Method for regulating gene expression intensity on microbial chromosome by using artificial regulatory element and its library
An artificial regulation element and gene regulation technology, which can be used in the introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, etc. It can solve the problems of large metabolic load of host cells, economic infeasibility, and difficulty in carrying long DNA fragments.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Embodiment 1, the construction of Escherichia coli promoter library 1 (P-Lib1)
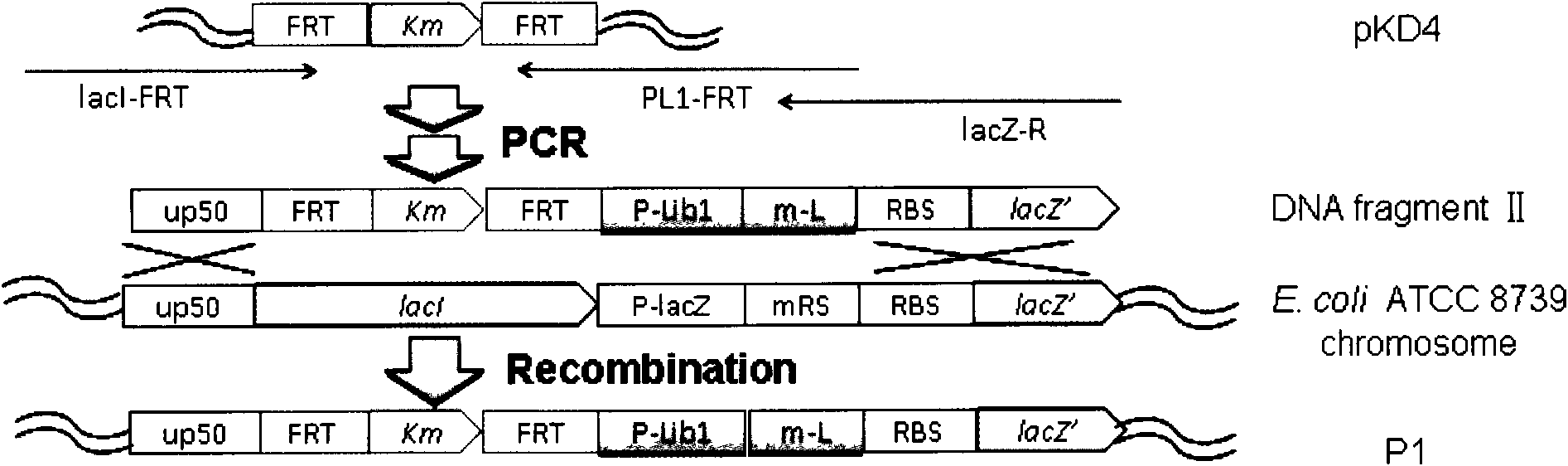
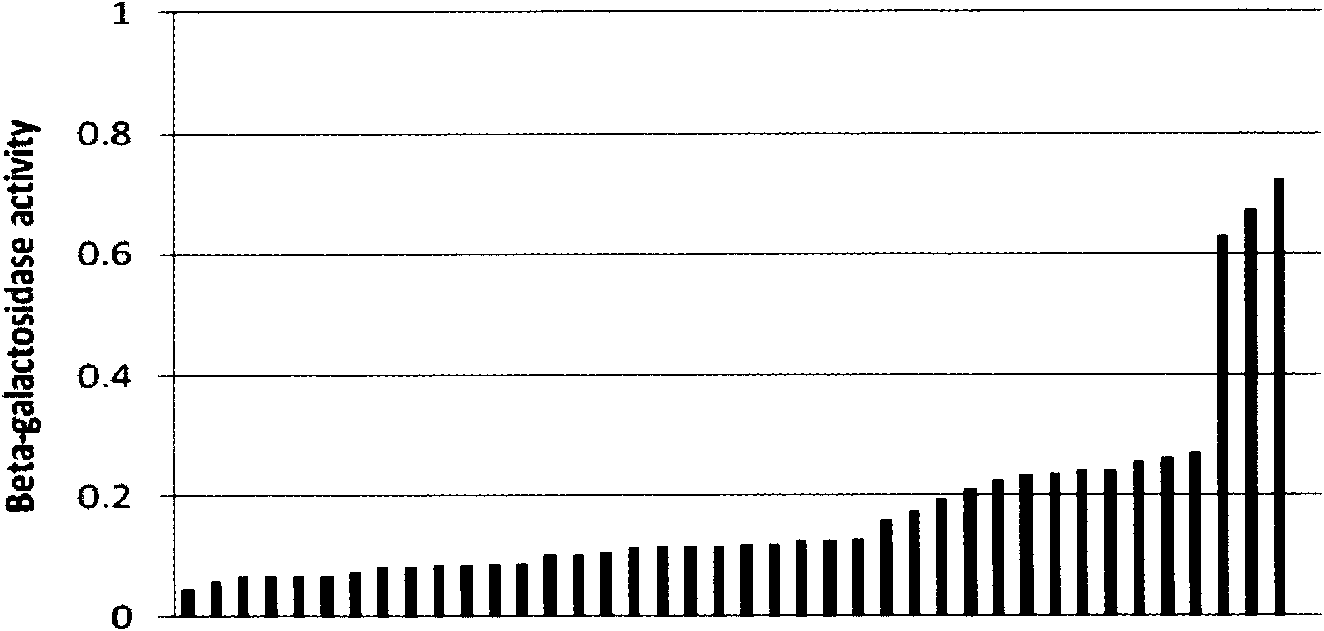
[0068] The strategy of Escherichia coli promoter library 1 (P-Lib1) construction is to combine Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 (the public can obtain from Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, and it has been recorded that Escherichia coli The non-patent literature of bacteria ATCC 8739 is Zhang, X., K.T.Shanmugam, L.O.Ingram.2010.Fermentation of glycerol tosuccinate by metabolically engineered strains of Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol, 76: 2397-2401) on chromosome The promoter of the glycosidase (lacZ) gene was replaced with an artificial promoter library 1 (P-Lib1) ( figure 1 ), and then determine the strength of each promoter by measuring the enzyme activity of β-galactosidase.
[0069] The promoter library 1 (P-Lib1) was designed based on the PL promoter sequence of bacteriophage lambda (Love et al., 1996, Gene, 176:49-53), and the sequence is sequence 1 in the sequence li...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2, the construction of Escherichia coli promoter library 2 (P-Lib2)
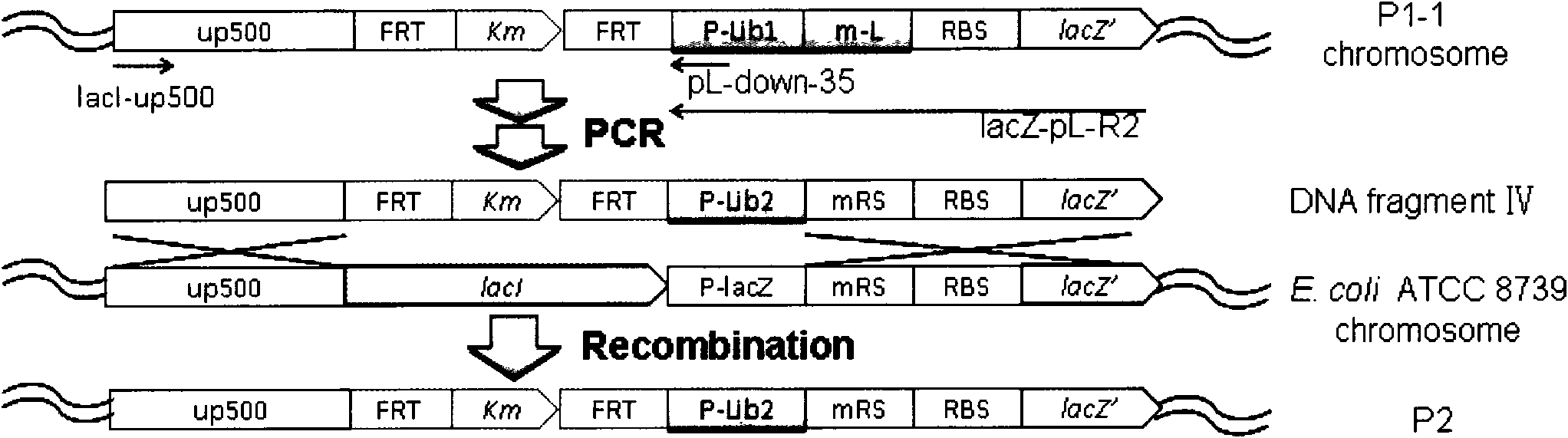
[0081] In order to improve the efficiency of homologous recombination and expand the storage capacity of the promoter library, the Escherichia coli promoter library 2 (P-Lib2) was constructed. When constructing P-Lib2, the length of the left homology arm was extended from 50 bases to 500 bases (500 bases upstream of lacI, relative to the region of -500-0 of the lacI start codon) ( image 3 ).
[0082] The sequence of P-Lib2 is sequence 2 in the sequence listing. Its characteristics are: the promoter-35 core region and the 15 bases upstream of the -35 region are the same as P-Lib1; the sequence of the -10 core region is changed to TATAAT; there are 14 random bases between the promoter-35 and the -10 core region bases and TGR. The downstream sequence of -10 core region was changed to 6 random bases.
[0083] The DNA fragment IV ( image 3 ). First, using the genomic DNA of the recombina...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Embodiment 3, the construction of Escherichia coli messenger RNA stable region library 1 (M-Lib1)
[0095] In order to improve the stability of messenger RNA after gene transcription, a messenger RNA stable region library (M-Lib1) was constructed between the promoter and ribosome binding site.
[0096] The sequence of M-Lib1 is sequence 9 in the sequence table, and it is characterized in that: the promoter sequence is the same as the P2-15 sequence of the strongest promoter in P-Lib2; the sequence of the messenger RNA stable region is 18 random bases and PmeI enzyme cutting site sequence.
[0097] The DNA fragment VI ( Figure 5 ). First, DNA fragment V was amplified using primers lacI-up500 and pL-down-3 using the genomic DNA of the recombinant strain P2-15 as a template. The primer sequences are:
[0098] pL-down-3: GGCTCAATTATATCAACG.
[0099] Then, using DNA fragment V as a template, DNA fragment VI was amplified using primers lacI-up500 and lacZ-pL-R3C. The p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com