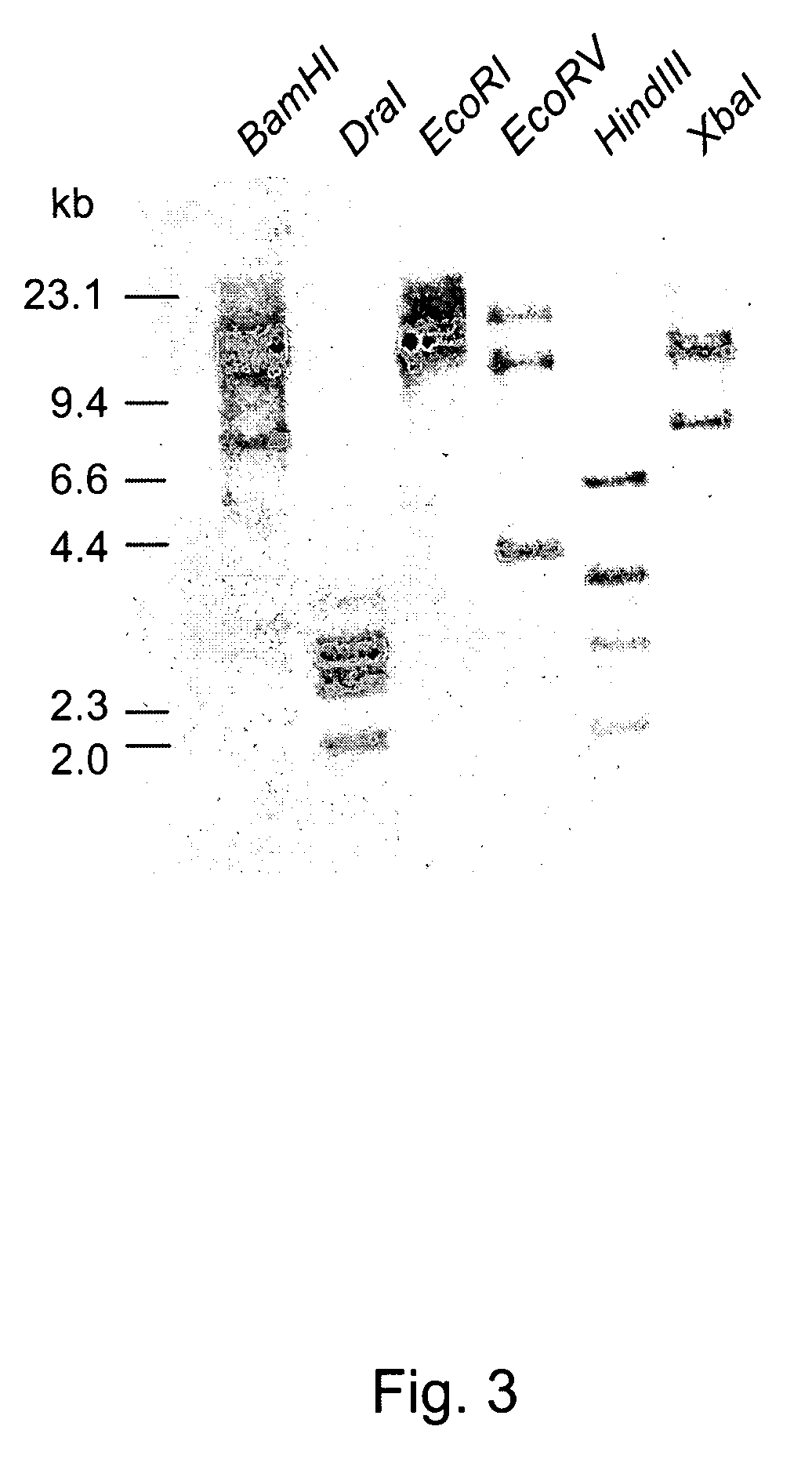
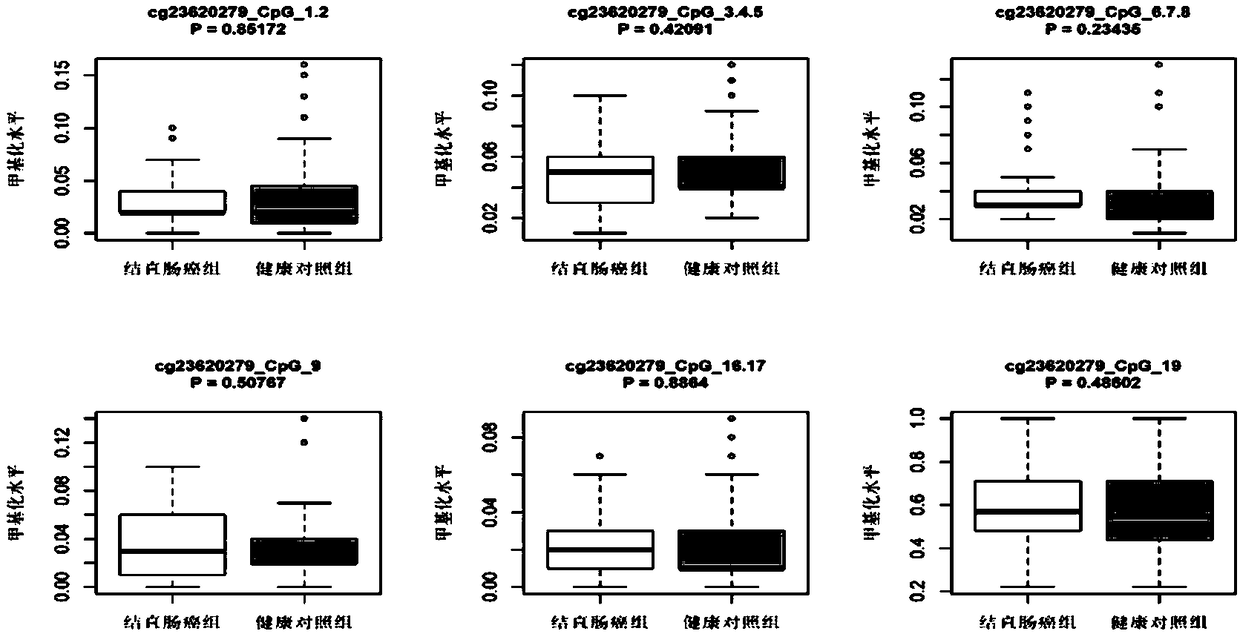
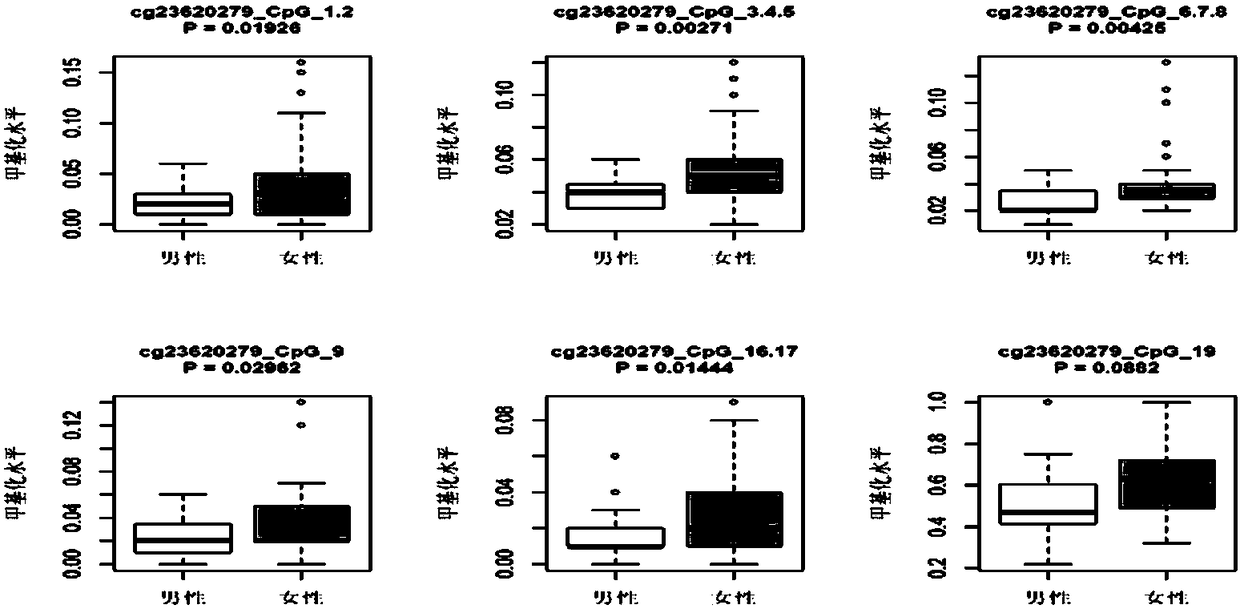
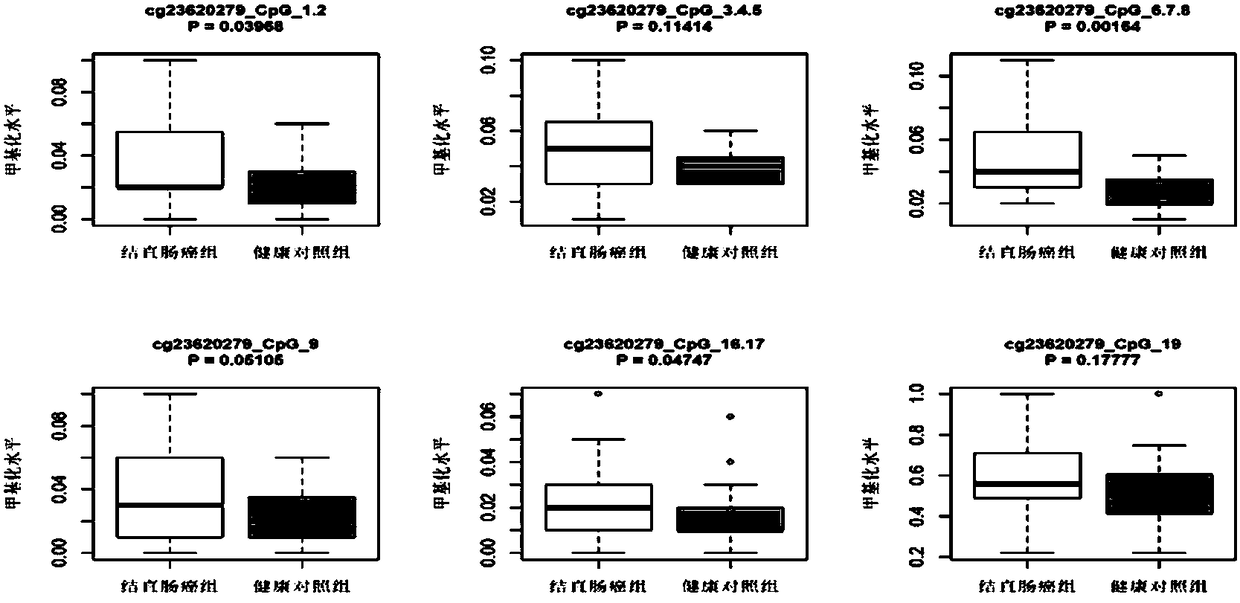
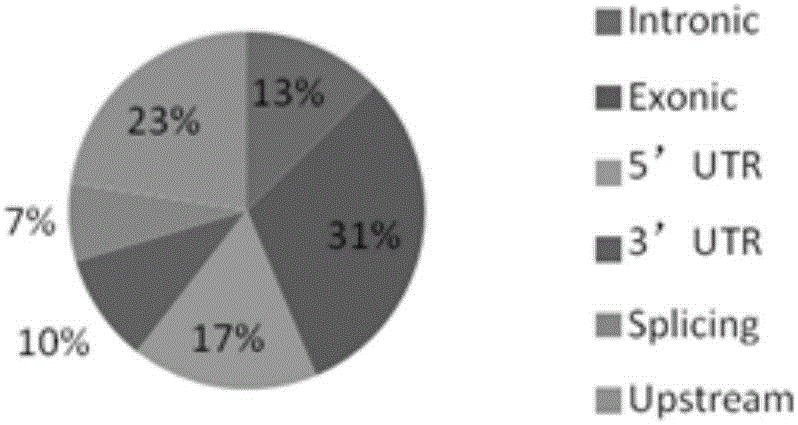
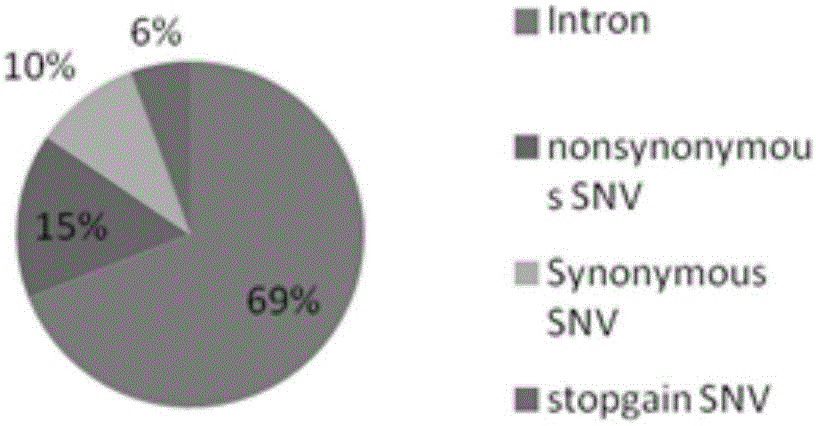
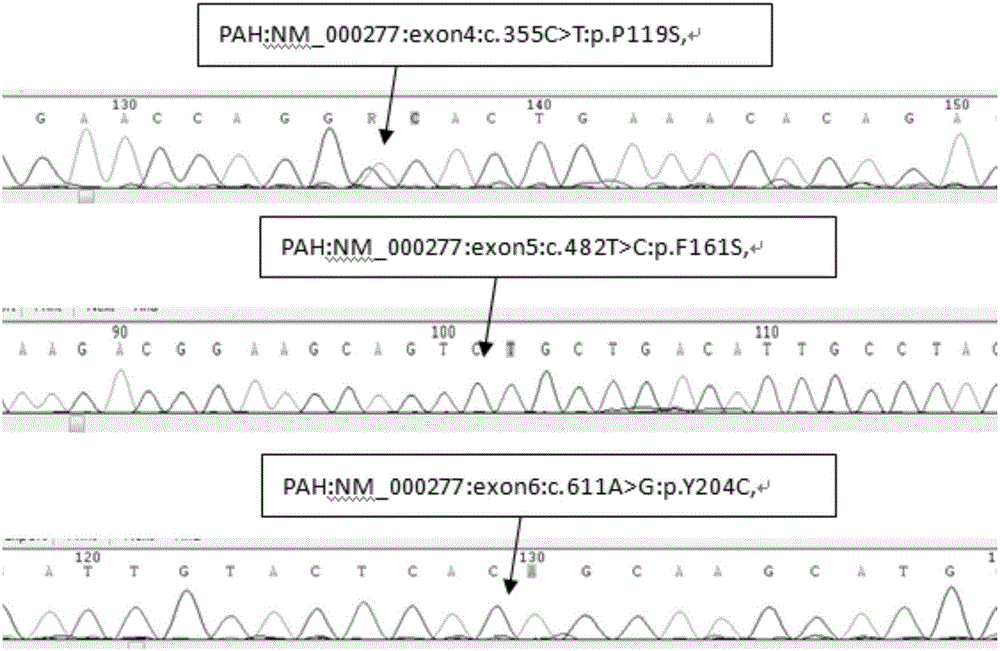
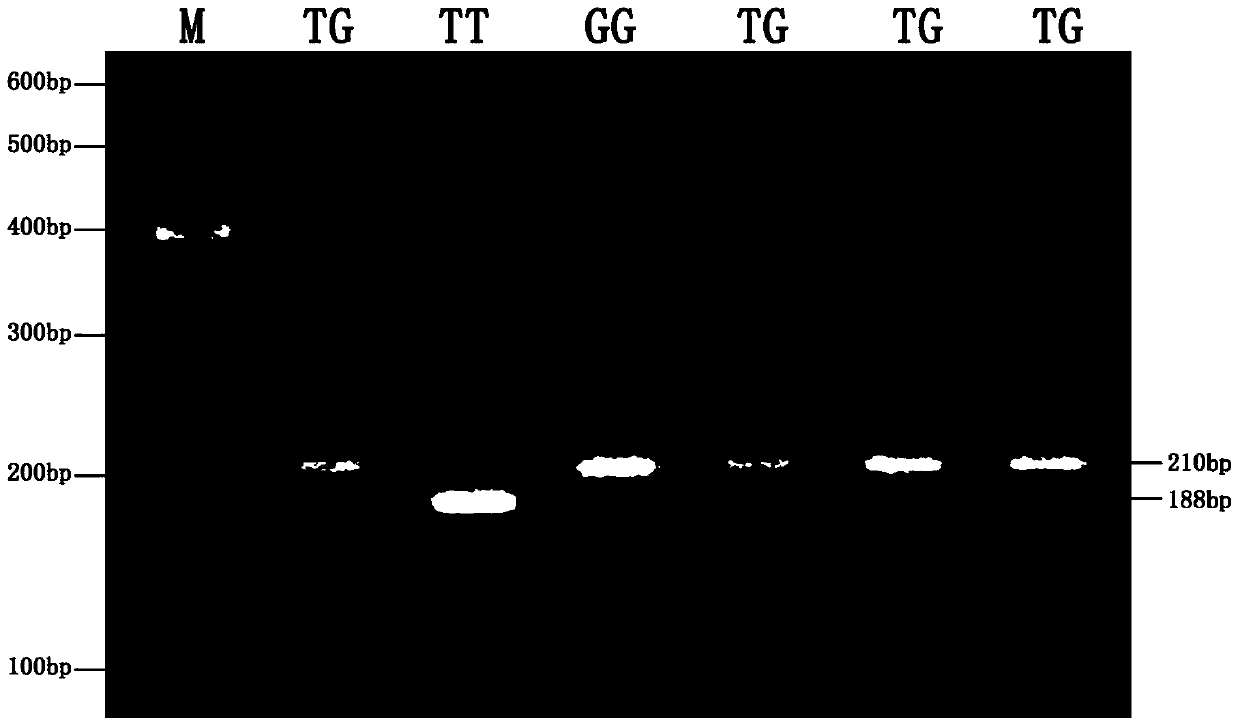
Patents
Literature
72 results about "Transcription start" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transcription start site. The nucleotide base at the upstream end of a gene where actual transcription of the gene begins. Transcription Start Site (TSS) Approximately -35.
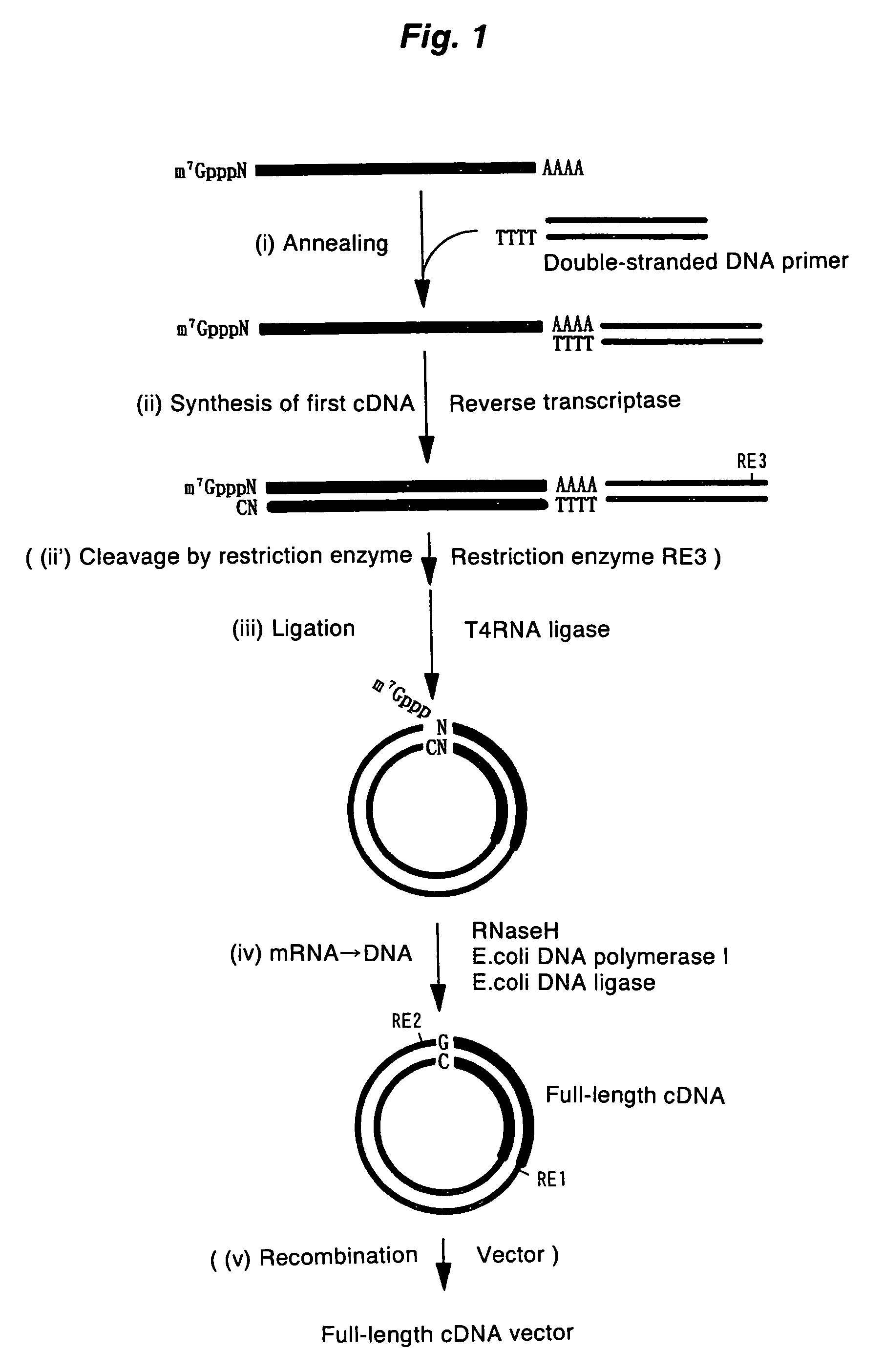
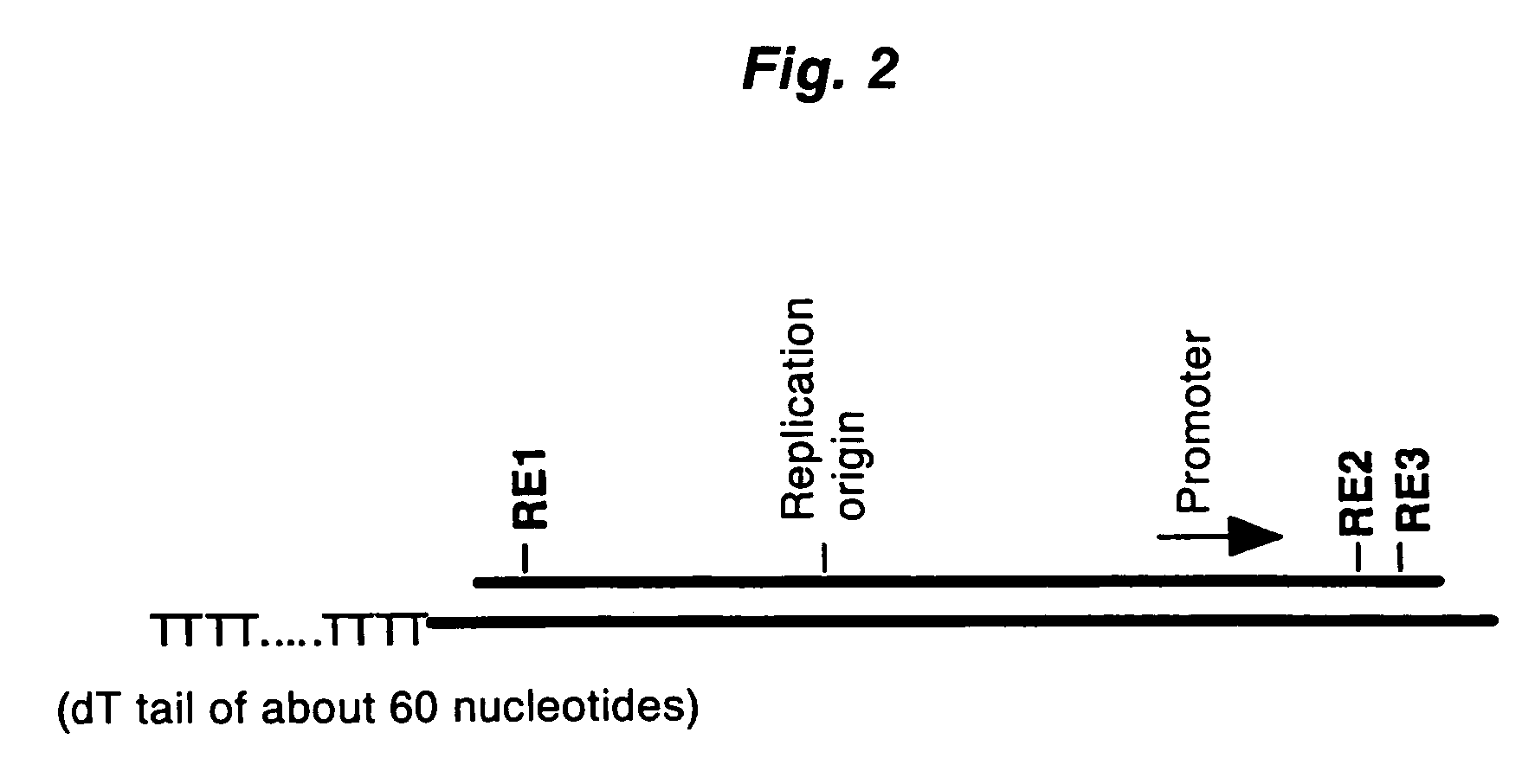
Method of synthesizing cdna
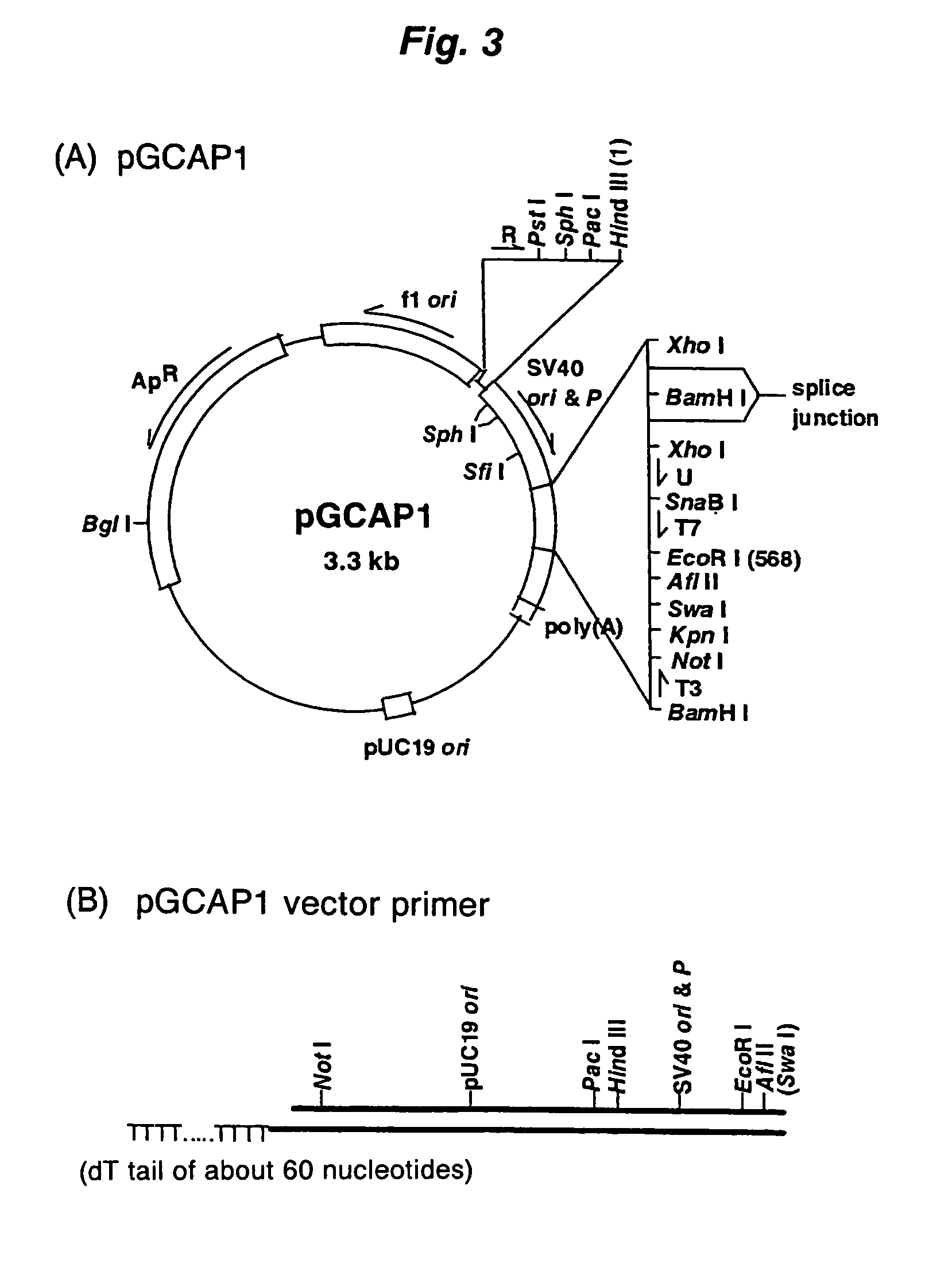
ActiveUS20060246453A1High yieldIncrease chanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexReverse transcriptase
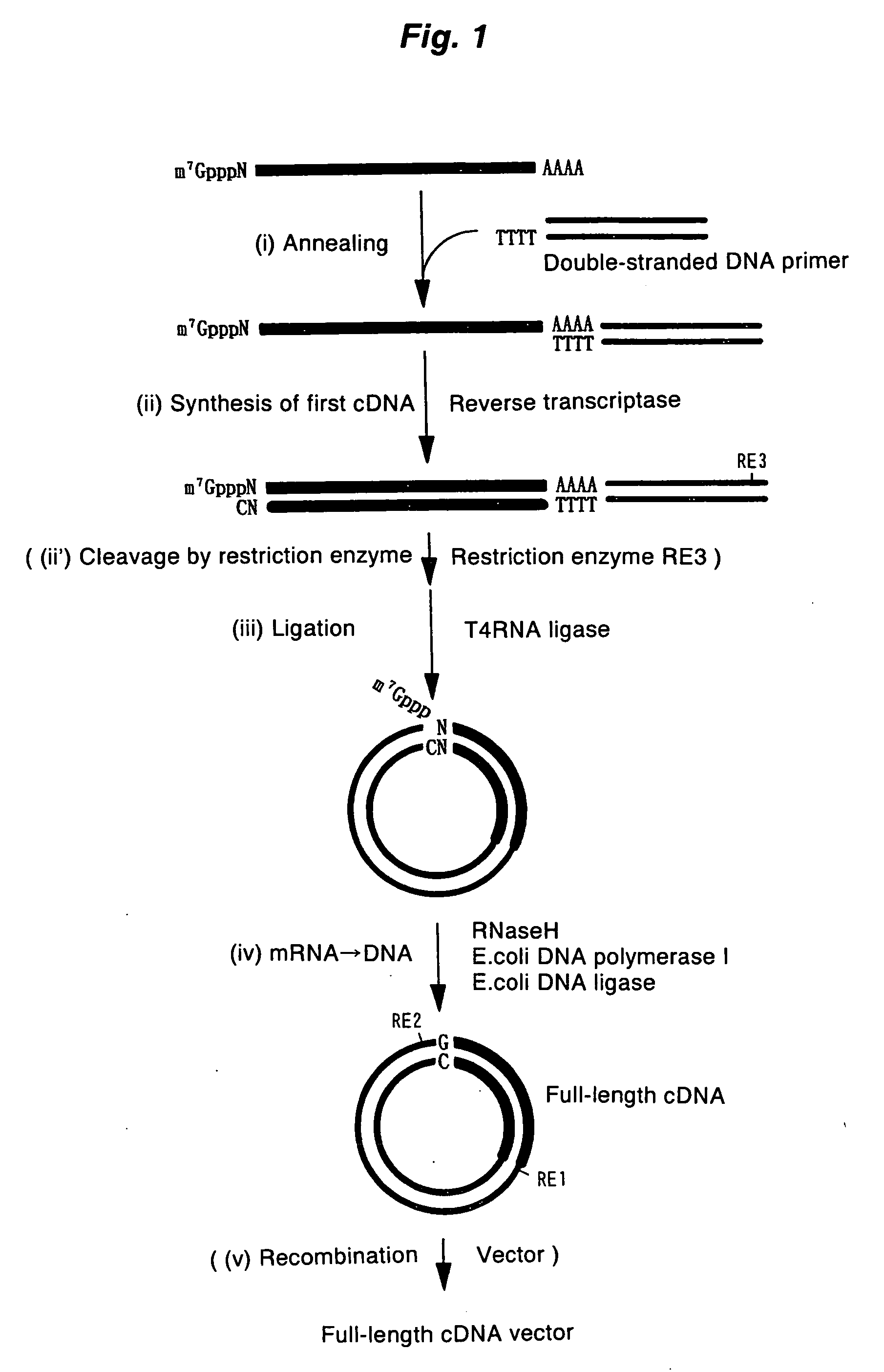
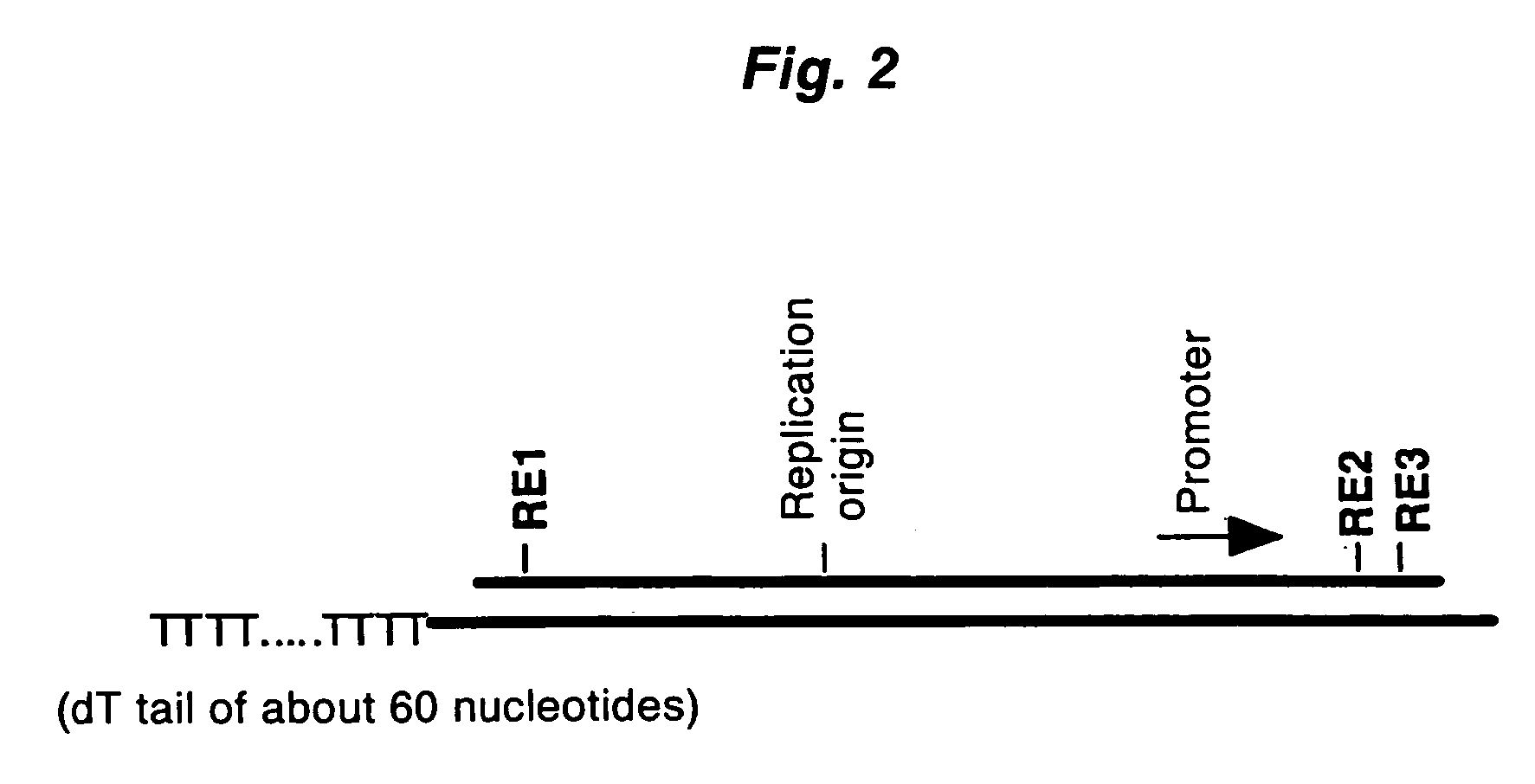
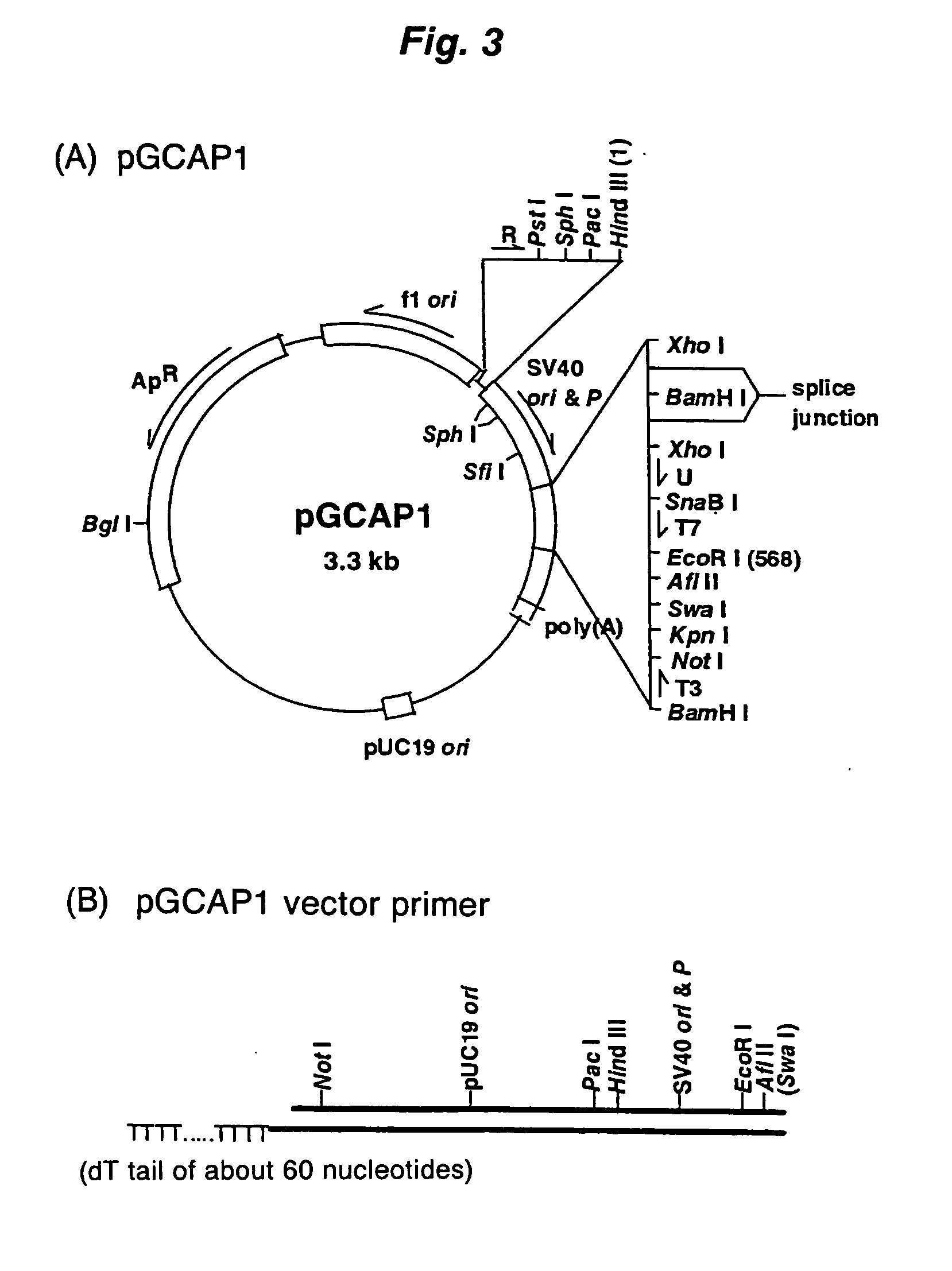
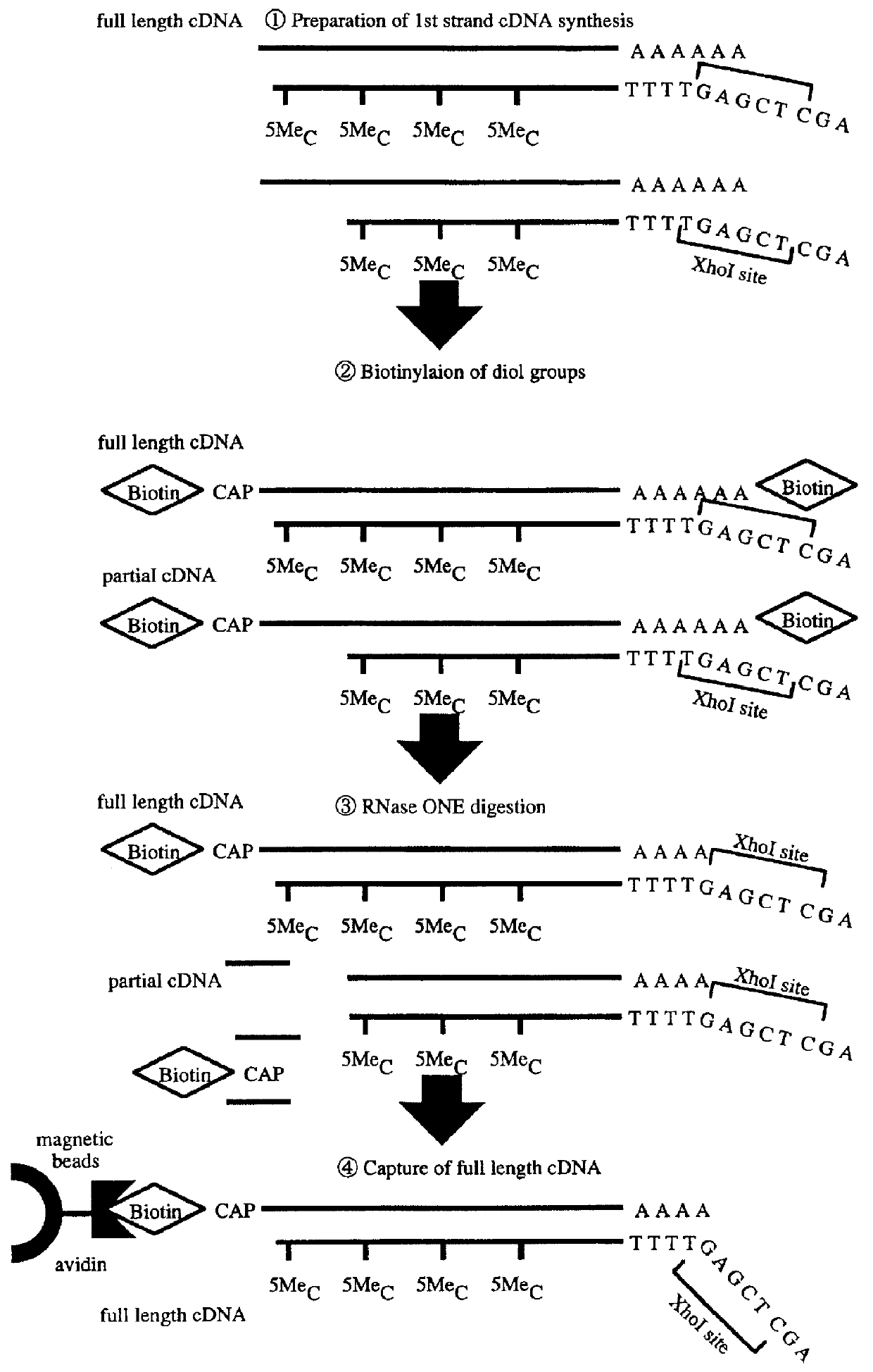
A method for synthesizing cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a nucleotide adjacent to a cap structure of mRNA, which comprises (i) a process for annealing a double-stranded DNA primer and an RNA mixture containing mRNA possessing a cap structure, (ii) a process for preparing a conjugate of an mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and a double-stranded DNA primer by synthesizing the first-strand cDNA primed with the double-stranded DNA primer using reverse transcriptase, and (iii) a process for circularizing the conjugate of the mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and the double-stranded DNA primer by joining the 3' and 5' ends of the DNA strand containing cDNA using ligase. This method enables us to efficiently synthesize a full-length cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a transcription-start-site nucleotide from a small amount of RNA by small processes.
Owner:KOKURITSU SHINTAI SHIYOUGAISHI +2
Method for forming full-length cDNA libraries
InactiveUS6143528AEasy to prepareEfficiently labeledSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodFull length cdna
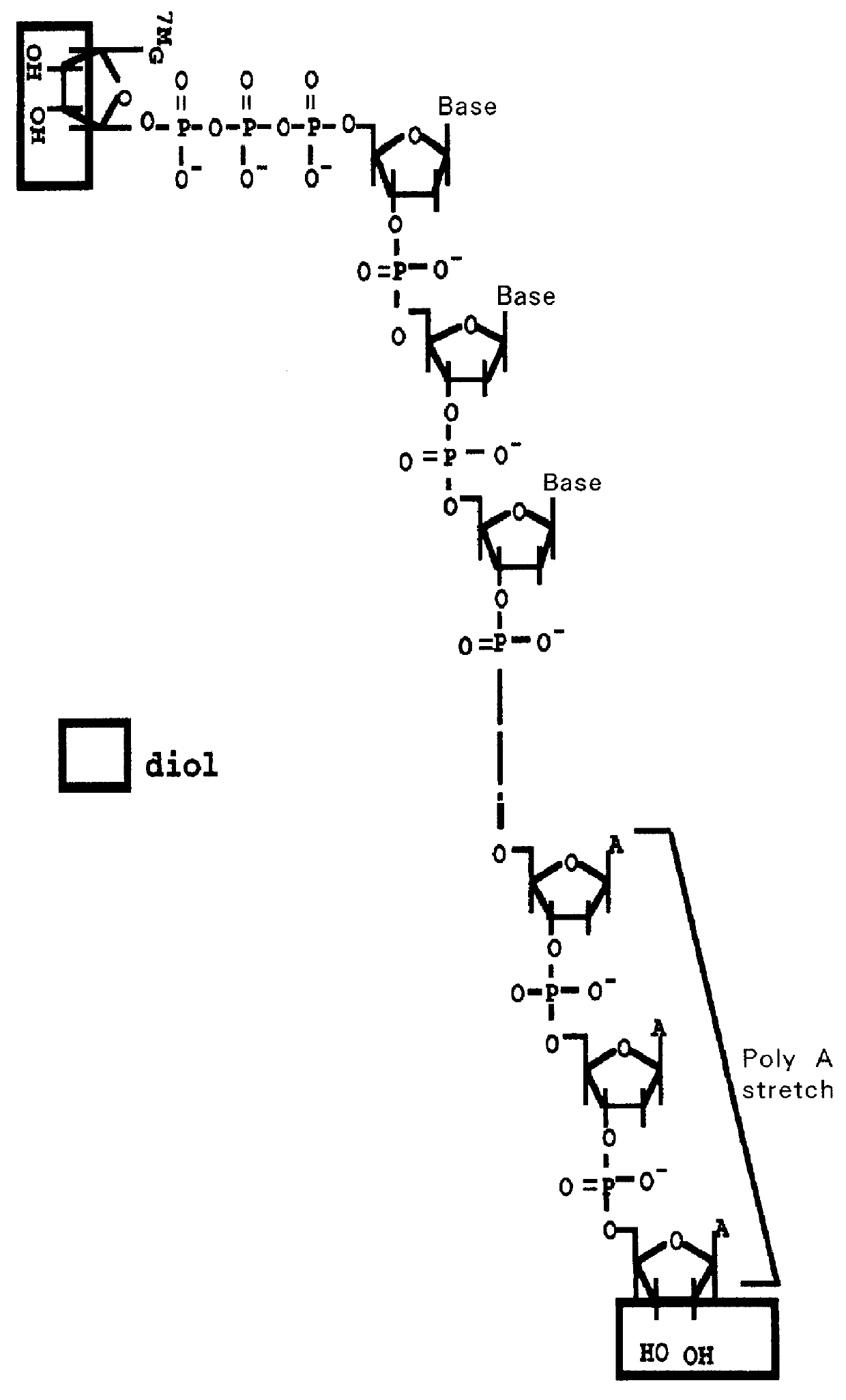
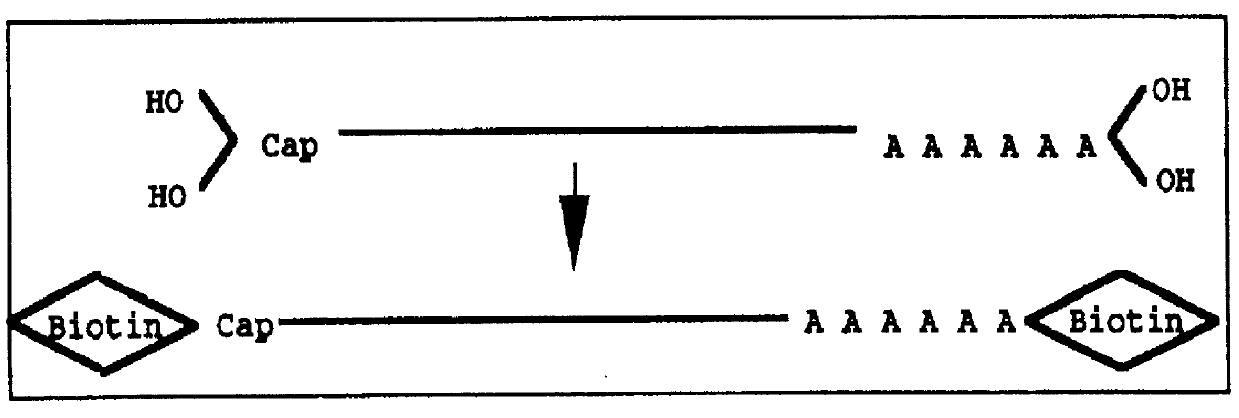
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 03992 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 16, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 16, 1999 PCT Filed Oct. 31, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 20122 PCT Pub. Date May 14, 1998Disclose is a method for making full-length cDNA libraries, which is for making libraries of cDNAs having lengths corresponding to full lengths of mRNAs and comprises the following steps of; forming RNA-DNA hybrids by reverse transcription starting from primers using mRNAs as templates, chemically binding a tag molecule to a diol structure present in the 5' Cap (7MeGpppN) site of a mRNA which is forming a RNA-DNA hybrid, and separating RNA-DNA hybrids carrying a DNA corresponding to a full-length mRNA from the RNA-DNA hybrids formed above by using a function of the tag molecule. The present method is a method for preparing full-length cDNA libraries utilizing a method for labeling the 5' Cap site more efficiently than protein enzyme reactions, which is avoidable a decrease of a full-length cDNA synthesis efficiency caused by cleavage of mRNA, and can synthesize a full-length cDNA more efficiently.
Owner:RIKEN
BNLEA3-1 promoter
InactiveUS20080244793A1Weakly inducibleSugar derivativesPlant peptidesEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
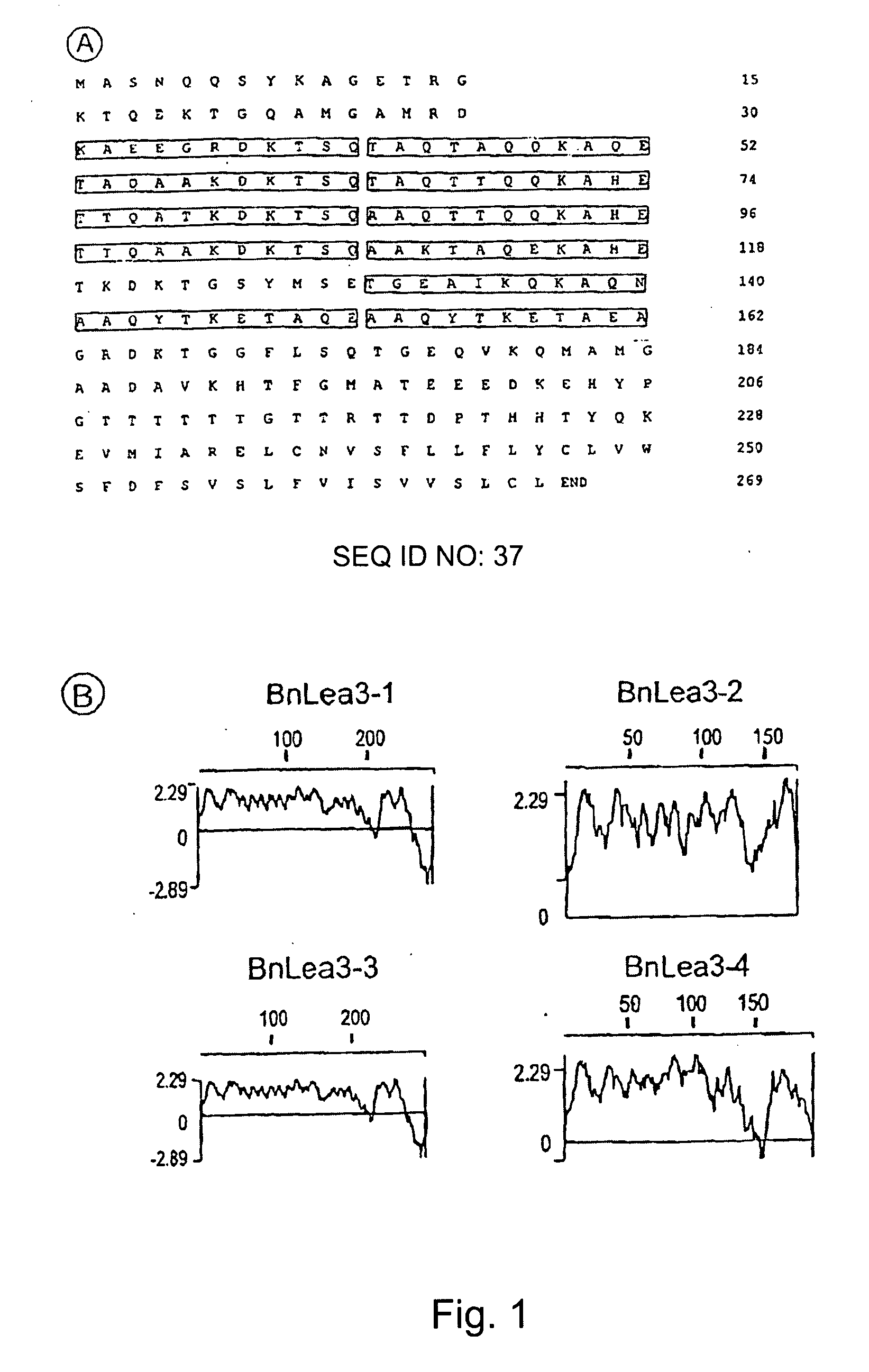
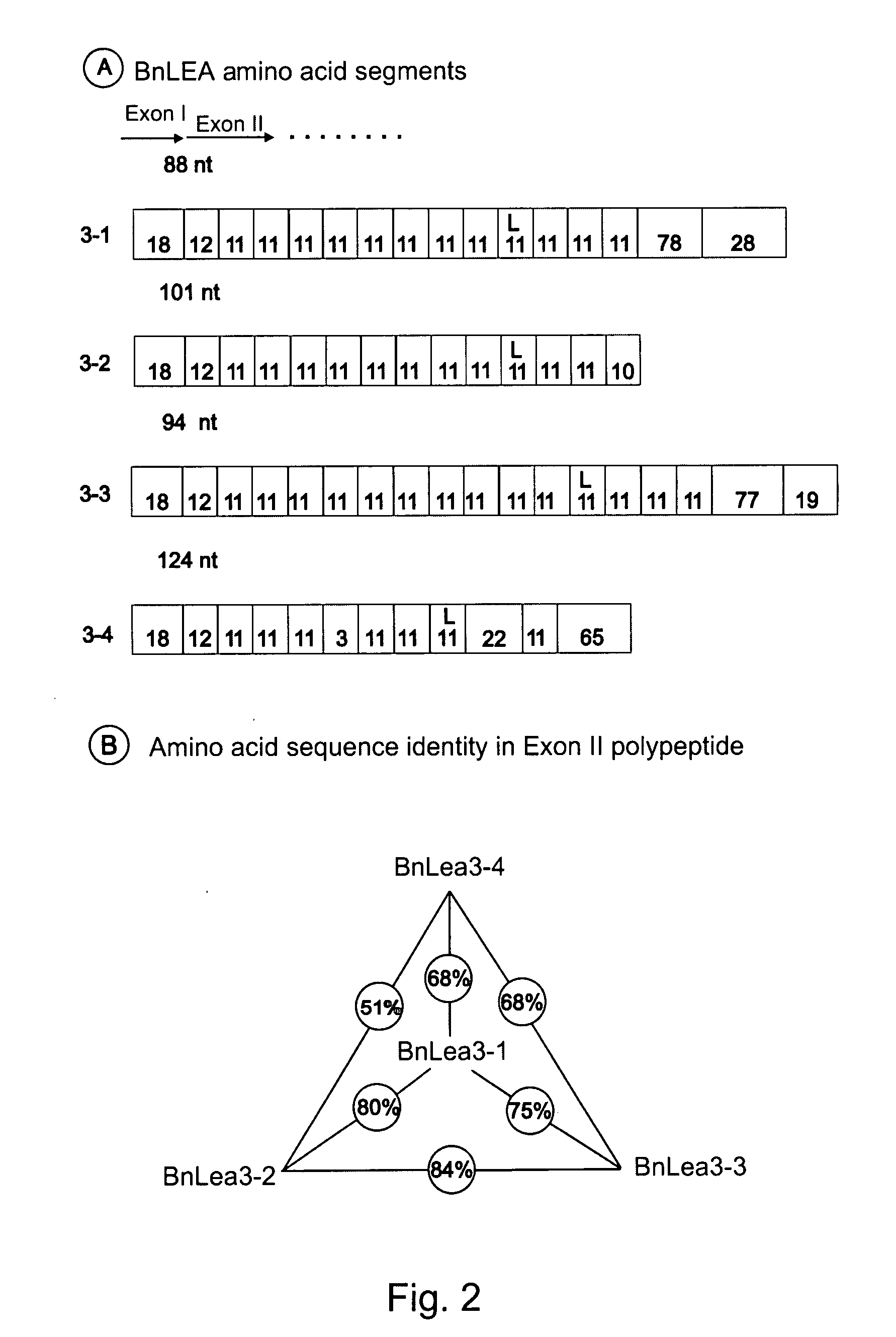
Late embryogenesis abundant (Lea) proteins accumulate in maturing seeds after many of the storage compounds have been synthesized, and they are considered relevant to maturation. We report here the molecular organization and expression of BnLea3-1, a novel Group 3 Lea gene from Brassica napus. BnLea3-1 contains a coding region of 798 bp, sharing 84.4% homology at the amino acid level with Lea76 of B. napus. Two tandem 11-mer repeats are truncated from the coding region of BnLea3-1, compared to the 13 conserved 11-mer repeats of Lea76. Substitutions of consensus residues are found at various positions within the 11-mer repeats. A 1561 bp 5′ flanking promoter fragment of BnLea3-1 fused to E. coli-glucuronidase (GUS) coding region conferred seed-specific GUS expression in stable transgenics of B. napus, tobacco and in transiently-transformed pea. A −137 bp minimal promoter preceding the first transcription start site, identified through progressive deletions from the upstream was sufficient for basal GUS expression in the seeds and in leaves treated with ABA. Deletion studies indicate the presence of enhancing elements located between −137 bp to −742 bp and suppressing elements located between −742 and −1561 bp. BnLea3-1 expression in seeds precedes that of Lea76. Unlike other Group 3 Lea members including HVA1 and Dc3, BnLea3-1 is active in seeds and responsive weakly in vegetative tissues to ABA and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) but not to stress treatments. Possible functions of BnLea3-1 and another member of the Group 3 Lea family BnLea3-2 in embryo development is discussed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method, marker, and kit used for colorectal cancer diagnosis, screening, and risk prediction
ActiveCN108315418AEasy to detectLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCpG siteComputer module
The invention discloses a DNA methylation marker used for diagnosis, screening, and prediction of male colorectal cancer. The DNA methylation marker is obtained via methylation of a combination of thefirst groups, or the first group with the second group, or the third groups, (1), +22, +27, and +29; (2), -24,-18, +89, and +92; and (3) +136; of three CpG sites in the front and back sequence of gene RPS24 transcription start site. The sequence number is based on sequence number in SEQ ID NO.1. The 143th site transcription start site A is recorded as +1. The invention also discloses a probe, a method, and a kit used for detecting the DNA methylation marker, and a computer module used for prediction of male colorectal cancer risk using the data of the DNA methylation sites.
Owner:太科航天智能康养技术(深圳)有限责任公司
Detection kit of gene mutations associated with phenylketonuria
InactiveCN106498059AWide detection rangeImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementGene defectMutation detection
The invention discloses a detection kit of gene mutations associated with phenylketonuria. The detection kit comprises ddH2O, 10*buffer (Takara), 2*GC buffer I, dNTP, MgCl2, HSTaq, a multiple PCR mixed primer liquid and an Illumina I5 / I7 primer. The detection kit has a wide detection range, comprehensively detects phenylketonuria caused by five gene defects, sequencing detection is conducted on the upstream 500bp of a genetic transcription start site, 5'UTR, a coding region, 8pp intron sequences of a splice site and transcription terminators, it is predicted that the mutation detection rate can reach 95% or above, and the detection kit can be better applied to clinical practice.
Owner:中国人民解放军新疆军区总医院 +1
PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of Pax3 gene of yellow cattle and application of method
InactiveCN103789406ASolve the cumbersomeFix instabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionTranscription start
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of a Pax3 gene of yellow cattle. The method comprises the following steps: detecting gene polymorphisms according to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) pool sequencing results, wherein the gene polymorphisms comprise SNP of a sequence transcription start site -580 T or G of the Pax3 gene of the yellow cattle; in the presence of a Taq DNA polymerase, a Buffer (a buffer environment), Mg<++> and dNTPs (deoxynucleoside triphosphate), performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the Pax3 gene of the yellow cattle, digesting a PCR amplification product by HinfI and HaeIII restriction enzymes respectively, and performing agarose gel electrophoresis on enzyme digestion segments. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a foundation is laid for creating a relationship between the SNP and the growth trait of the Pax3 gene, so that the marker assisted selection of the growth trait of the yellow cattle in China can be conveniently carried out and a new strain of high-quality special beef in China can be quickly, efficiently and accurately bred.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer
ActiveCN113215264AImprove complianceSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsOncologyGene targeting
The invention discloses a detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer. The detection kit is applied to early screening of endometrial cancer and comprises a methylation specific primer of a TMEM101 gene target site, a hydrolysis probe which is specific to the TMEM101 gene, and a primer of a reference gene and a hydrolysis probe of the reference gene, wherein the target site of the TMEM101 gene is at least one CpG site in an upstream and downstream 2000bp interval of a transcription start site of the TMEM101 gene; the reference gene is one or more of GAPDH and beta-actin; and the kit comprises a PCR pre-amplification reaction system and a PCR amplification reaction system. According to the provided detection kit for TMEM101 gene methylation in human peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA for early screening of endometrial cancer, the technical defects that in the prior art, the process is tedious, the detection time is long, the false positive is high, and the early screening of the endometrial cancer blood cannot be traced are overcome.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
Single-cell ATAC-seq data analysis method
ActiveCN110544509AEasy to dig deeperEasy to analyzeSequence analysisInstrumentsOriginal dataAccessibility
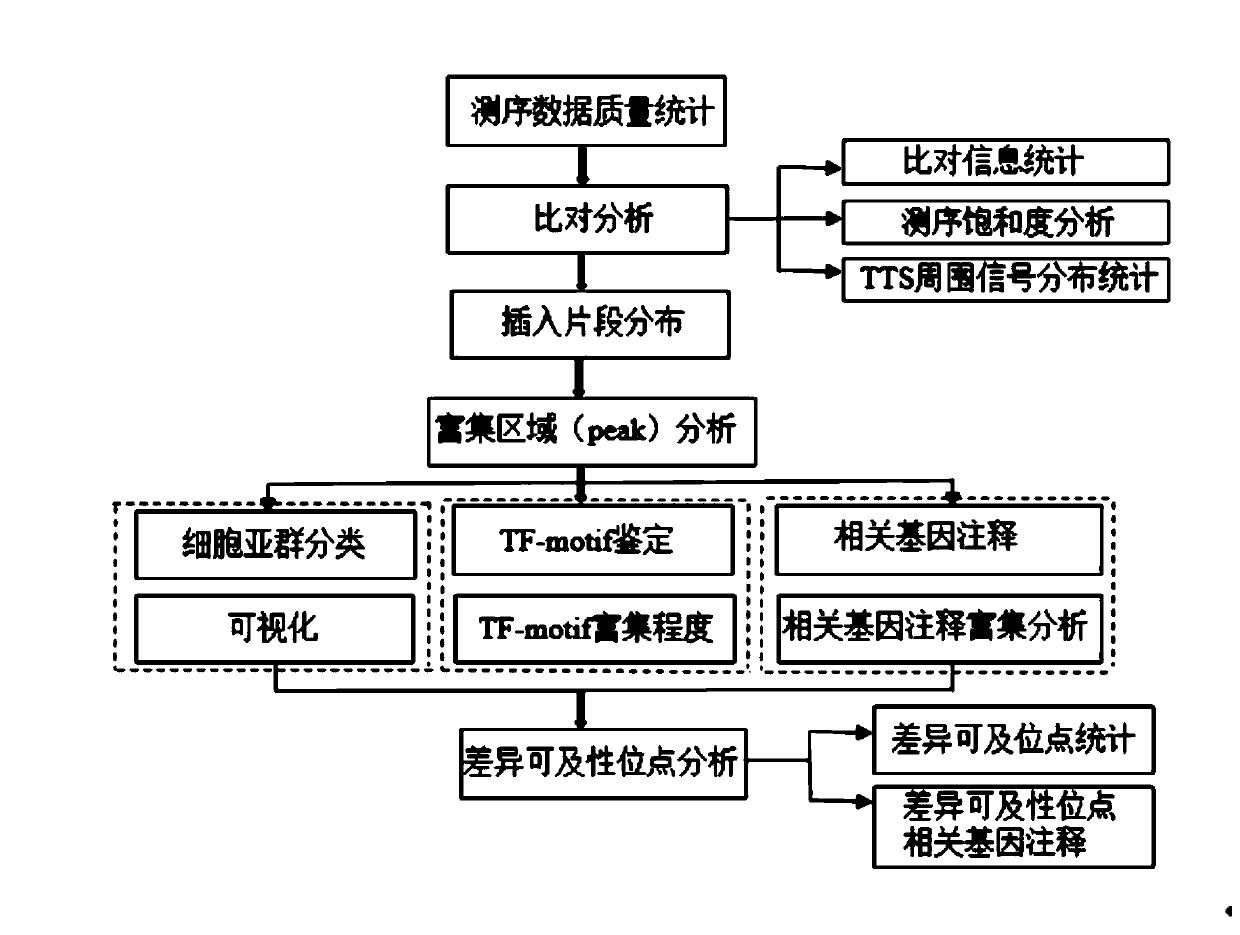
The invention provides a single-cell ATAC-seq data analysis method. The single-cell ATAC-seq data analysis method comprises the following steps: S1, performing data analysis and quality control on sequencing original data; S2, performing comparative analysis; S3, analyzing an insertion fragment; S4, carrying out Peak analysis on the enrichment region; S5, classifying the single-cell subgroups; S6,carrying out annotation and enrichment on the Peak related genes; S7, carrying out TF-motif analysis; S8, carrying out the subgroup accessibility difference analysis; S9, analyzing related genes of the difference accessibility sites, and annotating genes corresponding to the transcription start sites closest to the peak region where the identified difference TF-motif is located, and the like. According to the method, a comprehensive single-cell ATAC-seq data analysis process with rich analysis contents is constructed; the analysis result reveals a large amount of biological information, people can deeply excavate biological phenomena and characteristics contained in the single-cell level conveniently, the analysis process and result are visually displayed in the form of html, the analysiscontent is clear in hierarchy, the result display forms are diversified, and the readability of the report is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENE DENOVO BIOTECH
Method for increasing thaxtomin fermentation yield
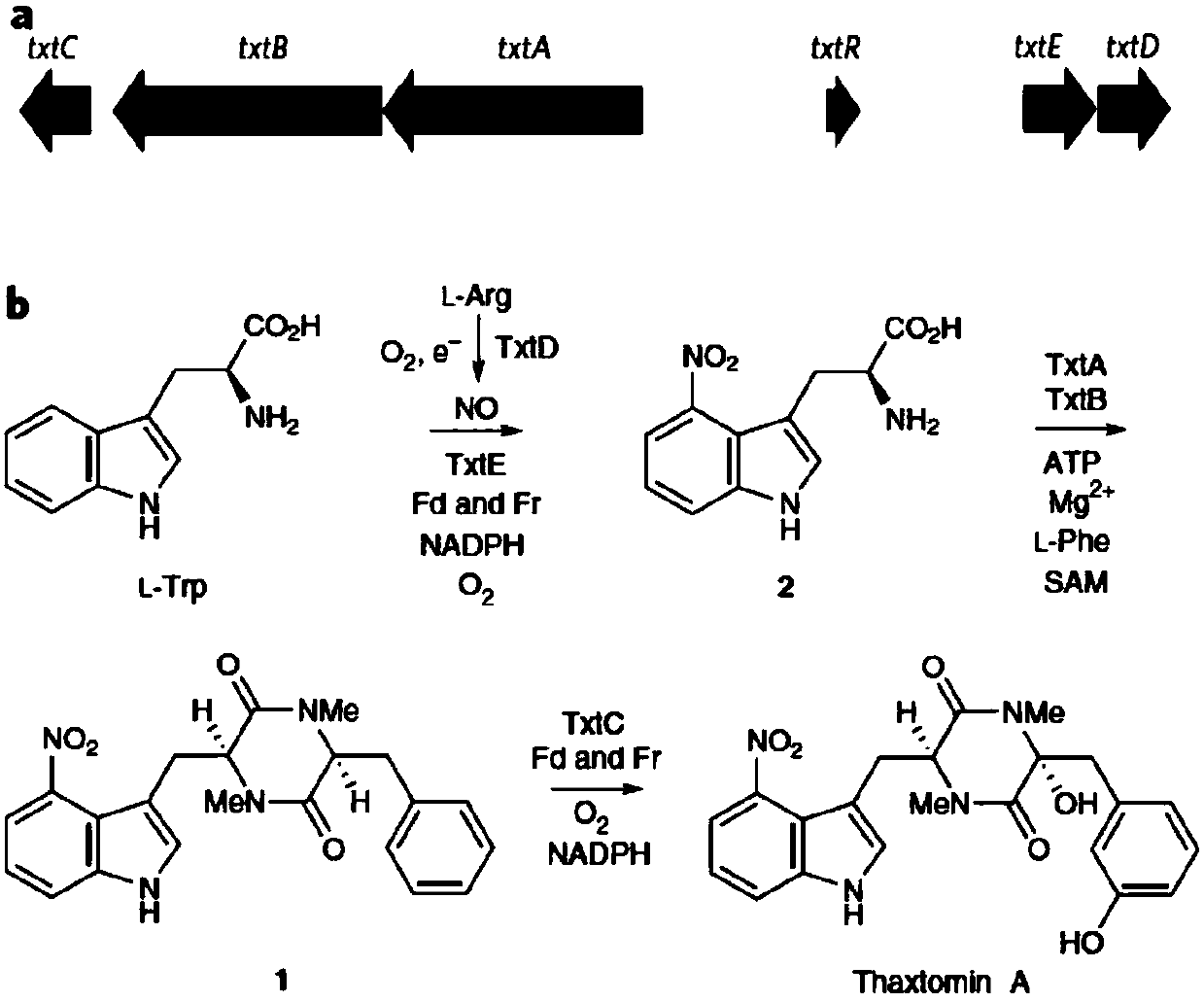
The present invention relates to a method for preparing thaxtomin A, thaxtomin B or thaxtomin D by heterologous expression of a thaxtomin biosynthetic gene cluster. In a preferred embodiment, a synthetic biology strategy is further applied to redesign a thaxtomin biosynthetic approach by using gene cluster editing technology, a constitutive strong promoter element is inserted in upstream of a transcription start site of the txtAB, txtED and / or txtC operons in the gene cluster, so that the yield of thaxtomin is increased.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Corn drought-inducible promoter and activity analysis
InactiveCN102417910ASolve food productionIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNAGMO Plants
A corn drought-inducible promoter and activity analysis belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention provides an obtained corn drought-inducible promoter sequence, a drought-inducible plant expression vector for corn transformation and genetically modified plants transformed by plant expression vector; the corn drought-inducible promoter sequence contains a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nucleotide sequence from the -1bp region to the -1444bp region relative to the transcription start site of SEQ ID NO: 1; the drought-inducible plant expression vector contains the corn drought-inducible promoter sequence and a 5' untranslated region of a corn drought-responding protein gene; the genetically modified plants transformed by the plant expression vector contain the corn drought-inducible promoter sequence and the 5' untranslated region of the corn drought-responding protein gene; and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers of SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 3 are suitable for amplifying the sequence DNA segment containing the SEQ ID NO: 1. The corn drought-inducible promoter can be used for promoting the high-efficiency expression of drought-resistant genes and in drought-resistant genetically modified plants, and has a positive significance in solving the problem in grain production in arid regions and increasing grain yield.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Promoter sequence of fructokinase gene in apple, and deletion mutants and application of
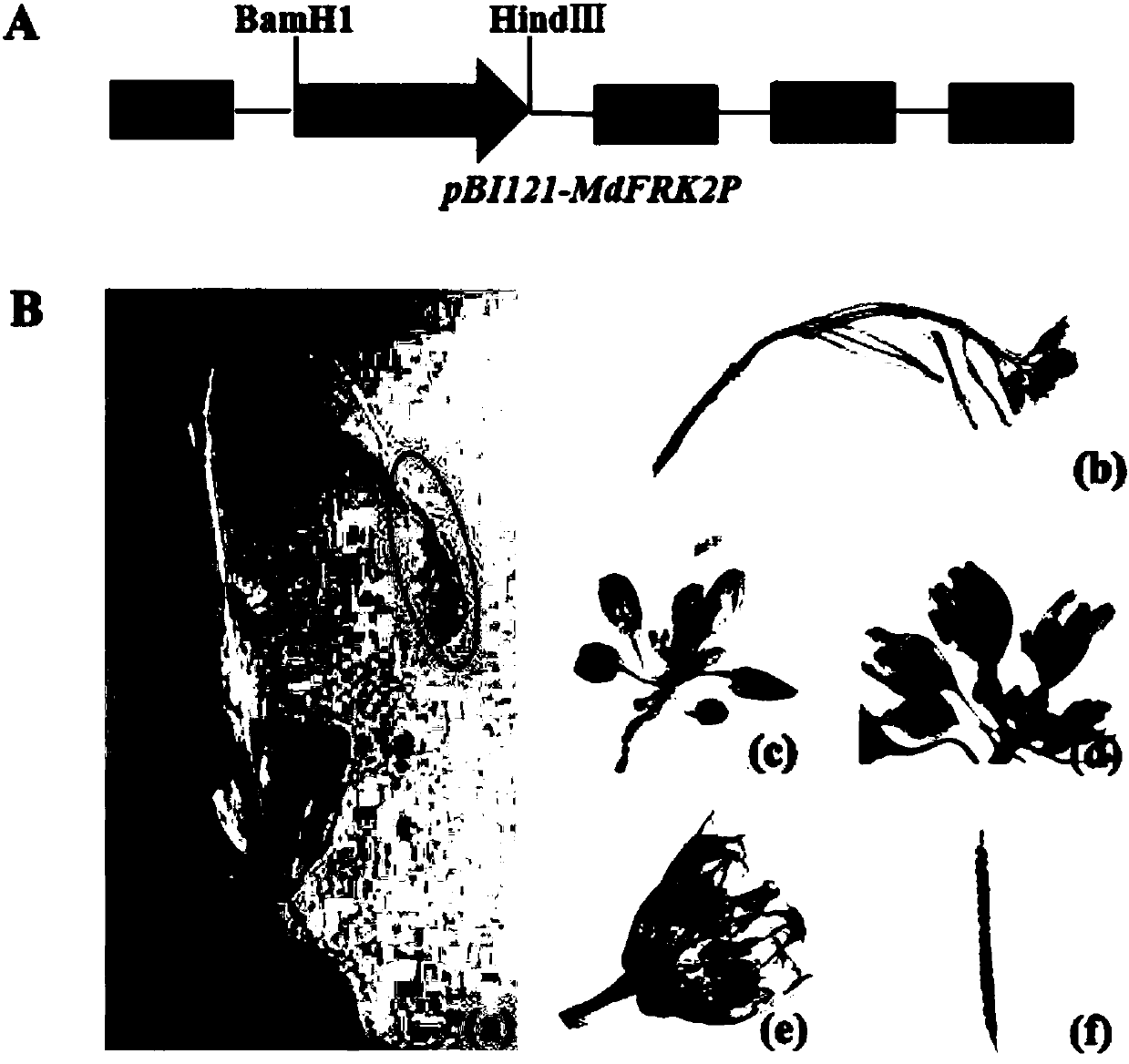
PendingCN111019943AFew research reportsRich researchTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
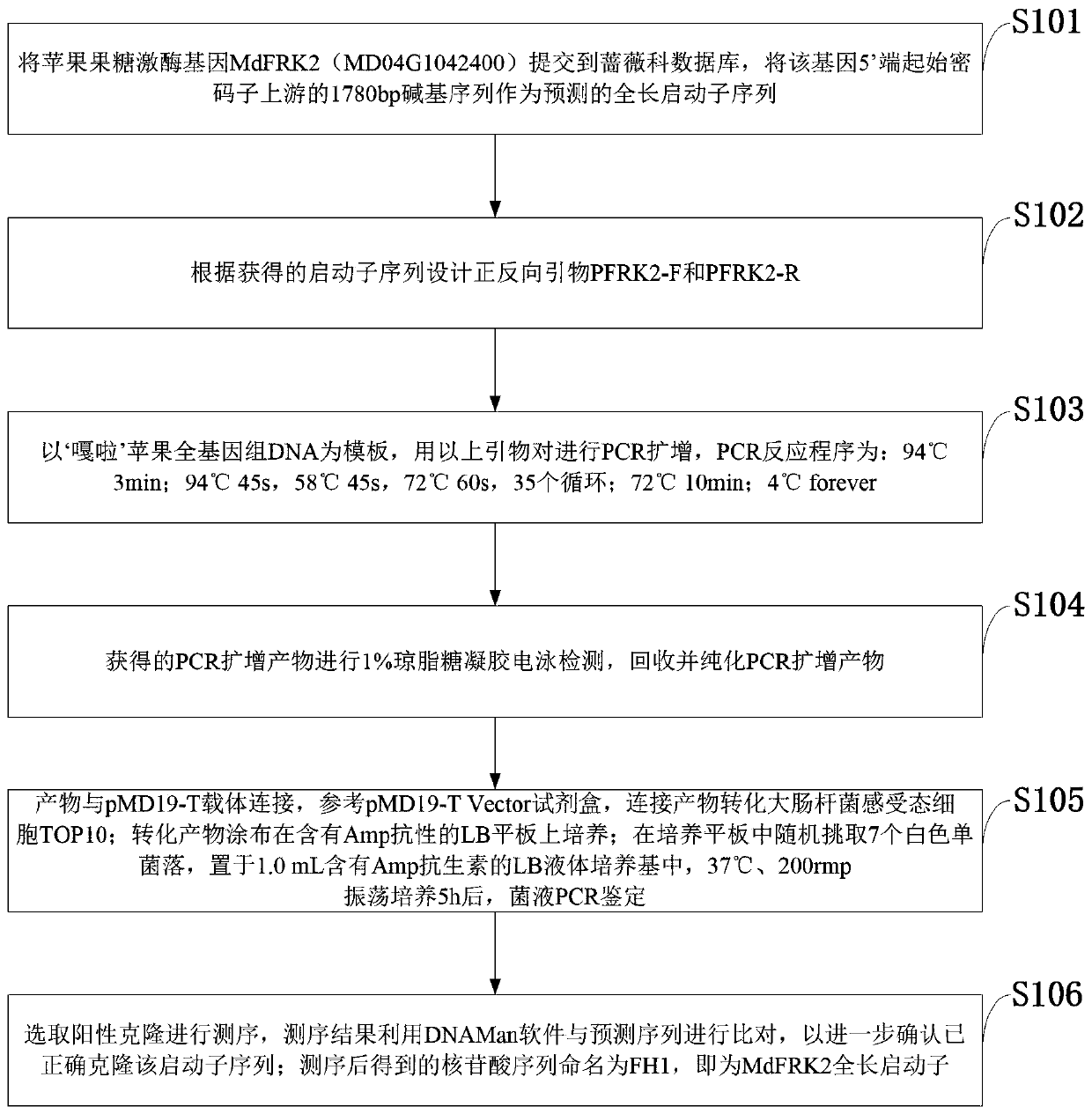
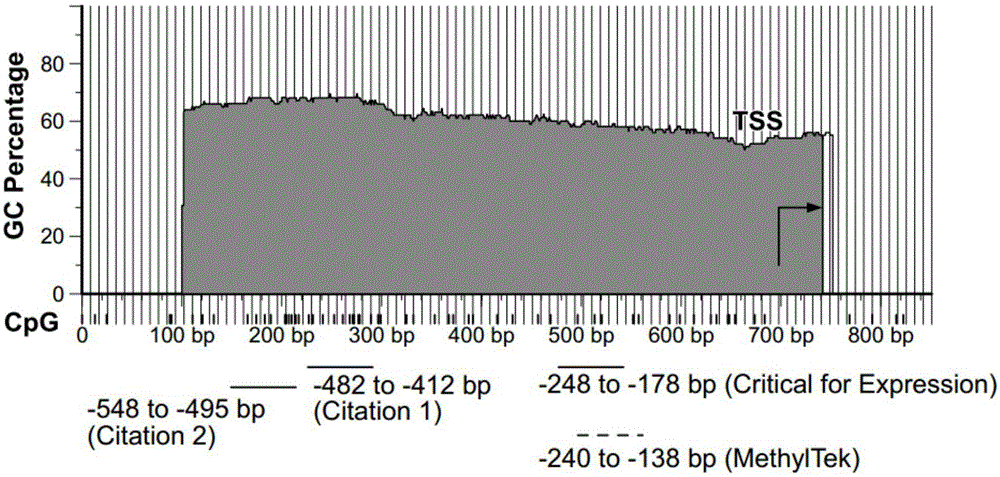
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological gene engineering and discloses a promoter sequence of a fructokinase gene in an apple, and deletion mutants and application of. A promoter isnamed as FH1 and is a 1780-bp nucleotide sequence at the upper stream of the 5'-end of an MdFRK2 gene coding frame in an apple; and the mutants are sequences obtained by deleting fragments with different lengths from the 5'-end of the sequence of FH1 and are named as FH2, FH3 and FH4 respectively. The invention further discloses application of the MdFRK2 promoter and the deletion mutants of the MdFRK2 promoter in research on plant functional genes. The MdFRK2 promoter can regulate and control the specific expression of a target gene in cambium of stem tip growth points, old leaves, functionalleaf margins and other library tissues of arabidopsis thaliana and poplar, and a fragment from a transcription starting site to upstream-600 bp is determined to be a core fragment of a promoter region of the MdFRK2 promoter. The full length of the MdFRK2 promoter is induced by exogenous sugar and drought, which indicates that the promoter has important application value in industrial developmentof plant genetic engineering.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Kit, method and primers for analyzing methylation status of MLH1 promoter in DNA sample
InactiveCN105018476AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnalysis dnaOligonucleotide primers
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a kit, a method and primers for analyzing methylation status of an MLH1 promoter in a DNA sample. The invention provides a kit for analyzing the methylation status of a neoplastic disease associated MLH1 promoter in a DNA sample. The kit comprises oligonucleotide primers, the oligonucleotide primers are complementary with at least part of the sequence of the MLH1 promoter in a zone from -248bp to -178bp relative to a transcription start site and overlap with the methylation sites in the zone. The present invention discloses accurate and sensitive test, composition and method for detection of differential methylation of genomic MLH1 promoter DNA in clinical sample. The test, composition and method can be used in allow diagnosis and symptom method; and the applicable characteristic is that the presenting level of methylation genomic MLH1 promoter DNA in the absence of a specific disorder is distinguished from illness of methylation genomic MLH1 promoter DNA level.
Owner:常州杰傲病理诊断技术有限公司
Cloning and function analysis of Zea mays adverse stress inducible promoter
InactiveCN102392020AStrong resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNucleotideBiology
The invention which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering provides a Zea mays adverse stress inducible promoter sequence. The adverse stress inducible promoter sequence is characterized in that: the promoter sequence comprises DNA nucleotide sequences relative to a zone from -1bp to -1150bp at the transcription start site of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also provides an adverse stress inducible plant expression vector for Zea mays transformation. The plant expression vector comprises the Zea mays adverse stress inducible promoter and a 5' untranslated region of ZmapH (Zea mays anionic peroxidase H); and PCR primers of SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3 are suitable for the amplification of DNA segments containing the SEQ ID NO:1. The Zea mays adverse stress inducible promoter can be used to promote adverse stress resistant gene to efficiently express, and has a positive meaning to the research of the transgenic technology of the Zea mays stress tolerant species and the cultivation of the strong comprehensive resistance high quality high yield new transgenic species.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
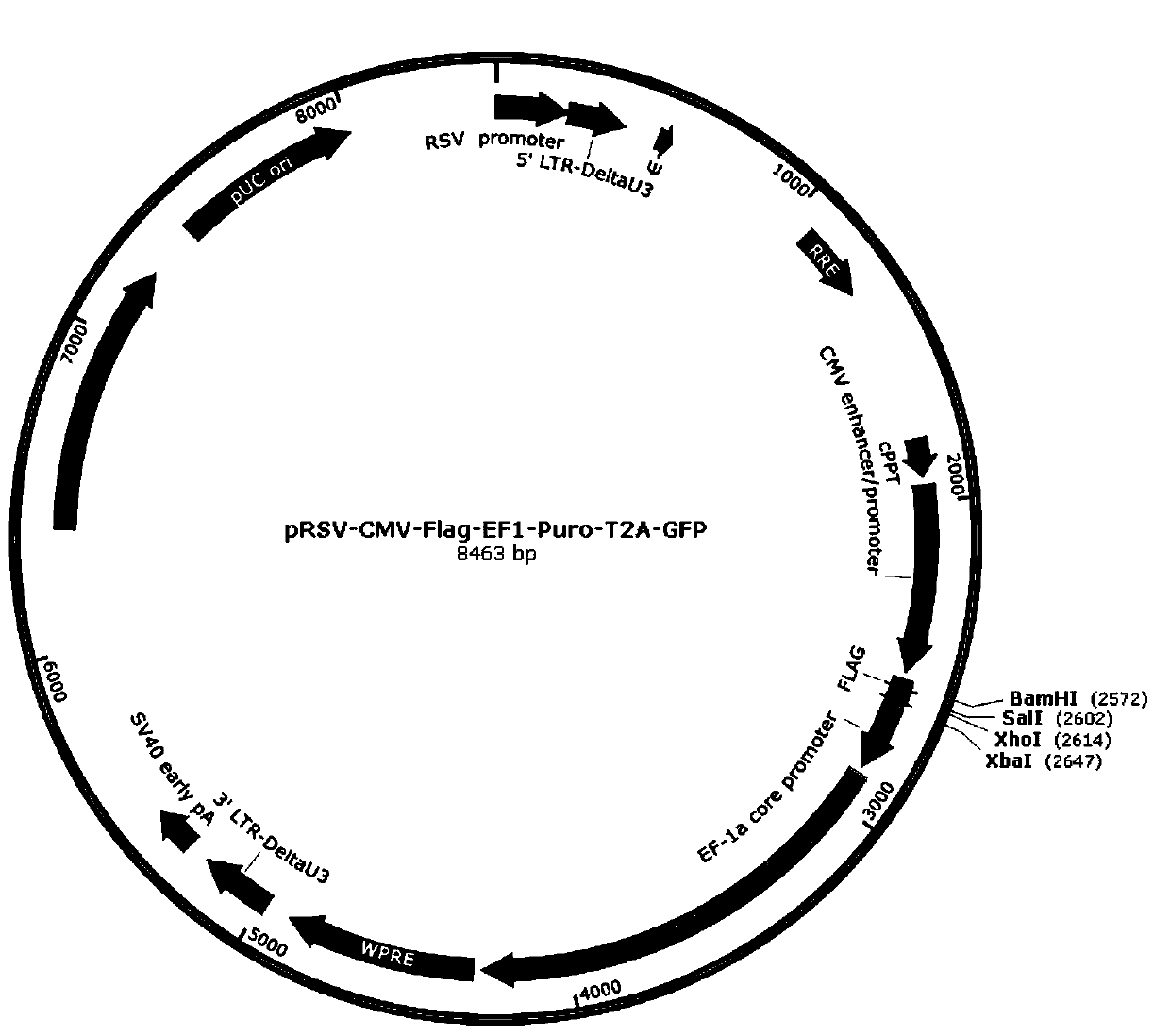
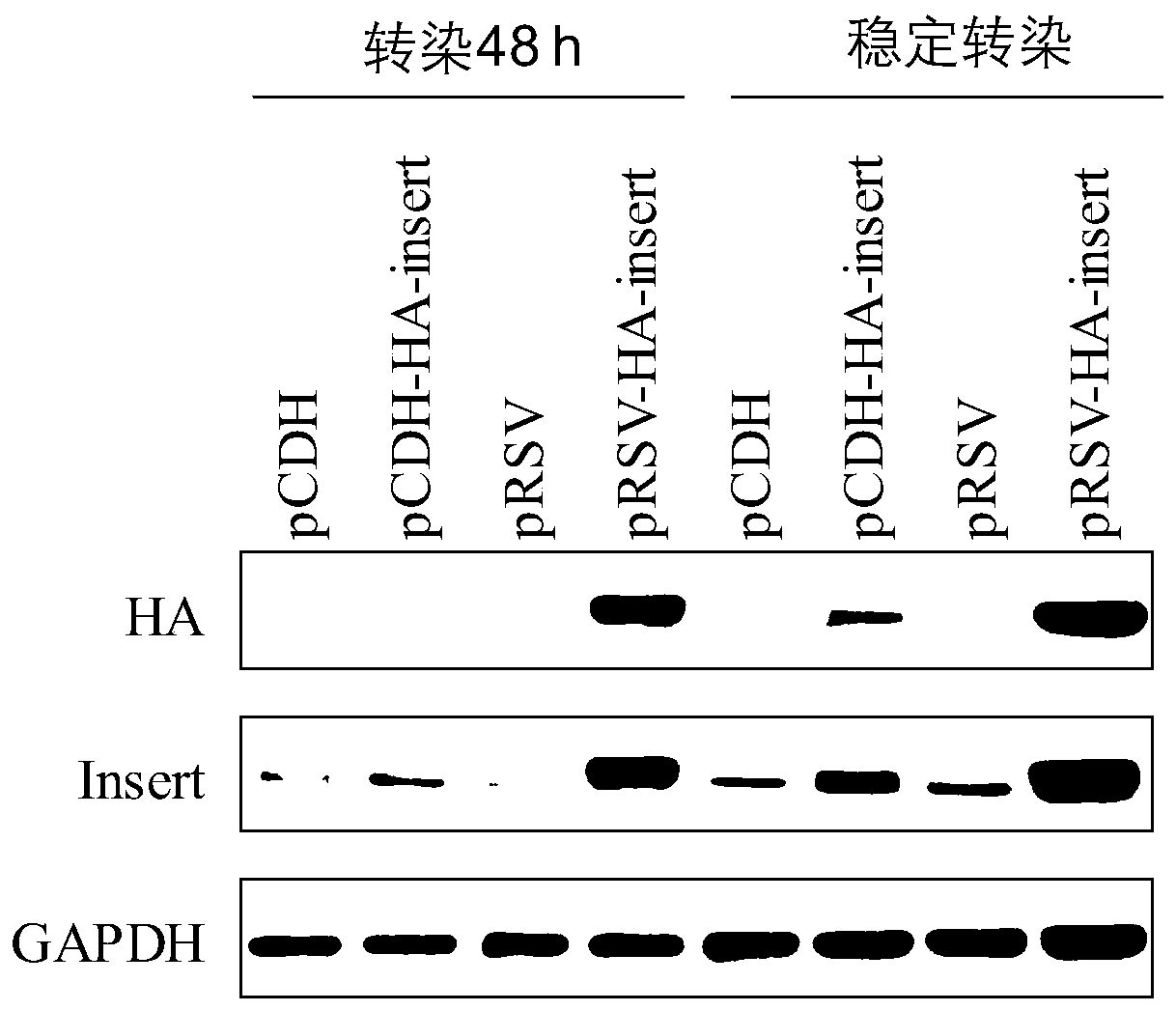
Design and application for lentiviral expression vector
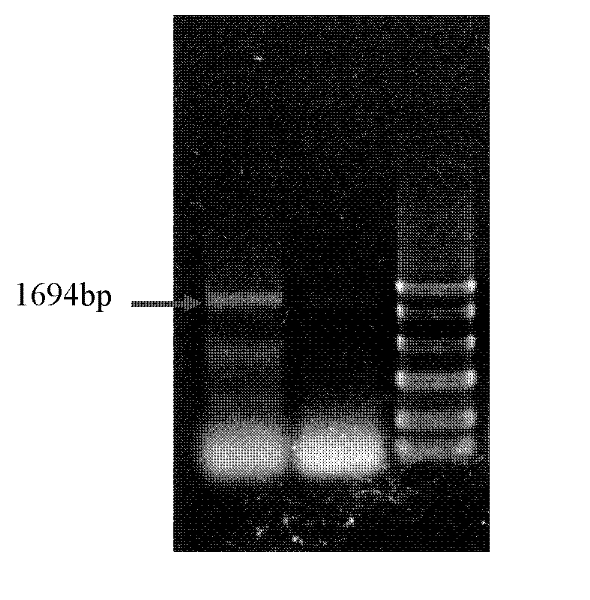
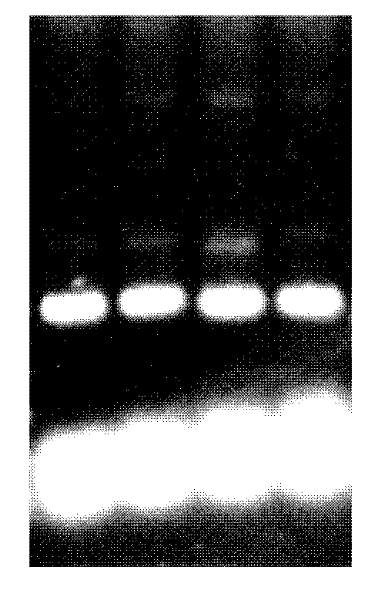
ActiveCN110982842AEfficient gene insertionMonitor transfection efficiency over timeBiological material analysisBiological testingTranscription startInsertion
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biology and cytobiology, and specifically relates to a design and an application for a lentiviral expression vector. According to the vector designed by the invention, a CMV enhancer and a CMV promoter are used as transcription starting elements of an insertion gene; an EF1a-core promoter is adopted as a transcription starting element for screeningand marking puromycin and green fluorescent protein (GFP), and a puromycin resistance gene and a GFP sequence are connected and expressed in series through T2A; a lentiviral vector is adopted as a vector skeleton, and two above-mentioned elements are inserted into the skeleton vector; thus, the lentiviral expression vector is obtained by reasonable design and optimization. By adoption of the lentiviral vector designed by the invention, the inserted gene can be efficiently expressed, and the expression efficiency of the lentiviral expression vector is superior to the expression efficiency of conventional vectors with the same type of characteristics.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Corn stress-inducible promoter and activity analysis
InactiveCN102417909ASolving the food crisisIncrease productionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsA-DNABio engineering
A corn stress-inducible promoter and activity analysis belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention provides an obtained corn stress-inducible promoter sequence, a stress-inducible plant expression vector for corn transformation and genetically modified plants transformed by plant expression vector; the corn stress-inducible promoter sequence contains a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nucleotide sequence from the -1bp region to the -1299bp region relative to the transcription start site of SEQ ID NO: 1; the stress-inducible expression vector contains the corn stress-inducible promoter sequence and a 5' untranslated region of a corn DRE-binding protein gene; the genetically modified plants transformed by the plant expression vector contain the corn stress-inducible promoter sequence and the 5' untranslated region of the corn DRE-binding protein gene; and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers of SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 3 are suitable for amplifying the sequence DNA segment containing the SEQ ID NO: 1. The corn stress-inducible promoter can be used for promoting the high-efficiency expression of drought-resistant genes and in drought-resistant genetically modifiedplants, and has a positive significance in solving grain crisis in arid regions and increasing grain yield.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
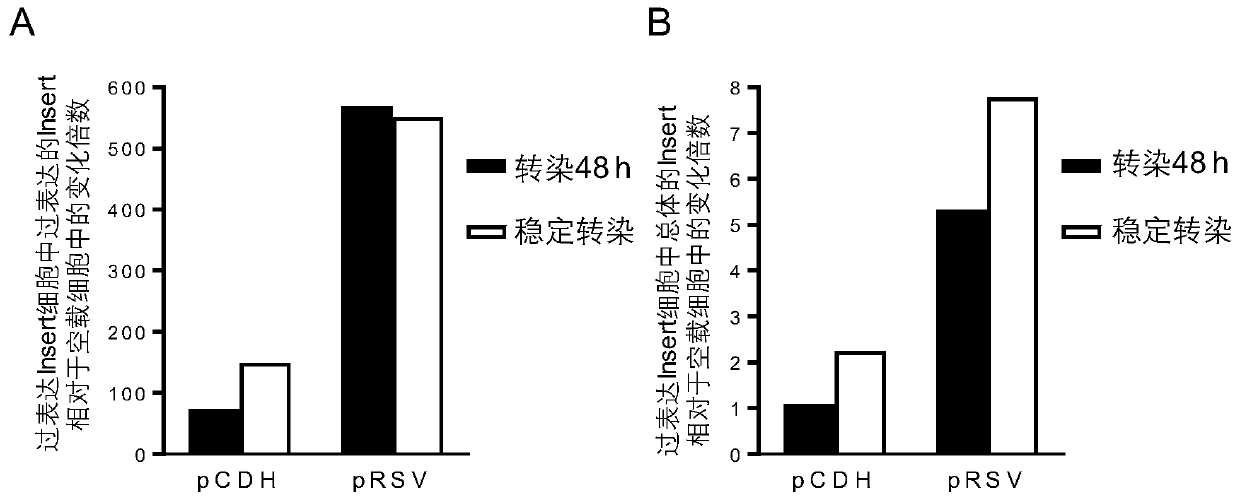
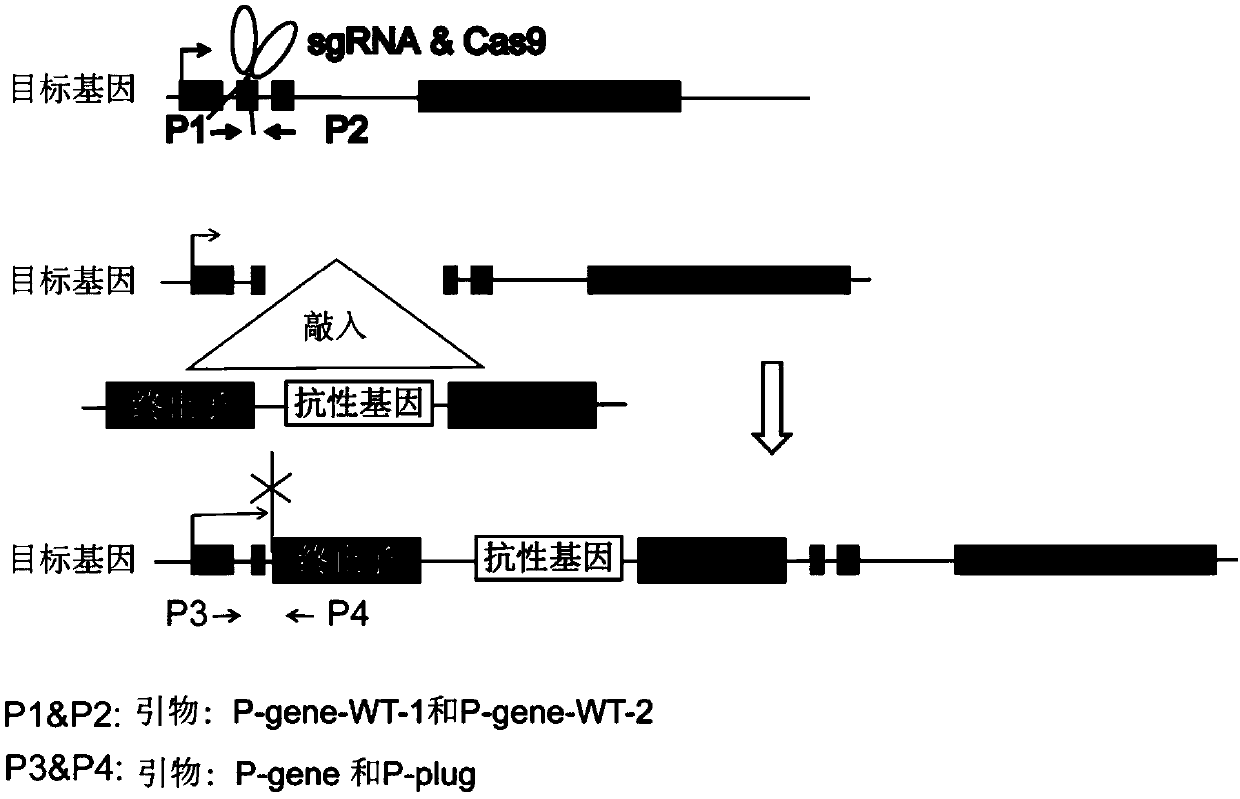
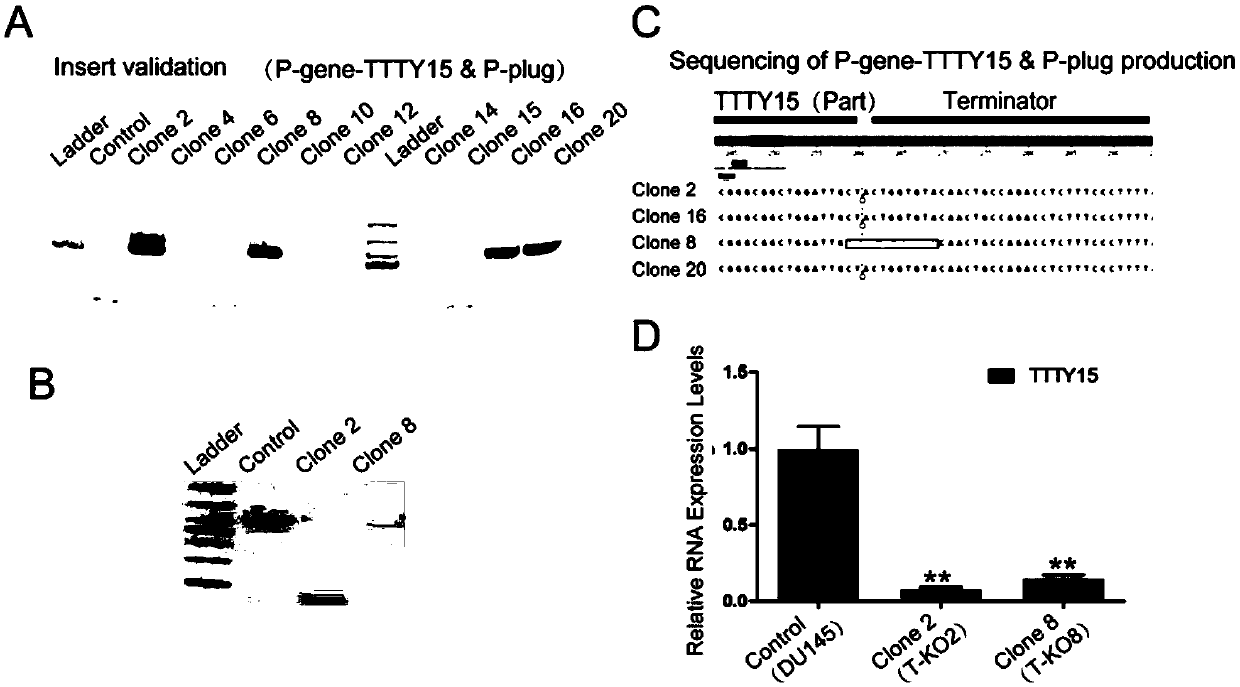
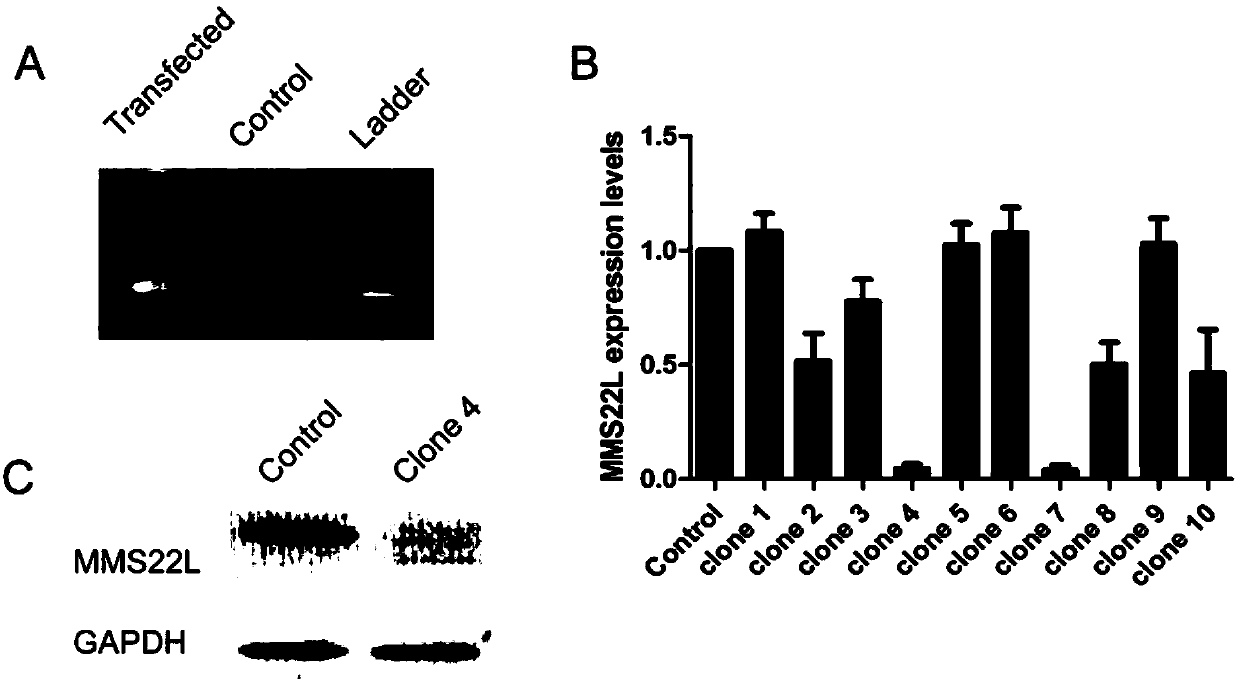
Method for knocking in terminator to achieve transcription factor knockout by using gene editing technology
PendingCN111218479AAchieve knockoutVersatilityStable introduction of DNATranscription initiation siteA-DNA
The invention relates to a method for knocking in a terminator to achieve efficient knockout of a transcription factor (including protein editing genes, non-encoding genes, and the like) by using a gene editing technology. Specifically, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) break is caused behind a transcription start site (TSS) of a gene to be knocked out by using a gene editing technology, meanwhile, a DNA donor with a transcription termination sequence (terminator) is introduced into cells, the doner does not comprise a target gene homologous sequence, the DNA donor is also linearized by using the gene editing technology, then after the terminator is knocked into a TSS of a target gene through a non-homologous repairing way, endogenous transcription of the target gene is terminated ahead of time,and thus knockout of the target gene is achieved. The method is wide in application scope, and all transcription facts can be knocked out by the method. The doner DNA has universality, has high efficiency, and in addition, has resistance genes, and the method is high in efficiency and has certain practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Expression control sequence
InactiveUS20050266525A1Increased controlled gene expressionControlled gene expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaA-DNABioinformatics
An expression control sequence which controls expression of a target gene linked downstream of the expression control sequence depending on an intracellular concentration of an amino acid, wherein in a bacterial cell which harbors a DNA construct comprising the expression control sequence, a promoter linked upstream of the expression control sequence and the target gene linked downstream of the expression control sequence, frequency of termination in the expression control sequence, of transcription starting from the promoter is lowered by increase of an intracellular concentration of an amino acid, whereby expression of the target gene increases.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Low-temperature drought induced promoter of zeamays and activity analysis
InactiveCN102399782ASolving the food crisisSolve problems such as ecological deteriorationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEmbryoBio engineering
The invention relates to a low-temperature drought induced promoter of zeamays and activity analysis, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention provides a low-temperature drought induced promoter sequence of the zeamays. The sequence comprises a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) nucleotide sequence relative to a -1 bp to -1,645 base pair (bp) region of the transcription starting point of SEQ ID No:1; a low-temperature drought induced plant expression vector for zeamays conversion is provided simultaneously, and comprises the low-temperature drought induced promotersequence of the zeamays and a 5' untranslated region of zeamays zinc finger protein (ZmZFP) gene; a transgenic zeamays mature embryo converted by the plant expression vector is provided; and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers of SEQ ID No: 2 and SEQ ID No: 3 are suitable for amplifying DNA fragments containing the sequence of SEQ ID No: 1. The low-temperature drought induced promoter can be used for promoting the high-efficiency expression of the low-temperature drought gene and is applied in drought transgenic plant which are not resistant to low temperature, so that the plants have thecharacters of low temperature and drought, and thus, the low-temperature drought induced promoter has a positive significance for solving the problem of food crisis in low-temperature and drought areas.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
PCR-RFLP method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of gene CREB 1
InactiveCN110734969ASolve the cumbersomeFix instabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionNucleotide
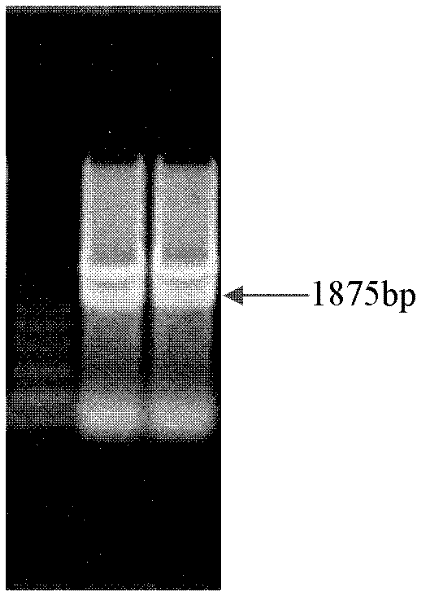
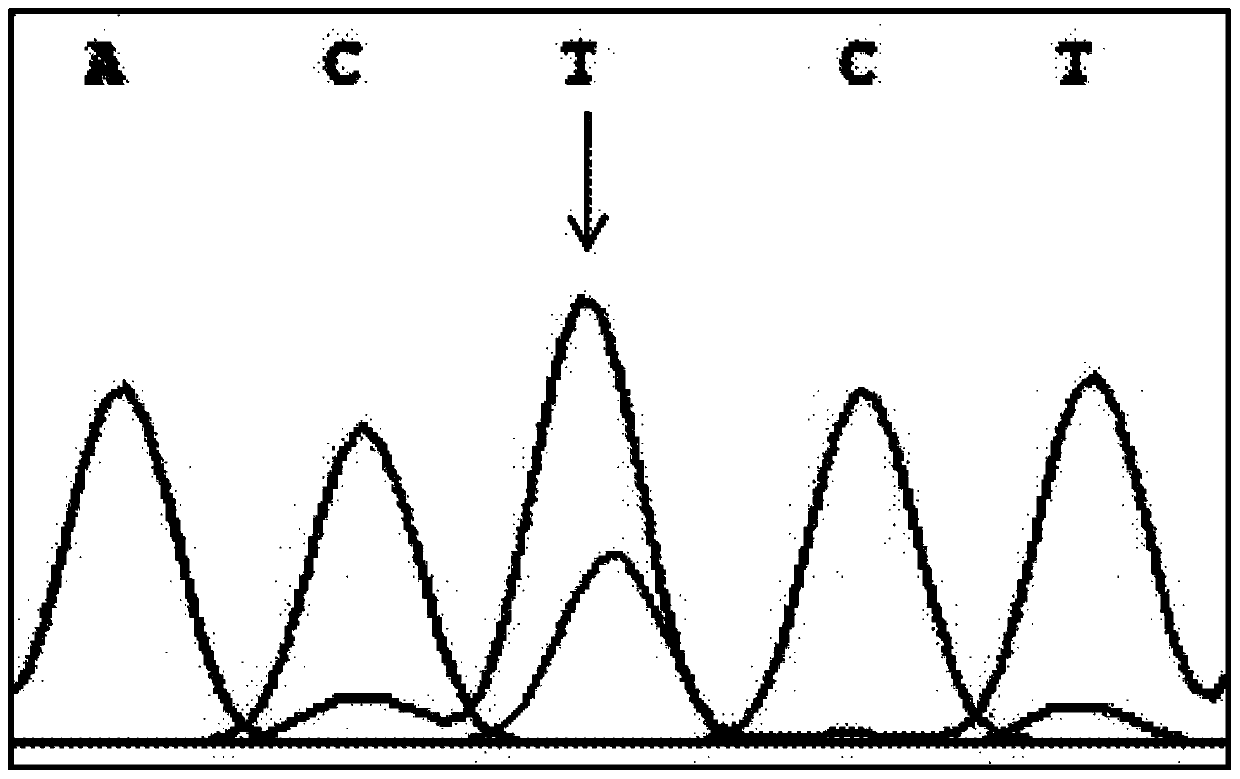
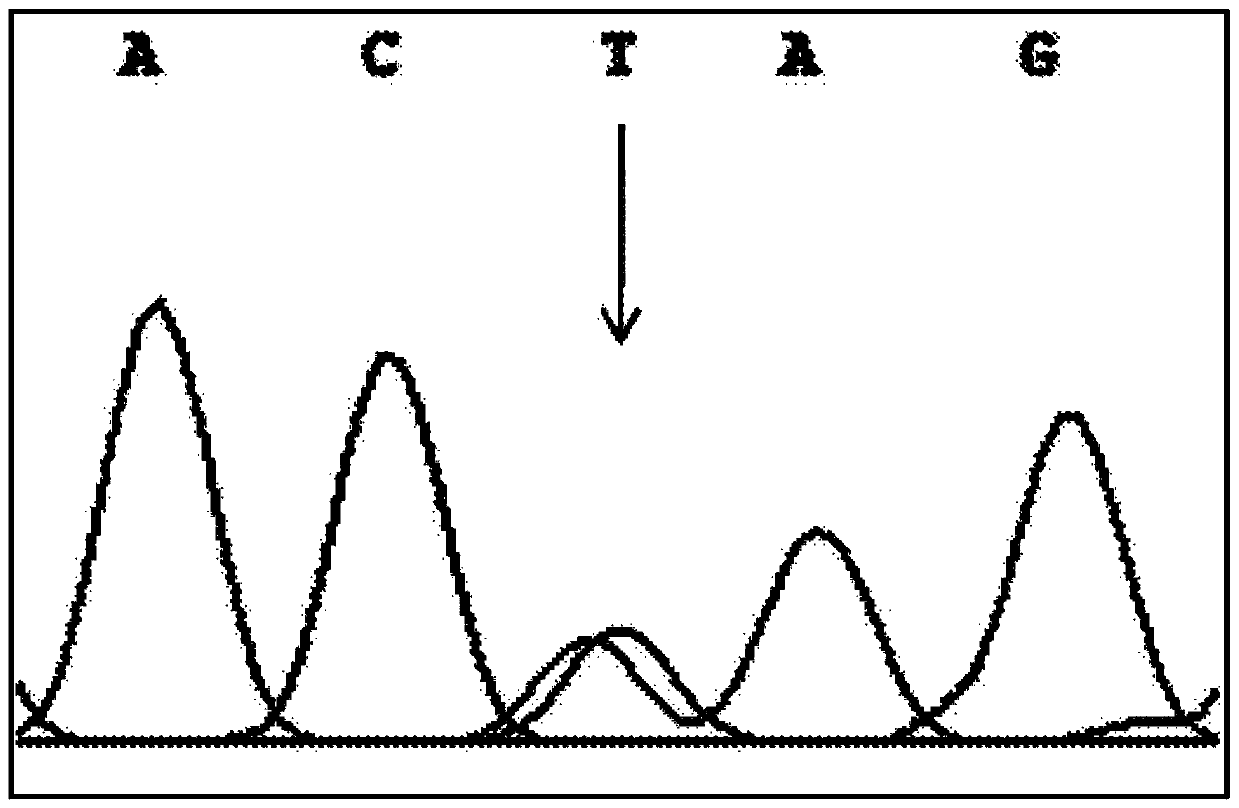
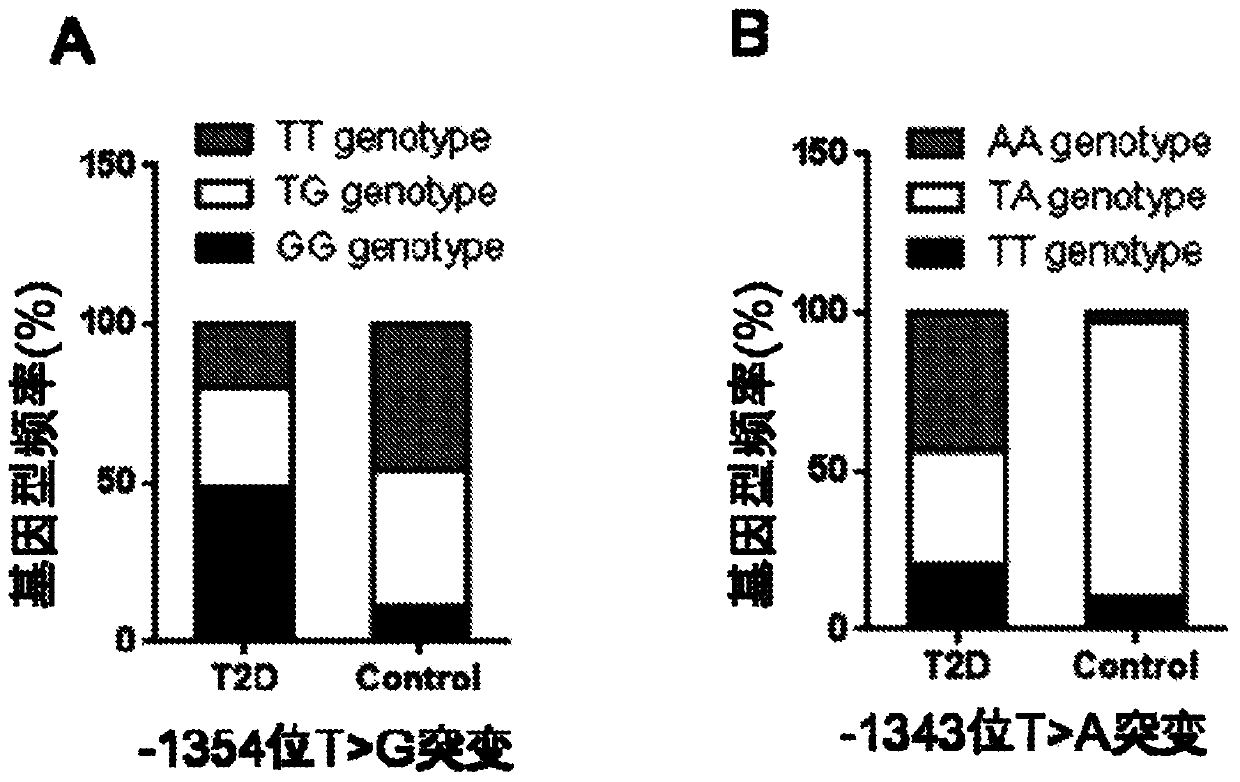
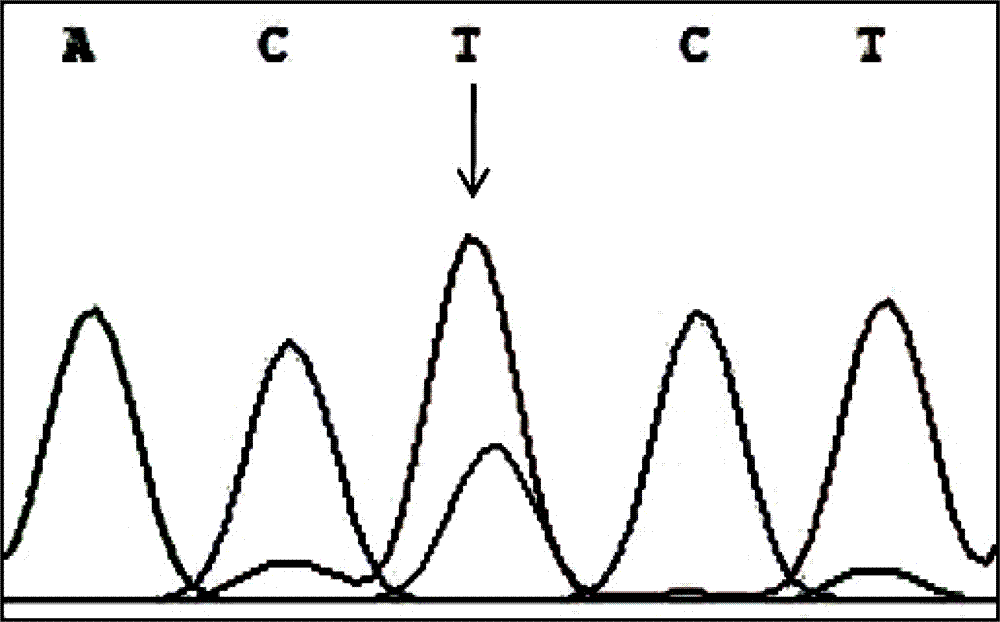
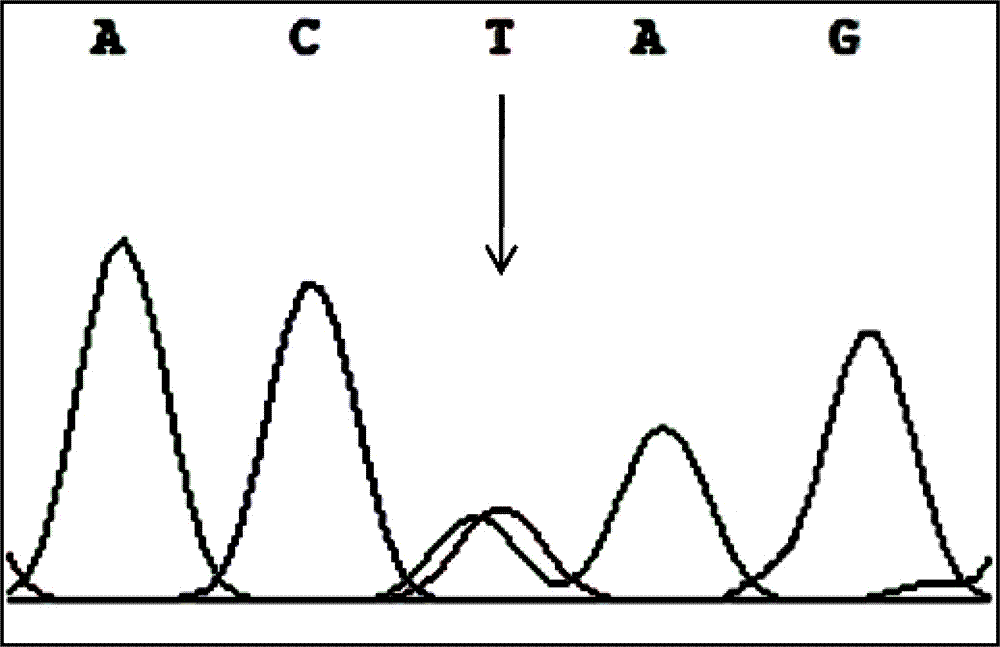
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP method for detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism of a gene CREB 1. Firstly, according to a DNA pool sequencing result, the detected gene polymorphism comprises single nucleotide polymorphism of T or G at the 1354th site from a CREB1 gene promoter region to a transcription starting point and single nucleotide polymorphism of T or A at the 1343th site. PCR amplification is conducted on a CREB1 gene sequence containing polymorphic sites in the presence of Taq DNA polymerase, Buffer (a buffer environment), Mg++ and dNTPs by taking genome DNA of a to-be-detected sample as a template and a primer pair P as a primer, a PCR product is divided into two parts, the two parts are digested by using restriction enzymes Hha I and Xsp I respectively, and enzyme digestion products are subjected to typing through agarose gel electrophoresis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
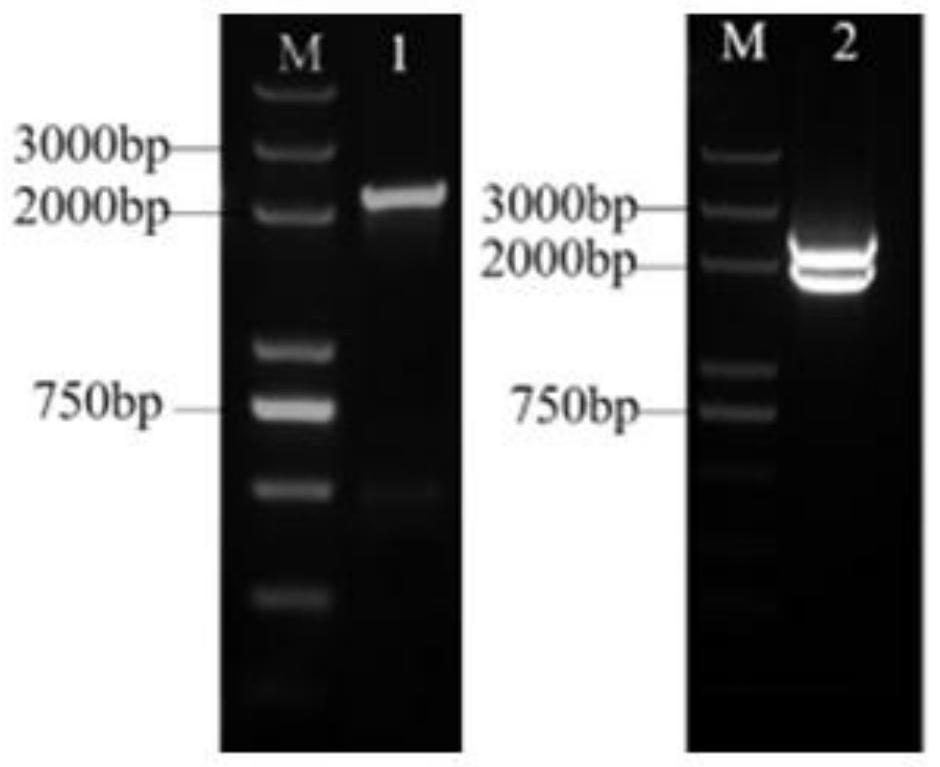
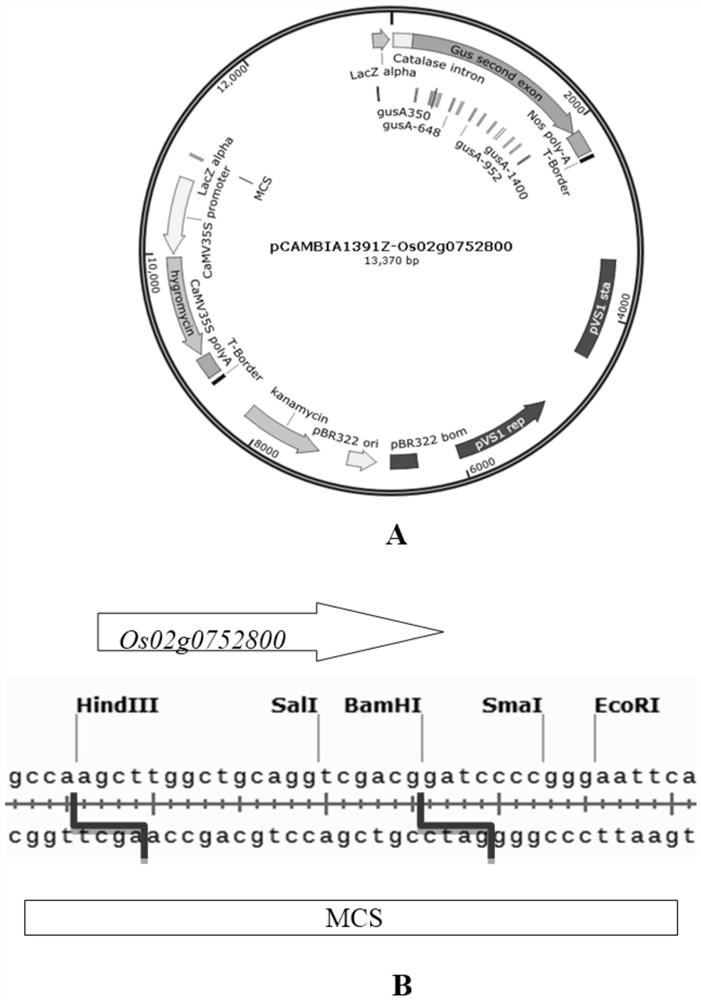
Rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 and application
ActiveCN112458091AEfficient expressionStable expressionClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyJaponica rice
The invention discloses a rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 and application, and relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The rice constitutive expression promoterOs02g0752800 is derived from a rice japonica rice variety Nipponbare, and the size of a promoter fragment is 2170 bp. The rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 has the following characteristics that (1) the rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 is located at the 5' end and the upstream of an Os02g0752800 gene; (2) the length of a basic group is 2170bp; (3) the rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 has a necessary site for initiating transcription and a transcription starting point; and (4) the rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 can be expressed in all tissues and organs of rice. The rice constitutive expression promoter Os02g0752800 disclosed by the invention can be effectively expressed in all the tissues and organs, and the functions of an exogenous gene expression product can be fully exerted, so that an exogenous gene is efficiently, stably and durably expressed in plants.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
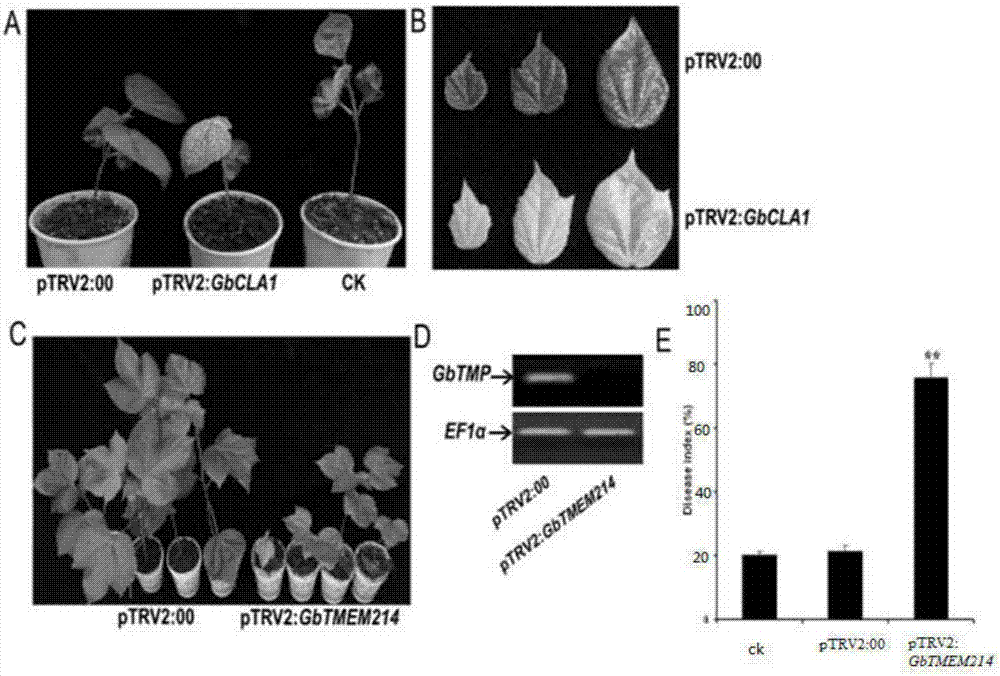
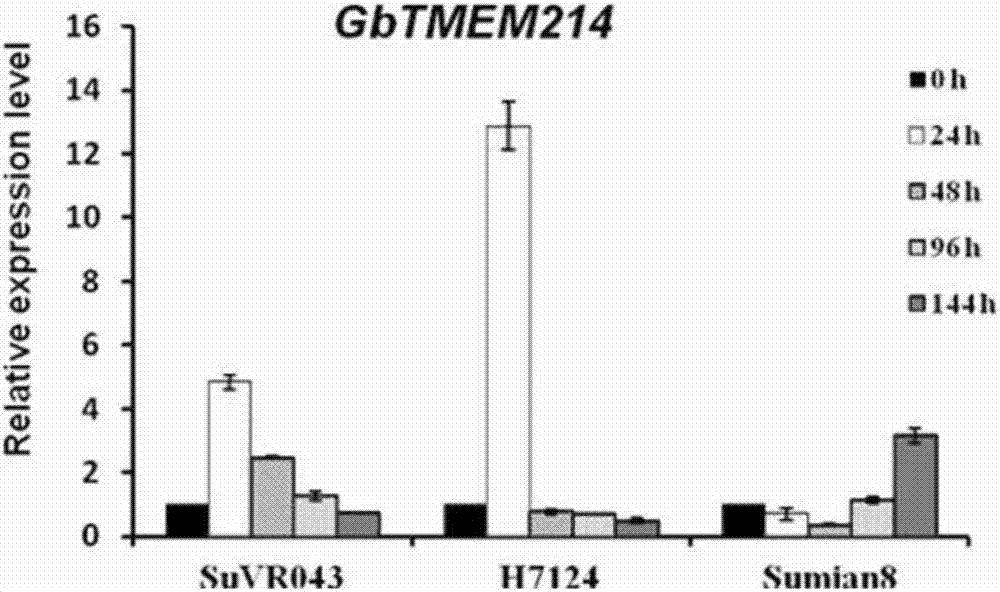
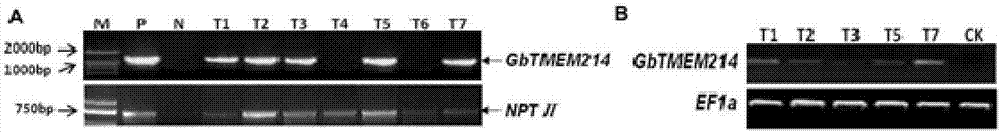
Gossypium barbadense transmembrane protein gene, primers, and application of Gossypium barbadense transmembrane protein gene
ActiveCN107254474ALower resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationDiseaseVerticillium wilt
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
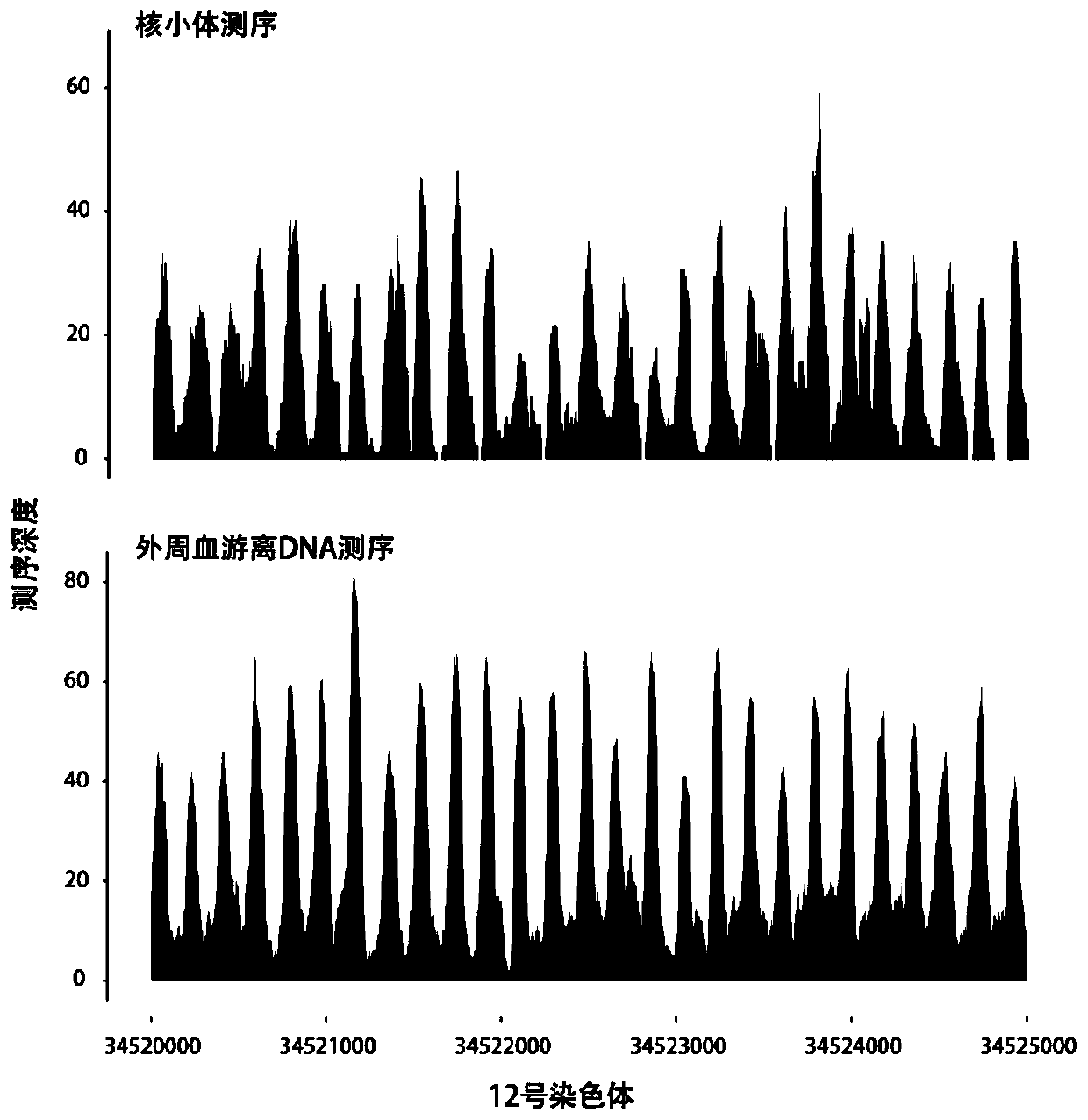
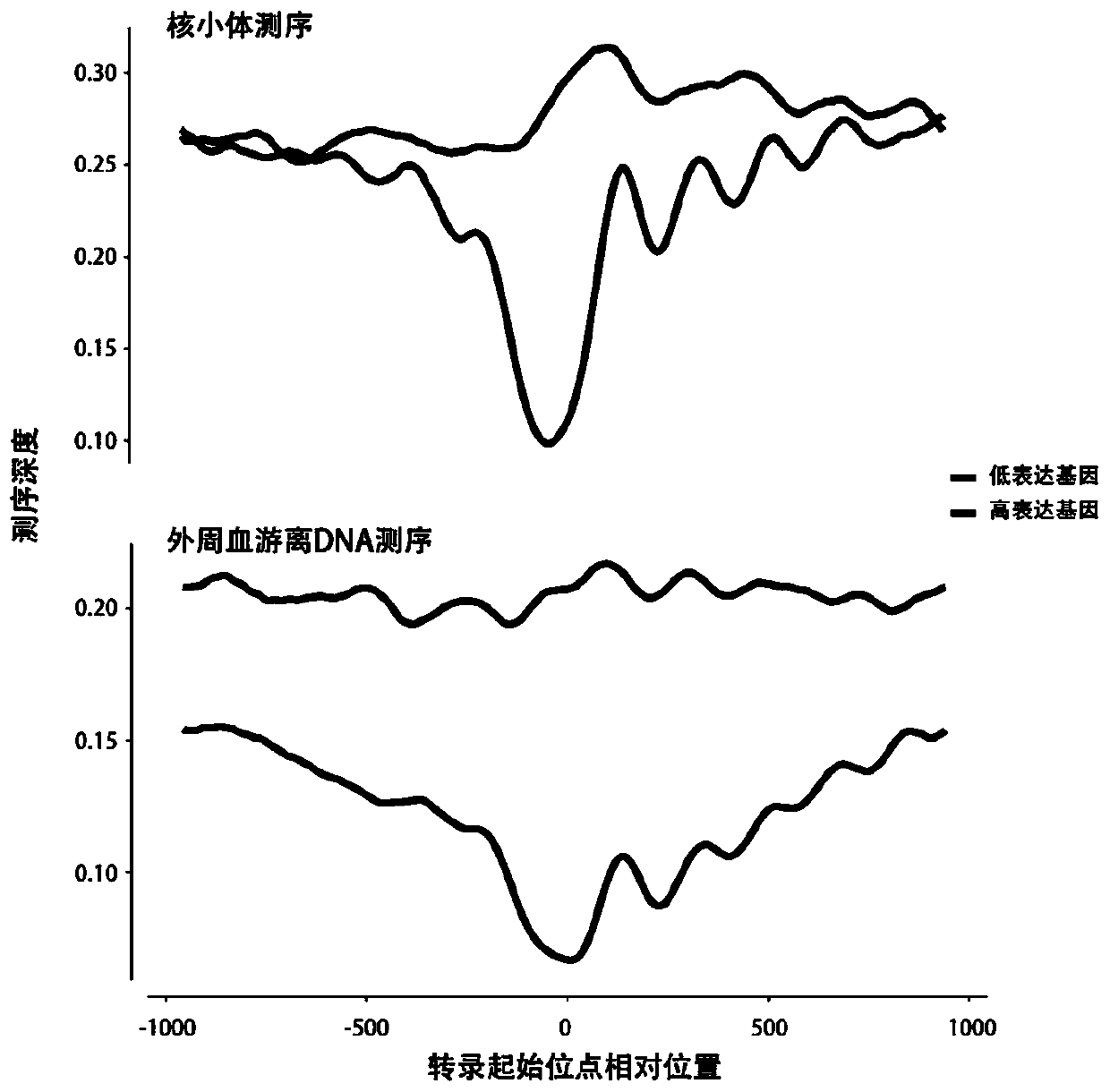
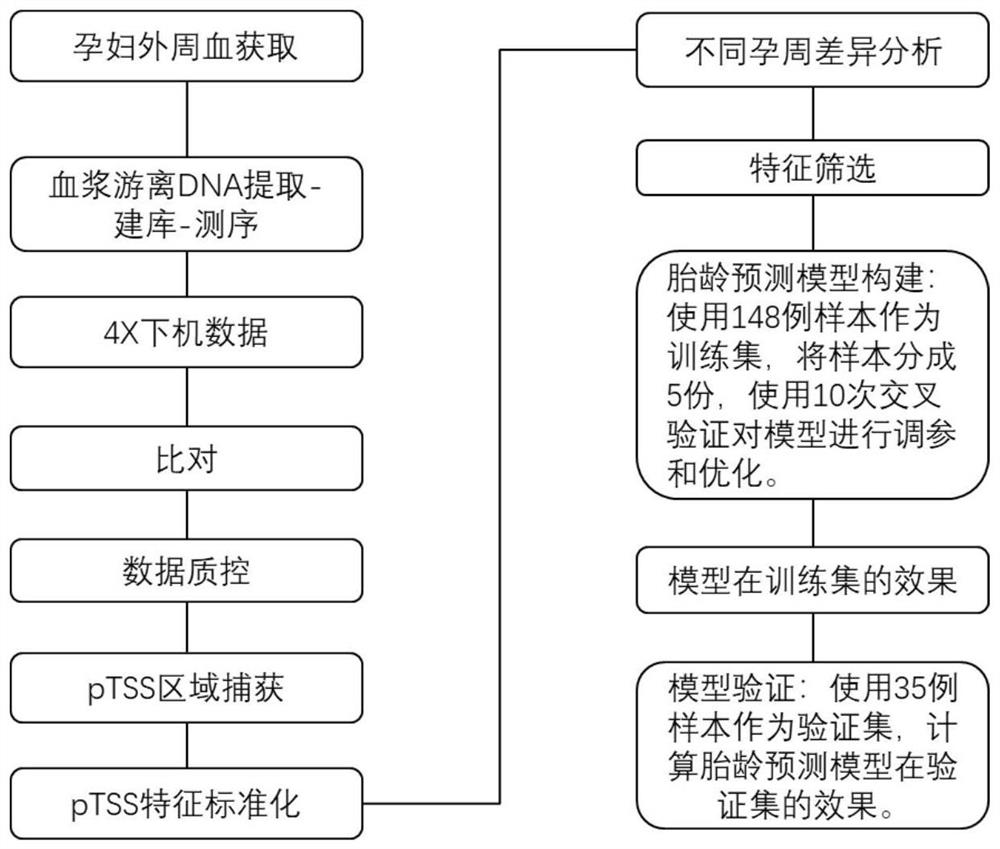
Method of predicting gestational related diseases based on peripheral blood free DNA high-throughput sequencing
ActiveCN110580934AEasy to degradeHigh degree of opennessMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsNon invasiveBiology
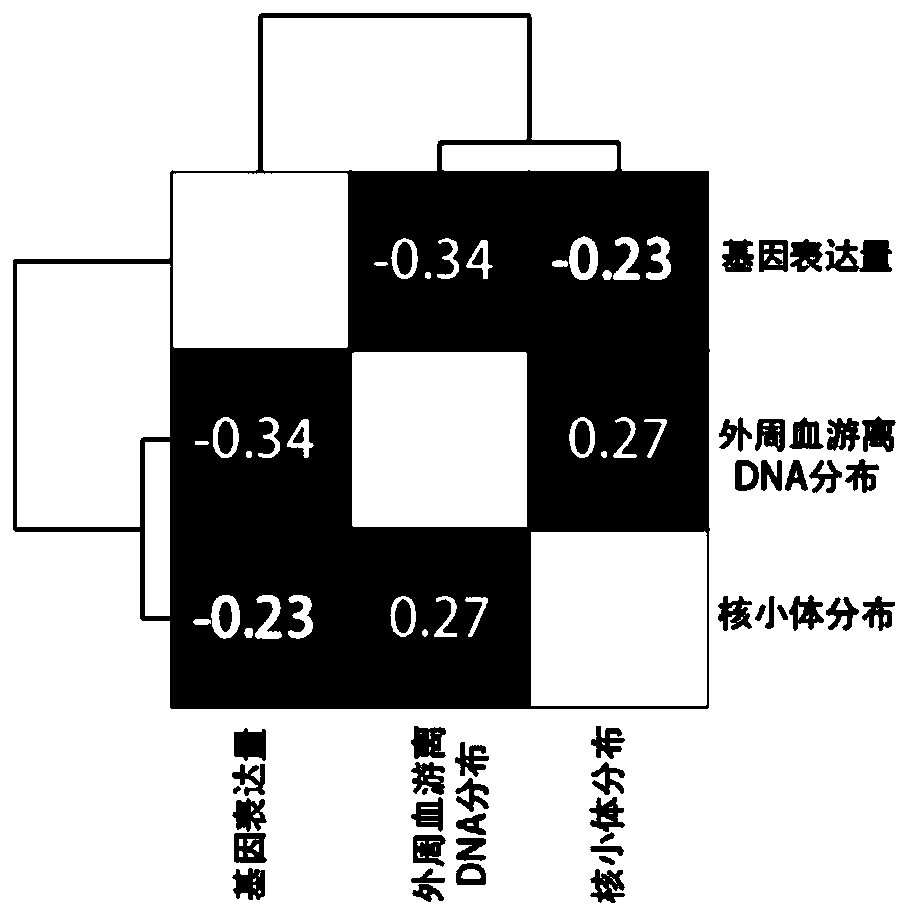
The invention discloses a method of predicting gestational related diseases based on pregnant woman peripheral blood free DNA high-throughput sequencing. A research discovers that the distribution condition of the pregnant woman peripheral blood free DNA in a gene transcription starting site region can reflect the physiological states of the pregnant woman and the fetus; the serum free DNA abundance based on the gene transcription starting site area has significant difference between a patient with a gestational related disease and a healthy pregnant woman, and can effectively predict the onset of the gestational related disease. A gestational related disease screening prediction model based on peripheral blood free DNA detection is constructed; the method can predict the onset of the gestational related disease before the clinical symptoms of the gestational related diseases occur, is a non-invasive, economical, convenient and accurate method for early prediction of the gestational related diseases, and has a good application prospect in development of prediction and screening products for the gestational related diseases.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for cultivating broad-spectrum bacterial leaf streak resistant rice, primer and expression cassette
PendingCN112522300AShort cycleImprove controllabilityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
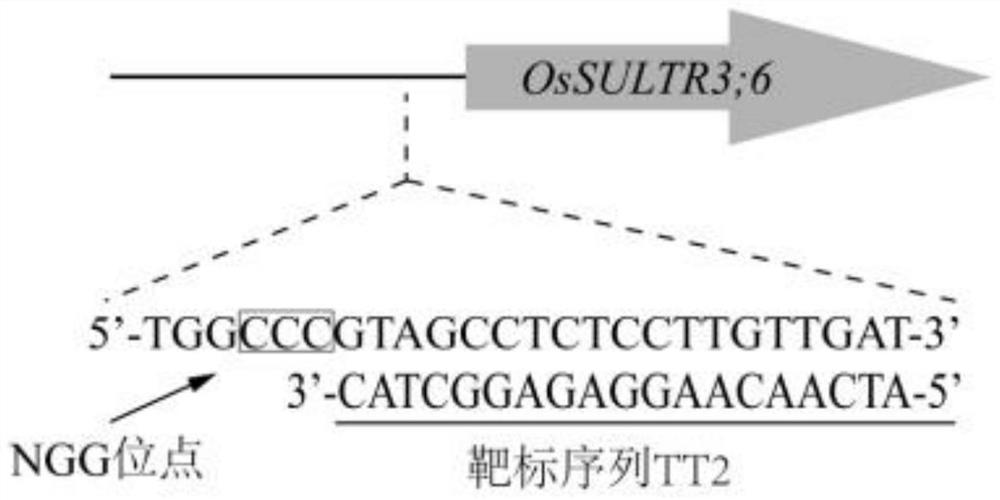
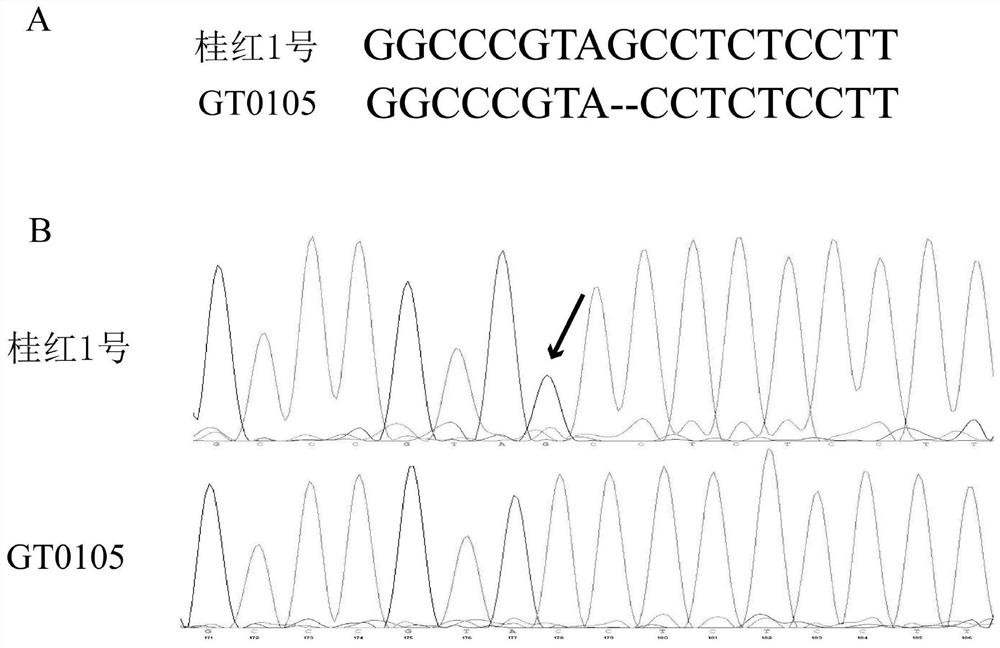
The invention discloses a method for cultivating broad-spectrum bacterial leaf streak resistant rice, a primer and an expression cassette. The method comprises the following step that an OsSULTR3;6 gene promoter region is edited, so target sequences from the 422th site to the 403rd site on the upstream of a transcription start site of the OsSULTR3;6 gene are mutated to obtain the broad-spectrum bacterial leaf streak resistant rice; and the target sequences are nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The provided method proposes constructing the bacterial leaf streak resistant rice through gene editing and breeding for the first time. According to the method, the OsSULTR3;6 gene promoter region is edited based on a CRISPR / Cas9 system; the obtained disease-resistant rice has no transgenic marker, the cultured new variety is similar to a natural mutation result, and the method can be widely applied to resistance breeding of various susceptible rice, is not limited by rice varieties, directionally changes rice characteristics, and is short in period and high in controllability.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
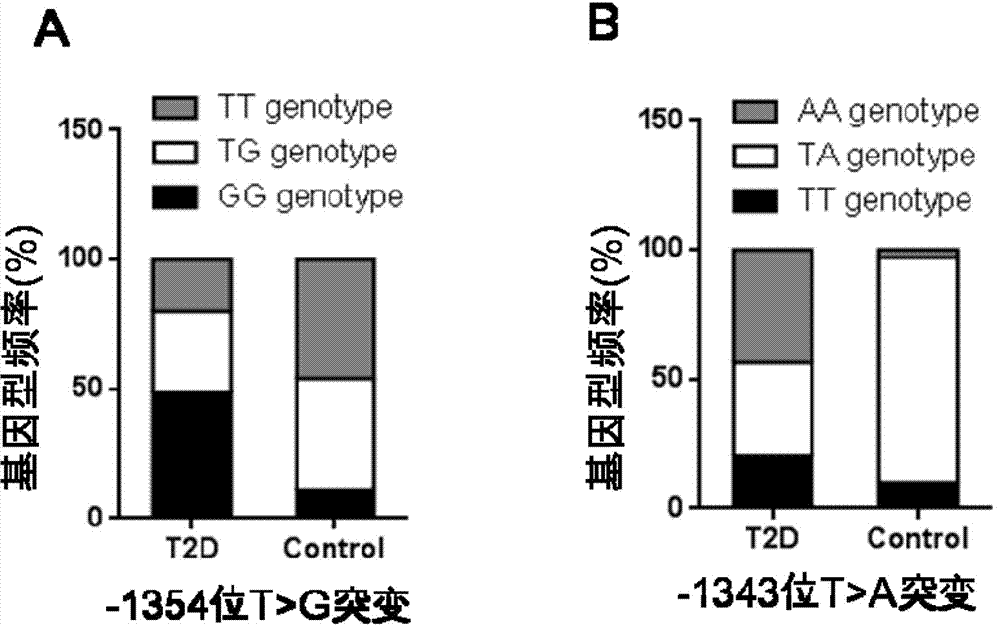
PCR-RFLP method for detecting single-nucleotide polymorphism of type II diabetes susceptibility gene CREB1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP method for detecting the single-nucleotide polymorphism of the type II diabetes susceptibility gene CREB1 and application thereof. According to the invention, the detected gene polymorphism comprises the single-nucleotide polymorphism of T or G located in the promoter region of the CREB1 gene and -1354 bp away from a transcription start site and the single-nucleotide polymorphism of T or A located in the promoter region of the CREB1 gene and -1343 bp away from the transcription start site according to the results of sequencing with DNA pools; the genome DNAs of a to-be-detected sample are used as a template, a primer pair P is used as a primers, and PCR amplification is carried out on a CREB1 gene sequence containing polymorphic sites in the presence of Taq DNA polymerase, Buffer (a buffer environment), Mg<++> and dNTPs; then a PCR product is divided into two parts which are respectively digested by using Hha I and Xsp I restriction enzymes; and enzyme-digested products are subjected to typing via agarose gel electrophoresis. Moreover, the above two polymorphic sites and clinical indicators of type II diabetes are subjected to association analysis, and results show that different genotypes are substantially related to the levels of fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
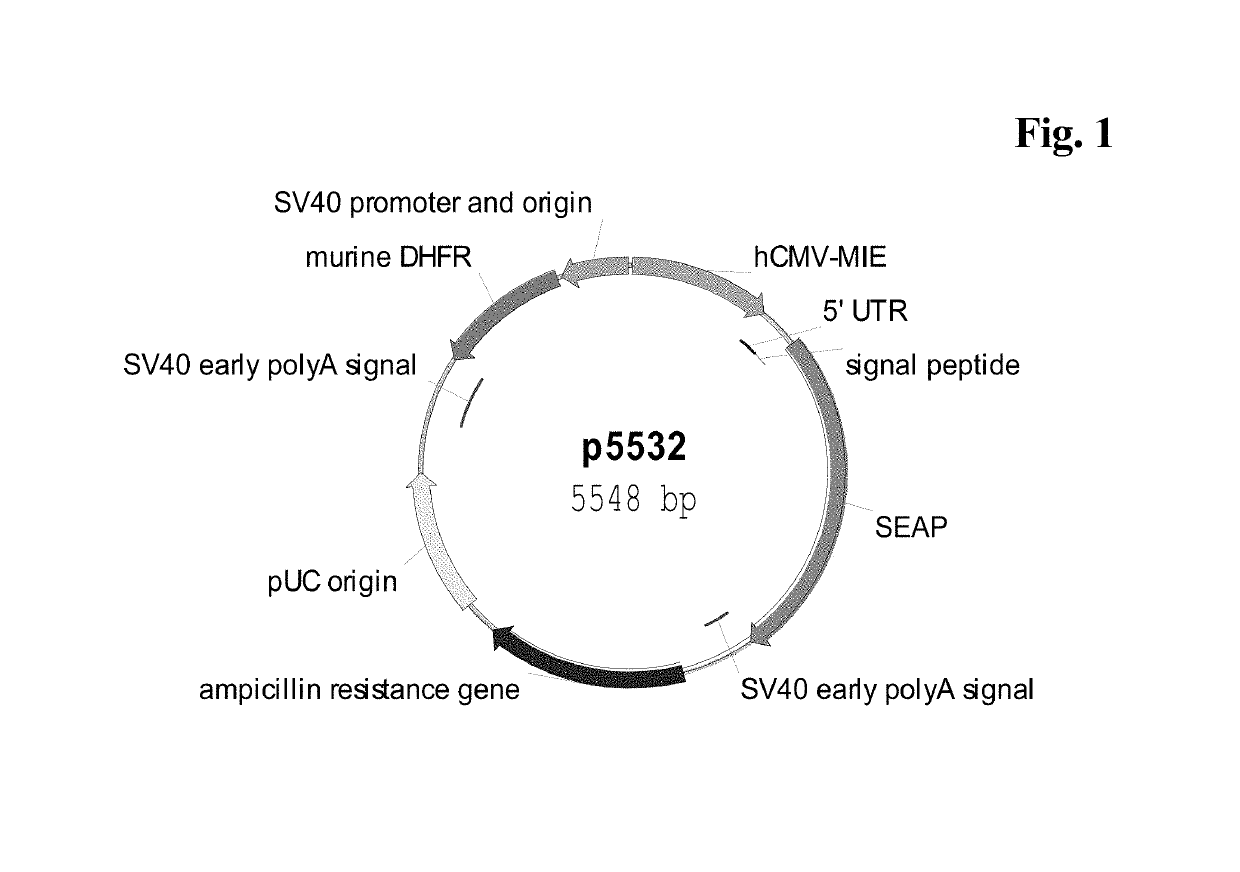
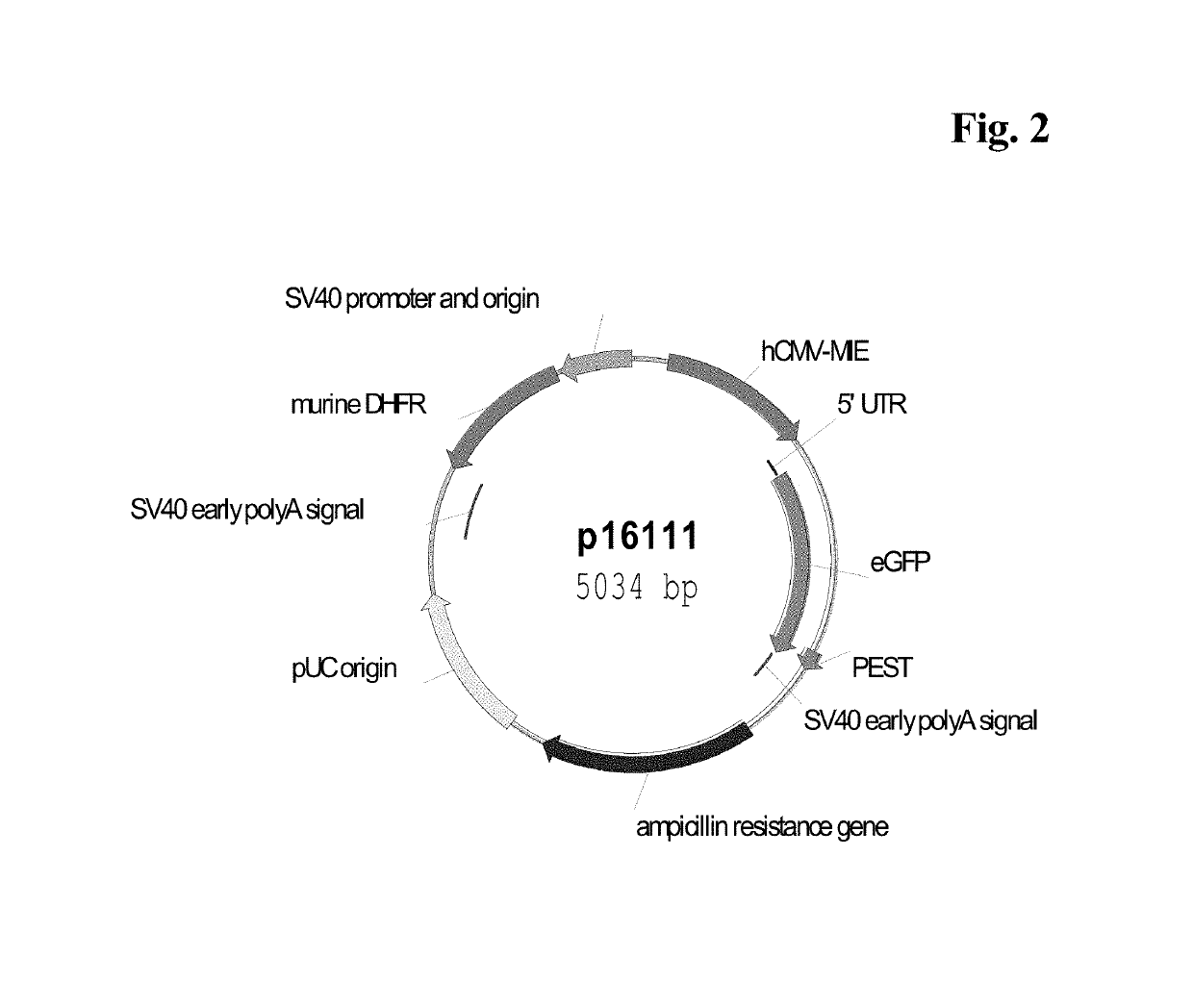
CMV promoter and method for production of polypeptides
ActiveUS10329595B2High potencyReduced promoter silencingGenetically modified cellsVirus peptidesTranscription initiationNucleic acid sequencing
The current invention reports a promoter that has the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 02 or SEQ ID NO: 03 which is a human CMV major immediate-early (hCMV-MIE) promoter / enhancer with C to G point mutation at position −41 and / or −179 relative to the transcription start site. This new promoter is especially useful for the production of polypeptides at large scale as it shows reduced promoter silencing and improved polypeptide production.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Method of synthesizing cDNA
ActiveUS8067205B2Increase chanceHigh yieldSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexNucleotide
A method for synthesizing cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a nucleotide adjacent to a cap structure of mRNA, which comprises (i) a process for annealing a double-stranded DNA primer and an RNA mixture containing mRNA possessing a cap structure, (ii) a process for preparing a conjugate of an mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and a double-stranded DNA primer by synthesizing the first-strand cDNA primed with the double-stranded DNA primer using reverse transcriptase, and (iii) a process for circularizing the conjugate of the mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and the double-stranded DNA primer by joining the 3′ and 5′ ends of the DNA strand containing cDNA using ligase. This method enables us to efficiently synthesize a full-length cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a transcription-start-site nucleotide from a small amount of RNA by small processes.
Owner:KOKURITSU SHINTAI SHIYOUGAISHI +2
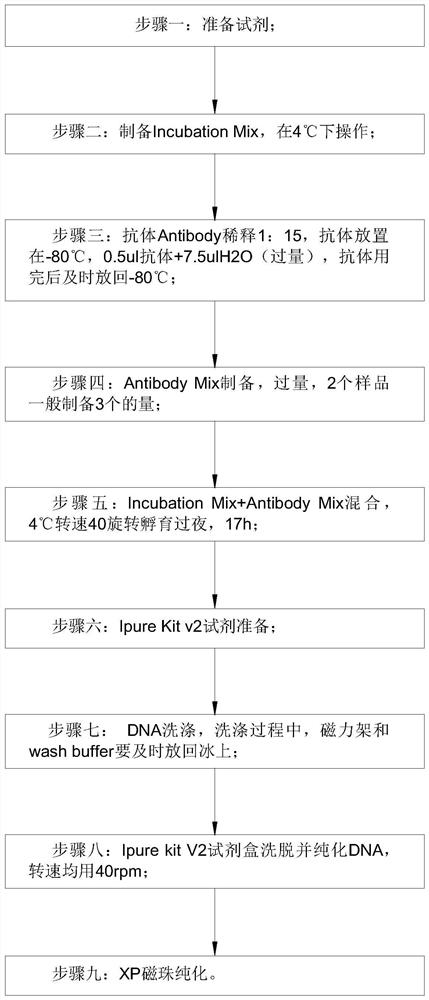
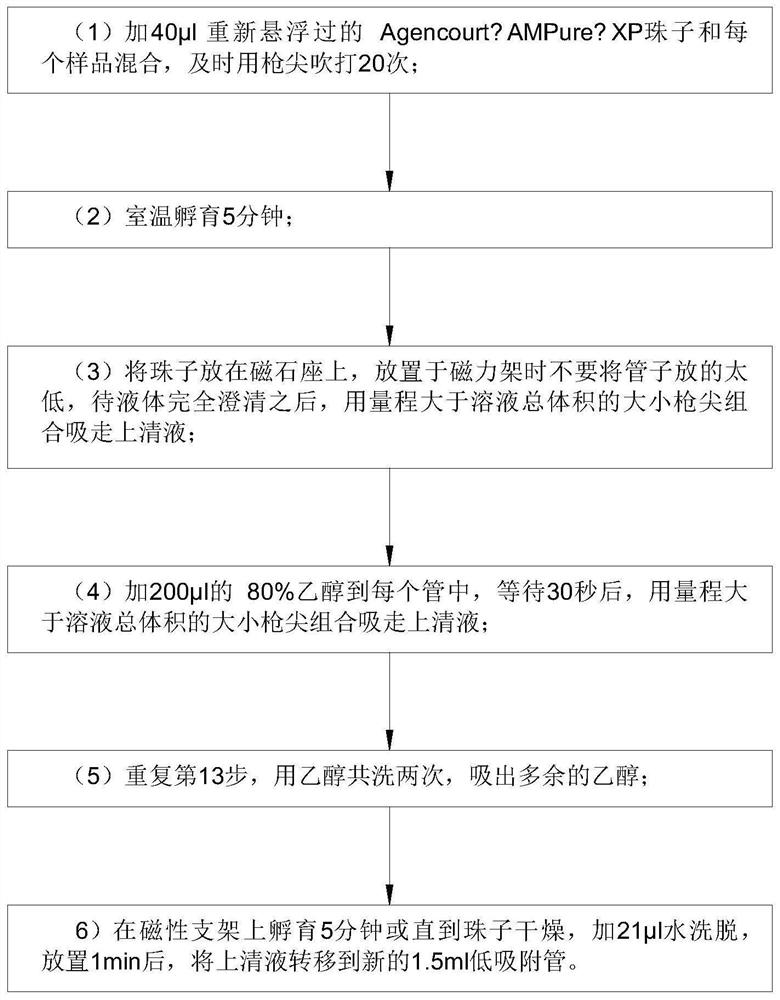
Detection method for capturing cfDNA5mC fragment
PendingCN113564226AImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription initiation siteMethyl palmoxirate
The invention discloses a detection method for capturing a cfDNA5mC fragment. The detection method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing reagents; step 2, preparing Inculation Mix, and operating at the temperature of 4 DEG C; step 3, diluting an Antibody at 1: 15, placing the antibody at -80 DEG C, adding 0.5 [mu] l of the antibody and 7.5 [mu] l of H2O (excess), and timely placing the antibody at-80 DEG C after the antibody is used up; step 4, preparation of Antibody Mix: the Antibody Mix is excessive, and three amounts of Antibody Mix are generally prepared for two samples; step 5, mixing an Inculation Mix and the Antibody Mix, rotating at the rotating speed of 40 at the temperature of 4 DEG C, and incubating overnight for 17 hours; and step 6, preparing an Ipre Kit v2 reagent. According to the detection method for capturing the cfDNA5mC fragment, methylation of fifth carbon of cytosine (5-methylcytosine: 5mC) is a methylation type excavated in eukaryotes at the earliest, in gene expression, a transcription start site region is generally non-methylated, and when the gene is expressed at a lower level, the methylation level of cytosine in a regulation region is higher, and library correlation generated by different initial quantities and different methods is an effective parameter for evaluating consistency and high performance.
Owner:深圳泰莱生物科技有限公司
Target gene combination related to gestational age and application thereof
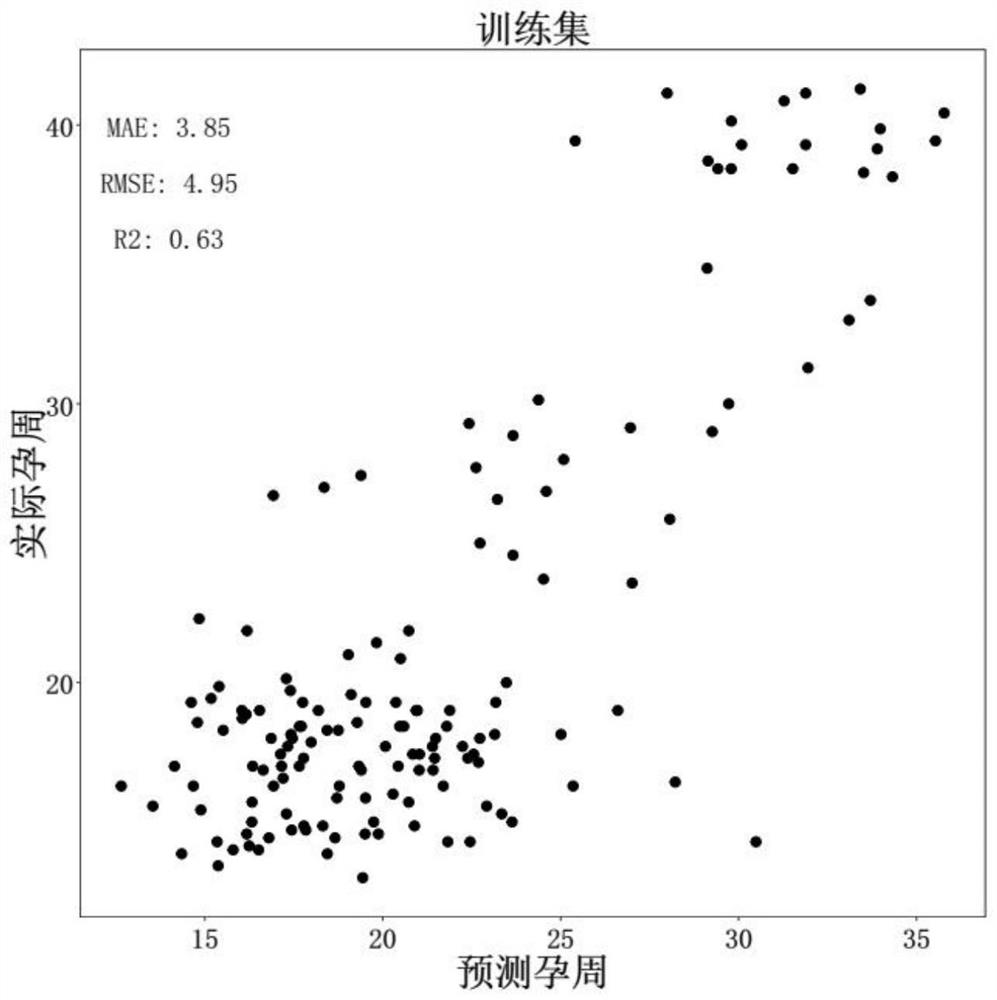
PendingCN114592074AGestational Age PredictionEffective predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsTranscription initiation siteFree dna
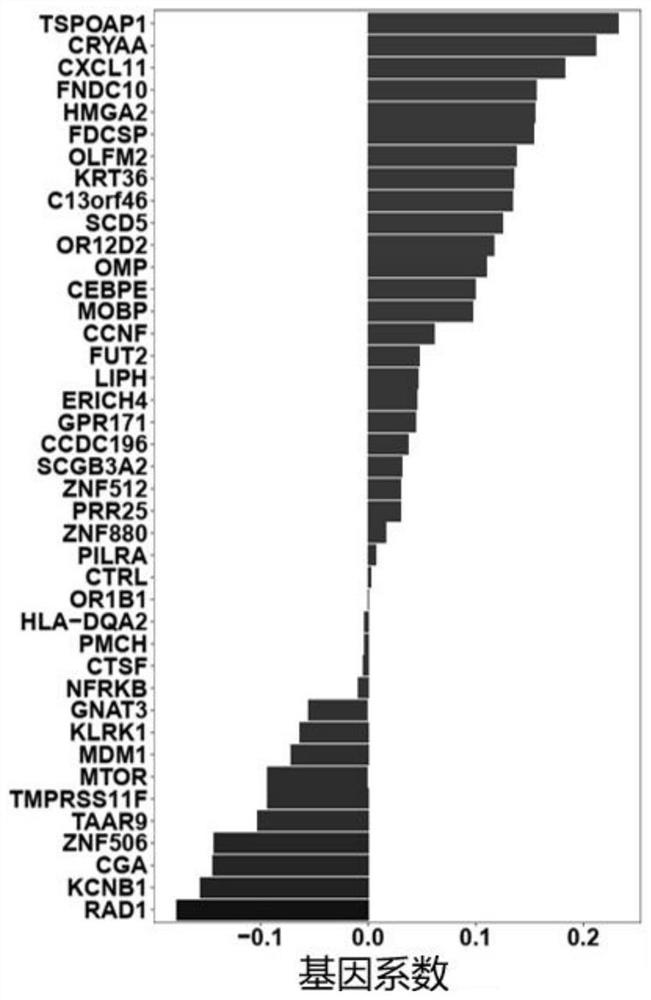
The invention discloses a target gene combination related to gestational age and application thereof. Based on the target gene combination, the target gene combination comprises TSPOAP1, CRYAA, CXCL11, FNDC10, HMGA2, FDCSP, OLFM2, KRT36, C13orf46, SCD5, OR12D2, OMP, CEBPE, MOBP, CCNF, FUT2, LIPH, ERICH4, GPR171 and the like. According to the method, the distribution condition of peripheral blood free DNA in some gene transcription start site areas can reflect different gestational weeks, and after the characteristics of the free DNA transcription start site areas are subjected to homogenization correction, a prediction model constructed by using a machine learning algorithm can effectively predict the fetal age of a fetus.
Owner:SUZHOU MUNICIPAL HOSPITAL +1
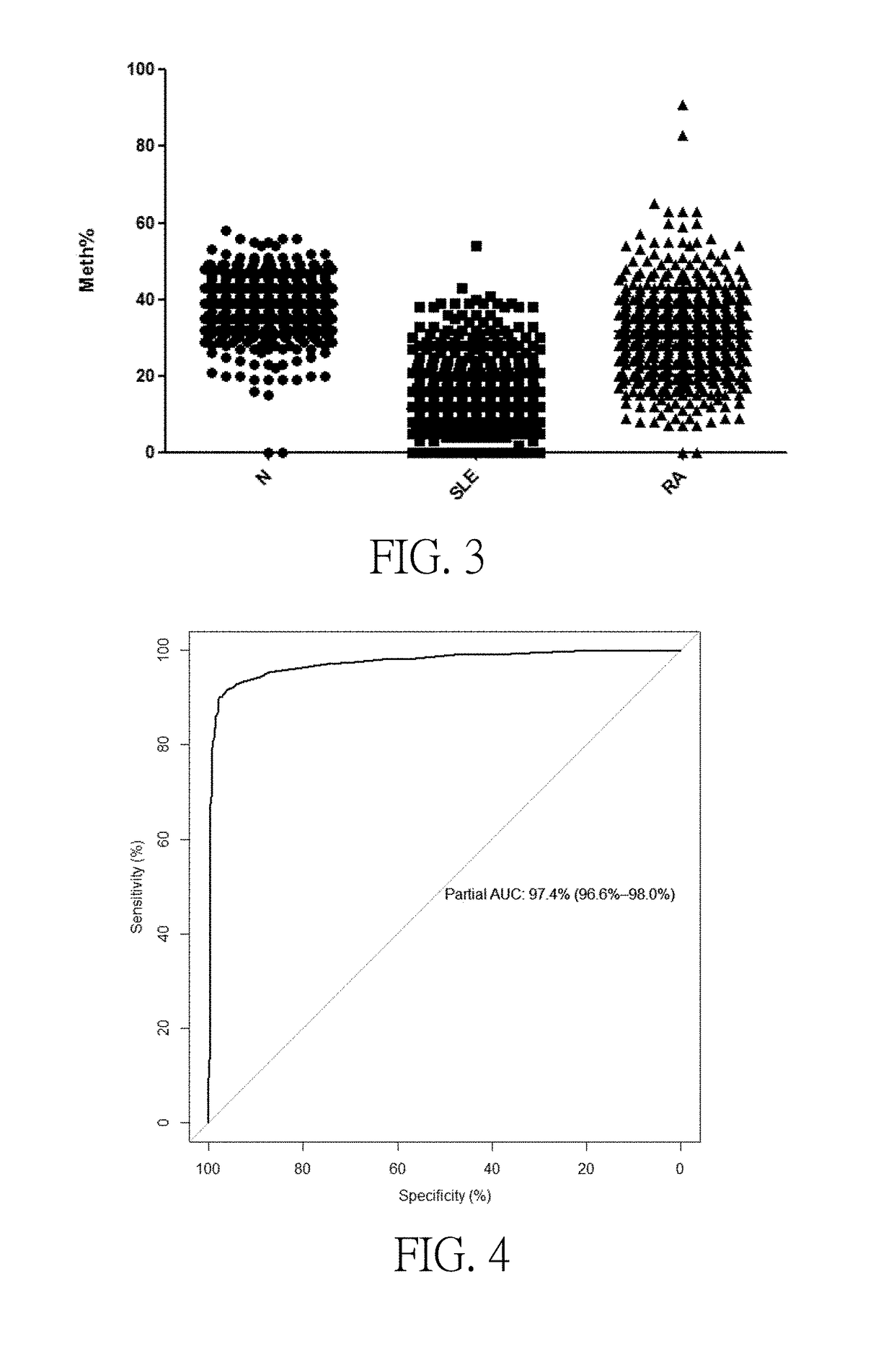
Systemic lupus erythematosus biomarker and diagnostic kit thereof
InactiveUS20180305745A1ChangeReduced DNA methylationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNABiomarker (petroleum)
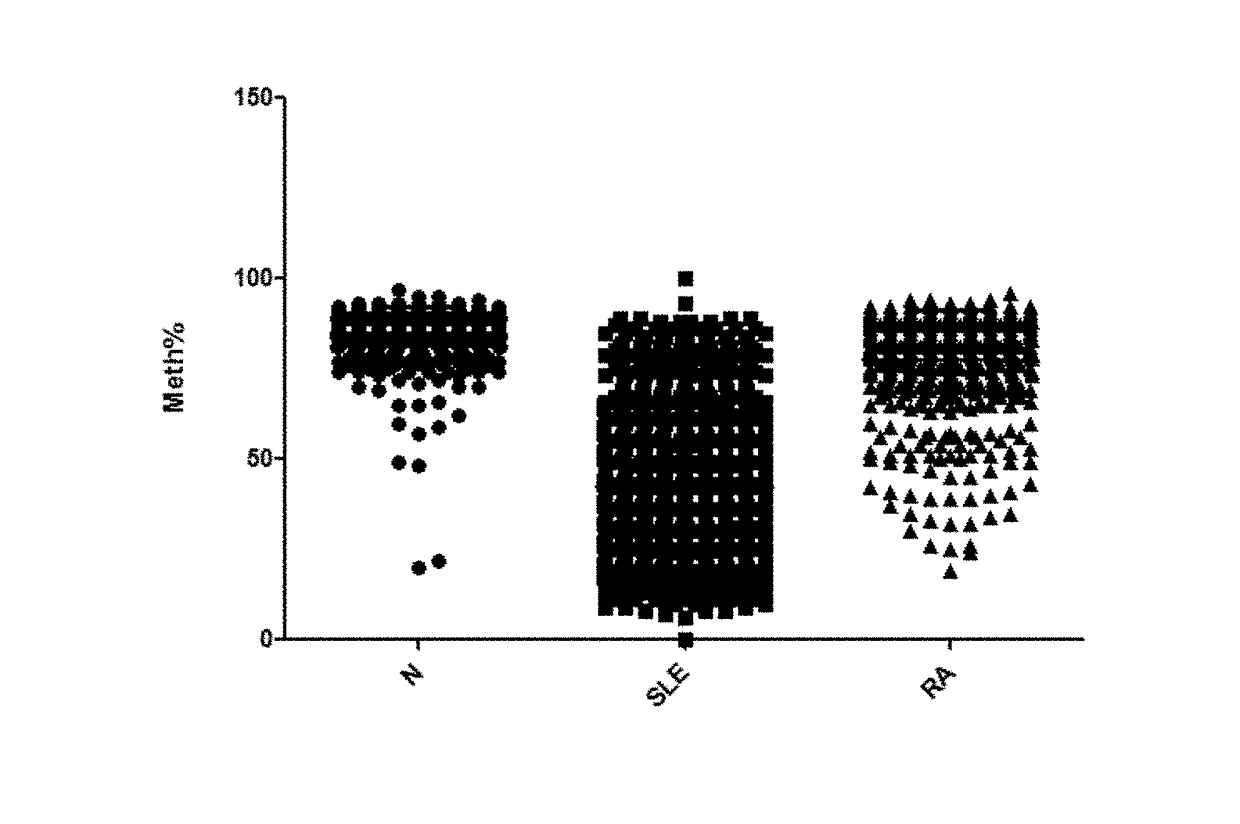
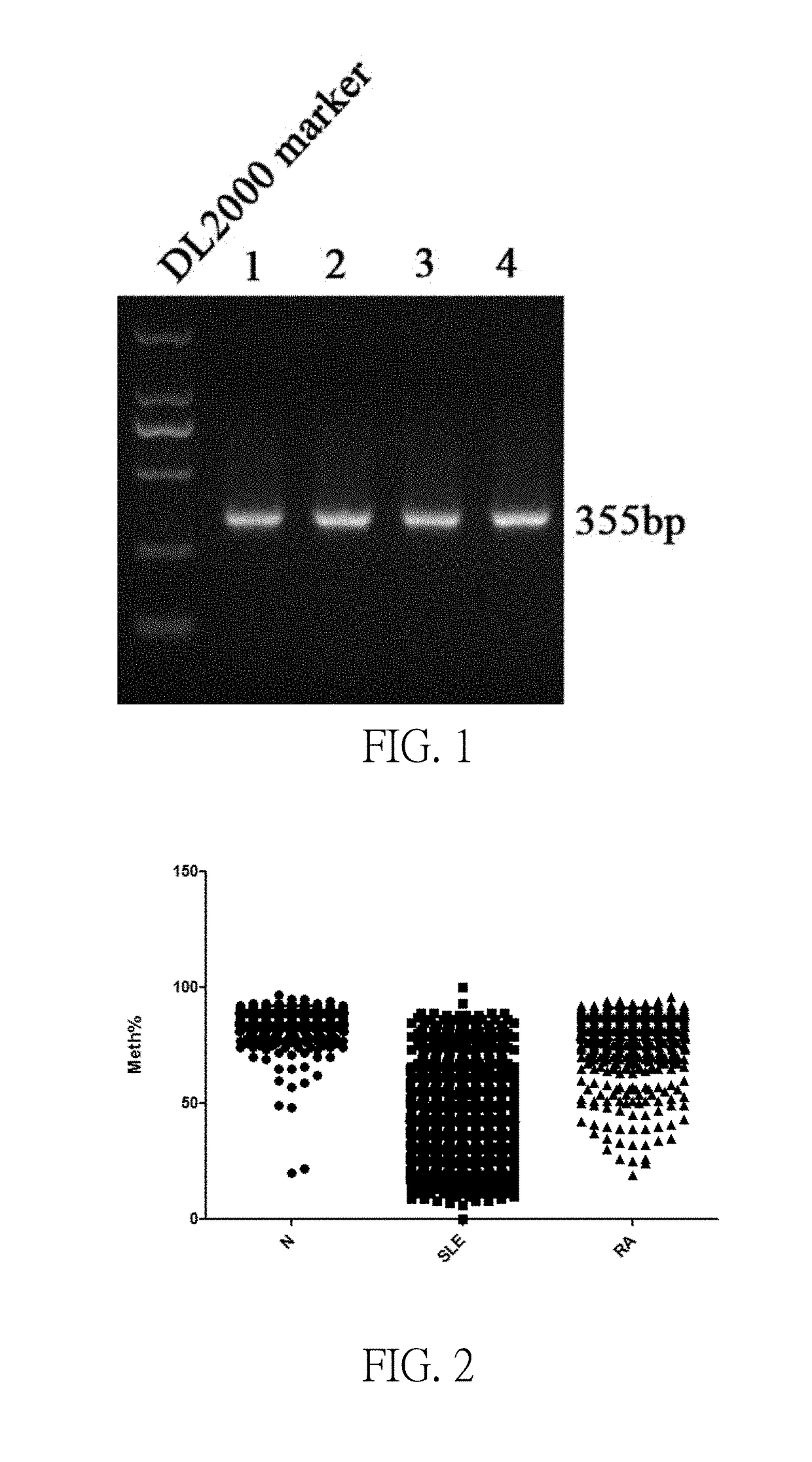
Disclosed are a systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) biomarker and diagnostic kit thereof. The SLE biomarker is a segment within 1500 bp upstream from a transcription start site of a human IFI44L gene, namely chr1: 79,085,190-79,085,311 (hg19), and a DNA sequence thereof is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The SLE diagnostic kit in the present invention comprises primers having sequences represented by SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3, and a probe having a sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.4.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Corn low-temperature inducible promoter and activity analysis
InactiveCN102399783ASolving the food crisisSolve problems such as ecological deteriorationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsA-DNAEmbryo
The invention discloses a corn low-temperature inducible promoter and activity analysis, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, and provides an obtained corn low-temperature inducible promoter sequence, which comprises a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) nucleotide sequence ranging from a -1bp region to a -1151bp region relative to a transcription start site of SEQ ID NO:1. The invention further provides a low-temperature inducible plant expression vector for transforming corn, which comprises a corn low-temperature inducible promoter sequence and a 5' non-translational region of a corn dehydration-responsive element (DRE) binding protein gene ZmDBP3, as well as a genetically-modified corn mature embryo transformed by the plant expression vector. PCR primers shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3 are suitable for amplifying DNA fragments, including the sequence SEQ ID NO:1. The corn low-temperature inducible promoter can be used for starting efficient expression of a low-temperature-resistant gene, can be applied to low-temperature-intolerant plants to realize the low-temperature resistance of plants, and plays a positive role in solving the problem of food crisis in low-temperature areas.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com