Selection of host cells expressing protein at high levels
a high-level protein and host cell technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and biotechnology, to achieve the effect of rapid and efficient creation of stable mammalian cell lines and increased probability of high expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction and Testing of a Zeocin-Resistance Gene Product with No Internal Methionine
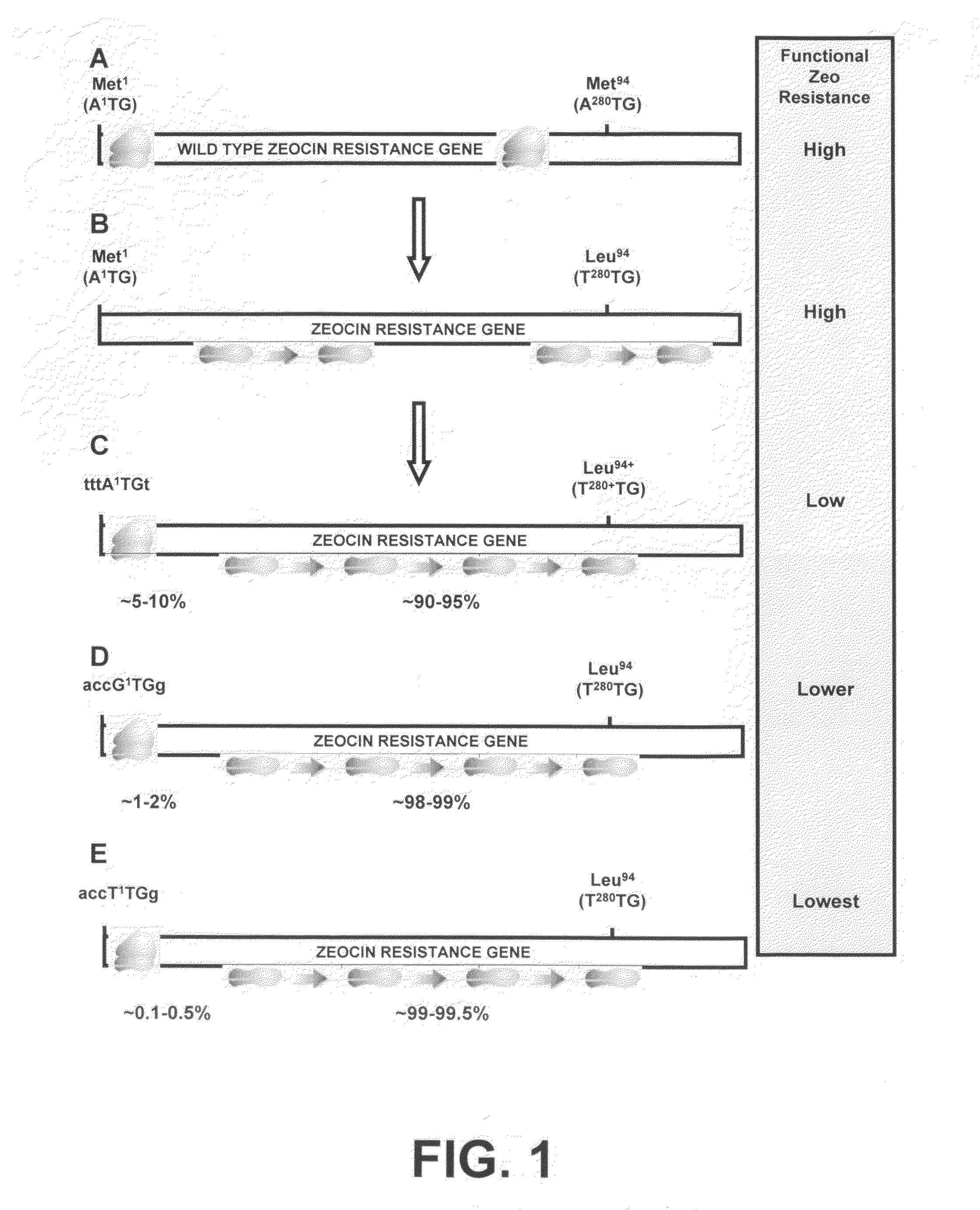
[0198]The basic idea behind the development of the novel selection system of the incorporated '525 application is to place the gene encoding the resistance gene upstream of a gene of interest, and one promoter drives the expression of this bicistronic mRNA. The translation of the bicistronic mRNA is such that only in a small percentage of translation events the resistance gene will be translated into protein and that most of the time the downstream gene of interest will be translated into protein. Hence the translation efficiency of the upstream resistance gene is severely hampered in comparison to the translation efficiency of the downstream gene of interest. To achieve this, three steps can be taken according to the invention of the '525 application:[0199]1) within the resistance gene on the mRNA, the searching ribosome preferably should not meet another AUG, since any downstream AUG may serve ...
example 2
Creation and testing of Zeocin-d2EGFP Bicistronic Constructs with Differential Translation Efficiencies
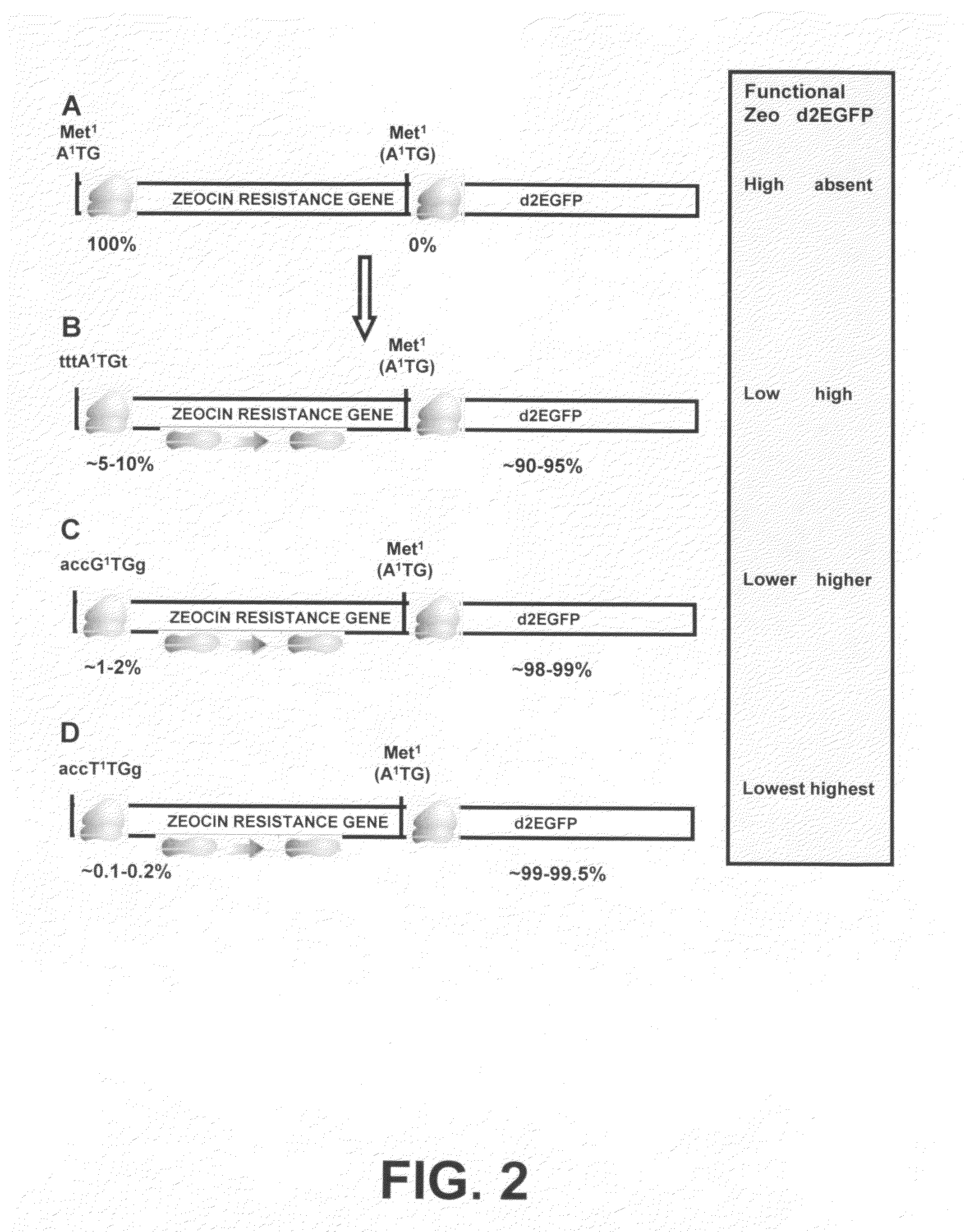
[0208]To create a bicistronic mRNA encompassing a mutated Zeocin-resistance mRNA with less translational efficiency, and the d2EGFP gene as downstream gene of interest, the start codon of the d2EGFP gene was first optimized (step 3 in Example 1). After that, the different versions of the Zeocin-resistance gene were created. The differences between these versions are that they have different start codons, with distinct translational efficiency (step 2 in Example 1, FIG. 1C-E). These different ZEOCIN®-resistance gene versions were cloned upstream of the modified d2EGFP gene (FIG. 2).
Materials and Methods
Creation of Plasmids
[0209]The d2EGFP reporter ORF was introduced into pcDNA3. The sequence around the start codon of this d2EGFP cDNA is GAATTCGG (start codon in bold; SEQ ID NO:73), which is not optimal. As a first step, d2EGFP was amplified from pd2EGFP (Clontech 6010-1) with primer...
example 3
Establishment of a Higher Number of TTG Zeo STAR Colonies and Comparison with an IRES-Zeo Construct
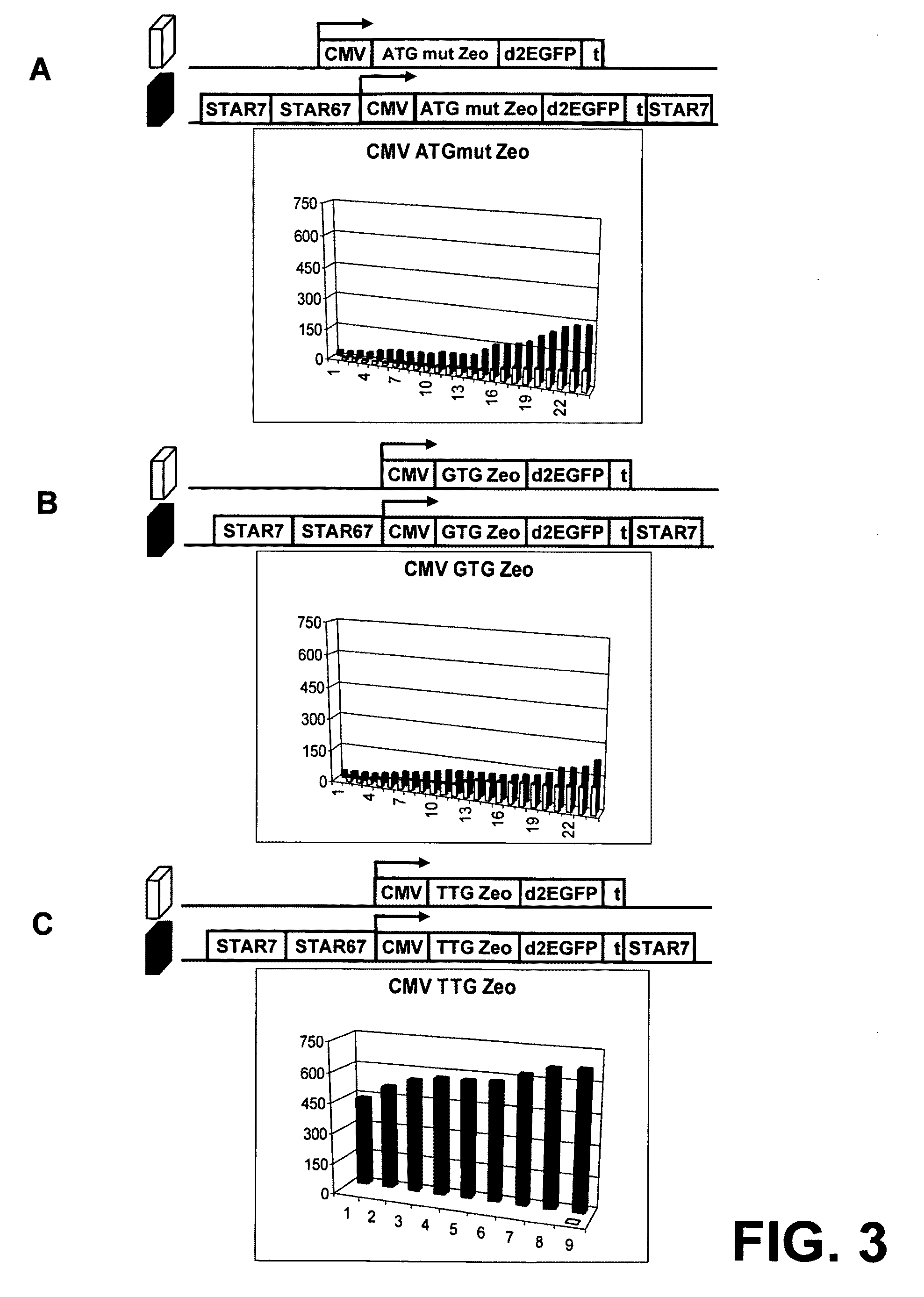
[0218]The results in example 2 indicate that the TTG Zeo has extremely stringent translation efficiency, which might be to high to convey ZEOCIN® resistance to the cells. The transfection was scaled up to test whether there would be some colonies that have such high expression levels that they survive. Scaling up the experiment could also address the question whether the high average of TTG Zeo STAR 7 / 67 / 7 would become higher when more colonies were analyzed.
Materials and Methods
[0219]CHO-K1 cells were transfected with the constructs that have the TTG Zeo gene as selection marker, with and without STAR elements 7 and 67 (FIG. 4). Transfections, selection, culturing etc were as in example 2, except that 6 times more cells, DNA and Lipofectamine 2000 were used. Transfections and selection were done in Petri dishes.
Results
[0220]FIG. 4A shows that transfection with the TTG Zeo STAR 7 / 67 / 7 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com