Patents
Literature
146 results about "Organ Model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Use of in vitro tissues or organ explants as surrogates for whole organism testing.
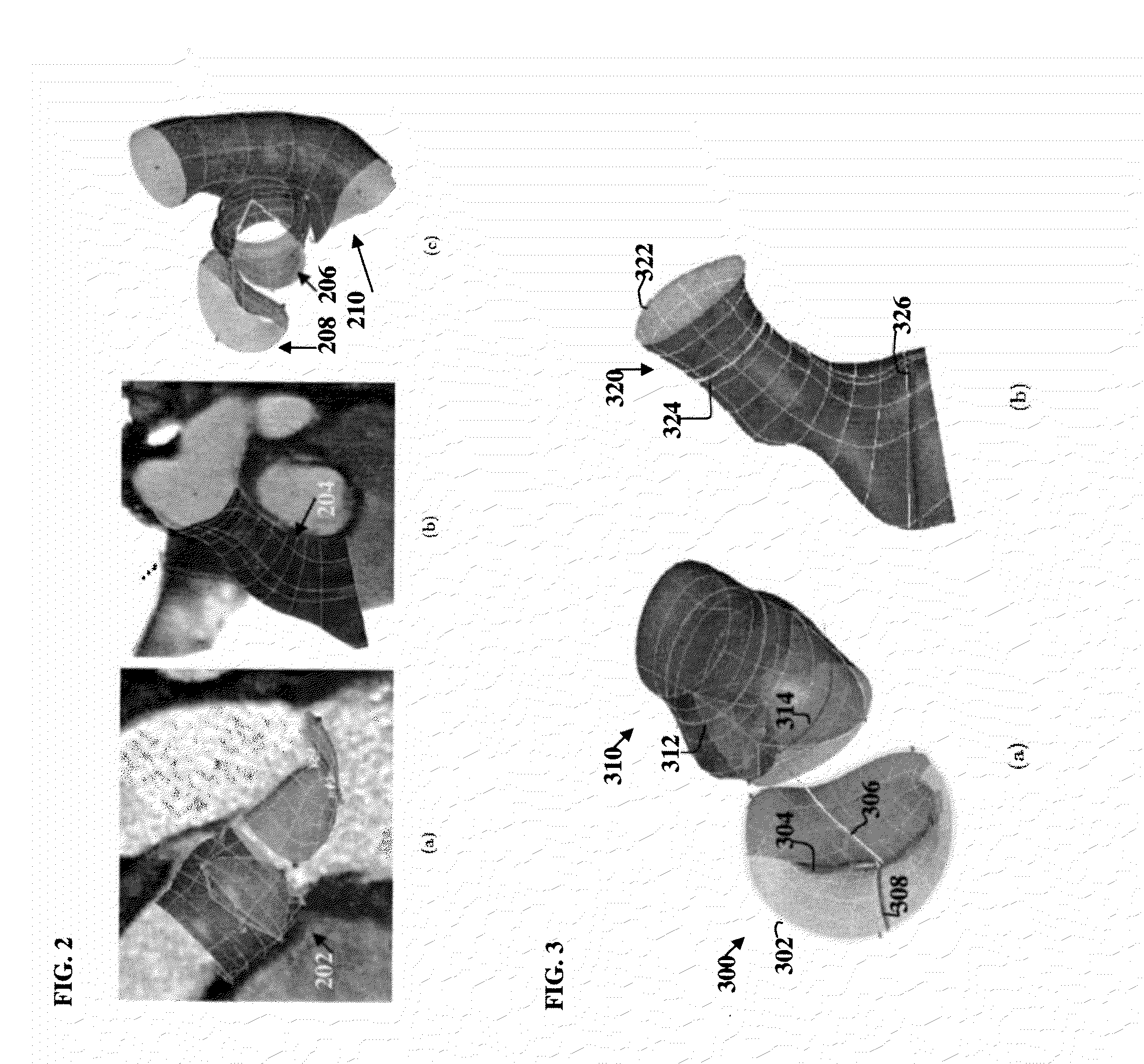
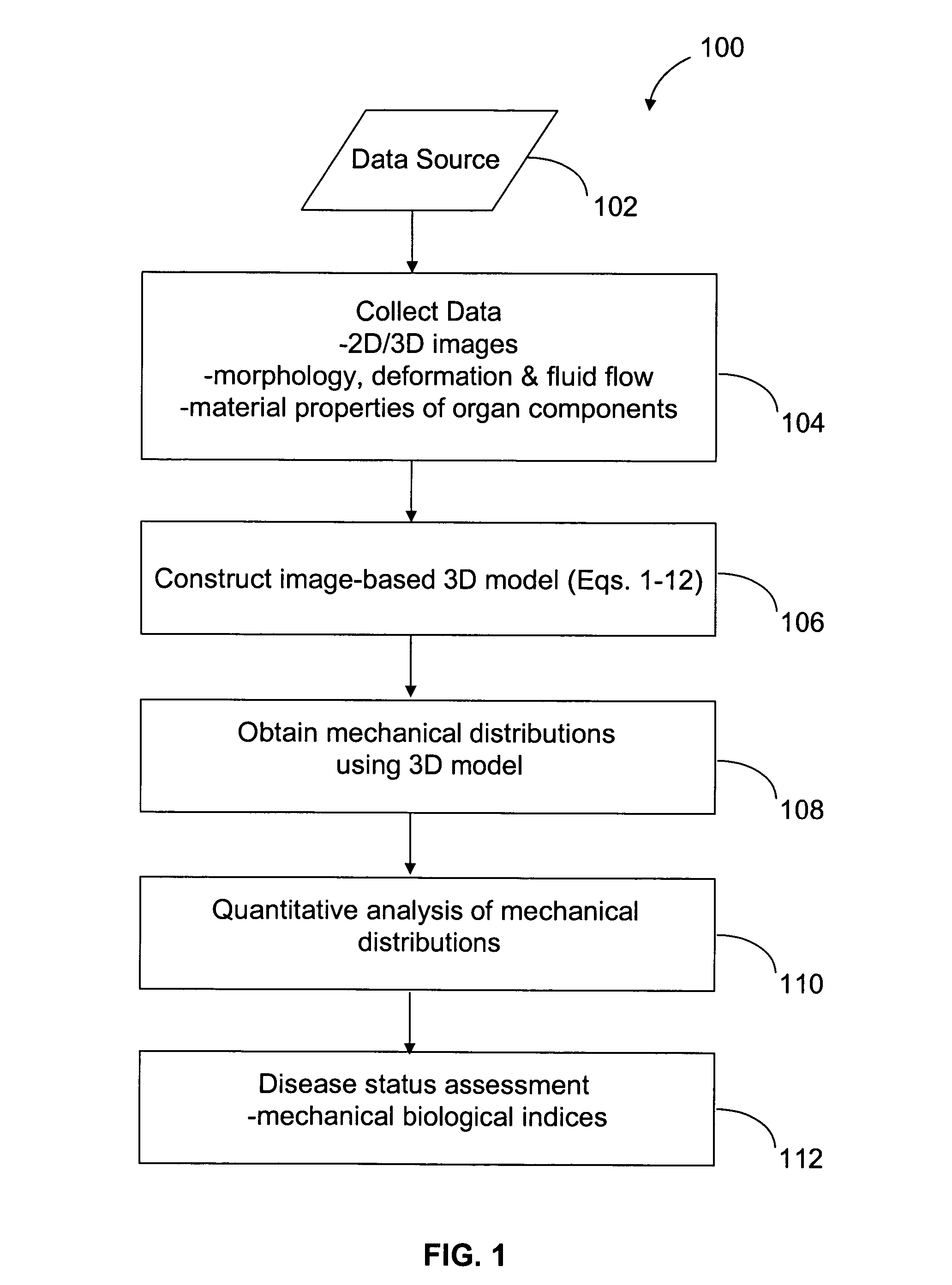
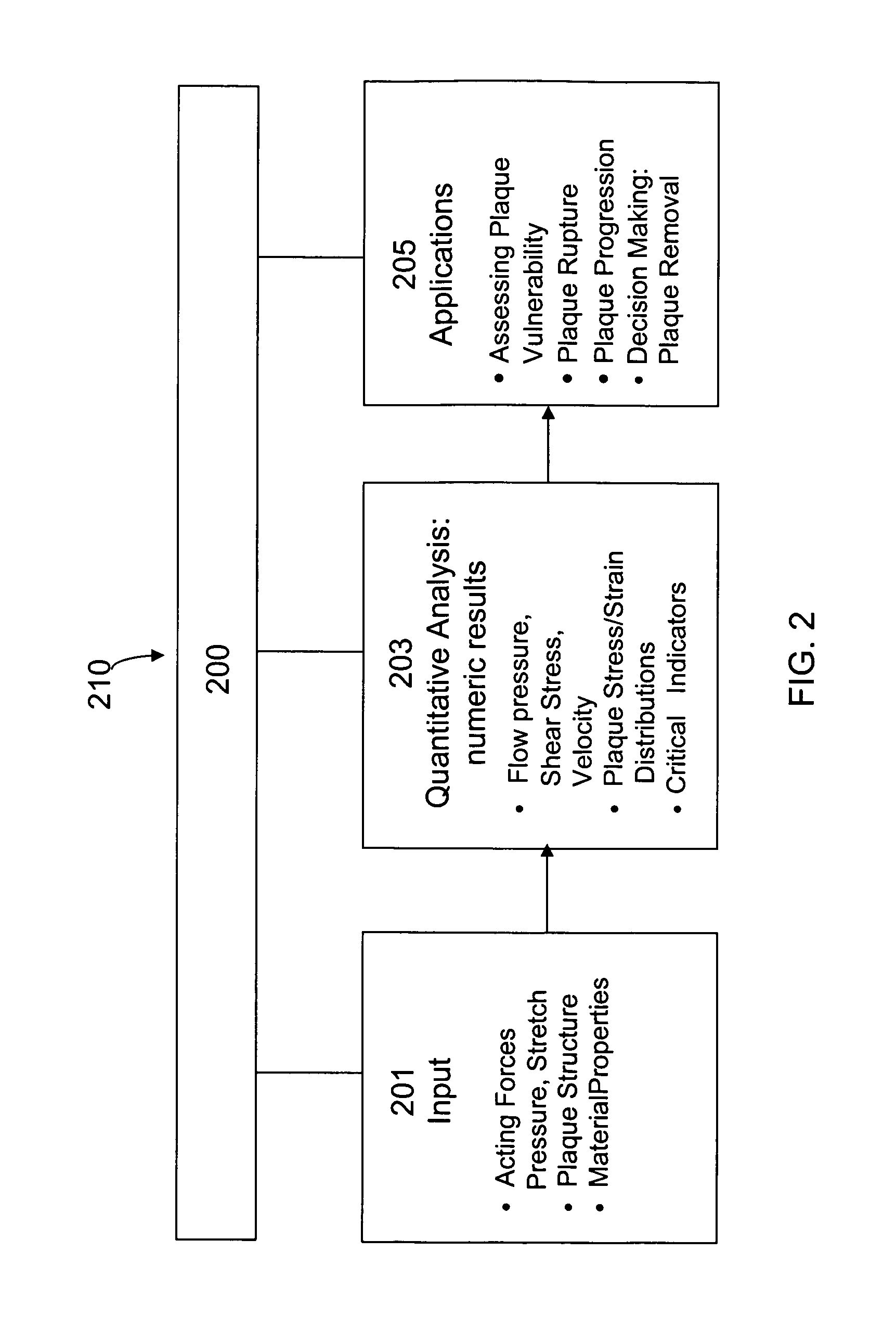
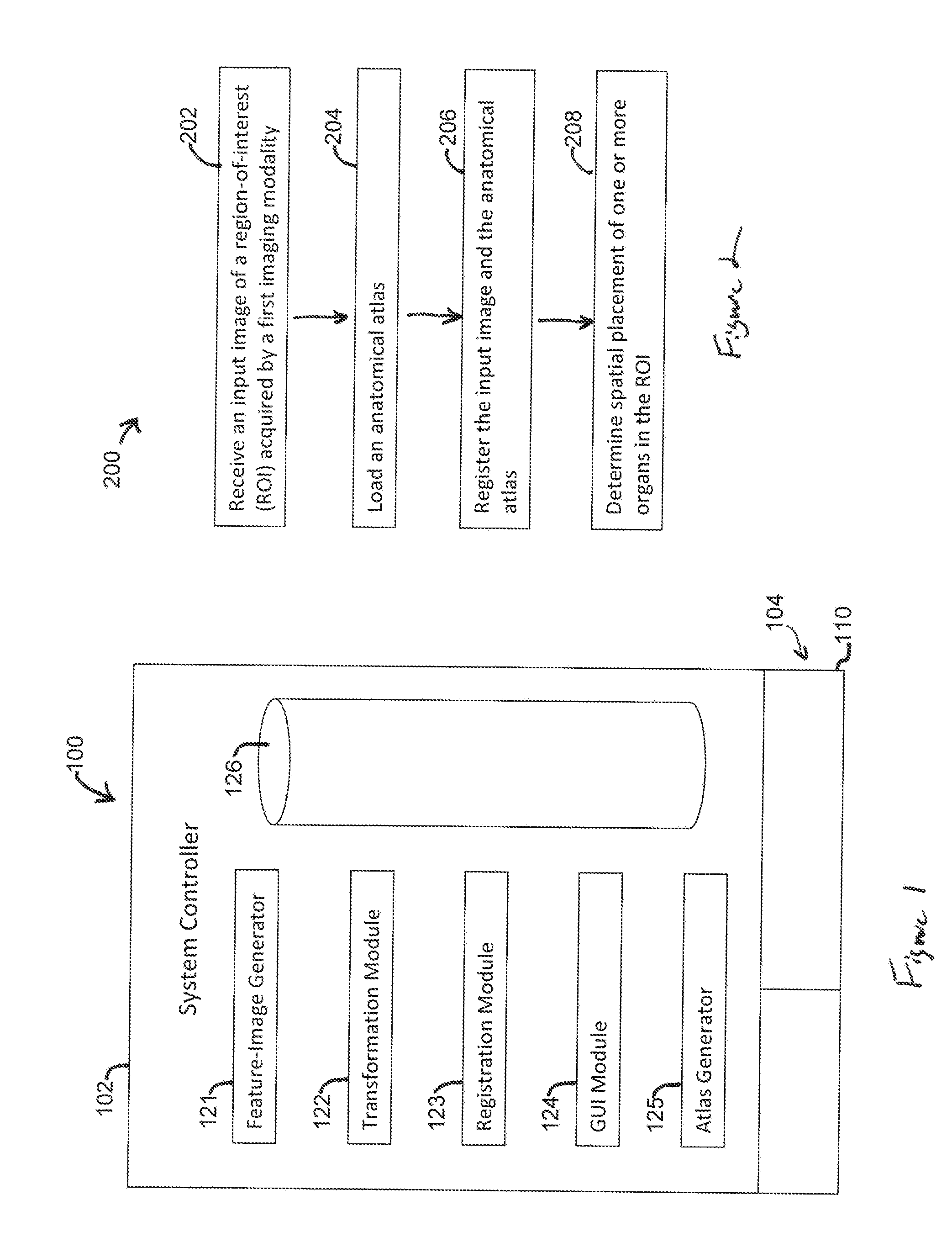
Image-based computational mechanical analysis and indexing for cardiovascular diseases
ActiveUS7751984B2Accurate modelingMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesOrgan ModelMedicine
A method and a computer system, for providing an assessment for disease status of a disease, such as a cardiovascular disease, employ construction of image-based 3D computational model of an organ representative of the disease status; computationally obtaining a certain mechanical distribution using the 3D-organ model; and computational, quantitative analysis of the mechanical distribution to provide an assessment for disease status of a disease. The image-based 3D computational model includes a fluid-structure interaction and multiple components within the organ.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Manipulation of tissue of organ type using the notch pathway
The present invention is directed to methods for altering the fate of a cell, tissue or organ type by altering Notch pathway function in the cell. The invention is further directed to methods for altering the fate of a cell, tissue or organ type by simultaneously changing the activation state of the Notch pathway and one or more cell fate control gene pathways. The invention can be utilized for cells of any differentiation state. The resulting cells may be expanded and used in cell replacement therapy to repopulate lost cell populations and help in the regeneration of diseased and / or injured tissues. The resulting cell populations can also be made recombinant and used for gene therapy or as tissue / organ models for research. The invention is directed to methods for of treating macular degeneration comprising altering Notch pathway function in retinal pigment epithelium cells or retinal neuroepithelium or both tissues. The present invention is also directed to kits utilizing the methods of the invention to generate cells, tissues or organs of altered fates. The invention also provides methods for screening for agonists or antagonists of Notch or cell fate control gene pathway functions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL +1
Model-based heart reconstruction and navigation
ActiveUS7773719B2Provide structureMinimize exposureImage enhancementImage analysisBase heartData set
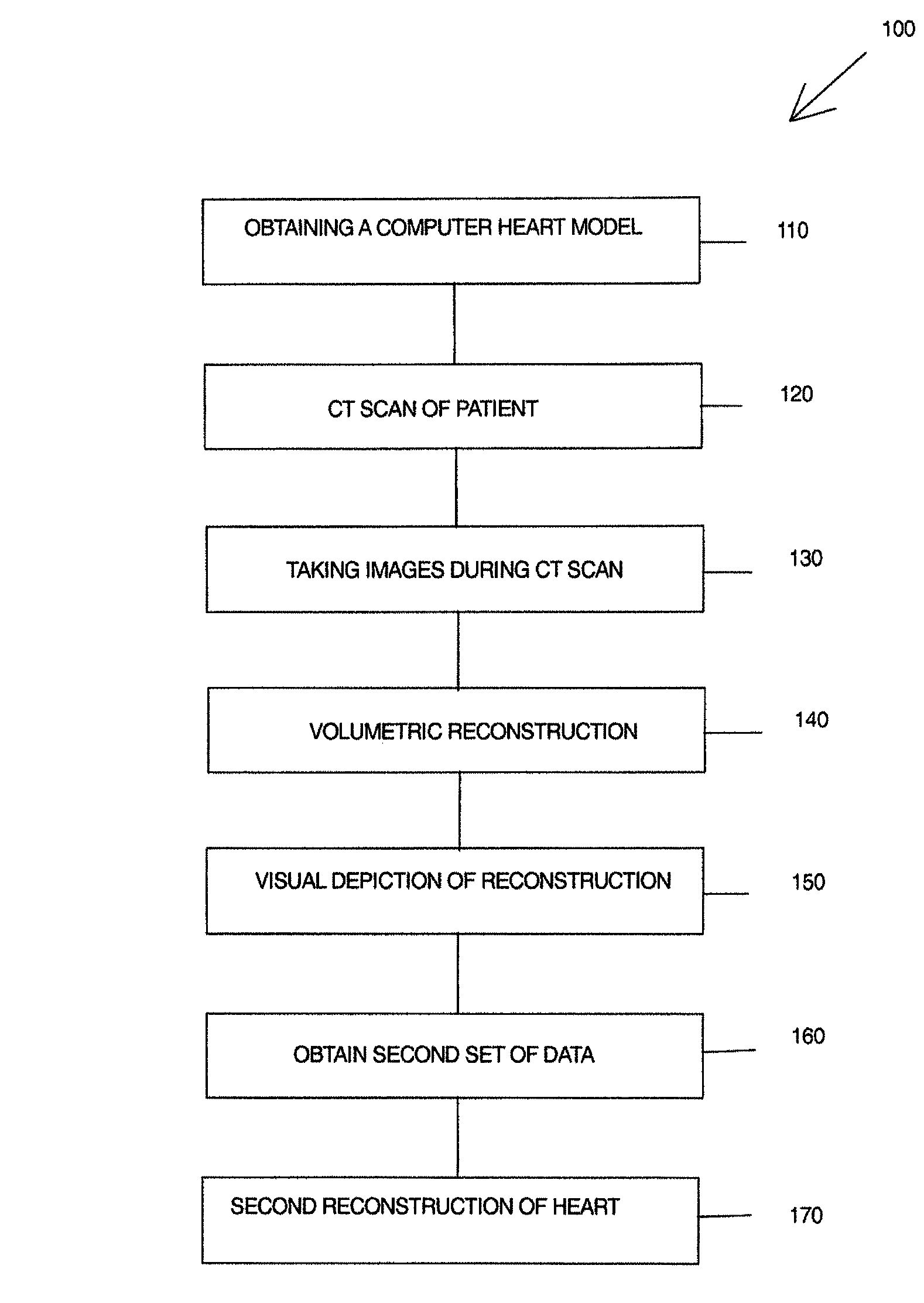
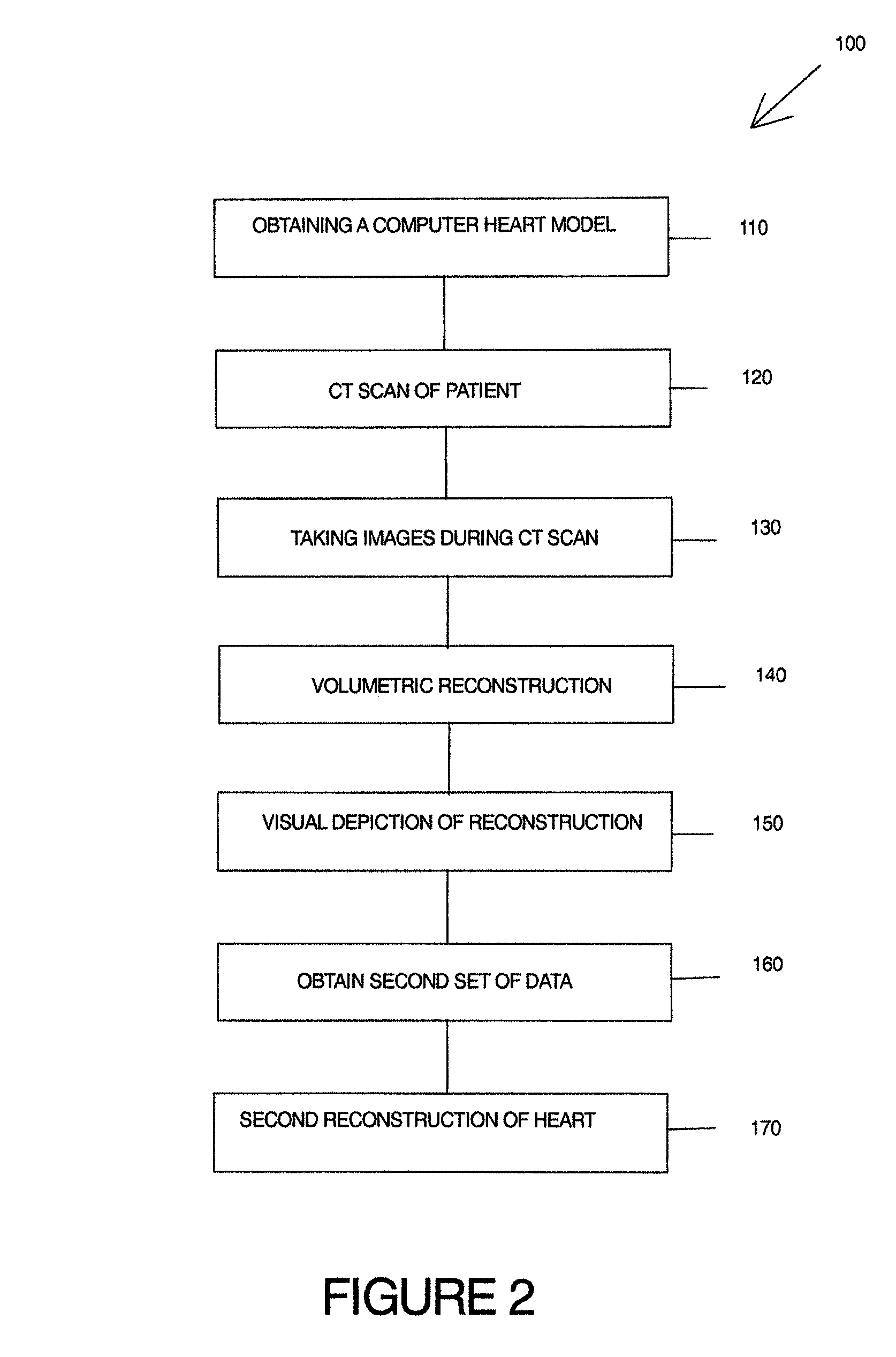
A method to obtain a patient based organ model from patient data, having steps of obtaining a computerized organ model based upon at least one data set of patients, the computerized organ model having a set of classifiers that are used to determine physical parameters of the patients heart, placing the patient in a diagnostic scanner device, taking representative data images of a patients organ while changing position of the image scan, the data images taken with ECG synchronization; and preparing the patient based organ model by evaluating the representative data images of the patients organ with the set of classifiers in the computerized organ model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Organ model
ActiveUS20120045743A1Suitable for operationSuitable for useSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesSilica particleSurface layer
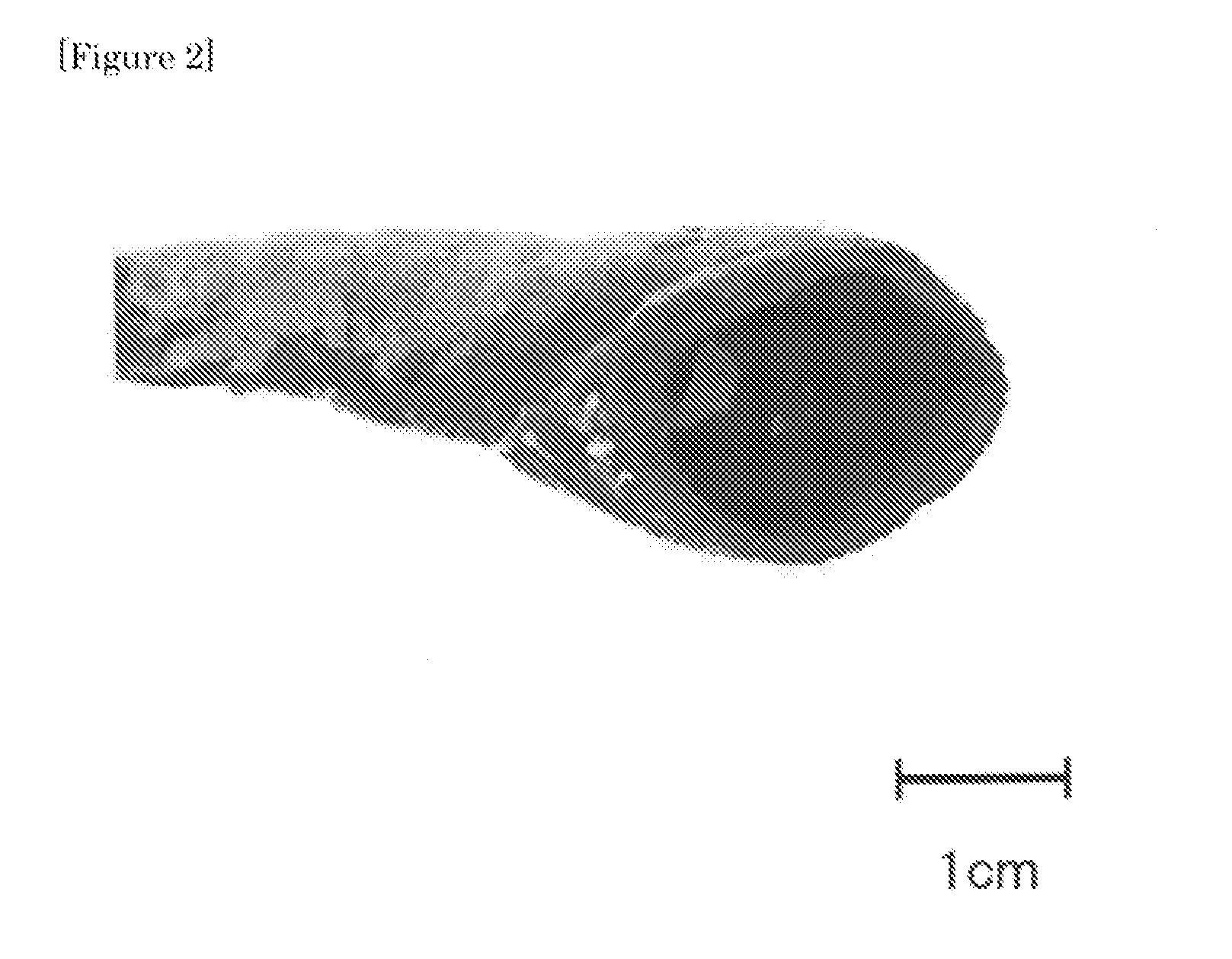
A material for forming an organ model containing an aqueous gel, which comprises polyvinyl alcohol having an average degree of polymerization of 300 to 3500 and a degree of saponification of not less than 90% by mole, and silica particles; a method for producing a material for forming an organ model, comprising cooling an aqueous polyvinyl alcohol solution which contains polyvinyl alcohol having an average degree of polymerization of 300 to 3500 and a degree of saponification of not less than 90% by mole and silica particles, to a temperature of −10° C. or lower, and thawing the resulting formed aqueous gel; and an organ model at least provided with a surface layer comprising the material for forming an organ model. Thus, it is possible to provide: an organ model which has a hydrophilic property similar to an organ of a human body, gives such an incision feel that an incised portion spreads just similar to a living human organ and, therefore can be appropriately used in, for example, exercising surgical procedures; a material for forming an organ model appropriately usable for the organ model; and a method for producing the same.
Owner:YUUGENGAISHA SEIWADENTAL
Method and system for medical decision support using organ models and learning based discriminative distance functions
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of operating a surgical navigation system and a system using the same
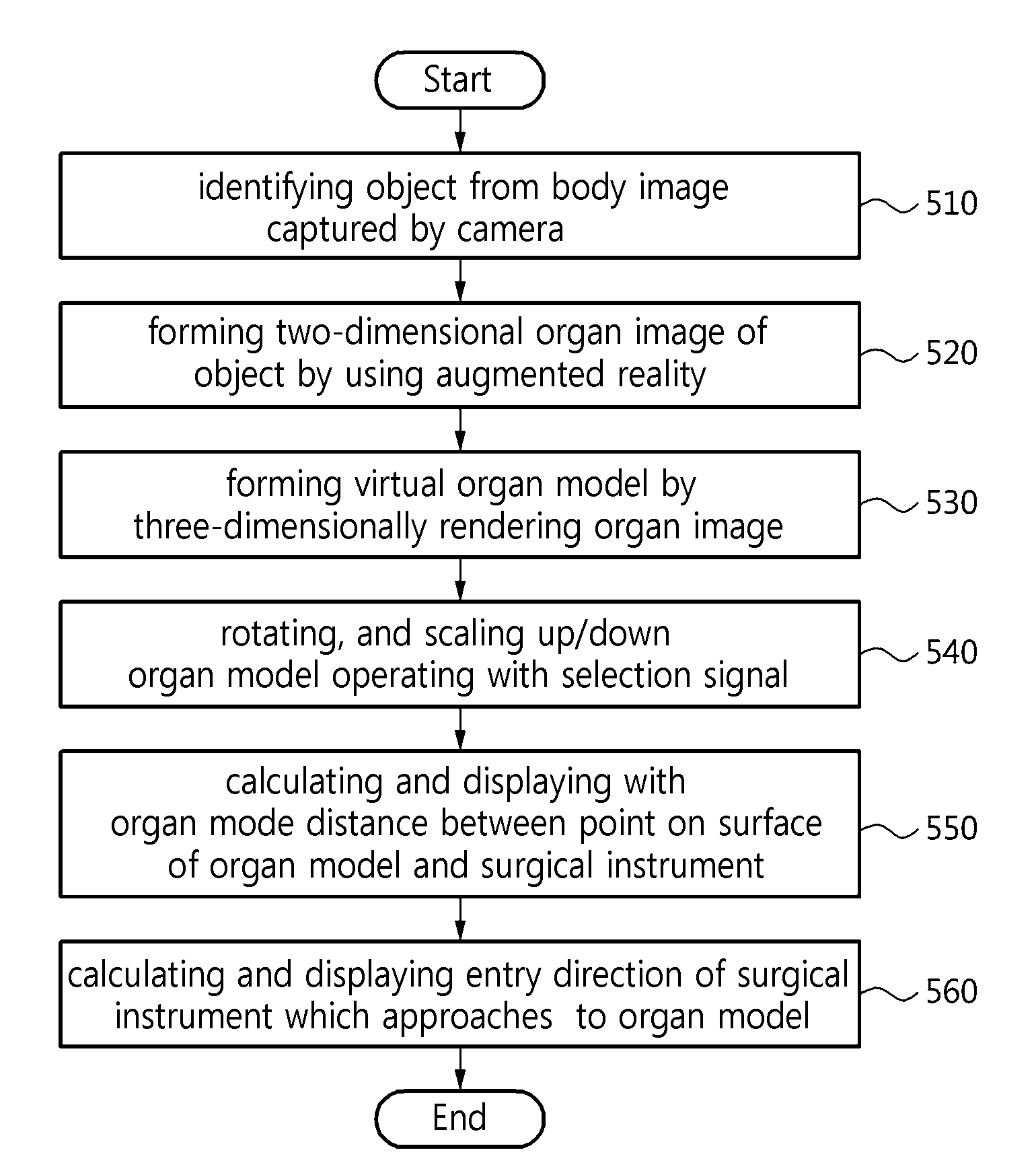
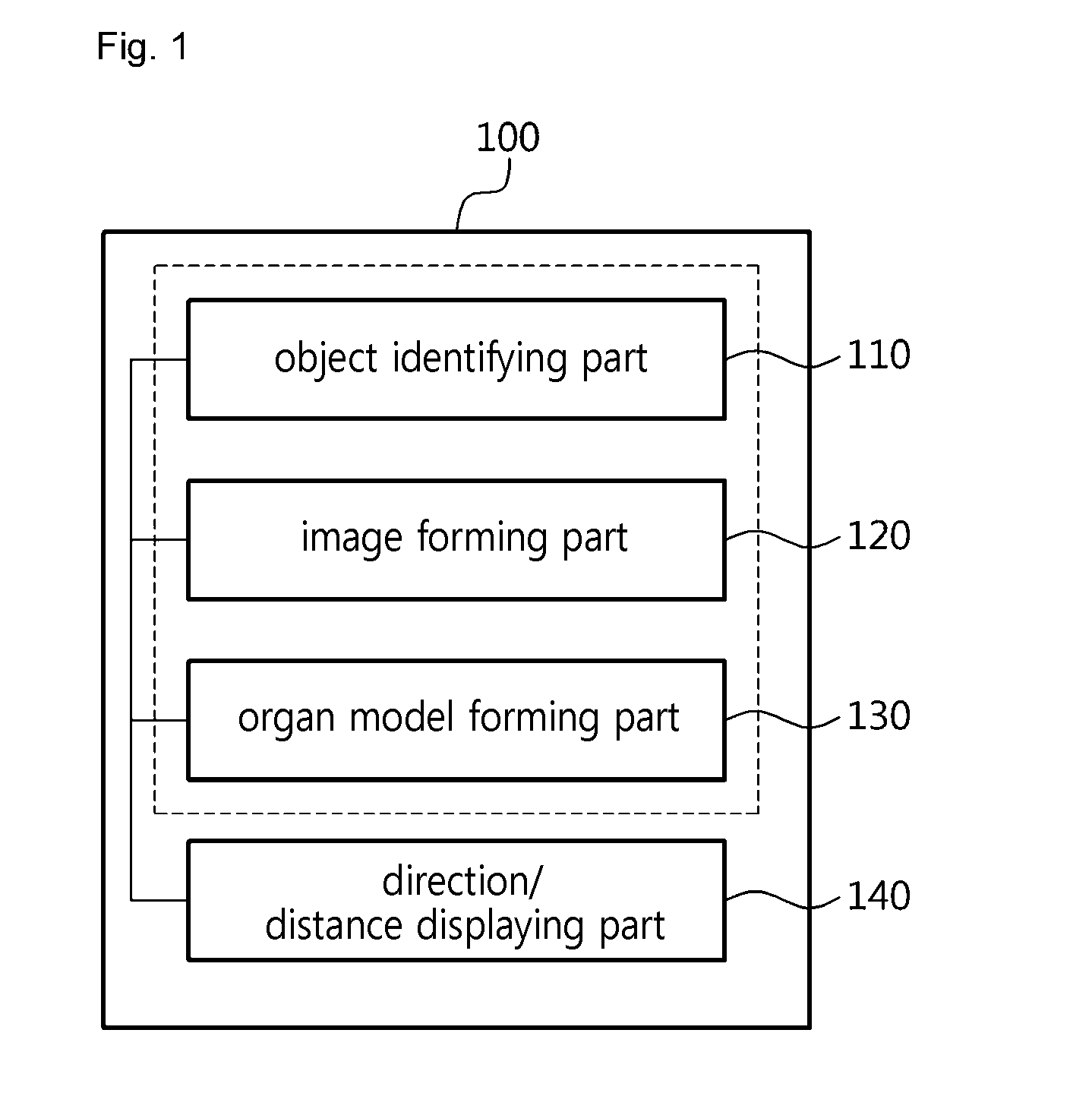
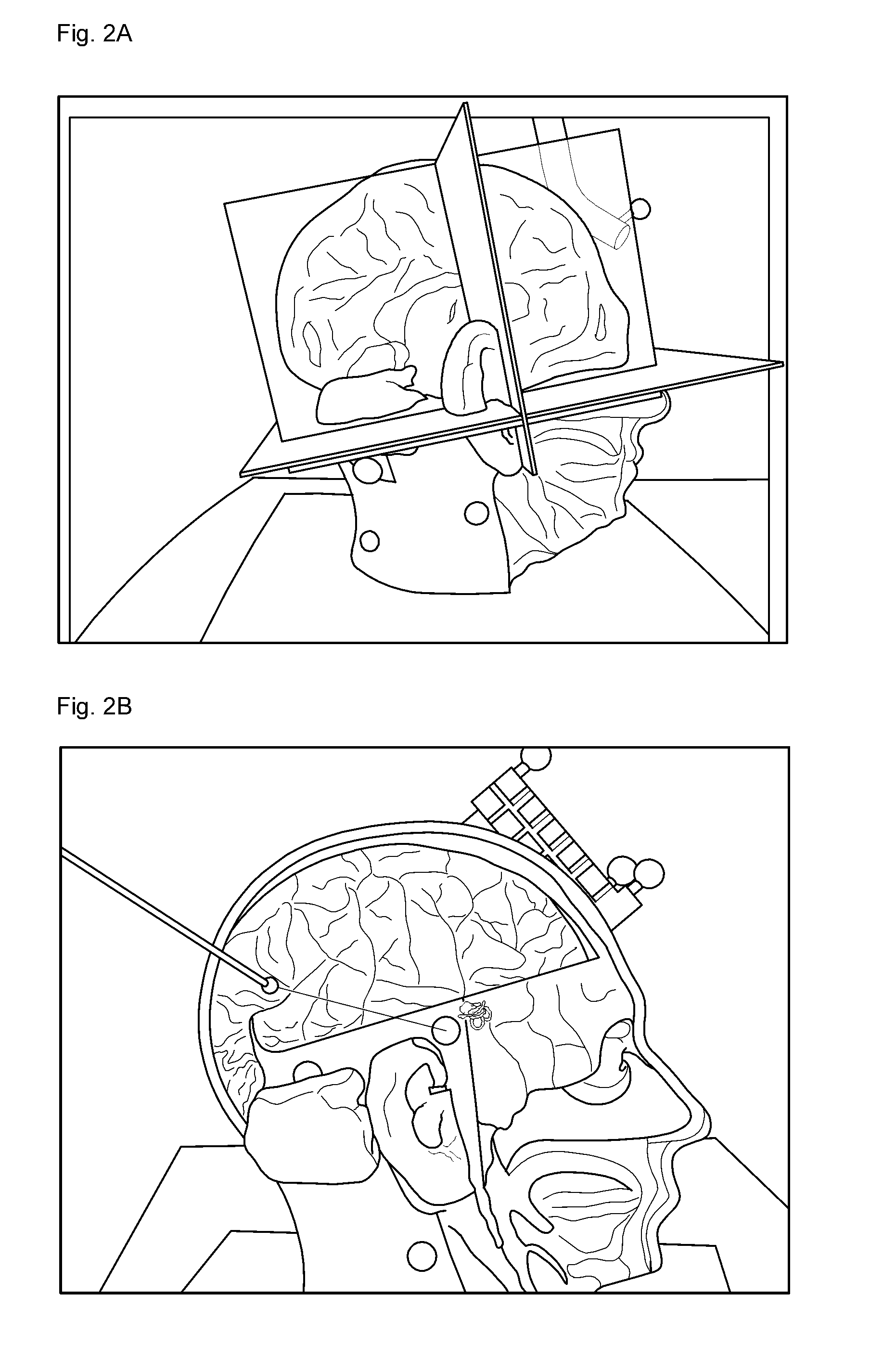
InactiveUS20160163105A1Easy to identifyAccurate identificationImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsOrgan ModelComputer graphics (images)
A method of operating a surgical navigation system is disclosed in which a user may easily recognize a depth perception between virtual organ models and a depth relationship between the virtual organ model and a surgical instrument by switching a two-dimensional organ image which is formed through an augmented reality to a virtual organ mode by three-dimensionally rendering the organ image. A method of operating a surgical navigation system comprises identifying an object from a body image captured by a camera, forming the object in a two-dimensional organ image by using an augmented reality, and forming a virtual organ model by three-dimensionally rendering the organ image.
Owner:KOHYOUNG TECH +1
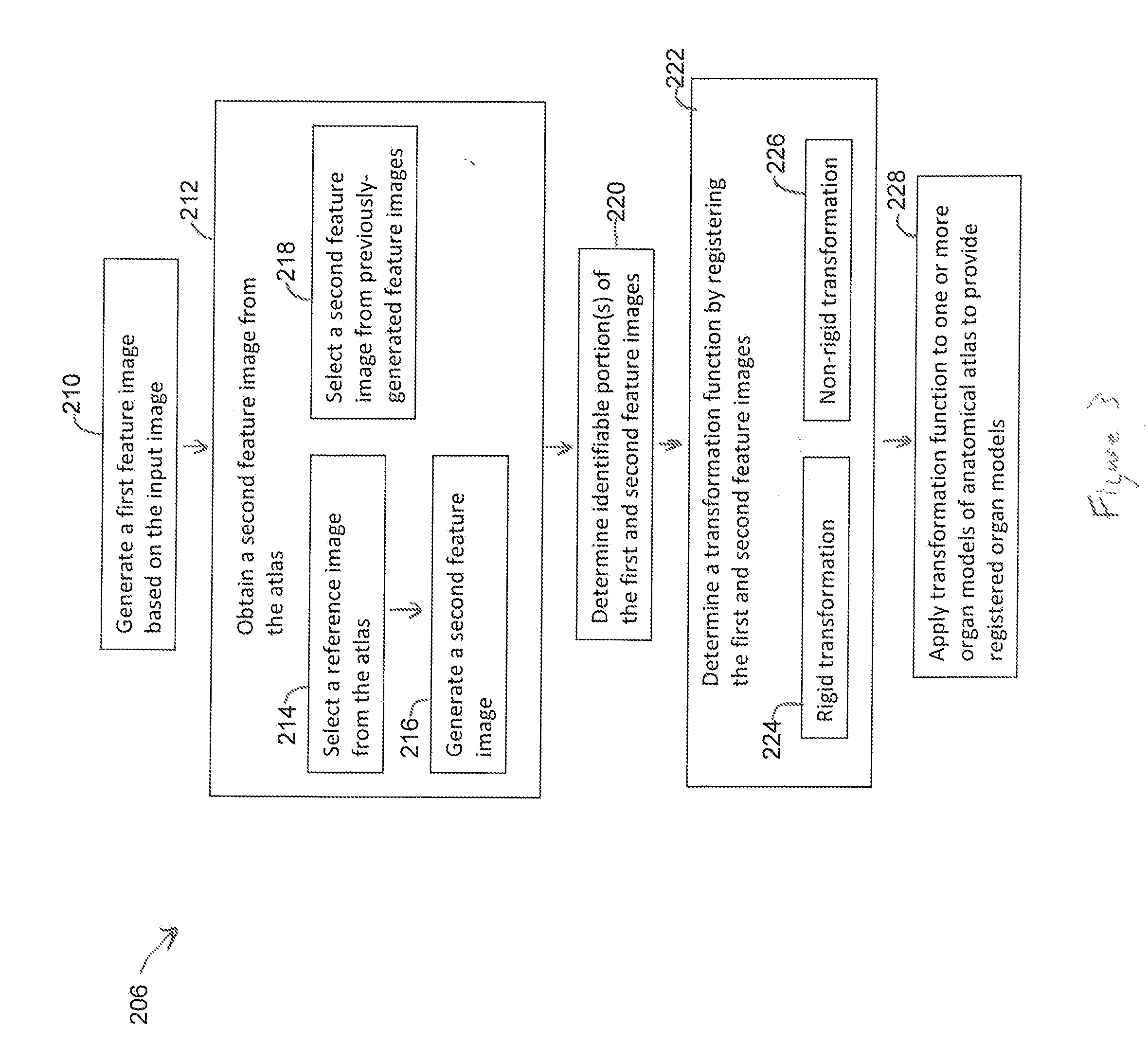
Methods and systems for determining a transformation function to automatically register different modality medical images
ActiveUS20140029812A1Image enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPattern recognition
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
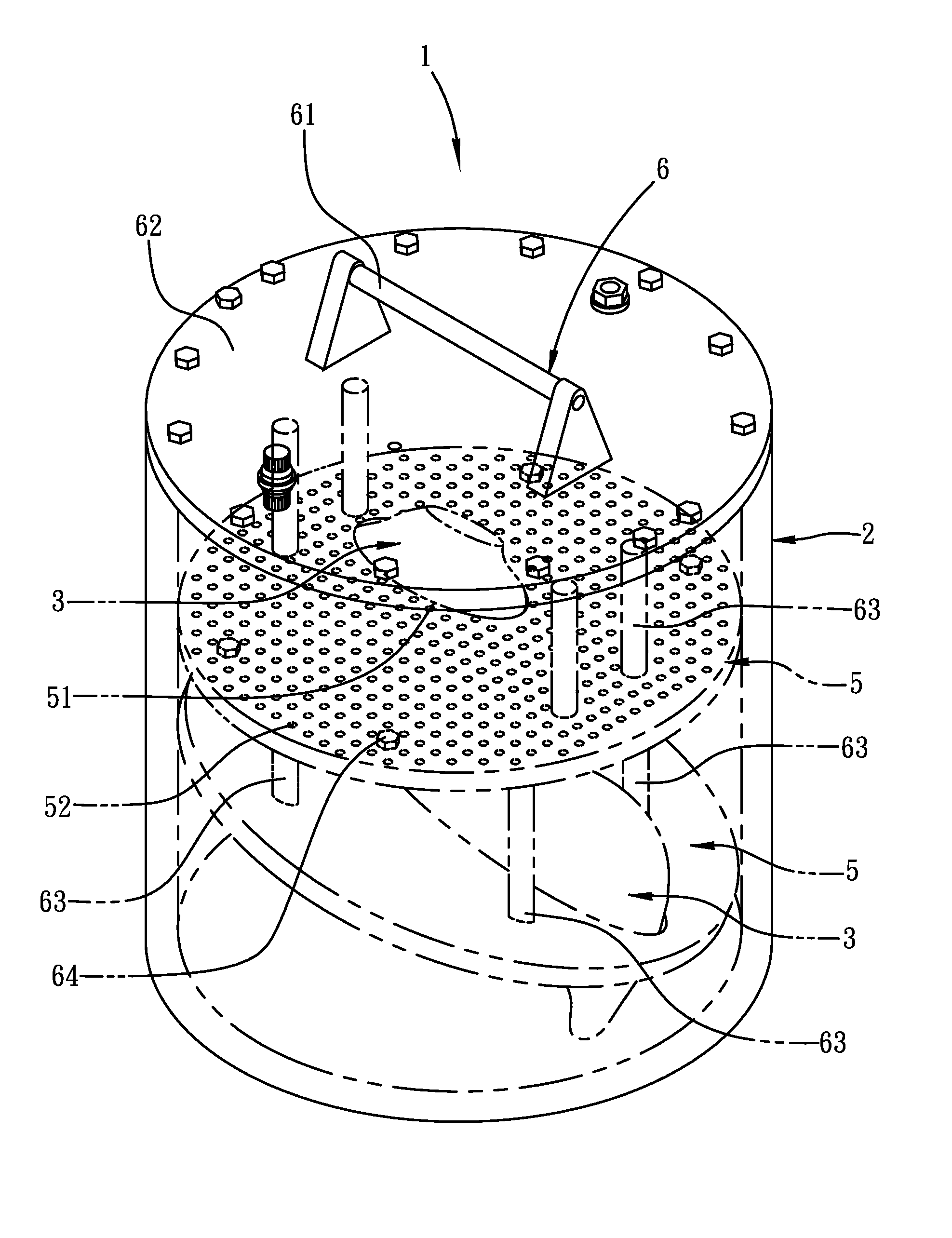
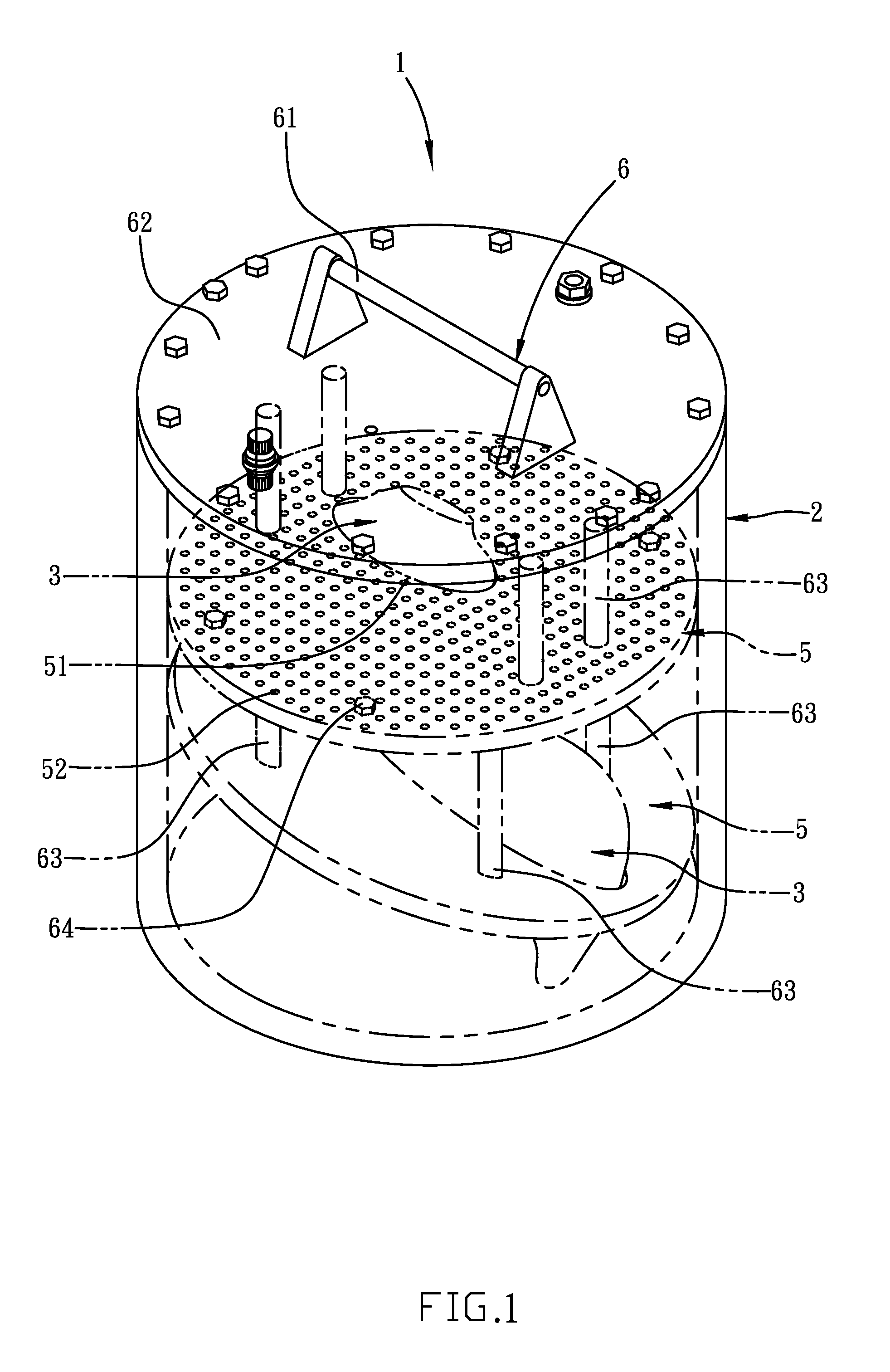
Anthropomorphic phantom for medical imaging systems
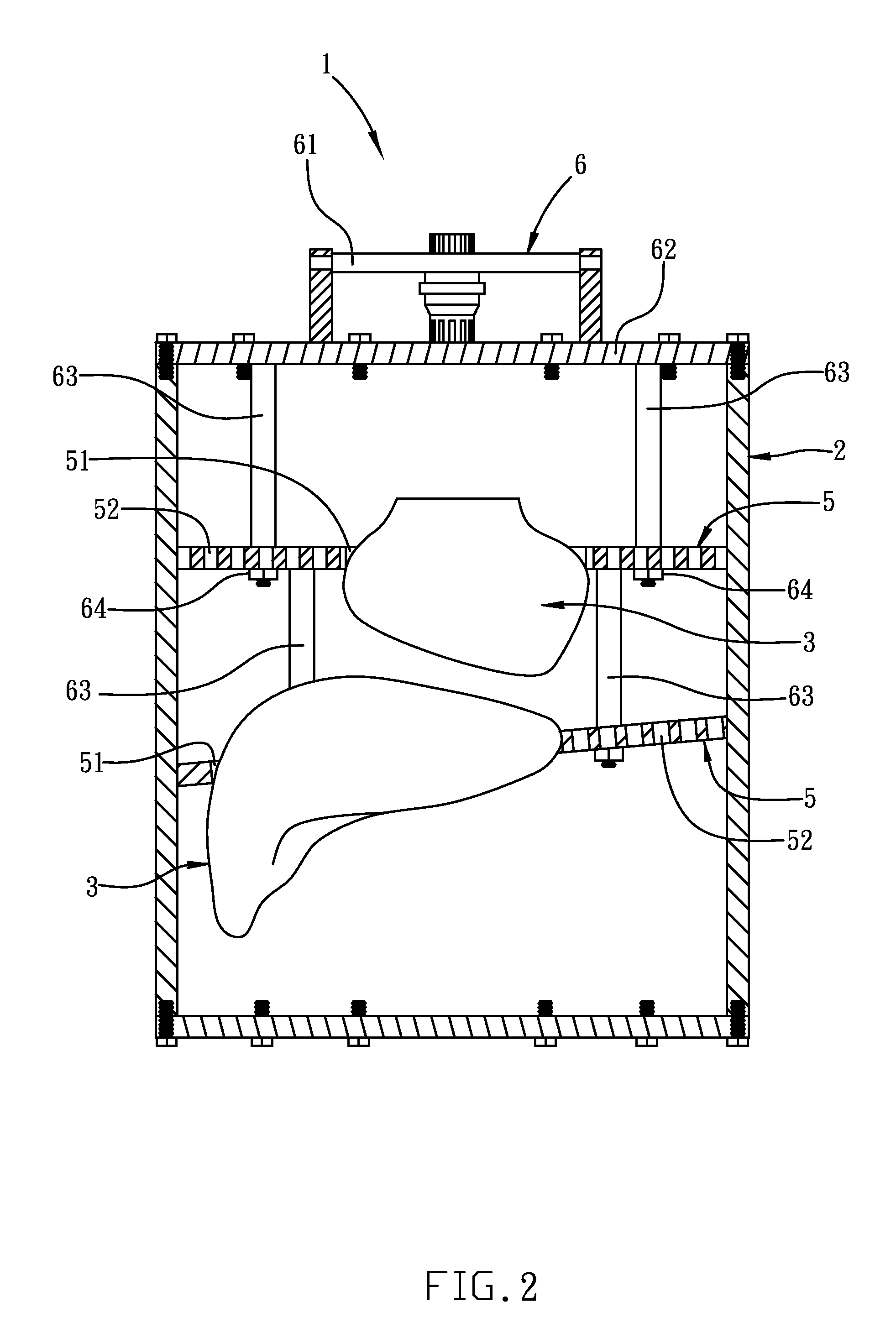
InactiveUS8966954B2Easy to assembleModular designMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesStatic/dynamic balance measurementAnthropomorphic phantomOrgan Model
An anthropomorphic phantom for medical imaging systems is disclosed, which is configured with organ models designed to mimic the three-dimensional shape of human organs, and also by the arrangement of plate-like first connecting elements inside their corresponding organ models, lesion phantoms for simulating tumors can be fixedly secured inside the corresponding organ model using a plurality of first connection holes formed on the first connecting element. Therefore, by the distribution of those first connection holes, not only the lesion phantoms can be arranged at any position inside the corresponding organ model at will as required, but also by modularized design of the anthropomorphic phantom, organ models can first be assembled to form a module structure while the whole module structure with the organ model can be moved into and assembled easily with a torso-like humanoid housing of the anthropomorphic phantom by the use of a handle element.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
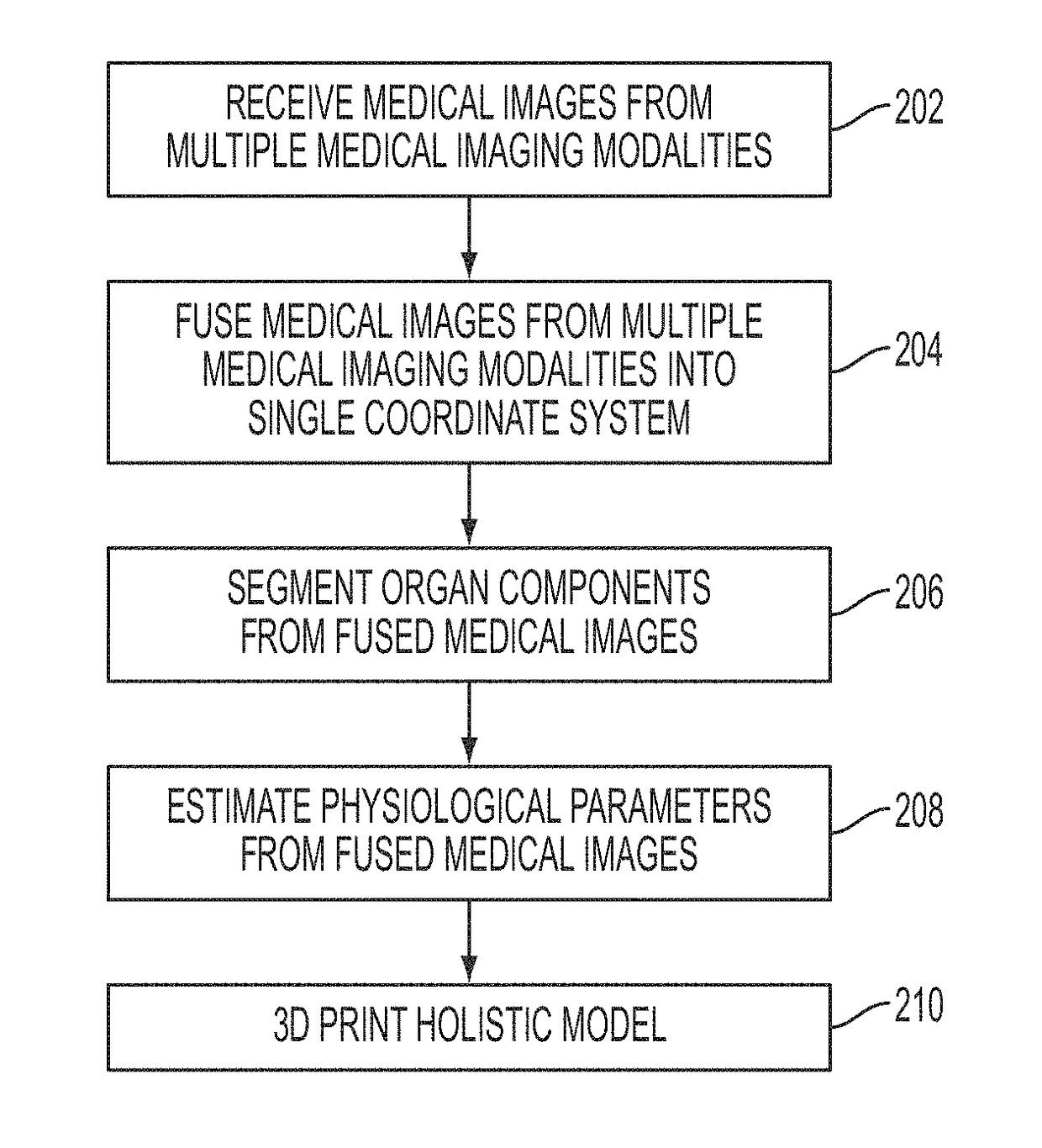
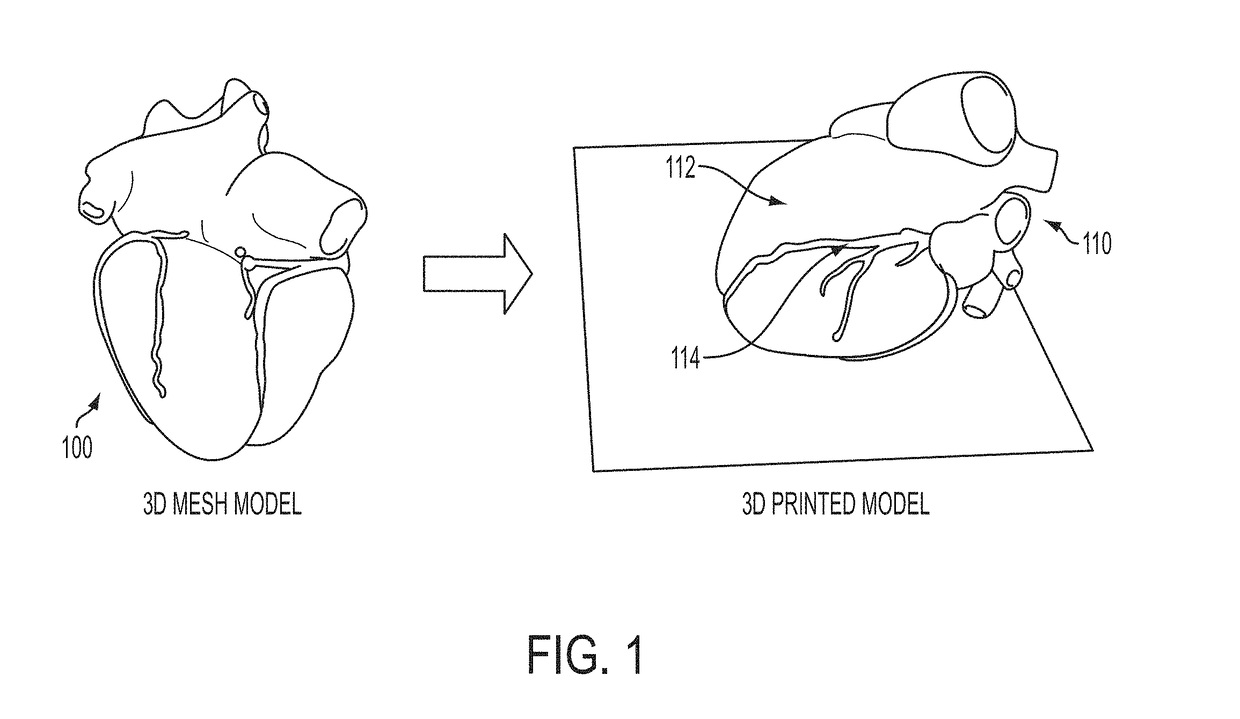
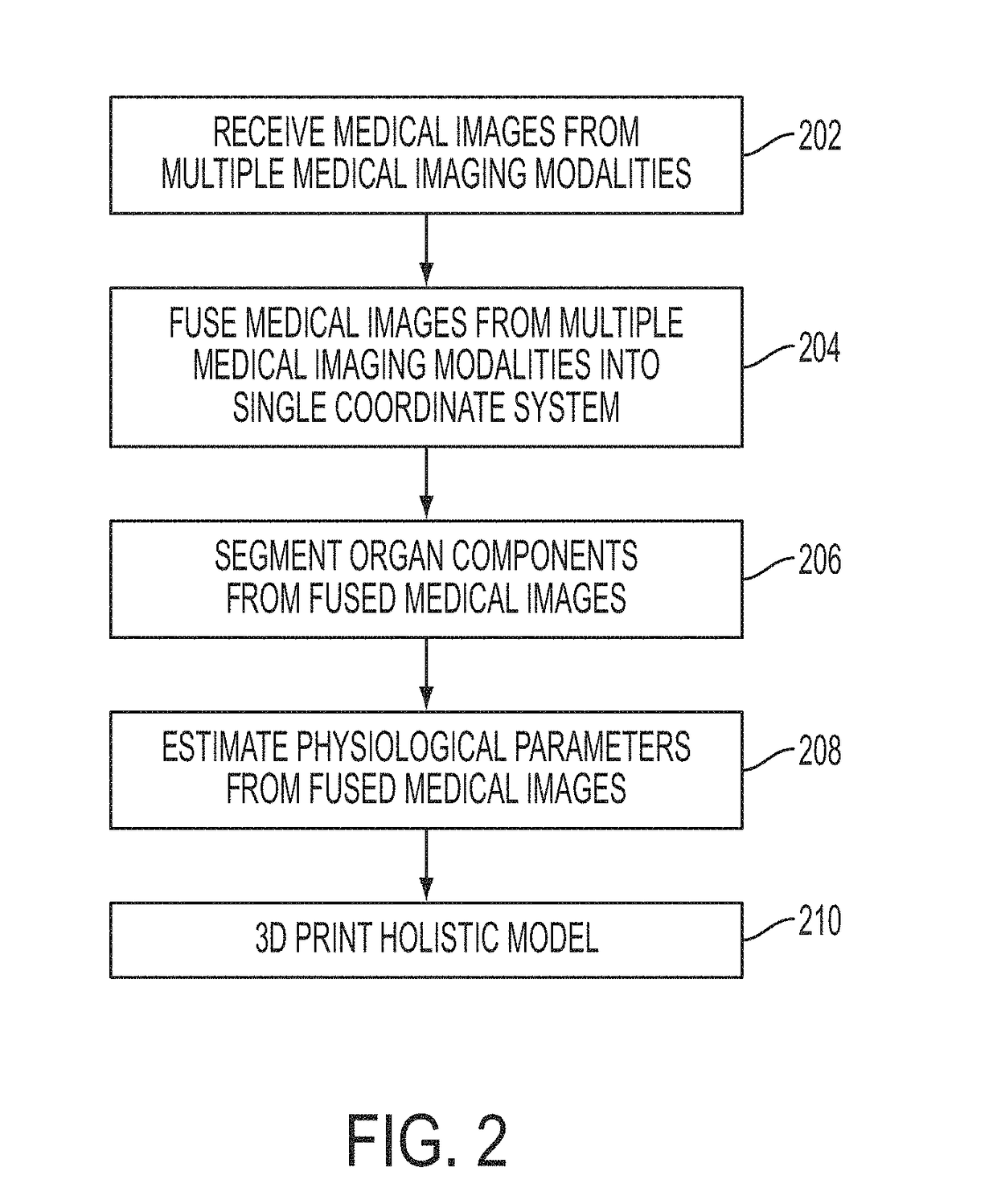
Multi-Modality Image Fusion for 3D Printing of Organ Morphology and Physiology
A system and method for multi-modality fusion for 3D printing of a patient-specific organ model is disclosed. A plurality of medical images of a target organ of a patient from different medical imaging modalities are fused. A holistic mesh model of the target organ is generated by segmenting the target organ in the fused medical images from the different medical imaging modalities. One or more spatially varying physiological parameter is estimated from the fused medical images and the estimated one or more spatially varying physiological parameter is mapped to the holistic mesh model of the target organ. The holistic mesh model of the target organ is 3D printed including a representation of the estimated one or more spatially varying physiological parameter mapped to the holistic mesh model. The estimated one or more spatially varying physiological parameter can be represented in the 3D printed model using a spatially material property (e.g., stiffness), spatially varying material colors, and / or spatially varying material texture.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
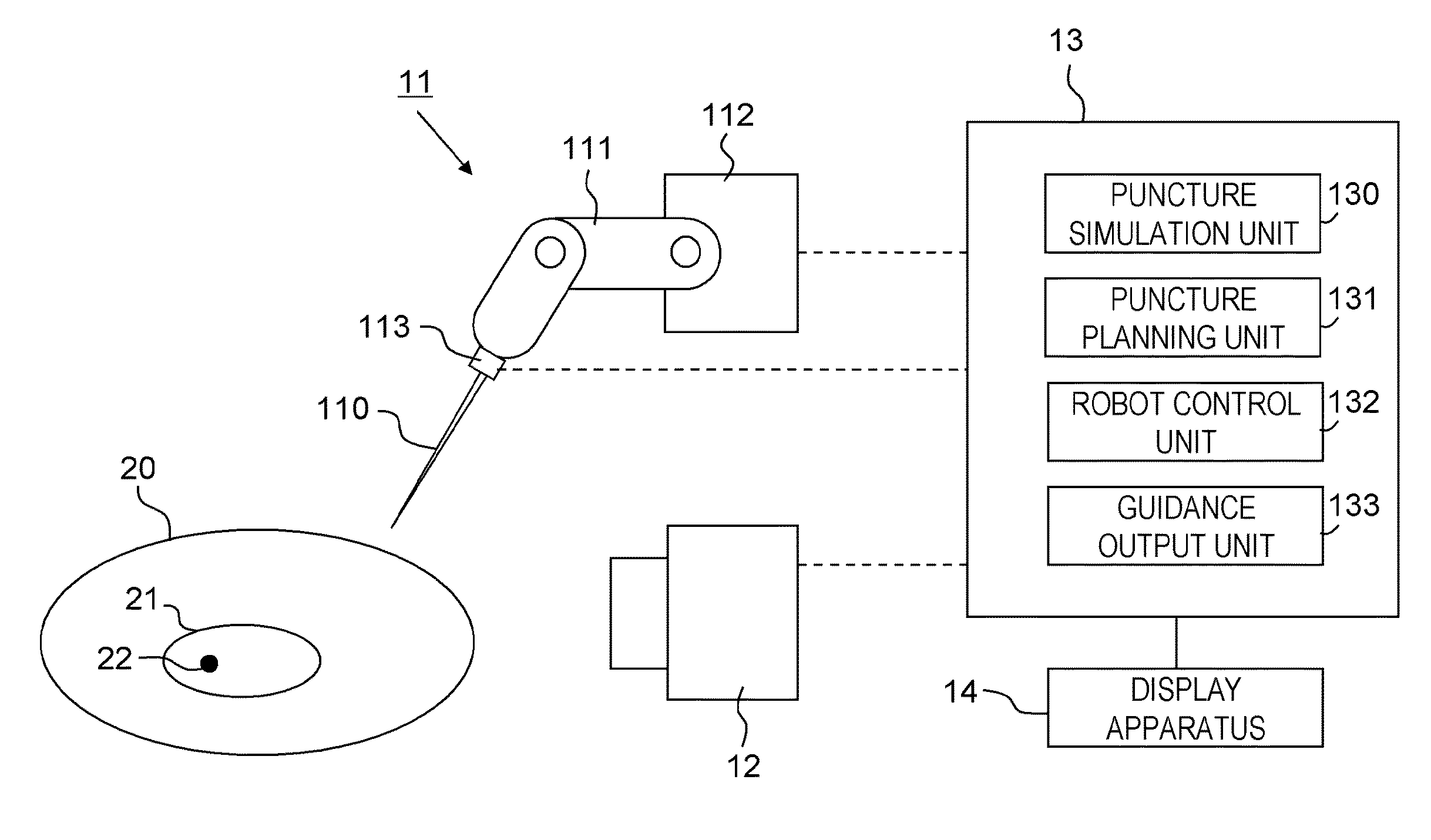
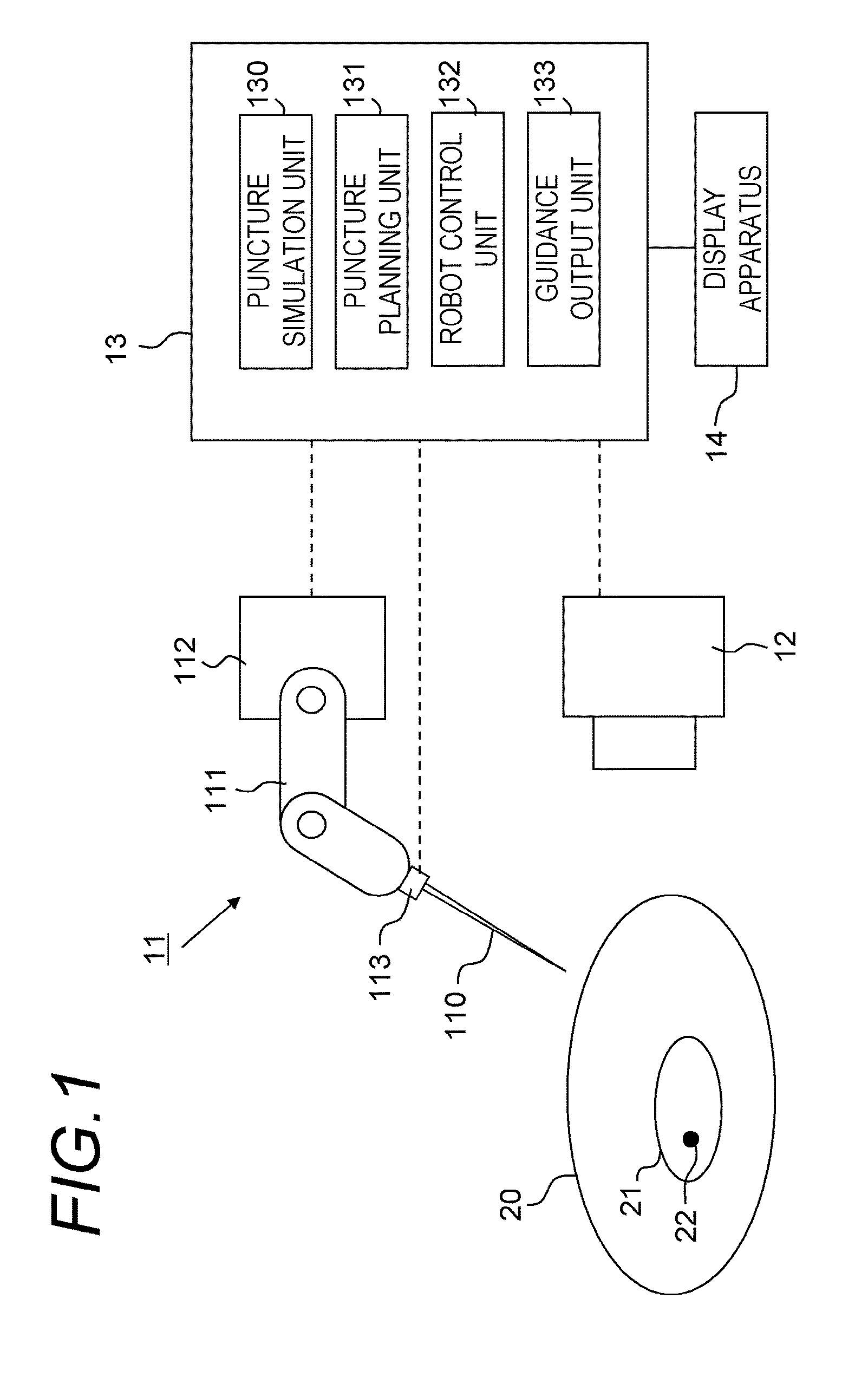
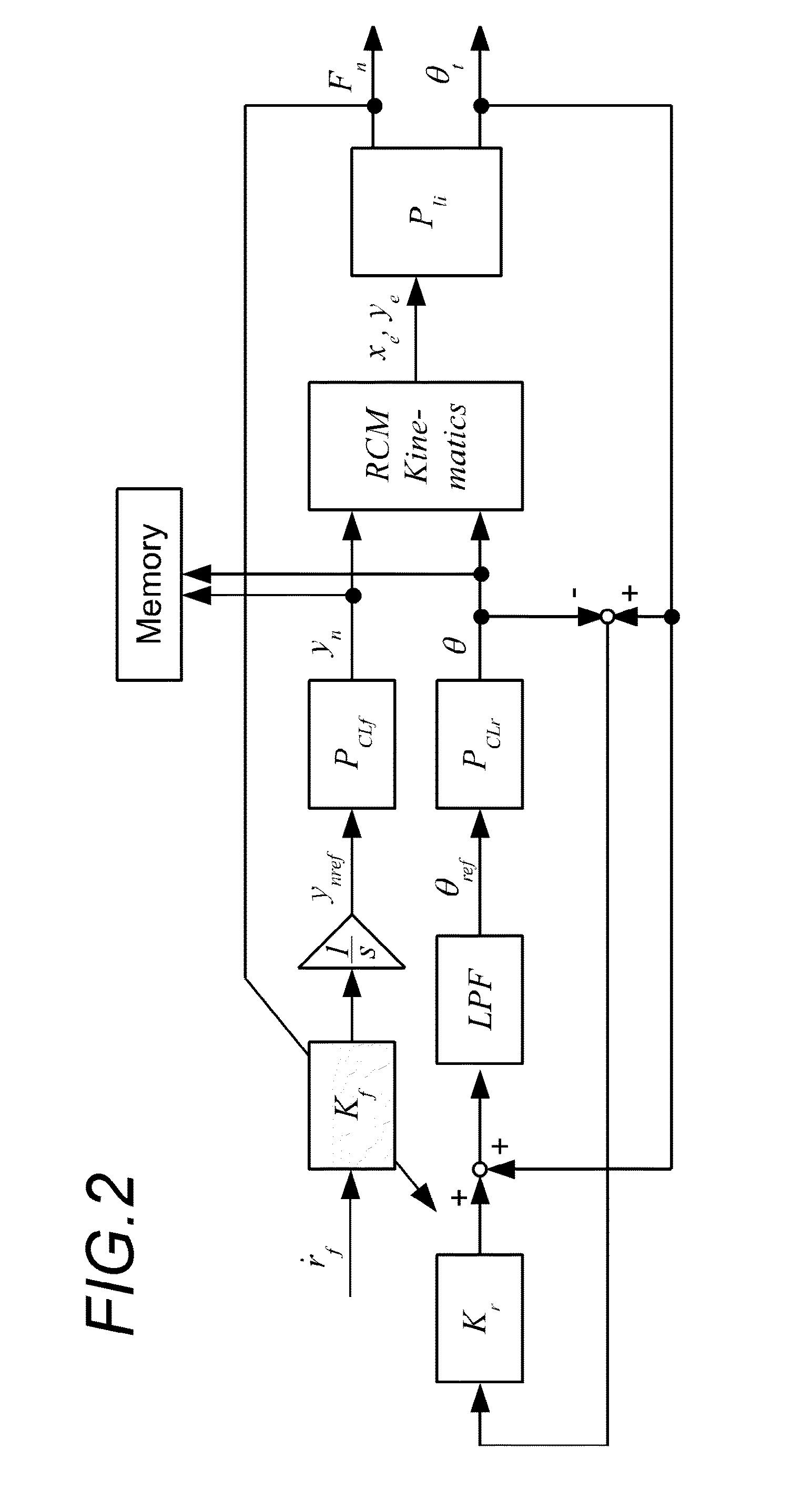
Puncture planning apparatus and puncture system
ActiveUS20160008082A1Minimize puncture errorError minimizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsOrgan ModelSimulation based
A puncture planning apparatus has: a simulation unit that simulates movement of an organ and a puncture needle by simulation using an organ model; and a planning unit that plans, based on the simulation result, how to move the puncture needle when an actual organ is punctured. The simulation unit executes a plurality of times of the simulation of an operation to advance the puncture needle while correcting an angle of the puncture needle so as to follow the movement of the target segment due to deformation of the organ, conditions of an advancement speed of the puncture needle are changed for each of the plurality times of the simulation, and the planning unit performs planning using the best simulation result out of the plurality of simulation results acquired under different conditions of the advancement speed.
Owner:CANON KK
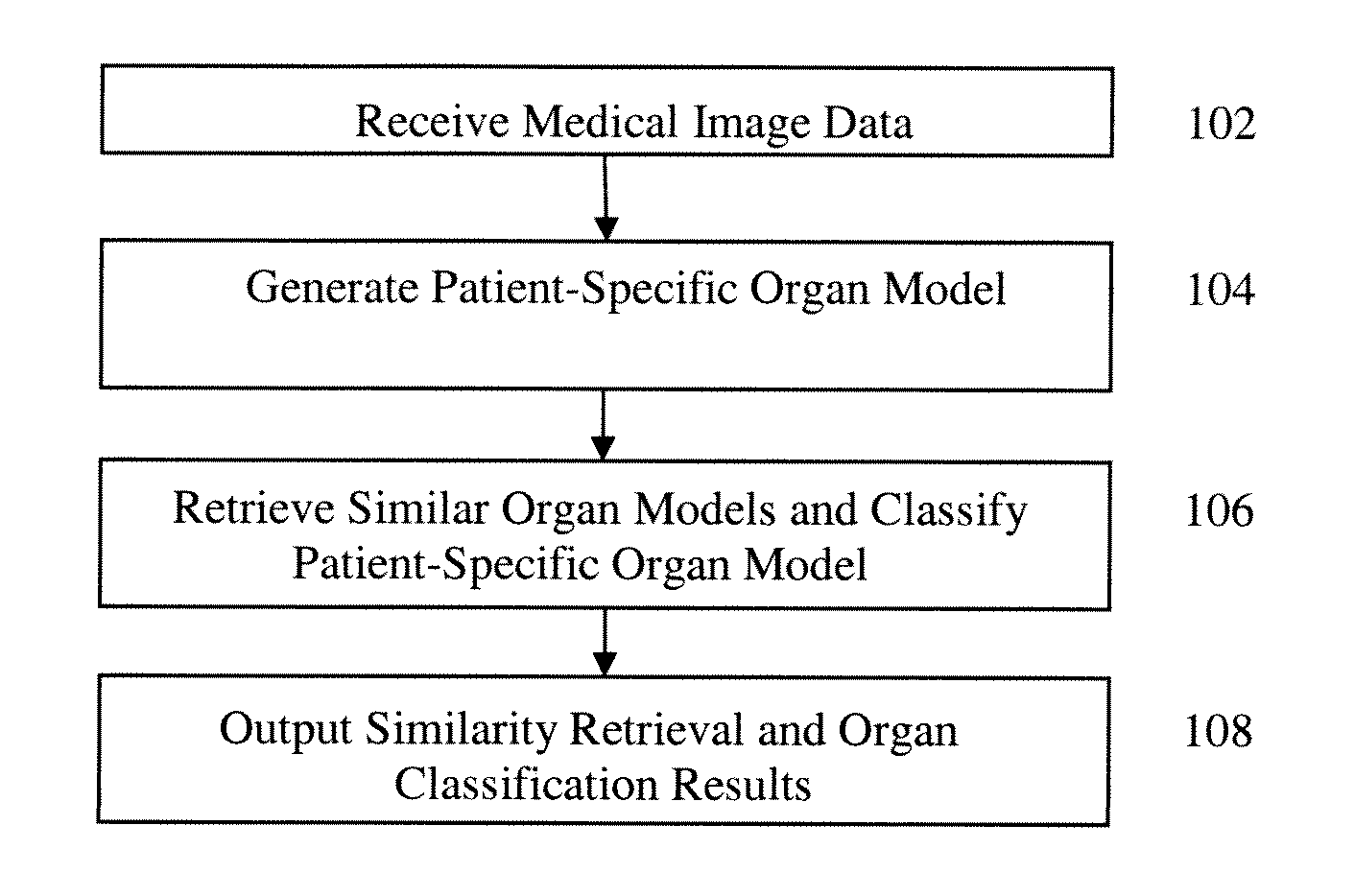
Method and System for Medical Decision Support Using Organ Models and Learning Based Discriminative Distance Functions
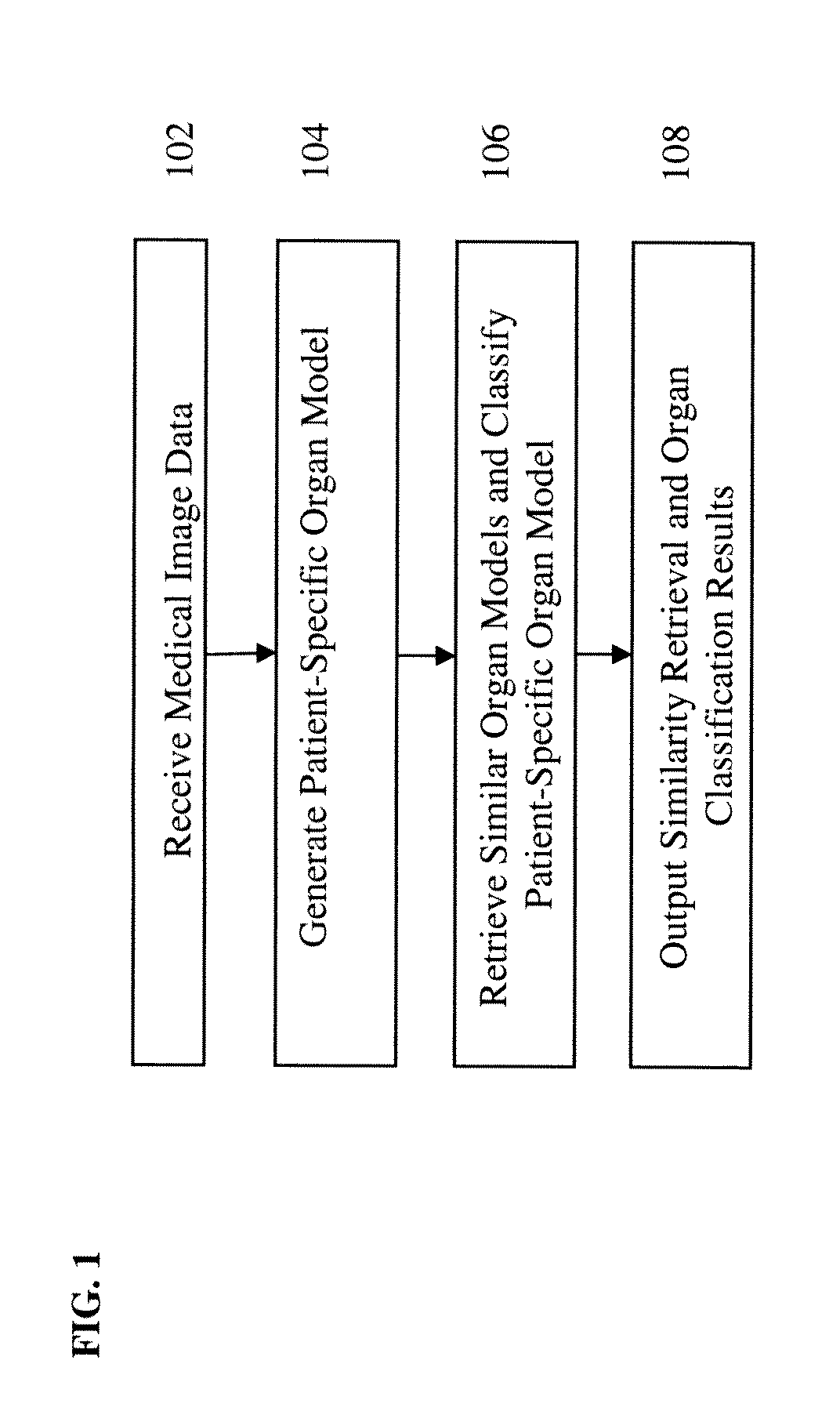
A method and system for providing medical decision support based on virtual organ models and learning based discriminative distance functions is disclosed. A patient-specific virtual organ model is generated from medical image data of a patient. One or more similar organ models to the patient-specific organ model are retrieved from a plurality of previously stored virtual organ models using a learned discriminative distance function. The patient-specific valve model can be classified into a first class or a second class based on the previously stored organ models determined to be similar to the patient-specific organ model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Puncture parameter generation method based on three-dimensional image
InactiveCN108784831AReduce the number of timesComputer-aided planning/modellingSkin surfaceOrgan Model
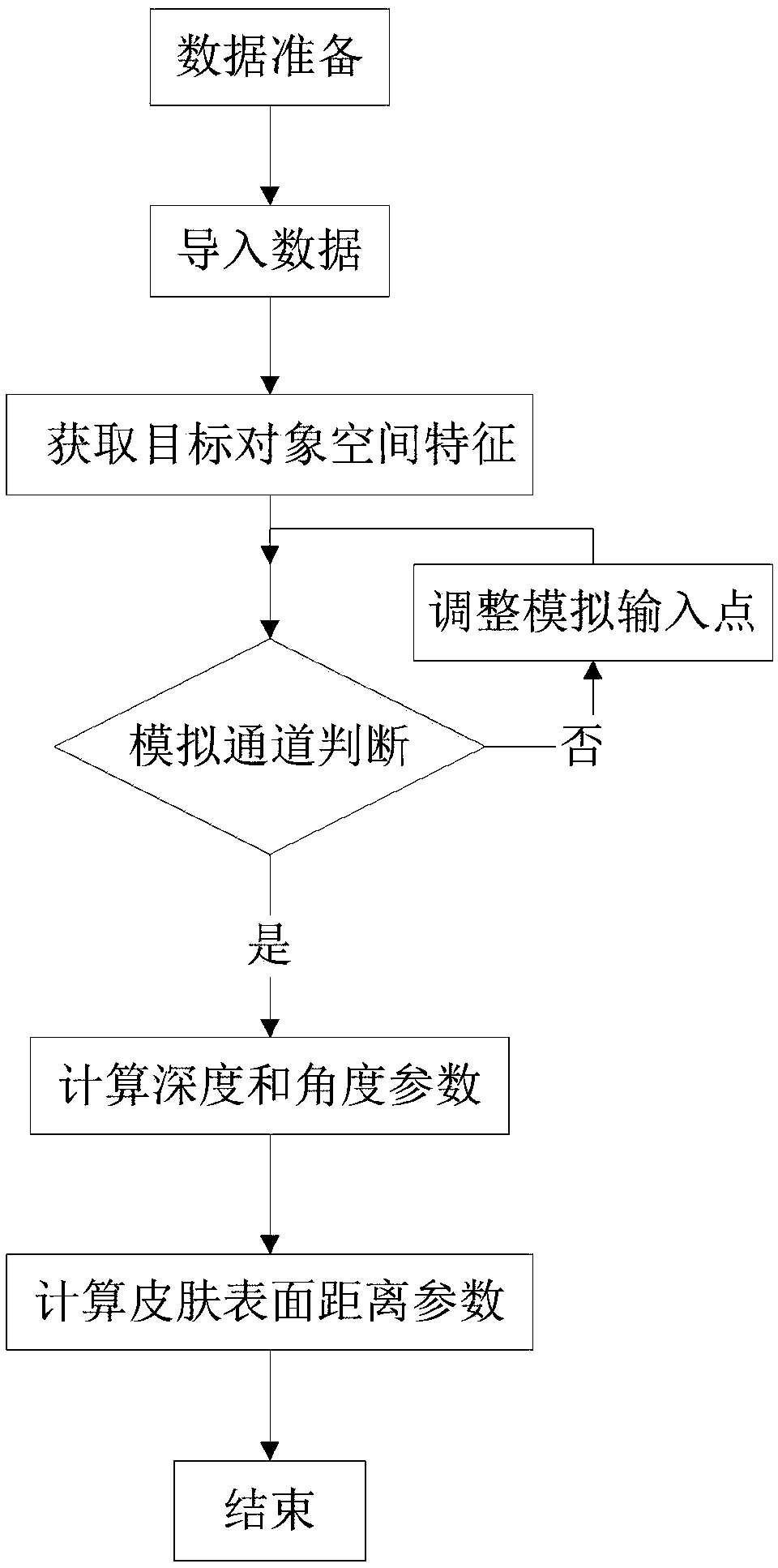
The invention discloses a puncture parameter generation method based on a three-dimensional image. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a medical image, and reconstructing 3D model data; acquiring central point coordinate position information of a target object model in 3D space; selecting a simulated puncture point from the skin surface in the 3D model data, obtaining three-dimensional space coordinates of the puncture point, and generating a connecting line between the selected puncture point and an objective target point; utilizing the puncture point and the objective target point ofthe connecting line not penetrating through an organ model for calculating a three-dimensional space intersection point of the connecting line and the surface of a target object, wherein the distancefrom the puncture point to the three-dimensional space intersection point is puncture depth; conducting skin transparent rendering and the bone rendering; determining an actual position of the puncture point according to the curve distance between the objective target point and the skin surface, and outputting the puncture depth and three-dimensional coordinate parameters. By means of the method,accurate quantitative data is obtained for individualized cases before the puncture operation, actual operating parameters are provided for minimally invasive treatment, and the clinical individualized and precise demands are met.
Owner:深圳市一图智能科技有限公司
Human anatomy teaching system
ActiveCN105632310ASimulated satisfactionReduce workloadCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsNODALHuman anatomy
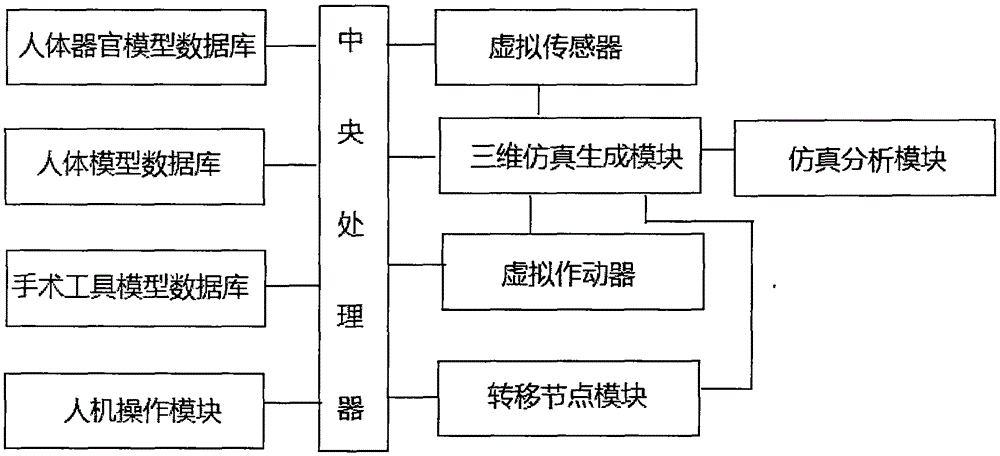
The invention discloses a human anatomy teaching system, and the system comprises a human organ model database, a human body model database, an operation tool model database, a three-dimensional simulation generation module, a virtual actuator, a virtual sensor, a simulation analysis module, a man-machine operation module, a central processor, and a transfer node module. The system simulates various types of human body models, human organs and operation tools through the three-dimensional simulation generation module, then carries out the simulation demonstration of an anatomy process according to a control command inputted by the man-machine operation module, enables students to be personally on the scene, and greatly improves the learning efficiency. Moreover, each database is provided with an updating module, thereby meeting the simulation of various types of model data, and greatly reducing the cost. Meanwhile, the system can achieve the teaching of an anatomy method in the whole anatomy process through various types of preset algorithms or methods, alleviates the workload of a teacher, employs a plurality of control command input modes, and further facilitates the teaching.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Lung cancer organ model and application thereof in tumor research
PendingCN109554346AFast and efficient buildPreserve genetic informationMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningAbnormal tissue growthCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a lung cancer organ model and an application thereof in tumor research. An establishment method of the lung cancer organ model comprises the steps as follows: (1) lung cancer tumor cells are added to a three-dimensional culture medium for culture, and the lung cancer tumor cells are added to a culture medium to be continuously cultured after a tumor layer is formed, whereinthe culture medium contains growth factors and extracellular matrix suitable for growth lung cancer tumor cells; (2) a system obtained through culture in step (1) forms single cell after protease enzymolysis, resuspension is performed by the culture medium after separation, and then, the lung cancer organ model is obtained. By use of the method, a specimen library containing a large number of lung cancer organ models can be established, heterogeneity and diversity of lung cancer are greatly covered, the defect of insufficient representativeness of traditional lung cancer cell lines is effectively overcome, and the lung cancer organ model becomes an efficient platform for research of occurrence and development mechanisms of lung cancer.
Owner:BEIJING CHEST HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Color-information-maintaining objectionable image detection method under deformation sensitive organ models
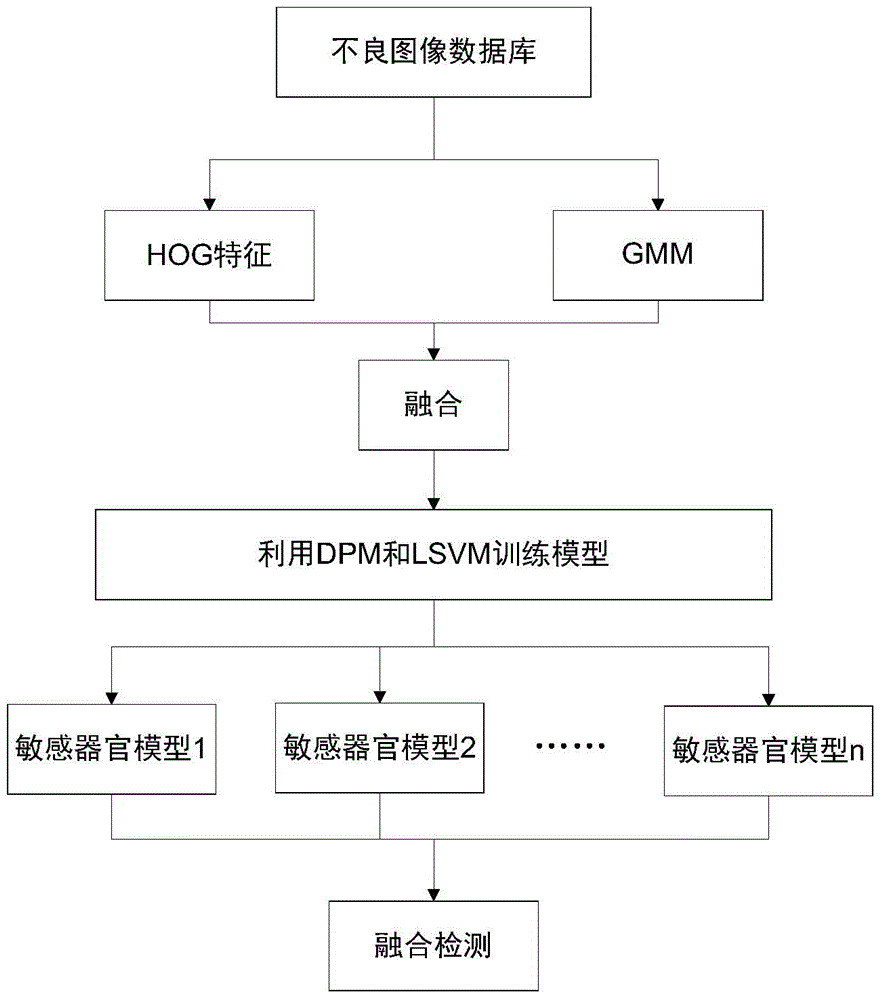
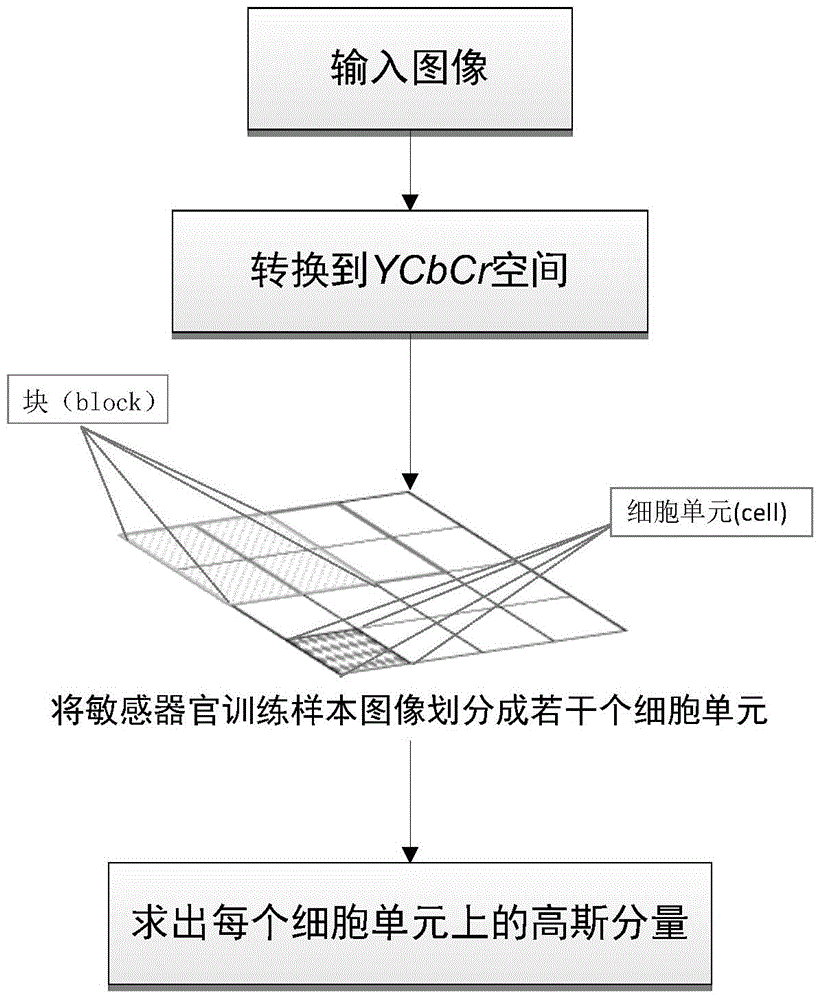
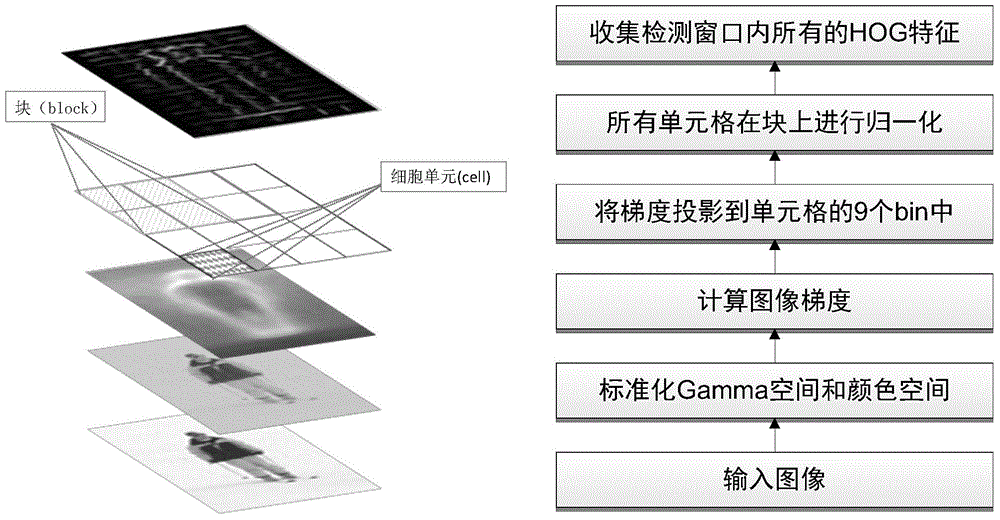
ActiveCN104134059AAccurate descriptionAvoid missing detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionOrgan ModelHistogram of oriented gradients
The invention discloses a color-information-maintaining objectionable image detection method under deformation sensitive organ models. The method comprises the following steps that: a GMM (Gaussian Mixture Model) is adopted for building color models of human body sensitive organs; HoG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients) features and GMM features of a sensitive organ training sample are extracted; for specific postures of each kind of human body sensitive organ, on the basis of features obtained after combining the HoG features and the GMM features of the human body sensitive organ, a deformable part model and a latent support vector machine are used for training detectors of the sensitive organ in the specific postures, and the detectors in various postures are integrated into a mixture deformation model of the sensitive organ; and various human body sensitive organ classifiers respectively detect test images, merge detection results and judge image properties. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that objectionable images are distinguished by using high-level semantic information of the sensitive organs in the objectionable images; the misjudging problem of normal images is effectively solved; and the method can be used for filtering pornographic information in the images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
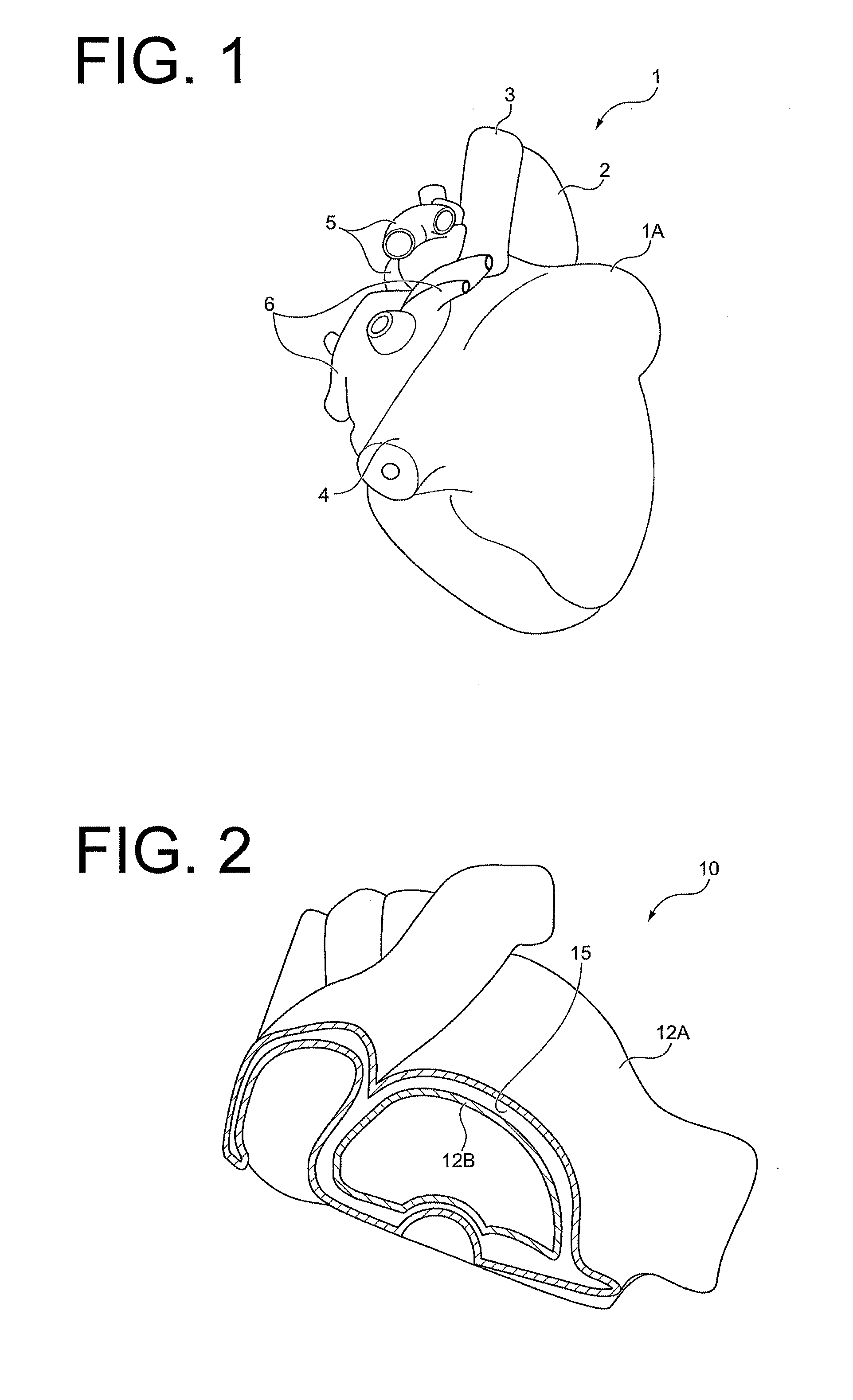
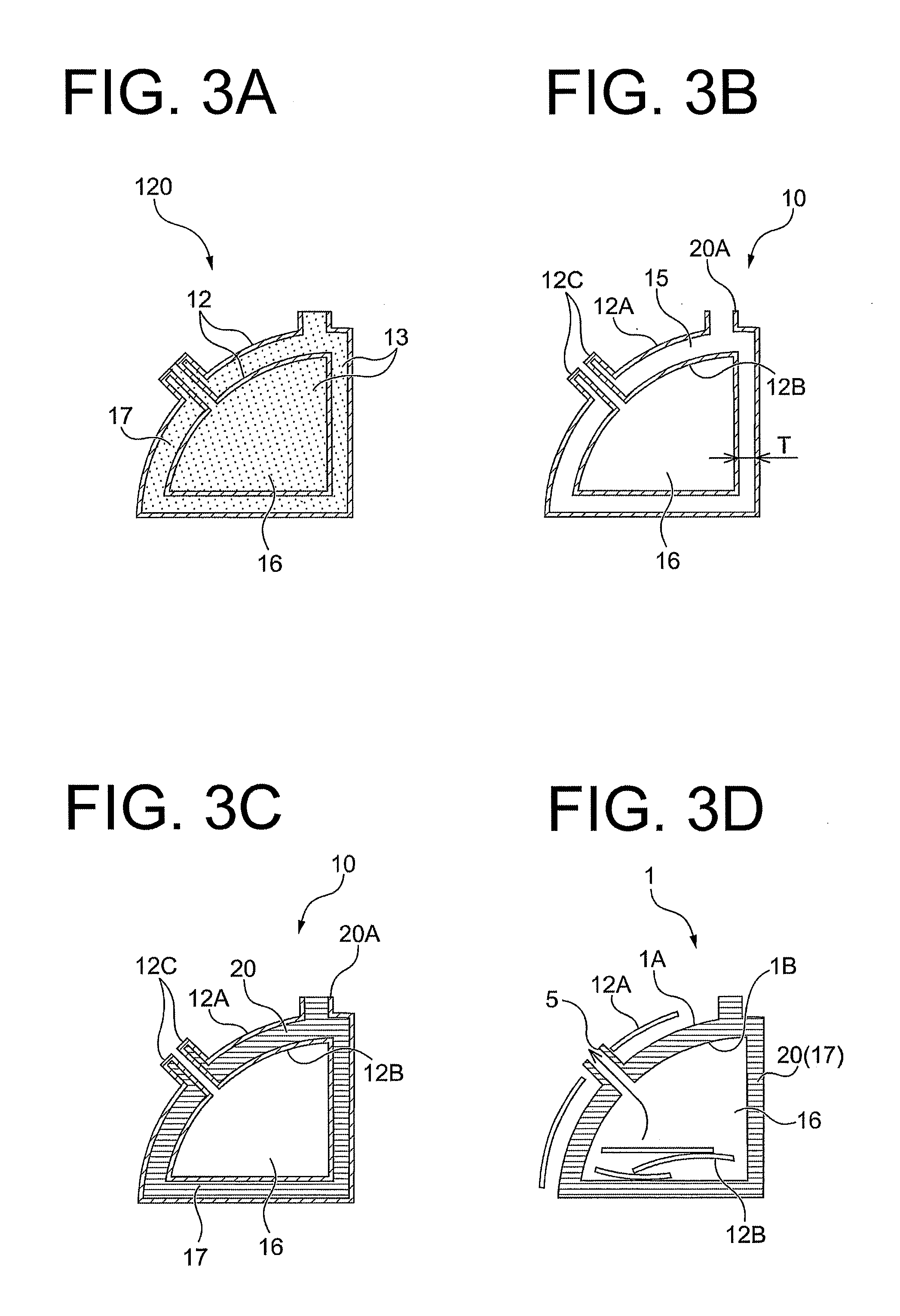
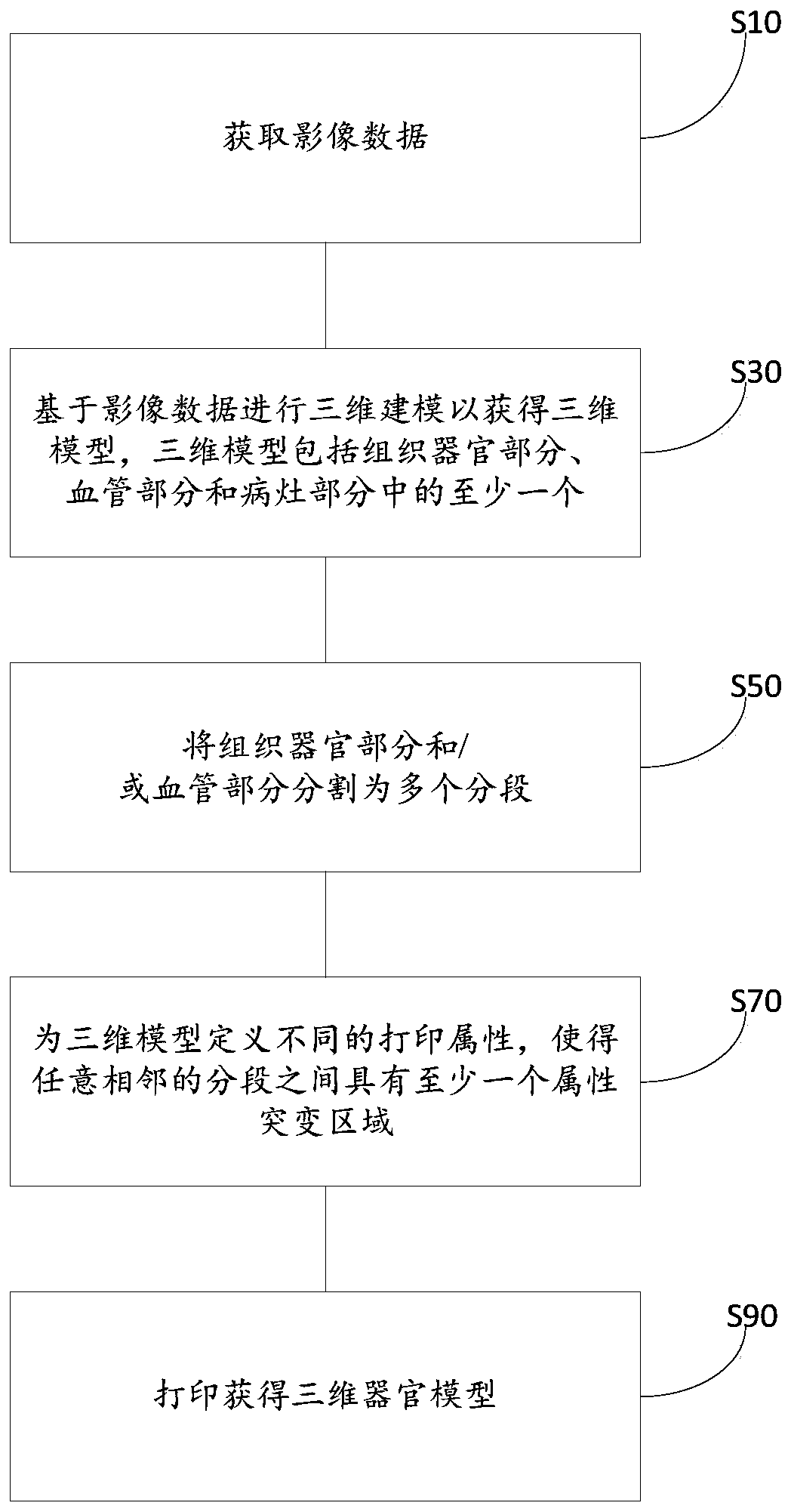
Method of producing organ model, mold for producing organ model, and organ model
InactiveUS20140106329A1Low costImprove accuracySurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsOrgan ModelMaterials science
The present invention provides a method of producing an organ model comprising; an outer-shape body forming step in which an outer-shape body 120 having regions 16, 17 to be a hollow portion and a structural wall of the organ model respectively is formed by irradiating curing light and cure the photocurable mold resin 12 and support resin 13 supporting the mold resin based on photographed data of a human organ, a mold shell forming step in which a mold shell 10 having outer and inner shell portions 12A, 12B covering outer and inner surfaces of the organ model respectively is formed by removing the support resin 13 from the outer-shape body 120, a filling step in which a space 15 between the outer and inner shell portions 12A, 12B is filled with a flexible injection molding material 20, and a removing step for removing the mold shell 10.
Owner:JMC
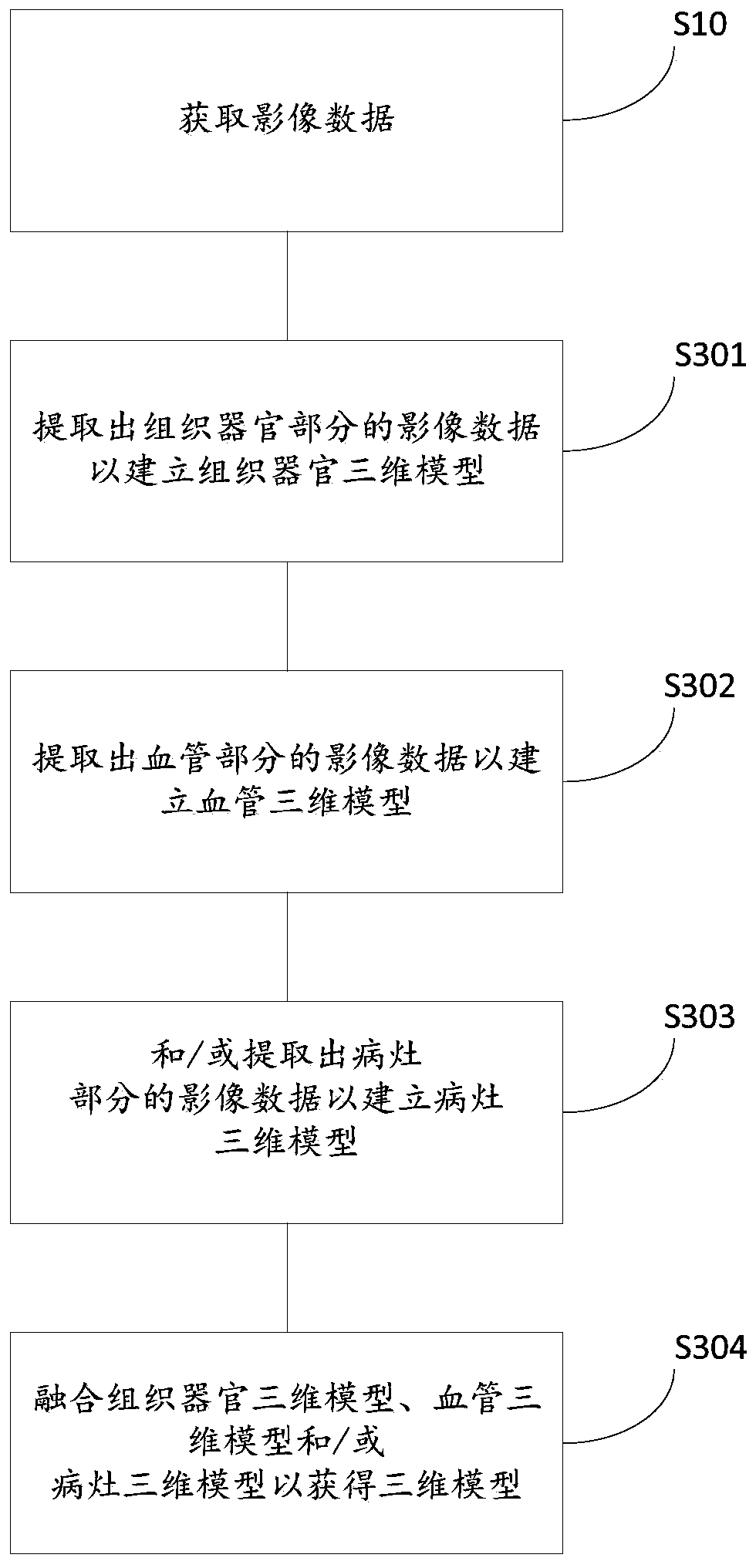
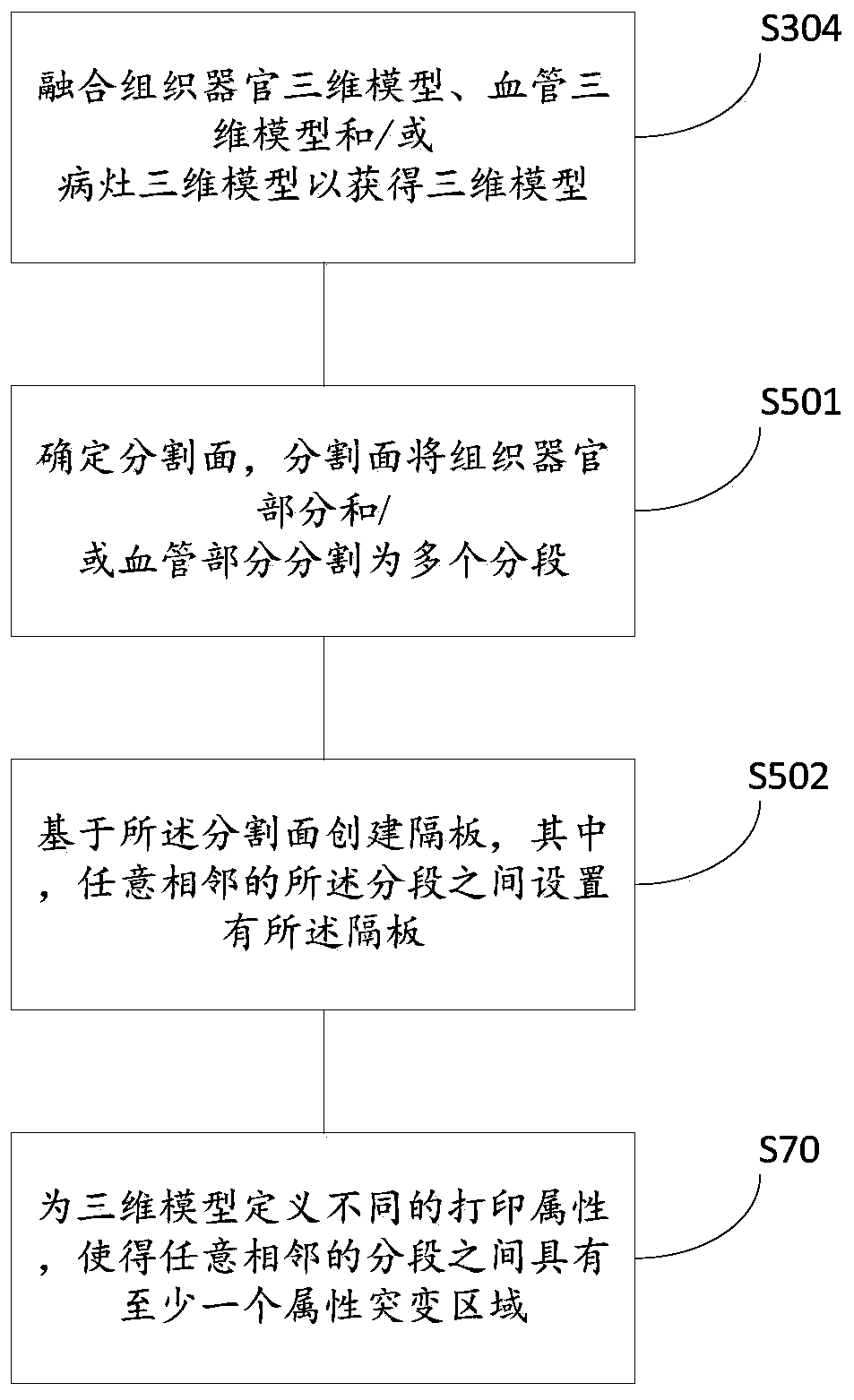
Three-dimensional organ model and printing method, device and equipment of three-dimensional organ model
ActiveCN110605853AIntuitive identificationAccurate identificationAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsOrgan ModelDimensional modeling
The invention relates to the technical field of printing and particularly relates to a three-dimensional organ model and a printing method, device and equipment of the three-dimensional organ model. The printing method of the three-dimensional organ model comprises the steps that image data are obtained; three-dimensional modeling is carried out based on the image data to obtain a three-dimensional model, wherein the three-dimensional model comprises at least one of a tissue organ part, a blood vessel part and a lesion part; the tissue organ part and / or the blood vessel part are / is divided into a plurality of sections; different printing attributes are defined for the three-dimensional model to make at least one attribute mutation area exist between any adjacent sections; and printing is carried out to obtain the three-dimensional organ model. By means of the three-dimensional organ model, the printing method, device and equipment of the three-dimensional organ model, all the sectionscan be visually and accurately distinguished, an operation path can be better planned, operation risks can be better reduced, and the purpose of precise medical treatment can be achieved.
Owner:ZHUHAI SAILNER 3D TECH CO LTD
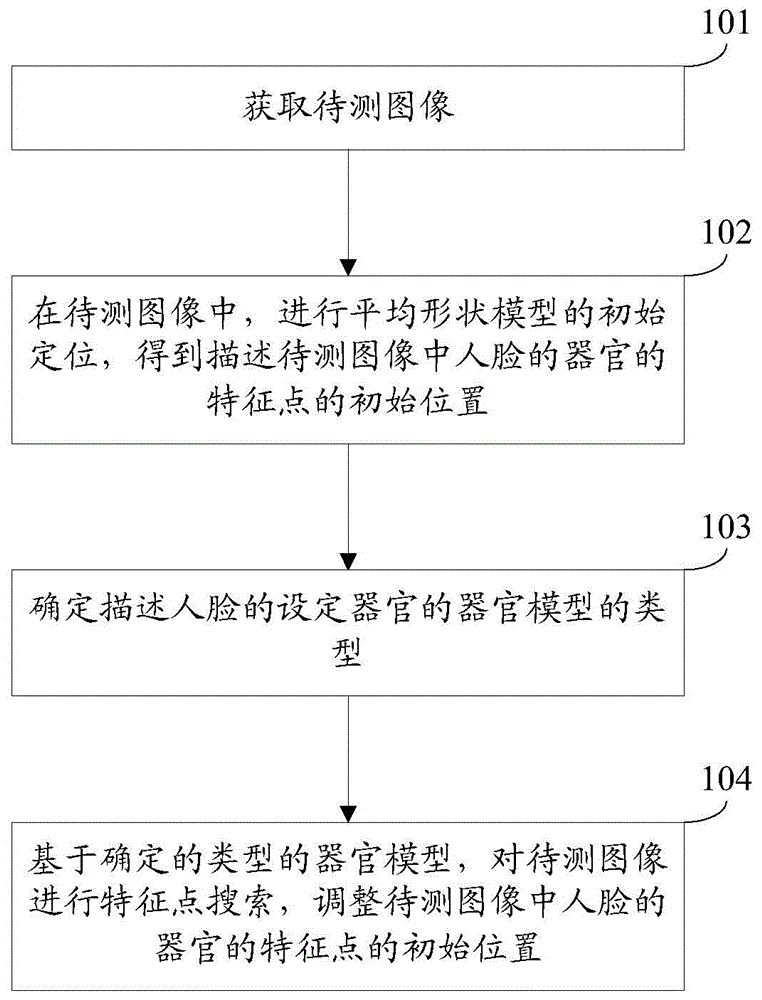
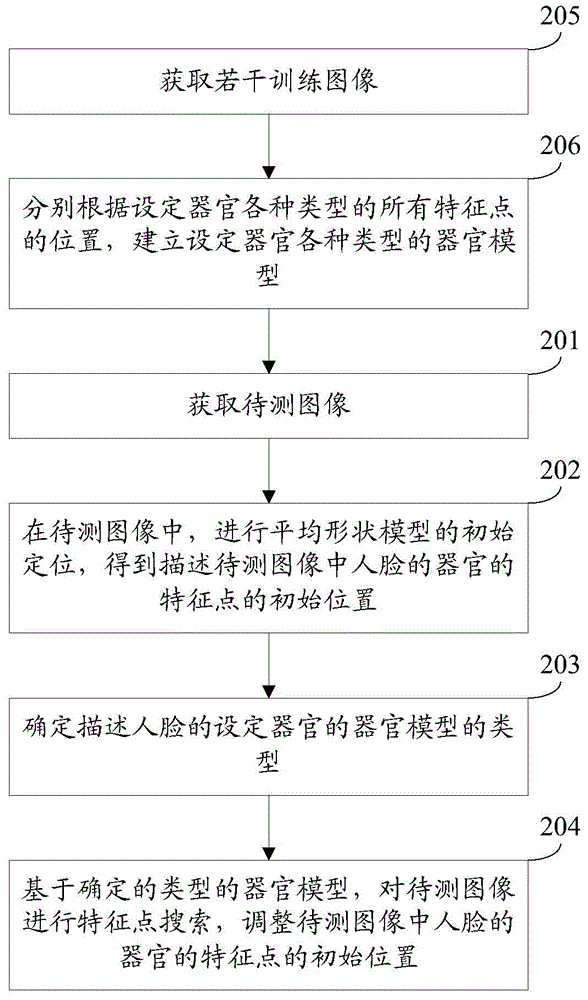
Facial feature point positioning method and device
ActiveCN104091148AHigh similarityReduce mistakesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses a facial feature point positioning method and device, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method includes the steps of obtaining an image to be detected, conducting initial positioning on an average shape model in the image to be detected so as to obtain initial positions of feature points for describing the organs of a face in the image to be detected, determining the types of organ models for describing the set organs of the face, conducting feature point search on the image to be detected on the basis of the organ models of the determined types, and regulating the initial positions of the feature points of the organs of the face in the image to be detected. According to the facial feature point positioning method and device, for different types of the set organs of the face in the image to be detected, the initial positions of the feature points of the organs of the face in the image to be detected are regulated on the basis of the organ shape models of different types, similarity between the feature points of the face and the image to be detected is improved, and errors between the face shape formed by the feature points of the face in the obtained image to be detected and the face shape in the image to be detected are reduced.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
In-vitro construction method of liver cancer organ model
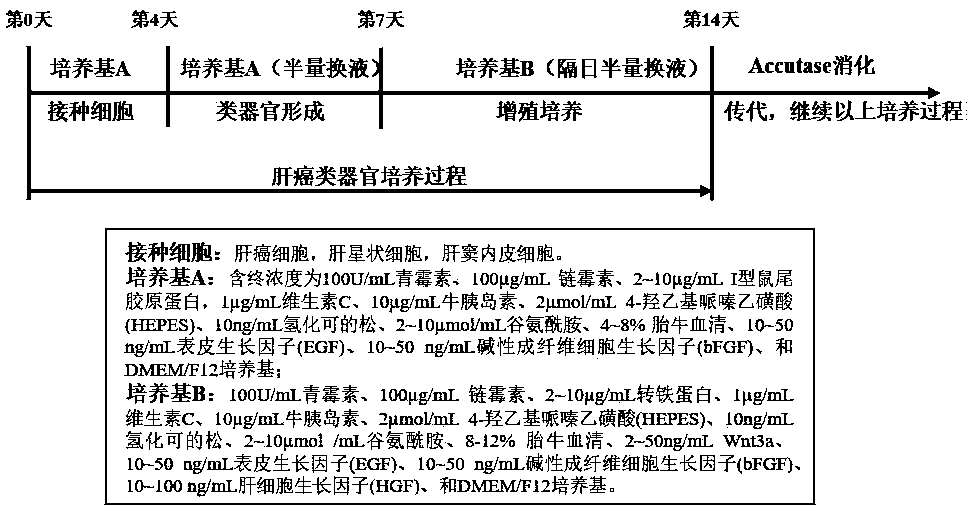
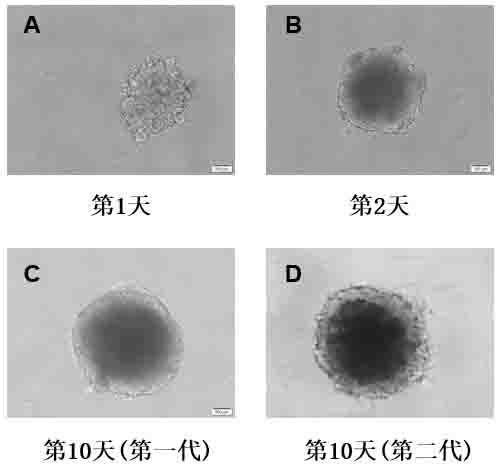
ActiveCN110004109AEasy constructionDetectable validityHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsOperability
The invention discloses an in-vitro construction method of a liver cancer organ model. Liver cancer cells, hepatic stellate cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are suspended in a culture medium A in a specific proportion; on the fourth day of culture, half of culture liquid is replaced, and culture is maintained; from the seventh day, the culture medium A is replaced with a culture mediumB, and then culture is continuously conducted for seven days; amplification subculture is conducted on the fourteenth day. On the basis of complex cellularity in a tumor microenvironment, the 3D liver cancer organ in-vitro model which is uniform in size, stable in structure, capable of being used for detecting the effectiveness of anticancer drugs and capable of achieving multiplication culture is quickly constructed. The constructed liver cancer organ model is simple in method, quick to construct, high in operability and suitable for researching a liver cancer generation and development mechanism, high-throughput screening of liver cancer drugs and the like, and has industrialization significance.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
Nidus and/or organ modeling method and apparatus used for model body making
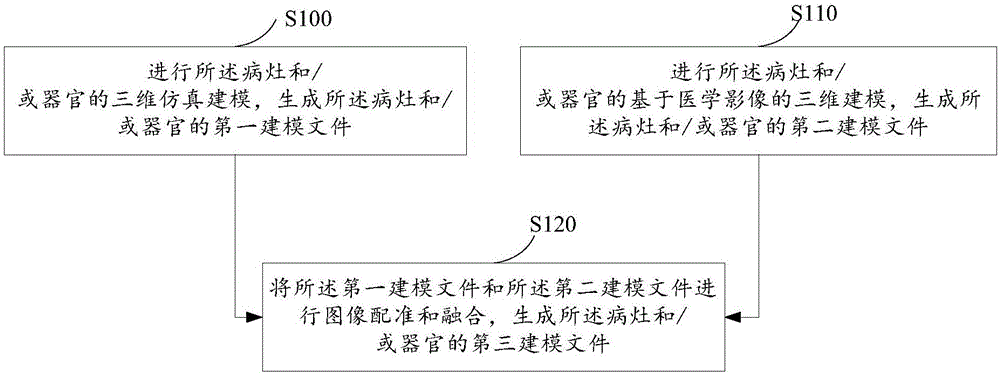
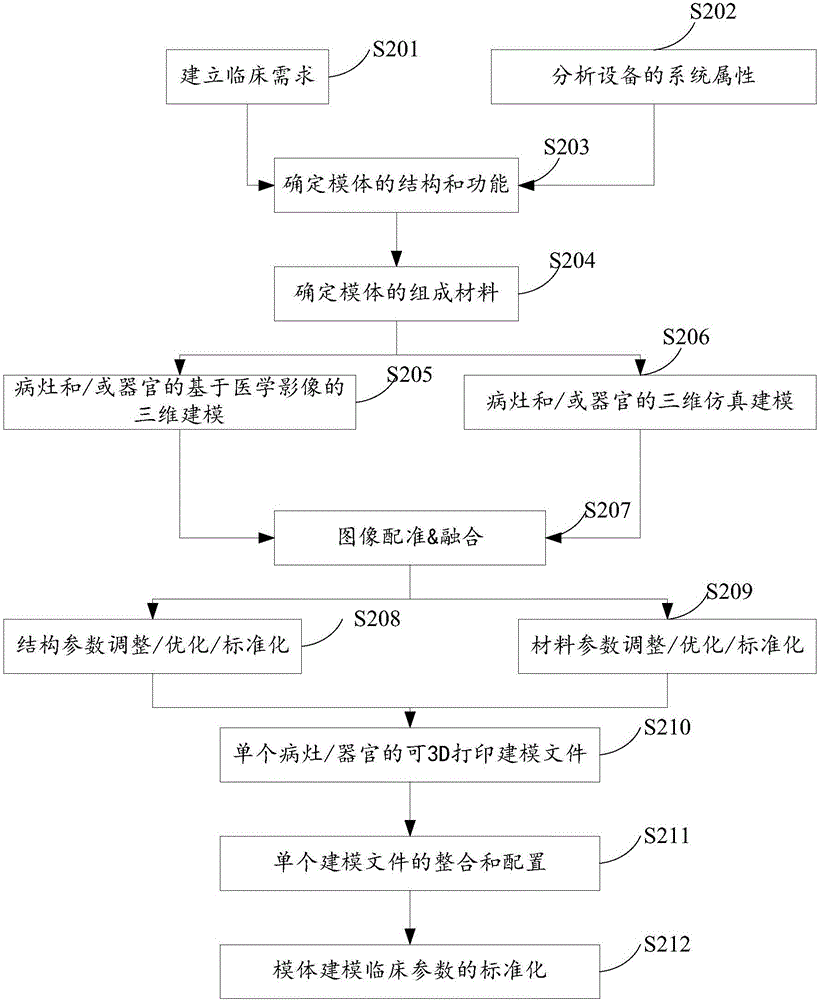
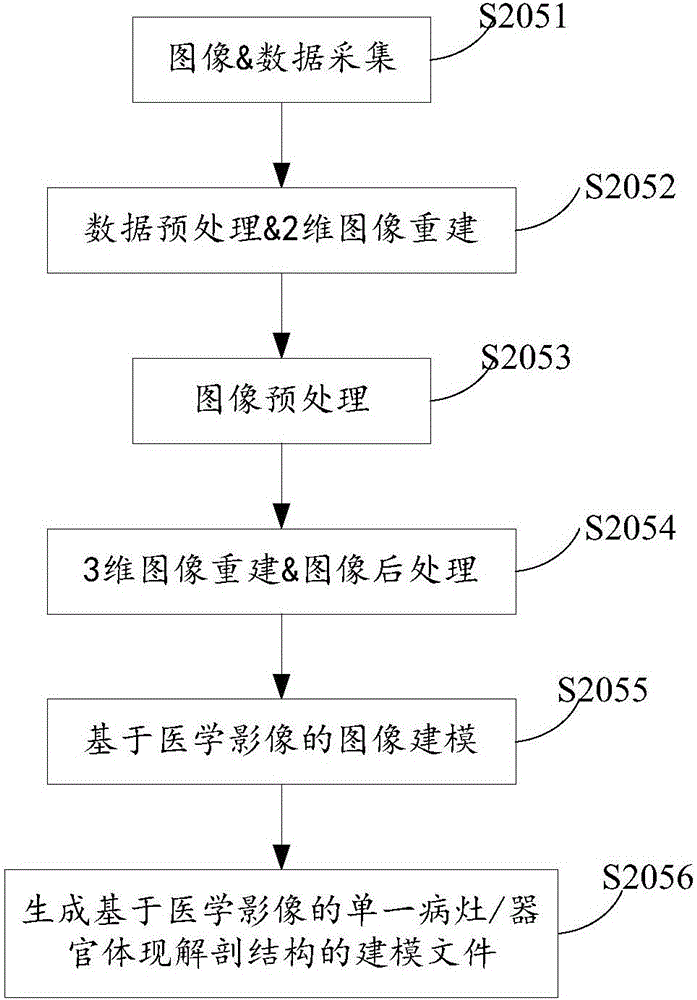
ActiveCN106709986AAccurately respond to detailed anatomical structuresPerformanceMedical simulationImage enhancementThree dimensional simulationOrgan Model
The invention relates to a nidus and / or organ modeling method and apparatus used for model body making. The nidus and / or organ modeling method used for model body making comprises the steps of performing three-dimensional simulation modeling of a nidus and / or an organ to generate a first modeling file of the nidus and / or the organ; performing medical image-based three-dimensional modeling of the nidus and / or the organ to generate a second modeling file of the nidus and / or the organ; and performing image registration and fusion on the first modeling file and the second modeling file to generate a third modeling file of the nidus and / or the organ. According to the method and the apparatus, nidus and / or organ modeling for model body making is realized through the registration and fusion of the three-dimensional simulation modeling and the medical image-based three-dimensional modeling.
Owner:上海术理智能科技有限公司
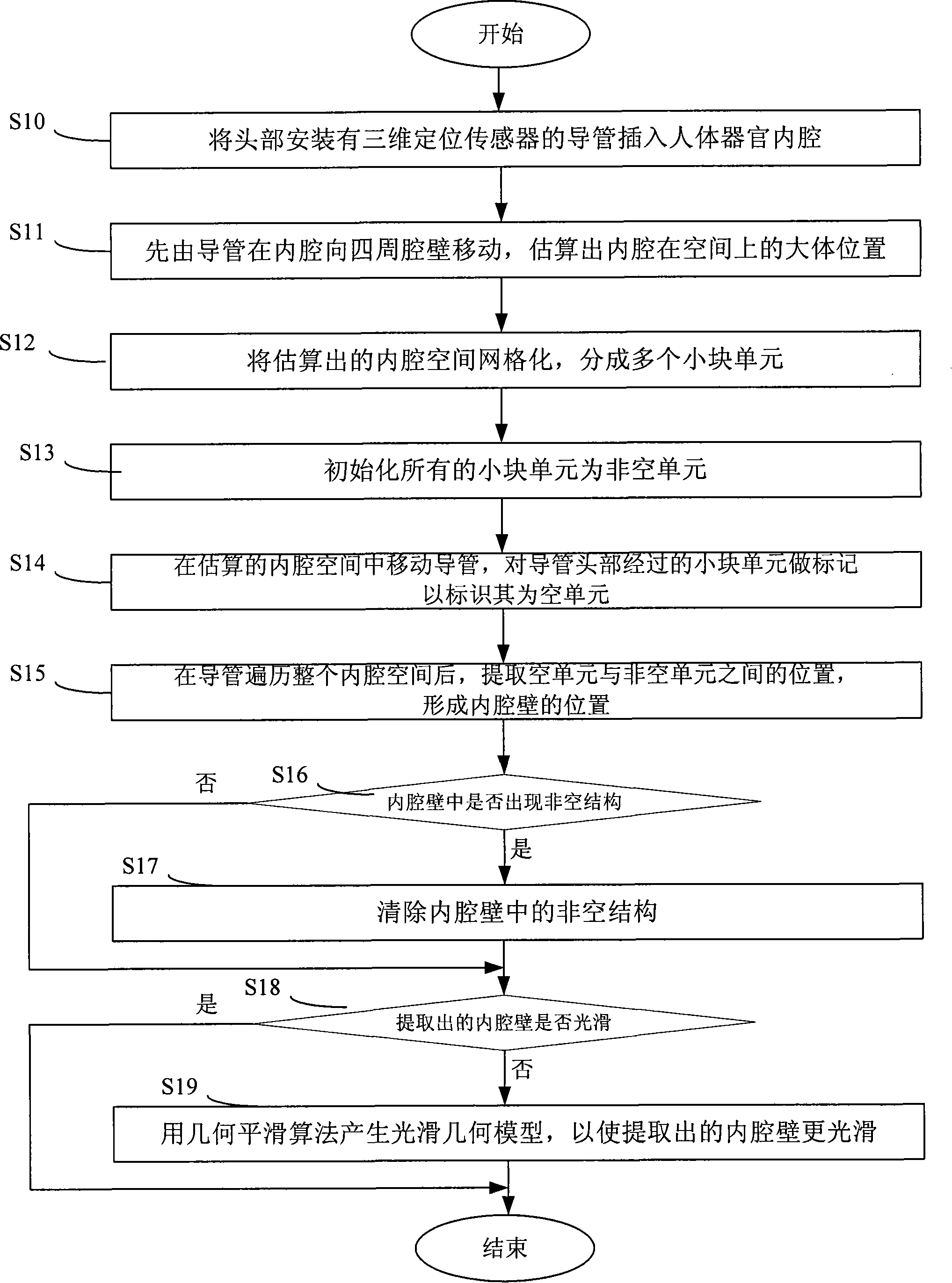
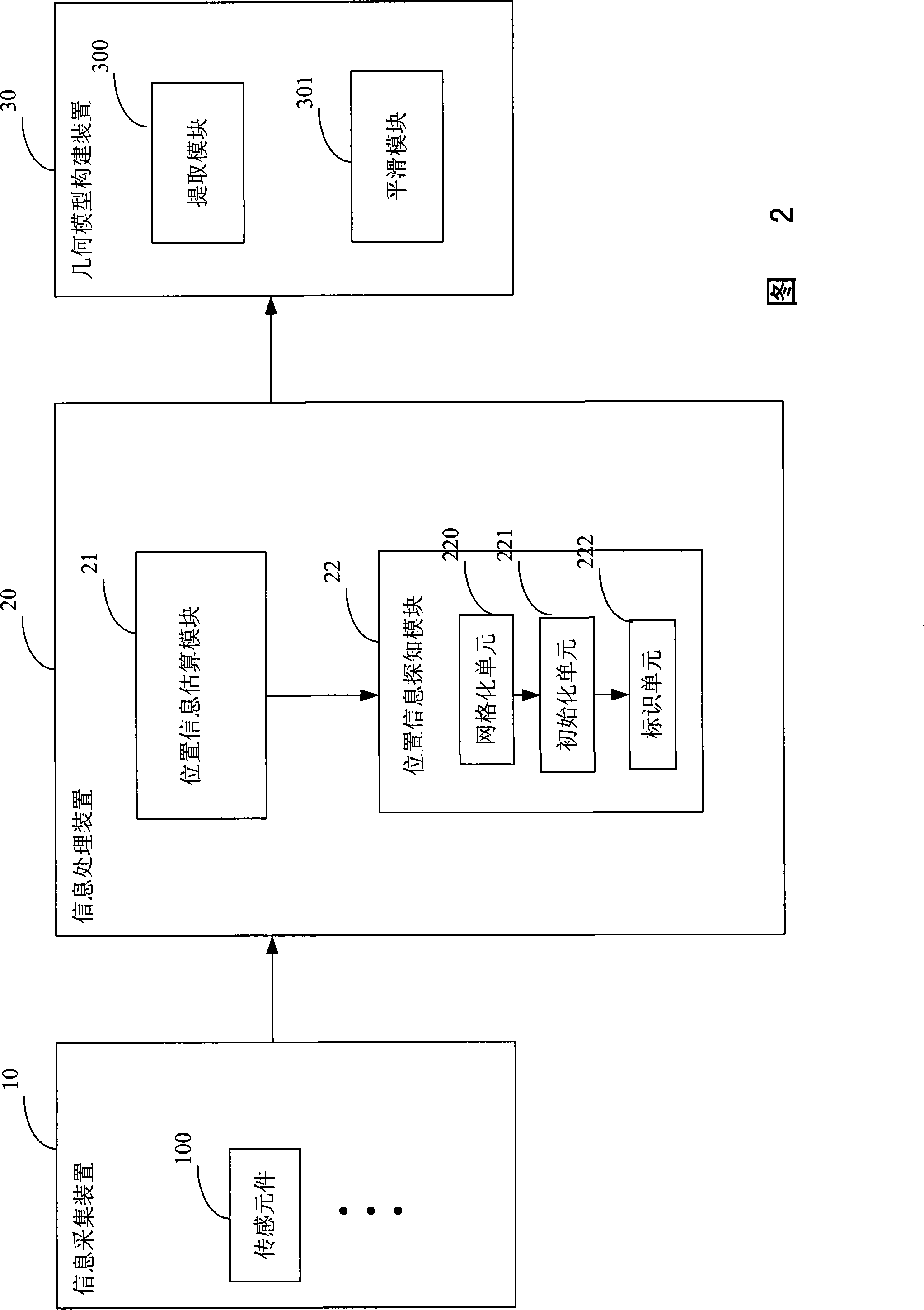
Method and system for rapidly constructing human body organ inner bore three-dimensional geometric model
The invention discloses a rapid construction method and system for human organ-intracavity three-dimensional geometry model, which is suitable for the rapid construction of complex cavities. The technical proposal is that: (1) one or more sensing elements are introduced into the intracavity; (2) in the intracavity the sensing elements are moved to collect the spatial location information of the intracavity to know the position or range of the intracavity; (3) according to the position or range of the intracavity, the intracavity surface three-dimensional geometry model is constructed. The rapid construction method and system for human organ-intracavity three-dimensional geometry model are applied in the field of organ model construction.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT EP MEDTECH CO LTD
Multi-stage suspension printing method for constructing complex heterogeneous tissue/organ
ActiveCN113290844AFacilitate the promotion of clinical applicationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCell culture supports/coatingOrgan ModelMicrosphere
The invention discloses a multi-stage suspension printing method for constructing a complex heterogeneous tissue / organ. The method comprises the following steps of S1, preparing bio-ink, wherein the bio-ink is formed by cross-linked cell-carrying gel microspheres, or is obtained by mixing the cross-linked cell-carrying gel microspheres with one or more non-cross-linked gel materials; S2, printing the bio-ink in a suspension medium to construct a specific tissue / organ structure; S3, further performing two-stage or multi-stage substructure printing in the tissue / organ structure obtained in S2; and S4, after printing, dissolving out the suspension medium after overall crosslinking. According to the multi-stage suspension three-dimensional printing method, the gel microsphere ink based on shear thinning and self-healing characteristics can be printed and formed in the suspension medium and then can be used as the suspension medium for printing a next-stage structure, is suitable for constructing the tissue and organ model with a blood vessel channel and a heterogeneous cell structure, and promotes the clinical application of the engineered tissue / organ in the aspect of regeneration and repair treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Liver organ model and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110373380AShorten the timeCutting costsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionChemical compoundOrgan Model
The invention discloses a liver organ model and a construction method and application thereof. The method includes steps: (1) subjecting embryonic stem cells to supported culture; (2) preparing cell balls, sequentially subjecting to differentiation culture through a mesoblast-entoderm stage, a liver induction stage and a mature stage to obtain different types of cells including liver cells, bile duct cells and endothelial cells, and subjecting the different types of cells to orderly arrangement and combination to form a liver organ. By control of exposure time of compounds in different differentiation stages, screening and evaluation of liver toxicity effects and liver early development influences of the compounds are carried out. In addition, by the liver organ model, high-flux short-timeevaluation of the liver development influences and the liver toxicity effects of one compound or various compounds can be realized, evaluation indexes are simple, direct and diversified, quick primary screening of a great quantity of new synthetic compounds can be realized, and a foundation is laid for subsequent compound modification, pharmacological and toxicological mechanism research or marketing for use.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tumor grid organ model 3D printing method
The invention relates to a tumor grid organ model 3D printing method. The method particularly comprises the following steps: a cross section and a sagittal section when a human body is in a supine position are used for building crossed multiple grids on the surface of an organ, while the 3D grids are built, 3D modeling software specially adopted for original data for medical imaging (CT or MRI) picks out an organ or a tumor or a blood vessel in need of 3D printing, and building of 3D data is carried out. 3D data for the organ or the tumor or the blood vessel are built at the same time, and organ surface 3D grid data are built. The 3D data are inputted to a 3D printer for 3D model printing. According to the printed model of the invention, the tumor can be intuitively observed via a hollow organ shell and the distance between the tumor and the organ surface can be measured, a guide is provided for surgical resection, and a spatial distance between the tumor or the blood vessel inside the organ and an anatomical site on the organ surface can be directly read from the model.
Owner:王峻峰
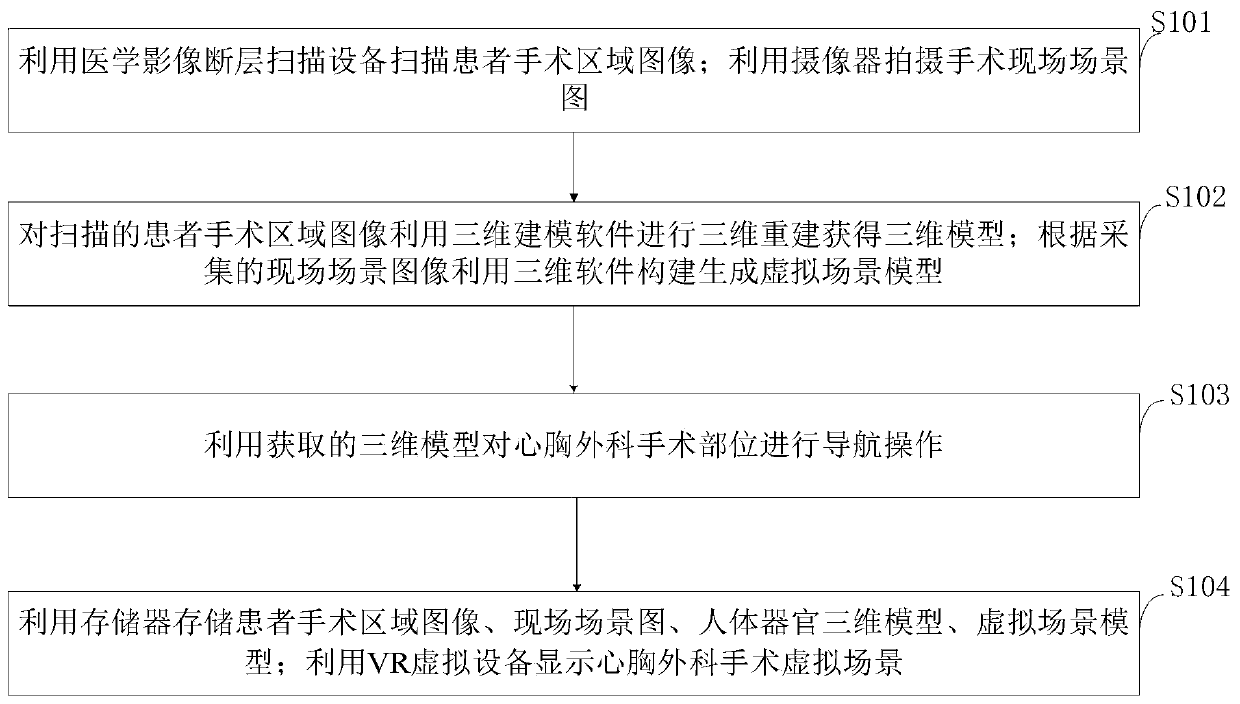
Cardiothoracic surgery auxiliary control system and method based on virtual reality
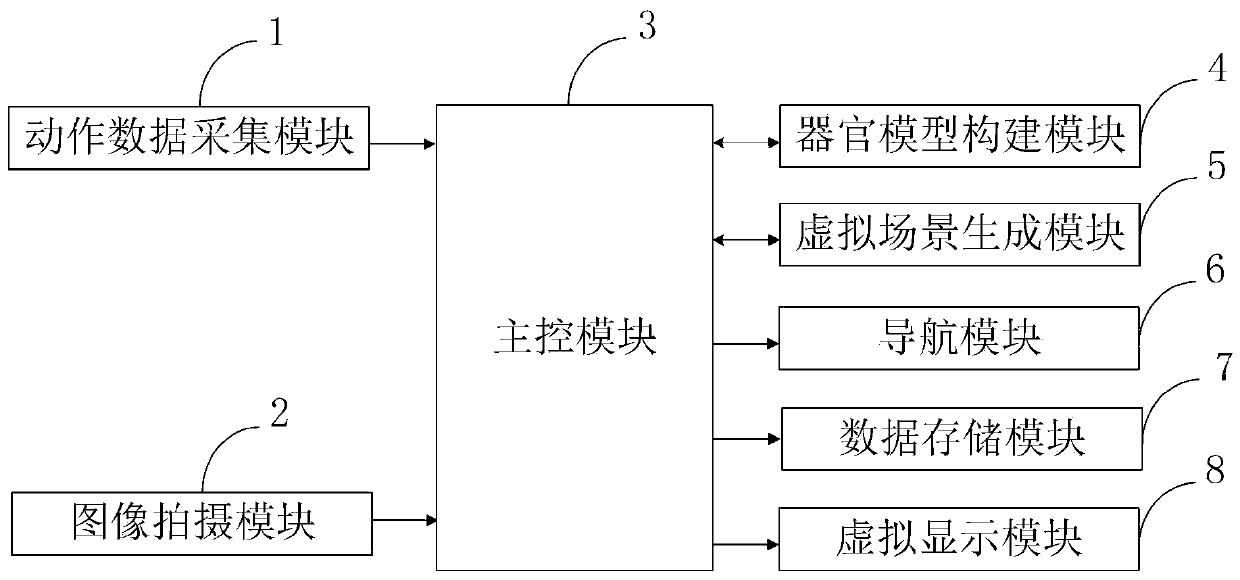
InactiveCN109730768ARealize the navigation functionImprove efficiencySurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingData acquisitionData acquisition module
The invention belongs to the technical field of cardiothoracic surgery, and discloses a cardiothoracic surgery auxiliary control system and method based on virtual reality. The cardiothoracic surgeryauxiliary control system based on virtual reality comprises an action data acquisition module, an image shooting module, a main control module, an organ model building module, a virtual scene generating module, a navigation module, a data storage module and a virtual display module. According to the cardiothoracic surgery auxiliary control system and method based on virtual reality, a specific scene is automatically shot through the image shooting module, the artificial resources are saved, and the more accurate shooting effect can be ensured; meanwhile, three-dimensional re-building is conducted on a medical image through the navigation module to obtain a virtual model; the virtual model is fused with the body part of a patient by utilizing an augmented reality technology, so that the navigation effect on the medical surgery is achieved in the fused state, a doctor conveniently and accurately controls surgical instruments, the efficiency of the surgery is greatly improved, and the success rate of the surgery is greatly increased.
Owner:黄德荣
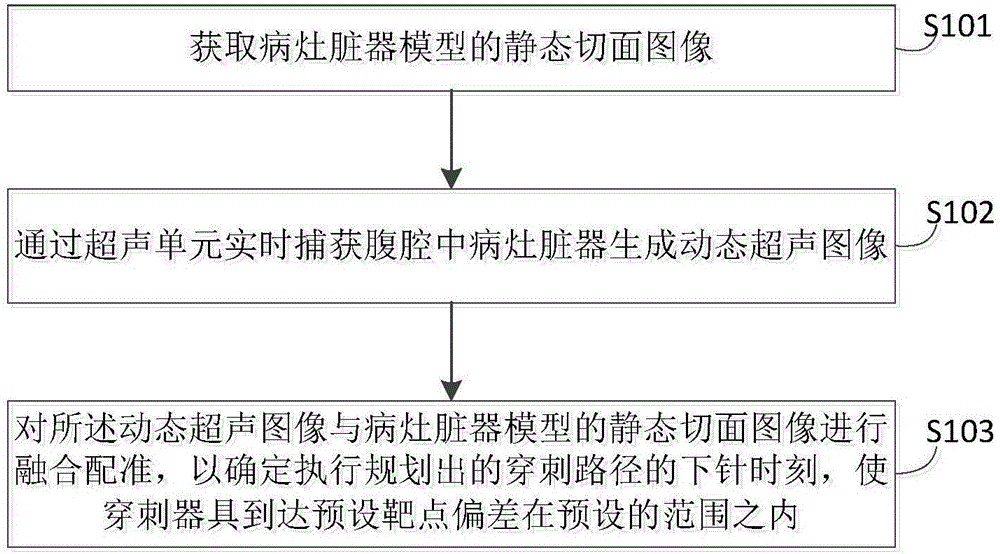
Abdominal cavity minimally invasive surgery system and needling time determination method
InactiveCN106109016AEnsure safetyGuaranteed validitySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsLess invasive surgeryAbdominal cavity
The invention embodiment provides an abdominal cavity minimally invasive surgery system and a needling time determination method; the method comprises the following steps: obtaining a static state section image of a focus internal organs model, and using an ultrasonic unit to capture the focus internal organs in the abdominal cavity in real time so as to form a dynamic ultrasonic image; fusing and rectifying the dynamic ultrasonic image with the static state section image of the focus internal organs model, thus determining the needling execution time of a planned puncture path, so the deviation of a puncture tool reaching a preset target can be limited in a preset scope. The system and method allow the tool to have the minimum deviation when reaching the preset target, thus further ensuring surgery safety and effectiveness, and reducing operational difficulty.
Owner:北京柏惠维康医疗机器人科技有限公司
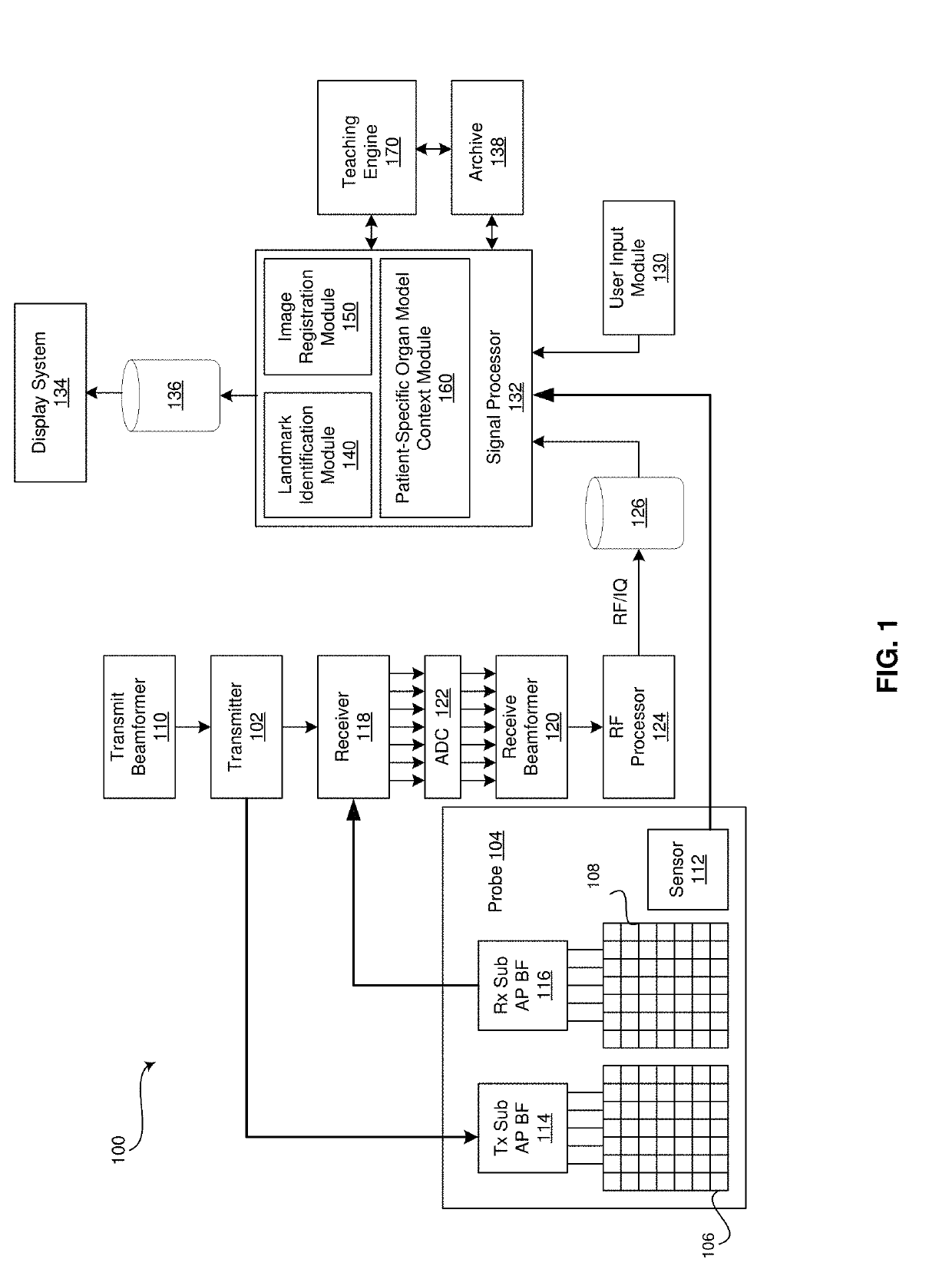
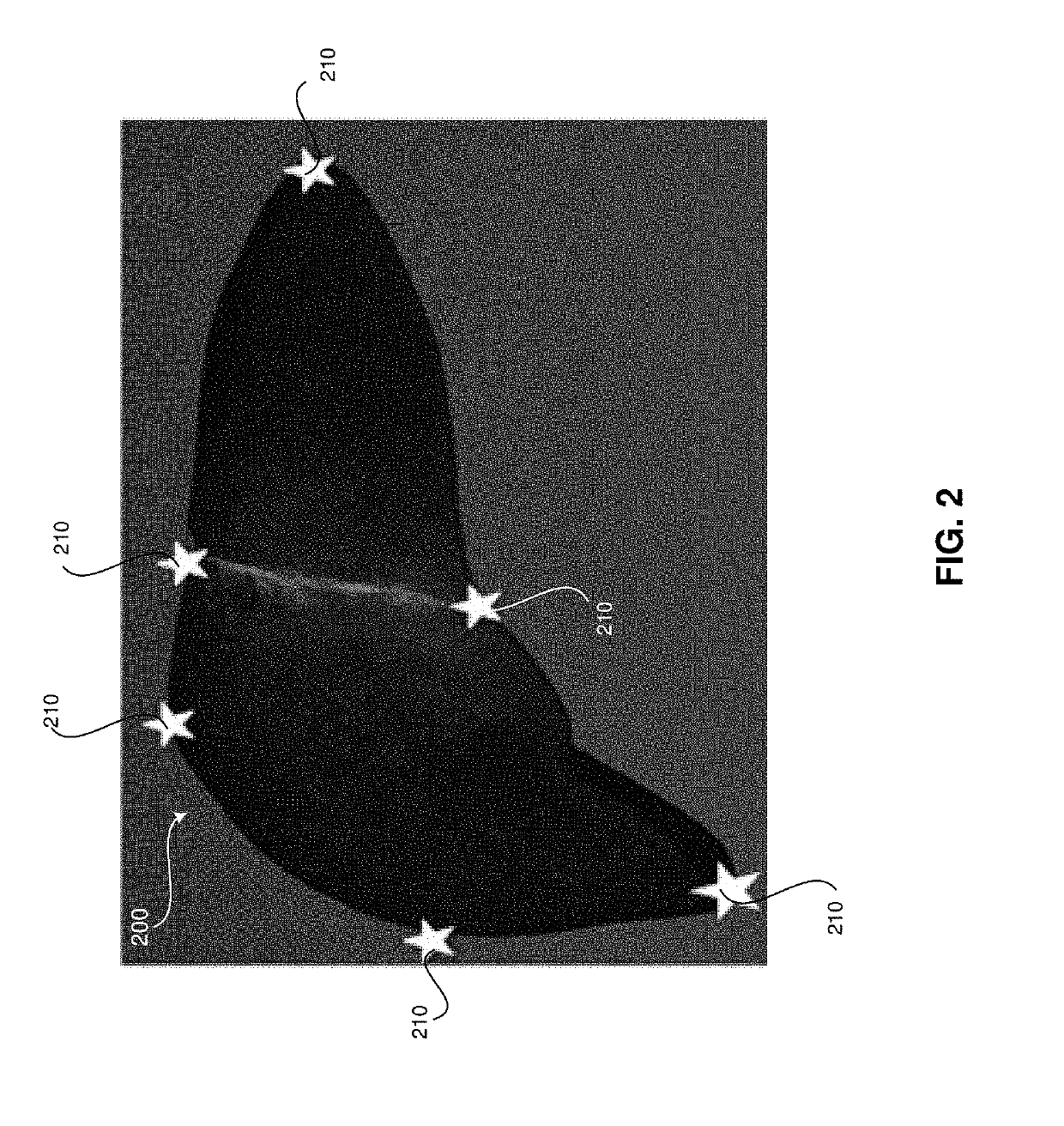
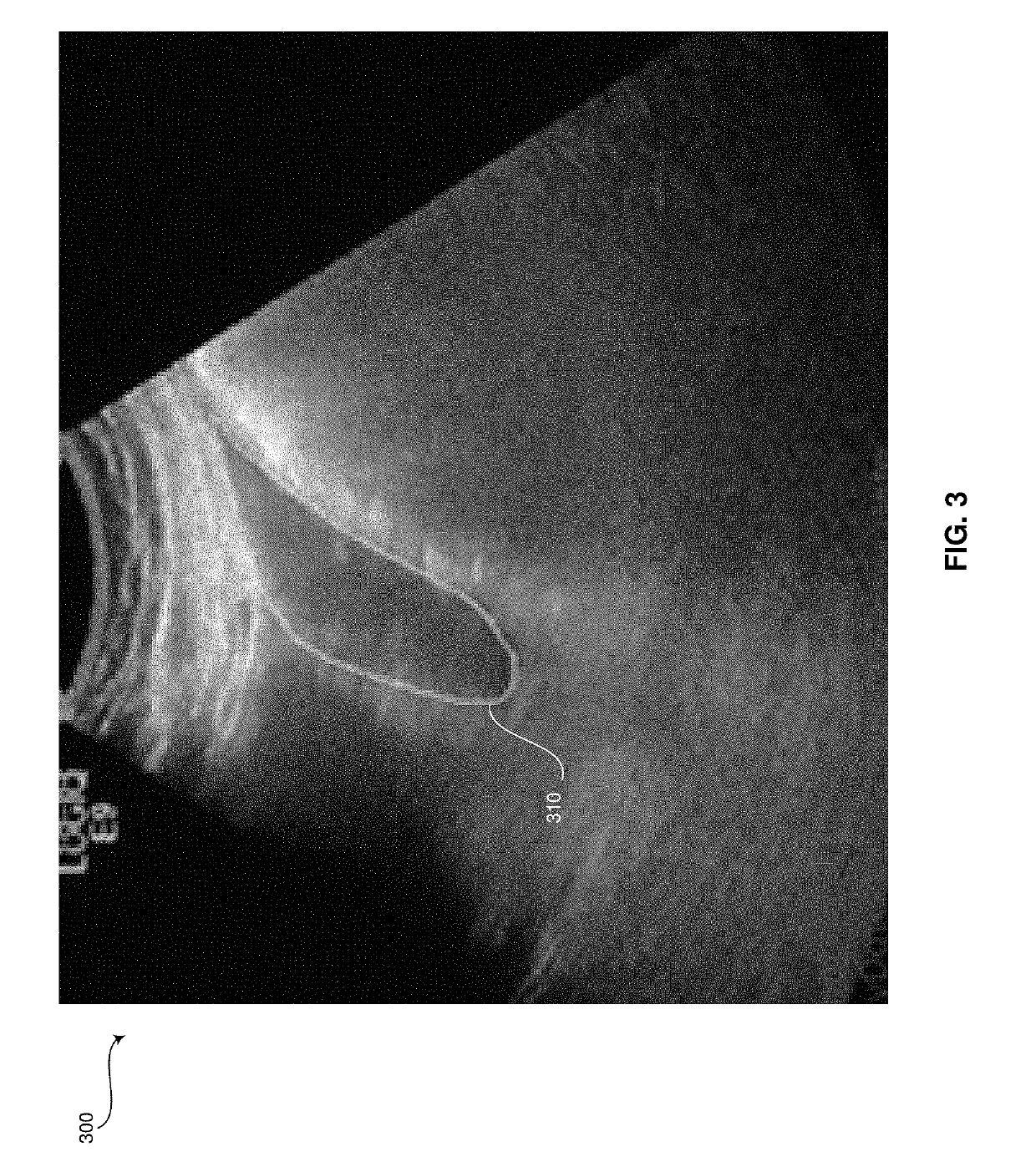
Method and system for creating and utilizing a patient-specific organ model from ultrasound image data
A system and method for generating a patient-specific organ model is provided. The method may include receiving ultrasound images of an organ and probe position data corresponding with each of the ultrasound images. The method may include receiving identification of landmarks in the ultrasound images corresponding with pre-defined landmarks of a generic geometric organ model. The method may include automatically identifying surface points of the organ in the ultrasound images. The method may include generating a patient-specific ultrasound point cloud of the organ based on the received identification of the landmarks, the automatically identified surface points of the organ, and the probe position data. The method may include registering a point cloud of the generic geometric model to the patient-specific ultrasound point cloud to create a patient-specific organ model. The method may include presenting the patient-specific organ model at a display system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
3D printing method for medical model
InactiveCN107139484AStrong toughnessLong storage timeAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresOrgan Model3D modeling
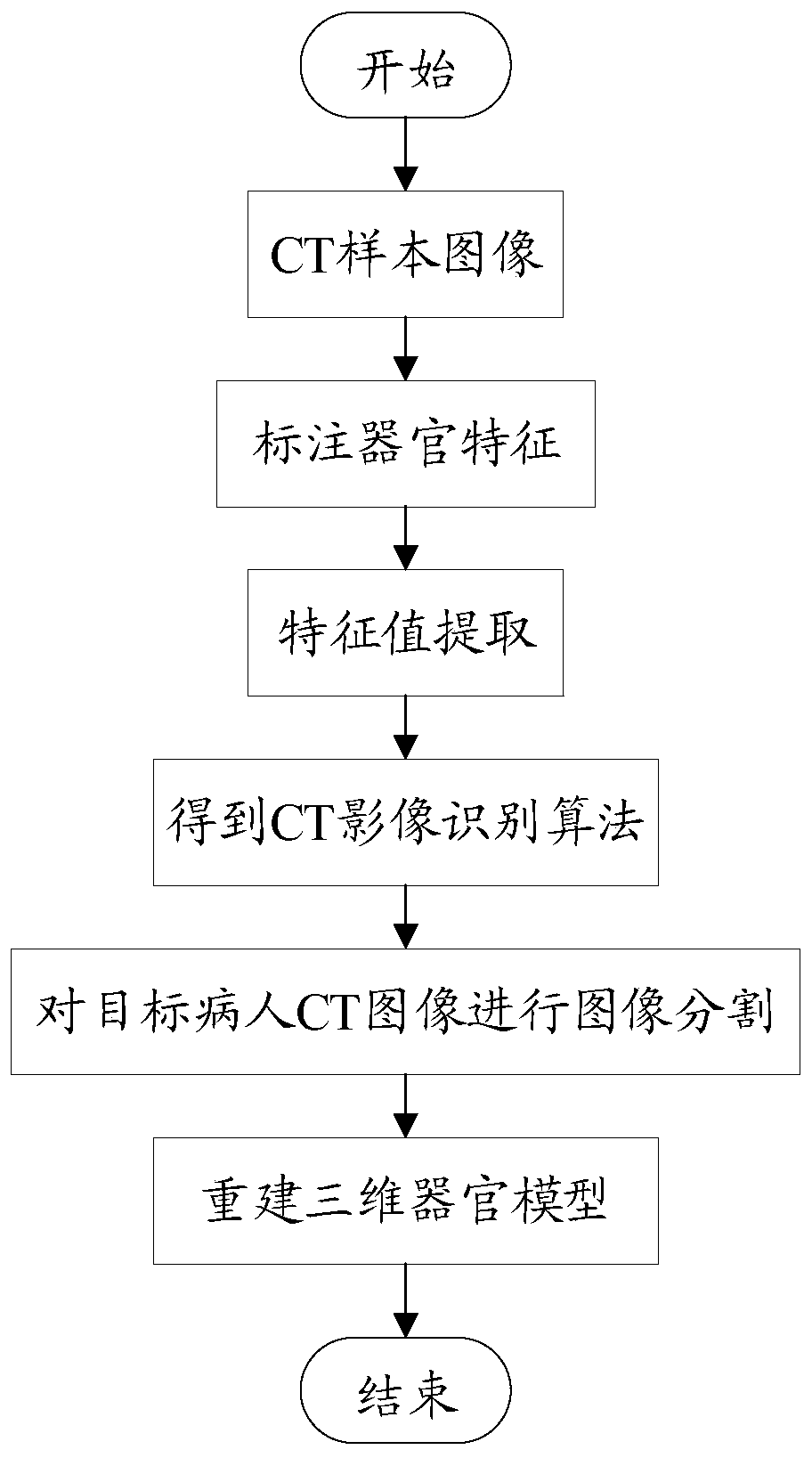
The invention discloses a 3D printing method for a medical model. The 3D printing method comprises the steps that A, three-dimensional model data are acquired, the model is imported into magics software through a STL file provided by a client so as to fix the positions of all parts of the model, and the output file with the STL format is then imported into 3DMAX software so as to modify and cut the model; B, according to the current situations of organs of the model, section lines are set along the maximum boundary of three-dimensional coordinates of all the organs after variation, and parts which are are sectioned and cut are exported to be STL files respectively; and C, the stored STL files are stored into Cura software, print files with the gcode format are output, and printing is started. The method has the advantages that the defects in the prior art can be overcome, and the precision of the 3D printed organ model can be improved.
Owner:宁夏上河科技有限公司
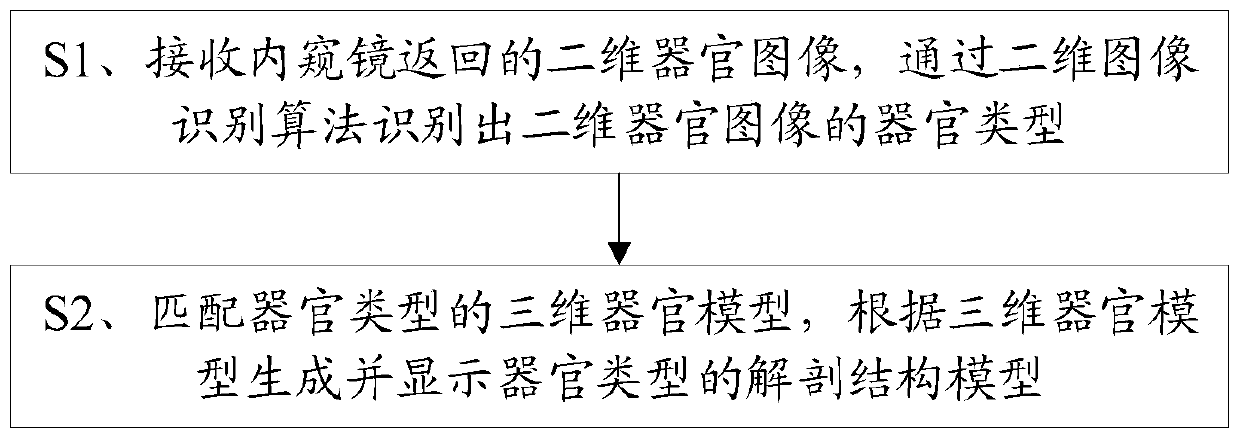
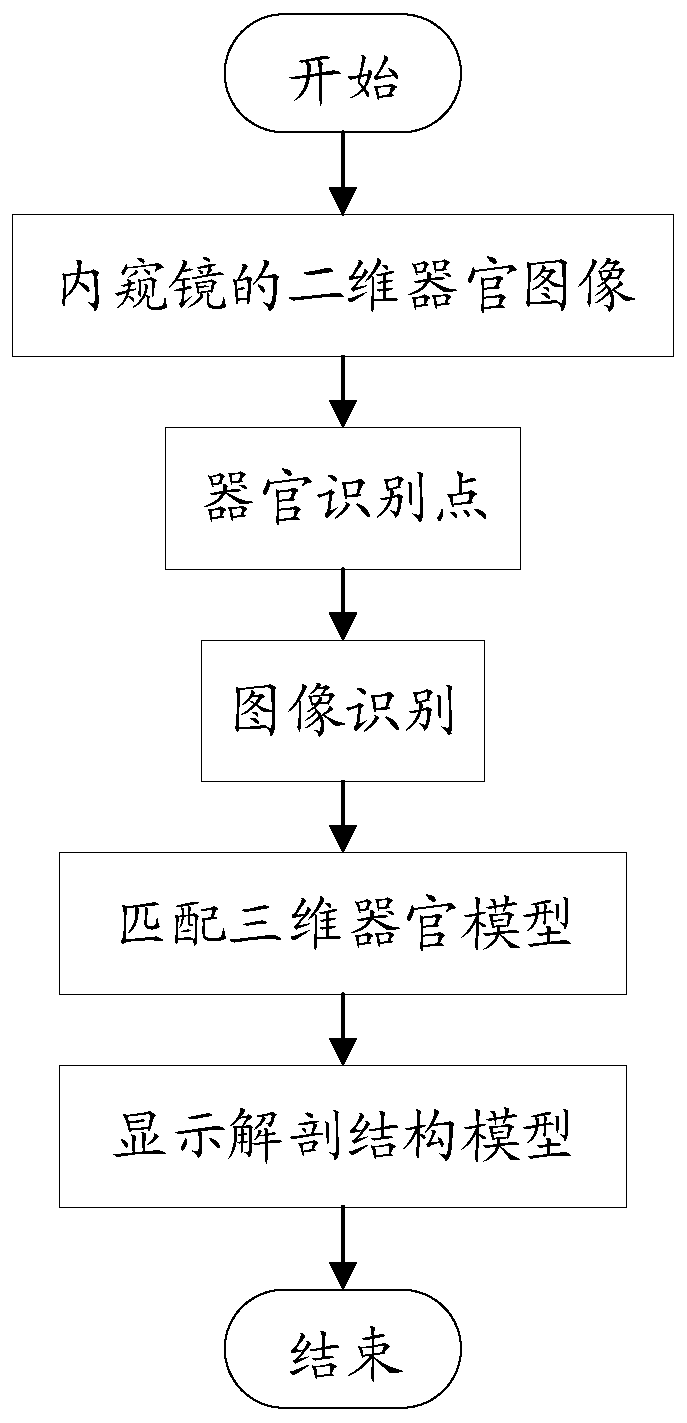
AR and endoscope combined surgical navigation method and terminal
InactiveCN110051434AUnderstand intuitiveEffectSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingOrgan ModelEndoscope
The invention discloses an AR and endoscope combined surgical navigation method and terminal. The method includes receiving a two-dimensional organ image returned by an endoscope and identifying an organ type of the two-dimensional organ image by a two-dimensional image identification algorithm; acquiring a three-dimensional organ model of the organ type and generating and displaying an anatomicalmodel of the organ type according to the three-dimensional organ model. The three-dimensional virtual anatomical model is generated through a two-dimensional organ image. On one hand, a doctor can see a real image presented by the two-dimensional organ image; on the other hand, a virtual image formed by the anatomical model can be seen, that is, the virtual reality contrast technology is adopted,so that the doctor can have a more intuitive understanding of the surrounding conditions of the endoscope, and the effect of surgical navigation can be achieved.
Owner:厦门强本科技有限公司
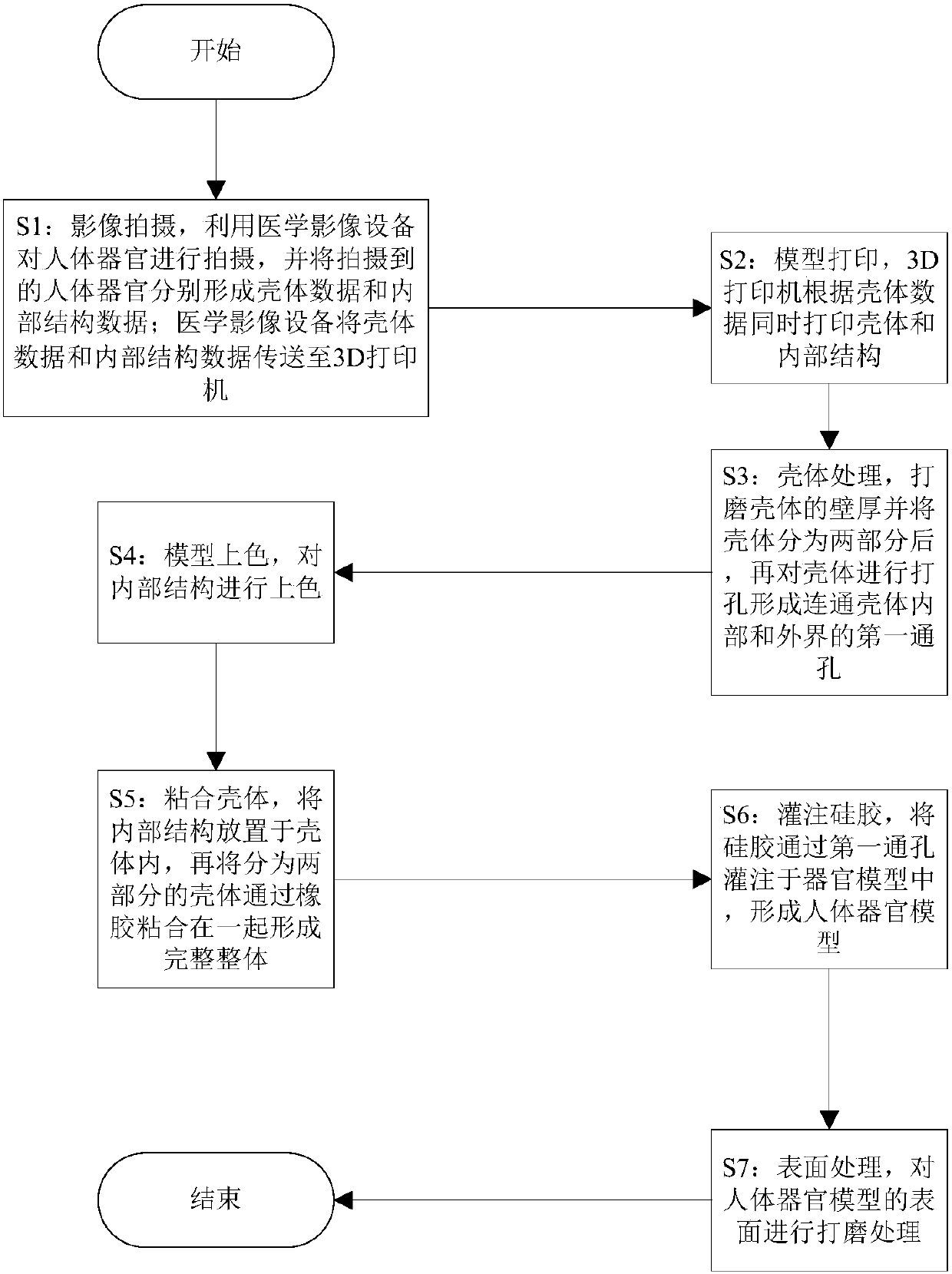
Manufacturing process of human organ model
InactiveCN107657880AGuaranteed firmnessGuaranteed fullnessEducational modelsOrgan ModelMedical imaging
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a human organ model. The human organ model comprises a shell body and an internal structure arranged inside the housing, and is characterized by comprising a 3D printer and medical imaging equipment. The manufacturing process of the human organ model comprises the steps of: S1, image photographing; S2, model printing; S3, shell body processing; S4, model coloring; S5, shell body adhering; S6, silica gel perfusion; S7, and surface treatment. The manufacturing process has the advantages and beneficial effects that: the firmness and plumpness ofthe human organ model are ensured through printing the shell body and the internal structures separately, placing the internal structure into the shell body and then perfusing silica gel into the shell body; and distinction degrees of tissues of the internal structure in the human organ model are ensured through coloring the internal structure and then implanting the internal structure into the shell body, the usage of full-color soft plastics is avoided, thus the manufacturing cost of the human organ model is further reduced, thereby being conductive to large-scale promotion and application.
Owner:上海光韵达数字医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com