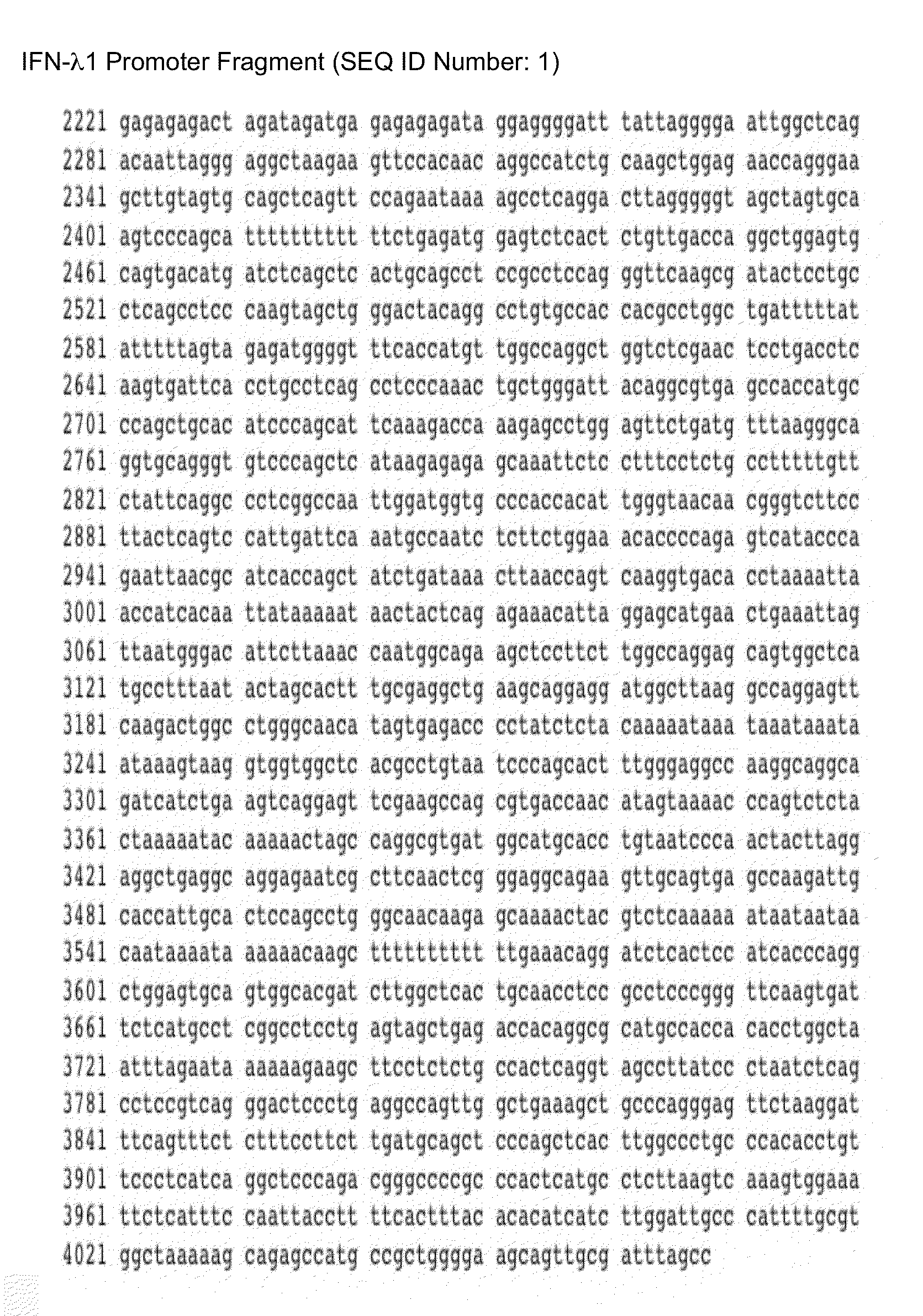Patents
Literature
38 results about "Translation initiation sites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
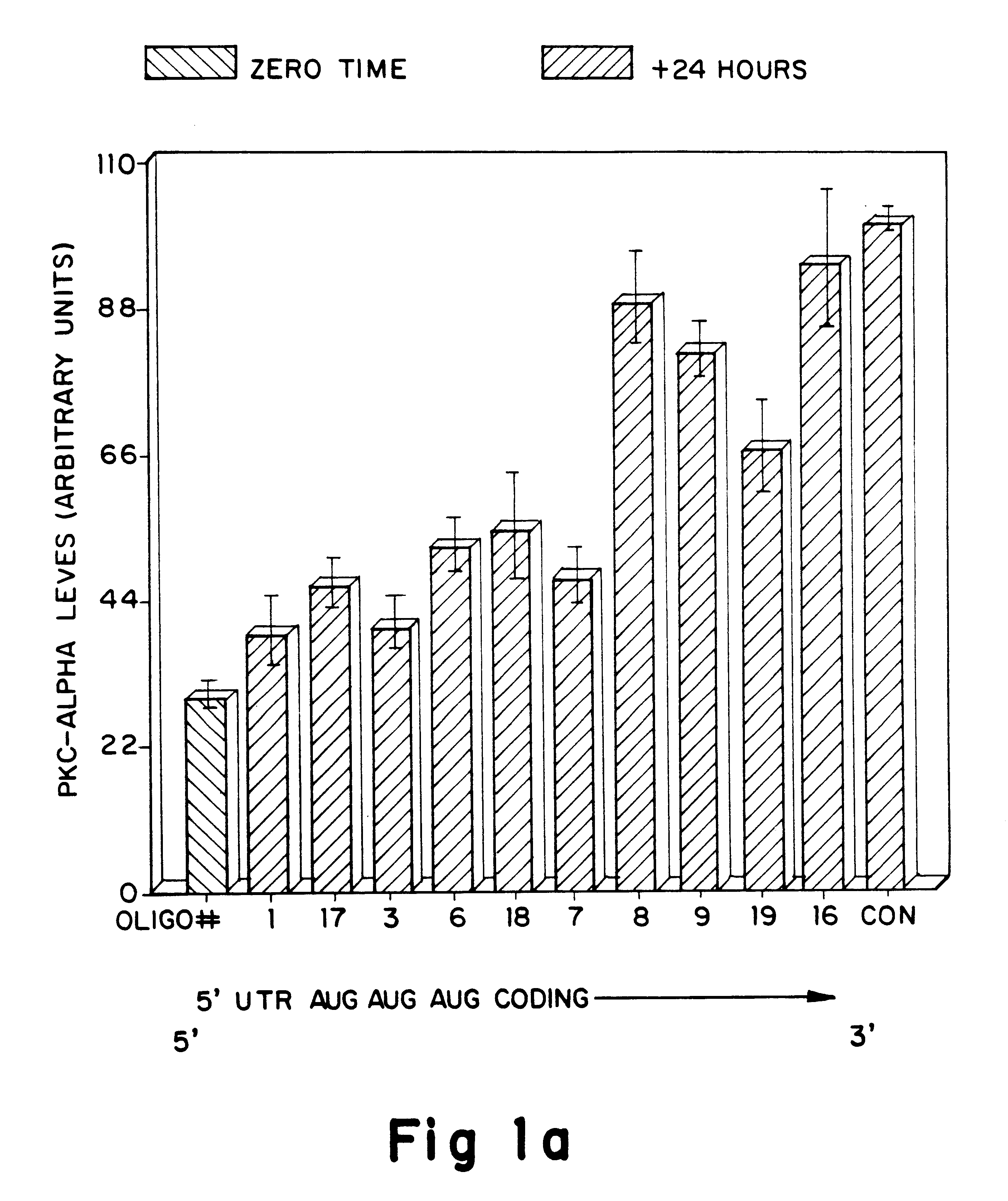
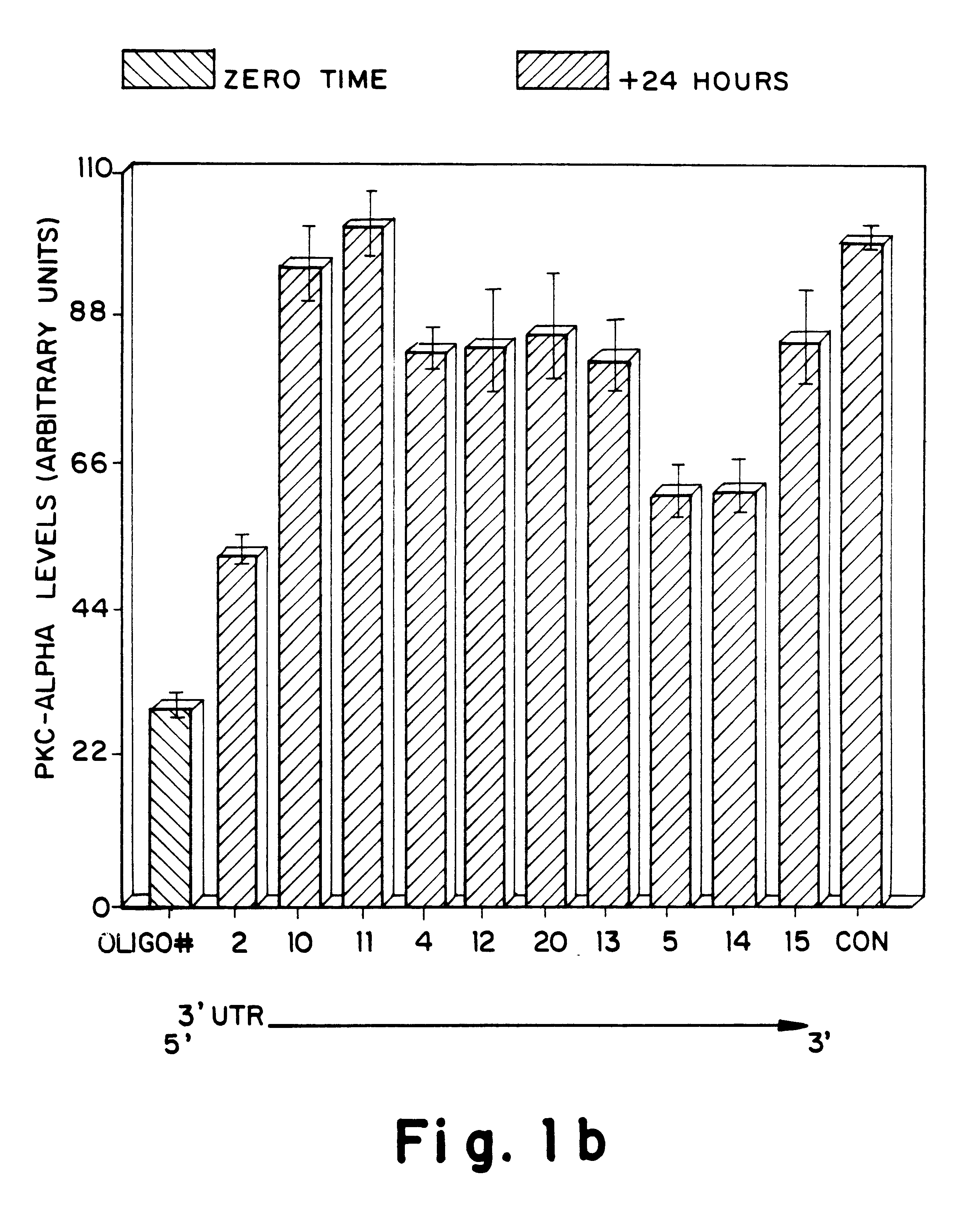
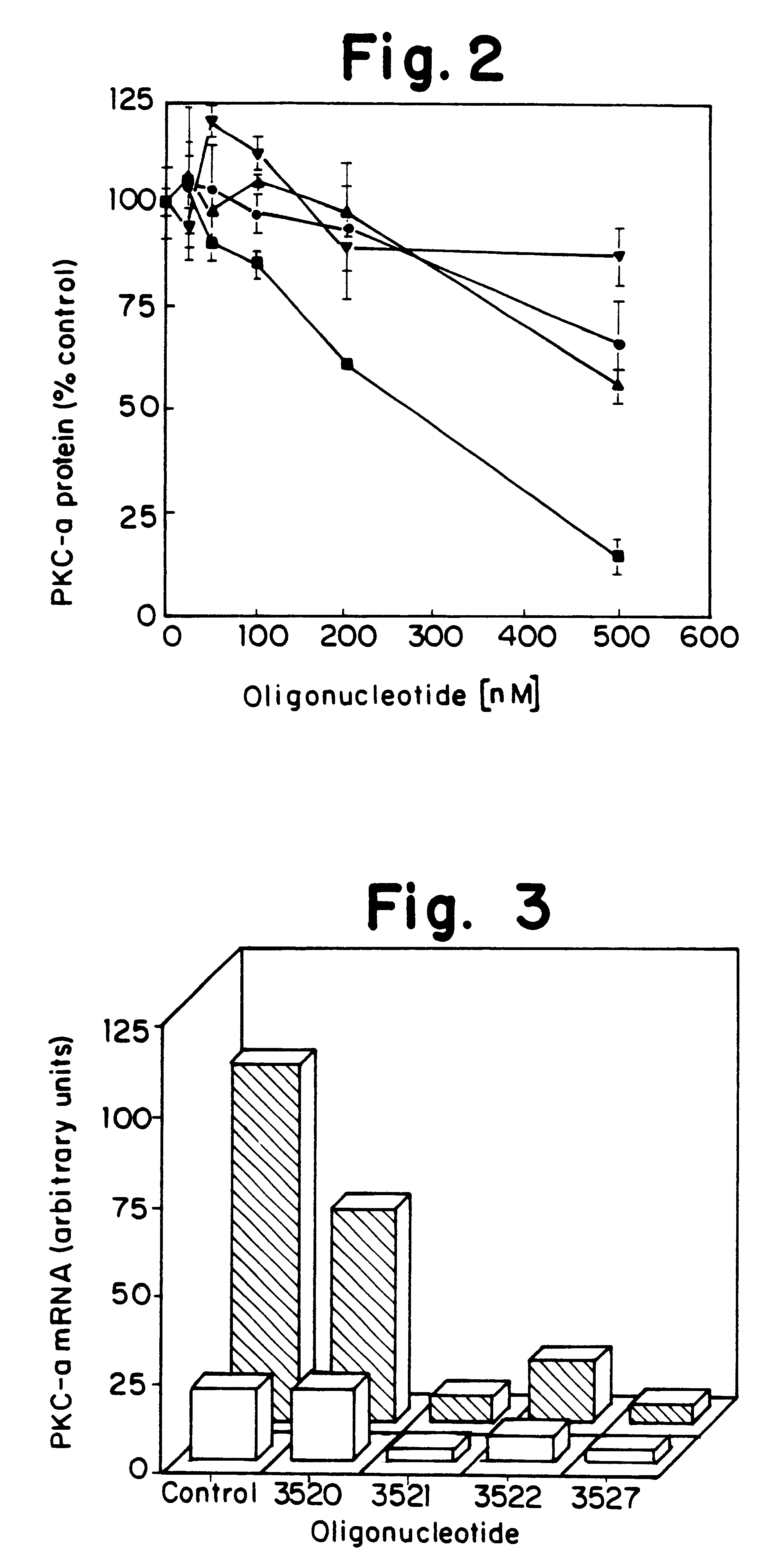
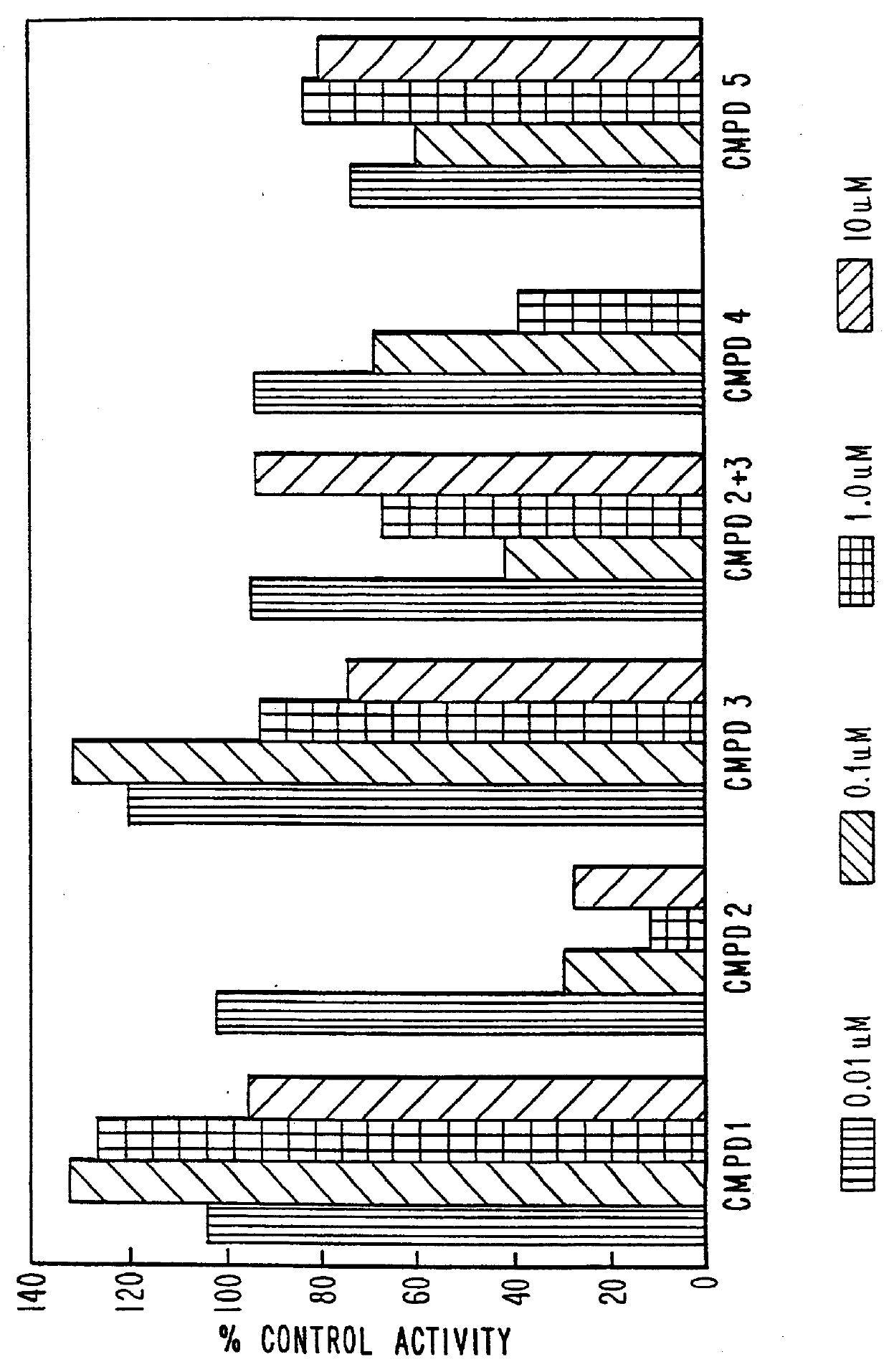
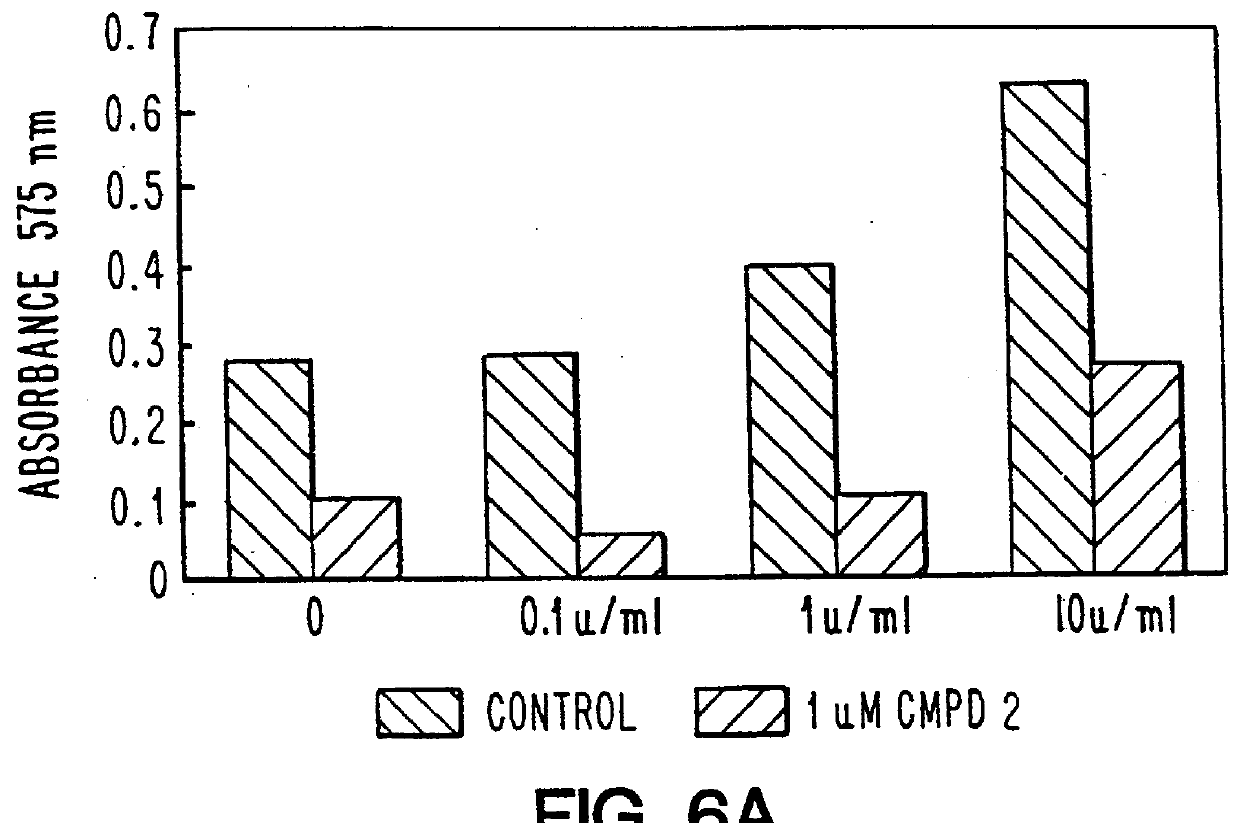
Antisense oligonucleotides which have phosphorothioate linkages of high chiral purity and which modulate betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, Ε, ζ and eta isoforms of human protein kinase C
InactiveUS6339066B1Modulate its functionImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseasePkc delta
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases associated with the expression of one or more of the betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoforms (isozymes) of protein kinase C (PKC). Oligonucleotides are provided which are targeted to nucleic acids encoding PKC-betaI, PKC-betaII, PKC-gamma, PKC-delta, PKC-epsi, PKC-ζ or PKC-eta. Provided herein are oligonucleotides specifically hybridizable with a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated region, 3'-untranslated region or other targeted region of a betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoform of PKC, wherein at least about 75% of the nucleoside units of a given oligonucleotide are joined together by a stereospecific (i.e., Sp or Rp) phosphorothioate 3' to 5' linkages. In preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides of the disclosure additionally contain one or more chemical modifications. Also disclosed are methods of using the oligonucleotides of the invention for modulating the expression of at least one of the betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoforms of PKC and for treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating the expression of one or more of the betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoforms of PKC.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
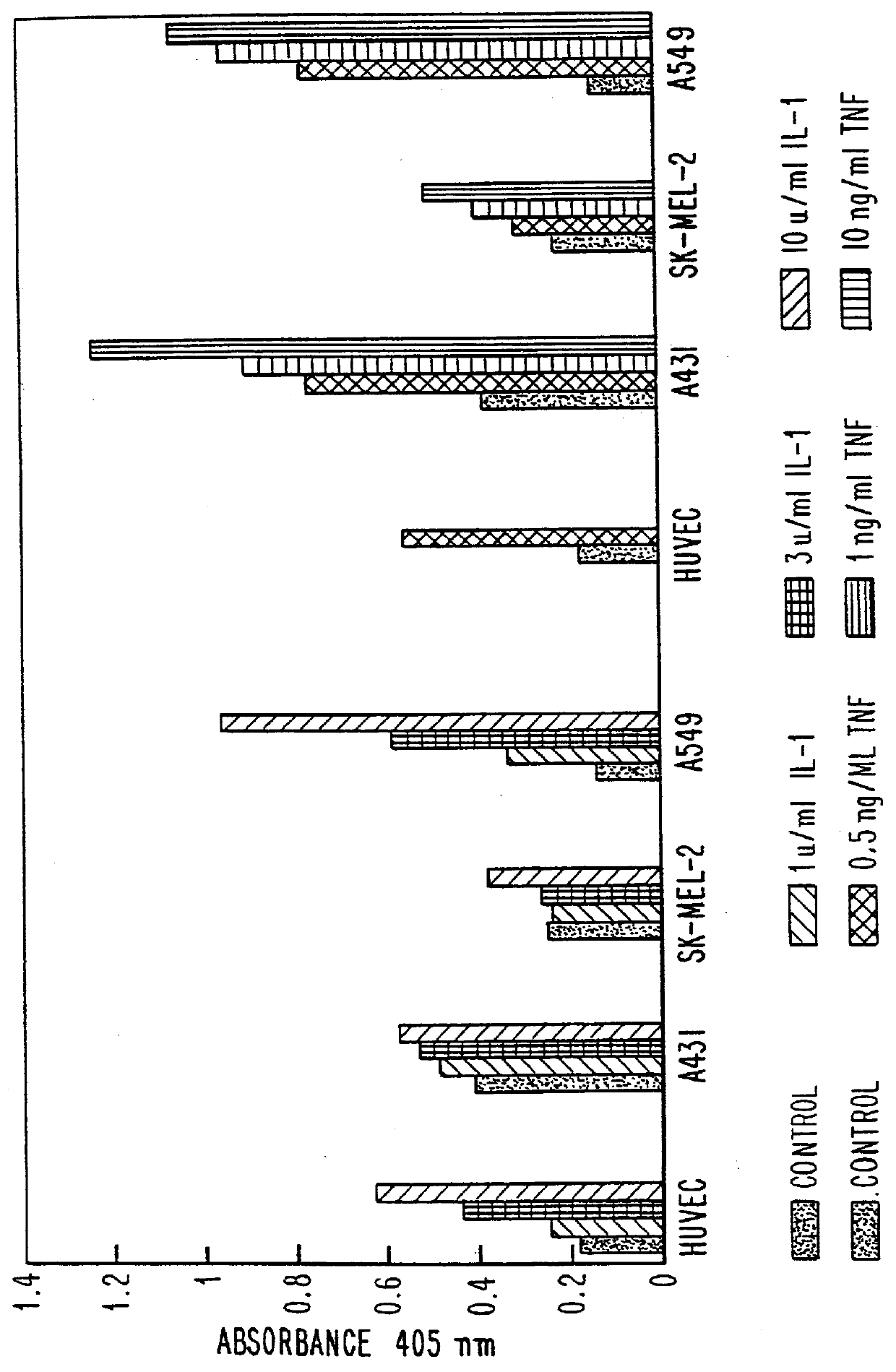
Oligonucleotide modulation of cell adhesion
InactiveUS6015894AHigh expressionAvoid inhibitionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTranscription initiation site
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to modulation cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
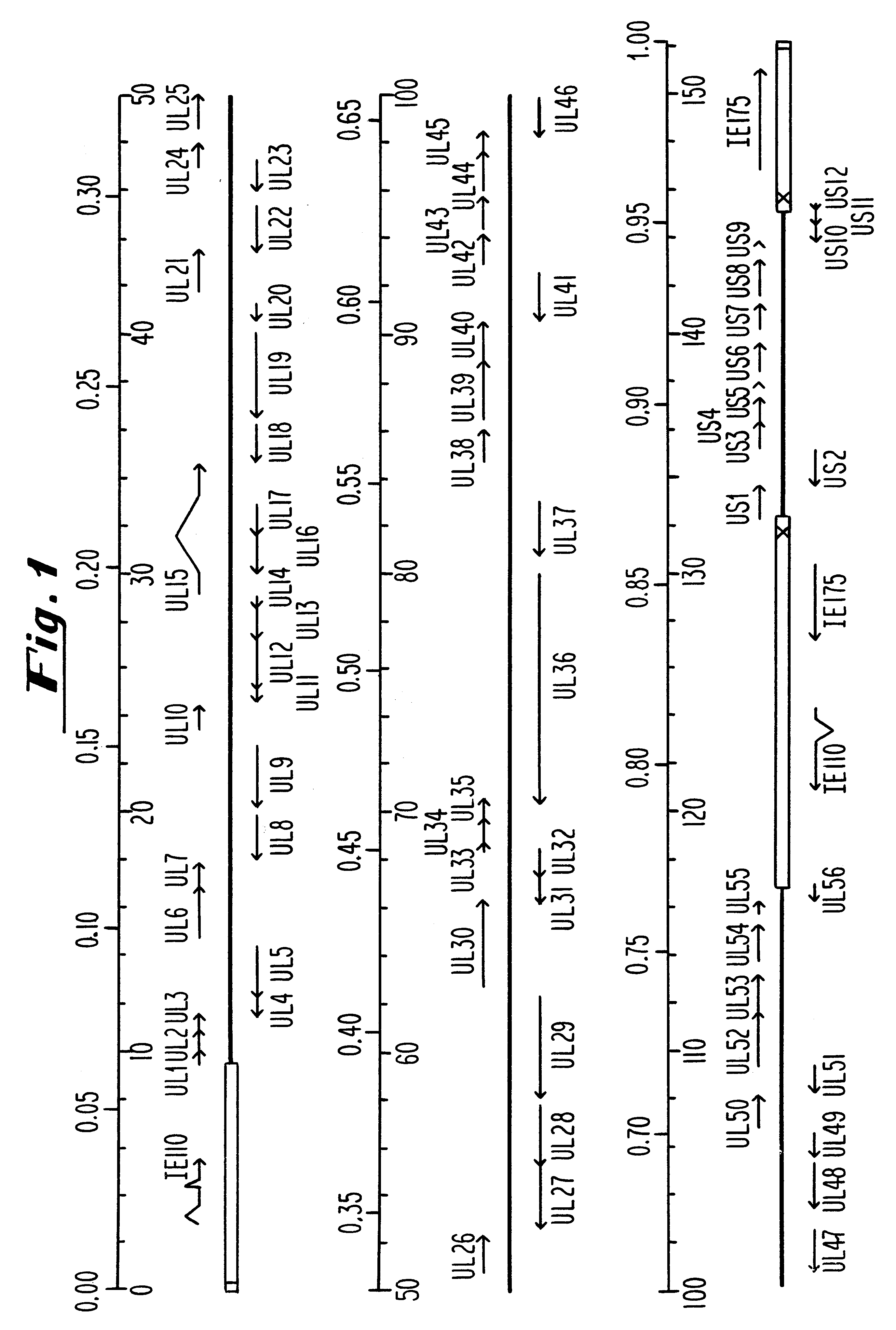
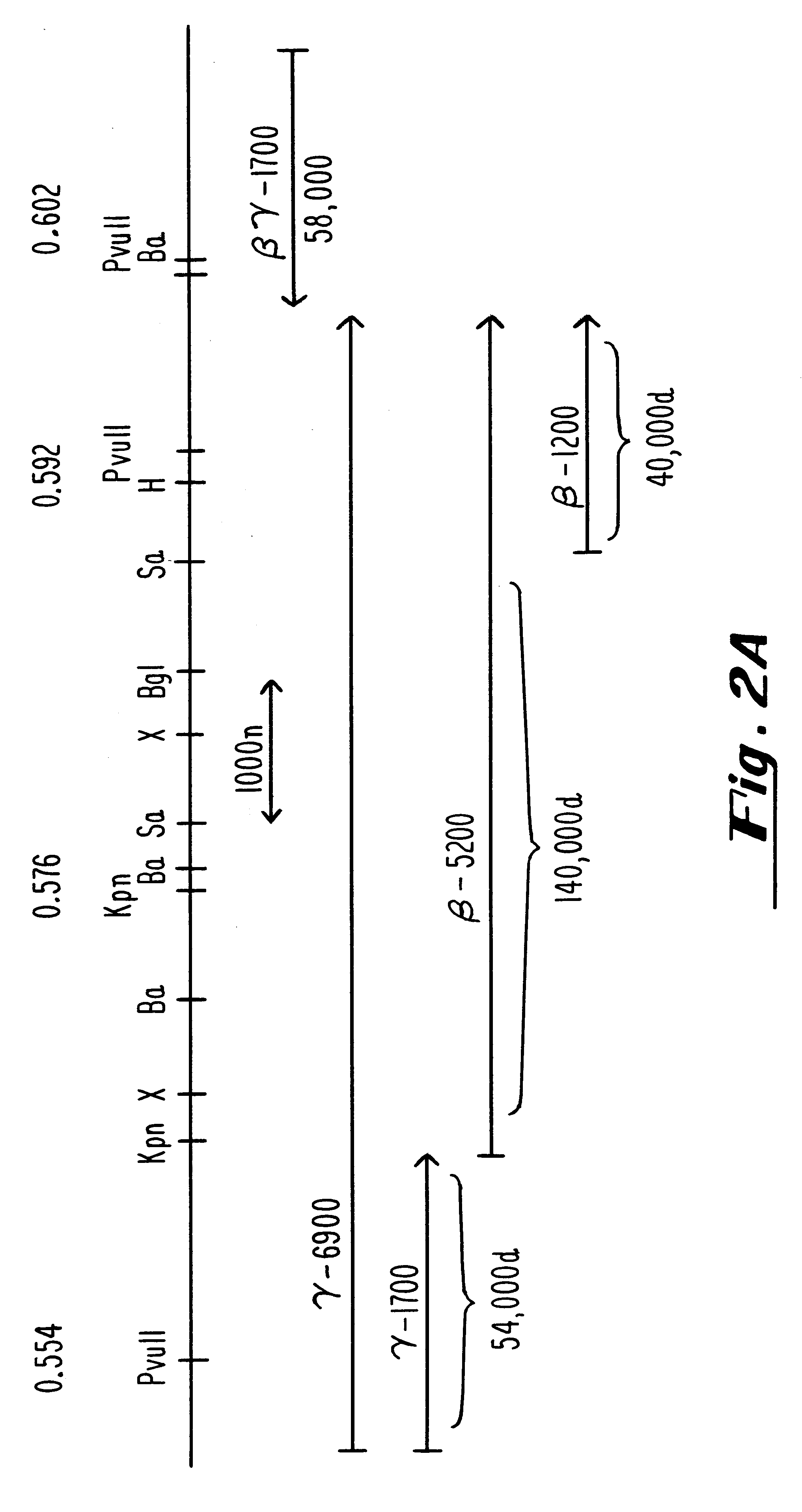
Oligonucleotide therapies for modulating the effects of herpesviruses
InactiveUS6310044B1Conveniently and desirably presentedFaster replicationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsOpen reading frameHerpesvirus infection
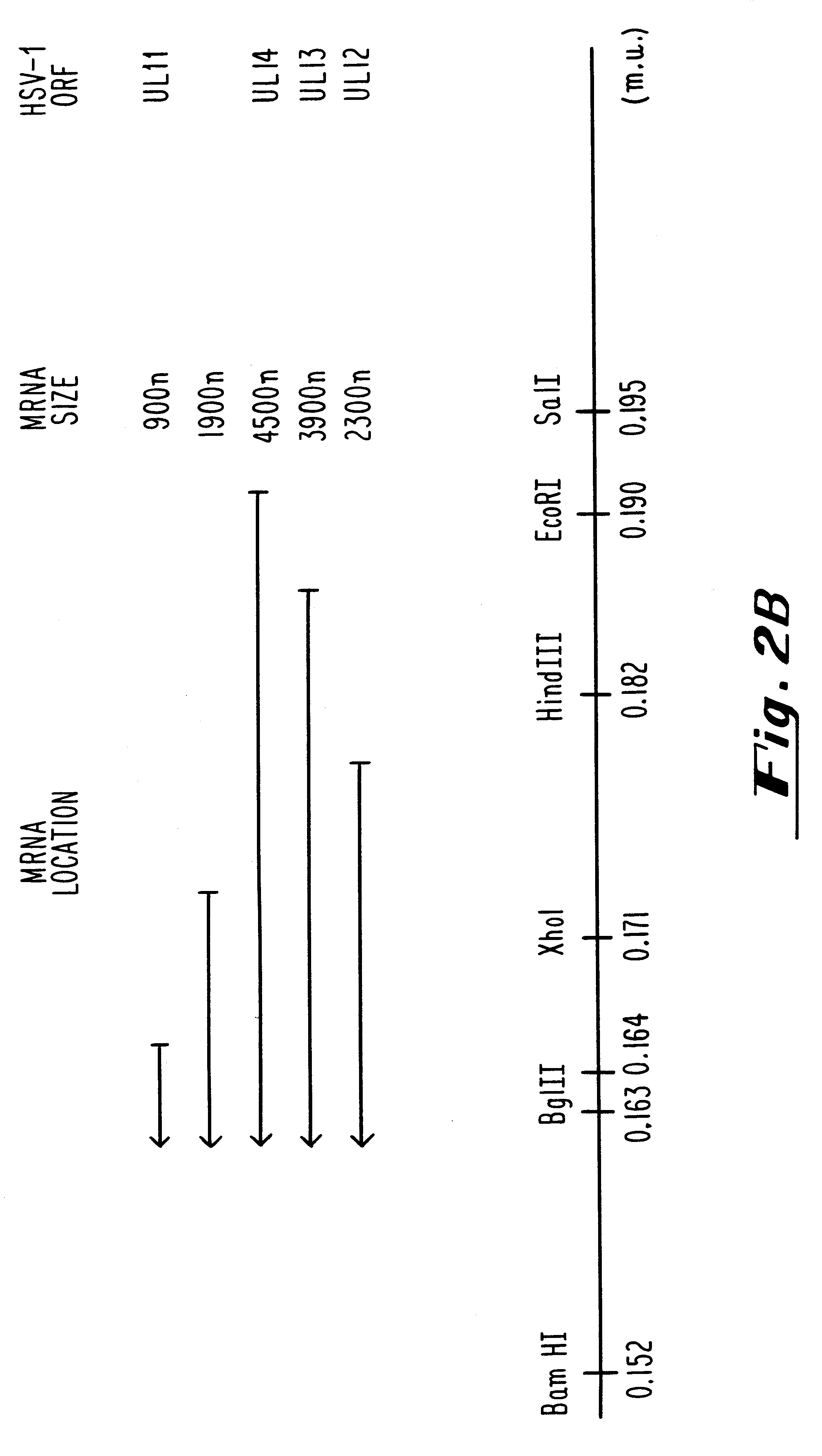
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of herpesvirus infections. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA deriving from a gene corresponding to one of the open reading frames UL5, UL8, UL9, UL13, UL29, UL30, UL39, UL40, UL42 AND UL52 of herpes simplex virus type 1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a translation initiation site; it is also preferred that they comprise the sequence CAT. Methods of treating animals suspected of being infected with herpesvirus comprising contacting the animal with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA deriving from one of the foregoing genes of the herpesvirus are disclosed. Methods for treatment of infections caused by herpes simplex virus type 1, herpes simplex virus type 2, cytomegalovirus, human herpes virus 6, Epstein Barr virus or varicella zoster virus are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
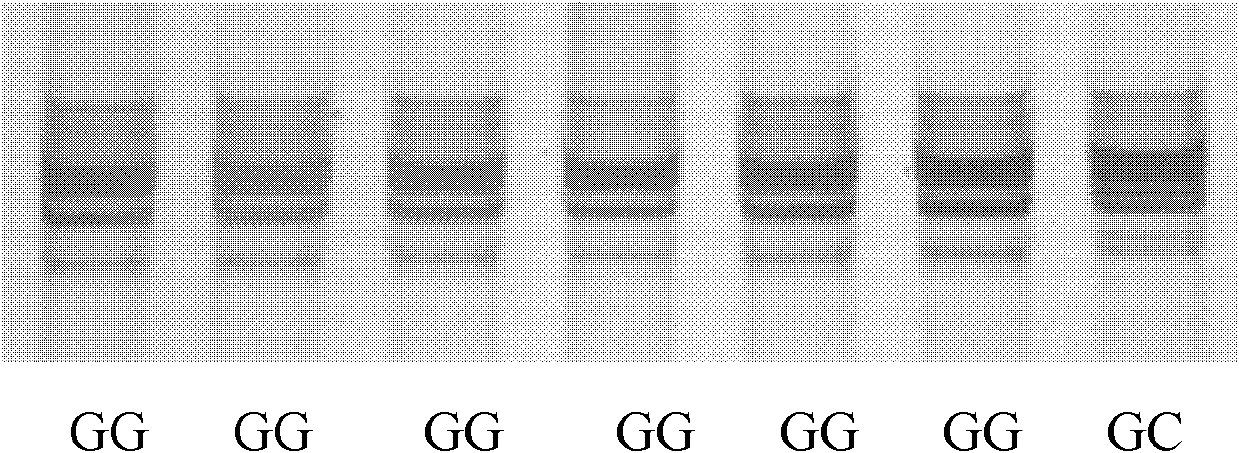
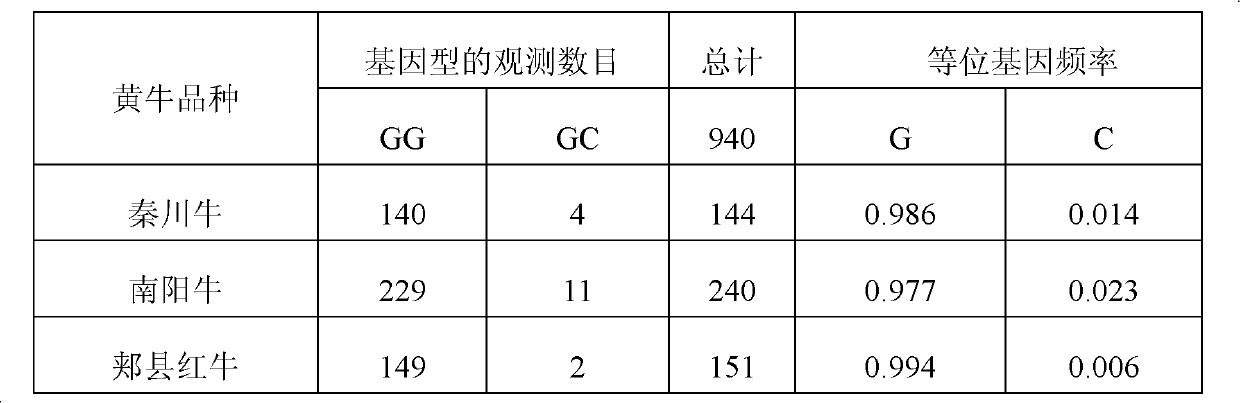
Application of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3888188 to detection of tuberculosis susceptibility
InactiveCN102808030AMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription initiation siteTranslation initiation sites
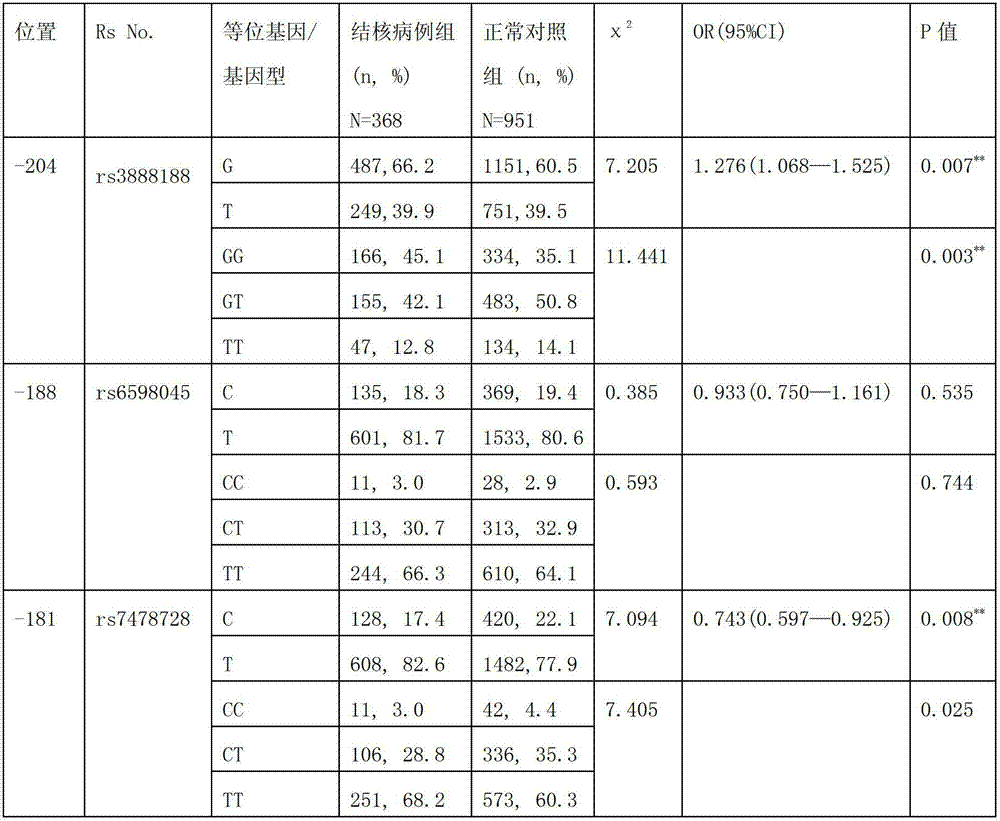
The invention discloses an application of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3888188 to detection of tuberculosis susceptibility. The SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) is the rs3888188 and is positioned in a human IFITM3 (interferon induced transmembrane protein) gene core promoter region (namely the upstream 103bp of a transcription initiation site / the upstream 204bp of a translation initiation site ATG), the rs3888188G is a risk factor of tuberculosis susceptibility, and the polymorphism of the rs3888188 is highly related with tuberculosis. When the genotype of the site is GG, the tuberculosis susceptibility or tuberculosis causing risk of an individual to be detected is increased. The application is of significant meaning and value in the aspects of diagnosing and treating the tuberculosis to reasonably prevent the tuberculosis.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Oligonucleotide inhibition of cell adhesion
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to inhibition of cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
FULL-LENGTH cDNA AND POLYPEPTIDES
InactiveUS20080032304A1Improve reliabilityReliable analysisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFull length cdnaNucleotide sequencing
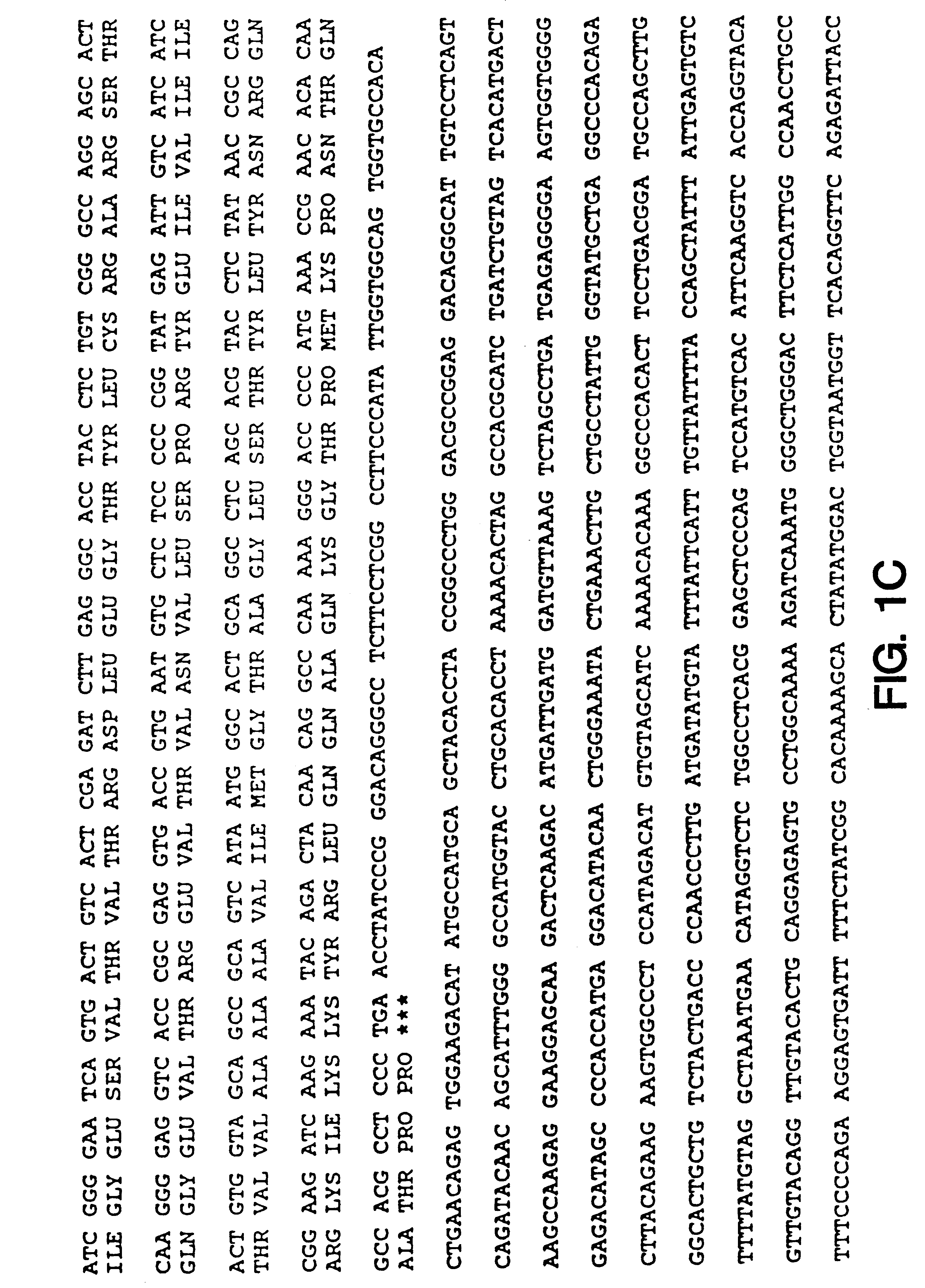
cDNA derived from human have been isolated. The full-length nucleotide sequences of the cDNA and amino acid sequences encoded by the nucleotide sequences have been determined. Because the cDNA of the present invention are full-length and contain the translation start site, they provide information useful for analyzing the functions of the polypeptide.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC
Tert promoter mutations in cancer
ActiveUS20160040250A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsTreatment modalityTert promoter
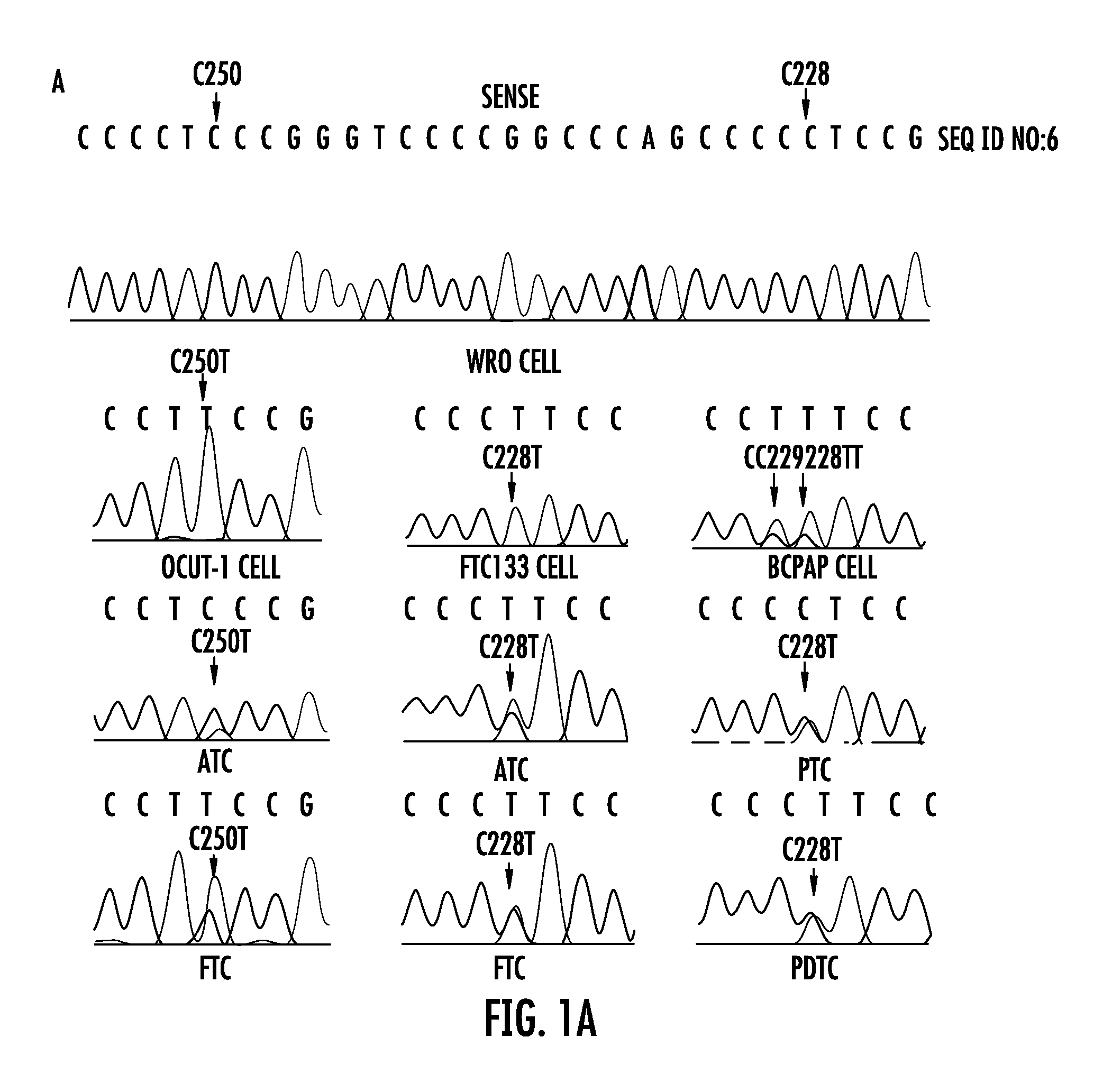
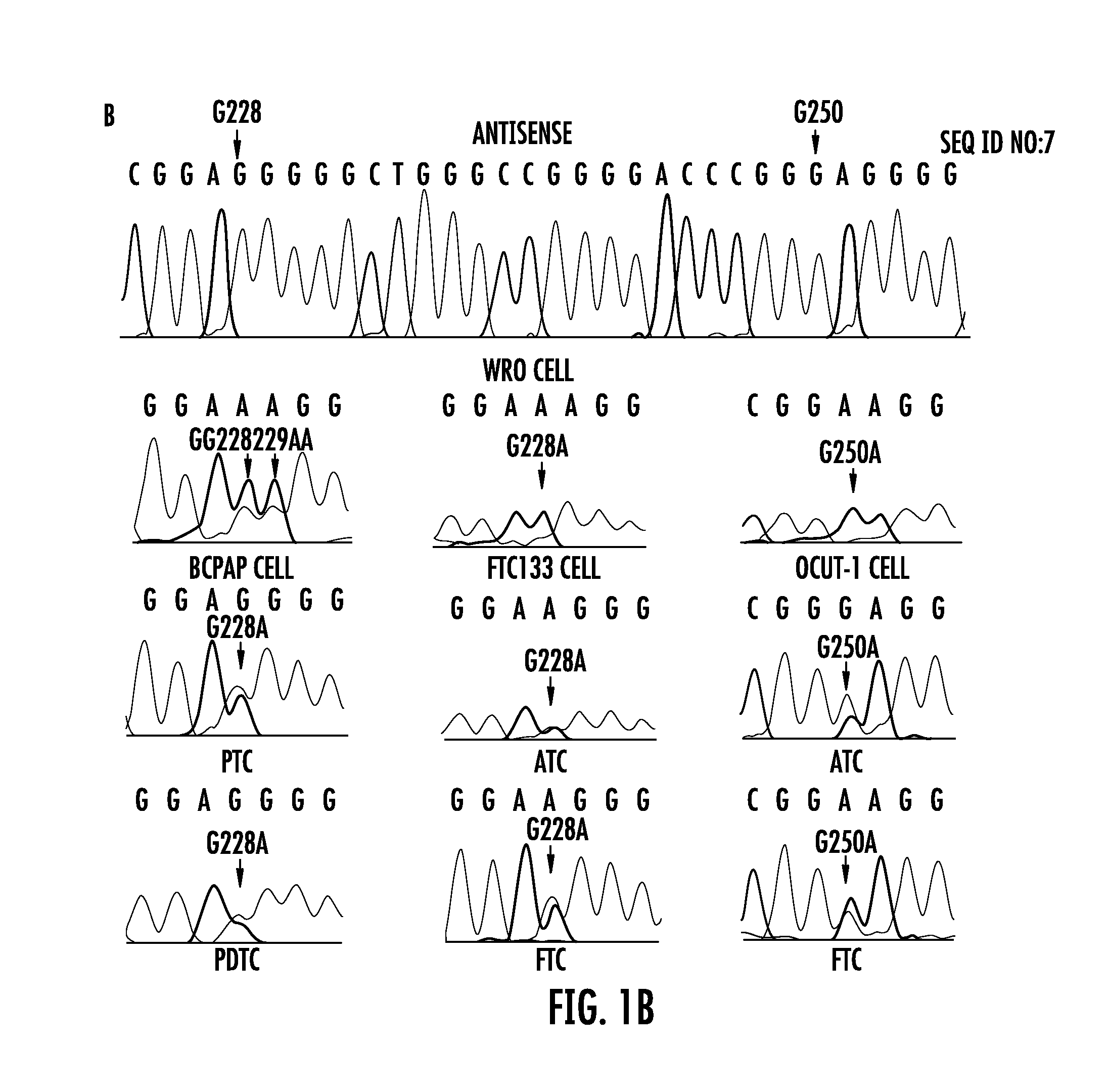
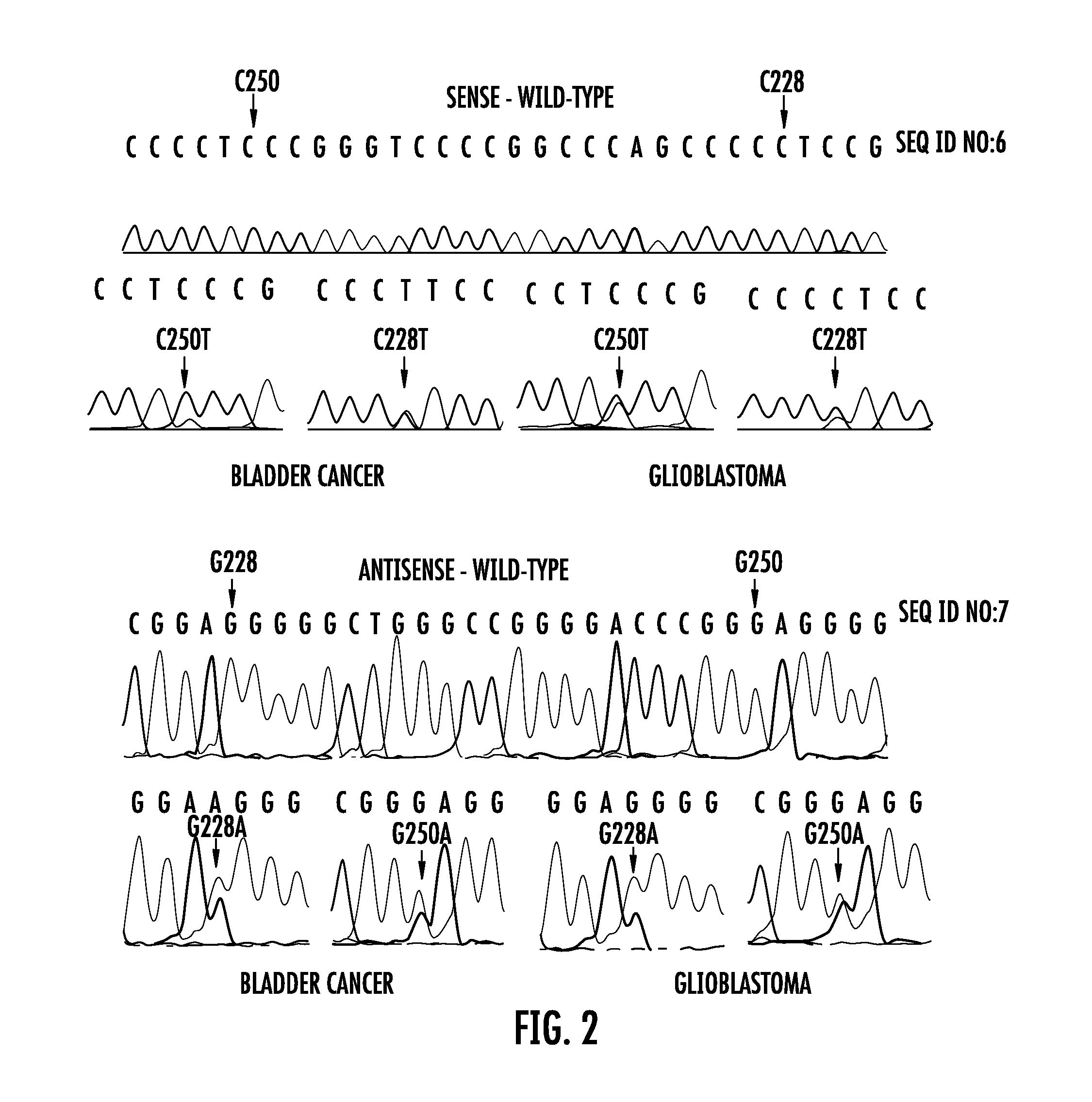
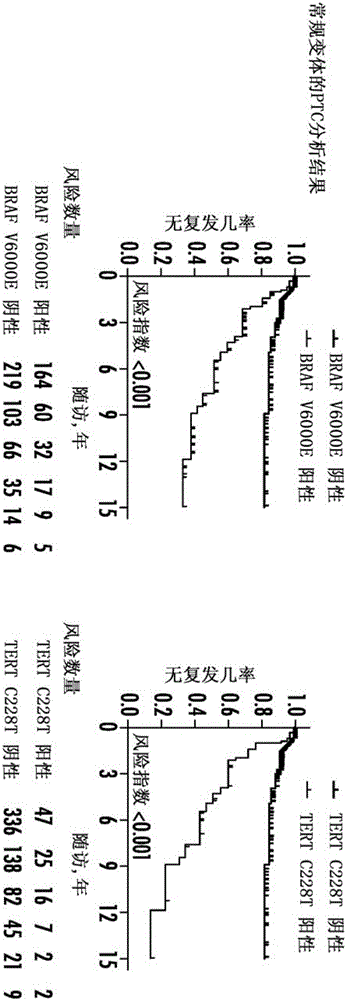
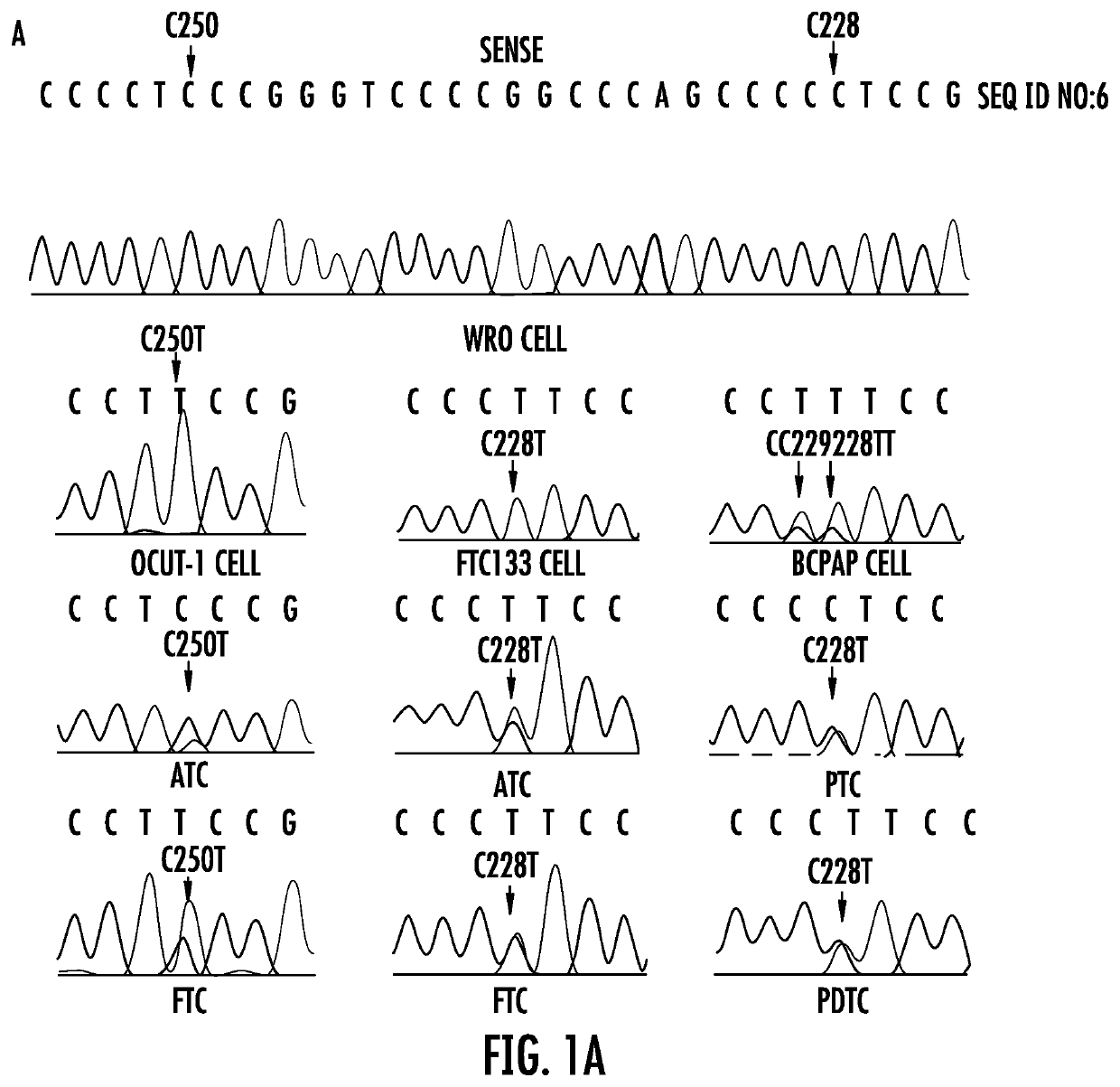
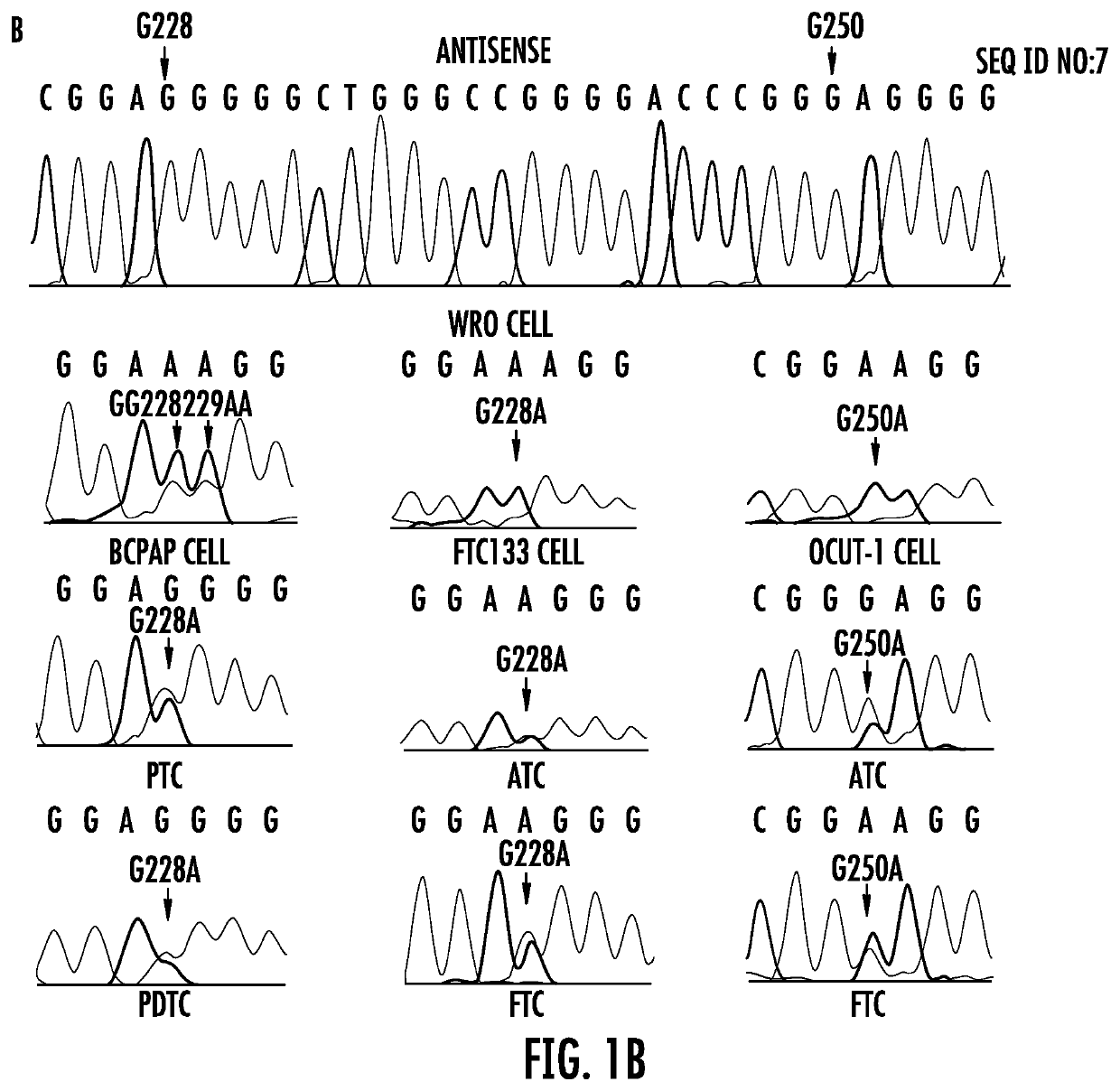
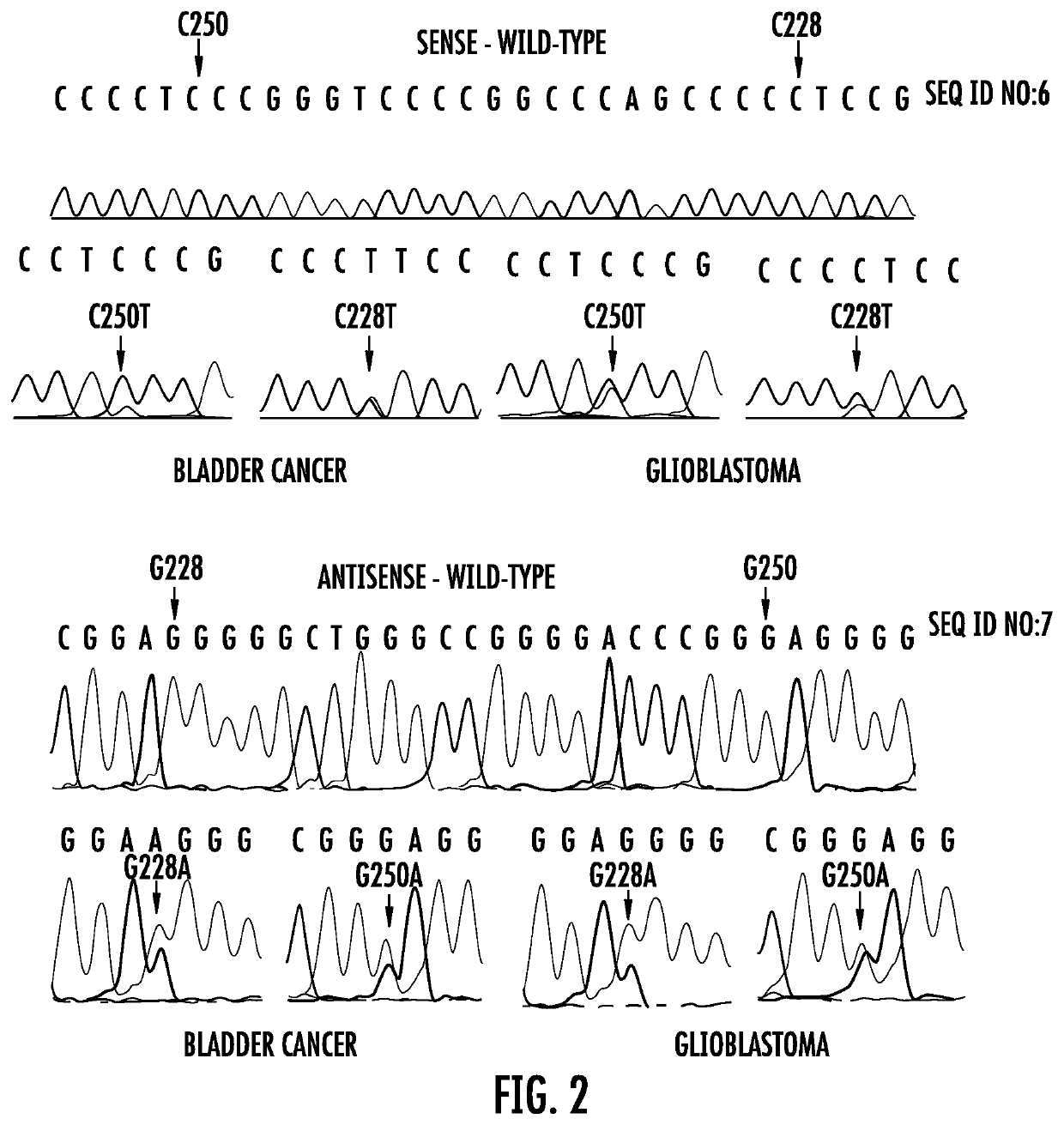
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions related to certain promoter mutations in cancer. In one embodiment, a method for treating a subject having thyroid cancer comprises the steps of (a) obtaining a biological sample from the subject; (b) performing an assay on the sample obtained from the subject to identify a mutation at 1 295 228 C>T (C228T) and 1 295 250 C>T (C250T), corresponding to −124 C>T and −146 C>T from the translation start site in the promoter of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) gene; (c) identifying the subject as having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer if the C228T and / or C250T mutation is identified; and (d) treating the subject with one or more treatment modalities appropriate for a subject having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
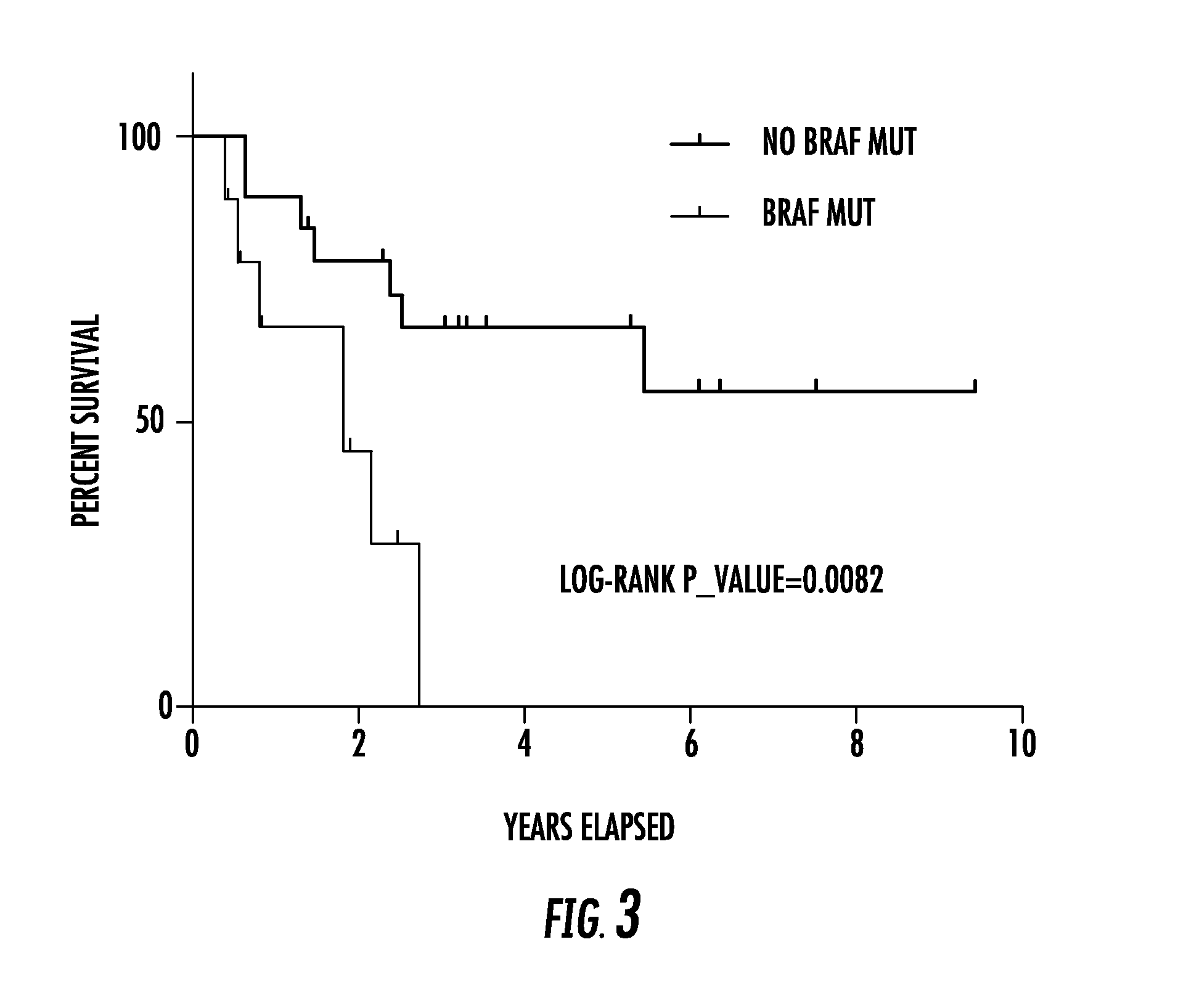
Tert and braf mutations in human cancer
ActiveUS20170022572A1Good risk stratificationEasy to manageMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseTert promoter
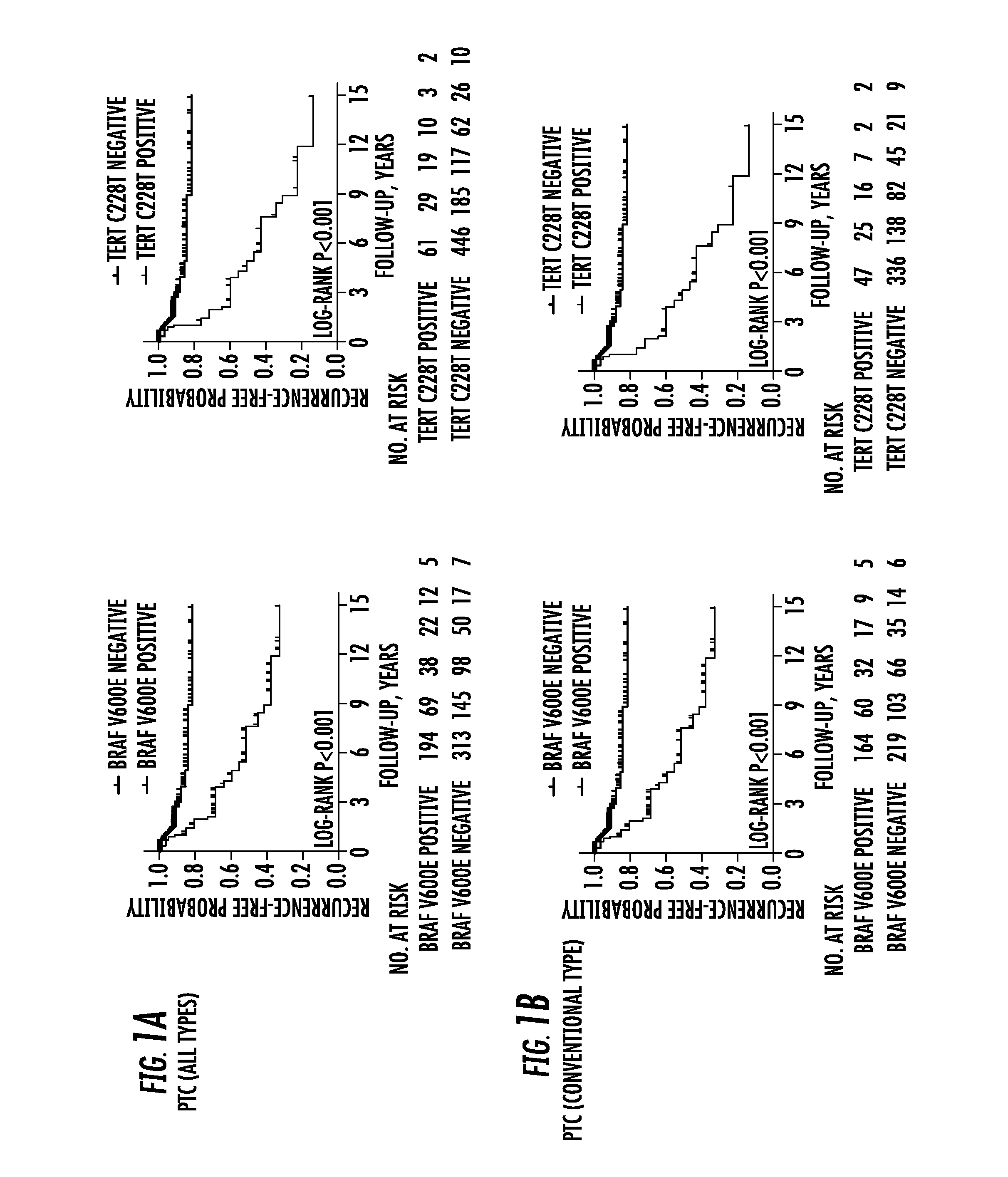
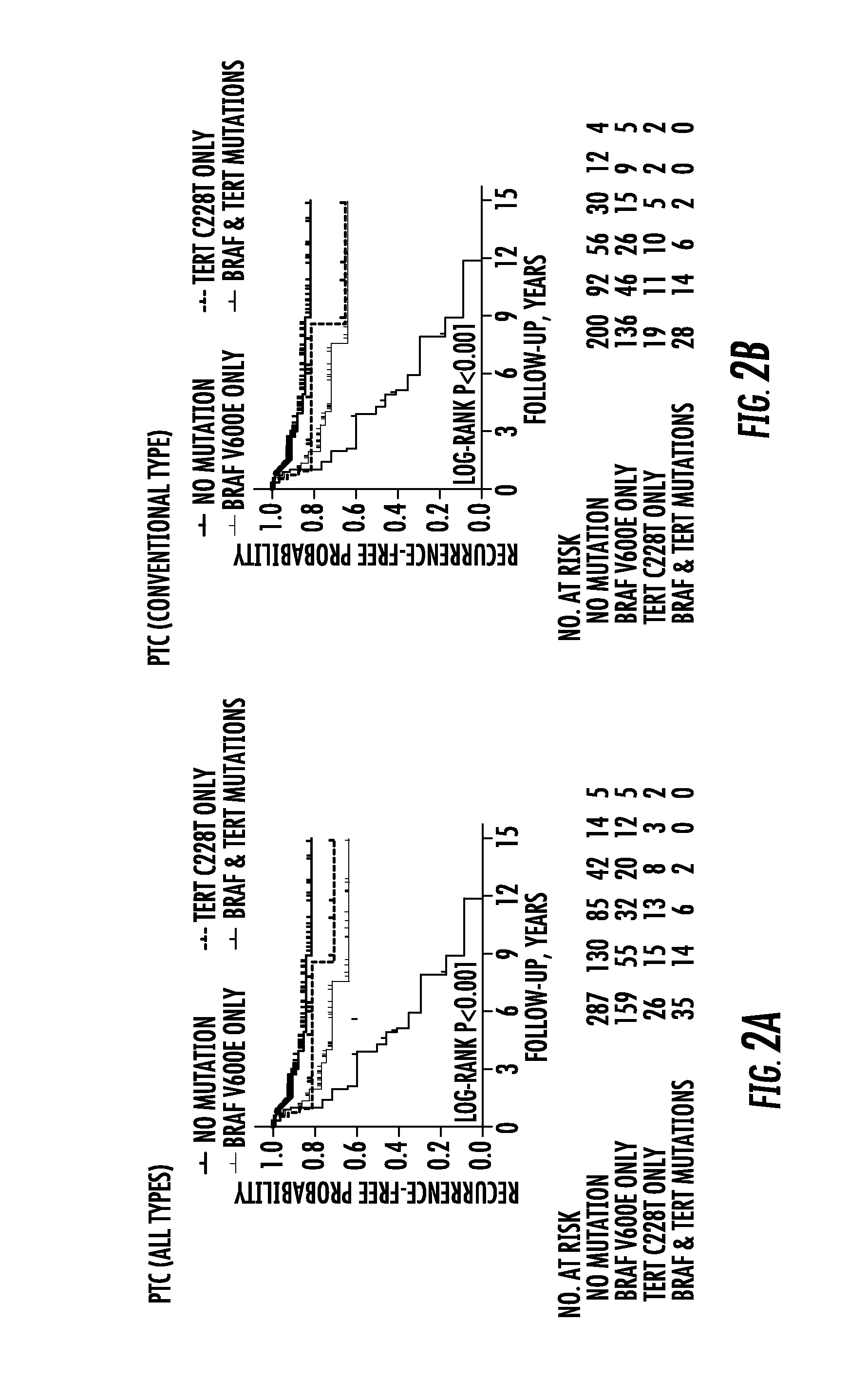
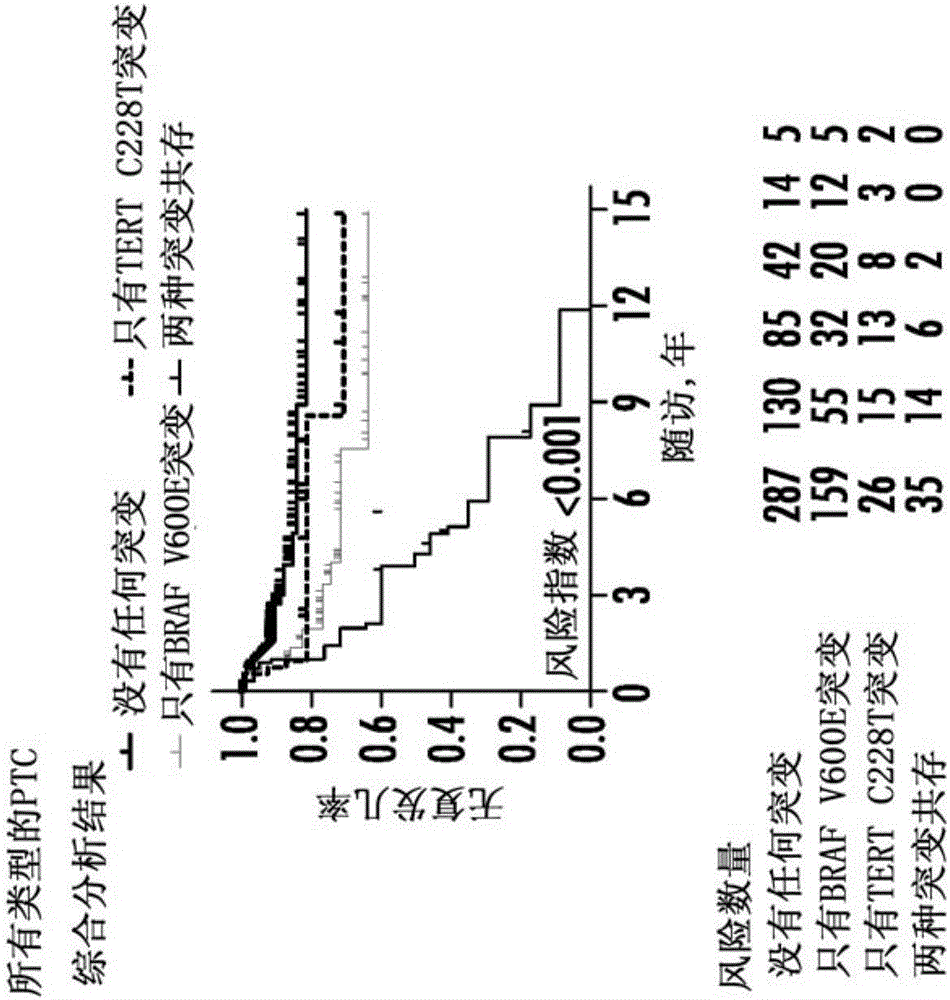
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions related to certain mutations in cancer. In one embodiment, a method for treating a subject having aggressive thyroid cancer comprises the steps of (a) obtaining a biological sample from the subject; (b) performing an assay on the sample obtained from the subject to identify a mutation at 1 295 228 C>T (C228T), corresponding to −124 C>T from the translation start site in the promoter of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) gene, and a T1799A mutation in the BRAF gene that results in a V600E amino acid change; (c) identifying the subject as having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer if the C228T and V600E mutations are identified; and (d) treating the subject with one or more treatment modalities appropriate for a subject having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer. Similar approaches are applied to other human cancers harboring both BRAF V600E mutation and TERT promoter mutations.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Plant leaf specific expression promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN107815452AWon't cause escapeReduce material energy consumptionPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic DNADNA fragmentation
The present invention relates to a plant leaf specific expression promoter and application thereof. An upstream promoter of a highly-active cotton leaf specific expression gene screened by gene microarray data and RT-PCR is cloned on the basis of upland cotton Goker Coker 312 genomic DNA as a template to obtain a DNA fragment of about 2kb at the upstream of a translation initiation site. Pant expression vector pGhlsp::GUS for the promoter to drive GUS is constructed, arabidopsis thaliana is transformed by agrobacterium floral dip method, the arabidopsis thaliana is observed by GUS histochemical staining, results show that the gene is mainly specifically expressed in leaves, and hardly expressed in roots and stems, and the plant leaf specific expression promoter is a new leaf specific expression promoter.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Tert and braf mutations in human cancer
InactiveCN106164299APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTert promoter mutationTranslation initiation sites
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions related to certain mutations in cancer.In one embodiment, a method for treating a subject having aggressive thyroid cancer comprises the steps of (a) obtaining a biological sample from the subject; (b) performing an assay on the sample obtained from the subject to identify a mutation at 1 295 228 C>T (C228T), corresponding to -124 C>T from the translation start site in the promoter of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) gene, and a T1799A mutation in the BRAF gene that results in a V600E amino acid change; (c) identifying the subject as having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer if the C228T and V600E mutations are identified; and (d) treating the subject with one or more treatment modalities appropriate for a subject having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer. Similar approaches are applied to other human cancers harboring both BRAF V600E mutation and TERT promoter mutations.
Owner:迈克明照邢
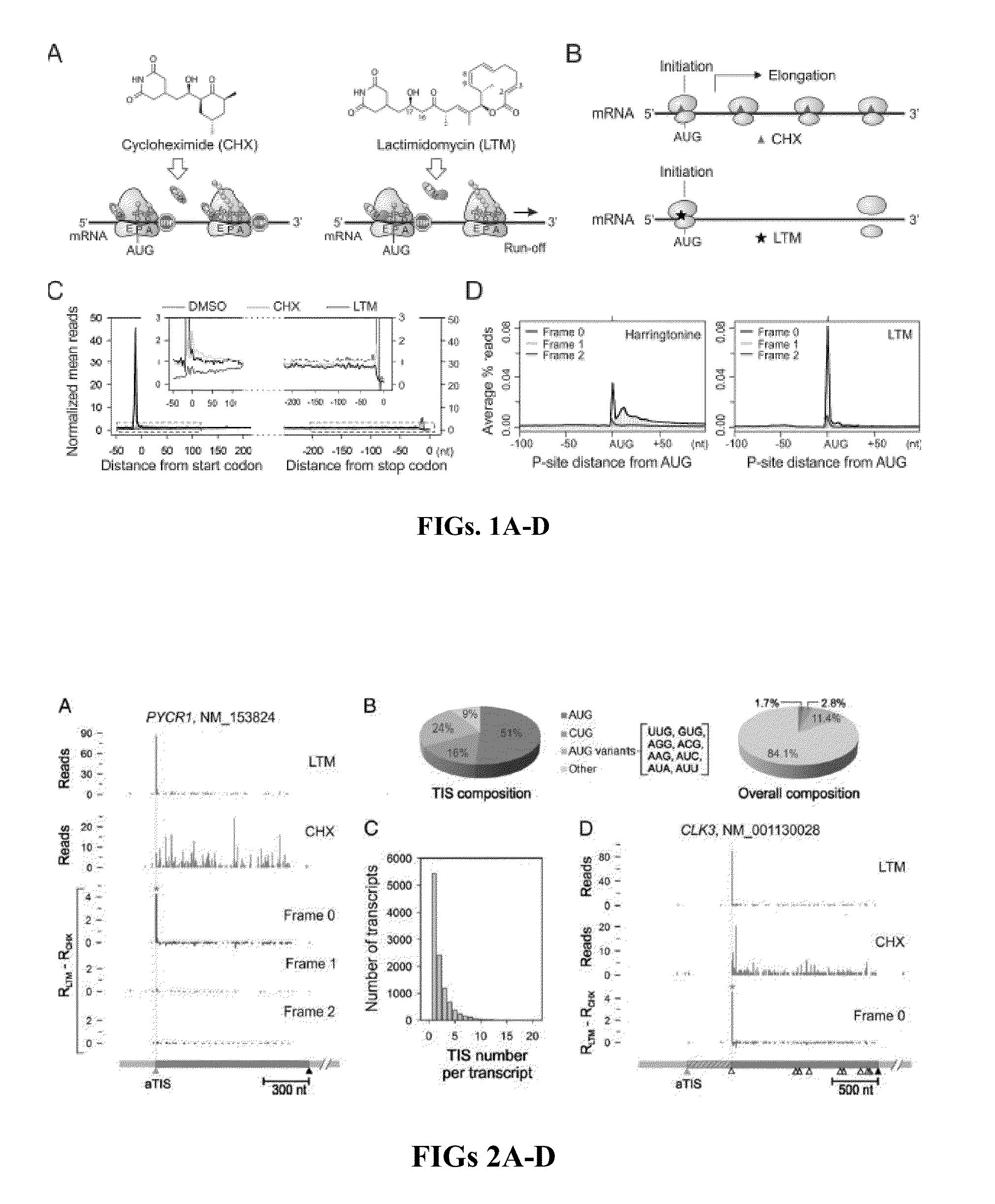
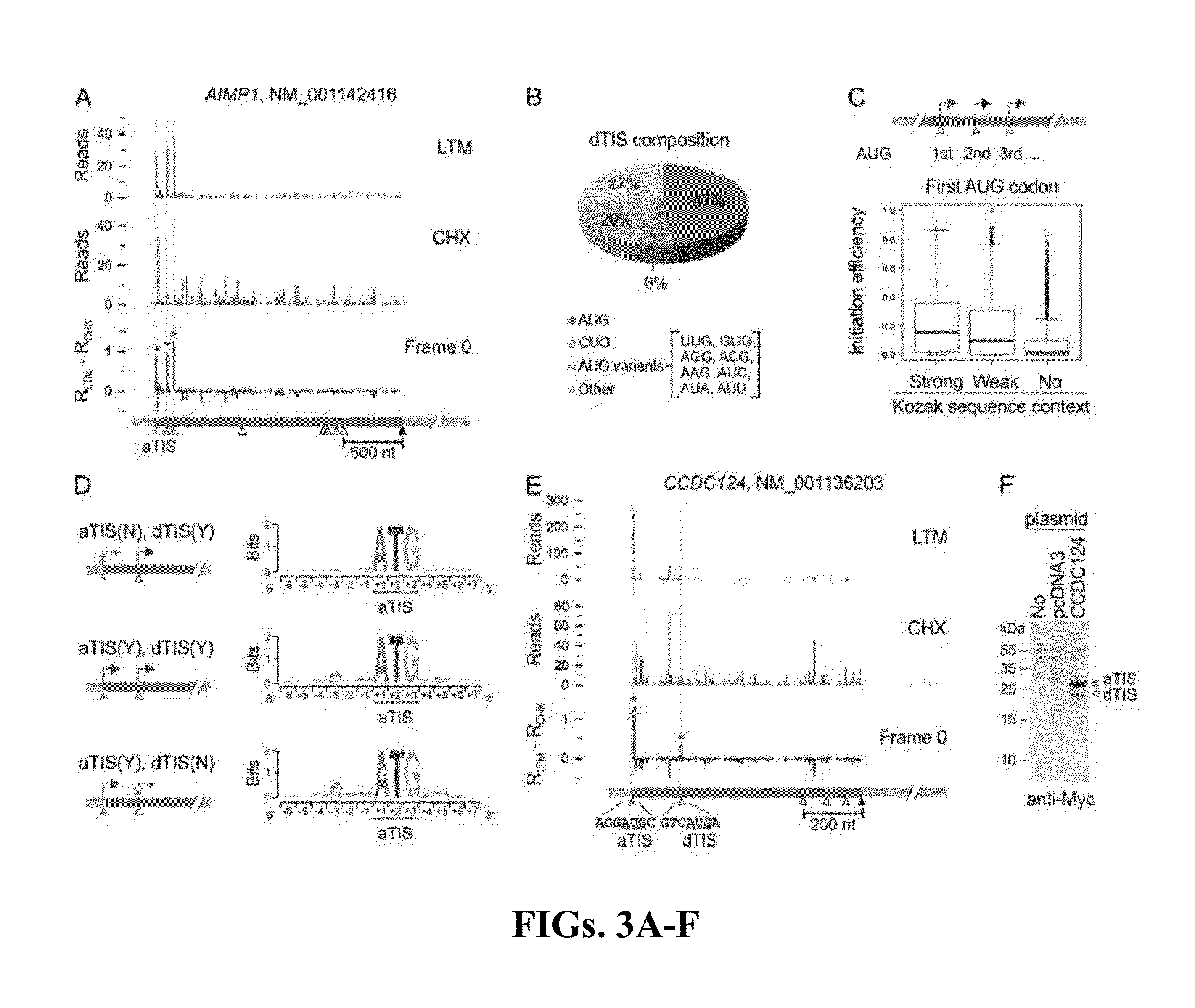
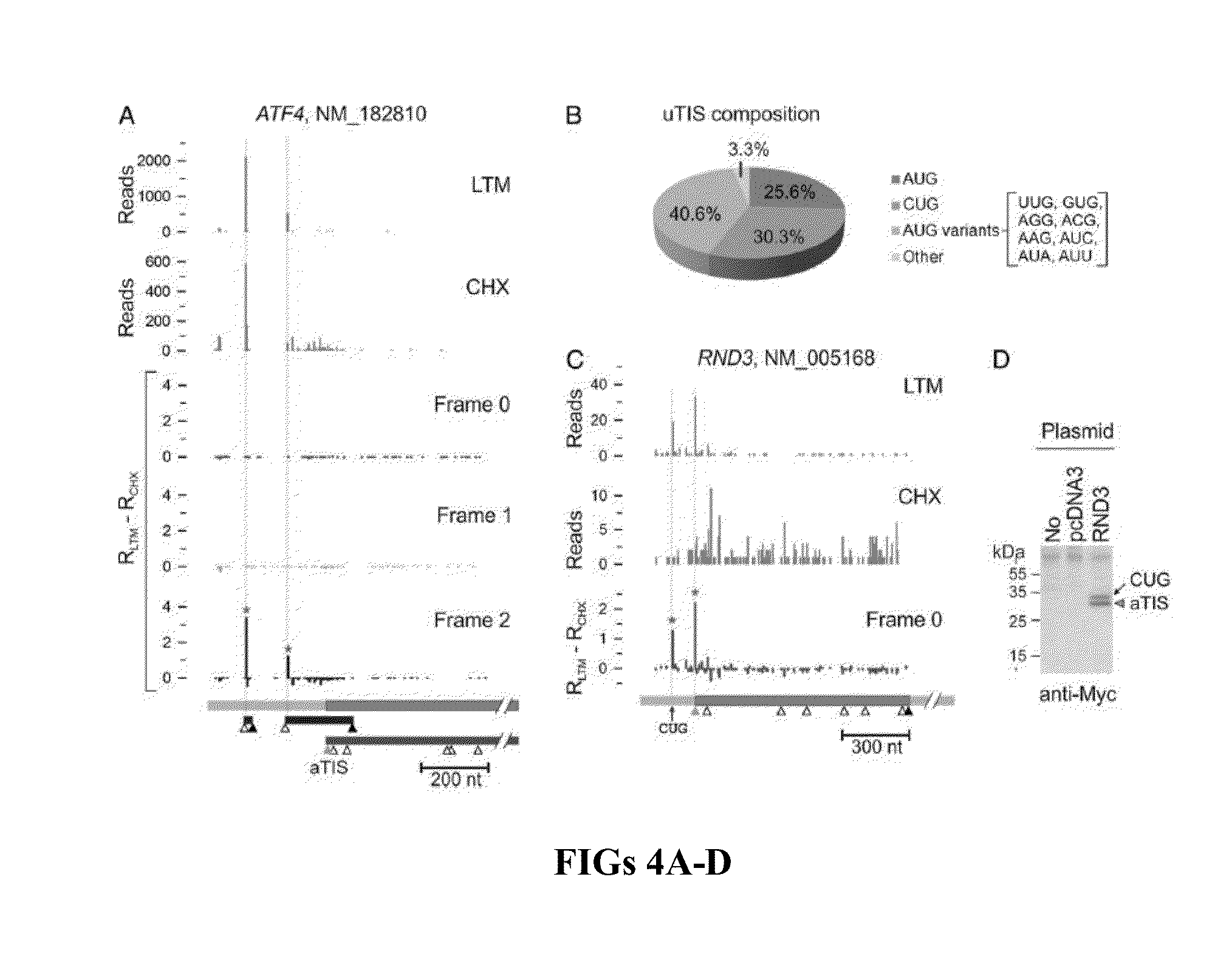
Method and kit for identifying a translation initiation site on an mRNA
InactiveUS20130096012A1Effectively lead to differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBiochemistryRibosome
The present invention relates to a method and kit for identifying a translation initiation site on an mRNA. The method involves contacting a first mRNA with a first translation inhibitor to preferentially stabilize one or more initiation ribosomes at translation initiation sites on the first mRNA. A second mRNA is contacted with a second translation inhibitor different from the first translation inhibitor to stabilize one or more initiation ribosomes and one or more elongation ribosomes on the second mRNA. The location of ribosomes stabilized on the first mRNA is compared to the location of ribosomes stabilized on the second mRNA.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting ox FTO (Fat Mass and Obesity-associated) gene single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
InactiveCN101906470AEasy to detectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionGenome
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Rice large-grain gene function marker and application
PendingCN110747288AValid identificationEfficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGermplasm
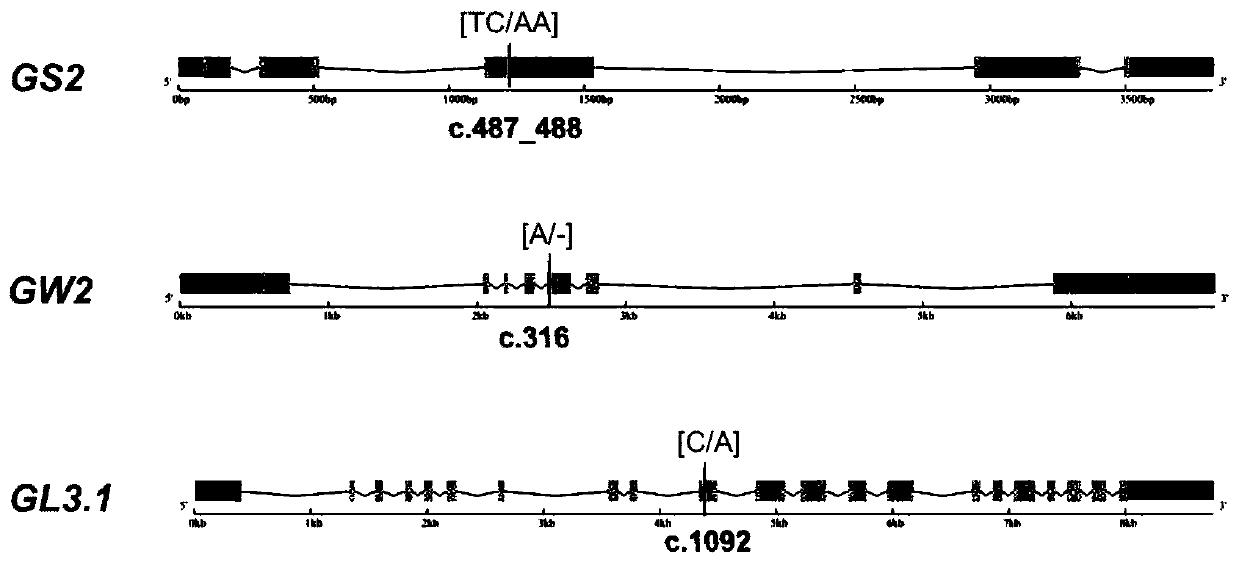
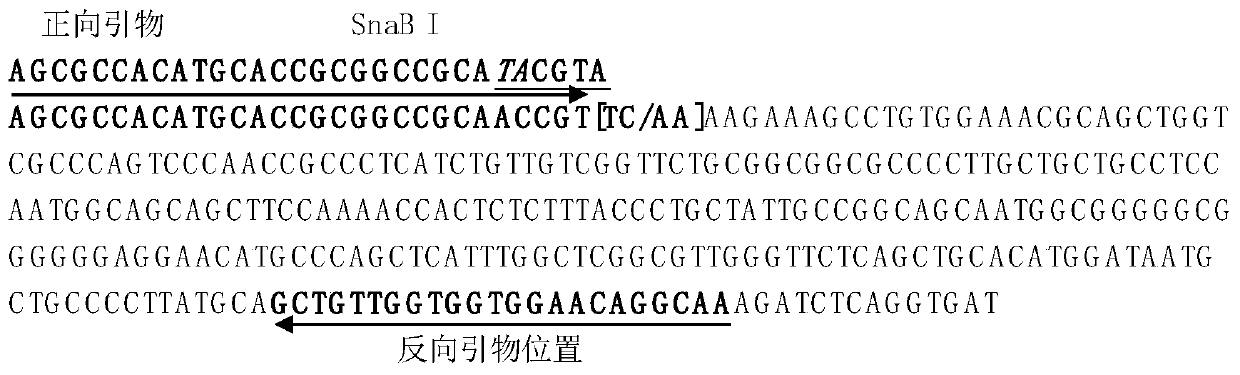
The invention discloses a rice large-grain gene function marker and application. The function marker is selected from one or more of a GS2 function marker, a GW2 function marker, a GL3.1 function marker and a GW2 promoter marker, wherein the GS2 function marker is a dCaps marker developed for TC / AA mutation of a third exon of a GS2 gene, the GW2 function marker is a dCaps marker developed for nucleotide A deletion mutation of a fifth exon of a GW2 gene, the GL3.1 function marker is a dCaps marker developed for single-base C / A mutation of a tenth exon of a GL3.1 gene, and the GW2 promoter marker is a dCaps marker developed for T / A mutation at upstream 858bp of a GW2 translation initiation site. The invention develops effective dCas markers for key variation sites of rice large-grain genes,can effectively identify large-grain rice germplasm and is applied to molecular breeding of rice.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
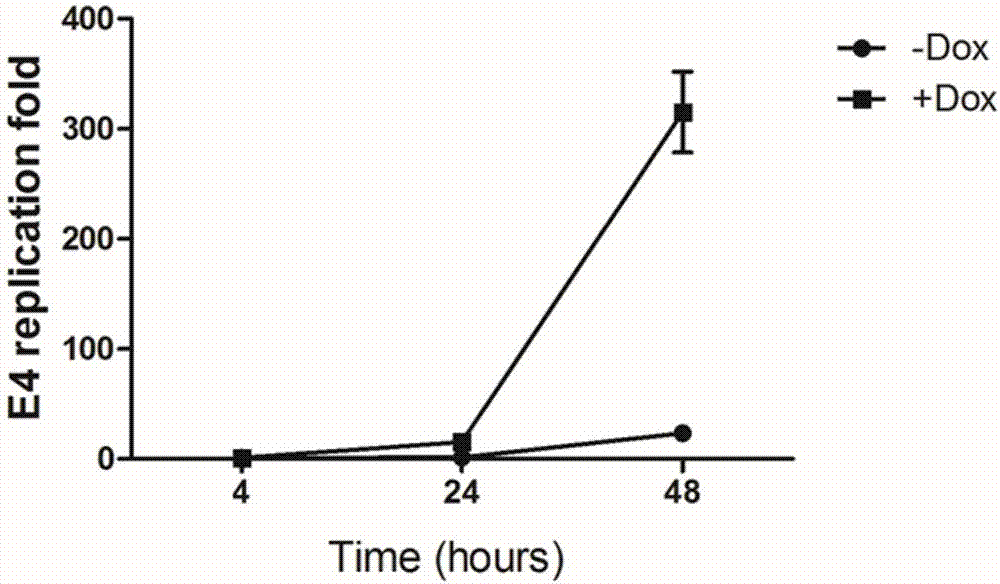
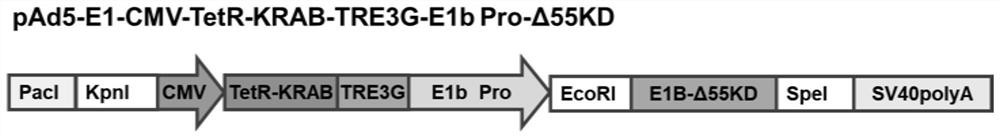
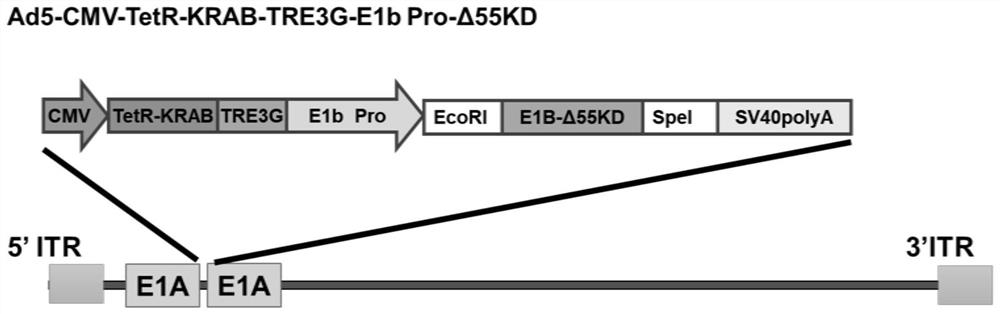
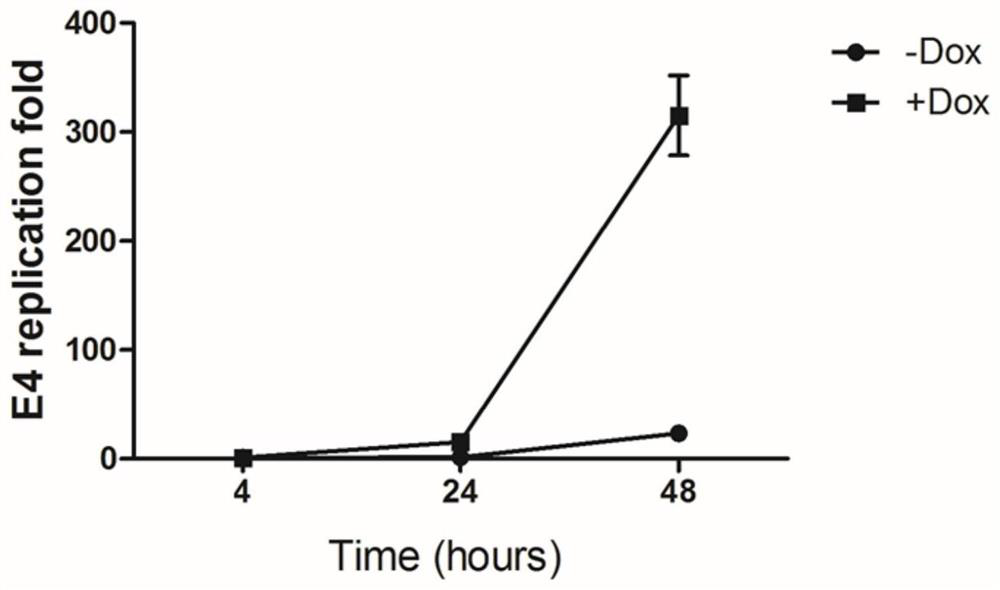
Conditionally replicating adenovirus vector for viral replication regulated by transcription inhibition type Tet-On system and application
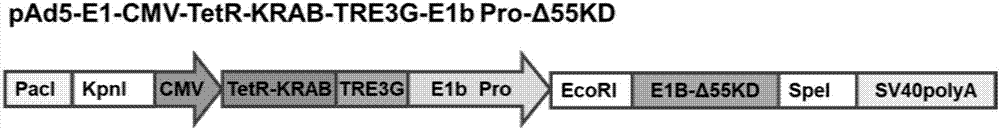
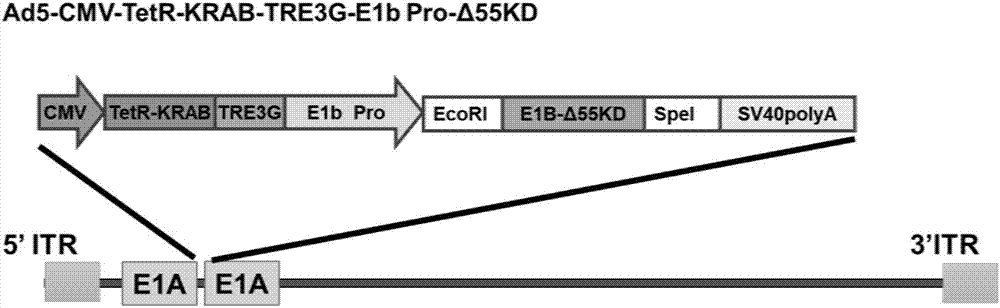
The invention discloses a conditionally replicating adenovirus vector for virus replication regulated by a TetR-KRAB-mediated transcription inhibition type Tet-On system, adenovirus E1 region comprises the following components in the following connection sequence: 5'-CMV promoter, TetR-KRAB gene, promoter TRE3G-E1b Pro containing a tetracycline responsive element, EcoR I enzyme cutting site, E1B Delta 55KD protein-deleted adenovirus E1A-E1B19KD gene sequence, enzyme cutting site Spe I and mRNA transcription termination signal SV40polyA-3'; the CMV promoter expresses transcription inhibitor TetR-KRAB; a gene sequence inserted into the two enzyme cutting sites of the EcoR I and the Spe I is a gene fragment from adenovirus E1A translation initiation site to adenovirus E1B19KD protein termination codon, the promoter TRE3G-E1b Pro containing the tetracycline responsive element expresses adenovirus E1A gene, adenovirus E1B19KD gene is expressed by the own promoter of the adenovirus E1B19KD, and the packed adenovirus is named as Ad5-CMV-TetR-KRAB-TRE3G-E1bPro-Delta 55KD. Tests show that the virus can be loaded into mesenchymal stem cells for application in study of tumor therapy.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Construction process of pig serum albumin locus targeting vector for producing foreign protein
The present invention constitutes three kinds of targeting vector capable of being located and integrated onto pig serum albumin locus and makes it possible to produce human serum albumin with pig serum. First, the 35 kb, including the 14 kb before translation starting site, all the exons and introns, and 3'-end translation 4 kb, of pig albumin genome are cloned and sequence analyzed. Then, two kinds of targeting vector capable of locating and integrating human serum albumin cDNA onto pig serum albumin and one kind of targeting vector capable of locating and integrating human serum albumin cDNA onto pig serum albumin locus are constituted. These targeting vectors are transfected pig fetus fibroblast or other cells, hitted cells are screened for nuclear transplantation of animal cells, and transgenic pig capable of producing human serum albumin in its serum is obtained.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
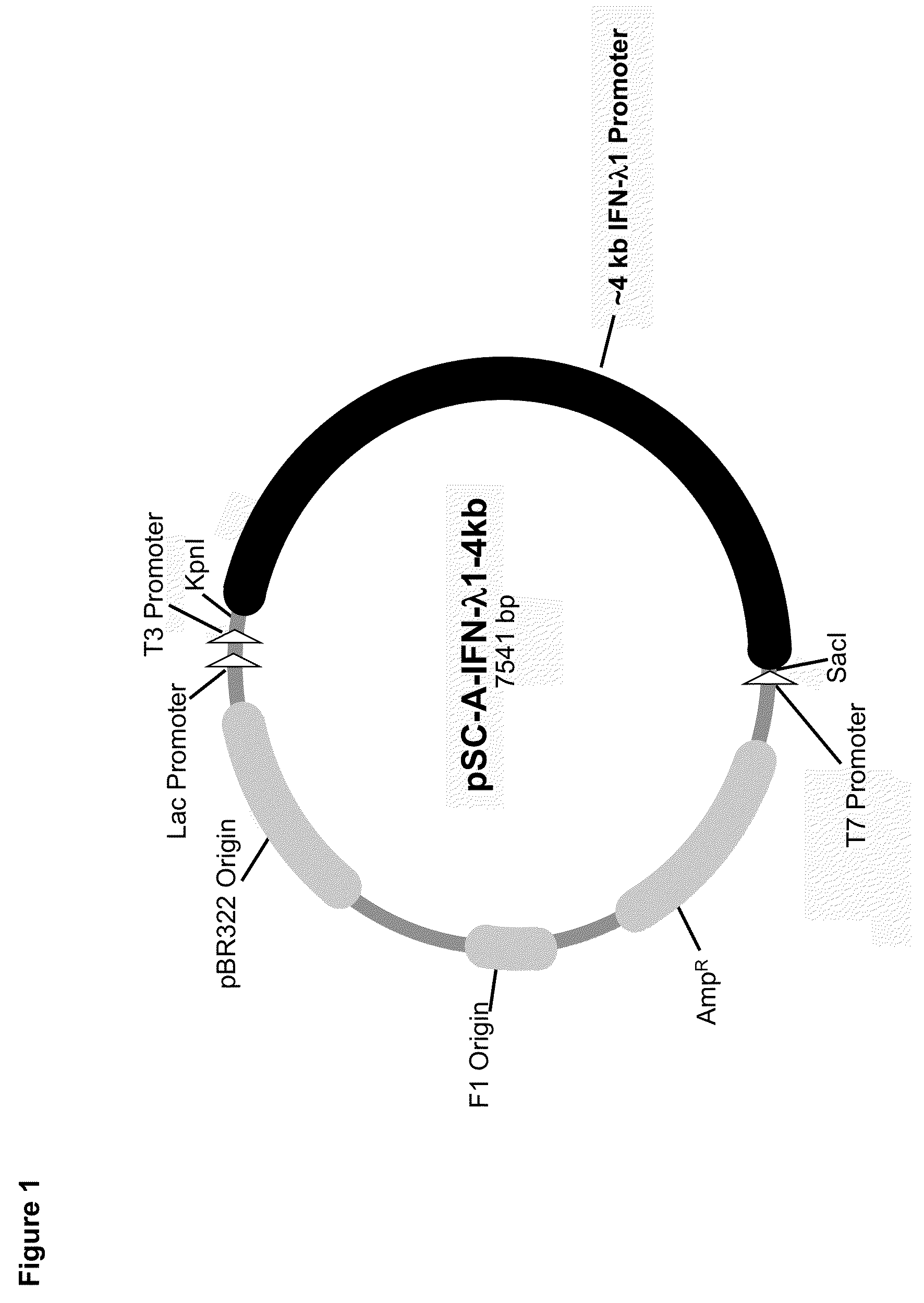
Novel repressor on ifn-lambda promoter and sirna against zeb1 and blimp-1 to increase ifn-lambda gene activity
InactiveUS20140057960A1High expressionIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePromoter activity
The present invention is directed to the identification of a novel repressor located between ˜1.2 kb to ˜1.6 kb from the translation start site of the IFN-λ1 promoter. The present invention provides a method of using siRNAs against ZEB1 (binds to the repressor region) and BLIMP-1 (binds outside the repressor region) and increases the promoter activity of IFN-λ1 (i.e., increases the production of IFN-λ1 protein). siRNAs against ZEB1 mRNA or BLIMP-1 mRNA increase IFN-λ1 gene activity. There is provided a therapeutic application of siRNAs against ZEB1 and BLIMP-1 mRNAs in treating a mammal (including a human) by increasing the production of IFN-λ1 protein that promotes an anti-viral response as well as treats asthma diseases and colon diseases.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
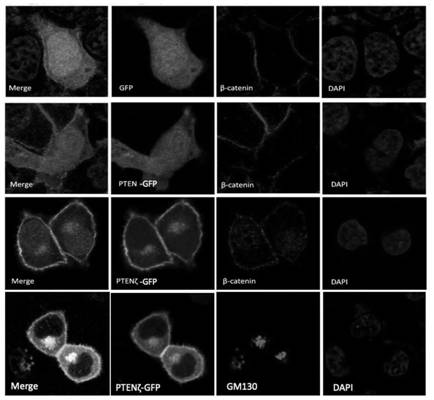
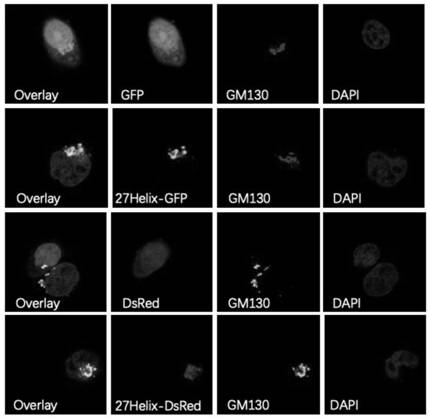
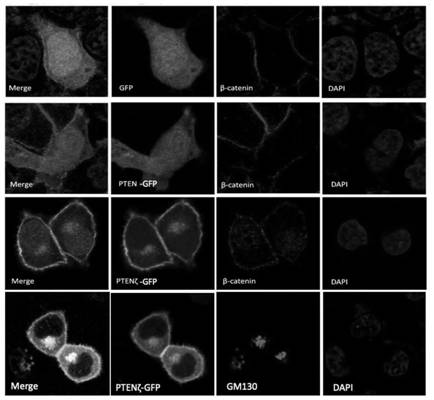
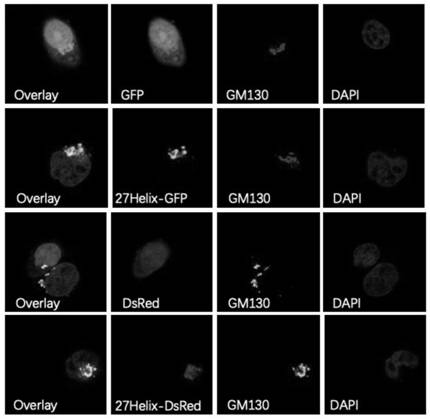
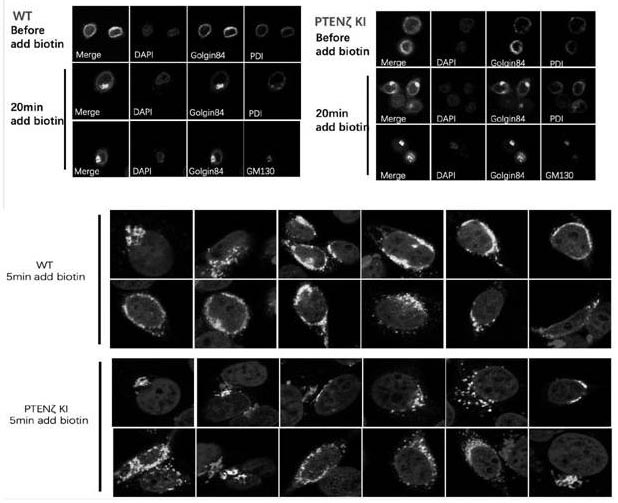
N-terminal extension type PTEN subtype PTEN zeta protein as well as coding gene and application thereof
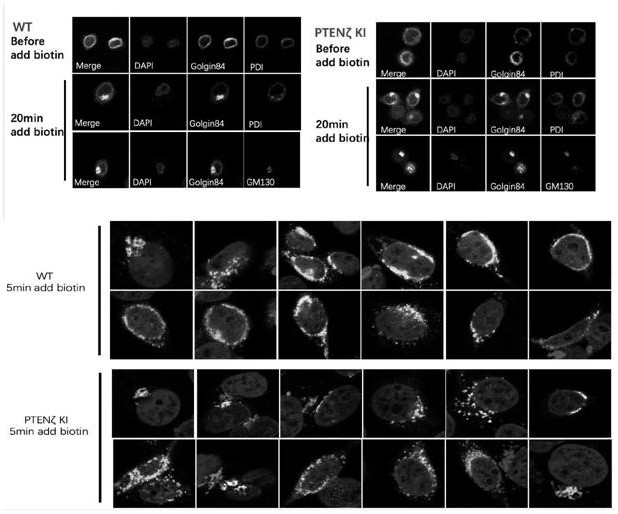
The invention provides an N-terminal extension type PTEN subtype PTEN zeta protein as well as a coding gene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of functional proteins. According to the PTEN subtype provided by the invention, a section of 28aa polypeptide is connected to the N end on the basis of PTEN protein, and the polypeptide is a Golgi positioning signal peptide section. Translation of the PTEN[zeta] protein starts from a non-classical AUG translation starting site-ATT948 in a 5'-UTR region, and a palindromic structure at the downstream of the site plays an important role in translation starting. The protein with 431 amino acid sequences, which is obtained by starting translation from ATT948, is named as PTEN[zeta]. PTEN[zeta] is mainly distributed in Golgi apparatus and cell membranes. According to the invention, PTEN[zeta] in Hela cells is specifically knocked out by using CRISPR-Cas9, and a RUSH system is used for verifying that the specific knockout of PTEN[zeta] leads to that the transport speed is obviously increased when endoplasmic reticulum is transported to vesicles of Golgi apparatus.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Combination therapy with liposomal antisense oligonucleotides
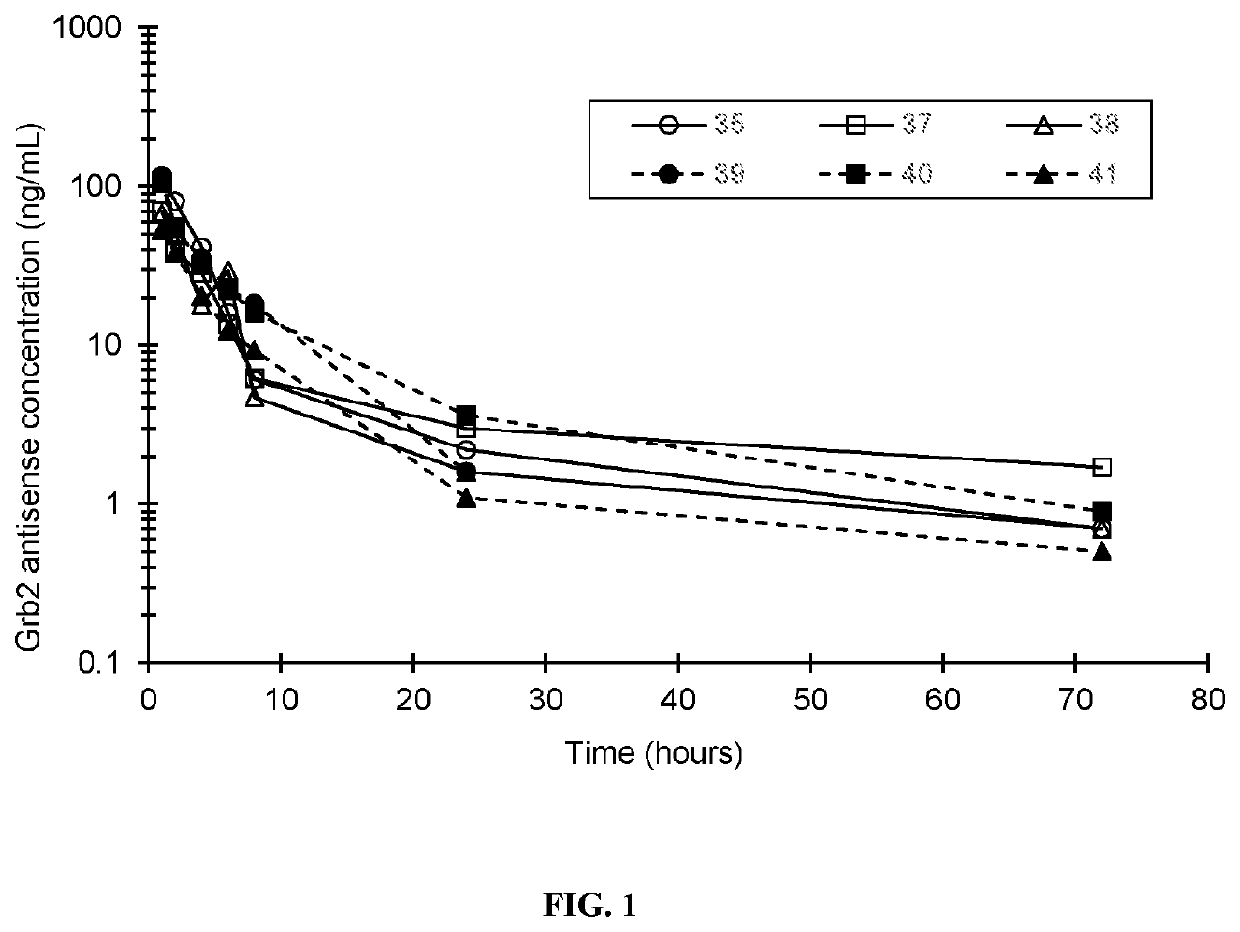
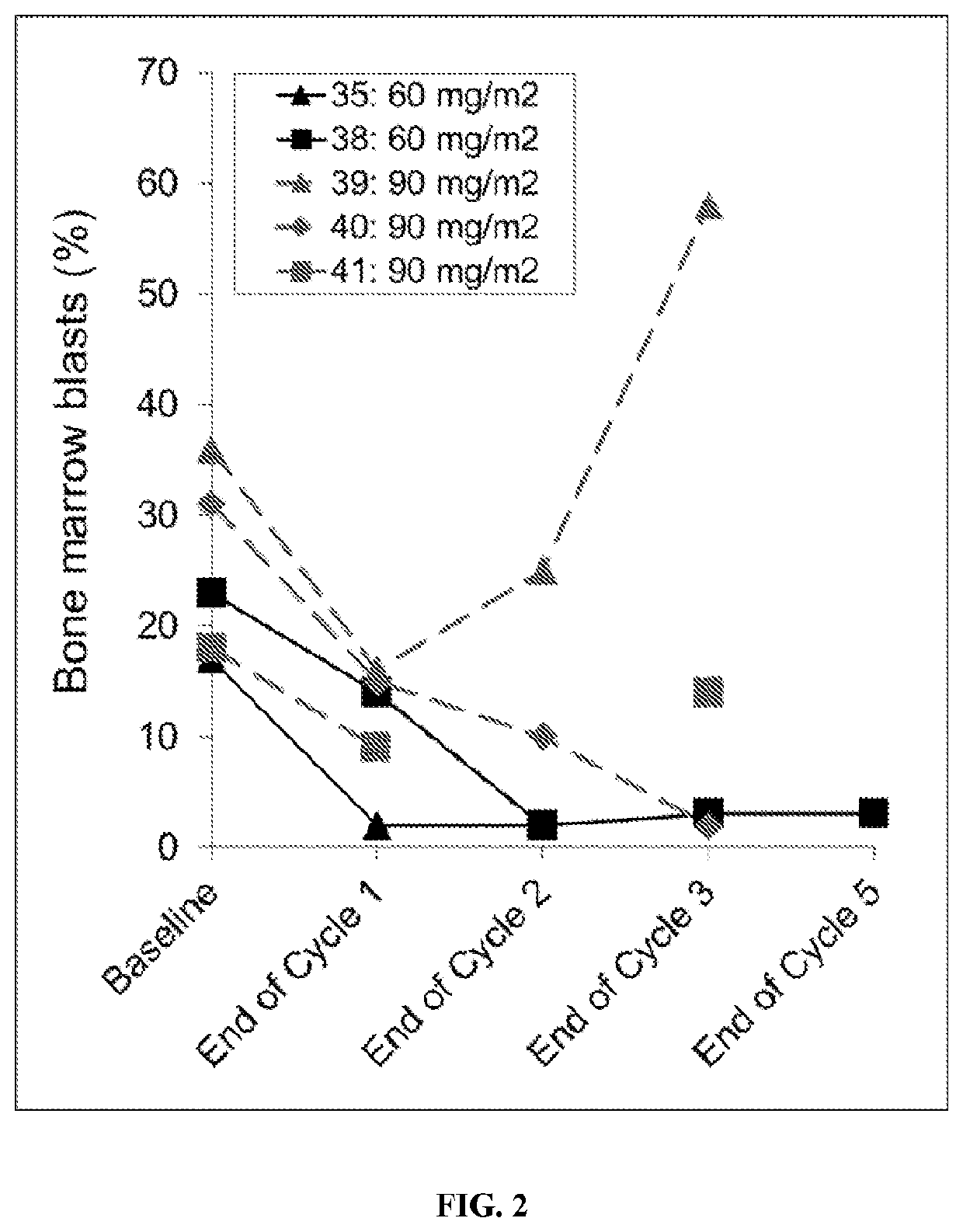
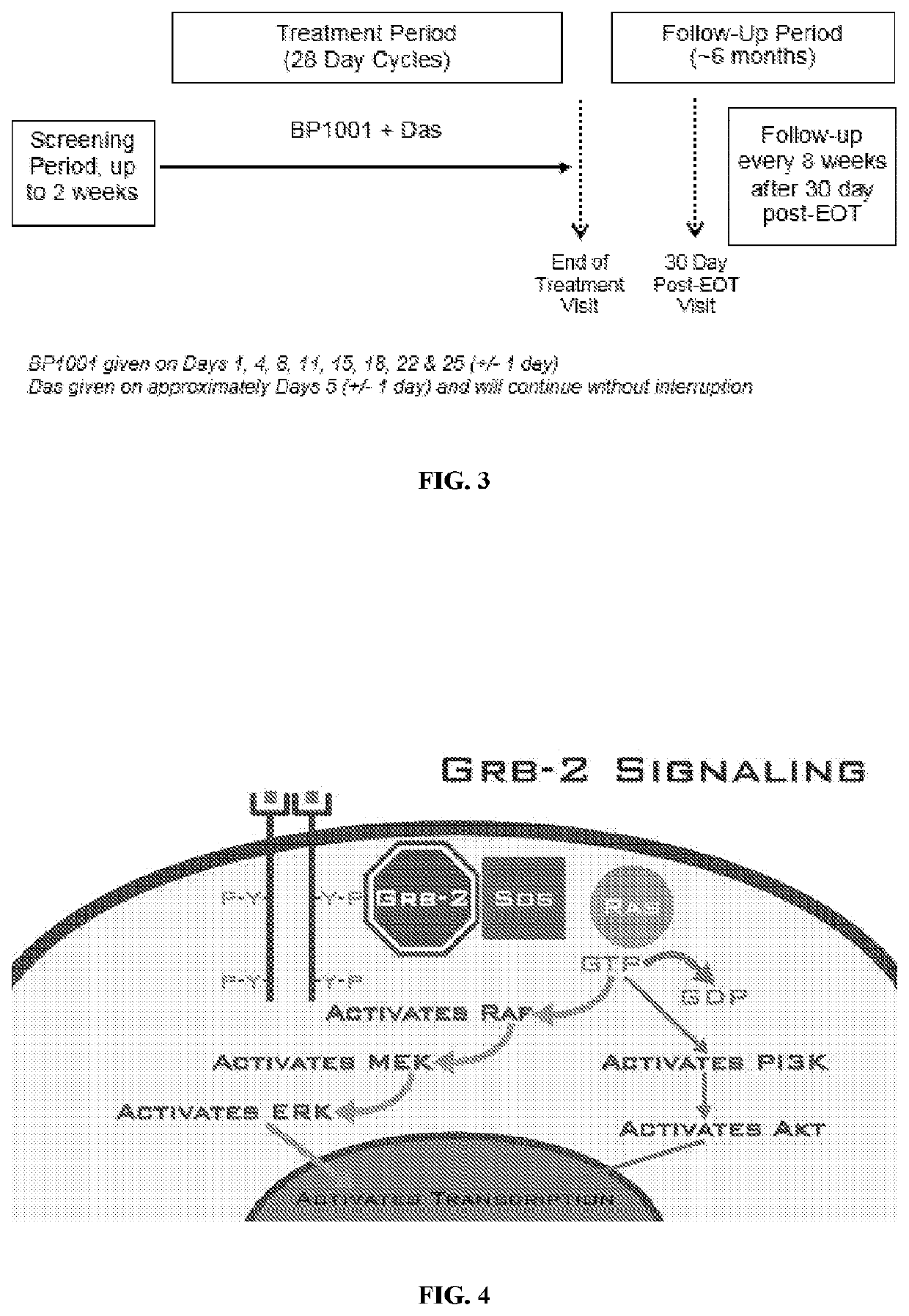
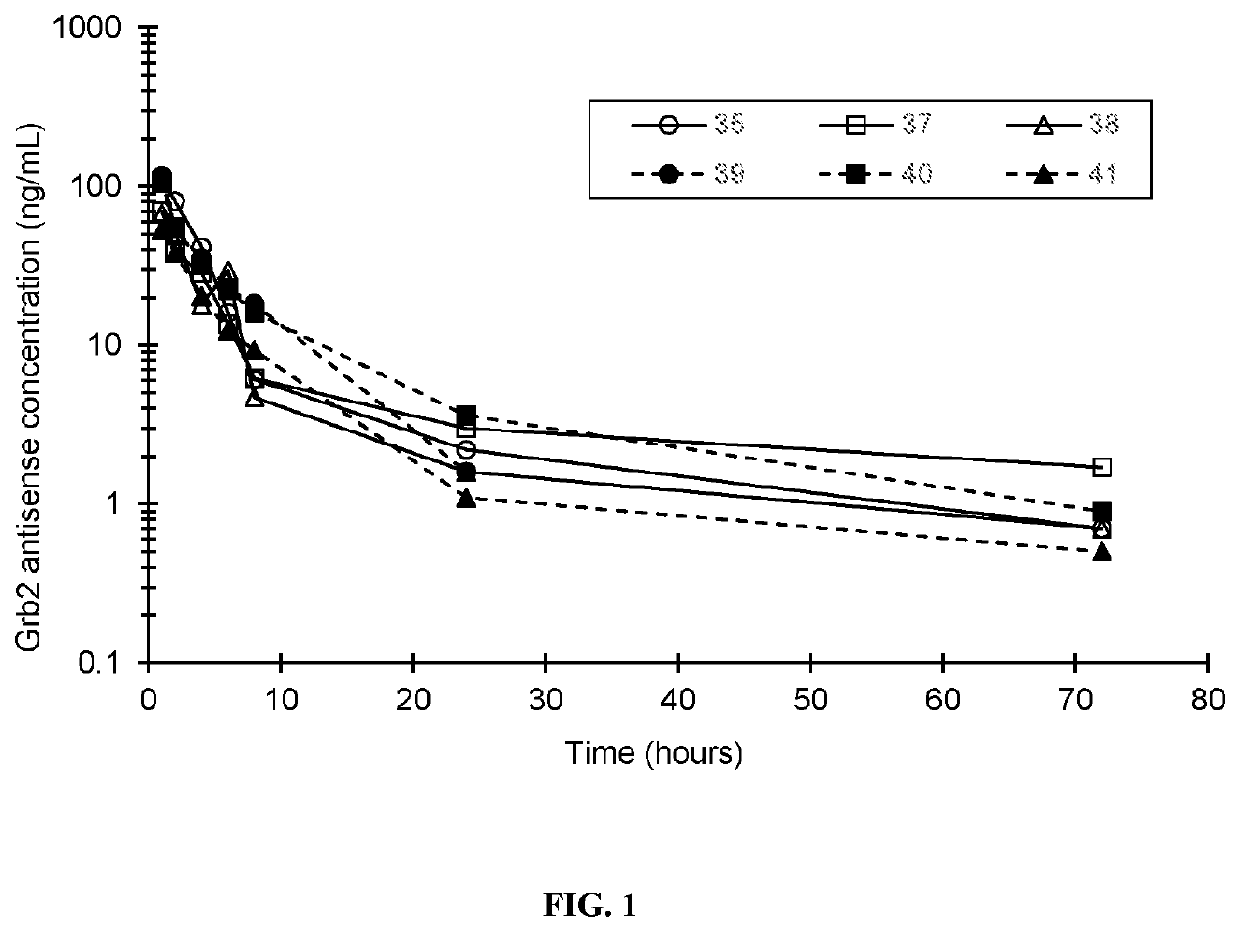
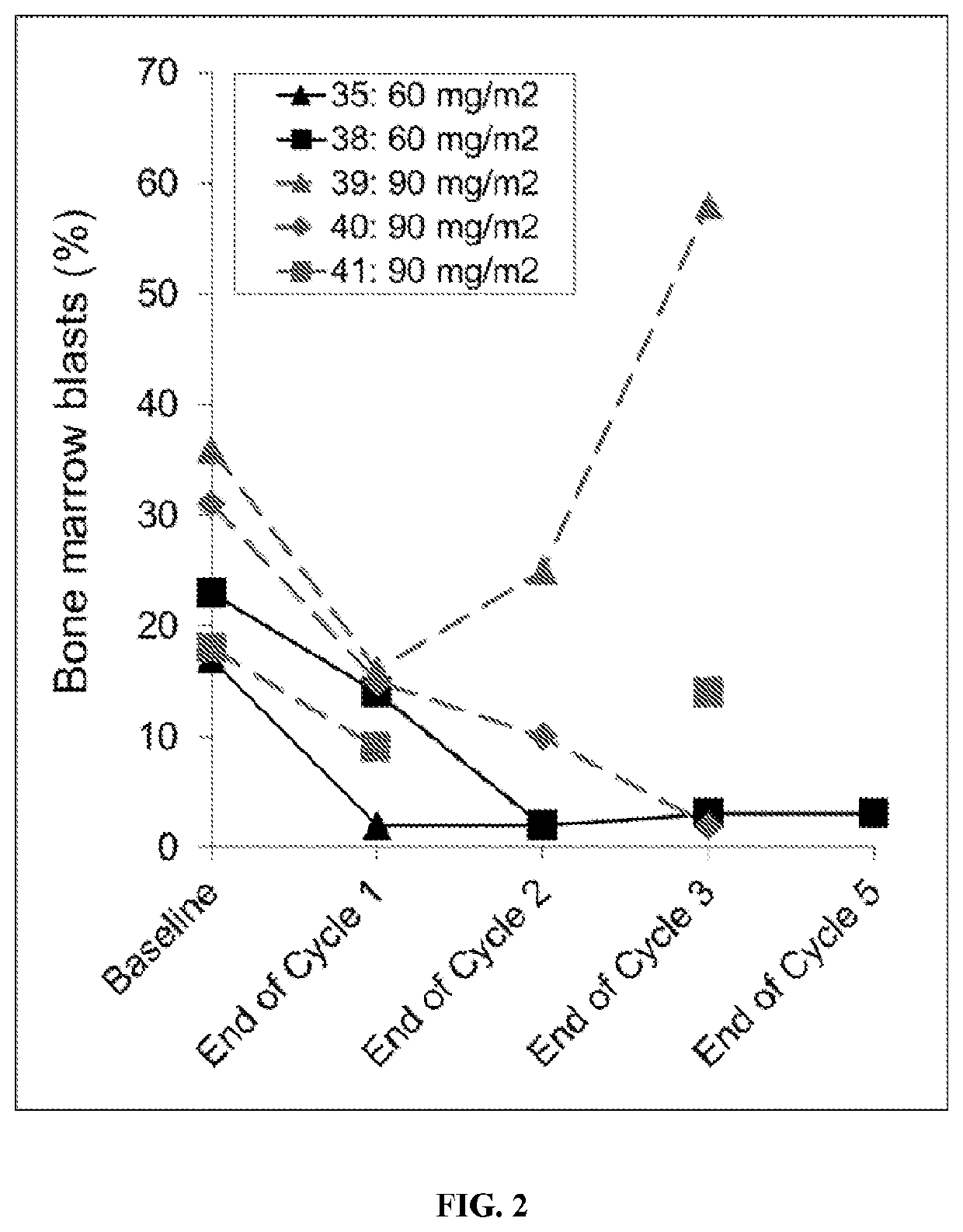
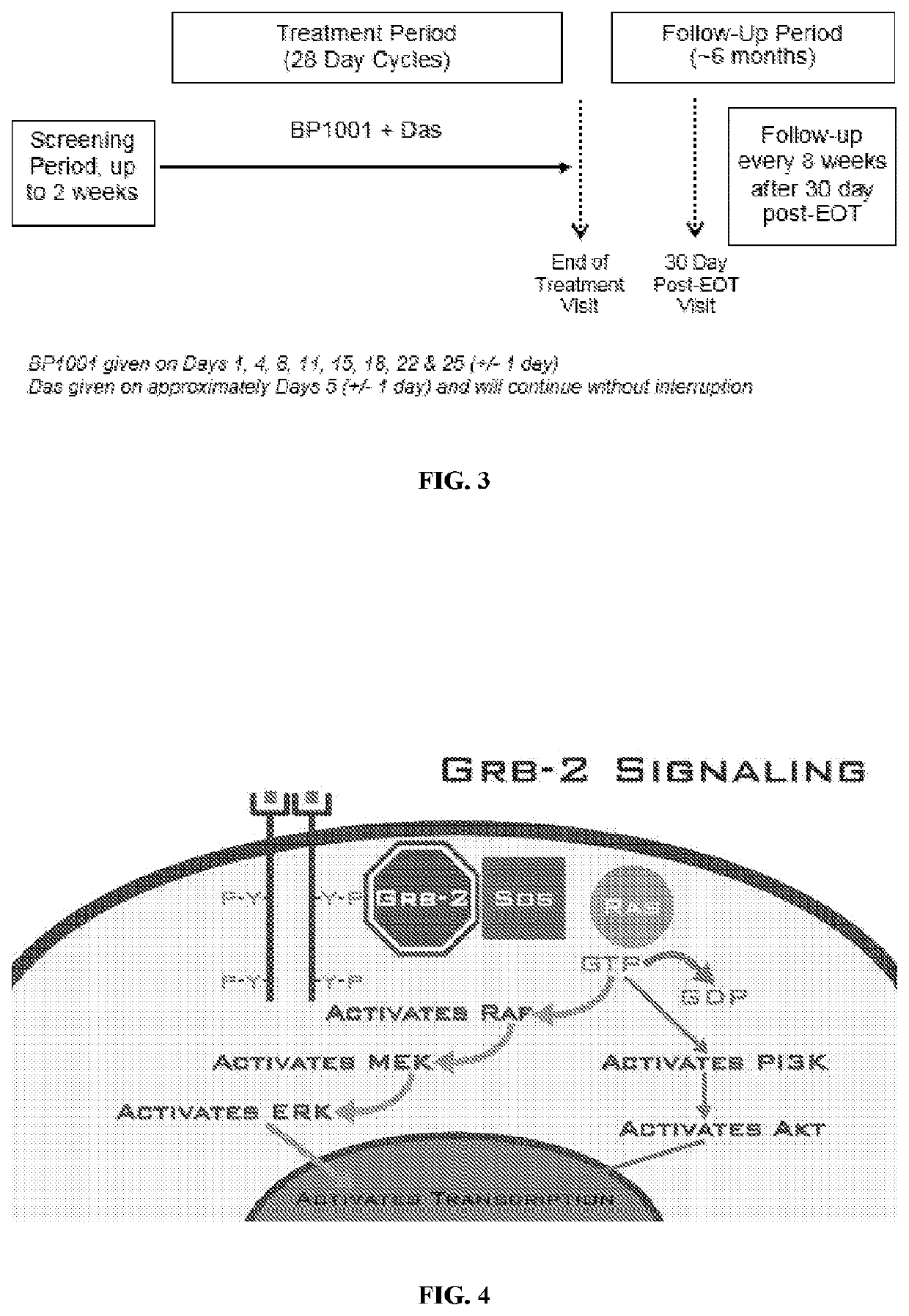
Provided herein are methods of treating a cancer in a patient comprising administration of an effective amount of a nuclease-resistant polynucleotide that hybridizes to the translation initiation site of a Grb2 nucleic acid in the patient and either a Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor (e.g., dasatinib) or a cytidine analogue (e.g., decitabine or cytarabine). The cancer may be Ph+ and / or Bcr-Abl positive chronic myelogenous leukemia or acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome.
Owner:BIO PATH HLDG INC
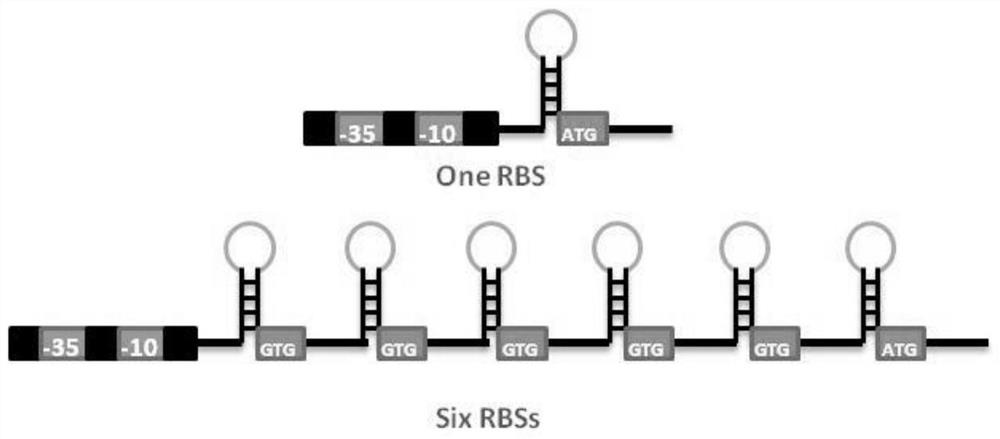
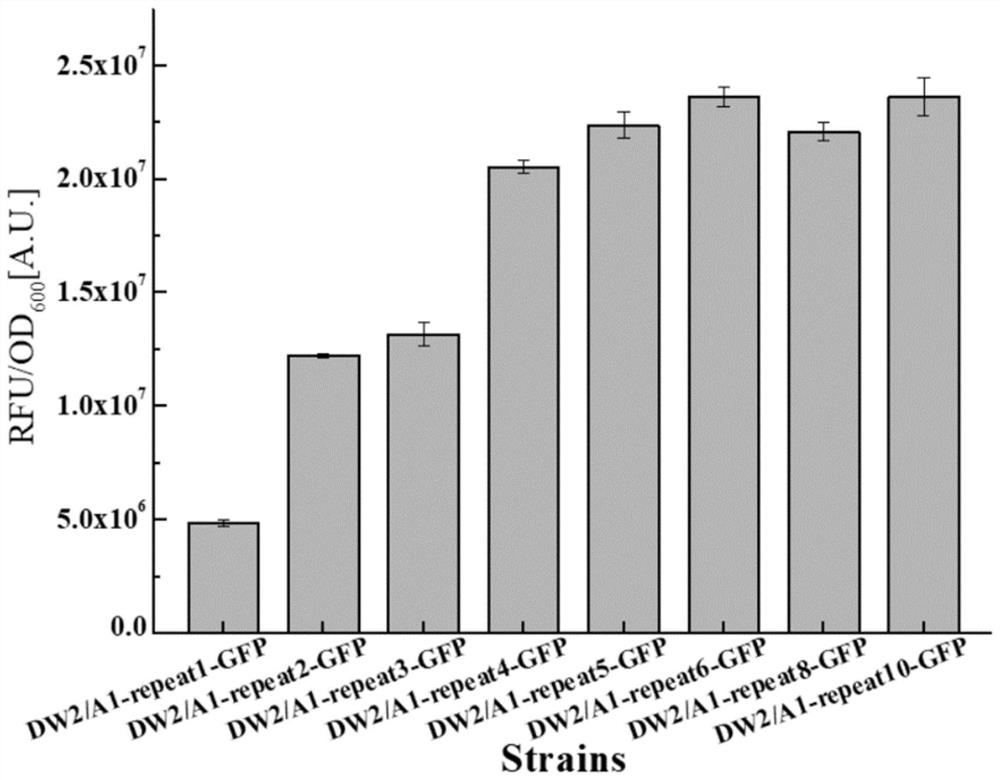
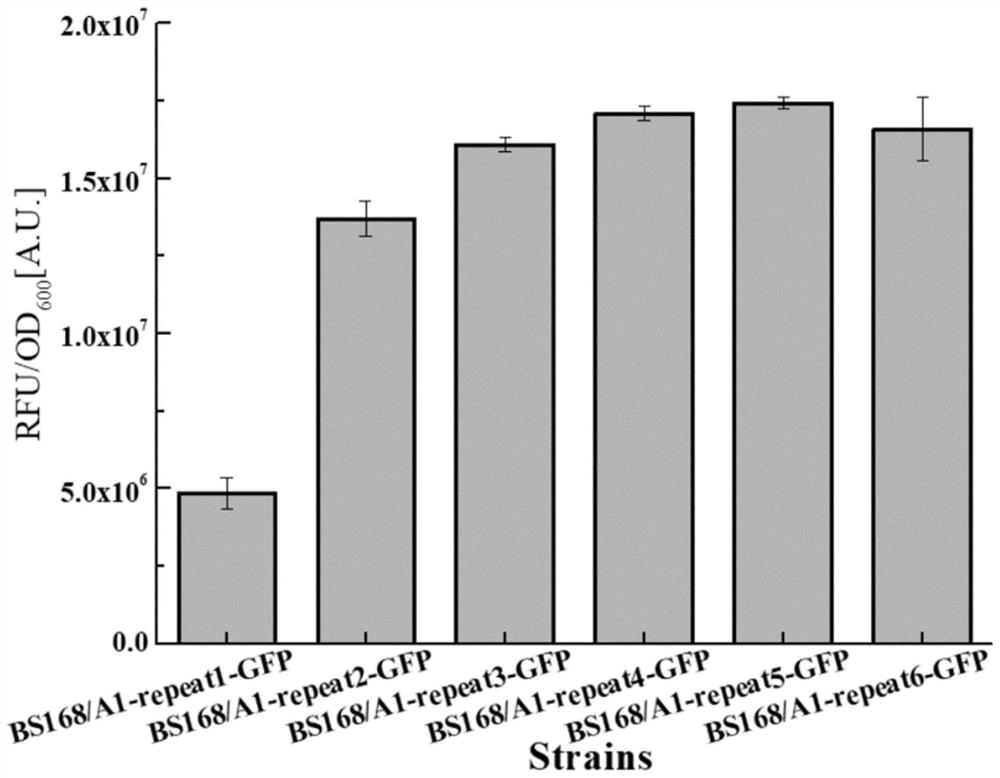
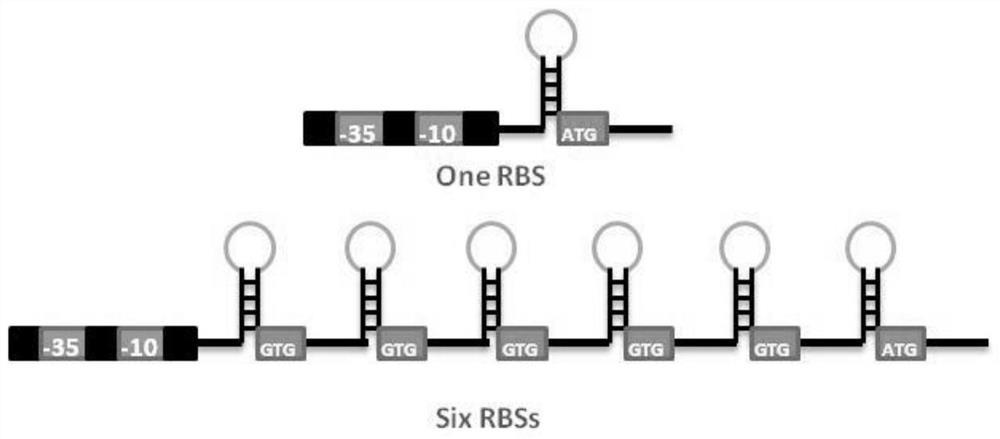
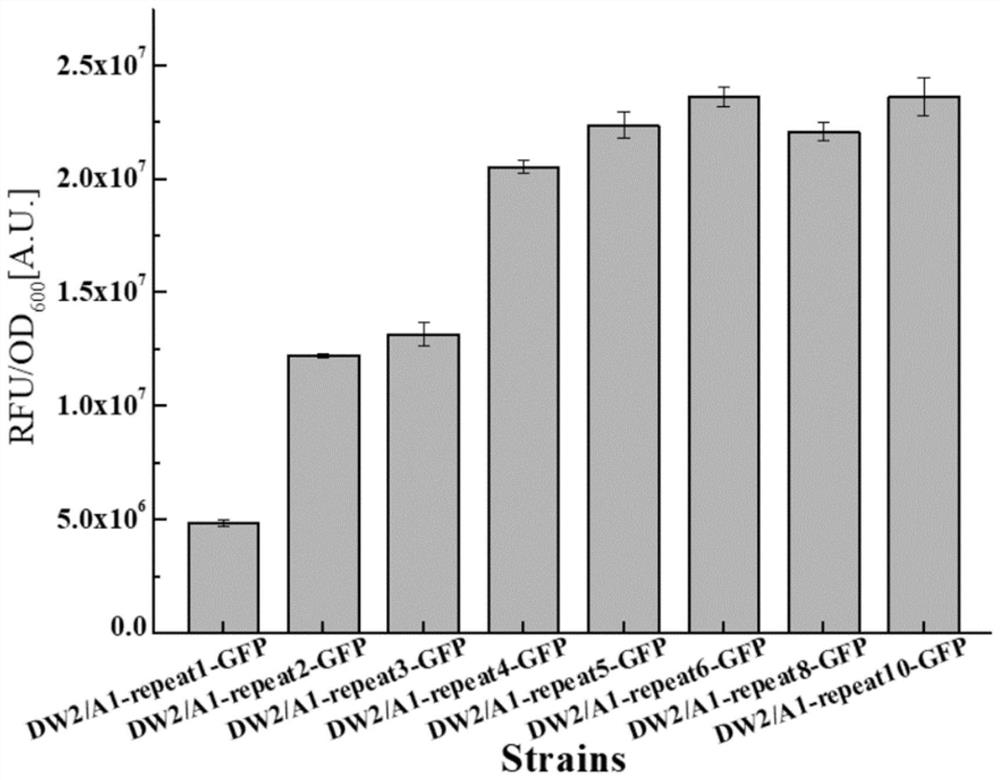
Sequence for increasing translation start sites of gram-positive bacteria and application of sequence in improving protein expression efficiency
ActiveCN113106095AHigh expressionThe increase in expression was further enhancedPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBacillus licheniformisGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbiological engineering, and discloses a sequence for increasing translation start sites of gram-positive bacteria and application of the sequence in improvement of protein expression efficiency, and the sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. According to the invention, a 5' untranslated region of the promoter is transformed, so that a target gene is prompted to translate from a plurality of translation start sites. In bacillus licheniformis and bacillus subtilis, the expression quantities of green fluorescent protein are respectively increased by about 150 times and 126 times compared with the original promoter P43. In corynebacterium glutamicum, the expression quantity of green fluorescent protein is increased by 36 times compared with that of an original promoter. Meanwhile, the mRNA leader sequence also remarkably improves the expression quantity of keratinase in bacillus licheniformis, and proves that the mRNA leader sequence is universal for improving the protein expression efficiency of gram-positive bacteria.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
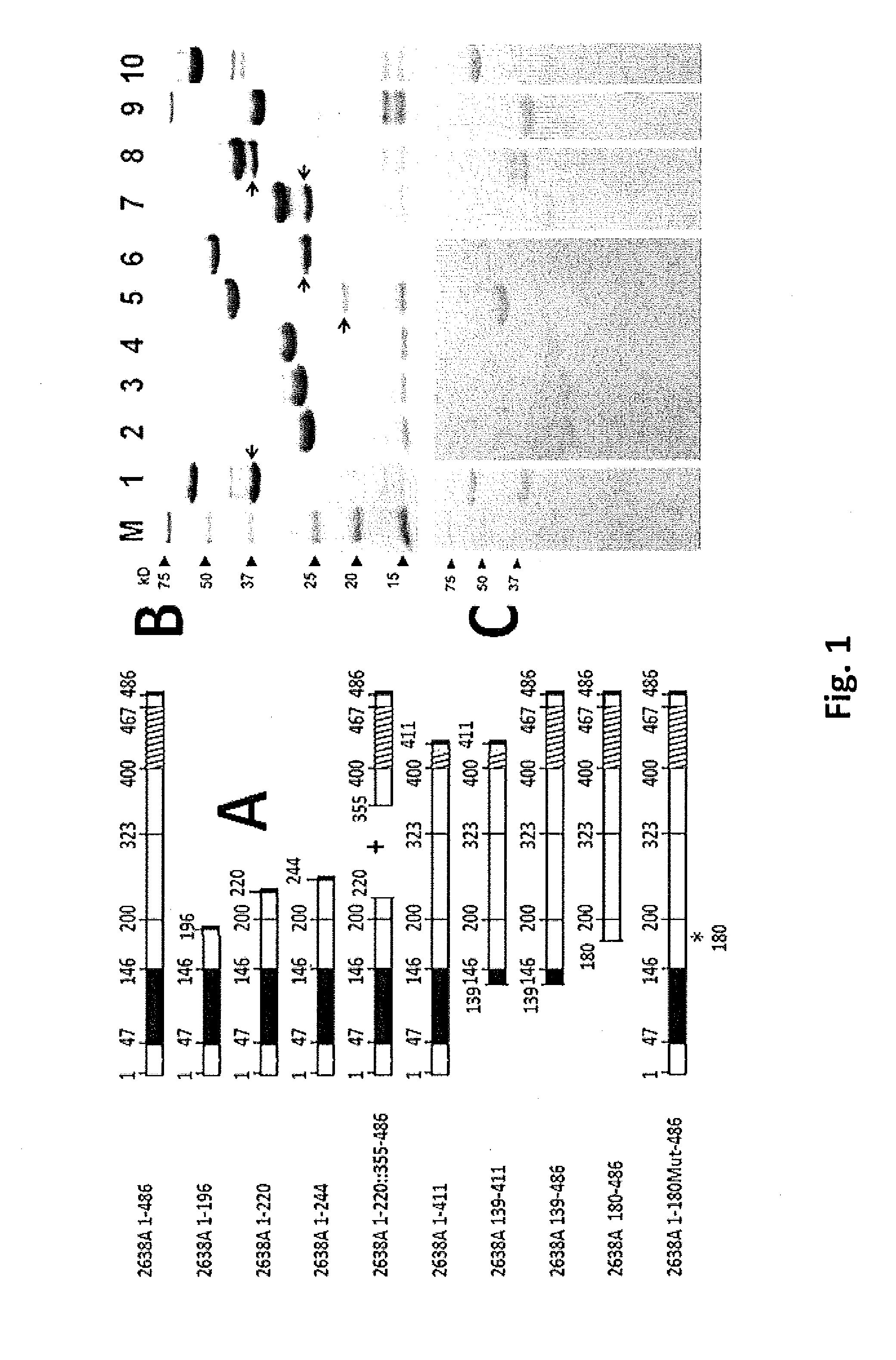
Staphylococcal Phage2638A endolysin amidase domain is lytic for Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS9206411B2Enhanced, specific antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaStaphylococcus cohniiPeptidoglycan Hydrolase
Staphylococcus aureus is notorious for developing resistance to virtually all antibiotics to which it is exposed. Staphylococcal phage 2638A endolysin is a peptidoglycan hydrolase that is lytic for S. aureus when exposed externally, making it a new antimicrobial candidate. It shares a common protein organization with over 40 other staphylococcal peptidoglycan hydrolases: a CHAP endopeptidase domain, a mid-protein amidase 2 domain and a C-terminal SH3b cell wall binding domain. It is the first phage endolysin reported with a cryptic translational start site between the CHAP and amidase domains. Deletion analysis indicates that the amidase domain confers most of the lytic activity and requires the full SH3b domain for maximal activity. It is common for one domain to demonstrate dominant activity over another; however, the phage 2638A endolysin is the first to show high amidase domain activity dominant over the N-terminal CHAP domain, an important finding for targeting novel peptidoglycan bonds.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for detecting ox FTO (Fat Mass and Obesity-associated) gene single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
InactiveCN101906470BEasy to detectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionMetapopulation
The invention discloses a method for detecting ox FTO (Fat Mass and Obesity-associated) gene single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), which comprises the following steps of: carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on an ox FTO gene by adopting FTO gene-contained ox whole genome DNA to be detected as a template and a primer pair P as a primer; after carrying out high-temperature denaturation on a PCR product, carrying out polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; and identifying the SNP of the 783rd site (+1 as a translation initiation site) of an ox FTO gene coding area according toa polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis result. Because the FTO gene function involves in body length and body height characters, the detecting method provided by the invention lays the foundation for establishing an SNP and growth character relation of the FTO gene so as to be used for marker-assisted selection (MAS) of growth characters for Chinese beef and rapidly establish an ox population with favorable genetic resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Combination therapy with liposomal antisense oligonucleotides
Provided herein are methods of treating a cancer in a patient comprising administration of an effective amount of a nuclease-resistant polynucleotide that hybridizes to the translation initiation site of a Grb2 nucleic acid in the patient and either a Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor (e.g., dasatinib) or a cytidine analogue (e.g., decitabine or cytarabine). The cancer may be Ph+ and / or Bcr-Abl positive chronic myelogenous leukemia or acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome.
Owner:BIO PATH HLDG INC
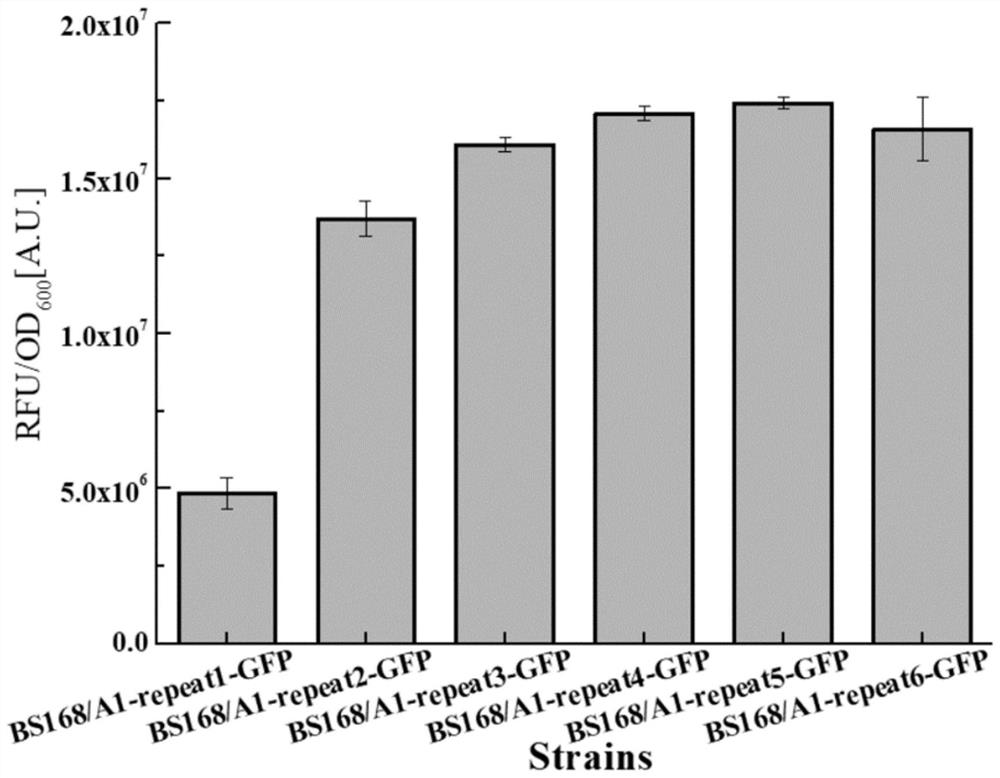
Sequence for increasing the translation initiation site of Gram-positive bacteria and its application in improving protein expression efficiency
ActiveCN113106095BHigh expressionThe increase in expression was further enhancedPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBacillus licheniformisGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbial engineering, and discloses a sequence for increasing the translation initiation site of Gram-positive bacteria and its application in improving protein expression efficiency. The sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1 Show. The invention promotes the translation of the target gene from multiple translation start sites by transforming the 5' untranslated region of the promoter. In Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis, the expression of green fluorescent protein increased by about 150 times and 126 times compared with the original promoter P43 promoter, respectively. In Corynebacterium glutamicum, the expression of green fluorescent protein was increased by 36 times compared with the original promoter. At the same time, the mRNA leader sequence also significantly increases the expression level of keratinase in Bacillus licheniformis, which proves the universality of the sequence for improving the protein expression efficiency of Gram-positive bacteria.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Conditional replicative adenoviral vector and application of viral replication regulated by transcriptional repressive tet-on system
The invention discloses a conditionally replicating adenovirus vector for virus replication regulated by a TetR-KRAB-mediated transcription inhibition type Tet-On system, adenovirus E1 region comprises the following components in the following connection sequence: 5'-CMV promoter, TetR-KRAB gene, promoter TRE3G-E1b Pro containing a tetracycline responsive element, EcoR I enzyme cutting site, E1B Delta 55KD protein-deleted adenovirus E1A-E1B19KD gene sequence, enzyme cutting site Spe I and mRNA transcription termination signal SV40polyA-3'; the CMV promoter expresses transcription inhibitor TetR-KRAB; a gene sequence inserted into the two enzyme cutting sites of the EcoR I and the Spe I is a gene fragment from adenovirus E1A translation initiation site to adenovirus E1B19KD protein termination codon, the promoter TRE3G-E1b Pro containing the tetracycline responsive element expresses adenovirus E1A gene, adenovirus E1B19KD gene is expressed by the own promoter of the adenovirus E1B19KD, and the packed adenovirus is named as Ad5-CMV-TetR-KRAB-TRE3G-E1bPro-Delta 55KD. Tests show that the virus can be loaded into mesenchymal stem cells for application in study of tumor therapy.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Oligonucleotide modulation of cell adhesion
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
A promoter pro-biutnt that efficiently drives the stable expression of target genes in apple protoplast cells
The invention discloses a promoter Pro-BIUTNT that efficiently drives the stable expression of a target gene in apple protoplast cells. The promoter is a polyubiquitin encoding gene that starts from A in the translation initiation site ATG (excluding A) Upward 1307bp nucleotide fragment. Experiments have shown that the Pro‑BIUTNT promoter can efficiently and stably drive and regulate the expression of 12 representative target genes involved in apple fruit ripening and immune response in apple protoplast cells, a breakthrough in apple protoplast cells. Using CaMV 35S promoter, some genes are not expressed, and some genes are weakly expressed, which lays a foundation for the application of apple protoplast cell protein expression technology to apple signal transduction research.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of n-terminal extended type pten subtype ptenζ protein and its coding gene and application
Owner:PEKING UNIV
TERT promoter mutations in cancer
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions related to certain promoter mutations in cancer. In one embodiment, a method for treating a subject having thyroid cancer comprises the steps of (a) obtaining a biological sample from the subject; (b) performing an assay on the sample obtained from the subject to identify a mutation at 1 295 228 C>T (C228T) and 1 295 250 C>T (C250T), corresponding to −124 C>T and −146 C>T from the translation start site in the promoter of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) gene; (c) identifying the subject as having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer if the C228T and / or C250T mutation is identified; and (d) treating the subject with one or more treatment modalities appropriate for a subject having or likely to develop aggressive thyroid cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Identification of a novel repressor on IFN-lambda promoter and siRNA against ZEB1 and BLIMP-1 to increase IFN-lambda gene activity
InactiveUS8349808B2High activityHigh expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePromoter activity
The present invention is directed to the identification of a novel repressor located between ˜1.2 kb to ˜1.6 kb from the translation start site of the IFN-λ1 promoter. The present invention provides a method of using siRNAs against ZEB1 (binds to the repressor region) and BLIMP-1 (binds outside the repressor region) and increases the promoter activity of IFN-λ1 (i.e., increases the production of IFN-λ1 protein). siRNAs against ZEB1 mRNA or BLIMP-1 mRNA increase IFN-λ1 gene activity. There is provided a therapeutic application of siRNAs against ZEB1 and BLIMP-1 mRNAs in treating a mammal (including a human) by increasing the production of IFN-λ1 protein that promotes an anti-viral response as well as treats asthma diseases.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
A kind of dna molecule and its application and method for obtaining high root mass ramie plants
The invention relates to the technical field of transgenics, in particular to a DNA molecule, its application and a method for obtaining ramie plants with high root mass. In the DNA molecule, the 2000-2500 bp sequence upstream of the translation start site of the 5' end untranslated region of the ramie BnWOX8 gene is replaced by the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention transfers the modified DNA molecule into the ramie plant, and the obtained ramie line shows higher production capacity of the root system, and has no significant influence on the total flavonoid content in the root system.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com