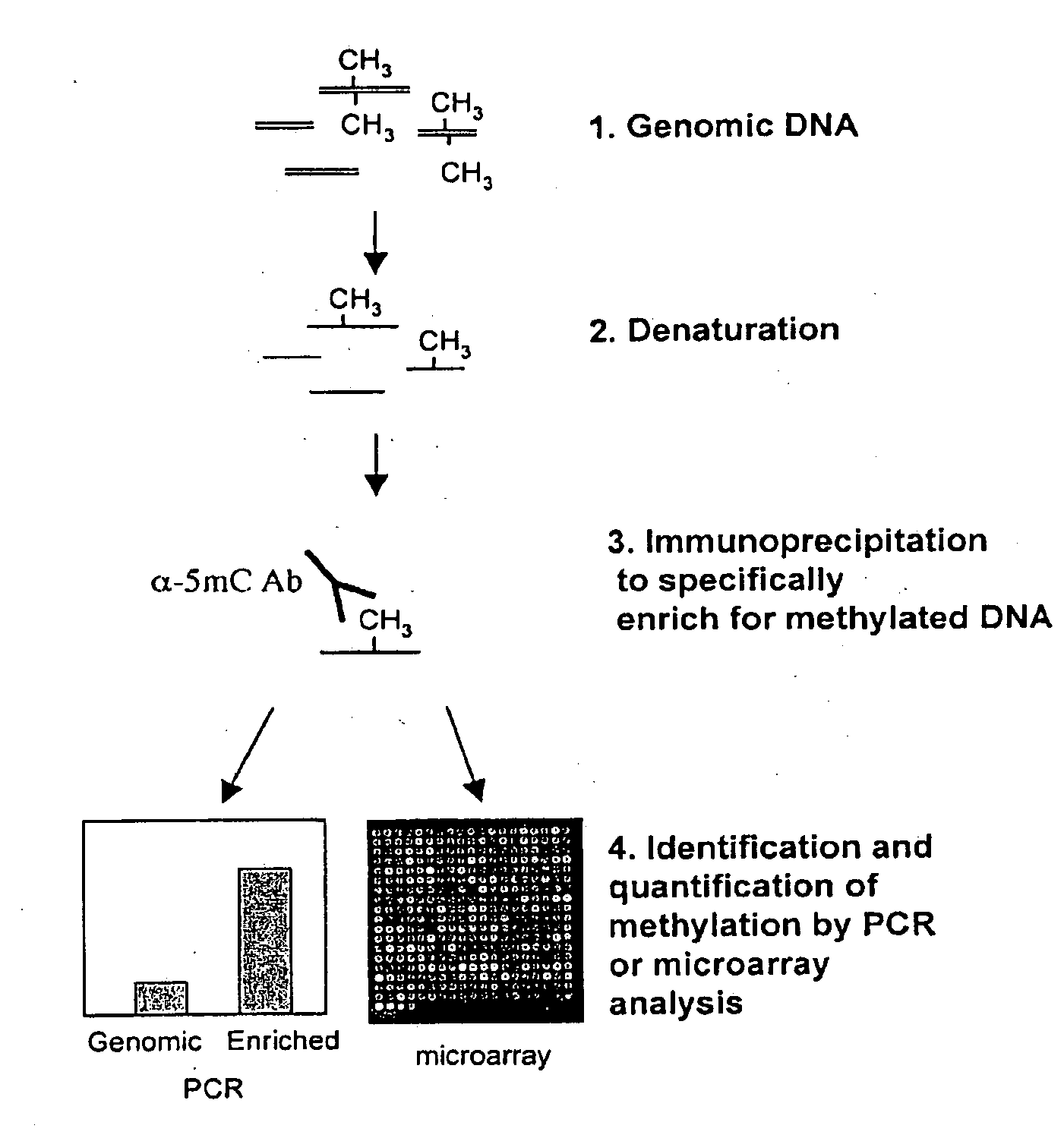
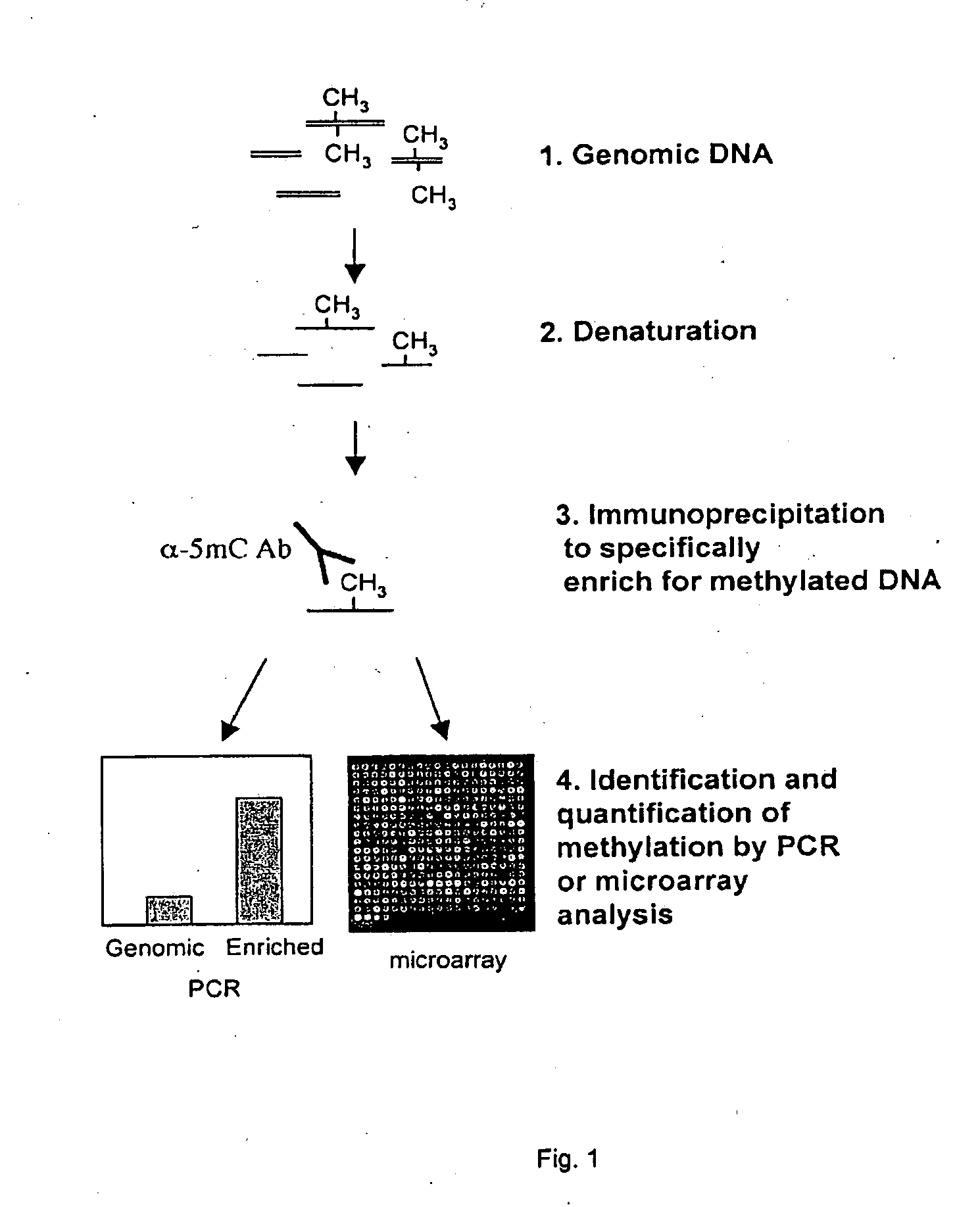
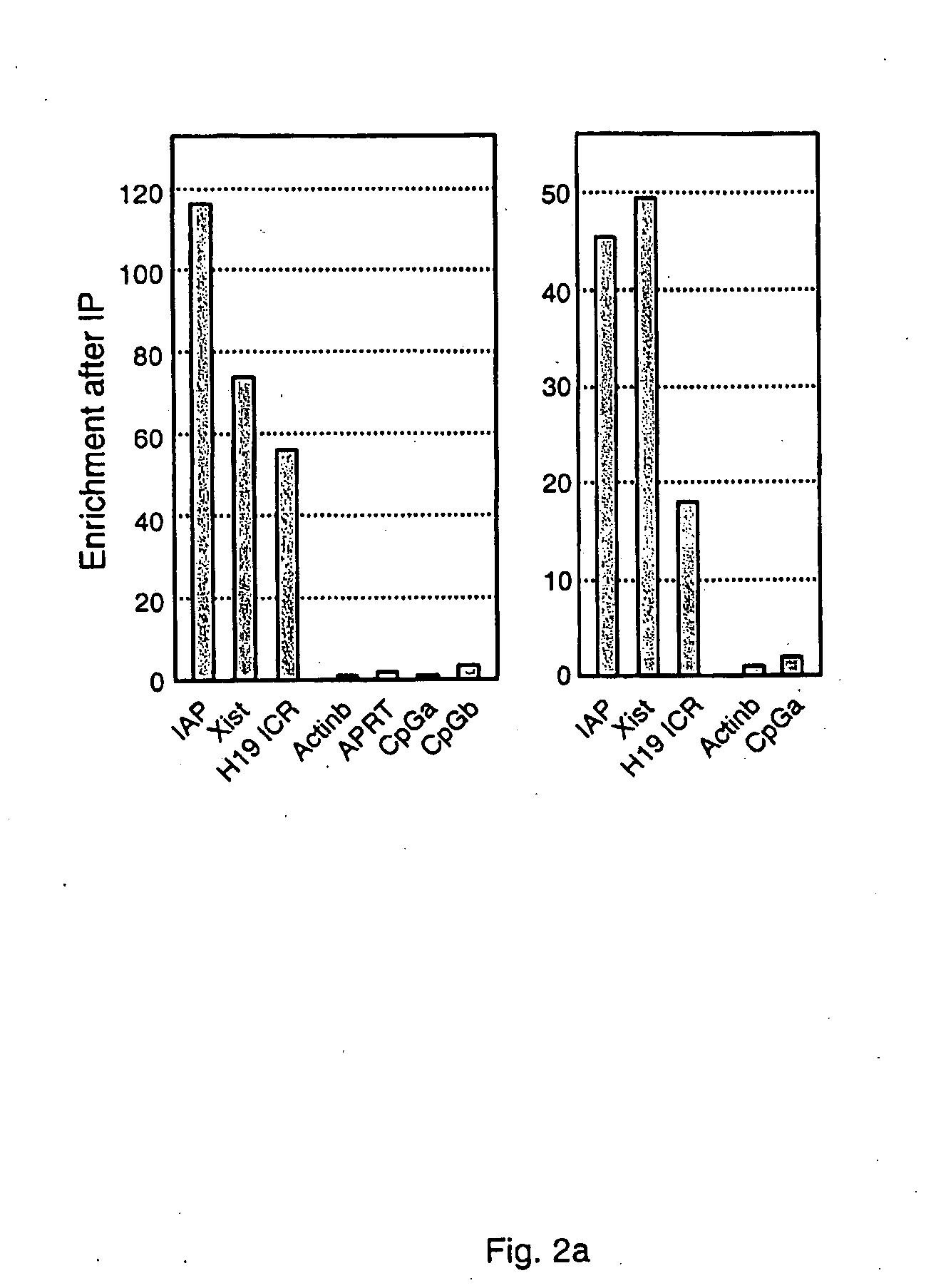
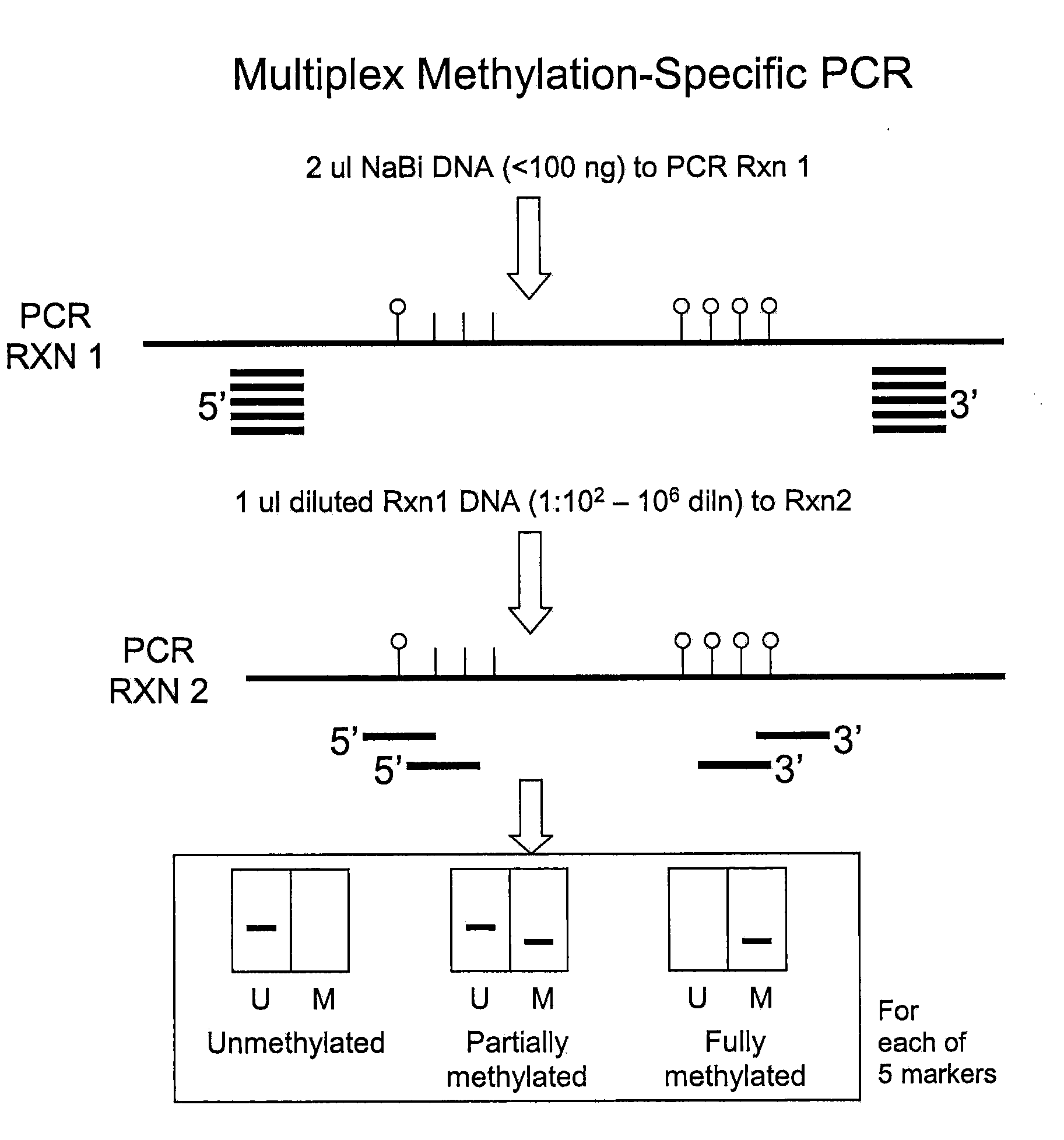
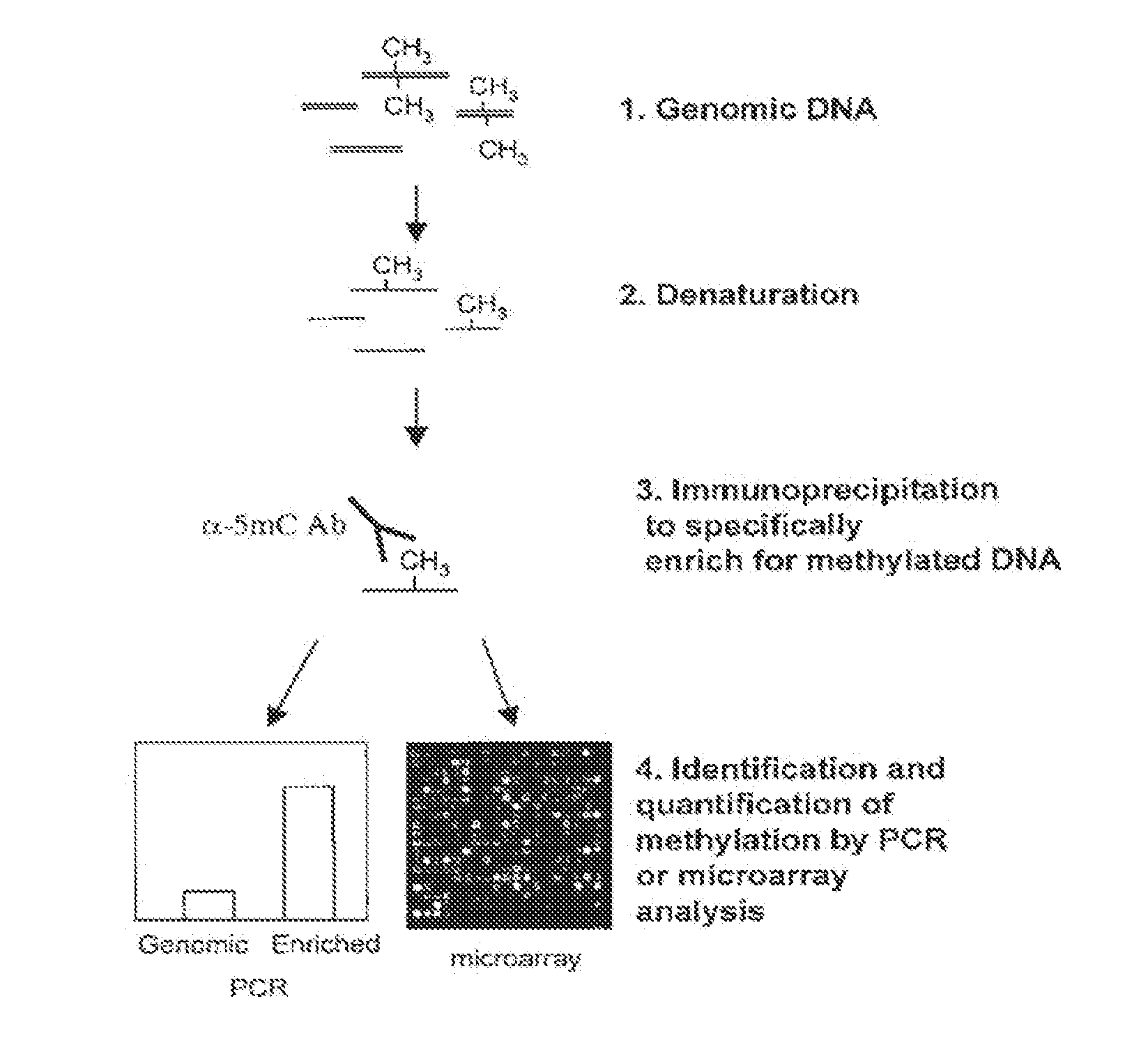
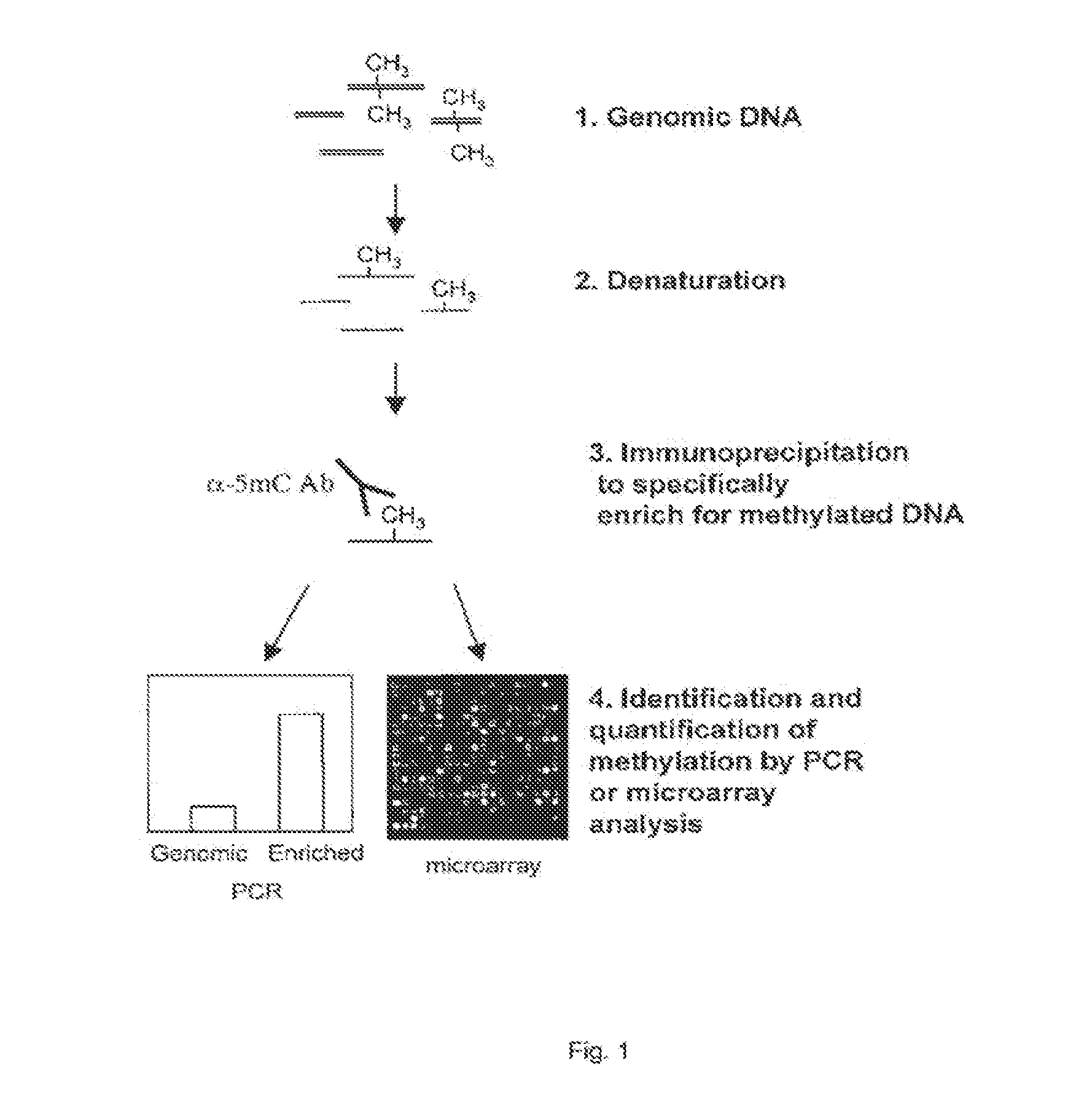
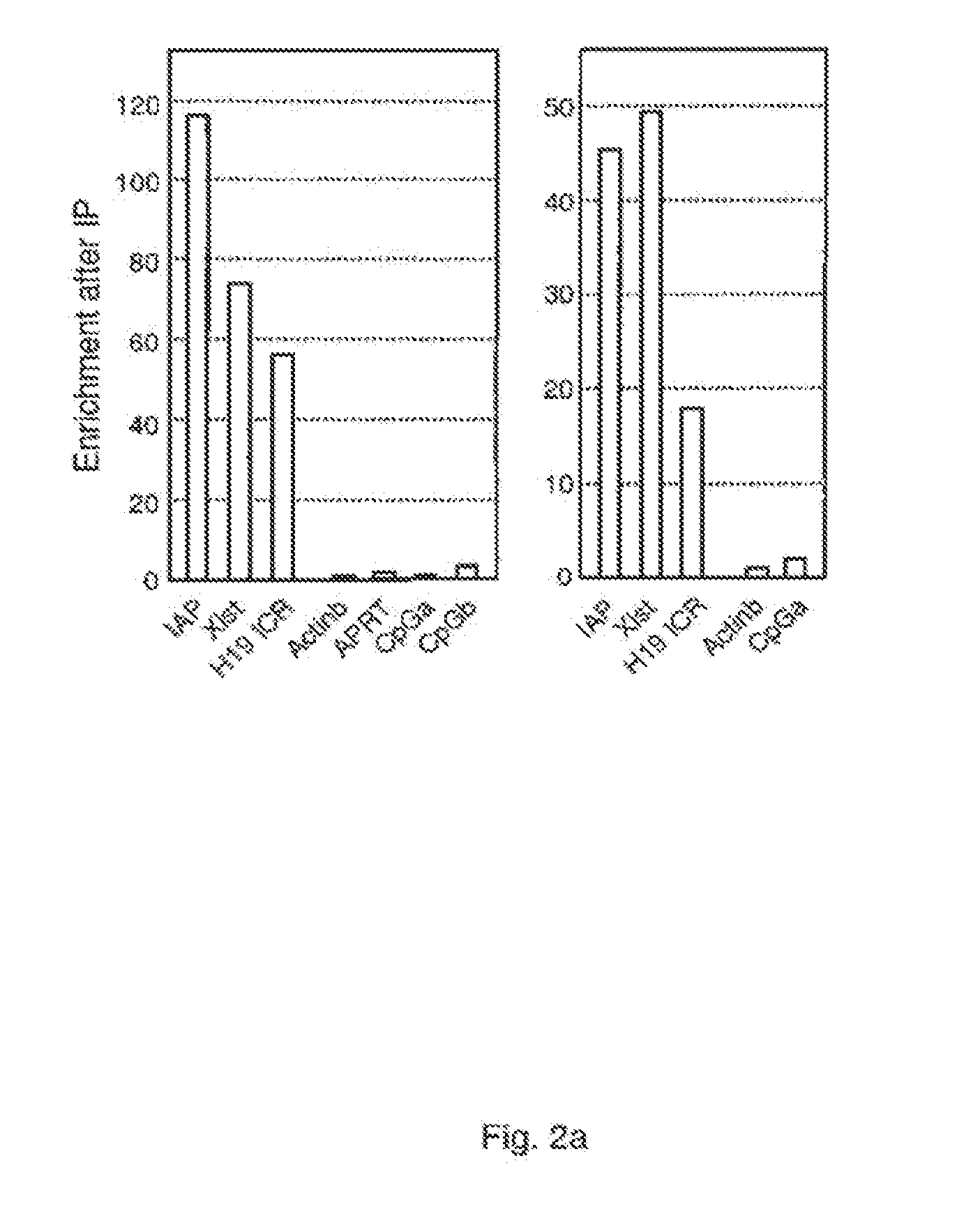
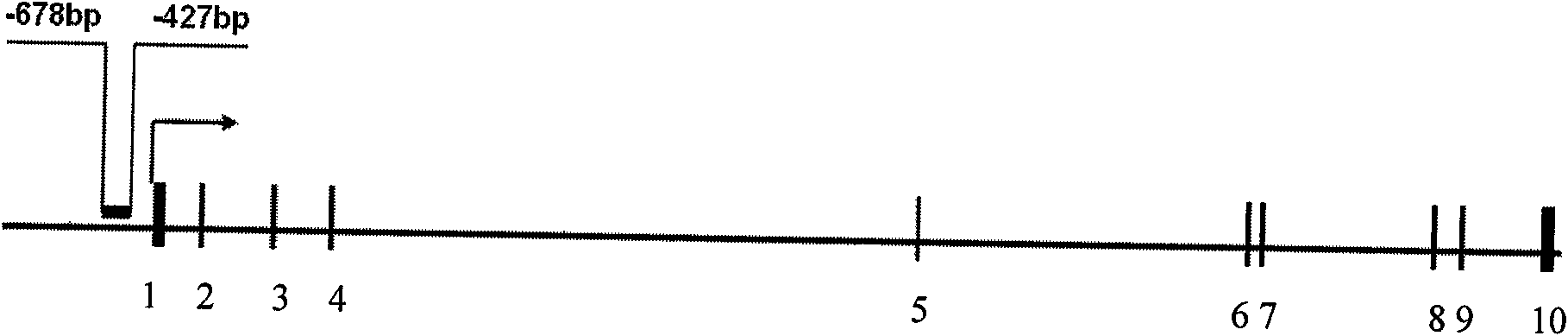
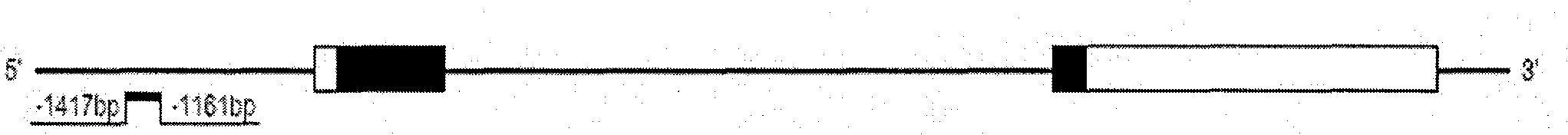Patents
Literature
33 results about "Aberrant methylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
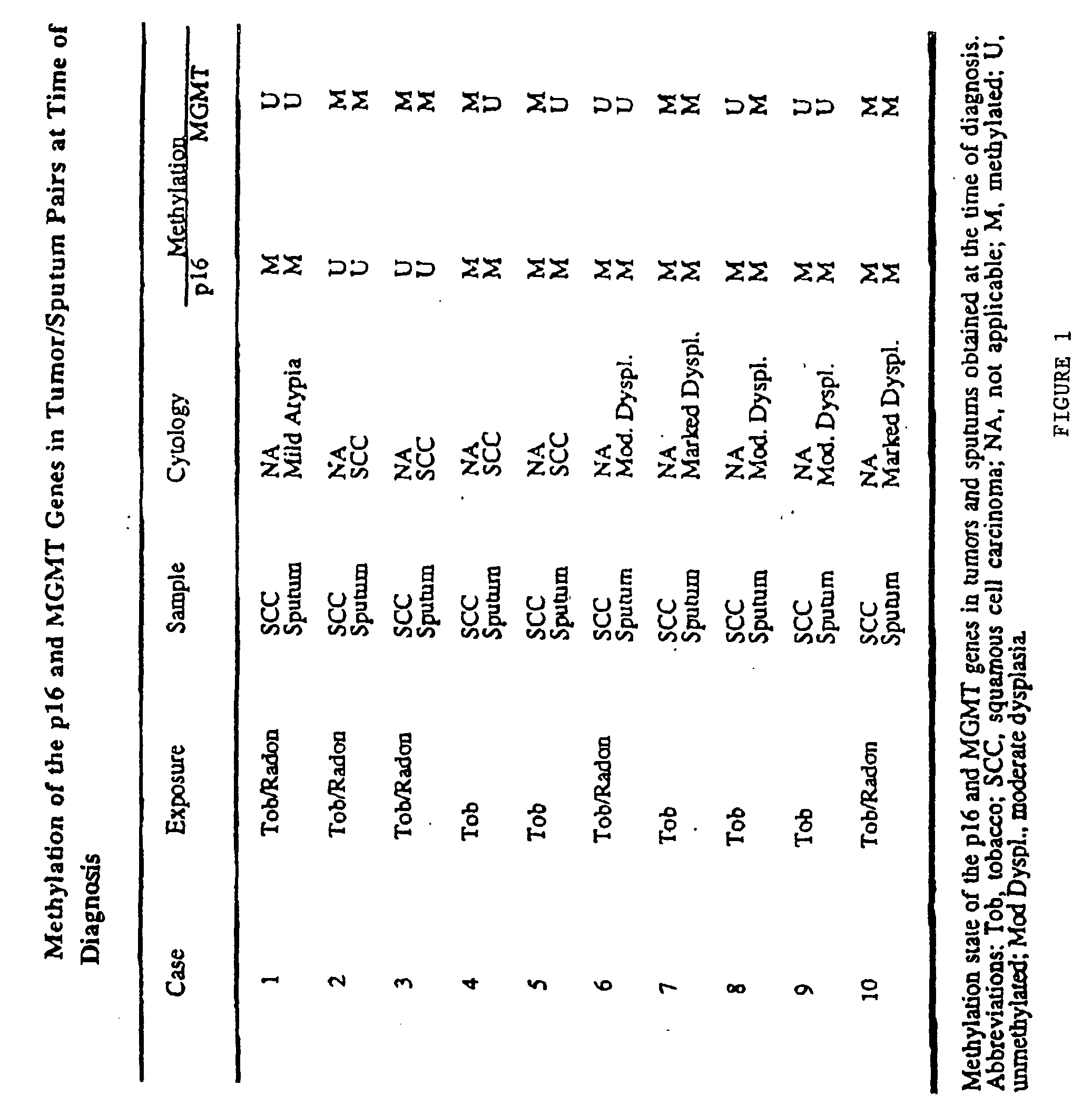
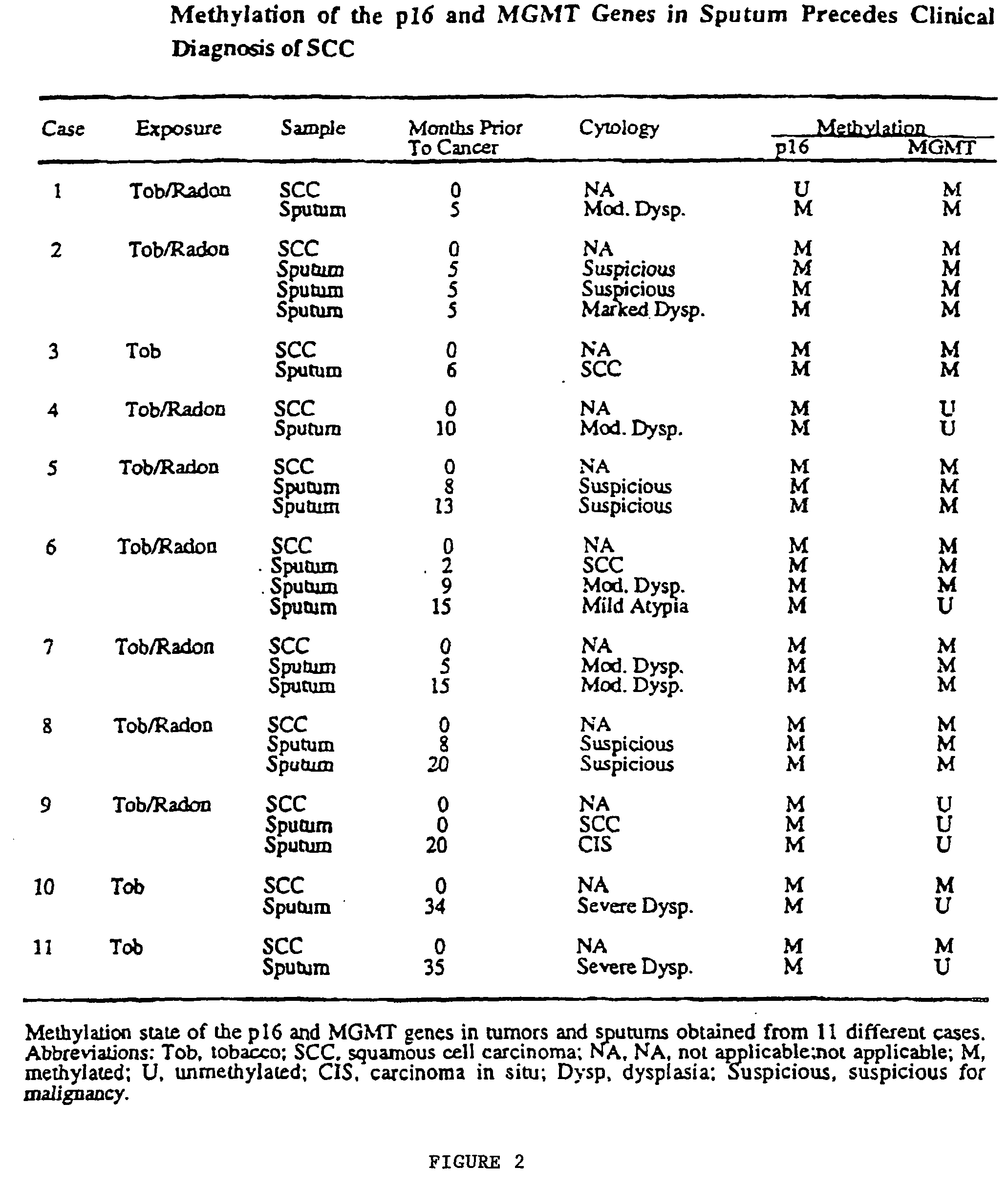
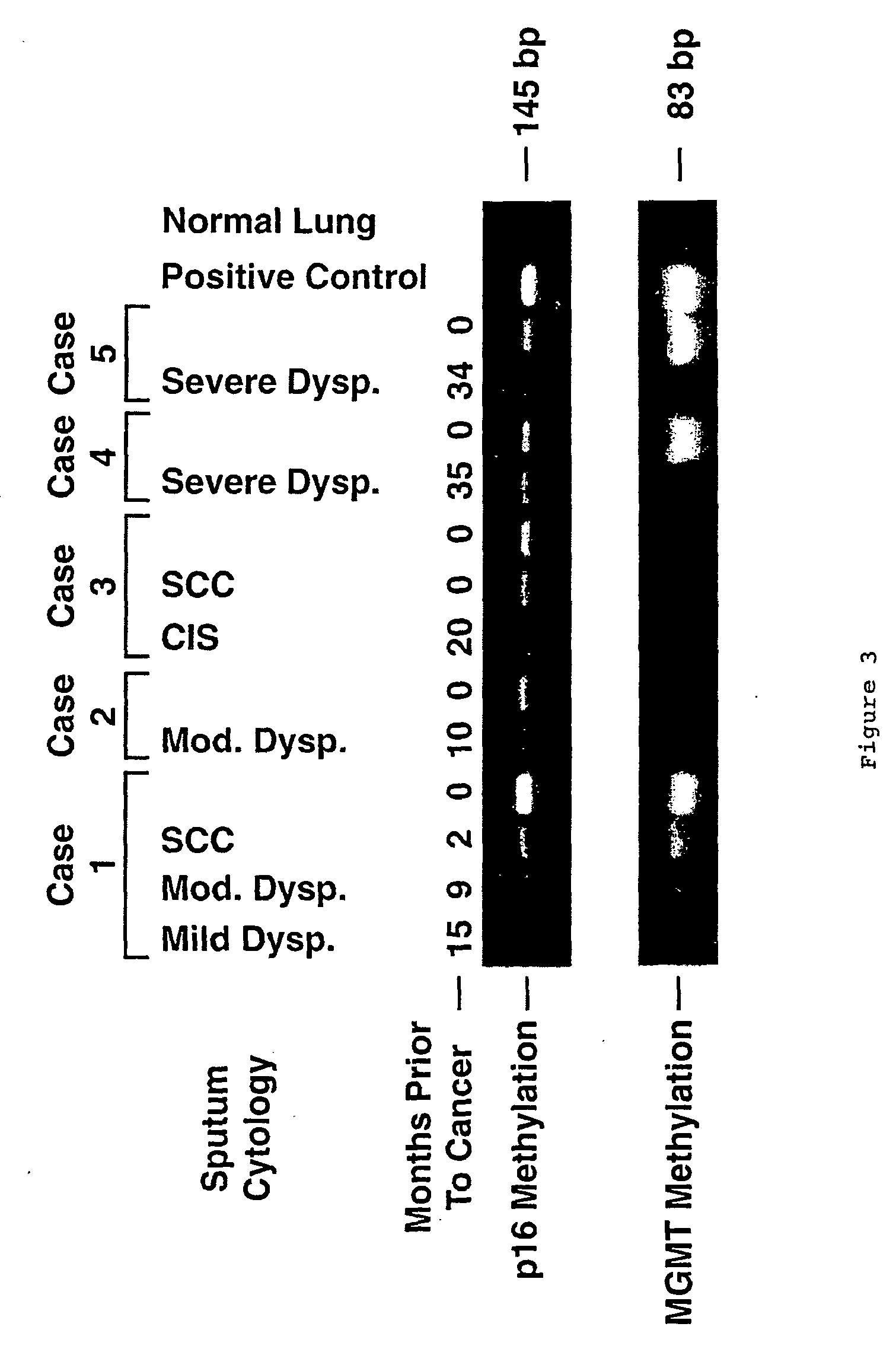
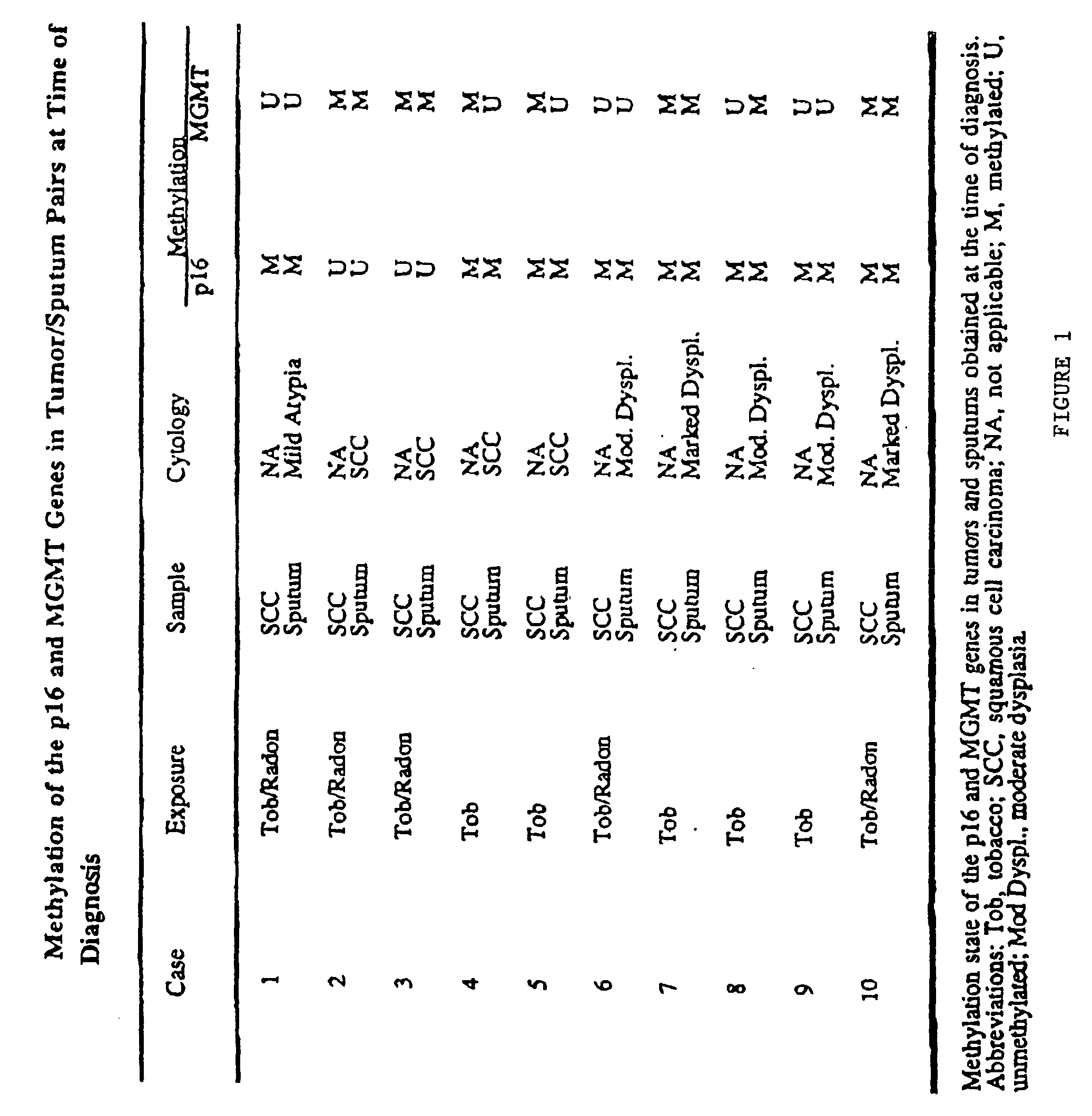
Nested methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction cancer detection method
A molecular marker-based method for monitoring and detecting cancer in humans. Aberrant methylation of gene promoters is a marker for cancer risk in humans. A two-stage, or "nested" polymerase chain reaction method is disclosed for detecting methylated DNA sequences at sufficiently high levels of sensitivity to permit cancer screening in biological fluid samples, such as sputum, obtained non-invasively. The method is for detecting the aberrant methylation of the p16 gene, O 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene, Death-associated protein kinase gene, RAS-associated family 1 gene, or other gene promoters. The method offers a potentially powerful approach to population-based screening for the detection of lung and other cancers.
Owner:LOVELACE RESPIRATORY RES INST
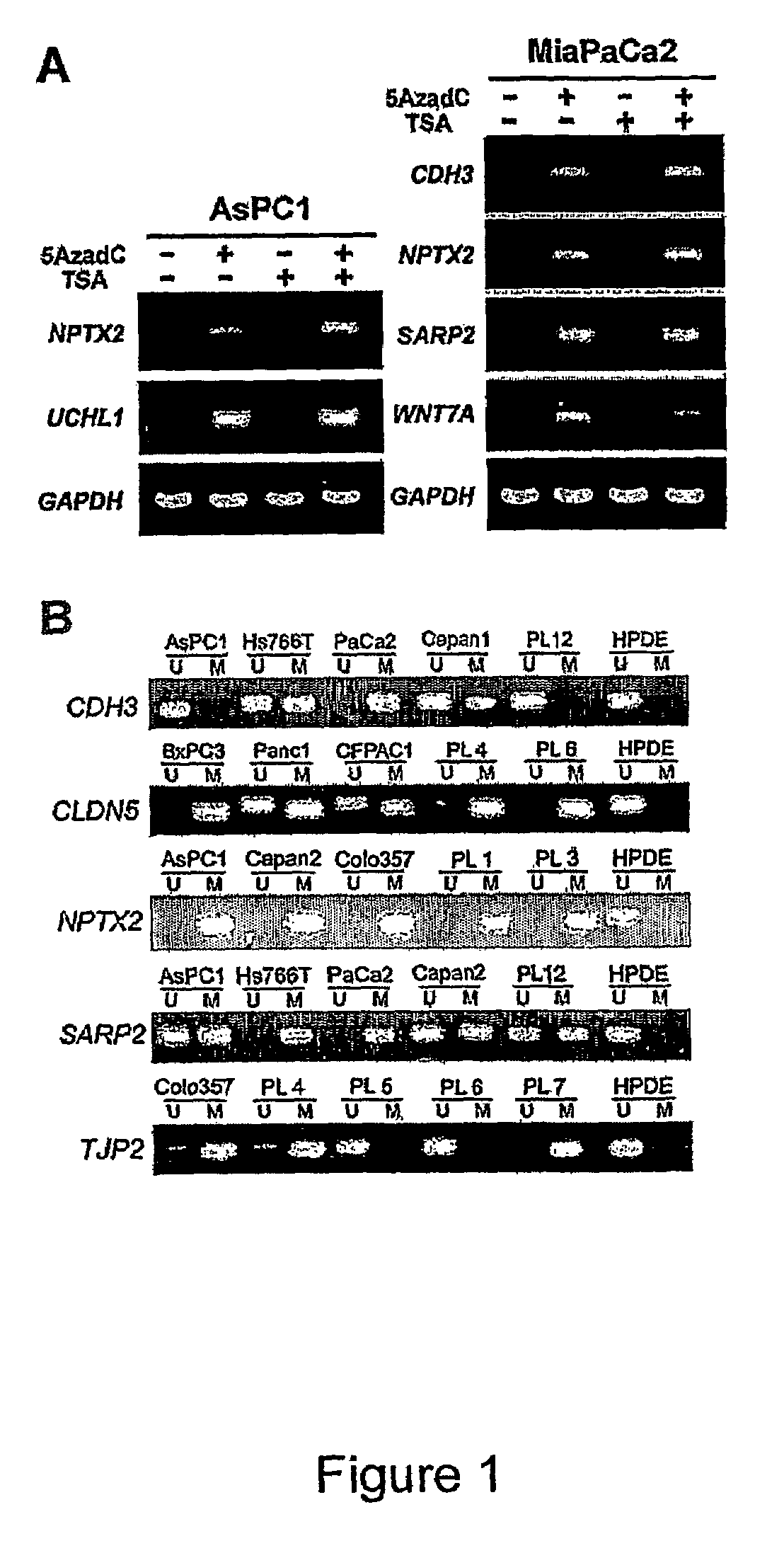
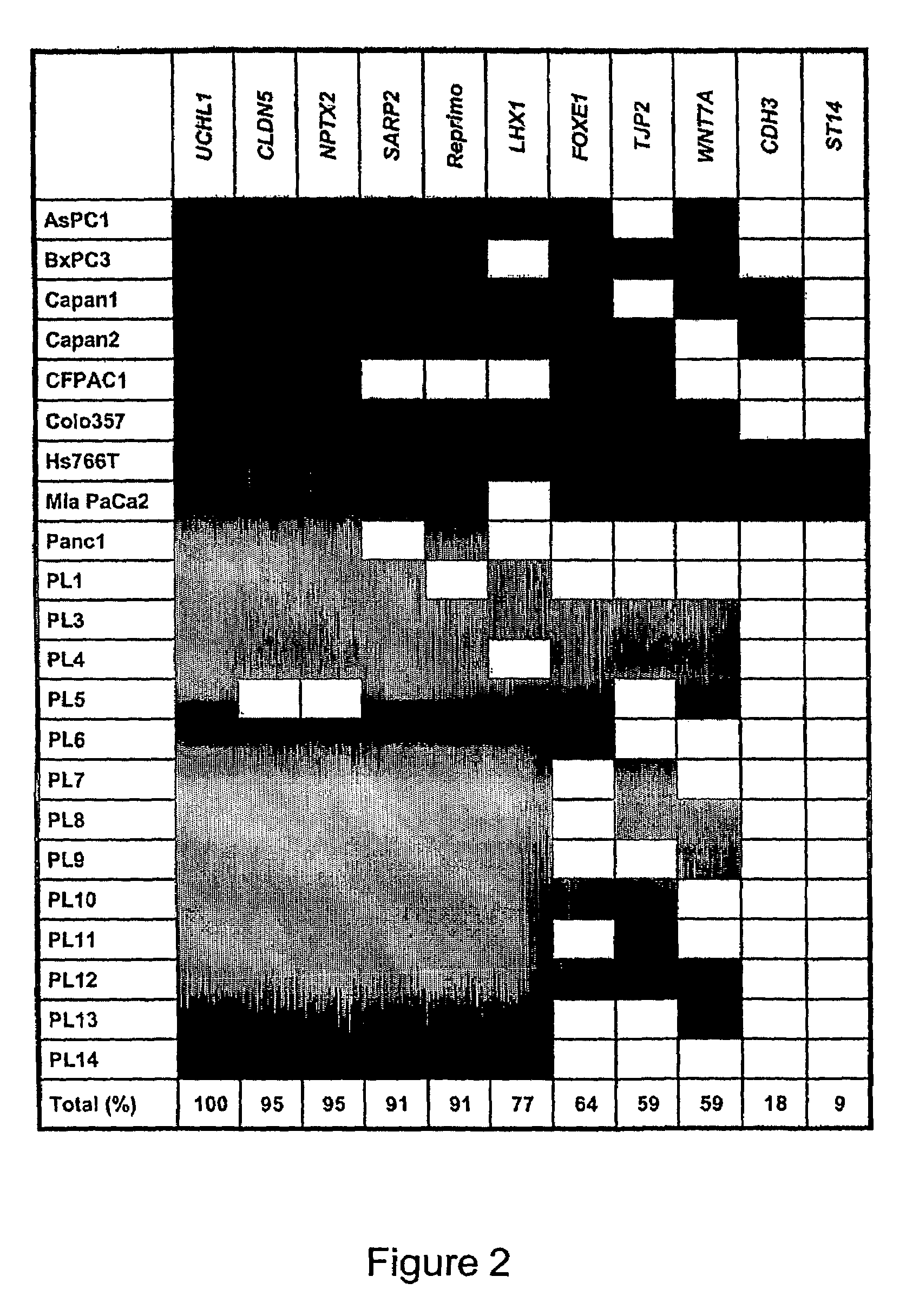
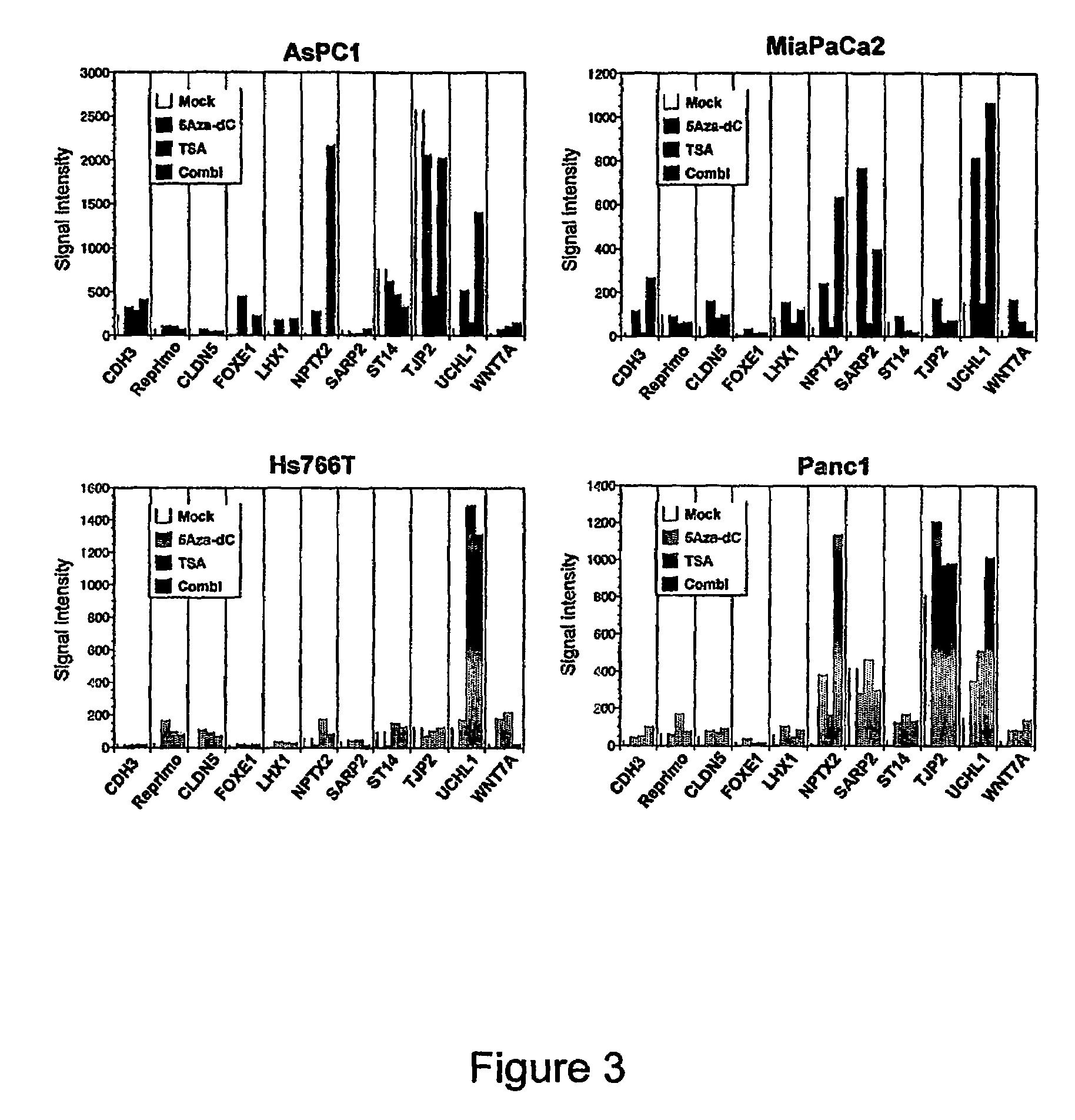
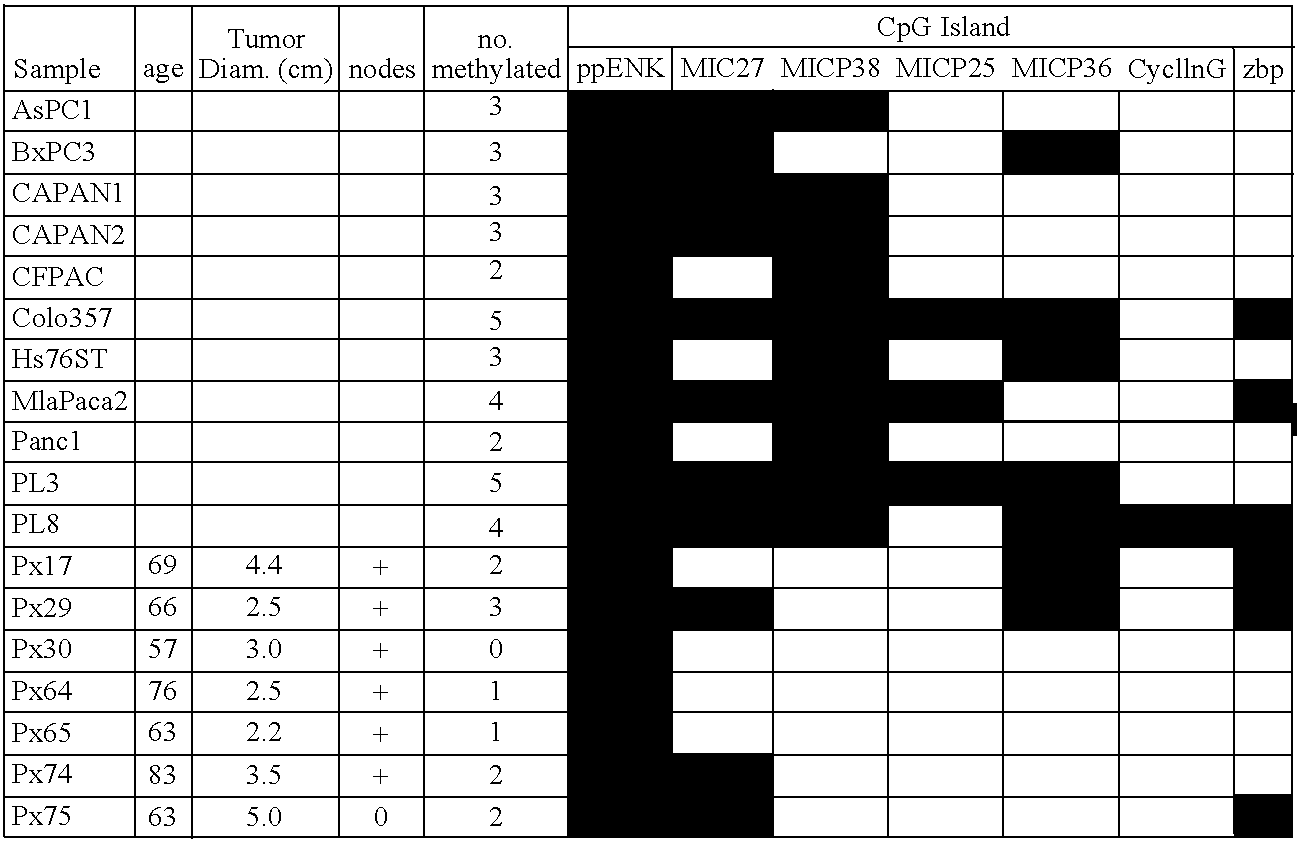
Aberrantly methylated genes in pancreatic cancer
ActiveUS7485418B2Raise the possibilityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsBiologyPancreatic carcinoma
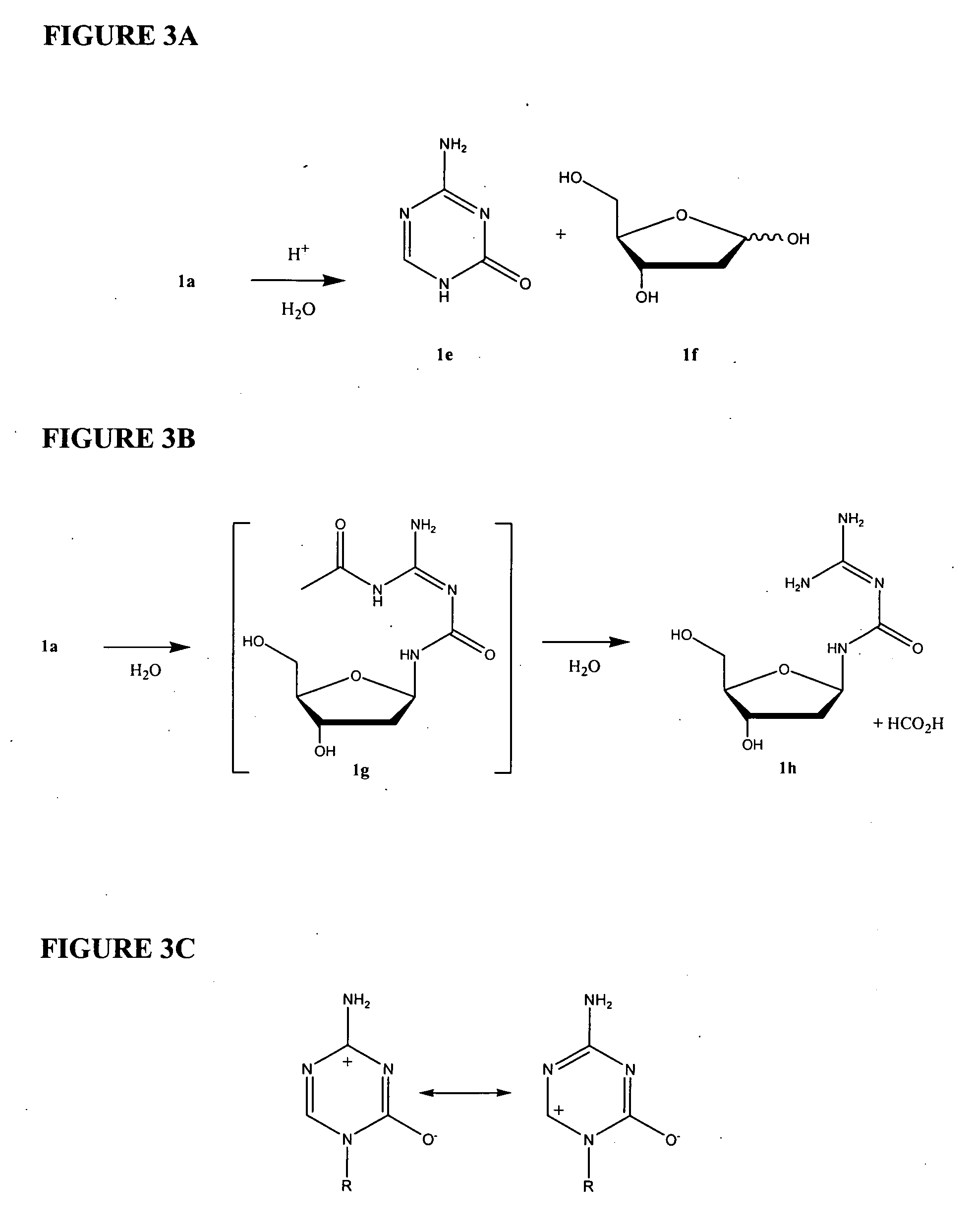
The present invention provides a method for detecting pancreatic carcinoma in a subject. The method includes contacting a nucleic acid-containing specimen from the subject with an agent that provides a determination of the methylation state of at least one gene or associated regulatory region of the gene and identifying aberrant methylation of regions of the gene or regulatory region, wherein aberrant methylation is identified as being different when compared to the same regions of the gene or associated regulatory region in a subject not having the pancreatic carcinoma, thereby detecting pancreatic carcinoma in the subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
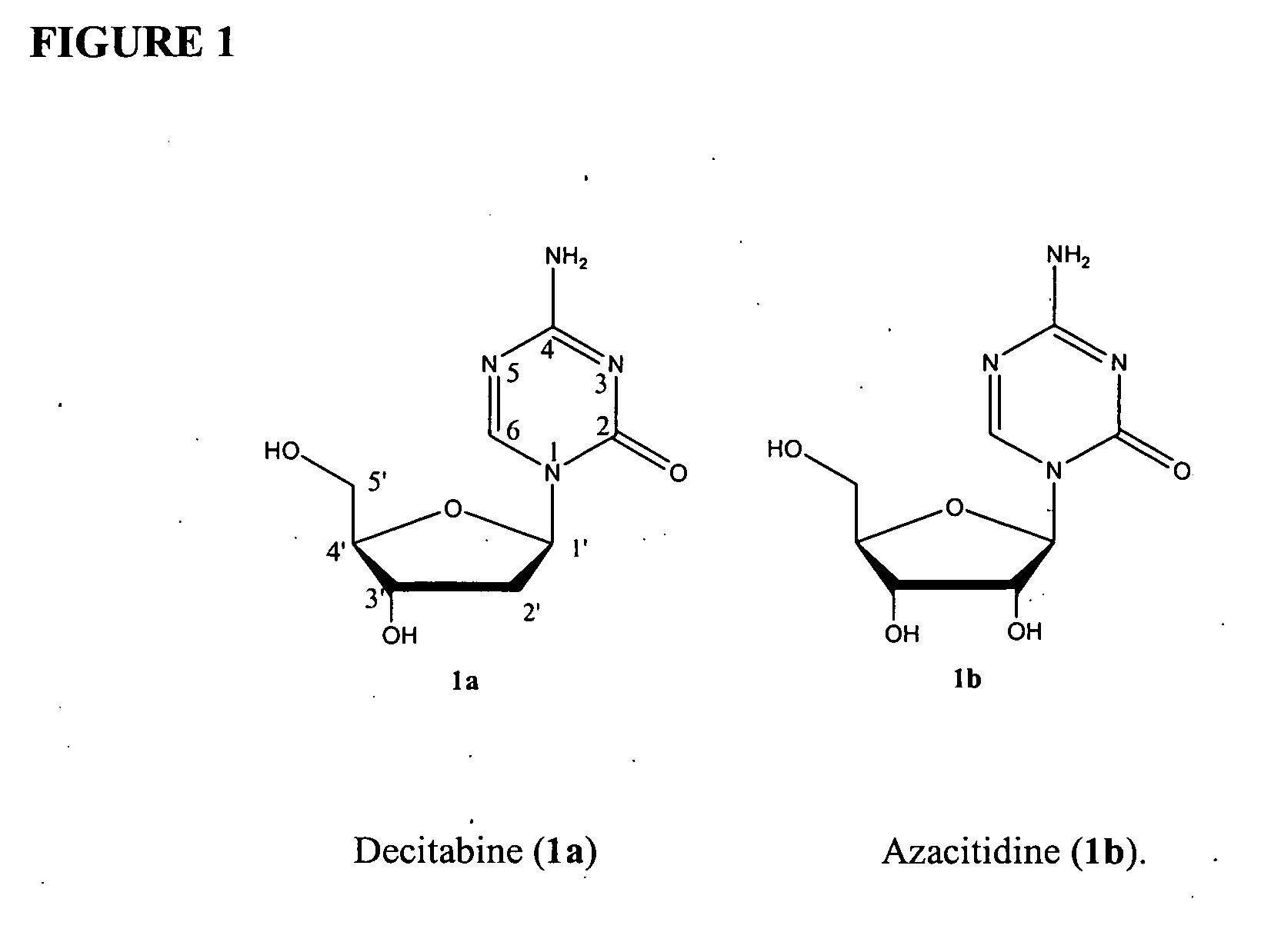
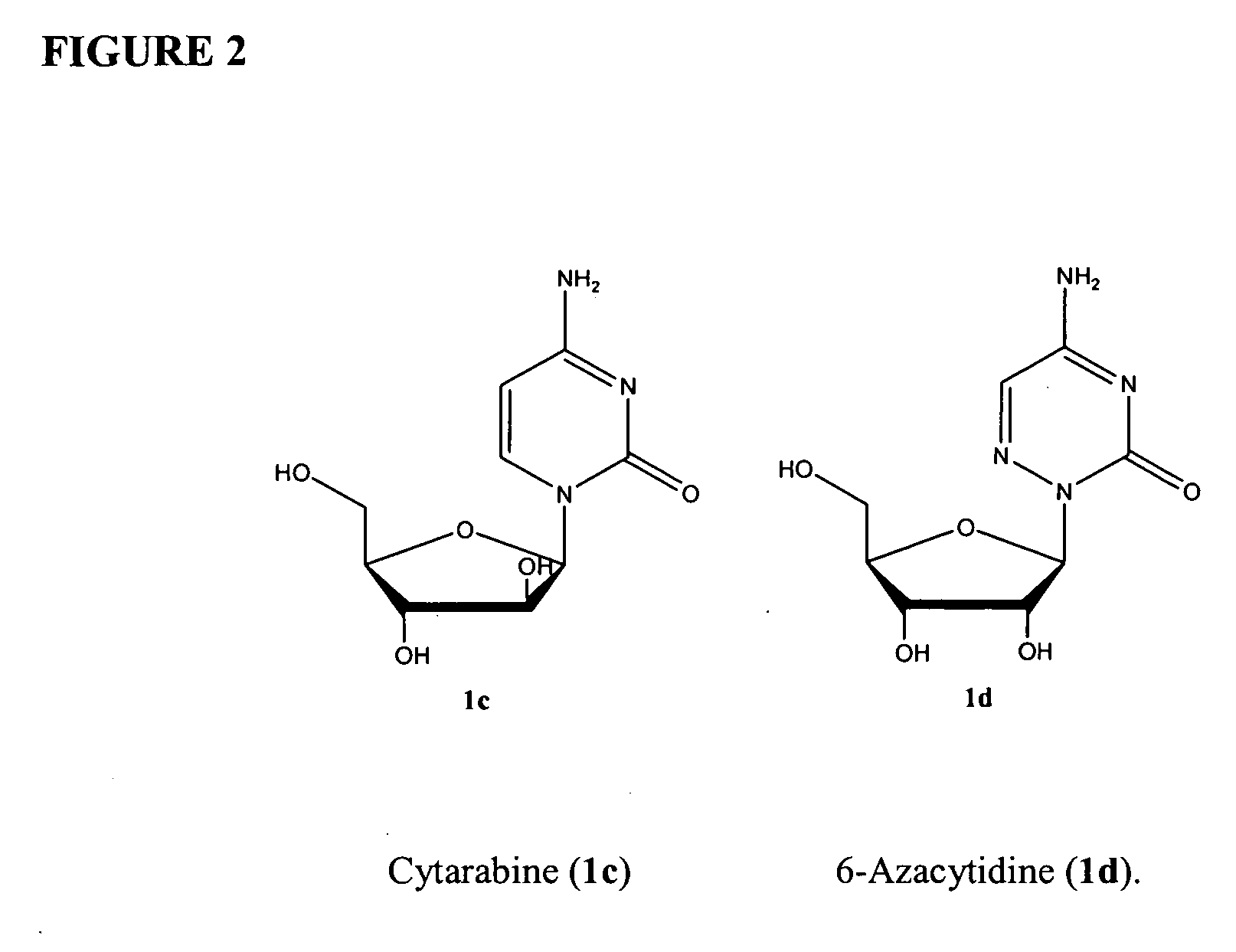
Azacytosine analogs and derivatives
InactiveUS20060205687A1Decrease electrophilicityBiocideSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthPyrimidine analogue
Compounds and compositions of azacytosine analogs and derivatives are provided. In one aspect of the invention, analogs or derivatives of decitabine and azacitidine are provided with modification at the 2-, 4-, or 6-position of the triazine ring, at the 1′-6′position of the ribose ring, or combinations thereof. Methods of using, synthesizing and manufacturing these analogs and derivatives are also provided. These compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutical compositions that can be used for treating any disease associated with aberrant DNA methylation, or a disease or condition that is sensitive to the treatment with decitabine or azacitidine, such as hematological disorders, tumors and cancers.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Administration Of DNA Methylation Inhibitors For Treating Epigenetic Diseases
Methods are provided for treating patients with epigenetic diseases, especially those associated with aberrant DNA methylation such as hematological disorders and cancer. By administering a DNA methylation inhibitor to the patients following unique dosing regimens, the disease can be efficaciously treated with reduced toxic side effects.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Aberrantly methylated genes in pancreatic cancer
ActiveUS20070015156A1Raise the possibilityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsBiologyPancreatic carcinoma
The present invention provides a method for detecting pancreatic carcinoma in a subject. The method includes contacting a nucleic acid-containing specimen from the subject with an agent that provides a determination of the methylation state of at least one gene or associated regulatory region of the gene and identifying aberrant methylation of regions of the gene or regulatory region, wherein aberrant methylation is identified as being different when compared to the same regions of the gene or associated regulatory region in a subject not having the pancreatic carcinoma, thereby detecting pancreatic carcinoma in the subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
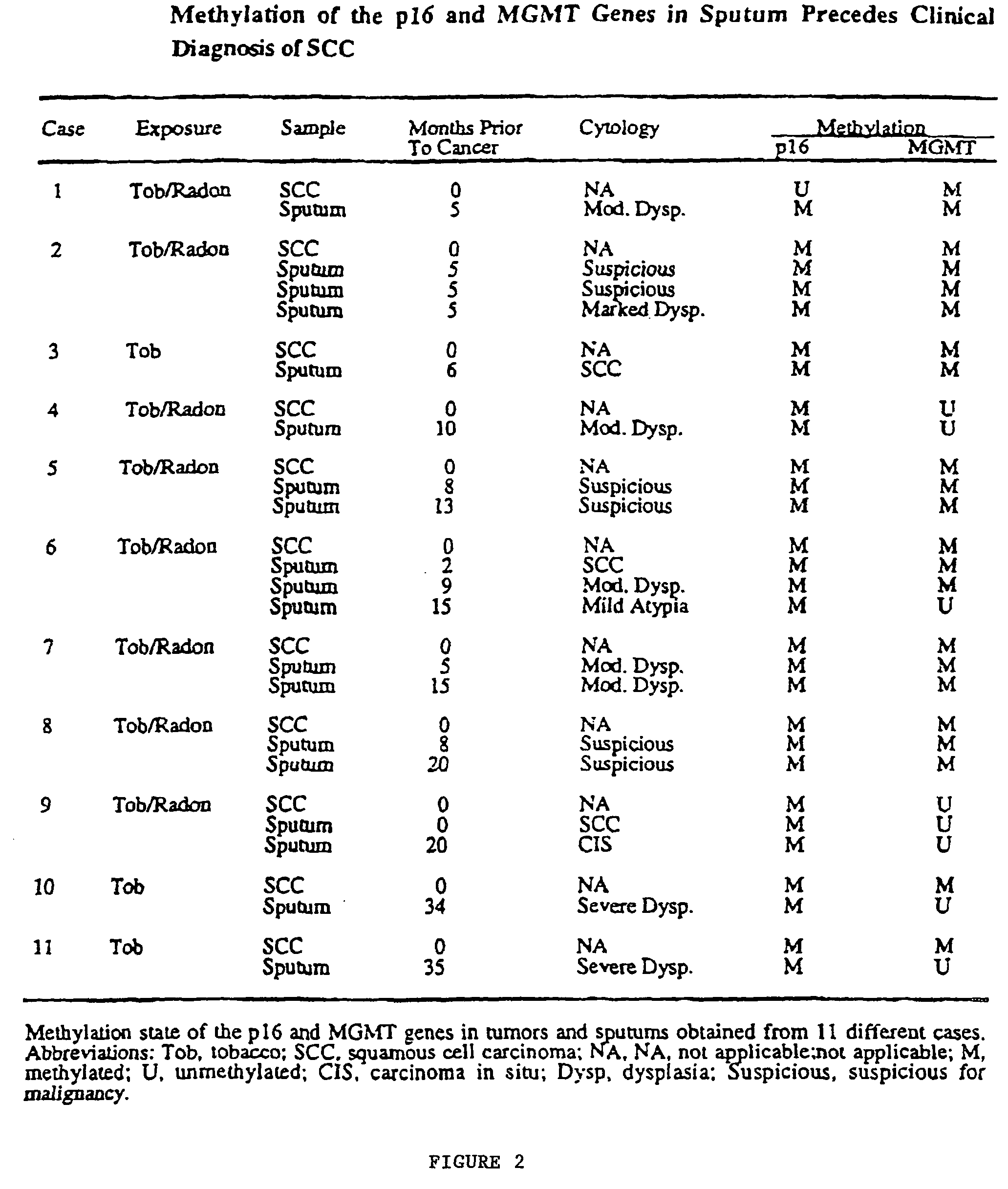
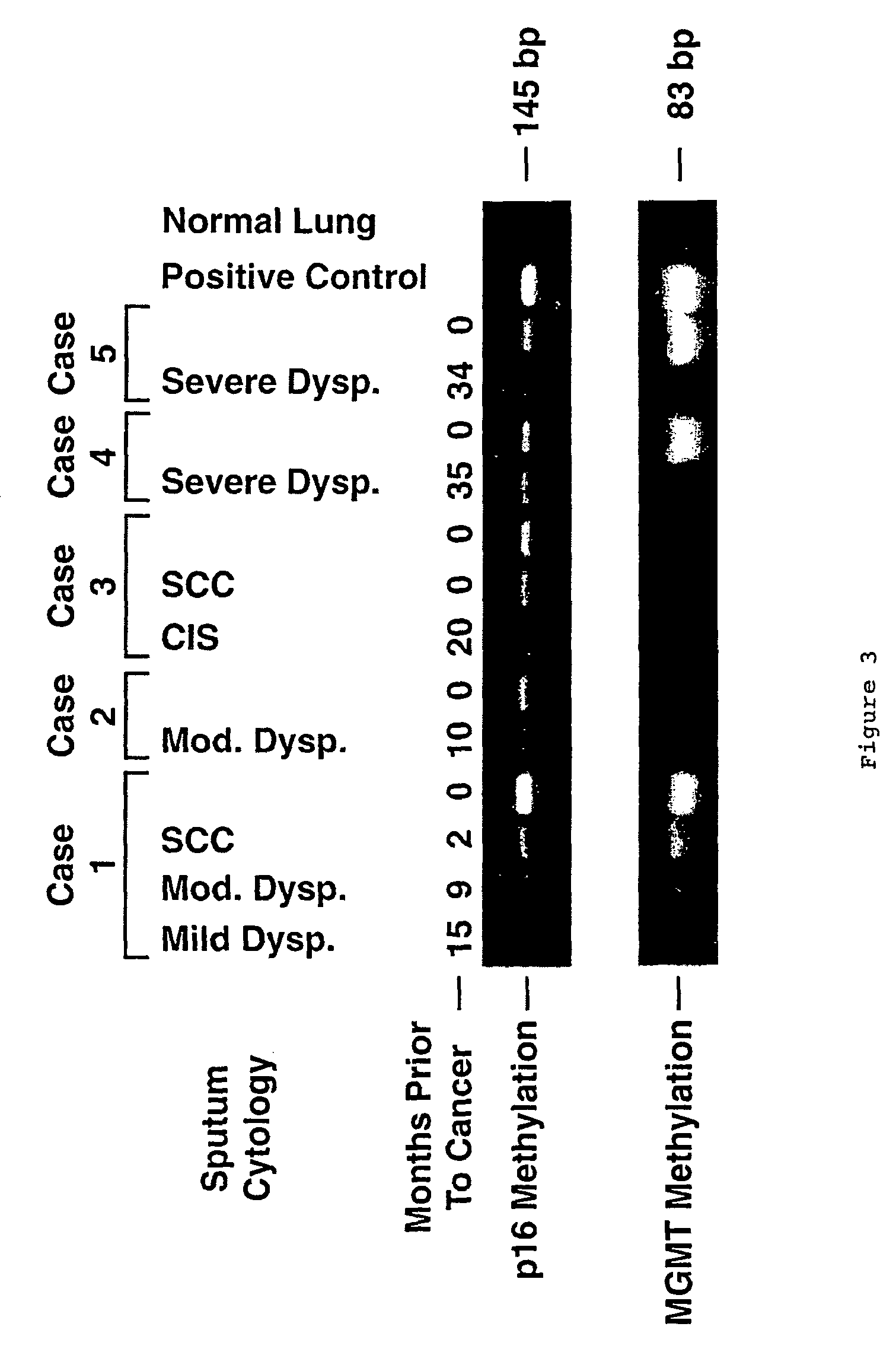
Nested methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction cancer detection method
A molecular marker-based method for monitoring and detecting cancer in humans. Aberrant methylation of gene promoters is a marker for cancer risk in humans. A two-stage, or “nested” polymerase chain reaction method is disclosed for detecting methylated DNA sequences at sufficiently high levels of sensitivity to permit cancer screening in biological fluid samples, such as sputum, obtained non-invasively. The method is for detecting the aberrant methylation of the p16 gene, O 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene, Death-associated protein kinase gene, RAS-associated family 1 gene, or other gene promoters. The method offers a potentially powerful approach to population-based screening for the detection of lung and other cancers.
Owner:LOVELACE RESPIRATORY RES INST
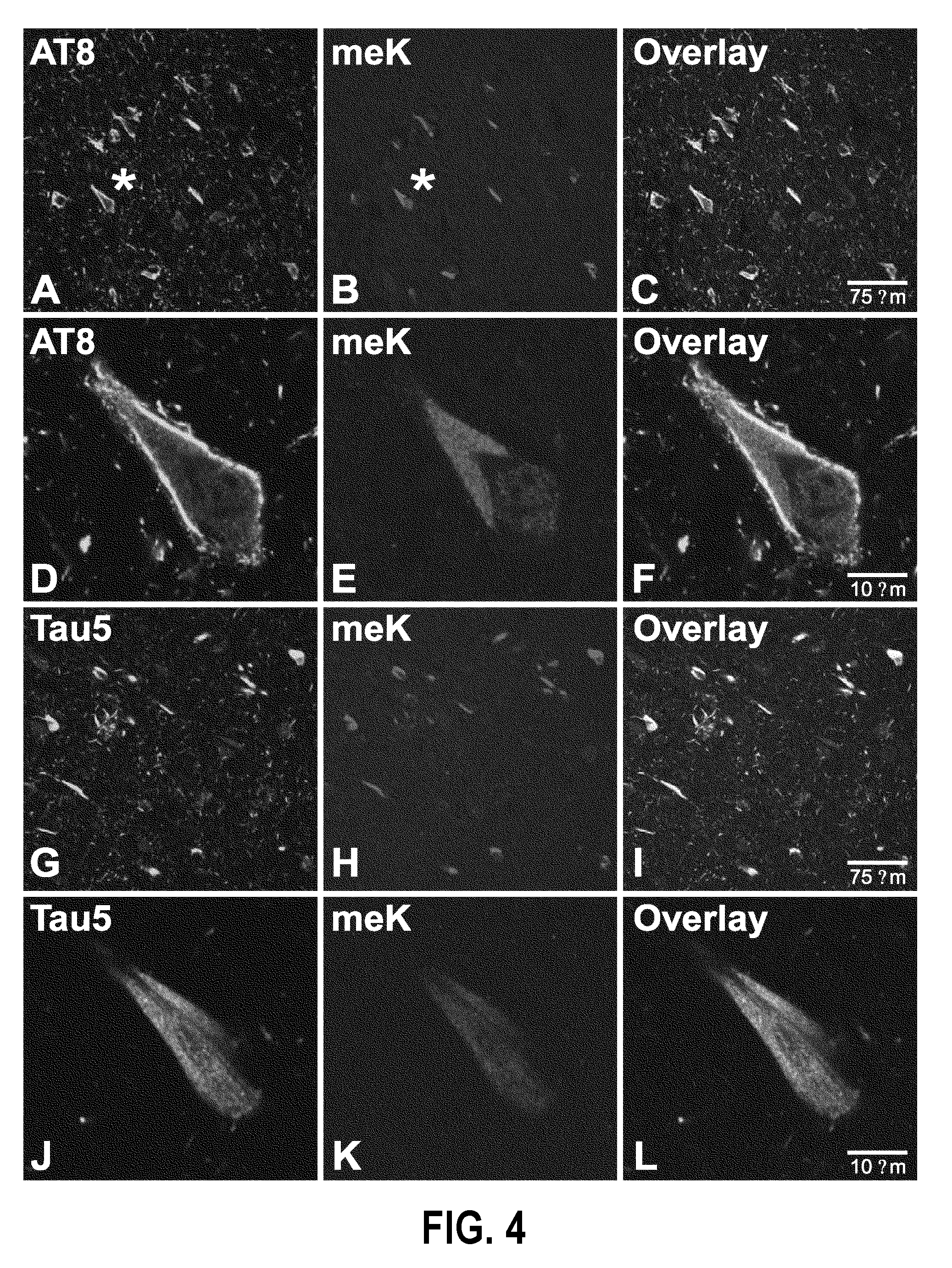
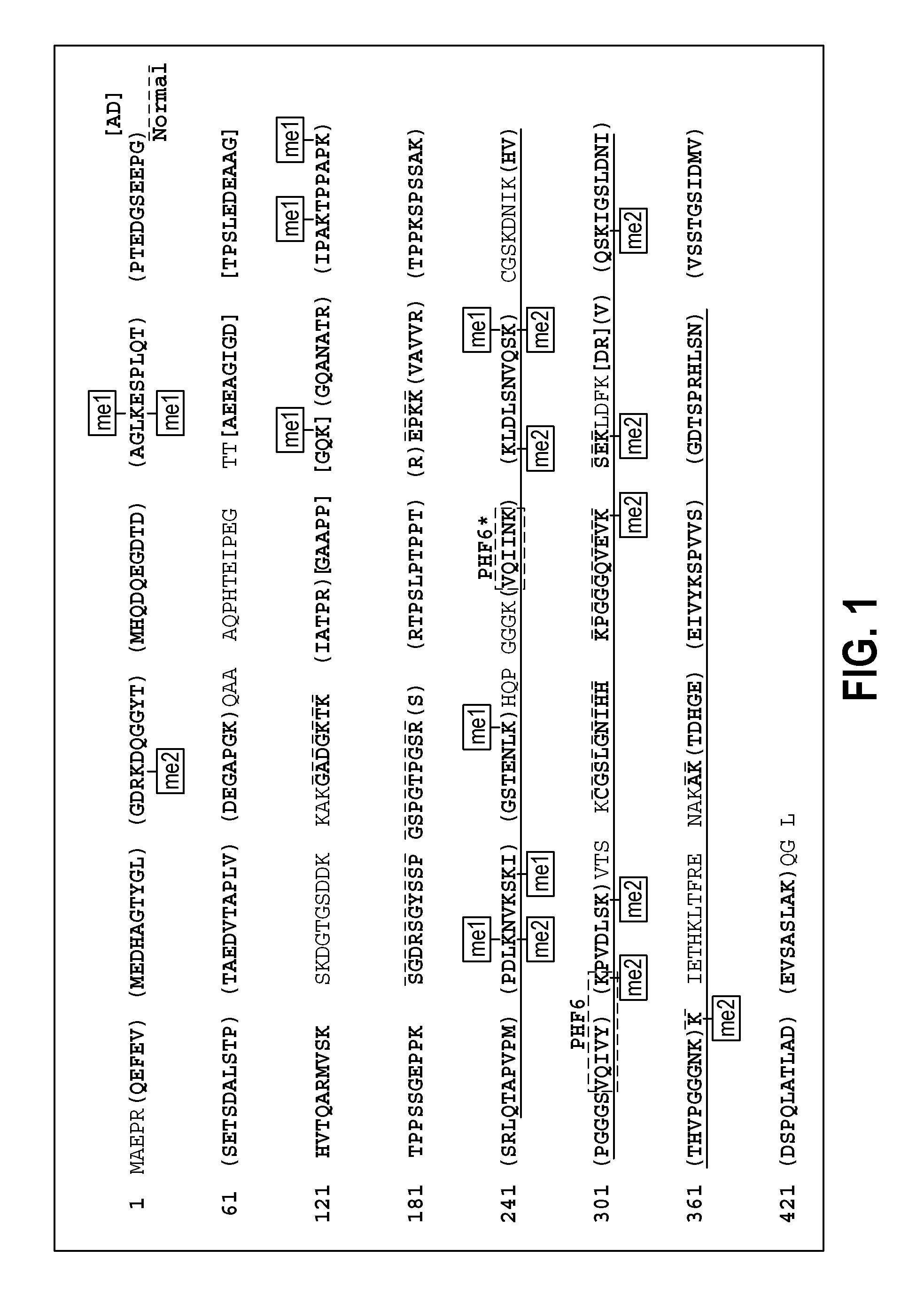
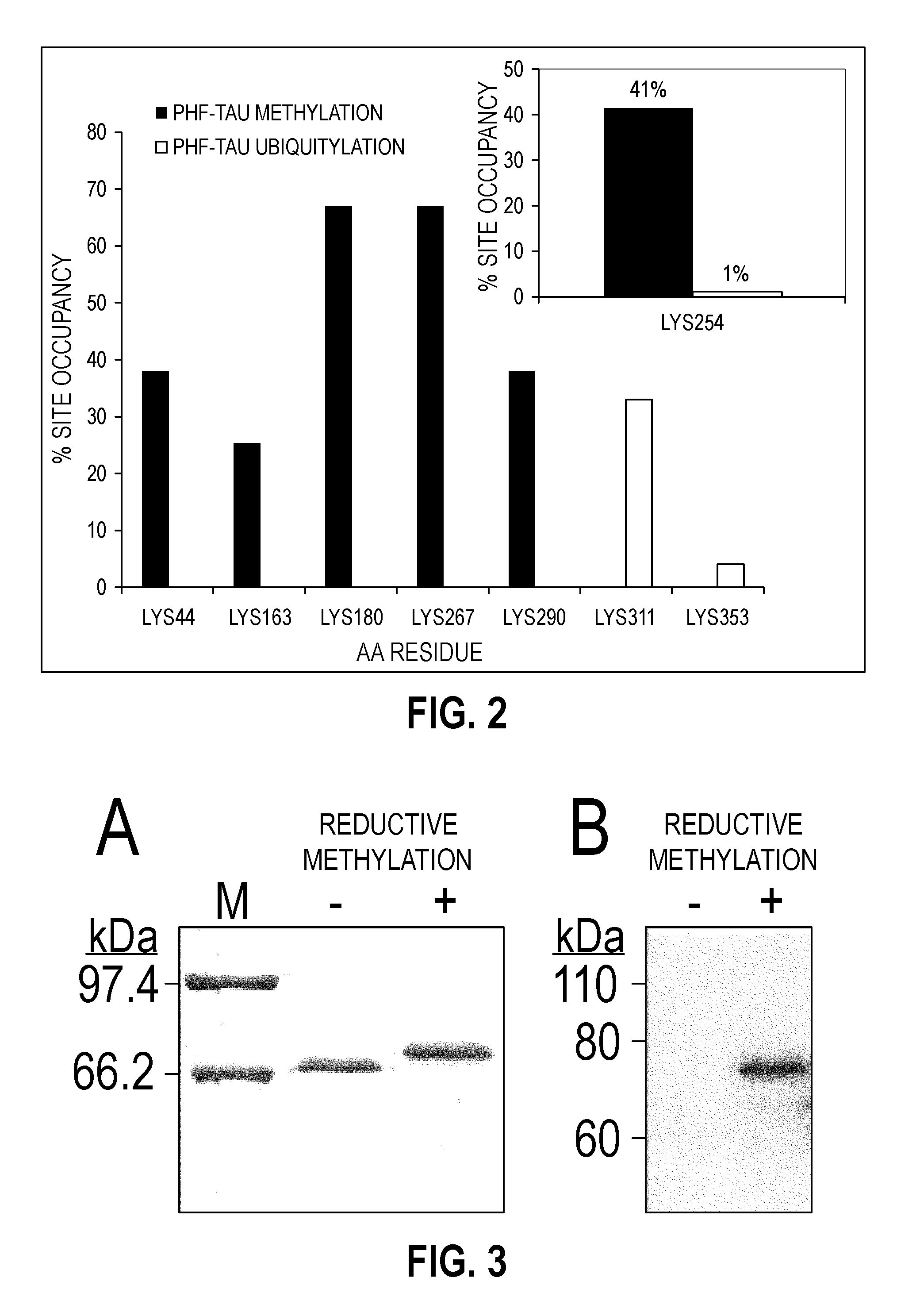
Methylated Peptides Derived from Tau Protein and Their Antibodies for Diagnosis and Therapy of Alzheimer's Disease
ActiveUS20140294839A1Low extensionImprove understandingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPost translational
In sporadic Alzheimer's disease, neurofibrillary lesion formation is preceded by extensive post-translational modification of the microtubule associated protein tau. Immunoassays have been developed recently that detect tau in biological specimens, thus providing a means for pre-mortem diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, which has remained elusive. These assays have been improved by the analysis of relevant post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, however opportunity for improvement remains. The present invention addresses this issue by disclosing synthetic methylated peptides derived from the tau protein of paired helical filaments and non-diseased control brain. Alzheimer's disease specificity is provided by the presence or absence of methyl moieties on lysine residues and differences between mono-, di-, and tri-methylation. The methylated peptide is useful as an antigen and a binding partner for identifying compounds that interact with the peptide and the methylated tau protein, including antibodies that can distinguish non-diseased brain from that affected by Alzheimer's disease. The resulting antibodies are useful diagnostically and therapeutically. The compounds that specifically bind to methylated tau proteins are useful for eliminating abnormally methylated tau.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +1
Methylation quantitative detection method of PCDH8 gene
InactiveCN101967515AQuantitative determination of abnormal methylation levelsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesBisulfite sequencing
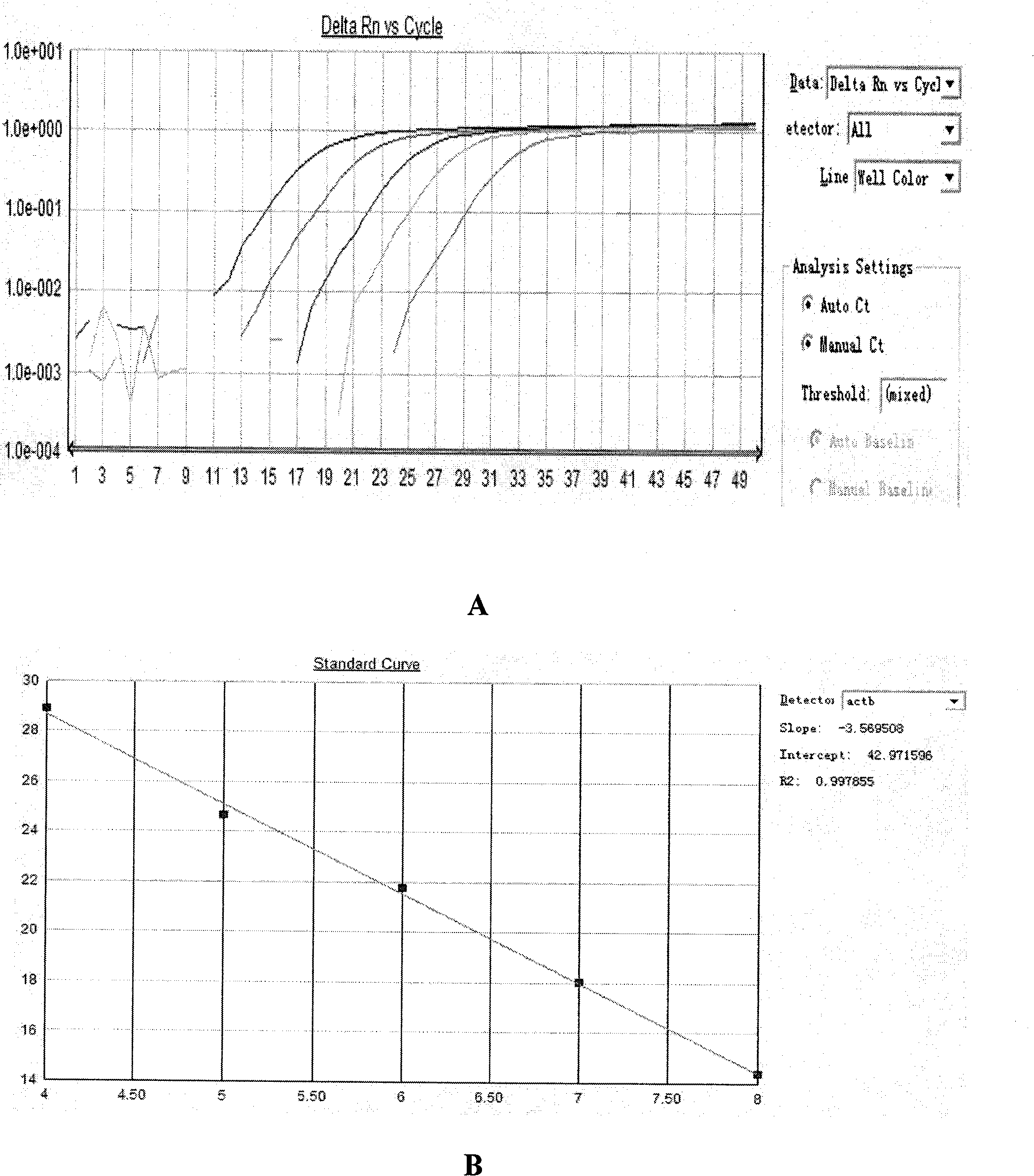
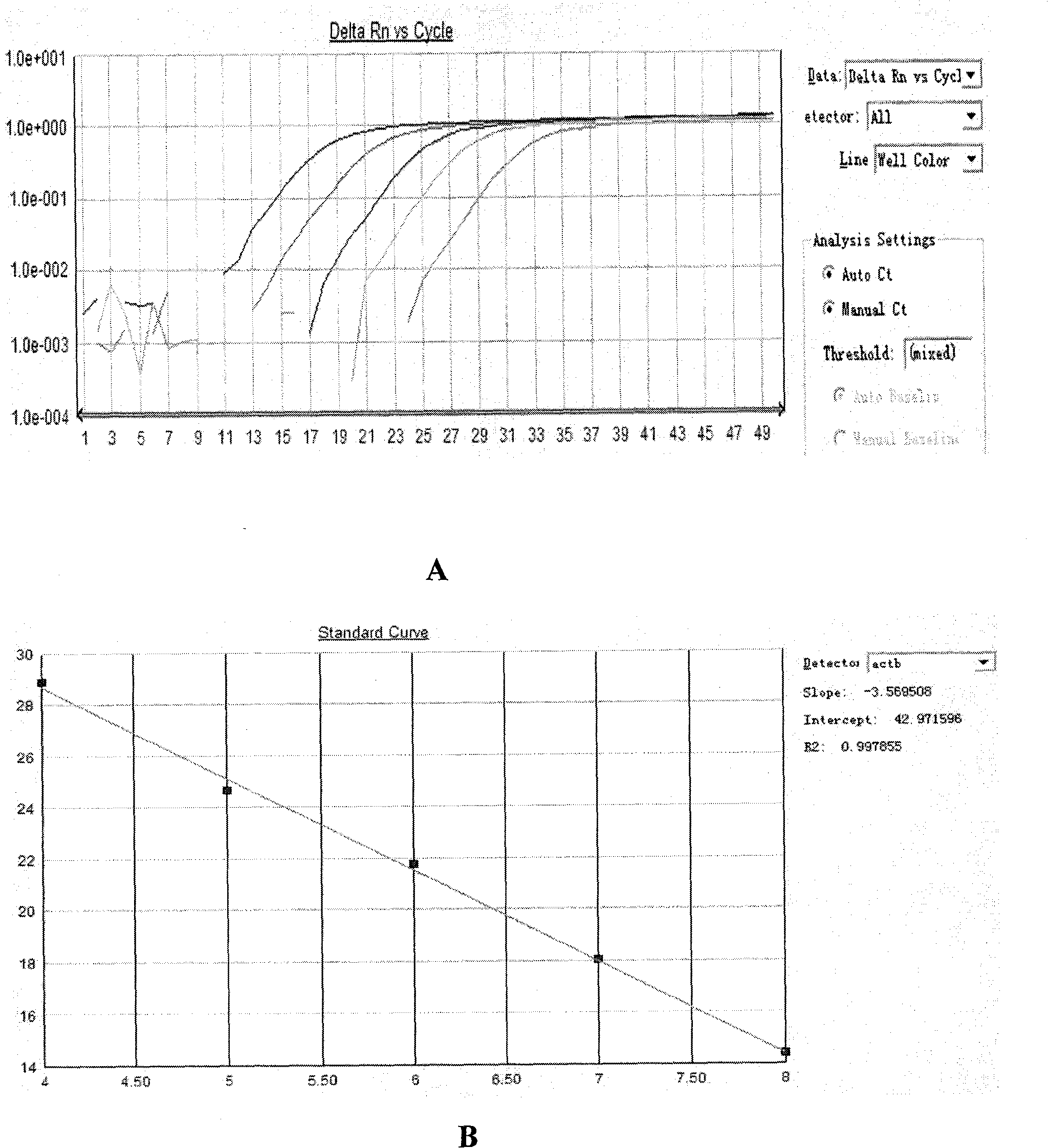
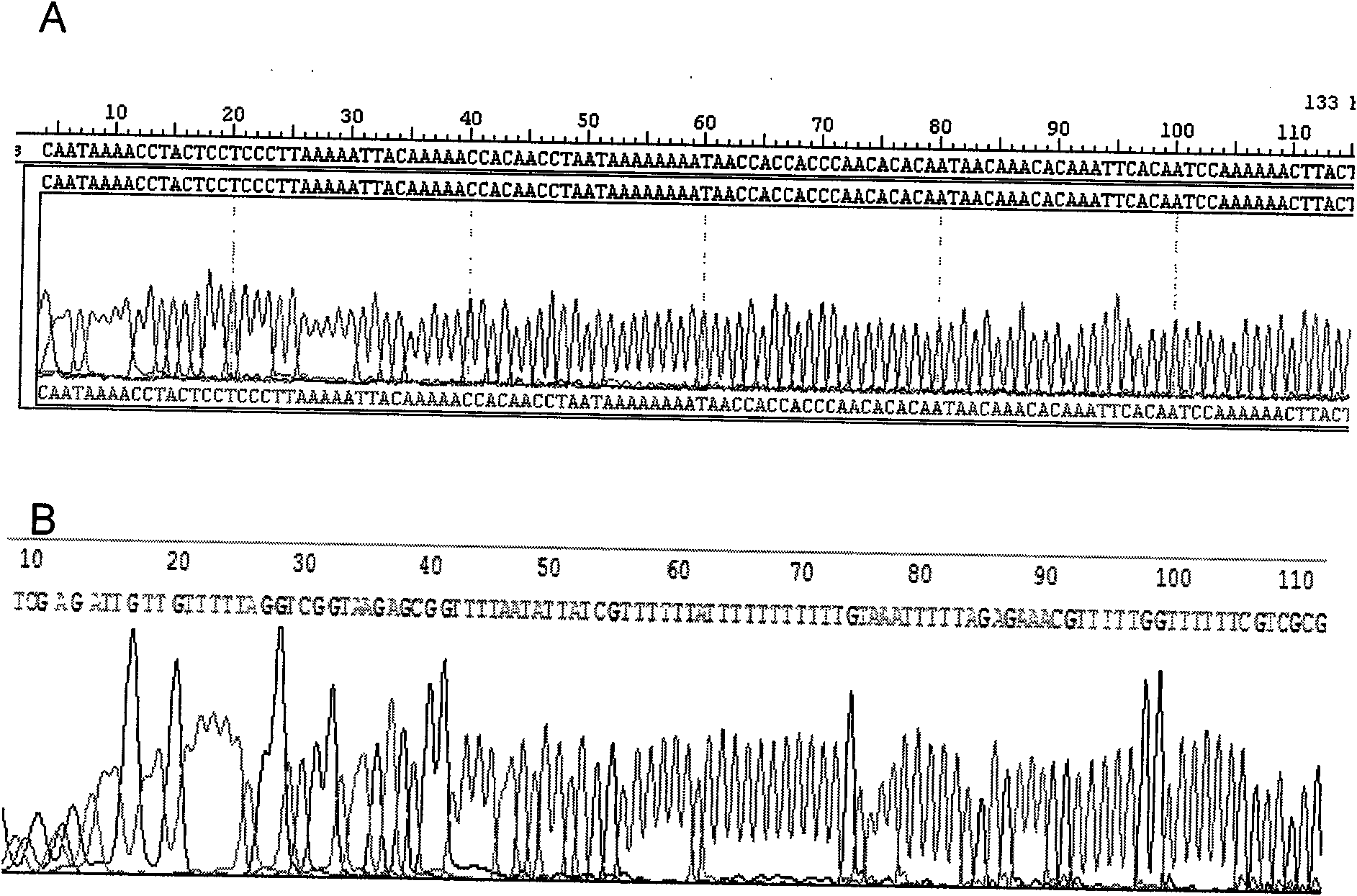
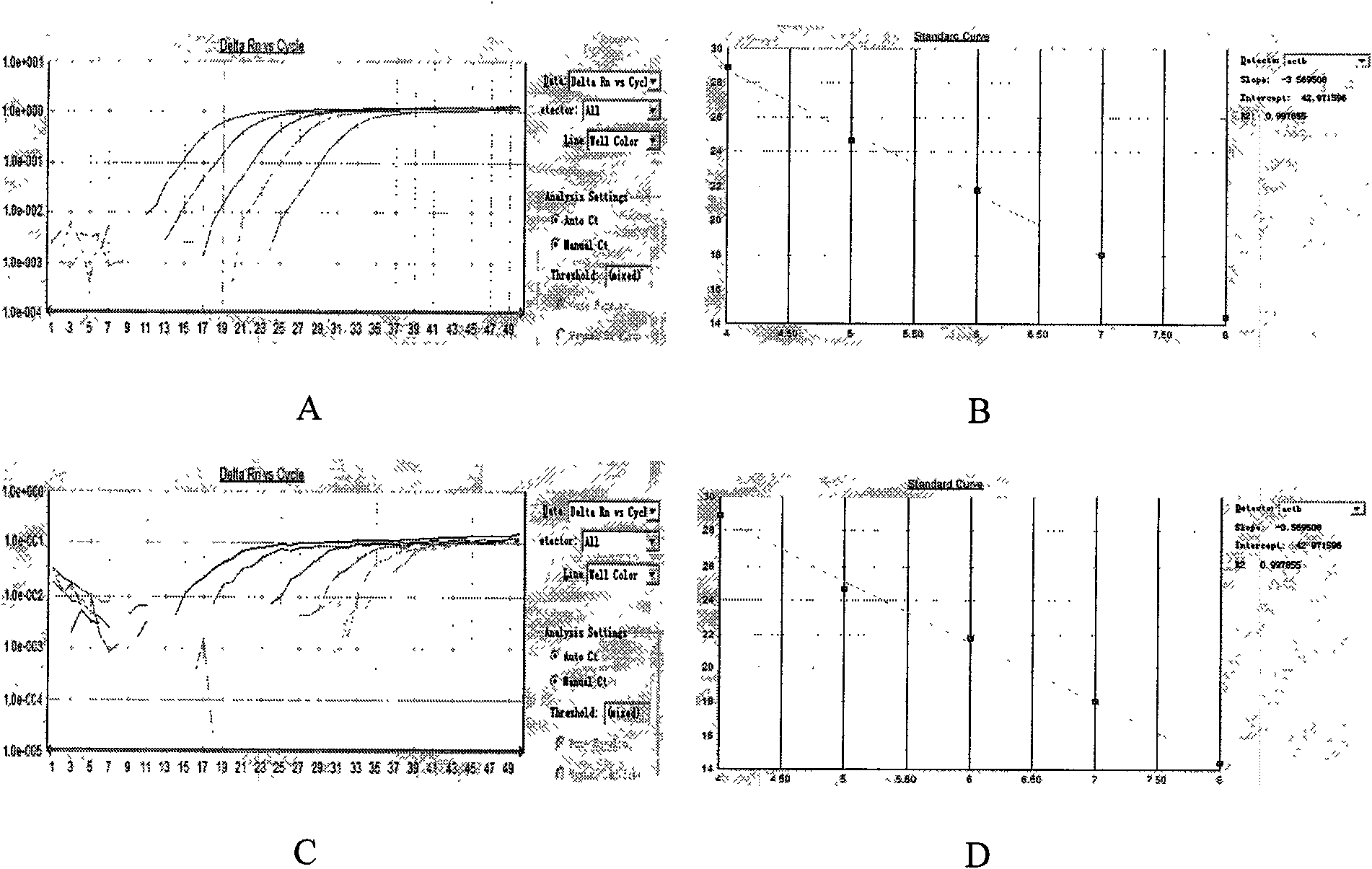
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. Based on the fact that the abnormal methylation of genes are involved in the generation and development of tumors, the invention aims to overcome the defects of a methylation sensitive restriction enzyme method, a bisulfite sequencing method and a methylation specificity PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method, and provide a methylation quantitative detection method of the PCDH8 (Protocadherin-8) gene, with simple and convenient operation and high sensitivity. The detection method comprises the steps of: taking pancreatic cancer tissues, extracting DNA to prepare a standard curve sample of ACTB (Actin, Beta), and preparing a standard curve sample of PCDH8; extracting the DNA of a tissue to be detected, carrying out chemical decoration, designing a methylation primer and a probe for a CPG island in a human PCDH8 gene promoter area, and designing a BSP primer and a probe for a CPG island in a human reference gene ACTB promoter area, carrying out real-time quantitative PCR on the DNA subjected to the sulfite treatment by using a Taqman-MGB real-time quantitative PCR method, and calculating out a quantitative value on the methylation degree of a PCDH8 gene. The method has the advantages of rapidness, correctness and high sensitivity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Analysis of methylated nucleic acid
InactiveUS20090270482A1Readily susceptibleOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis dnaDisease markers
The present invention provides a method for analysis methylation patterns in DNA and identifying aberrantly methylated genes in disease tissue. The invention also provides a method of identifying novel targets for therapeutic intervention and disease markers. Novel cancer targets are provided.
Owner:SCHUEBELER DIRK +1
Aberrantly Methylated Genes as Markers of Breast Malignancy
InactiveUS20090136944A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBreast malignant tumorsBreast malignancy
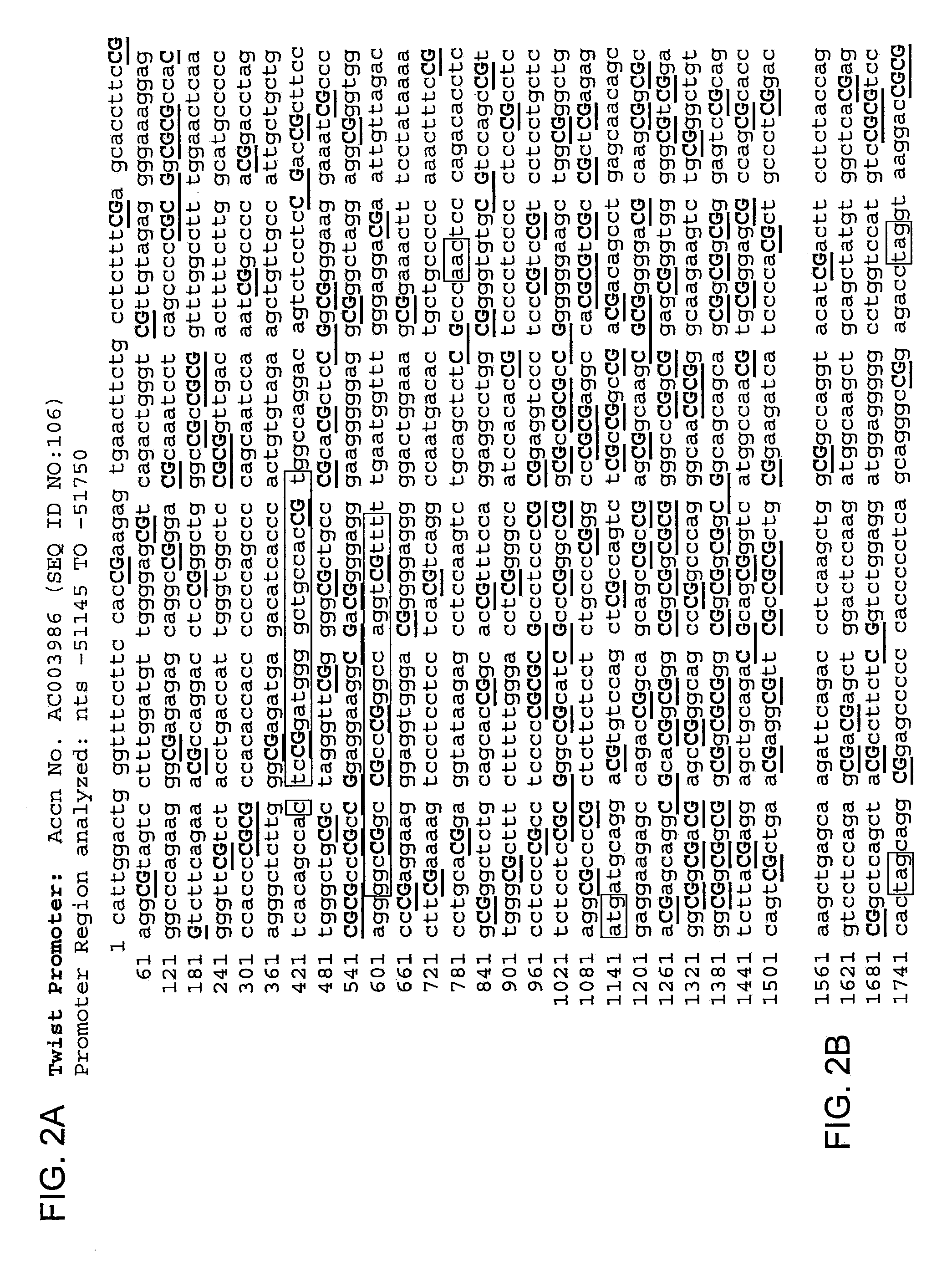
The invention is directed to a method of diagnosing a cell proliferative disorder of breast tissue by determining the methylation status of nucleic acids obtained from a subject. Aberrant methylation of several genes including TWIST, HOXA5, NES-1, retinoic acid receptor beta (RARβ), estrogen receptor (ER), cyclin D2, WT-1, 14.3.3 sigma, HIN-1, RASSF1A, and combinations of such genes serve as markers of breast malignancy.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
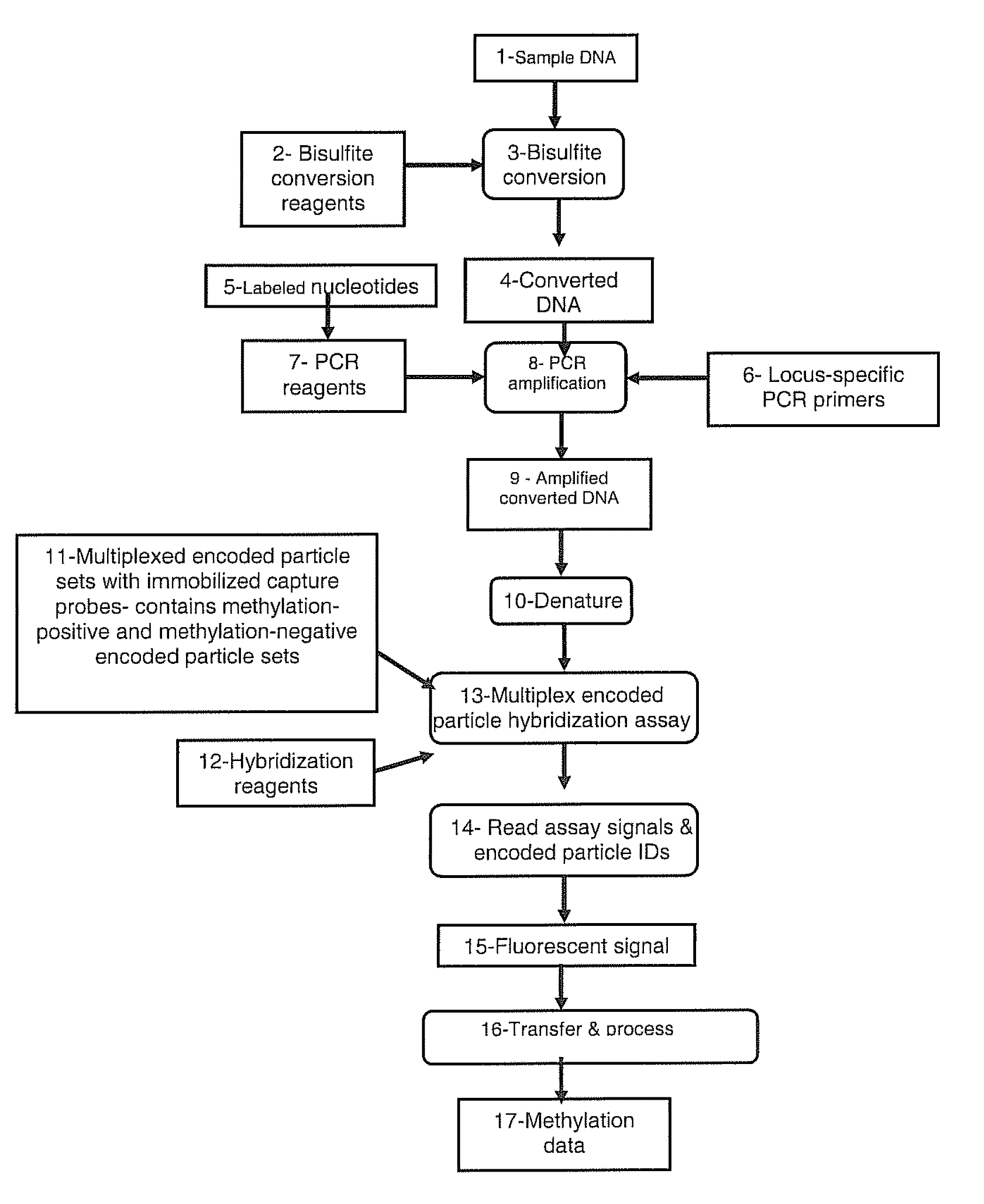
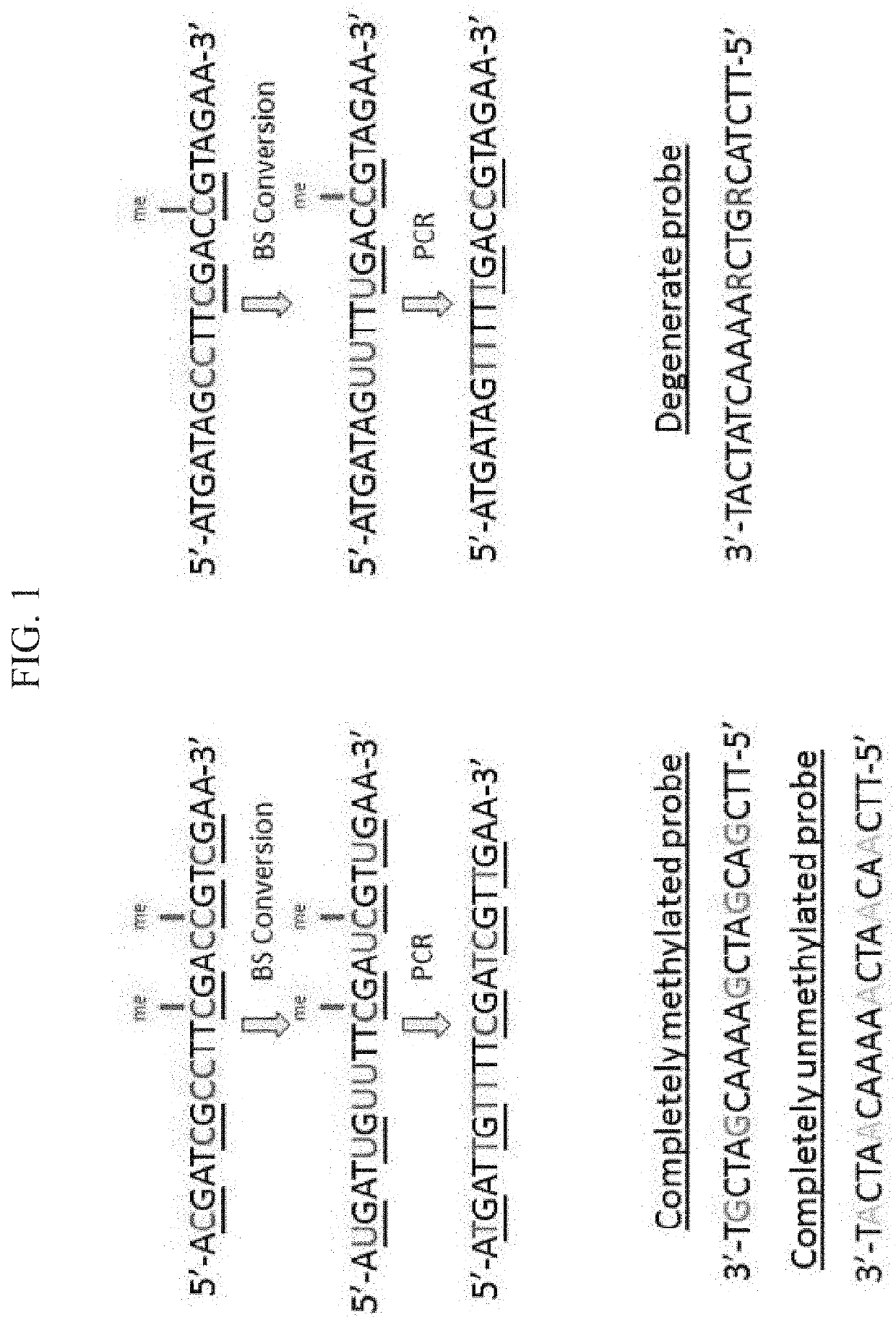
Methods for detecting DNA methylation using encoded particles
Methods for detecting the methylation status of a target genomic locus are provided. Methods described allow for simultaneous assay of multiple cytosines in a target genomic locus. Assays of multiple cytosines in a target genomic locus provide detection of an aggregate cytosine methylation state of the target genomic locus. Methods to detect methylation of a genomic locus associated with a disease or disorder characterized by aberrant methylation of the genomic locus, such as, but not limited to, Fragile X mental retardation syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Angelman sydrome, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, and Russell-Silverman syndrome, diabetes, cancer, multiple sclerosis or schizophrenia are described herein.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
LRRC55 gene methylation quantitative detection method
InactiveCN101967514ASimple and fast operationIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesBisulfite sequencing
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The abnormal methylation of genes participates in the occurrence and the development of tumors. The invention aims at overcoming the defects of the methylation sensitivity restriction enzyme method, the bisulfite sequencing method and the methylation specificity PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method and providing an LRRC55 gene methylation quantitative detection method with easy and simple operation and high sensitivity. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a pancreatic cancer tissue, extracting DNA, preparing a standard curve sample of ACTB (Actin, Beta), and preparing a standard curve sample of LRRC55 by using a complete methylation template; extracting the DNA of a tissue to be tested, performing chemical modification, designing a methylation primer and probe aiming at the CpG island of a promoter region of the human LRRC55 gene, designing a BSP primer and probe aiming at the CPG island of a promoter region of human reference gene ACTB, performing real-time quantitative PCR on the DNA treated by sulfite by using the Tagman-MGB real-time quantitative PCR method, and calculating the quantitative value of the methylation degree of the LRRC55 gene. The method is rapid and accurate and is high in sensitivity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Differentially methylated sequences in pancreatic cancer
InactiveUS7153653B2Raise the possibilityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDifferential MethylationCancer research
The present invention provides a method for detecting a cellular proliferative disorder in a subject. The method includes contacting a nucleic acid-containing specimen from the subject with an agent that provides a determination of the methylation state of at least one gene or associated regulatory region of the gene and identifying aberrant methylation of regions of the gene or regulatory region, wherein aberrant methylation is identified as being different when compared to the same regions of the gene or associated regulatory region in a subject not having said cellular proliferative, thereby detecting a cellular proliferative disorder in the subject.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
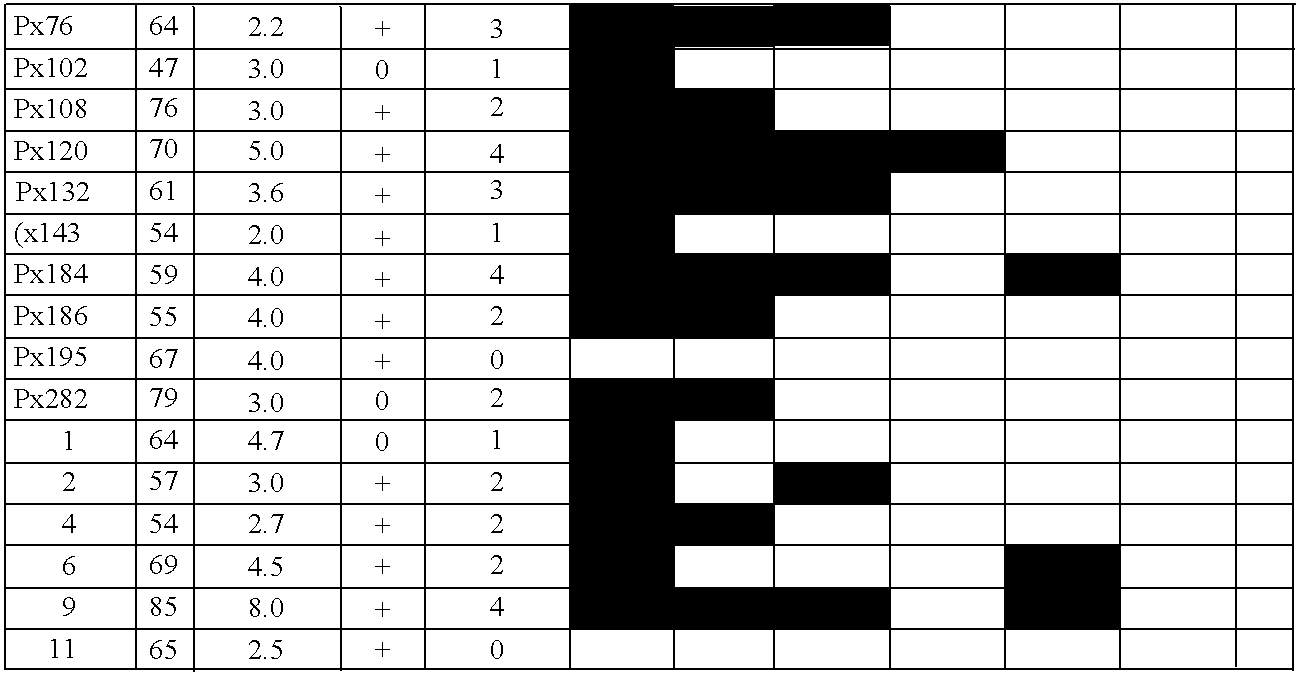
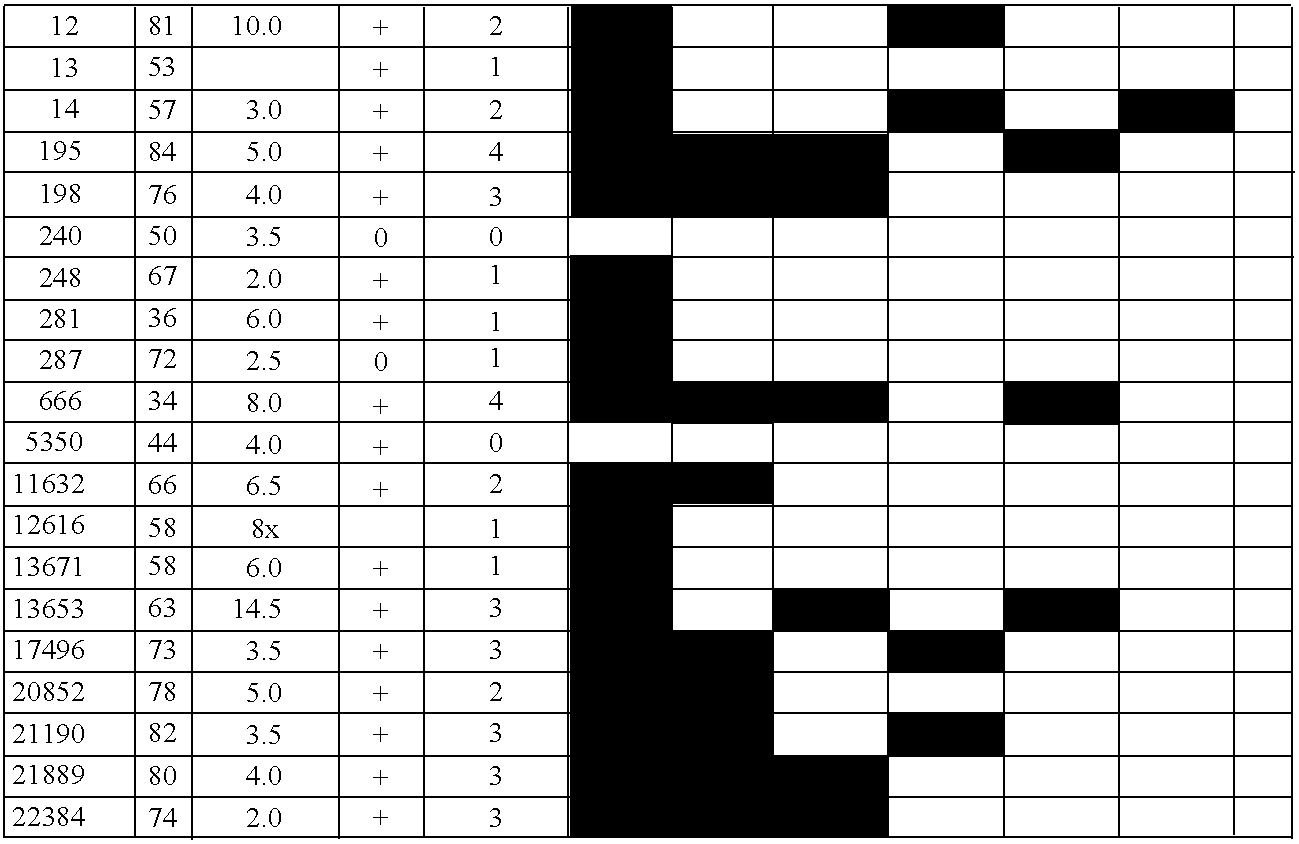
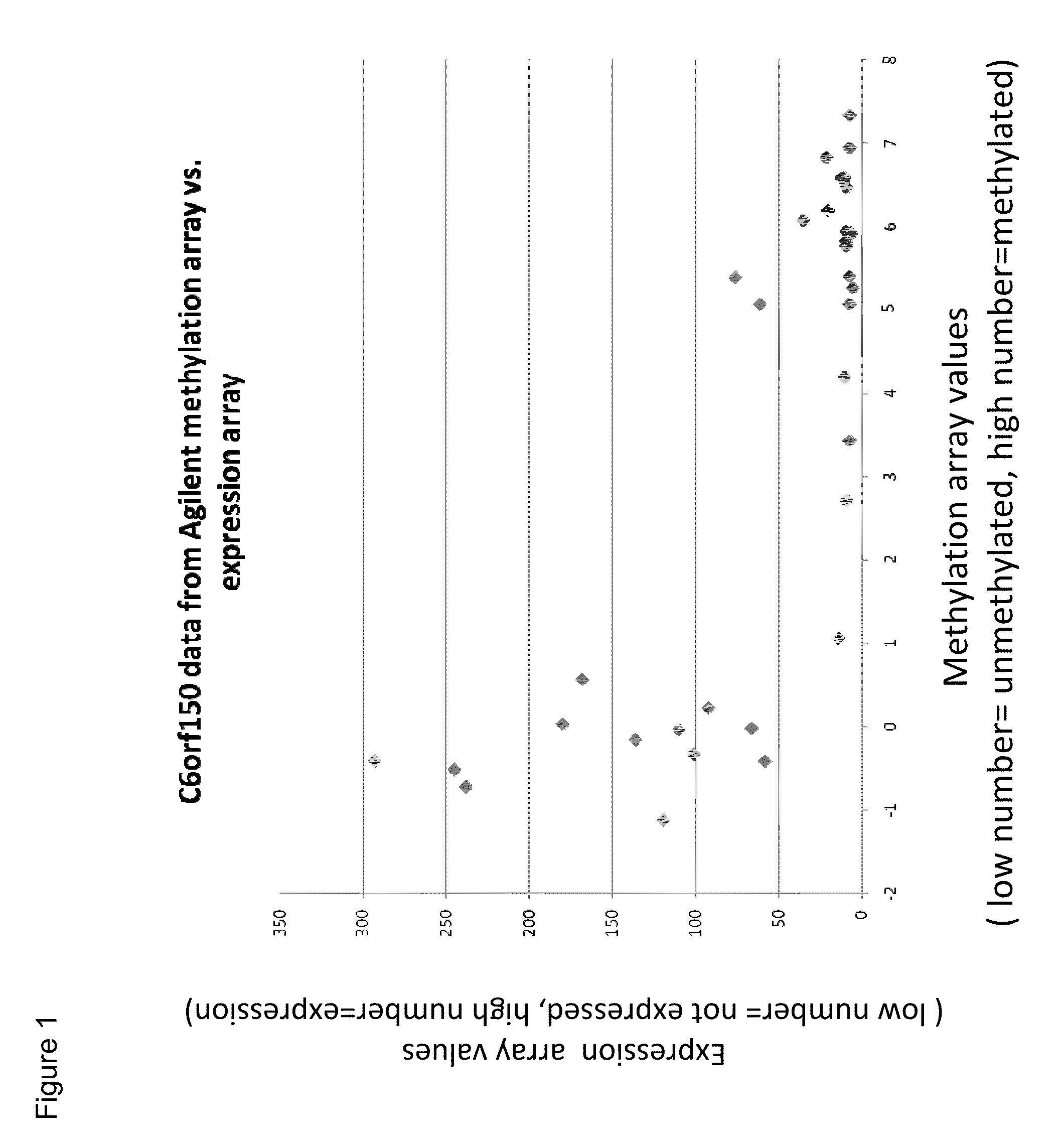
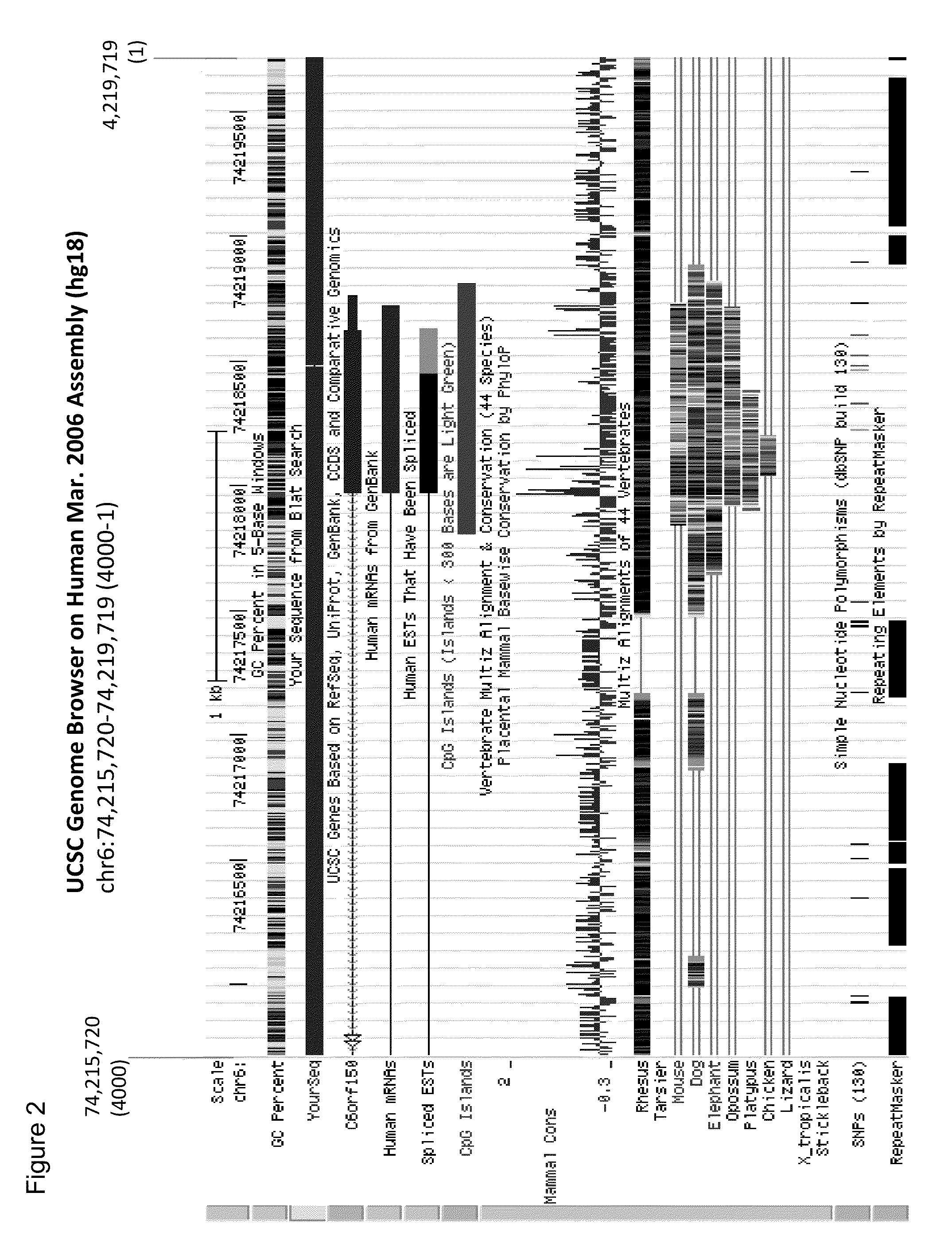
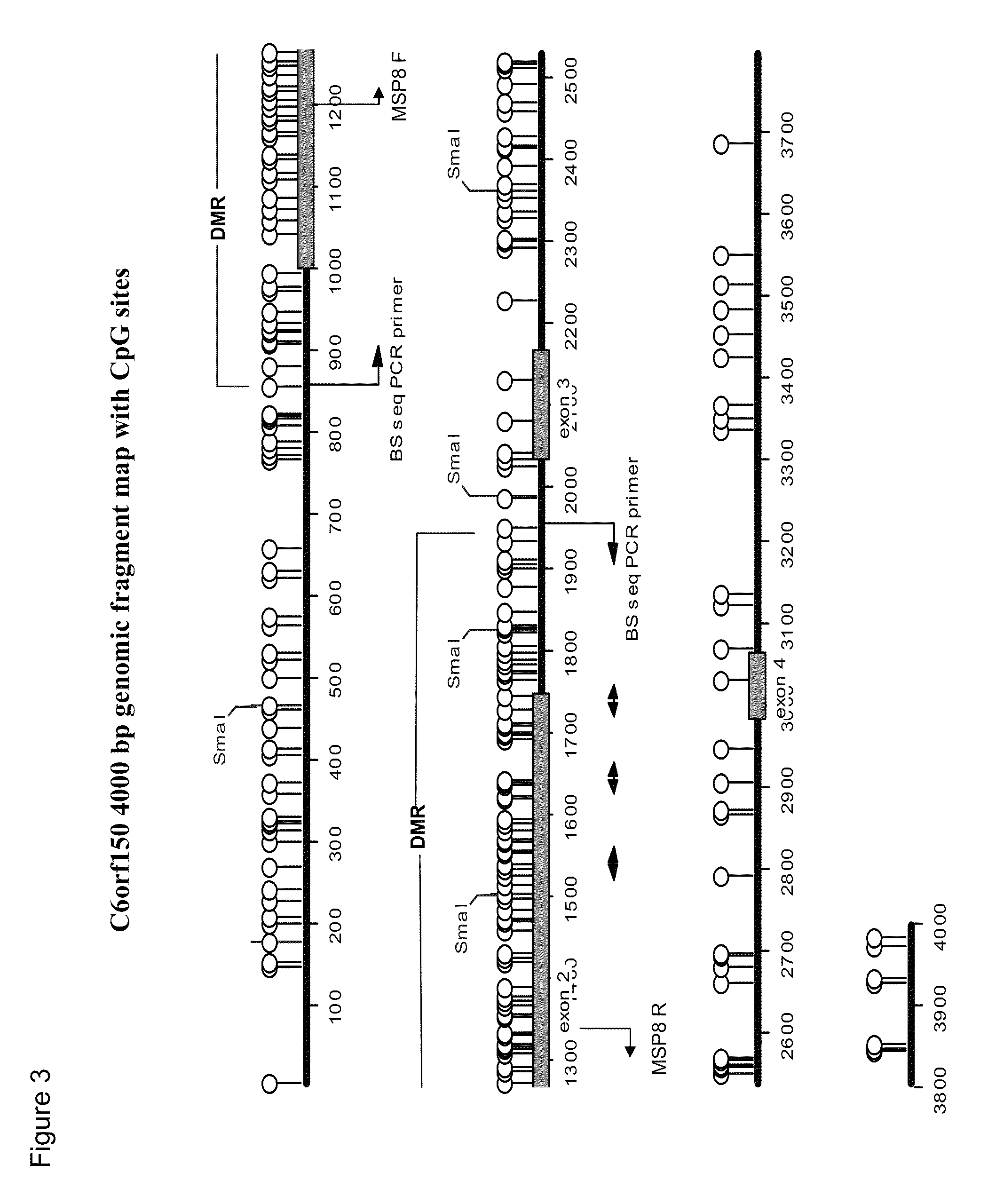
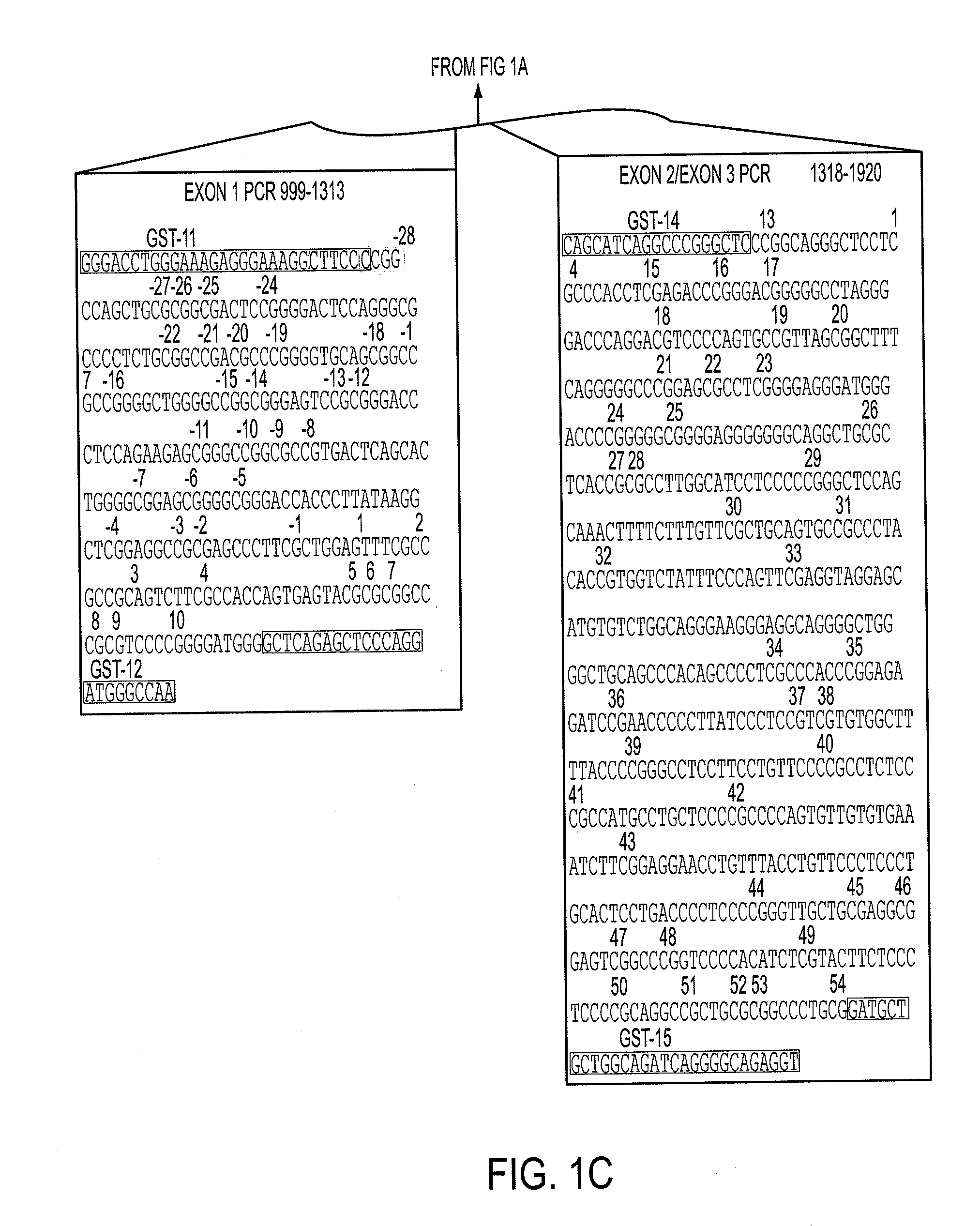
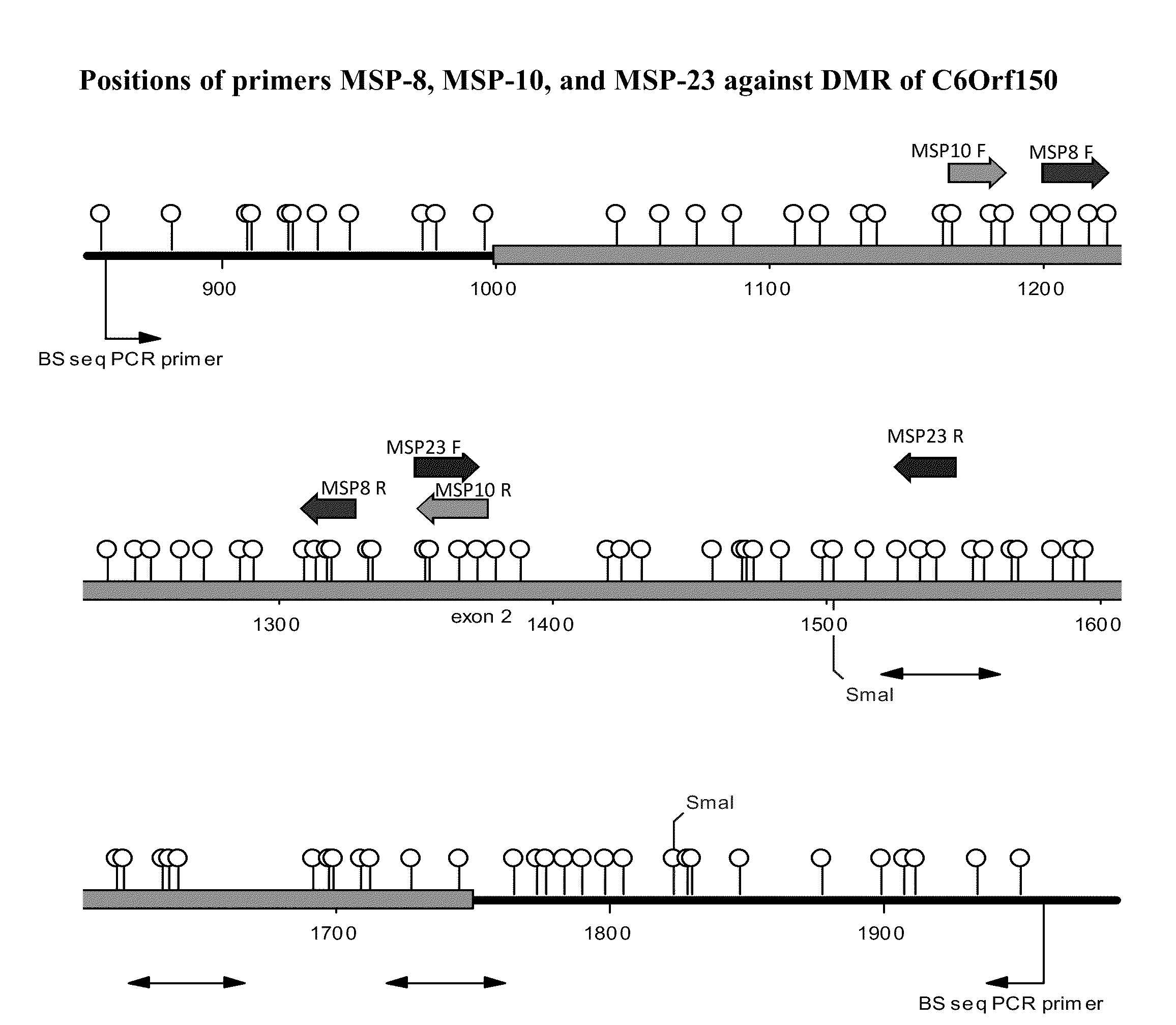
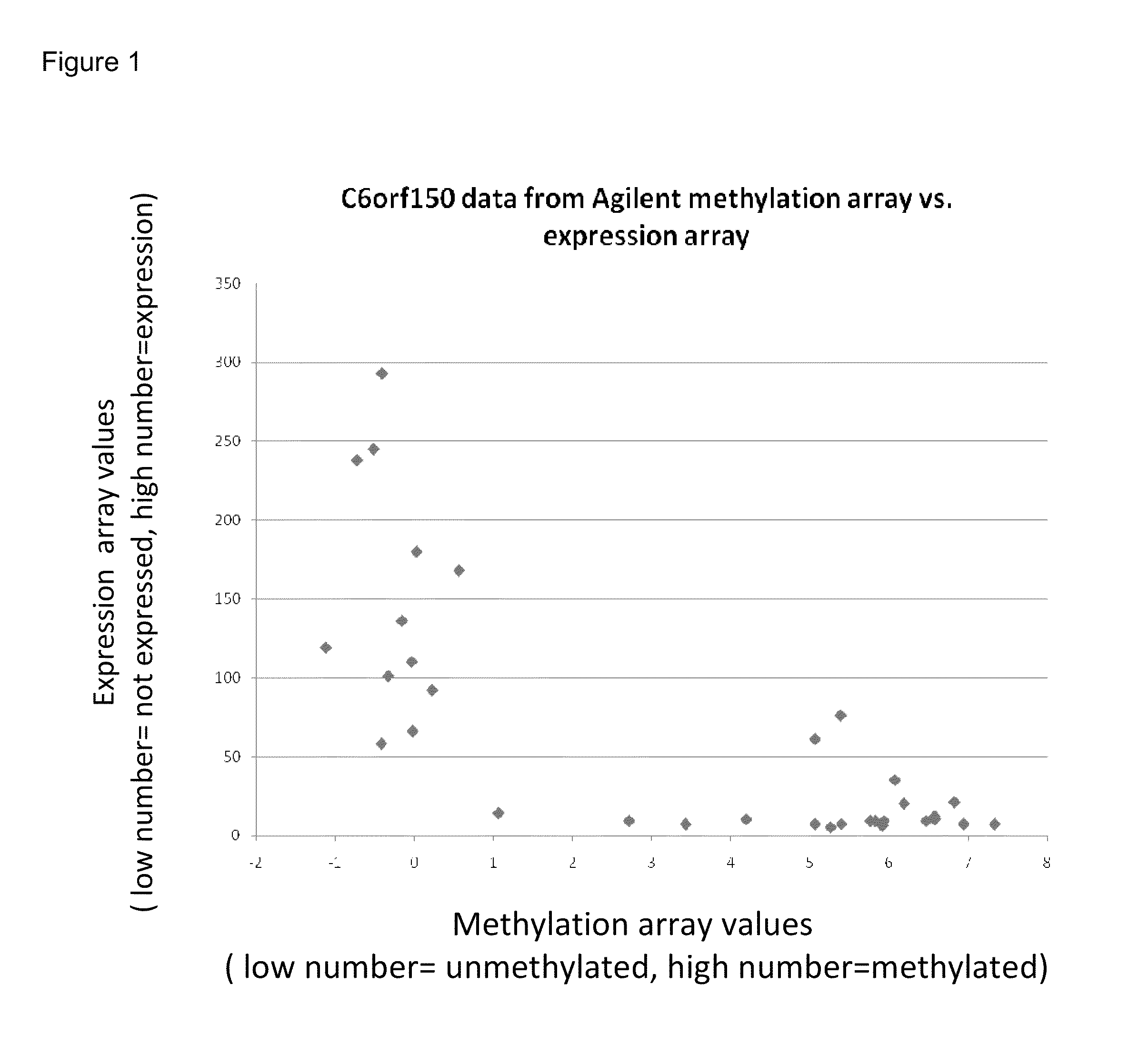
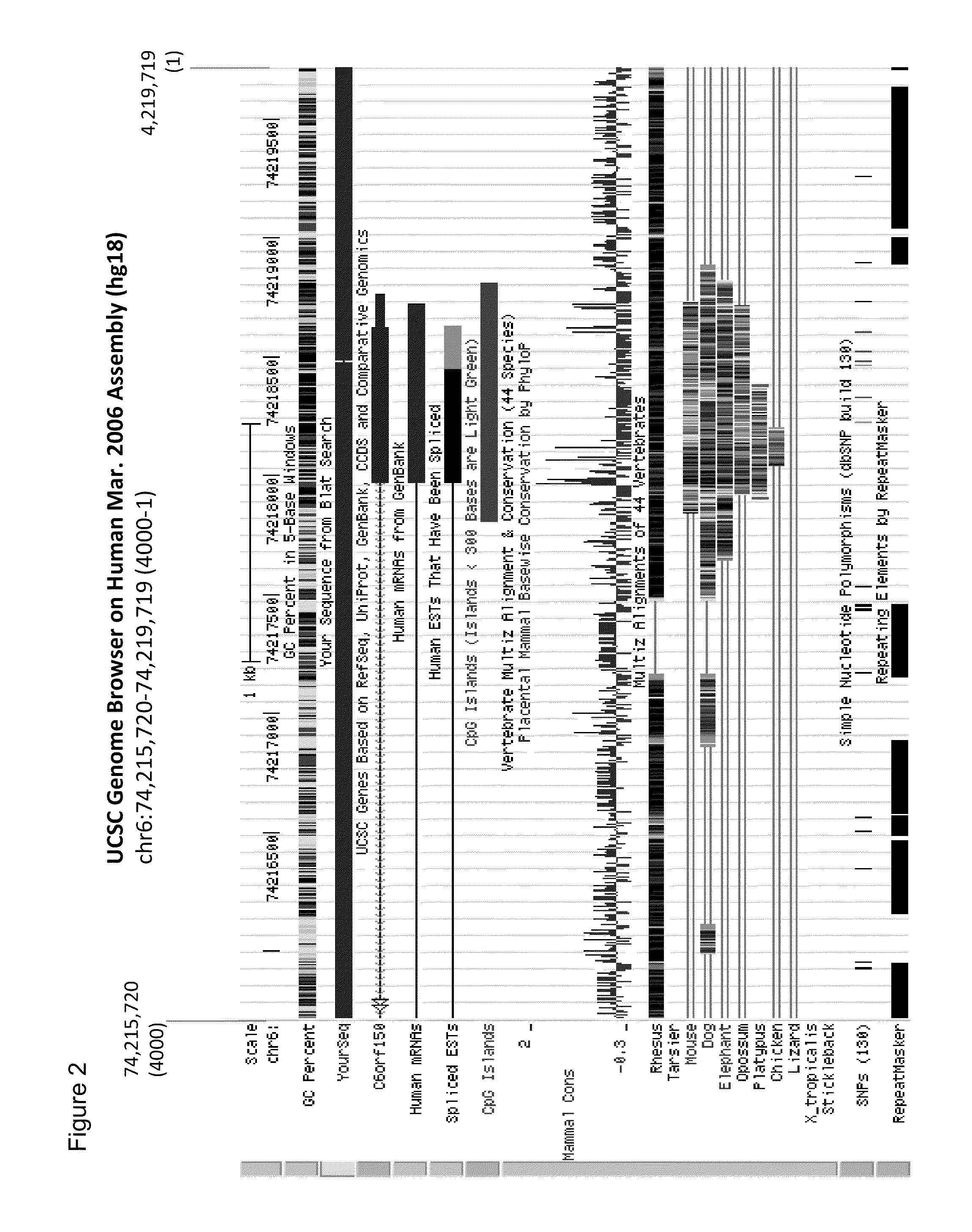
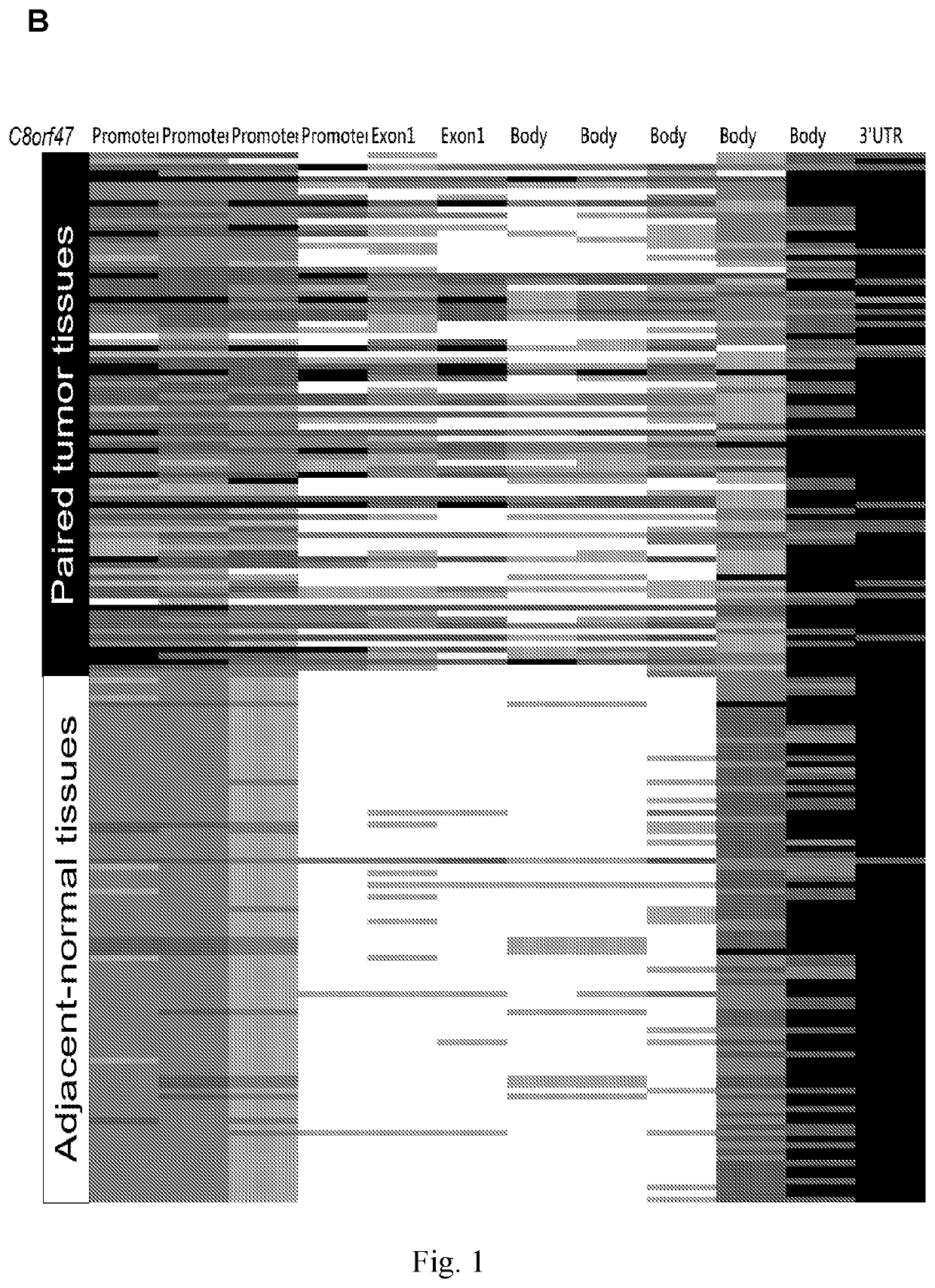
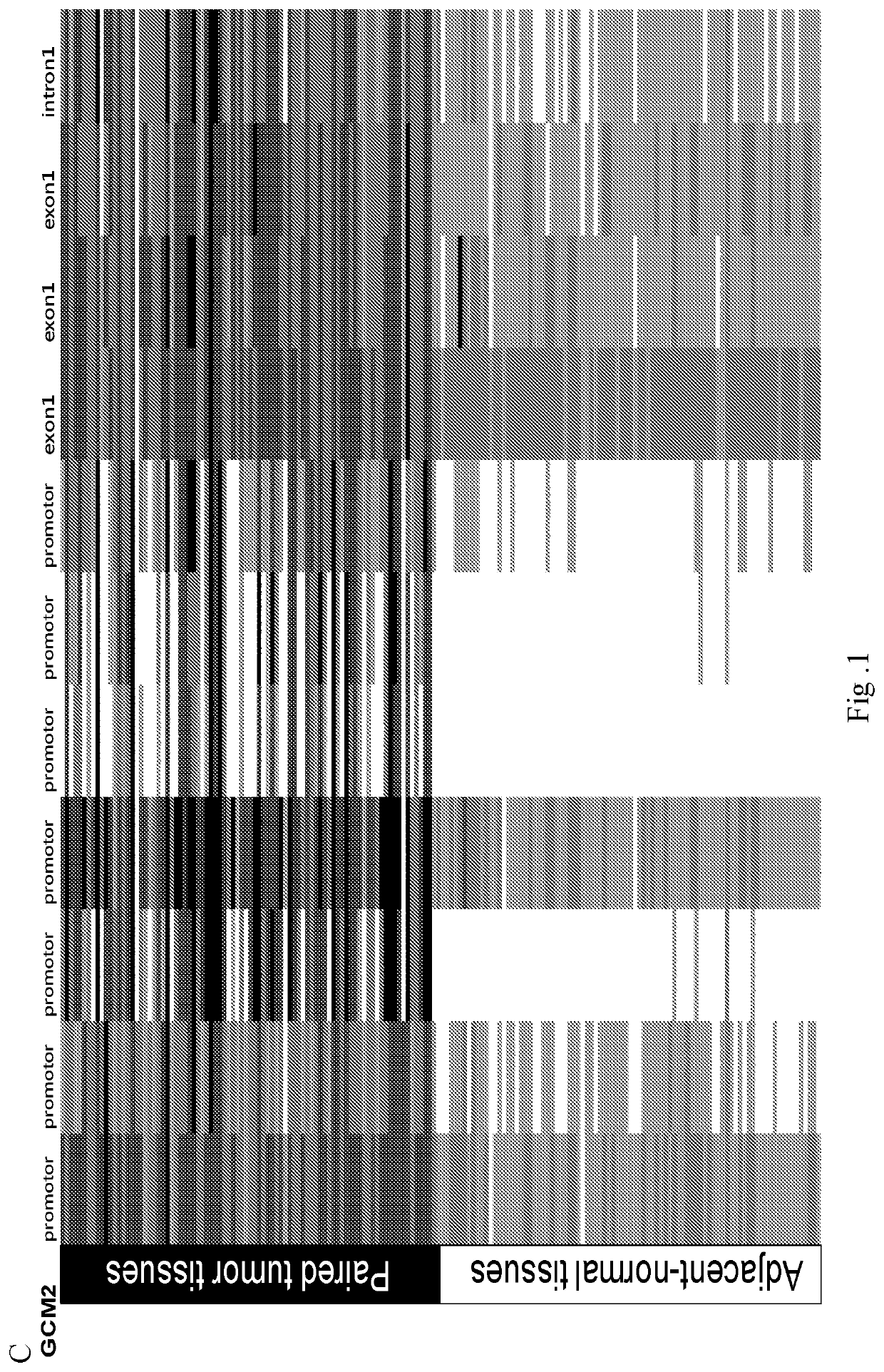
Aberrant methylation of C6Orf150 DNA sequences in human colorectal cancer
InactiveUS8642271B2Compound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
This application describes methods and compositions for detecting and treating C6Orf150-associated neoplasia. Differential methylation of the C6Orf150 nucleotide sequences has been observed in C6Orf150-associated neoplasia such as colon neoplasia.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Assays, methods and compositions for diagnosing cancer
InactiveUS20140242583A1Improve the level ofScalable automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementActin genesDNA
The present invention provides a method and single-tube assay for identification and quantitative analysis of differentially methylated MLH1 promoter sequences that are associated with certain types of cancer in an individual by obtaining a biological sample comprising DNA from the individual, detecting the presence of and measuring the level of methylated MLH1 promoter sequences, and comparing the presence of and level of methylation in the sample to a normalization reference of “normal” beta-actin gene promoters, wherein a difference in the level or pattern of MLH1 methylation of the sample compared to the Actin gene reference level identifies abnormally methylated MLH1 promoter sequences associated with cancer.
Owner:GO PATH GLOBAL
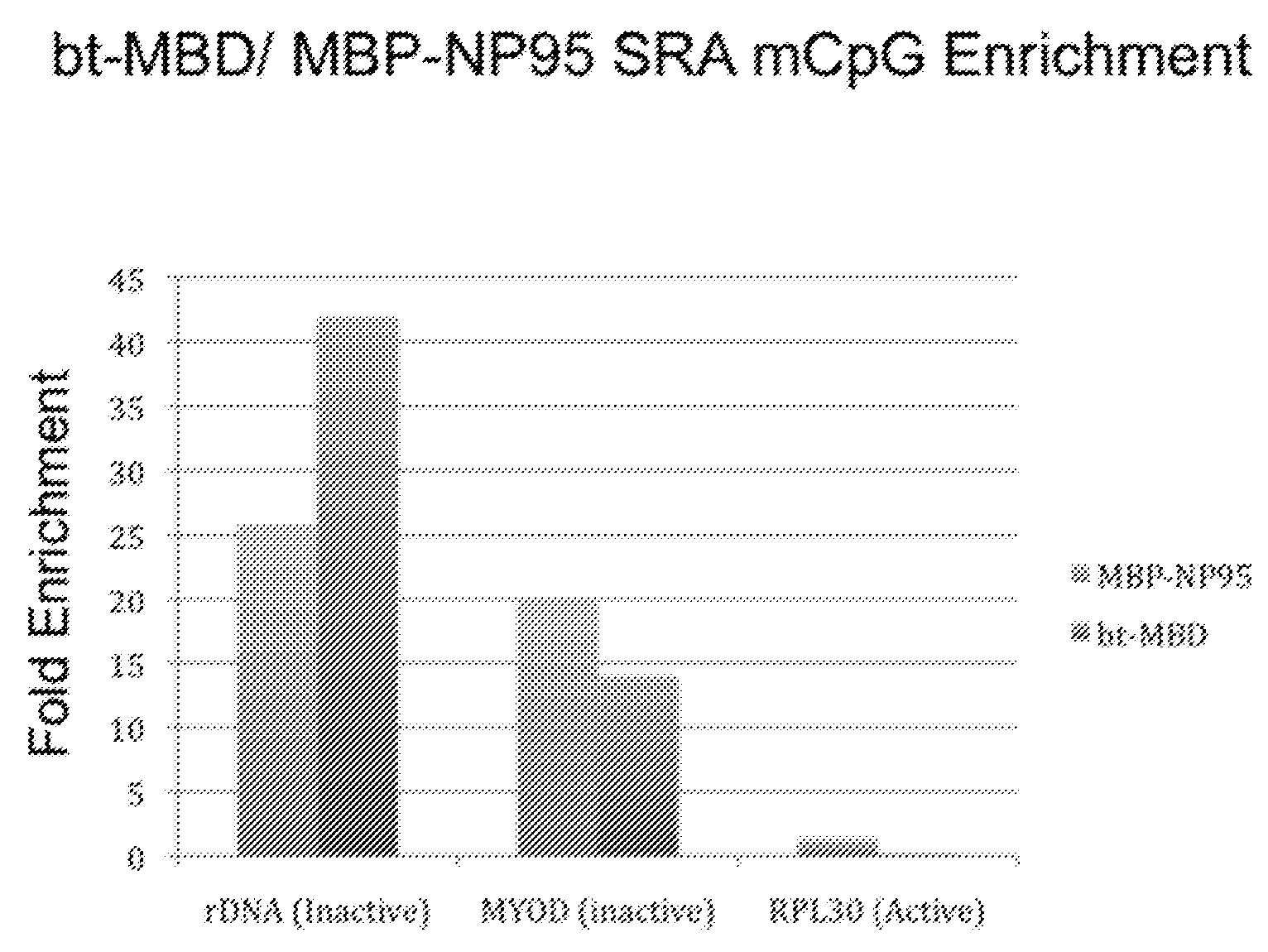
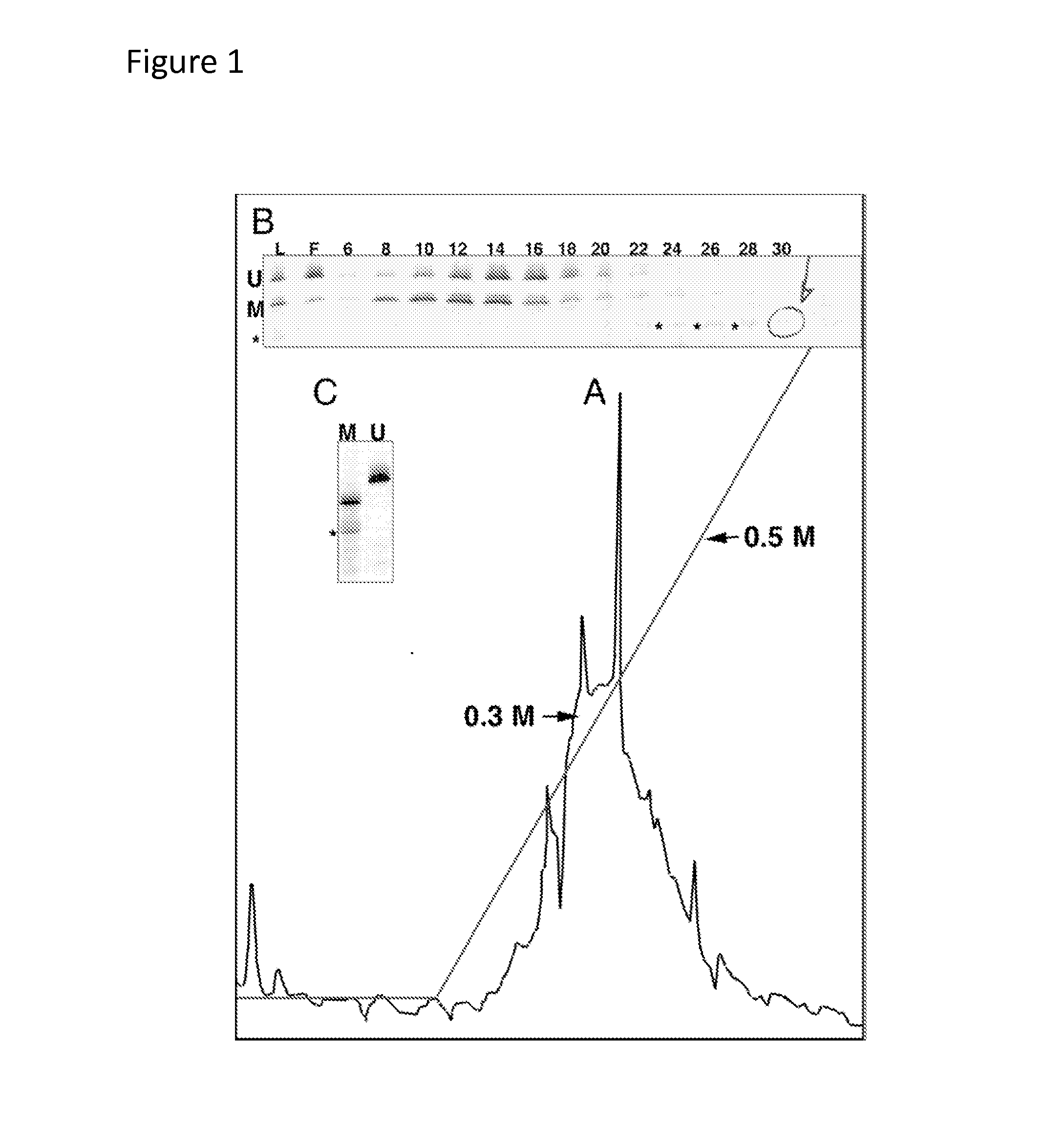
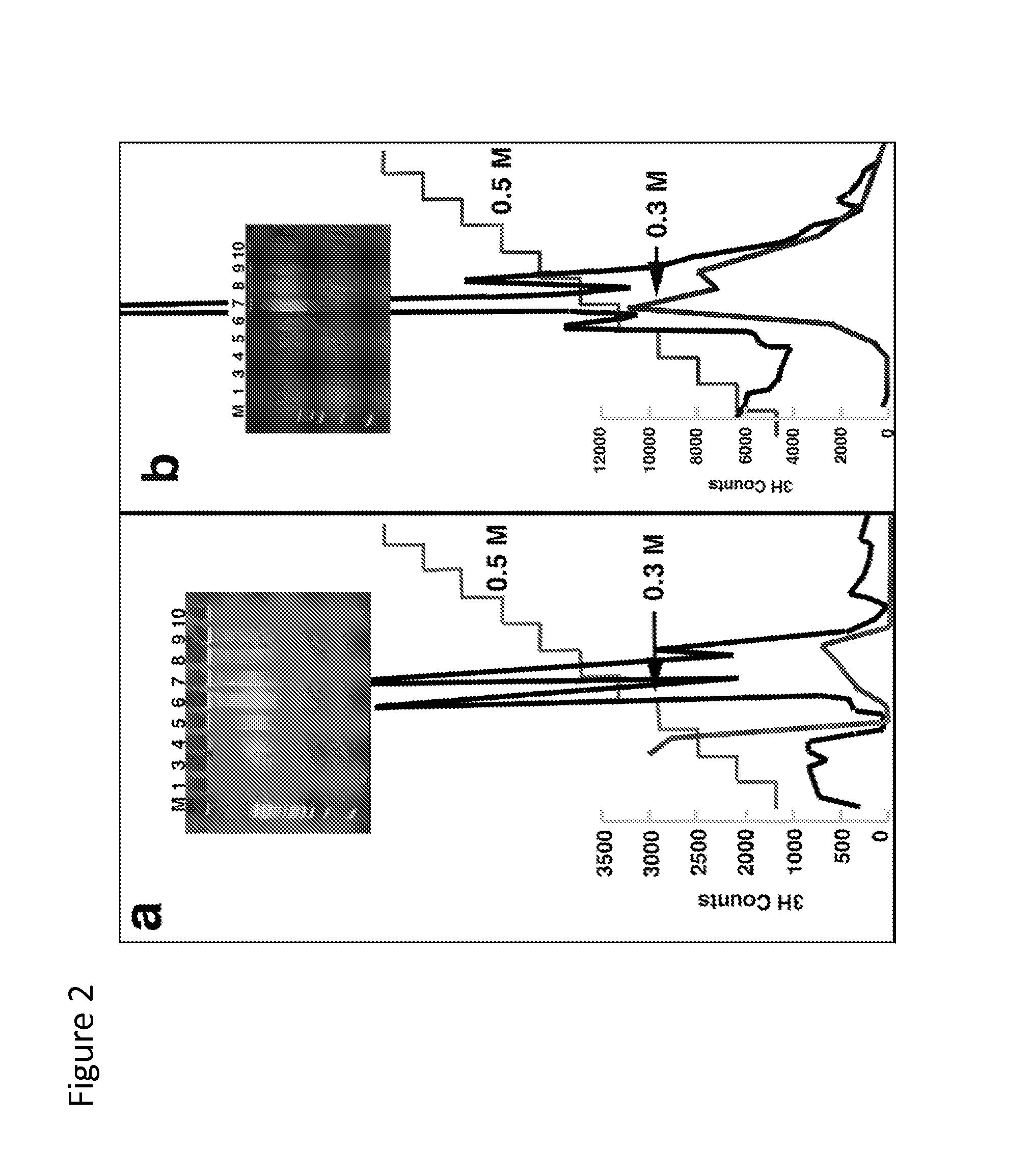
Method for Enriching Methylated CpG Sequences
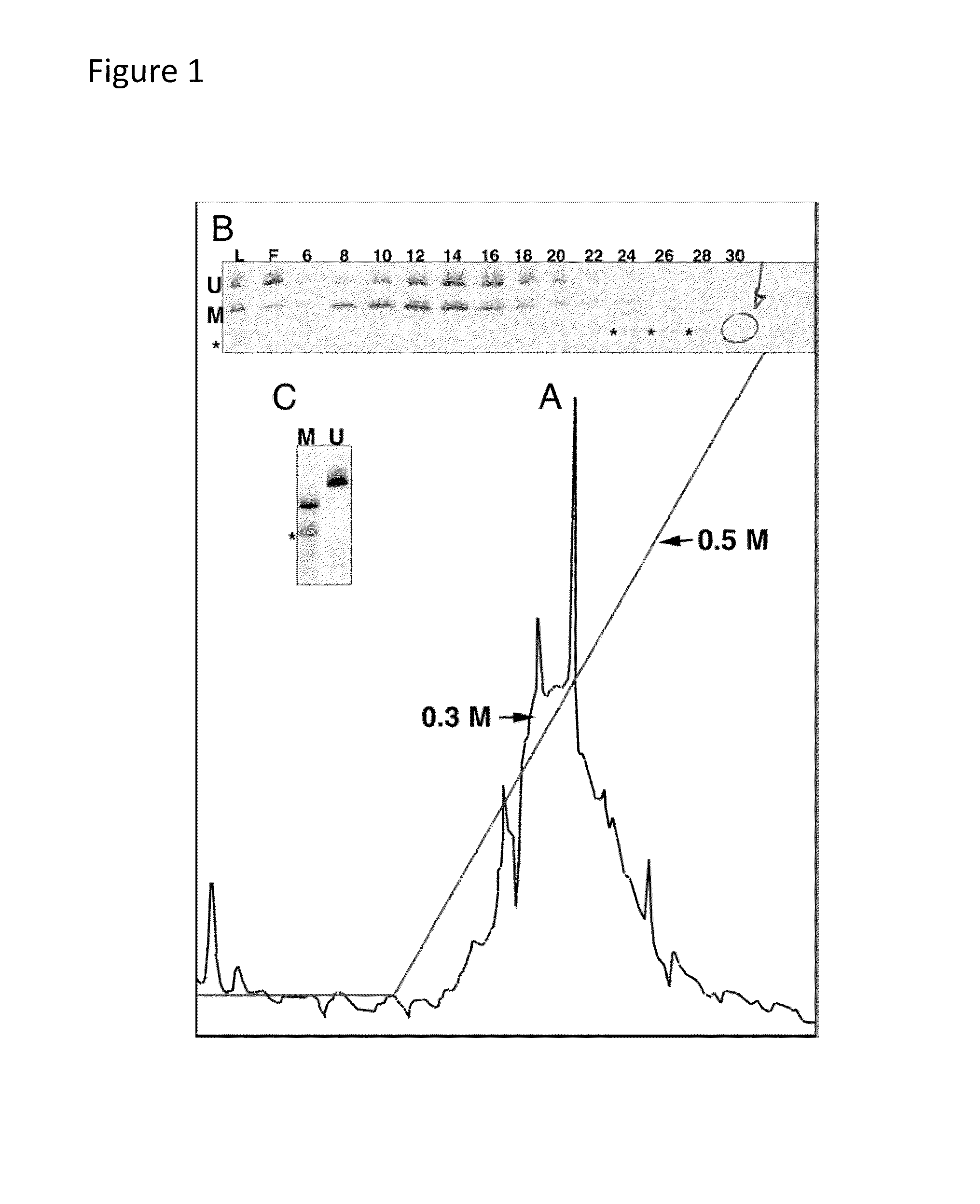
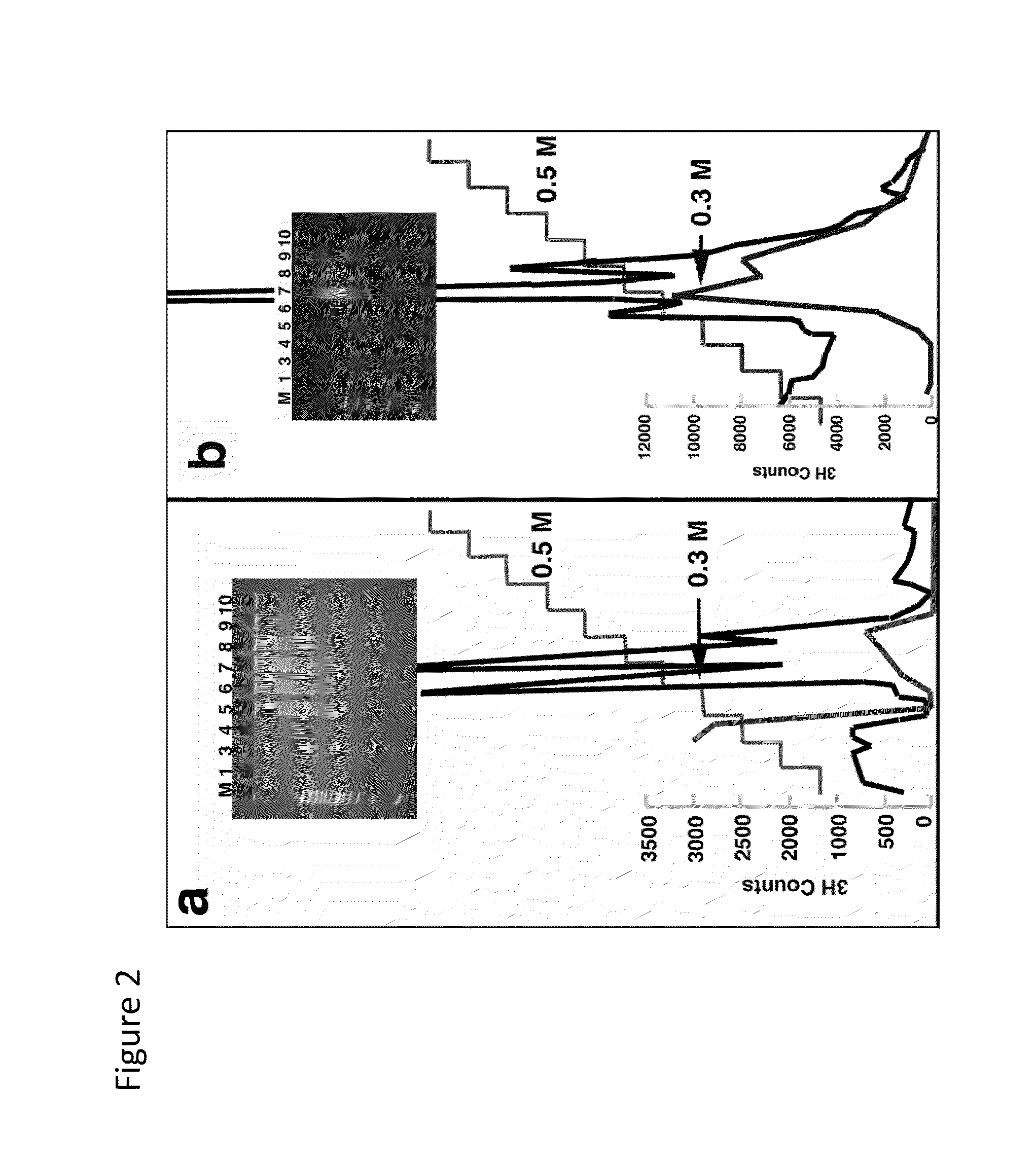
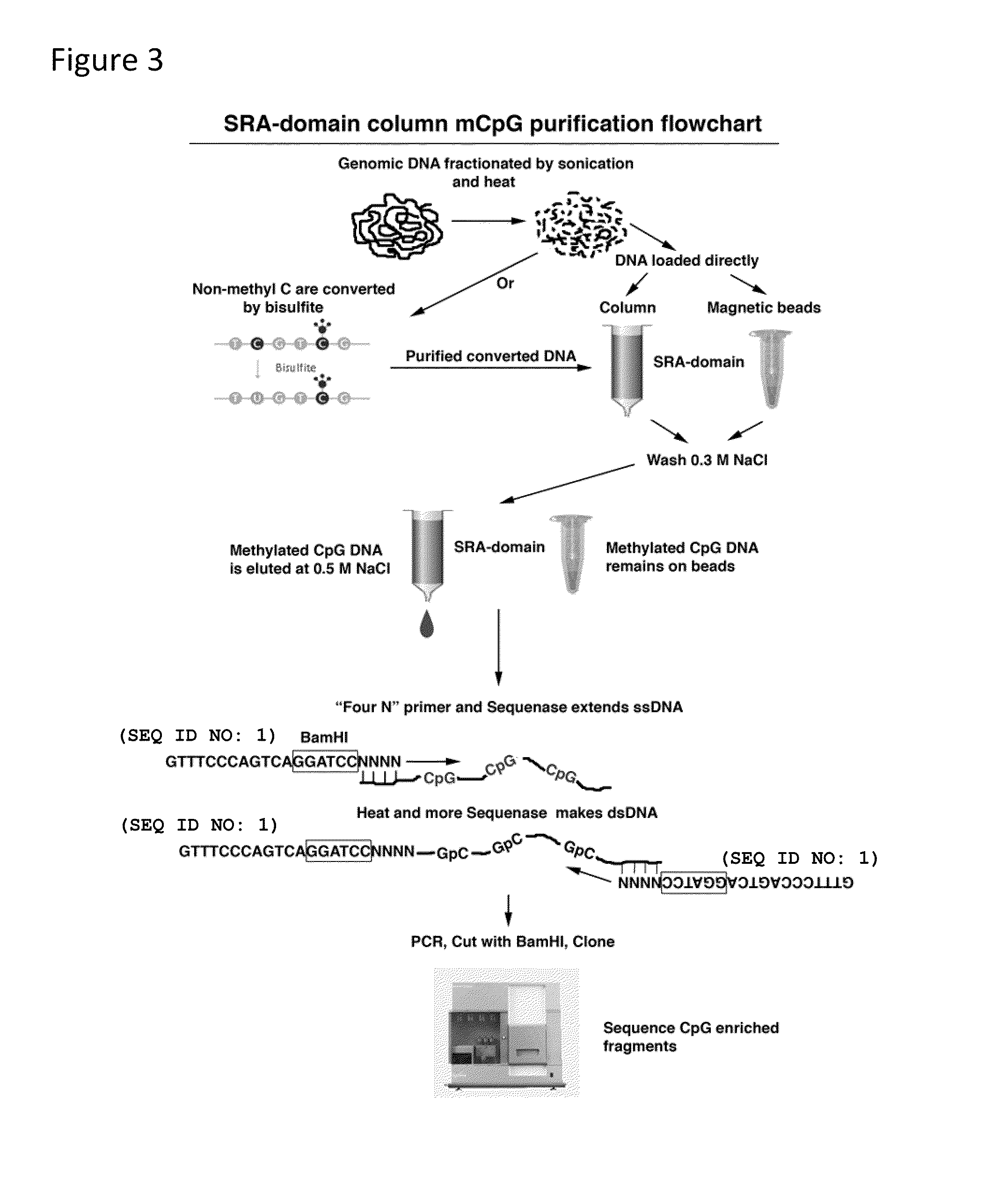
ActiveUS20100112585A1Promote recoveryFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesDiseaseSingle strand dna
Compositions and methods are provided for facilitating the enrichment of single-stranded DNA containing methylated CpG in a mixture containing methylated and unmethylated DNA. The compositions relate to methylation-binding protein domains that selectively bind to methylated single strand DNA. In embodiments of the invention, the methylated DNA is eluted in 0.4M-0.6M NaCl while the unmethylated single strand DNA is eluted in less than 0.4M salt. The ability to readily enrich for methylated DNA permits high throughput sequencing of the methylated DNA and identification of abnormal methylation patterns associated with disease.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Aberrantly methylated genes as markers of breast malignancy
InactiveUS7858317B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBreast malignant tumorsBreast malignancy
The invention is directed to a method of diagnosing a cell proliferative disorder of breast tissue by determining the methylation status of nucleic acids obtained from a subject. Aberrant methylation of several genes including TWIST, HOXA5, NES-1, retinoic acid receptor beta (RARβ), estrogen receptor (ER), cyclin D2, WT-1, 14.3.3 sigma, HIN-1, RASSF1A, and combinations of such genes serve as markers of breast malignancy.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Aberrantly methylated genes as markers of breast malignancy
InactiveUS20050191640A1Accurate and effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementBreast malignant tumorsBreast malignancy
The invention is directed to a method of diagnosing a cell proliferative disorder of breast tissue by determining the methylation status of nucleic acids obtained from a subject. Aberrant methylation of several genes including TWIST, HOXA5, NES-1, retinoic acid receptor beta (RARβ), estrogen receptor (ER), cyclin D2, WT-1, 14.3.3 sigma, HIN-1, RASSF1A, and combinations of such genes serve as markers of breast malignancy.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methylated quantitative detection method of GSH2 (glutathione 2) gene
InactiveCN101818203ASimple and fast operationIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesBisulfite sequencing
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical sciences. Abnormal methylation of genes participates in the development of tumors. The invention aims at overcoming the defects of a methylation-sensitive restrictive endonuclease method, a bisulfite sequencing method and a methylation-specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method and provides a methylated quantitative detection method of a GSH2 (glutathione 2) gene, which has simple and convenient operation and high senibilitiy. The method comprises the following steps of: taking pancreatic cancer tissues, extracting DNA and preparing an ACTB (Actin, Beta) standard curve sample, and preparing a GSH2 (Glutathione 2) standard curve sample by utilizing a full methylation template; extracting DNA of tissues to be detected, and carrying out chemical modification; designing methylation primers and probes aiming at CPG islands at a human GSH2 gene promoter region, designing BSP (Bisulfite) primers and probes aiming at CPG islands at a human reference gene ACTB promoter region, carrying out real-time quantitive PCR on DNA after bisulfite treatment by adopting a Taqman-MGB real-time quantitive PCR method, and calculating a quantitive value of the GSH2 gene methylation degree. The method is rapid, accurate and high in sensitivity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Quantitative comparison method for detecting fragile X syndrome based on methylation level and primer used in quantitative comparison method
InactiveCN104498607AStable detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFmr1 geneFragile X chromosome
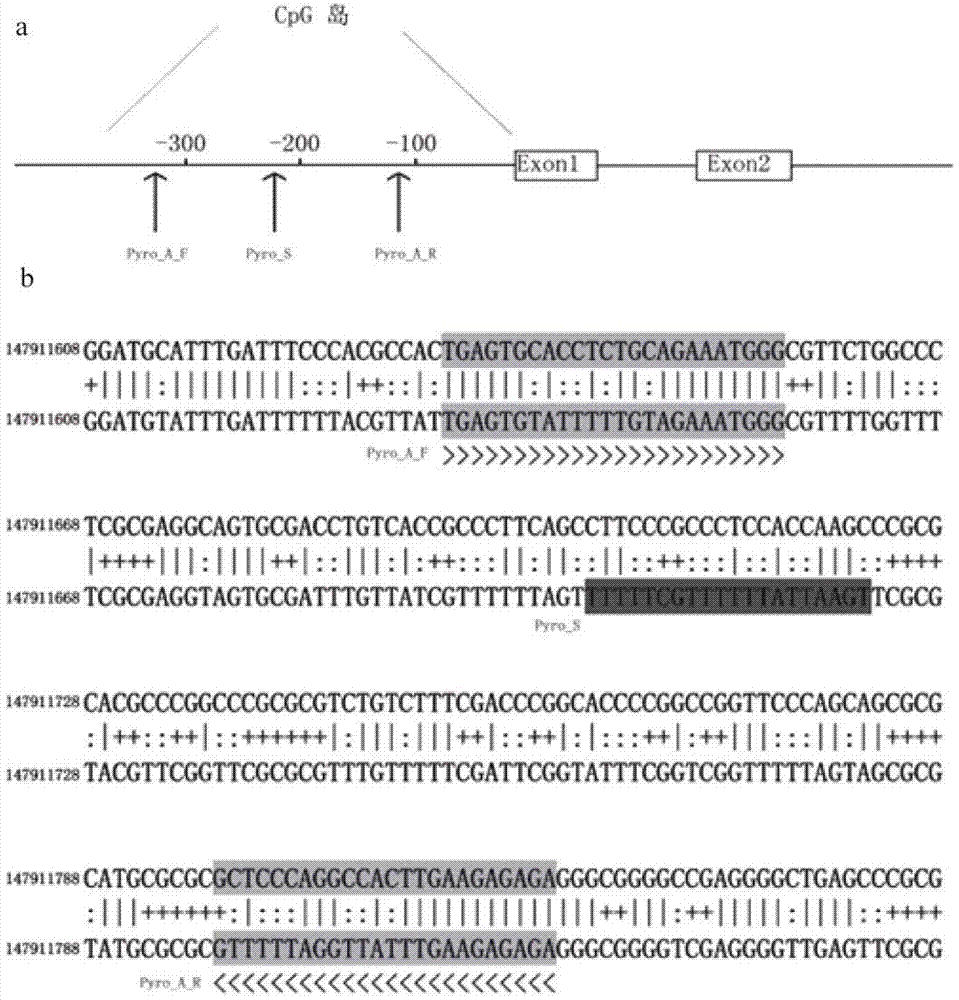
The invention discloses a method for setting a primer used in a detection method of abnormal methylation of upstream CpG island of fragile X chromosome syndrome FMR1 gene. The designed position of an amplification primer does not cover any CG dinucleotide to ensure that PCR amplification treated by a hydrosulphite has no bias. The method is specifically as follows: a pair of amplification primers designed for the upstream CpG island area of the FMR1 gene: PyroAF: TGAGTGTATTTTTGTAGAAATGGG, PyroAR: TCTCTCTTCAAATAACCTAAAAAC. The invention further provides a method for detecting fragile X syndrome by quantitatively comparing the methylation level of the CpG island stably and quickly. By adopting the method, the defects that the existing method for quantitatively detecting abnormal methylation of a FMR1 promoter is still not mature and especially cannot achieve quantitative detection of a single CpG site are solved.
Owner:绍兴迪安华因生物科技有限公司
Differentially methylated sequences in pancreatic cancer
InactiveUS20050069924A1Raise the possibilityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDifferential MethylationPancreatic cancer
The present invention provides a method for detecting a cellular proliferative disorder in a subject. The method includes contacting a nucleic acid-containing specimen from the subject with an agent that provides a determination of the methylation state of at least one gene or associated regulatory region of the gene and identifying aberrant methylation of regions of the gene or regulatory region, wherein aberrant methylation is identified as being different when compared to the same regions of the gene or associated regulatory region in a subject not having said cellular proliferative, thereby detecting a cellular proliferative disorder in the subject.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Macrophage polarization inhibitor and application thereof
InactiveCN109929803AFully understandEnriching understanding of polarization mechanismsBlood/immune system cellsMacrophage polarizationAberrant methylation
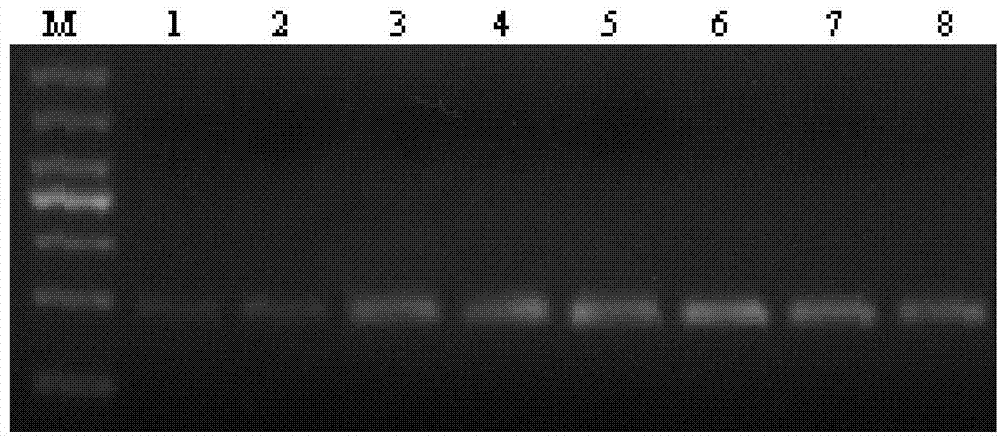
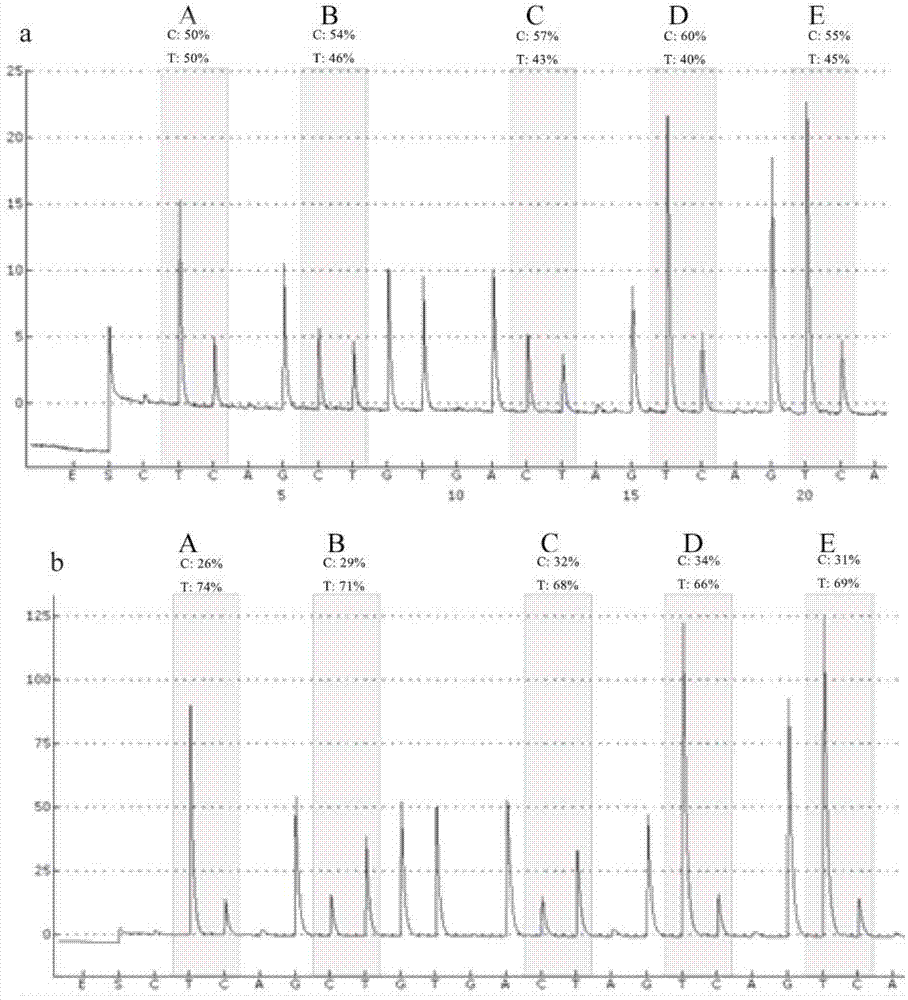
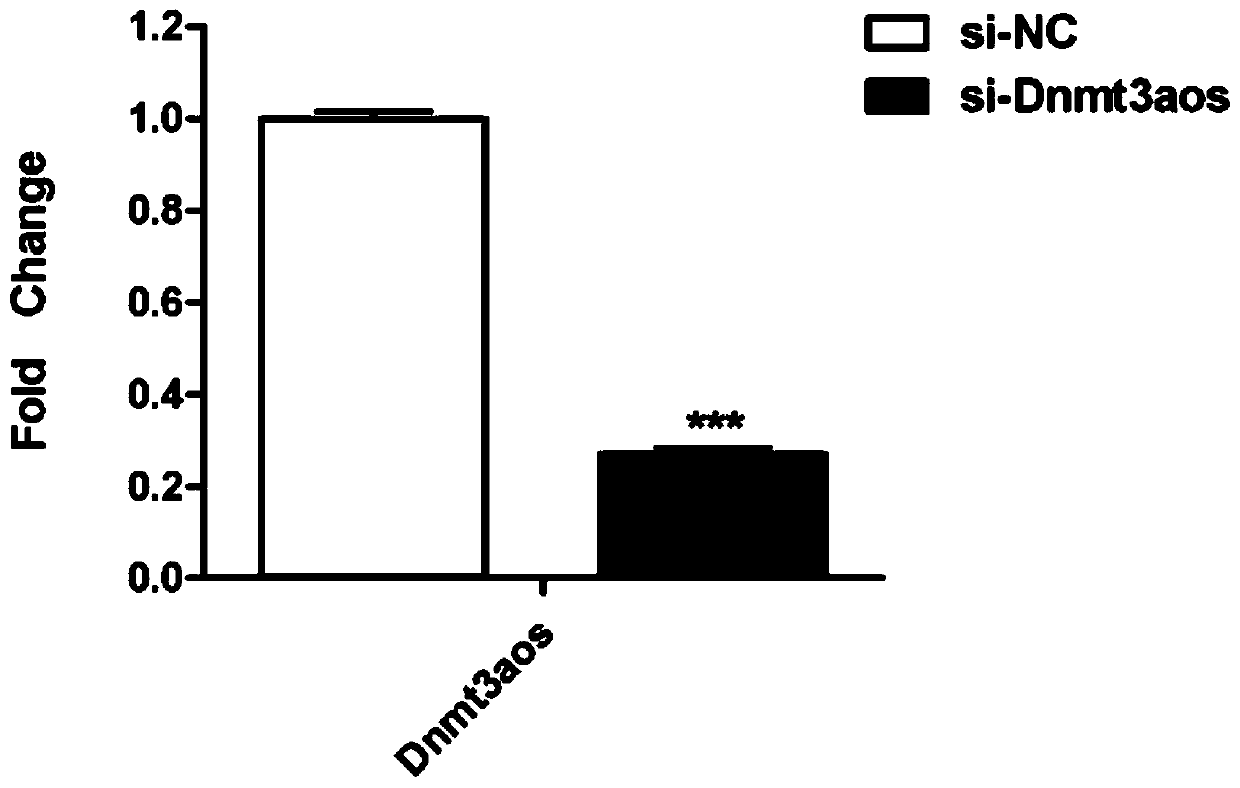
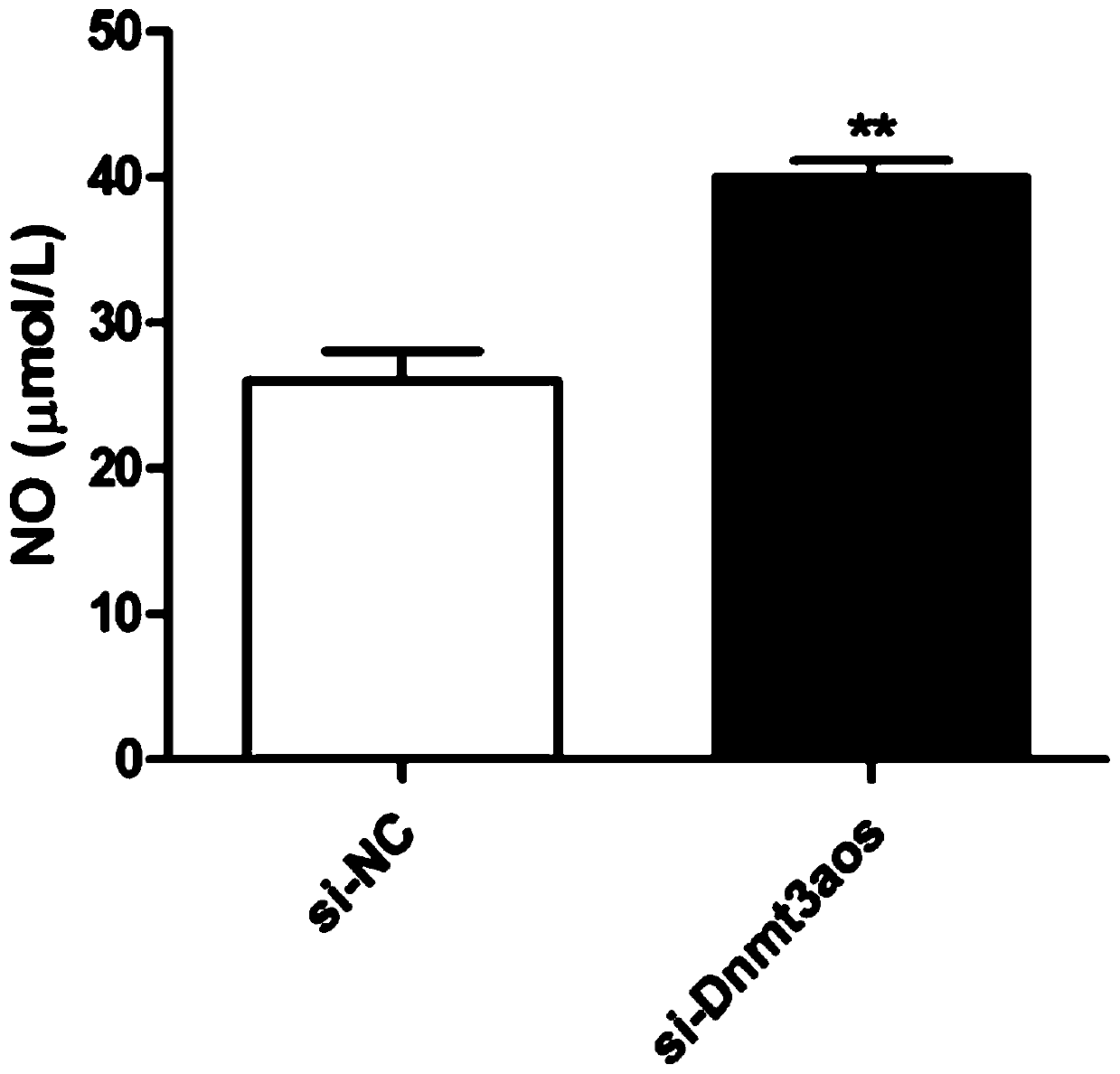
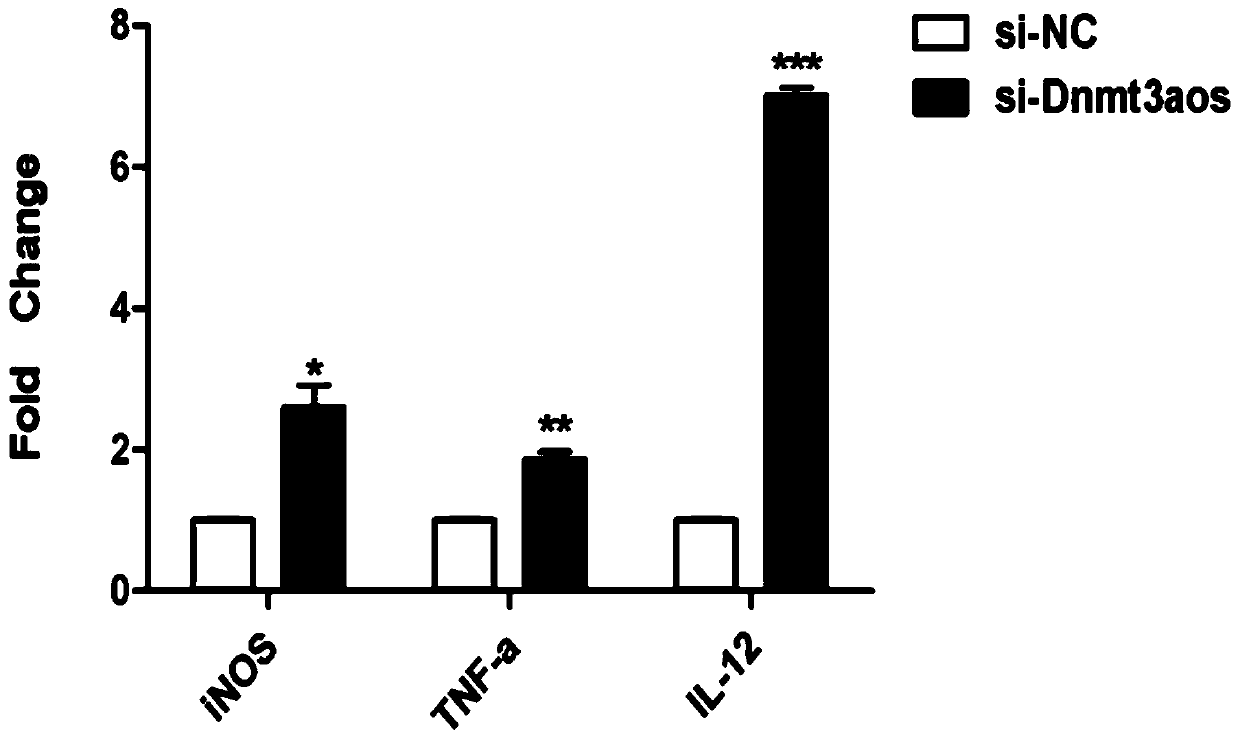
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to a macrophage polarization inhibitor and application thereof. A macrophage polarization inhibitor Dnmt3aos, a kit containing the inhibitor Dnmt3aos claimed in Claim 1 and the application of the macrophage polarization inhibitor Dnmt3aos are provided. The Dnmt3aos plays a crucial role in macrophage polarization, Dnmt3aos-Dnmt3a axis-mediated DNA aberrant methylation may play a key role in the macrophage polarization, and the inhibitor enriches the understanding of the macrophage polarization mechanism and provides theoreticaldata support for studying the macrophage polarization.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WANNAN MEDICAL COLLEGE YIJISHAN HOSPITAL OF WANNAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
Method for enriching methylated CpG sequences
ActiveUS8367331B2Promote recoveryFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesSingle strand dnaBiology
Compositions and methods are provided for facilitating the enrichment of single-stranded DNA containing methylated CpG in a mixture containing methylated and unmethylated DNA. The compositions relate to methylation-binding protein domains that selectively bind to methylated single strand DNA. In embodiments of the invention, the methylated DNA is eluted in 0.4M-0.6M NaCl while the unmethylated single strand DNA is eluted in less than 0.4M salt. The ability to readily enrich for methylated DNA permits high throughput sequencing of the methylated DNA and identification of abnormal methylation patterns associated with disease.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Analysis of methylated nucleic acid
InactiveUS20120288509A1Readily susceptiblePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease markersDNA
The present invention provides a method for analysis methylation patterns in DNA and identifying aberrantly methylated genes in disease tissue. The invention also provides a method of identifying novel targets for therapeutic intervention and disease markers. Novel cancer targets are provided.
Owner:SCHUEBELER DIRK +1
Quantitative detection method of HPP1 gene methylation
InactiveCN101665835AQuantitative determination of abnormal methylation levelsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReference genesBisulfite sequencing
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The abnormal methylation of the gene participates in the occurrence and the development of tumors, therefore, the invention aims at overcoming the defects of a methylation sensitive restriction enzyme method, a bisulfite sequencing method and a methylation specificity PCR method, and providing a quantitative detection method of HPP1 genemethylation with convenient operation and high sensitivity. The method comprises the steps of: taking pancreatic cancer tissue; extracting NDA to prepare a standard curve sample of ACTB; using a fullmethylated template to prepare a standard curve sample of HPP1; extracting the DNA of tissue to be tested, and chemically modifying; designing methylated primer and probe by aiming at the human HPP1gene promoter area CPG island; designing BSP primer and probe by aiming at the human reference gene ACTB promoter area CPG island; conducting real-time and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR)to the DNA of processed sulfite by means of Taqman-MGB real-time quantitative PCR method; and counting the quantitative value of the HPP1 gene methylation degree. The method is fast and accurate, andhas high sensitivity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Assay for Methylation in the GST-PI Gene
InactiveUS20090215056A1Variability in methylation statusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineAssay
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
ABERRANT METHYLATION OF C6Orf150 DNA SEQUENCES IN HUMAN COLORECTAL CANCER
InactiveUS20110165567A1High stringent conditionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
This application describes methods and compositions for detecting and treating C6Orf150-associated neoplasia. Differential methylation of the C6Orf150 nucleotide sequences has been observed in C6Orf150-associated neoplasia such as colon neoplasia.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Methods for early prediction, treatment response, recurrence and prognosis monitoring of breast cancer
The present invention discloses a set of novel epigenetic biomarkers for early prediction, treatment response, recurrence and prognosis monitoring of a breast cancer. Aberrant methylation of the genes can be detected in tumor tissues and plasma samples from breast cancer patients but not in normal healthy individual. The present disclosure also discloses primers and probes used herein.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
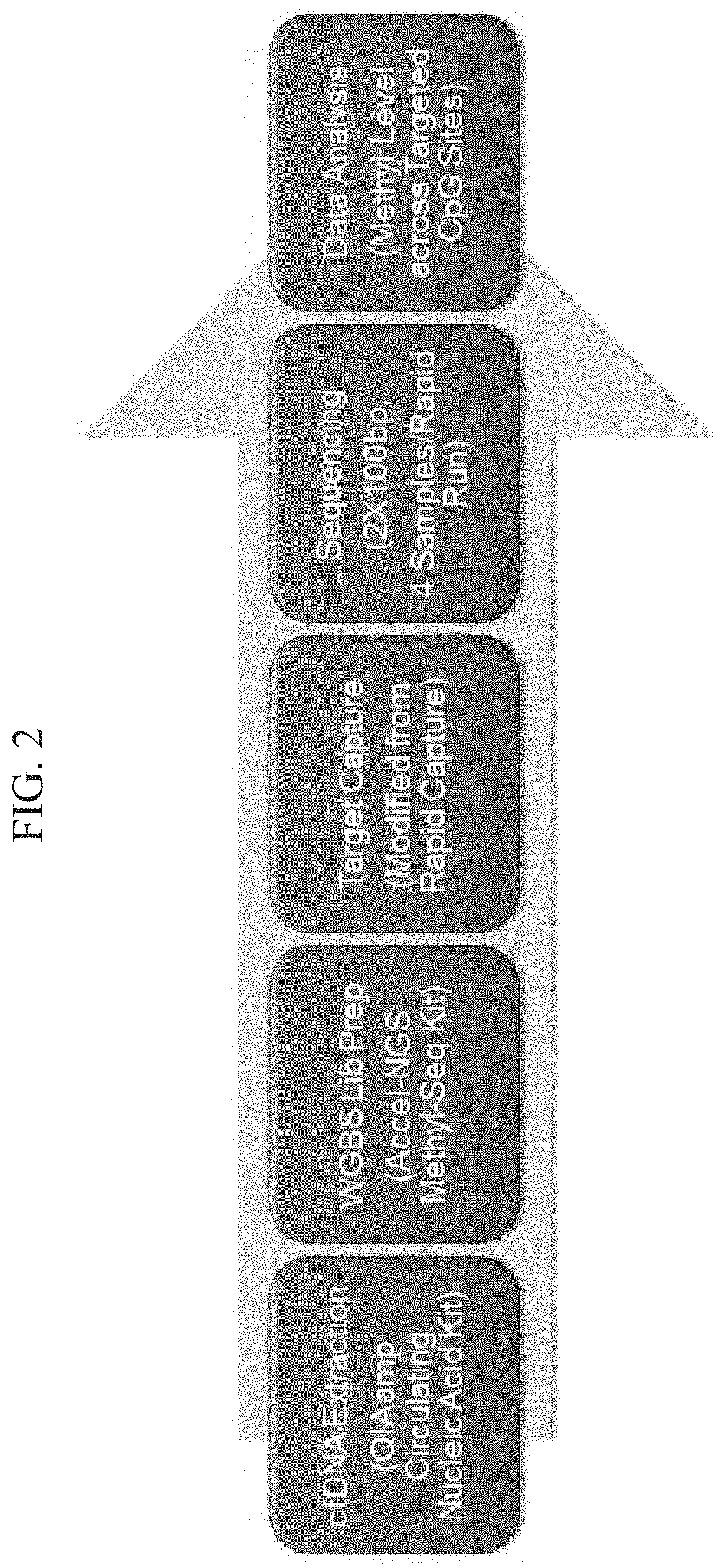
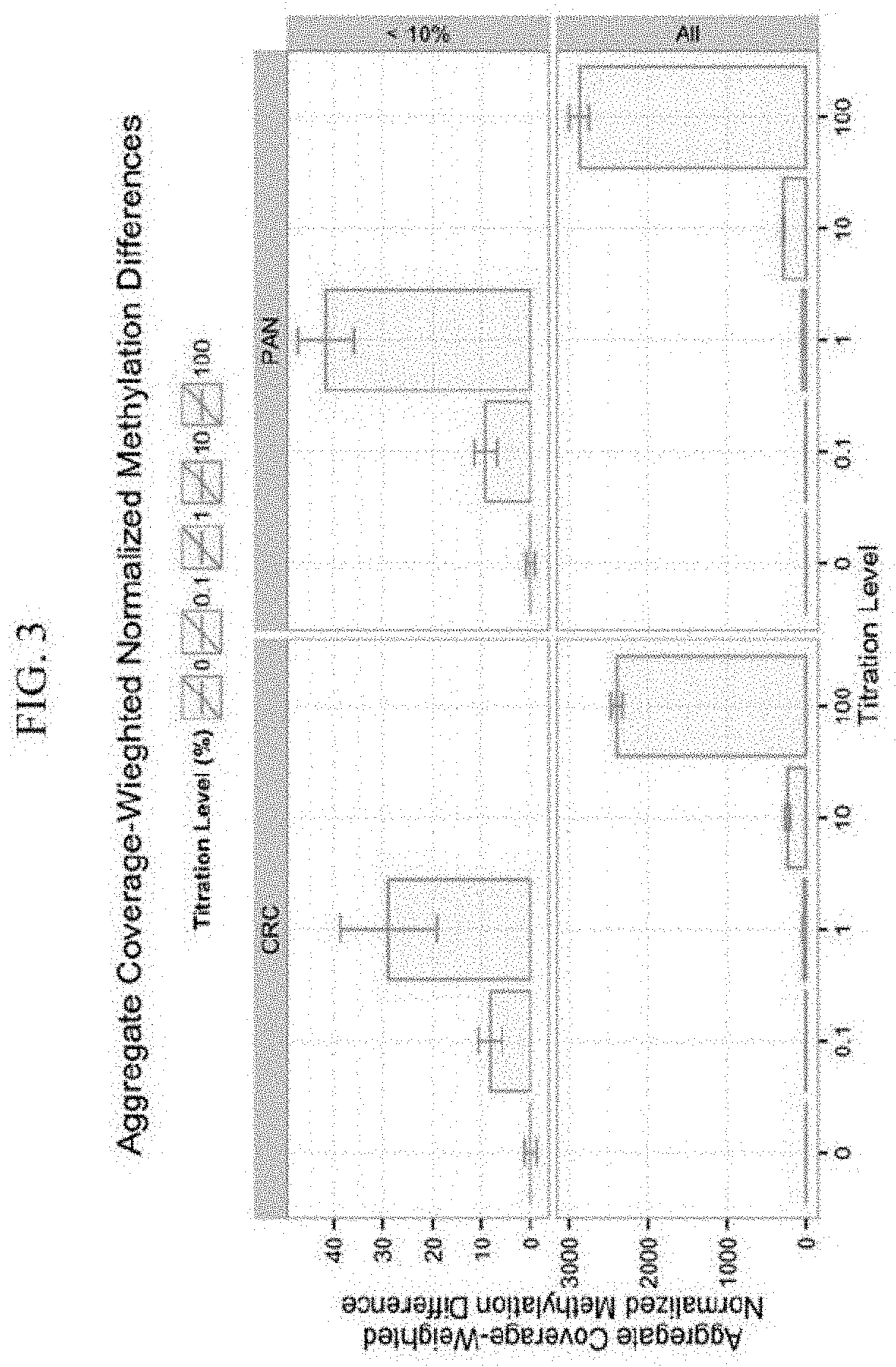
Distinguishing methylation levels in complex biological samples
PendingUS20220170113A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellCancer type
Provided herein is a method for distinguishing an aberrant methylation level for DNA from a first cell type, including steps of (a) providing a test data set that includes (i) methylation states for a plurality of sites from test genomic DNA from at least one test organism, and (ii) coverage at each of the sites for detection of the methylation states; (b) providing methylation states for the plurality of sites in reference genomic DNA from one or more reference individual organisms, (c) determining, for each of the sites, the methylation difference between the test genomic DNA and the reference genomic DNA, thereby providing a normalized methylation difference for each site; and (d) weighting the normalized methylation difference for each site by the coverage at each of the sites, thereby determining an aggregate coverage-weighted normalized methylation difference score. Also provided herein are sensitive methods for using genomic DNA methylation levels to distinguish cancer cells from normal cells and to classify different cancer types according to their tissues of origin.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
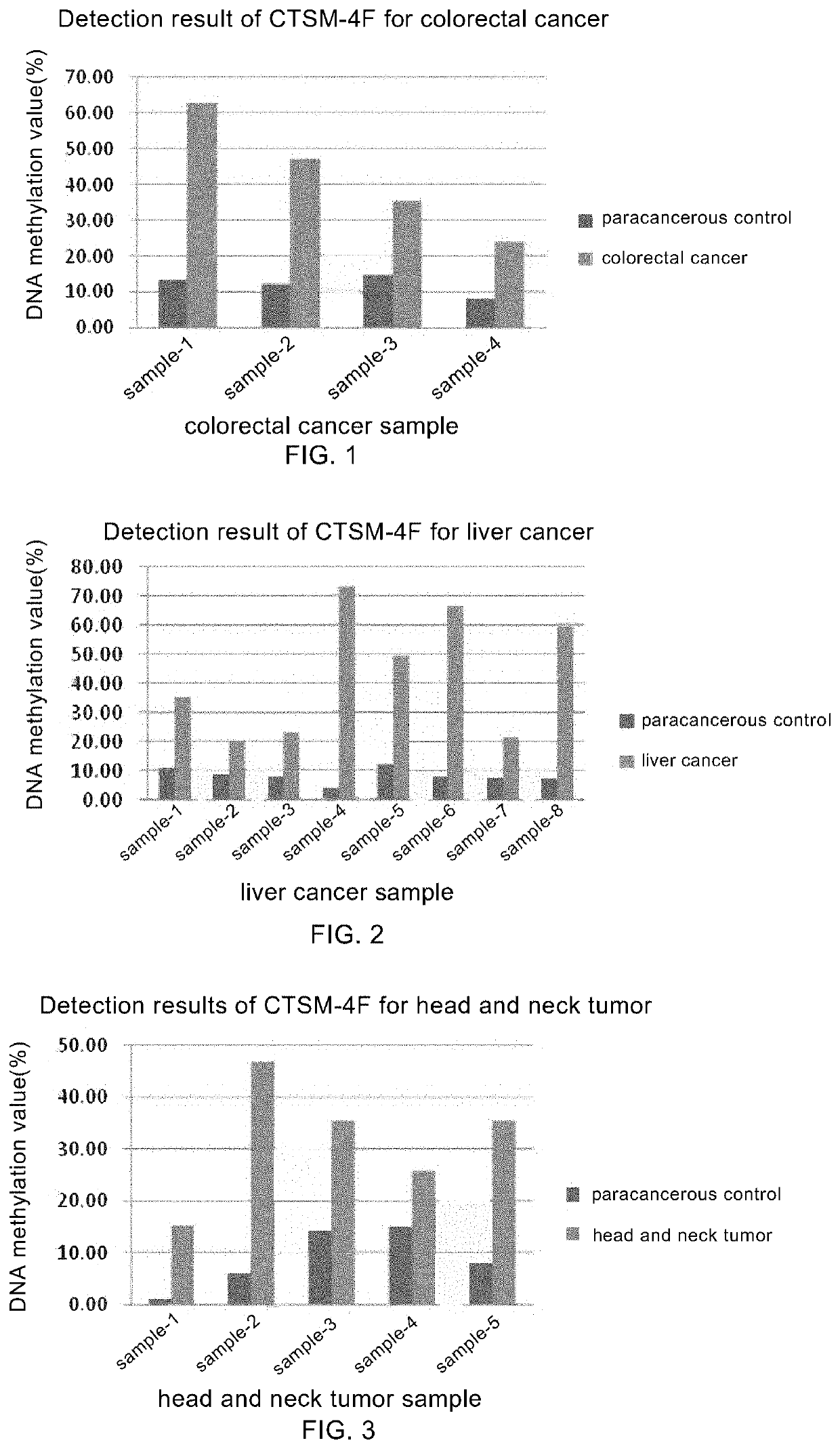
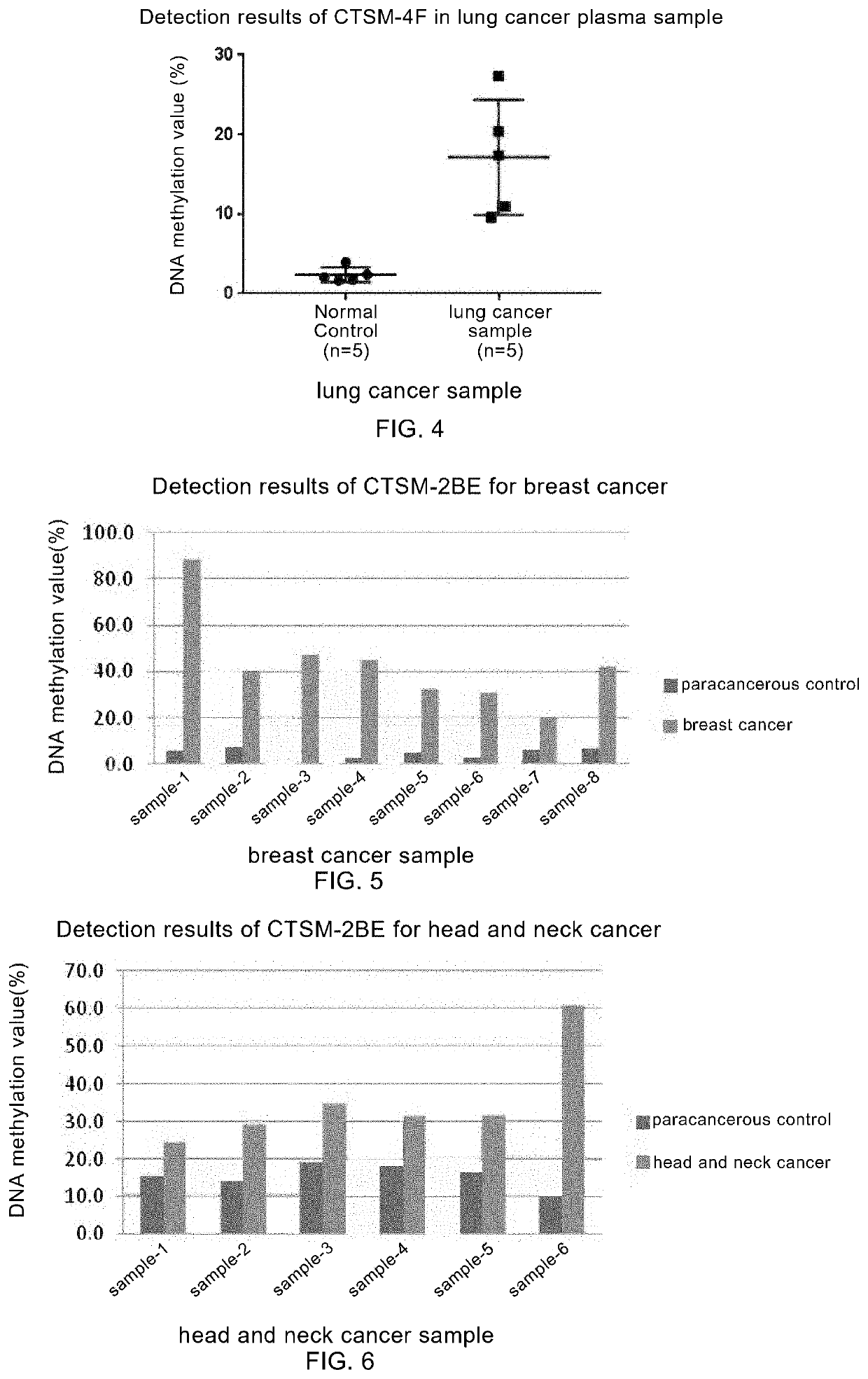
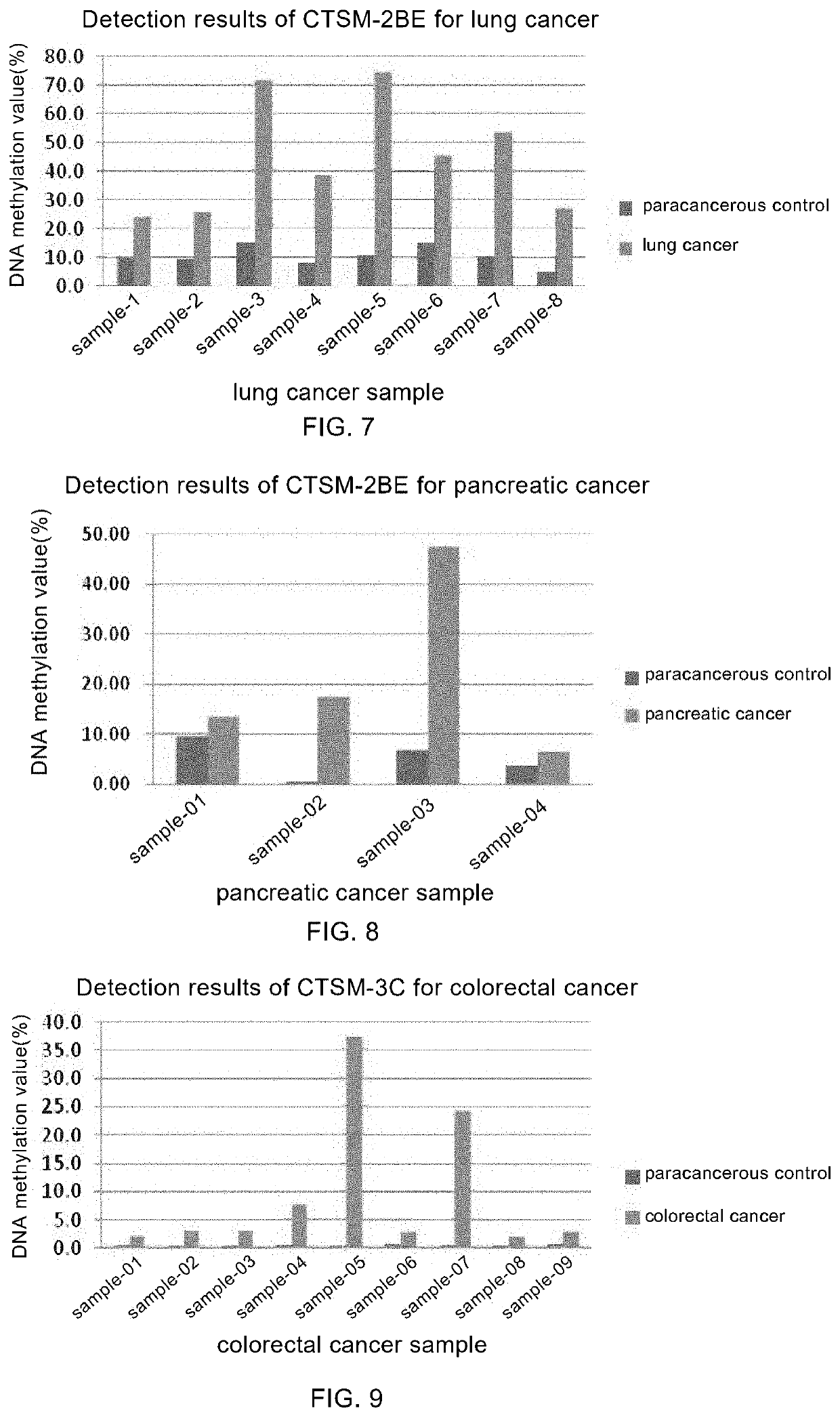
DNA methylation-related marker for diagnosing tumor, and application thereof
Provided are DNA methylation related markers for diagnosis of tumors and application thereof. Disclosed are gene sequence regions having abnormal DNA methylation in the genome, named tumor markers CTSM-4F, CTSM-2BE, CTSM-3C, CTSM-4I. The methylation levels of those sequence regions are significantly different between tumor tissues and non-tumor tissues, with their CpG(s) hypermethylated in tumor tissues.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com