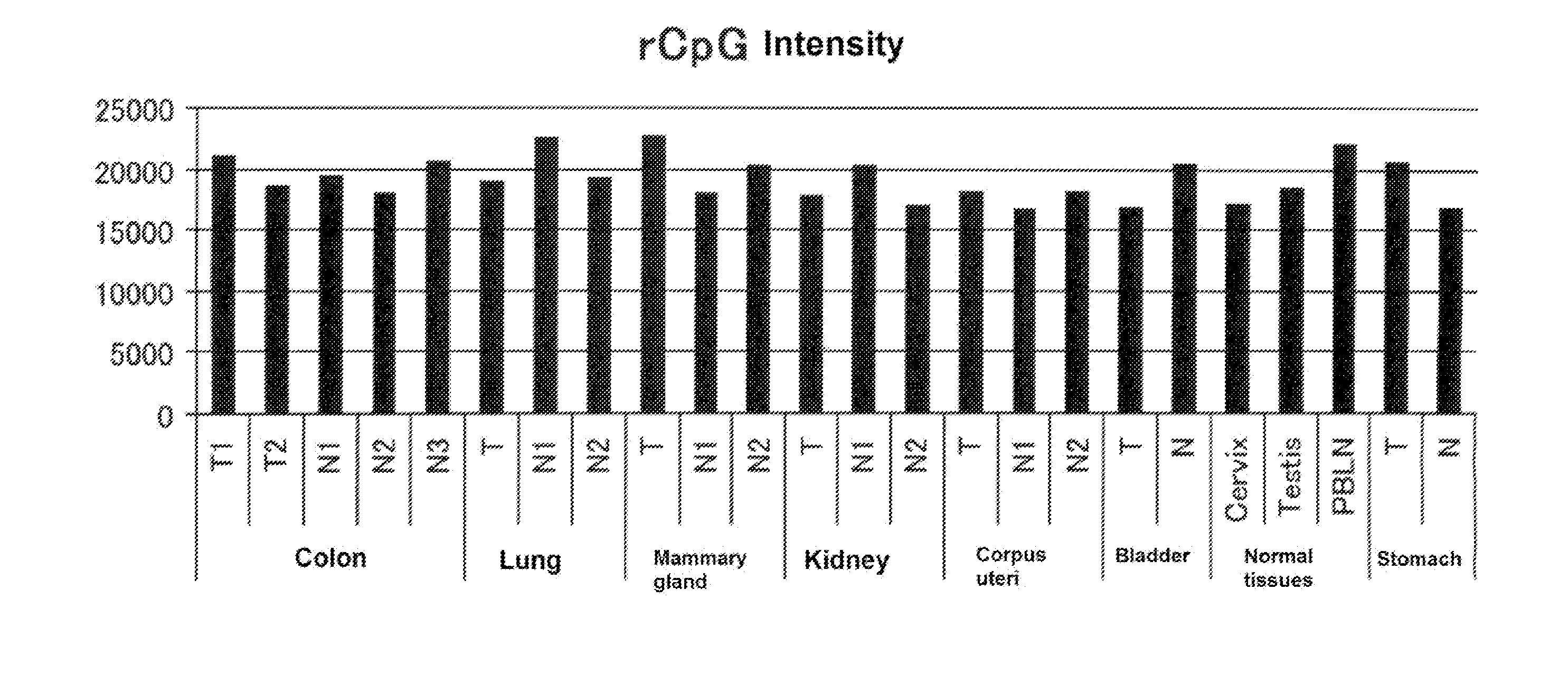
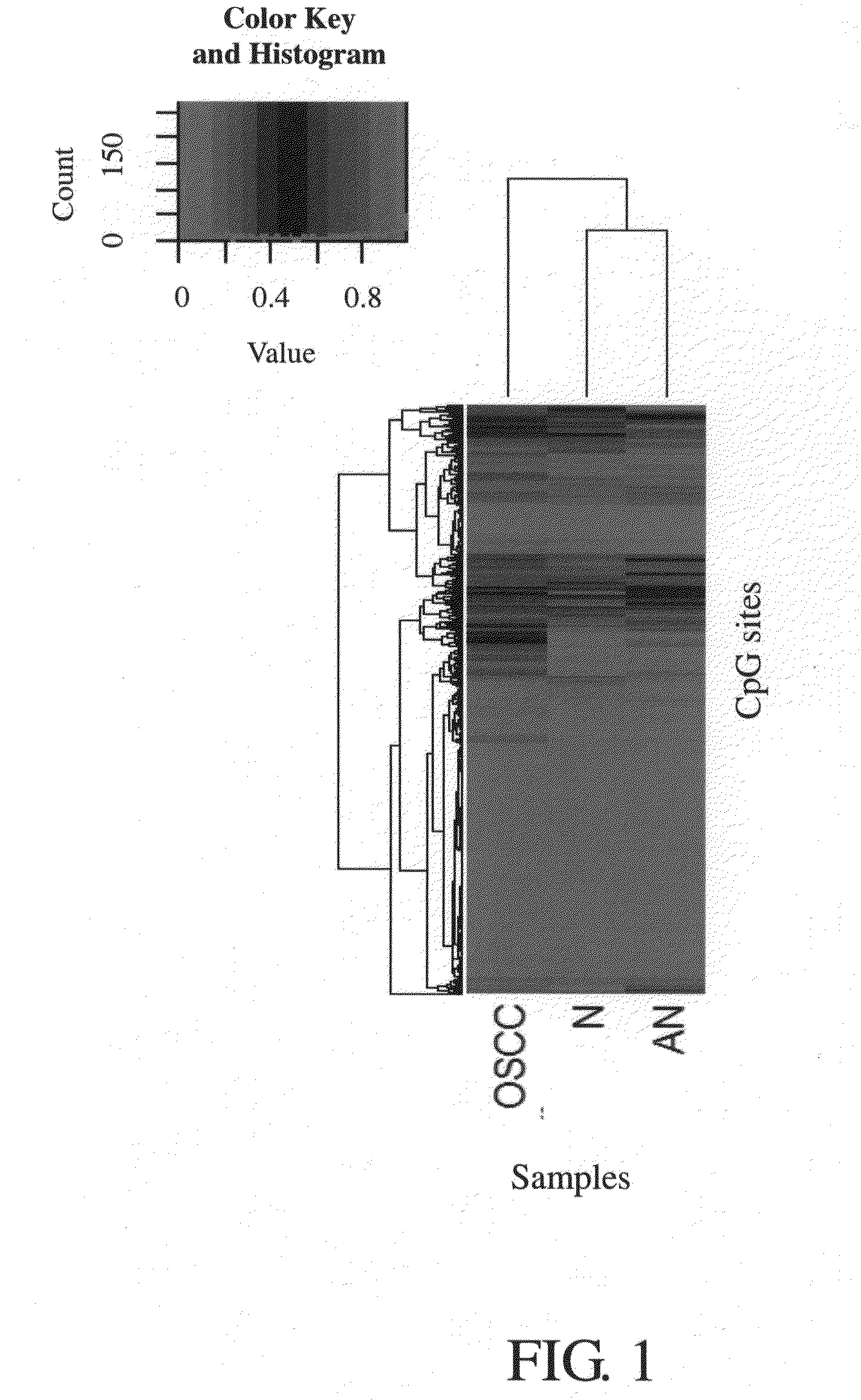
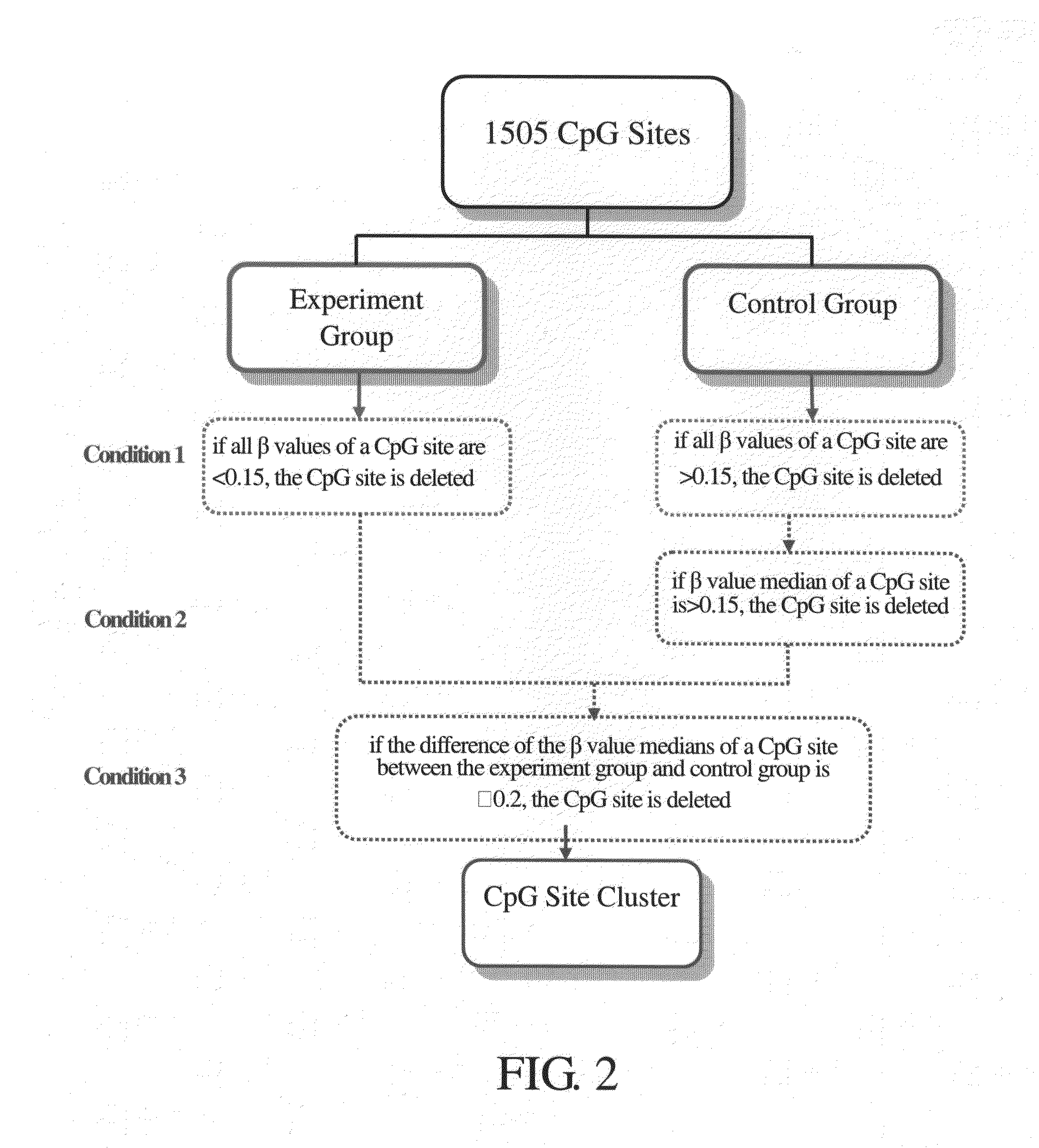
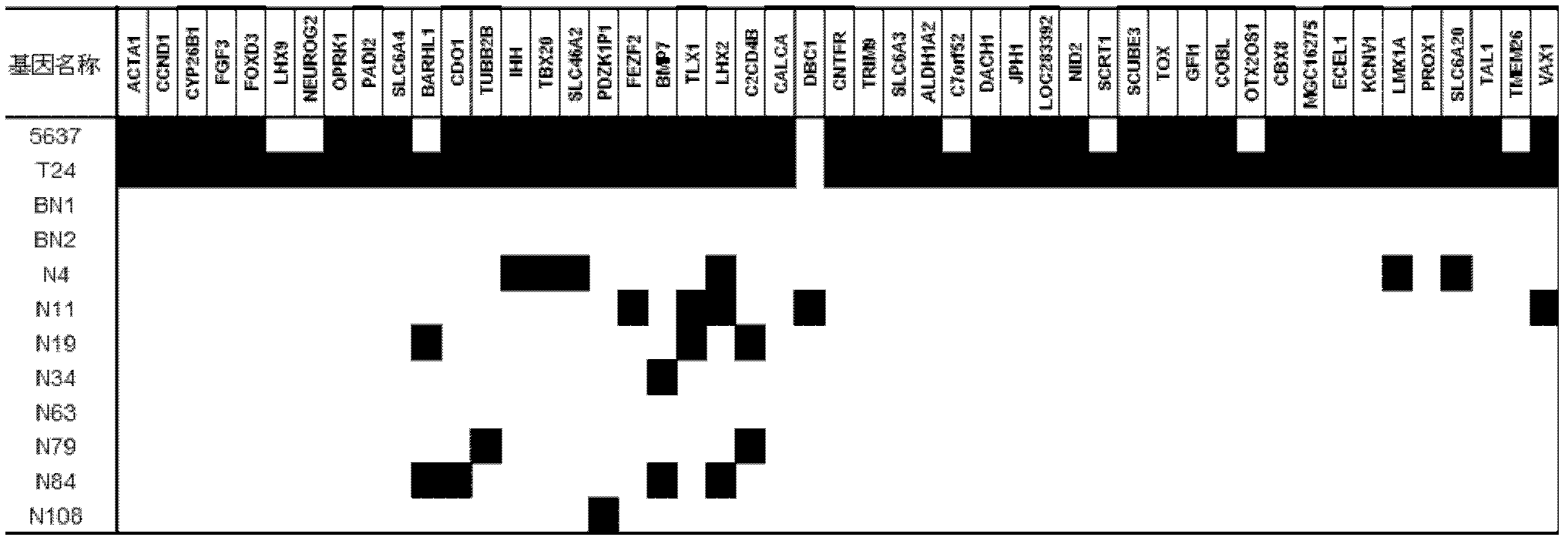
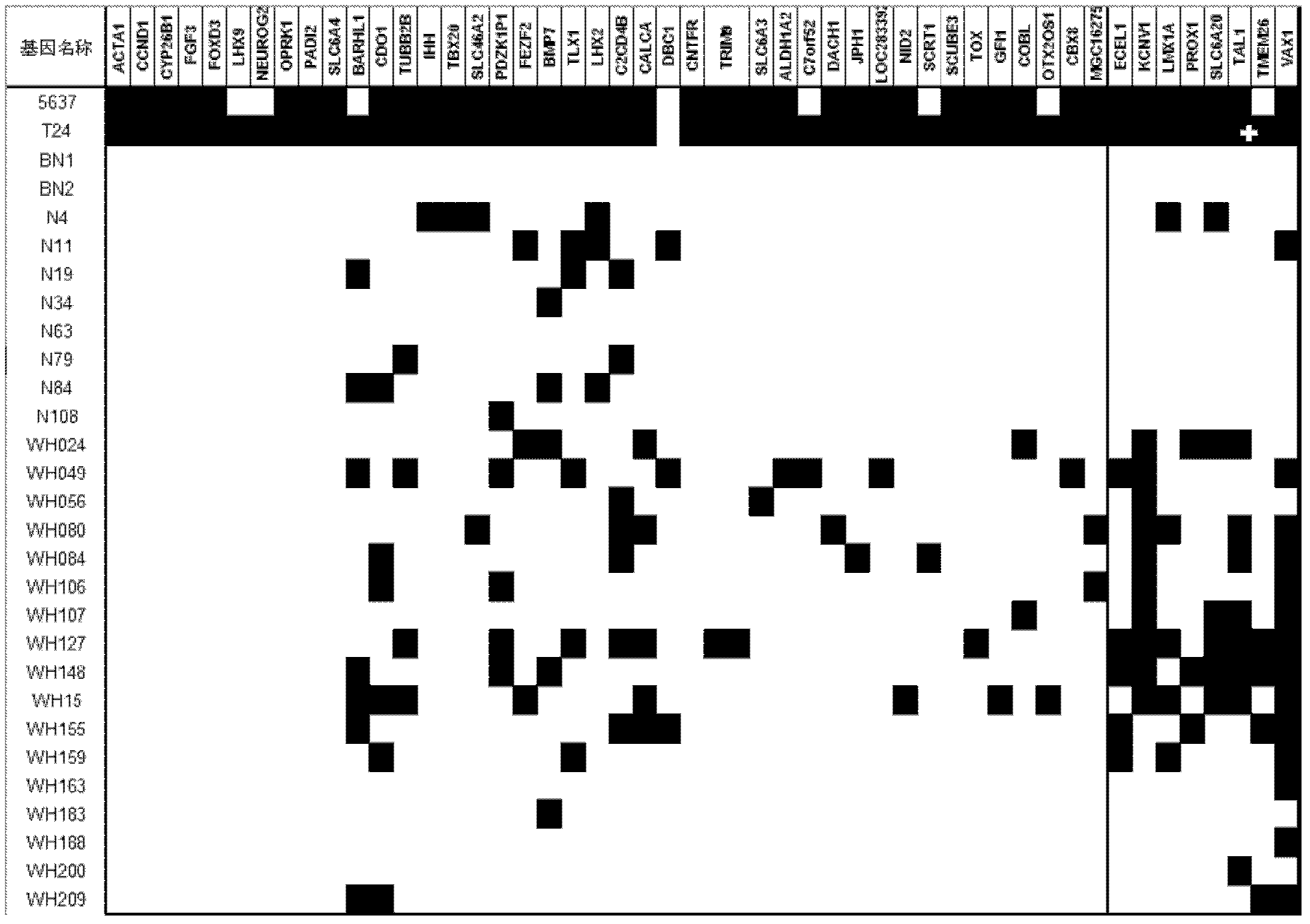
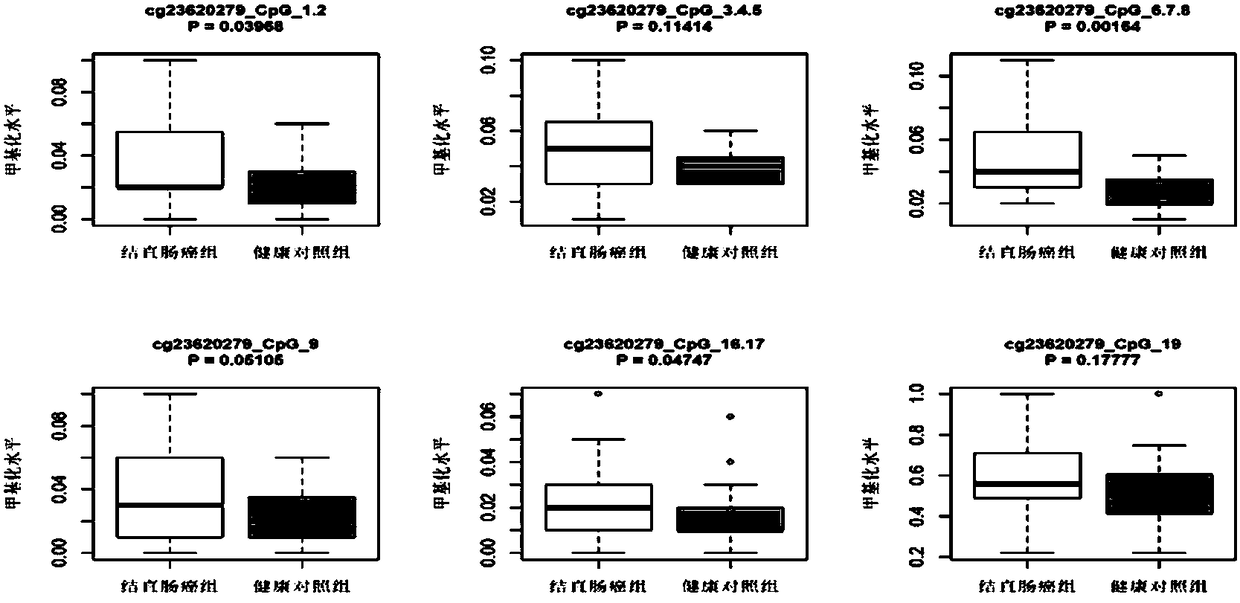
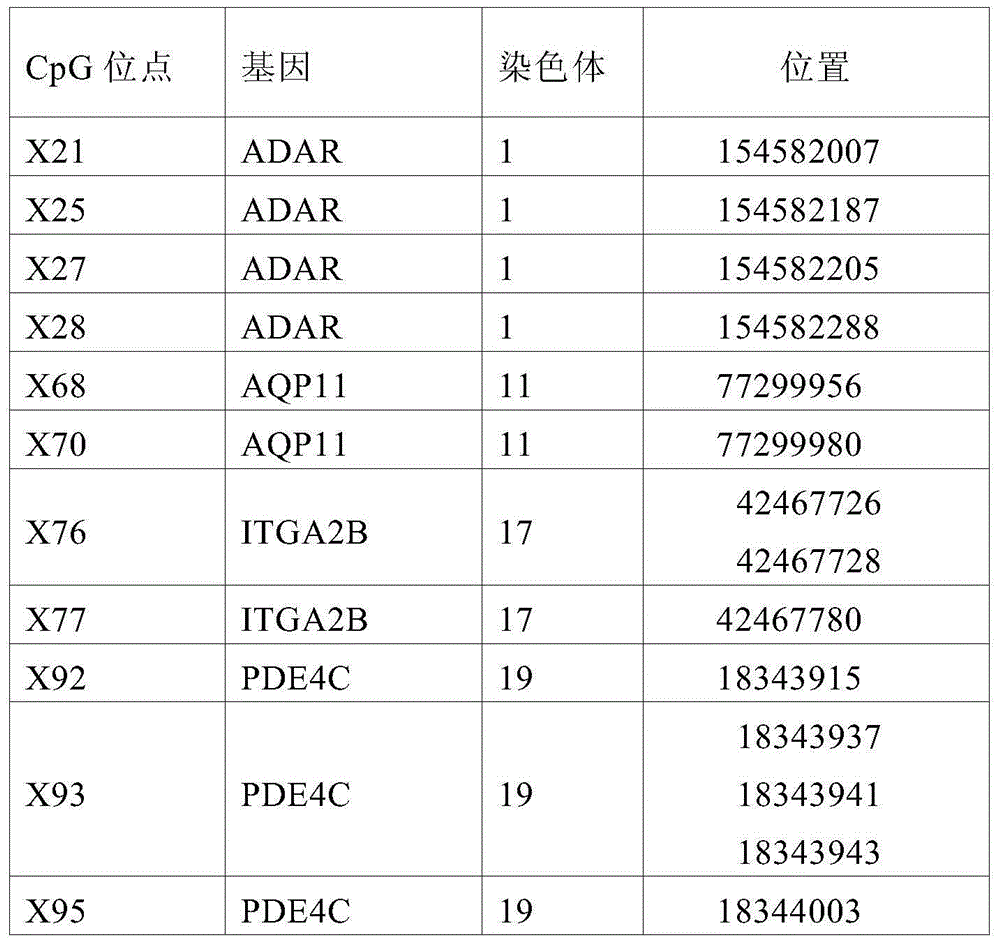
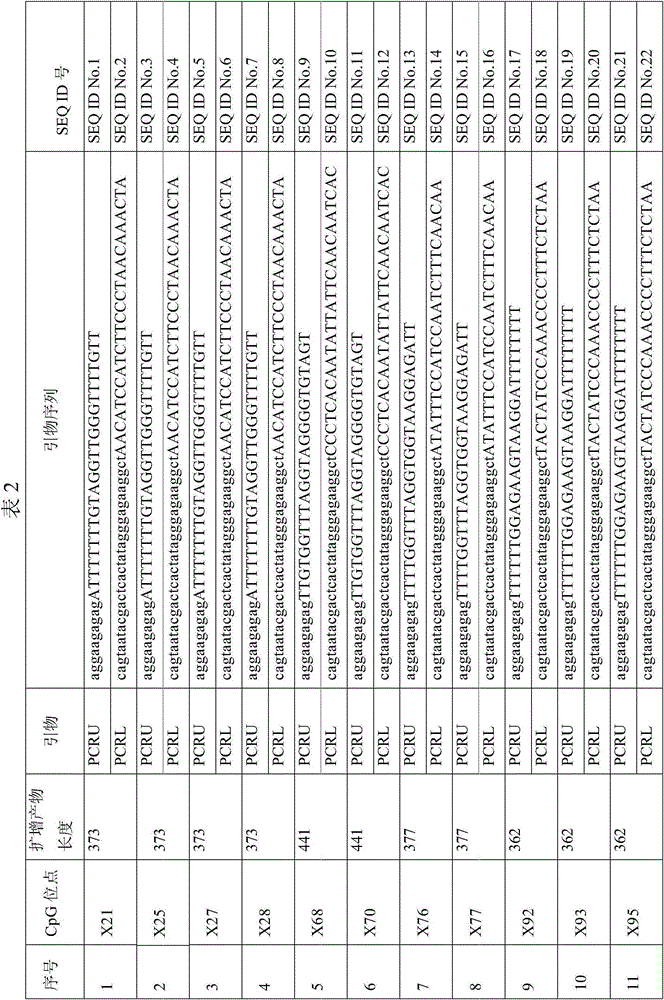
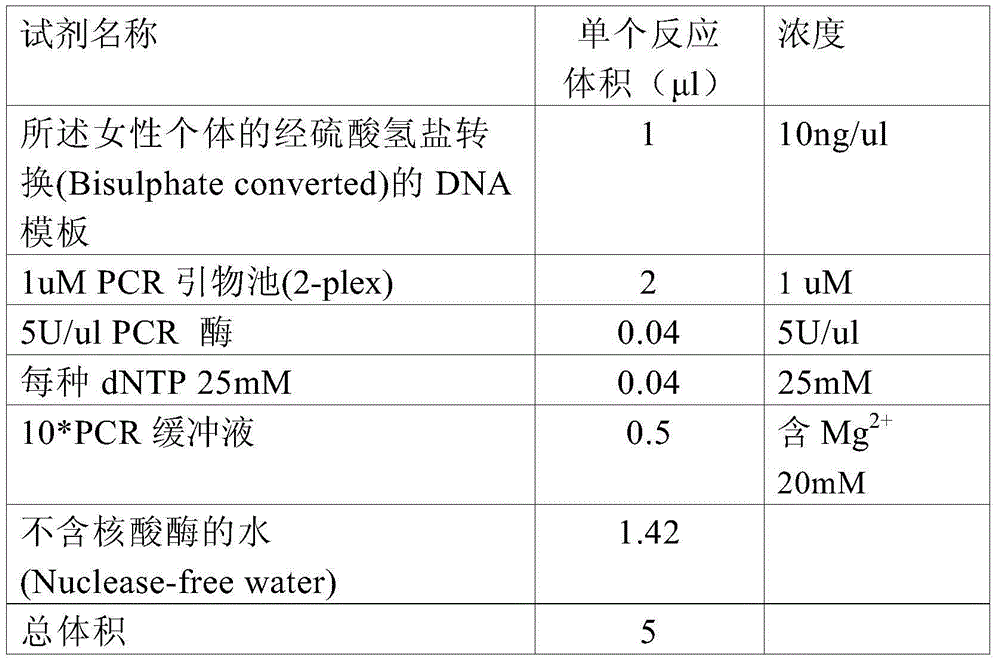
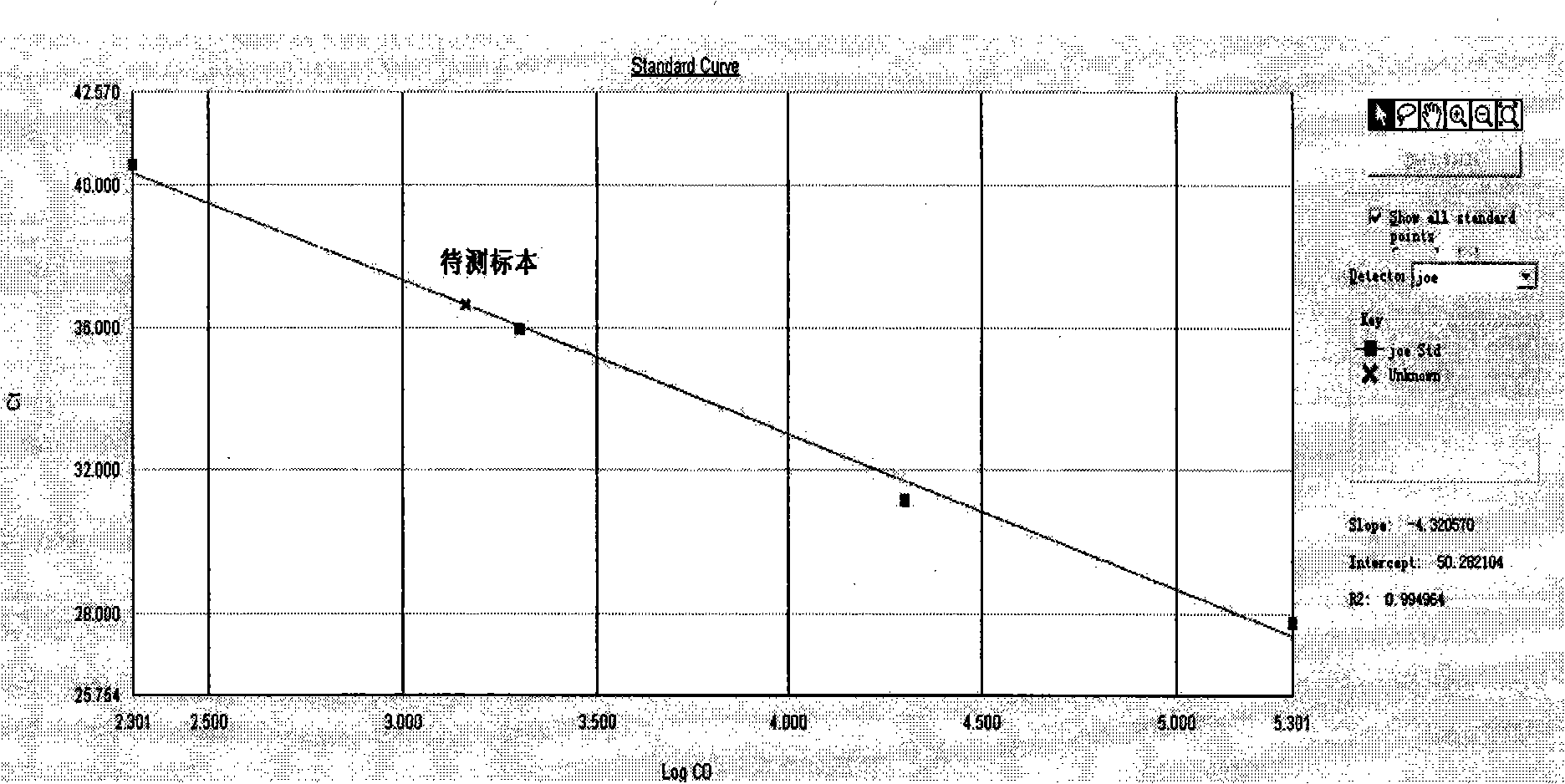
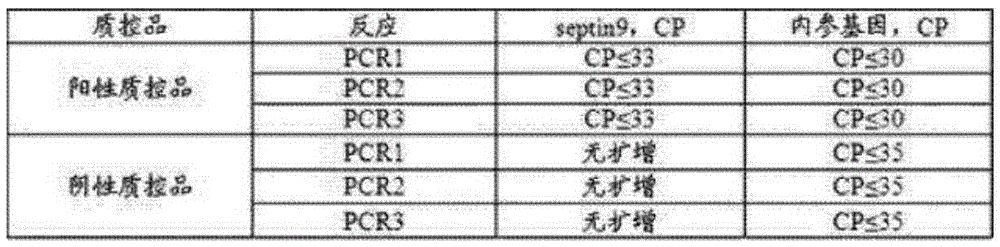
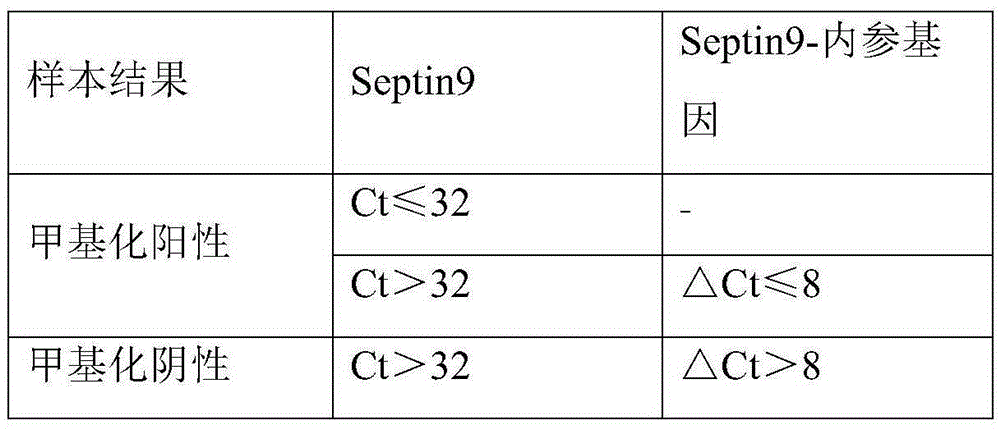
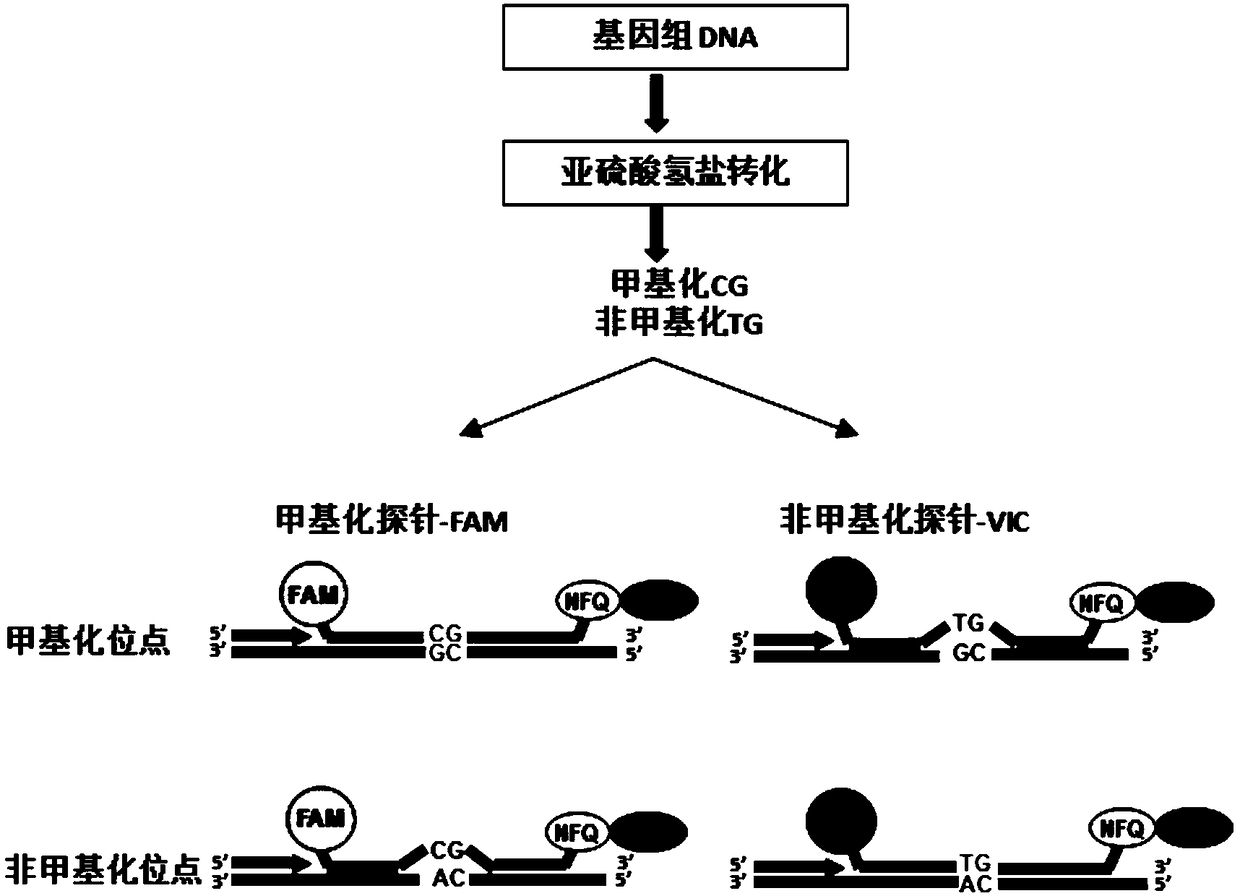
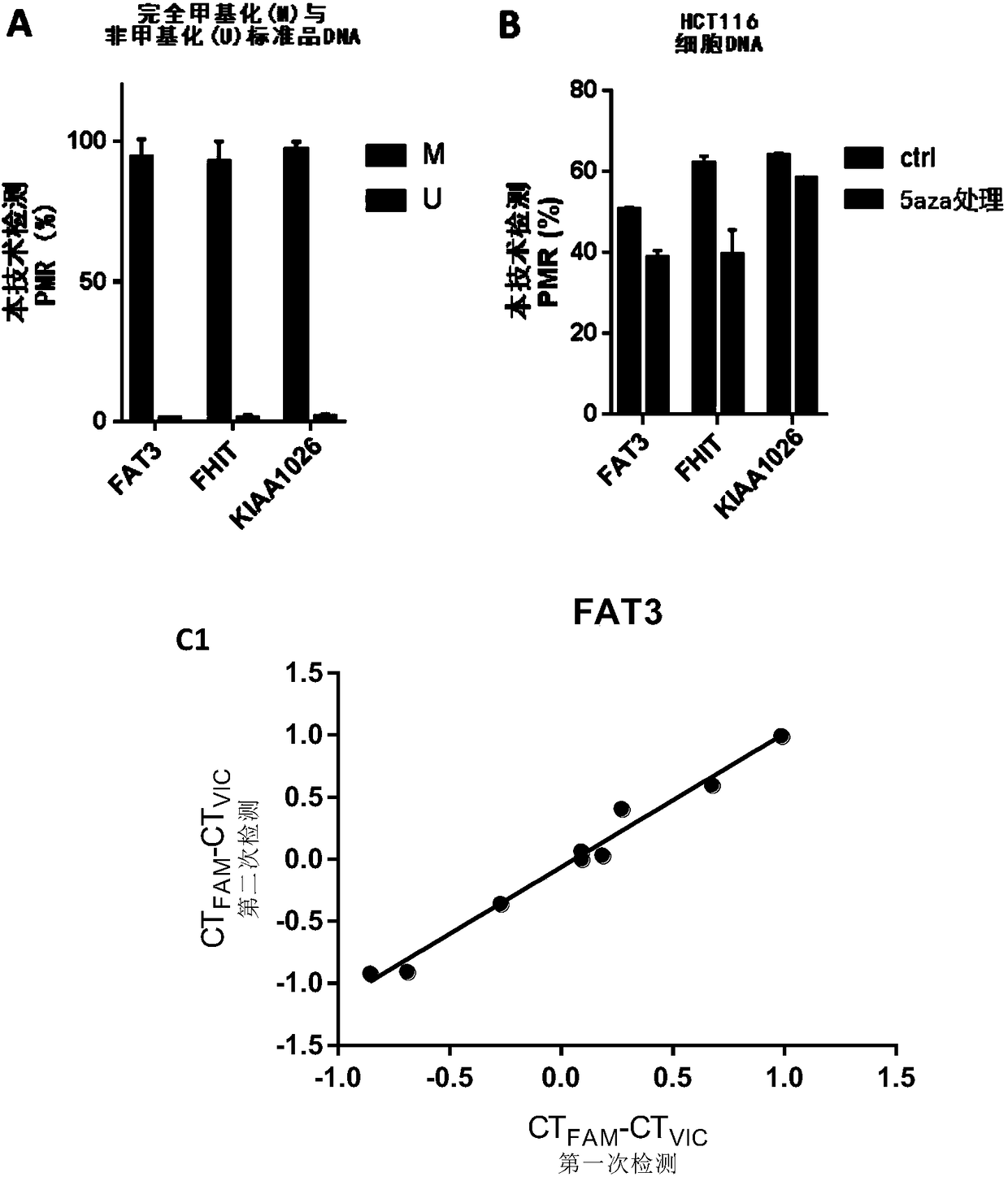
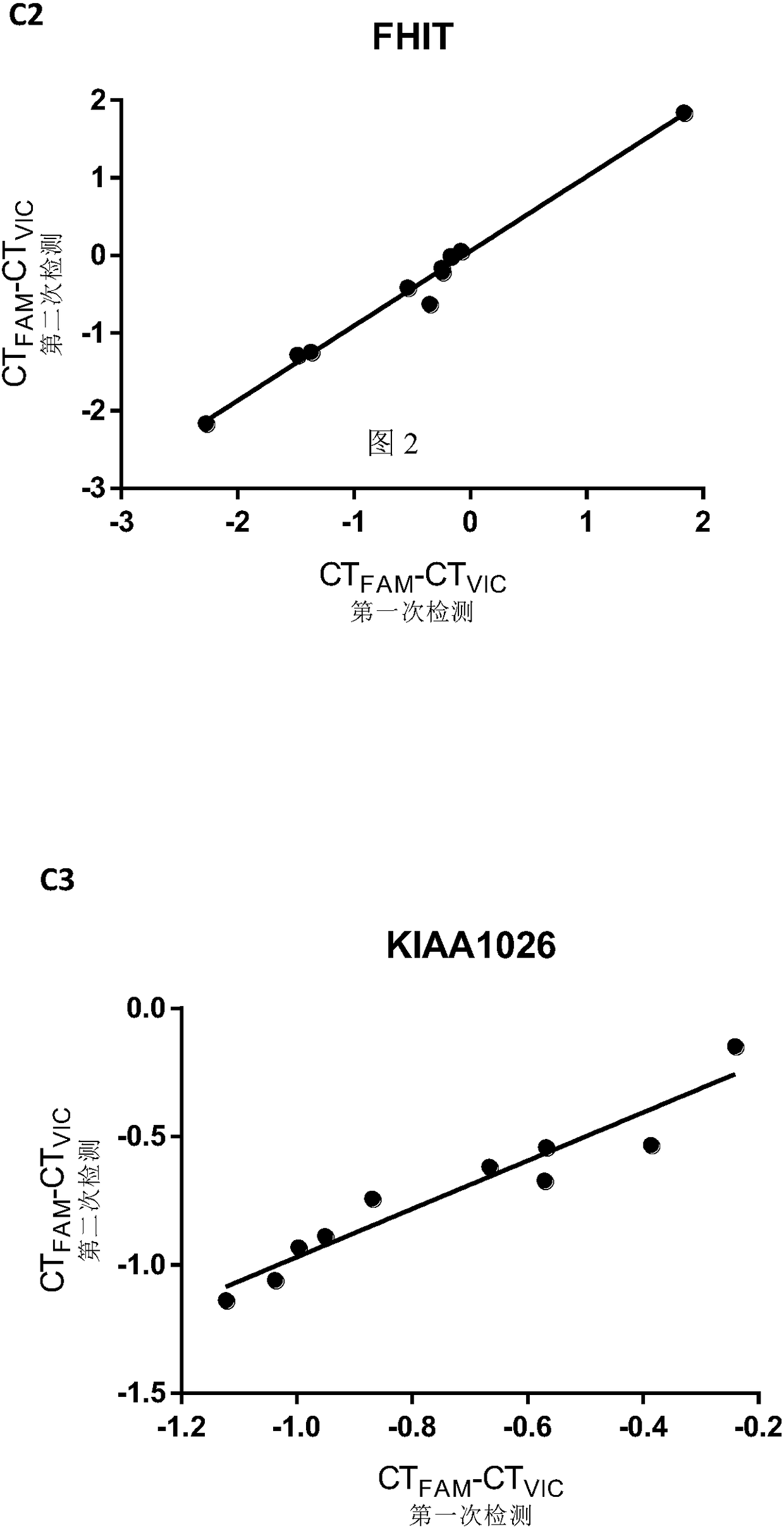
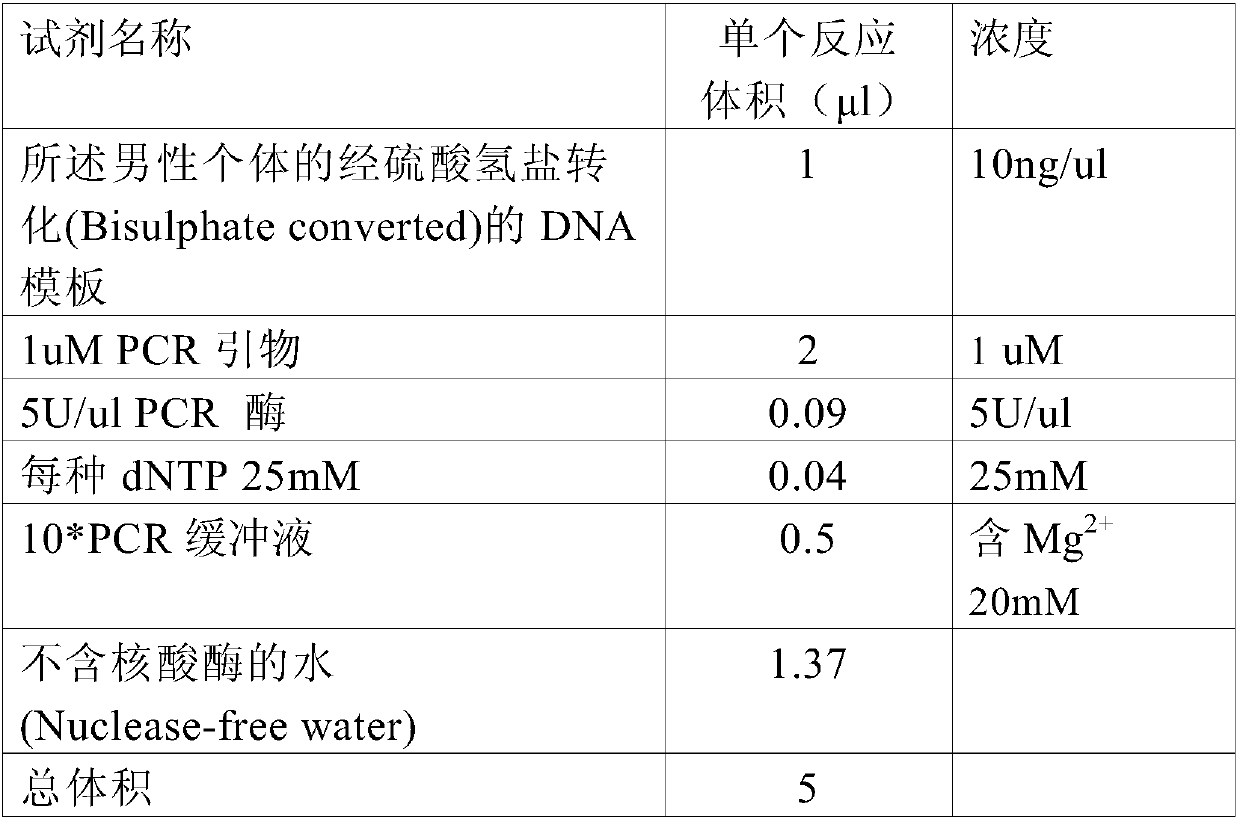
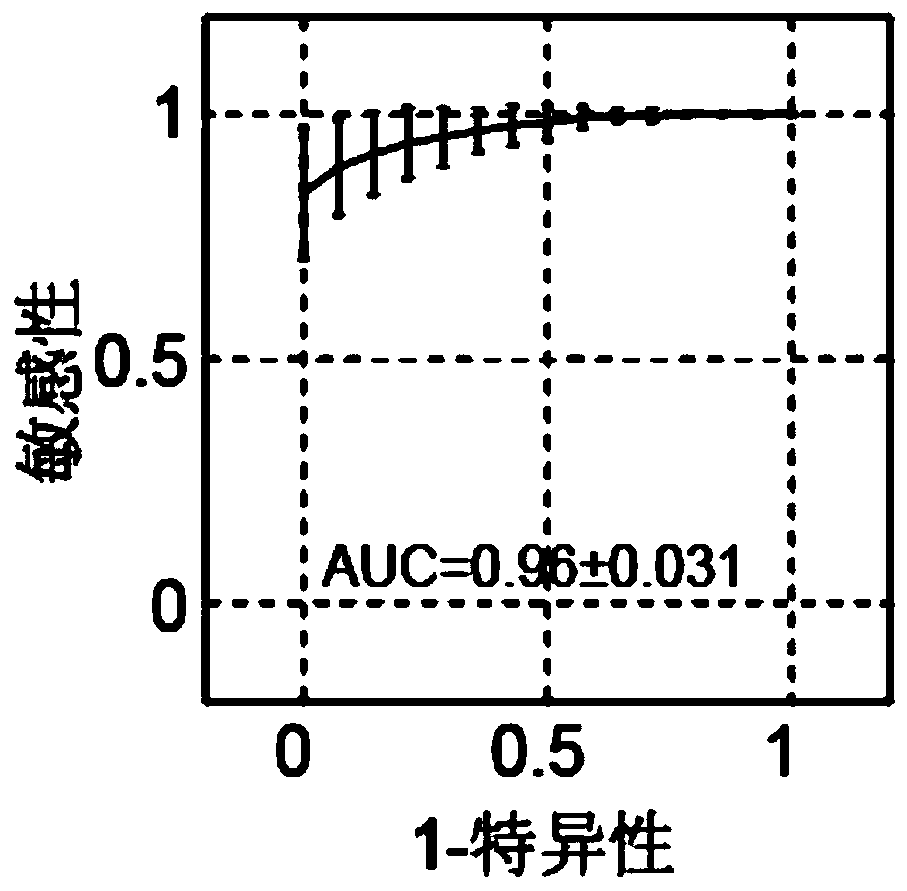
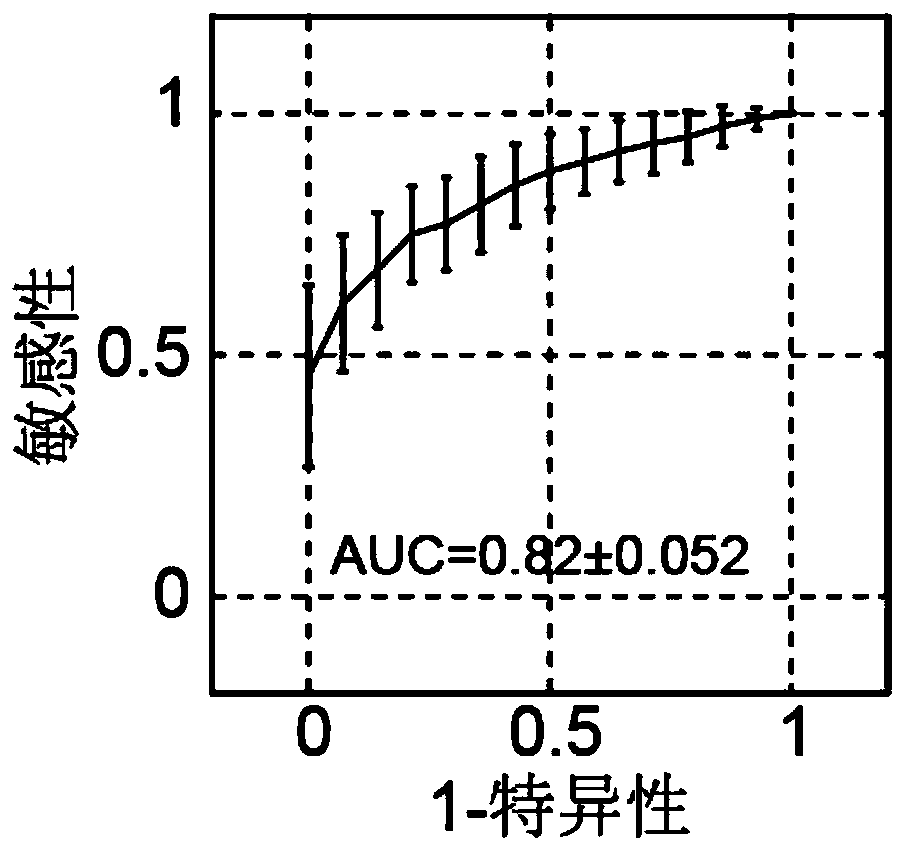
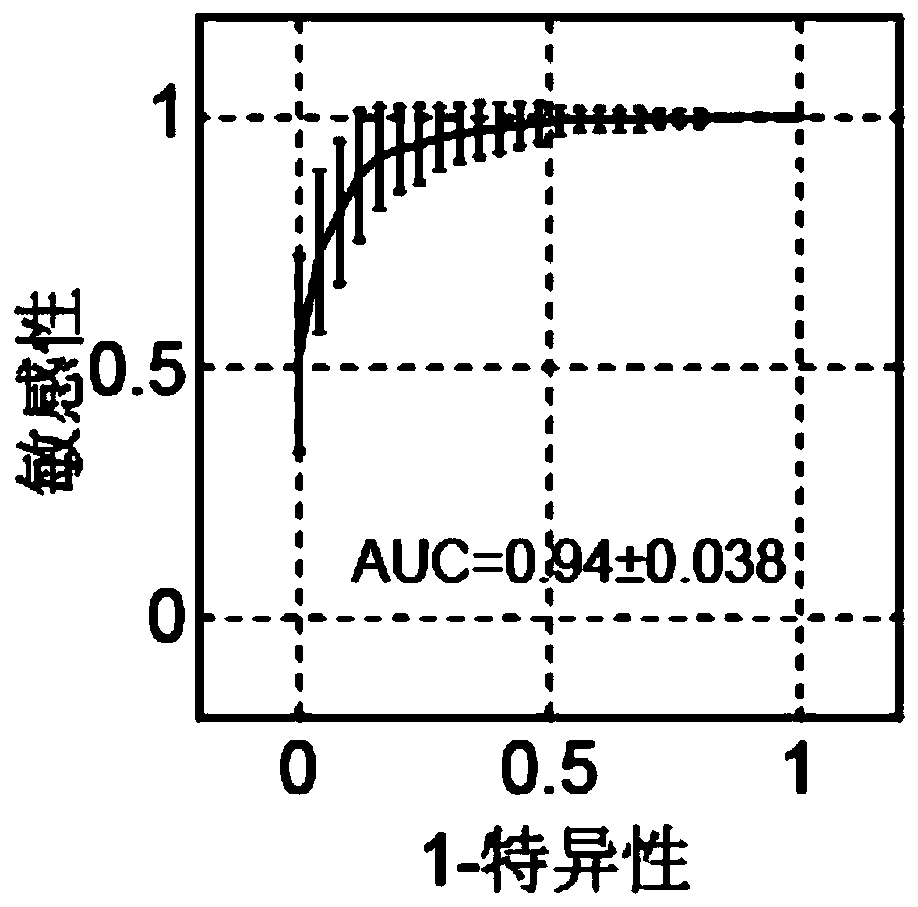
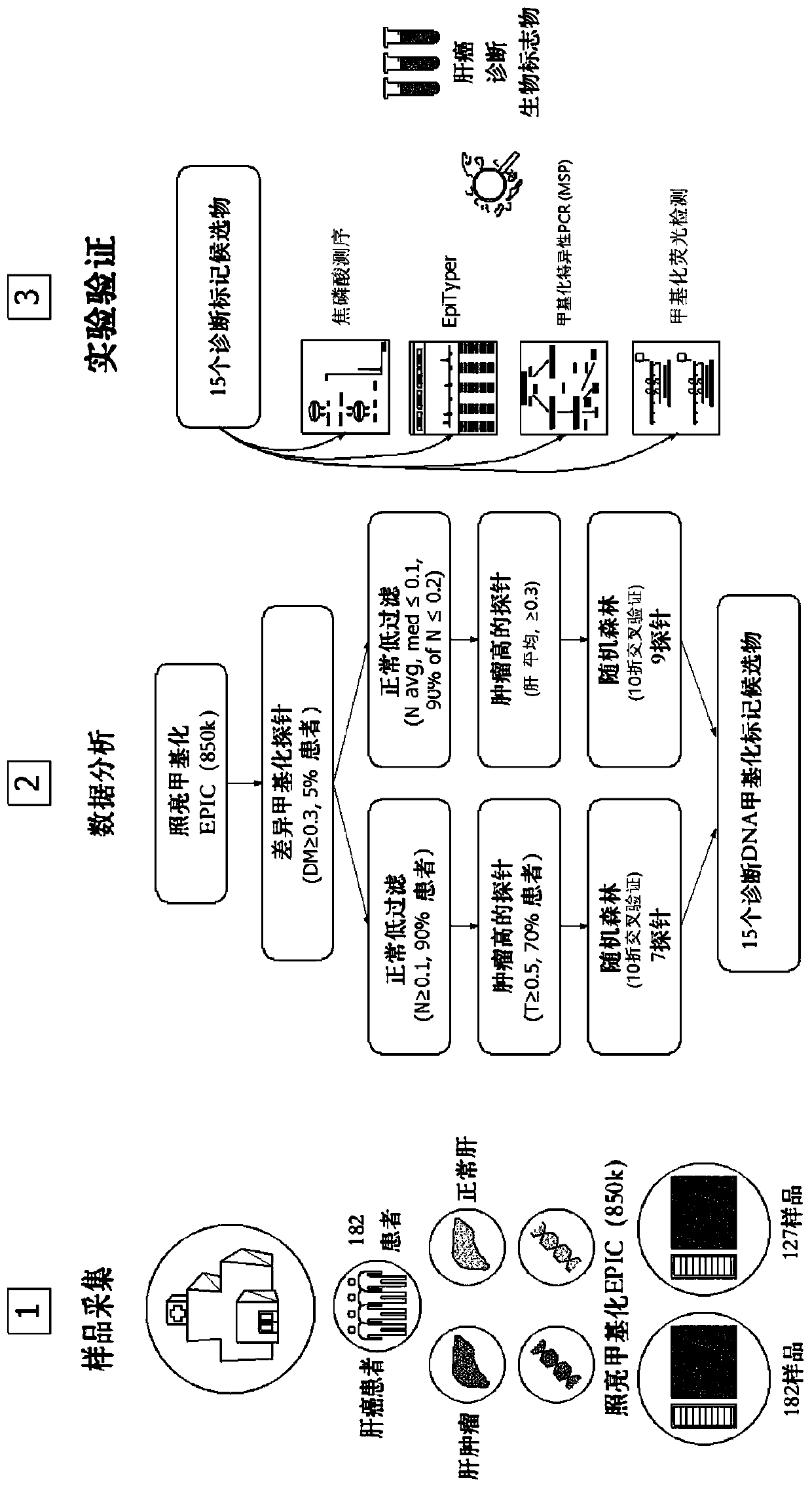
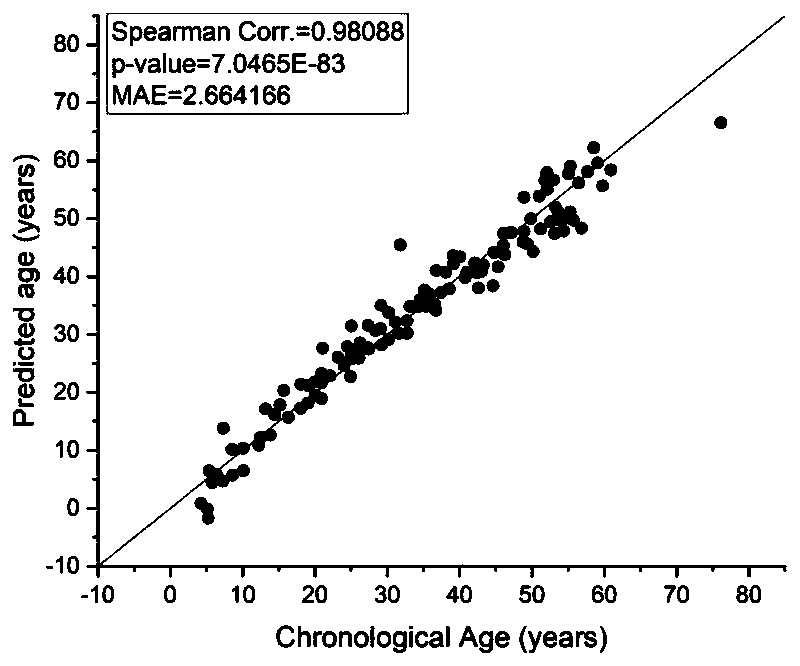
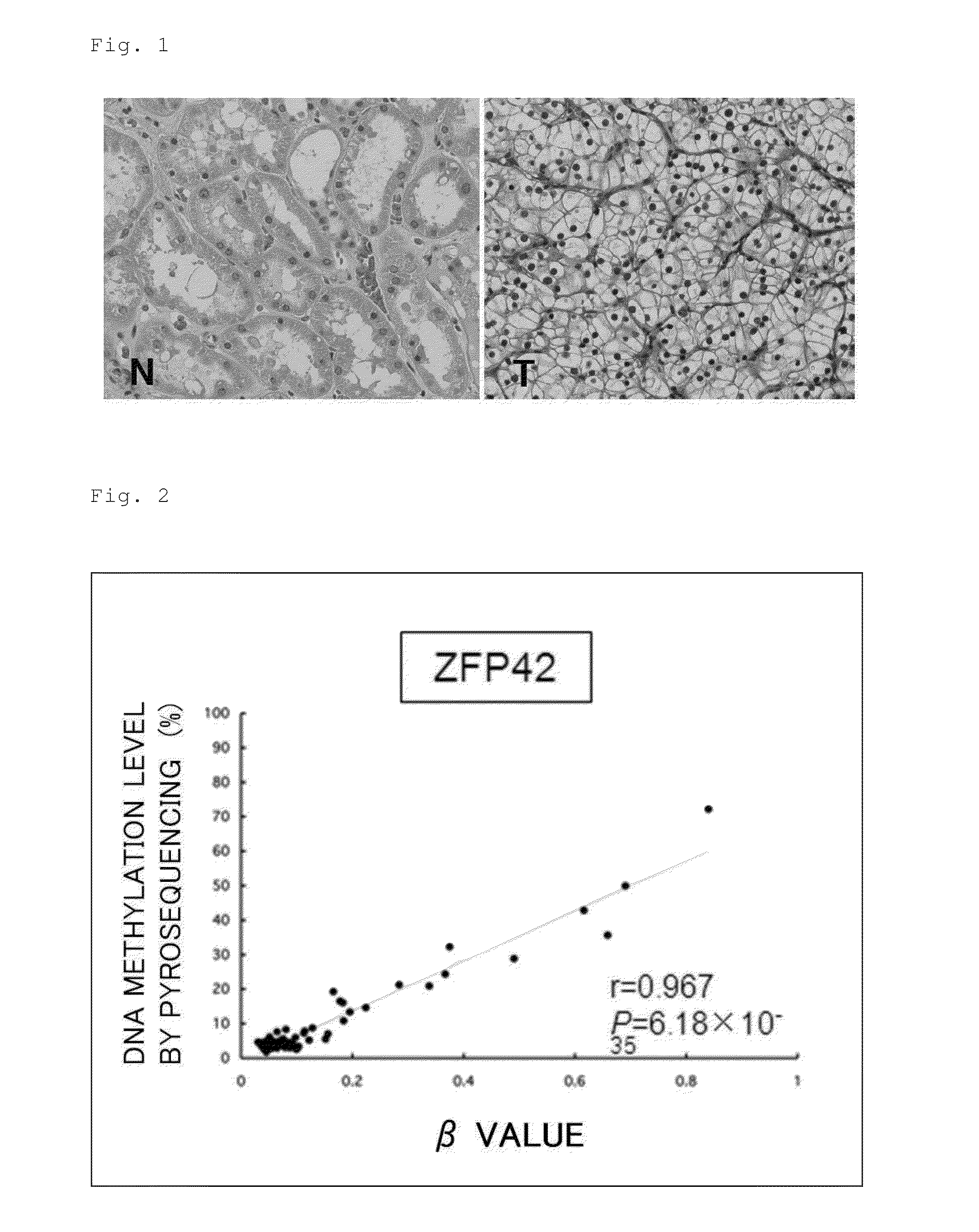
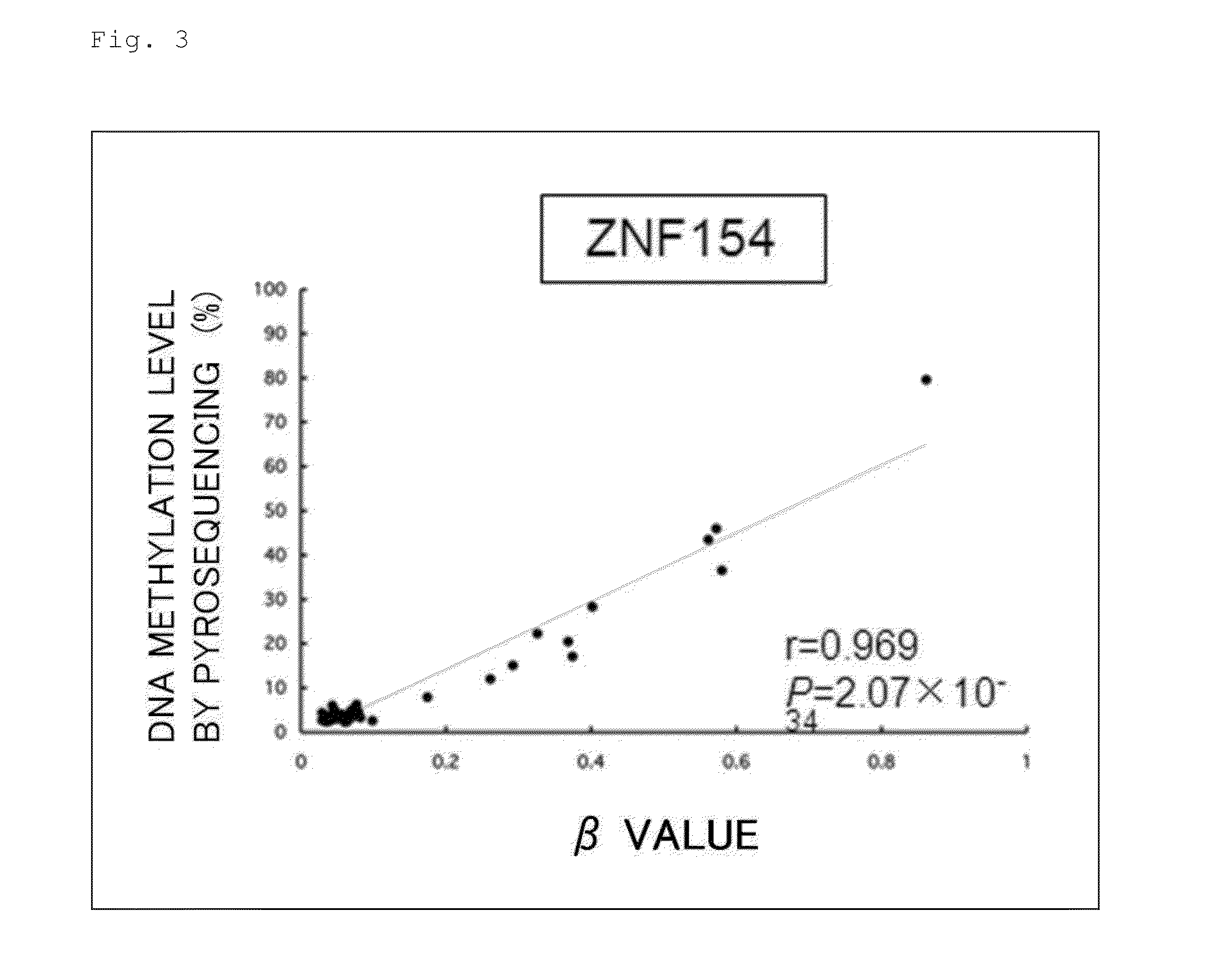
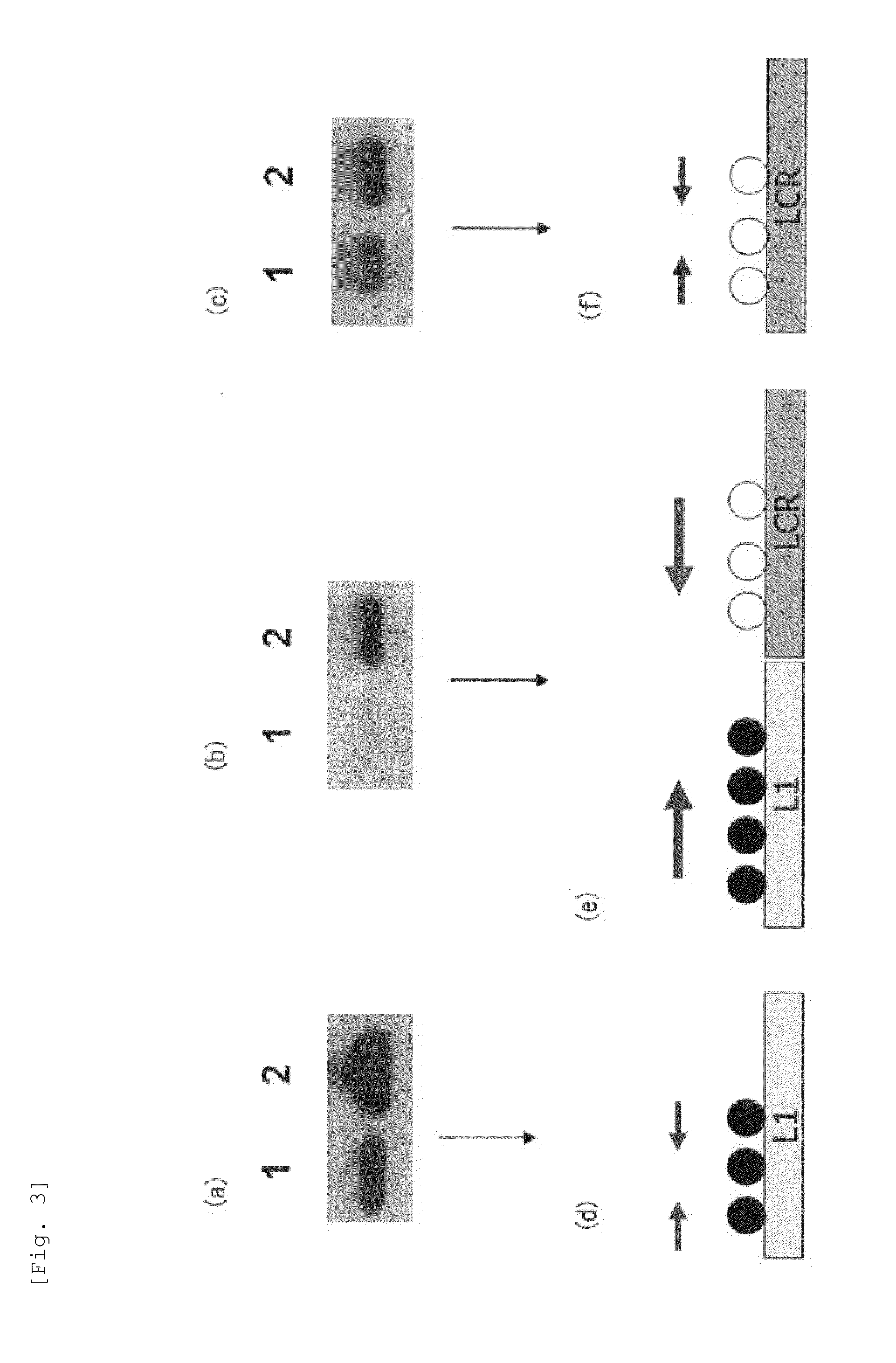
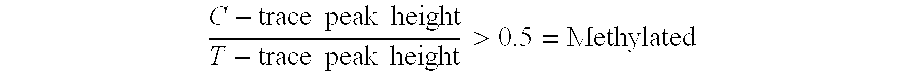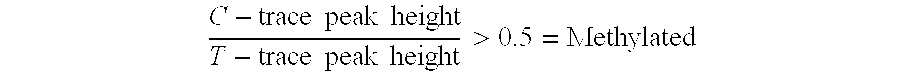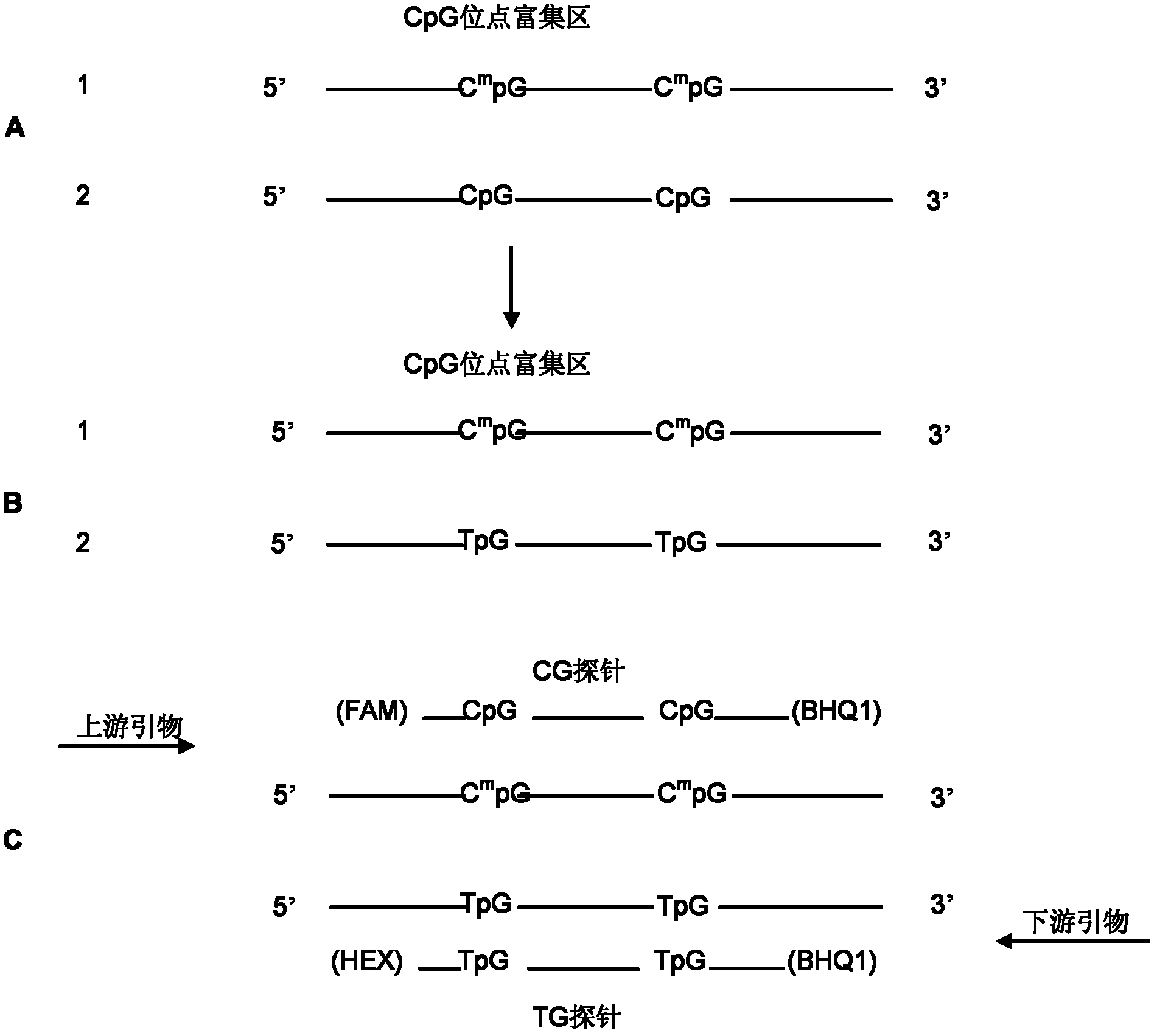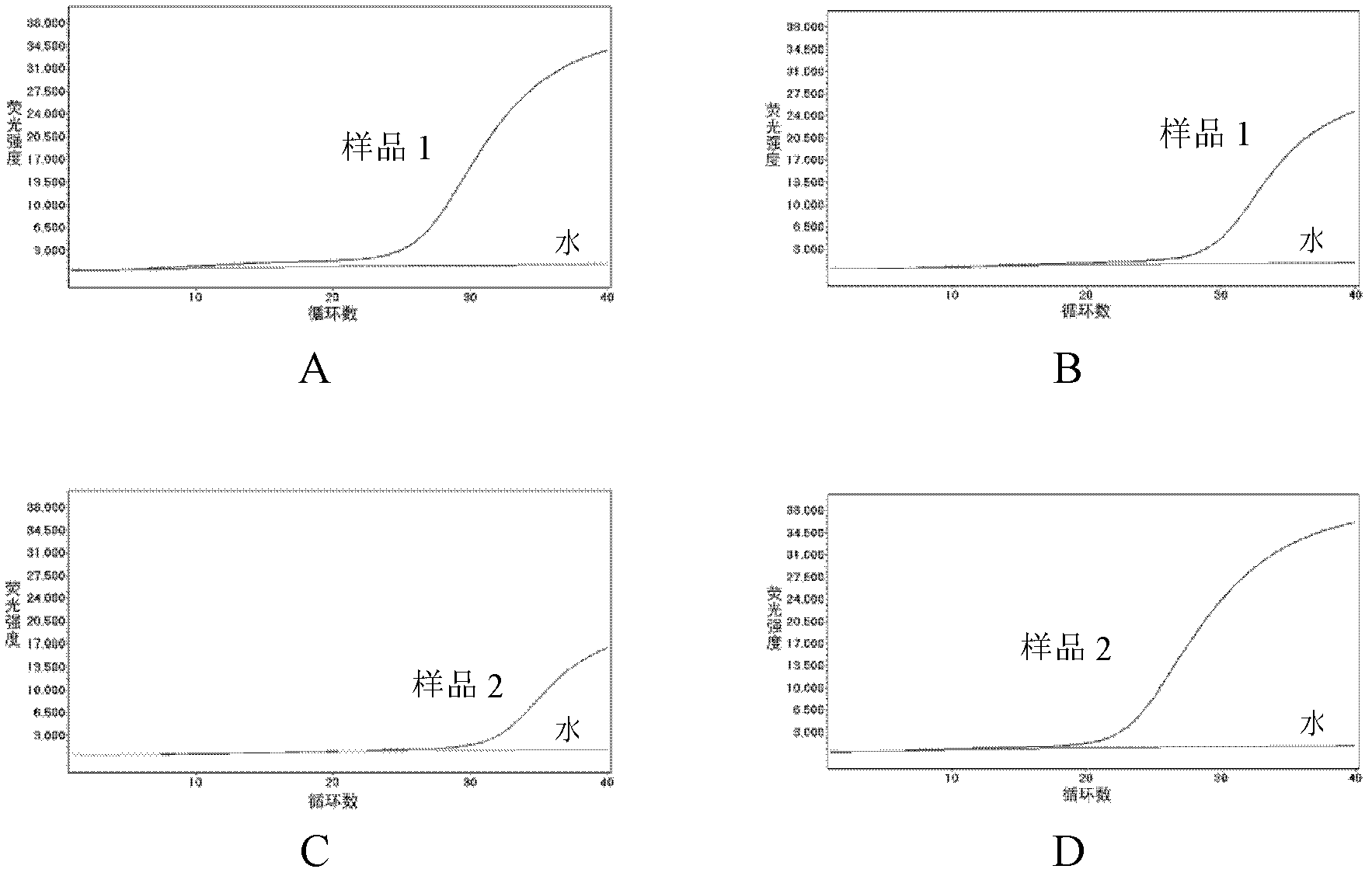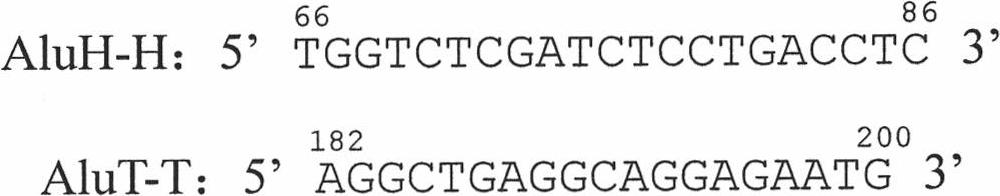Patents
Literature
146 results about "CpG site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
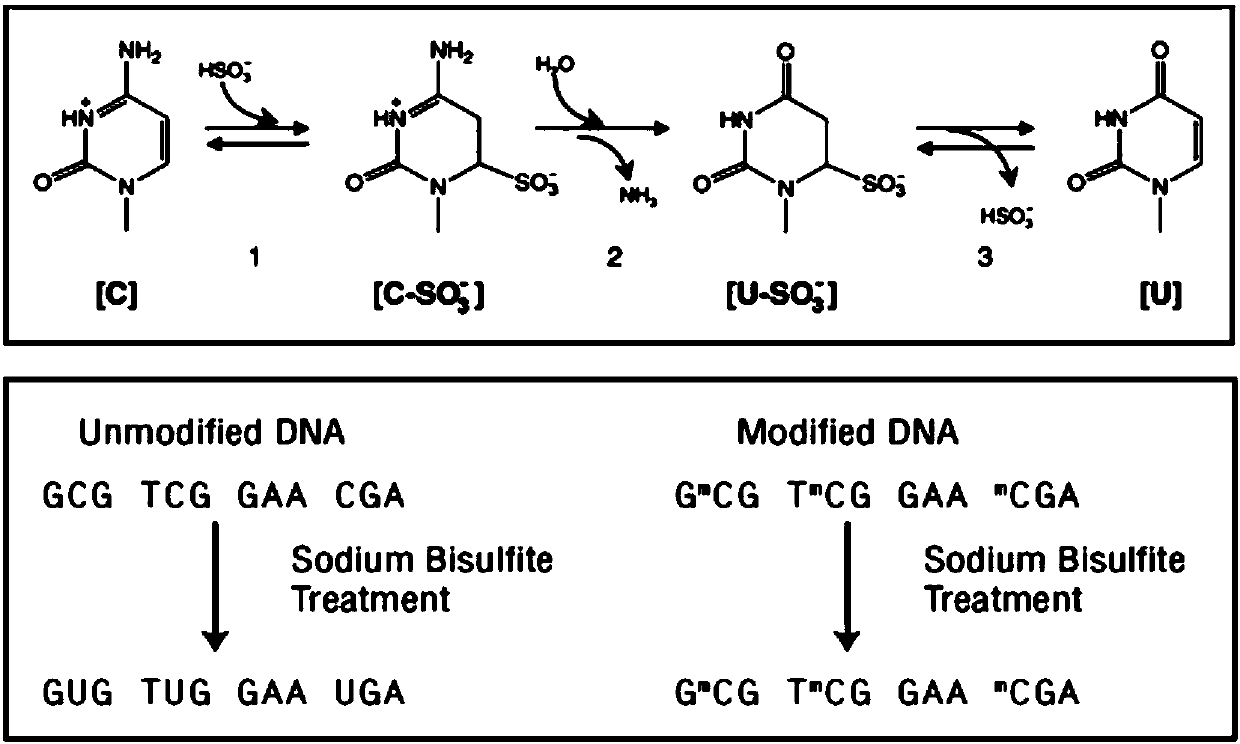
The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG islands (or CG islands). Cytosines in CpG dinucleotides can be methylated to form 5-methylcytosines. Enzymes that add a methyl group are called DNA methyltransferases. In mammals, 70% to 80% of CpG cytosines are methylated. Methylating the cytosine within a gene can change its expression, a mechanism that is part of a larger field of science studying gene regulation that is called epigenetics.
Cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences
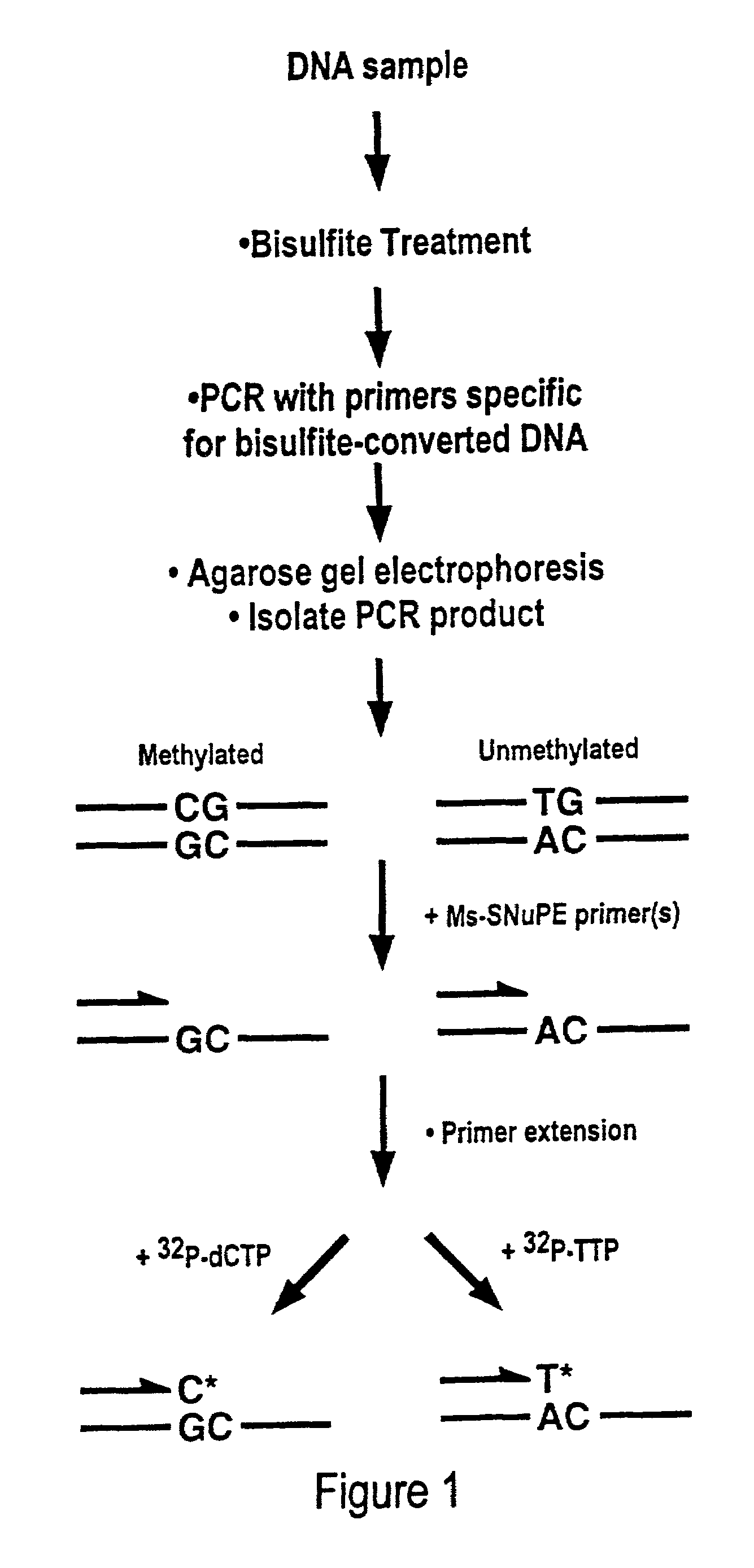
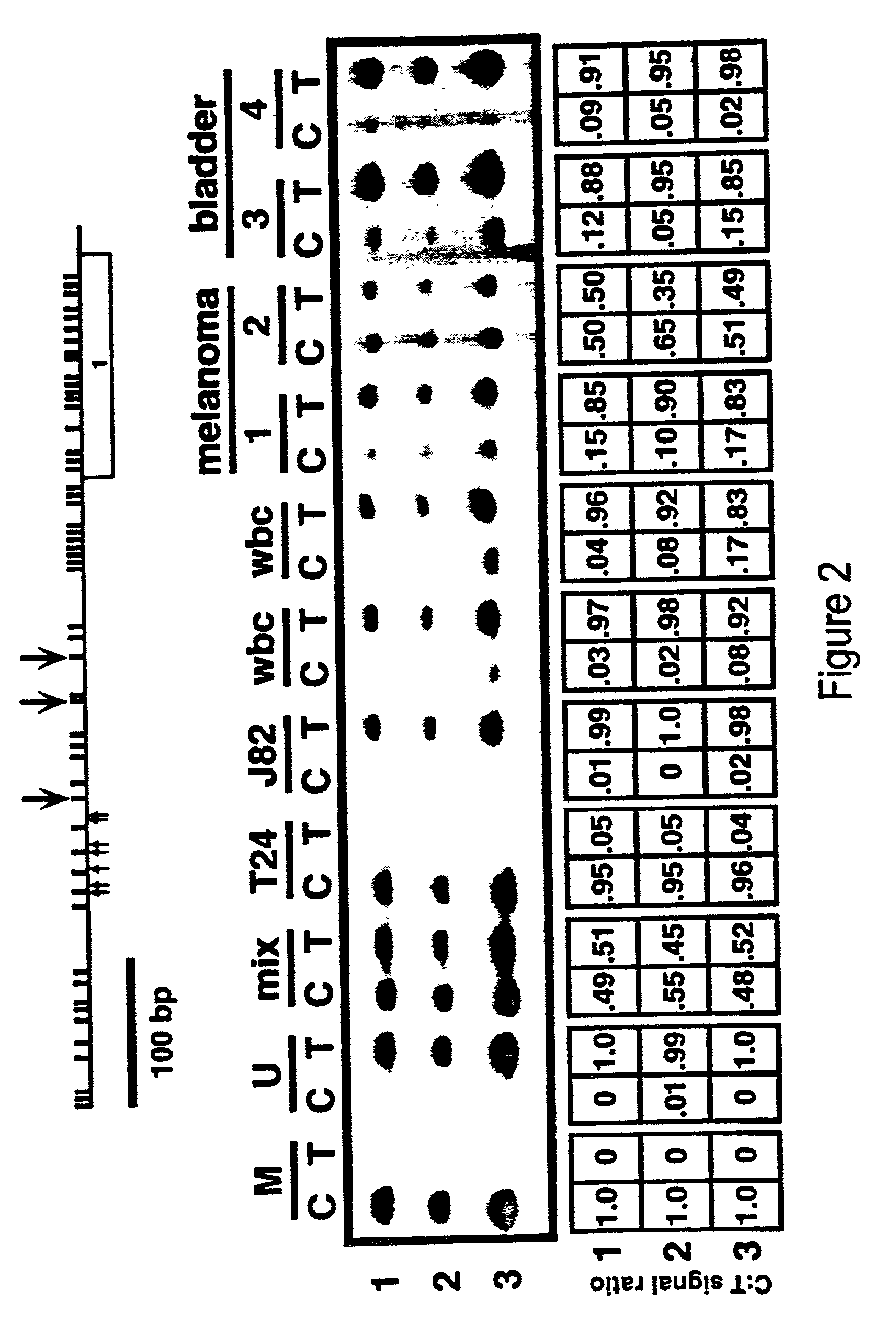
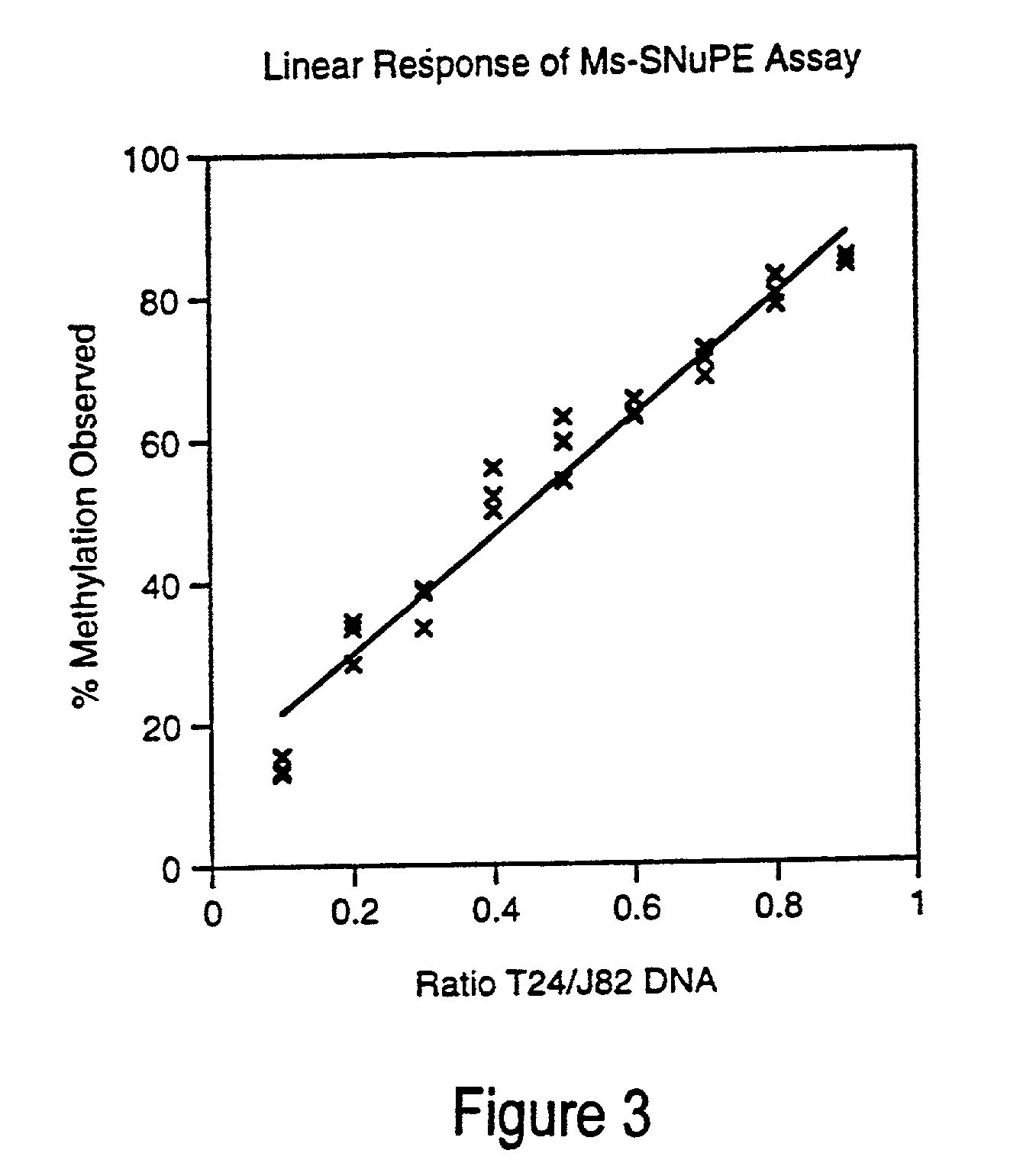
There is disclosed a cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences at specific CpG sites. Specifically, the inventive method provides for a bisulfite treatment of DNA, followed by methylation-sensitive single nucleotide primer extension (Ms-SNuPE), for determination of strand-specific methylation status at cytosine residues.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Identification and verification of methylation marker sequences
InactiveUS20050130170A1Improve throughputReduce the burden onMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteBioinformatics
The present invention relates to methods for identifying among the genes that are down-regulated in cells or tissues having disease including cancer, the CpG sites within the CpG islands of said genes, wherein the identified CpG sites show great potential for diagnostic utility. In another aspect, the present invention also provides methods of using the selected CpG sites for purposes of diagnosis, prognosis, staging, assessing or monitoring the therapy of or recovery from a disease such as cancer.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Identification and verification of methylation marker sequences
InactiveUS20050130172A1Reduce removalSmall sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCpG siteDisease
The present invention relates to methods for identifying among the genes that are down-regulated in cells or tissues having disease including cancer, the CpG sites within the CpG islands of said genes, wherein the identified CpG sites show great potential for diagnostic utility. In another aspect, the present invention also provides methods of using the selected CpG sites for purposes of diagnosis, prognosis, staging, assessing or monitoring the therapy of or recovery from a disease such as cancer.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Methylated CpG island amplification (MCA)
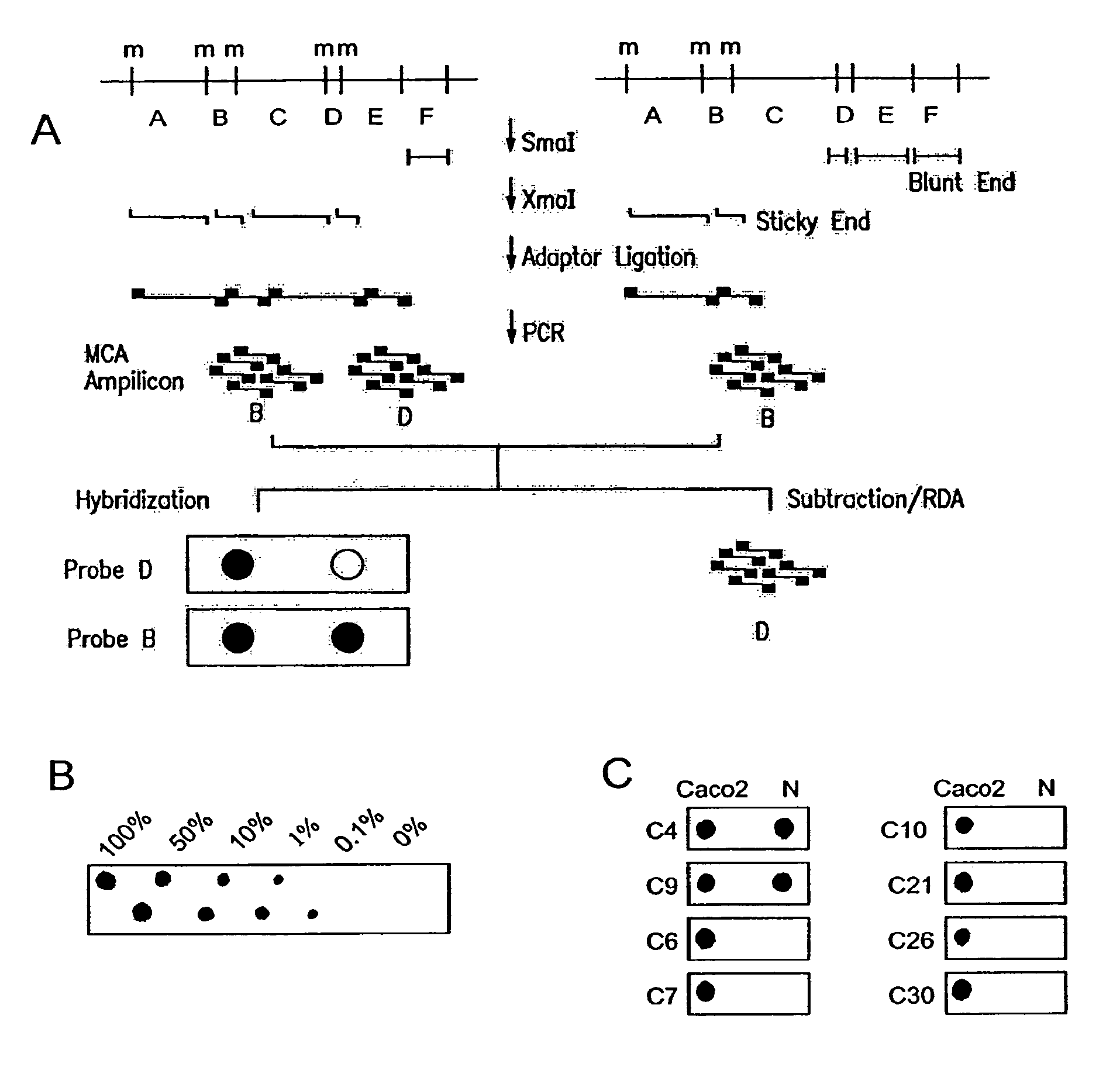
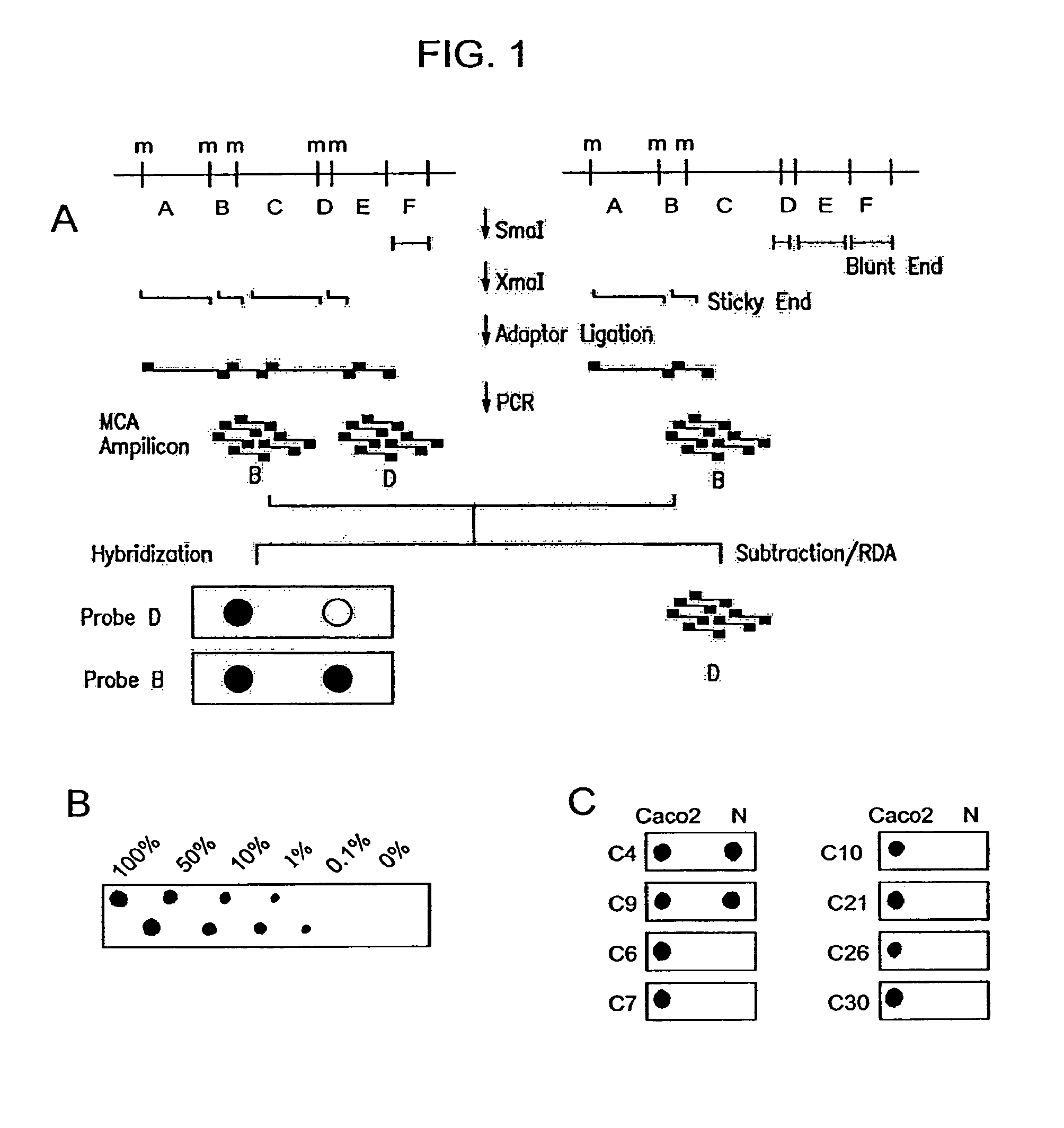
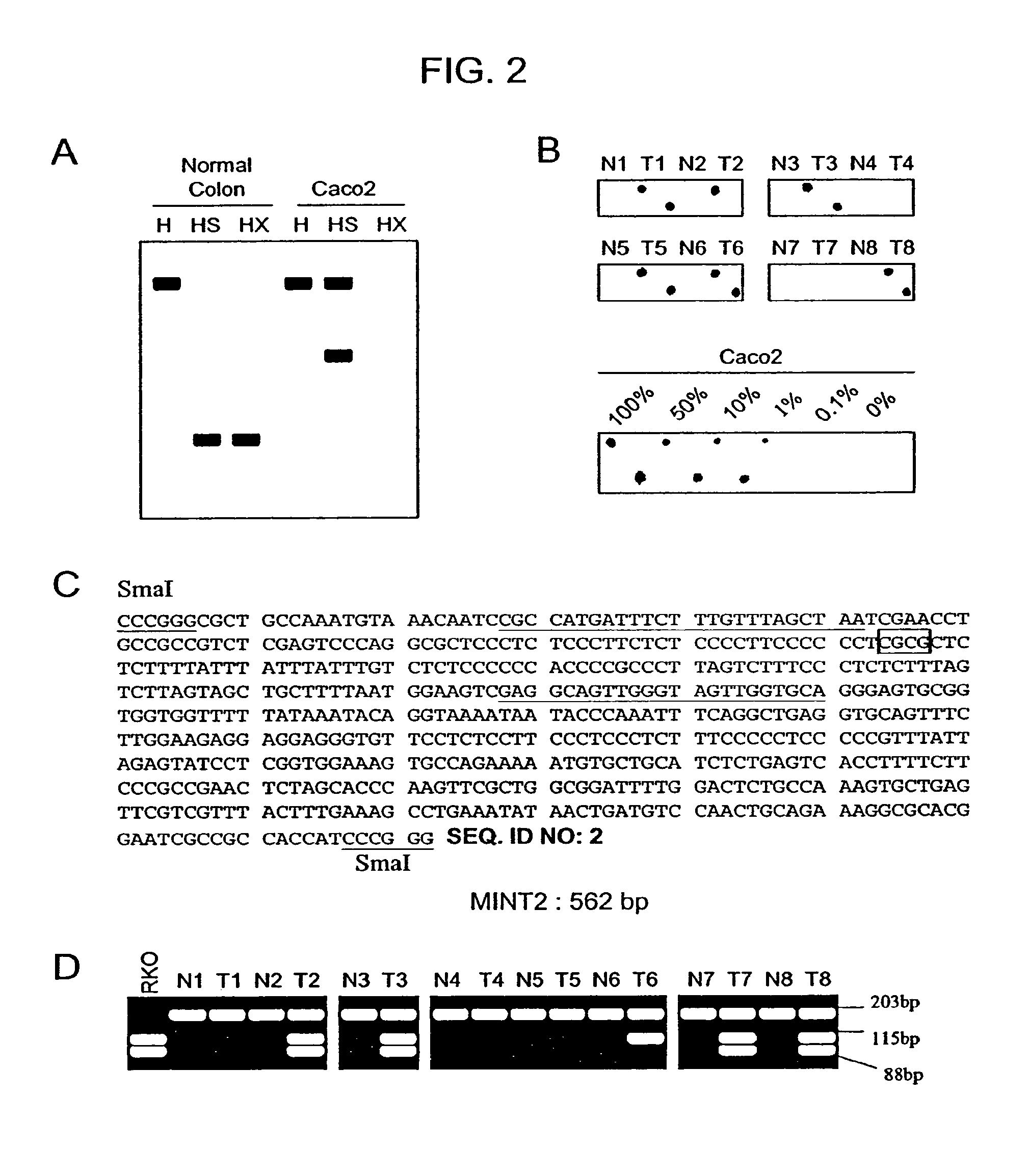
The present invention provides a method for identifying a methylated CpG containing nucleic acid by contacting a nucleic acid with a methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease that cleaves unmethylated CpG sites and contacting the sample with an isoschizomer of the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease, which cleaves both methylated and unmethylated CpG sites. The method also includes amplification of the CpG-containing nucleic acid using CpG-specific oligonucleotide primers A method is also provided for detecting an age associated disorder by identification of a methylated CpG containing nucleic acid. A method is further provided for evaluation the response of a cell to an agent A kit useful for detection of a CpG containing nucleic acid is also provided. Nucleic acid sequences encoding novel methylated clones.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
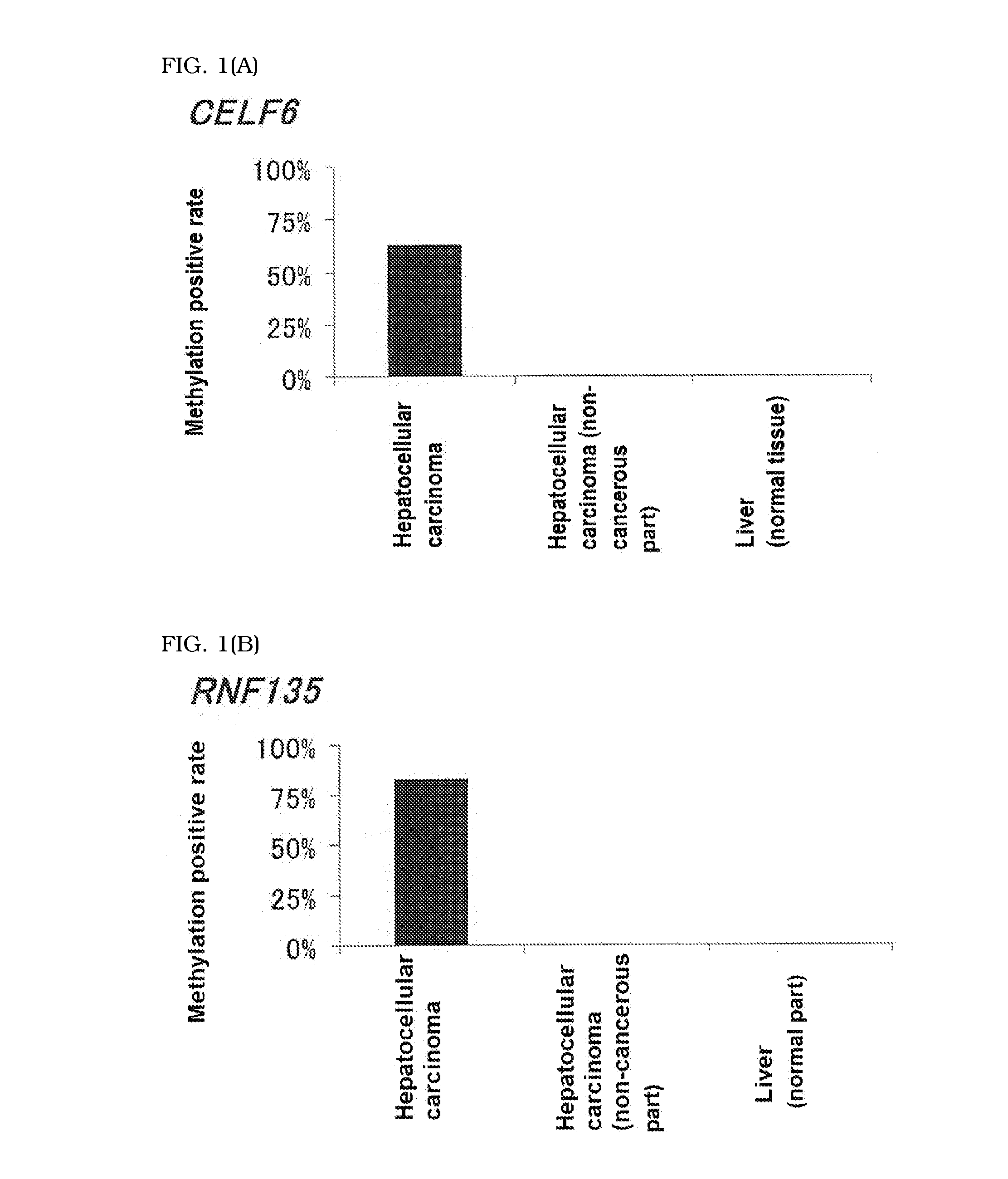
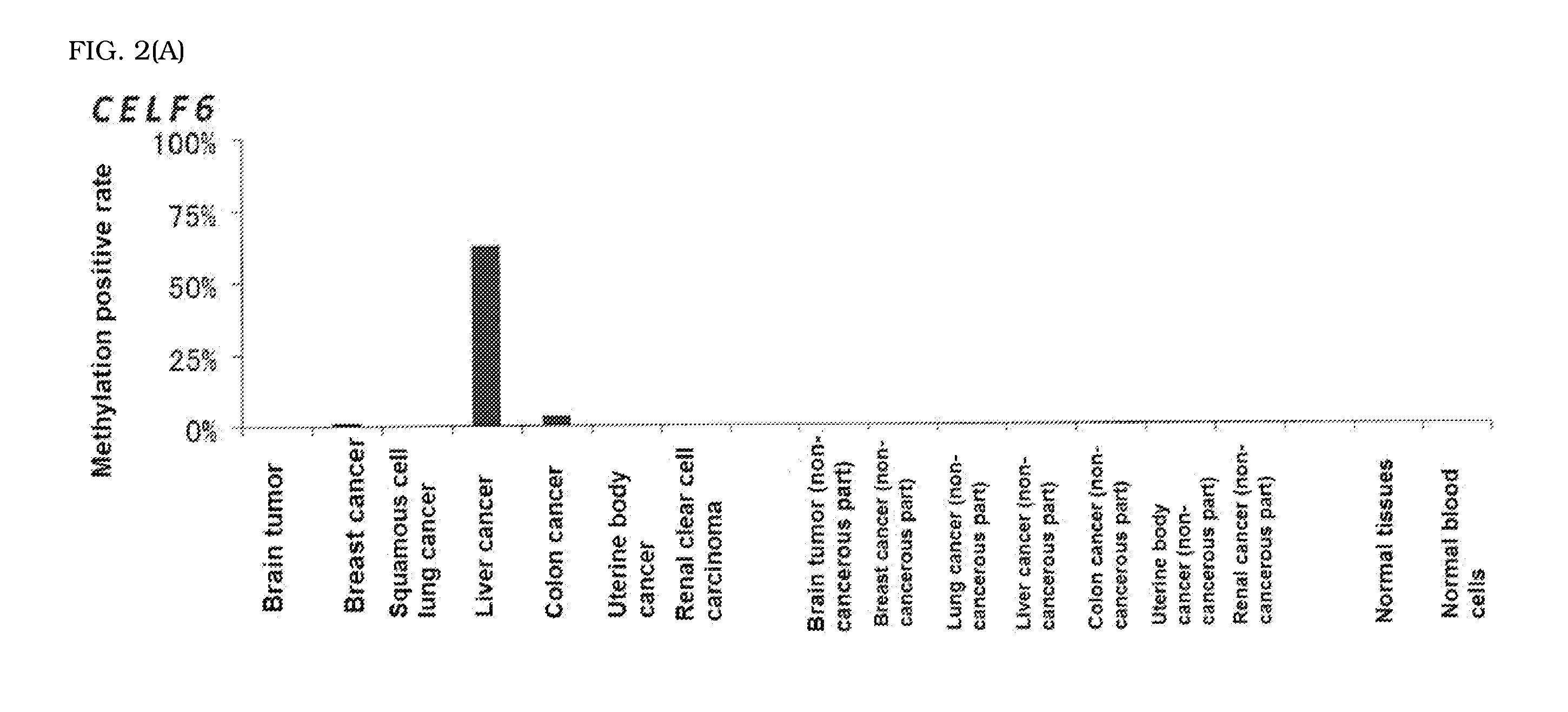
Computer readable medium for enabling a computer to carry out provision of information on hepatocellular carcinoma and marker and kit for obtaining information on hepatocellular carcinoma
InactiveUS20140358448A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteHepatocellular carcinoma
The present invention is to provide a computer readable medium comprising a computer program for enabling a computer to carry out provision of information on hepatocellular carcinoma in a subject based on an analysis result on methylation status of a novel marker specific for hepatocellular carcinoma.The above object is achieved by obtaining the analysis result on methylation status of a CpG site located in a promoter region of at least one gene selected from CELF6 and RNF135 in a DNA sample derived from the subject and providing information on hepatocellular carcinoma in the subject based on the resulting analysis result.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP +1
Gene marker and method for detection of oral cancer
A gene marker for the detection of oral cancer, comprising methylated CpG sites in target genes, is provided. The CpG sites in the target genes are selected from a group consisting of the following CpG sites: FLT4_E206_F, ASCL1_E24_F, KDR_E79_F, TFPI2_P9_F, TERT_E20_F, ADCYAP1_P455_R, MT1A_P49_R, and combinations thereof. A method for the detection of oral cancer, comprising the following steps is also provided: a) providing a sample to be examined from an individual; b) detecting a methylation state of at least one CpG site in a target gene on the genomic DNA from cells of the sample, wherein the CpG site in the target gene is selected from a group consisting of the following CpG sites: FLT4_E206_F, ASCL1_E24_F, KDR_E79_F, TFPI2_P9_F, TERT_E20_F, ADCYAP1_P455_R, and MT1A_P49_R; and c) determining if the individual has oral cancer based on the methylation state of the selected CpG site in the target gene.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Method and kit for diagnosing bladder cancer with urine
InactiveCN102311953AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCommunity health centerBiomarker (petroleum)
The invention relates to a method and a kit for diagnosing bladder cancer with urine. The invention discloses a group of methylated sensitive genes, comprising ECEL1, KCNV1, LMX1A, PROX1, SLC6A20, TAL1, TMEM 26, and VAXI gene. In urine samples of bladder cancer patients, the specific CpG sites of the genes are showed the highest methylation levels. Accordingly, the genes are the biological marker of bladder cancer. The method and the kit can be used as the basic of designing diagnostic reagents of bladder cancer, and are suitable for auxiliary detection of cancer in hospitals, postoperative followup, screening of high risk group of bladder cancer in community health centers, and screening of common people and high risk practitioners of bladder cancer in physical examination center.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Method and kit for quantitatively detecting methylation degree of DNA specific site
ActiveCN102321745AGuaranteed accuracyEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteA-DNA
The invention provides a method and kit for quantitatively detecting the methylation degree of a DNA specific site. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1) designing a PCR primer in accordance with a DNA sequence to be detected, and using the PCR primer for amplifying the DNA to be detected; 2) designing a pair of TaqMan probes in accordance with a CpG site-enriched region in the PCR product obtained by amplification in the step 1), wherein one probe is a CG probe designed in accordance with the DNA of which the CpG site is completely methylated, and the other probe is a TG probe designed in accordance with the DNA of which the CpG site is completely non-methylated and is used for specifically combining the PCR product and detecting the PCR product; and 3) carrying out real-time quantitative PCR based on the primer designed in the step 1) and the probes designed in the step 2), thus detecting the methylation degree of the DNA to be detected. By using the method, a specific methylated site can be detected, and the methylation states of other sites can not affect the detection result. The kit provided by the invention can be used for detecting the methylation degree of a DNA specific site.
Owner:BIOCHAIN BEIJING SCI & TECH
Method for detecting activity of DNA methylase and DNA methyltranseferase by unlabeled fluorescent detection based on restriction endonuclease and exonuclease III
InactiveCN103993083ALow costAvoid accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSignalling moleculesSingle strand dna
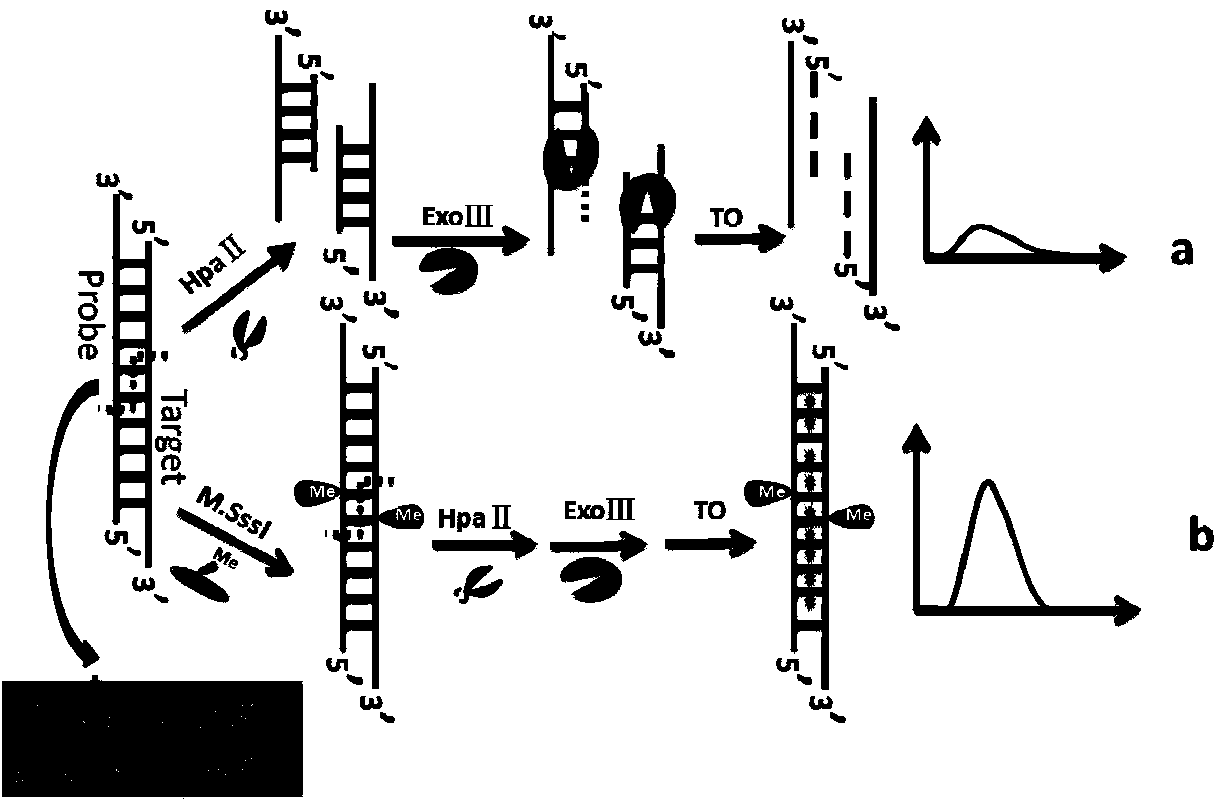
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of DNA methylase and DNA methyltranseferase based on restriction endonuclease Hpa pi and exonuclease III. An unlabeled DNA probe is prepared and the sequence of the probe comprises a cleavage site of the restriction endonuclease and a methylated CpG site. The purpose of detecting the activity of the methylase and methyltranseferase is reached by steps of hybridizing the unlabeled DNA probe with the target DNA, carrying out methylation treatment by the methylase, carrying out the specific cleavage of the restriction endonuclease Hpa pi and enabling exonuclease III having the activity of 3'->5' exonuclease to act on the double-stranded DNA and then adding fluorescence signal molecules thiazole orange which having different signals to single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA. According to the method, since no complex material or labeling of DNA probes need to be prepared, the defects of high detection cost, cumbersome operations and poor reproducibility caused by the preparation of the material and labeling of DNA probes are avoided. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost and high sensitivity and is fast and simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method, marker, and kit used for colorectal cancer diagnosis, screening, and risk prediction
ActiveCN108315418AEasy to detectLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCpG siteComputer module
The invention discloses a DNA methylation marker used for diagnosis, screening, and prediction of male colorectal cancer. The DNA methylation marker is obtained via methylation of a combination of thefirst groups, or the first group with the second group, or the third groups, (1), +22, +27, and +29; (2), -24,-18, +89, and +92; and (3) +136; of three CpG sites in the front and back sequence of gene RPS24 transcription start site. The sequence number is based on sequence number in SEQ ID NO.1. The 143th site transcription start site A is recorded as +1. The invention also discloses a probe, a method, and a kit used for detecting the DNA methylation marker, and a computer module used for prediction of male colorectal cancer risk using the data of the DNA methylation sites.
Owner:太科航天智能康养技术(深圳)有限责任公司
Method and system for acquiring age of female individual of Chinese population
ActiveCN104357561ANarrow your searchImprove the efficiency of solving crimesMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteRegression analysis
The invention provides a method and a system for acquiring an age of a female individual of Chinese population. The method comprises the following steps: extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of the female individual, acquiring methylation indexes of 11 CpG loci of the DNA, conducting regress analysis to the methylation indexes of each GpG loci, the 11 CpG loci and the age with SPSS 17 (Statistic Package for Social Science) software, and constructing a regression model to obtain the age of the female individual of the Chinese population. The scheme provided by the invention can accurately obtain the age of the female individual of the Chinese population, deduces the age of the individual with a biologically examined blood or blood stain sample remained in a crime scene of the public security actual combat, so as to facilitate targeting of the range of criminal suspects, provide clues for investigation of the case, and increase the detection speed of the case.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Diagnostic methylation markers of epithelial or mesenchymal phenotype and response to EGFR kinase inhibitor in tumours or tumour cells
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methylation quantitative detection method of APC gene in human plasma
InactiveCN101354347AOvercoming the need for electrophoresisOvercoming pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansLoss rateFluorescence
The invention relates to a methylation quantitative test method of APC gene in the DNA of human blood plasma. The methylation quantitative test method obtains venous blood and the blood plasma, prepares a DNA standard curve sample of the blood plasma, extracts the DNA of the blood plasma to be detected, the DNA of a standard curve blood plasma sample and the DNA of healthy human blood plasma, realizes chemical modification of the DNA of the blood plasma to be detected, the standard curve blood plasma sample and the healthy human blood plasma, designs particularity primers and Taqman fluorescent probes according to 707 CpG locus of a 1A sequence in a human APC gene sub-promoter, builds a standard curve according to the augmentation result of the DNA of the standard blood plasma after the augmentation, and implements methylation quantitative result analysis of the sample to be detected. The methylation quantitative test method of the APC gene solves the defects that the blood plasma has less DNA content, high loss rate, DNA degradation and carcinogenic pollutant, etc. The methylation quantitative test method of the APC gene utilizes a primer pair and a Taqman fluorescent probe that aim at the 1A sequence in the APC gene sub-promoter, realizes the detection aiming at the 707 CpG locus in the APC gene sub-promoter with high methylation developing rate, implements quantitative analysis, and can be used in the aspects of cure effect observing as well as prognosis and relapse monitoring of tumor patients.
Owner:潘世扬
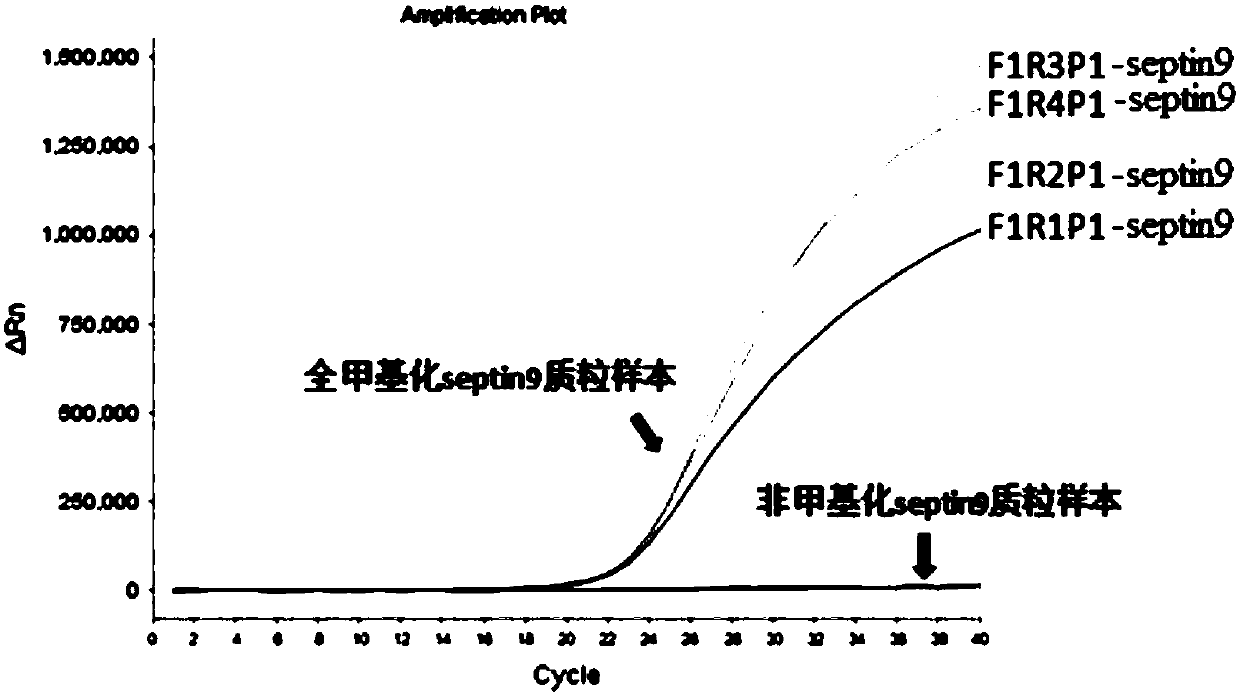
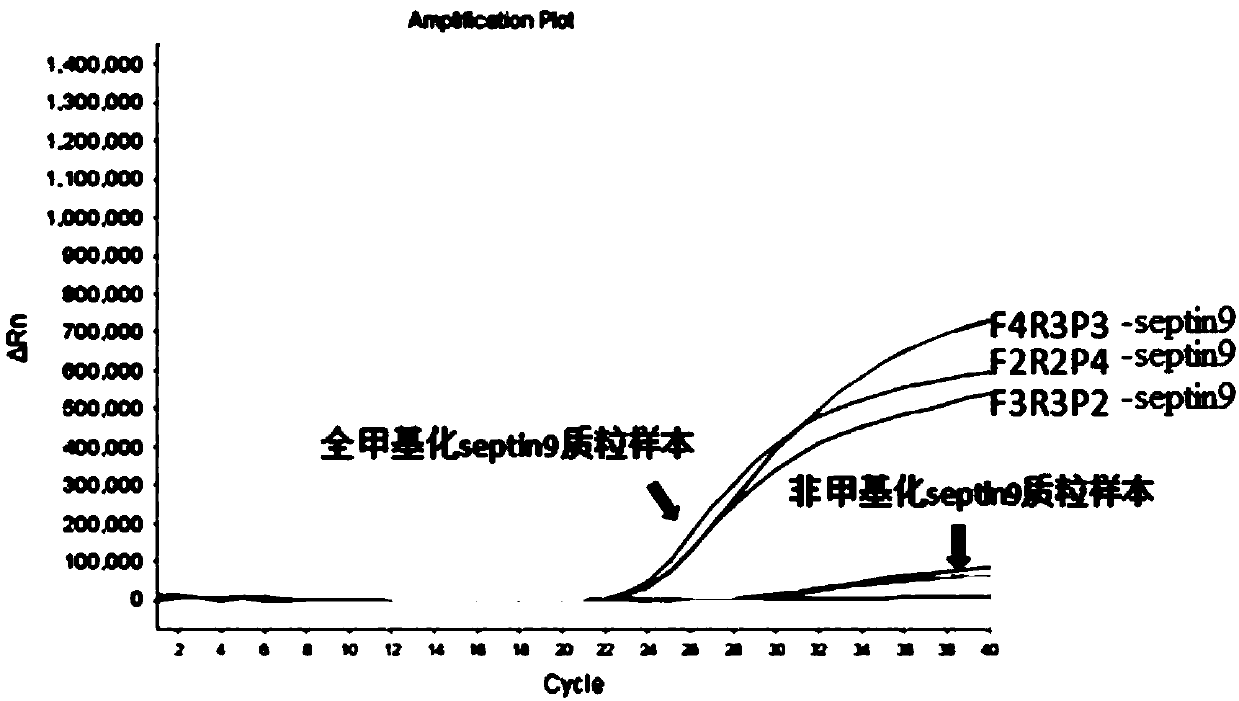
Detection reagent kit for methylation of septin 9 genes in human peripheral blood circulation tumor DNA
ActiveCN105331727AEasy to detectEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteOperability
Owner:湖南宏雅基因技术有限公司
Detection kit and method for DNA methylation
InactiveCN109385464AEfficient detectionRaise the annealing temperatureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCpG siteOpen sea
The invention relates to a detection kit and method for DNA methylation, especially to a detection kit and method for DNA methylation without CpG sites at flanking sequences. The kit and method employa Taqman probe binding to a minor groove binder (MGB) and can determine the methylation of both a CpG island (CGI) and isolated CpG sites in CpG open sea and the like without CpG at two flanking sequences. The kit and method provided by the invention are specific and sensitive, simple to operate, and does not require a control reaction or a fully-methylated standard DNA substance as a reference,thereby overcoming defects resulting from the control reaction and the fully-methylated standard DNA substance. In addition, the kit and method have higher repeatability and accuracy than the existingMethyLight technology.
Owner:THE SIXTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
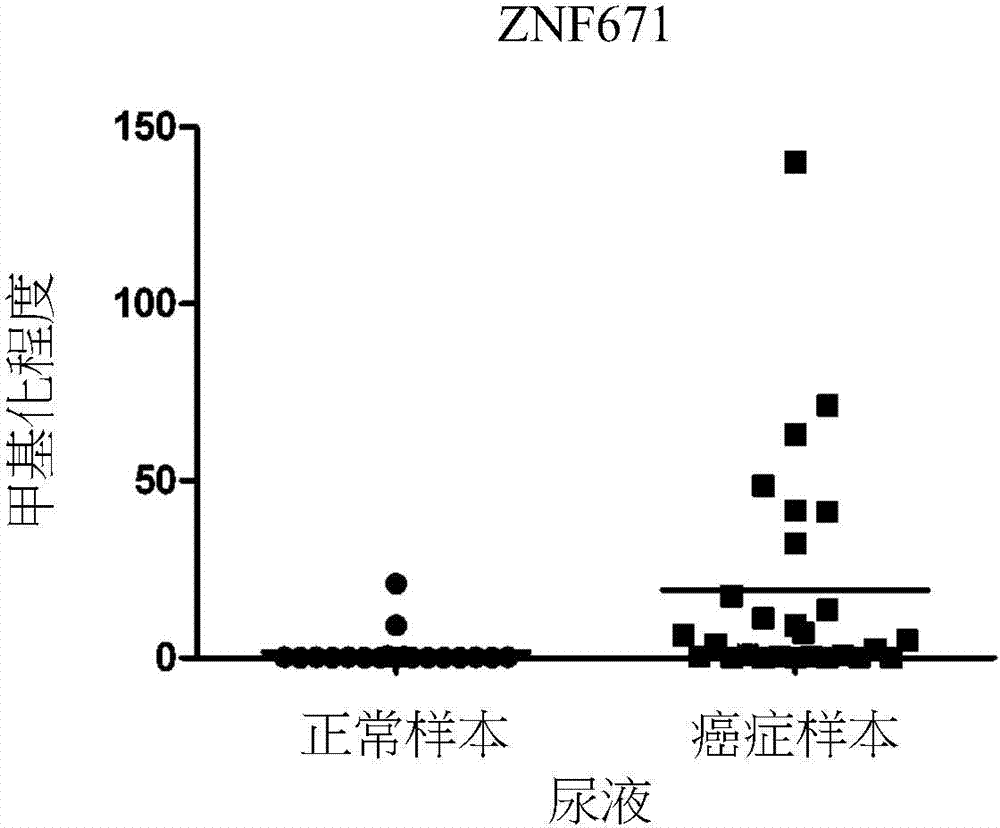
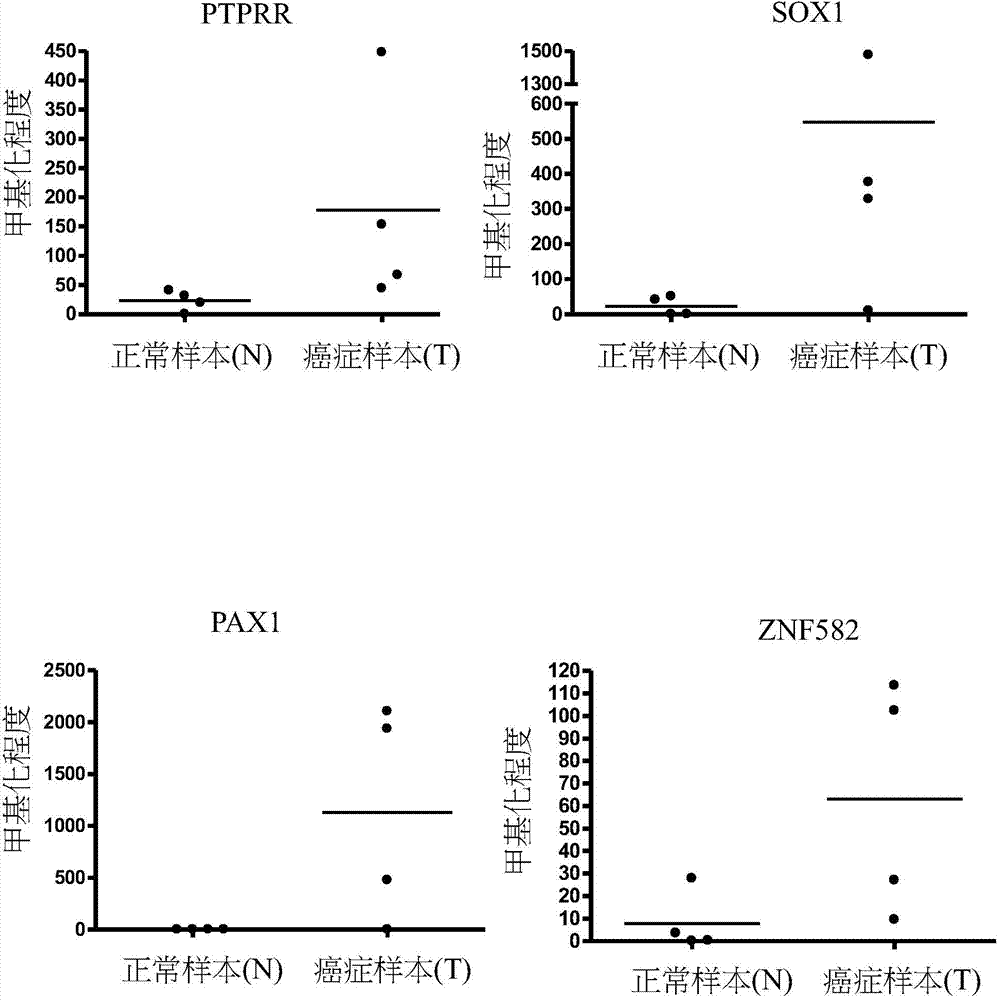
Novel epigenetic biomarker for detecting bladder cancer and method thereof
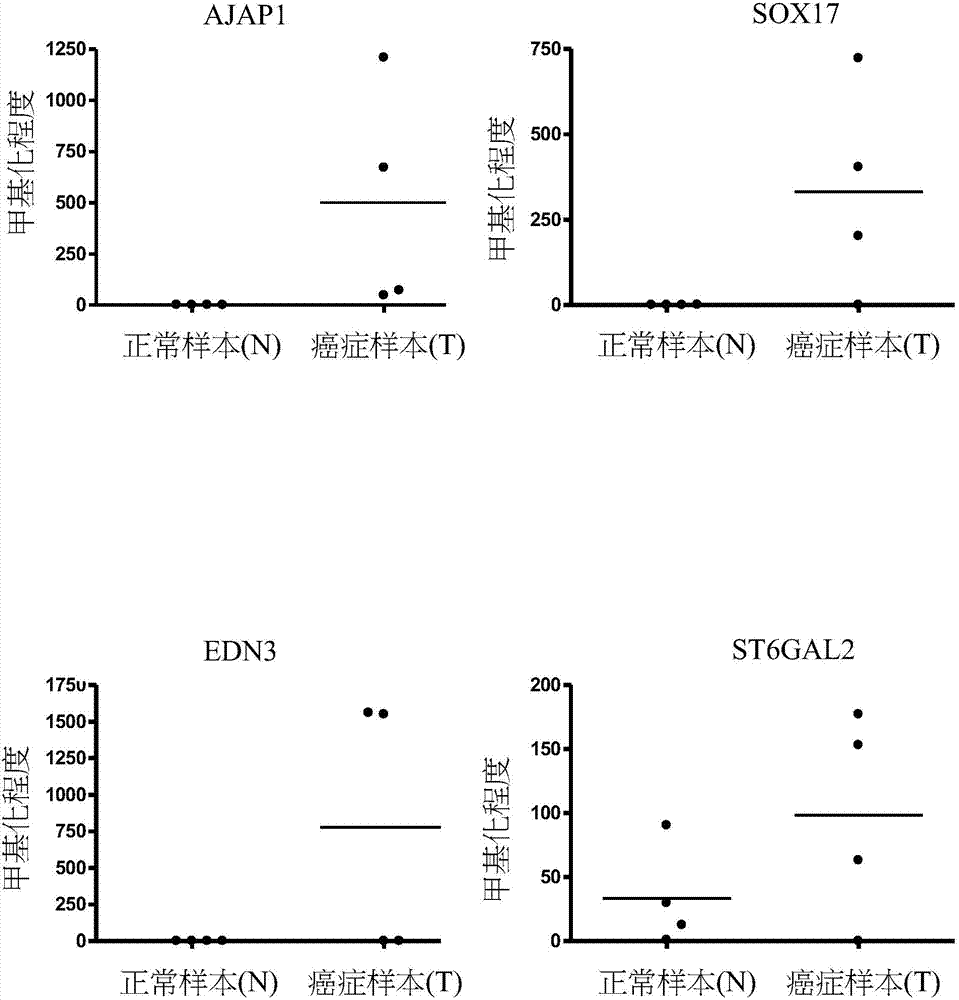
A novel epigenetic biomarker for detecting bladder cancer and a method thereof. The method comprises following steps: (1) providing a to-be-detected specimen; (2) detecting a CpG sequence methylation status of at least one targeted gene in genome DNA of the to-be-detected specimen, wherein the targeted gene is selected from at least one of the group consisting of ZNF671, PTPRR, SOX1, PAX1, ZNF582, AJAP1, SOX17, EDN3, ST6GAL2, ZNF614, PTGDR, SYT9, SOX8, HS3ST2, POU4F3, ADRA1D, MAGI2, EPO, NEFH, POU4F2, STC2 and THRB; and determining whether the specimen is suffered from cancer or precancerous lesions or not according to whether the methylation status of the targeted gene exists or not, or employing the determination of the existence of the methylation status of the targeted gene as treatment prognosis. The invention also discloses a novel epigenetic biomarker for detecting the bladder cancer, wherein the biomarker comprises a methylated CpG locus of the target gene. The methylated CpG locus can be detected in urine.
Owner:GUZIP BIOMARKERS CORP
Urine-based method and kit for diagnosing relapse risk of bladder cancer patient
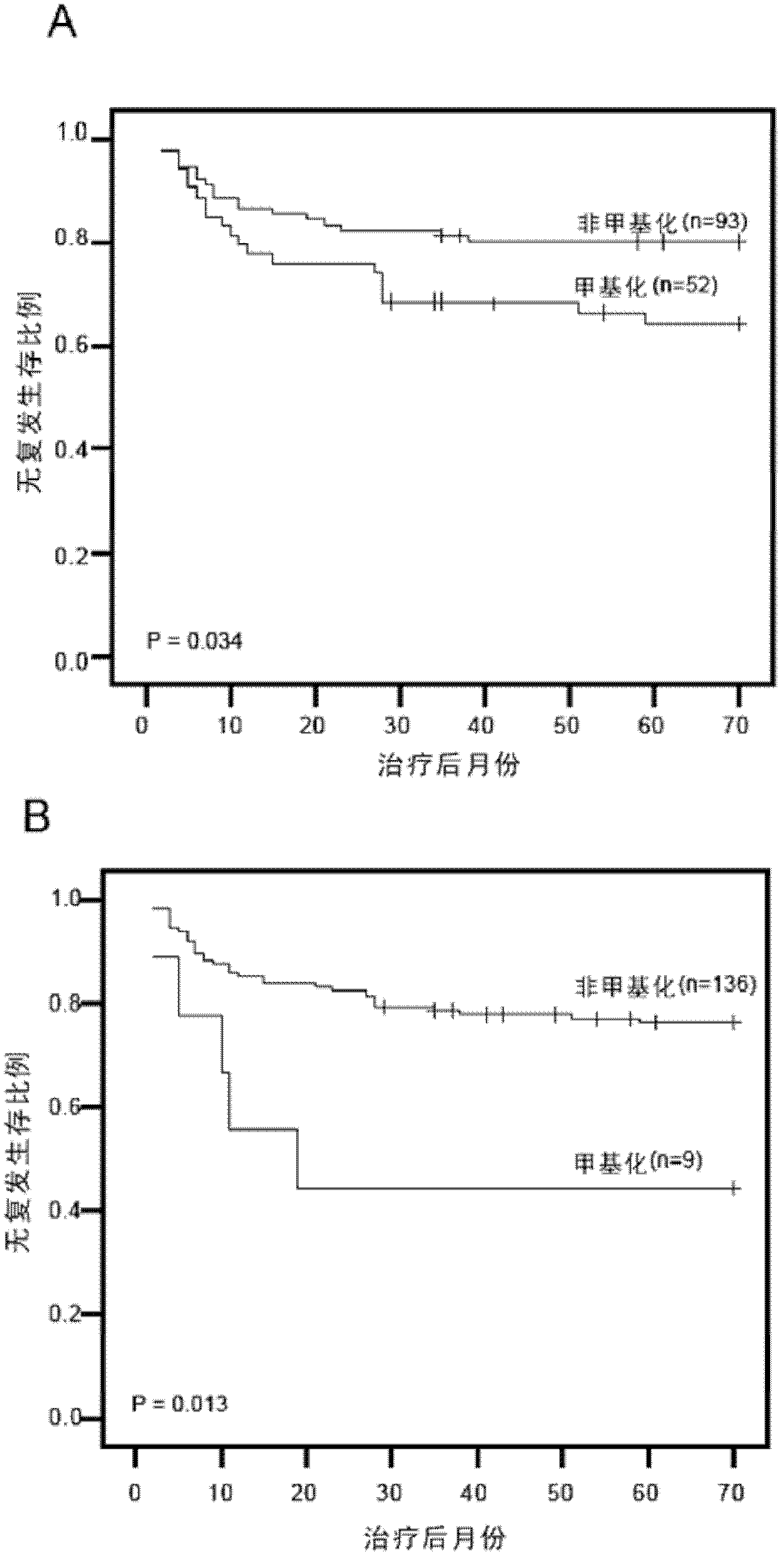
The invention relates to a urine-based method and kit for diagnosing the relapse risk of a bladder cancer patient. The invention discloses two methylation-sensitive genes, namely an LMX1A gene and a VAX1 gene. A urine sample is kept before the operation of a detected bladder cancer patient, and the specific CpG sites of the genes are subjected to high methylation among people who are determined to suffer from a relapse in the follow-up visit process. Thus, the two genes can be used as biological markers for the relapse of bladder cancer. The invention can be used as the basis for designing a kit for prognosing and diagnosing the relapse of bladder cancer, and is applicable to the prognosis detection of bladder cancer in hospital, the postoperative follow-up visit and the postoperative monitoring of the community health center on people subjected to bladder cancer operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
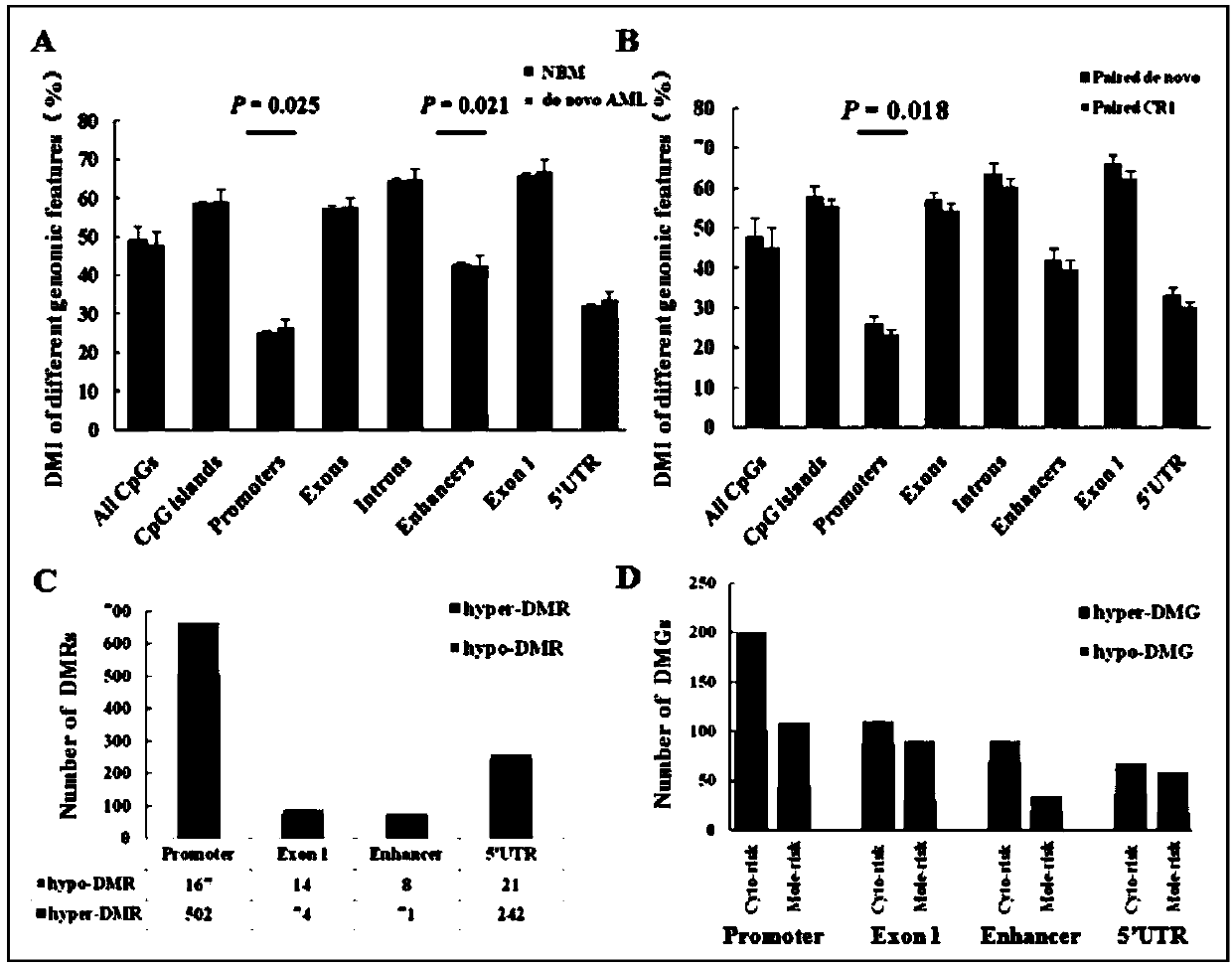
Method for screening prognostic markers of DNA methylation in acute myeloid leukemia
ActiveCN109852672AImproved prognosisIncrease conversion rateMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG sitePrognosis biomarker
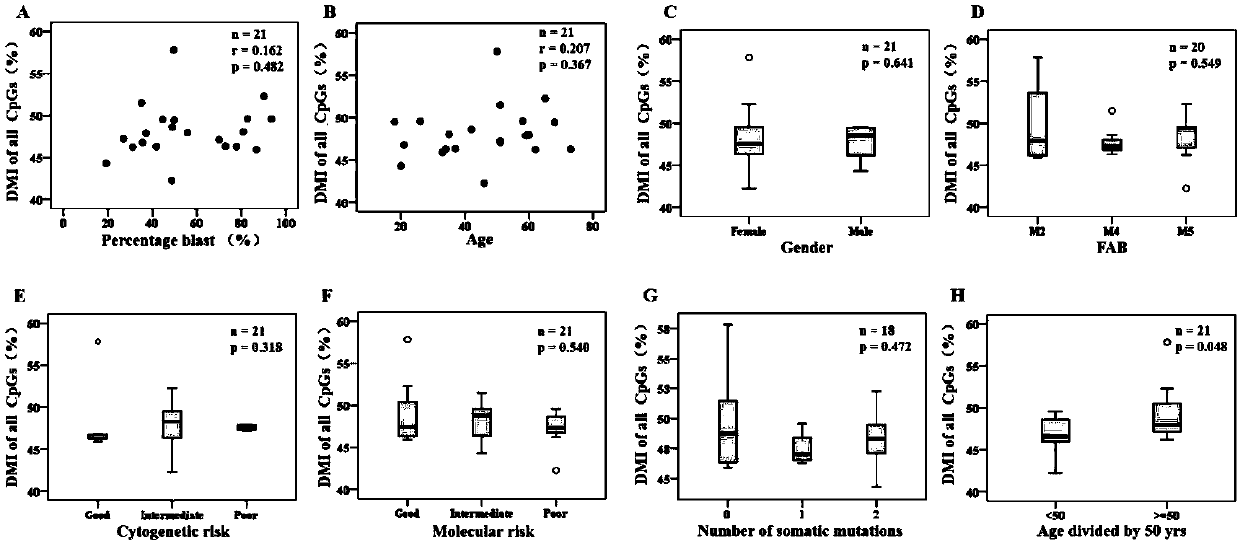
The invention discloses a method for screening prognostic markers of DNA methylation in acute myeloid leukemia. The method includes the following steps: (1) sample and clinical data collection; (2) sample preparation; (3) genomic DNA extration; (4) whole-genome CpG site methylation capture sequencing; and (5)methylation sequencing data analysis and marker screening. The method uses the whole-genome CpG site methylation capture sequencing technology to detect DNA methylation in acute myeloid leukemia and perform prognosis analysis, and screens genetic markers which are regulated by DNA methylation and has prognostic significance through information of integrative genetics and epigenetics to guide accurate diagnosis and treatment of AML, thereby improving the curative effect and improving the prognosis of patients.
Owner:深圳豪石生物科技有限公司
Nucleic acid combination and kit for detecting septin9 gene methylation
InactiveCN108048566AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCpG siteSpecific detection
The invention discloses a nucleic acid combination and kit for detecting septin9 gene methylation, and relates to the field of molecular biology. The nucleic acid combination includes a primer pair for detecting septin9 gene methylation. The primer pair includes an upstream primer having a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.11 and a downstream primer having a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.17. Theprimer pair can specifically amplify the target site of a septin9 gene, wherein the target site is the third CpG island containing six CpG sites in a septin9 gene promoter region, so that specific detection of septin9 gene methylation is achieved. The nucleic acid combination and kit are high in sensitivity and have the detection limit as low as 100 copies, and the difficulty that the content ofctDNA in blood plasma is low and ctDNA cannot be detected is overcome.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
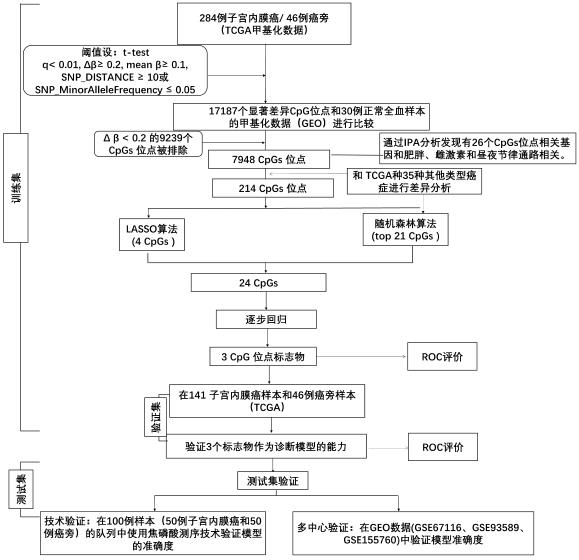
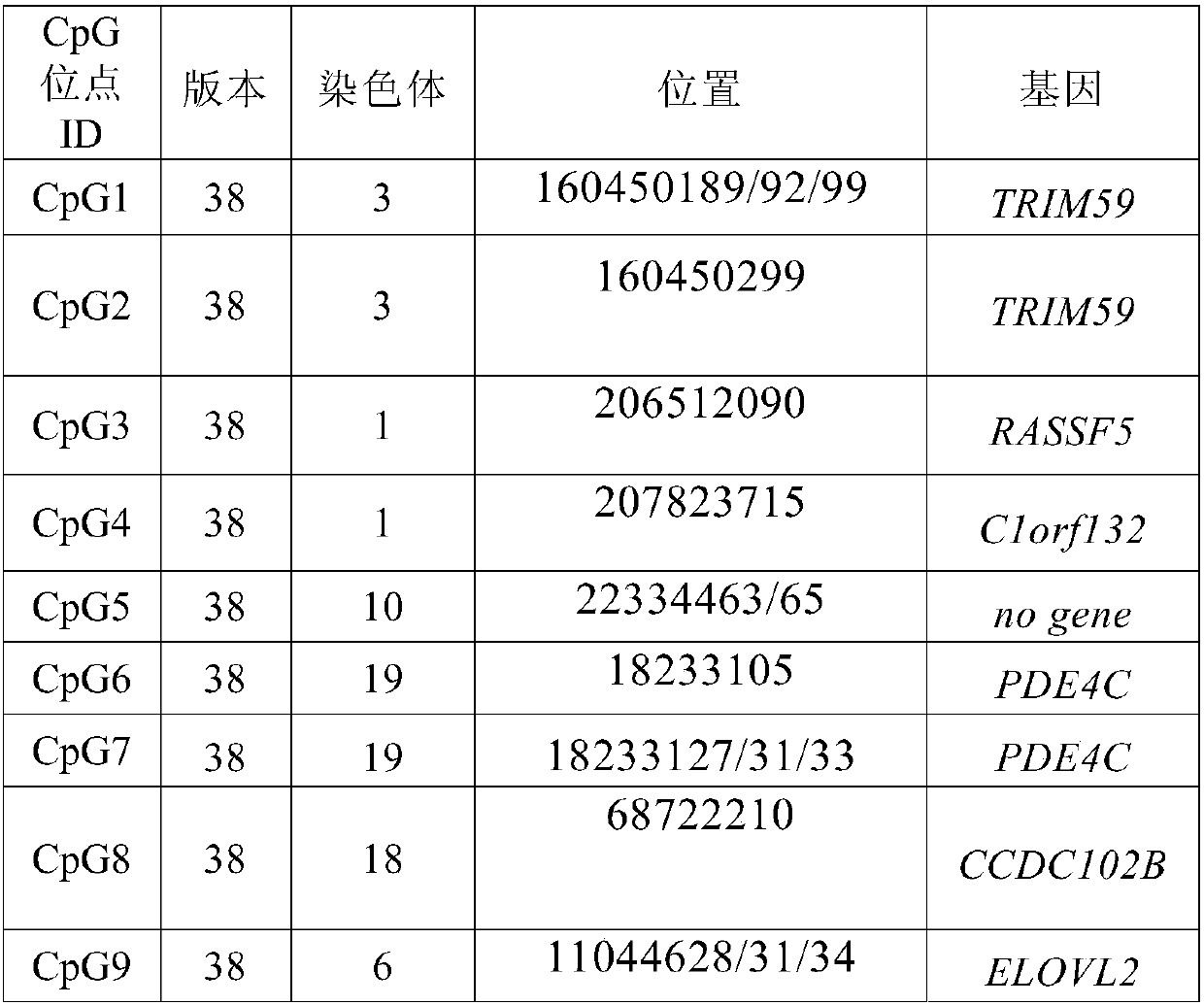
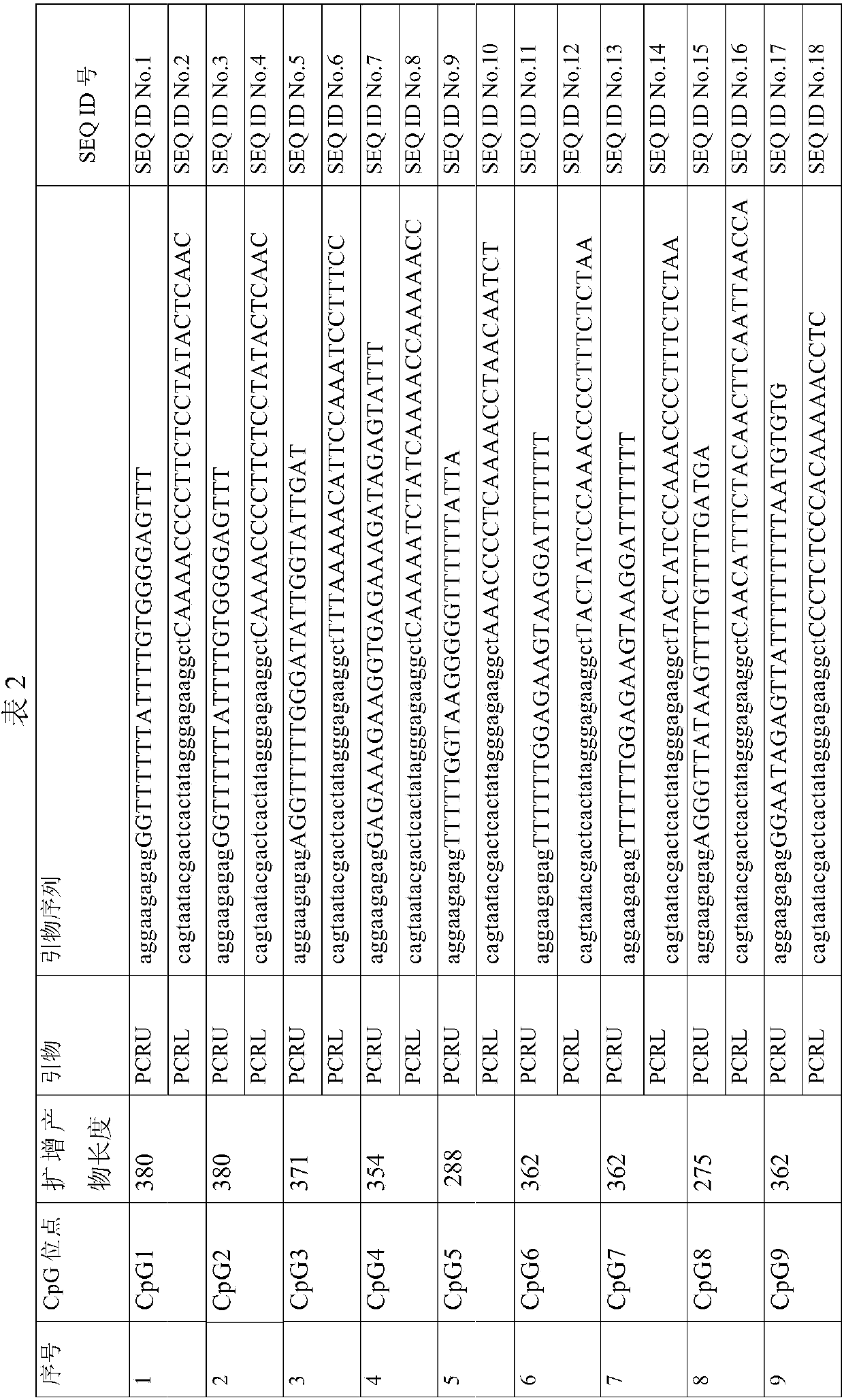
Detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer
ActiveCN113215264AImprove complianceSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsOncologyGene targeting
The invention discloses a detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer. The detection kit is applied to early screening of endometrial cancer and comprises a methylation specific primer of a TMEM101 gene target site, a hydrolysis probe which is specific to the TMEM101 gene, and a primer of a reference gene and a hydrolysis probe of the reference gene, wherein the target site of the TMEM101 gene is at least one CpG site in an upstream and downstream 2000bp interval of a transcription start site of the TMEM101 gene; the reference gene is one or more of GAPDH and beta-actin; and the kit comprises a PCR pre-amplification reaction system and a PCR amplification reaction system. According to the provided detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer, the technical defects that in the prior art, the process is tedious, the detection time is long, the false positive is high, and the early screening of the endometrial cancer blood cannot be traced are overcome.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
Method and system for acquiring age of male individual in Chinese population
ActiveCN109593862ANarrow your searchImprove the efficiency of solving crimesMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteRegression analysis
The invention provides a method and a system for acquiring the age of a male individual in a Chinese population. The method comprises the following steps: extracting DNA of the male individual; acquiring the methylation rates of 9 CpG sites of the DNA; and according to the methylation rates of the respective CpG loci, performing regression analysis on the 9 CpG loci and the age by R software to construct a regression model so as to acquire the age of the male individual in the Chinese population. According to a scheme provided by the invention, the age of the male individual in the Chinese population can be accurately acquired, and the age of the individual can be inferred from biodetection materials, such as blood or a blood mark sample, which are left on a crime scene in an actual publicsecurity combat, so that quick locking of a criminal suspect scope is facilitated, a clue is provided for case detection and the speed of the case detection is increased.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Ribosome DNA methylation marker for detection of cancer in peripheral blood and application thereof
ActiveCN110195107AHigh copy numberTimely diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCancers diagnosisRibosomal DNA
The invention provides a ribosome DNA methylation marker for detection of cancer in peripheral blood and an application thereof. The markers comprise at least one selected from the group consisting of, by taking a human ribosomal DNA repeat fragment unit reference sequence U13369.1 as a reference, CpG sites at positions of 38974, 37148, 37013, 37082, 37076, 32936, 21740, 23407, 34657, and 28277 orthe modified CpG site. The invention also provides a system, a kit, and the like for any combination of the markers for cancer diagnosis. The methylation status of the markers is significantly different between tumor tissues and non-tumor tissues, and the markers are hypomethylated in tumor tissues, and the ROC of combination of the markers in a test set to distinguish patients with liver cancer,lung cancer, and colorectal cancer can respectively reach 96%, 94%, and 92%.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for assessing prognosis or risk stratification of liver cancer by using cpg methylation variation in gene
PendingCN111386352APredict the likelihood of onsetMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteHematological test
The present invention relates to a method for assessing the prognosis or risk stratification of liver cancer by using a clinical specimen mixed with a normal tissue, wherein at least one CpG site thatshows a low methylation level in normal and blood tissues but a high methylation level in only a cancer tissue is measured for methylation level.
Owner:LEPIDYNE CO LTD
Method and system for acquiring individual age of Chinese population and amplification detection system
ActiveCN110257494ANarrow your searchImprove the speed of solving crimesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRegression analysisR software
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to a method and system for acquiring the individual age of Chinese population and an amplification detection system. The method includes: extracting the genome DNA of an individual; performing hydrosulphite treatment on the DNA; acquiring the methylation rate of one group of CpG sites in the DNA; using R software to perform regression analysis on the methylation rate of the CpG sites and the age of the individual to build a regression model for inferring the age of the individual. The method and system has the advantages that the individual age of the Chinese population can be accurately inferred, and mean absolute deviation of the inferred age is 2-4; the method and system is especially applicable to police practice, age inferring is performed through the individual blood or blood stain sample extracted in a crime scene, the age range of a suspect or a victim can be obtained, information can be provided for case investigation, the search range can be narrowed, and case cracking speed can be increased.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for predicting prognosis of renal cell carcinoma
InactiveUS20150118681A1Sure easyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteRenal Cell Cancers
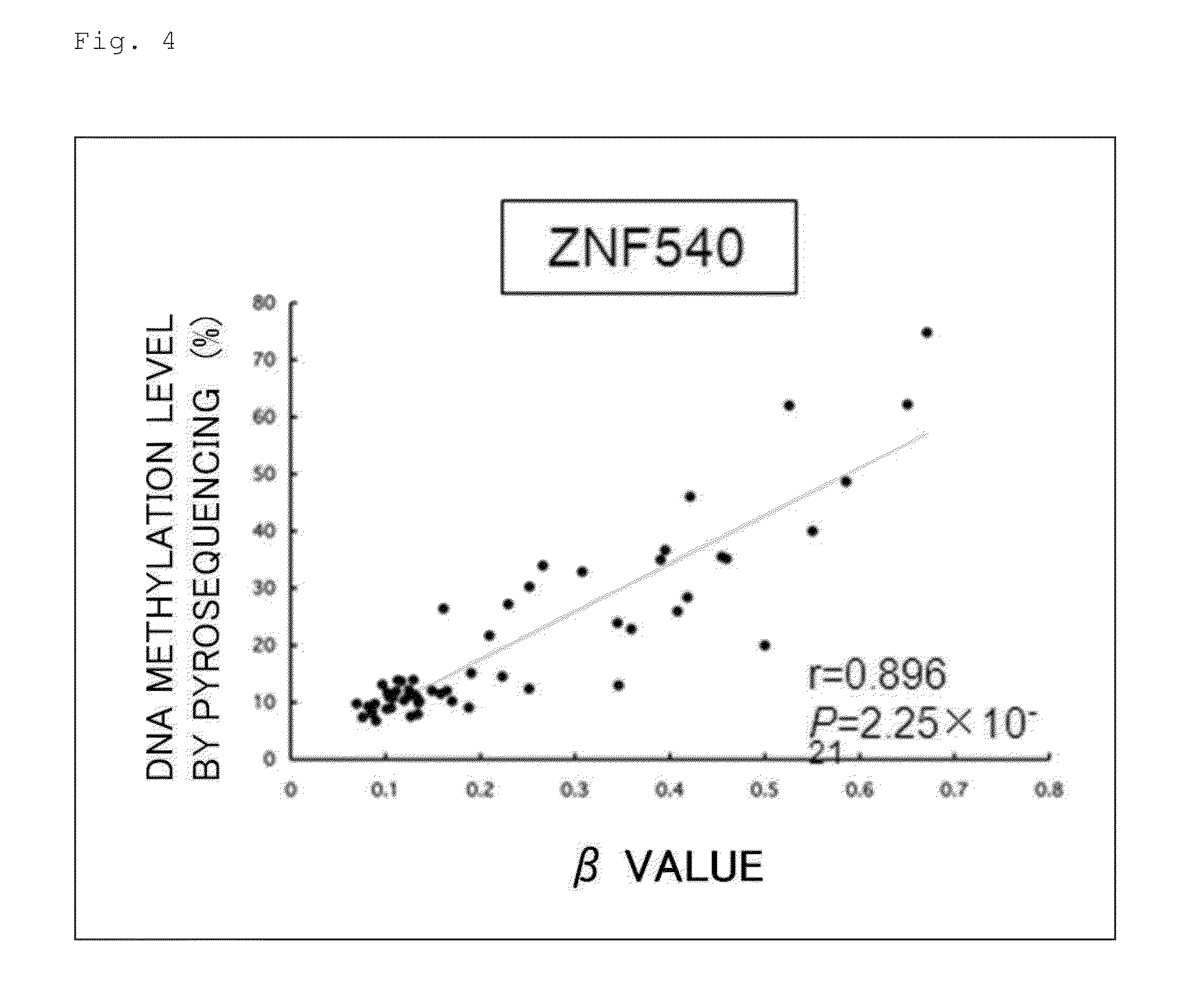
In order to provide a method for detecting an unfavorable prognostic risk of renal cell carcinoma easily with quite high sensitivity and specificity, a methylome analysis was performed on normal renal tissues, and non-cancerous tissues and renal cell carcinomas derived from patients with renal cell carcinomas. The result revealed that it was possible to detect an unfavorable prognostic risk of renal cell carcinoma by detecting a DNA methylation level at at least one CpG site of FAM150A, GRM6, ZNF540, ZFP42, ZNF154, RIMS4, PCDHAC1, KHDRBS2, ASCL2, KCNQ1, PRAC, WNT3A, TRH, FAM78A, ZNF671, SLC13A5, and NKX6-2 genes.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
Method for detecting characteristics of gene region based on inter-alu polymerase chain reaction
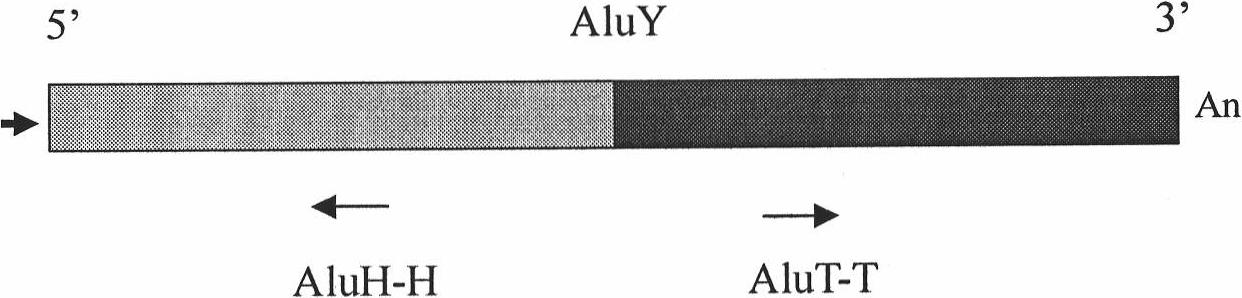
The invention relates to a method for centralized expanding and detecting the gene region of a genome DNA, which aims to verify the characteristics of the gene area in the genome. The characteristics comprise single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), point mutuation, sequence insertion / deletion and the levels of dideoxy nucleotide (DNA) methylated CpG sites. With an Alu family, particularly an AluY subfamily common sequence as the main oligonucleotide primer, the method expands the DNA and copies all gene regions which are mostly concentrated in the genome with the oligonucleotide primer inter-alu PCR expanded genome DNA. The method is characterized in that the inter-Alu PCR can filter some non-gene sequences, so that a novel generation of sequencing technology detects the SNP, the point mutuation, the sequence insertion / deletion and the levels of DNA methylated CpG sites of the gene region in a centralized way, so as to save the consumption of the genome DNA required by the sequencing.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HKUST FOK YING TUNG RES INST
Expansion method for DNA methylation chip data
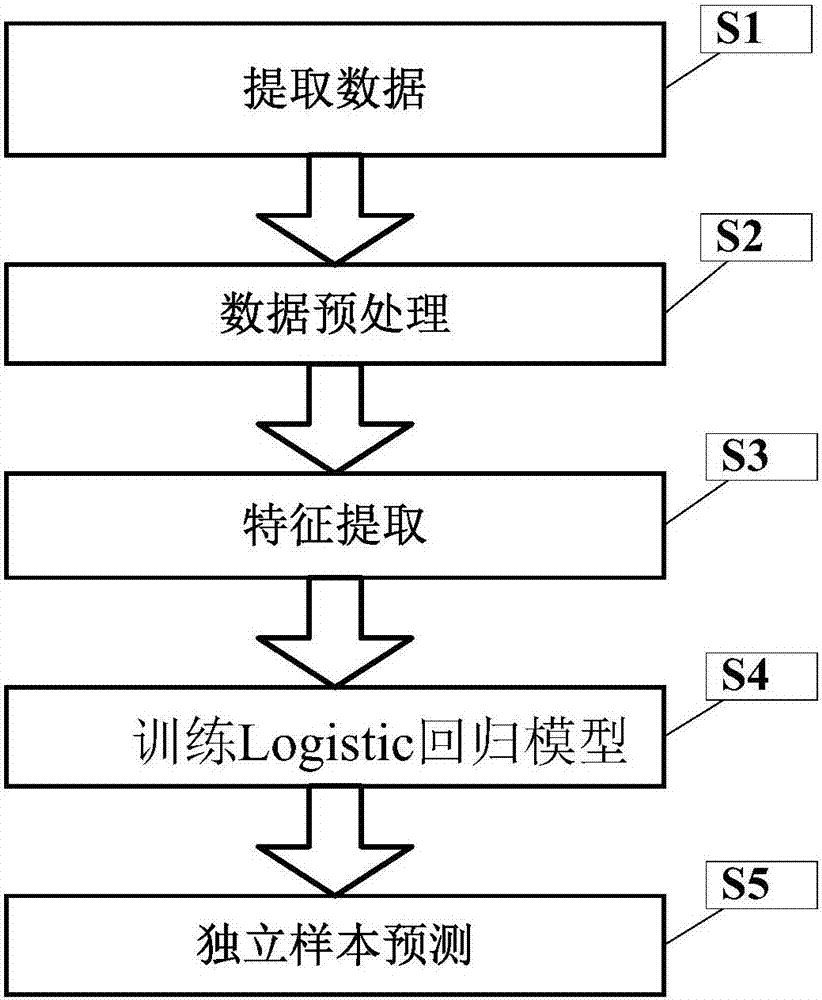
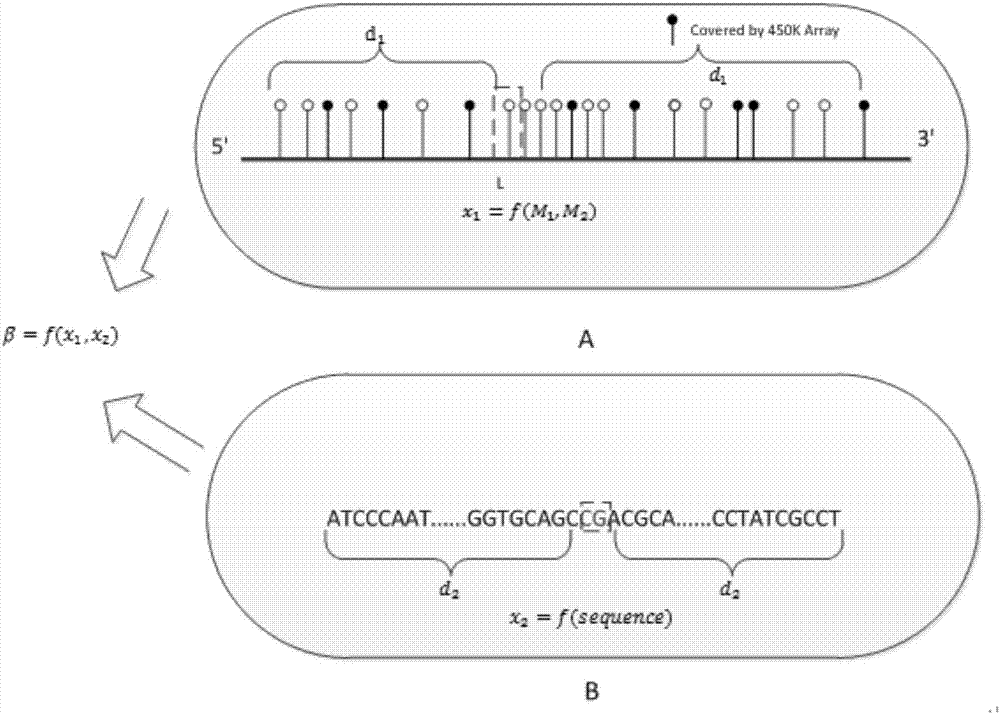
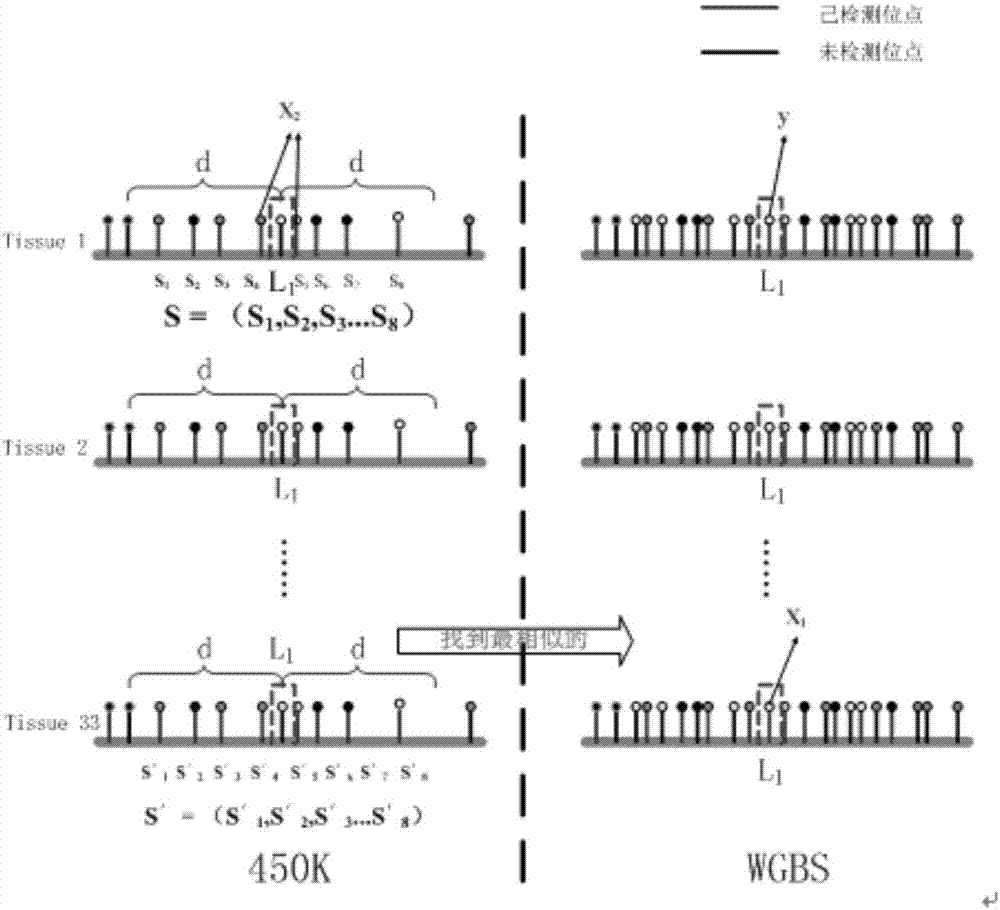
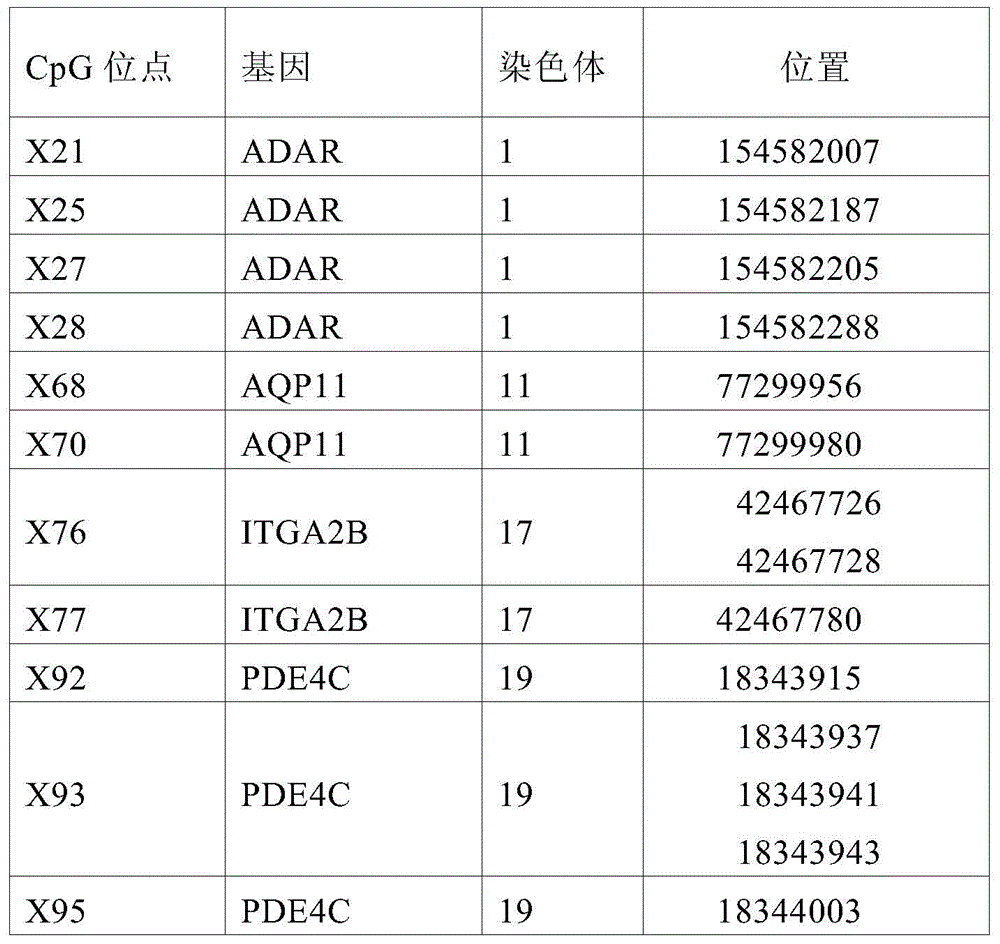
The invention discloses an expansion method for DNA methylation chip data. Expansion of the DNA methylation chip data is realized by predicting a CpG locus not covered by a DNA methylation chip. Specifically, first, features of the CpG locus to be predicted are extracted based on measured data of the DNA methylation chip and sequencing data of other whole-genome sulfite with similar tissue; second, a methylation value measured through a whole-genome sulfite sequencing method of the CpG locus to be predicted is combined to train a Logistic regression model; and last, the trained regression model is used to predict new data.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A method and system for obtaining the individual age of women in Chinese population
ActiveCN104357561BNarrow your searchImprove the efficiency of solving crimesMicrobiological testing/measurementRegression analysisCrowds
The invention provides a method and a system for acquiring an age of a female individual of Chinese population. The method comprises the following steps: extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of the female individual, acquiring methylation indexes of 11 CpG loci of the DNA, conducting regress analysis to the methylation indexes of each GpG loci, the 11 CpG loci and the age with SPSS 17 (Statistic Package for Social Science) software, and constructing a regression model to obtain the age of the female individual of the Chinese population. The scheme provided by the invention can accurately obtain the age of the female individual of the Chinese population, deduces the age of the individual with a biologically examined blood or blood stain sample remained in a crime scene of the public security actual combat, so as to facilitate targeting of the range of criminal suspects, provide clues for investigation of the case, and increase the detection speed of the case.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
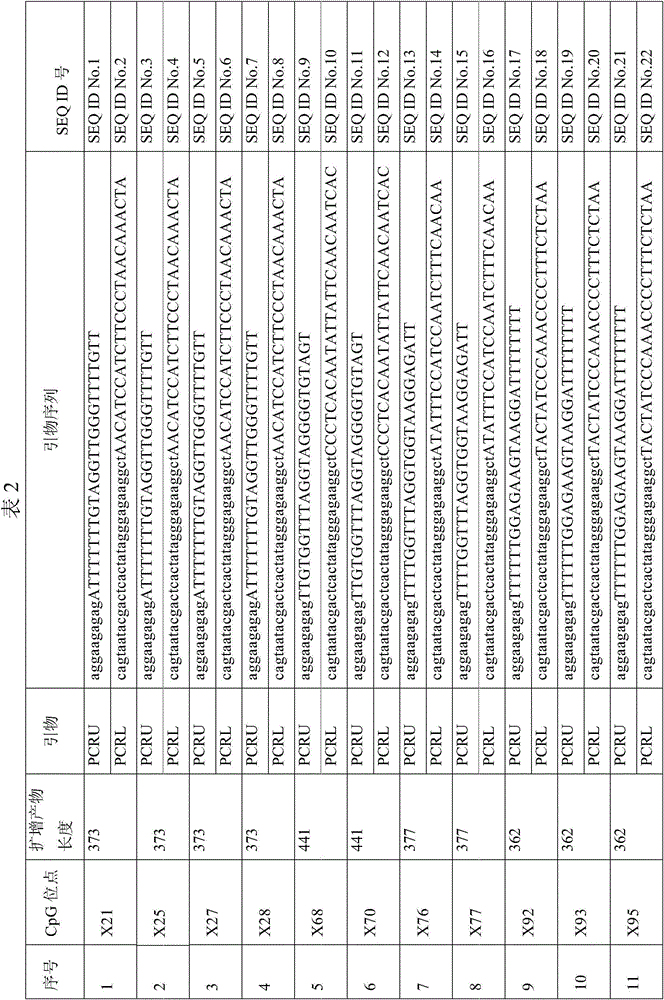
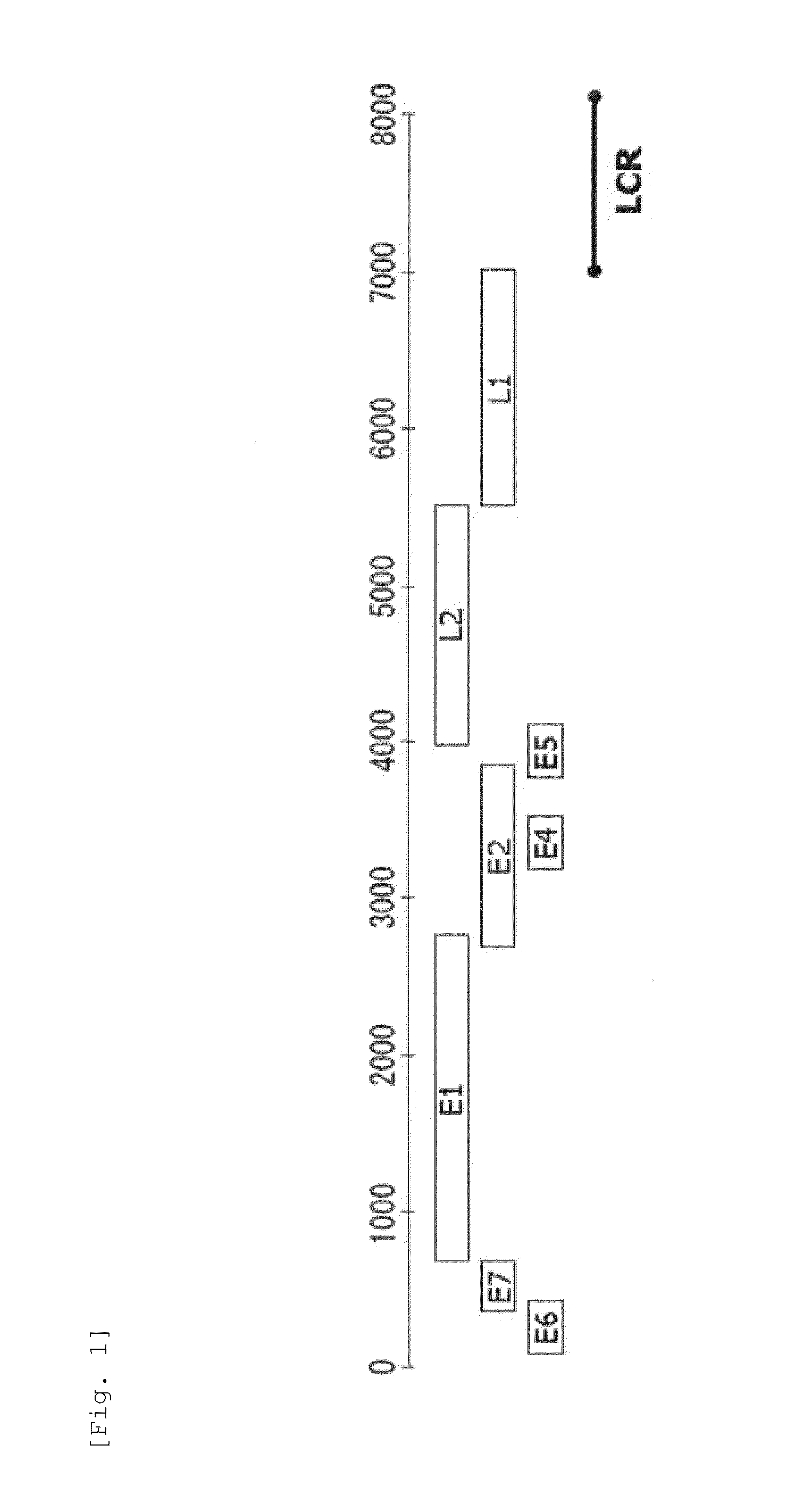
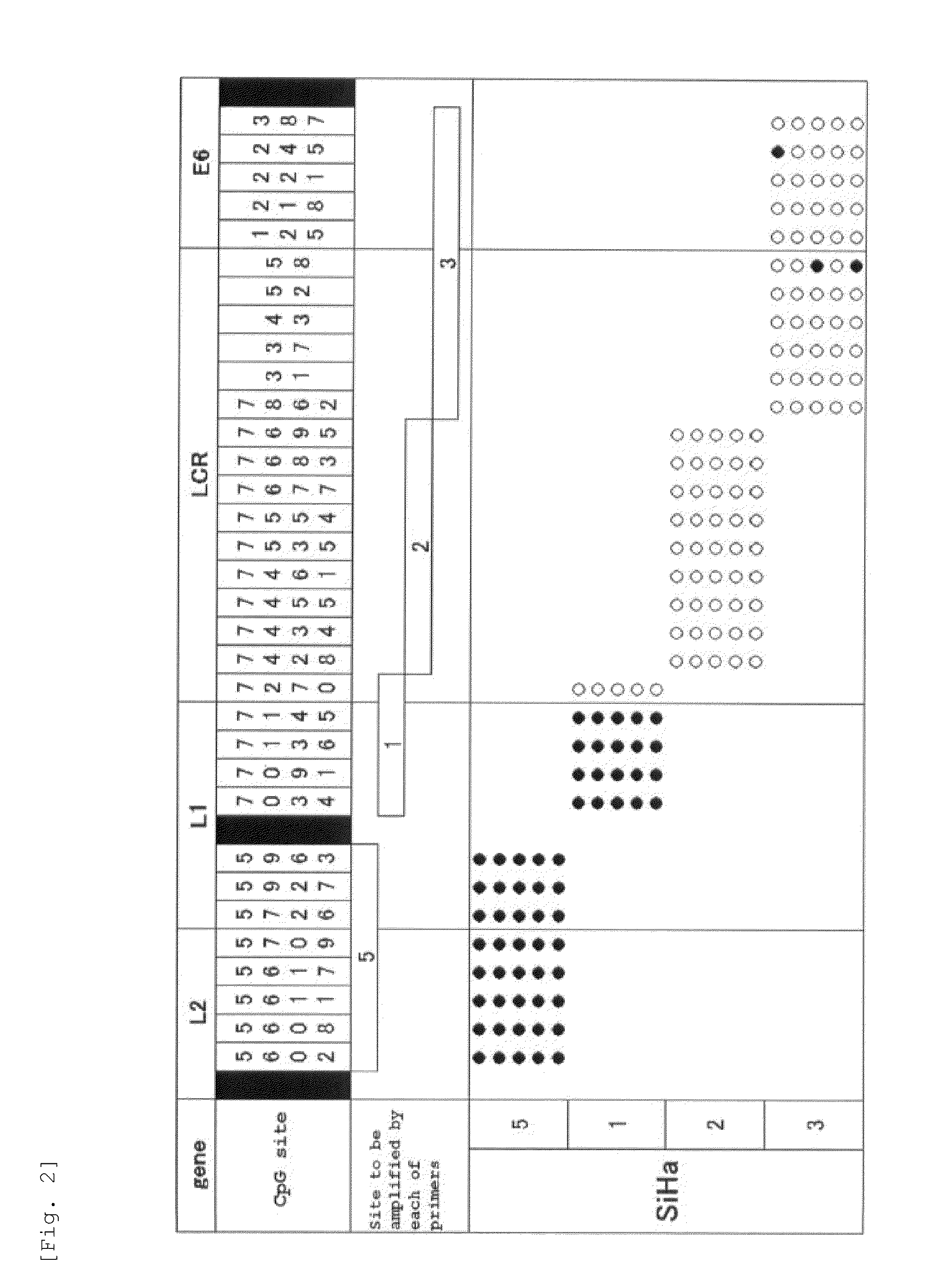
Method for detecting cancer cell caused by hpv, method for determining whether or not tissue is at stage of high-grade dysplasia or more severe stage, and primer set and kit used therefor
InactiveUS20110020832A1Easy diagnosisImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementCpG siteCytosine
Provided are a primer set, a method and a kit therefor, which can easily perform with high accuracy the detection of a cancer cell caused by HPV and the determination of whether or not a tissue is a tissue with high-grade dysplasia or in a more severe phase. As a primer set, used is a primer set consisting of a first primer which hybridizes with a nucleic acid consisting of a nucleotide sequence in which cytosine present in a site other than a CpG site is converted into another base in a nucleotide sequence having a CpG site in L1 region or L2 region of HPV and a second primer which hybridizes with a nucleic acid consisting of a nucleotide sequence in which cytosine is converted into another base in a nucleotide sequence having a CpG site in LCR or E6 region of HPV.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Human repeat element DNA methylation as markers for early diagnosis of liver cancer and application thereof
ActiveCN109825583AHigh copy numberAchieve early diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCpG siteCvd risk
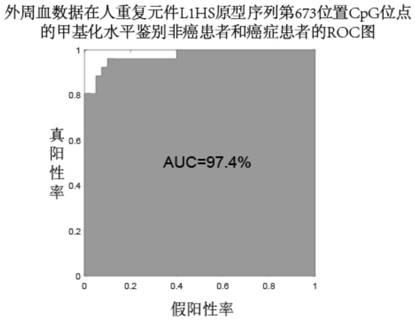
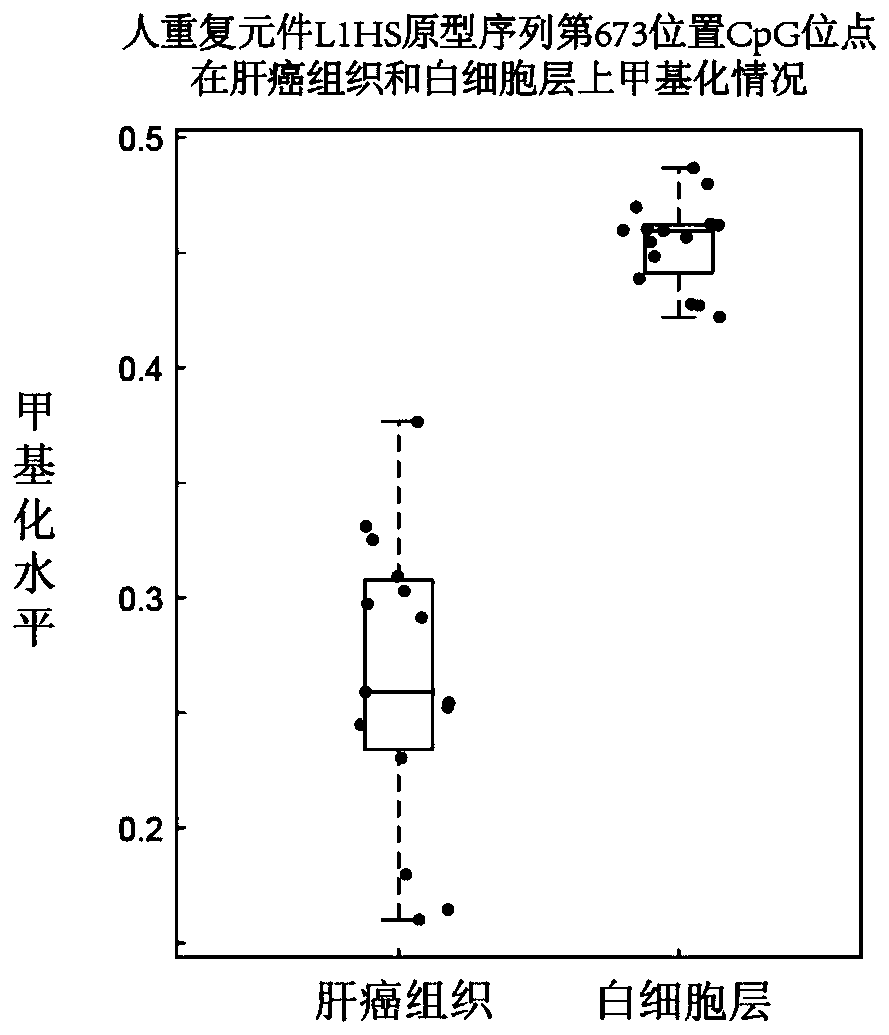
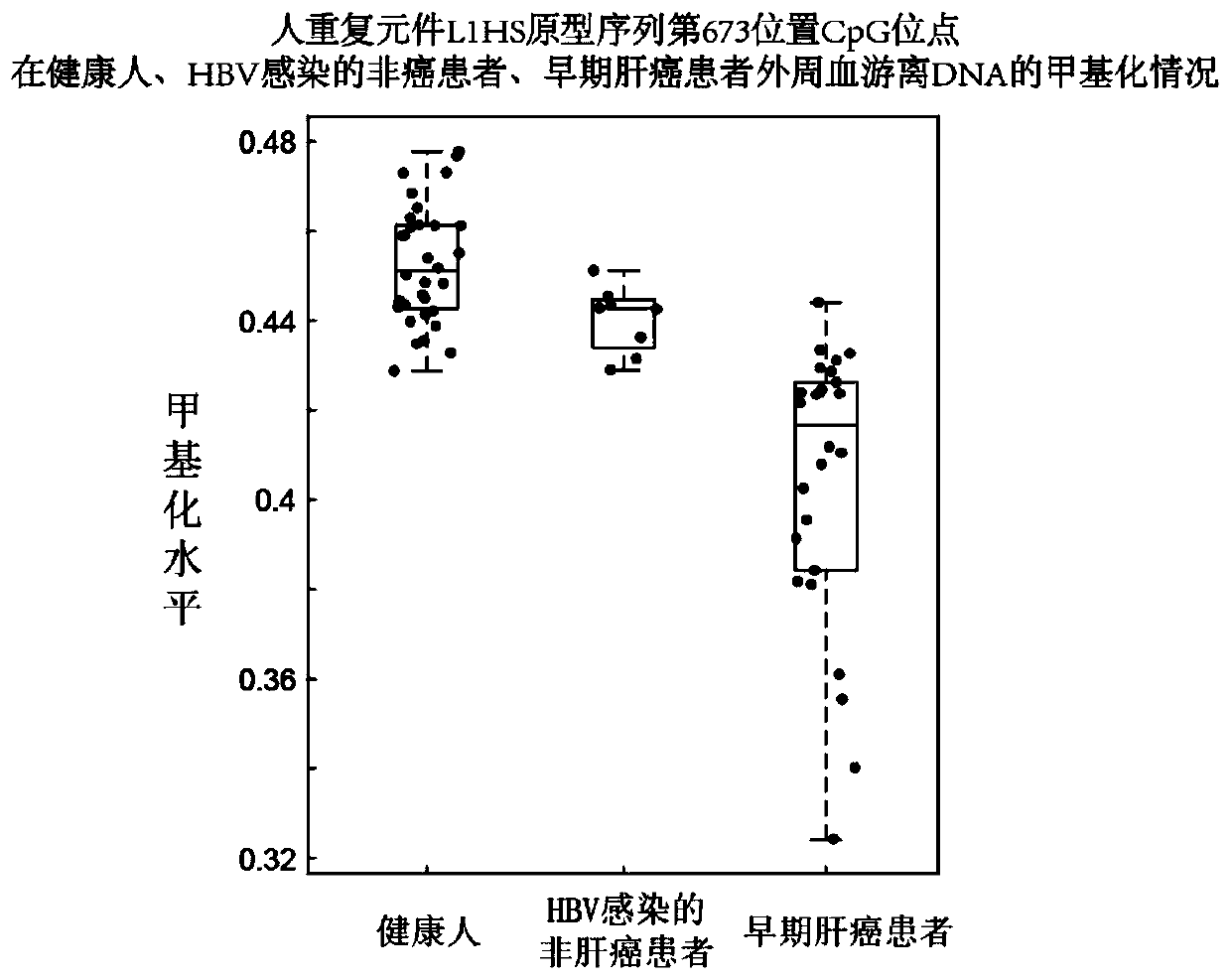
The invention discloses an human repeat element DNA methylation as markers for early diagnosis of liver cancer and an application thereof.The invention belongs to the field of biological detection, and relates to markers for liver cancer and the application thereof.These markers are selected from one or more of the CpG sites modified at positions 64 on AluYg6,72,231 on AluSp,447,493,673 on L1HS,380,448 on L1,230 on AluYba3a2,1569 on LSAU, and 446 on LTR12E in Repbase data published by the Genetic Information Research Institute (GIRI).The invention further provides a system for diagnosing livercancer or predicting the risk of liver cancer by using the combination of the markers.The methylation states of the markers are obviously different in tumor tissues and non-tumor tissues; the methylation of the markers is low in the tumor tissues, and the accuracy rate of distinguishing whether or not a patient suffers from liver cancer in a test set by the marker combination reaches 90 percent.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com