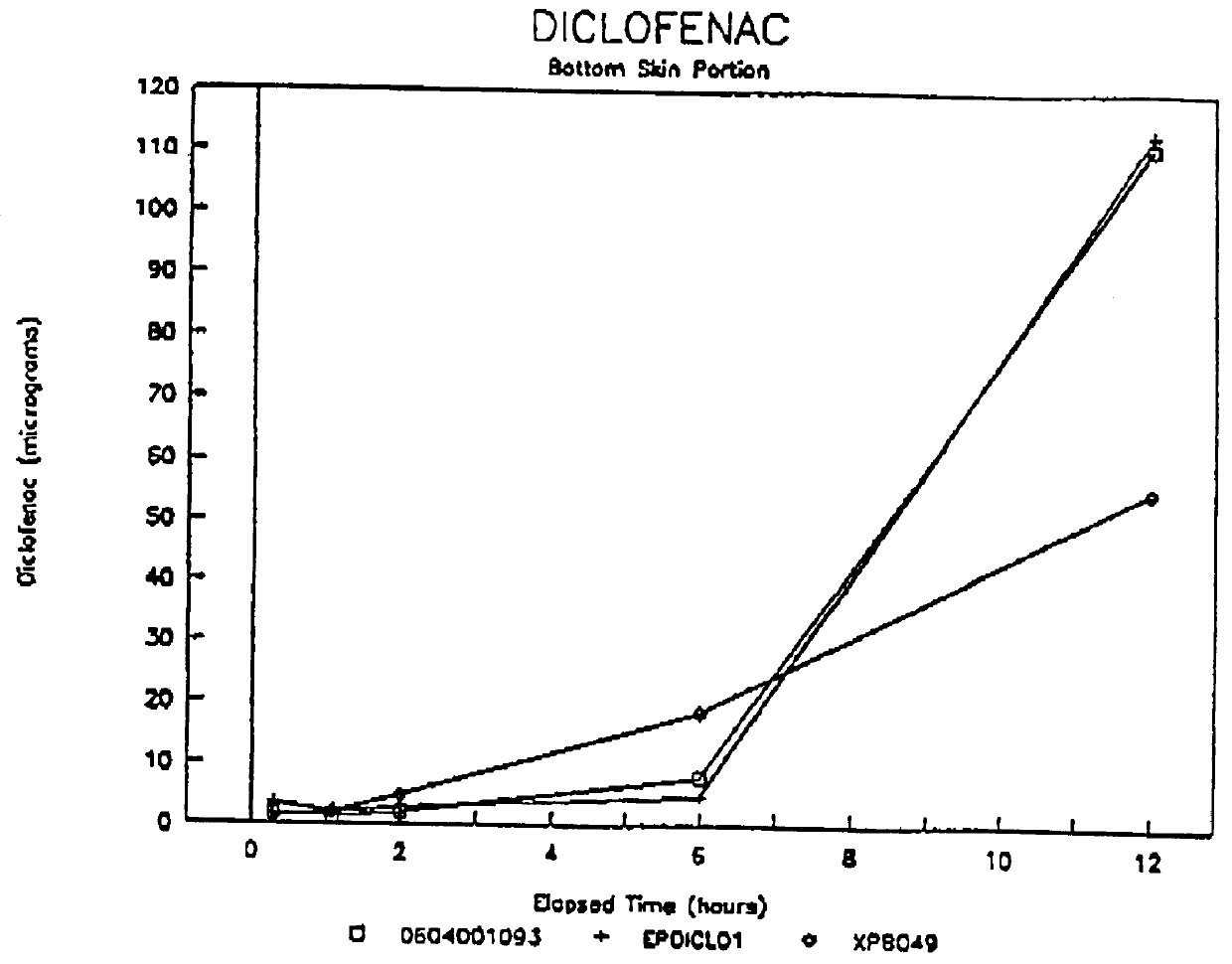
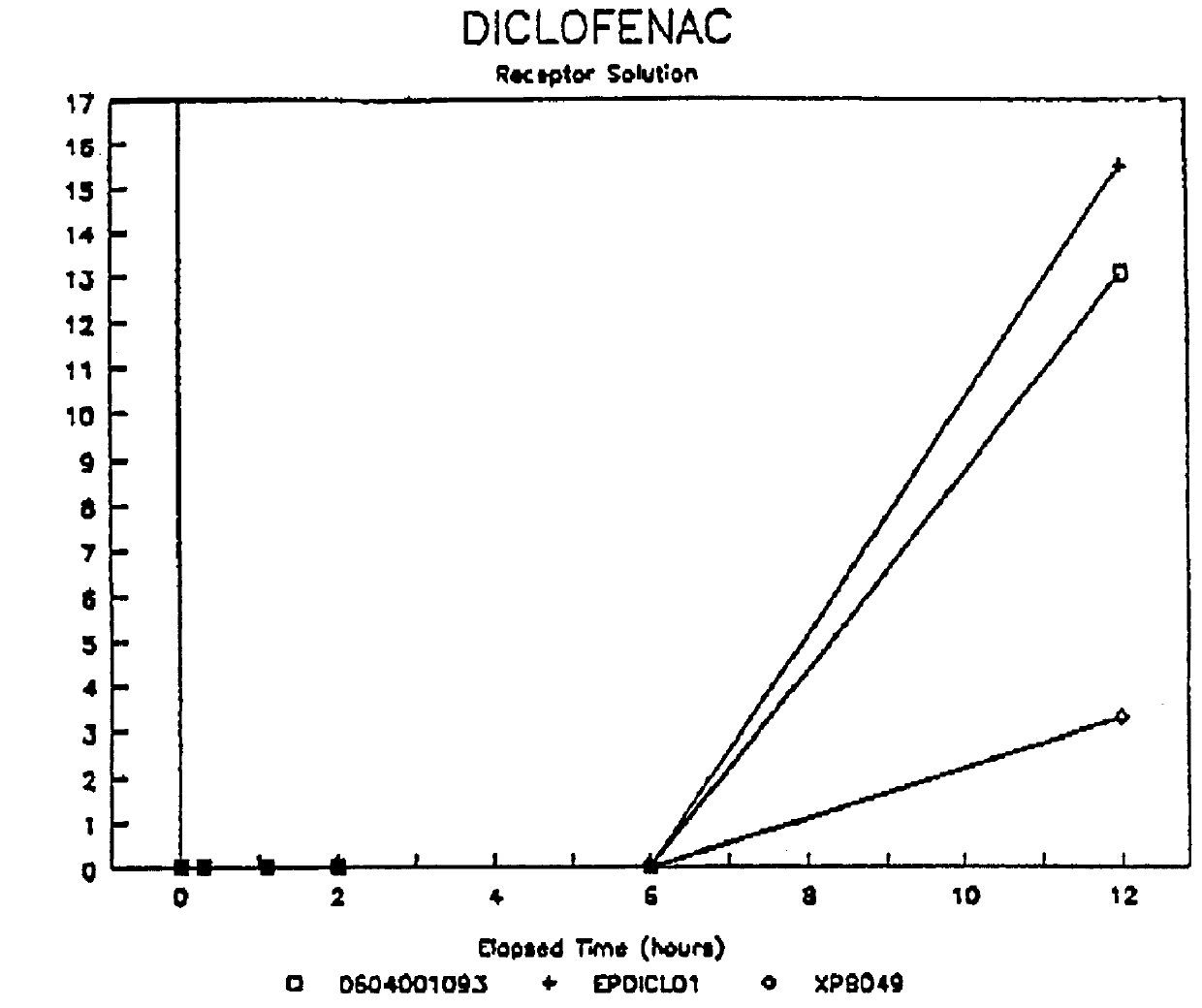
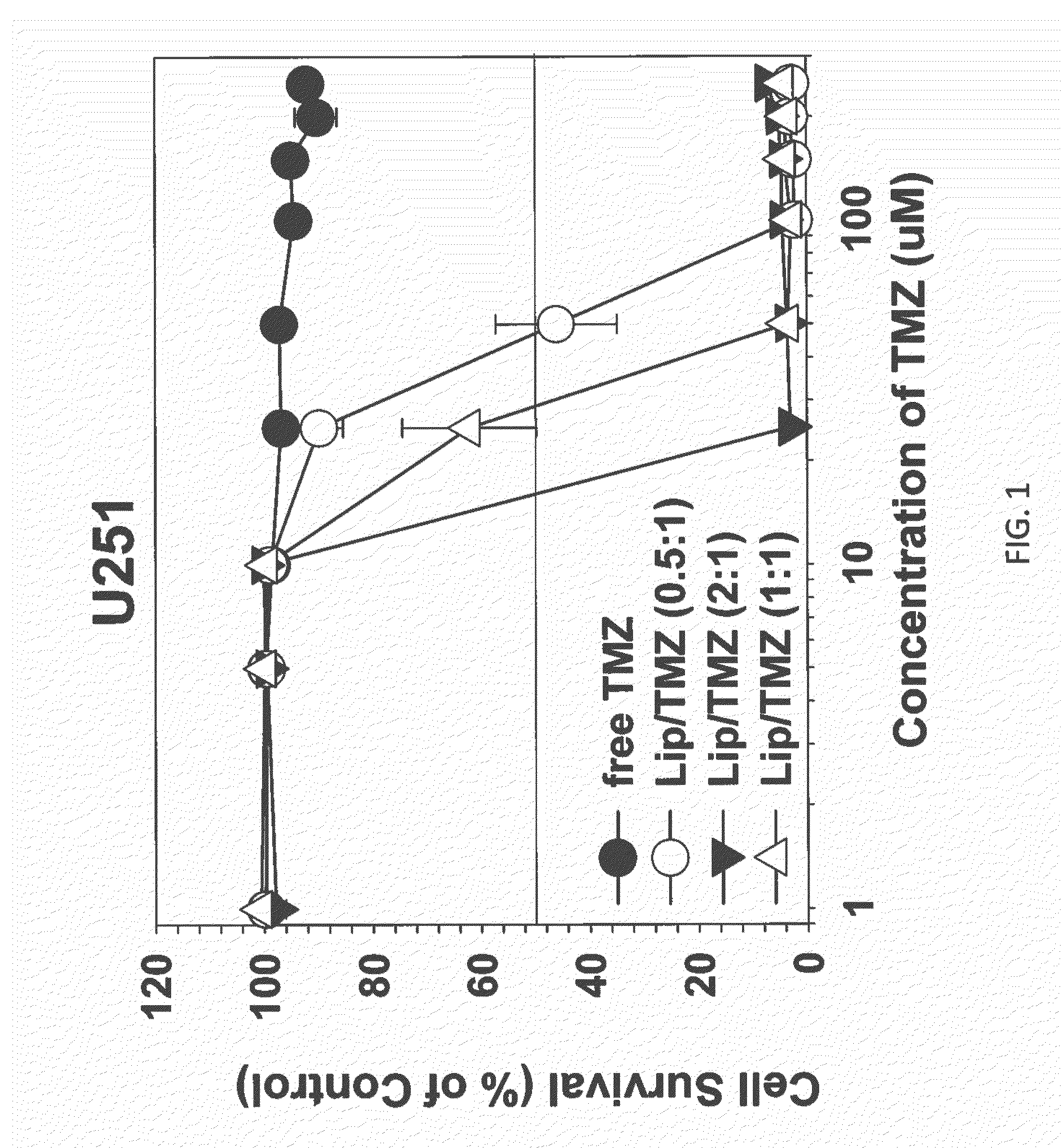
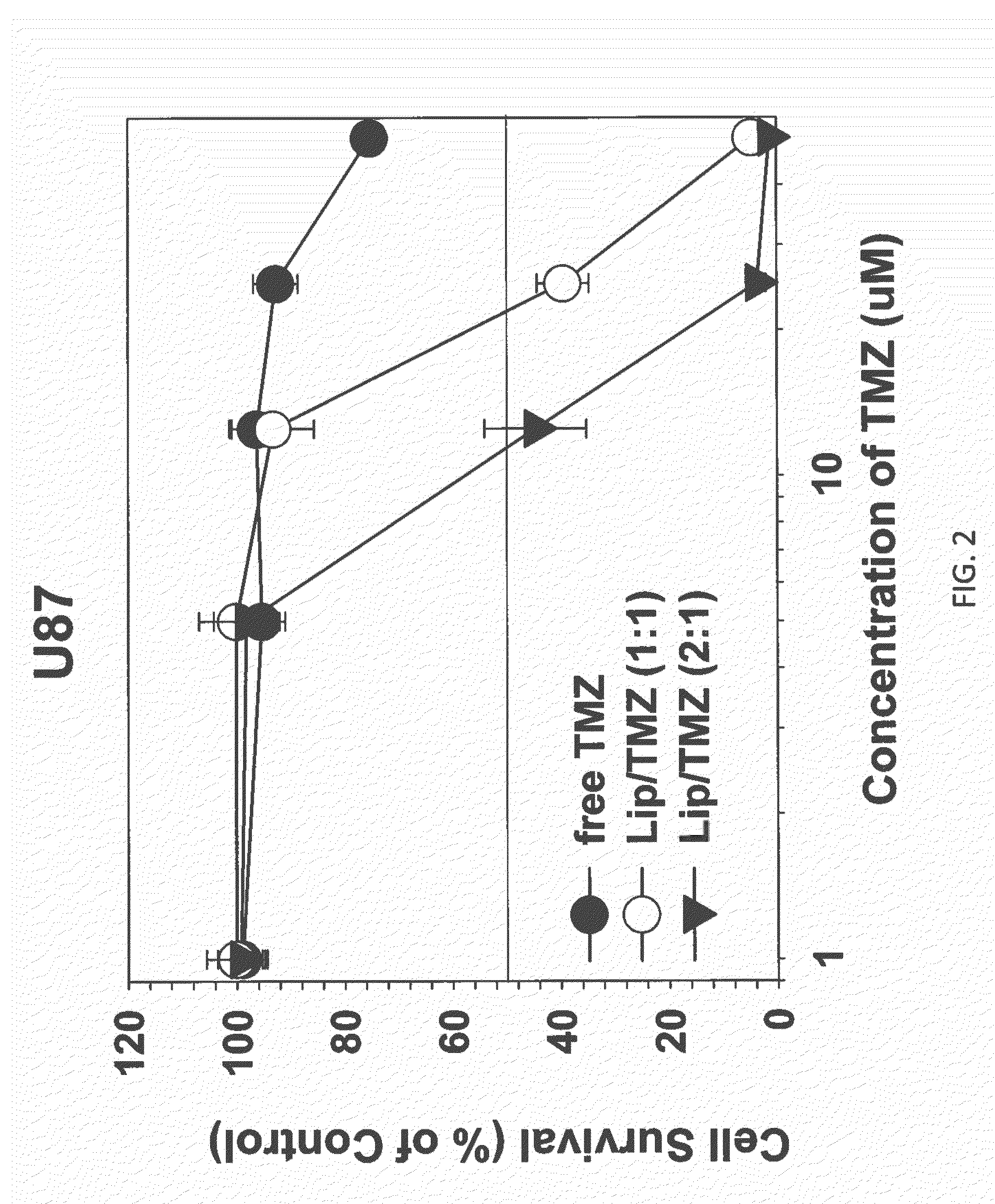
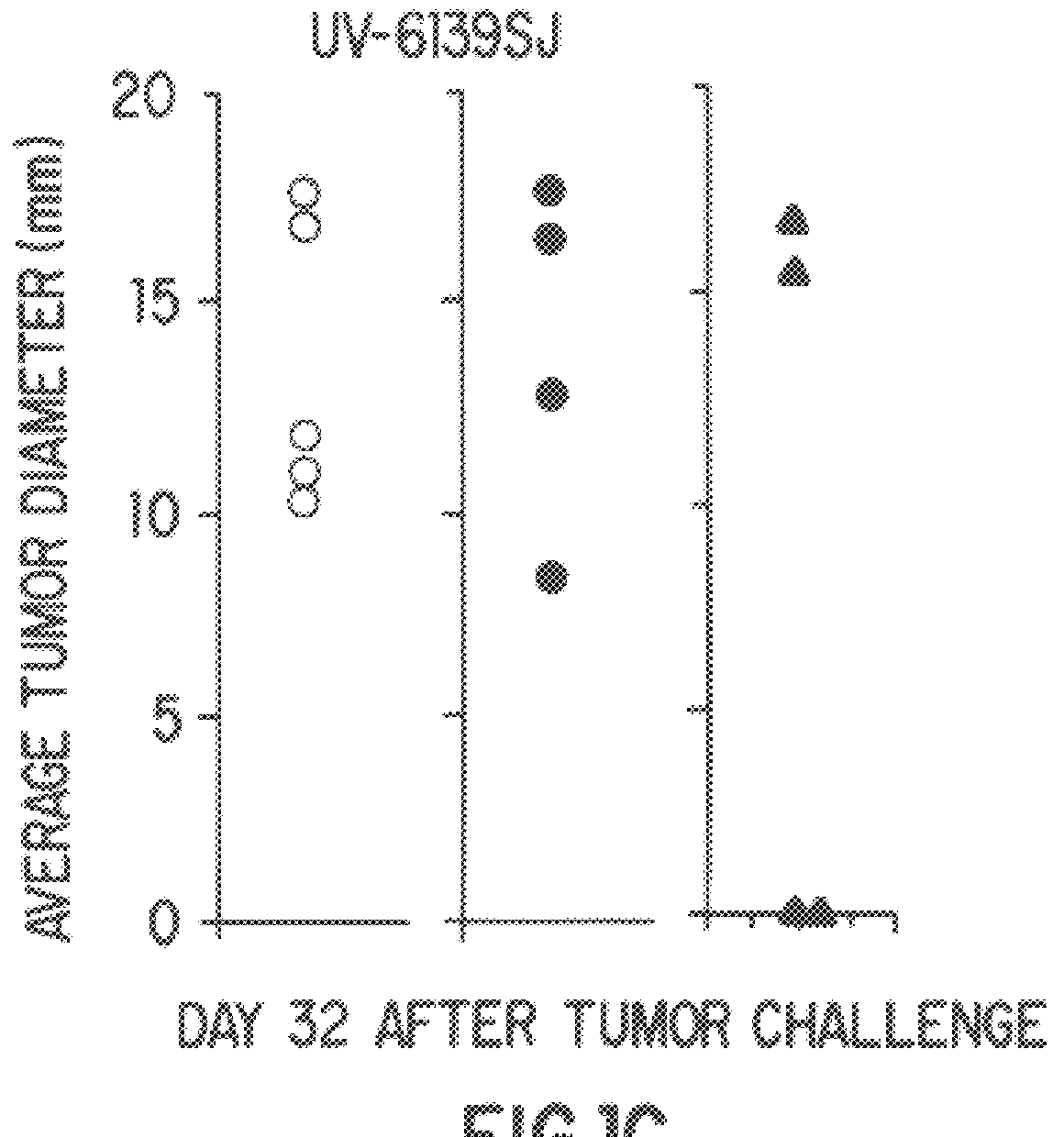
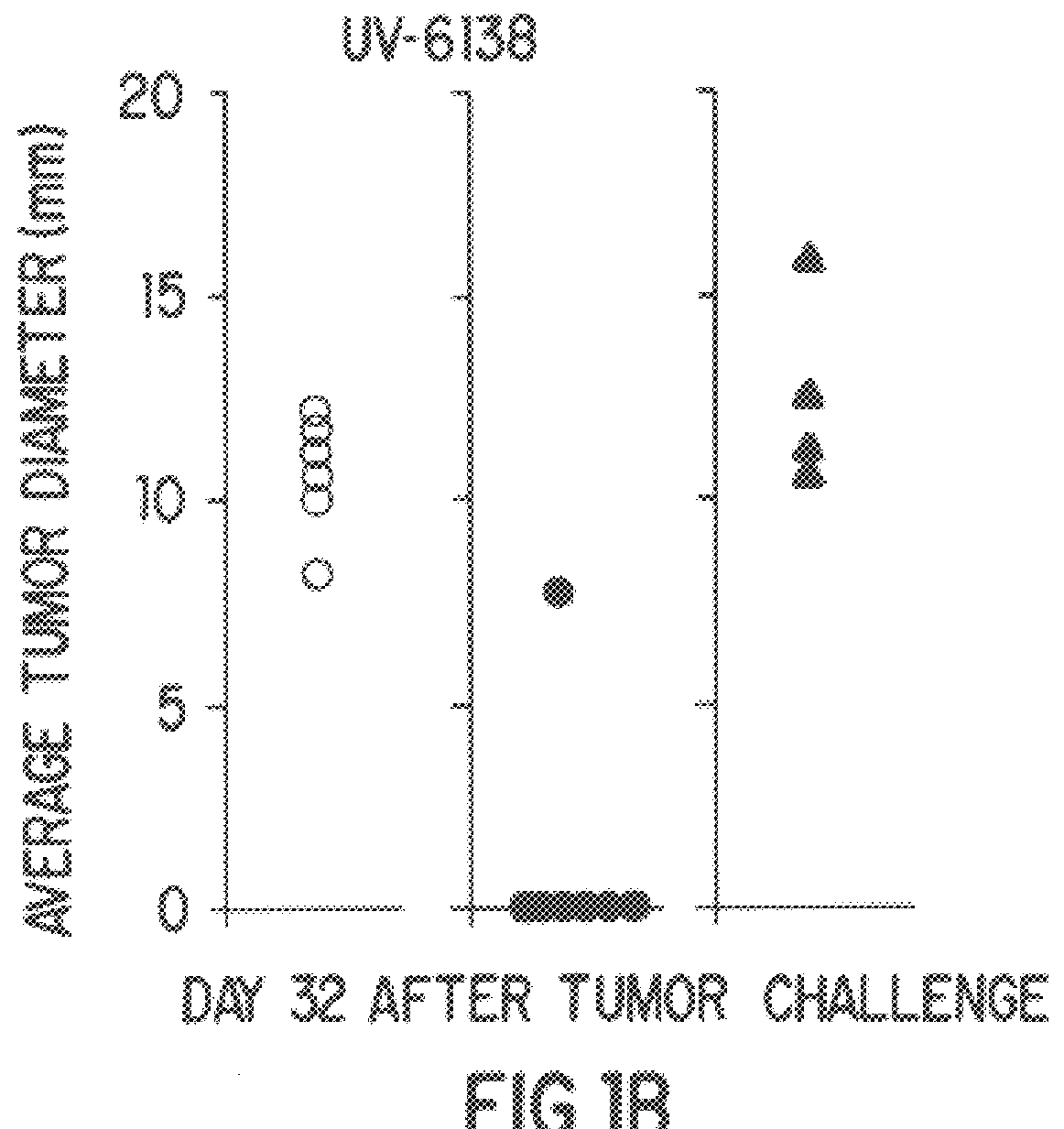
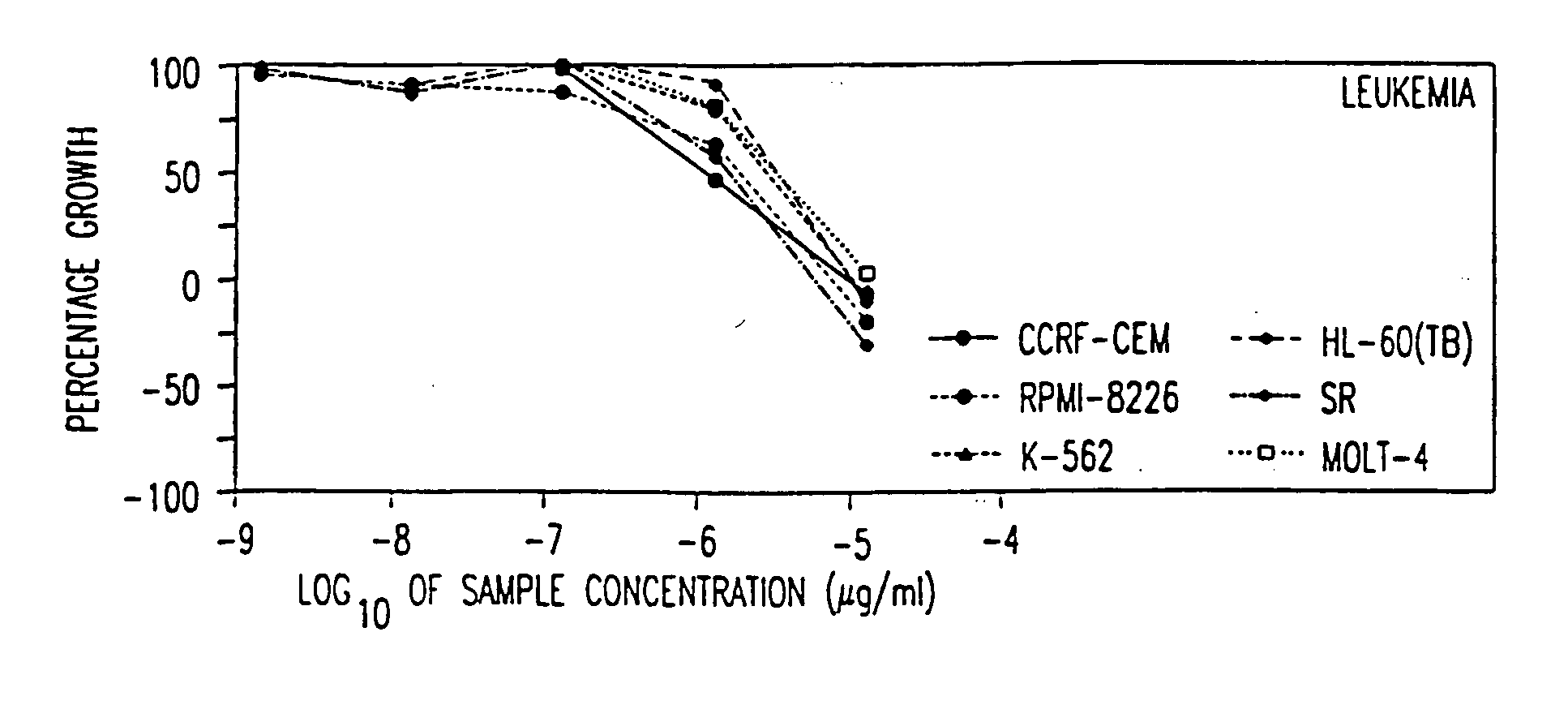
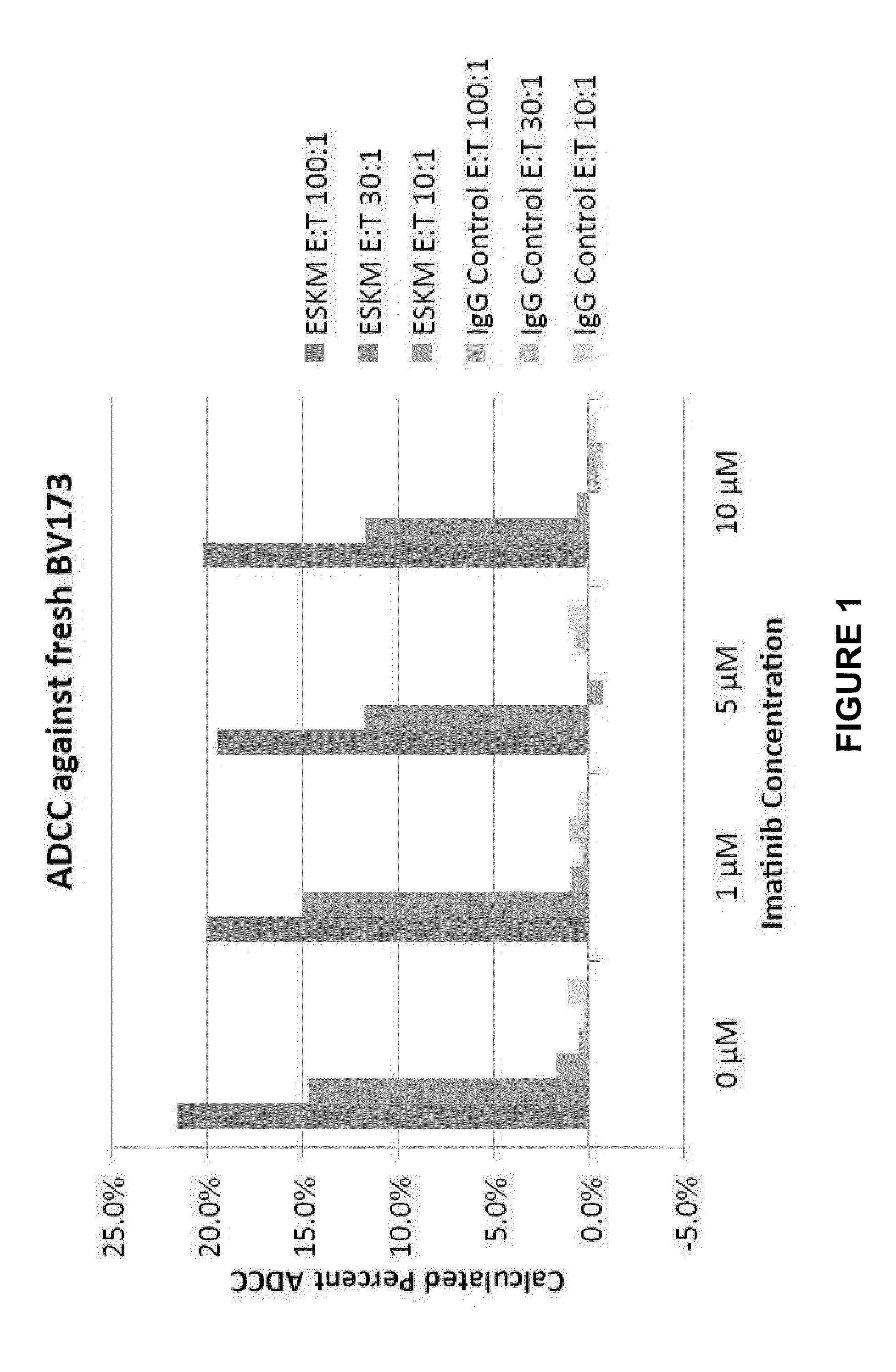
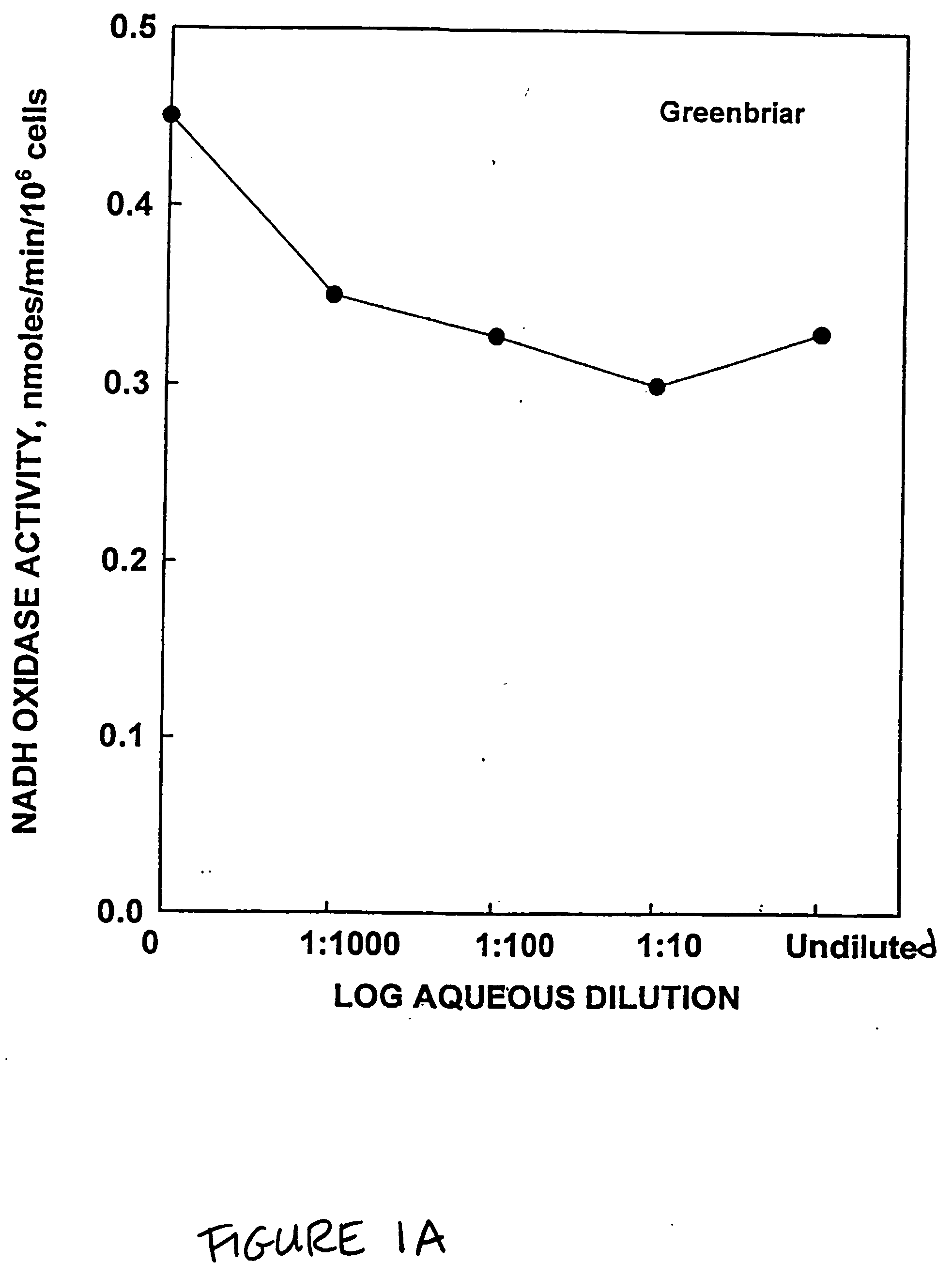
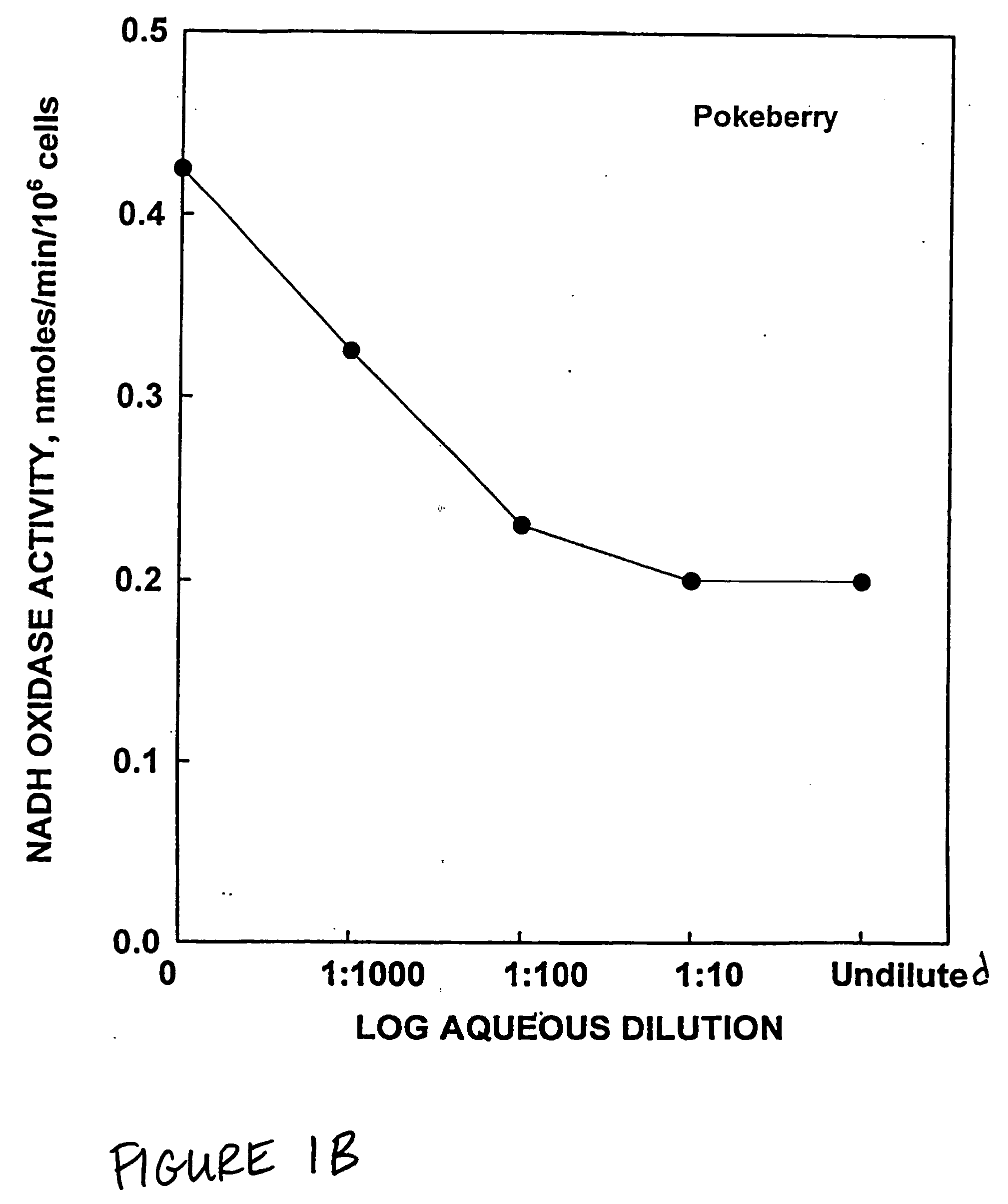
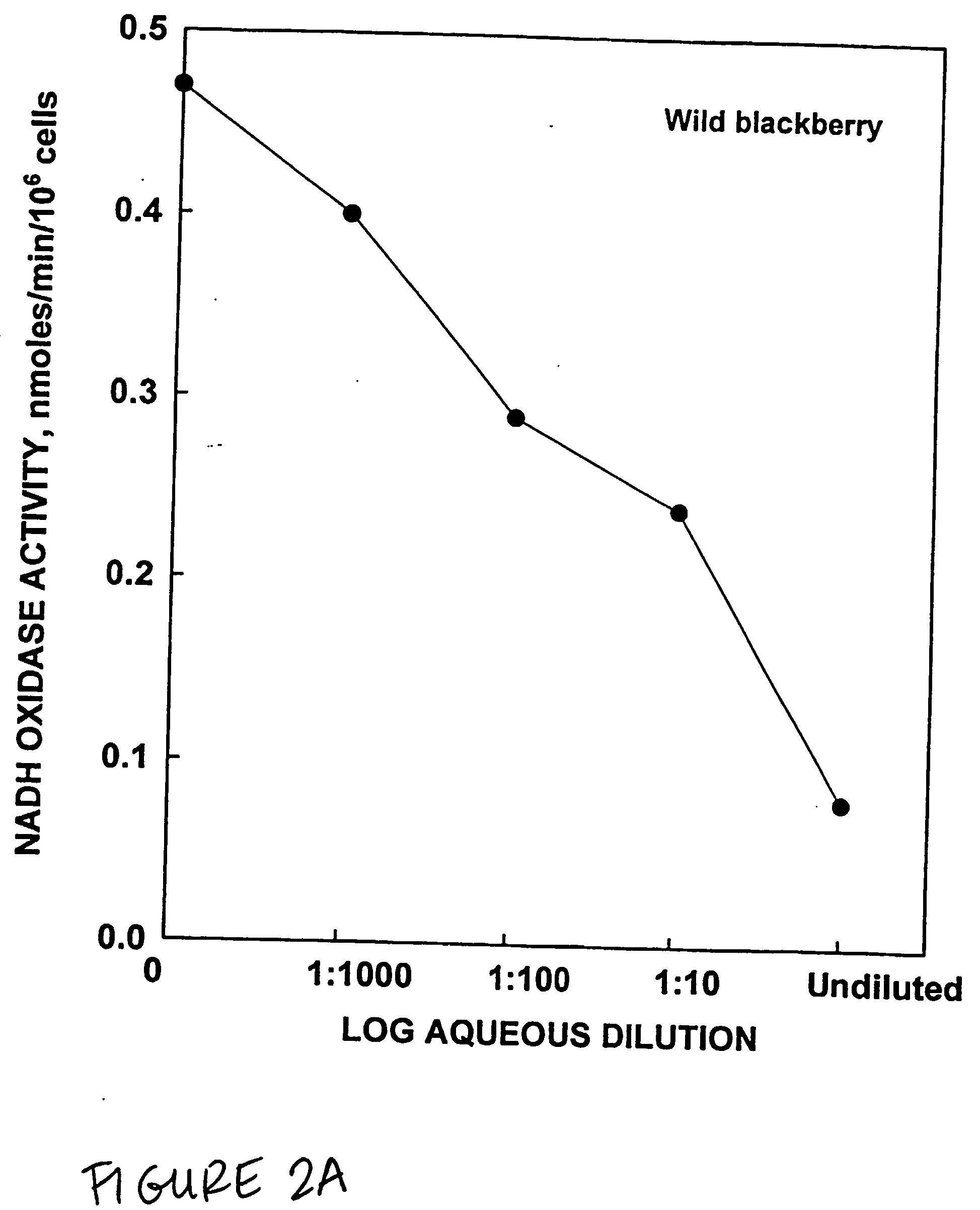
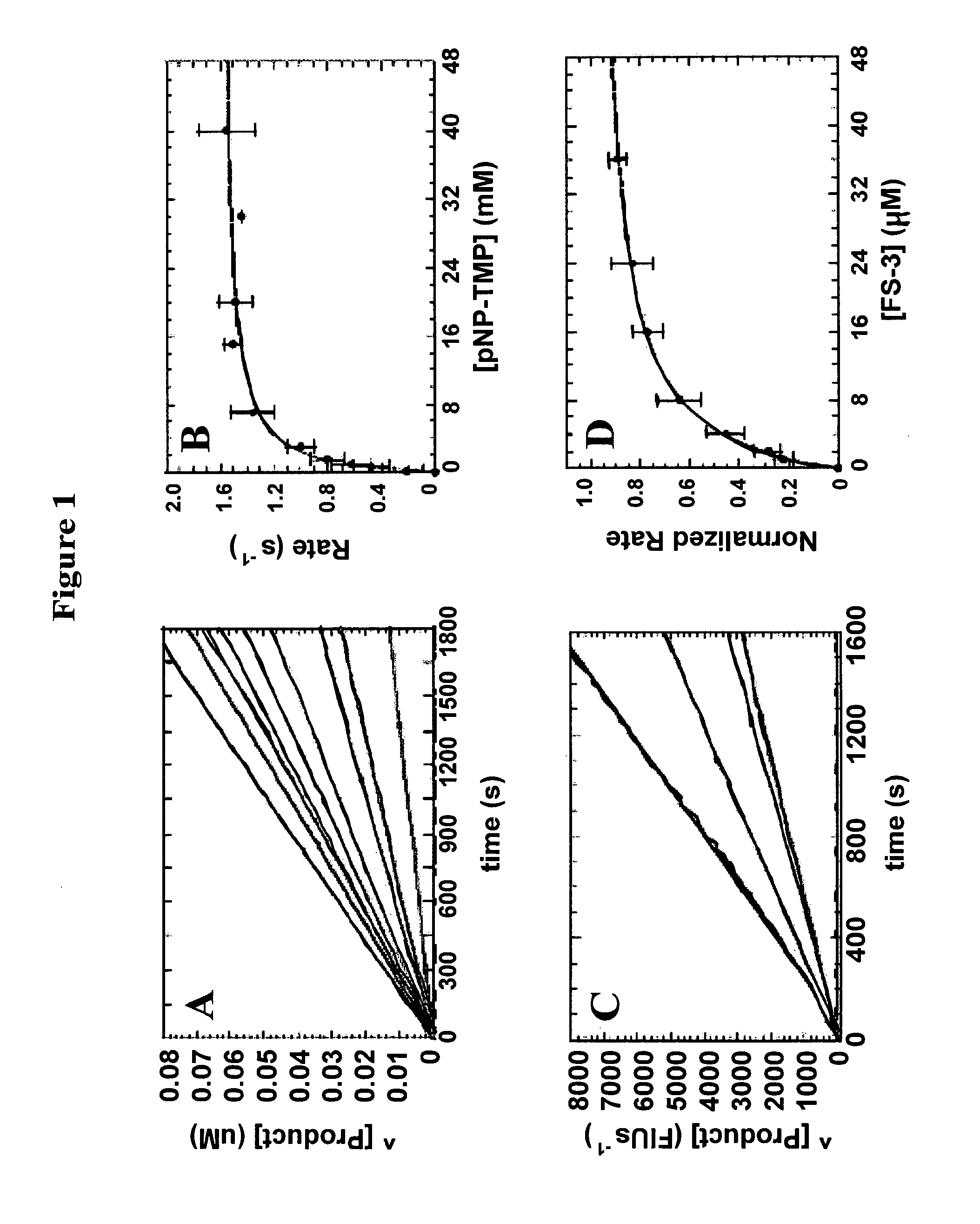
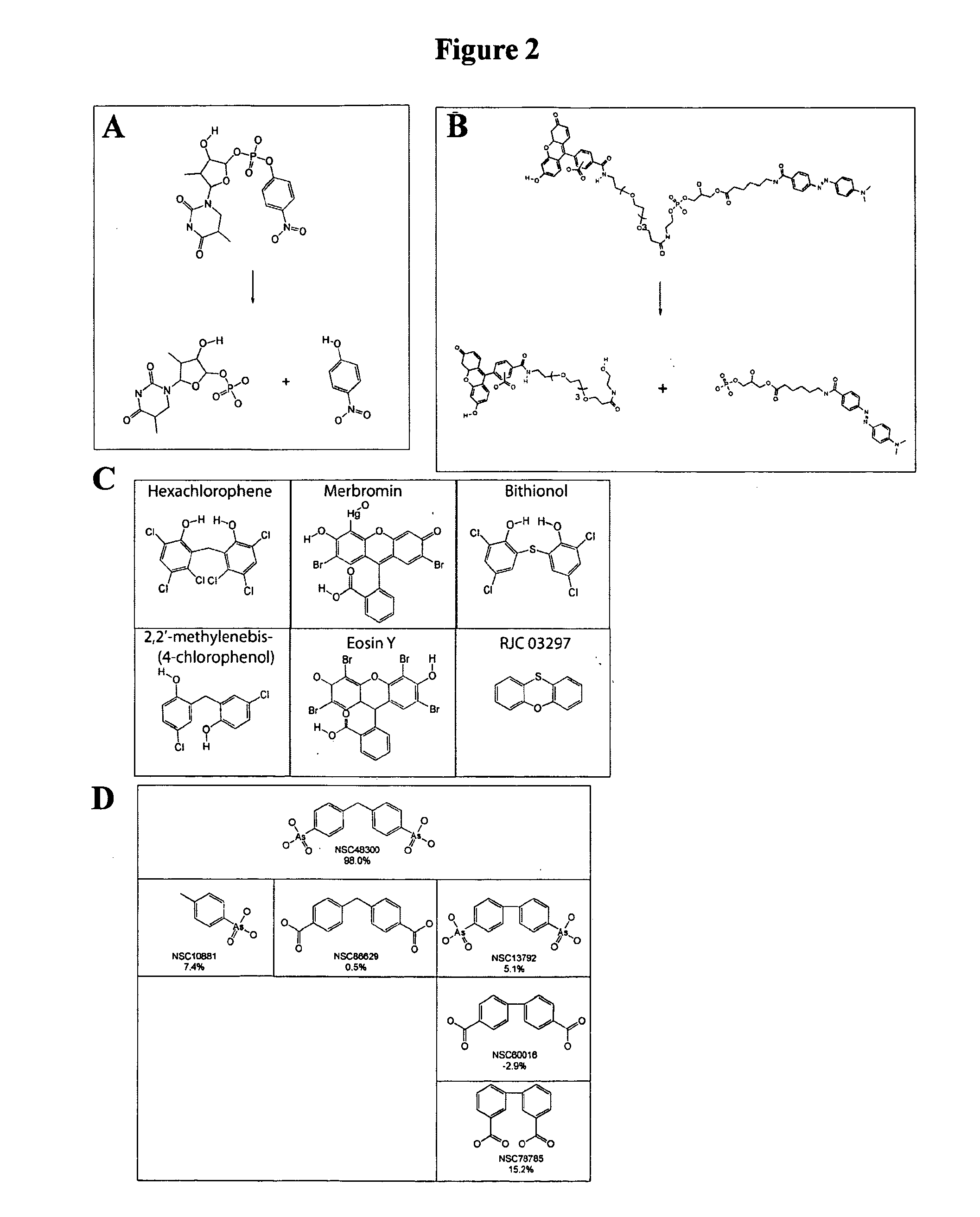
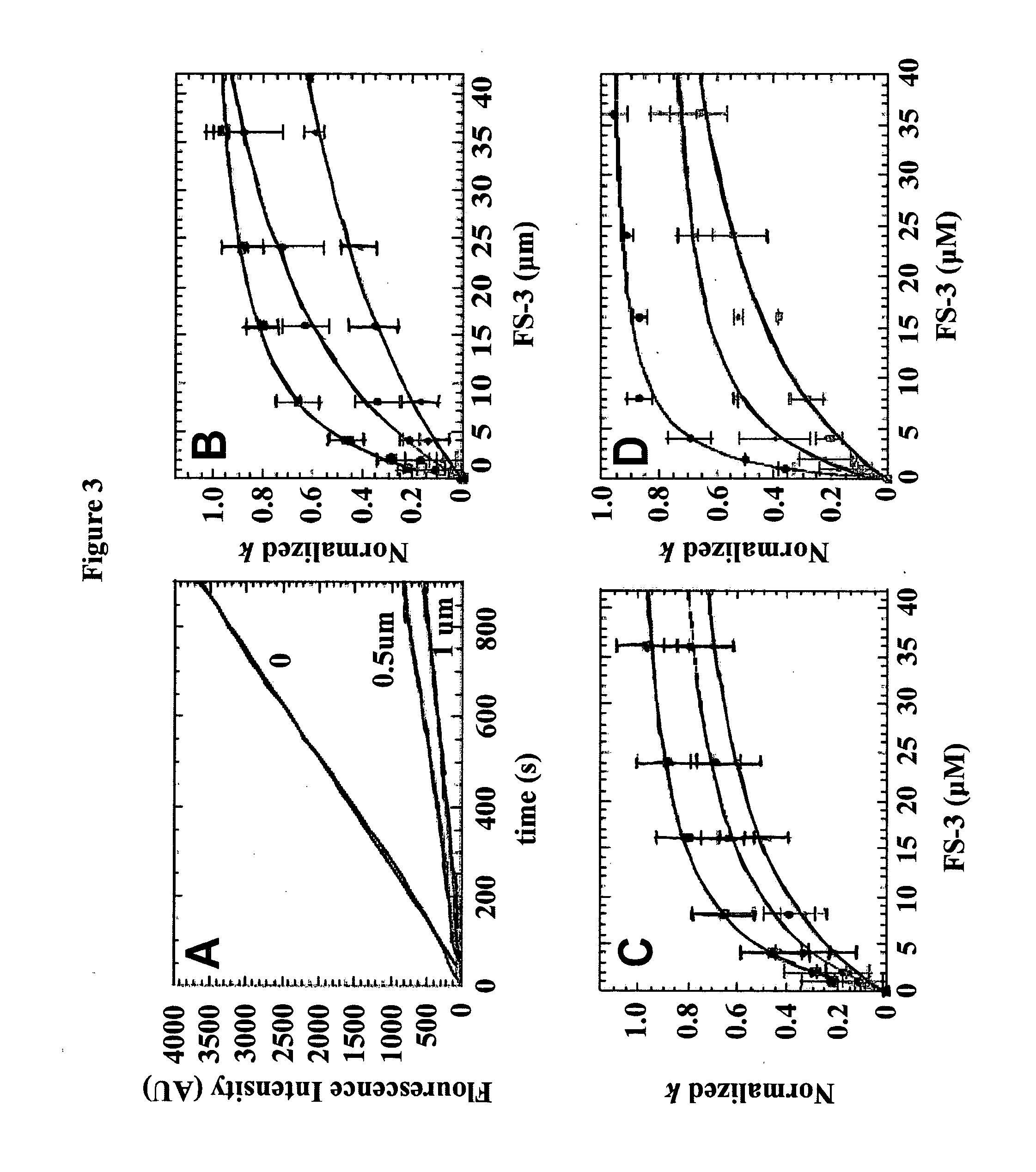
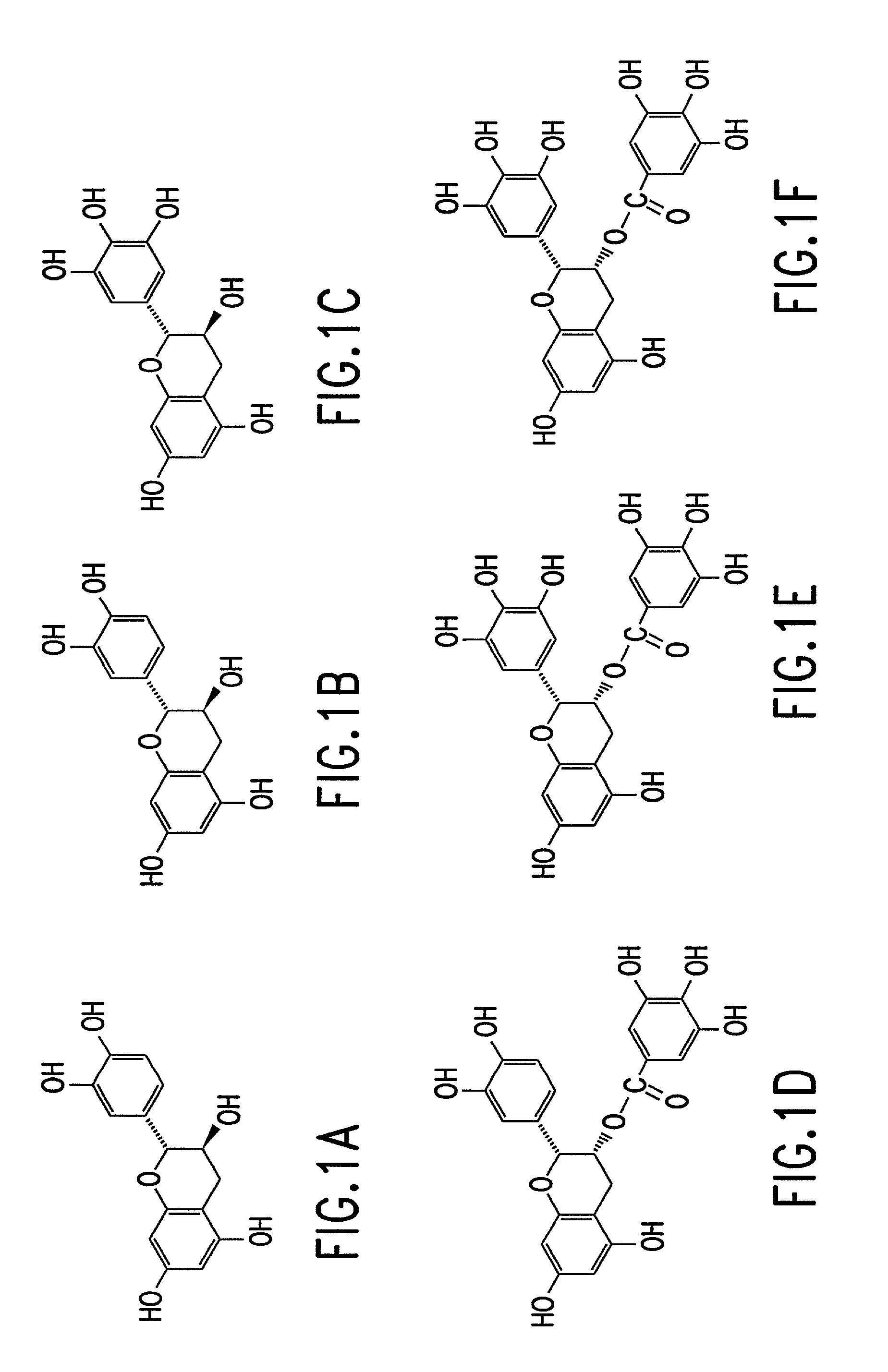
Patents
Literature
345 results about "Unknown primary" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
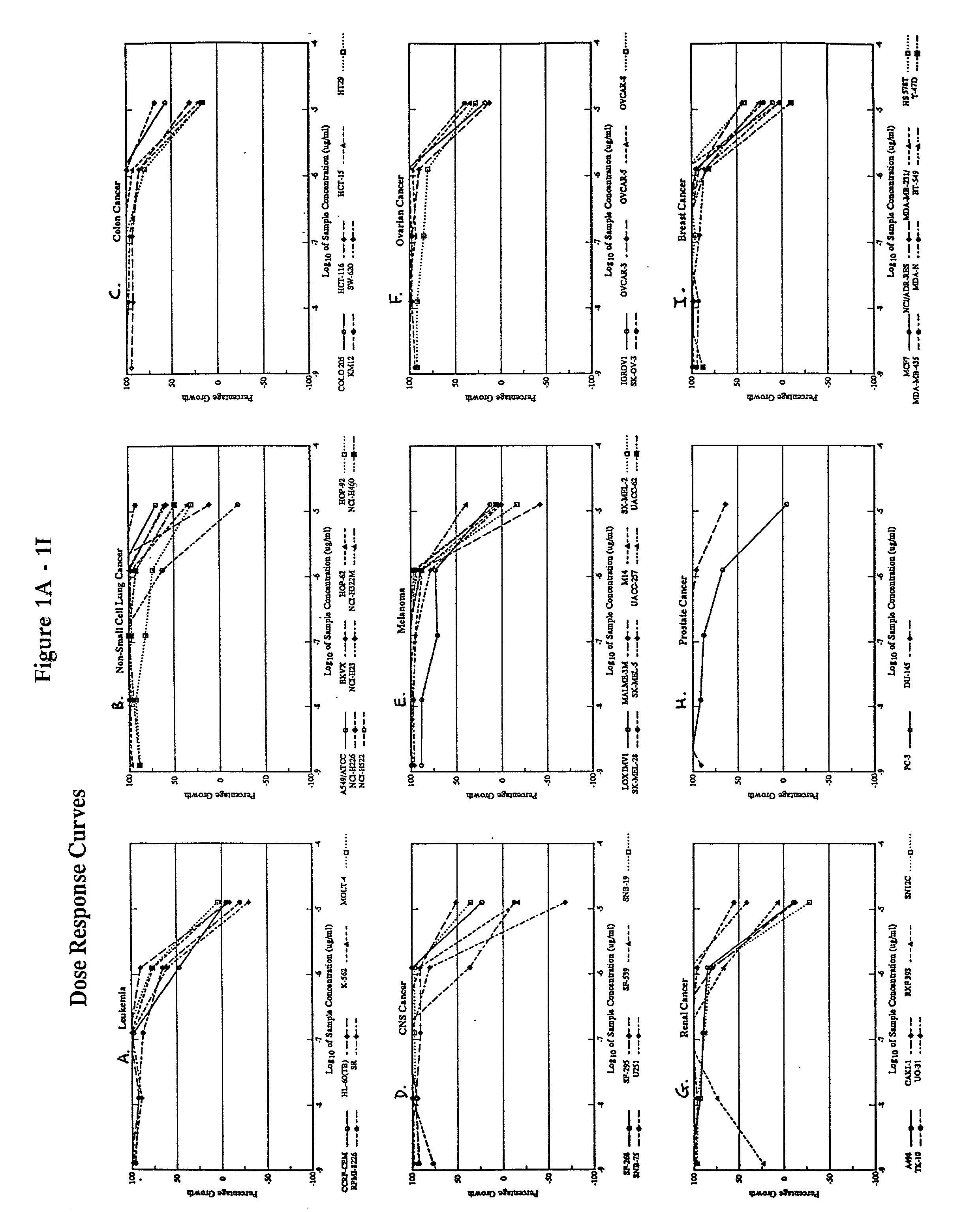
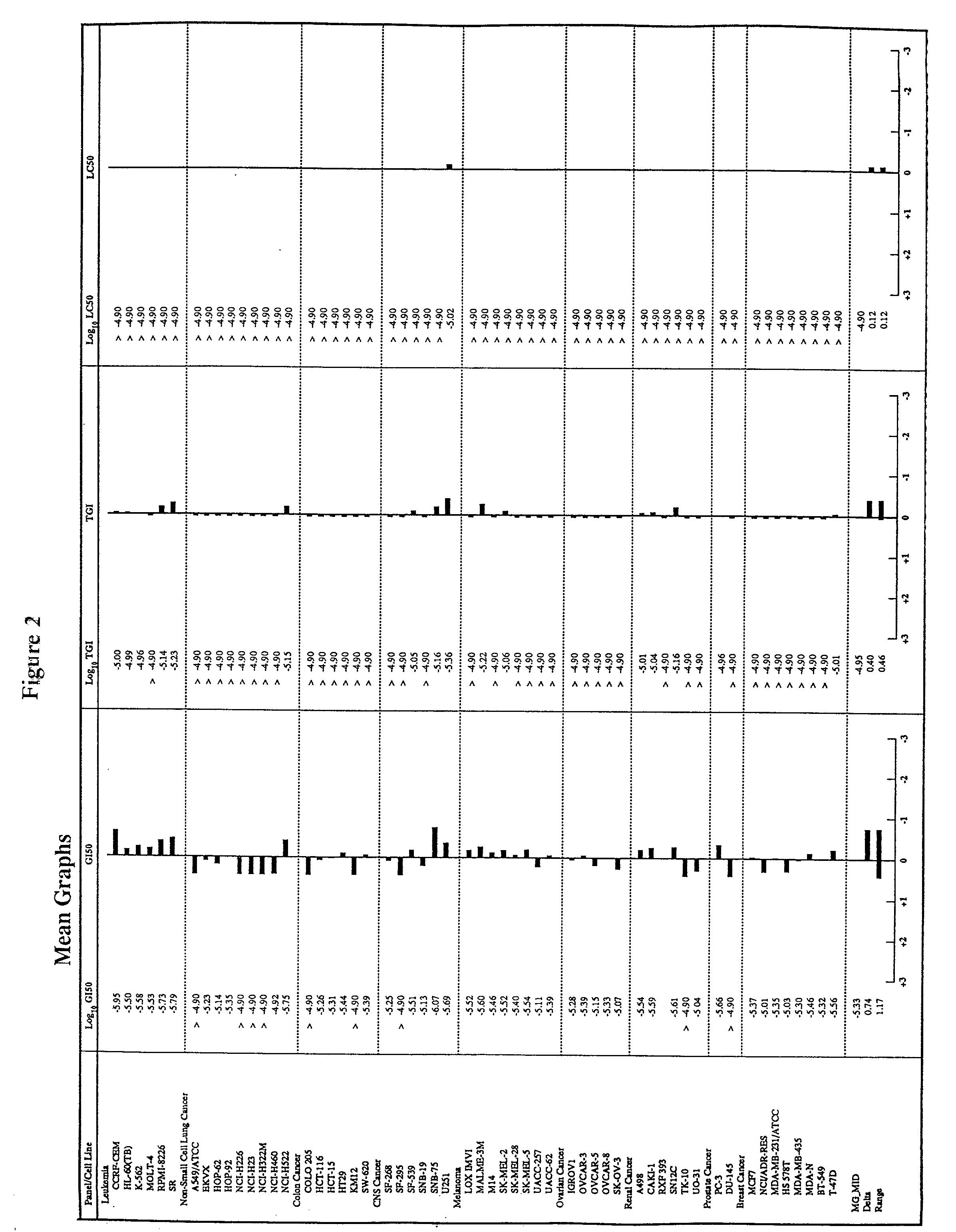
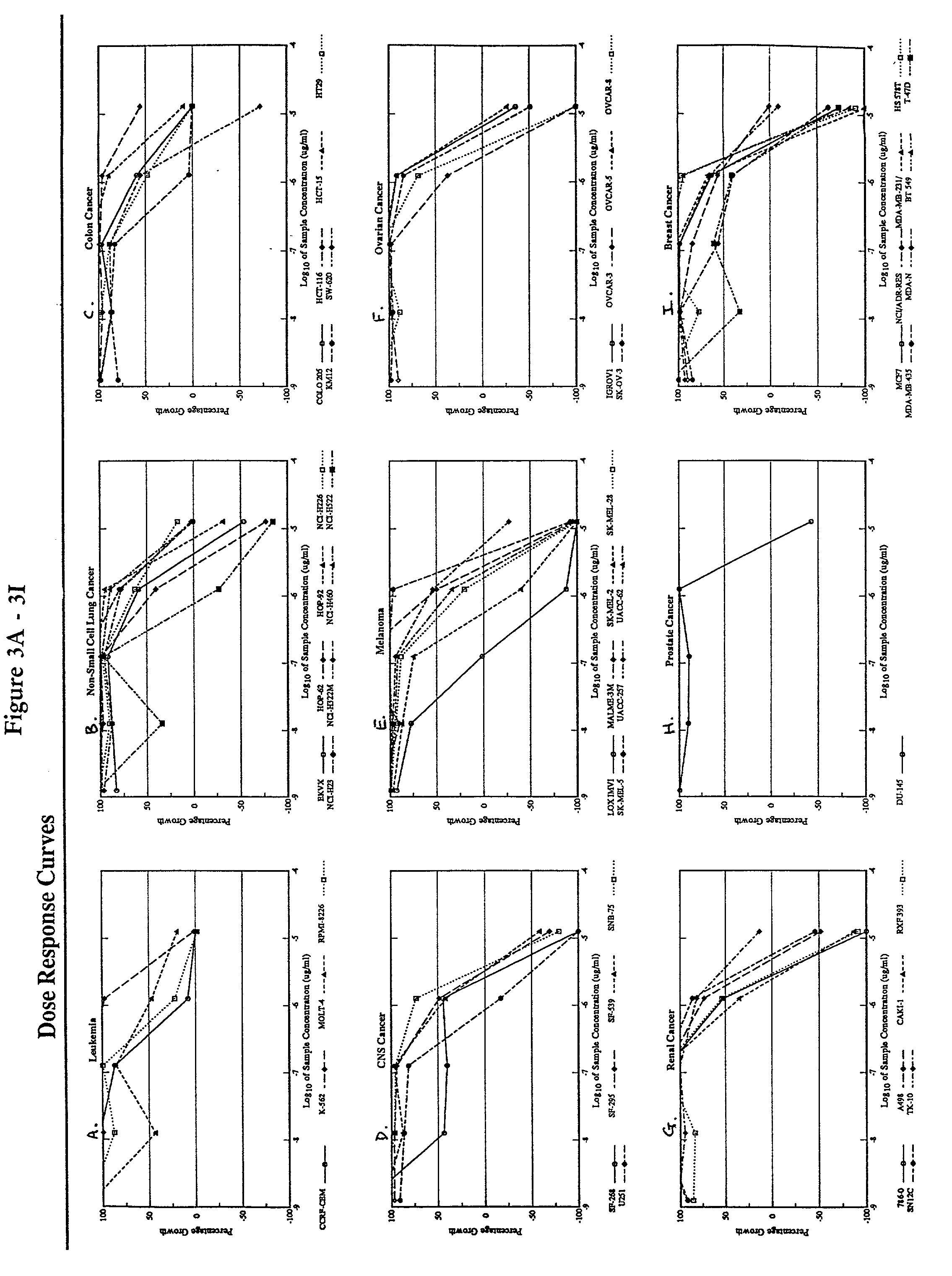
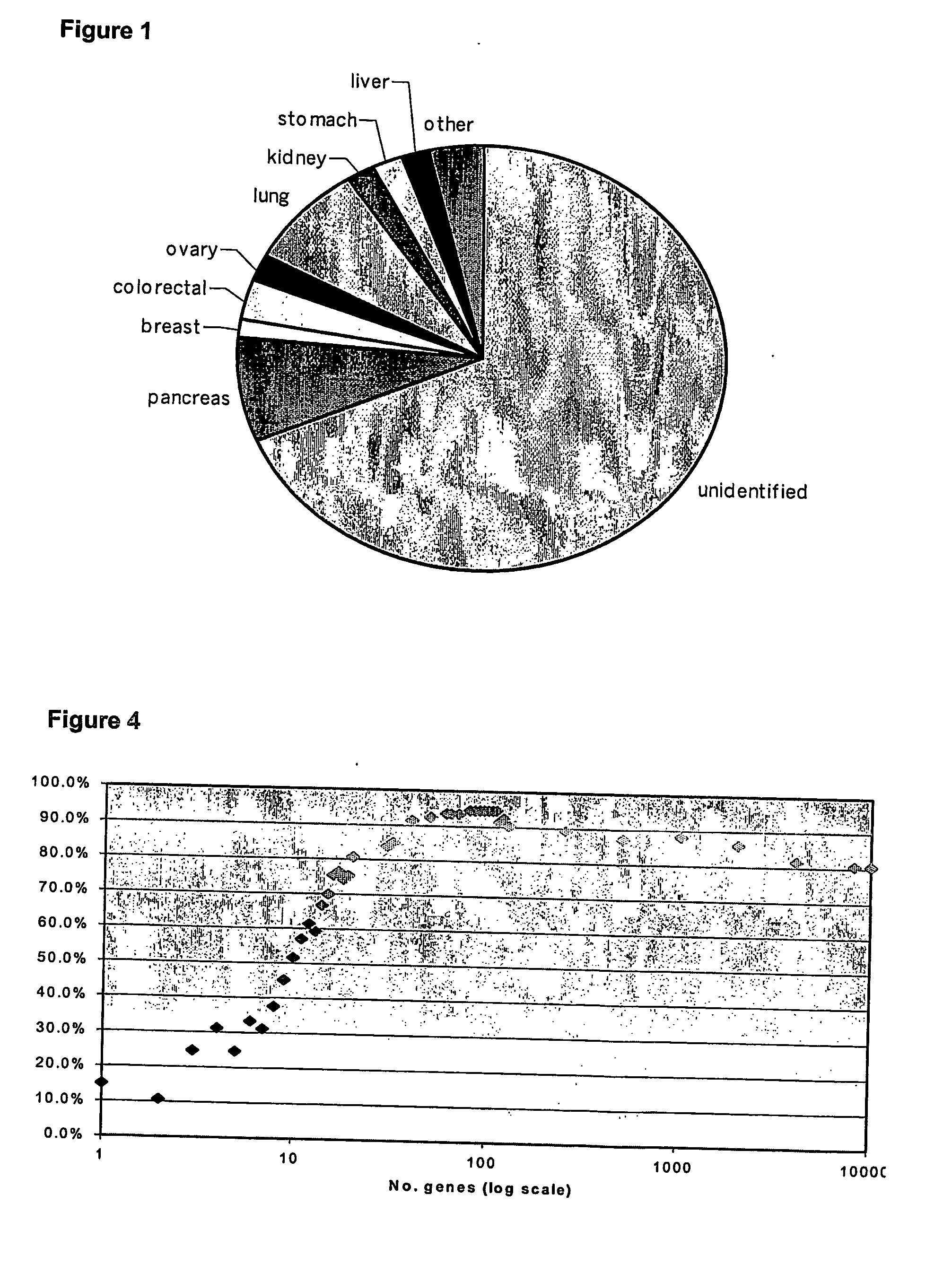
It is generally accepted that cancer of unknown primary site exists because the primary tumor is not identified due to clinical or technological inefficiencies, or because the primary tumor regresses or stays dormant after spreading the cancer cells that generate the metastases.
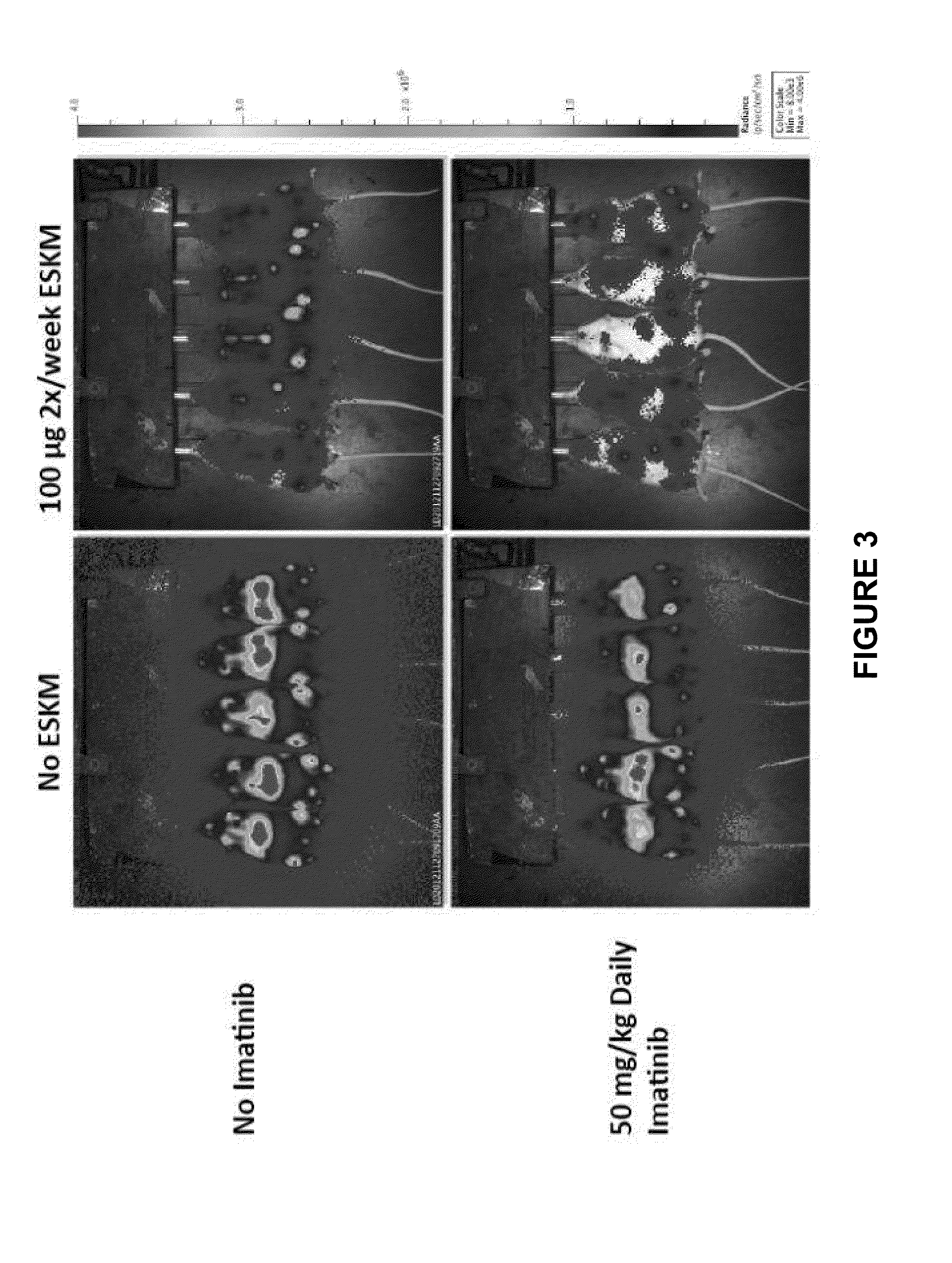
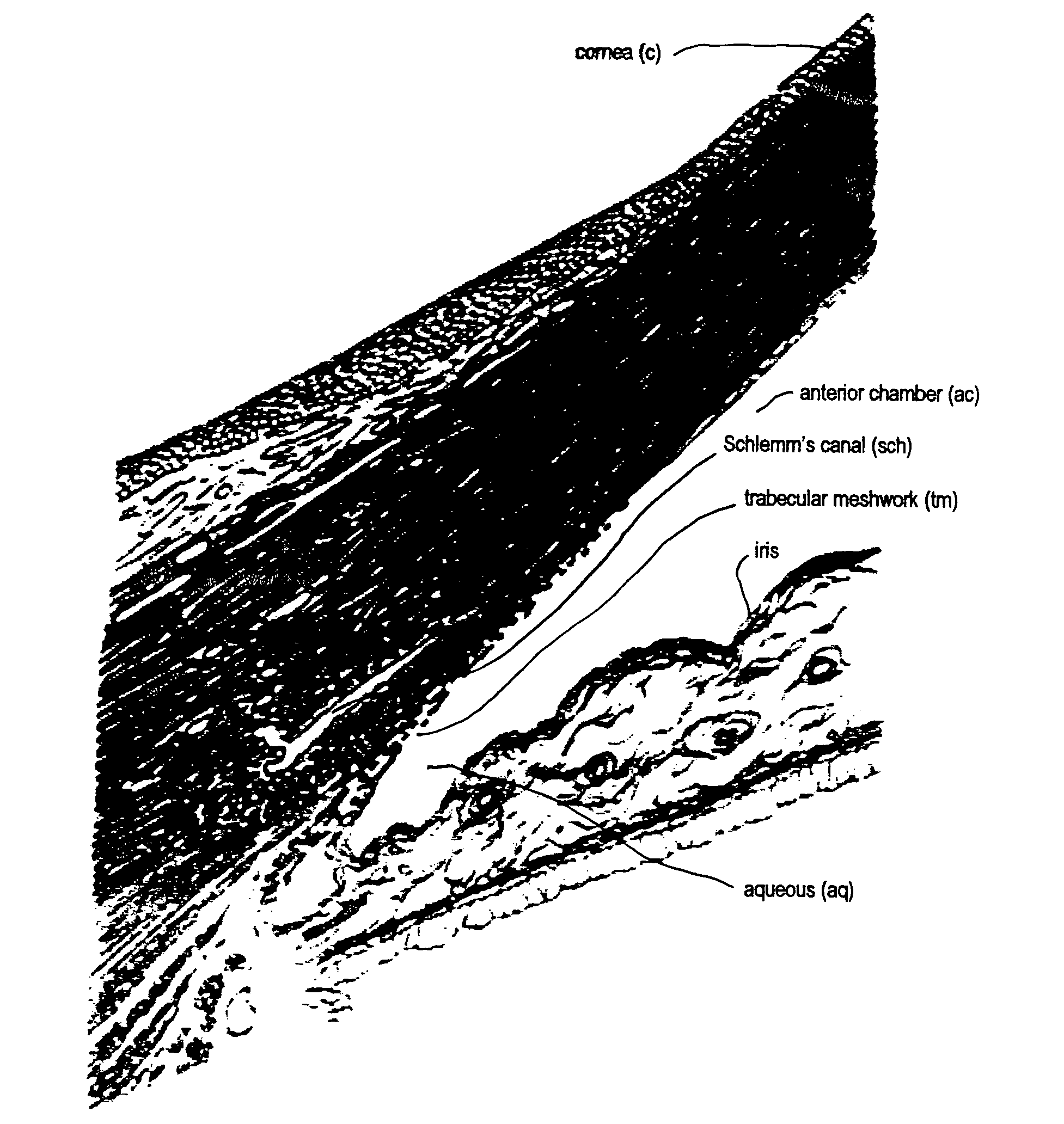
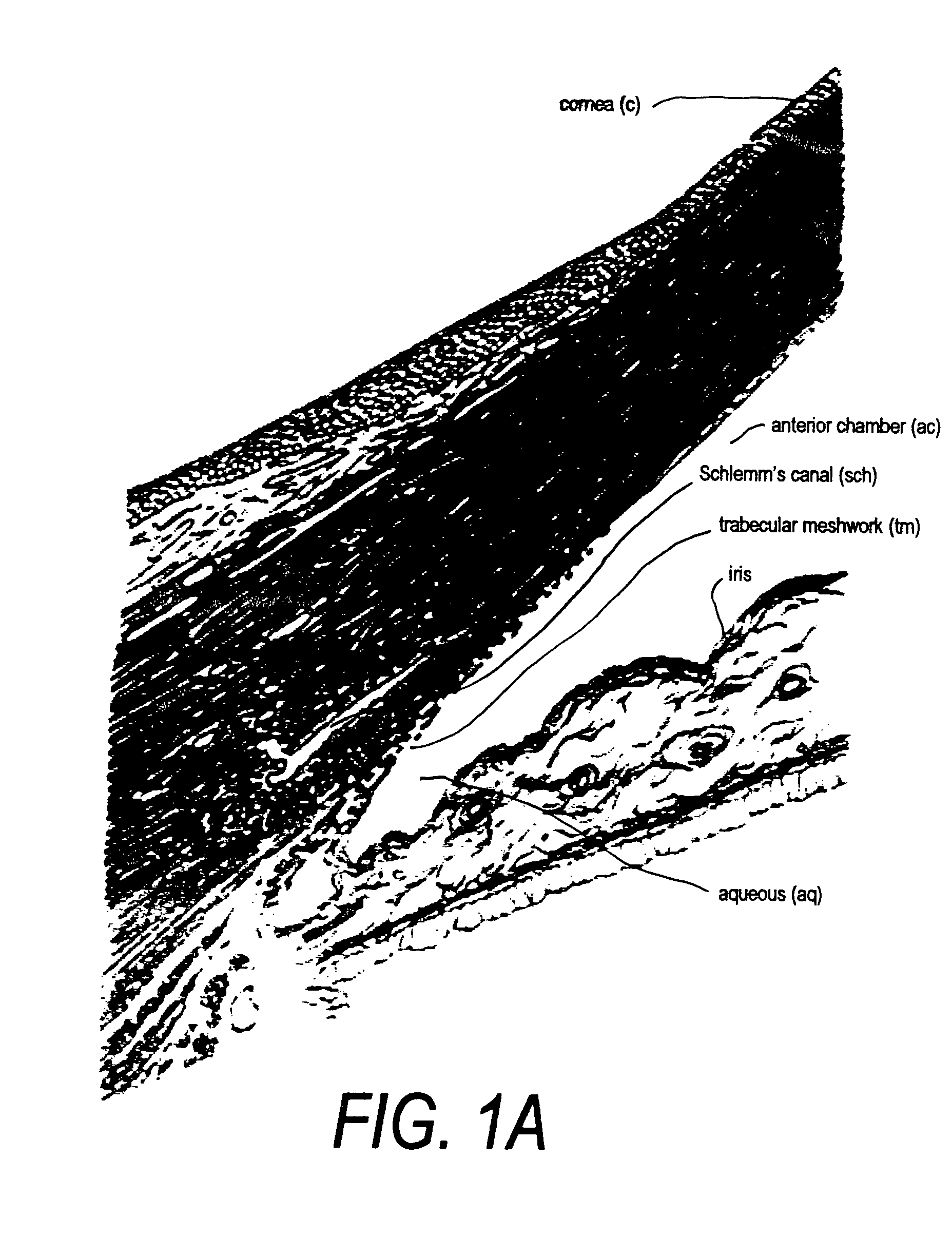
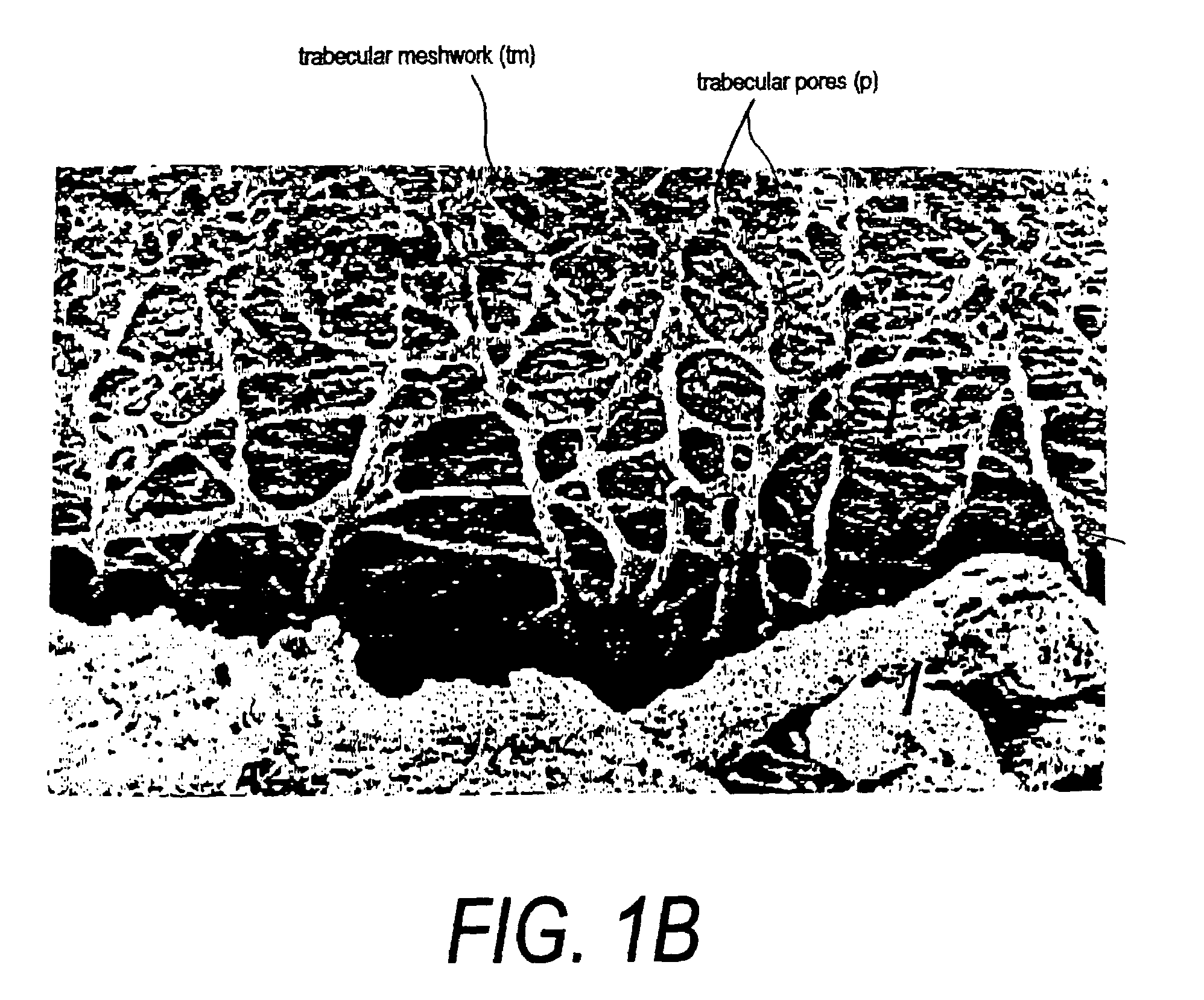
Devices and techniques for treating glaucoma
InactiveUS6989007B2Improve facilitiesGood mannersLaser surgeryDiagnosticsOpen angle glaucomaAqueous outflow
A system for non-invasive treatment of a patient's trabecular meshwork to treat primary open-angle glaucoma. The system and technique applies energy directly to media within clogged spaces in a patient's trabecular meshwork to increase aqueous outflow facility by (i) localization of microimplantable bodies carrying a selected exogenous chromophore, such as particles with a gold surface, in deeper regions of the trabecular meshwork, and (ii) irradiation of the microimplantables with a selected coherent wavelength having a power level and pulse duration that is strongly absorbed by the surfaces of the microimplantables.
Owner:OCCULOGIX CORP
Prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases with heat shock/stress protein-peptide complexes
InactiveUS6017540AEnhancing host 's immunocompetenceHigh activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsStress ProteinsIn vivo
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. Optionally, the methods further comprise administering antigen presenting cells sensitized with complexes of hsps noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. In a specific embodiment, the effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 0.1 to 9.0 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp70, 5 to 49 micrograms for hsp90, and 0.1 to 9.0 micrograms for gp96.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
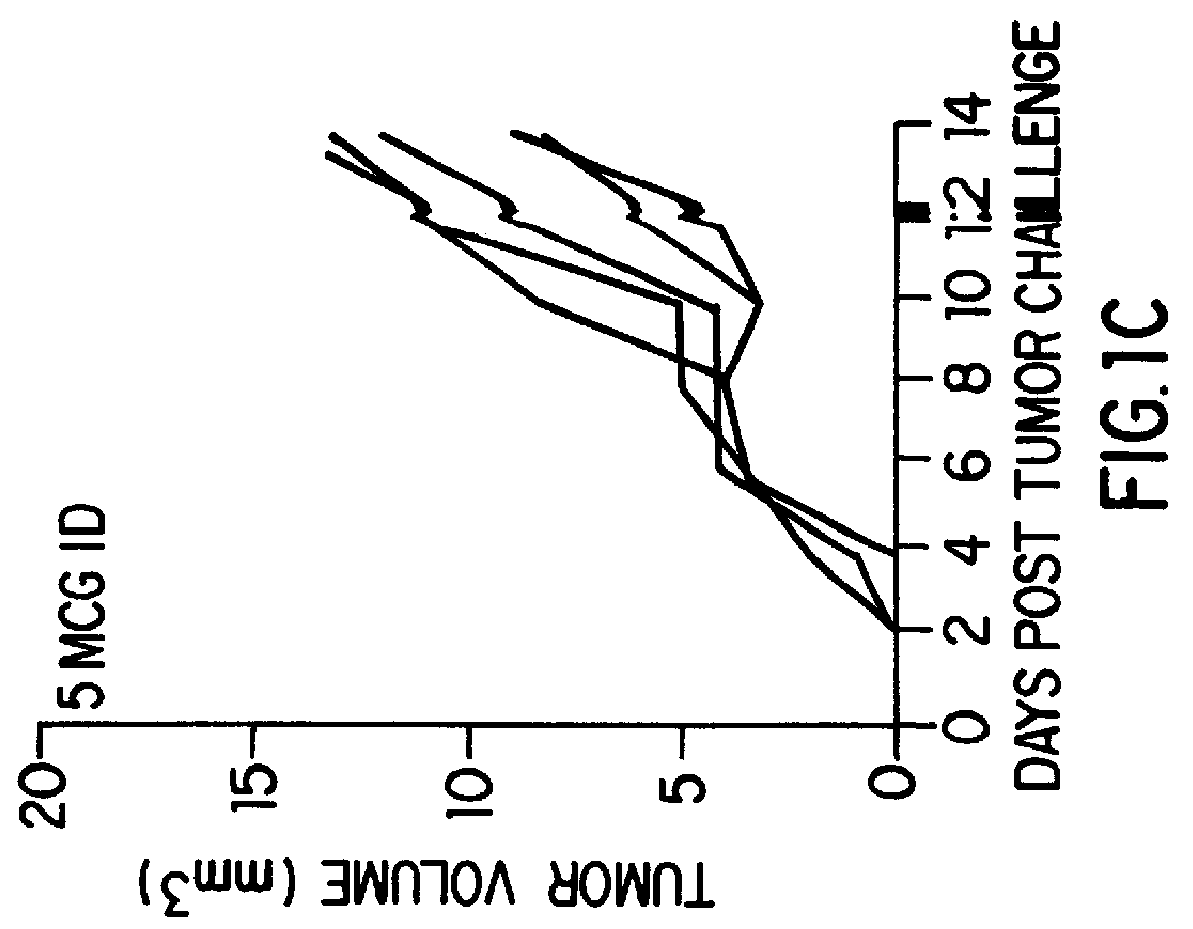
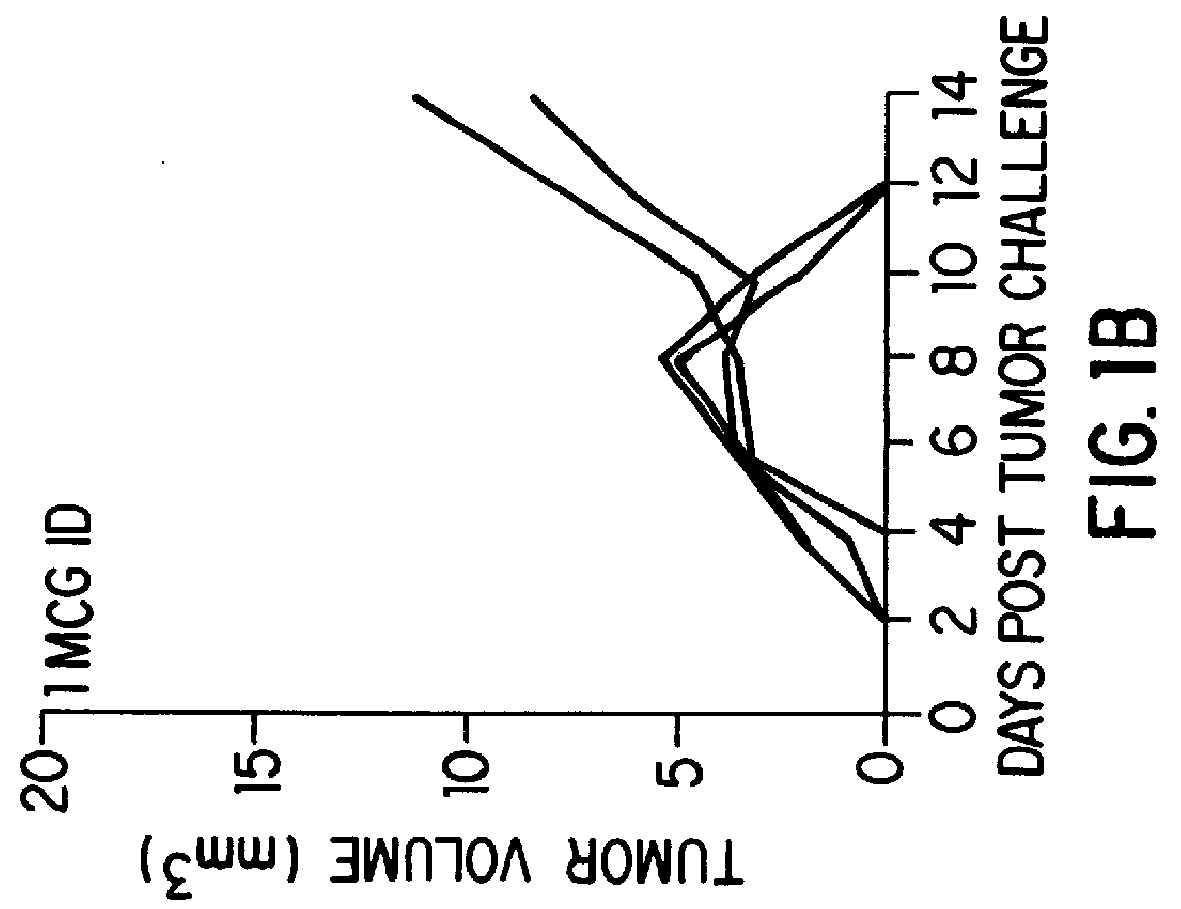
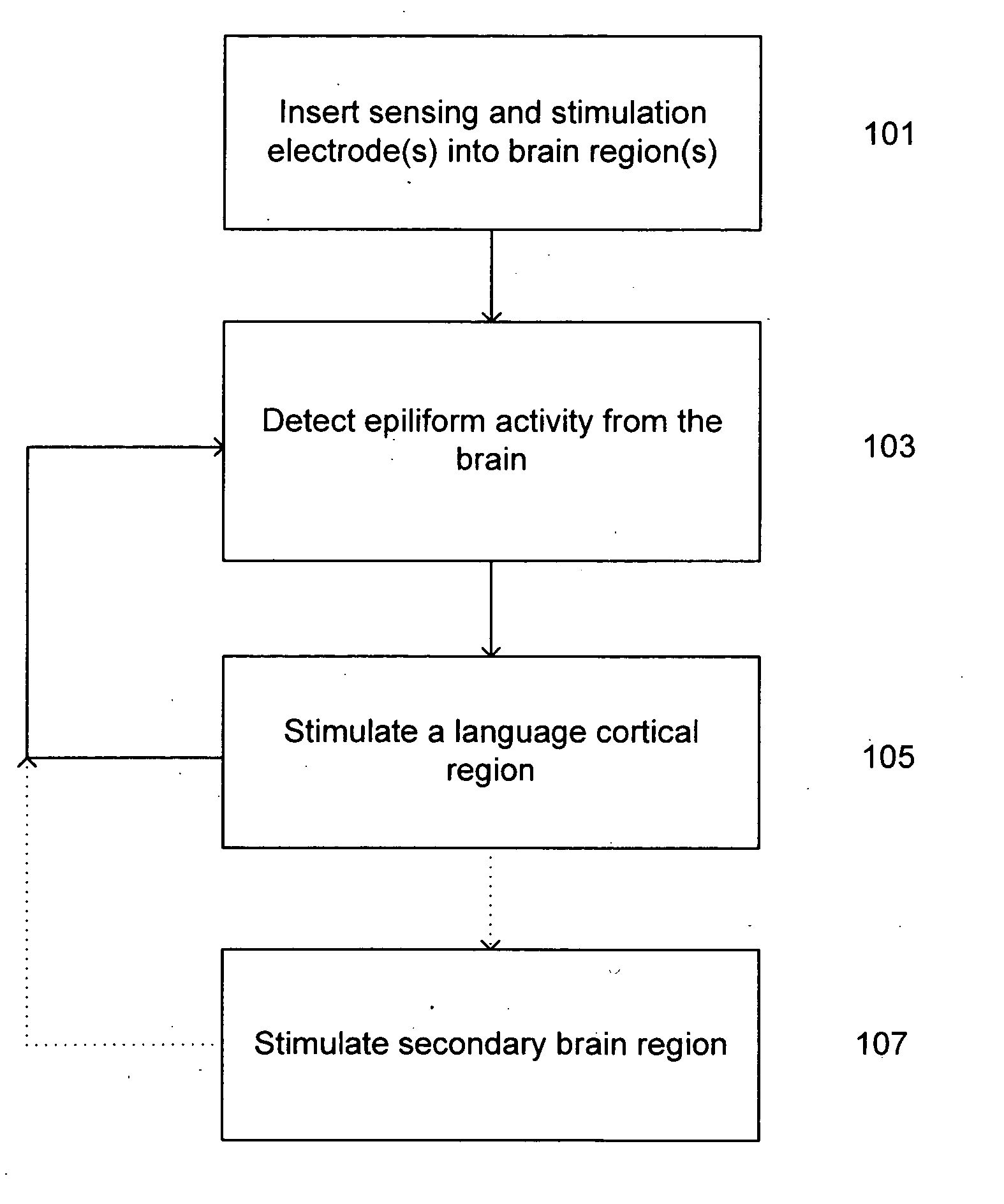
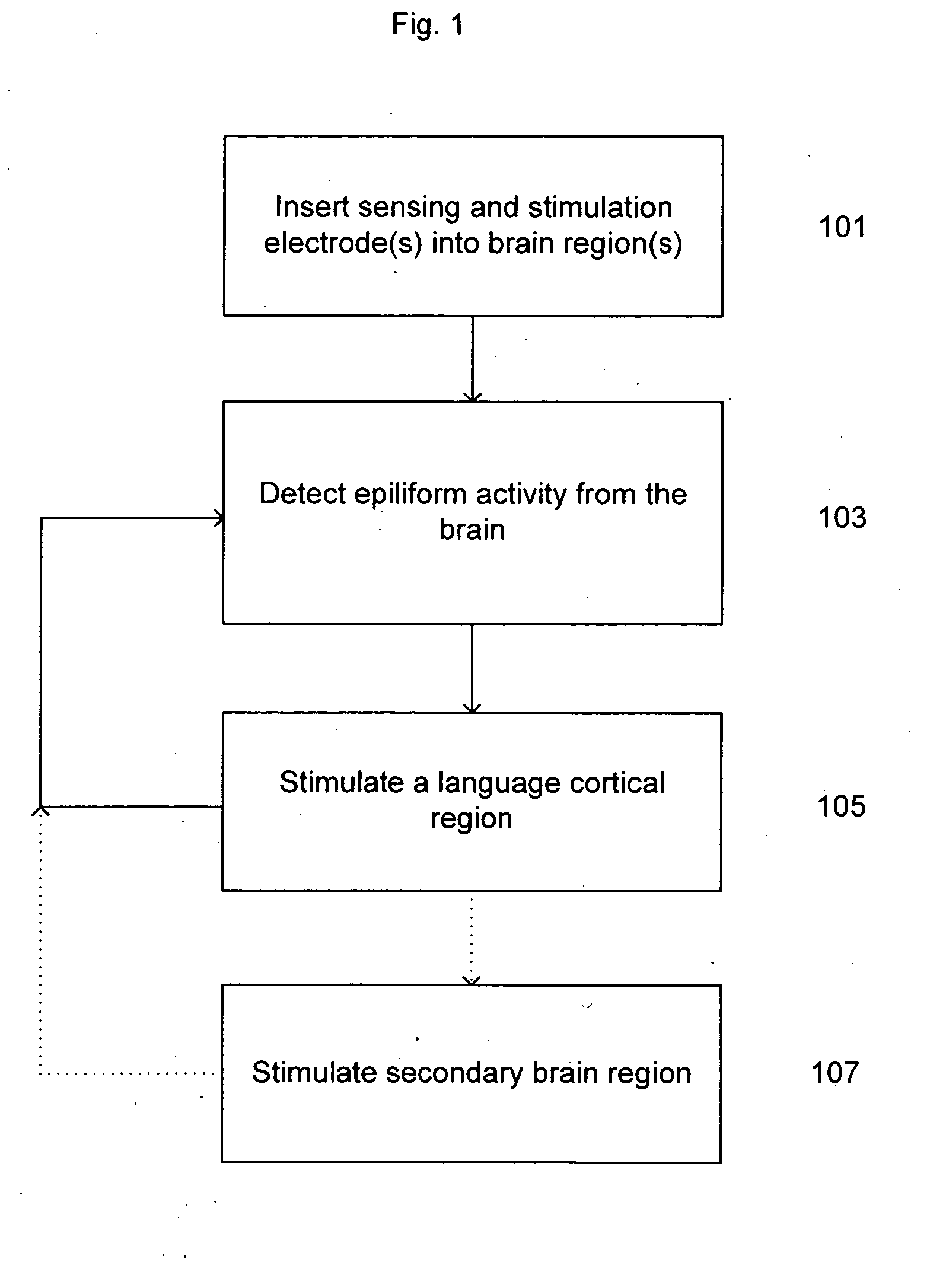
Treatment of language, behavior and social disorders
ActiveUS20080077191A1Improve socialImprove emotional disabilityElectroencephalographyHead electrodesMedicineAutism spectrum disorder
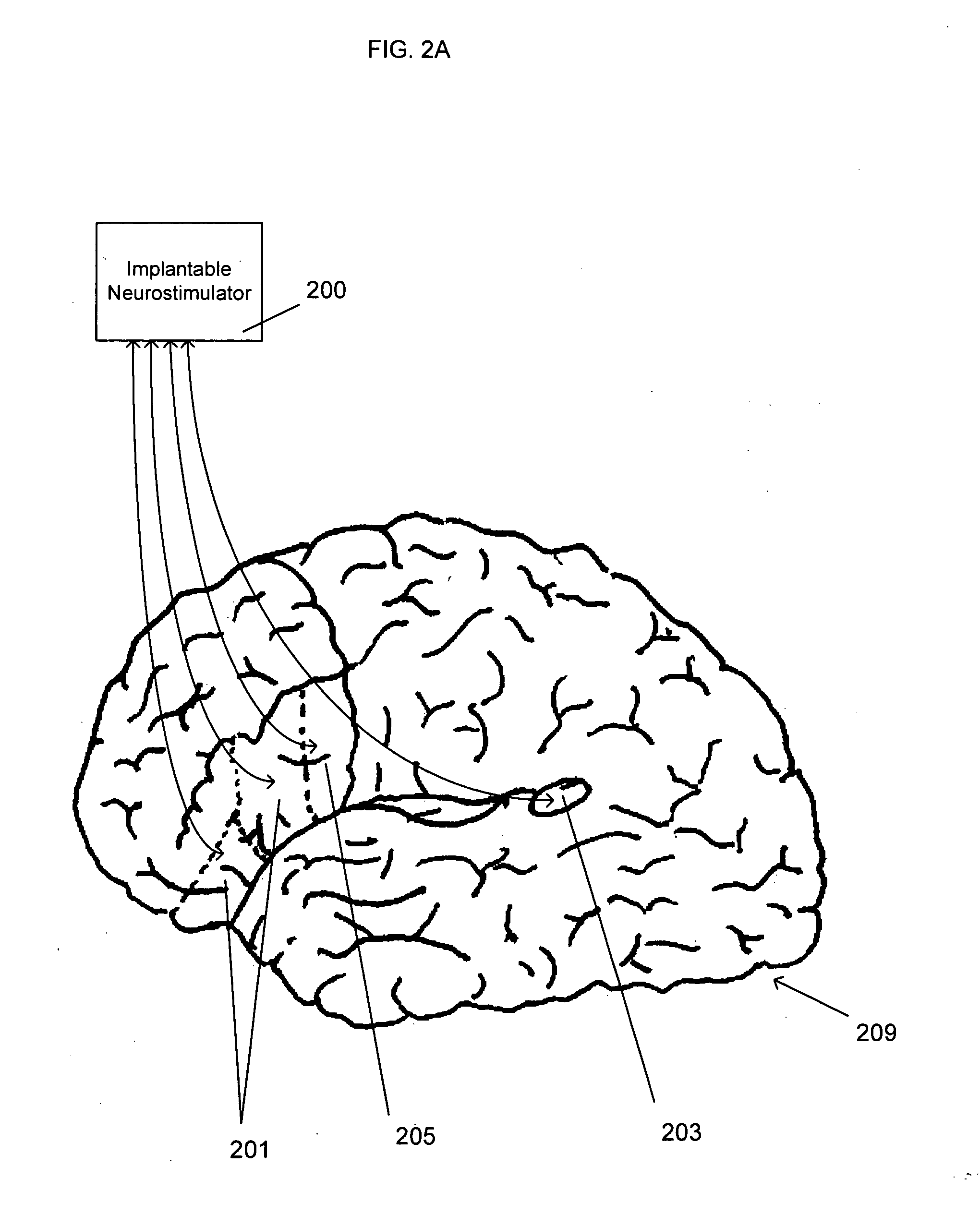
Methods of treating language, behavioral and social disorders are described, including methods of treating language disorders associated with electrographic abnormalities in the primary or associative language cortex of persons with autism spectrum disorders, pervasive developmental delay or acquired epileptic aphasia. A language, behavioral and social disorder may be treated by detecting epileptiform activity or an electrographic seizure for a subject's brain and applying neurostimulation to a language cortical region of the subject's brain (e.g., a primary or associative language cortical region). Detection of epileptiform activity or an electrographic seizure and stimulation of language cortex may be performed by a sensing and / or stimulation electrode that is inserted into a subject's brain and connected to one or more neurostimulation devices for monitoring and / or stimulating the language cortex.
Owner:NEUROPACE
Compositions and methods for the treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases using arsenic compounds
InactiveUS20020183385A1Improve the quality of lifeRestricted blood flowHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The invention relates to the use of arsenic compounds to treat a variety of neoplastic diseases. The present invention encompasses the administration to a mammal of arsenic in the form of a salt, complex, organic compound or ionic solution to treat tumors of epithelial tissue, connective tissue, central nervous system, lymphoid tissue, hematopoietic cells and tumors associated with oncogenic viruses. This invention also encompasses the treatment of hematopoietic disorders in mammals by the administration of one or more arsenic compounds to said mammal. Further, the arsenic compounds may be used to treat metastatic neoplastic diseases.
Owner:POLARX BIOPHARM
Compositions and methods using complexes of heat shock protein 90 and antigenic molecules for the treatment and prevention of neoplastic diseases
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. The effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 10-600 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp7o, 50-1000 micrograms for hsp9o, and 10-600 micrograms for gp96. The invention also provides a method for measuring tumor rejection in viva in an individual, preferably a human, comprising measuring the generation by the individual of MHC Class I-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific to the tumor. Methods of purifying hsp7o-peptide complexes are also provided.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
Adoptive immunotherapy using macrophages sensitized with heat shock protein-epitope complexes
InactiveUS6156302AEnhancing host 's immunocompetenceHigh activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseInterleukin 6
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for enhancing immunological responses and for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases or primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases based on the administration of macrophages and / or other antigen presenting cells (APC) sensitized with heat shock proteins non-covalently bound to peptide complexes and / or antigenic components. APC are incubated in the presence of hsp-peptide complexes and / or antigenic components in vitro. The sensitized cells are reinfused into the patient with or without treatment with cytokines including but not limited to interferon- alpha , interferon- alpha , interleukin-2, interleukin-4, interleukin-6 and tumor neurosis factor.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
Expression profiling of tumours
InactiveUS20060265138A1Easy translationImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsPrimary tumorTissue sample
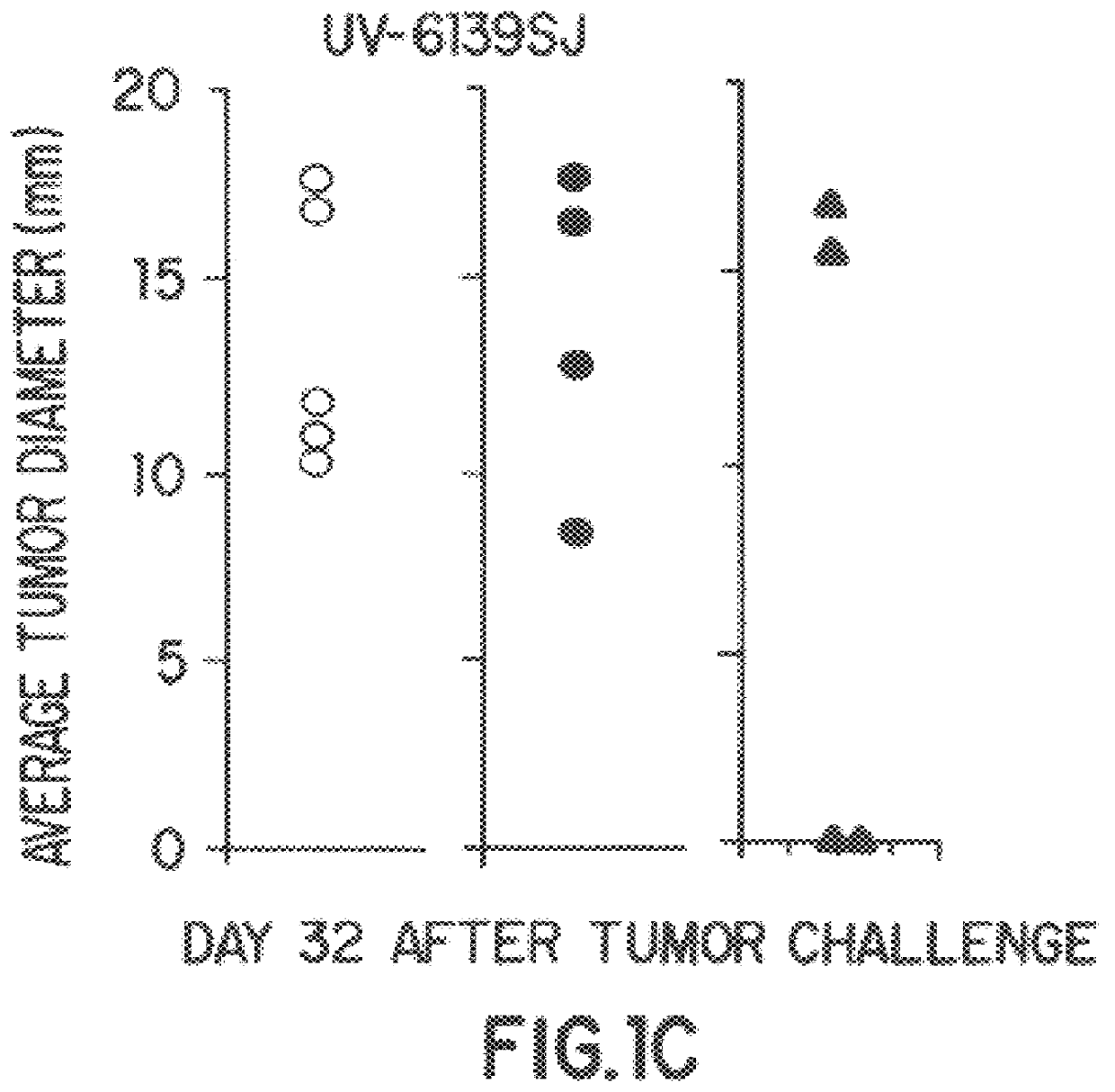
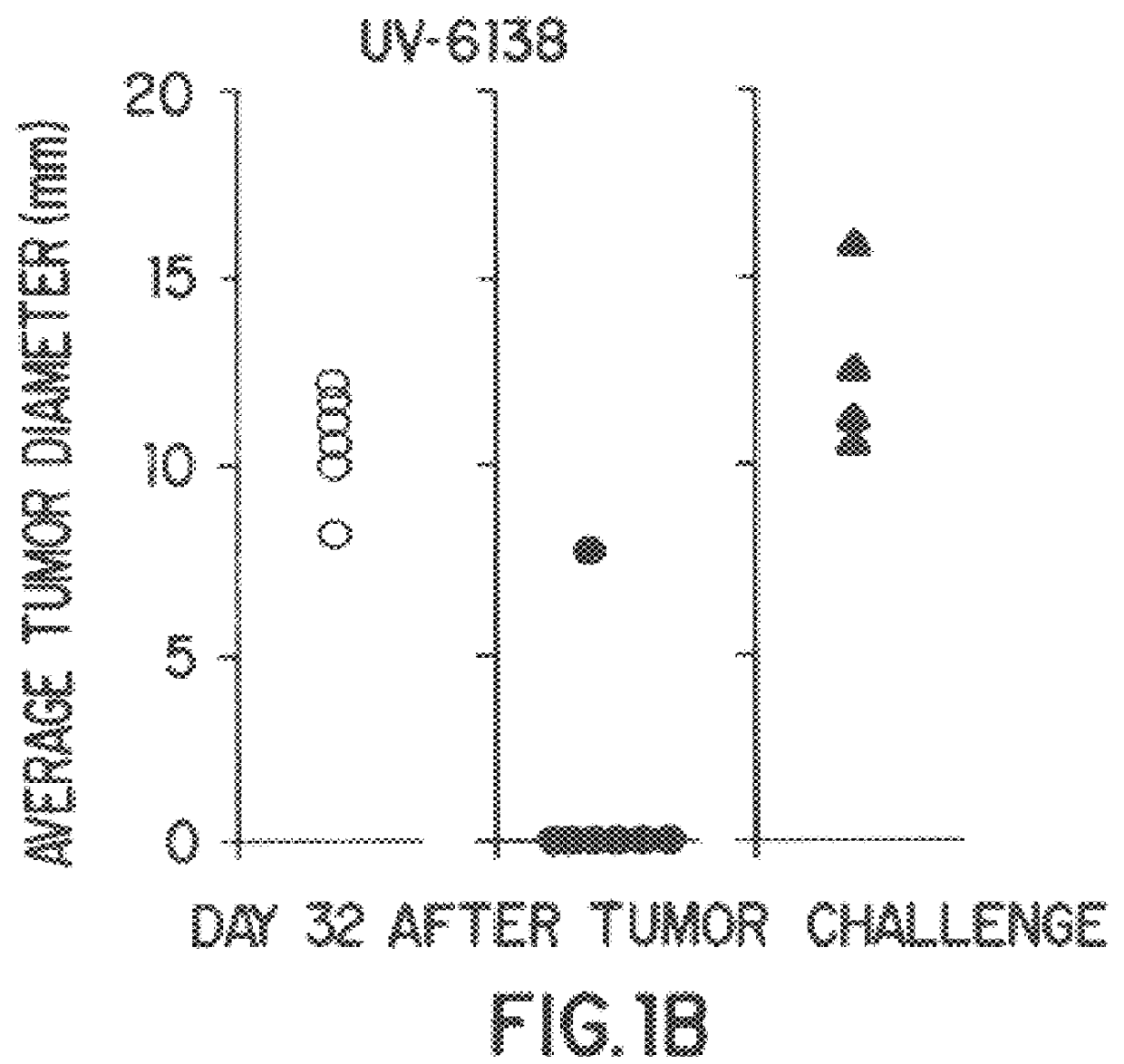
The present invention relates to methods of profiling tumours and characterisation of the tissue types associated with the tumours. A gene expression profile is obtained from the tissue sample, the genes ranked in order of their relative expression levels and the tissue type identified by comparing the gene ranking obtained with a database of relative gene expression level rankings of different tissue types. This gives a means to identify primary tumours and to determine the identity of a tumour of unknown primary. The invention also provides a method of treatment of a tumour by diagnosis of primary tumours identified by the methods described.
Owner:PETER MACCALLUM CANCER INST
Inhibitors of proteasomal activity for stimulating hair growth
Compounds that inhibit the activity of NF-κB or inhibit the activity of the proteasome or both promote bone formation and hair growth and are thus useful in treating osteoporosis, bone fracture or deficiency, primary or secondary hyperparathyrdidism, periodontal disease or defect, metastatic bone disease, osteolytic bone disease, post-plastic surgery, post-prosthetic joint surgery, and post-dental implantation; they also stimulate the production of hair follicles and are thus useful in stimulating hair growth, including hair density, in subject where this is desirable.
Owner:OSTEOSCREEN IP +1
Compositions comprising heat shock proteins or alpha(2) macroglobulin, antigenic molecules and saponins, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20020037290A1Growth inhibitionEffective amountBiocideSenses disorderAutoimmune ReactionsAutoimmune responses
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases. In the practice of the invention, the compositions are employed comprising: (a) a heat shock protein (hsp) or an alpha(2)macroglobulin (alpha2M); (b) a saponin; and, optionally, (c) an antigenic molecule. The antigenic molecule displays the antigenicity of an antigen of: (a) a cell that elicits an autoimmune response; (b) an agent of an infectious disease; (c) a cancerous cell; or (d) a cell or structure associated with a neurodegenerative or amyloid disease. The hsps that can be used in the practice of the invention include but are not limited to hsp70, hsp90, gp96, calreticulin, hsp 110, grp 170, and PDI, alone or in combination with each other. The antigenic molecule can be covalently or noncovalently bound to the hsp or alpha2M, free in solution, and / or covalently bound to the saponin. The compositions of the invention can be administered alone or in combination with the administration of antigen presenting cells sensitized with an hsp- or alpha2M-antigenic molecule complex.
Owner:ANTIGENICS
Method for treating primary and secondary forms of glaucoma
InactiveUS20070197491A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderOpen angle glaucomaAngiostatic Agents
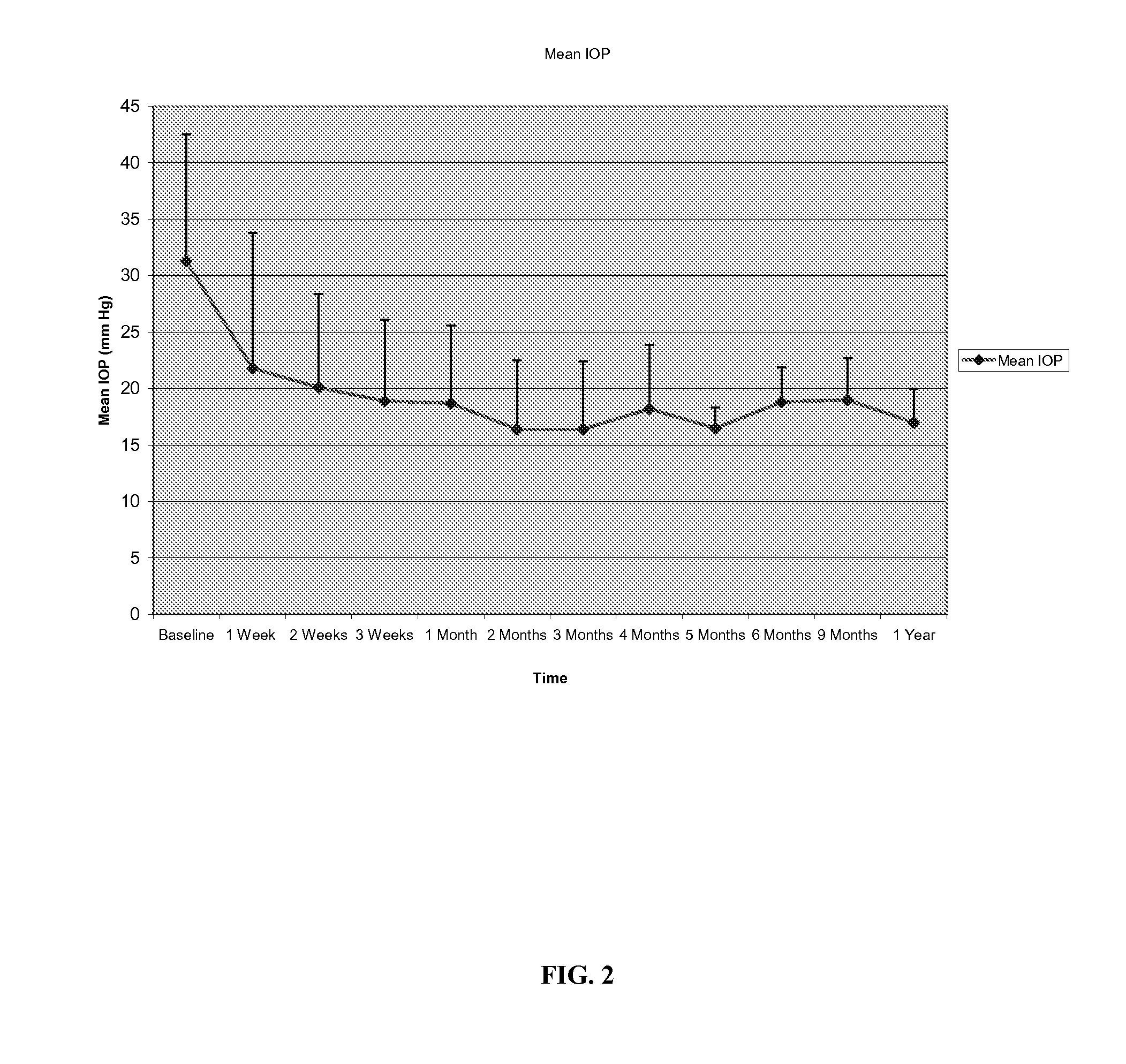
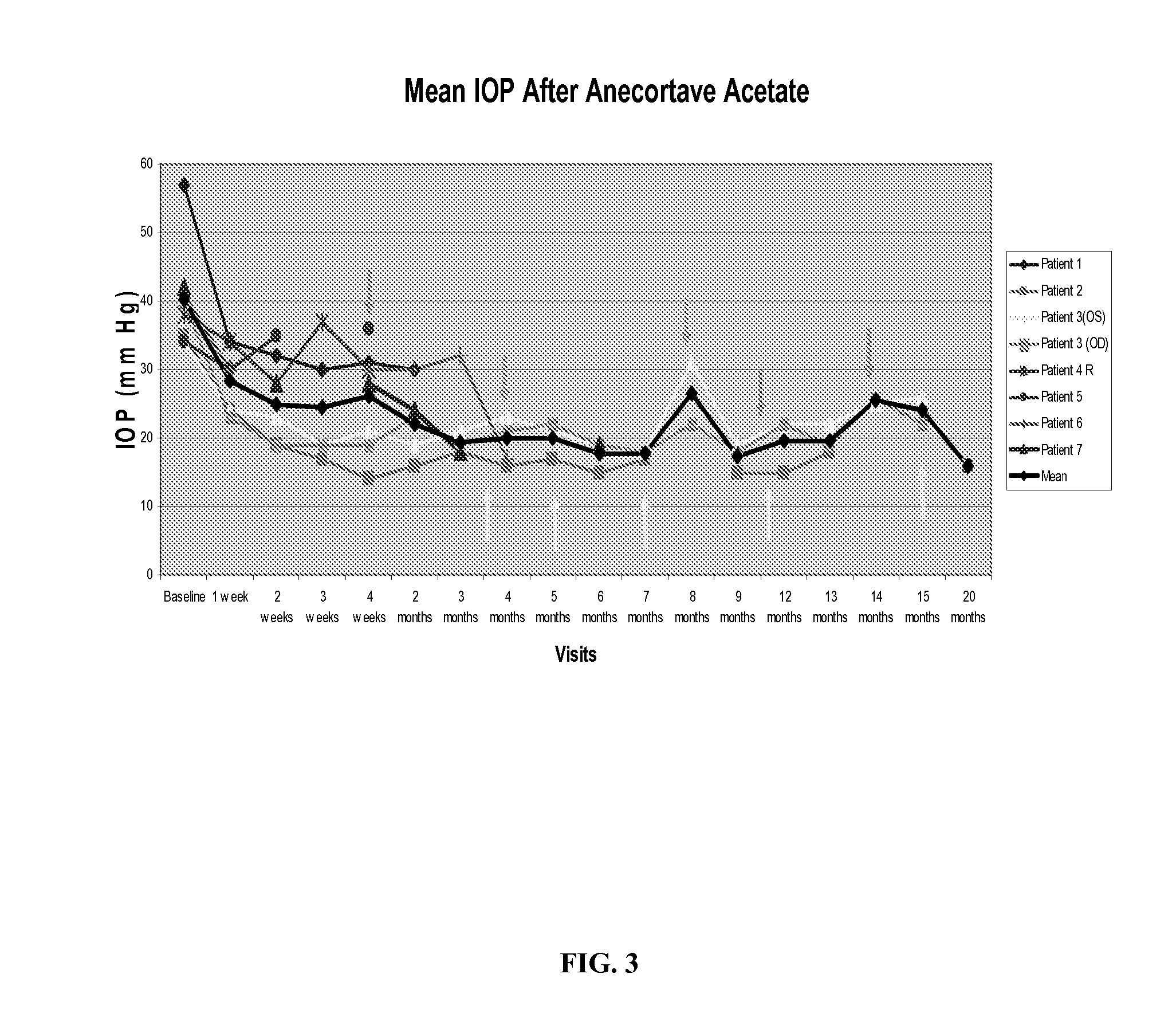
Methods and compositions for controlling ocular hypertension associated with (i) primary open angle glaucoma (POAG), (ii) other forms of glaucoma, or (iii) glucocorticoid therapy are disclosed. The methods involve administration of angiostatic agents and other IOP-lowering agents via local injections in the anterior segment of the eye. The most preferred IOP-lowering agents are angiostatic steroids, particularly anecortave acetate, and the most preferred route of administration is an anterior juxtascleral injection or implant. The invention is based in part on the discovery that anterior juxtascleral injections of anecortave acetate are capable of controlling intraocular pressure for sustained periods of from one to several months or more. This result is believed to be attributable to facilitation of access of the anecortave acetate to the trabecular meshwork via the anterior juxtascleral route of administration. This route of administration is also believed to be advantageous for other types of IOP-lowering agents, particularly molecules that cannot readily penetrate the cornea due to size or other physical properties.
Owner:ALCON INC
Therapeutic treatment of human cancers using simple salts of zinc
InactiveUS20110117210A1Functional impairmentOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseTumor regression
The present invention is a non-topical method of therapeutically treating human cancer patients which comprises an administration of an anti-cancer medicament comprising at least one simple organic or inorganic salt of zinc in at least a minimally effective concentration to suppress malignant tumor growth and induce tumor regression in-vivo. Administration can be performed by oral, parenteral, and / or body cavity routings; and the therapeutic treatment method is effective for the treatment of a diverse range of primary human cancers and metastatic diseases.
Owner:UGOLKOV ANDREY
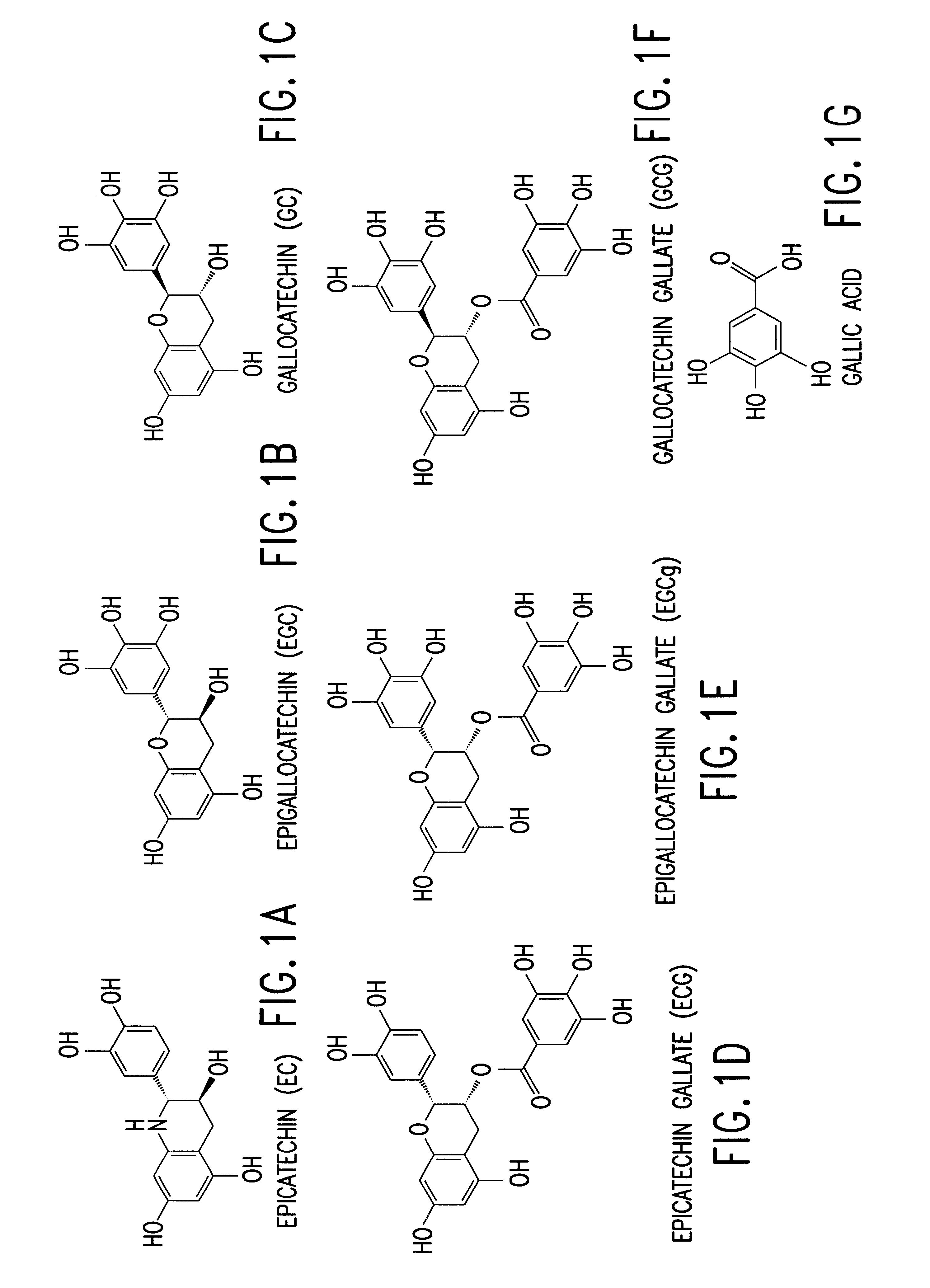
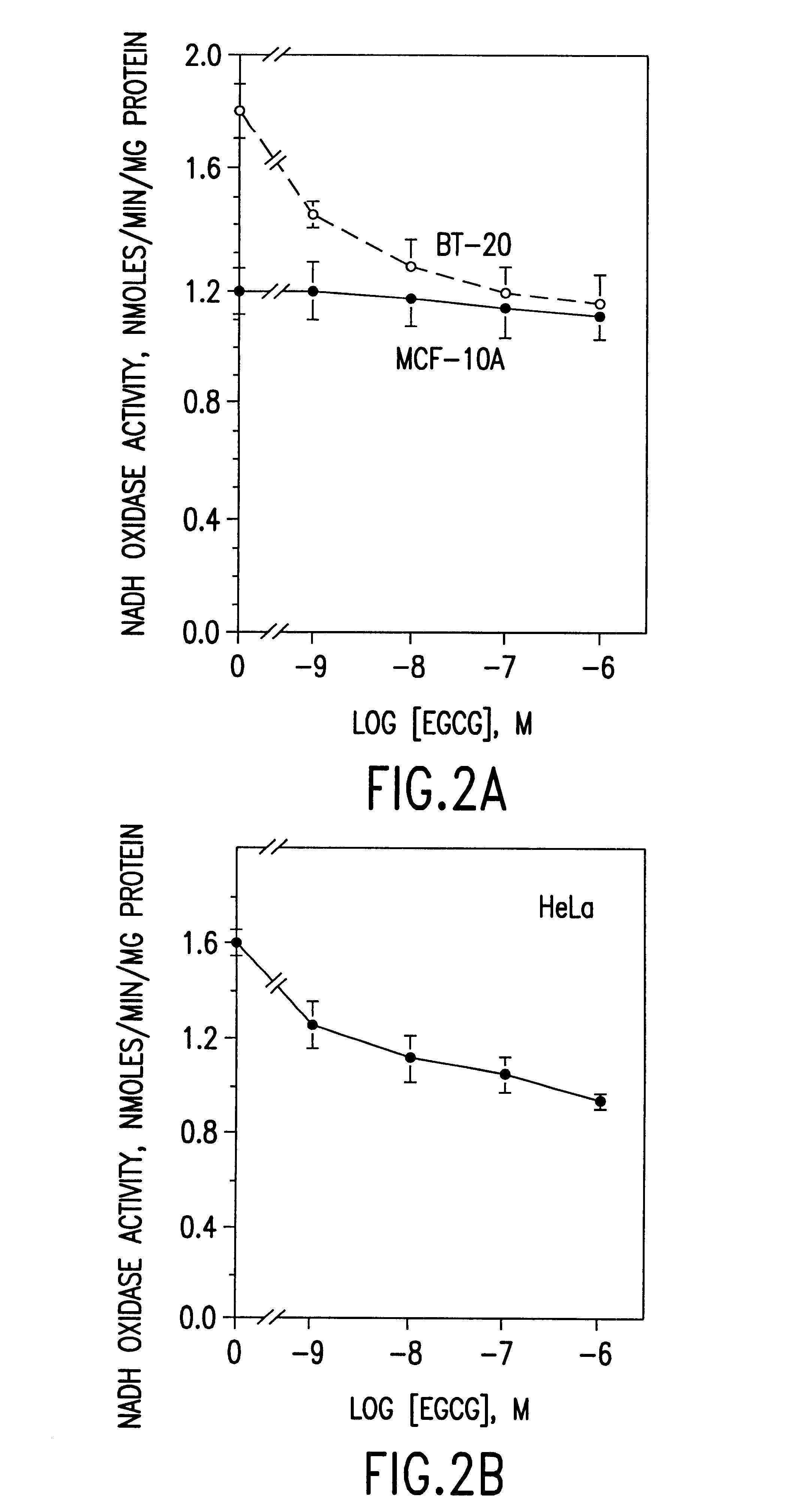
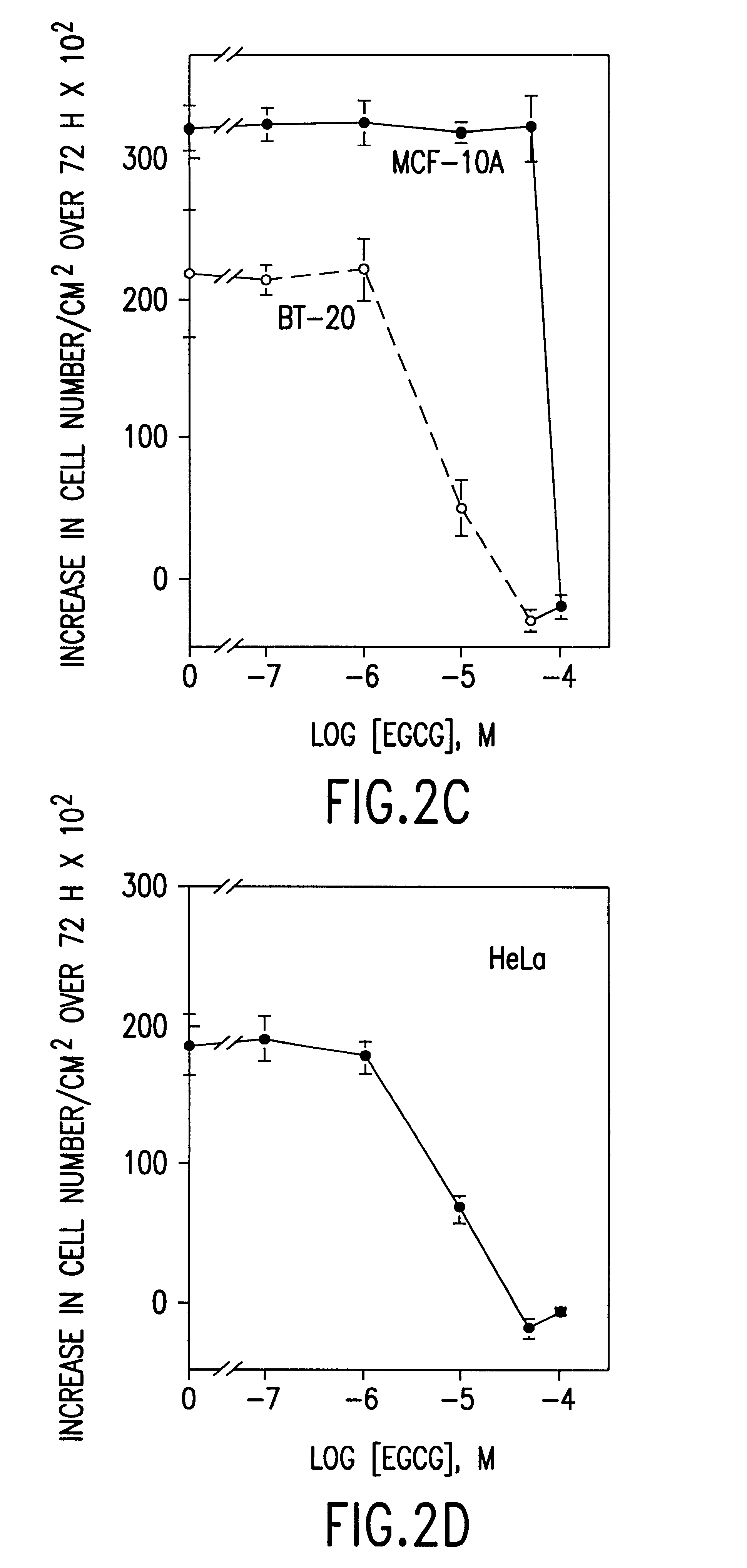
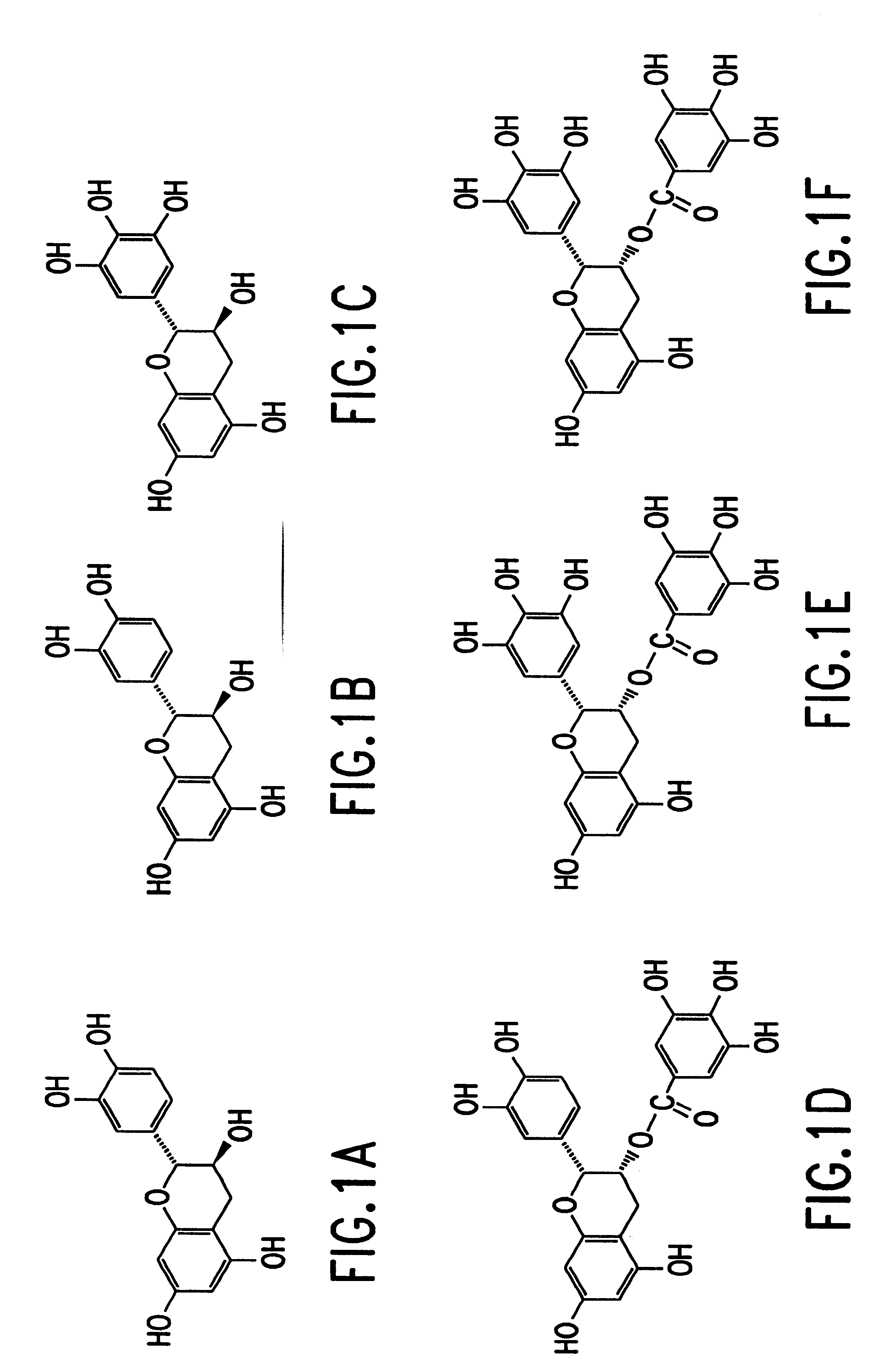
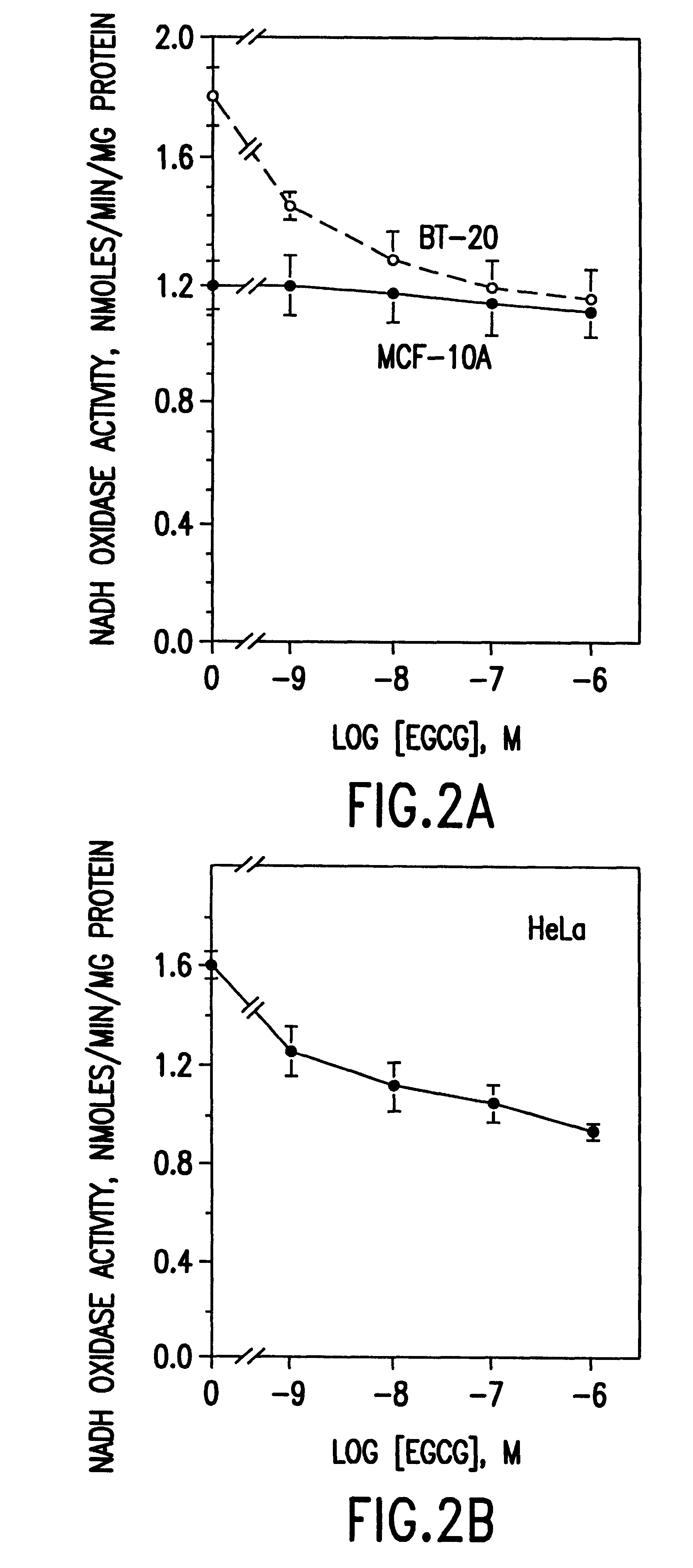
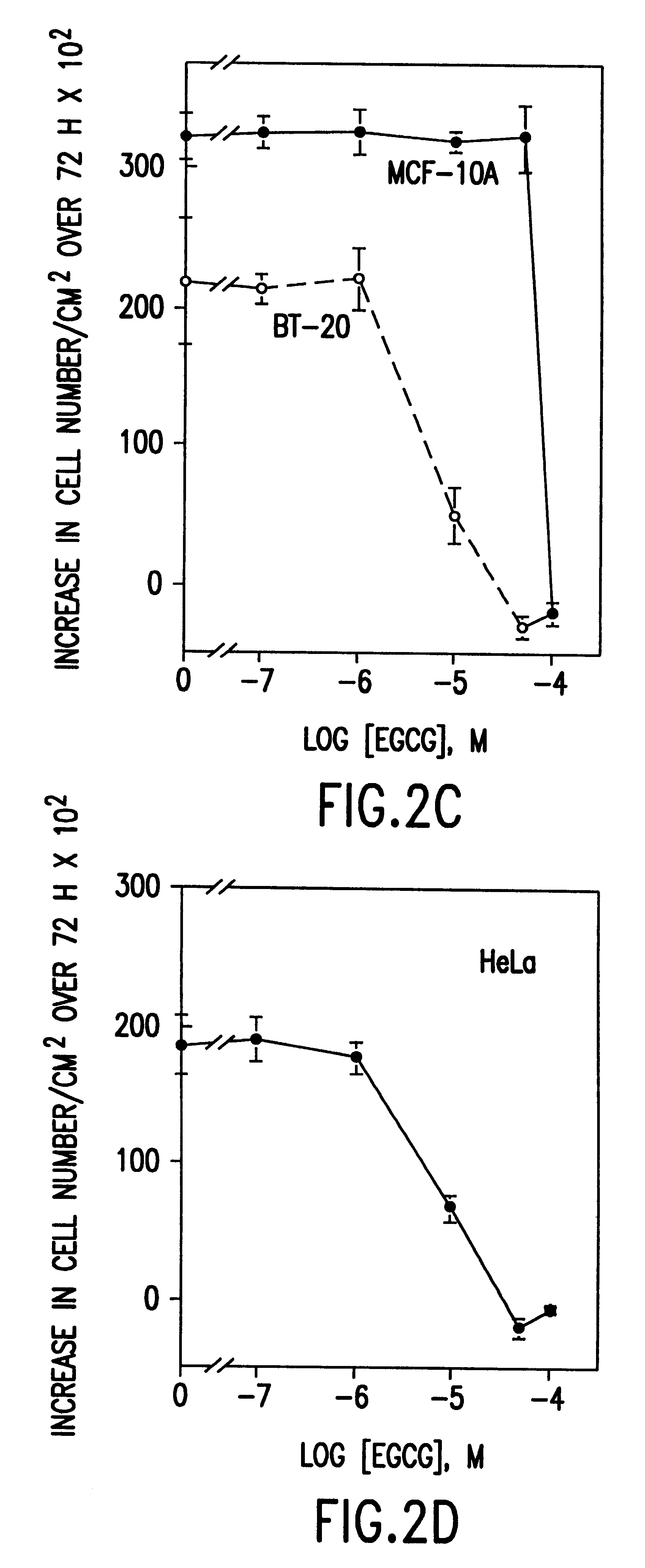
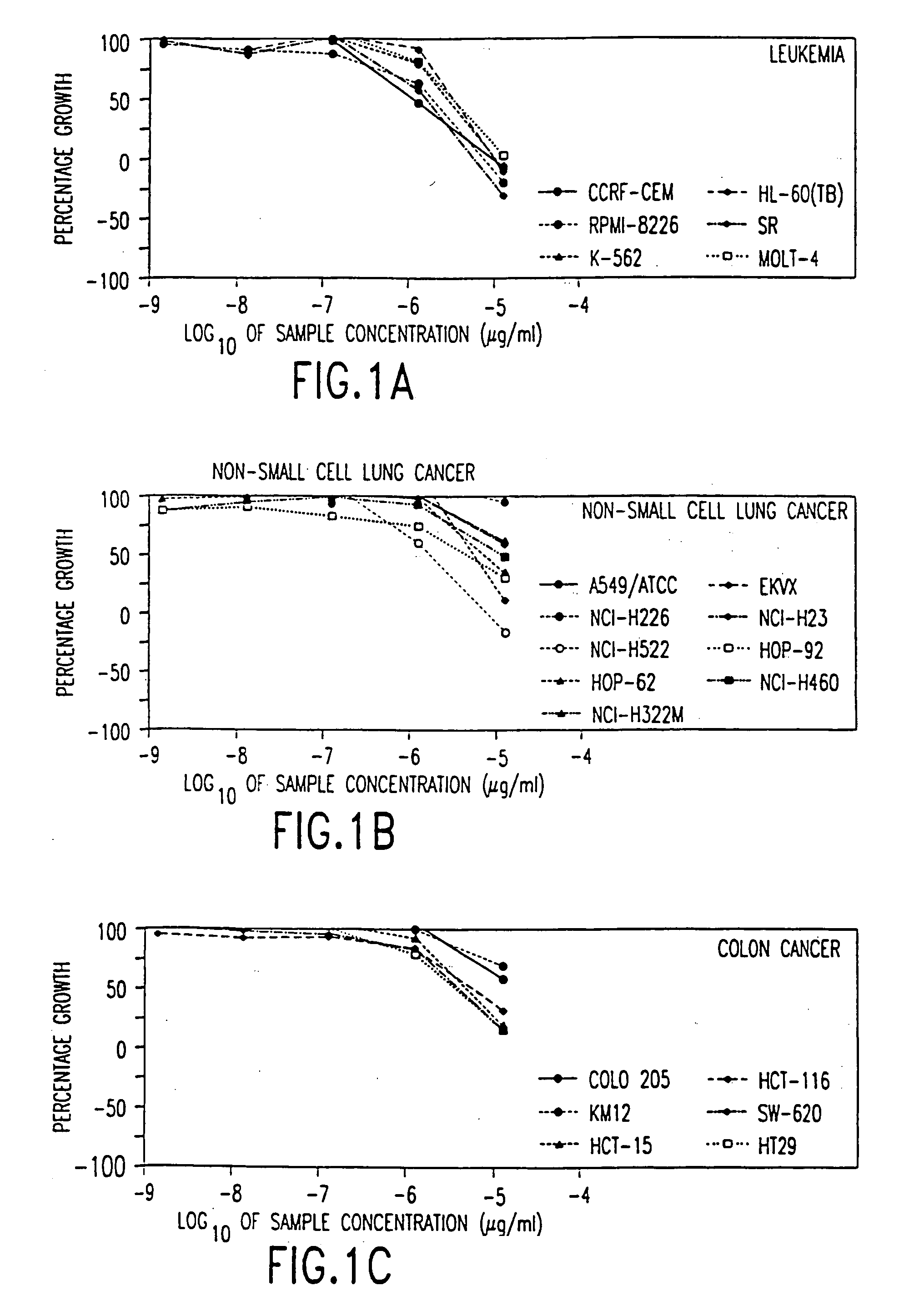
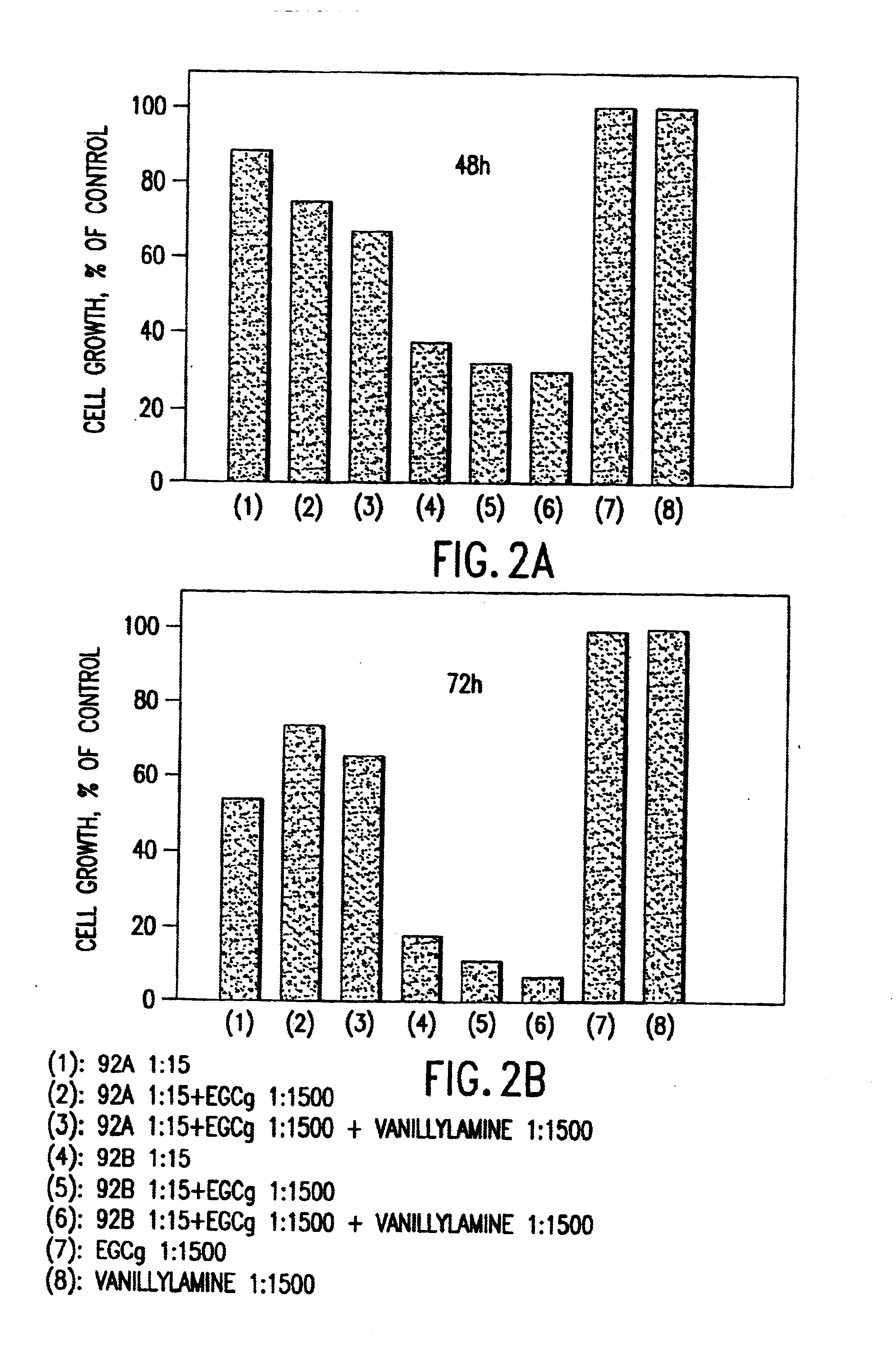
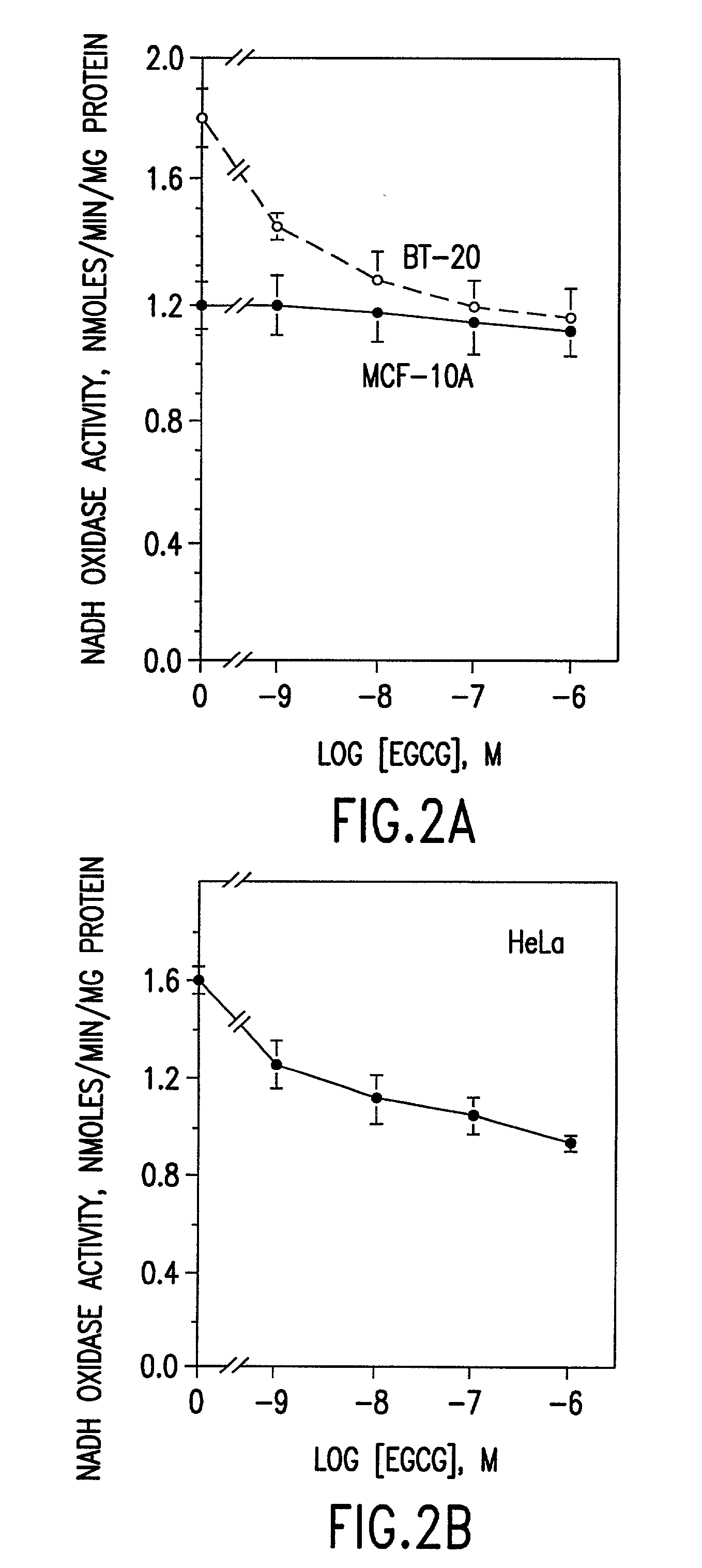
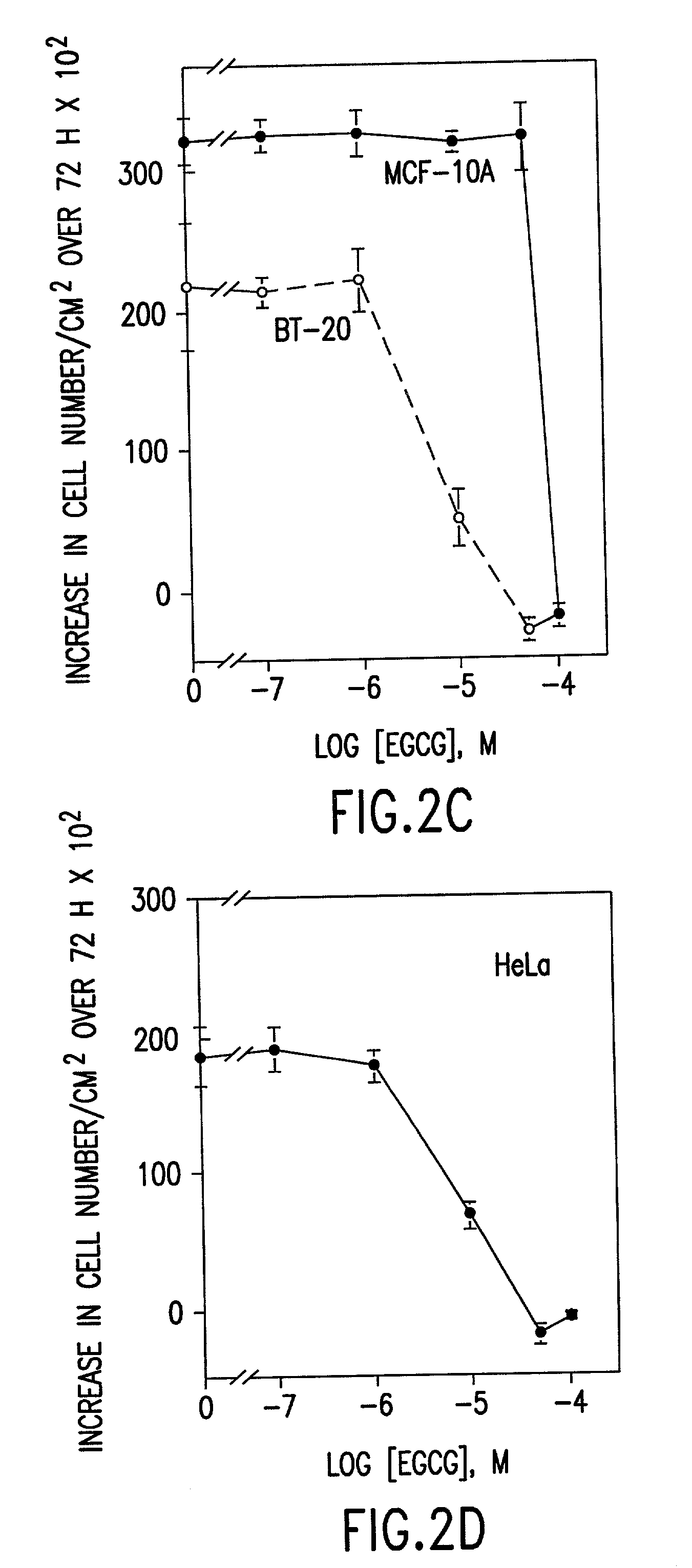
Tea catechin formulations and processes for making same
InactiveUS6428818B1Inhibit activity of specificMinimal levelBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsSolid tumorGreen tea
The invention described herein encompasses methods and compositions of treating cancer or solid tumors comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of catechins, a group of polyphenols found in green tea, to a mammal in need of such therapy. Compositions of catechins include but not limited to, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC). The unique compositions of the invention contain various combinations of the catechins with reduced levels of EGCg, alone or in combination with each other or other therapeutic agents and are used to treat primary and metastatic cancers in humans. The invention also encompasses the varying modes of administration of the therapeutic compounds.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Cancer treatments
The invention relates to a product comprised of specific combinations of cell lines intended for use as an allogeneic immunotherapy agent for the treatment of prostate cancer in humans. The heterogeneity of the immunotherapeutic matches the heterogeneity of the antigenic profile in the target prostate cancer and immunises the recipients with many of the potential TAA and TSA which are expressed at various stages of the disease. The invention discloses a vaccine comprising a combination of three different cell lines prepared from primary or metastatic prostate cancer biopsy material. The cell lines are lethally irradiated utilising gamma irradiation at 50-300 Gy to ensure that they are replication incompetent.
Owner:ONYVAX
Tea catechins as cancer specific proliferation inhibitors
InactiveUS6410061B1Good treatment effectReduce adverse effectsBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsSolid tumorGreen tea
The invention described herein encompasses a methods and compositions of treating cancer or solid tumors comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of catechins, a group of polyphenols found in green tea, to a mammal in need of such therapy. Compositions of catechins include but not limited to, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC). The unique compositions of the invention contain various combinations of the catechins, alone or in combination with each other or other therapeutic agents and are used to treat primary and metastatic cancers in humans. The invention also encompasses the varying modes of administration of the therapeutic compounds.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
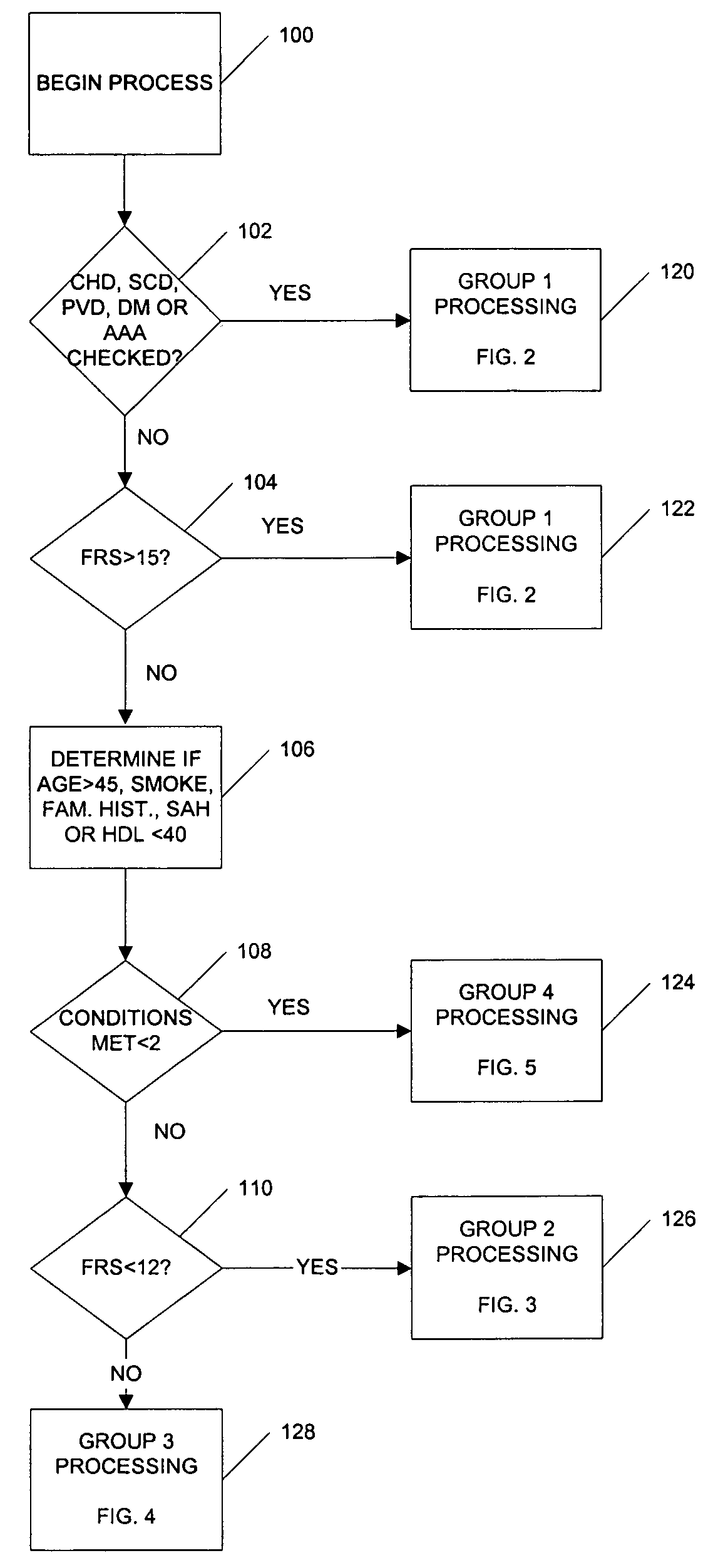
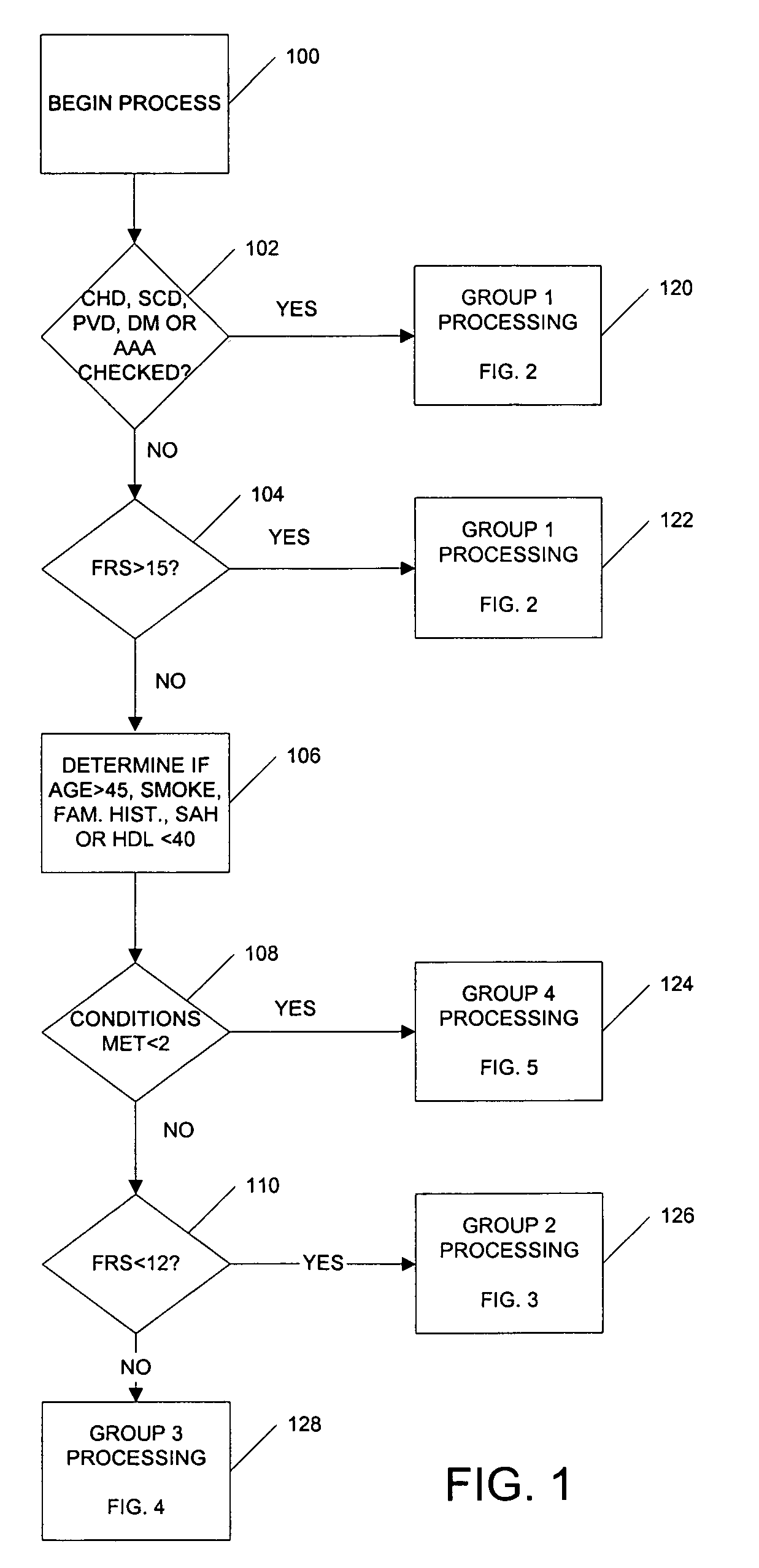
Medical risk assessment method and program product
ActiveUS7306562B1Physical therapies and activitiesData processing applicationsGuidelineRisk classification
A medical risk assessment method and computer program product resident on a computer or a hand-held device that allows a physician to determine the best strategy for primary and secondary cardiovascular disease prevention utilizing current guidelines and published medical literature. The computer program product evaluates a number of risk factors to determine specific recommendations for an individual patient, including Framingham risk scoring (FRS), pertinent medical history, individual lipid panel and advanced lipoprotein profiling, patient laboratory test results, and published literature on the effects of anti-lipid medicines on plasma concentration and / or composition of lipoprotein molecules and clinical outcomes. The risk assessment method establishes a cardiovascular treatment therapy strategy for a patient by determining a cardiac risk classification group, determining a cardiovascular treatment therapy based on the patient's lipoprotein profile and the patient's cardiac group risk classification, and presenting the cardiovascular treatment therapy for the patient to a medical practitioner on a patient evaluation display.
Owner:MEDICAL SOFTWARE
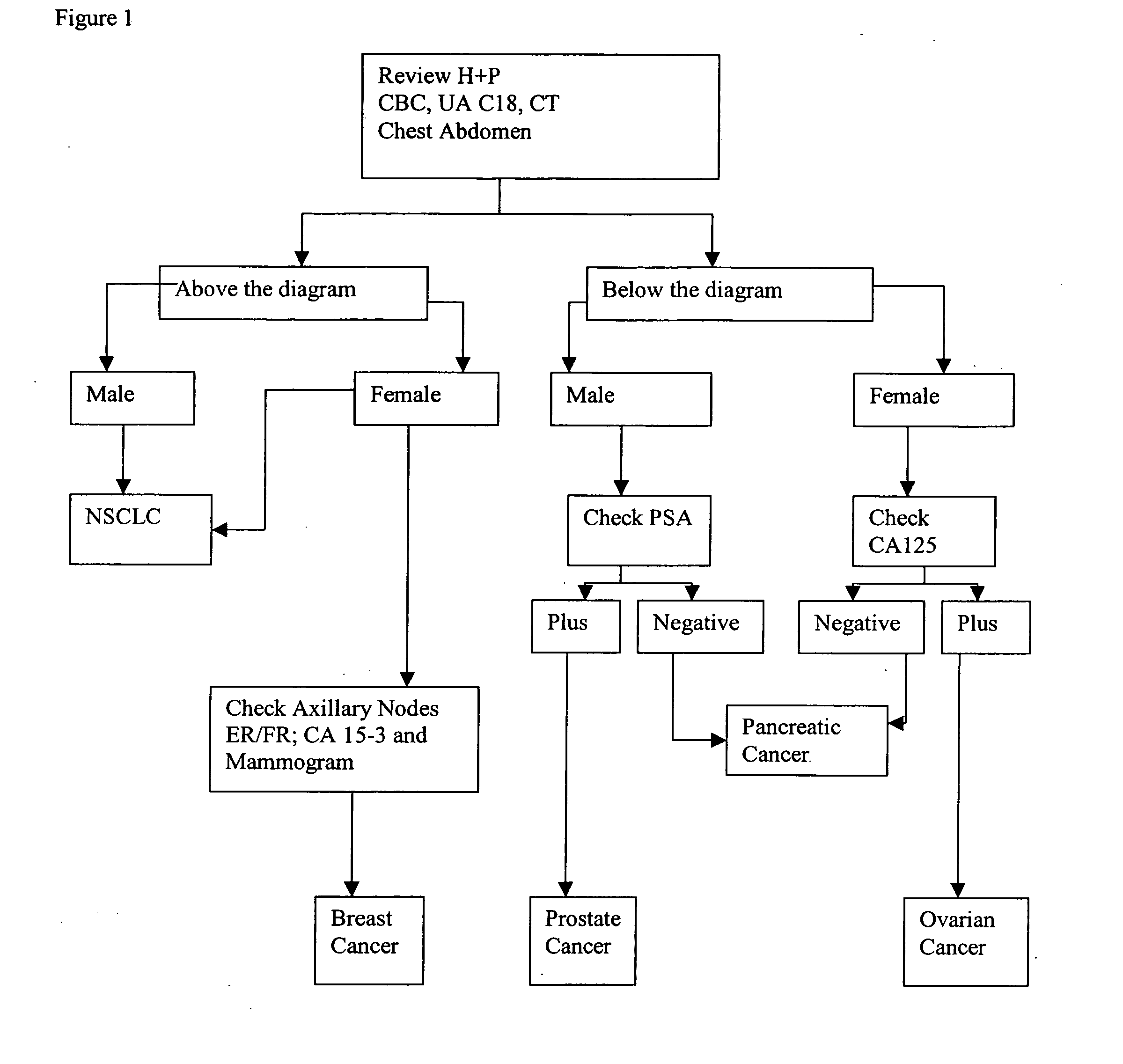
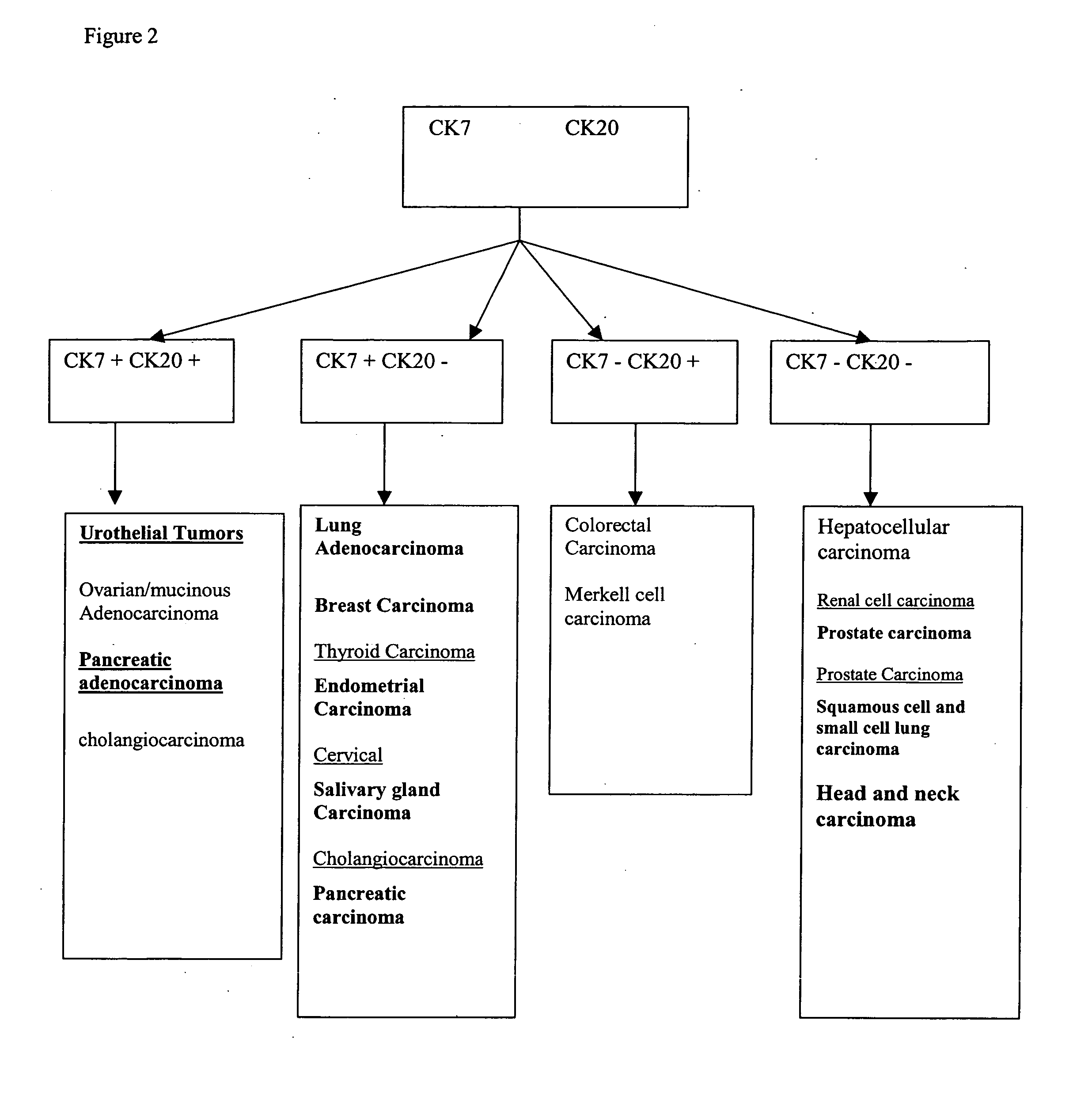
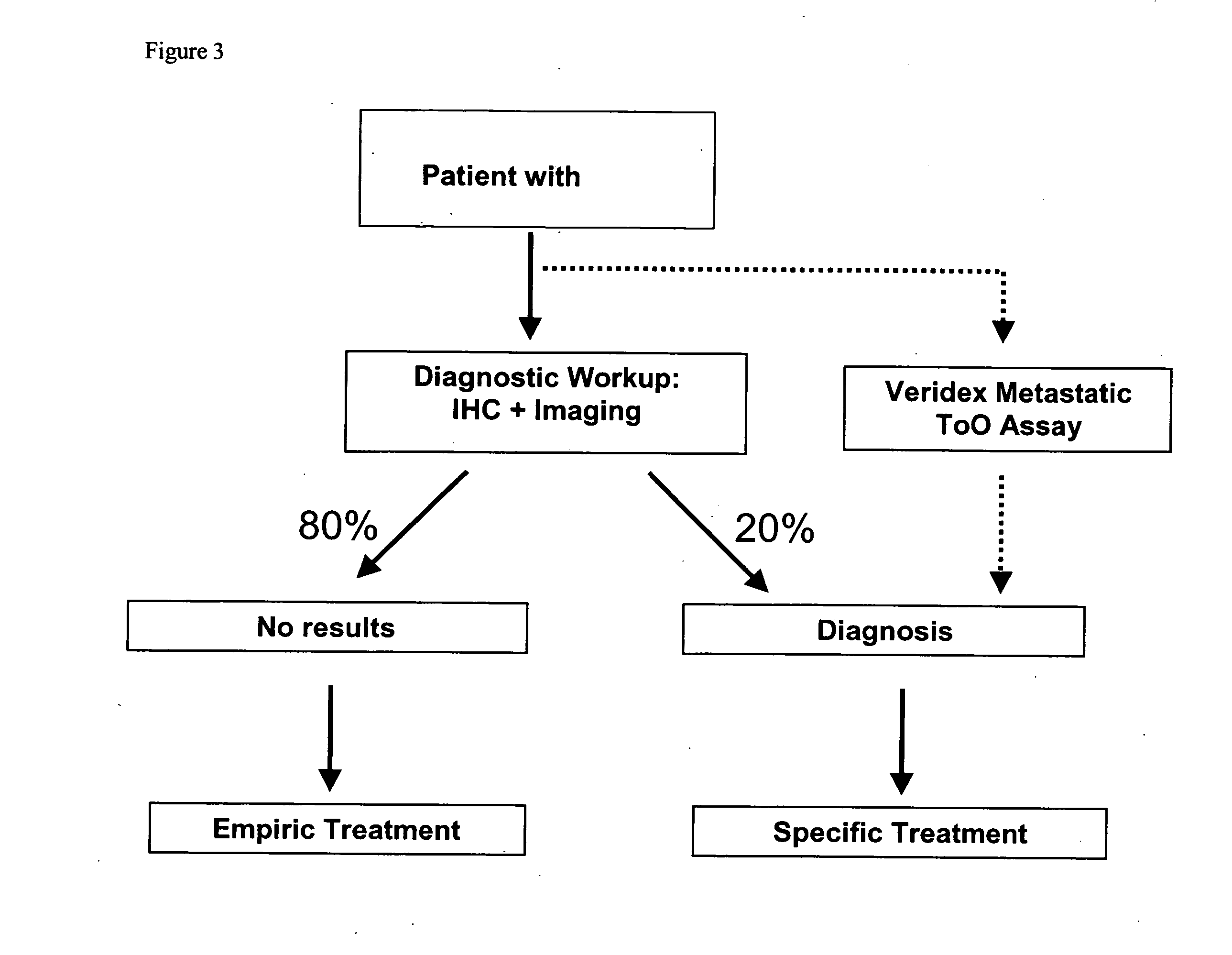
Methods and materials for identifying the origin of a carcinoma of unknown primary origin
InactiveUS20070065859A1High sensitivityStrong specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLymphatic SpreadHigh probability
The present invention provides a method of identifying origin of a metastasis of unknown origin by obtaining a sample containing metastatic cells; measuring Biomarkers associated with at least two different carcinomas; combining the data from the Biomarkers into an algorithm where the algorithm normalizes the Biomarkers against a reference; and imposes a cut-off which optimizes sensitivity and specificity of each Biomarker, weights the prevalence of the carcinomas and selects a tissue of origin determining origin based on highest probability determined by the algorithm or determining that the carcinoma is not derived from a particular set of carcinomas; and optionally measuring Biomarkers specific for one or more additional different carcinoma, and repeating the steps for additional Biomarkers.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Formulations containing hyaluronic acid
InactiveUS6114314AInhibit synthesisQuick to penetrate into skinBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseActinic keratoses
Topically applied transdermally quick penetrating (best targeting the epidermis and subsequently remaining there for a prolonged period of time) systemic independent acting, combinations and formulations which employ, combine, or incorporate a therapeutically effective non-toxic (to the patient) amount of a drug which inhibits prostaglandin synthesis together with an amount of hyaluronic acid and / or salts thereof (for example the sodium salt) and / or homologues, analogues, derivatives, complexes, esters, fragments, and / or sub units of hyaluronic acid to treat a disease and condition of the skin and exposed tissue for example, basal cell carcinoma, the precancerous, often recurrent, actinic keratoses lesions, fungal lesions, "liver" spots and like lesions (found for the most part in the epidermis), squamous cell tumours, metastatic cancer of the breast to the skin, primary and metastatic melanoma in the skin, genital warts cervical cancer, and HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) including HPV of the cervix, psoriasis (both plaque-type psoriasis and nail bed psoriasis), corns on the feet and hair loss on the head of pregnant women and remain in the skin for a prolonged period of time.
Owner:JAGOTEC AG +1
Targeted liposomes
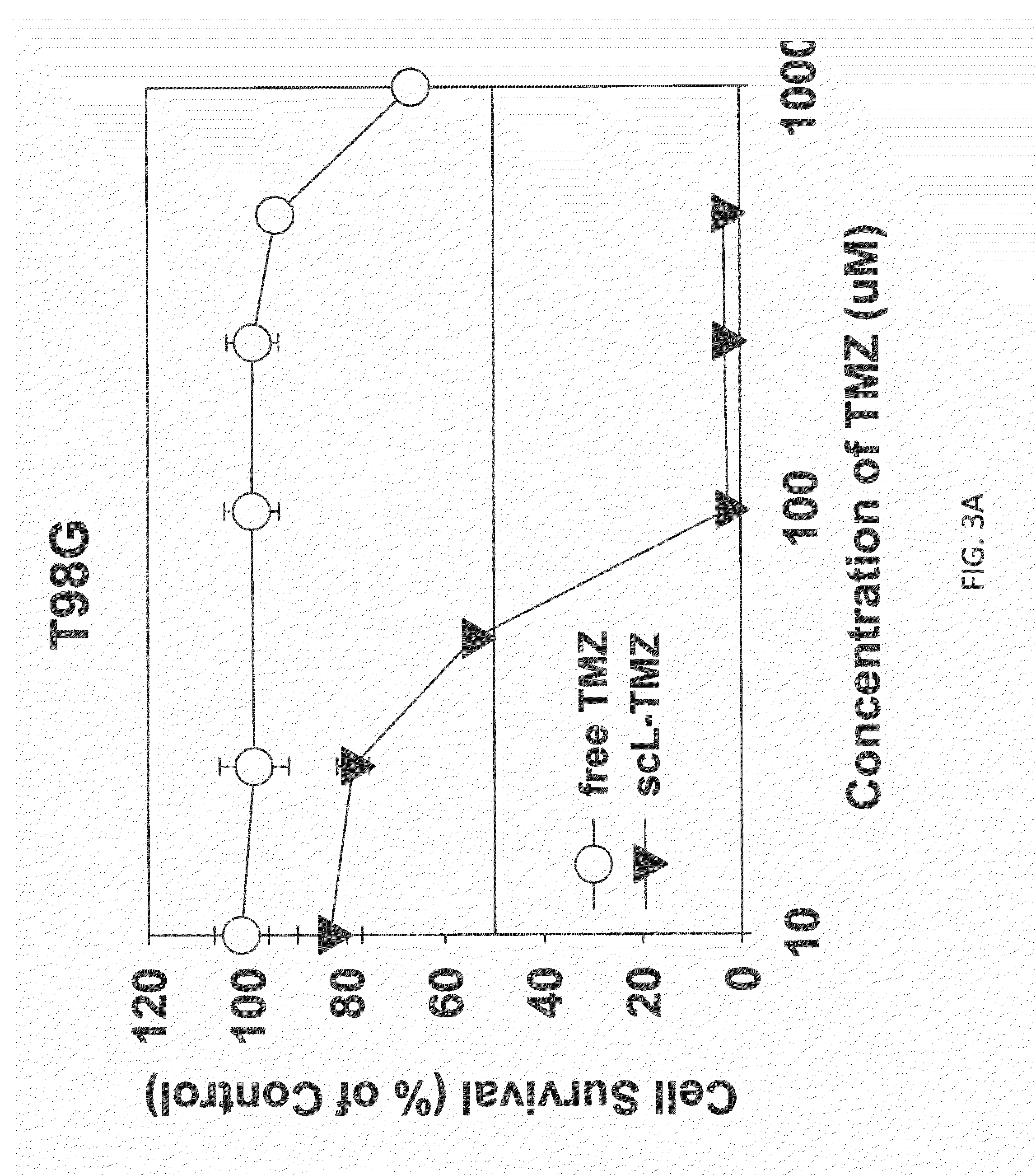
The present invention is in the field of drug delivery, and specifically, cationic liposome-based drug delivery. In embodiments, this invention provides methods of making ligand-targeted (e.g., antibody- or antibody fragment-targeted) liposomes useful for the delivery of liposomes to tumors, including brain tumors. In embodiments, the liposomes deliver temozolomide across the blood-brain barrier for treatment of primary or metastatic brain tumors. Additional cancers that can be treated with the liposomes include neuroendocrine tumors, melanoma, prostate, head and neck, ovarian, lung, liver, kidney, breast, urogenital, gastric, colorectal, cervical, vaginal, angiosarcoma, liposarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, choriocarcinoma, pancreatic, retinoblastoma and other types of cancer. In another embodiment the liposomes deliver melphalan for the treatment of multiple myeloma, other tumors of the blood or other solid tumors. In still other embodiments the liposomes can deliver other drugs such as pemetrexed or irinotecan for treatment of cancer or drugs including atropine for treatment of organophosphate poisoning.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Kit for diagnosing gene of Leber optic neuropathy in heredity and detecting method
InactiveCN1661116ASolve difficult collection problemsShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseLesion
A reagent kit for the gene diagnosis of Leber's hereditary optical nerve (LHON) lesion which is caused by the mutations on 3 primary pathogenic sites (G11778A, G3460A and T14484C) is disclosed. Its detecting process includes such steps as designing and synthesizing the site specific PCR primer, using whole blood as DNA template, PCR amplification, and detecting said mutant sites of LHON patient.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
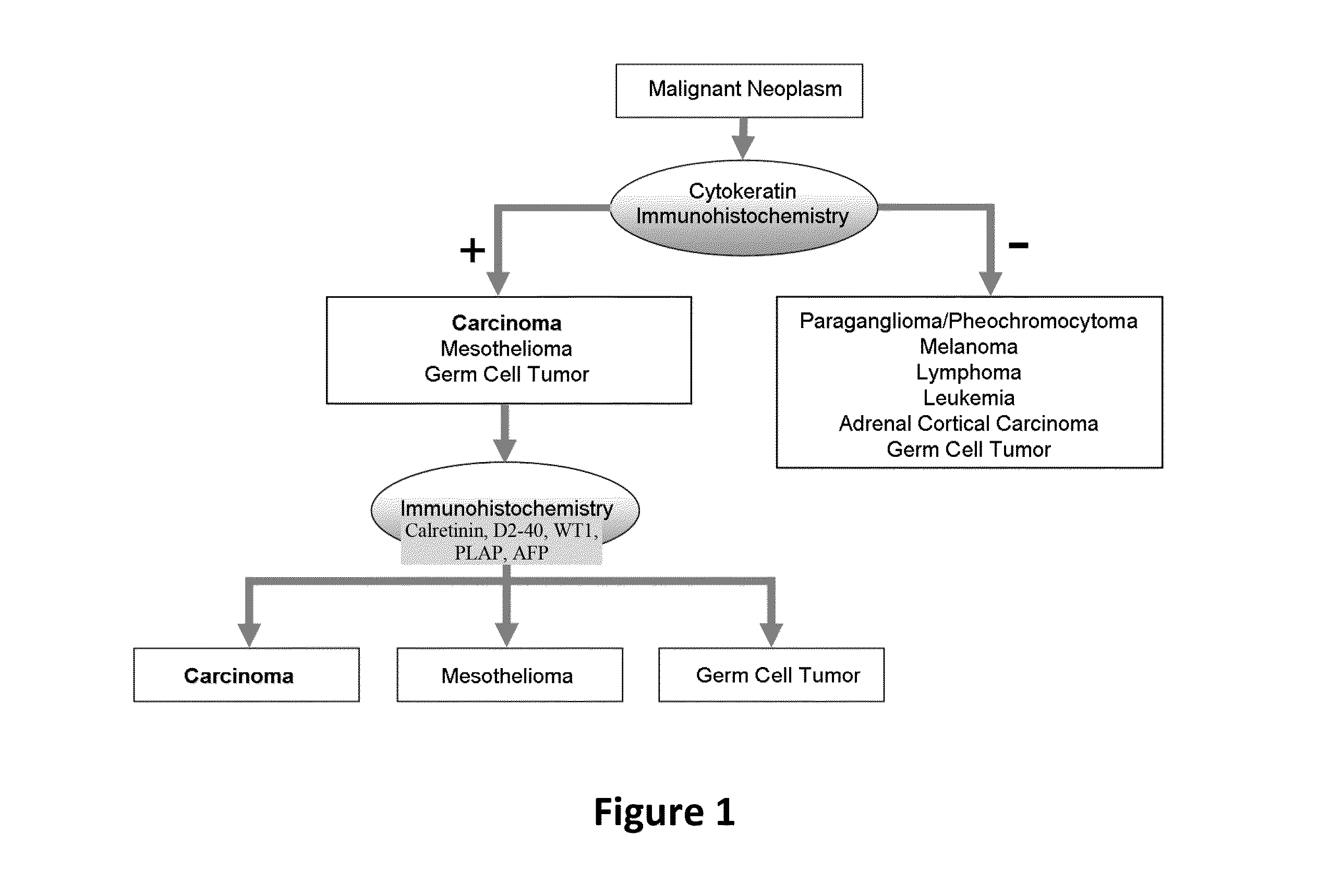
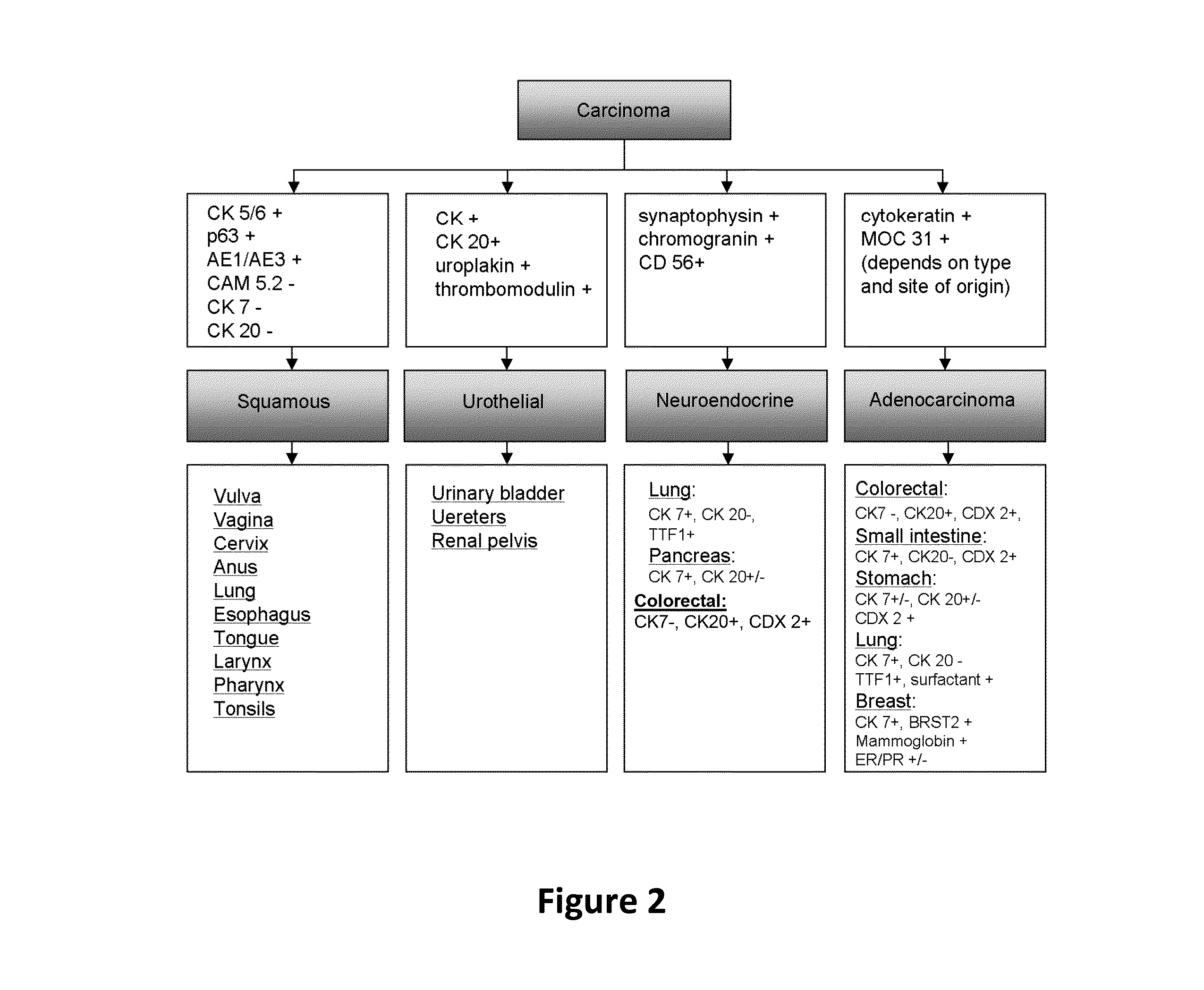
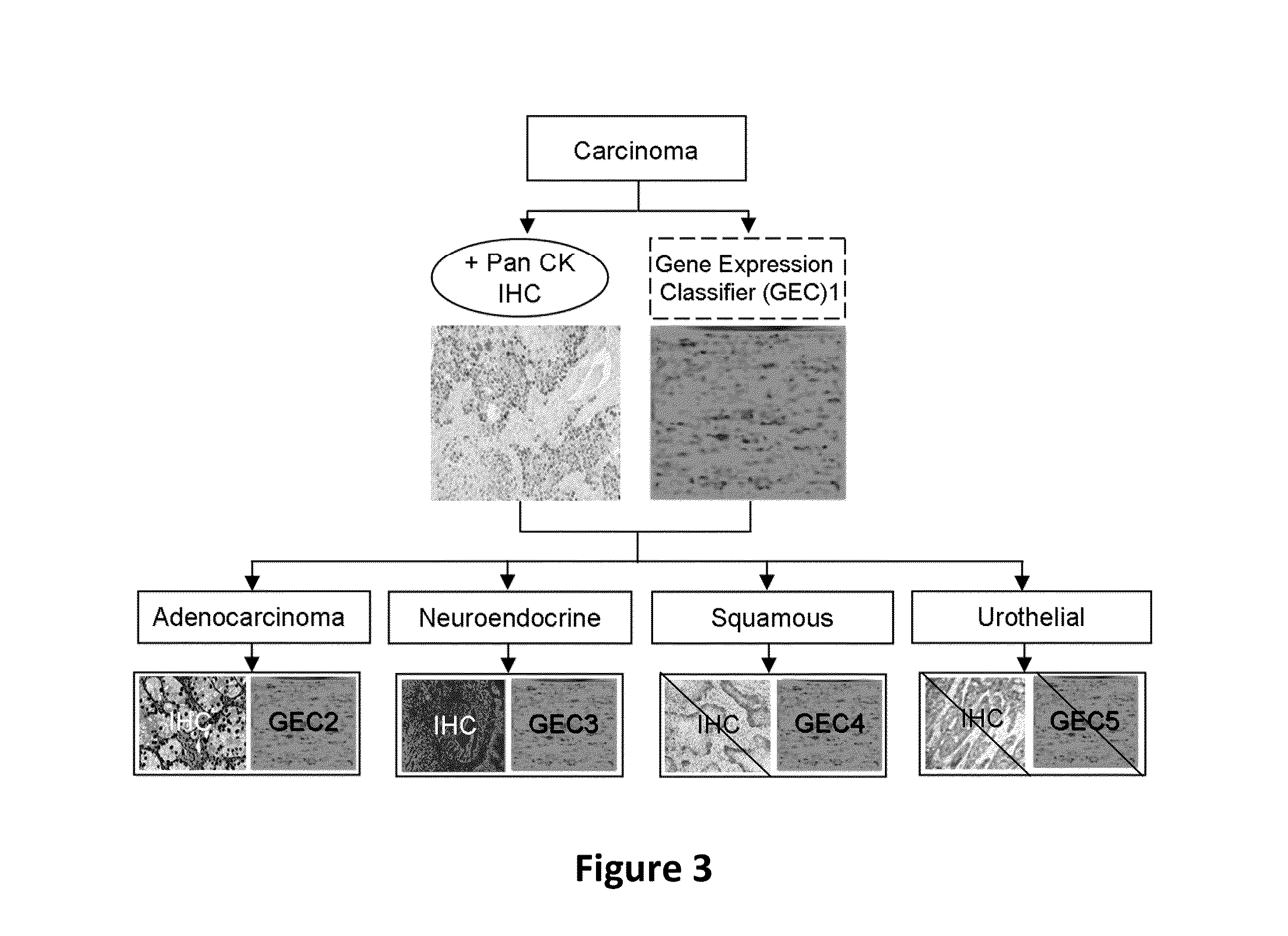
Hybrid model for the classification of carcinoma subtypes
ActiveUS20130172203A1Effective treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSquamous CarcinomasPrimary sites
A two-tiered classification system that can be integrated with the current algorithm used by pathologists for identification of the site of origin for ‘malignancy with unknown primary ’ is presented. In use, morphology, immunohistochemical (IHC) studies, and microarry-based top tier gene expression classifiers first subclassify cytokeratin positive carcinomas into adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, neuroendocrine carcinoma and urothelial carcinoma. Subsequently, organ-specific IHC-markers, if available, are used in conjunction with microarray-based second tier gene expression classifiers to assign the primary site of origin to the sample. This new hybrid approach combines IHC with a hierarchy of quantitative gene expression based classifiers into an algorithmic method that can assist pathologists to further refine and support their decision making process.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Compositions and methods using complexes of heat shock protein gp96 and antigenic molecules for the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases
InactiveUS6143299AElicit immune responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMHC class IAntigenic valence
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. The methods of the invention comprise administering a composition comprising an effective amount of a complex, in which the complex consists essentially of a heat shock protein (hsp) noncovalently bound to an antigenic molecule. "Antigenic molecule" as used herein refers to the peptides with which the hsps are endogenously associated in vivo as well as exogenous antigens / immunogens (i.e., with which the hsps are not complexed in vivo) or antigenic / immunogenic fragments and derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the complex is autologous to the individual. The effective amounts of the complex are in the range of 10-600 micrograms for complexes comprising hsp70, 50-1000 micrograms for hsp90, and 10-600 micrograms for gp96. The invention also provides a method for measuring tumor rejection in vivo in an individual, preferably a human, comprising measuring the generation by the individual of MHC Class I-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific to the tumor. Methods of purifying hsp70-peptide complexes are also provided.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for the treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases using arsenic compounds
The invention relates to the use of arsenic compounds to treat a variety of neoplastic diseases. The present invention encompasses the administration to a mammal of arsenic in the form of a salt, complex, organic compound or ionic solution to treat tumors of epithelial tissue, connective tissue, central nervous system, lymphoid tissue, hematopoietic cells and tumors associated with oncogenic viruses. This invention also encompasses the treatment of hematopoietic disorders in mammals by the administration of one or more arsenic compounds to said mammal. Further, the arsenic compounds may be used to treat metastatic neoplastic diseases.
Owner:POLARX BIOPHARM
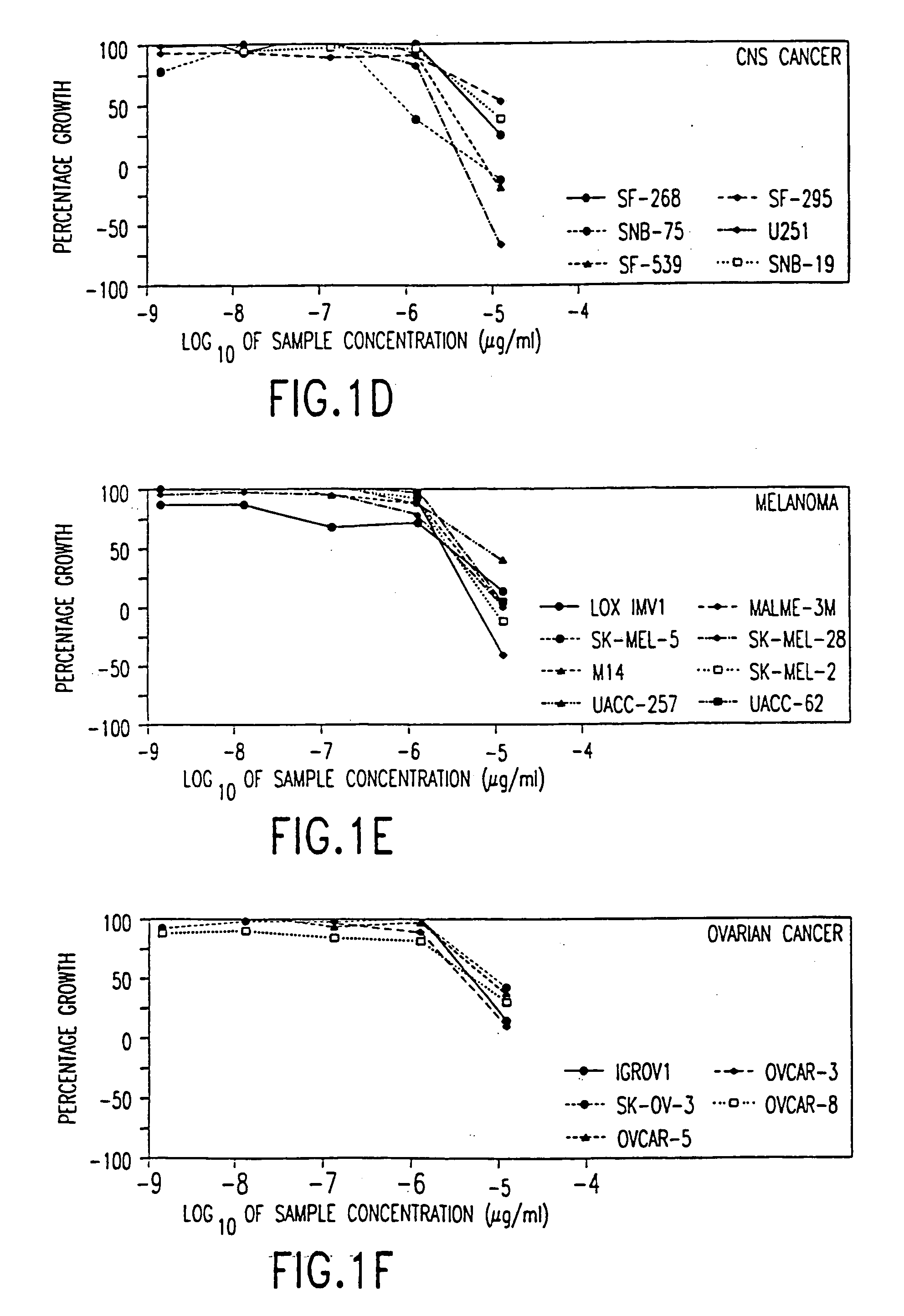
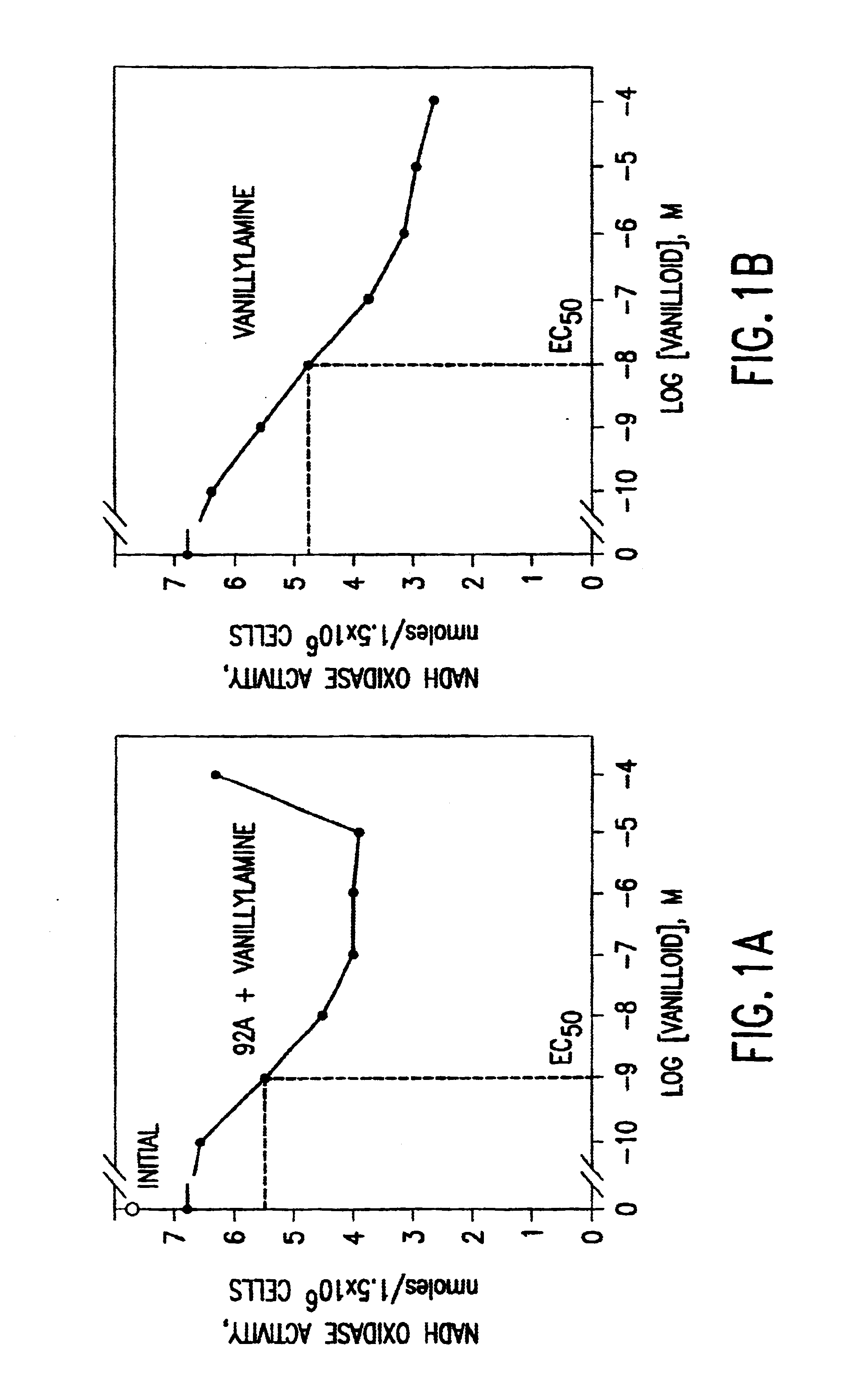
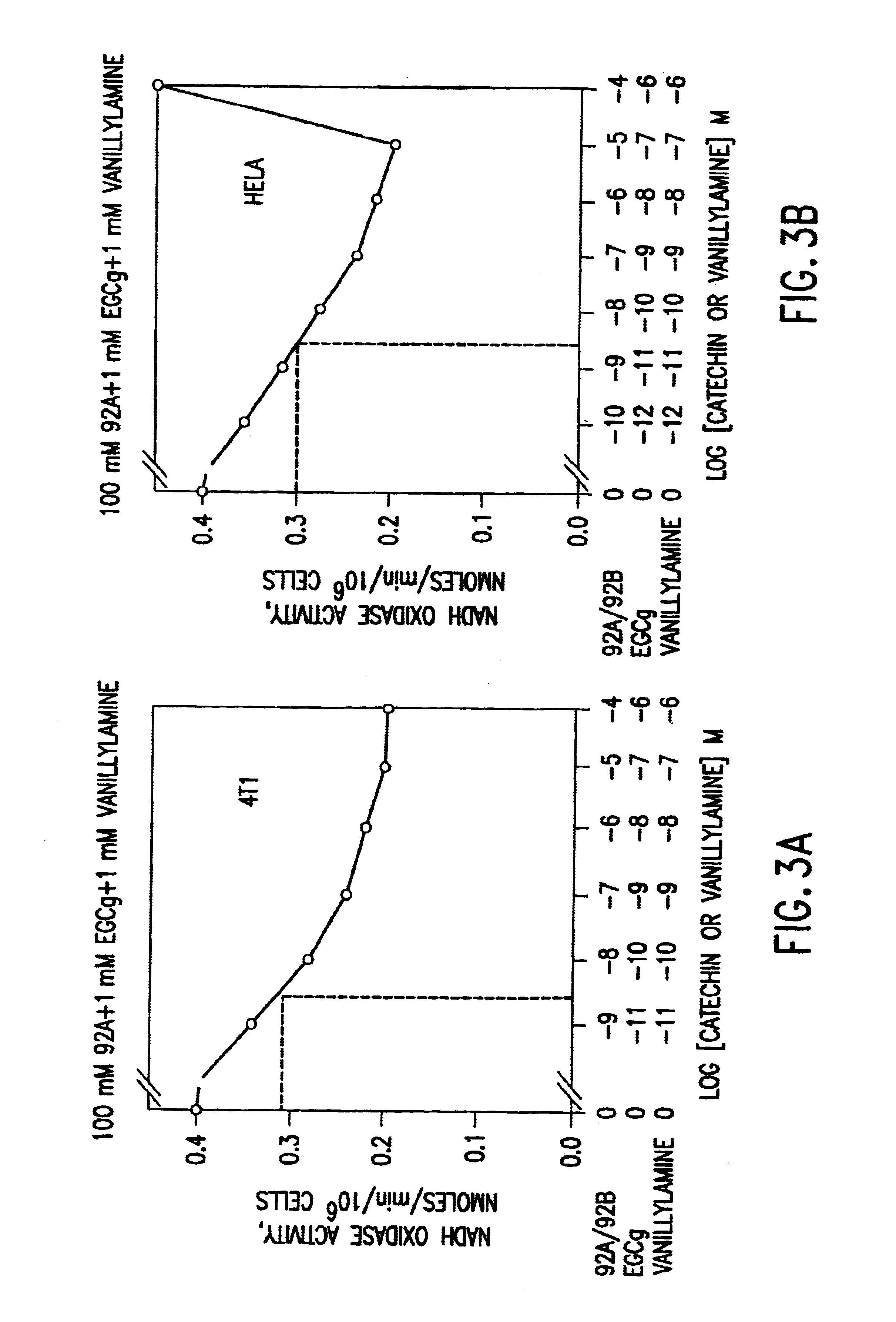
Compositions based on vanilloid-catechin synergies for prevention and treatment of cancer
InactiveUS6759064B2Reduce adverse effectsInhibitory activityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMedicineTannase
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
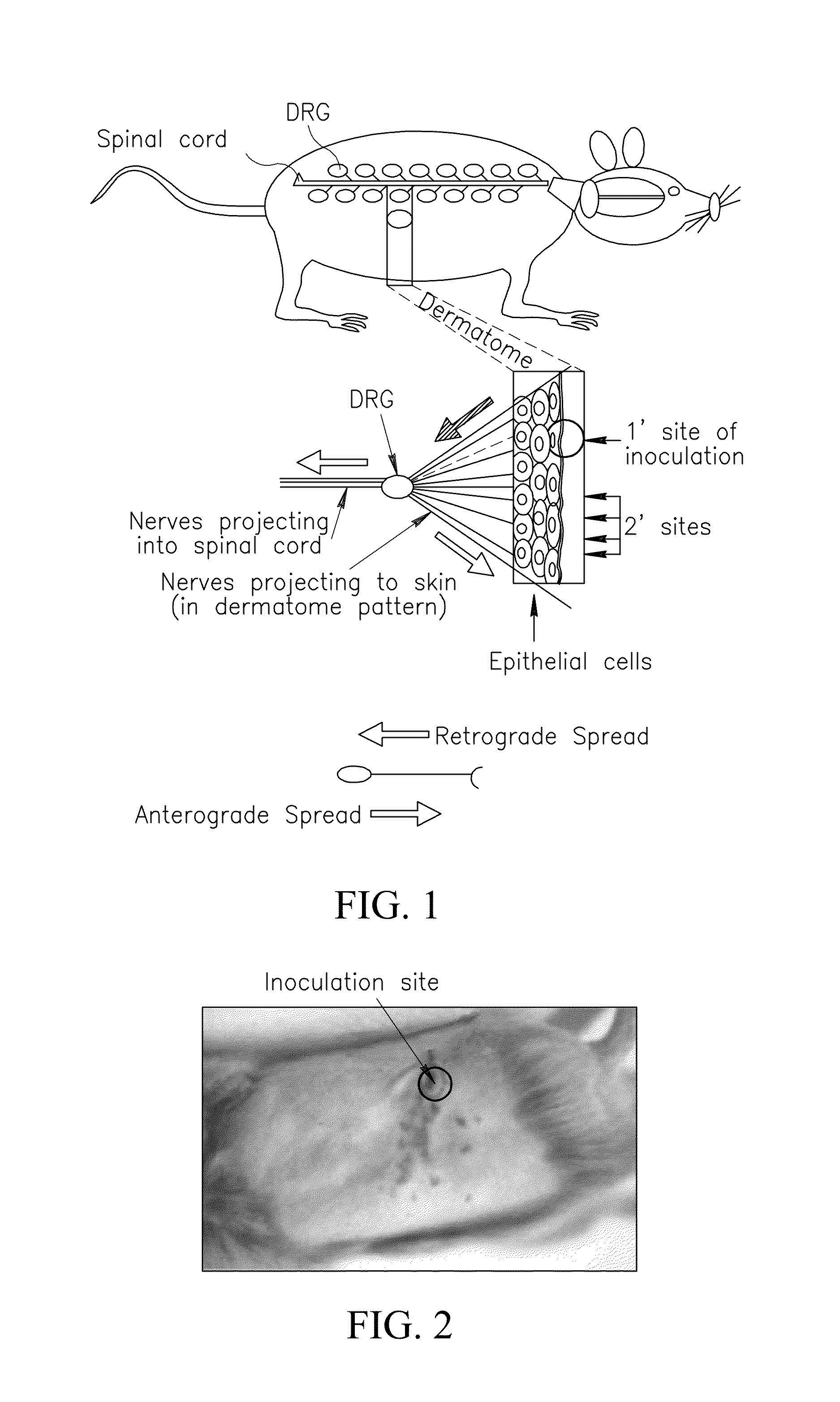
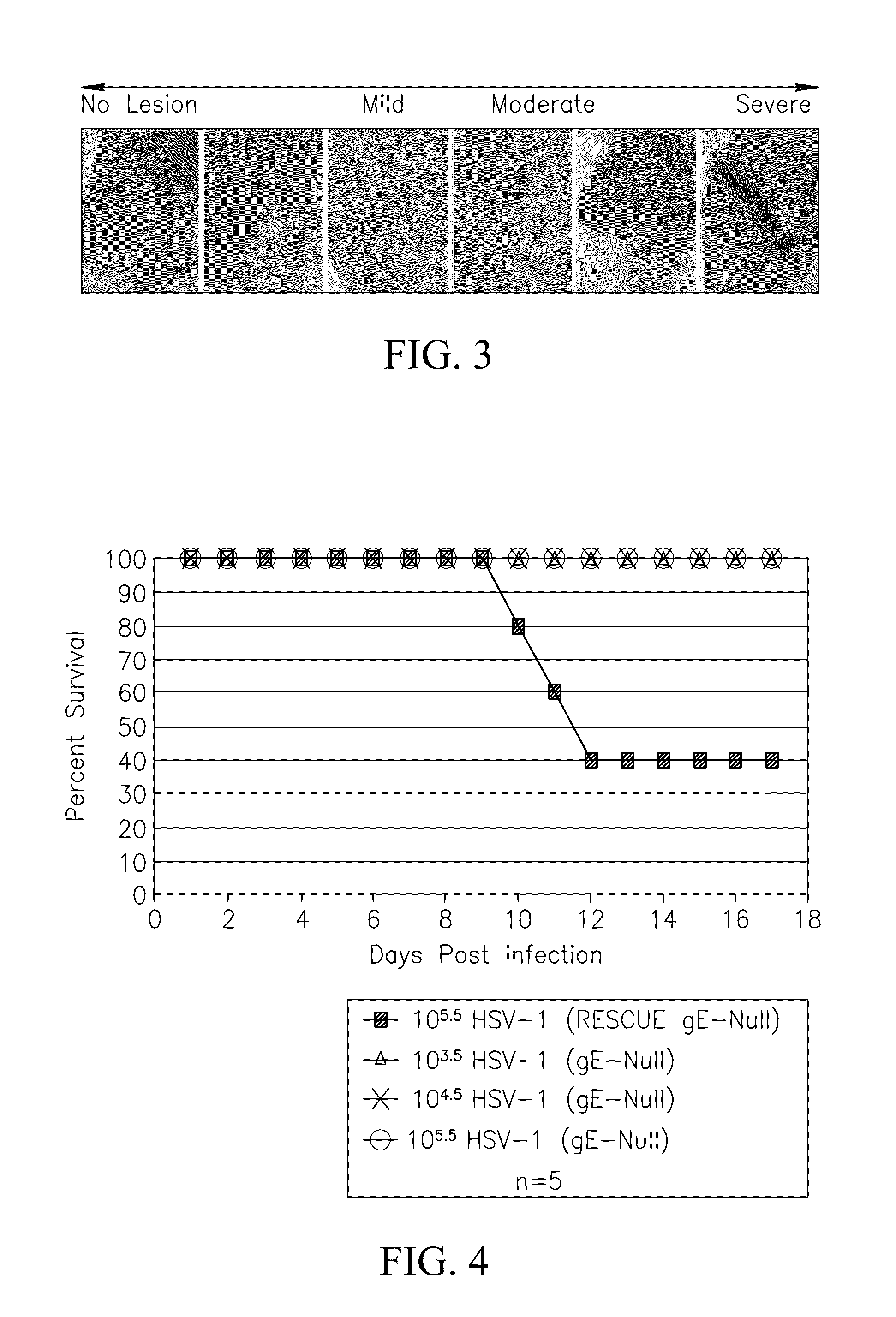
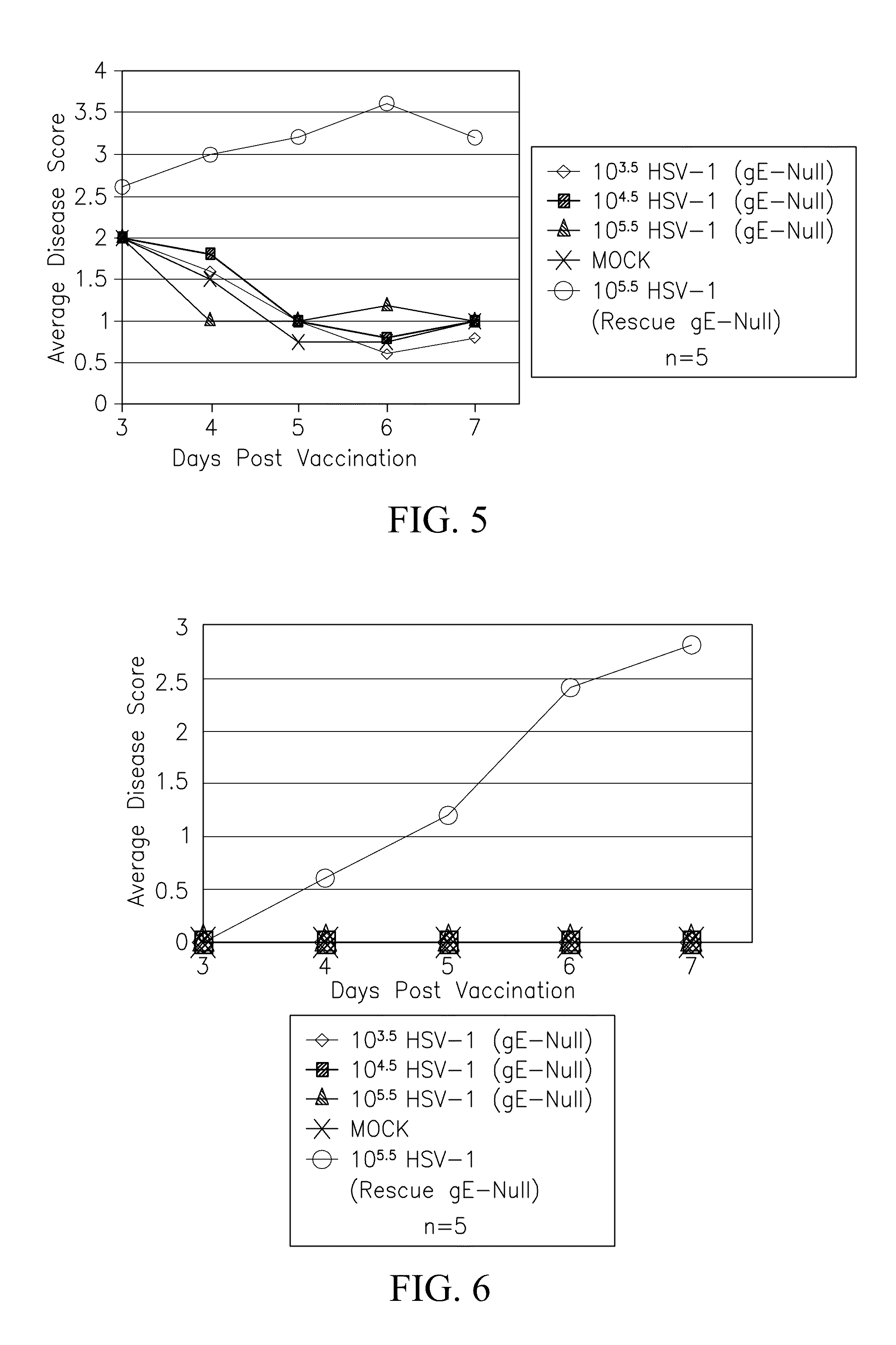
Methods of use for hsv-1 and hsv-2 vaccines
ActiveUS20090246227A1Reduce decreaseSymptoms improvedViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesRecurrent herpes simplexHsv infection
This invention provides methods of treating, suppressing, inhibiting, reducing an incidence, reducing the pathogenesis of, ameliorating the symptoms of, or ameliorating the secondary symptoms of a primary or recurring Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) infection, or prolonging the latency to a relapse of an HSV infection, and disorders and symptoms associated with same and inducing an anti-HSV immune response in a subject comprising the step of contacting the subject with a composition comprising a mutant HSV strain comprising an inactivating mutation in a Us8 gene, followed by a second contacting with the composition.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Combination/adjuvant therapy for wt-1-positive disease
InactiveUS20140271644A1Early inhibitionEnhance anti-tumor responseOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer cellTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
In an attempt to improve primary disease responsiveness and / or to overcome resistant disease, the present disclosure provides a method for treating or inhibiting the proliferation of a WT-1-dependent cancer comprising providing to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor along with an anti-WT-1 / HLA antibody, that is, an antibody that specifically binds to a peptide of Wilms' tumor protein (WT-1) presented on the surface of the cancer cells in an HLA-restricted fashion.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Botulinum toxin and the treatment of primary disorders of mood and affect
ActiveUS8926991B2Reduce transmissionRelieve symptomsBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBotulinum toxin typeClinical psychology
The invention provides methods for treating primary disorders of mood and affect, including depressive disorders, anxiety and sleep disorders and CNS disorders comprising the administration of a neurotoxin.
Owner:REVANCE THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions based on proanthocyanadin-catechin synergies for prevention and treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20040142048A1Reduced and no adverse effectInhibitory activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBetacyaninsProanthocyanidin
The invention described herein encompasses methods and compositions of preventing or treating cancer comprising the administration of a combination of catechins and proanthocyanadins. Compositions of catechins include but not limited to, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC). Compositions of proantho-cyanains include, but are not limited to, blue fruit extracts. The unique compositions of the invention contain various combinations of the catechins and proanthocyanadins, in combination with each other or other therapeutic agents and are used to treat primary and metastatic cancers in humans. The invention also encompasses various modes of administration of the therapeutic compounds, including formulations which may be used as a dietary or nutritional supplement or as a therapeutic compound.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Small molecule inhibitors of autotaxin and methods of use
InactiveUS20110110886A1Inhibit and reduce and growthInhibit and reduce likelihoodHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMetastatic melanoma
Autotaxin (ATX) is a prometastatic enzyme initially isolated from the conditioned media of human melanoma cells that stimulates a myriad of biological activities including angiogenesis and the promotion of cell growth, survival, and differentiation through the production of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). ATX increases the aggressiveness and invasiveness of transformed cells, and ATX levels directly correlate with tumor stage and grade in several human malignancies. To study the role of ATX in the pathogenesis of malignant melanoma, we developed antibodies and small molecule inhibitors against recombinant human protein. Immunohistochemistry of paraffin embedded human tissue demonstrates that ATX levels are markedly increased in human primary and metastatic melanoma relative to benign nevi. Chemical screens identified several small molecule inhibitors with binding constants ranging from nanomolar to low micromolar. Cell migration and invasion assays with melanoma cell lines demonstrate that ATX markedly stimulates melanoma cell migration and invasion, an effect suppressed by ATX inhibitors. The migratory phenotype can be rescued by the addition of ATX's enzymatic product, LPA, confirming that the observed inhibition is linked to suppression of LPA production by ATX. Chemical analogues of the inhibitors demonstrate structure activity relationships important for ATX inhibition and indicate pathways for their optimization. These studies suggest that ATX is an approachable molecular target for the rational design of chemotherapeutic agents directed against human malignancies driven by the ATX / LPA axis, especially including malignant melanoma, among numerous others including breast and ovarian cancers.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Tea catechins in sustained release formulations as cancer specific proliferation inhibitors
InactiveUS20020176898A1Good treatment effectReduce adverse effectsBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsCancer preventionDietary supplement
The invention described herein encompasses a methods and compositions of treating cancer or solid tumors comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of catechins, a group of polyphenols found in green tea, to a mammal in need of such therapy. Compositions of catechins include but not limited to, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC). The unique compositions of the invention contain various combinations of the catechins, alone or in combination with each other or other therapeutic agents and are used to treat primary and metastatic cancers in humans. The invention also encompasses the varying modes of administration of the therapeutic compounds, including a sustained release formulation which may be used as a therapeutic compound for the treatment of cancer or as a dietary supplement for the prevention of cancer.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
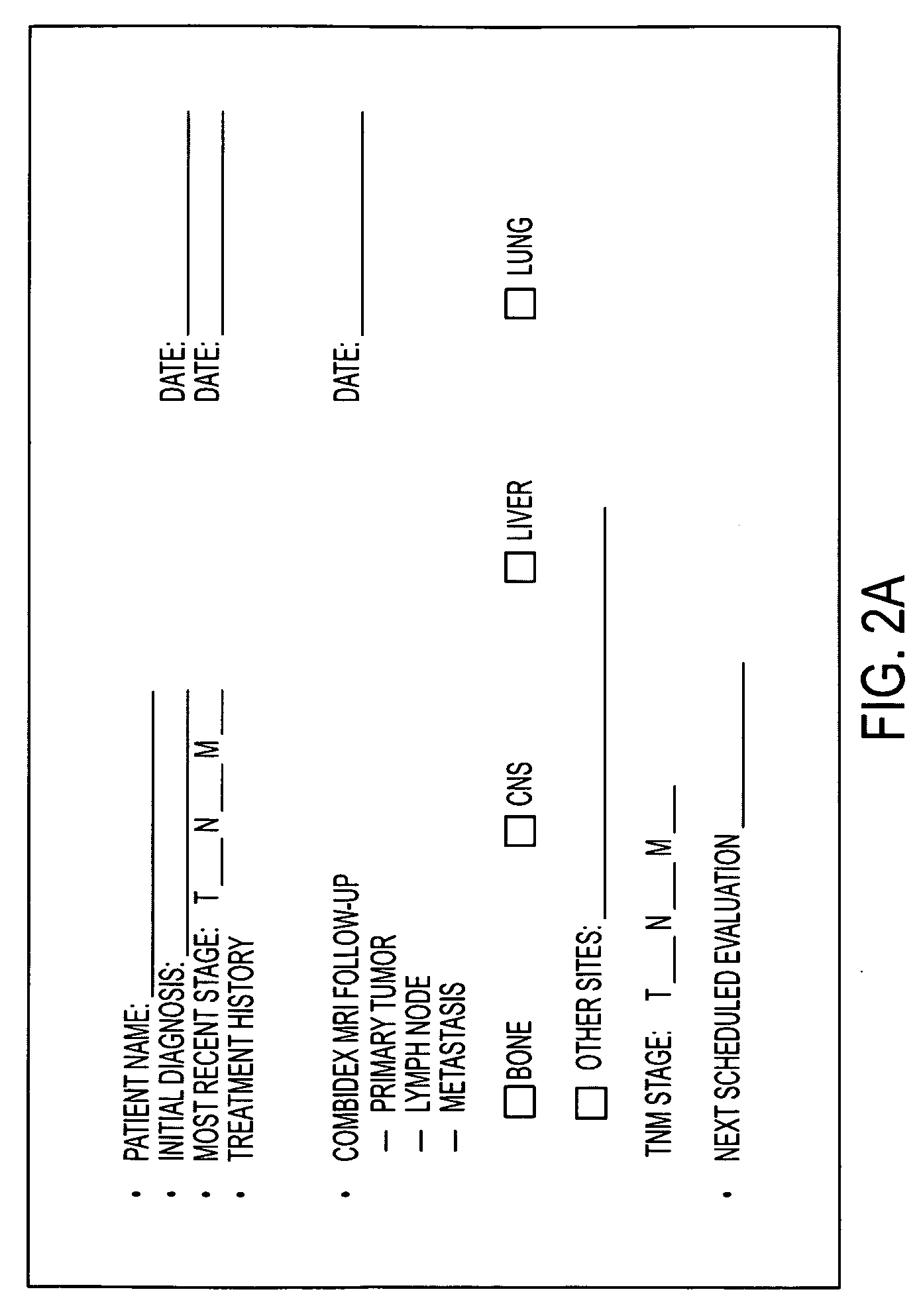
Macrophage-Enhanced MRI (MEMRI)
Methods for assessing stage of cancer in a subject are provided, comprising administering a macrophage imaging agent to the subject, making a magnetic resonance image of regions of the subject's body at cancer risk, and using the image to assess macrophage density and displacement associated with any primary cancer or metastatic cancer in the subject, such density and displacement being indicative of neoplasia. The macrophage imaging agent may be an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particle and in particular embodiments, the macrophage imaging agent has a blood half-life sufficient to permit microphage trapping throughout the regions at cancer risk. Additional embodiments provide methods for assessing efficacy of an anticancer treatment in a subject, methods for determining frequency of follow-up MEMRI evaluation in a subject, methods for determining metastatic potential of cancer foci in a subject, and methods for determining prognosis of cancer in a subject. Methods for directing site of biopsy in a subject by performing a whole body MEMRI evaluation of the subject to identify macrophage density at a tumor site of interest and assessing the macrophage density to identify the site of biopsy in the subject, macrophage density being an indicator of tumor growth are also provided, in addition to methods for providing individualized cancer treatment to a subject in need thereof using whole body MEMRI evaluation.
Owner:AMAG PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com