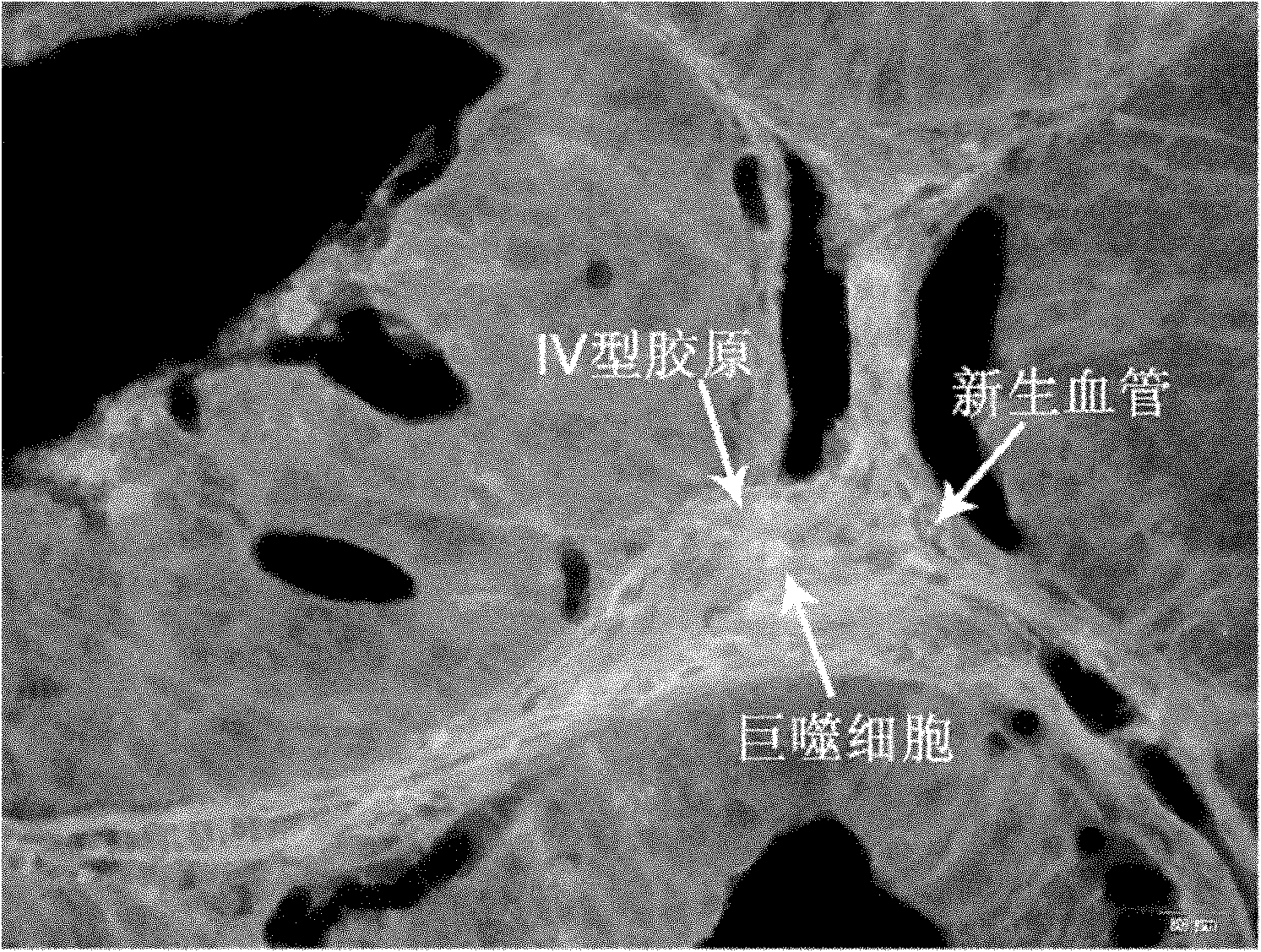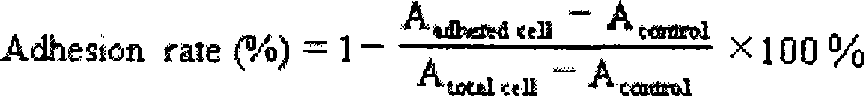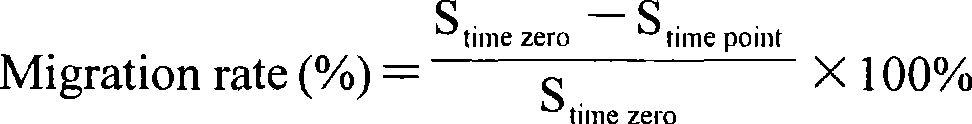Patents
Literature
123 results about "Type IV collagen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Collagen IV (ColIV or Col4) is a type of collagen found primarily in the basal lamina. The collagen IV C4 domain at the C-terminus is not removed in post-translational processing, and the fibers link head-to-head, rather than in parallel. Also, collagen IV lacks the regular glycine in every third residue necessary for the tight, collagen helix. This makes the overall arrangement more sloppy with kinks. These two features cause the collagen to form in a sheet, the form of the basal lamina. Collagen IV is the more common usage, as opposed to the older terminology of "type-IV collagen". Collagen IV exists in all metazoan phyla.
Drug Carrier and Drug Carrier Kit for Inhibiting Fibrosis
ActiveUS20080193512A1Minimize side effectsPreventing and suppressing and improving fibrosisBiocidePowder deliveryDiseaseSide effect
An astrocyte-specific drug carrier containing a retinoid derivative and / or a vitamin A analog as a constituent; a drug delivery method with the use of the same; a drug containing the same; and a therapeutic method with the use of the drug. By binding a drug carrier to a retinoid derivative such as vitamin A or a vitamin A analog or encapsulating the same in the drug carrier, a drug for therapeutic use can be delivered specifically to astrocytes. As a result, an astrocyte-related disease can be efficiently and effectively inhibited or prevented while minimizing side effects. As the drug inhibiting the activity or growth of astrocytes, for example, a siRNA against HSP47 which is a collagen-specific molecule chaperone may be encapsulated in the drug carrier. Thus, the secretion of type I to type IV collagens can be inhibited at the same time and, in its turn, fibrosis can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Nanofibrous biocomposite prosthetic vascular graft
The present invention provides a bioactive, small-diameter (typically less than 6 mm in internal diameter) vascular graft prosthesis, and is a textile conduit preferably manufactured using a novel electrospinning perfusion methodology. One preferred embodiment is a nanofibrous biocomposite textile conduit which comprises a prepared liquid admixture of polyester (Dacron), a biodurable implantable synthetic polymer, and Type IV collagen, an extracellular matrix protein. This prepared admixture and blending of diverse fibrous matter is utilized in a novel electrospinning perfusion process to form a small-diameter (less than 6 mm) fabricated textile conduit, a discrete article of manufacture, which then serves as an antecedent tangible workpiece for a subsequently-made prosthetic vascular graft construct.
Owner:BIOSURFACES +2
Drug carrier and drug carrier kit for inhibiting fibrosis
ActiveUS8173170B2Preventing and suppressing and improving fibrosisInhibited efficiently and effectivelyBiocidePowder deliveryDiseaseSide effect
An astrocyte-specific drug carrier containing a retinoid derivative and / or a vitamin A analog as a constituent; a drug delivery method with the use of the same; a drug containing the same; and a therapeutic method with the use of the drug. By binding a drug carrier to a retinoid derivative such as vitamin A or a vitamin A analog or encapsulating the same in the drug carrier, a drug for therapeutic use can be delivered specifically to astrocytes. As a result, an astrocyte-related disease can be efficiently and effectively inhibited or prevented while minimizing side effects. As the drug inhibiting the activity or growth of astrocytes, for example, a siRNA against HSP47 which is a collagen-specific molecule chaperone may be encapsulated in the drug carrier. Thus, the secretion of type I to type IV collagens can be inhibited at the same time and, in its turn, fibrosis can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Novel method for constructing tissue engineering skin
The invention provides a method for constructing tissue engineering skin. In the method, human epidermal stem cells and hypodermal fibroblasts are taken as seed cells, and a homologous acellular dermal matrix modified by a human placental type IV collagen is taken as a stent, so that active dual-layer engineering skin is compounded and constructed by using a gas-liquid interface separate culture method. The tissue engineering skin constructed by using the method is closer to the structure of natural skin; and as proved by histomorphology, the tissue engineering skin has an epidermal and hypodermal double-layer structure, wherein the hypodermal collagen stent has a complete structure, an epidermal layer is provided with a plurality of layers of cells of different differentiation degrees, and the morphological requirement of the tissue engineering skin is met.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Nanofibrous biocomposite prosthetic vascular graft
The present invention provides a bioactive, small-diameter (typically less than 6 mm in internal diameter) vascular graft prosthesis, and is a textile conduit preferably manufactured using a novel electrospinning perfusion methodology. One preferred embodiment is a nanofibrous biocomposite textile conduit which comprises a prepared liquid admixture of polyester (Dacron), a biodurable implantable synthetic polymer, and Type IV collagen, an extracellular matrix protein. This prepared admixture and blending of diverse fibrous matter is utilized in a novel electrospinning perfusion process to form a small-diameter (less than 6 mm) fabricated textile conduit, a discrete article of manufacture, which then serves as an antecedent tangible workpiece for a subsequently-made prosthetic vascular graft construct. In this manner, after the biocomposite textile conduit has been fabricated as a tangible article, one or more pre-chosen biologically-active compounds are then subsequently permanently bound (covalently or ionically) via a bifunctional linking agent to the wall surface(s) of the textile conduit. These permanently bound compounds retain their characteristic biological activity after becoming permanently immobilized to the textile wall surface; and, via such immobilization, provide the textile conduit wall with many of the highly desired attributes and properties characteristic of naturally occurring blood vessels. Accordingly, after the immobilization of one or more biologically active compounds to the wall surfaces, the completely prepared article is then suitable for use in-vivo as a prosthetic vascular graft construct.
Owner:BIOSURFACES +2
Type IV collagen high molecular form and production and diagnostic use thereof
InactiveUS6060255AClarify degreeRaise the ratioPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymologyType IV collagenPepsin digestion
A type IV collagen high molecular form having a higher molecular weight than the 7S domain of type IV collagen and including the 7S domain in its structure, is obtained from the supernatant being recovered from a collagen solution digested by pepsin in the following steps; 1) salt precipitating with sodium chloride at a concentration no higher than 1.2 M, 2) dissolving the precipitates, 3) salt precipitating with sodium chloride at a concentration no higher than previous concentration. By reacting a sample with an antibody which reacts with this form, the type IV collagen high molecular form in the sample can be measured to allow diagnosis of the degree of liver fibrosis in patients with liver diseases.
Owner:TOSOH CORP +1
Reconstruction method of tissue engineering human corneal epithelium
The invention relates to a reconstruction method of tissue engineering human corneal epithelium. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting a DMEM / F12 culture medium containing 20% calf serum to carry out the in vitro culture on human corneal epithelium cells to a logarithmic growth phase, and adopting trypsin and a trypsin-EDTA digestion method to obtain a digestive amniotic carrier bracket of which the epithelium is completely removed; and after the digestive amniotic carrier bracket of which the epithelium is removed is flatly laid in a plug-in Petri dish and is firmly and pasted in a drying way, inoculating the human corneal epithelium cells at the logarithmic growth phase suspended in the DMEM / F12 culture medium containing IV type collagen and 20% calf serum to the plug-inPetri dish flatly laid with the digestive amniotic carrier bracket of which the epithelium is removed, and carrying out the in vitro reconstruction on the tissue engineering human corneal epithelium by a gas-liquid interface culture method. The invention has scientific and reasonable process, the reconstructed tissue engineering human corneal epithelium can be used for mass production, a lot of demands of vast blind patients with corneal epithelium diseases for the tissue engineering human corneal epithelium in clinical corneal transplantation treatment can be met, and the costs of the in vitro reconstruction and clinical treatment of the tissue engineering human corneal epithelium are low.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
Lingzhiol A and application of lingzhiol A in drug production and foods
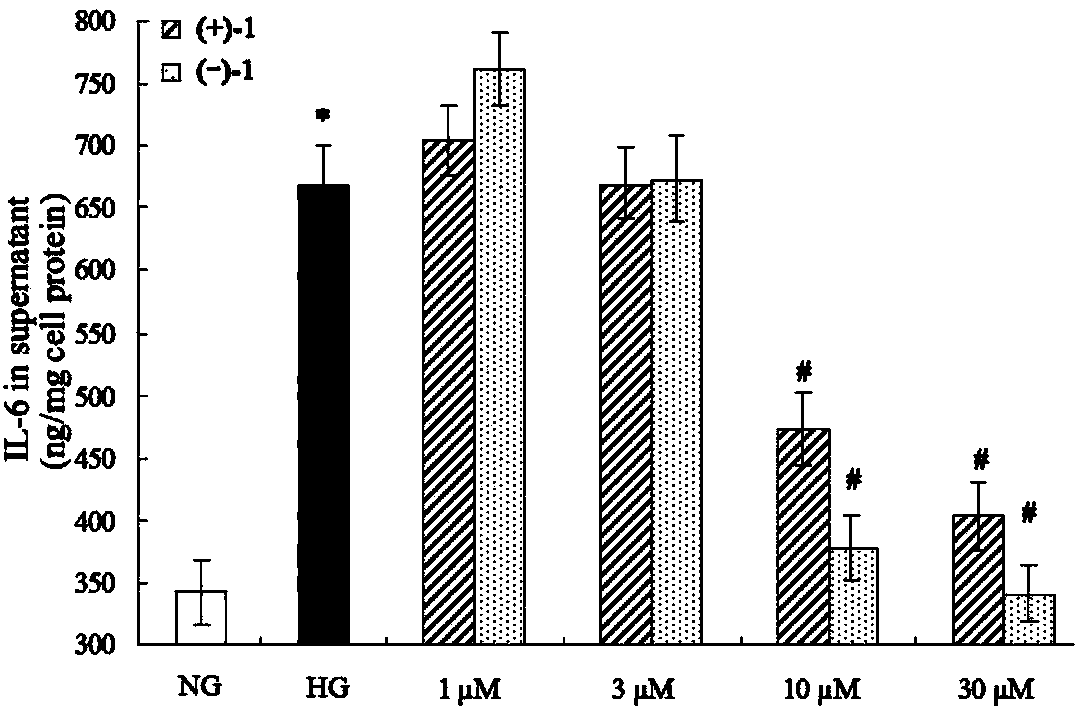
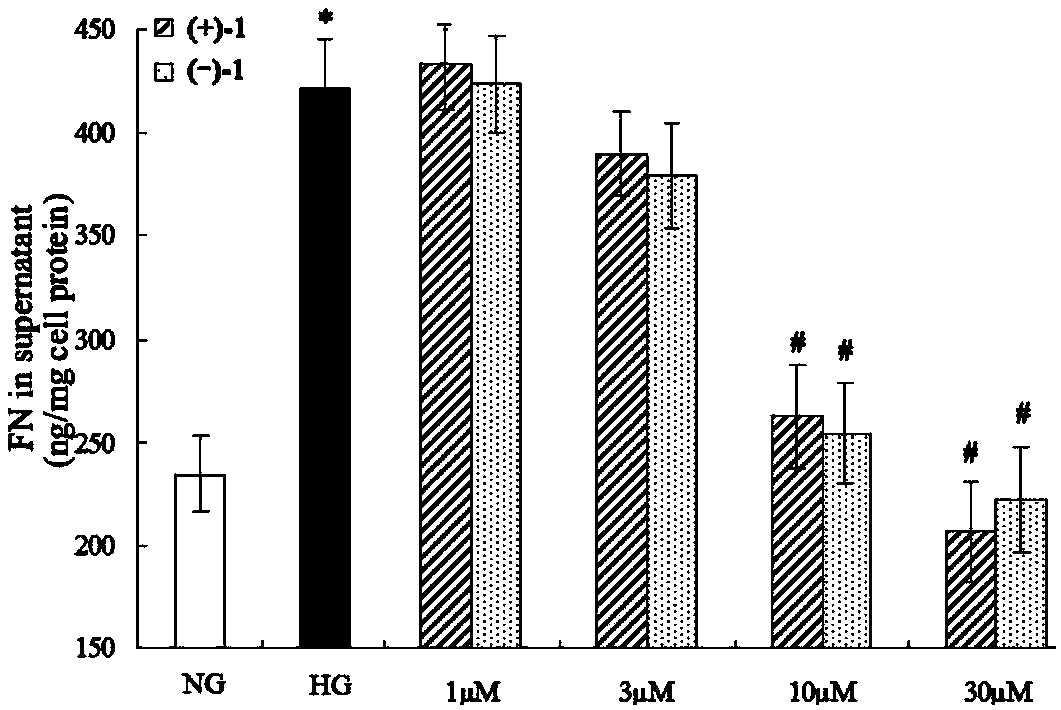
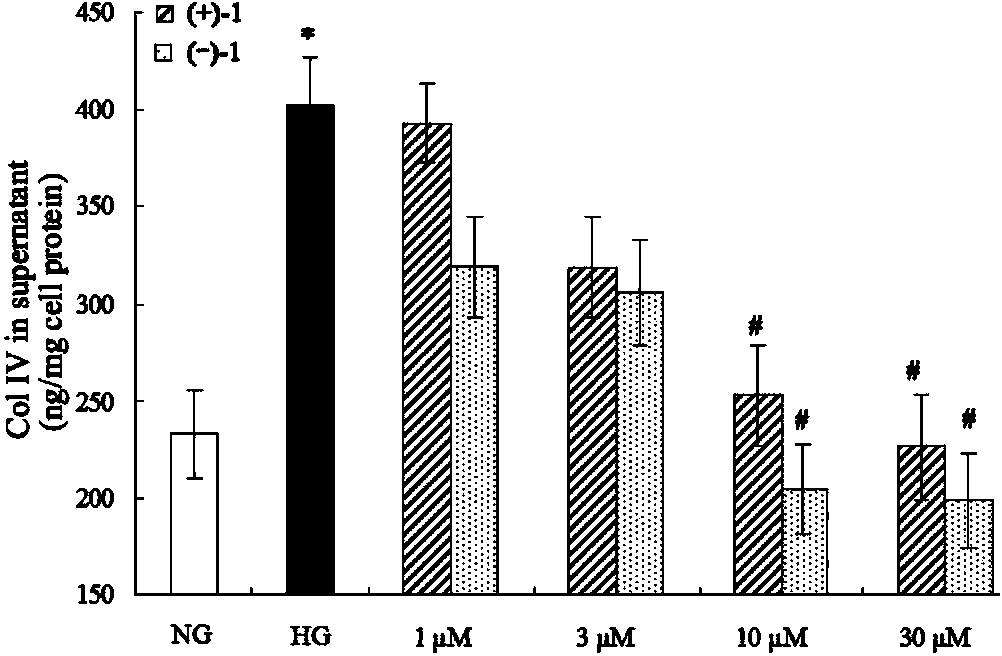
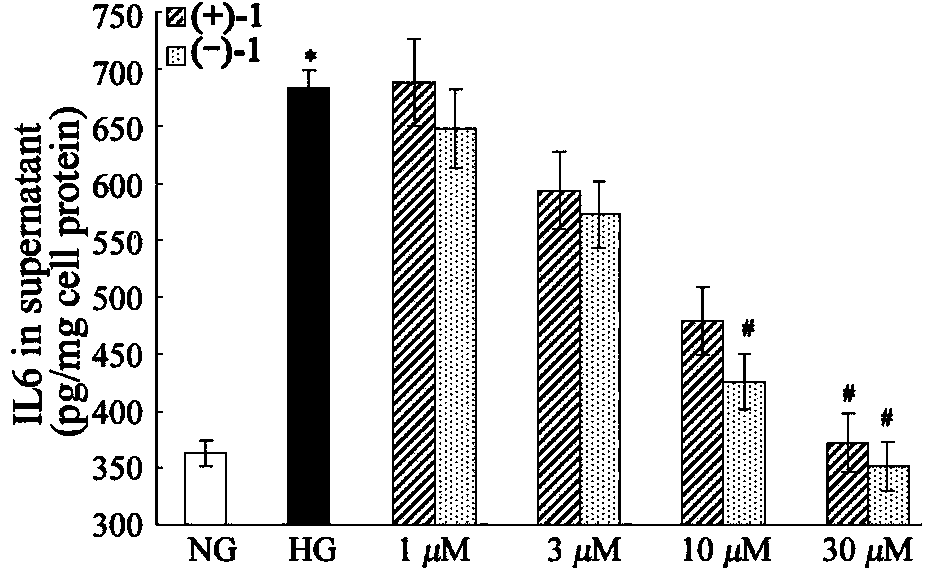
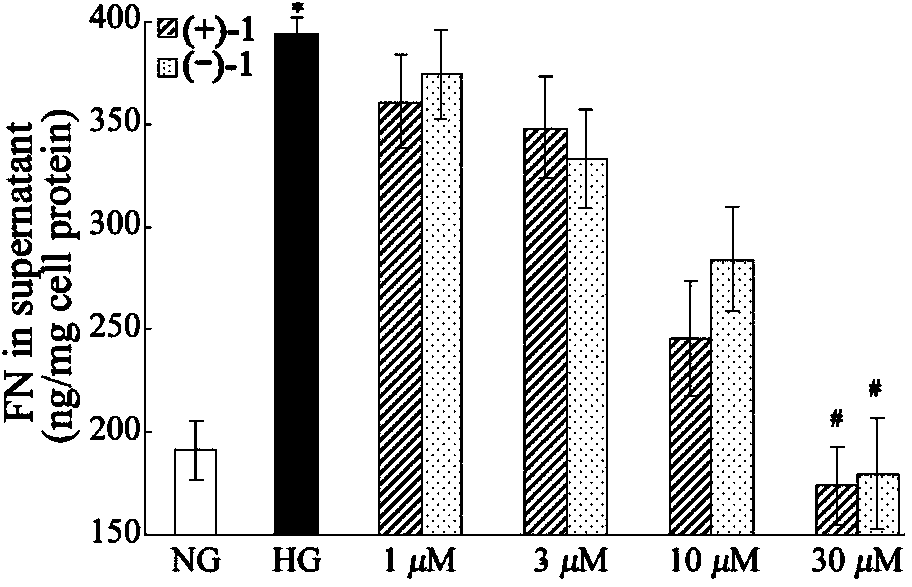
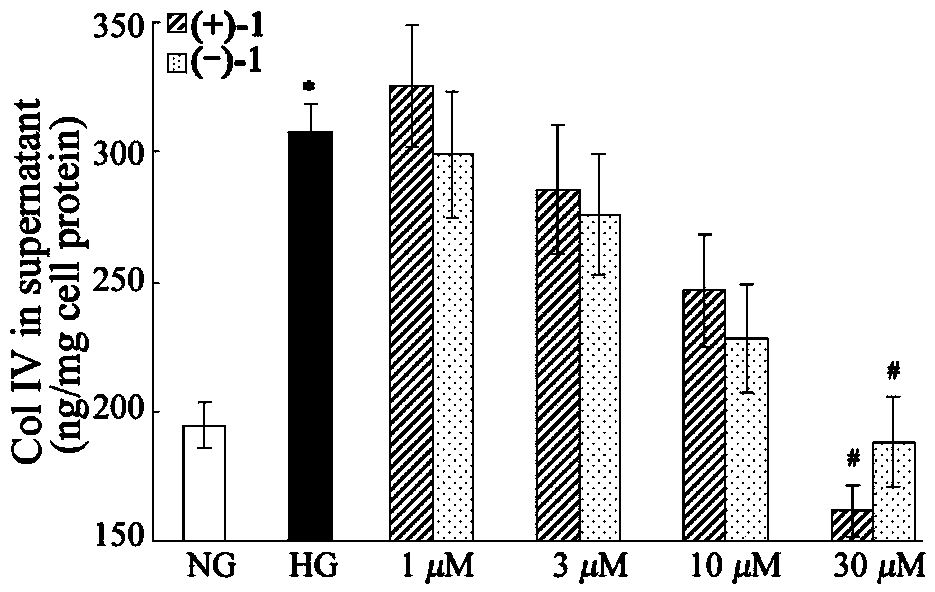
Glossy ganoderma as a traditional Chinese medicine is called immortal grass since ancient times and known as the ability to treat various diseases; a pair of lingzhiol A optical enantiomers is purified from ganoderma lucidum, and the lingzhiol A optical enantiomers have obvious effects on inhibiting rat renal mesangial cell strains induced by high glucose to generate reactive oxide species, IL-6, fibronectin and IV type collagen, and also can obviously inhibit the phosphorylation of the renal tubular epithelial cell Smad3 induced by TGF-beta1, so that the application prospect of the compound in preparation of medicines for treating diabetic nephropathy and chronic nephropathy is shown.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cultural method for inducing human embryonic stem cell to directionally differentiate into corneal limbal stem cell
ActiveCN102952779AGood in vitro differentiation and proliferation abilitySuppress generationArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsImmunofluorescenceMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a cultural method for inducing a human embryonic stem cell to directionally differentiate into a corneal limbal stem cell, which comprises the following steps that firstly, a DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium) / F12 conditioned medium is adopted to culture a human primary corneal limbal stem cell to prepare a corneal limbal stem cell conditioned medium, and then the corneal limbal stem cell conditioned medium is utilized and combined with IV type collagen culture in vitro to induce the human embryonic stem cell to directionally differentiate into the corneal limbal stem cell. According to the corneal limbal stem cell obtained by utilizing the cultural method, through light microscope observation in vitro, electron microscope observation, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, cloning efficiency determination and the like, the induced cell has a similar shape and phenotype with a normal corneal limbal stem cell, has good differentiation and proliferation capacity in vitro, can be transferred in vitro for more than four generations and can be used as a seed cell for preparing a corneal graft.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Mesenchymal stem cells, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102517251AIncrease vitalityImprove securitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisDigestionBottle
The invention relates to the field of cell engineering and discloses mesenchymal stem cells, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of cutting an umbilical cord into small pieces after removing an umbilical artery and umbilical veins, digesting with an alpha MEM (minimum essential medium) culture medium containing 0.1% of type IV collagenase and a complete medium, then centrifugating cell suspension obtained after digestion, removing supernatant liquid, then washing, further performing resuspension with the complete medium, transferring suspension after resuspension into a culture bottle coated by a wall-adhered matrix for culture till the emergence of shuttle-shaped wall-adhered cells, washing, and replacing the new complete medium for continuing the culture so as to get the shuttle-shaped wall-adhered cells after the culture, namely the mesenchymal stem cells. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the culture medium without serum or foreign protein is used for preparation, a recombinase with a single component is used for passage, and the prepared mesenchymal stem cells are smaller in diameter, have no sensibiligen and can improve the vitality of the cells and increase the safety in regeneration treatment of a patient.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
Erythroculter ilishaeformis spermatogonia stem cell separation and culture method
InactiveCN104830756AGood retention propertiesPromote proliferationGerm cellsSterile environmentErythroculter ilishaeformis
The invention relates to an erythroculter ilishaeformis spermatogonia stem cell separation and culture method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting spermatic tissues: collecting spermary of erythroculter ilishaeformis with an age of seven months in a sterile environment, then rinsing spermary in PBS containing double-antibody, and finally grinding the spermary to disperse the spermary tissues; (2) digesting and separating spermatogonia stem cell: adding IV type collagenase (0.1%) into the dispersed spermary tissues, subjecting the digestive fluid to centrifugal separation, collecting the precipitate, digesting the precipitate by trypsin (0.25%), stopping the digestion by a culture medium containing FBS (10%), and collecting the cells; (3) carrying out primary culture of spermatogonia stem cell: using a DMEM / F12 complete medium containing cell factors to re-suspend the cells obtained in the step (2), adjusting the cell concentration, then paving the suspension liquid on a 24-hole cell culture plate coated by gelatin, and culturing the cells at a temperature of 26 DEG C. Trough the provided method, the in-vitro growth of primary cells of erythroculter ilishaeformis spermatogonia stem cell becomes easier, and an effective cell platform is provided for the research on reproduction and growth of erythroculter ilishaeformis.
Owner:HUZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
Method for separating primary adult hepatocytes, and special sterile apparatus box thereof
InactiveCN102220278AGuaranteed sterilityFor long-term storageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSerum freeType IV collagen
The invention discloses a method for separating primary adult hepatocytes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out multi-point puncture on surface of isolated adult hepatic tissue through a needle syringe, and injecting a preperfusate, wherein connective tissues are removed from the isolated adult hepatic tissue; (2) carrying out the multi-point puncture on the surface of the isolated adult hepatic tissue through the needle syringe again, and injecting a IV collagenase solution; (3) separating the isolated adult hepatic tissue, followed by adding the IV collagenase solution and carrying out digesting through vibration at a temperature of 37 DEG C to obtain digest; (4) carrying out filtering for the digest, followed by centrifuging and collecting cell aggregate in the underlayer, then resuspending the adult hepatocyte aggregate through a hepatocyte wash buffer, followed by filtering and centrifuging, then abandoning supernatant and collecting the adult hepatocyte aggregate in the underlayer; (5) washing the adult hepatocyte aggregate in the underlayer from the step (4) through a serum-free DMEM medium to obtain the primary adult hepatocytes. The invention further discloses a disposable special sterile apparatus box for separating the primary adult hepatocytes. With the present invention, the disposable special sterile apparatus box is adopted, the primary adult hepatocytes are separated through the multi-point puncture on the surface of the tissue and the injection, such that operation is simplified, cost is reduced, and the method and the apparatus box are applicable for extracting the hepatocytes from small pieces of the irregular isolated adult hepatic tissues of recovery of liver resection.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for constructing human corneal epithelial cell system
ActiveCN102168064ANot tumorigenicLow costMicroorganism based processesArtificial cell constructsCuticleCell system
The invention relates to a method for constructing a human corneal epithelial cell system. The construction method comprises the following steps of: disinfecting cornea, digesting the cornea, taking off corneal epithelium with a front elastic layer, cutting the corneal epithelium into small tissue blocks, flatly attaching the tissue blocks to the bottom of culture holes downwards, adding culture solution into a carbon dioxide culture box, and performing plate-attaching culture at the temperature of 37 DEG C, changing the culture solution during culturing, performing subculture when the cells grow into a single layer, and presently, completing the construction of the human corneal epithelial cell system above 60 generations, wherein the culture solution contains 20 percent of fetal calf serum, 0.002 to 0.004 percent of human epidermic cell growth factor, 0.001 to 0.002 percent of human alkali fibroblast growth factor, 0.04 to 0.1 percent of carboxymethyl chito-oligosaccharide, 0.025 to0.1 percent of DMEM / F12 culture solution of chondroitin sulfate, and 0.008 to 0.01 percent of IV type collagen. In the construction method, the non-transfection human corneal epithelial cell system is successfully constructed by utilizing the human corneal epithelial tissues, and the constructed cell system can realize continuous transfer of culture, and a great number of human corneal epithelialcells are provided.
Owner:青岛彩晖生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of fish single-cell suspension
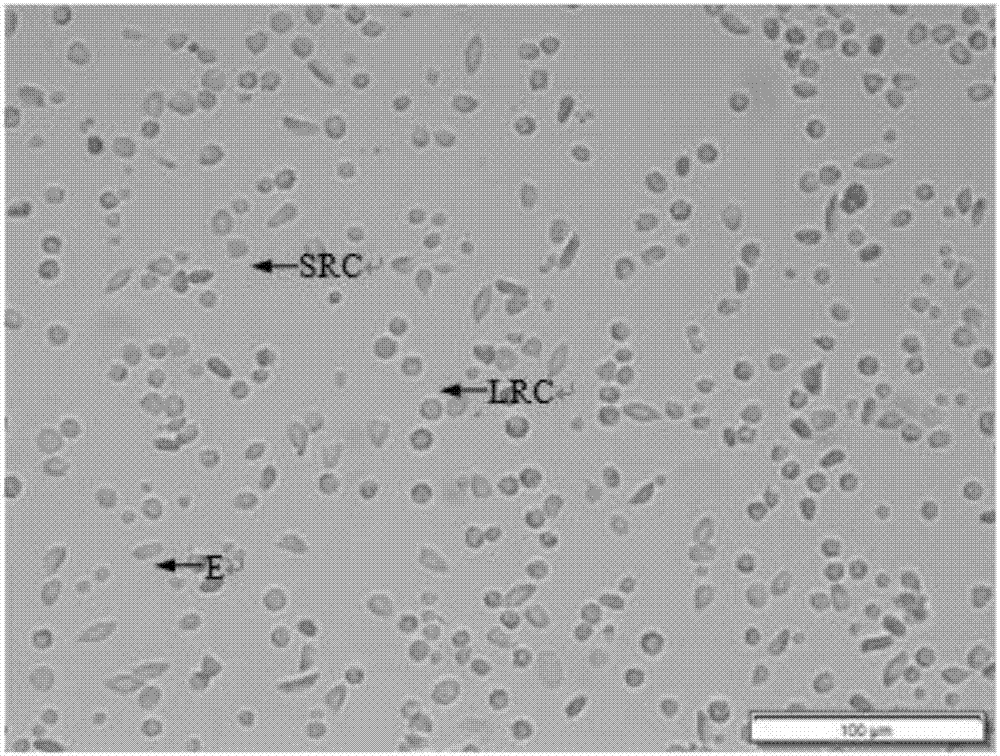
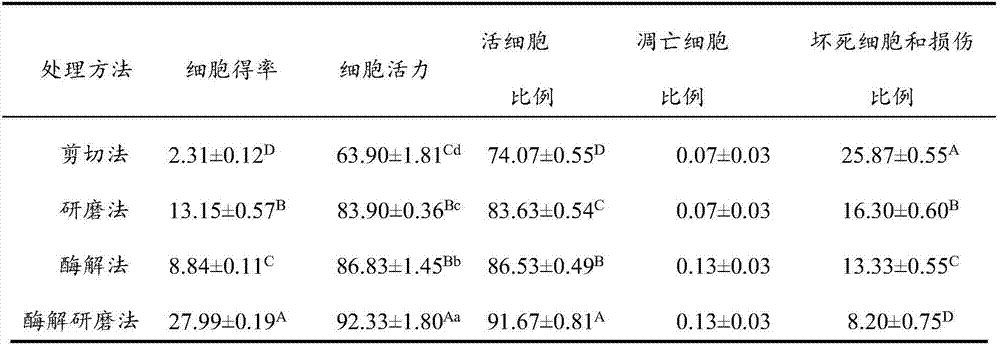
InactiveCN106929468ABest preparation methodGood dispersionCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsEnzymatic digestionFiltration
The application discloses a preparation method of a fish single-cell suspension. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a PBS reagent, a D-Han liquid and an IV type collagenase liquid, preparing a kidney tissue block of a fish, and washing the kidney tissue for more than three times with PBS; putting the kidney tissue block in a flat vessel of an ice bath, adding PBS, shearing the kidney tissue block into small pieces, and putting the tissue blocks in a high throughput tissue centrifuge tube of a burnisher; adding the IV type collagenase liquid into the centrifuge tube and meanwhile, adding PBS to fix the volume to 4ml, putting a zirconium oxide wall to grind, and performing enzymatic digestion on a tissue homogenate; and performing filtration, centrifugalization, washing with PBS, performing centrifugalization to abandon supernate and removing cell debris, filtering the cell suspension and fixing the volume to 3ml with PBS, and storing the cell suspension for later use at 4 DEG C. By adopting an enzymatic hydrolysis grinding method, advantages of a griding method and an enzymatic hydrolysis method are combined. The tissue is more fully treated by enzymatic hydrolysis grinding, so that the problem that the cell yield is low and the cell viability is low for preparing the fish single-cell suspension can be solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
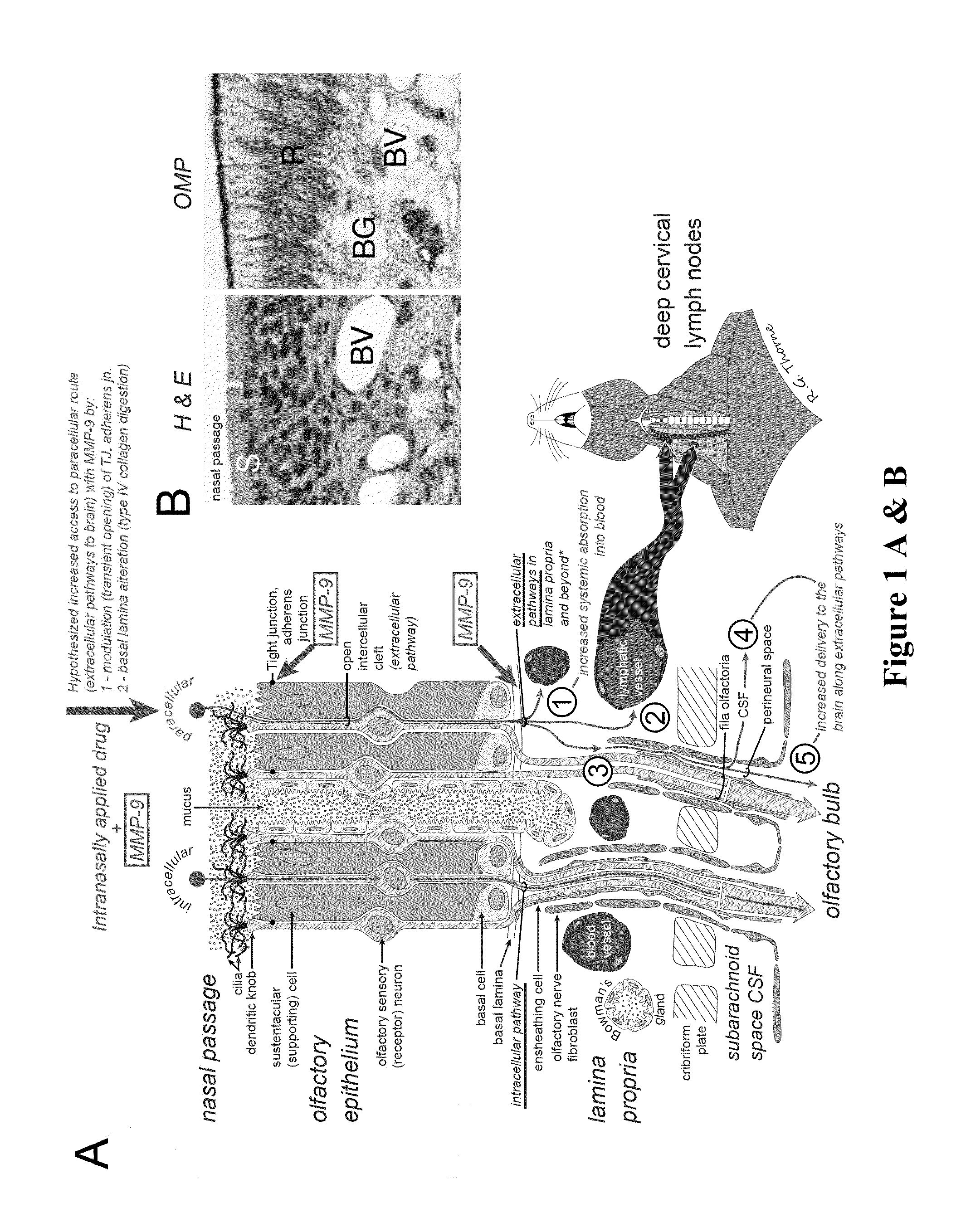
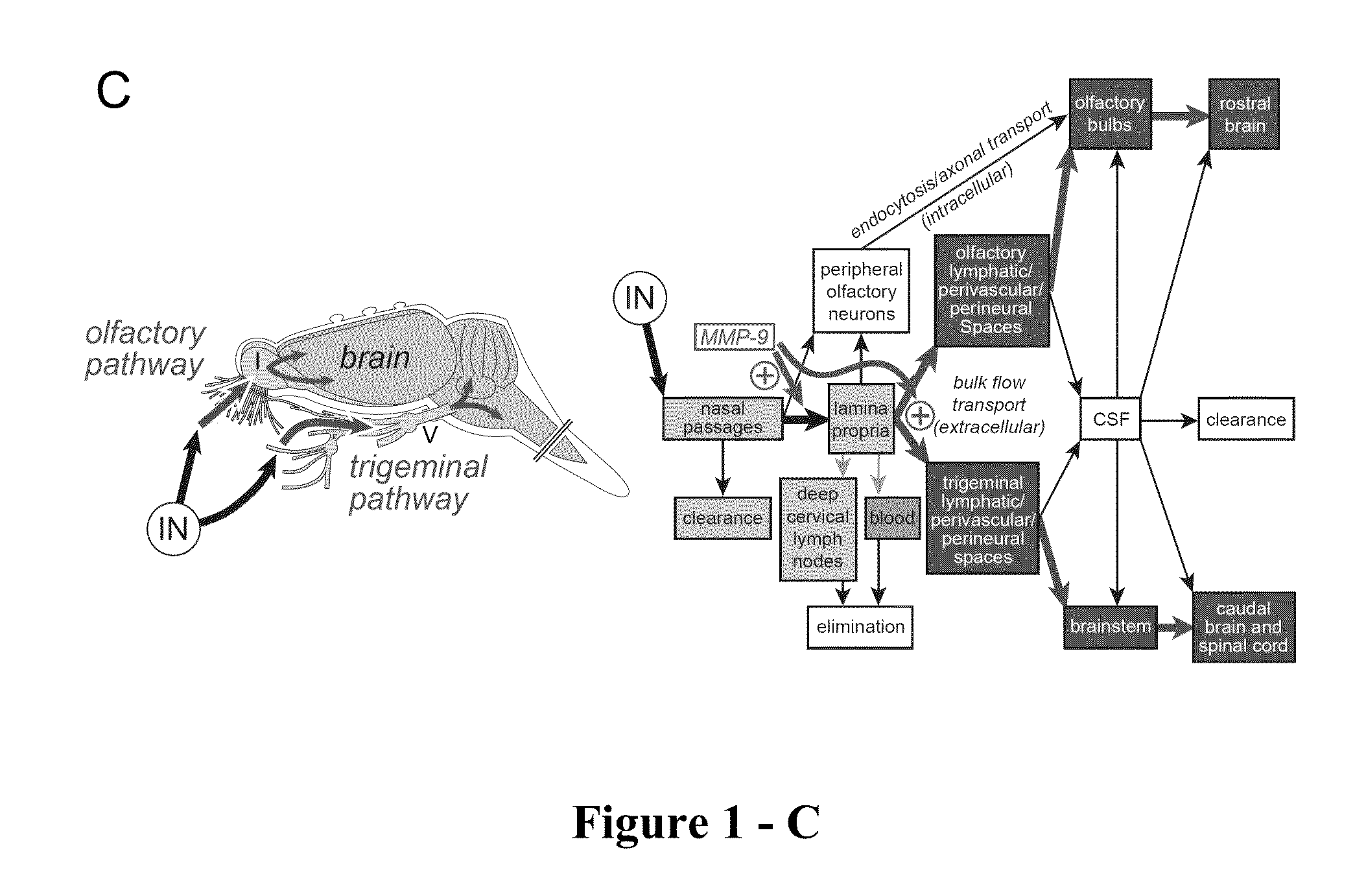
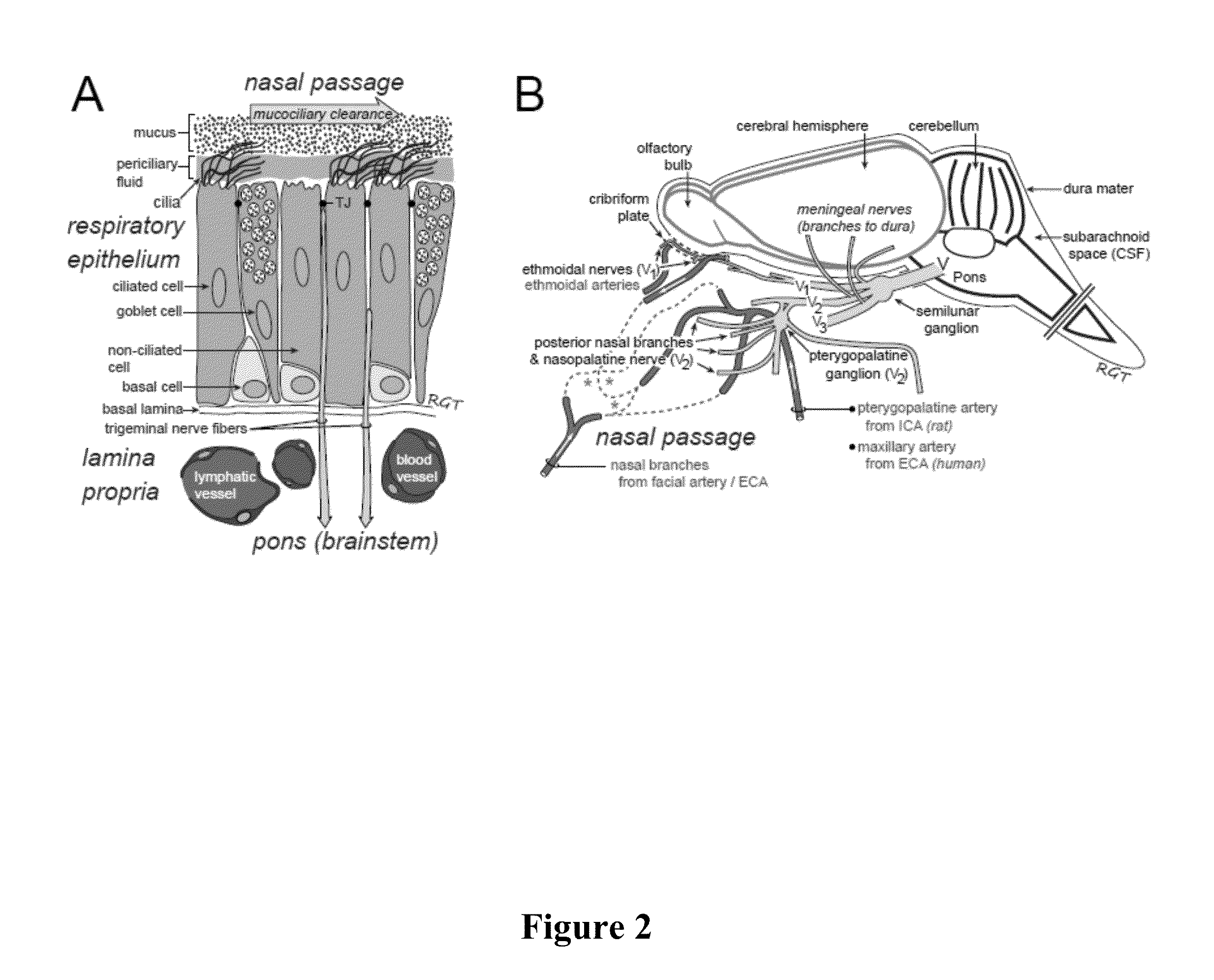
Methods and Compositions for Enhancing Intranasal Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20140050718A1Easy accessNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBasal laminaPerivascular Satellitosis
A method for treating a patient suffering from a condition with an active compound comprising the steps of (a) treating the patient intranasally with an effective amount of MMP-9 or a functionally equivalent fragment, wherein the tight junctions of the patient's nasal epithelial cells are modulated or wherein the basal lamina of the patient is partially digested and type IV collagen of the patient is degraded or wherein access to the patient's perineural, perivascular, or lymphatic compartment spaces is facilitated and (b) treating the patient intranasally with an active compound is disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for separating and extracting hUC-MSC (human Umbilical Cord mesenchymal stem cells) from wharton jelly tissue of umbilical cord
InactiveCN105462919AReduce incubation timeImprove securityCell dissociation methodsCulture processSerum free mediaUmbilical cord tissue
The invention provides a method for rapidly separating and extracting hUC-MSC (human Umbilical Cord mesenchymal stem cells). The method comprises the following steps: taking the freshly collected umbilical cord tissue of a healthy newborn baby, carrying out on-ice transportation on the freshly collected umbilical cord tissue in umbilical cord storage transportation liquid containing double antibodies, carrying out cleaning and disinfection by adopting 75% alcohol and normal saline, removing blood vessels, carrying out blunt dissection on wharton jelly, carrying out mechanical pulverization, treating the obtained product I by adopting red blood cell lysis buffer for 3 min, digesting the obtained product II by adopting IV collagenase, screening the obtained product III by adopting a 100-200-mesh sieve, carrying out suspension culture on the obtained product IV by adopting a serum-free medium, wherein the liquid is changed every 3-5 days, taking supernatant, detecting cell pollution, after the adherent rate in a plate reaches 30-70%, carrying out trypsinization, carrying out centrifugation, collecting cells, carrying out passage amplification, carrying out merging when the cell merging rate reaches 90% or above, collecting the cells, carrying out cryopreservation on the cells, and detecting the biological characteristics of hUC-MSC.
Owner:郭镭 +1
Method for guiding the derivation of endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells employing two-dimensional, feeder-free differentiation
InactiveUS20150017724A1Artificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingInduced pluripotent stem cellSingle cell suspension
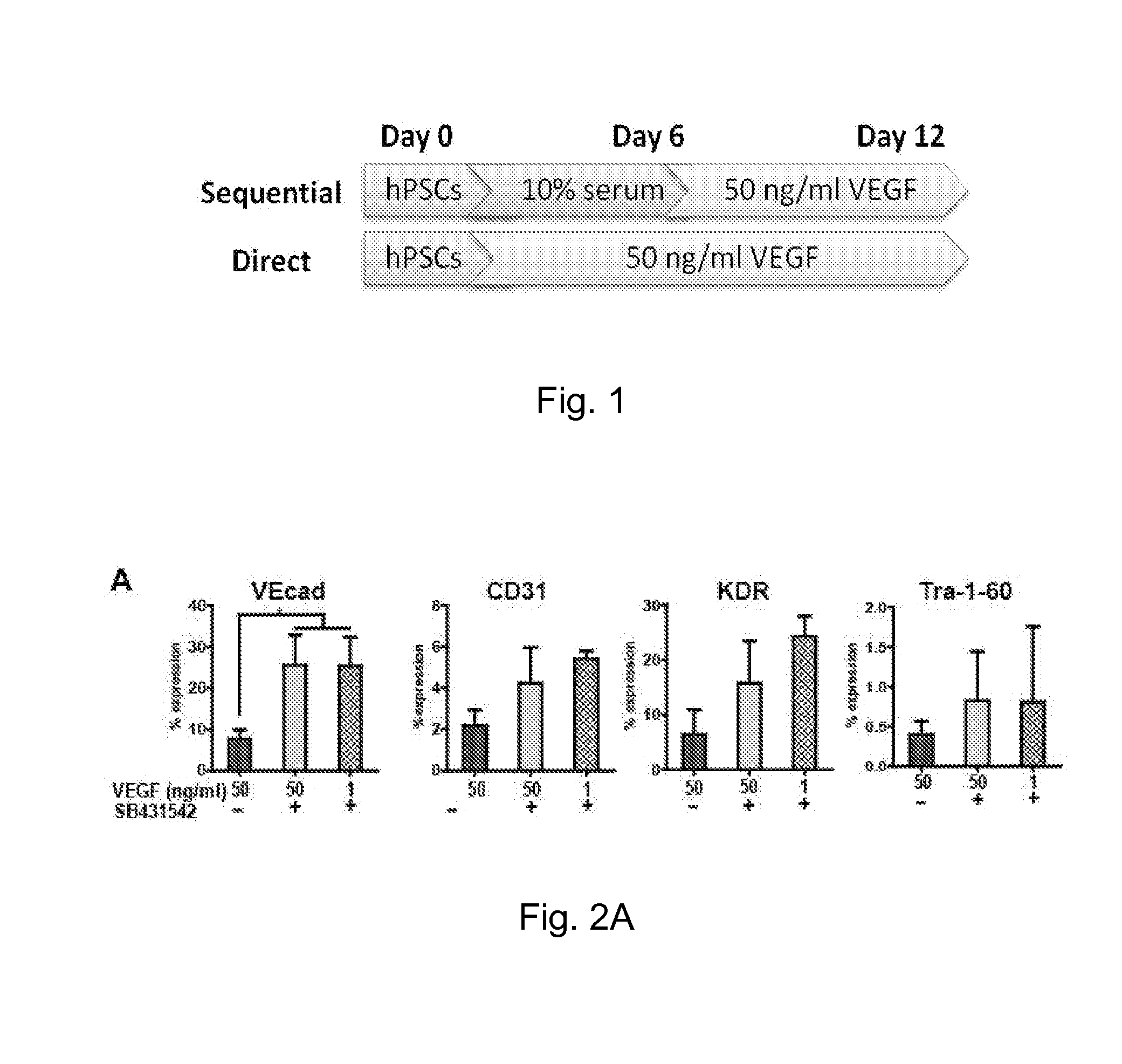
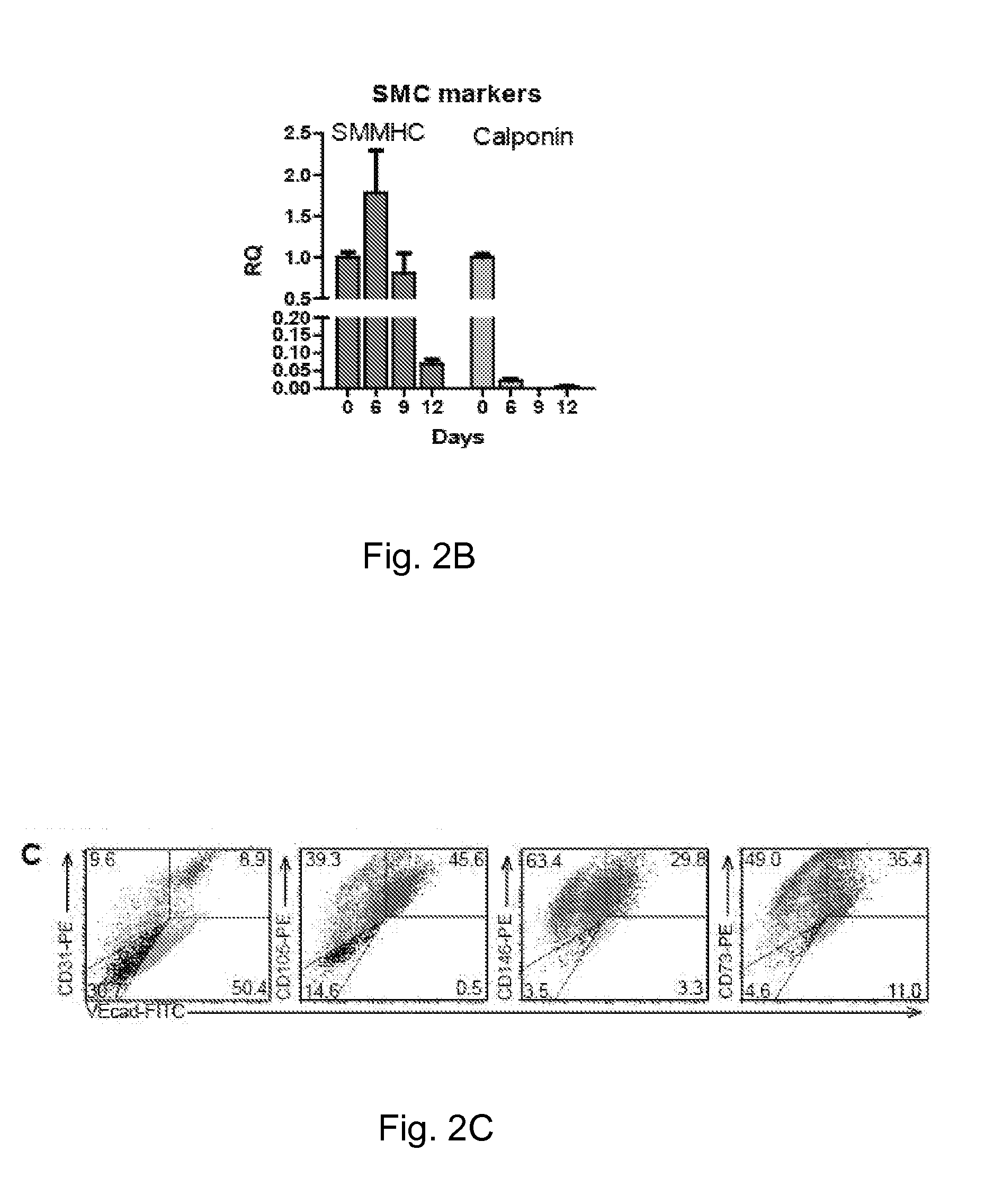
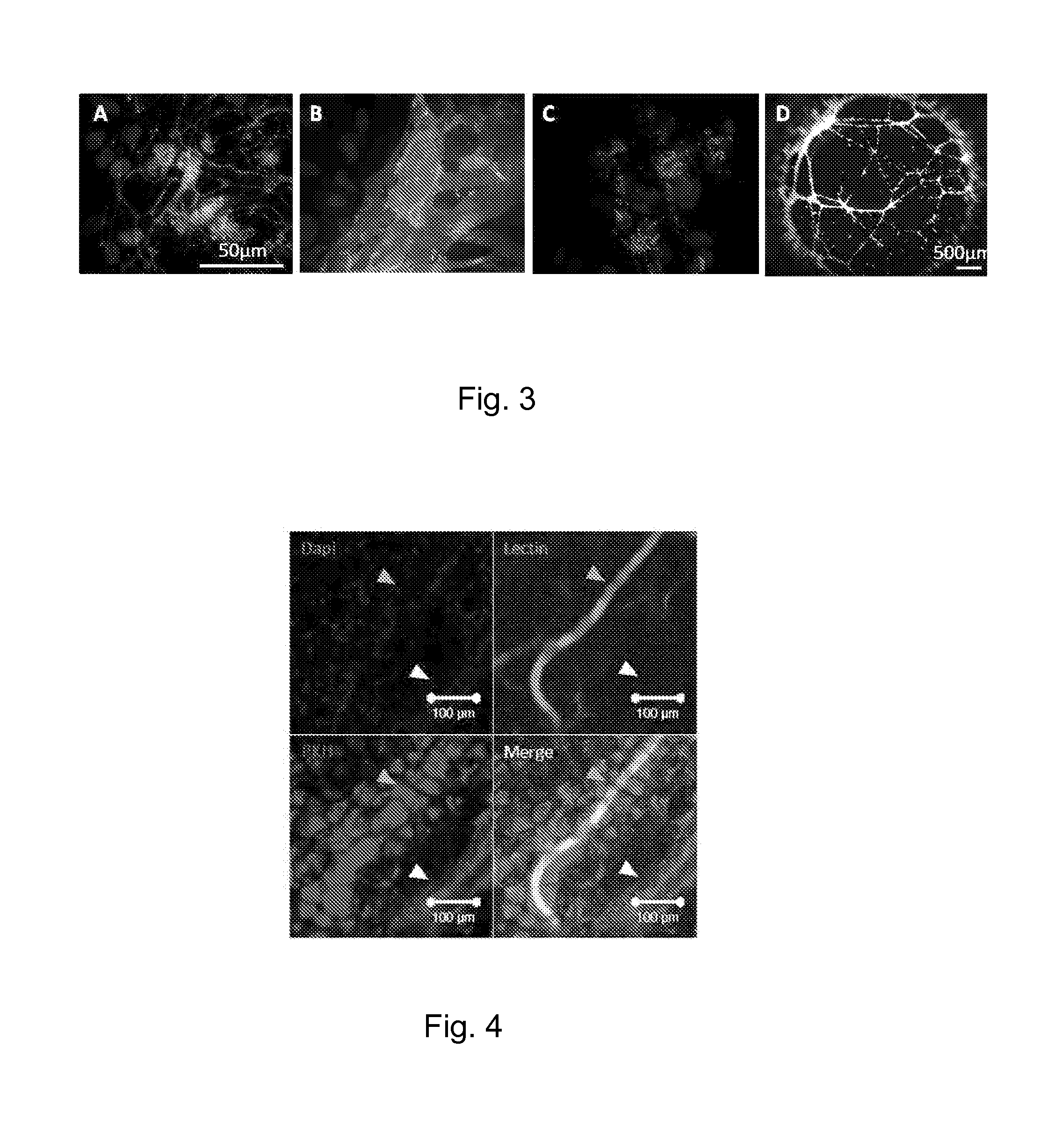
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for differentiating mammalian (e.g., human) pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) into endothelial cells (ECs) in vitro, by plating a single-cell suspension of PSCs onto a suitable surface such as type IV collagen and culturing the cells with VEGF after which ECs can be harvested. A preferred embodiment of the method first cultures the cells without VEGF and then sequentially cultures the cells with VEGF. Differentiation can be enhanced by adding an inhibitor of transforming growth factor β to the culturing with VEGF.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Vivo assay for anti angiogenic compounds
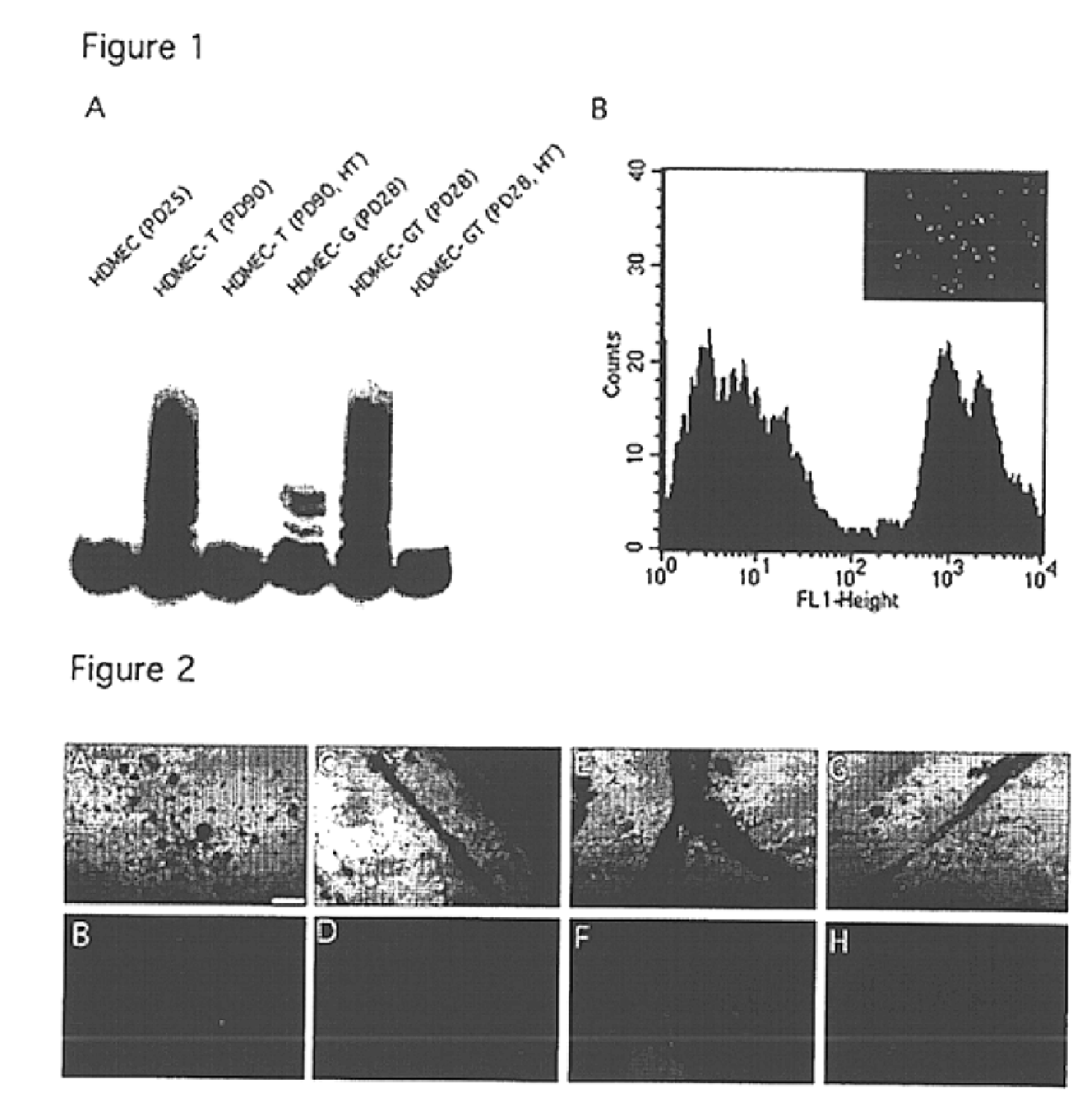
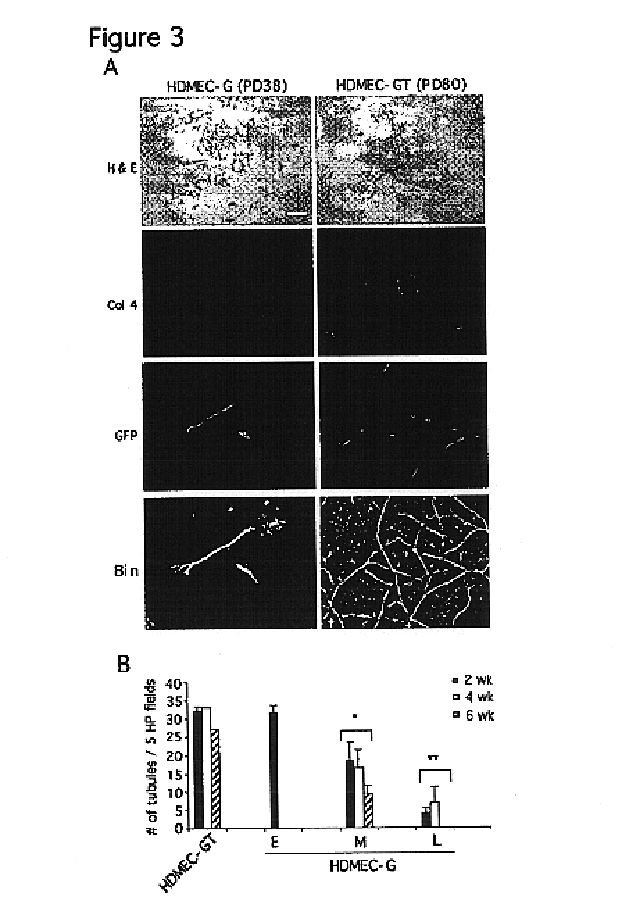
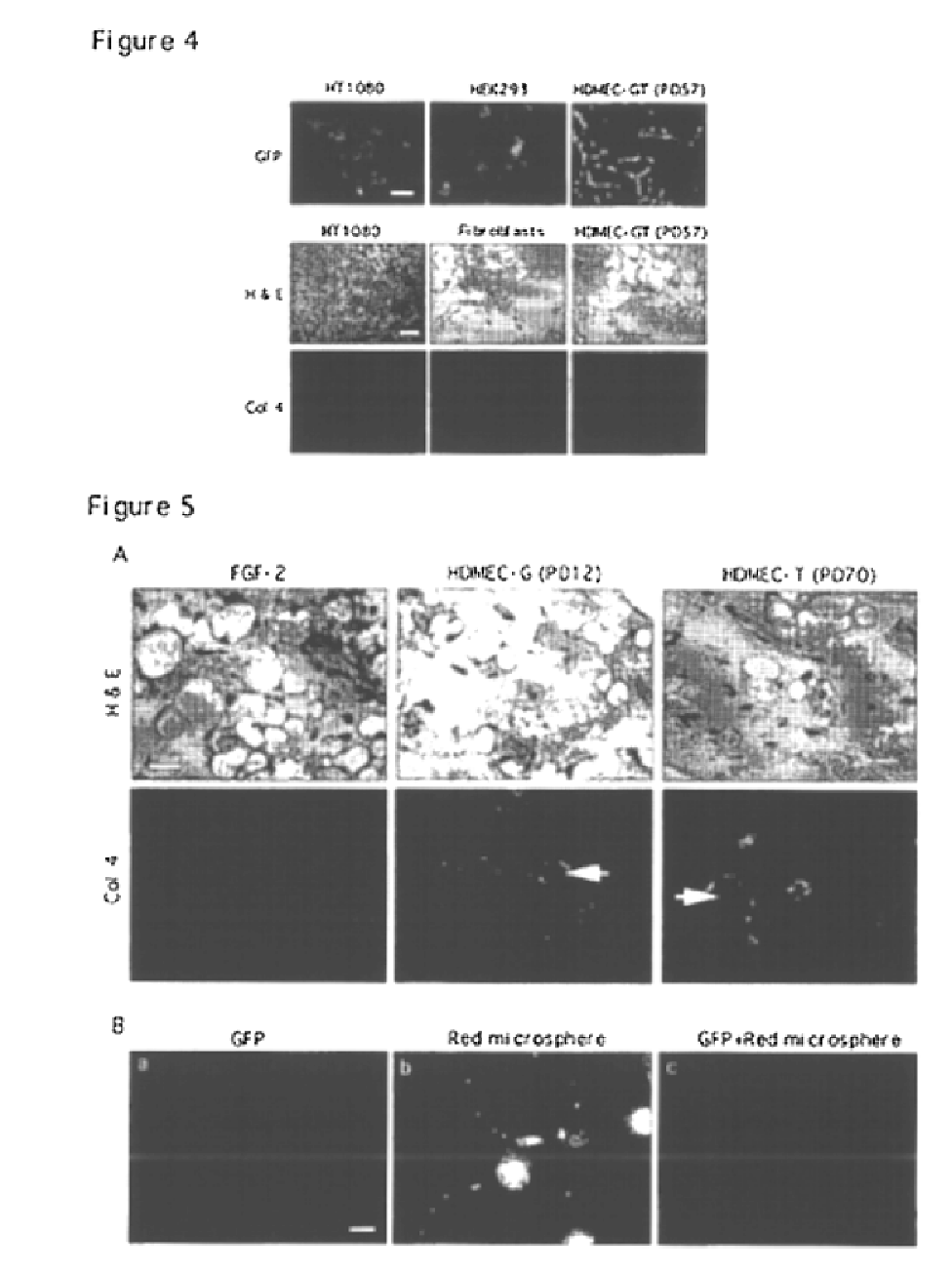
We report the use of telomerase-immortalized human microvascular endothelial cells in the formation of functional capillary blood vessels in vivo. Previously we showed the superior in vitro survival of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT)-transduced human endothelial cells. Here we show that retroviral-mediated transduction of hTERT in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) results in cell lines that form microvascular structures when subcutaneously implanted in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. The human origin of xenografted microvaculature was confirmed both by basement membrane immunoreactivity with anti-human type IV collagen staining and visualization of fluorescent vessels containing HDMEC that were co-transduced with hTERT and green fluorescent protein (eGFP). The lack of human vascular structures after implantation of HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells, 293 human embryonic kidney cells or human skin fibroblasts demonstrated the specificity of HDMEC at forming capillaries. Intravascular red fluorescent microspheres injected into the host circulation were found within green “telomerized” microvessels indicating functional murine-human vessel anastamoses. Whereas primary HDMEC-derived vessel density decreased steadily with time, telomerized HDMEC maintained durable vessels 6 weeks after xenografting. Modulation of implant vessel density by exposure to different angiogenic and angiostatic factors demonstrated the utility of this system for the study of human microvascular remodeling in vivo.
Owner:HERRON G SCOTT
Method for simultaneously labelling collagen type IV, macrophage and neovascularisation of tumors
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously labelling collagen type IV, macrophage and neovascularisation of tumors. The method comprises the following steps: 1. immobilizing tissue sections on a plus microscope slide processed by polylysine; 2. dewaxing the tissue sections in dimethylbenzene; 3. carrying out antigen retrieval; 4. washing the sections; 5. carrying out confining; 6. addingprimary antibodies; 7. washing the sections; 8. carrying out confining in the same way as the step 5; 9. using the fragment antigen-binding F(ab')2-QDs525 of goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G labelledby quantum dot QDs525, the fragment antigen-binding F(ab')2-QDs585 of goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G labelled by quantum dot QDs585 and the fragment antigen-binding F(ab')2-QDs655 of rabbit anti-goat immunoglobulin G labelled by quantum dot QDs655 as secondary antibodies and dropwise adding the mixture after removing the confining liquid; 10. washing the sections; and 11. sealing the sections:preparing buffered glycerol with glycerol and 10ml of tris buffered saline (TBS) and storing the sections after sealing the sections with the buffered glycerol. The method is used for efficiently, accurately, rapidly and simultaneously detecting various components in tumor tissue microenvironment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
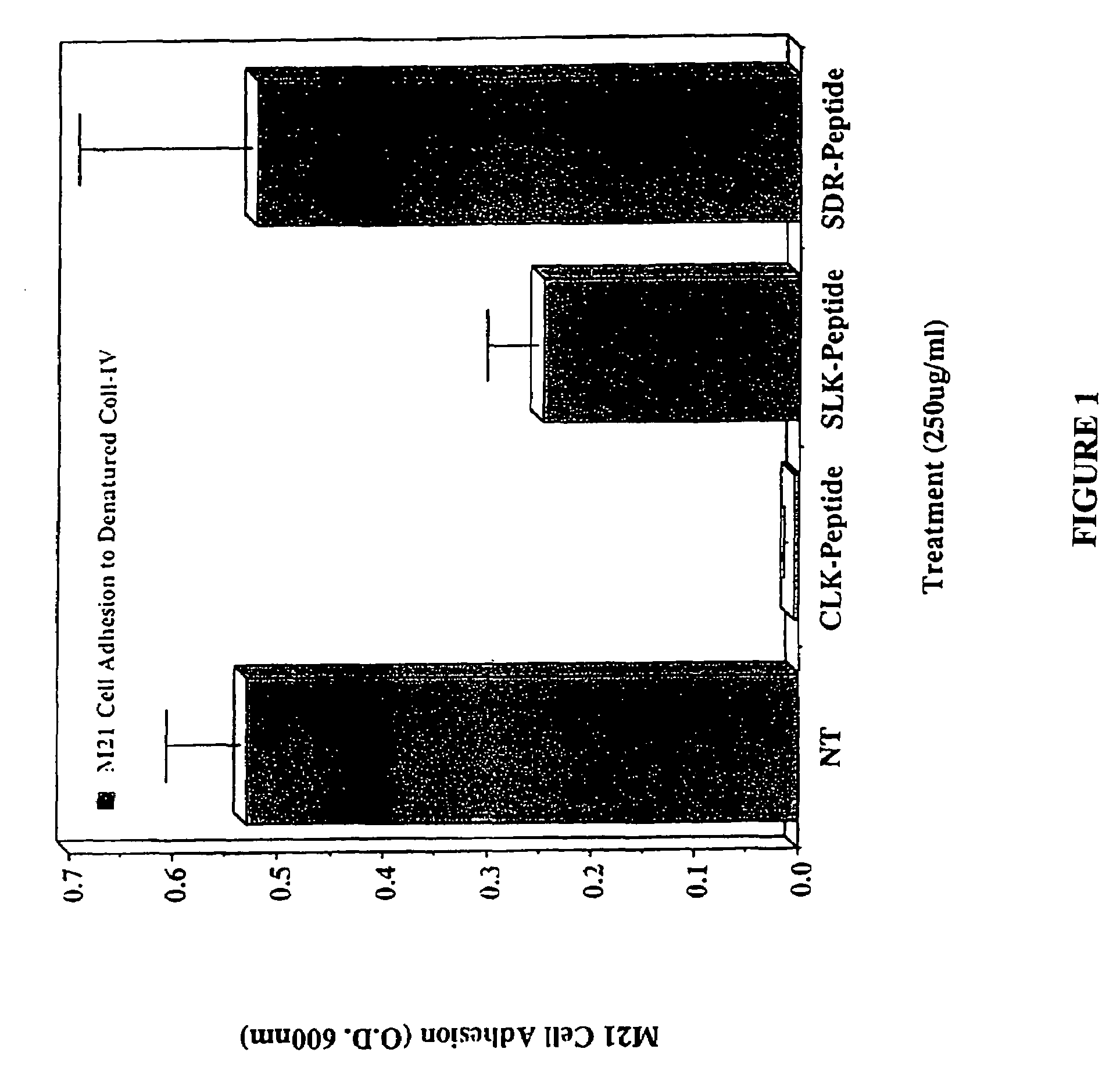
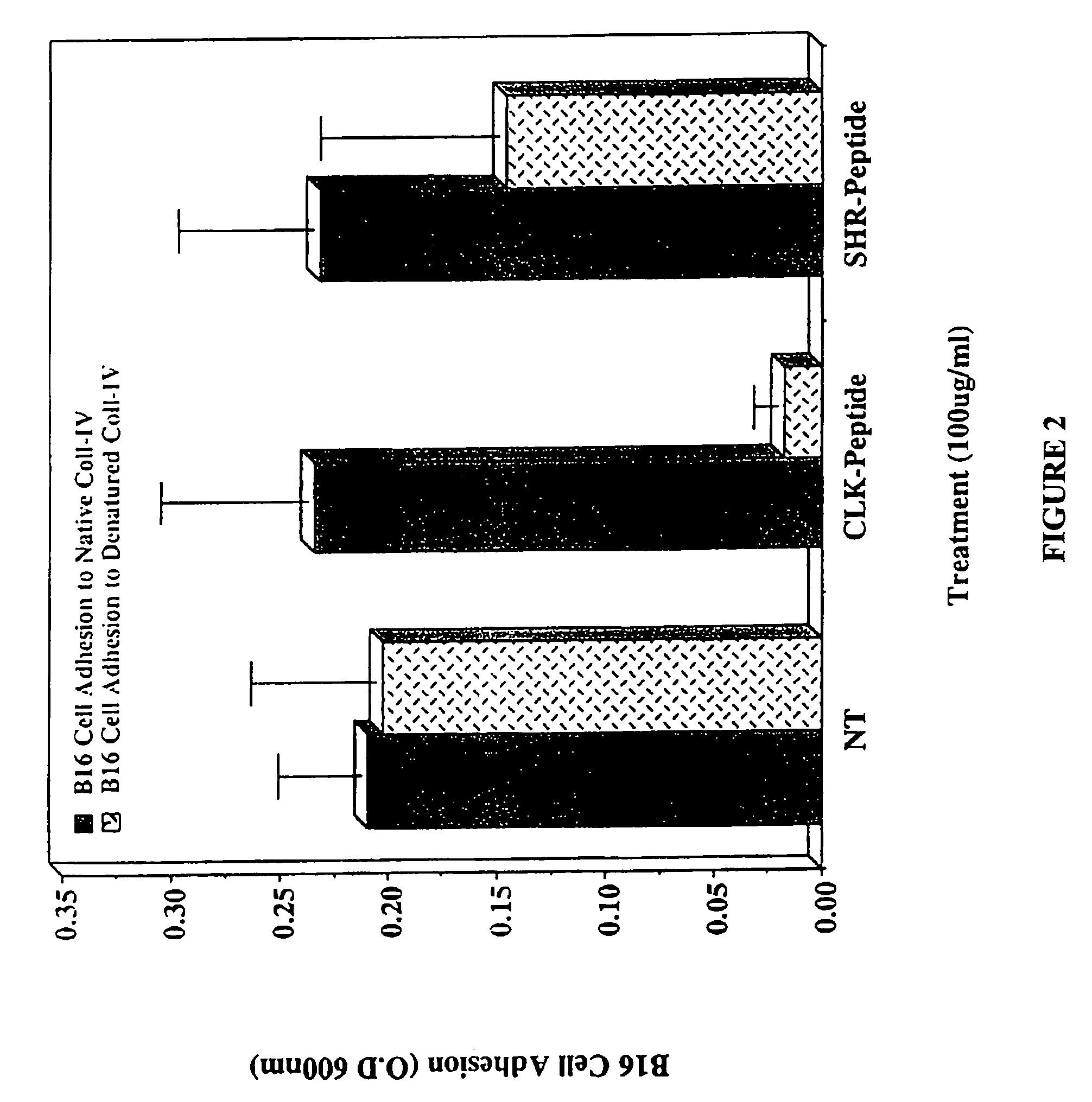
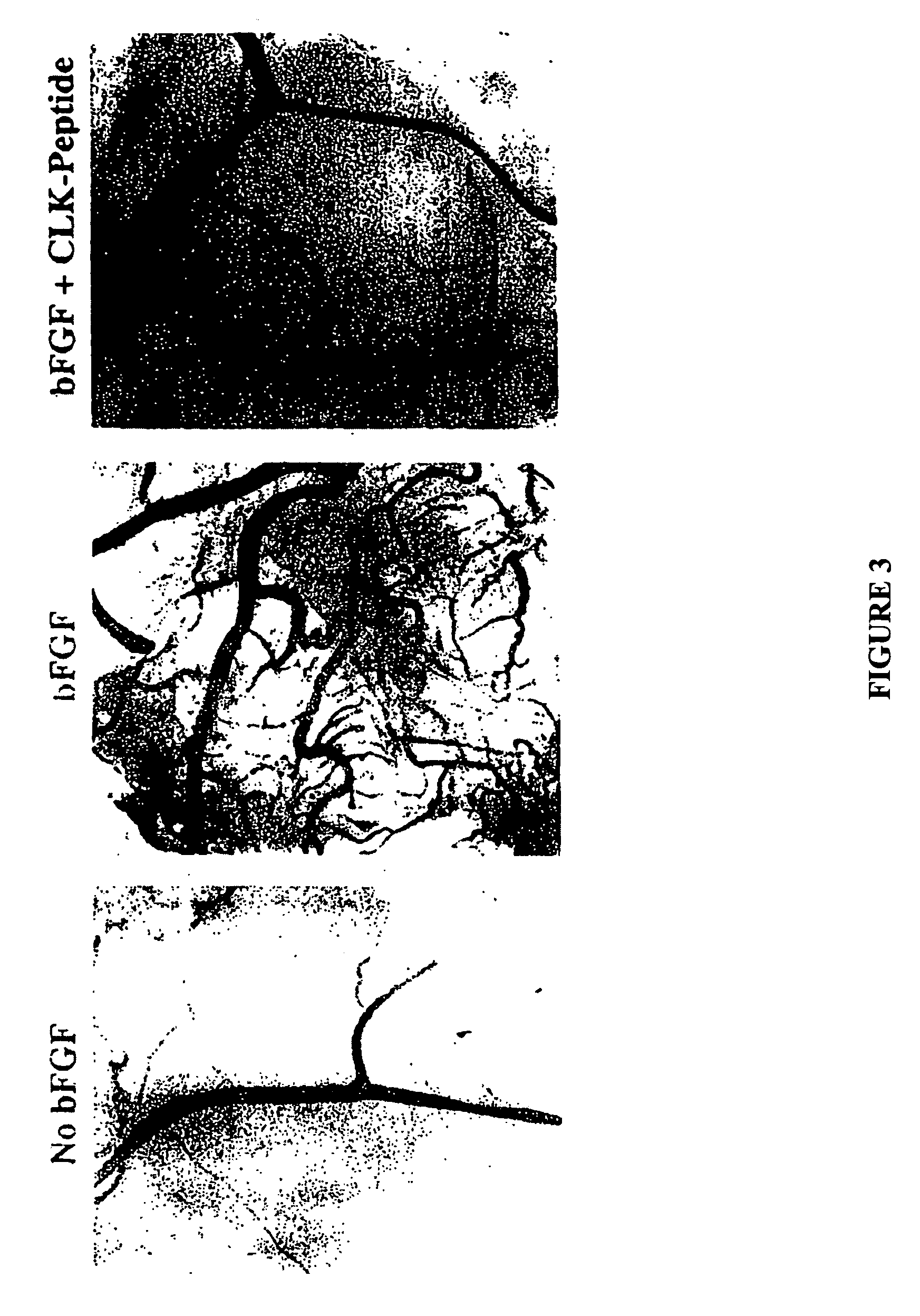
CLK-peptide and SLK-peptide
InactiveUS7662783B2Improve efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Separation and culture method and application of human testis mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN105331579AIncrease serum testosterone levelsMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDiseaseTissue biopsy
The invention discloses a separation and culture method and application of human testis mesenchymal stem cells. The separation method comprises the steps that an obstructive azoospermia patient testis specimen which is processed through tissue biopsy separation is digested with type IV collagenase, digested cell suspension is filtered to remove tissue clumps, and human testis cells are obtained; the human testis cells are marked with a CD51 antibody, separation is performed with a flow cytometer, the cells expressing the CD51 are collected, and then the human testis mesenchymal stem cells with the positive CD51 are separated. The invention further provides the human testis mesenchymal stem cells which are obtained through the separation method and have the positive CD51, the culture method of the stem cells and application of the stem cells in preparation of medicine for treating related diseases caused by low testosterone level.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Artificial skin tissue, artificial skin model and manufacturing method therefor
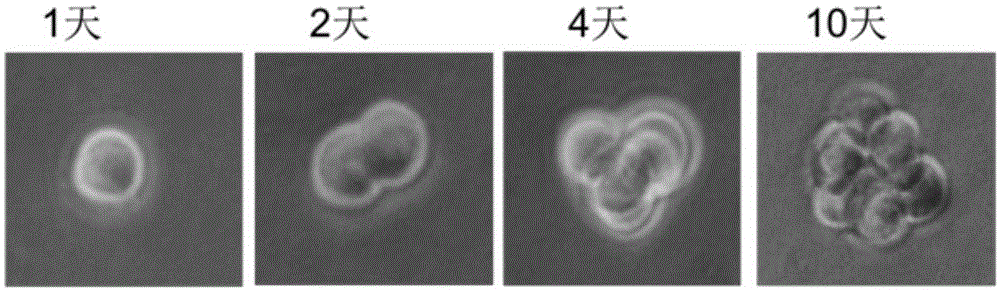
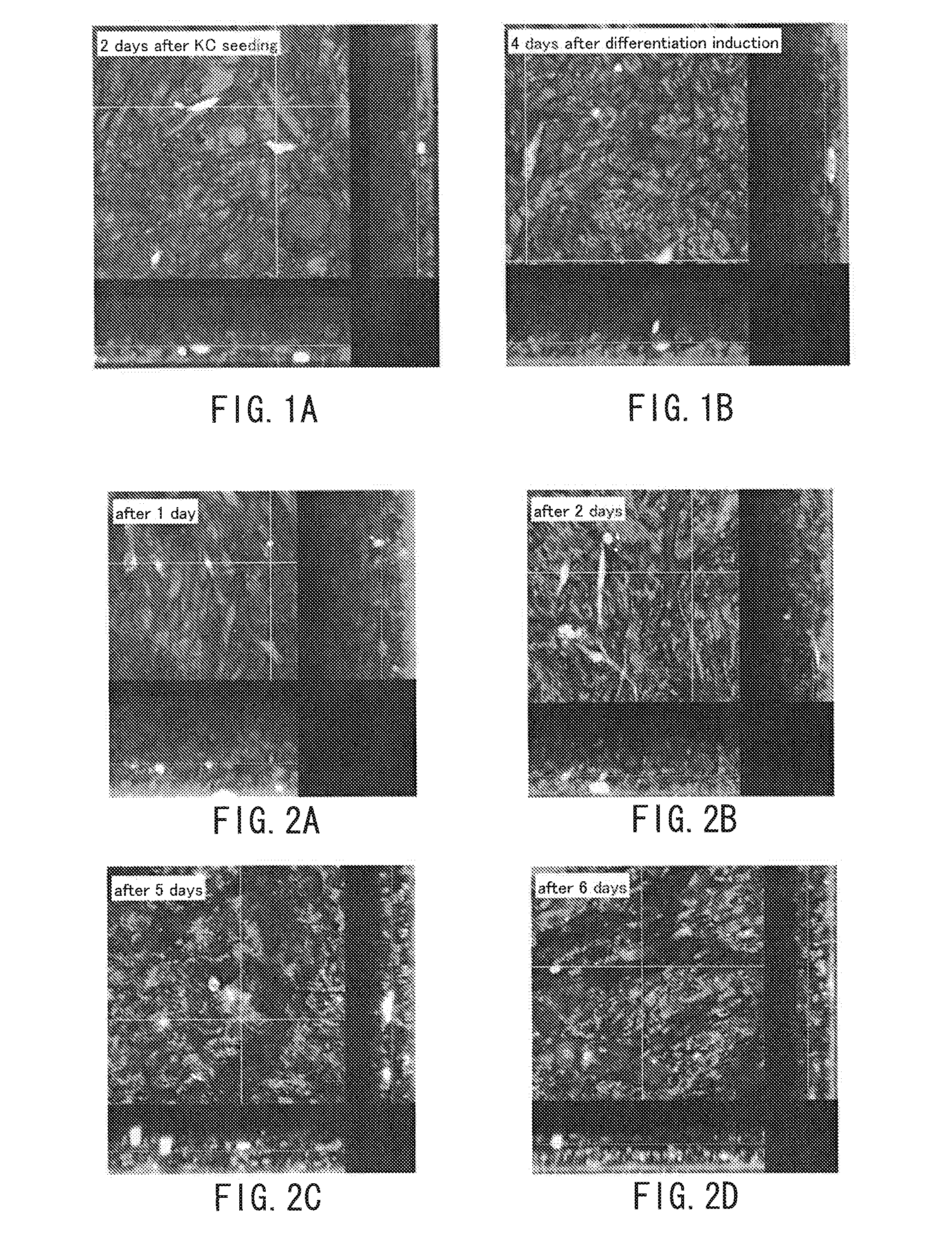
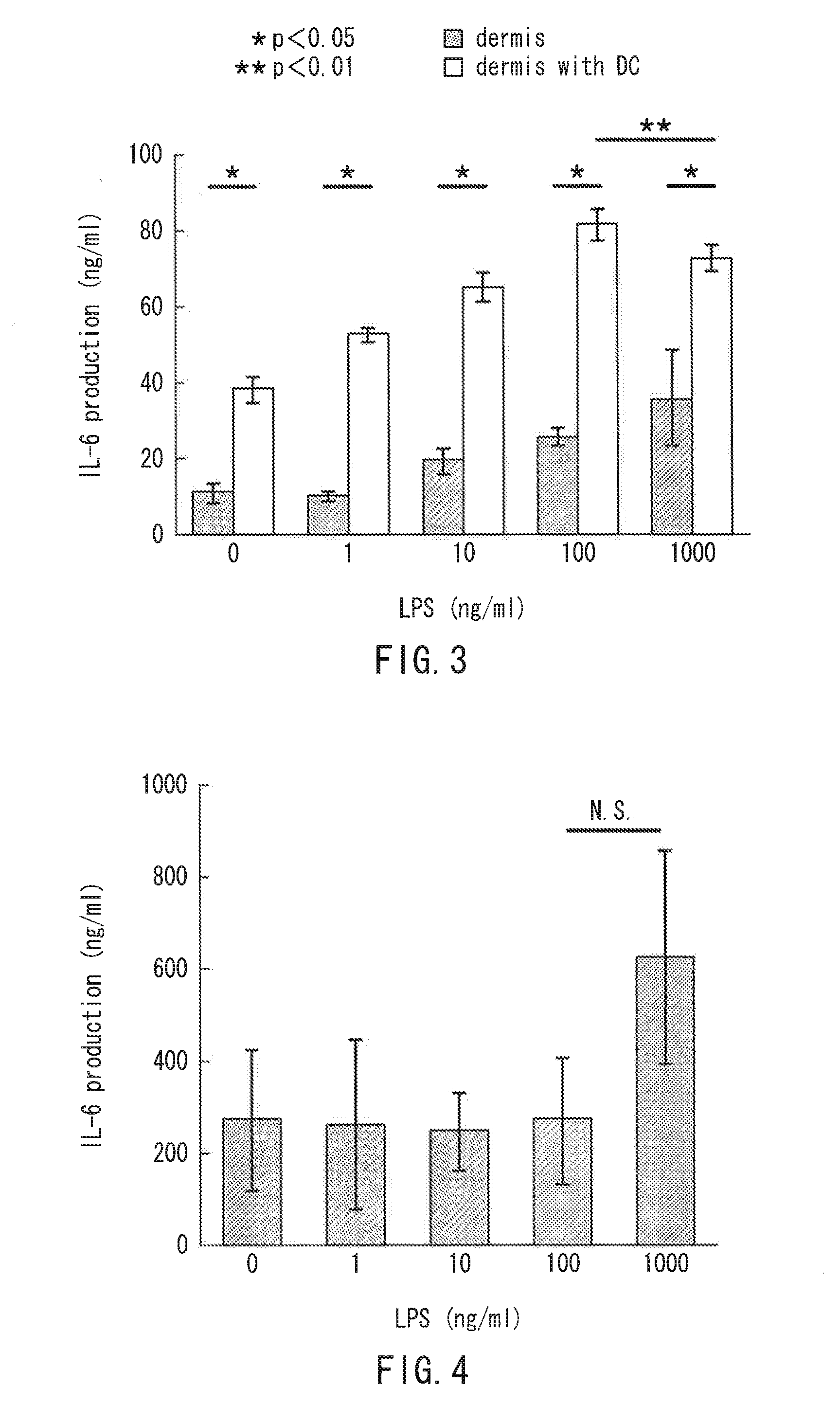
Provided is a novel method capable of manufacturing an artificial skin model including dendritic cells. A method for manufacturing an artificial skin model includes the following: forming a dermal tissue layer by culturing coated cells in which a cell surface is coated with a coating film containing an extracellular matrix component, so that the coated cells are layered; forming a basal layer including type IV collagen on the dermal tissue layer by bringing type IV collagen into contact with the dermal tissue layer; and forming an epidermal layer by arranging epidermal cells on the basal layer. At least one of the dermal tissue layer and the epidermal layer includes dendritic cells.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL TECH HYBRID +1
Liquid phase chip used for detecting liver fibrosis and method of producing the same
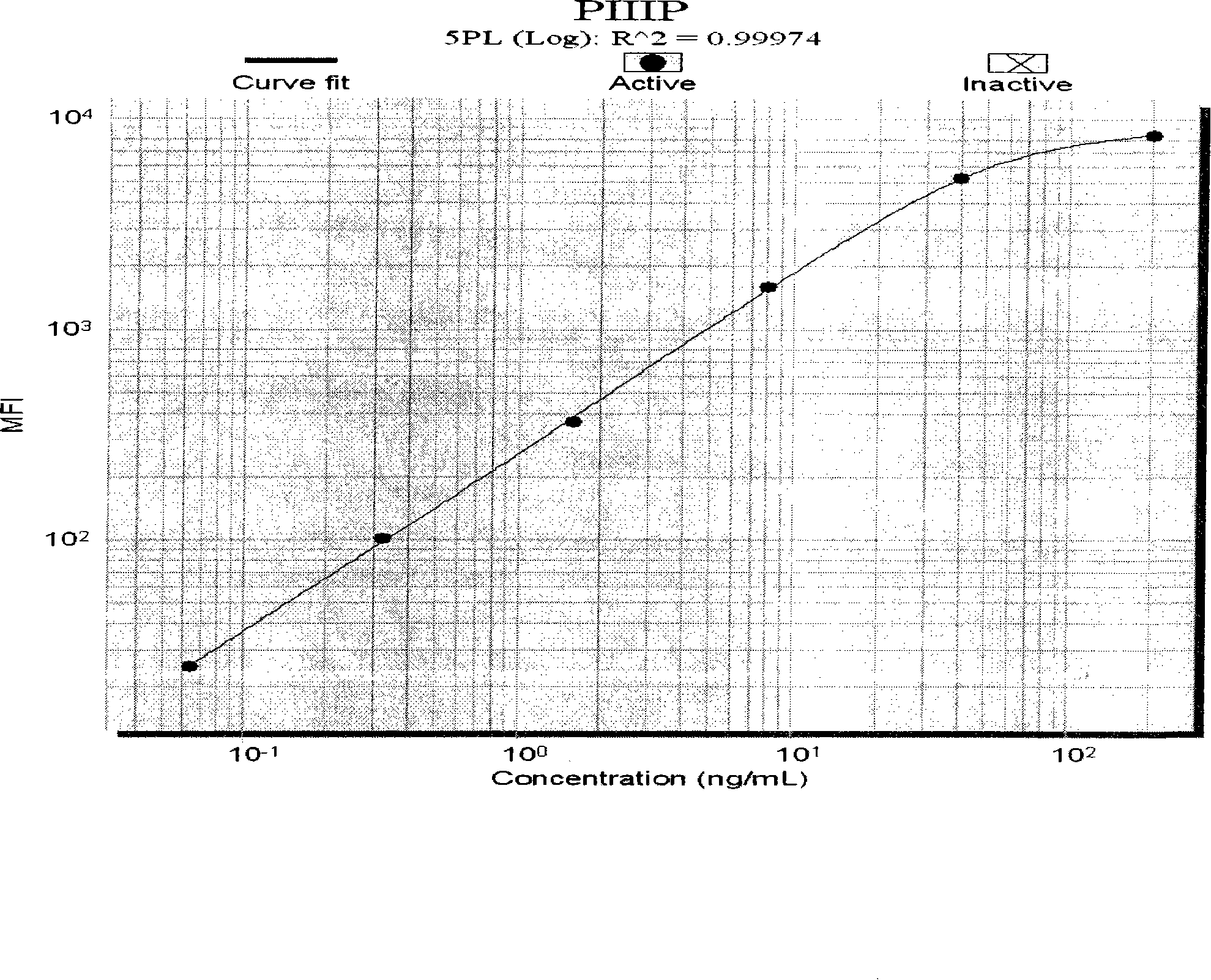
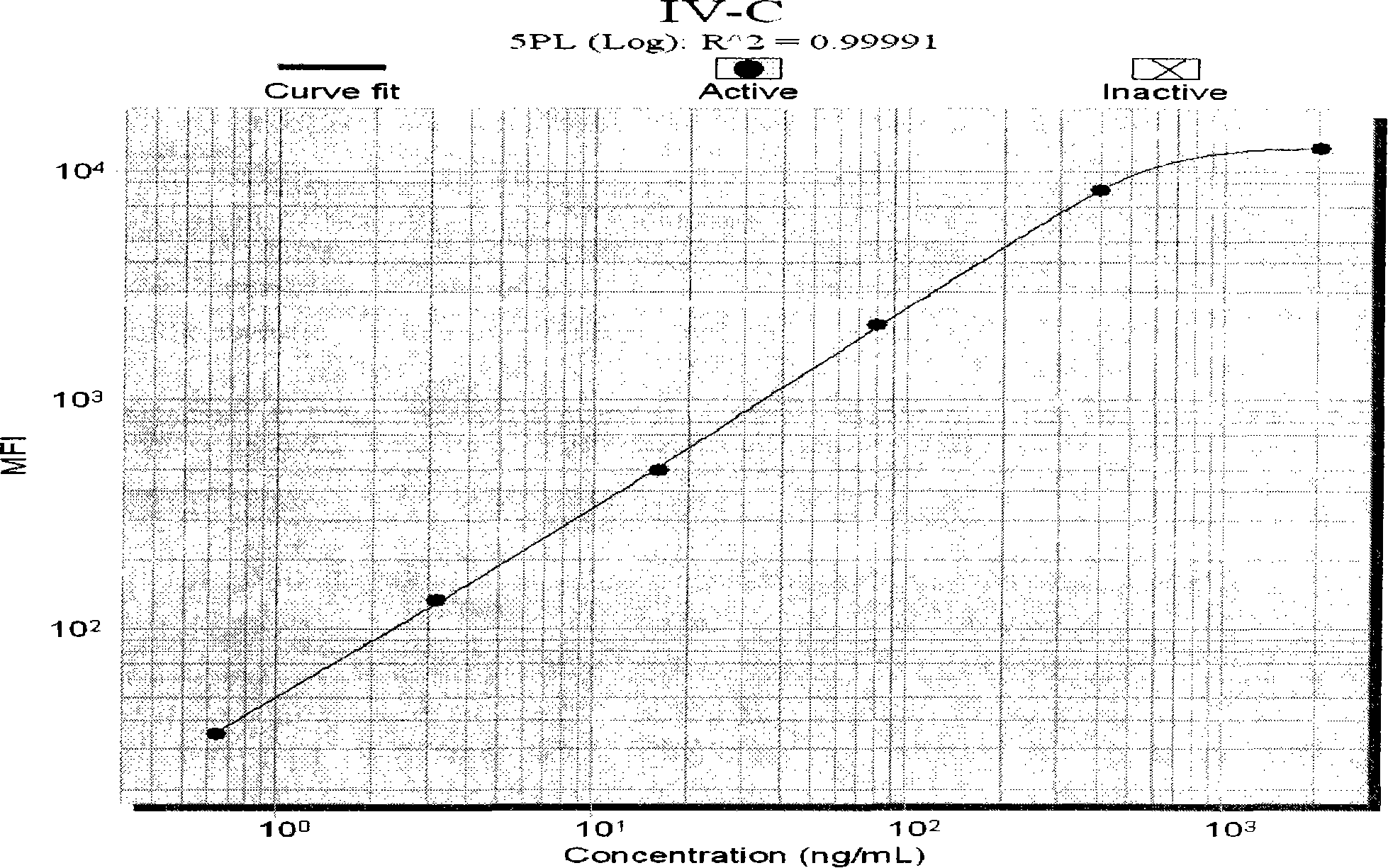
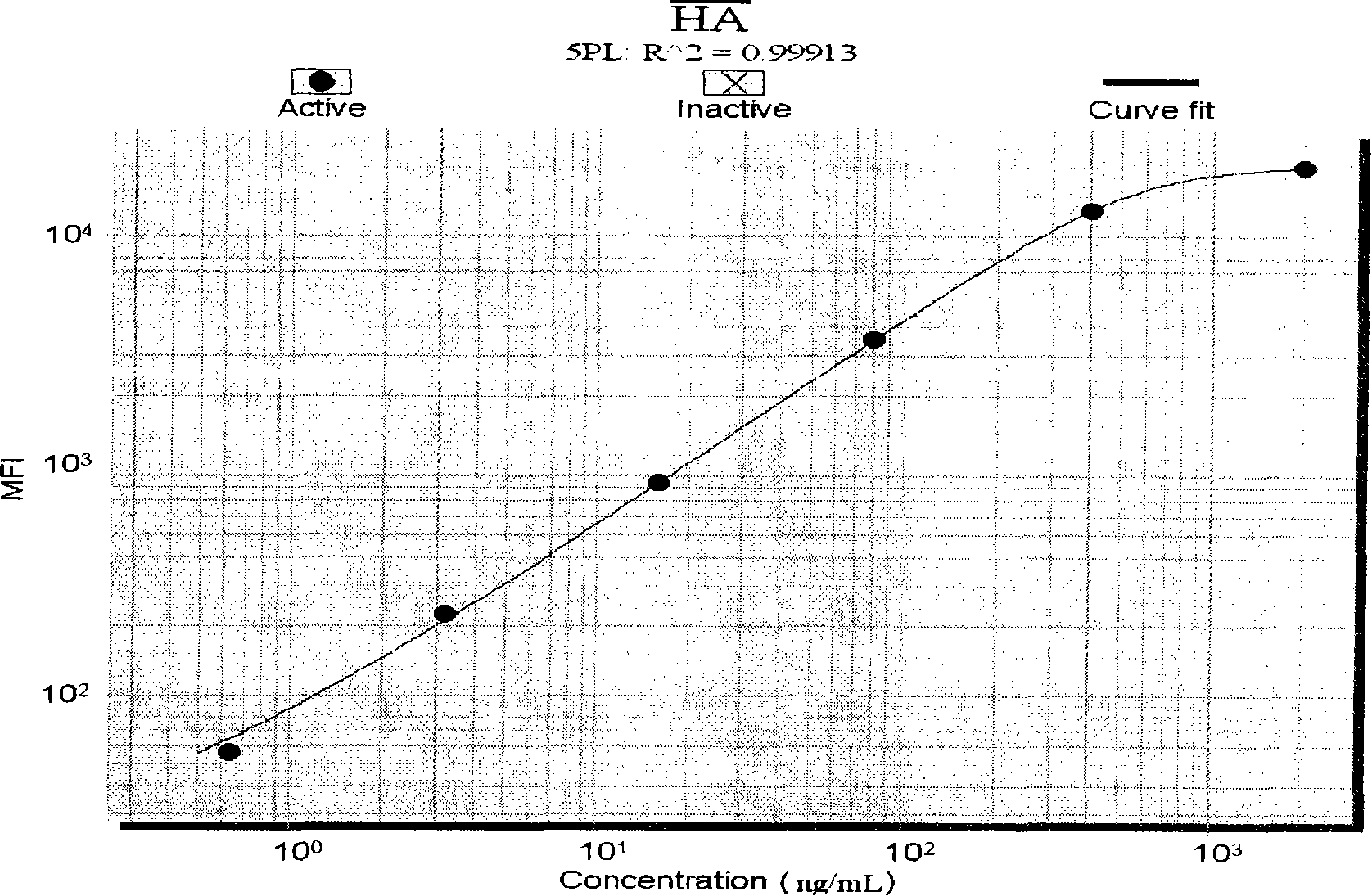
The invention discloses a liquid phase chip for detecting liver fibrosis, which mainly includes: (1) 4-plex coated microspheres: containing respectively coated type III procollagen (PIIIP) capture antibody, type IV collagen and its fragment (IV-C) capture antibody, laminin (LN) capture antibody and hyaluronidase (HA) capture antibody with different color-coded microspheres; (2) 4-plex biotin-labeled detection antibody: respectively Biotin-labeled detection antibodies of PIIIP, IV-C, LN, HA; and (3) streptavidin phycoerythrin. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the liquid phase chip. The liquid phase chip for liver fibrosis detection of the present invention has the advantages of no side effects, high throughput, multi-indicator parallel detection, high sensitivity, good repeatability, rapid and accurate detection, low cost and the like.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Ganoderma lucidum lactone compound and pharmaceutical composition, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103788038AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTGanoderma lucidum
The invention provides six novel terpene compounds obtained by purifying traditional Chinese medicine ganoderma lucidum, a pharmaceutical compound using six novel terpene compounds as active ingredients, a preparation method of the novel terpene compounds and application of the novel terpene compounds in the preparation process of pharmaceuticals and health-care foods for treating diabetic nephropathy or chronic kidney diseases. The compound has the remarkable inhabitation effect on rat glomerular cell strain secretion IL-6 induced by high glucose, Fibronectin and IV collagen and active oxygen effect. The compound has application prospect in preparation of the pharmaceuticals for treating diabetic nephropathy or chronic kidney diseases.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lotion for treating hormonous dermatitis
InactiveCN105012220AReasonable compositionSignificant effectCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsInflammatory edemaAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a lotion for treating hormonous dermatitis. Besides multiple moisturizing effective ingredients, a pseudoalteromonas leavening extract is added to serve as a core of the lotion, is exopolysaccharide extracted from pseudoalteromonas, and can be used for promoting synthesis of I-type, III-type and IV-type collagen, so that the collagen has better quality; the capability of repairing a wound surface can be improved by means of the function of activating immune cells, and the defense capability of the skin system can be improved; because the skin barrier of hormonous dermatitis is destroyed, the collagen binding capability is reduced, the skin barrier is reconstructed by activating resistant cells of the skin, the metabolic cycle is improved, and the skin can quickly metabolize dermatitis to achieve a curing effect. The lotion is reasonable in formula, natural in ingredients, remarkable in curative effect and extremely low in recurrence rate, and can be used for effectively treating flushed face, acne rosacea, serious acne, inflammatory edema, acute pustular eruption and other symptoms caused by hormonous dermatitis, and the hormonous dermatitis can be finally cured.
Owner:陈见芬
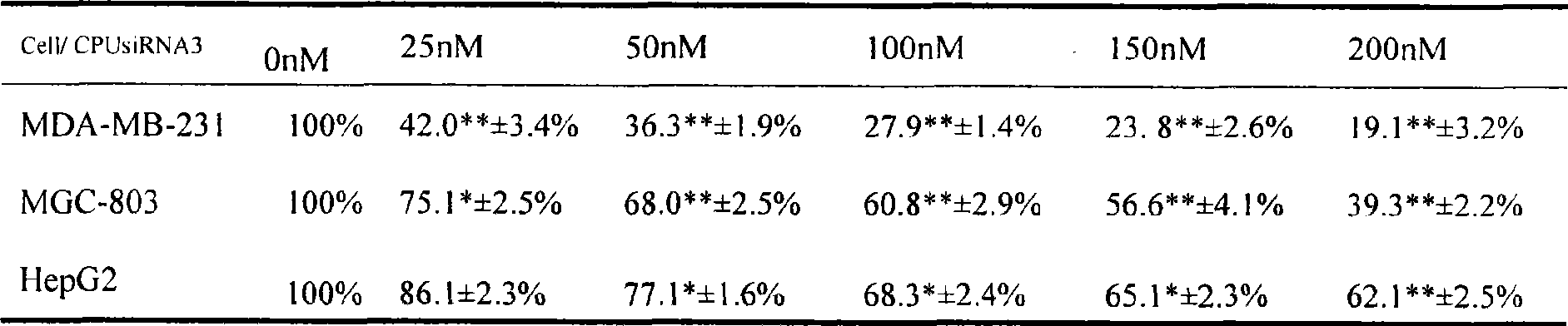
Use of high efficiency siRNA for preparing tumor migration inhibition drug
InactiveCN101445534AInhibit migrationInhibited DiffusionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthType IV collagen
The invention belongs to the biological medicine field, in particular relating to the use of a high efficiency small interfering RNA for preparing a tumor migration inhibition drug. The high efficiency small interfering RNA can silence the expression of survivin, change the adhesive force of breast cancer, gastric cancer and liver cancer cells against IV collagen, and inhibit the migrating ability of the breast cancer, gastric cancer and liver cancer cells at two-and three-dimensional levels. The small interfering RNA can also prepare the drug for inhibiting the tumor migration.
Owner:YICHUN UNIVERSITY
Method for producing tissue engineering skin outside of the body with scarifiskin stem cell
InactiveCN101152580AImprove proliferative abilityGuarantee normal developmentProsthesisDispaseBiology
The invention provides a method of manufacturing tissue engineering skin out of the body with epithelial stem cells. The method includes the following steps: (1) preparation of the epithelial stem cells: epithelial cells are made into cell suspension liquid, adhered and screened by IV collagen, and cultivated with epithelial stem cell media; (2) preparation of deepitheliarizing derma; (3) construction of the tissue engineering skin: epithelial stem cells for 2nd to 5th generation cultivation are selected, Dispase enzyme is adopted to digest the bossy cell patches in the size of rice to soya beam, the patches are inoculated to the deepitheliarizing derma, the tissue media is added, to cultivate the tissue engineering skin underwater or on the water. The tissue engineering skin constructed by the method of the invention is more suitable for the biological characteristics of human skin.
Owner:陆洪光
Serum-free cryoprotectits agent
InactiveCN102578077ANo serum components remainClear ingredientsDead animal preservationSerum igeExtracellular
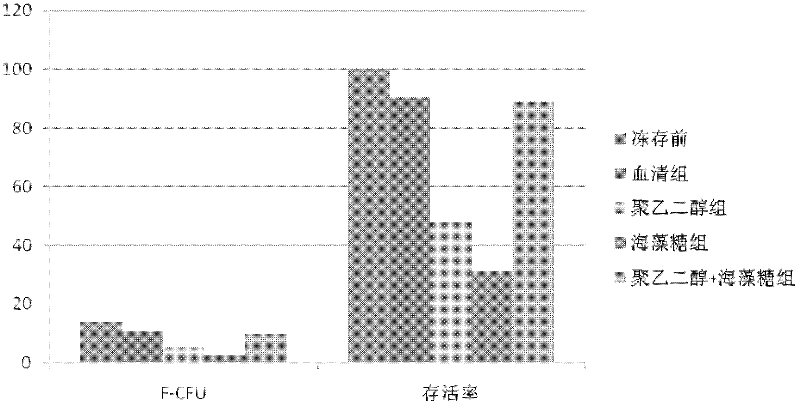
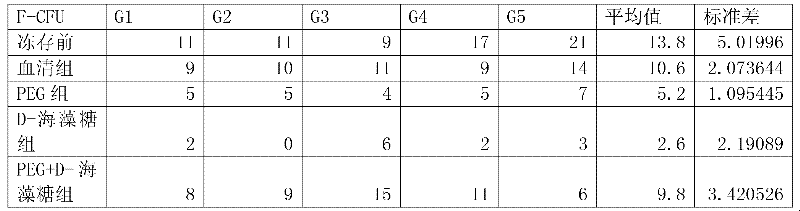
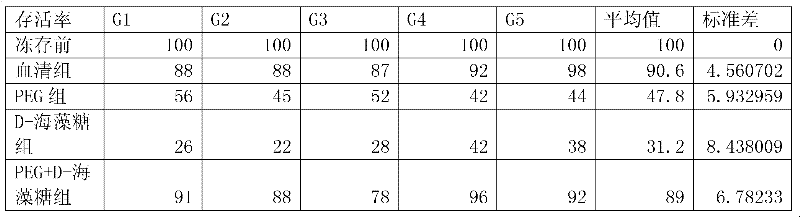
The invention disclose a serum-free cryoprotectits agent which comprises an intracellular permeating protecting agent and an extracellular protecting agent, wherein, the extracellular protecting agent comprise NaCL, KCL, Na2HPO4.12H2O, KH2PO4, PEG(400 to 2000), D-trehalose and type-IV collagen; and the intracellular permeating protecting agent is DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide). The invention further discloses a method for preparing the serum-free cryoprotectits agent. The serum-free cryoprotectits agent does not contain serum from any source, and serum cannot be left over when cells are stored under low temperature; and in addition, the serum-free cryoprotectits agent has definite and simple components, is easy to prepare, and can be used for storing mesenchymal stem cells under low temperature.
Owner:四川全组生命科技有限公司
Method for separating and extracting hUC-MSC from umbilical cord outer layer amnion tissue
InactiveCN105420185AReduce incubation timeImprove securitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsUmbilical cord tissueDigestion
The invention provides a method for fast separating and extracting human Umbilical Cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSC) from umbilical cord outer layer amnion tissue. The method includes the following steps that fresh collected umbilical cord tissue of a healthy newborn is taken, transported on ice in double-antibody-containing umbilical cord storing transporting liquid, washed and disinfected with 75% ethyl alcohol and normal saline, outer layer amnions are separated bluntly after blood vessels are rejected, mechanically smashed and treated with erythrocyte lysate for 3 min, IV type collagenase digestion is used, and a digestion product is cultured in a suspension mode with a serum-free culture medium after being screened through a 100-200-mesh sieve; medium change is carried out every three to five days, supernatant is taken to detect cell contamination, after the attachment rate in a plate reaches 30-70% and trypsinization is used, cell passage amplification is collected centrifugally, and confluence is carried out when the cell confluence rate reaches 90% or above, the cells are collected for cryopreservation, and the biological characteristics of hUC-MSC are detected.
Owner:郭镭 +1
Application of artesunate in preparation of medicine for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveCN105078964AReduce infiltrationReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDrugType IV collagen
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUILIN MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com