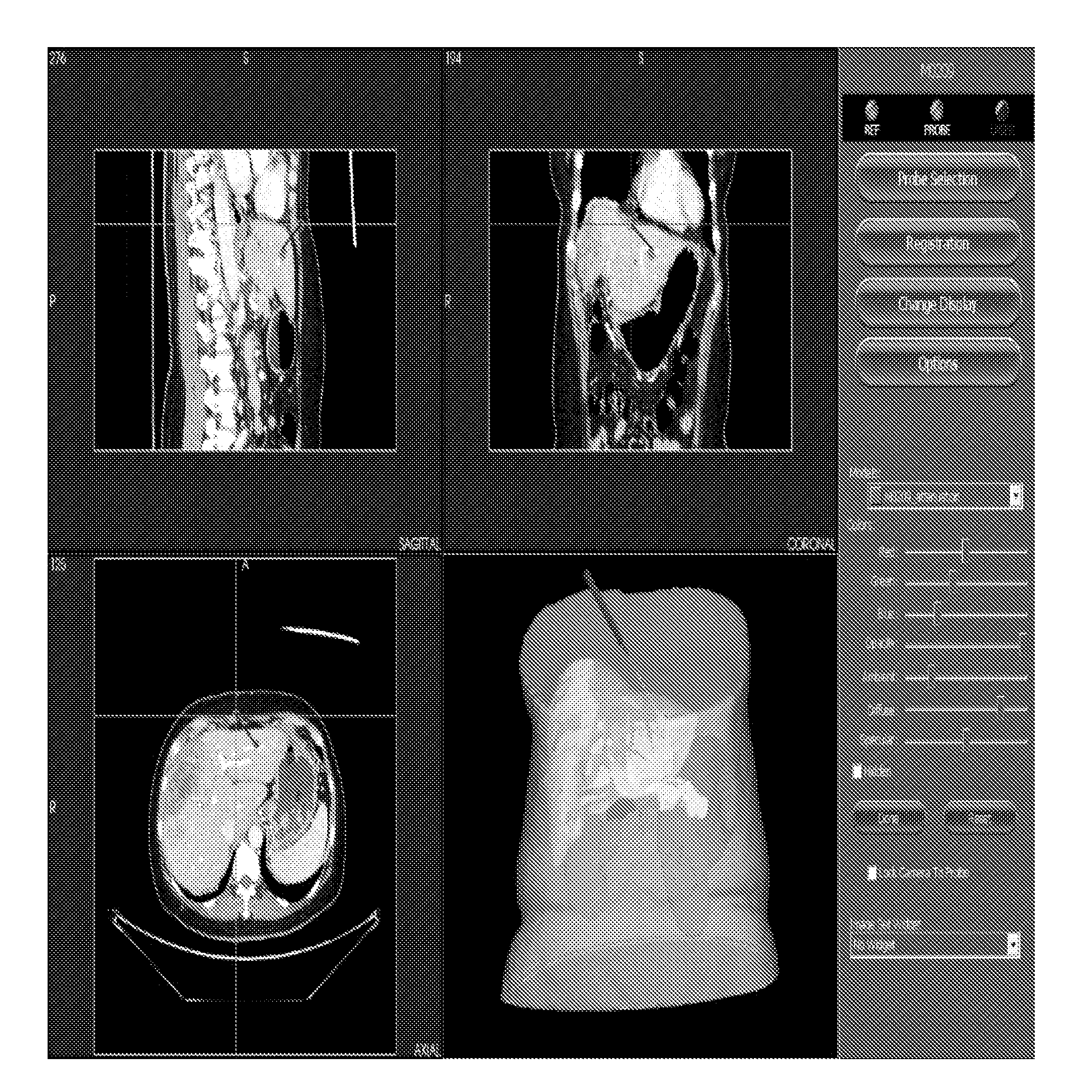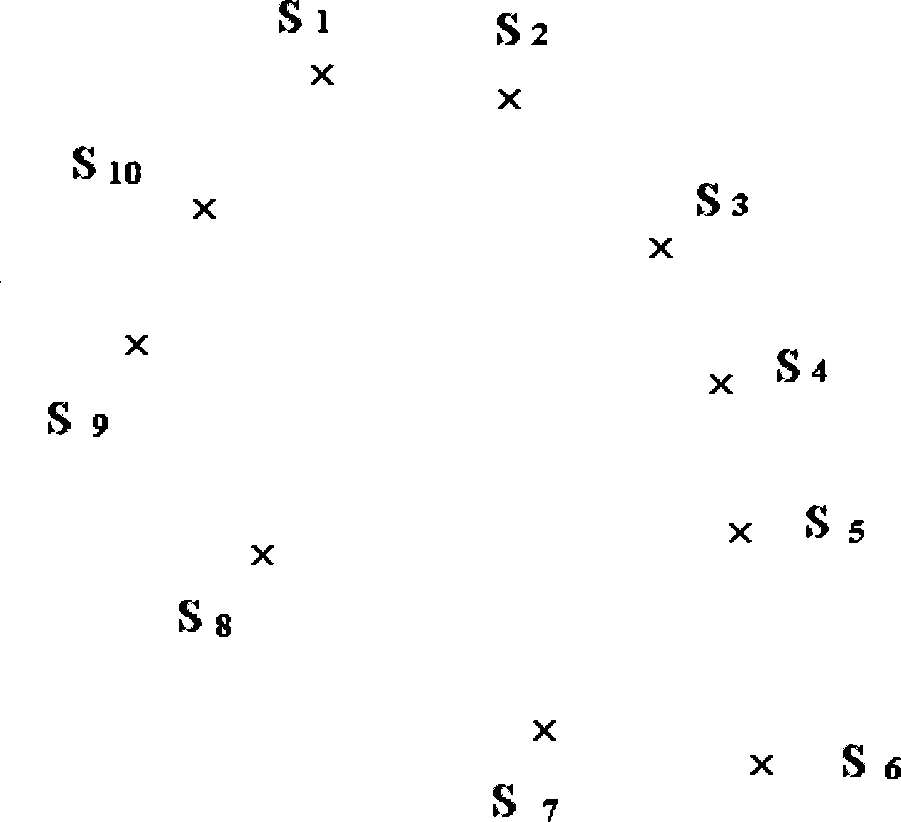Patents
Literature
60 results about "Organ surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
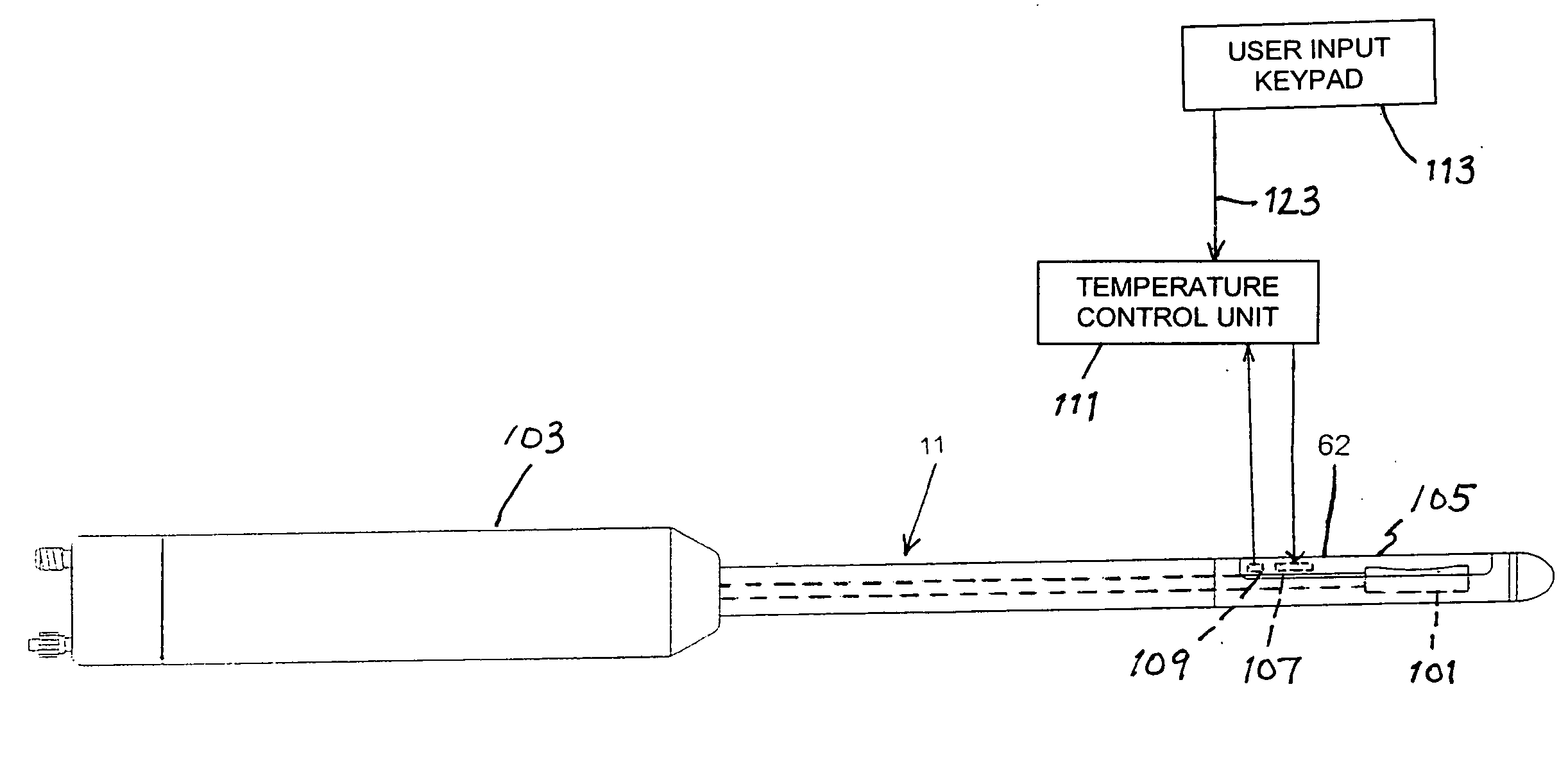
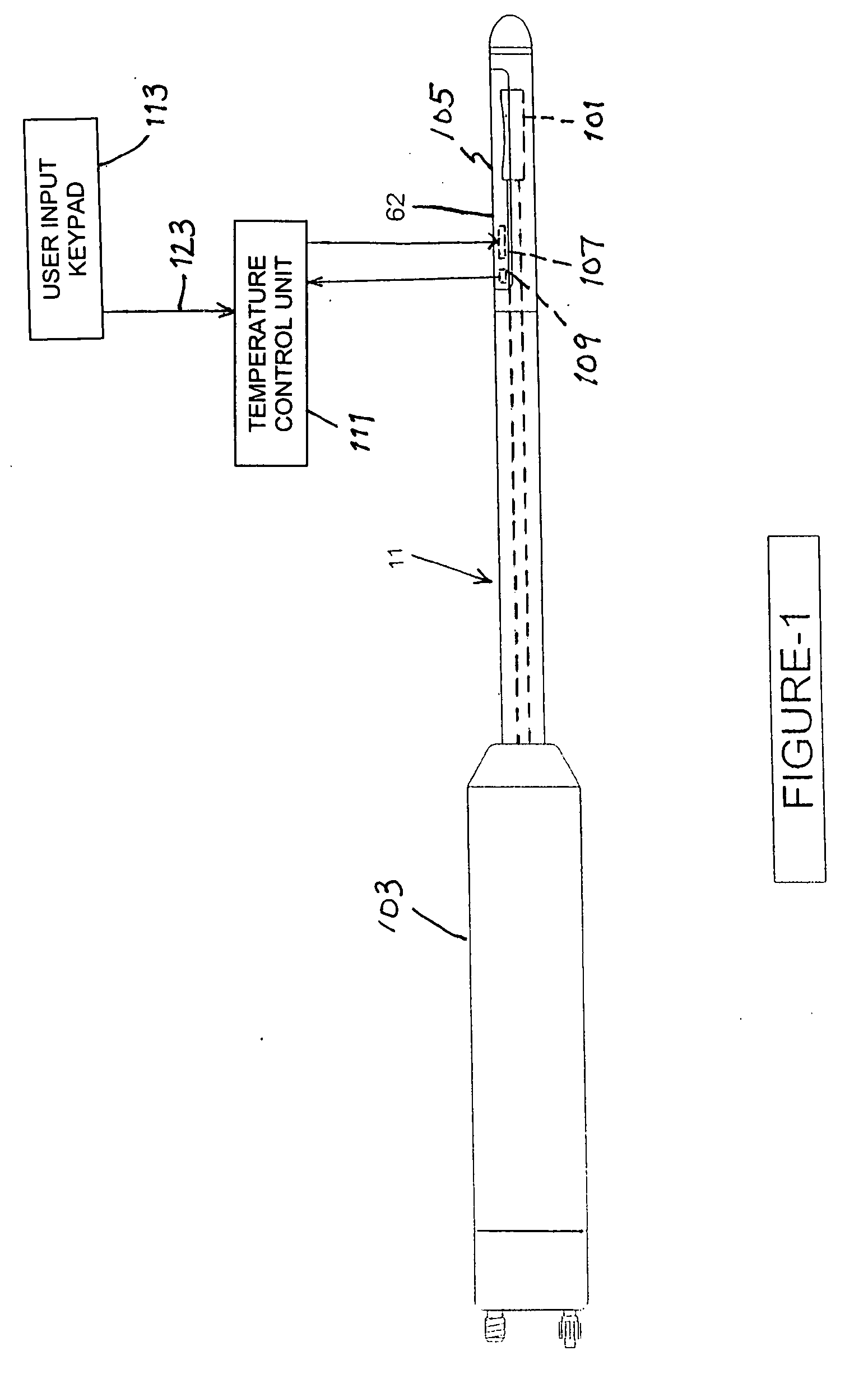
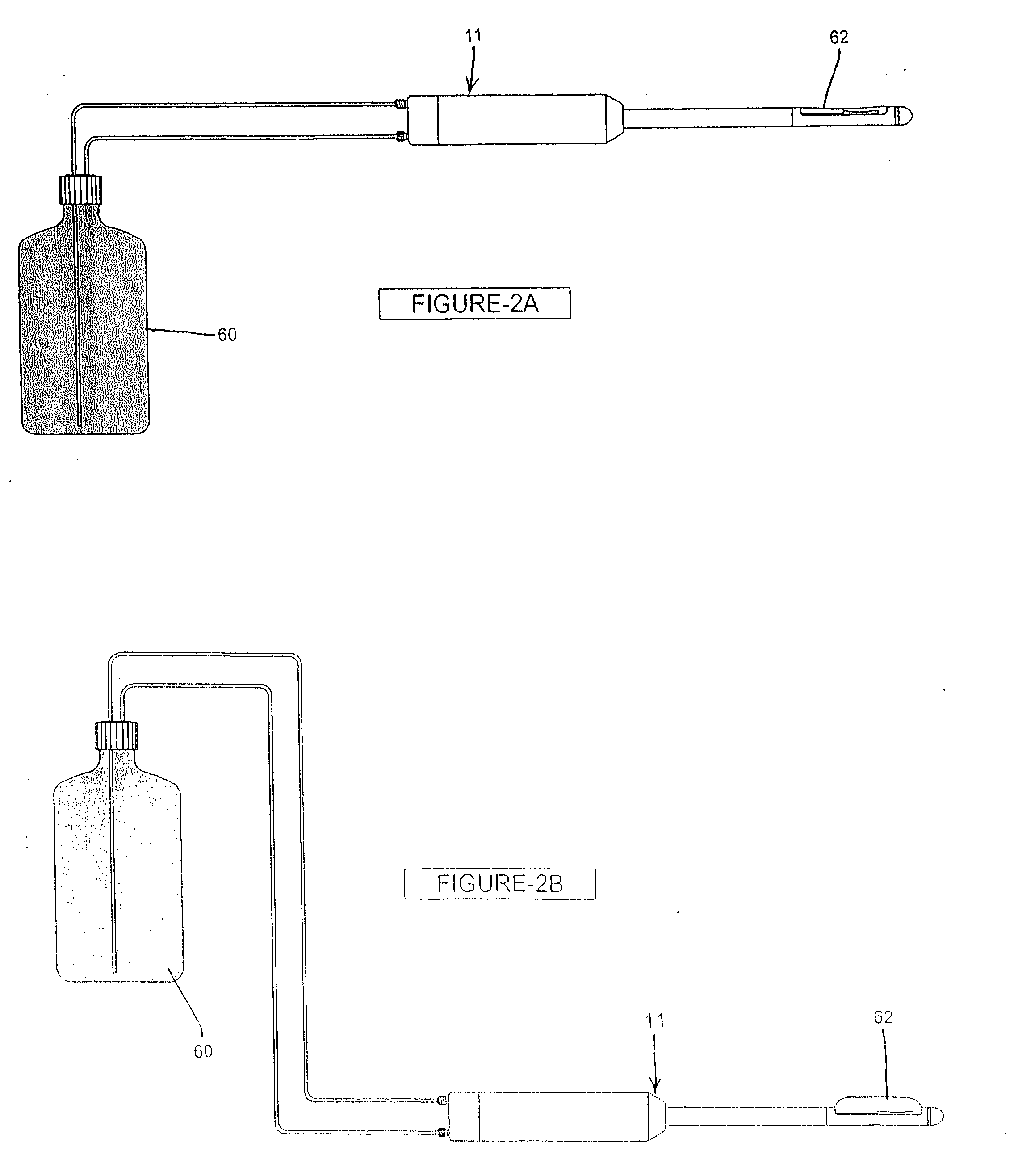
Elevated coupling liquid temperature during HIFU treatment method and hardware
InactiveUS20080281200A1Avoid necrosisEnhanced couplingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyLiquid temperatureUltrasonic vibration
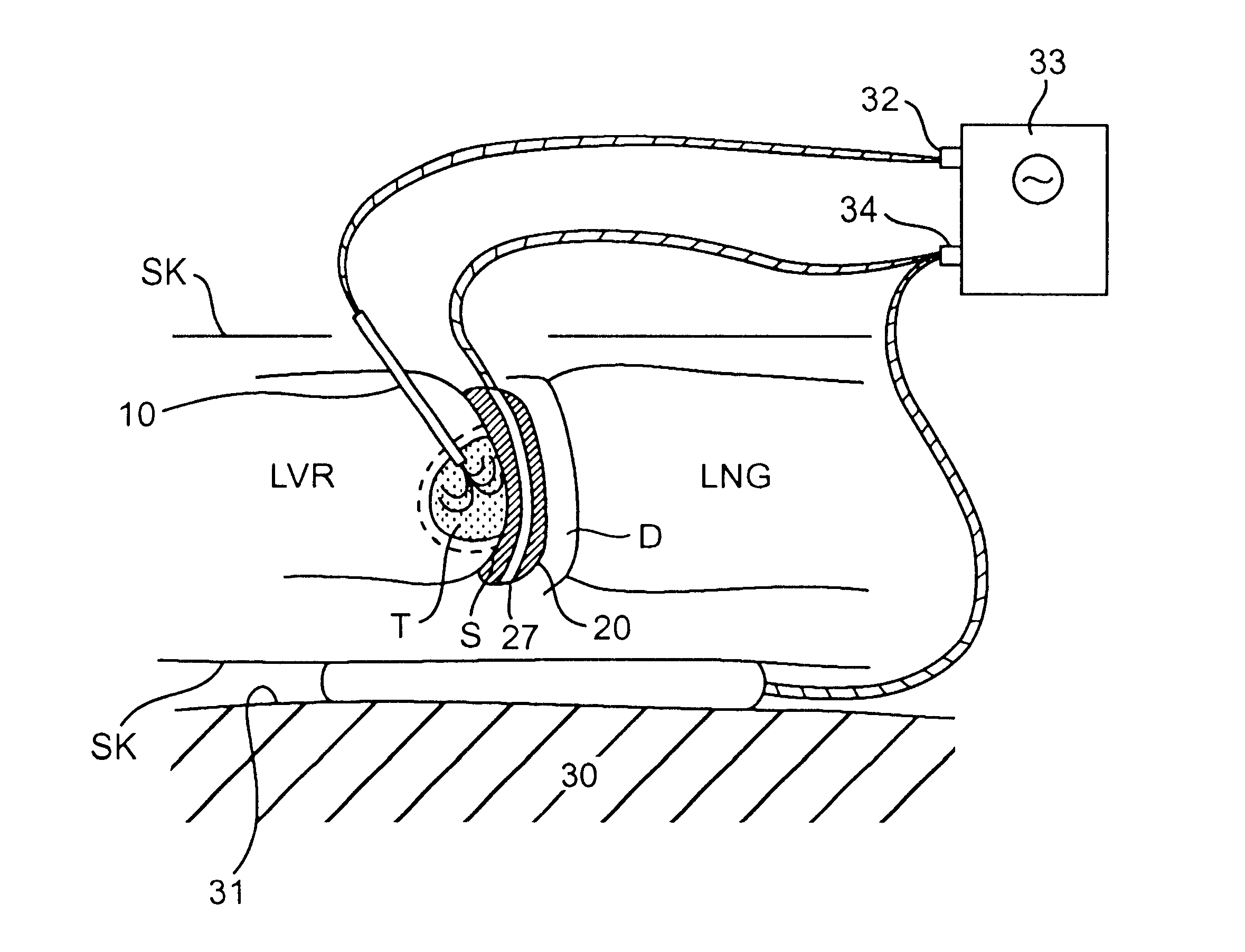
A medical procedure utilizes a high-intensity focused ultrasound instrument having an applicator surface, a liquid-containing bolus or expandable chamber acting as a heat sink, and a source of ultrasonic vibrations, the applicator surface being a surface of a flexible wall of the bolus, the source of ultrasonic vibrations being in operative contact with the bolus. The applicator surface is placed in contact with an organ surface of a patient, the source is energized to produce ultrasonic vibrations focused at a predetermined focal region inside the organ, and a temperature of liquid in the bolus is controlled while the applicator surface is in contact with the organ surface to control temperature elevation in tissues of the organ between the focal region and the organ surface to necrose the tissues to within a desired distance from the organ surface.
Owner:US HIFU
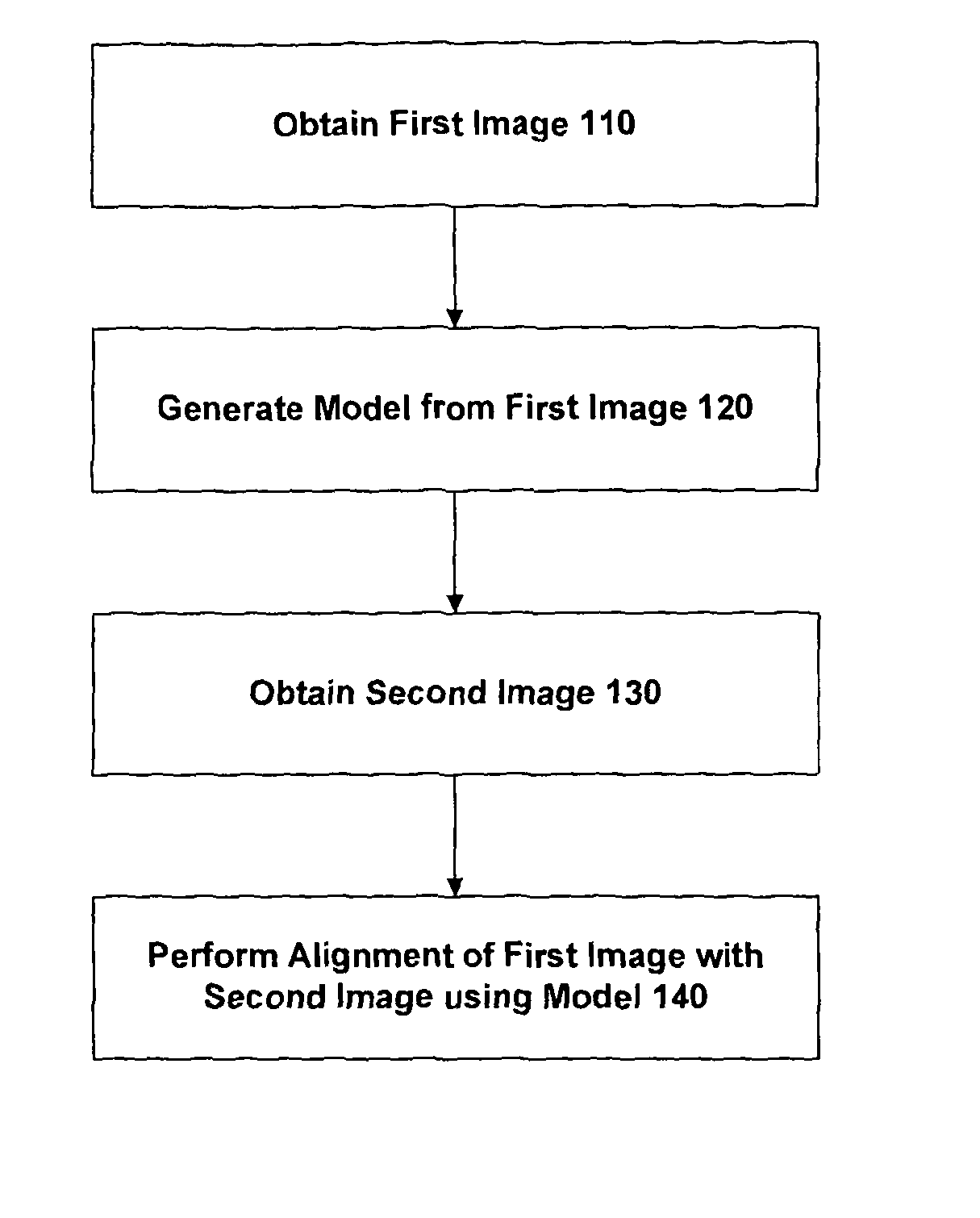
Apparatus and method for registering two medical images
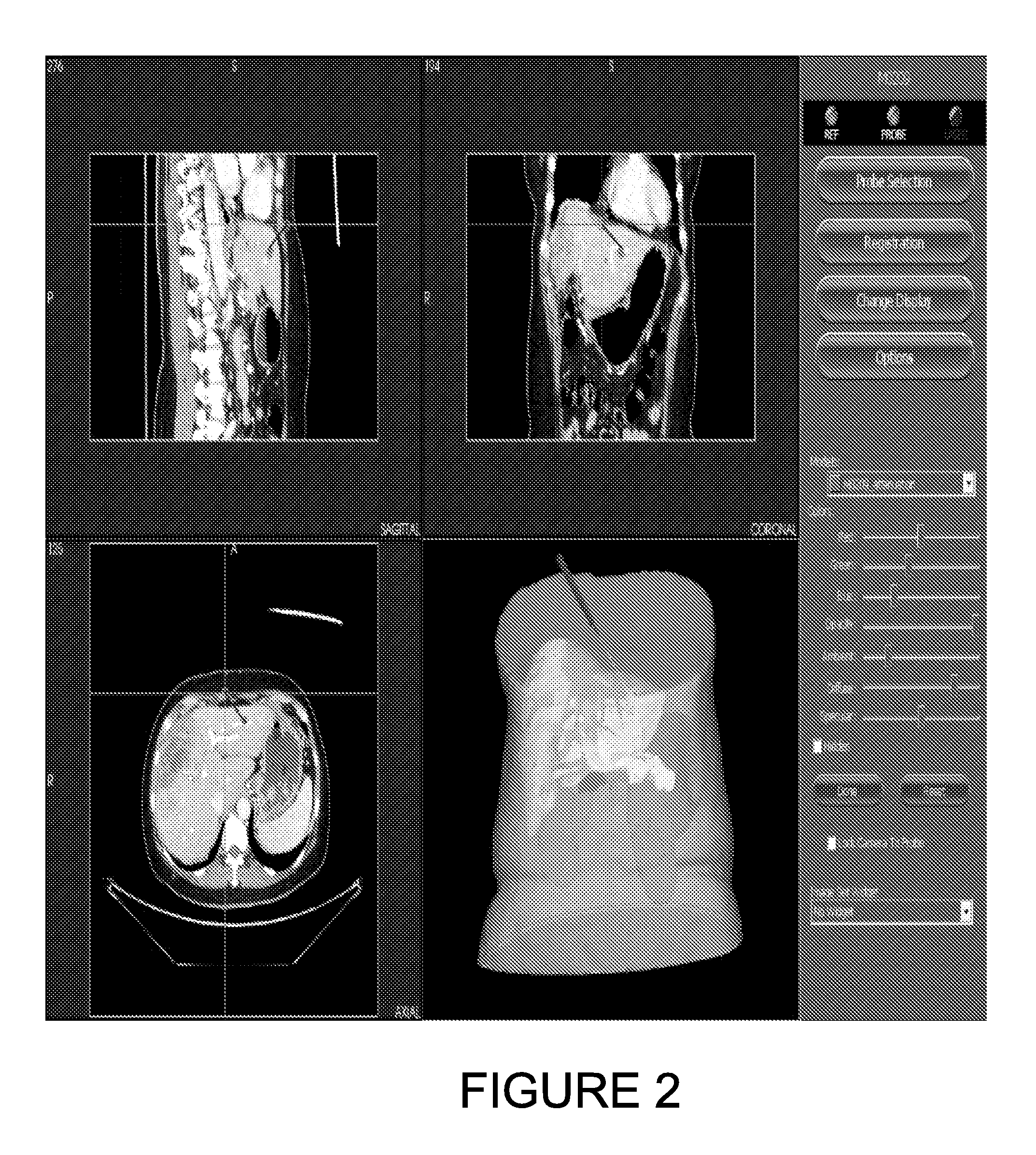
ActiveUS8620055B2Time requiredShorten the timeImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGeometric modelingOrgan surface
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Method and apparatus for continuous guidance of endoscopy
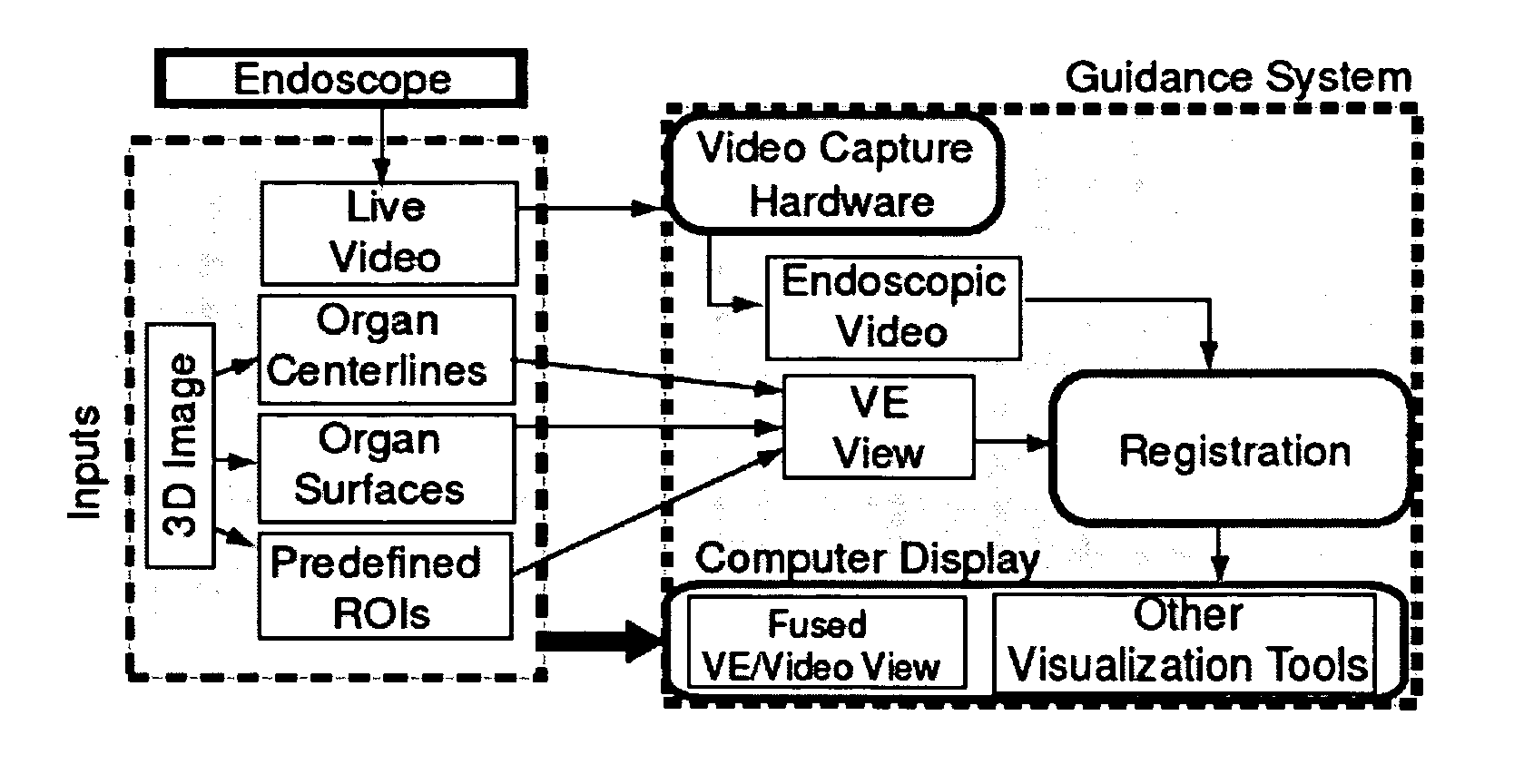
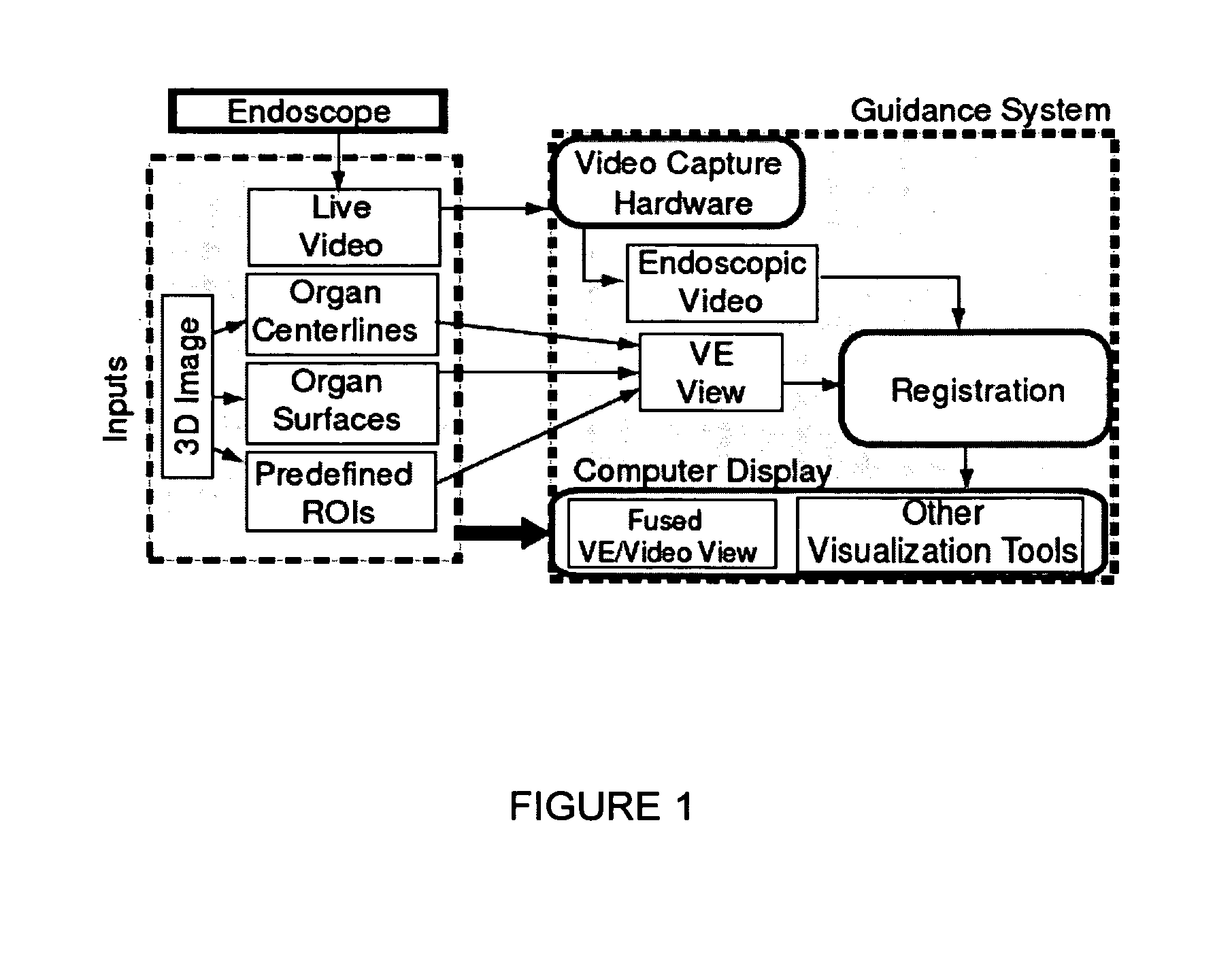
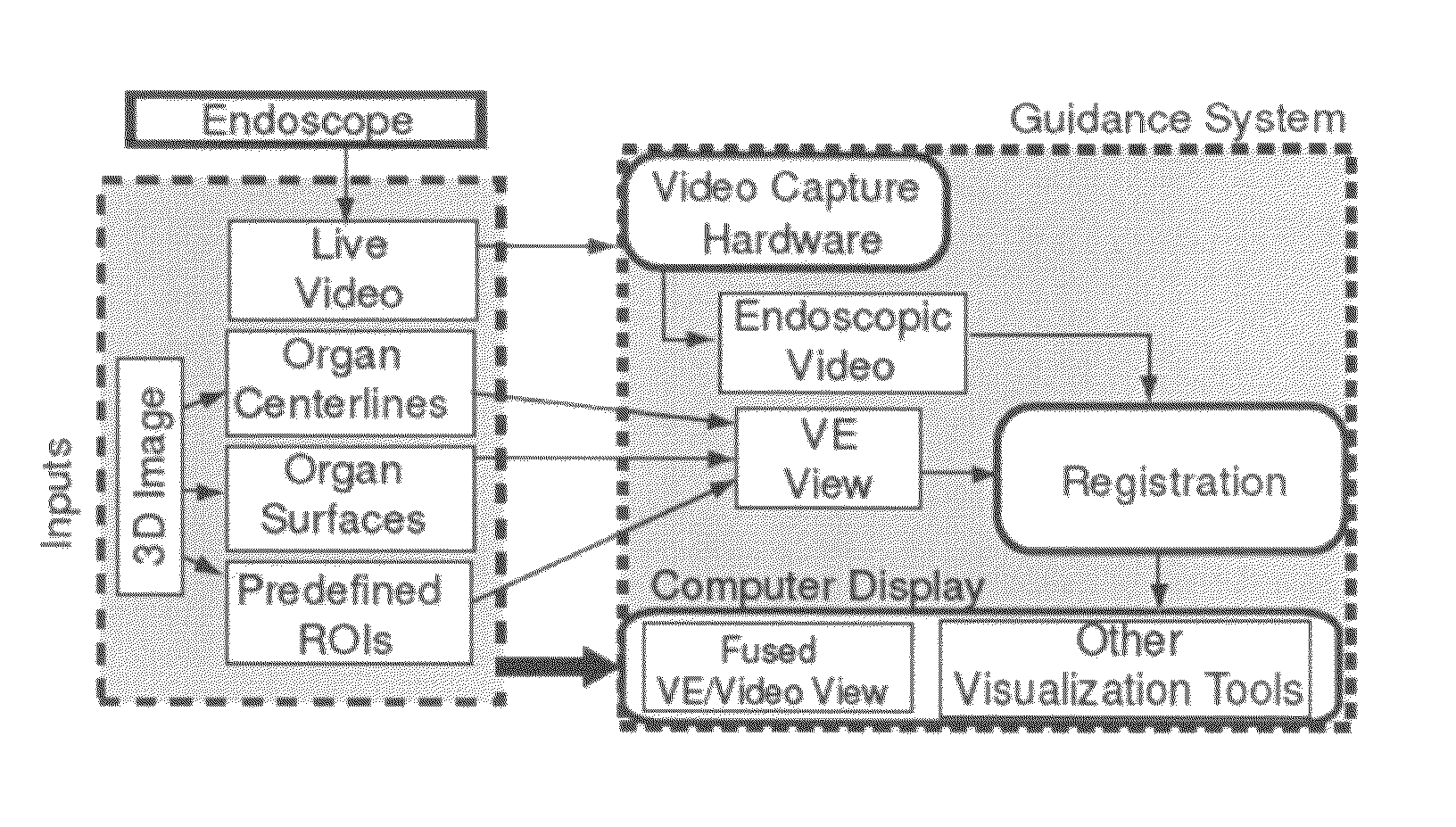
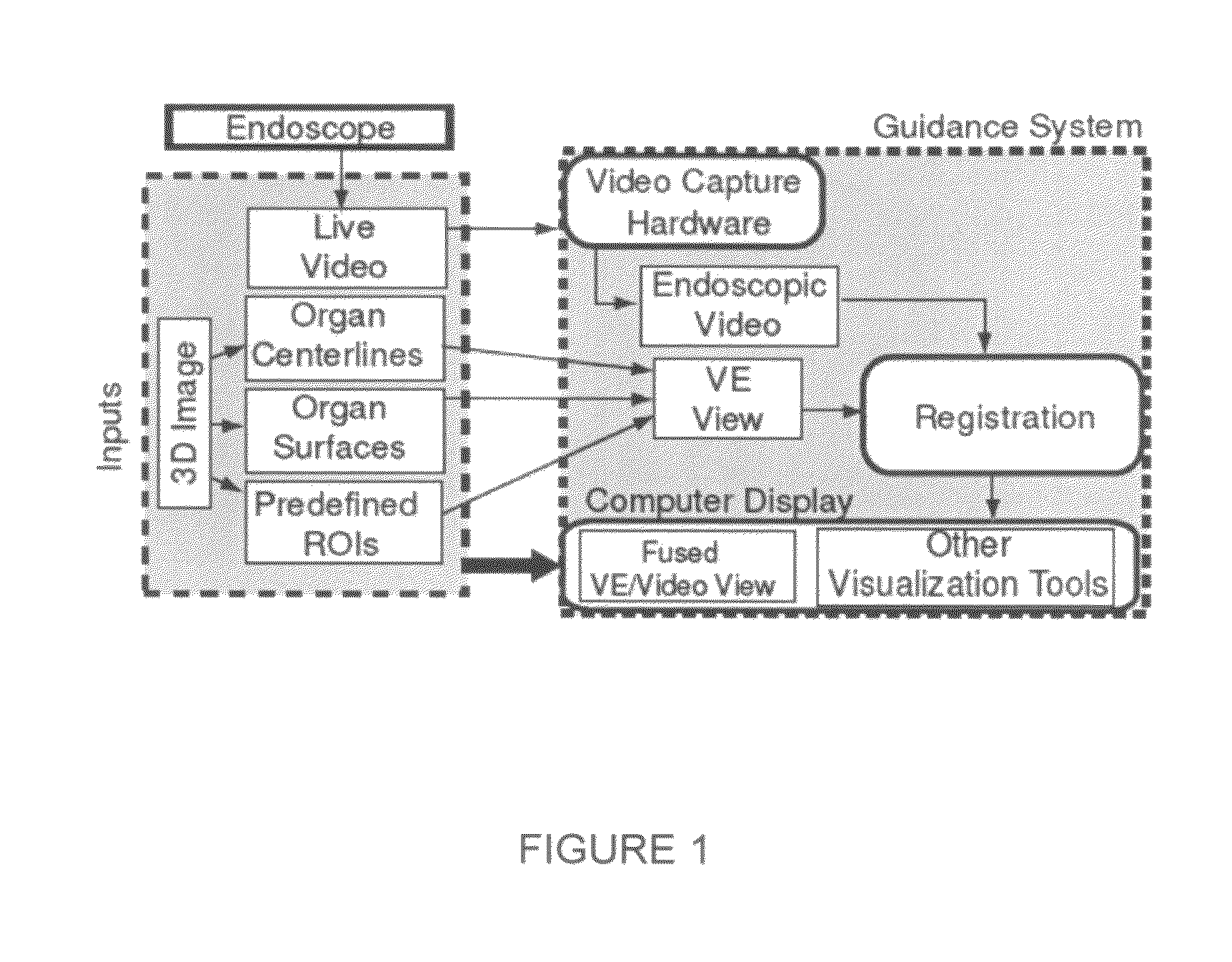
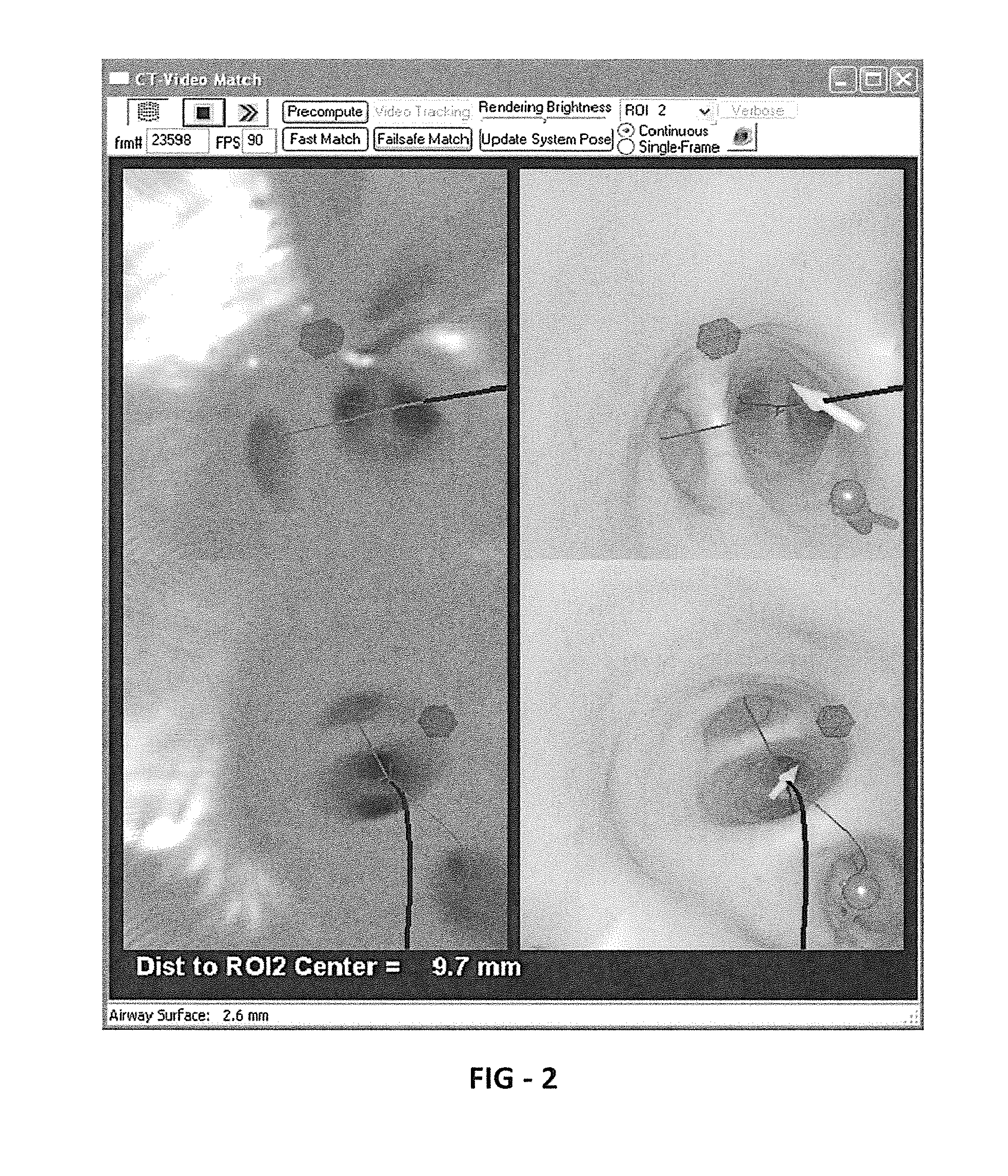
Methods and apparatus provide continuous guidance of endoscopy during a live procedure. A data-set based on 3D image data is pre-computed including reference information representative of a predefined route through a body organ to a final destination. A plurality of live real endoscopic (RE) images are displayed as an operator maneuvers an endoscope within the body organ. A registration and tracking algorithm registers the data-set to one or more of the RE images and continuously maintains the registration as the endoscope is locally maneuvered. Additional information related to the final destination is then presented enabling the endoscope operator to decide on a final maneuver for the procedure. The reference information may include 3D organ surfaces, 3D routes through an organ system, or 3D regions of interest (ROIs), as well as a virtual endoscopic (VE) image generated from the precomputed data-set. The preferred method includes the step of superimposing one or both of the 3D routes and ROIs on one or both of the RE and VE images. The 3D organ surfaces and routes may correspond to the surfaces and paths of a tracheobronchial airway tree extracted, for example, from 3D MDCT images of the chest.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Fat removal and nerve protection device and method
A fat removal device includes a screen which includes passages through which fat can be extruded, to be cut or melted away from the surface of an internal organ. The device includes a blade to cut the fat or radiofrequency monopolar or bipolar electrodes to melt the fat, aspiration to remove the fat away from the screen and blade, irrigation to irrigate the screen and blade, and an electrocautery member to cauterize the capillary bed of the fat. Methods of using removing the fat layer from the surface of an internal body organ are also described.
Owner:BROWN TONY R
System and method for abdominal surface matching using pseudo-features
InactiveUS8781186B2Enhanced informationFacilitates extensive pre-procedural planningImage enhancementImage analysisAbdominal surfaceAbdomen
A system and method for using pre-procedural images for registration for image-guided therapy (IGT), also referred to as image-guided intervention (IGI), in percutaneous surgical application. Pseudo-features and patient abdomen and organ surfaces are used for registration and to establish the relationship needed for guidance. Three-dimensional visualizations of the vasculature, tumor(s), and organs may be generated for enhanced guidance information. The invention facilitates extensive pre-procedural planning, thereby significantly reducing procedural times. It also minimizes the patient exposure to radiation.
Owner:PATHFINDER THERAPEUTICS +1
Method and apparatus for continuous guidance of endoscopy
Methods and apparatus provide continuous guidance of endoscopy during a live procedure. A data-set based on 3D image data is pre-computed including reference information representative of a predefined route through a body organ to a final destination. A plurality of live real endoscopic (RE) images are displayed as an operator maneuvers an endoscope within the body organ. A registration and tracking algorithm registers the data-set to one or more of the RE images and continuously maintains the registration as the endoscope is locally maneuvered. Additional information related to the final destination is then presented enabling the endoscope operator to decide on a final maneuver for the procedure. The reference information may include 3D organ surfaces, 3D routes through an organ system, or 3D regions of interest (ROIs), as well as a virtual endoscopic (VE) image generated from the precomputed data-set. The preferred method includes the step of superimposing one or both of the 3D routes and ROIs on one or both of the RE and VE images. The 3D organ surfaces and routes may correspond to the surfaces and paths of a tracheobronchial airway tree extracted, for example, from 3D MDCT images of the chest.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for registering two medical images
ActiveUS20120155734A1Maximize joint probabilityMinimize cost functionImage enhancementImage analysisOrgan surfaceImage vector
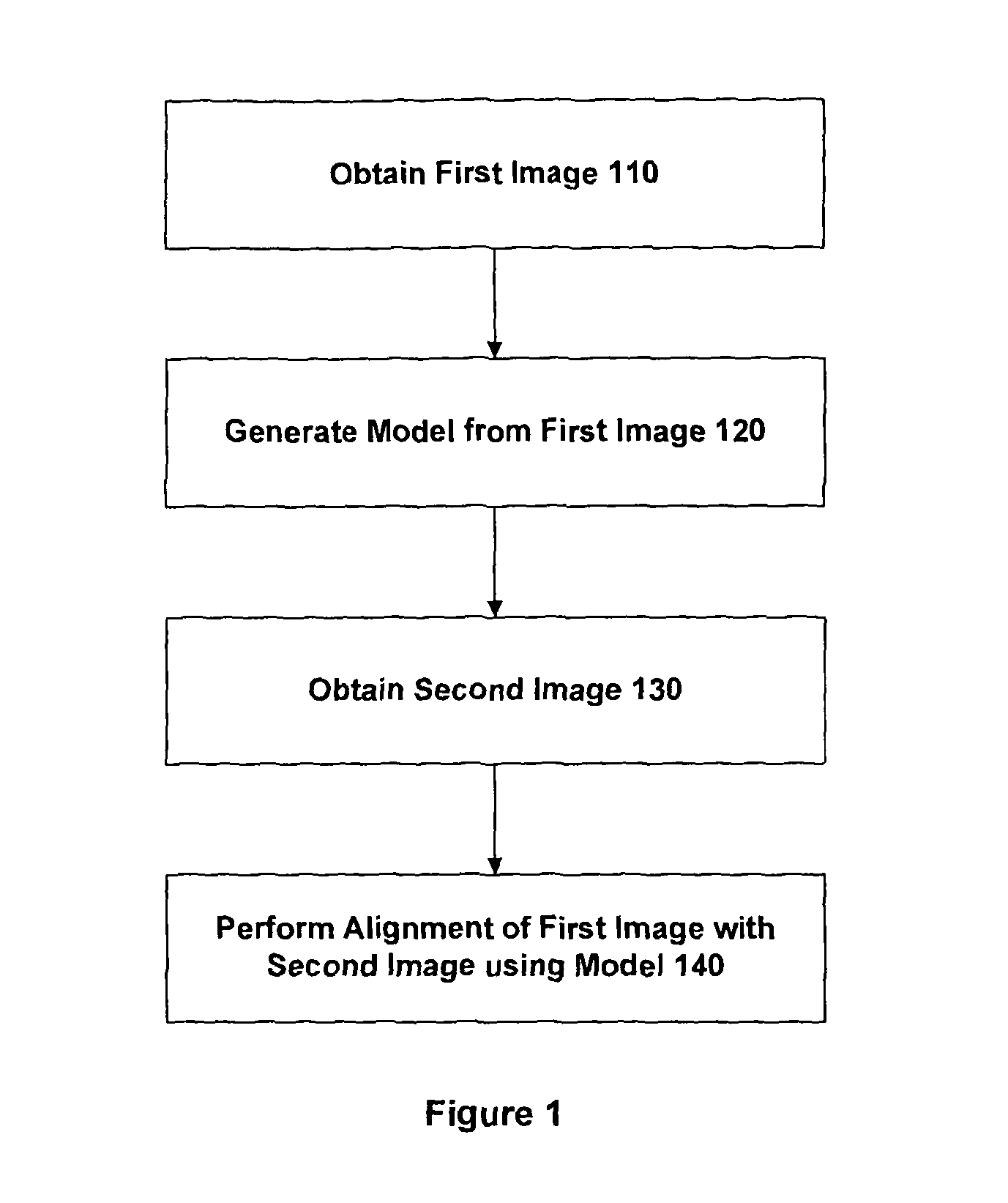
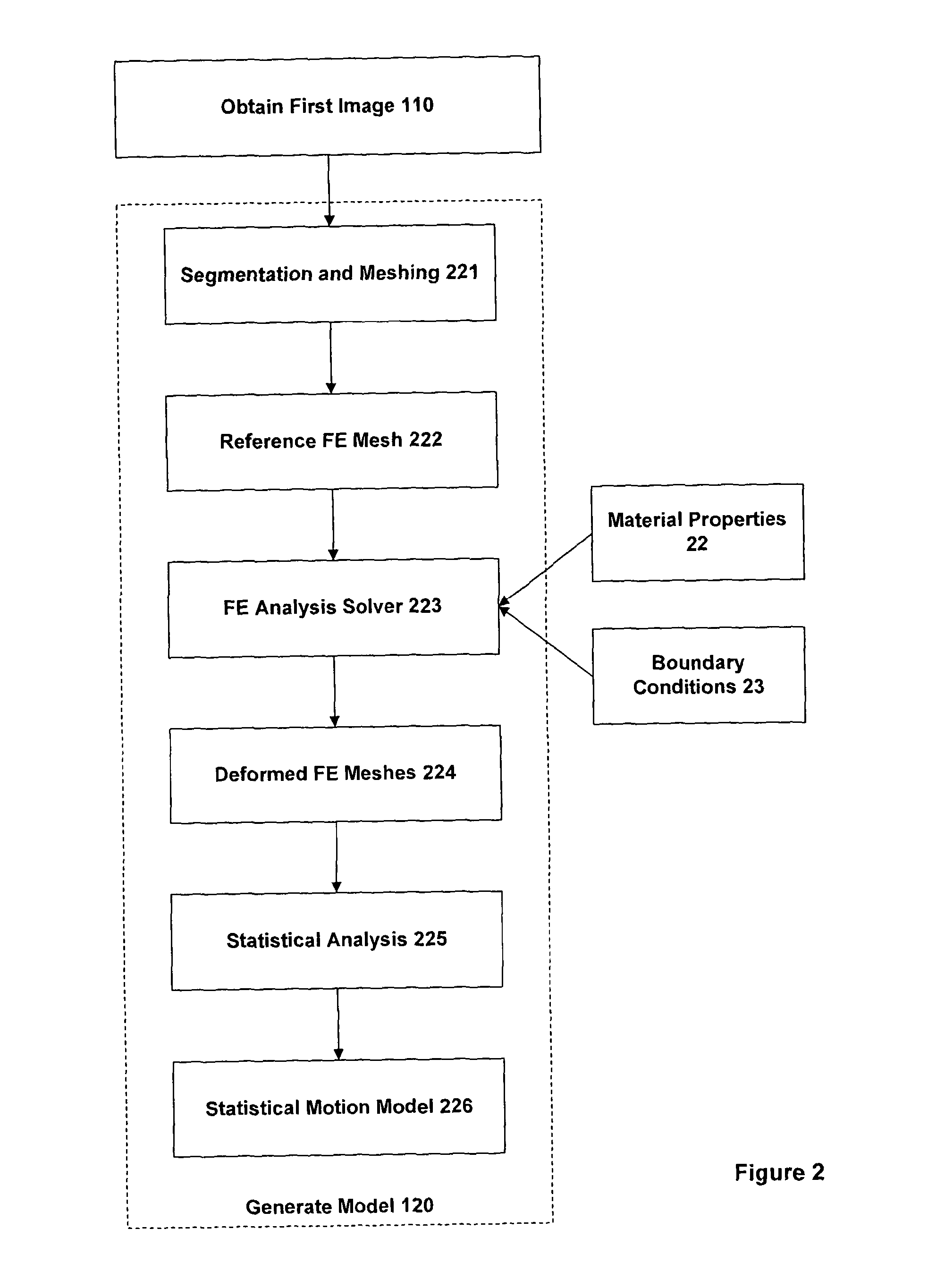
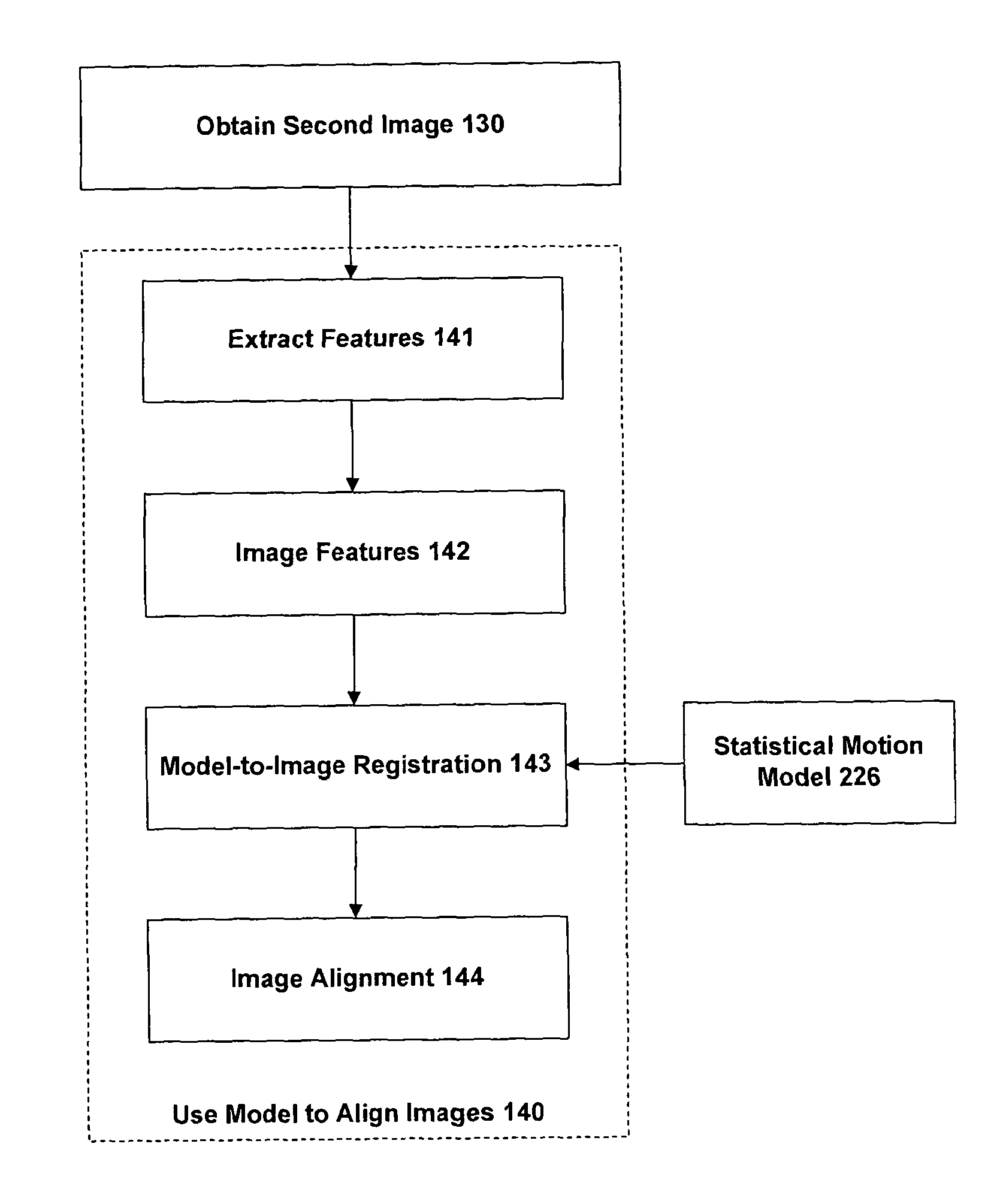
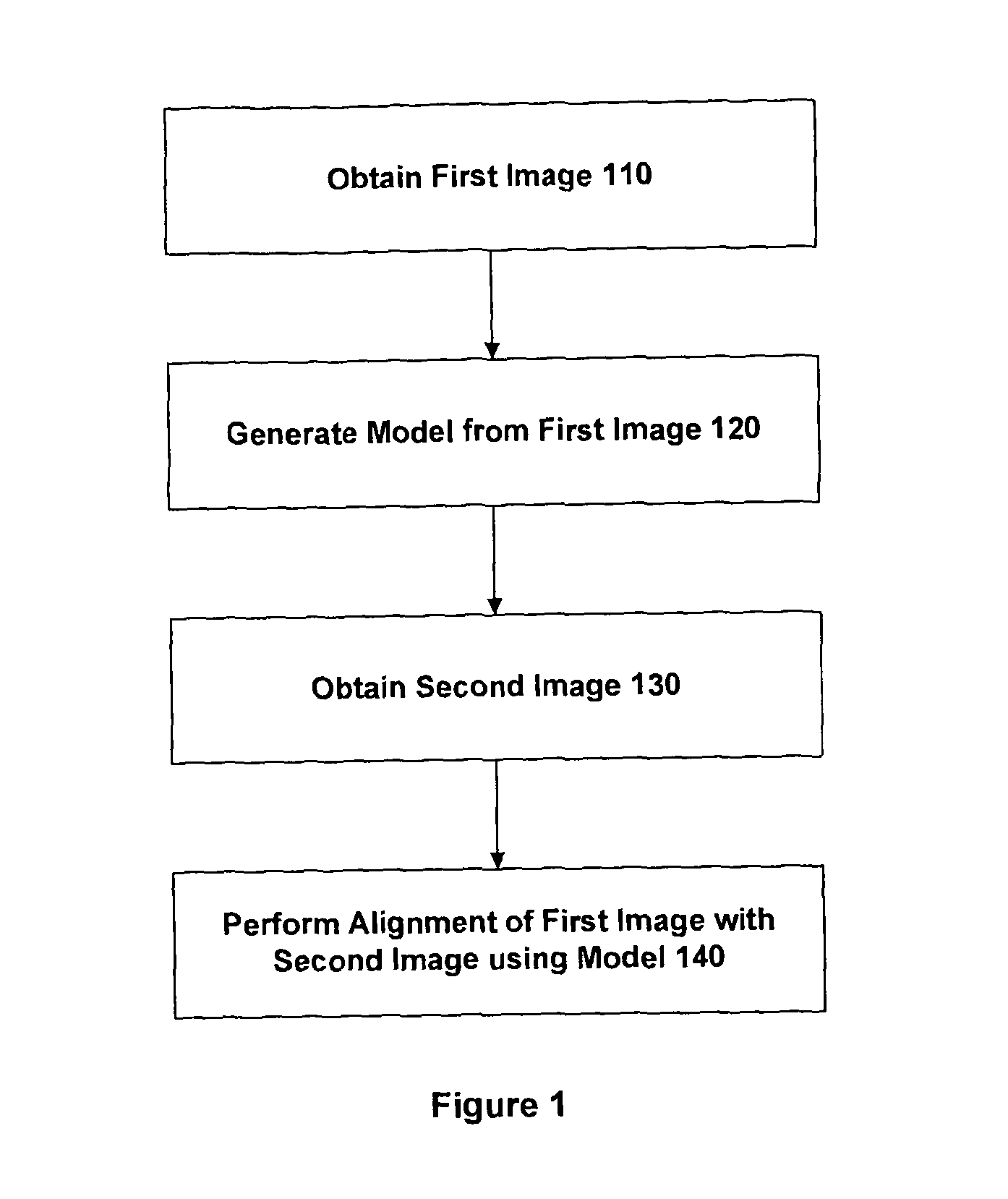
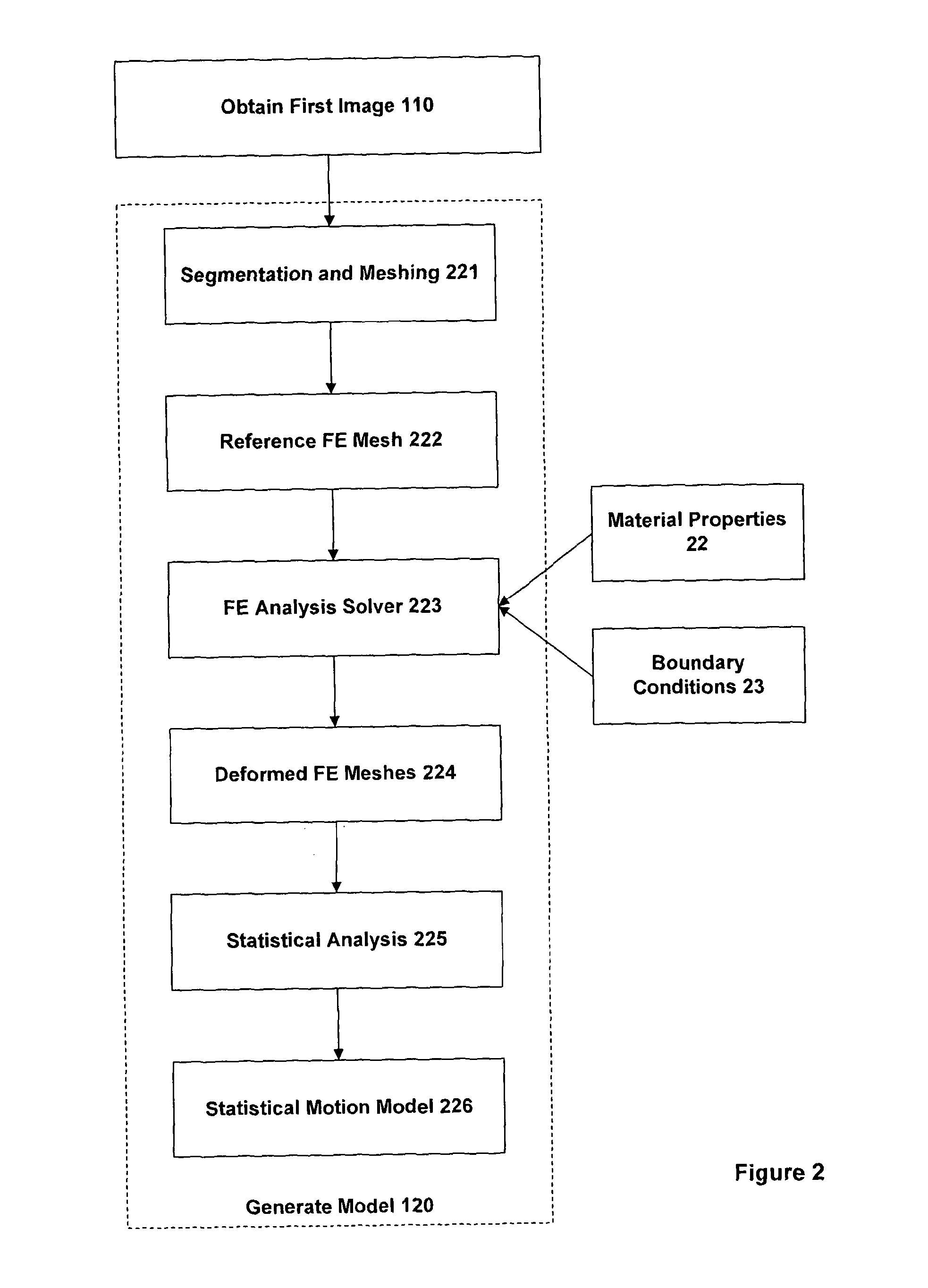
An embodiment of the invention provides a method and apparatus for registering two medical images with one another. A first medical image including a representation of a biological organ of a subject or for a population is obtained and the surface of the organ is identified in the first medical image. The identified surface is then used to construct a 3D geometric surface model of the organ. The geometric model is used to derive a motion model that incorporates information on the physical material properties of the organ and external forces that cause the organ to move and deform. A second medical image including a representation of the organ of the subject (or another subject, in the case that the first medical image is an atlas image) is obtained and an alignment is determined between a first surface normal vector field for the organ surface, derived from the geometric model, and a second surface normal vector field for the organ surface, derived by filtering the second medical image. The alignment accommodates deformation of the geometric model in accordance with the motion predicted by the motion model. The first and second medical images can then be registered with one another based on said determined model-to-image vector alignment (MIVA).
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Physiological stress detector device and system
InactiveUS7171251B2Accurate readingAccurate pulse oximetry readingCatheterSensorsOrgan regionOrgan surface
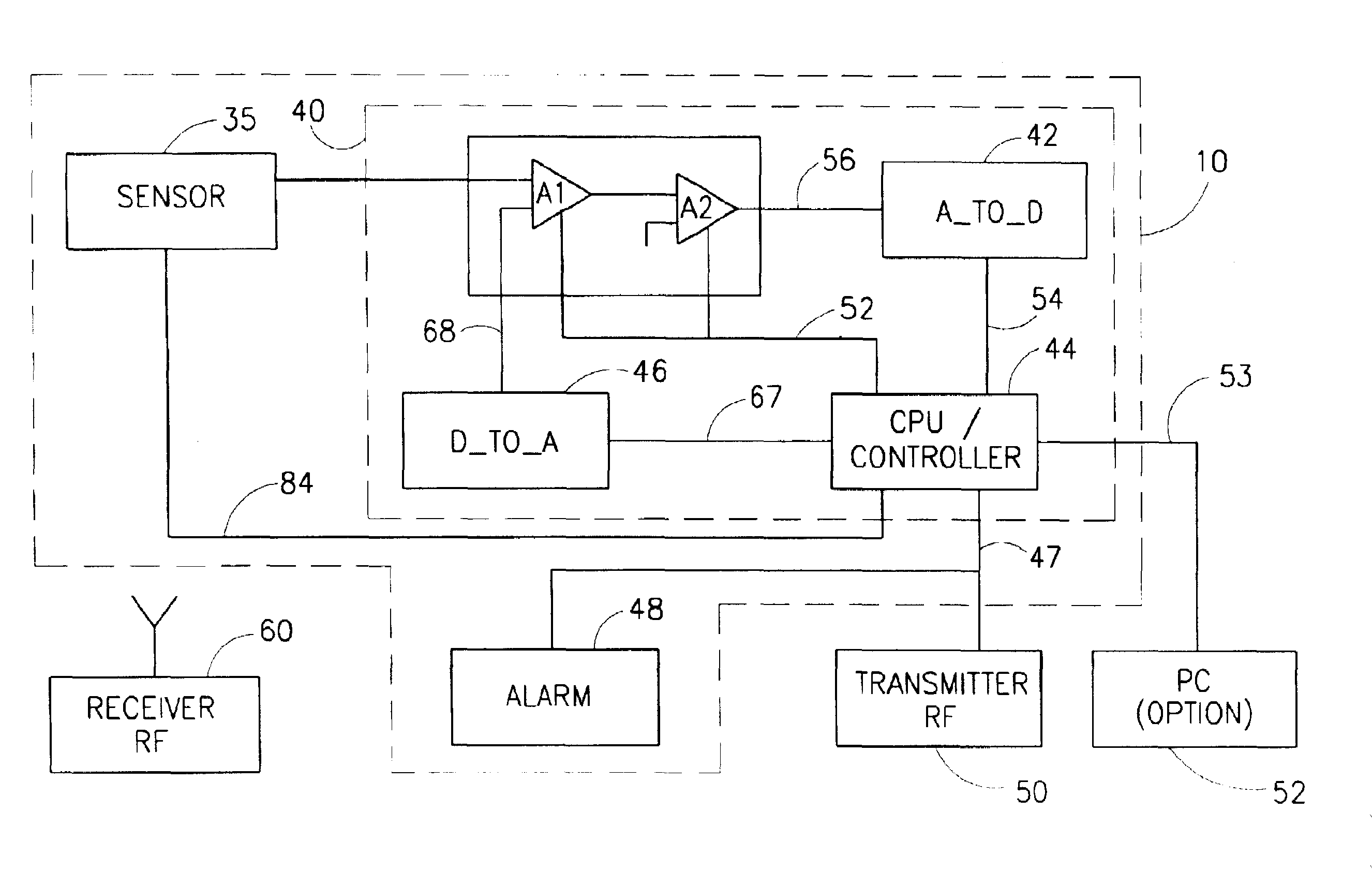
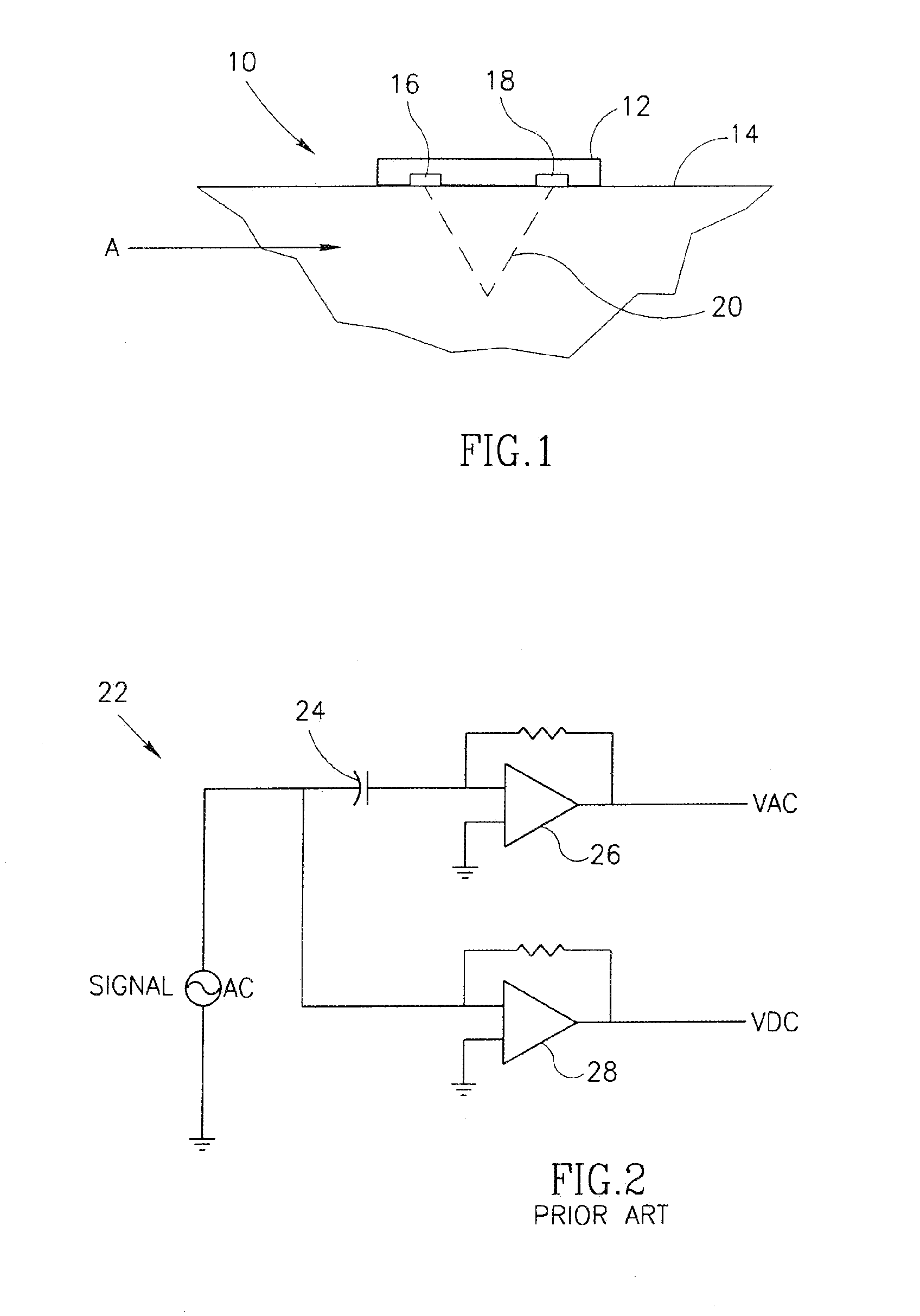
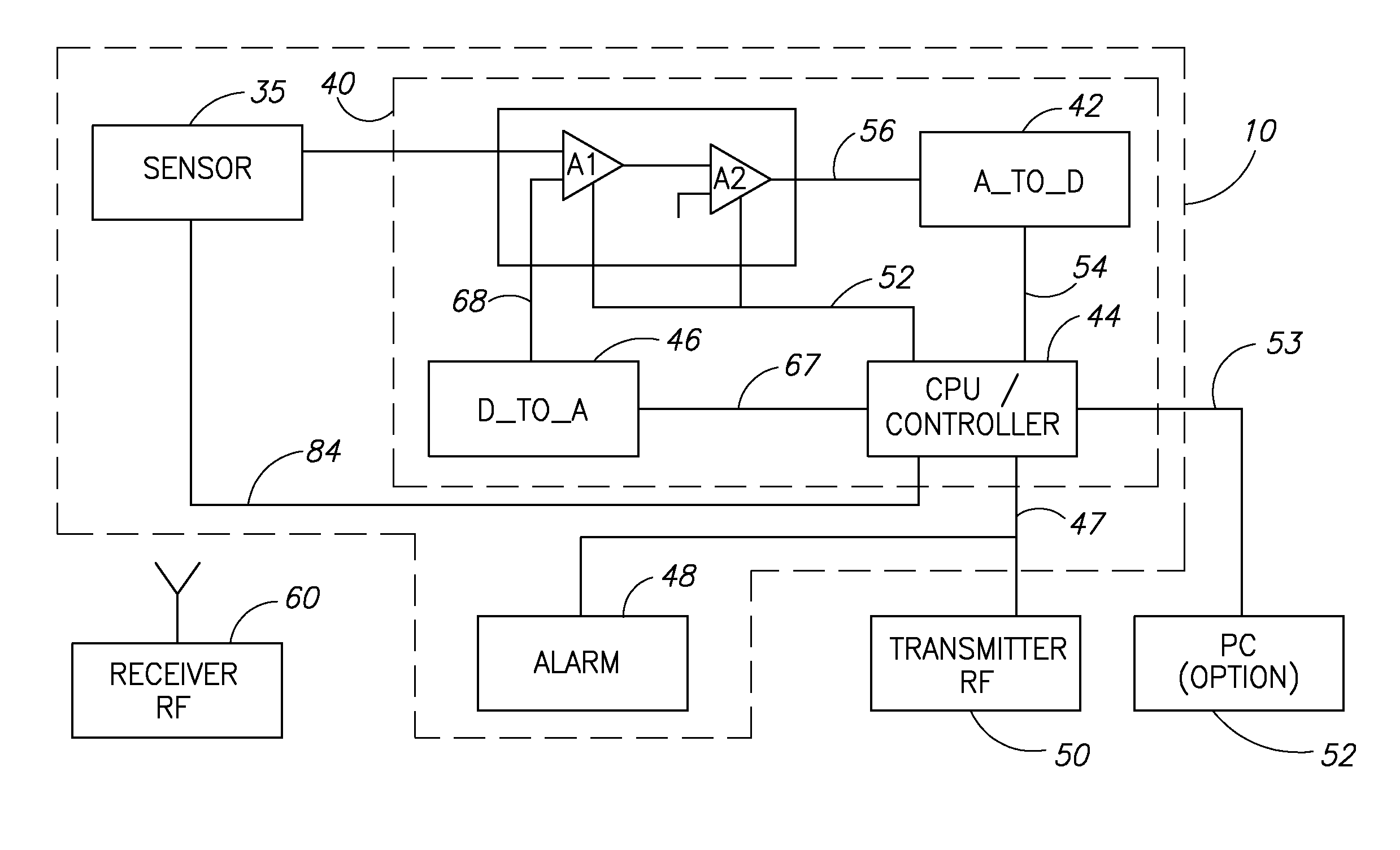
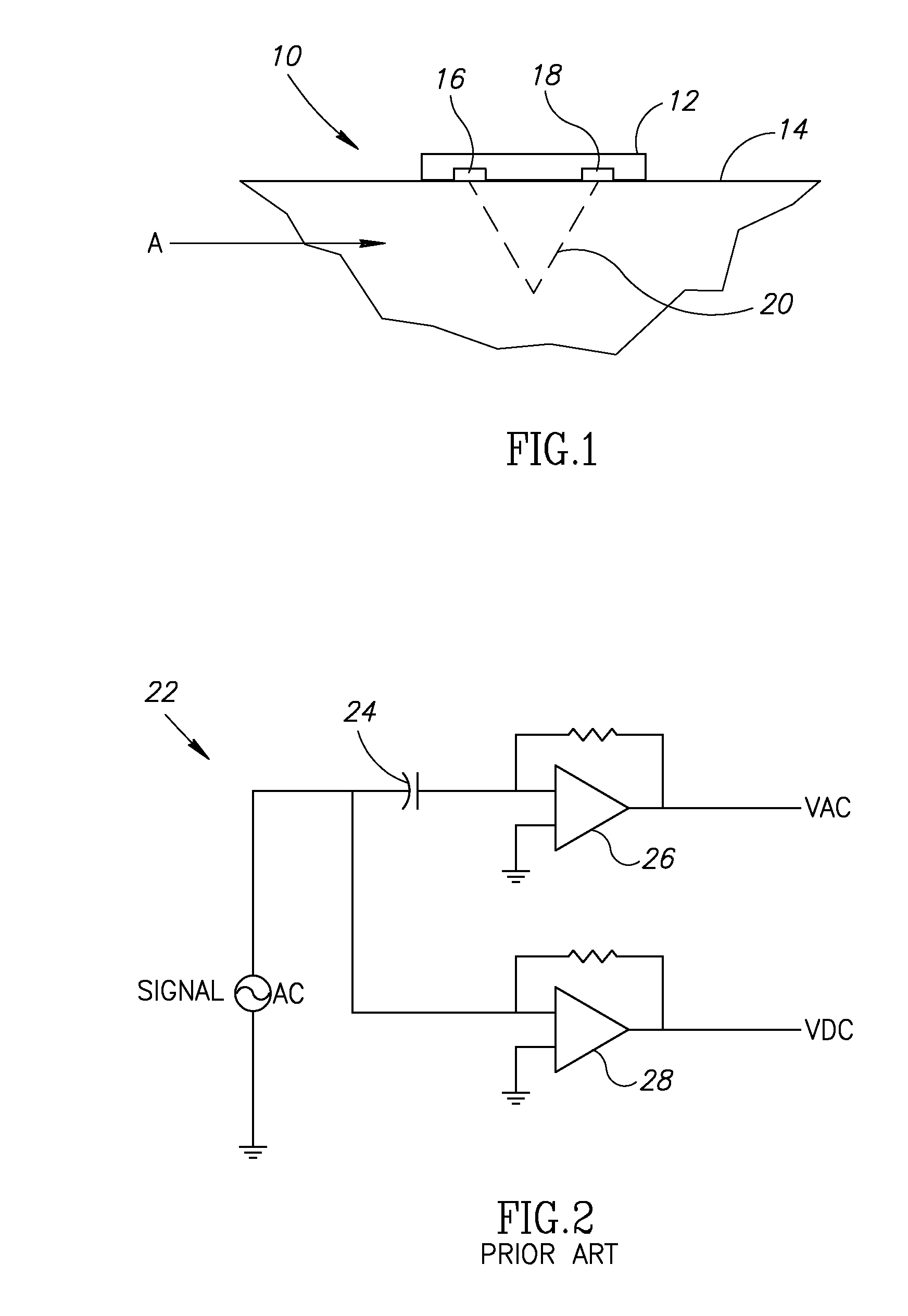
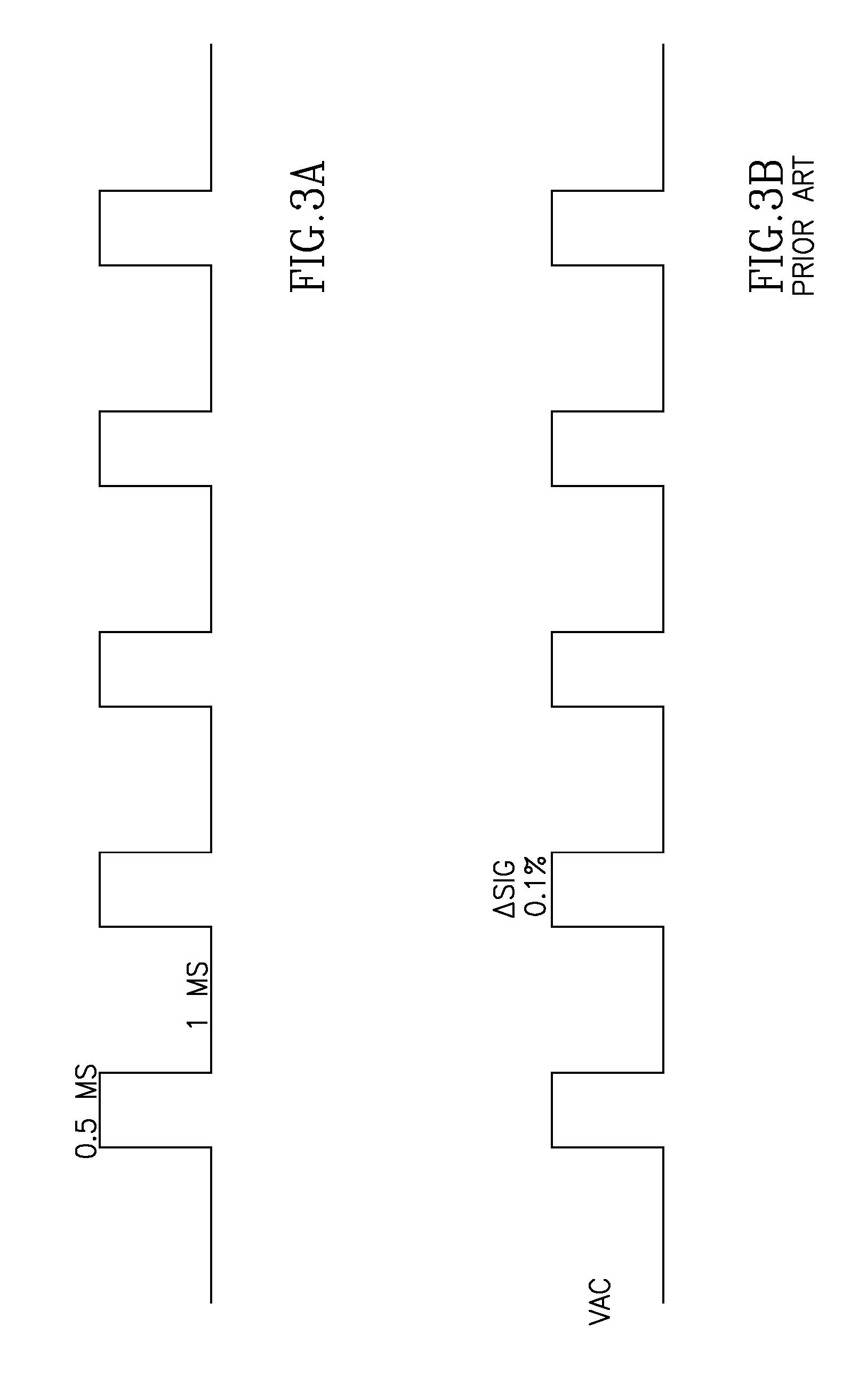
A method, system and device for measurement of a blood constituent level, including a light source, a light detector proximate an organ surface, adjustable gain amplifiers, and a processor / controller connected within a processing unit operative to separate AC and DC signal components. The device may determine the level of blood constituent, may use this level for monitoring and / or to activate an alarm when the level falls outside a predetermined range, may be applied to monitoring conditions of apnea, respiratory stress, and reduced blood flow in organ regions, heart rate, jaundice, and blood flow velocity, and may be incorporated within a monitoring system.
Owner:SPO MEDICAL EQUIP
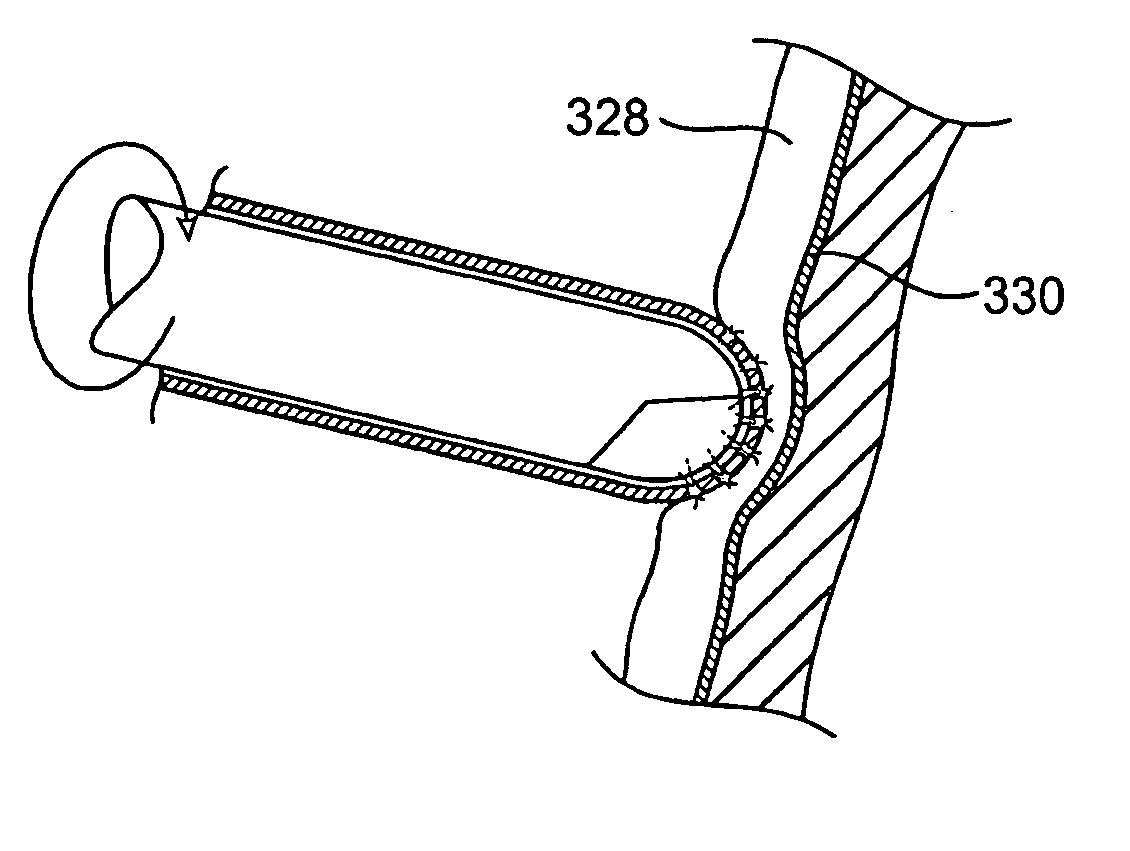
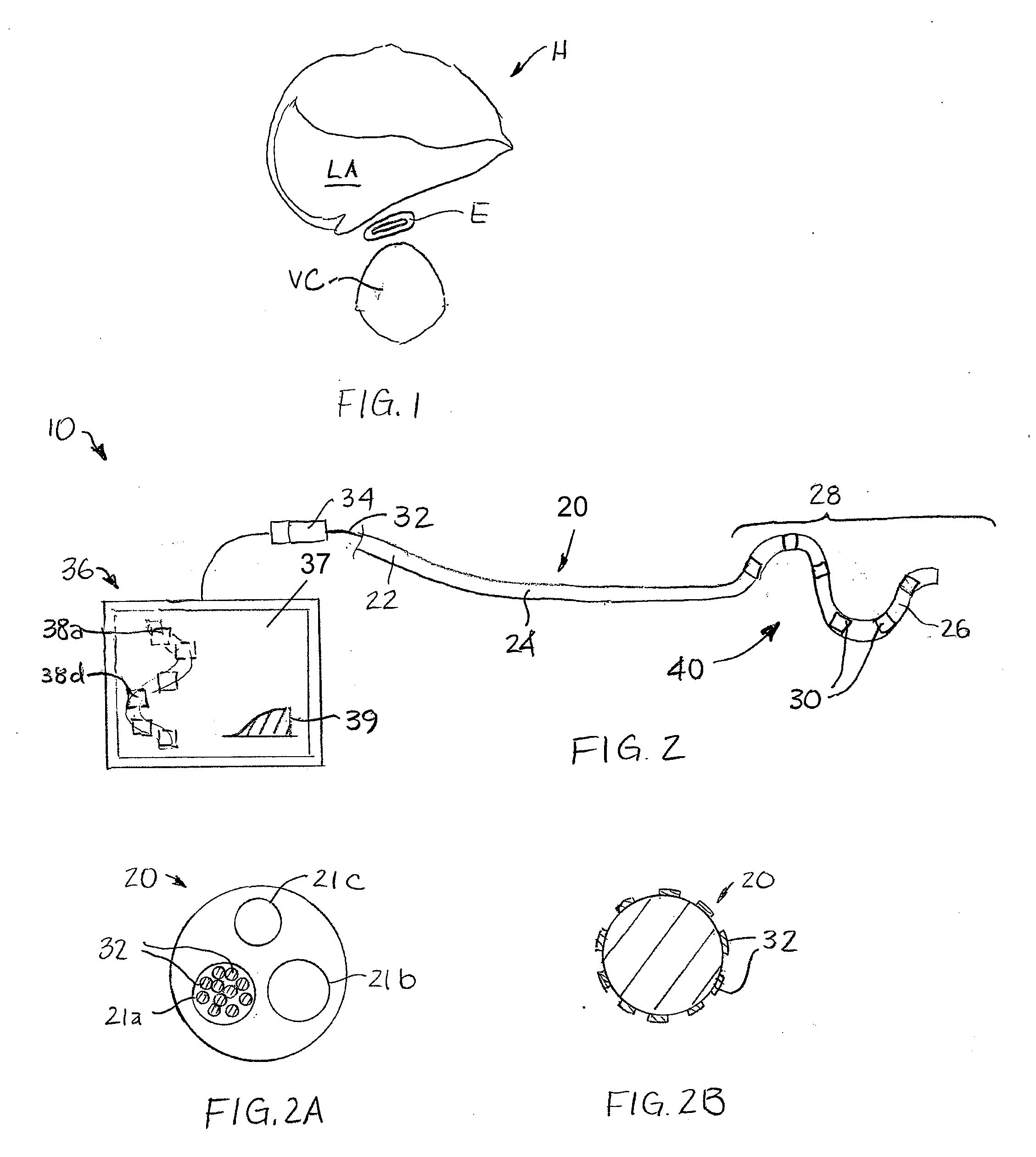
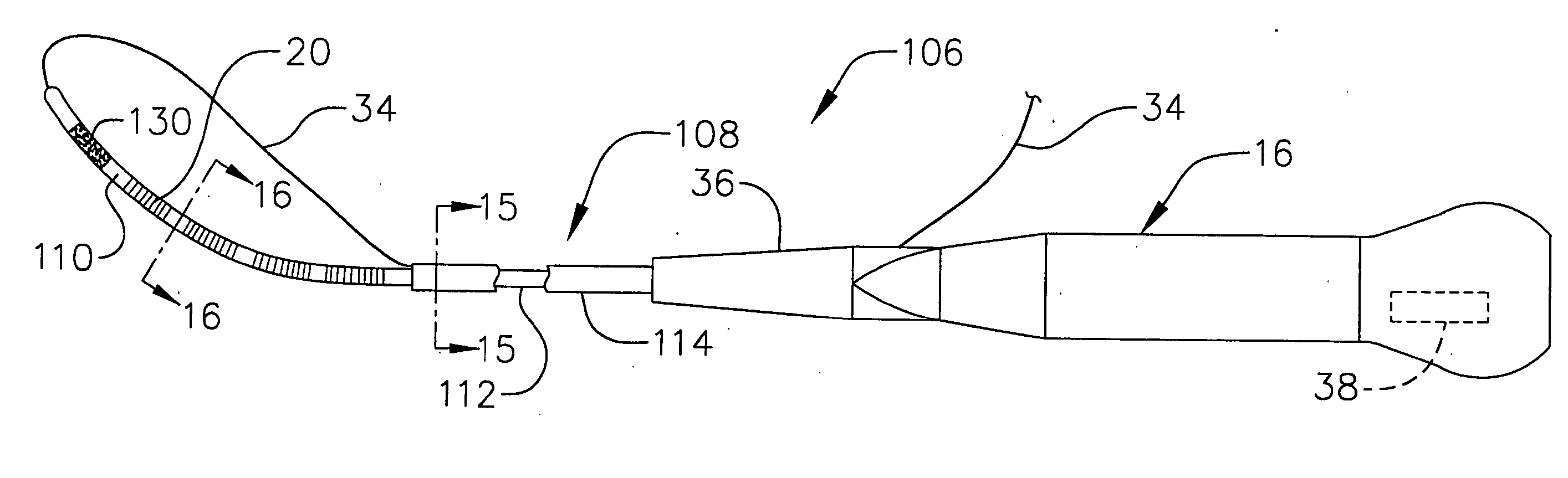
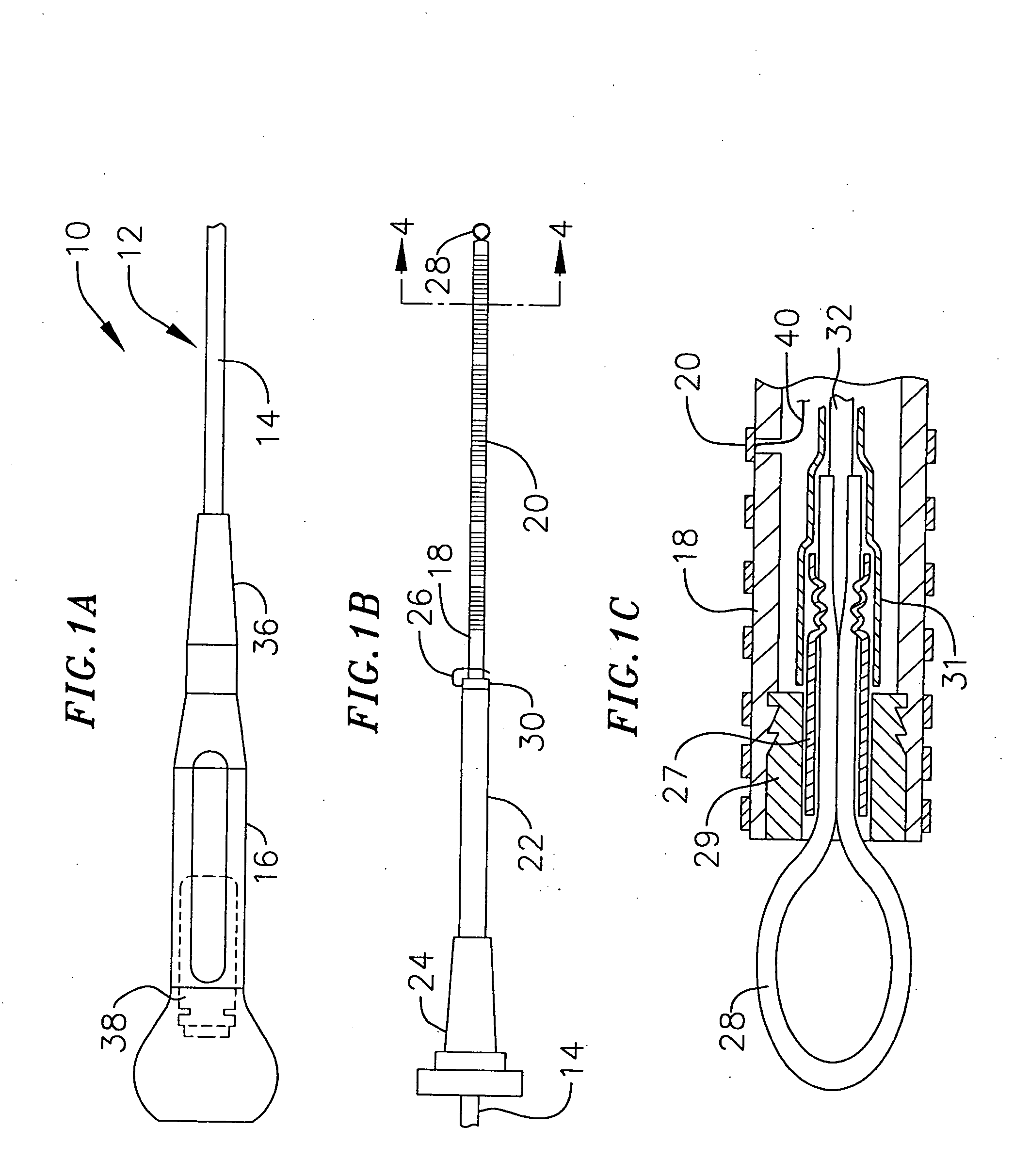
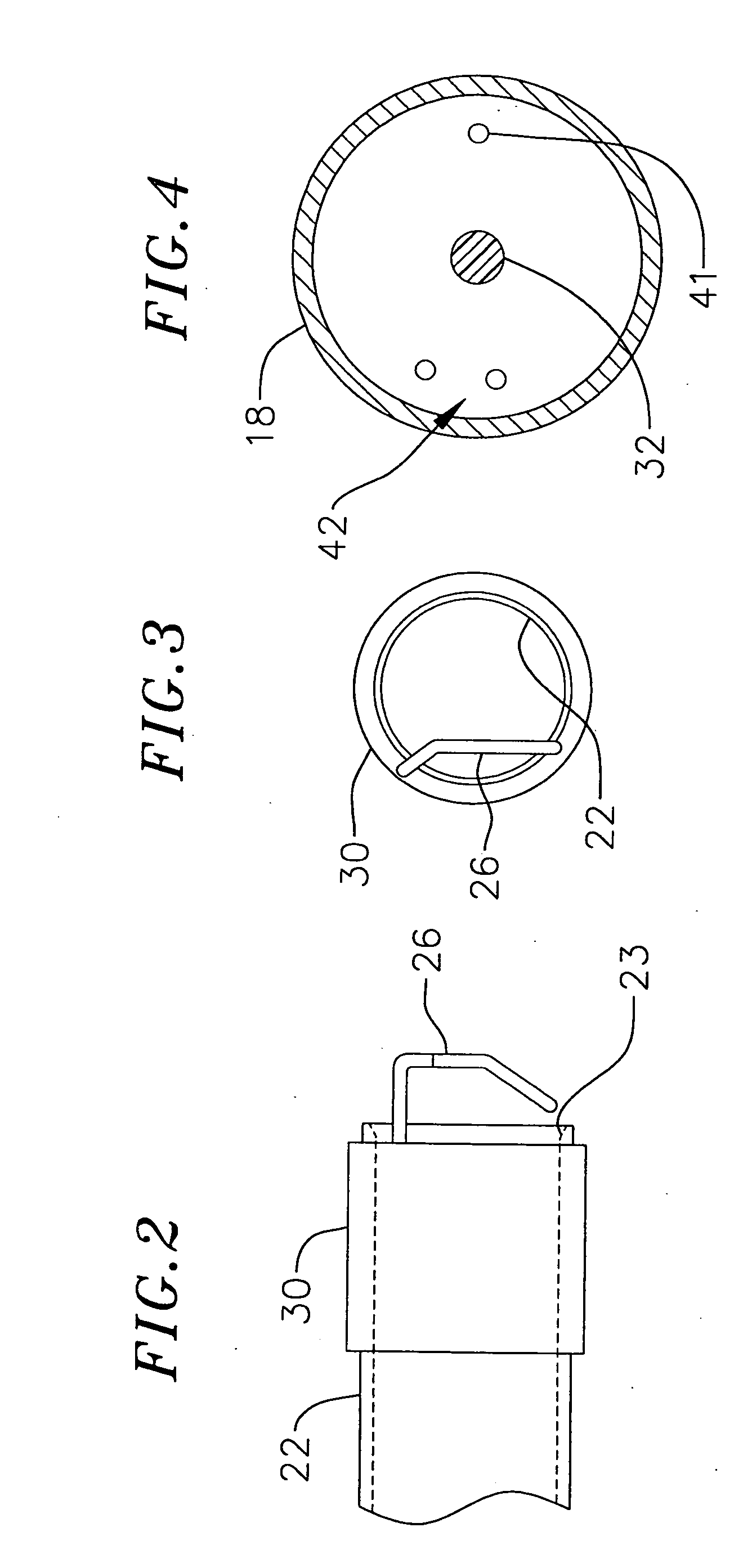
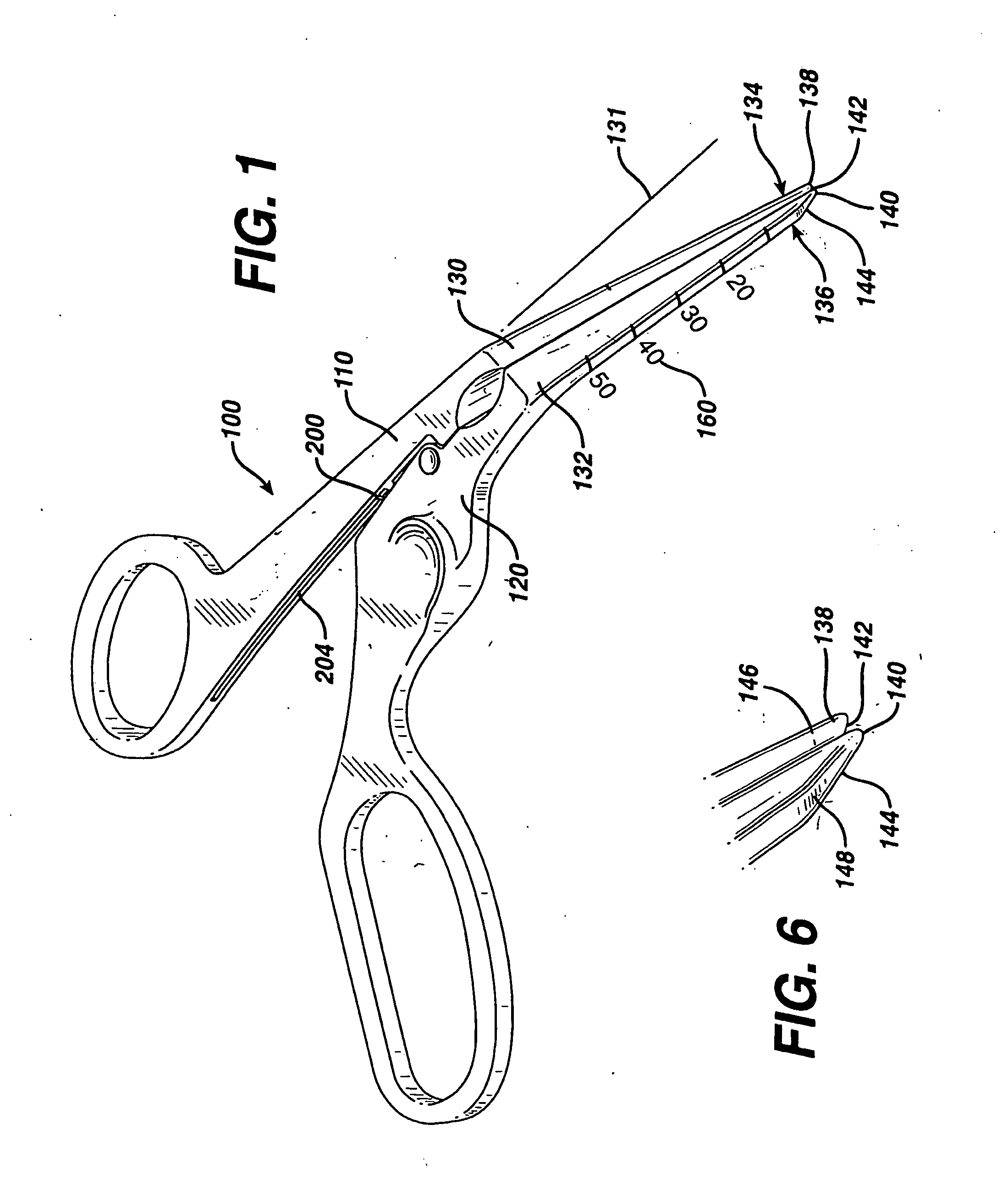
Loop structures for positioning a diagnostic or therapeutic element on the epicardium or other organ surface
InactiveUS7175619B2Creating lesionPromote formationTransvascular endocardial electrodesInstrument handpiecesLoop of HenleSurgery
Loop structures for positioning diagnostic an therapeutic elements on the epicardium or other organ surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
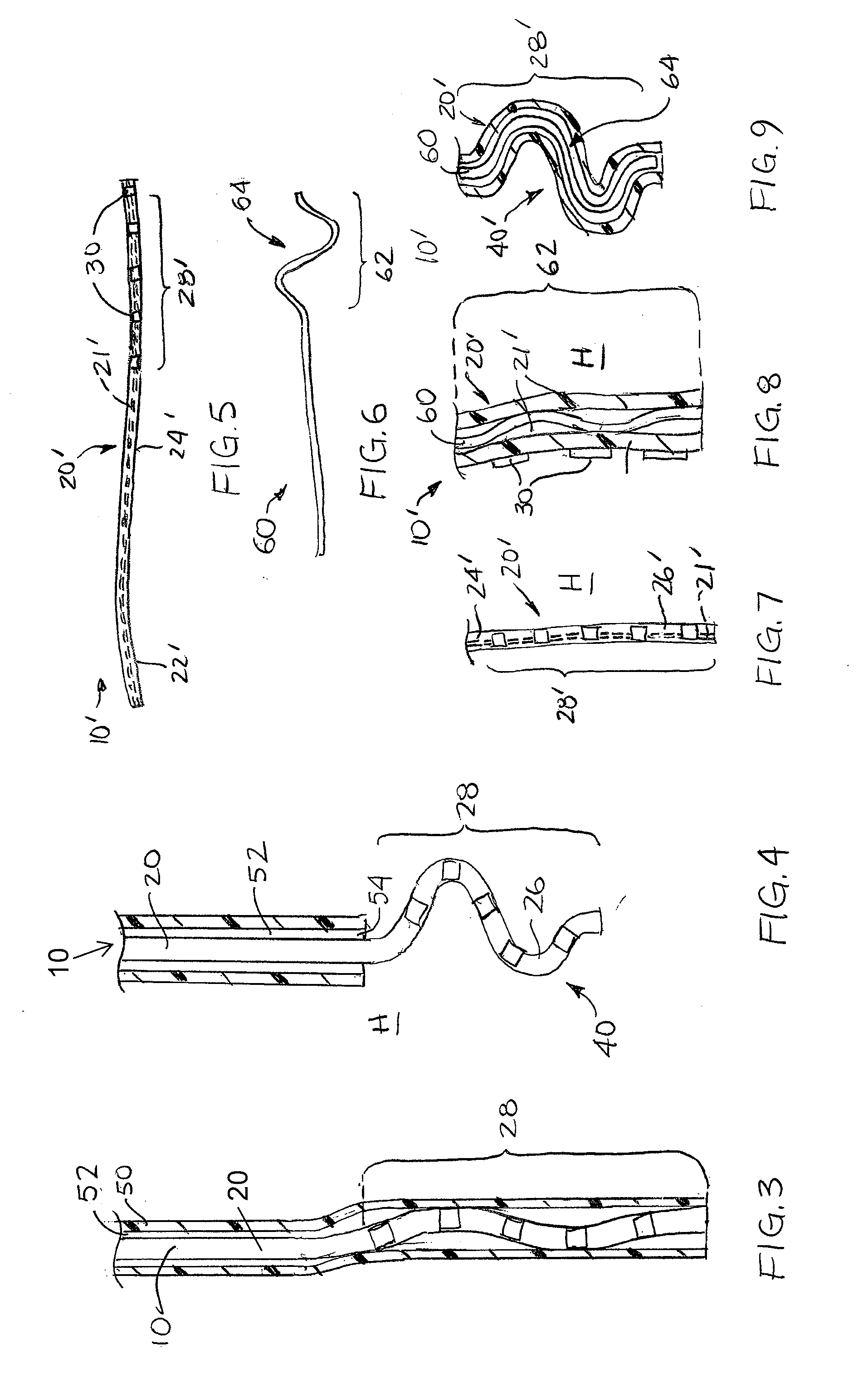
Fluid cooled apparatus for supporting diagnostic and therapeutic elements in contact with tissue
InactiveUS7303558B2Create efficientlyWider and deep lesionDiagnosticsInstrument handpiecesOrgan surfaceBiomedical engineering
Surgical methods and apparatus for positioning diagnostic an therapeutic elements on the epicardium or other organ surface. The apparatus includes a tissue cooling apparatus.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Physiological stress detector device and system
InactiveUS20070149871A1Accurate readingAccurate pulse oximetry readingCatheterSensorsOrgan regionEngineering
A method, system and device for measurement of a blood constituent level, including a light source, a light detector proximate an organ surface, adjustable gain amplifiers, and a processor / controller connected within a processing unit operative to separate AC and DC signal components. The device may determine the level of blood constituent, may use this level for monitoring and / or to activate an alarm when the level falls outside a predetermined range, may be applied to monitoring conditions of apnea, respiratory stress, and reduced blood flow in organ regions, heart rate, jaundice, and blood flow velocity, and may be incorporated within a monitoring system.
Owner:SPO MEDICAL EQUIP
Large surface area temperature sensing device
A temperature probe for monitoring temperatures of a surface of a tissue or organ within the body of a subject includes a section with a substantially two-dimensional arrangement and a plurality of temperature sensors positioned across an area defined by the substantially two-dimensional arrangement. Such an apparatus may be used in conjunction with procedures in which thermal techniques are used to diagnose a disease state or treat diseased tissue. Specifically, a temperature probe may be used to monitor temperatures across an area of a surface of a tissue or organ located close to the treated tissue to prevent subjection of the monitored tissue or organ to potentially damaging temperatures.
Owner:CIRCA SCI
Method and apparatus for stabilization and positioning during surgery
InactiveUS20080009668A1Stabilize target areaCannulasSurgical needlesExtracorporeal circulationEngineering
Novel surgical devices for off-pump surgery are described herein. The disclosed apparatus employs a novel suction element that releasably couples to a surgical connector. In an embodiment, a surgical device comprises a suction element adapted to be releasably coupled to a surgical connector. The suction element has an opening for stabilizing said surgical connector against the surface of an organ by suction. The surgical device further comprises a flexible arm connected to the suction element. The flexible arm is capable of being fixed in a stationary position to hold the surgical connector and the organ in place. The novel suction element in combination with a flexible arm not only positions and stabilizes an organ during surgery, but also positions and stabilizes the surgical connector on the organ during a surgical procedure such as an LVAD implantation.
Owner:TEXAS HEART INST
Scanning light imager
InactiveUS20100198081A1Reduce chanceUniform structureDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionFiberCancer cell
This invention describes the detection of atherosclerotic plaque or cancer cells by a light probe inside a blood vessel or internal to an elongate organ. In one embodiment, vessel wall is imaged by employing a scanning mechanism using one emitting and one receiving fiber, whereby light is directed at a spinning mirror, approximately normal to the vessel or elongate organ surface. The light is reflected circumferentially around the vessel or elongate organ surface as the mirror rotates and received by a low-numerical aperture (NA) fiber, which transmits it to a light detector, thereby generating a set of light amplitudes circumferentially around the vessel / elongate organ surface. Multiple rings are acquired by translating the probe within the vessel / elongate organ. In another embodiment, adding a piezoelectric transducer in proximity to the distal ends of the fibers permits simultaneous ultrasound and light images to be created.
Owner:HANLIN JOHN HAROLD +1
System and method for abdominal surface matching using pseudo-features
InactiveUS20110274324A1Enhanced guidance informationFacilitates extensive pre-procedural planningImage enhancementImage analysisAbdominal surfaceOrgan surface
A system and method for using pre-procedural images for registration for image-guided therapy (IGT), also referred to as image-guided intervention (IGI), in percutaneous surgical application. Pseudo-features and patient abdomen and organ surfaces are used for registration and to establish the relationship needed for guidance. Three-dimensional visualizations of the vasculature, tumor(s), and organs may be generated for enhanced guidance information. The invention facilitates extensive pre-procedural planning, thereby significantly reducing procedural times. It also minimizes the patient exposure to radiation.
Owner:PATHFINDER THERAPEUTICS +1
Human body organ three-dimensional surface rebuilding method and system
ActiveCN101249019AAccurate reconstructionConforms to smooth continuous propertiesDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingHuman bodyCell restriction
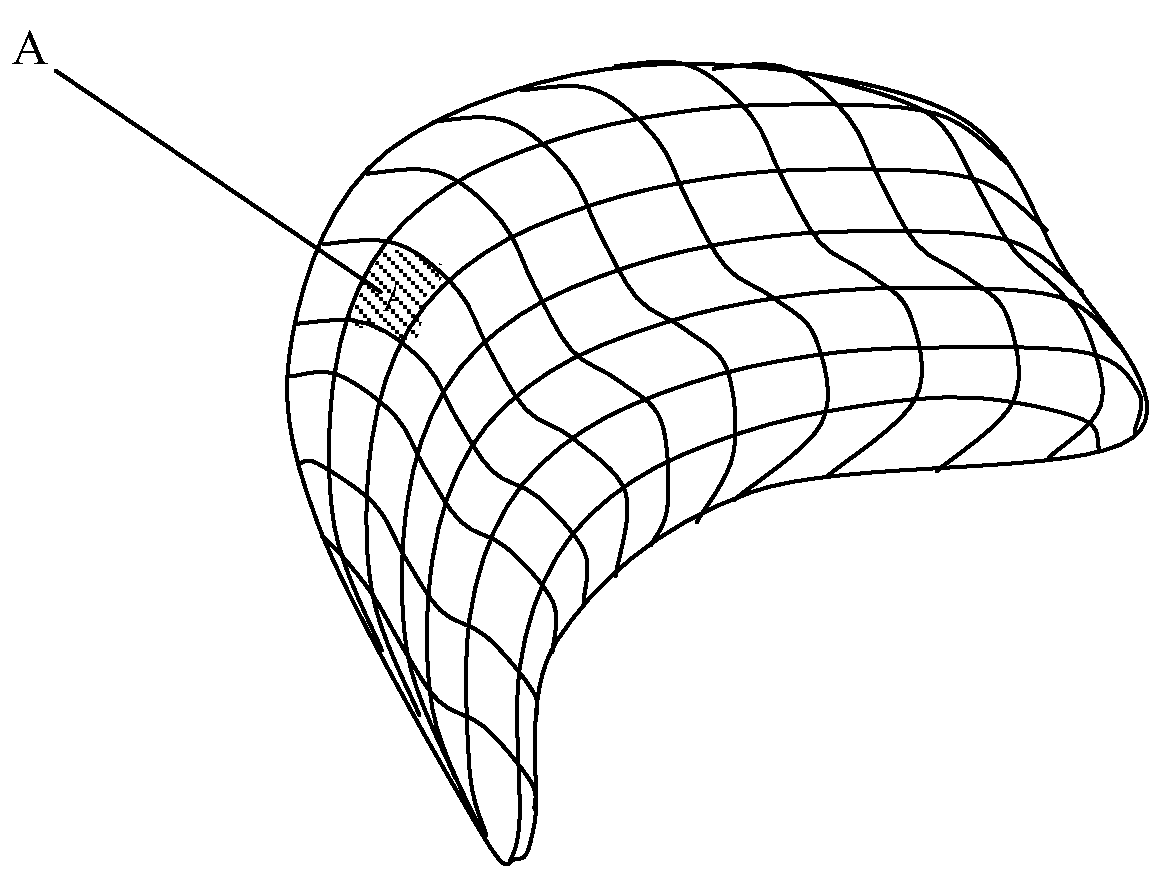
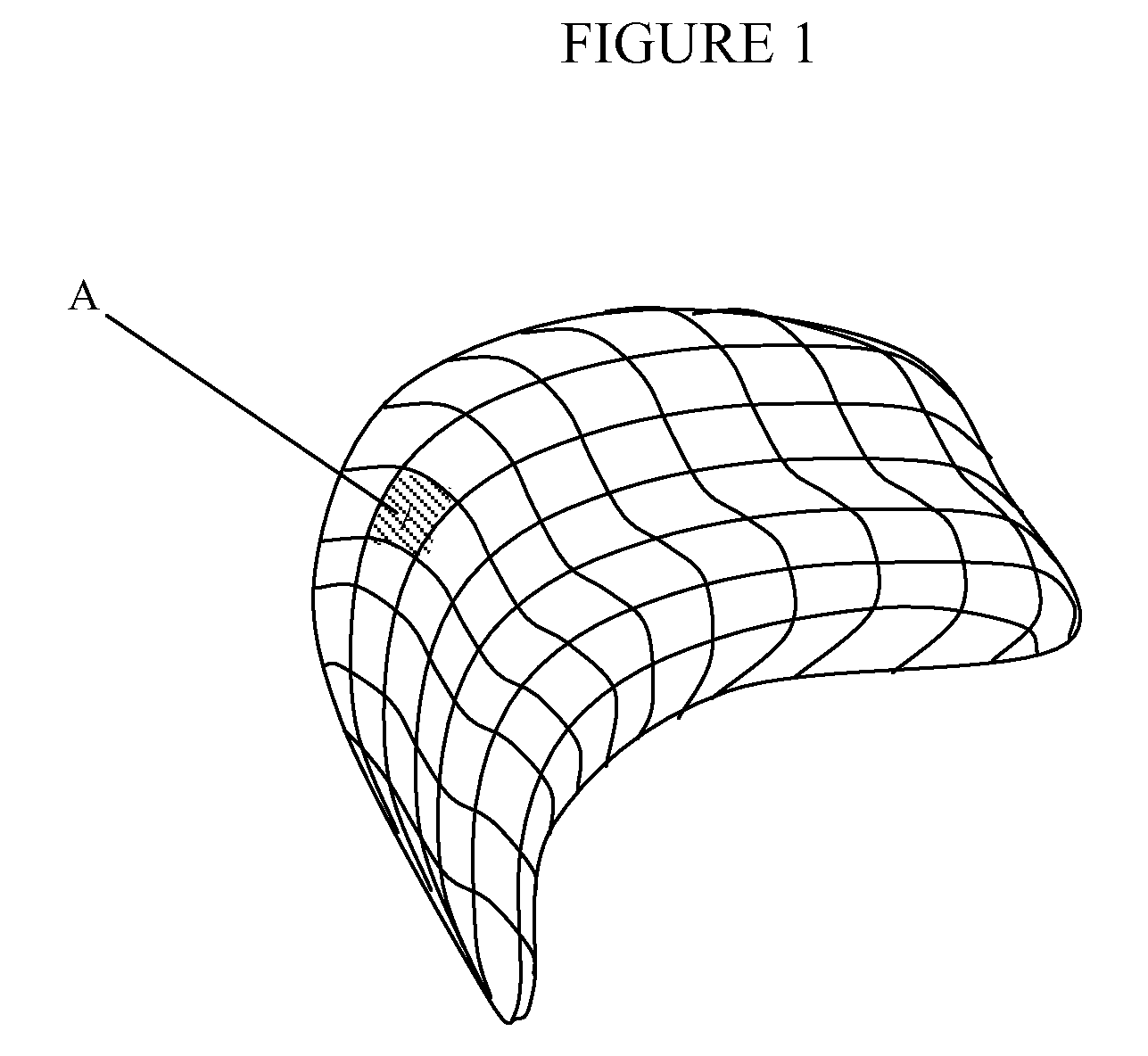
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing three-dimensional surface of human organs and a system thereof, aiming to solve the problems in the prior cavity surface reconstruction method, including rough reconstruction surface and inability to reconstruct surface of multi-furcate complex organ cavity. The method comprises the following steps of collecting spatial position information of a plurality of points on the surface of an organ; adding one or more restriction points containing spatial position information; constructing and solving a function according to the spatial position information at the sampling point and the restriction points; and performing isosurface extraction of all points with the same functional value of the sampling point to obtain a reconstructed surface of the organ. The inventive method and system can accurately reconstruct the surface model of multi-furcate complex organs, and can obtain smooth surface model, which nearly approaches to the geometry of the original cavity.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT EP MEDTECH CO LTD
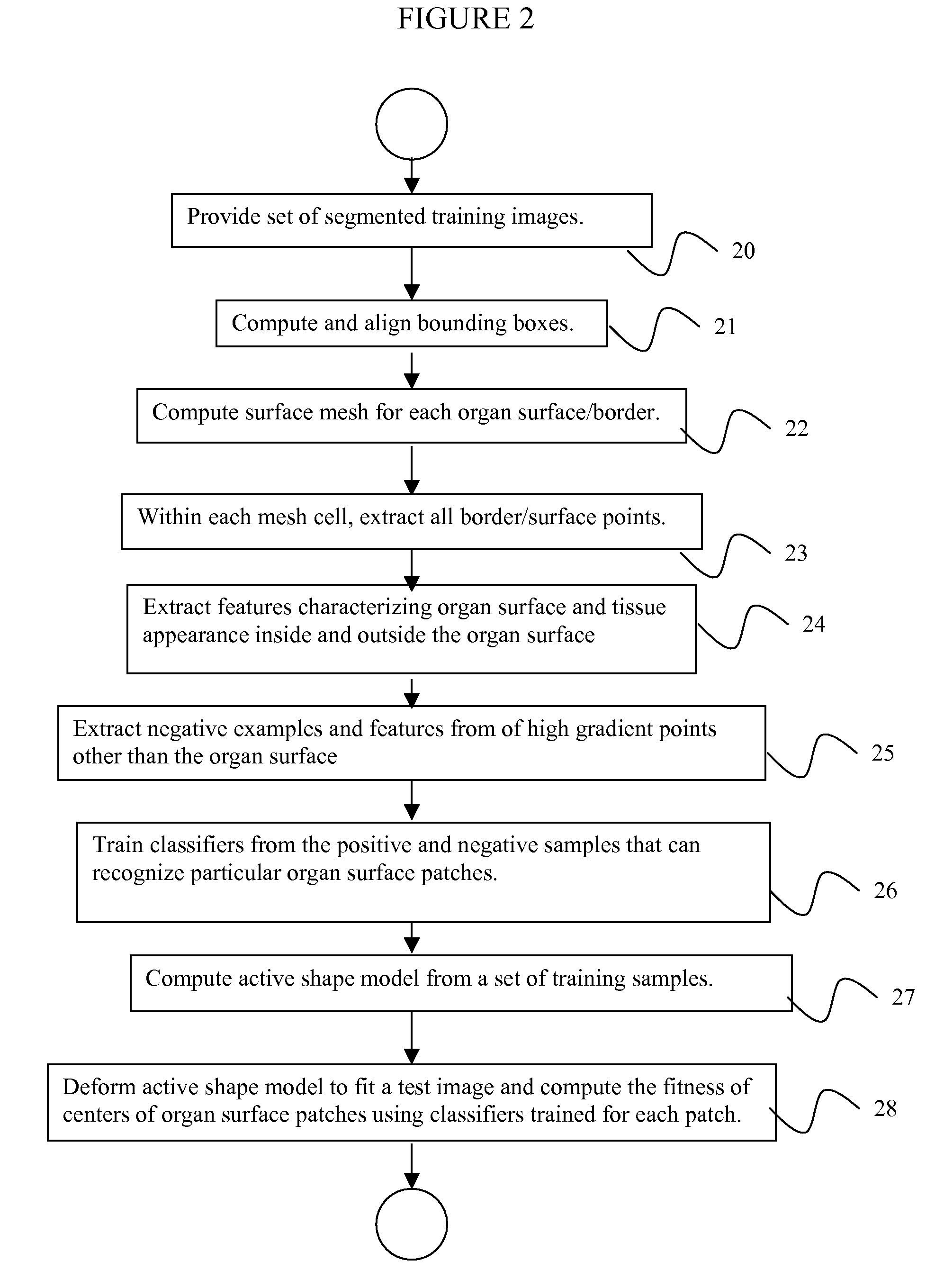
System and Method for Organ Segmentation Using Surface Patch Classification in 2D and 3D Images
A method for segmenting organs in digitized medical images includes providing a set of segmented training images of an organ, computing a surface mesh having a plurality of mesh cells that approximates a border of the organ, extracting positive examples of all mesh cells and negative examples in the neighborhood of each mesh cell which do not belong to the organ surface, training from the positive examples and negative examples a plurality of classifiers for outputting a probability of a point being a center of a particular mesh cell, computing an active shape model using a subset of center points in the mesh cells, generating a new shape by iteratively deforming the active shape model to fit a test image, and using the classifiers to calculate a probability of each center point of the new shape being a center of a mesh cell which the classifier was trained to recognize.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
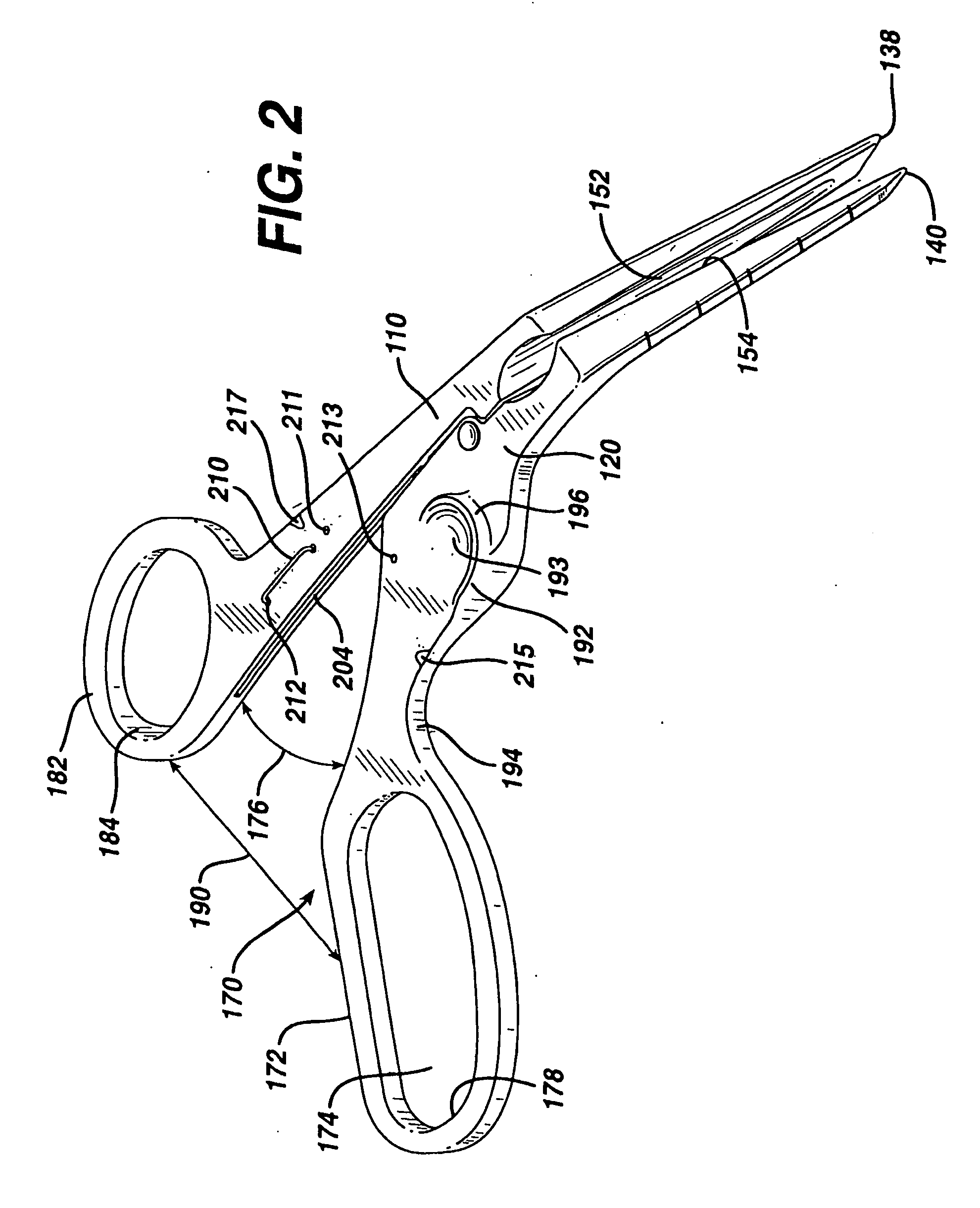
Method and apparatus for positioning a diagnostic or therapeutic element within the body and tip electrode for use with same
InactiveUS7186250B2Avoid problemsCreating lesionInstrument handpiecesSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringOrgan surface
Surgical methods and apparatus for positioning diagnostic an therapeutic elements on the epicardium or other organ surface. The apparatus include a relatively short shaft and an adjustable loop structure that supports
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Augmented reality surgery navigation method based on video superposing, system and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110010249AFully automatedRealize the deformation registration functionMedical simulationImage data processingFully automaticTarget tissue
The invention discloses an augmented reality surgery navigation method based on video superposing, a system and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a preoperative three-dimensional anatomical model of a target tissue organ; according to laparoscope video information which is acquired by a three-dimensional laparoscope in the surgery, constructing point cloud data on the surface of the target tissue organ; registering the preoperative three-dimensional model and the point cloud data, according to a registering result, obtaining a target transforming relation between the preoperative three-dimensional anatomical model and the point cloud data which correspond with a current laparoscope view; and according to the target transforming relation, superposing and displaying the preoperative three-dimensional anatomical model on the laparoscope view through augmented reality technology. Therefore fully automatic non-rigid registering can be realized without artificial manual intervention. Furthermore no any marking point or external tracking equipment is required. Augmented reality displaying of the visual field in the surgery can be finished in a standard clinical surgery process, and furthermore real-time navigation of the whole surgery process is finished through image tracking technology, thereby realizing imaging guiding of a doctor in surgery.
Owner:BEIJING DIACRID MEDICAL TECH
Apparatus and method for shielding tissue during tumor ablation
InactiveUS6471695B1Resistance to penetrationHigh proportionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAbnormal tissue growthTherapeutic effect
The present invention provides improved methods, systems, and kits for protecting body tissues which are adjacent to tissues undergoing thermal treatment. Thermal treatment is often prescribed for tumors and other disease conditions within body organs and other tissue masses. The methods, systems, and kits are particularly useful for treating tumors which lie at or near the surface of an organ, such as the kidney, pancreas, stomach, spleen, and particularly the liver. One risk of treating such tumors is the possibility of mistargeting the tumor and penetrating a delivery cannula or portions of a treatment device beyond the surface into the adjacent tissues or organs. In the case of radiofrequency or electrosurgical treatment, healthy surrounding tissue may be directly ablated. An additional risk, present even when the tumor is correctly targeted, is the possibility of thermal damage to the surrounding, non-targeted tissue. In radiofrequency or electrosurgical treatment, heat may dissipate into surrounding tissues which are more fragile and heat sensitive than the tissue in the organ being treated, thus causing unwanted tissue damage. These risks and others may be lessened or avoided with the use of an interface shield between the target region and adjacent body tissues to shield surrounding organs and tissue from treatment effects.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Exogenous matrix-supported topical application of stem cells to organ surface
A process of tissue regeneration is provided that includes the administration of a stem cell topically to a surface of a tissue. The tissue being in vivo in a subject or in vitro. The tissue has a biocompatible matrix applied around the stem cell and in contact with the surface. After sufficient time, the stem cell infiltrates and regenerates the tissue. A composition is also provided that includes an injured or diseased tissue with a plurality of stem cells proximal to the tissue surface in a biocompatible. A process of increasing a level of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, anti-apoptotic or anti-necrotic factors in a tissue is provided that includes the administration of a stem cell topically to a surface of a tissue in a biocompatible matrix. After sufficient time, the stem cell releases soluble pro-regenerative factors to increase the levels in the tissue.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
Preparation method for infant cleft lip facial simulation model
InactiveCN101673481ASpecial data processing applicationsTeaching apparatusHuman bodyIncomplete bilateral cleft lip
The invention belongs to the design of a surface model of a medical simulation human organ and a preparation method, in particular to a preparation method for an infant cleft lip facial simulation model, which comprises the following steps: (1) collecting three-dimensional original data of faces of cleft lip illness children; (2) rebuilding digital facial models of the faces of the cleft lip illness children; (3) automatically layering and scattering model files and forming processing files; (4) automatically processing resin part models of the faces of the cleft lip illness children; (5) duplicating silastic cleft lip facial models; and (6) coloring the silastic facial models. The invention can provide a personalized customization facial simulation model which is in high consistence withthe shape, color, texture and the like of the faces of the cleft lip illness children with three age of months; the simulation model not only provides the real reference for a surgeon before operation, causes the surgeon to know fairly well during the operation, and simultaneously provides postoperative facial esthetic effects for parents of cleft lip and palate patients.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Loop structures for positioning a diagnostic or therapeutic element on the epicardium or other organ surface
InactiveUS20050015083A1Avoid problemsCreating lesionTransvascular endocardial electrodesInstrument handpiecesPericardiumOrgan surface
Loop structures for positioning diagnostic an therapeutic elements on the epicardium or other organ surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
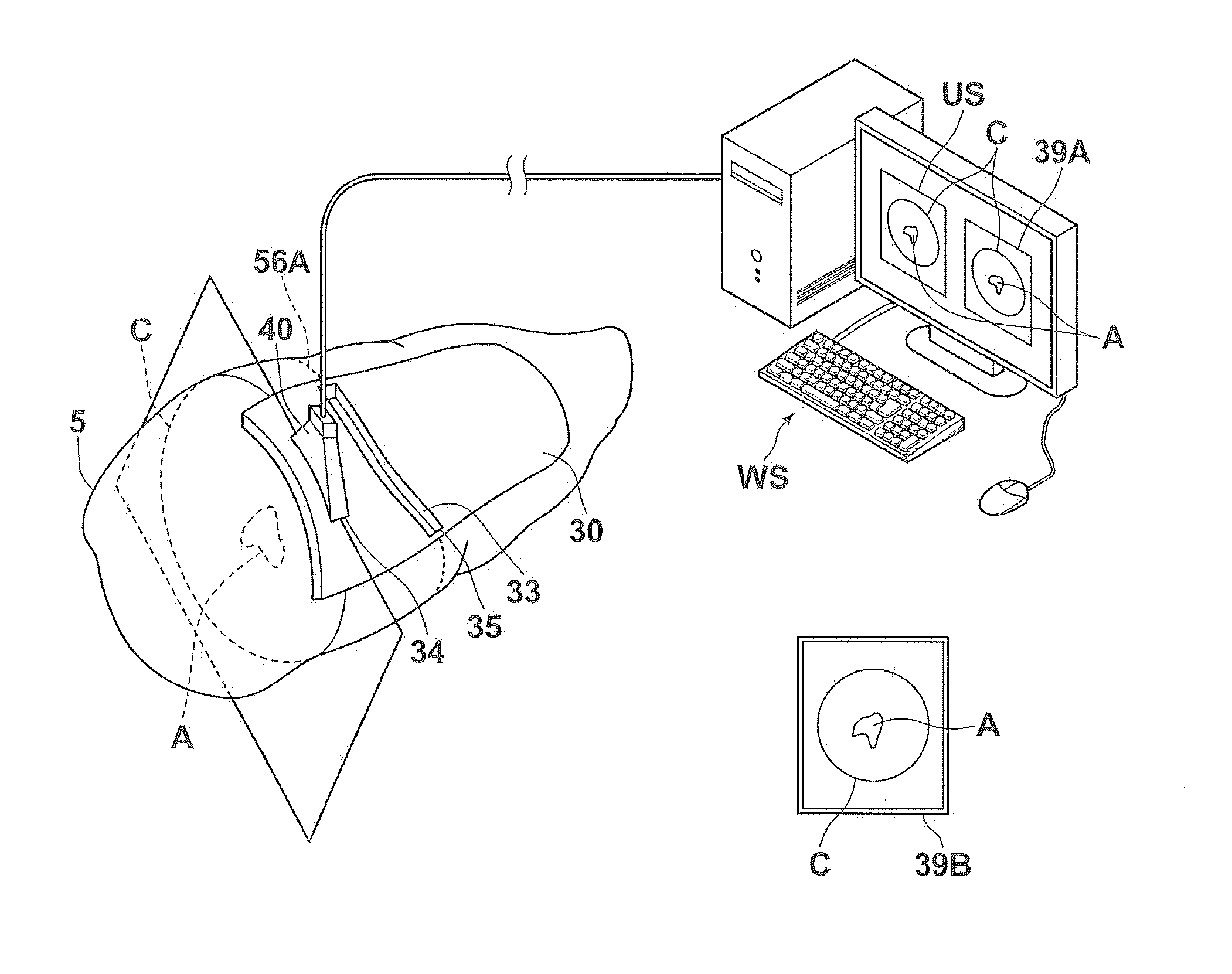
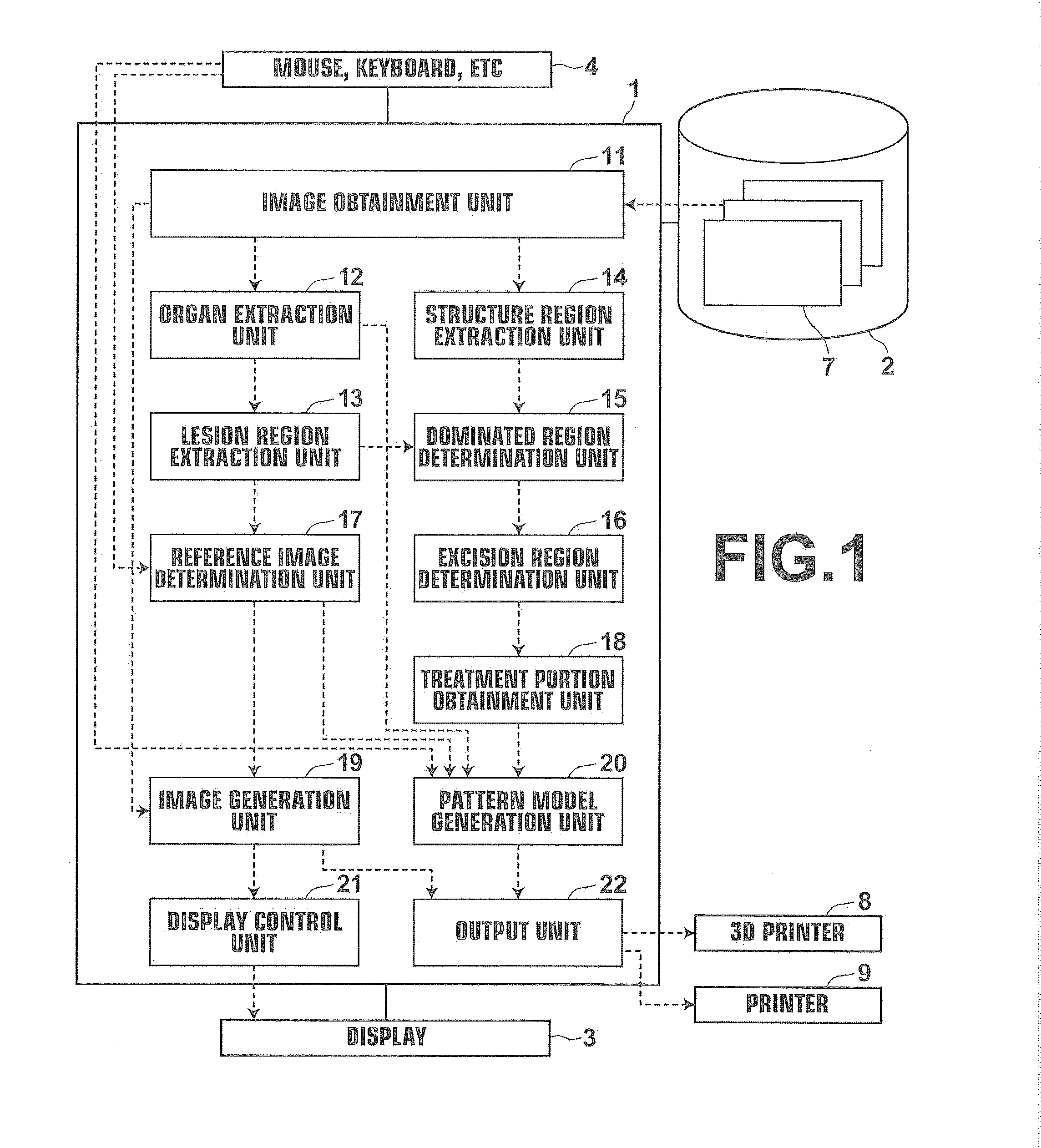
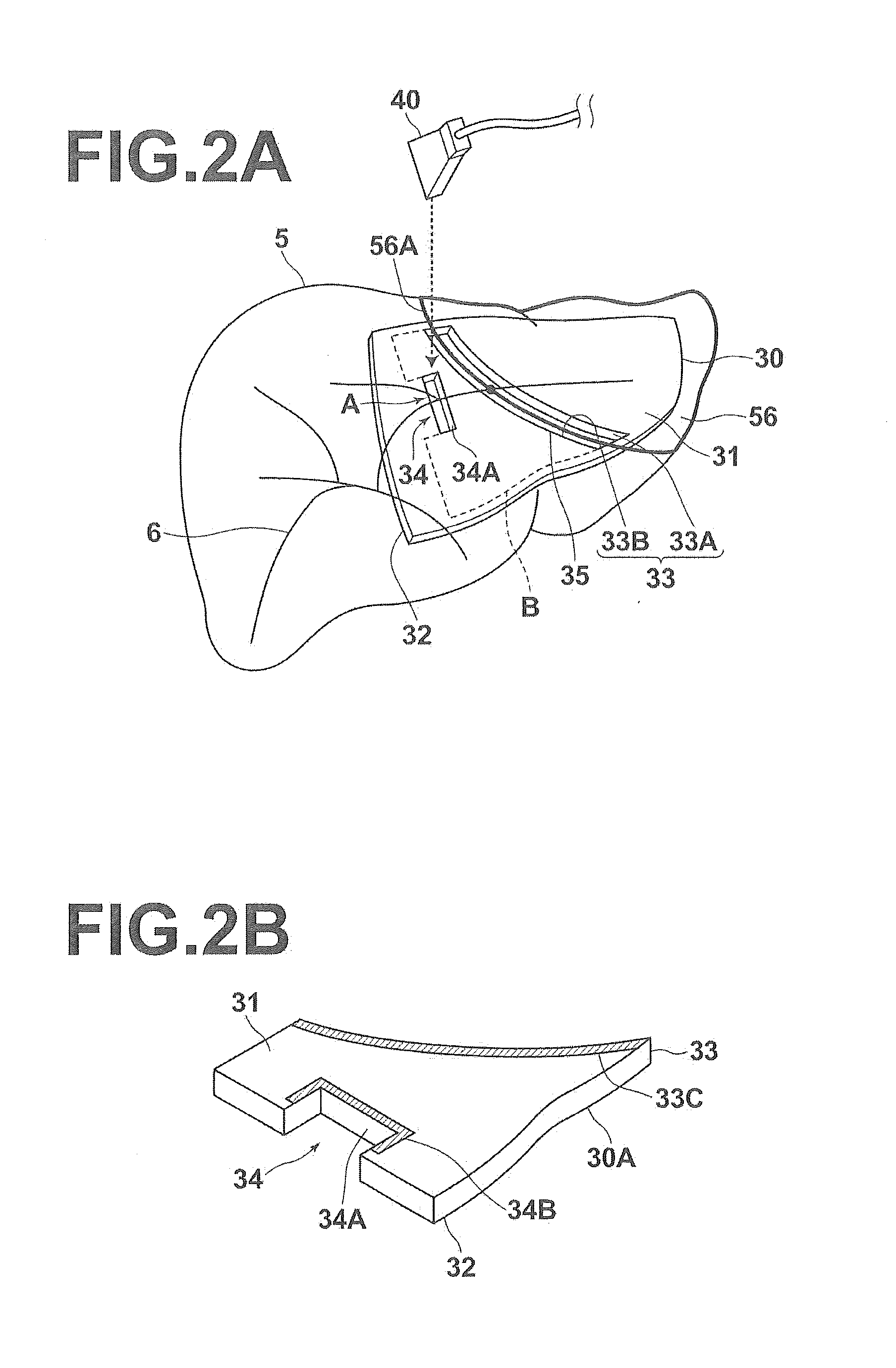
Pattern and surgery support set, apparatus, method and program
ActiveUS20140333617A1Convenient ArrangementDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgeryTomographic image
A three-dimensional image representing a patient's organ is obtained. The organ is extracted from the three-dimensional image. A treatment portion, at which desirable treatment for the organ is performed, on a surface of the organ is obtained. A pattern model including an outer surface, an inner surface having a surface form along an organ's outer surface of the organ, a guide wall connecting, along the treatment portion, the outer surface and the inner surface, and a positioning portion is generated. The positioning portion positions a predetermined imaging probe in such a manner that a tomographic image of a cross section of the organ including a target portion of the organ is imageable when the guide wall is arranged along the treatment portion on the organ.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Multiple energy radioactive source CT imaging method for realizing color organ surface mapping
InactiveCN1857161AEasy diagnosisImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsImaging processingAbsorbed energy
The multiple energy radioactive source CT imaging method for realizing color organ surface mapping belongs to the field of image processing technology. The method includes first multiple energy radioactive source CT imaging to obtain original image and 3D reconstruction of the organ to be observed and diagnosed, the subsequent converting the difference of energy values obtained with the multiple energy radioactive source CT imaging near the organ into different colors, and the final endowing the colors to the surface of the organ before displaying. The present invention distinguishes different tissues based on their difference in absorbing energy rays, like that different matters absorb light of different energy to show different colors. The present invention makes it possible to simulate relatively realistic colors on the surface of organ by means of neural network method for doctor to diagnose conveniently.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Tumor grid organ model 3D printing method
The invention relates to a tumor grid organ model 3D printing method. The method particularly comprises the following steps: a cross section and a sagittal section when a human body is in a supine position are used for building crossed multiple grids on the surface of an organ, while the 3D grids are built, 3D modeling software specially adopted for original data for medical imaging (CT or MRI) picks out an organ or a tumor or a blood vessel in need of 3D printing, and building of 3D data is carried out. 3D data for the organ or the tumor or the blood vessel are built at the same time, and organ surface 3D grid data are built. The 3D data are inputted to a 3D printer for 3D model printing. According to the printed model of the invention, the tumor can be intuitively observed via a hollow organ shell and the distance between the tumor and the organ surface can be measured, a guide is provided for surgical resection, and a spatial distance between the tumor or the blood vessel inside the organ and an anatomical site on the organ surface can be directly read from the model.
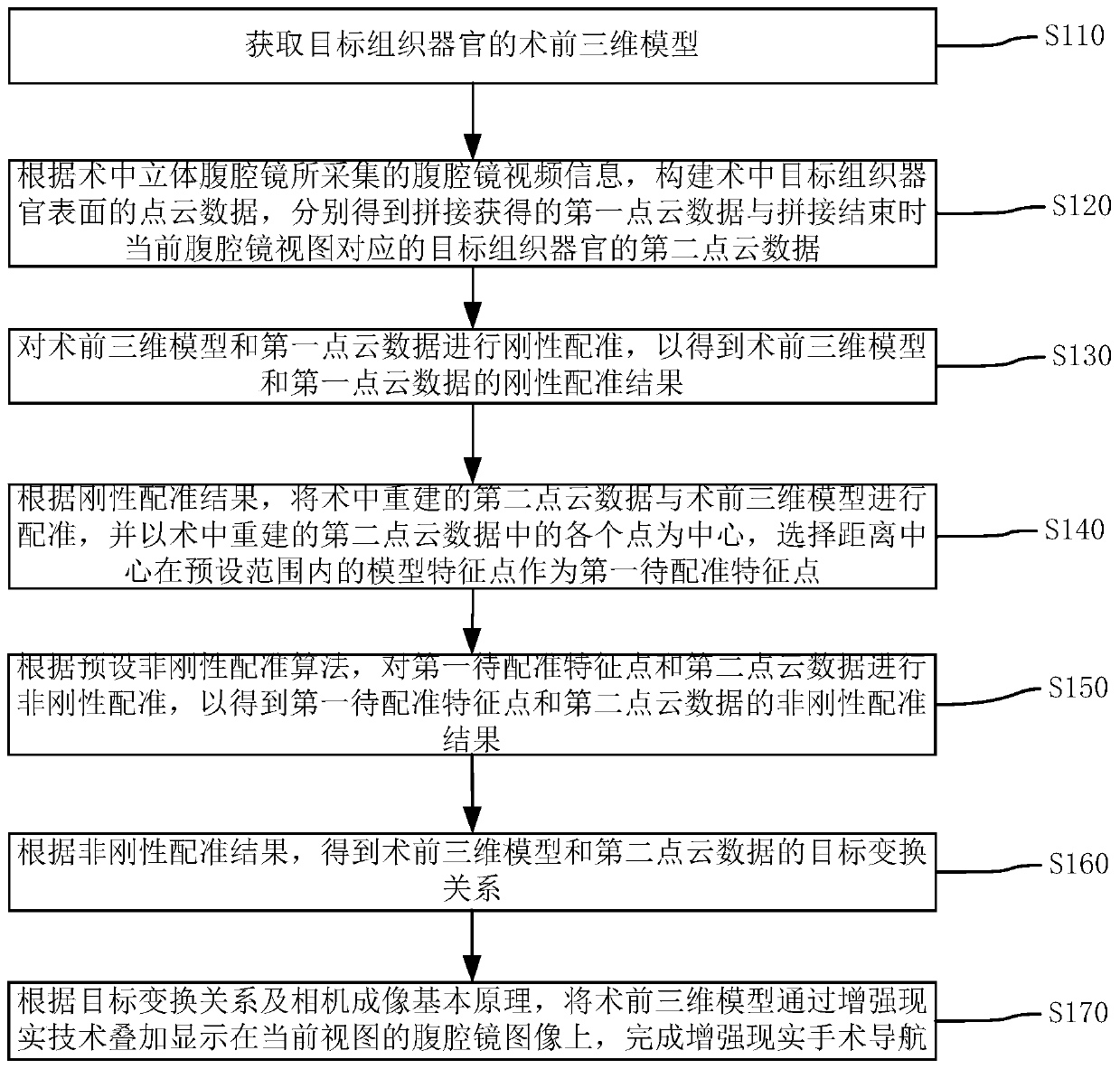
Owner:王峻峰
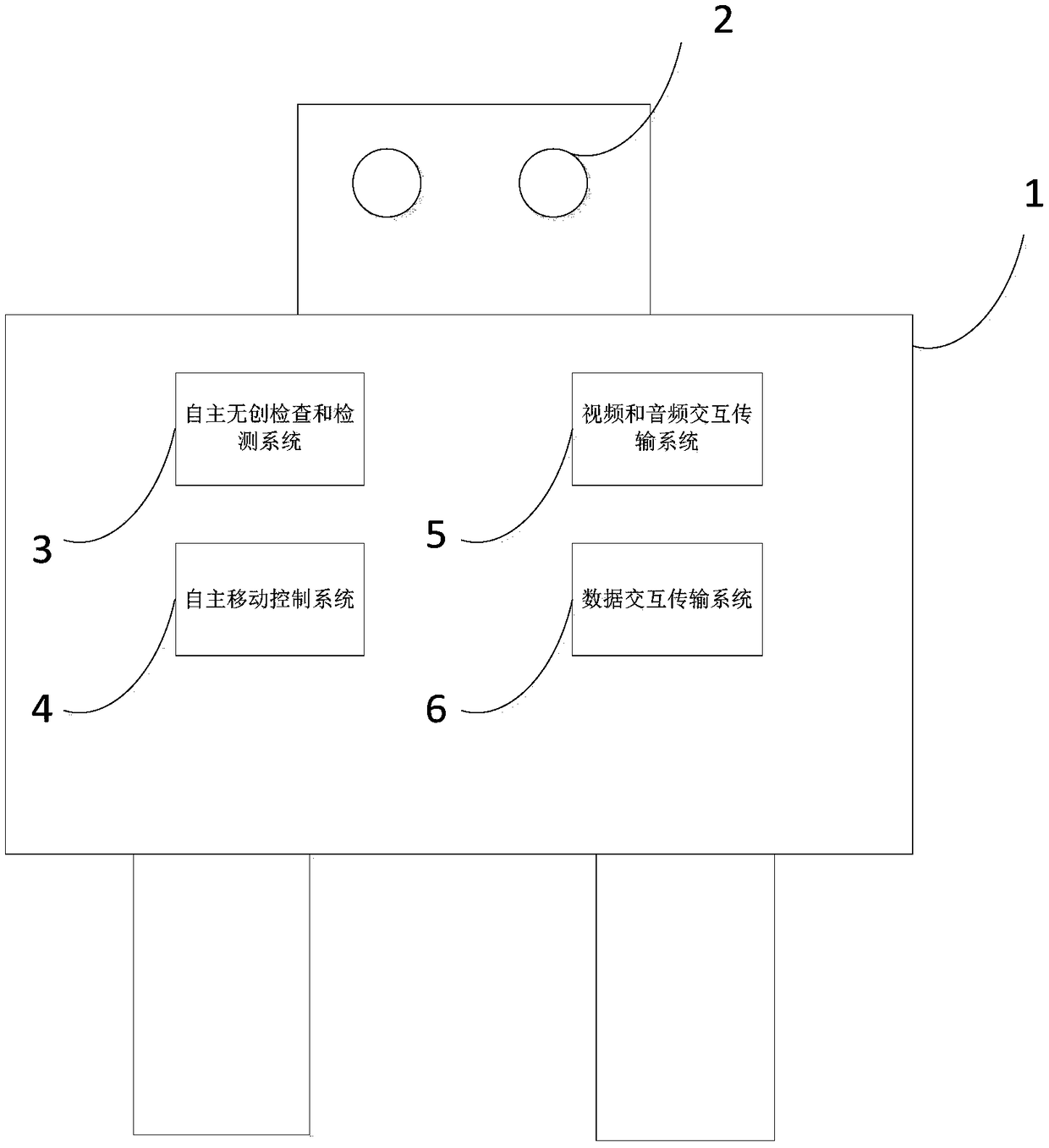
Medical robot
PendingCN108942952AImplement diagnosticsGet inspection/detection dataManipulatorMedical robotNon invasive
The invention discloses a medical robot. The robot comprises an autonomous movement control system, an automatic infrared scanning target-seeking patient positioning and organ surface positioning system, an autonomous non-invasive inspection and detection system, a real-time video and audio interactive transmission system and an interactive transmission system which is used for integrating information and is automatically connected with a consultation center robot and a multi-party consultation robot or an expert mobile phone APP, wherein all the systems are integrated in a robot body. According to the robot, remote consultation is easy to implement, so that primary hospitals easily obtain diagnosis and treatment support and medical support of experts in large hospitals, and the problems that it is difficult, expensive and far for common people to see a doctor are solved. By means of the robot, especially the autonomous non-invasive inspection and detection system arranged in the robotbody, various non-invasive detection and inspection instruments are integrated, required examinations, detection, tests and the like can be immediately conducted near patient beds, and the robot plays an important role in timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment and rescue of critical patients.
Owner:杨水祥
Percutaneous access conduit and methods
A tubular conduit is used to access blood vessels or other structures in the human body. The conduit has a distal tip angled to match the angle of entry into the body and an end contour adapted for the surface of the target vessel or organ. The contour may be curved to match the curve on the outer surface of the vessel or organ. The conduit's angled and contoured distal end may be adapted to engage, and align the conduit with, the surface of the vessel or organ. The conduit bears a longitudinal groove along its lower, inner surface. When the conduit is appropriately aligned, the groove may be used to guide a needle tip to the desired location, for example, the mid-line of the vessel or organ.
Owner:GRAYZEL JEFFREY +5
Method applied in adding sealing reinforcement strips in process of manufacturing organ zipper bag
ActiveCN102233689AEasy to produceImprove sealingEnvelopes/bags making machineryPlastic filmOrgan surface
The invention discloses a method, which can improve the bonding strength of a bag, is suitable for mass production and is applied in adding sealing reinforcement strips in the process of manufacturing an organ zipper bag. In the method, a plastic film on the front plane, the front ends of a left organ surface and a right organ surface and the sealing reinforcement strips are firstly heat-sealed together, and then concave and convex embedding zippers, the sealing reinforcement strips and a plastic film on the rear plane are heat-sealed once, so that the organ zipper bag with the sealing reinforcing rib can be simply and conveniently produced, the sealing performance of the bag is enhanced, the processing procedure for producing the whole bag is also reduced, the production cost is saved and the method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:FOSHAN NANHAI LIDA PACKAGING
Blocking material capable of stopping bleeding, preparation method thereof, and blocking product capable of stopping bleeding
ActiveCN108785732AImprove adhesionImprove water absorptionSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberBiological body
The invention provides a blocking material capable of stopping bleeding, a preparation method thereof, and a blocking product capable of stopping bleeding. The blocking material comprises a matrix, and a wet state adhesive layer which is arranged on at least one surface of the matrix; the matrix comprises nonwoven fiber filament; the linear density of the nonwoven fiber filament ranges from 0.5dtex to 5dtex, and the carboxylation degree ranges from 12 to 25%; the wet state adhesive layer is obtained through contact of at least one surface with an adhesive solution; the adhesive solution contains an amino compound and a buffer solution; the amino compound is dissolved in the buffer solution. The blocking material possesses excellent adhesion performance and water adsorption performance, iscapable of realizing effective adhesion with organism surfaces or parenchyma organ surfaces, and can be degraded and absorbed; deposition in internal organs is avoided; internal organs function damageis not caused; and the blocking material is safe to be used for stopping bleeding.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com