Bioreactor of artificial liver
A bioreactor and artificial liver technology, applied in biochemical instruments, biochemical equipment and methods, suction devices, etc., can solve the problems of decreased biological activity, death, and shedding of liver cells, so as to promote reproduction and growth, and improve biological activity , the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0017] 1. Preparation of nanofibrous scaffolds: select different solvents to dissolve polymers (alginate, polylysine, chitosan, agarose, polyvinyl alcohol, etc.) to prepare electrospinning solutions. According to the different properties of the polymer solution, different electrospinning conditions (voltage, receiving distance, injection speed) are formulated, and then spinning is carried out. Adjustable shape and thickness. The nanofiber scaffolds of different materials are modified and sterilized accordingly to prepare nanofiber scaffolds that can be placed in cell culture fluid as cell growth substrates.
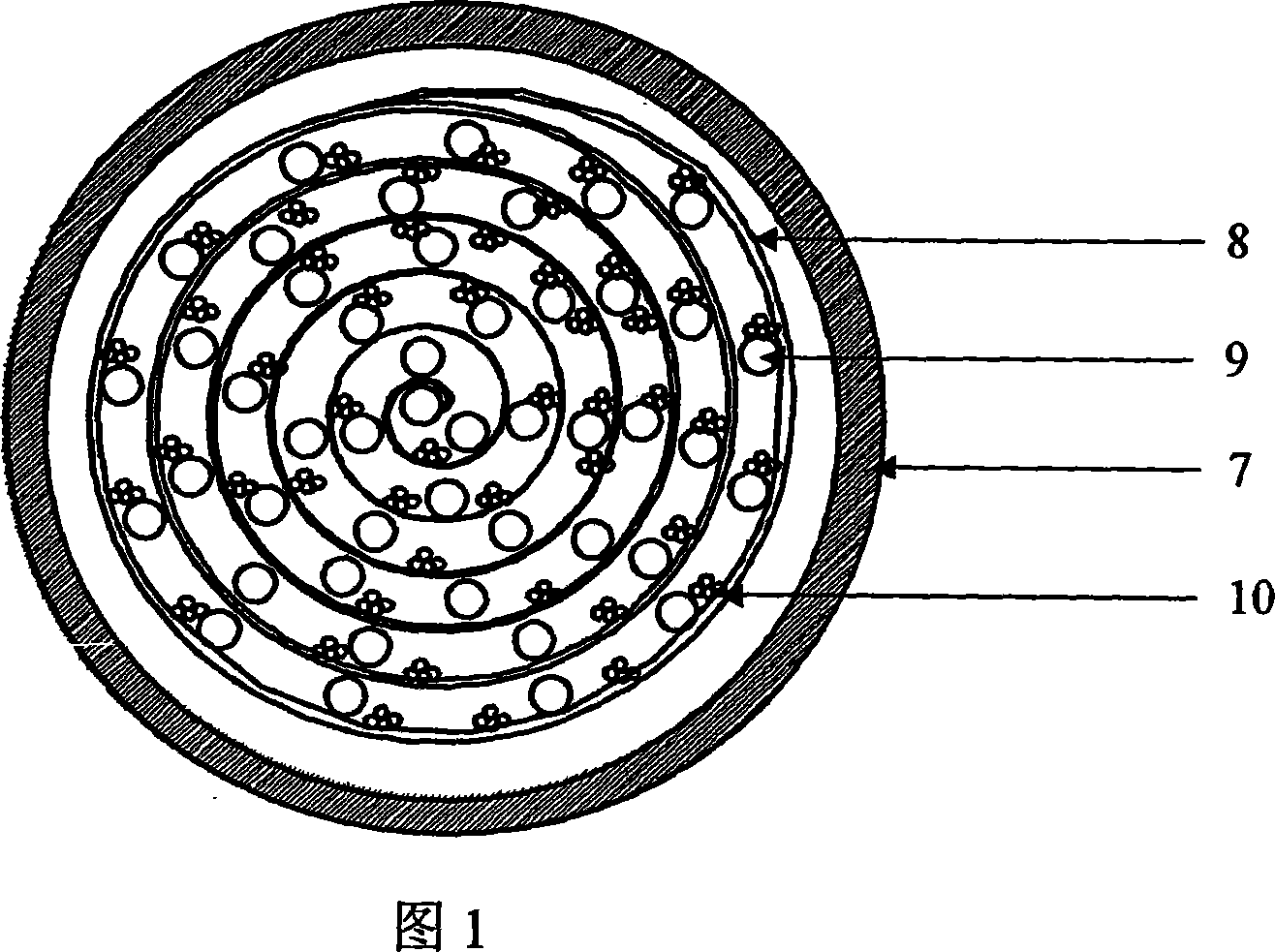
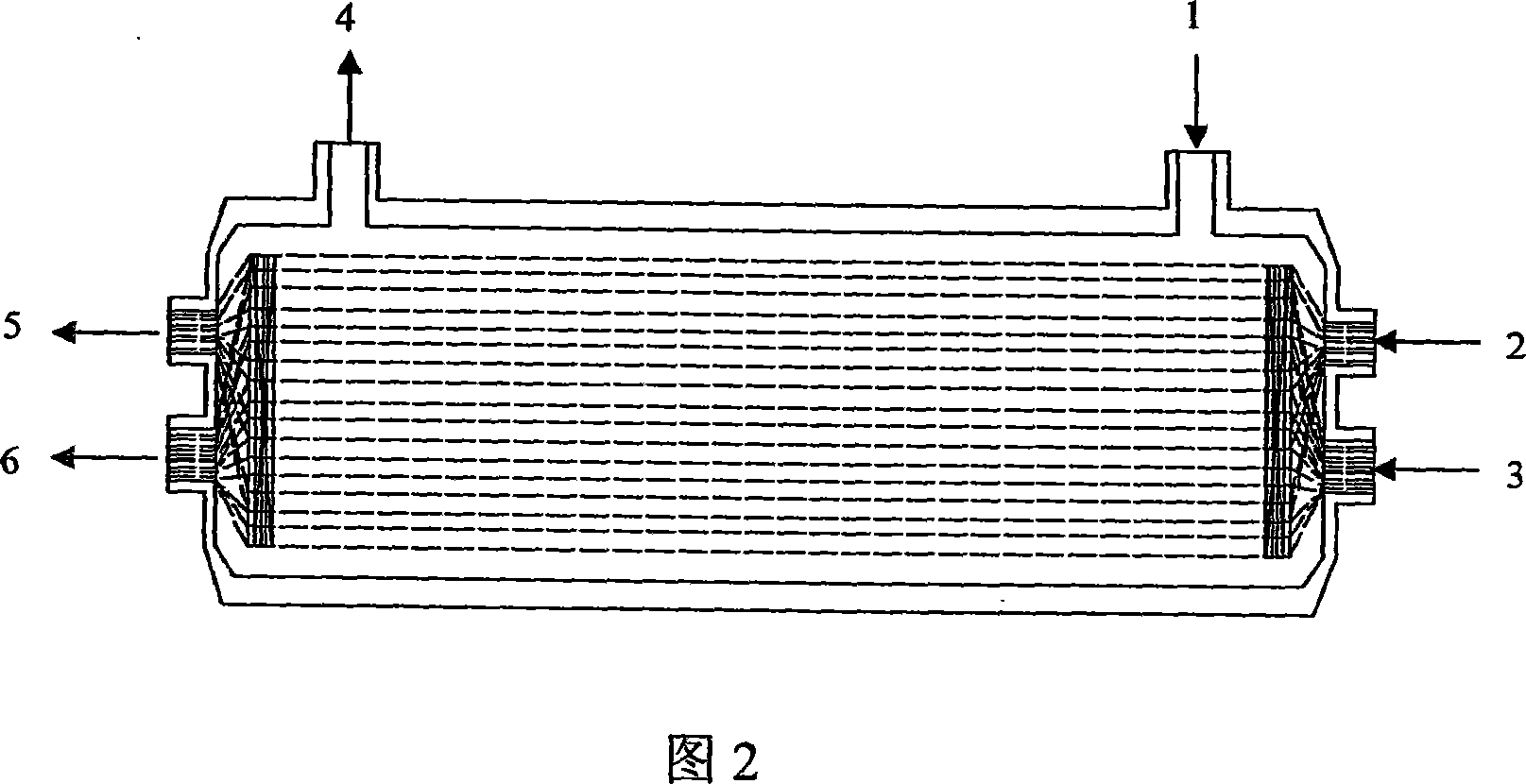
[0018] 2. Structural design of hollow fiber and nanofiber support: flatten the nanofiber non-woven fabric support, arrange polysulfone hollow fibers in sequence on the support (with a distance of 0.5mm to 2mm), and then curl the nanofiber support to wrap the hollow fiber in it. Inside, the core components of the bioreactor are made. One hollow fiber is selected at inter...
example 1
[0020] Example 1: This new type of bioreactor was fabricated using alginate as the raw material of the nanofiber scaffold.
[0021] 1. Preparation of nanofiber scaffold: (1) Preparation of electrospinning solution: Sodium alginate was dissolved in deionized water to prepare concentration as mass ratio W 海藻酸钠 :W 去离子水 = 4% solution. Polyethylene oxide (Mw=900kD) was dissolved in deionized water to prepare a concentration of mass ratio W 聚氧化乙烯 :W 去离子水 = 4% solution. Then the two solutions are mixed in the volume ratio V 海藻酸钠溶液 :V 聚氧化乙烯溶液 = Mix at a ratio of 8:2, stir at room temperature for 100 min until uniformly mixed, and obtain a mixed solution of sodium alginate and polyethylene oxide. Then by volume ratio V 表面活性剂 :V 混 合溶液 =0.5% ratio Add surfactant Triton X-100, keep stirring for 10min. Then according to the volume ratio V 助溶剂 :V 混合溶液 The co-solvent dimethyl sulfoxide was added at a rate of =10%. Stirring was continued for 60 min at room temperature. That is, a...
example 2
[0024] Example 2: Using chitosan as the raw material of the nanofiber scaffold to make this new bioreactor.
[0025] 1. Preparation of nanofiber support: (1) Preparation of electrospinning solution: dissolving chitosan (Mw=190kD, Deacetylation=85%) in an acetic acid solution with a mass ratio of 5% is prepared into a concentration of mass ratio W 壳聚糖 :W 醋酸溶液 = 2% solution. Polyethylene oxide (Mw=900kD) is dissolved in the acetic acid solution that the mass ratio is 5% and is prepared into the concentration that the mass ratio is W 聚氧化乙烯 :W 醋酸溶液 = 3% solution. Then the two solutions are mixed in the volume ratio V 壳聚 糖溶液 :V 聚氧化乙烯溶液 = 9: 1 ratio mixing, stirring at room temperature for 100min until mixing evenly, to obtain a mixed solution of chitosan and polyethylene oxide. Then by volume ratio V 表面活性剂 :V 混合溶液 =0.3% ratio Add surfactant Triton X-100, keep stirring for 10min. Then according to the volume ratio V 助溶剂 :V 混合溶液 The co-solvent dimethylformamide was added a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com