Preparation method for novel non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model
A non-alcoholic and fatty liver disease technology, applied in the field of human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) model preparation, can solve the problems of large developmental differences, difficult to control, high sugar, etc., to achieve strong pertinence, promote occurrence, and reasonable route Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
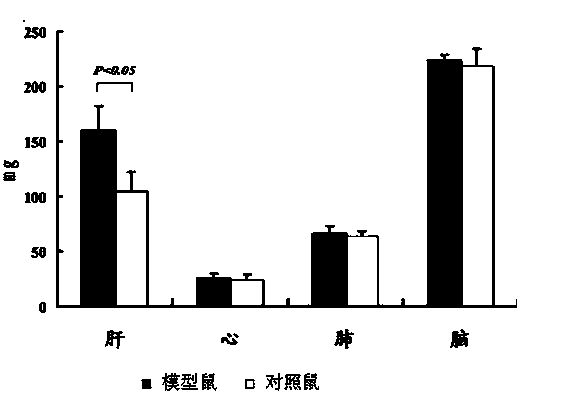
[0050] The livers of the model mice and control mice were compared after 2 weeks, and the size and shape of the livers were as follows: Figure 5 Shown: Fatty liver animal model sees massive hepatic fat accumulation ( Figure 5 A). There was no change in the rat liver of the control group ( Figure 5 B). Visually, there was a clear difference in liver size.
Embodiment 2
[0052] After the two groups of mice were treated, 5ml of blood was collected from the hearts of the mice, and the serum was separated in time and stored at -20°C; the liver was removed from the mice, and the liver tissue was divided into 1. 5 cm × 1. 5 cm × 0. 3 cm , respectively placed in AAF mixed fixative solution (ethanol, acetic acid, neutral formaldehyde, V / V / V, refer to the method introduced by Xu Ping (Journal of Henan Medical University, 1999, 34 (4): 75) for fixation.
[0053] The liver tissues of the two groups of mice were routinely frozen into sections using a Leica-CM1900 cryostat and Feather disposable blades. The samples were collected, embedded in ordinary glue (frozen), sectioned, and sealed after staining.
[0054] Routine pathological examination (H&E staining) was performed on the mice of the two groups; the liver tissue of the mice was stained with oil red O method for fat accumulation, and the fat accumulation in the liver tissue was dynamically analyzed....
Embodiment 3
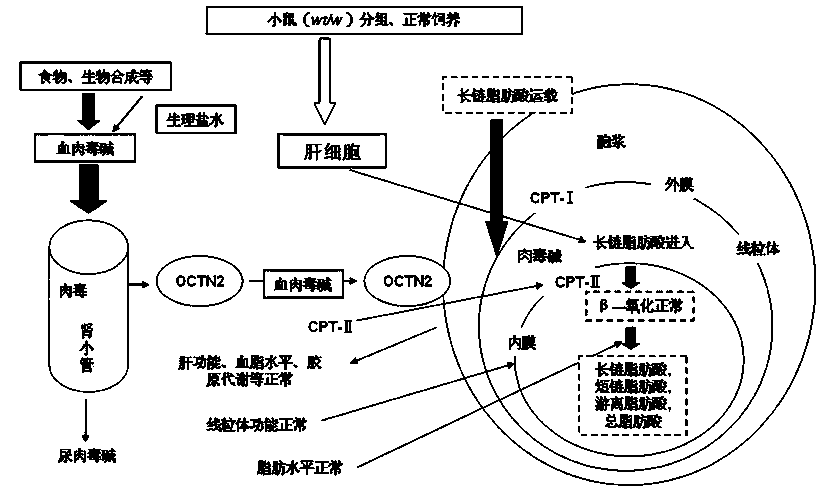
[0066] Dynamic analysis of liver tissue fat. The liver tissue of the two groups of rats after staining was dynamically analyzed, and the obtained dynamic analysis of liver tissue fat was compared, and it was obtained that during the establishment of the dynamic change model of fatty acids and total fatty acids, fat accumulation in liver tissue, long-chain fatty acids, short-chain fatty acids and Total fatty acid level (attached table); changes in peripheral blood, long-chain fatty acid, short-chain fatty acid and total fatty acid levels. For example, the changes of fatty acid concentration in mouse liver tissue are as follows:
[0067] The change of fatty acid concentration in rat liver in the attached table for two weeks (n=5, nMol / gram wet weight liver tissue)
[0068] group total fatty acids free fatty acid short chain fatty acids long chain fatty acids model mouse 392.16±53.08* 252.28±28.21* 61.56±23.28* 78.32±9.51* Control mice 323.78±5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com