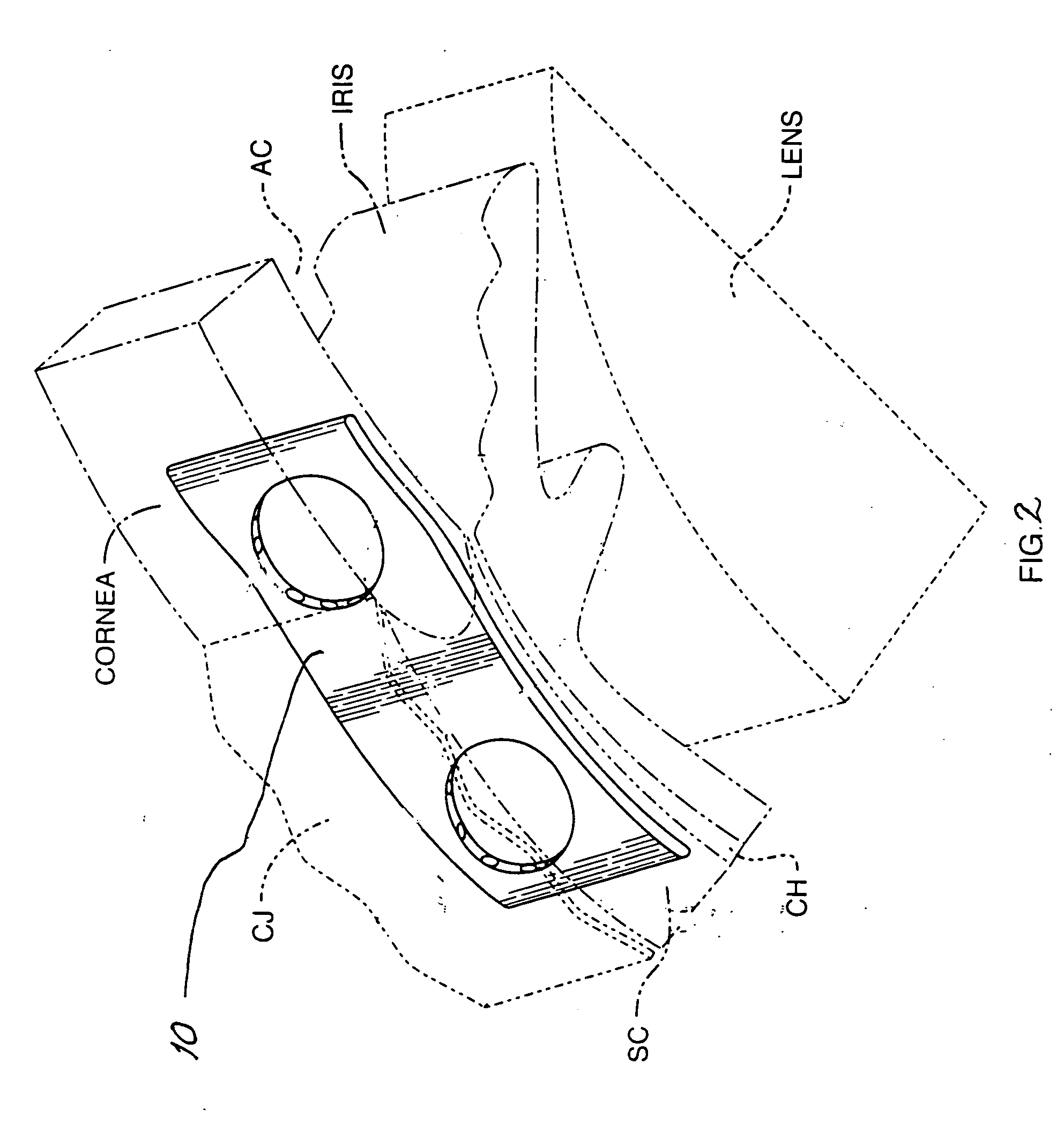
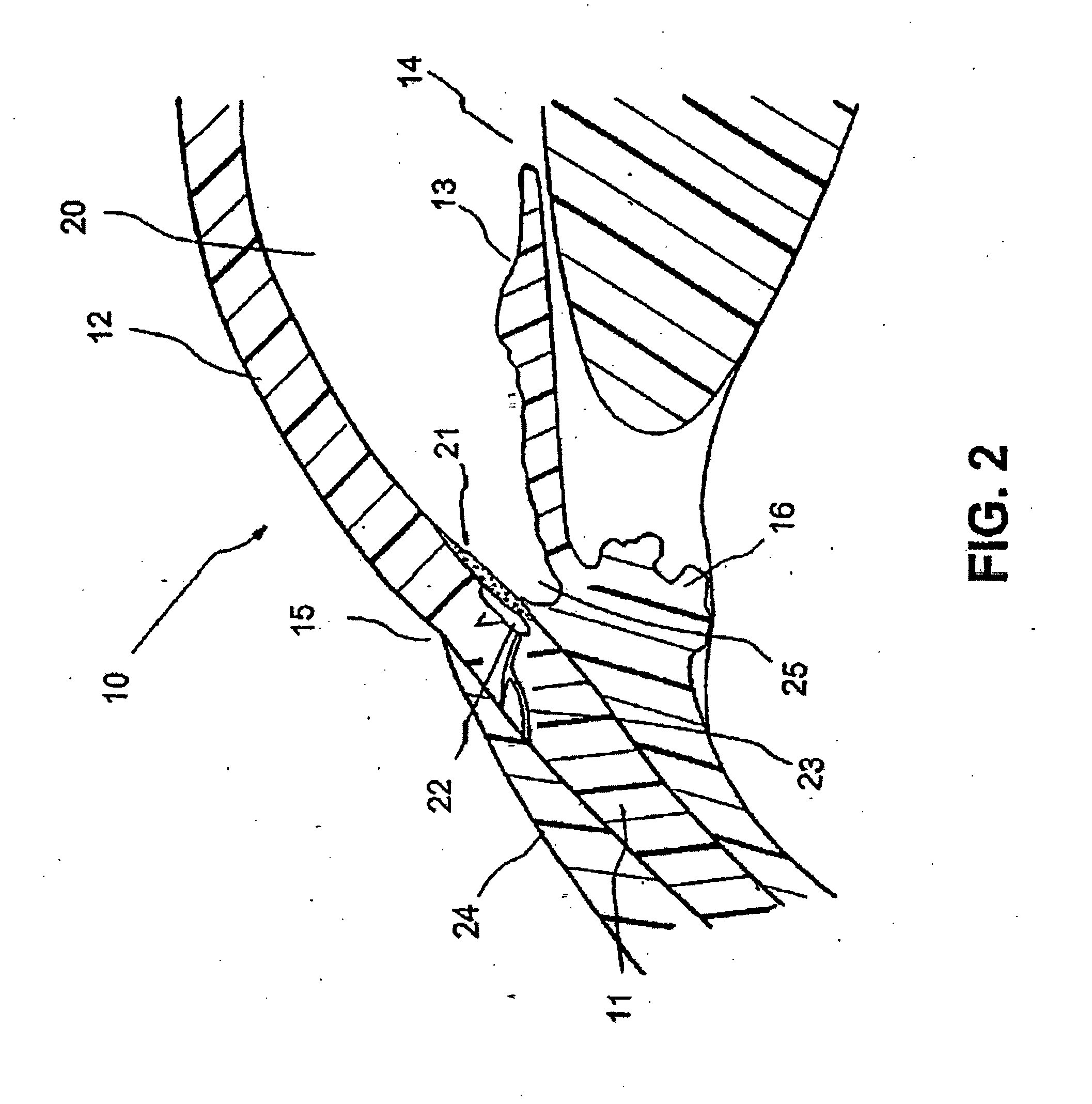
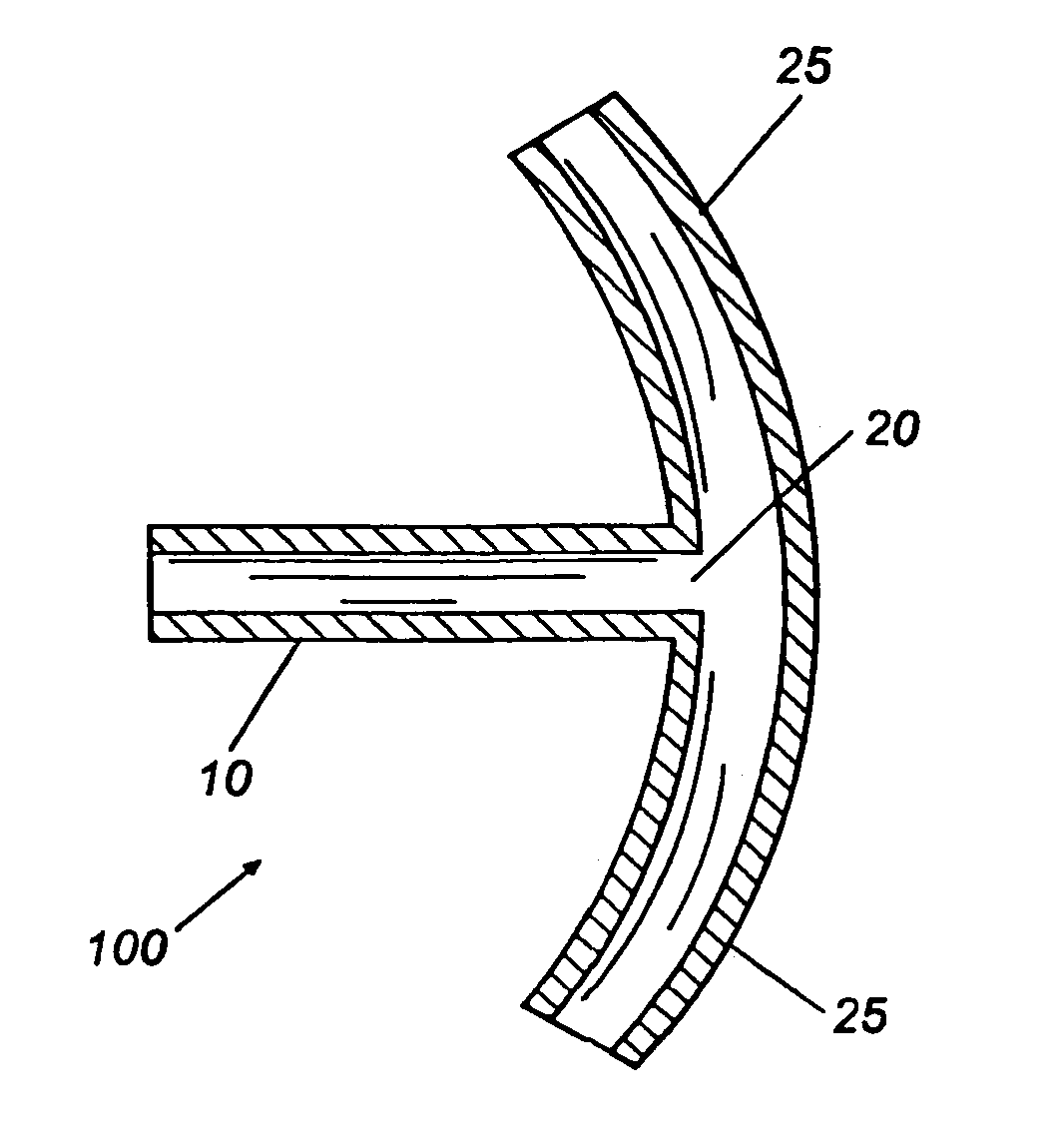
Devices and methods are provided for the treatment of glaucoma. An ocular implant is adapted such that aqueous humor flows controllably from the anterior chamber of the eye to Schlemm's canal, bypassing the trabecular meshwork. The implant may utilize one or more bioactive agents effective in treating glaucoma or other pathology.
Owner:DOSE MEDICAL CORP
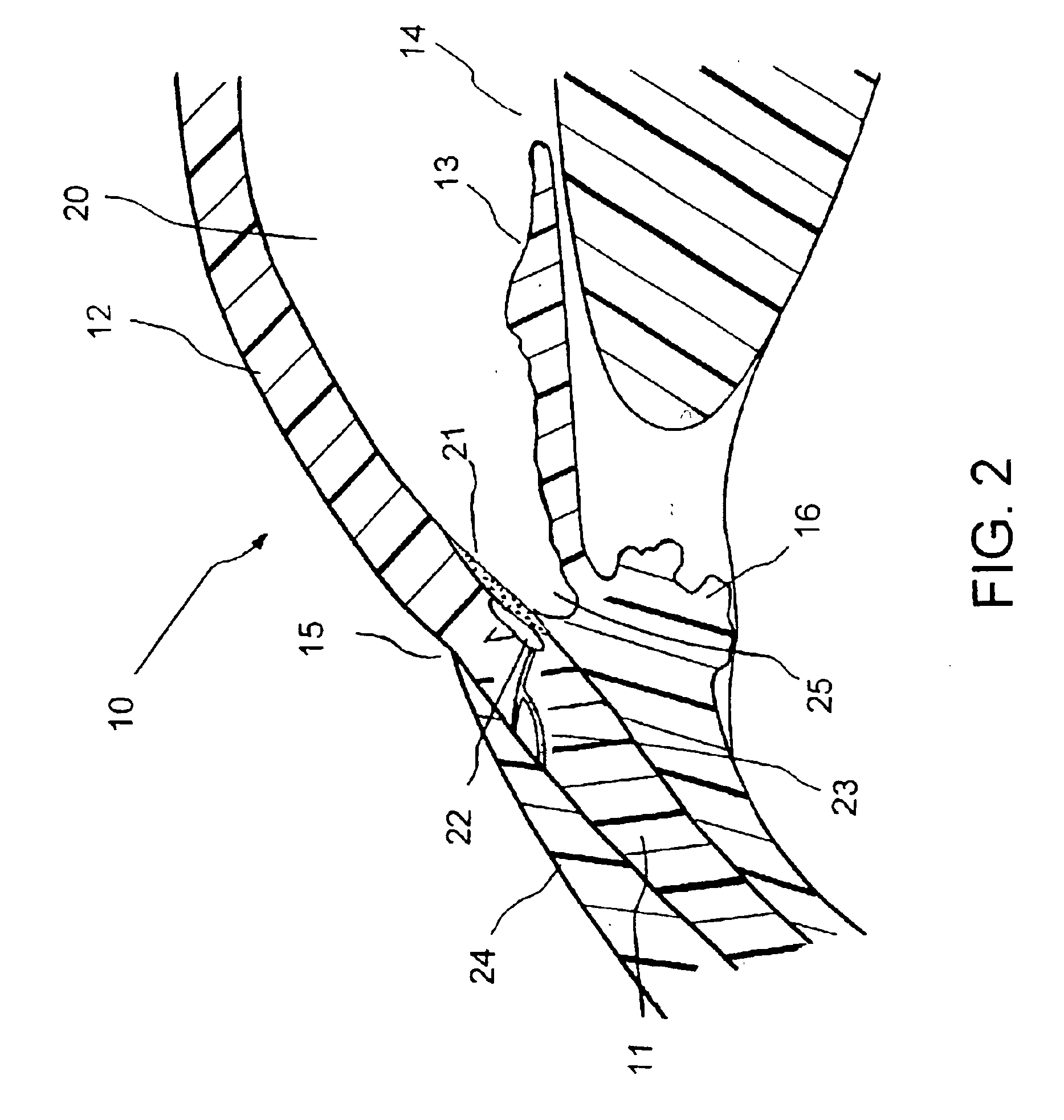
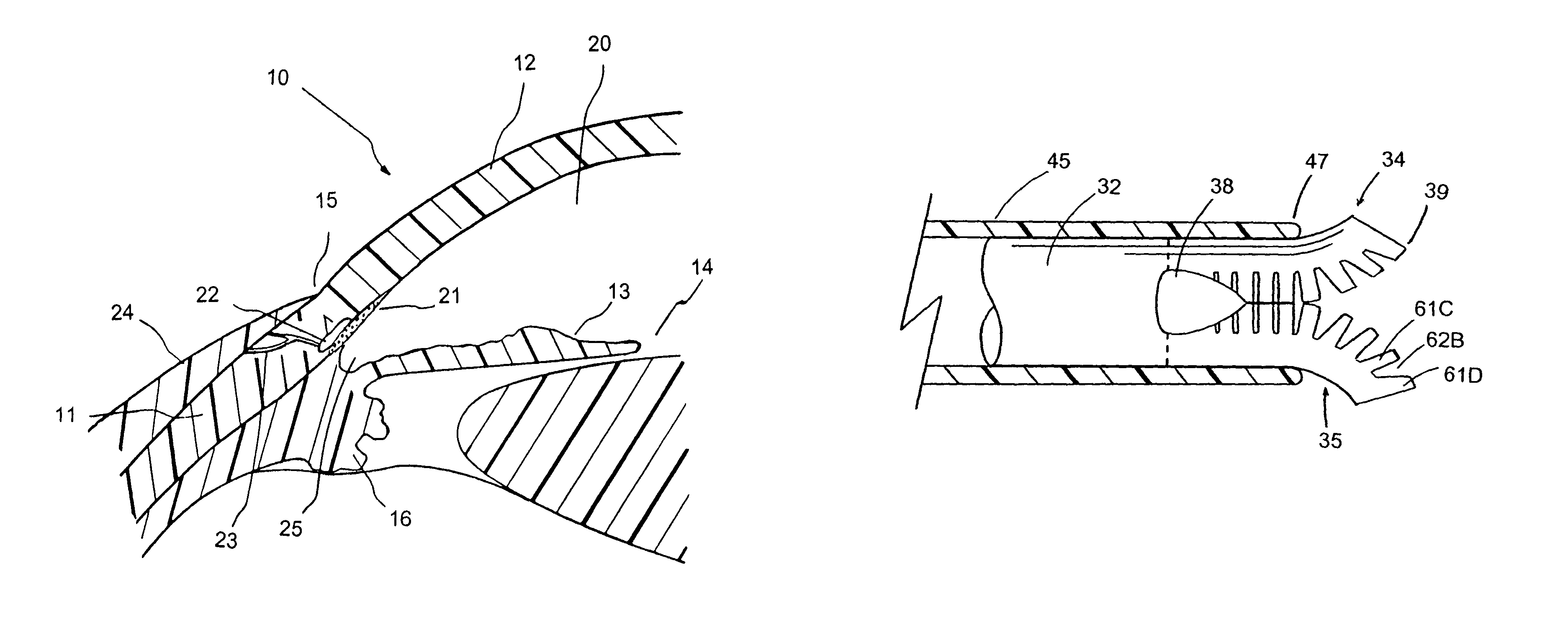
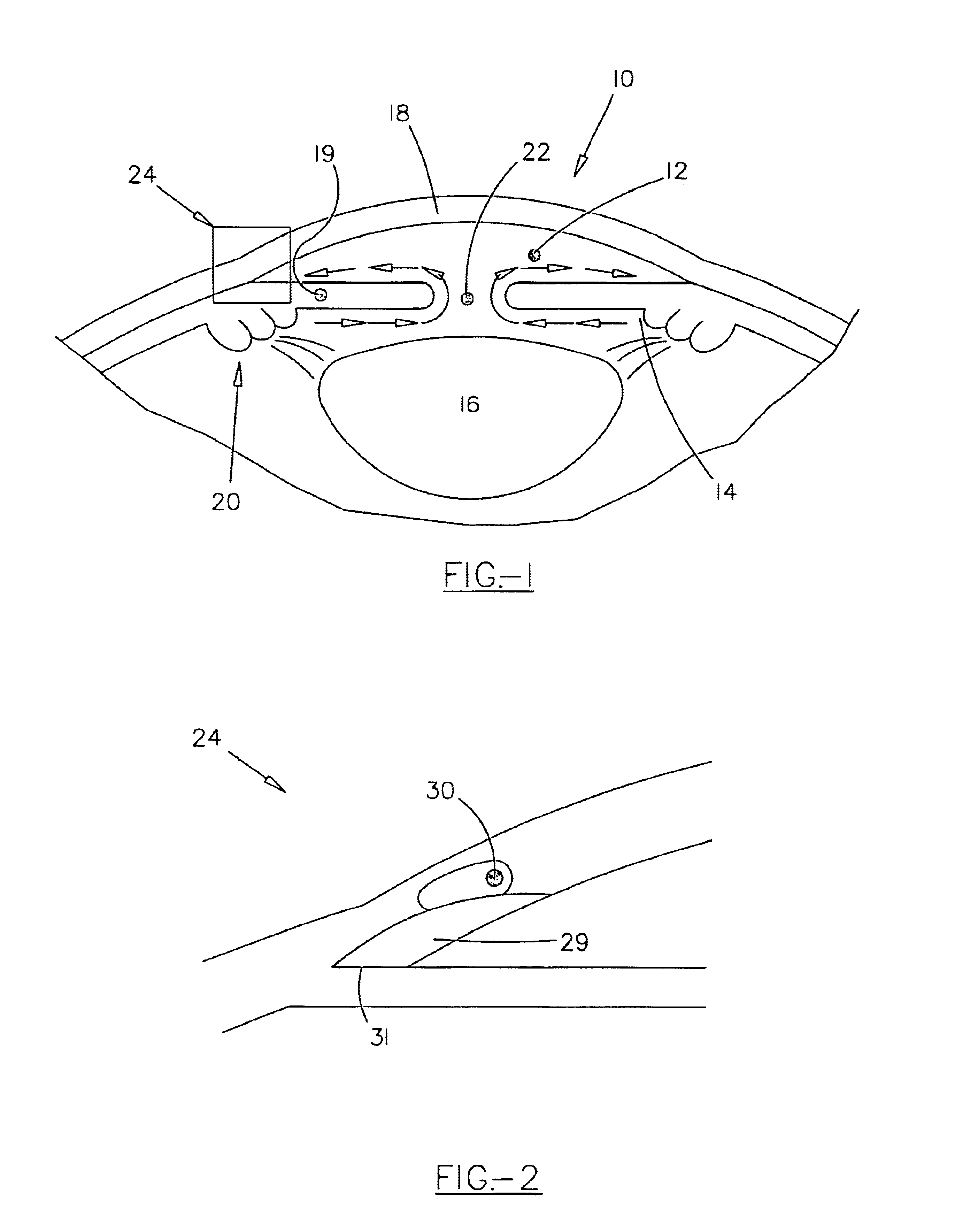
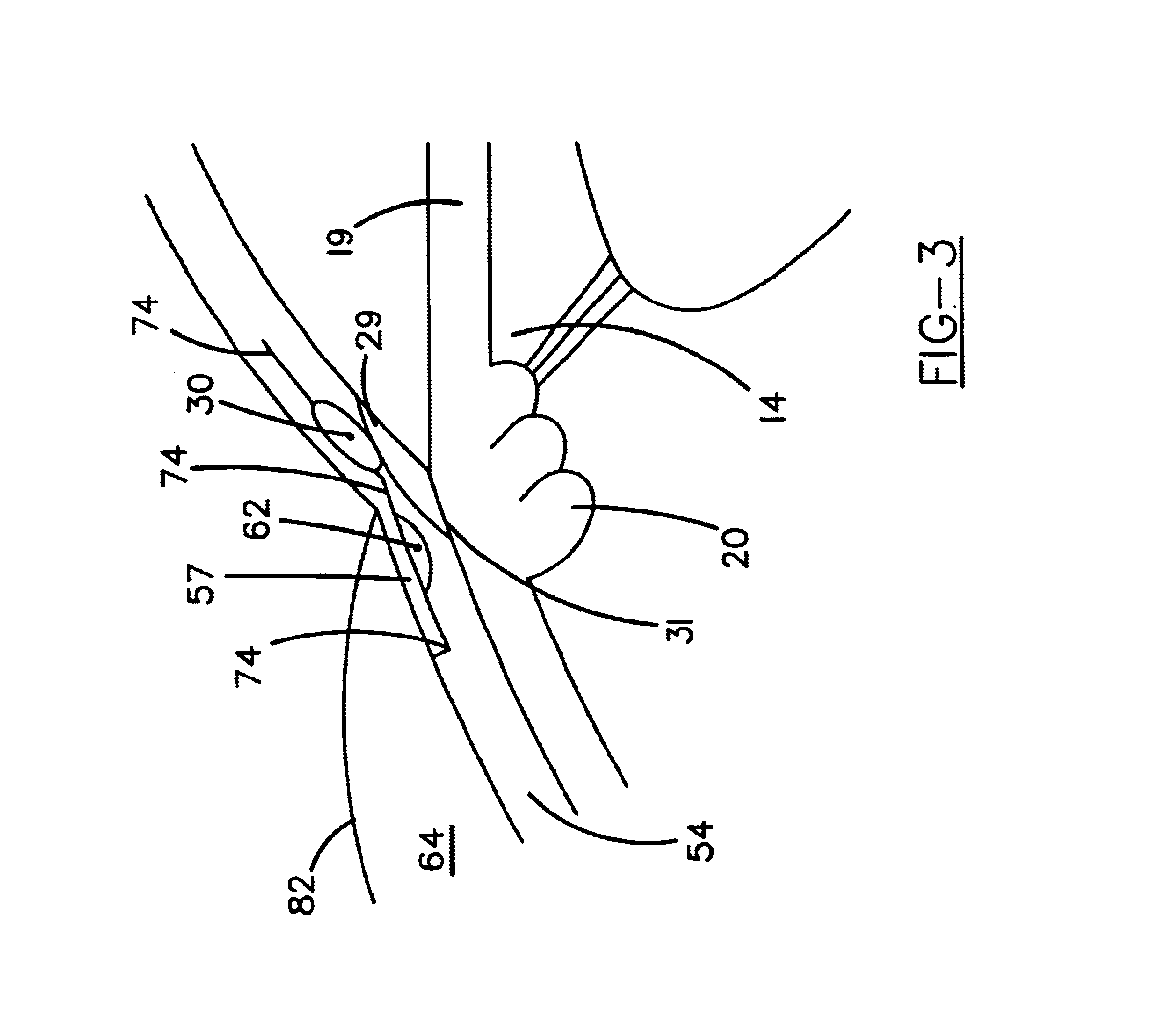
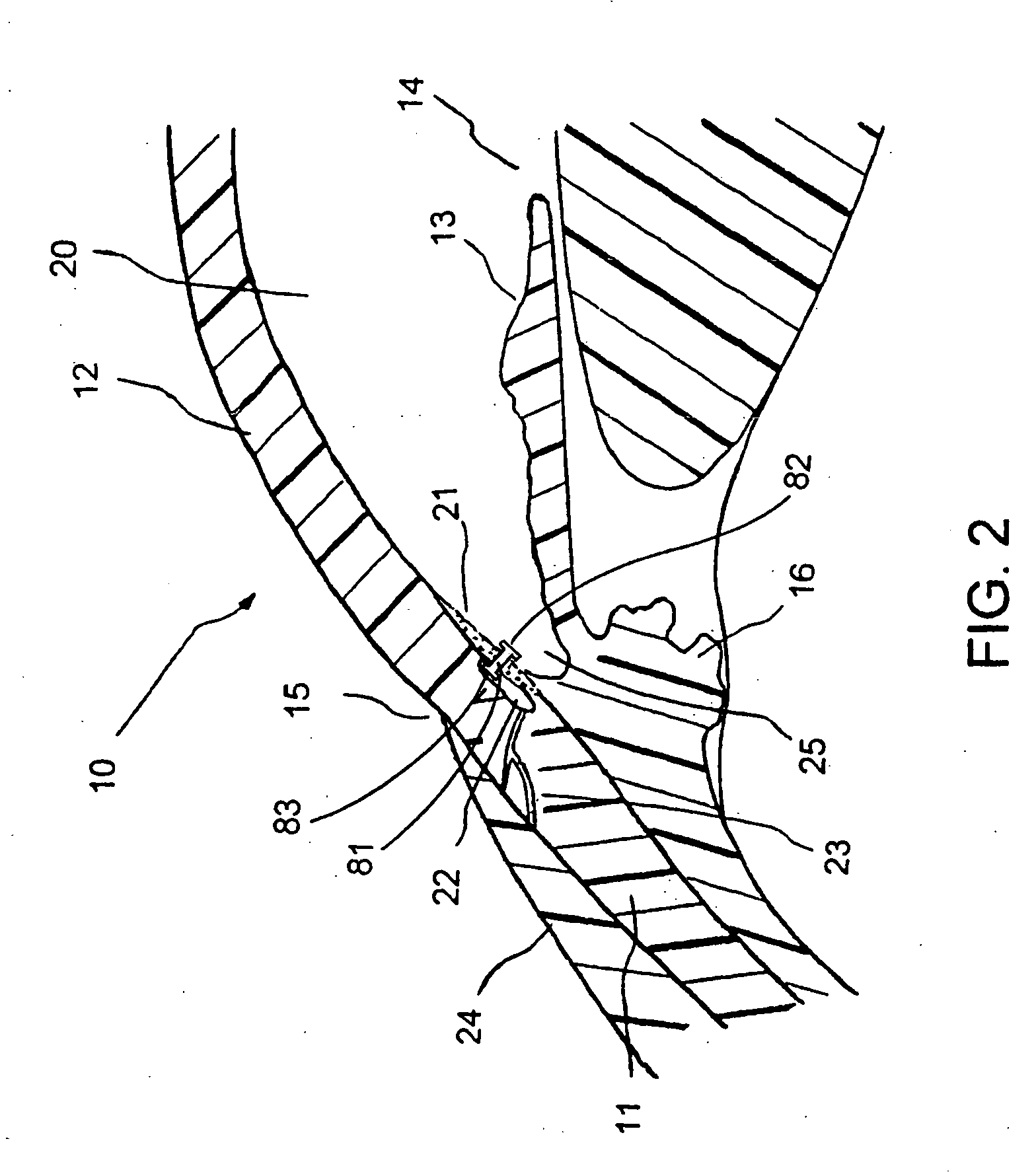
Apparatus and method for treating glaucoma
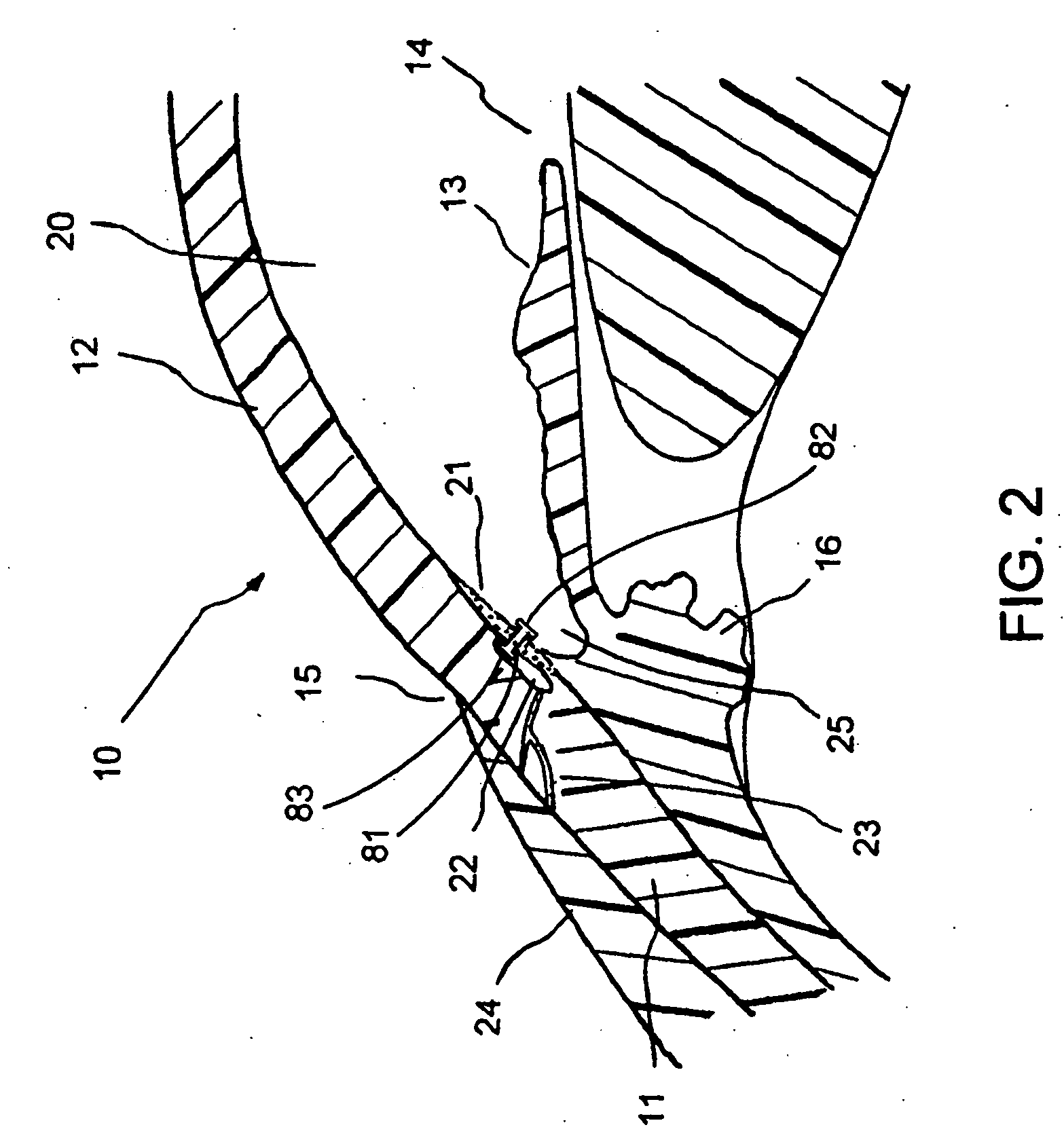
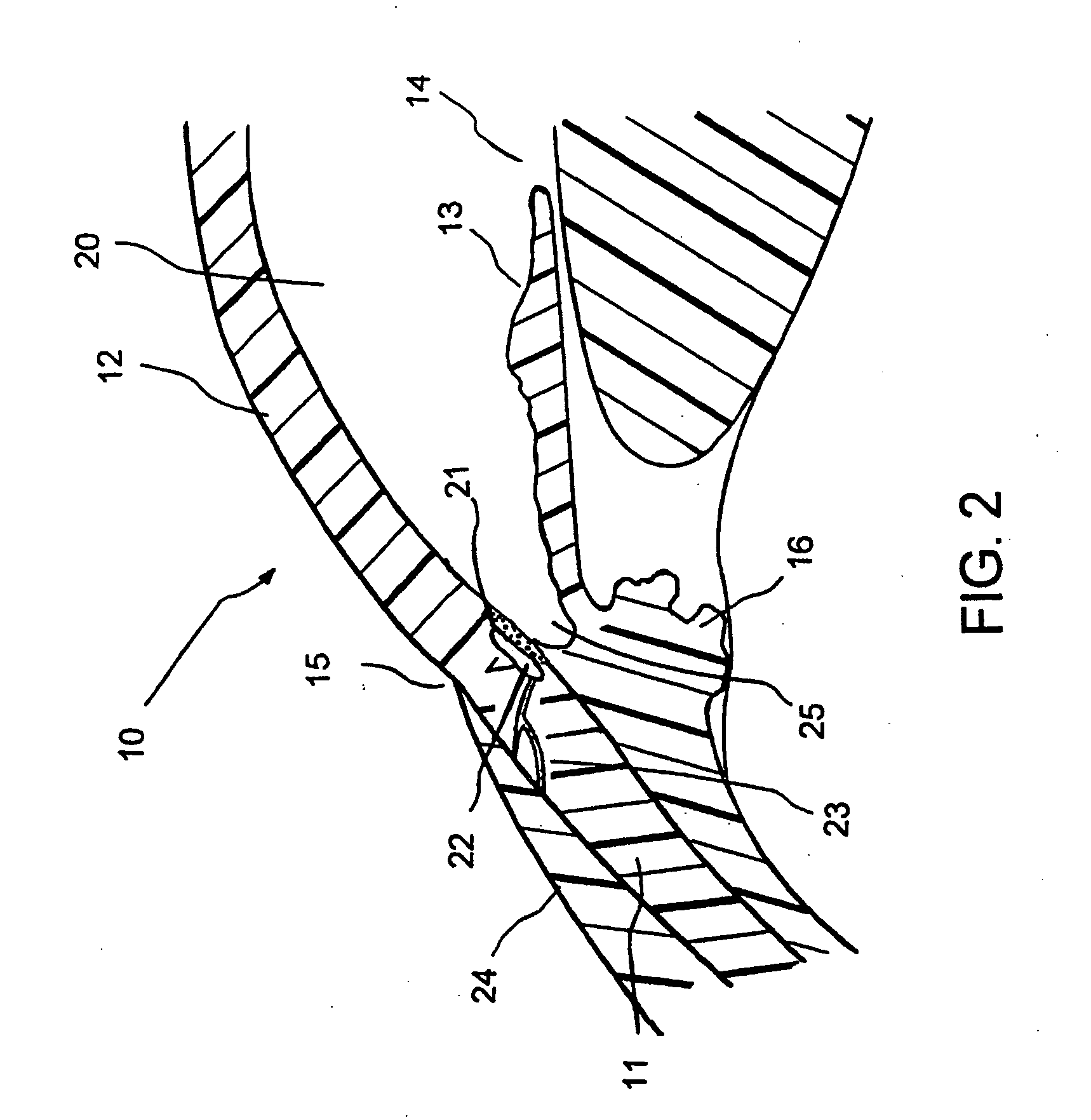
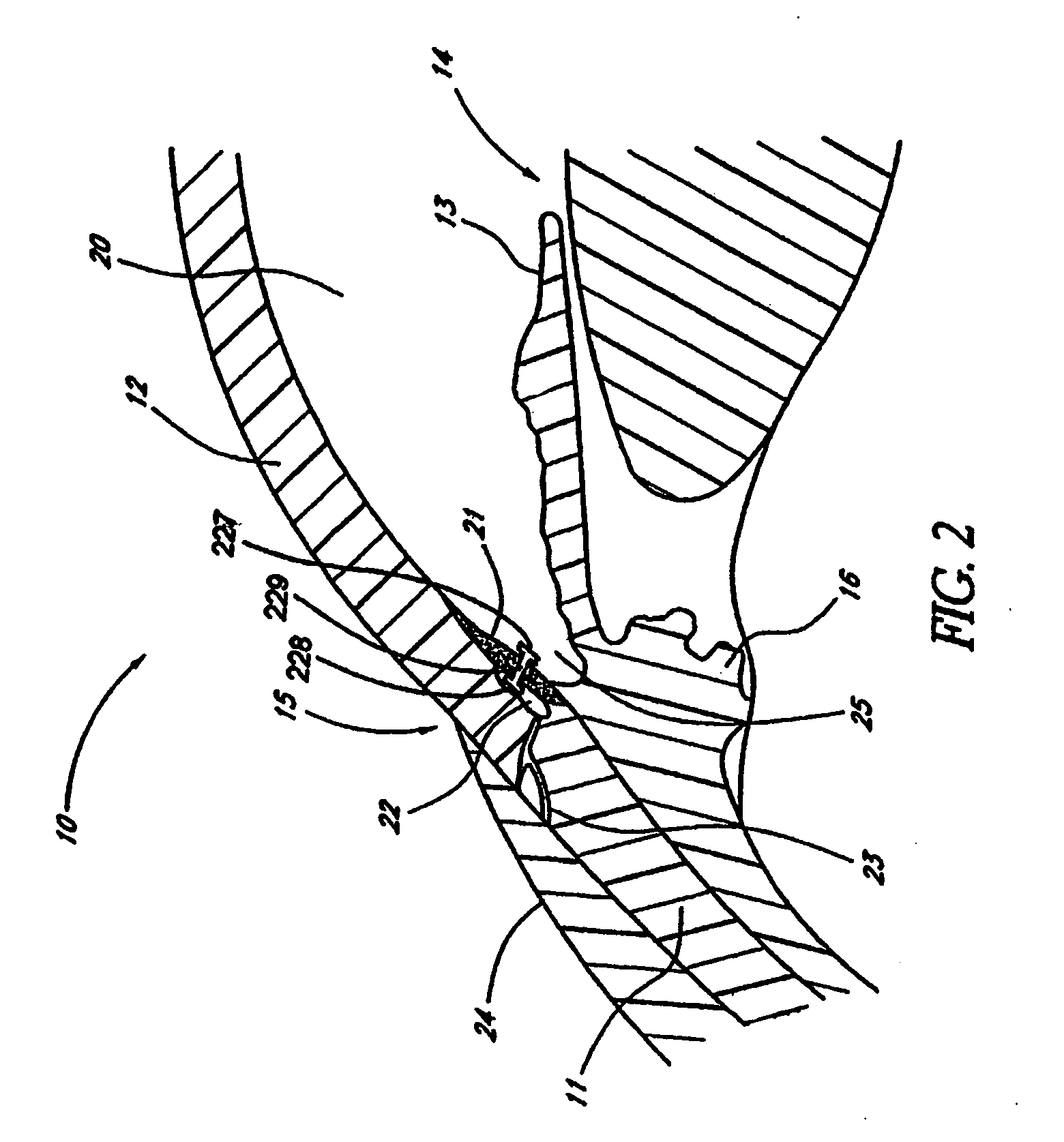
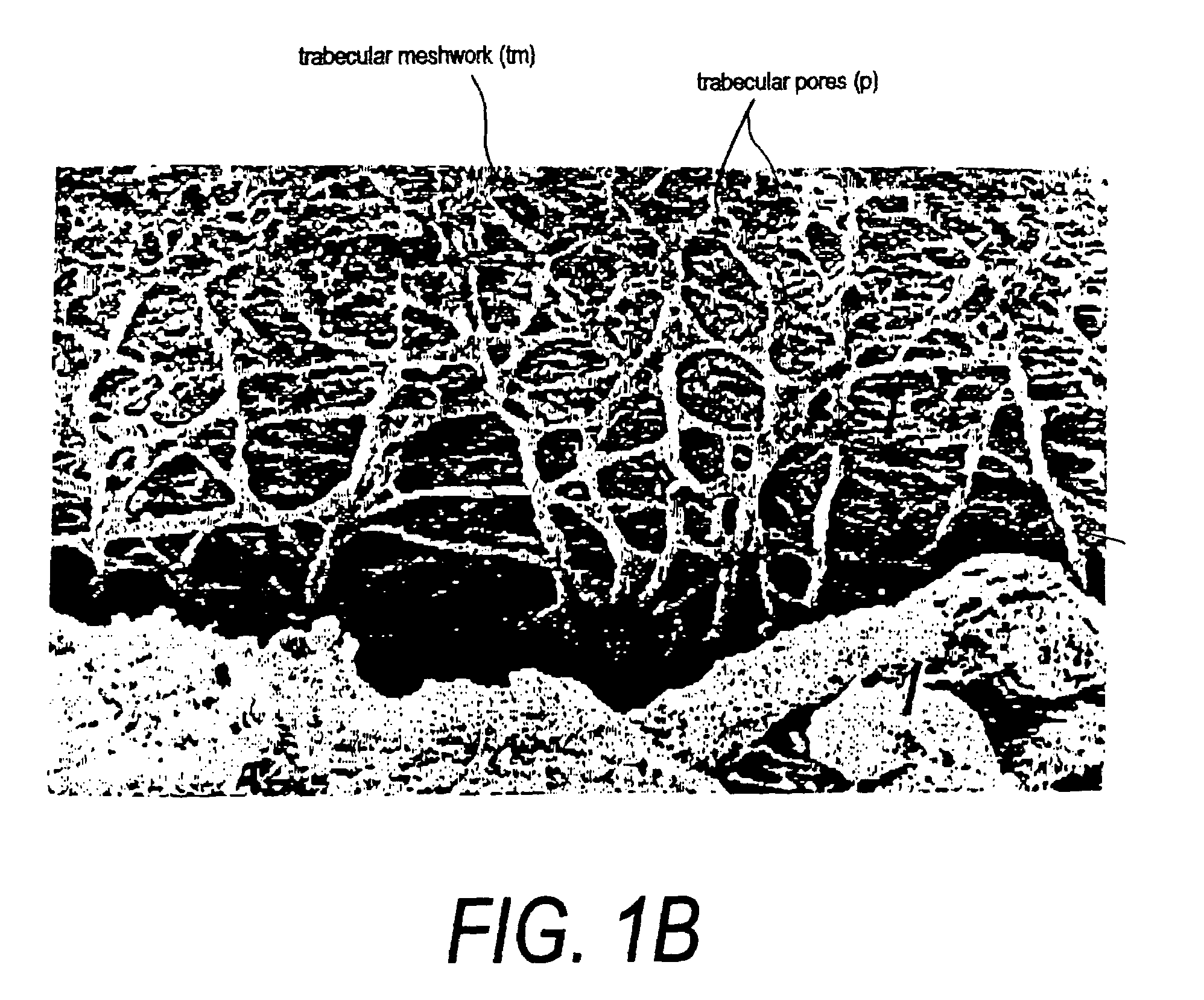
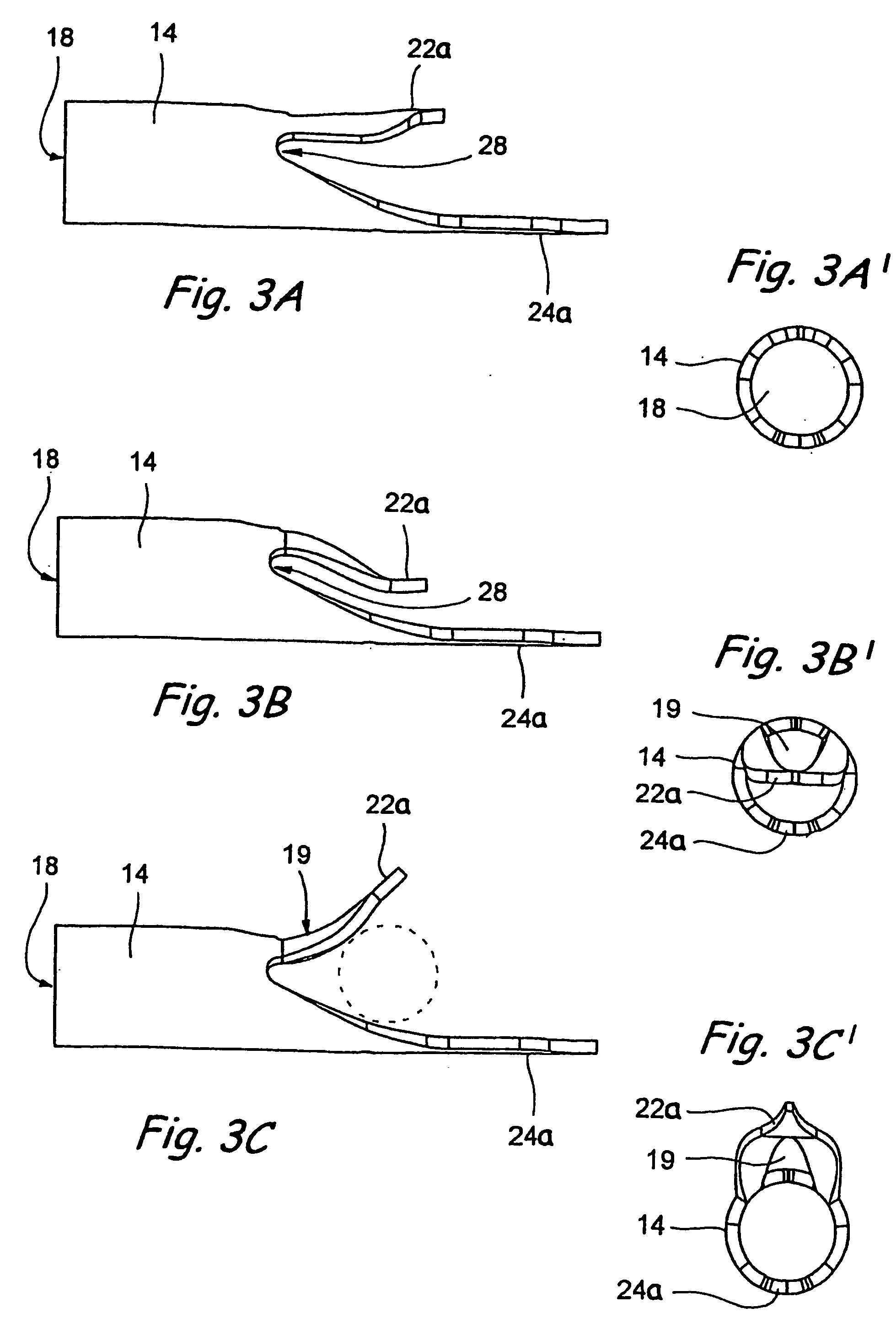
Surgical methods and related medical devices for treating glaucoma are shown. The method includes trabecular bypass surgery, which involves bypassing diseased trabecular meshwork with the use of a seton implant. The seton implant is used to prevent a healing process known as filling in, which has a tendency to close surgically created openings in the trabecular meshwork. The surgical method and novel implant are addressed to the trabecular meshwork, which is a major site of resistance to outflow in glaucoma. In addition to bypassing the diseased trabecular meshwork at the level of the trabecular meshwork, existing outflow pathways are also used or restored. The seton implant is positioned through the trabecular meshwork so that an inlet end of the seton implant is exposed to the anterior chamber of the eye and an outlet end is positioned into fluid collection channels at about an exterior surface of the trabecular meshwork or up to the level of aqueous veins.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Implant with pressure sensor for glaucoma treatment
InactiveUS6981958B1Reduce morbidityAvoiding hypotonyEye surgeryInfusion needlesSchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
A trabecular shunt and methods for treating glaucoma are disclosed. One of the methods comprises transporting fluid from the anterior chamber of an eye to Schlemm's canal through an implant, the implant extending between the anterior chamber and Schlemm's canal; sensing an intraocular pressure using a sensor incorporated into the implant; and transmitting a signal indicative of the sensed pressure to an external receiver.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Injectable glaucoma implants with multiple openings
ActiveUS20050271704A1Reduce morbidityAvoiding hypotonyEye implantsEye surgerySchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
Intraocular stents and applicators are disclosed for treating glaucoma. The stents are configured to extend between the anterior chamber of the eye and Schlemm's canal for enhancing outflow of aqueous from the anterior chamber so as to reduce intraocular pressure. The stents can have features for anchoring the stent into Schlemm's canal as well as preventing the walls of Schlemm's canal from closing the outlet of the stents. The applicators can be steerable so as to make implantation easier. Additionally, the applicators can be configured to hold a plurality of stents so that multiple stents can be implanted through one incision without removing the applicator from the incision between serial implantations.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
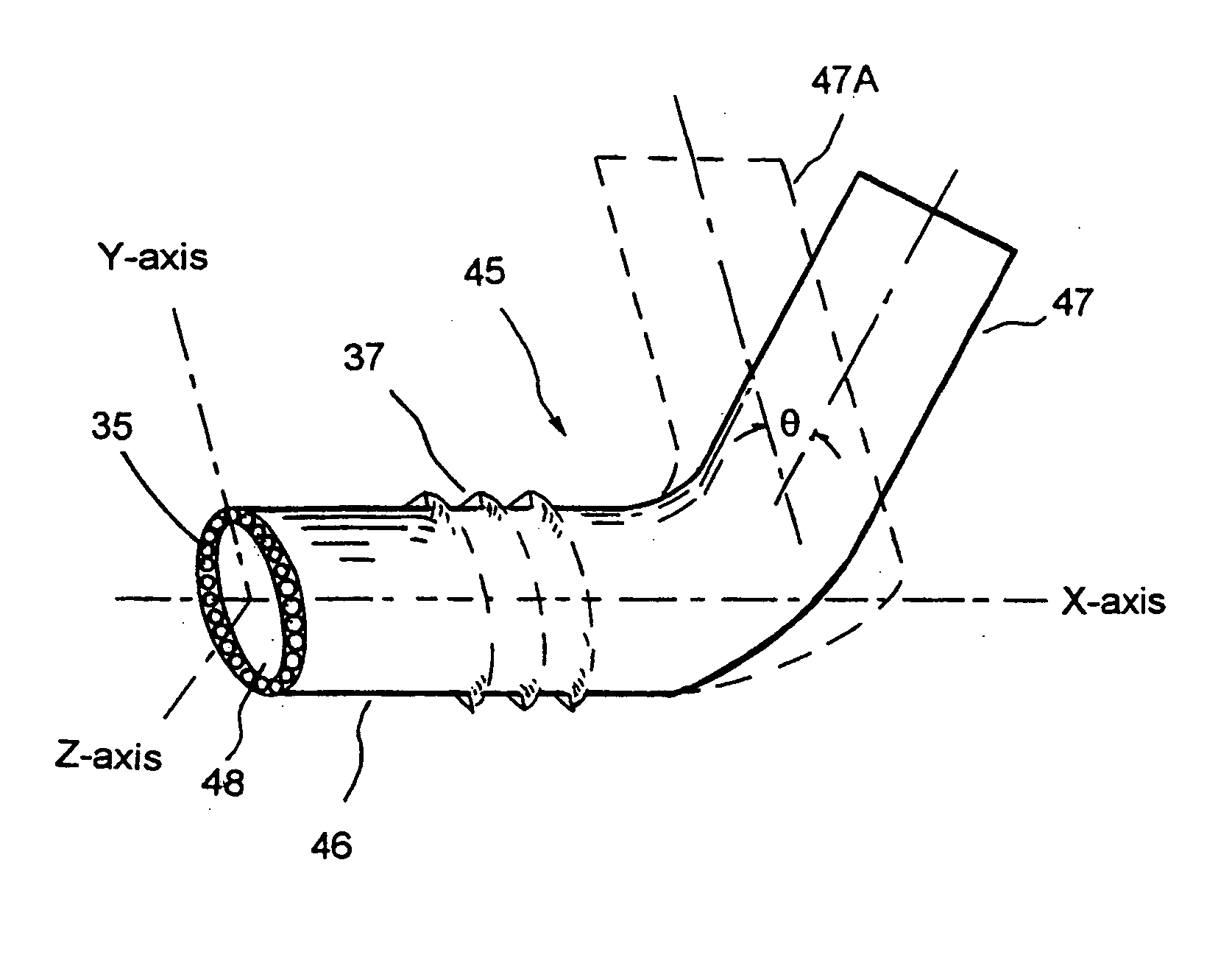
Liquid jet for glaucoma treatment
Methods of treating glaucoma are described including treatment of an eye with a liquid jet. The liquid jet can be generated by a laser-induced liquid jet instrument which is inserted through an incision in an eye. A stent can also be used, the stent having an inflow portion that is in fluid communication with an outflow portion. The stent can be inserted into the eye and transported from the incision through the anterior chamber of the eye toward the trabecular meshwork of the eye. In some embodiments, the stent can be advanced through the anterior chamber of the eye and provide fluid communication between the anterior chamber and Schlemm's canal. The method includes infusing fluid into an aqueous cavity and increasing the pressure of the fluid within the aqueous cavity.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Method and apparatus for treatment of glaucoma
InactiveUS6699211B2Slowing and stopping progressionLower eye pressureEar treatmentEye surgeryVeinAqueous humor
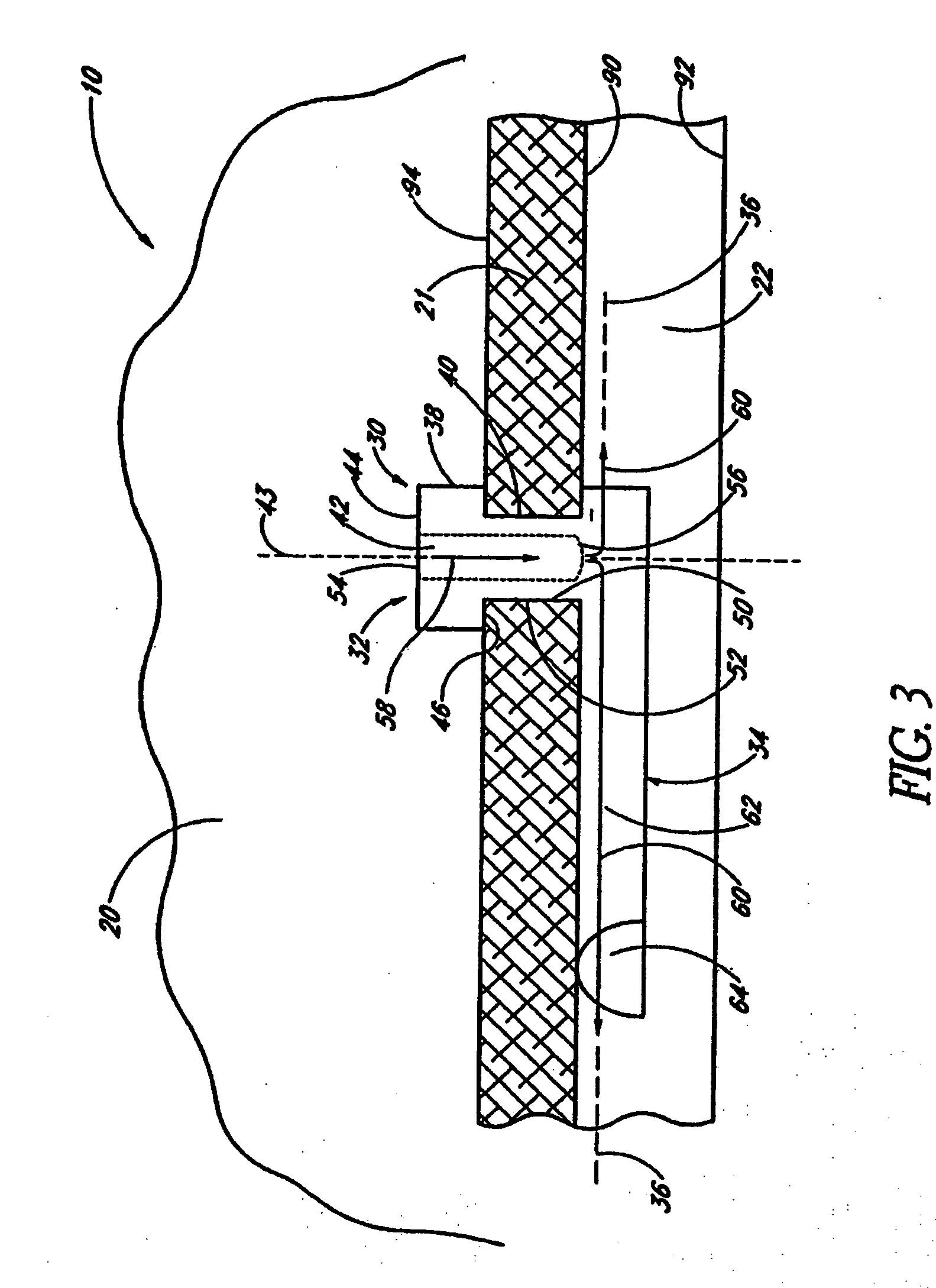
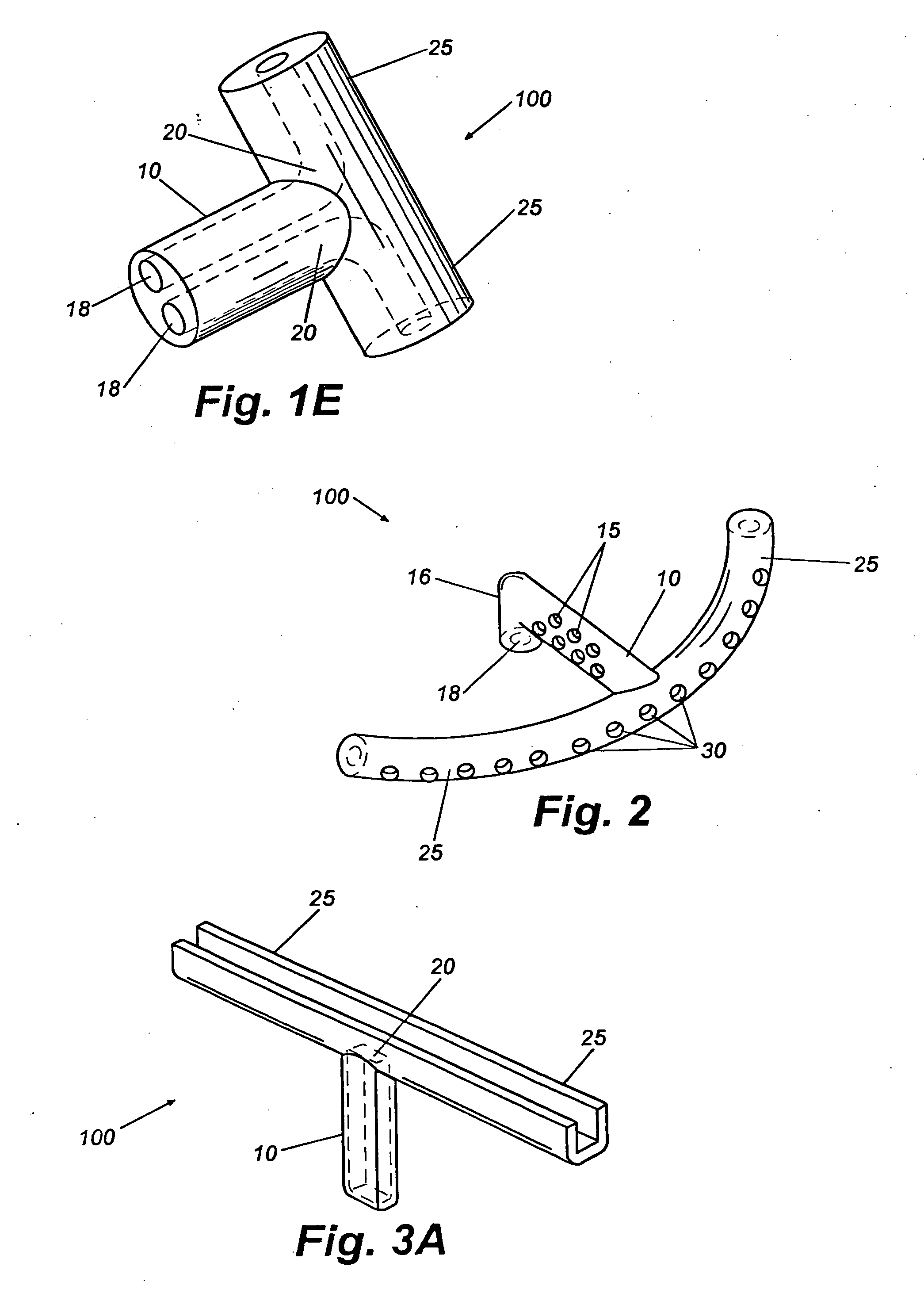
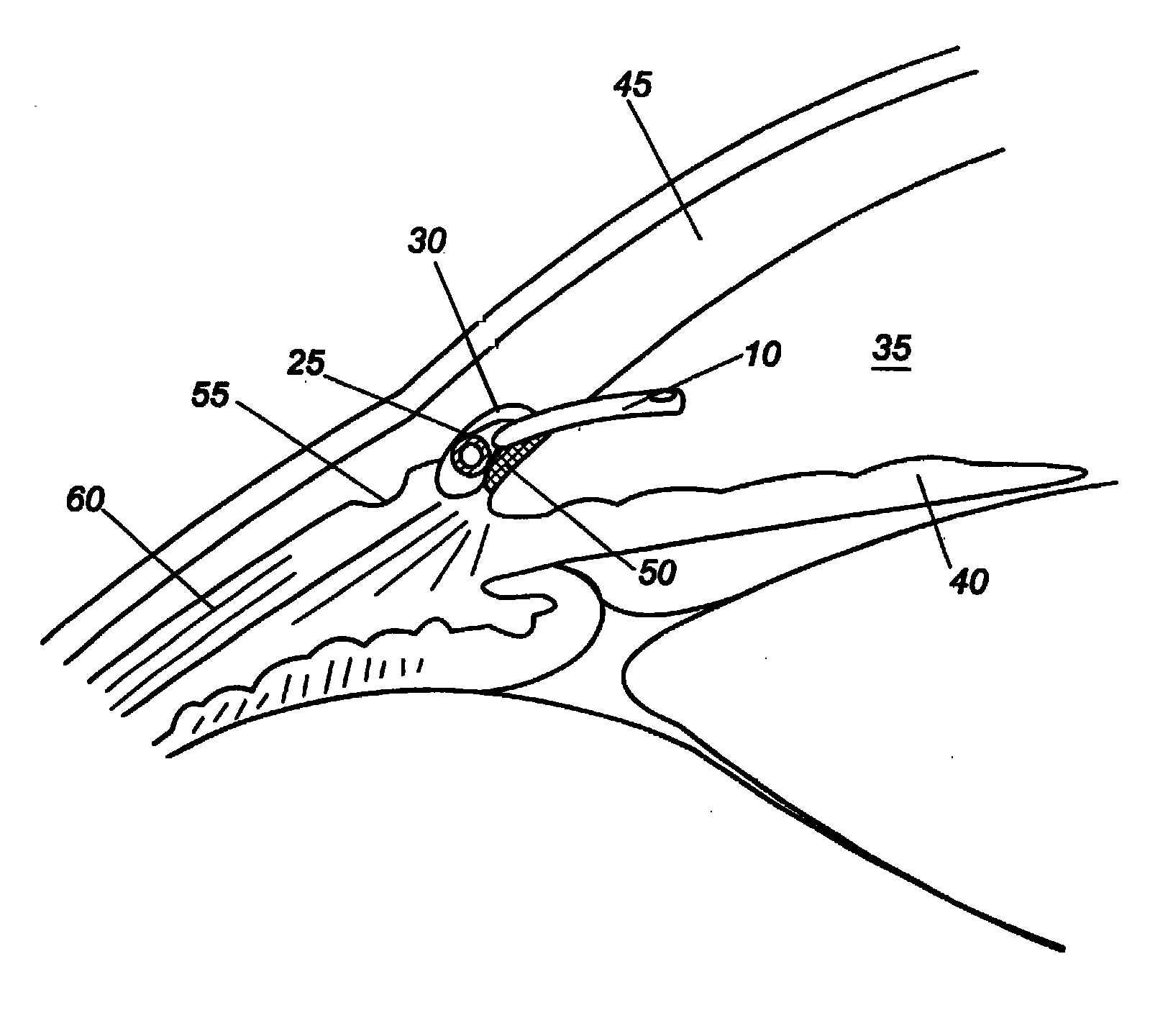
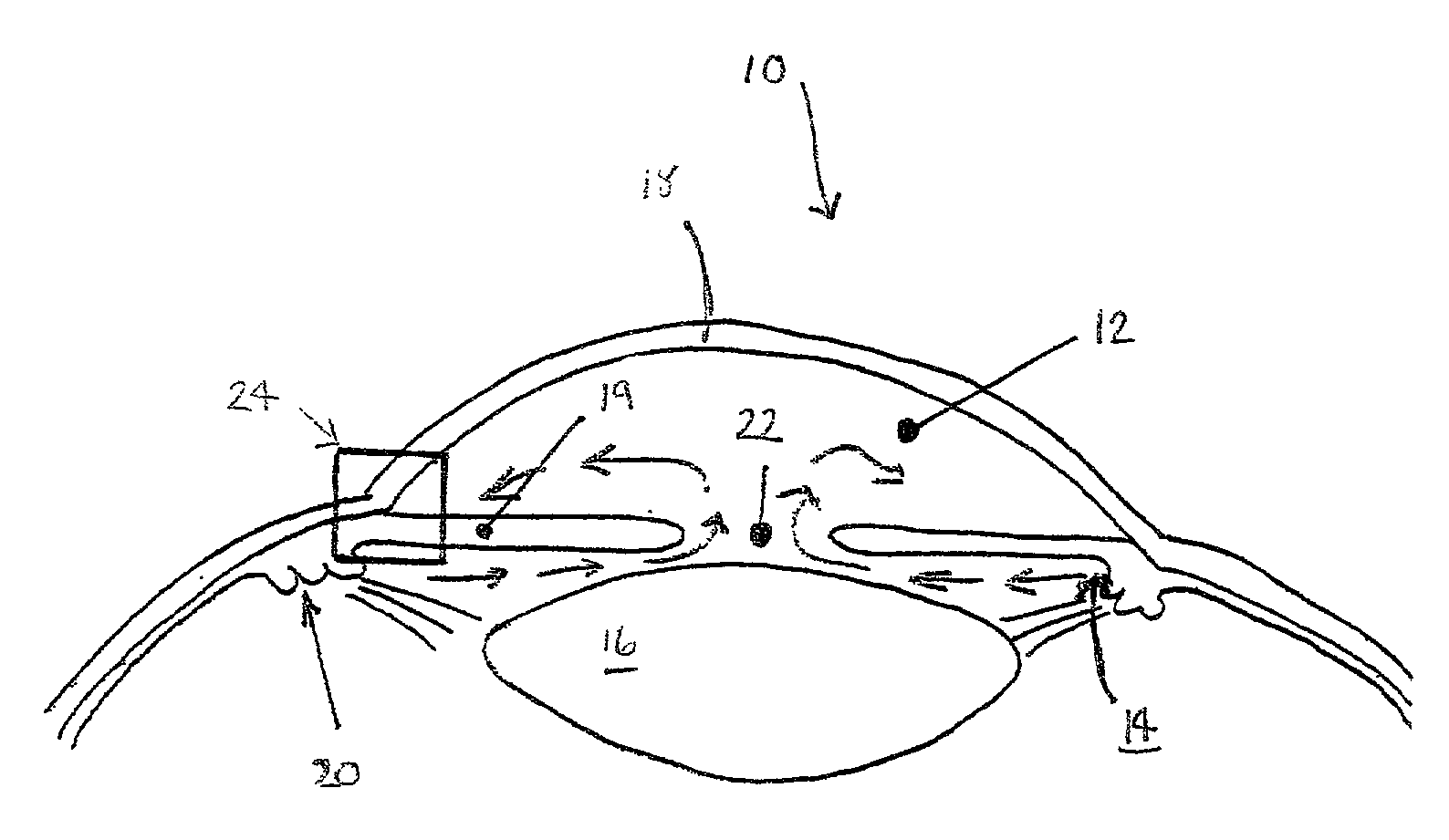
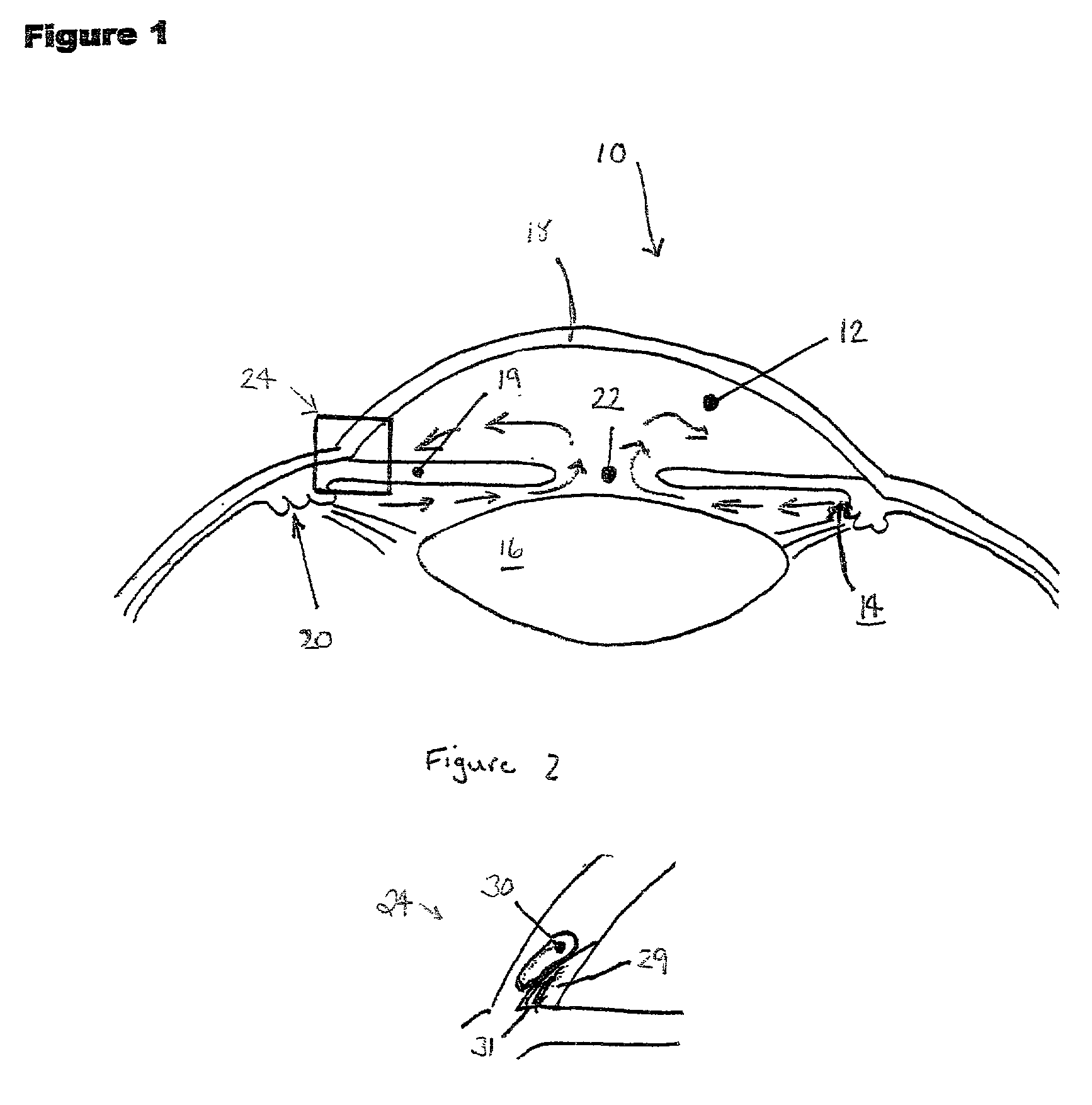
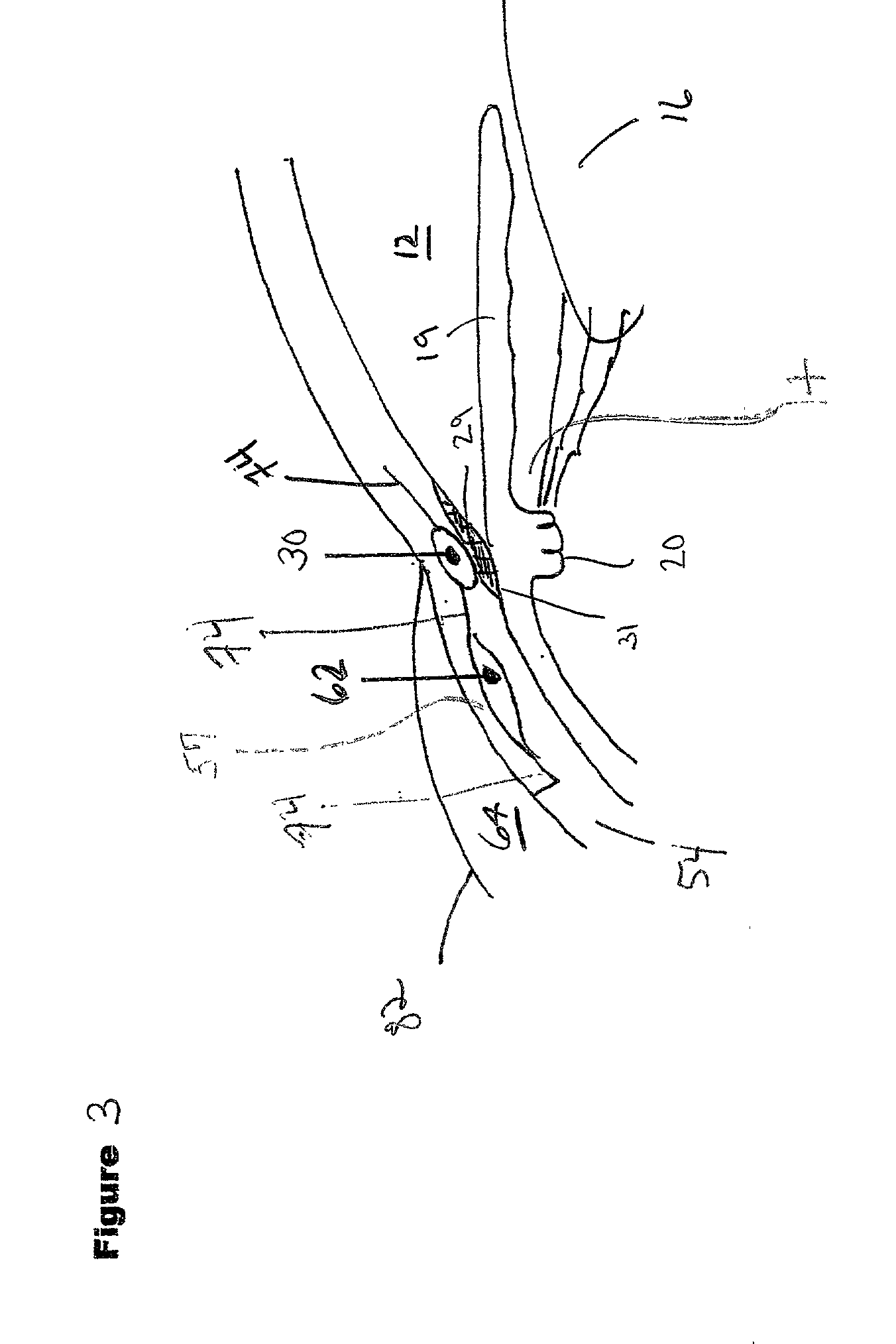
A new and improved method and apparatus for treating glaucoma is described herein. A device for directing aqueous humor from an anterior chamber to Schlemm's canal comprises a seton, and may further comprise a pump operatively connected to the seton. The seton conducts aqueous directly from the anterior chamber to Schlemm's canal so that it can drain directly into the aqueous veins leading to the venous circulation. The seton for lowering intraocular pressure of an associated eye comprises a first tube adapted to be inserted into an associated anterior chamber of the eye; and, two wing tubes extending from the first tube. The two wing tubes are adapted to be inserted into Schlemm's canal. The two wing tubes and the first tube form a substantially continuous passageway, such that aqueous humor flows from the anterior chamber into Schlemm's canal through the substantially continuous passageway.
Owner:SAVAGE JAMES A
Ophthalmology implants and methods of manufacture
The present disclosure provides an ophthalmology implant and methods for treating glaucoma or optic neural transmission deficiency, wherein at least a portion of the implant is made of or includes a nanometer-sized substance, such as nanotubes, nanofibers, sheets from nanotubes, nanowires, nanofibrous mesh and the like.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
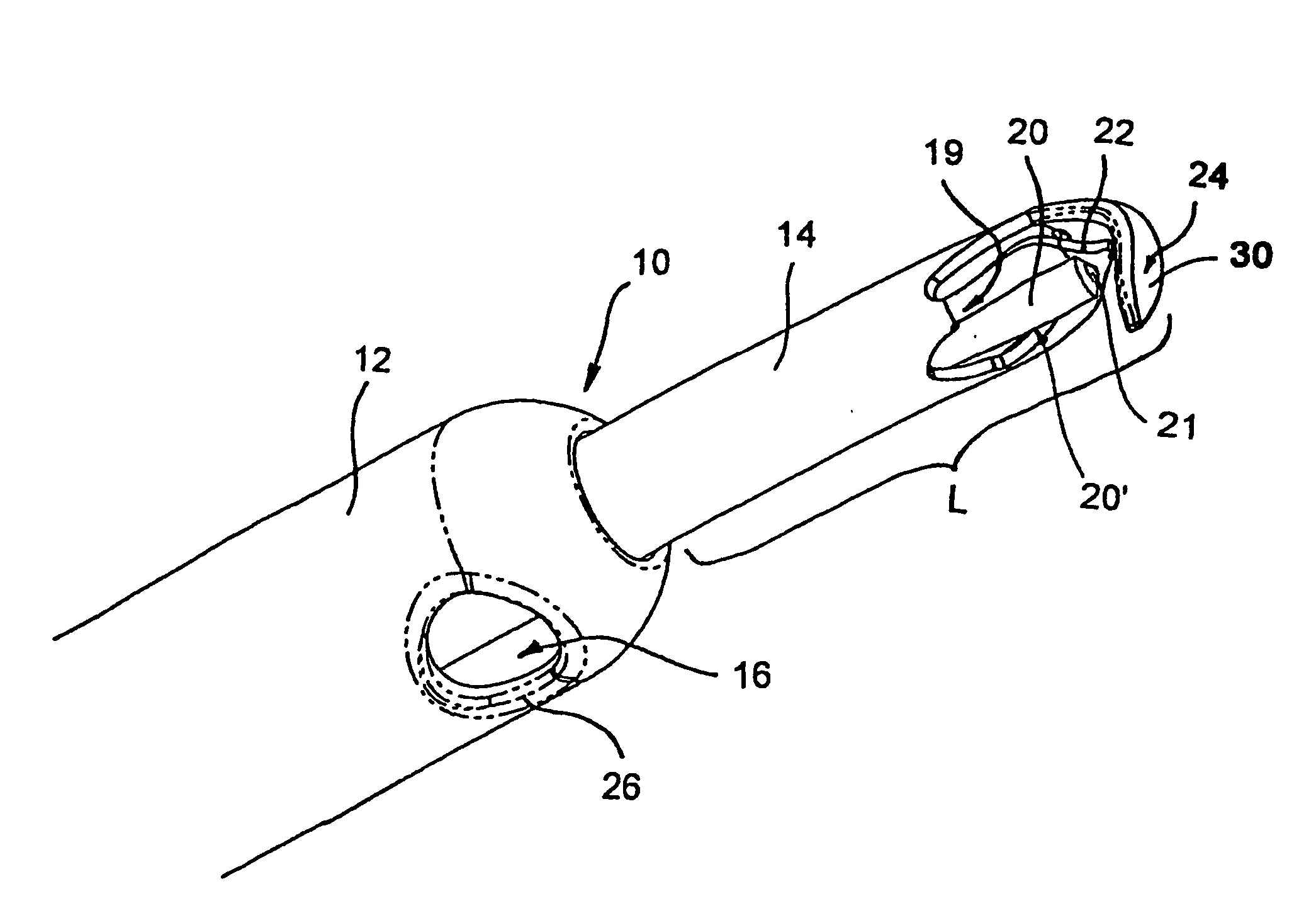
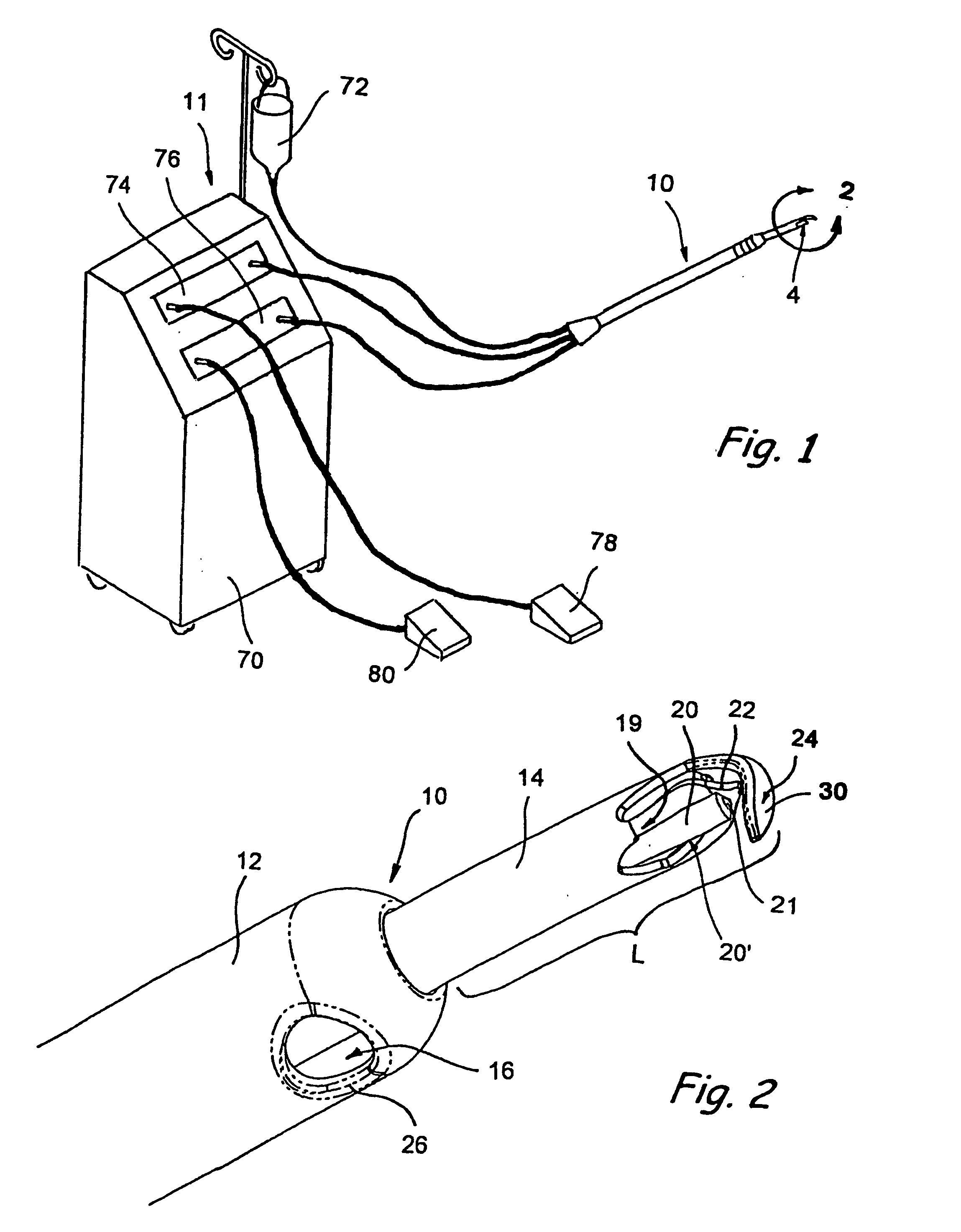
Minimally invasive glaucoma surgical instrument and method
InactiveUS6979328B2Easy to solveEasy accessSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringSchlemm's canalSurgical instrumentation
A surgical instrument and methods for the treatment of glaucoma are provided. The instrument uses either cauterization, a laser to ablate, sonic or ultrasonic energy to emulsify, or mechanical cutting of a portion of the trabecular meshwork. The instrument may also be provided with irrigation, aspiration, and a footplate. The footplate is used to enter Schlemm's canal, serves as a guide, and also protects Schlemm's canal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Glaucoma implant with extending members
InactiveUS20050192527A1Avoiding hypotonyEliminate riskEye surgeryIntravenous devicesSchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
A trabecular shunt and methods for treating glaucoma are disclosed. One of the methods comprises transporting fluid from the anterior chamber of an eye to Schlemm's canal through an implant, the implant extending between the anterior chamber and Schlemm's canal; sensing an intraocular pressure using a sensor incorporated into the implant; and transmitting a signal indicative of the sensed pressure to an external receiver.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Injectable glaucoma implants with multiple openings
InactiveUS20050266047A1Faster and safe and less-expensive surgical procedureRapid visual recoveryOrganic active ingredientsEye surgerySchlemm's canalImplant
Intraocular stents and applicators are disclosed for treating glaucoma. The stents are configured to extend between the anterior chamber of the eye and Schlemm's canal for enhancing outflow of aqueous from the anterior chamber so as to reduce intraocular pressure. The stents can have features for anchoring the stent into Schlemm's canal as well as preventing the walls of Schlemm's canal from closing the outlet of the stents. The applicators can be steerable so as to make implantation easier. Additionally, the applicators can be configured to hold a plurality of stents so that multiple stents can be implanted through one incision without removing the applicator from the incision between serial implantations.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Minimally invasive glaucoma surgical instrument and method
InactiveUS20060106370A1Easy accessEasy to solveLaser surgeryDiagnosticsSchlemm's canalMinimally invasive glaucoma surgery
Apparatuses and methods for the treatment of glaucoma are provided. The instrument uses either cauterization, a laser to ablate, sonic or ultrasonic energy to emulsify, or mechanical cutting of a portion of the trabecular meshwork. The instrument may also be provided with irrigation, aspiration, and a footplate. The footplate is used to enter Schlemm's canal, serves as a guide, and also protects Schlemm's canal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Shunt for the treatment of glaucoma
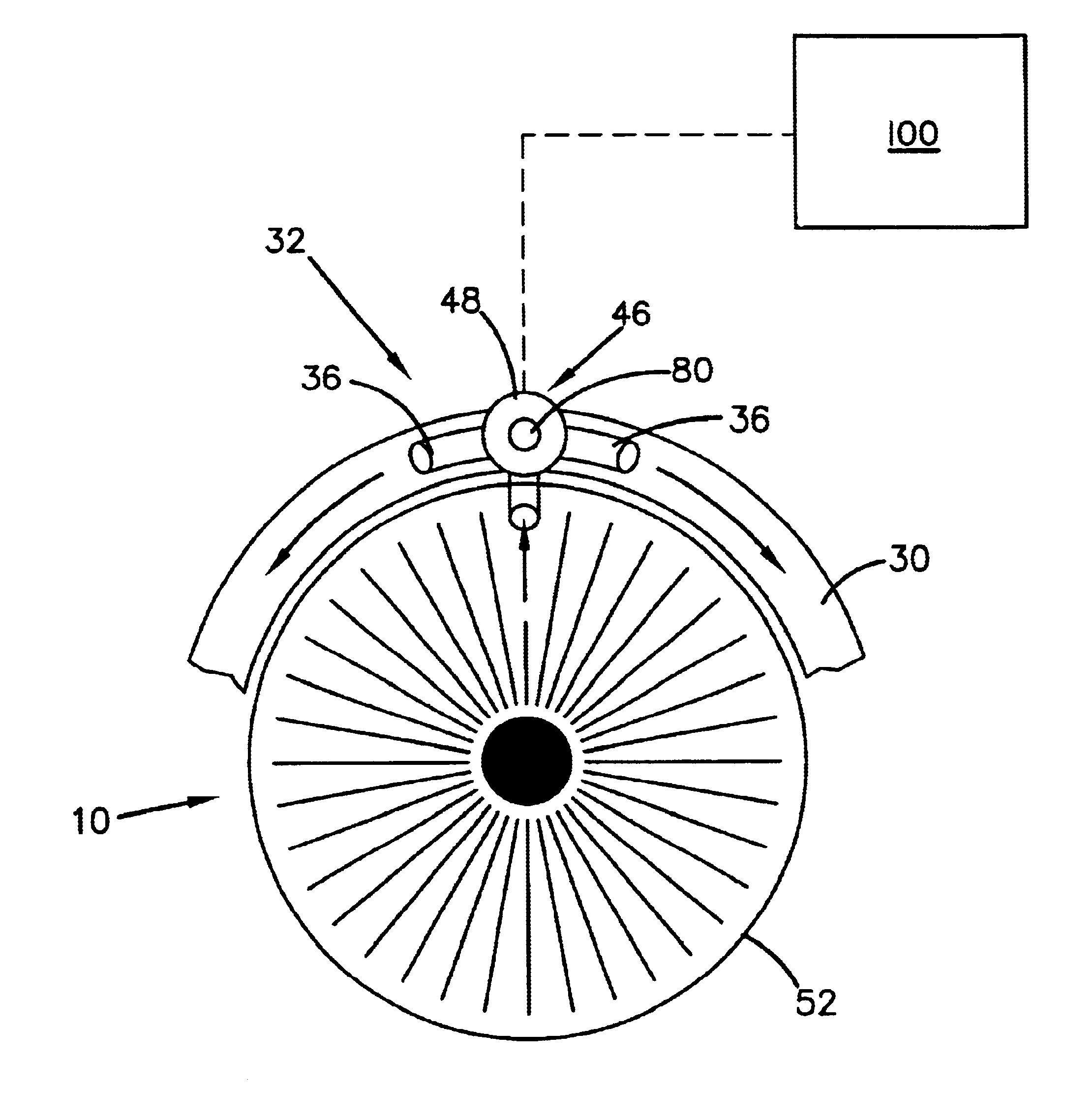
InactiveUS20060069340A1Reducing ocular hypertensionLaser surgeryEye implantsIntraocular pressureFlow diverter
A system is provided for reducing intraocular pressure, the system having: an implantable shunt, the implantable shunt with a planar member, at least one microchannel disposed within that planar member, and a laser whereby at least one fenestration may be introduced into the microchannel.
Owner:SOLX
Ocular implants with anchors and methods thereof
InactiveUS7431710B2Reduce morbidityAvoiding hypotonyOrganic active ingredientsEye surgerySchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
Intraocular stents and applicators are disclosed for treating glaucoma. The stents are configured to extend between the anterior chamber of the eye and Schlemm's canal for enhancing outflow of aqueous from the anterior chamber so as to reduce intraocular pressure. The stents can have features for anchoring the stent into Schlemm's canal as well as preventing the walls of Schlemm's canal from closing the outlet of the stents. The applicators can be steerable so as to make implantation easier. Additionally, the applicators can be configured to hold a plurality of stents so that multiple stents can be implanted through one incision without removing the applicator from the incision between serial implantations.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Devices and techniques for treating glaucoma
InactiveUS6989007B2Improve facilitiesGood mannersLaser surgeryDiagnosticsOpen angle glaucomaAqueous outflow
A system for non-invasive treatment of a patient's trabecular meshwork to treat primary open-angle glaucoma. The system and technique applies energy directly to media within clogged spaces in a patient's trabecular meshwork to increase aqueous outflow facility by (i) localization of microimplantable bodies carrying a selected exogenous chromophore, such as particles with a gold surface, in deeper regions of the trabecular meshwork, and (ii) irradiation of the microimplantables with a selected coherent wavelength having a power level and pulse duration that is strongly absorbed by the surfaces of the microimplantables.
Owner:OCCULOGIX CORP
Shunt and method treatment of glaucoma
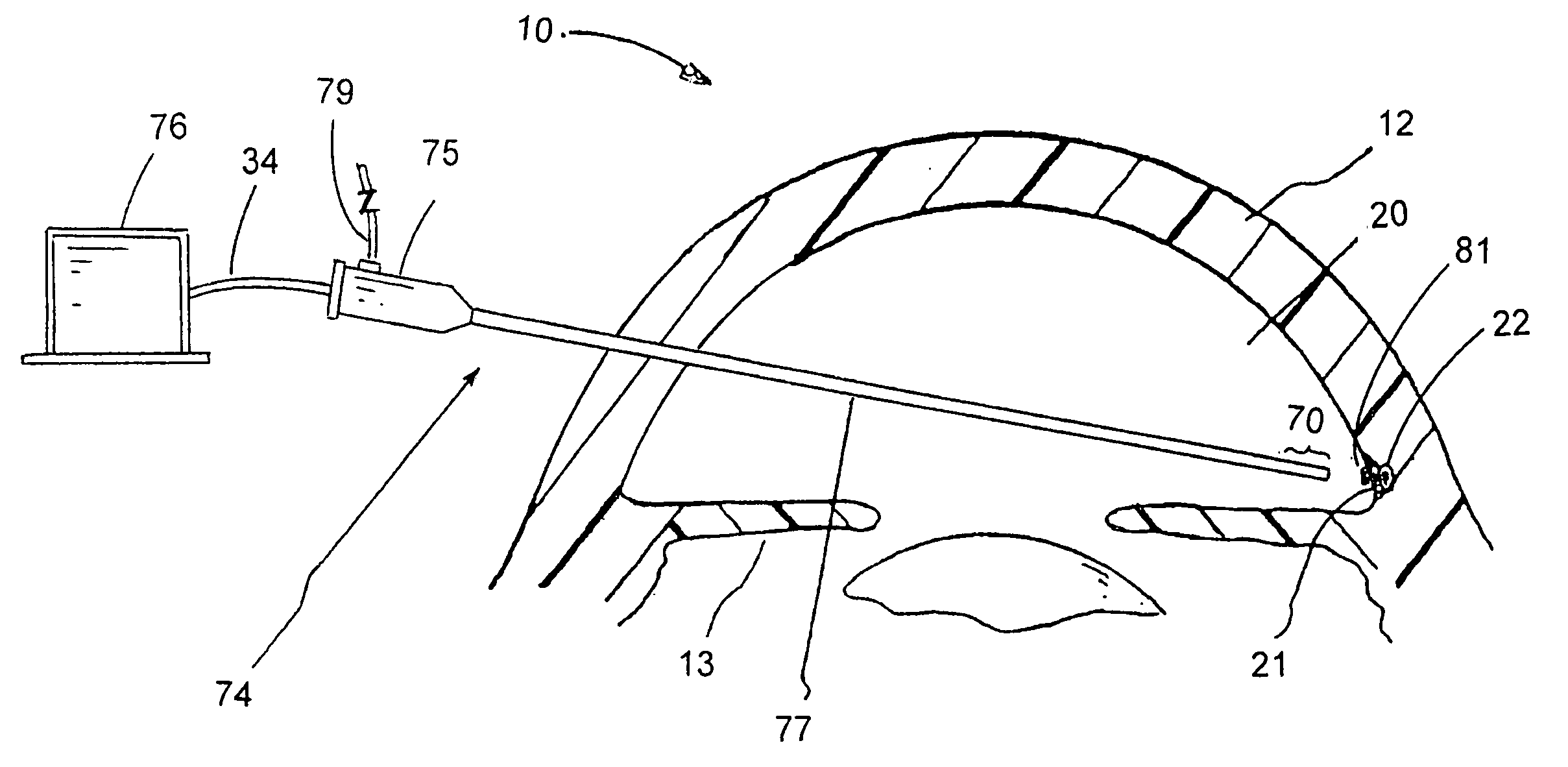
InactiveUS20050273033A1Avoid insufficient lengthEye surgeryWound drainsAqueous humorLeft frontal sinus
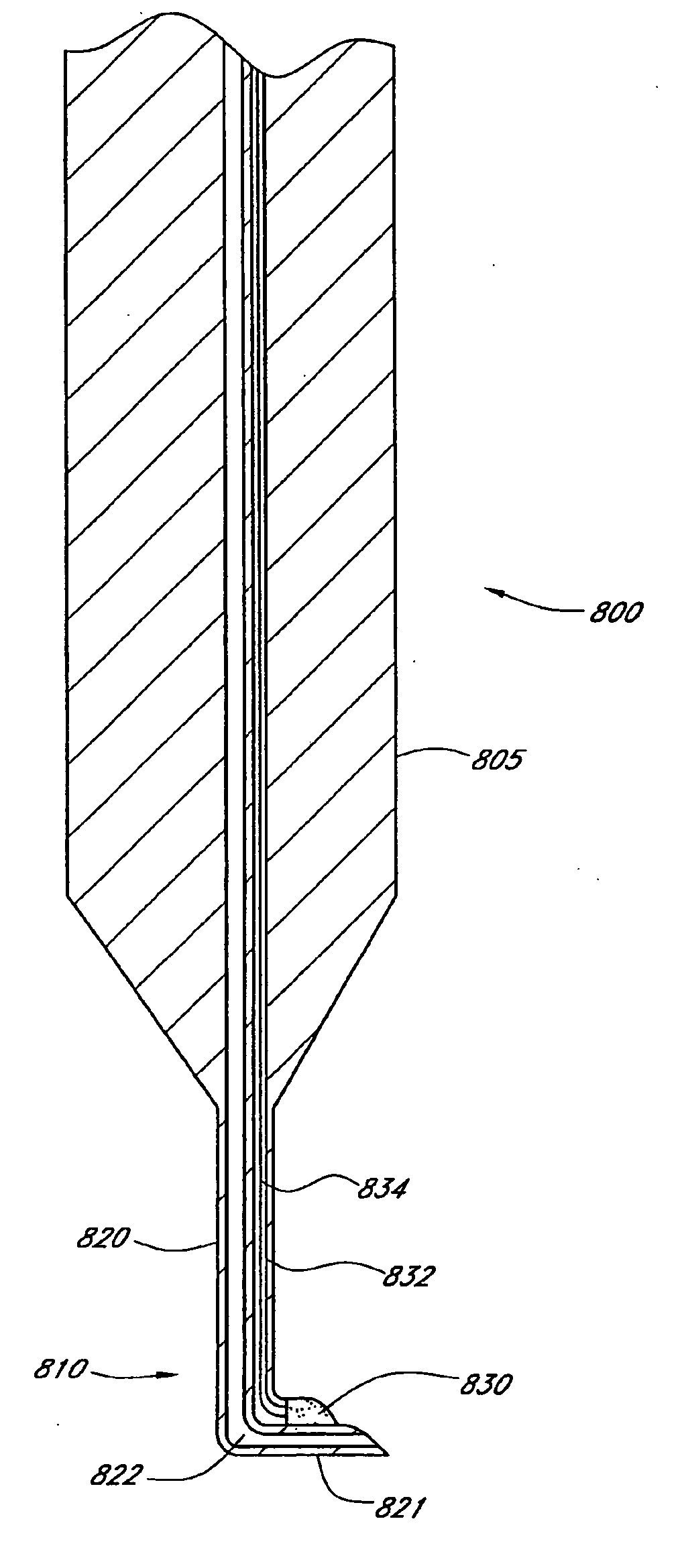
This invention provides a shunt for implantation between the anterior chamber of the eye and the epithelial-lined space through the frontal sinus bone of a patient for the treatment of glaucoma. The shunt includes a tube having a length sufficient to span the distance between the anterior chamber of the eye and the epithelial-lined space of the patient, the tube having an open anterior chamber end and a closed epithelial-lined space end, and a seal device associated with the tube between the anterior chamber and epithelial-lined space ends, for sealing a hole in the frontal sinus bone, and for anchoring the tube against movement from the frontal sinus bone. The shunt also includes a fluid pressure openable valve in the tube, located at or near the epithelial-lined space sinus end, allowing for controlled flow of aqueous humor through the tube when implanted. The invention also extends to a method of treating glaucoma in a patient by surgically implanting the shunt between the anterior chamber of the eye and the frontal sinus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Shunt for the treatment of glaucoma
A system is provided for reducing intraocular hypertension, the system having an implantable shunt, with a planar member having at least one microchannel disposed within the planar member. There is an inflow port disposed proximate to a first end of the microchannel and an outflow port disposed proximate to a second end of the microchannel. The inflow port is configured such that when the implantable shunt is implanted, the inflow port is located approximately within the region of an angle of an anterior chamber.
Owner:SOLX
Biodegradable glaucoma implant
InactiveUS20050288619A1Reduce morbidityAvoiding hypotonyEye surgeryIntravenous devicesSchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
A trabecular shunt and methods for treating glaucoma are disclosed. One of the methods comprises transporting fluid from the anterior chamber of an eye to Schlemm's canal through an implant, the implant extending between the anterior chamber and Schlemm's canal; sensing an intraocular pressure using a sensor incorporated into the implant; and transmitting a signal indicative of the sensed pressure to an external receiver.
Owner:GHARIB MORTEZA +2
Shunt device and method for treating glaucoma
InactiveUS20050119601A9Expand exportsFacilitates the normal physiologic pathwayEye surgeryMedical devicesShunt DeviceAqueous humor
The present invention provides a shunt for the flow of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber of the eye to Schlemm's canal. The device comprises at least one lumen and optionally has at least one anchor extending from the proximal portion within the anterior chamber to assist in placement and anchoring of the device in the correct anatomic position.
Owner:GMP VISION SOLUTIONS
Dual drainage pathway shunt device and method for treating glaucoma
A shunt is provided for the flow of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber of the eye to Schlemm's canal and to other anatomical spaces of the eye. The shunt comprises at least one lumen and optionally has at least one anchor extending from a proximal portion of the shunt to assist in placement and anchoring of the device in the correct anatomic position.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Devices and methods for glaucoma treatment
ActiveUS20070276316A1Reduce morbidityAvoiding hypotonyStentsEye surgerySchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
Intraocular stents and applicators are disclosed for treating glaucoma. The stents are configured to extend between the anterior chamber of the eye and Schlemm's canal for enhancing outflow of aqueous from the anterior chamber so as to reduce intraocular pressure. The stents can have features for anchoring the stent into Schlemm's canal as well as preventing the walls of Schlemm's canal from closing the outlet of the stents. The applicators can be steerable so as to make implantation easier. Additionally, the applicators can be configured to hold a plurality of stents so that multiple stents can be implanted through one incision without removing the applicator from the incision between serial implantations.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Method and apparatus for treatment of glaucoma
InactiveUS20020026200A1Slowing and stopping progressionLower eye pressureEar treatmentEye surgeryVeinAqueous humor
A new and improved method and apparatus for treating glaucoma is described herein. A device for directing aqueous humor from an anterior chamber to Schlemm's canal comprises a seton, and may further comprise a pump operatively connected to the seton. The seton conducts aqueous directly from the anterior chamber to Schlemm's canal so that it can drain directly into the aqueous veins leading to the venous circulation. The seton for lowering intraocular pressure of an associated eye comprises a first tube adapted to be inserted into an associated anterior chamber of the eye; and, two wing tubes extending from the first tube. The two wing tubes are adapted to be inserted into Schlemm's canal. The two wing tubes and the first tube form a substantially continuous passageway, such that aqueous humor flows from the anterior chamber into Schlemm's canal through the substantially continuous passageway.
Owner:SAVAGE JAMES A
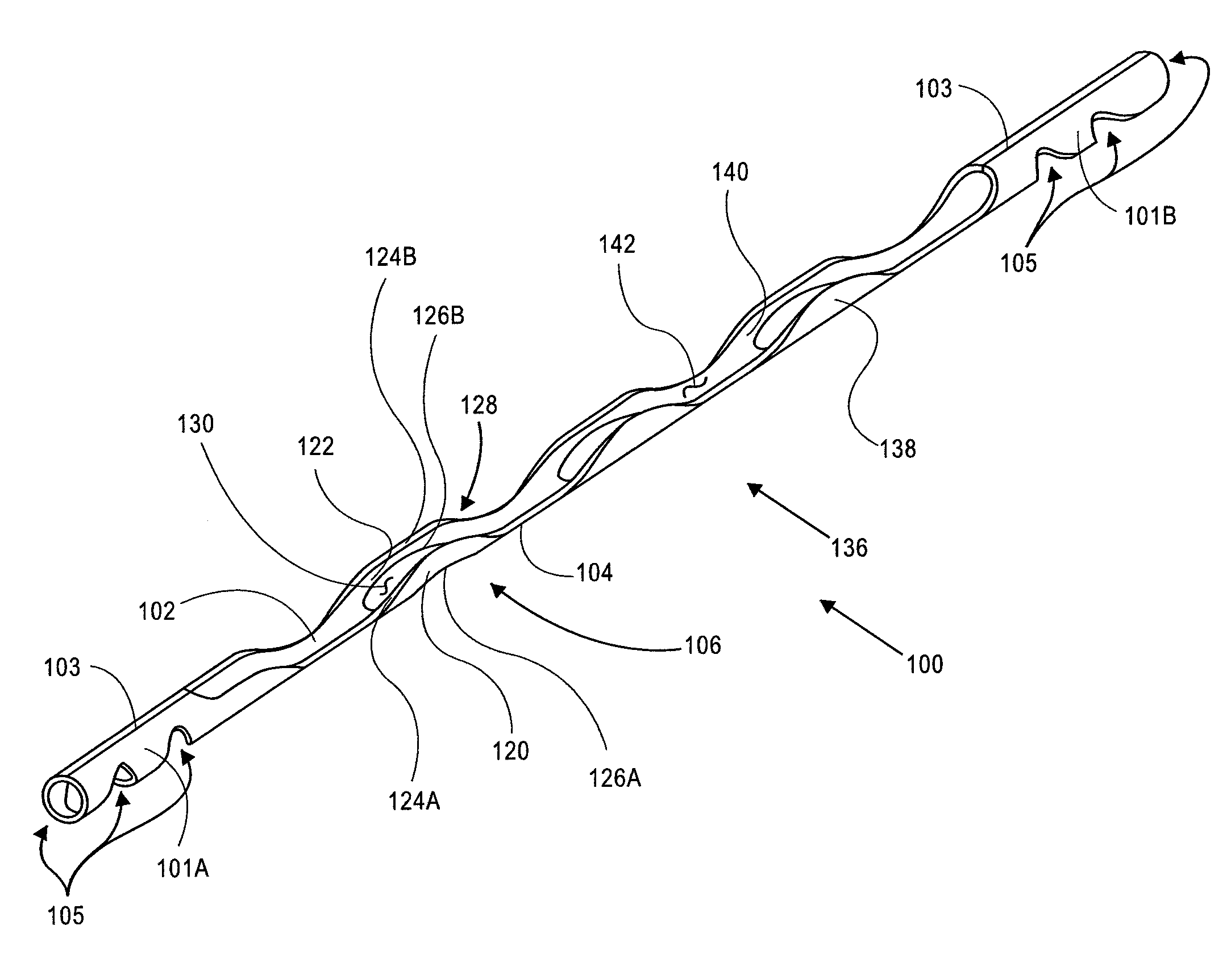
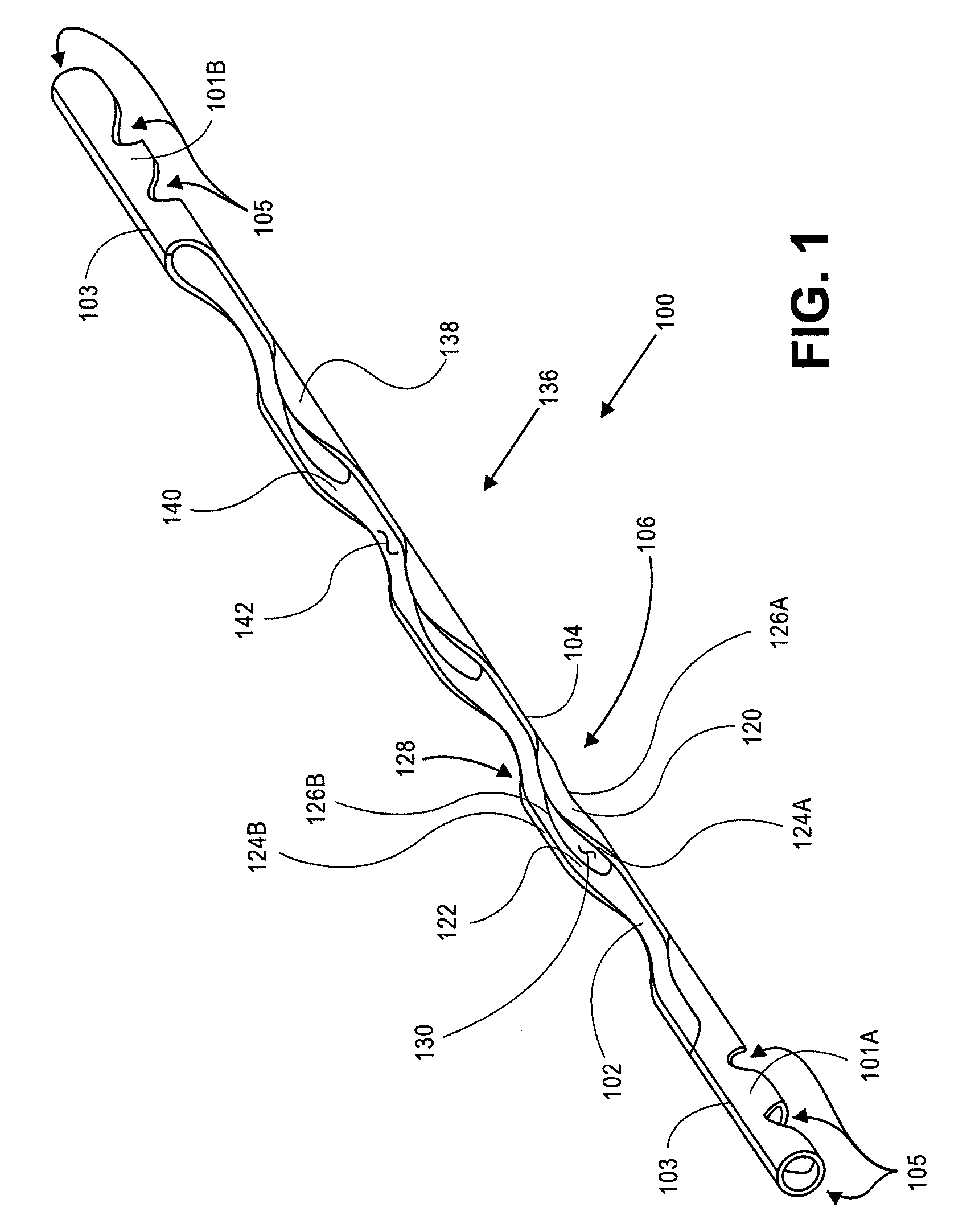
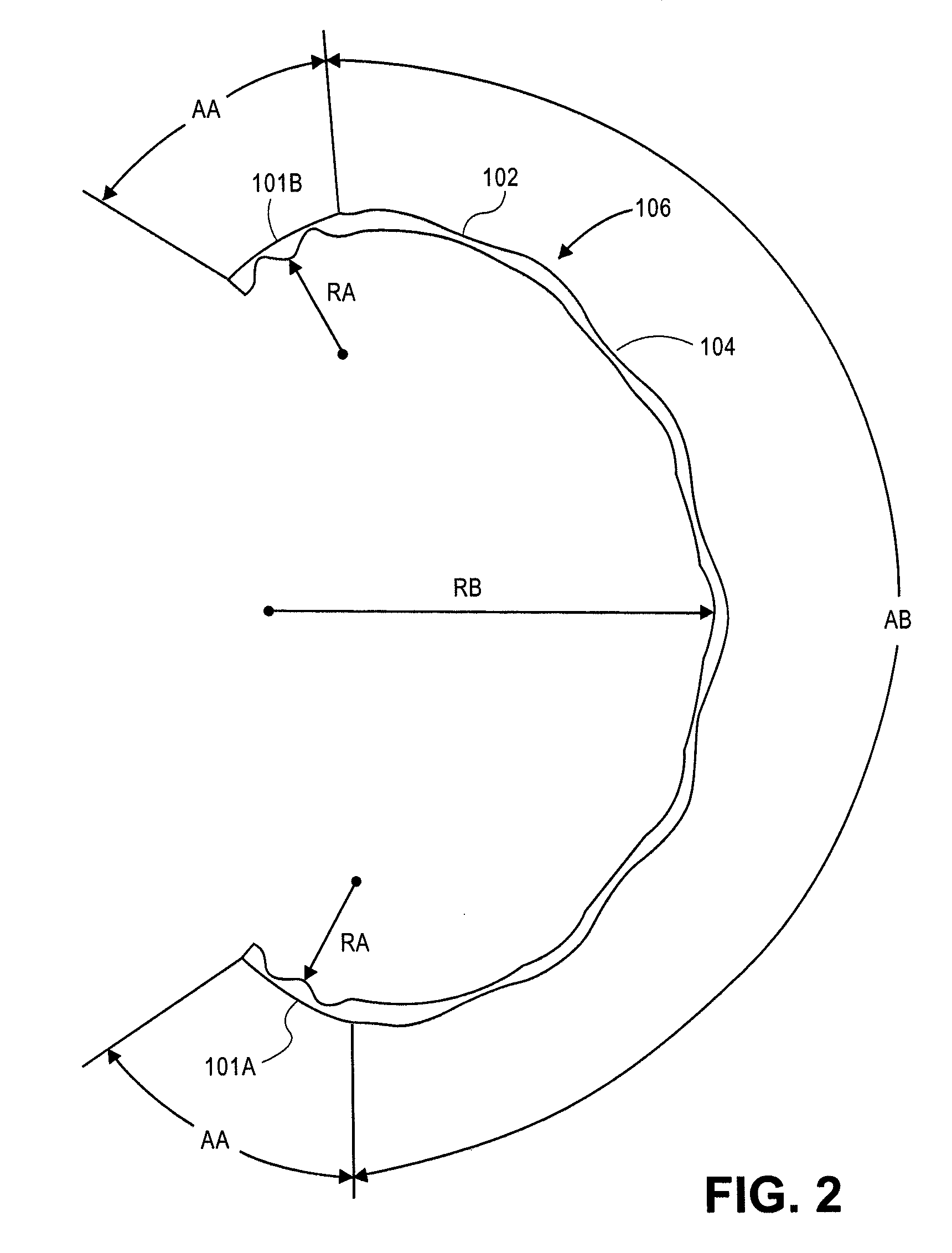
Fluid infusion methods for glaucoma treatment
InactiveUS20060116626A1Convenient treatmentReduce and inhibit and slow effectLaser surgeryEye implantsFluid infusionInsertion stent
Methods of treating glaucoma are disclosed, such as a method that includes inserting a stent through an incision in an eye; the stent having an inflow portion that is in fluid communication with an outflow portion of the stent; transporting the stent from the incision through the anterior chamber of the eye to an aqueous cavity of the eye, such that the inflow portion of the stent is positioned in the anterior chamber and the outflow portion of the stent is positioned at the aqueous cavity; and infusing fluid from the inflow portion to the outflow portion of the stent.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Device and methods useable for treatment of glaucoma and other surgical procedures
InactiveUS20060241580A1Not to damageAvoiding significant and irreparable damageEye surgerySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical departmentTissue protection
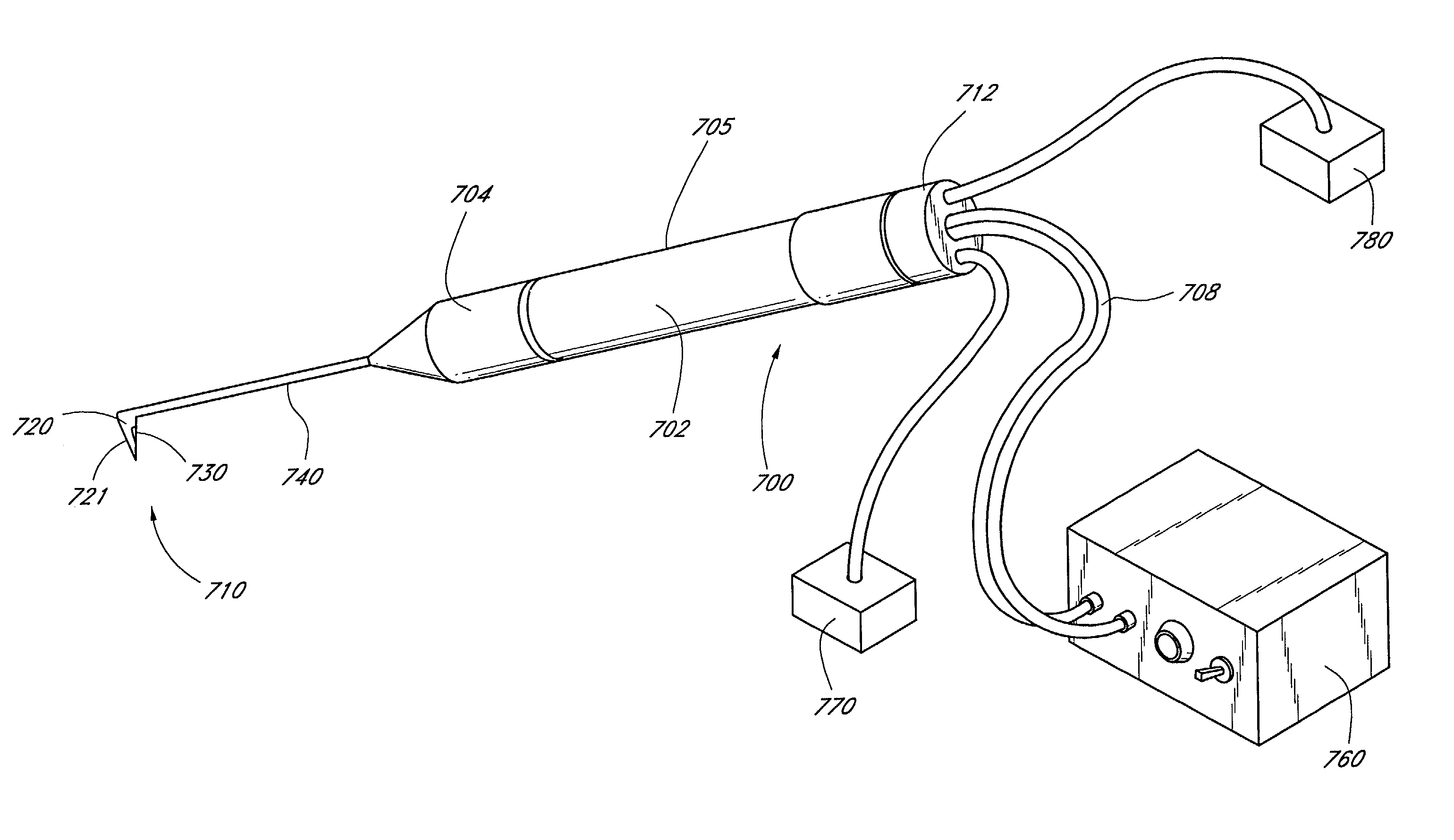
A device and method for cutting or ablating tissue in a human or veterinary patient includes an elongate probe having a distal end, a tissue cutting or ablating apparatus located adjacent within the distal end, and a tissue protector extending from the distal end. The protector generally has a first side and a second side and the tissue cutting or ablating apparatus is located adjacent to the first side thereof. The distal end is structured to be advanceable into tissue or otherwise placed and positioned within the patient's body such that tissue adjacent to the first side of the protector is cut away or ablated by the tissue cutting or ablation apparatus while tissue that is adjacent to the second side of the protector is not substantially damaged by the tissue cutting or ablating apparatus.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK +1
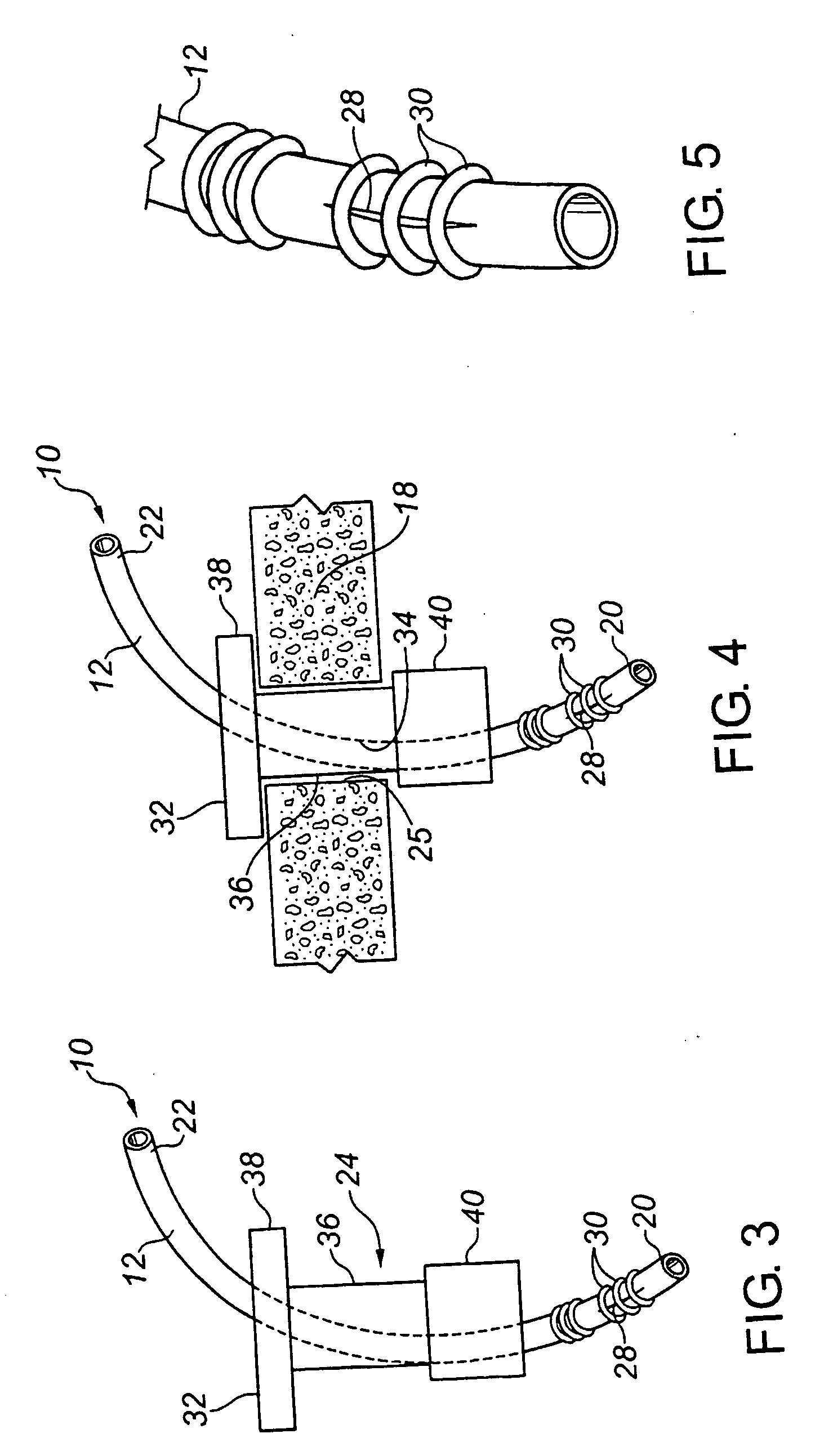
Apparatus and method for surgical bypass of aqueous humor
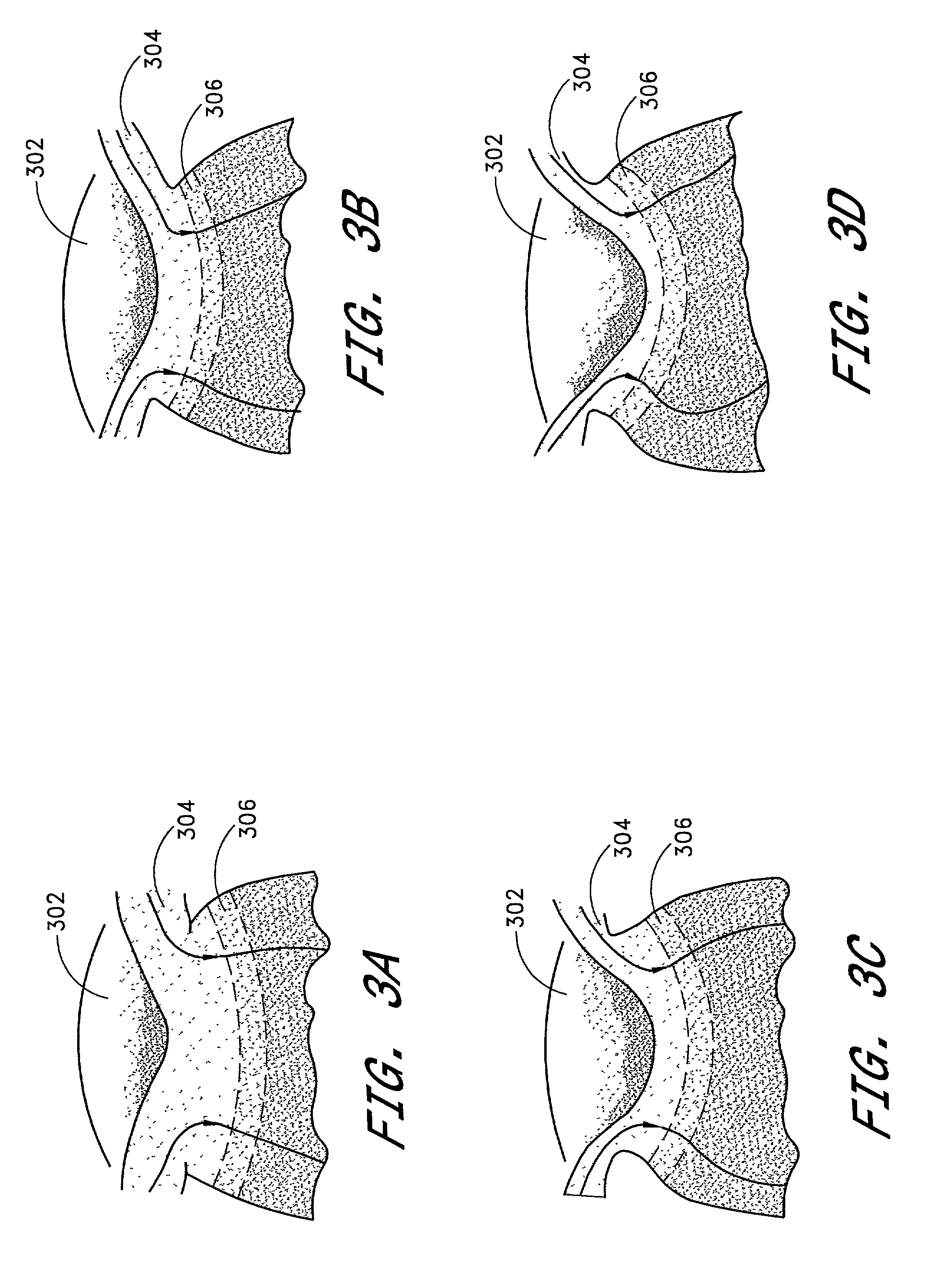
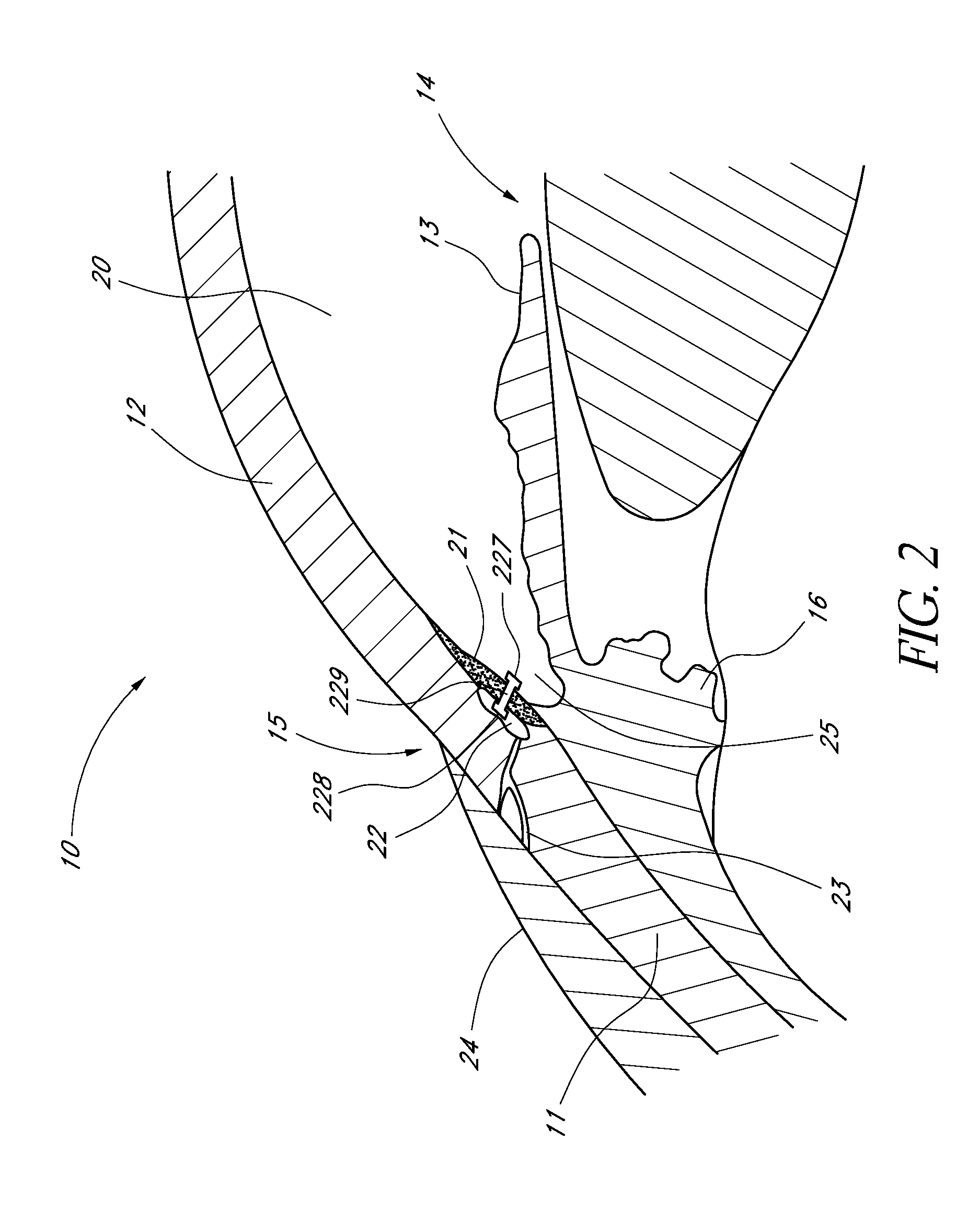
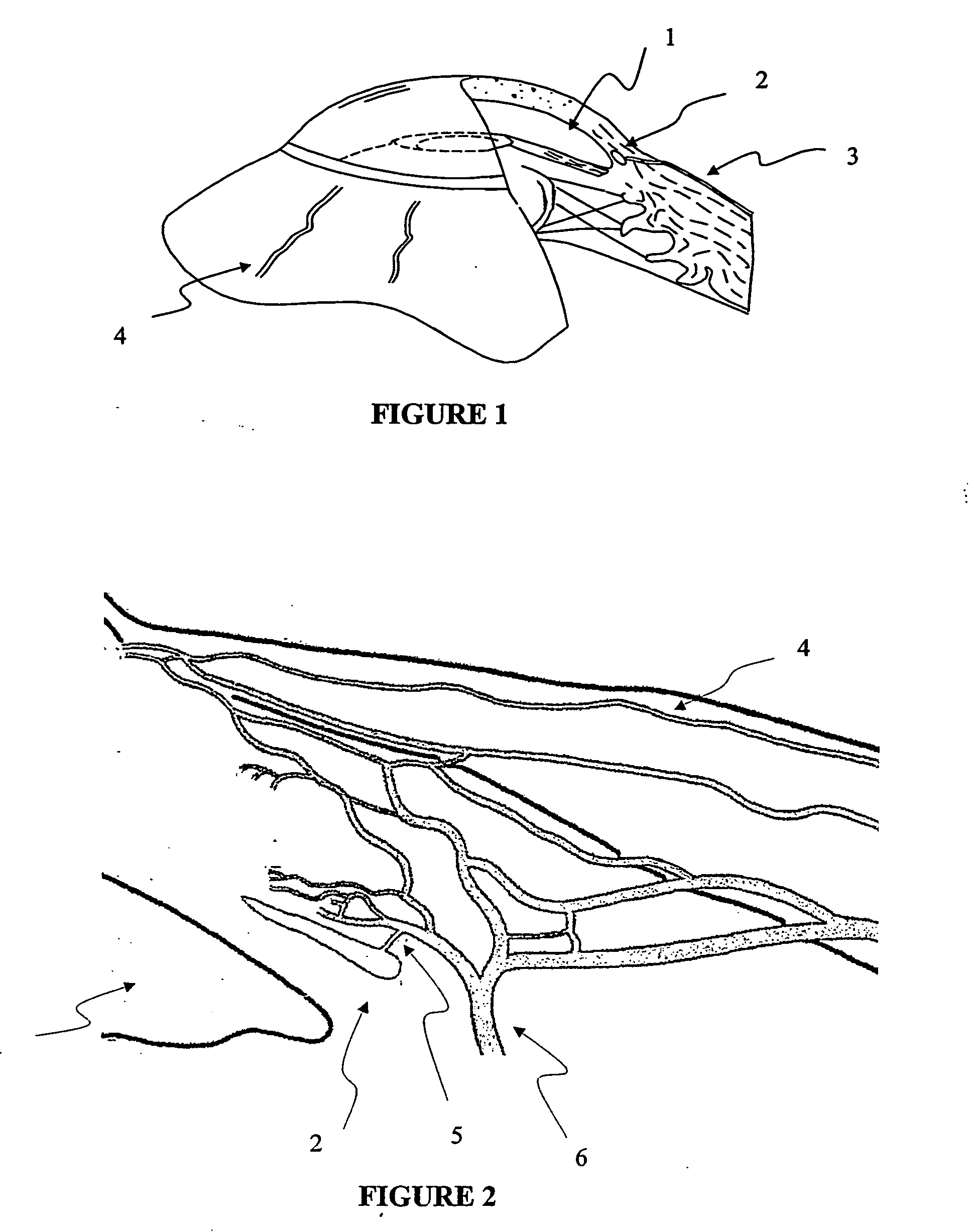
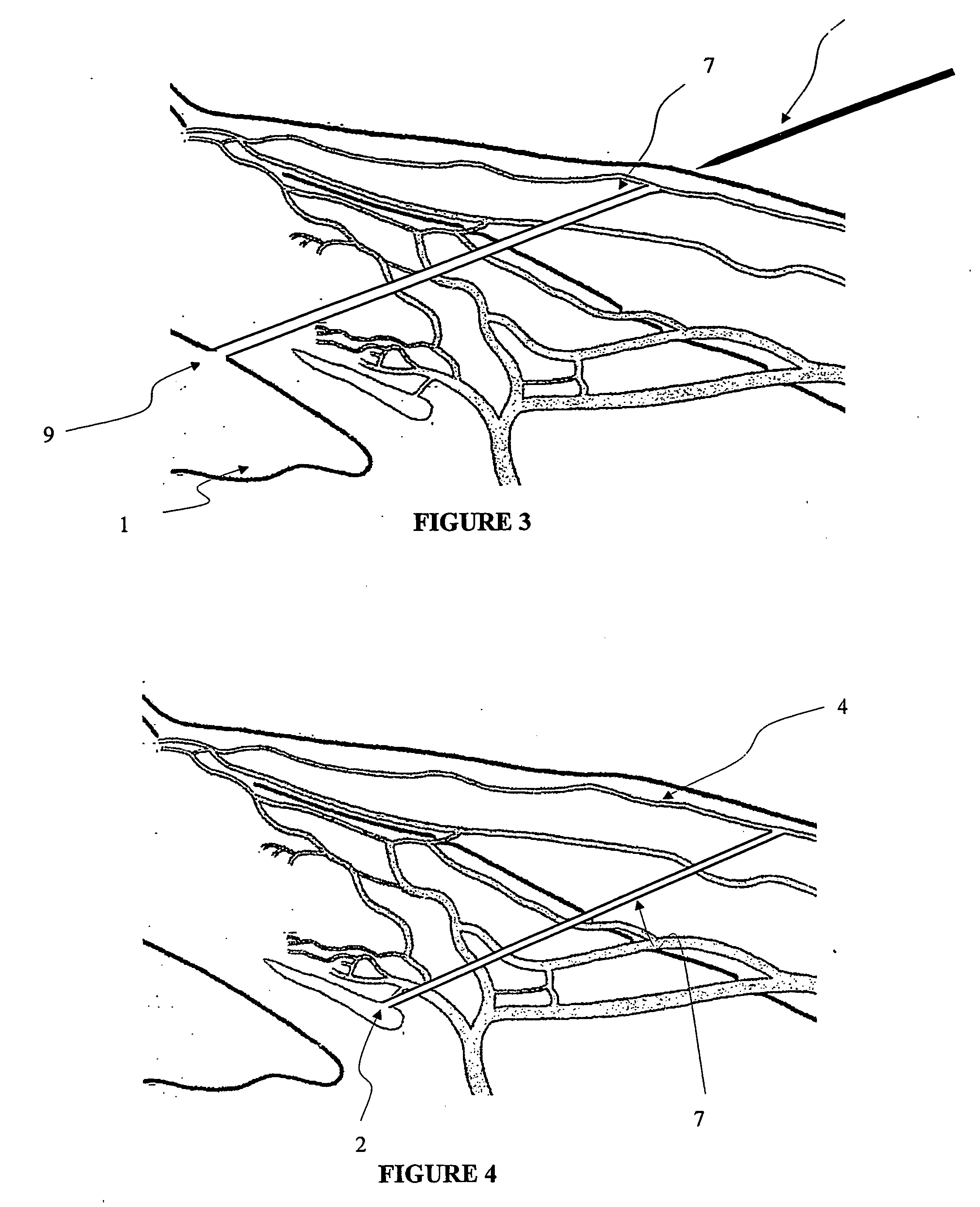
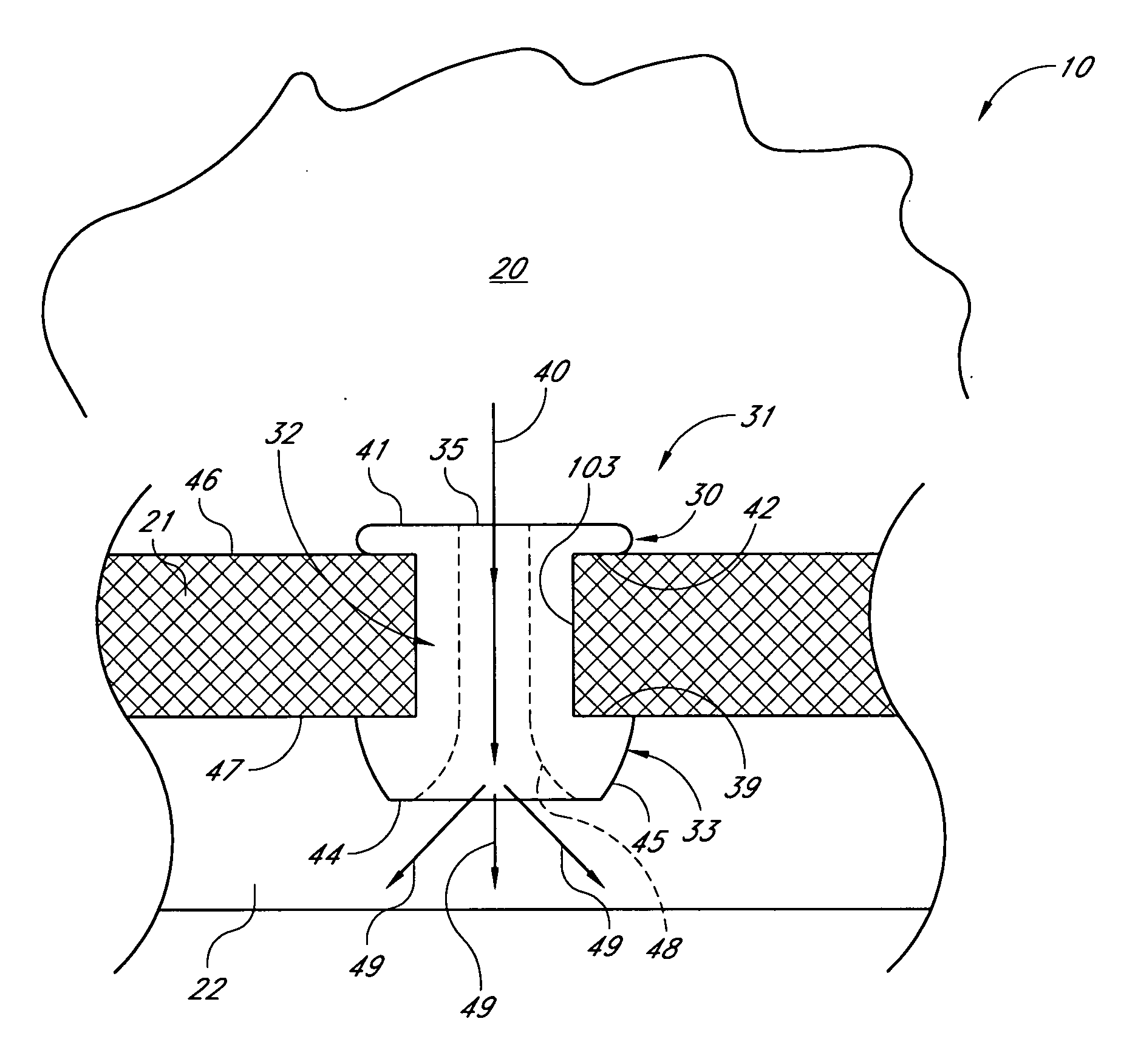
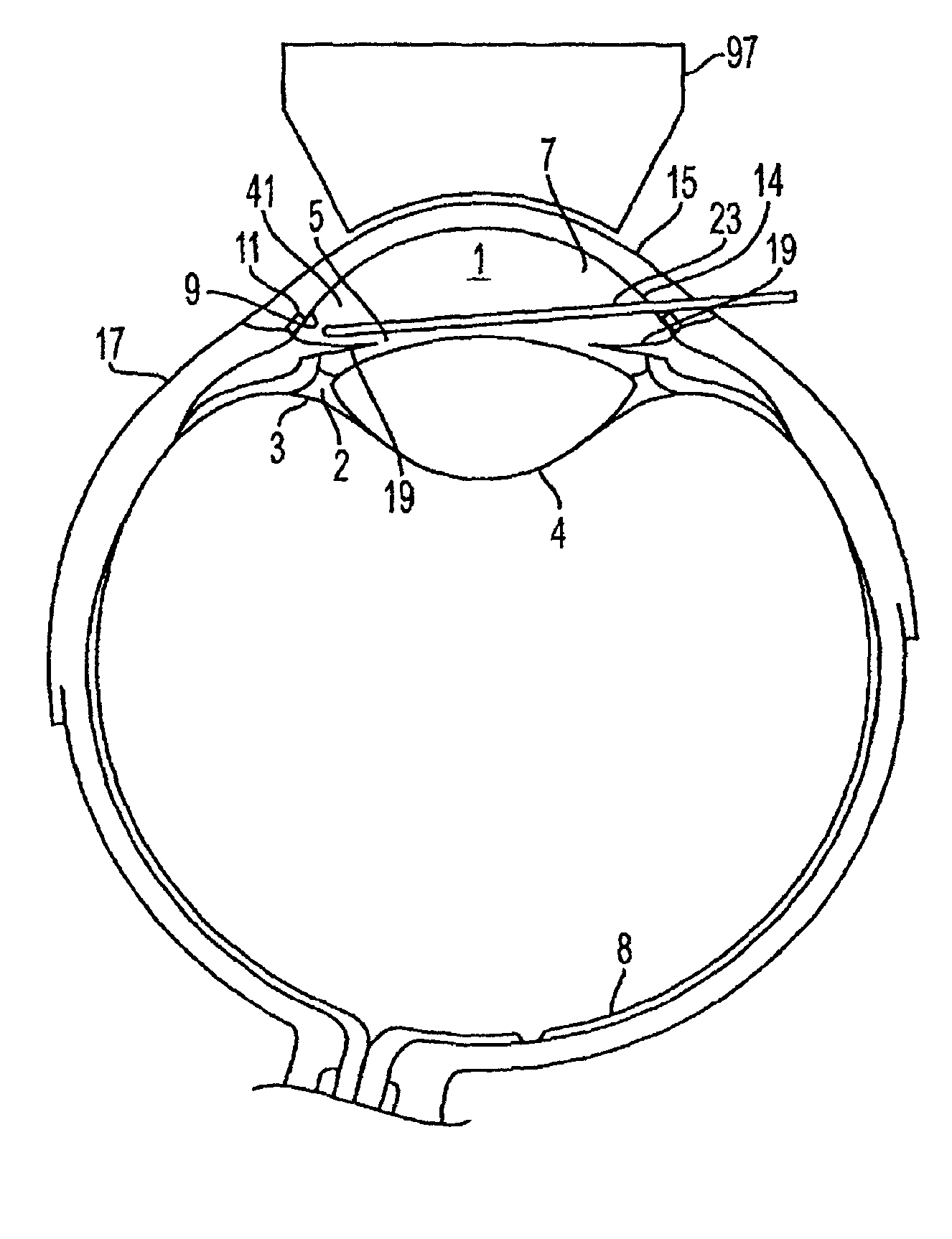
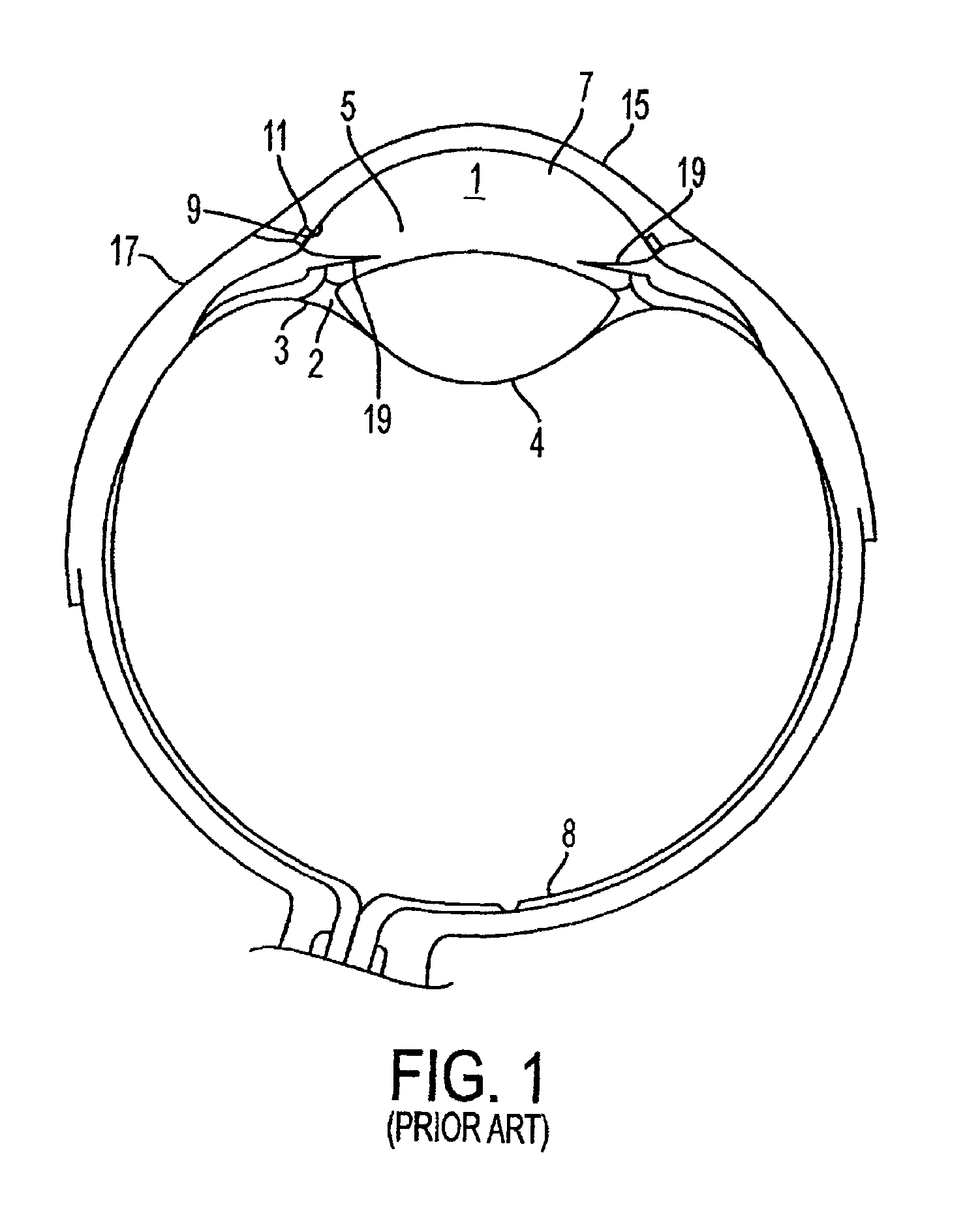
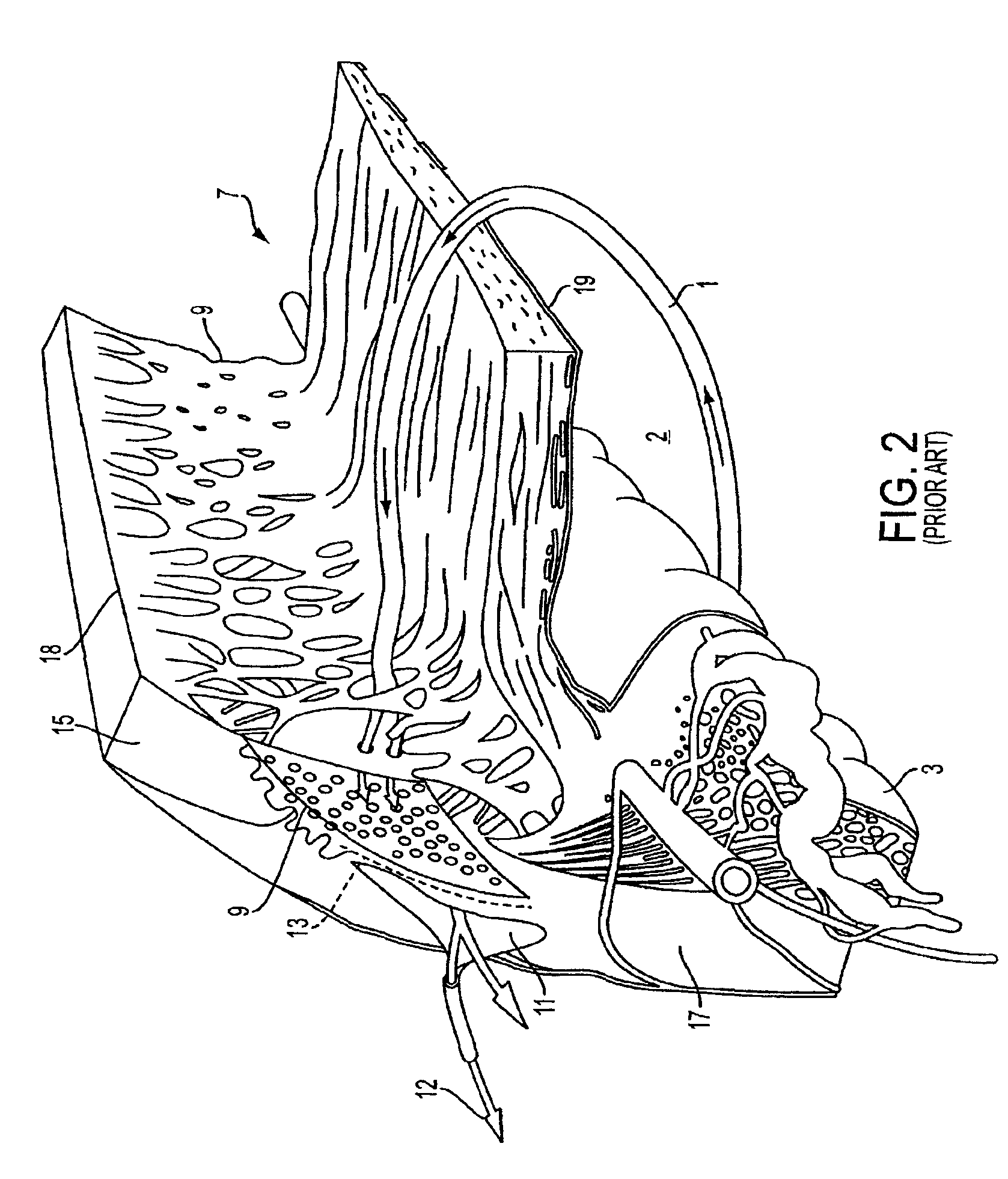
The invention provides minimally invasive microsurgical tools and methods to form an aqueous humor shunt or bypass for the treatment of glaucoma. The invention enables surgical creation of a tissue tract (7) within the tissues of the eye to directly connect a source of aqueous humor such as the anterior chamber (1), to an ocular vein (4). The tissue tract (7) from the vein (4) may be connected to any source of aqueous humor, including the anterior chamber (1), an aqueous collector channel, Schlemm's canal (2), or a drainage bleb. Since the aqueous humor passes directly into the venous system, the normal drainage process for aqueous humor is restored. Furthermore, the invention discloses devices and materials that can be implanted in the tissue tract to maintain the tissue space and fluid flow.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
Glaucoma stent system
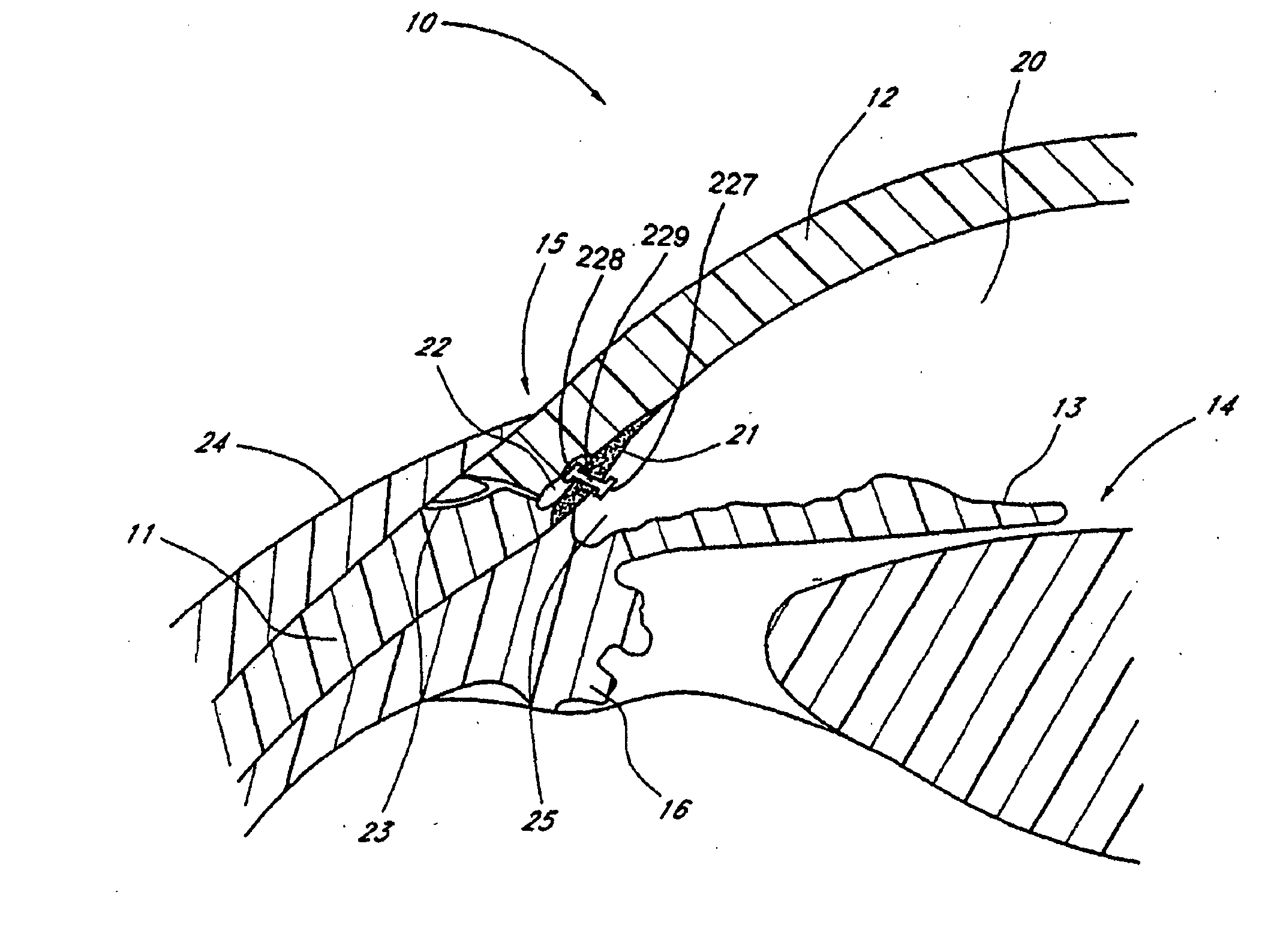
Surgical methods and related medical devices for treating glaucoma are disclosed. The method comprises trabecular bypass surgery, which involves bypassing diseased trabecular meshwork with the use of a stent implant. The stent implant is inserted into an opening created in the trabecular meshwork by a piercing member that is slidably advanceable through the lumen of the stent implant for supporting the implant insertion. The stent implant is positioned through the trabecular meshwork so that an inlet end of the stent implant is exposed to the anterior chamber of the eye and an outlet end is positioned into fluid collection channels at about an exterior surface of the trabecular meshwork or up to the level of aqueous veins.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Glaucoma surgery methods and systems
InactiveUS20080082078A1Reducing collateral tissue damageObviating benefitLaser surgeryElectrotherapyAqueous flowSchlemm's canal
Methods and systems are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Some embodiments described apparatus and methods useful in photoablation of tissues. In some embodiments, a photoablation apparatus is used to perforate a tissue, forming an aperture into a space behind the tissue. Gases formed during a photoablation process can be used to pressurize the space behind the tissue to enhance patency of the space. In some embodiments the tissue is the trabecular meshwork of the eye and a wall of Schlemm's canal, and the space behind the tissue is a portion of the lumen of Schlemm's canal. In some embodiments, the method is useful in the treatment of glaucoma by improving outflow from the anterior chamber of the eye into Schlemm's canal, reducing intraocular pressure.
Owner:BERLIN MICHAEL S
Devices and methods for glaucoma treatment
InactiveUS20070276315A1Reduce morbidityAvoiding hypotonyStentsEar treatmentSchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
Intraocular stents and applicators are disclosed for treating glaucoma. The stents are configured to extend between the anterior chamber of the eye and Schlemm's canal for enhancing outflow of aqueous from the anterior chamber so as to reduce intraocular pressure. The stents can have features for anchoring the stent into Schlemm's canal as well as preventing the walls of Schlemm's canal from closing the outlet of the stents. The applicators can be steerable so as to make implantation easier. Additionally, the applicators can be configured to hold a plurality of stents so that multiple stents can be implanted through one incision without removing the applicator from the incision between serial implantations.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Methods and apparatus for treating glaucoma
ActiveUS8267882B2Reduce the possibilityImprove fluid flowLaser surgeryEar treatmentSchlemm's canalOcular implant
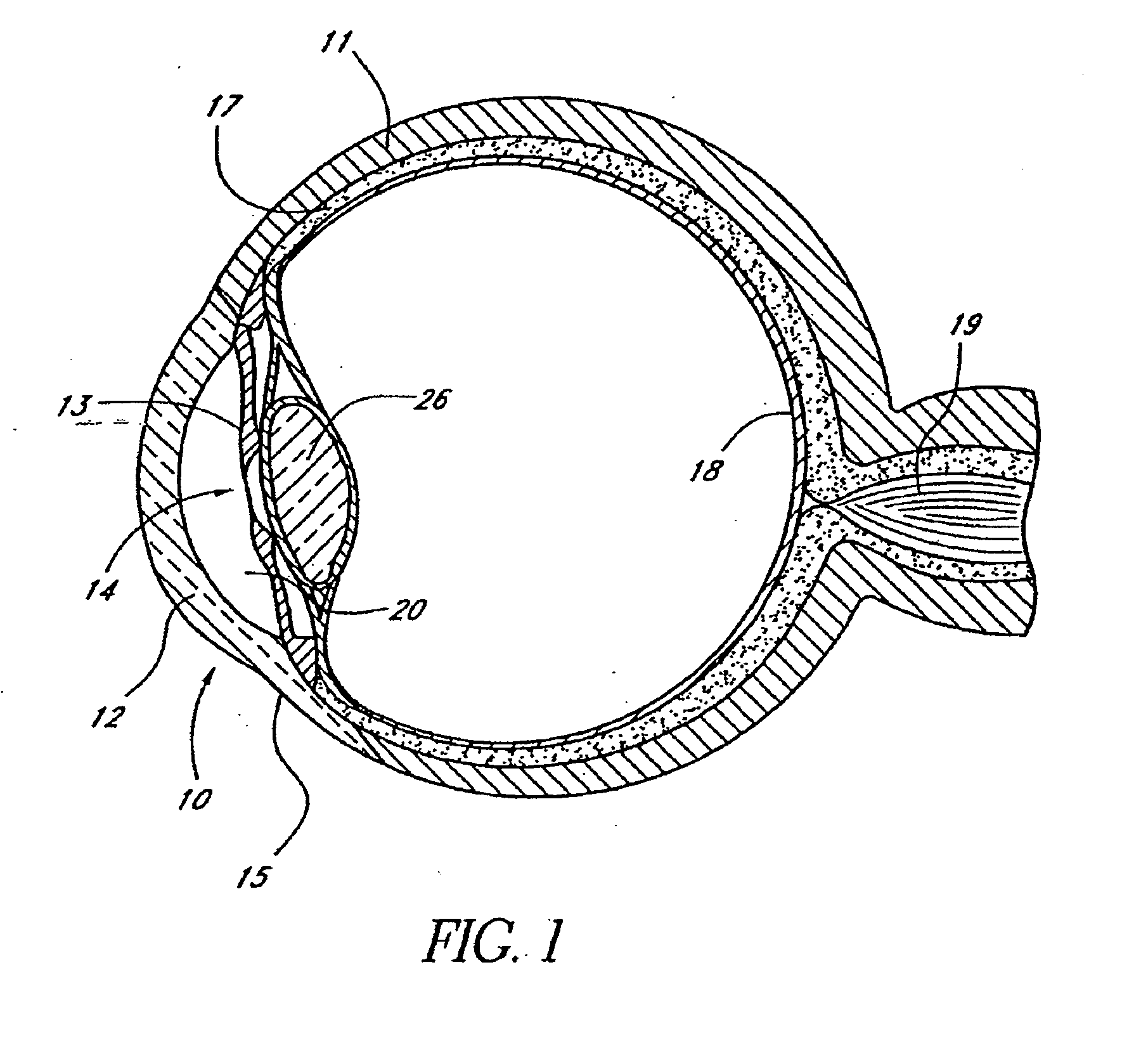
An ocular implant for treating glaucoma is provided, which may include any number of features. More particularly, the present invention relates to implants that facilitate the transfer of fluid from within one area of the eye to another area of the eye. One feature of the implant is that it includes a proximal inlet portion and a distal inlet portion adapted to be inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye, and an intermediate portion adapted to be inserted into Schlemm's canal. Another feature of the implant is that it can be biased to assume a predetermined shape to aid in placement within the eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Devices and techniques for light-mediated stimulation of trabecular meshwork in glaucoma therapy
An apparatus and technique for transscleral light-mediated biostimulation of the trabecular plates of a patient's eye in a treatment for glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The apparatus includes; (i) a working end geometry for contacting the anterior surface of the sclera and cornea to insure that a laser emission reaches the trabecular meshwork from a particular location on the anterior surface of the sclera, (ii) a laser energy source providing a wavelength appropriate for absorption beneath the anterior scleral surface to the depth of the trabecular plates, and (iii) a dosimetry control system for controlling the exposure of the laser emission at the particular spatial locations. The device uses a light energy source that emits wavelengths in the near-infrared portion of the spectrum, preferably in the range of about 1.30 mum to 1.40 mum or from about 1.55 mum to 1.85 mum. The depth of absorption of such wavelength ranges will extend through most, if not all, of the thickness of the sclera (750 mum to 950 mum). In accordance with a proposed method of trabecular biostimulation, the targeted region is elevated in temperature to a range between about 40° C. to 55° C. for a period of time ranging from about 1 second to 120 seconds or more.
Owner:SOLX
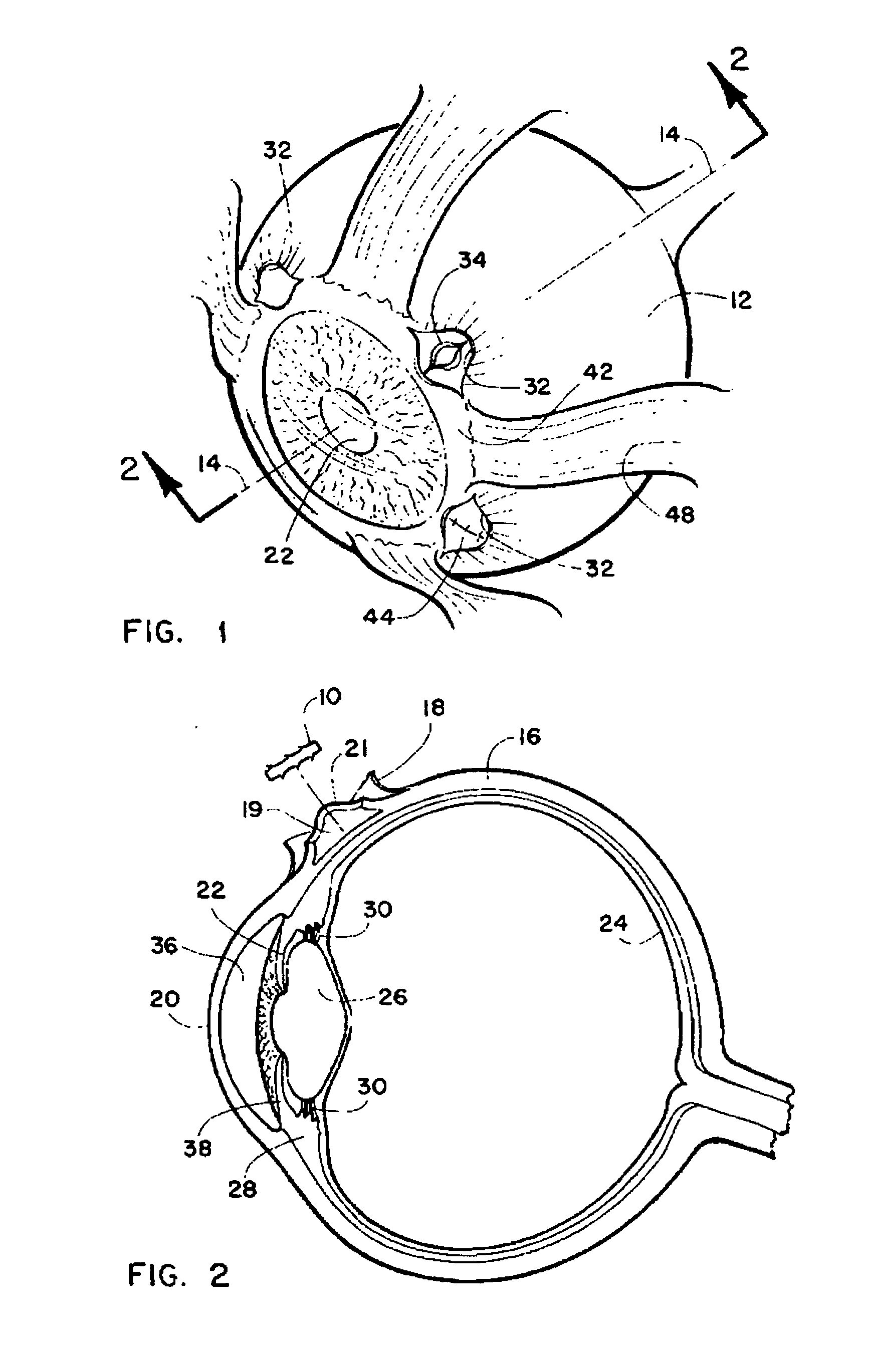
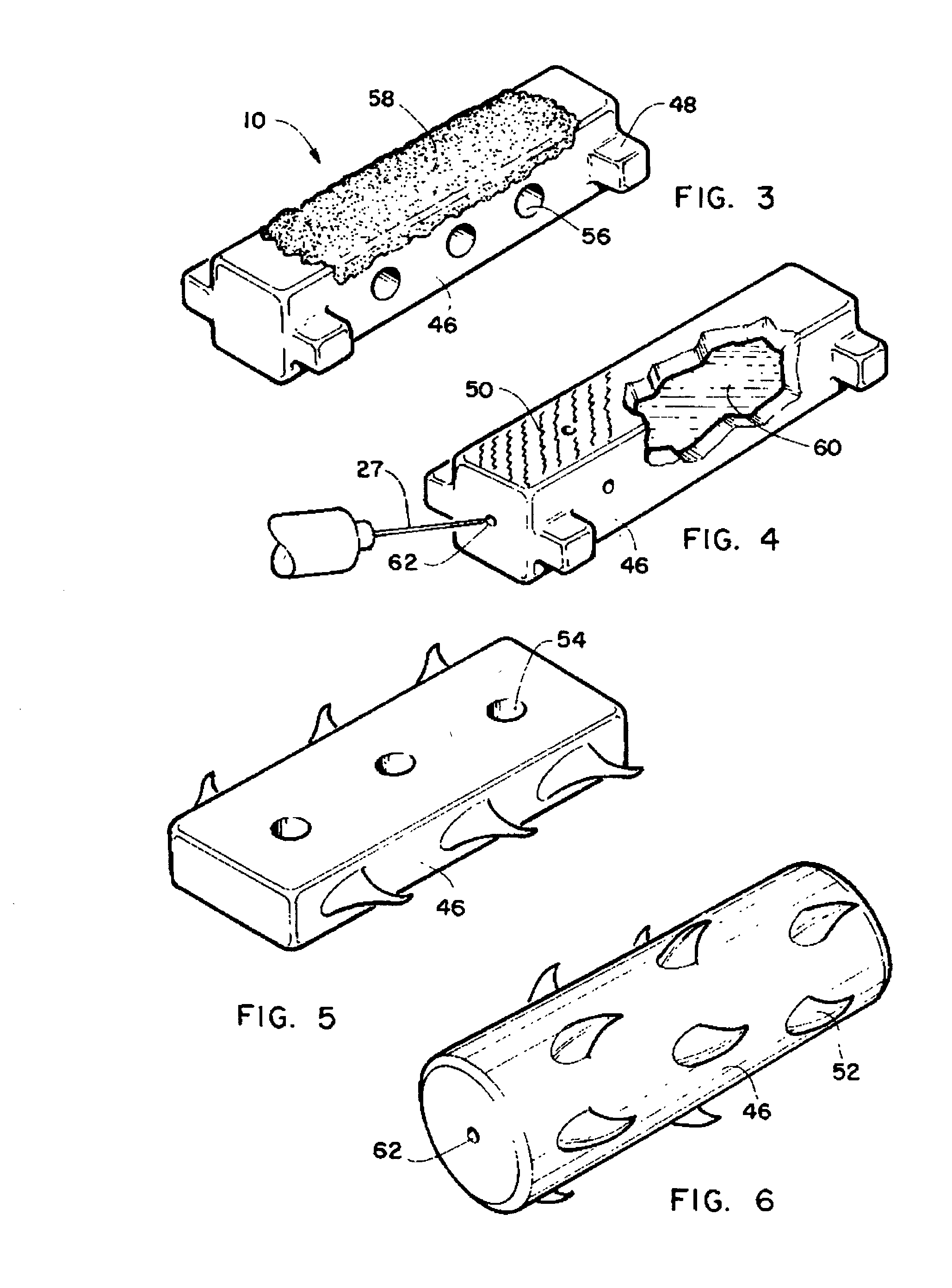
Method and intra sclera implant for treatment of glaucoma and presbyopia
An intra scleral implant and method of implantation for use in the treatment of intraocular pressure and presbyopia. The implant features a body portion and protrusions from the body portion to anchor the device in a cavity formed in the scleral wall of the eye. Optionally a drug delivery function is provided to allow long term communication of drugs to tissue surrounding the implant.
Owner:GLAUCOMA RES TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com