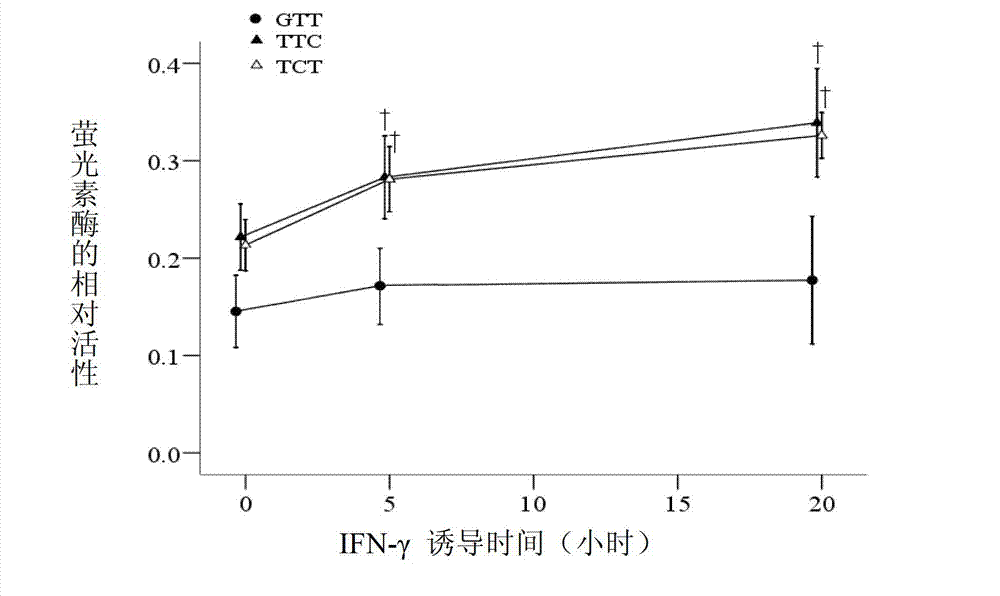
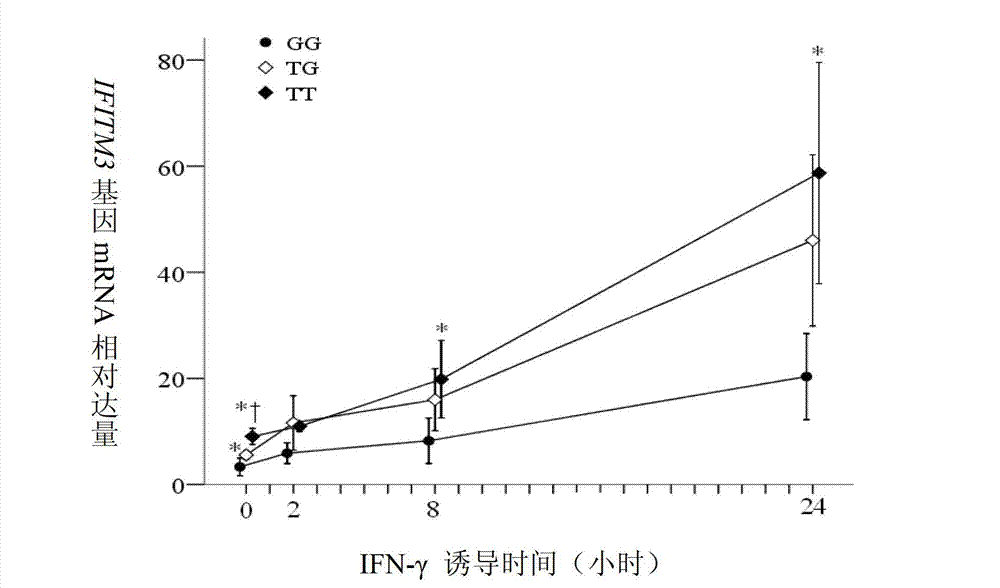
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Transcription initiation site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for knocking off animal myostatin gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN104531705AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal myostatin gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second myostatin exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second myostatin exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal myostatin gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of synthesizing cdna
ActiveUS20060246453A1High yieldIncrease chanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexReverse transcriptase
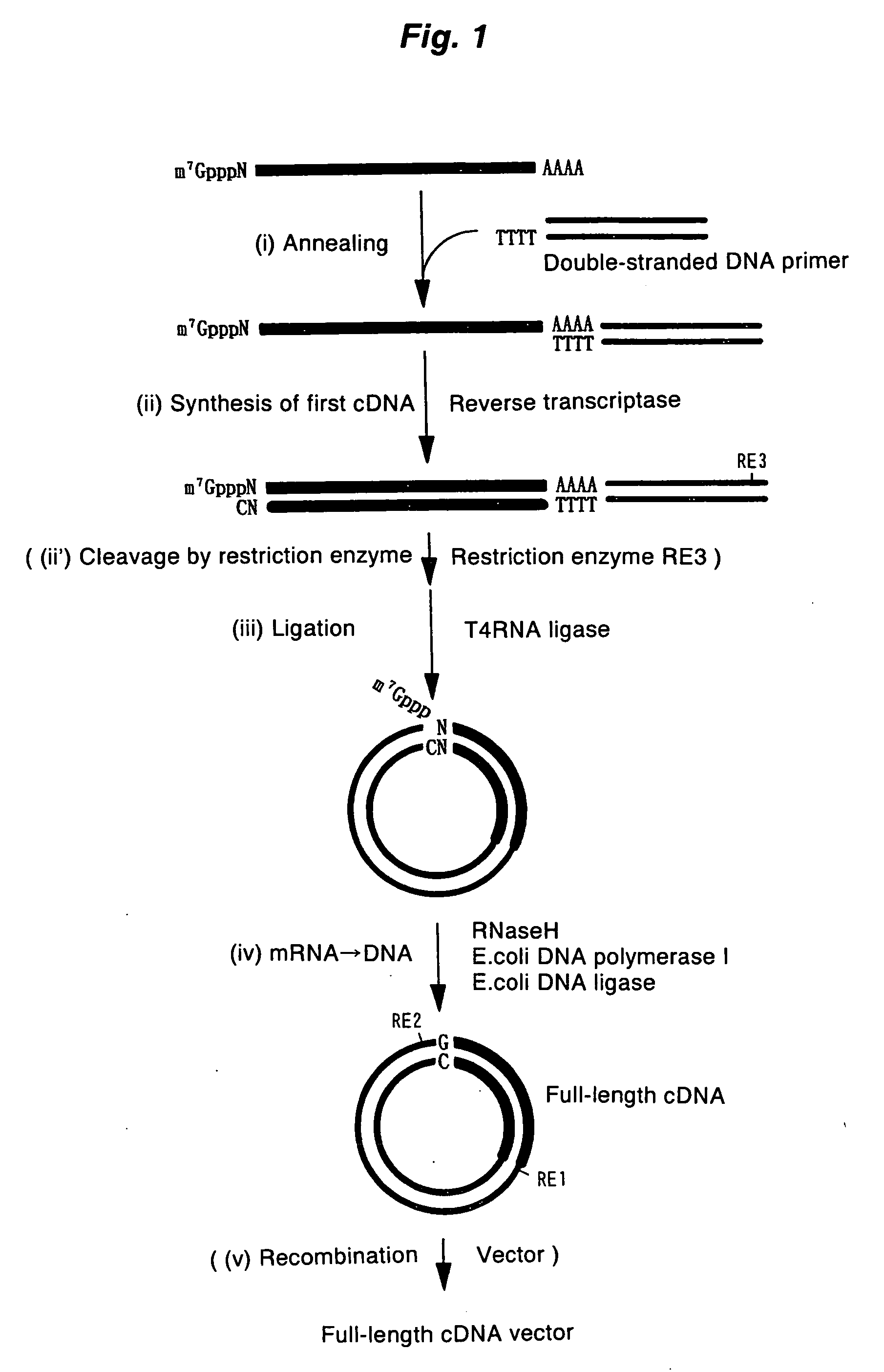
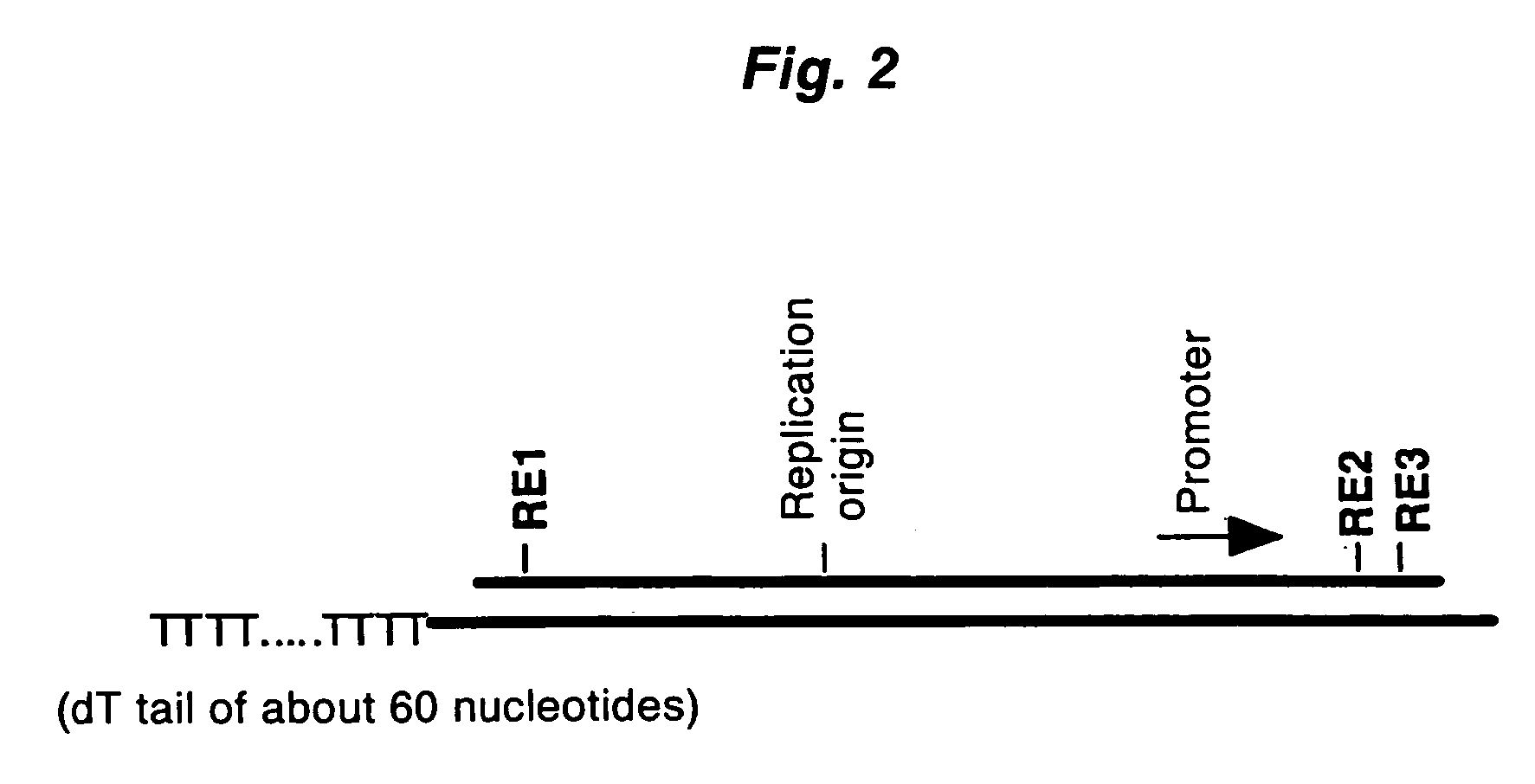
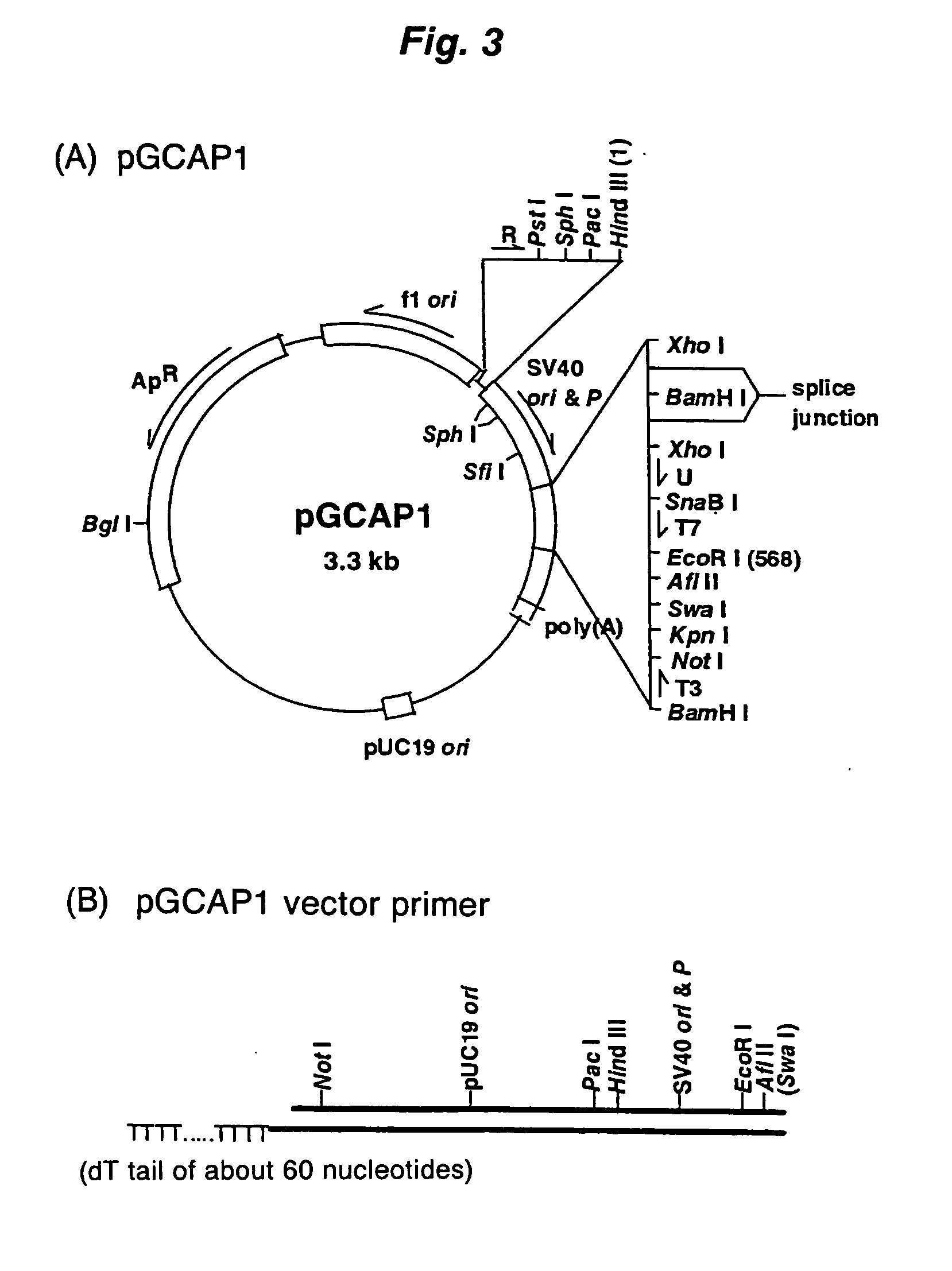
A method for synthesizing cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a nucleotide adjacent to a cap structure of mRNA, which comprises (i) a process for annealing a double-stranded DNA primer and an RNA mixture containing mRNA possessing a cap structure, (ii) a process for preparing a conjugate of an mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and a double-stranded DNA primer by synthesizing the first-strand cDNA primed with the double-stranded DNA primer using reverse transcriptase, and (iii) a process for circularizing the conjugate of the mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and the double-stranded DNA primer by joining the 3' and 5' ends of the DNA strand containing cDNA using ligase. This method enables us to efficiently synthesize a full-length cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a transcription-start-site nucleotide from a small amount of RNA by small processes.
Owner:KOKURITSU SHINTAI SHIYOUGAISHI +2
Oligonucleotide modulation of cell adhesion
InactiveUS6015894AHigh expressionAvoid inhibitionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTranscription initiation site
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to modulation cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Ribosome binding site reconstruction-based promoter optimization method
ActiveCN106939310AIncreased binding levelsImprove expression levelPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionTranscription initiation siteBinding site
A ribosome binding site reconstruction-based promoter optimization method comprises the following steps: 1, amplifying the sequence of a ribosome binding site behind the transcription initiation site of a P43 promoter in Bacillus subtillis; and 2, amplifying a P43 promoter with the ribosome binding site sequence through primer design to obtain a sequence with at least one structure function. The ribosome binding site in the P43 promoter is optimized through the method to make the binding level of the optimized promoter and mRNA improved in order to improve the expression level of target gene.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
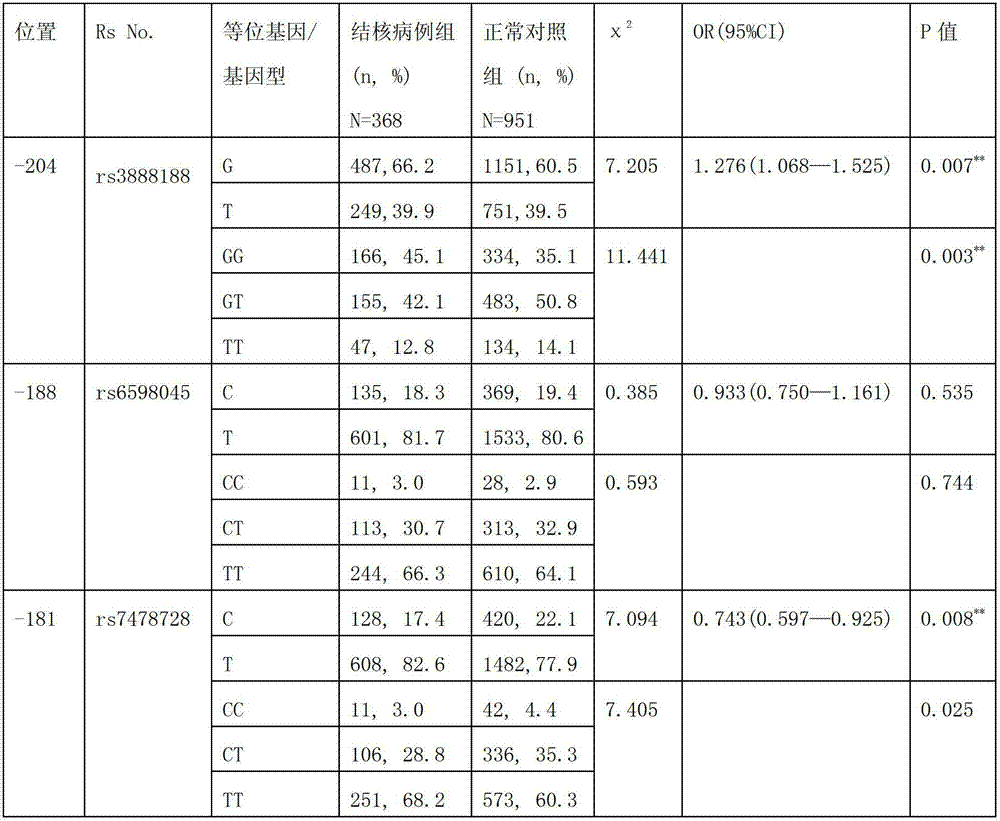
Application of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3888188 to detection of tuberculosis susceptibility
InactiveCN102808030AMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription initiation siteTranslation initiation sites
The invention discloses an application of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3888188 to detection of tuberculosis susceptibility. The SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) is the rs3888188 and is positioned in a human IFITM3 (interferon induced transmembrane protein) gene core promoter region (namely the upstream 103bp of a transcription initiation site / the upstream 204bp of a translation initiation site ATG), the rs3888188G is a risk factor of tuberculosis susceptibility, and the polymorphism of the rs3888188 is highly related with tuberculosis. When the genotype of the site is GG, the tuberculosis susceptibility or tuberculosis causing risk of an individual to be detected is increased. The application is of significant meaning and value in the aspects of diagnosing and treating the tuberculosis to reasonably prevent the tuberculosis.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Methods for Obtaining Gene Tags
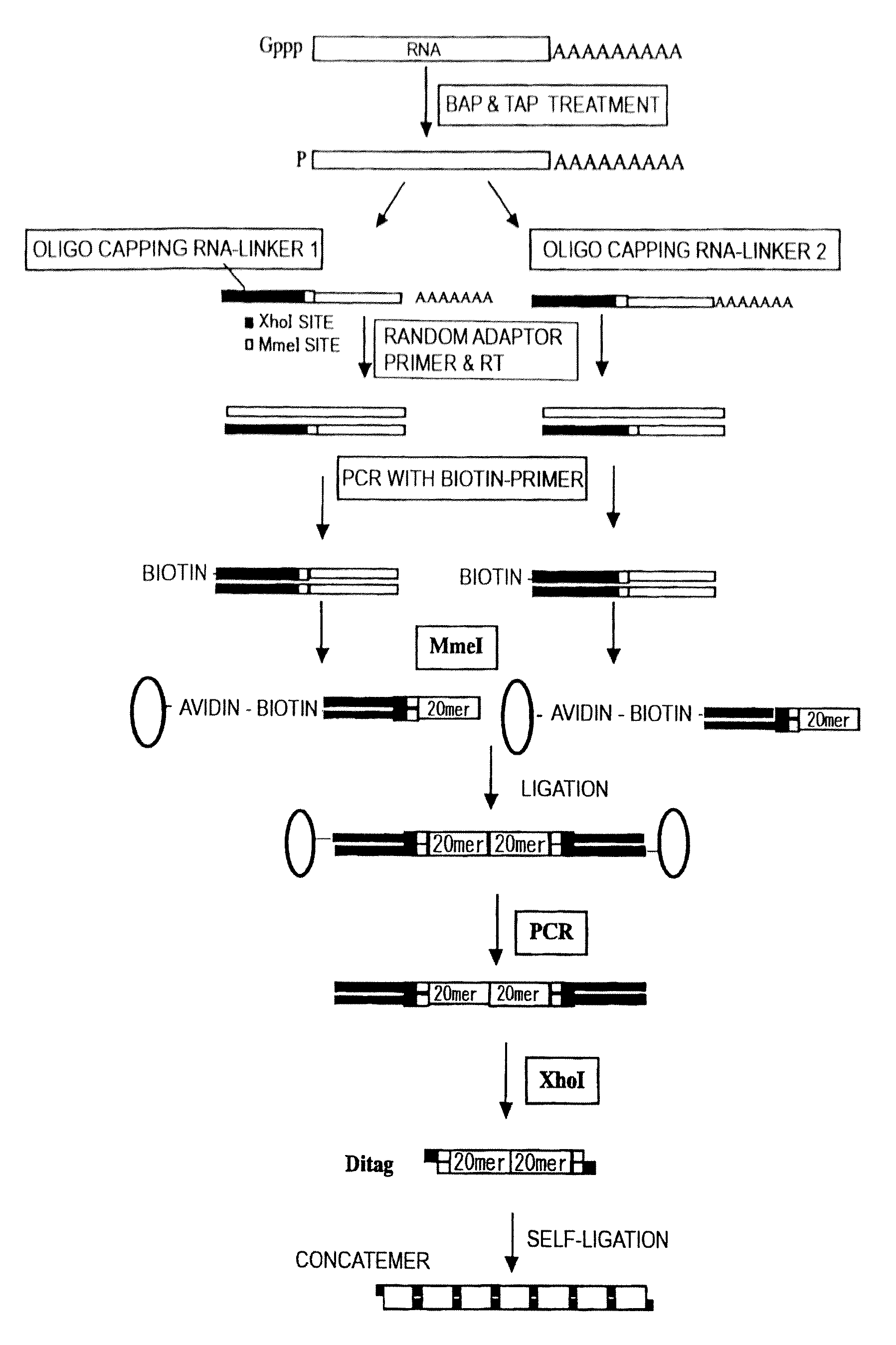
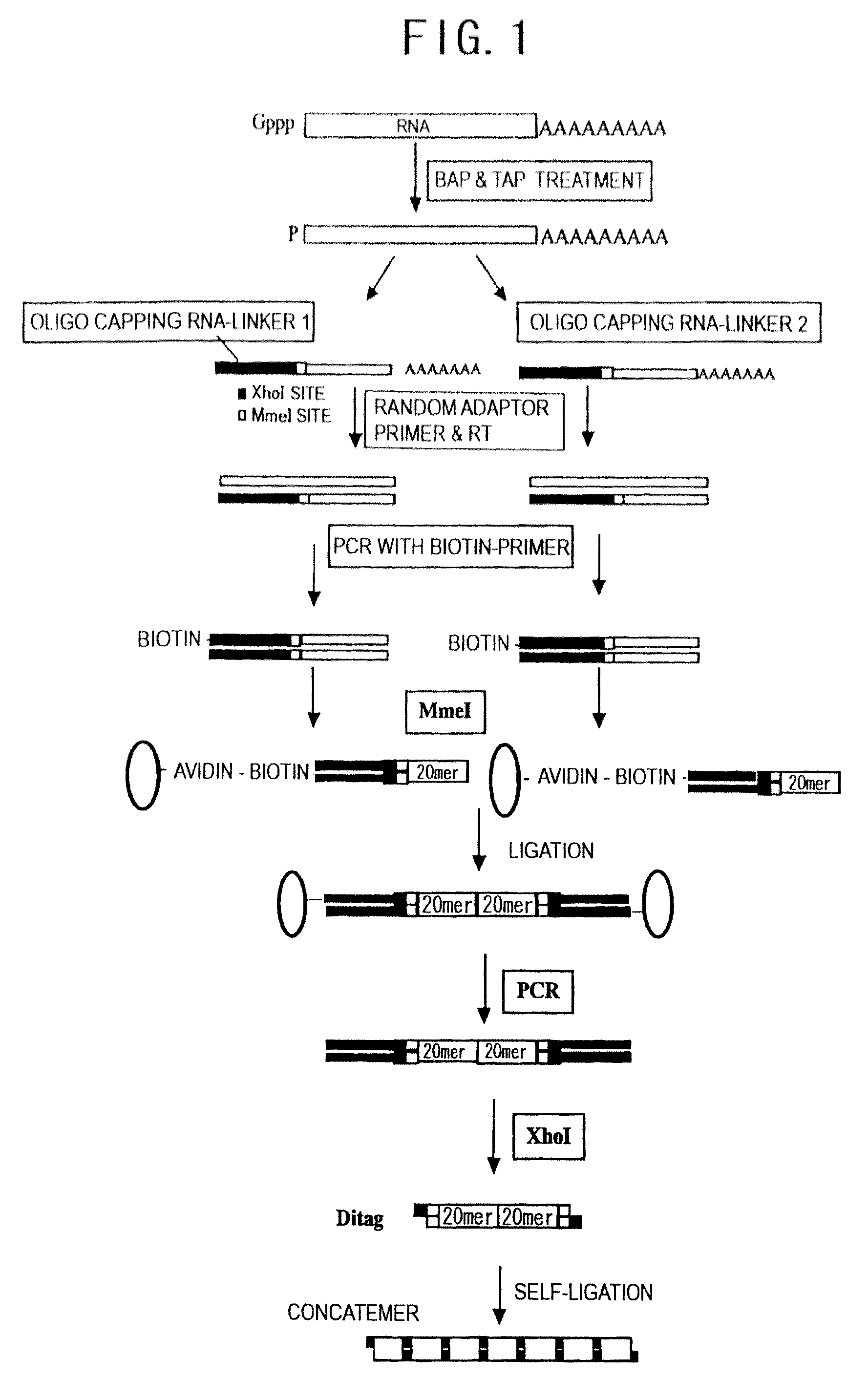
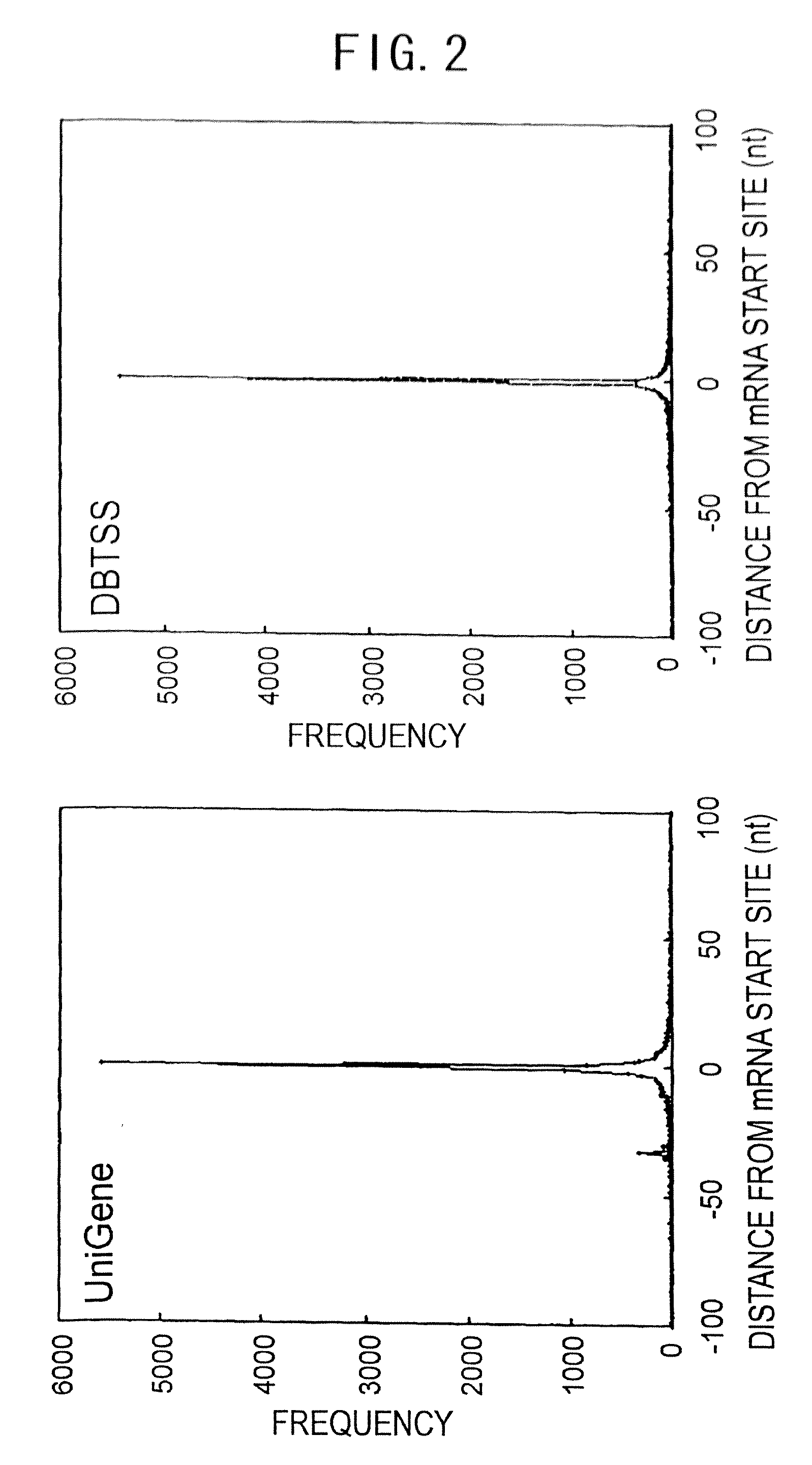
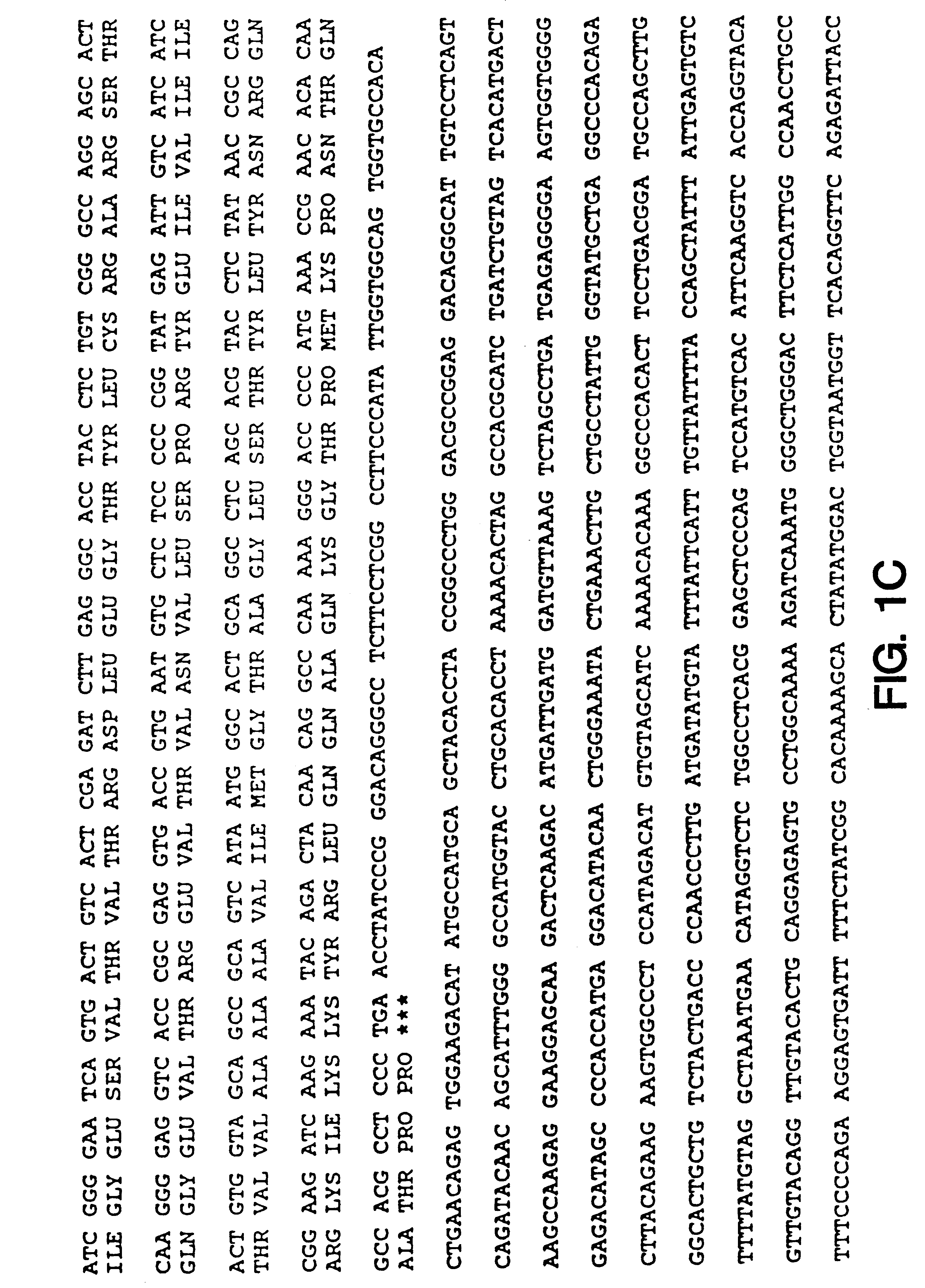
The present invention provides methods for providing as tags the nucleotide sequences at the 5′ end of mRNA. The method of the present invention comprises the step of synthesizing cDNA using, as a template, mRNA whose CAP structure is linked with a IIs linker having a type IIs endonuclease recognition sequence. Tags including the nucleotide sequence from the 5′ end of mRNA are generated by reacting the type IIs endonuclease to cDNA. Tags can be generated from all mRNA, independently of their nucleotide sequences. Methods for identifying transcriptional start sites and primers for full-length cDNA synthesis are provided based on the nucleotide sequence information of tags of the present invention.
Owner:POST GENOME INST CO LTD
Oligonucleotide inhibition of cell adhesion
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to inhibition of cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Application of skin color-associated SNP marker in genotyping of black-bone chickens
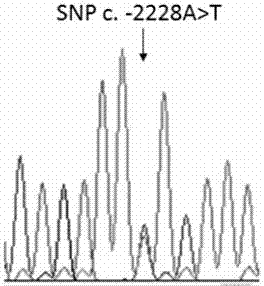
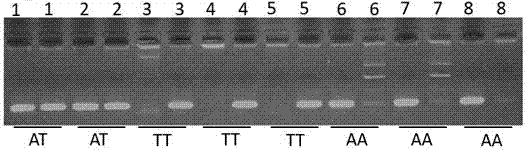
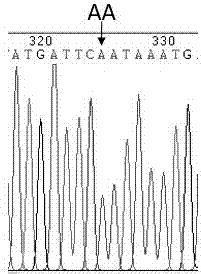
ActiveCN107988376AStrong specificitySingle detection bandMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiation siteTyping
The invention provides an application of a skin color-associated SNP marker in genotyping of black-bone chickens. The SNP marker is located at 2228 bp upstream of a transcription initiation site in apromoter region of a TYR gene, and a base with polymorphism is adenine A or thymine T. The SNP genotype detection primer has high specificity, single detection band and accurate typing results. In combination with a provided detection method, the whole operation process is simpler and more efficient, and the cost is lower. Rapid and accurate individual screening is achieved, and a basis for breeding development and protection of black-bone chicken varieties is provided.
Owner:LESHAN NORMAL UNIV
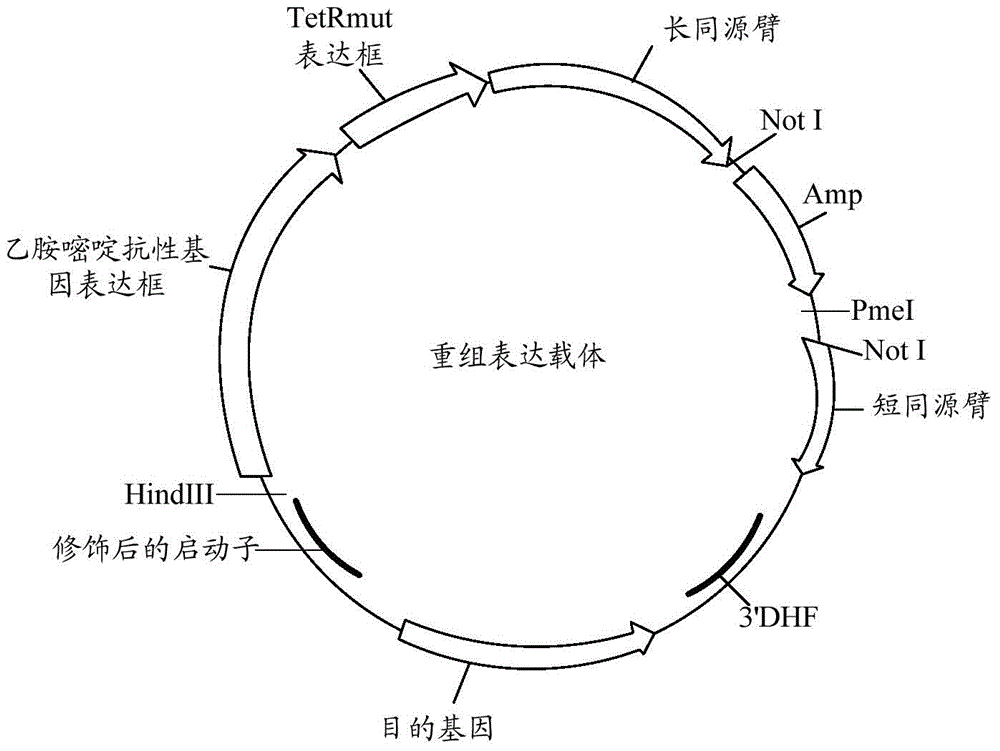
Controllable genome-modified plasmodium, recombinant expression vector and construction method and application of controllable genome-modified plasmodium and recombinant expression vector
The invention relates to a controllable genome-modified plasmodium, a recombinant expression vector and the construction method and application of the controllable genome-modified plasmodium and the recombinant expression vector. The recombinant expression vector comprises a gene targeting long homologous arm, a gene targeting short homologous arm, a tetracycline repression protein gene expression cassette, a pyrimethamine resistance gene expression cassette and a target gene expression cassette, wherein the tetracycline repression protein gene expression cassette, the pyrimethamine resistance gene expression cassette and the target gene expression cassette are located between the gene targeting long homologous arm and the gene targeting short homologous arm, and tetracycline operator gene sequences are inserted in multiple transcriptional start sites of a target gene promoter, so that the recombinant expression vector can be used for conditional research of the functions of a certain functional gene in a plasmodium genome. Furthermore, a functional gene expression sequence, corresponding to a target gene, in the plasmodium genome is knocked out by means of the gene knockout technique; meanwhile, the recombinant expression vector is transfected into a plasmodium with genes knocked out, so that the controllable genome-modified plasmodium is obtained; a new technical scheme is provided for further research of the functions of all functional genes in the plasmodium genome, and application prospects are broad.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
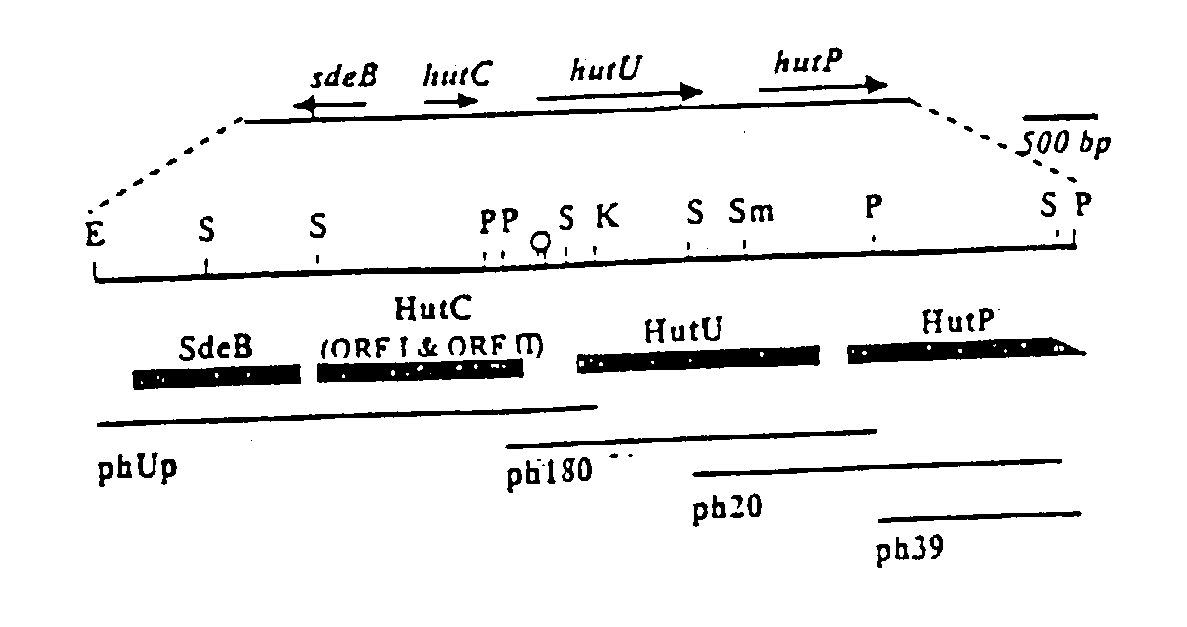
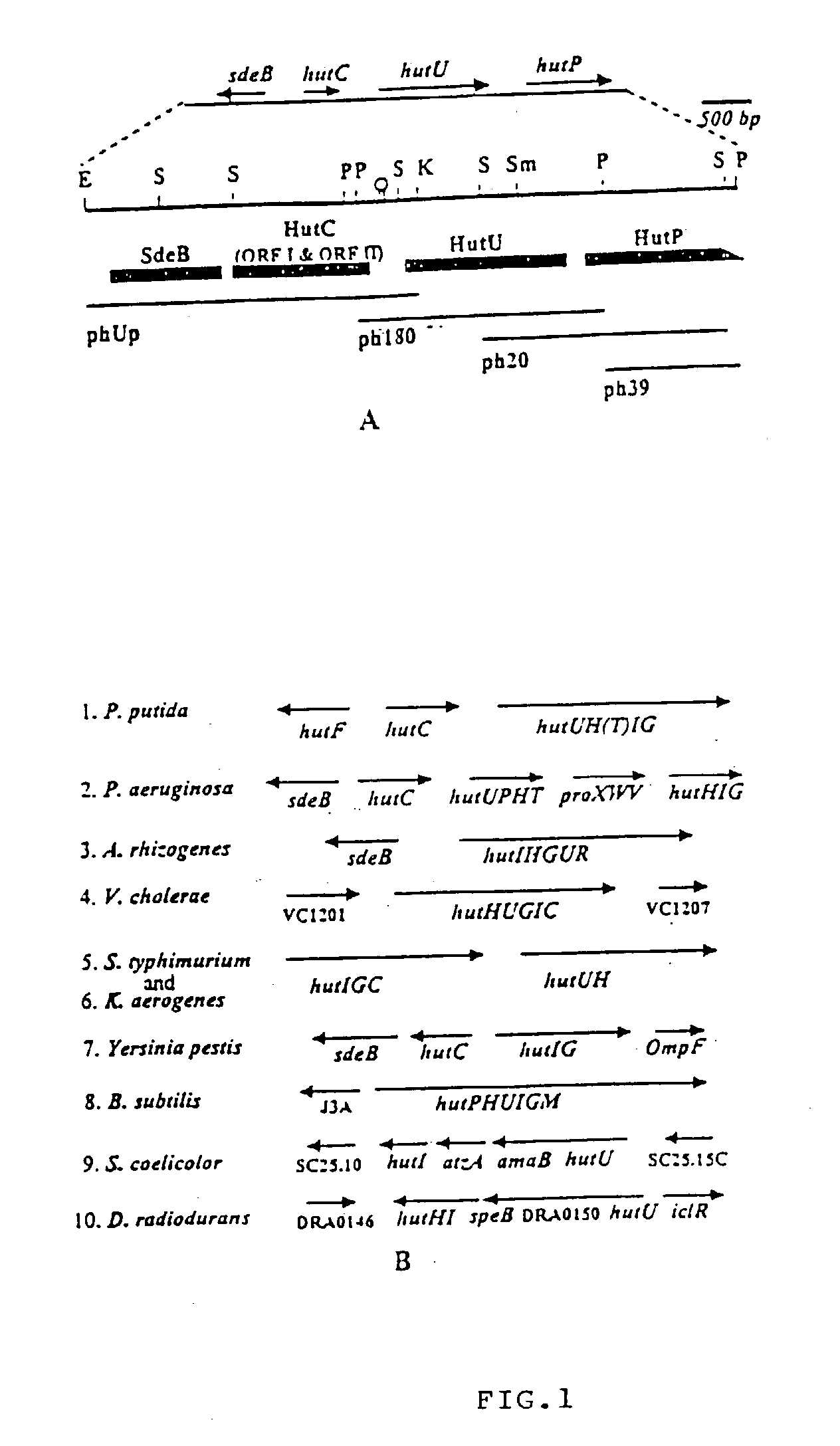
Novel regulatory elements of cold-inducible hutU gene from the Antarctic psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas Syringae
A DNA sequence from the upstream region of cold-inducible hutU gene of the Antarctic Psychrotrophic Bacterium Pseudomonas Syringae, comprising promoter elements and other regulatory sequences, with unique 'CAAAA' nucleotide sequence at -10 site of multiple transcription start sites and using said promoter to express genes of interest in the said bacterium at temperature as low as 4° C. and using the said bacterium with generation time ranging between two and half to three hours, as a system to produce low temperature labile proteins of pharmaceutical significance.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
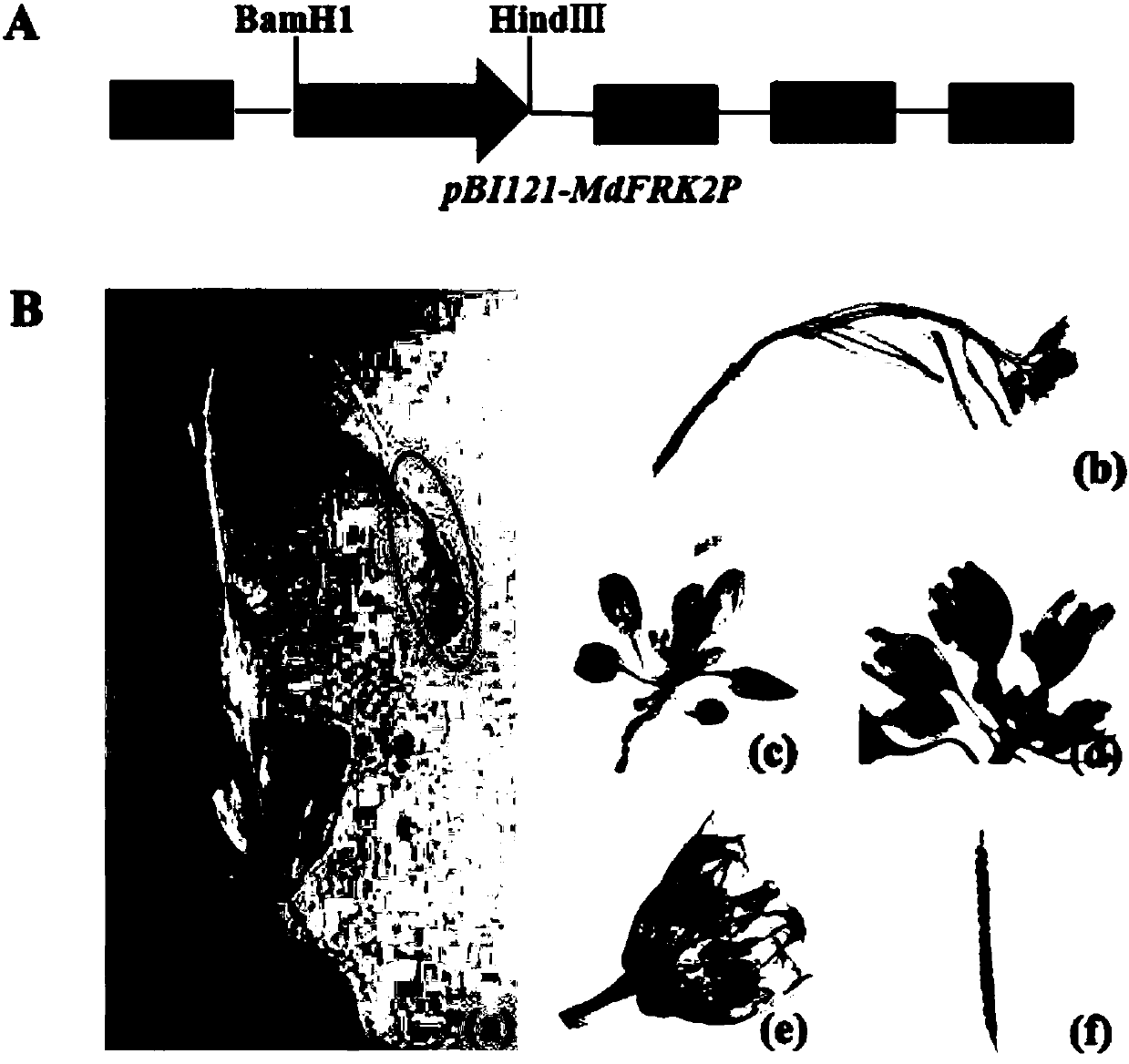
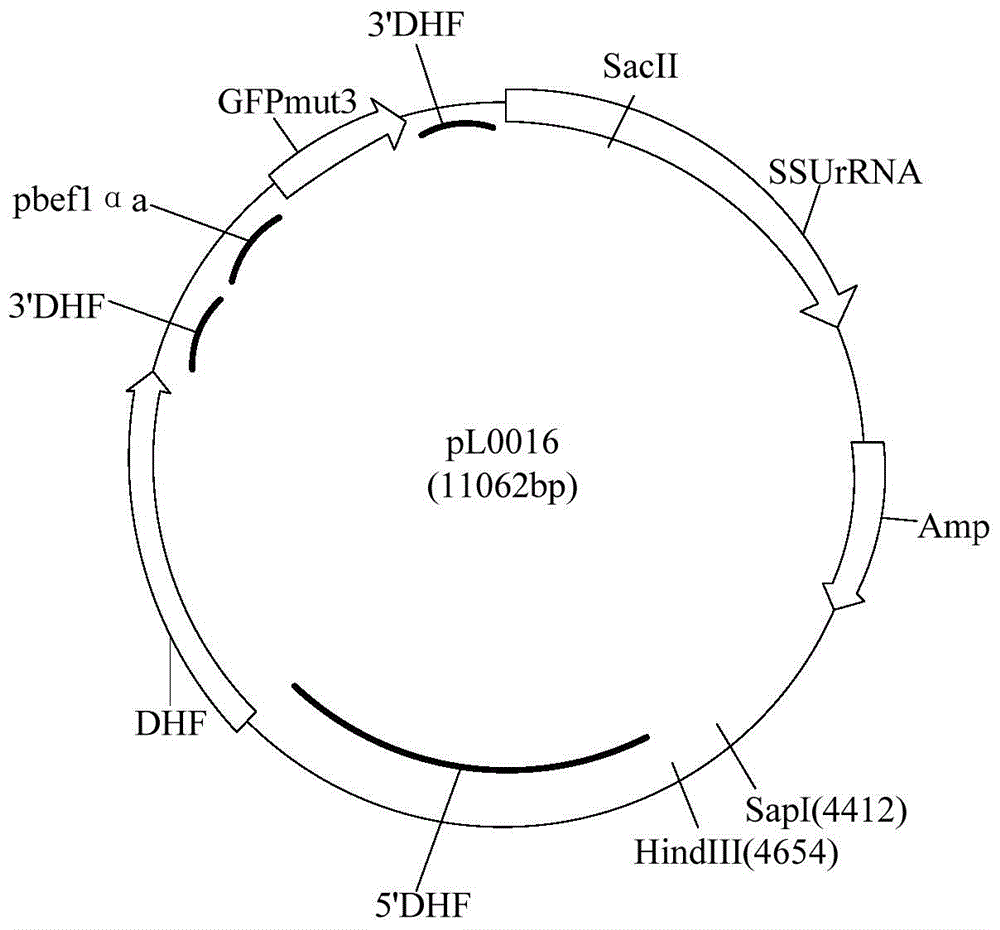
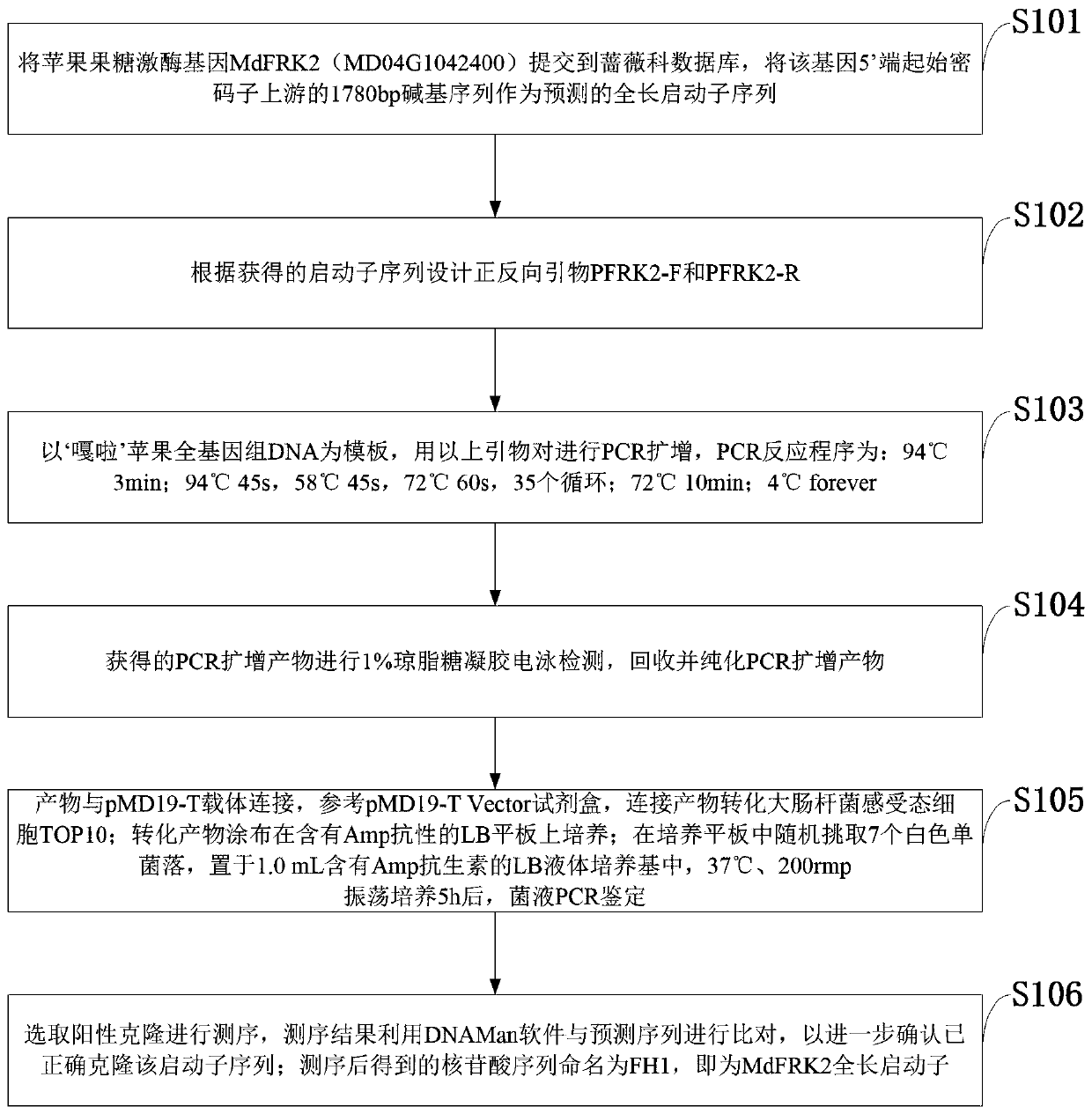
Promoter sequence of fructokinase gene in apple, and deletion mutants and application of
PendingCN111019943AFew research reportsRich researchTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological gene engineering and discloses a promoter sequence of a fructokinase gene in an apple, and deletion mutants and application of. A promoter isnamed as FH1 and is a 1780-bp nucleotide sequence at the upper stream of the 5'-end of an MdFRK2 gene coding frame in an apple; and the mutants are sequences obtained by deleting fragments with different lengths from the 5'-end of the sequence of FH1 and are named as FH2, FH3 and FH4 respectively. The invention further discloses application of the MdFRK2 promoter and the deletion mutants of the MdFRK2 promoter in research on plant functional genes. The MdFRK2 promoter can regulate and control the specific expression of a target gene in cambium of stem tip growth points, old leaves, functionalleaf margins and other library tissues of arabidopsis thaliana and poplar, and a fragment from a transcription starting site to upstream-600 bp is determined to be a core fragment of a promoter region of the MdFRK2 promoter. The full length of the MdFRK2 promoter is induced by exogenous sugar and drought, which indicates that the promoter has important application value in industrial developmentof plant genetic engineering.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Small molecule RNA, preparation method thereof and application in pharmaceuticals for transcriptional activity of specificity up-regulated genes
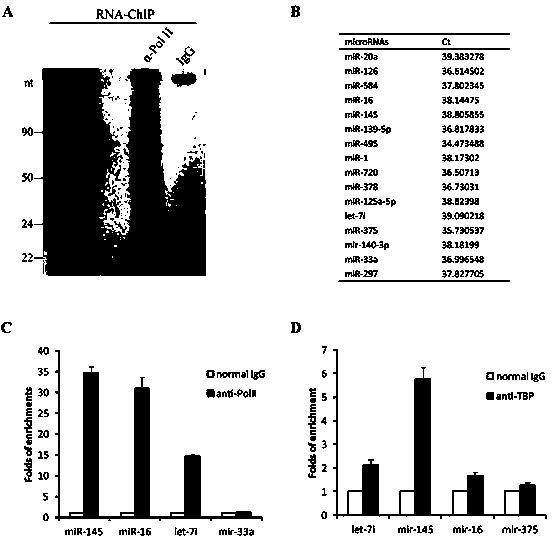
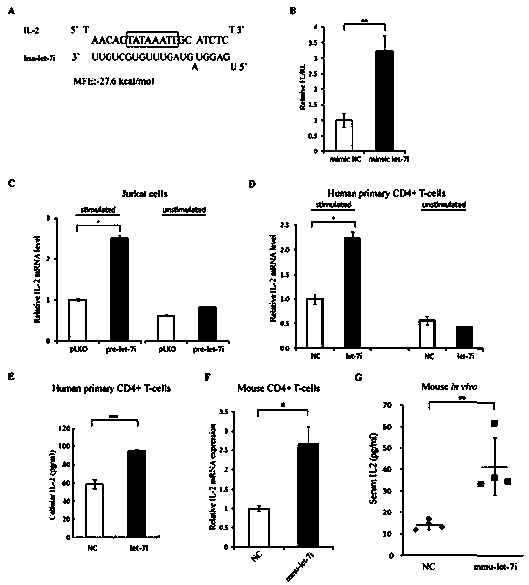
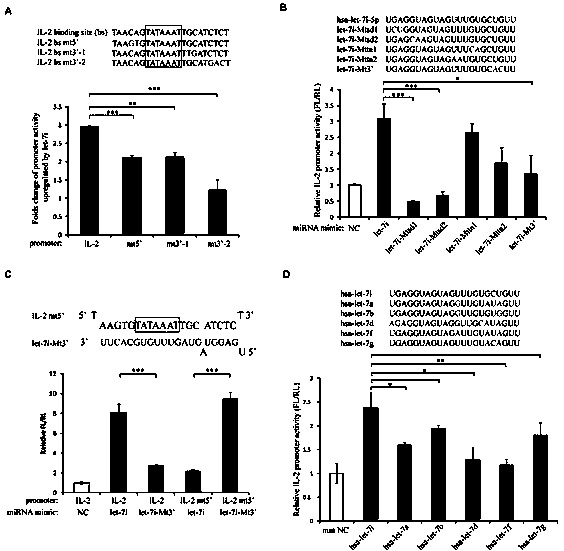
ActiveCN103509797AHigh expressionUpregulates gene transcription activityGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyTranscription initiation siteBase J
The invention discloses a method for specificity up-regulated gene expression through a targeting core promoter utilizing small molecule RNAs (including micro-RNAs and small interfering RNAs) and a series of regulation target genes. According to the invention, when a TATAbox sequence is contained in the promoter, a target site is in the range of expanding 20 basic groups from the upstream and downstream sides respectively by taking the TATAbox sequence as the center; when no TATAbox sequence is contained in the promoter, the target site is a 1-50 sequences on the upstream side of the genetic transcription initiation site. The micro-RNAs hsa-let-7i, hsa-miR-138, hsa-miR-92a, hsa-let-7c and hsa-miR-181d specifically regulate up the expression of interleukin-2, insulin, thyrocalcitonin, histone and c-myc gene respectively. Besides, aiming to the randomly-selected 19 gene promoters, the artificially-synthesized small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can enhance the transcriptional activities of 78.9% of the genes. The invention aims to provide the method for specificity up-regulated gene expression utilizing micro-RNAs and has higher application values and broad application prospects in the biotechnology and the biomedicine field.
Owner:GUANGZHOU QIANYANG BIO-TECH PHARM CO LTD
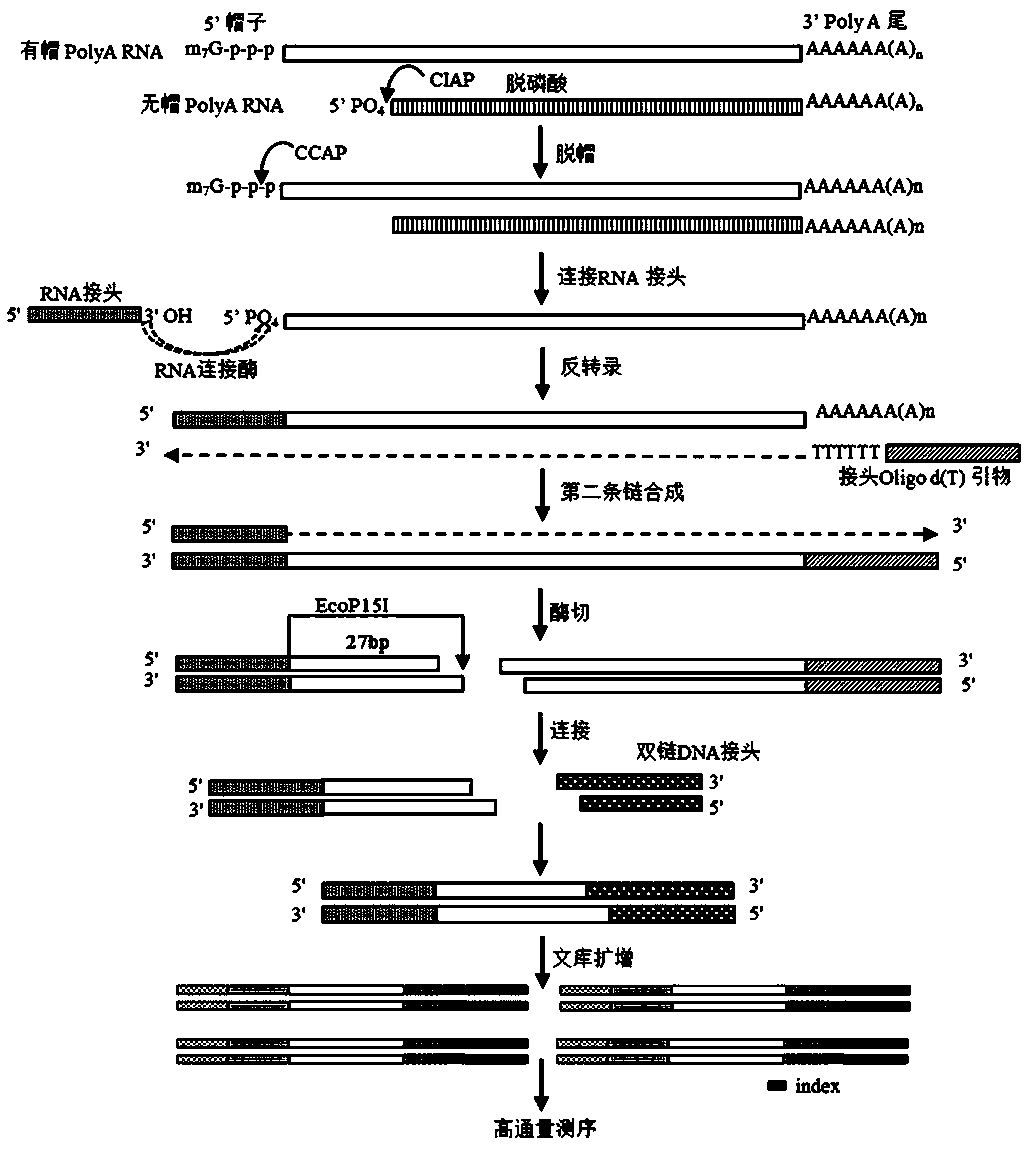
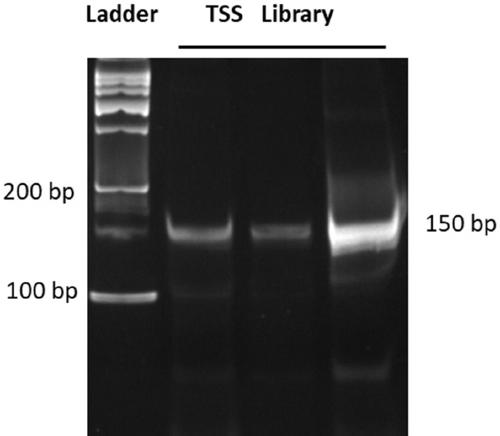
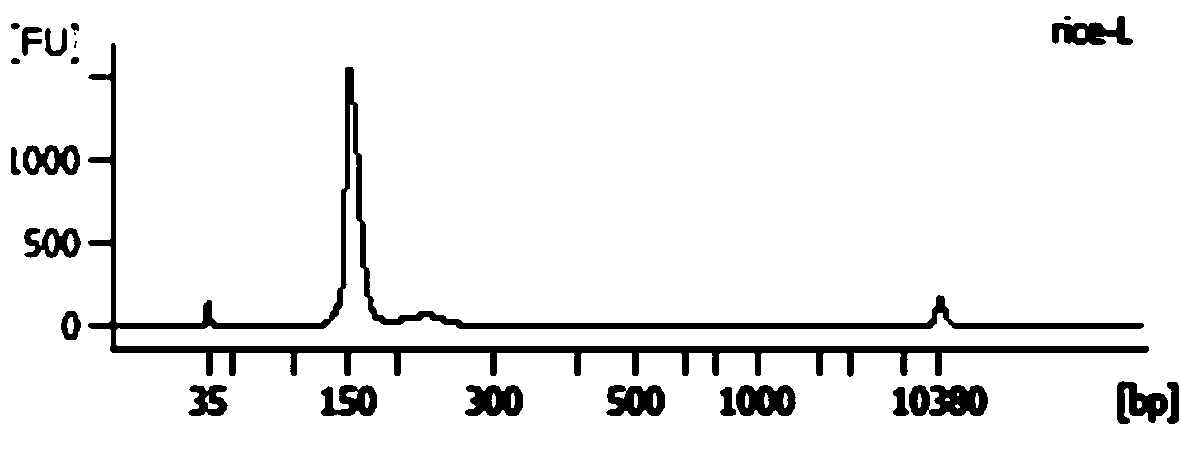
Library construction method capable of detecting transcription initiation sites of eukaryotes by using high-throughput sequencing technology
PendingCN109750031AEfficient constructionPrecise positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationTranscription initiation siteEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a library construction method capable of detecting poly (A) RNA transcription initiation sites of eukaryotes by using a high-throughput sequencing technology. The method is used for RNA with poly (A) tail and cap structure in the eukaryotes, and comprises the following steps: purifying to obtain the poly(A) RNA, removing phosphorylation, removing the cap structure, connecting RNA adapter, carrying out reverse transcription, carrying out PCR amplification, carrying out enzyme digestion, connecting double-stranded DNA adapter, carrying out PCR enrichment transcription initiation sites library, carrying out purification and analysis of the library. The method has the advantages of high cap removalefficiency, capability of efficiently constructing a transcription initiation sites library, convenience for accurately positioning the transcription initiation sites, simplicity and convenience in sequencing method, contribution to improving the accuracy of a transcription initiation sites analysis result and the like; the technique can be used for the study of all RNA transcription initiation sites with the cap structure with a slight improvement.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
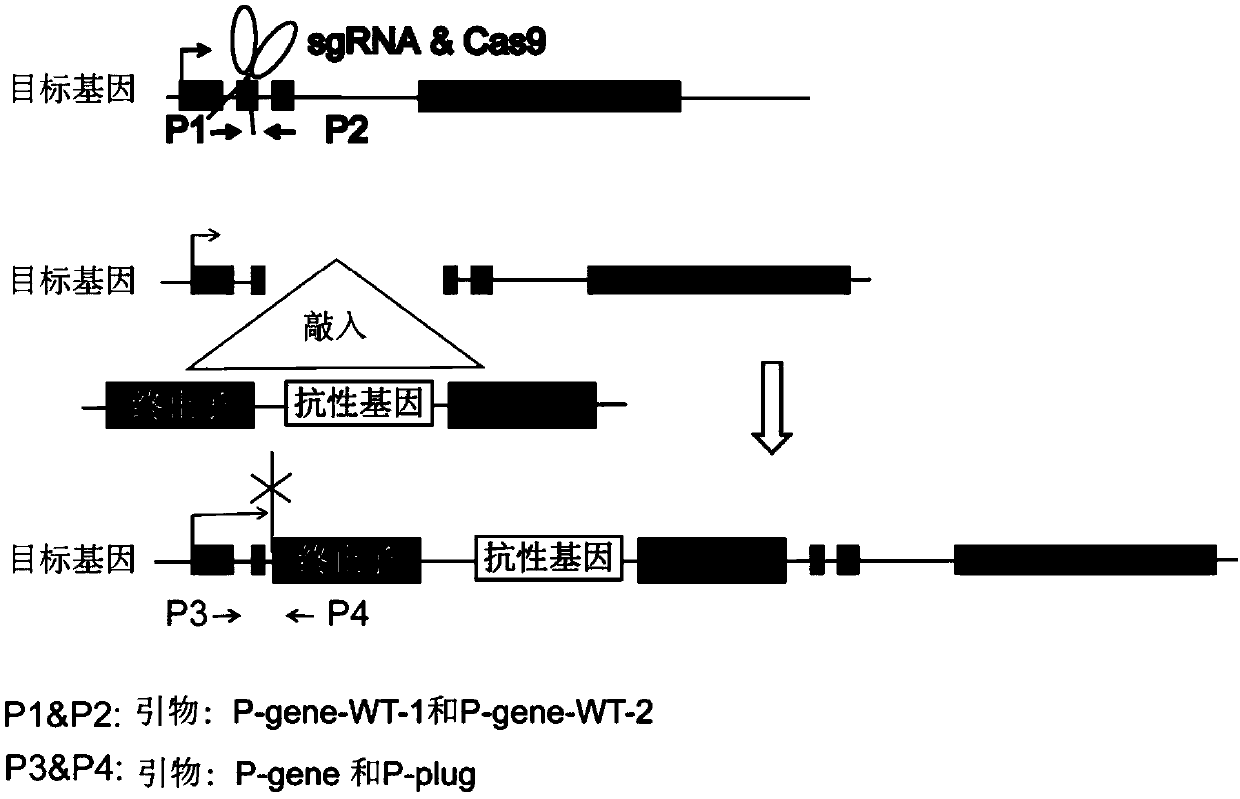
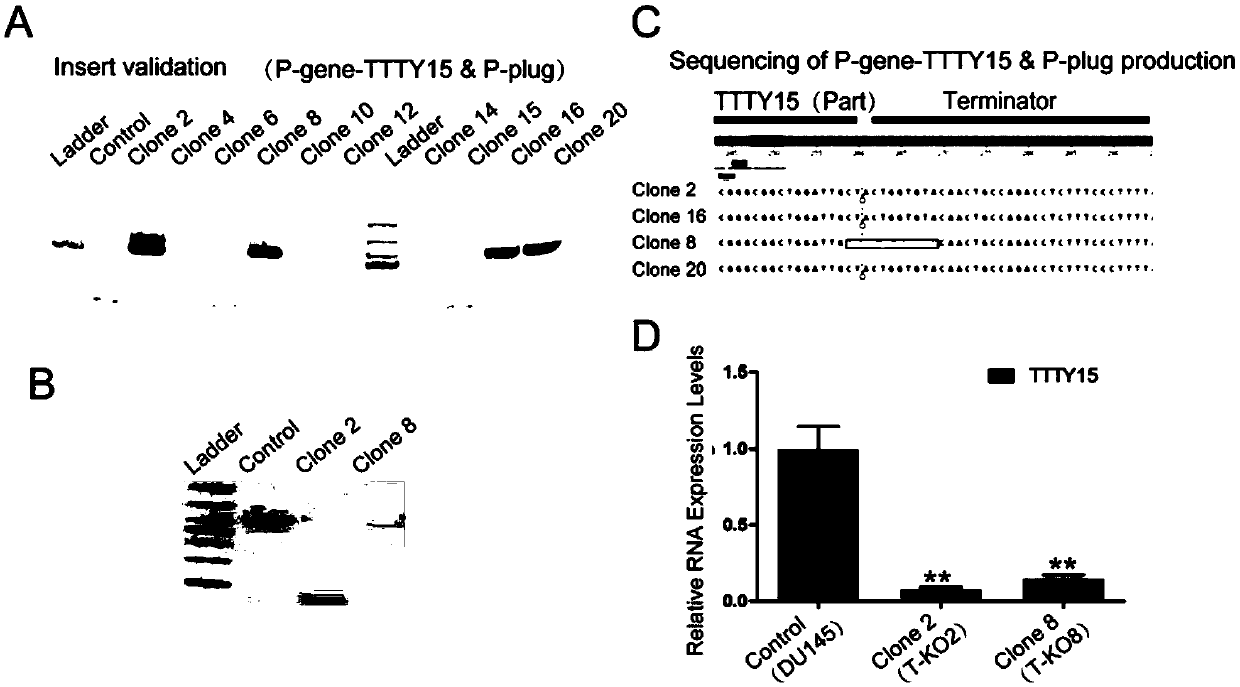
Method for knocking in terminator to achieve transcription factor knockout by using gene editing technology
PendingCN111218479AAchieve knockoutVersatilityStable introduction of DNATranscription initiation siteA-DNA
The invention relates to a method for knocking in a terminator to achieve efficient knockout of a transcription factor (including protein editing genes, non-encoding genes, and the like) by using a gene editing technology. Specifically, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) break is caused behind a transcription start site (TSS) of a gene to be knocked out by using a gene editing technology, meanwhile, a DNA donor with a transcription termination sequence (terminator) is introduced into cells, the doner does not comprise a target gene homologous sequence, the DNA donor is also linearized by using the gene editing technology, then after the terminator is knocked into a TSS of a target gene through a non-homologous repairing way, endogenous transcription of the target gene is terminated ahead of time,and thus knockout of the target gene is achieved. The method is wide in application scope, and all transcription facts can be knocked out by the method. The doner DNA has universality, has high efficiency, and in addition, has resistance genes, and the method is high in efficiency and has certain practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
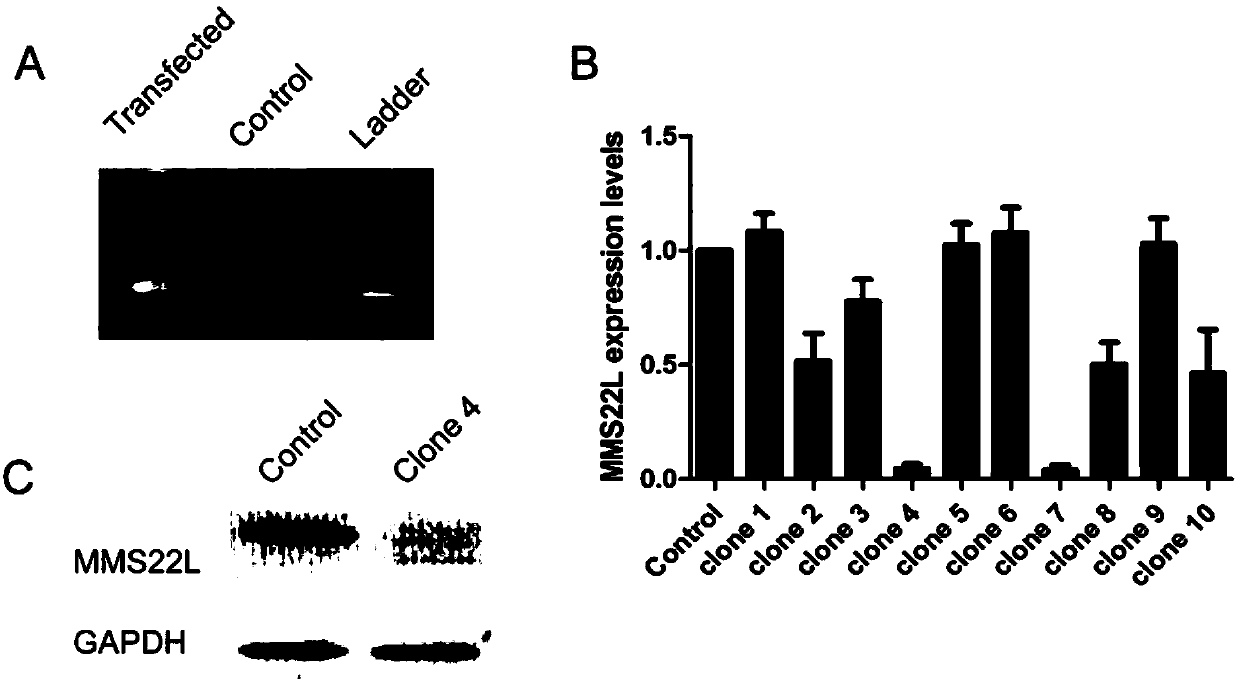
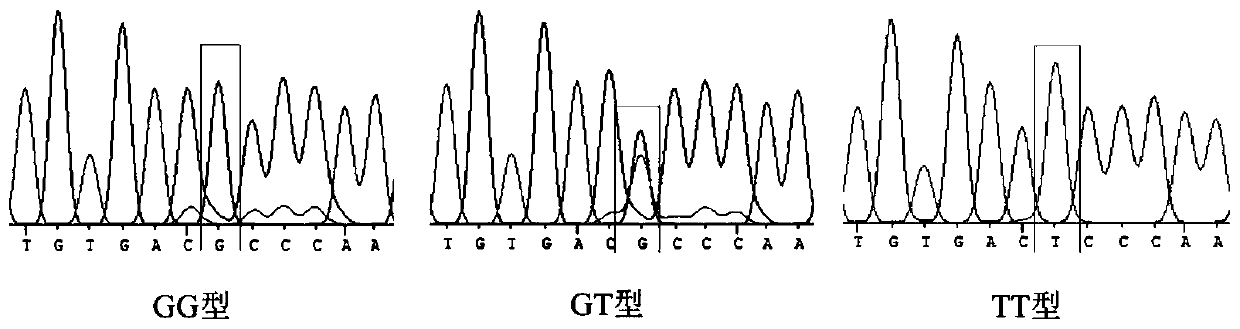
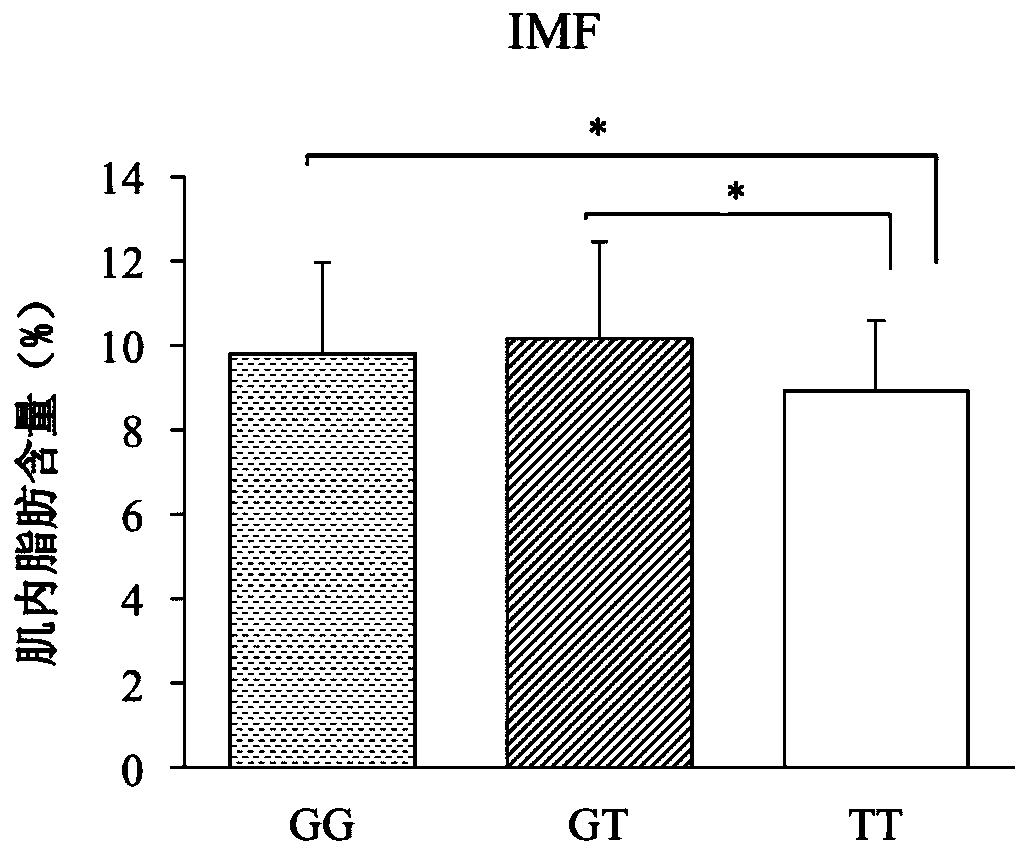
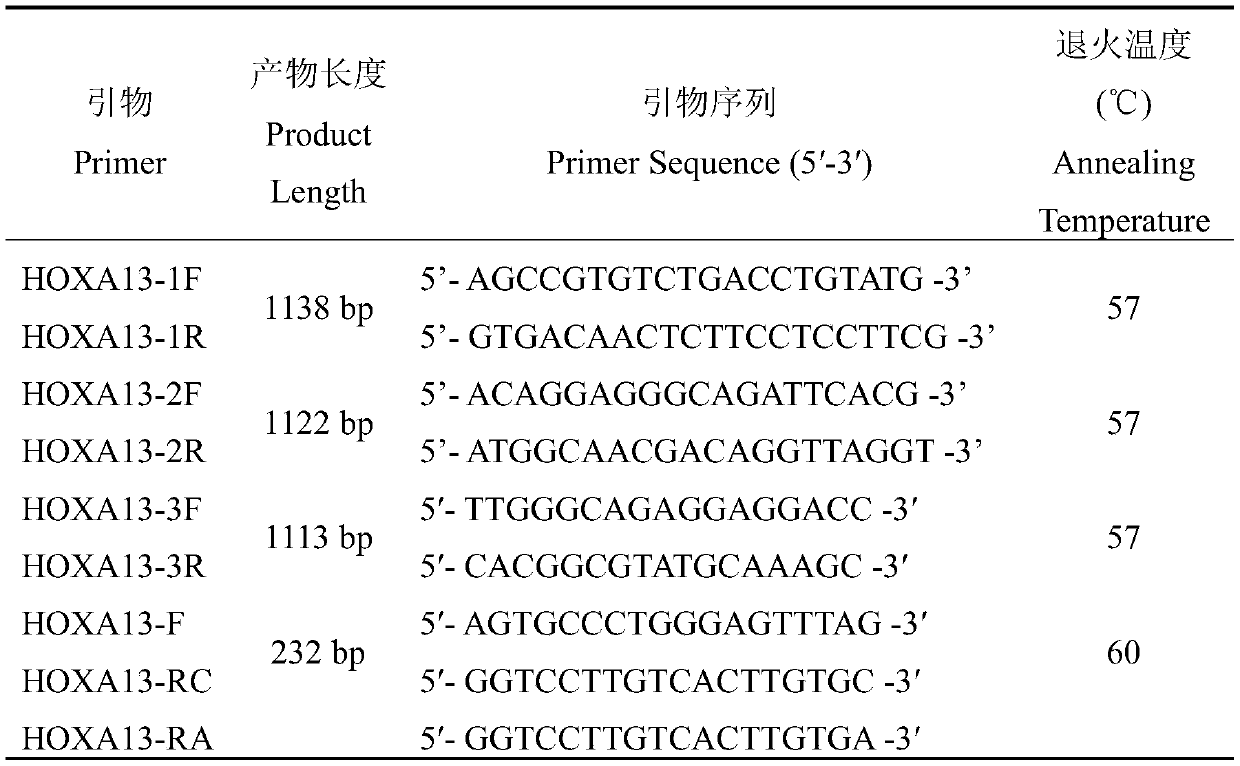
HOXA13 gene promoter region SNP site and application thereof to detection on intramuscular fat content of pigs
ActiveCN110079616AIncrease intramuscular fat contentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiation siteIntramuscular fat
The invention provides an SNP site for detecting the intramuscular fat content of pork. The SNP site is positioned at the upstream 1311bp position of a pig HOXA13 gene transcription initiation site; and the genotype of the SNP site is GG, GT or TT. Therefore, the SNP is named as (the formula is as shown in the description). The invention also provides a method for detecting the intramuscular fat content of the pork. The method comprises the steps of extracting the DNA of a to-be-detected pork sample, parting amplified fragments and judging the intramuscular fat content of a pork sample throughthe parting result. The method for detecting the intramuscular fat content of the pig is obtained by researching the correlation of the muscle development key gene HOXA13 and the intramuscular fat content; and based on the method, breeding of the pigs is benefited, foundation is laid for further increasing the intramuscular fat content of the pork and judging the intramuscular fat content of thepork conveniently and rapidly, and important significance in cultivating the pigs with excellent meat varieties is achieved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
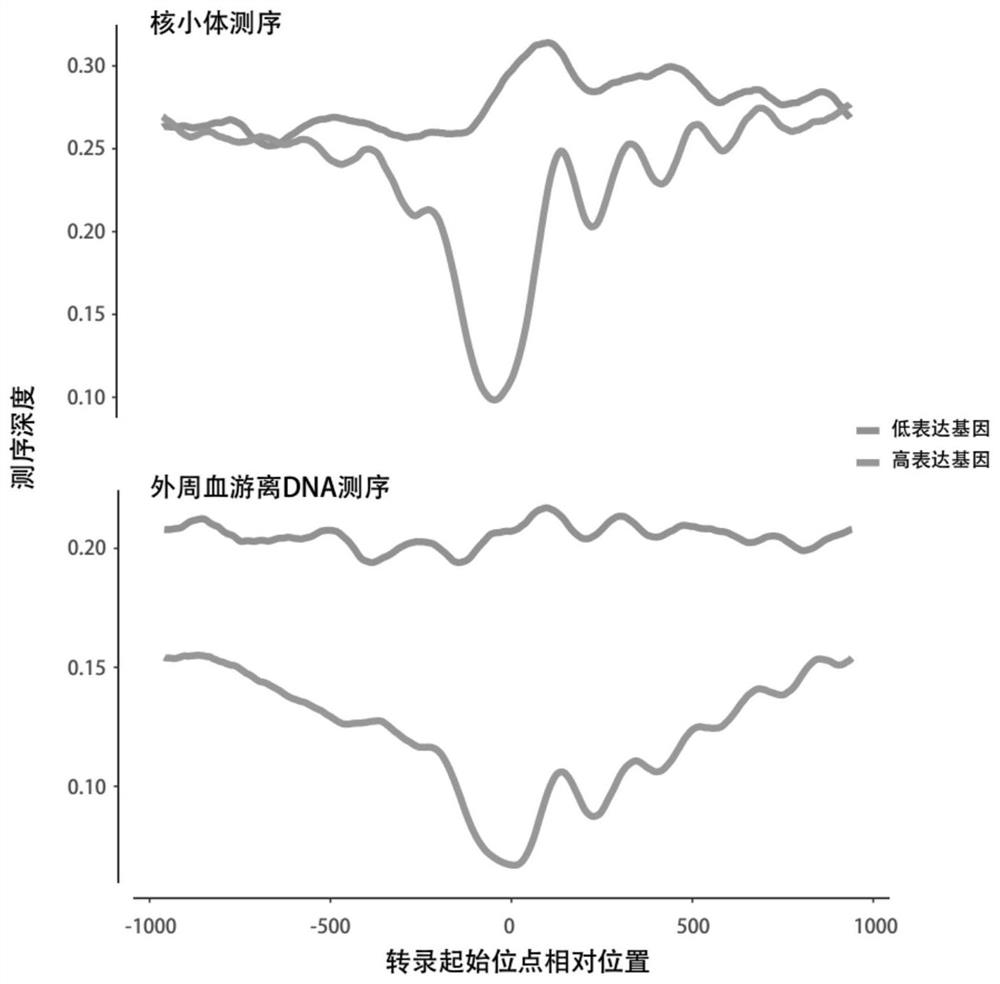
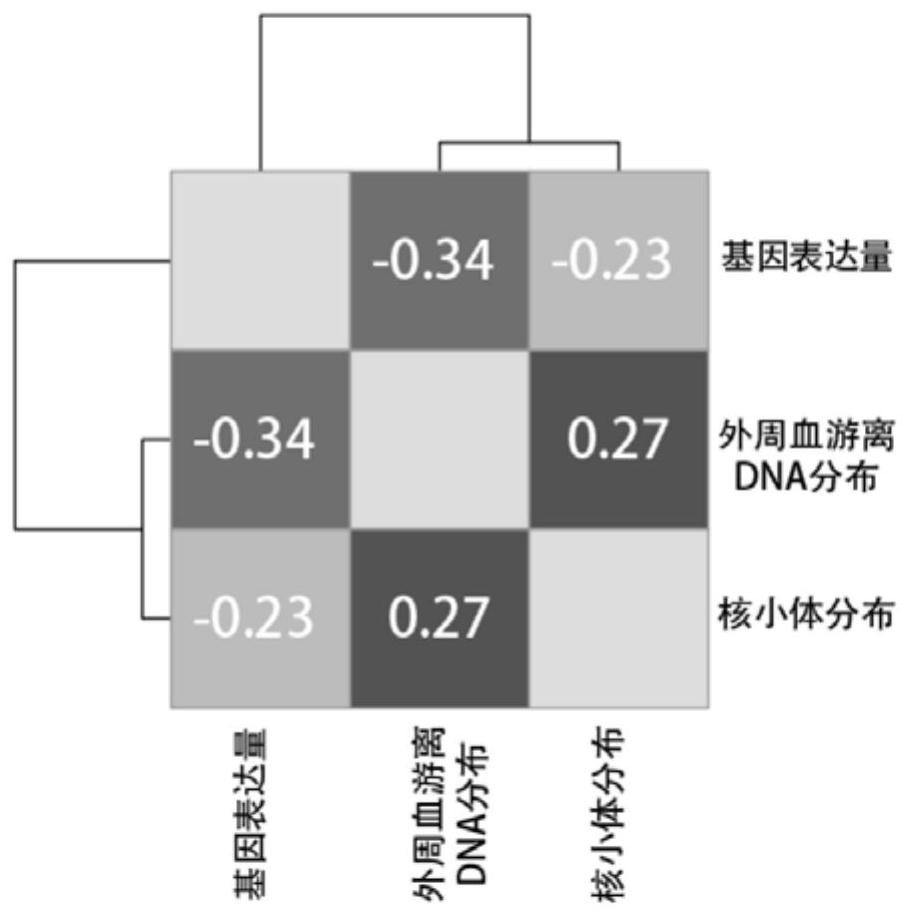
Giant baby forecasting model based on peripheral blood free DNA detection
ActiveCN110305970AEffectively predict the onsetMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription initiation siteSerum free
The invention discloses a giant baby forecasting model based on peripheral blood free DNA detection. Through research, the inventor finds that the distribution situation of peripheral blood free DNA in a genetic transcription initiation site region can reflect the physiological status of a pregnant woman and a foetus, based on significant differences of serum free DNA abundance in the genetic transcription initiation site region between a giant baby pregnant women and a healthy pregnant women, the free DNA abundance is subjected to uniform calibration, a machine learning algorithm is used, andthrough preferable selection combination of different difference genes, effective forecast of pathogenesis of a giant baby can be realized. Therefore, the screening and forecasting model based on peripheral blood free DNA forecasting is constructed, an optimized target gene combination is constructed, forecast of pathogenesis of the giant baby can be realized before the giant baby was born, and arelatively non-invasive, economic and convenient early giant baby forecasting method is adopted, and has good application prospects in the respect of developing giant baby forecasting and screening products.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Model for predicting gestational diabetes mellitus by using peripheral blood free DNA
ActiveCN110387414AEffectively predict the onsetEasy to combineMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisTranscription initiation siteNeonatal diabetes
The invention discloses a model for predicting gestational diabetes mellitus by using peripheral blood free DNA. According to research finding of the model, distribution of the peripheral blood free DNA in the region of a gene transcription initiation site can reflect the physiological status of pregnant women and fetuses, after the free DNA abundance is subjected to homogenization correction based on the fact that the serum free DNA abundance in the region of the gene transcription initiation site has the significant difference between gestational diabetes patients and healthy pregnant women,a machine learning algorithm is used, and optimal combination of different differential genes can effectively predict the incidence of gestational diabetes; and thus a screening prediction model forgestational diabetes based on peripheral blood free DNA prediction and an optimized combination of target genes are constructed, the incidence of gestational diabetes can be predicted before the onsetof the clinical symptoms of gestational diabetes, a relatively non-invasive, economical and convenient method for predicting early gestational diabetes is achieved, and good application prospects indeveloping predictive screening products for gestational diabetes are achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
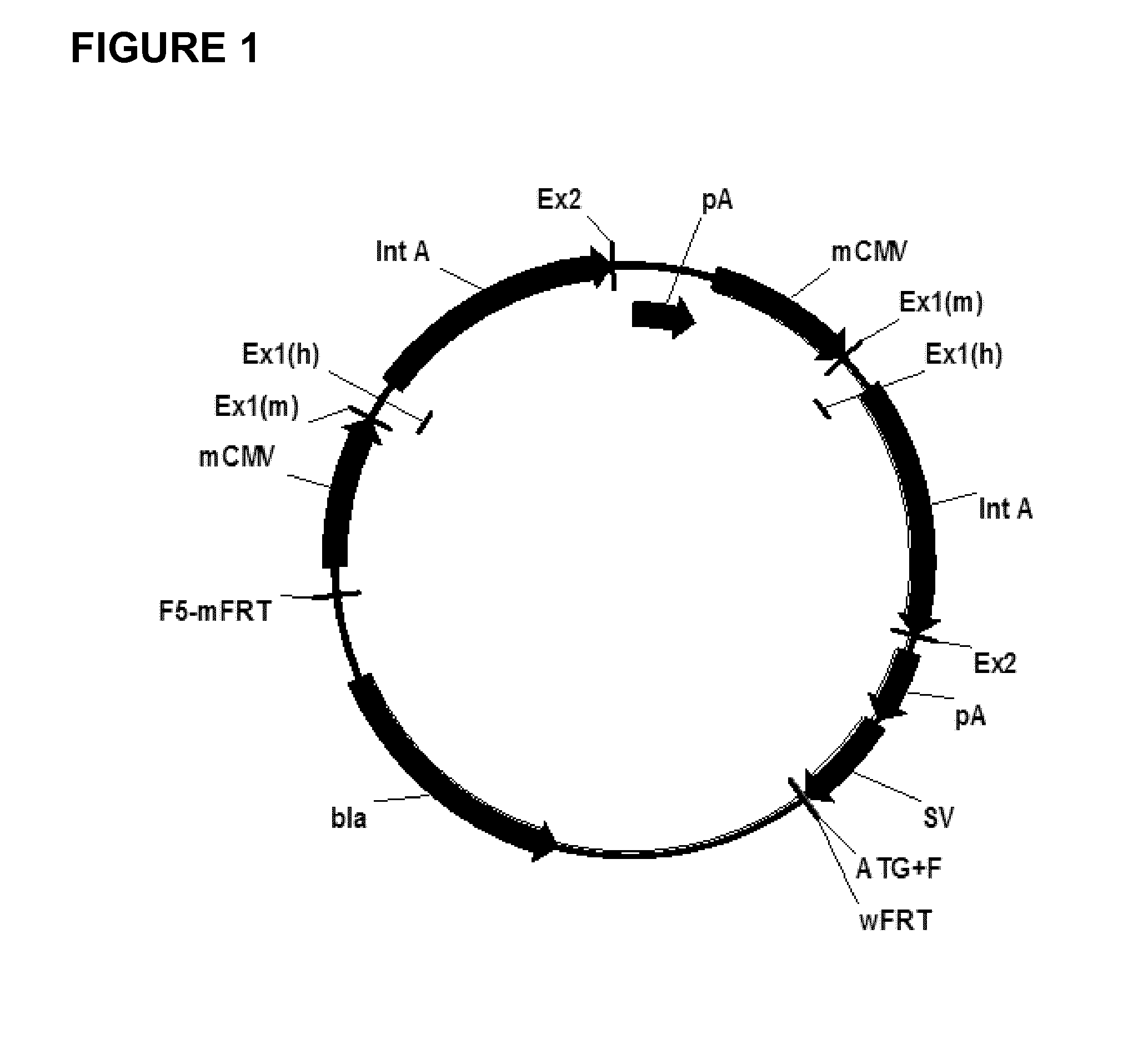
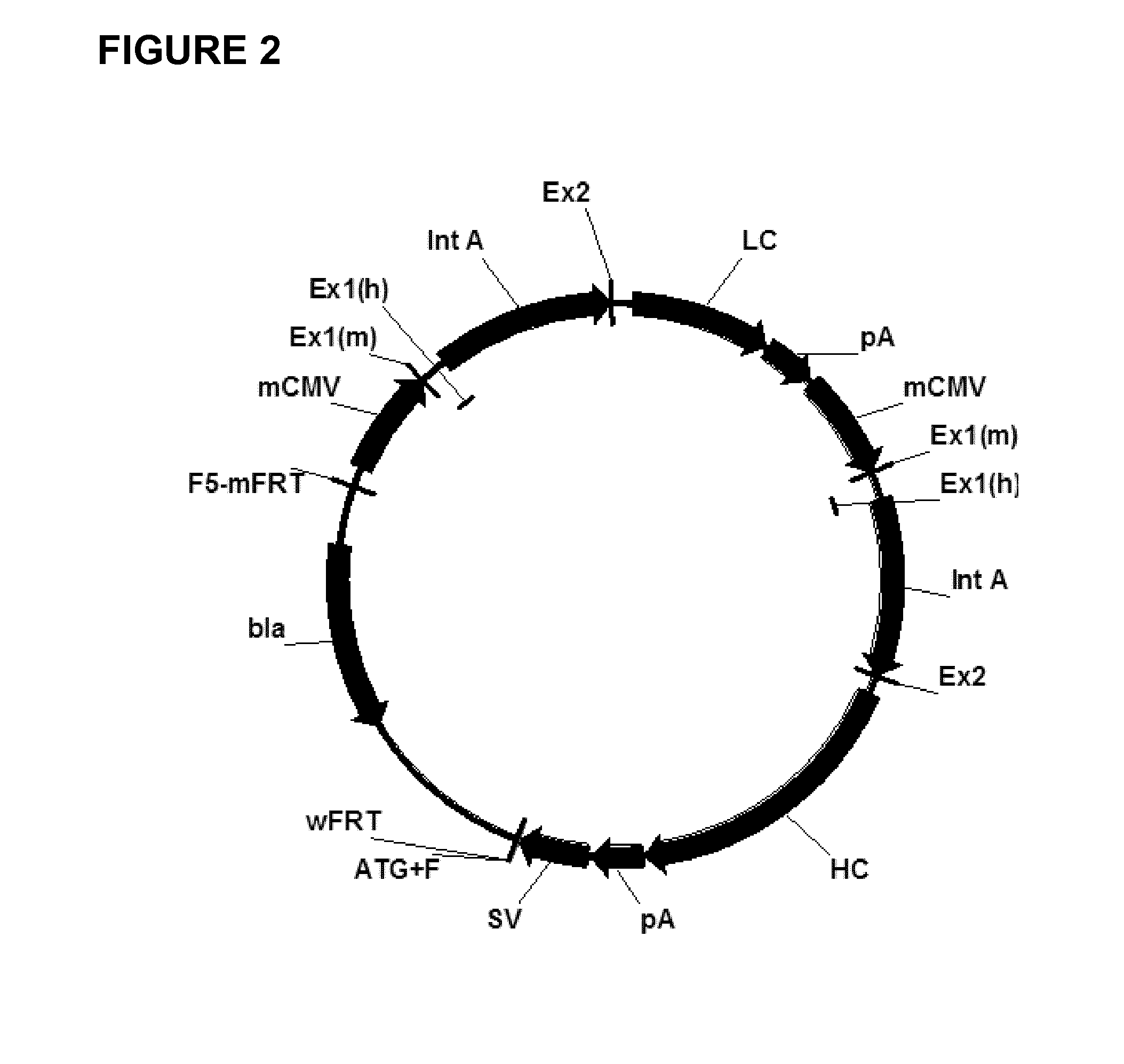
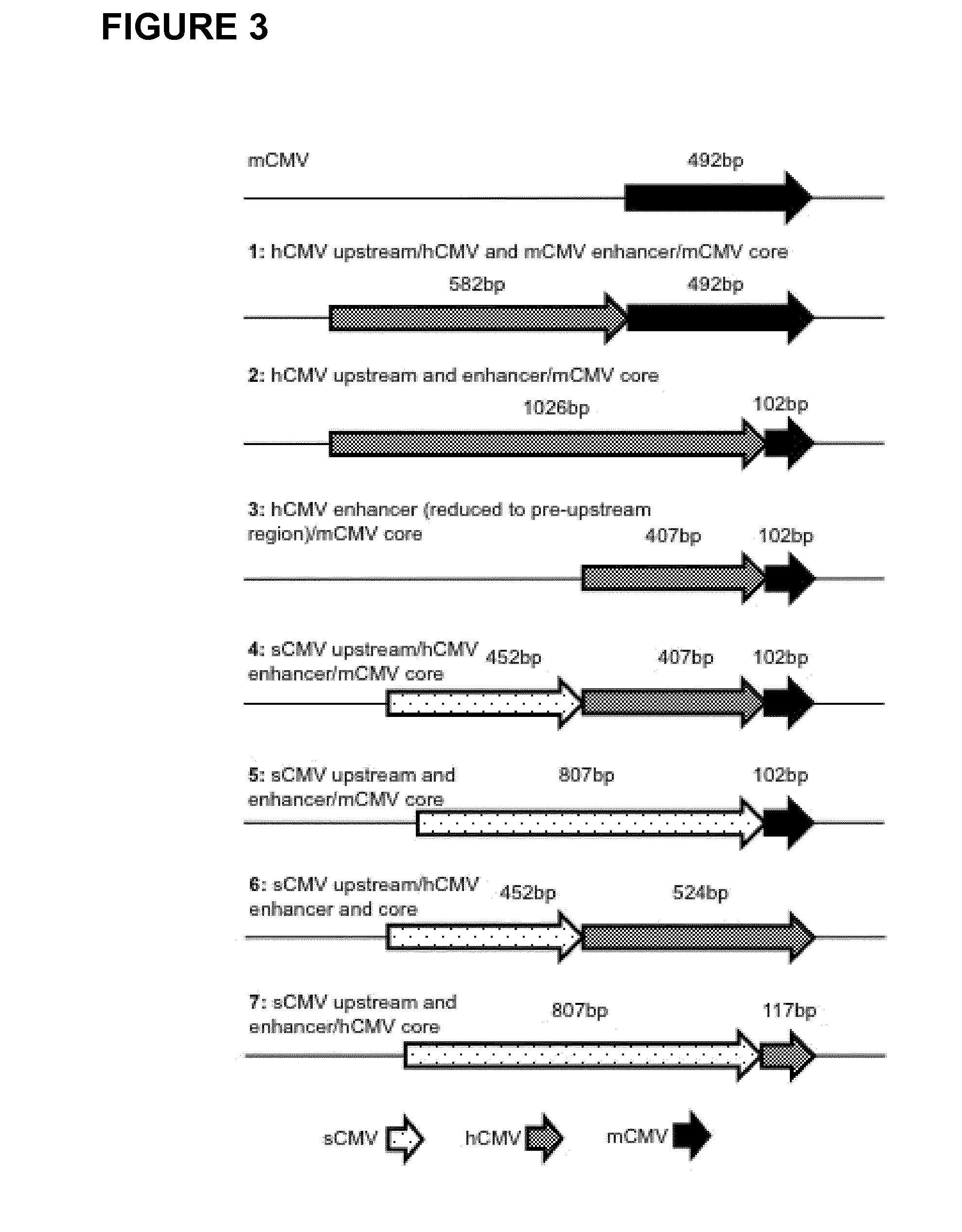
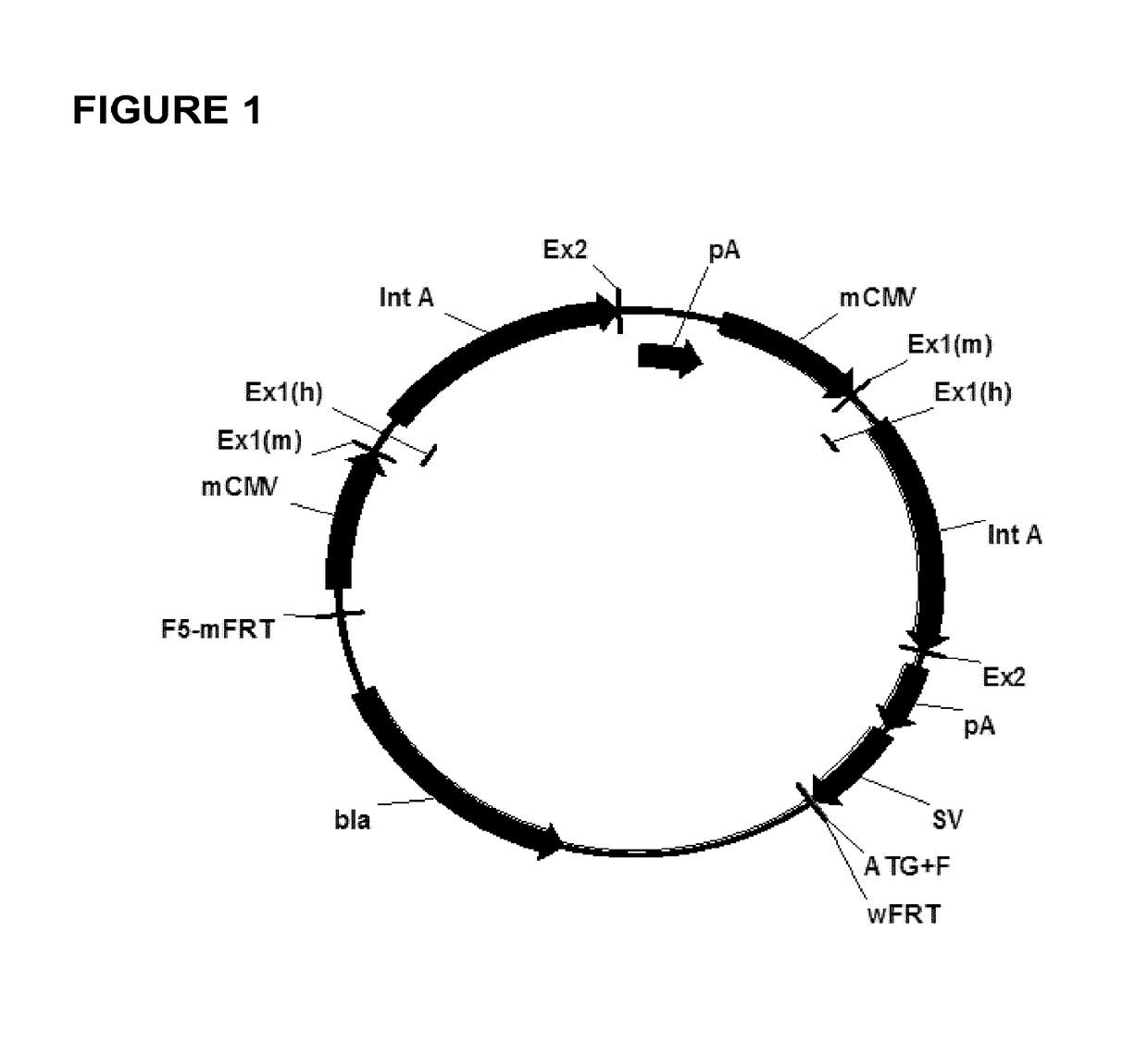
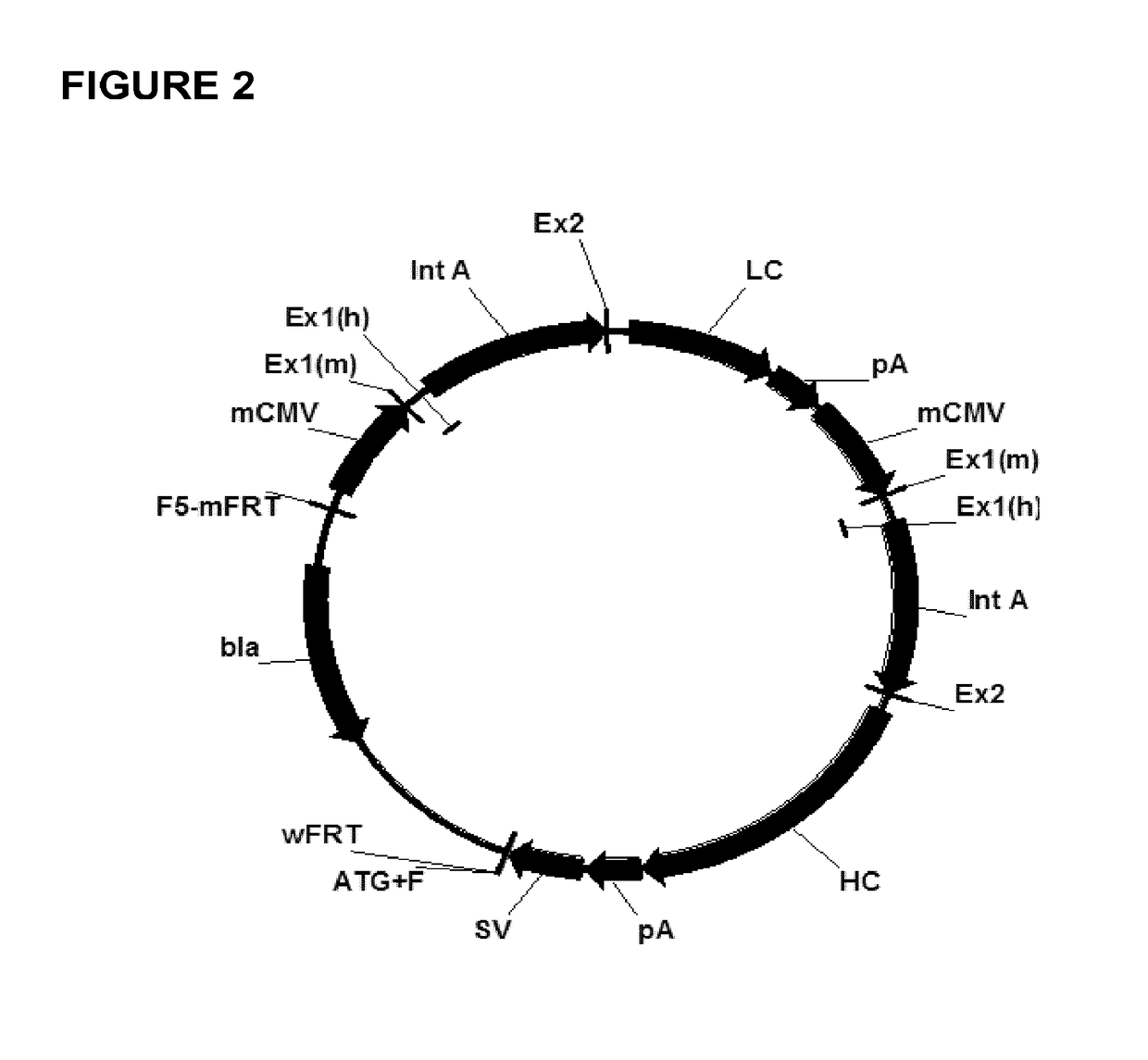
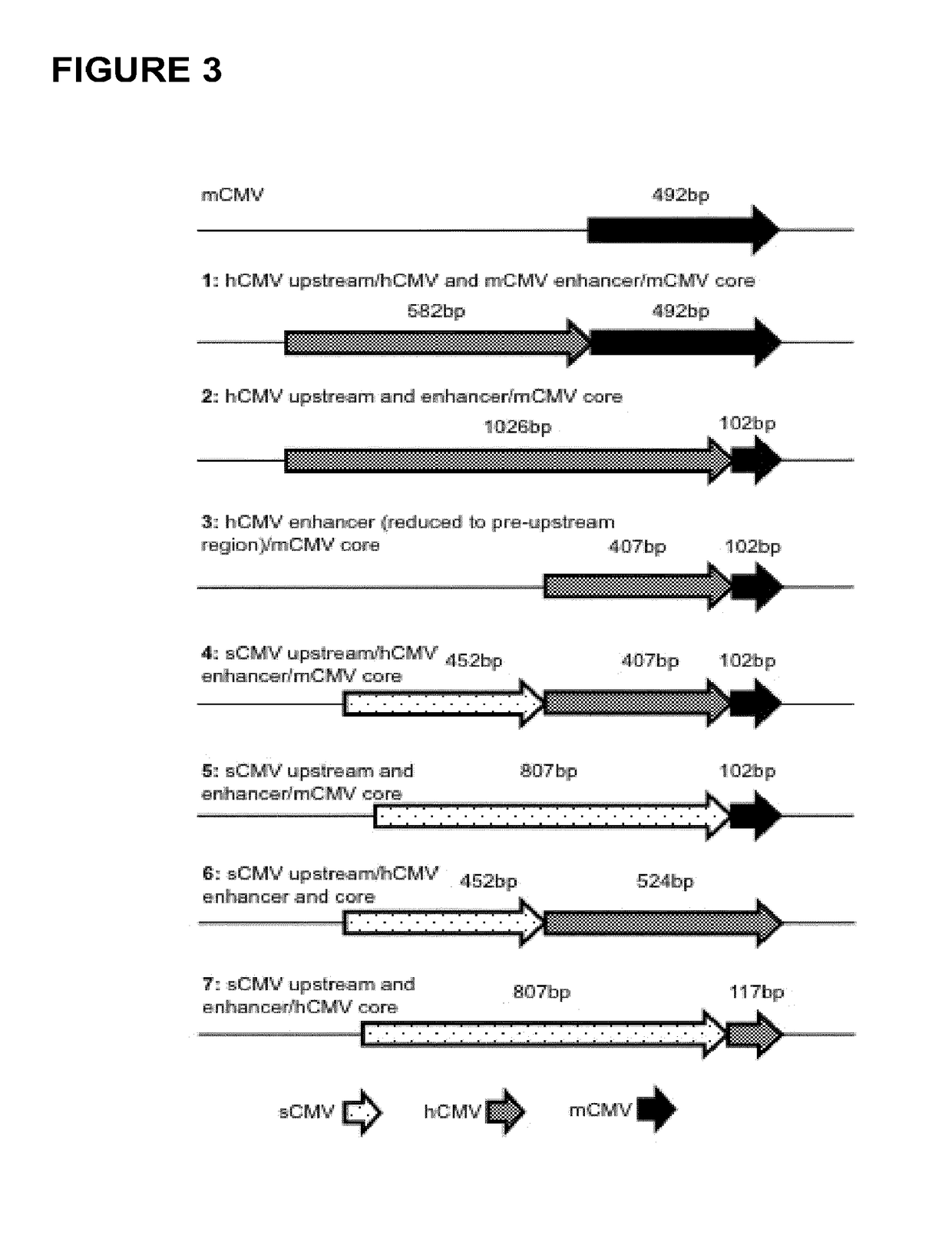
Expression vectors comprising chimeric cytomegalovirus promoter and enhancer sequences
The present invention relates to expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence of interest in mammalian cells, the vectors comprising a chimeric promoter regulatory sequence being operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence to be expressed, wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises a cytomegalovirus promoter sequence derived from murine cytomegalovirus or from human cytomegalovirus and being operably linked to the transcriptional start site of the nucleic acid sequence to be expressed; and a cytomegalovirus upstream region and / or enhancer sequence derived from human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus, wherein the upstream region and / or enhancer sequence is located 5′ of and operably linked to the murine or the human promoter sequence, and wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements being derived from at least two of the group consisting of murine cytomegalovirus, human cytomegalovirus and simian cytomegalovirus. In particular embodiments, the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements derived from the murine or the human cytomegalovirus IE1 promoter and from the human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus IE1 region. The invention also relates to mammalian host cells transfected with such expression vectors, a method for heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence in a mammalian host cell by employing such expression vectors, and the use of such expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
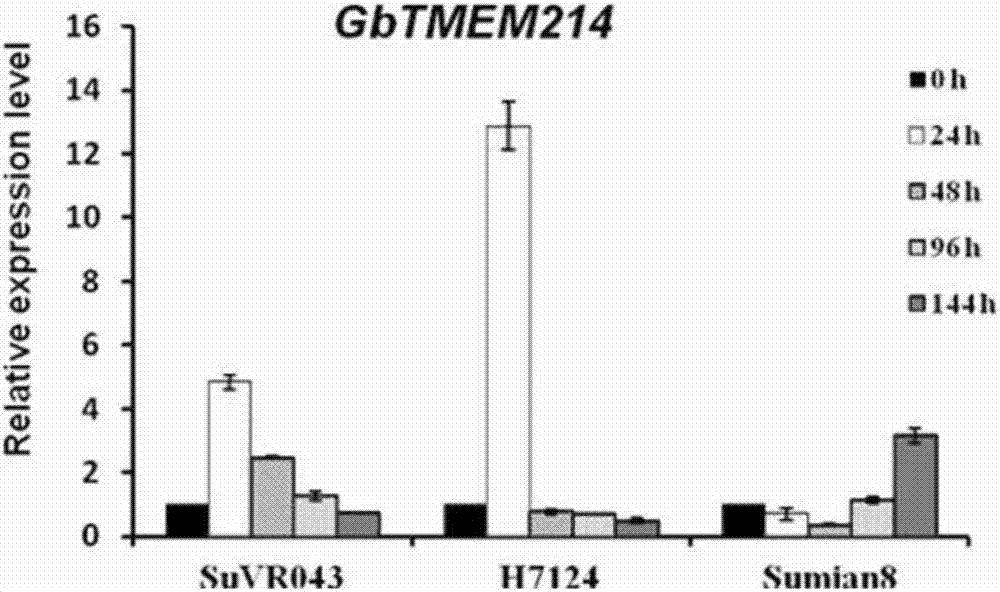
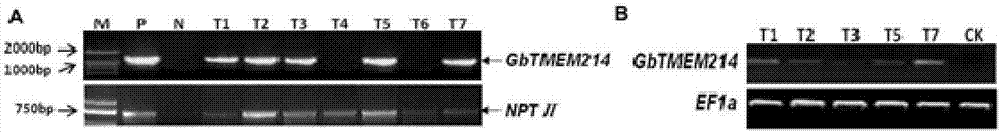
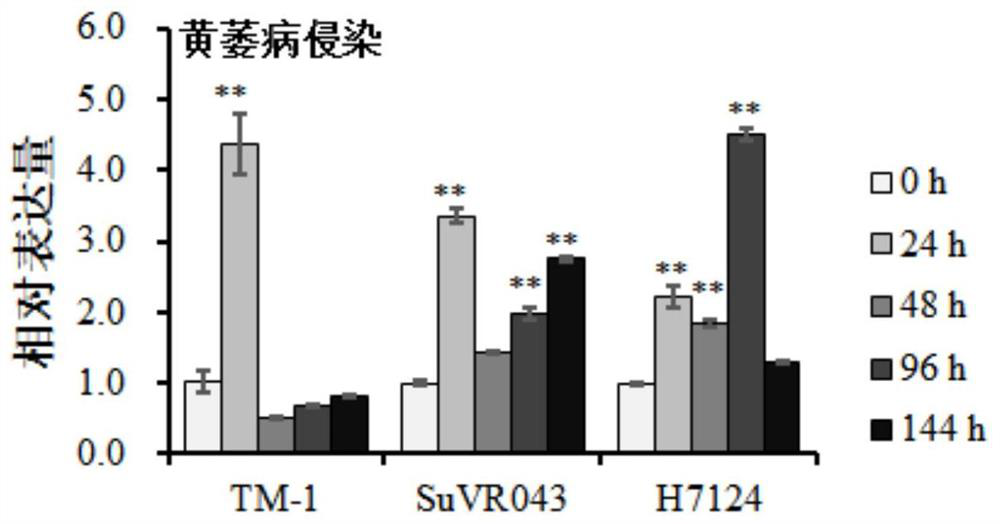
Gossypium barbadense transmembrane protein gene, primers, and application of Gossypium barbadense transmembrane protein gene
ActiveCN107254474ALower resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationDiseaseVerticillium wilt
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
CMV promoter and method for production of polypeptides
ActiveUS10329595B2High potencyReduced promoter silencingGenetically modified cellsVirus peptidesTranscription initiationNucleic acid sequencing
The current invention reports a promoter that has the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 02 or SEQ ID NO: 03 which is a human CMV major immediate-early (hCMV-MIE) promoter / enhancer with C to G point mutation at position −41 and / or −179 relative to the transcription start site. This new promoter is especially useful for the production of polypeptides at large scale as it shows reduced promoter silencing and improved polypeptide production.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
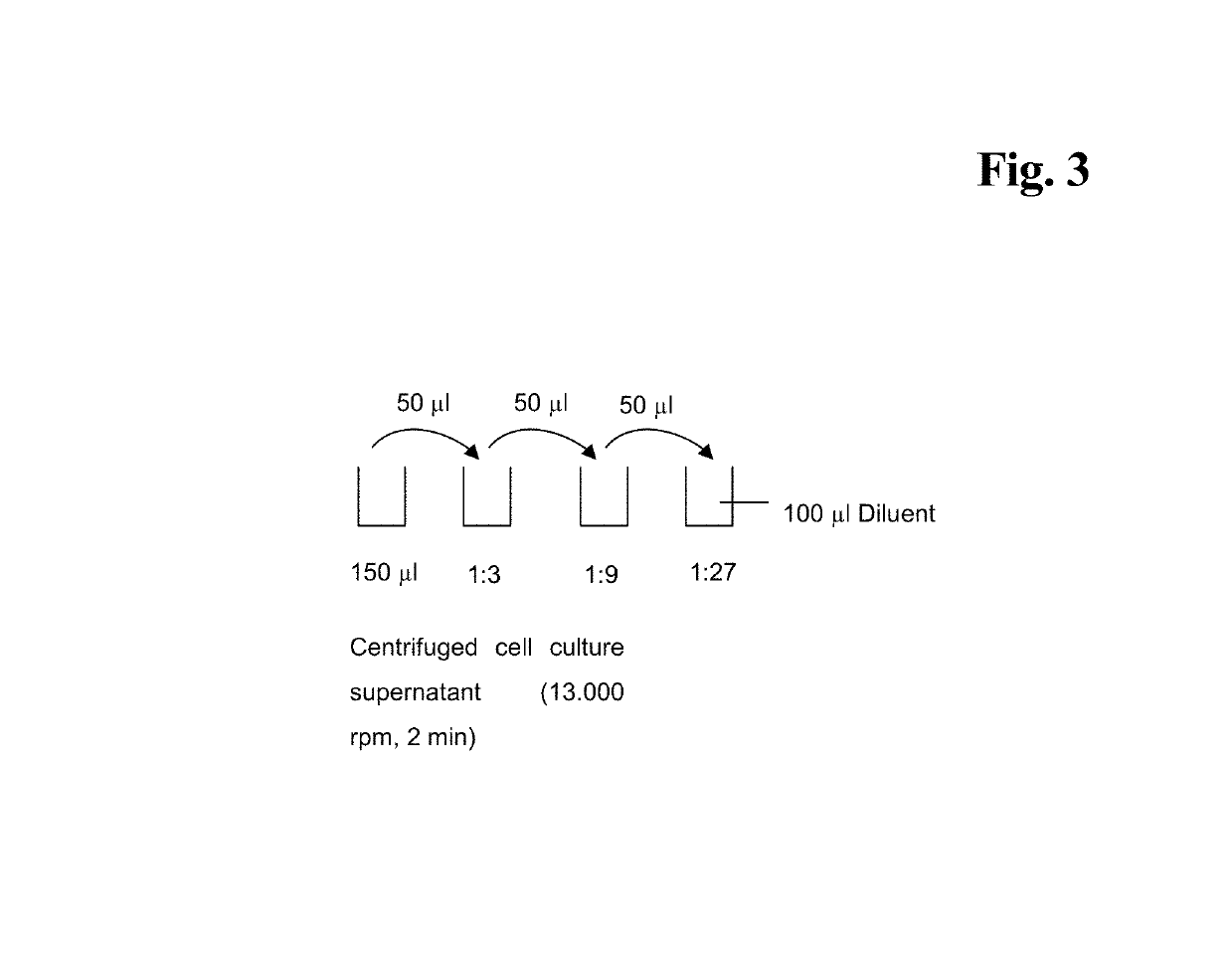
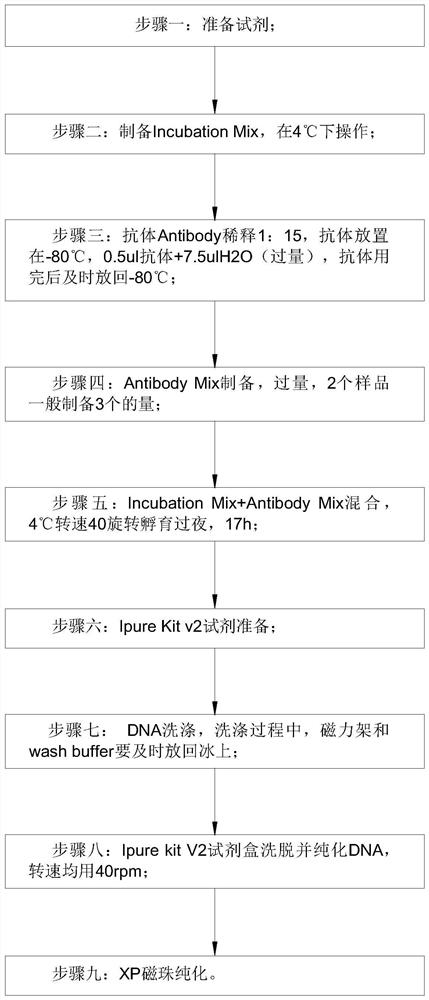
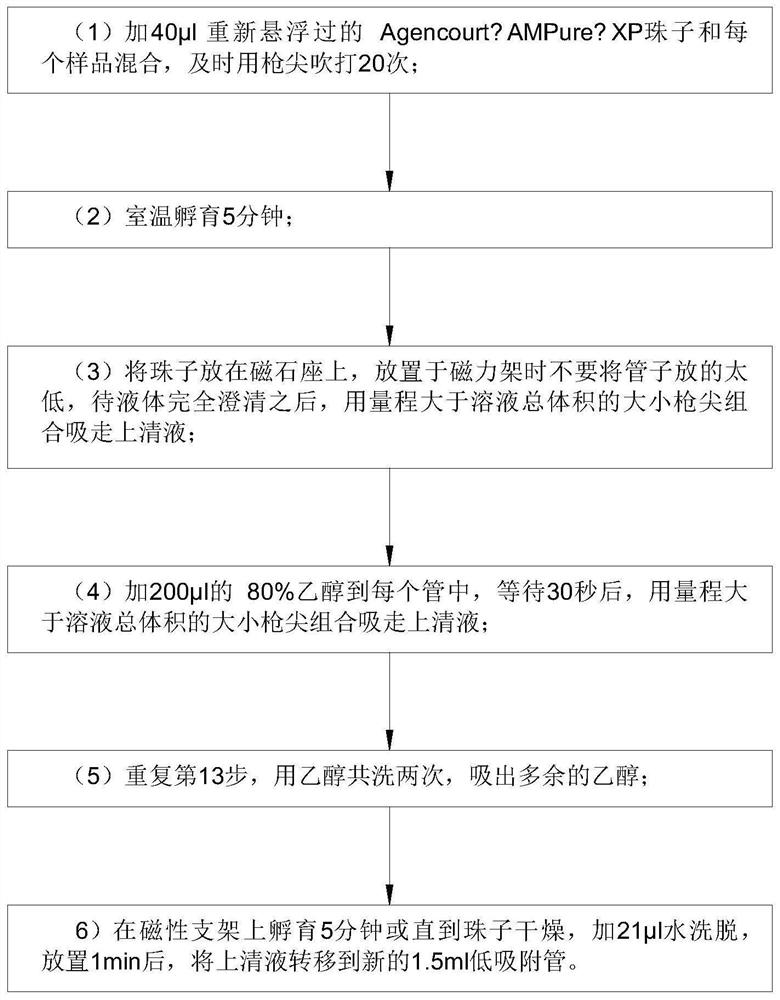
Detection method for capturing cfDNA5mC fragment
PendingCN113564226AImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription initiation siteMethyl palmoxirate
The invention discloses a detection method for capturing a cfDNA5mC fragment. The detection method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing reagents; step 2, preparing Inculation Mix, and operating at the temperature of 4 DEG C; step 3, diluting an Antibody at 1: 15, placing the antibody at -80 DEG C, adding 0.5 [mu] l of the antibody and 7.5 [mu] l of H2O (excess), and timely placing the antibody at-80 DEG C after the antibody is used up; step 4, preparation of Antibody Mix: the Antibody Mix is excessive, and three amounts of Antibody Mix are generally prepared for two samples; step 5, mixing an Inculation Mix and the Antibody Mix, rotating at the rotating speed of 40 at the temperature of 4 DEG C, and incubating overnight for 17 hours; and step 6, preparing an Ipre Kit v2 reagent. According to the detection method for capturing the cfDNA5mC fragment, methylation of fifth carbon of cytosine (5-methylcytosine: 5mC) is a methylation type excavated in eukaryotes at the earliest, in gene expression, a transcription start site region is generally non-methylated, and when the gene is expressed at a lower level, the methylation level of cytosine in a regulation region is higher, and library correlation generated by different initial quantities and different methods is an effective parameter for evaluating consistency and high performance.
Owner:深圳泰莱生物科技有限公司
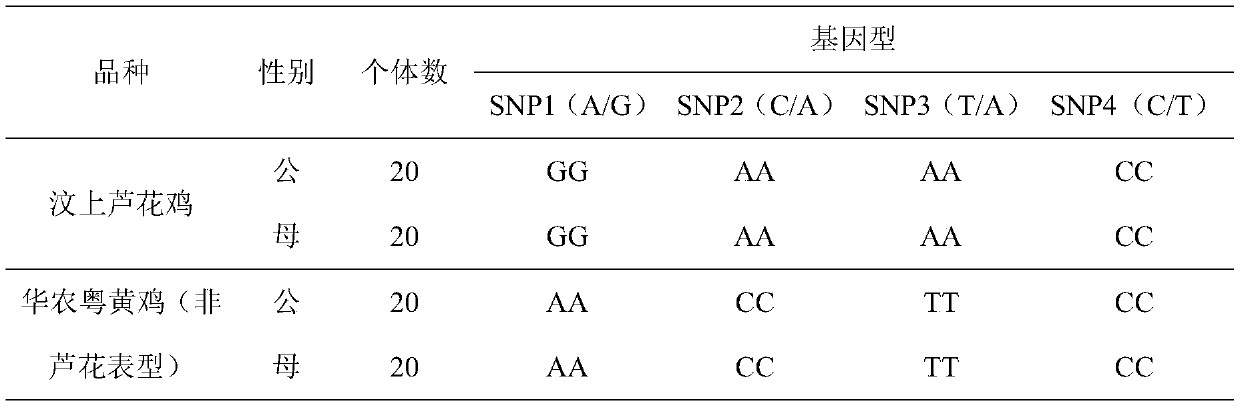
Identification method of sex-linkage Luhua chicken genotype of Chinese native chickens
ActiveCN110016508AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiation siteGallus gallus gallus
The invention discloses an interlocking SNP site combination related to the sex-linkage Luhua phenotype of Chinese native chickens. The SNP sites comprise SNP1, SNP2 and SNP3, wherein the SNP1 is a position of 267 bp of a CDKN2A gene promoter region and transcription initiation site upstream, the SNP2 is a position of 380 bp of CDKN2A gene intron 1, and the SNP3 is a position of 170 bp of CDKN2A gene exon 1. The invention finds the three SNP sites related to the sex-linkage Luhua chicken phenotype of Chinese native chickens for the first time, and establishes a method for detecting the phenotype and the genotype of sex-linkage Luhua chickens by the SNP sites. The method has the advantages of simple operation, high accuracy, good repeatability and time saving, is available to mutual detection, realizes 100% accuracy, can be used for cultivating auto-sexing commercial strains, performs auto-sexing by using feather colors, is high in accuracy and simple and convenient to operate, saves time and cost, has good application value, and is worthy of great popularization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
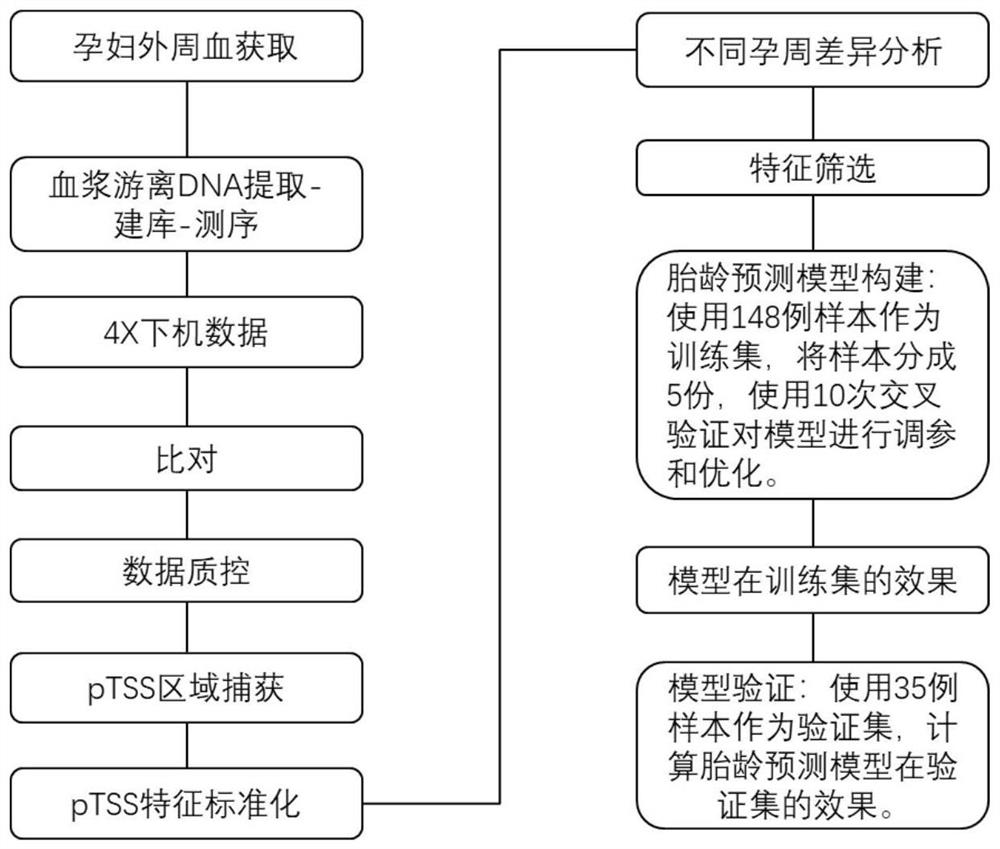
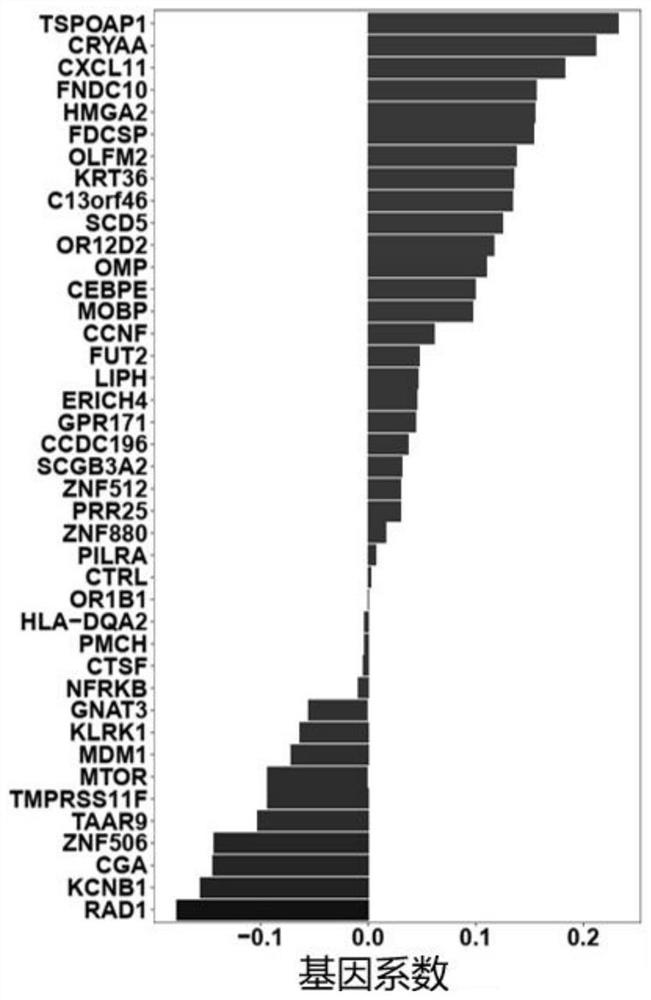
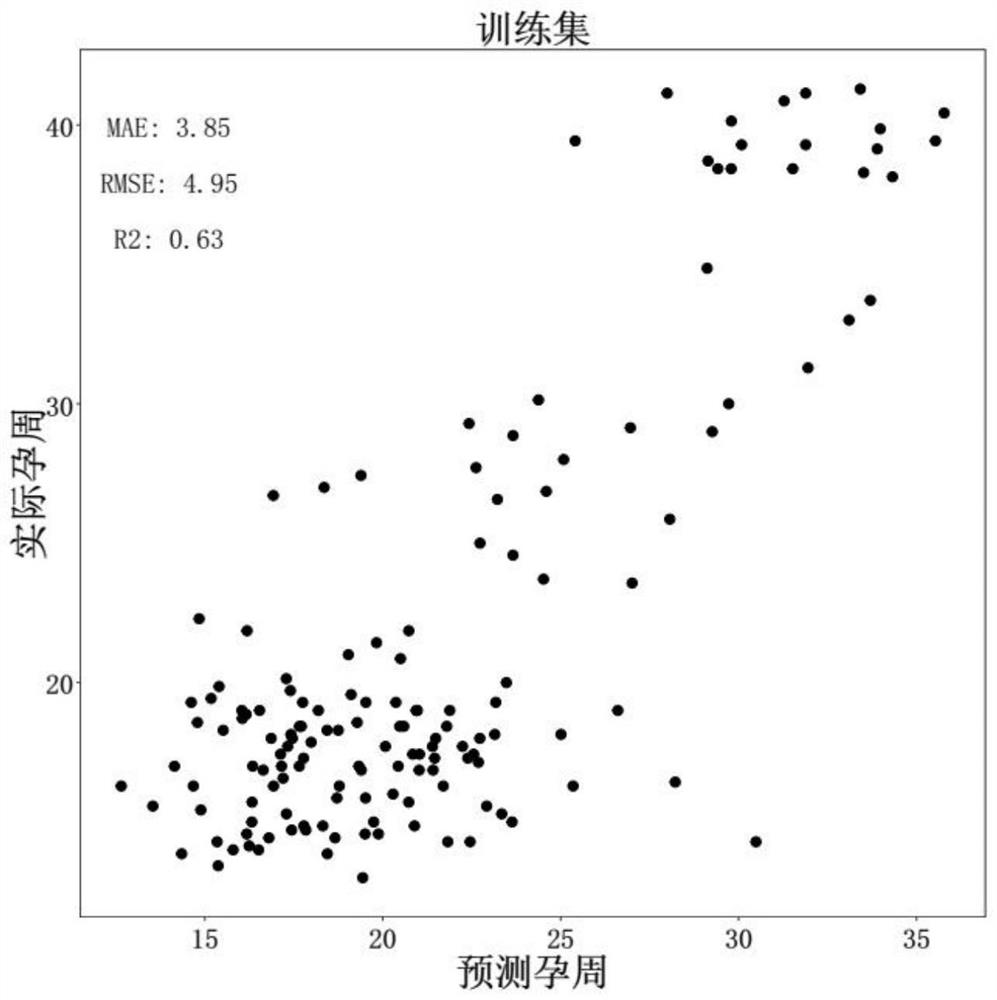
Target gene combination related to gestational age and application thereof
PendingCN114592074AGestational Age PredictionEffective predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsTranscription initiation siteFree dna
The invention discloses a target gene combination related to gestational age and application thereof. Based on the target gene combination, the target gene combination comprises TSPOAP1, CRYAA, CXCL11, FNDC10, HMGA2, FDCSP, OLFM2, KRT36, C13orf46, SCD5, OR12D2, OMP, CEBPE, MOBP, CCNF, FUT2, LIPH, ERICH4, GPR171 and the like. According to the method, the distribution condition of peripheral blood free DNA in some gene transcription start site areas can reflect different gestational weeks, and after the characteristics of the free DNA transcription start site areas are subjected to homogenization correction, a prediction model constructed by using a machine learning algorithm can effectively predict the fetal age of a fetus.
Owner:SUZHOU MUNICIPAL HOSPITAL +1
Expression vectors comprising chimeric cytomegalovirus promoter and enhancer sequences
The present invention relates to expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence of interest in mammalian cells, the vectors comprising a chimeric promoter regulatory sequence being operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence to be expressed, wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises a cytomegalovirus promoter sequence derived from murine cytomegalovirus or from human cytomegalovirus and being operably linked to the transcriptional start site of the nucleic acid sequence to be expressed; and a cytomegalovirus upstream region and / or enhancer sequence derived from human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus, wherein the upstream region and / or enhancer sequence is located 5′ of and operably linked to the murine or the human promoter sequence, and wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements being derived from at least two of the group consisting of murine cytomegalovirus, human cytomegalovirus and simian cytomegalovirus. In particular embodiments, the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements derived from the murine or the human cytomegalovirus IE1 promoter and from the human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus IE1 region. The invention also relates to mammalian host cells transfected with such expression vectors, a method for heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence in a mammalian host cell by employing such expression vectors, and the use of such expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
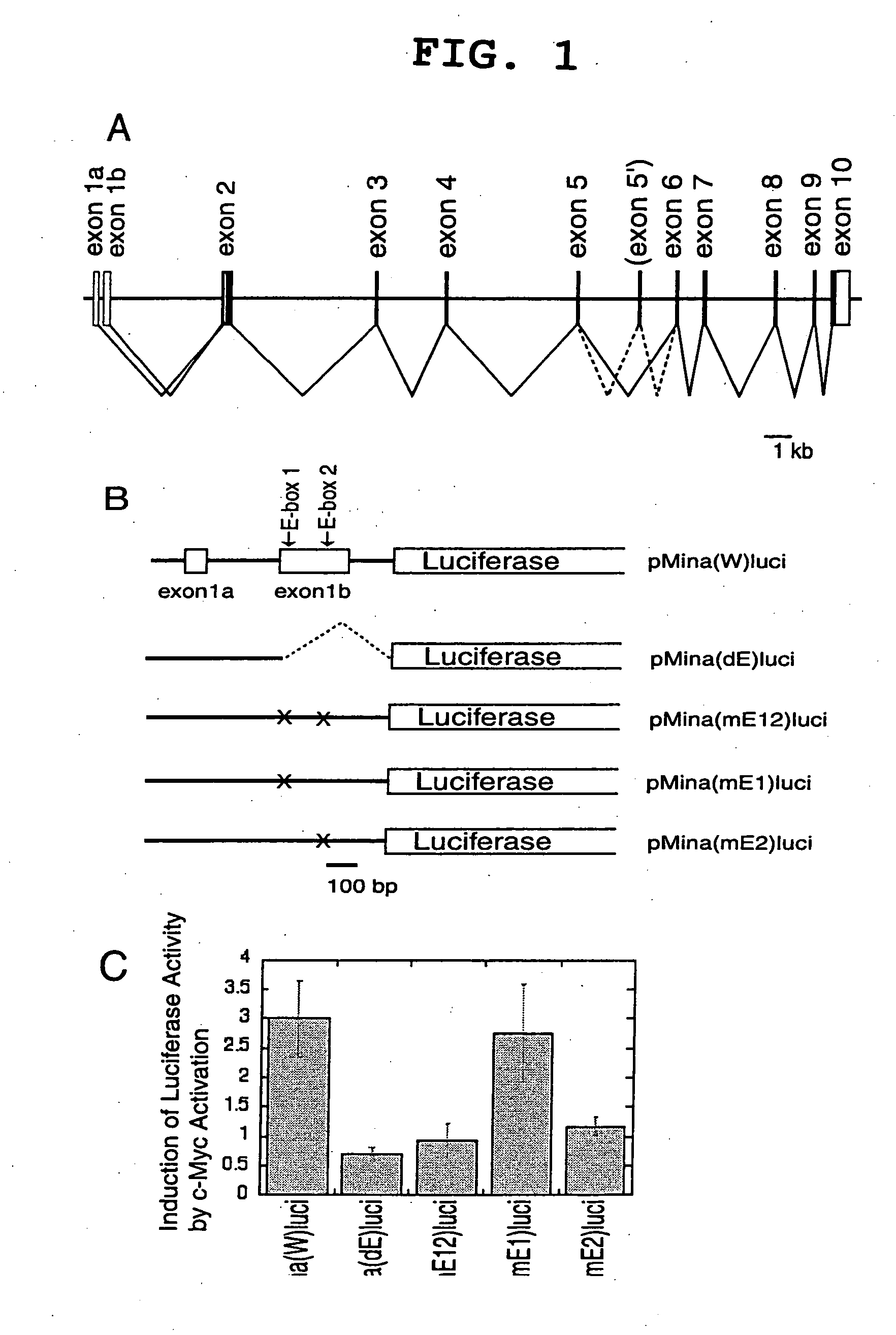
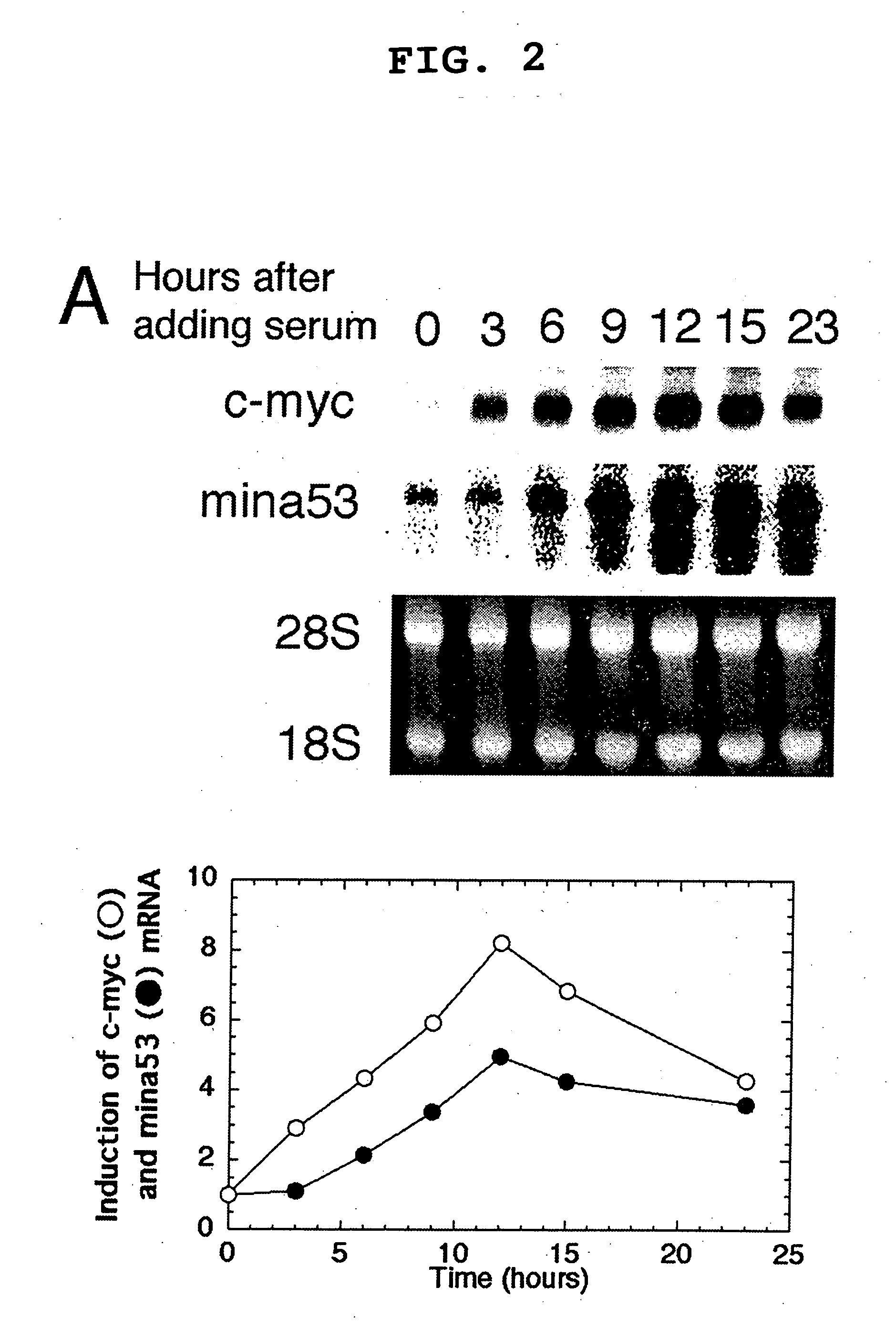
Cancer associated gene mina 53, protein mina 53 and monoclonal antibody thereof
InactiveUS20060234318A1Prevent proliferationAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTranscription initiation siteFhit gene
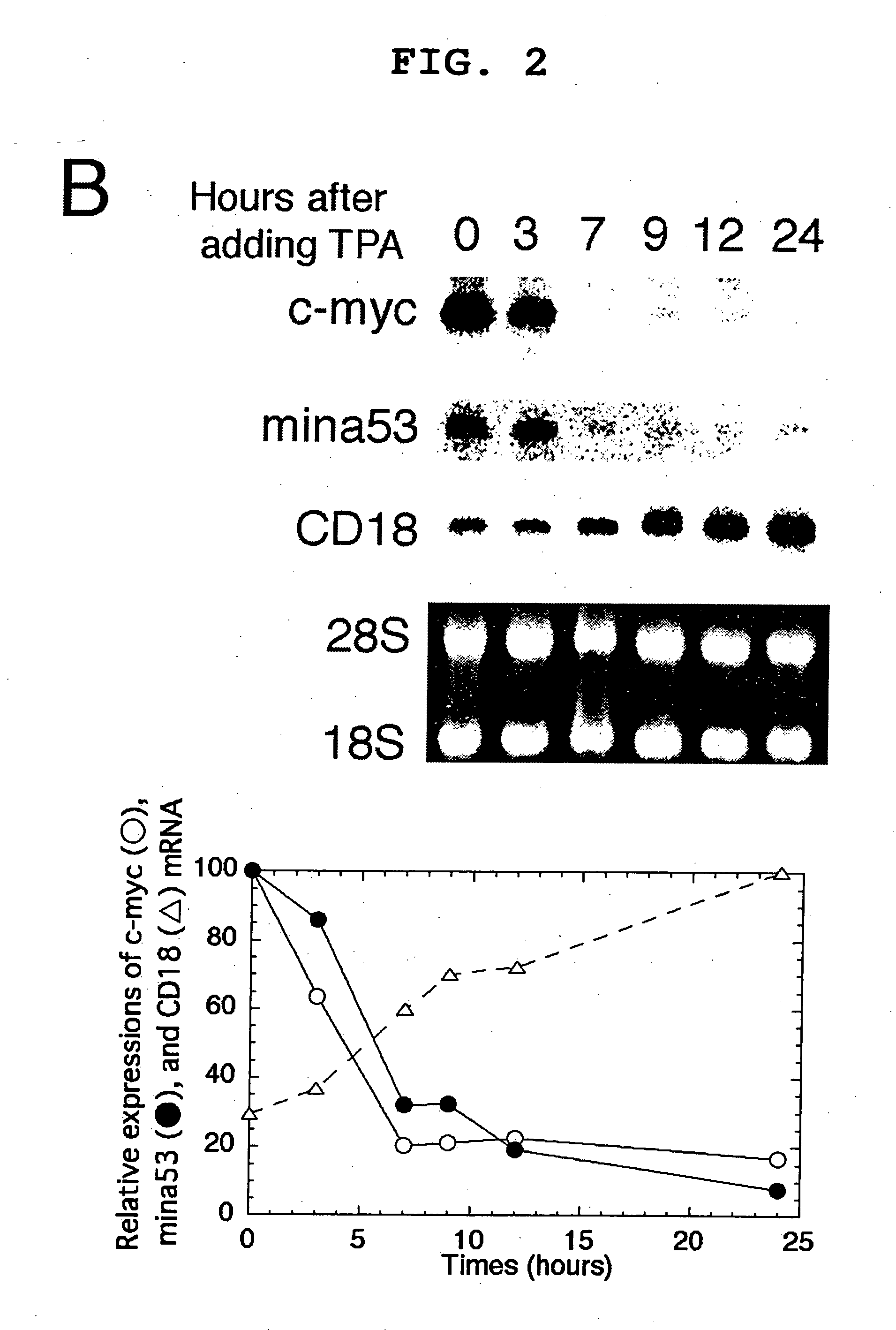
Myc protein is an unevenly distributed intermediate agent for cell proliferation, and activates a gene expression via E.box. Mina 53 gene encodes a protein of 53 kDa molecular weight and is present in the nucleoplasm and nucleolus. Mina 53 mRNA and protein expression are induced by artificial introduction of c-Myc activity. E.box site is present in the vicinity of the transcription initiation site of mina 53 gene, and the expression from mina 53 promoter is activated by the c-Myc through the medium of E.box. Specific inhibition of the mina 53 expression in HeLa cells and rat fibroblast cells 3Y1 having high expression c.myc strikingly inhibited the cell proliferation. Combination of these results shows that the mina 53 is a Myc target gene and is associated with the cell proliferation of mammal.
Owner:GAKKOUHOUJIN KURUME UNIV
Cloning and activity analysis of corn adversity inducing promoter
InactiveCN102373208ASolving the food crisisSolve problems such as ecological deteriorationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTranscription initiation siteA-DNA
The invention discloses cloning and activity analysis of a corn adversity inducing promoter, which belong to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The invention provides an obtained corn adversity inducing promoter sequence which comprises a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence ranging from a -1bp region to a -1273bp region relative to the transcription initiation site of SEQ ID NO:1, and provides an adversity inducing plant expression vector for transforming corn, which comprises a corn adversity inducing promoter sequence and a 5' non-translational region of a corn lipoxygenase gene, and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO 3. The primers are characterized by being suitable for amplifying DNA fragments comprising the SEQ ID NO:1. The inducing promoter can be used for promoting high-efficiency expression of an adversity-relevant gene, is applied to cold-resistant, drought-resistant and salt-resistant transgenic plants, and plays a positive role in solving the problems of coldness, drought, crisis in food in salt damage regions, ecological degeneration and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A method for predicting pregnancy-related diseases based on high-throughput sequencing of peripheral blood cell-free DNA
ActiveCN110580934BEasy to degradeHigh degree of opennessMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsTranscription initiation sitePhysiology
The invention discloses a pregnancy-related disease prediction model based on high-throughput sequencing of free peripheral blood DNA. The study of the present invention found that the distribution of free DNA in the gene transcription start site region of pregnant women can reflect the physiological state of pregnant women and fetuses. There are significant differences between healthy pregnant women and can effectively predict the onset of pregnancy-related diseases. Based on this, the present invention constructs a pregnancy-related disease screening and prediction model based on peripheral blood cell-free DNA detection, which can predict the onset of pregnancy-related diseases before the clinical symptoms of pregnancy-related diseases appear, and is a non-invasive, economical, convenient, The method for accurate early prediction of pregnancy-related diseases has a good application prospect in the development of predictive screening products for pregnancy-related diseases.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
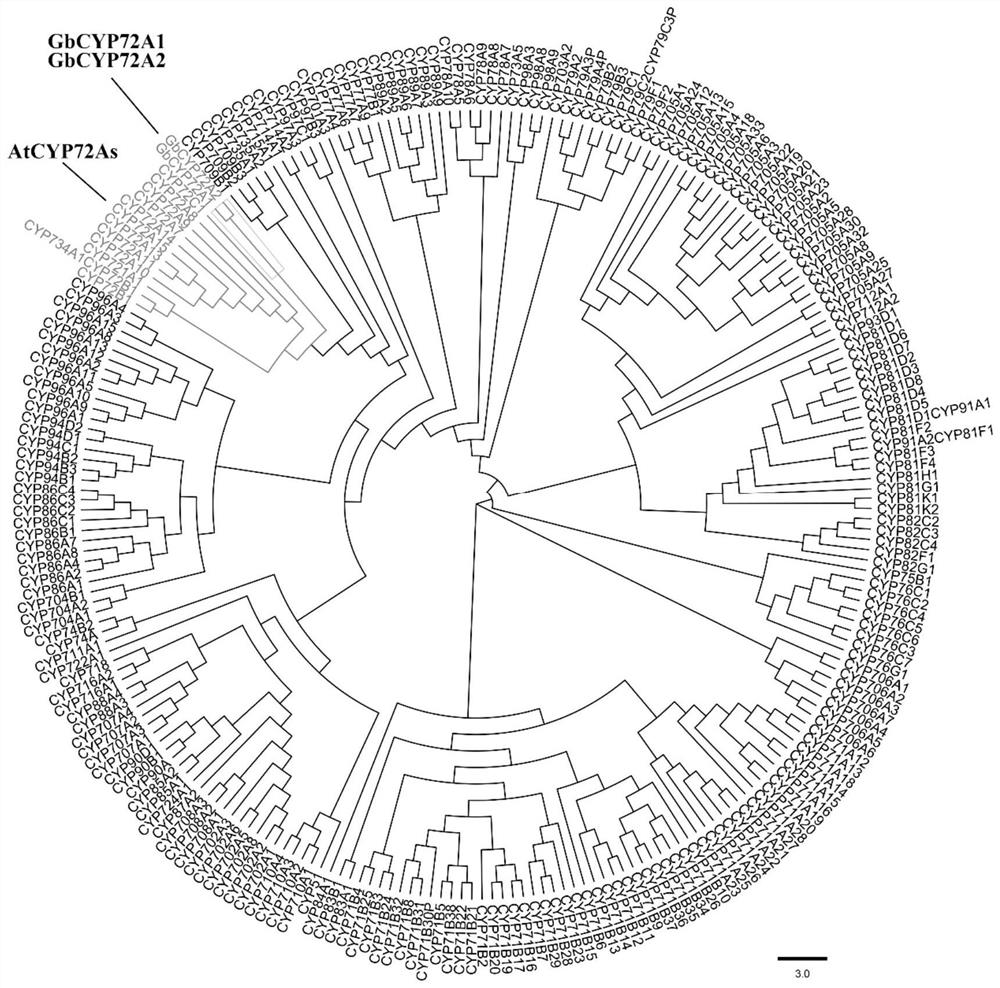
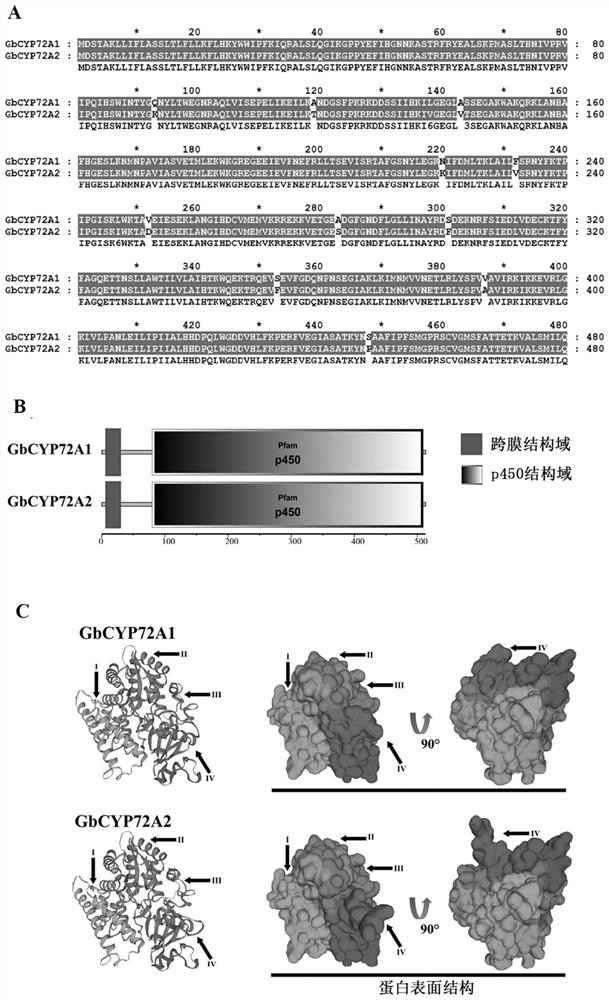
Sea island cotton GbCYP72A2 gene as well as encoding protein and application thereof
PendingCN111635906ALower resistanceIncrease resistanceOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Cloning and activity analysis of corn adversity inducing promoter
InactiveCN102373208BMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTranscription initiation siteA-DNA
The invention discloses cloning and activity analysis of a corn adversity inducing promoter, which belong to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The invention provides an obtained corn adversity inducing promoter sequence which comprises a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence ranging from a -1bp region to a -1273bp region relative to the transcription initiation site of SEQ ID NO:1, and provides an adversity inducing plant expression vector for transforming corn, which comprises a corn adversity inducing promoter sequence and a 5' non-translational region of a corn lipoxygenase gene, and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO 3. The primers are characterized by being suitable for amplifying DNA fragments comprising the SEQ ID NO:1. The inducing promoter can be used for promoting high-efficiency expression of an adversity-relevant gene, is applied to cold-resistant, drought-resistant and salt-resistant transgenic plants, and plays a positive role in solving the problems of coldness, drought, crisis in food in salt damage regions, ecological degeneration and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A molecular marker method for pig growth traits
ActiveCN108707675BShorten the generation intervalShorten the selection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiation siteAnimal science
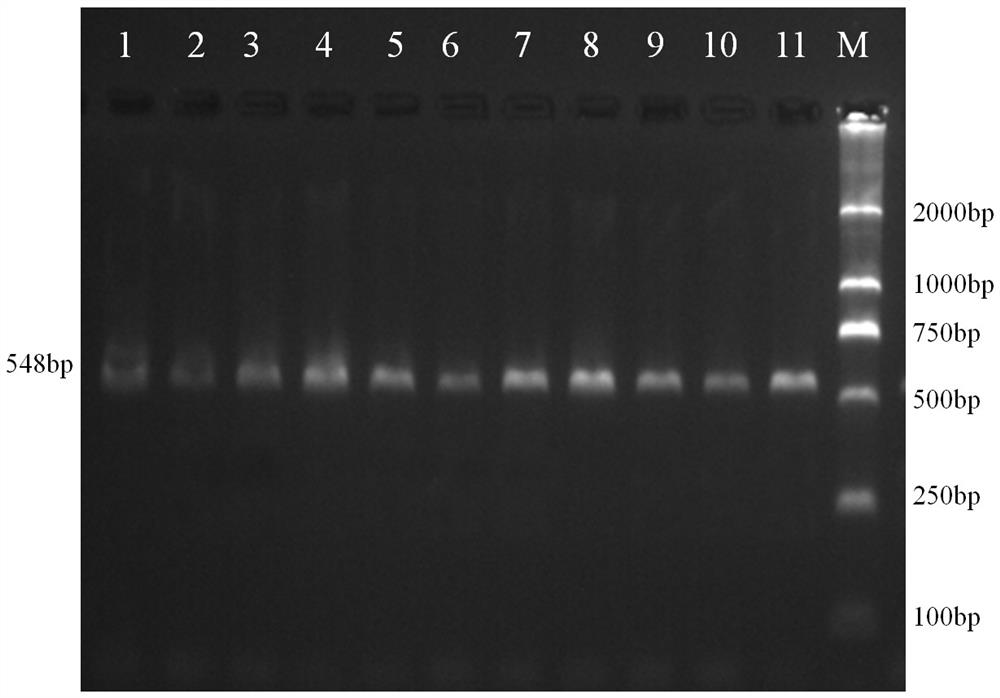
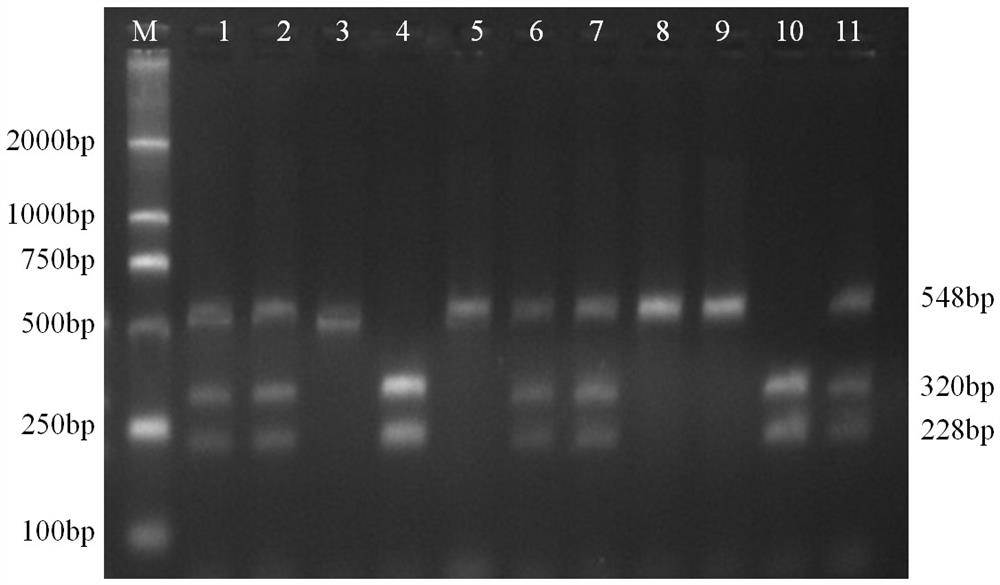
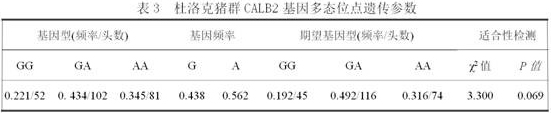
The invention relates to a molecular marker method for growth traits of pigs. The operation steps are as follows: extract porcine genomic DNA from porcine ear margin tissue; design a pair of primers between -1201bp and -654bp of the initiation transcription site of porcine calcium-binding protein 2 (CALB2) gene, that is, upstream primers and downstream primers Obtain the 548bp long in vitro amplification product between the upstream -1201bp and -654bp of the pig CALB2 gene transcription start site by polymerase chain reaction; Carry out the restriction endonuclease HhaI enzyme digestion reaction to the in vitro amplification product; The cut product was tested for polymorphism (RLFP), and the AA type was obtained as the genotype with excellent growth speed, that is, the mutant type. Therefore, the piglets with the AA type were selected for breeding, and the growth and fattening cycle of the AA type pigs was shorter than that of the GG type. Pigs shortened by 3.6 to 4.0 days.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com