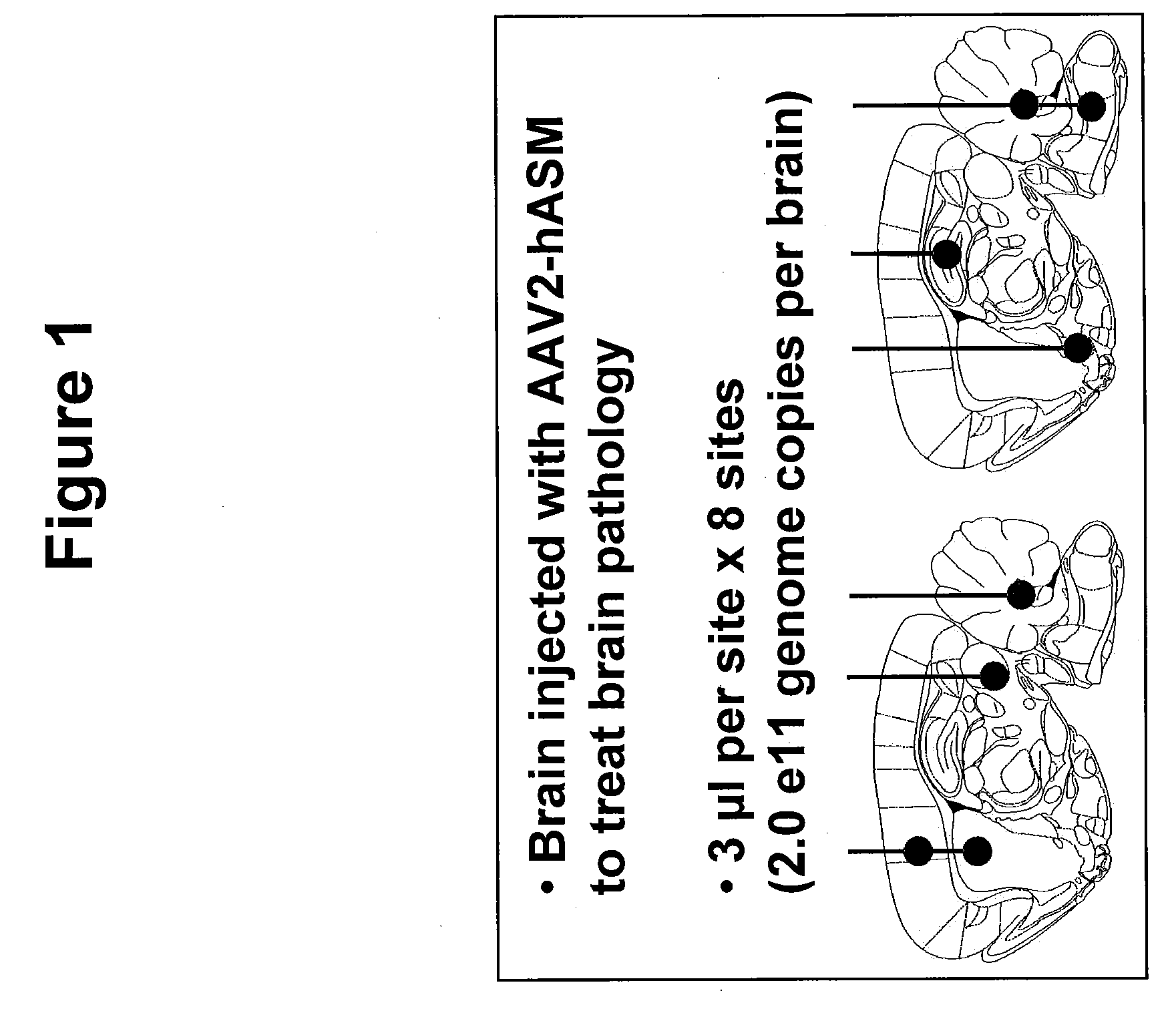
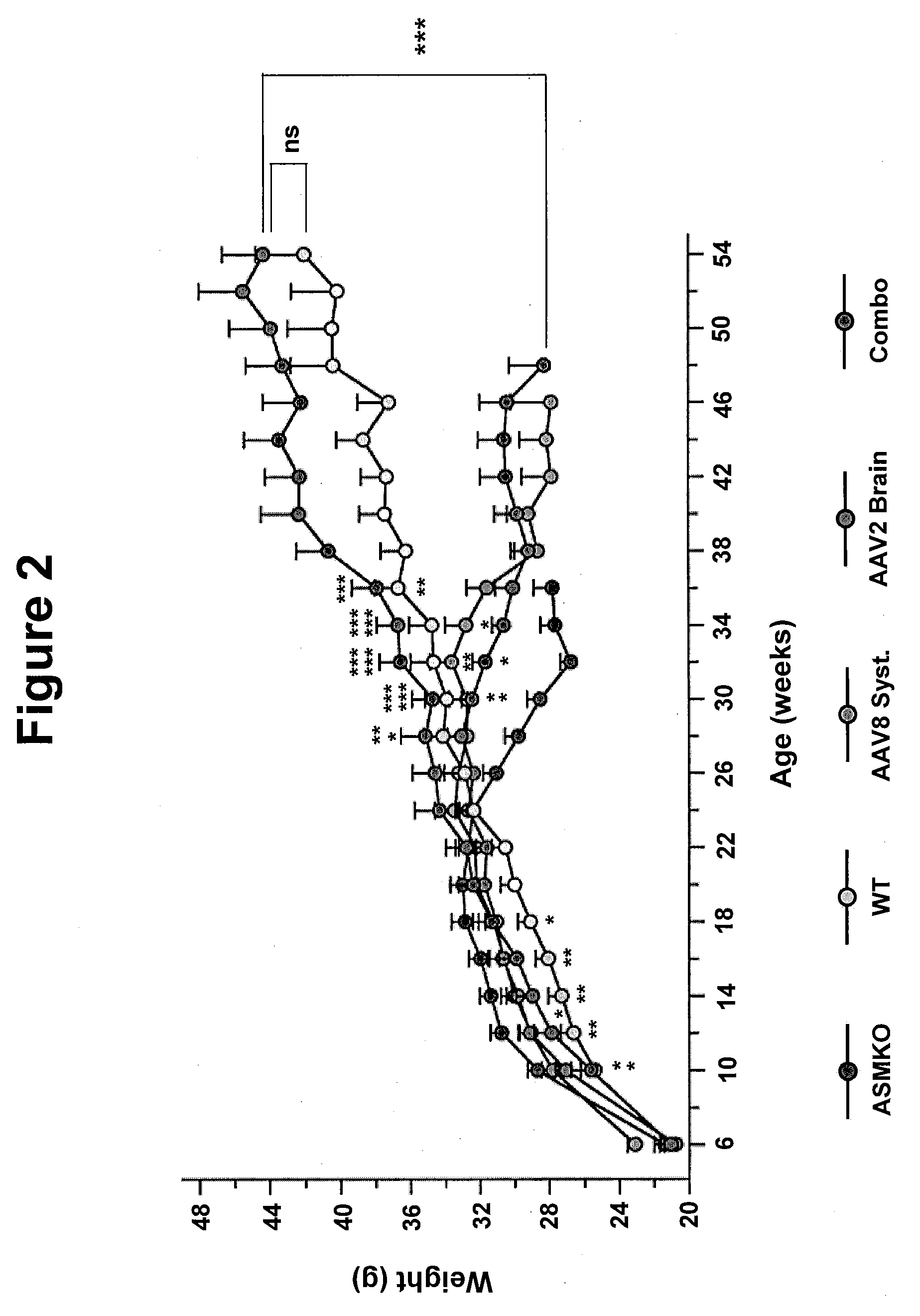
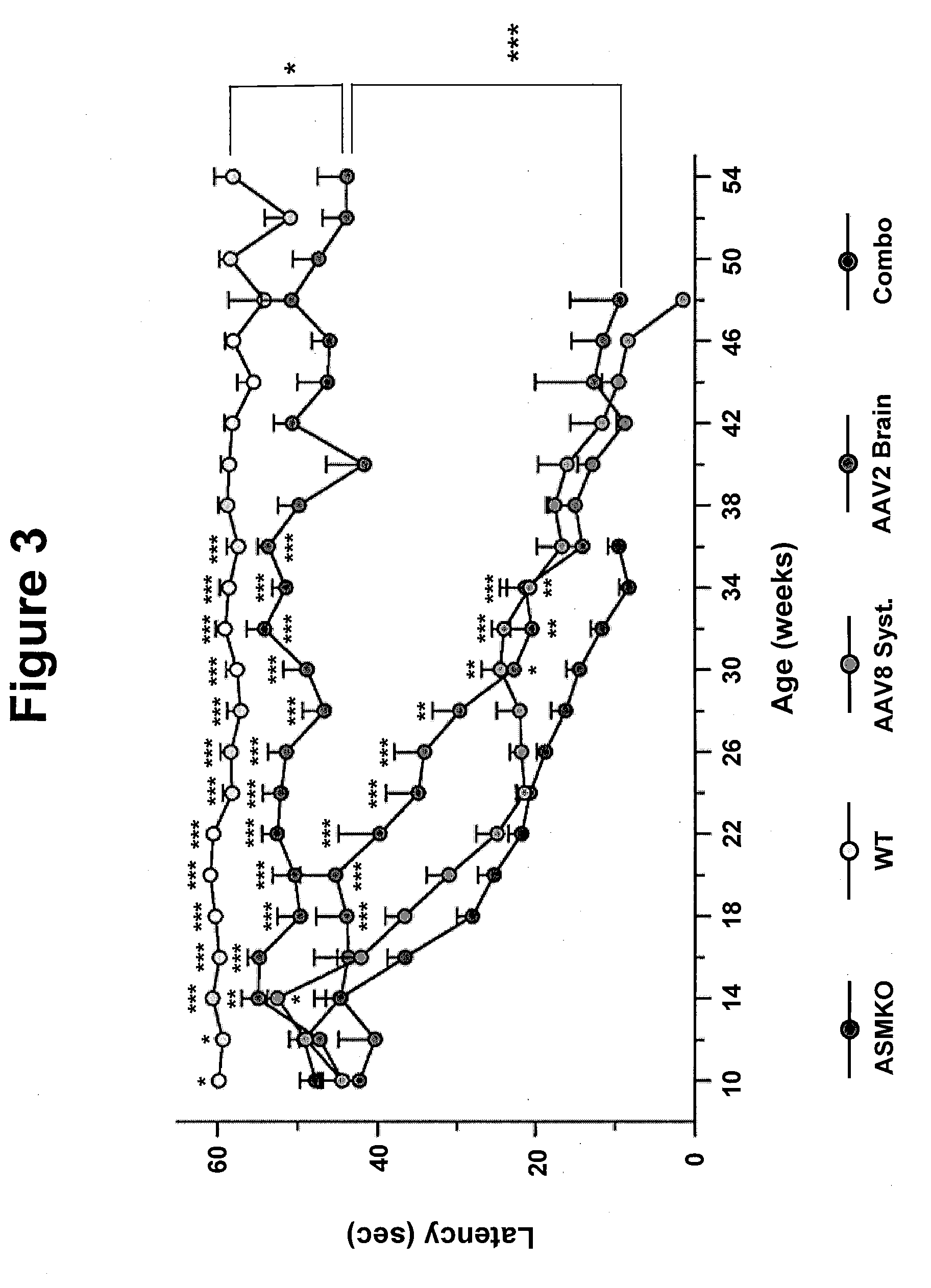
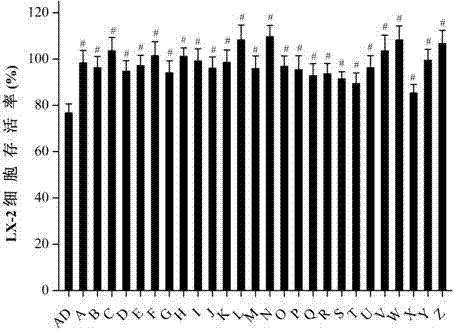
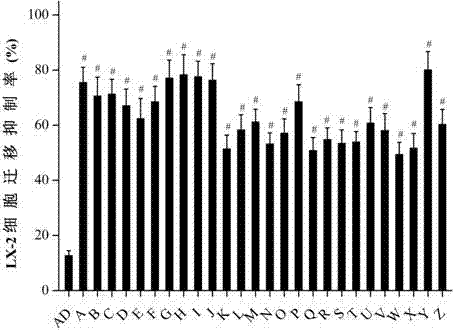
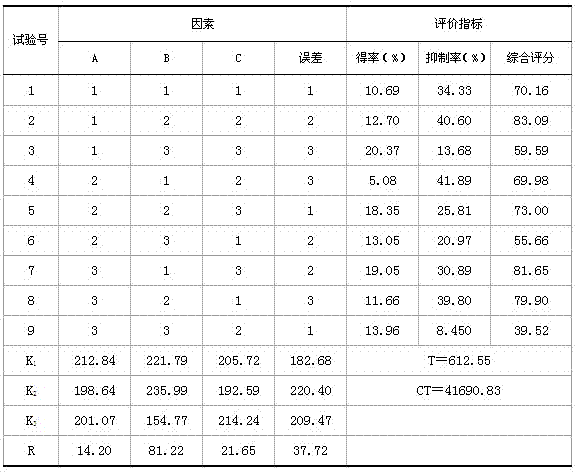
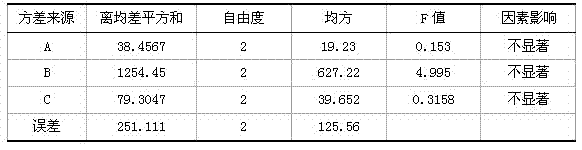
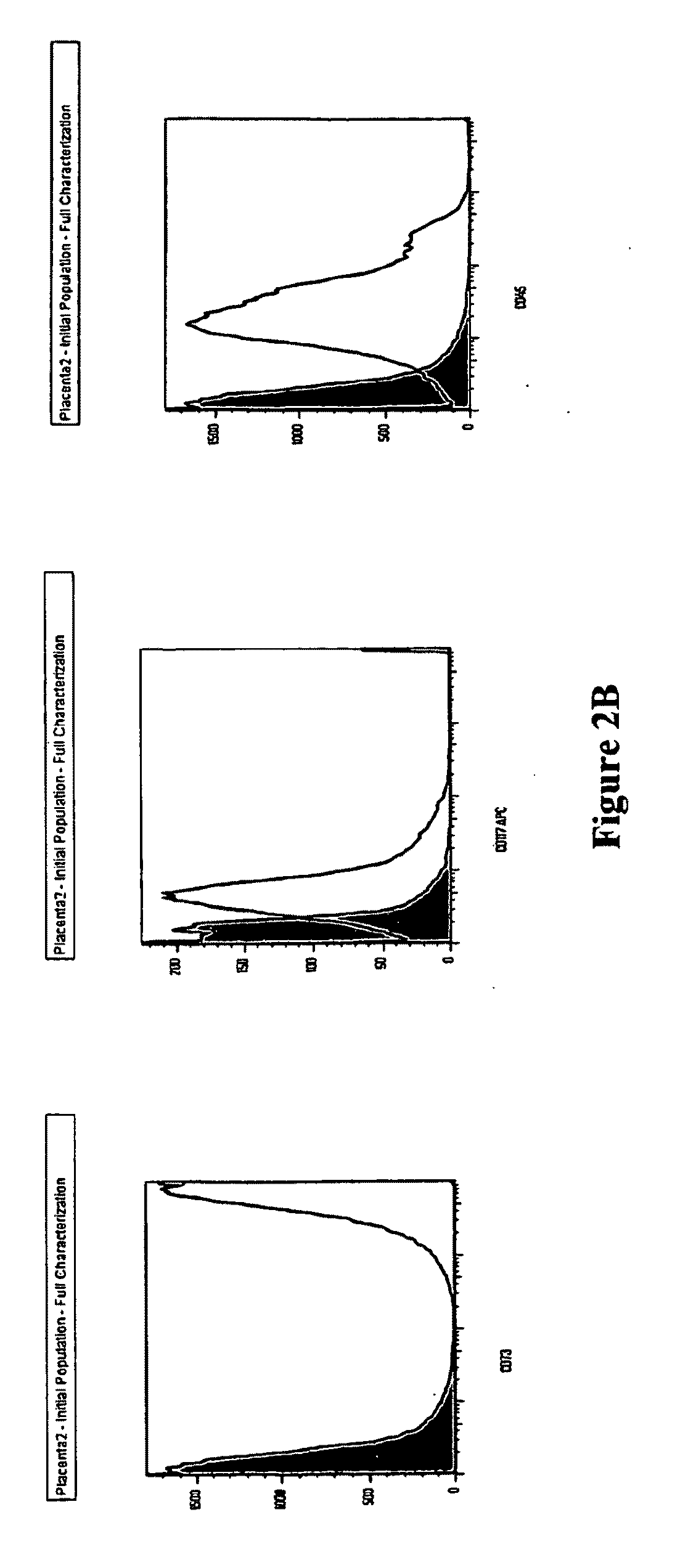
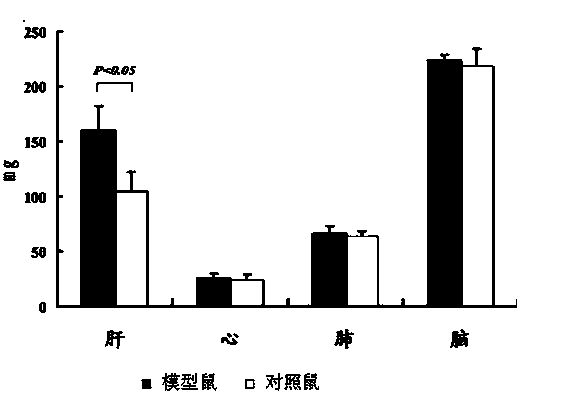
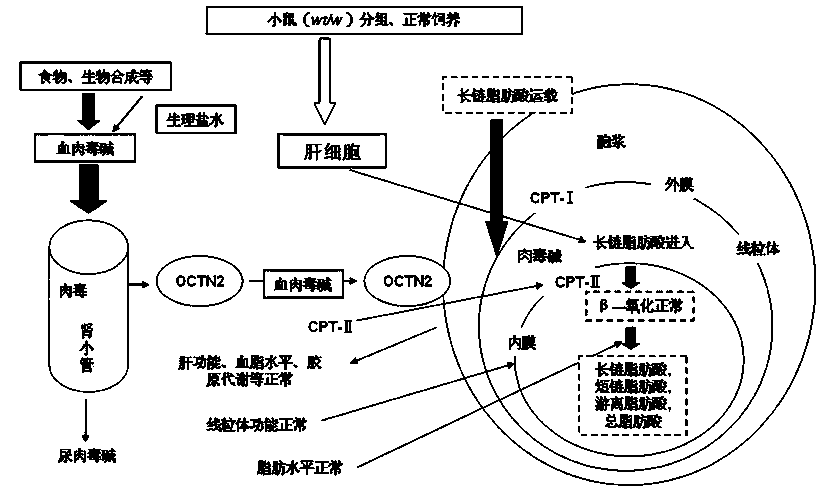
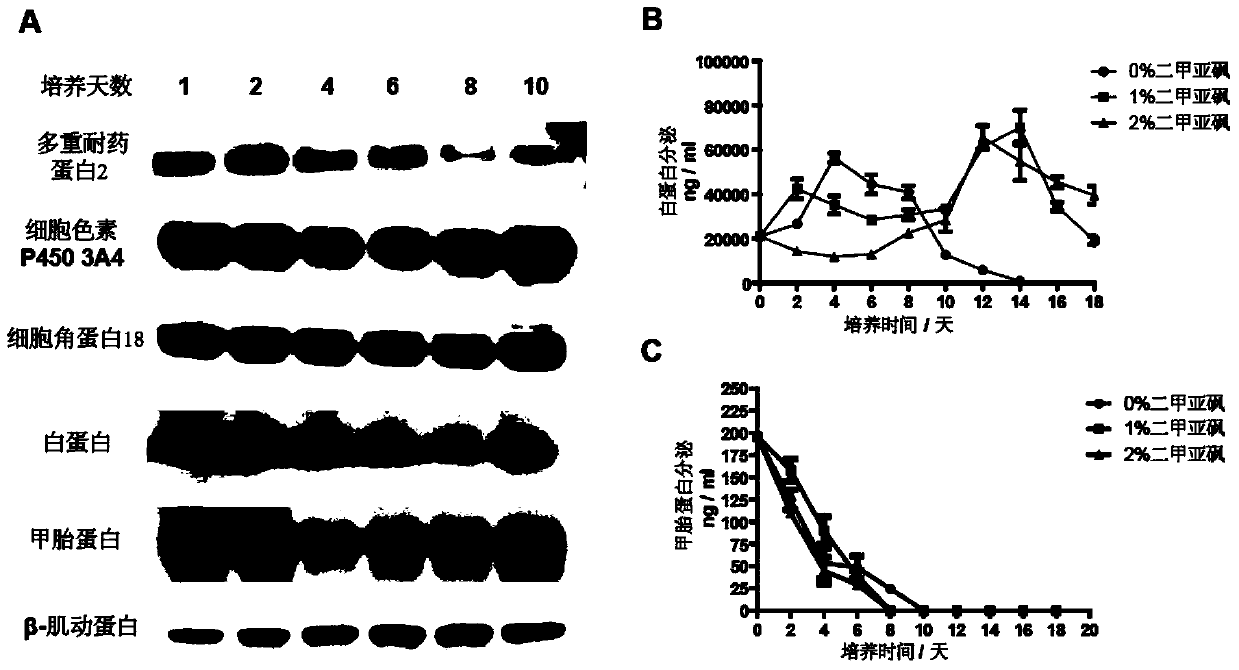
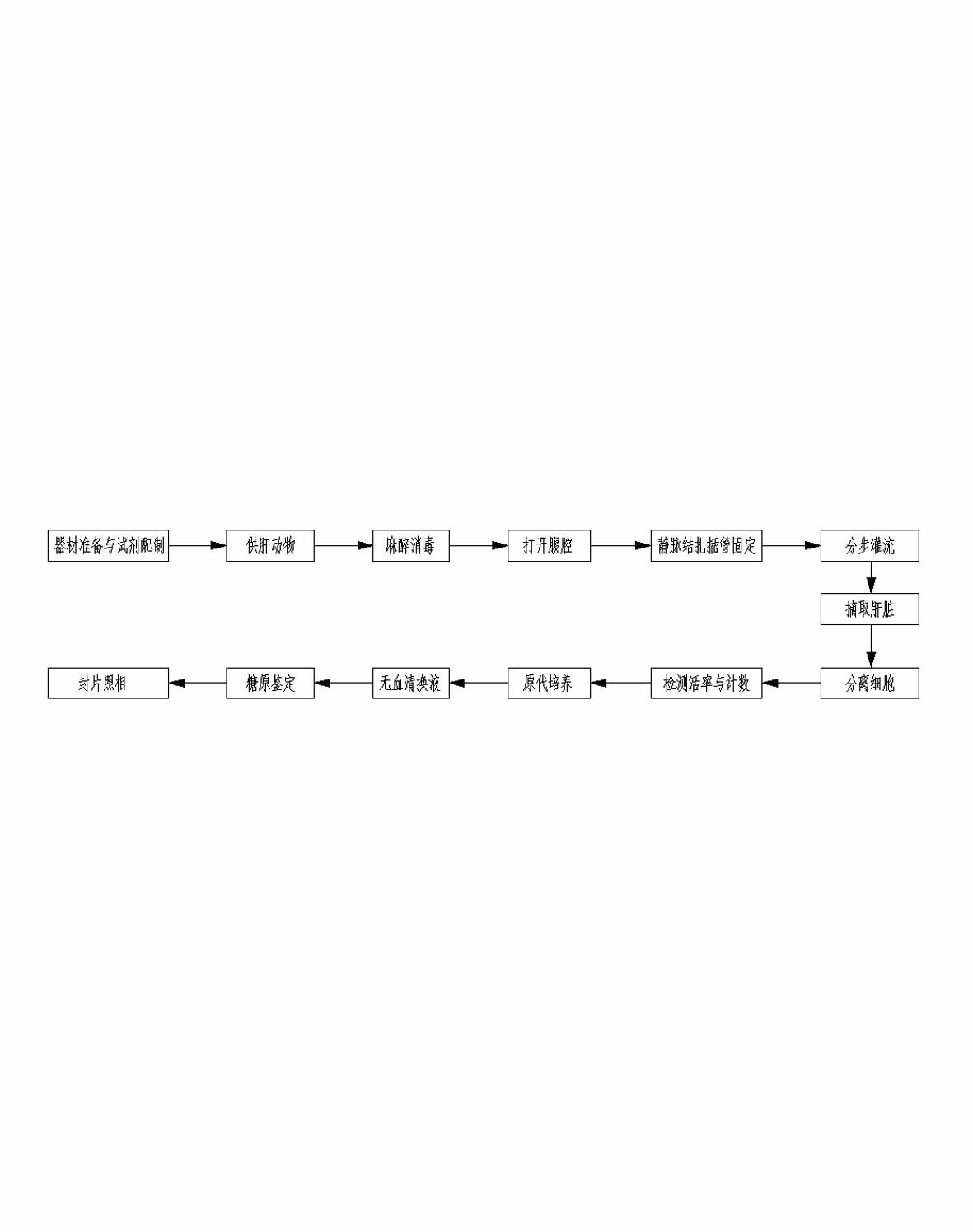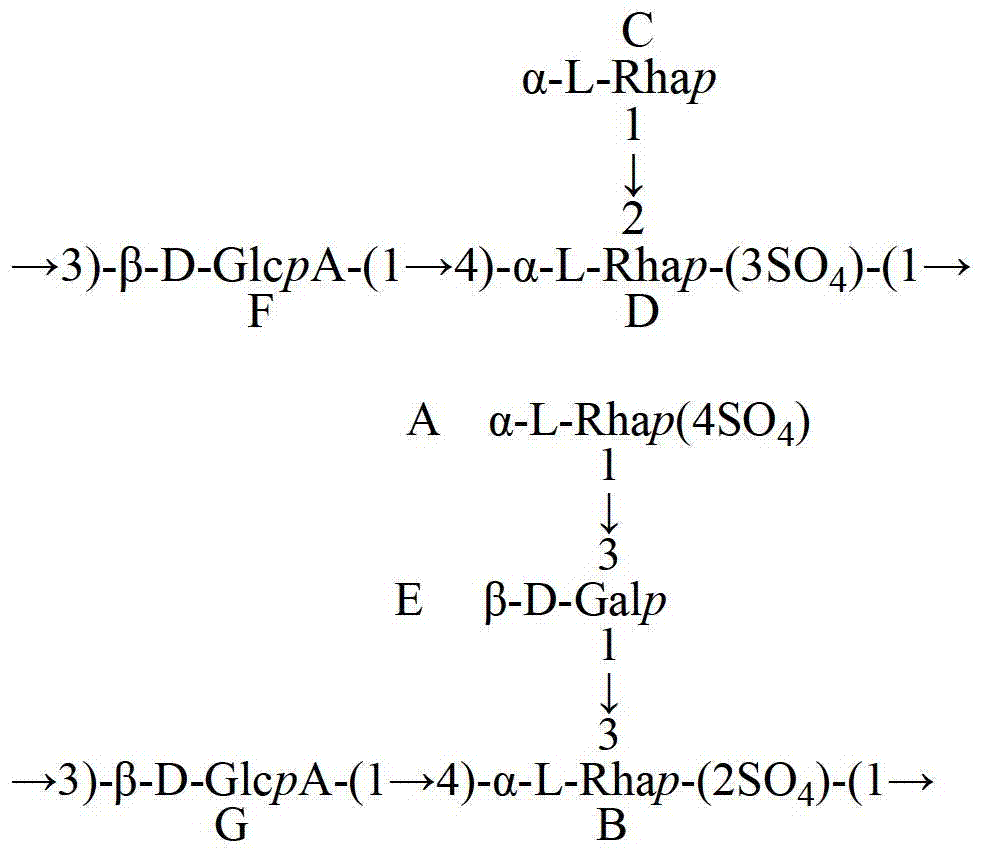Patents
Literature
202 results about "Hepatic tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hepatic Tissue. The tissue of the liver. It includes the hepatic lobules, hepatic sinusoids, perisinusoidal spaces, and portal triad. The hepatic lobules are composed of hepatocytes.
Compositions and methods for enhanced biostability and altered biodistribution of oligonucleotides in mammals
InactiveUS6753423B1Improve biostabilityBiodistribution can be alteredOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalBiodistribution
The invention is directed to oligonucleotides and oligonucleosides functionalized to include lipophilic moieties and having improved biostability and altered biodistribution in mammals. In one embodiment, such lipophilic oligonucleotide conjugates are used in a method of targeting antisense oligonucleotides to hepatic tissues and thereby preferentially modulating gene expression in the liver and associated tissues of a mammal.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Gene therapy for niemann-pick disease type a
InactiveUS20090117156A1Symptoms improvedCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsMedicineTransgene
This disclosure pertains to methods and compositions for tolerizing a mammal's brain to exogenously administered acid sphingomyelinase polypeptide by first delivering an effective amount of a transgene encoding the polypeptide to the mammal's hepatic tissue and then administering an effective amount of the transgene to the mammal's central nervous system (CNS).
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for isolating and culturing human primary hepatocytes
InactiveCN102061284AOvercome the disadvantage of inability to in vitro perfusionReduce usageVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsLow speedTropocollagen
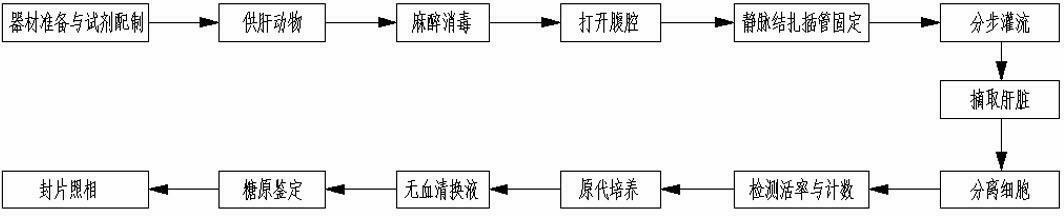
The invention provides a method for isolating and culturing human primary hepatocytes, comprising the following steps: cleaning blood clots on surfaces of hepatic tissues by using D-Hank's solution and cutting off connective tissues; using a needle syringe for puncturing on multipoints to perfuse anterior perfusion solution preheated to 38 DEG C so that a hepatic tissue block changes from dark red to gray and the effluent anterior perfusion solution becomes clear; using the needle for puncturing on multipoints to perfuse preheated recyclable type II collagenase solution until the hepatic tissue block is loosened and inelastic and has turtleback cracks on the surface; scissoring the hepatic tissue block, passively isolating the hepatic tissues, removing residual envelops and fibrillar connective tissues and continuously shaking and digesting in the type II collagenase solution at 37 DEG C; blowing and beating digest into hepatocyte suspension, filtering the suspension under ice bath condition, collecting filtered suspension, transferring the filtered suspension to a centrifuging tube and centrifuging at low speed; adding bottom precipitate produced from the primary low-speed centrifuging of the filtered suspension to erythrocyte lysate, blowing and beating, standing at room temperature, adding Dulbecco's modified eagle medium (DMEM), mixing the mixture uniformly, cleaning, centrifuging at low speed, adding DMEM again, mixing uniformly, centrifuging at low speed for 2-4 times and adding bottom precipitate produced from the last-time low-speed centrifuging to Williams' MediumE complete medium suspension; adjusting the hepatocytes density to 1*105 / ml, inoculating the hepatocytes in a culture bottle laid with rat tropocollagen, carrying out constant culturing in a CO2 incubator at 37 DEG C, changing the suspension to remove died hepatocytes and non-adherent hepatocytes after the hepatocytes are adhered to the wall and continually culturing the hepatocytes.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Applications of andrographolide derivatives and 3,19 esterified compounds thereof in preparation of anti-hepatic fibrosis medicines
ActiveCN106946821ADefinitive anti-hepatic fibrosis activityInhibit migrationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCell-Extracellular MatrixHepatic stellate cell activation
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, discloses applications of andrographolide derivatives in preparation of medicines preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis, and relates to 15-benzylidene-14-deoxy-11,12-dehydroandrographolide derivatives and 3,19 esterified compounds thereof. Experiments prove that the compounds significantly inhibit human hepatic stellate cell LX-2 metastasis and activation, significantly reduce the fibrosis level of hepatic tissues of rats affected with hepatic fibrosis, reduce contents of extracellular matrix protein (ECM) related components, significantly reduce the level of immune inflammation correlation factors of rats affected with hepatic fibrosis, effectively inhibit immuno-inflammatory responses, inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation in hepatic tissues, and promote collagen degradation. The compounds are used as active components for preparing the anti-hepatic fibrosis medicines, and are efficient and low in toxicity, thus providing a novel medicine route for hepatic fibrosis treatment and prevention, and expanding the optional range of clinical medicine application. The compounds and the applications have good development prospects.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Method for minim hepatic tissue in vitro incubation and detecting CYP450 enzymatic activity
InactiveCN101308119AHigh simulationSave costsComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteCytochrome p450 enzyme
Disclosed is a method for detecting CYP450 enzymatic activity by means of micro-liver tissue incubation in vitro, which is characterized in that: a liver trace puncturing method used in clinic takes micro-liver tissues of 0.1 to 0.2g, or kills a mouse to take out the liver in an animal experiment, and builds a micro-liver tissue in vitro incubation system, then uses a one-probe medicine to perform the liquid phase chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for detecting probe substrates and concentration of corresponding metabolites, and obtains the activity of P450 enzyme according to metabolite ratios thereof. The method has the advantages of: 1. micro scale: only micro-liver tissues of 0.1 to 0.2g are needed for detecting cytochrome P450enzyme activity, and can be used for animal experiment and checking clinic micro-liver tissue liver drug enzyme activity; 2. time saving and convenience: costly ultracentrifugation equipment used in the conventional method is saved, costs and time for detection are greatly saved, and liver enzyme metabolic condition simulation is better; and 3. establishing indexes for evaluating the enzyme metabolic activity: metabolite ratios.
Owner:CENT HOSPITAL XUHUI DISTRICT SHANGHAI CITY
Method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) using molecular markers
InactiveUS20060135420A1Easy and reliable evaluationEase of evaluationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntioxidant proteinSelenium-Binding Proteins
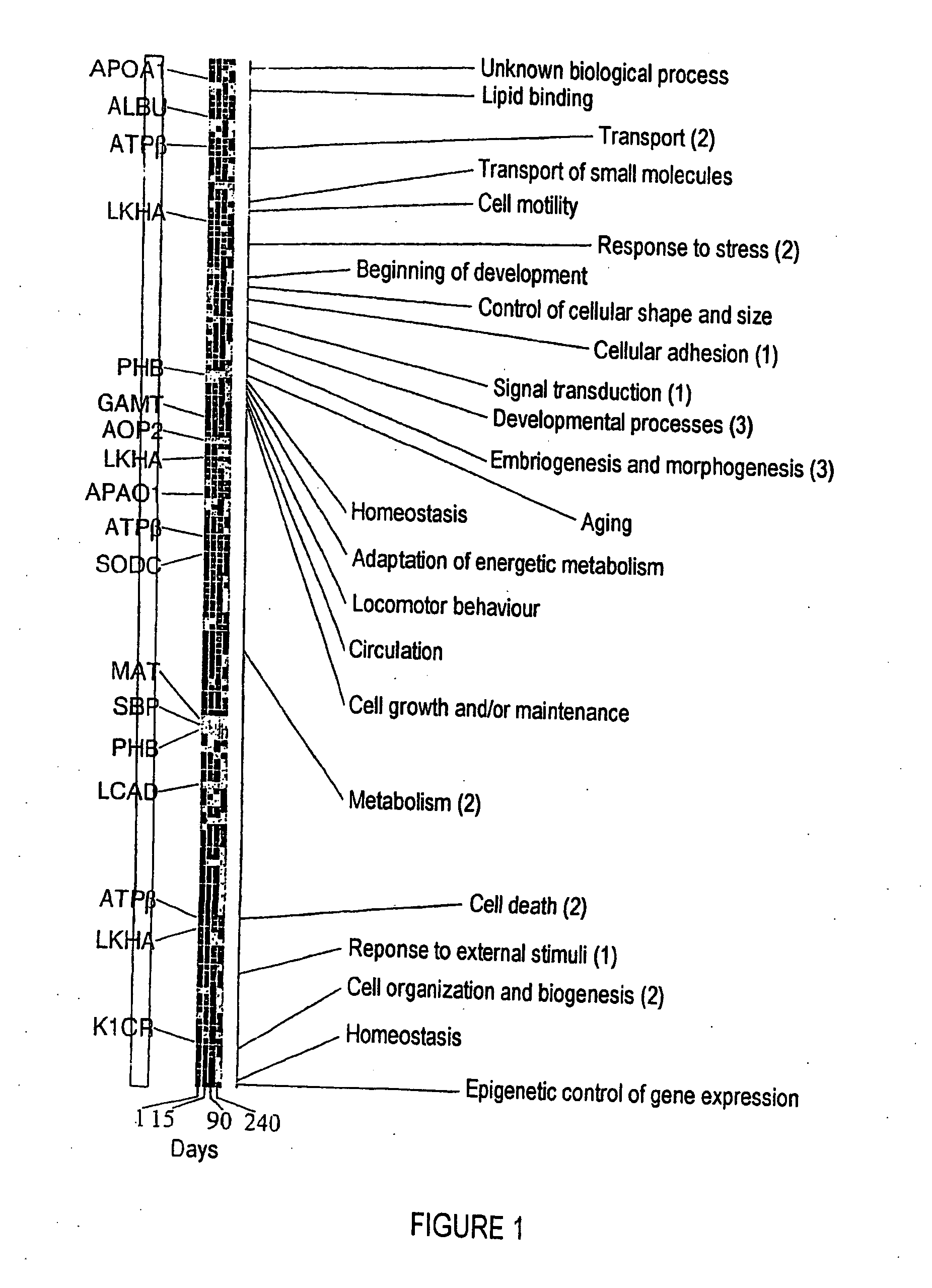
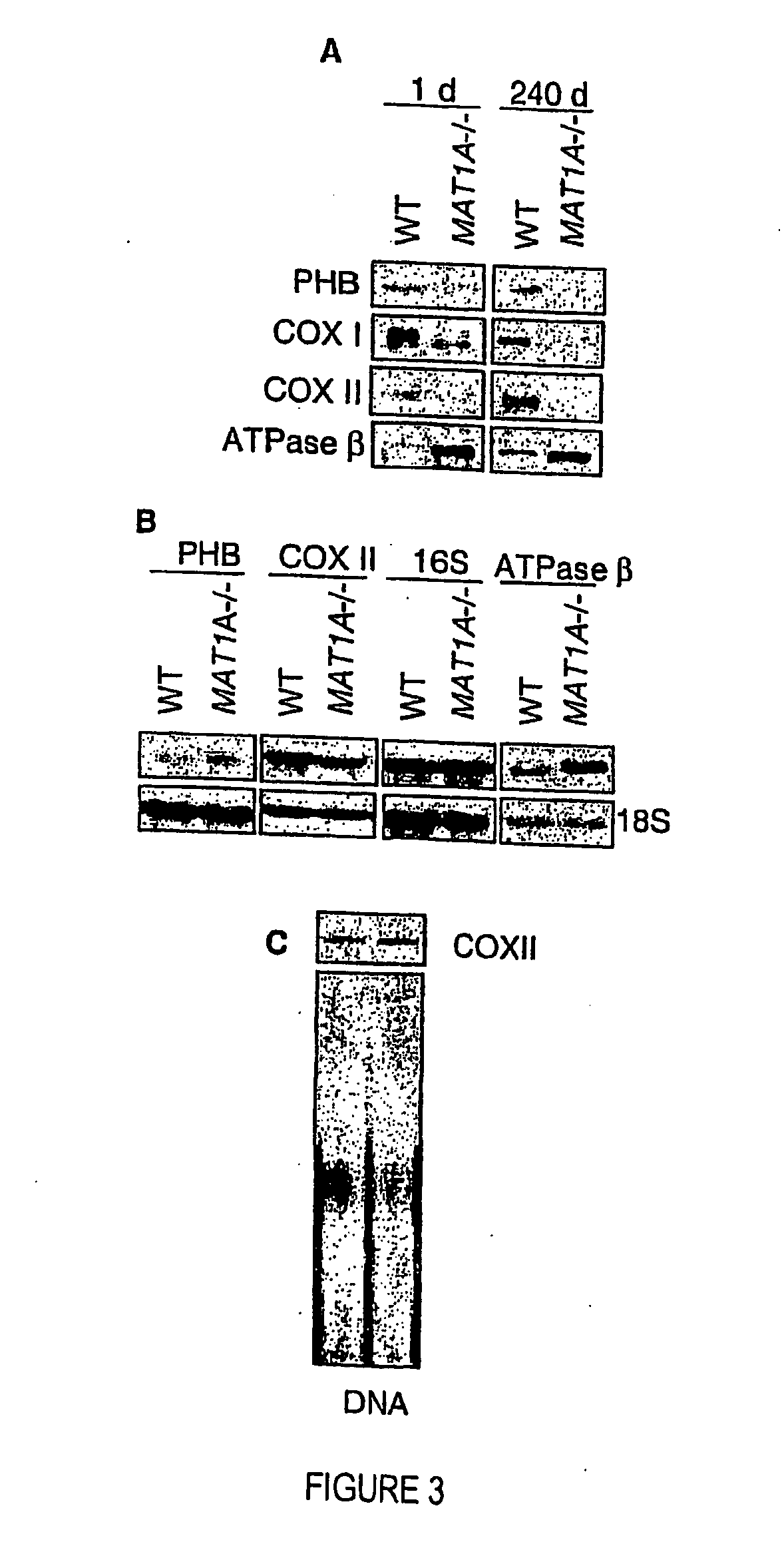
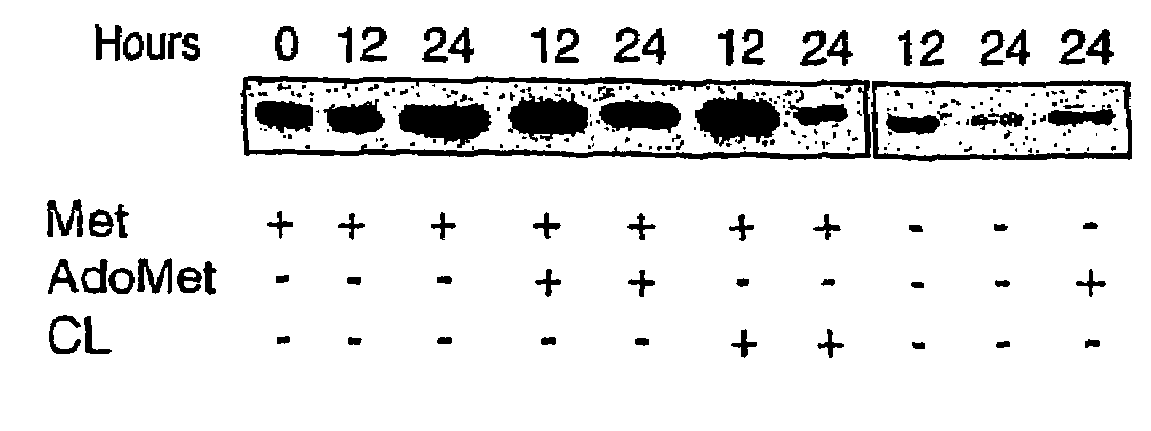
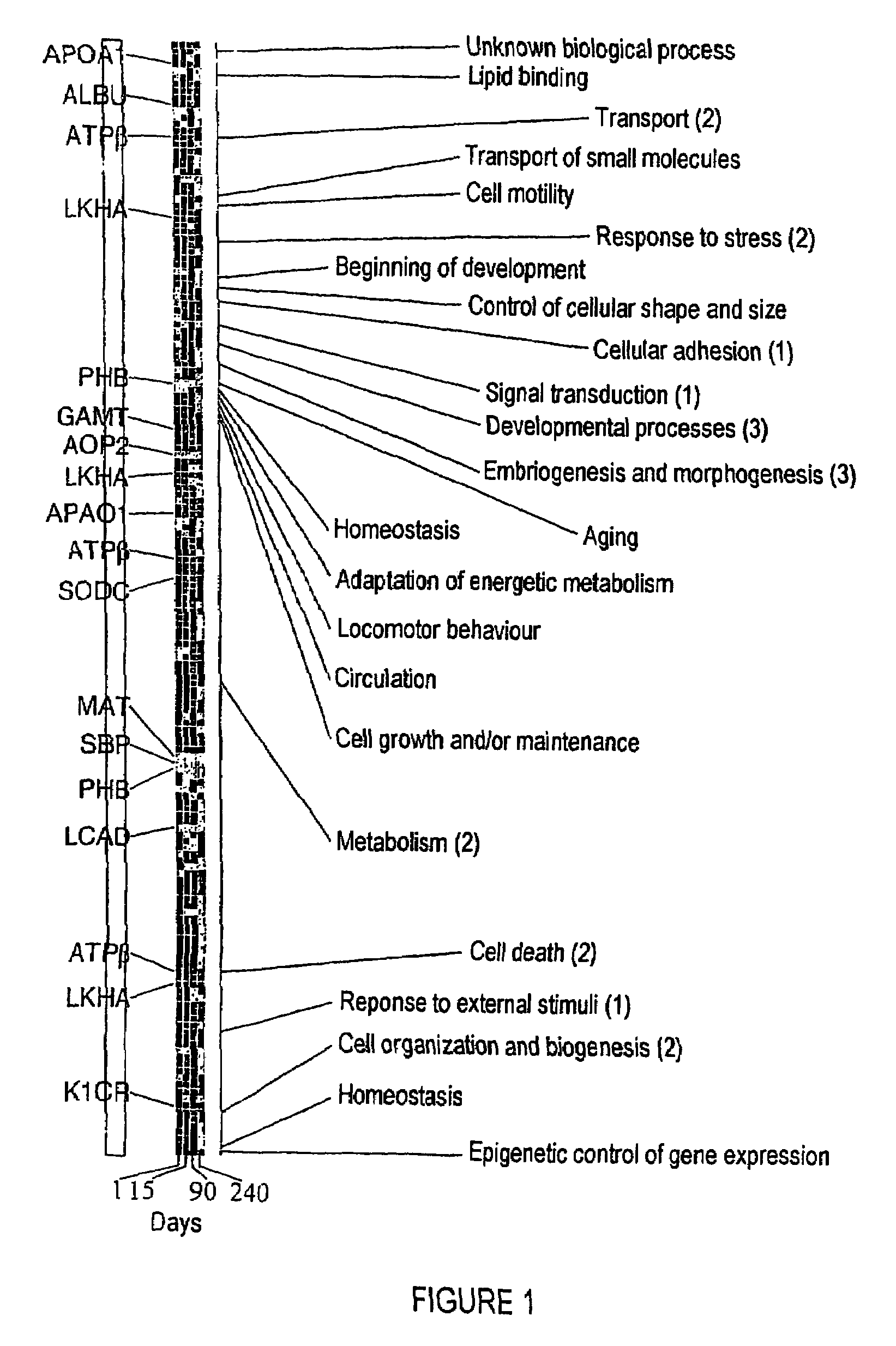
The invention relates to a method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) using molecular markers. The inventive method consists in detecting and quantifying, in vitro in a hepatic tissue sample, the levels of a protein which can be used as a NASH molecular marker and which is selected from apolipoprotein A1, sub-unit β of the mitochondrial ATPase, leukotriene A4 hydrolase, keratin 18, guanidine acetate N-methyltransferase, superoxide dismutase, albumin, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 1), prohibitin 1, methionine adenosyl transferase, long-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase, selenium binding protein, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 2), and combinations of same. The invention further consists in comparing the results obtained with the normal values of said proteins in healthy hepatic tissue. Said method can be used to diagnose NASH and / or to assess a patient's potential risk of developing NASH.
Owner:ONE WAY LIVER GENOMICS
A kind of spirulina active polysaccharide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102286109AGood anti-lipid peroxidation activityAvoid destructionOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsPretreatment methodAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to an active spirulina polysaccharide and a preparation method thereof. By introducing an activity evaluation index, discussing the influence of a raw material pretreatment method and different extraction processing technologies on spirulina polysaccharide yield, polysaccharide preservation rate, protein removal rate and polysaccharide lipid peroxidation resistance and evaluating and screening an extraction processing technology capable of well keeping the bioactivity of the spirulina polysaccharide and with relatively high spirulina polysaccharide yield, the active spirulina polysaccharide is prepared by preferable process conditions; the main active ingredients of the active spirulina polysaccharide are binding protein polysaccharides, the molecular weights of which are 100,000 and 95,000 respectively; the active spirulina polysaccharide has remarkable hepatic tissue lipid peroxidation activity resistance; and the two binding protein polysaccharides are qualitycontrol index ingredients of a spirulina lipid peroxidation activity resistant polysaccharide product. Compared with a method discussed in the conventional technology, the protection of the extraction, separation and purification processes on the activity of the spirulina polysaccharide is stressed; and by comprehensively evaluating and optimizing the preparation process conditions, blindness of the process discuss and destroy and loss of the active ingredients in the extraction and purification processes can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
3D hepatoma tissue construction method based on biological 3D printing hydrogel
InactiveCN107400661APromote formationBeneficial methodWeighing by removing componentAdditive manufacturing apparatusSwelling ratioTissue material
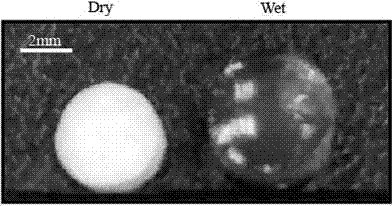
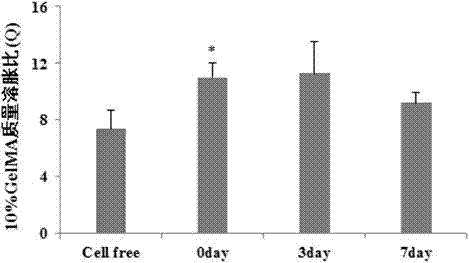
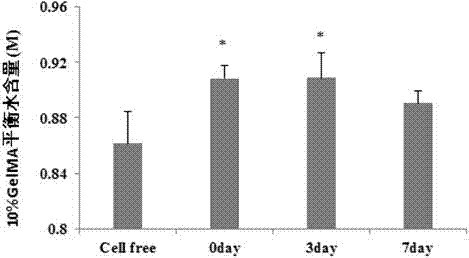
The invention discloses a 3D hepatoma tissue construction method based on biological 3D printing hydrogel. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) a GelMA biomaterial is synthesized, and the acylation rate and light polymerization time of the GelMA biomaterial are detected; 2) after GelMA and an photoinitiator are uniformly mixed and dissolved, human hepatoma cell HepG2 and GelMA solutions are uniformly mixed, the cell concentration is adjusted to 1*10<6> / mL, and biological printing ink is prepared. Biological printed cells and a hydrogel system are placed under an ultraviolet lamp for light polymerization for 5 min to be cured, the cured system is placed in a 10%FBS culture solution to be cultured for 7 d, and a hepatoma tissue engineered unit containing an HepG2 source is prepared and saved for later use; 3) the swelling ratio and balance water content of a 3D hepatoma tissue material are detected; 4) the growth states of 2D and 3D on the seventh day are detected with a BE histochemistry method. The method is reliable, convenient to operate and high in repeatability and can effectively promote formation of hepatoma tissue functions and provide beneficial reference for scientific research of hepatic tissue engineering and clinical treatment of hepatoma.
Owner:武汉枫霖科技有限公司
Animals comprising human hepatocellular tissue.
Non-human mammalian hosts are provided, comprising functional human hepatocytes. Isolated human hepatocytes or fragments of human hepatic tissue are introduced into the xenogeneic host in conjunction with one or more agent that stimulates human hepatocyte growth factor receptor. The human hepatocytes are maintained in the host by administration of one or more agent that stimulates human hepatocyte growth factor receptor, either continuously (e.g., via an implanted catheter or intravenous apparatus) or in discrete, regular dosages of the agent (e.g., via intravenous injections or oral dosages). The human hepatocytes are able to survive and function in the host animal for a period of at least 5 months.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method for separating, culturing and identifying primary hepatic cells of livestock and fowl
InactiveCN102643778AIncreased dispersionHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to a method for separating, culturing and identifying primary hepatic cells of livestock and fowl, which integrates a chelation process and an in-situ two-step perfusion process. Ca<2+> and Mg<2+> in hepatic tissues of livestock and fowl are previously removed so that the hepatic tissues maximally release the primary hepatic cells; and the formula of additives of the culture fluid is adjusted to perfect the serum-free culture system and identify the glycogen of the obtained primary hepatic cells. The invention can effectively enhance the quantity, motility and purity of the separated primary hepatic cells of livestock and fowl, and is applicable to various animals; and the obtained primary hepatic cells have the advantages of fewer traumas, high wall attaching tendency and high activity, can be widely used for physiological function adjustment, metabolic diseases, and pharmacological and toxicological mechanisms of hepatic cells of livestock and fowl, can establish a virus infected cell model, and can be used for research in the fields of physics and chemistry, toxicant factor influence and the like.
Owner:SHAOGUAN COLLEGE
Use of pepper amide compound in preparation of drug or healthcare product for reducing blood fat
InactiveCN1634029AReduce cholesterolLower triglyceridesOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseTG - Triglyceride
The invention relates to the use of pepper amide compound in preparation of drug or healthcare product for reducing blood fat with the general formula (I), wherein R, R1, R2 are defined in the specification, the piperamide compounds represented by formula (1) have the actions of substantially reducing cholesterin, triglyceride and increasing high density lipoprotein, fully activating lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase, forwarding extra-hepatic tissue cholesterol to liver, cleaning out plasma lipoproteins, plasma cholesterol and cholesterol esters, thus can be applied to the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as atherosclerotic, cerebrovascular, coronary artery and peribiliary vessel pathology and hyperlipemia.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Method for separating primary adult hepatocytes, and special sterile apparatus box thereof
InactiveCN102220278AGuaranteed sterilityFor long-term storageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSerum freeType IV collagen
The invention discloses a method for separating primary adult hepatocytes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out multi-point puncture on surface of isolated adult hepatic tissue through a needle syringe, and injecting a preperfusate, wherein connective tissues are removed from the isolated adult hepatic tissue; (2) carrying out the multi-point puncture on the surface of the isolated adult hepatic tissue through the needle syringe again, and injecting a IV collagenase solution; (3) separating the isolated adult hepatic tissue, followed by adding the IV collagenase solution and carrying out digesting through vibration at a temperature of 37 DEG C to obtain digest; (4) carrying out filtering for the digest, followed by centrifuging and collecting cell aggregate in the underlayer, then resuspending the adult hepatocyte aggregate through a hepatocyte wash buffer, followed by filtering and centrifuging, then abandoning supernatant and collecting the adult hepatocyte aggregate in the underlayer; (5) washing the adult hepatocyte aggregate in the underlayer from the step (4) through a serum-free DMEM medium to obtain the primary adult hepatocytes. The invention further discloses a disposable special sterile apparatus box for separating the primary adult hepatocytes. With the present invention, the disposable special sterile apparatus box is adopted, the primary adult hepatocytes are separated through the multi-point puncture on the surface of the tissue and the injection, such that operation is simplified, cost is reduced, and the method and the apparatus box are applicable for extracting the hepatocytes from small pieces of the irregular isolated adult hepatic tissues of recovery of liver resection.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation technology of promoting hepatocyte growth factor solution
InactiveCN101225101AReduce outputLower unit costPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemFreeze thawingNeutral protease
The invention discloses a preparation technique for promoting hepatocyte growth factor solution, which comprises a hepatic-cleaning step, a hepatic tissue smashing step, an active component extracting step, a heating and denaturing step, a solid-liquid separation and pH value regulating step. The preparation technique is characterized in that: the active components extracting is a chemical extraction method of enzymatic hydrolysis or acid hydrolysis; enzyme for the enzymatic hydrolysis extraction method is about papain or tryptic enzyme or stomach enzyme or neutral protease; acid of the acid hydrolysis extraction method is about hydrochloric acid or phosphoric acid or acetic acid. The preparation technique for promoting hepatocyte growth factor solution has the advantages of overcoming the drawback of repeated freeze thaw method for prior art, simplifying the preparation operation for promoting hepatocyte growth factor solution, shortening production period, fully being in conformity with relative standard requirement upon national drug regulated by State Drug Administration for prepared promoting hepatocyte growth factor solution, having high preparation rate and low production cost.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUAJIN PHARMA
Health food with effect of relieving alcoholic liver injury
InactiveCN106135891AReduce MDA contentReduce contentDigestive systemTea substituesHas active ingredientMalonicdialdehyde
The invention provides a natural drug oral preparation for relieving or neutralizing effects of alcohol. The natural drug oral preparation comprises, by mass, 10-15% of curcumin, 15-25% of kudzu vine root extract flavonoids, 10-25% of Chinese magnoliavine fruit total lignins, 0.05-5% of VB6, 0.05-5% of VE, 0.05-5% of VC and the balance auxiliary materials. The natural drug oral preparation is processed to form common oral preparations such as particles, tablets and capsules. Curcumin, kudzu vine root total flavonoids and Chinese magnoliavine fruit total lignins are obtained through extraction and then macroporous resin separation purification. The natural drug oral preparation has active ingredient content of 30-80%. A product test proves that the natural drug oral preparation can obviously reduce malonaldehyde, triglyceride and glutathione content of mouse hepatic tissue, inhibit alcohol-caused small intestine permeability increasing, reduce a blood alcohol concentration and relieve discomfort after drinking and alcoholic liver injury.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
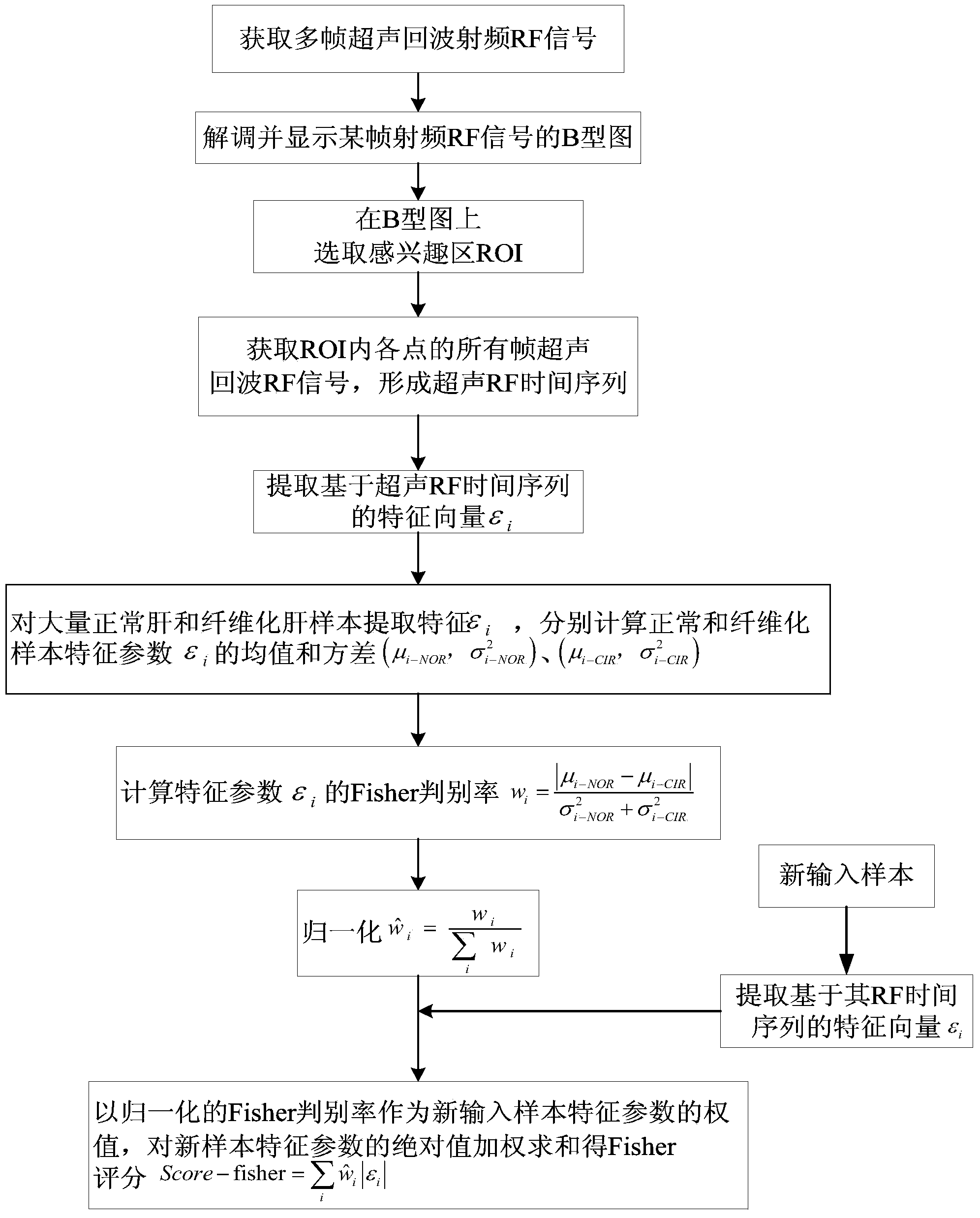
Hepatic fibrosis degree Fisher identification method based on ultrasonic radio frequency (RF) time sequence
InactiveCN103637821AImprove characterization accuracyNo extra costTomographySonificationDynamic monitoring
The invention belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic medicine and particularly relates to a hepatic fibrosis degree Fisher identification method based on an ultrasonic radio frequency (RF) time sequence. The method includes that first, a broadband ultrasonic linear array probe is used for scanning a living hepatic tissue, and multi-frame ultrasonic echo RF signals are recorded; a certain frame of B type pattern is demodulated and displayed, a region of interest (ROI) is selected, all frame RF signals of each point in the ROI are taken to form the ultrasonic RF time sequence; SMR fractal dimension mean values and a plurality of characteristic parameters of the RF time sequence in the ROI are extracted, the 7 features are extracted for a large amount of normal and fibrosis hepatic samples, Fisher distinguishing rate of each feature parameter is collected and obtained, the normalization Fisher distinguishing rate is used as the weight of a new input sample corresponding feature parameter, and the absolute value of each feature parameter of a new sample is weighted and summed to obtain Score-fisher. The hepatic fibrosis degree Fisher identification method based on the ultrasonic RF time sequence is brought up for the first time and provides quantification reference for clinical hepatic fibrosis diagnosis and dynamic monitoring.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Silybin nanostructured lipid carrier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101632638AImprove bioavailabilityExtend cycle timePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationLow temperature curing
The invention discloses a silybin nanostructured lipid carrier, comprising the following components: 0.05-0.5wt% of silybin, 0.1-5wt% of a solid lipid material, 0.02-2wt% of liquid lipid, 0.2-5wt% of liposoluble emulsifier, 0.2-5wt% of water-soluble emulsifier, and the balance of water. The preparation method is an improved microemulsion technology-emulsification and evaporation-low-temperature curing method. The silybin nanostructured lipid carrier prepared by the method has the advantages of a particle size of about 200nm, a slow release function in vivio, prolonged cycle time of medicines, passive targeting in a hepatic tissue, improved bioavailability of the silybin, good biocompatibility, easy degradation, high encapsulation rate, high drug-loading rate and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Combination of biomarkers for the detection and evaluation of hepatitis fibrosis
InactiveUS20130323720A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHepatic fibrosisOrganism
The application concerns means for determining the stage of hepatic tissue damage, in particular the hepatic fibrosis score of subjects infected with one or more hepatitis viruses. In particular, the means of the invention involve measuring the levels of expression of selected genes, said selected genes being:SPP1, andat least one gene from among A2M and VIM, andat least one gene from among IL8, CXCL10 and ENG, andoptionally, at least one gene from among the list of the following sixteen genes: IL6ST, p14ARF, MMP9, ANGPT2, CXCL11, MMP2, MMP7, S100A4, TIMP1, CHI3L1, COL1A1, CXCL1, CXCL6, IHH, IRF9 and MMP1.
Owner:BIO RAD EURO GMBH +4
Pluripotent adult stem cells
InactiveUS20100196923A1Artificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAdipogenesisTissues types
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Refined glossy privet fruit total glycosides capable of preventing and treating liver injury, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103301205AHigh content of active ingredientsImprove protectionDigestive systemFood preparationSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseChemical constituents
The invention discloses refined glossy privet fruit total glycosides capable of preventing and treating liver injury and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized in that the chemical compositions and pharmacological activity of the glossy privet fruit are researched and selected systematically; and the experiment results show that the selected refined glossy privet fruit total glycosides can obviously reduce serum ALT (Alanine Transaminase) and AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) activities of a CCl4-induced liver injury model mice and the MDA (Methyl Di Aldehyde) content in the hepatic tissue of an alcohol-induced liver injury model mice and improve the GSH (Glutathione) activity of the liver, and also show that the refined glossy privet fruit total glycosides provided by the invention not only can obviously protect the liver from chemical liver injury and long-term drinking induced liver injury and can be developed into novel medicines or health products for preventing liver injury.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Use of piperic acid ester compound in preparation of drug or healthcare product for reducing blood fat
InactiveCN1634030AReduce cholesterolLower triglyceridesOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseTG - Triglyceride
The invention relates to the use of piperic acid ester compound in preparation of drug or healthcare product for reducing blood fat, wherein R1, R2, R3 are defined in the description, the piperic acid ester compounds represented by formula (1) have the actions of substantially reducing cholesterin, triglyceride and increasing high density lipoprotein, fully activating lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase, forwarding extra-hepatic tissue cholesterol to liver, cleaning out plasma lipoproteins, plasma cholesterol and cholesterol esters, thus can be applied to the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, cerebrovascular, coronary artery and peribiliary vessel pathology and hyperlipemia.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) using molecular markers
InactiveUS7314720B2Ease of evaluationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntioxidant proteinMitochondrial ATPase
The invention relates to a method of diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) using molecular markers. The inventive method consists in detecting and quantifying, in vitro in a hepatic tissue sample, the levels of a protein which can be used as a NASH molecular marker and which is selected from apolipoprotein A1, sub-unit β of the mitochondrial ATPase, leukotriene A4 hydrolase, keratin 18, guanidine acetate N-methyltransferase, superoxide dismutase, albumin, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 1), prohibitin 1, methionine adenosyl transferase, long-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase, selenium binding protein, antioxidant protein 2 (isoform 2), and combinations of same. The invention further consists in comparing the results obtained with the normal values of said proteins in healthy hepatic tissue. Said method can be used to diagnose NASH and / or to assess a patient's potential risk of developing NASH.
Owner:ONE WAY LIVER GENOMICS
Preparation method for novel non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model
ActiveCN103462948AReasonable routingEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsStainingLipid profiling
The invention discloses a preparation method for a novel non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, randomly dividing fed mice into two groups, with one group being a model group and the other group being control mice, recording states everyday and taking urine, hepatic tissue and blood for lipid analysis; b, processing experimental subjects; c, building a model; d, collecting hepatic tissue and blood; e, preparing conventional frozen sections from hepatic tissue specimens of the mice, taking materials, wrapping the frozen sections with common glue and then successively carrying out dyeing and sealing; f, carrying out conventional pathological examination on model mice; g, carrying out conventional pathological examination on control mice; and h, comparing results of dynamic analysis of hepatic tissue fat obtained in step f and step g. The novel non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model established in the invention has the advantages of reasonable route, easy operation and strong pertinency and is an effective tool for further research on the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
Method for separating, freezing and resuscitating human fetal hepatocytes susceptible to hepatitis B virus and application of method
InactiveCN103740637AObvious morphological featuresIncrease proliferative activityMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationHepatitis B immunizationPetri dish
The invention discloses a method for separating, freezing and resuscitating human fetal hepatocytes susceptible to hepatitis B virus and an application of the method. The method comprises the following steps of thoroughly rinsing fresh hepatic tissues by utilizing a filling solution through an exposed blood vessel until complete digestion; placing the fresh separated hepatic cells into a culture dish containing cell washing liquid, and filtering the cells by utilizing a cell sieve to obtain single cell suspended liquid; precipitating washed single cells, re-suspending the cells, and storing the precipitated single cells to liquid nitrogen by utilizing a gradual freezing method; and establishing compact cell single-layer culture by optimizing planking density of high-vitality fetal hepatic cells, purifying the low-vitality hepatic cells through a Percoll centrifugal medium, subsequentially culturing the cells so as to resuscitate the fetal hepatic cells. By adopting the method, a great amount of fetal hepatic cells can be separated, stored and high-efficiently resuscitated, and the resuscitated fetal hepatic cells can maintain good characteristics of the hepatic cells, good differentiation state and good susceptibility to the hepatitis B virus, so that the problem that the primary hepatic cells are in shortage can be solved, and a stable hepatitis B virus medicinal sieve platform can be established.
Owner:康珞生物科技(武汉)有限公司
Co-culturing method of human primary hepatocytes and liver nonparenchymal cells
ActiveCN103509751AAchieve in vitro expansionNo blocking operation requiredVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsSeparation technologySingle cell suspension
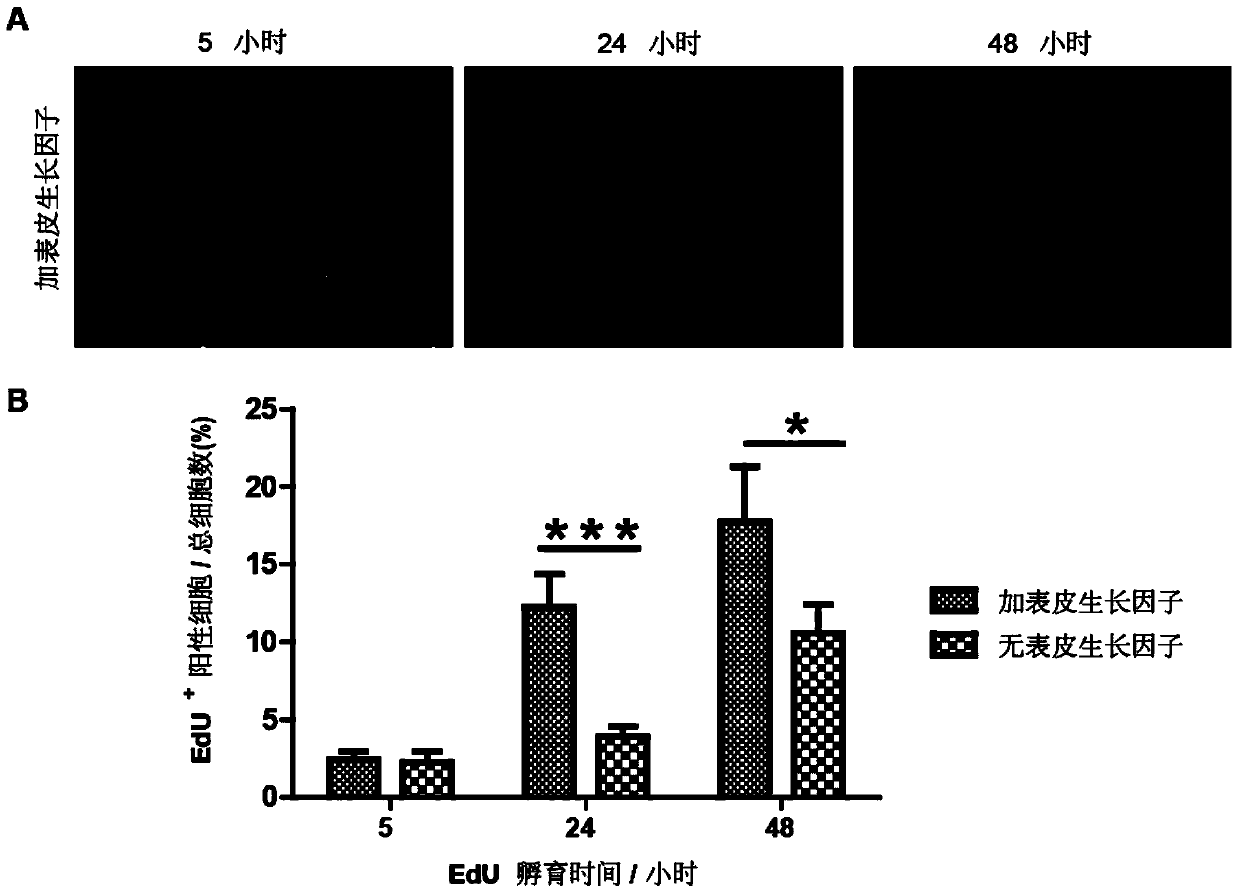
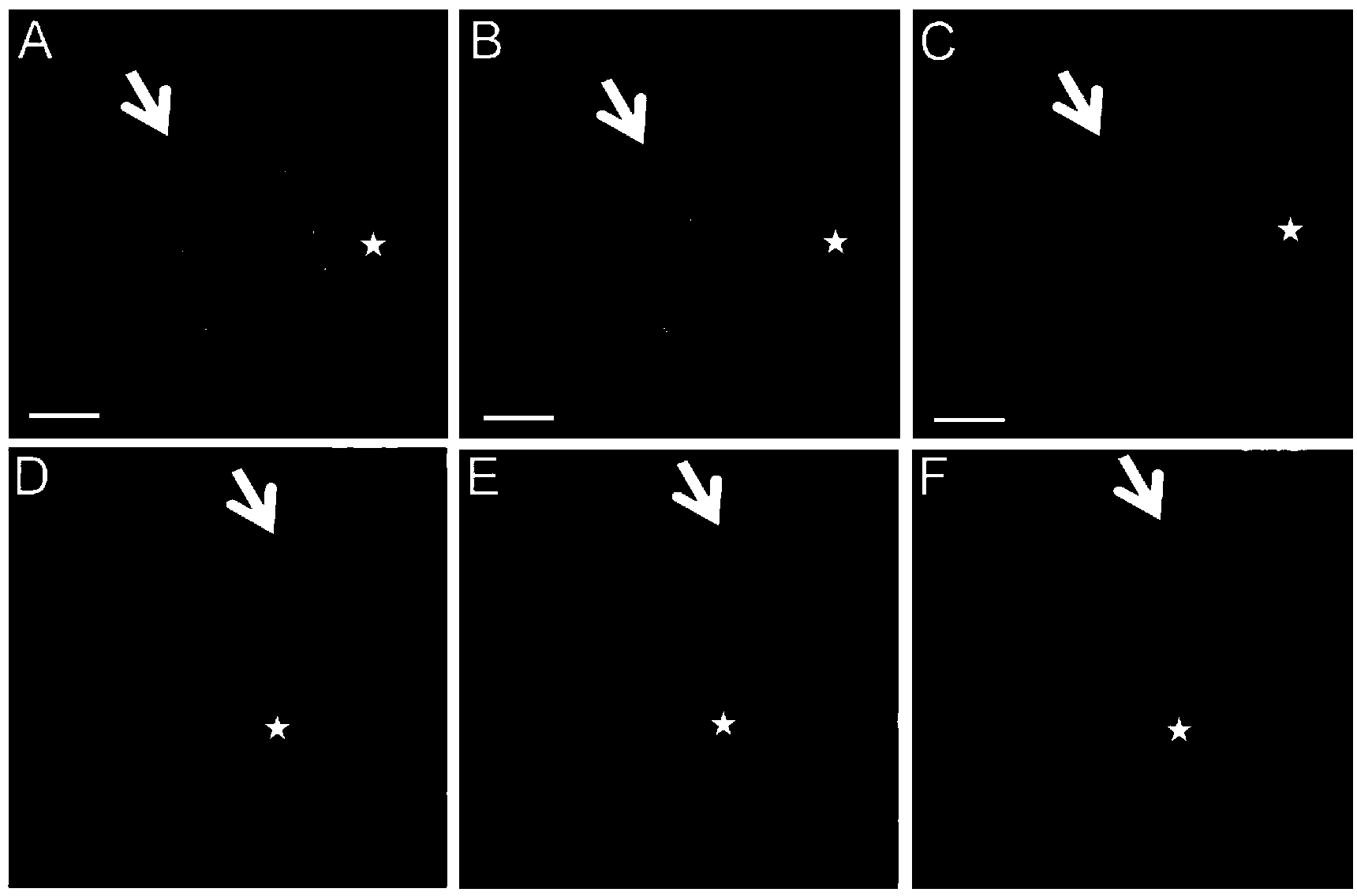
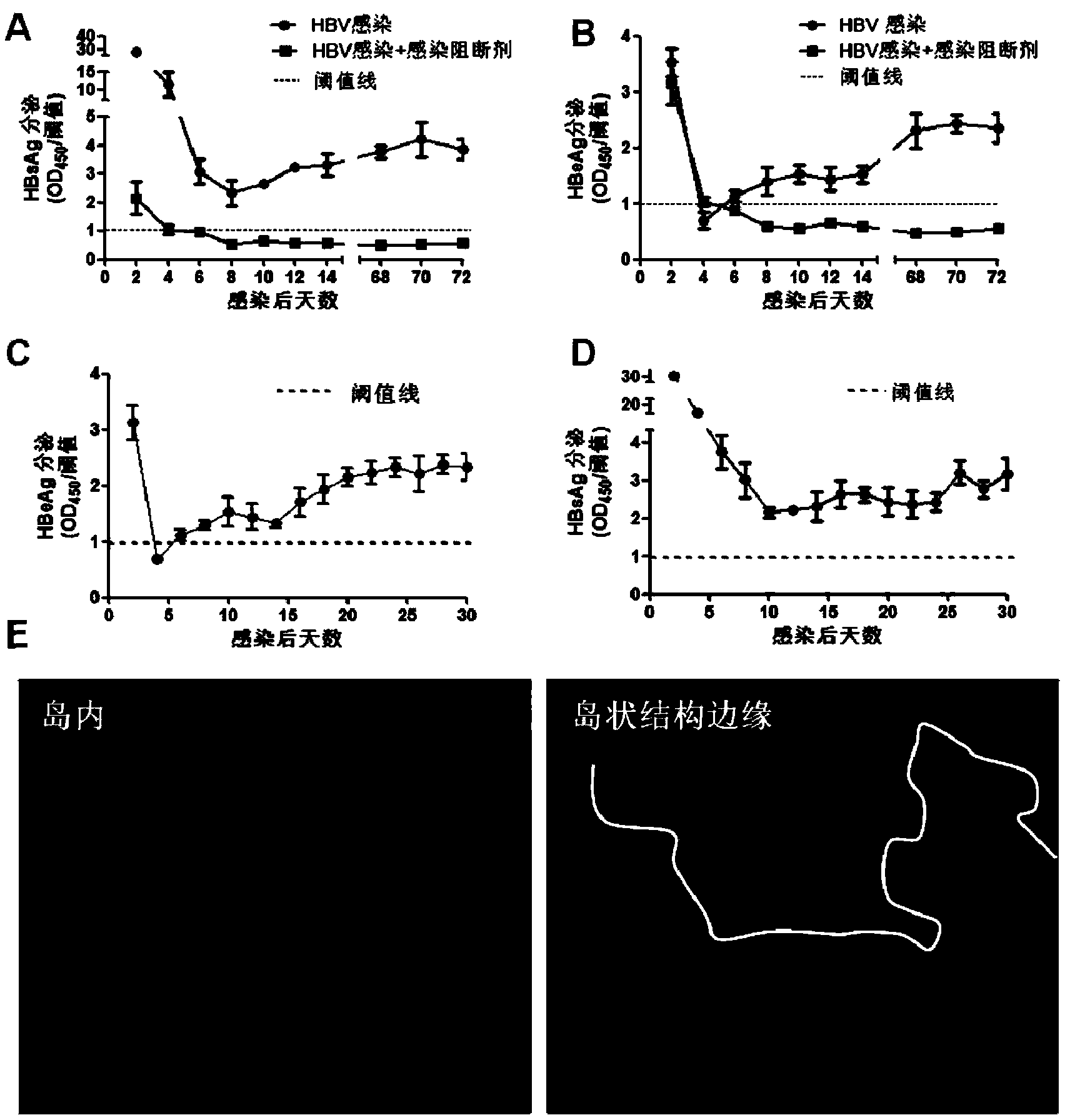
The invention discloses a co-culturing method of human primary hepatocytes and liver nonparenchymal cells. The co-culturing method comprises following steps: fresh hepatic tissue is washed thoroughly with exposed blood vessel perfusate I and perfusate II until elasticity of the hepatic tissue is lost, and complete digestion is realized; the hepatic tissue is delivered into a culture dish filled with a cell washing liquor, and is screened so as to obtain a single-cell suspension; a culture plate or a culture dish coated with collagen is inoculated with the single-cell suspension with a low inoculum density so as to obtain monolayer co-cultured cells with a fusion degree of 100% in the presence of growth factors; and a maintaining culture medium containing 2% DMSO is added into the culture plate or the culture dish for culturing, and then a liver island structure is formed by accumulation of hepatic cells, wherein the liver island structure is surrounded and invaded by liver nonparenchymal cells. Routine hepatocyte separation technology is employed in the co-culturing method, in vitro long-term culturing of hepatocytes as long as 120 days are realized, and HBV susceptibility is maintained for as long as 72 days. In addition, the co-culturing method can be used for screening and evaluating anti-HBV medicines, and possesses significant importance on researches of antiviral medicines.
Owner:康珞生物科技(常州)有限公司
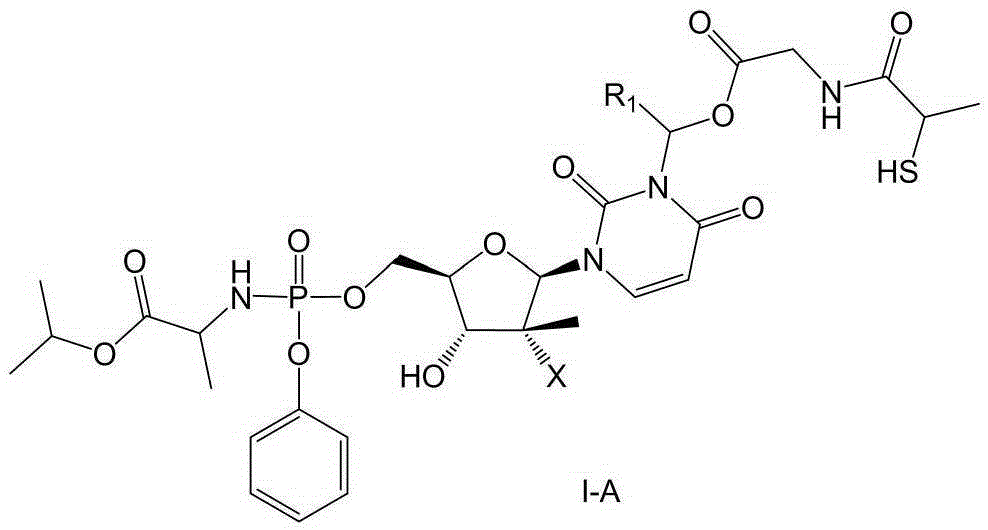
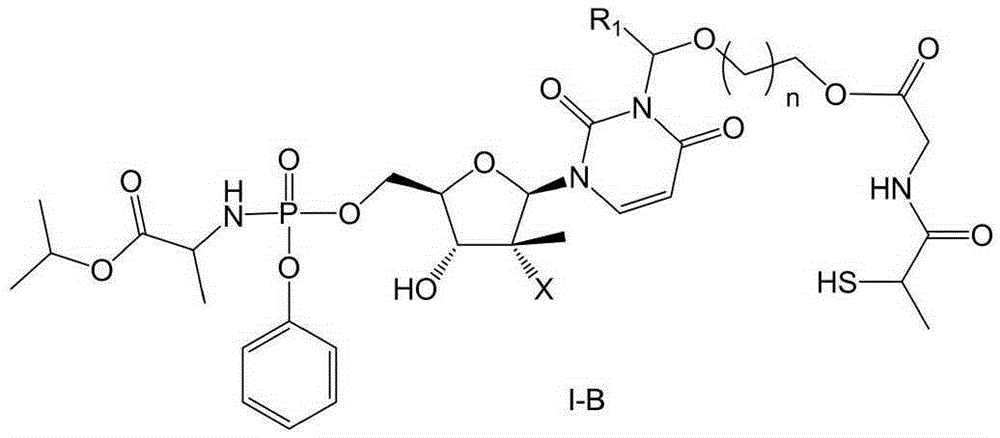
Prodrug containing tiopronin structure, preparation method of prodrug, pharmaceutical composition and application of pharmaceutical composition
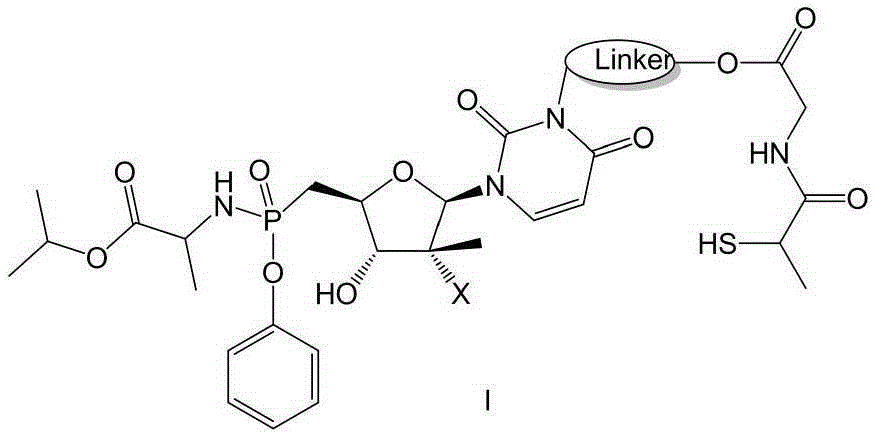
InactiveCN105348345AAvoid damageReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesStereoisomerismHepatic tissue
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry. Specifically, the invention relates to a prodrug containing a tiopronin structure showed by the following general formula I or a tautomer and a stereisomer of the prodrug, a stereisomer mixture or pharmaceutically acceptable solvate of the stereisomer mixture, a preparation method of the prodrug, a pharmaceutical composition, and application of the pharmaceutical composition serving as an anti-hepatitis c drug. This type of compounds or pharmaceutical compositions thereof can be used for curing hepatitis c, and also has the effects of protecting hepatic tissues and hepatic cells, and improving hepatic function.
Owner:HANGZHOU HERTZ PHARMA
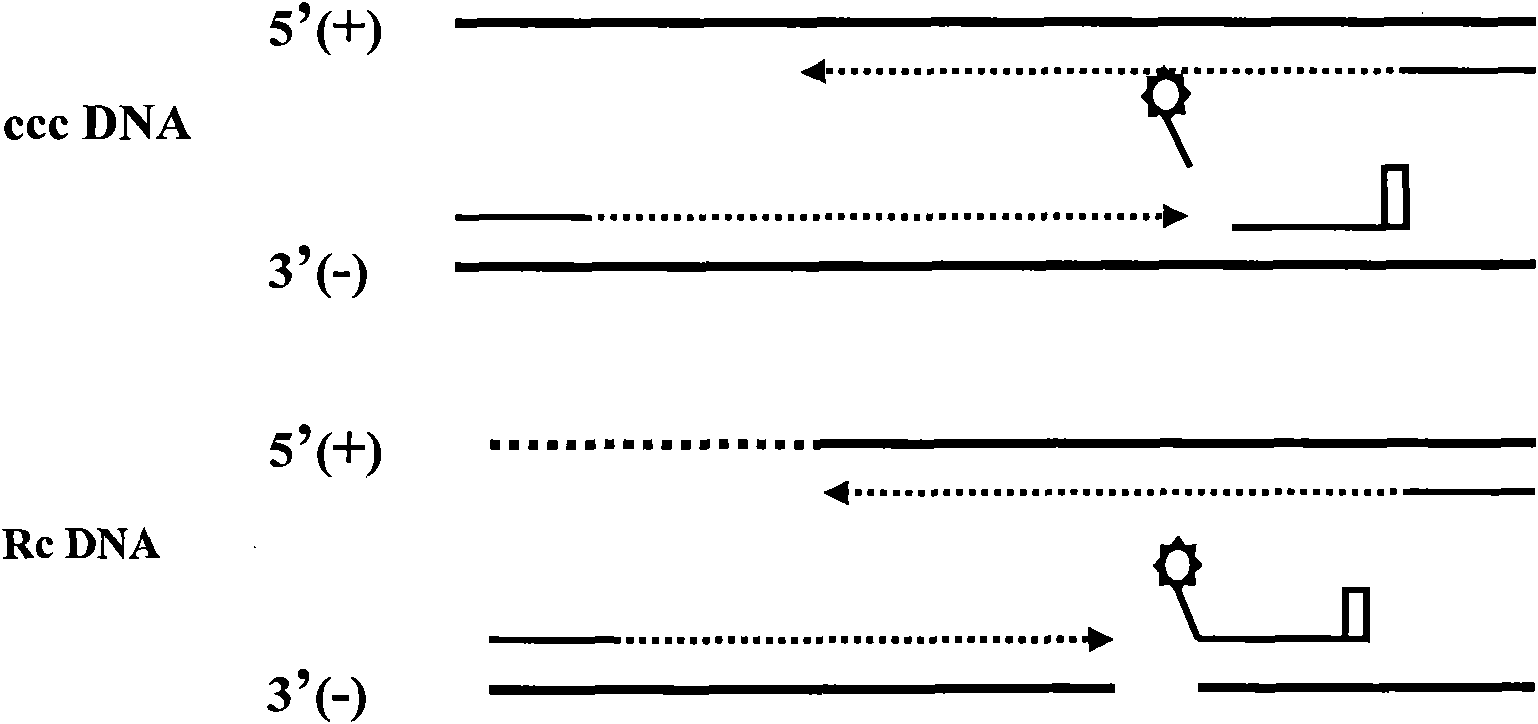
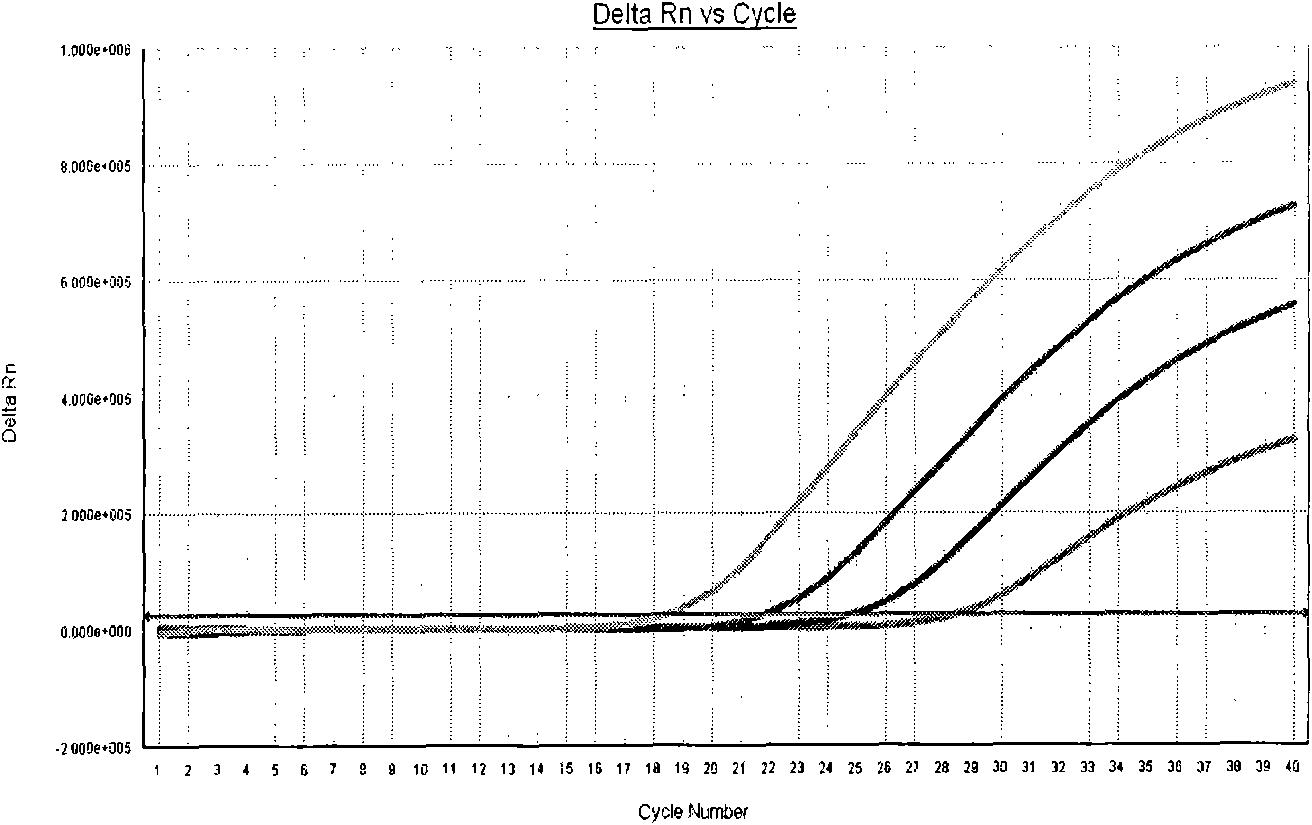
Method for performing two-color fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection on hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA, and application of kit
InactiveCN101967522AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesQuality controlHepatitis B virus
The invention provides a method for detecting hepatitis B virus covalently-closed circular DNA (HBV ccc DNA) from the samples of peripheral blood, hepatic tissues and the like by utilizing two-color fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, namely a PCR-two-color fluorescence probe method, and a kit therefor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting the samples; (2) extracting the DNA; (3) detecting the samples by a two-color fluorescence quantitative PCR in-vitro amplification method; and (4) analyzing the samples according to the fluorescence intensity of the amplification reaction of the corresponding samples after the amplification reaction is finished, thereby judging the existence of the HBV ccc DNA in the collected samples and accurately quantifying the HBV ccc DNA by using the standard curve of a positive quality control material to realize the real-time, fast and quantitative detection of the HBV ccc DNA.
Owner:BEIJING SUOAO BIOMEDTECH
Functional feed for preventing and treating white liver lesion of micropterus salmoides, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107410674AMeet basic nutritional needsEnhanced exchange refluxFood processingClimate change adaptationJuvenile fishFish oil
The invention relates to a functional feed, in particular to the functional feed for preventing and treating a white liver lesion of micropterus salmoides, and a preparation method thereof. The feed comprises, by weight percentage, 15-25% of fish meal, 20-35% of chicken powder, 16-22% of soybean meal, 8-15% of flour, 4-8% of squid extractum, 1-2% of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 1-2% of a multi-vitamin premix, 1-2% of a multi-mineral premix, 2-4% of fish oil, 1-2% of soybean oil, 1-2% of phosphatide oil, 2-7% of corn protein powder, 0.2-0.5% of pennisetum sinese herb extract, 0.1-0.5% of mulberry leaf fermentation liquid, and 0.1-0.3% of red rooted saliva root fermentation liquid. Compared with a common puffed feed for the micropterus salmoides, a feed formula provided by the invention can meet the basic nutrient demands of juvenile fishes, medium fishes and adult fishes of the micropterus salmoides, also can effectively enhance exchangeable backflow between artery blood and vein blood in hepatic tissue blood circulation, and has a good prevention effect and a repair treatment effect on the white liver lesion and hepatic tissue hypofunction caused by the white liver lesion.
Owner:清远海贝生物技术有限公司
Abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose and health-care product containing abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose and application of abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose
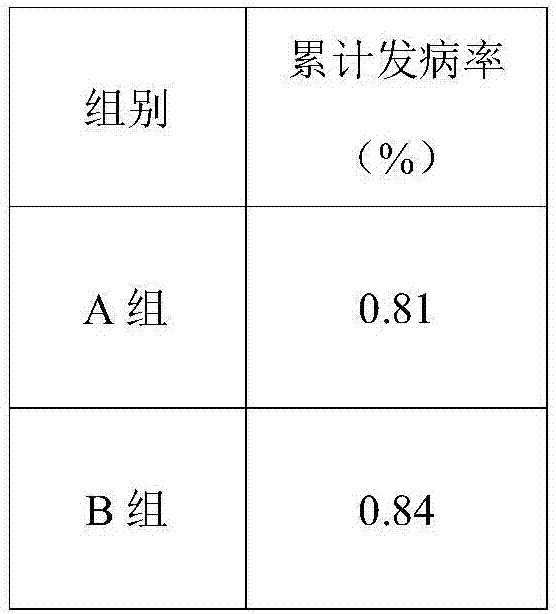
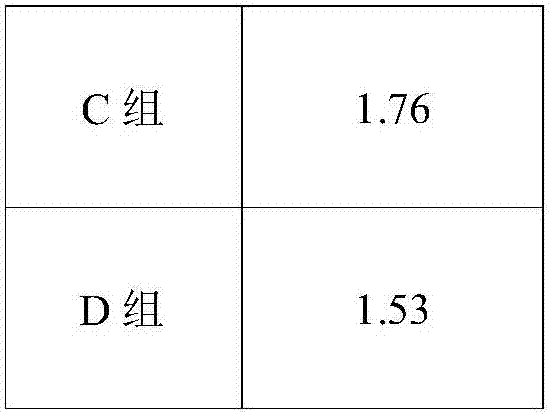
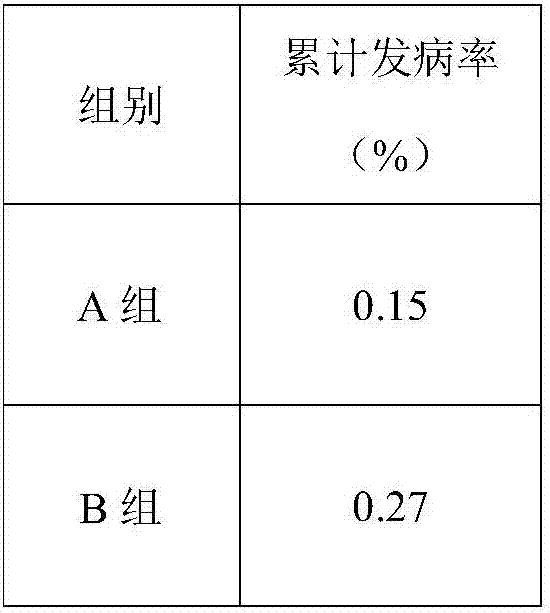
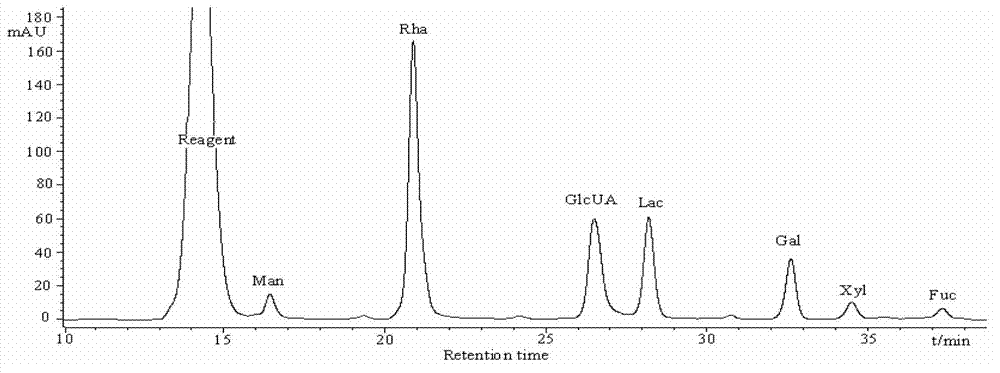
ActiveCN102898538APromote proliferationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemIn vivoHepatic tissue
The invention provides abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose. According to the abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose, a main chain comprises rhamnose and glucuronic acid, wherein a C-2 position or C-3 position of the rhamnose in the main chain is subjected to sulphating; and the rhamnose in the main chain is connected with the rhamnose or galactose to form a branched chain structure. The abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose which is extracted from abalone viscera can promote the proliferation of hepatoma carcinoma cells (HepG2) in vitro obviously, and has a certain effect of dose dependency; and experiments of studying a repair effect of the abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose on the HepG2 cells which are subjected to oxidative damage and on rat hepatic tissues which are subjected to acute hepatic damage caused by carbon tetrachloride in vivo indicate that the abalone viscera acidic polysaccharose can be used as a functional factor for protecting liver.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Soft capsule health food capable of protecting liver and preparation method of food
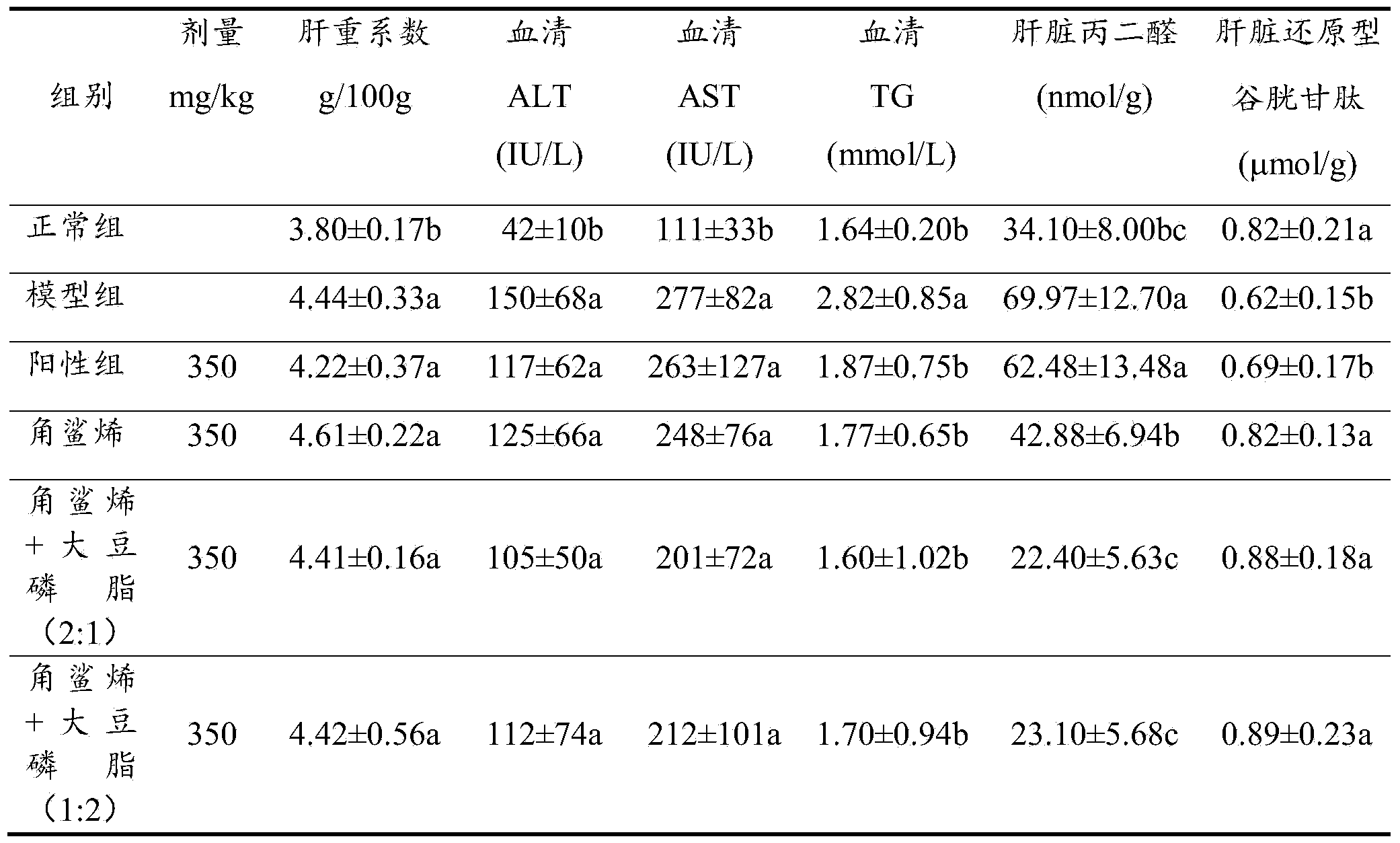
ActiveCN104068397AReduce MDA contentIncreased reduced glutathione contentHydrocarbon active ingredientsDigestive systemAlcoholPhospholipid
The invention provides a soft capsule health food capable of protecting the liver. The food is characterized by comprising squalene and soybean lecithin soft capsules and plant oil. The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the health food. According to the food, squalene is compounded with soybean lecithin, so that the content of rat serum triglyceride and malondialdehydle of an alcohol model can be remarkably reduced and the content of reduced glutathione in hepatic tissues is increased, which fully shows that a squalene and soybean lecithin compound has a remarkable protection effect on alcohol-induced liver damage; therefore, the protection effect on chemical liver damage can be improved. Compared with single soyabean lecithin, the squalene and soybean lecithin compound has a better protection effect on chemical liver damage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HAILISHENG BIOTECH +2
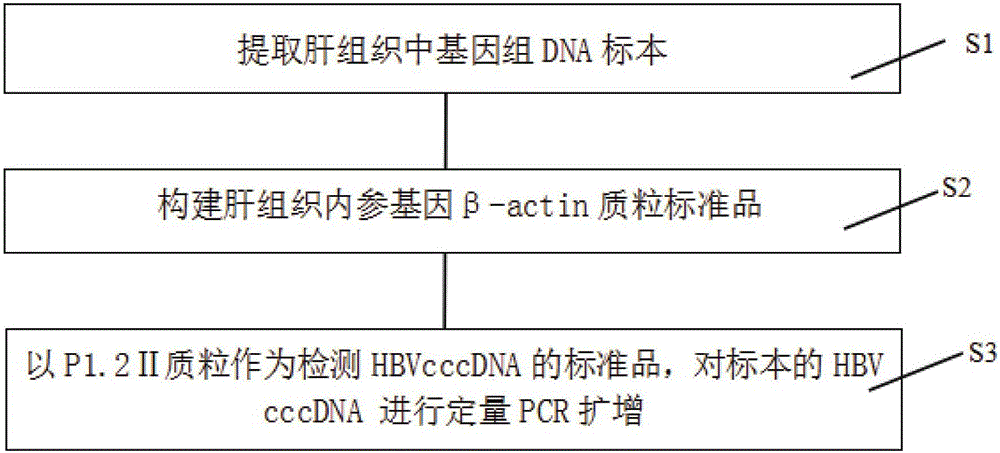
Quantitative PCR detection method for hepatic tissue HBVcccDNA
InactiveCN105755151AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a quantitative PCR detection method for hepatic tissue HBVcccDNA. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a genome DNA specimen in hepatic tissues; establishing a beta-actin plasmid standard; taking total RNA of adult peripheral blood cells as a template, performing inverse transcription to synthesize cDNA; performing PCR amplification on corresponding cDNA target fragments of human beta-actin genes by taking the cDNA as a template, establishing to form recombinant plasmid by taking pMD18-T as a carrier, performing electrophoresis and sequencing identification, and making a beta-actin standard curve by using fluorescent quantitative PCR. According to the method disclosed by the invention, HBVcccDNA and beta-actin in the hepatic tissues can be subjected to sensitive and specific amplification, quantification of the HBVcccDNA in hepatic cells is realized, and the method can be used for detection and application of HBVcccDNA in the clinical hepatic tissue and hepatic cells.
Owner:陈延平
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com