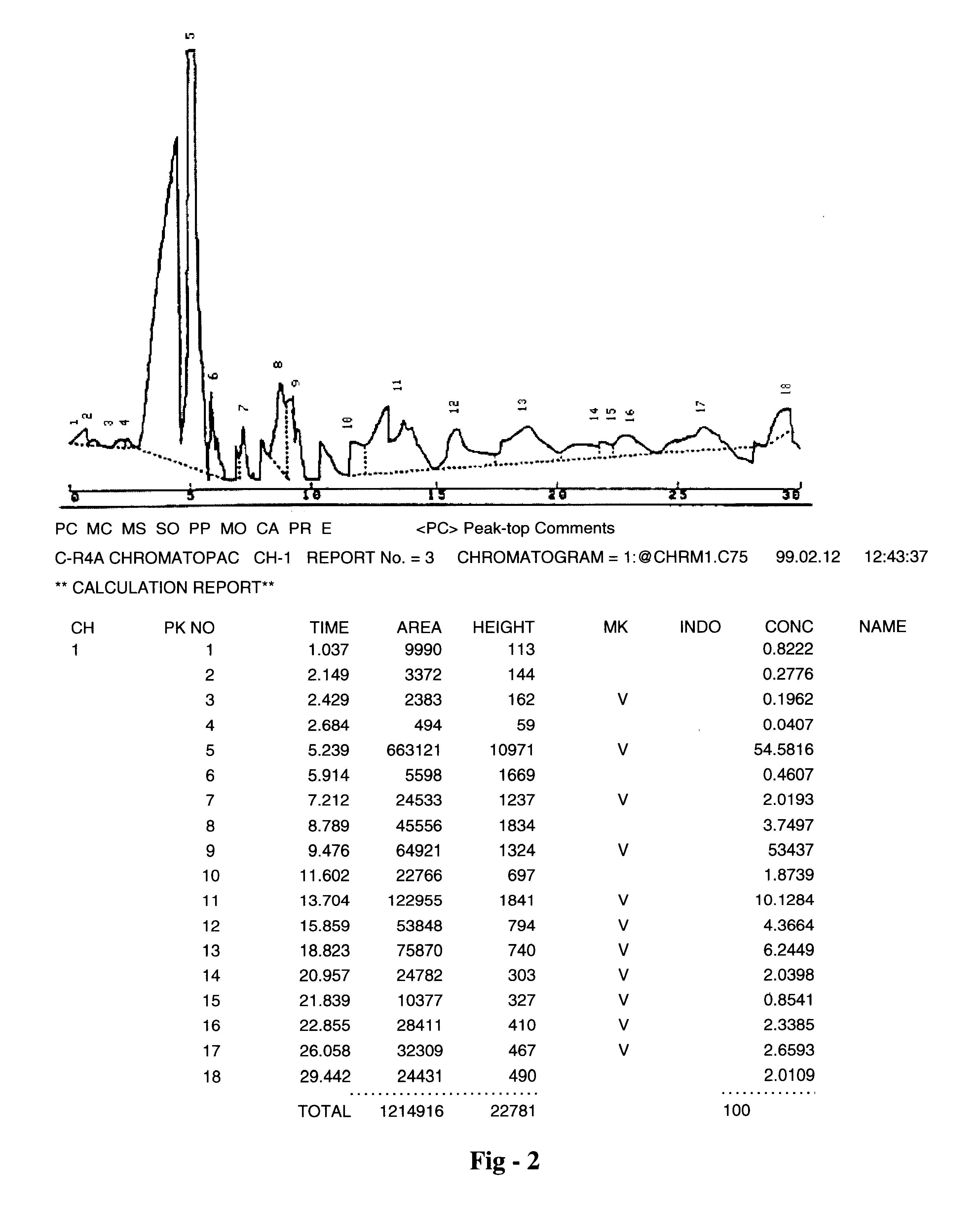
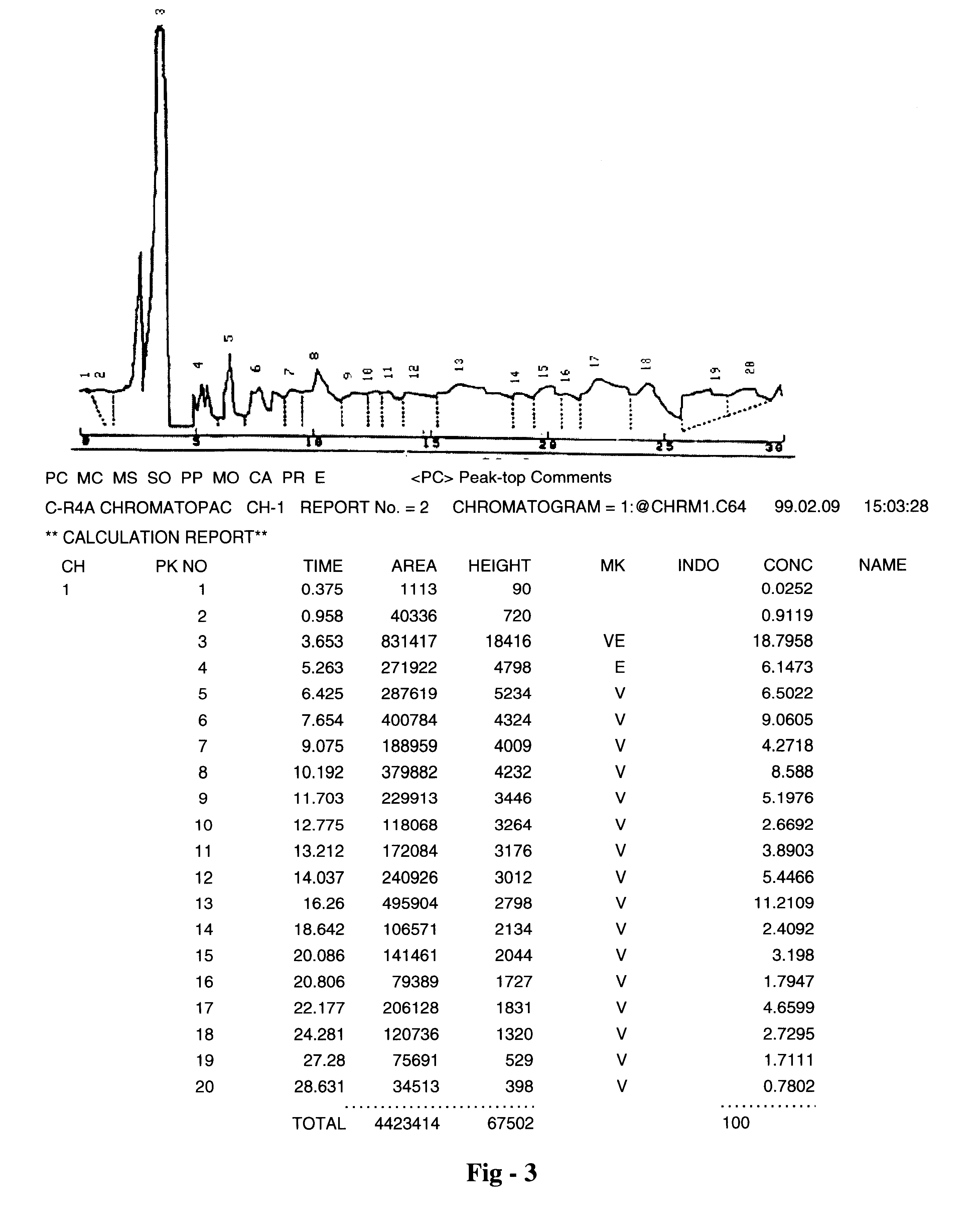
Patents
Literature
352 results about "Hepatica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hepatica (hepatica, liverleaf, or liverwort) is a genus of herbaceous perennials in the buttercup family, native to central and northern Europe, Asia and eastern North America. Some botanists include Hepatica within a wider interpretation of Anemone.
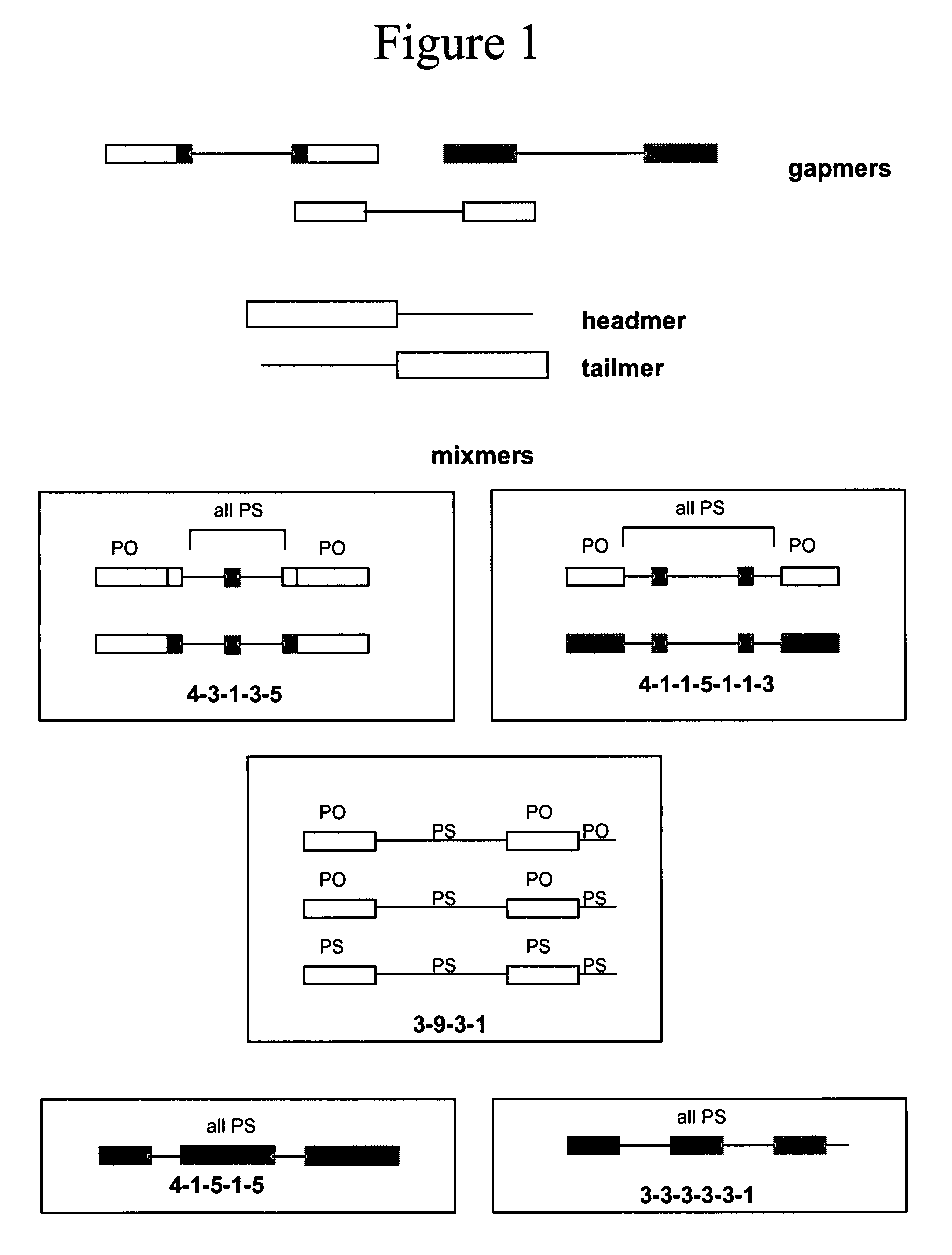
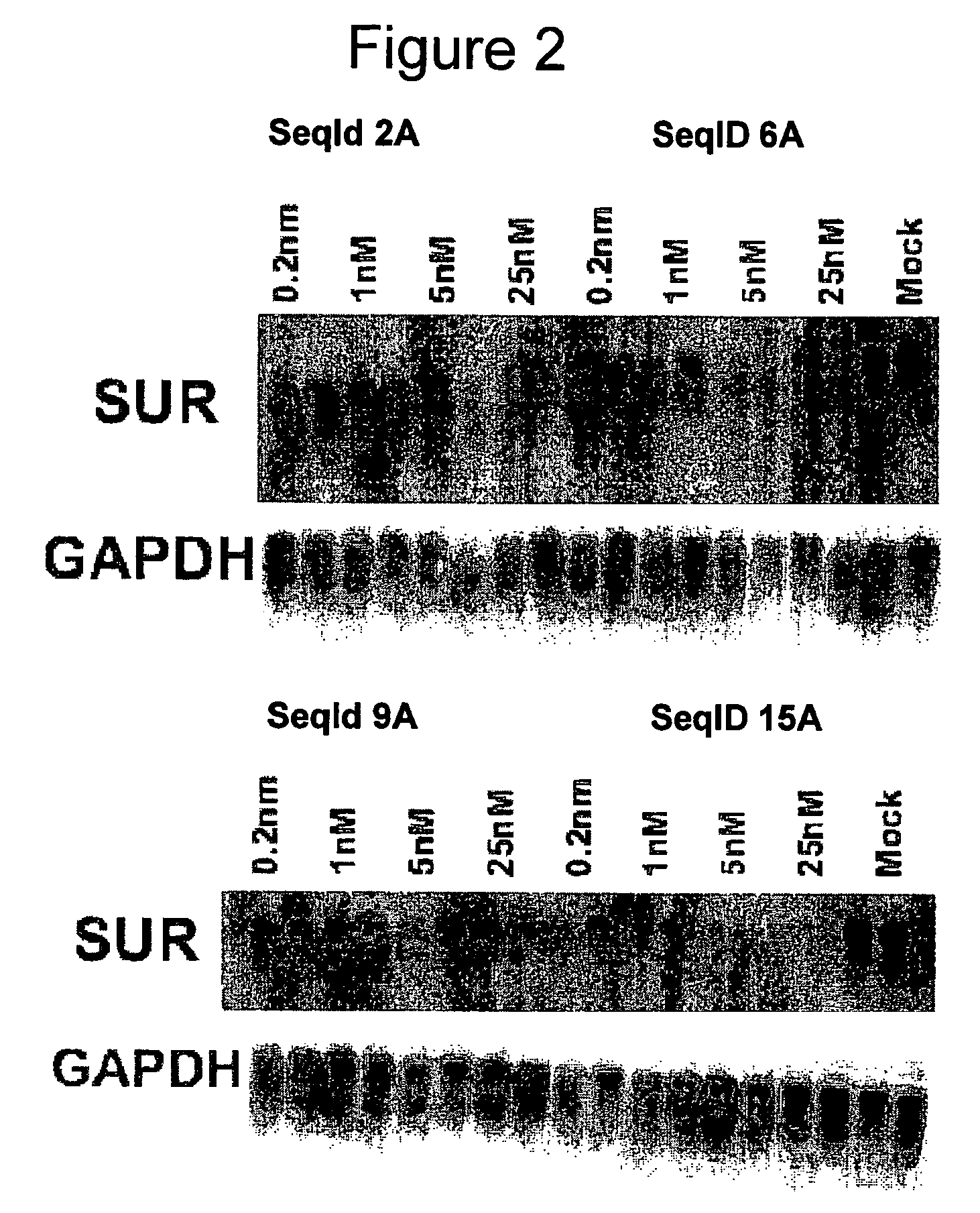
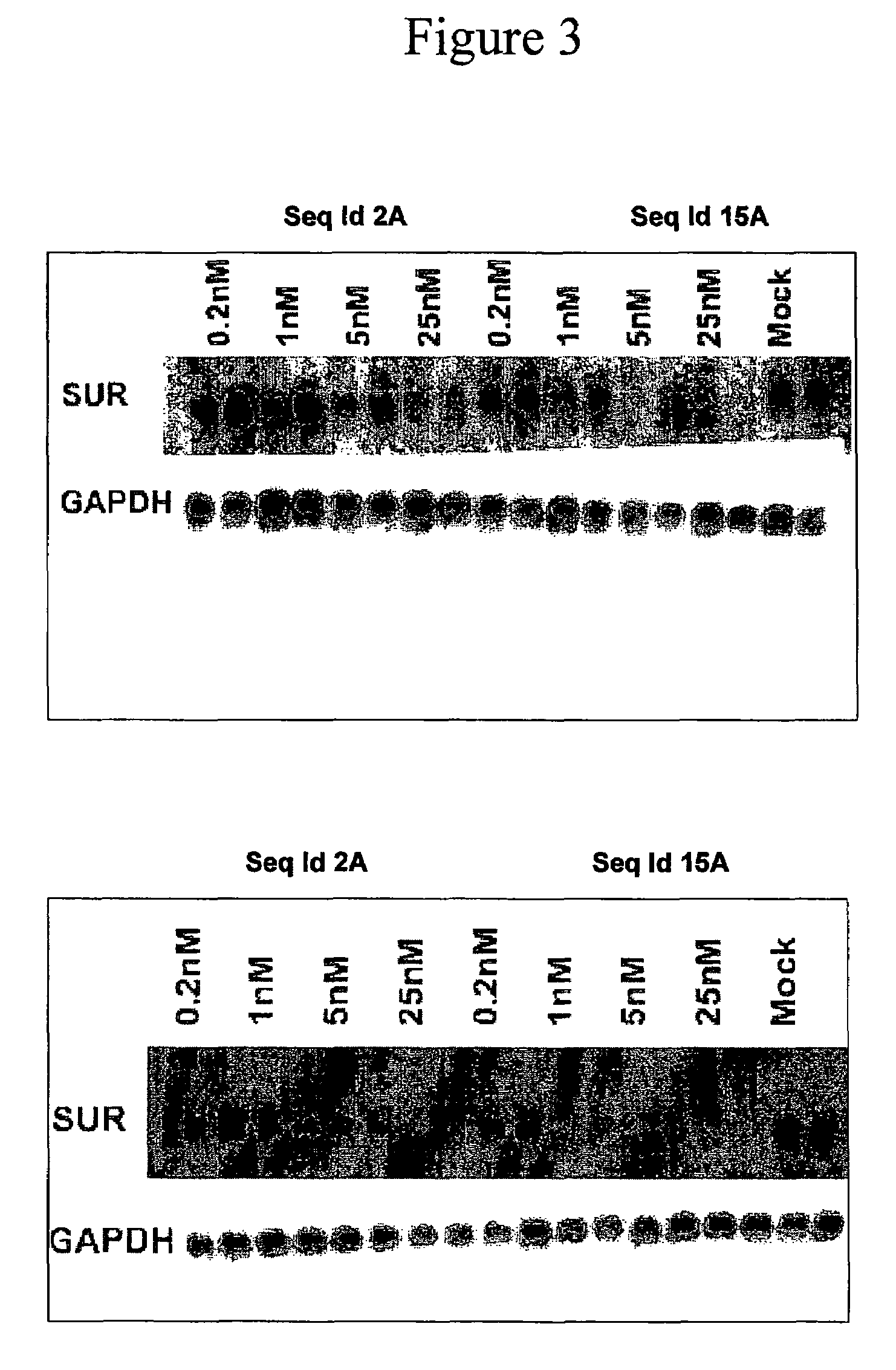
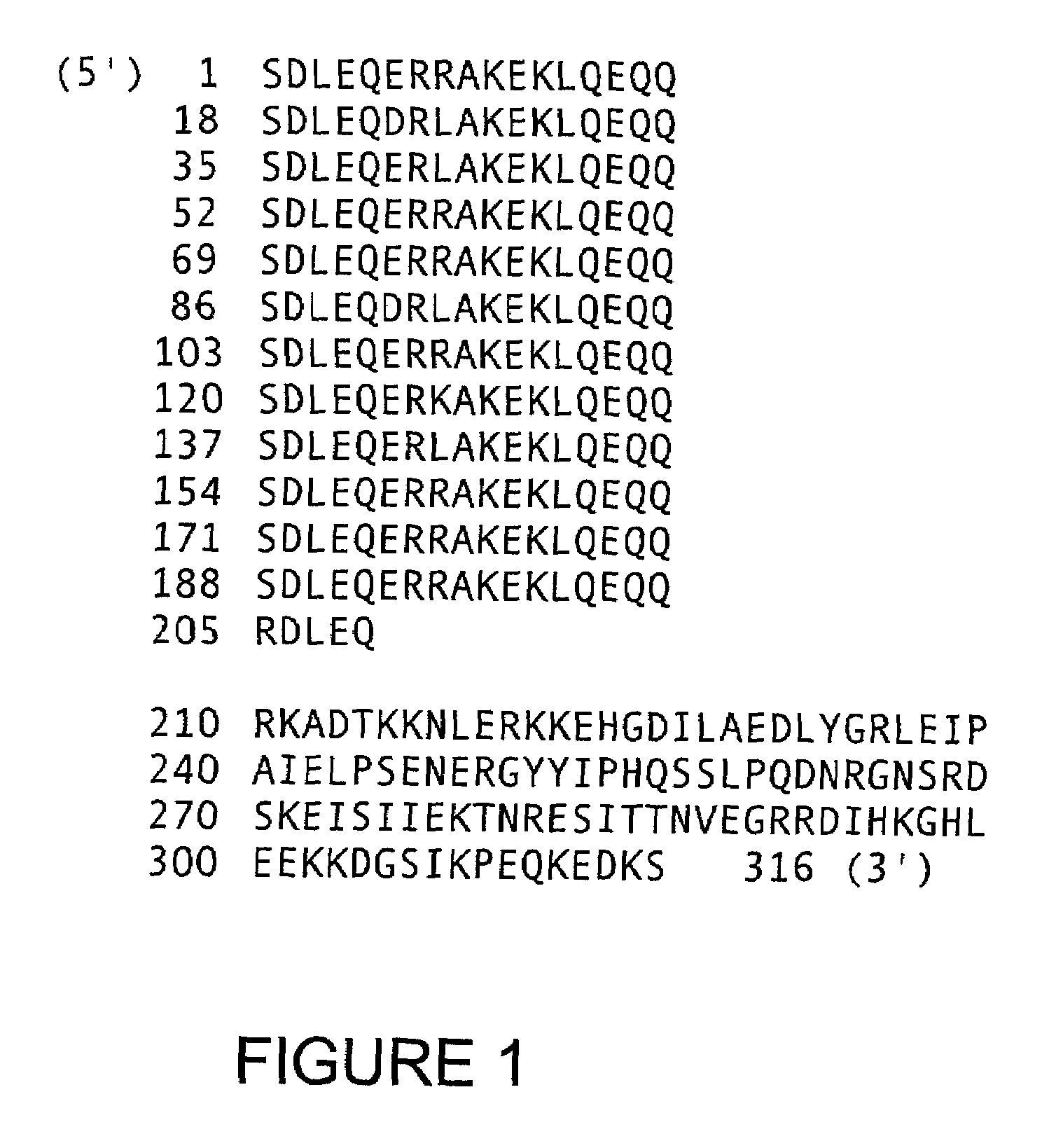
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
Peptide sequences specific for the hepatic stages of P. falciparum bearing epitopes capable of stimulating the T lymphocytes
The present invention relates to an in vitro diagnostic method for malaria in an individual comprising placing a tissue or a biological fluid taken from an individual in contact with a molecule or polypeptide composition, wherein said molecule or polypeptide composition comprises one or more peptide sequences bearing all or part of one or more T epitopes of the proteins resulting from the infectious activity of P. falciparum, under conditions allowing an in vitro immunological reaction to occur between said composition and the antibodies that may be present in the tissue or biological fluid, and in vitro detection of the antigen-antibody complexes formed. The invention further relates to a polypeptide comprising at least one T epitope from a liver-stage specific protein produced by P. falciparum and a vaccine composition directed against malaria comprising a molecule having one or more peptide sequences bearing all or part of one or more T epitopes resulting from the infectious activity of P. falciparum in the hepatic cells.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
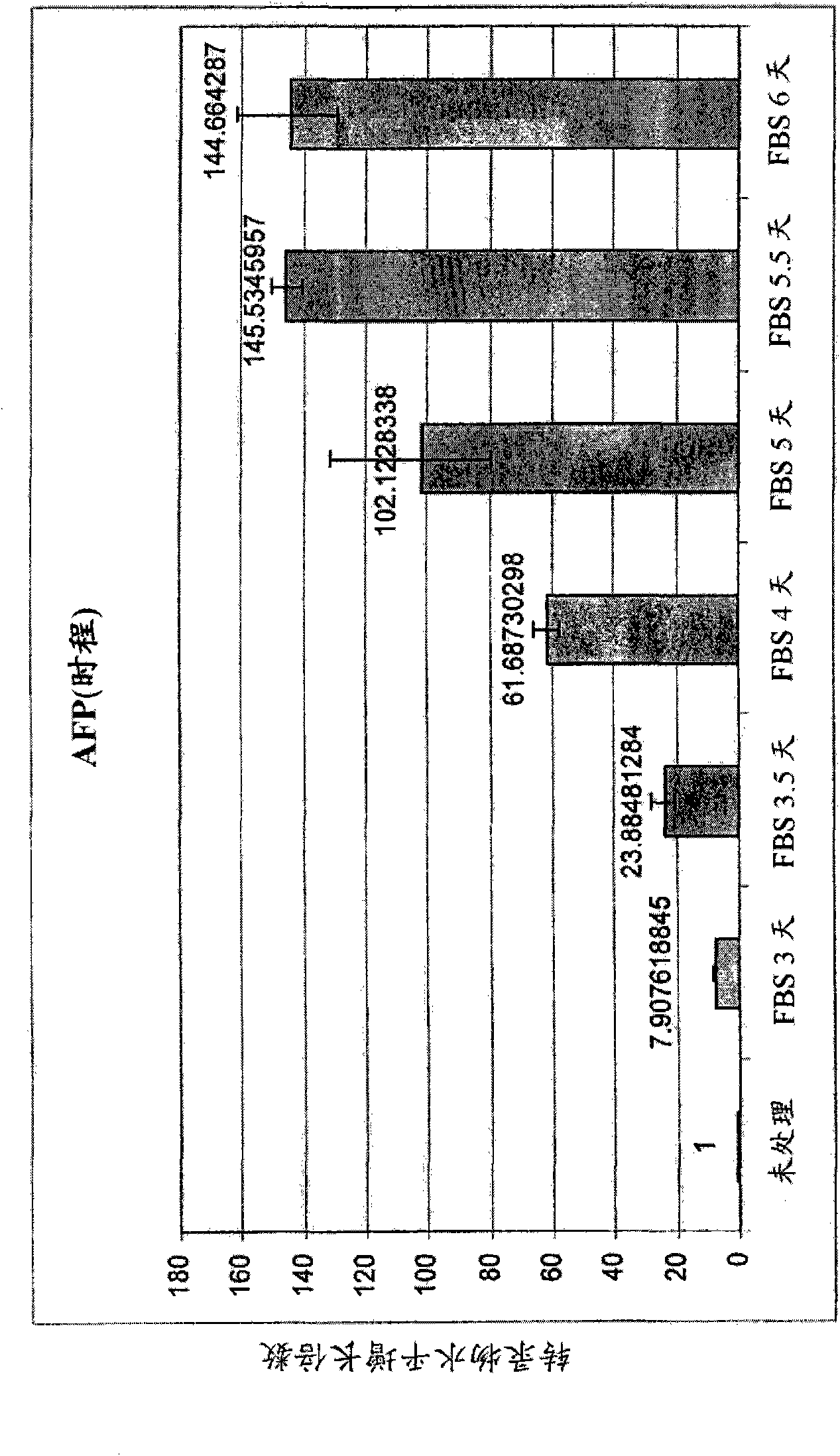
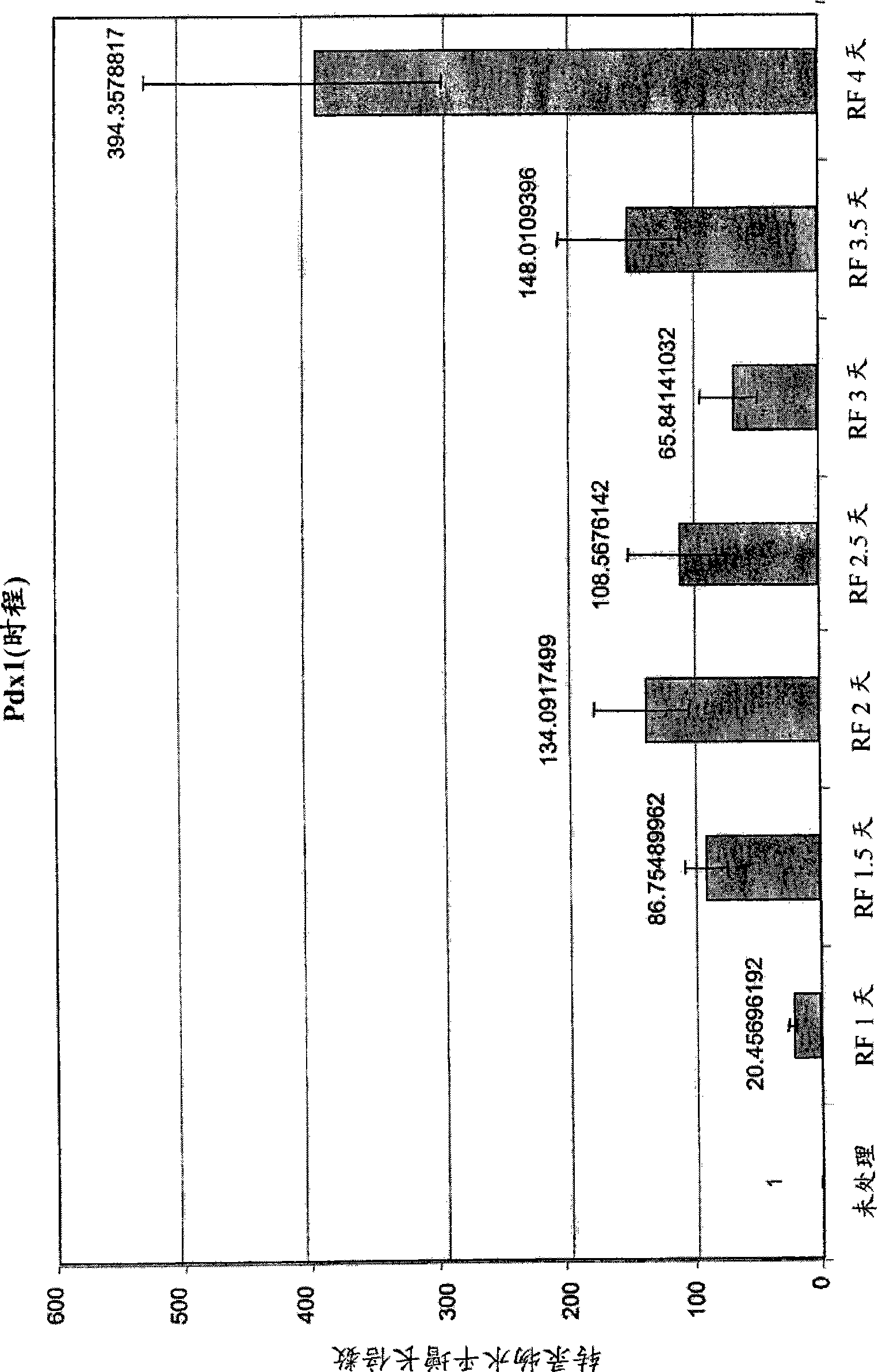
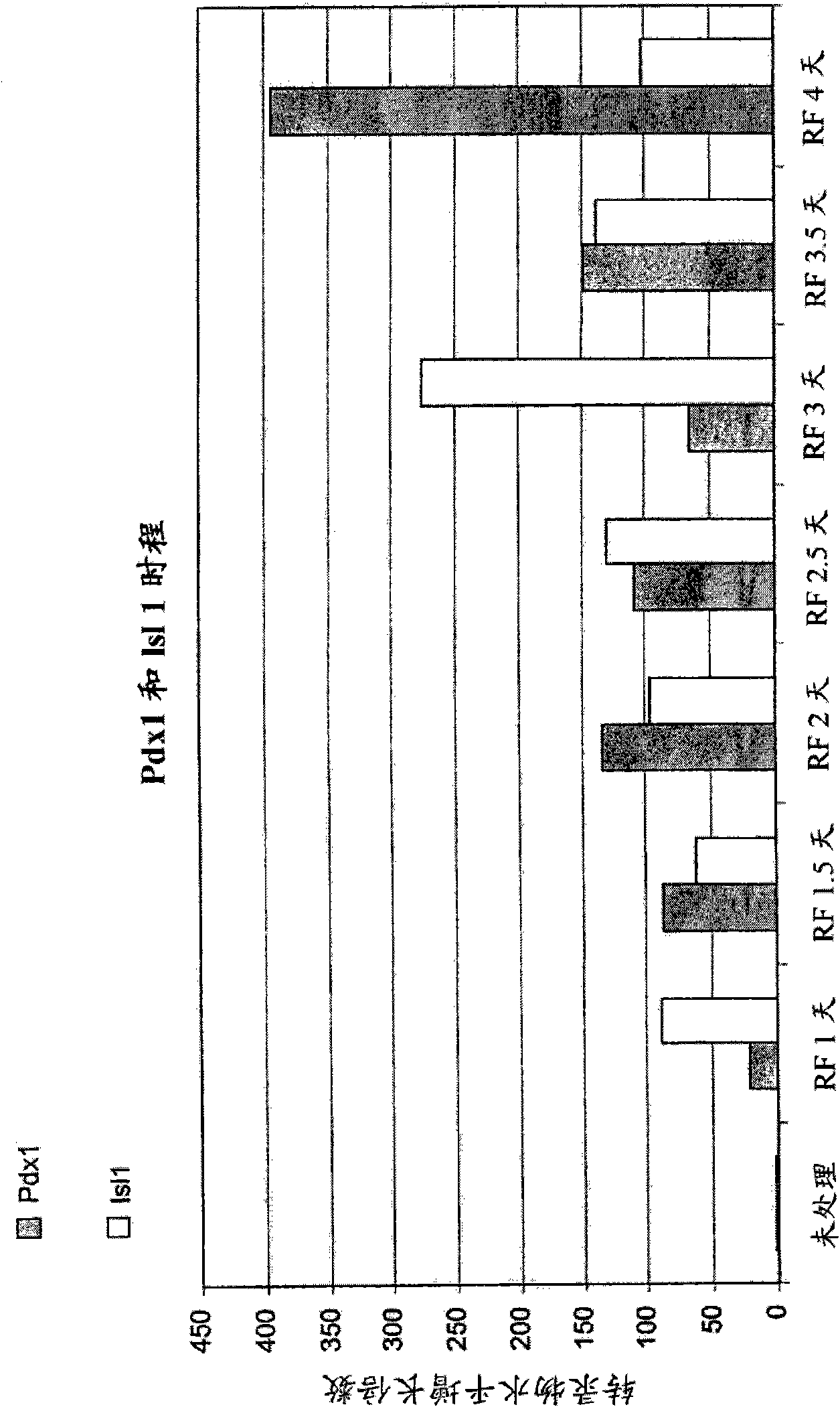
Pancreatic and liver endoderm cells and tissue by differentiation of definitive endoderm cells obtained from human embryonic stems
The invention relates to methods that allow for the efficient differentiation to form pancreatic endoderm cells from pluripotent stem cells such as human embryonic stem cells and definitive endoderm cells. The invention is directly applicable to the ultimate generation of pancreatic beta cells that could be used as part of a therapy to treat or even cure diabetes. Additionally, the present invention may be used to generate liver endoderm cells from human embryonic stem cells and definite endoderm cells as well. This invention relates to a method for generating definitive endoderm and pancreatic endoderm cells from stem cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells using defined media in the absence of feeder cells. A simply two step procedure to provide pancreatic endoderm cells from embryonic stem cells represents further embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
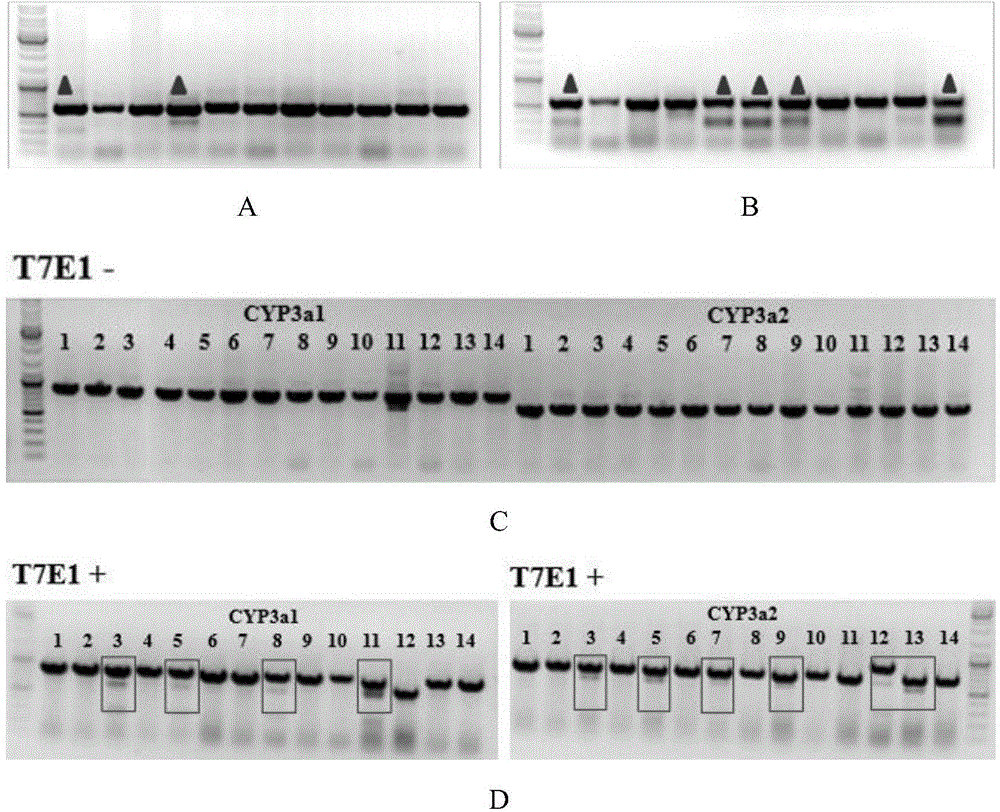
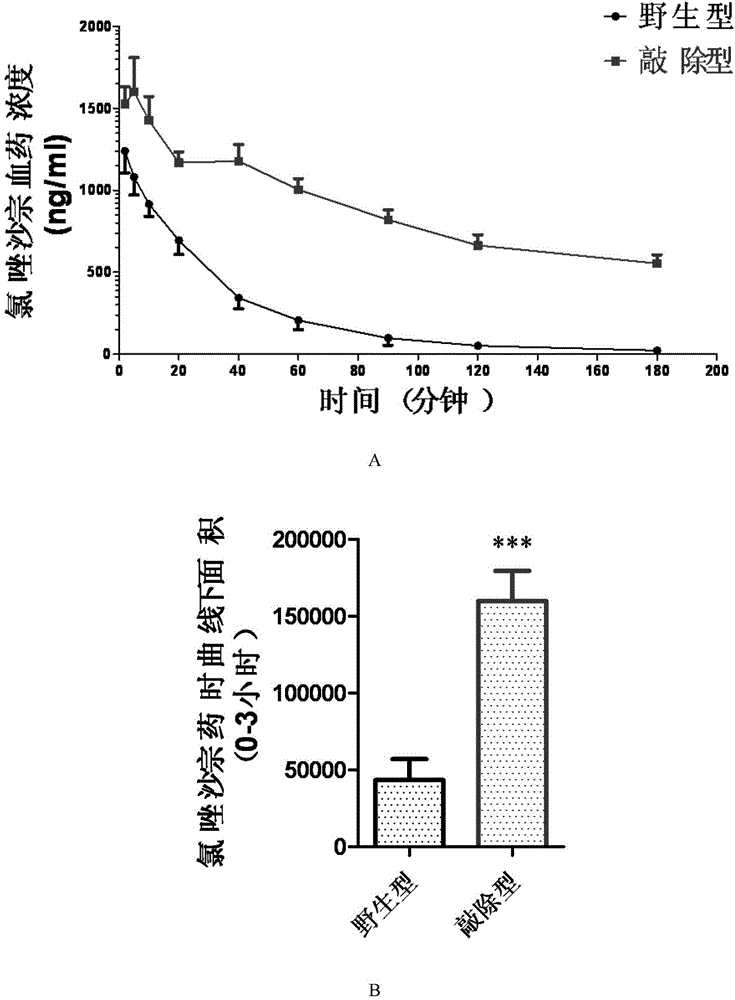
Cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and preparation method of liver microsome of the rats
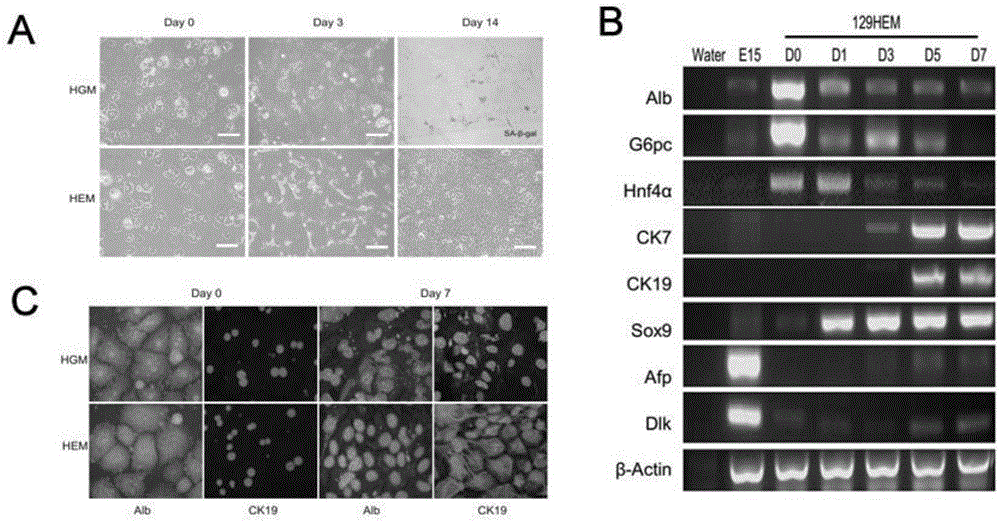
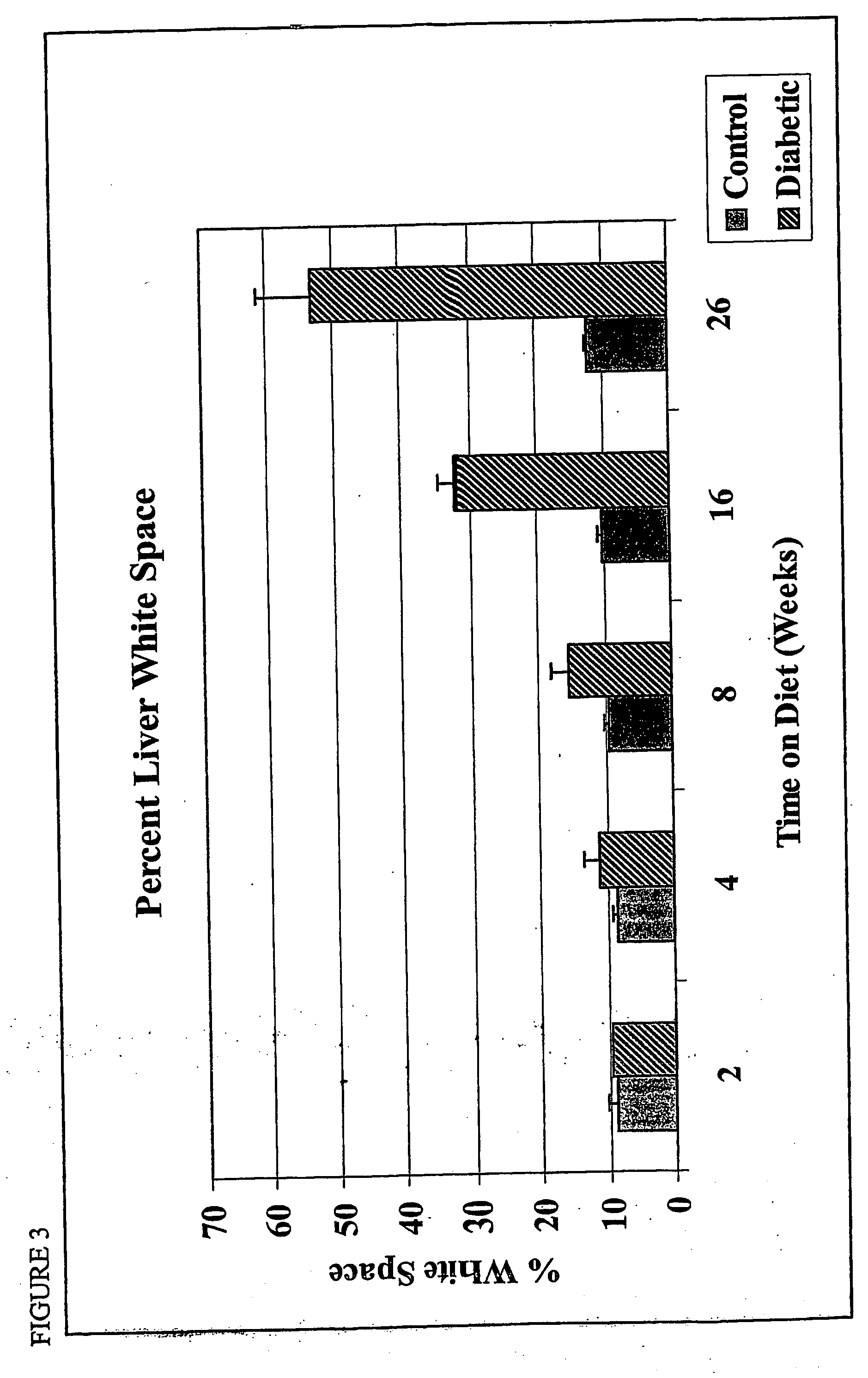
ActiveCN106148416ADiverse in vitro modelsImprove transfer abilityMicroinjection basedFermentationHepaticaMicro injection
The invention provides a cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and a preparation method of liver microsome of the rats. The Cyp gene knock-out herein includes Cyp single gene knock-out and Cyp multiple gene knock-out. In the method, firstly a Cyp gene knocked-out rat is constructed by means of a CRISPR / Cas system, which includes selection of a knocked-out target site, in-vitro synthesis and transcription of sg RNA and Cas9m RNA, preparation of a pseudopregnant female rat, in-vitro micro-injection and transplanting of a single-cell embryo, and cultivation of the rat, and finally, a homozygote Cyp gene knocked-out rat can be cultured. Furthermore, the liver of the Cyp gene knocked-out rat is extracted and is subjected to homogenization and differential centrifugation to prepare the liver microsome of the rat in Cyp gene deletion. The invention also provides an application of the Cyp gene knocked-out rats and the liver microsome thereof in study on drug metabolism.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
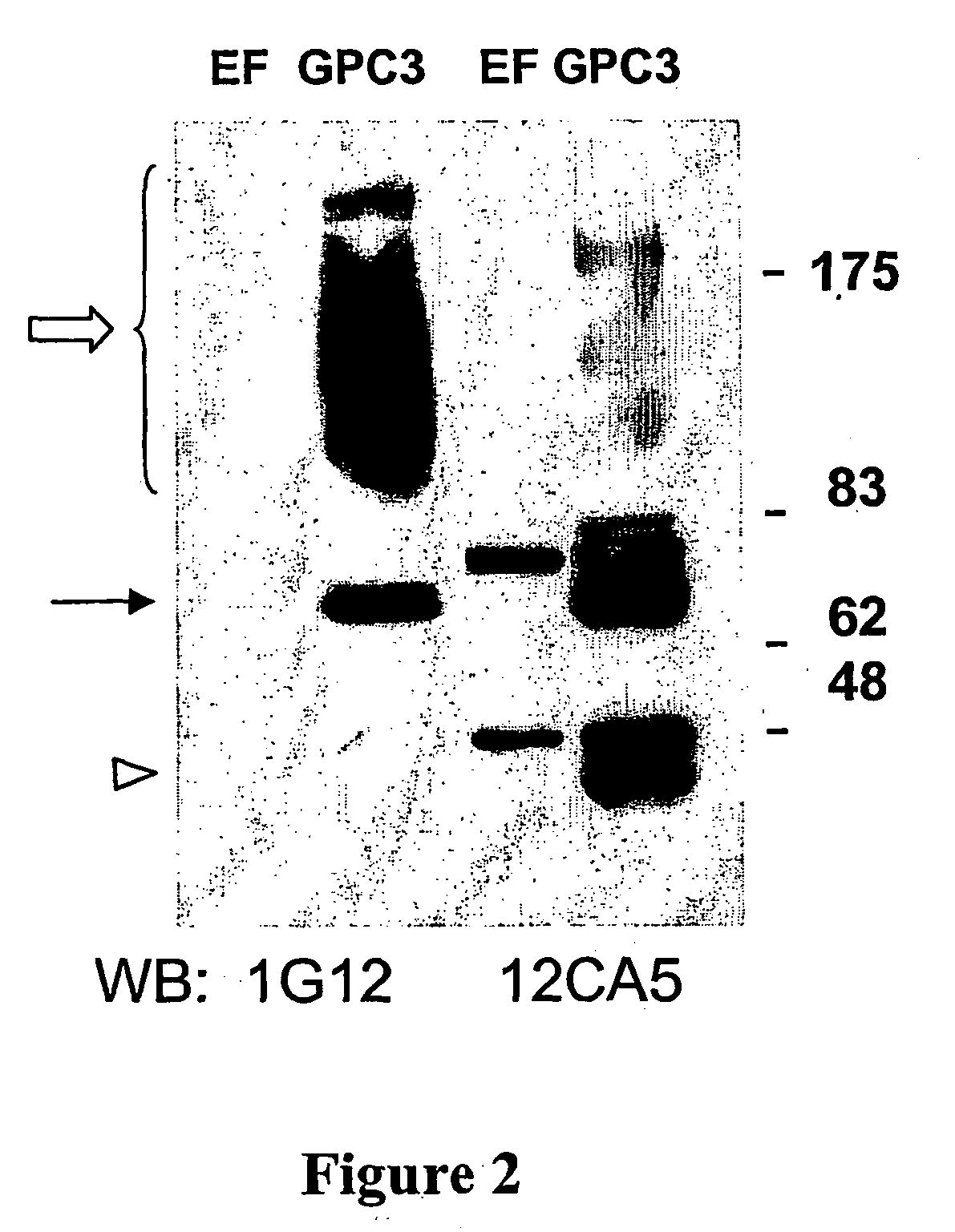
Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
InactiveUS20050233392A1Strong specificityThe process is convenient and fastImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingHepaticaLiver tissue sample
A method is provided for screening a subject for hepatocellular carcinoma by determining the level of glypican-3 (GPC3) in a body fluid sample from the subject. A further method is provided for diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma by detecting GPC3 in a liver tissue sample. Also provided are antibodies which bind specifically to GPC3.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
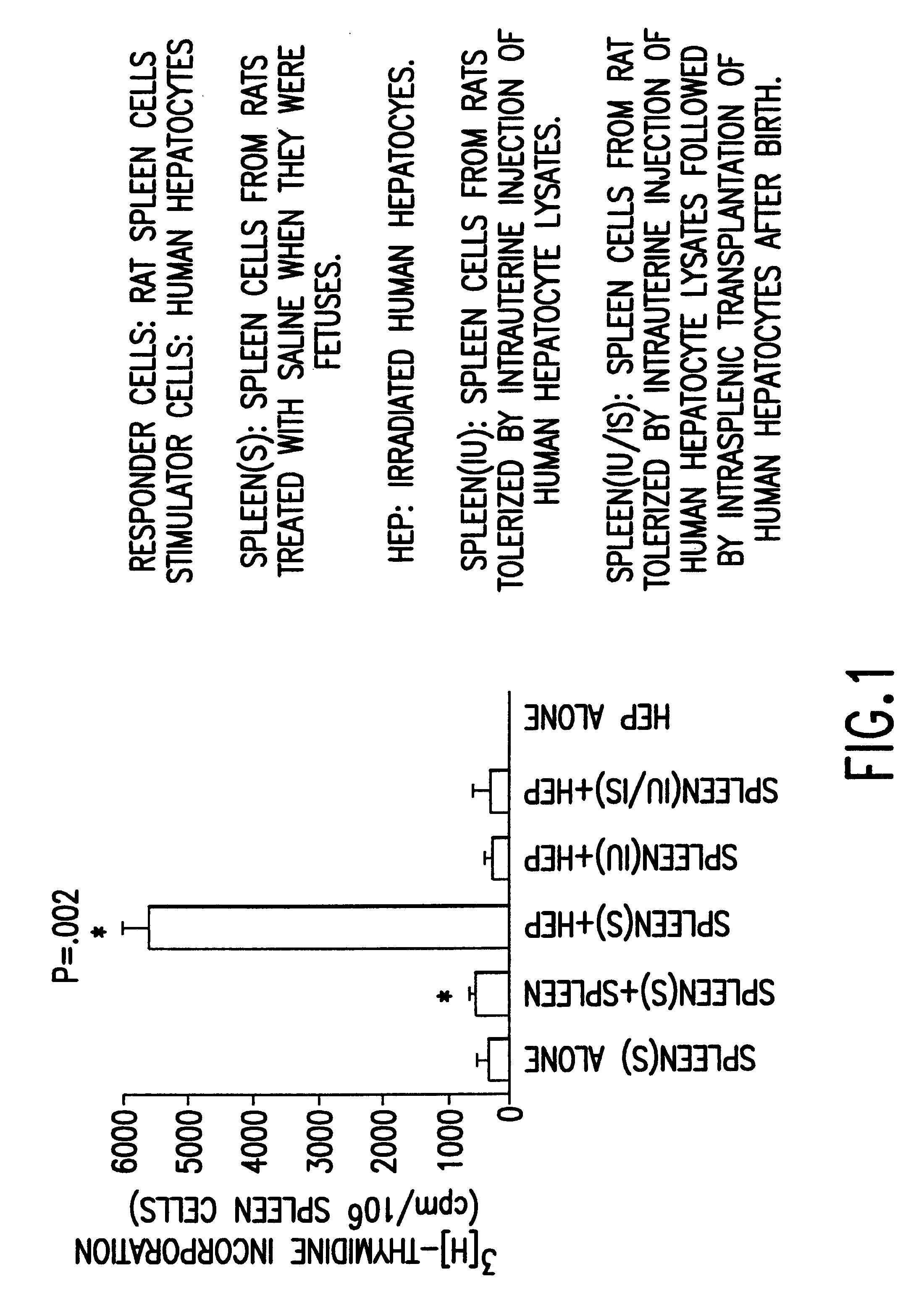
Propagation of human hepatocytes in non-human mammals
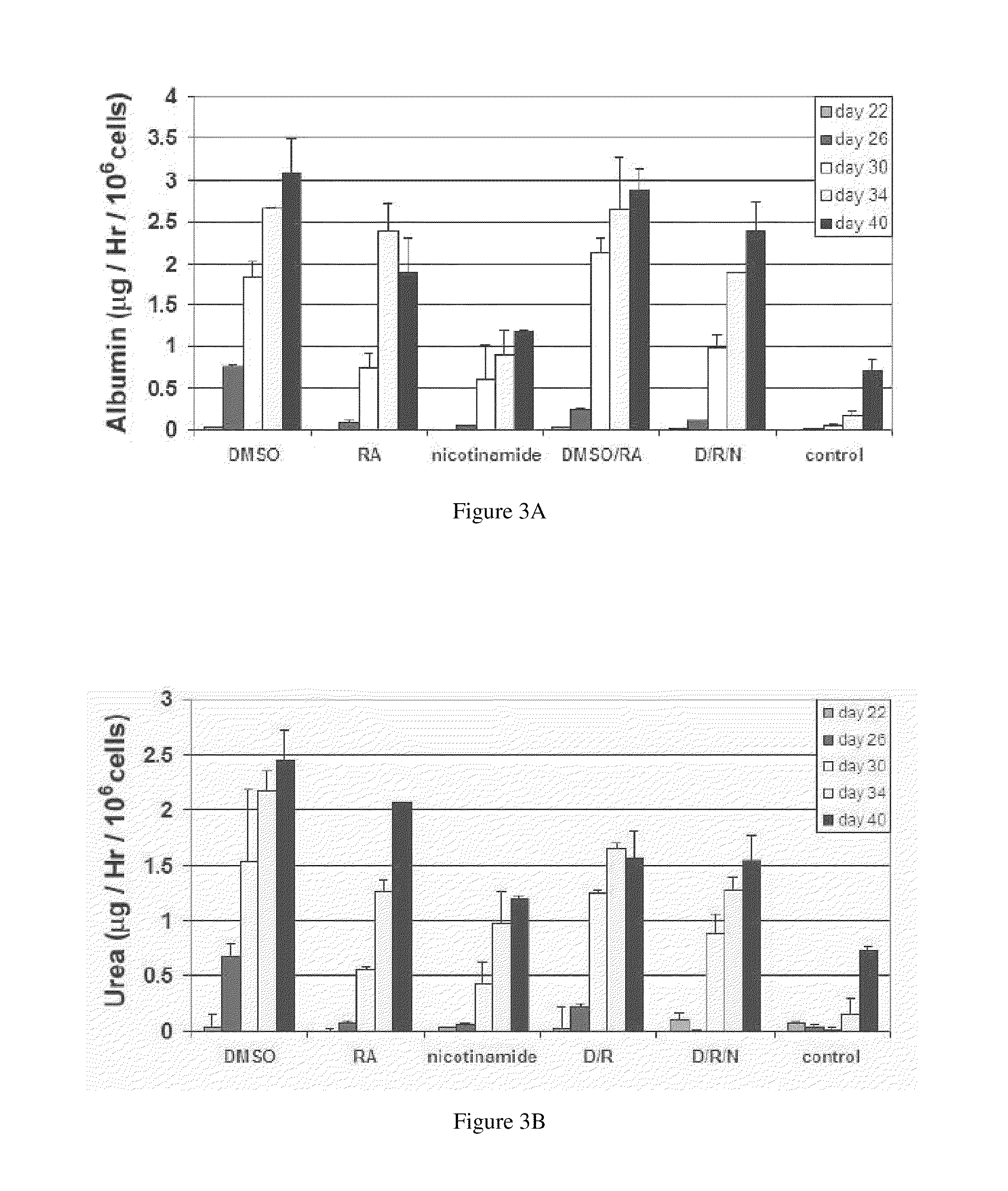
The present invention relates to the preparation of non-human animals having chimeric livers, whereby some or substantially all of the hepatocytes present are human hepatocytes. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that rats, tolerized in utero against human hepatocytes, were found to serve as long-term hosts for human hepatocytes introduced post-natally, and the introduced hepatocytes maintained their differentiated phenotype, as evidenced by continued production of human albumin.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Method of screening candidate compounds for susceptibility to biliary excretion
InactiveUS7601494B2More compoundedFast processSugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsBiliary excretionHepatica
A method of screening a candidate compound for susceptibility to biliary excretion by a hepatocyte transport protein. The method includes the steps of providing a culture of hepatocytes comprising a transport protein, the culture having at least one bile canaliculus; exposing a candidate compound to the culture; and determining an amount of candidate compound in the at least one bile canaliculus, the amount of candidate compound in the at least one bile canaliculus indicating the susceptibility of the candidate compound to biliary excretion by the transport protein. In some embodiments determining the amount of candidate compound in the bile canaliculus comprises inhibiting expression of the transport protein, measuring the amount of candidate compound in the bile canaliculus and comparing amounts of compound in the canalicules with and without inhibition of the transport protein. A difference in the amount of candidate compound in the canaliculus indicates susceptibility of the candidate compound to biliary excretion by the transport protein. In one embodiment, expression of the transport protein is inhibited through introduction of a RNA having a sequence corresponding to a coding strand of the gene encoding the transport protein into the hepatocyte. Optionally, the culture of hepatocytes is a long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. The method is particularly applicable to the screening of multiple candidate compounds in a single effort.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Homogeneous differentiation of hepatocyte-like cells from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20100143313A1Rapid and direct differentiationImprove survivalBiocideHepatocytesLiver morphologyBioartificial liver device
One of the major hurdles of cellular therapies for the treatment of liver failure is the low availability of functional human hepatocytes. Although embryonic stem (ES) cells represent a potential cell source for therapy, current methods for differentiation result in mixed cell populations or low yields of the cells of interest. The present invention provides for a rapid, direct differentiation method that yields a homogeneous population of endoderm-like cells with 95% purity. In one embodiment, mouse ES cells cultured on top of collagen-sandwiched hepatocytes differentiate and proliferate into a uniform and homogeneous cell population of endoderm-like cells. The endoderm-like cell population was positive for Foxa2, Sox17 and AFP, and could further differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells that demonstrate hepatic morphology, functionality, and gene and protein expression. Incorporating the hepatocyte-like cells into a bioartificial liver device to treat fulminant hepatic failure improved animal survival, thereby underscoring the therapeutic potential of these cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
In vivo, animal model for expression of hepatitis C virus
Disclosed is a method for expressing hepatitis C virus in an in vivo, animal model. Viable, hepatitis C virus-infected, human hepatocytes are transplanted into a liver parenchyma of a scid / scid mouse host. The scid / scid mouse host is then maintained in a viable state, for up to five days or greater, whereby viable, morphologically intact human hepatocytes persist in the donor tissue and hepatitis C virus is replicated in the persisting human hepatocytes.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Animal model having a chimeric human liver
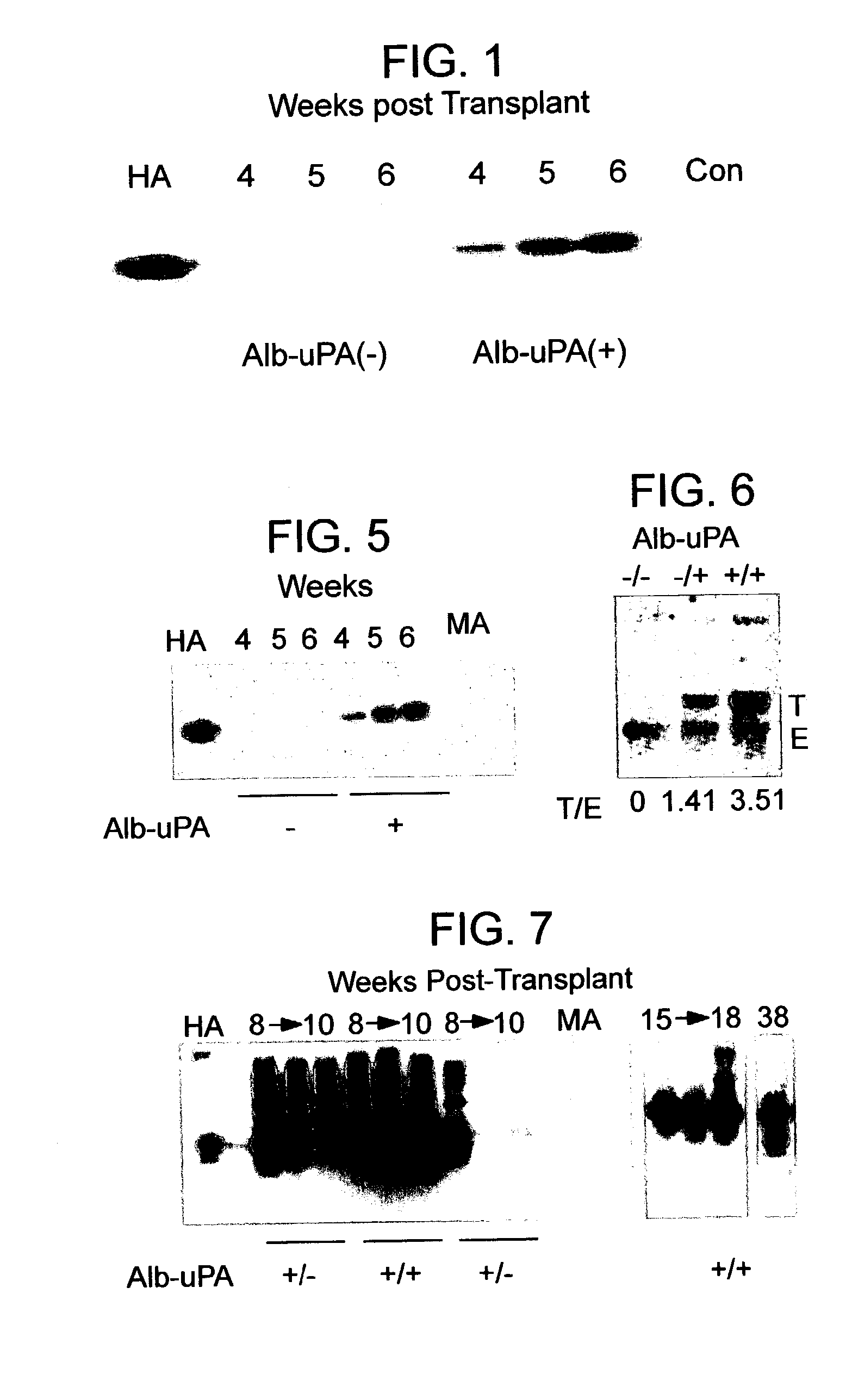
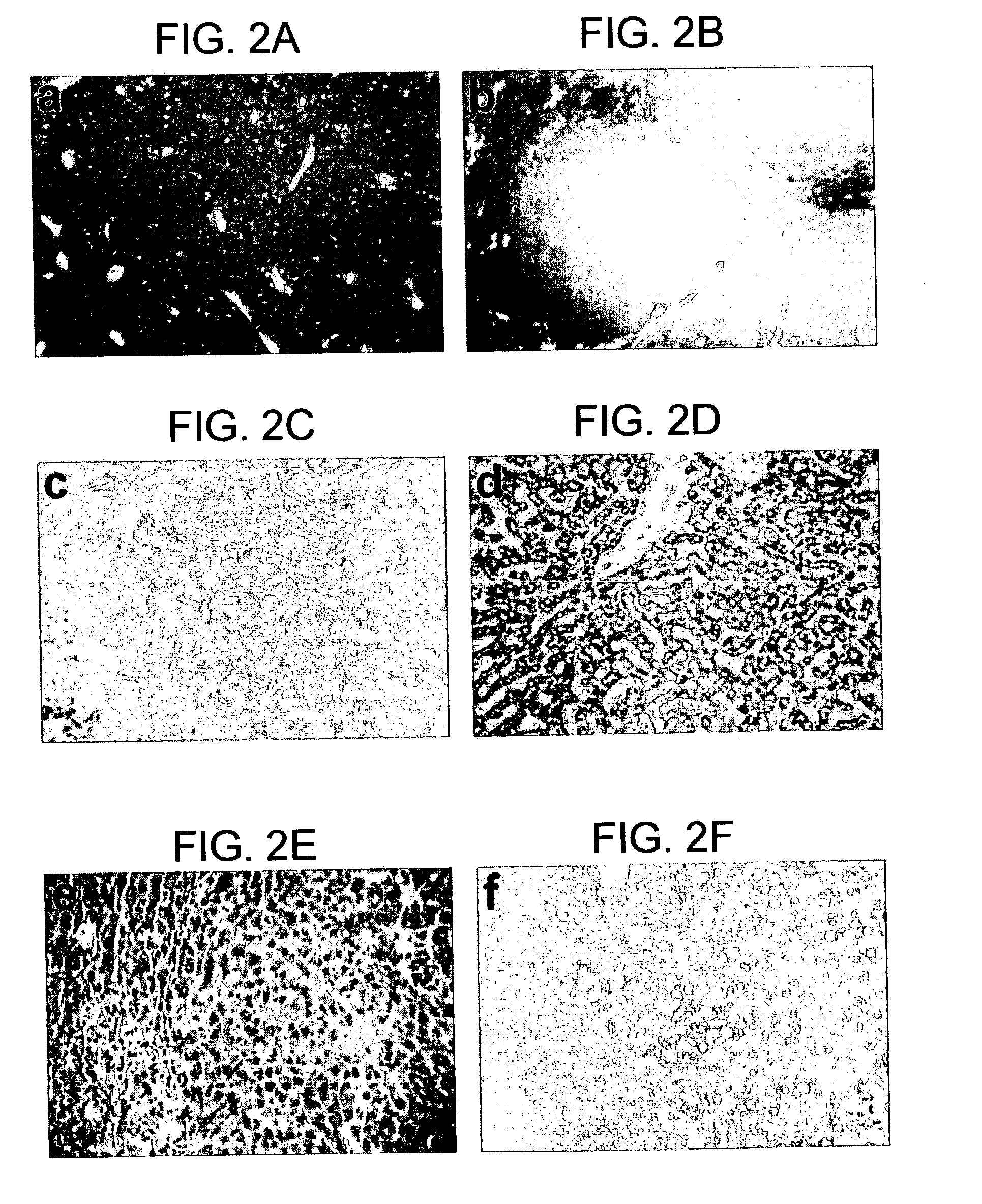
The present invention features a non-human animal model that is susceptible to infection by human hepatotrophic pathogens, particularly human hepatitis C virus (HCV). The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having antiviral activity against HCV infection. The animals of the invention are also useful in assessing toxicity of various agents, as well as the activity of agents in decreasing blood lipids.
Owner:KMT HEPATECH
Improved diagnosis of liver fibrosis or cirrhosis
InactiveCN102334122AImprove the accuracy of a single diagnosisHigh industrial interestOrgan movement/changes detectionMedical automated diagnosisMedical imaging dataBlood test
This invention relates to method of diagnosing the presence and / or severity of a liver pathology and / or of monitoring the effectiveness of a curative treatment against a liver pathology in an individual, leading to a score, comprising the combination, of at least one blood test and of at least one data issued from a physical method of diagnosing liver fibrosis, said data being selected from the group consisting of medical imaging data and clinical measurements, said combination being performed through a mathematical function.This invention also relates to a method wherein the combination through a mathematical function, of at least one blood test and of at least one data issued from a physical method of diagnosing liver fibrosis, is performed at least twice and the at least two resulting scores are combined in an algorithm based on the diagnostic reliable intervals.
Owner:UNIV DANGERS +1
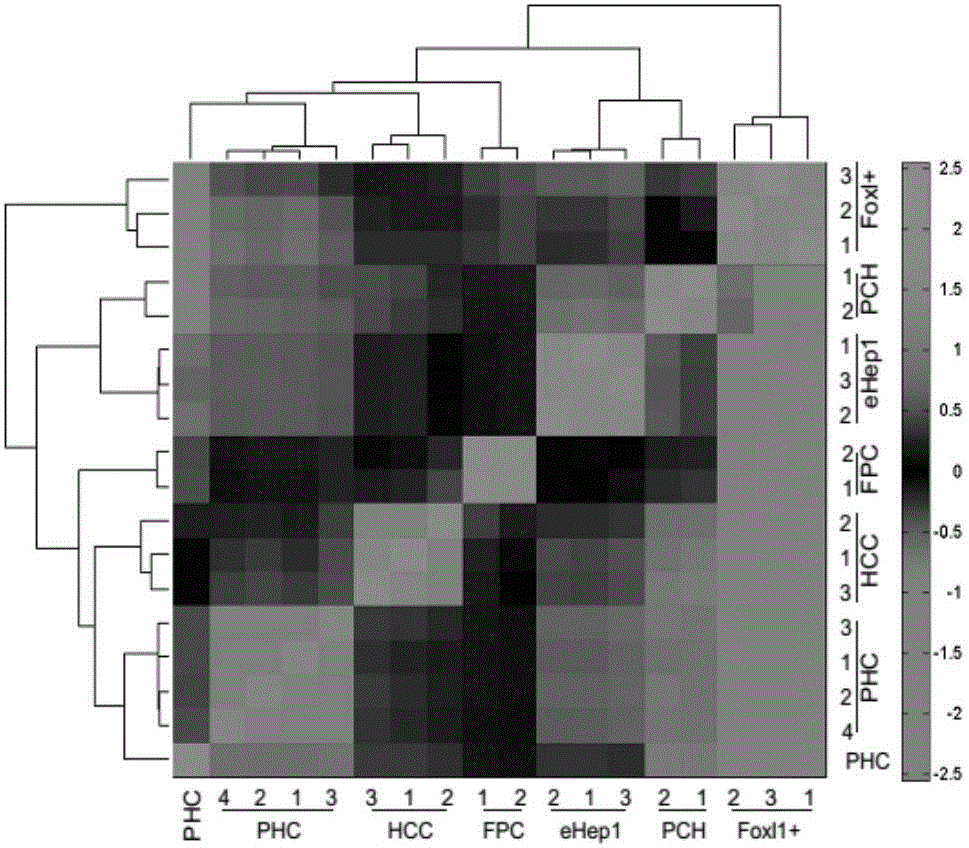
Method for in-vitro induction of cholangiocyte-like transformation of primary hepatocytes and for long-term culture, amplification and differentiation and application of method
ActiveCN106754636AStable proliferationSolve problems that cannot be cultivated for a long timeVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsIn vitro transformationHepatica
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering technology, and in particular to a method for in-vitro induction of cholangiocyte-like transformation of primary hepatocytes and for long-term culture, amplification and differentiation and an application of the method. The invention provides a hepatocyte cholangiocyte-like transformation medium determined by chemical ingredients and / or a system which is composed of a hepatocyte mature medium and is applicable to long-term stable culture, amplification and differentiation of the primary hepatocytes; the invention also provides the method for in-vitro induction of cholangiocyte-like transformation of the primary hepatocytes and for long-term culture, amplification and differentiation; and with the application of the method, the cholangiocyte-like hepatocyte conversion of the primary hepatocytes can be induced in vitro, so that the obtained hepatocytes have characteristics of biliary epithelial cells and hepatic precursor cells, and the hepatocytes are applicable to long-term stable culture and amplification. The breedable cholangiocyte-like hepatocytes and hepatocytes, which are mature in differentiation, prepared by the invention are applicable to such aspects as toxicologic and pharmacological evaluation of compounds and drugs, researches and diagnosis & treatment of hepatitis viruses, treatment by hepatocyte transplantation, preparation of bioartificial liver and the like.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Pharmaceutical formulation useful for the treatment of hepatitis B, hepatitis C and other viral infections of the liver and a process for its preparation
InactiveUS6589570B1Easy to inactivateAvoid multiplicationBiocideDigestive systemChemical standardizationHepatica
The invention disclosed in this application relates to a pharmaceutical formulation prepared from the biotyped variety of the medicinal plant, Phyllanthus amarus which is useful for the treatment of Hepatitis B (both acute and chronic), Hepatitis C (both acute and chronic) and other related viral infections of the liver with antihepatotoxic and liver cell regenerating potentials and immunomodulating properties. The invention confirms, that when pars of the biotyped variety of the medicinal plant, Phyllanthus amarus are extraceted separately with a polar solvent alone, polar solvent and water in specific ratios and water alone and when such extracts are mixed together, the resultant formulation has all the essential antiviral and biological properties, while the individual polar or aqueous extracts alone does not possess one or more of these properties. The present invention also relates to a process for the preparation of the above said new pharmaceutical formulation with biological and chemical standardisation protocols.
Owner:MADRAS UNIV OF
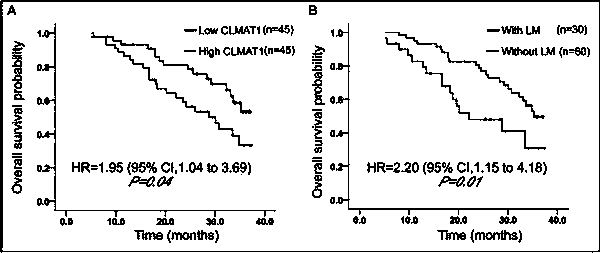
Long noncoding RNA CLMAT1 related with colorectal liver metastasis and application of long non-coding RNA CLAMT1
The invention provides long noncoding RNA (ribonucleic acid) CLMAT1 related with colorectal liver metastasis and application of the long noncoding RNA CLAMT1. The long noncoding RNA CLAMT1 is positioned at a 14th chromosome chr14: 101379770-101381326, hg19; the gene sequence length is 1557bp. Compared with normal intestinal tissues, intestinal tissues with the intestinal cancer has high expression of CLAMT1 which is positively correlated with liver metastases of colorectal cancer; in addition, bad prognosis of patients also indirectly prompts that the liver metastasis probability of the patients is relatively high.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
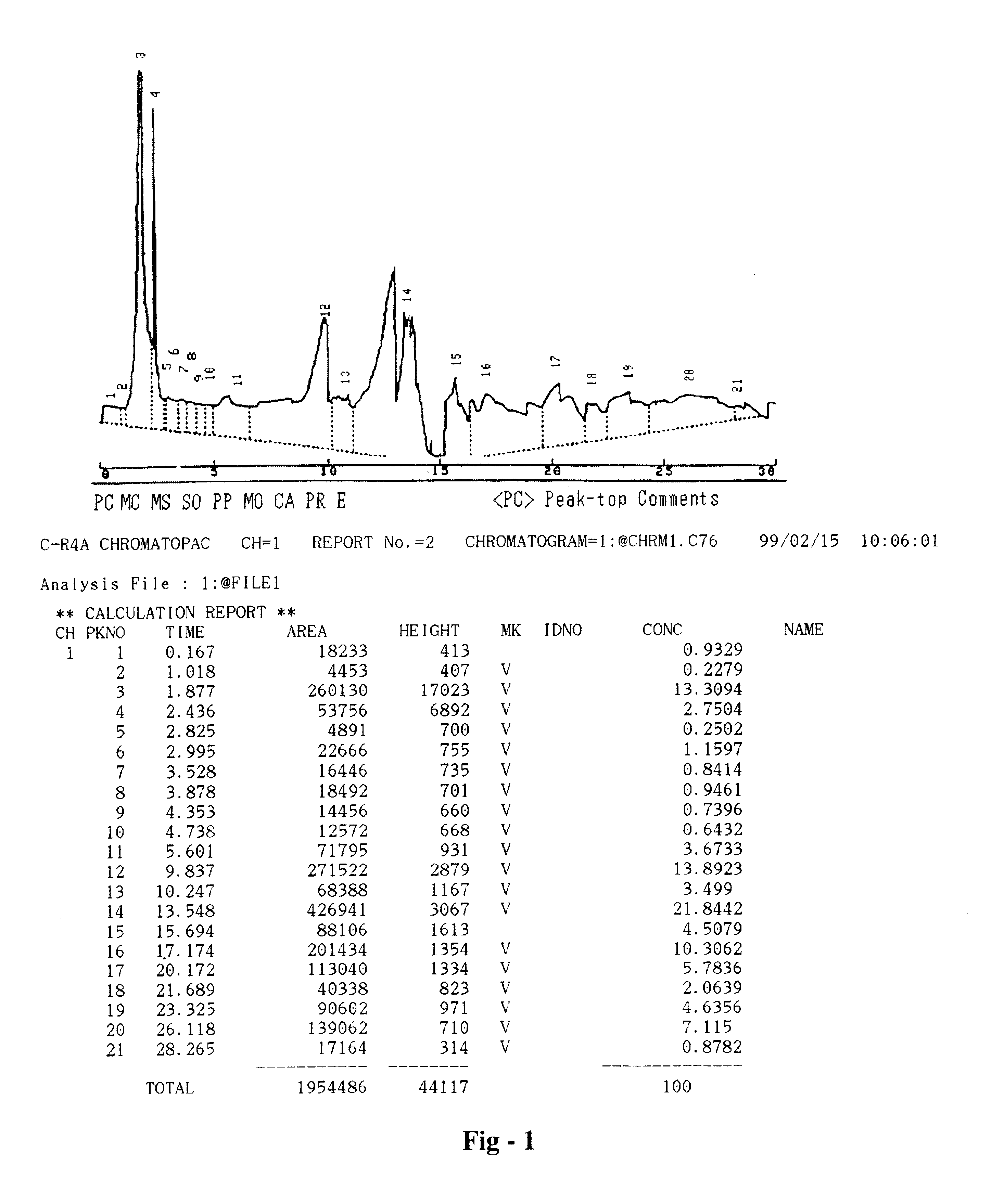
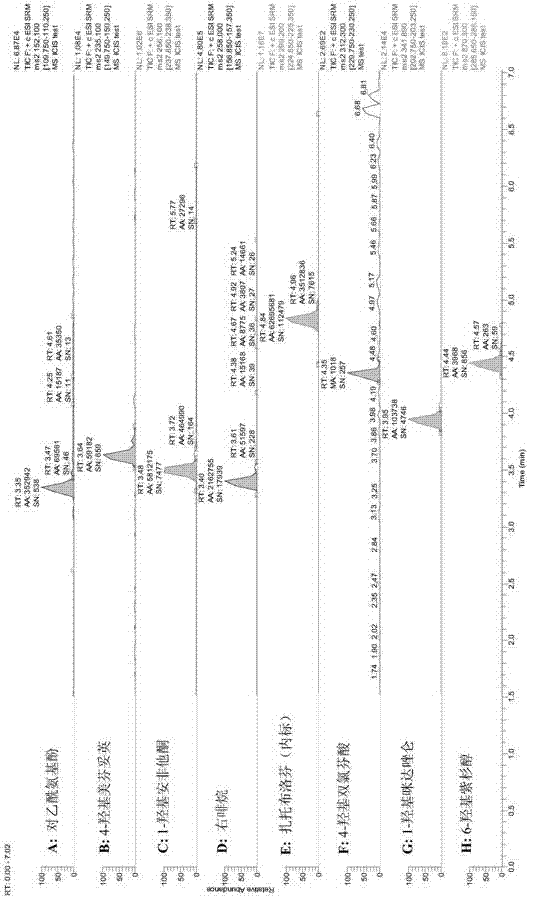
Detection method for simultaneously determining metabolic products of seven CYP450 enzyme probe substrates in human liver microsomes
InactiveCN104849371AThe pretreatment method is simpleSuitable for routine testingComponent separationMetaboliteHepatica
The invention relates to a detection method for simultaneously determining the metabolic products of seven CYP450 enzyme probe substrate in human liver microsomes, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The detection method comprises the following steps: performing incubation on specificity probe substrates of CYP450 enzyme and the human liver microsomes for different periods of reaction time to generate corresponding metabolic products, using Zaltoprofen as an interior label, adopting a high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after protein precipitation pretreatment, and thus simultaneously detecting the concentrations of the metabolic products of seven probe substrates. The method disclosed by the invention is high in specificity, high in sensitivity and simple and convenient in operation, and has already successfully been applied to the research of baicalin on CYP450 enzyme inhibiting action of the human liver microsomes.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Liver-tonifying kidney-boosting medicinal liquor
InactiveCN101297908AHeavy metal active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsVasculitisAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a medicinal liquor which has the functions of liver nourishing and kidney tonification. The medicinal liquor of the invention comprises ingredients of 30g prepared rehmannia root, 10 centipedes, 20g rhizoma atractylodis, 1 seal genital, 20g mulberry, 30g Morinda officinalis, 30g herba cistanches, 150g actinolite, 300g medlar, 200g polygonum, 200g herba epimedii, 300g fructus rosae laevigatae, 70g cornu cervi pantotrichum, 200g ginseng, 100g earthworm, 100g rhizoma curculiginis, 150g amur corktree bark, 150g rhizoma anemarrhenae, 300g semen cuscutae, 200g himalaya teasel, 300g semen psoraleae, 80g cordyceps sinensis, 15 pairs of geckos, 15 snow lotuses and 30g saffron, which are added with 25 kg grain liqueur with more than 100 proof to be soaked for above half a year. Drinking 50 to 100g of the obtained liquor for each day can result in endocrine balance in various ways, fundamental human immunity enhancement and reasonable addition of nutrition and has curative effect on rheumatoid arthritis, lumbar disc protrusion, arthritis, sciatica, vasculitis and impotence.
Owner:秦汉富
Diagnosis and treatment methods related to aging, especially of liver
InactiveUS20070111933A1Reduce probabilityReduce severityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHepaticaGene
Mouse genes differentially expressed in comparisons of older and younger livers by gene chip analysis have been identified, as have corresponding human genes and proteins. The human molecules, or antagonists thereof, may be used for protection against faster-than-normal biological aging, or to achieve slower-than-normal biological aging. The human molecules may also be used as markers of biological aging.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
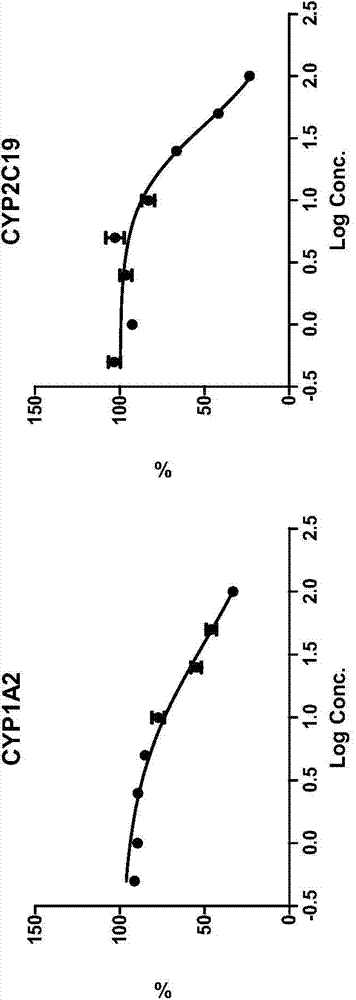
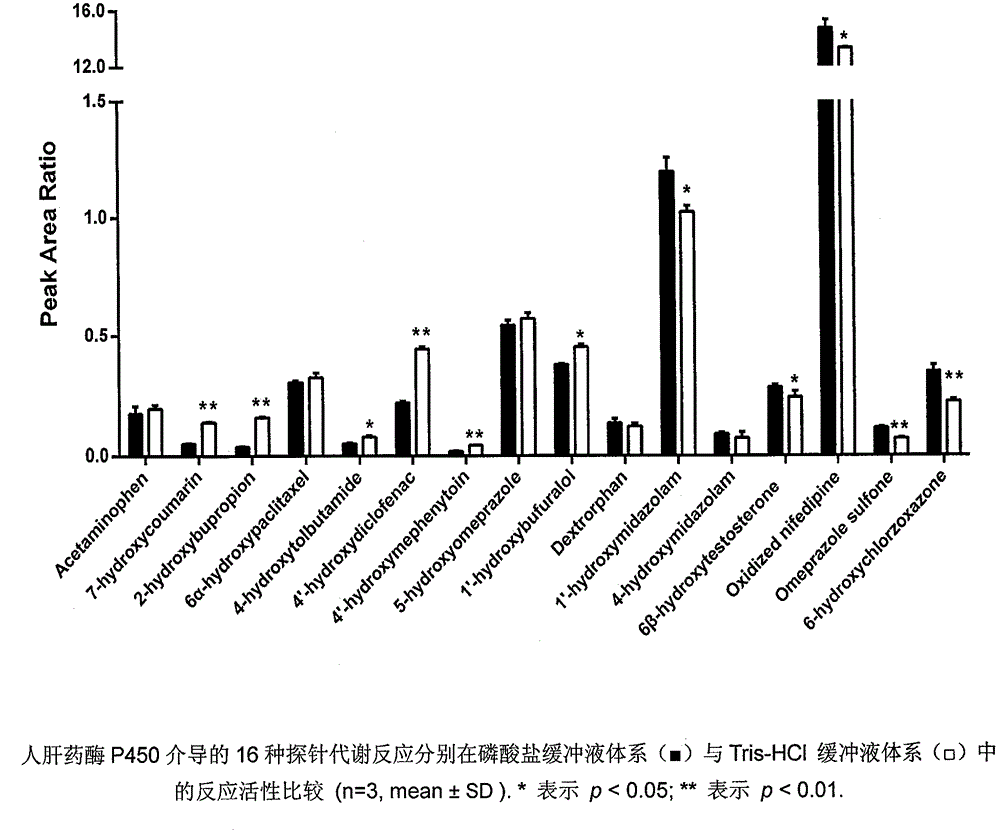
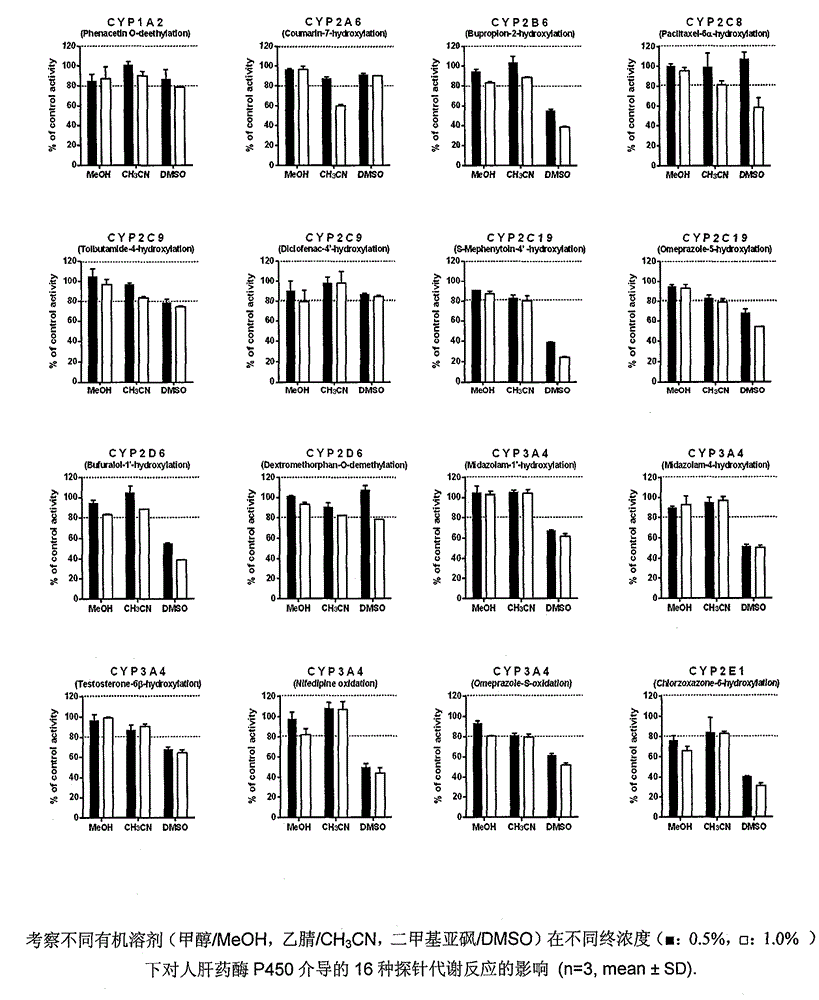
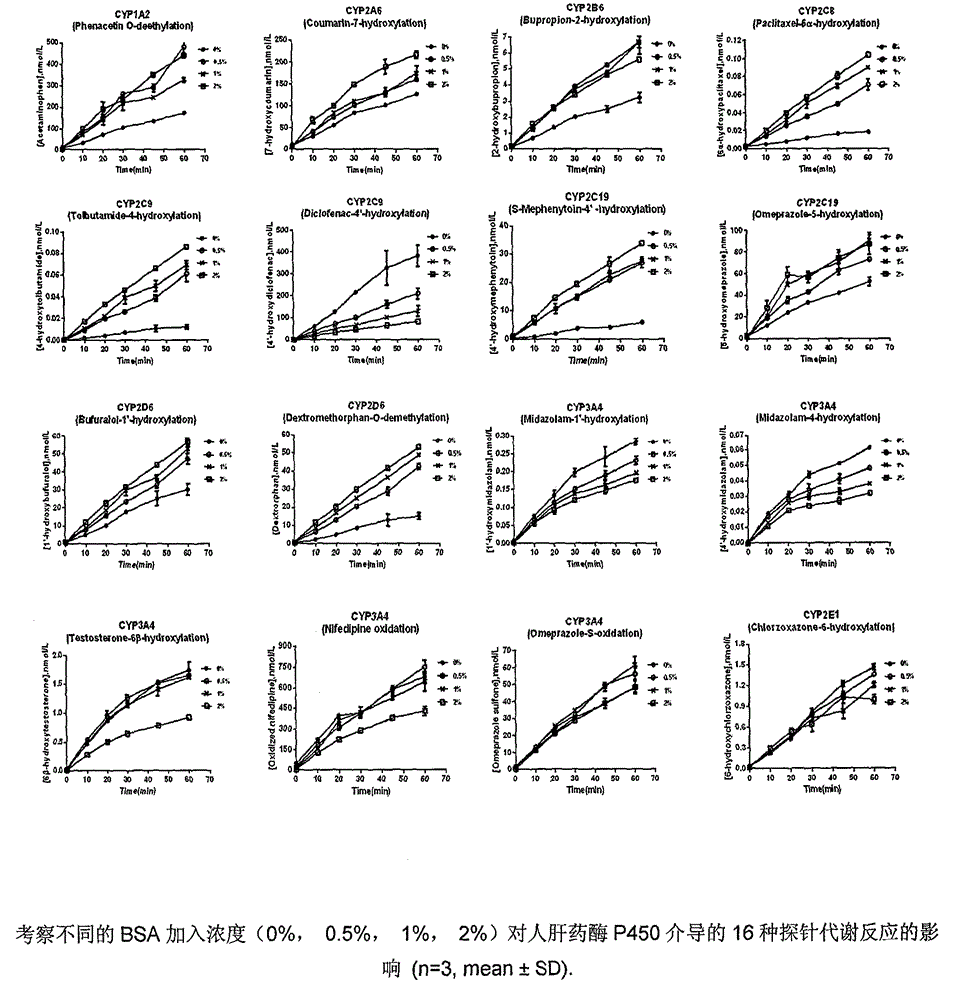
Method for rapidly screening in-vitro inhibitory effect of nine human liver CYP450 enzymes
ActiveCN104928350AImprove accuracyReduce the incidence of false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
The invention discloses a rapid screening method for comprehensively evaluating the in-vitro inhibitory effect of nine human liver CYP450 metabolic enzymes by utilizing 14 probe substrates and 16 probe reaction. The invention mainly relates to a method for monitoring metabolic activity variation of 9 human liver CYP450 enzymes and rapidly and comprehensively evaluating an inhibitory effect of a tested compound on the metabolic enzyme by adopting an in-vitro mixed probe incubation method and LC / MS / MS. According to the method, the exclusiveness and diversity of the probe substrate, interaction of the probe substrates, influence of different inoculation conditions (by charging organic solvent, buffer solution and BSA) in a warm inoculation system and the enzyme kinetics characteristics of 16 probe reactions under the selected inoculation condition are comprehensively considered, a brand new in-vitro system is established by integrating high-sensitive and high-selective LC-MS / MS technology, so that the inhibitory effect of the tested compounds on the nine human liver main metabolic enzymes can be more accurately and comprehensively predicted in the high-throughput screening of the novel drug development, and the predictability on the interaction of the later metabolism can be improved.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
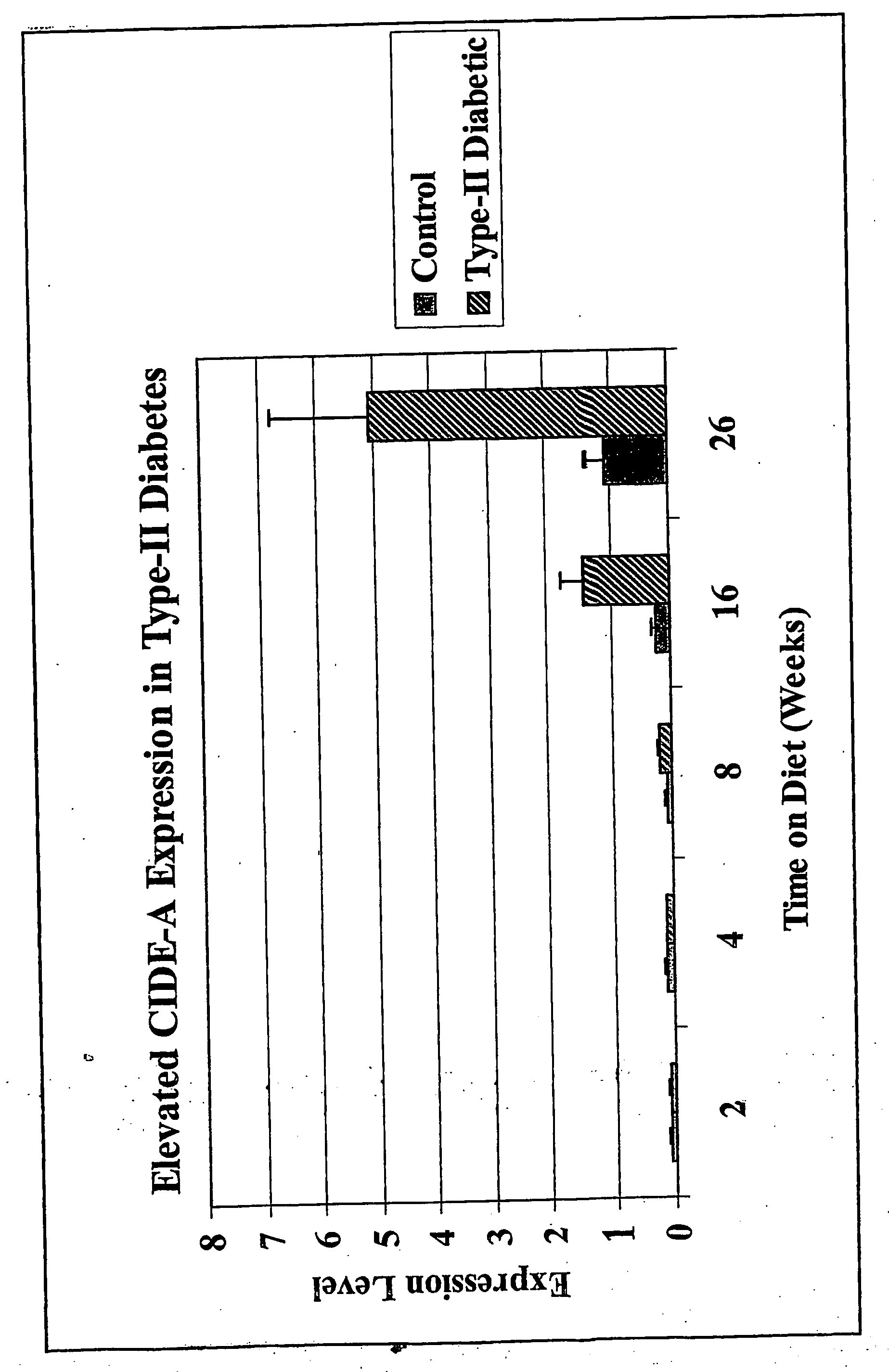
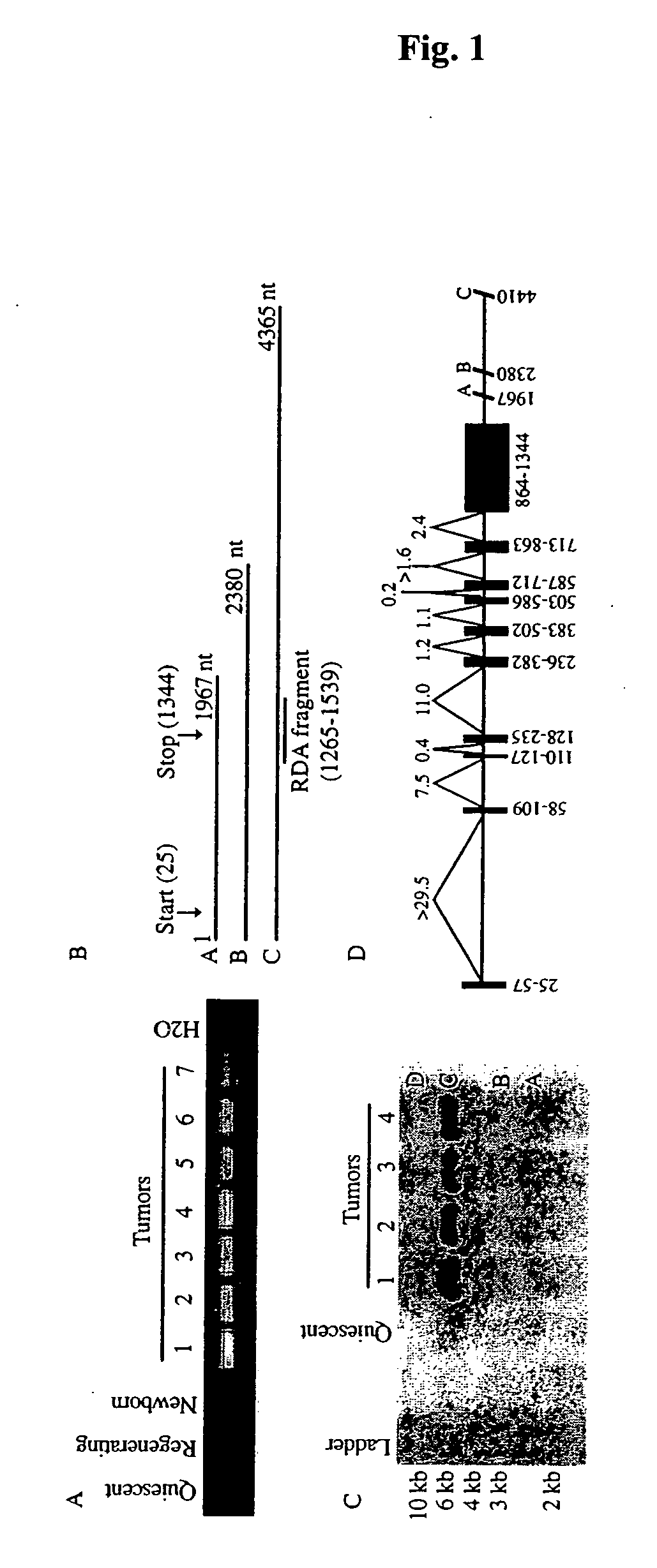
Gene up-regulated in regenerating liver
InactiveUS6027935AImprove scalabilityPromote regenerationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsRaspLiver disorder
The novel gene, Rasp-1, which is up-regulated in regenerating liver, is disclosed. The novel RASP-1 protein, which is encoded by the Rasp-1 gene, is also disclosed. In addition, antibodies against the Rasp-1 gene products are also disclosed. Furthermore, the use of Rasp-1 nucleic acid sequences, Rasp-1 gene products, and antibodies against Rasp-1 gene products in the treatment and diagnosis of liver disorders is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED TISSUE SCIENCES INC +1
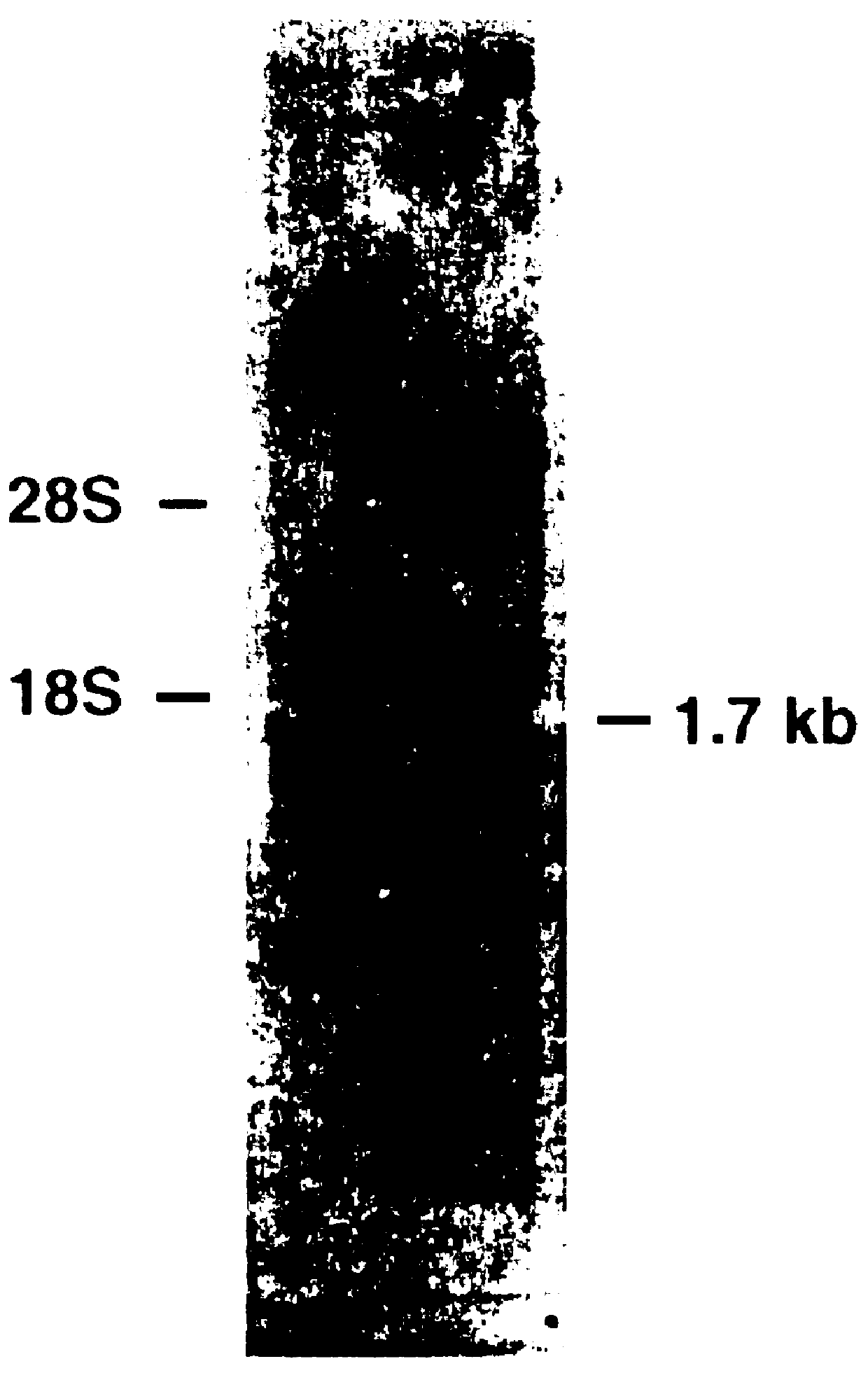
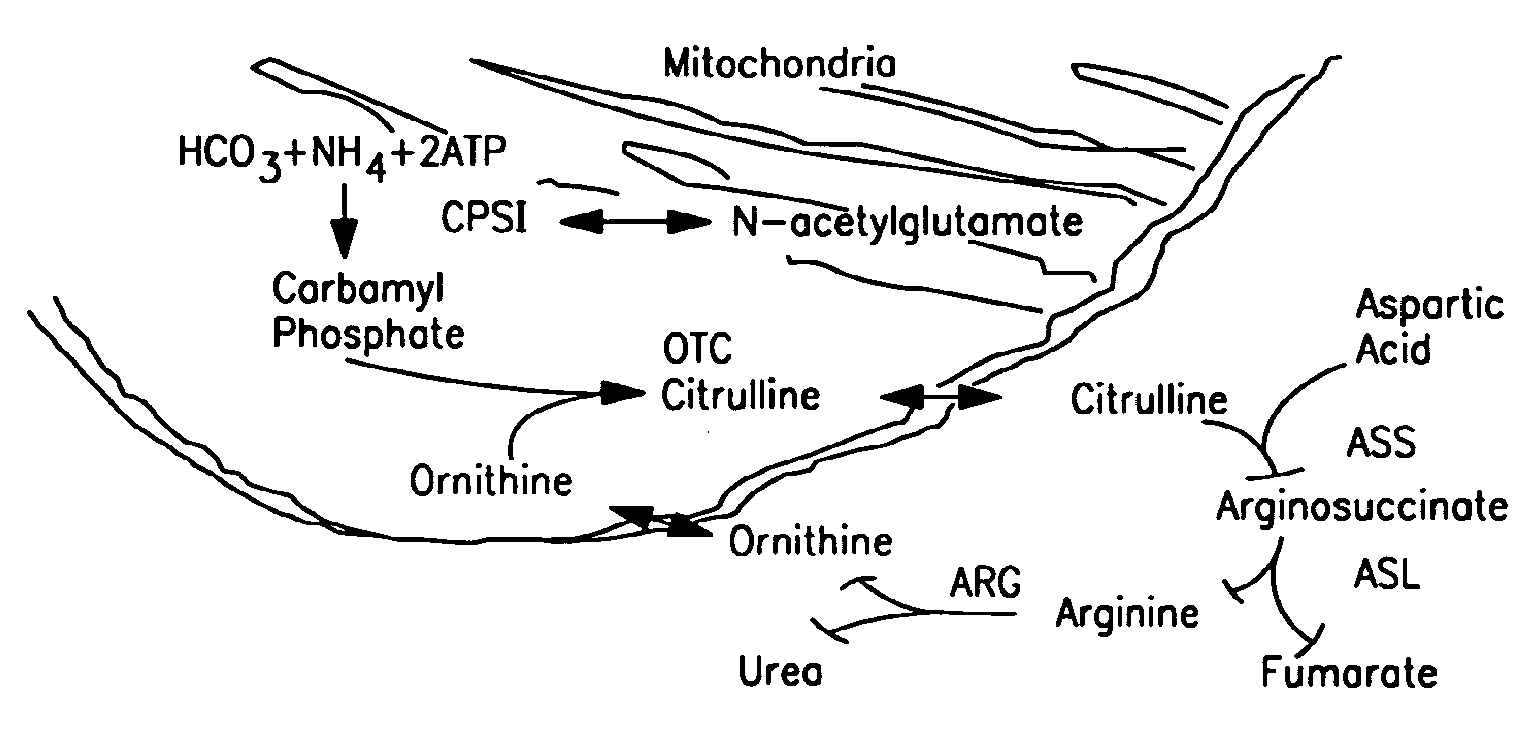
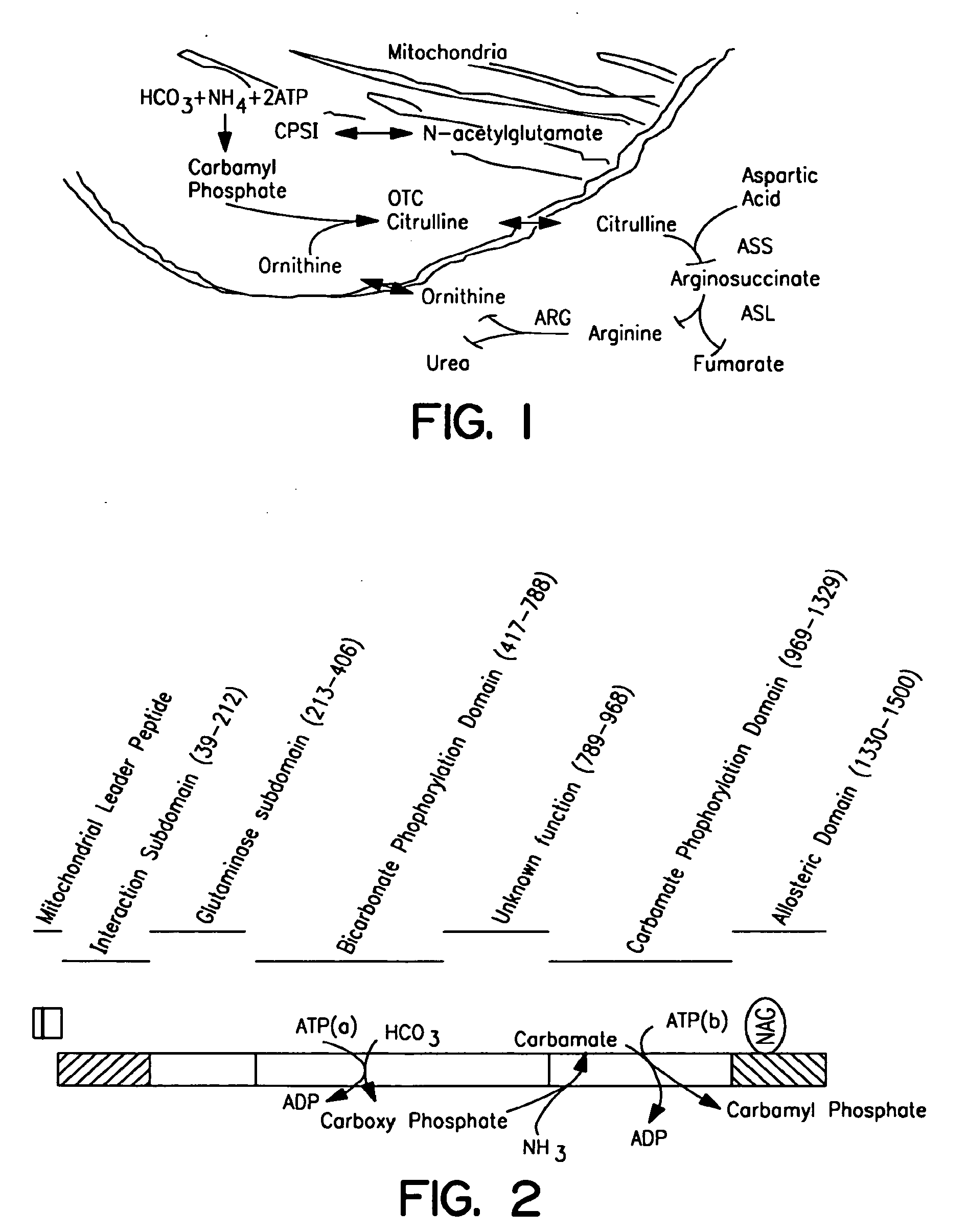
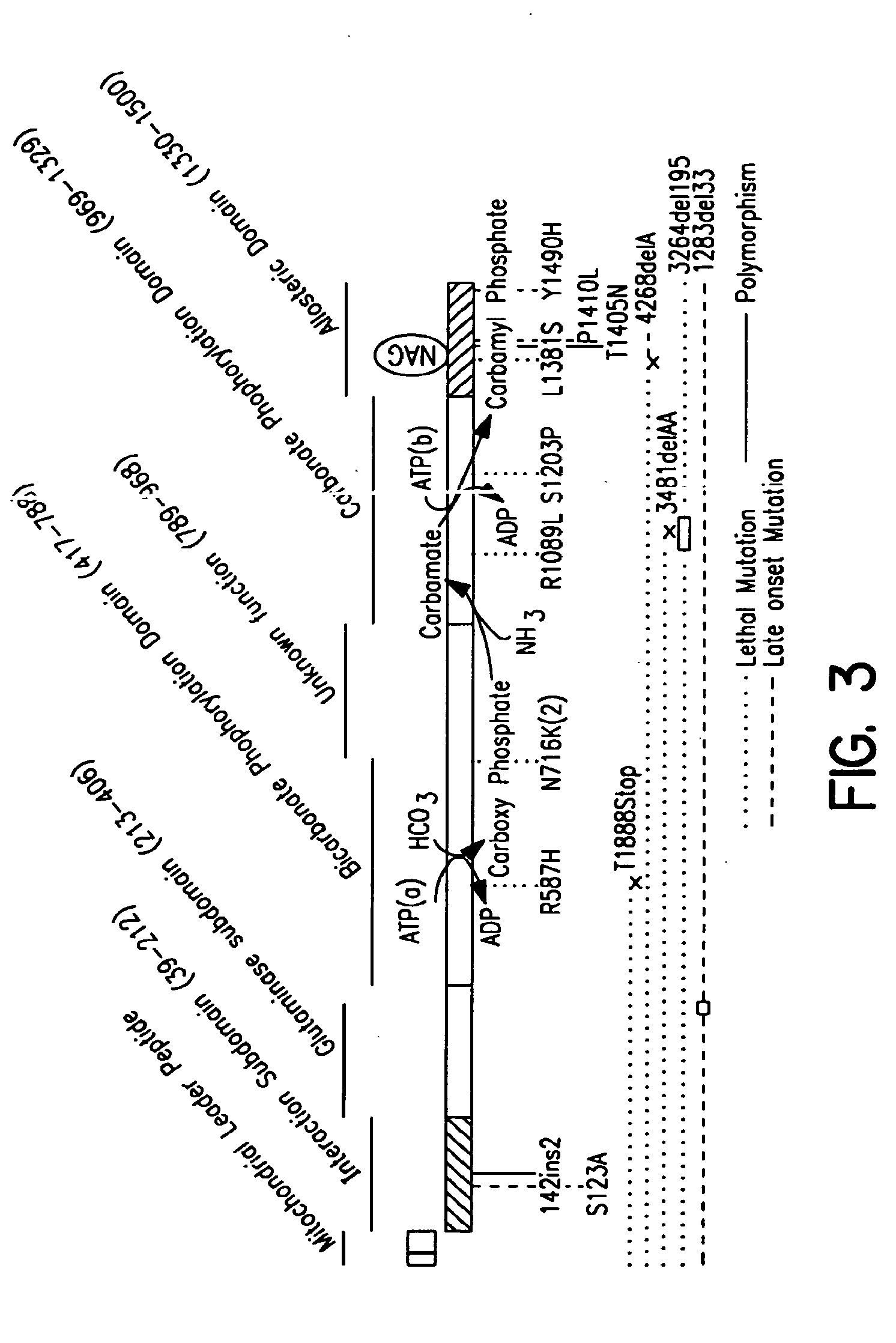
Therapeutic methods employing nitric oxide precursors
Isolated polynucleotide molecules and peptides encoded by these molecules are used in the analysis of human carbamyl phosphate synthetase I phenotypes, as well as in diagnostic and therapeutic applications, relating to a human carbamyl phosphate synthetase I polymorphism. By analyzing genomic DNA or amplified genomic DNA, or amplified cDNA derived from mRNA, it is possible to type a human carbamyl phosphate synthetase I with regard to the human carbamyl phosphate synthetase I polymorphism, for example, in the context of diagnosing and treating hepatic veno-occlusive disease (HVOD) associated with bone marrow transplants.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
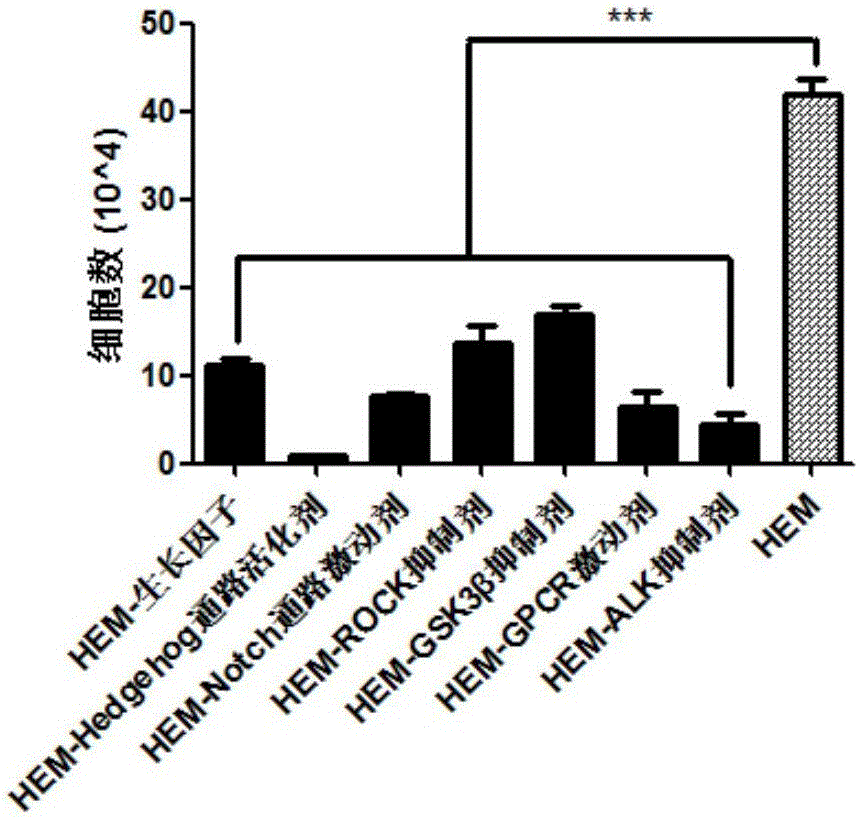
Animals comprising human hepatocellular tissue.
Non-human mammalian hosts are provided, comprising functional human hepatocytes. Isolated human hepatocytes or fragments of human hepatic tissue are introduced into the xenogeneic host in conjunction with one or more agent that stimulates human hepatocyte growth factor receptor. The human hepatocytes are maintained in the host by administration of one or more agent that stimulates human hepatocyte growth factor receptor, either continuously (e.g., via an implanted catheter or intravenous apparatus) or in discrete, regular dosages of the agent (e.g., via intravenous injections or oral dosages). The human hepatocytes are able to survive and function in the host animal for a period of at least 5 months.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Human liver progenitors
InactiveUS20050148072A1Low densityReduce in quantityHepatocytesGenetic material ingredientsProgenitorGlycophorin
Methods of isolating and cryopreserving progenitors from human liver are disclosed which include processing human liver tissue to provide a substantially single cell suspension comprising progenitors and non-progenitors of one or more cell lineages found in human liver; subjecting the suspension to a debulking step, which reduces substantially the number of non-progenitors in the suspension, and which provides a debulked suspension enriched in progenitors exhibiting one or more markers associated with at least one of the one or more cell lineages; and selecting from said debulked suspension those cells, which themselves, their progeny, or more mature forms thereof express one or more markers associated with at least one of the one or more cell lineages. Among these markers are CD14, CD34, CD38, CD45, and ICAM. Hepatic progenitors are characterized as being 6-15μ in diameter, diploid, glycophorin A−, CD45−, AFP+++, ALB+, ICAM+, and with subpopulations varying in expression of CD14+. CD34++, CD38++, CD117+. These progenitor subpopulations have characteristics expected for cells that are particularly useful in liver cell and gene therapies and for establishing bioartificial organs.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Animal model having a chimeric human liver
The present invention features a non-human animal model that is susceptible to infection by human hepatotrophic pathogens, particularly human hepatitis C virus (HCV). The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having antiviral activity against HCV infection. The animals of the invention are also useful in assessing toxicity of various agents, as well as the activity of agents in decreasing blood lipids.
Owner:KMT HEPATECH
Eight human miRNAs
InactiveCN1800388AConform to structural featuresGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseGenetics
Owner:RADIOLOGY INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE SCI PLA
In-vitro construction method of liver cancer organ model
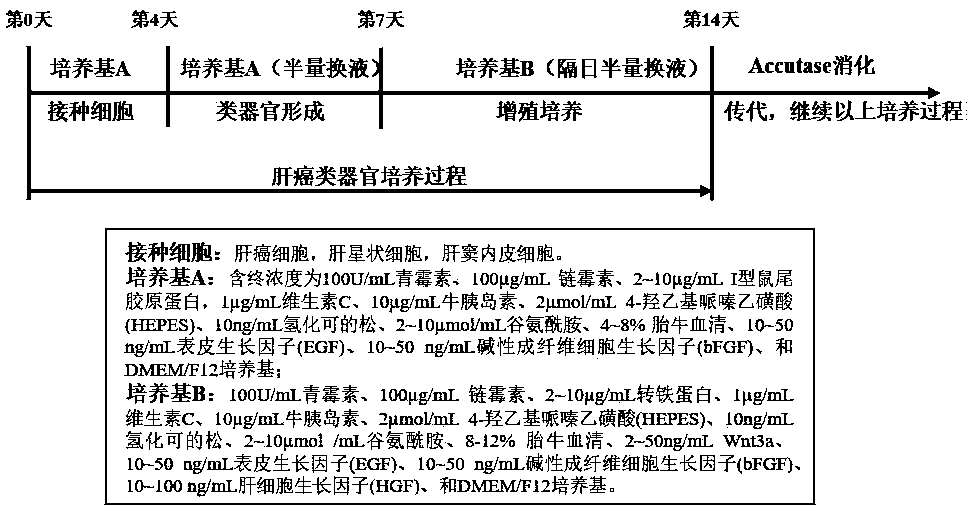
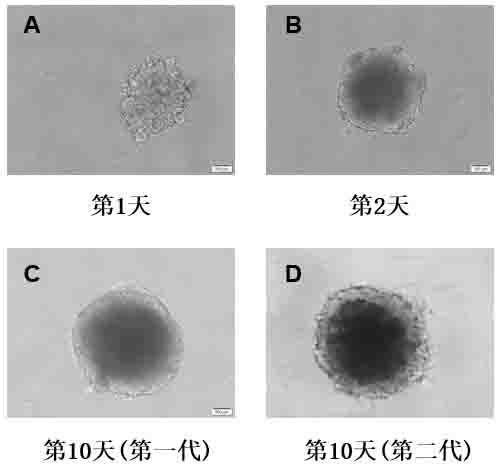
ActiveCN110004109AEasy constructionDetectable validityHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsOperability
The invention discloses an in-vitro construction method of a liver cancer organ model. Liver cancer cells, hepatic stellate cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are suspended in a culture medium A in a specific proportion; on the fourth day of culture, half of culture liquid is replaced, and culture is maintained; from the seventh day, the culture medium A is replaced with a culture mediumB, and then culture is continuously conducted for seven days; amplification subculture is conducted on the fourteenth day. On the basis of complex cellularity in a tumor microenvironment, the 3D liver cancer organ in-vitro model which is uniform in size, stable in structure, capable of being used for detecting the effectiveness of anticancer drugs and capable of achieving multiplication culture is quickly constructed. The constructed liver cancer organ model is simple in method, quick to construct, high in operability and suitable for researching a liver cancer generation and development mechanism, high-throughput screening of liver cancer drugs and the like, and has industrialization significance.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
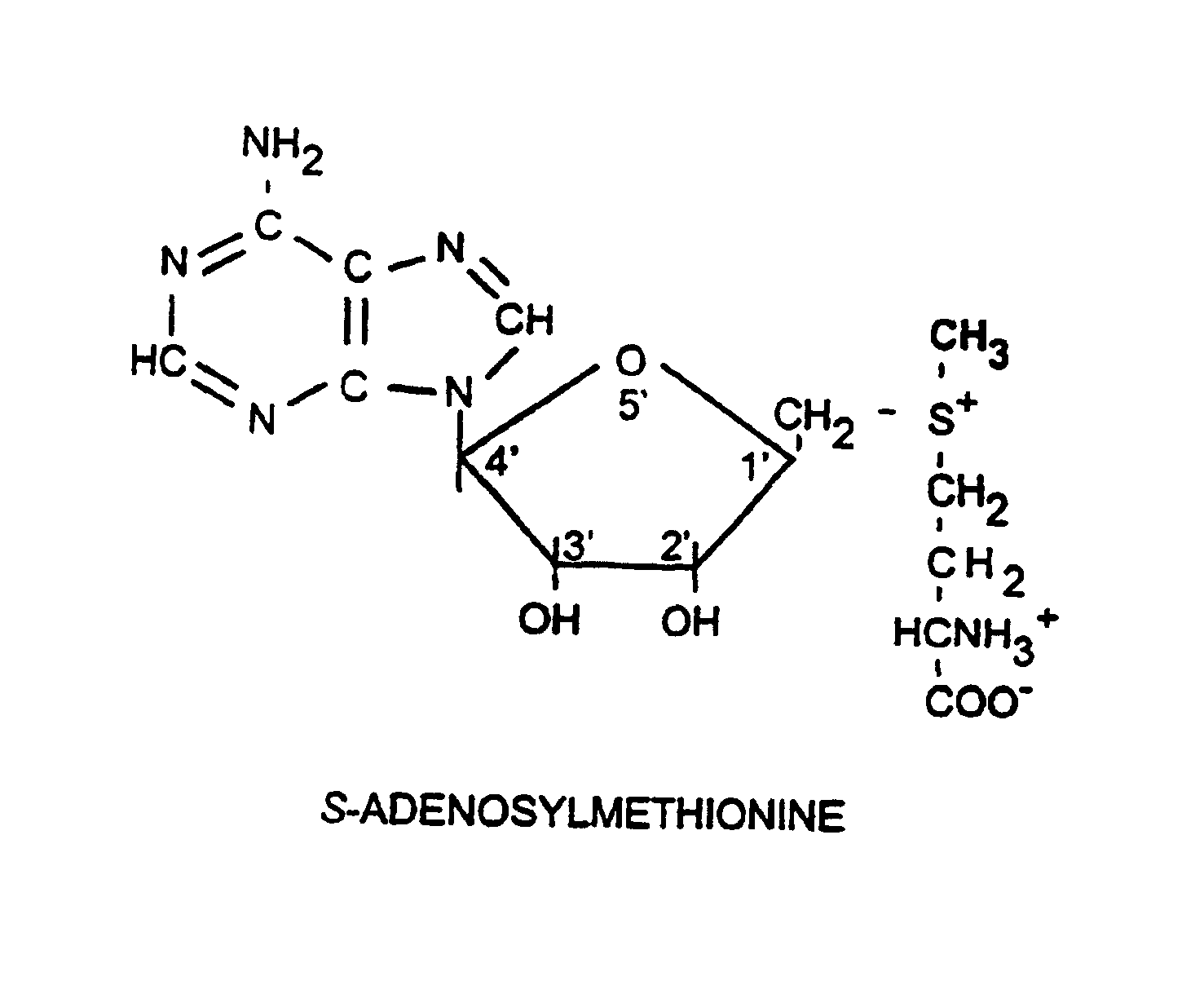
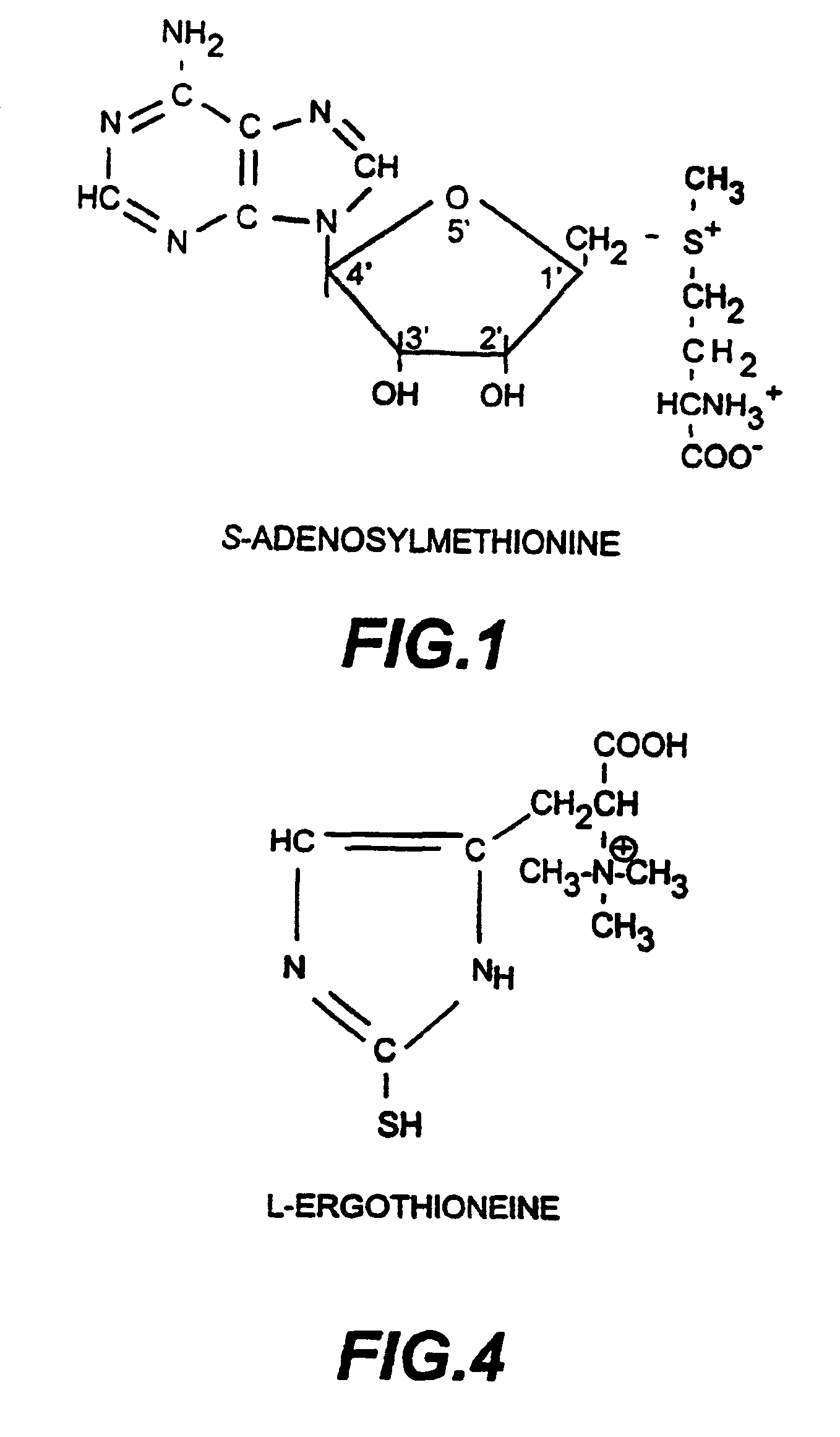
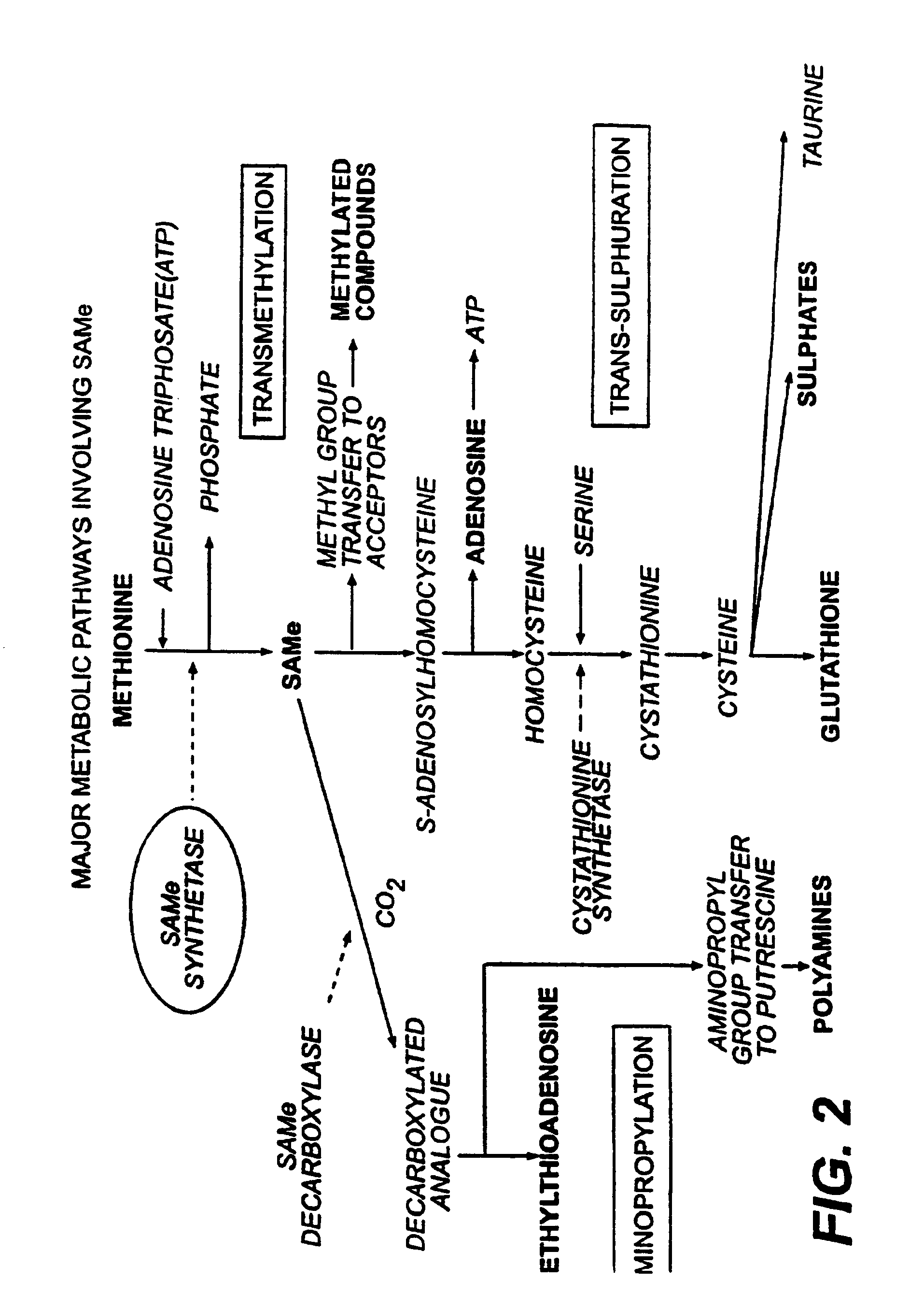
L-ergothioneine, milk thistle, and S-adenosylmethionine for the prevention, treatment and repair of liver damage
This invention provides therapeutic compositions and combinations for the protection, treatment and repair of liver tissue. The invention relates to novel compositions and combinations comprising two or more compounds selected from the group consisting of S-adenosylmethionine, L-ergothioneine, and a substance selected from the group consisting of constituents of Milk thistle (Silybum marianum), silymarin and active components of silymarin, whether naturally, synthetically, or semi-synthetically derived, and to methods of preventing and treating liver disease and of repairing damaged liver tissue. The invention also provides a method of administering these compositions and combinations to humans or animals in need thereof.
Owner:NUTRAMAX LABORATORIES INC
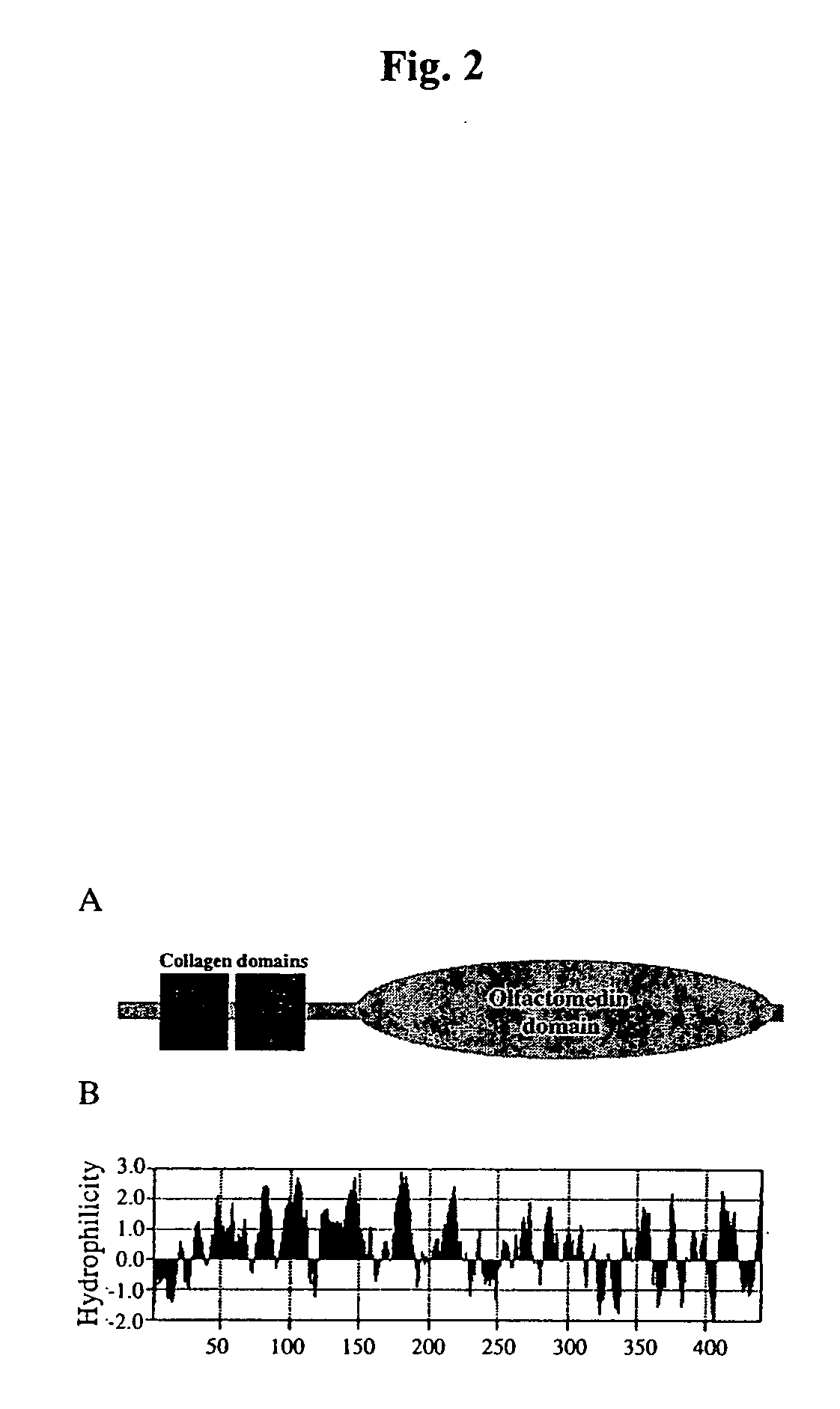
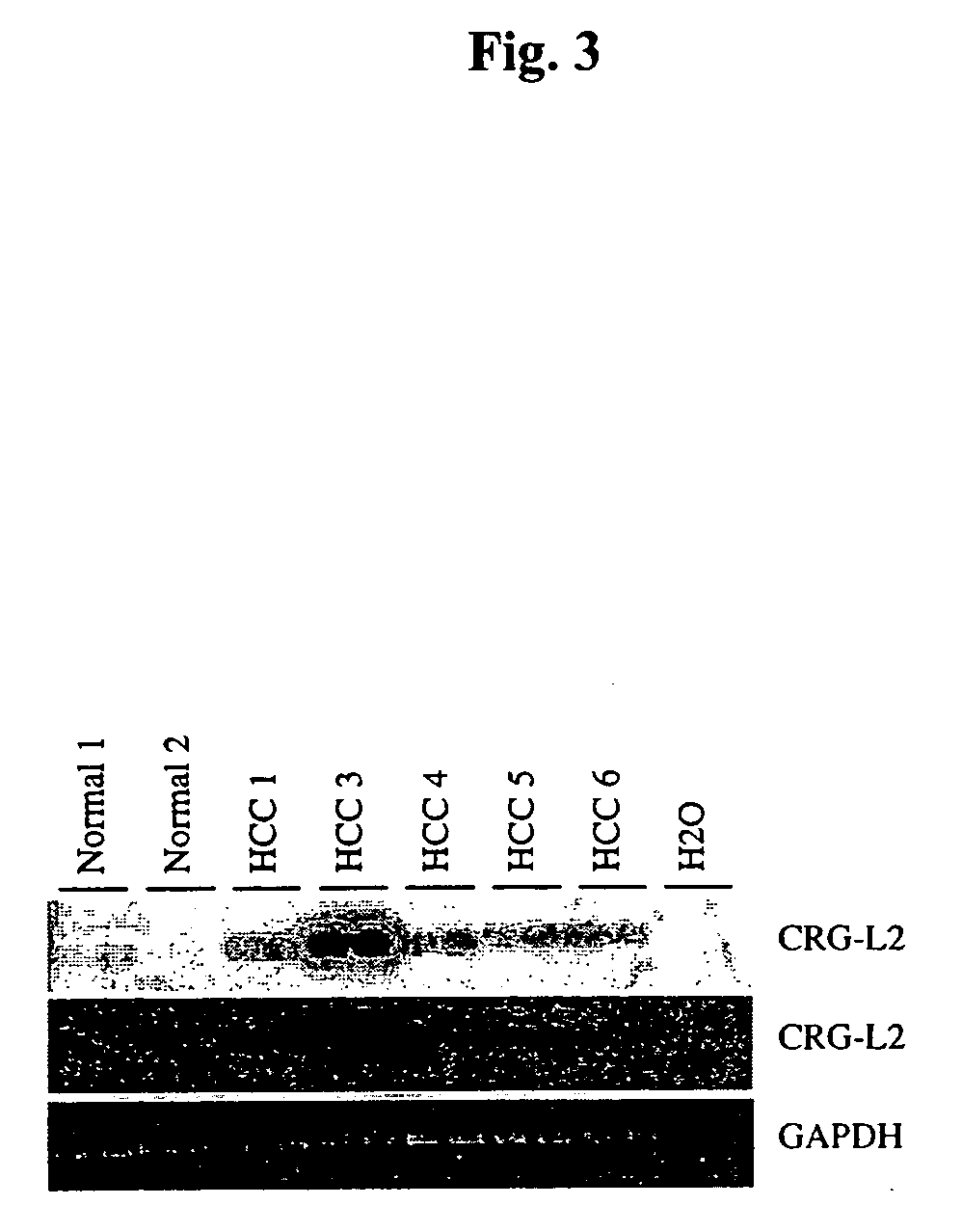
Liver tumor marker sequences
InactiveUS20070042420A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsKidney cancerPreneoplastic foci
Polypeptides whose expression is upregulated in liver tumor cells and cells from liver preneoplastic foci relative to expression in normal liver cells are disclosed as are polynucleotides that encode the polypeptides. In humans, the polynucleotide maps to a region of chromosome 15. The overexpression has also been confirmed in human liver, breast, colon and kidney cancer cell lines. It is believed that the polypeptides are overexpressed in tumor and preneoplastic cells in general.
Owner:FARNHAM PEGGY J +2
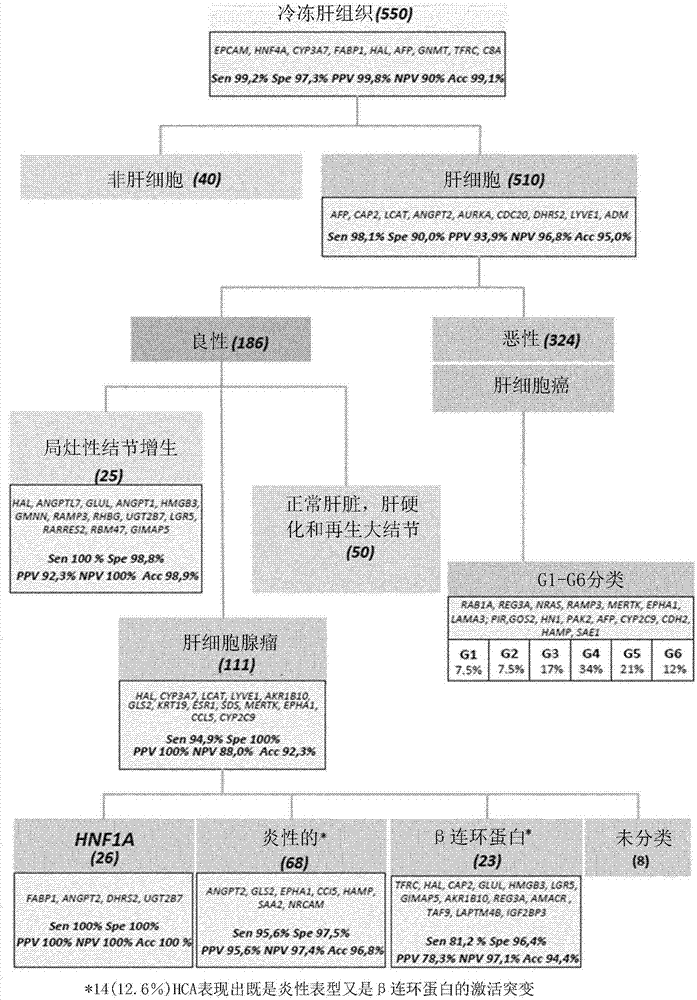
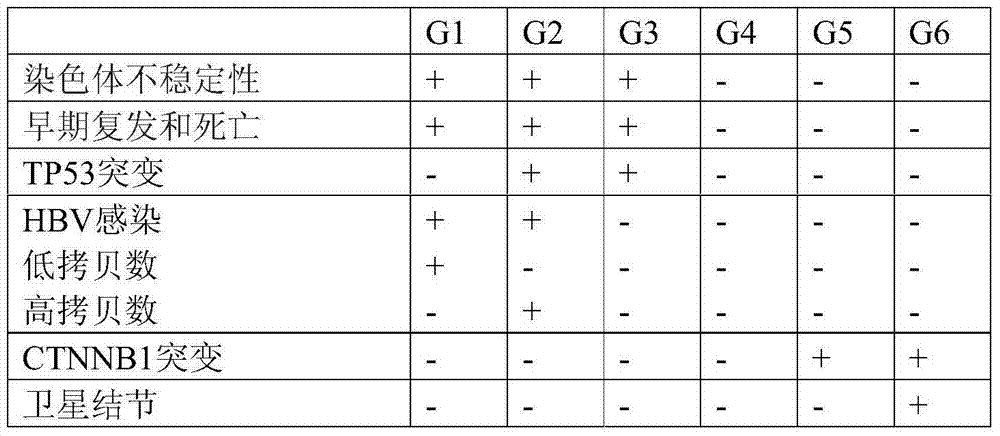
A new method for classification of liver samples and diagnosis of focal nodule dysplasia, hepatocellular adenoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma
The present invention relates to the technical field of liver diseases, their classification and diagnosis. It provides a new method for classifying a liver sample between non- hepatocellular sample; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) sample with further classification into one of subgroups G1 to G6; focal nodule dysplasia (FNH) sample; hepatocellular adenoma (HCA) sample with further classification into HNF1A mutated HCA, inflammatory HCA, β catenin mutated HCA or other HCA sample; and other benign liver sample, based on determination in vitro of genes expression profiles and analysis of the expression profile using algorithms calibrated with reference samples. The invention also provides kits for the classification of liver samples, and methods of treatment of liver disease in a subject based on a preliminary classification of a liver sample of said subject.
Owner:INTEGRAGEN +2
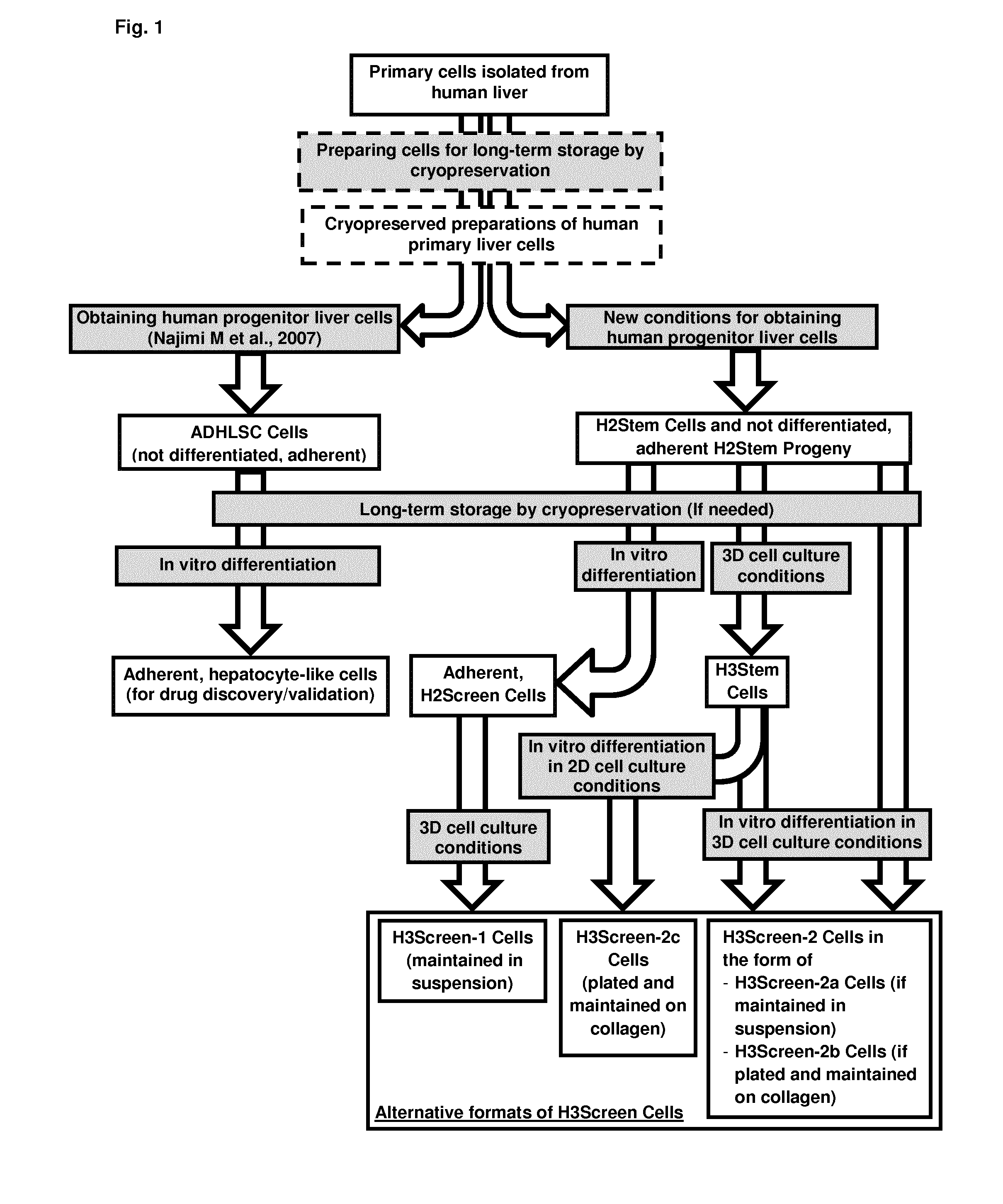
Method for producing adult liver progenitor cells
Novel adult liver progenitor cells (called H2Stem Cells) have been have been characterized on the basis of a series of biological activities and markers. Methods for producing H2Stem Cells allow providing such cells in the form of adherent cells and three-dimensional cell clusters in suspension that can be differentiated into cells having strong liver-specific activities and / or that can be used for treating liver diseases or for evaluating the efficacy, the metabolism, and / or toxicity of a compound.
Owner:PROMETHERA THERAPEUTICS SA
Bioreactor of artificial liver
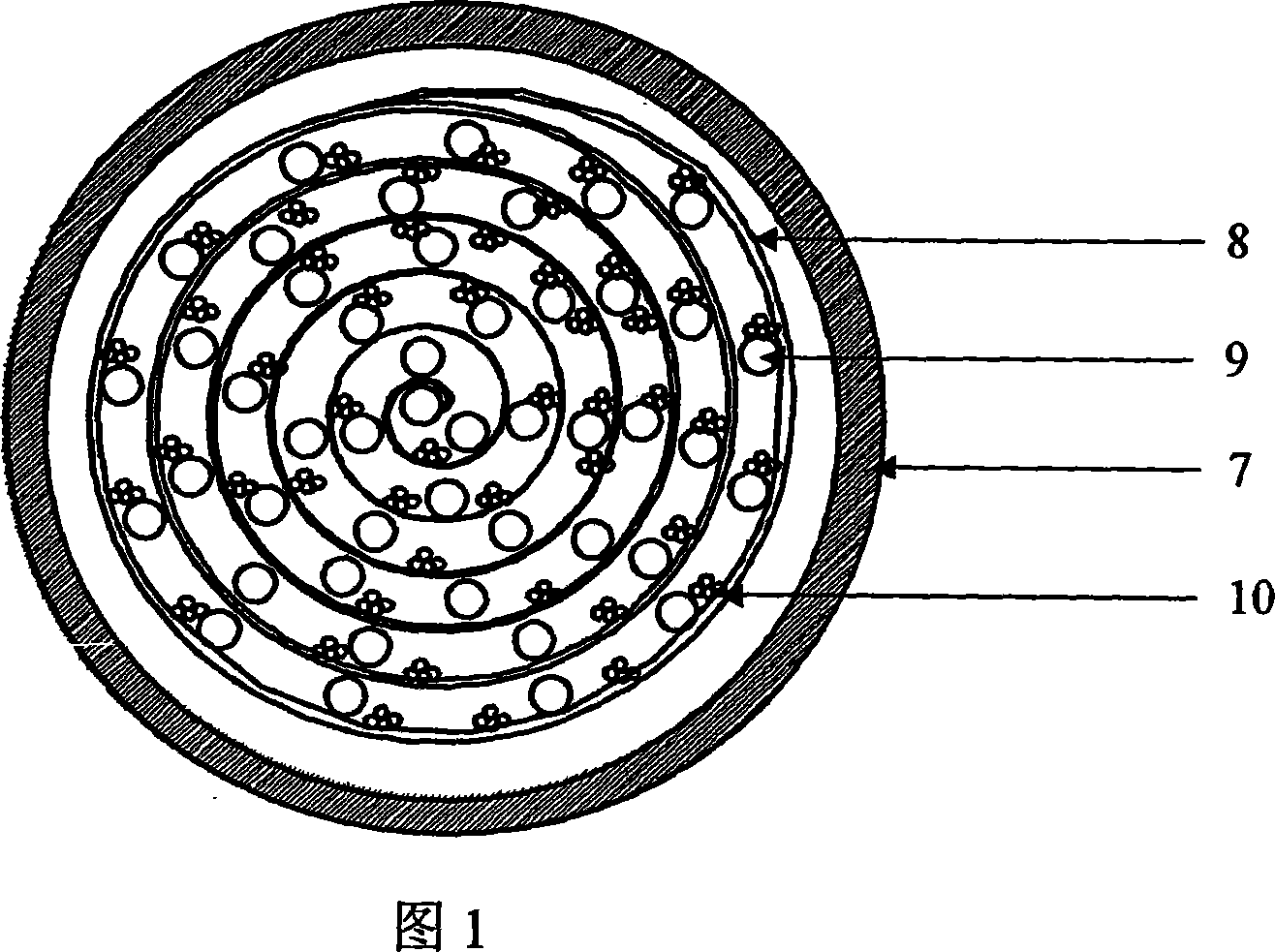
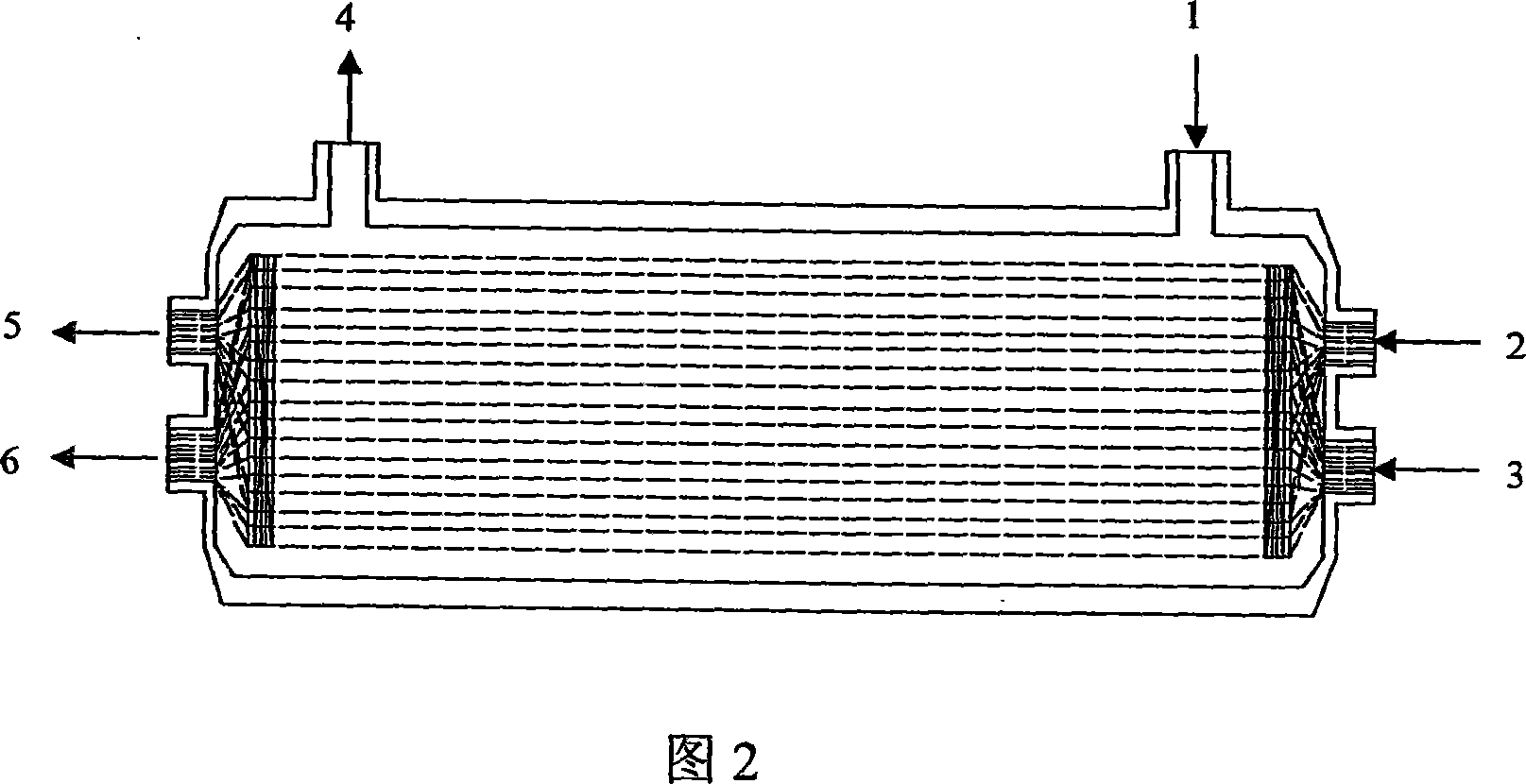
InactiveCN101050418AInnovative designAchieve adherent growthTissue/virus culture apparatusProsthesisFiberHollow fibre
This invention relates to an artificial live bioreactor with nanofiber scaffold material as the culture medium for liver cells. A plasma inlet and an oxygen inlet are set at one end of the bioreactor hull, while a plasma outlet and an oxygen outlet are set at the other end. A nutrient solution inlet and an outlet are set at both ends of one side of the bioreactor hull, respectively. A culture medium composed of nanofiber scaffold and hollow fibers is set in the bioreactor hull. The nanofiber scaffold and the hollow fibers form coiled sandwich structure, with the nanofiber scaffold coiled into spiral drum and the hollow fibers encapsulated in the interlayer. The liver cell aggregates are adhered to the hollow fibers. An oxygen passage is set in the bioreactor to realize real-time oxygen supplement.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com