Patents
Literature
308 results about "Cancer detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Detection of cancer is actually the detection of such abnormal cells formed during the generation of cancerous tumors. These abnormal cells spread to various parts of the body through lymph nodes and the bloodstream. ... Cancer detection is very important to predict the extent of damage the cancerous cells may cause to the body. A proper and reliable treatment can be planned only when the presence of cancerous tumors is confirmed.
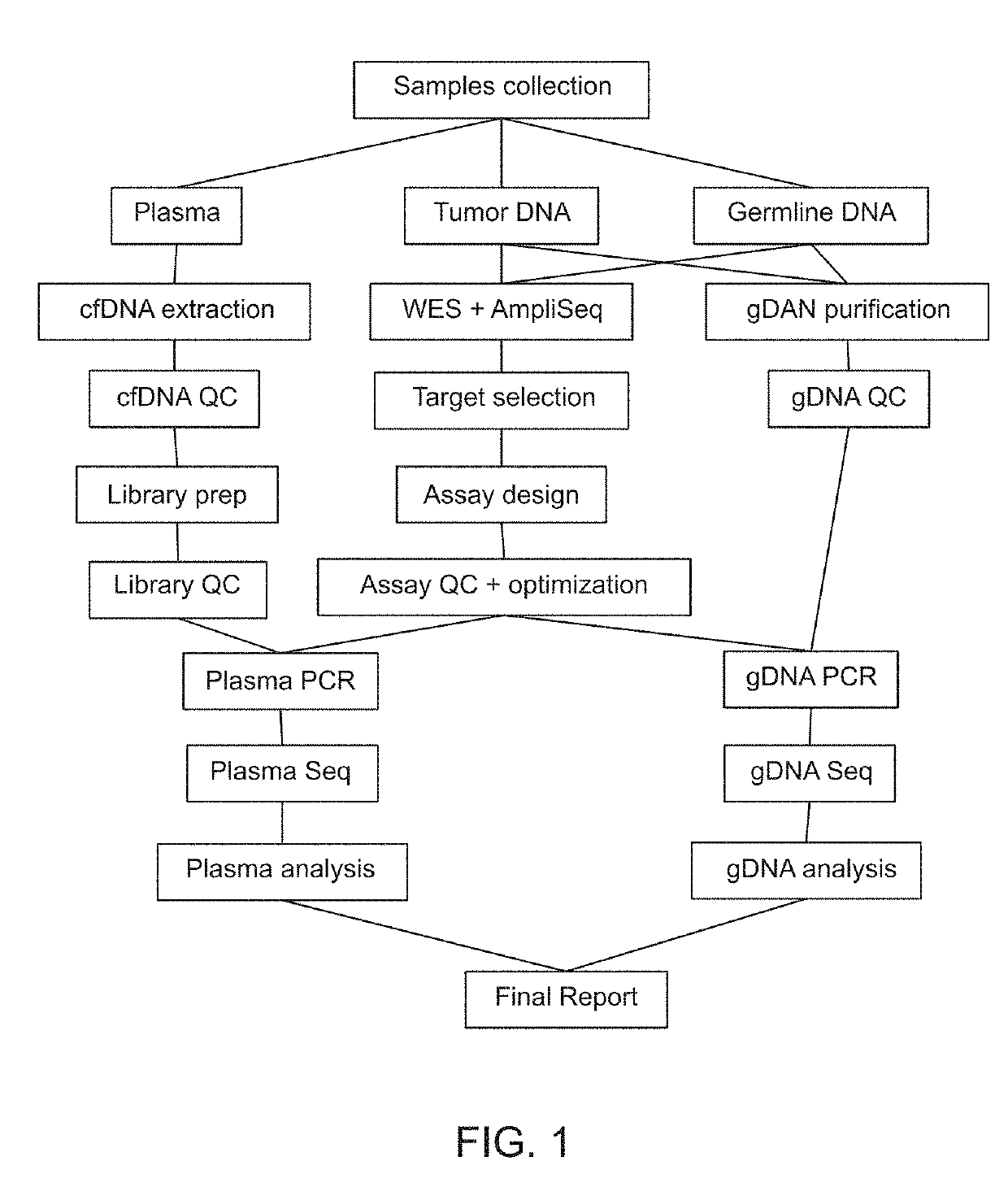
Mutational analysis of plasma DNA for cancer detection
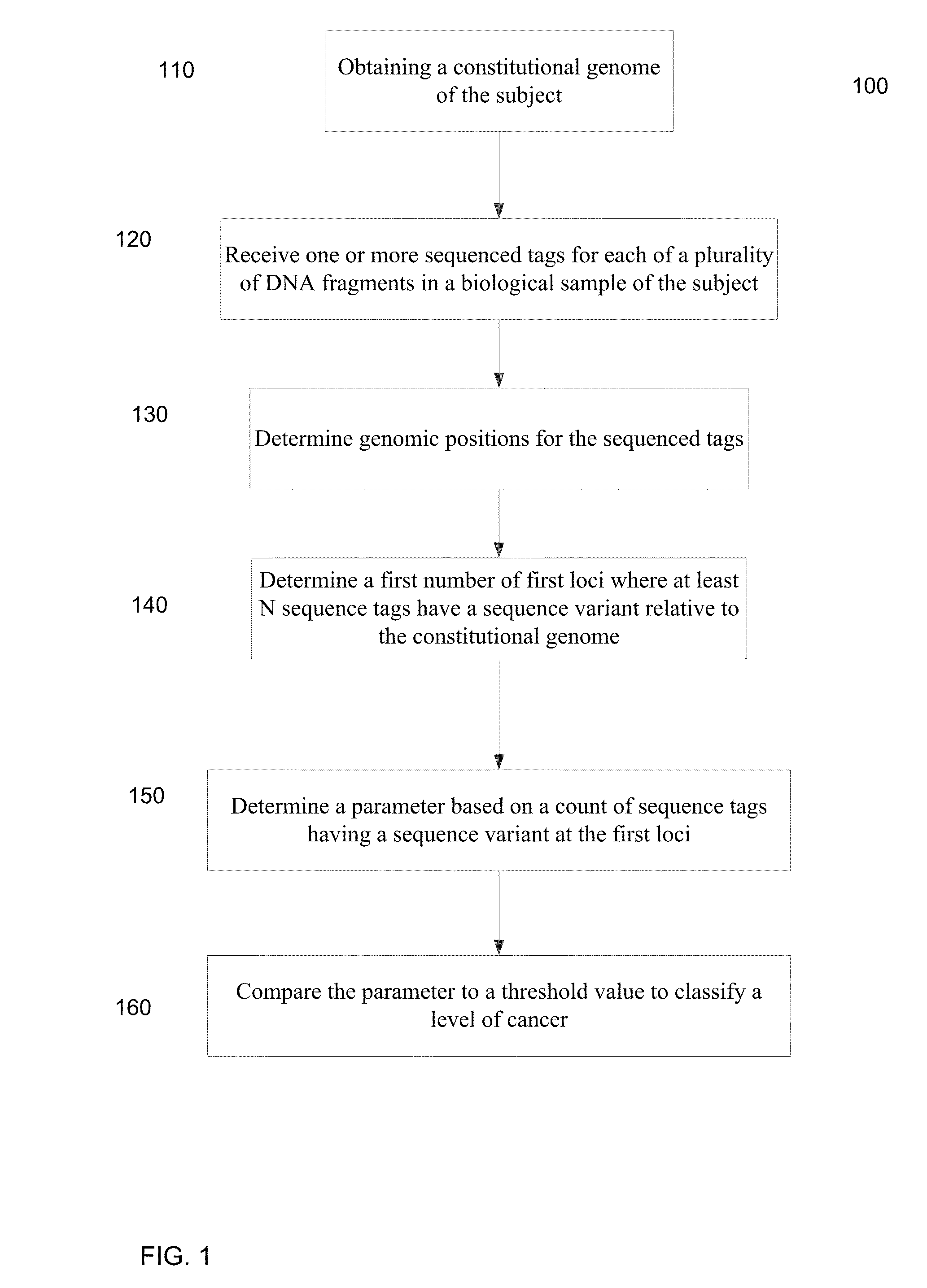
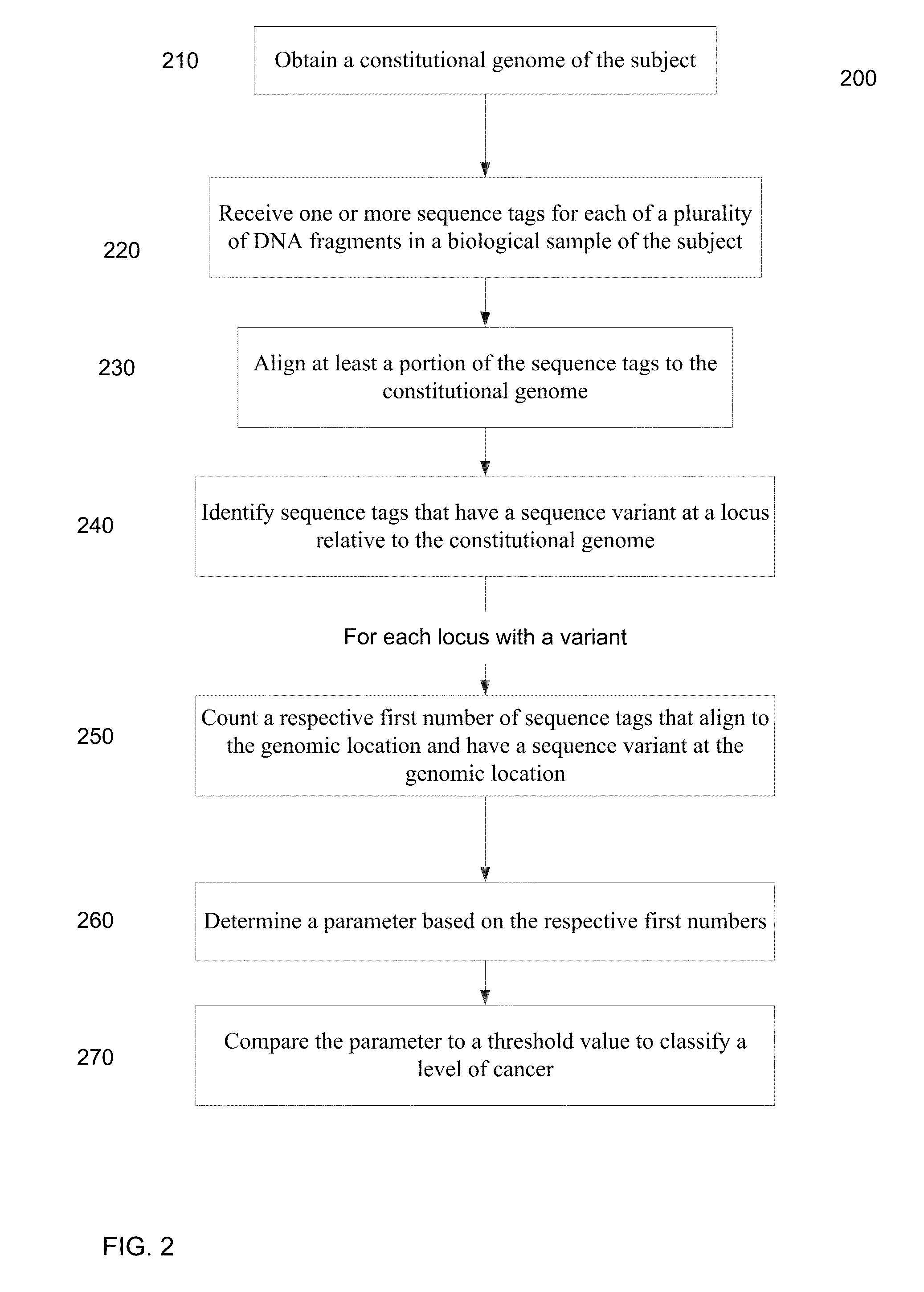
ActiveUS20140100121A1Accurate parameterLevel of heterogeneity of tumorsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation frequencyBlood plasma
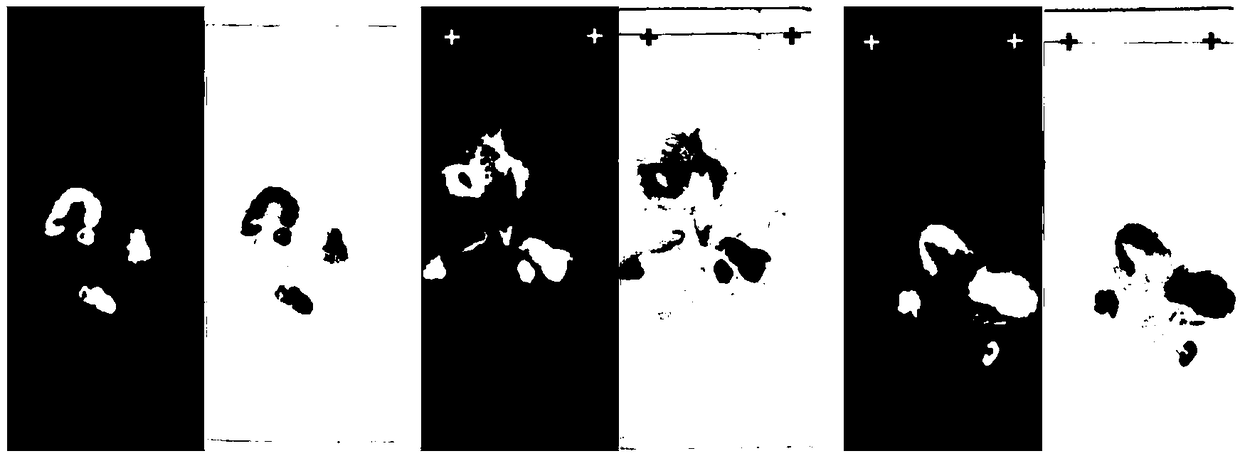
A frequency of somatic mutations in a biological sample (e.g., plasma or serum) of a subject undergoing screening or monitoring for cancer, can be compared with that in the constitutional DNA of the same subject. A parameter can derived from these frequencies and used to determine a classification of a level of cancer. False positives can be filtered out by requiring any variant locus to have at least a specified number of variant sequence reads (tags), thereby providing a more accurate parameter. The relative frequencies for different variant loci can be analyzed to determine a level of heterogeneity of tumors in a patient.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for cancer detection, diagnosis and prognosis
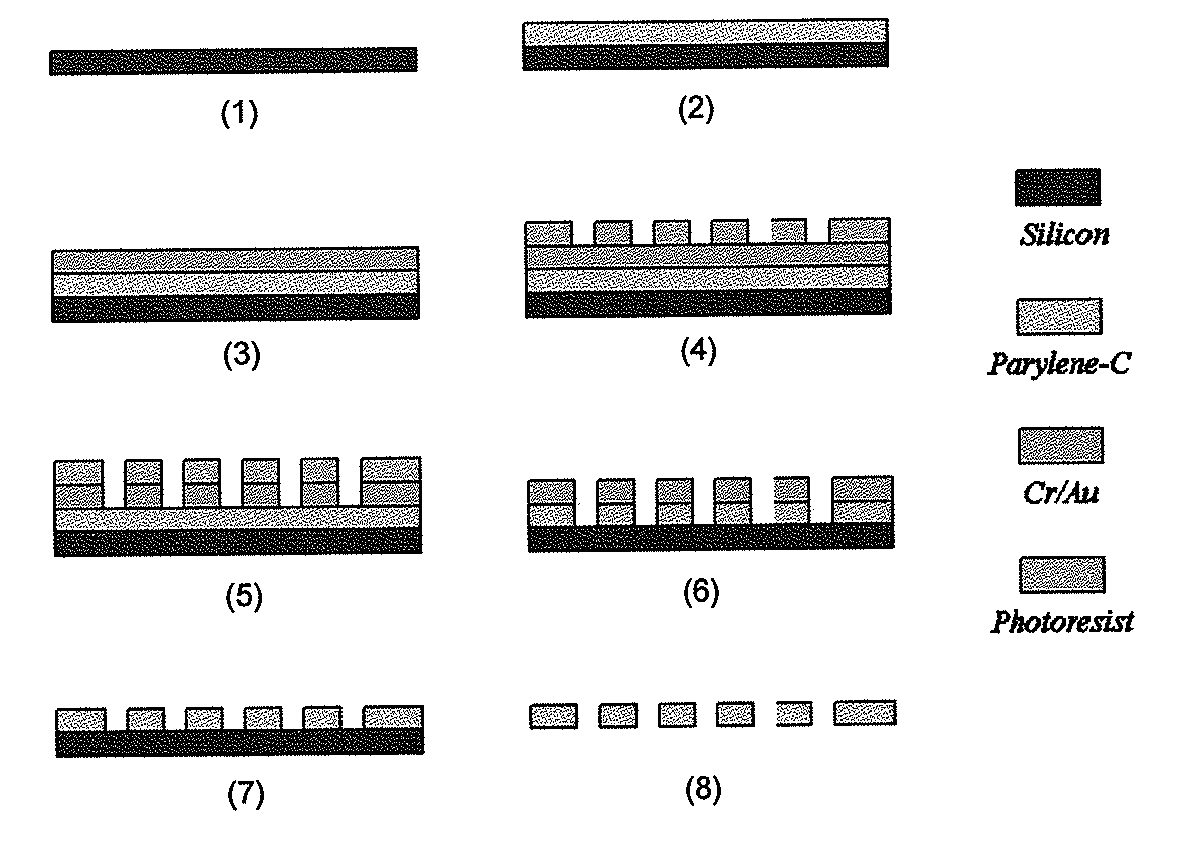
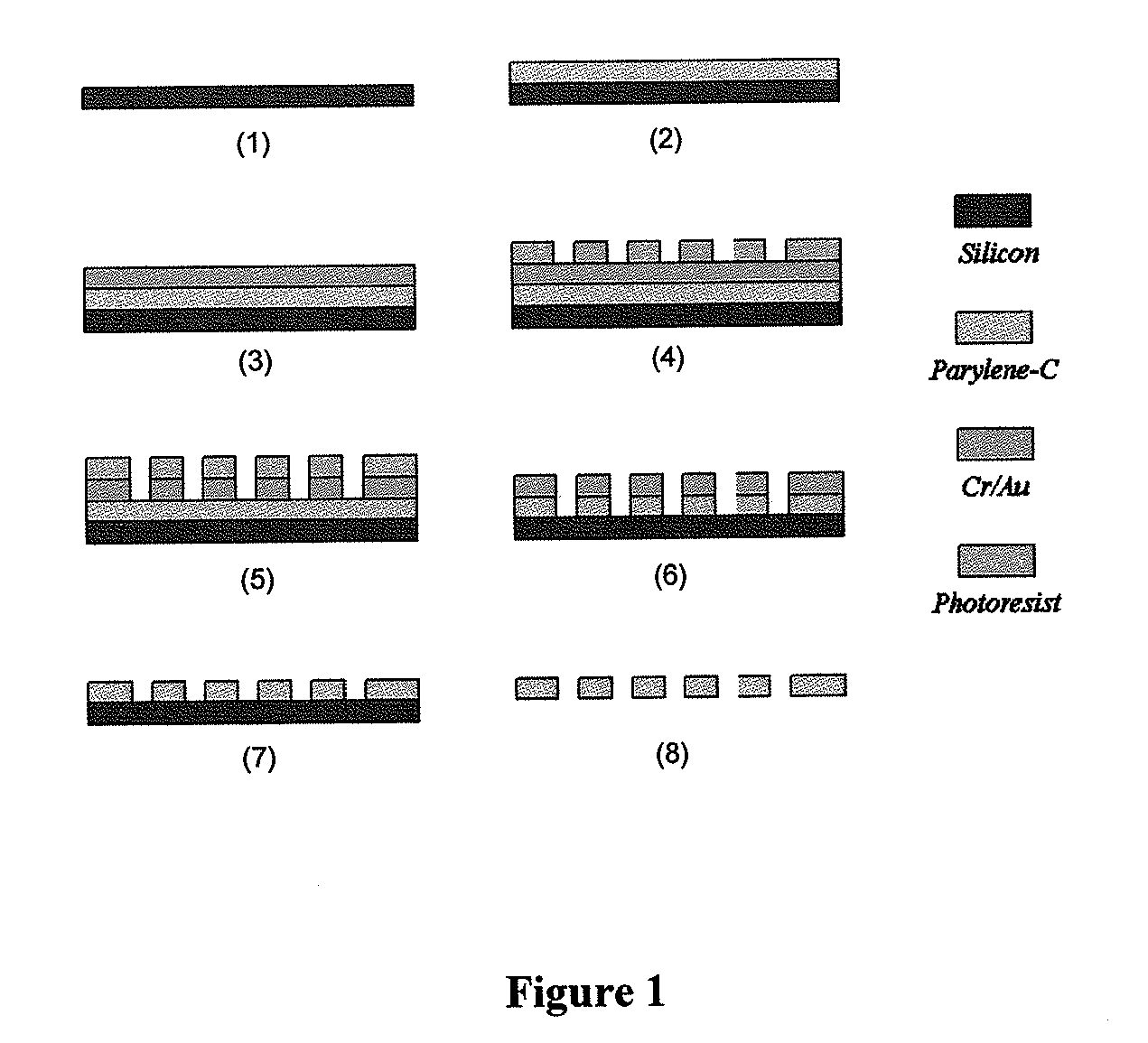
ActiveUS20110053152A1Rapidly and efficiently captureImprove capture efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTelomeraseParylene
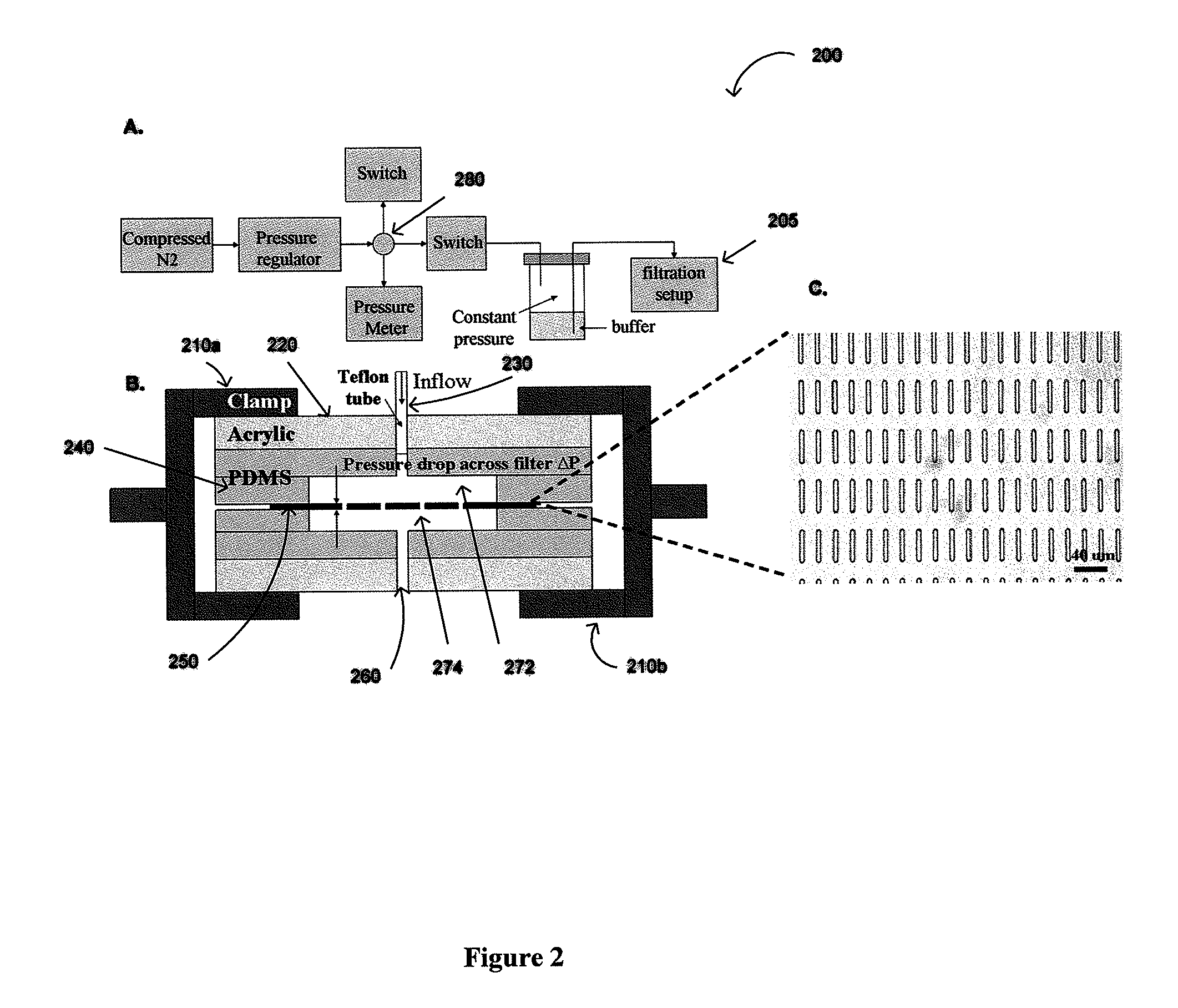
The present invention provides a method for diagnosing cancer, predicting a disease outcome or response to therapy in a patient sample. The method involves isolating a circulating tumor cell (CTC), for example, a viable CTC, from a sample using a parylene microfilter device comprising a membrane filter having or consisting of a parylene substrate, which has an array of holes with a predetermined shape and size; and detecting and quantifying telomerase activity in blood circulating tumor cells. The invention further provides methods of using cells live-captured in various applications.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Methods for cancer imaging
InactiveUS6989140B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCancer cellFluorescence
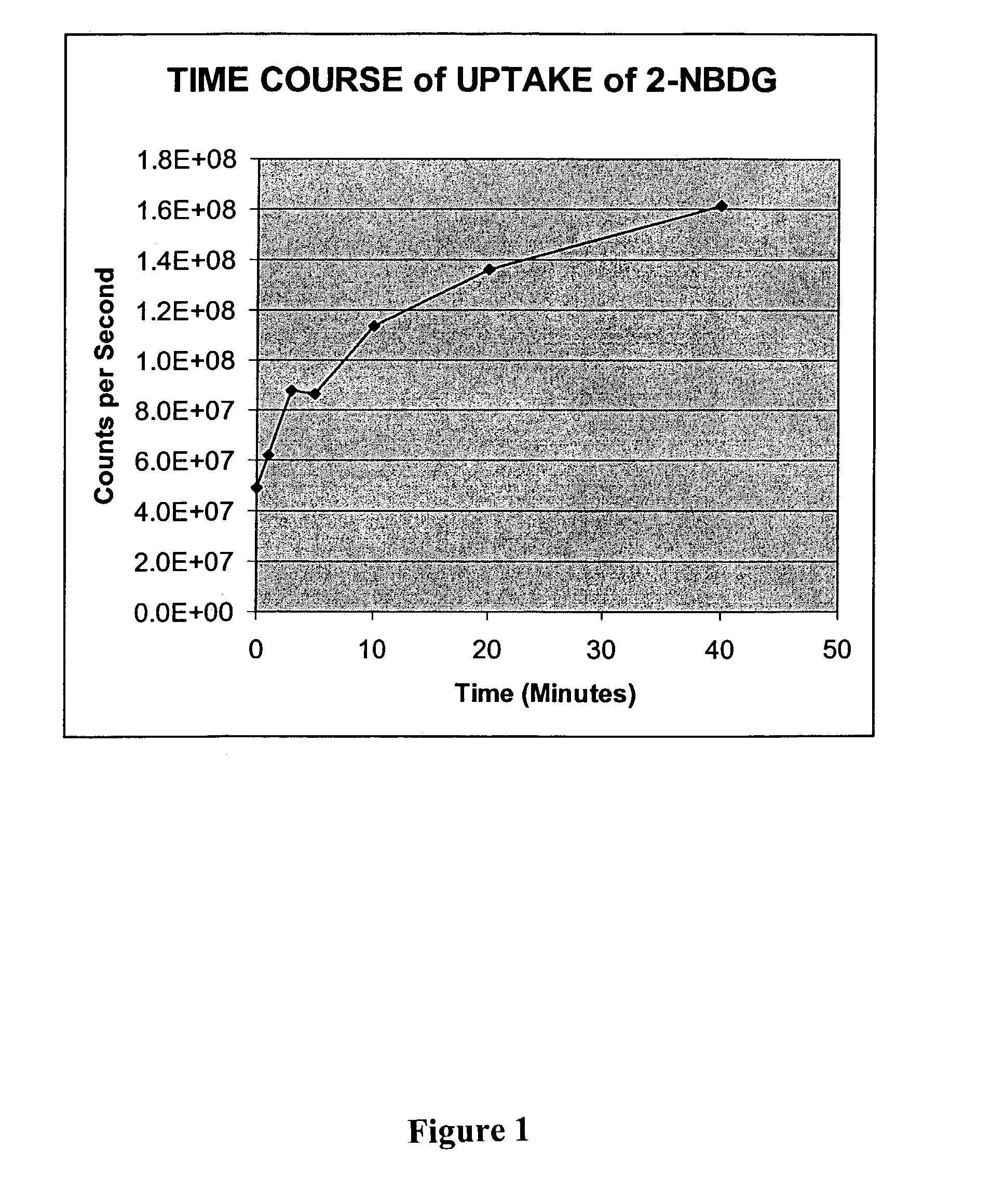
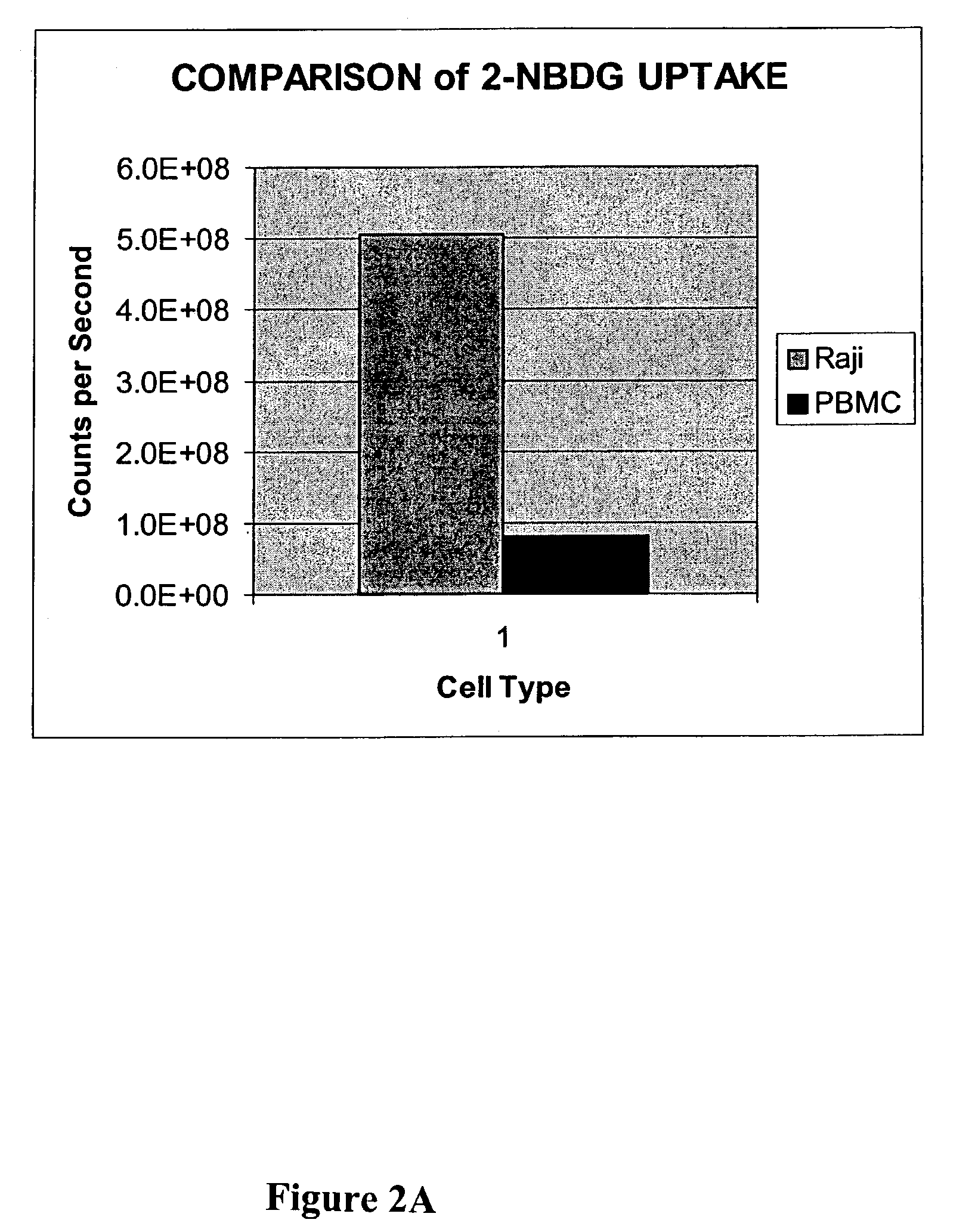
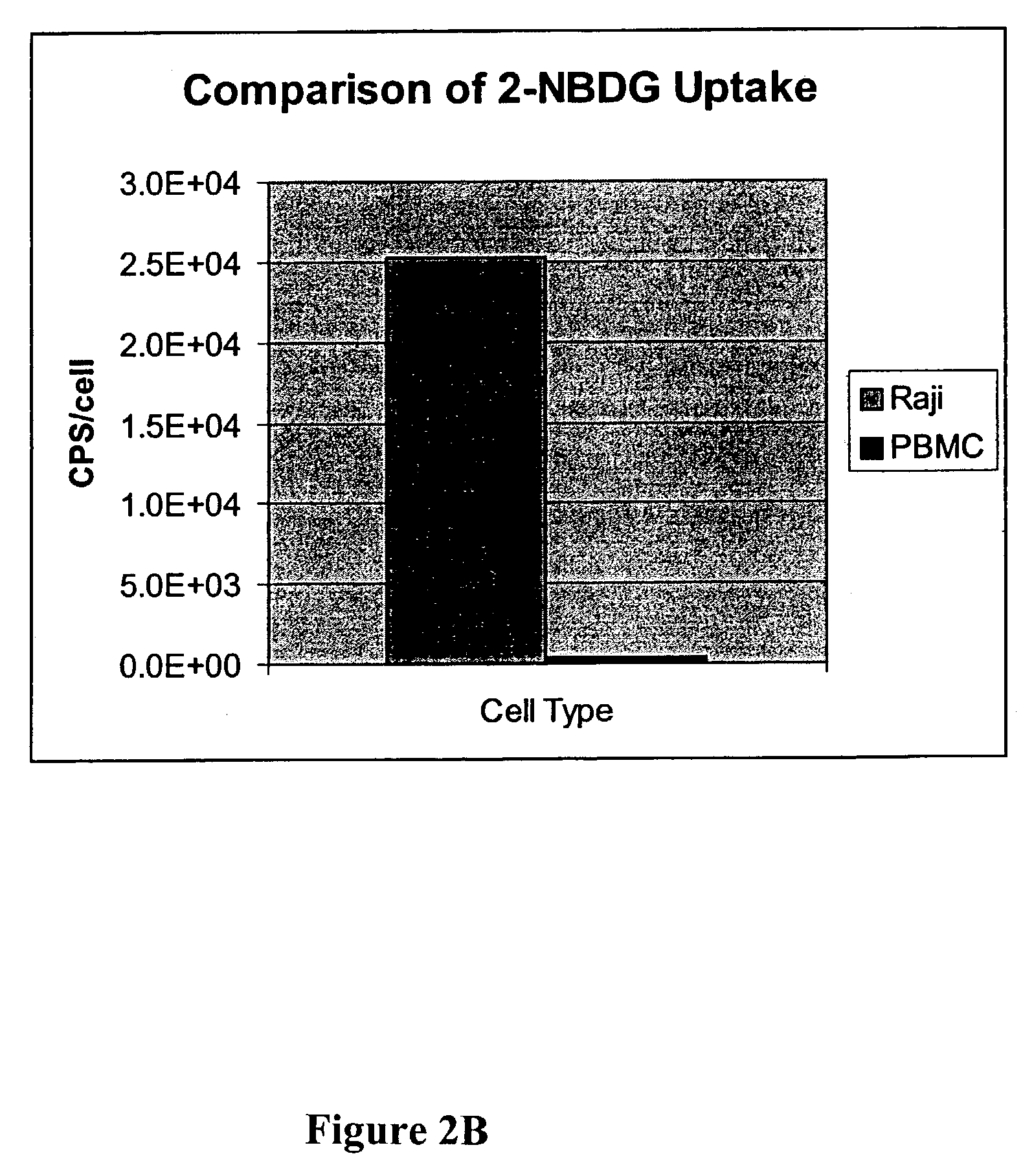
Methods are provided for cancer and pre-cancer detection by increased uptake of fluorophore glucose or deoxyglucose conjugates in cancerous and pre-cancerous cells relative to normal cells.
Owner:THRESHOLD PHARM INC
Multifactorial assay for cancer detection
InactiveUS20050069963A1Rapid and early detectionPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnti her2Anti-MUC-1
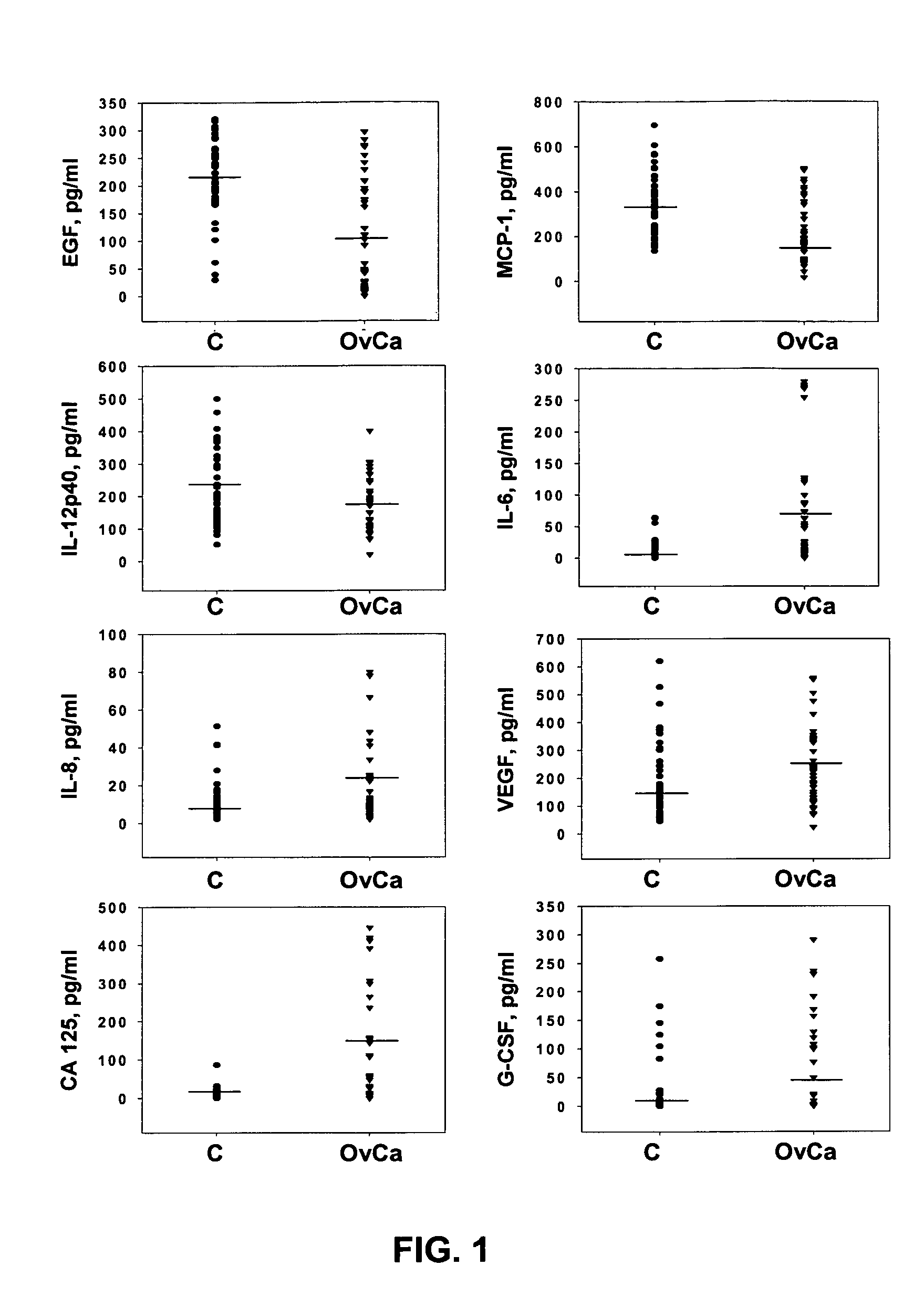
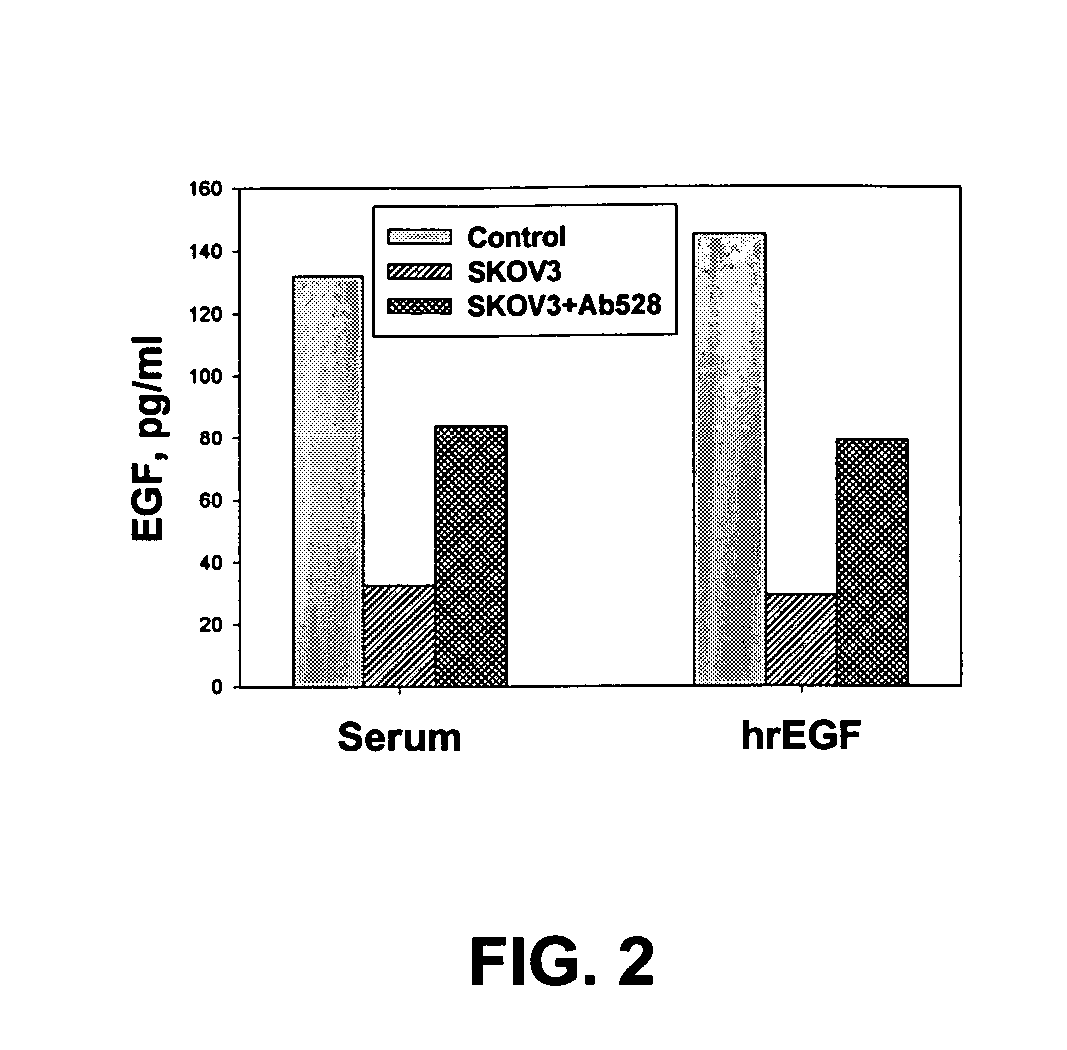
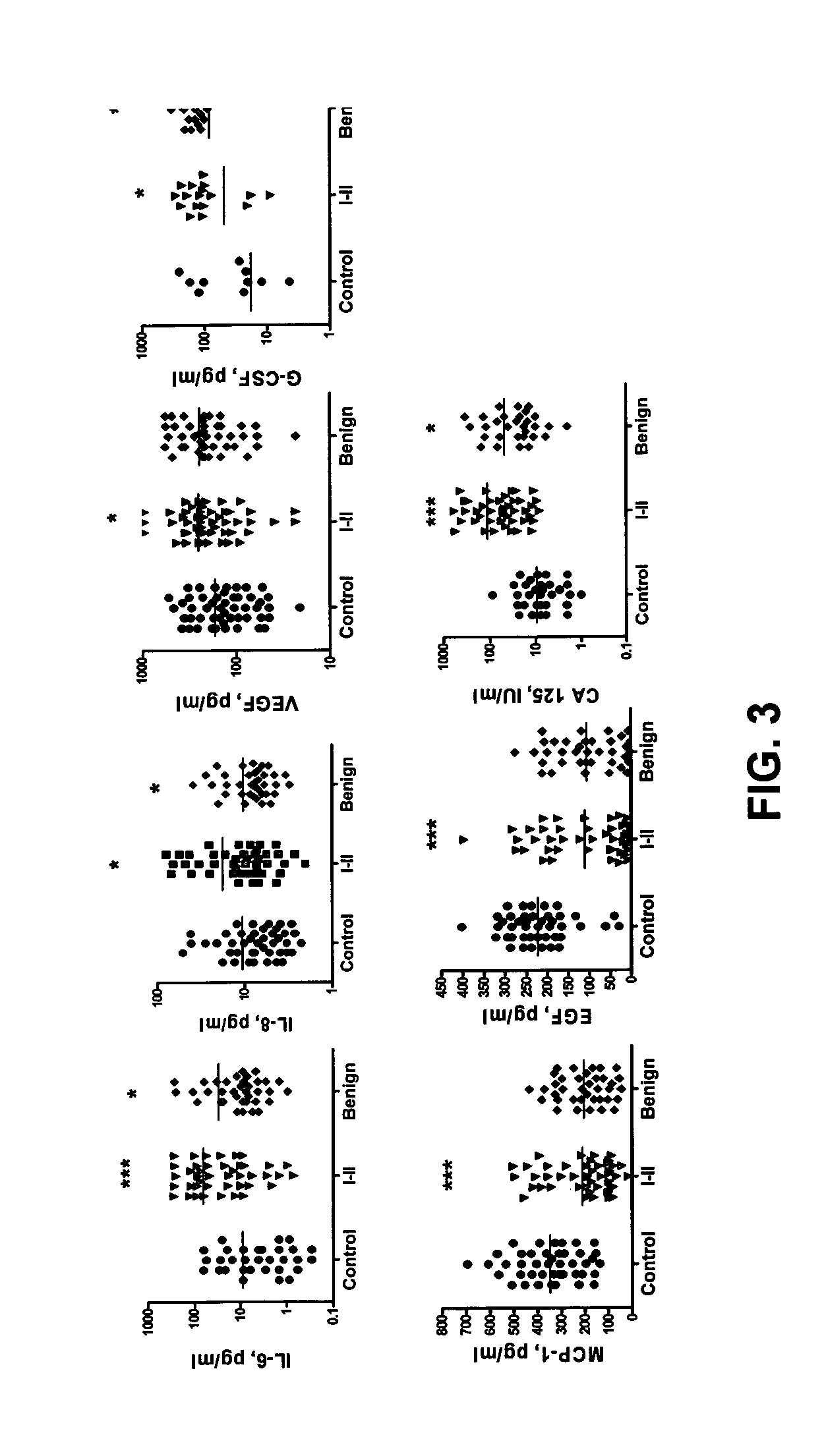
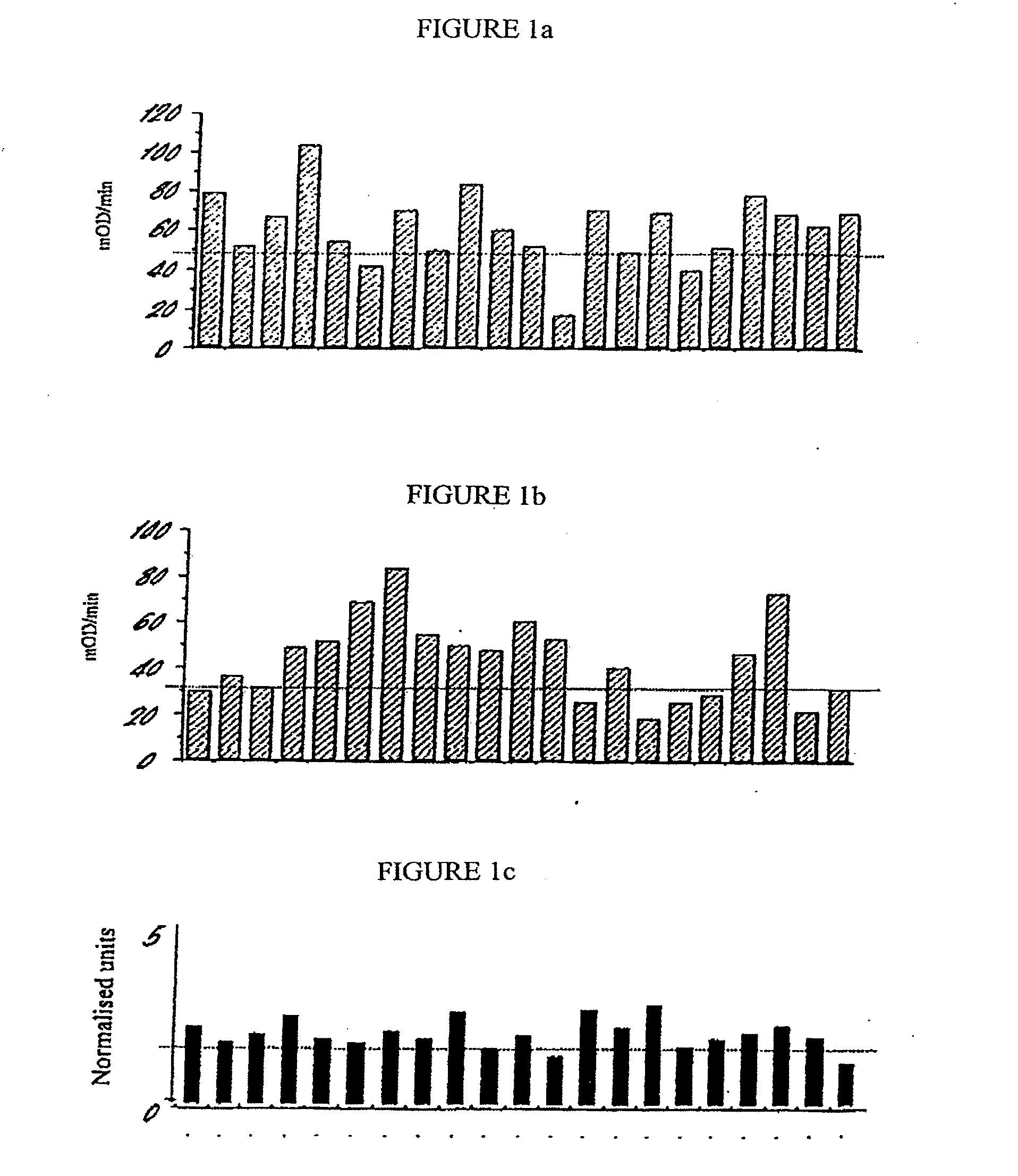
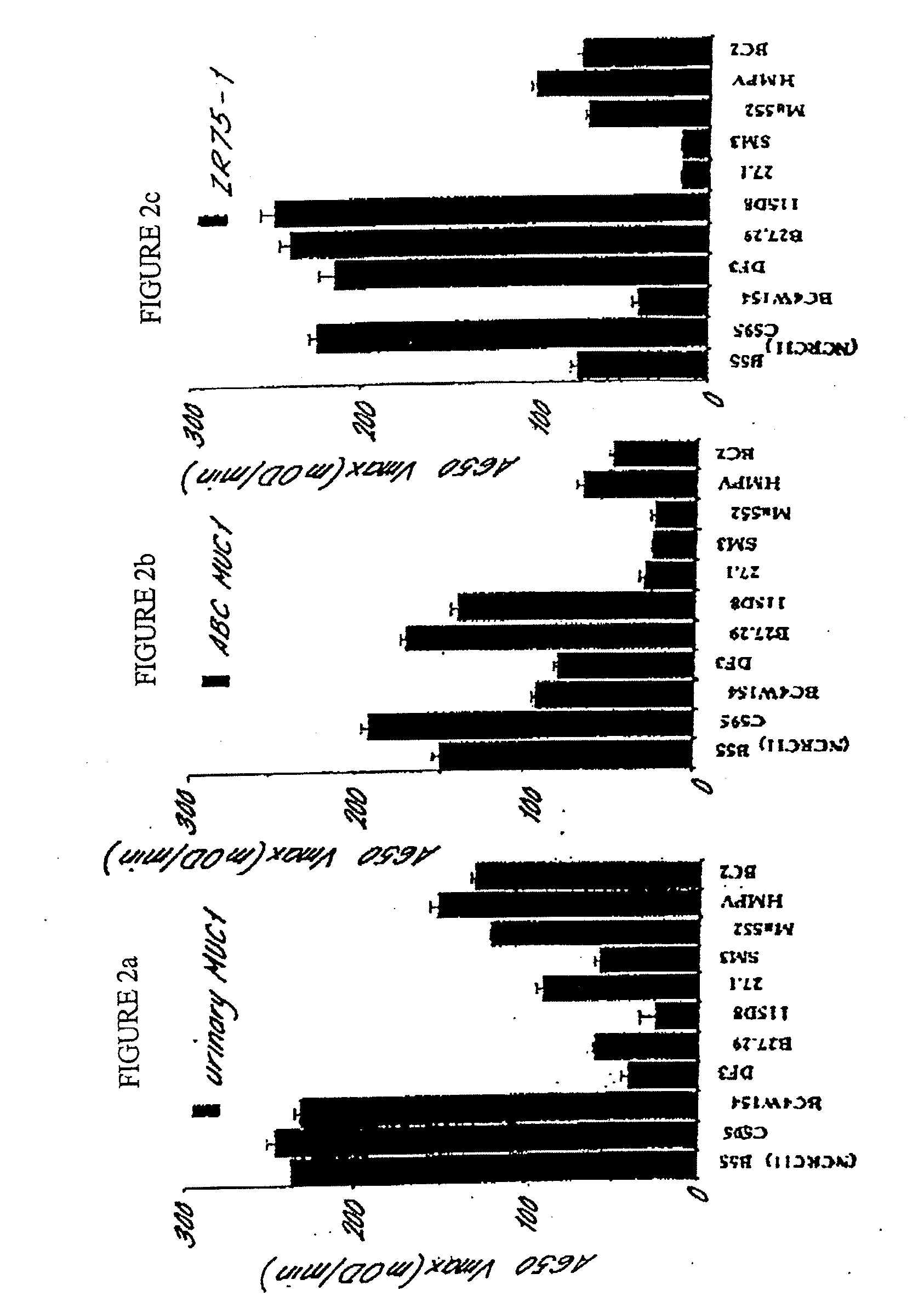
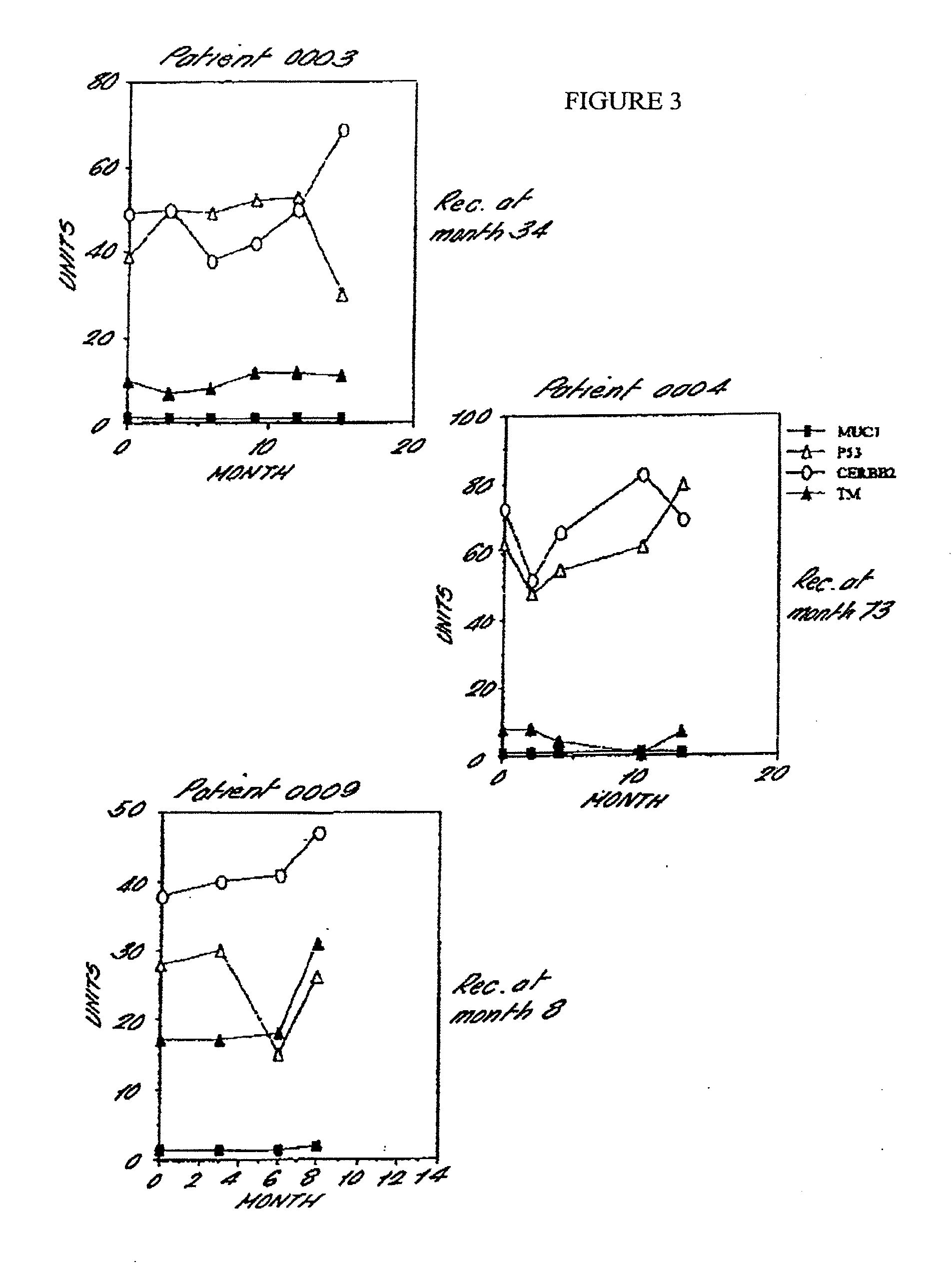
Provided are methods for the rapid detection of ovarian cancer. The methods employ a multiplex immunoassay to detect levels of two or more of the markers EGF, G-CSF, IL-6, IL-8, CA-125, VEGF, MCP-1, anti-IL6, anti-IL8, anti CA-125, anti-c-myc, anti-p53, anti-CEA, anti-CA 15-3, anti-MUC-1, anti-survivin, anti-bHCG, anti-osteopontin, anti-PDGF, anti-Her2 / neu, anti-Akt1, anti-cytokeratin 19, cytokeratin 19, EGFR, CEA, kallikrein-8, M-CSF, FasL, ErbB2 and Her2 / neu in a sample of the patient's blood, where the presence of abnormal levels of two or more of the markers indicates the presence of ovarian cancer in the patient. An array also is provided to quantitate levels of these markers in a patient's blood. Also provided is a method of predicting onset of clinical ovarian cancer comprising determining the change in concentration over time of two or more of anti-Her2 / neu, anti-MUC-1, anti-c-myc, anti-p53, anti-CA-125, anti-CEA, anti-CA 72-4, anti-PDGFRα, IFNγ, IL-6, IL-10, TNFα, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, EGFR and Her2 / neu in a patient's blood.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Methods for cancer detection and monitoring
PendingUS20190316184A1Minimize dimer formationHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadEarly Relapse
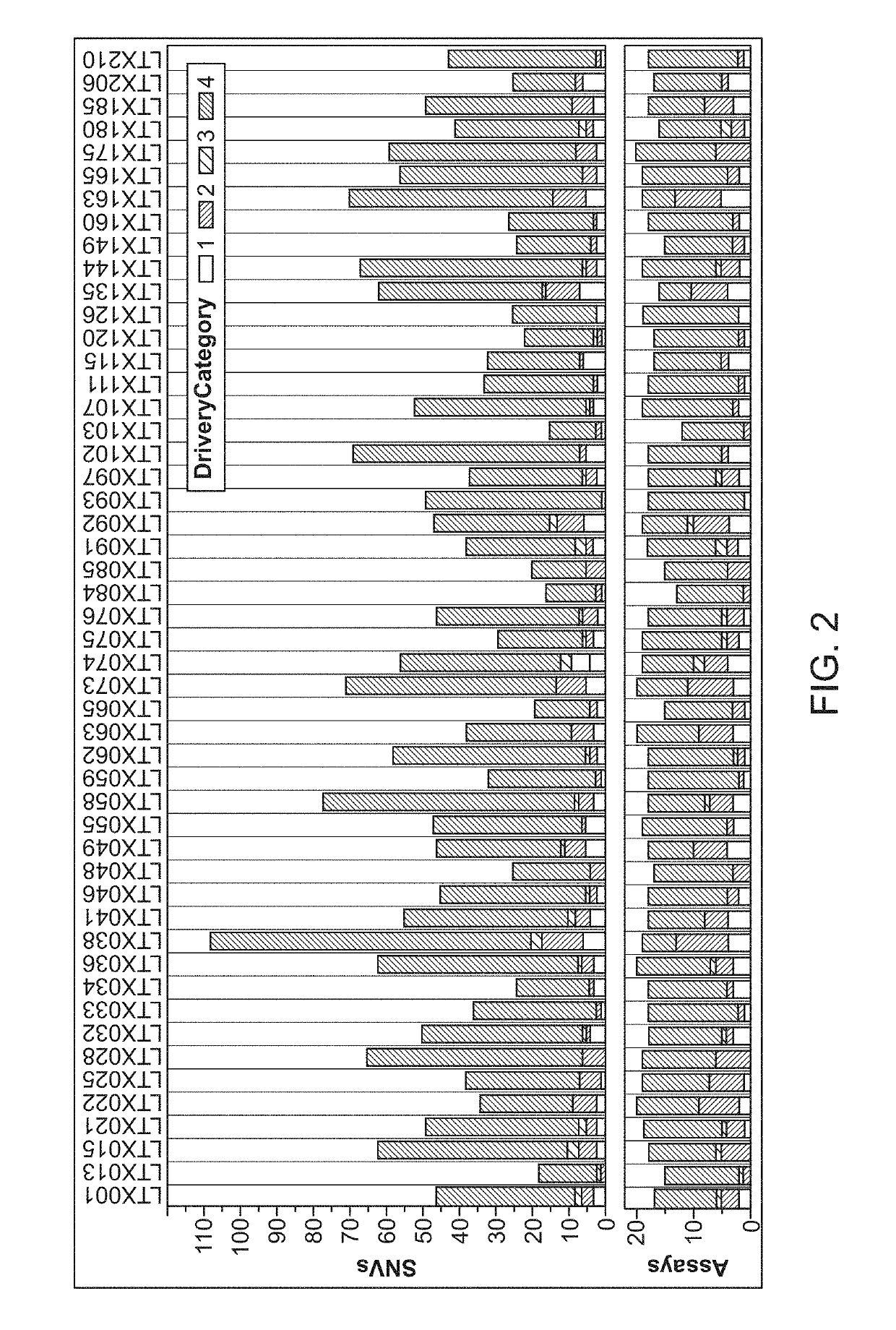
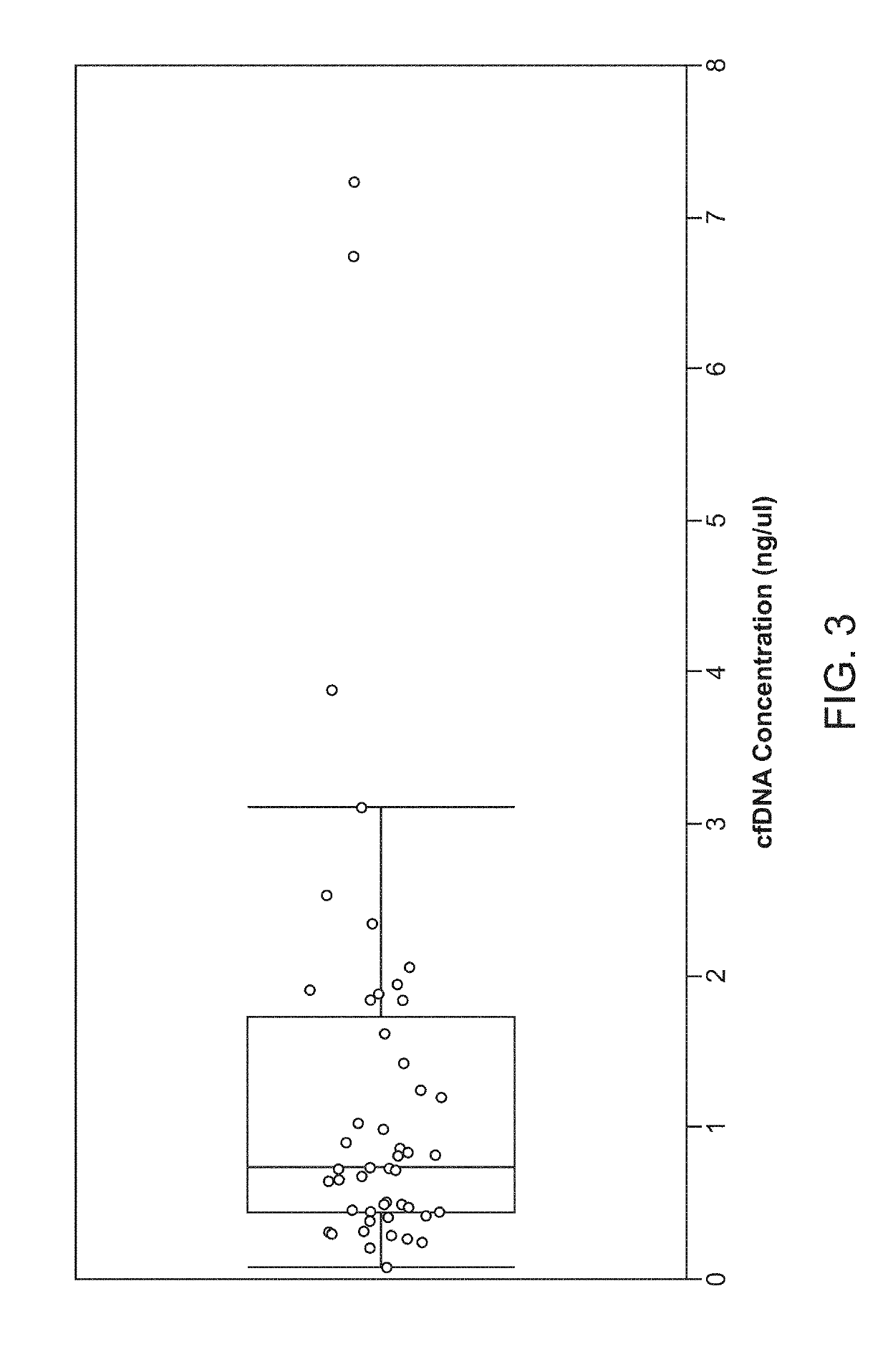
The invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide variants in breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer. Additional methods and compositions, such as reaction mixtures and solid supports comprising clonal populations of nucleic acids, are provided. For example, provided here is a method for monitoring and detection of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, comprising generating a set of amplicons by performing a multiplex amplification reaction on nucleic acids isolated from a sample of blood or urine or a fraction thereof from a patient who has been treated for a breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, wherein each amplicon of the set of amplicons spans at least one single nucleotide variant locus of a set of patient-specific single nucleotide variant loci associated with the breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer; and determining the sequence of at least a segment of each amplicon of the set of amplicons that comprises a patient-specific single nucleotide variant locus, wherein detection of one or more patient-specific single nucleotide variants is indicative of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer.
Owner:NATERA
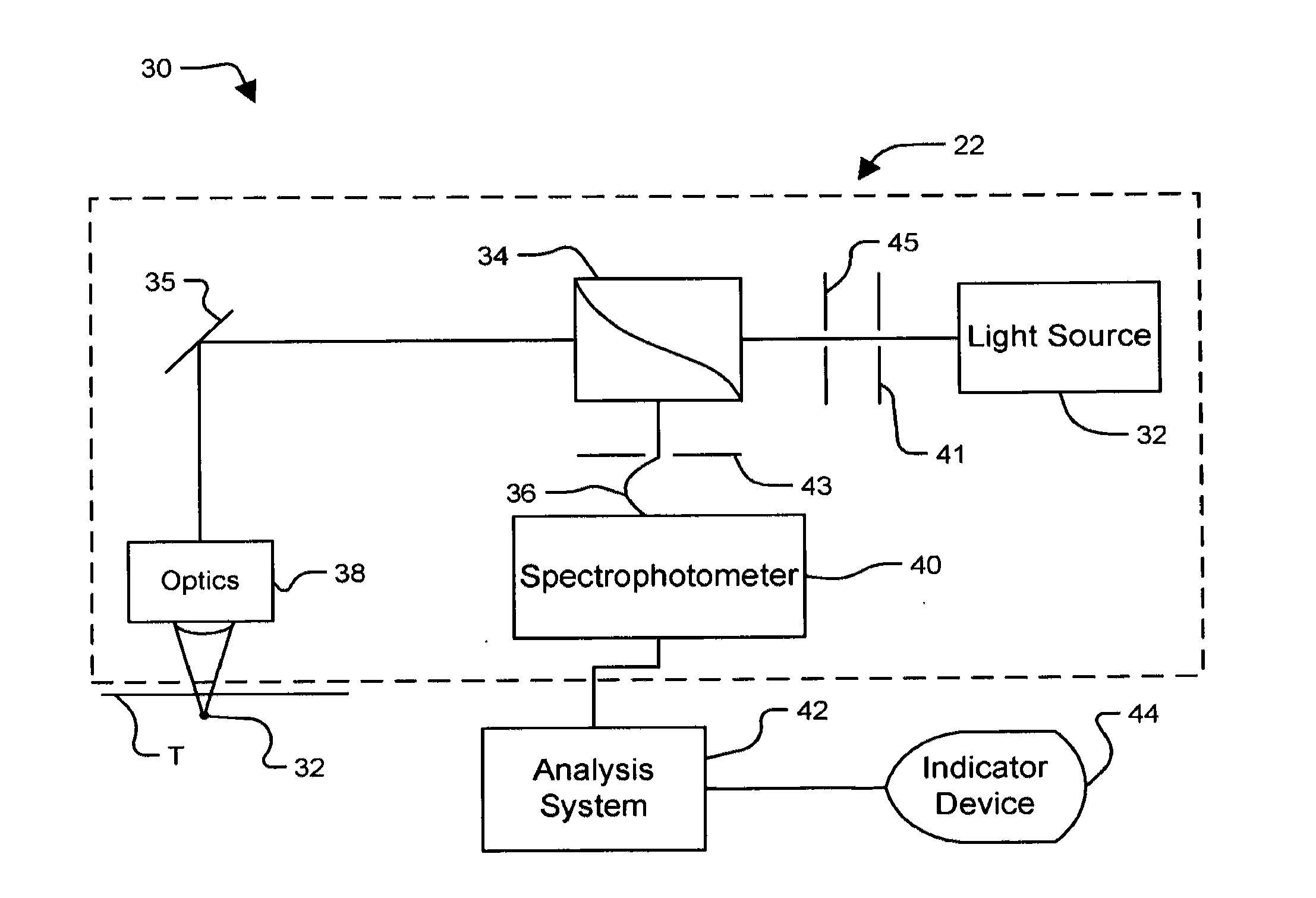
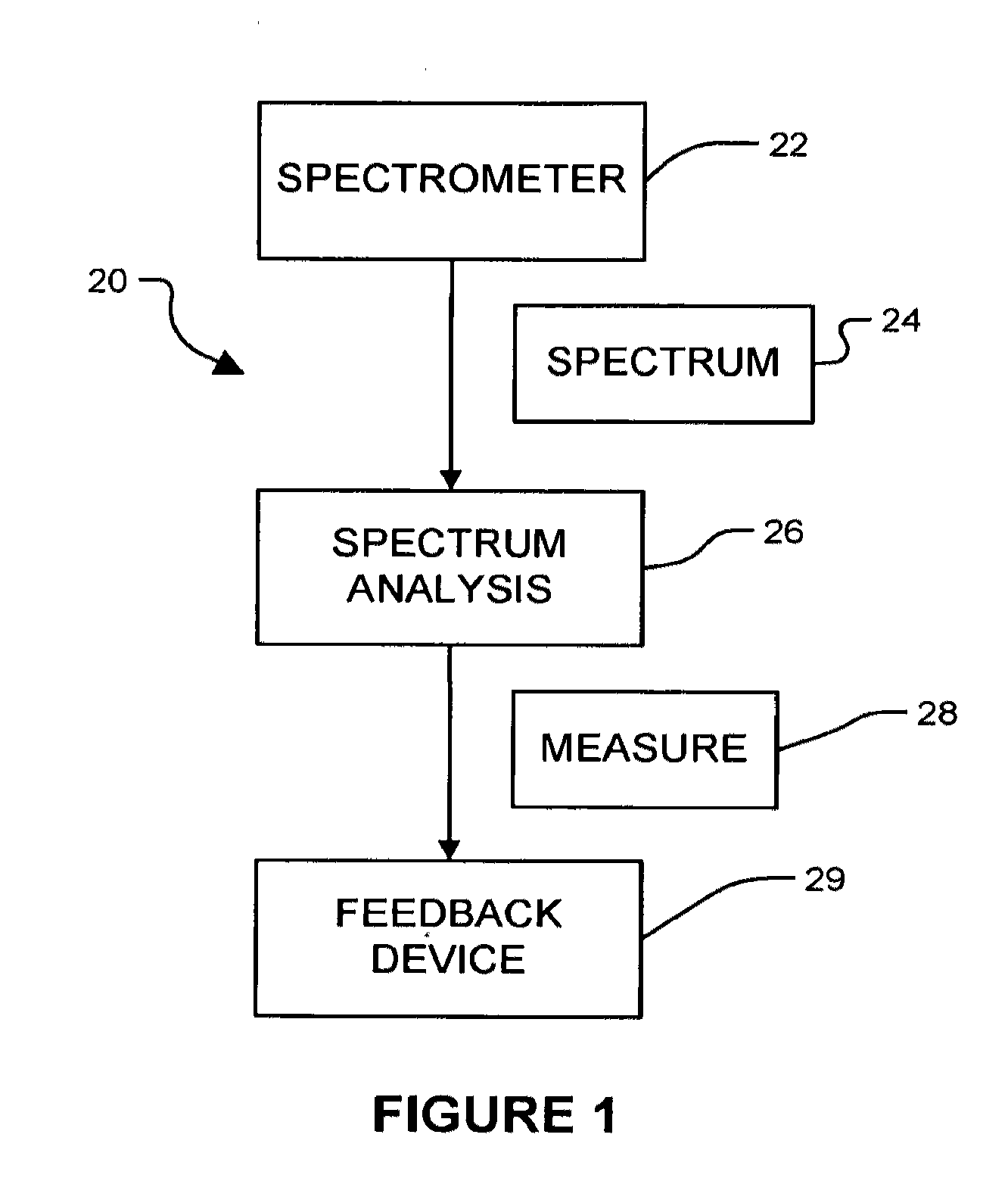
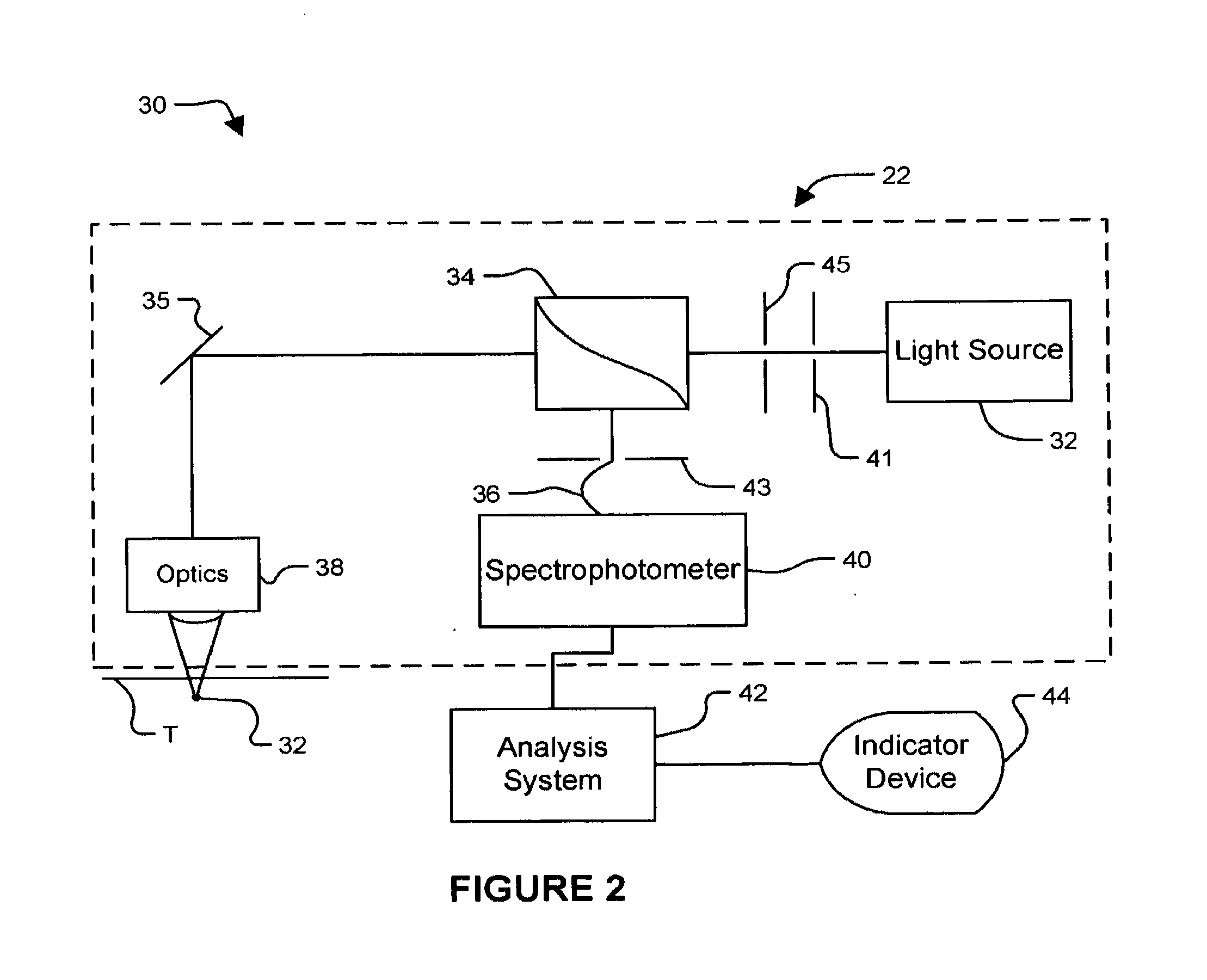
Method and apparatus for measuring cancerous changes from reflectance spectral measurements obtained during endoscopic imaging
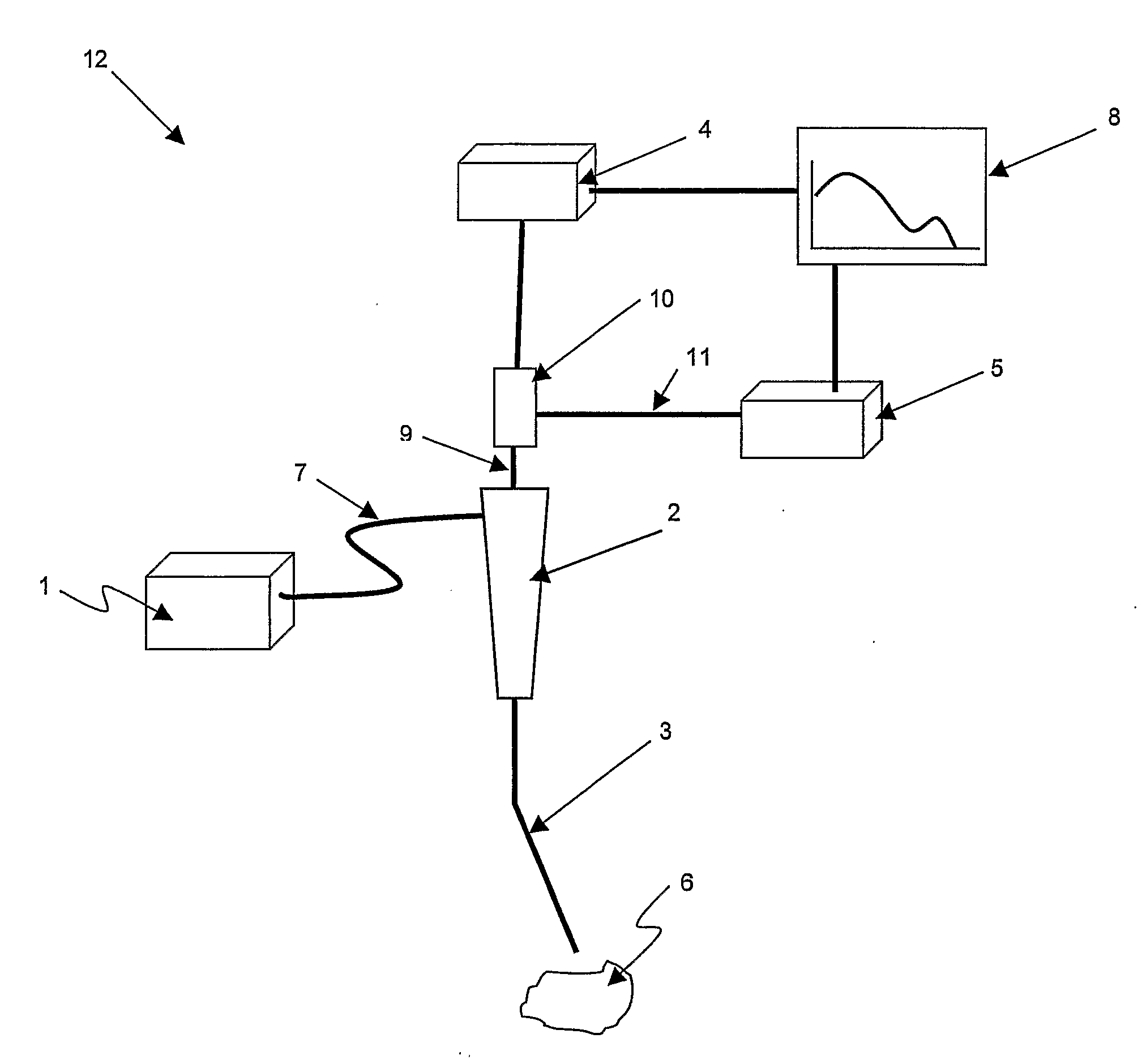
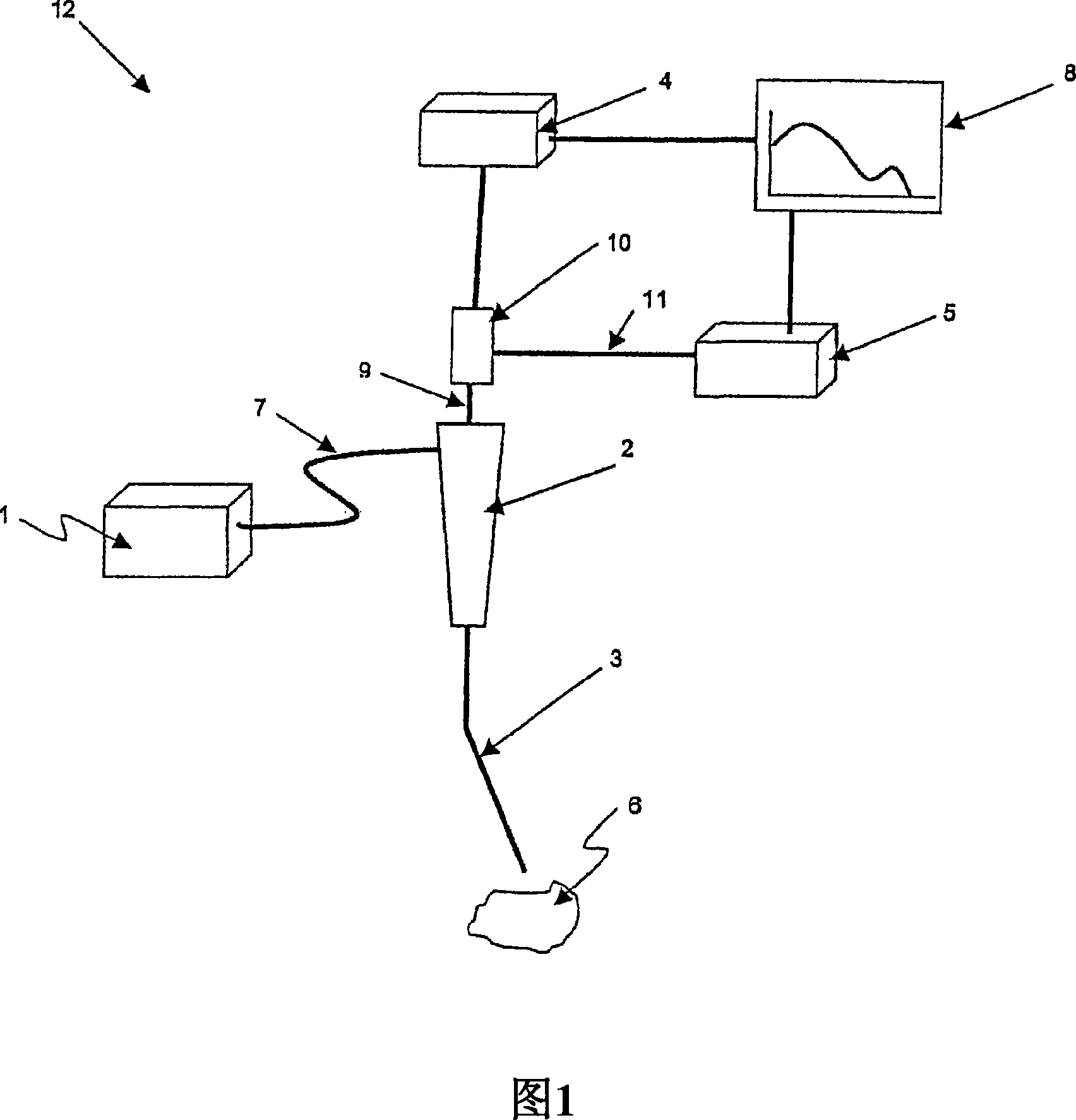
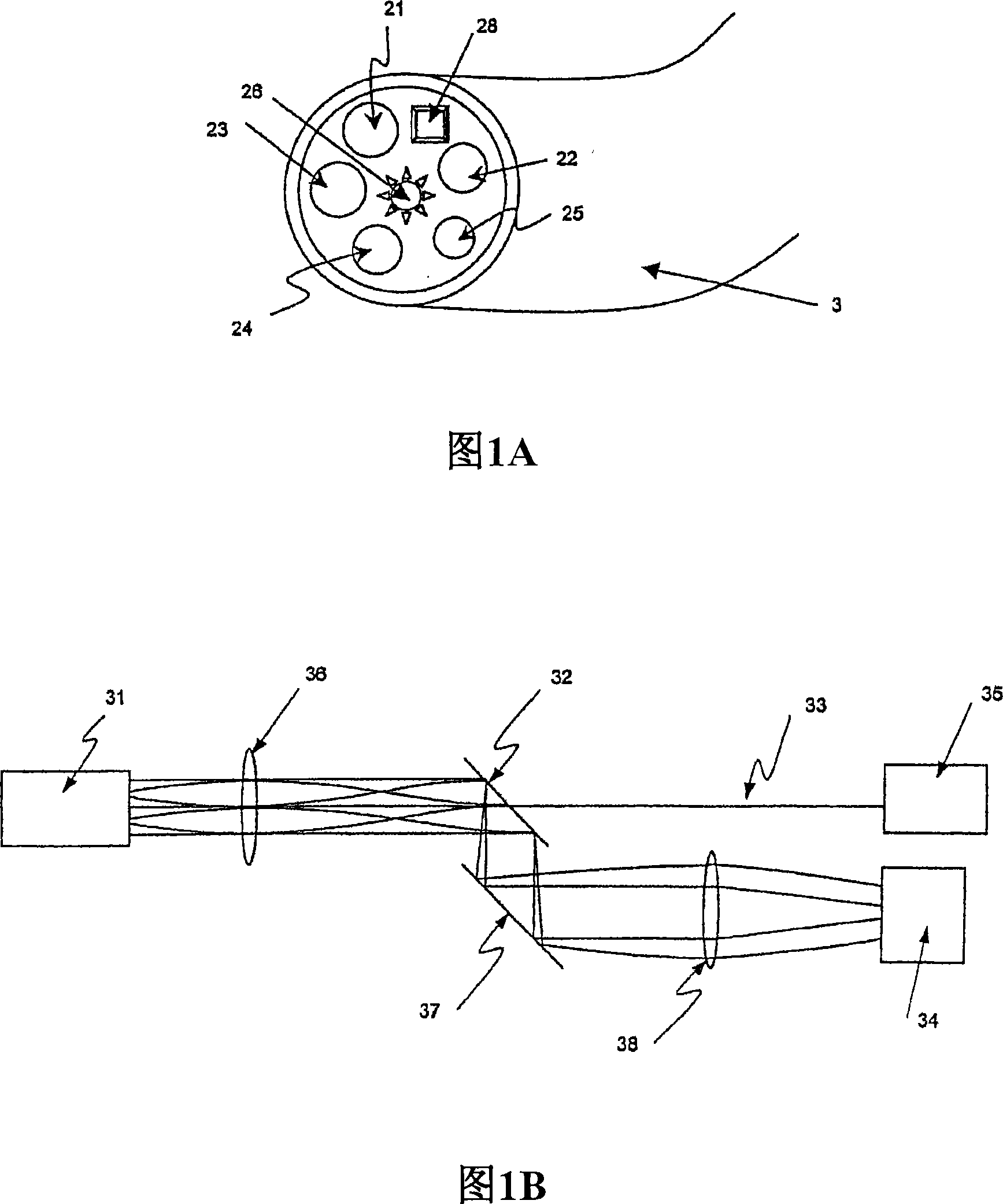
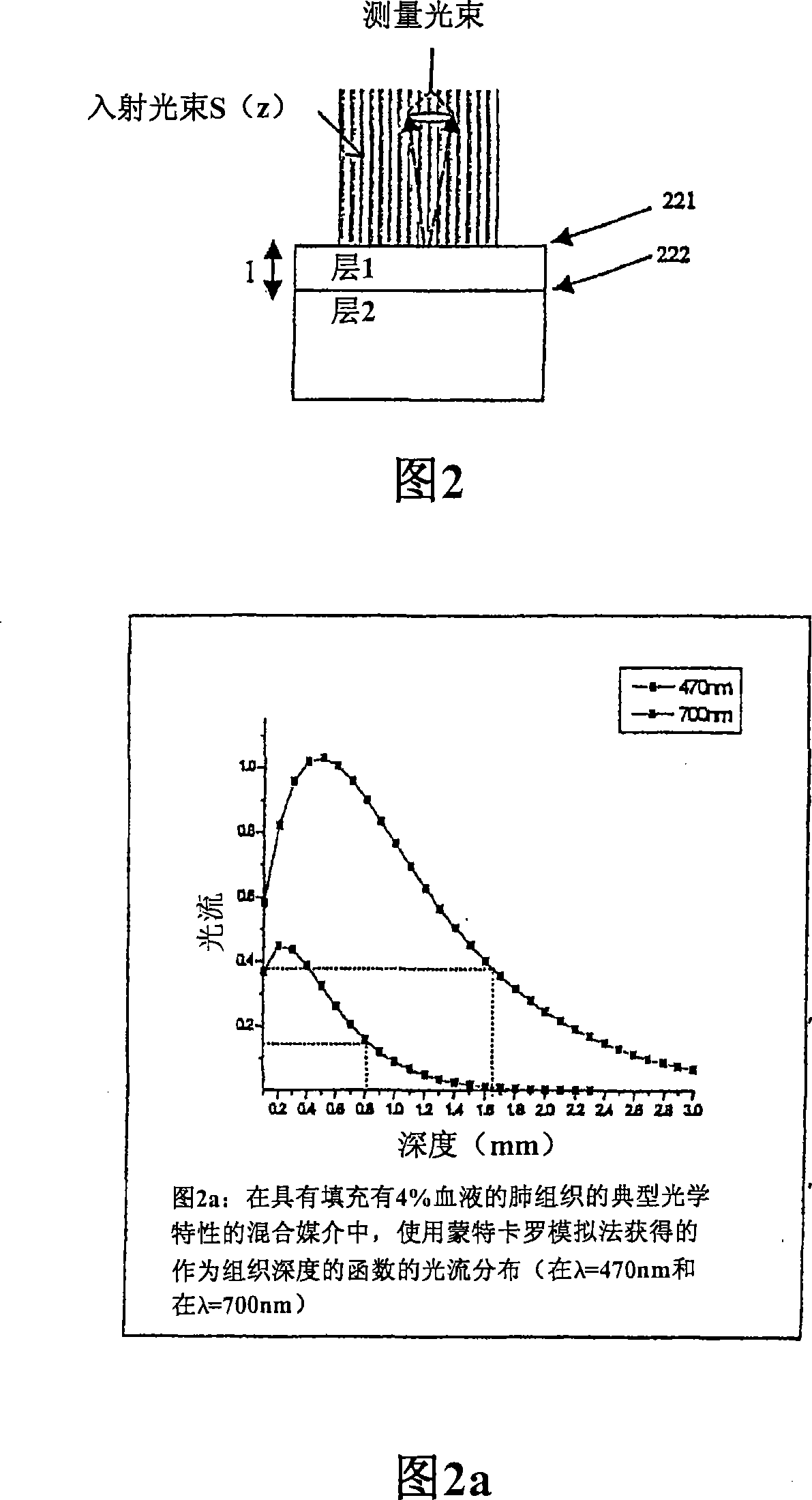
The present invention provides a new method and device for disease detection, more particularly cancer detection, from the analysis of diffuse reflectance spectra measured in vivo during endoscopic imaging. The measured diffuse reflectance spectra are analyzed using a specially developed light-transport model and numerical method to derive quantitative parameters related to tissue physiology and morphology. The method also corrects the effects of the specular reflection and the varying distance between endoscope tip and tissue surface on the clinical reflectance measurements. The model allows us to obtain the absorption coefficient (μa) and further to derive the tissue micro-vascular blood volume fraction and the tissue blood oxygen saturation parameters. It also allows us to obtain the scattering coefficients (μs and g) and further to derive the tissue micro-particles volume fraction and size distribution parameters.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL +1
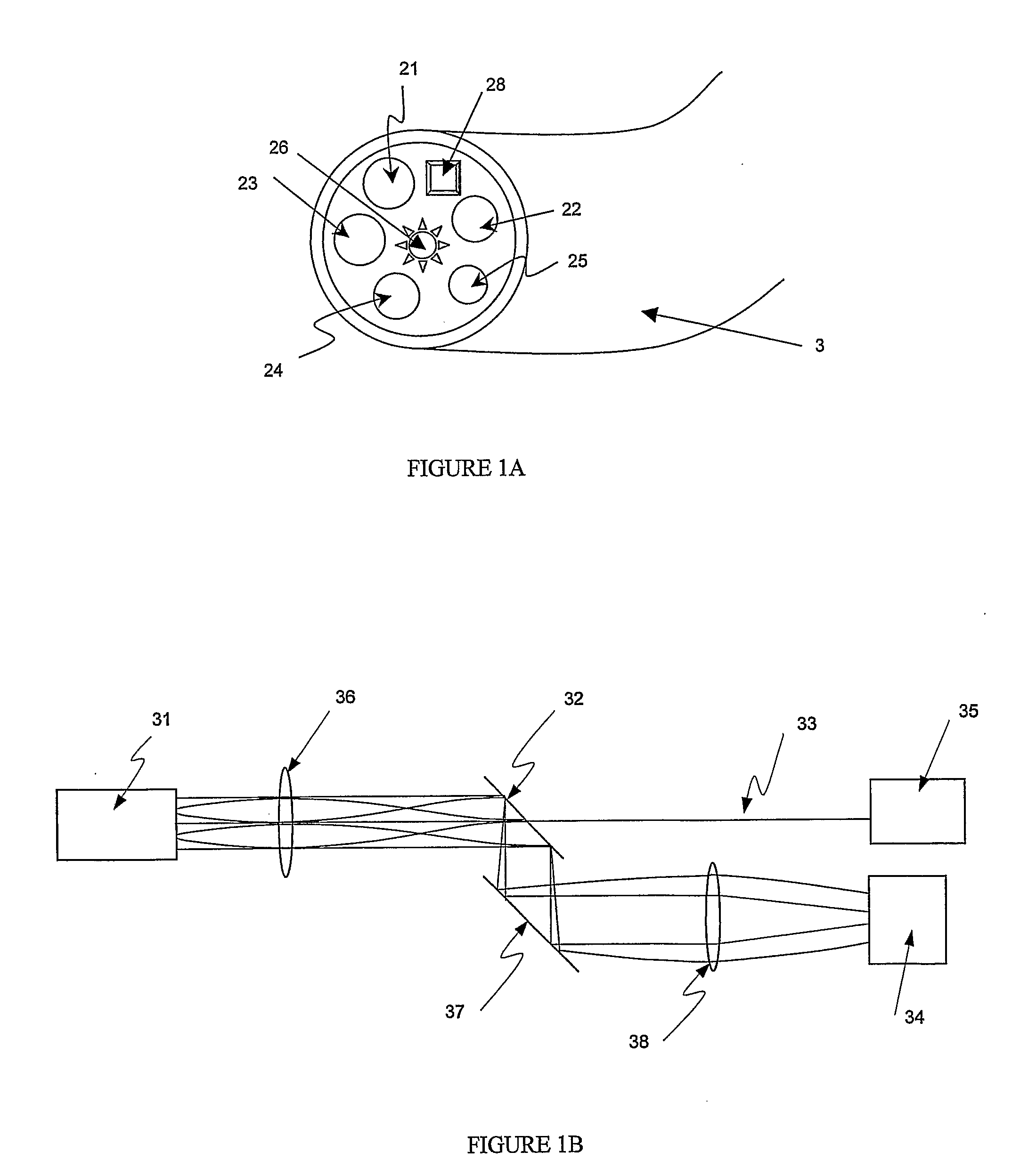
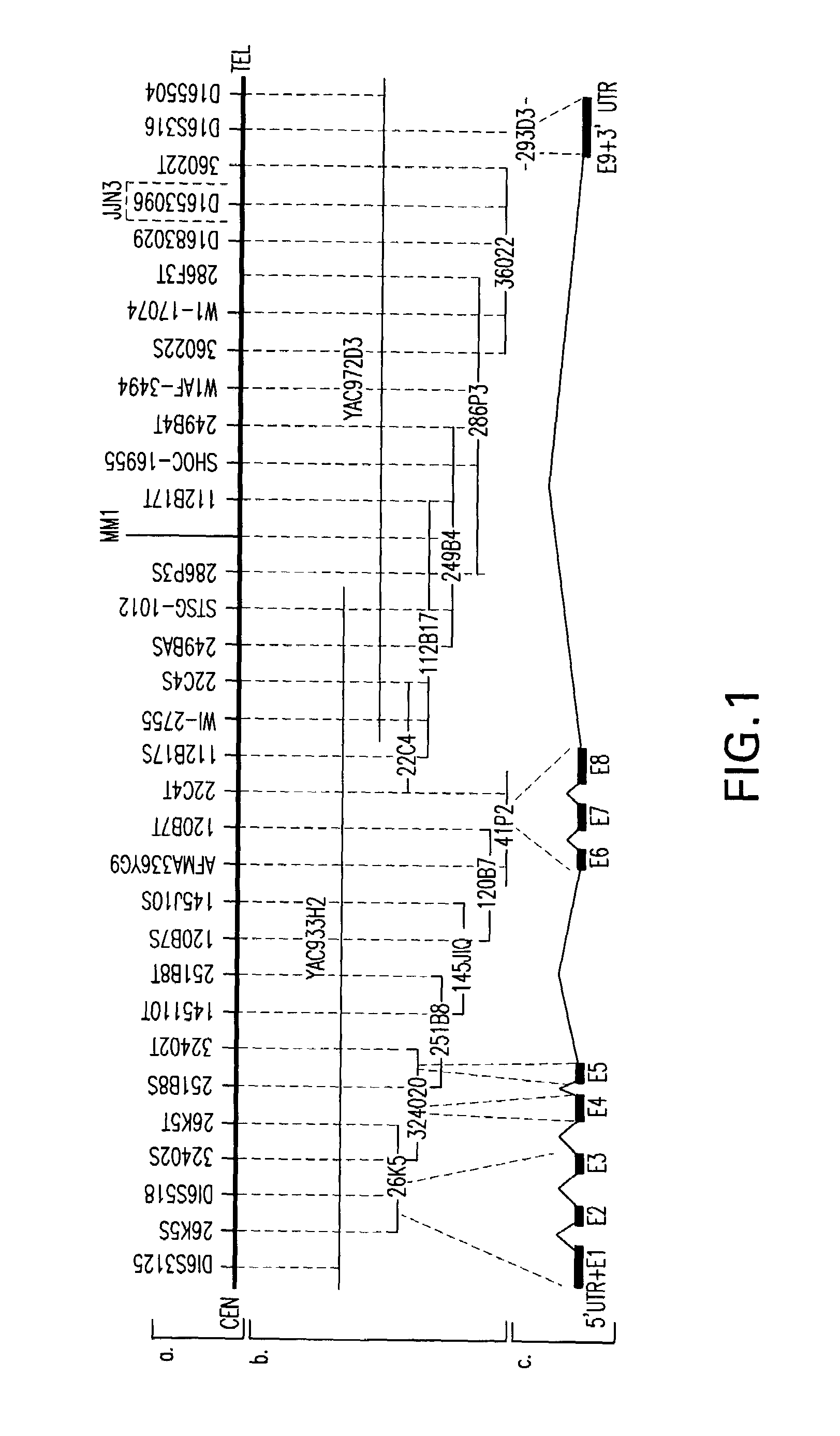
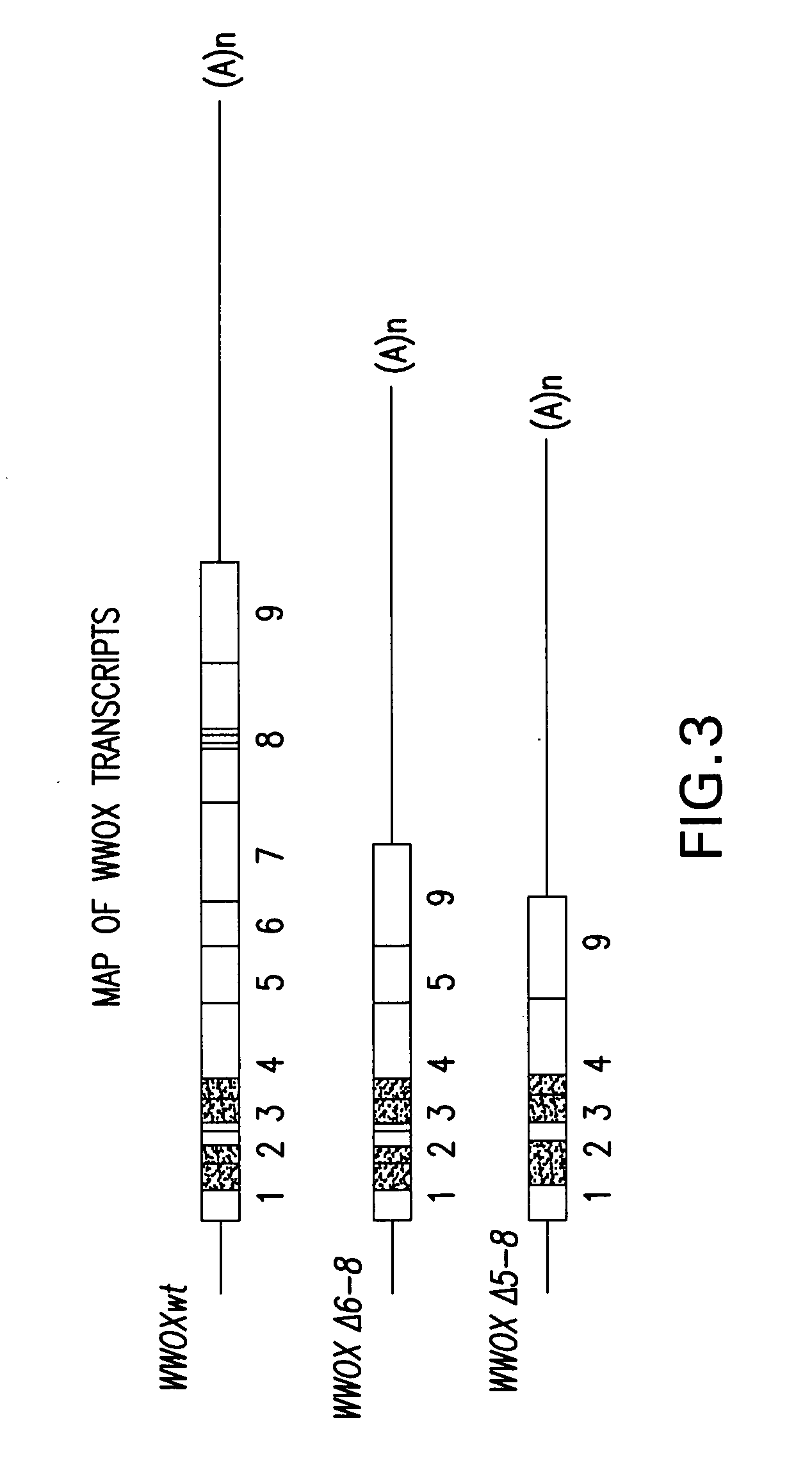
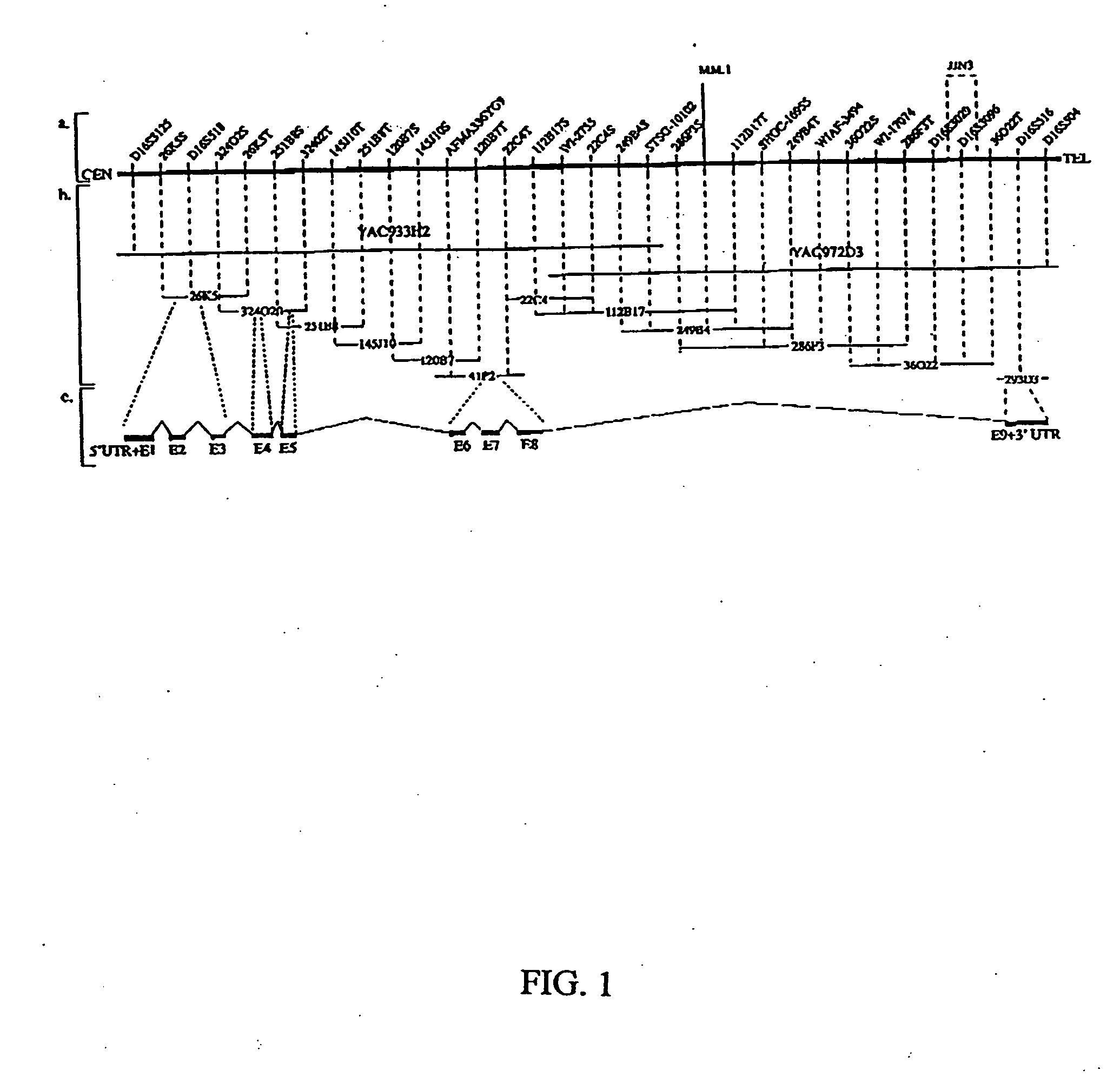
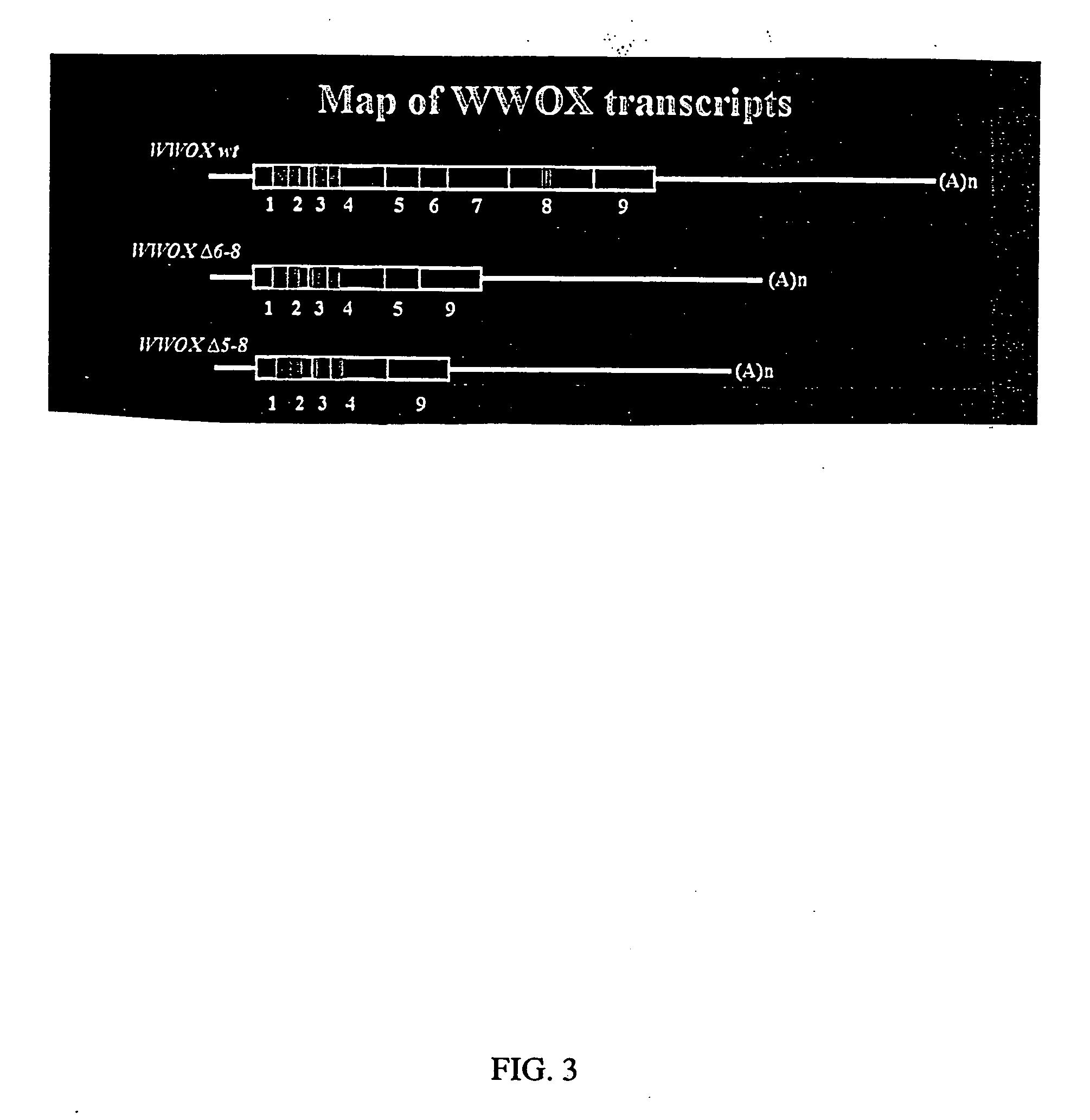
WWOX: a tumor suppressor gene mutated in multiple cancers
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Wwox: a tumor suppressor gene mutated in multiple cancers
InactiveUS20060024780A1Sugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsAbnormal tissue growthTumour suppressor gene
The present invention provides the isolation and cloning of WWOX, a novel WW domain-containing protein mapping to human chromosome 16q23.3-24.1, a region frequently affected in several cancers. This gene encodes a tumor suppressor with apoptotic functions. The invention provides WWOX nucleic acid- and polypeptide-based cancer therapies. The invention also provides methods for cancer detection, diagnosis and prognosis involving WWOX nucleic acids and polypeptides.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
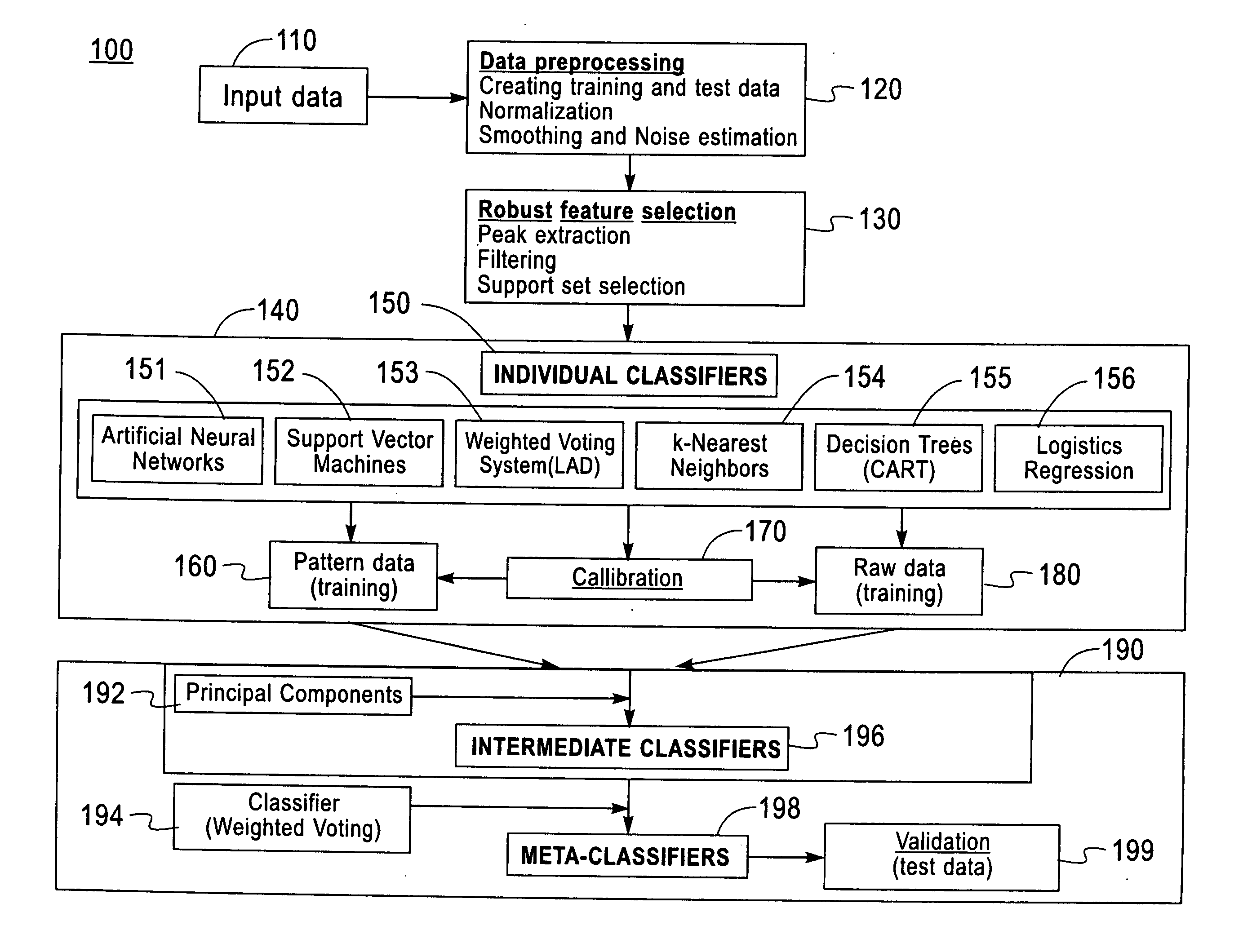
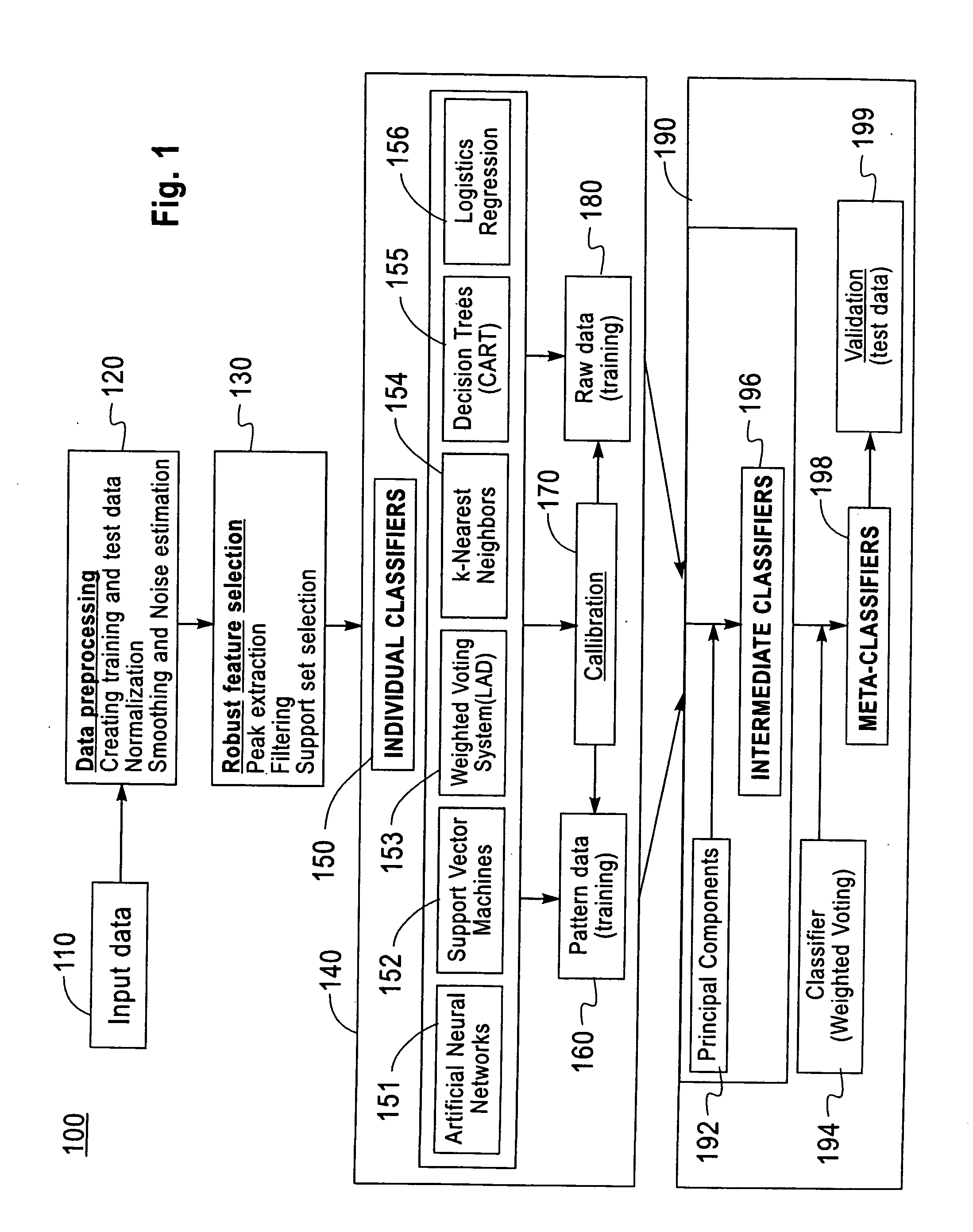
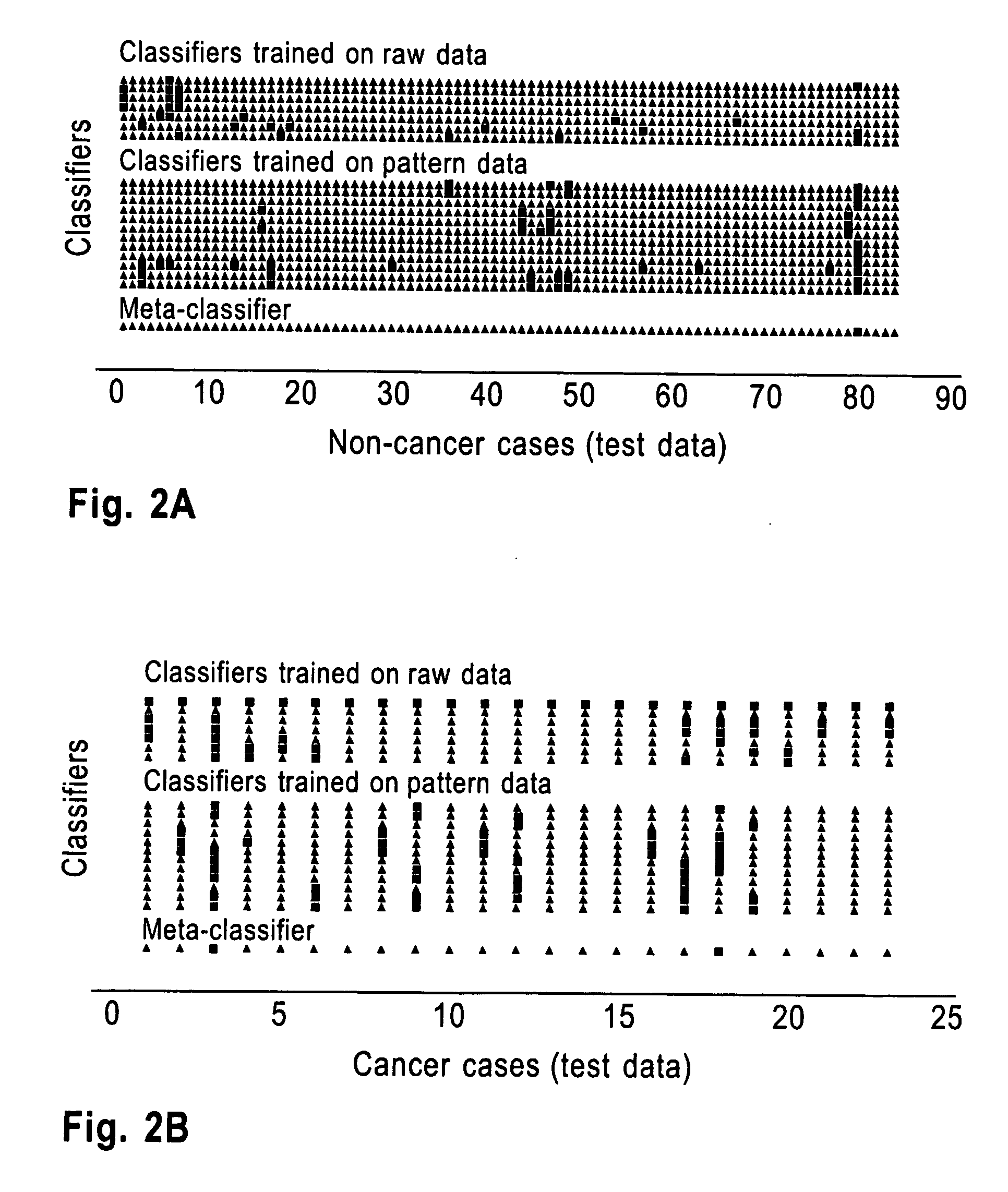
Method and system for robust classification strategy for cancer detection from mass spectrometry data
InactiveUS20080025591A1Reduce sensitivity to noiseEasy to predictDigital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusData setClassification methods
A robust classification method for cancer detection from mass spectrometry data includes inputting the mass spectrometry data, preprocessing the spectrometry data, conducting robust feature selection, generating predictions for the test data sets using multiple data classifiers, the multiple data classifiers including artificial neural networks, support vector machines, weighted voting on data patterns, classification and regression trees, k-nearest neighbor classification, and logistic regression, and constructing and validating a meta-classifier by combining individual predictions of the multiple data classifiers to generate a robust prediction of a phenotype. The test data sets are used exclusively for validation of the meta-classifier.
Owner:IBM CORP
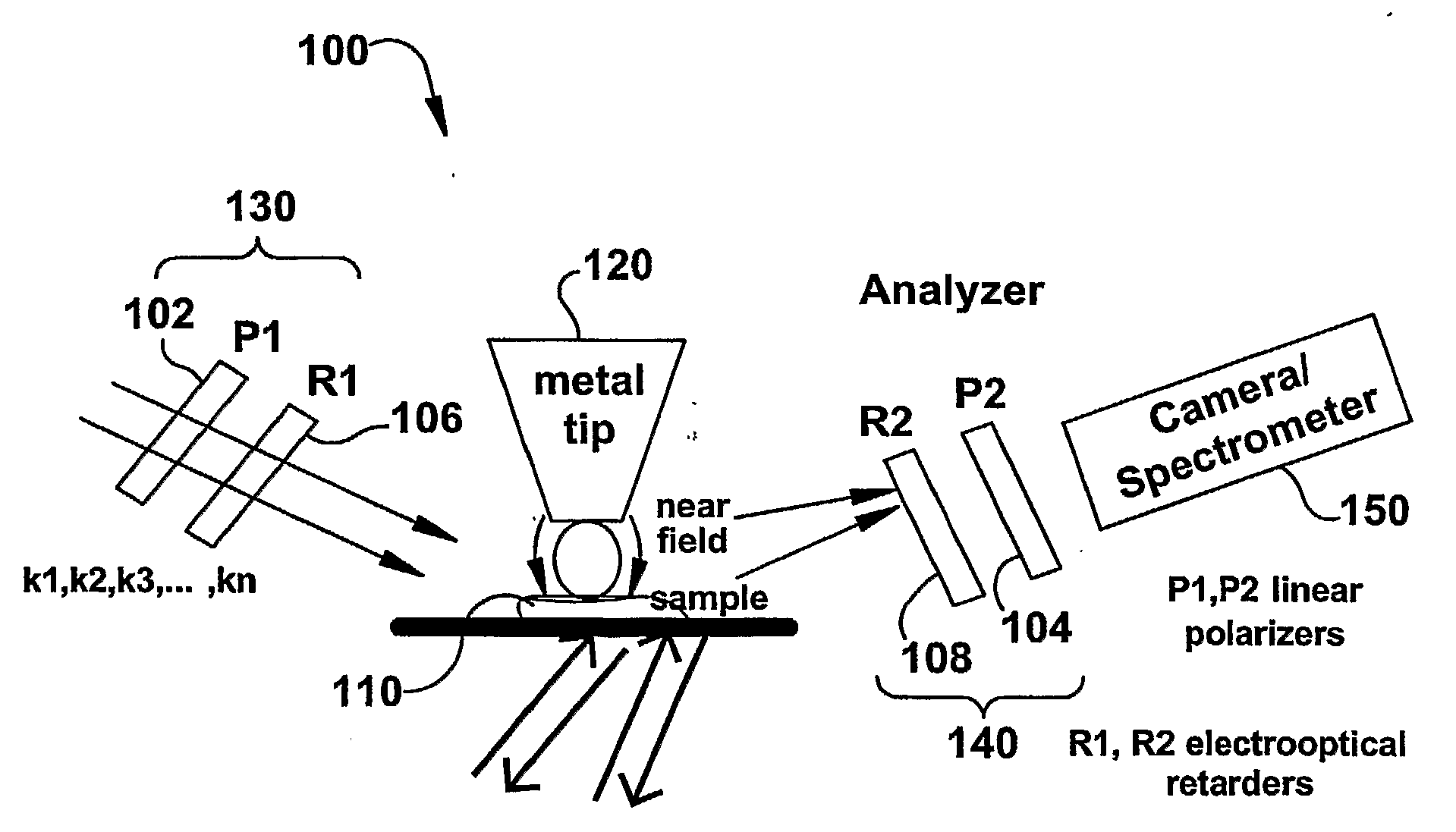
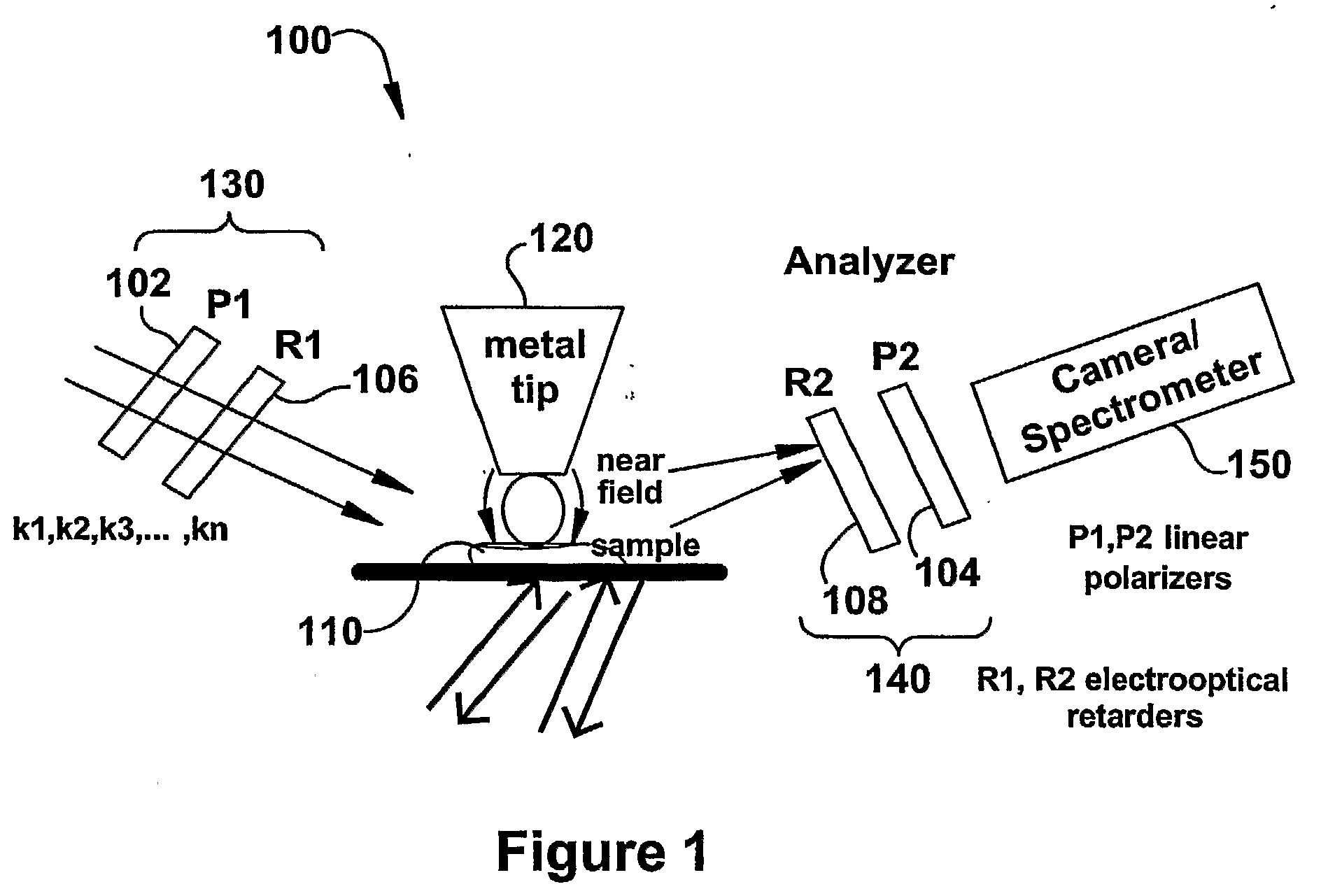
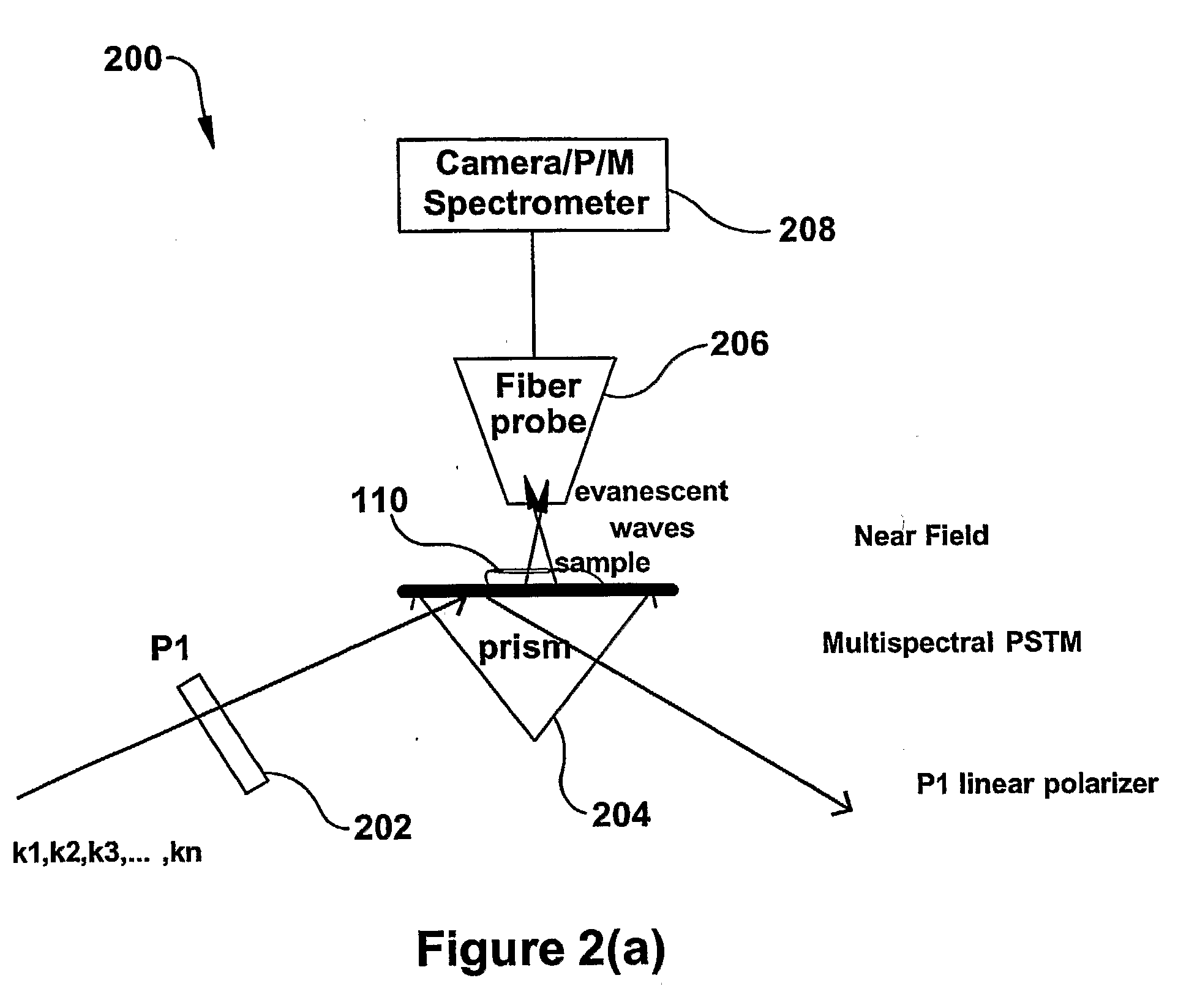
Molecular imaging and nanophotonics imaging and detection principles and systems, and contrast agents, media makers and biomarkers, and mechanisms for such contrast agents
InactiveUS20090119808A1Enhanced sub-surfaceEnhanced in-depth imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesSurface/boundary effectDepth imagingImage resolution
The present invention relates to near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) and near-field / far-field scanning microscopy methods, systems and devices that permit the imaging of biological samples, including biological samples or structures that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the present invention permits the production of multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field microscopy systems that can achieve a spatial resolution of less than 100 nanometers. In another embodiment, the present invention permits the production of a multifunctional, multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field / far-field microscopy that can achieve enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imaging of biological samples. In still another embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of polar molecules as new optical contrast agents for imaging applications (e.g., cancer detection).
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
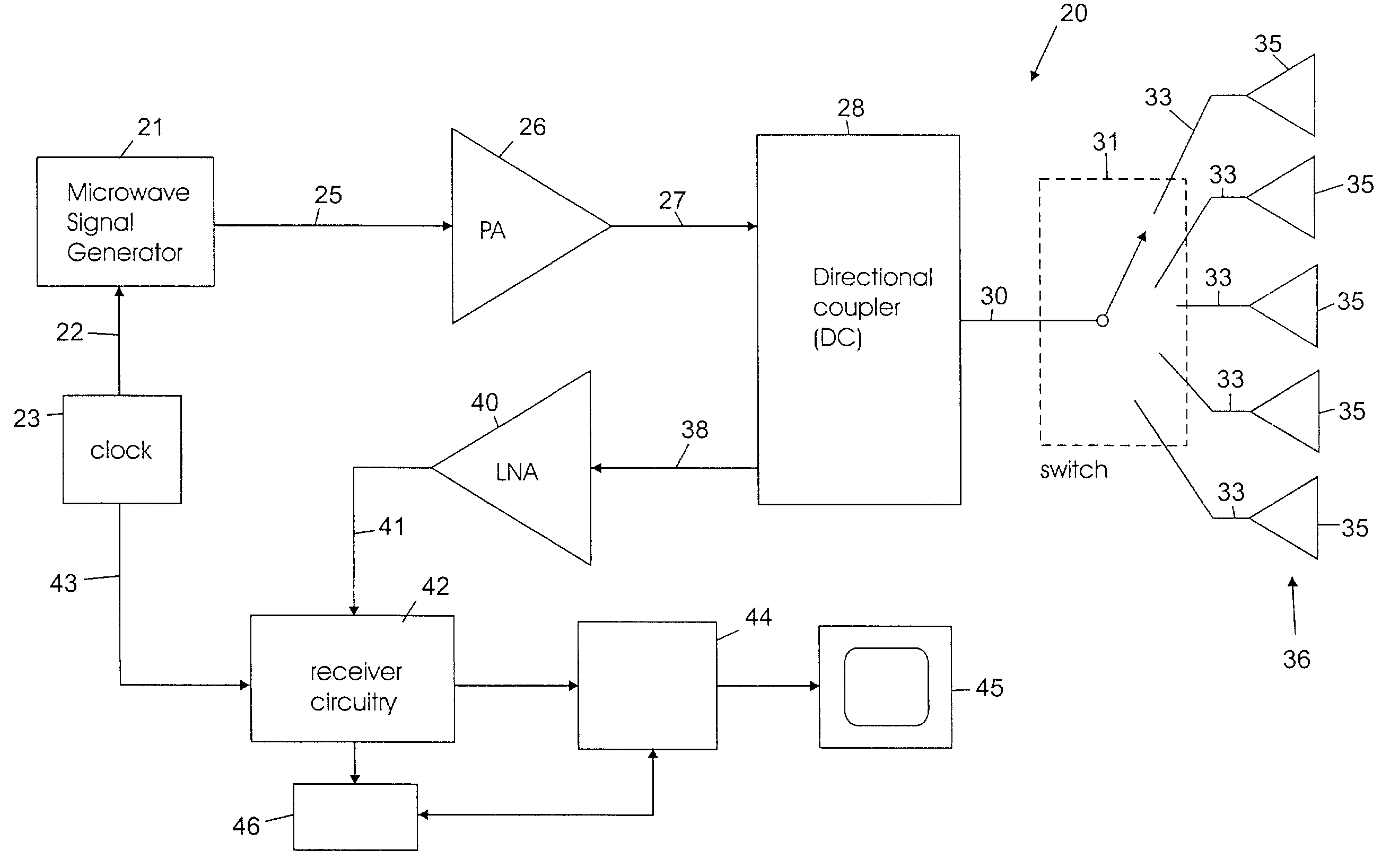
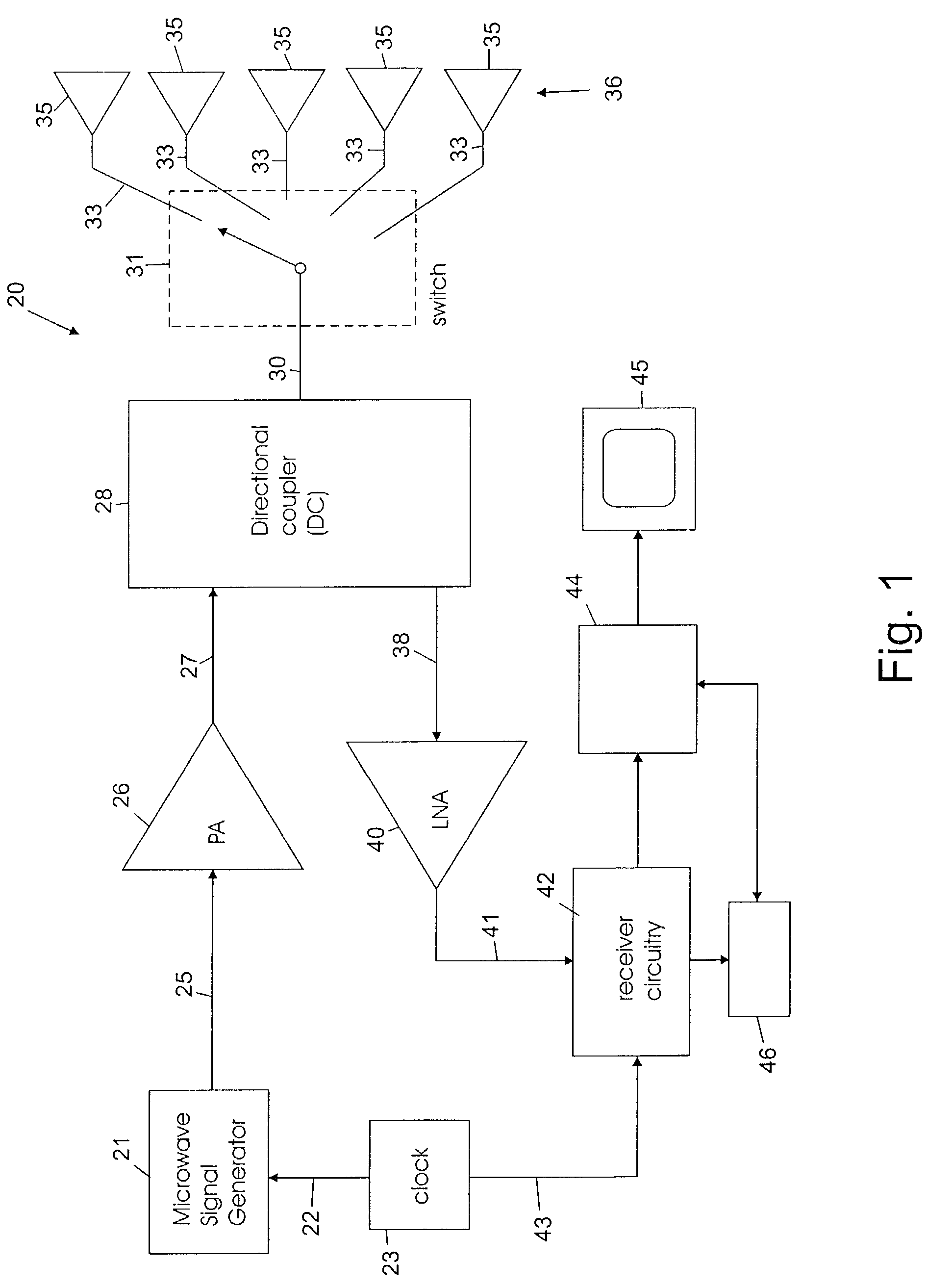
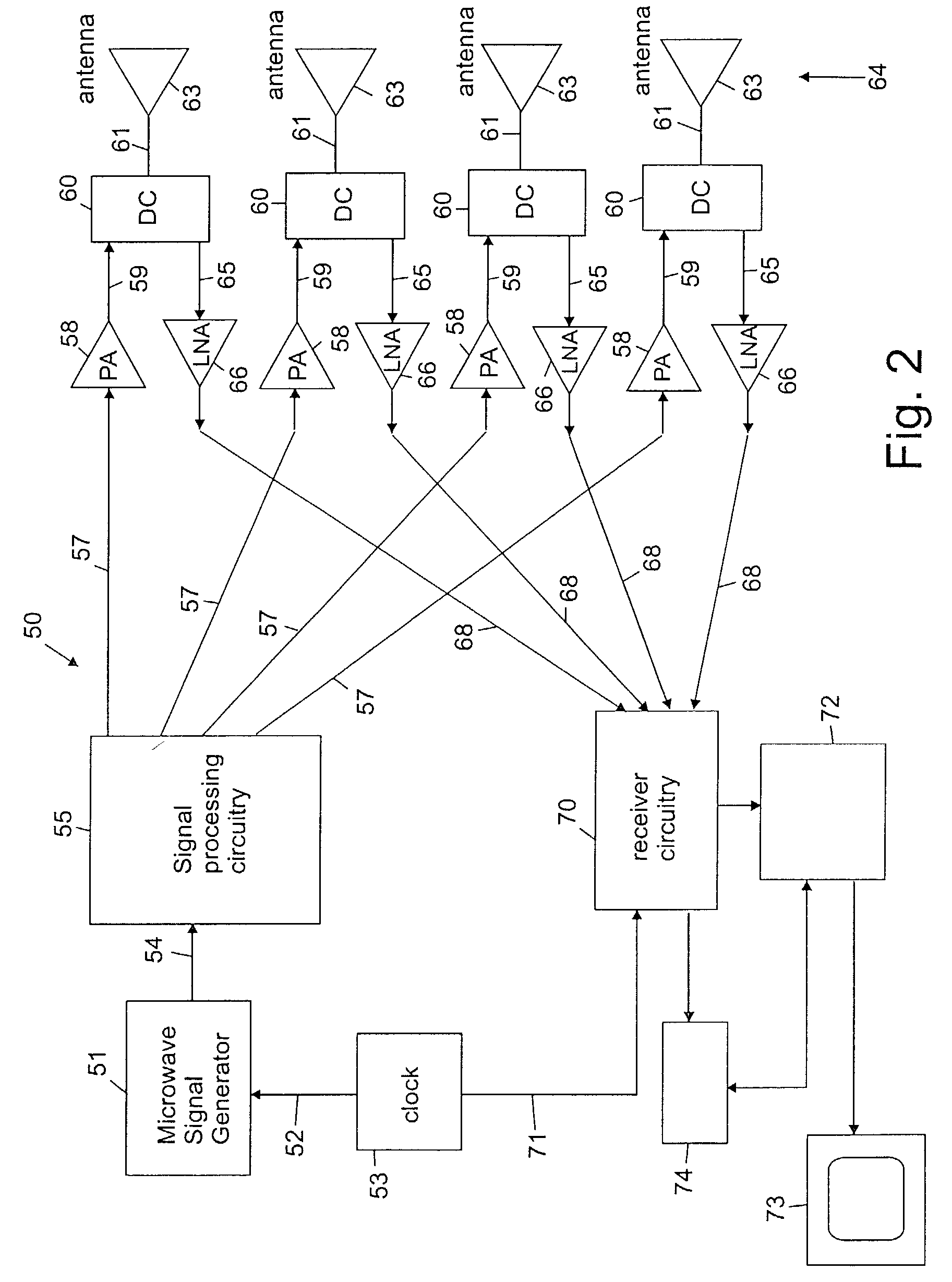
Space-time microwave imaging for cancer detection
ActiveUS7570063B2Reduce in quantityAvoid the needResistance/reactance/impedenceDiagnostic recording/measuringTime gatingEngineering
Microwave imaging via space-time beamforming is carried out by transmitting microwave signals from multiple antenna locations into an individual to be examined and receiving the backscattered microwave signals at multiple antenna locations to provide received signals from the antennas. The received signals are processed in a computer to remove the skin interface reflection component of the signal at each antenna to provide corrected signal data. The corrected signal data is provided to a beamformer process that time shifts the received signals to align the returns from a scatterer at a candidate location, and then passes the time aligned signals through a bank of filters, the outputs of which are summed, time-gated and the power therein calculated to produce the beamformer output signal at a candidate location. The beamformer is then scanned to a plurality of different locations in the individual by changing the time shifts, filter weights and time-gating of the beamformer process. The output power may be displayed as a function of scan location, with regions of large output power corresponding to significant microwave scatterers such as malignant lesions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
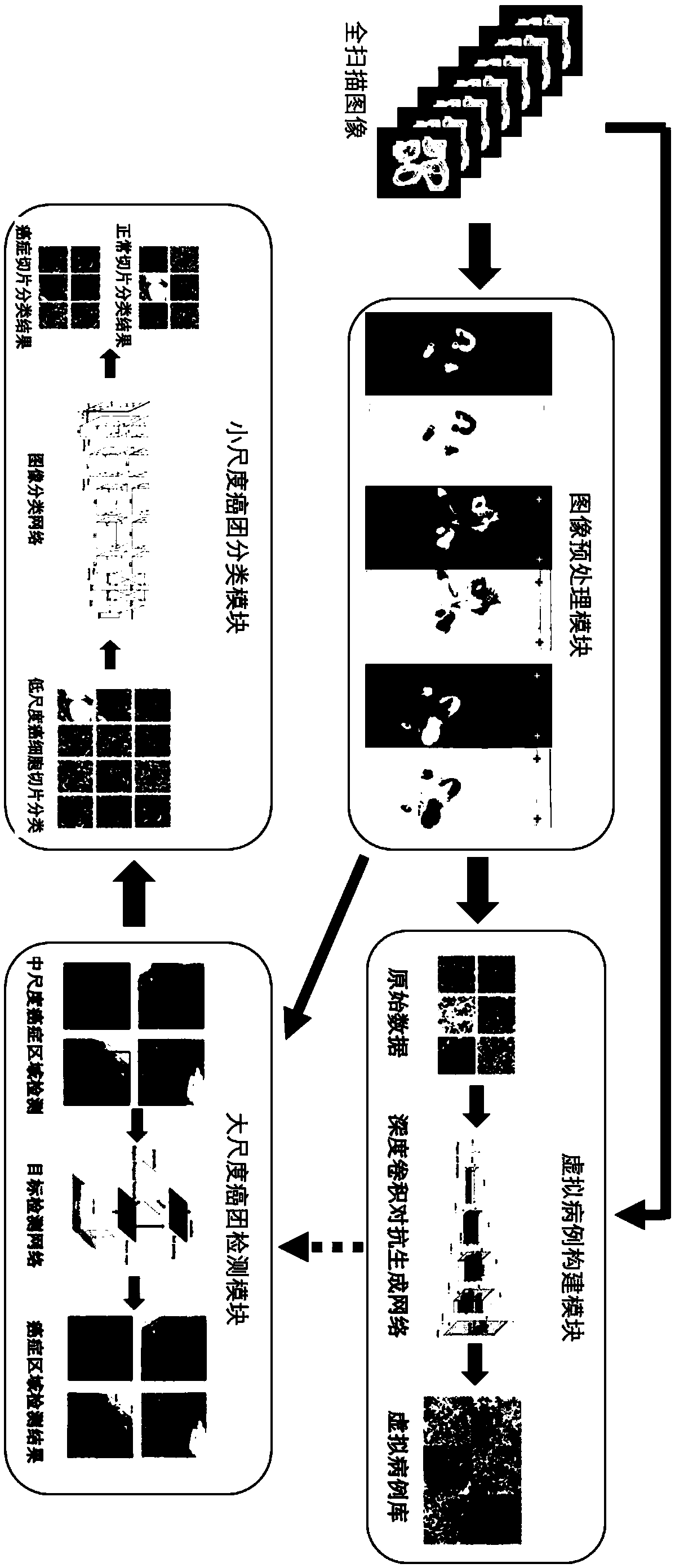
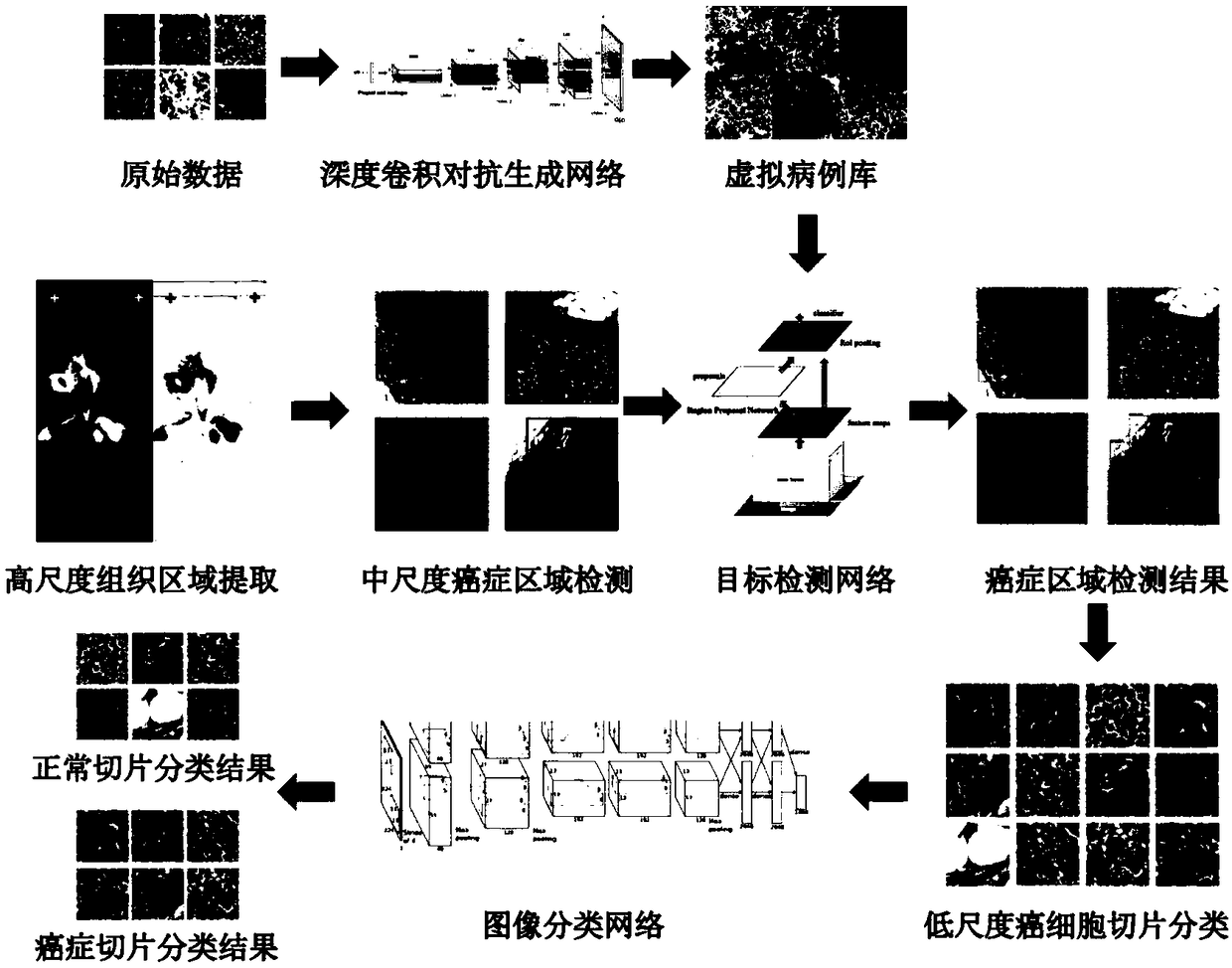
Method for constructing virtual case library of cancer pathological images and multi-scale cancer detection system based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN108765408AIncrease diversityReduce redundant calculationsImage enhancementImage analysisData setStudy methods
The invention discloses establishment of a virtual case library of cancer pathological images and a multi-scale cancer detection system based on a convolutional neural network. The system is based ona method of a convolution neural network, a cancer mass region is detected on a pathological full-scan section, and the system includes four modules: 1) a pathological section image preprocessing module; 2) a virtual case database construction module; 3) a high-scale cancer mass detection module; and 4) a small-scale cancer mass classification module. The multi-scale cancer detection system provided by the invention can make full use of the multi-scale information of a pathological image, on different scales, according to the characteristics of the image, different strategies are designed to detect a suspected cancer area, and at the same time, under the condition of insufficient training data, the virtual case library method established by the invention can provide more training data setsfor an existing data-driven deep learning method. The multi-scale cancer detection system based on a convolutional neural network has the characteristics of multi-scale detection, driving of a relatively small amount of data and the like, and has the characteristic of reducing computing resources required for one-time recognition and improving time efficiency of an algorithm on the basis of ensuring the overall recall rate and accuracy.
Owner:杭州同绘科技有限公司
Nested methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction cancer detection method
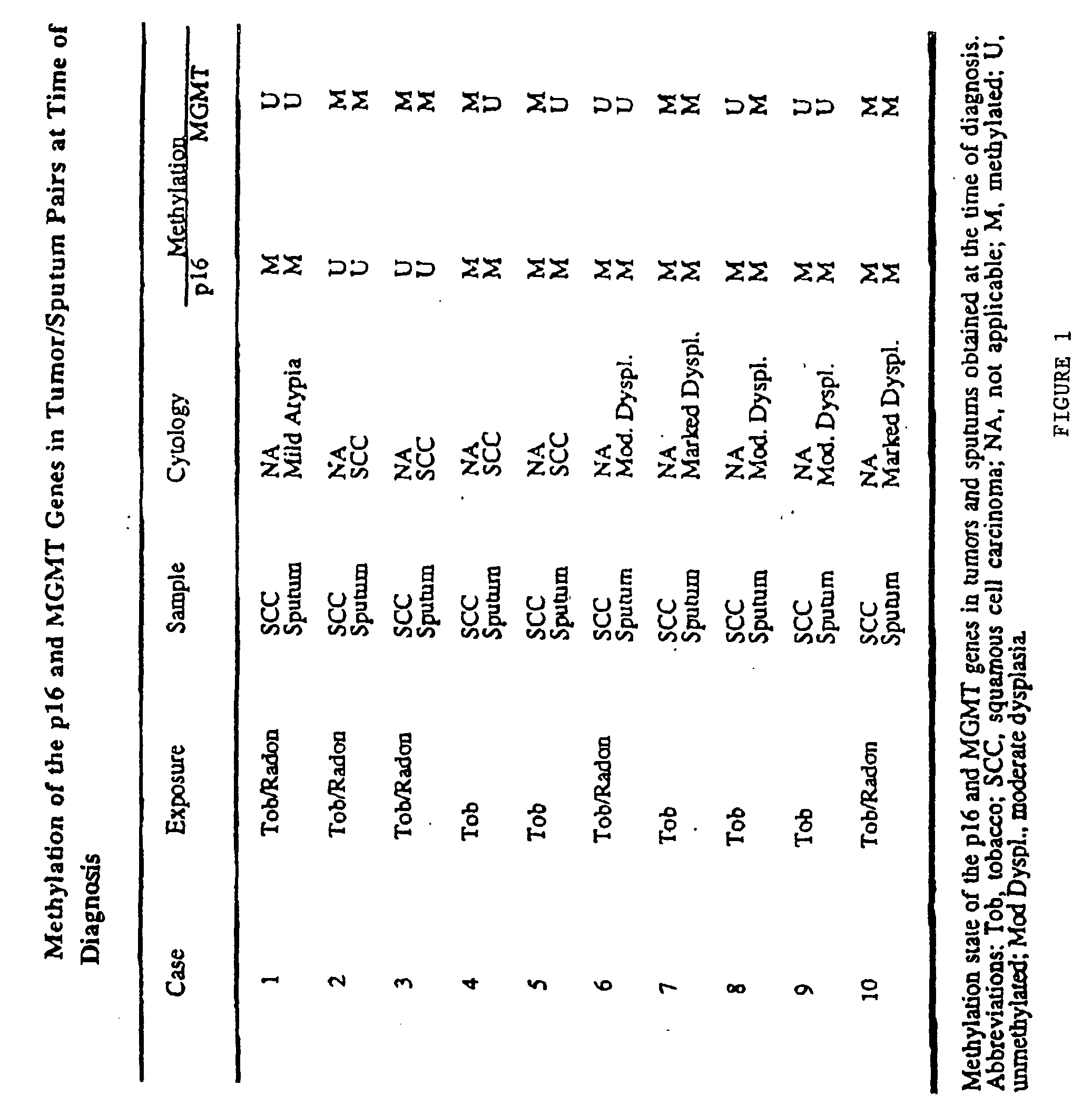
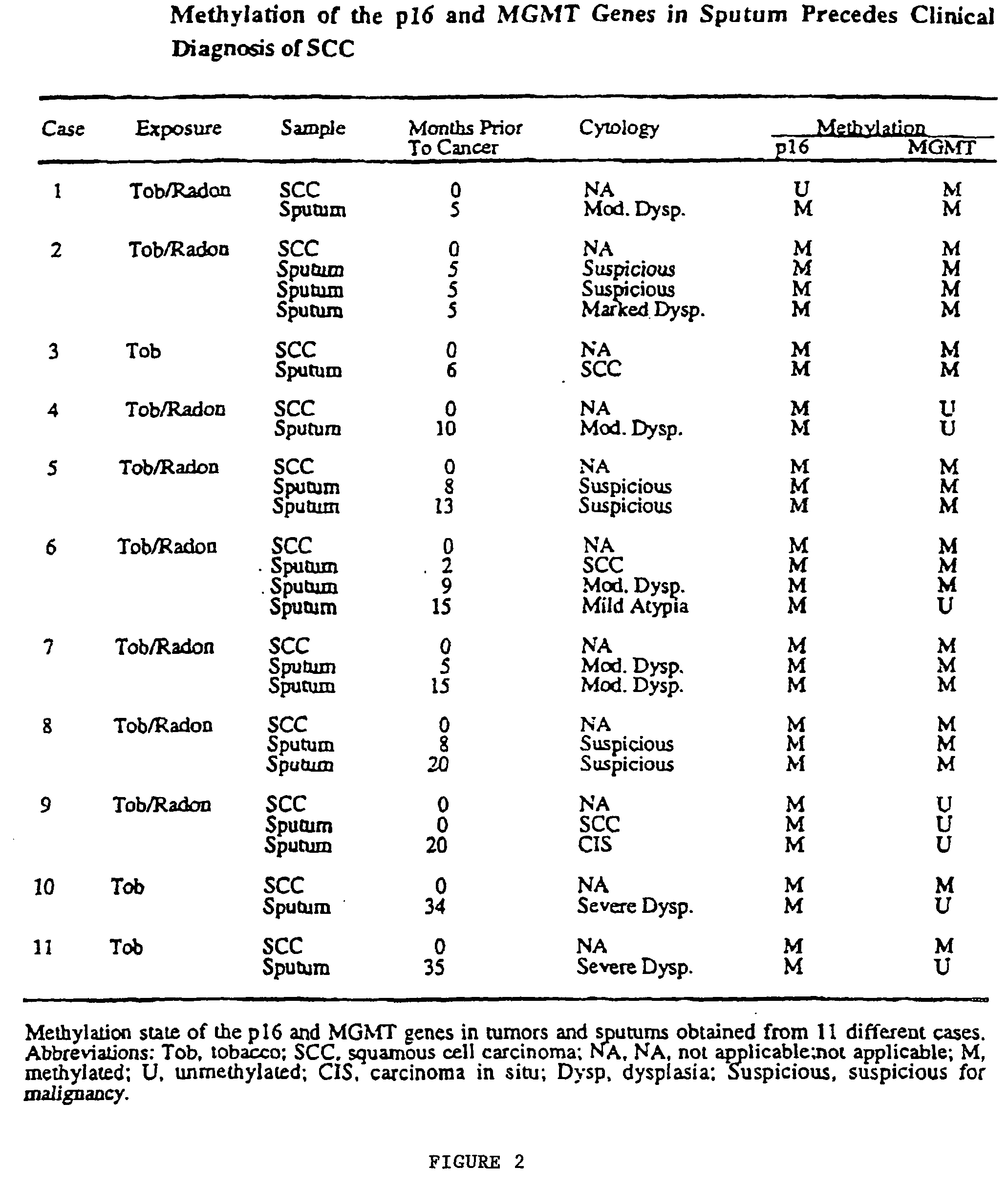
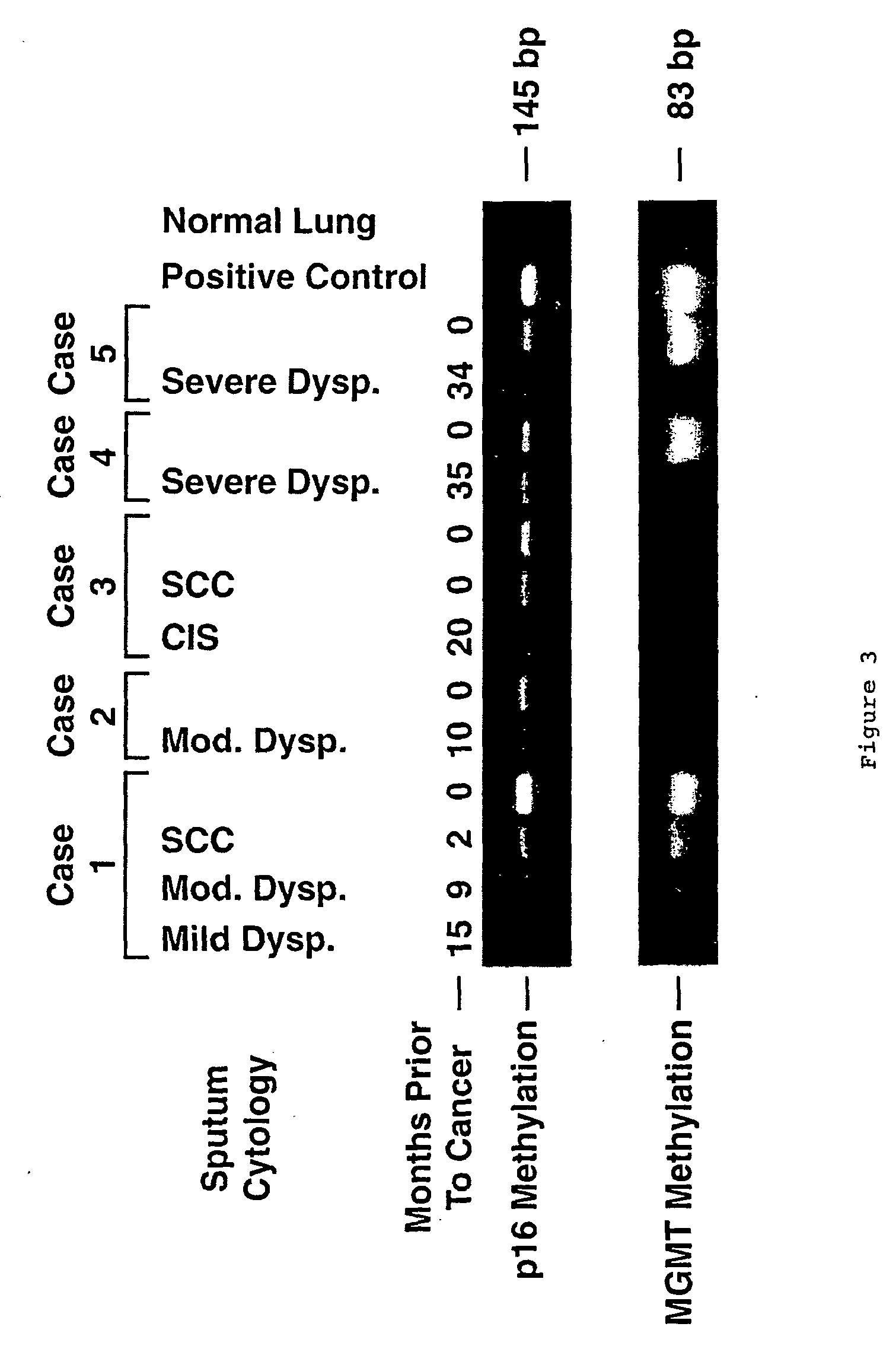
A molecular marker-based method for monitoring and detecting cancer in humans. Aberrant methylation of gene promoters is a marker for cancer risk in humans. A two-stage, or "nested" polymerase chain reaction method is disclosed for detecting methylated DNA sequences at sufficiently high levels of sensitivity to permit cancer screening in biological fluid samples, such as sputum, obtained non-invasively. The method is for detecting the aberrant methylation of the p16 gene, O 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene, Death-associated protein kinase gene, RAS-associated family 1 gene, or other gene promoters. The method offers a potentially powerful approach to population-based screening for the detection of lung and other cancers.
Owner:LOVELACE RESPIRATORY RES INST
Markers for cancer detection
InactiveUS20120039811A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGastrointestinal Tract CancersOncology
The present invention relates to methods for detecting, prognosing and staging cancers, in particular cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. The methods of the invention comprise detecting specific protein markers in a tissue of interest, wherein the detected levels thereof may be indicative of pre-cancerous or cancerous tissue, or the stage or prognosis of a cancer. Further provided are methods of treating cancer, and cancer detection kits.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method for Detection of Cancer Cells Using Virus
InactiveUS20090311664A1Microbiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsNon cancerCancer cell
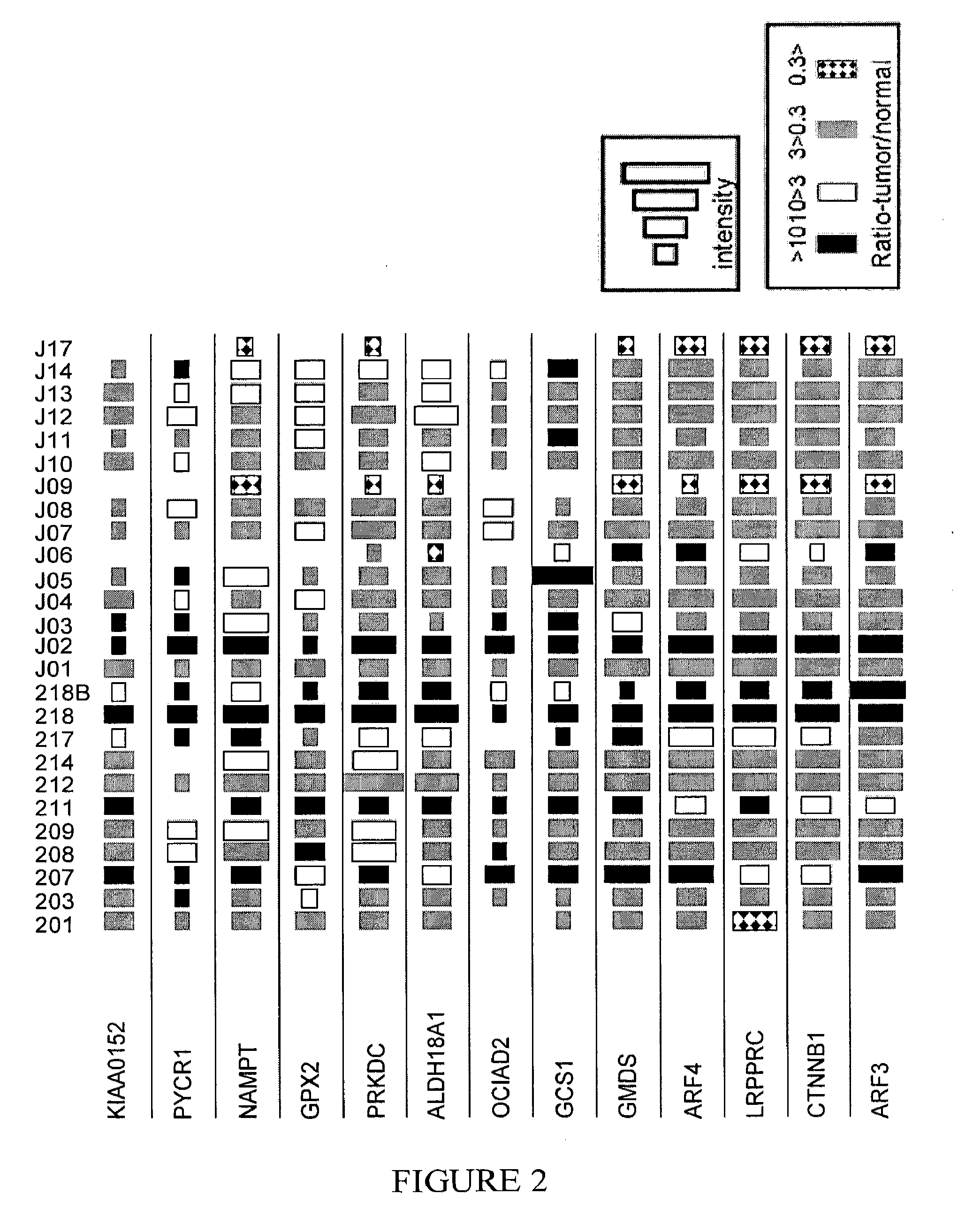
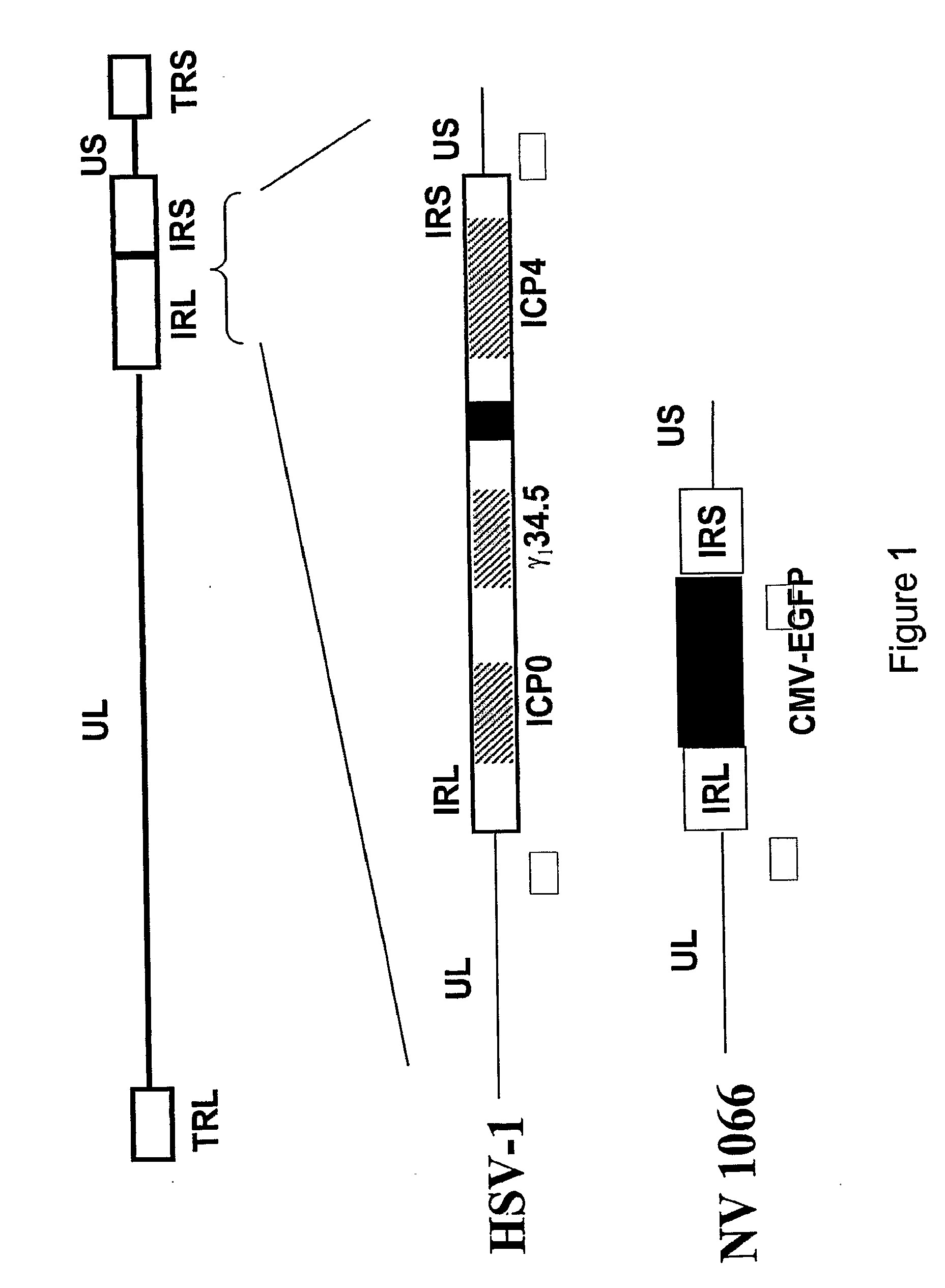
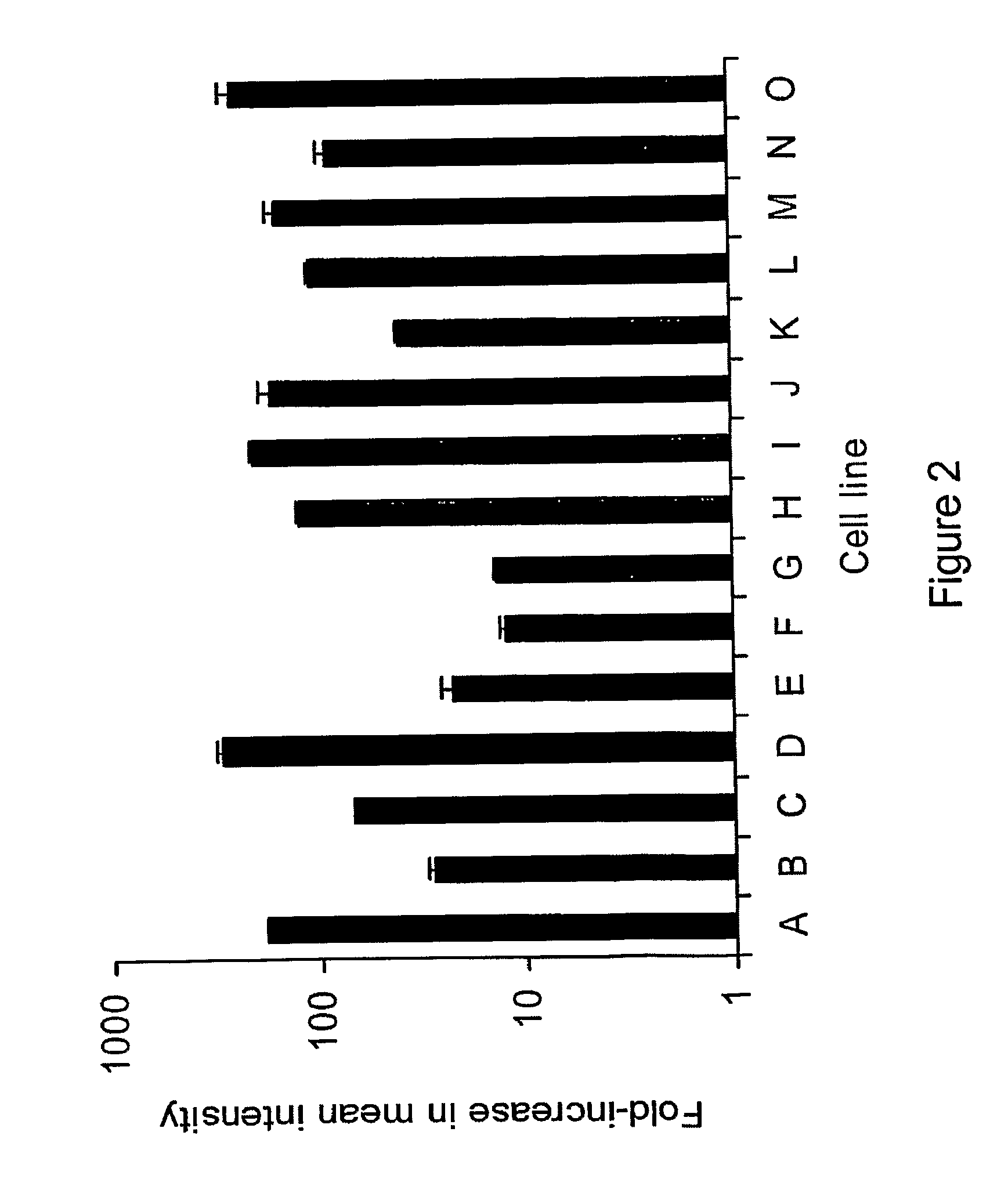
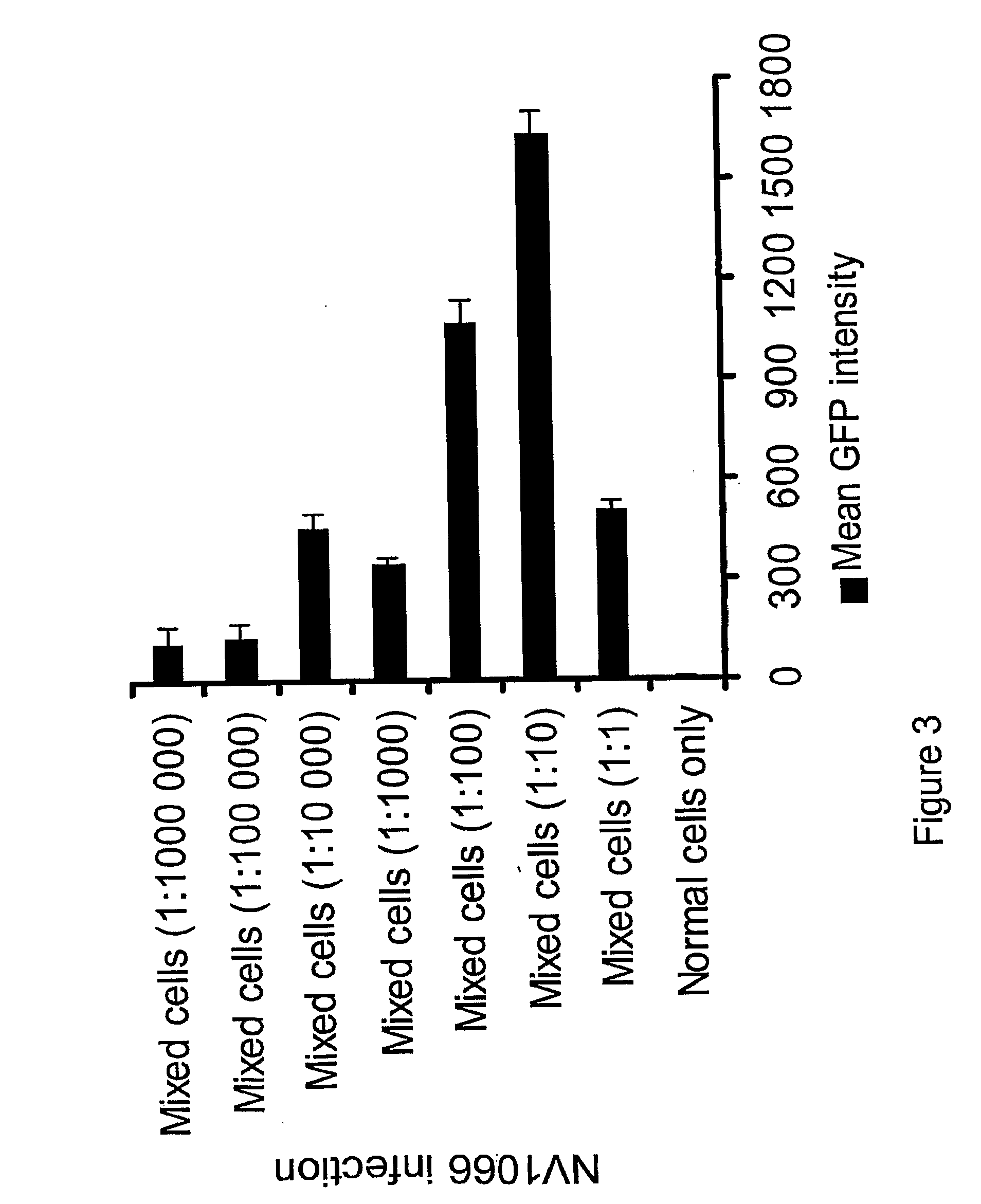
The invention relates to compositions and methods for cancer cell detection in bodily samples wherein a cancer cell can be detected within a mixed population of cancer cells and non-cancer cells. The invention also relates to compositions and methods that may be used in cancer cell detection, specifically viruses that are replication-competent conditional to a cancer cell, in particular an oncolytic herpes virus, such as NV 1066 and a vaccinia virus, such as GLV-1h68. Provided are methods and kits for using these viruses that preferentially replicate in cancer cells and may also preferentially infect cancer cells for specific identification of such cancer cells, even when a cancer cell is present, for example, at a ratio of one infected cancer cell in a background often thousand non-cancer cells, thus further providing a reproducible and sensitive screening method for cancer detection, monitoring and prognosis.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
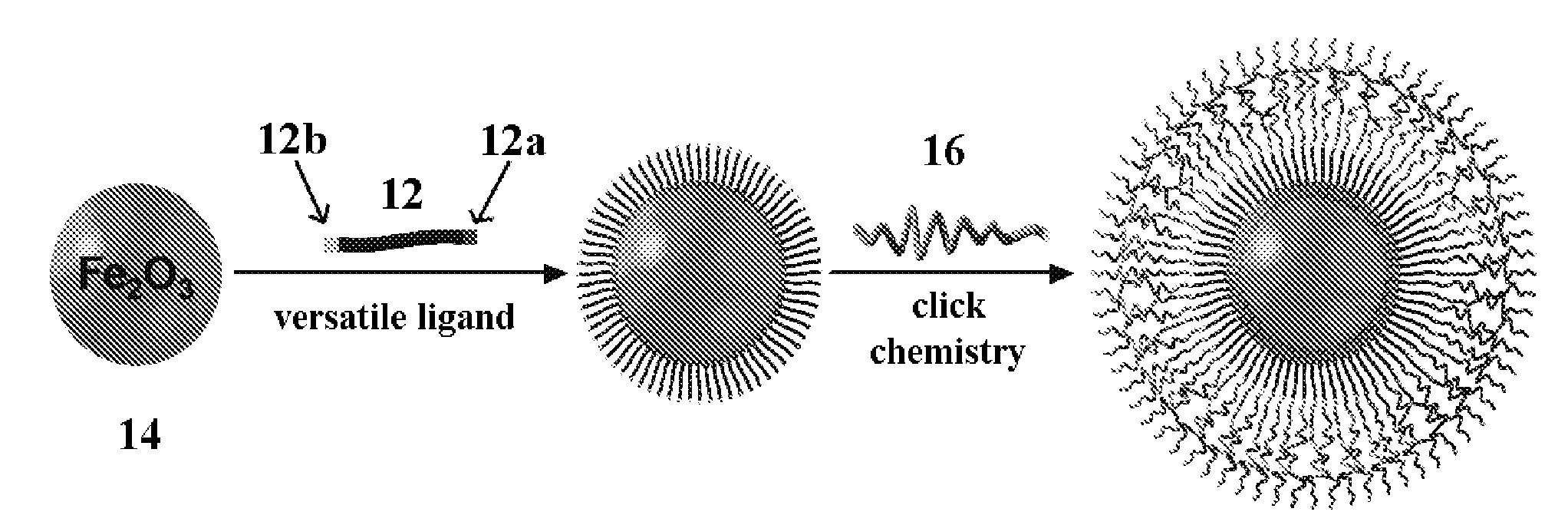
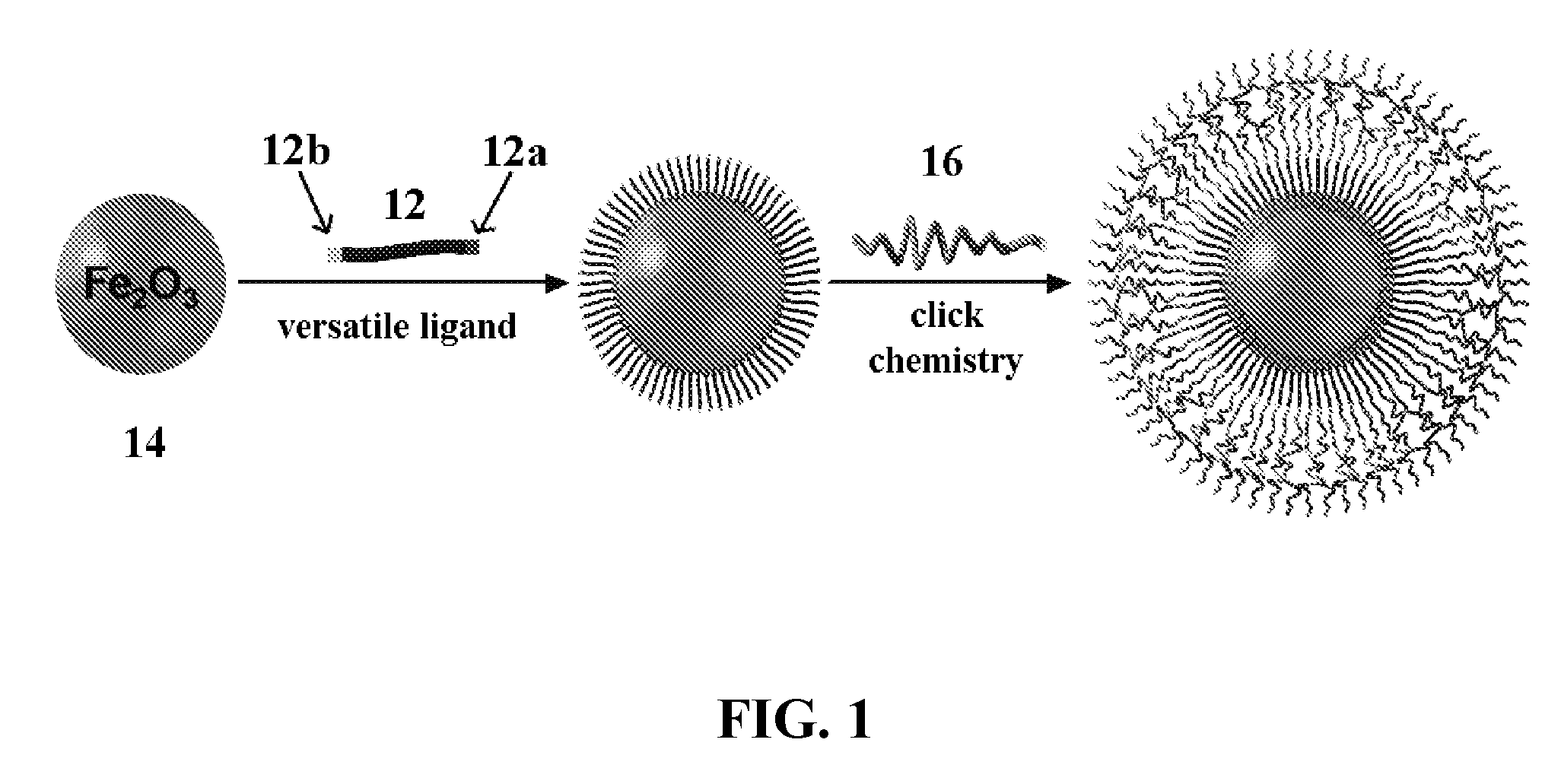
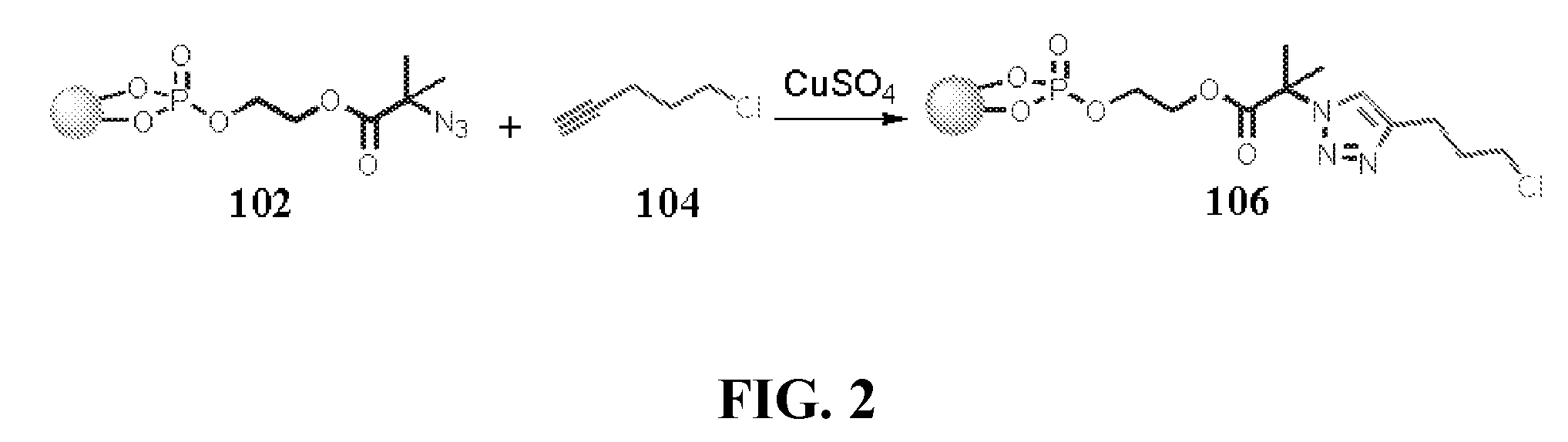
Methods for controlling surface functionality of metal oxide nanoparticles, metal oxide nanoparticles having controlled functionality, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080299046A1High dielectric constantPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyMetal oxide nanoparticlesMagnetic storage
Methods for controlling surface functionality of metal oxide nanoparticles, nanoparticles having controlled surface functionality, and uses thereof are described herein. Methods for controlling the surface functionality of a metal oxide nanoparticle are can include attaching a ligand to a metal oxide nanoparticle, where the ligand can include a functional portion that is capable of forming an irreversible bond with an object at a site that is complementary to the functional portion without reacting with other reactive sites that may be present. Moreover, metal oxide nanoparticles having versatile ligands can include an anchoring portion that binds to the surface of the metal oxide nanoparticle and a functional portion that is capable of forming an irreversible bond with an object at a site that is complementary to the functional portion without reacting with other reactive sites that may be present. Uses thereof can include cancer detection, electronics, cosmetics, cellular delivery carriers, magnetic storage media, drug delivery carriers, nanocomposite formation for improved mechanical properties, and the like.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
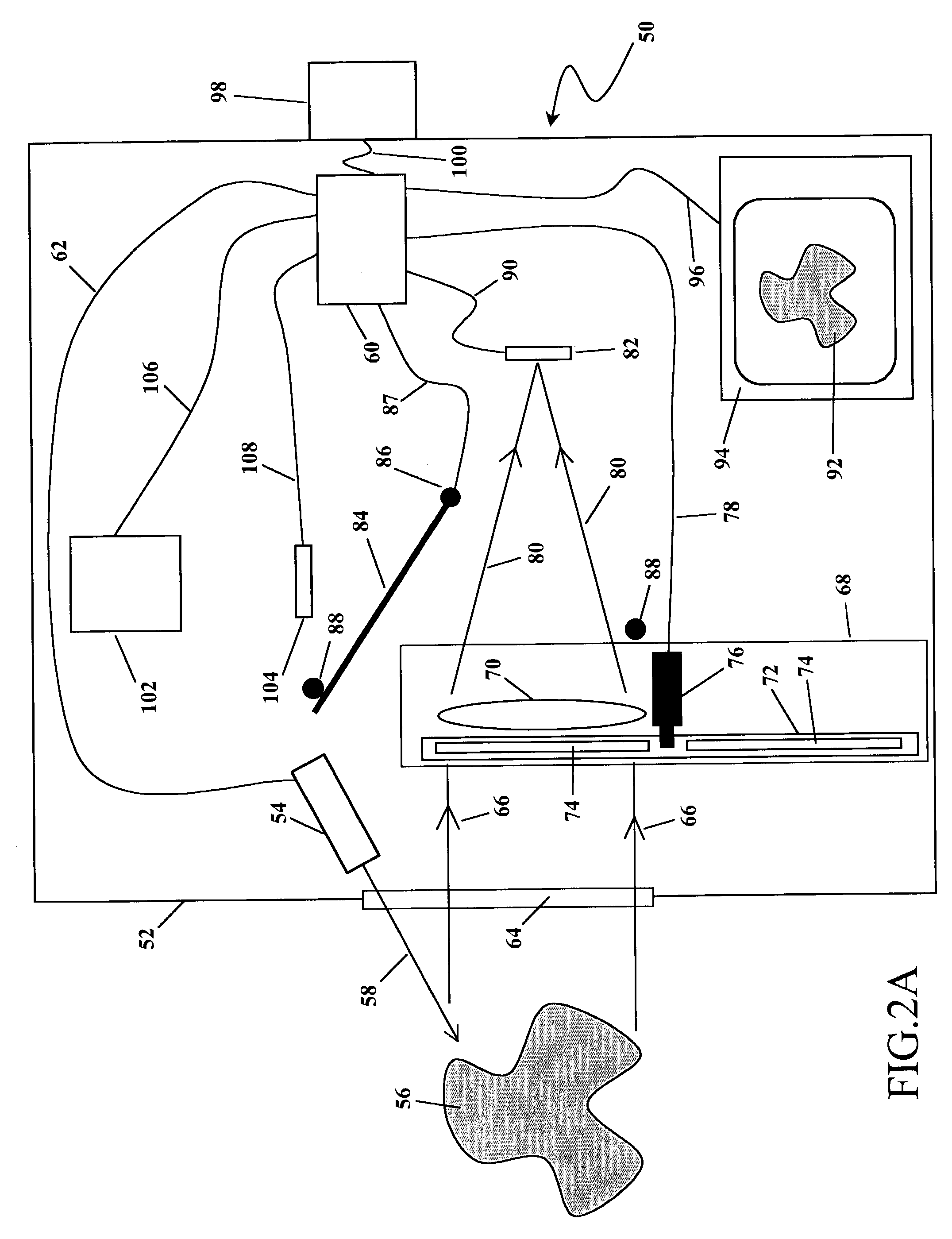
System and method for cancer detection
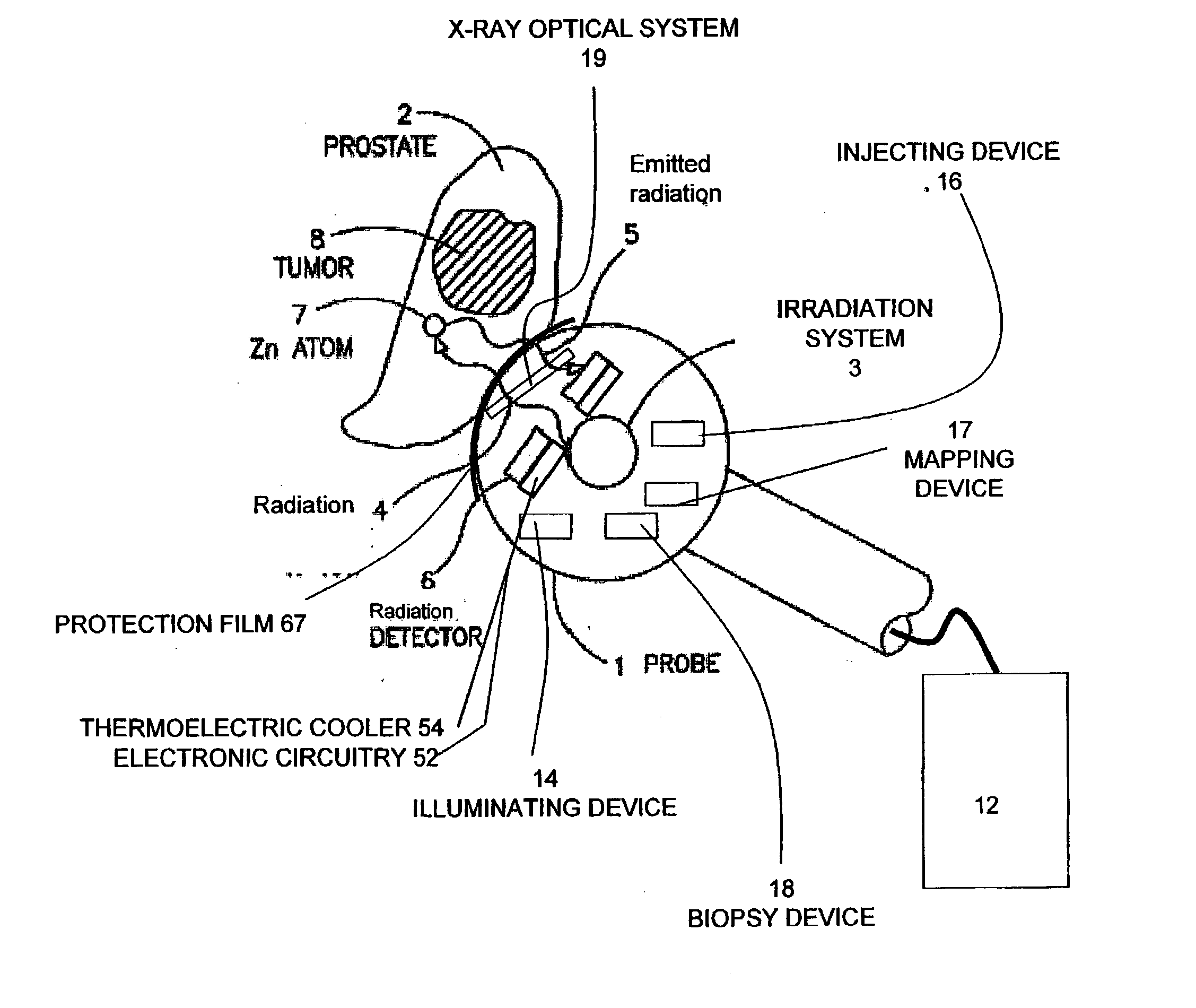
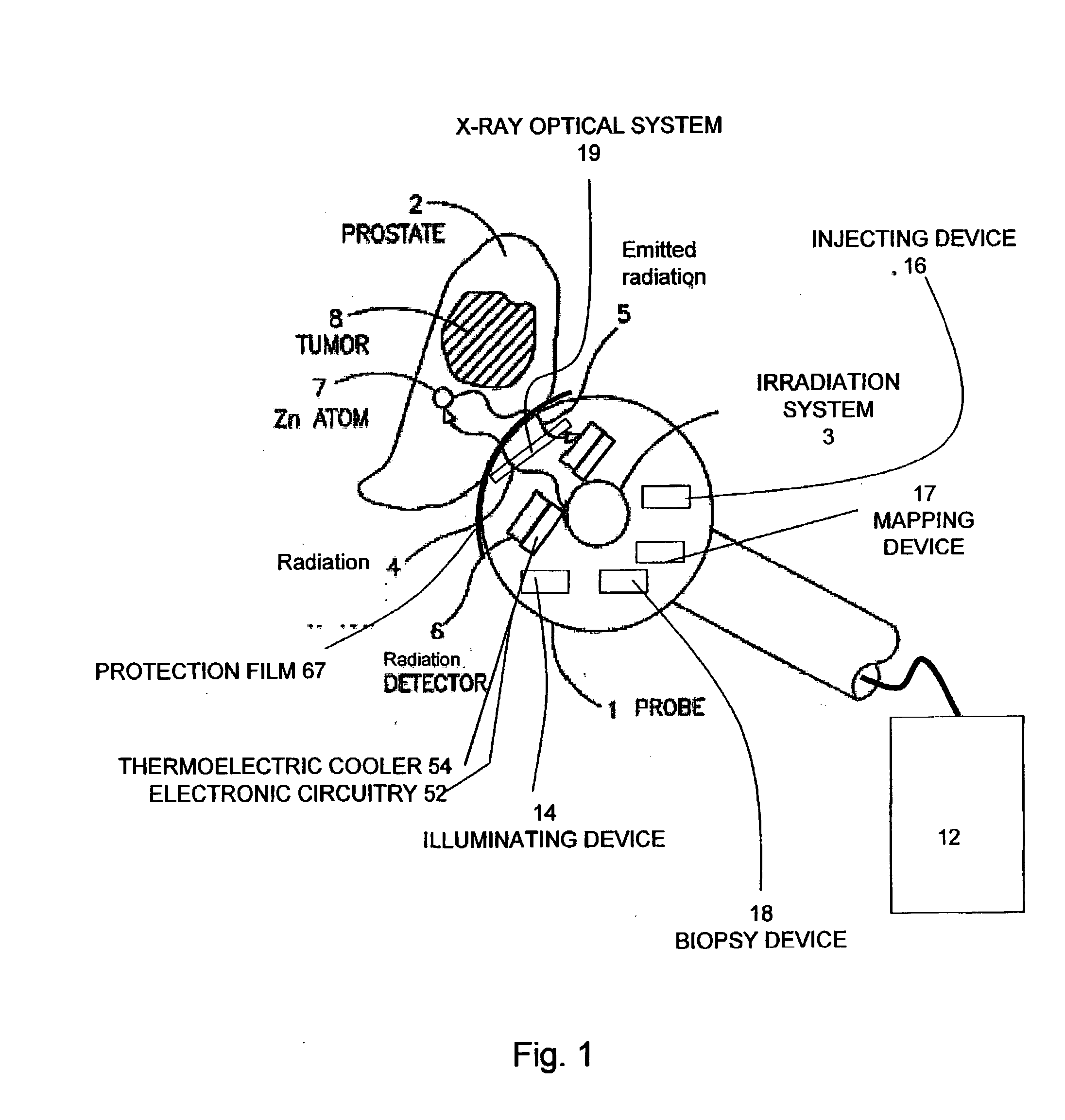
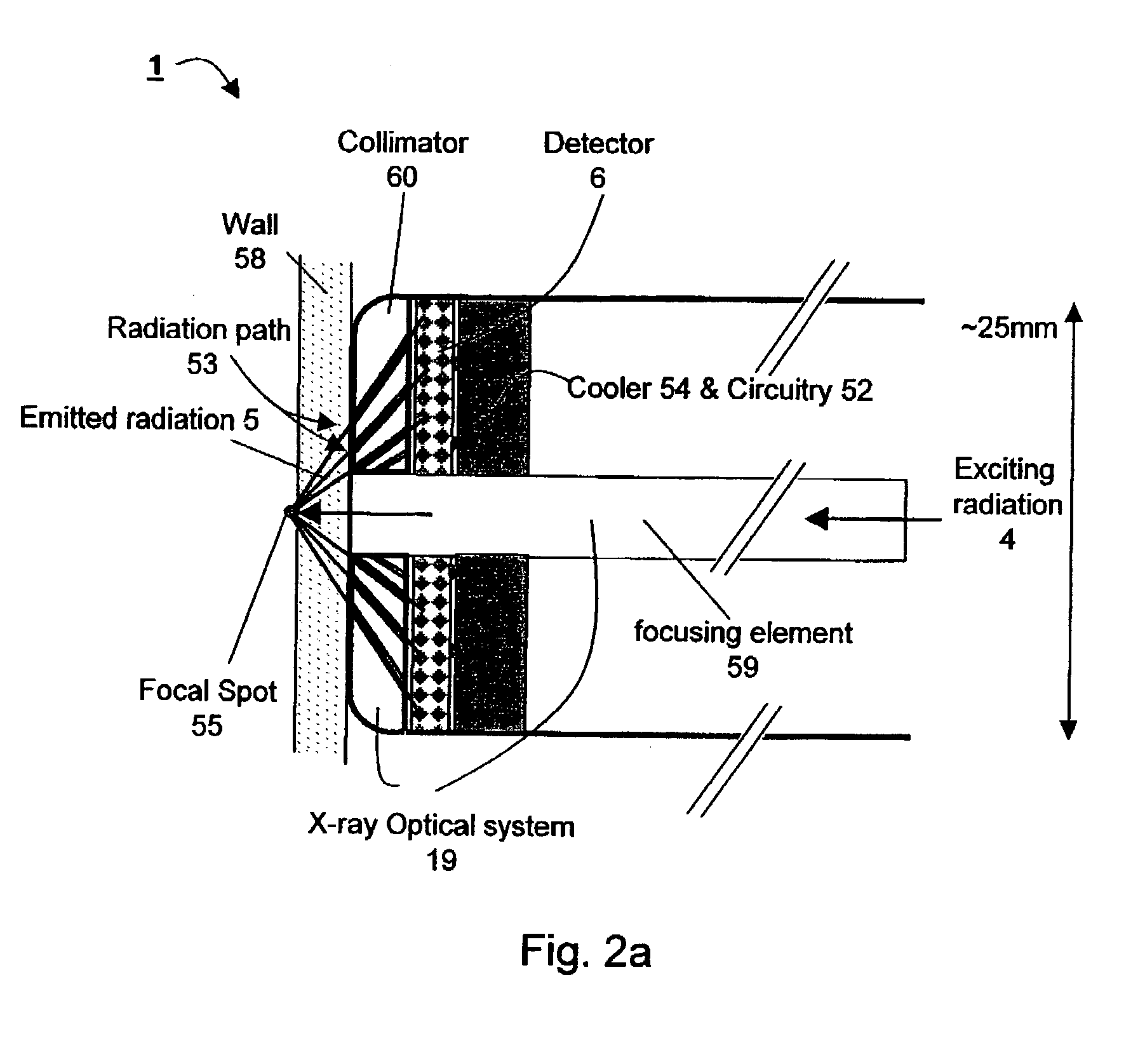
Apparatus for non-invasive in vivo detection of a chemical element in the prostate of a subject, comprising: (a) a probe adapted for being inserted into at least one of the rectum or the urethra of the subject; (b) an irradiation system capable of exciting the chemical element to emit radiation to form emitted radiation; (c) a radiation detector located within the probe, wherein the radiation detector is capable of detecting the emitted radiation and wherein the radiation detector is suitable for mapping the emitted radiation; and (d) a signal recording, processing and displaying system for mapping the level of tie chemical element in the prostate of the subject at a plurality of different points in the prostate according to the mapping of the emitted radiation. In one embodiment, the irradiation system is capable of delivering exciting radiation through the probe to the prostate; in another embodiment the emitted radiation comprises fluorescent X-ray radiation.
Owner:SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION +1
Ultrasonic sensor garment for breast tumor
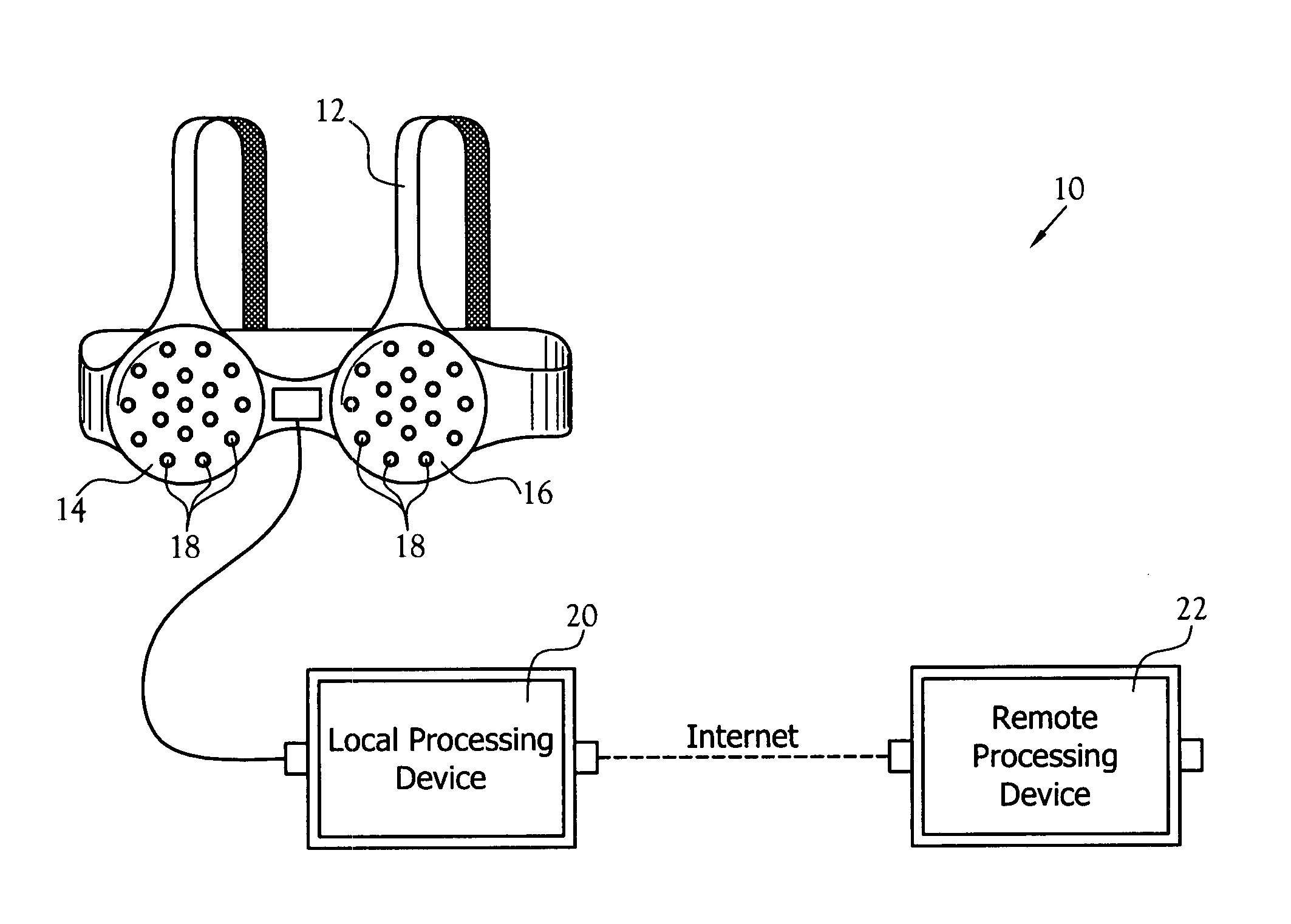
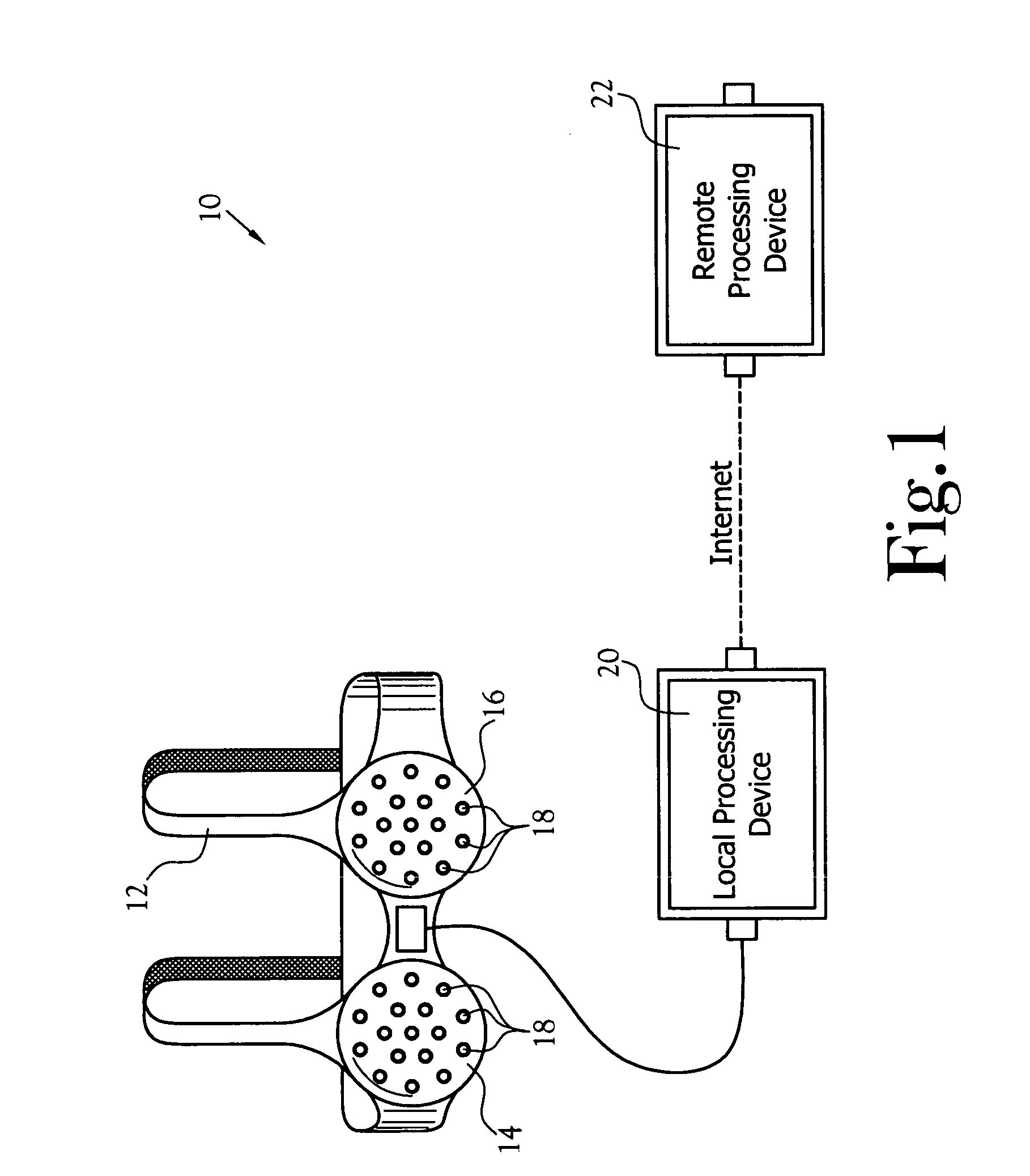
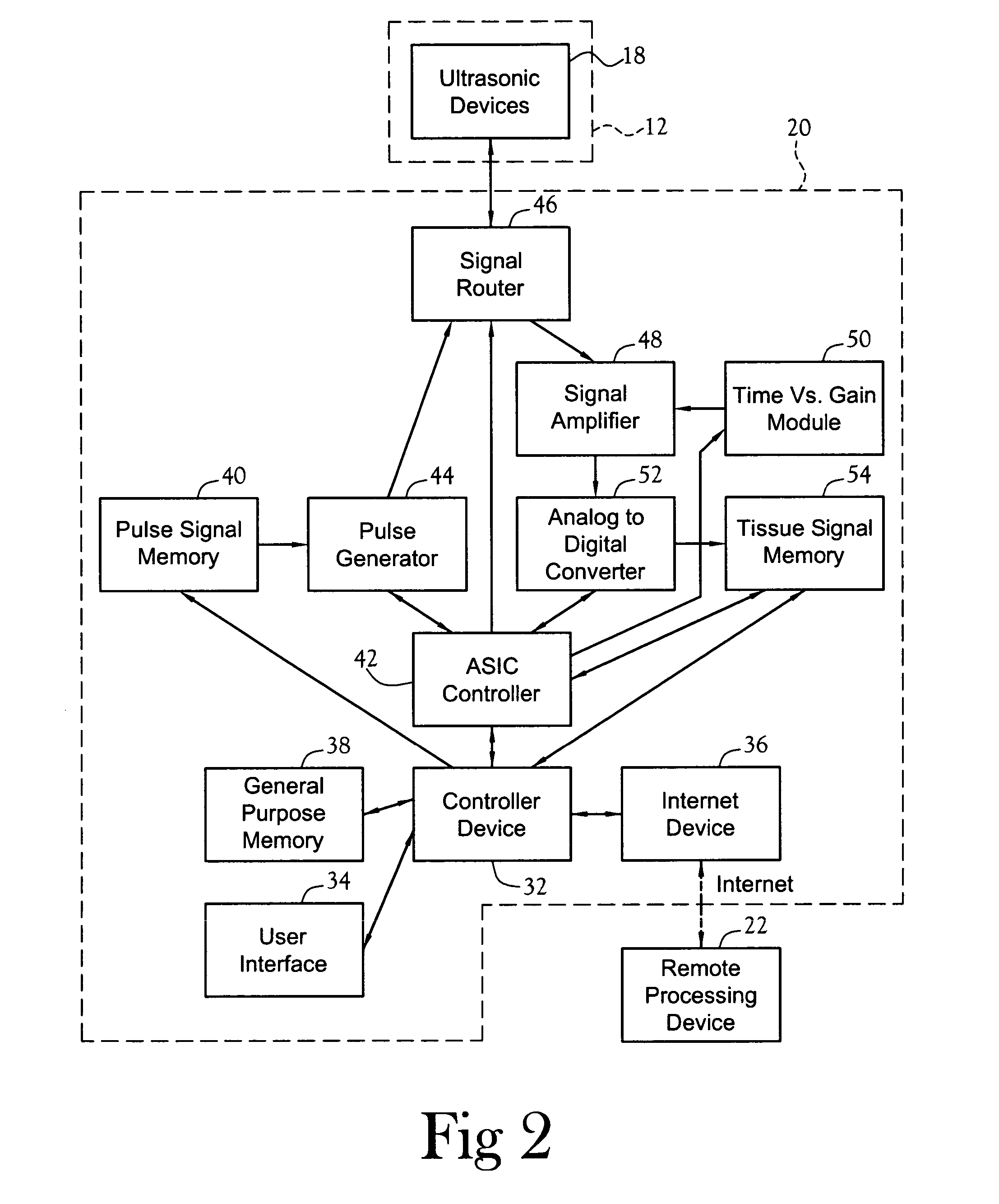
InactiveUS20050020921A1Increase probabilityAvoid developmentOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonic sensorStructure analysis
A cancer detection system having a plurality of ultrasonic sensors positioned about a garment worn over at least one breast. The sensors transmit a signal that is received by the other sensors. A processor records the amplitude and time-of-flight of the received signals. The signals include both direct line-of-flight signals and reflected signals. In one embodiment, the processor performs tissue structure analysis. In another embodiment, the recorded data is sent to a remote processor for long term storage, tissue structure analysis, and / or addition to a chronological profile.
Owner:TPG APPLIED TECH
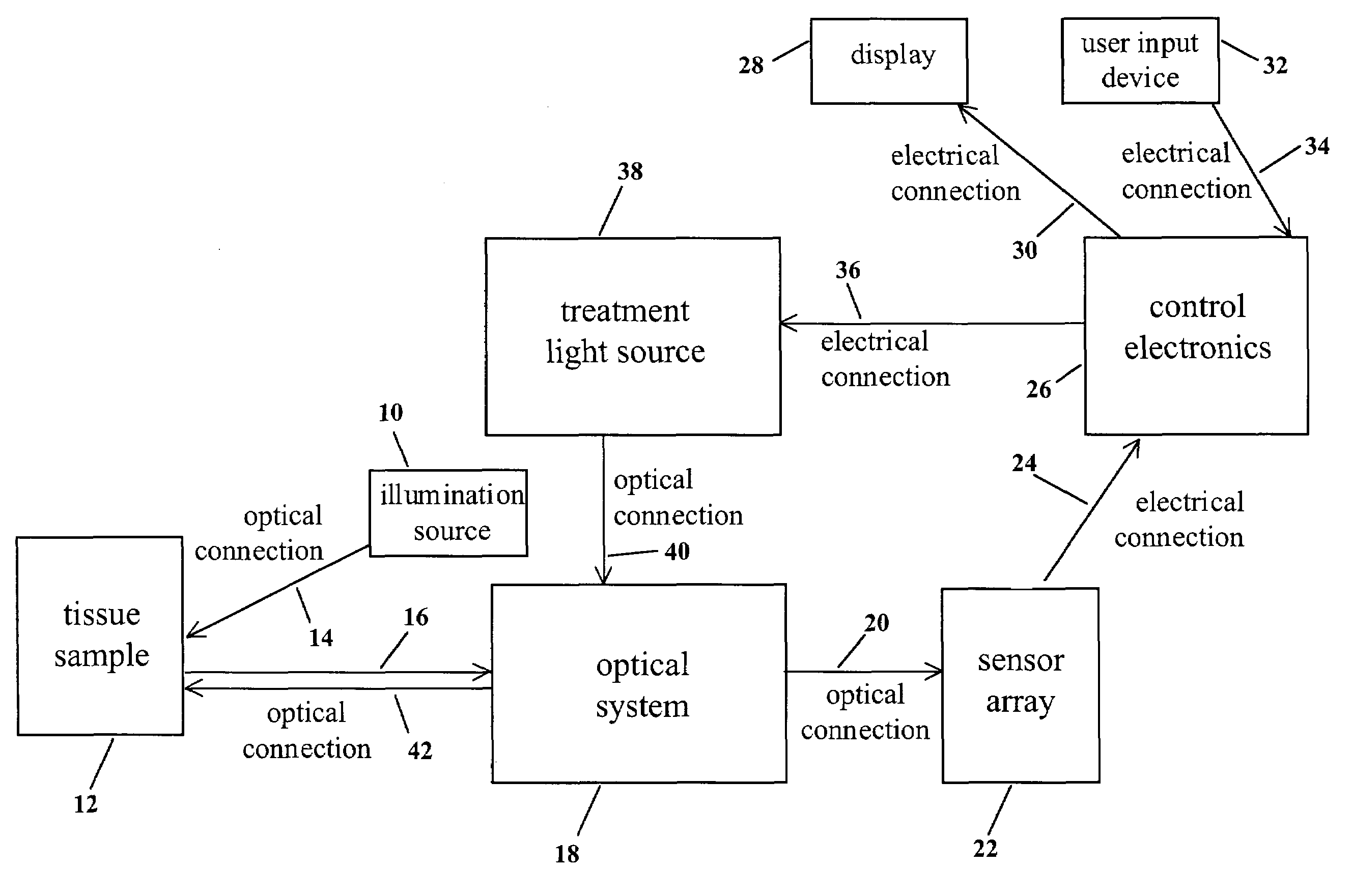
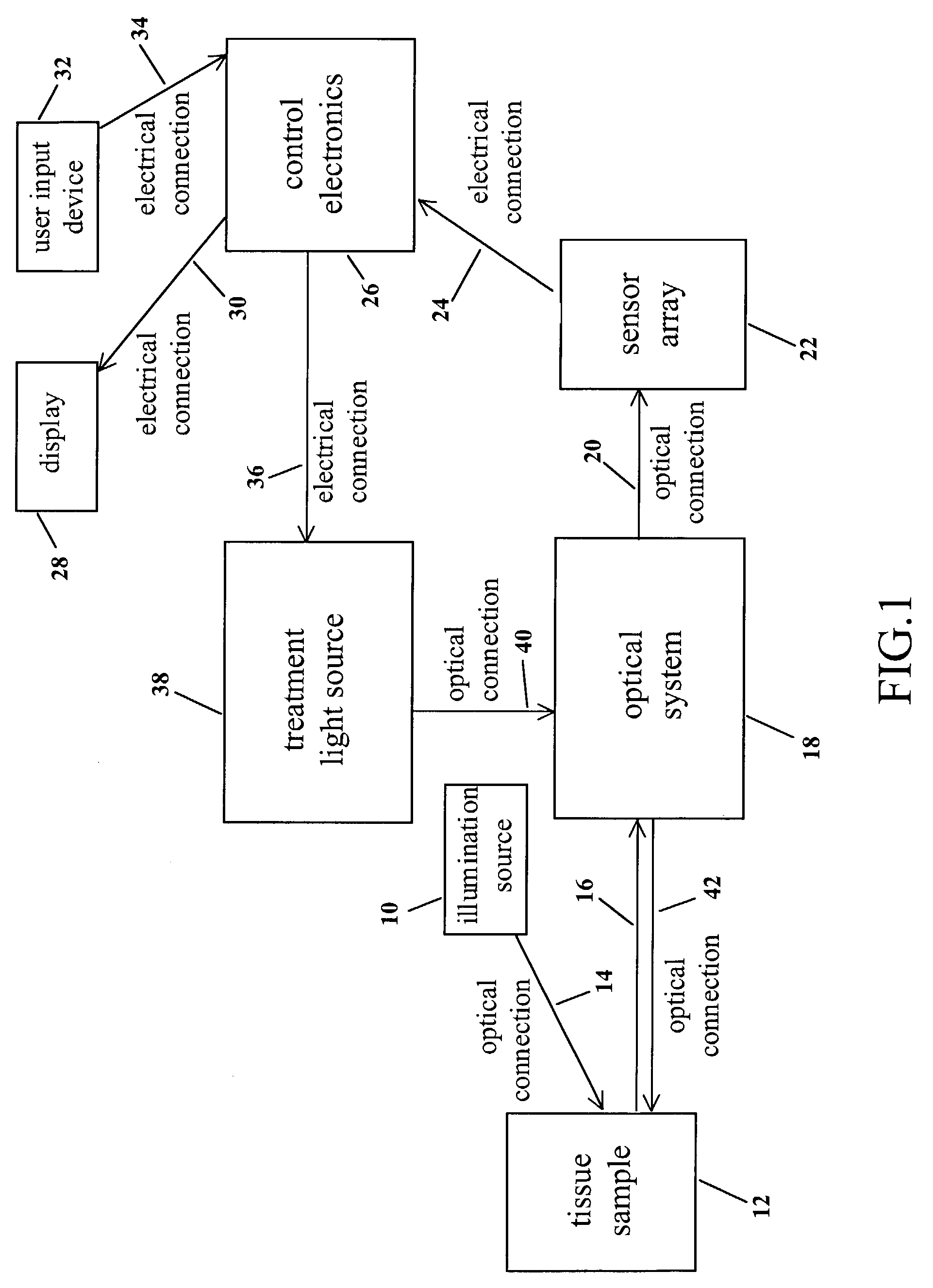
Cancer detection and adaptive dose optimization treatment system
The present invention utilizes a series of optical and electronic elements to detect and image cancerous and / or pre-cancerous cells in living tissue. The invention further uses the images thus obtained to adaptively and dynamically shape a treatment light beam so as to maximize the beam's intensity in proportion to the areas with the most cancer or pre-cancer and to minimize the irradiation of normal tissue by the beam.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
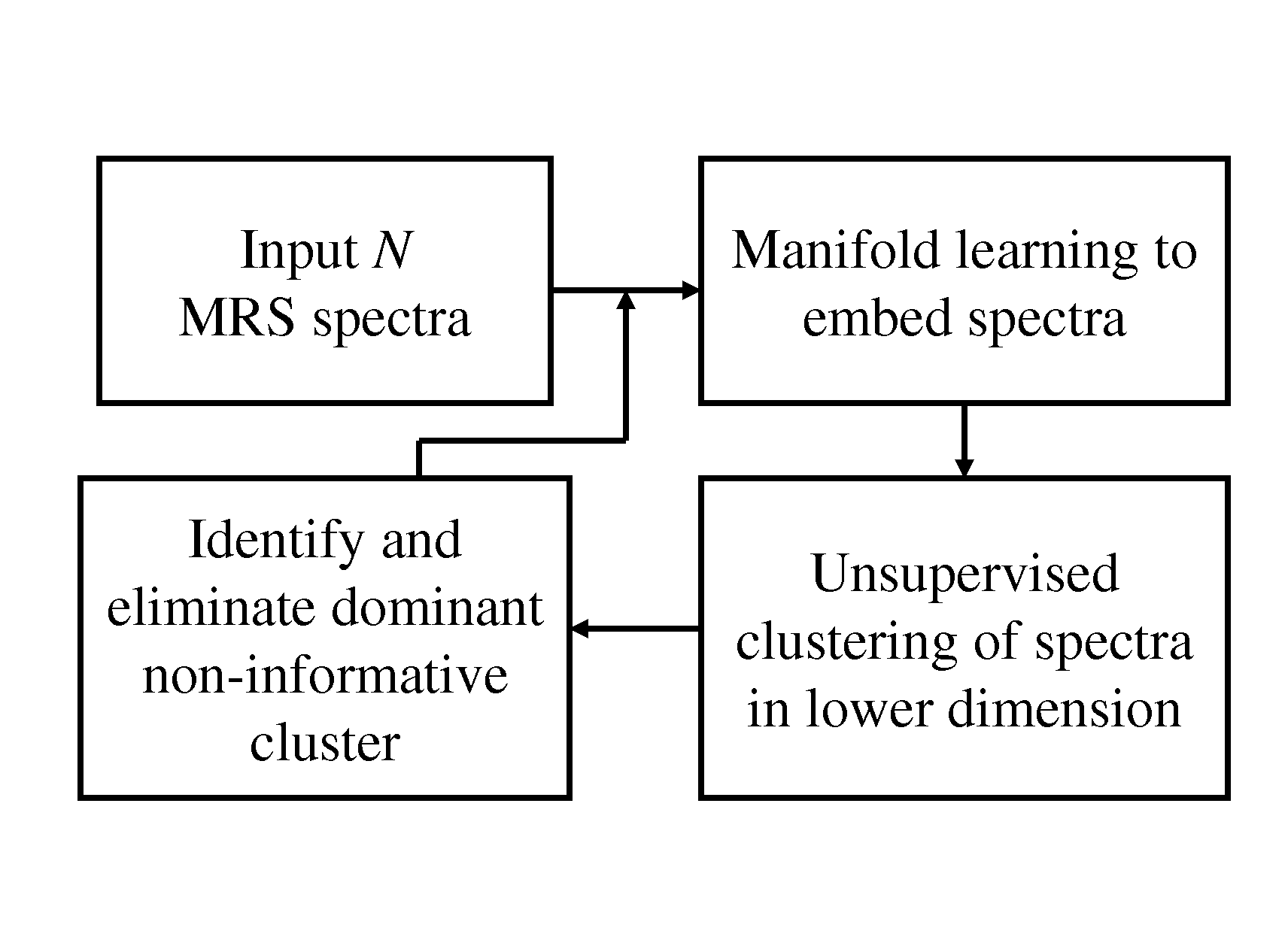
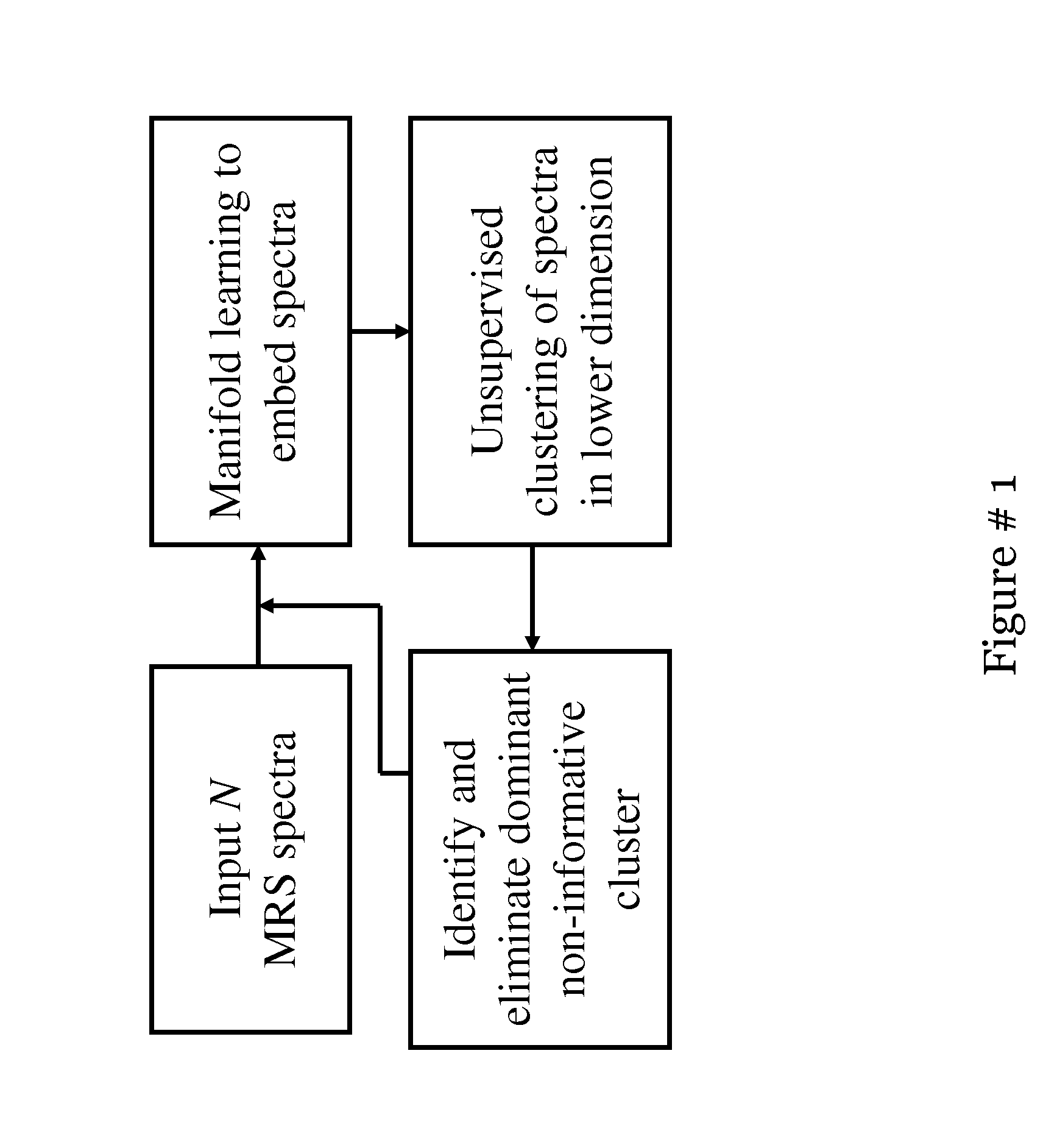
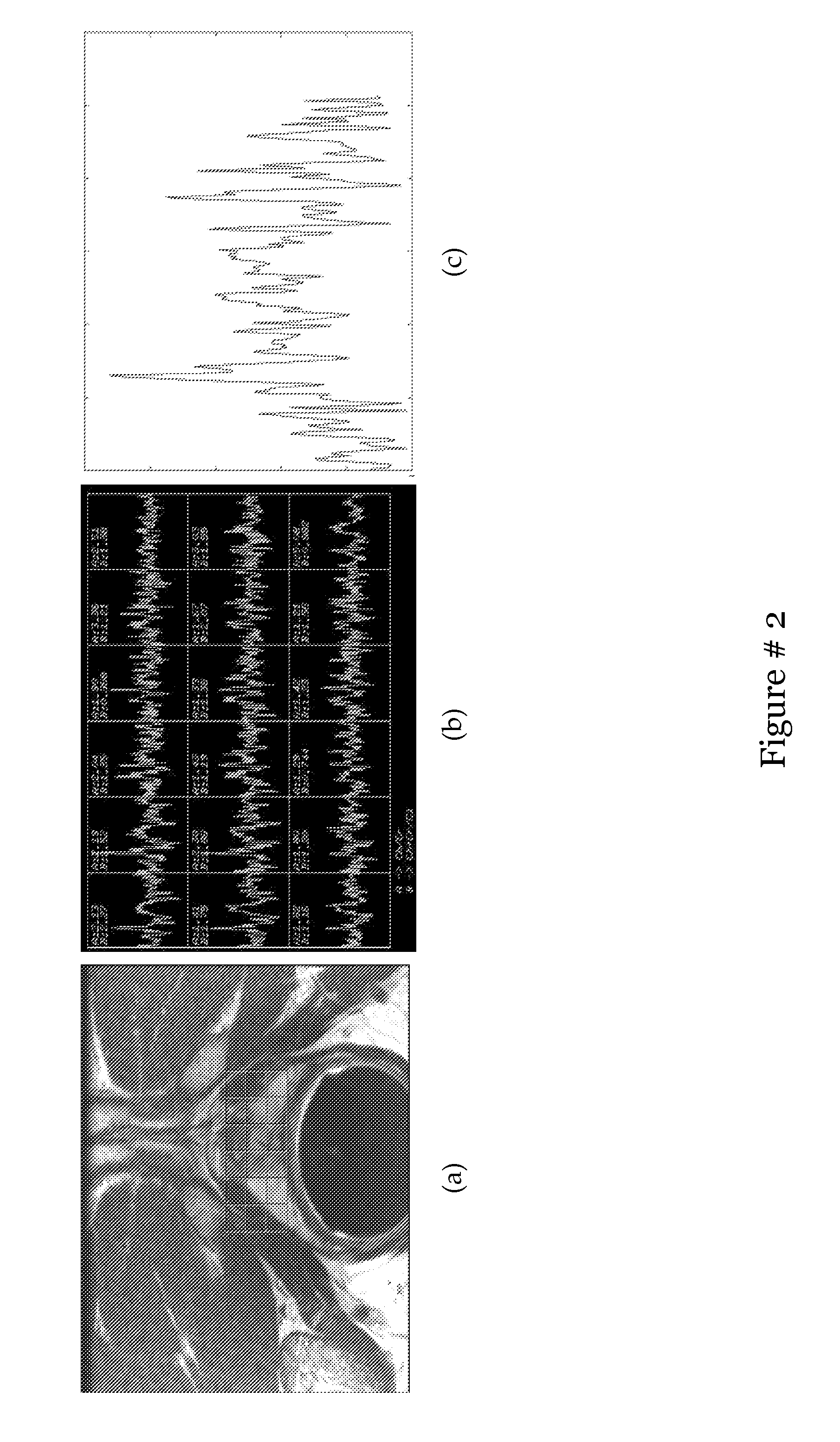
Computer assisted diagnosis (CAD) of cancer using multi-functional, multi-modal in-vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and imaging (MRI)
This invention relates to computer-assisted diagnostics and classification of prostate cancer. Specifically, the invention relates to segmentation of the prostate boundary on MRI images, cancer detection using multimodal multi-protocol MR data; and their integration for a computer-aided diagnosis and classification system for prostate cancer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Abnormal pattern detection processing method and system
InactiveUS7162061B1Improvement of detection processing algorithmStrong specificityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern detectionOutput device
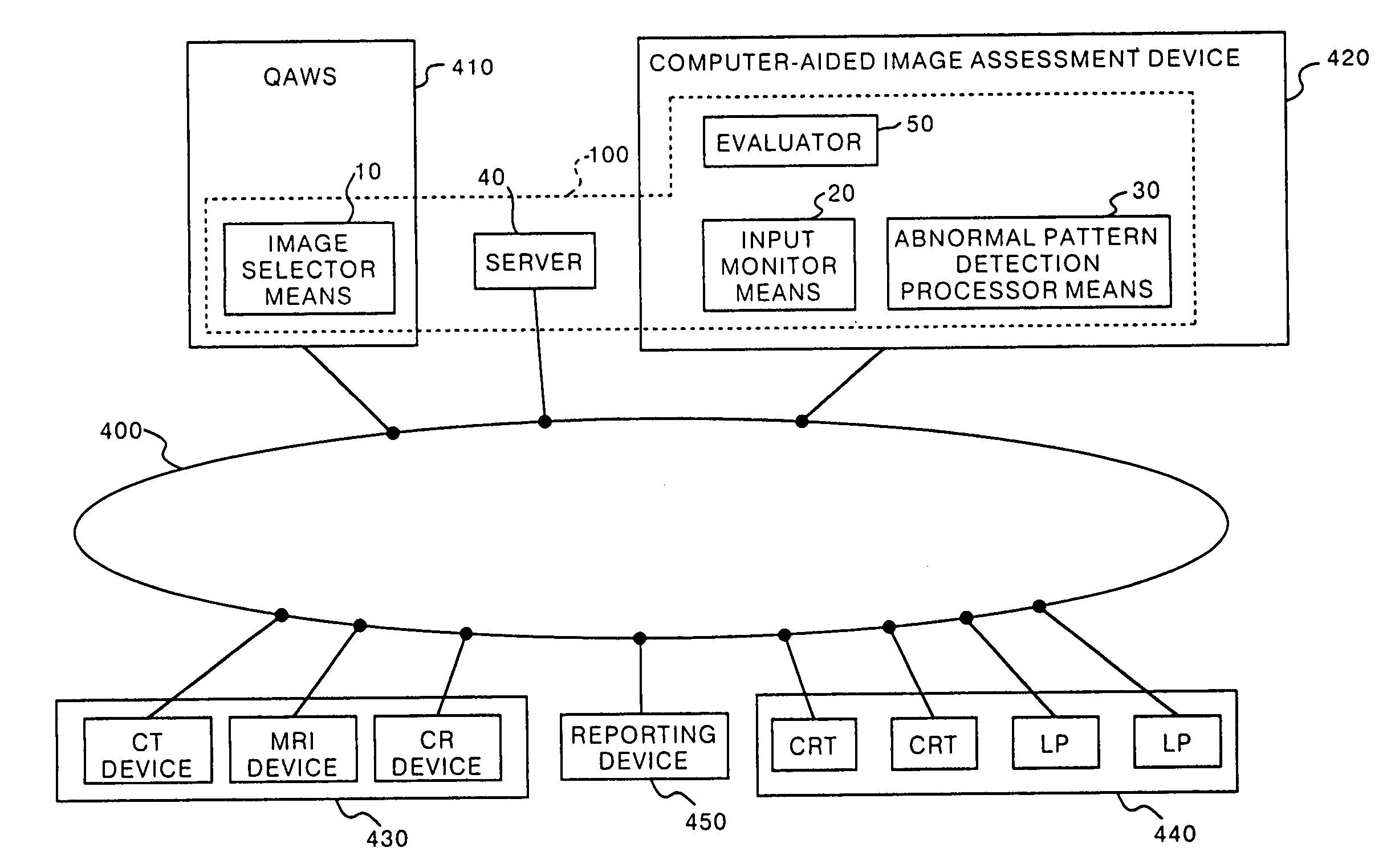
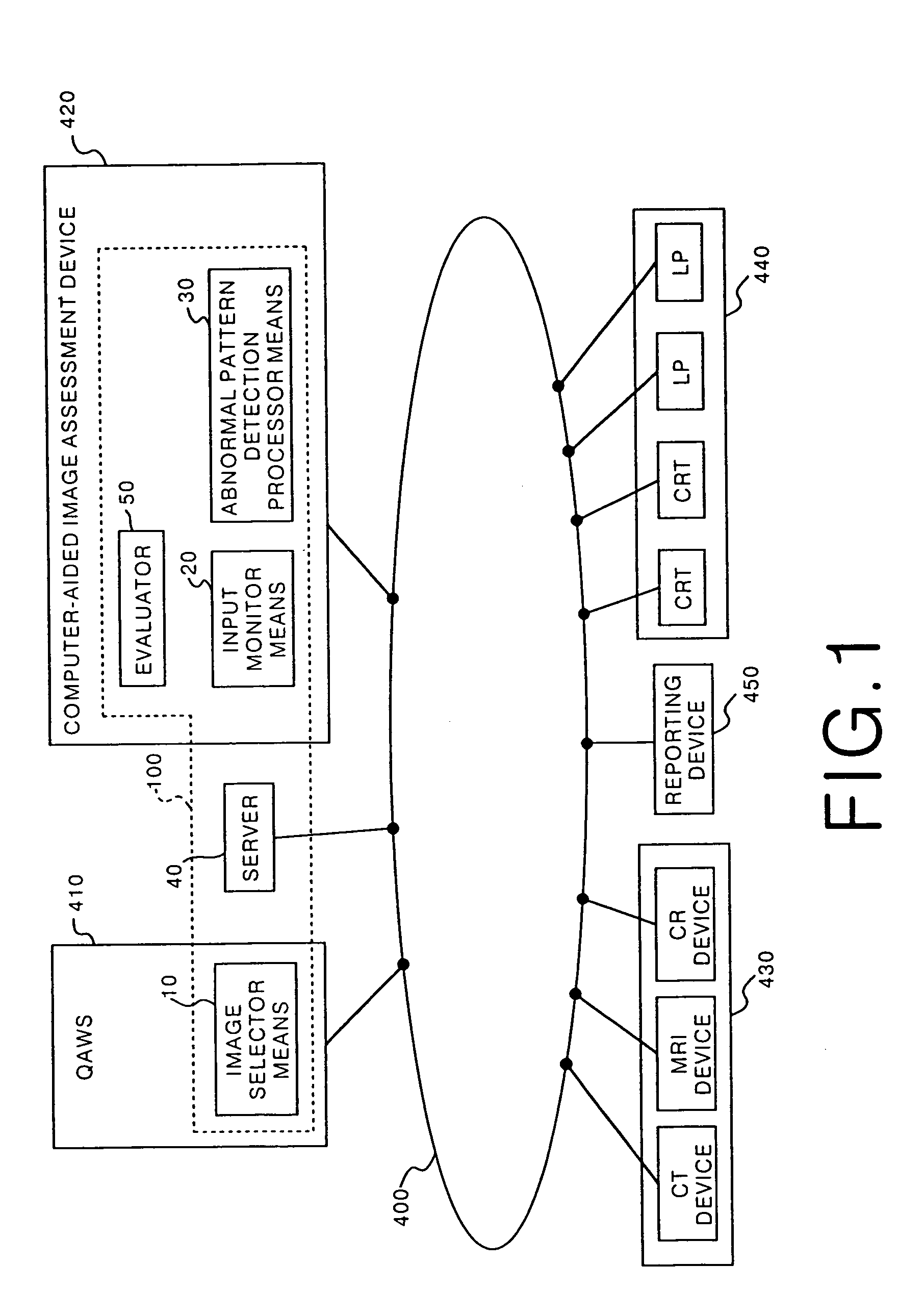
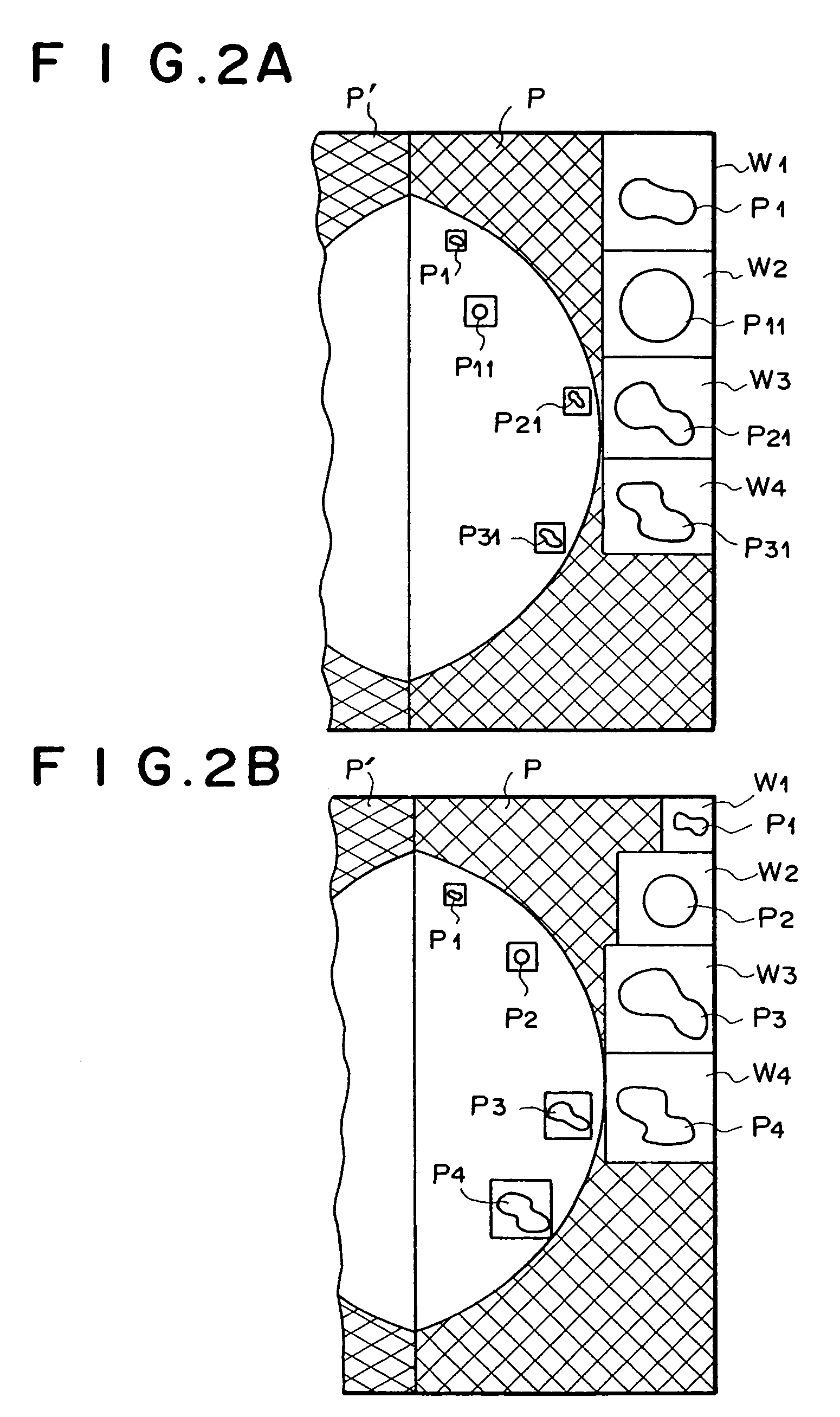
The result of detection processing by abnormal pattern detection processor means 30 is stored in a server 40. In addition, the output image on an image output device 440 is read for pattern, and the supporting contents, such as the result of judgment by a doctor (which, when differing from the result of detection processing, corresponds to the corrected result), the comment, and the assessment category, are stored in the server 40 in conformity with the BI-RADS proposed by the ACR. The result of pathologic assessment corresponding to the abnormal pattern is related to the supporting contents and stored in the server 40. The statistical processing in conformity with the follow-up method of the BI-RADS is performed to find the specificity, the cancer detection rate, etc.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
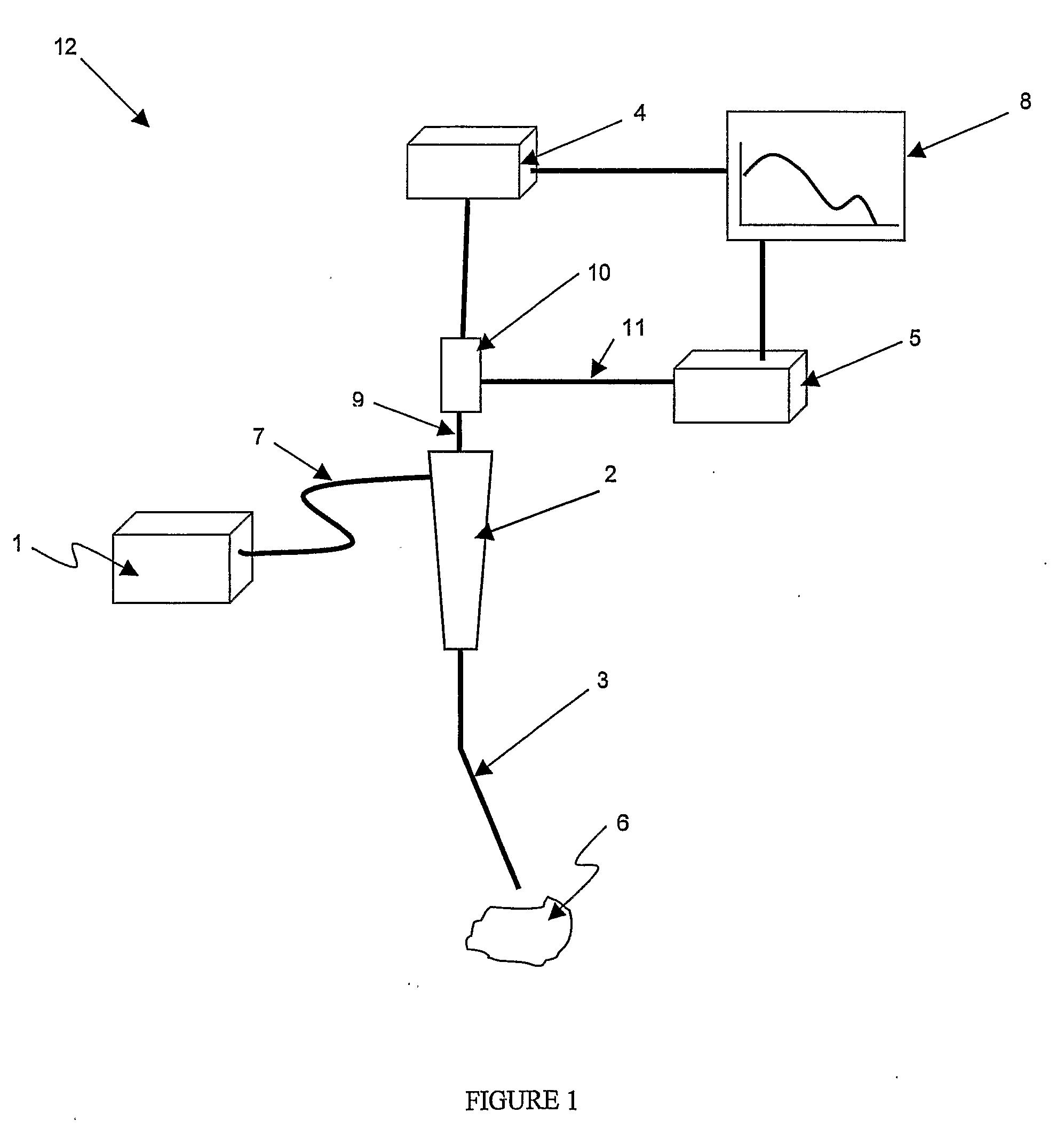
Method and apparatus for measuring cancerous changes from reflectance spectral measurements obtained during endoscopic imaging
The present invention provides a new method and device for disease detection, more particularly cancer detection, from the analysis of diffuse reflectance spectra measured in vivo during endoscopic imaging. The measured diffuse reflectance spectra are analyzed using a specially developed light-transport model and numerical method to derive quantitative parameters related to tissue physiology and morphology. The method also corrects the effects of the specular reflection and the varying distance between endoscope tip and tissue surface on the clinical reflectance measurements. The model allows us to obtain the absorption coefficient ([mu]a) and further to derive the tissue micro-vascular blood volume fraction and the tissue blood oxygen saturation parameters. It also allows us to obtain the scattering coefficients ([mu]s and g) and further to derive the tissue micro-particles volume fraction and size distribution parameters.
Owner:维利桑特技术公司 +1
Cancer Detection and Treatment Instrument
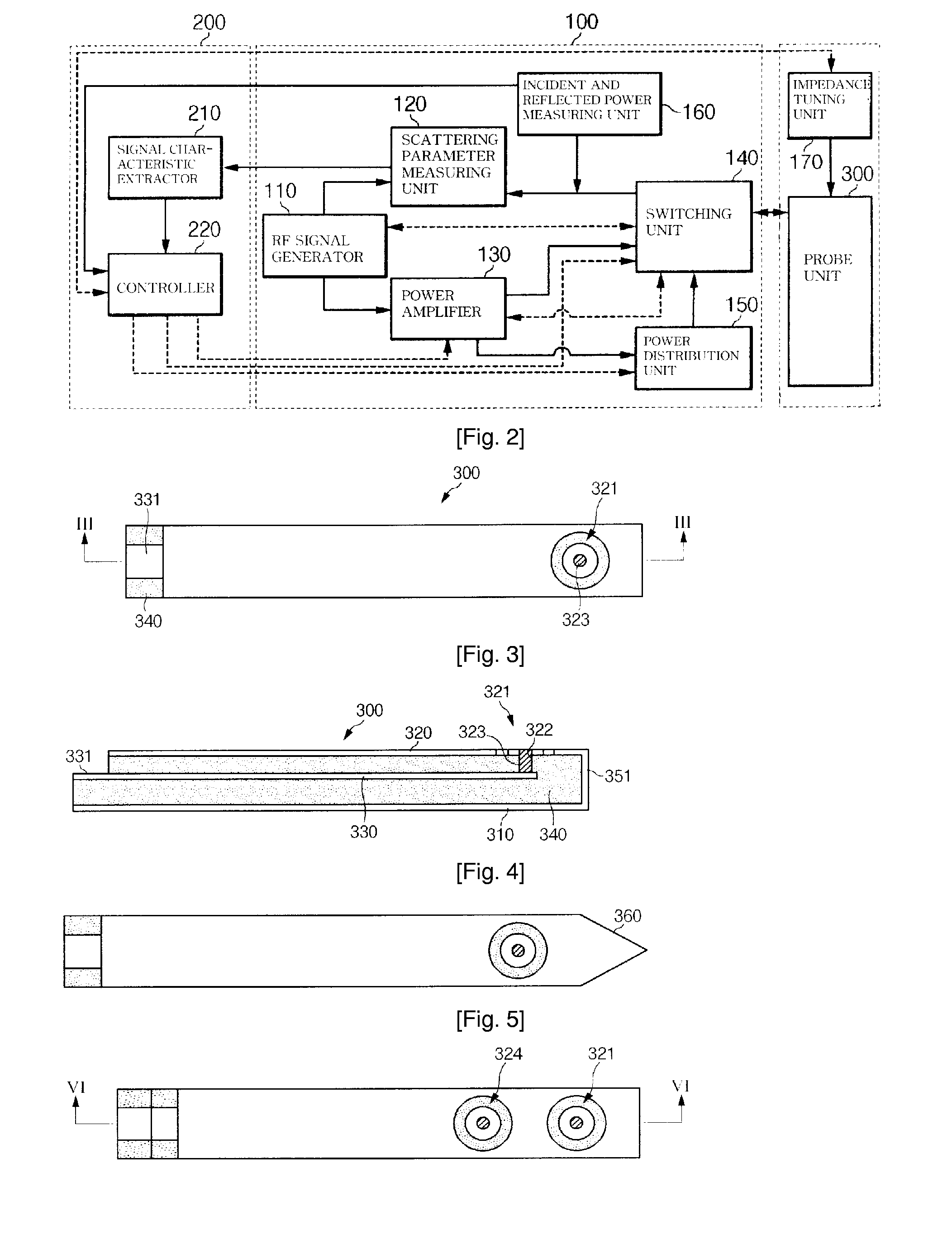
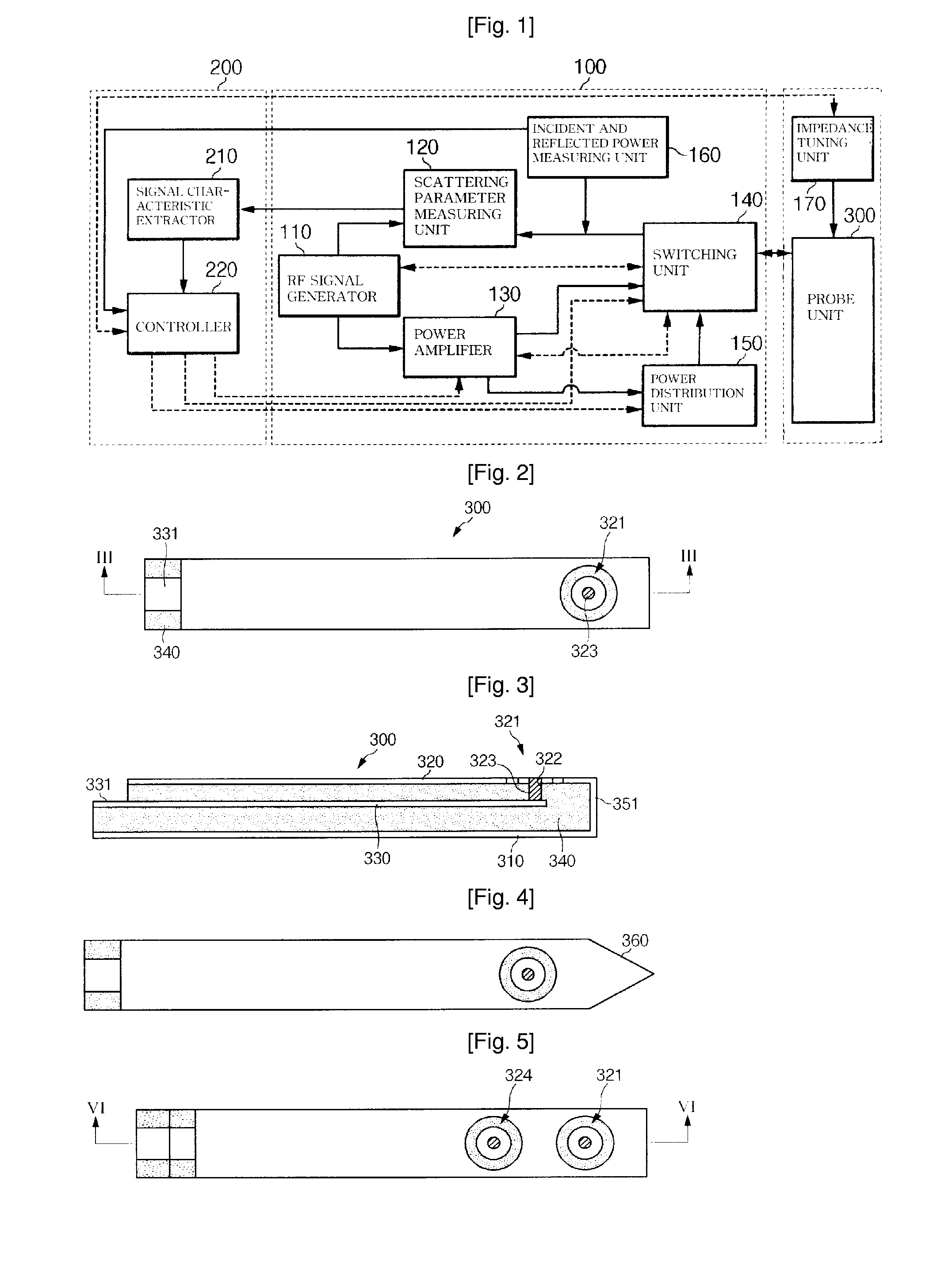
InactiveUS20080200803A1Accurately detecting cancerMetal rolling stand detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringDamages tissueCancer detection
Provided herein is a cancer detection and treatment instrument comprising: a first conductive plate; a second conductive plate which is opposed to the first conductive plate and has a first opening; a first signal line disposed between the first conductive plate and the second conductive plate; a first contact member of which one end is exposed through the first opening and of which the other end is connected to the first signal line; a dielectric portion filled between the first and second conductive plates and the first signal line; and a conductive layer surrounding both side surfaces and a front end surface of the dielectric portion which are exposed. Therefore, it is possible to accurately detect cancer by the use of the ultrahigh-frequency signal and to treat a diseased portion without damaging tissues around the diseased portion.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Electromagnetic system and method
InactiveUS20120035457A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsTissue sampleEngineering
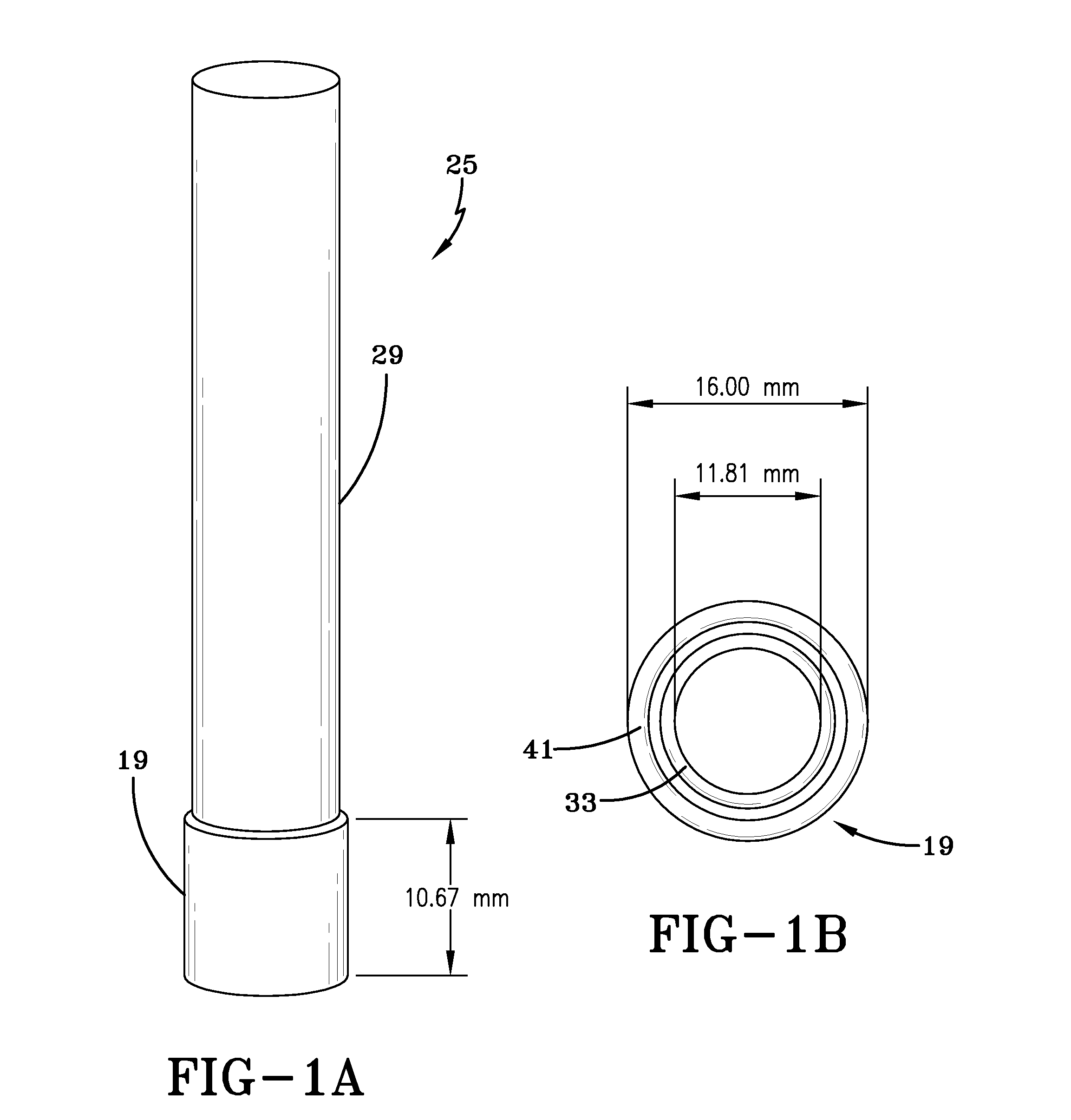
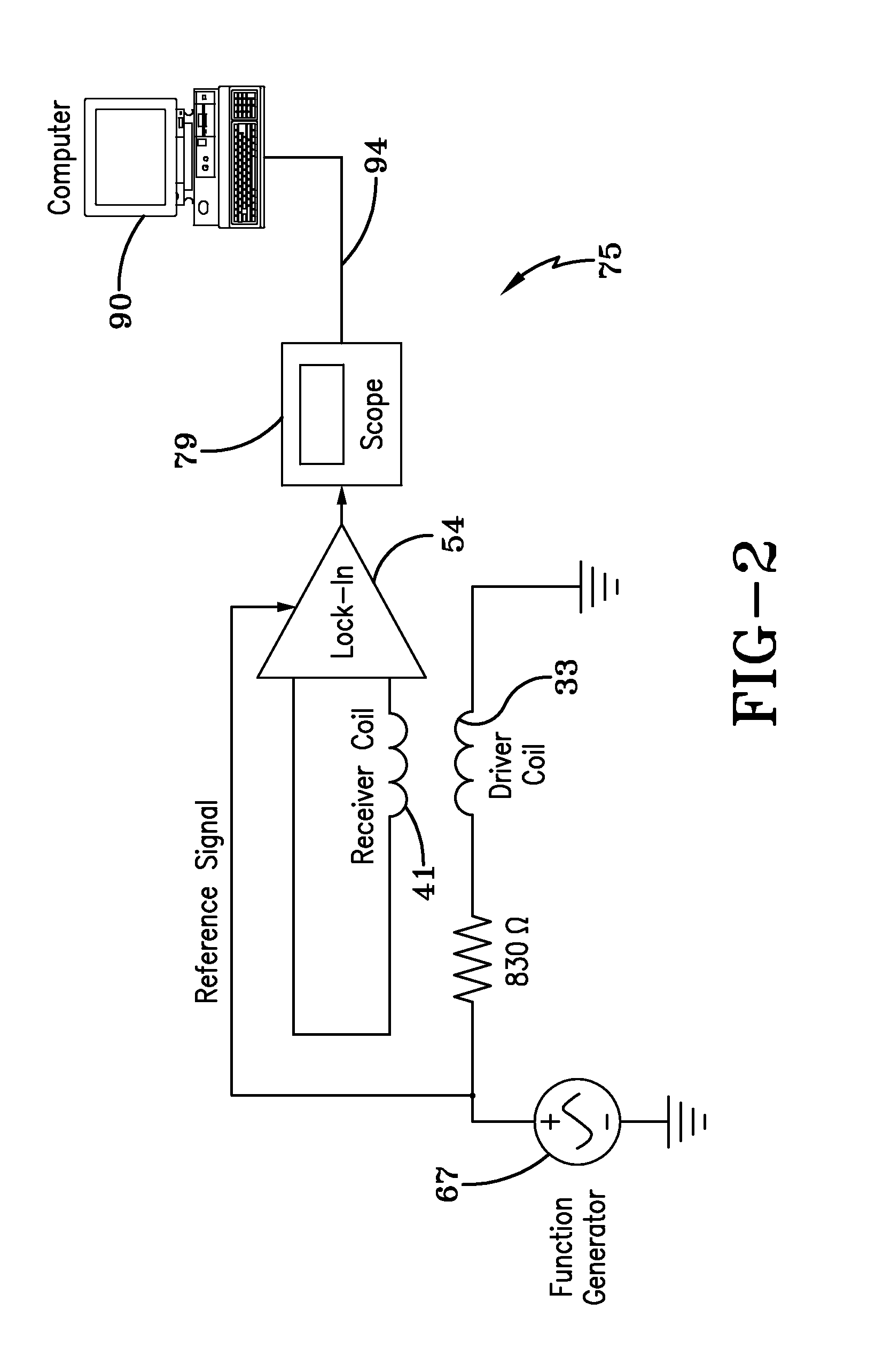
Differences of electromagnetic (EM) properties between healthy and cancerous tissues allow detection of abnormal conditions occurring in a tissue of an animal, for example, intra-operative cancer detection. By using a time-varying EM field, electrical eddy currents are generated in the tissue sample, and assessed using phase-sensitive detection. In some aspects, a change in phase shift between the voltage in a receiver coil and the voltage in a driver coil provide a direct and immediate indication of differences in EM properties of specimens.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Cancer Detection Methods and Reagents
InactiveUS20110086061A1High sensitivityViral antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAntigenAutoantibody
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for detecting cancer in an individual comprising autoantibodies to cancer-associated antigens. Specifically, the present invention comprises methods and compositions for detecting autoantibodies to cancer-associated antigen in a bodily fluid as well as use of said autoantibodies as a means to detect the presence of cancer-associated antigens.
Owner:ONCIMMUNE
Method for detecting cancer and a method for suppressing cancer
InactiveUS20070161018A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellNormal cell
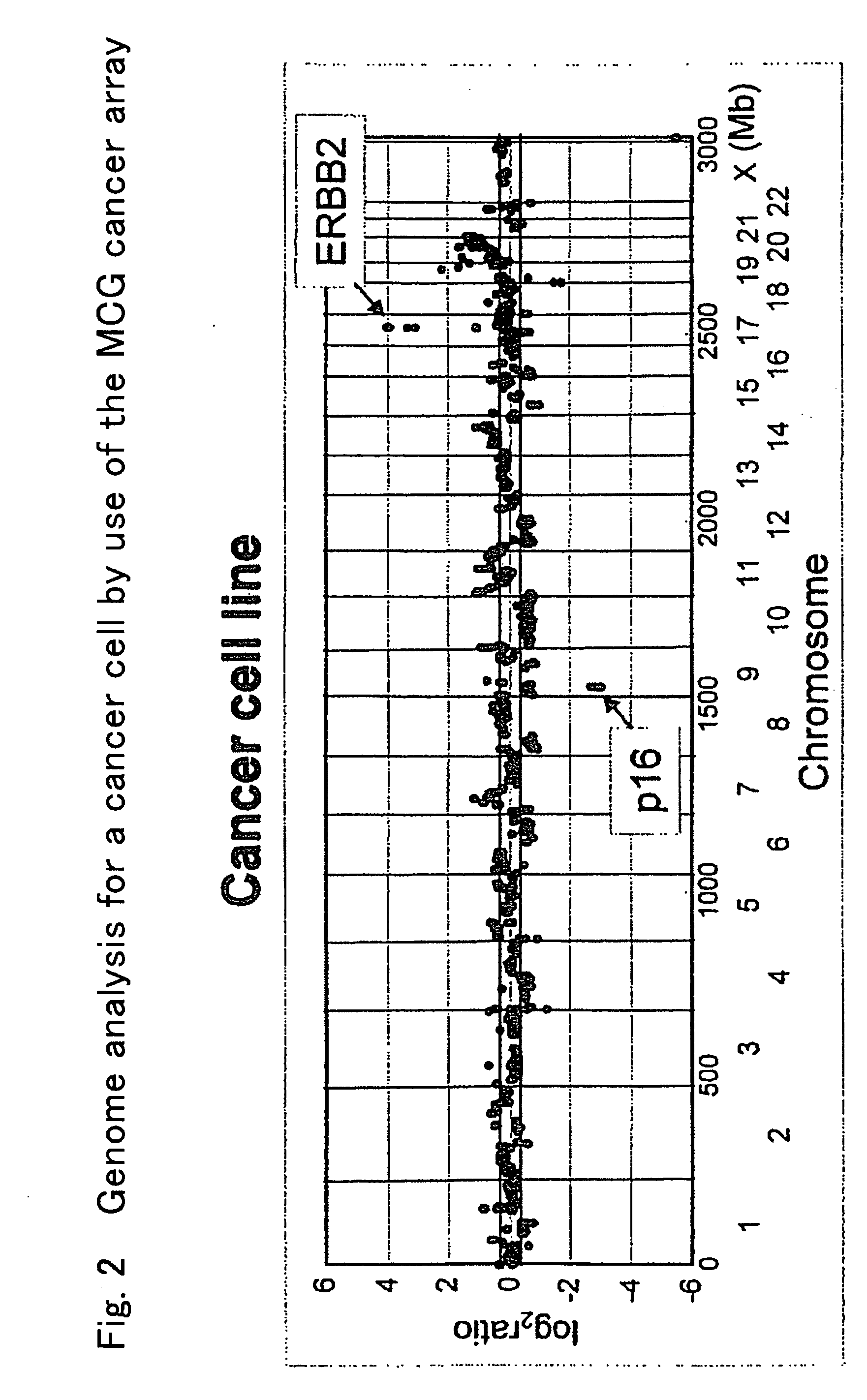
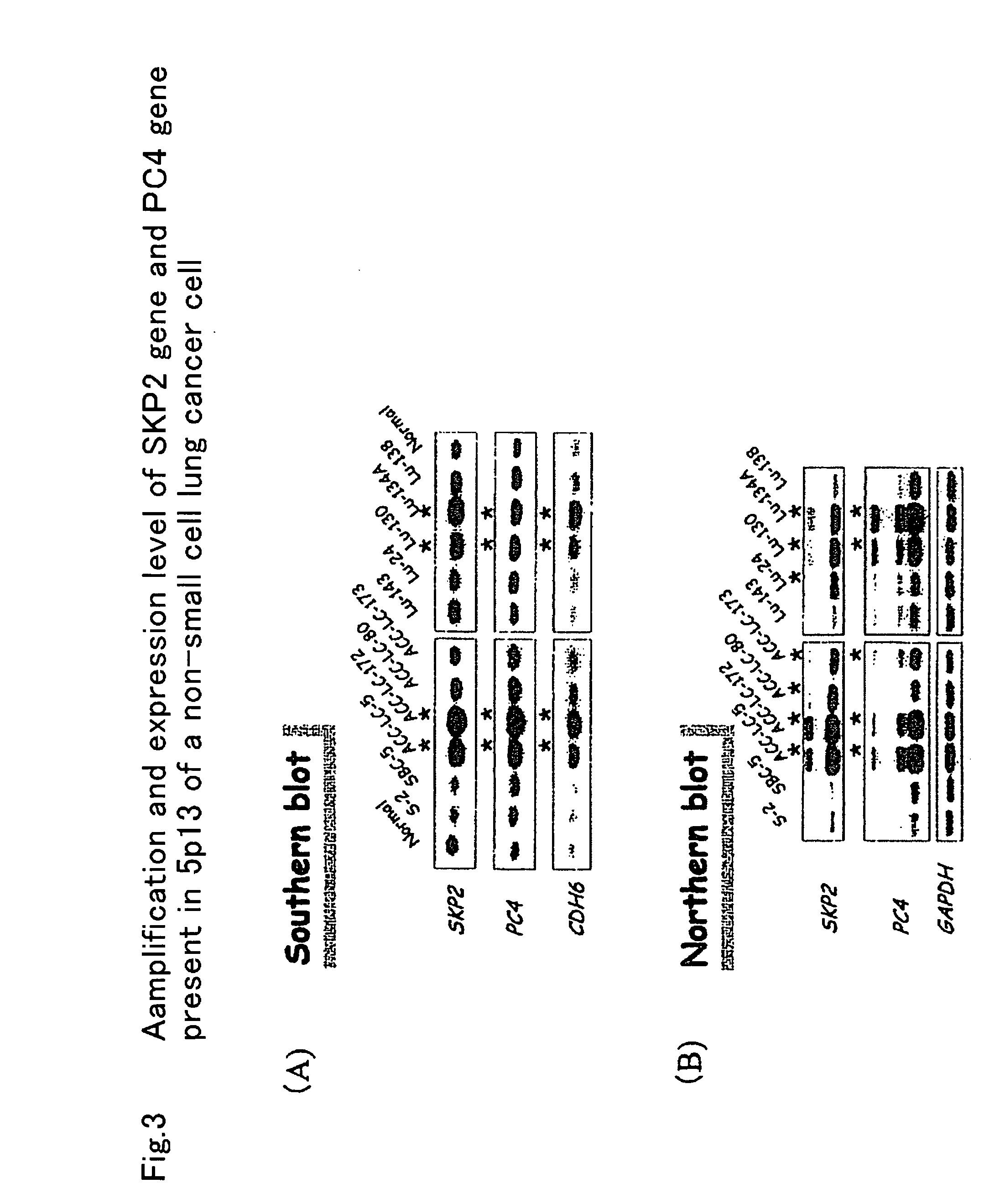
An object of the invention is to find a cancer-associated gene to be used as an index for detecting canceration of cells and degree of malignancy of cancer, so as to to provide a method for detecting cancer using the cancer-associated gene as an index and provide a method of suppressing / treating cancer using the cancer-associated gene as essential part. According to the present invention, specific genes which are amplified or deleted in bile duct cancer as compared with normal cell have been collectively found, and a method for detecting cancer using amplification or deletion of these cancer-associated genes as an index is provided. Further, cancer can be suppressed by introducing a gene which is deleted in cancer cells amond these cancer-associated genes into cancer and inhibiting the transcription product of the gene amplified.
Owner:BML INC +2
Apparatus and methods for in vivo tissue characterization by raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120259229A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyRaman scatteringNormal skinTissue characterization
A micro-Raman spectrometer system for use in differentiating tumor lesions from normal skin detects specific characteristics of Raman spectra indicative of cancer. A peak at 899 cm−1 and a higher intensity region in the 1325 cm−1 to 1330 cm−1 range indicate the presence of tumors. The spectrometer system may be applied for skin cancer detection and for mapping the margins of lesions. Cancer detection methods as described herein have achieved diagnostic sensitivity of 95.8% and specificity of 93.8%.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
Cancer detection method
ActiveCN102171570AHigh serum antibody levelsStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBiological bodyAntigen-antibody reactions
Disclosed is a cancer detection method comprising measuring the expression of a polypeptide in a sample separated from a living body, wherein the polypeptide has a reactivity to bind, through an antigen-antibody reaction, to an antibody directed against CAPRIN-1 protein comprising an amino acid sequence depicted in any even-numbered sequence selected from SEQ ID NO:2 to SEQ ID NO:30 shown in the Sequence Listing. Also disclosed is a cancer detection reagent comprising CAPRIN-1 protein or a fragment thereof, an antibody directed against CAPRIN-1 protein or the fragment thereof, or a polynucleotide encoding CAPRIN-1 protein or the fragment thereof.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Nanoparticle drug conjugates
ActiveUS20150343091A1Maintain good propertiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticle drug conjugateMedicine
Described herein are nanoparticle drug conjugates (NDCs), which, in certain embodiments, comprise a non-toxic, multi-modality, clinically proven silica-based nanoparticle platform with covalently attached drug molecules / moieties. The nanoparticle drug conjugates (NDCs) demonstrate imaging capability and targeting ligands which efficiently clear through the kidneys. Furthermore, the conjugates incorporate therapeutic agents for cancer detection, prevention, and / or treatment.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +1
Lung cancer marker detection immunochromatographic test paper and application
InactiveCN101609096AAchieve early diagnosisIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysisAntigenWilms' tumor
The invention belongs to the cancer detection technology, relating to a lung cancer marker detection immunochromatographic test paper and an application. The detection of a single tumour marker in the prior art can not meet the requirements of clinical early diagnosis and differential diagnosis. The invention realizes the early diagnosis of lung cancer by jointly detecting NSE and CEA in serum with a double antibody sandwich immunochromatography. The invention comprises the following preparation steps: preparing aurosol-neure NSE and aurosol-carcinoembryonic antigen CEA antibody compounds; preparing double antibody sandwich NSE and CEA detection test strips. The invention comprises the following steps in lung cancer detection: configurating series concentration NSE and CEA standard substances; preparing NSE and CEA mixed antigen solution with serum of normal people; inserting the sample pad ends of the test strips into the above concentration series standard substances respectively to observe the changes in colours of T and C lines on a NC film. The invention has the advantages of convenient detection operation, high sensitivity and precise result, and can determine lung cancer recurrence 4-12 weeks ahead.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com