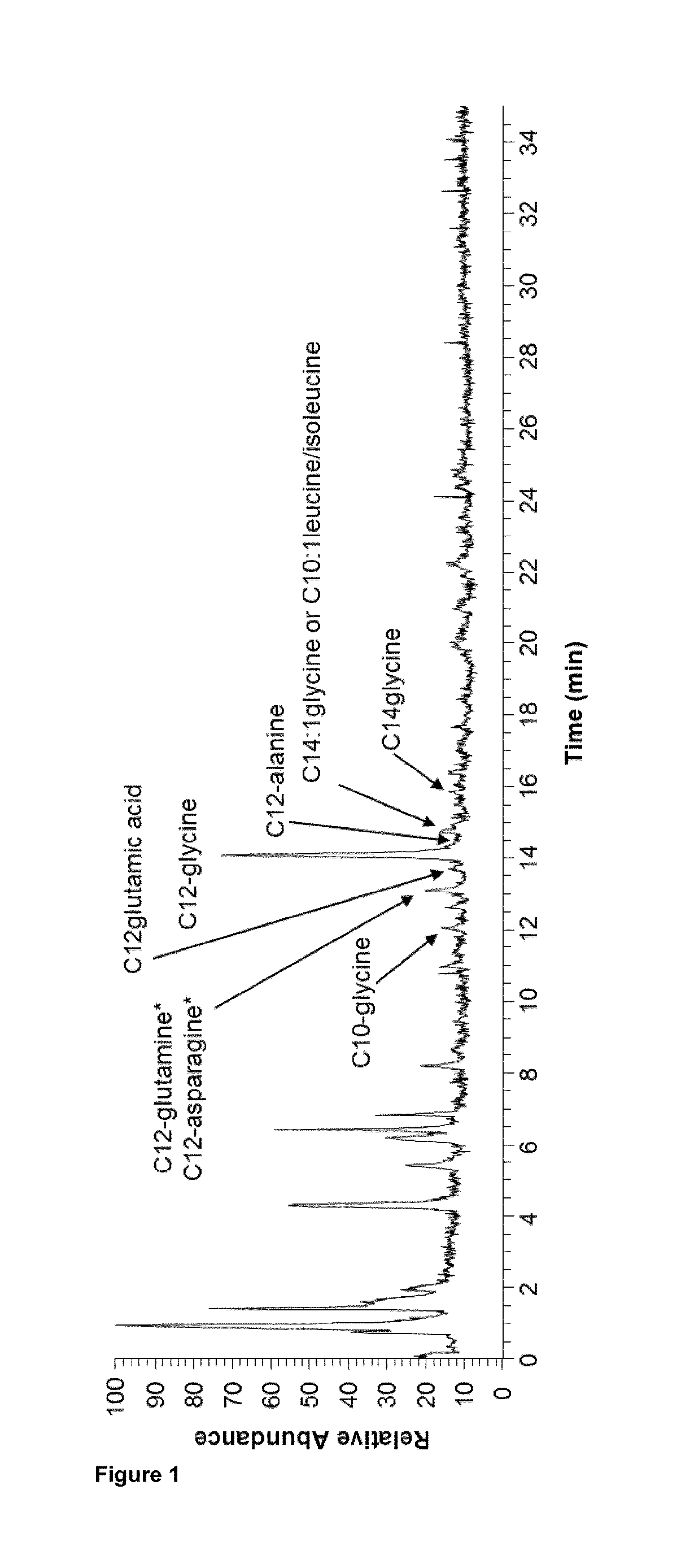
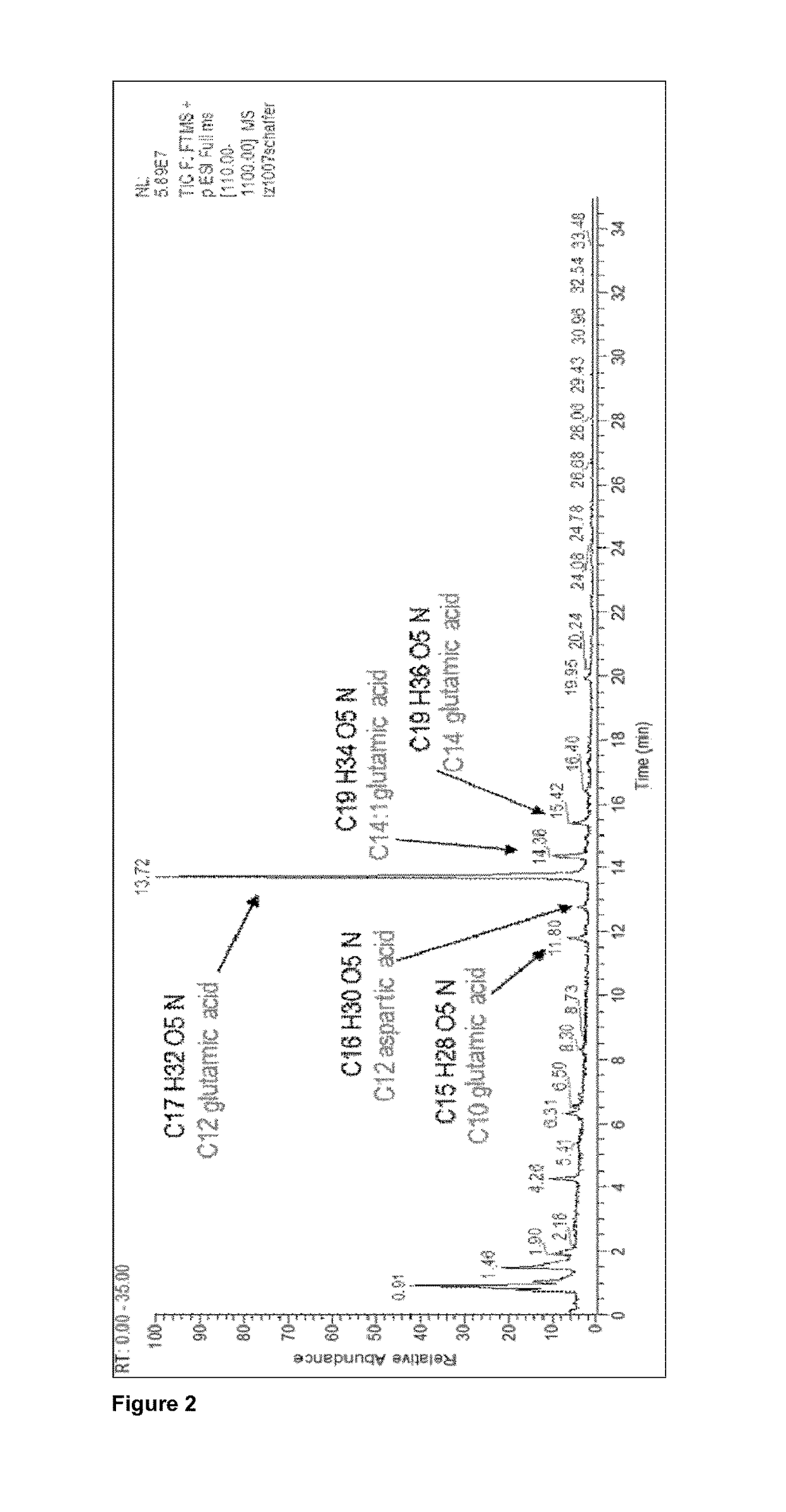
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Acyl transferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In muscle disease: Lipid storage myopathies …the presence of the enzyme acylcarnitine transferase. The acylcarnitine that is formed crosses the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes and then is split in the presence of another form of the enzyme acyltransferase to give carnitine and the acyl molecule, which is then oxidized.
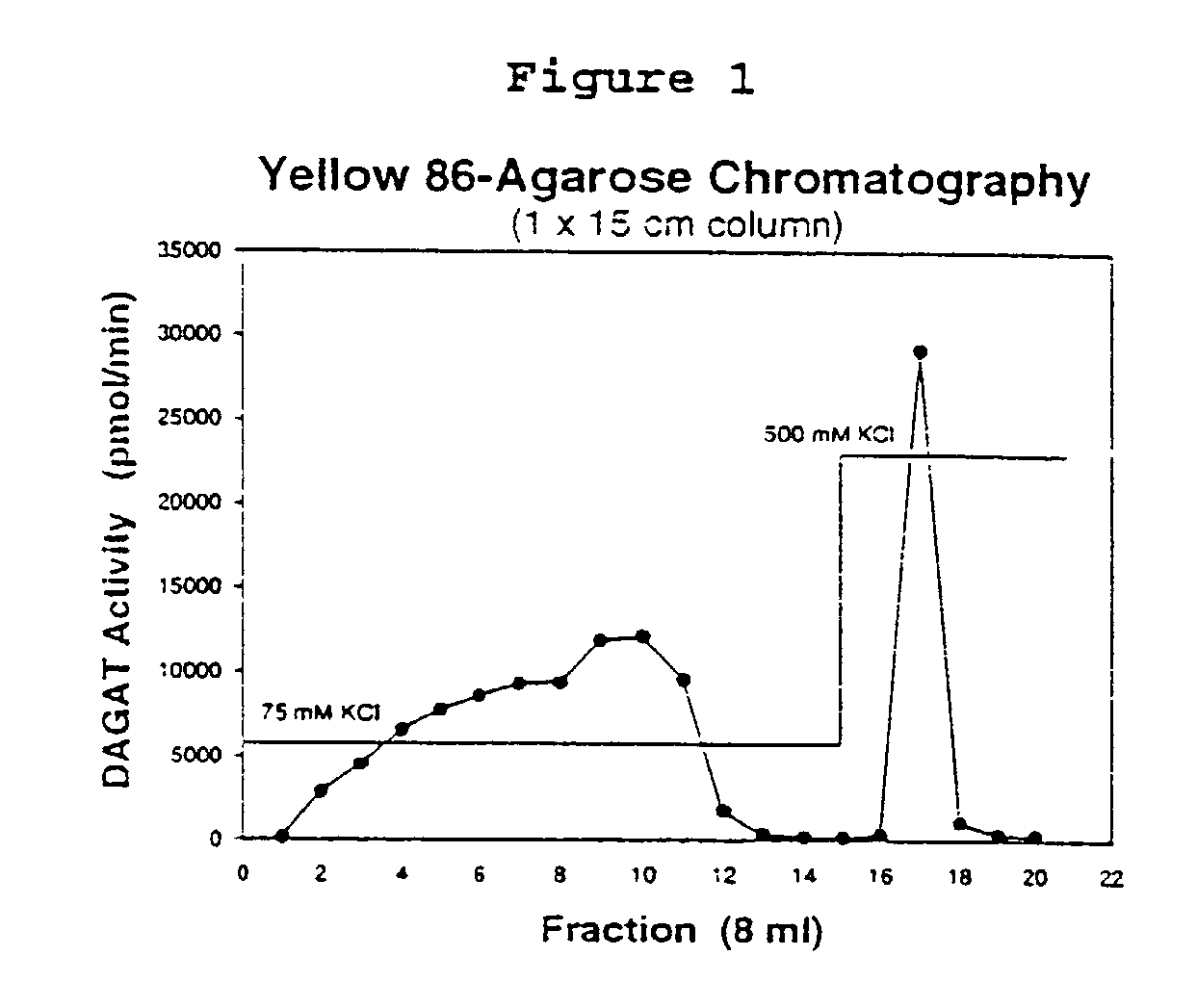
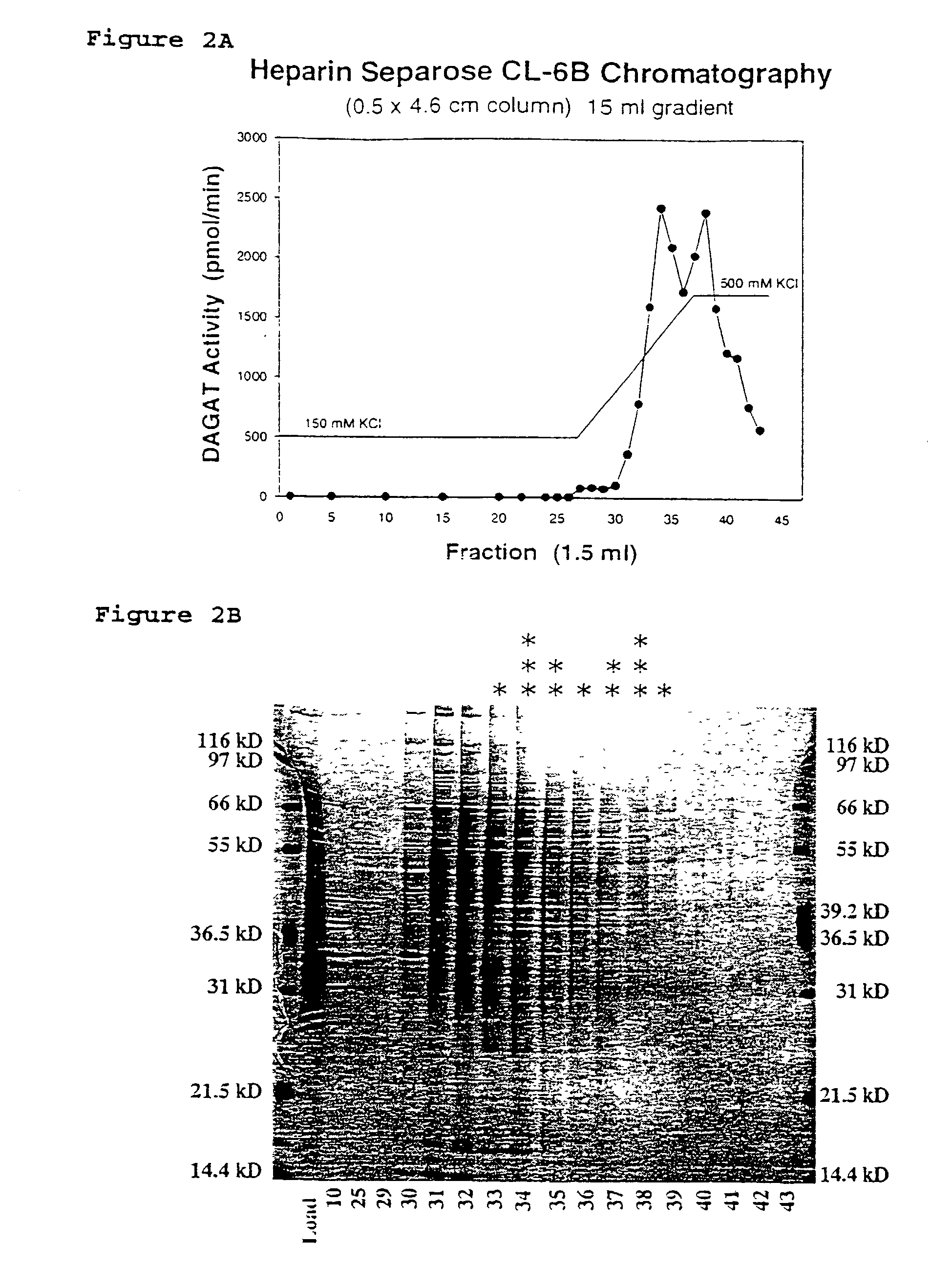
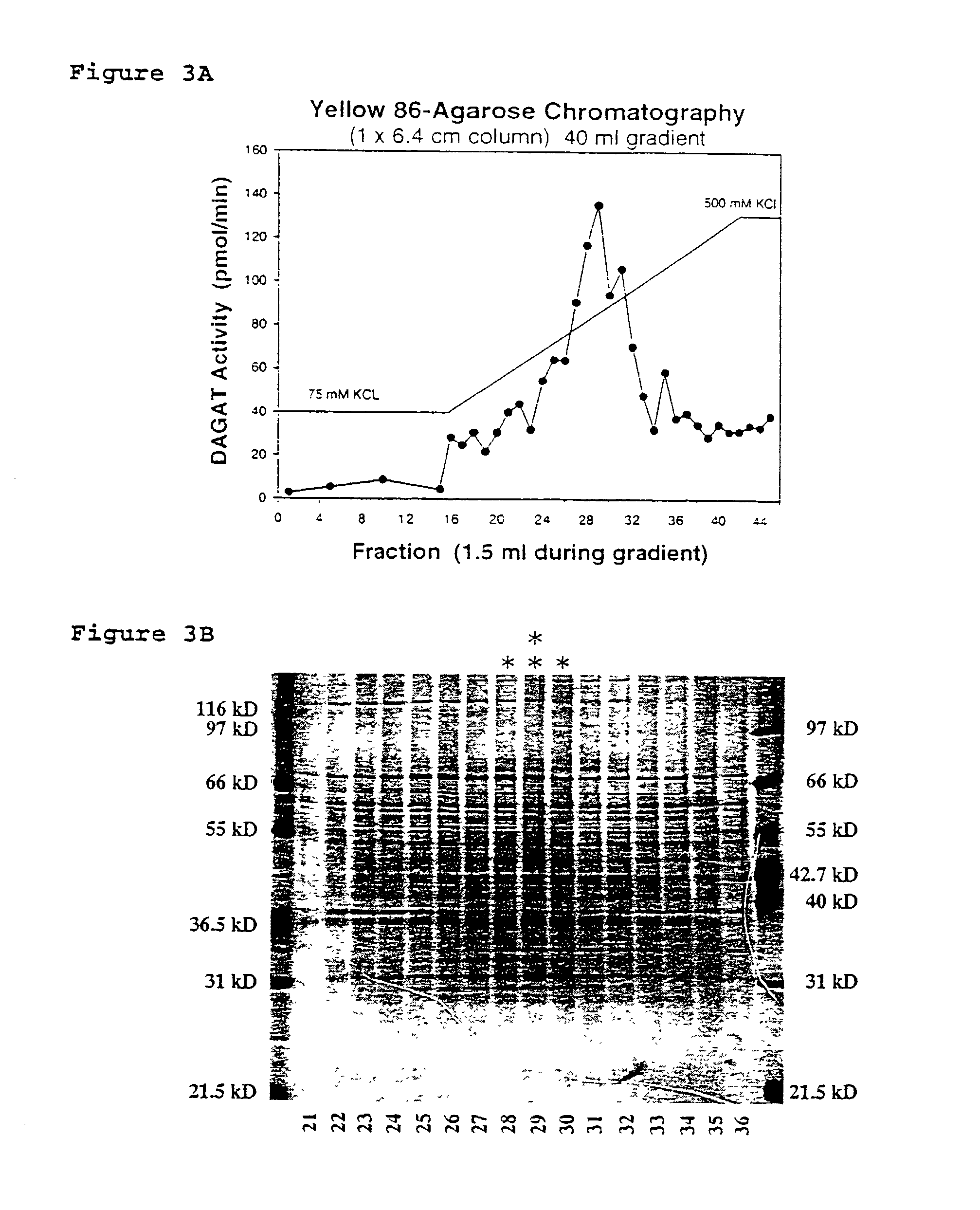
Diacylglycerol acyl transferase proteins
InactiveUS7135617B2Increase percentageIncreased DAGAT activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMortierella ramanniana
The invention provides diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DAGAT) proteins, wherein said proteins are active in the formation of triacylglycerol from fatty acyl and diacylglycerol substrates. In one aspect, Mortierella ramanniana DAGAT proteins have been isolated and have molecular weights of between approximately 36 and 37 kDa as measured by SDS-PAGE. The invention also provides novel DAGAT polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences and to methods of producing such polypeptides using recombinannt techniques. In addition, methods are provided for using such sequences to alter triacylglycerol levels in plants and to treat diseases associated with altered DAGAT activity or expression.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
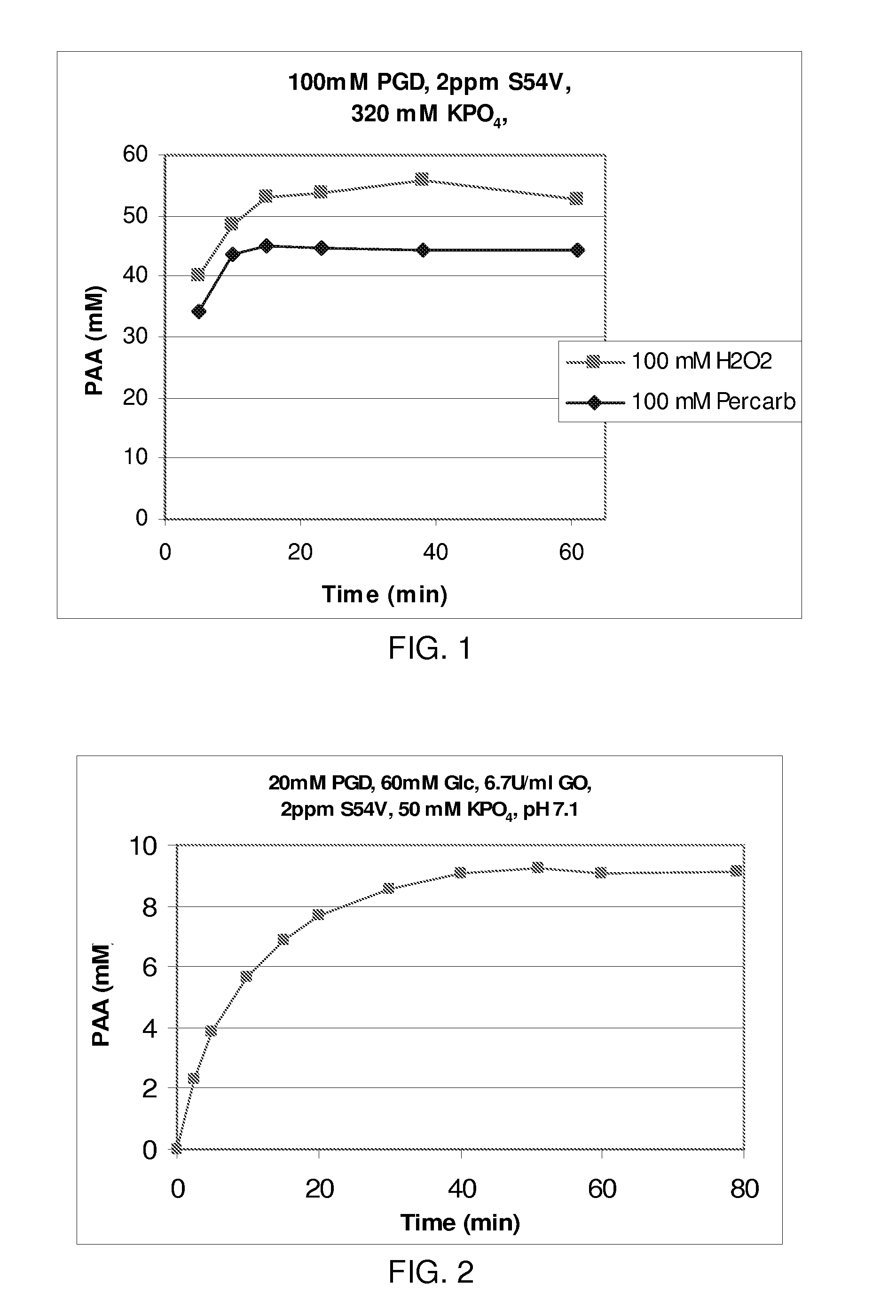
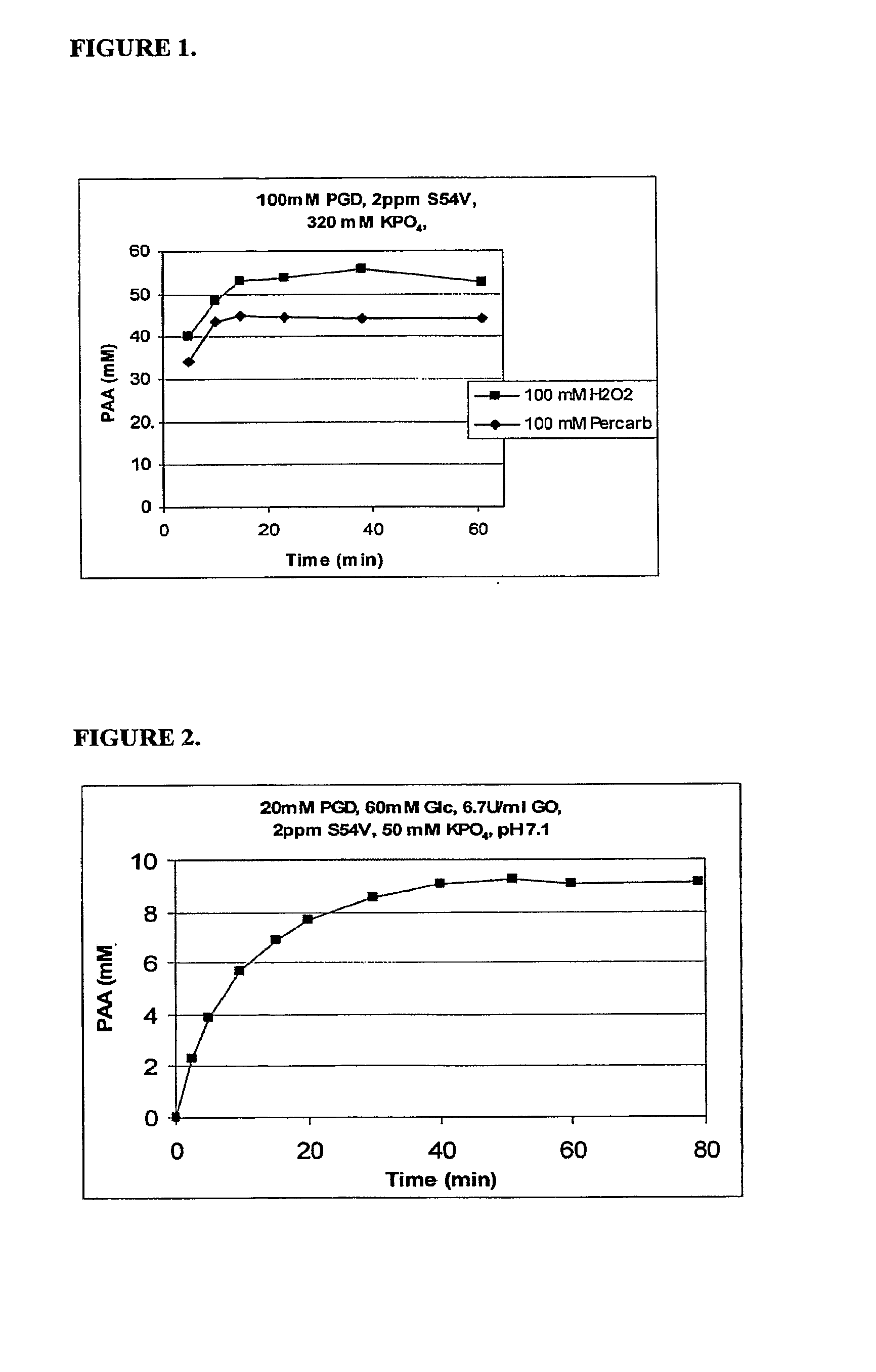
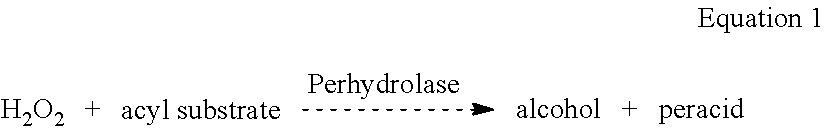
Stable Enzymatic Peracid Generating Systems
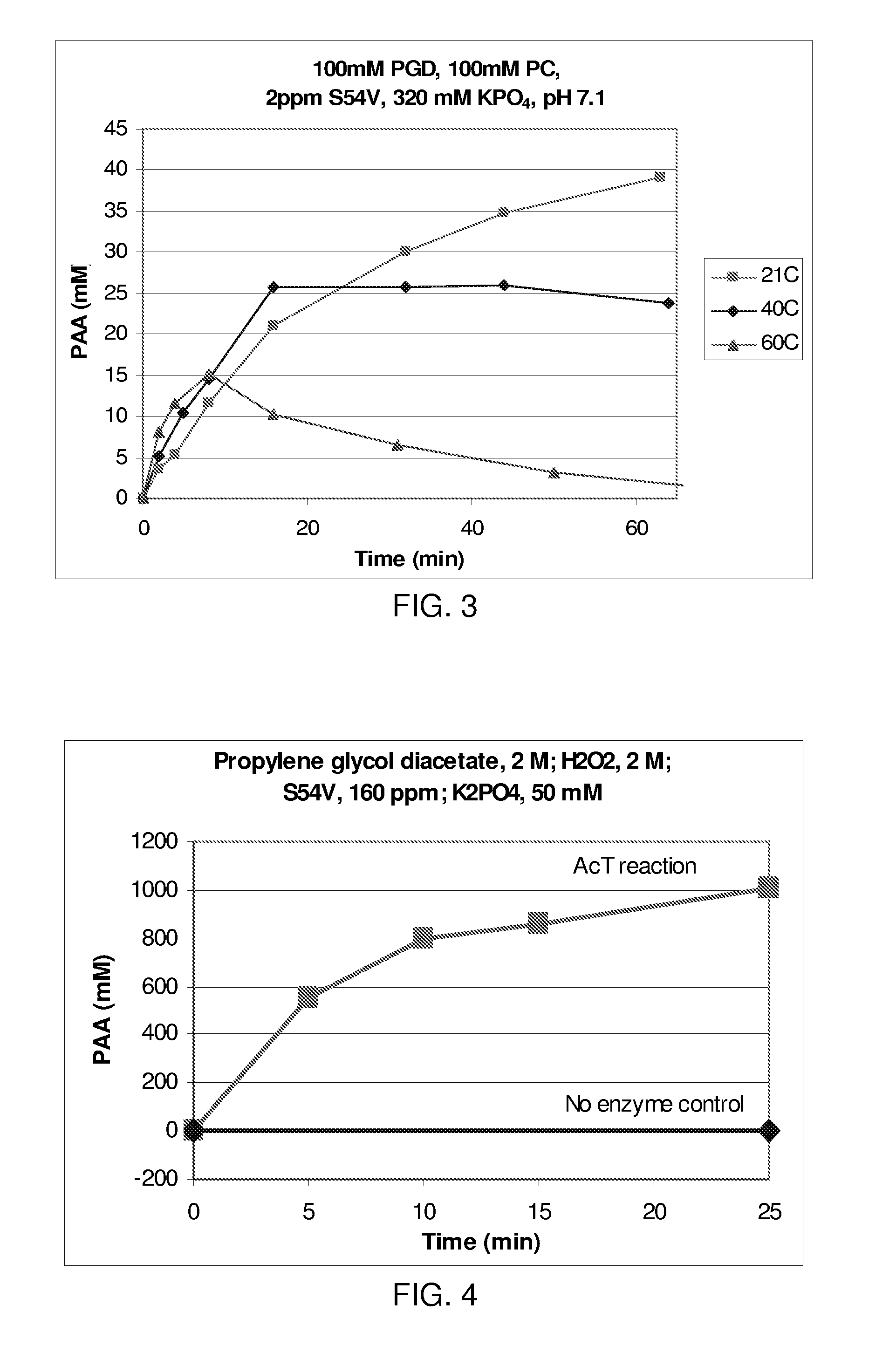
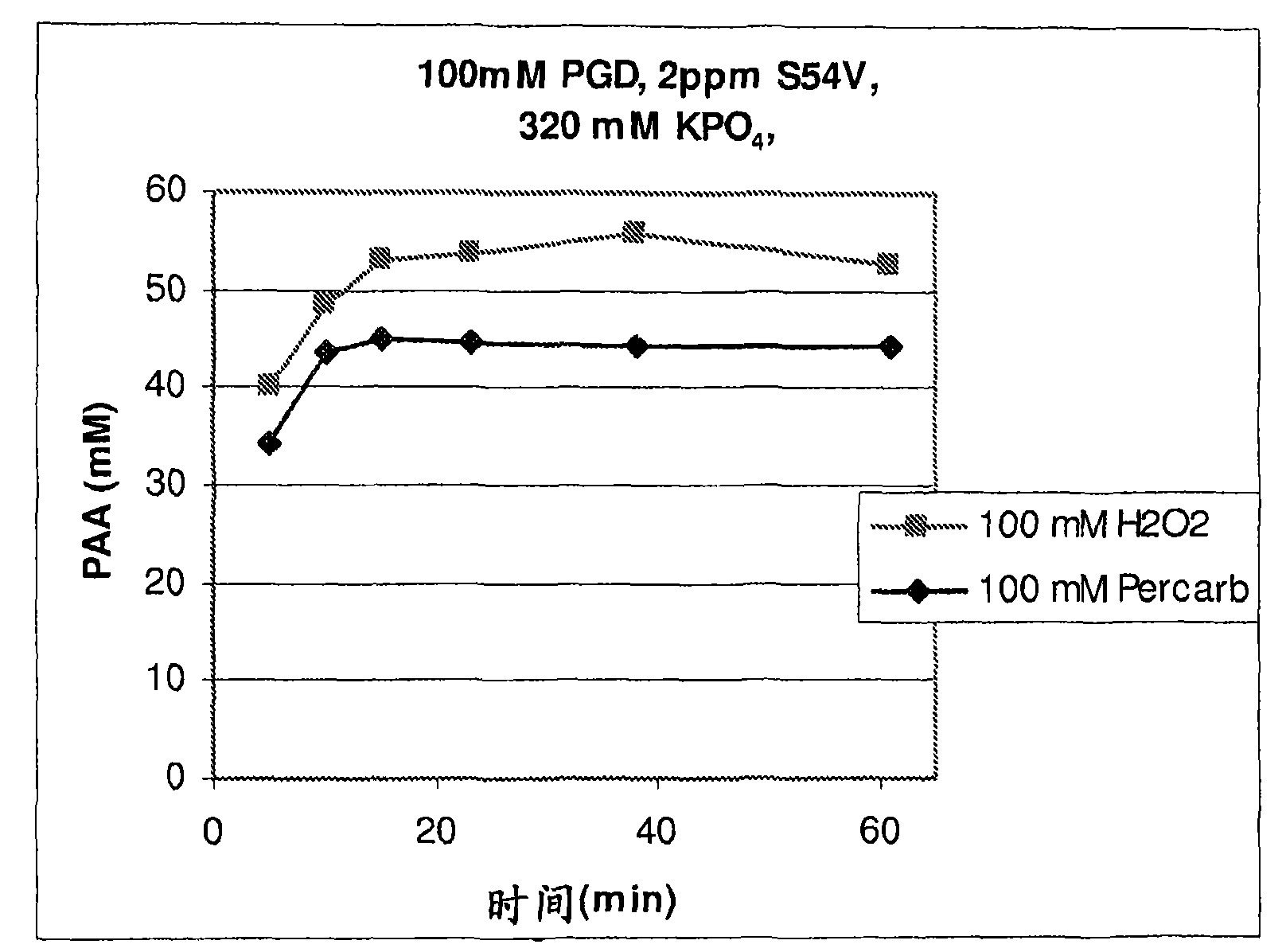
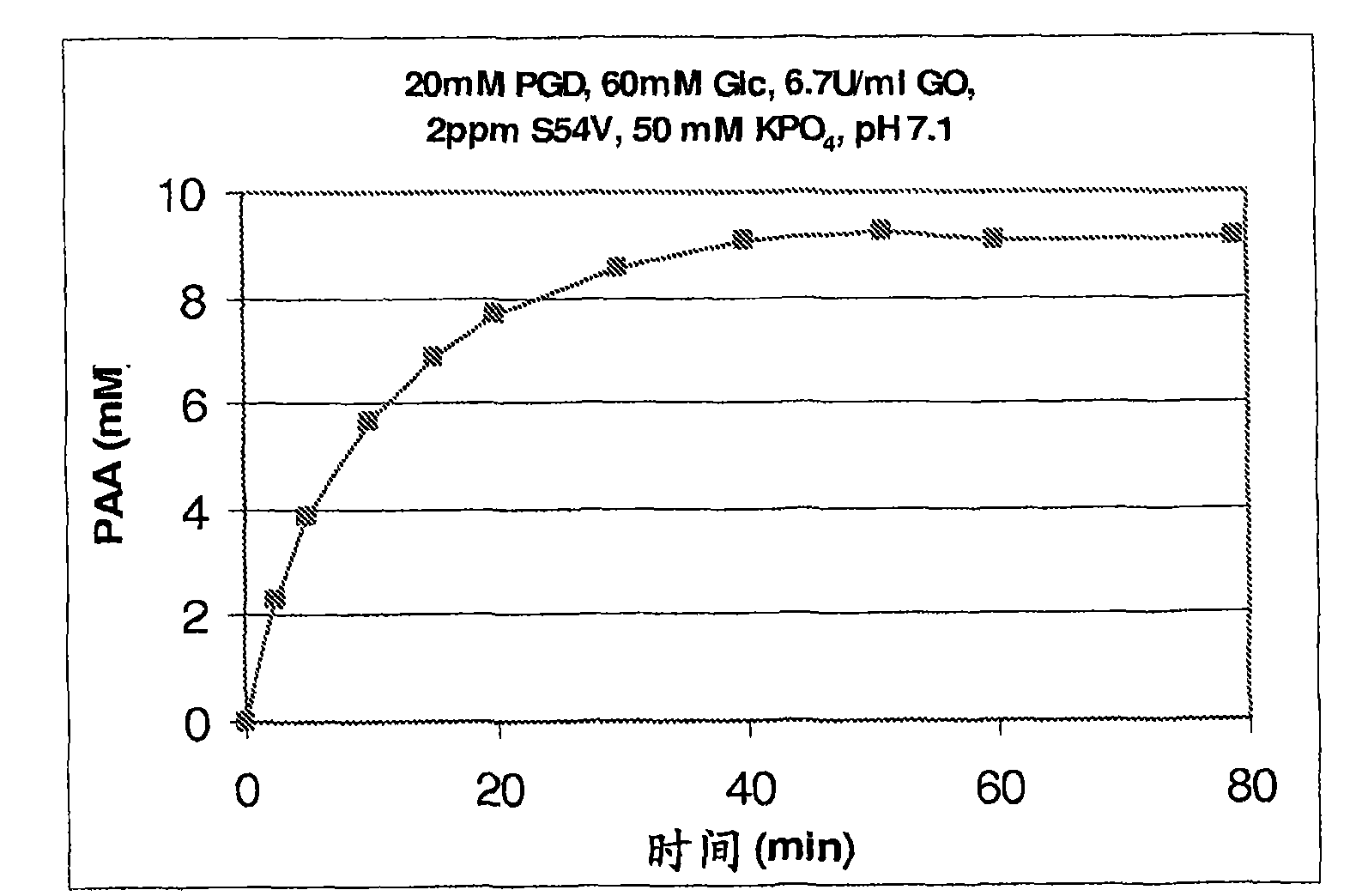
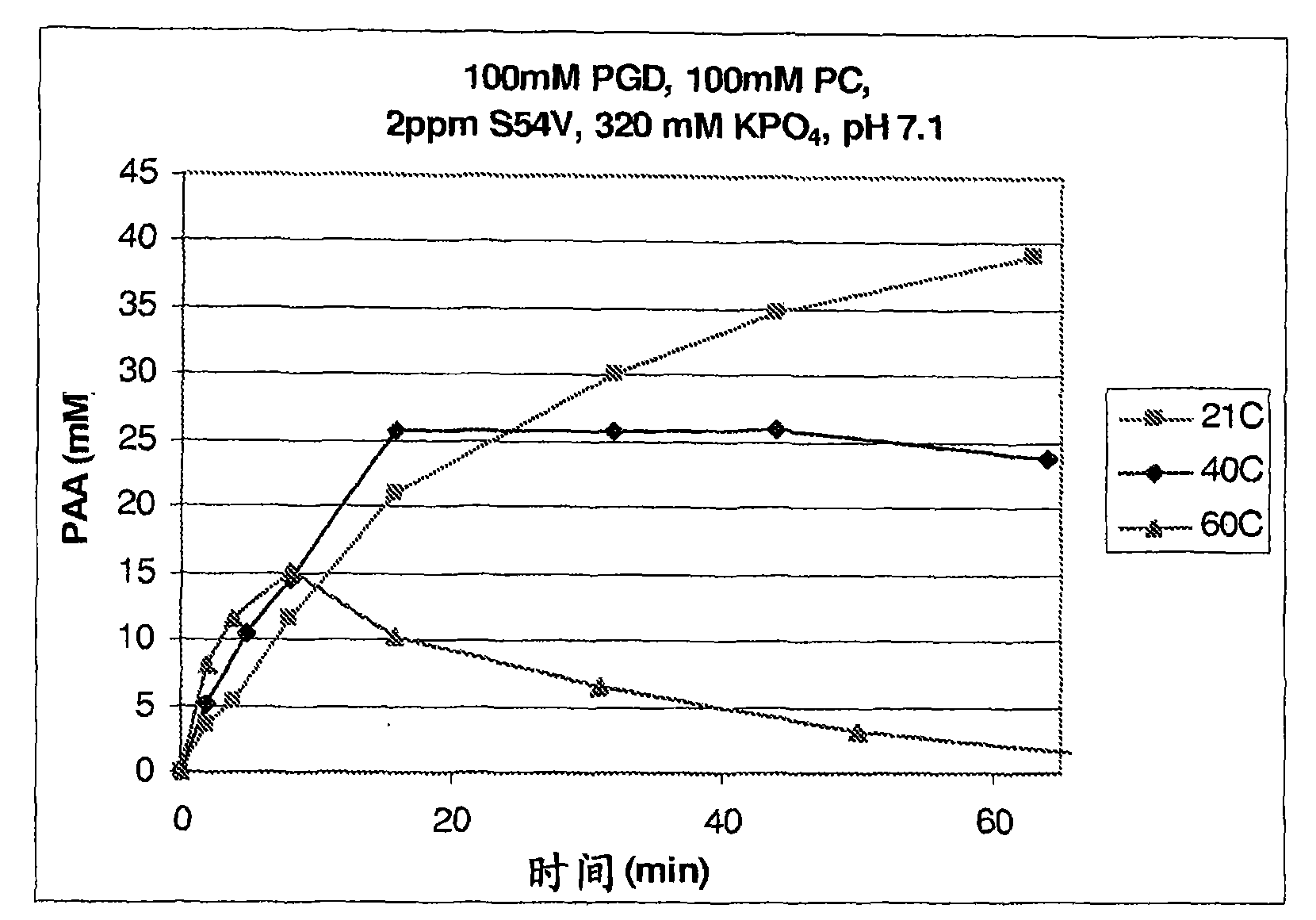
The present invention provides stable compositions comprising a perhydrolase enzyme, a hydrogen peroxide source, and an ester substrate that efficiently generate aqueous peracid solutions. The generated peracid solutions are suitable for decontaminating and / or sanitizing a wide range of materials and equipment contaminated with pathogens or toxic chemicals. In one preferred embodiment, the stable composition comprises an acyl transferase enzyme, sodium percarbonate, and propylene glycol diacetate, and is stable for 30 days or longer. Upon addition to water, the composition is activated and generates an aqueous solution with a high ratio of peracetic acid to acetic acid.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Diacylglycerol acyl transferase proteins
The invention provides diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DAGAT) proteins, wherein said proteins are active in the formation of triacylglycerol from fatty acyl and diacylglycerol substrates. In one aspect, Mortierella ramanniana DAGAT proteins have been isolated and have molecular weights of between approximately 36 and 37 kDa as measured by SDS-PAGE. The invention also provides novel DAGAT polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences and to methods of producing such polypeptides using recombinant techniques. In addition, methods are provided for using such sequences to alter triacylglycerol levels in plants and to treat diseases associated with altered DAGAT activity or expression.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for improving yield of arginine by mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase
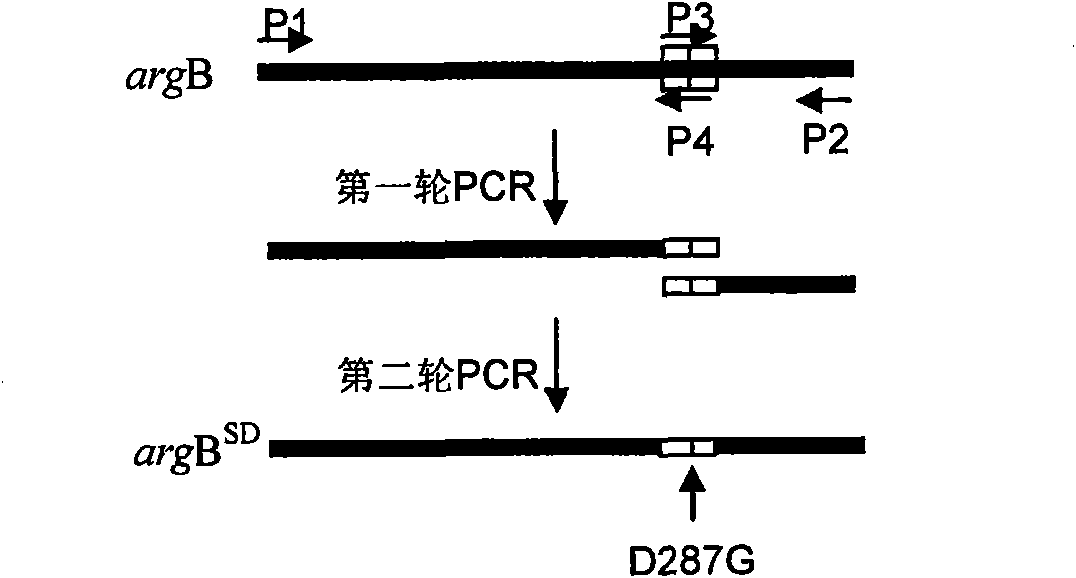
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of arginine by the mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase. L-arginine is one of semi-essential basic amino acids for a human body, and has various particular physiology and pharmacology functions. High-yield arginine mutant strain C. crenatum SYPA5-5 is compounded into the arginine through a circulating way, and N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the compounding way and is subject to the feedback inhibition of the product arginine. By using an overlapping PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, a GAT (glycerol phosphate acyl transferase) codon used for coding aspartic acid is used for substituting a GGA (General Gonadotropic activity) codon used for coding glycine at the site 287 in the coding NAGK albumen, and the NAGK which has high activity and arginine with obviously reduced by the feedback inhibition can be obtained after the mutation. An argBSD gene is brought into the Corynebacterium crenatum of the high-yield arginine through pJCl-tac, and the expression volume of the key enzyme is further improved. The final acid yield is increased to 36.3g / L from original 28g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 29.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Diacylglycerol acyl transferase 2 inhibitors
ActiveUS10071992B2Lower capability requirementsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseBiochemistry
Compounds of Formula I that inhibit the activity of the diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) and their uses in the treatment of diseases linked thereto in animals are described herein.
Owner:PFIZER INC
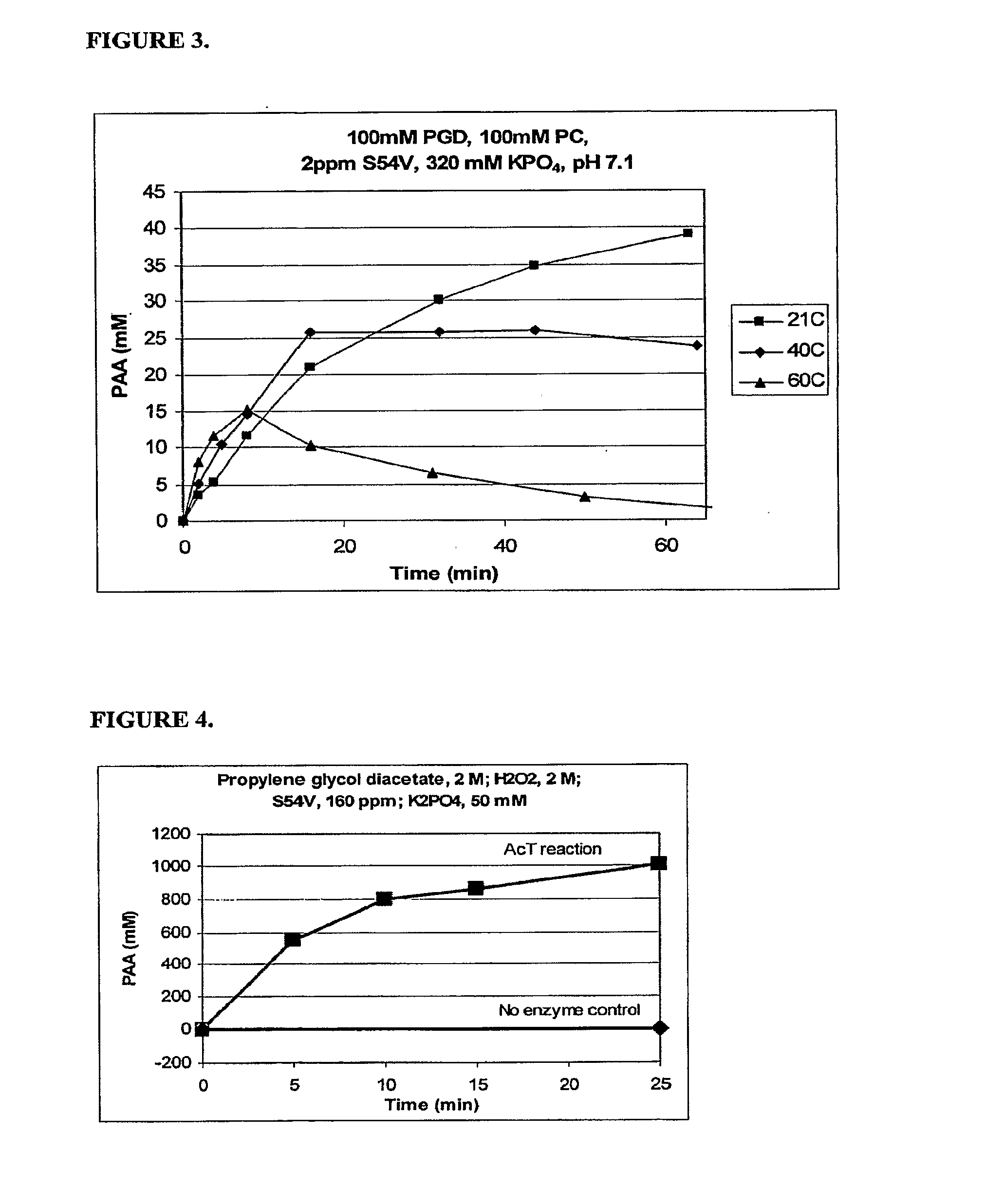
ACYL Transferase Useful for Decontamination
InactiveUS20090311395A1Small chemical footprintWide temperature rangeTransferasesOxidoreductasesAcetic acidSurface cleaning
The present invention provides an enzyme system that efficiently generates peracetic acid for use in decontamination applications. In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides a system that comprises an ester substrate, a hydrogen peroxide, and at least one acyl transferase. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the system further comprises at least one surfactant. In alternatively preferred embodiments, the present invention provides at least one wild-type and / or variant acyl transferase. The present invention finds particular use in decontamination involving a wide variety of chemical and biological warfare materials, as well as for general surface cleaning and decontamination.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
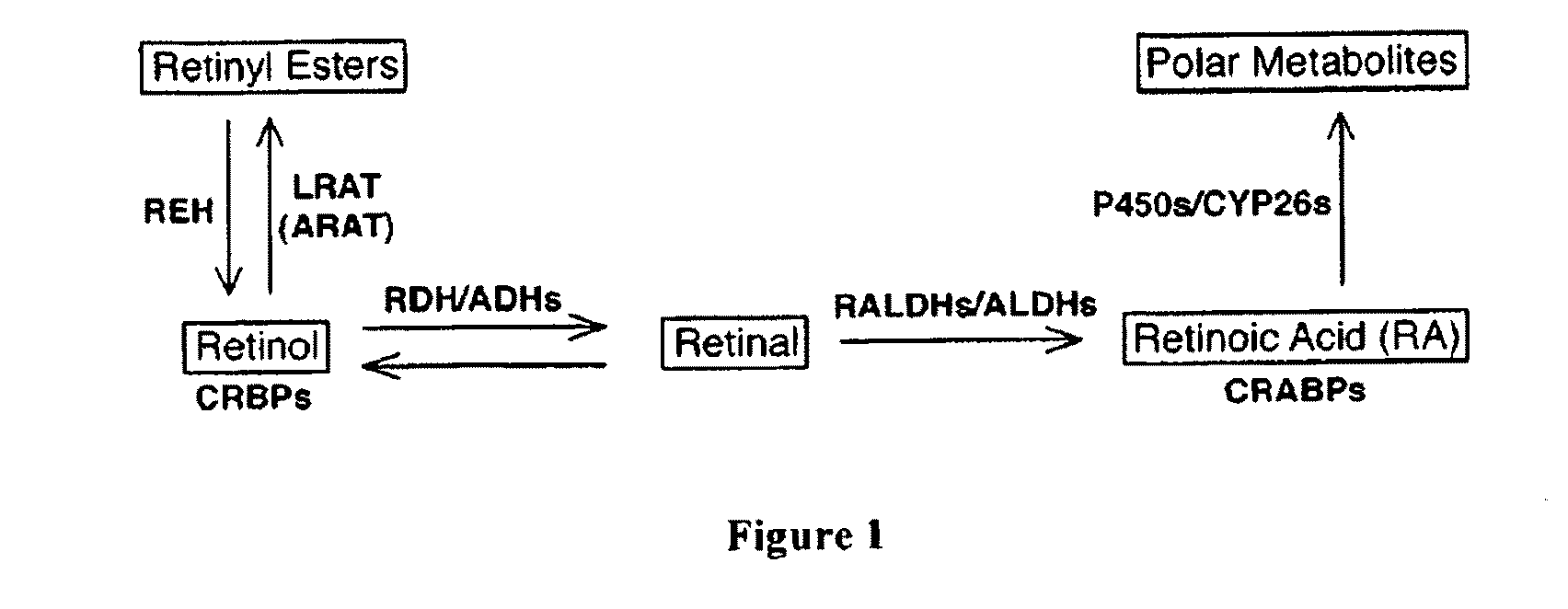
Use of lecithin:retinol acyl transferase gene promoter methylation in evaluating the cancer state of subject
The present invention relates to a method of evaluating the cancer state of a subject using lecithin:retinol acyl transferase (LRAT) gene promoter methylation status. Methods of analyzing and quantifying LRAT gene promoter methylation level are also disclosed. The present invention also relates to methods of determining the prognosis for s subject having cancer by assessing LRAT mRNA expression and LRAT protein expression. Methods of cancer detection, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment are also disclosed.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +2
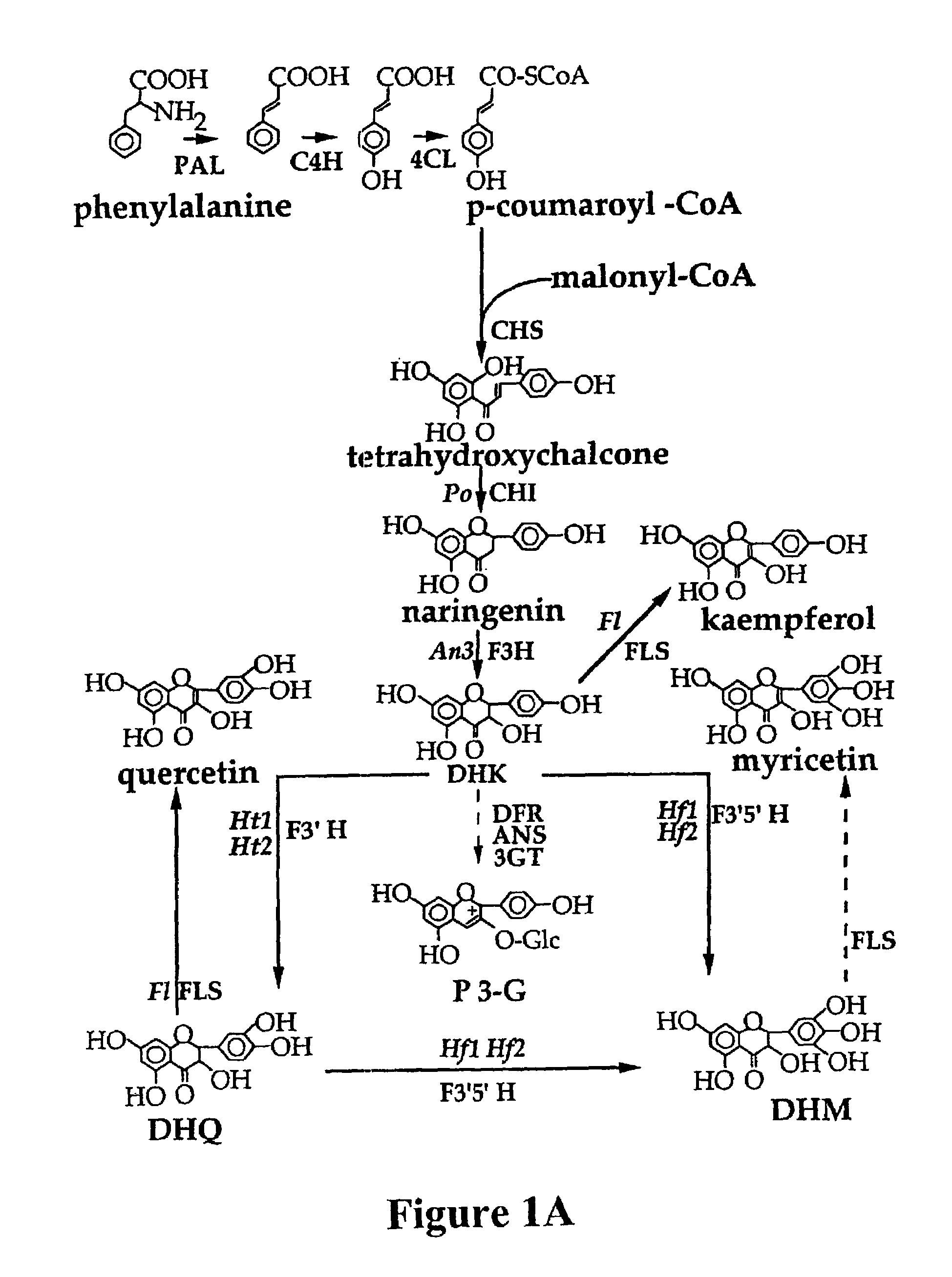
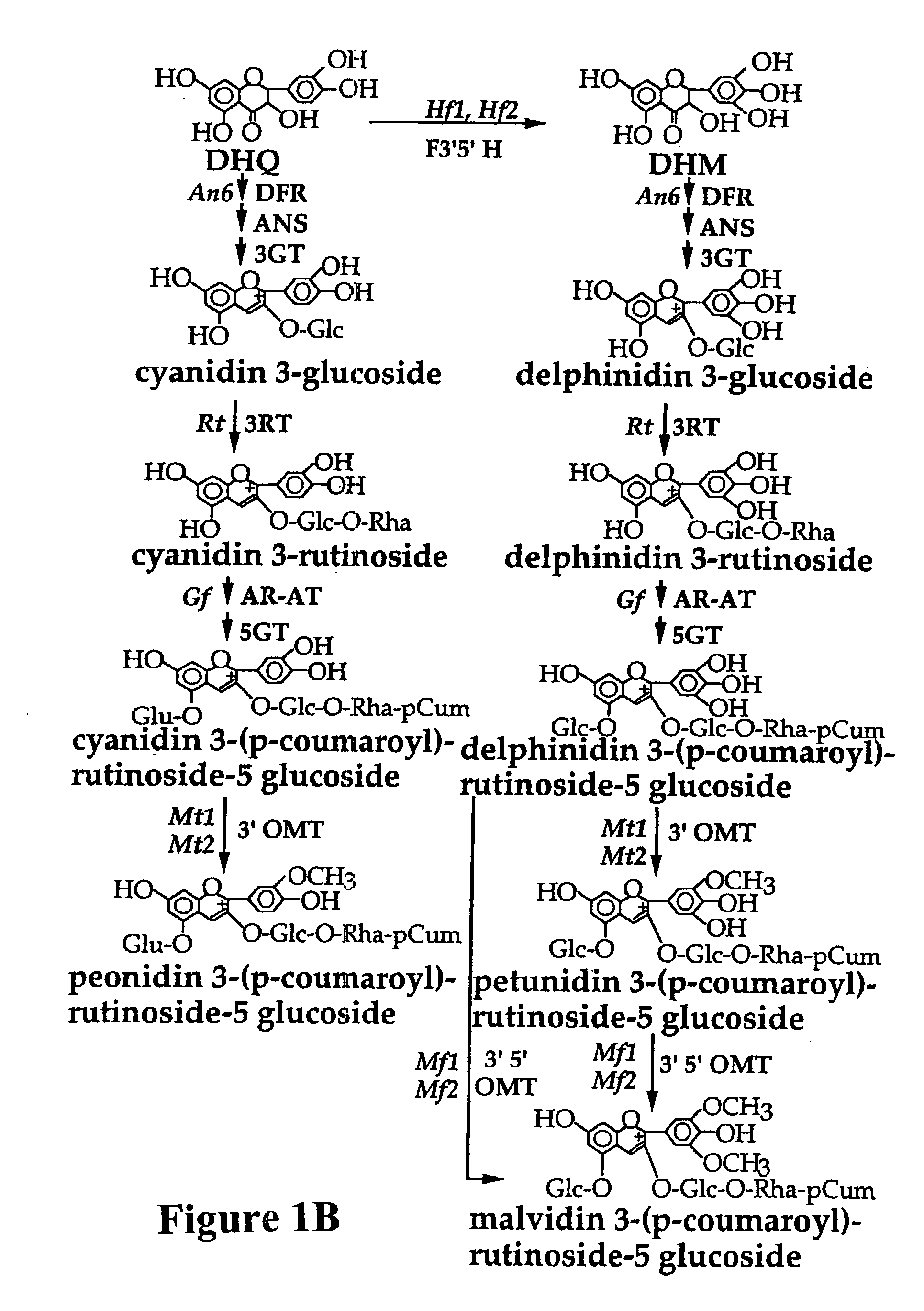
Plant anthocyanidin rutinoside aromatic acyl transferases
The present invention relates generally to a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having aromatic acyl group transfer activity and the use of the genetic sequence and / or its corresponding polypeptide thereof. More particularly, the present invention provides a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having aromatic acyl group transfer activity derived from Petunia, Nierembergia and Viola spp. Even more particularly, the present invention relates to a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having aromatic acyl group transferase activity to anthocyanidin-rutinoside. The present invention also provides a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having aromatic acyl group transferase activity to anthocyanidin 3-O-rutinoside. The instant invention further relates to antisense and sense molecules corresponding to all or part of the subject genetic sequence as well as genetically modified plants as well as cut flowers, parts and reproductive tissue from such plants.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Inhibitors of diacylglycerol acyl transferase
InactiveUS20120289505A1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to heterocyclic compounds in all their stereoisomeric and tautomeric forms; and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, pharmaceutically acceptable solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable polymorphs. The invention also relates to processes for the manufacture of the heterocyclic compounds and to pharmaceutical compositions containing them. The said compounds and their pharmaceutical compositions are useful in the prevention and treatment of diseases or disorders mediated by diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT), particularly DGAT1. The present invention further provides a method of treatment of such diseases or disorders by administering a therapeutically effective amount of said compounds or their pharmaceutical compositions, to a mammal in need thereof.
Owner:PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD
Biosynthetic production of acyl amino acids
InactiveCN107075463ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Stable enzymatic peracid generating systems
The present invention provides stable compositions comprising a perhydrolase enzyme, a hydrogen peroxide source, and an ester substrate that efficiently generate aqueous peracid solutions. The generated peracid solutions are suitable for decontaminating and / or sanitizing a wide range of materials and equipment contaminated with pathogens or toxic chemicals. In one preferred embodiment, the stable composition comprises an acyl transferase enzyme, sodium percarbonate, and propylene glycol diacetate, and is stable for 30 days or longer. Upon addition to water, the composition is activated and generates an aqueous solution with a high ratio of peracetic acid to acetic acid.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Organic compounds
InactiveUS20100022513A1Rational designUseful solubilityBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseAcyl coenzyme A
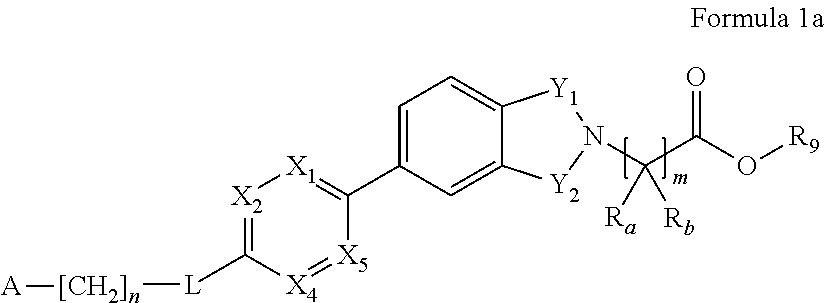
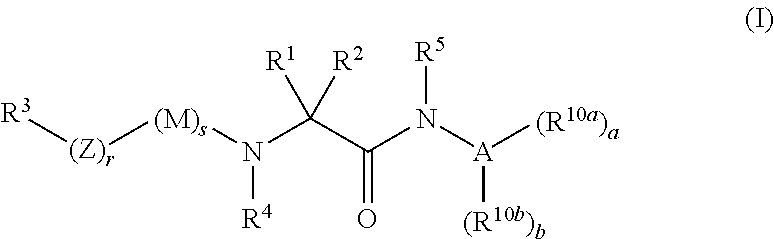
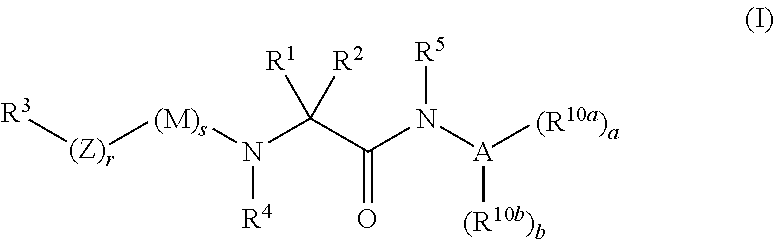
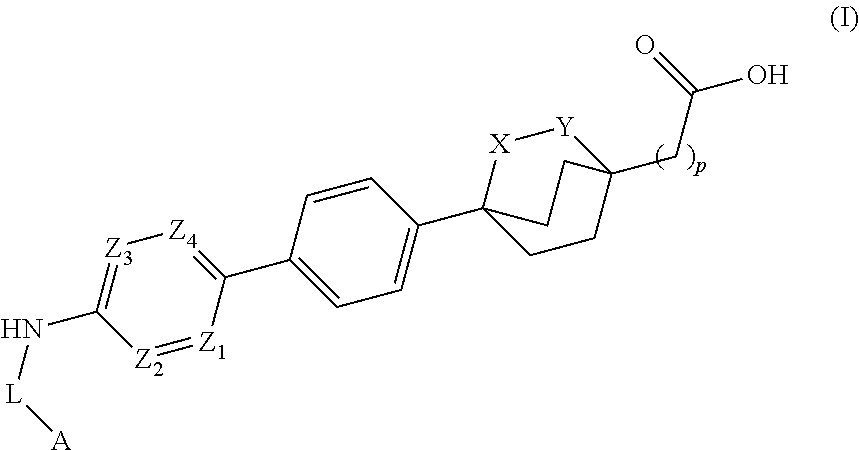
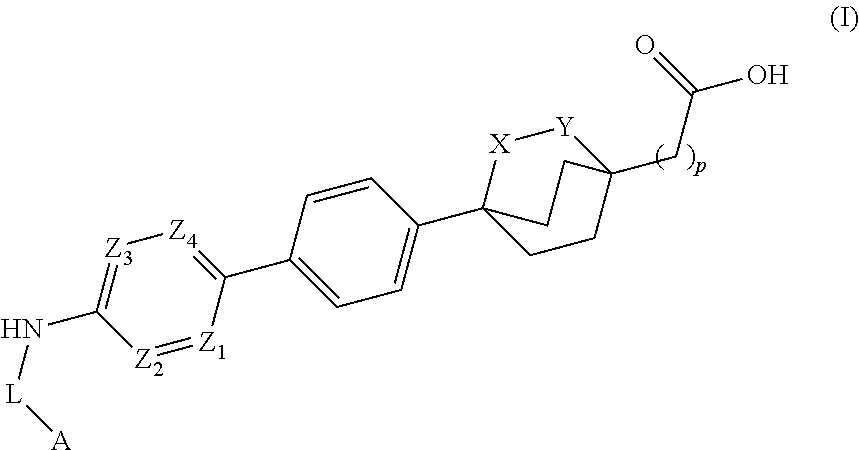
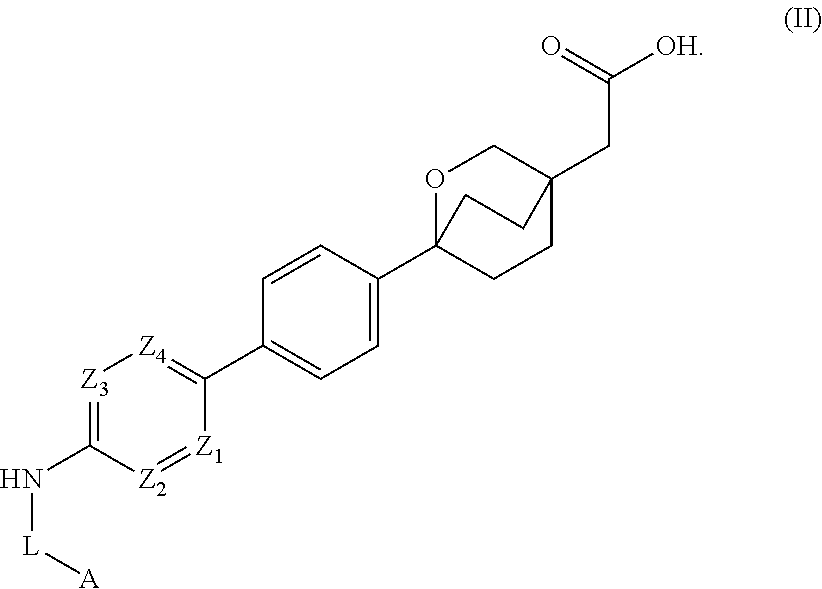
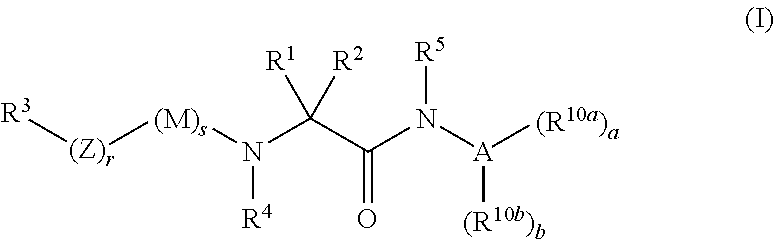
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I):where A is an optionally substituted heteroaryl, useful for treating disorders mediated by acyl coA-diacylglycerol acyl transferase 1 (DGAT1), e.g. metabolic disorders. The invention also provides methods of treating such disorders, and compounds and compositions etc. for their treatment.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
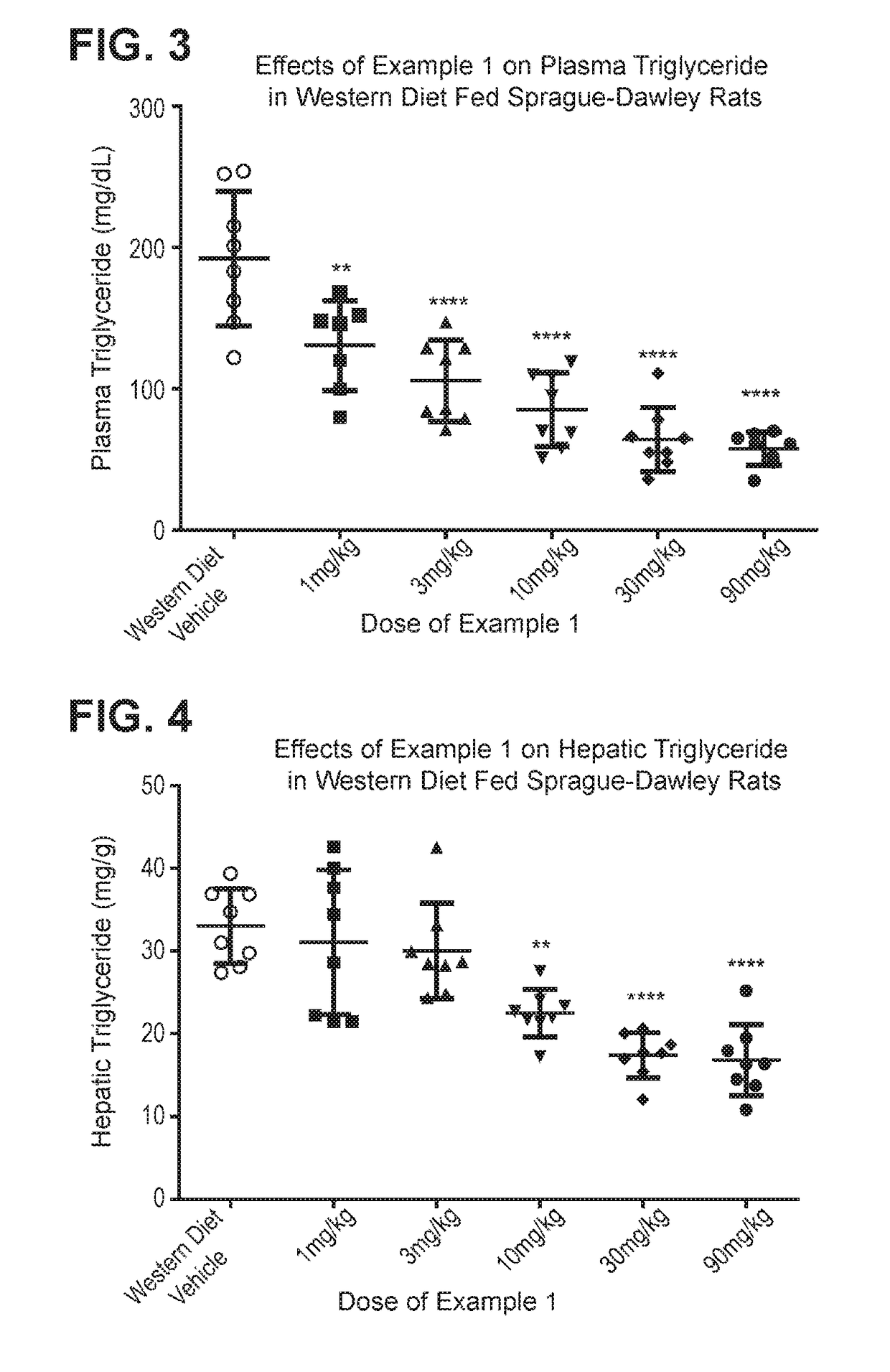
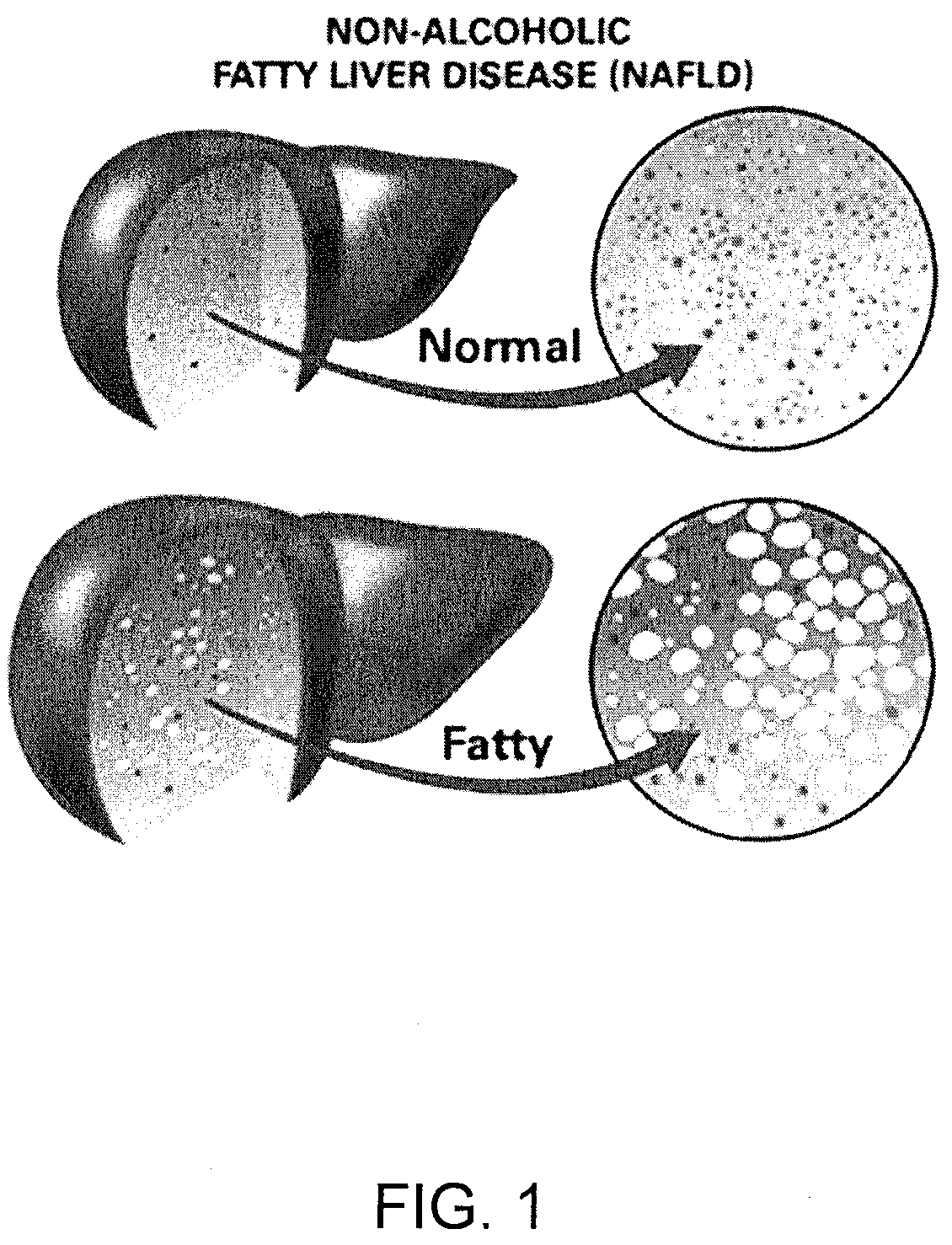
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of developing liver cancer in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ActiveUS20200121743A1Inhibit progressEarly detectionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseIntestinal microorganisms
A method for reducing the likelihood of developing liver cancer in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease involves providing in the gut of an individual a population of beneficial bacteria selected from the group consisting of Lactobacillus species, and administering fiber to the individual to maintain a therapeutically effective amount of the beneficial bacteria in the gut of the individual. In certain embodiments, monoacylglycerolacyltransferase-3 (MGAT3) synthesis is inhibited to lower triacylglycerol (TAG) production, while in others, expression of diacylglycerolacyltransferase-2 (DGAT-2) is inhibited. The beneficial bacteria are preferably modified to produce increased amounts of butyrate and may also be encapsulated in a frangible enclosure. Levels of Roseburia are preferably increased while the levels of Akkermansia spp. in the individual's gut microbiome are reduced. In other embodiments, a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is administered, or a composition comprising modified L. reuteri bacteria having the ability to survive conditions in the duodenum or jejunum of the individual's small intestine. Other embodiments include the administration of a bacterial formulation comprising at least one of Coprococcus, Veillonella, Roseburia, Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Prevotella.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Byosynthetic Production of Acyl Amino Acids
InactiveUS20170130248A1PurityYield andLigasesAcyltransferasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
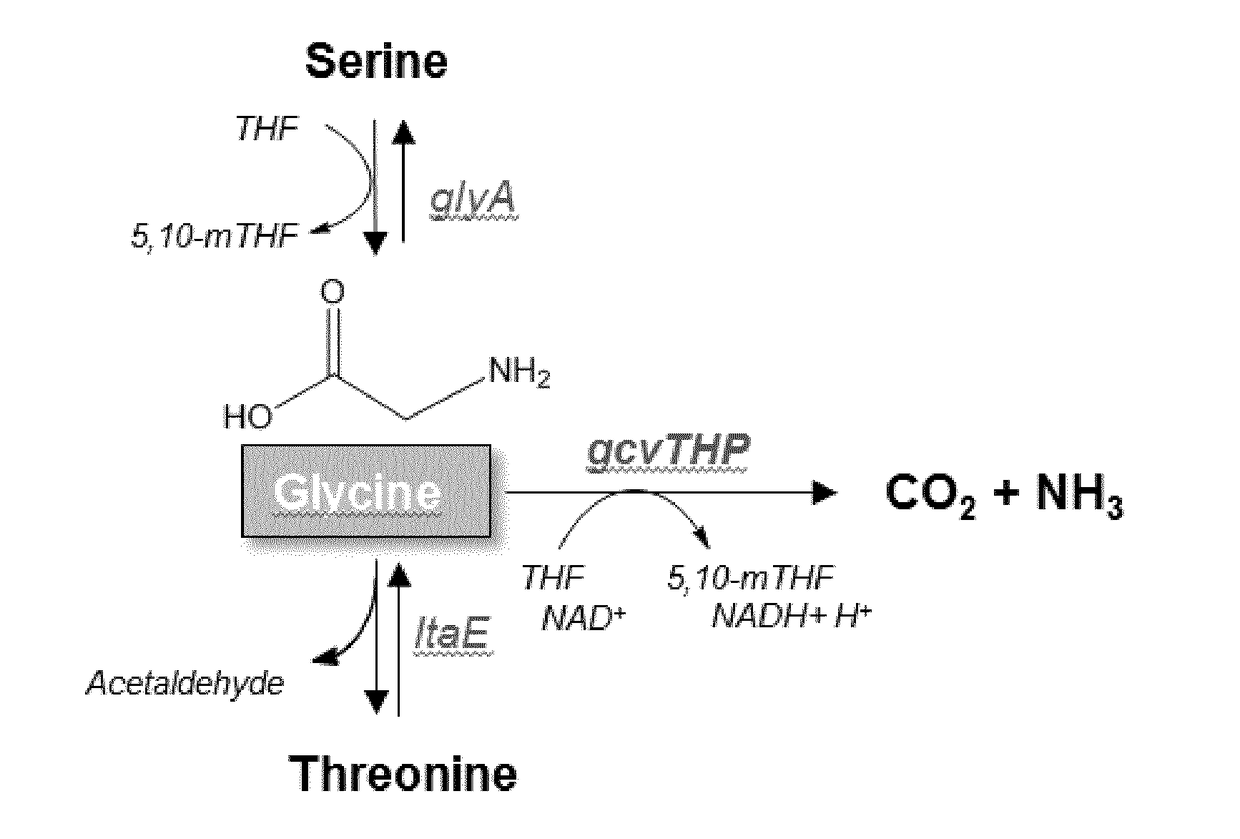
The present invention relates to a cell for producing acyl glycinates wherein the cell is genetically modified to compriseat least a first genetic mutation that increases the expression relative to the wild type cell of an amino acid-N-acyl-transferase,at least a second genetic mutation that increases the expression relative to the wild type cell of an acyl-CoA synthetase, andat least a third genetic mutation that decreases the expression relative to the wild type cell of at least one enzyme selected from the group consisting of an enzyme of the glycine cleavage system, glycine hydroxymethyltransferase (GlyA) and threonine aldolase (LtaE).
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and method for making the same
InactiveCN103119170AClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesPopulus trichocarpaDEAD-box RNA Helicases
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a CER2-like (CER2- like (CER2-like acyl transferase) polypeptide) polypeptide or an At1 g68440-like (putative IMP dehydrogenase / GMP reductase from Populus trichocarpa) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a CER2-like polypeptide or an At1 g68440-like polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield- related traits relative to control plants.; The invention also provides hitherto unknown encoding nucleic acids, and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. The present invention also relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by reducing or substantially eliminating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an endogenous DEAD-box RNA helicase polypeptide and / or the level and / or the activity of a DEAD-box RNA helicase polypeptide in said plant. The present invention also concerns plants having a reduction or substantial elimination of the expression of an endogenous nucleic acid encoding a DEAD-box RNA helicase polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides hitherto unknown DEAD-box RNA helicase encoding nucleic acids, and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
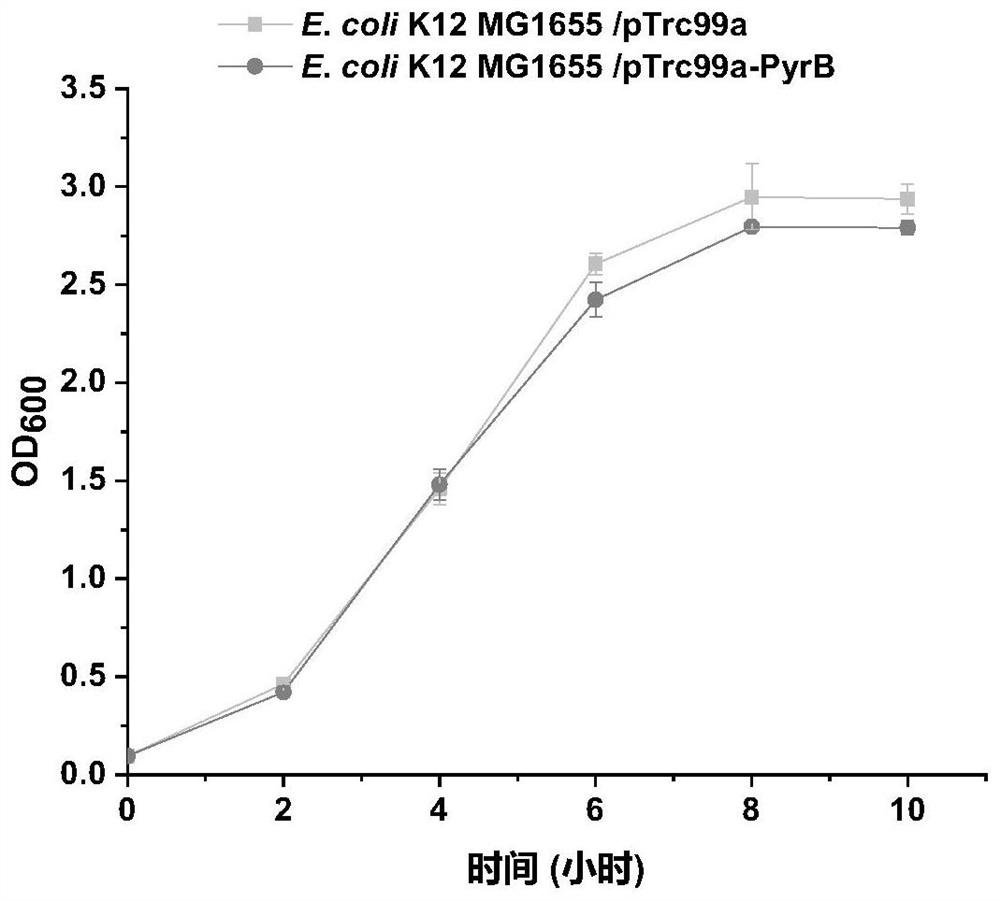
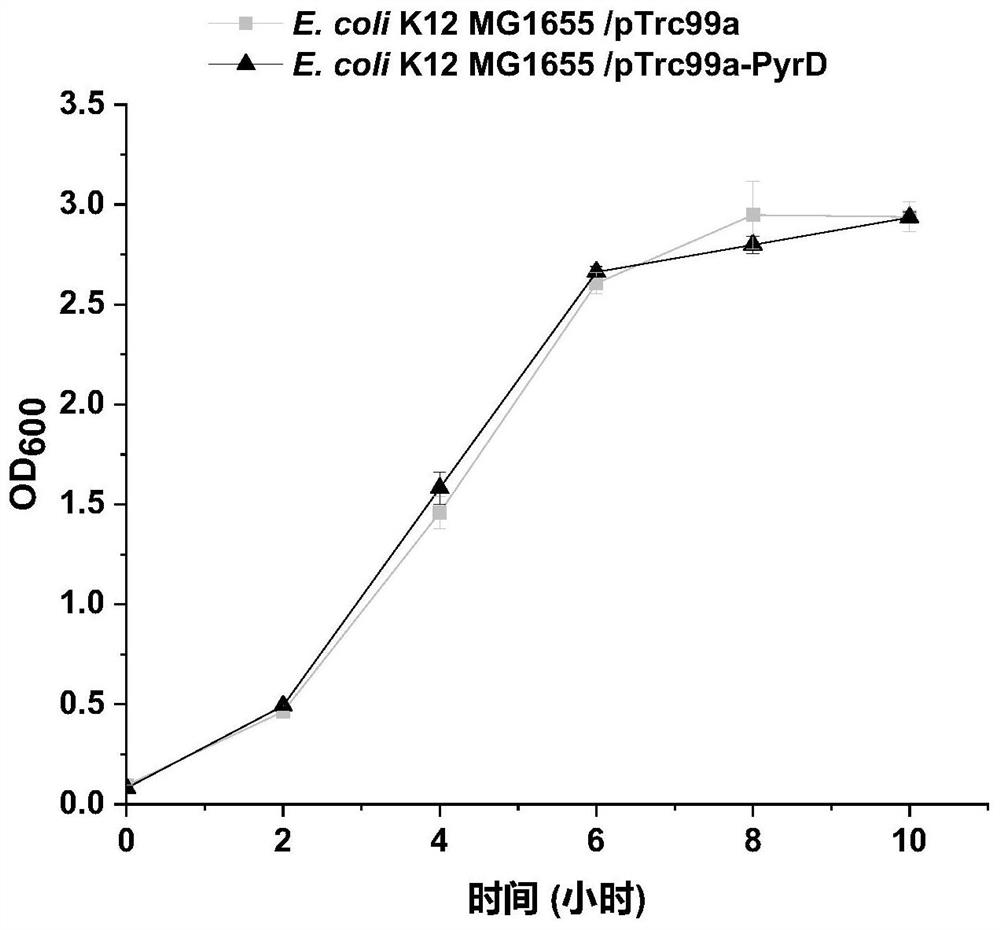
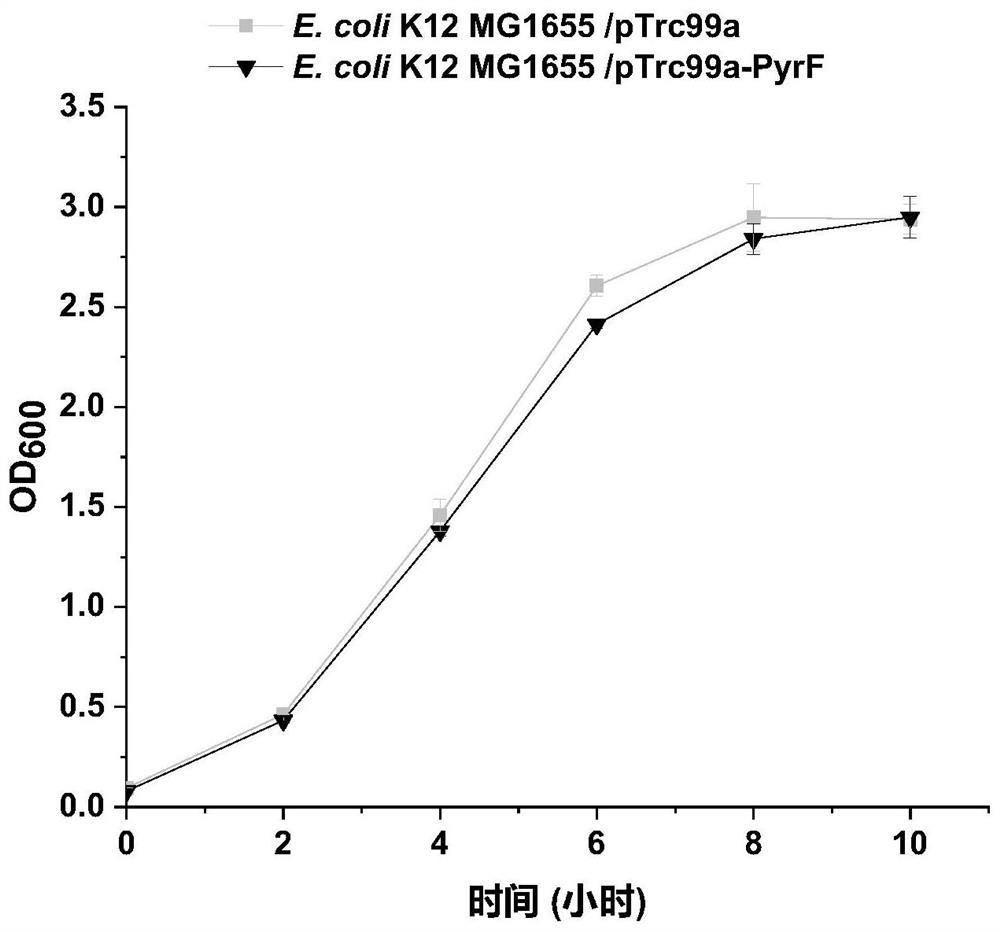
Escherichia coli engineering bacteria with improved acid stress resistance and application of escherichia coli engineering bacteria
ActiveCN112391329AImprove acid stress resistanceEasy to operateBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses escherichia coli engineering bacteria with improved acid stress resistance and application of the escherichia coli engineering bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. According to the invention, aspartate carbamoyl transferase is overexpressed in escherichia coli to catalyze subunits PyrB, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase PyrD and Orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase protein PyrF, so that the escherichia coli engineering bacteria with improved acid stress resistance, which can be widely applied to preparation of food, medicines, feeds and chemicals, is constructed successfully; and compared with a control strain, the stress resistance of the recombinant strain to itaconic acid, D-lactic acid and succinic acid is remarkably improved. The escherichia coli engineering bacteria are simple to operate and can be widely applied to industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
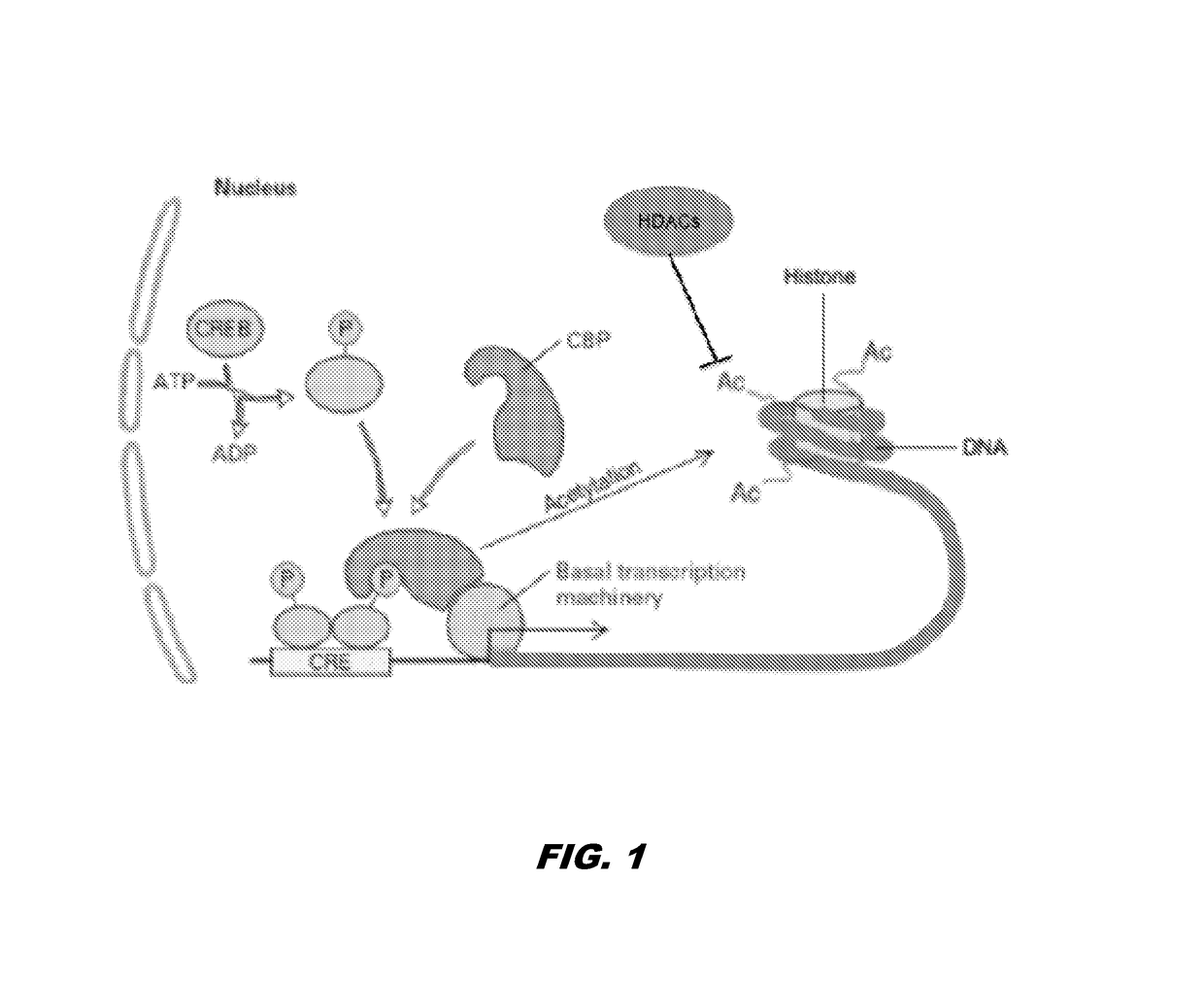
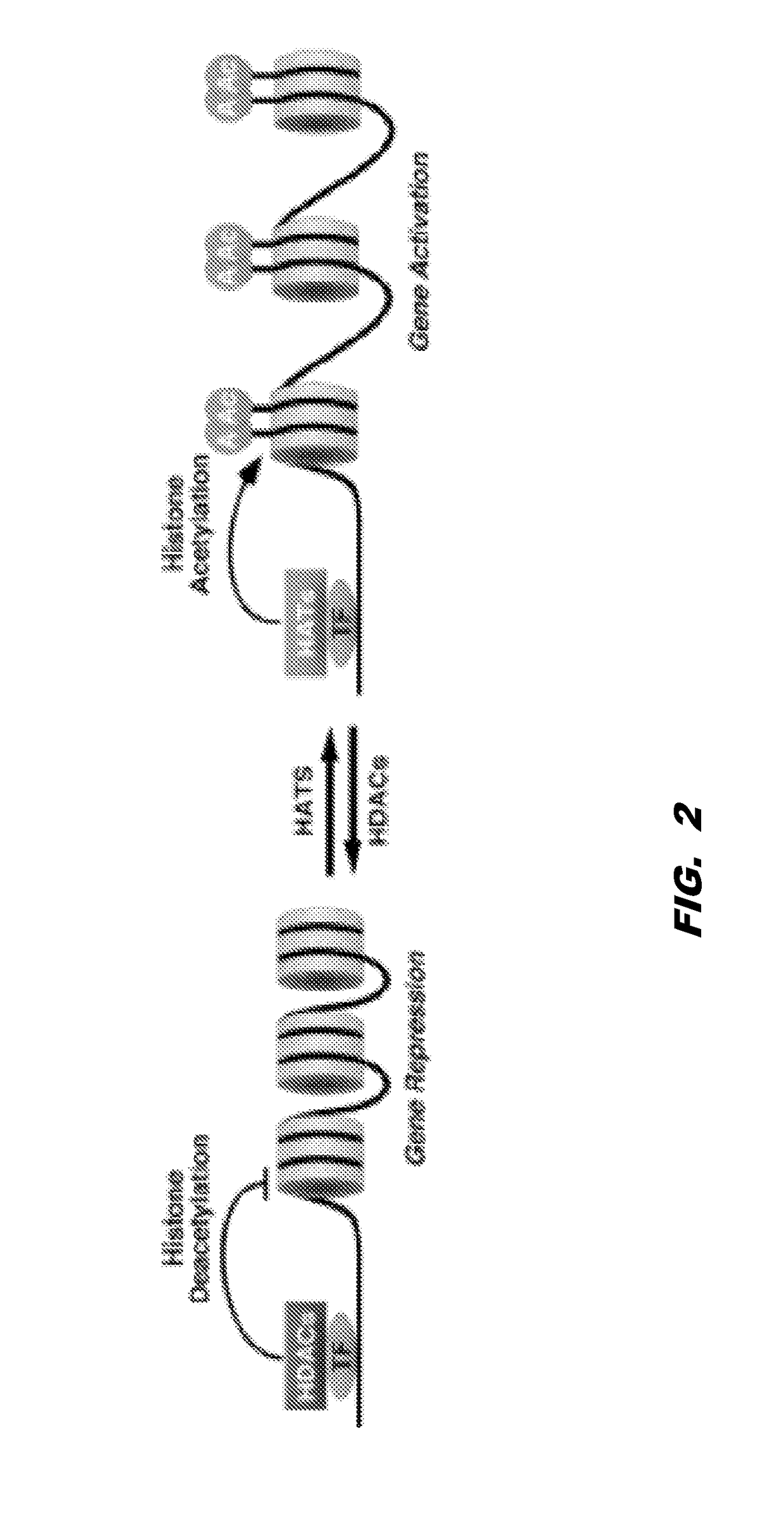
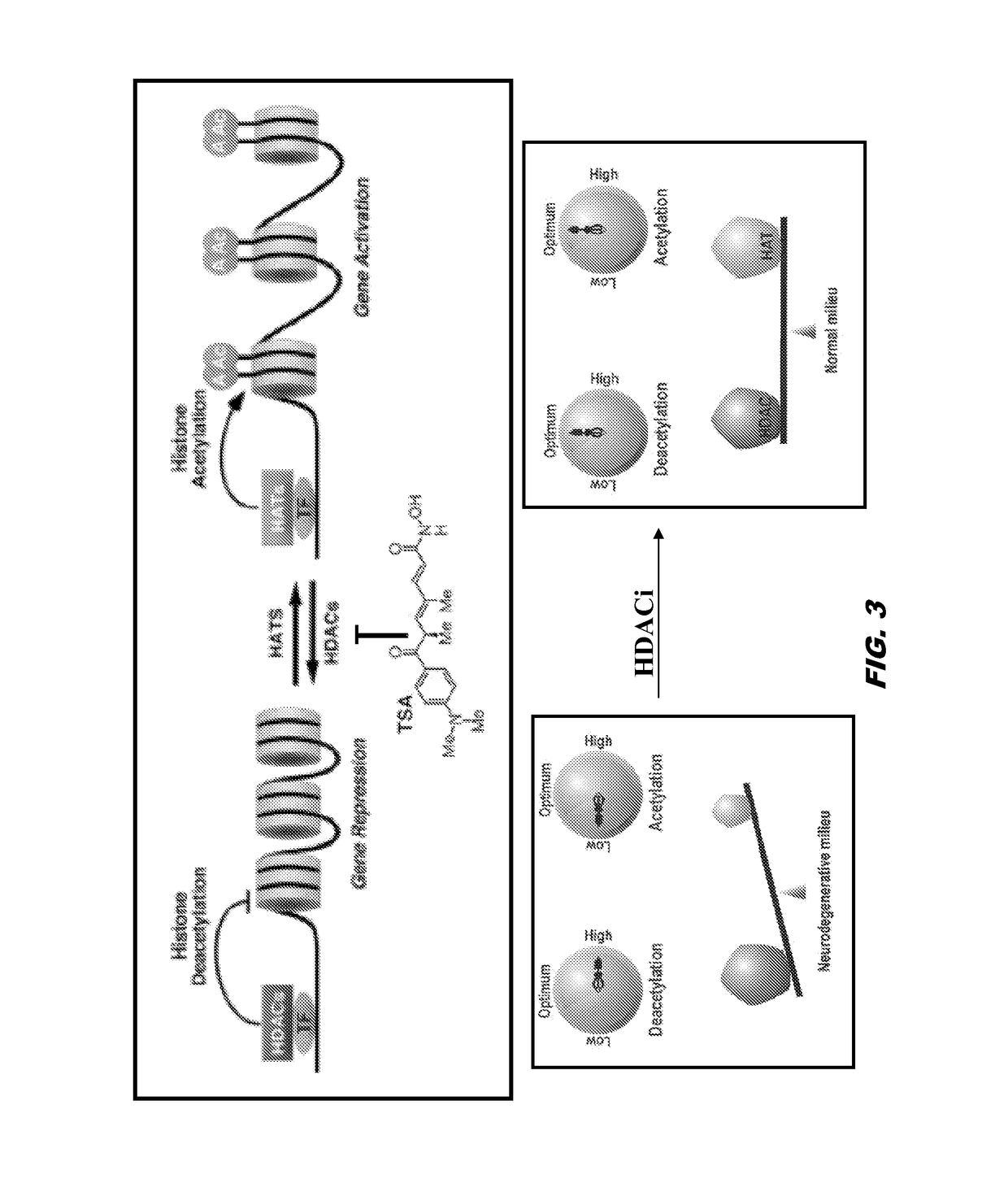
Histone acetyltransferase modulators and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170121276A1Increasing synaptic plasticityIncrease histone acetylationNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAmyloid betaSynuclein
The invention provides compounds and compositions comprising compounds that modulate histone acyl transferase (HAT). The invention further provides methods for treating neurodegenerative disorders, conditions associated with accumulated amyloid-beta peptide deposits, Tau protein levels, and / or accumulations of alpha-synuclein as well as cancer by administering a compound that modulates HAT to a subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Cyclic bridgehead ether DGAT1 inhibitors
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I):useful for treating disorders mediated by acyl coA-diacylglycerol acyl transferase 1 (DGAT1), e.g. metabolic disorders. The invention also provides methods of treating such disorders, and compounds and compositions etc. for their treatment.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
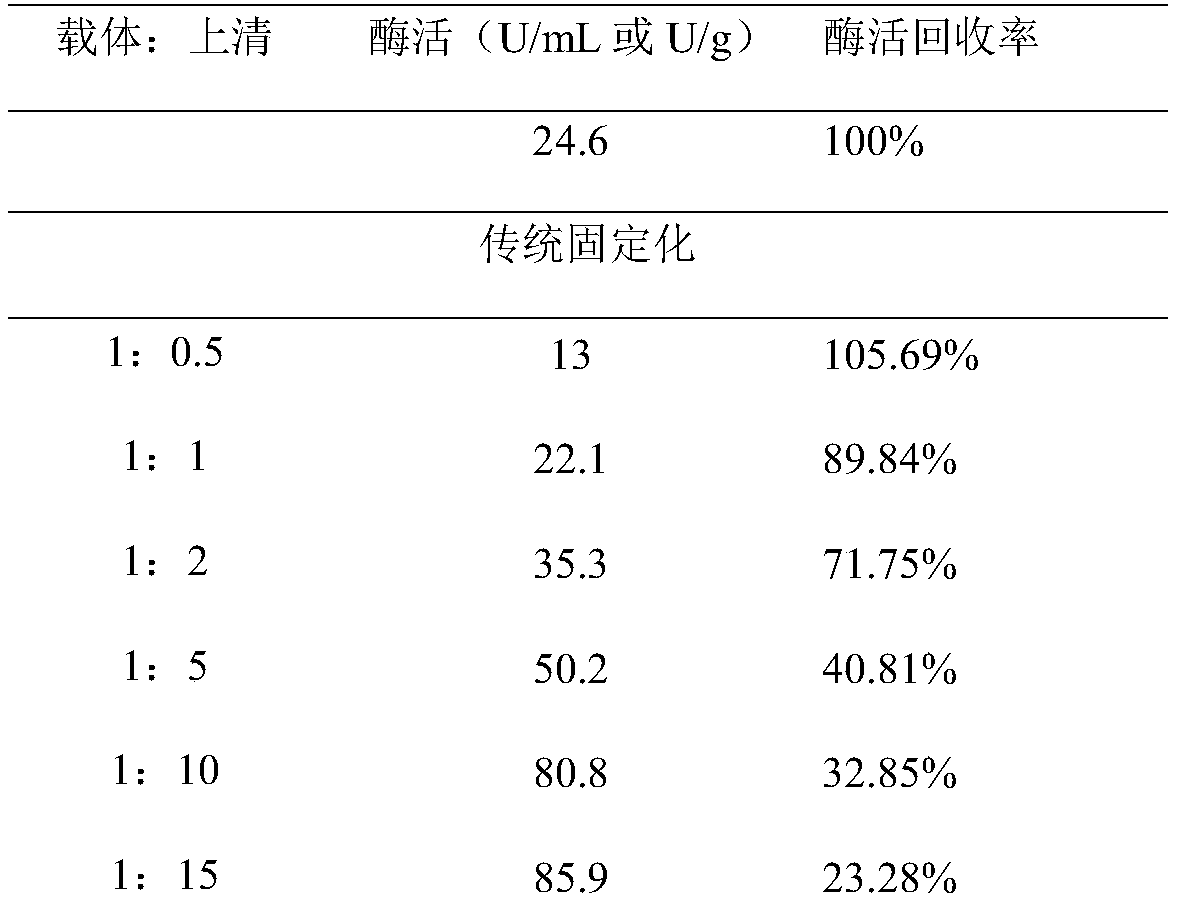
Method for performing one-step purification and immobilization on alpha-amino acid fatty acyl transferase
ActiveCN108728424AAchieve one-step purificationReduced purification stepsTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetAcyl group
The invention relates to the technical field of enzyme immobilization and particularly discloses a method for performing one-step purification and immobilization on alpha-amino acid fatty acyl transferase. The method comprises the following steps: performing aldehyde labeling on the alpha-amino acid fatty acyl transferase, performing synchronous induction on the alpha-amino acid fatty acyl transferas and formylglycine synthetase in host cells to obtain a bacterial strain with high expression quantity, crushing the thallus, taking supernatant, and mixing the supernatant and an amino carrier torealize one-step immobilization of the alpha-amino acid fatty acyl transferase, wherein an additional purification step is not needed. By the method, the operation steps are saved, expression of the target protein is guaranteed, immobilization can be realized by the common amino carrier, and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:HEBEI FITNESS BIOTECH CO LTD
Organic compounds
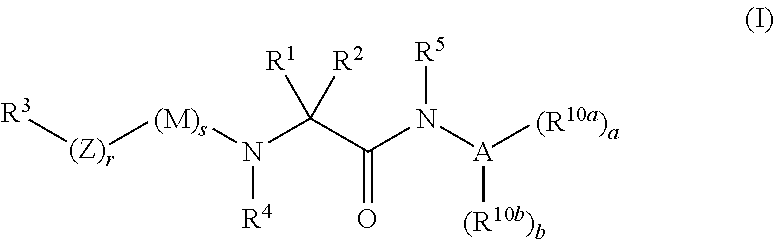
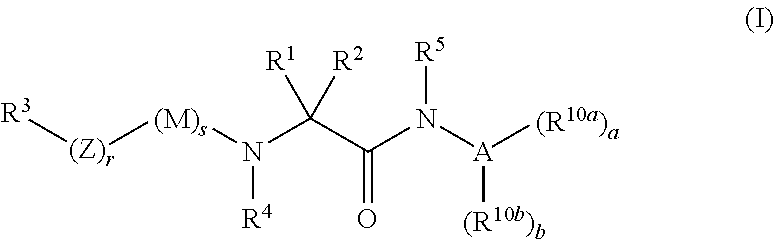
InactiveUS8703761B2Rational designUseful solubilityBiocideOrganic chemistryOrganic compoundMetabolic disorder
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I):where A is an optionally substituted heteroaryl, useful for treating disorders mediated by acyl coA-diacylglycerol acyl transferase 1 (DGAT1), e.g. metabolic disorders. The invention also provides methods of treating such disorders, and compounds and compositions etc. for their treatment.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Tetrazolone-substituted dihydropyridinone mgat2 inhibitors
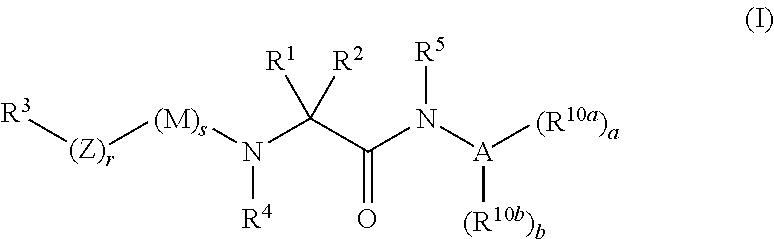
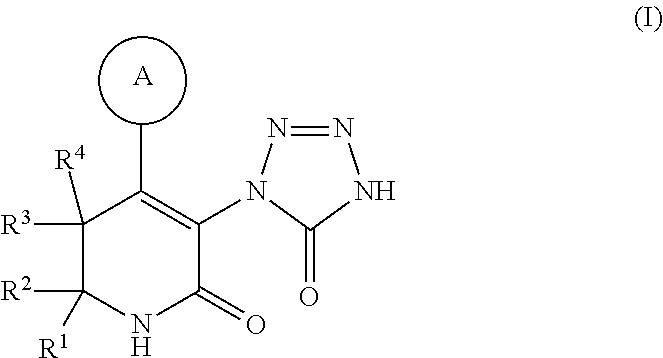
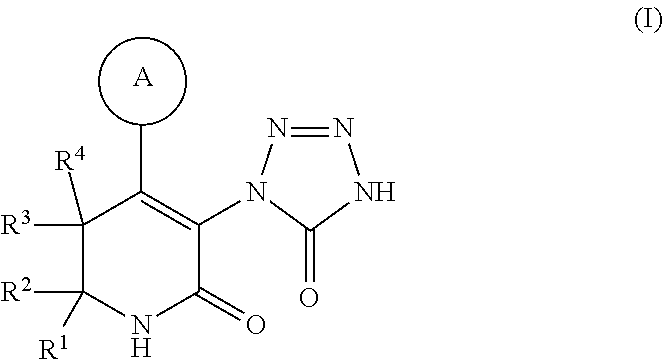
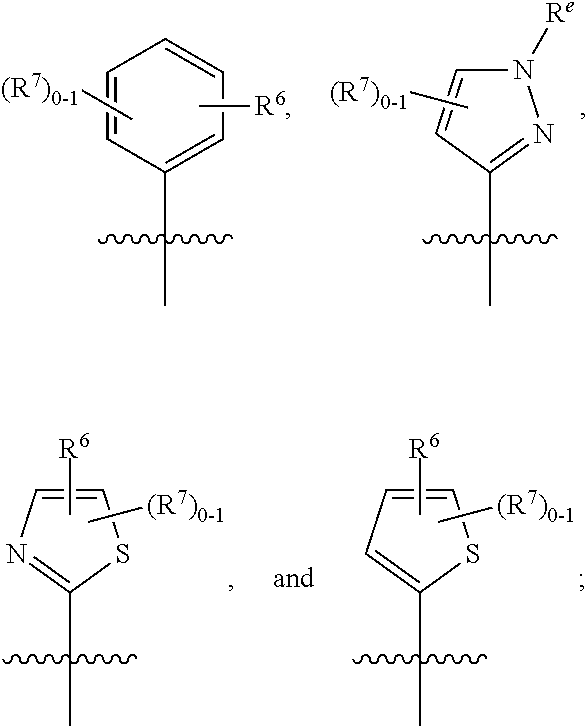
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I): a stereoisomer, a tautomer, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a polymorph, a solvate thereof, wherein all of the variables are as defined herein. These compounds are monoacylglycerol acyl-transferase type 2 (MGAT2) inhibitors which may be used as medicaments.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for increasing lipid content of diatom through metabolism gene engineering
InactiveCN105219649AHigh fat contentAchieve integrationUnicellular algaeFermentationPhosphateGlycerol
The invention provides a method for increasing the lipid content of diatom through metabolism gene engineering. A glycerinum-3-phosphate acyl transferase gene cDNA of phaeodactylum tricornutum which belongs to marine lipid-producing diatom is cloned, the function is verified in a glycerinum-3-phosphate acyl transferase gene mutant of yeast, a diatom overexpression carrier is established, phaeodactylum tricornutum cells are introduced with an electroporation method or a particle bombardment method, screening is performed through glufosinate, an engineered strain with increased TAG (triglyceride) is obtained and can be used for extracting microalgae lipid after being subjected to scale-up culture. Glycerinum-3-phosphate acyl transferase in the diatom is taken as a target regulated in diatom lipid metabolism gene engineering, the lipid content of the diatom is increased with the metabolism engineering method, and a new concept and a new focus are provided for lipid research of the diatom.
Owner:南通中国科学院海洋研究所海洋科学与技术研究发展中心 +1
Application of dendrobium nobile water extract in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus
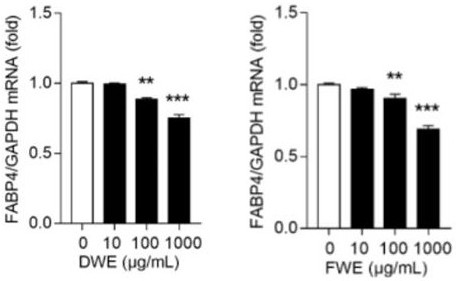
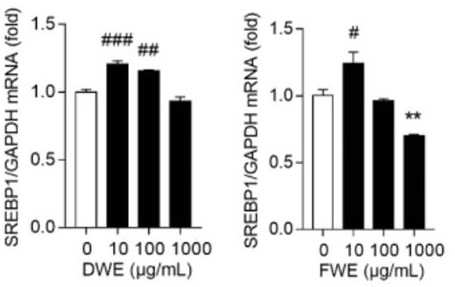
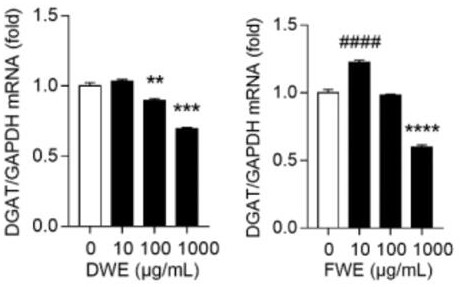
InactiveCN111773323ASuppressed expression levelImprove the immunityMetabolism disorderEndocrine system disorderBeta-cell FunctionSterol
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmacy, and relates to an application of a dendrobium nobile water extract in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus, in particular to regulation of insulin resistance and triglyceride synthesis of a dry dendrobium water extract and a fresh dendrobium water extract in a high-sugar state. Experimental results prove that the dendrobium nobile water extract prepared by the invention can obviously inhibit the expression level of mRNA of fatty acid binding protein, improve the peripheral insulin resistance, protect the pancreatic beta cell function, increase insulin sensitivity, obviously inhibit the expression level of diacylglycerol acyltransferase mRNA, reduce the TG biosynthesis, improve the sensitivity of the body to insulin and leptin, increasethe mRNA expression level of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1, and effectively regulate the triglyceride biosynthesis so as to achieve inhibition of type 2 diabetes mellitus from multipleaspects. Therefore, the dendrobium nobile water extract disclosed by the invention can be used for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus and has a good development prospect in the aspect of treating type2 diabetes mellitus.
Owner:安徽同济生生物科技有限公司
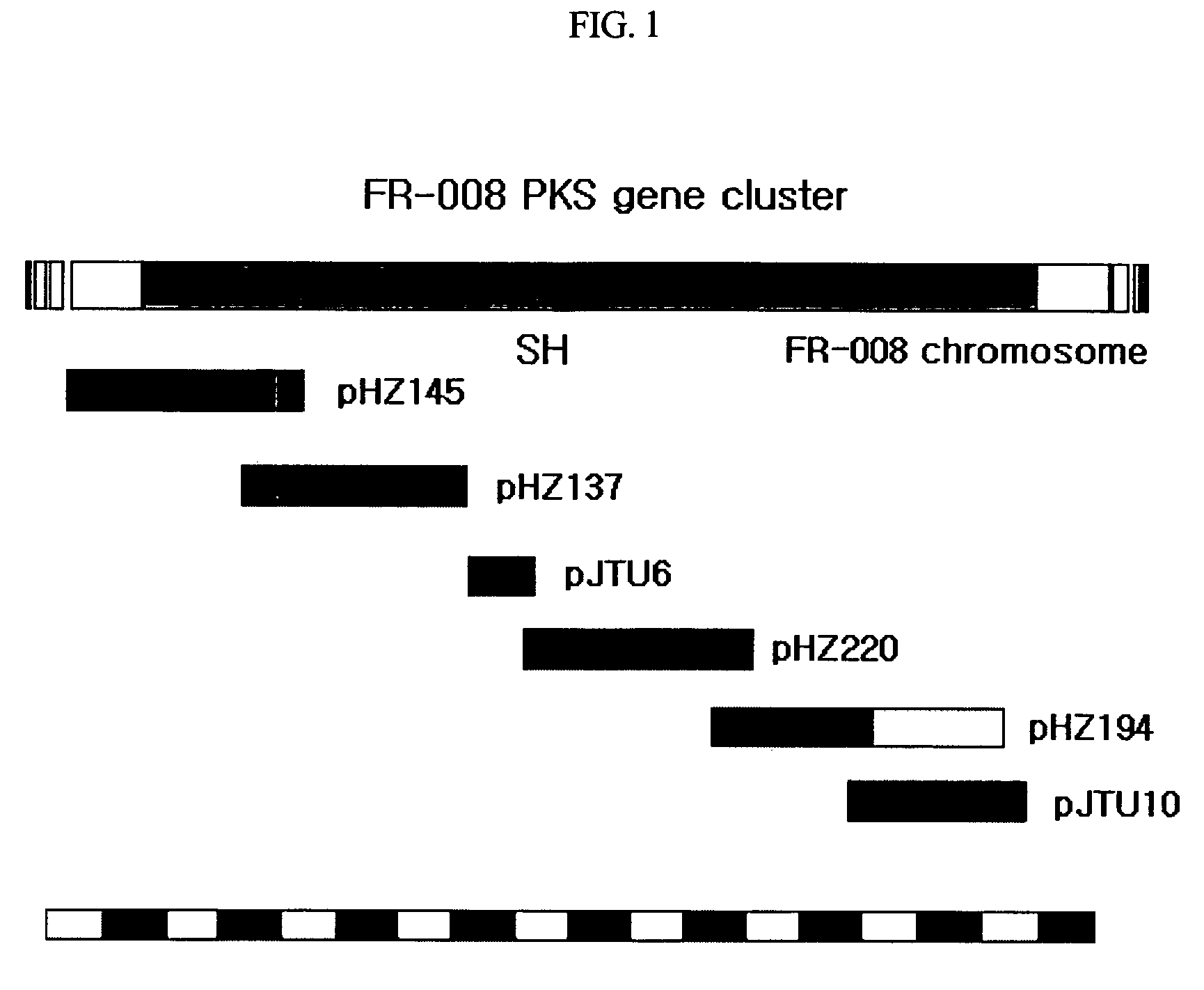
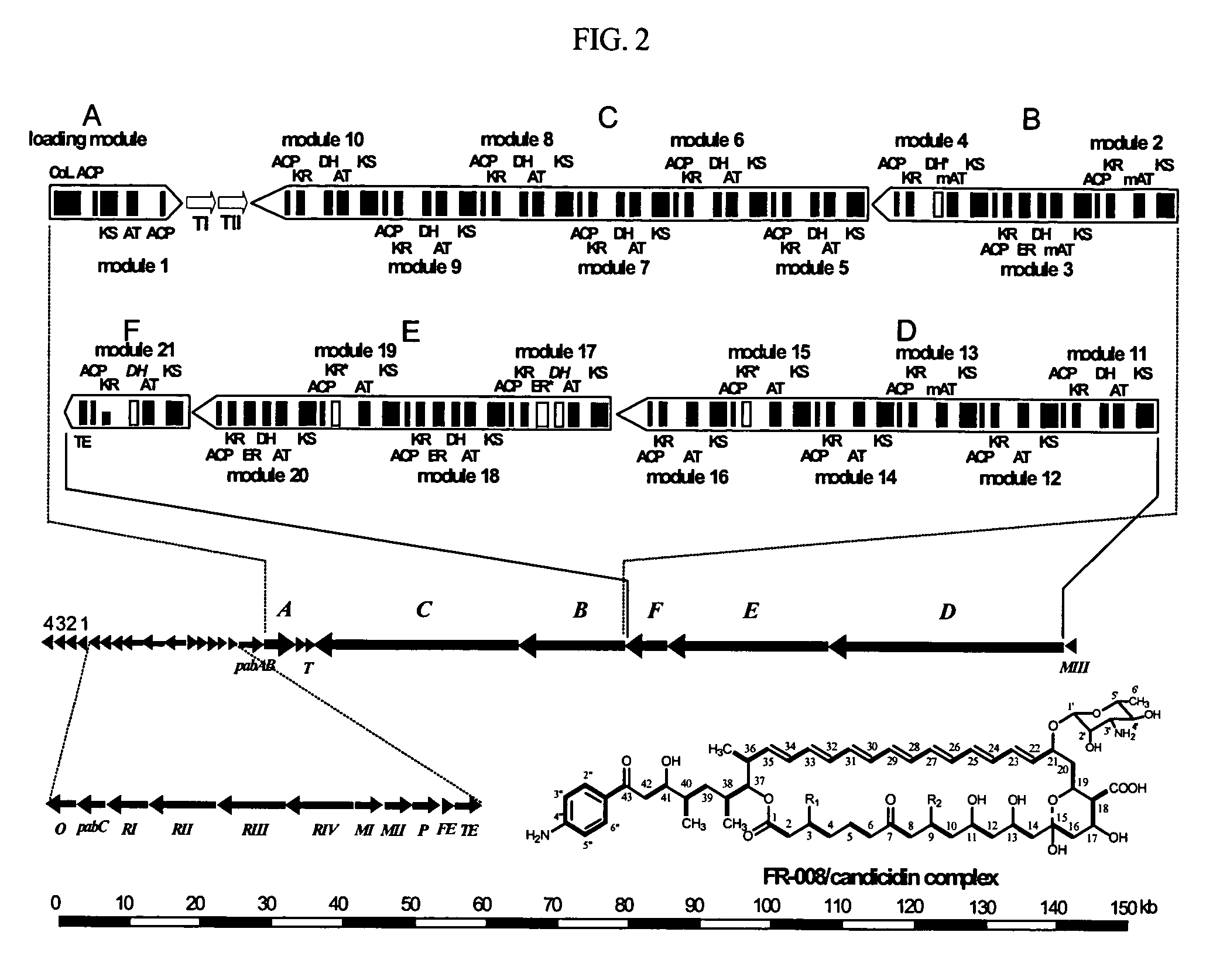
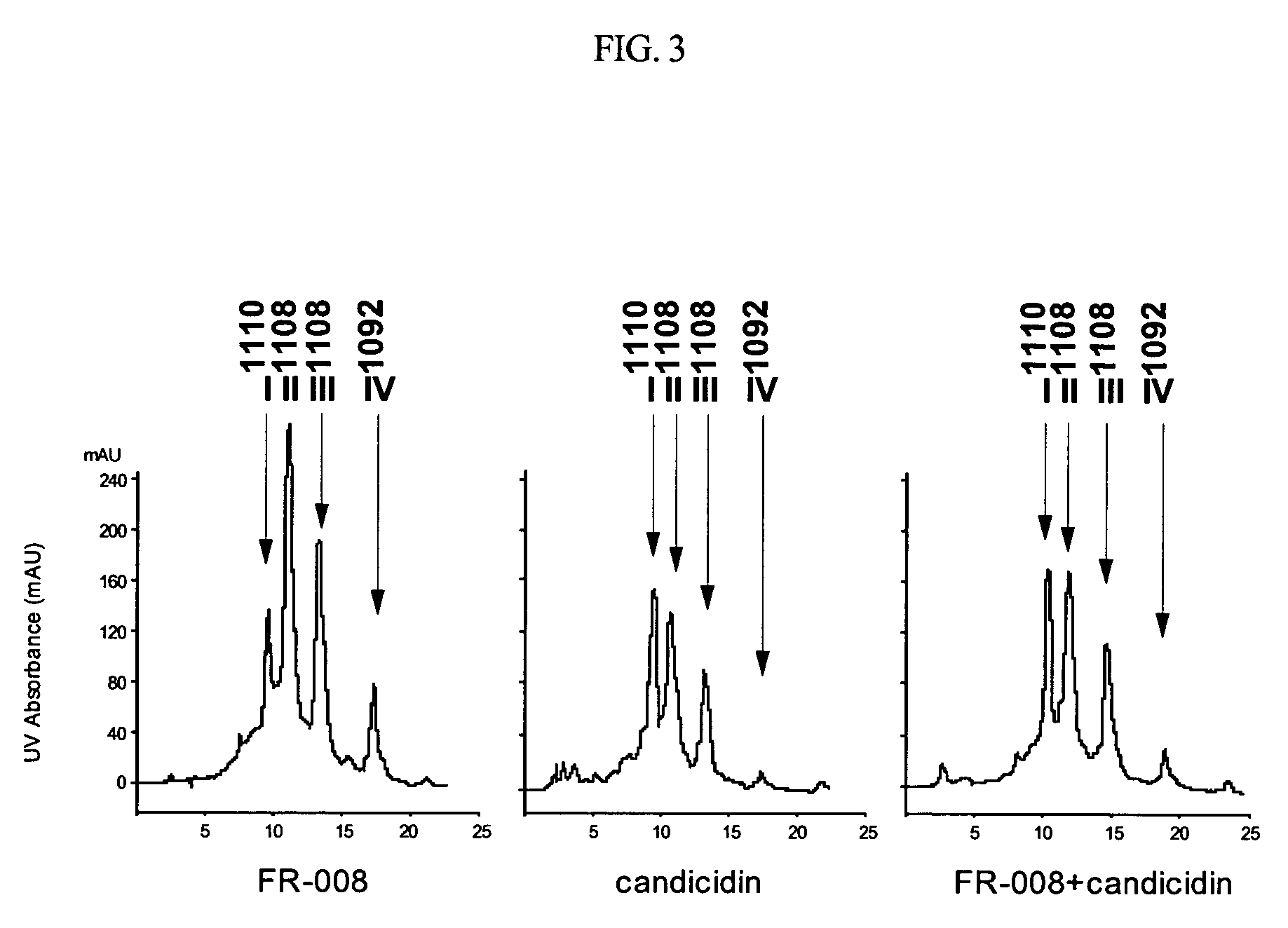
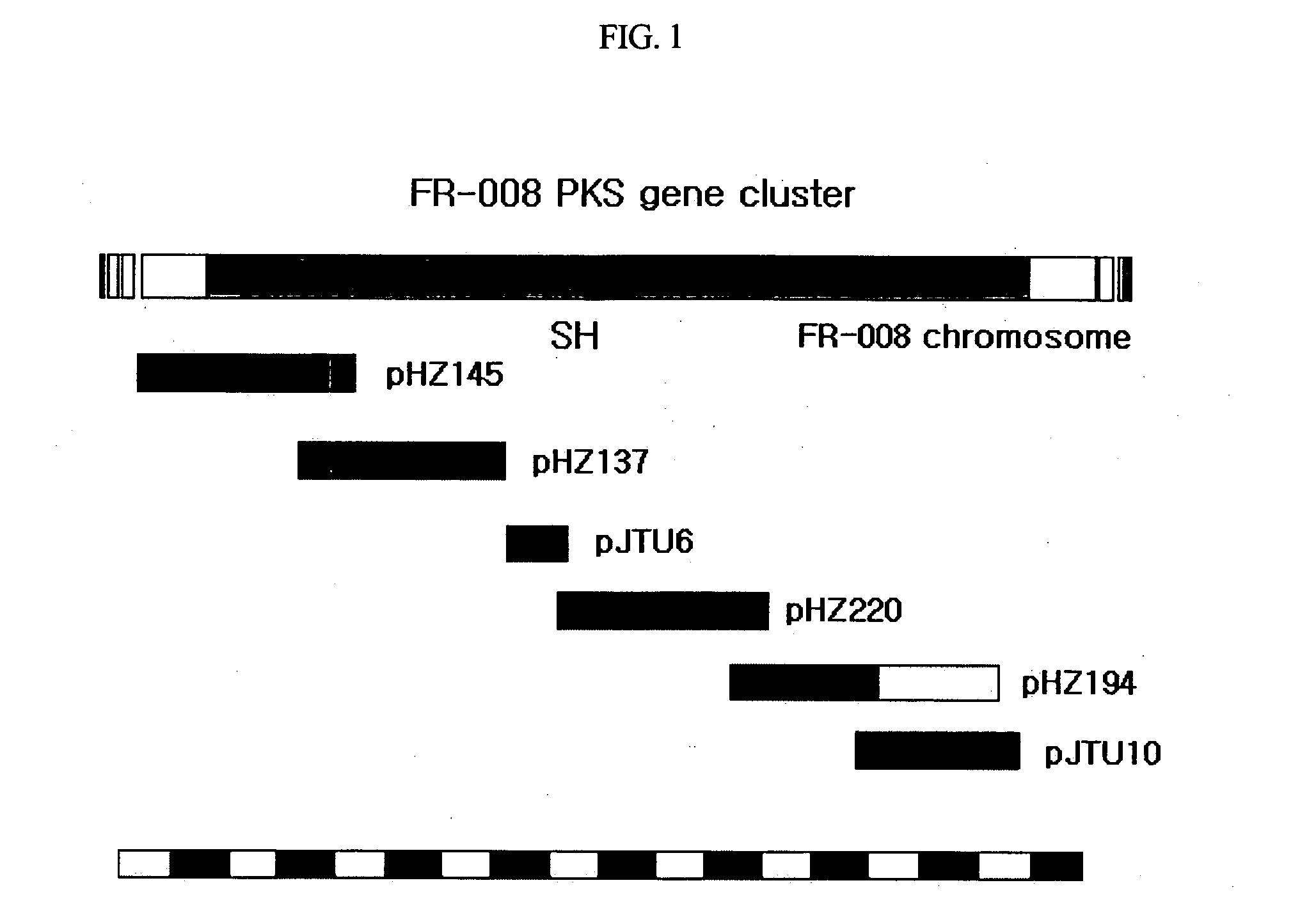
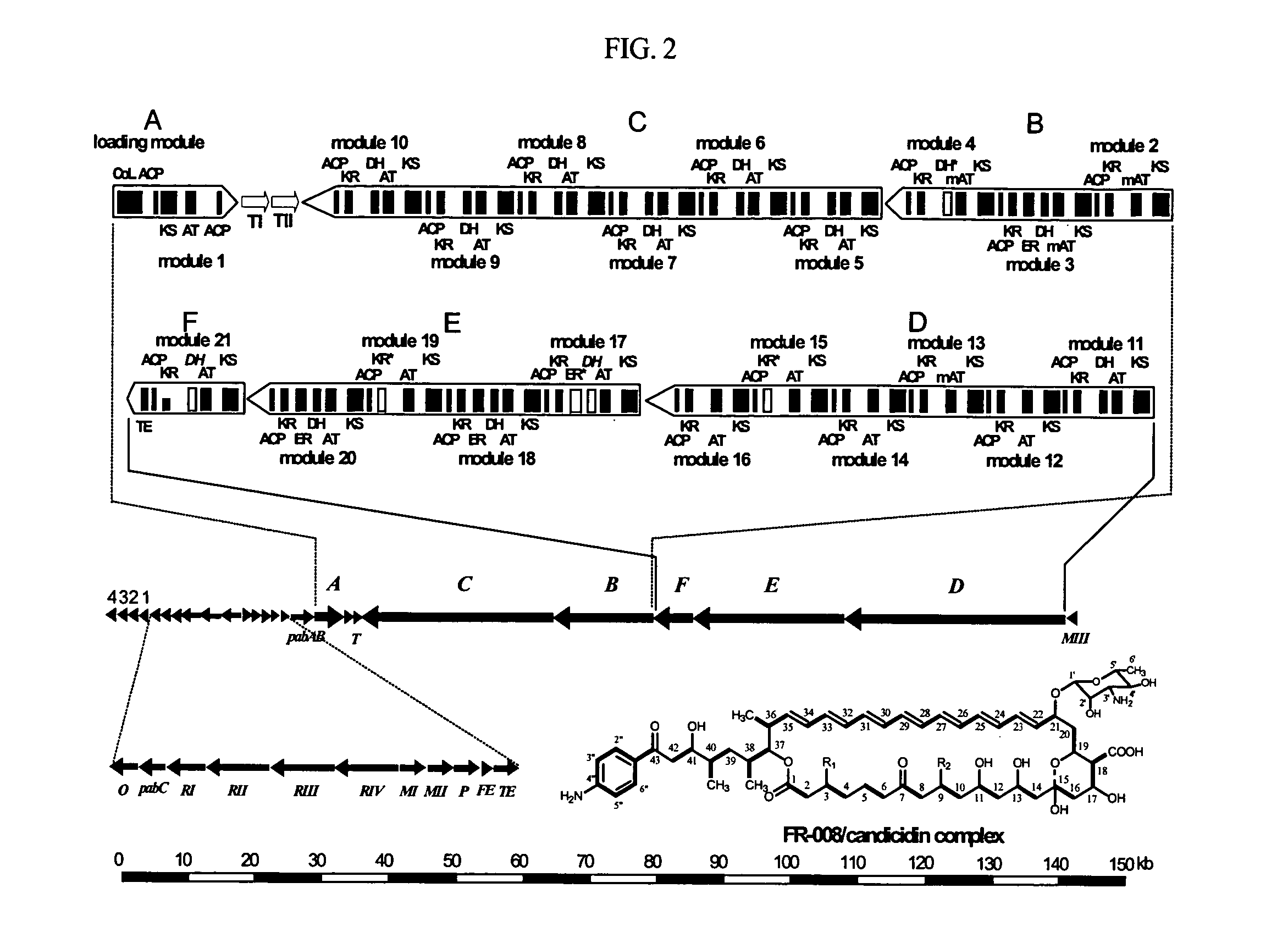
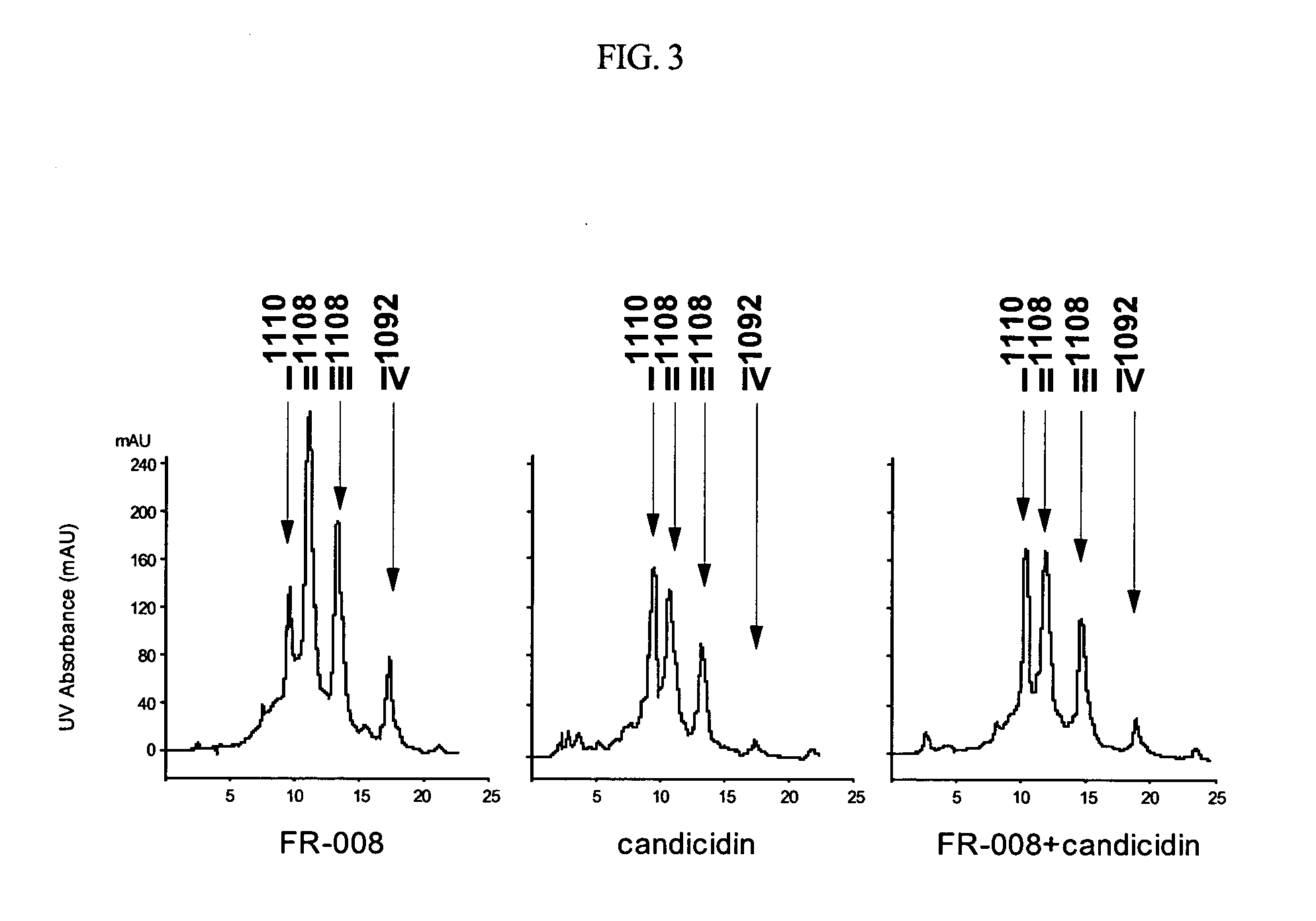
Genes for synthesis of FR-008 polyketides
The present invention relates to the base sequence of whole genes involved in the biosynthesis of FR-008 polyketides derived from Streptomyces sp. FR-008. This base sequence comprises genes coding for ketosynthase (KS), acyl transferase (AT), acyl carrier protein (ACP), ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH) and enoyl reductase (ER) domains, and genes coding for modifier enzymes, such as ABC transporter, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, ferredoxin, thioesterase, sugar synthetic protein, FAD-dependent monooxygenase, 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate (ADC) synthase and ADC lyase. The gene base sequence according to the present invention can be used to increase the productivity of the existing FR-008 polyketides or produce new FR-008 polyketides, through modification of its parts.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
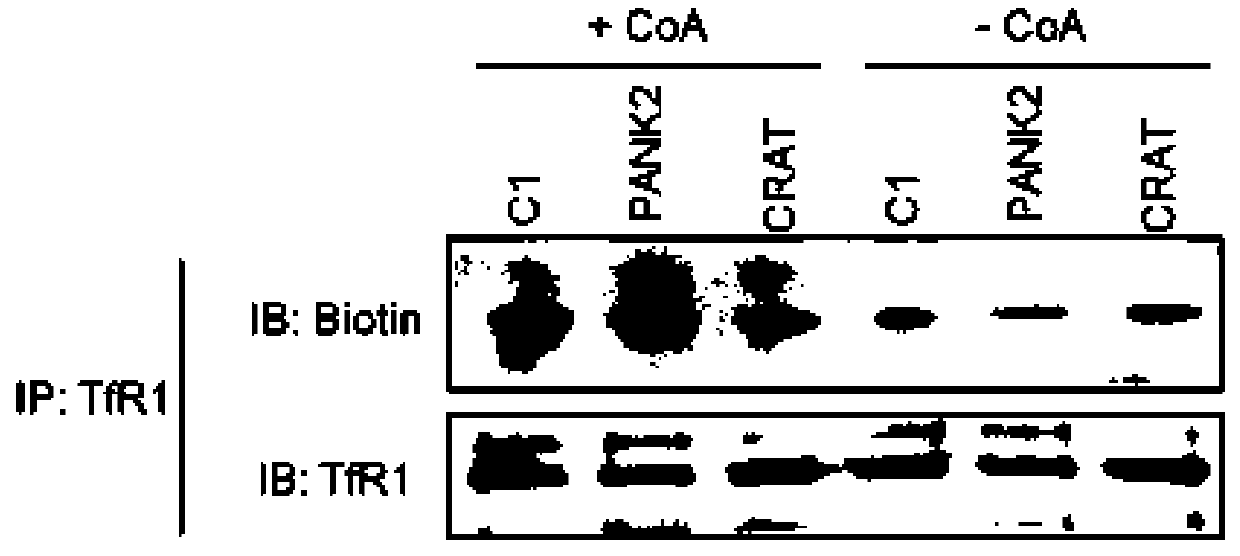
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation
ActiveUS10874637B2Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderNovel geneNeurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation
The present invention relates to methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of neurodegeneration in with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). Studying two novel genes, namely, CRAT encoding the carnitine acetyltransferase and REPS1 involved in endocytosis and vesicle transport, and a series of known NBIA genes, the inventors reported on iron overload related to increased levels and abnormal recycling of transferrin receptor as a common feature in NBIA. They ascribe this anomaly, at least in part, to impaired palmitoylation of the receptor as a common consequence of the various disease causing mutations. Finally, the inventors show that Artesunate improved TfR1 palmitoylation in NBIA fibroblasts. In particular, the present invention relates to a method of treating neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a drug increasing TfR1 palmitoylation.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
Method of treating fabrics
InactiveUS20190055499A1Eliminate riskLess likelihood of chemical and physical incompatibilityCationic surface-active compoundsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsAqueous mediumPeroxide
A method of treating fabrics including the steps of: providing a fabric comprising an ester containing compound pre-deposited thereon; and (ii) contacting the fabric with an aqueous medium comprising an acyl transferase enzyme and a peroxide source, wherein the acyl transferase enzyme causes generation of peracid in situ in the aqueous medium.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Benzyl-, (pyridin-3-yl)methyl- or (pyridin-4-yl)methyl-substituted oxadiazolopyridine derivatives as ghrelin O-acyl transferase (GOAT) inhibitors
The present invention relates to compounds of general formula (I), wherein the groups R1 and R2 are defined as in claim 1, which have valuable pharmacological properties, in particular bind to ghrelinO-acyl transferase (GOAT) and modulate its activity. The compounds are suitable for treatment and prevention of diseases which can be influenced by this receptor, such as metabolic diseases, in particular obesity.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Genes for synthesis of FR-008 polyketides
The present invention relates to the base sequence of whole genes involved in the biosynthesis of FR-008 polyketides derived from Streptomyces sp. FR-008. This base sequence comprises genes coding for ketosynthase (KS), acyl transferase (AT), acyl carrier protein (ACP), ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH) and enoyl reductase (ER) domains, and genes coding for modifier enzymes, such as ABC transporter, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, ferredoxin, thioesterase, sugar synthetic protein, FAD-dependent monooxygenase, 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate (ADC) synthase and ADC lyase. The gene base sequence according to the present invention can be used to increase the productivity of the existing FR-008 polyketides or produce new FR-008 polyketides, through modification of its parts.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
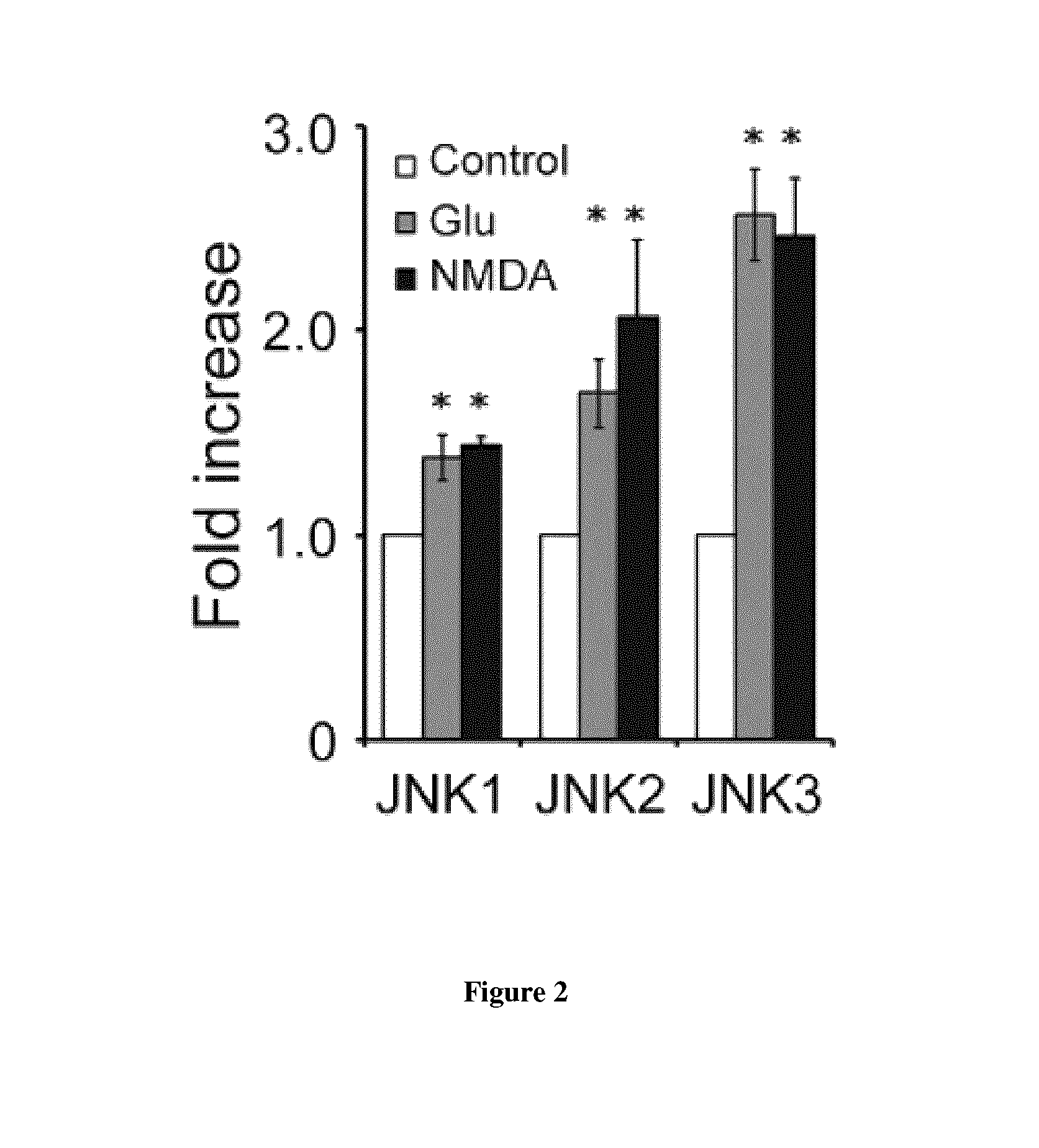
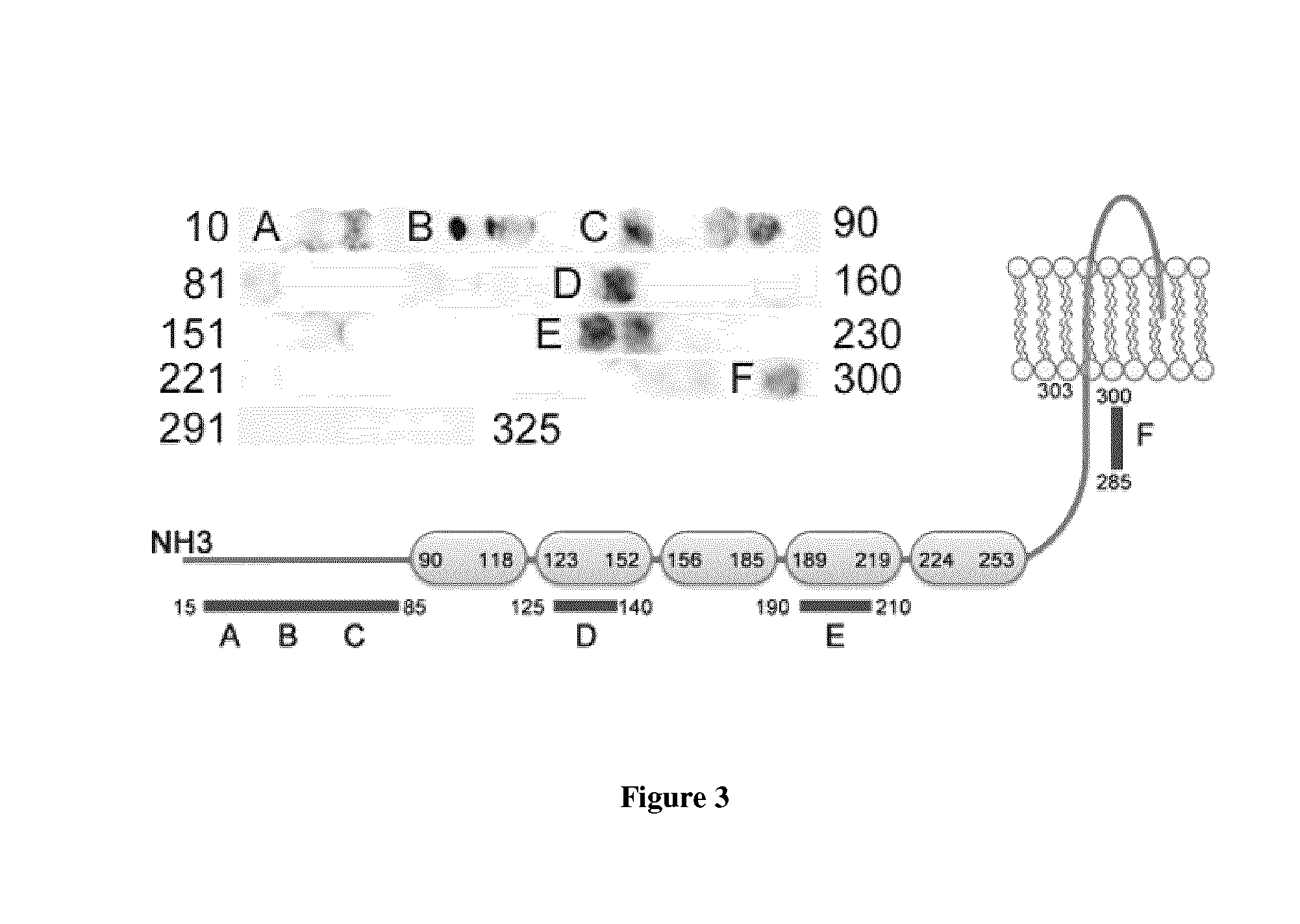
Neuroprotective peptides that inhibit interaction of palmitoyl acyl transferase zinc-finger dhhc type containing 17 (ZD17) and c-jun n-terminal kinase (JNK)
ActiveUS20150225704A1Stress protectionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCell membrane
Isolated polypeptides are disclosed herein, the isolated polypeptides comprising at least 90% identity to any one of: SEQ ID NO:1; SEQ ID NO:2; or SEQ ID NO:3, wherein the isolated polypeptide inhibits an interaction between palmitoyl acyl transferase zinc-finger DHHC type containing 17 (z D17) and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The polypeptides may be conjugated to a delivery and targeting moiety, such as the cell-membrane transduction domain of the HIV-1 Tat protein. There are also provided methods for treating a disease associated with cytotoxicity or excitotoxicity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Histone acetyltransferase modulators and uses thereof
ActiveUS9969677B2Decreasing inclusion bodyImprove the level ofNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAmyloid betaProtein level
The invention provides compounds and compositions comprising compounds that modulate histone acyl transferase (HAT). The invention further provides methods for treating neurodegenerative disorders, conditions associated with accumulated amyloid-beta peptide deposits, Tau protein levels, and / or accumulations of alpha-synuclein as well as cancer by administering a compound that modulates HAT to a subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com