Patents
Literature
42 results about "Perivascular Satellitosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
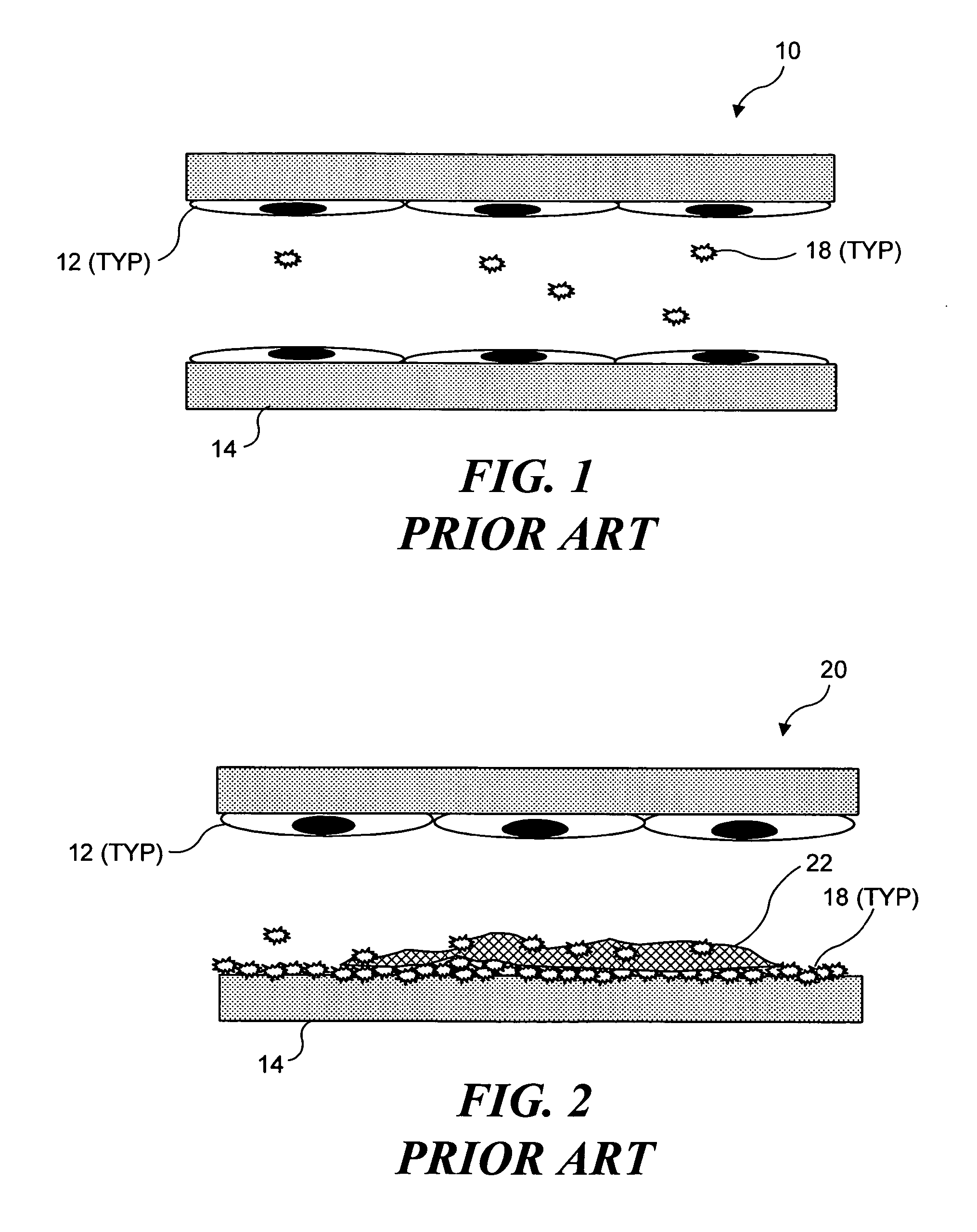
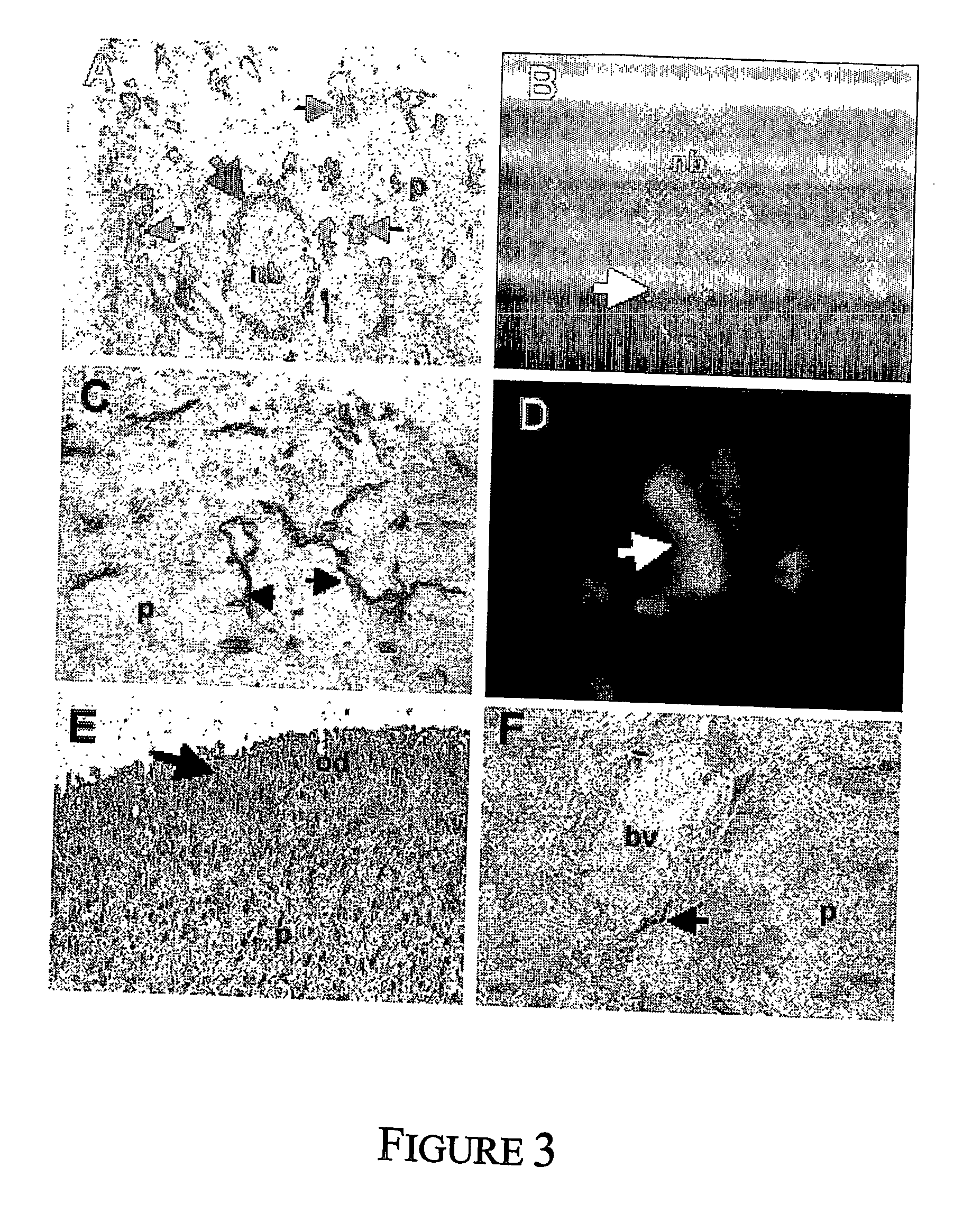
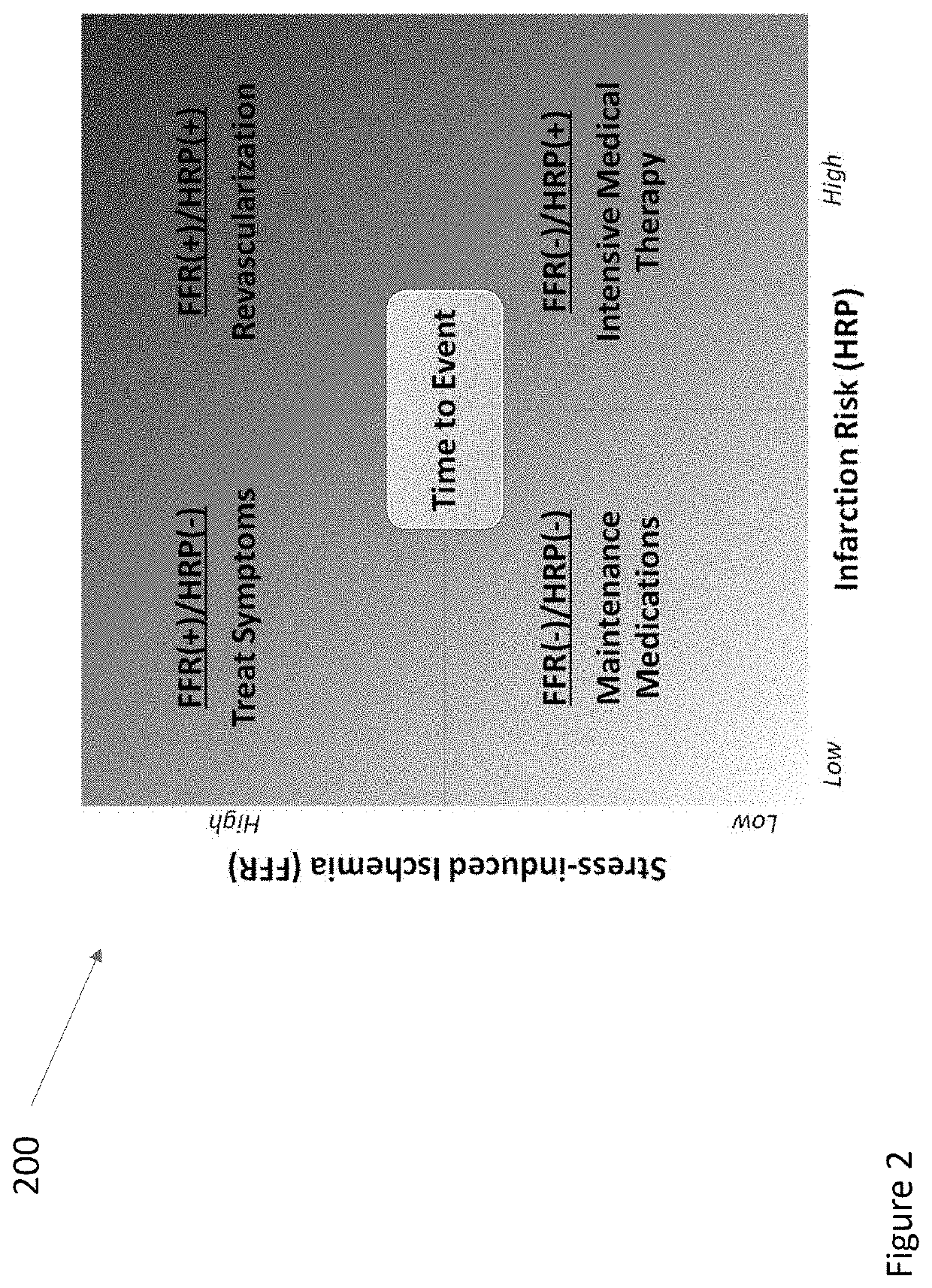
A morphologic finding that refers to the accumulation of glial cells encircling vessels in a tissue specimen.
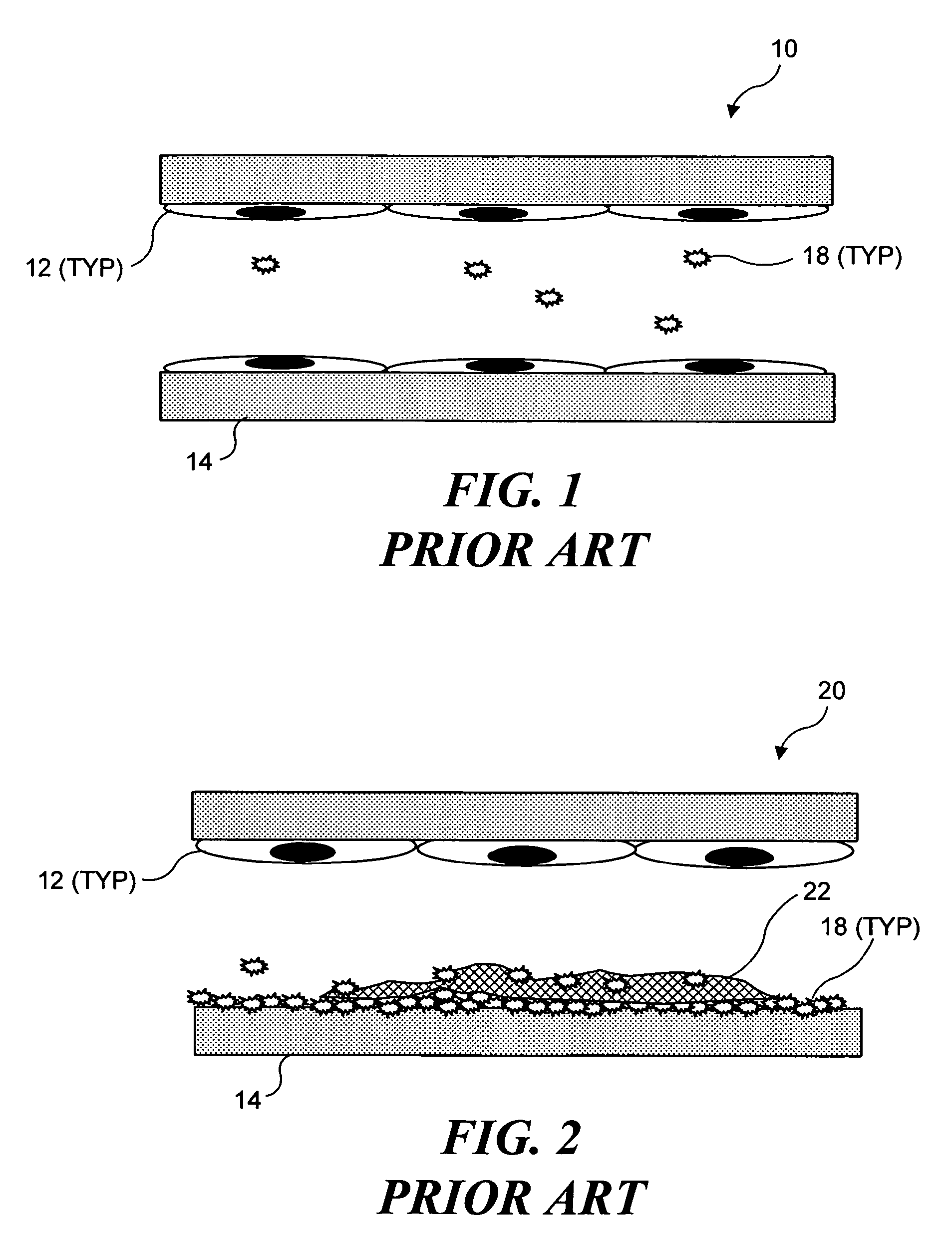
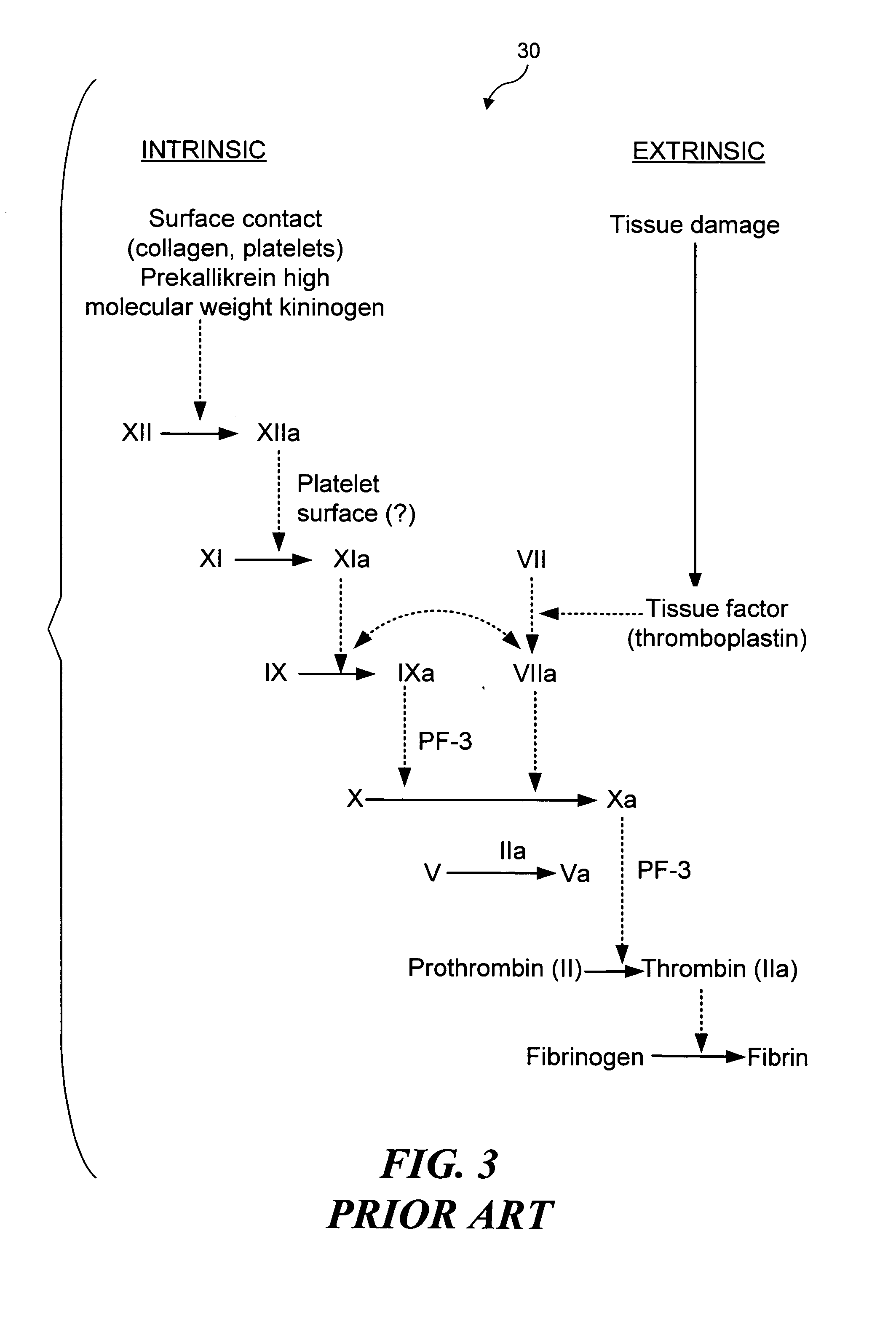
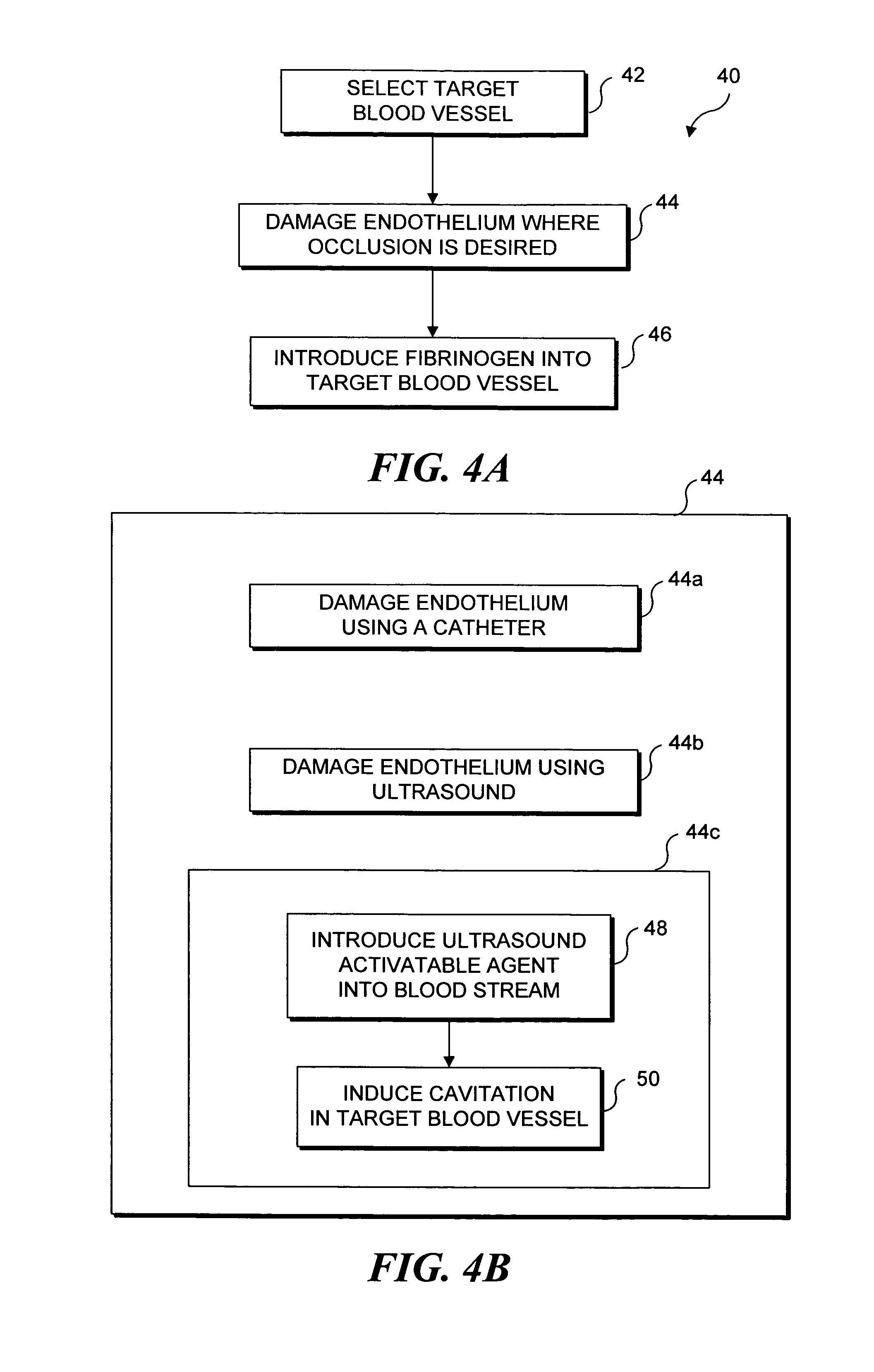
Ultrasound target vessel occlusion using microbubbles
InactiveUS7591996B2Eliminate heat damageFew techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationThrombus
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
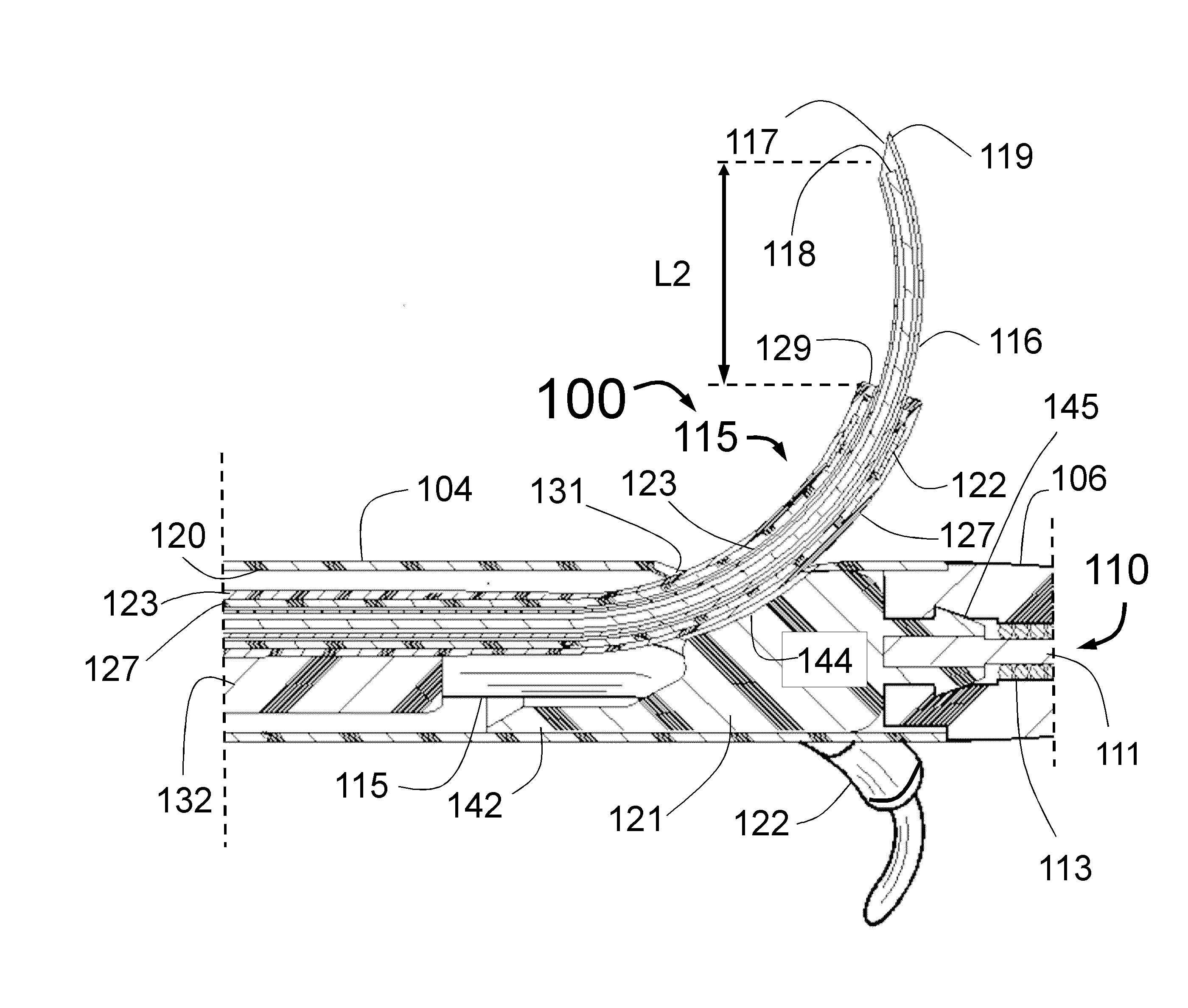
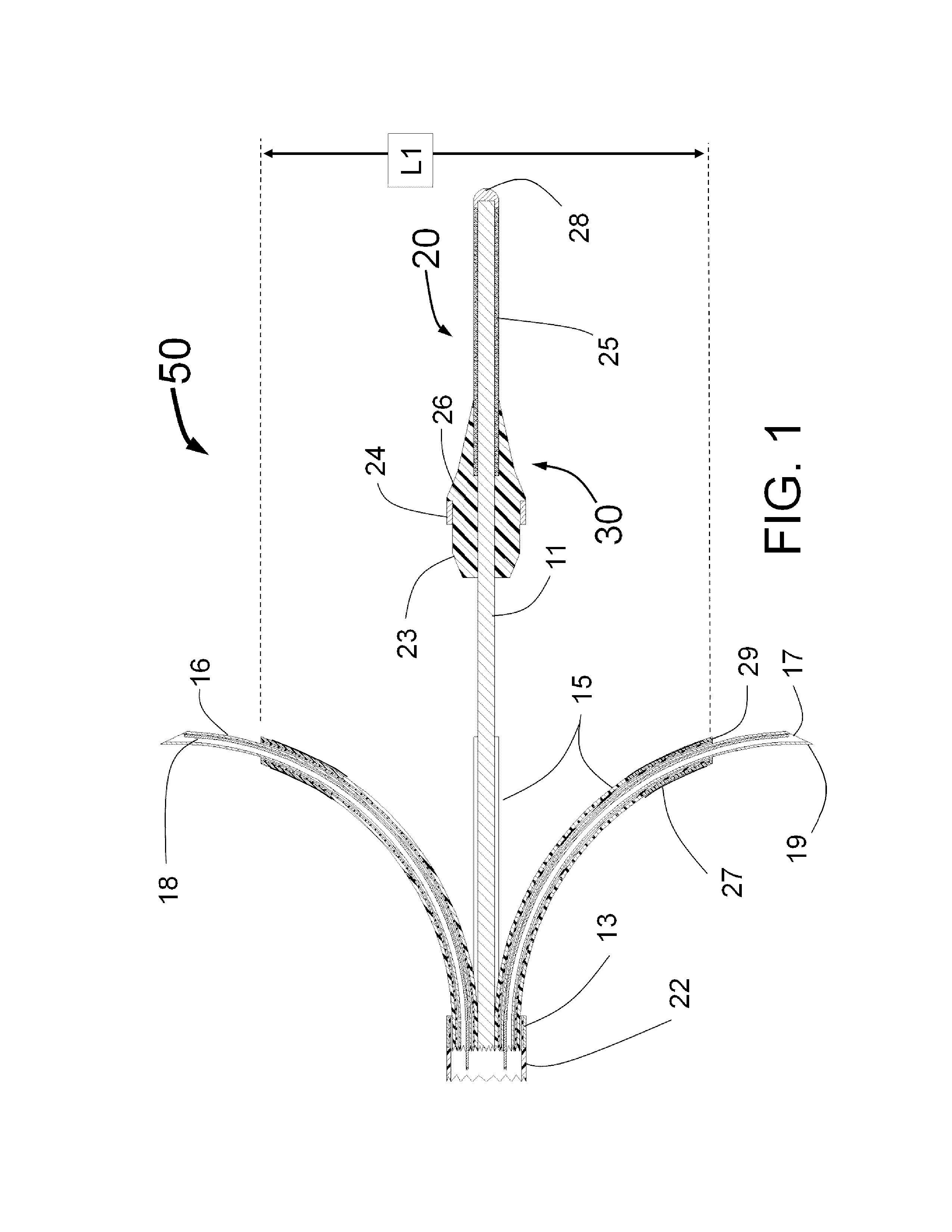
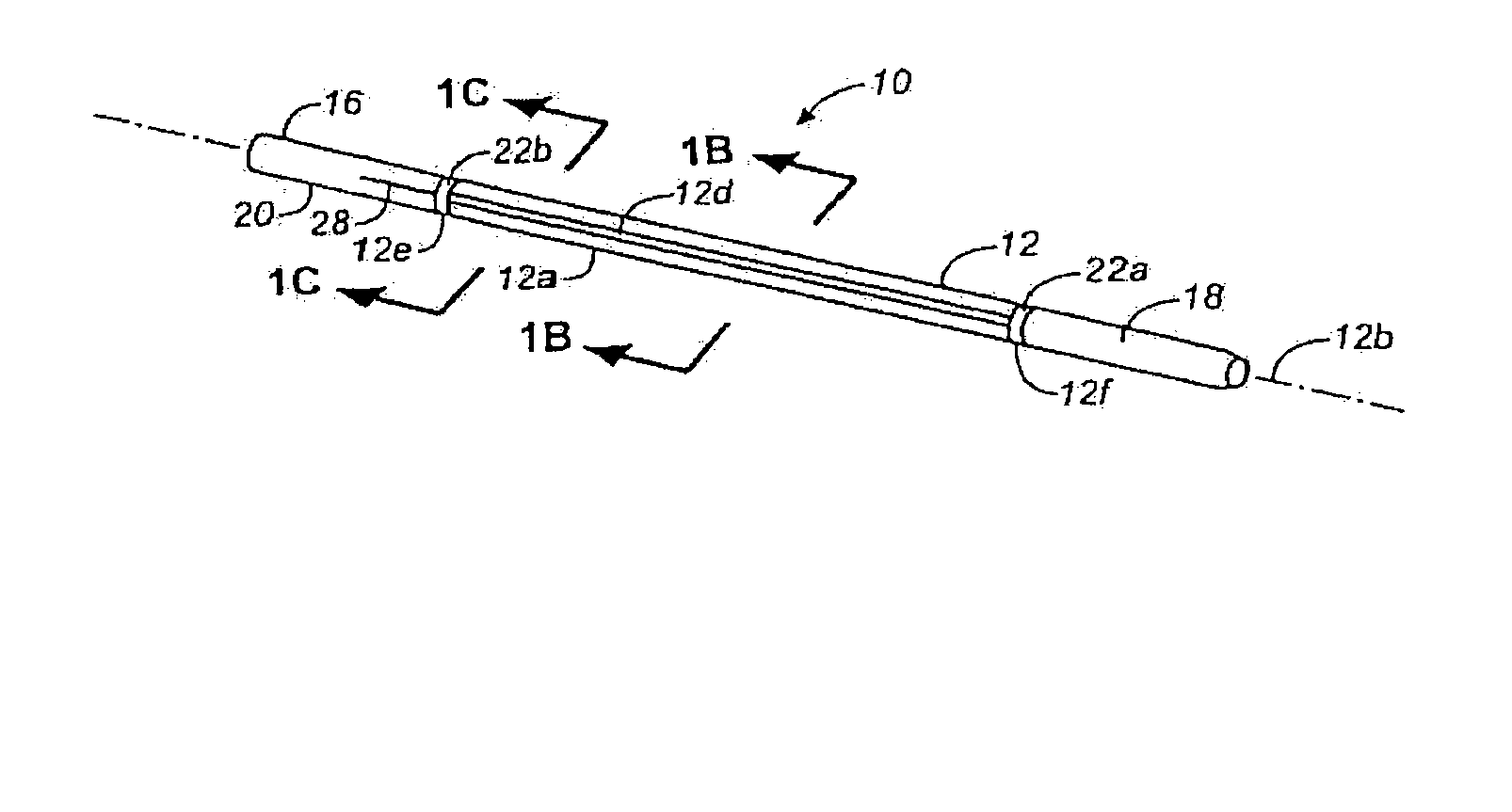
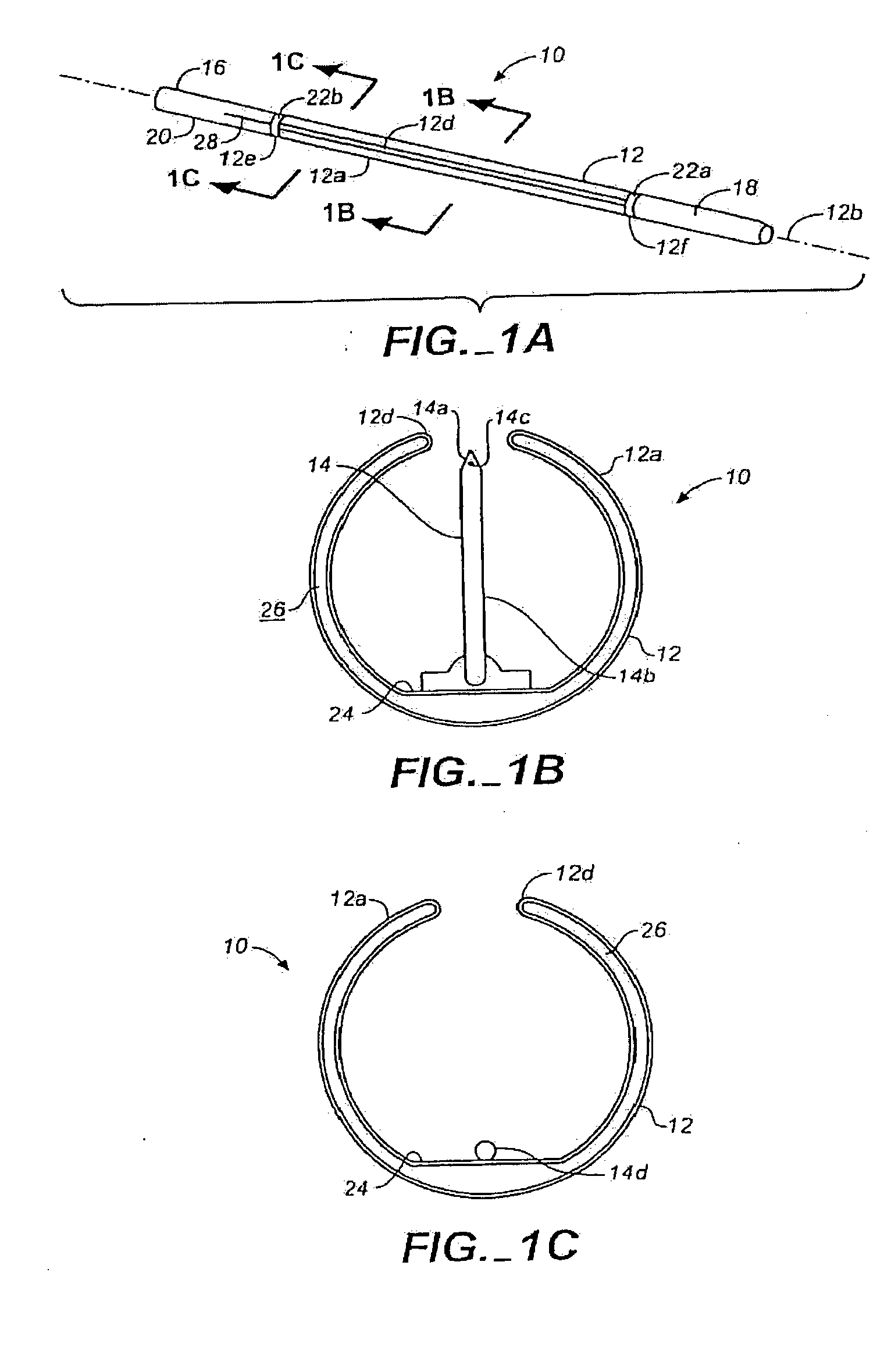
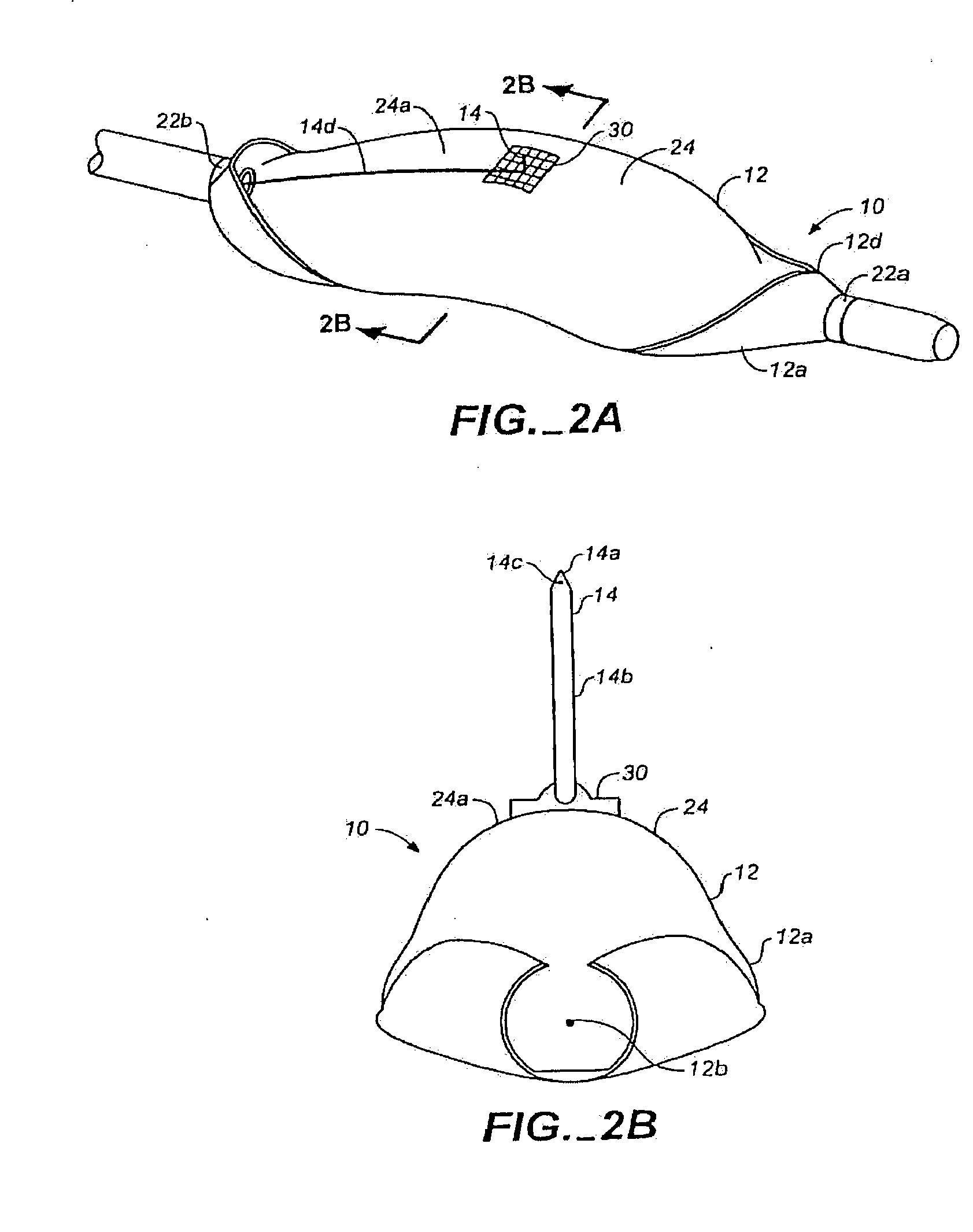
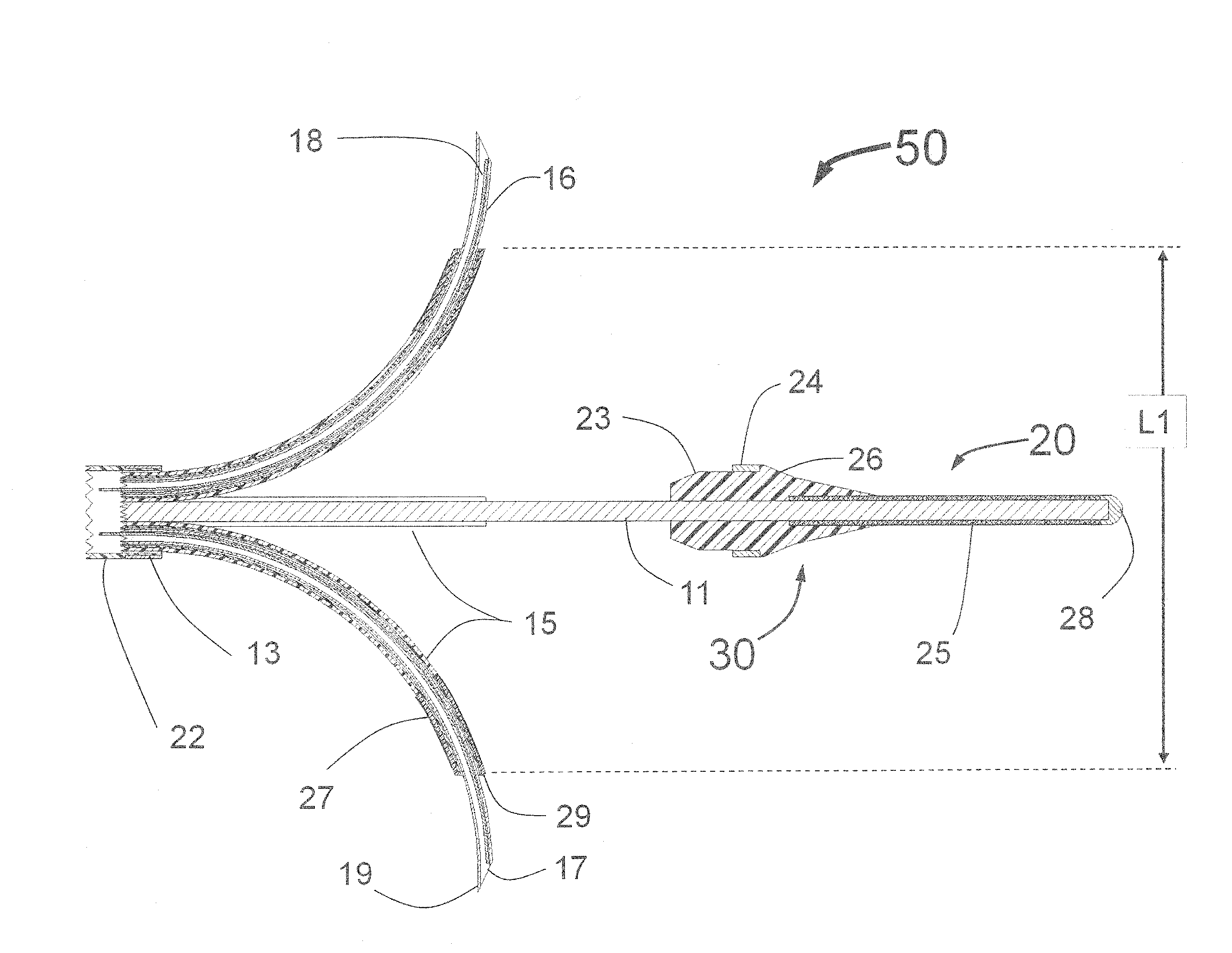
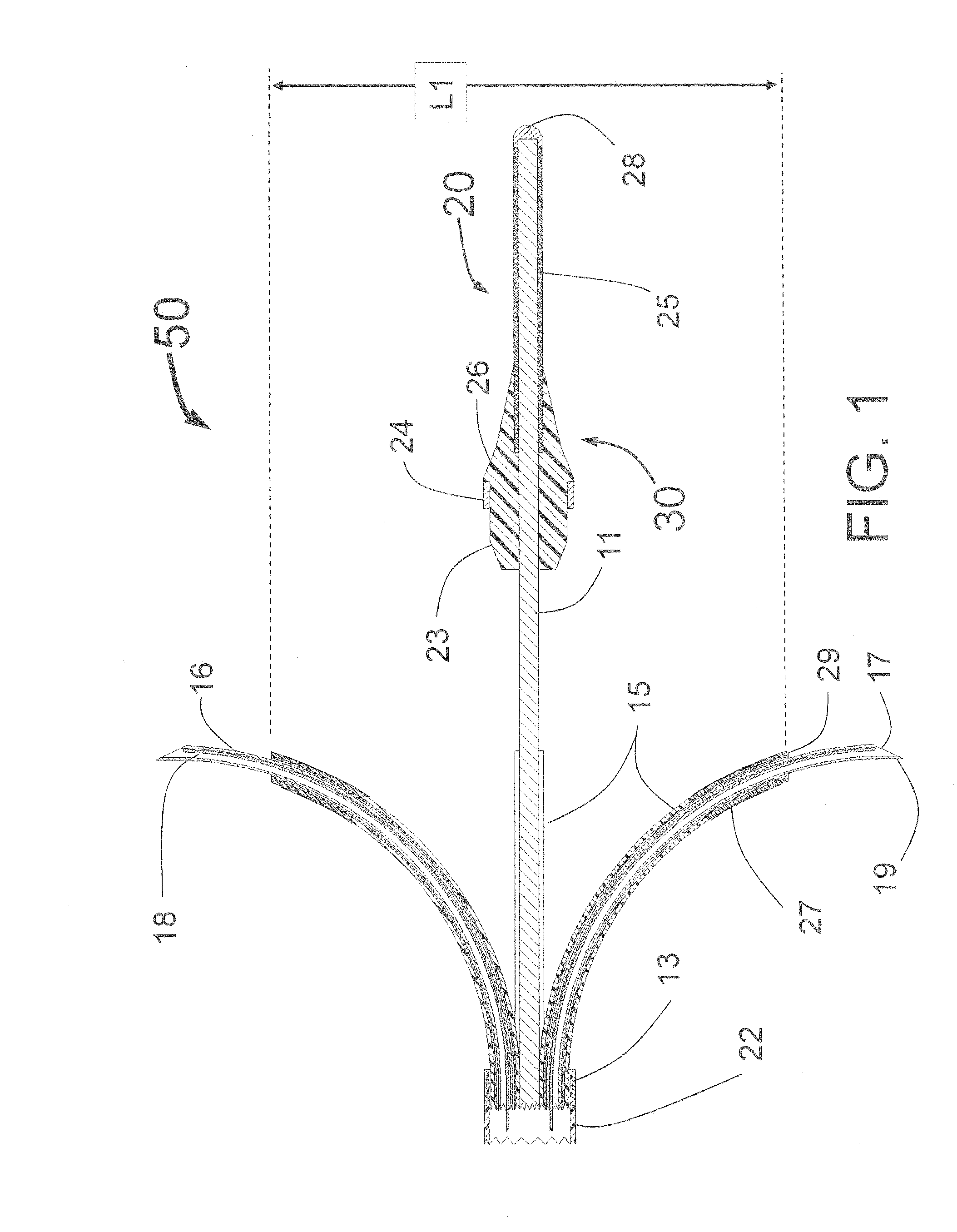
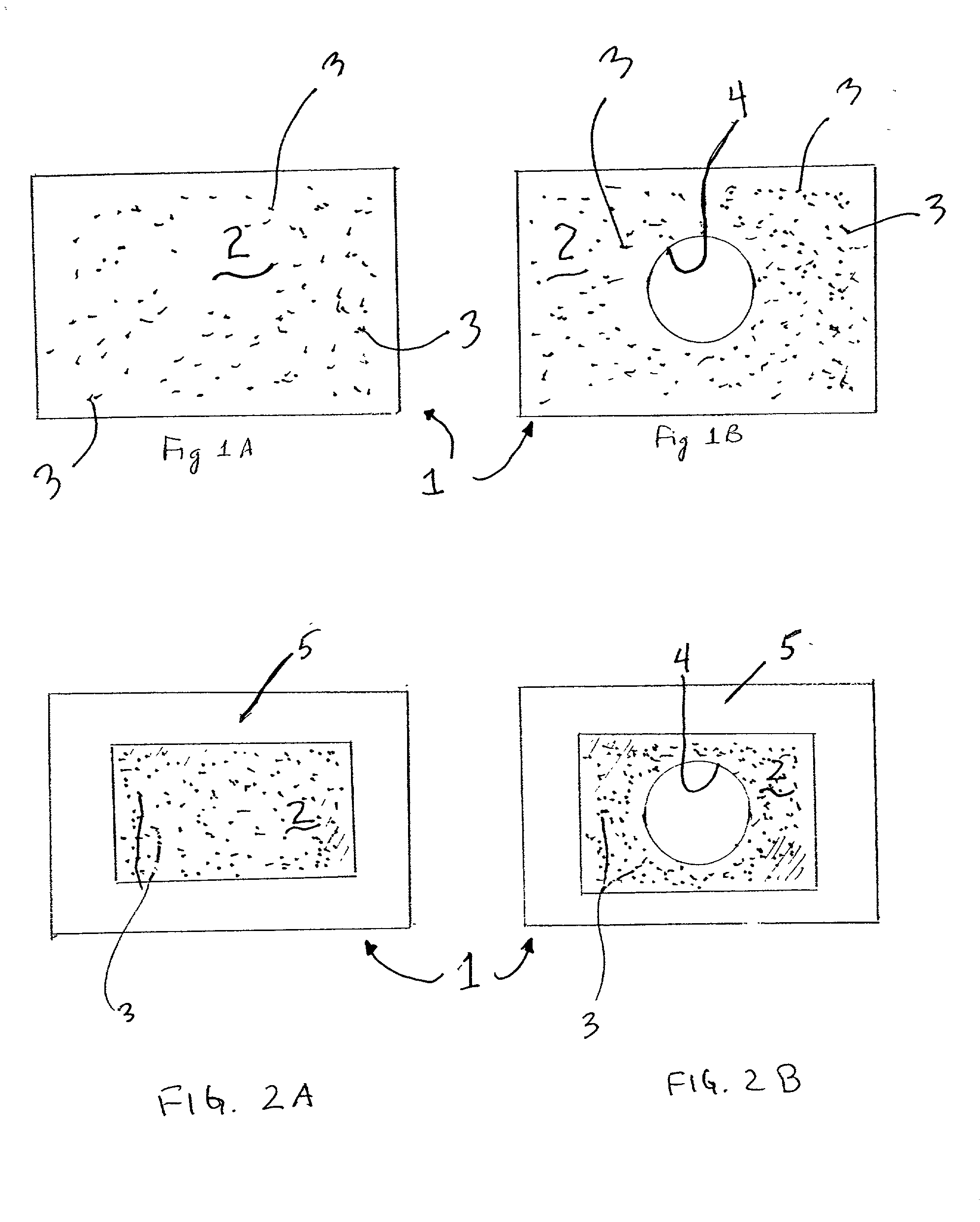
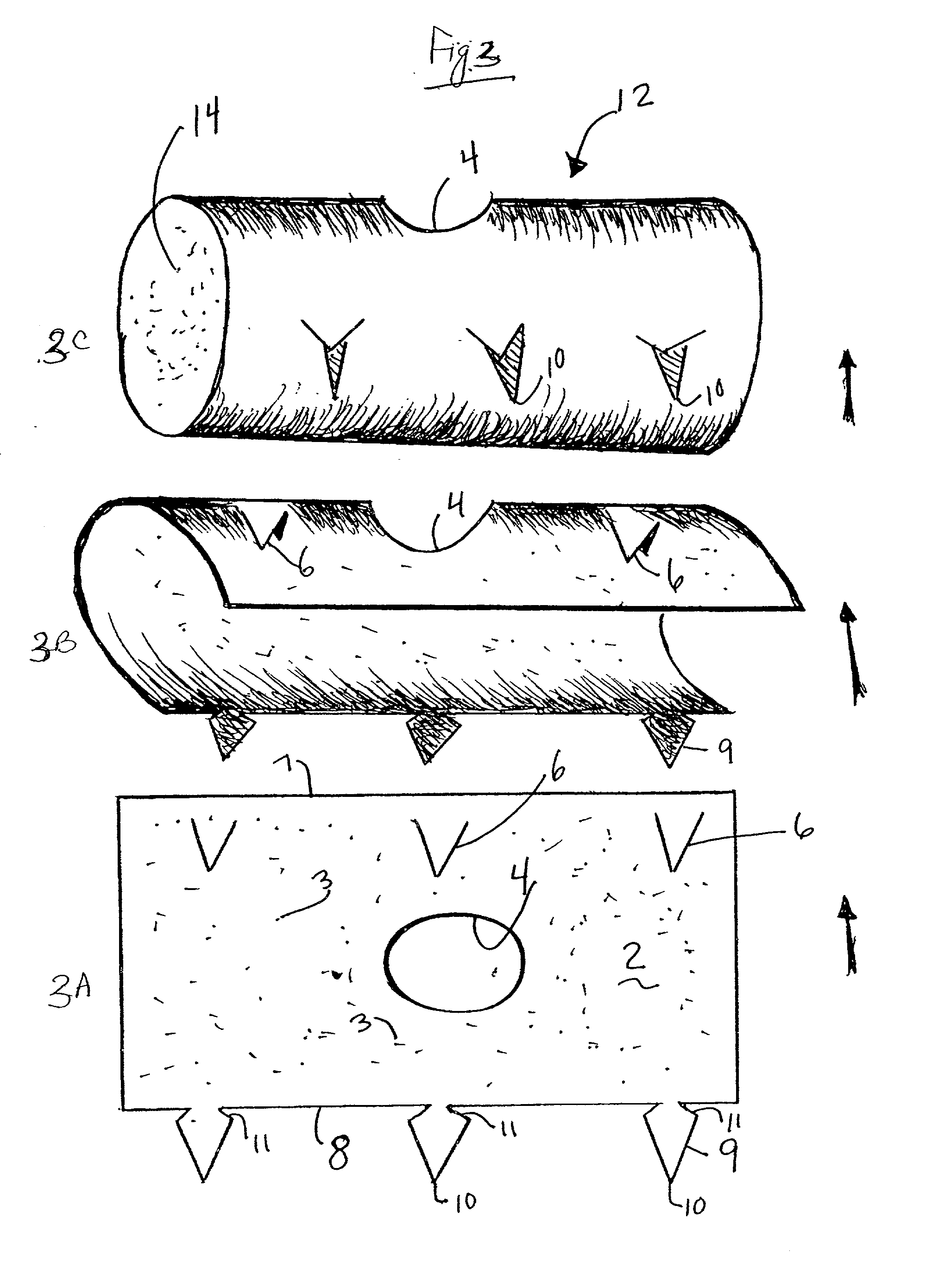
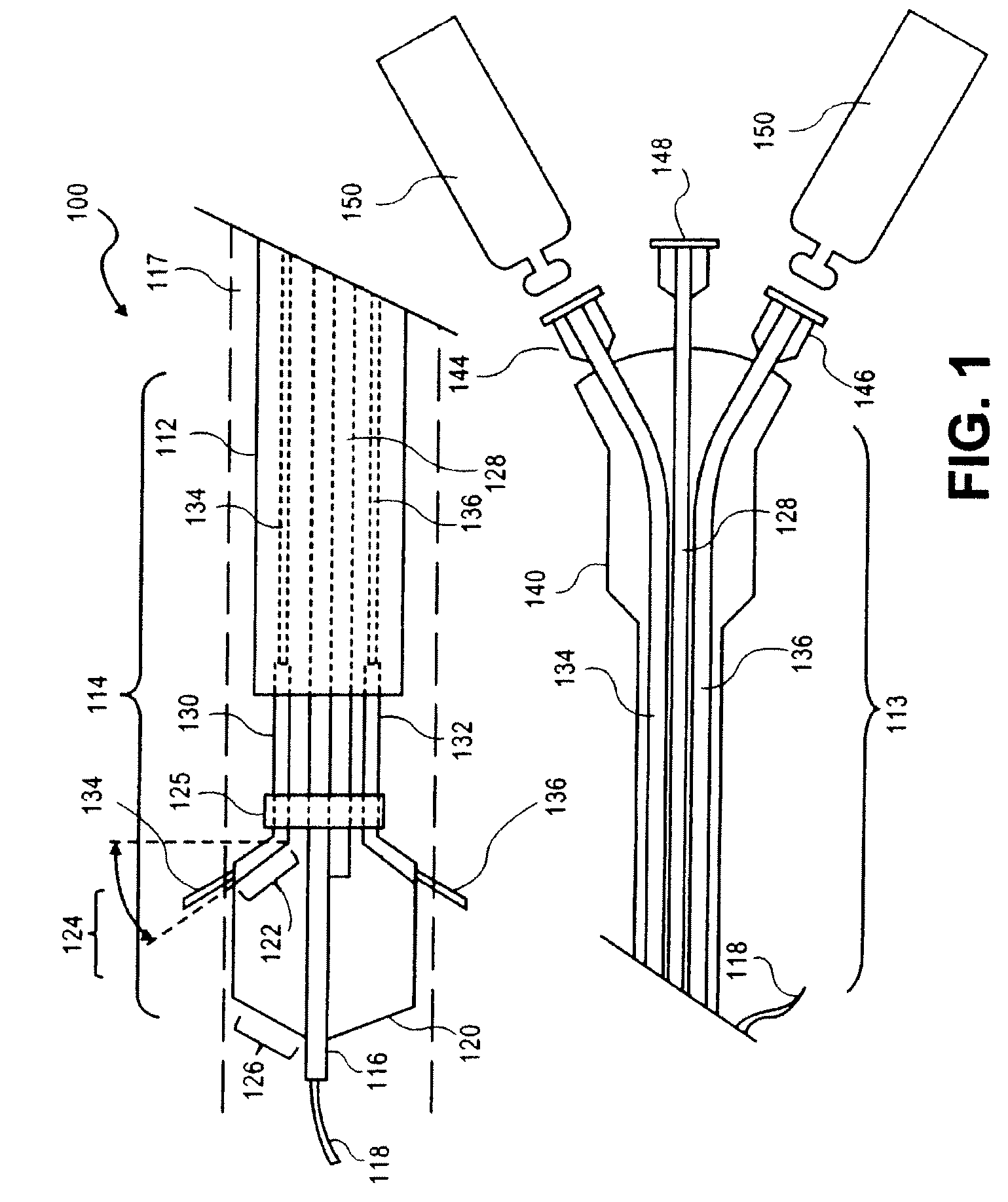
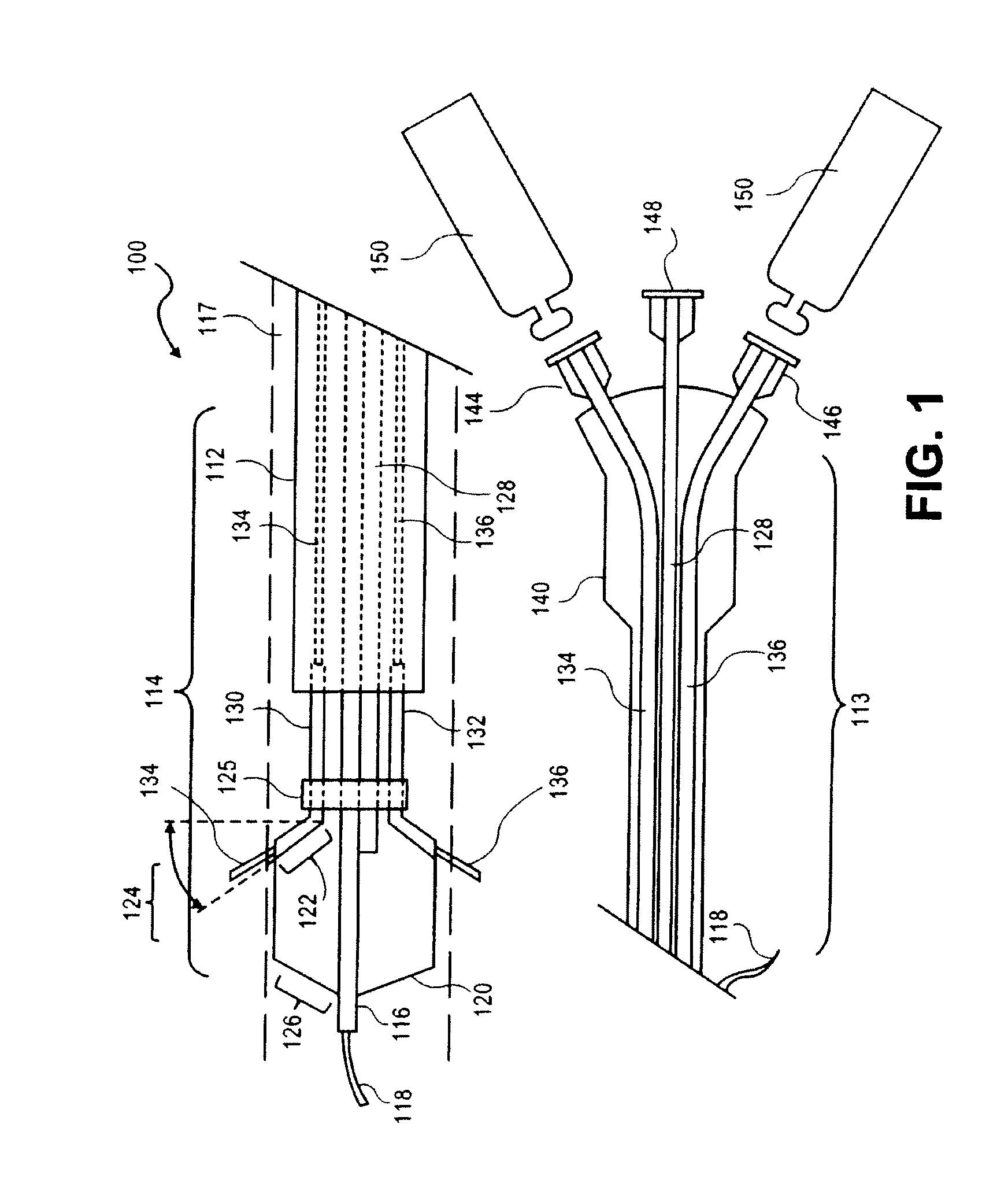
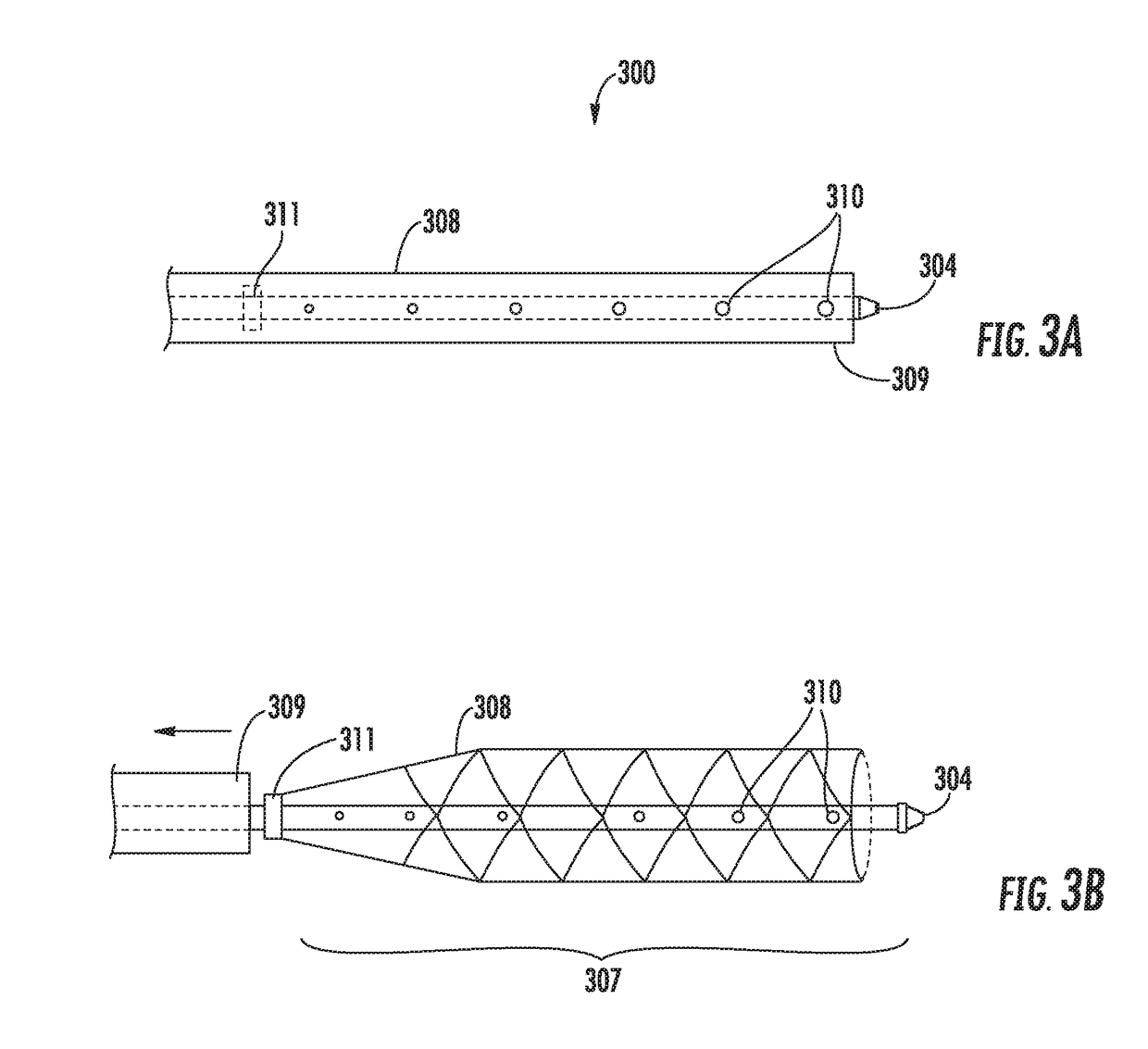
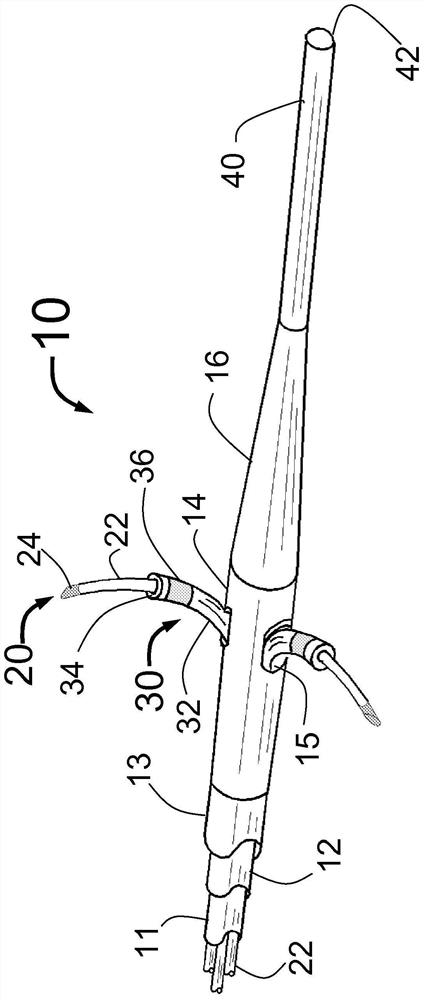
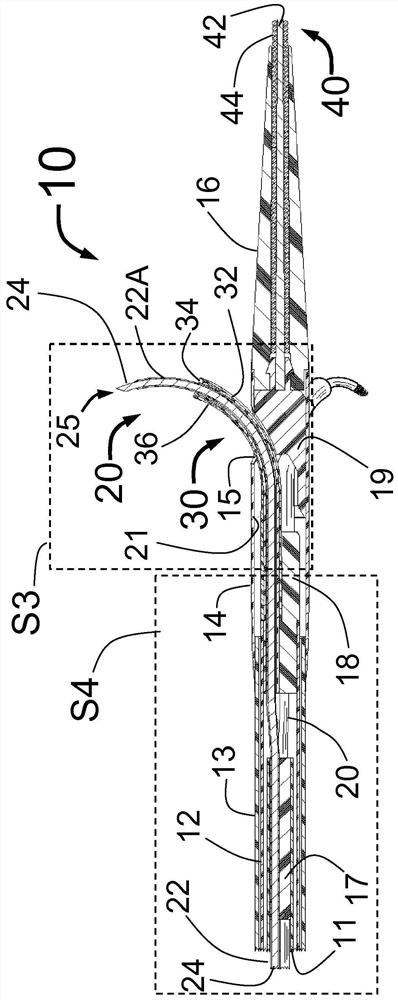
Peri-vascular tissue ablation catheter with support structures
ActiveUS8740849B1Add supportImprove uniformityHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiagnosticsVascular tissueGuide tube
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through supported guide tubes which expand with open ends around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The system also includes means to limit and / or adjust the depth of penetration of the ablative fluid into and beyond the tissue of the vessel wall. The preferred embodiment of the catheter includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened injection needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Ultrasound target vessel occlusion using microbubbles
InactiveUS20070041961A1Less invasive techniqueSimple technologyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationThrombus
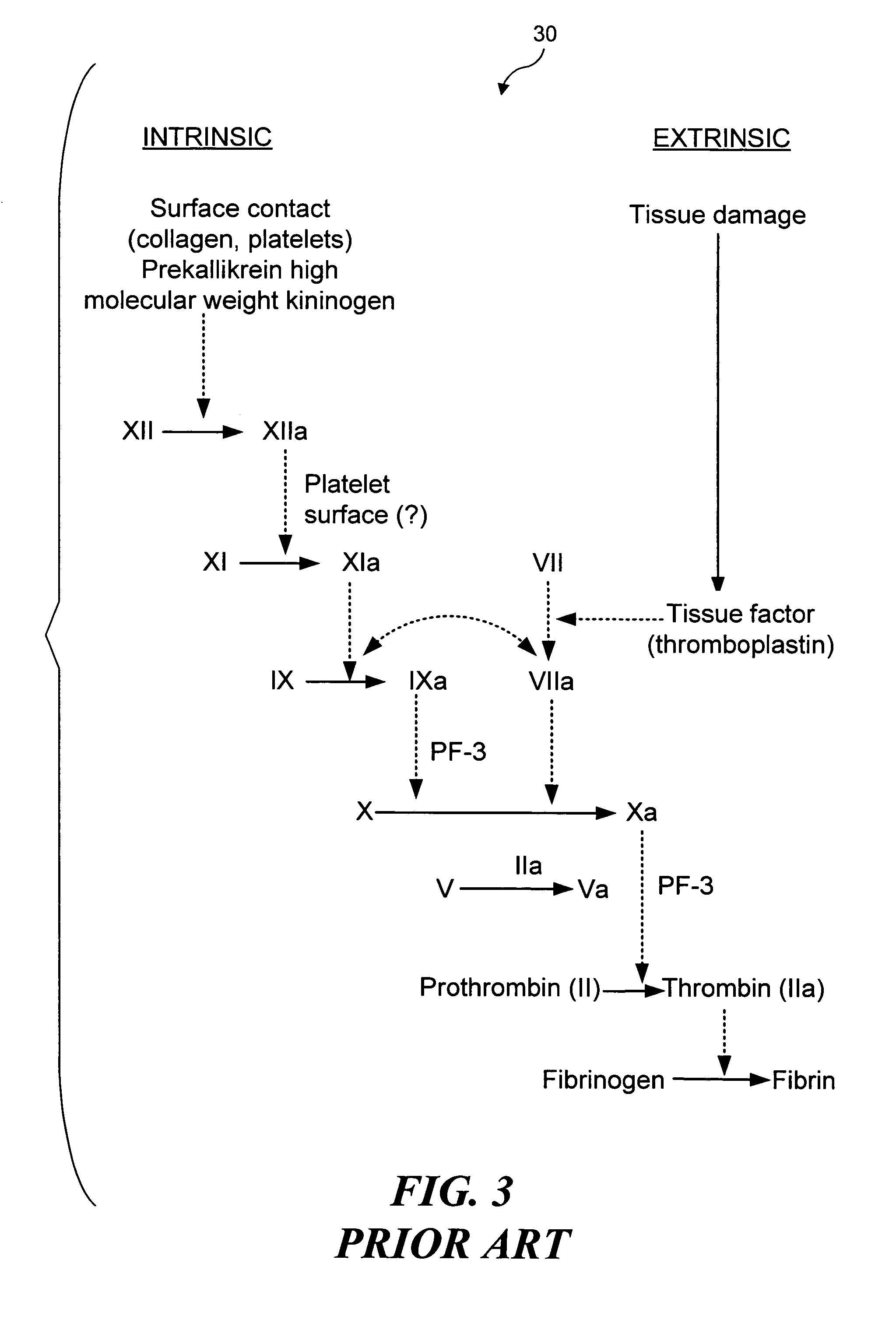
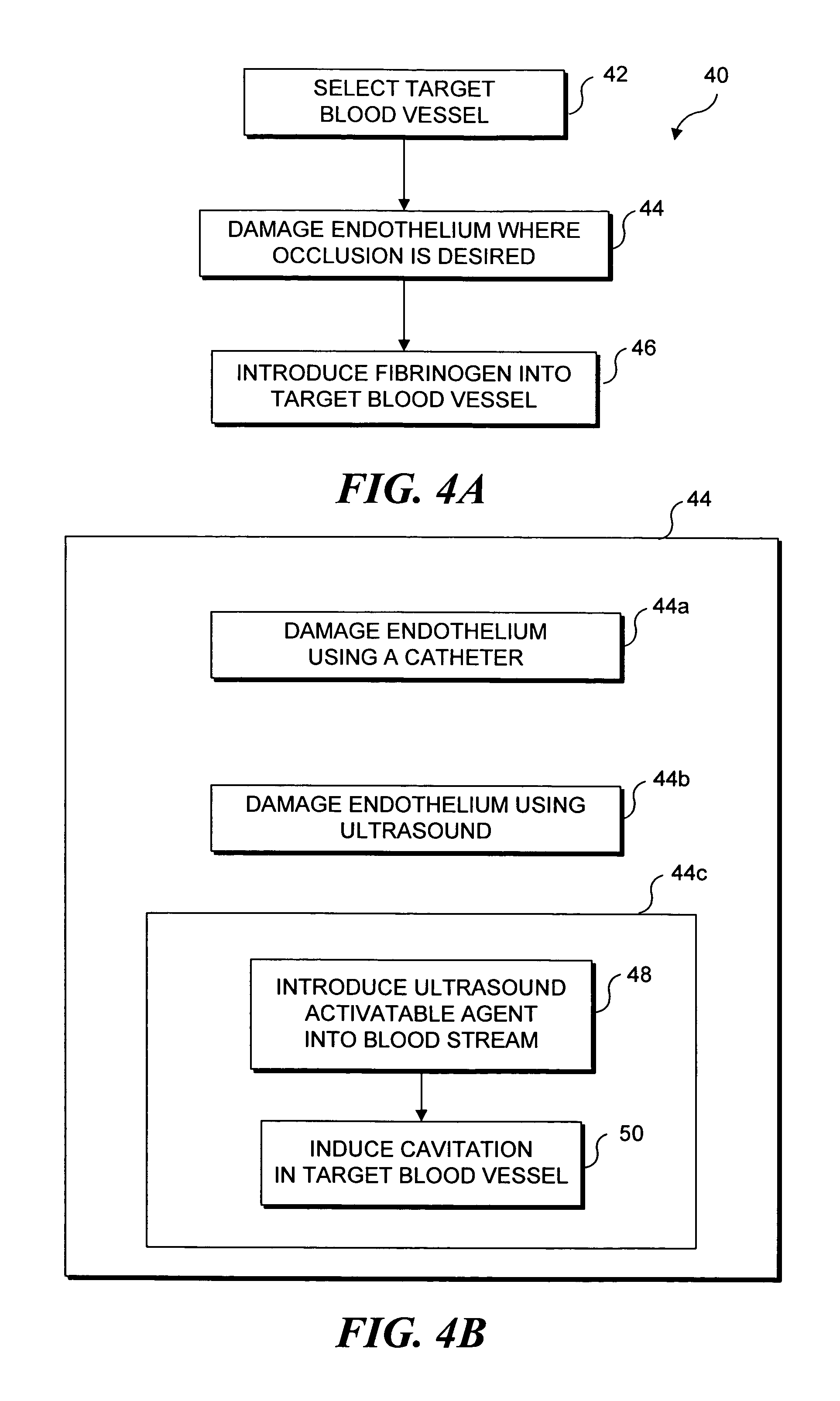
Selective occlusion of a blood vessel is achieved by selectively damaging endothelial cells at a target location in the blood vessel, resulting in the formation of a fibrin clot proximate to the damaged endothelial cells. Additional fibrinogen can then be introduced into the blood vessel if occlusion is not achieved, as the fibrinogen is converted to fibrin by enzymes released by the exposed thrombogenic tissue and activated platelets. Endothelial cells are selectively damaged using thermal effects induced by ultrasound, by mechanical effects induced by ultrasound, or by mechanical effects produced by a tool introduced into the blood vessel (such as a catheter-based tool). A particularly preferred technique for selectively damaging endothelial cells involves introducing an ultrasound activatable agent into the blood vessel, and causing cavitation in that agent using pulses of high-intensity focused ultrasound having a duration insufficient to induce thermal damage in adjacent perivascular tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Methods and systems for ablating tissue
InactiveUS20080045890A1Improve side effectsLess damage to the heart's electrical functionsBalloon catheterMedical devicesAbnormal tissue growthHypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Methods and systems for treating patients requiring tissue ablation for volumetric tissue reduction rely on the injection of ethanol and other tissue-ablating agents into the perivascular space surrounding body lumens, particularly blood vessels or vessels of the alimentary canal, reproductive system and urinary tract. Injection of tissue-ablating agents is intended treat conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, benign and malignant tumors, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and uterine fibroids, for example. Injection may be achieved using intravascular catheters which advance needles radially outward from a body vessel lumen or by transmyocardial injection from an epicardial or endocardial surface of the heart.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
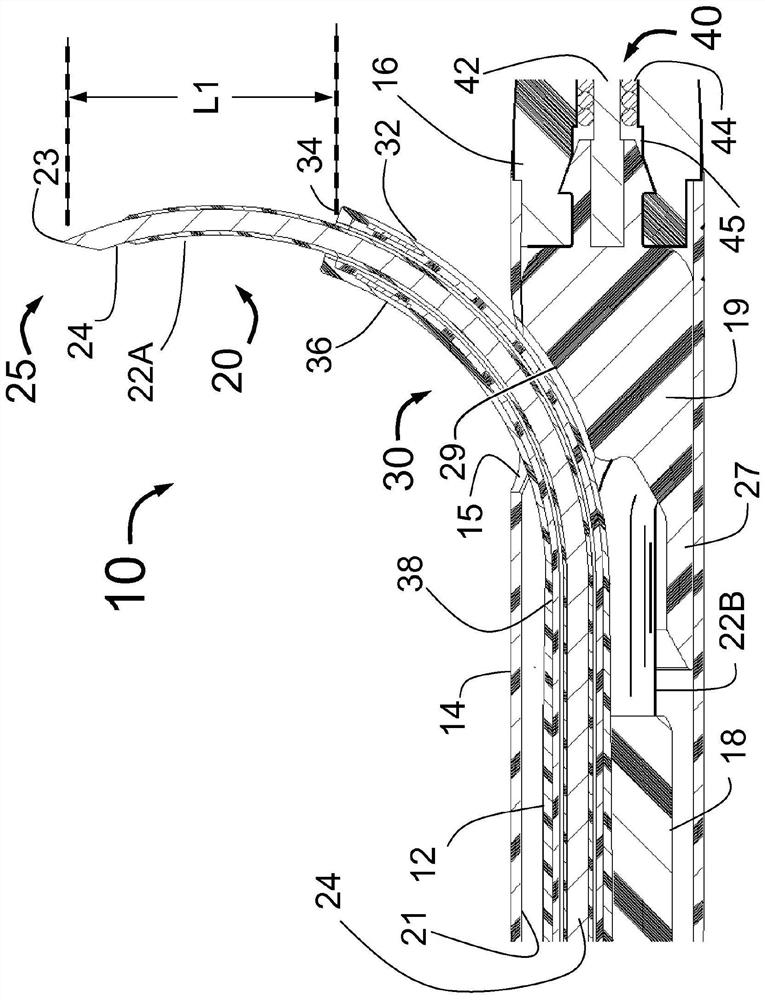
Peri-vascular tissue ablation catheter with support structures
ActiveUS20140236103A1Add supportImprove uniformityBalloon catheterDiagnosticsVascular tissueGuide tube
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through supported guide tubes which expand around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The system may also include a means to limit and / or adjust the depth of penetration of the ablative fluid into and beyond the tissue of the vessel wall. The catheter may also include structures which provide radial and / or lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes expand uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened injection needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
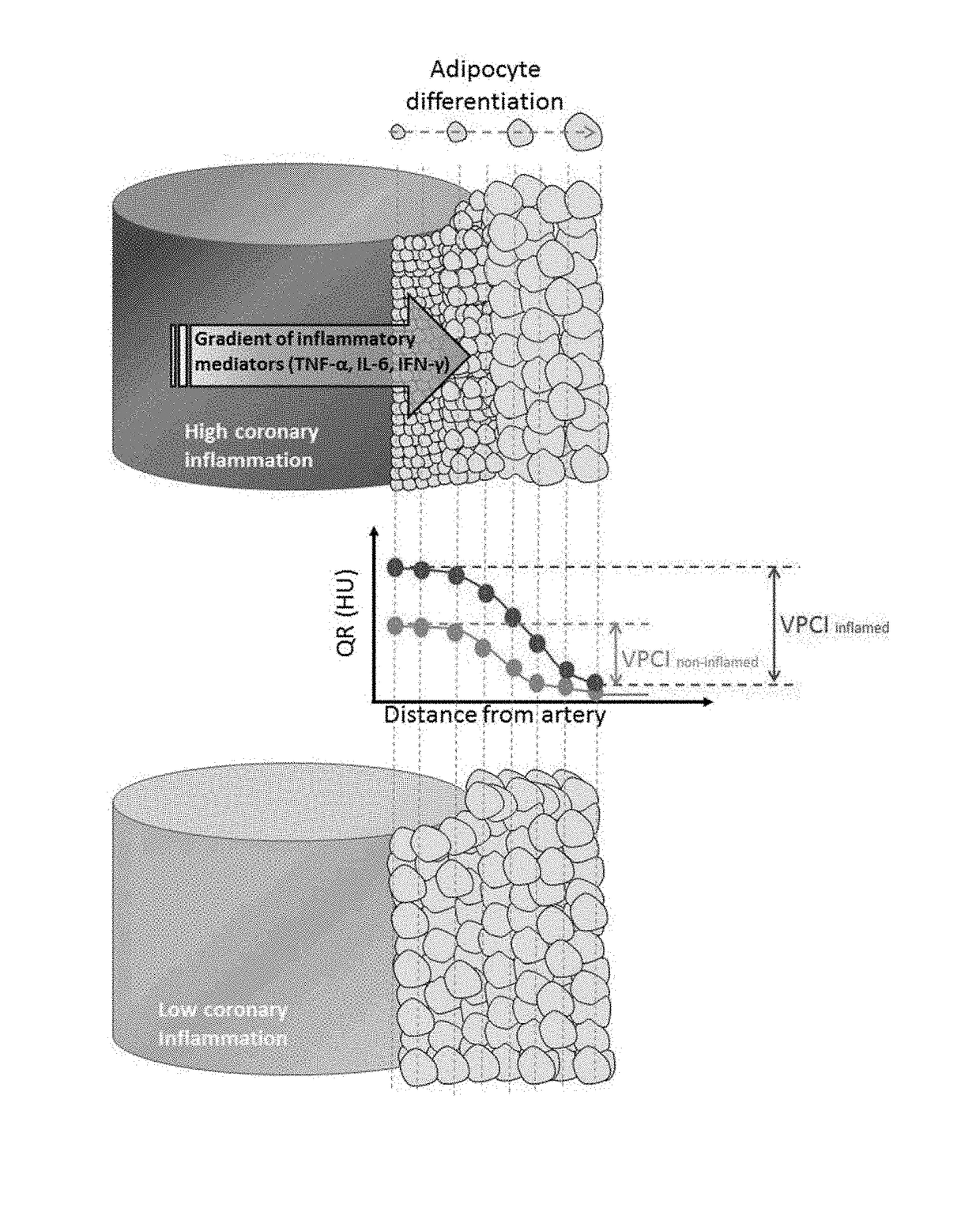
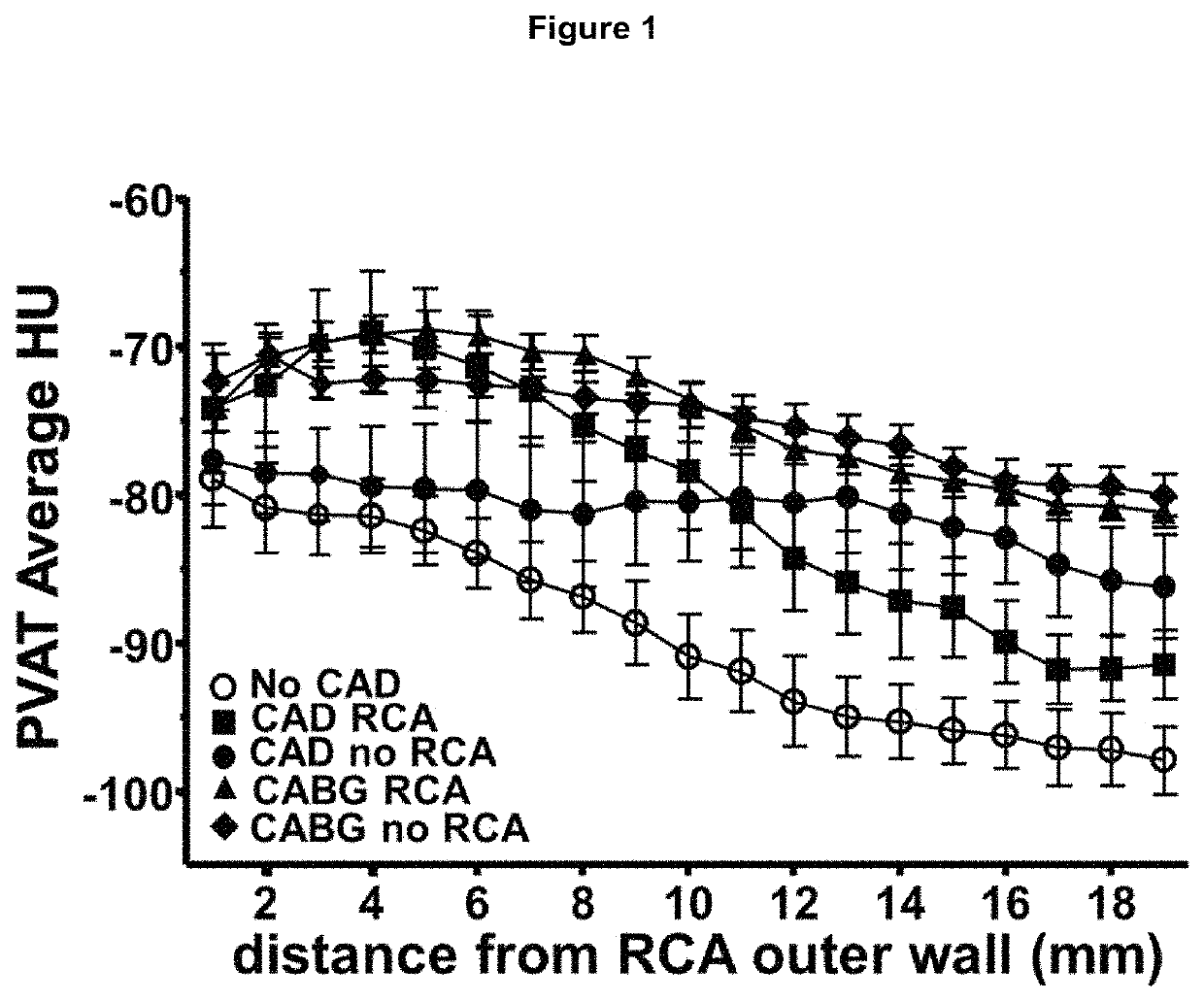
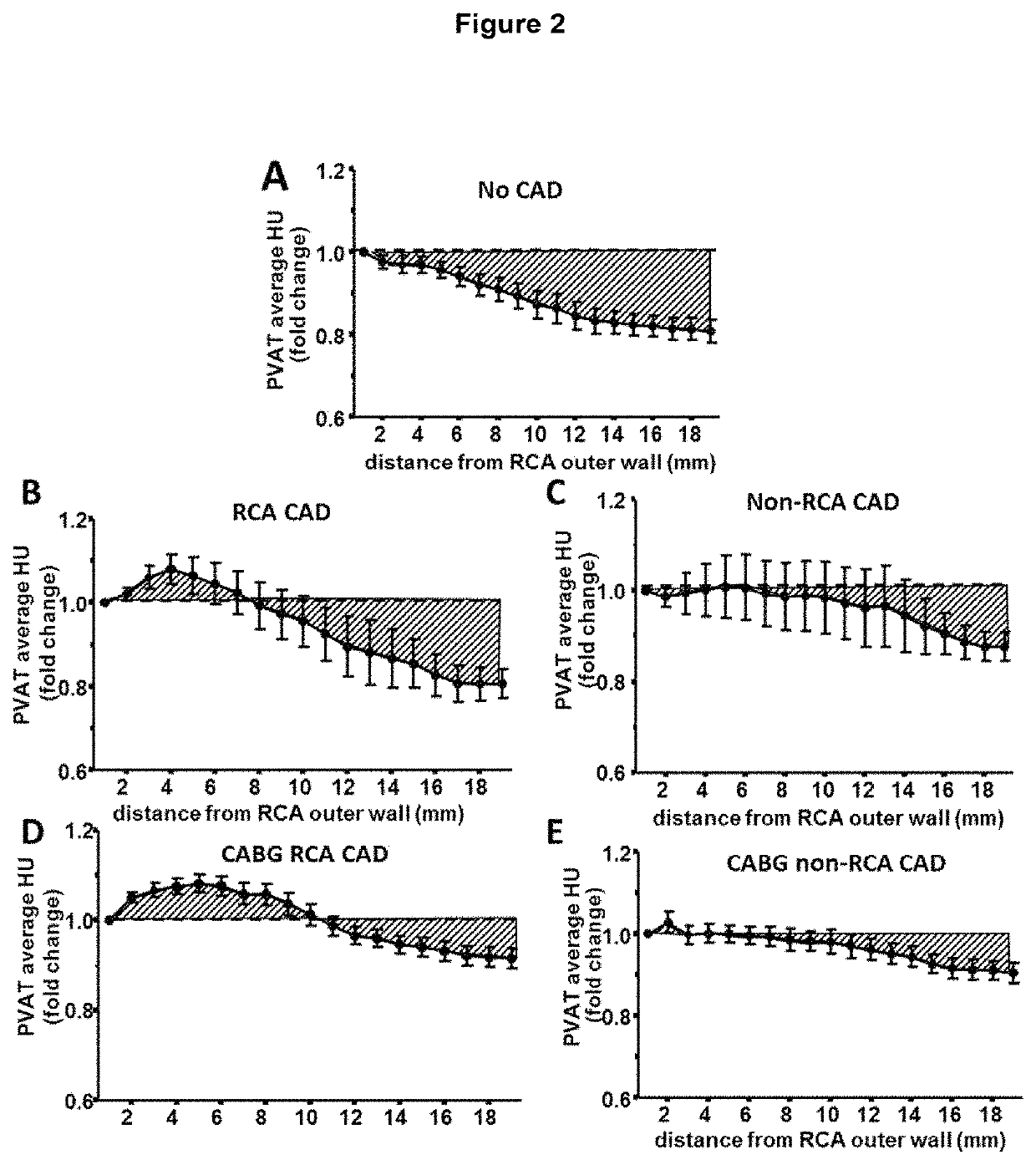
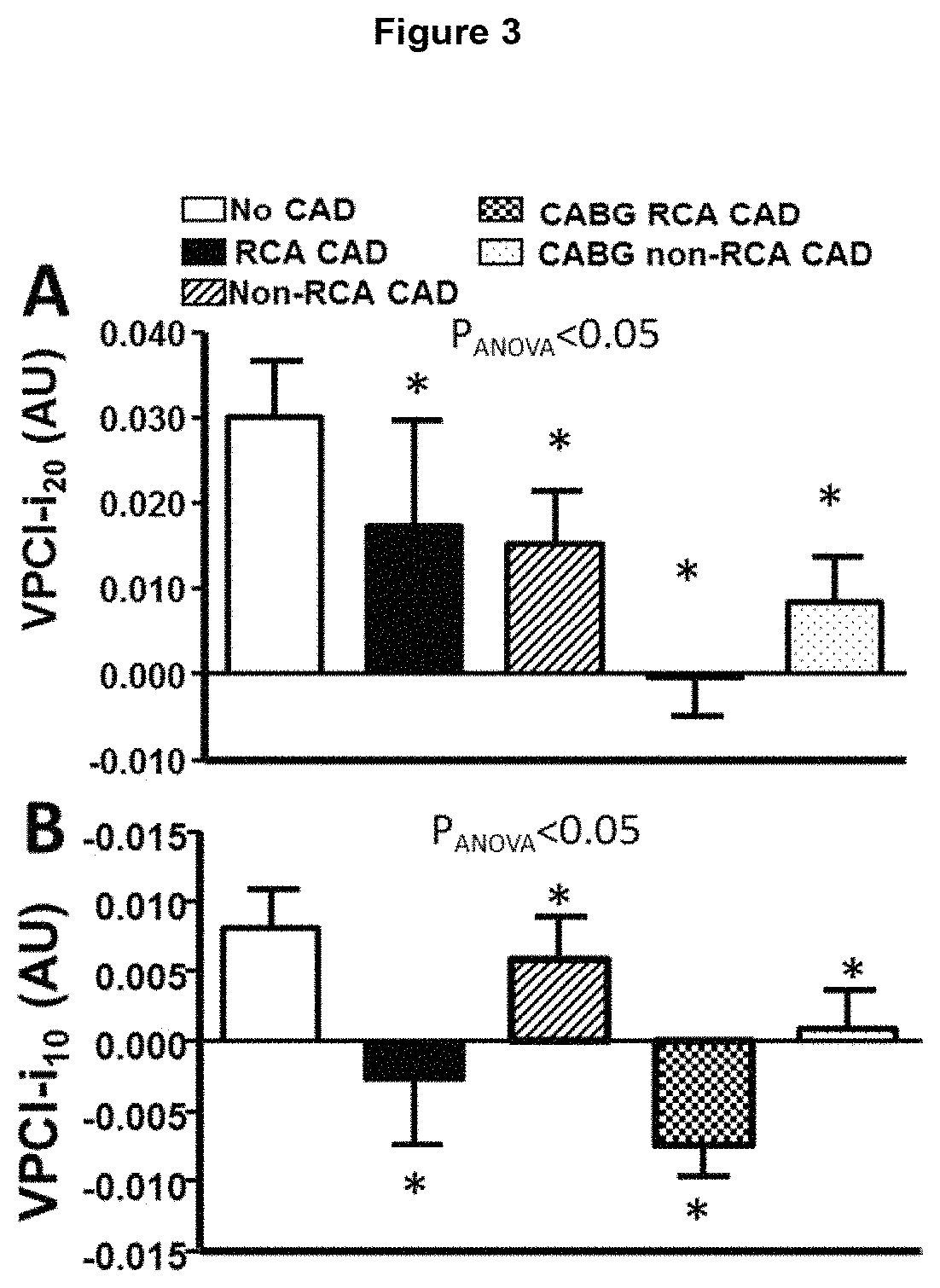
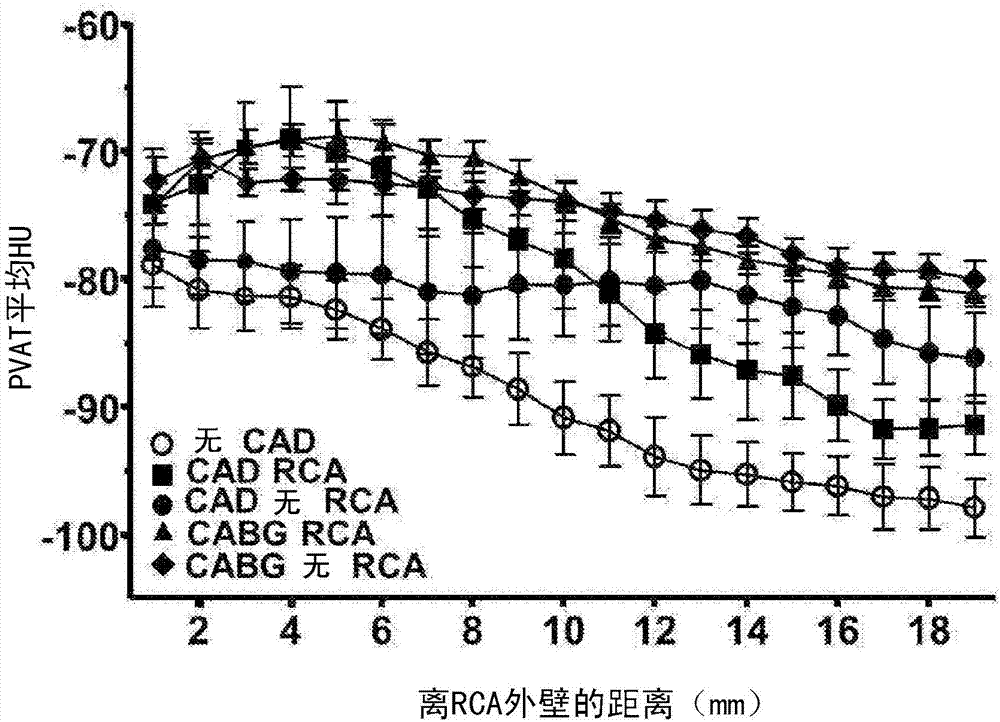
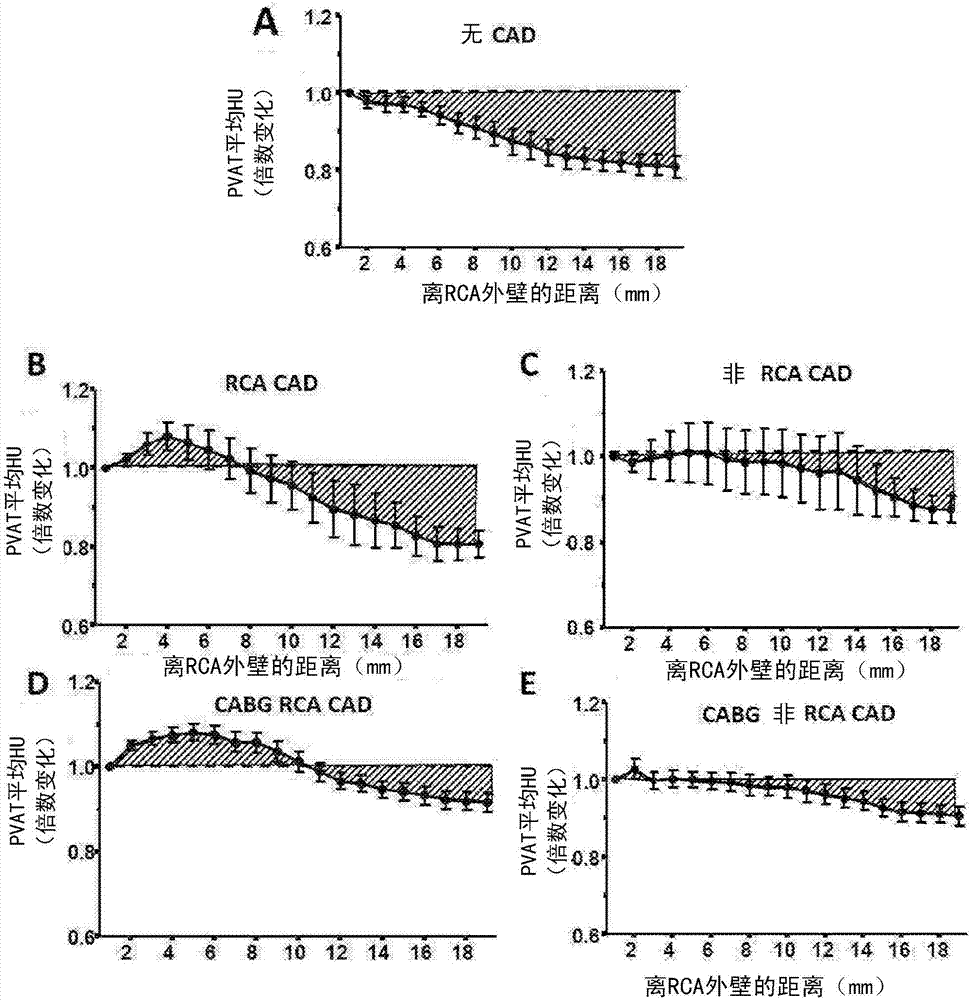
Method for characterisation of perivascular tissue
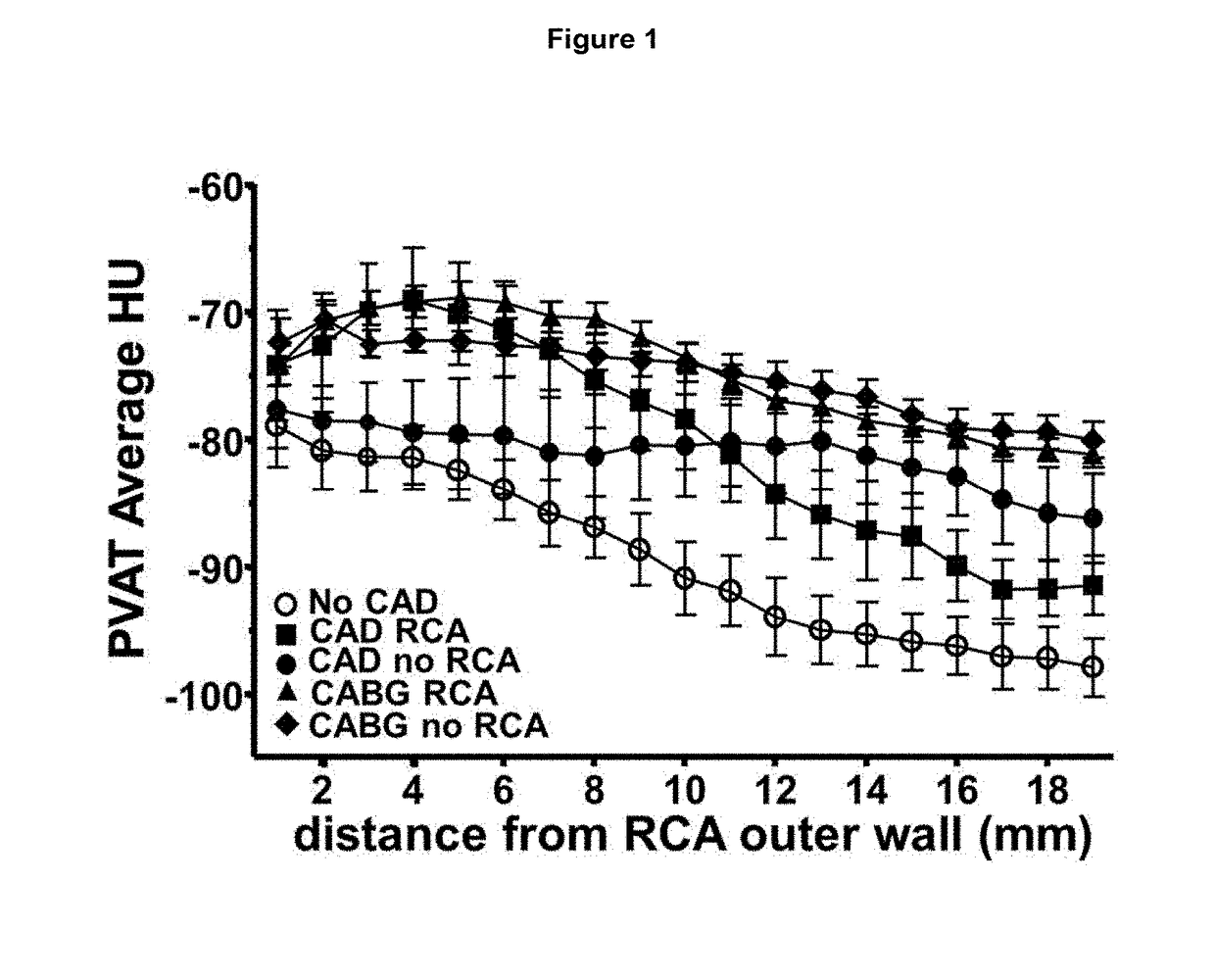
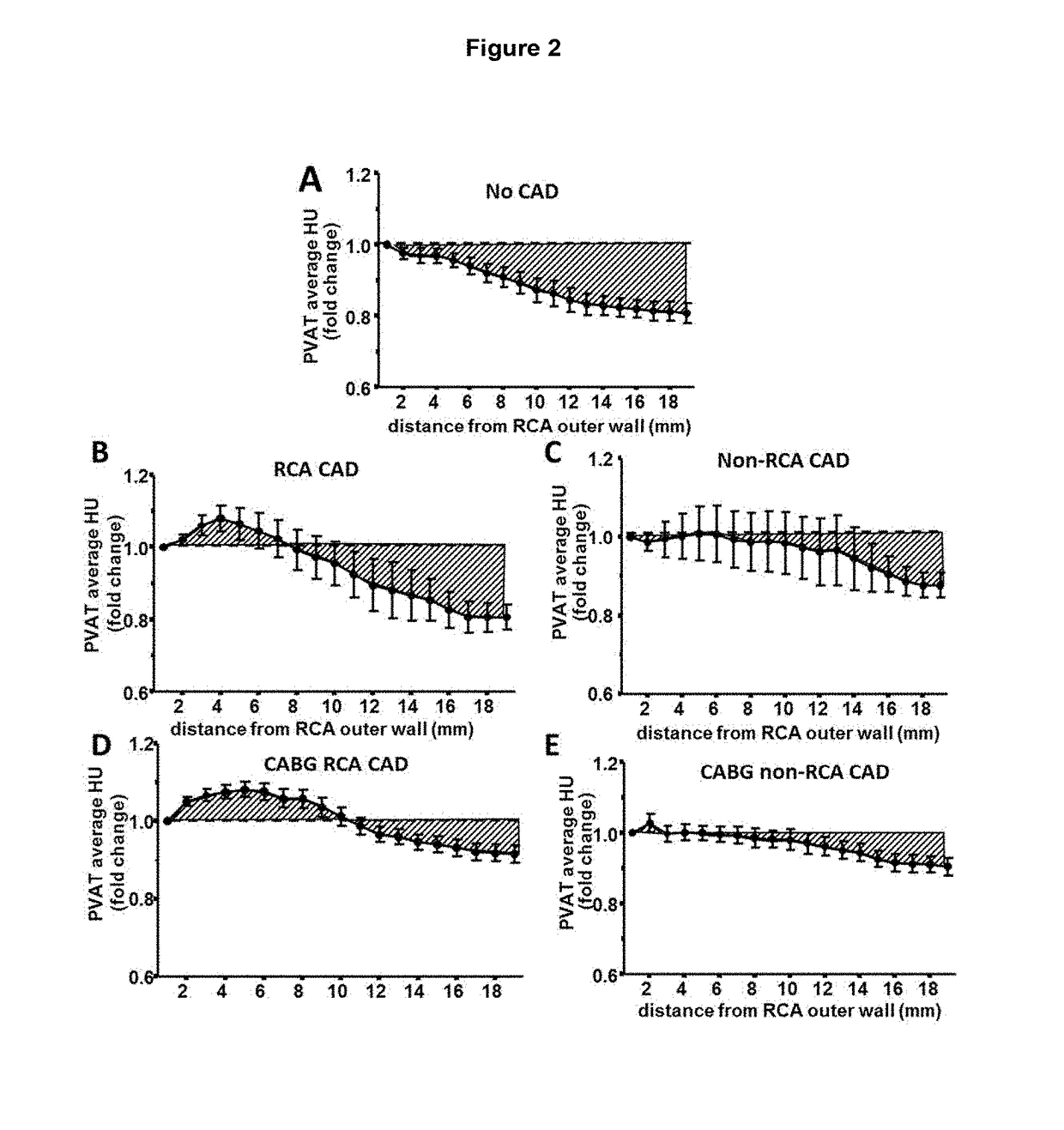
ActiveUS20170265832A1Health-index calculationComputerised tomographsVascular diseasePerivascular Satellitosis
Methods for volumetric characterisation of perivascular adipose tissue use data collected by computed tomography (CT) scanning. The volumetric characterisation of perivascular adipose tissue allows the inflammatory status of underlying blood vessels to be established by CT scanning. This is of use in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of coronary and vascular disease.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
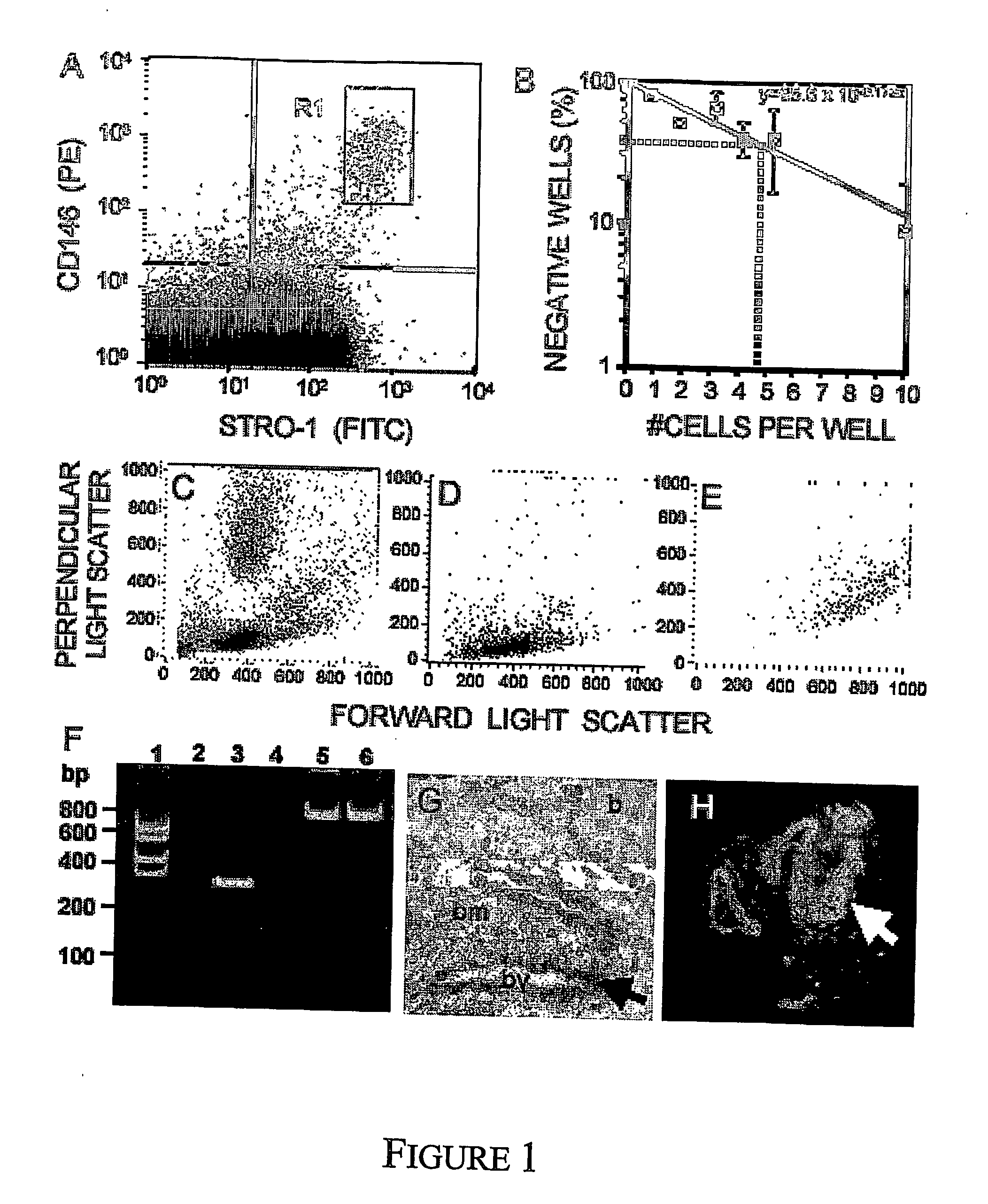
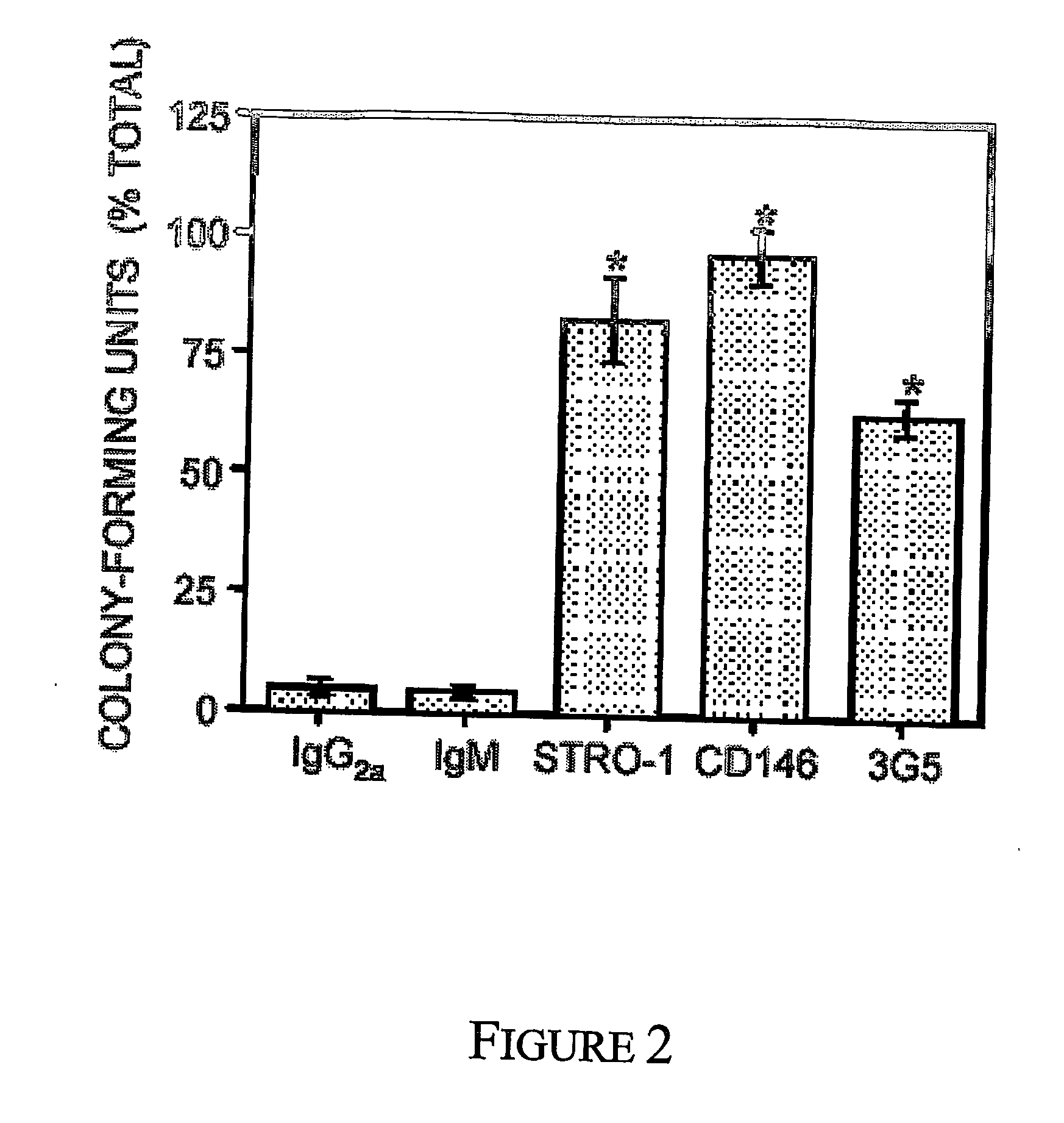
Perivascular mesenchymal precursor cell induced blood vessel formation
Mesenchymal precursors cells have been isolated from perivascular niches from a range of tissues utilizing a perivascular marker. A new mesenchymal precursor cell phenotype is described characterized by the presence of the perivascular marker 3G5, and preferably also alpha smooth muscle actin together with early developmental markers such as STRO-1 and CD146 / MUC18. The perivascular mesenchymal precursor cell is shown to induce neovascularisation and improvement in cardiac function. Suitable administration of preparations of the mesenchymal precursor cells are useful for treatment of cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular diseases and peripheral vascular diseases.
Owner:MESOBLAST
Apparatus and methods for preventing or treating failure of hemodialysis vascular access and other vascular grafts
This invention is a prosthetic device generally placed on the outside surface of the vessel or graft which then elutes antiproliferative drugs or agents from a drug-eluting matrix material. Methods of perivascular antiproliferative drug administration also are disclosed.
Owner:VASCULAR THERAPIES INC
Materials and methods for prevention and treatment of RNA viral diseases
InactiveUS20040009152A1Preventing and decreasing severity of symptomBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMononuclear cell infiltration
The subject invention concerns a method of inhibiting an RNA virus infection within a patient by increasing the amount of 2-5 oligoadenylate synthetase (2-5 AS) activity within the patient. Preferably, the preventative and therapeutic methods of the present invention involve administering a nucleotide encoding 2-5 AS, or at least one catalytically active fragment thereof, such as the p40, p69, p100 subunits, to a patient in need thereof. The present inventors have determined that overexpression of 2-5AS causes a reduction in epithelial cell damage, reduction in infiltration of mononuclear cells in the peribronchiolar and perivascular regions, and reduction in thickening of the septa in the lungs. Levels of chemokines, such as MIP1-alpha, are also reduced upon overexpression of 2-5AS. The subject invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions containing a nucleotide sequence encoding 2-5 AS and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, as well as vectors for delivery of the 2-5 AS nucleotide sequence.
Owner:IB SECURITYHOLDERS +1
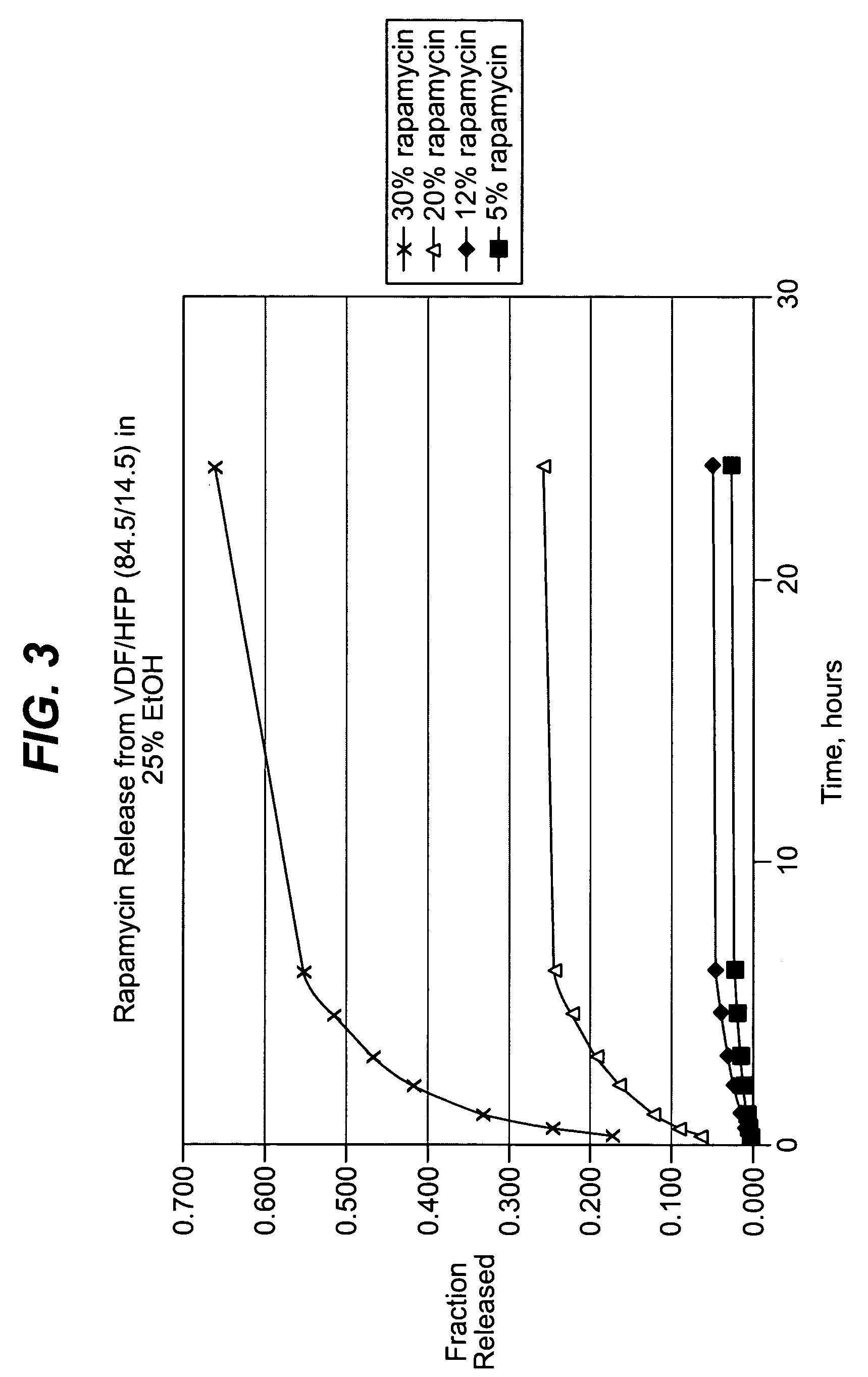
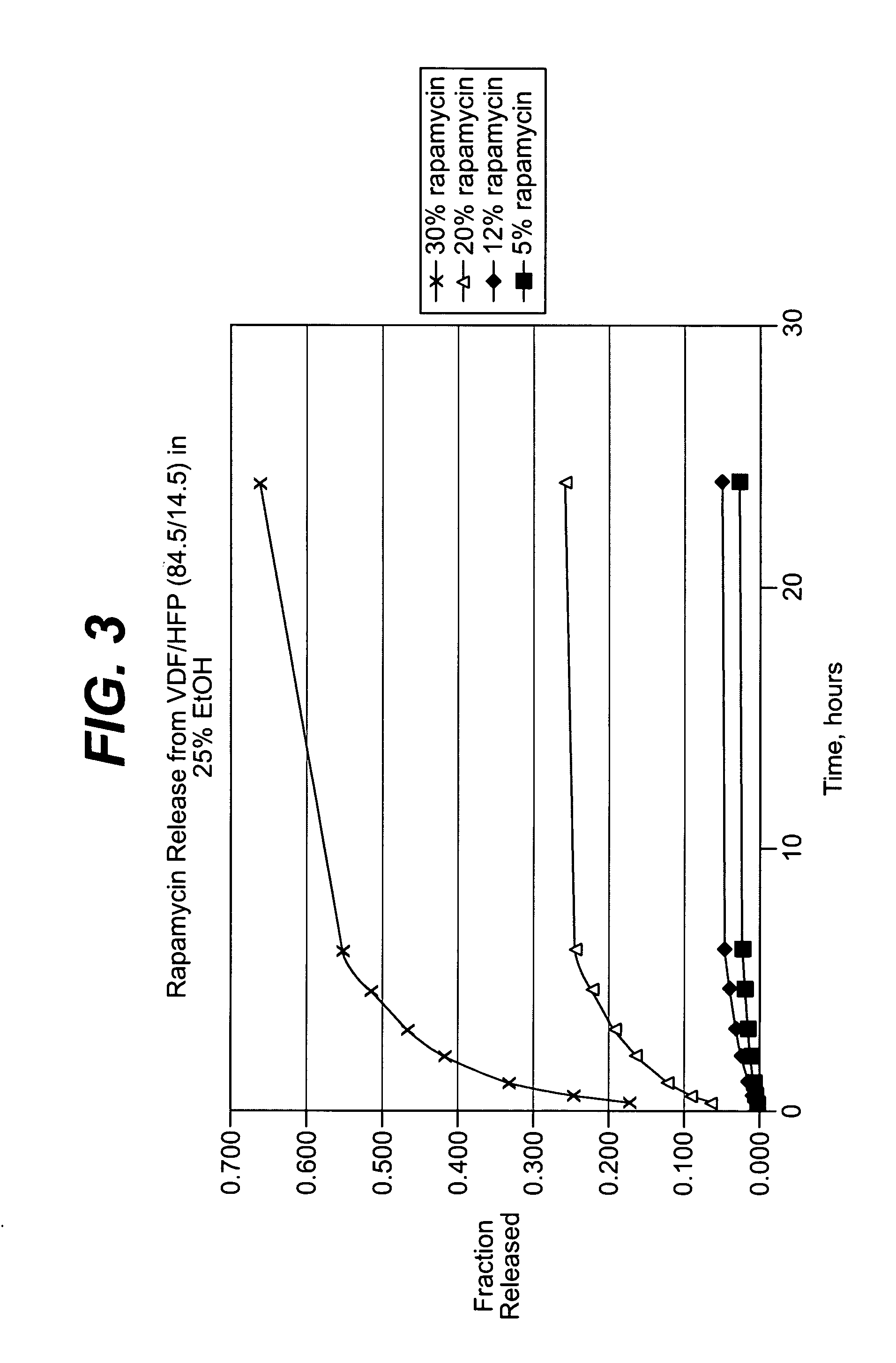
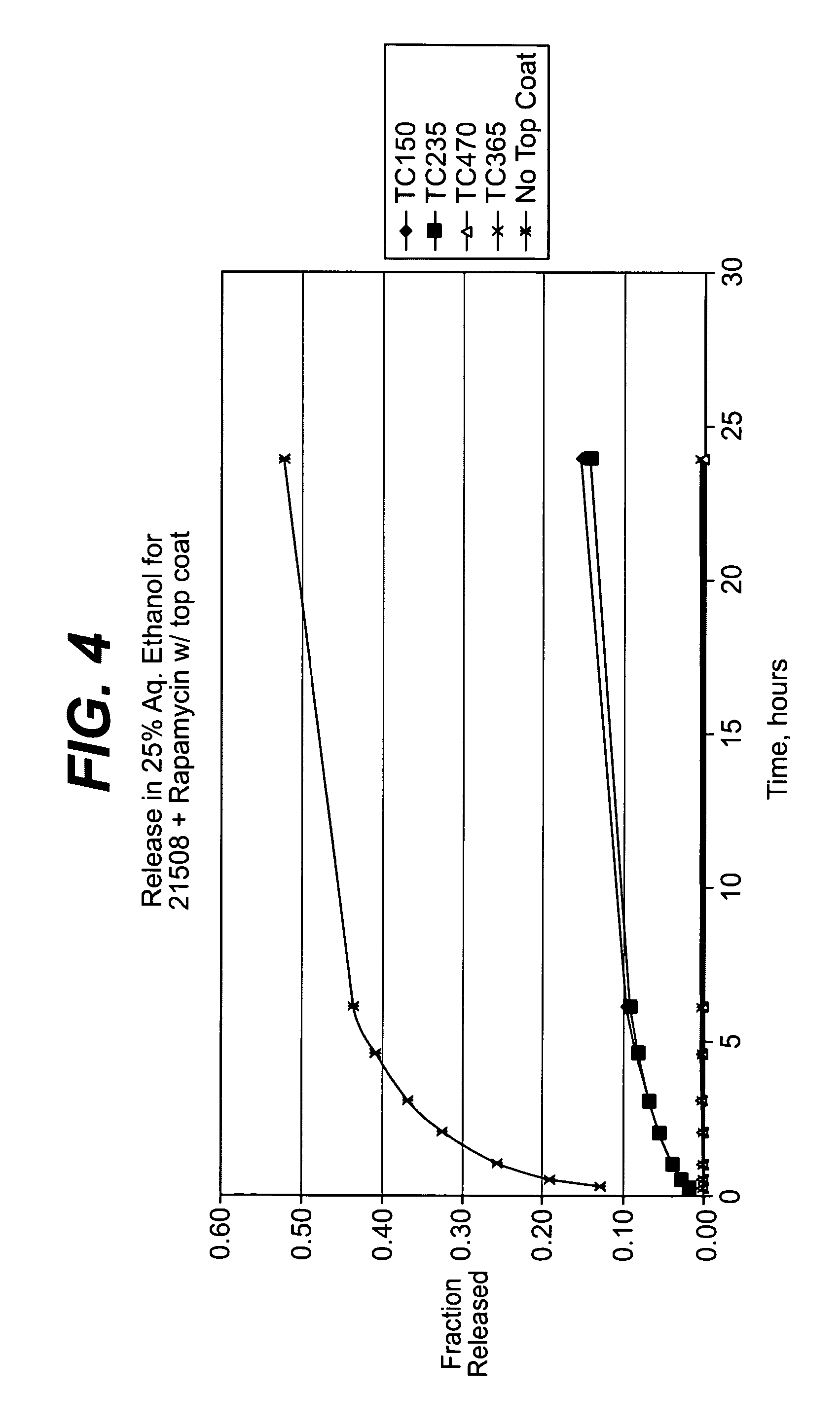
Local vascular delivery of mycophenolic acid in combination with rapamycin to prevent restenosis following vascular injury
ActiveUS20050158360A1Minimize potential risk of damageReduce frictionStentsOrganic active ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisBlood vessel
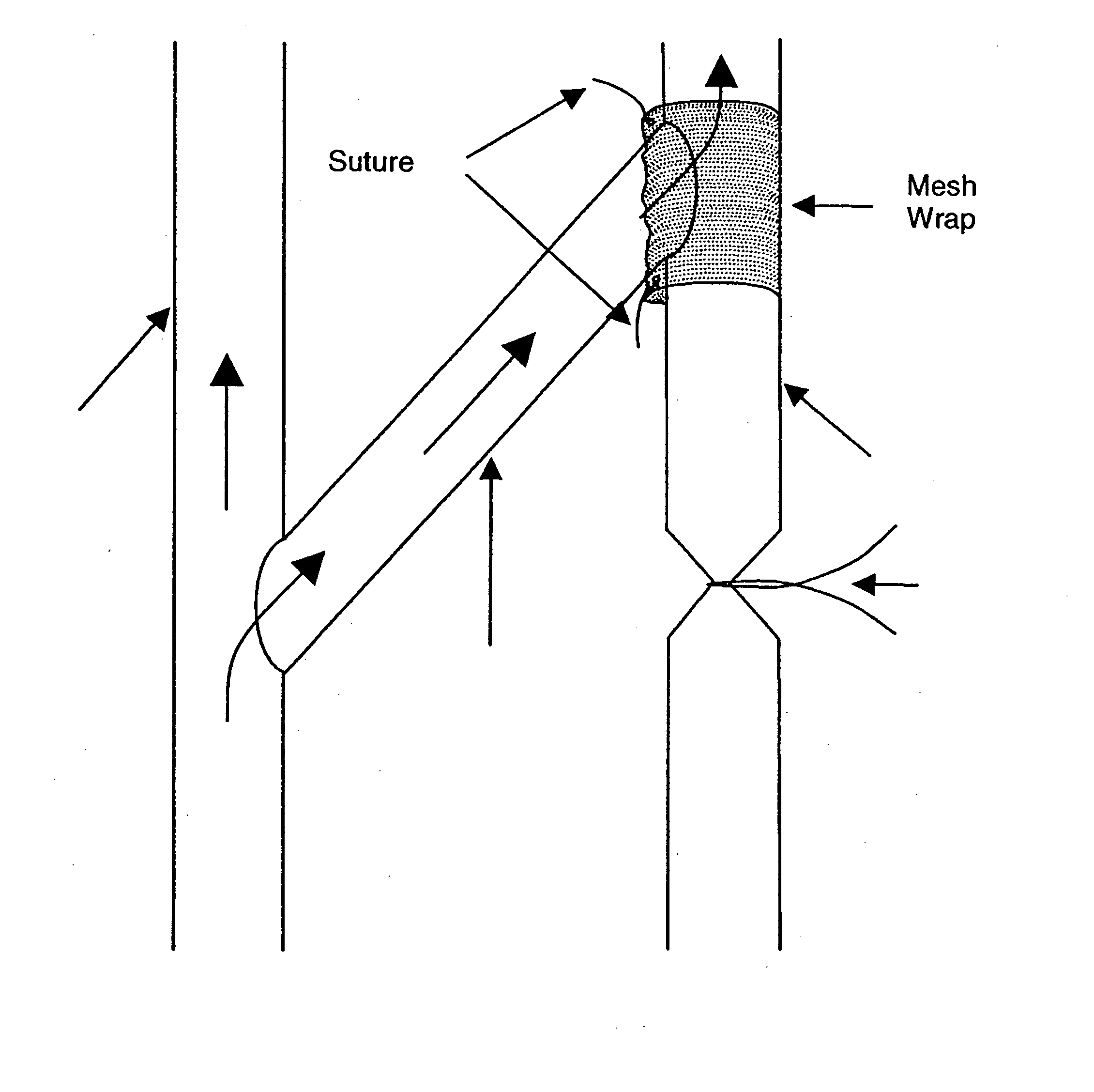
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. Also, the devices may be modified to promote endothelialization. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned. In addition, the devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment. Medical devices include stents, grafts, anastomotic devices, perivascular wraps, sutures and staples. In addition, various polymer combinations may be utilized to control the elution rates of the therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds from the implantable medical devices.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Local vascular delivery of mycophenolic acid in combination with rapamycin to prevent restenosis following vascular injury
ActiveUS7303758B2Prevent elutionProvide controlStentsOrganic active ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisBlood vessel
Owner:WYETH LLC
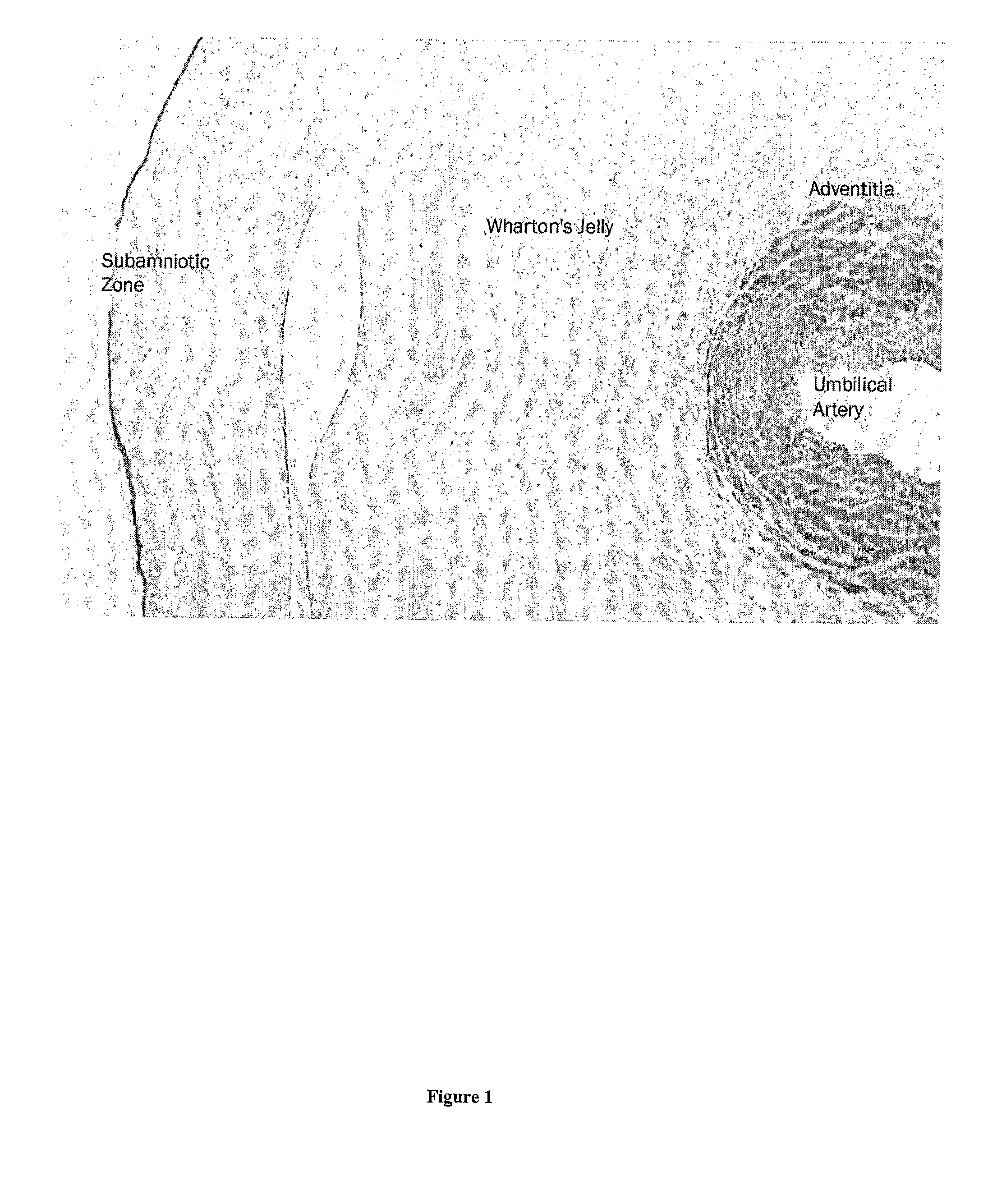
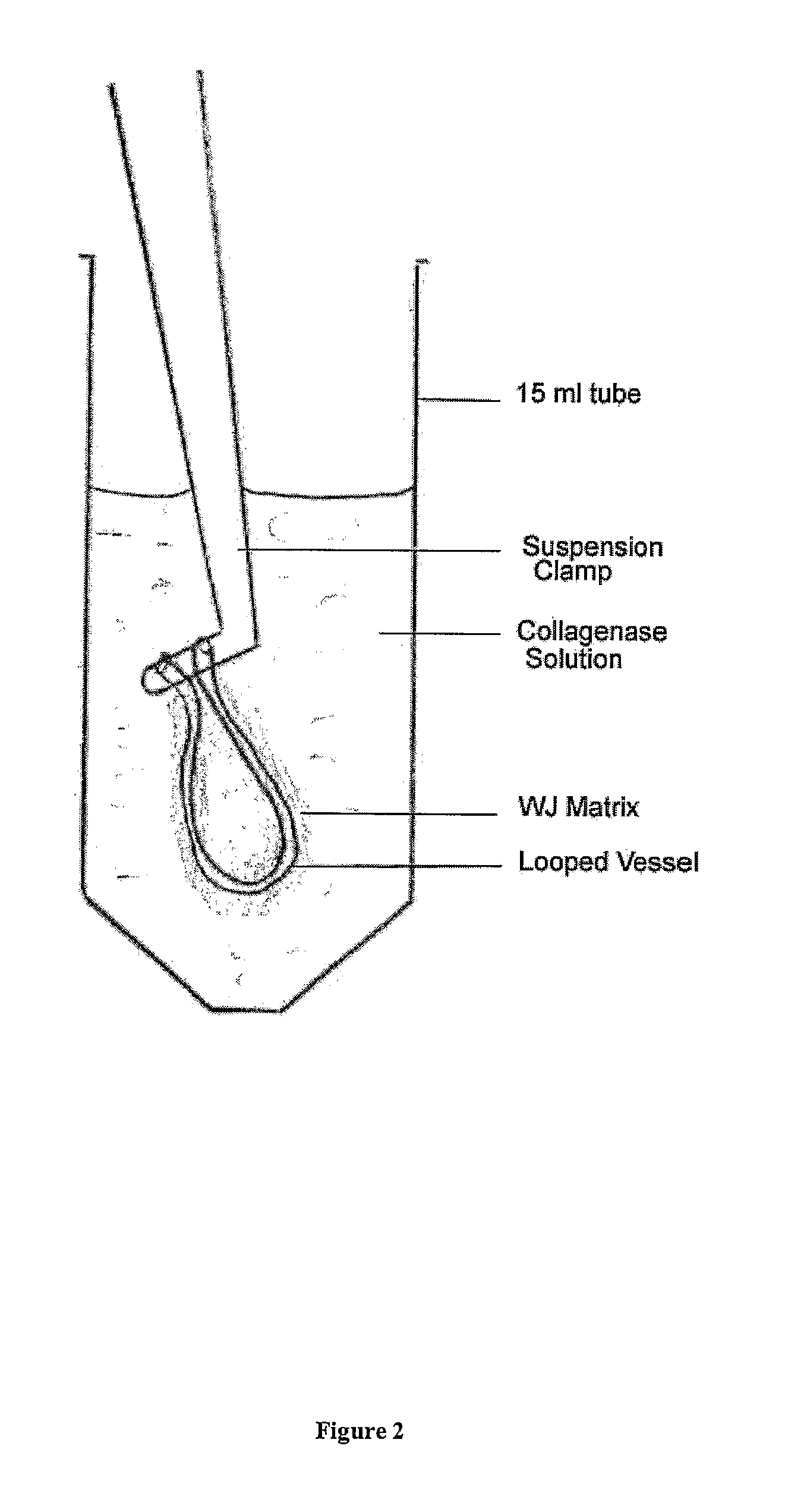
Viable cells from frozen umbilical cord tissue
Viable progenitor cells are extracted from frozen umbilical cord tissue. In embodiments, the umbilical cord tissue is a blood vessel bearing perivascular Wharton's jelly, and the extracted progenitor cells are HUCPVCs.
Owner:TISSUE REGENERATION THERAPEUTICS
Method for characterisation of perivascular tissue
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
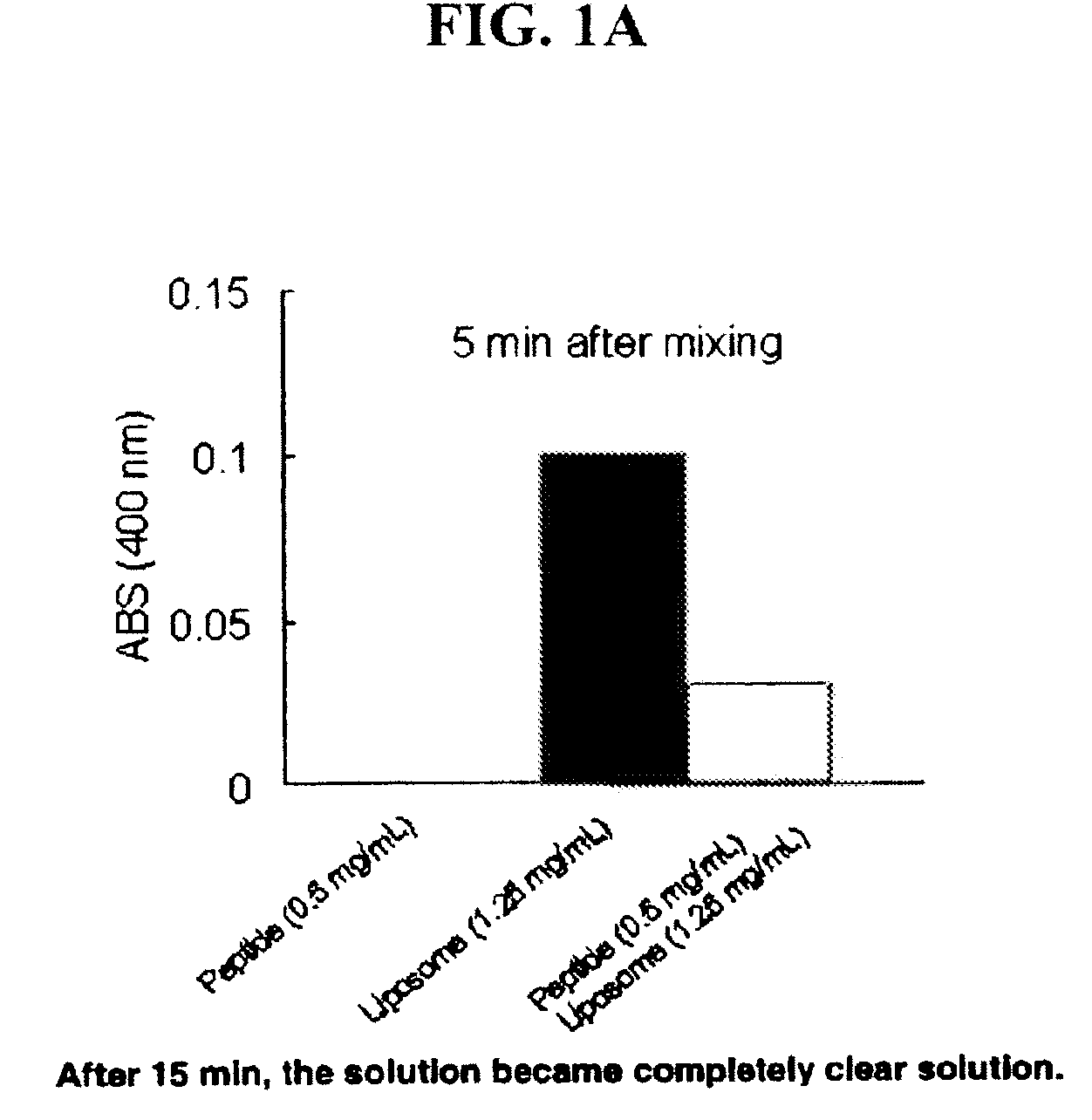
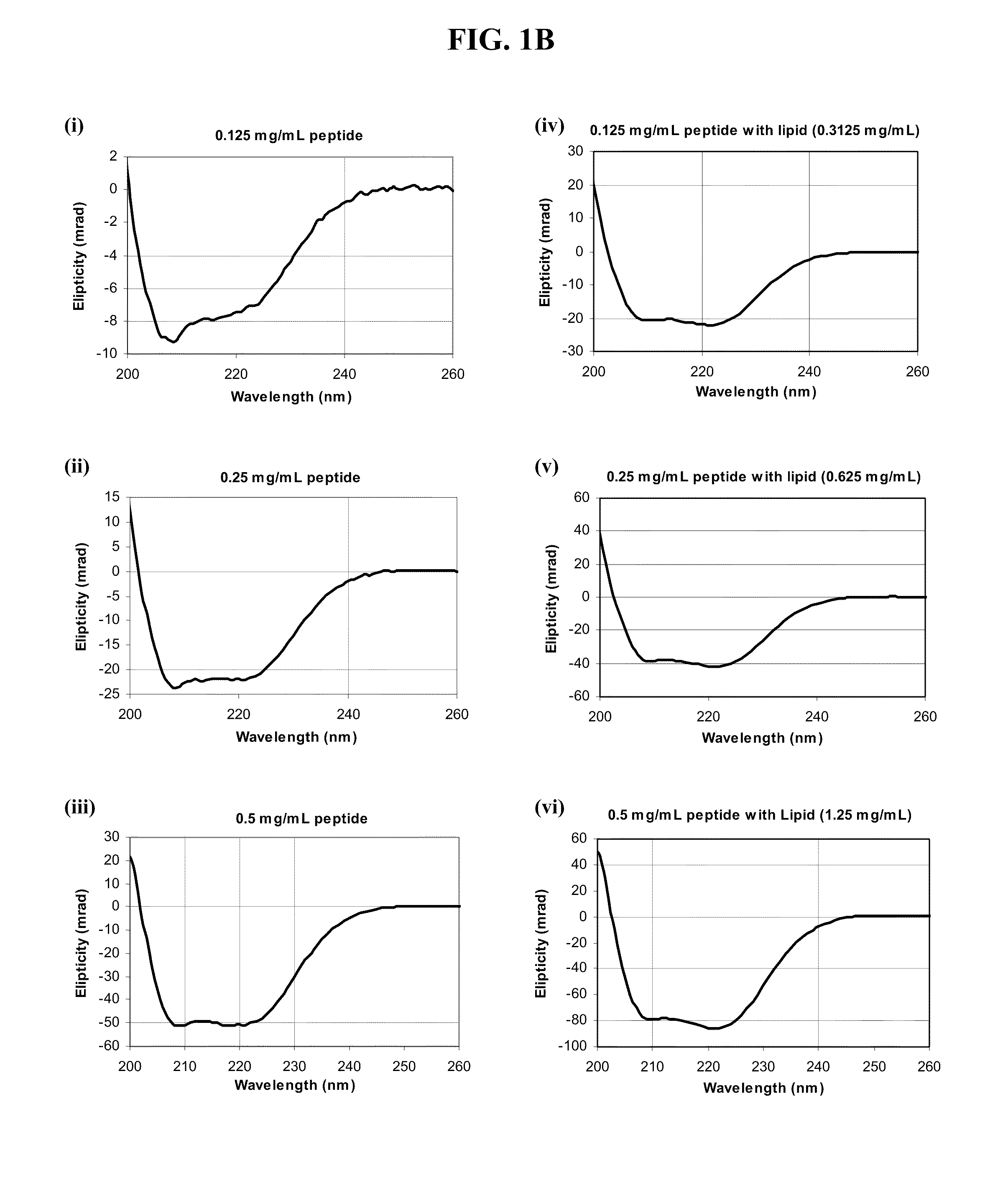
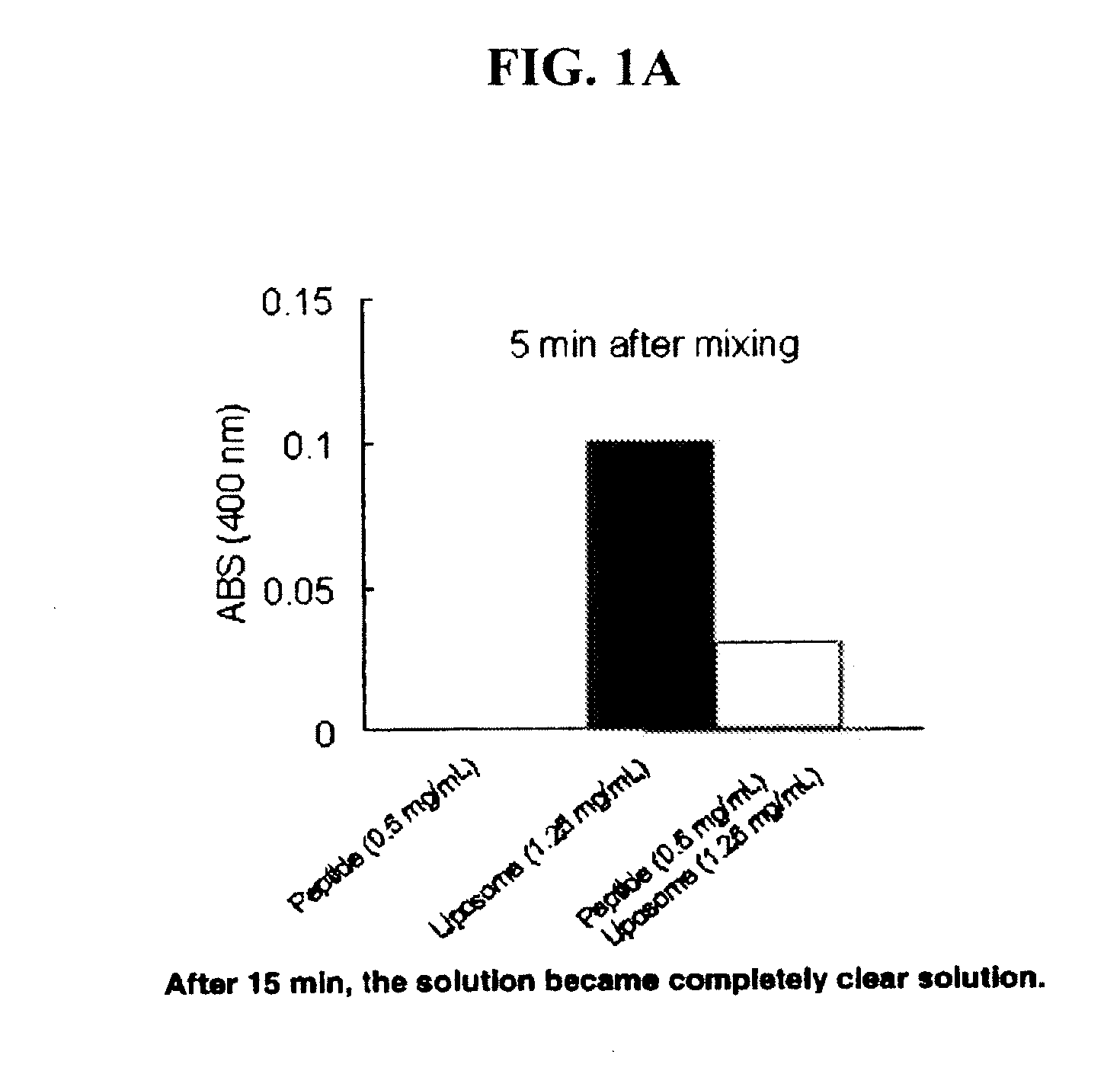
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081299A1Improve concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Local vascular delivery of topotecan in combination with rapamycin to prevent restenosis following vascular injury
ActiveUS20050202059A1Minimize potential risk of damageReduce frictionStentsSurgeryThrombusPercent Diameter Stenosis
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. Also, the devices may be modified to promote endothelialization. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned. In addition, the devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment. Medical devices include stents, grafts, anastomotic devices, perivascular wraps, sutures and staples. In addition, various polymer combinations may be utilized to control the elution rates of the therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds from the implantable medical devices.
Owner:WYETH LLC
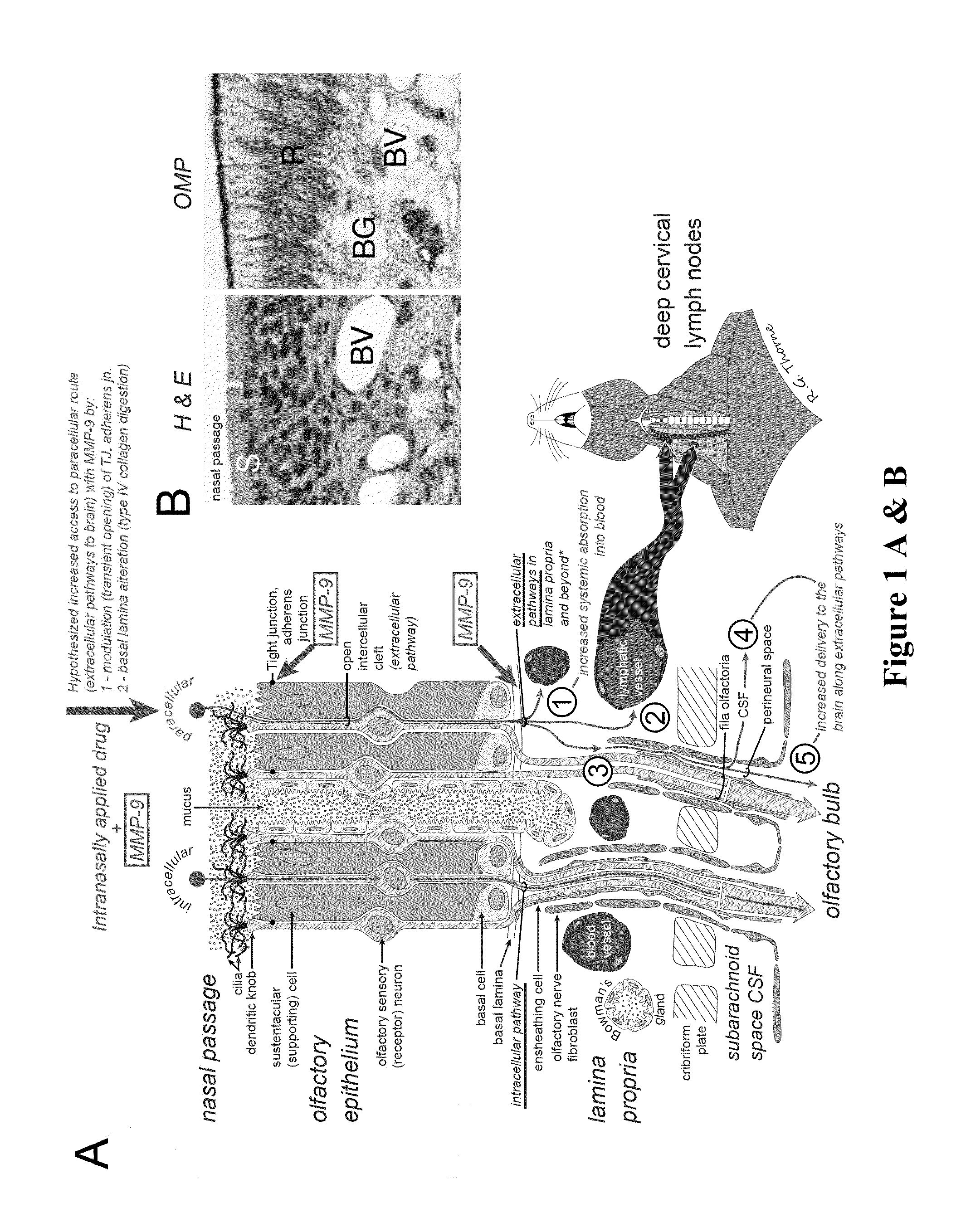
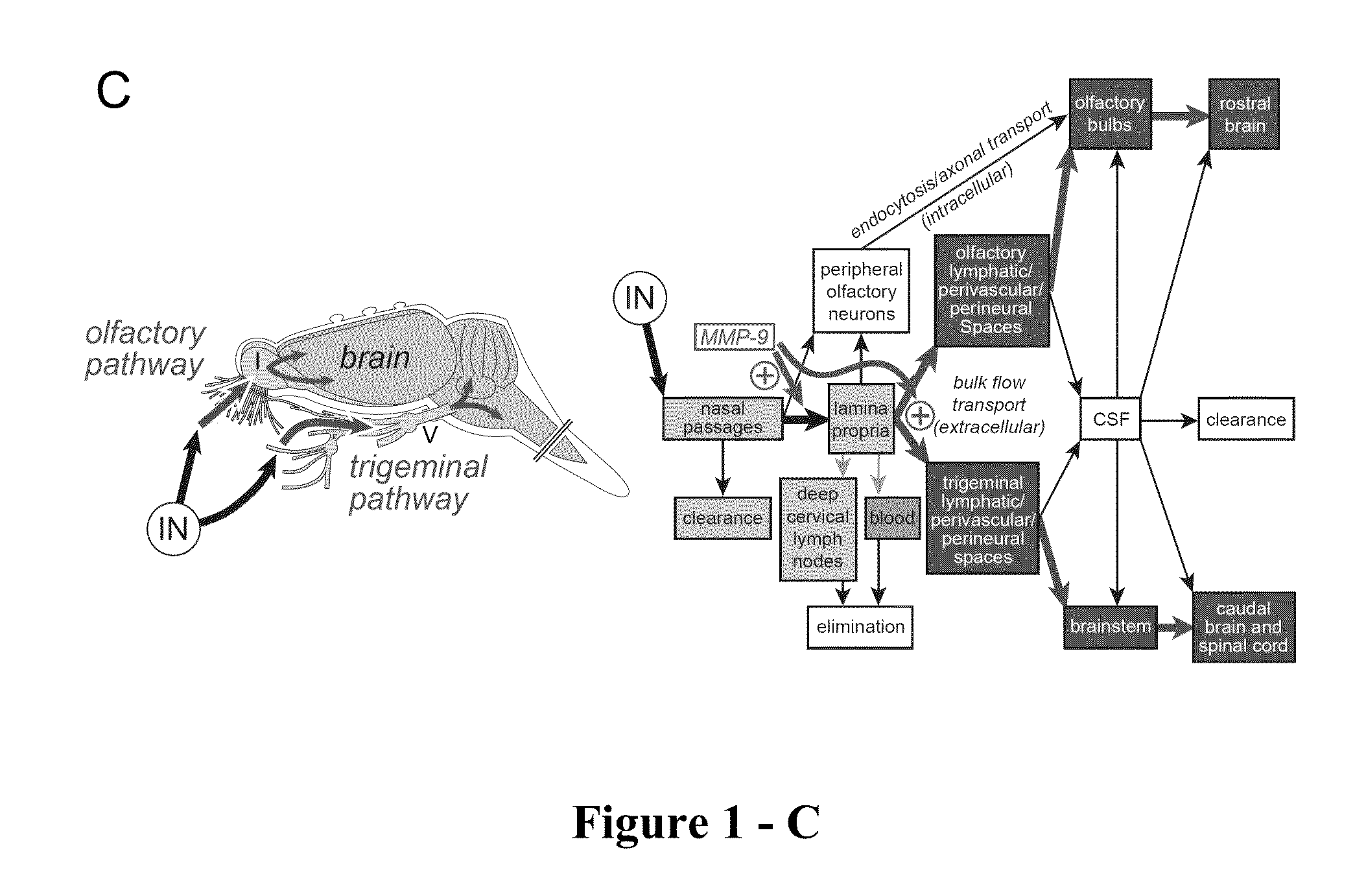
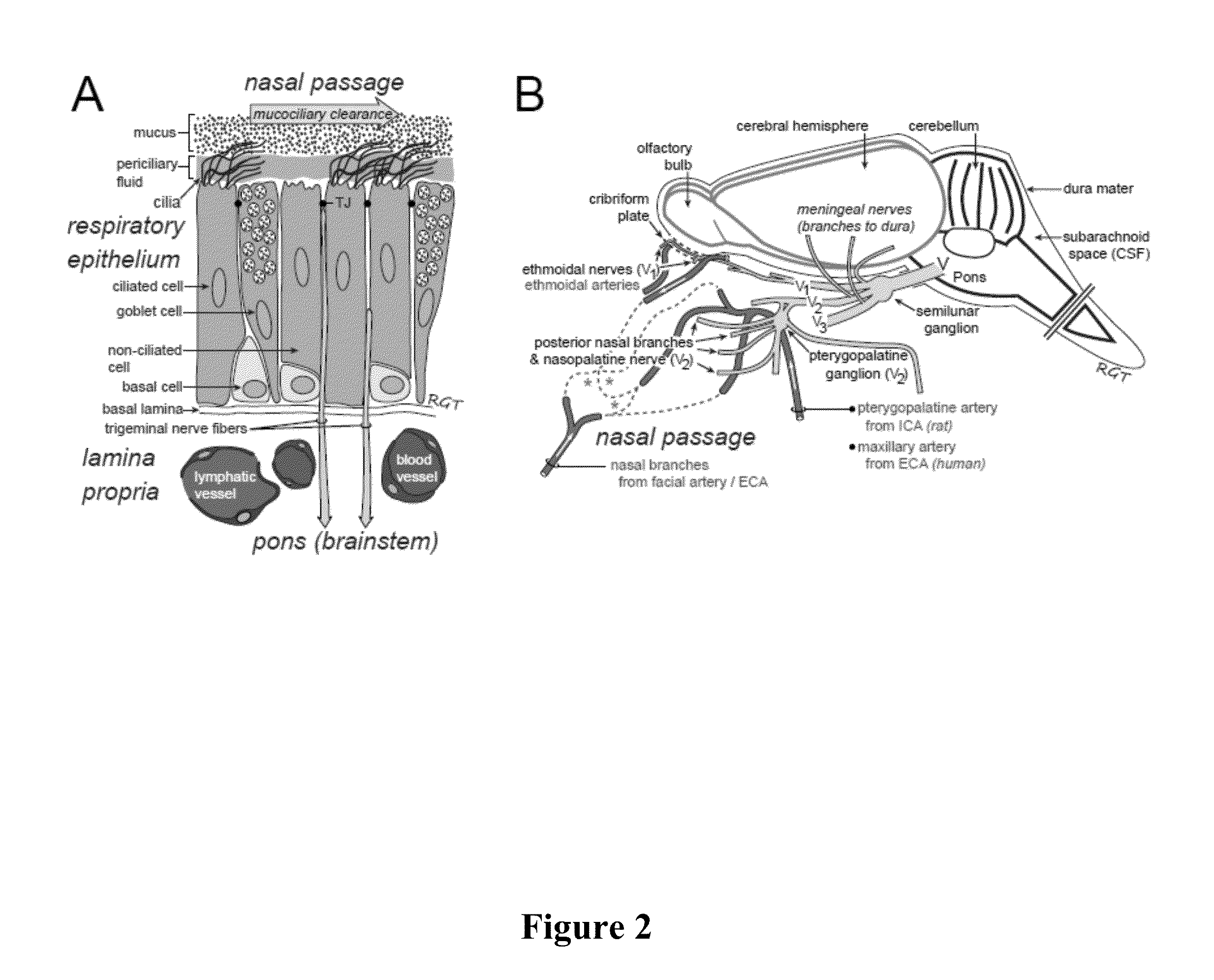
Methods and Compositions for Enhancing Intranasal Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20140050718A1Easy accessNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBasal laminaPerivascular Satellitosis
A method for treating a patient suffering from a condition with an active compound comprising the steps of (a) treating the patient intranasally with an effective amount of MMP-9 or a functionally equivalent fragment, wherein the tight junctions of the patient's nasal epithelial cells are modulated or wherein the basal lamina of the patient is partially digested and type IV collagen of the patient is degraded or wherein access to the patient's perineural, perivascular, or lymphatic compartment spaces is facilitated and (b) treating the patient intranasally with an active compound is disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081298A1Improve concentrationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSterol transportReverse cholesterol transport
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for characterisation of perivascular tissue
ActiveCN106999122AQuantitative radiodensity reductionHealth-index calculationTomographyVascular diseasePerivascular Satellitosis
The present invention defines methods for volumetric characterisation of perivascular adipose tissue using data collected by computed tomography (CT) scanning. The volumetric characterisation of perivascular adipose tissue allows the inflammatory status of underlying blood vessels to be established by CT scanning. This is of use in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of coronary and vascular disease..
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Sustained release of apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS8044021B2Organic active ingredientsPowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
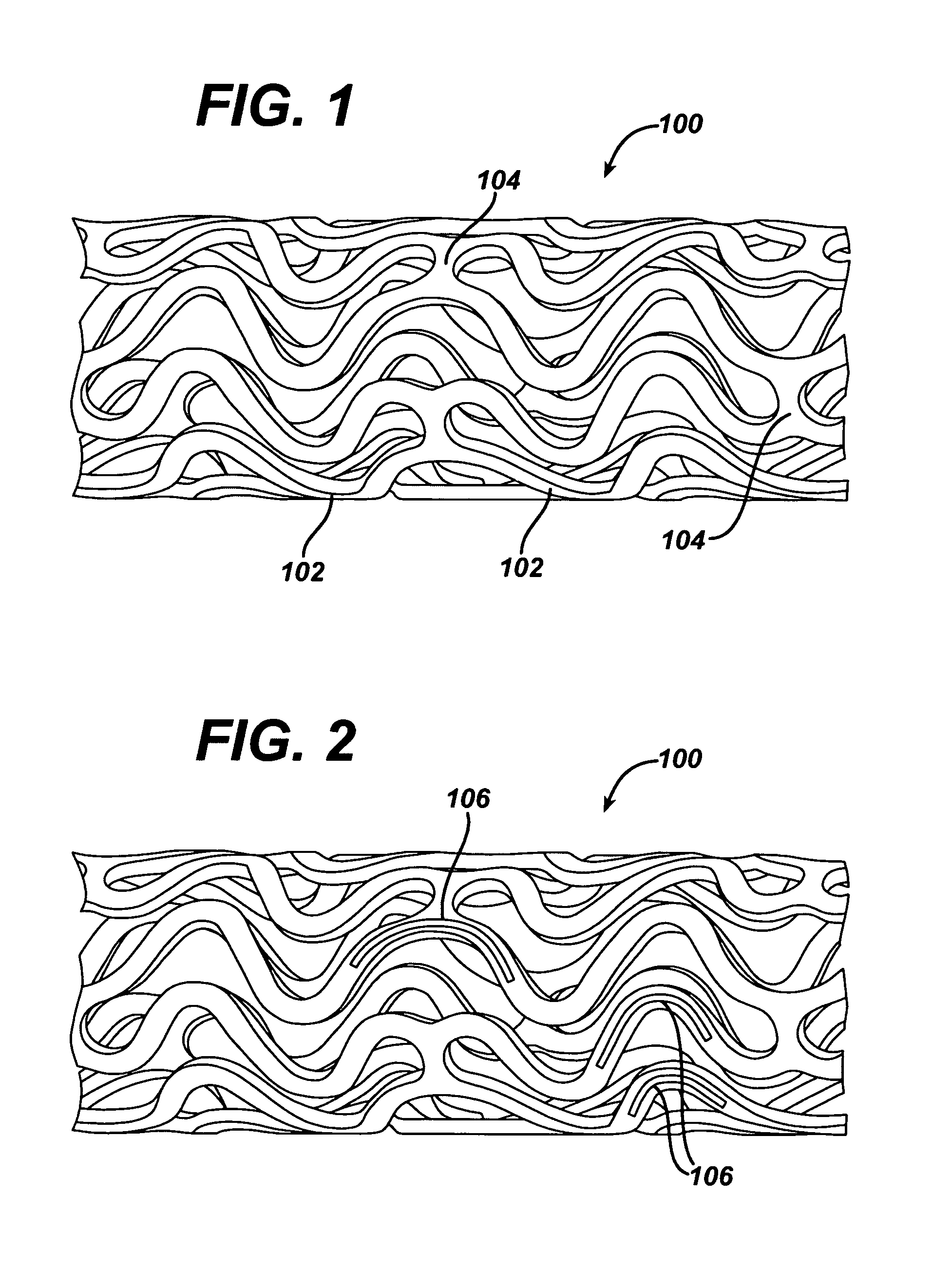
Perivascular wraps
InactiveUS20080085855A1Preventing and reducing biological responseImprove integrityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSmooth musclePerivascular Satellitosis
The present invention provides compositions, devices, and methods for maintaining or improving the integrity of body passageways following surgery, such as at a graft site, or injury. Delivery devices including one or more therapeutic agents and a mesh are described. Representative examples of therapeutic agents include microtubule stabilizing agents, anti-angiogenic factors, inhibitors of smooth muscle cell growth or proliferation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and other factors useful preventing and / or reducing a proliferative biological response that may obstruct or hinder the optimal functioning of the passageway or cavity.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Systems and methods for improving soft tissue contrast, multiscale modeling and spectral ct
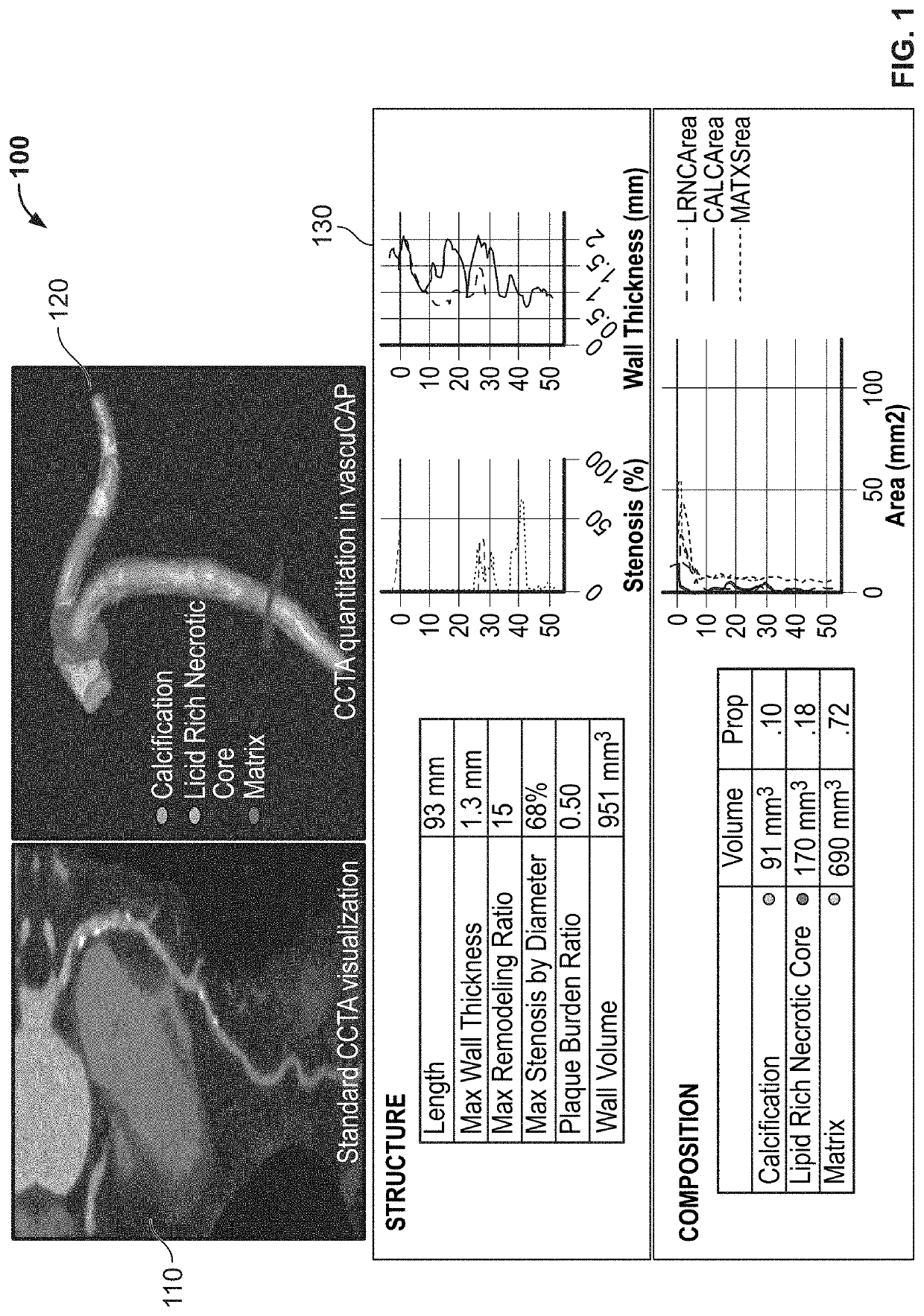
ActiveUS20220253992A1Improving soft tissue analysisEasy to analyzeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementBlood vesselSoft tissue contrast
Systems and methods for improving soft tissue contrast, characterizing tissue, classifying phenotype, stratifying risk, and performing multi-scale modeling aided by multiple energy or contrast excitation and evaluation are provided. The systems and methods can include single and multi-phase acquisitions and broad and local spectrum imaging to assess atherosclerotic plaque tissues in the vessel wall and perivascular space.
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
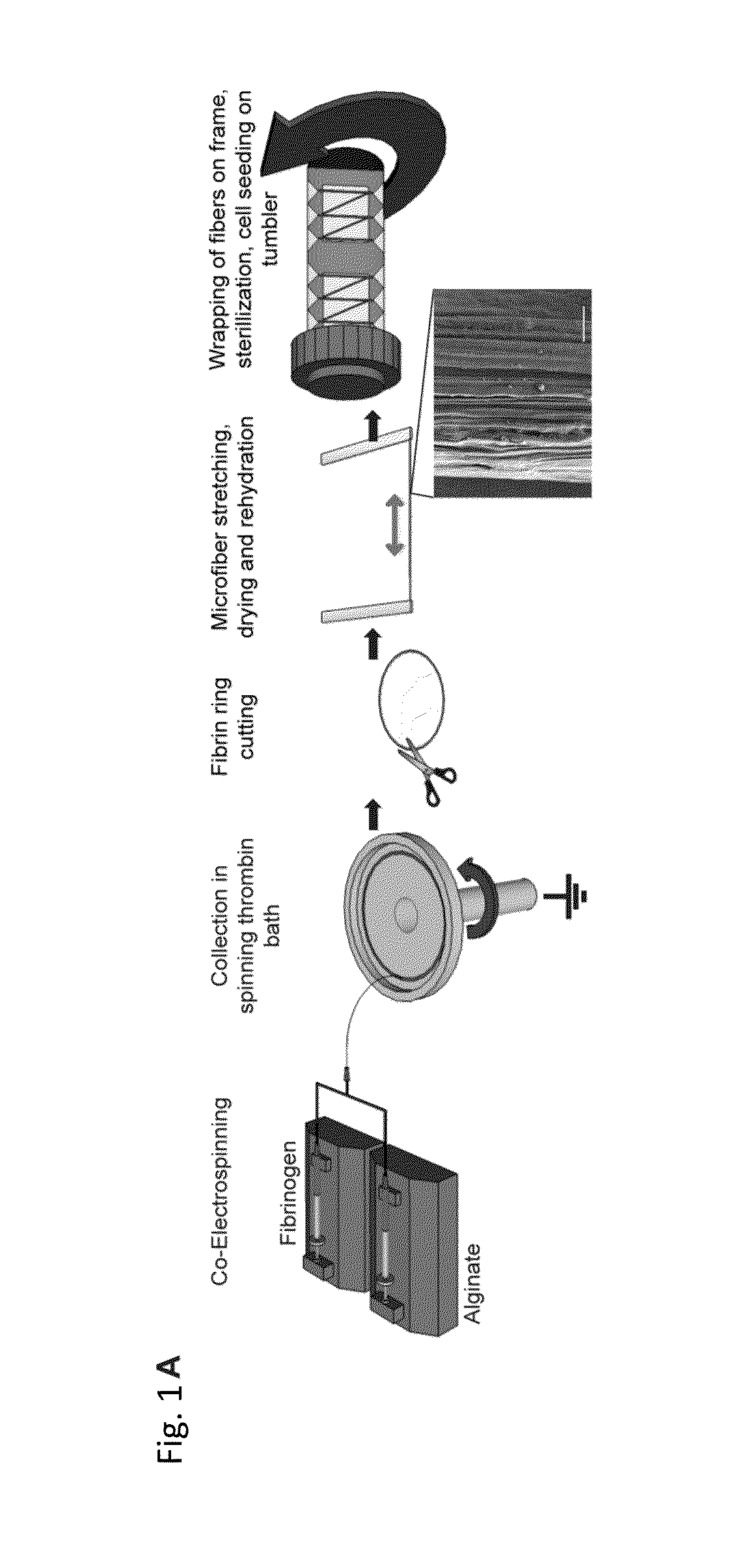
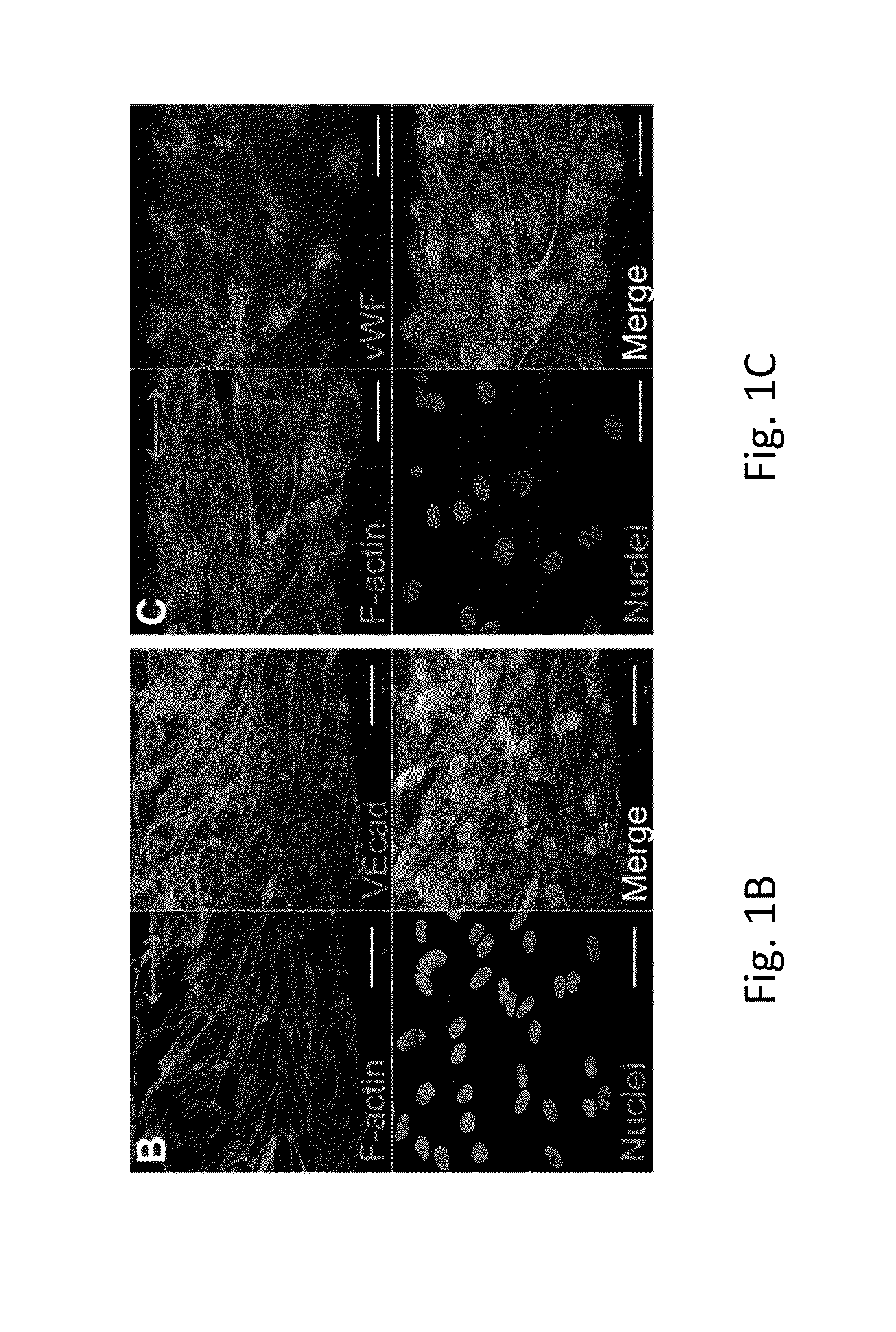
Electrostretched polymer microfibers for microvasculature development
An in vitro model system that guides the development of microvasculature, recapitulating the detailed organization of both its cellular and a-cellular components is established. Use of electrostretched fibrin microfibers enables both endothelial layer organization and co-culture of supporting perivascular (mural) cells such as vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes. The fiber curvature affects the circumferential deposition of endothelial-produced ECM independently of cellular organization and induces deposition of higher quantities of vascular ECM proteins. Further, a luminal multicellular microvascular structure is disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Sustained release of Apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
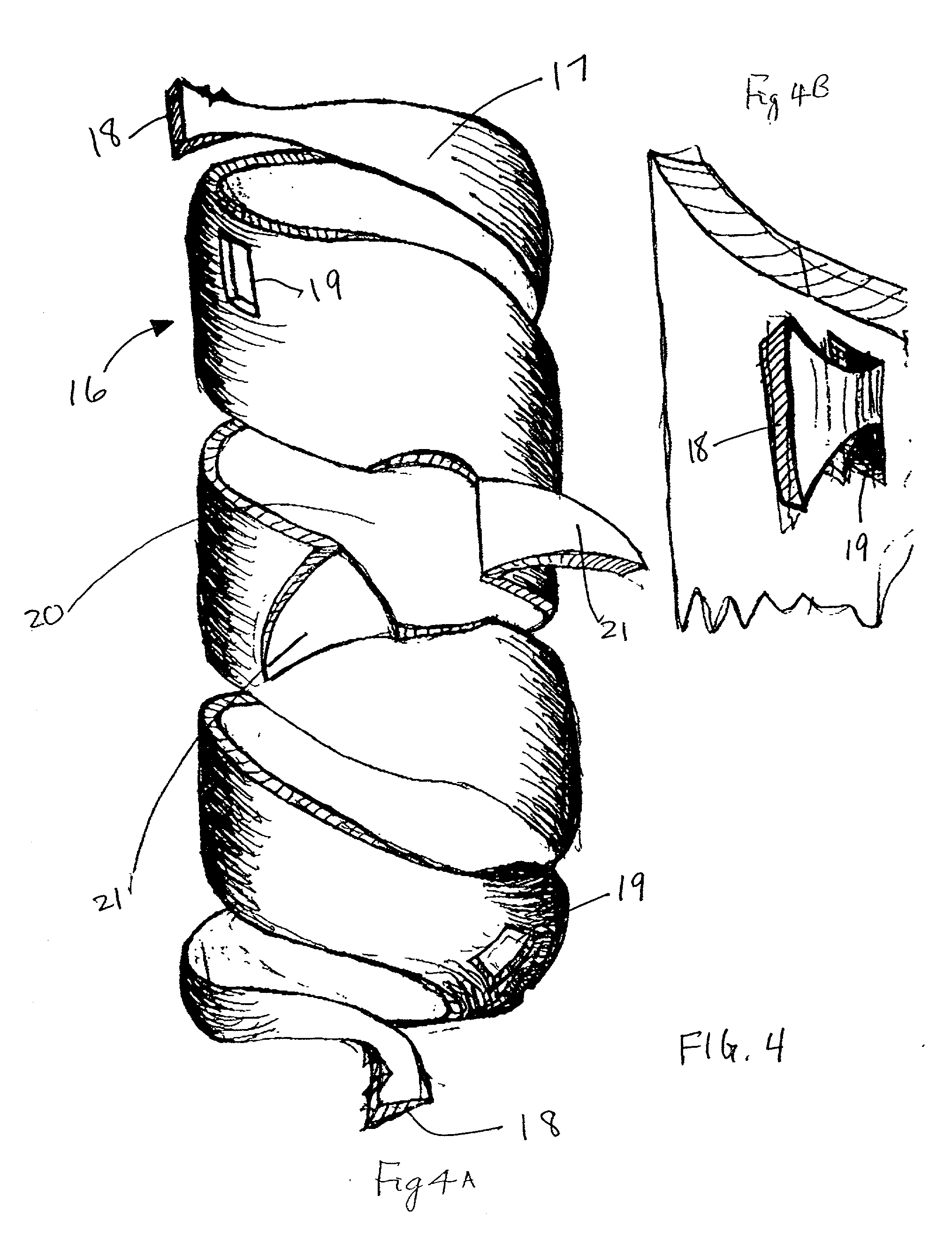
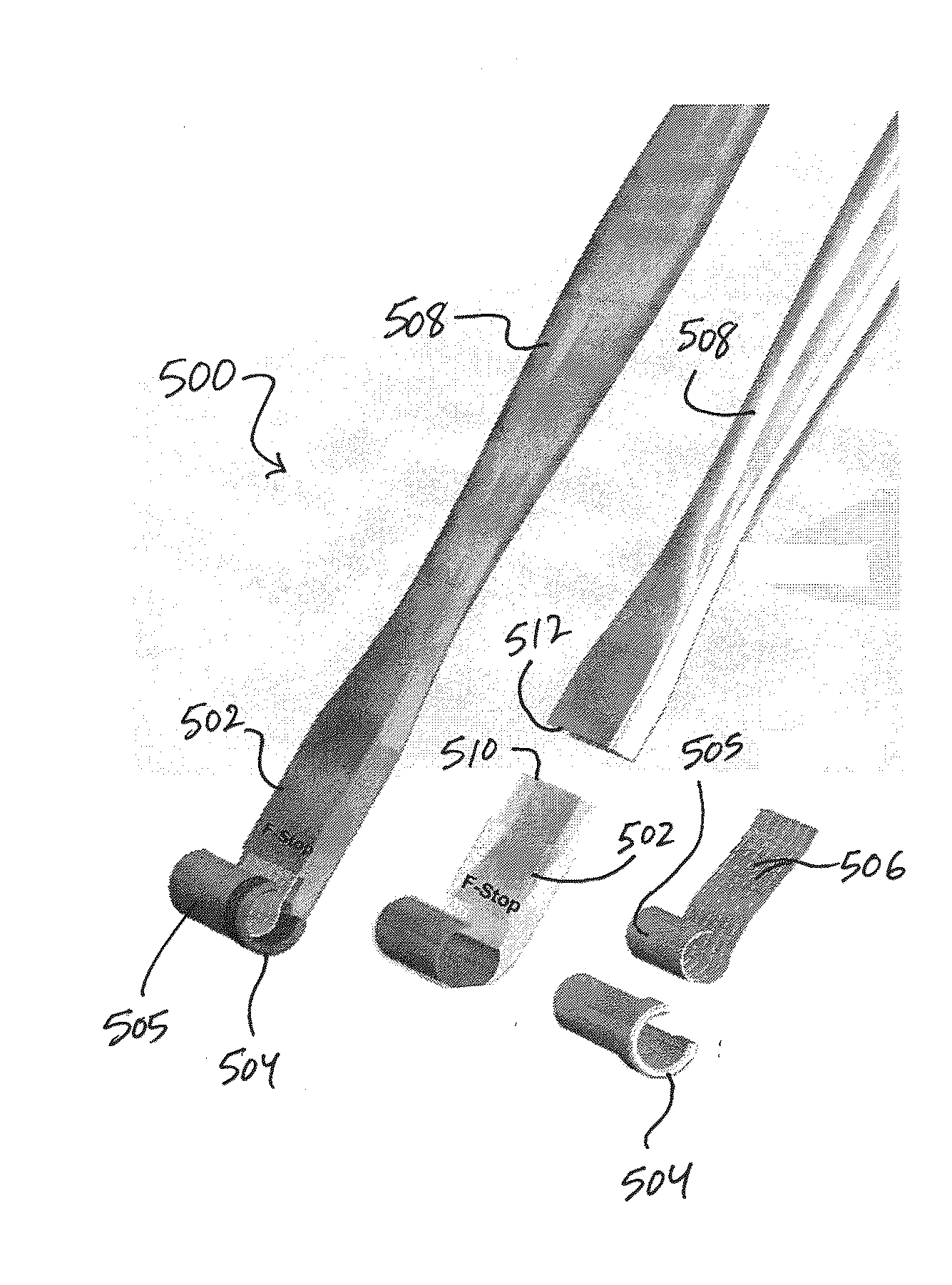
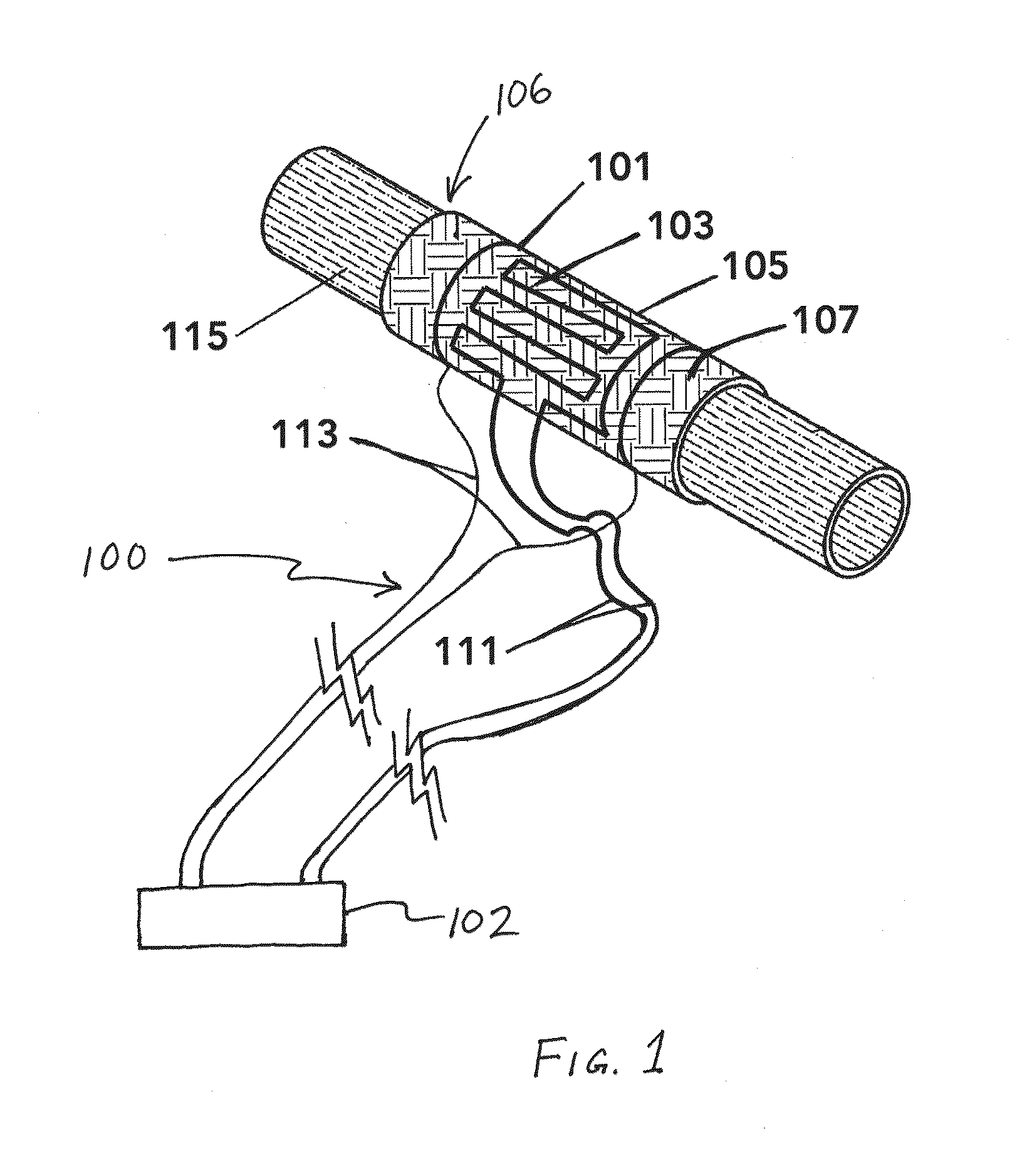
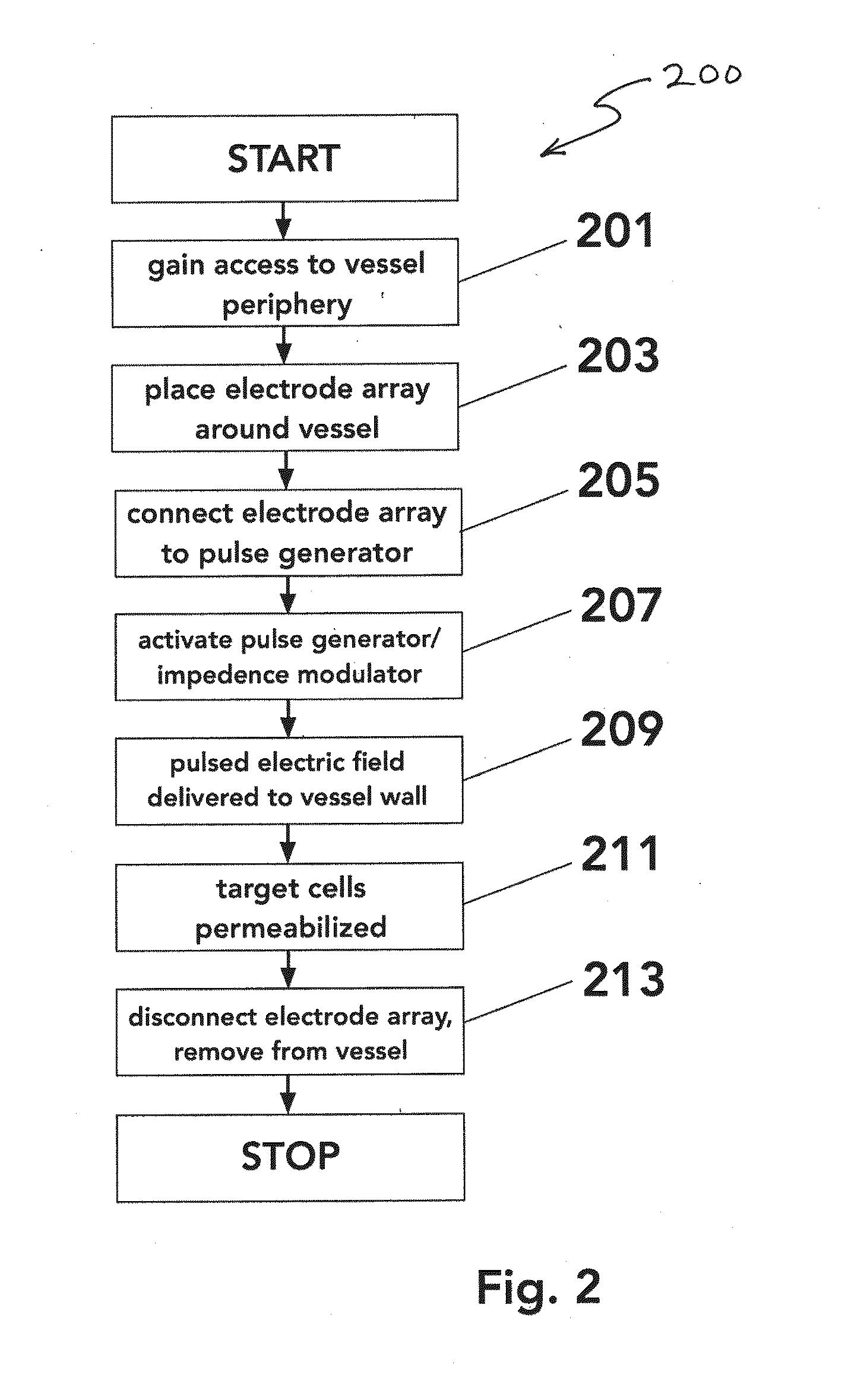
Perivascular Electroporation Device and Method for Extending Vascular Patency
InactiveUS20160256218A1Mitigate host responseReduce riskSurgical instruments for heatingMedicinePerivascular Satellitosis
A system for performing perivascular electroporation of a blood vessel may include a tissue treatment device configured to contact and surround at least part of a circumference of an outer surface of a blood vessel wall and a control device coupled with the tissue treatment device. The control device may include an electric pulse generator and a tissue impedance modulator. A method for performing perivascular electroporation of a blood vessel may involve coupling a tissue treatment device of a perivascular electroporation system with an outer surface of a wall of the blood vessel and delivering electric pulses to an outermost layer of the blood vessel wall, while limiting a depth of penetration of the electric pulses such that they do not reach an innermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
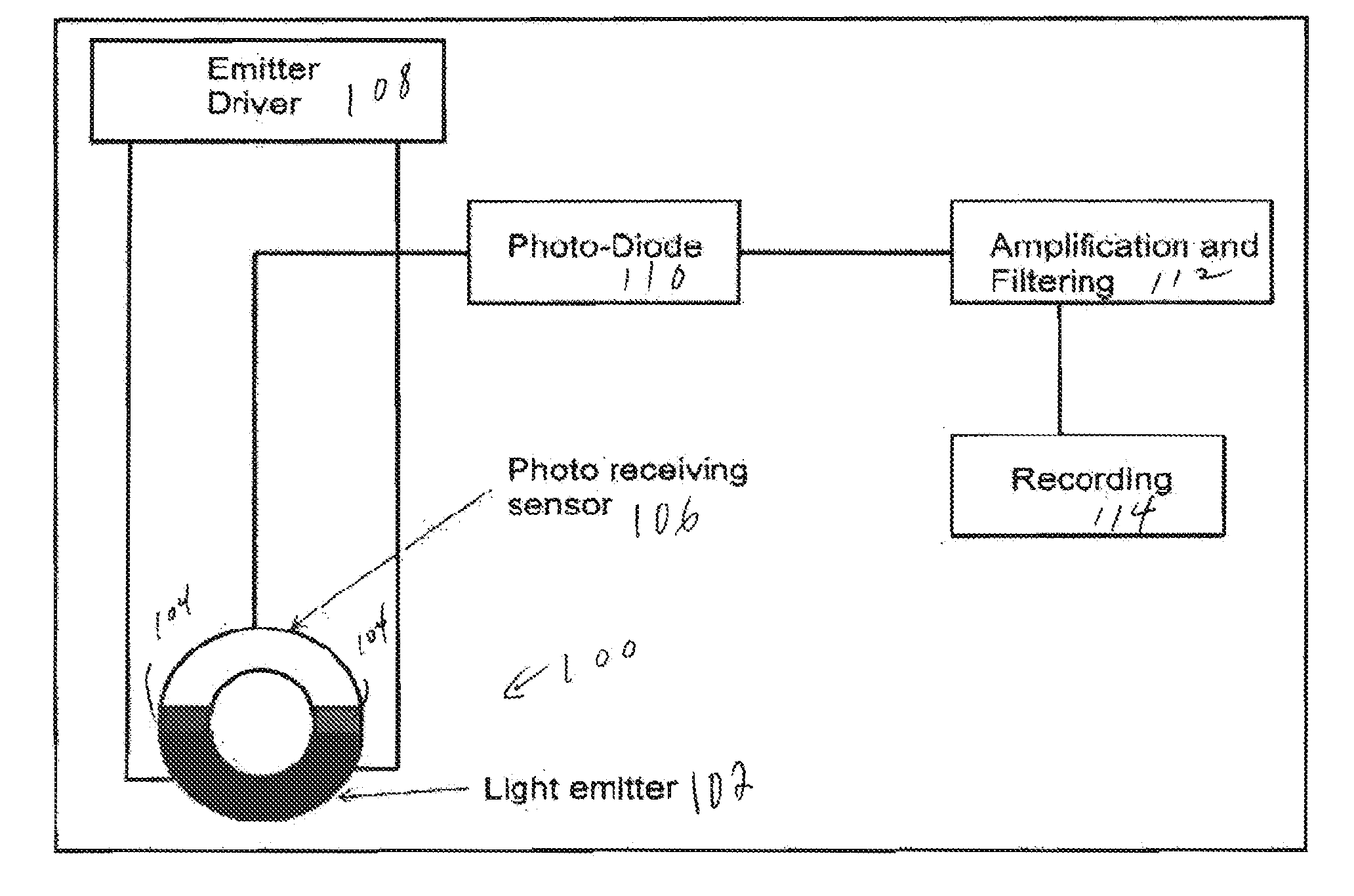
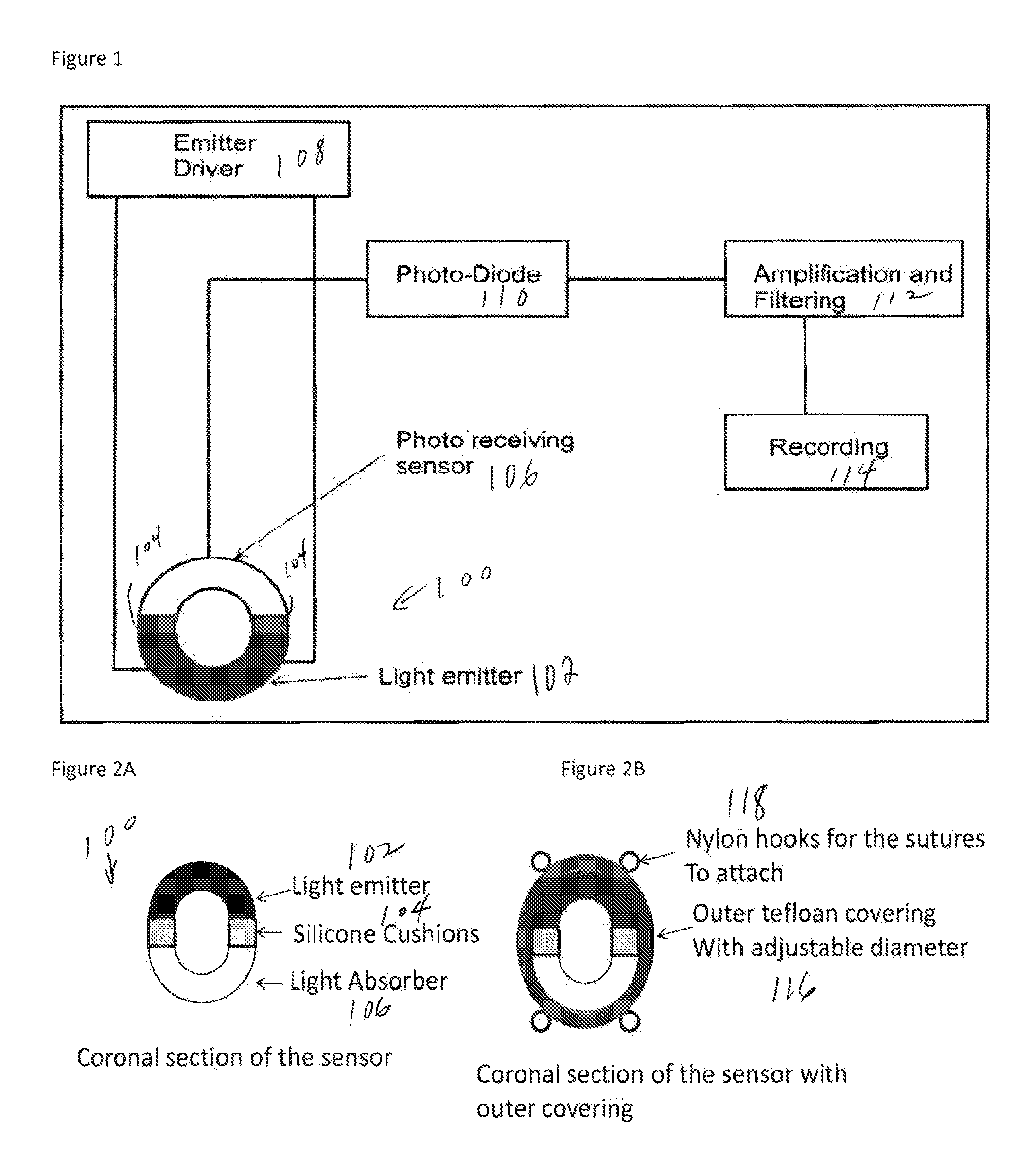
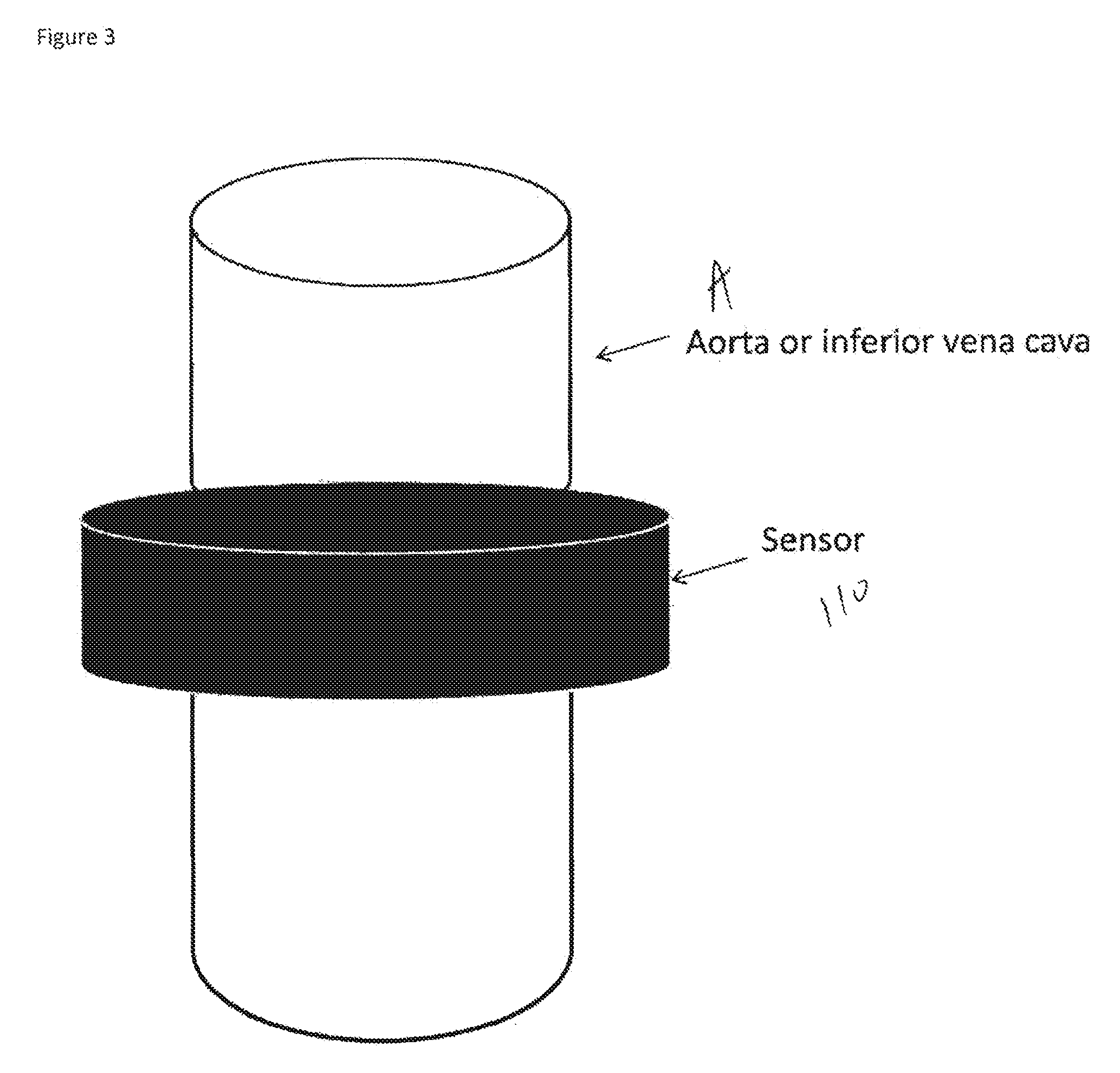
Implantable Real-Time Oximeter To Determine Potential Strokes And Post-Traumatic Brain-Injury Complications
ActiveUS20150073240A1Increase the areaRapid diagnosisCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse oximetersPerivascular Satellitosis
A first embodiment of an oximetry probe is attached around a blood vessel near the site of a likely stroke. That will be useful to monitor large and medium size cerebral arteries. Another type of pulse oximeter can be passed within cerebral blood vessels to monitor the oxygenation status of the surrounding cerebral tissues. In that version, the emitter and detector are coplanar and contained in a small area, e.g., 50-12 μm.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Apparatus and method for promoting angiogenesis in ischemic tissue
InactiveUS20180369539A1Promote absorptionReduce washoutMedical devicesCatheterPerivascular SatellitosisAngiogenesis growth factor
A biologics delivery device and method of use for promoting angiogenesis in occluded vessels and ischemic tissue of a patient are provided, wherein the biologics delivery device includes a catheter having a proximal end, a distal region having a distal end, and a side wall defining a catheter lumen; an expandable member disposed in the distal region, the expandable member configured to support a subintimal space in an occluded blood vessel of a patient, and to transition between a collapsed state and an expanded state; and a hollow needle having a penetration tip deployable from inside the catheter lumen to outside the catheter lumen, and into tissue surrounding the occluded blood vessel, wherein the expandable member in the expanded state allows the flow of oxygenated blood to the occluded blood vessel. Methods of using the inventive biologics delivery device also are provided to deposit the biologic from a subintimal space to tissue surrounding the occluded blood vessel.
Owner:ROCHA SINGH KRISHNA +1
Sustained release of Apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
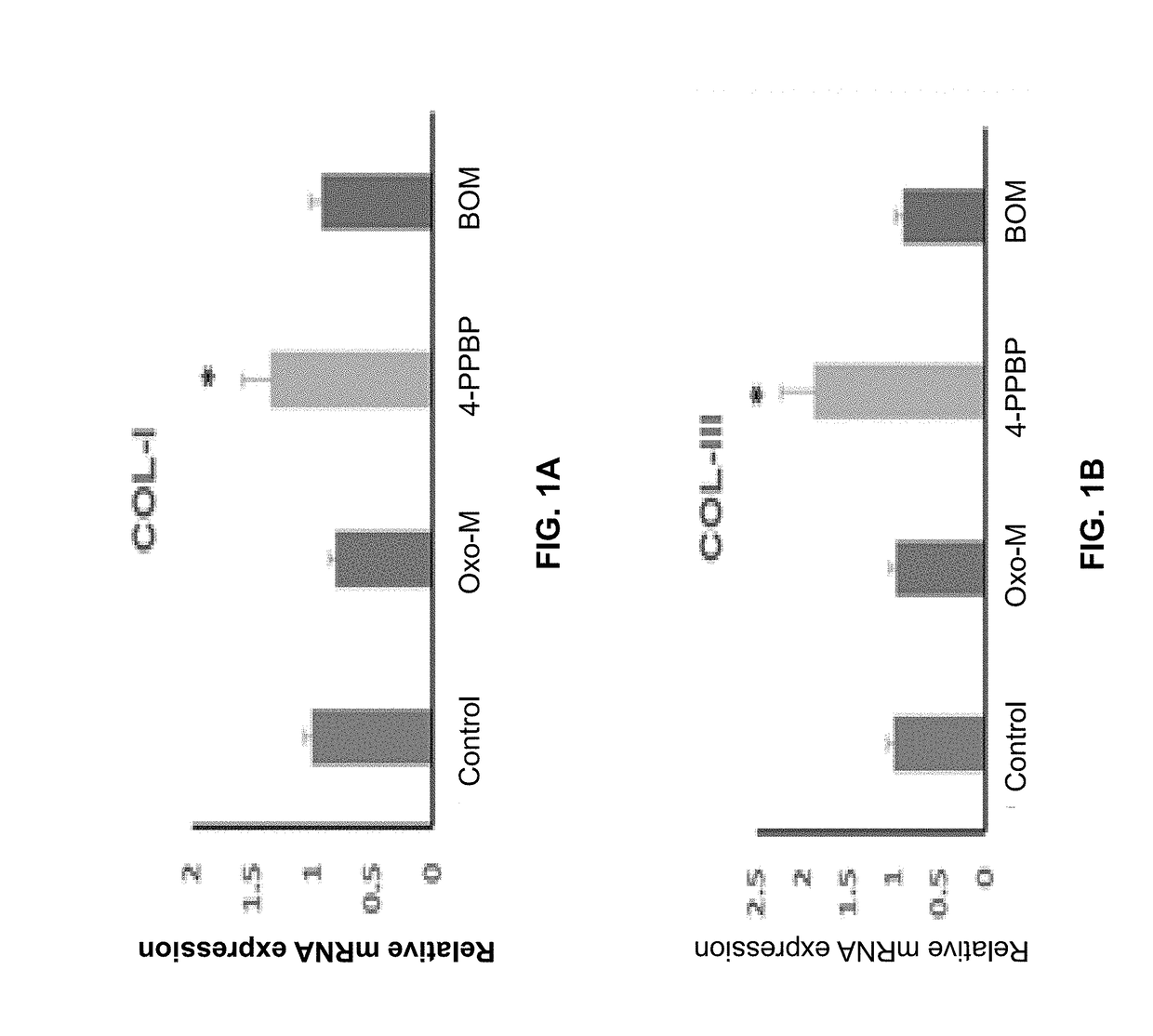
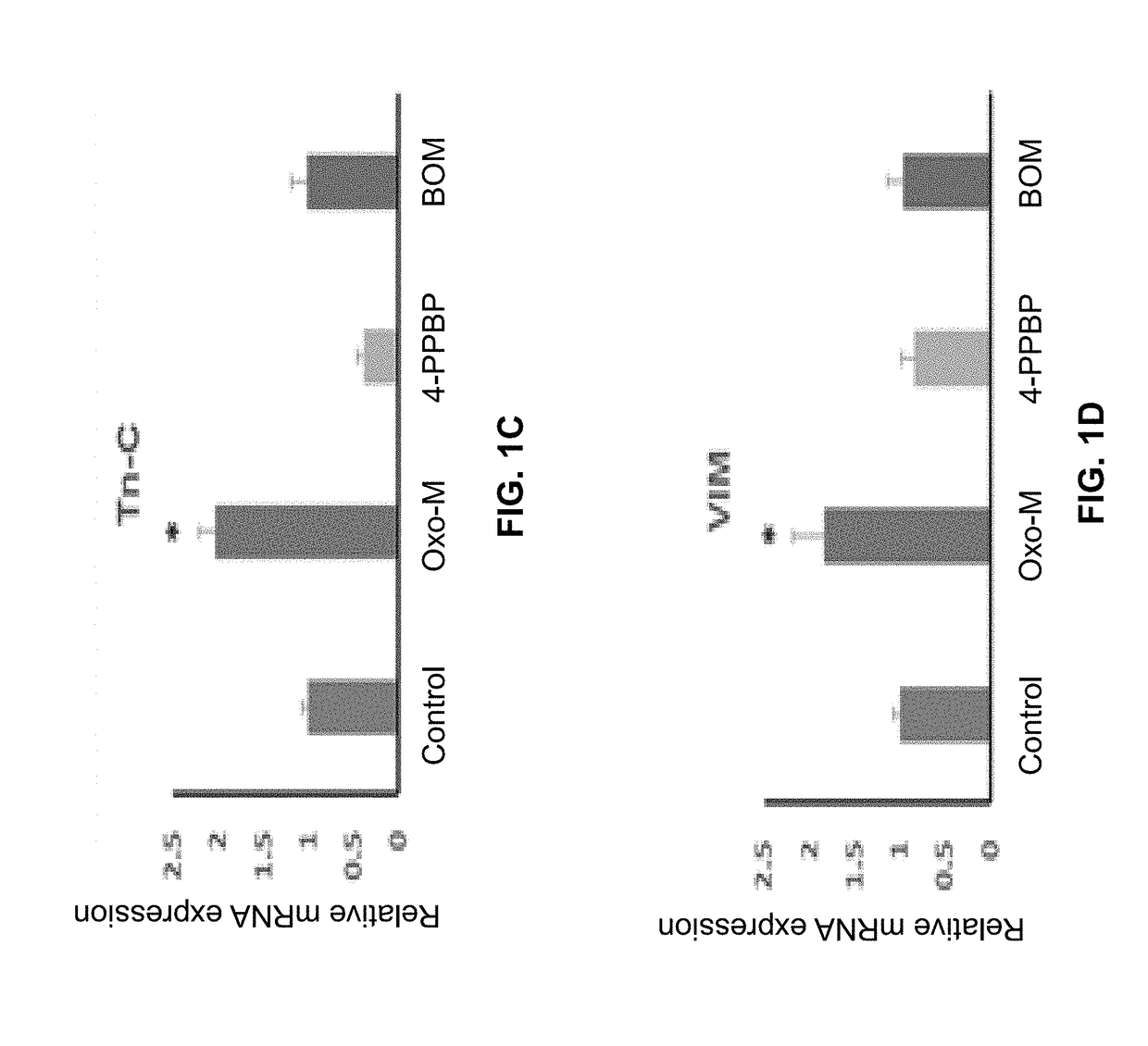
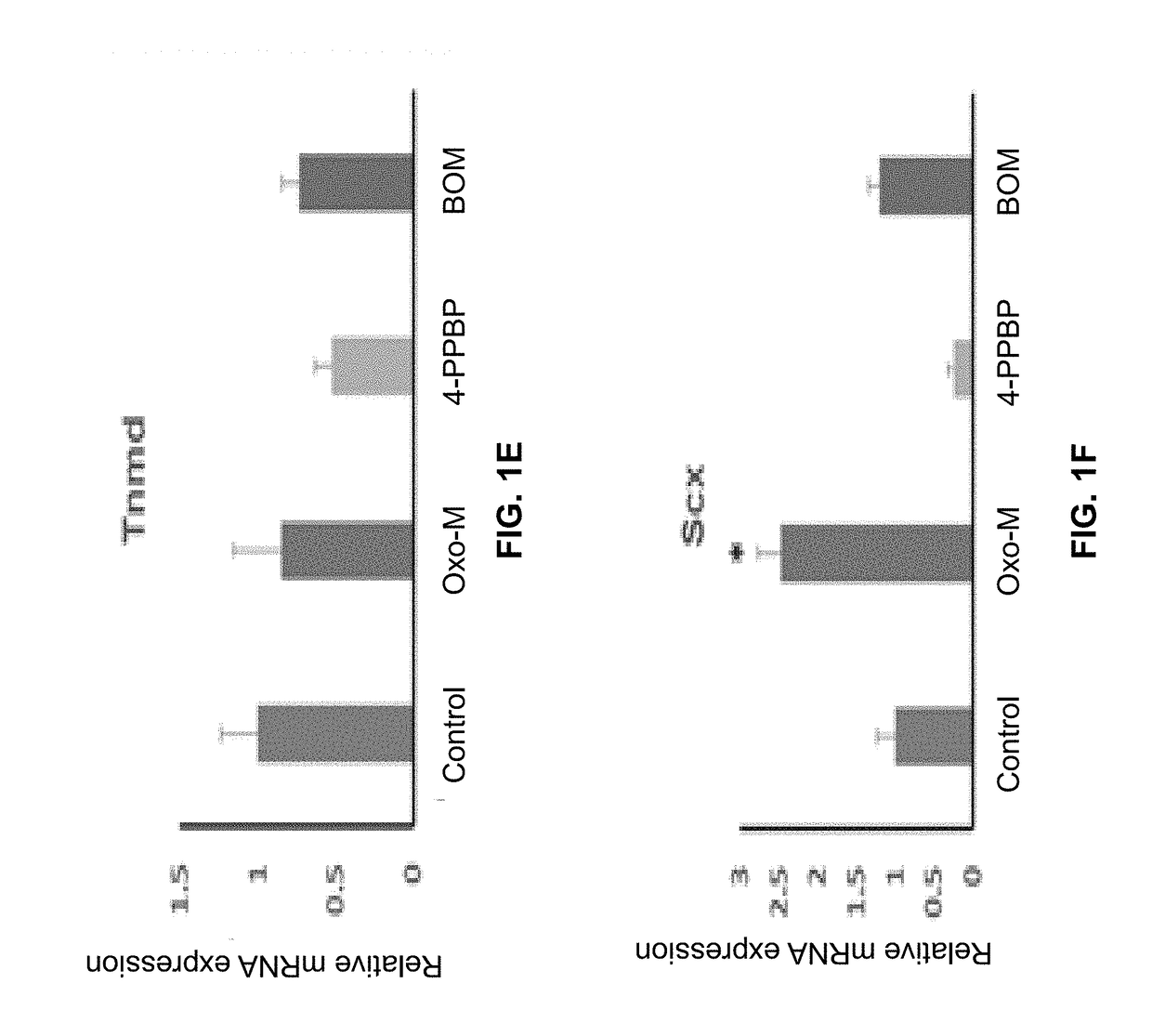
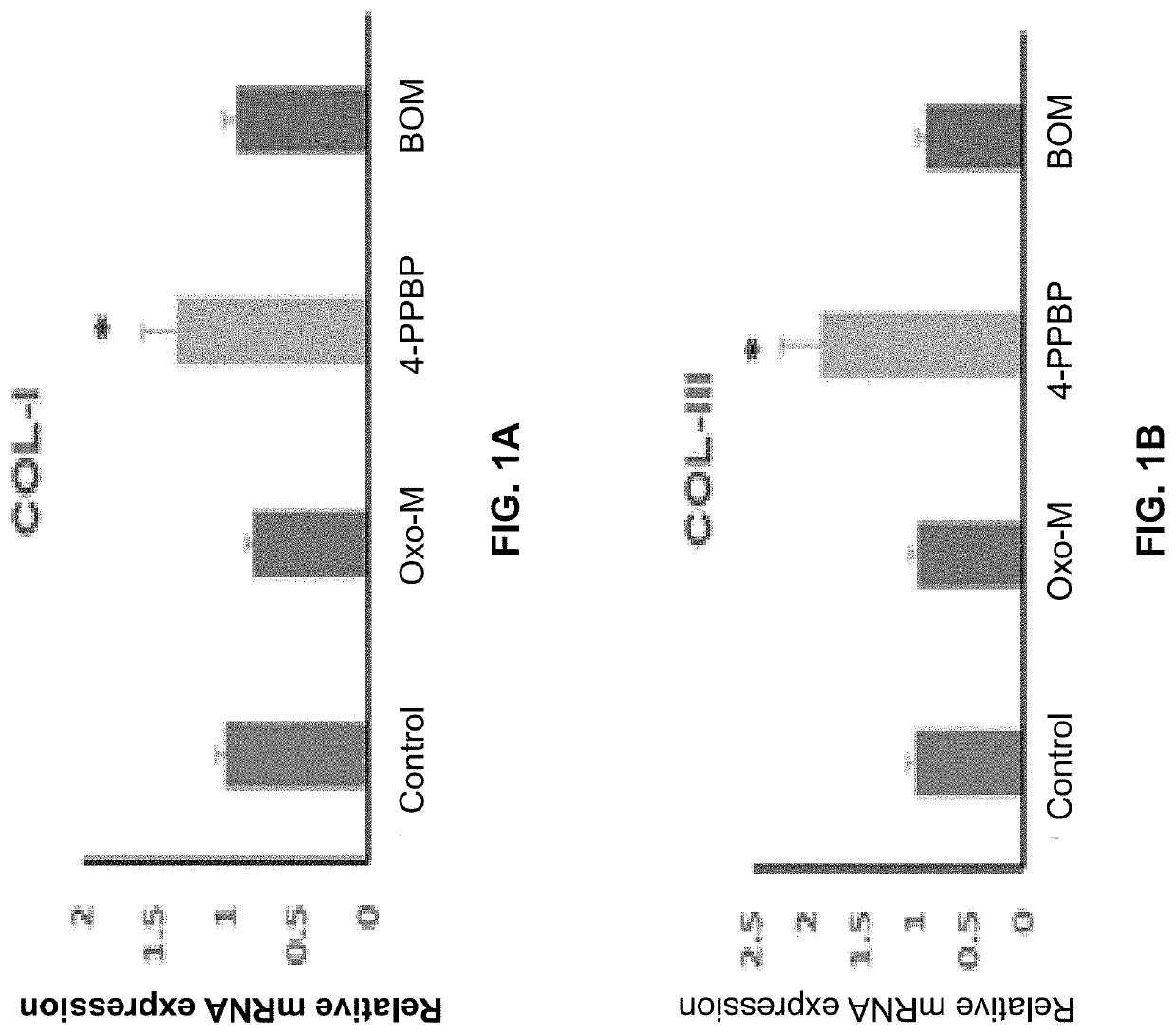
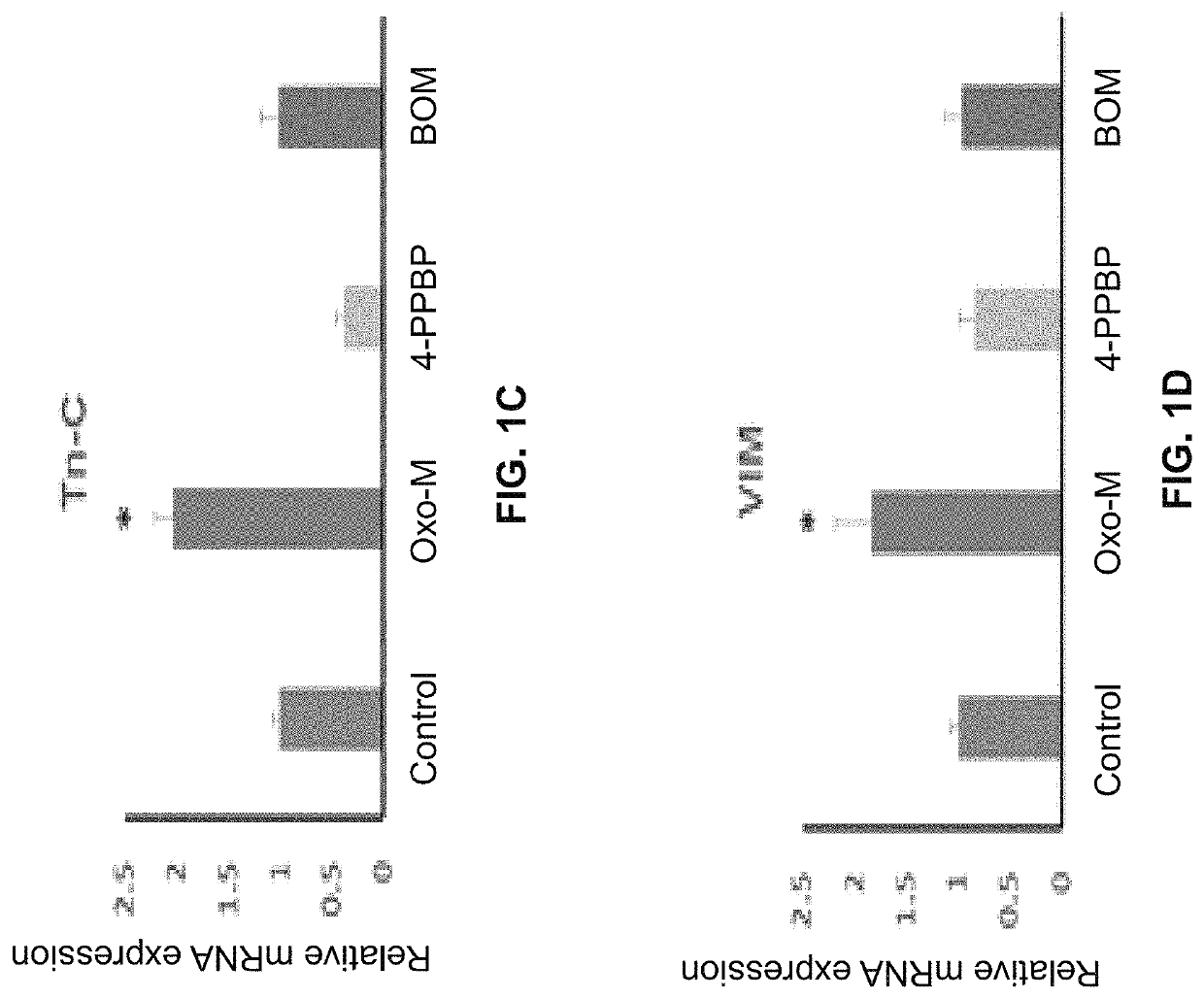
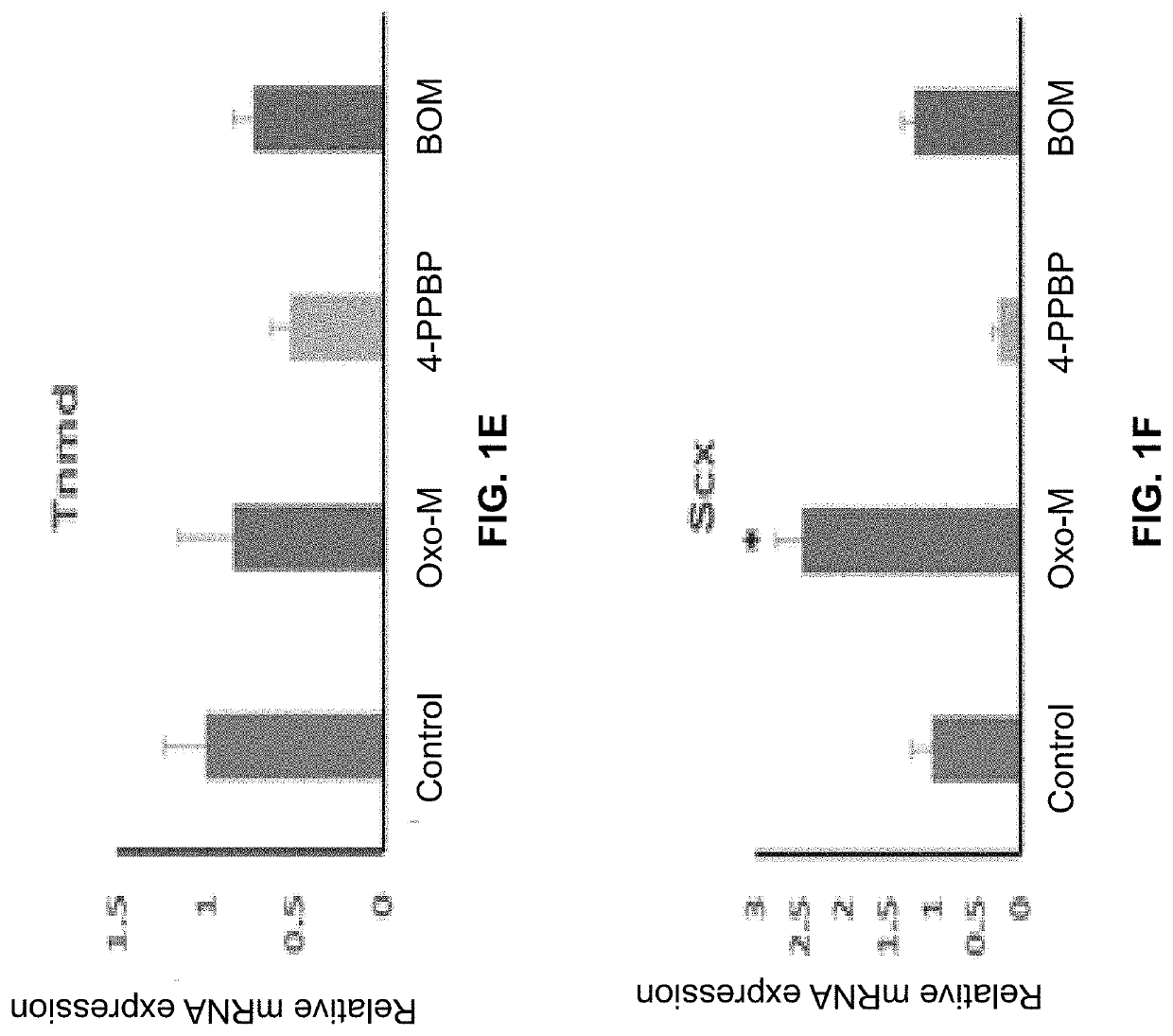
Oxo-M and 4-PPBP induction of tenogenic differentiation of perivascular tendon stem cells
ActiveUS20190015386A1Reduce gapStructure morePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMethiodideMedicine
Provided herein are compositions including oxotremorine (e.g., oxotremorine methiodide or Oxo-M) and 4-PPBP (e.g., 4-PPBP maleate). Also provided are methods of treating a connective tissue defect in a subject with oxotremorine and 4-PPBP. In addition, provided are scaffolds and methods of making same that include multiple fibers that include Oxo-M, 4-PPBP, and optionally icariin or kartogenin.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
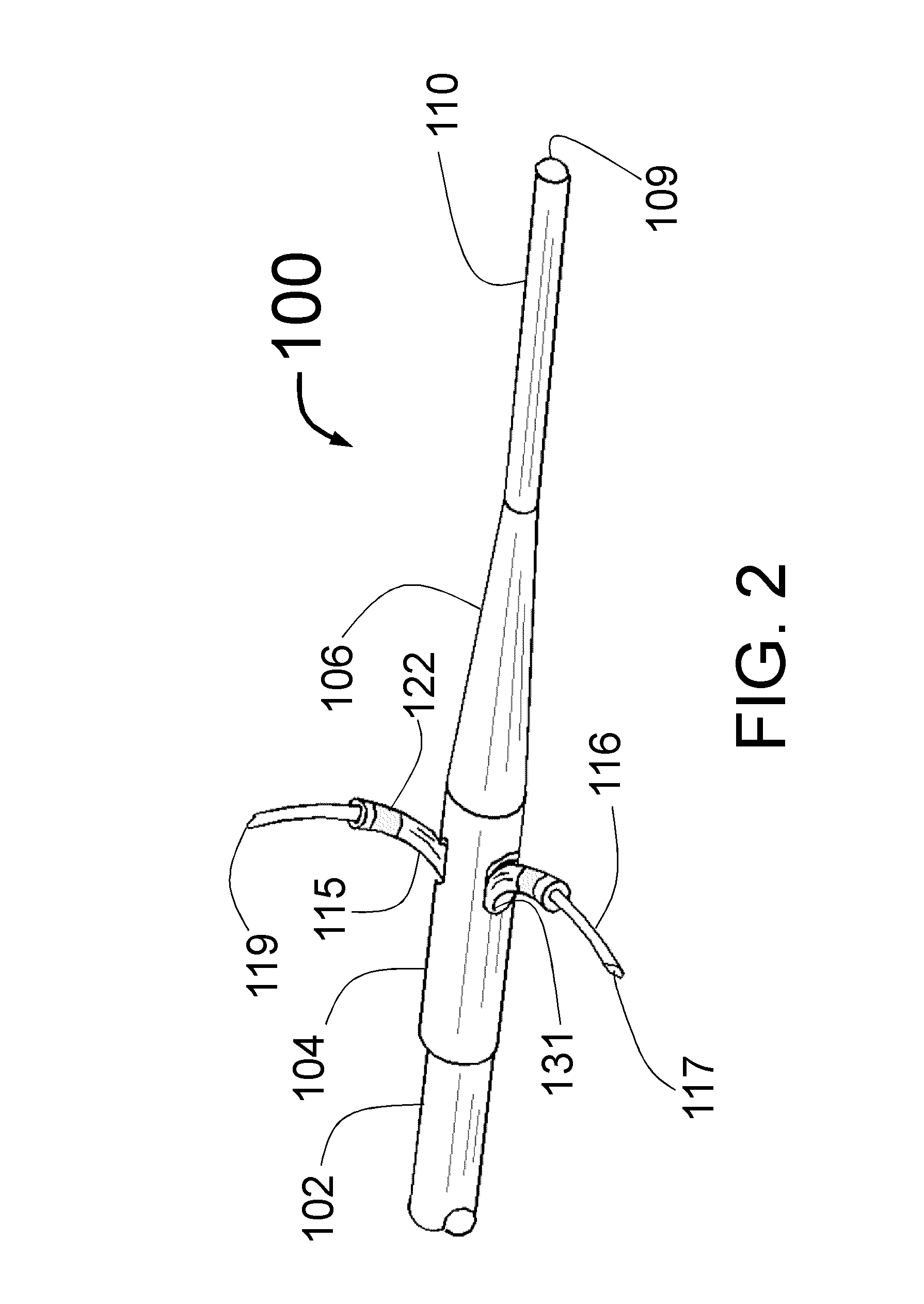
Intravascular catheter with sensor for peripheral nerve activity
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Oxo-M and 4-PPBP induction of tenogenic differentiation of perivascular tendon stem cells
ActiveUS10583117B2High expressionInduced differentiationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsConnective tissue fiberMethiodide
Provided herein are compositions including oxotremorine (e.g., oxotremorine methiodide or Oxo-M) and 4-PPBP (e.g., 4-PPBP maleate). Also provided are methods of treating a connective tissue defect in a subject with oxotremorine and 4-PPBP. In addition, provided are scaffolds and methods of making same that include multiple fibers that include Oxo-M, 4-PPBP, and optionally icariin or kartogenin.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com