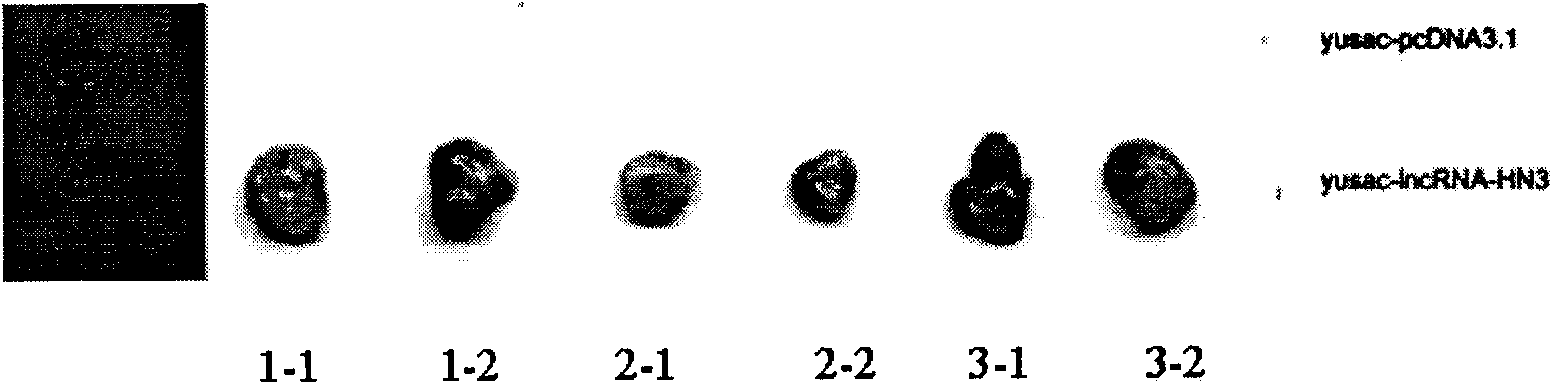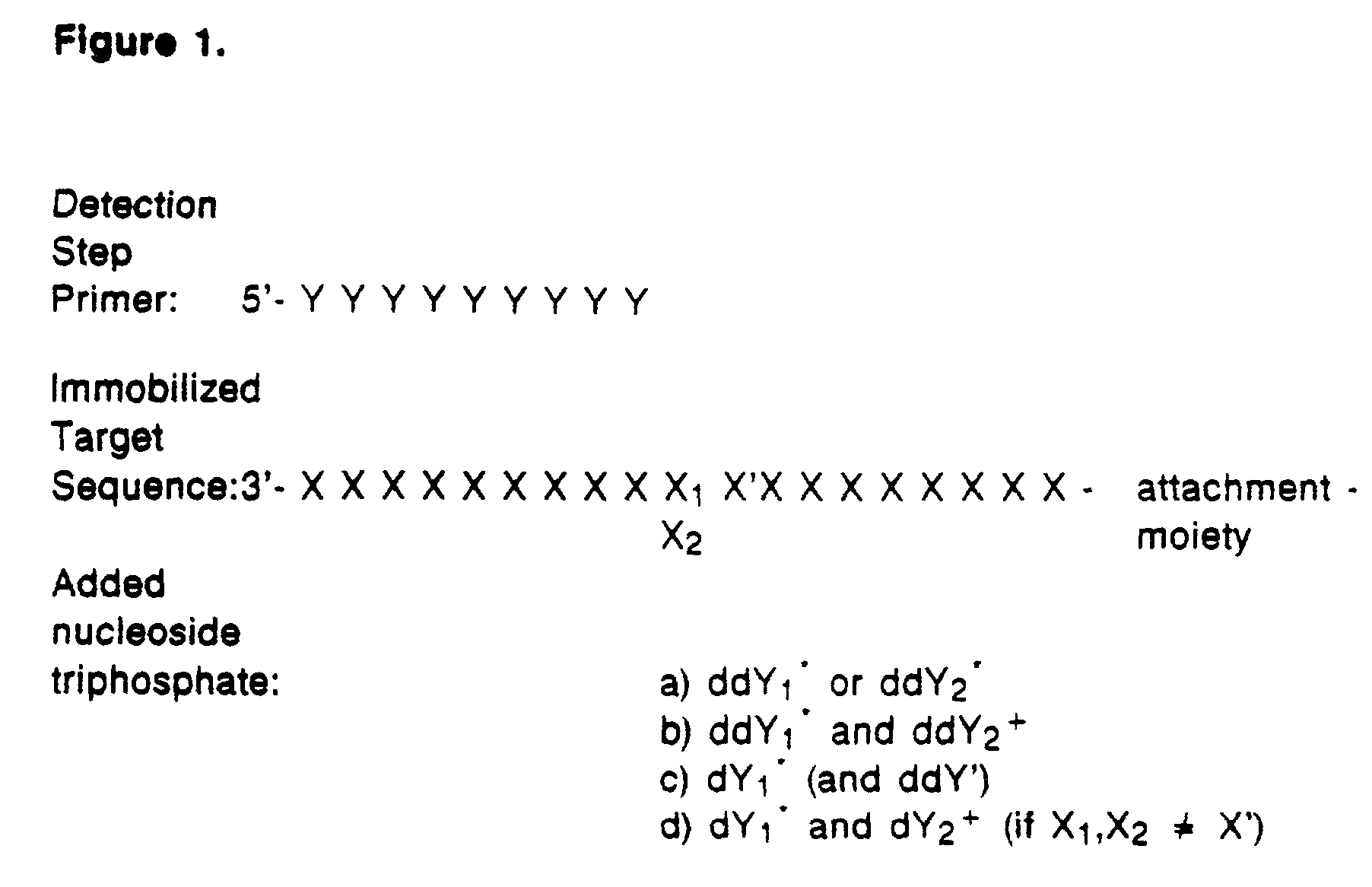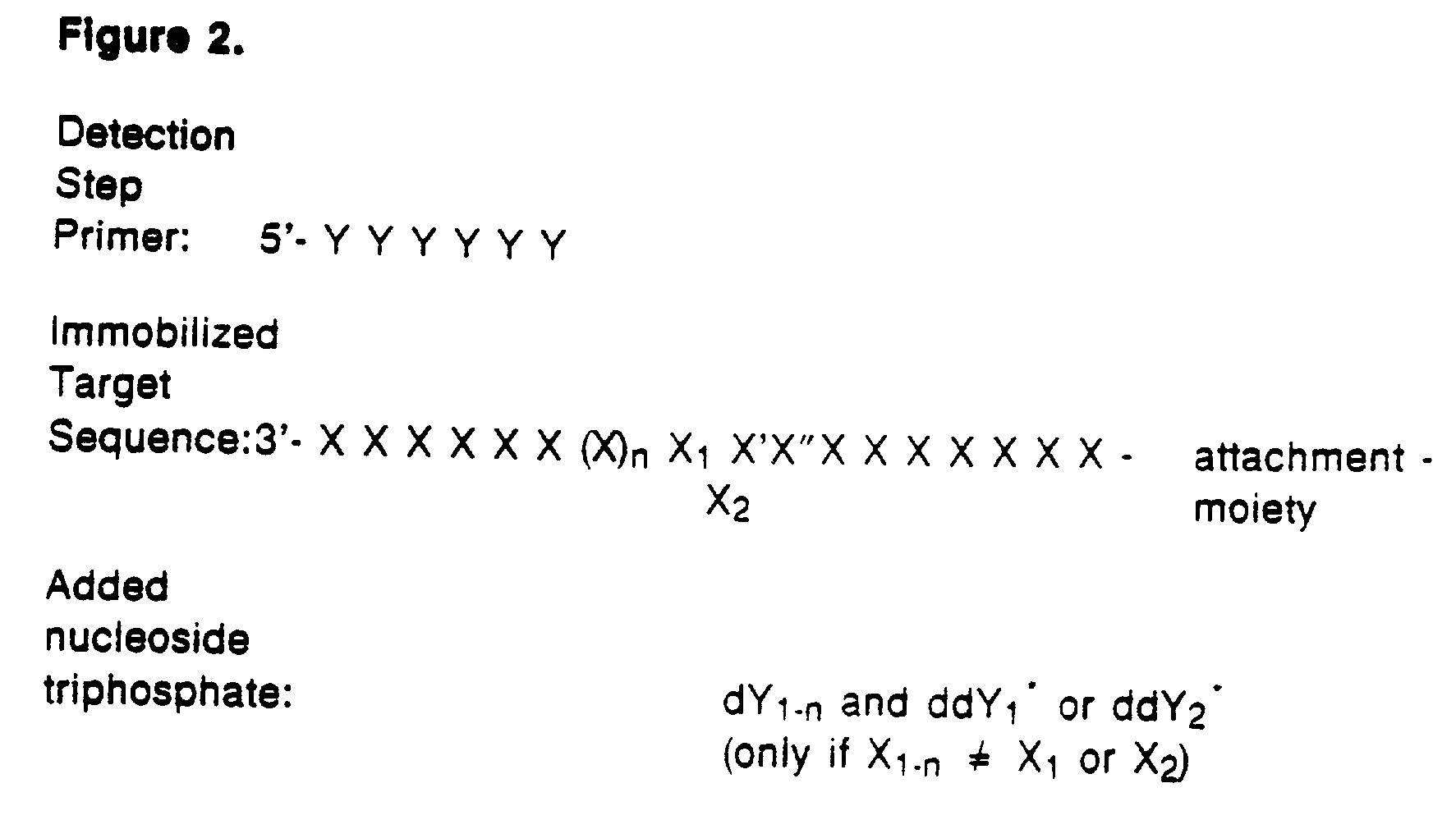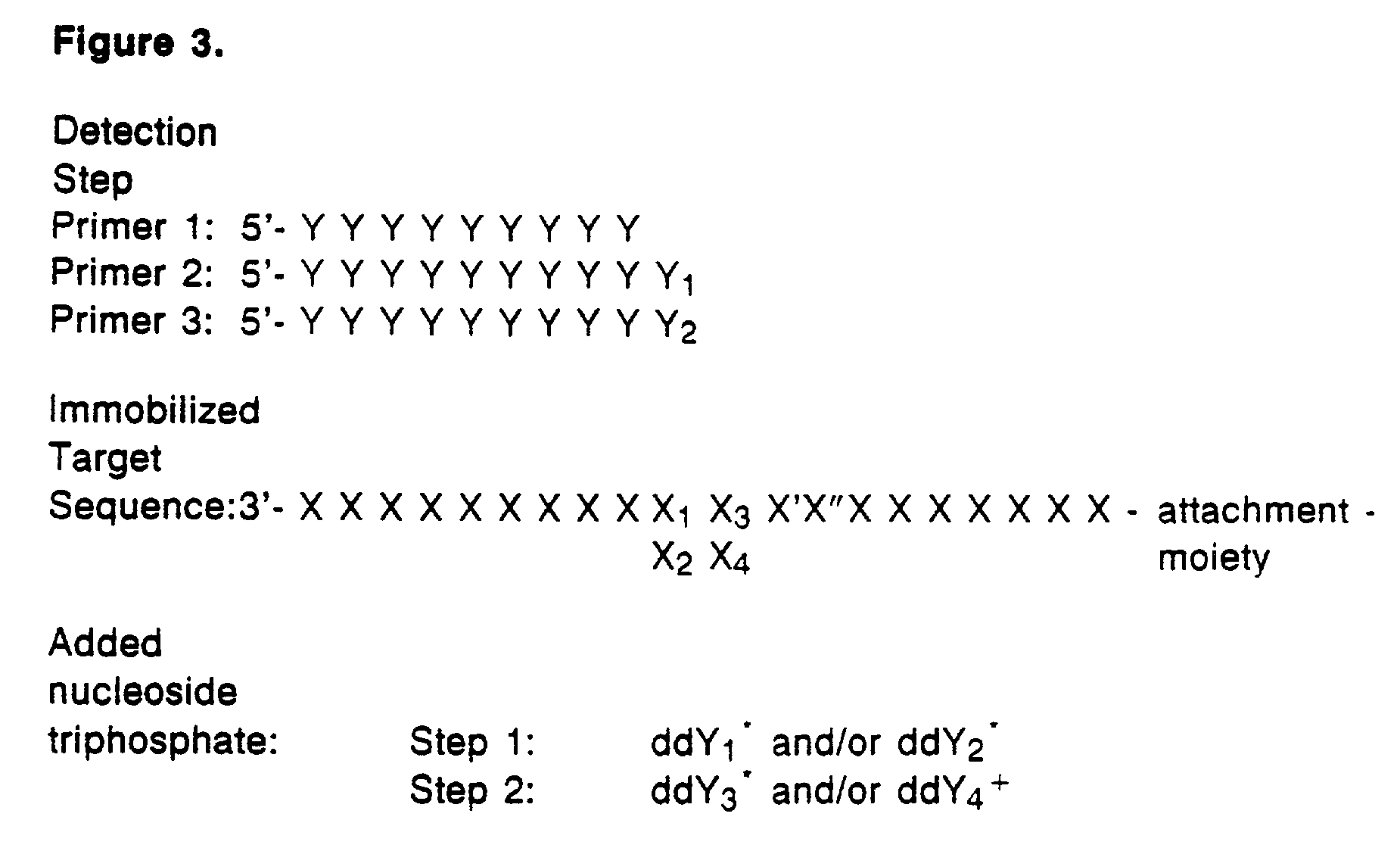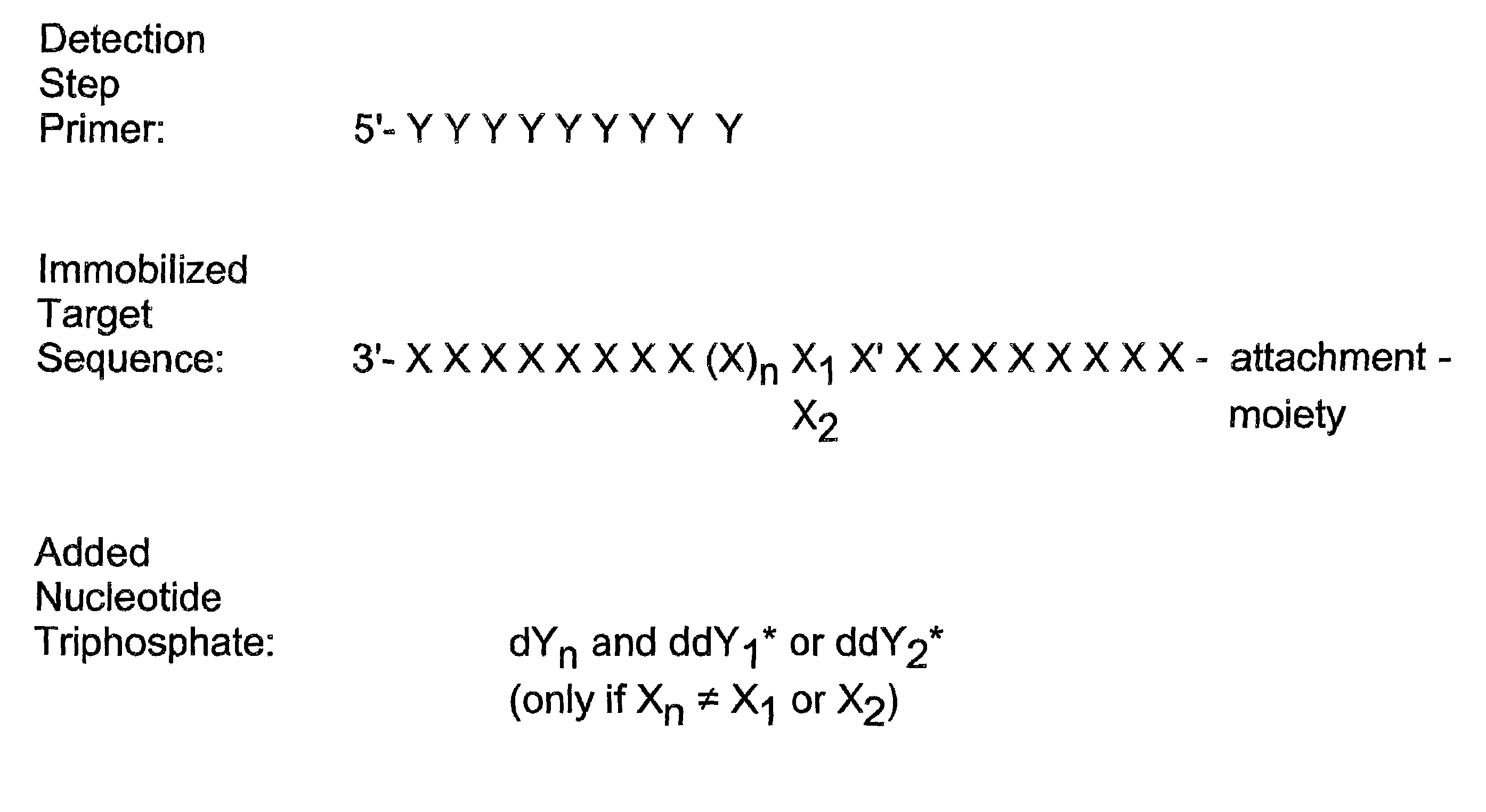Patents
Literature
51 results about "Coding strand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
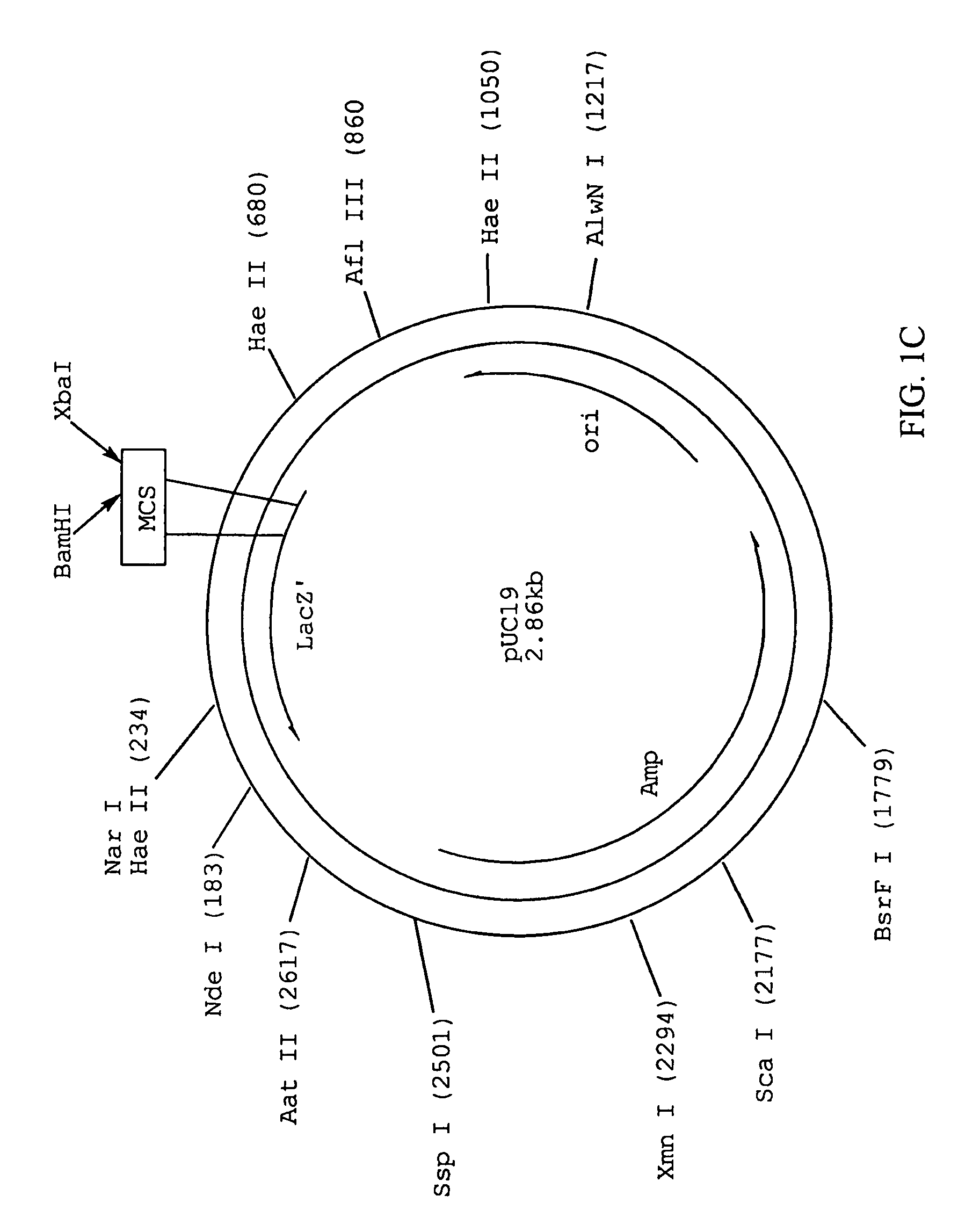
When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand is the DNA strand whose base sequence corresponds to the base sequence of the RNA transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). It is this strand which contains codons, while the non-coding strand contains anticodons. During transcription, RNA Pol II binds to the non-coding strand, reads the anti-codons, and transcribes their sequence to synthesize an RNA transcript with complementary bases.
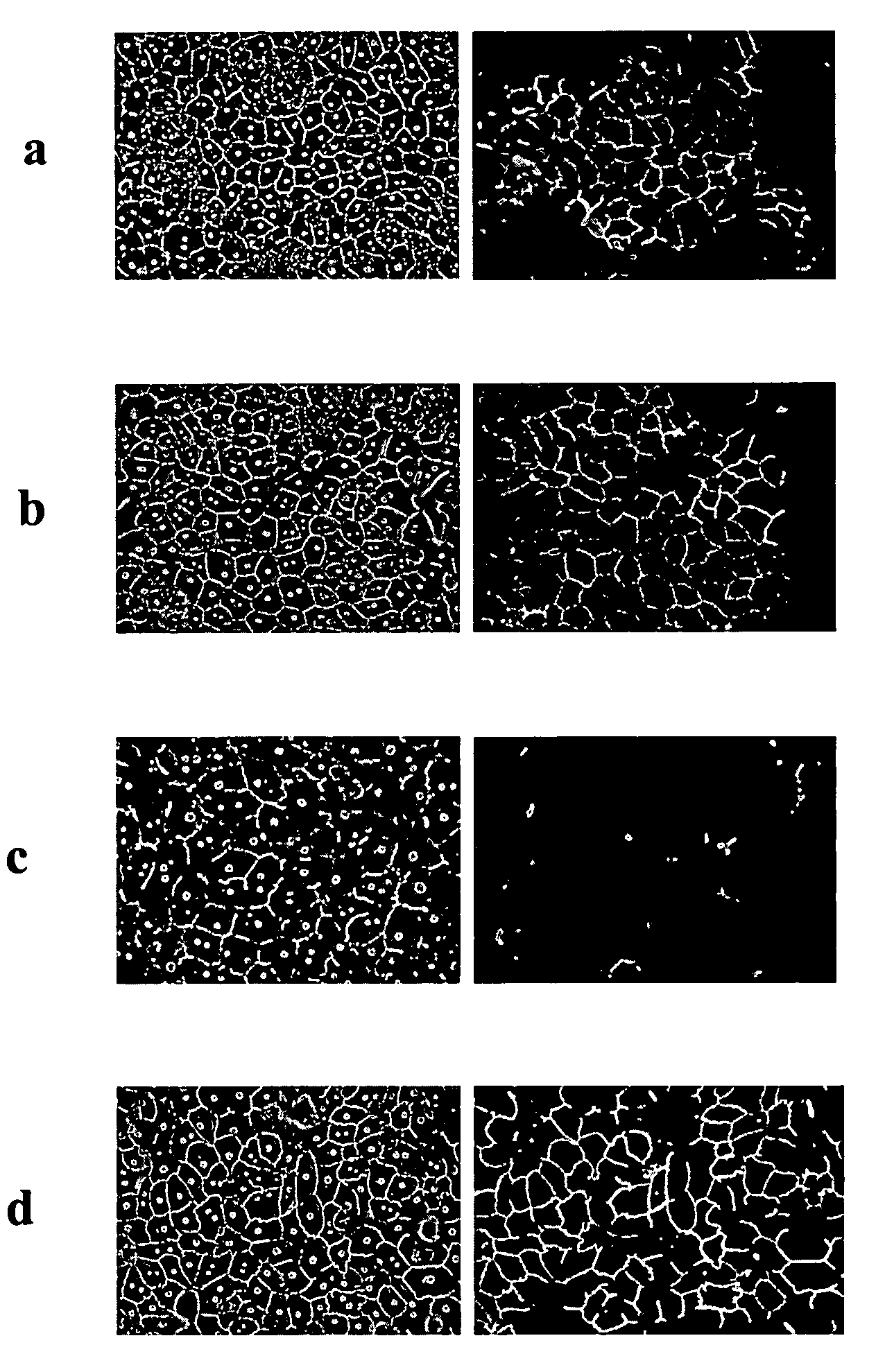
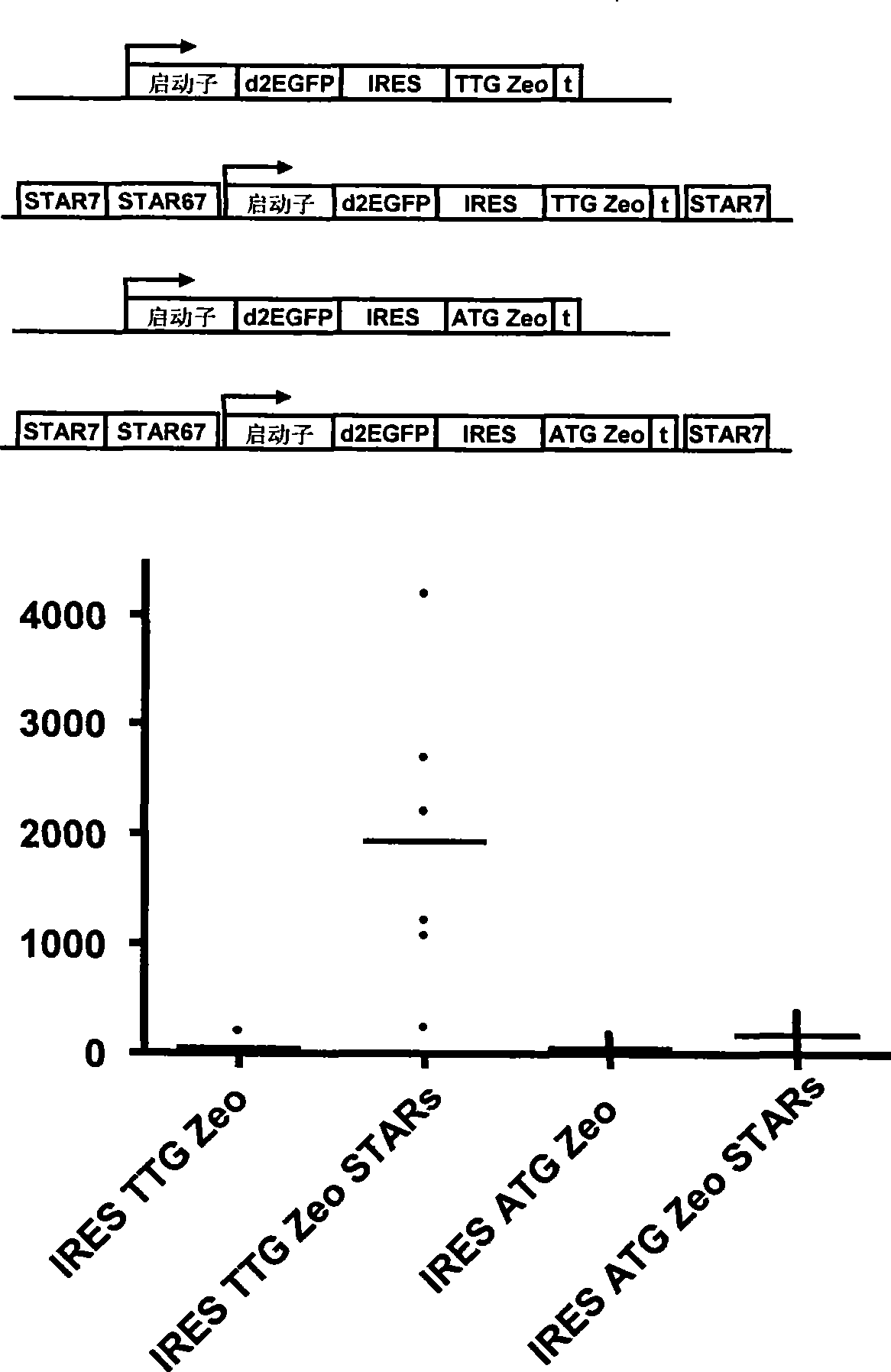
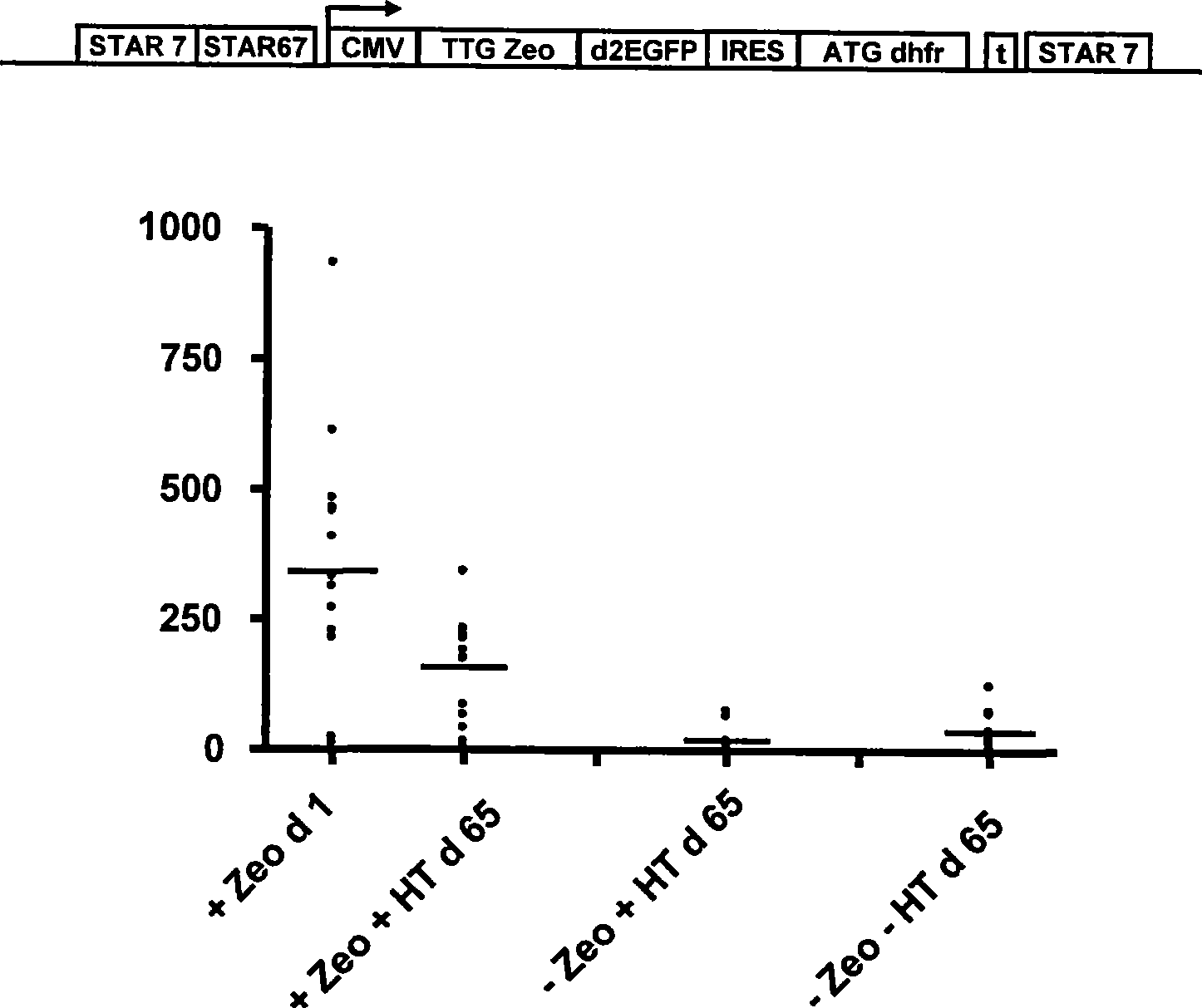
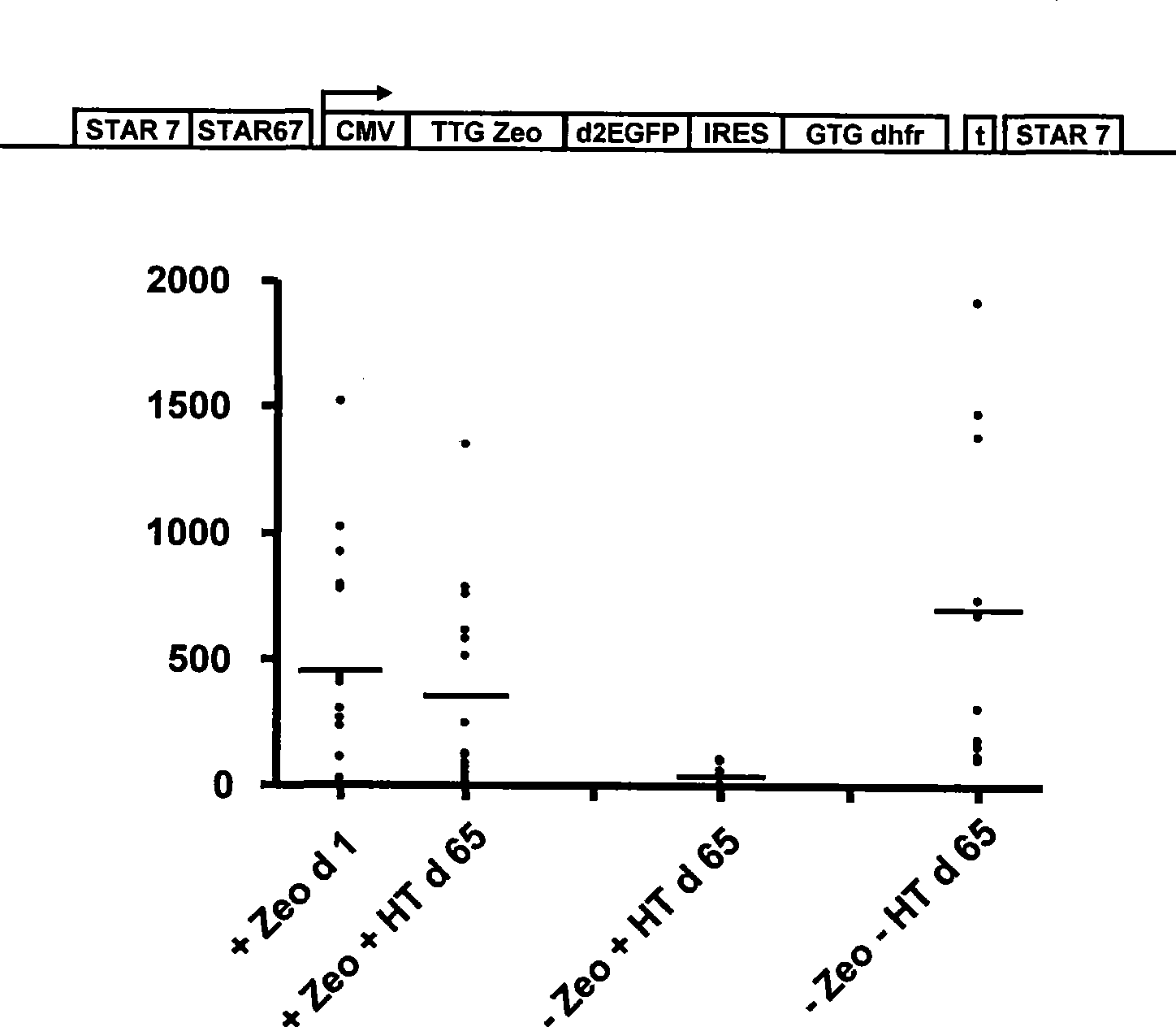
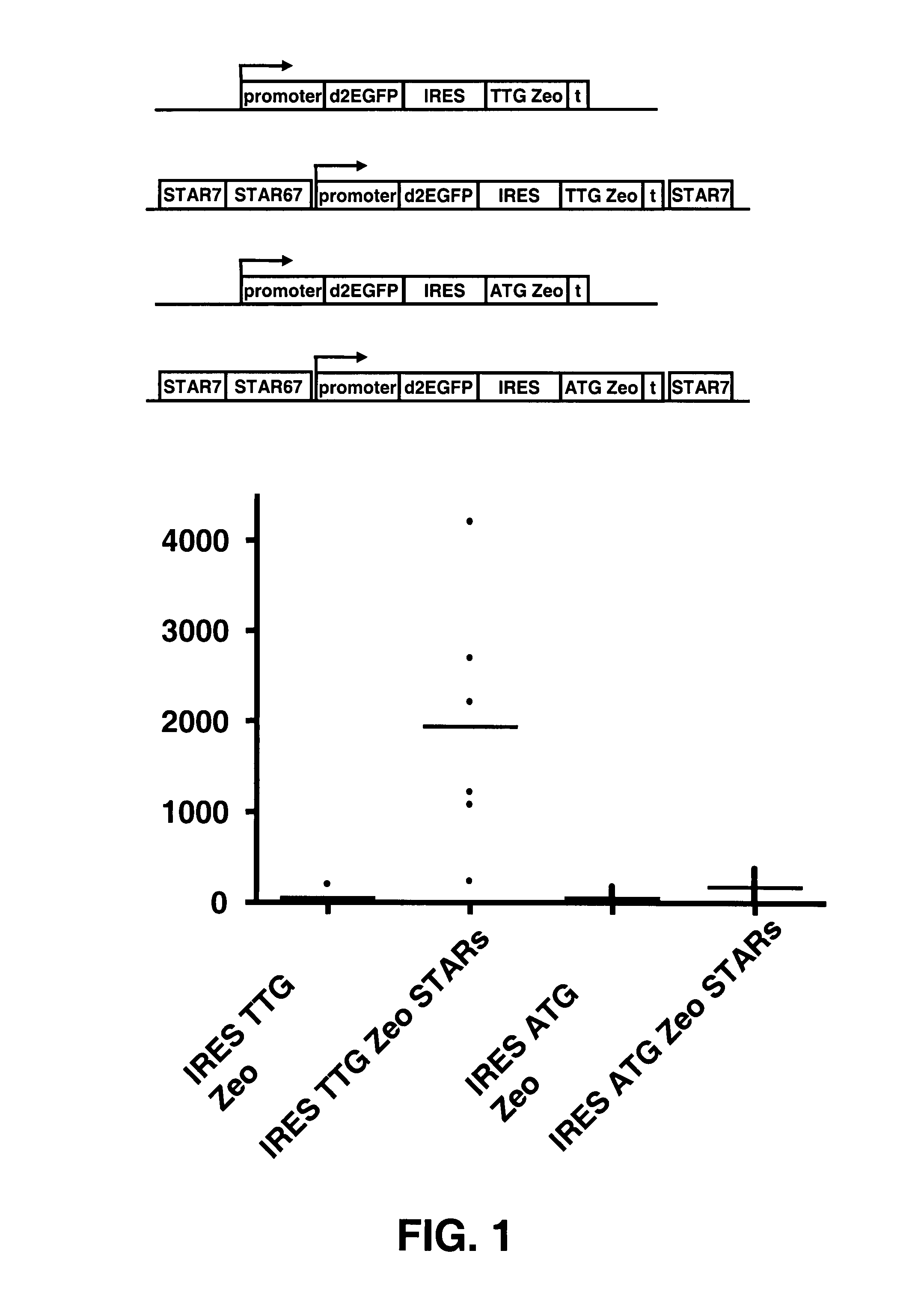
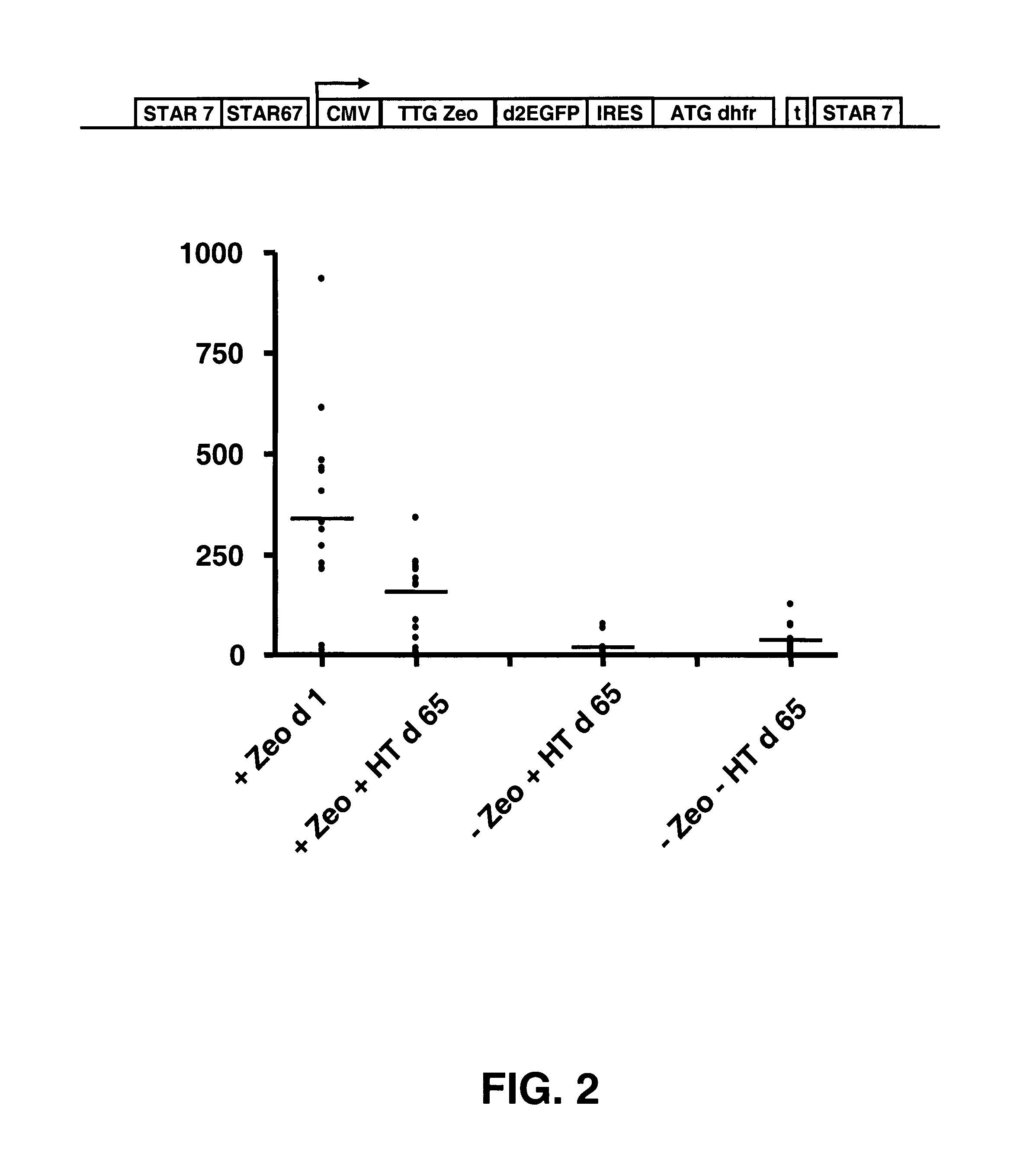
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
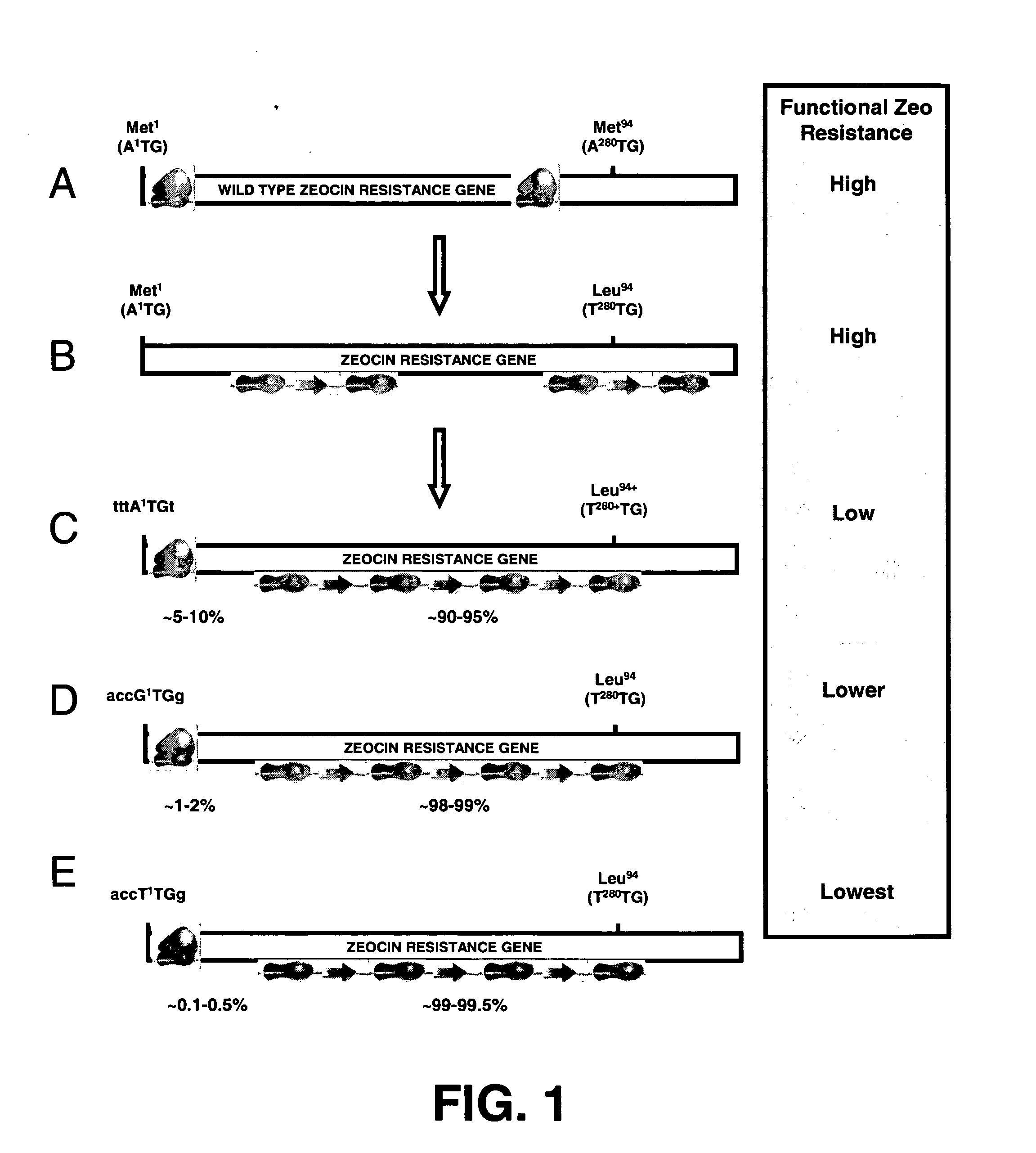
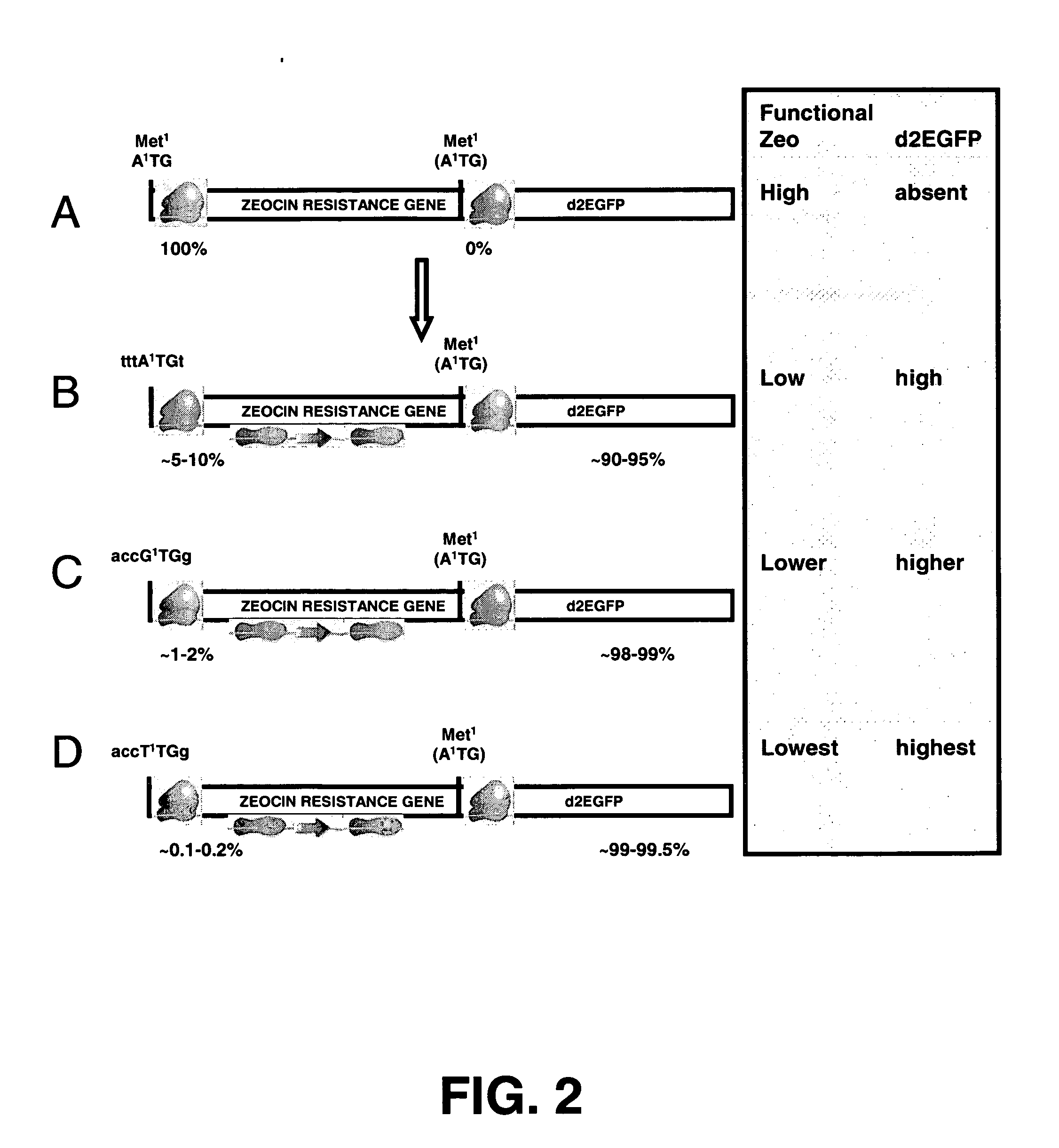
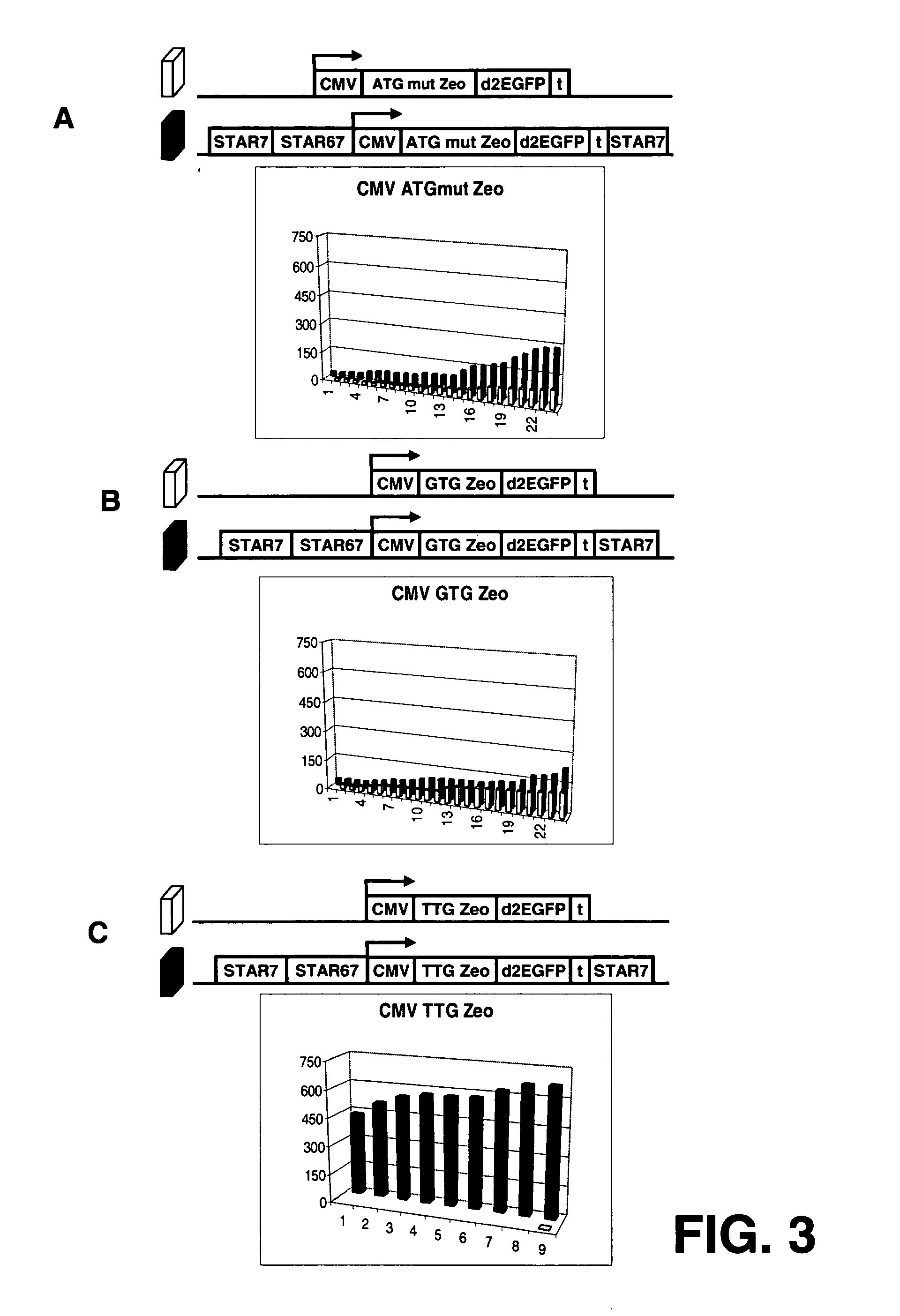
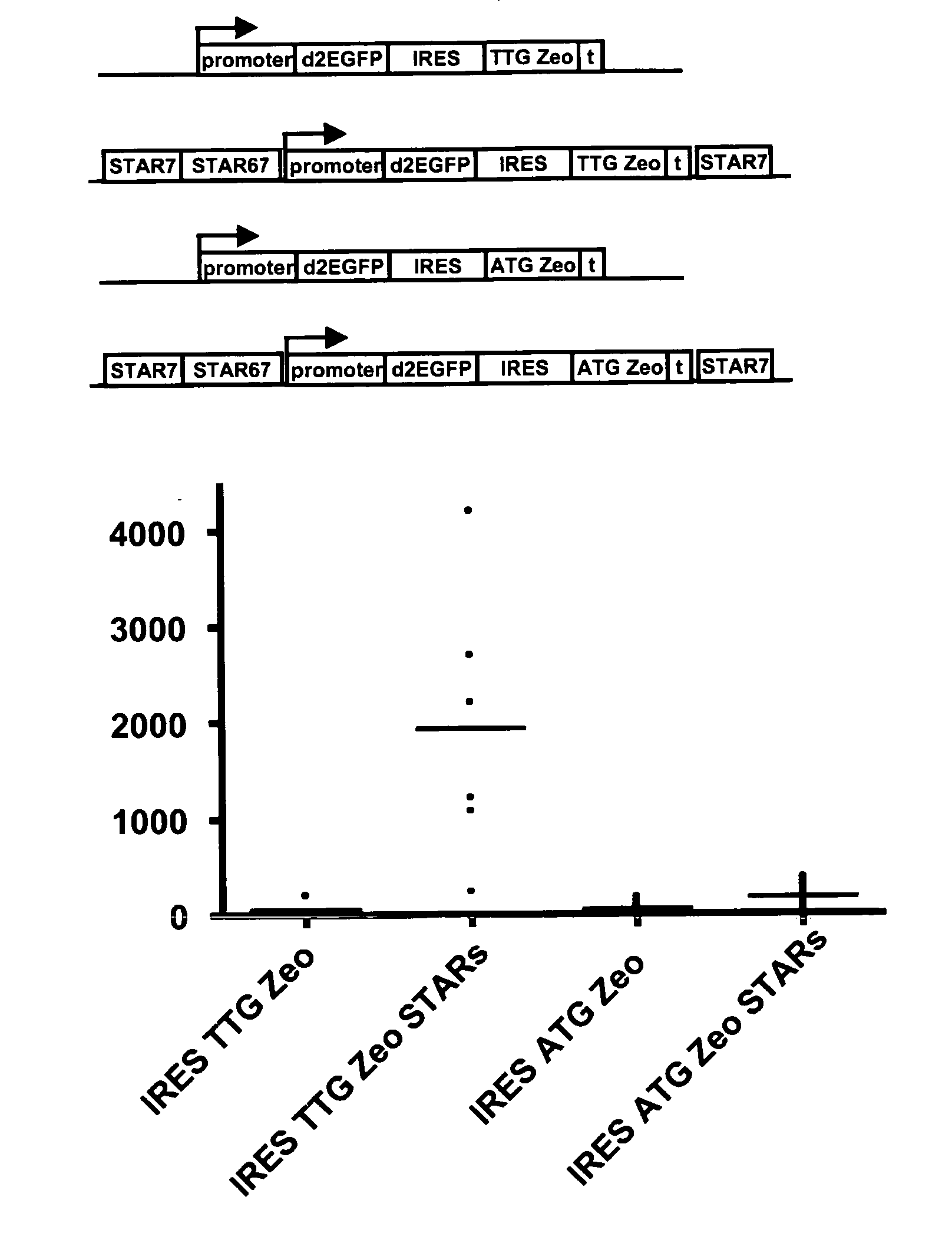
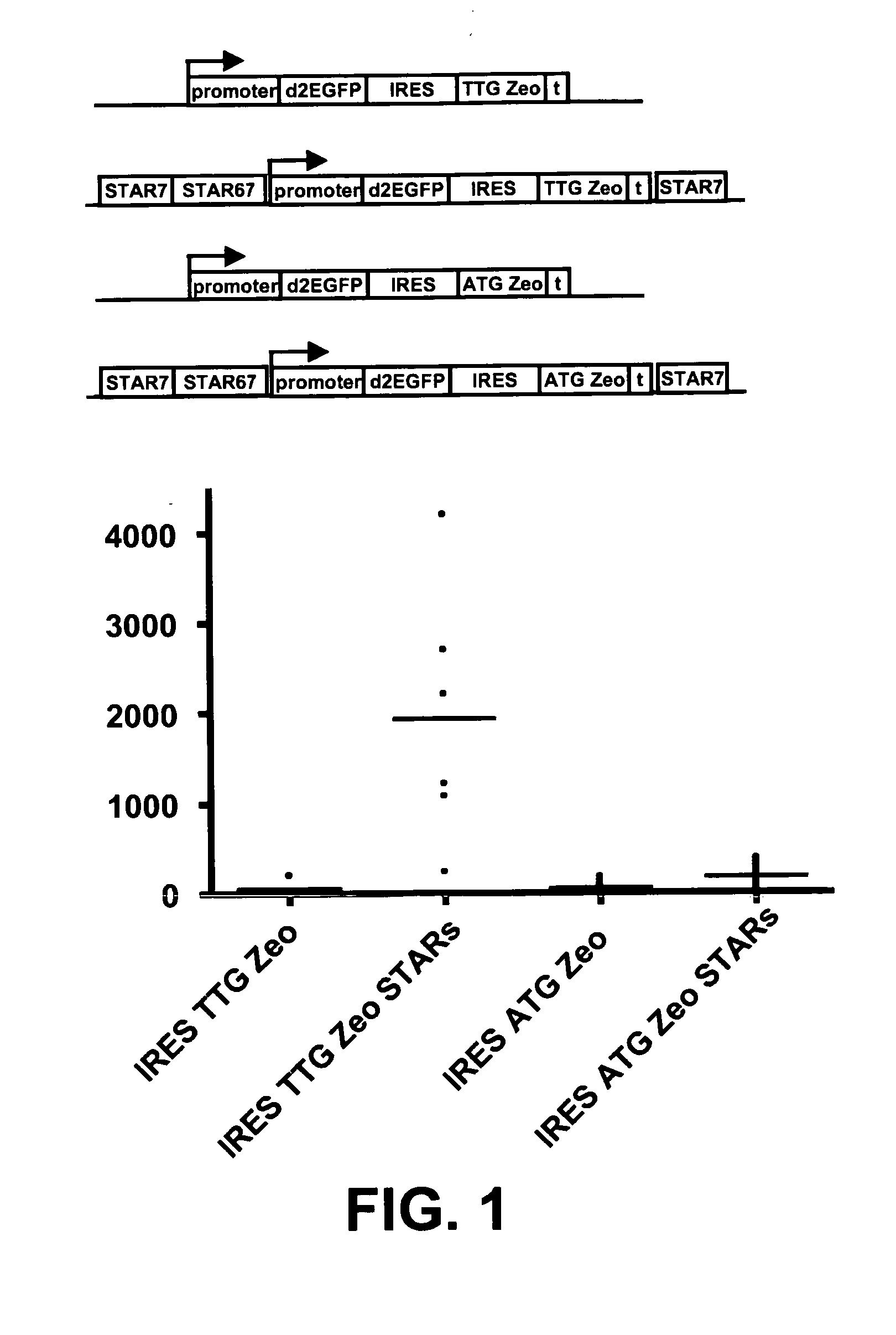
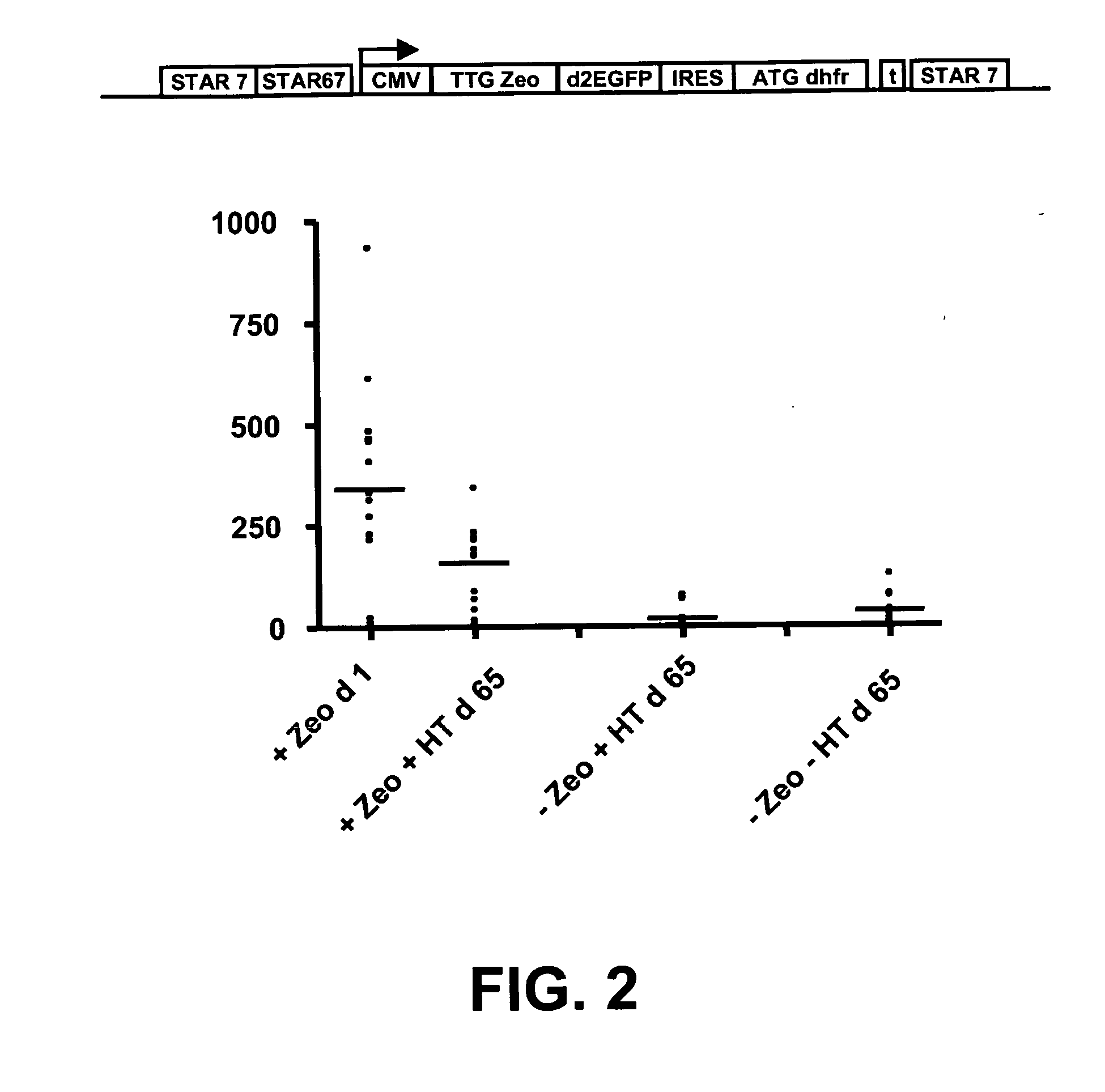
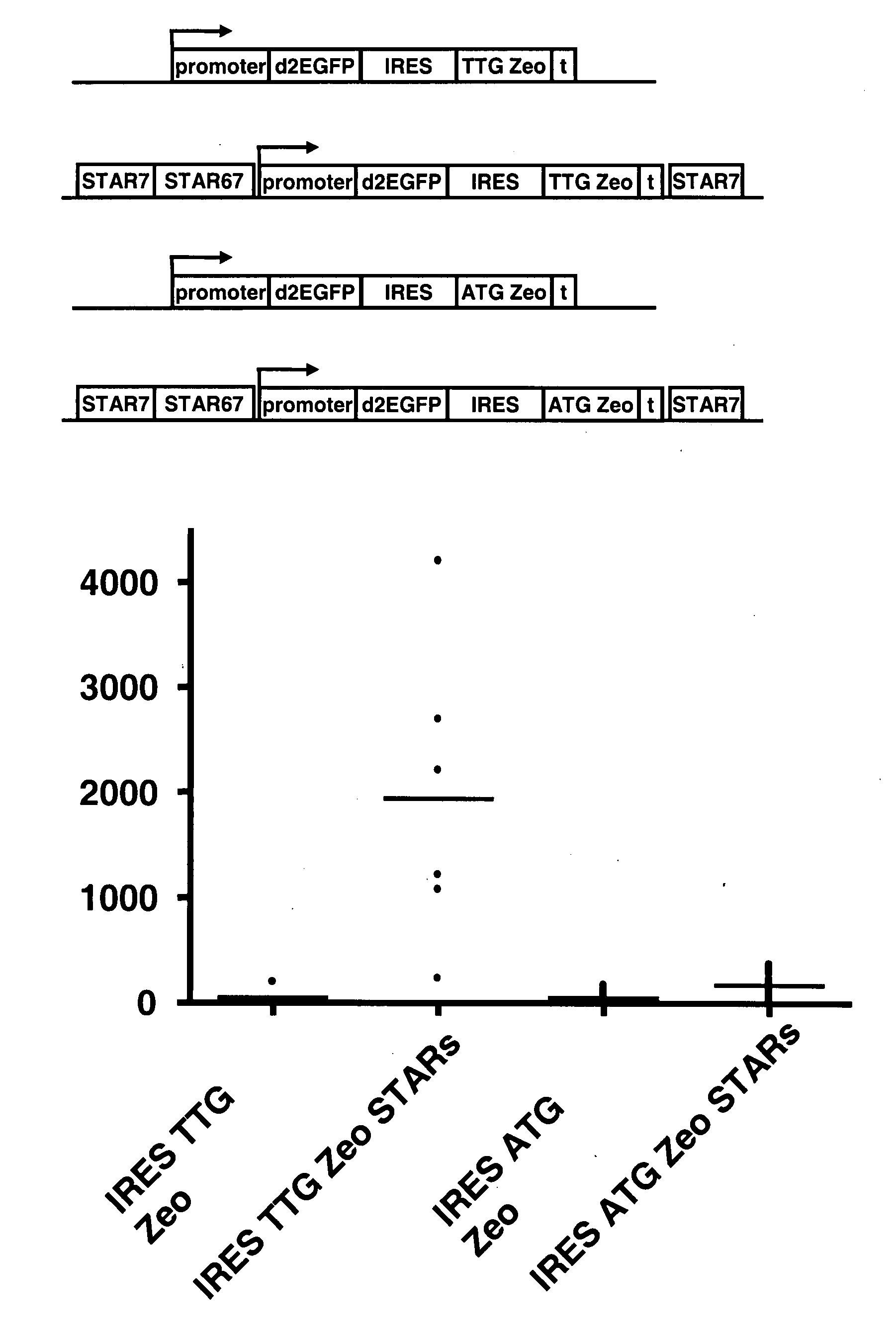
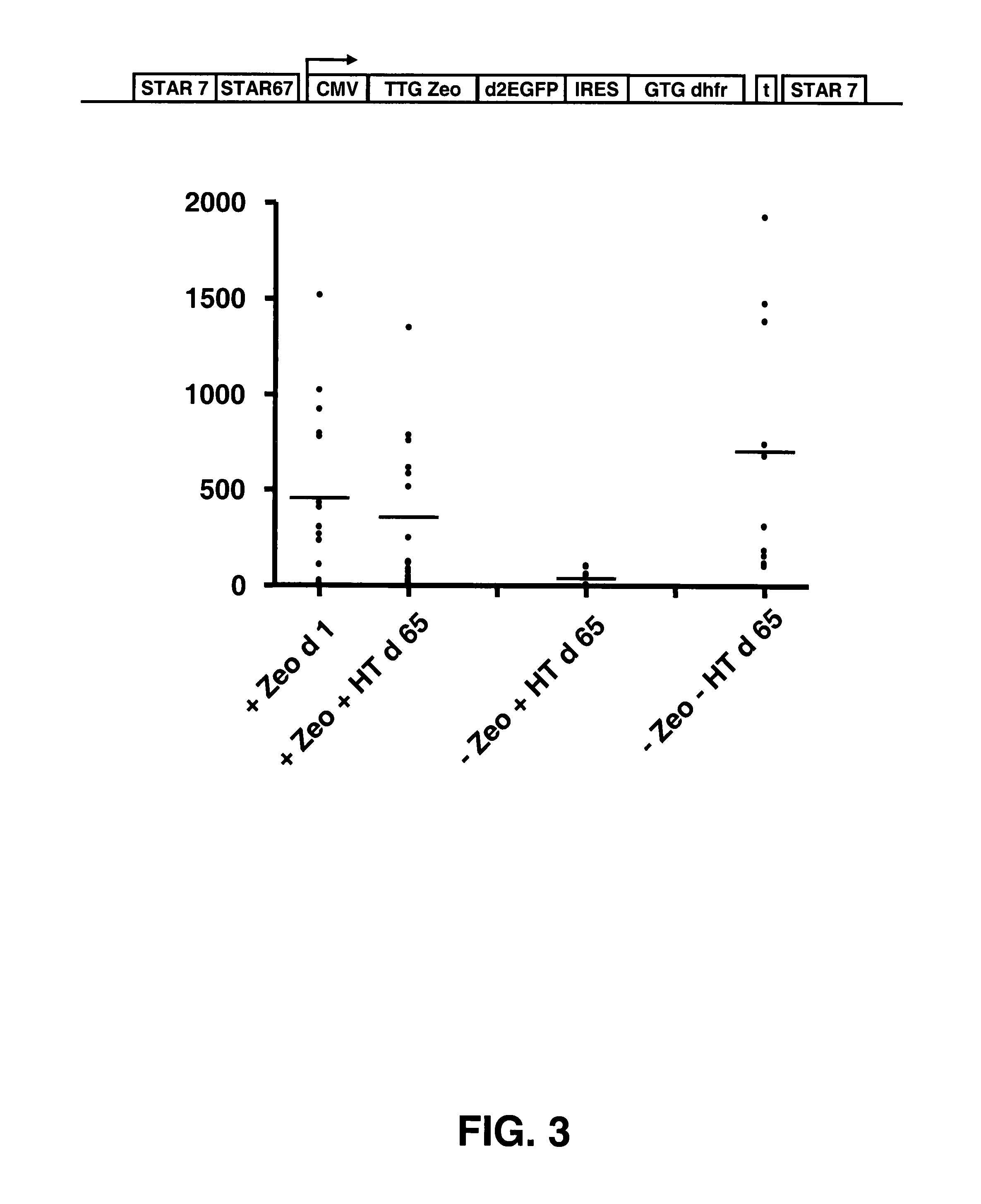
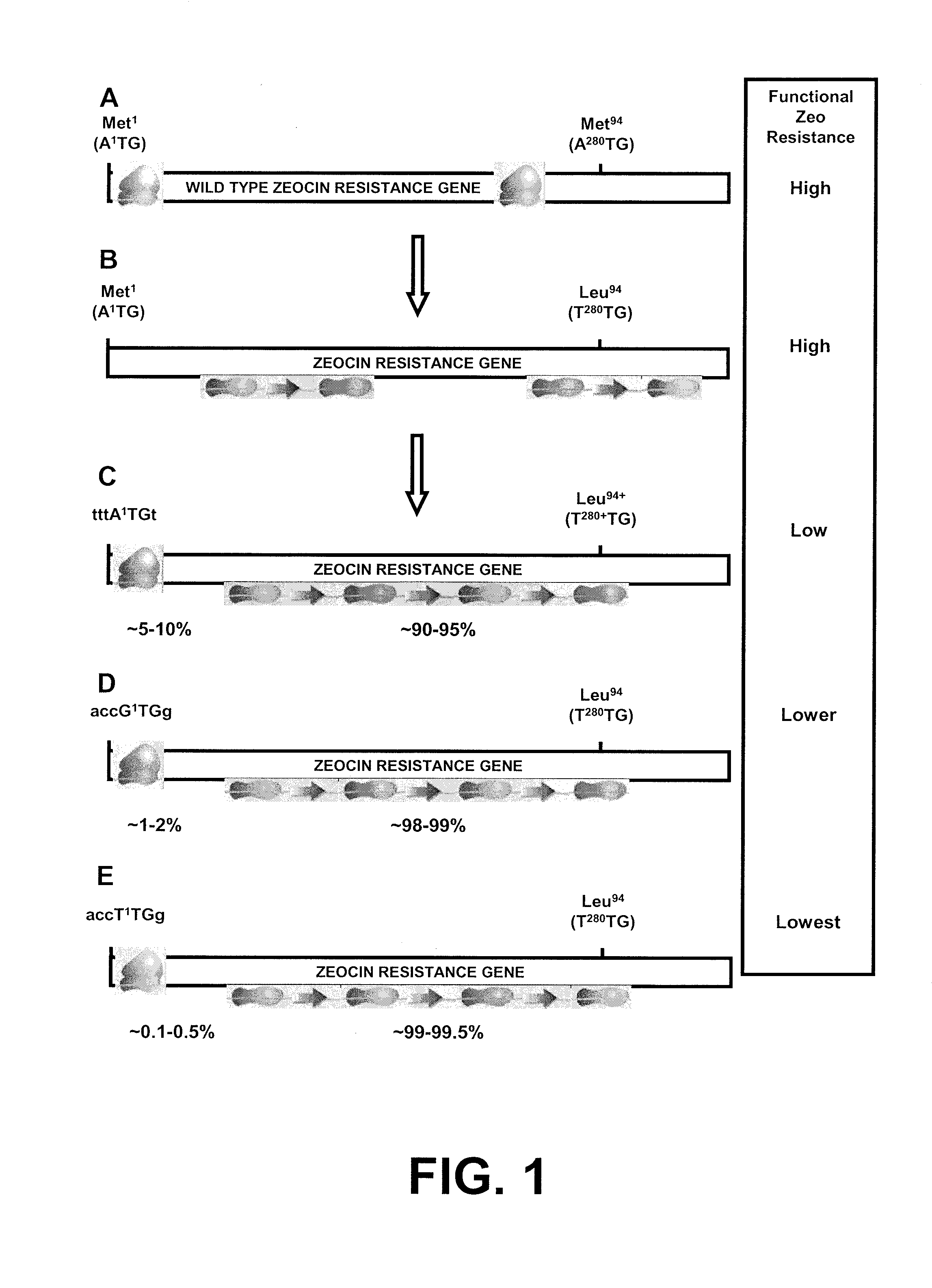
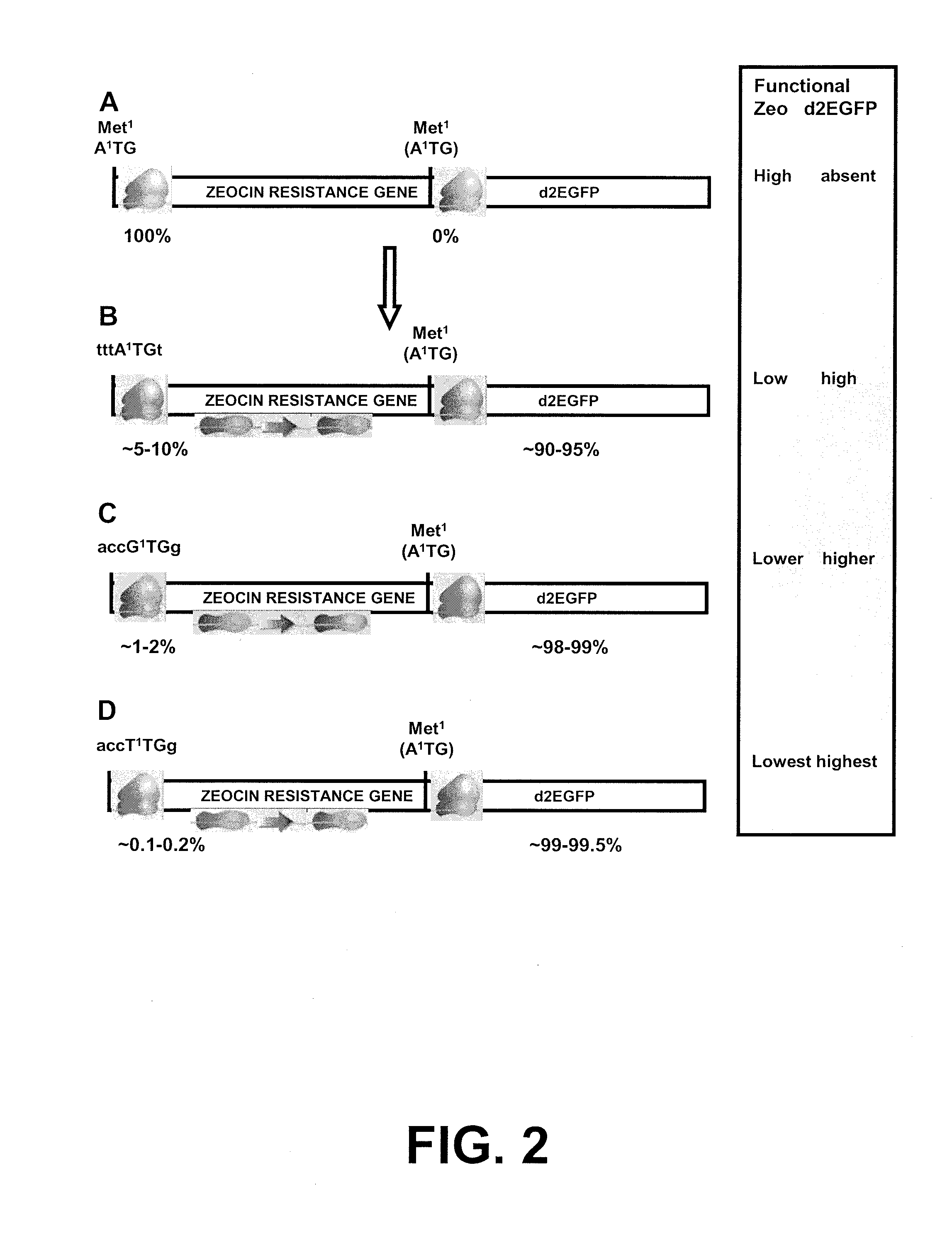
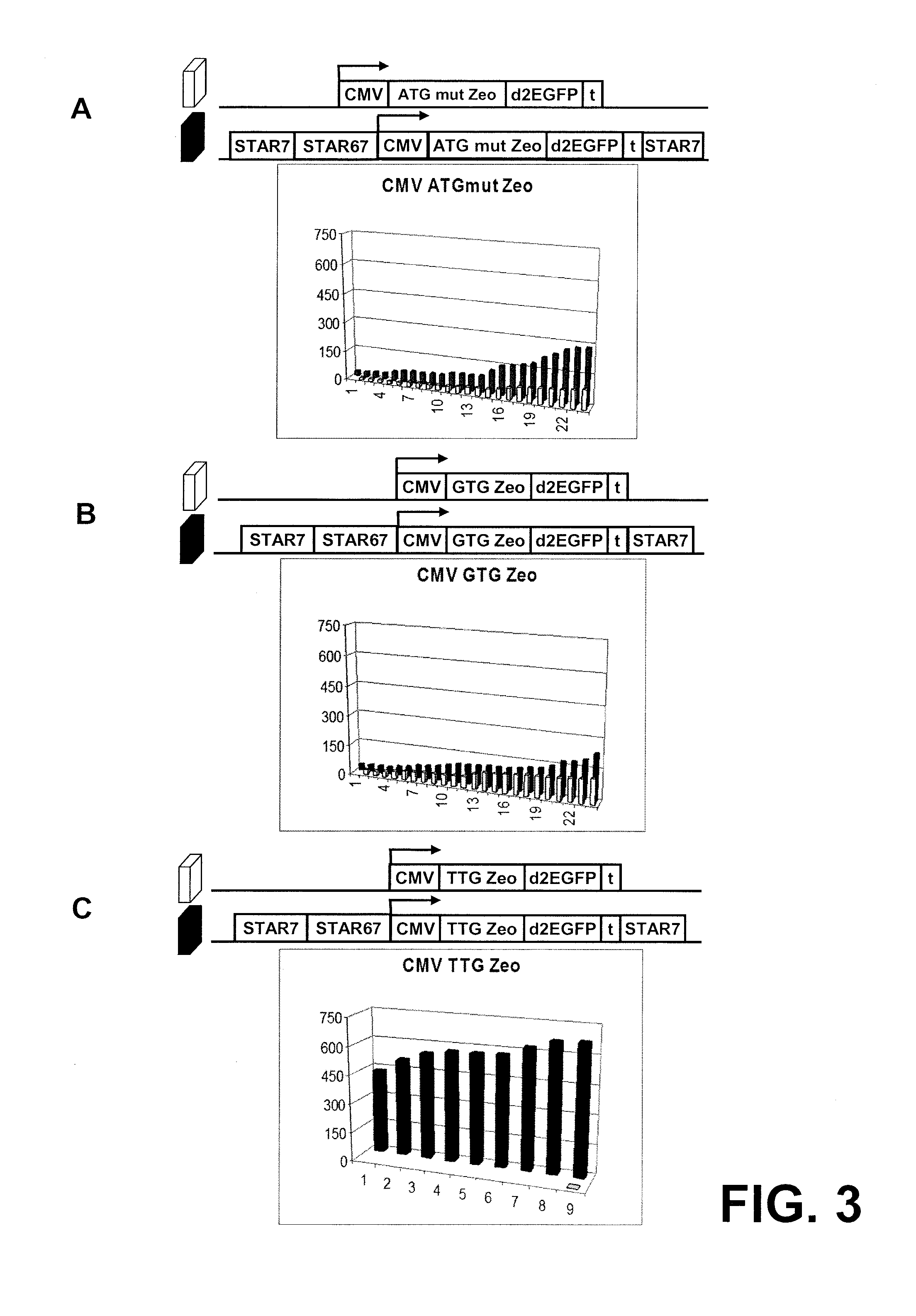
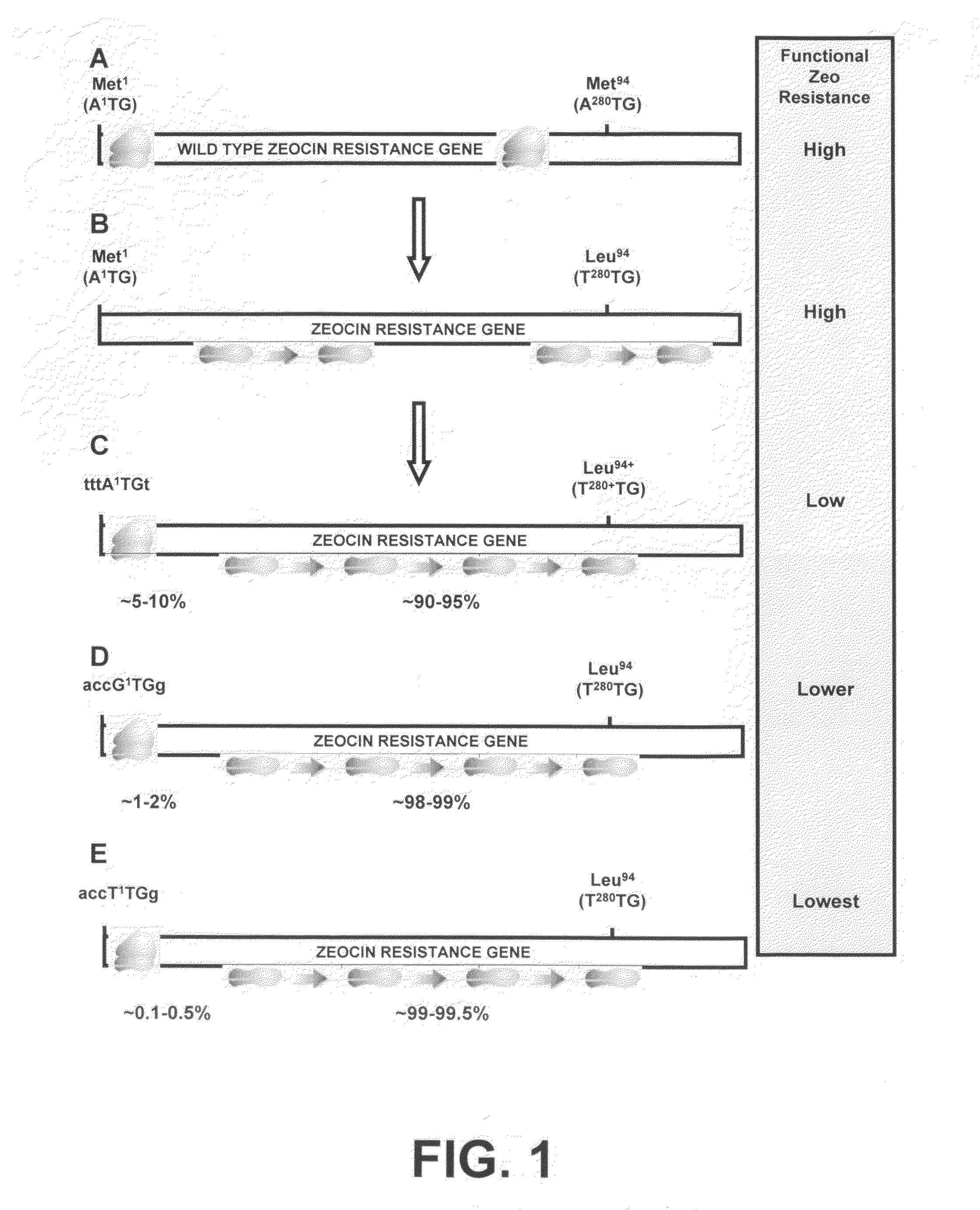
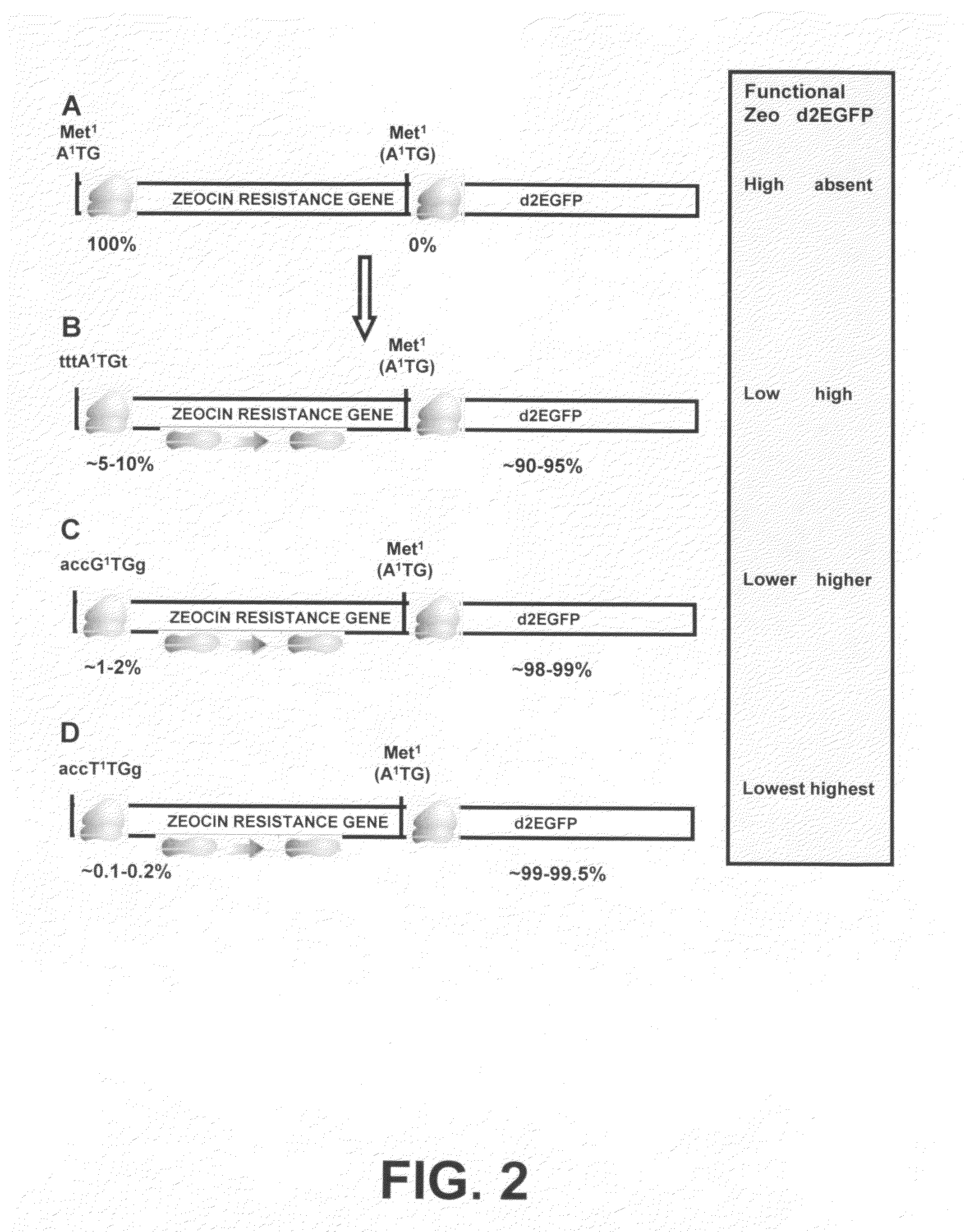
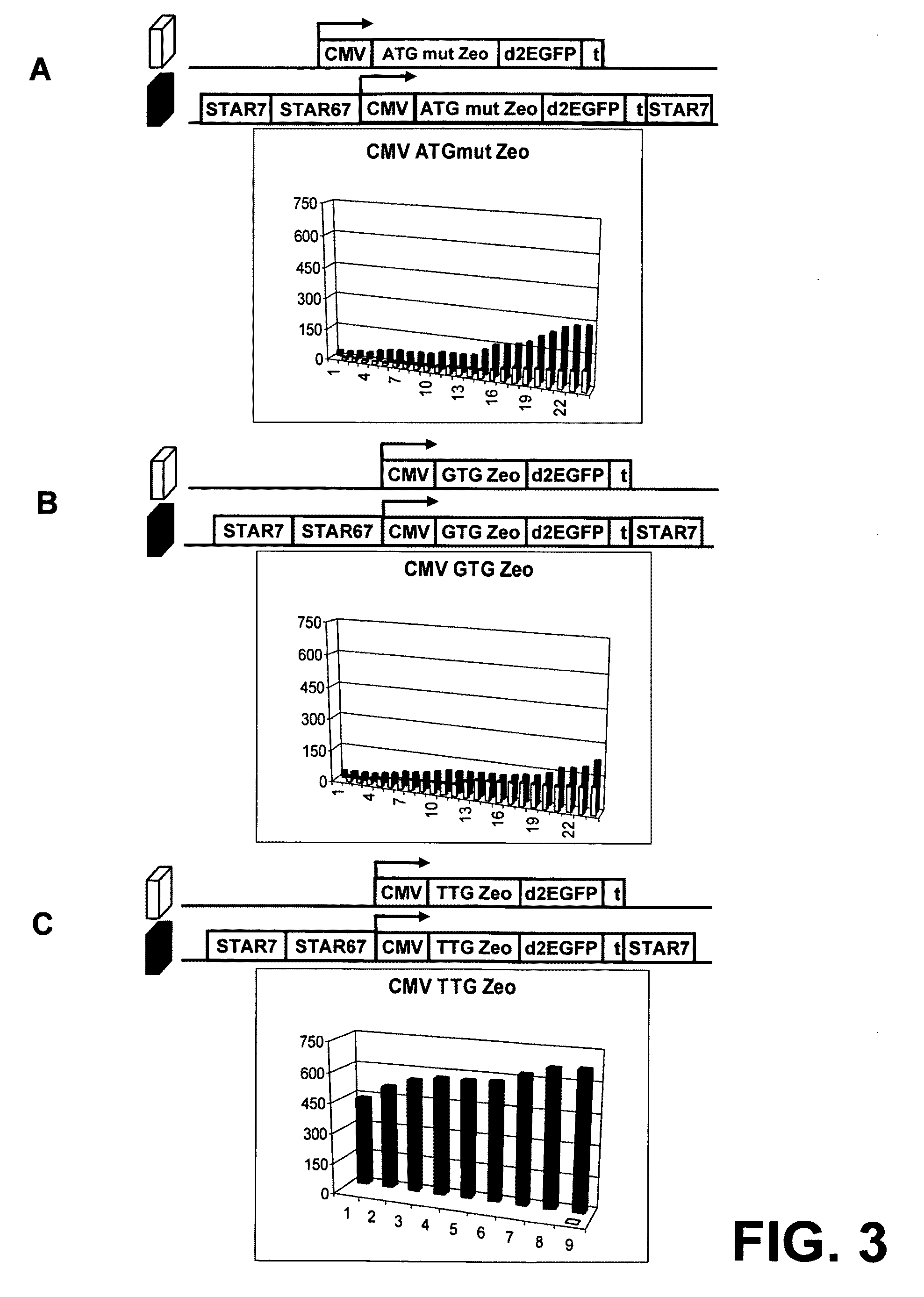
InactiveUS20060141577A1Decreases translation initiation efficiencyVectorsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsStart codonA-DNA
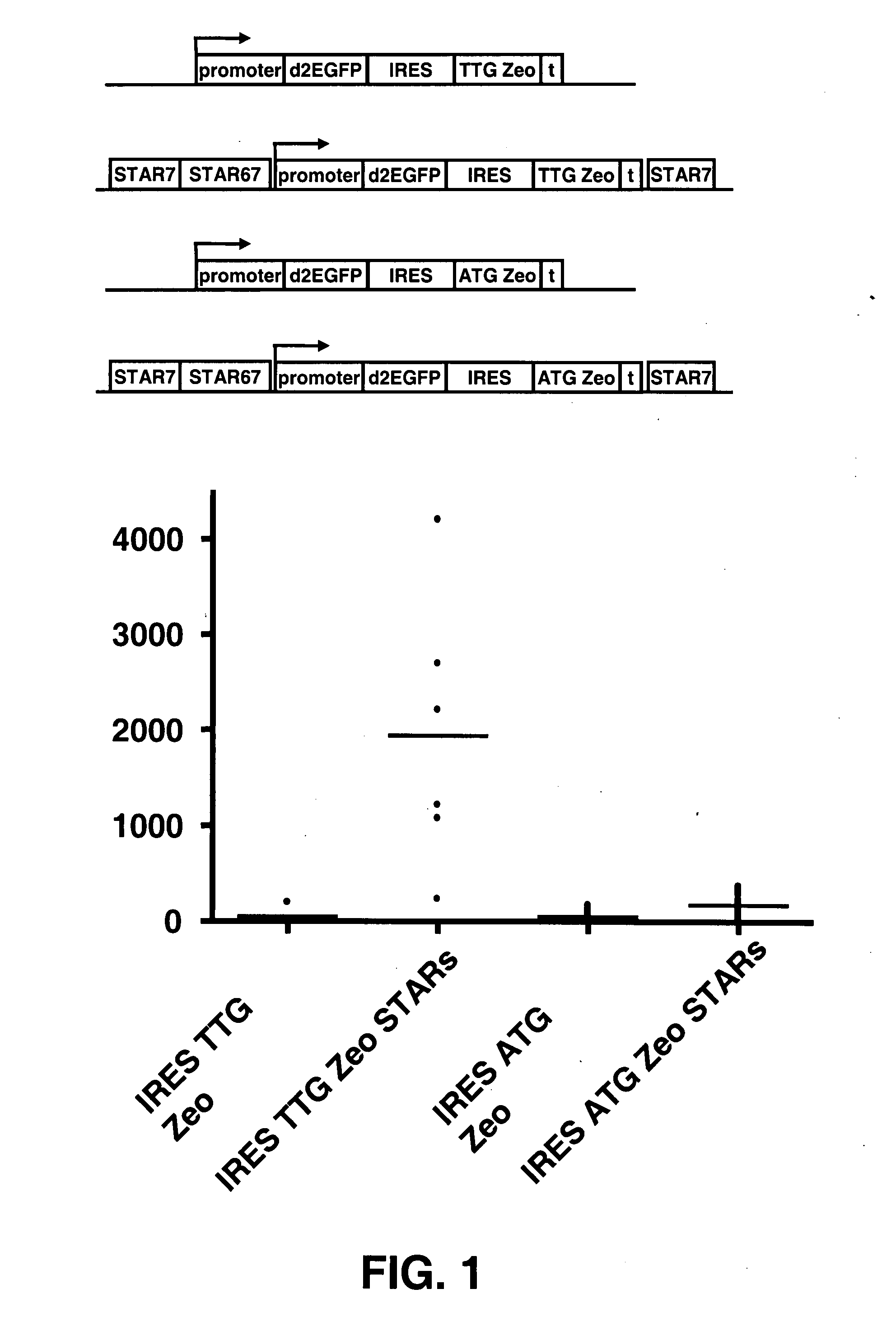
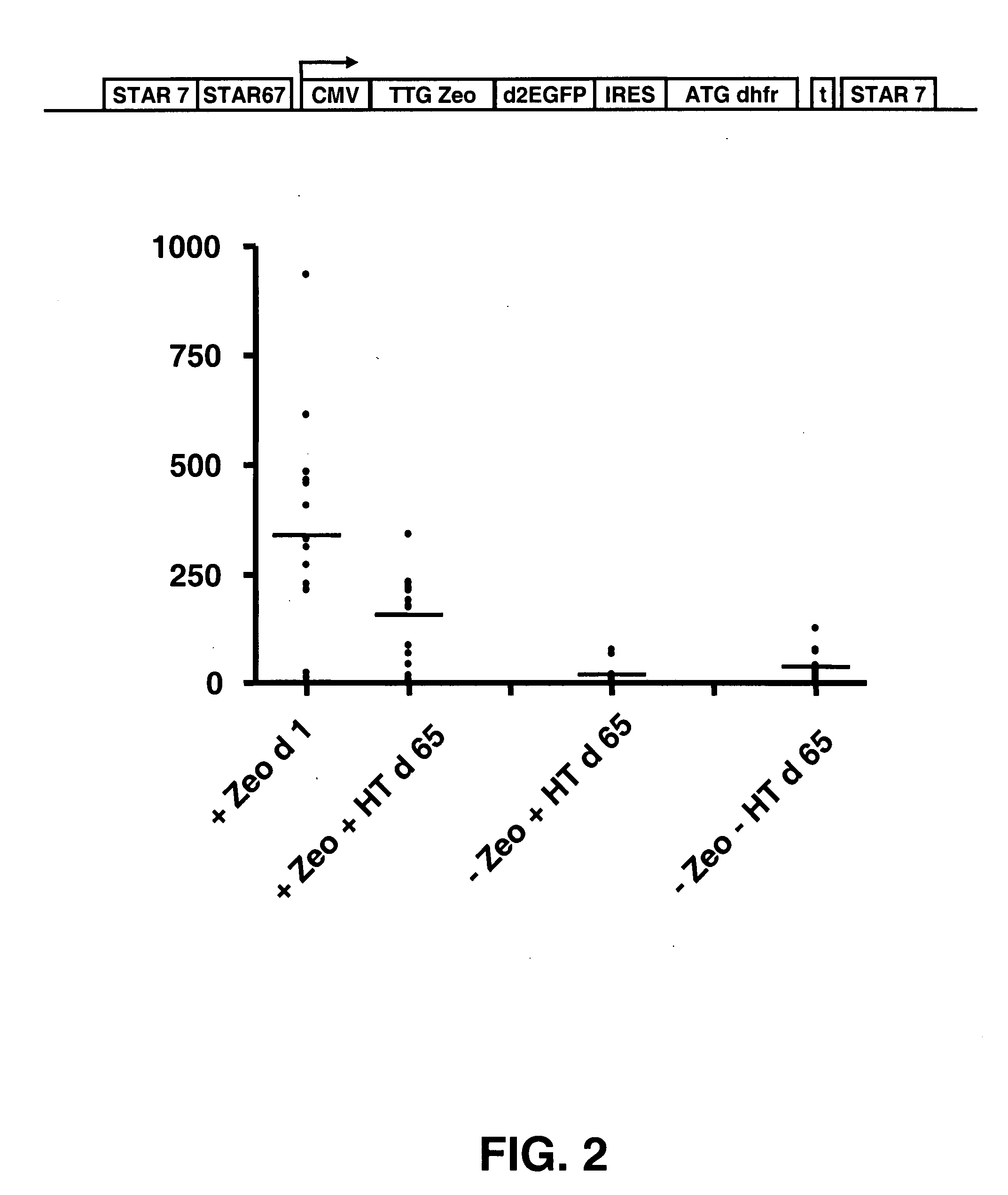
The invention provides a DNA molecule comprising a multicistronic transcription unit coding for i) a polypeptide of interest, and for ii) a selectable marker polypeptide functional in a eukaryotic host cell, wherein the polypeptide of interest has a translation initiation sequence separate from that of the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest is upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide in said multicistronic transcription unit, and wherein an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is present downstream from the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest and upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the nucleic acid sequence coding for the selectable marker polypeptide in the coding strand comprises a GTG or a TTG startcodon. The invention also provides methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, said host cells comprising the DNA molecules of the invention. The invention further provides the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules according to the invention.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
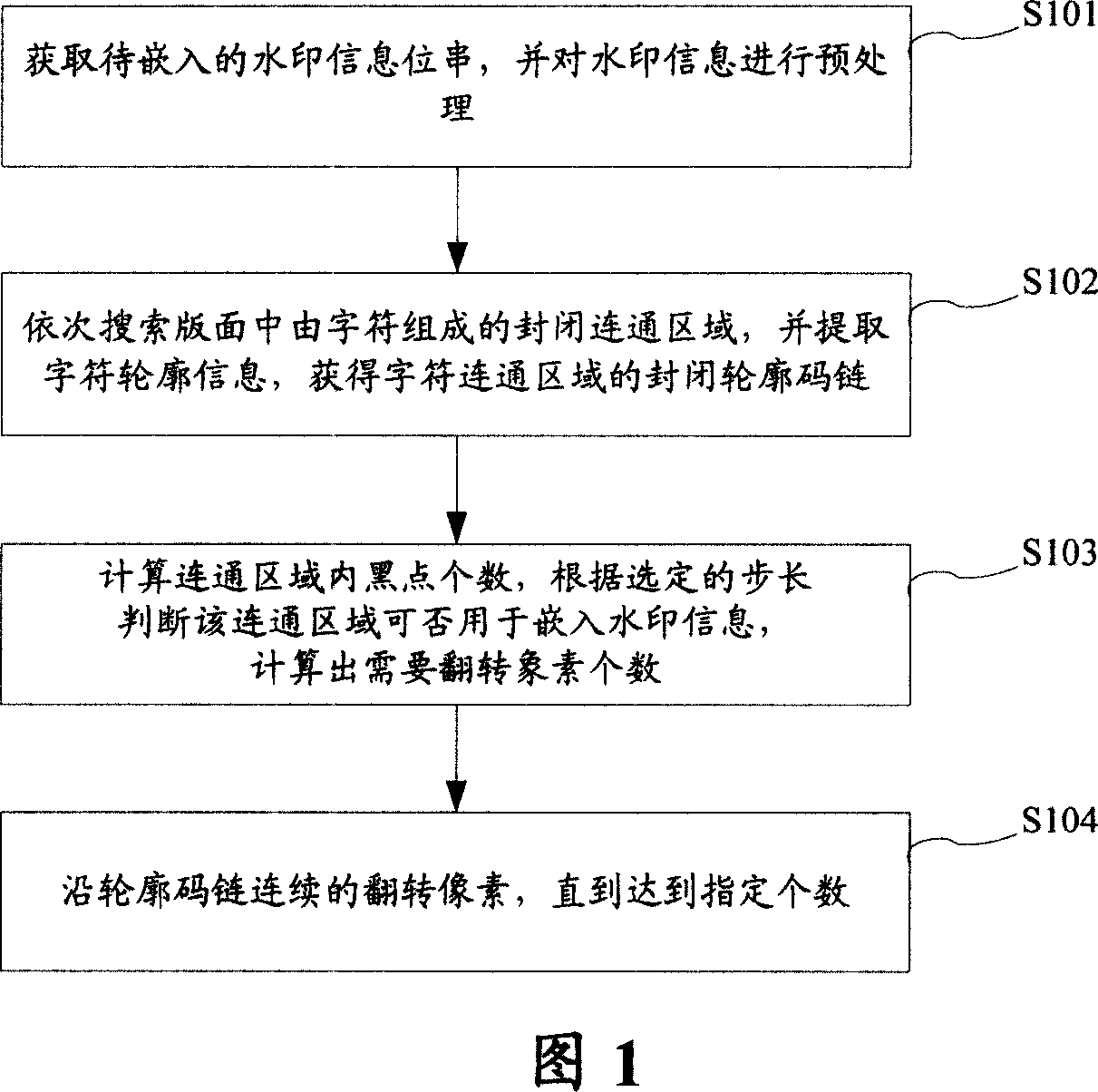
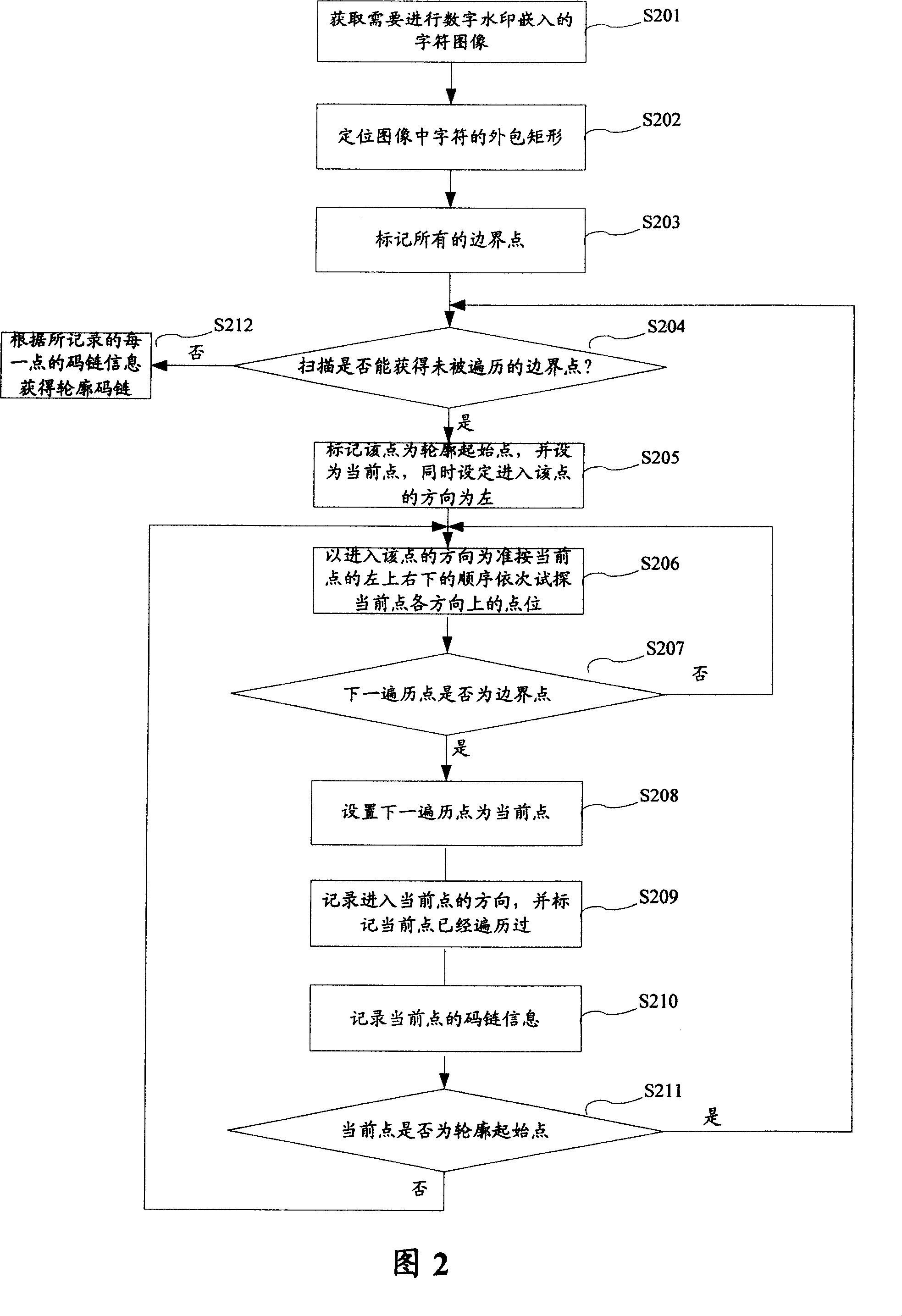
Digital watermark embedded and extracting method and device
InactiveCN101119429AVersatilityTo achieve the purpose of digital watermark embeddingImage data processing detailsPictoral communicationDocumentationComputer science
The present invention relates to a method and device of embedding and extraction of digital watermarking. The invention is to solve the prior art problem that the method for embedding and extracting of digital watermarking in the binary document image has no commonality. The embedding method of digital watermarking includes the steps as follows: acquiring the message bit string of watermarking which needs embedded; searching for the closed connect region consisted of characters, obtaining the profile code strand of connect region; calculating the first pixel value of pixel which needs to turn according to the smudge number in the connect region, the message bit string of watermarking and the first step; turning the pixel along the profile code strand based on the first pixel value. The method of the present invention has a simple embedding and extraction procedure without blocking or scrambling process in advance as well as not depends on the makeup of the text content; therefore, the calculating rate is increased, and the attack during the printing and scanning is effectively prevented, facilitating the follow of the message.
Owner:BEIJING FOUNDER ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method of screening candidate compounds for susceptibility to biliary excretion
InactiveUS7601494B2More compoundedFast processSugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsBiliary excretionHepatica
A method of screening a candidate compound for susceptibility to biliary excretion by a hepatocyte transport protein. The method includes the steps of providing a culture of hepatocytes comprising a transport protein, the culture having at least one bile canaliculus; exposing a candidate compound to the culture; and determining an amount of candidate compound in the at least one bile canaliculus, the amount of candidate compound in the at least one bile canaliculus indicating the susceptibility of the candidate compound to biliary excretion by the transport protein. In some embodiments determining the amount of candidate compound in the bile canaliculus comprises inhibiting expression of the transport protein, measuring the amount of candidate compound in the bile canaliculus and comparing amounts of compound in the canalicules with and without inhibition of the transport protein. A difference in the amount of candidate compound in the canaliculus indicates susceptibility of the candidate compound to biliary excretion by the transport protein. In one embodiment, expression of the transport protein is inhibited through introduction of a RNA having a sequence corresponding to a coding strand of the gene encoding the transport protein into the hepatocyte. Optionally, the culture of hepatocytes is a long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. The method is particularly applicable to the screening of multiple candidate compounds in a single effort.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
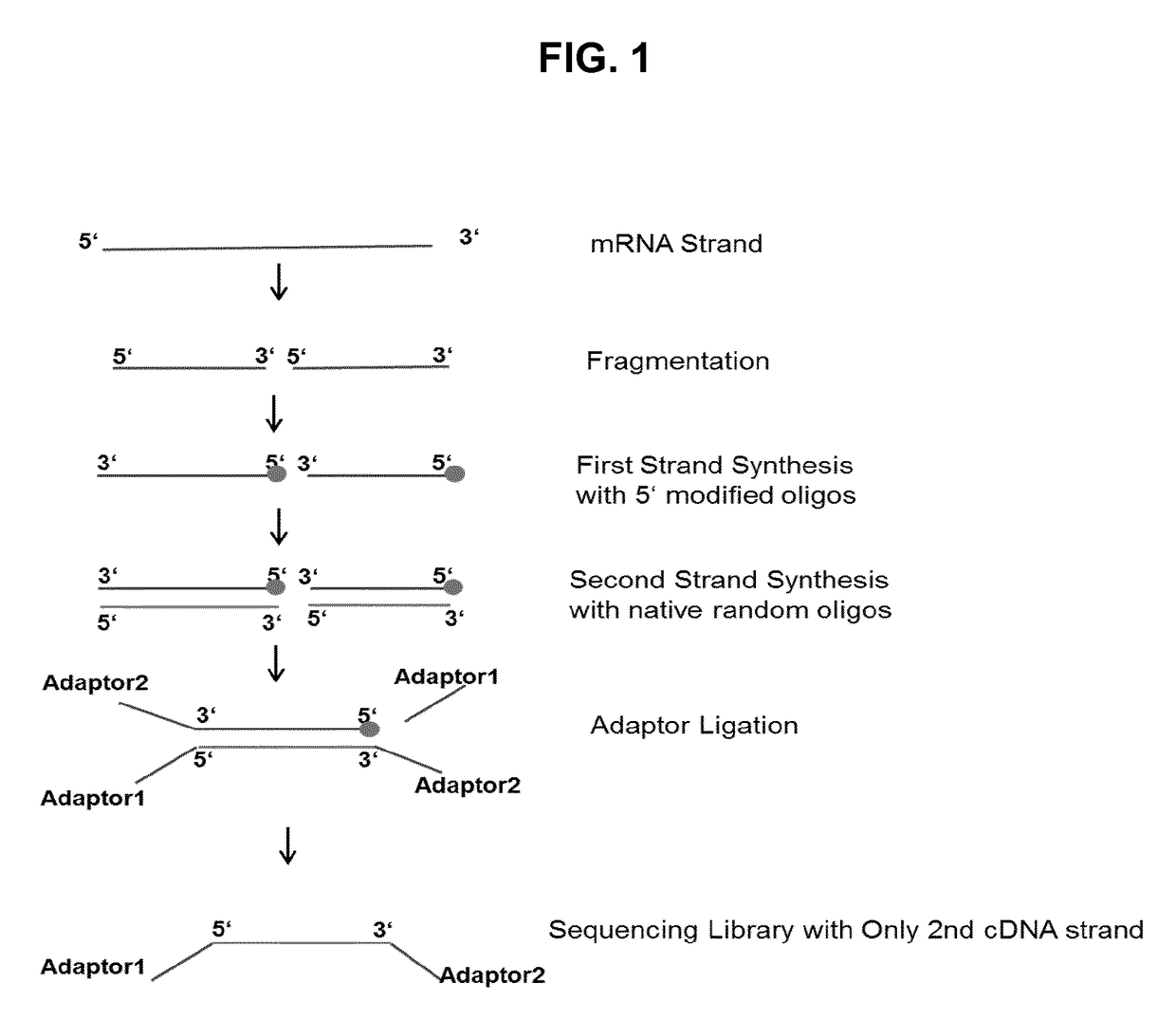
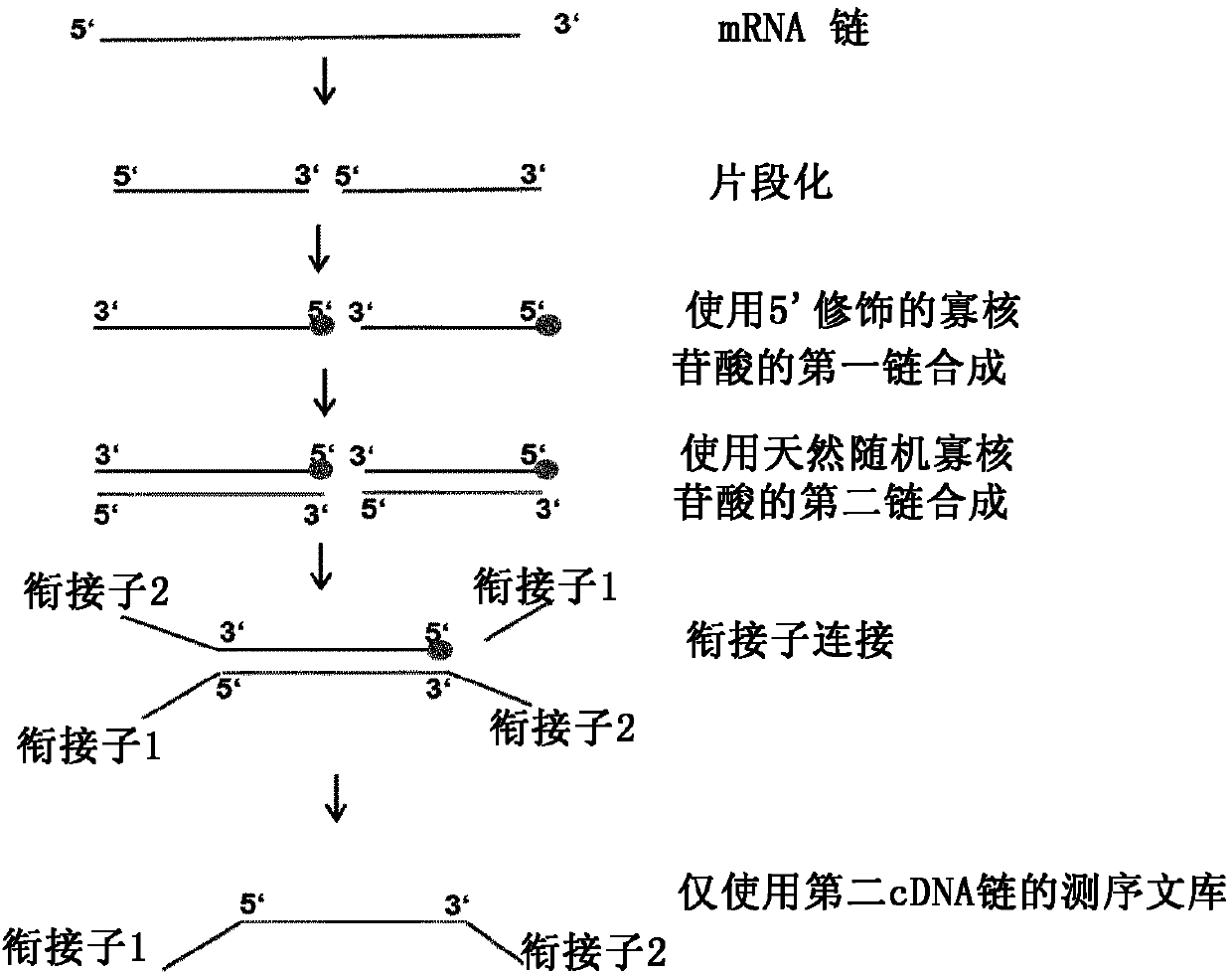
Method for generating a rna-sequencing library
The invention refers to a novel method of preparing strand-specific RNA-sequencing libraries that can be used to identify DNA coding and non-coding strands that are transcribed mRNA Strand to RNA. Such strand-specific RNA-sequencing libraries are especially useful in discovering anti-sense RNA and non-coding RNA. Random primer oligonucleotides, covalently coupled to a moiety, which blocks ligation, are used for RT reaction or the subsequent generation of the second DNA strand so that only one strand of the generated double-stranded DNA is ligated to sequencing adapters at the 5′ nucleotide and sequenced by paired-end sequencing.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method for inhibiting expression of a protein in a hepatocyte
InactiveUS20090325297A1Fast processQuick filterSugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsBiliary excretionBile canaliculus
A method of screening a candidate compound for susceptibility to biliary excretion by a hepatocyte transport protein. The method includes the steps of providing a culture of hepatocytes comprising a transport protein, the culture having at least one bile canaliculus; exposing a candidate compound to the culture; and determining an amount of candidate compound in the at least one bile canaliculus, the amount of candidate compound in the at least one bile canaliculus indicating the susceptibility of the candidate compound to biliary excretion by the transport protein. In some embodiments determining the amount of candidate compound in the bile canaliculus comprises inhibiting expression of the transport protein, measuring the amount of candidate compound in the bile canaliculus and comparing amounts of compound in the canalicules with and without inhibition of the transport protein. A difference in the amount of candidate compound in the canaliculus indicates susceptibility of the candidate compound to biliary excretion by the transport protein. In one embodiment, expression of the transport protein is inhibited through introduction of a RNA having a sequence corresponding to a coding strand of the gene encoding the transport protein into the hepatocyte. Optionally, the culture of hepatocytes is a long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. The method is particularly applicable to the screening of multiple candidate compounds in a single effort.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
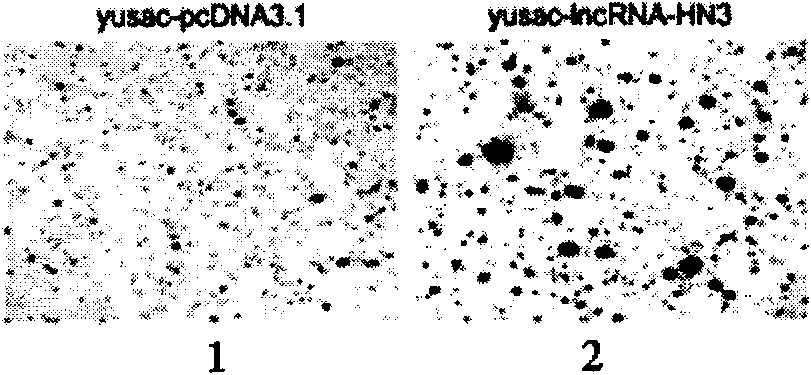
Long non-coding RNA sequence relevant to human melanoma cells and application thereof
InactiveCN101633923AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEukaryotic plasmids
The invention provides a long non-coding RNA (long non-coding RNA, 1ncRNA)-incRNA-HN3 sequence relevant to human melanoma cells, and an RNA interference (RNA interference, RNAi) target spot sequence, a short-hairpin RNA (short-hairpin RNA, shRNA) sequence, an shRNA coded small molecule interference RNA (small interference RNA, siRNA), a coding shRNA coding strand and an anti-sense strand DNA sequence, coding shRNA recombinant plasmids of the long non-coding RNA sequence, and the invention relates to the applications of the long non-coding RNA sequence for preparing reagents for diagnosing melanoma diseases and drugs for treating the melanoma diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Selection of Host Cells Expressing Protein at High Levels
InactiveUS20100136616A1Impaired translationImprove translationAnimal cellsVectorsHigh level expressionA-DNA
The invention provides a DNA molecule comprising a multicistronic transcription unit coding for i) a polypeptide of interest, and for ii) a selectable marker polypeptide functional in a eukaryotic host cell, wherein the polypeptide of interest has a translation initiation sequence separate from that of the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest is upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide in said multicistronic transcription unit, and wherein an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is present downstream from the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest and upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the nucleic acid sequence coding for the selectable marker polypeptide in the coding strand comprises a GTG or a TTG startcodon. The invention also provides methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, said host cells comprising the DNA molecules of the invention. The invention further provides the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules according to the invention.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
The invention provides a DNA molecule comprising a multicistronic transcription unit coding for i) a polypeptide of interest, and for ii) a selectable marker polypeptide functional in a eukaryotic host cell, wherein the polypeptide of interest has a translation initiation sequence separate from that of the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest is upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide in the multicistronic transcription unit, and wherein an internal ribosome entry site is present downstream from the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest and upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the nucleic acid sequence coding for the selectable marker polypeptide in the coding strand comprises a GTG or a TTG start codon. Also provided are methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, such host cells comprising DNA molecules of the invention. Further provided is the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules of the invention.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
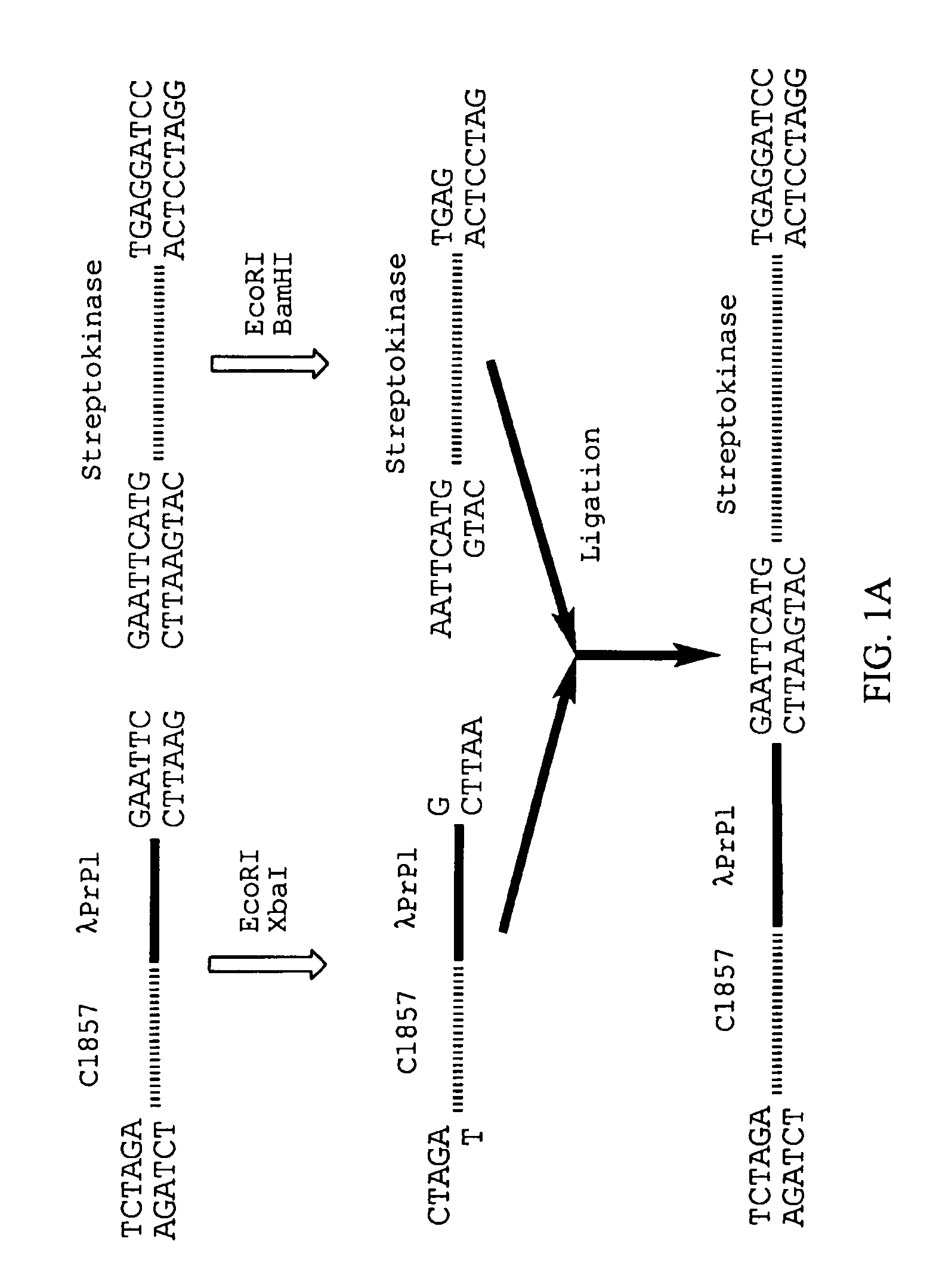
Recombinant streptokinase
The present invention is based on the isolation of a gene coding for streptokinase from Streptococcus equisimilis (ATCC 9542), its cloning, and expression in E. coli. Two different strategies were carried out for the production of enzymatically-active streptokinase. In the first strategy, streptokinase was expressed as an inclusion body without its signal sequence followed by purification, solubulization, and renaturation to obtain an active preparation. The purified enzyme was formulated and lyophilized. In the second strategy, enzymatically-active streptokinase is secreted into the culture medium. The enzyme was purified, formulated and lyophilized.
Owner:BHARAT BIOTECH INTERNATIONAL
Linear double stranded DNA coupled to a single support or a tag and methods for producing said linear double stranded DNA
ActiveUS20200392572A1Accelerate CuAAC reactionProtects against oxidative damageMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle supportDouble strand
The present invention is concerned with linear double stranded DNA, which is coupled to a single support or a tag at the 3′ end of its non-coding strand and methods for producing said linear double stranded DNA. The present invention further relates to the use of said linear double stranded DNA in an RNA in vitro transcription reaction and also to a method for producing RNA in vitro. The present invention also relates to a bioreactor for RNA in vitro transcription.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
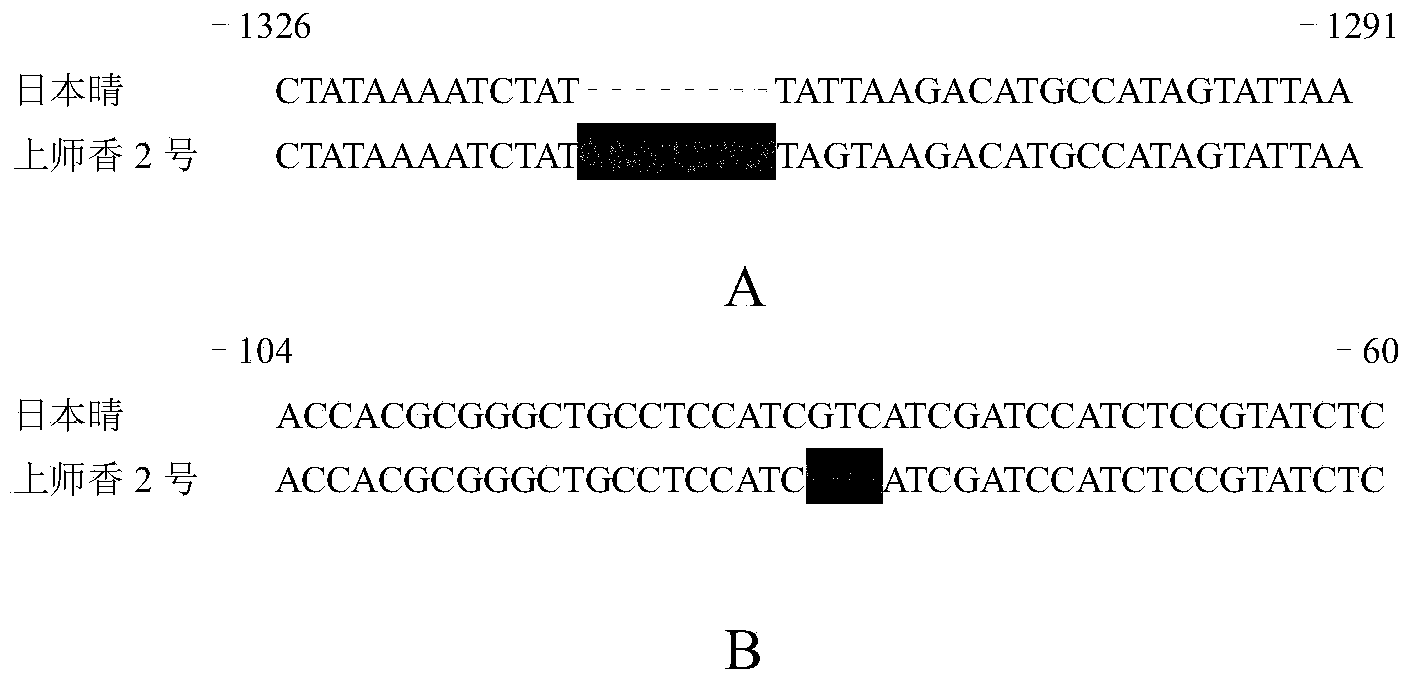
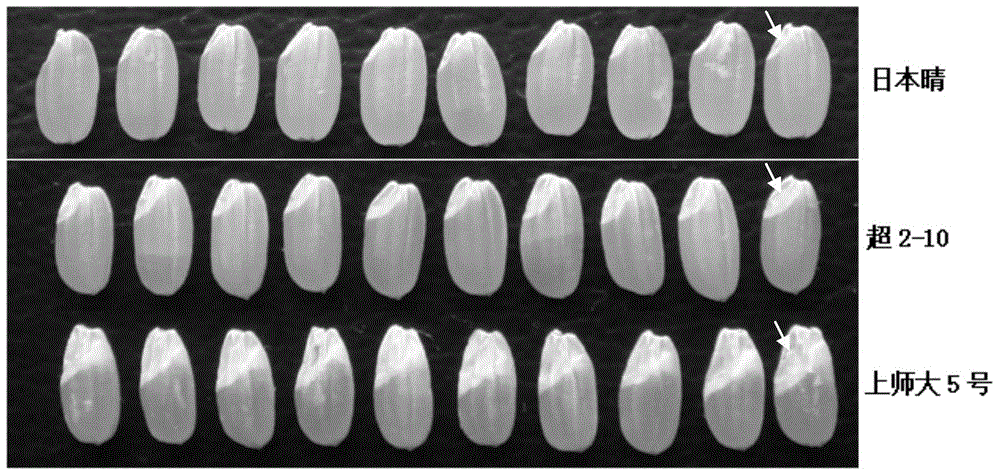
Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 fragrance gene in paddy rice, primer of molecular marker and screening method
InactiveCN103525840AMeet needsOvercome biasMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a new betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene enabling paddy rice to have the characteristic of light fragrance, and compared with non-fragrant paddy rice nipponbare, the mutation site is not located in coding strand but belongs to the mutation-type betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene at the upstream of the coding strand. Three nucleotides are lost at the -81 site at the upstream of the first nucleotide of the initiation codon of the coding strand, and eight nucleotides are inserted into the -1314 site. A new light-fragrance type paddy rice species is cultivated once homozygous progeny is obtained by transferring the gene into non-fragrant paddy rice via hybridization. The invention also discloses a method for screening the paddy rice possessing the light-fragrance type characteristic and a primer of a molecular marker. The new gene is provided for cultivation of the light-fragrance type paddy rice; also the betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 fragrance gene in paddy rice, the primer of molecular marker and the screening method help to perform assistant selection on plants containing light-fragrance gene, are beneficial to improve selection effect, and also help to identify whether the inbred progeny light-fragrance gene formed at the later stage of breeding is in a homozygous state, so that the breeding target can be realized rapidly and effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
The invention provides a DNA molecule comprising a multicistronic transcription unit coding for i) a polypeptide of interest, and for ii) a selectable marker polypeptide functional in a eukaryotic host cell, wherein the polypeptide of interest has a translation initiation sequence separate from that of the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest is upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide in the multicistronic transcription unit, and wherein an internal ribosome entry site is present downstream from the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest and upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the nucleic acid sequence coding for the selectable marker polypeptide in the coding strand comprises a GTG or a TTG start codon. Also provided are methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, such host cells comprising DNA molecules of the invention. Further provided is the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules of the invention.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
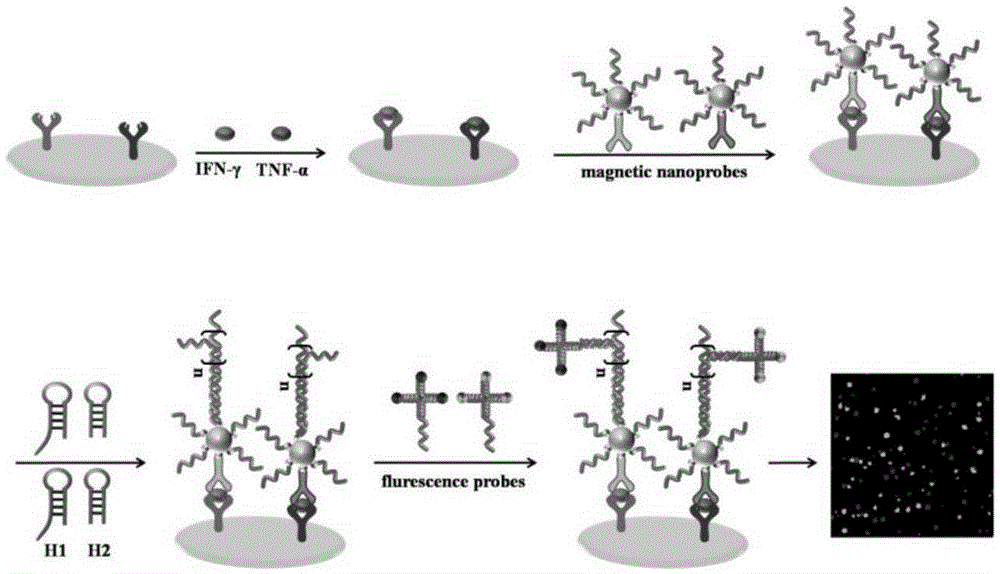
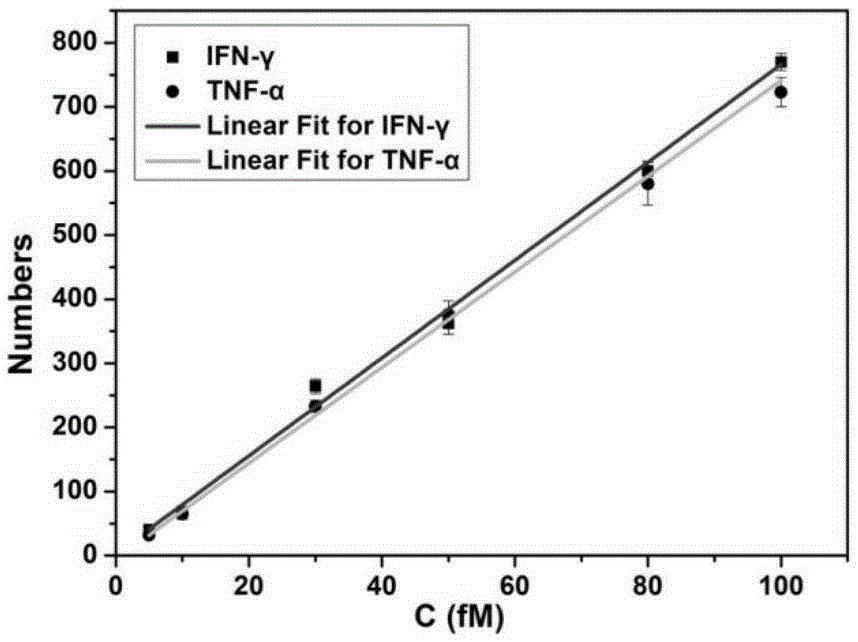
Cytokine multiple detection method based on dual coding and monomolecular counting
ActiveCN105353131AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionGreat application potentialBiological testingImmune complex depositionFluorescence
The invention discloses a cytokine multiple detection method based on dual coding and monomolecular counting. The method is characterized in that a first antibody is fixed on a same glass substrate, through interaction of antigen-antibodies, the target objects can be respectively fixed; simultaneously, a secondary antibody and a first coding strand are modified on magnetic nano-particles to obtain a magnetic nano probe; then specific binding effect between the secondary antibody and antigen is used, the magnetic nano probe is fixed on a substrate to form an immune complex having a sandwich structure, the first coding strand on the magnetic nano probe is taken as an amplification unit to trigger a multi-branches hybridization chain reaction, and a double-chain structure having multiple branches; the branched chain is a secondary coding strand; finally, the secondary coding strand and a polymolecule-labeled fluorescence probe are combined, an enhanced fluorescence signal is generated, and quantification on the target object is carried out by counting the amount of phosphor dots. The method realizes multiple and sensitive detection for cytokine, and a detection limit of two target objects is 5fM.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Gene sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN104911193AHigh content of maltooligosaccharidesHigh in Total Vitamin EGenetic engineeringFermentationEmbryoOligosaccharide
The invention provides a new gene sequence and an application thereof. The gene sequence is characterized in that am adenine deoxynucleotide is inserted between the upstream-777 and the upstream-778 of the first deoxynucleotide of the first codon of a giant embryo allele coding strand corresponding to normal embryo rice, and guanine deoxynucleotide in the downstream+125 of the first deoxynucleotide of the first codon of the coding strand mutates to adenine deoxynucleotide. The GABA content, the vitamin E content, the glutathione content and the malto-oligosaccharide content of homozygous brown rice with the gene sequence are obviously higher than those of brown rice without the gene sequence. The gene sequence is transferred to normal embryo rice to obtain homozygous giant embryo progeny, so a new species of giant embryo rice with giant embryo phenotype and with obviously improved content of various nutrients in brown rice can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for generating a RNA-sequencing library
The invention refers to a novel method of preparing strand-specific RNA-sequencing libraries that can be used to identify DNA coding and non-coding strands that are transcribed to RNA. Such strand-specific RNA-sequencing libraries are especially useful in discovering anti-sense RNA and non-coding RNA. Random primer oligonucleotides, covalently coupled to a moiety, which blocks ligation,are used for RT reaction or the subsequent generation of the second DNA strand so that only one strand of the generated double-stranded DNA is ligated to sequencing adapters at the 5 nucleotide and sequenced by paired-end sequencing.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Reagent kit for determining specific nucleotide variations
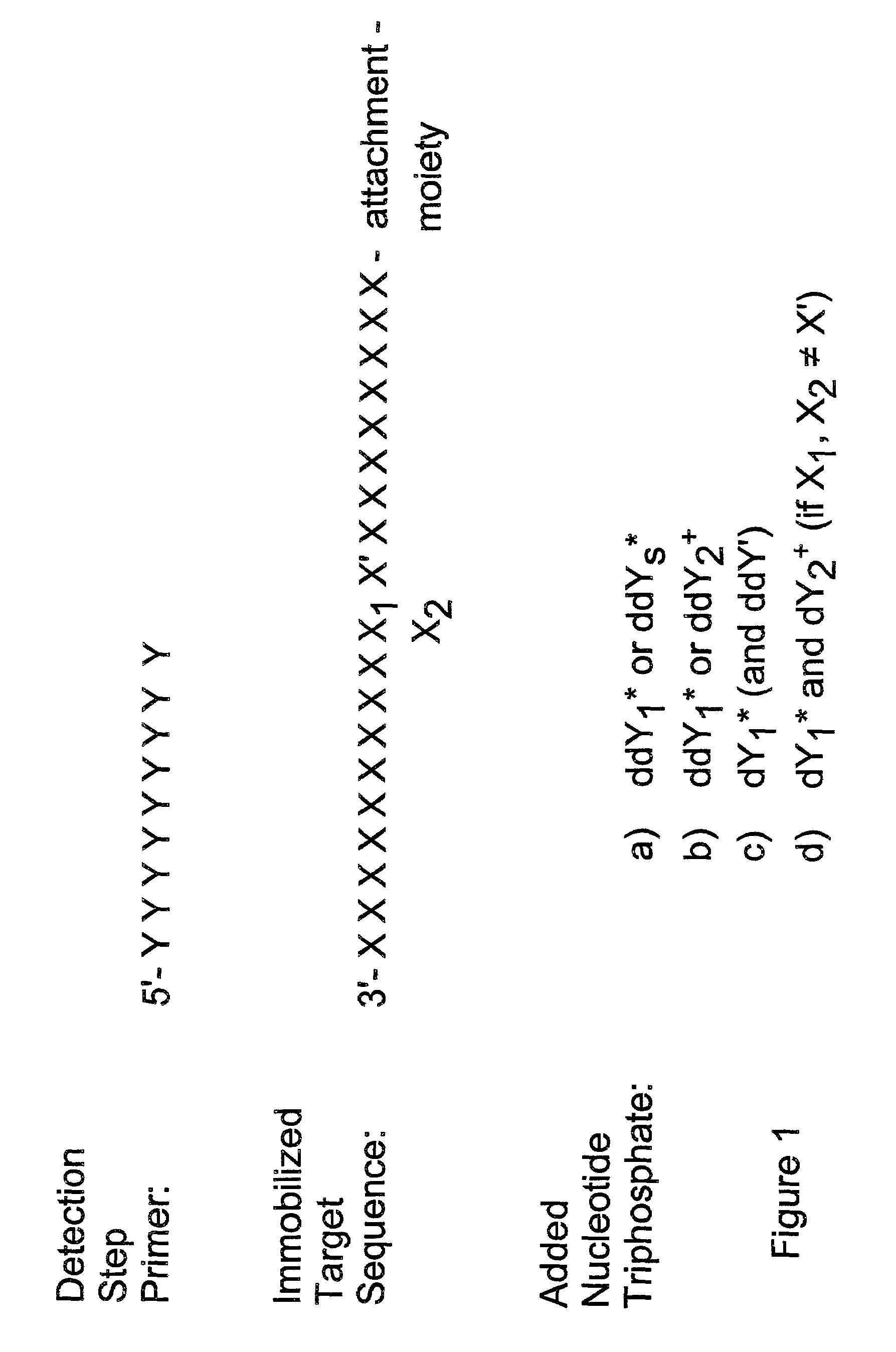
InactiveUS7132235B2Improve automationFew and easily procedureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide variationNucleotide sequencing
Detection of variable nucleotide(s) is based on primer extension and incorporation of detectable nucleoside triphosphates. By selecting the detection step primers from the region immediately adjacent to the variable nucleotide, this variation can be detected after incorporation of as few as one nucleoside triphosphate. Labelled nucleoside triphosphates matching the variable nucleotide are added and the incorporation of a label into the detection step primer is measured. The selection of the detection step primer is important to the method according to this invention and is dependent on the nucleotide sequence of interest. The detection step primers are preferably selected so as to span the region immediately toward the 3′ end from the variable nucleotide to be detected. The detection step primers can also be complementary to a sequence beginning several nucleotides removed from the variable nucleotide. The only limitation concerning the position of the detection step primers is that the sequence between the 3′ end of the detection step primer and the variable nucleotide to be detected must not contain a nucleotide residue of the same type as the one to be detected. The detection step primers can equally well be chosen to be complementary to either the coding or non-coding strands of the nucleotide sequence of interest.
Owner:ORCHID CELLMARK INC
Method for determining specific nucleotide variations
InactiveUS7026117B2Improve automationFew and easily procedureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide variationNucleotide sequencing
Detection of variable nucleotide(s) is based on primer extension and incorporation of detectable nucleoside triphosphates. By selecting the detection step primers from the region immediately adjacent to the variable nucleotide, this variation can be detected after incorporation of as few as one nucleoside triphosphate. Labelled nucleoside triphosphates matching the variable nucleotide are added and the incorporation of a label into the detection step primer is measured. The selection of the detection step primer is important to the method according to this invention and is dependent on the nucleotide sequence of interest. The detection step primers are preferably selected so as to span the region immediately toward the 3′ end from the variable nucleotide to be detected. The detection step primers can also be complementary to a sequence beginning several nucleotides removed from the variable nucleotide. The only limitation concerning the position of the detection step primers is that the sequence between the 3′ end of the detection step primer and the variable nucleotide to be detected must not contain a nucleotide residue of the same type as the one to be detected. The detection step primers can equally well be chosen to be complementary to either the coding or non-coding strands of the nucleotide sequence of interest.
Owner:LAB OF AMERICA HLDG
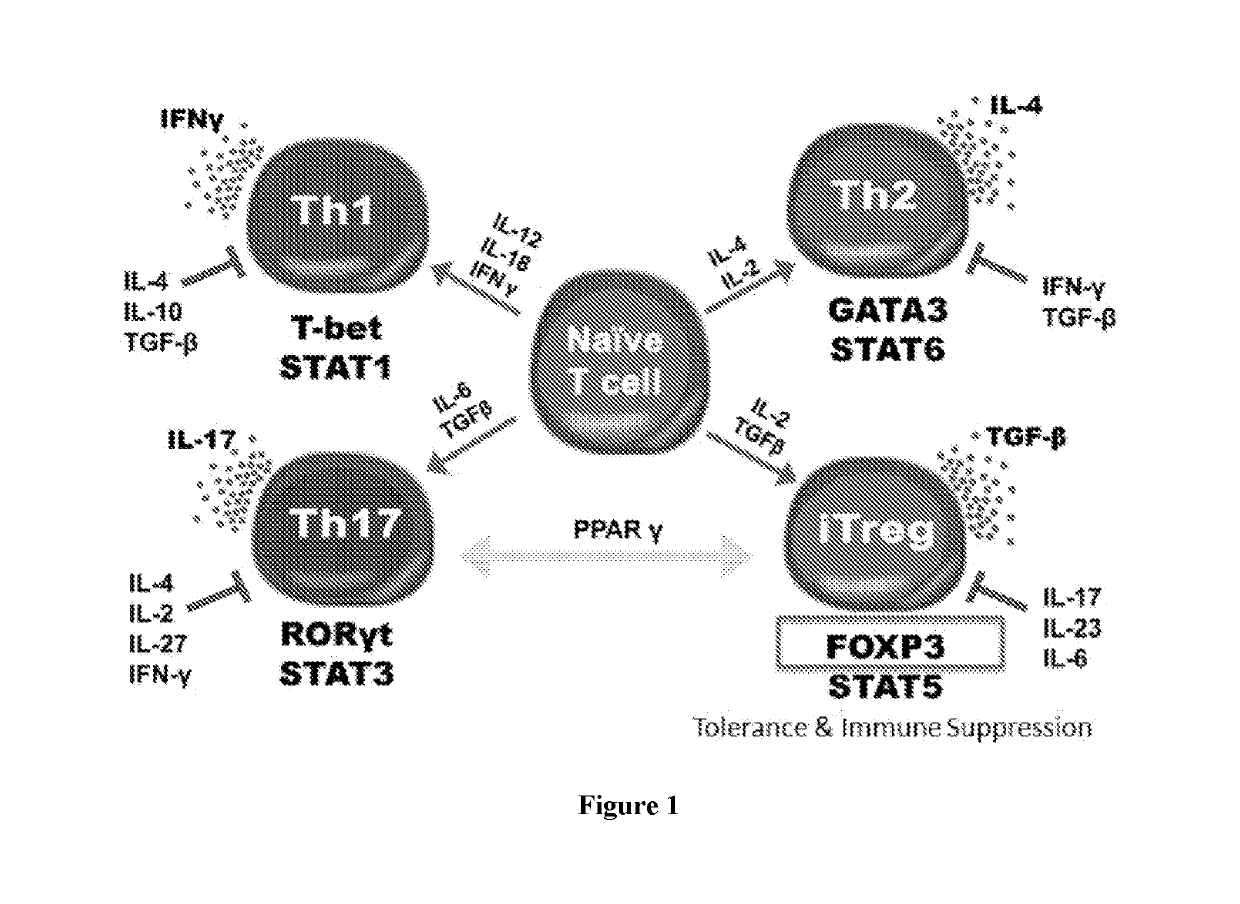
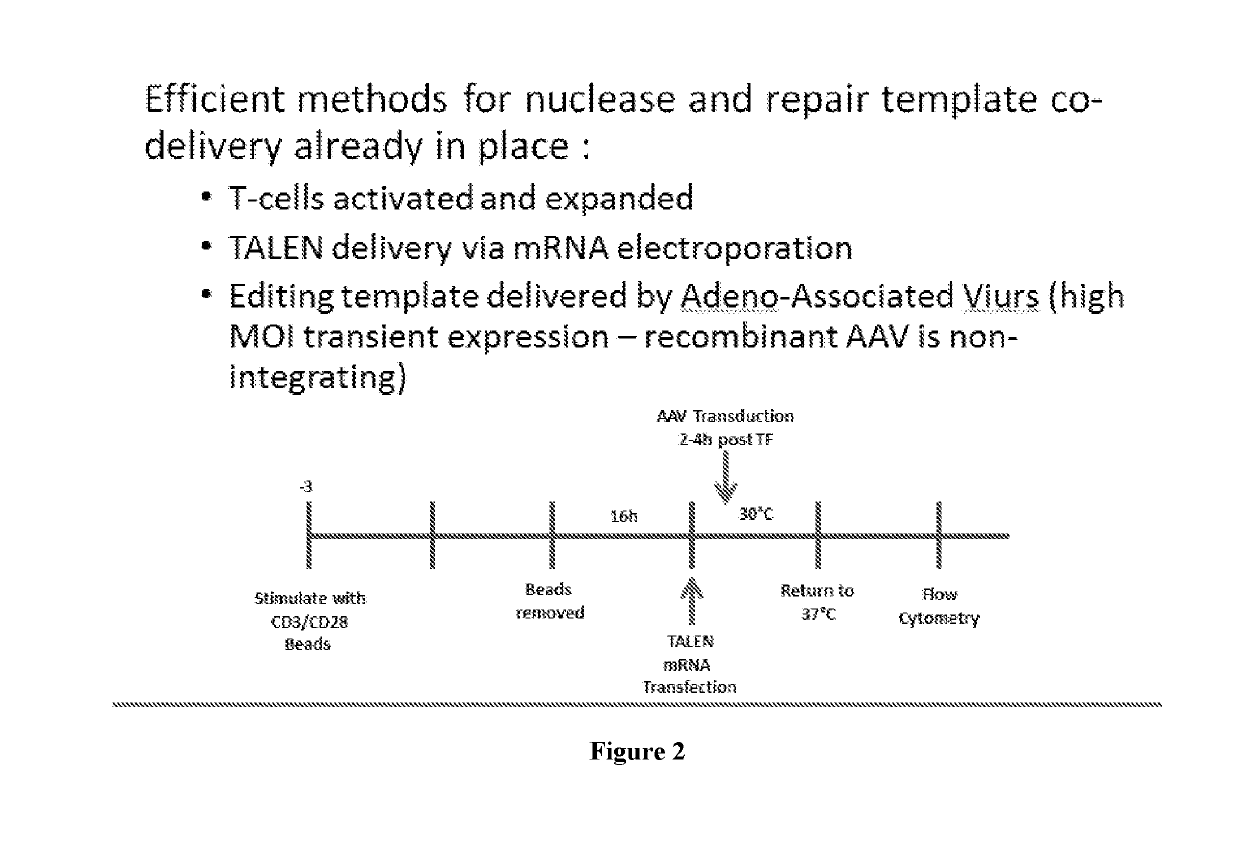
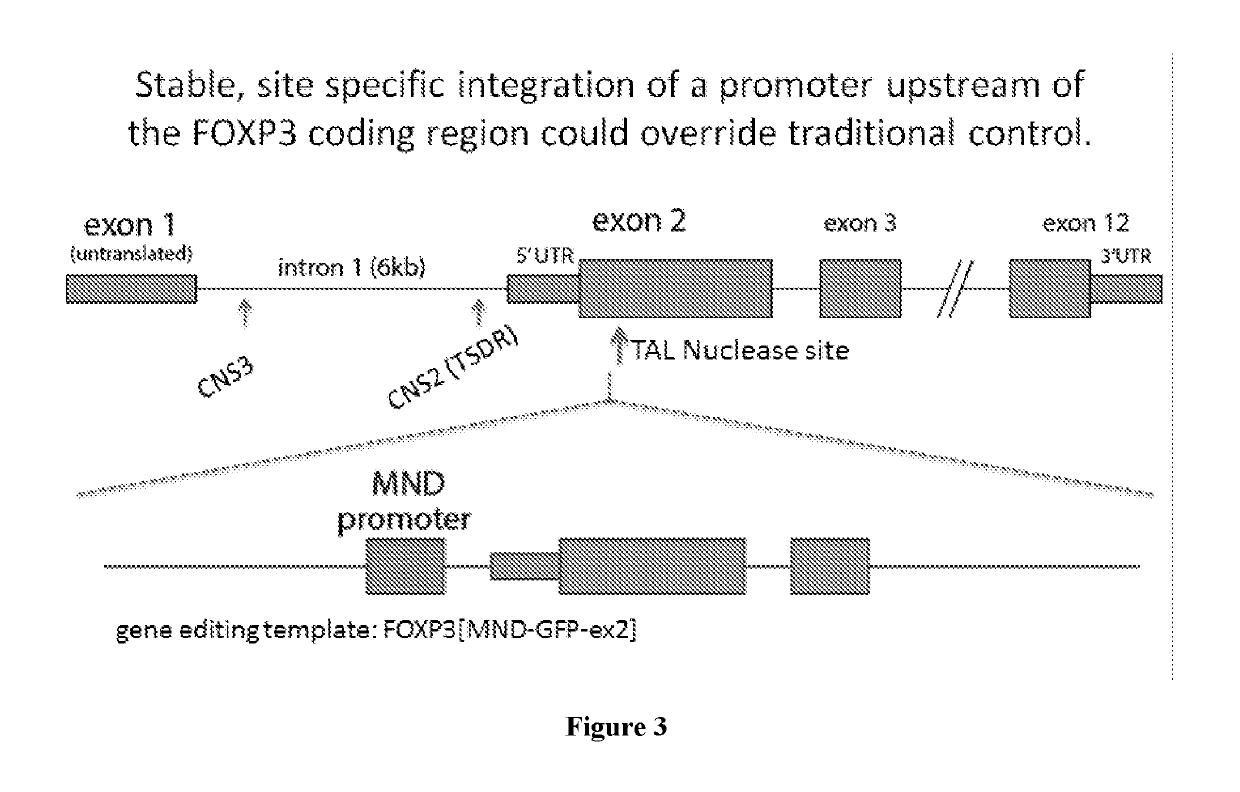
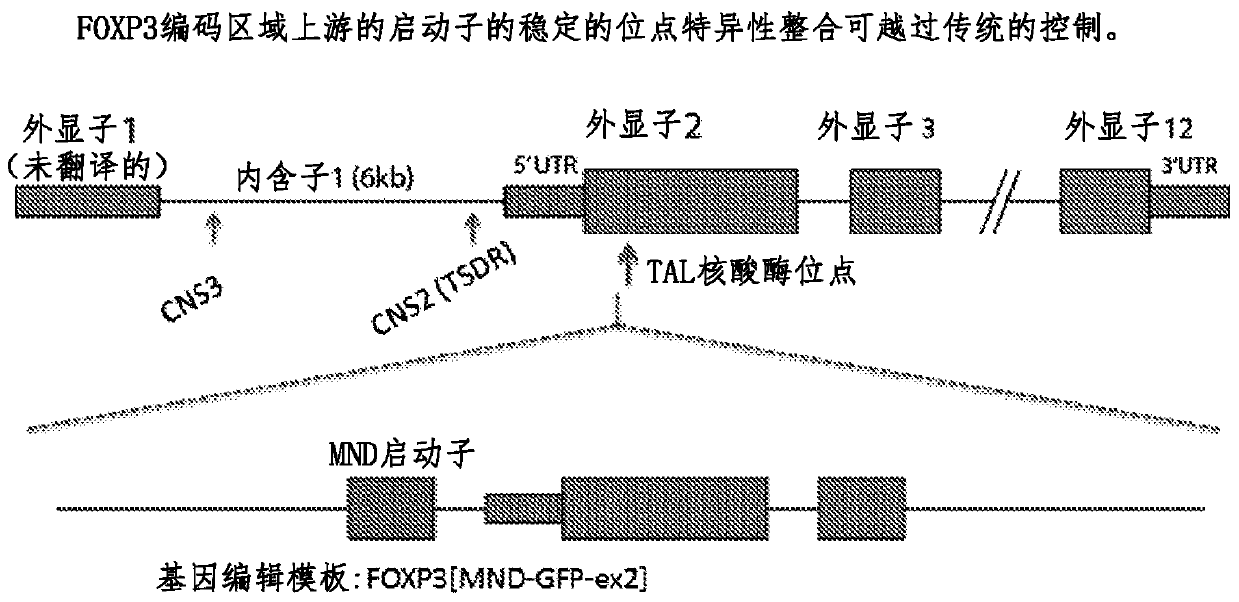
Method for treating autoimmune disease using cd4 t-cells with engineered stabilization of expression of endogenous foxp3 gene
PendingUS20190247443A1Stable expressionImprove propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseNucleotide
Disclosed are methods of making a genetically cell that expressed FOXP3 and methods of treatment. In some embodiments, the method can providing a first nucleotide sequence, wherein the first nucleotide sequence comprises a coding strand, the coding strand comprising one or more regulatory elements and a FOXP3 gene or portion thereof providing a nuclease and performing a gene editing process on the first nucleotide sequence, which edits said one or more regulatory elements, and optionally edits the FOXP3 gene or portion thereof. Methods of treating a subject suffering from an autoimmune disease and subjects suffering the effects of organ transplantation are also provided.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL (DBA SEATTLE CHILDRENS RES INST)
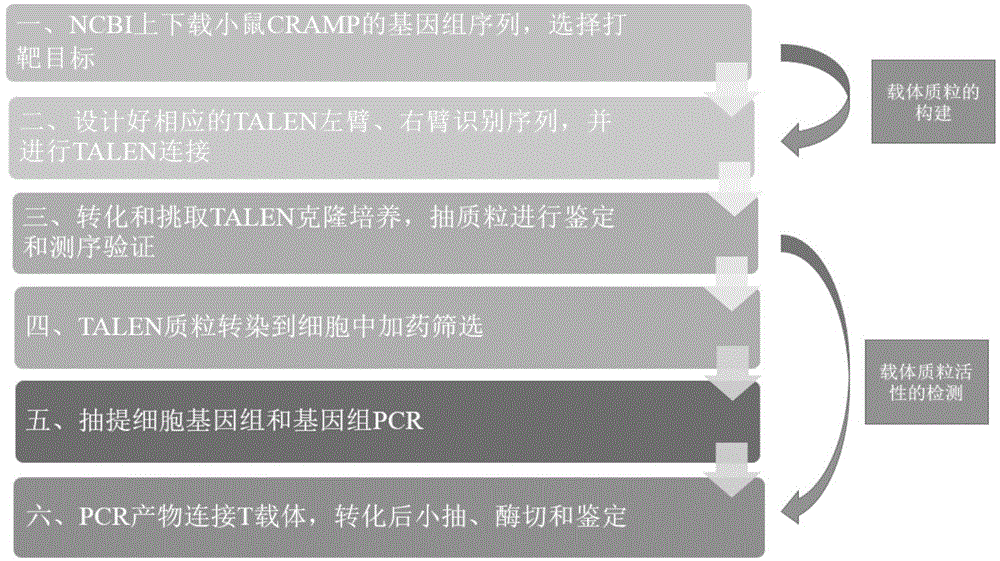
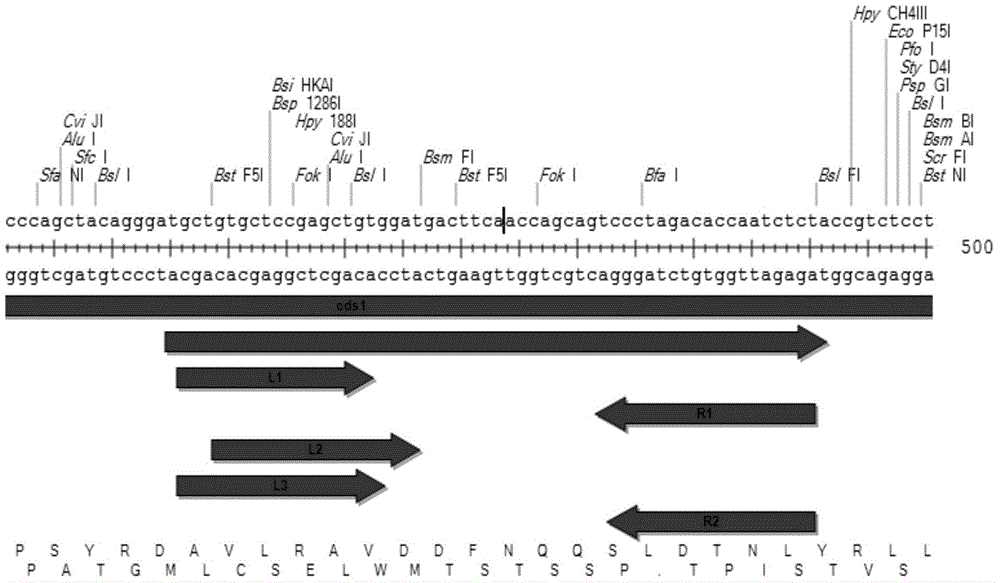
Method for establishing plasmid capable of knocking out mouse CRAMP gene by use of TALEN technique
InactiveCN104694539AShort cycleHigh transfection efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionRecognition sequenceExpression vector
The invention discloses a TALEN recognition sequence pair for directionally knocking out a mouse cell CRAMP gene and a carrier plasmid established by use of the recognition sequences. The gene sequences of the TALEN recognition sequence pair are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 9 and SEQ ID NO. 12, respectively. The carrier plasmid comprises a TALEN chain L and a TALEN chain R; the TALEN chain L is encoded by the bases of the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the TALEN chain R is encoded by the bases of the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses a preparation method of an endogenous CRAMP gene knockout cell; the nucleotide sequences encoding the TALEN chain L and the TALEN chain R are inserted into prokaryotic expression vectors, respectively, before transfection into the cell containing the endogenous CRAMP gene, and then the endogenous CRAMP gene knockout cell can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
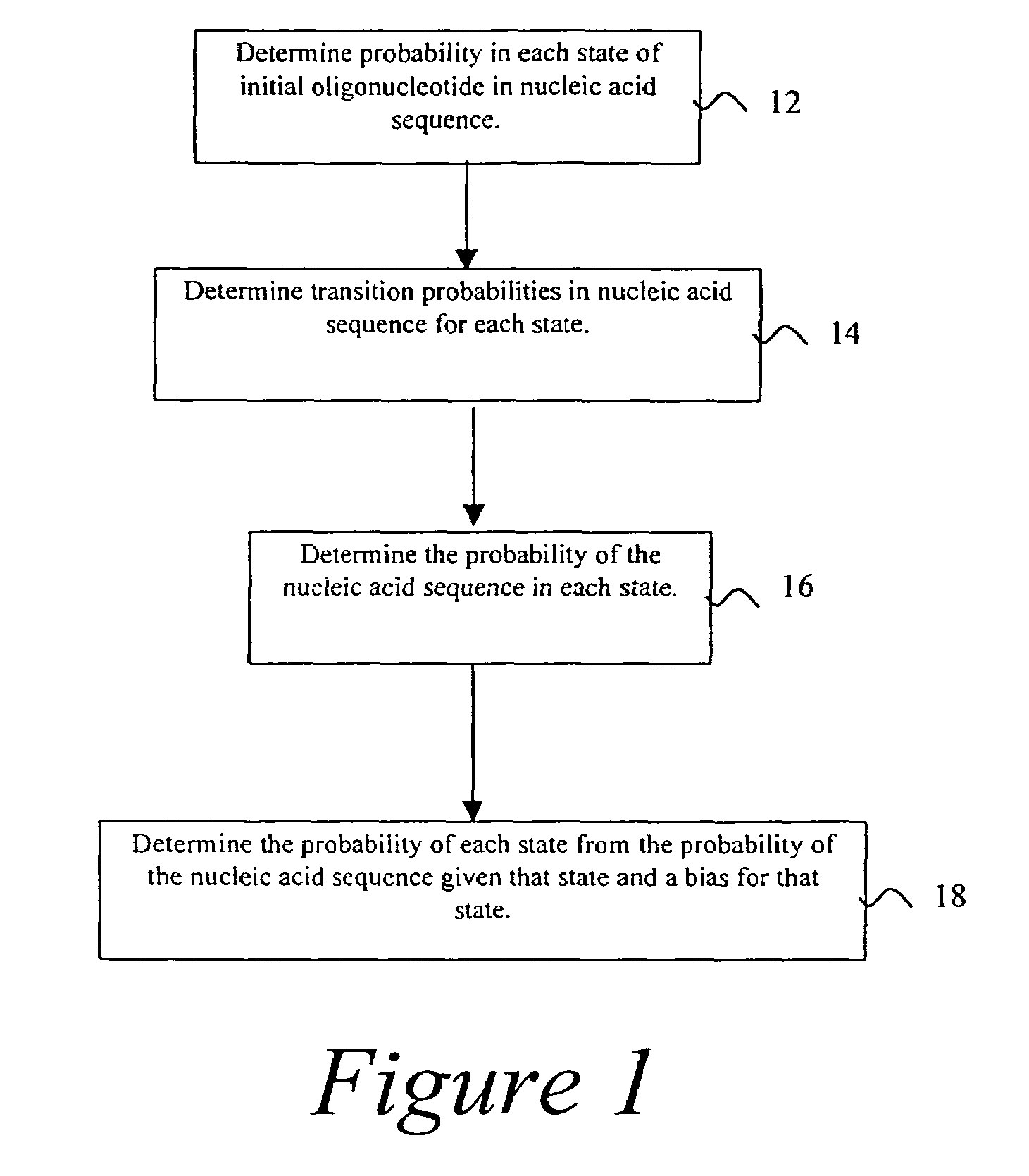
Probabilistic method for determining nucleic acid coding features
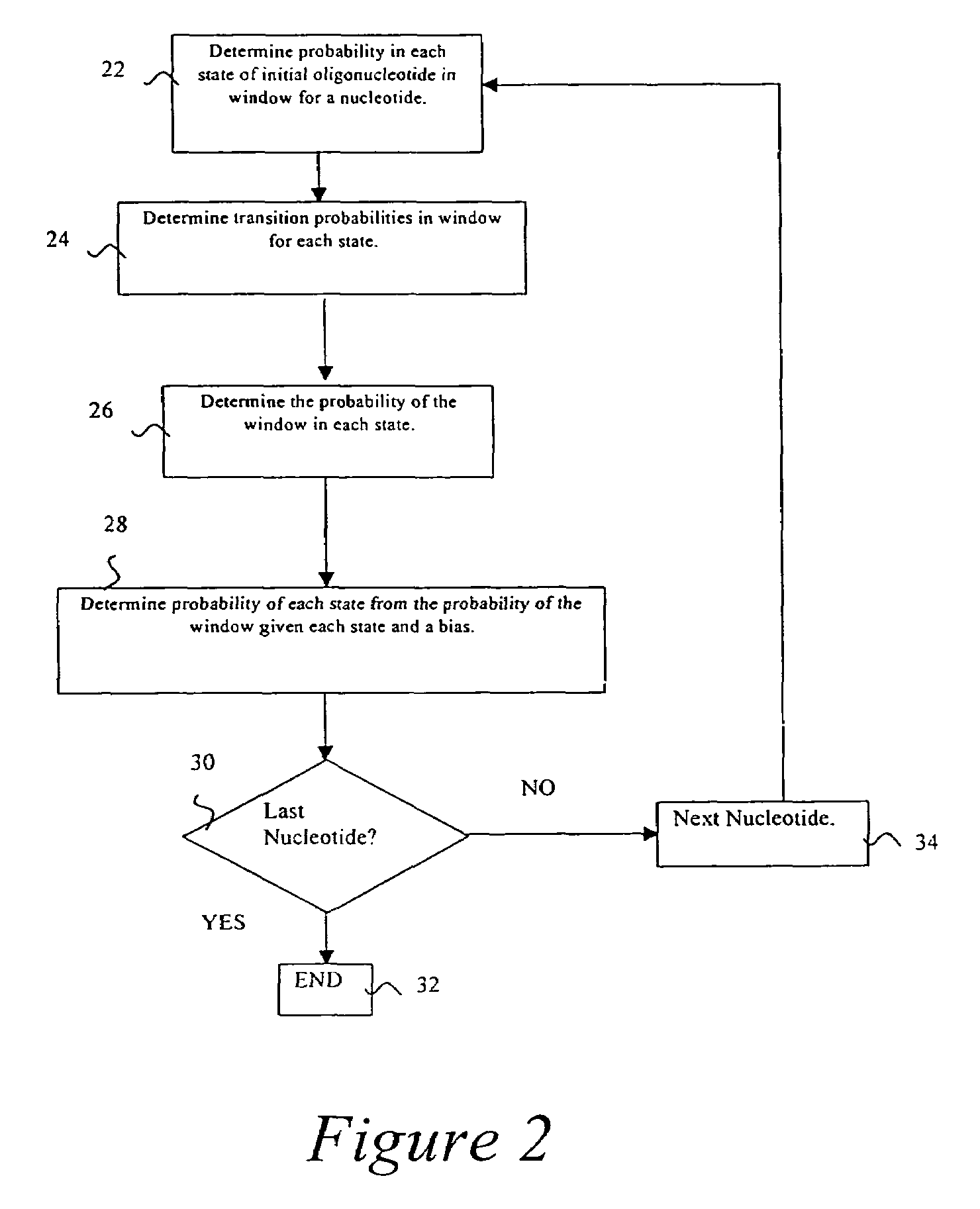
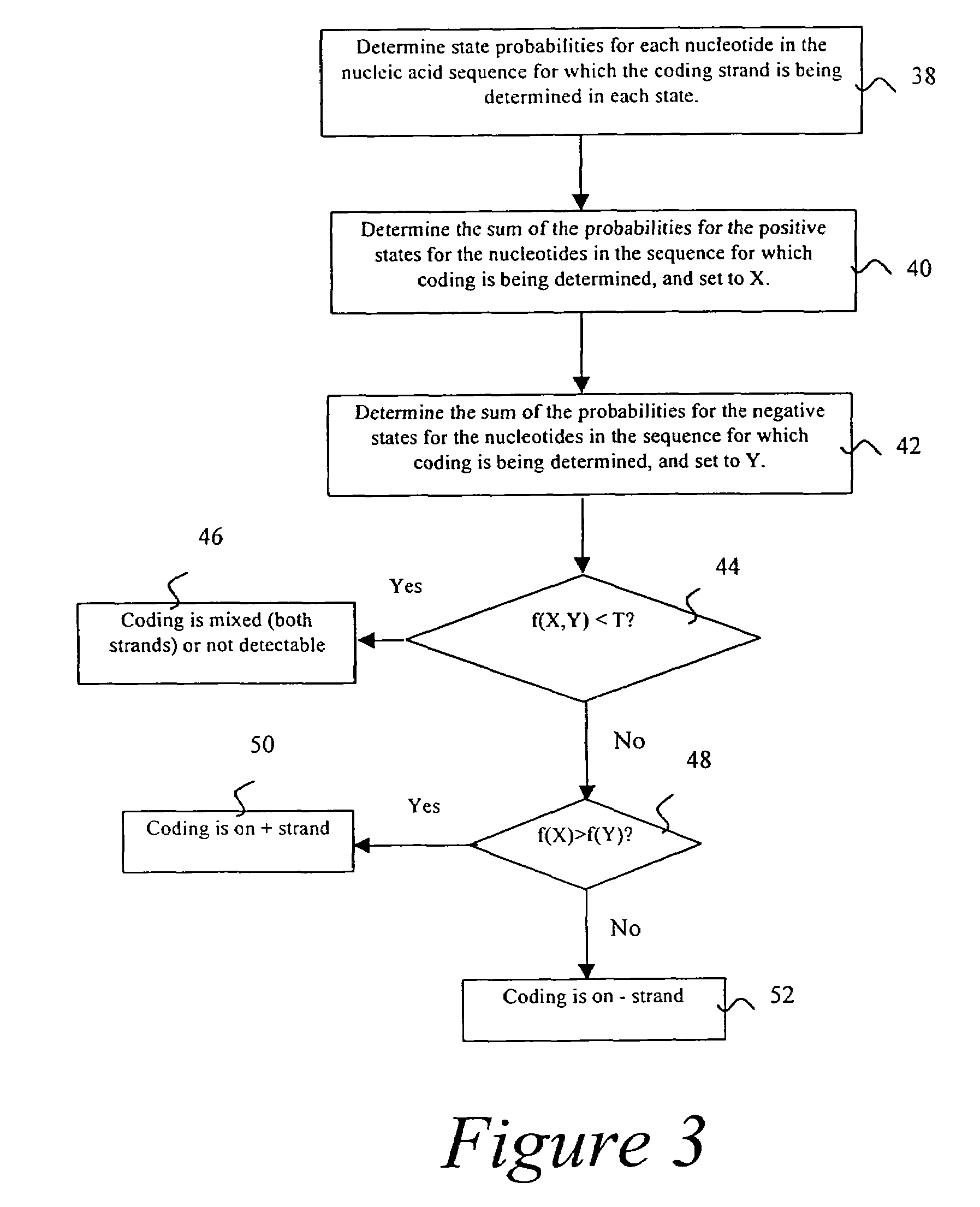
InactiveUS7444243B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesProbabilistic methodOpen reading frame
The present invention is in the field of bioinformatics, particularly as it pertains to gene prediction. More specifically, the invention relates to the probabilistic analysis of nucleic acid sequences for the determination of coding features, including determination of state probabilities for each nucleotide in a nucleic acid sequence, determination of coding strand, determination of open reading frame extent, determination of insertion and deletion location, determination of exon location, and determination of protein sequence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Preparation method and application of target protein
InactiveCN103014048AHormone peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetNucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation and application of target protein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining a nucleotide sequence fragment of the target protein; constructing a recombinant expression vector of the target protein; inductively expressing and purifying the target protein; cleaving; introducing a single cleavage site to the downstream of the nucleotide sequence fragment of the target protein; synthesizing a coding strand and a template strand; and hybridizing the coding strand and the template strand, thus obtaining the target protein, wherein a recognition site for monomer cleavage is introduced while synthesizing the coding strand and the template strand; and preferably, the target protein can be a human nerve growth factor, thymosin, Huwentoxin-XI and Huwena analgesic peptide. The target protein prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention is high in expression quantity and easy to purify; the gene expression product is the target protein monomer and brings no extra amino acid residue, and thus the high biological activity of the target protein is ensured, and the multi-copy cleavage cost is saved; and the target protein is simple to purify and easy for mass production.
Owner:SINOBIOWAY BIOMEDICINE
Method for treating autoimmune disease using cd4 t-cells with engineered stabilization of expression of endogennous foxp3 gene
ActiveCN110139675APeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAutoimmune conditionNucleotide
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL (DBA SEATTLE CHILDRENS RES INST)
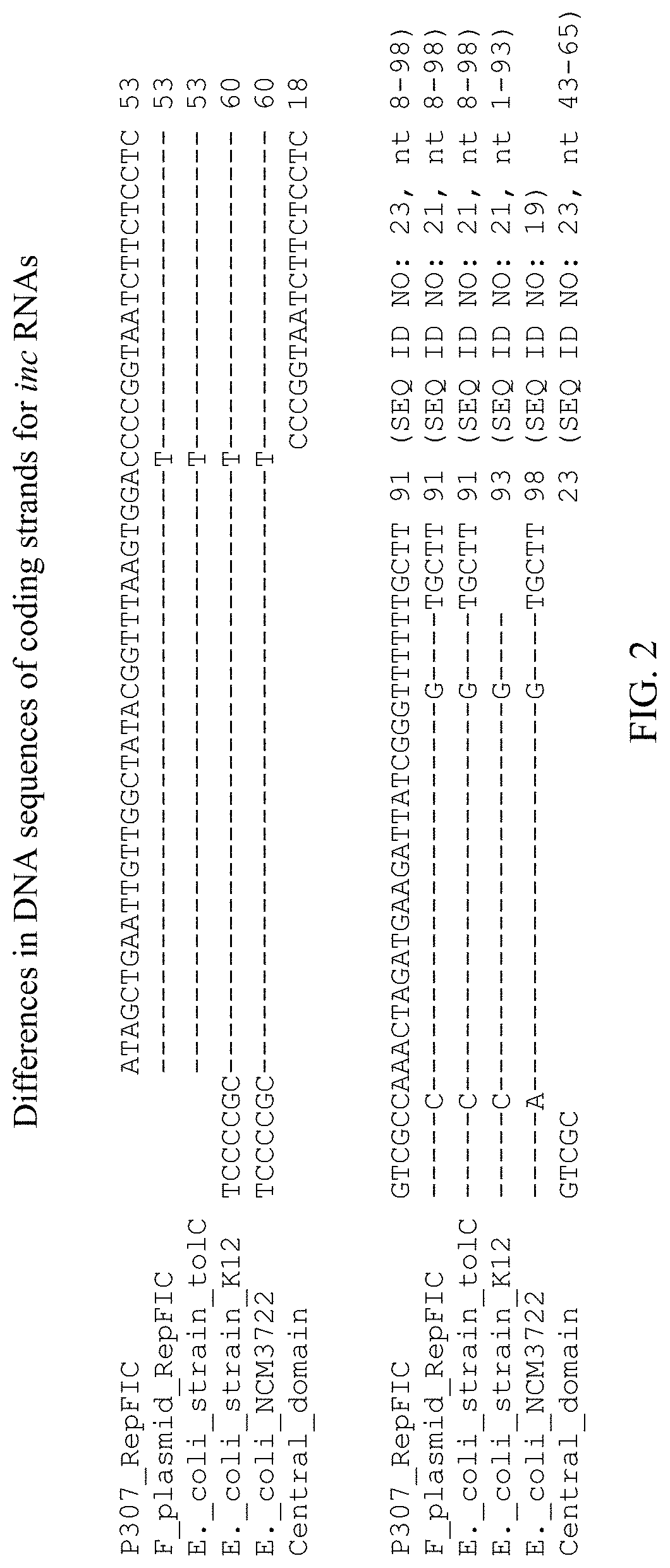
Nucleic Acid Molecules Comprising a Variant inc Coding Strand
ActiveUS20200048642A1High copy numberIncrease productionTransferasesNucleic acid vectorOrigin of replicationMicroorganism
A nucleic acid molecule comprising a variant inc coding strand is disclosed as a regulator of plasmid copy number. Also disclosed is a replicon comprising the nucleic acid molecule, a promoter, and an origin of replication. Also disclosed is a vector comprising the replicon. Also disclosed is a recombinant microorganism comprising the vector.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
The invention provides a DNA molecule comprising a multicistronic transcription unit coding for i) a polypeptide of interest, and for ii) a selectable marker polypeptide functional in a eukaryotic host cell, wherein the polypeptide of interest has a translation initiation sequence separate from that of the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest is upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide in the multicistronic transcription unit, and wherein an internal ribosome entry site is present downstream from the coding sequence for the polypeptide of interest and upstream from the coding sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide, and wherein the nucleic acid sequence coding for the selectable marker polypeptide in the coding strand comprises a GTG or a TTG start codon. Also provided are methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, such host cells comprising DNA molecules of the invention. Further provided is the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules of the invention.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
Described is a DNA molecule comprising an open reading frame sequence encoding a selectable marker polypeptide, wherein the DNA molecule in the coding strand comprises a translation start sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide having a GTG or TTG start codon, and wherein the ORF sequence that encodes the selectable marker protein has been mutated to replace at least half of its CpG dinucleotides as compared to the native ORF sequence that encodes the selectable marker protein. Further provided are such DNA molecules wherein the ORF sequence that encodes a selectable marker polypeptide is part of a multicistronic transcription unit that further comprises an open reading frame sequence encoding a polypeptide of interest. Also described are methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, wherein the host cells comprise the DNA molecules described herein. Further provided is the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules described herein.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
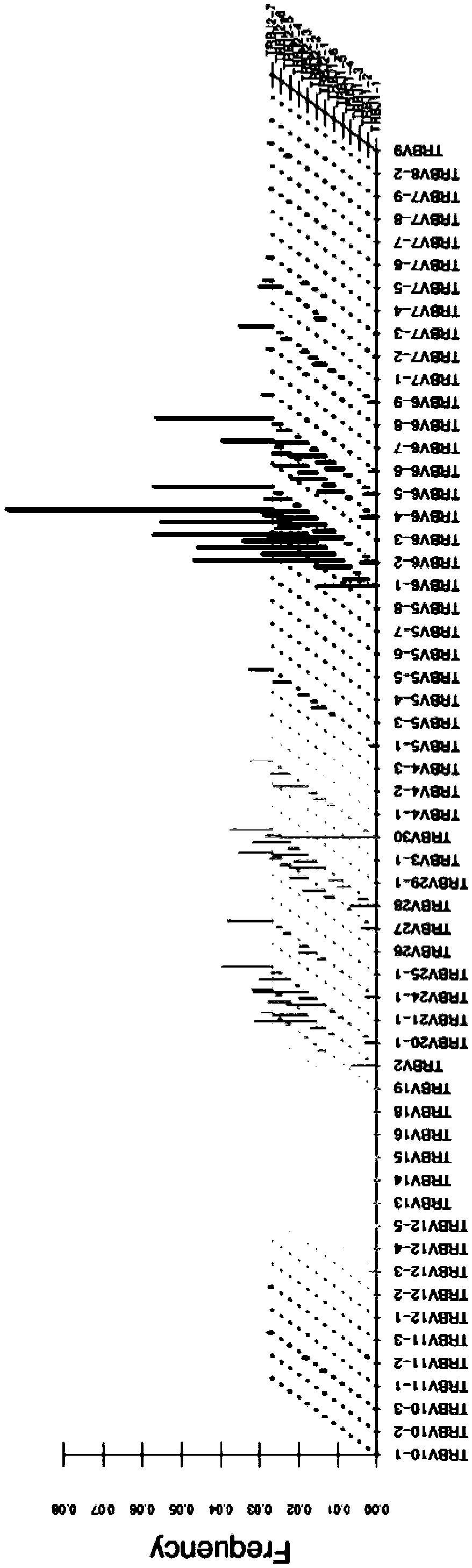
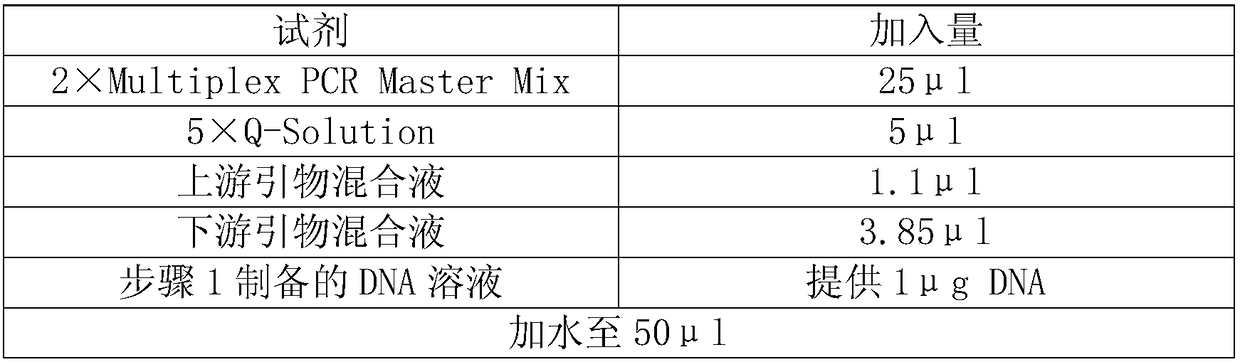
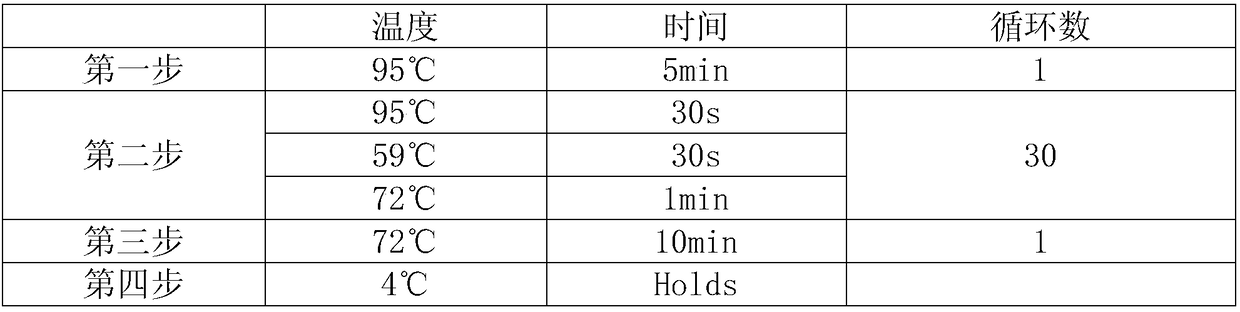
Method for detecting human DNA TCR beta chain immune repertoire based on high-throughput sequencing and specific primer group thereof
InactiveCN109486926AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNAHigh throughput sequence
The invention discloses a method for detecting a human DNA TCR beta chain immune repertoire based on high-throughput sequencing and a specific primer group thereof. The invention protects a primer group, which comprises 45 primers as shown from sequence 1 to sequence 45 in a sequence table. The invention further protects a method for establishing a DNA library, which sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) performing PCR amplification by adopting a primer group and using the genome DNA of a to-be-detected sample as a template, and reclaiming an amplified product; and (2) performing PCRamplification by adopting a universal upstream primer and a universal downstream primer of a sequencing platform and taking the amplified product as a template, and reclaiming the amplified product,which is the DNA library encoding TCR beta chain immune repertoire in a human DNA. The primer group can realize multiple PCR amplification in a tube. The TCR beta chain immune repertoire acquired by adopting the primer group or method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, high repeatability and low experiment cost.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
RNA molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140316126A1High expressionSugar derivativesVector-based foreign material introductionNon-coding RNANucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a method of designing a short RNA molecule to increase the expression of a target gene in a cell through the down-regulation of a non-coding RNA transcript, said method comprising the steps of: a) obtaining the nucleotide sequence of the coding strand of the target gene, at least between 200 nucleotides upstream of the gene's transcription start site and 200 nucleotides downstream of the gene's transcription start site; b) determining the reverse complementary RNA sequence to the nucleotide sequence determined in step a); and c) designing a short RNA molecule which is the reverse complement or has at least 80% sequence identity with the reverse complement of a region of the sequence determined in step b); wherein said method does not include a step in which the existence of said non-coding RNA transcript is determined; and to such short RNA molecules and uses thereof.
Owner:MINA THERAPEUTICS
Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
Described is a DNA molecule comprising an open reading frame sequence that encodes a selectable marker polypeptide, wherein the DNA molecule in the coding strand comprises a translation start sequence for the selectable marker polypeptide having a GTG start codon or a TTG start codon, and wherein the ORF sequence that encodes the selectable marker protein has been mutated to replace at least half of its CpG dinucleotides as compared to the native ORF sequence that encodes the selectable marker protein. Further provided are such DNA molecules wherein the ORF sequence that encodes a selectable marker polypeptide is part of a multicistronic transcription unit that further comprises an open reading frame sequence encoding a polypeptide of interest. Also described are methods for obtaining host cells expressing a polypeptide of interest, wherein the host cells comprise the DNA molecules described herein. Further provided is the production of polypeptides of interest, comprising culturing host cells comprising the DNA molecules described herein.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
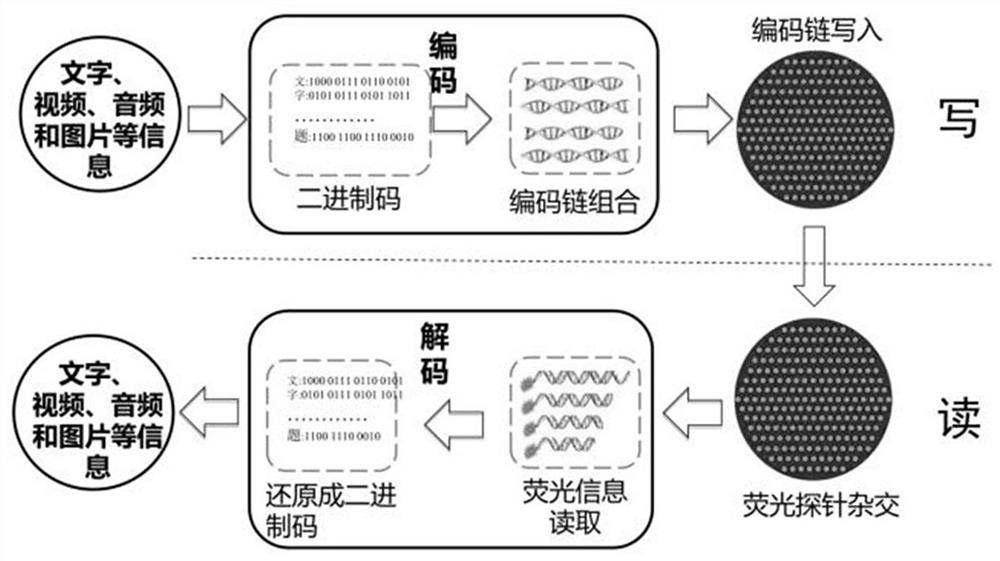
DNA hybridization information storage encryption method based on addition and removal of coding chain hairpin structure
ActiveCN113539379ARealize hard encryption functionAvoid accessDigital data protectionHybridisationComputer hardwareA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA storage encryption method based on specific removal of a hairpin structure of a coding chain. The DNA storage encryption method comprises a set of combination of a DNA coding chain with a hairpin structure and a restriction enzyme recognition site and a restriction enzyme, wherein the specific restriction enzyme can cut off the hairpin structure of the specific coding chain, so that the coding region is exposed and activated. In the information reading process, if a DNA coding chain is not correctly activated, the information cannot be effectively read due to the fact that hybridization is hindered by a hairpin structure. When the method is implemented, a sender selects one group from a code chain combination for data writing, sends a storage disk to a receiver, and sends a secret key (namely correct incision enzyme information) by using another confidential way. After receiving the secret key, the receiver can correctly process and activate the coding chain, but cannot activate the coding chain due to wrong processing, and even may cause self-destruction of the memory disk. Hard encryption of the DNA hybrid storage technology is realized, and application of the storage technology is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A gene sequence and its application
InactiveCN104911193BHigh content of maltooligosaccharidesHigh in Total Vitamin EFermentationGenetic engineeringEmbryoNovel gene
The present invention provides a new gene sequence and its application. The gene sequence includes the following characteristics: the first deoxynucleoside of the first codon of the coding chain of the giant embryo allele corresponding to the normal embryo rice "Nipponbare" An adenine deoxynucleotide is inserted between the upstream ‑777 and ‑778 deoxynucleotides of the acid, and at +125 downstream of the first deoxynucleotide of the first codon in the coding strand, a guanine Deoxynucleotides are mutated to adenine deoxynucleotides. The GABA content and vitamin E content of rice brown rice homozygous for this gene sequence are significantly higher than those of rice brown rice without this gene sequence. At the same time, the glutathione and maltooligosaccharide content in brown rice are also significantly higher than those without this gene sequence Rice Brown Rice Raised. Therefore, by transferring the gene sequence into normal embryo rice and obtaining homozygous giant embryo offspring, a new variety of giant embryo rice with a giant embryo phenotype and the content of various nutrients in brown rice can also be significantly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com