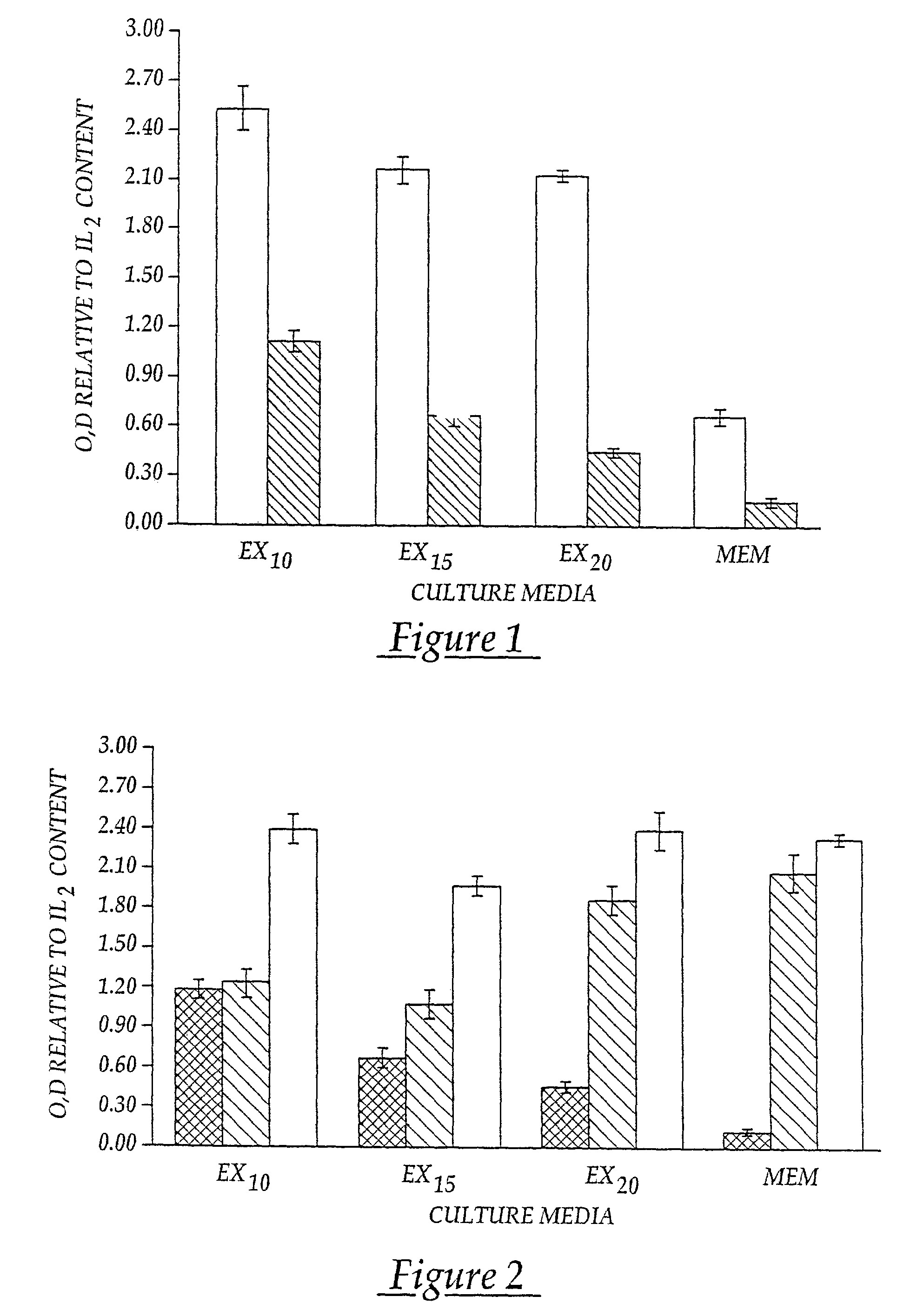
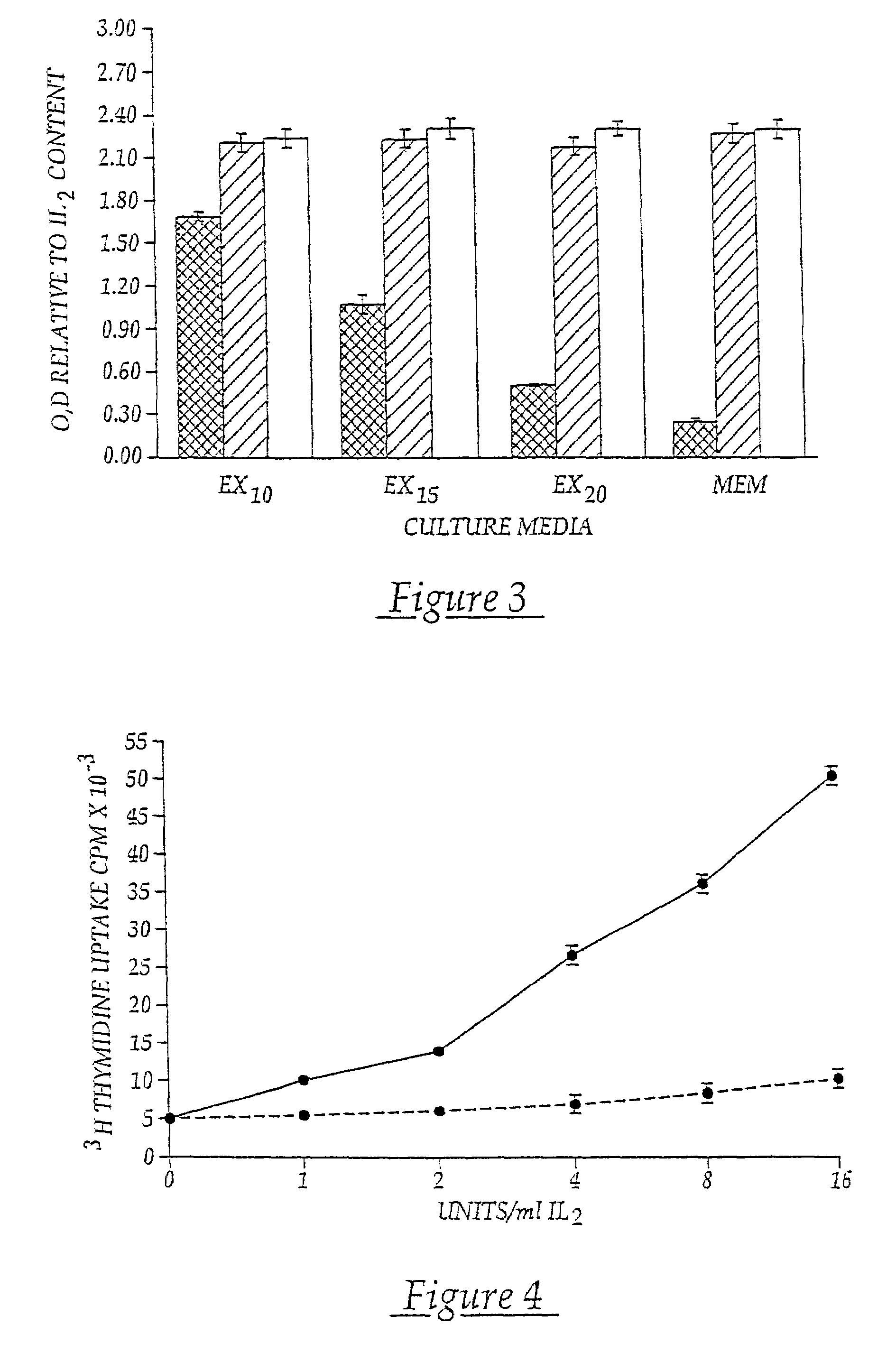
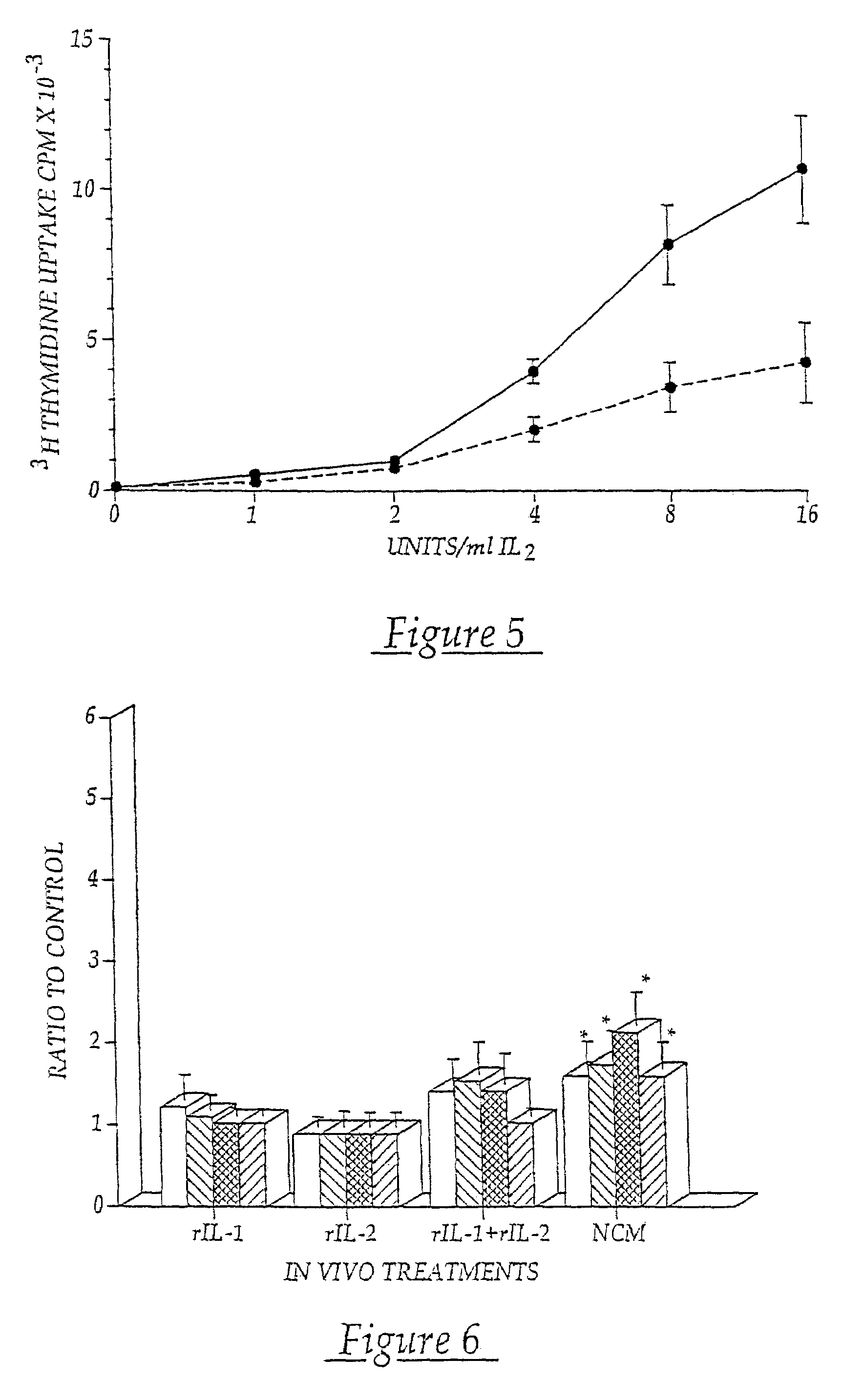
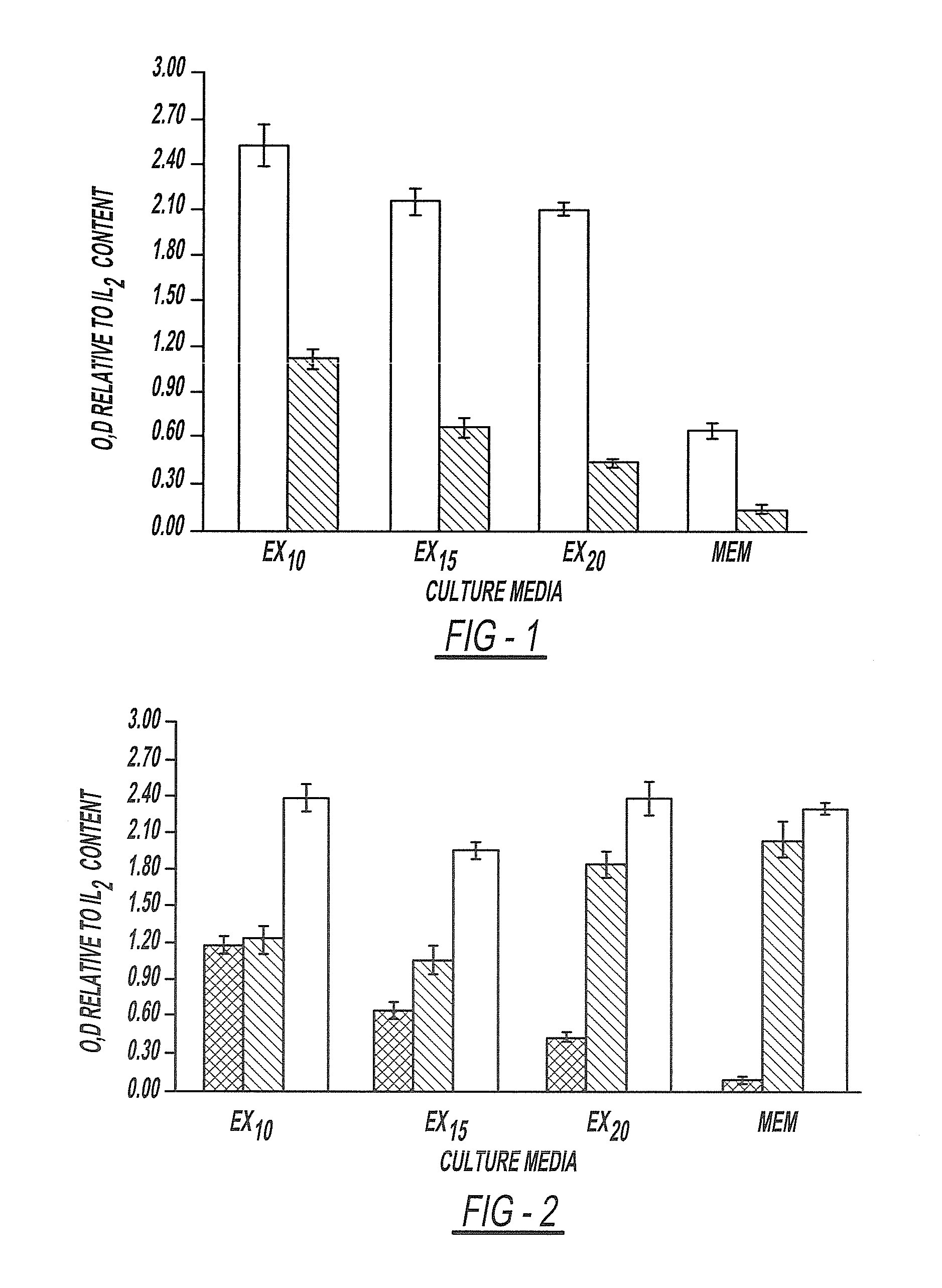
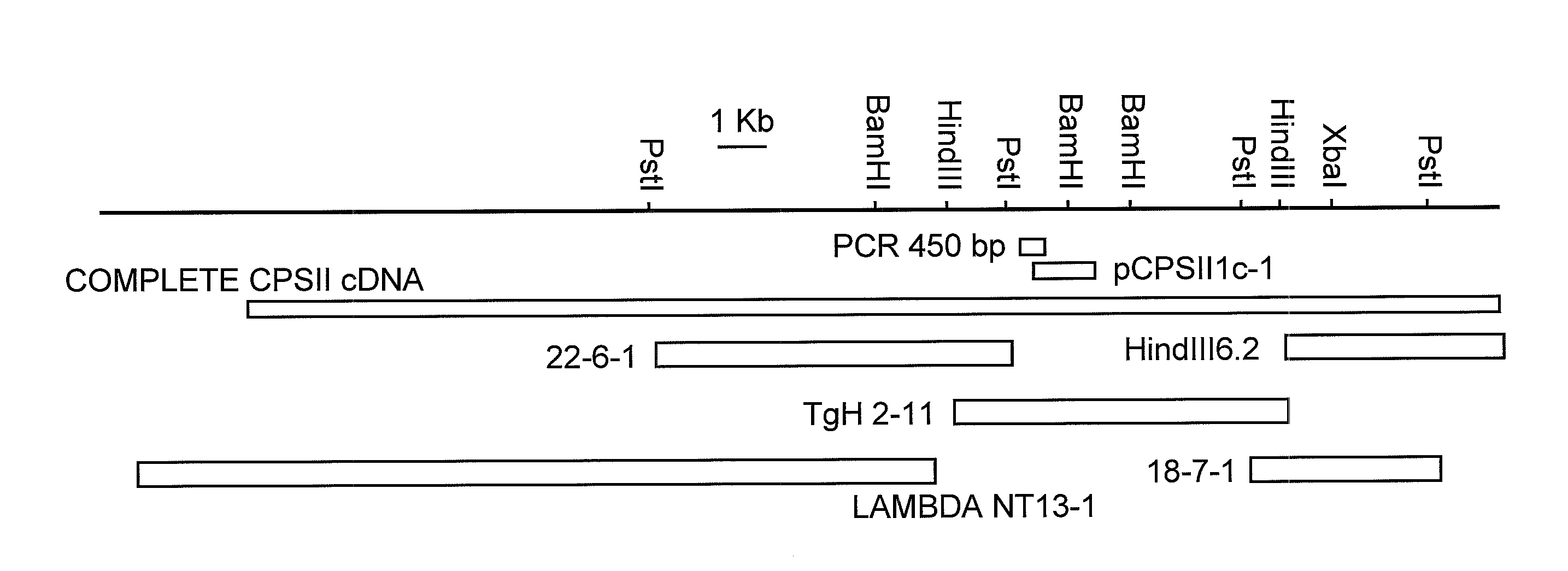
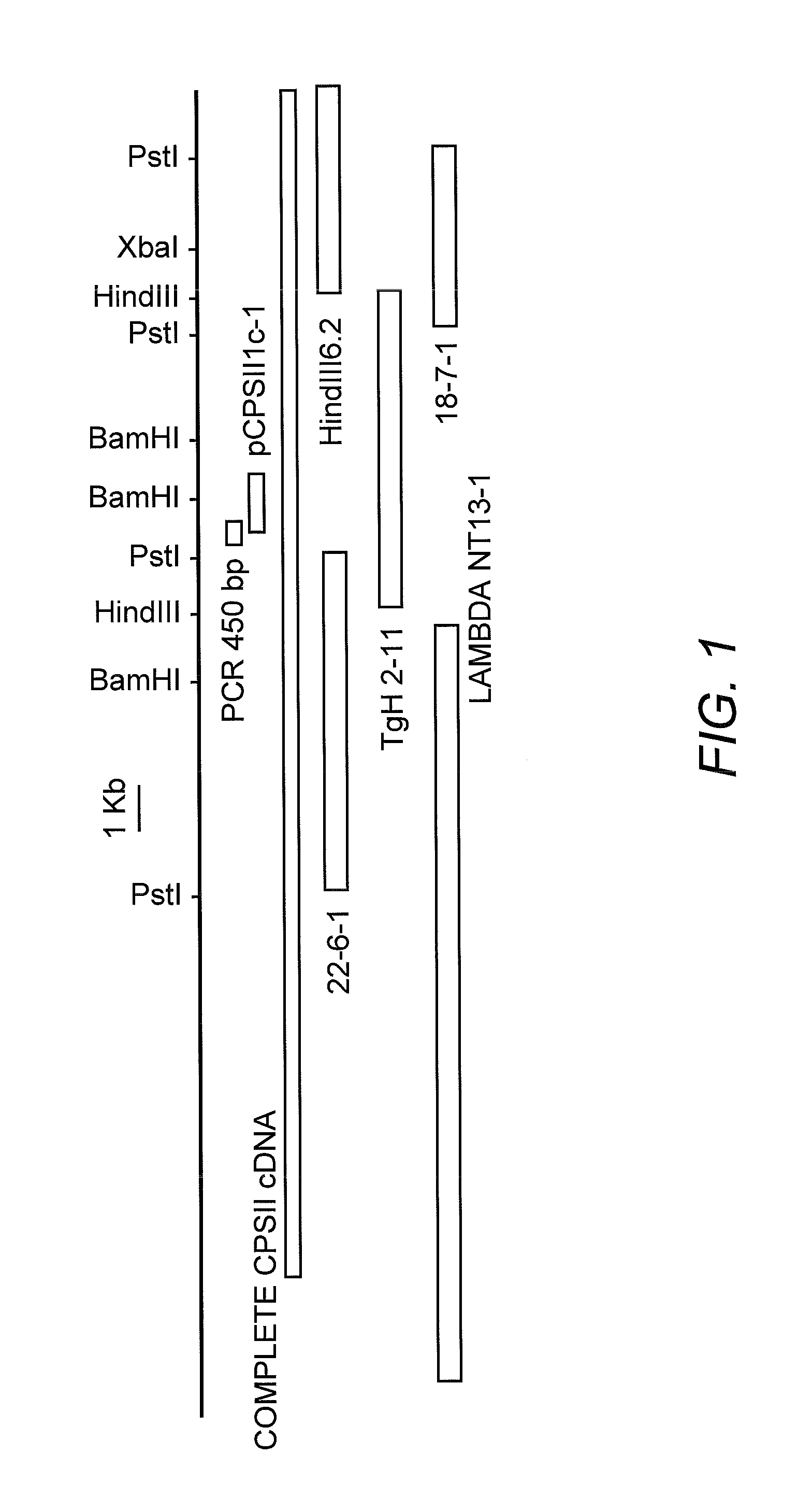
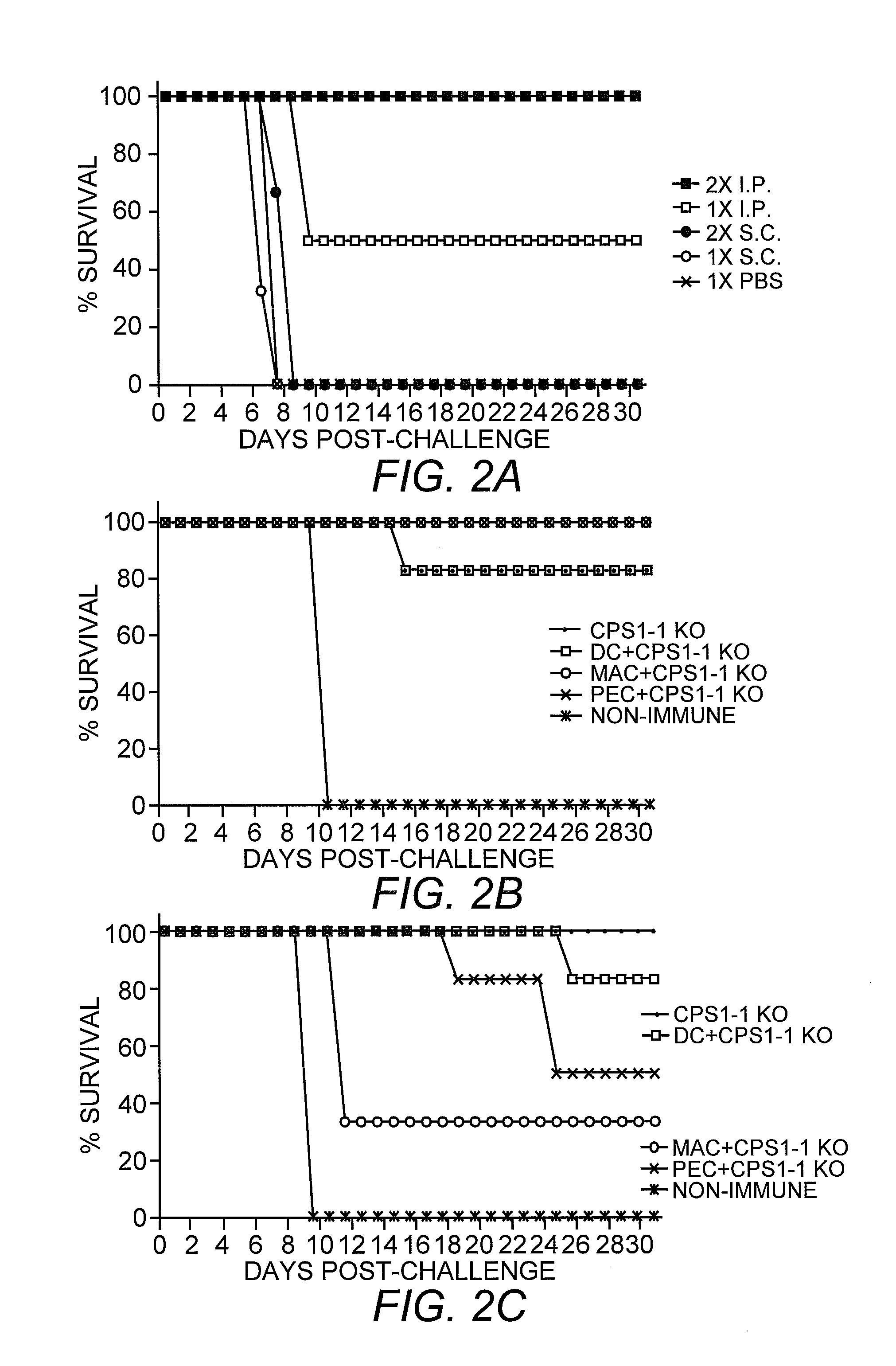
Patents
Literature
85 results about "Exogenous antigen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exogenous antigen. Definition. noun. Antigen that enters the body of the organism from the outside, e.g. through inhalation, ingestion, or injection. Supplement. Exogenous antigens include particles considered foreign within the organism.
Prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases with heat shock/stress protein-peptide complexes
InactiveUS6017540AEnhancing host 's immunocompetenceHigh activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsStress ProteinsIn vivo
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. Optionally, the methods further comprise administering antigen presenting cells sensitized with complexes of hsps noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. In a specific embodiment, the effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 0.1 to 9.0 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp70, 5 to 49 micrograms for hsp90, and 0.1 to 9.0 micrograms for gp96.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for immunomodulation
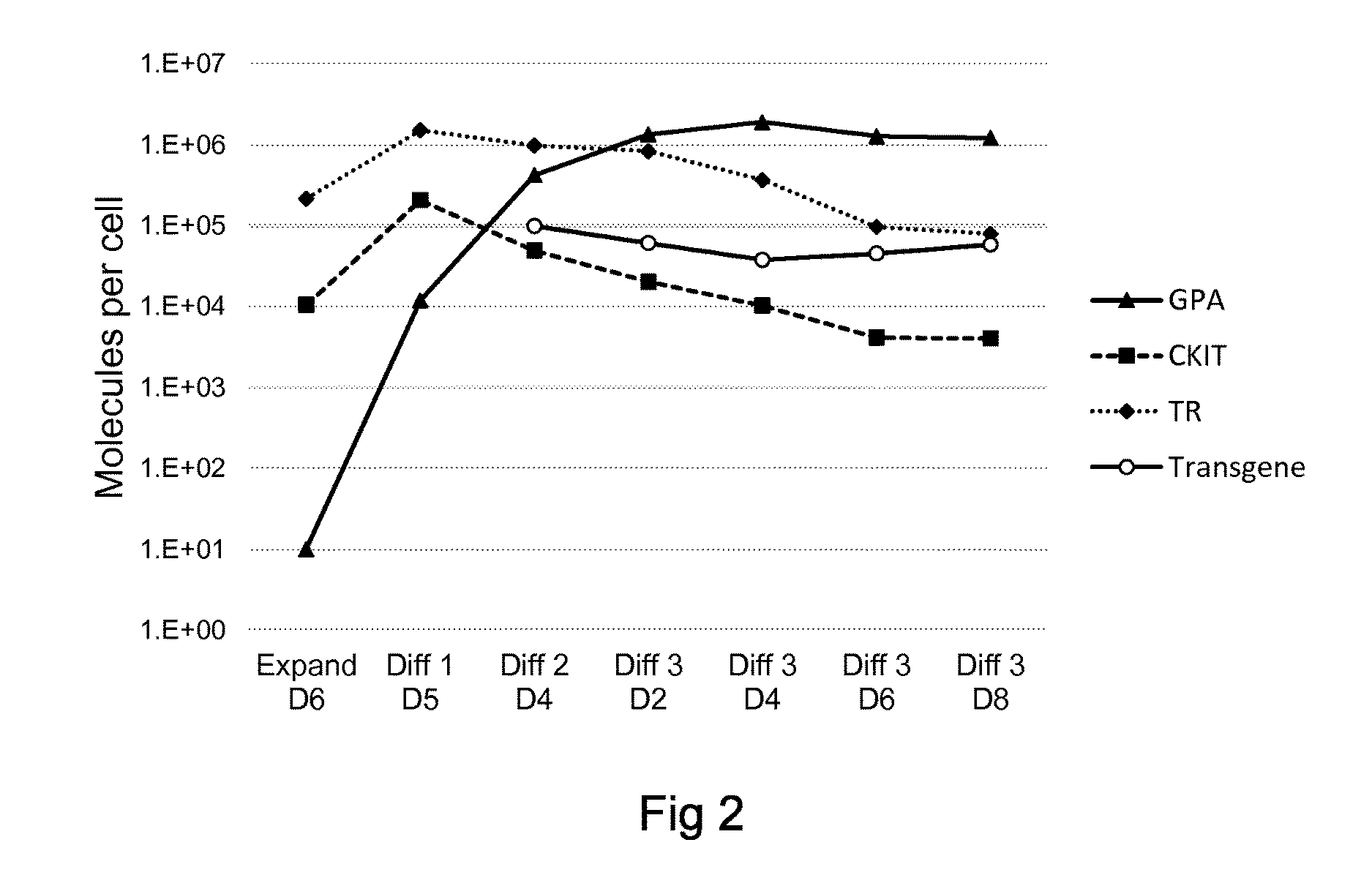
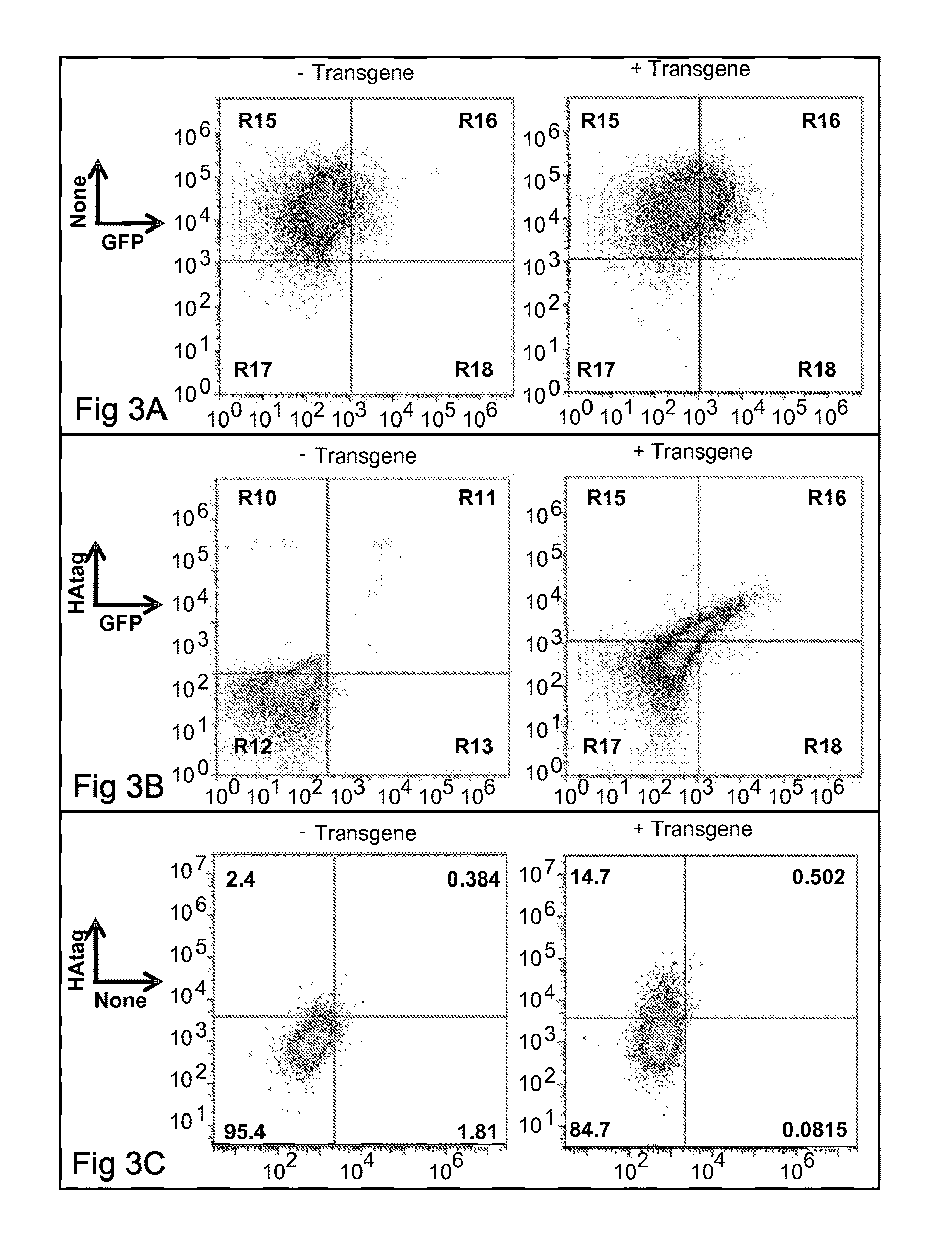
ActiveUS20170020926A1Efficient managementLess side effectsNervous disorderAntipyreticImmunomodulationsExogenous antigen
Owner:RUBIUS THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and methods using complexes of heat shock protein 90 and antigenic molecules for the treatment and prevention of neoplastic diseases
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. The effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 10-600 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp7o, 50-1000 micrograms for hsp9o, and 10-600 micrograms for gp96. The invention also provides a method for measuring tumor rejection in viva in an individual, preferably a human, comprising measuring the generation by the individual of MHC Class I-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific to the tumor. Methods of purifying hsp7o-peptide complexes are also provided.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for increased priming of t-cells through cross-presentation of exogenous antigens
InactiveUS20080171059A1Easy to demonstrateEffective vaccineTissue cultureCancer antigen ingredientsDiseaseVaccination
Methods for eliciting in an animal in need thereof a cell-mediated immune response specific to an antigen, the method comprising providing an antigen preparation comprising particles on the surface of which the antigen is attached, and administering the antigen preparation to the animal, wherein the particles are taken up by antigen presenting cells (APC) of the animal via phagocytosis, forming a phagosome inside the APC, wherein the antigen is attached to the surface of the particle in such a way that the antigen is released in the phagosome before the phagosome fuses with a late endosome or a lysosome, and wherein the antigen is cross-presented on a Class I MHC molecule. Also provided are particulate antigen preparations or particulate vaccines that can be delivered to an animal in need thereof for vaccination against, for preventing or treating, a disease related to the antigen, such as cancer and a viral infection.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Compositions and methods using complexes of heat shock protein gp96 and antigenic molecules for the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases
InactiveUS6143299AElicit immune responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMHC class IAntigenic valence
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. The effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 10-600 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp70, 50-1000 micrograms for hsp90, and 10-600 micrograms for gp96. The invention also provides a method for measuring tumor rejection in vivo in an individual, preferably a human, comprising measuring the generation by the individual of MHC Class I-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific to the tumor. Methods of purifying hsp70-peptide complexes are also provided.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
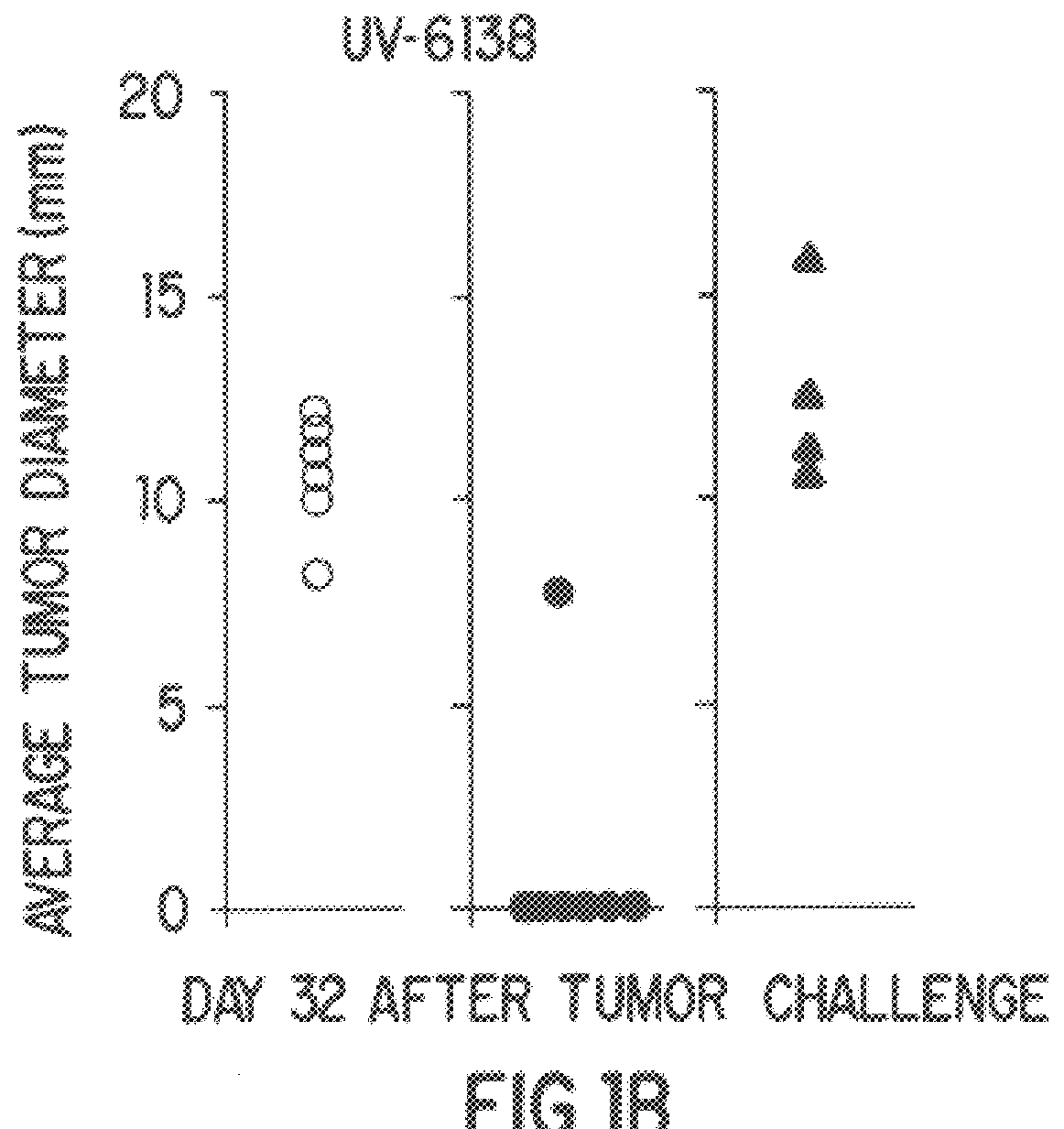
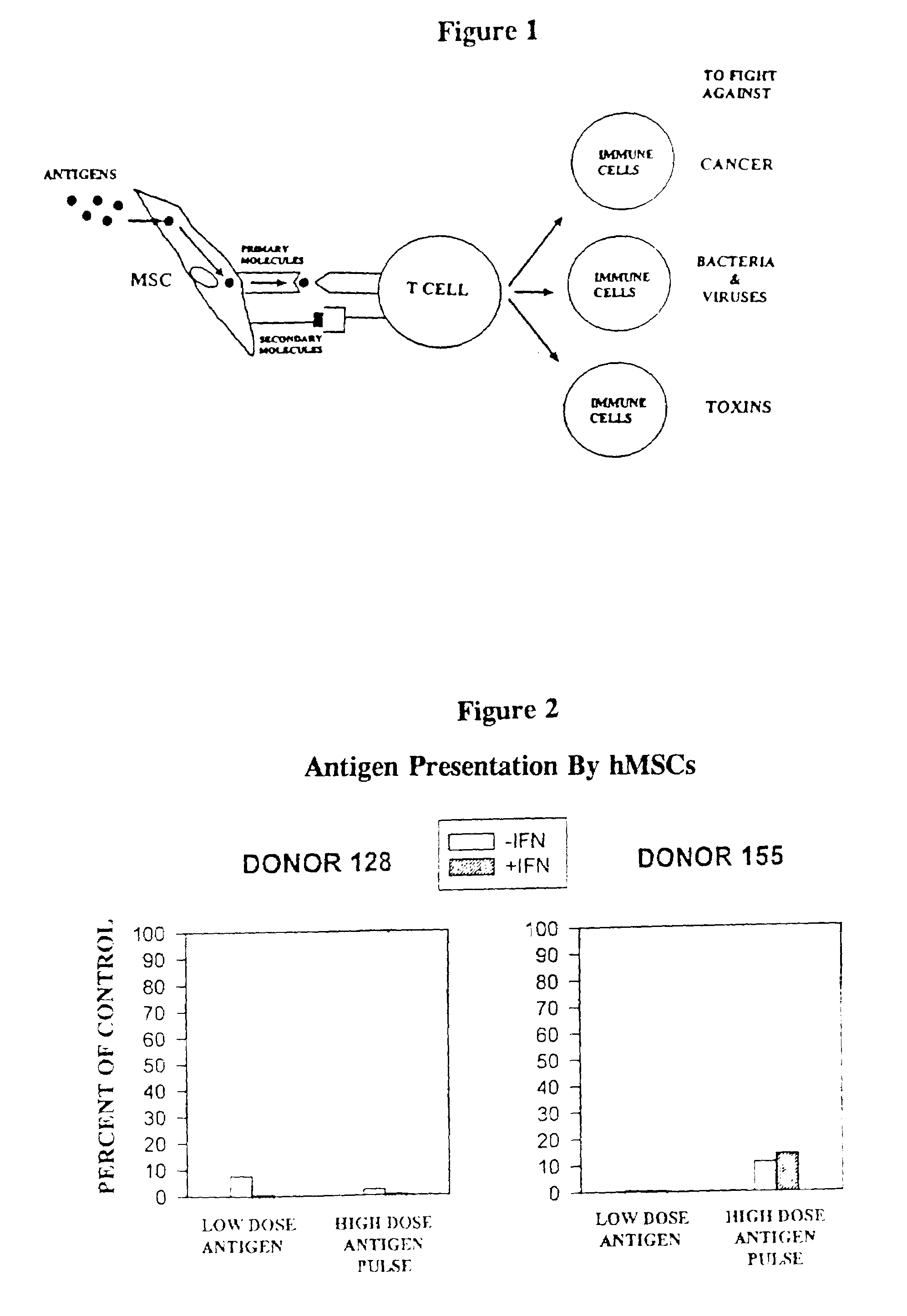
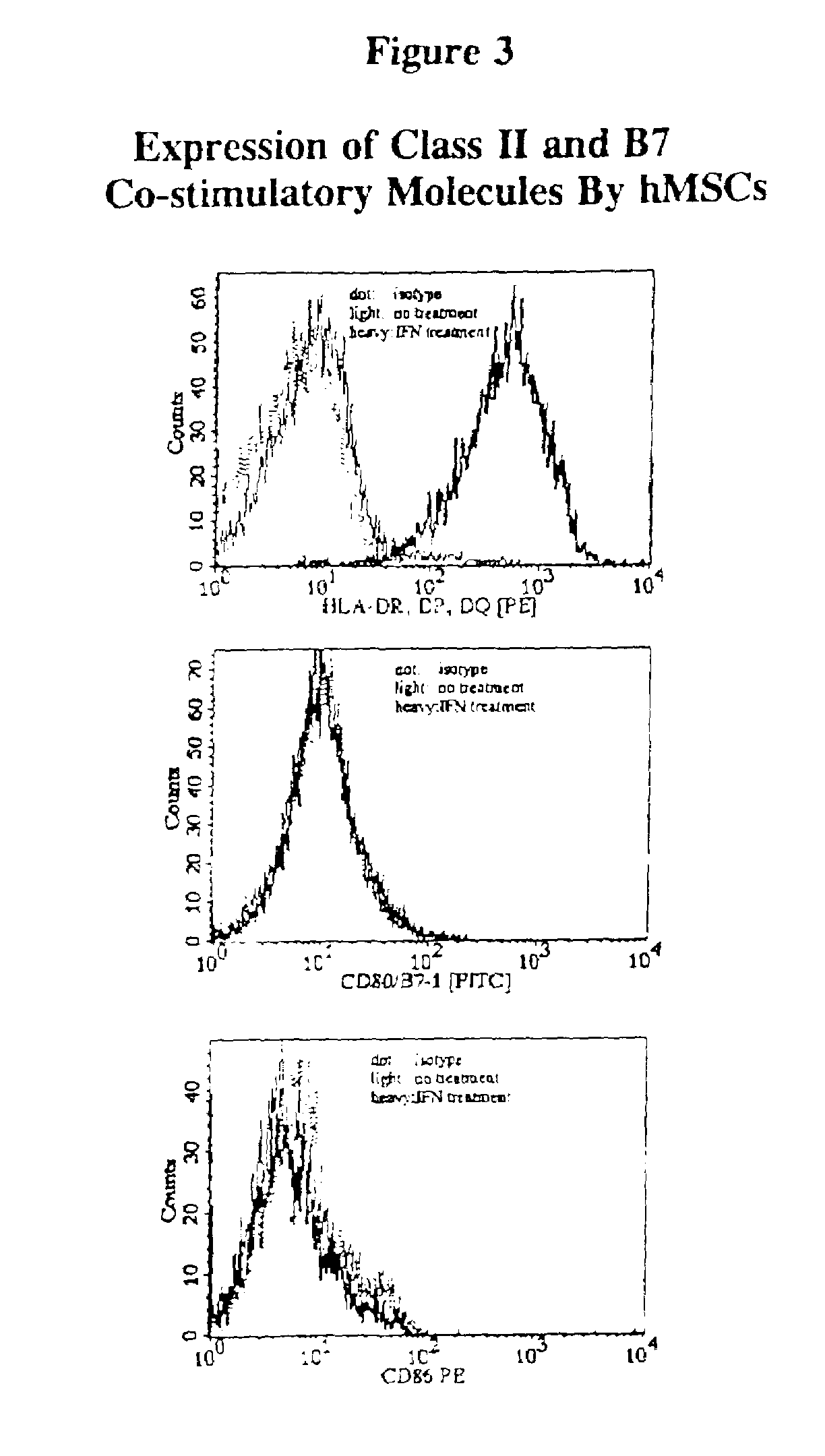
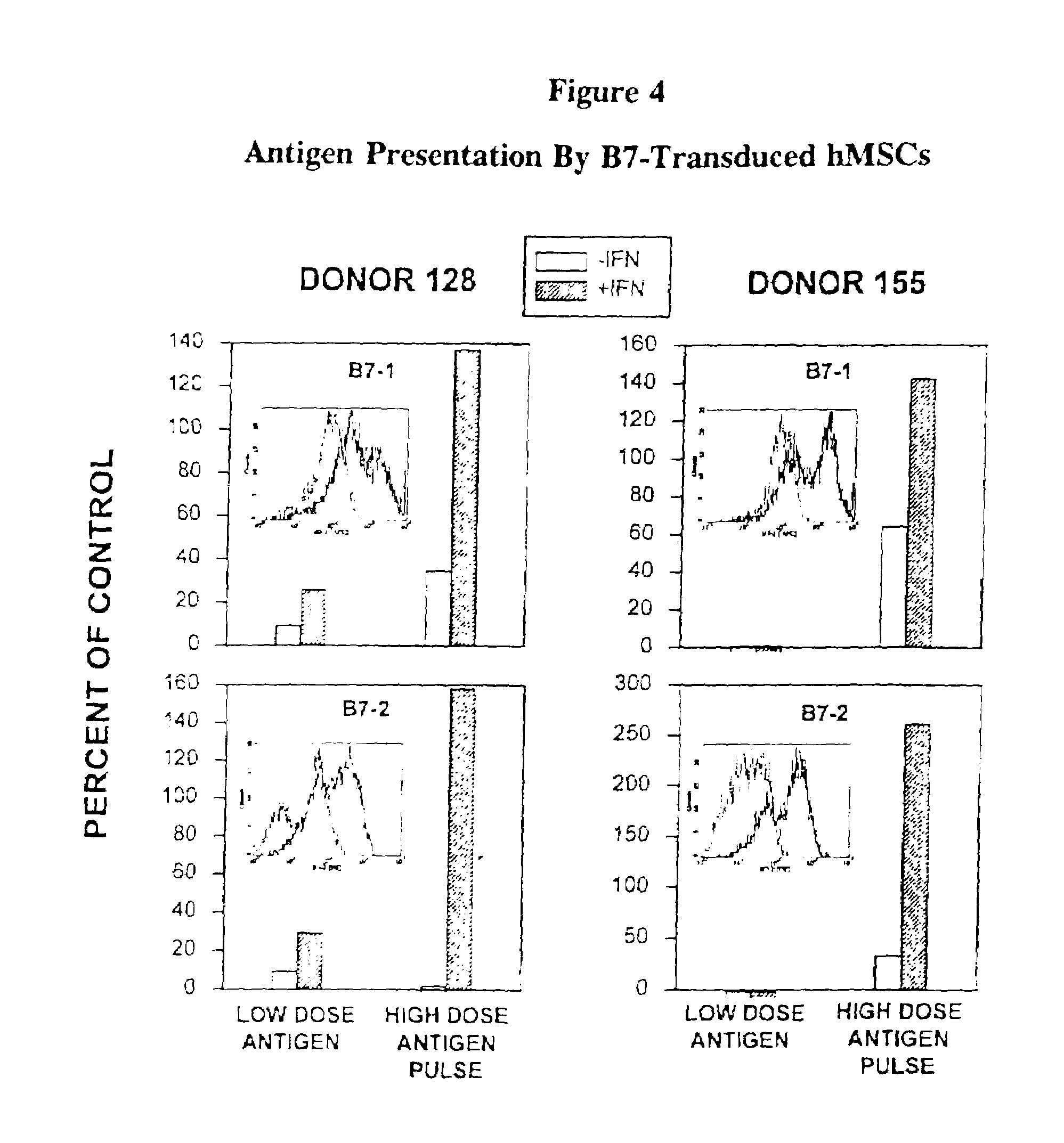
Antigen presenting mesenchymal stem cells
Disclosed is a mesenchymal stem cell and / or cell of the adipocyte lineage that (i) has been modified to have at least one exogenous antigen bound to at least one primary surface molecule of said cell such that said at least one antigen can initiate an immune response and (ii) also expresses at least one co-stimulatory molecule. The antigen is preferably a protein, polypeptide, lipid or glycolipid. The primary surface molecule is MHC I, MHC II or CD1. Also disclosed is a method for stimulating presentation of at least one exogenous antigen fragment on a mesenchymal stem cell primary surface molecule by contacting a mesenchymal stem cell that is capable of expressing at least one co-stimulatory molecule with (i) an exogenous antigen or (ii) genetic material that codes for the exogenous antigen which the mesenchymal stem cell processes into at least one antigen fragment. The method can further include contacting the mesenchymal stem cell with interferon-γ. Also disclosed are a method for determining the state of activation of a T lymphocyte population and a method for the treatment or prevention of a disease in an animal.
Owner:MESOBLAST INT
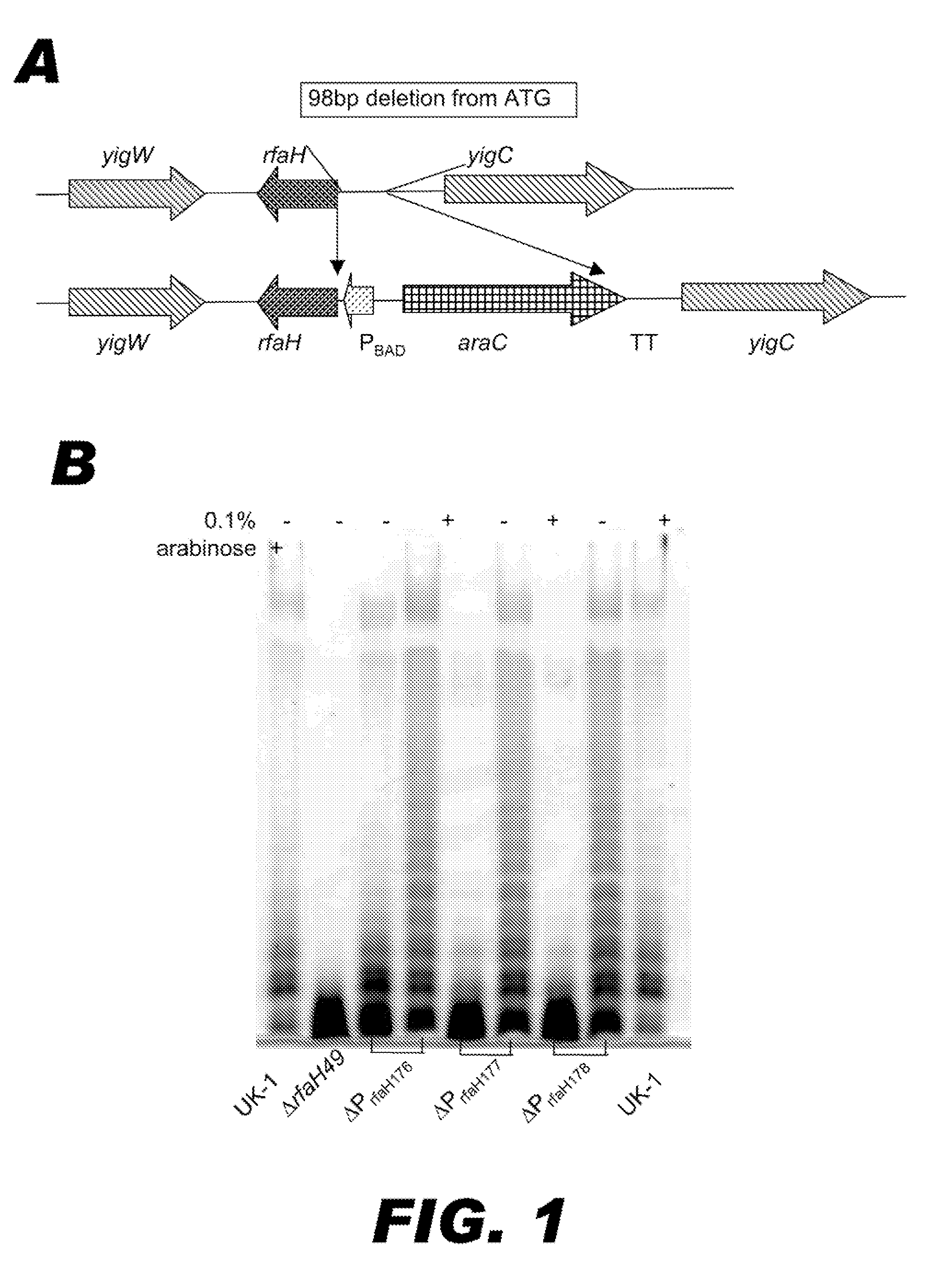
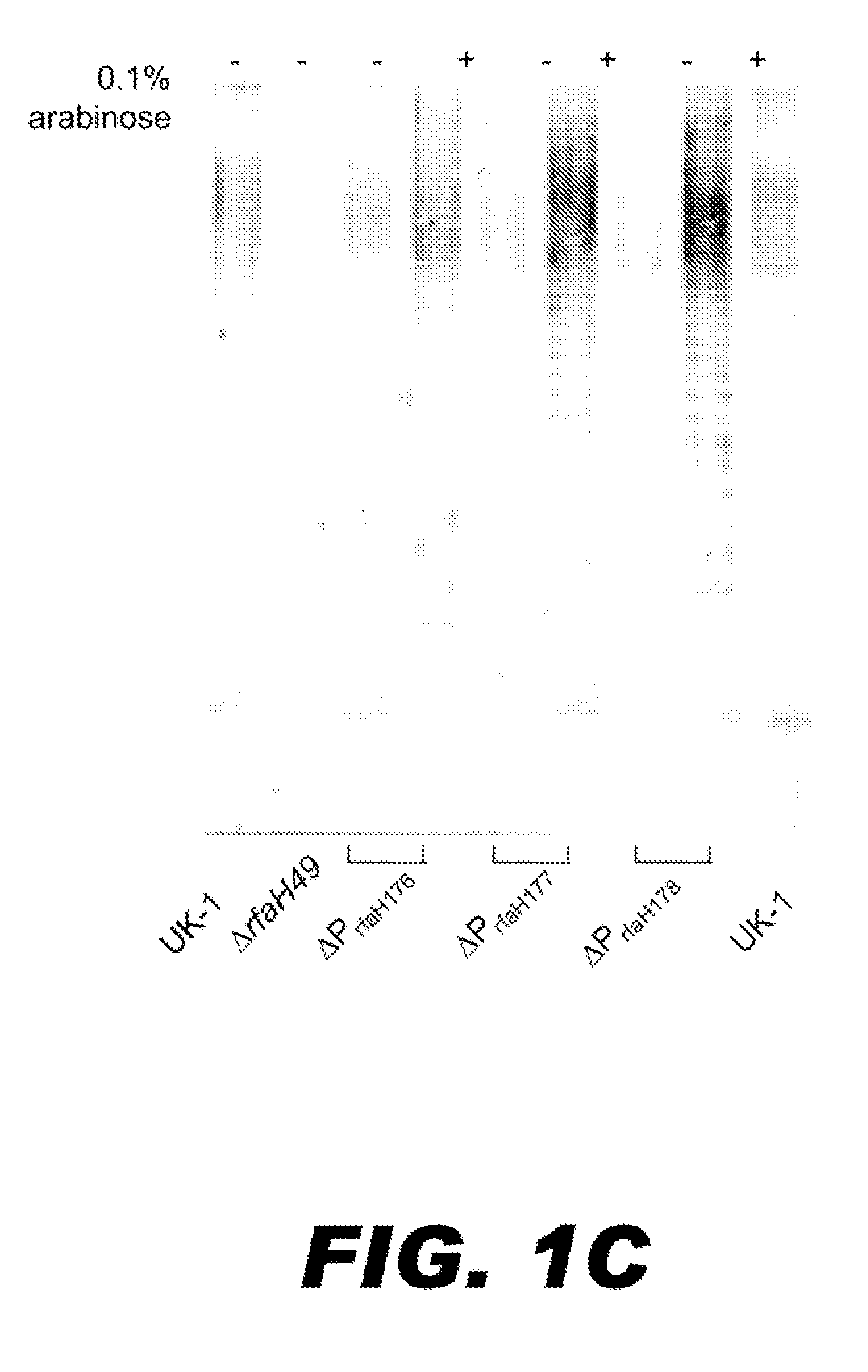
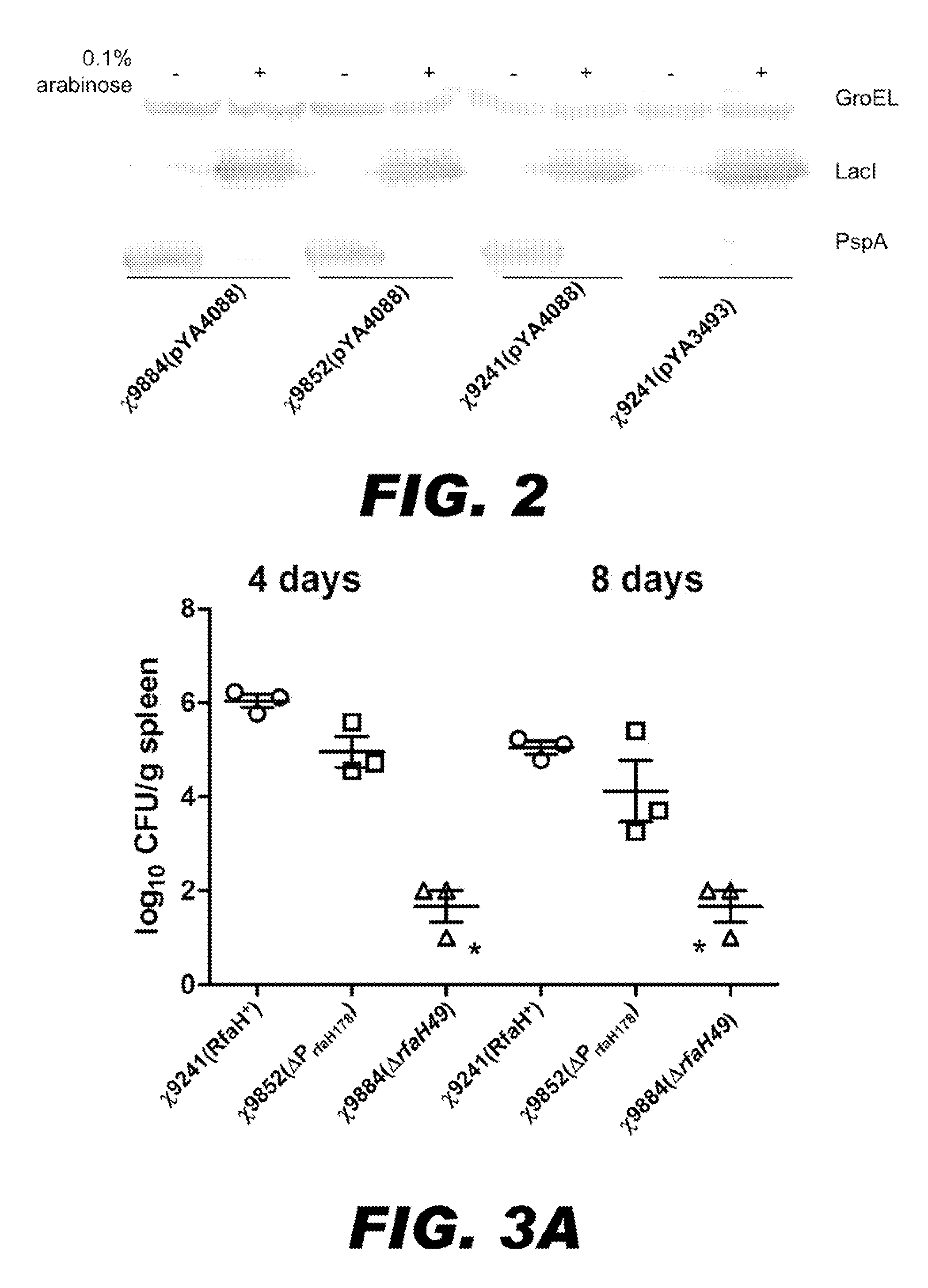
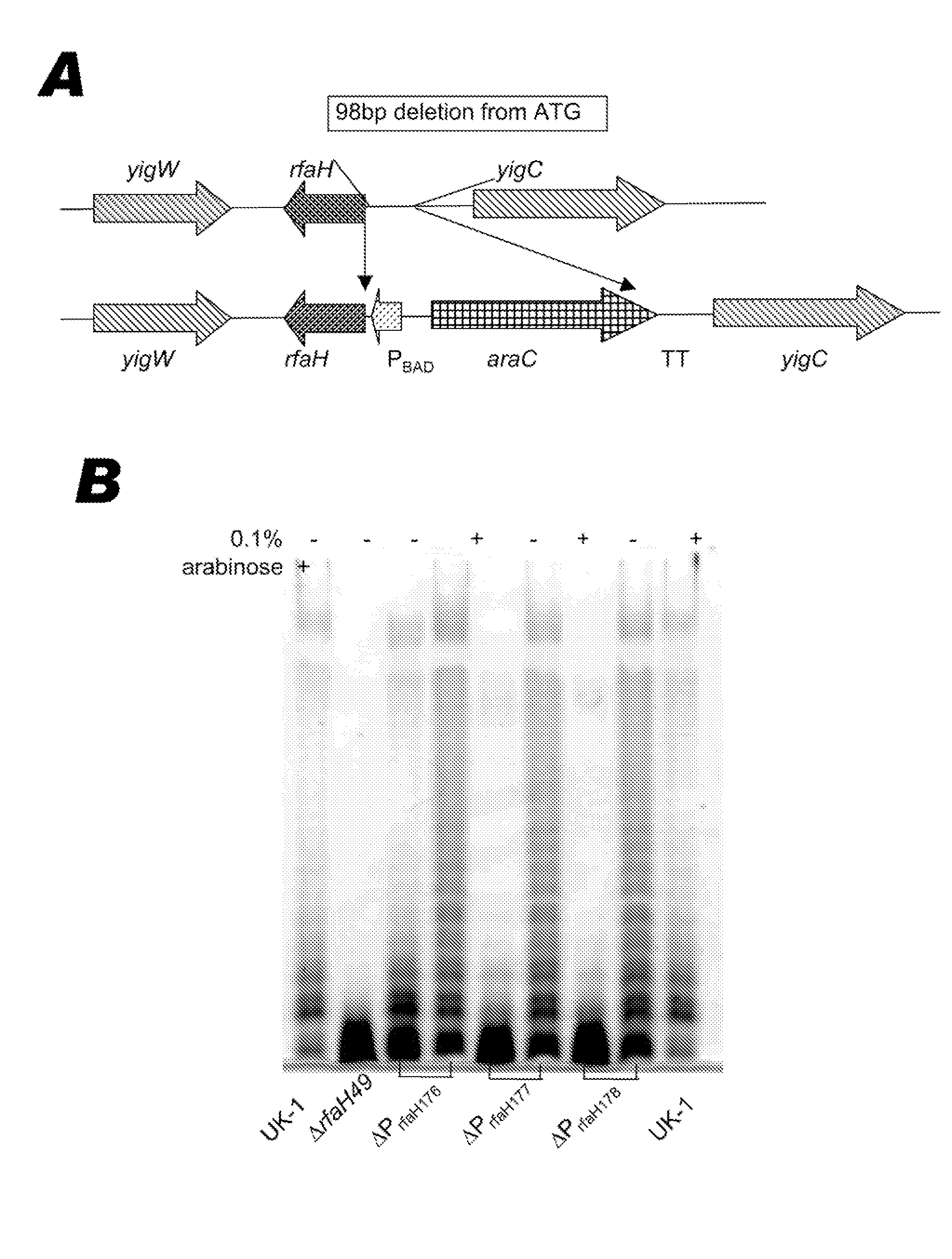
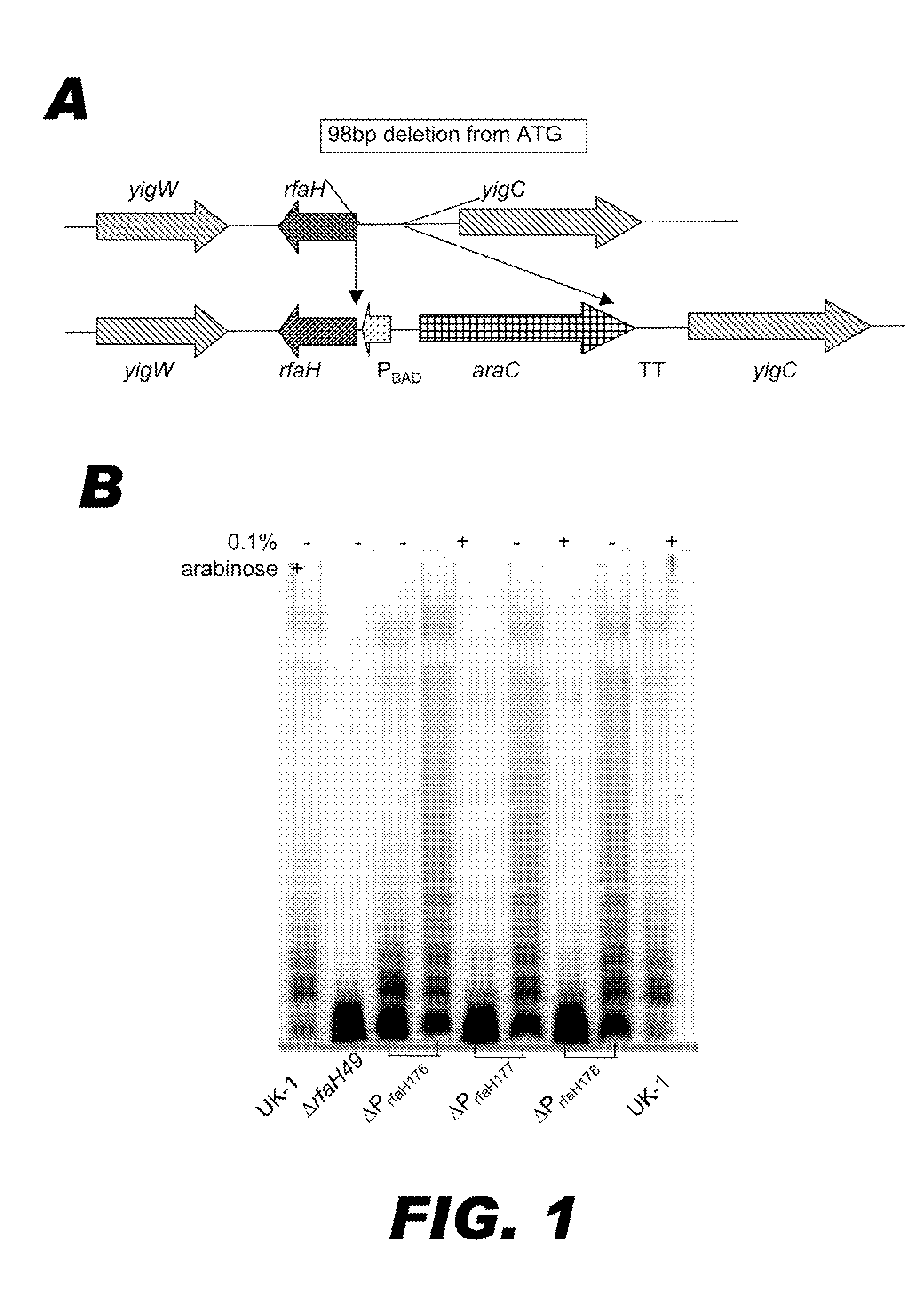
BACTERIUM COMPRISING A REGULATED rfaH NUCLEIC ACID
The present invention encompasses a recombinant bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid, as well as a vaccine comprising said recombinant bacterium. Other embodiments of the present invention encompass a recombinant bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid and a regulated rfc nucleic acid, while additional embodiments encompass a recombinant bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid and at least one nucleic acid encoding at least one exogenous antigen.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods of enhancing the immunogenicity of mycobacteria and compositions for the treatment of cancer, tuberculosis, and fibrosing lung diseases
InactiveUS20110243992A1Enhance recruitmentIncreased activationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMycobacterium immunogenumCancer cell
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for enhancing the immunogenicity of cellular microorganisms for use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria or for use as vectors to express exogenous antigens and induce responses against other infectious agents or cancer cells. The present invention involves an additional method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme produced by the intracellular microbe is reduced by expressing a mutant copy of the enzyme, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Methods and compositions for immunomodulation
ActiveUS20180271910A1Efficient managementLess side effectsNervous disorderAntipyreticImmunomodulationsExogenous antigen
Owner:RUBIUS THERAPEUTICS
Vaccine immunotherapy
ActiveUS20130243723A1Enhance immune responseEnhance immune functionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAdjuvantPrimary cell
Owner:BROOKLYN IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS LLC
Vaccine immunotherapy for immune suppressed patients
A method for overcoming mild to moderate immune suppression includes the steps of inducing production of naïve T-cells and restoring T-cell immunity. A method of vaccine immunotherapy includes the steps of inducing production of naïve T-cells and exposing the naïve T-cells to endogenous or exogenous antigens at an appropriate site. Additionally, a method for unblocking immunization at a regional lymph node includes the steps of promoting differentiation and maturation of immature dendritic cells at a regional lymph node and allowing presentation of processed peptides by resulting mature dendritic cells, thus, for example, exposing tumor peptides to T-cells to gain immunization of the T-cells. Further, a method of treating cancer and other persistent lesions includes the steps of administering an effective amount of a natural cytokine mixture as an adjuvant to endogenous or exogenous administered antigen to the cancer or other persistent lesions.
Owner:BROOKLYN IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS LLC
Immunotherapy for reversing immune suppression
InactiveUS7731945B2Restoring T cell immunityPromoting differentiationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRegion lymph nodeDendritic cell
A method for overcoming immune suppression includes the steps of inducing production of naïve T cells and restoring T cell immunity. A method of vaccine immunotherapy includes the steps of inducing production of naïve T cells and exposing the naïve T cells to endogenous or exogenous antigens at an appropriate site. Additionally, a method for unblocking immunization at a regional lymph node includes the steps of promoting differentiation and maturation of immature dendritic cells at a regional lymph node and allowing presentation of processed peptides by resulting mature dendritic cells, thus, for example, exposing tumor peptides to T cells to gain immunization of the T cells. Further, a method of treating cancer and other persistent lesions includes the steps of administering an effective amount of a natural cytokine mixture as an adjuvant to endogenous or exogenous administered antigen to the cancer or other persistent lesions; preferably the natural cytokine mixture is administered in combination with thymosin α1.
Owner:BROOKLYN IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS LLC
Arabinogalactan for enhancing the adaptive immune response
The present invention discloses a composition containing Arabinogalactan for enhancing the adaptive immune response in subjects to foreign antigen(s) by administering said composition prior, during and after the phase of exposure to said foreign antigen(s). Furthermore, the present invention relates to a vaccination kit comprising a composition comprising Arabinogalactan and a vaccine.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Immunotherapy for reversing immune suppression
InactiveUS20110044941A1Promoting differentiation and maturationRestore immunityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRegion lymph nodeDendritic cell
A method for overcoming immune suppression includes the steps of inducing production of naïve T cells and restoring T cell immunity. A method of vaccine immunotherapy includes the steps of inducing production of naïve T cells and exposing the naïve T cells to endogenous or exogenous antigens at an appropriate site. Additionally, a method for unblocking immunization at a regional lymph node includes the steps of promoting differentiation and maturation of immature dendritic cells at a regional lymph node and allowing presentation of processed peptides by resulting mature dendritic cells, thus, for example, exposing tumor peptides to T cells to gain immunization of the T cells. Further, a method of treating cancer and other persistent lesions includes the steps of administering an effective amount of a natural cytokine mixture as an adjuvant to endogenous or exogenous administered antigen to the cancer or other persistent lesions; preferably the natural cytokine mixture is administered in combination with thymosin α1.
Owner:IMMUNO RX
Vaccine immunotherapy for immune suppressed patients
InactiveUS20050152874A1Promoting differentiation and maturationRestore immunityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthAdjuvant
Owner:IRX THERAPEUTICS
Method to increase class i presentation of exogenous antigens by human dendritic cells
InactiveUS20080171023A1Enhance MHC-class I processingEnhance immune responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsMHC class IDendritic cell
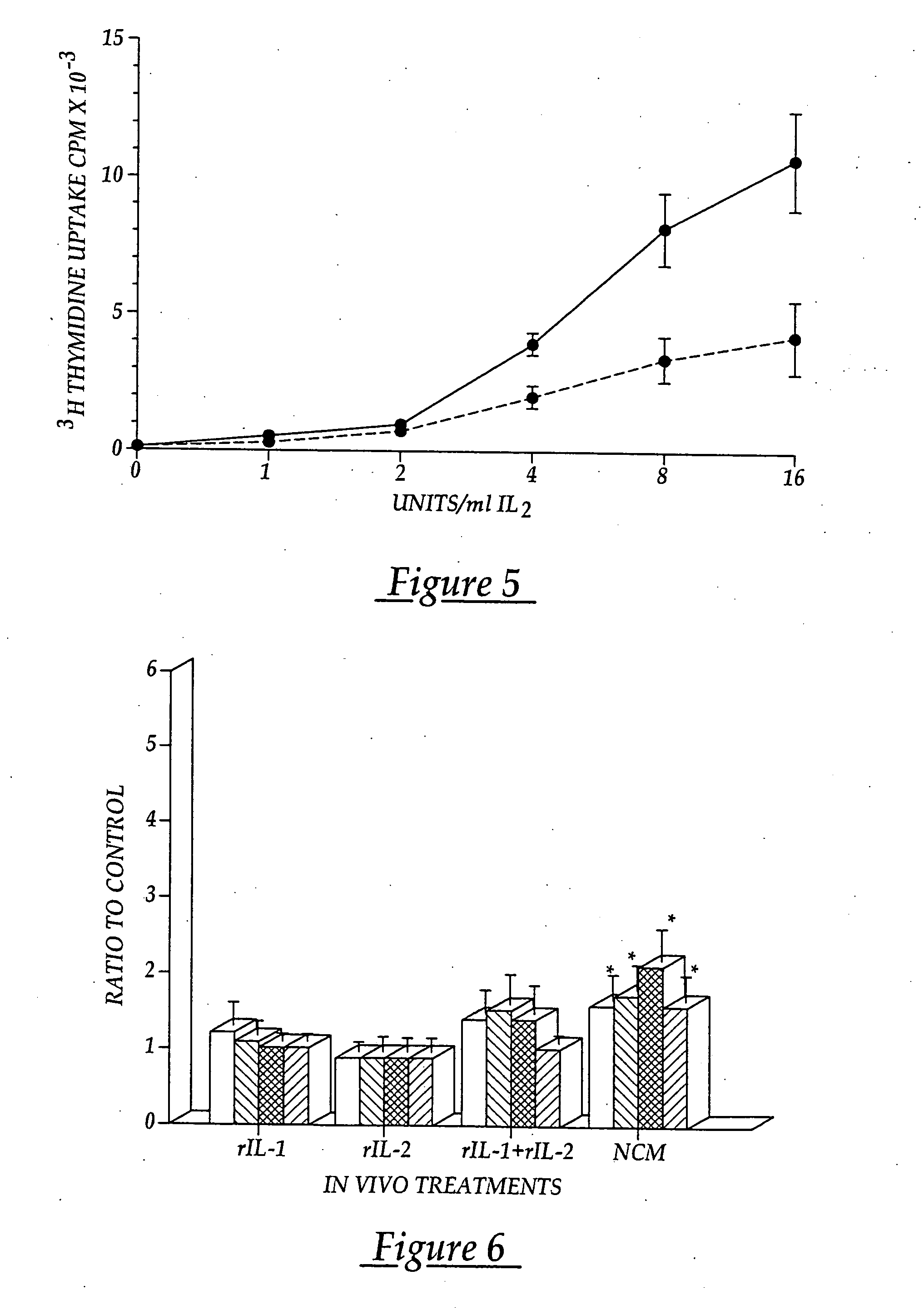
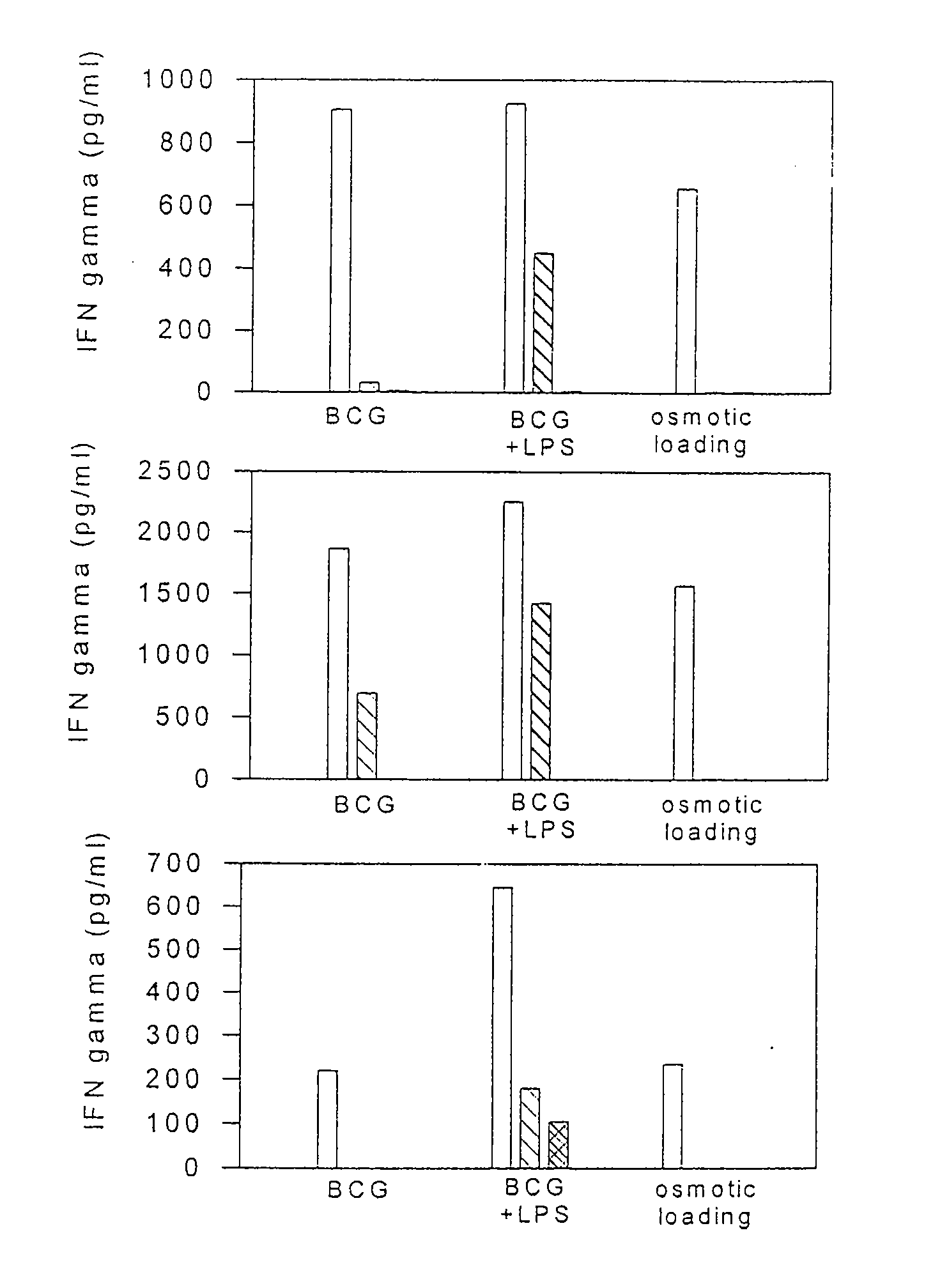
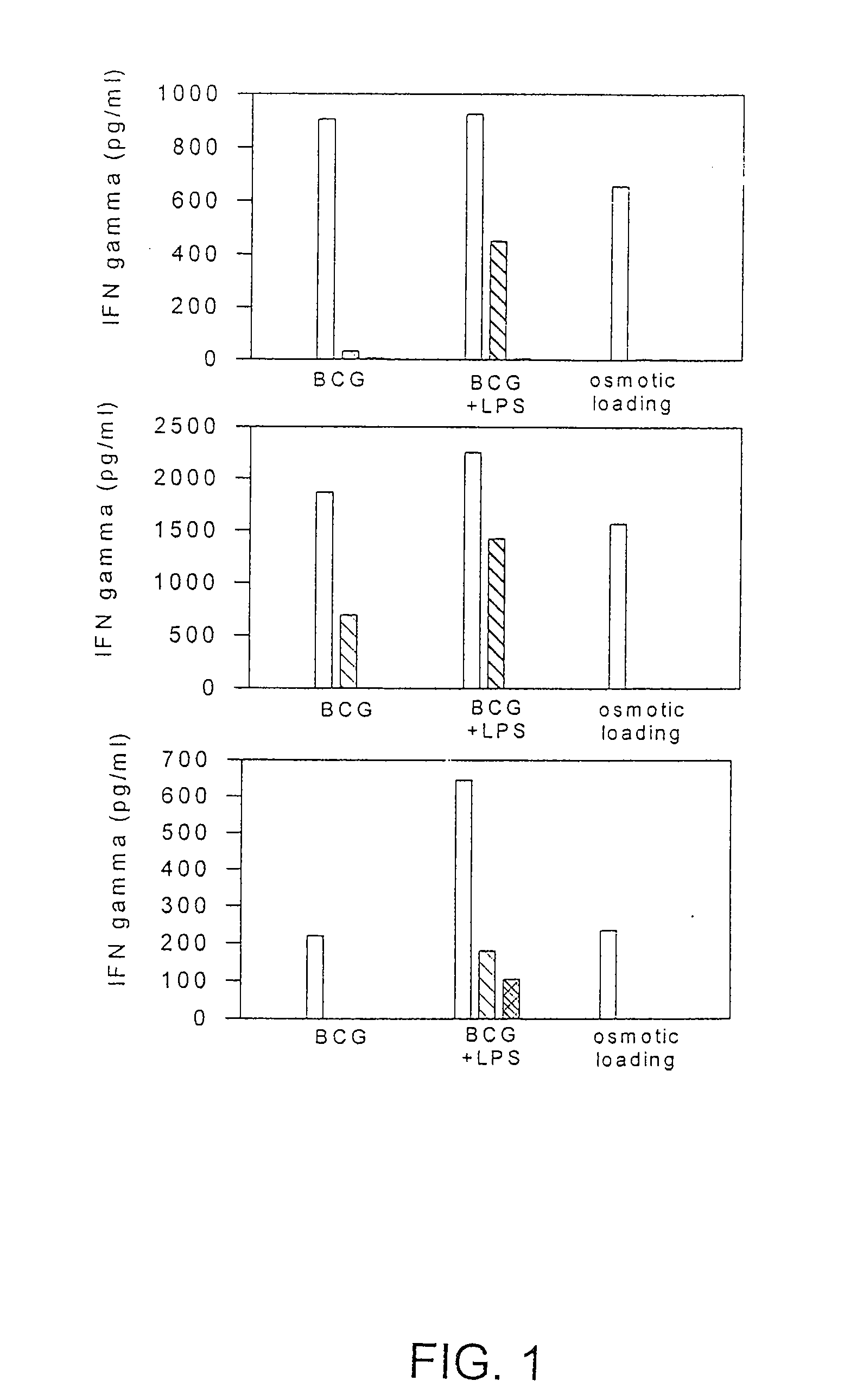
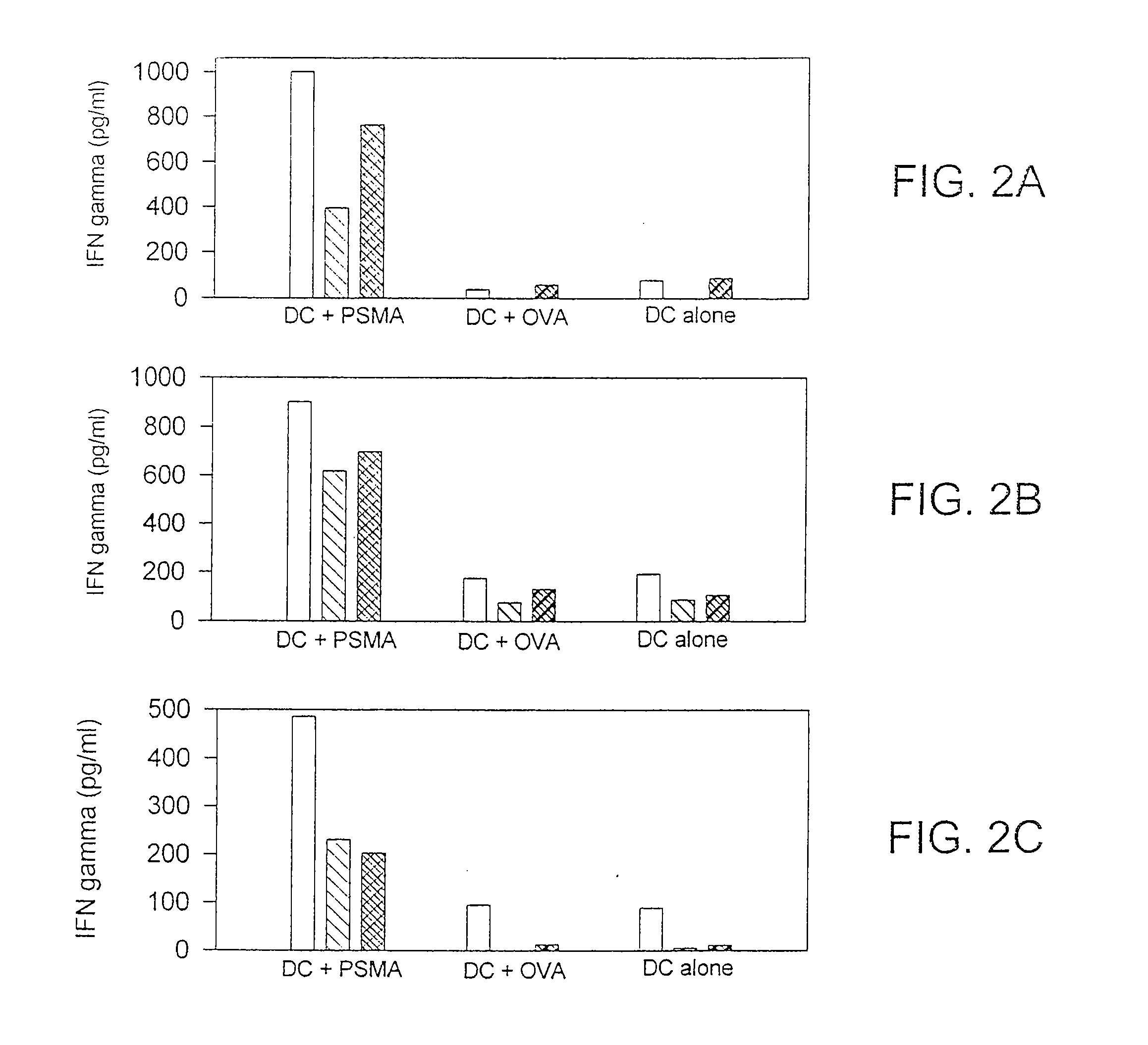
Methods and compositions for use of human dendritic cells to activate T cells for immunotherapeutic responses against primary and metastatic cancer are disclosed. In one embodiment, human dendritic cells exposed to a tumor associated antigen, or an antigenic fragment thereof in combination with bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), are administered to a cancer patient to activate a predominantly CD8+T cell response in vivo. In an alternate embodiment, human dendritic cells are exposed to a tumor associated antigen or a specific antigenic peptide in combination with BCG in vitro and incubated or cultured with primed or unprimed T cells to activate a predominantly CD8+T cell response in vitro. The activated T cells are then administered to a cancer patient. Antigen in combination with BCG is processed by dendritic cells through the MHC-CLASS I compartment which provides for a predominantly CD8+T cell response. The addition of LPS provides for a greater number of mature dendritic cells enhancing the T cell response to antigen. Methods and compositions for human dendritic cells with extended life span and cryopreserved dendritic cells are disclosed.
Owner:NORTHWEST BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid
The present invention encompasses a recombinant bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid, as well as a vaccine comprising said recombinant bacterium. Other embodiments of the present invention encompass a recombinant bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid and a regulated rfc nucleic acid, while additional embodiments encompass a recombinant bacterium comprising a regulated rfaH nucleic acid and at least one nucleic acid encoding at least one exogenous antigen.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Cloned enzyme-donor immunoassay (CEDIA) ImmunoChip drug detecting kit
Rapid drug detection is a regular detection item for public security departments, drug control organizations, sports events, enlistment and entry departments. At present, colloidal gold test paper is a basic choice for rapid drug detection, but the sensitivity of the colloidal gold test paper is low, the possibility of fake positive and fake negative results is high, the repeatability is low and the quantification is impossible. The invention discloses a cloned enzyme-donor immunoassay (CEDIA) ImmunoChip drug detecting kit. The kit comprises an immuno chip on which the combination of an enzyme donor and an enzyme receptor is immobilized, wherein the enzyme donor can be coupled with a drug micromolecule by a chemical bond to form an enzyme-donor-labeled exogenous antigen so as to be used for detecting whether a specific anti-drug antibody which can be competitively combined with the enzyme-donor-labeled exogenous antigen exists in a sample to be detected by a CEDIA ImmunoChip drug detecting method and calibration is carried out by using a novel fluorogenic substrate. The kit has the advantages of sensitive reaction, high accuracy, no cross reaction and high repeatability, and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIHANG BIOTECH
Prevention of infectious diseases with gp96-peptide complexes
InactiveUS6379672B1Enhancing host 's immunocompetence and activityEasy to returnAntibacterial agentsBiocideIn vivoHSP90 Heat-Shock Proteins
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. Optionally, the methods further comprise administering antigen presenting cells sensitized with complexes of hsps noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. In a specific embodiment, the effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 0.1 to 9.0 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp70, 5 to 49 micrograms for hsp90, and 0.1 to 9.0 micrograms for gp96.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
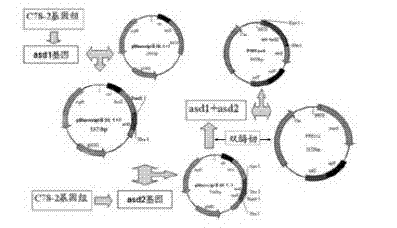
Construction method for delaying attenuation and increasing expression exogenous antigen salmonella suipestifer carrier through regulation and control of gene
ActiveCN104498418ALarge market applicabilityImmunogenicBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
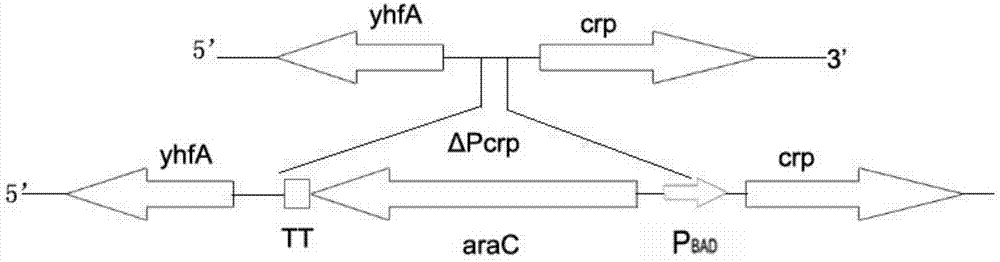
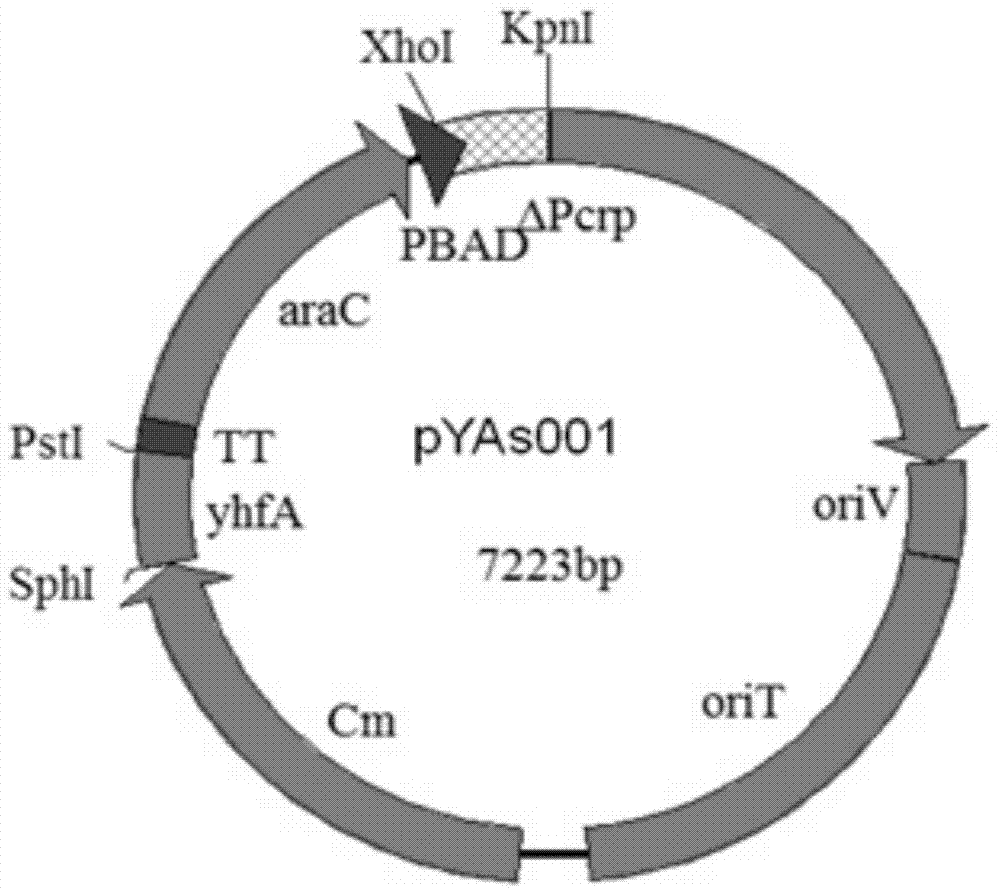
The invention provides a construction method for delaying attenuation and increasing an expression exogenous antigen salmonella suipestifer carrier through regulation and control of gene, which is characterized in that receptor bacterium C78-3 is combined with manA, crp, relA and asd -containing deleted suicide carrier escherichia coli donor bacterium, mutants delta manA, delta Pcrp: : TT ara C PBAD crp, delta relA: : araC PBAD lacI TT and delta asd A are introduced in wild-type salmonella suipestifer C78-3, the introduced salmonella suipestifer after mutation can be called x0011; and four types of mutation enable phenotype identification. The method of the invention makes salmonella suipestifer to become safe and effective vaccine carrier of many exogenous antigens; and provides the delaying attenuation and increasing expression exogenous antigen salmonella suipestifer carrier through regulation and control of gene for various pig diseases, especially many bacteria diseases of pig, and has great market applicability.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Attenuated vector bacterium of salmonella choleraesuls and construction method of attenuated vector bacterium
InactiveCN106754594AReduce usageHas attenuated safety featuresBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesAntibiotic Y
The invention provides an attenuated vector bacterium of salmonella choleraesuls and a construction method of the attenuated vector bacterium and belongs to the technical field of animal bacterium genetic engineering. The attenuated vector bacterium is C78-3 salmonella choleraesuls without deltamanA, deltacrp::TT araC PBAD, deltarelA:: araC PBAD lacI TT, deltasoB and deltaasdA genes and is named as rSC0016. The method for taking a suicide vector without a resistance marker as a salmonella choleraesuls constructing vector is adopted and the utilization of the vector marked with antibiotics can be avoided; the vector can be safely used in clinical practice; furthermore, a balanced lethal system carries an exogenous antigen and can guarantee that only vaccine strains carrying the exogenous antigen can be used for producing vaccines and enter a host and survive, so that the immunity efficiency of the vaccines is improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Pro-Apoptotic Bacteria and Compositions for Delivery and Expression of Antigens
InactiveUS20090325298A1Enhance antigen presentationImproves vaccine efficacyBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaCancer cellApoptosis
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for enhancing the immunogenicity of cellular microorganisms for use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria or for use as vectors to express exogenous antigens and induce responses against other infectious agents or cancer cells. The present invention involves an additional method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme produced by the intracellular microbe is reduced by expressing a mutant copy of the enzyme, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
Antigenic epitope displaying method based on single domain antibody
ActiveCN102952193AOvercoming the problem of poor immunogenicityAvoid technical complexityPeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsEpitopeSingle-domain antibody
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and specifically relates to an antigenic epitope displaying method based on a single domain antibody. Specifically, an exogenous antigenic epitope is displayed in a CDR3 region of the single domain antibody, and the single domain antibody skeleton protein which displays the exogenous antigenic epitope on the surface of a molecule can be used for preparing an antibody with a too small epitope, be also used as a substitutive antigen of an exogenous antigen and used for immunizing animals and preparing antibodies aiming at the exogenous antigen. In addition, the antigenic epitope displaying method based on a single domain antibody skeleton can also be used for preparing epitope vaccins.
Owner:BEIJING VICNOVO SCI TECH
Recombined cattle parainfluenza carrier for expressing protein VP1 of porcine O type foot-and-mouth disease virus
InactiveCN103773803ACapable of copyingVector-based foreign material introductionAntigen epitopeHeterologous
The invention relates to a recombined cattle parainfluenza carrier pcDNA-NM09-VP1 for expressing the protein VP1 of a porcine O type foot-and-mouth disease virus. The recombined cattle parainfluenza carrier is characterized in that an RNA (ribonucleic acid) extracted from a strain BPIV3NM09 is used as a template; a virus total-length gene group is segmentally amplified through RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction); the total-length cDNA of cattle parainfluenza is subjected to primary modification, namely AgeI is introduced between P and M, so that insertion and replacement of exogenous antigen gene fragments are facilitated; due to secondary modification, antigen epitope which is inserted into a heterologous virus in a modified manner is the protein VP1 of the O type foot-and-mouth disease virus; the amino acid sequence is SEQIDNO1, and the nucleotide sequence is SEQIDNO2. The foundation is laid for further development of a gene engineering recombined vaccine for preventing and controlling the porcine foot-and-mouth disease and research on the III-type toxicity factor and the molecular pathogenesis of the cattle parainfluenza; the recombined cattle parainfluenza carrier has the replication capacity.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS +1
Attenuated uracil auxotroph of an apicomplexan and use thereof
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Recombined sheep poxvirus transfer vector and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103966262AEasy to detectEasy to insertViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesCapripoxvirusRecombinant vaccines
The invention provides a recombined sheep poxvirus transfer vector. A vector containing resistance genes and a plasmid replicon sequence and adopting Hind III and Avr II for digestion, such as a pVAX1 vector, is adopted, a DNA segment is inserted via introducing Hind III and Avr II enzyme cutting sites; the DNA segment comprises a gene sequence of a homologous arm with bidirectional poxvirus promoters and a sheep poxvirus TK gene. The invention further provides a recombined sheep poxvirus containing the recombined sheep poxvirus transfer vector and application of the recombined sheep poxvirus in the transfer of an exogenous antigen. Exogenous genes can be conveniently inserted into the recombined sheep poxvirus transfer vector, provided by the invention; moreover, the recombined sheep poxvirus transfer vector is improved according to a recombination result, and finally higher recombination efficiency is realized, accordingly, a good basis for the research and preparation of such recombination vaccines is laid.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Improved therapeutic T cell
The invention, which belongs to the field of biological medicines, in particular, relates to an improved therapeutic T cell and a method of making the same. Specifically, according to the invention, co-expression of exogenous antigen-specific receptor protein (for example, TCR or CAR) and a dominant negative TGF-beta type II receptors in a T cell is realized by means of ransduction by a lentiviralvector and thus an improved therapeutic T cell ( a TCR-T or CAR-T cell) is prepared.
Owner:IMMUNOTECH BIOPHARM CO LTD +1
Methods for generating immune responses to influenza antigens with a secretable CD40L fusion protein
ActiveUS9533036B2Enhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseInfectious agentExogenous antigen
Owner:MICROVAX LLC
Salmonella choleraesuis double-gene-deletion strain free of resistance marker and application thereof
InactiveCN102732442AImprove securityClear genetic backgroundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesVirulent characteristicsExogenous antigen
The invention relates to a Salmonella choleraesuis double-gene-deletion strain free of a resistance marker, Salmonella choleraesuis C7822 (with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2011402 ). The strain is obtained by carrying out deletion of the asd gene, one of the important nutrition and metabolism genes of Salmonella choleraesuis, on Salmonella choleraesuis C7821 (with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2010102 ) which has undergone deletion of the crp virulence gene. The gene-deletion strain C7822 loses the capability of synthesizing diaminopimelic acid (DAP), so the strain cannot survive in a DAP negative environment. After plasmids containing the asd gene are transformed into C7822, the asd gene in the plasmids can form a complementary gene with C7822, which enables C7822 to regain the capability of surviving in a DAP negative environment. The double-gene-deletion strain C7822 obtained in the invention has distinct genetic background, strong security and no resistance marker and can stably carry and express exogenous antigens; the double-gene-deletion strain is a good carrying vector and expression strain for exogenous antigens and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
New swine influenza vaccine
ActiveUS20180080044A1Low costSimilar efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsNucleotideHerpes simplex virus DNA
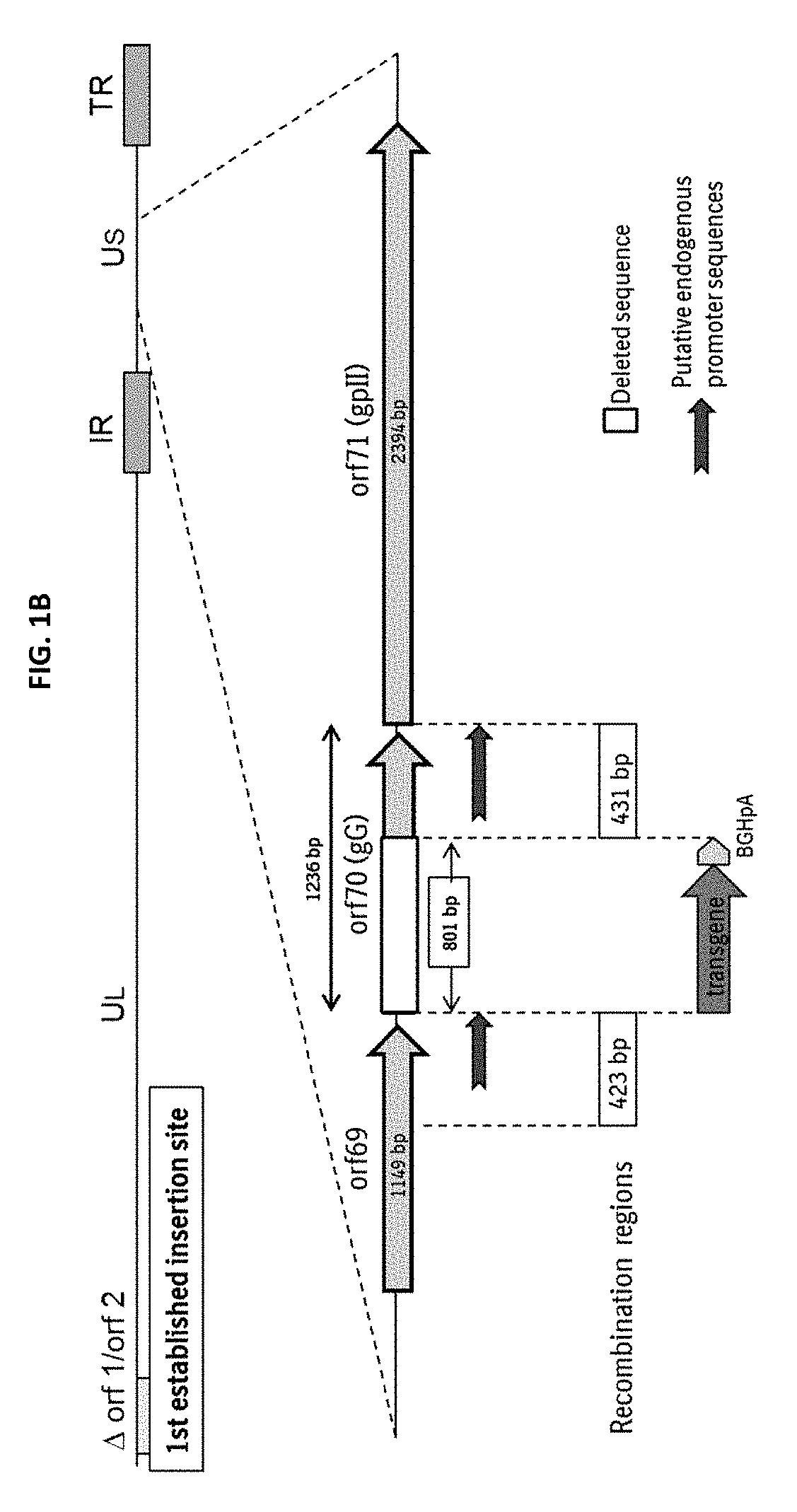
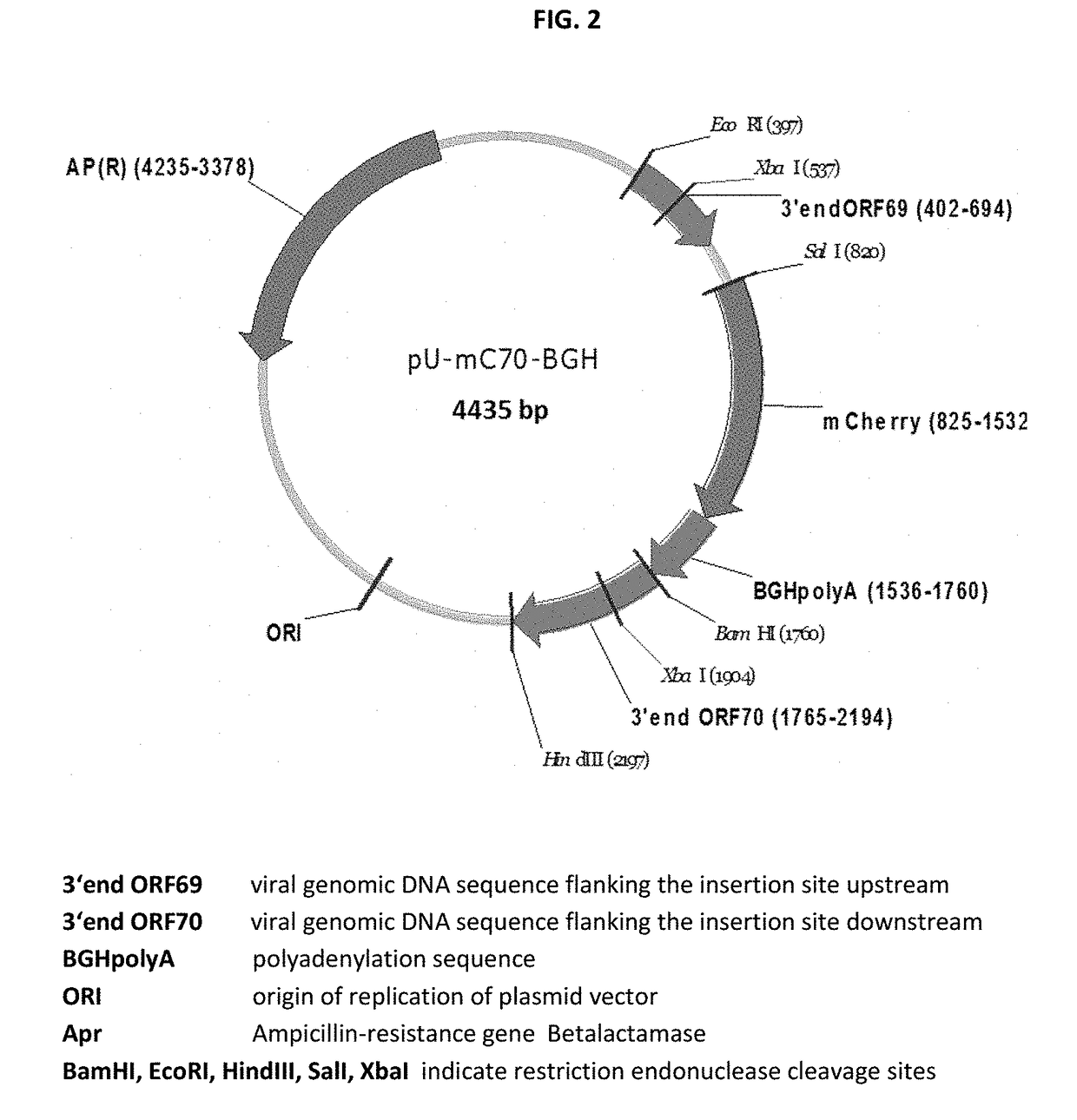
The present invention relates to Equine Herpes Virus (EHV) vectors comprising at least one exogenous antigen encoding sequence relating to a pathogen infecting food producing animals, wherein said exogenous antigen encoding sequence is inserted into an insertion site, preferably ORF70, and said exogenous antigen encoding sequence is operably linked to a promoter sequence, preferably the promoter sequence comprising 4pgG600 (SEQ ID NO:1) or 4pMCP600 (SEQ ID NO:2) or the complementary nucleotide sequences thereof or a functional fragment or a functional derivative thereof or the complementary nucleotide sequences thereof. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods for immunizing a food producing animal comprising administering to such food producing animal an immunogenic composition comprising embodiments of the present invention. Moreover, the present invention relates to methods for the treatment or prophylaxis of clinical signs caused by swine influenza virus in a food producing animal.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com