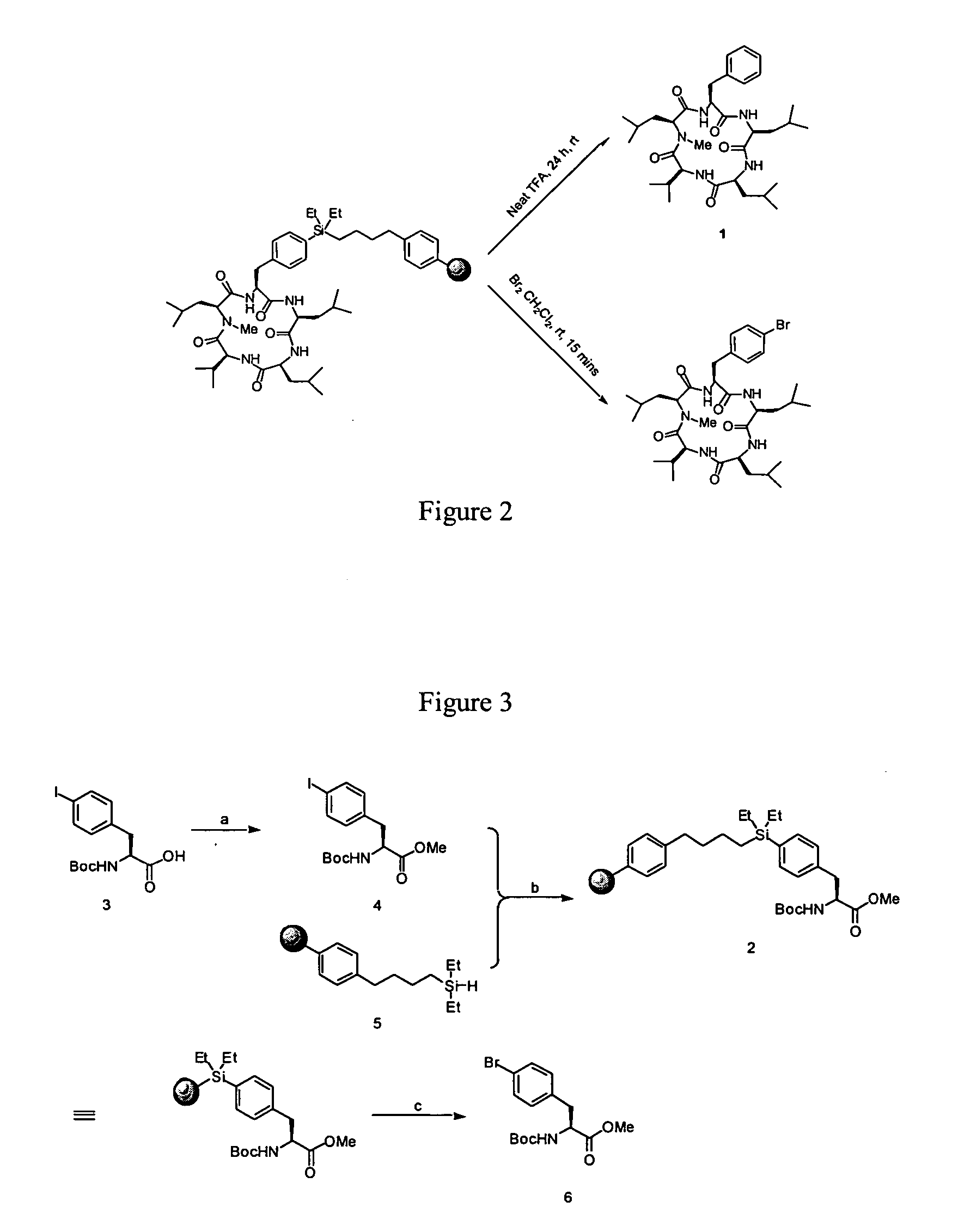
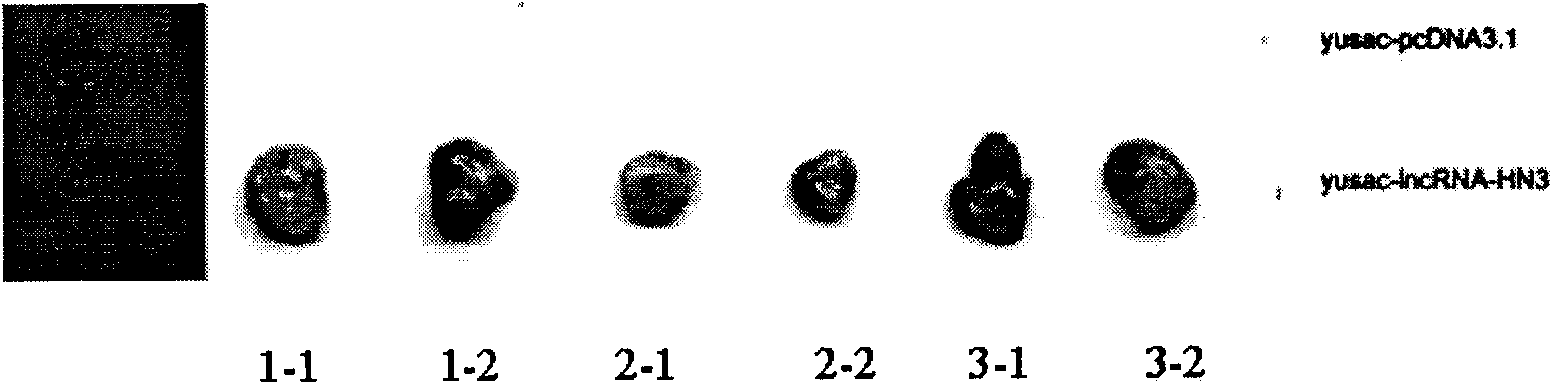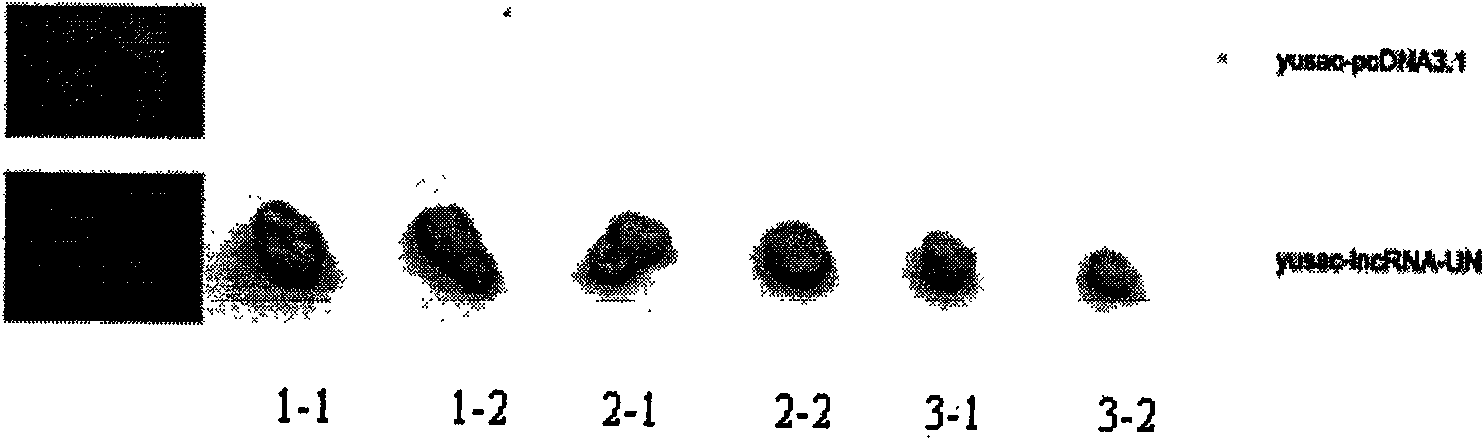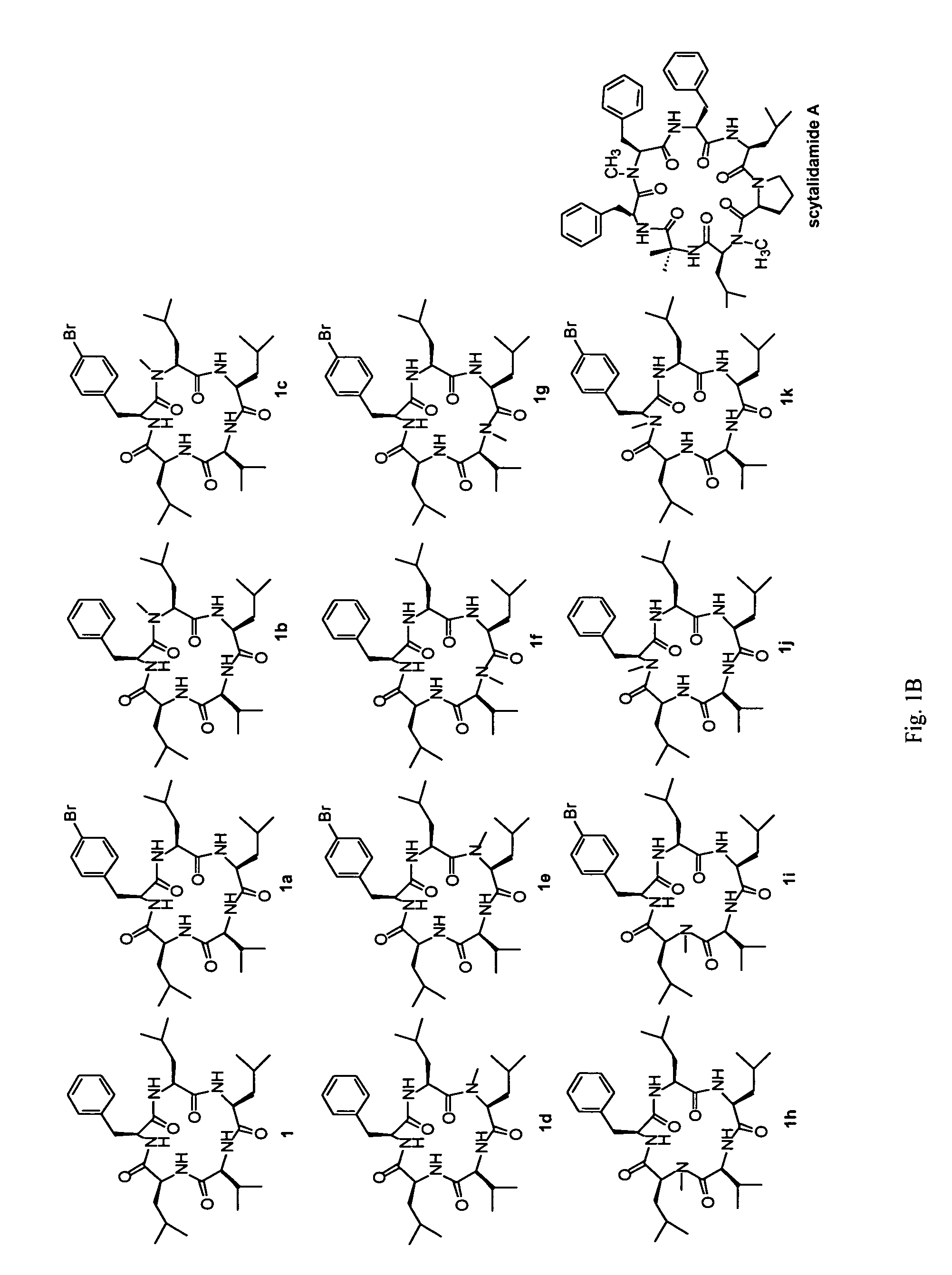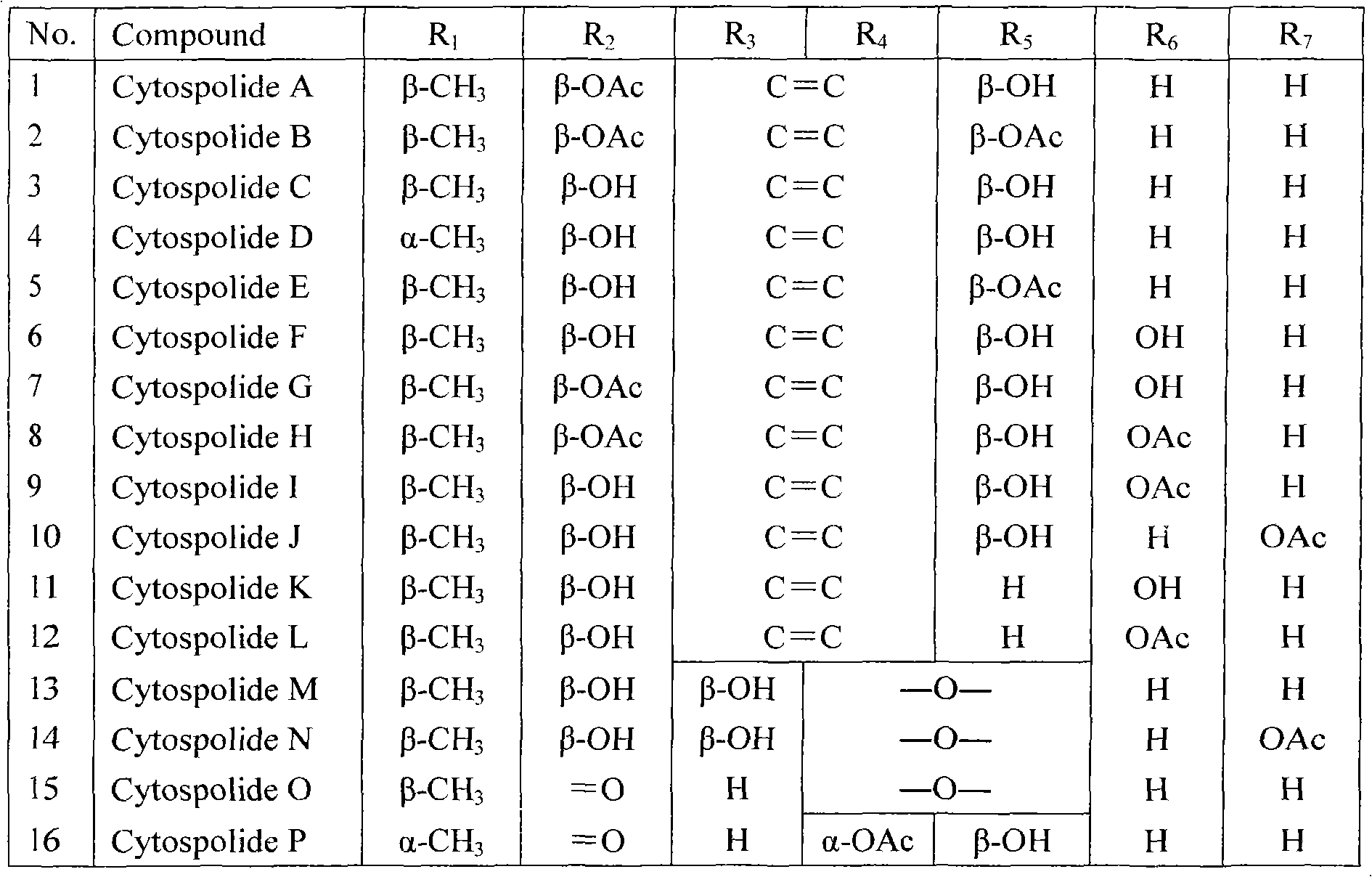Patents
Literature
107 results about "Human melanoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
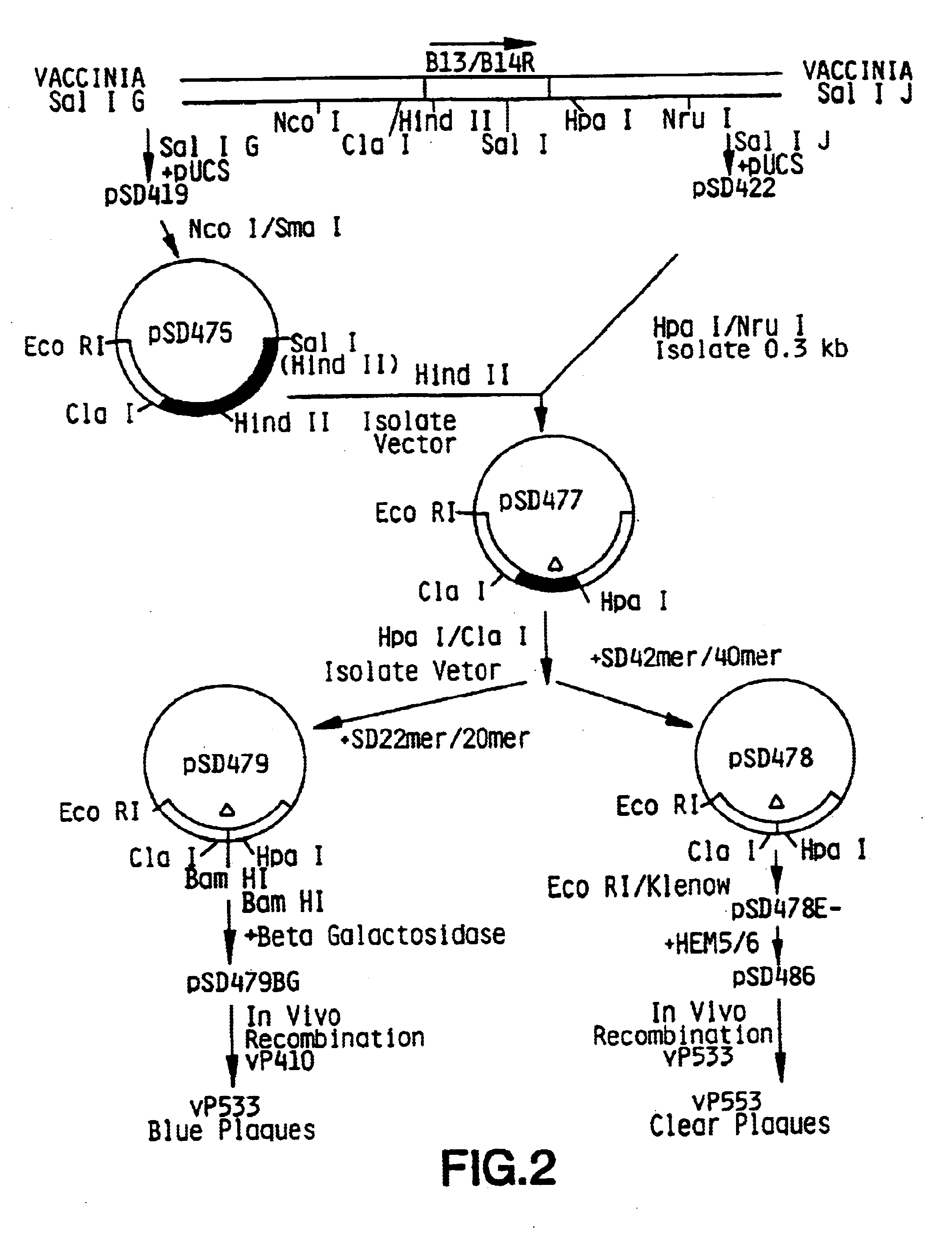
Pox virus containing DNA encoding a cytokine and/or a tumor associated antigen
InactiveUS6265189B1Improve securityImprove security levelVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorWild type
Attenuated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a cytokine and / or a tumor associated antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least on of: human tumor necrosis factor; nuclear phosphoprotein p53, wildtype or mutant; human melanoma-associated antigen; IL-2; IFNgamma; IL-4; GNCSF; IL-12; B7; erb-B-2 and carcinoembryonic antigen. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:VIROGENETICS
Vaccina virus comprising cytokine and/or tumor associated antigen genes
InactiveUS6537594B1Improve securityImprove security levelVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorWild type
Owner:VIROGENETICS
Pox virus comprising DNA sequences encoding CEA and B7 antigen
Attenutated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a cytokine and / or a tumor associated antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least one of: human tumor necrosis factor; nuclear phosphoprotein p53, wiltype or mutant; human melanoma-associated antigen; IL-2; IFNgamma; IL-4; GMCSF; IL-12; B7; erb-B-2 and carcinoembryonic antigen. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for cancer therapy.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated protein 9) target knockout human Lin28A gene and specific gRNA (guide Ribonucleic Acid) of CRUSPR/Cas9 target knockout human Lin28A gene
InactiveCN106868008AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHuman melanomaWilms' tumor
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and biomedicine and in particular relates to application of a gRNA (guide Ribonucleic Acid) sequence based on a CRISPR / Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated protein 9) system on knockout of a human Lin28A gene and application to tumor treatment. According to a design principle of CRISPR / Cas9, 6 guide RNAs (gRNA) are designed and a sequence table is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.6; the guide RNAs are constructed on a PX458 carrier and two efficient target gRNAs are obtained through activity detection and screening. The CRISPR / Cas9 system guided by the two gRNAs is utilized in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HepG2) and human melanoma cell lines (A375), and the human Lin28A gene can be effectively knocked out; the system is easy to operate and the human Lin28A gene knockout efficiency is high, so that the system is applicable to various tumor cell models. The gRNA provided by the invention is hopefully applied to a new drug for treating tumors.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
Small molecule inhibitors of autotaxin and methods of use
InactiveUS20110110886A1Inhibit and reduce and growthInhibit and reduce likelihoodHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMetastatic melanoma
Autotaxin (ATX) is a prometastatic enzyme initially isolated from the conditioned media of human melanoma cells that stimulates a myriad of biological activities including angiogenesis and the promotion of cell growth, survival, and differentiation through the production of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). ATX increases the aggressiveness and invasiveness of transformed cells, and ATX levels directly correlate with tumor stage and grade in several human malignancies. To study the role of ATX in the pathogenesis of malignant melanoma, we developed antibodies and small molecule inhibitors against recombinant human protein. Immunohistochemistry of paraffin embedded human tissue demonstrates that ATX levels are markedly increased in human primary and metastatic melanoma relative to benign nevi. Chemical screens identified several small molecule inhibitors with binding constants ranging from nanomolar to low micromolar. Cell migration and invasion assays with melanoma cell lines demonstrate that ATX markedly stimulates melanoma cell migration and invasion, an effect suppressed by ATX inhibitors. The migratory phenotype can be rescued by the addition of ATX's enzymatic product, LPA, confirming that the observed inhibition is linked to suppression of LPA production by ATX. Chemical analogues of the inhibitors demonstrate structure activity relationships important for ATX inhibition and indicate pathways for their optimization. These studies suggest that ATX is an approachable molecular target for the rational design of chemotherapeutic agents directed against human malignancies driven by the ATX / LPA axis, especially including malignant melanoma, among numerous others including breast and ovarian cancers.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Long non-coding RNA sequence relevant to human melanoma cells and application thereof
InactiveCN101633923AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEukaryotic plasmids
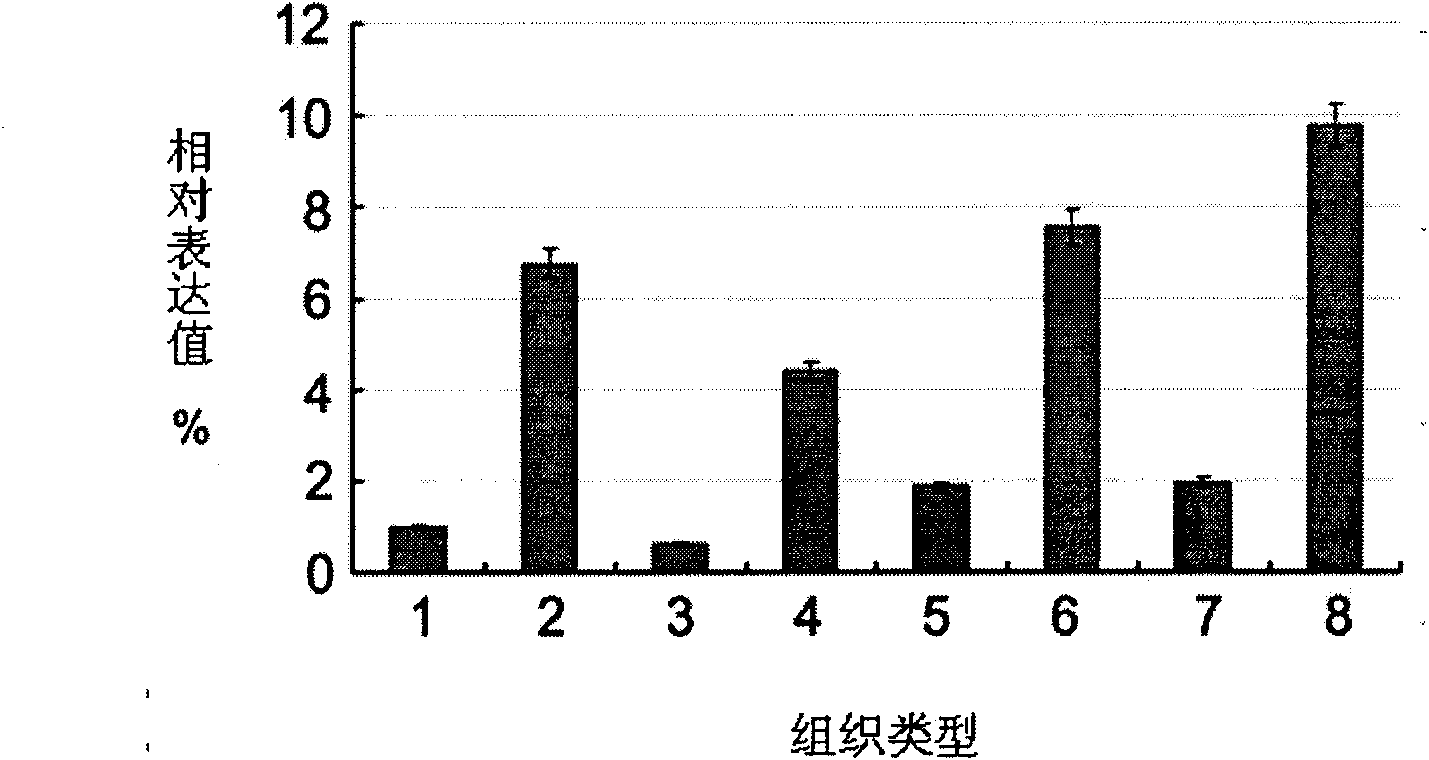
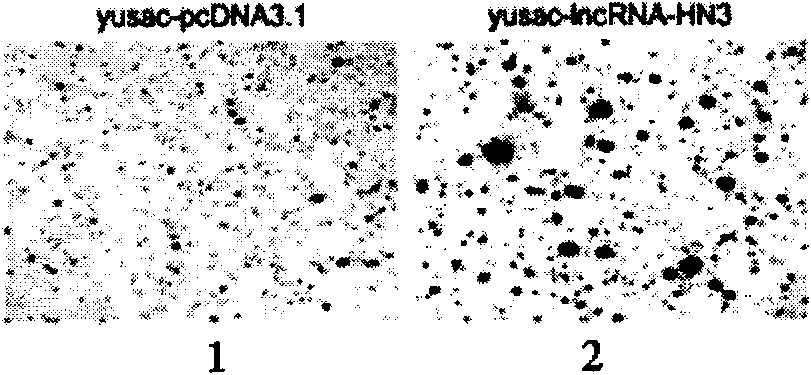
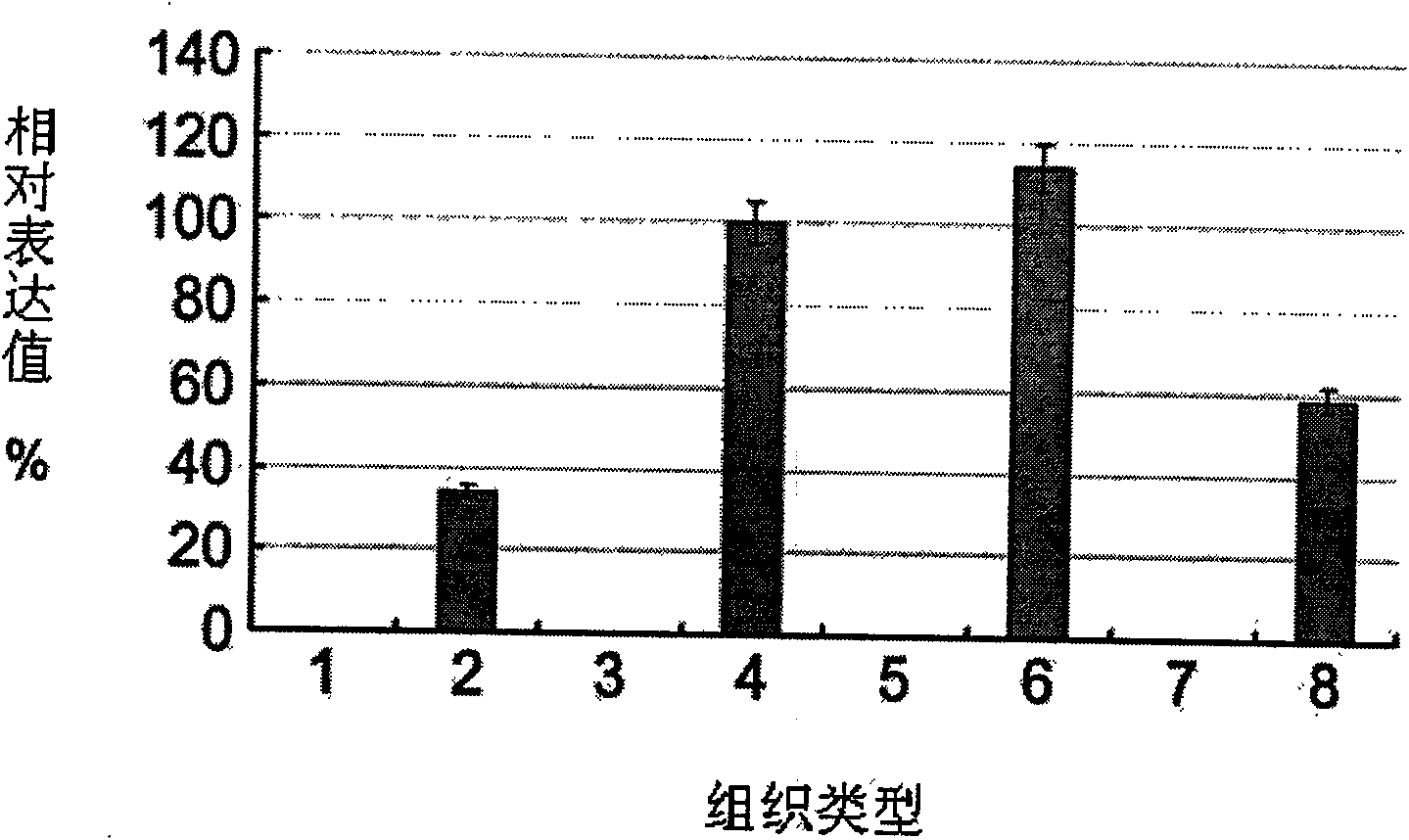
The invention provides a long non-coding RNA (long non-coding RNA, 1ncRNA)-incRNA-HN3 sequence relevant to human melanoma cells, and an RNA interference (RNA interference, RNAi) target spot sequence, a short-hairpin RNA (short-hairpin RNA, shRNA) sequence, an shRNA coded small molecule interference RNA (small interference RNA, siRNA), a coding shRNA coding strand and an anti-sense strand DNA sequence, coding shRNA recombinant plasmids of the long non-coding RNA sequence, and the invention relates to the applications of the long non-coding RNA sequence for preparing reagents for diagnosing melanoma diseases and drugs for treating the melanoma diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Long non-coding RNA sequence of human melanoma cell specific expression and application thereof
InactiveCN101619312AEasy diagnosisGood treatment effectGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell specificDisease
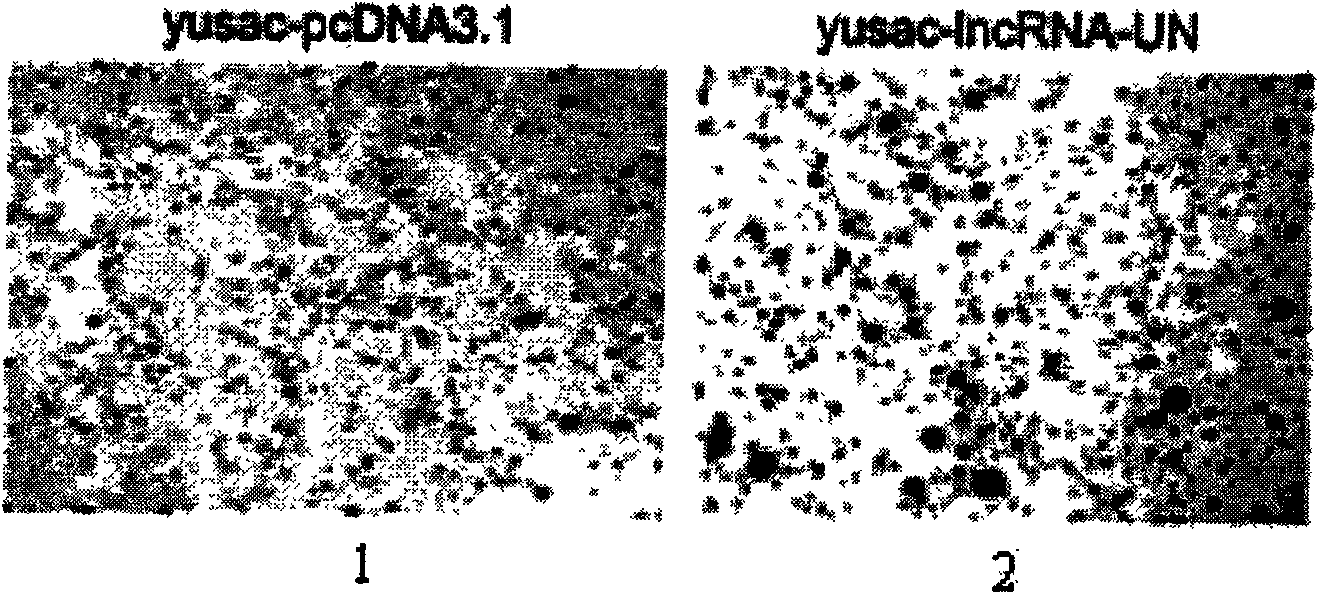
The invention discloses a long non-coding RNA (lnc RNA-UN) of human melanoma cell specific expression, an RNA interfering target spot thereof, a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) of the RNA interfering target spot, a small interfering RNA (siRNA), a sense strand DNA and an antisense strand DNA of the coding short hairpin RNA and a recombinant plasmid of a transcription short hairpin RNA. Proved by experiments, the lnc RNA-UN is highly expressed in a melanoma tissue and not expressed in a peficancerous tissue and can be applied to preparing a reagent for diagnosing melanoma diseases. Proved by the experiments, the recombinant plasmid of the transcription short hairpin RNA expresses the shRNA and the siRNA in a melanoma cell and can obviously degrade the cell endogenous lncRNA-UN and restrain the malignant growth of the melanoma cell, thus the shRNA and the siRNA of the RNA interfering target spot of the lncRNA-UN and the recombinant plasmid of the transcription short hairpin RNA can be applied to medicaments for treating the melanoma diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
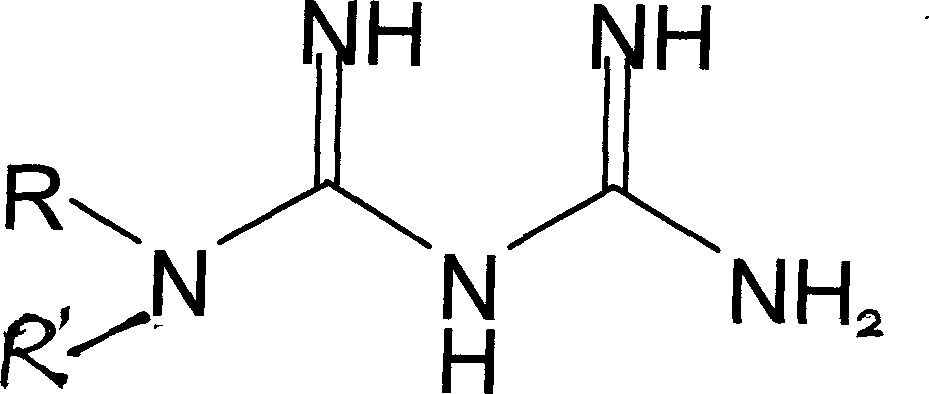
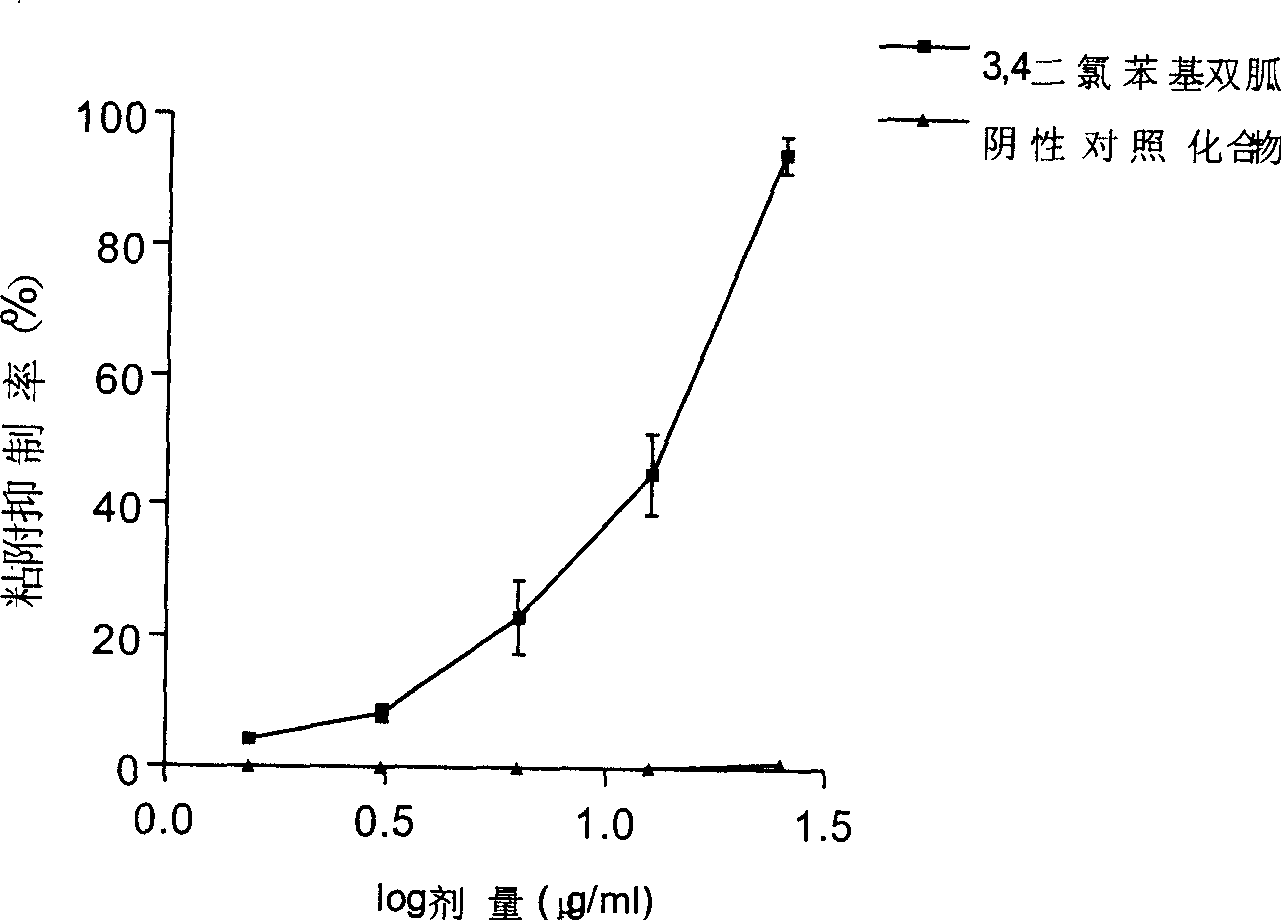
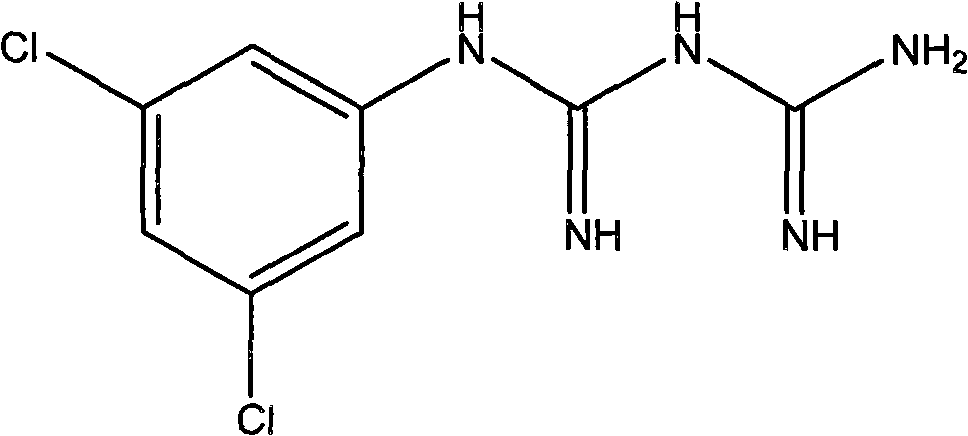
Substituted aromatic radical biguanide compounds and the application of their medicine composition in preparing medicine for resisting malignant tumors
The present invention relates to substituted aromatic radical biguanide compounds and the application of their medicine composition in preparing medicine for treating malignant tumors. The substituted aromatic radical biguanide compounds possess, extracorporeal and intracorporeal experiments shows, obvious tumor cell inhibiting effect and the features of high efficiency and low toxicity, so that the medicine compounds are expected to be applied in inhibiting tumor attack and metastasis, inhibiting angiogenesis, and treating human melanoma, glioma, lung cancer and other malignant tumors with high expression of integrin.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
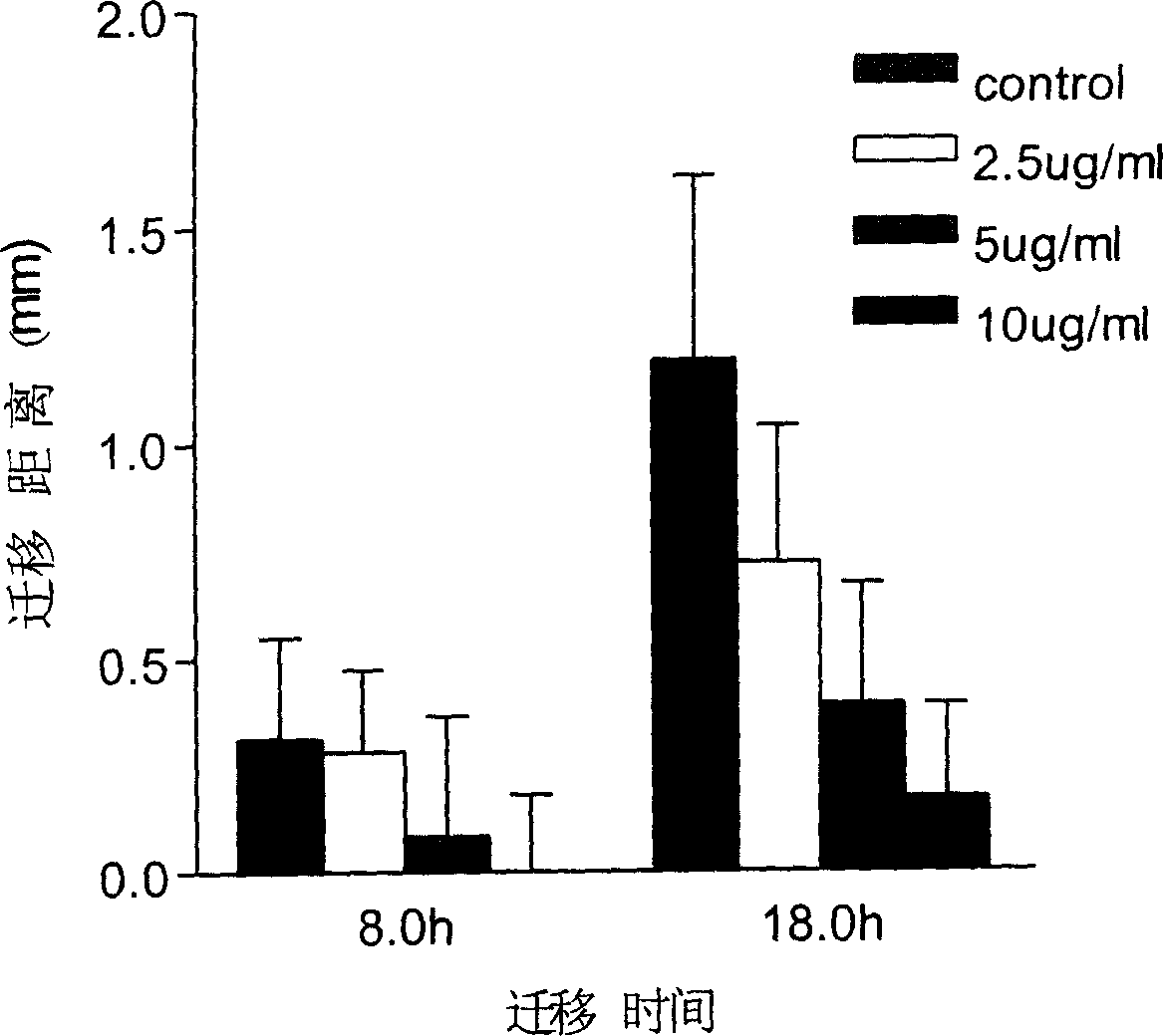
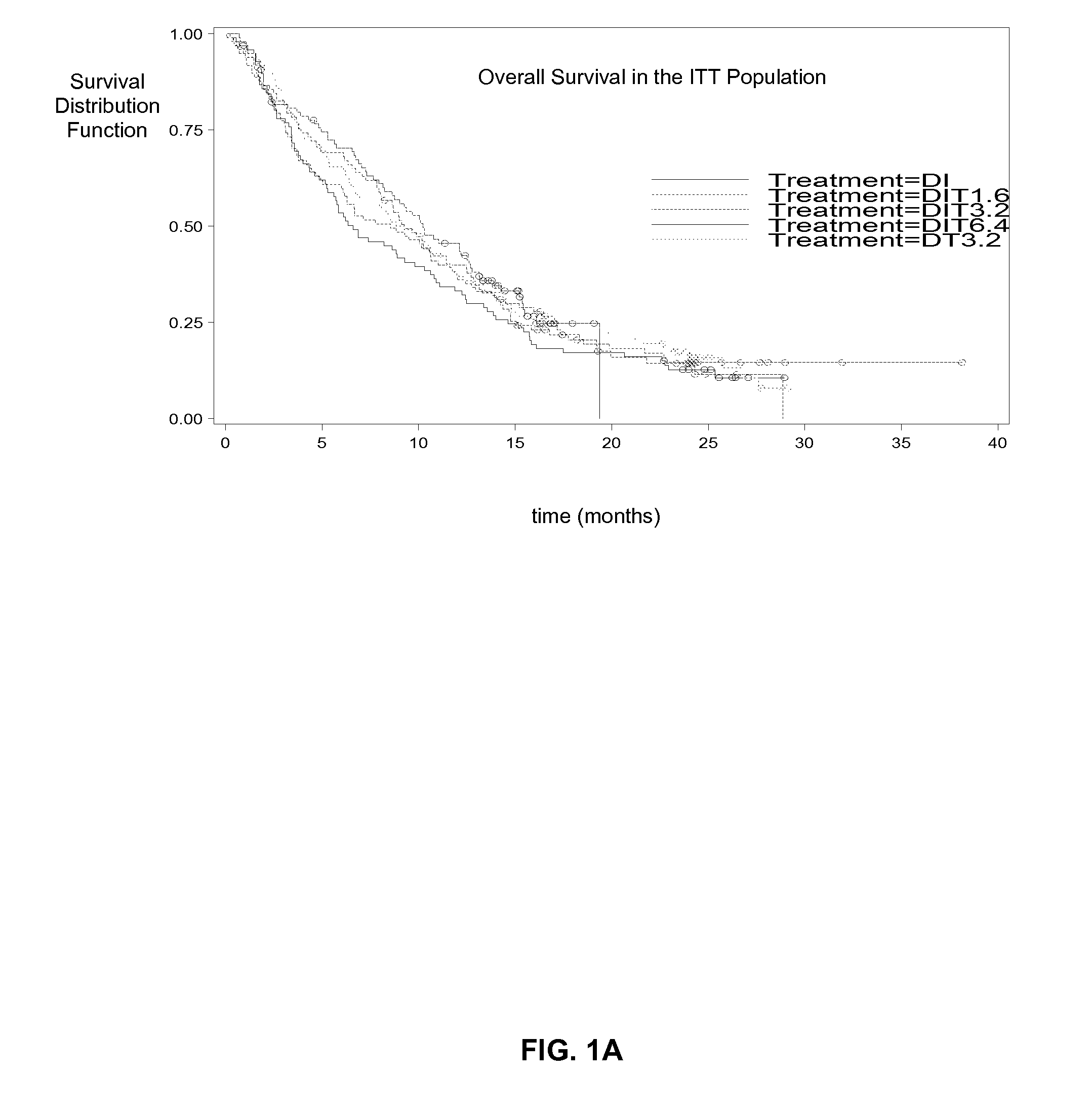
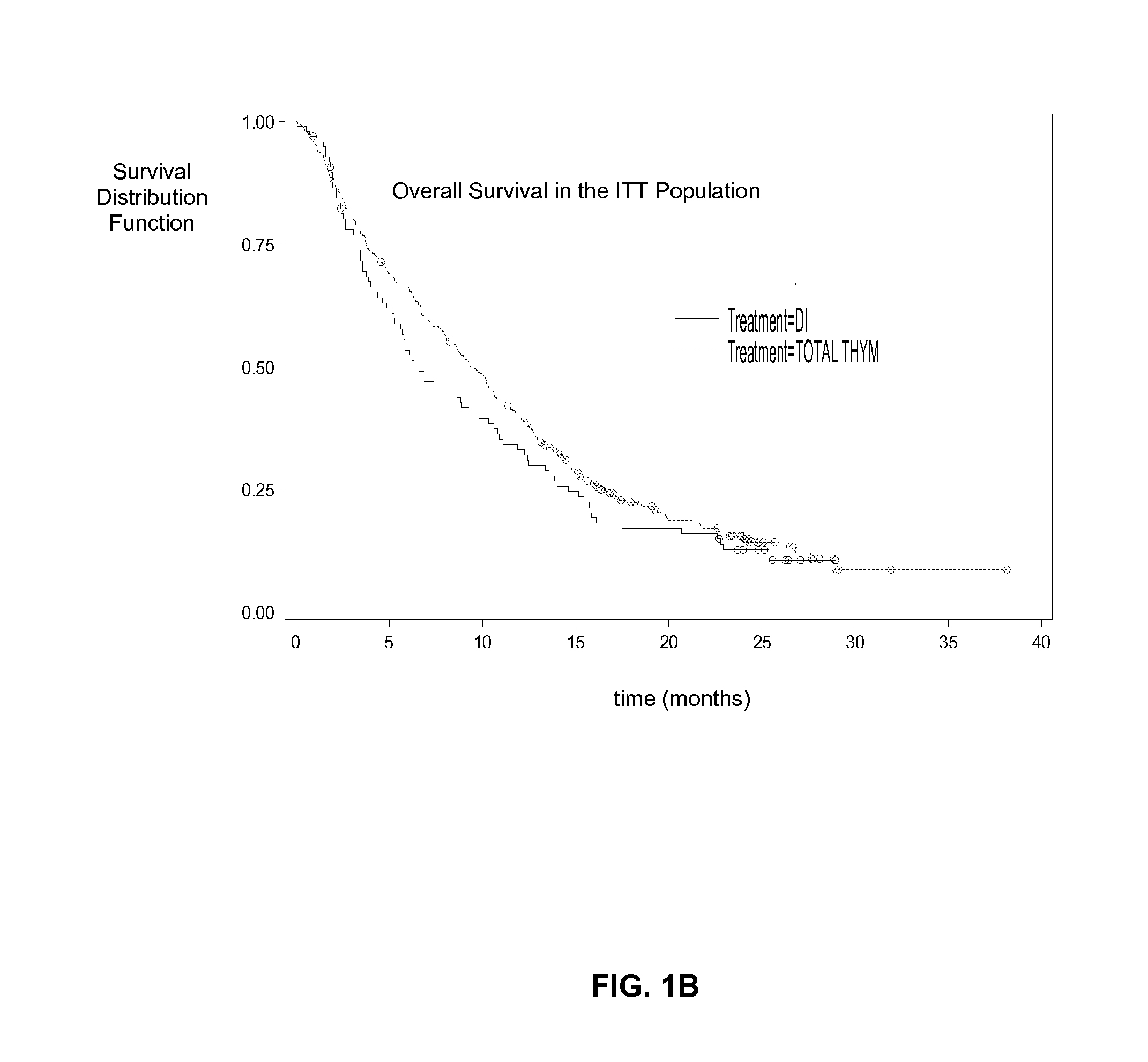
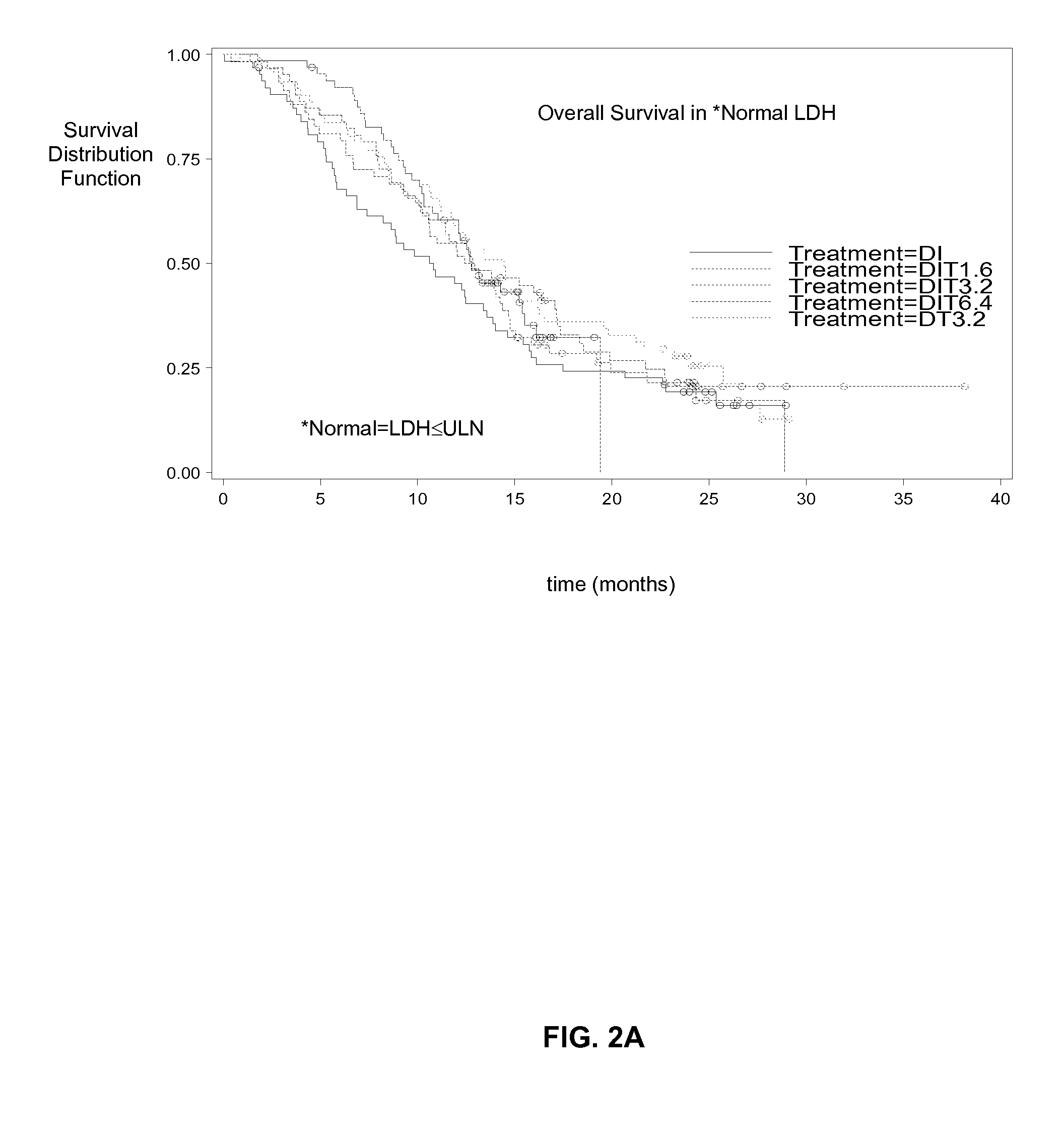
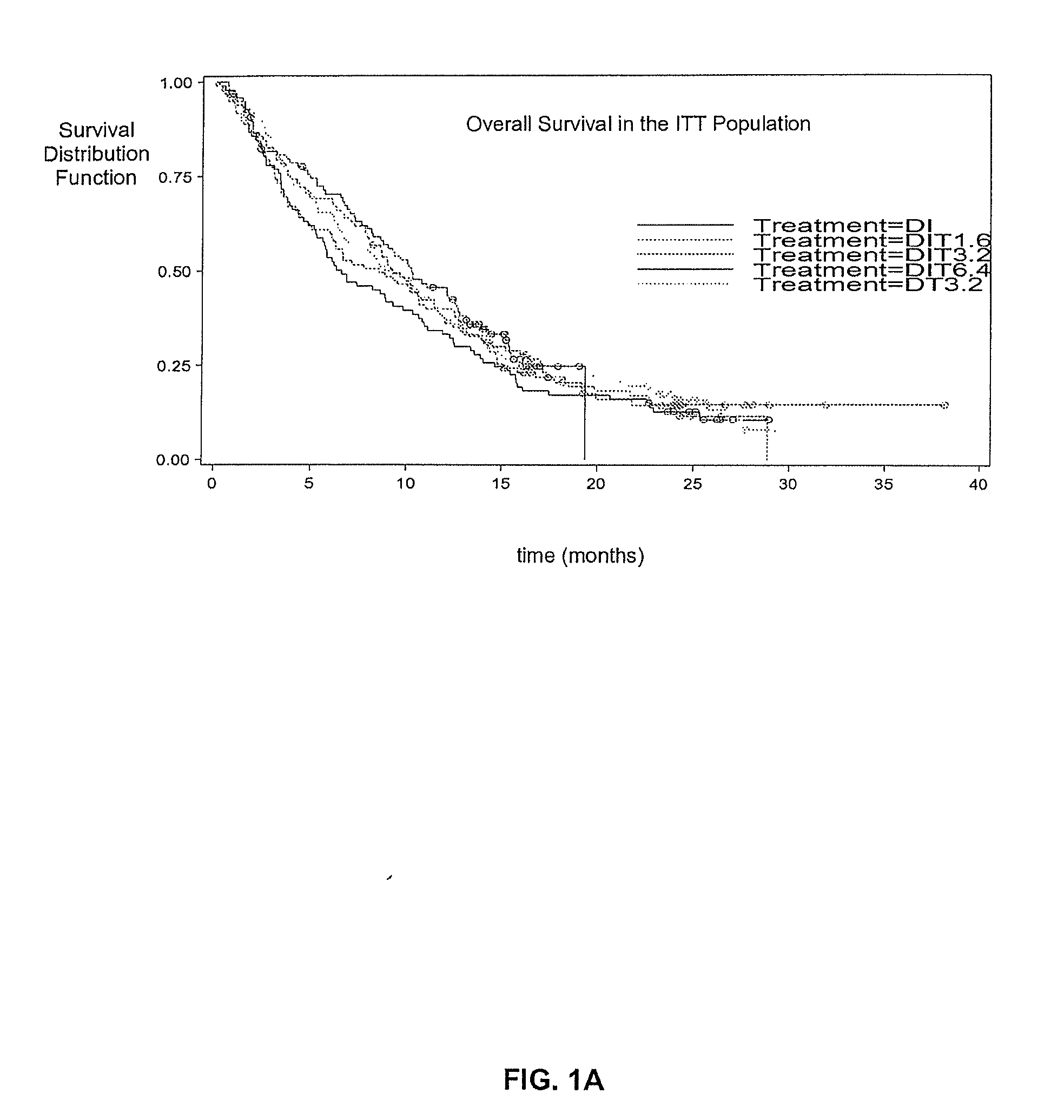
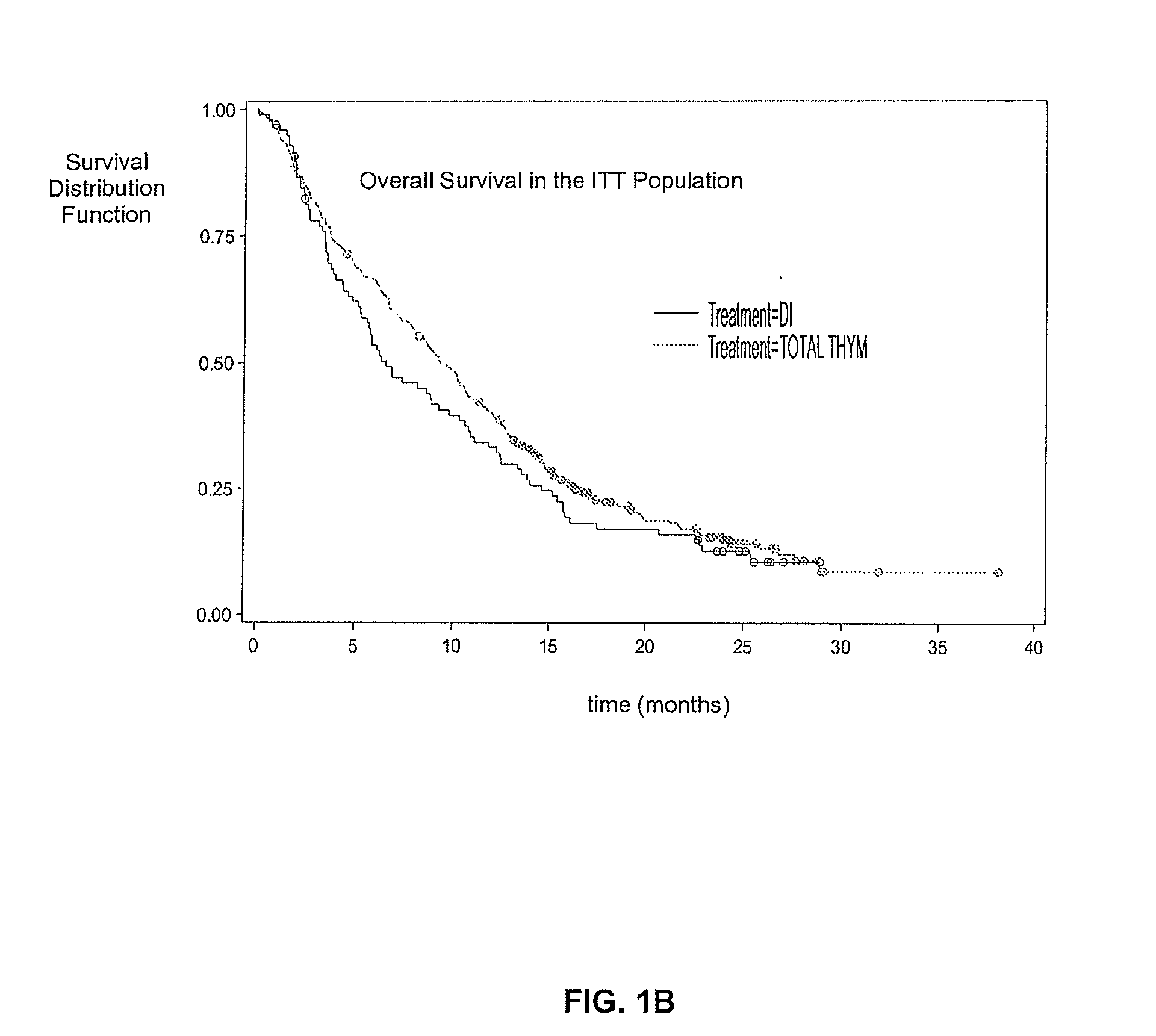
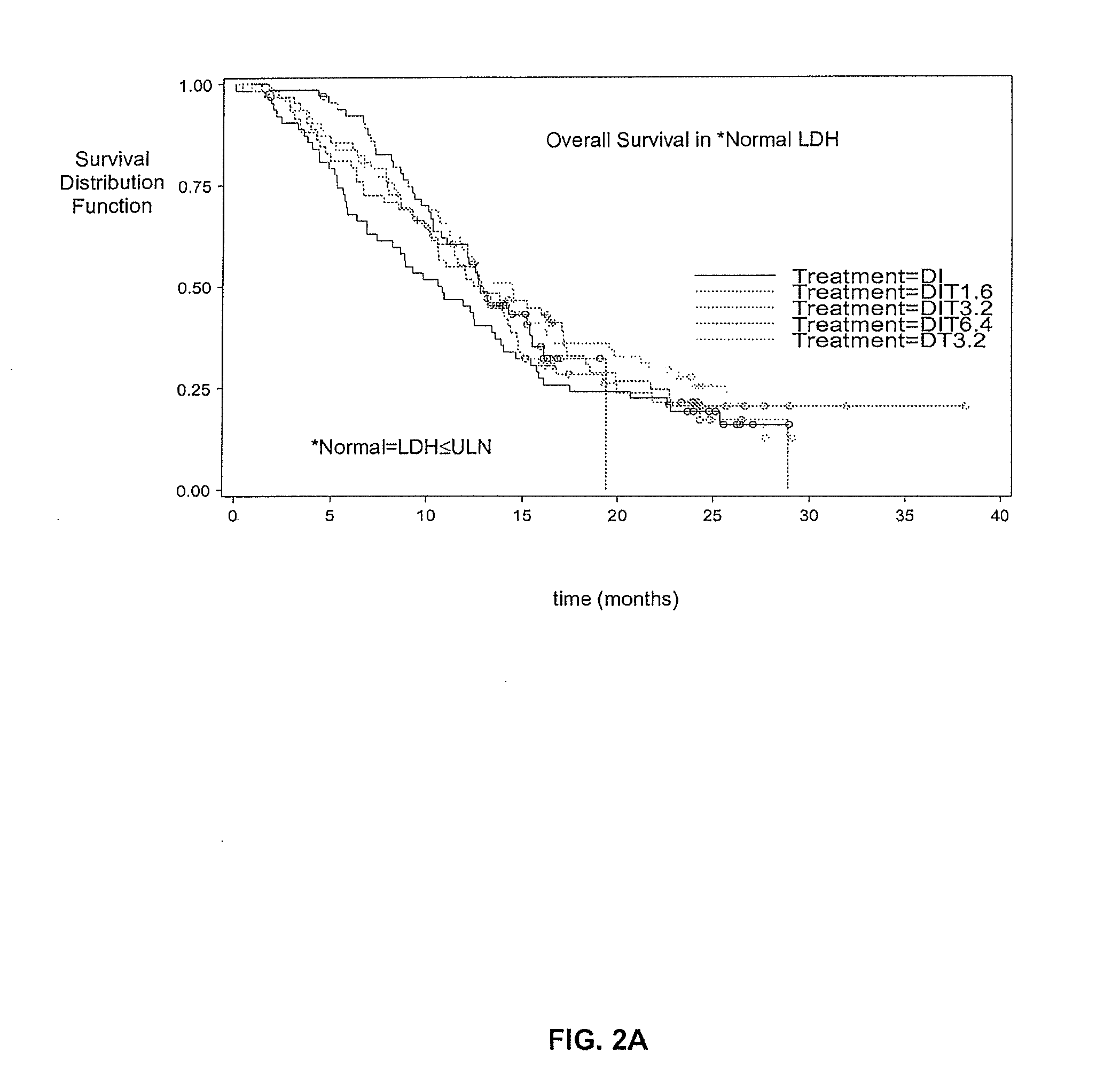
Treatment of Melanoma with Alpha Thymosin Peptides
InactiveUS20080300166A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSulfonylurea active ingredientsBlood levelLymphatic Spread
A method of treating melanoma or a metastasis thereof in a human patient by administering a melanoma-treating effective amount of an alpha thymosin peptide to a human melanoma patient, wherein the human melanoma patient does not have a substantially elevated LDH blood level.
Owner:SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICAL INC
Treatment of melanoma with alpha thymosin peptides in combination with antibodies against cytotoxic t lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4)
Melanoma or a metastasis thereof is treated in a human patient in a combination therapy which includes administering a melanoma-treating combination to a human melanoma patient during a treatment regimen, the combination including an alpha thymosin peptide and antibodies against cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4).
Owner:SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICAL INC
Highly metastatic model of human melanoma, cell subline, creation methods, and dynamic detection of metastasis
InactiveCN102067828AMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsMetastatic melanomaLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses a highly metastatic model of human melanoma, a highly metastatic cell subline of the human melanoma, creation methods for the highly metastatic model and the highly metastatic cell subline, and the dynamic detection of metastasis. The subcutaneously-transplanted mouse highly metastatic model and the corresponding cell subline are established in an in-vivo screening way in a mouse with severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) by using mouse lung metastasis, namely human malignant melanoma cell strain A375 pulmonary metastasis, wherein the highly metastatic cell subline of the human melanoma is A375sci, and has a human tumor cell karyotype; and 60 to 75 hypo-triploid-dominated chromosomes are acrocentric and have a heteroploid karyotype. The cell subline has the two routes of metastasis of blood trails and lymph. The in-vivo screening of the highly-metastatic model is performed by using animals with severe immune deficiency, and is expressed and applied in nude mice. A method for detecting Alu genes by using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is simple, highly sensitive and highly specific, and can be used for detecting organ metastasis, particularly micrometastasis, in a human tumor animal-xenotransplantation model.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Cyclic peptide antitumor agents
InactiveUS20050159346A1High cytotoxic activityImprove effectivenessCyclic peptide ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCyclic peptideProstate cancer cell
Cyclic peptide compounds and derivatives thereof having antitumor activity as shown by treatment of human melanoma, pancreatic, breast, prostate cancer cells.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
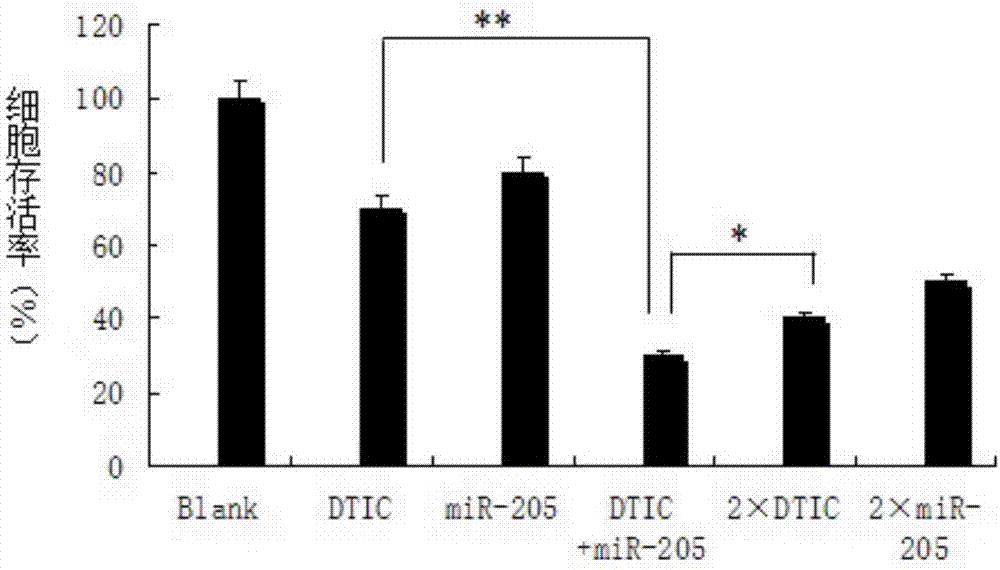
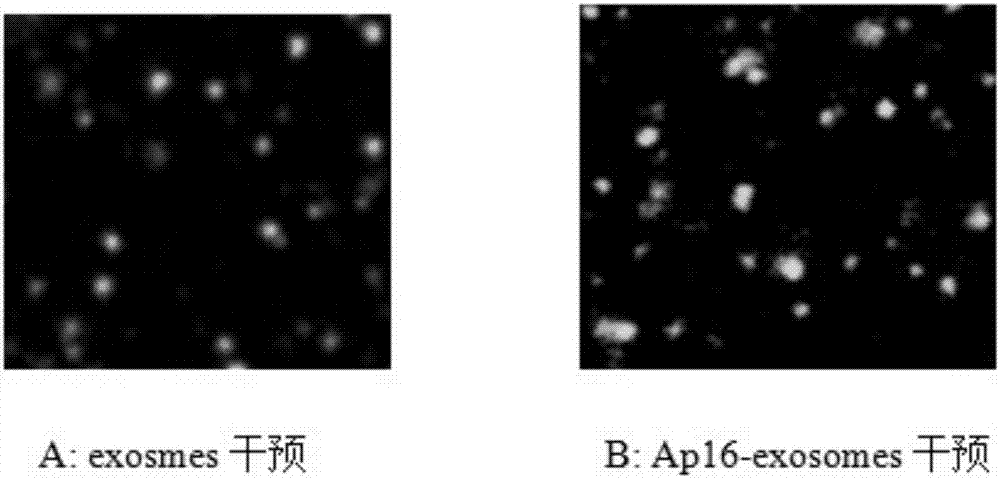
Targeted anti-malignant-melanoma DTIC (dacarbazine) and miR-205 co-carrying exosome as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107375944APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFreeze thawingModified dna
The invention relates to a targeted anti-malignant-melanoma DTIC (dacarbazine) and miR-205 co-carrying exosome as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The condition that DTIC and miR-205 achieve a cooperated inhibition effect on the human melanoma through being used in a combined way is discovered; a cholesterol modified DNA aptamer Ap16 is used as a targeted head; exosomes from the middle lactation period of milk are coated and carried with DTIC and miR-205; an Ap16-exosome / (DTIC / miR-205) nanometer medication system is successfully built by a freeze thawing method; the cooperated anti-tumor effect of the DTIC and miR-205 is proved; the aptamer Ap16 mediated co-carrying exosomes improve the feasibility of the miR-205 for enhancing the anti-malignant-melanoma effect of the DTIC. The invention provides a novel path for building the anti-malignant-melanoma nanometer medication system, and also provides the theoretical basis for the combined use of gene therapy and chemotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL
Treatment of melanoma with alpha thymosin peptides in combination with an antineoplastic heat shock apoptosis activator (HSAA)
Melanoma or a metastasis thereof is treated in a human patient in a combination therapy which includes administering a melanoma-treating combination to a human melanoma patient during a treatment regimen, the combination including an alpha thymosin peptide and an antineoplastic heat shock apoptosis activator (HSAA) such as STA-4783 (and optionally an antineoplastic cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agent such as paclitaxel), and / or optionally one or more additional anti-melanoma agents.
Owner:SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICAL INC
BANCR (BRAF-activated non-protein coding RNA) overexpressed human skin melanoma stable cell strain and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a BANCR (BRAF-activated non-protein coding RNA) overexpressed human skin melanoma stable cell strain and a preparation method and application thereof and relates to the technical field of molecular biology. BANCR gene is inserted into an expression vector to obtain a recombinant lentiviral vector, packaging cells are co-transfected by the recombinant lentiviral vector and packaging plasmid to obtain recombinant lentivirus, human skin melanoma cells are infected with the recombinant lentivirus to obtain the BANCR overexpressed human skin melanoma stable cell strain. The construction method provided herein integrates a target gene to a host cell through a lentivirus system, and finally acquires the efficient stable BANCR overexpressed human skin melanoma stable cell strain by screening and identifying; the cell strain is used for studying BANCR and tumor relevancy and its mechanism, and reliable study basis is provided for the deep study on possible occurrence and developing mechanisms of BANCR and human melanoma.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Human melanoma mutation
InactiveUS20080003603A1Negative regulatory effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementActivating mutationMedicine
The present invention relates to the field of melanoma diagnosis and therapy. In particular, the present invention relates to c-kit activating mutations present in melanoma, and their use for melanoma evaluation and diagnosis, melanoma prognosis, melanoma progression monitoring, and prescribing therapeutic strategies such as treatment with imatinib or other kinase inhibitors.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
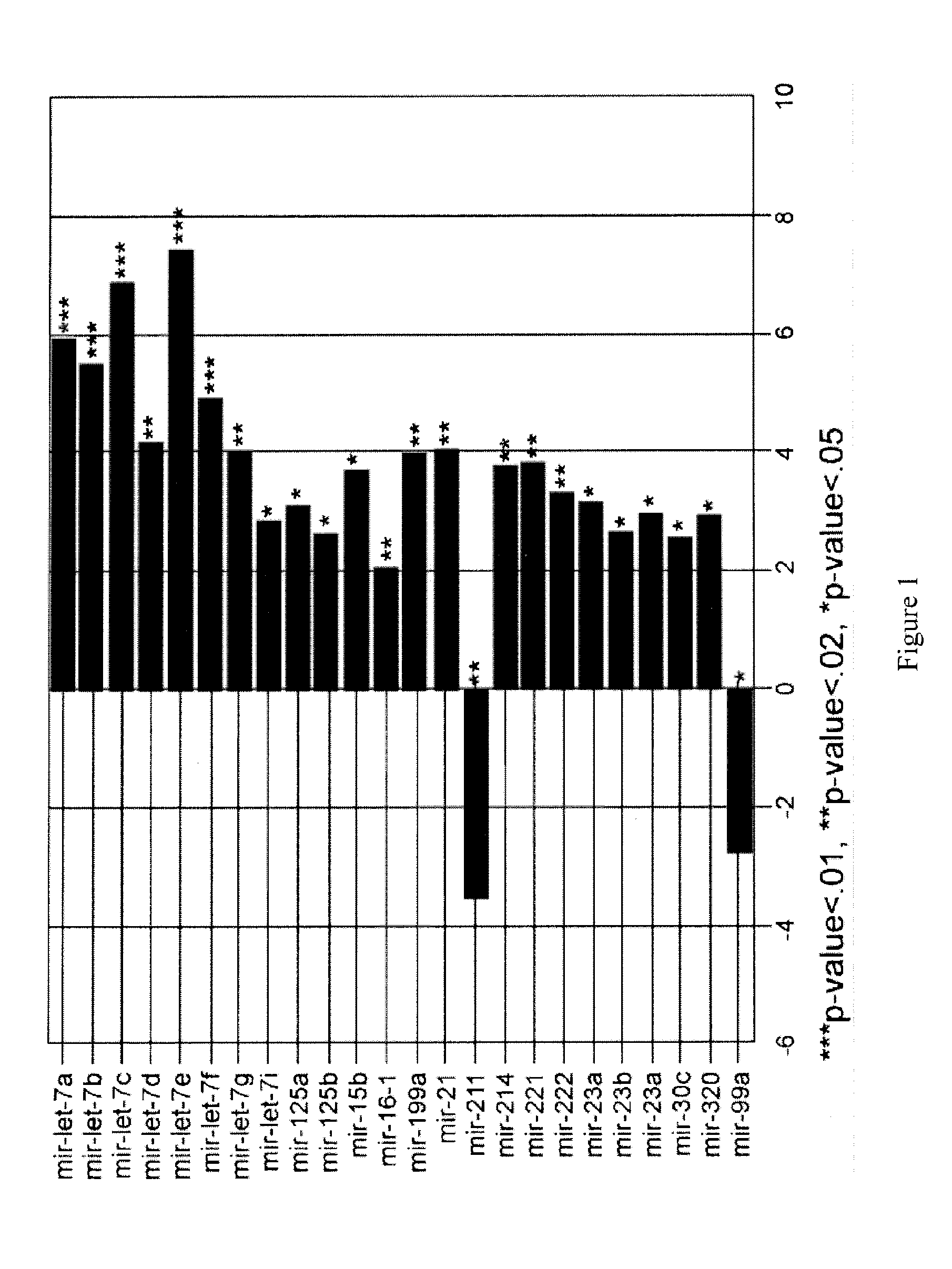
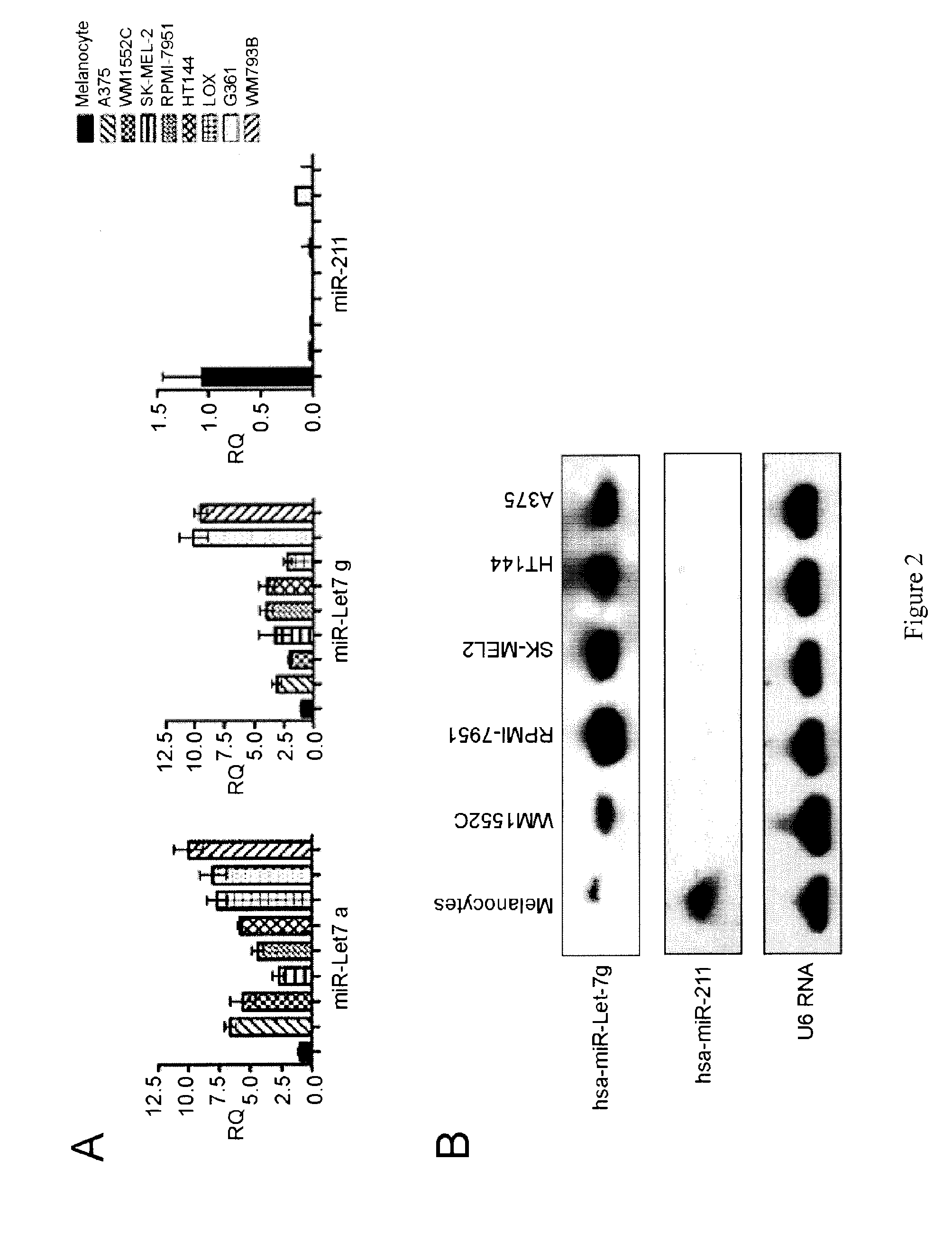
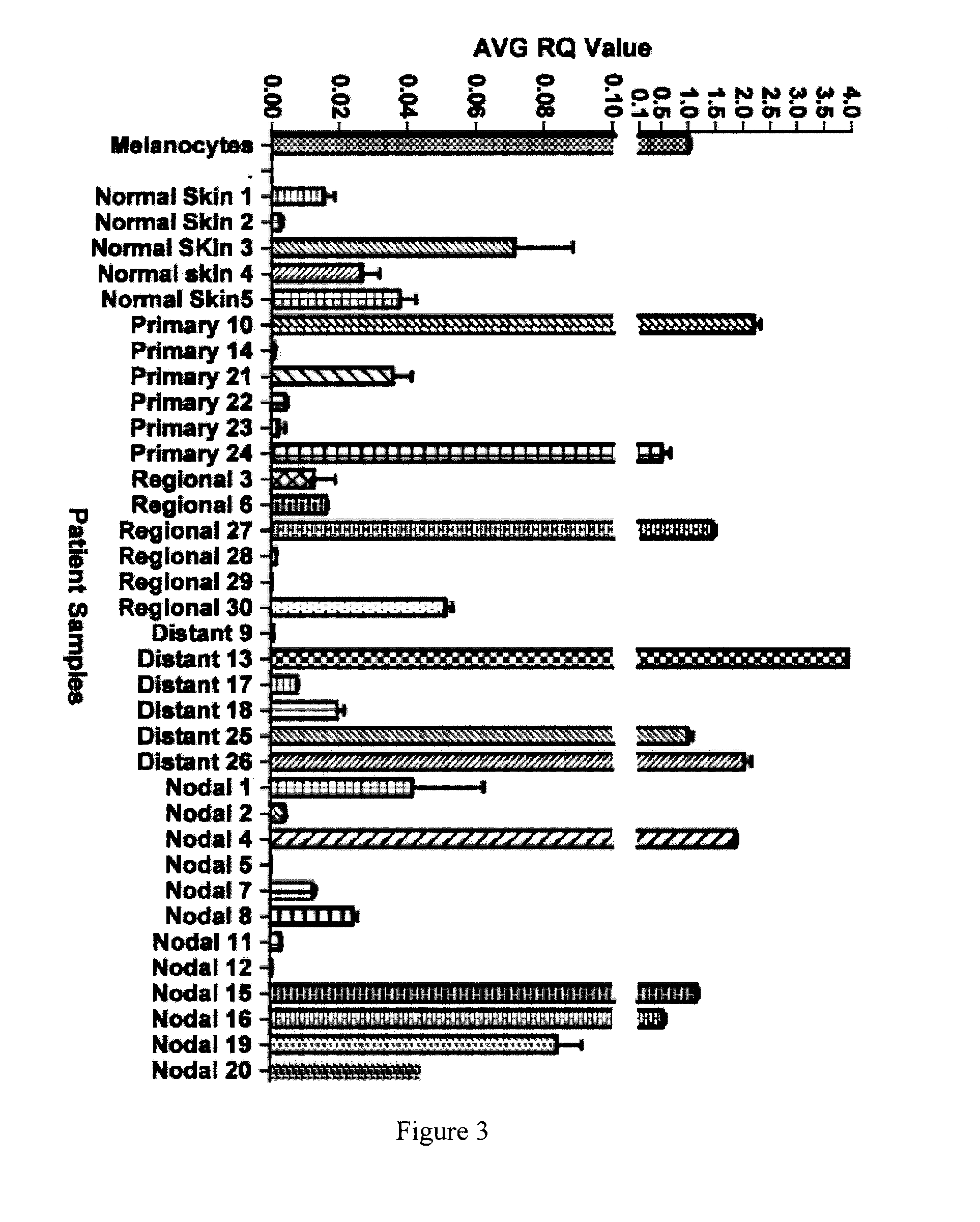
Mir-211 expression and related pathways in human melanoma
InactiveUS20140134231A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman melanomaBiology
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM MEDICAL RES INST
Application of disubstituted phenyl biguanide to inducing malignant tumor cell for anoikis
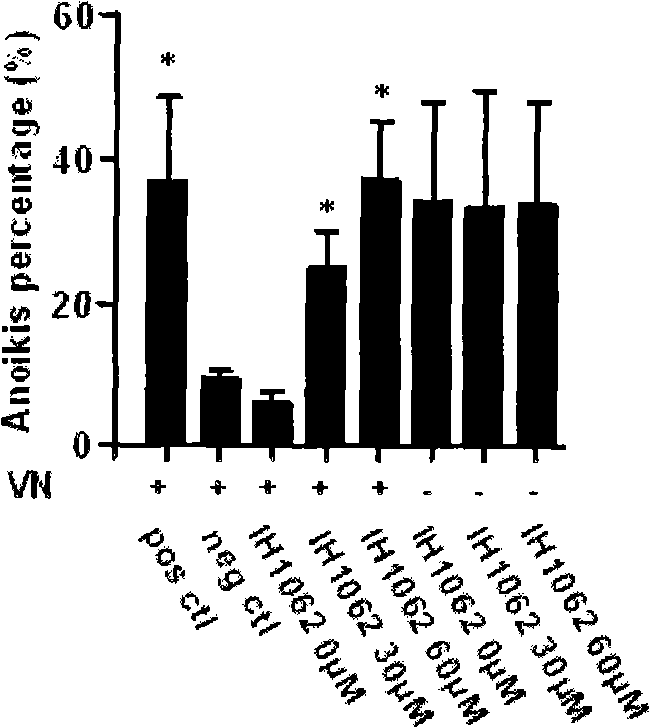
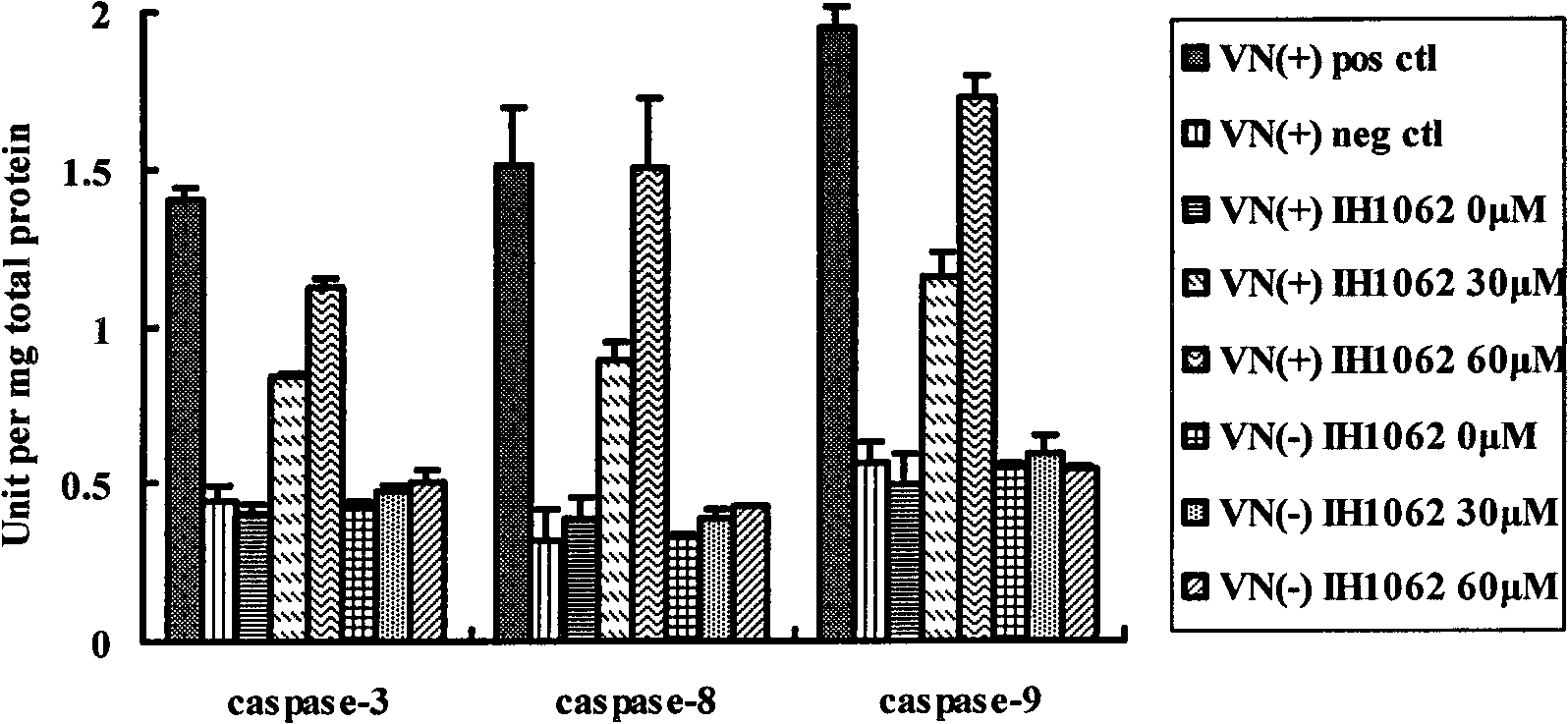
InactiveCN101862315AOvert anoikisGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLymphatic SpreadProstate cancer
The invention relates to disubstituted phenyl biguanide compounds and application containing the same to inducing malignant tumor cell for anoikis and inhibiting tumor growth and transfer. Proved by in vitro-in vivo experiments, the disubstituted phenyl biguanide compounds show the remarkable functions of inducing the malignant tumor cell for anoikis, starting caspase cascade and inhibiting tumor growth and transfer and also have the characteristics of high efficiency and low toxicity, so the disubstituted phenyl biguanide compounds as pharmaceutical compounds are expected to be applied to a plurality of malignant tumor medicaments for inhibiting the tumor growth, invasion and metastasis and treating human melanoma, neurospongioma, lung cancer, gastric cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer and the like.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Preparation method and application of nose comforting tablet
The invention provides a preparation method of a nose comforting tablet which is prepared from crude drugs including 100g of scutellaria baicalensis, 150g of Fructus Xanthii, 100g of violet magnolia, 75g of mint, 100g of radix angelicae, 25g of asarum, and 500g of dandelion through supercritical extraction and microwave extraction, so that the content of baicalein is greatly improved. The invention also provides the application of the nose comforting tablet in preparing a medicine for restraining proliferation of human melanoma cell, M14 cell.
Owner:海门江海建设投资有限公司
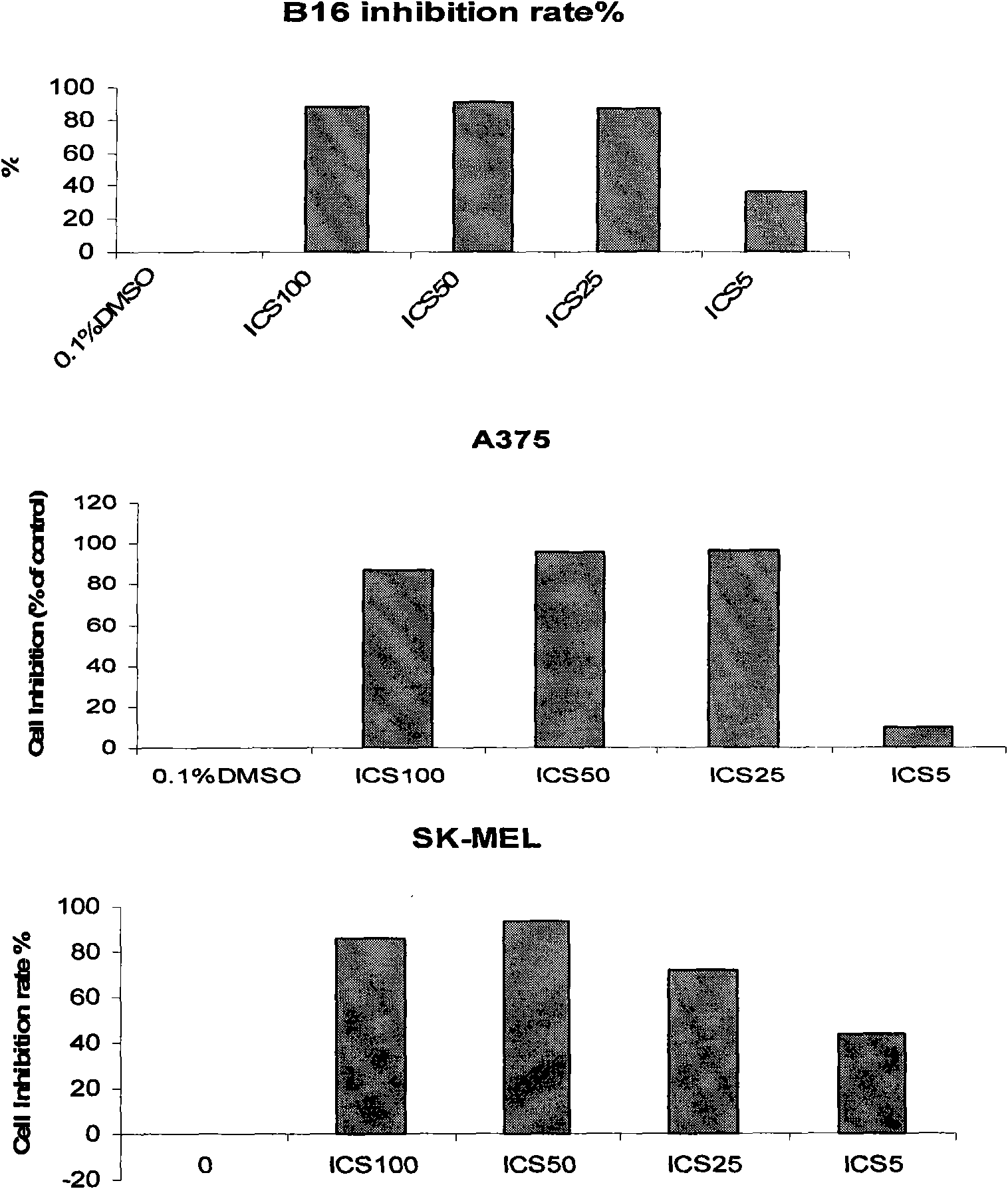
Application of icariside II in preparation of anti-melanoma medicament
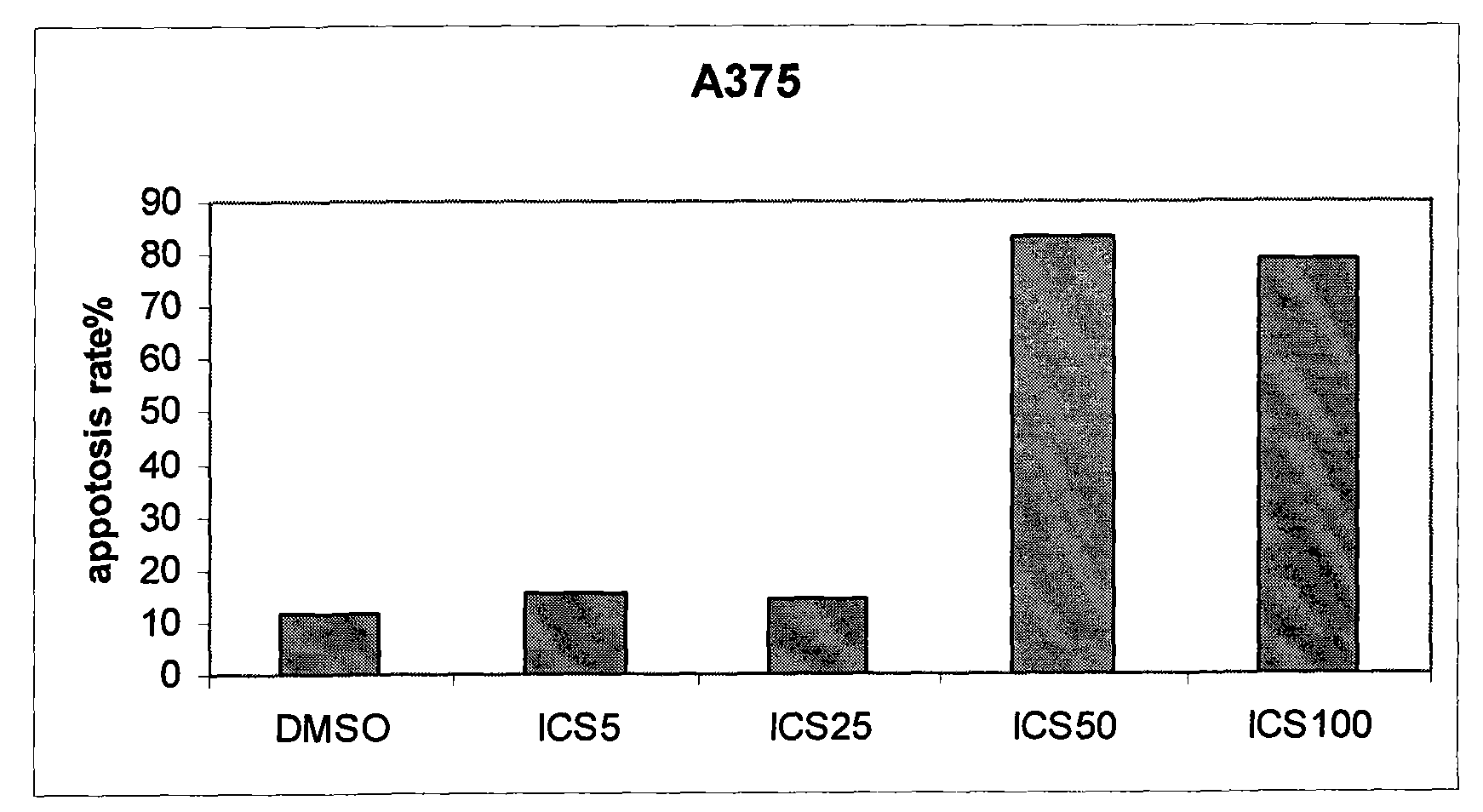
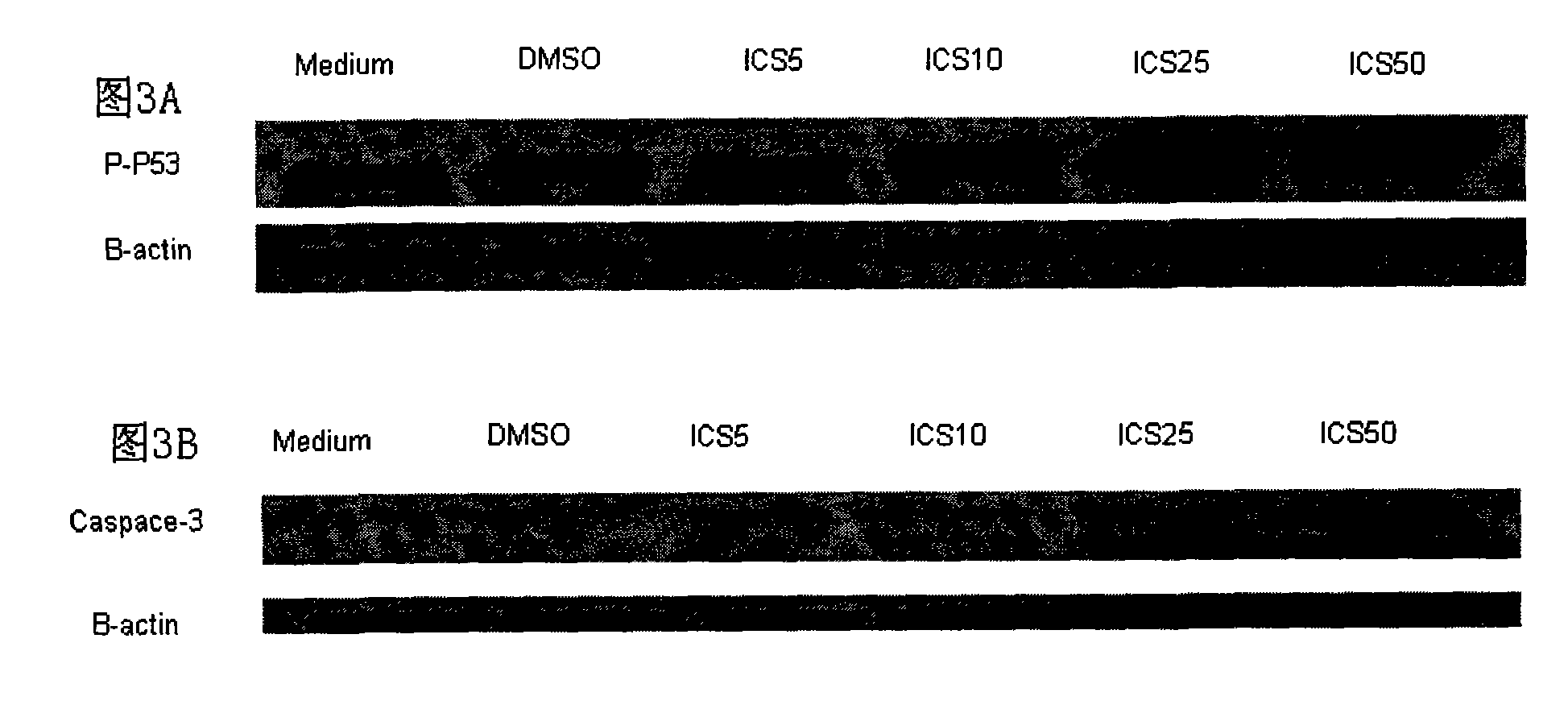
The invention belongs to the field of medicament preparation, relates to new medicinal application of icariside II, and particularly relates to application of icariside II in preparation of an anti-melanoma medicament. The icariside II is adopted for intervention experiments of mouse melanoma cell strains and human melanoma cell strains; by observing the inhibiting condition of the icariside II on cell proliferation, the results show that the icariside II can remarkably inhibit the proliferation of B16, A375 and SK-MEL-2 cells in vitro, obviously promote apoptosis of the cells and increase P53 protein phosphorylation and caspace protein expression; and the icariside II can remarkably inhibit loaded B16 mouse subcutaneous transplant tumor volume. Experiment results prove that the icariside II can effectively inhibit the melanoma. The icariside II can further be used for preparing the anti-melanoma medicament by adding proper pharmaceutically-acceptable carriers.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Specific nNOS Inhibitors for the Therapy And Prevention Of Human Melanoma
ActiveUS20120238016A1Diminish nitric oxide stressOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMedicineHuman melanoma
Methods for melanoma treatment and prevention with selective nitric oxide synthase inhibitor compounds and related pharmaceutical compositions, alone or in conjunction with one or more other melanoma therapies.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
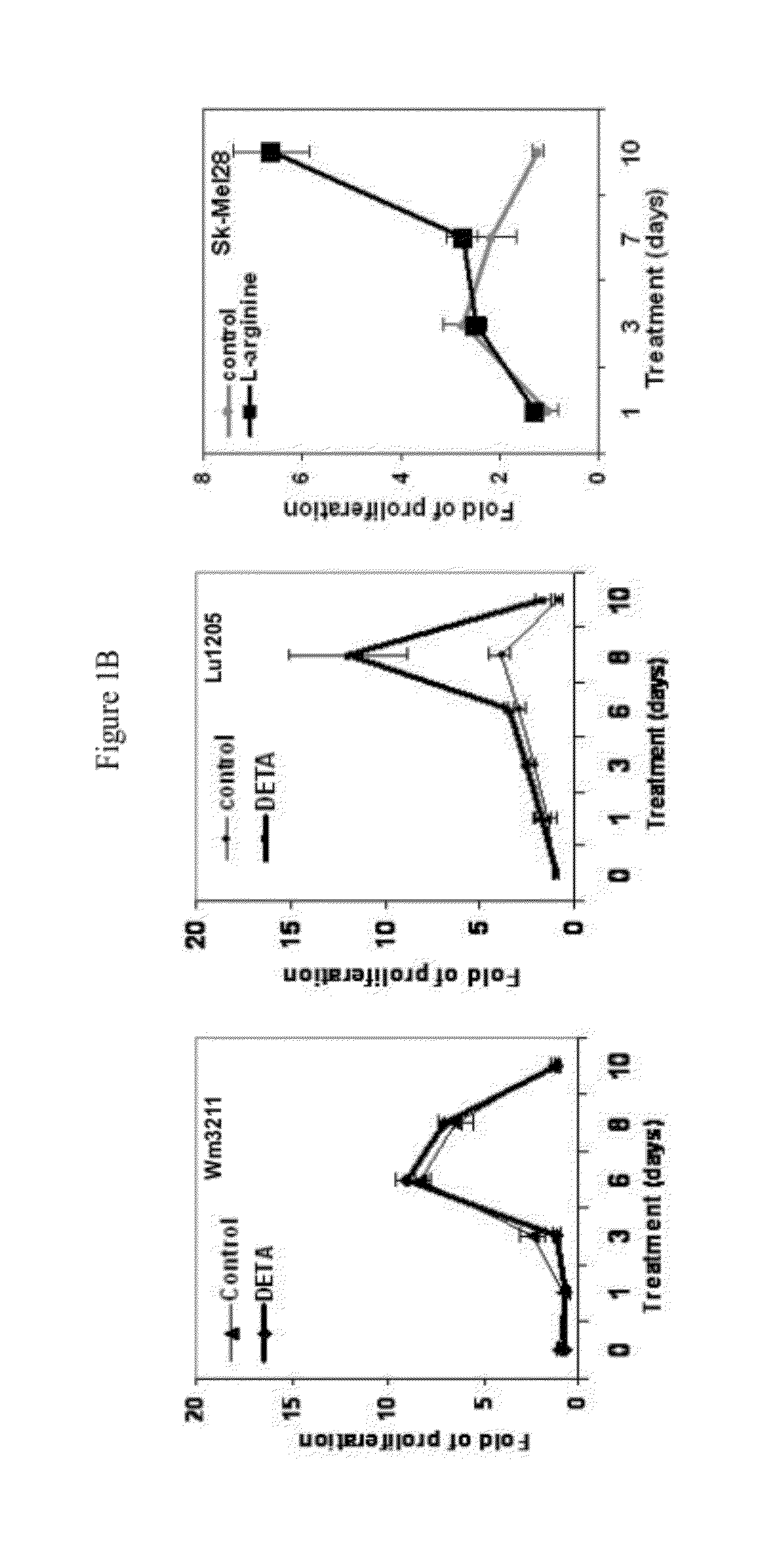
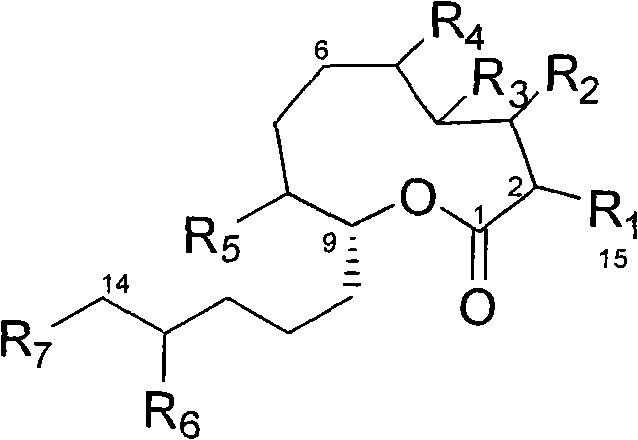
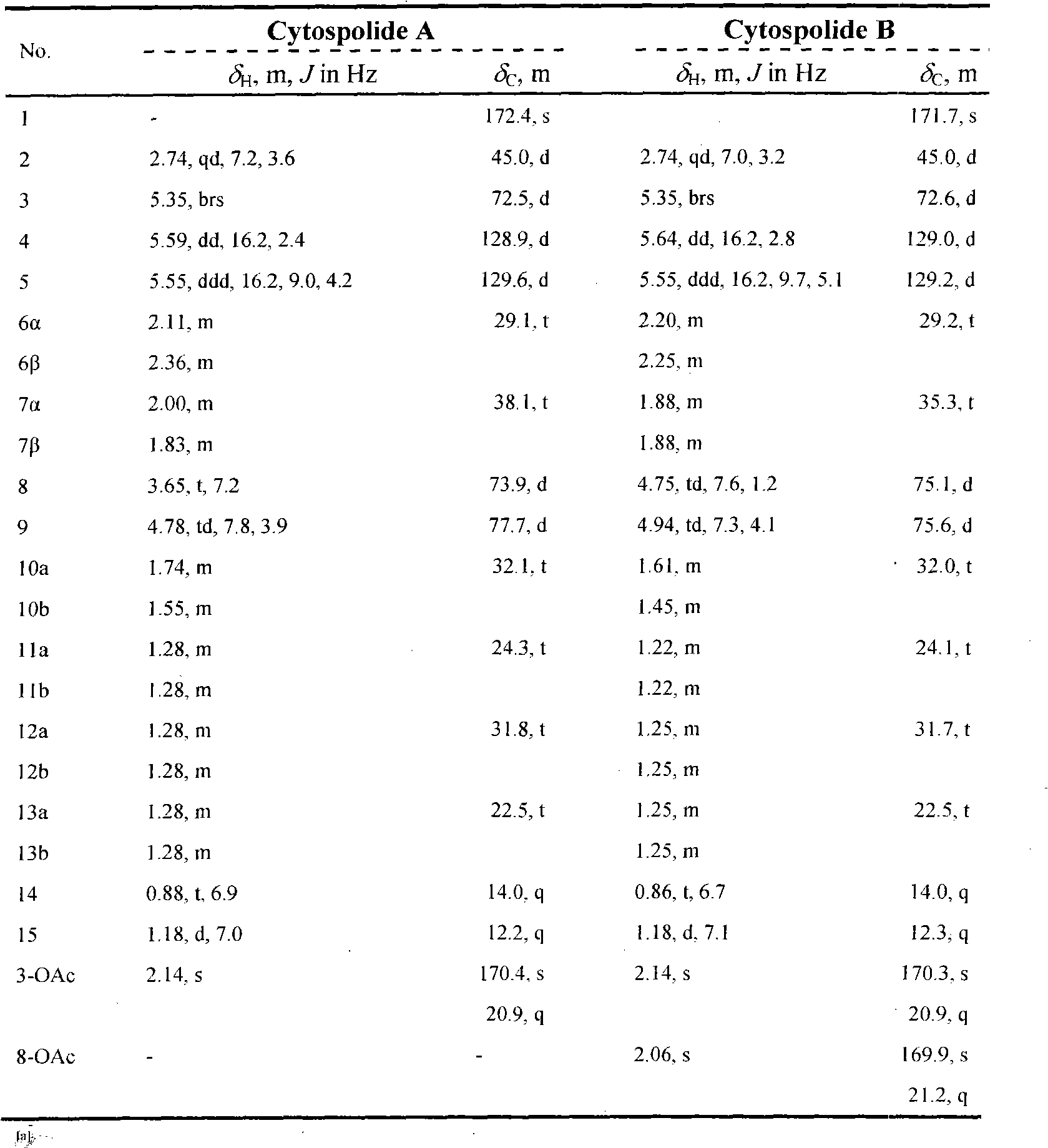
Cytospolides with anti-tumor and antibacterial activity
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, in particular to 16 cytospolides A-P which are separated from a plant endophytic fungus cytospora sp. fermentation product and have anti-tumor and antibacterial activity. The in-vitro anti-tumor test proves that the cytospolides A-P have the effect of obviously inhibiting HCT116 (human colon cancer cells), A549 (human lung cancer cells), QGY-7703 (human liver cancer cells), A375 (human melanoma cells), and U937 (human leukemia cells) tumor cell strains; and the in-vitro antibacterial test proves that the cytospolides A-P have the effect of obviously inhibiting microbotryum violaceum, septoria tritici, Escherichia coli and bacillus megaterium. Therefore, the cytospolides A-P can be used for preparing anti-tumor or antibacterial medicines, are novel lead compounds for developing the anti-tumor and antibacterial medicines, and have great significance for developing and utilizing plant endophyte resources.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Treatment of Melanoma With Alpha Thymosin Peptides
InactiveUS20100016211A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSulfonylurea active ingredientsBlood levelLymphatic Spread
A method of treating melanoma or a metastasis thereof in a human patient by administering a melanoma-treating effective amount of an alpha thymosin peptide to a human melanoma patient, wherein the human melanoma patient does not have a substantially elevated LDH blood level.
Owner:SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICAL INC
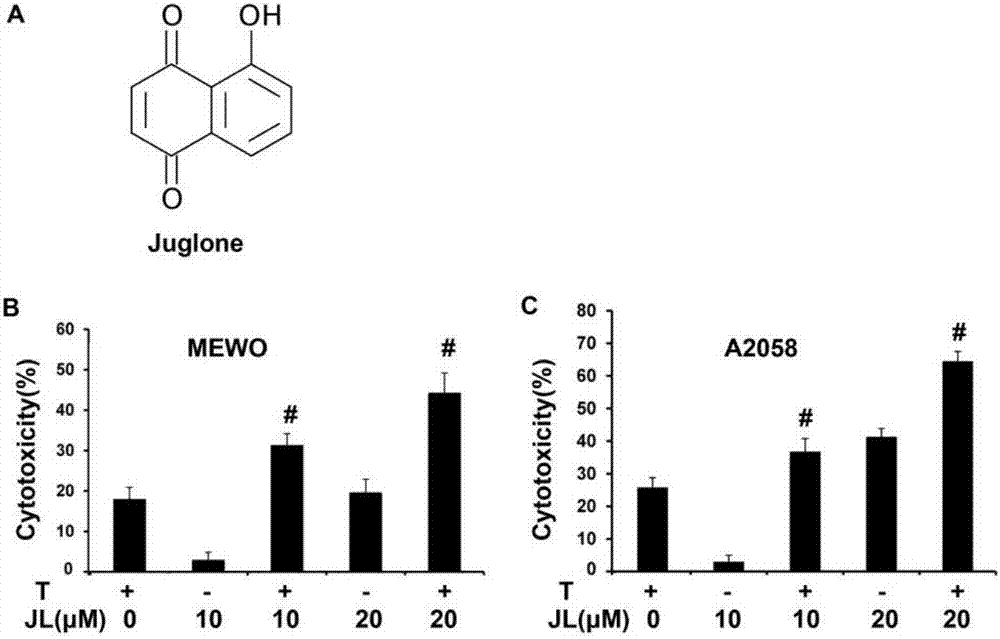
Application of juglone in preparation of TRAIL sensitizer
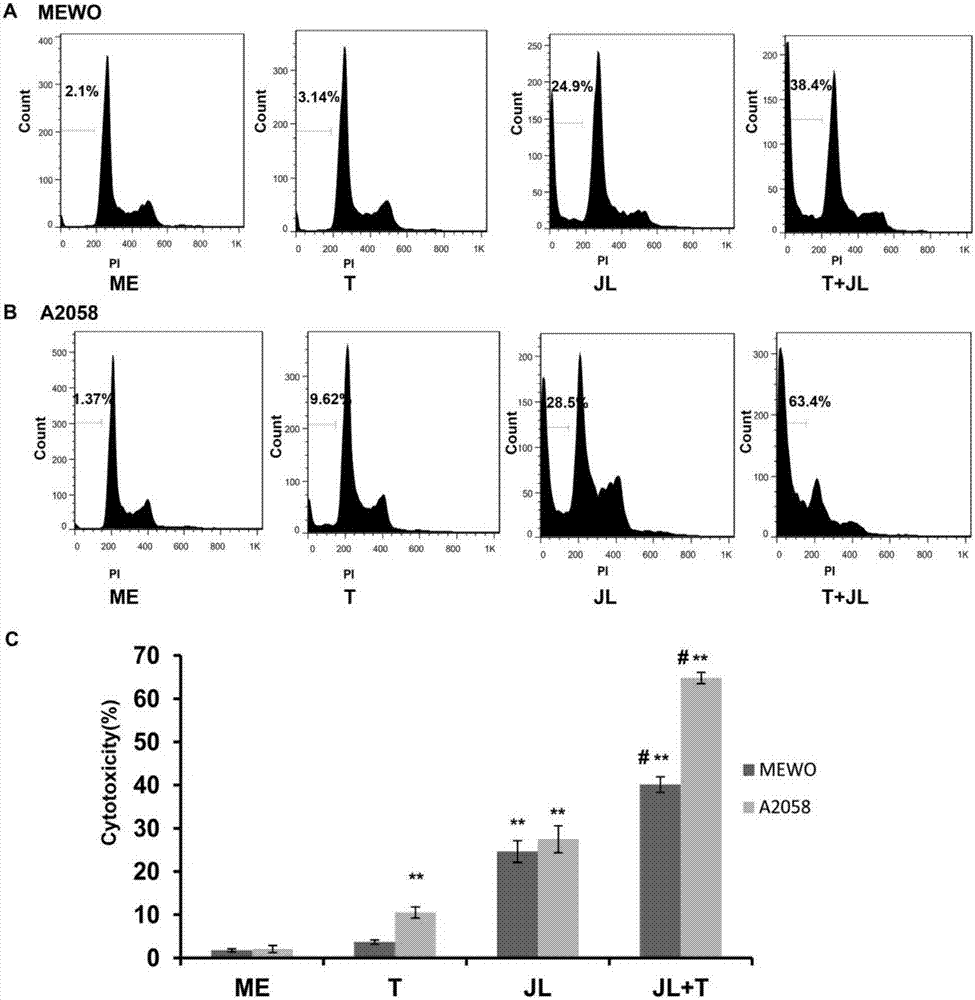
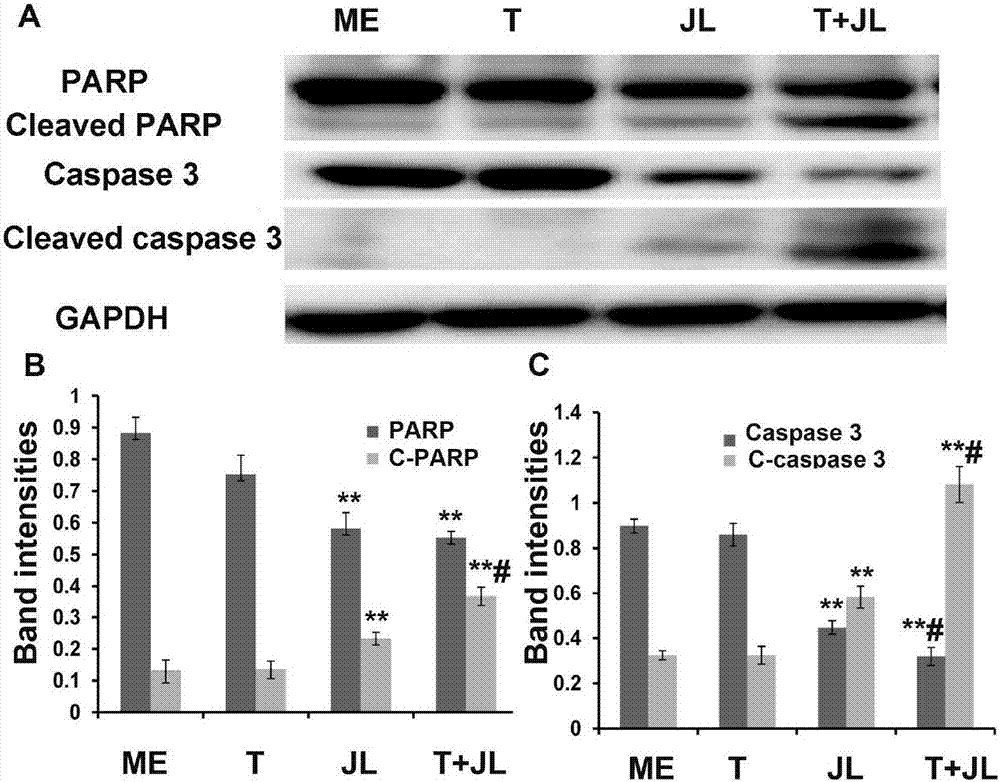
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicines, relates to a novel medicinal application of a natural drug active ingredient juglone, and particularly relates to an application of juglone in preparation of a TRAIL sensitizer. An experiment proves that the killing effect of a TRAIL on two tumor cell lines, namely human melanoma cell lines MEWO and A2058 can be significantly strengthened through combined utilization of the juglone and the TRAIL, and separate application of the RAIL does not have an obvious effect on cell proliferation and apoptosis of the human melanoma cell lines MEWO and A2058.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
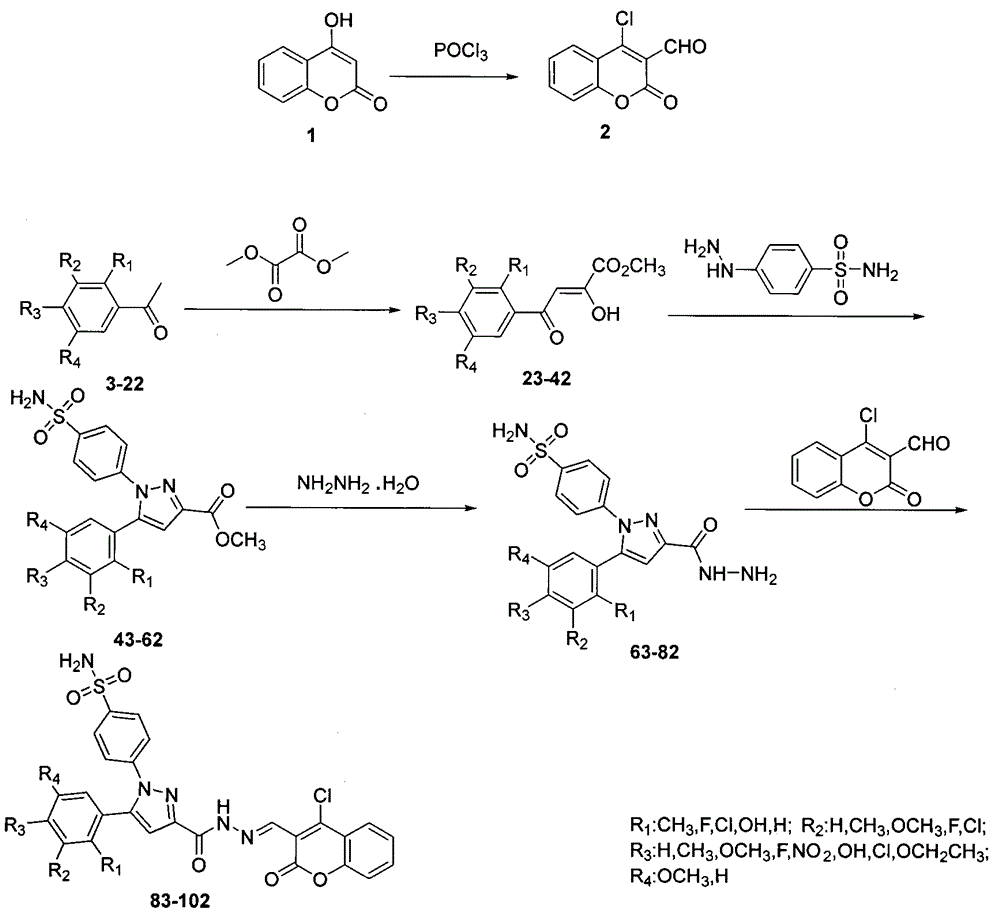
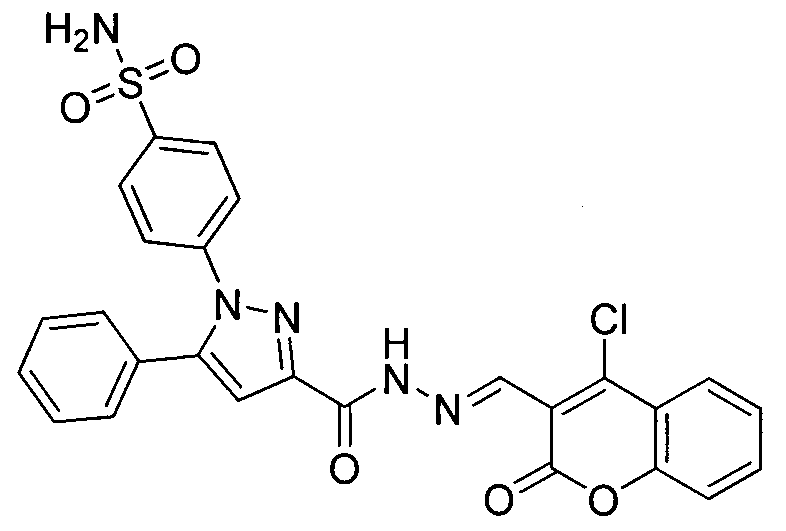
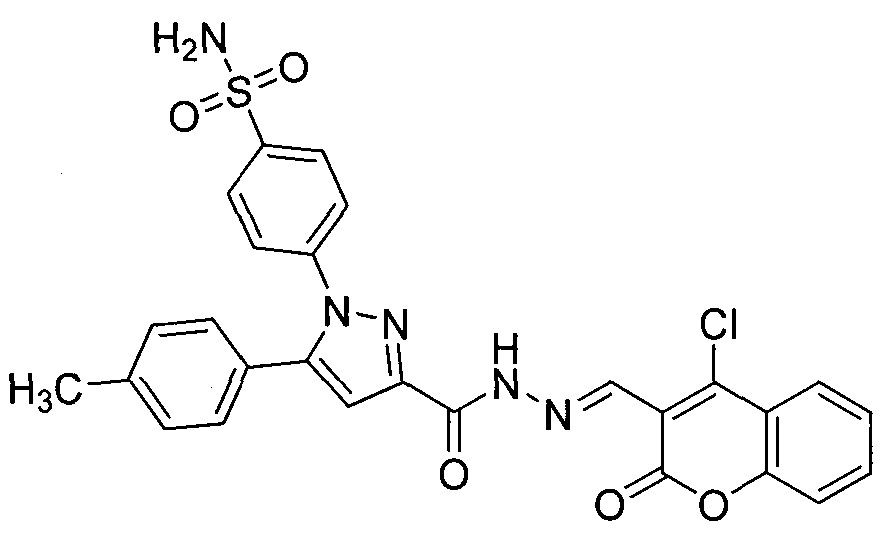
Preparing method for 4-(3-(3-(4-clocoumarol)-acylhydrazone)-5-phenyl-pyrazol) benzene sulfonamide derivate and application to anti-cancer drugs
The invention provides synthesis for a 4-(3-(3-(4-clocoumarol)-acylhydrazone)-5-phenyl-pyrazol) benzene sulfonamide derivate. The synthesis is characterized by being implemented according to the general formula (please see the formula in specification). The 4-(3-(3-(4-clocoumarol)-acylhydrazone)-5-phenyl-pyrazol) benzene sulfonamide derivate has the obvious inhibiting effect on culture of cervical cancer cells (Hela), human melanoma cells (F10) and hepatoma carcinoma cells (HepG2) and has cytotoxicity equivalent to or better than that of positive control drugs for human kidney epithelial cells (293T). Accordingly, the 4-(3-(3-(4-clocoumarol)-acylhydrazone)-5-phenyl-pyrazol) benzene sulfonamide derivate can be used for preparing anti-tumor drugs. The invention discloses a preparing method of the benzene sulfonamide derivate and anti-tumor biological activity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
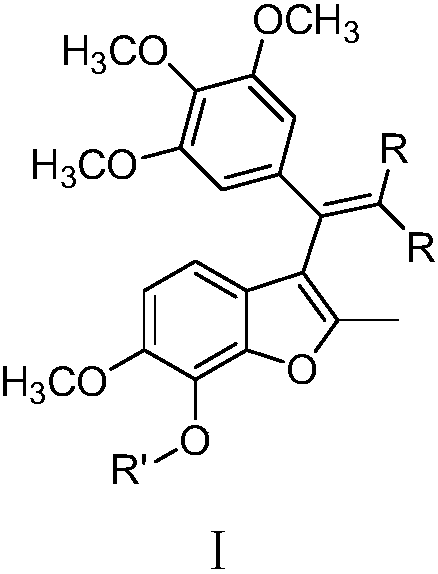
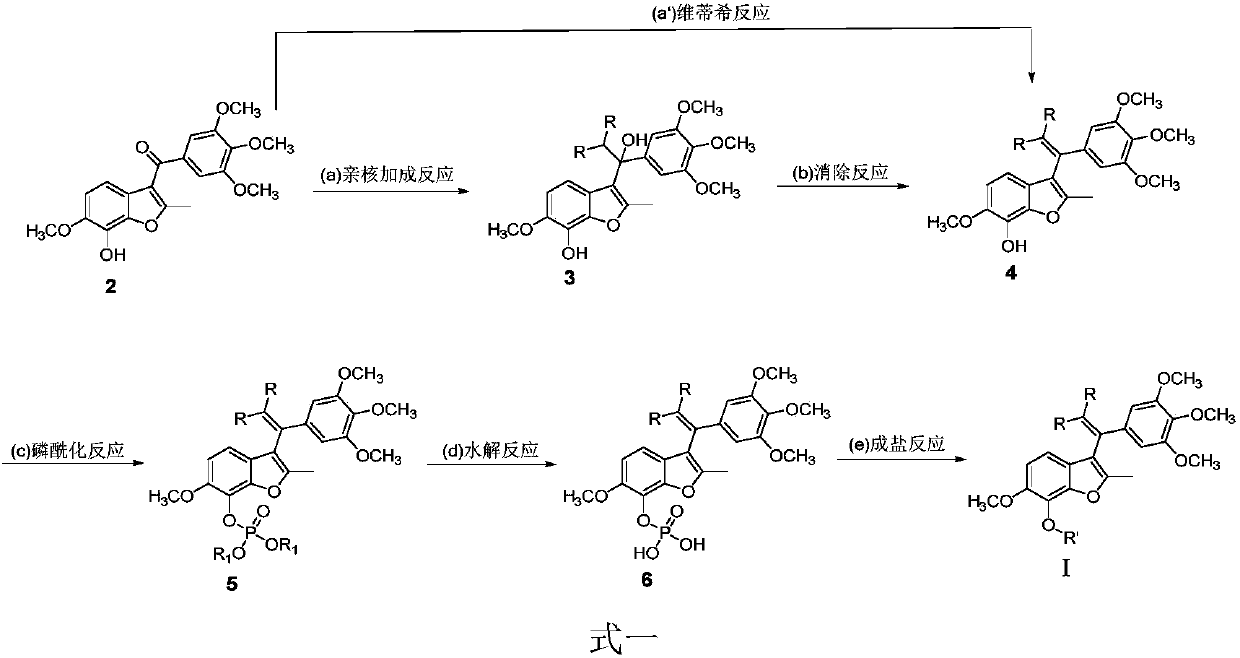
Substituted benzofuran derivative, preparation and application thereof in preparing antitumor drug
InactiveCN108976187AGood antitumor activityLow acute toxicityOrganic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolubilityChemical structure
The invention provides a substituted benzofuran derivative. A chemical structure of the derivative is as shown in general formula I. The invention further provides a preparation method of the formulaI, the preparation method is as shown in the following reaction formula described in the specification, wherein R and R' are defined the same as the specification. In-vitro proliferation inhibition experiment researches of human tumor cells show that the substituted benzofuran derivative has excellent inhibition effects on tumor cells such as human hepatoma cells HLF, human intestinal cancer cellsHCT116, human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231, human prostate cancer cells DU145, human melanoma cells A375, human colon cancer cells Lovo, human kidney cancer cells 786-o, human chronic myeloid leukemia cells K562, human gastric cancer cells MGC-803, human pancreatic cancer cells PANC-1, can be used for preparing an anti-tumor drug, has low acute toxicity and good water solubility, and has good clinical application prospects. The preparation method provided by the invention is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI QINGDONG BIOTECH CO LTD
Preparation method and application of angelica sinensis and radix paeoniae alba liujun pill
ActiveCN103599292ARich in active ingredientsReduce dosagePill deliveryAntineoplastic agentsAtractylis carduusCodonopsis
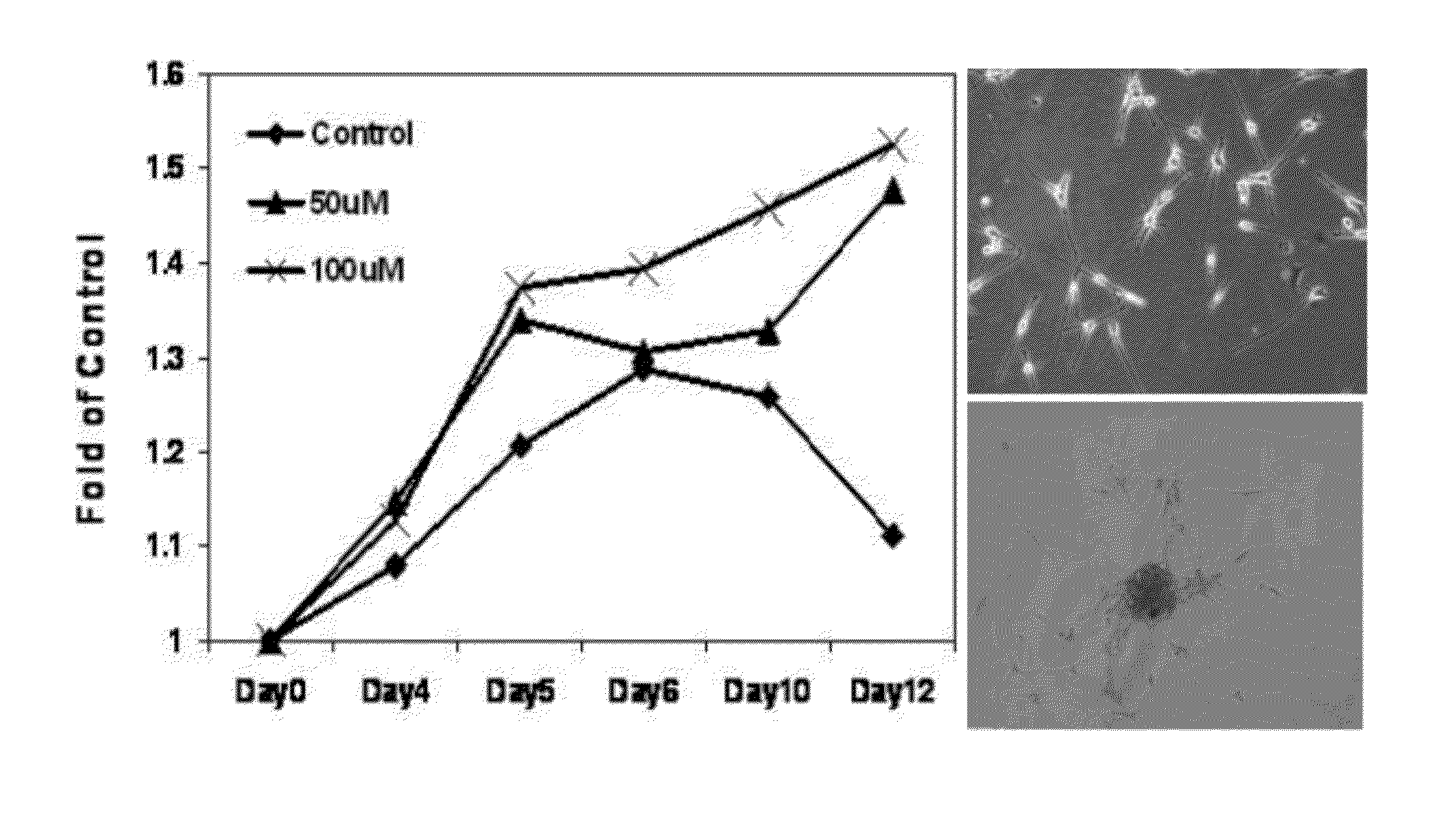
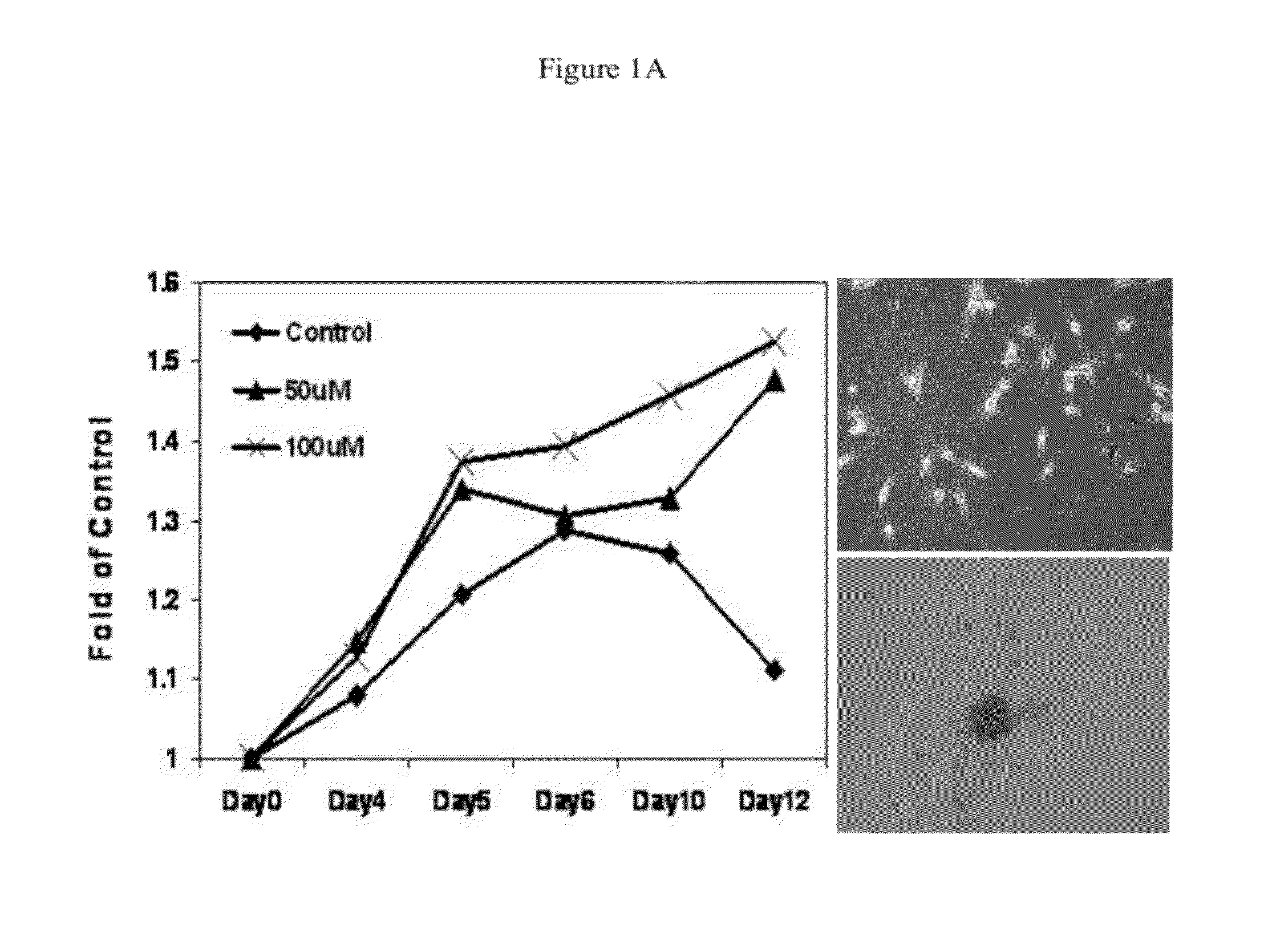
The invention provides a preparation method of an angelica sinensis and radix paeoniae alba liujun pill. The angelica sinensis and radix paeoniae alba liujun pill is prepared from 100g of angelica sinensis, 100g of fried white atractylodes rhizome, 100g of codonopsis pilosula, 100g of radix paeoniae alba, 100g of poria cocos, 50g of honey-fried licorice root, 50g of pericarpium citri reticulatae and 50g of ginger processed pinellia which are used as crude drugs by adopting supercritical extraction. Thus, the content is greatly improved, and the dose is reduced. The invention also provides application of the angelica sinensis and radix paeoniae alba liujun pill in preparation of a medicine for inhibiting cell proliferation of human melanoma cells (MV3).
Owner:山东天成钢结构有限公司
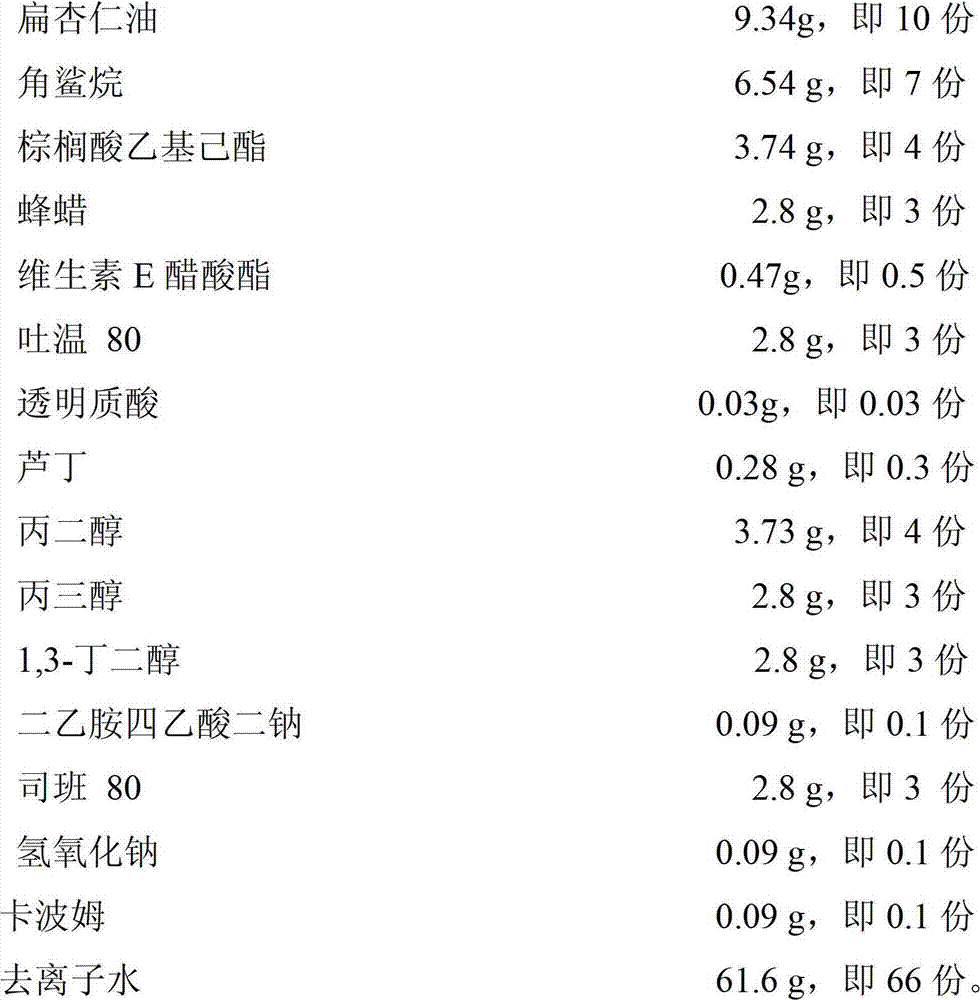
Application of composition of flat almond soil and rutin in sun-screening agent
InactiveCN102727400AInhibits tyrosinase activityFor sun protection and skin careCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNatural productIrritation
The invention relates to application of composition of flat almond soil and rutin in a sun-screening agent. According to the invention, the composition comprises the following components in parts by mass: 5 to 15 parts of flat almond soil and 0.1 to 0.5 part of rutin. An experiment proves that the composition of the flat almond soil and the rutin can obviously inhibit the activity of tyrosinase in human melanoma cell A875 which is damaged by ultraviolet rays, and the composition also has the synergistic effect. The composition can be applied to the sun-screening agent as a natural additive; and moreover, the flat almond soil and the rutin are both natural products, are softer on the skin, and have no irritation; and the composition can play a role in screening the sun and caring the skin if being used for a long term.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
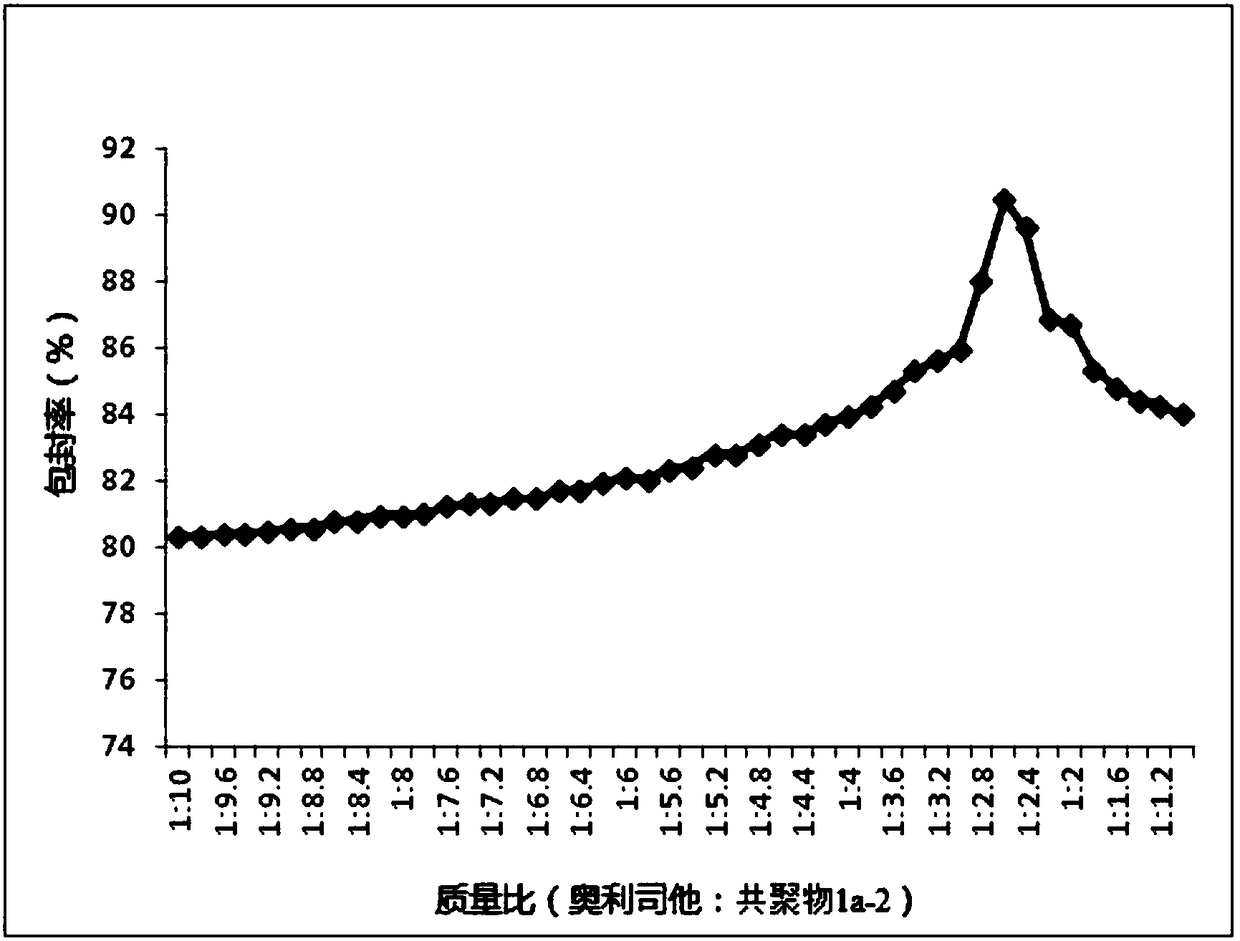
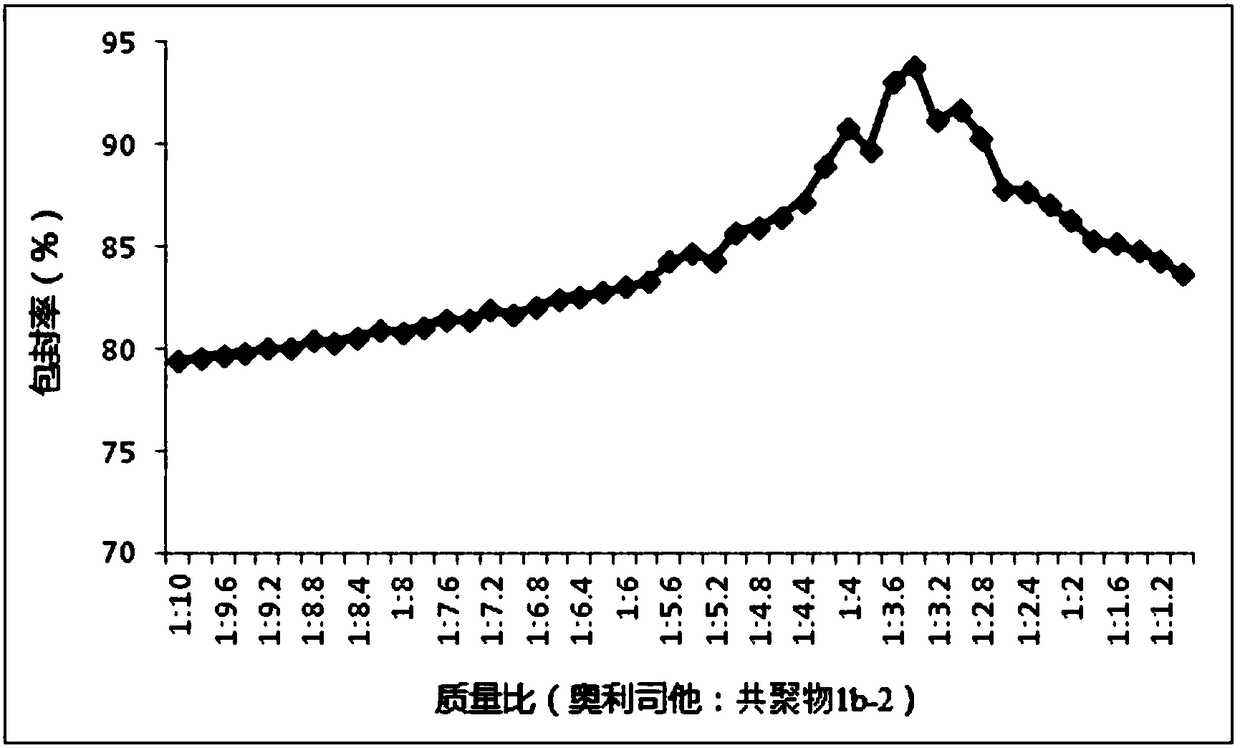
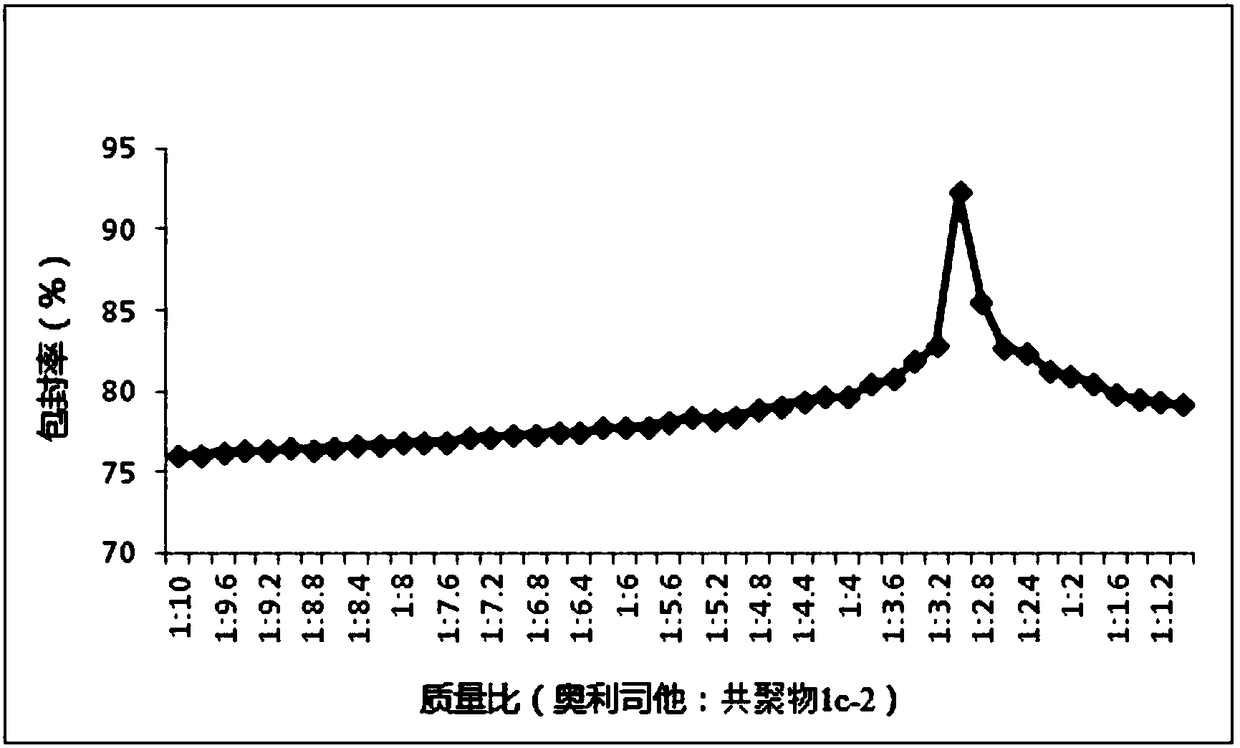
Application of nano-microsphere containing orlistat in preparing antineoplastic drugs
ActiveCN108578390AHigh encapsulation efficiencyPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredients2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholinePhosphorylcholine
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and in particular to an application of nano-microsphere containing orlistat in preparing antineoplastic drugs. The nano-microsphere consistsof the orlistat as well as any copolymer which is selected from a vitamin A methacrylate-2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine copolymer, a vitamin E methacrylate-2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine copolymer and a vitamin D methacrylate-2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine copolymer. Based upon in vitro test results, it is indicated that antineoplastic activity of the nano-microsphereprovided by the invention on human prostate cancer cells DU145, human melanoma cells A375 and human pancreatic cancer cell lines bxpc-3 is obviously higher than that caused by independent administration of the orlistat, and the antineoplastic activity is better than that of control nano-microsphere which is prepared by taking PMB30 as a carrier as well as nano-microsphere which contains the orlistat and polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN WANHAN PHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com