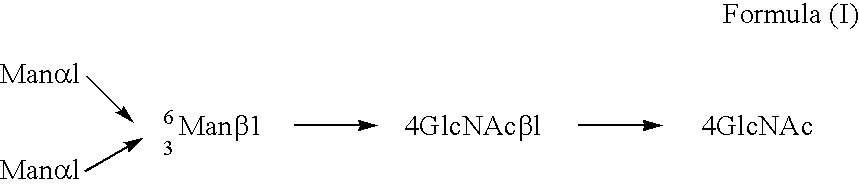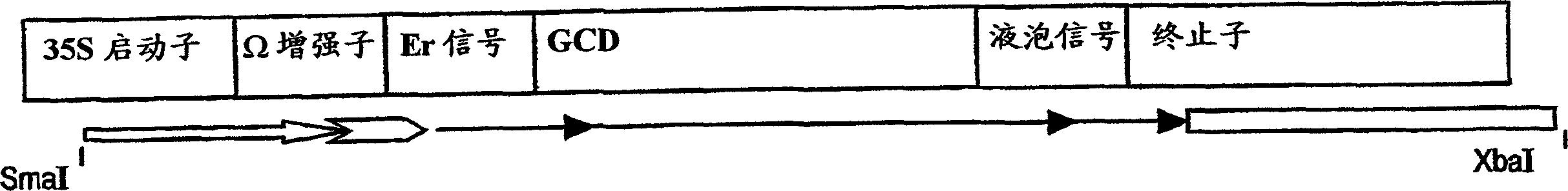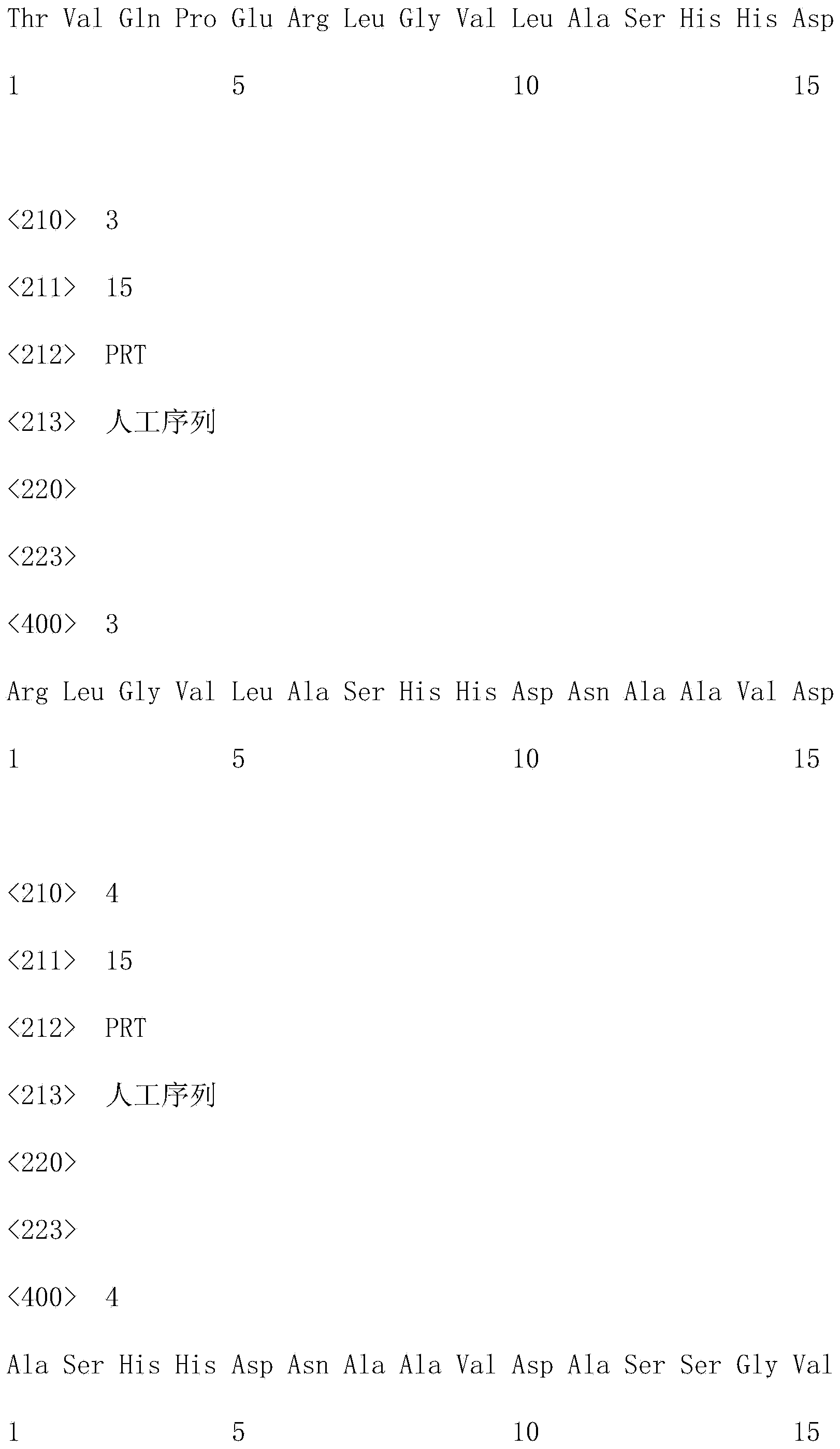Patents
Literature
89 results about "Golgi apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and named after him in 1898.
Process for producing glycoprotein composition
InactiveUS20060223147A1Raise the ratioAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticComplex typeN-Acetylglucosamine
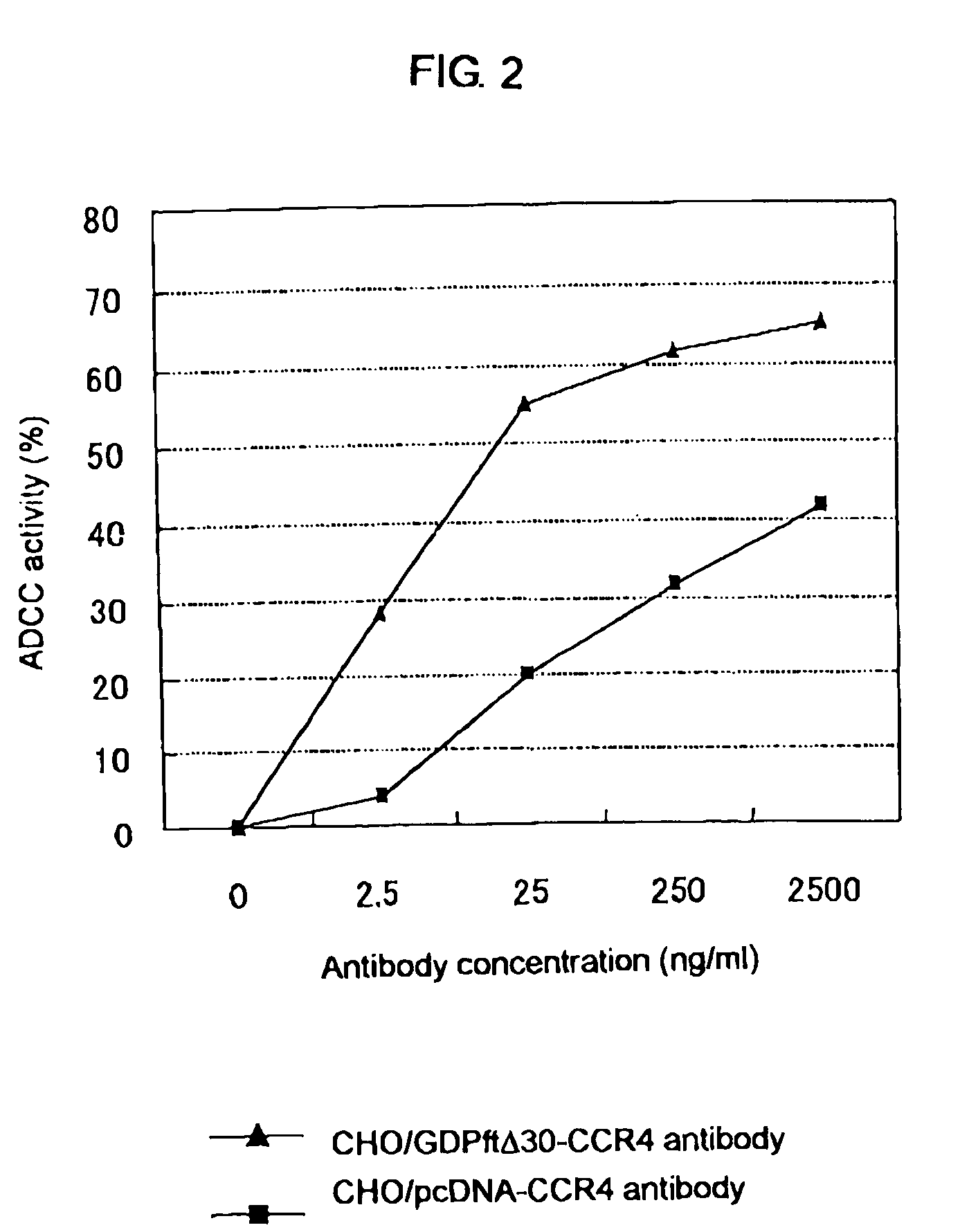
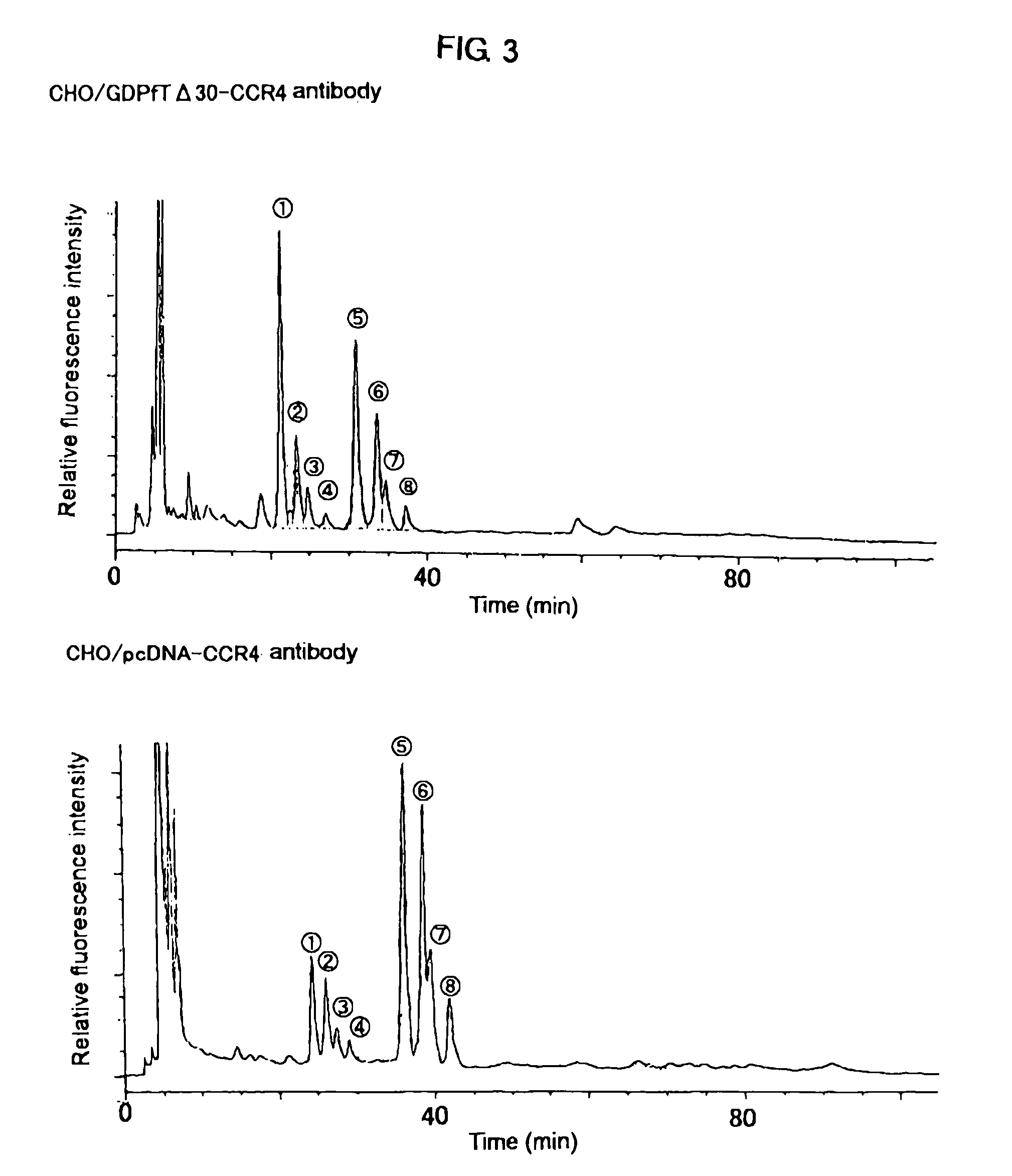
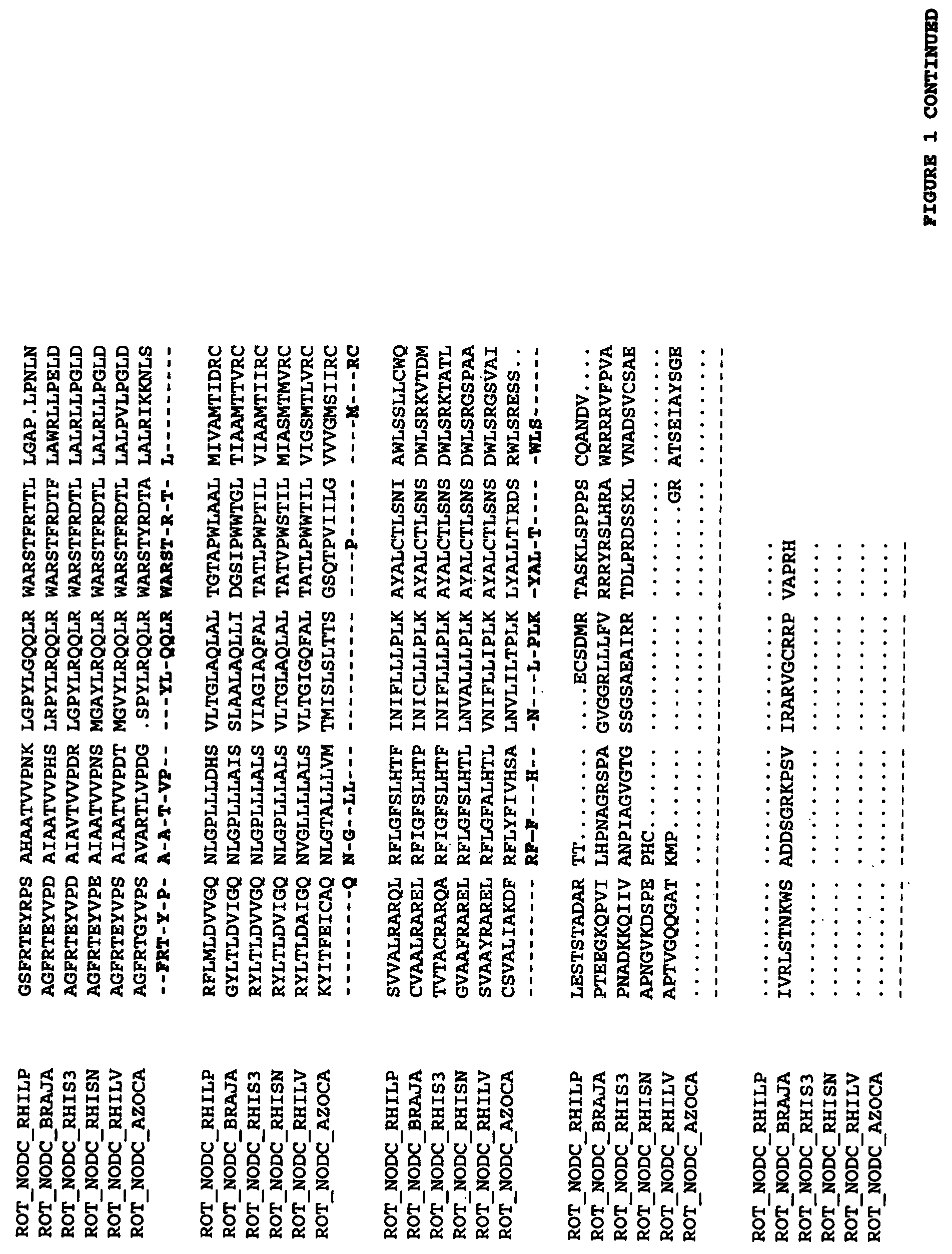
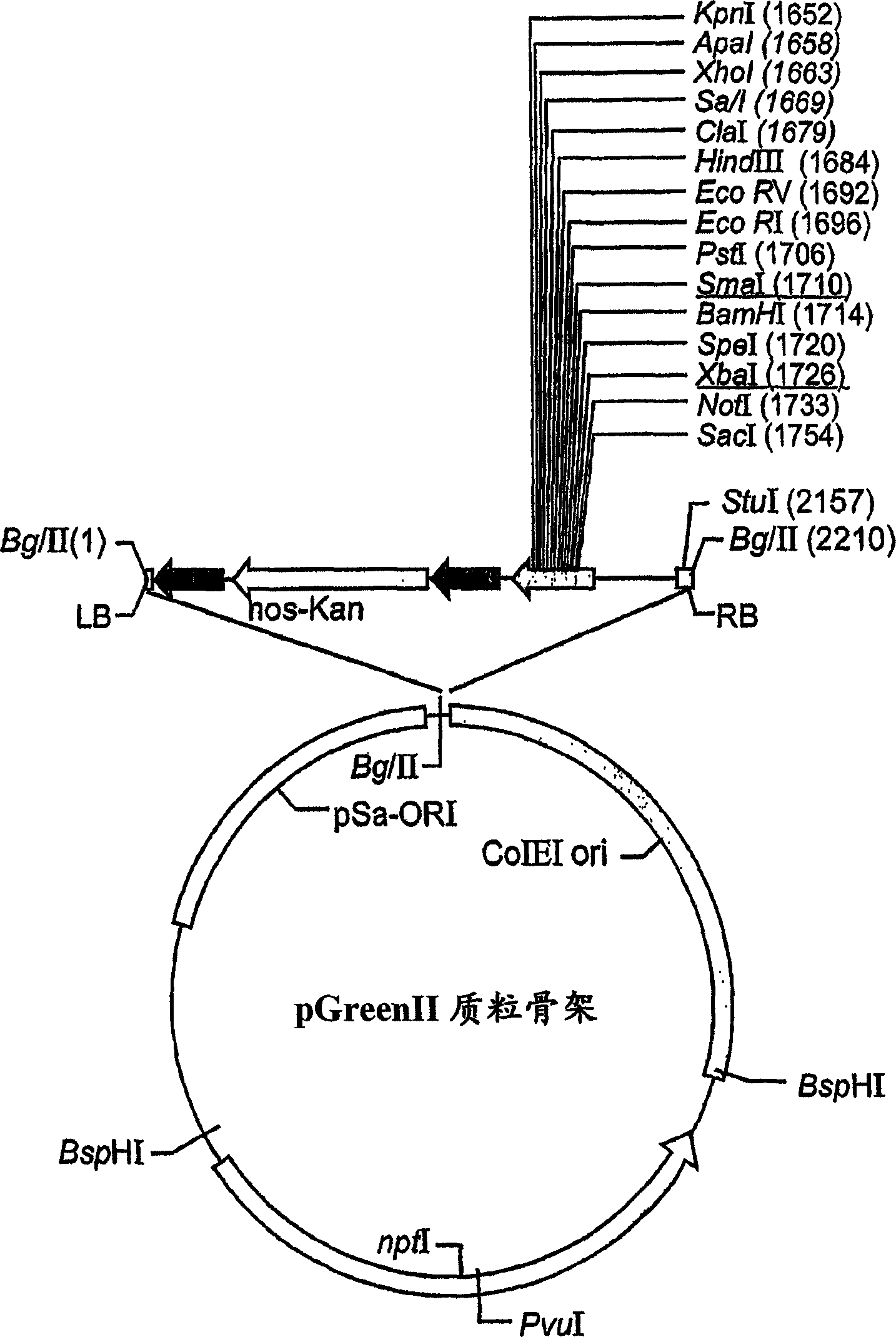
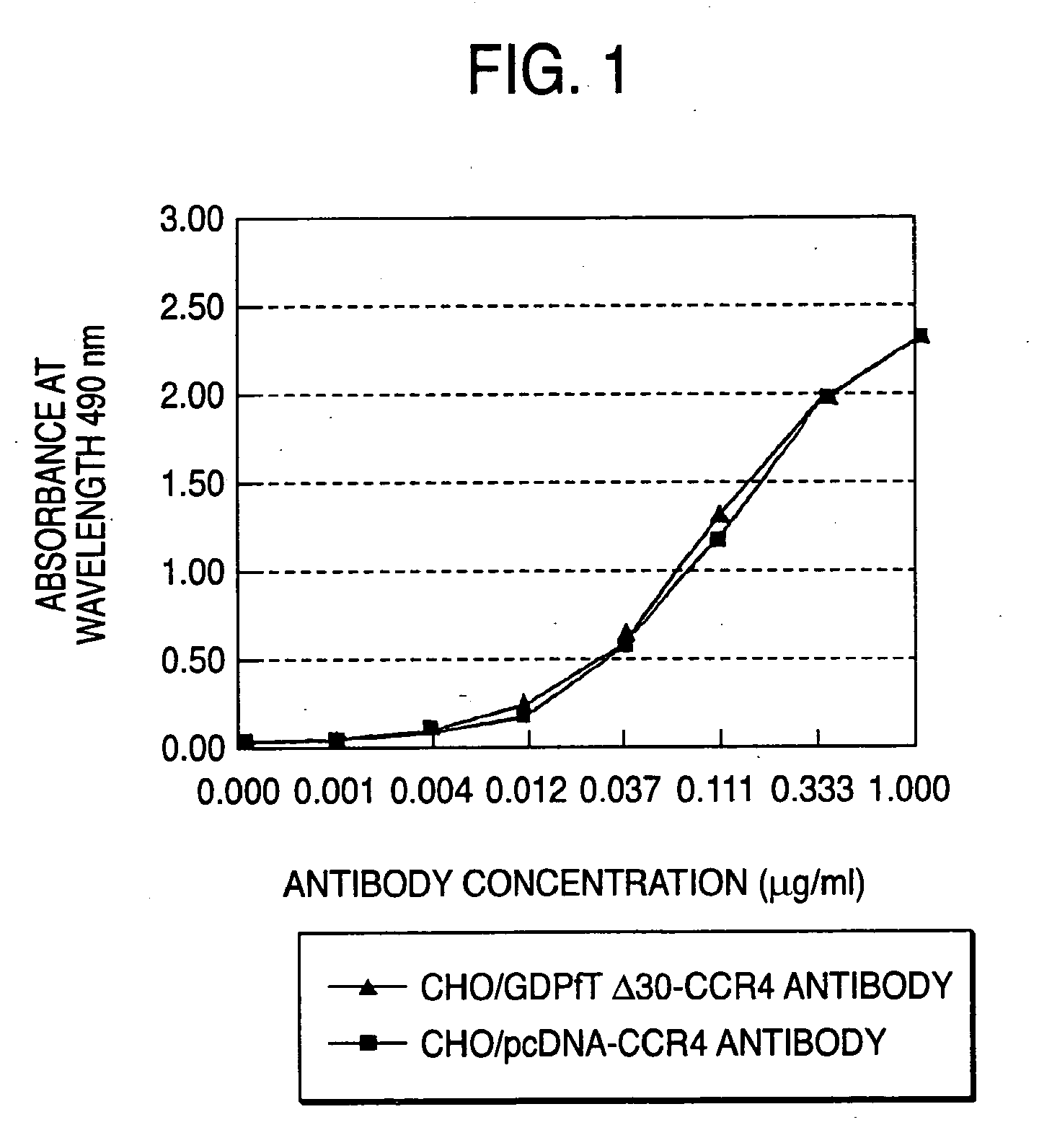
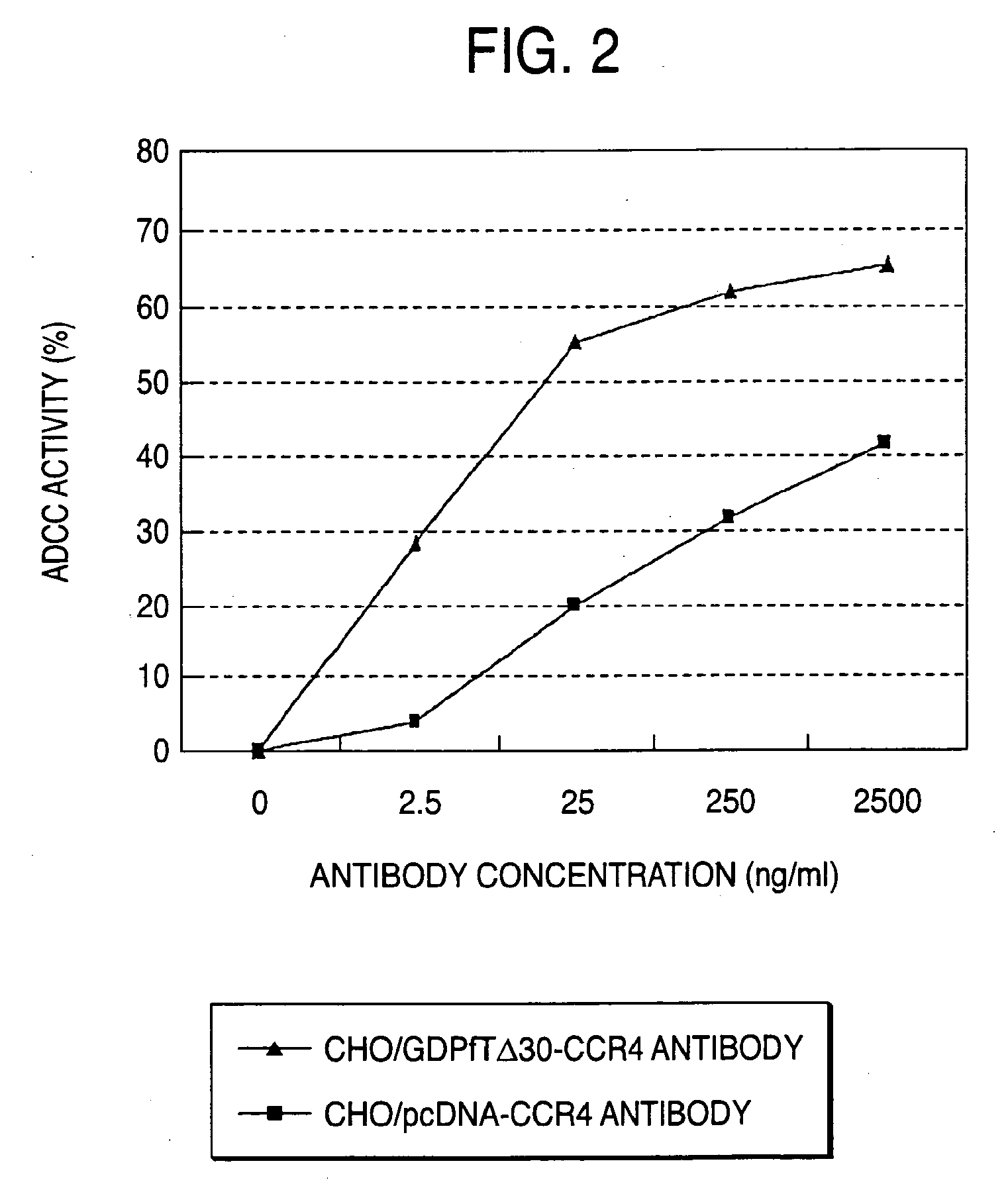
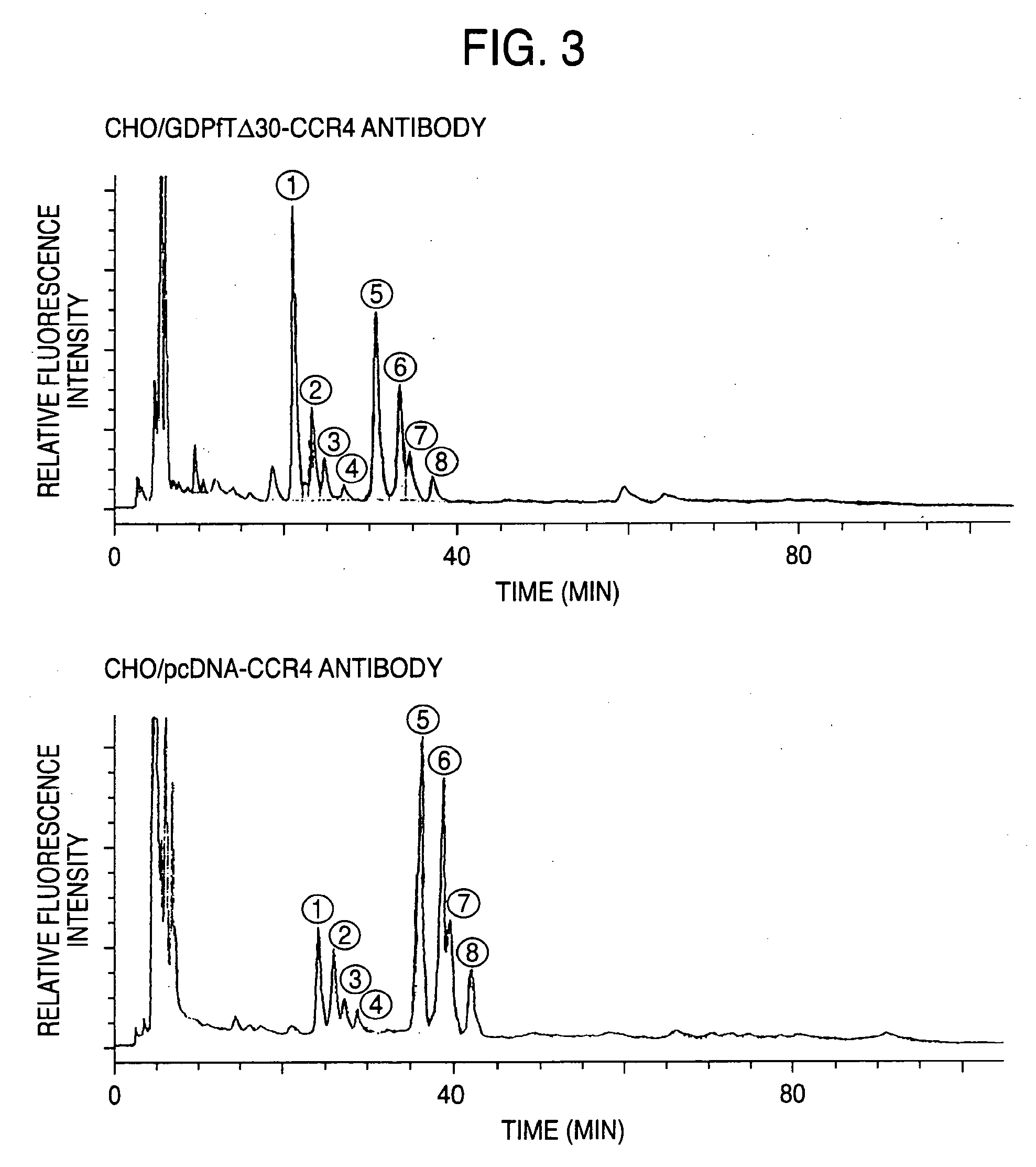
The present invention relates to a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme catalyzing a reaction which converts GDP-mannose into GDP-4-keto,6-deoxy-GDP-mannose is introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein using the cell; a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, and an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to synthesis of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, or an RNA capable of suppressing the function of a protein relating to transport of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, to the Golgi body are introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein composition using the cell; and the like.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Cells in which activity of the protein involved in transportation of GDP-fucose is reduced or lost
A cell in which the activity of a protein relating to transport of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, to the Golgi body is more decreased or deleted than its parent cell; a process for producing an antibody composition using the cell; a transgenic non-human animal or plant or the progenies thereof, in which genome is modified so as to have a decreased or deleted activity of a protein relating to transport of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, to the Golgi body; a process for producing an antibody composition from the animal or plant; and a medicament comprising the antibody composition.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Method for remodelling cell wall polysaccharide structures in plants
InactiveUS20030159178A1Reduce the ratioImprove gel propertiesSurgical adhesivesDead animal preservationReticulum cellNucleotide
Methods for providing transgenic plants and parts hereof that, relative to the wild type state, is modified in a complex cell wall polysaccharide structure including pectins and hemicelluloses, the modification being in the overall glycosidic linkage pattern or the monosaccharide profile, comprising transforming a plant cell with a nucleotide sequence that causes an altered production of a complex cell wall polysaccharide-modifying enzyme such as endo-rhamnogalacturonan hydrolase, an endo-rhamnogalacturonan lyase, an endo-galactanase, an endo-arabinanase, an arabinofuranosidase, a galactosidase such as a beta-galactosidase, a xylosidase and an exo-galacturosidase. The modification can occur in vivo or post harvest, in which latter case the modifying enzyme is separated in the growing plant from its substrate, e.g. by targeting the enzyme to the Golgi, the endoplasmic reticulum or a vacuole, or is in a form that is inactive in the plant. After harvest the enzyme is brought into contact with its substrate or it is activated to provide the desired post harvest modification of the cell wall polysaccharide. The transgenic plant materials have improved functionalities and are useful in food and feed manufacturing and as pharmaceutically or medically active substances.
Owner:POALIS
Methods for altering the reactivity of plant cell walls
InactiveUS8008544B2Increase the amount addedImprove responseSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellN-Acetylglucosamine
Methods and means are provided for the modification of the reactivity of plant cell walls, particularly as they can be found in natural fibers of fiber producing plants by inclusion of positively charged oligosaccharides or polysaccharides into the cell wall. This can be conveniently achieved by expressing a chimeric gene encoding an N-acetylglucosamine transferase, particularly an N-acetylglucosamine transferase, capable of being targeted to the membranes of the Golgi apparatus in cells of a plant.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
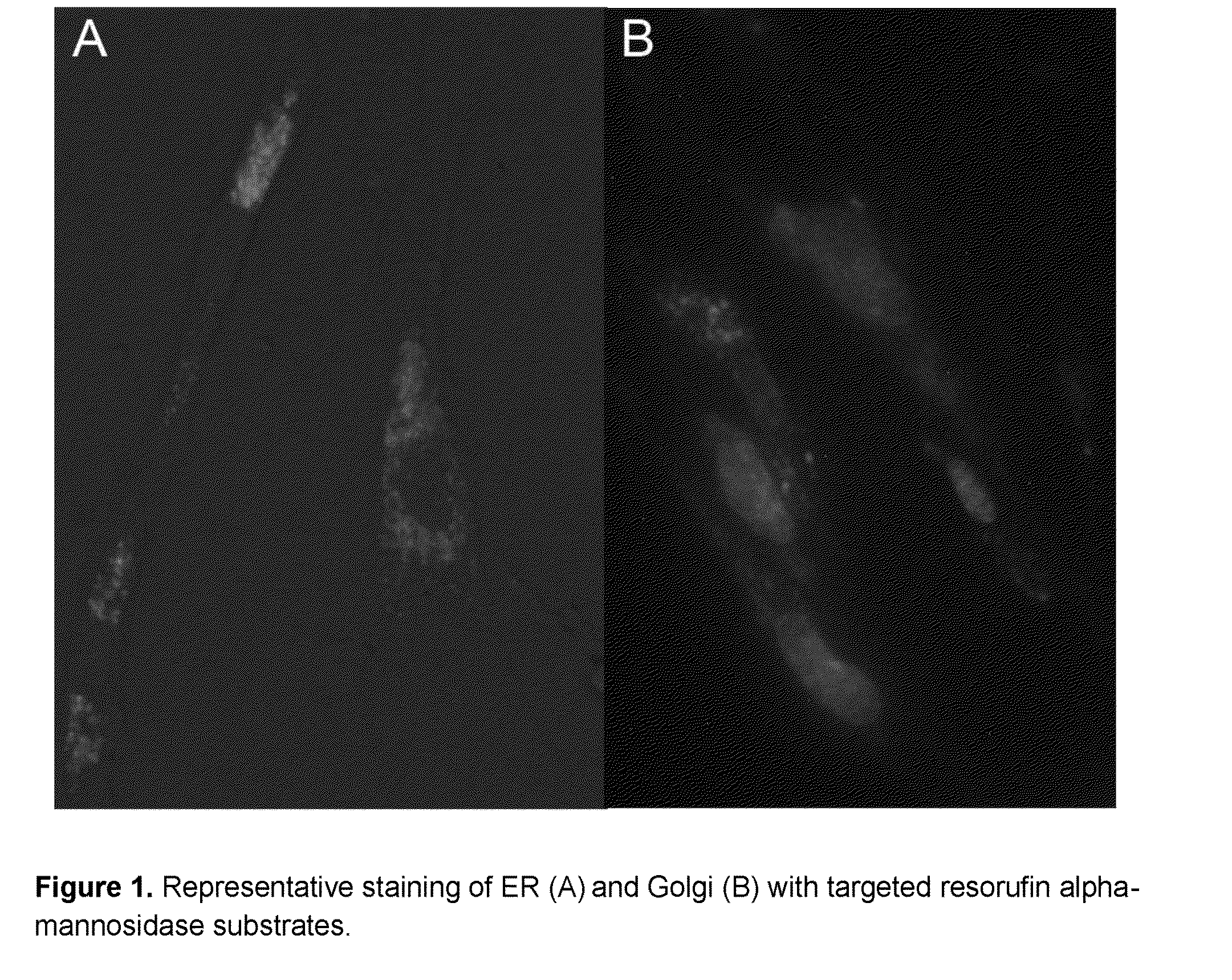
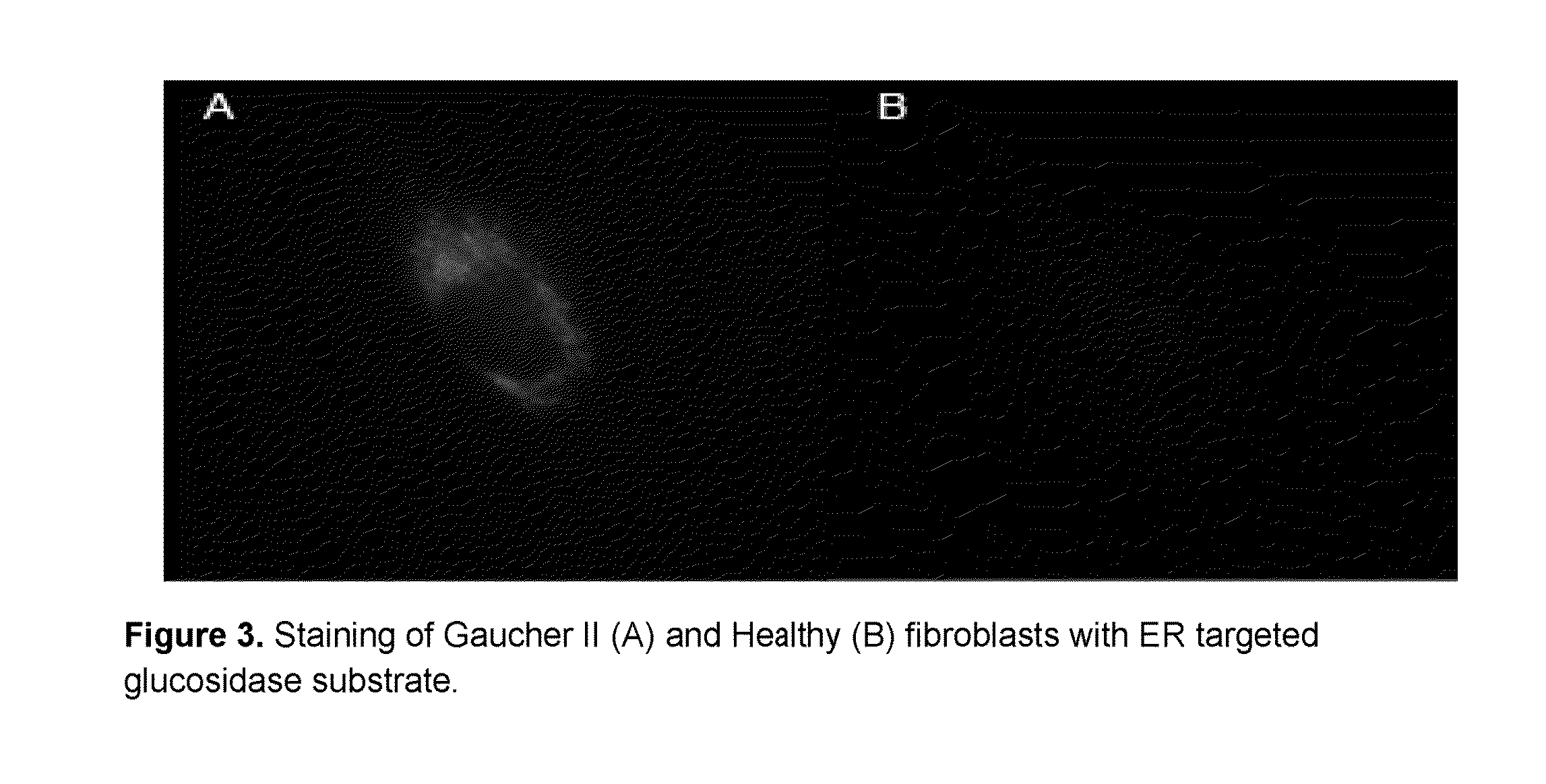
Intracellular organelle peptide targeted enzyme substrates
ActiveUS20150219654A1High fluorescenceSufficient timeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFluorescencePeptide
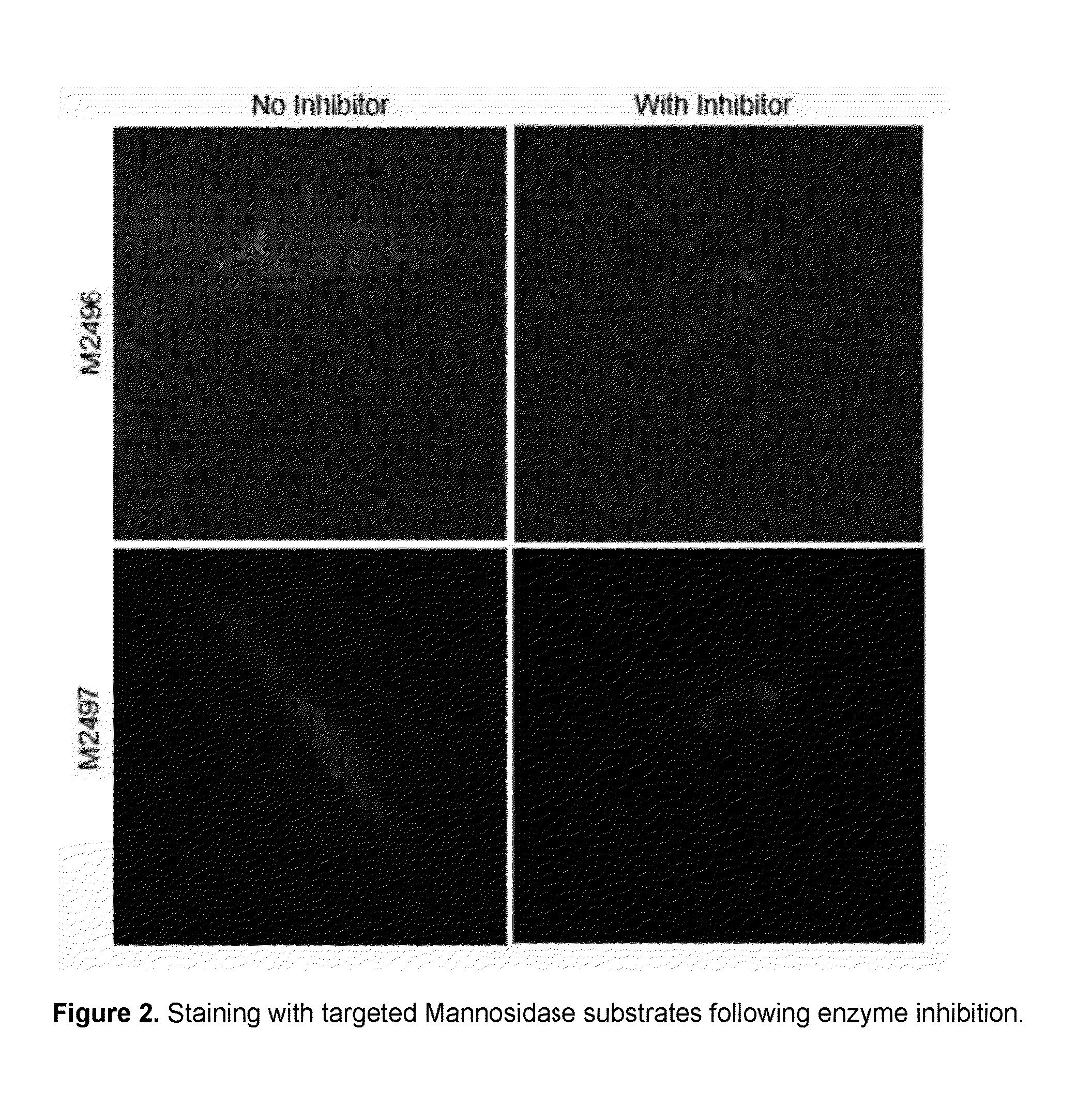
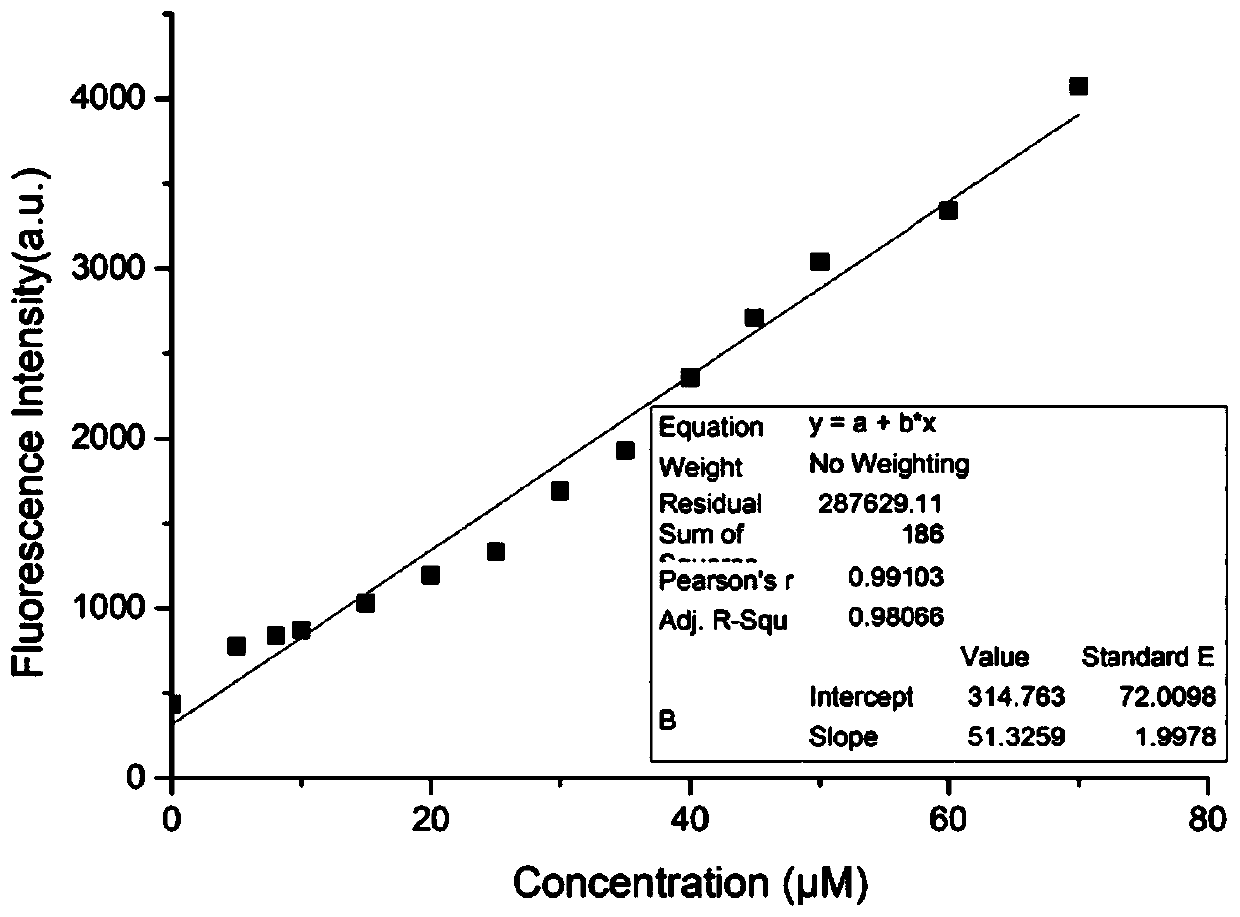
This invention relates to substrates and methods for the visualization of intracellular organelles, such as the lysosome, peroxiosome, nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus, based upon organelle enzyme activity. Such compounds represent a novel combination of chemically distinct enzyme substrates with targeting and detection substrates which are activated by enzyme activity inside target organelles to produce a detectable signal. The organelle targeted enzyme substrates of this invention are designed to provide high fluorescence at lower pH values found in some organelles and can be used for monitoring enzyme activity inside cells at very low concentrations.
Owner:MARKER GENE TECH
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
Owner:普罗塔里克斯有限公司
Cells in which activity of the protein involved in transportation of GDP-fucose is reduced or lost
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Methods for Altering the Reactivity of Plant Cell Walls
InactiveUS20090028837A1Increase the amount addedImprove responseBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberPlant cell
Methods and means are provided for the modification of the reactivity of plant cell walls, particularly as they can be found in natural fibers of fiber producing plants by inclusion of positively charged oligosaccharides or polysaccharides into the cell wall. This can be conveniently achieved by expressing a chimeric gene encoding an N-acetylglucosamine transferase, particularly an N-acetylglucosamine transferase, capable of being targeted to the membranes of the Golgi apparatus in cells of a plant.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Pichia pastoris strains for producing predominantly homogeneous glycan structure
ActiveUS9617550B2GlycosyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
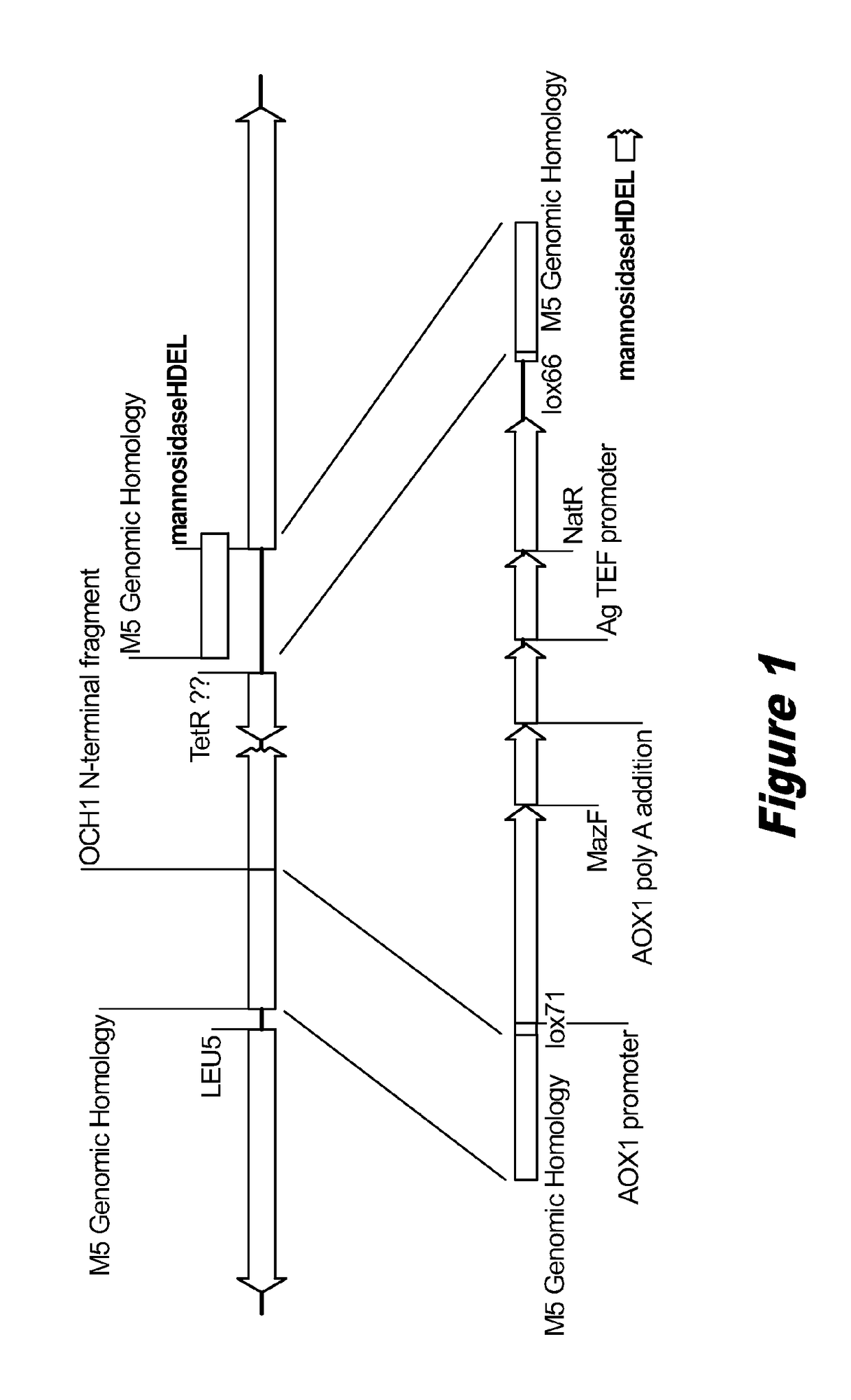
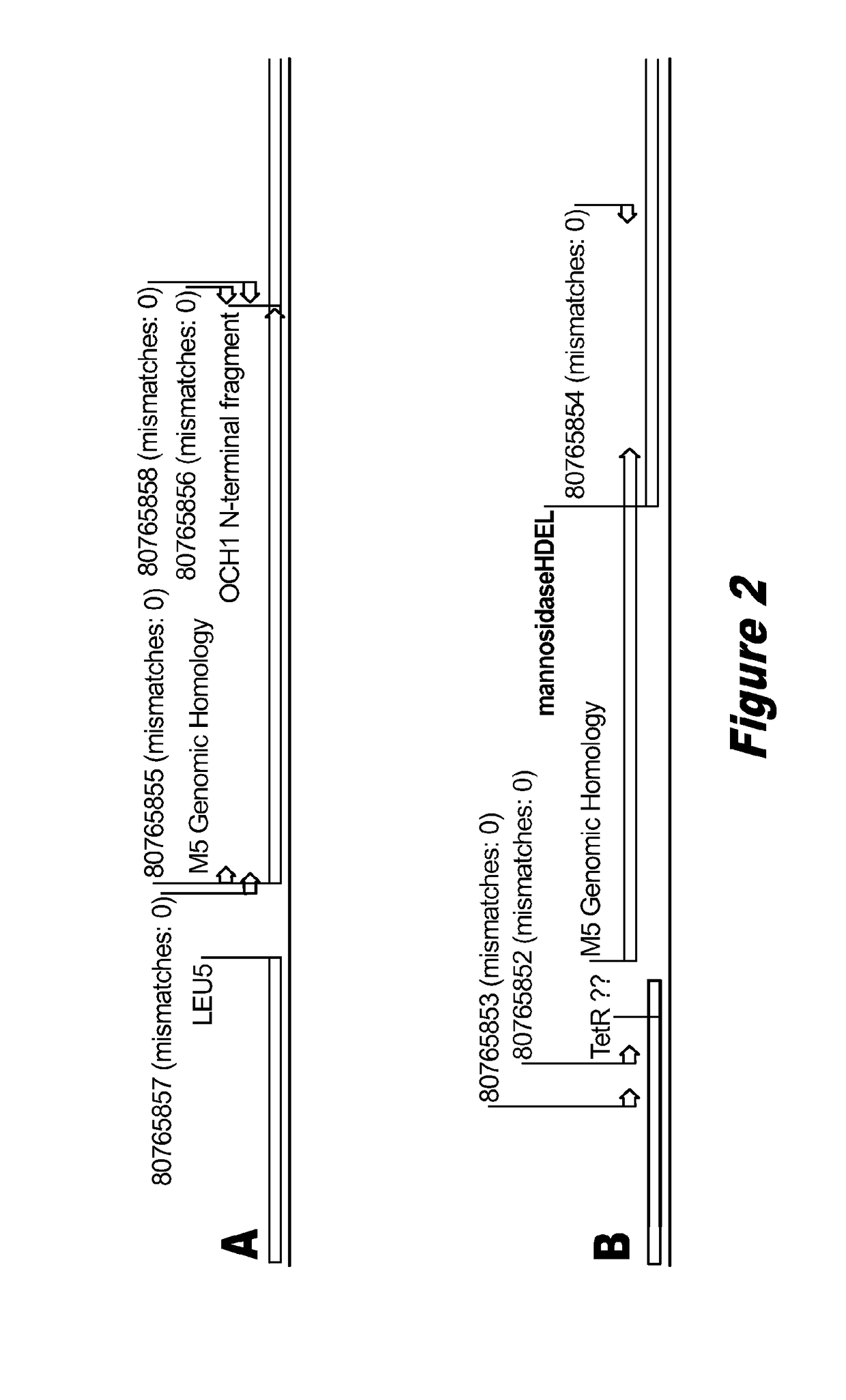
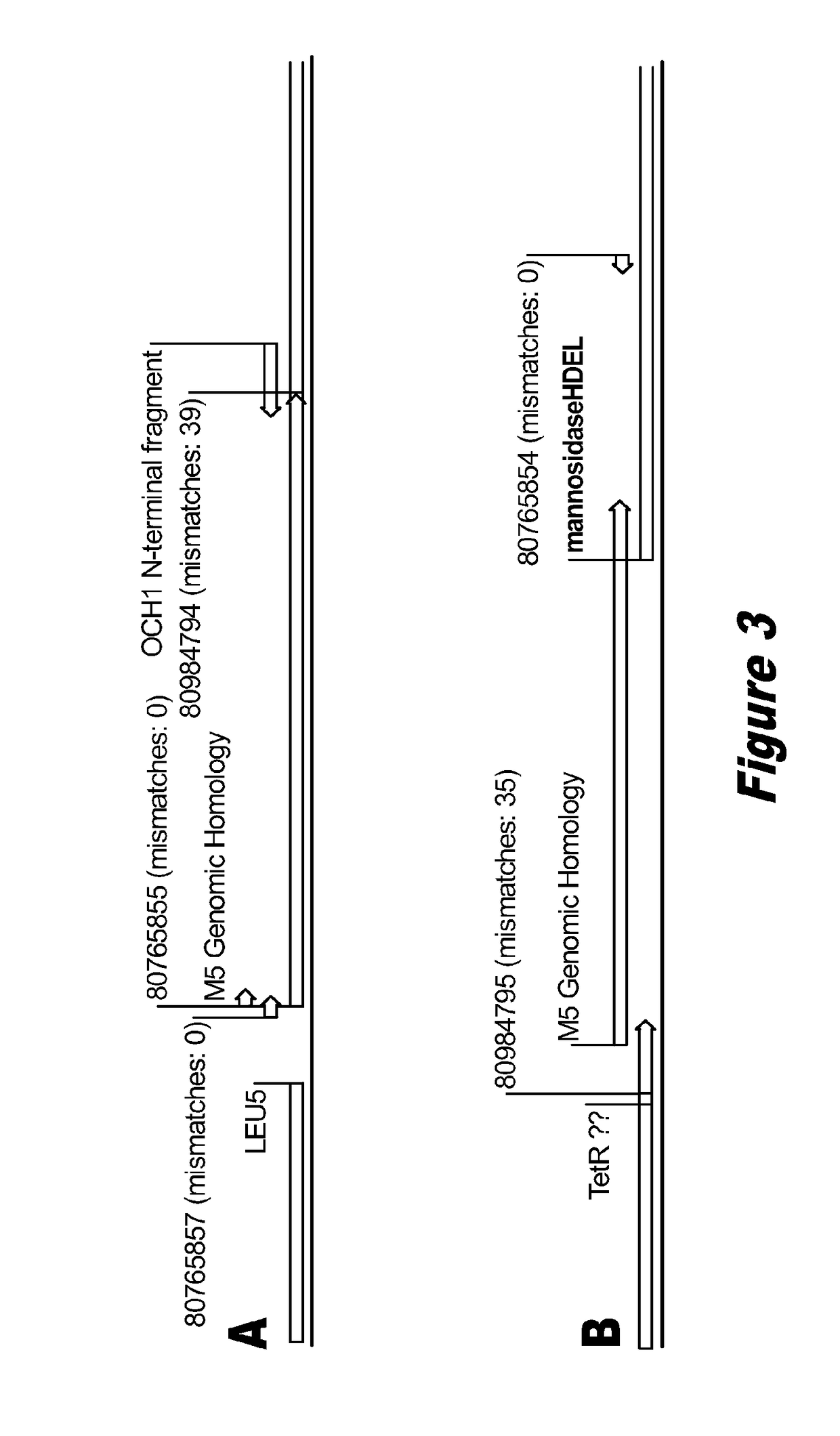
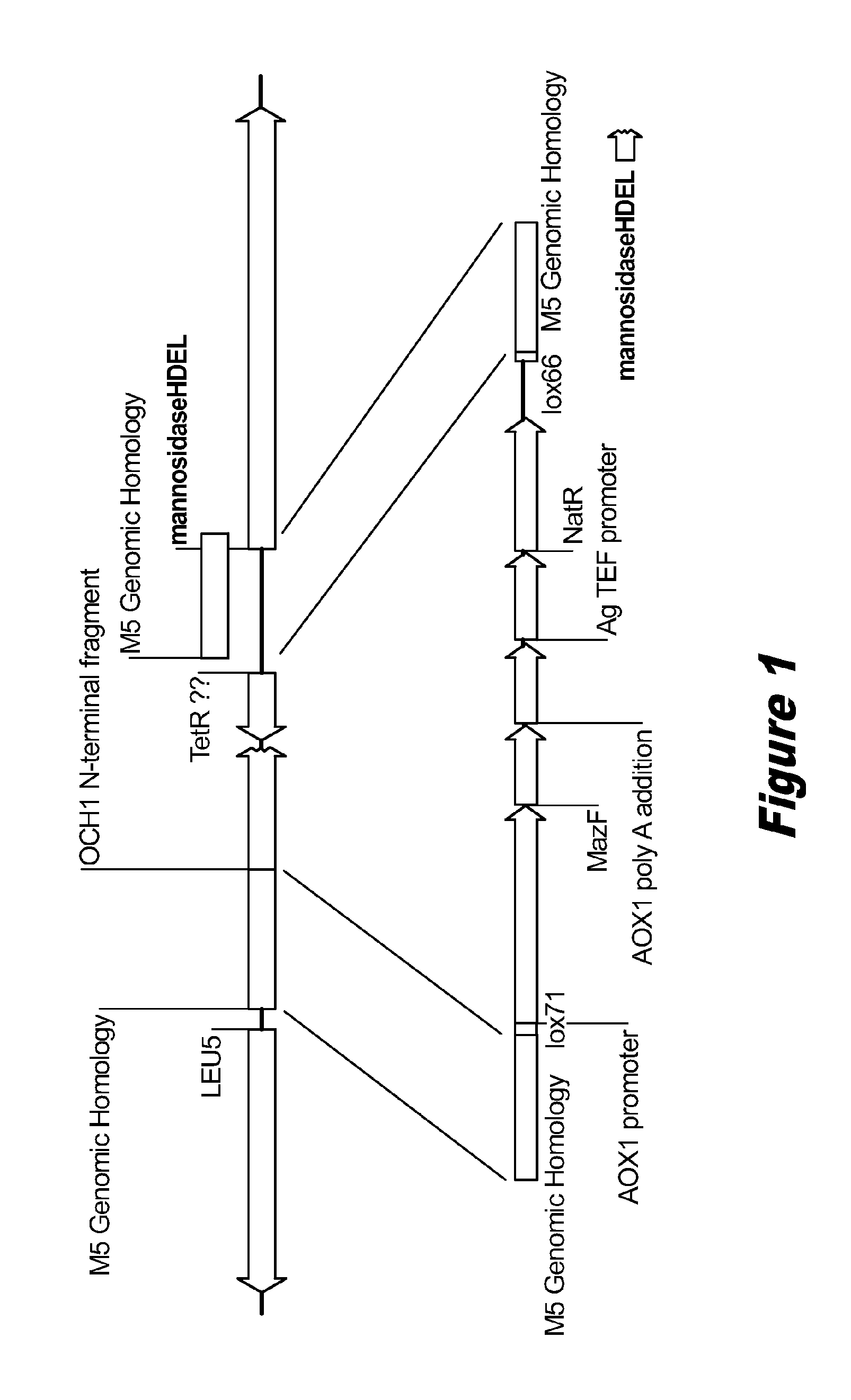
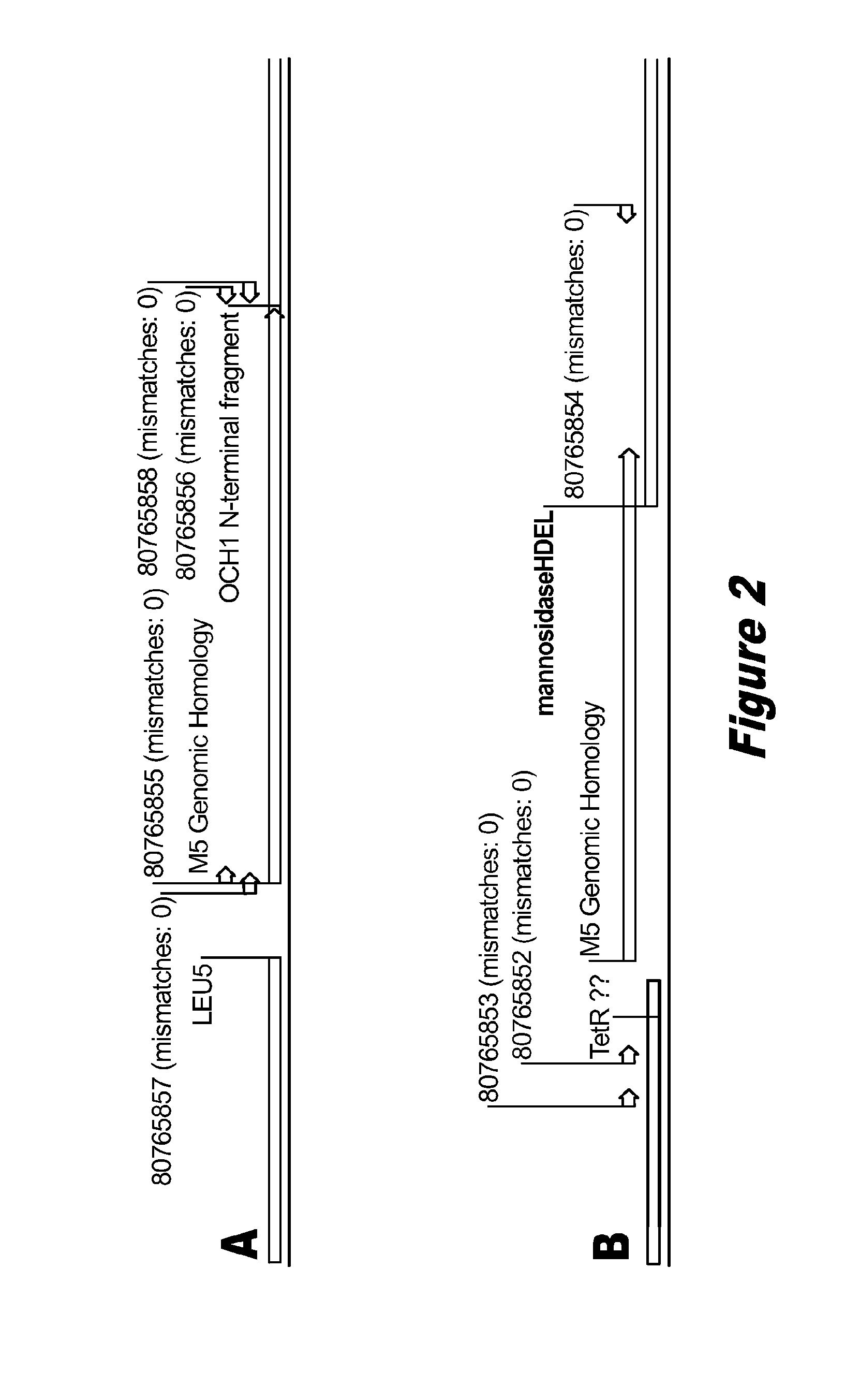
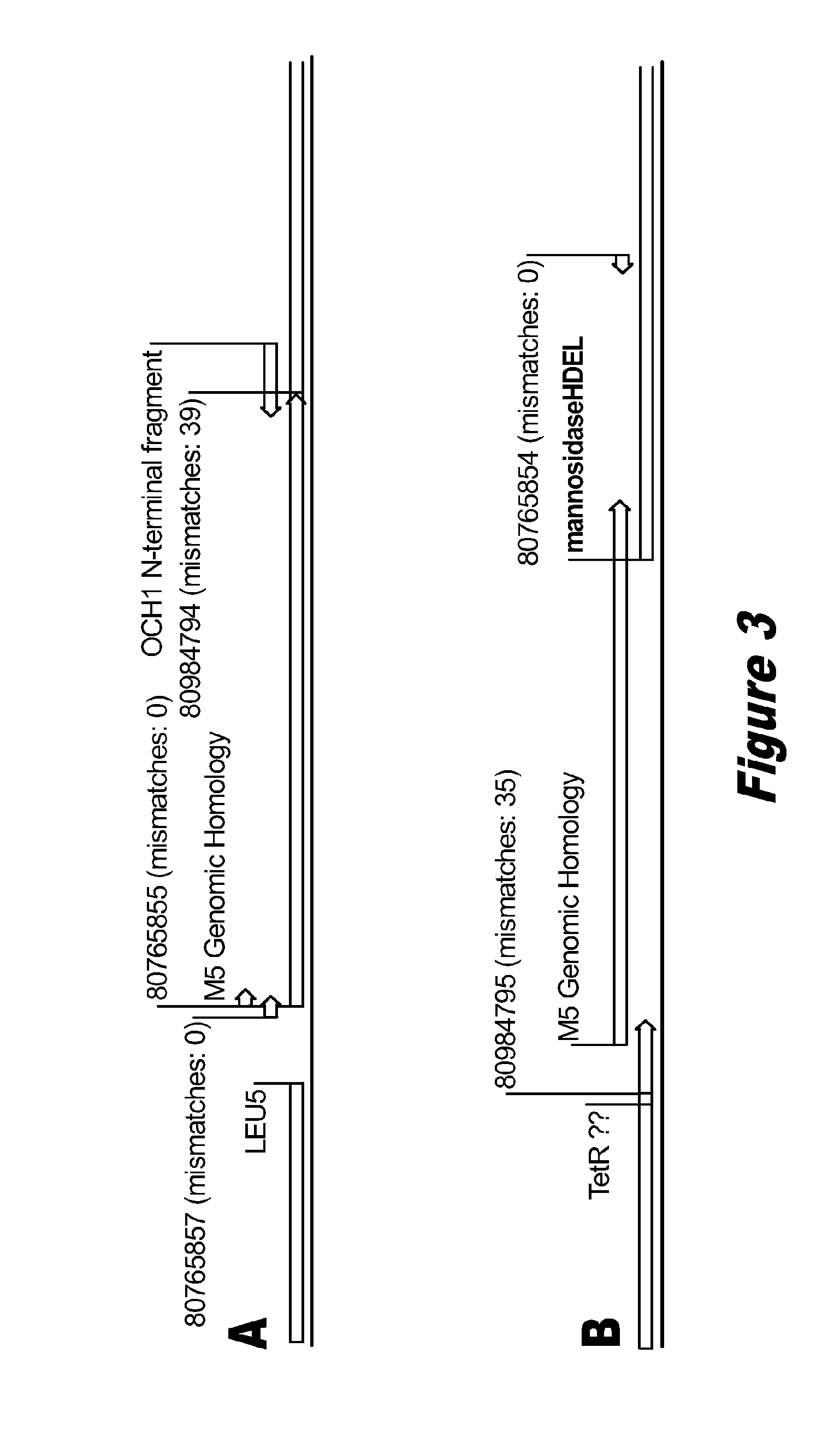
Disclosed herein are novel Pichia pastoris strains for expression of exogenous proteins with substantially homogeneous N-glycans. The strains are genetically engineered to include a mutant OCH1 allele which is transcribed into an mRNA coding for a mutant OCH1 gene product (i.e., α-1,6-mannosyltransferase, or “OCH1 protein”). The mutant OCH1 protein contains a catalytic domain substantially identical to that of the wild type OCH1 protein, but lacks an N-terminal sequence necessary to target the OCH1 protein to the Golgi apparatus. The strains disclosed herein are robust, stable, and transformable, and the mutant OCH1 allele and the ability to produce substantially homogeneous N-glycans are maintained for generations after rounds of freezing and thawing and after subsequent transformations.
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
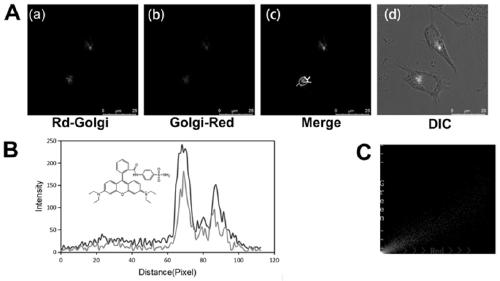
Novel quinoline dye capable of being used as Golgi apparatus organelle probe
ActiveCN104529893AQuick tagLow costOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementQuinolineU2os cell
The invention relates to a novel quinoline dye capable of being used as a Golgi apparatus organelle probe. In comparison of dye with a commercial Golgi apparatus organelle dye in term of imaging results in human osteosarcoma cells U2OS, the result proves that the dye disclosed by the invention can be used for targeted localization of the Golgi apparatus organelle. The dye has a great potential effect in the field of marking of the Golgi apparatus organelle.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Carbon dot with continuous golgi apparatus target imaging capability and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104987862AHigh blue fluorescence intensityHigh Absolute Quantum YieldNanoopticsFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseQuantum yield
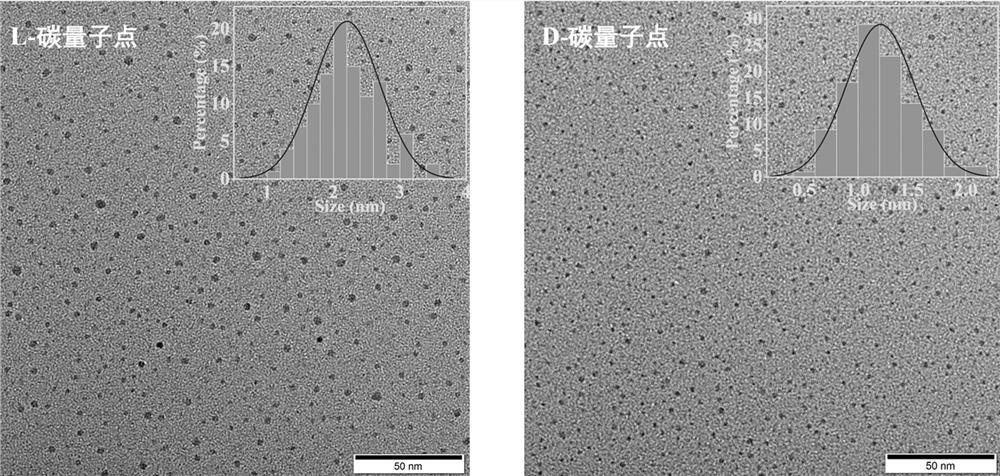
The invention discloses a photobleaching-resisting carbon dot with the continuous golgi apparatus target imaging capability and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that a small carbon dot skeleton is prepared from citric acid through pyrolysis and condensation at high temperature at first, and then the carbon dot skeleton and L-cysteine are in condensation to form a carbon dot. The surface of the carbon dot has a large number of cysteine residues. According to the carbon dot with the high blue-fluorescence intensity and the continuous golgi apparatus target imaging capability, tedious follow-up modification steps needed by conventional methods are avoided. The absolute quantum yield of the blue carbon dot obtained through the preparation method reaches up to 68%. The blue carbon dot has the good photobleaching resistance and biocompatibility, and brings more accurate help to cell process detection, disease diagnosis and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
InactiveUS20100196345A1Efficient productionSufficient quantityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPlant rootsHigh mannose
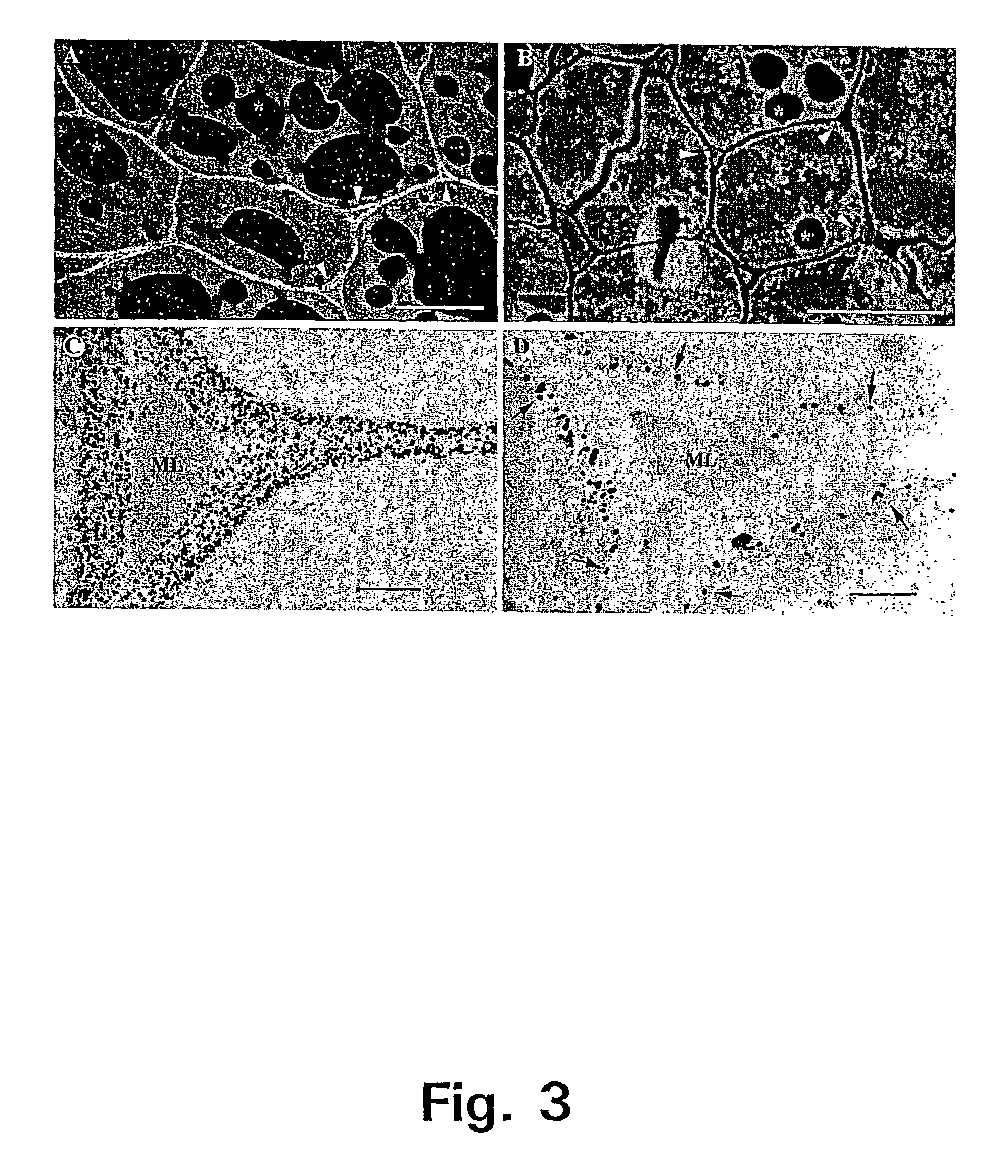
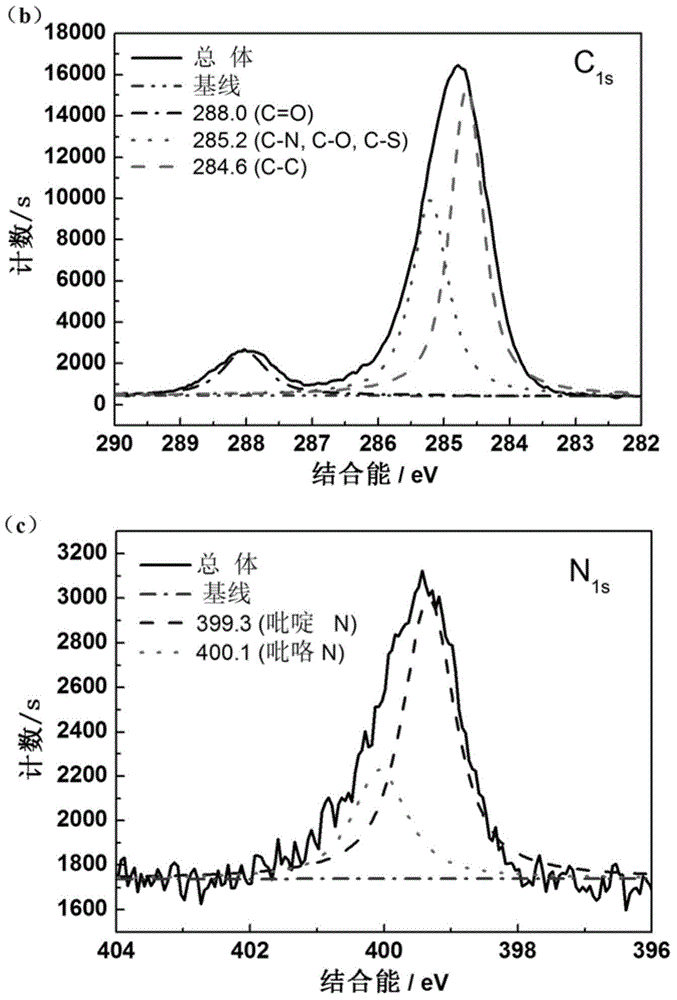
A device, system and method for producing glycosylated proteins in plant culture, particularly proteins having a high mannose glycosylation, while targeting such proteins with an ER signal and / or by-passing the Golgi. The invention further relates to vectors and methods for expression and production of enzymatically active high mannose lysosomal enzymes using transgenic plant root, particularly carrot cells. More particularly, the invention relates to host cells, particularly transgenic suspended carrot cells, vectors and methods for high yield expression and production of biologically active high mannose Glucocerebrosidase (GCD). The invention further provides for compositions and methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:PROTALIX
Kit for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by using peripheral blood and application of kit
The invention discloses a kit for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by using peripheral blood. The kit provided by the invention comprises the following substances: (1) a mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3615c mixed polypeptide library which consists of all or a part of 19 polypeptides consisting of amino acid sequences shown as sequences 1 to 19 in a sequence table, (2) an anti-CD3 antibody labeled with a fluorescent dye A, (3) an anti-gamma-interferon antibody labeled with a fluorescent dye B, and (4) a Golgi apparatus blocking agent, wherein the fluorescent dye A and the fluorescent dye B emit different fluorescent colors. A novel method which can be used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection is provided. As proved by experiments, antigenic stimulation can be performed by directly using the peripheral blood without separating single karyocytes of the peripheral blood. As indicated by experimental data, the kit has high sensitivity and high specificity when being used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Moreover, the kit is easy and convenient to operate and low in cost, and has high clinical application value.
Owner:北京同生时代生物技术有限公司
Pichia pastoris strains for producing predominantly homogeneous glycan structure
Disclosed herein are novel Pichia pastoris strains for expression of exogenous proteins with substantially homogeneous N-glycans. The strains are genetically engineered to include a mutant OCH1 allele which is transcribed into an mRNA coding for a mutant OCH1 gene product (i.e., α-1,6-mannosyltransferase, or “OCH1 protein”). The mutant OCH1 protein contains a catalytic domain substantially identical to that of the wild type OCH1 protein, but lacks an N-terminal sequence necessary to target the OCH1 protein to the Golgi apparatus. The strains disclosed herein are robust, stable, and transformable, and the mutant OCH1 allele and the ability to produce substantially homogeneous N-glycans are maintained for generations after rounds of freezing and thawing and after subsequent transformations.
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
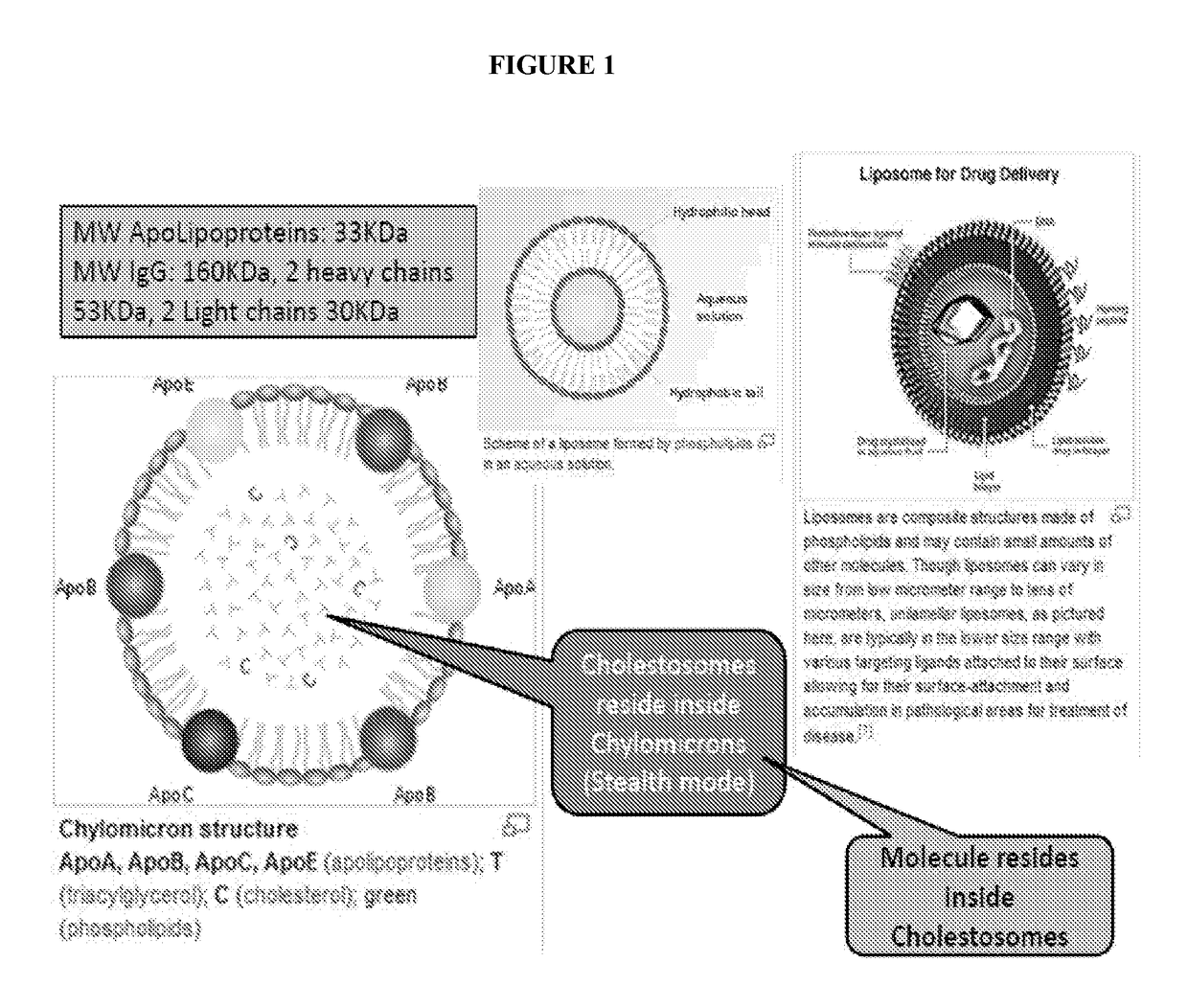
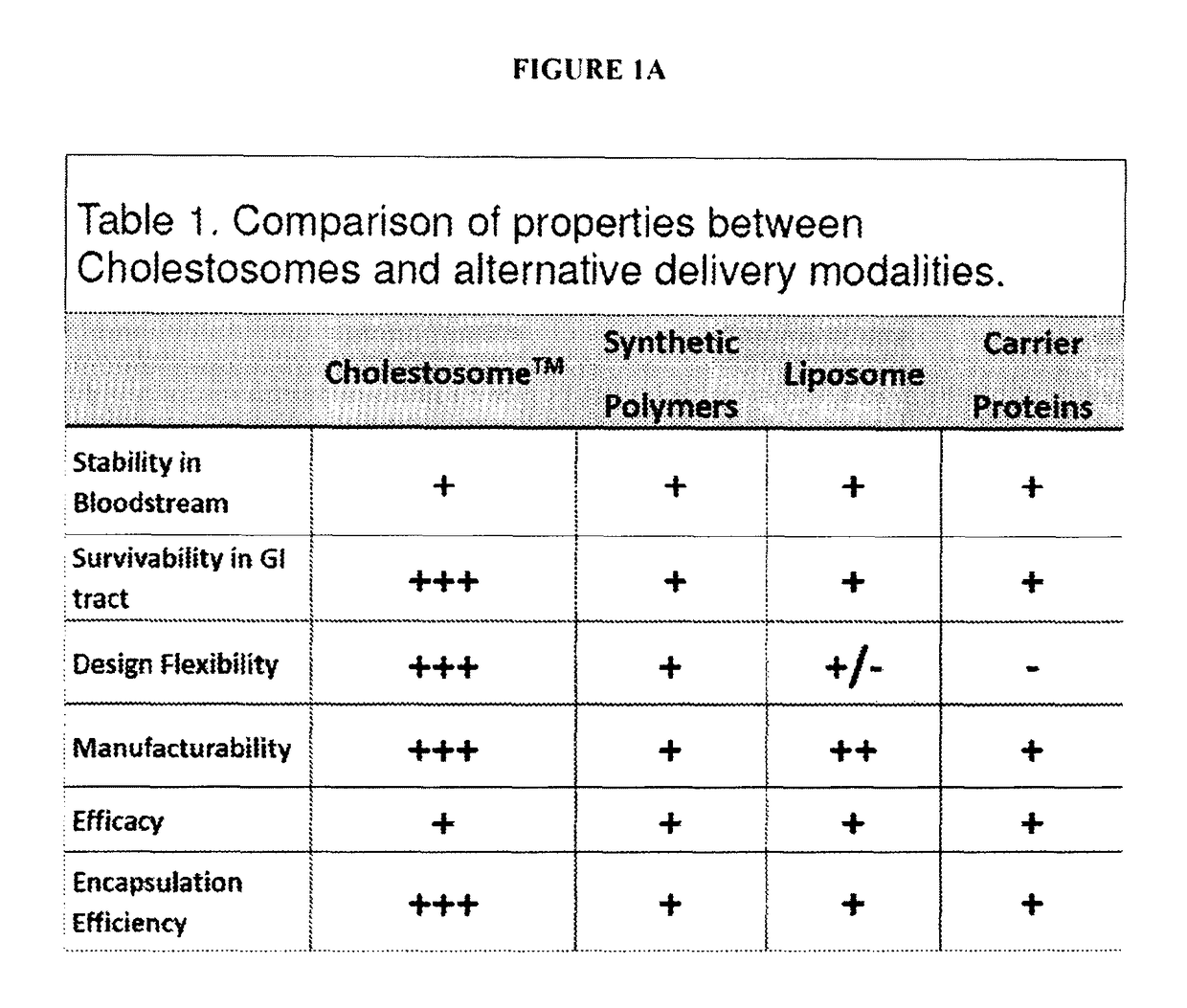
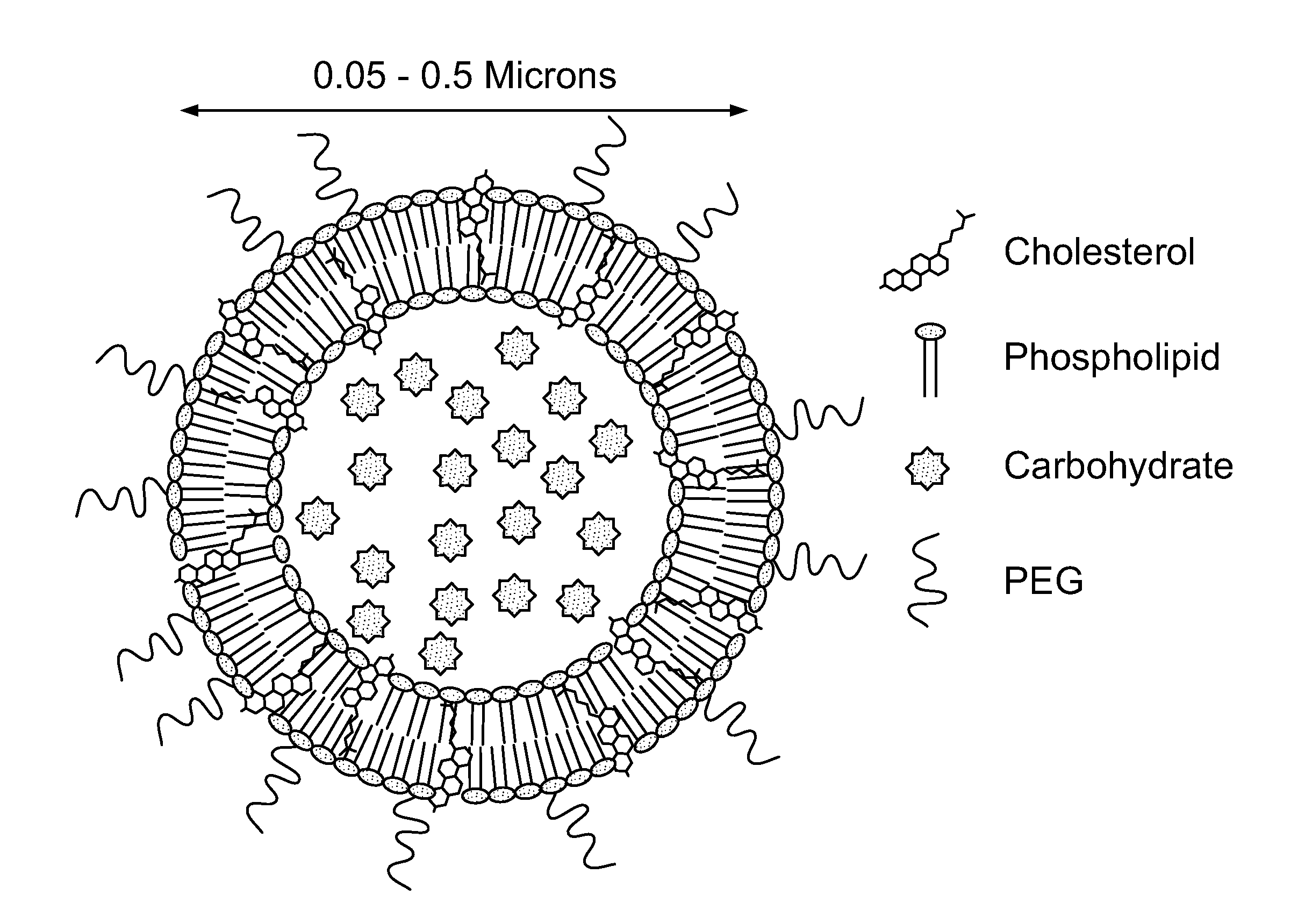
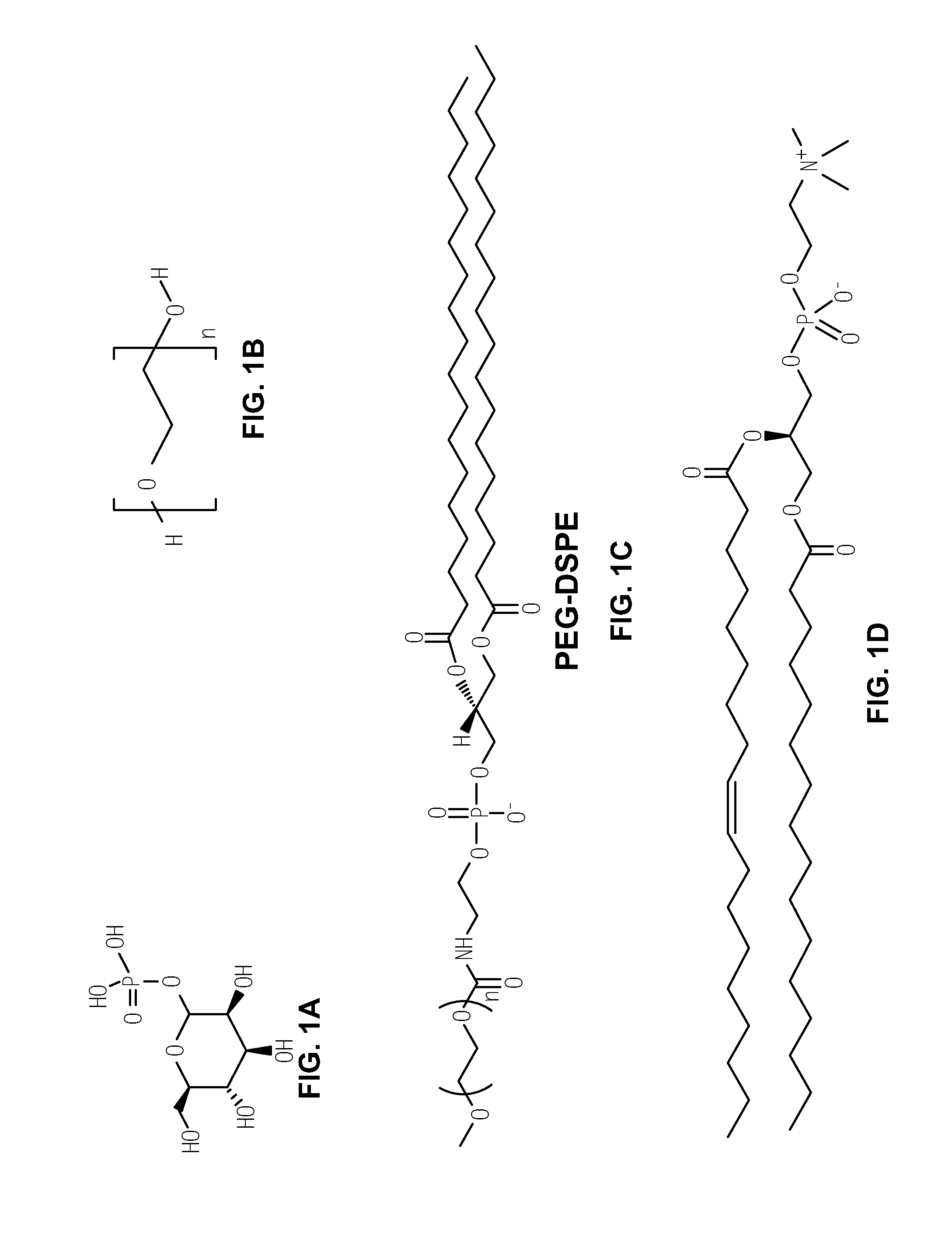
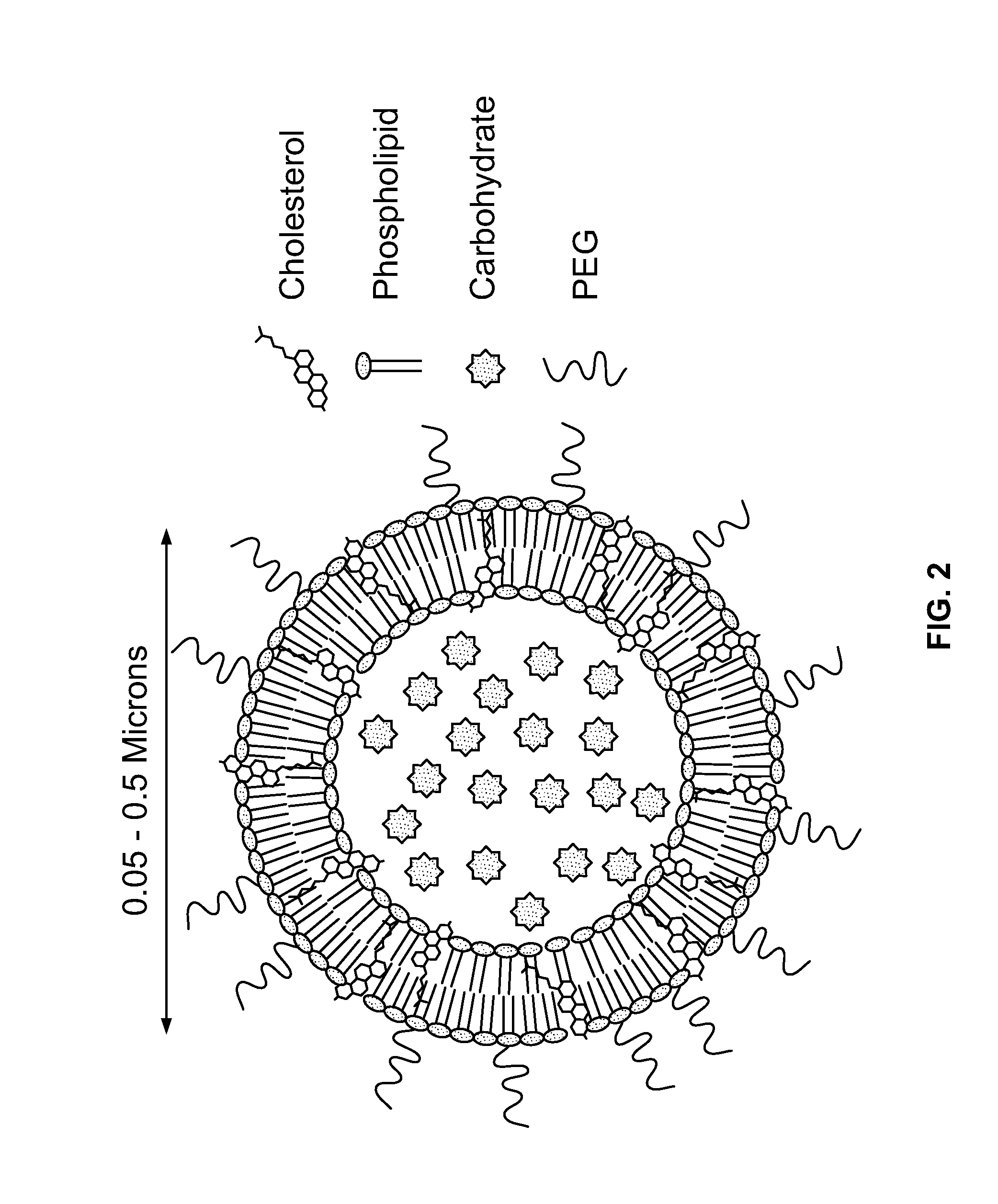
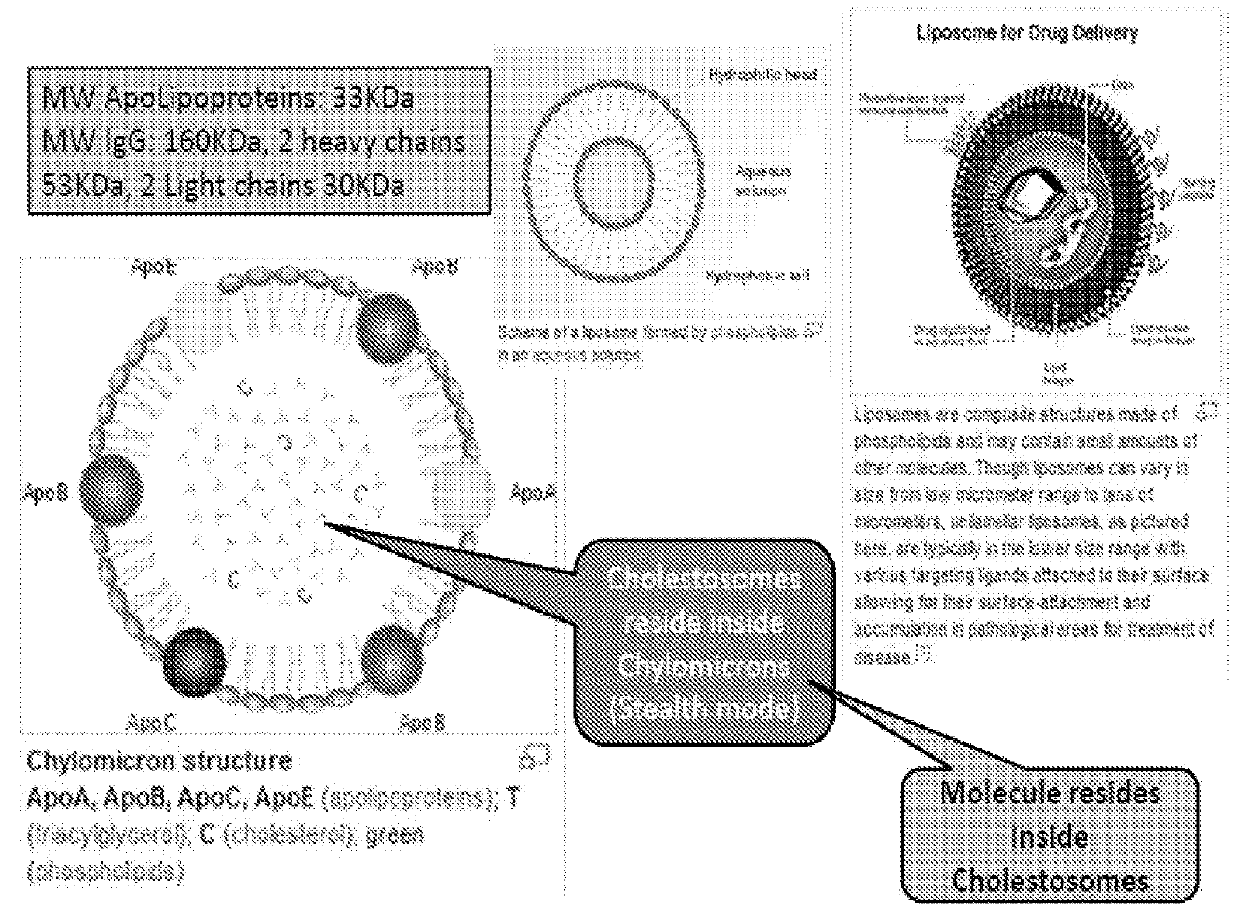
Cholestosome vesicles for incorporation of molecules into chylomicrons
The present invention is directed to a cargo-loaded cholesteryl ester nanoparticle with a hollow compartment (“cholestosome”) consisting essentially of at least one non-ionic cholesteryl ester and one or more encapsulated active molecules which cannot appreciably pass through an enterocyte membrane in the absence of said molecule being loaded into said cholestosome, the cholestosome having a neutral surface and having the ability to pass into enterocytes in the manner of orally absorbed nutrient lipids using cell pathways to reach the golgi apparatus. Pursuant to the present invention, the novel cargo loaded cholestosomes according to the present invention are capable of depositing active molecules within cells of a patient or subject and effecting therapy or diagnosis of the patient or subject.
Owner:THERASYN SENSORS
Quantitative Golgi apparatus protein GP73 determination kit and detecting method thereof
The invention relates to a quantitative Golgi apparatus protein GP73 determination kit which comprises a GP73 antibody coating plate, a GP73 standard substance, a concentrated enzyme conjugate, a concentrated enzyme conjugate diluent, concentrated washing liquid, color developing agent liquid A, color developing agent liquid B, termination liquid and a sealing plate film. A quantitative Golgi apparatus protein GP73 determination method comprises the steps of experiment preparation and detection, wherein the detection step includes sample adding, warm bathing, washing, enzyme conjugate adding, warm bathing, washing, color development, determination and data treatment. The quantitative Golgi apparatus protein GP73 determination kit is high in detection sensitivity, low in sample consumption, simple in operation, short in reaction time and good in stability, and the sensitivity and specificity of the quantitative Golgi apparatus protein GP73 determination kit is 39%-64% and 76%-91% respectively.
Owner:天津金虹生物科技开发有限公司
Kit for building a model of a cell
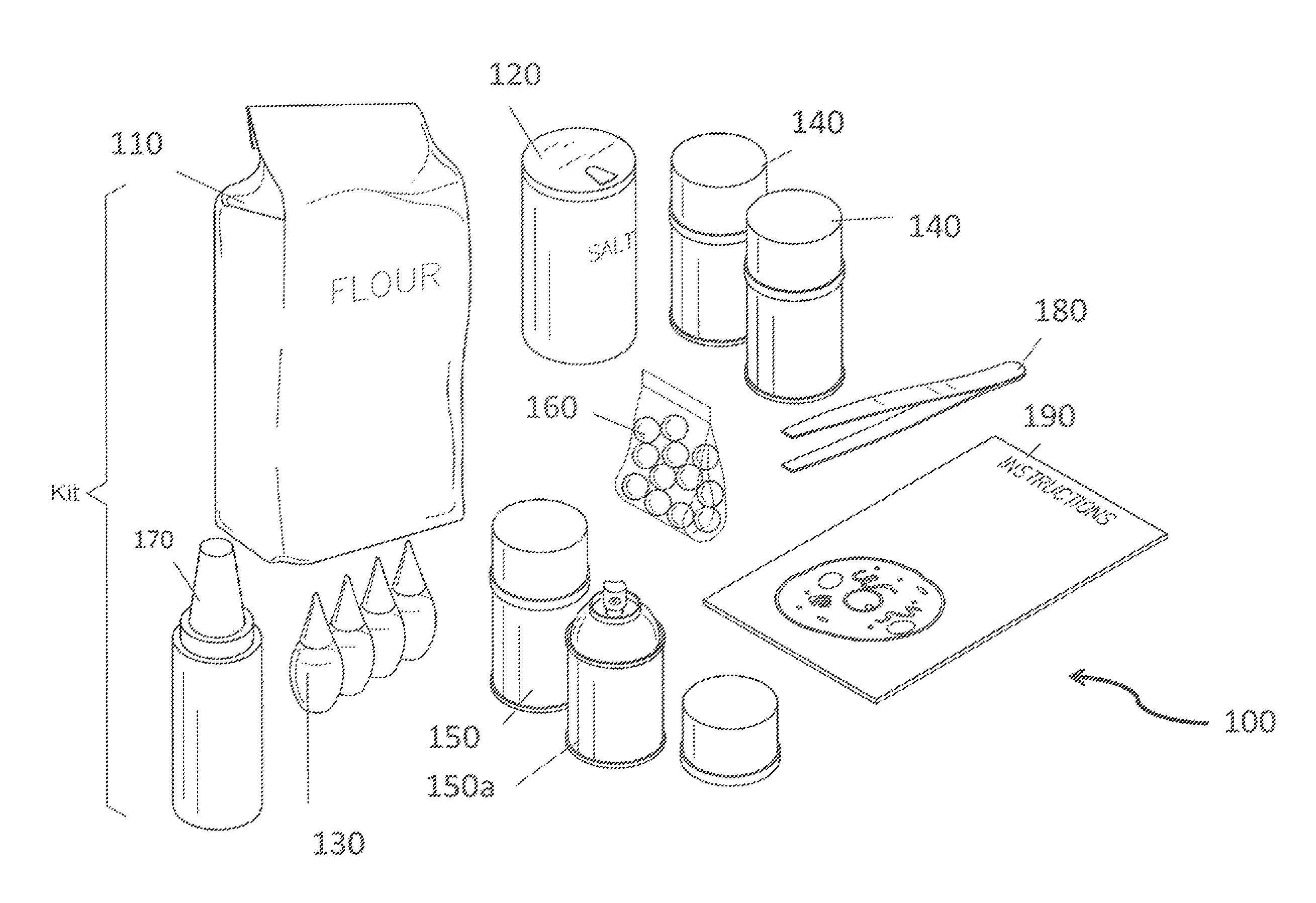
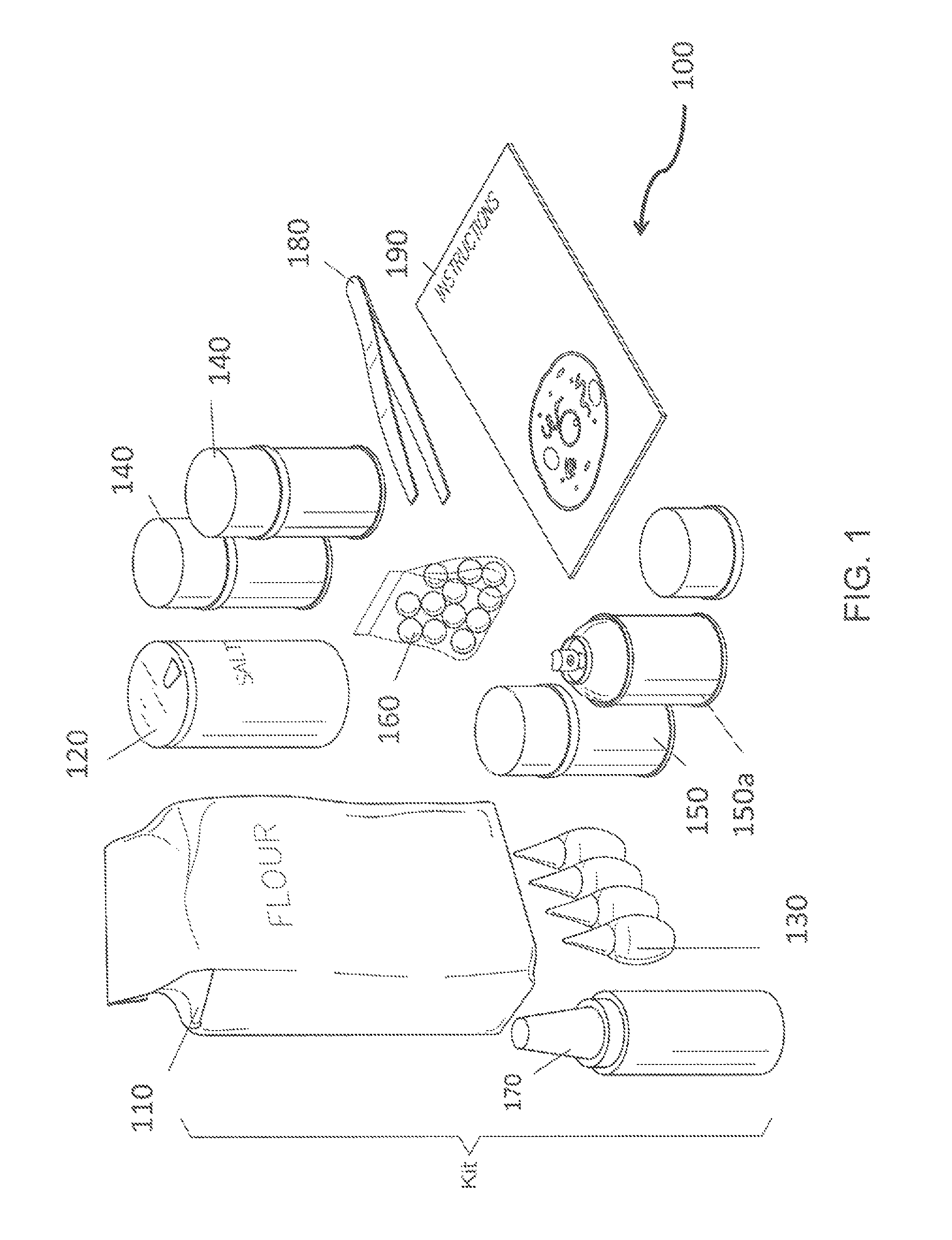
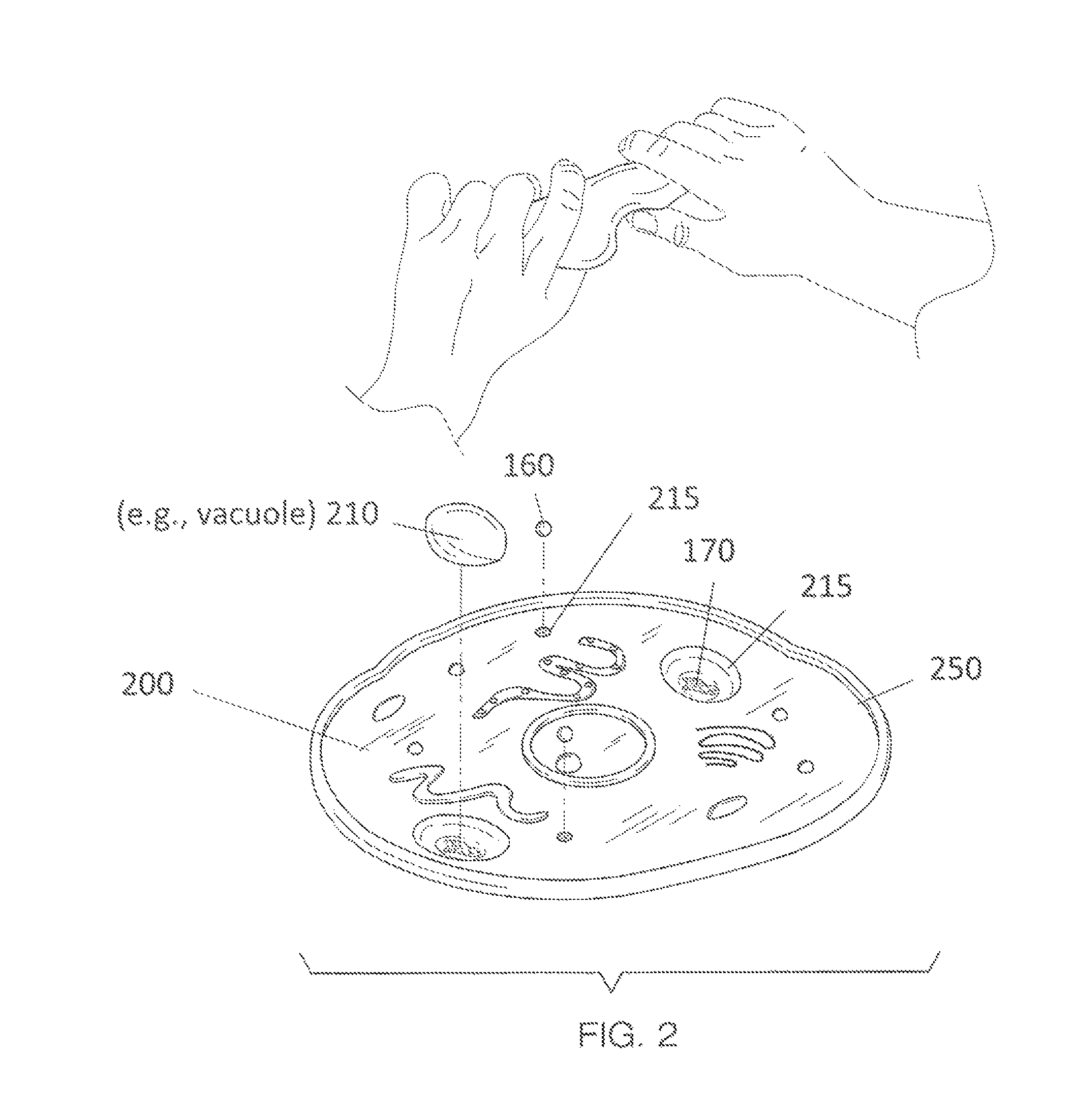
A method of creating a model of a biological cell. The method features providing a circular base with indentations disposed therein, forming a cell membrane and at least one organelle from a mixture formed by mixing all-purpose flour and water. Organelles may include a nuclear membrane, a cell wall, mitochondria, a smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a rough ER, a vacuole, a golgi apparatus, a nucleolus, a nucleoplasm, chromatin, a ribosome, DNA, RNA, transcription machinery, a histone, and a microtubule. The outside edge of the base is lined with the cell membrane. The organelles are inserted into indentations or atop the base. The organelles can be secured with glue.
Owner:POMPEY AUDREY SIOUX
Pharmaceutical preparation of carbohydrates for therapeutic use
InactiveUS20160228364A1Promote circulationImprove retentionOrganic active ingredientsLiposomal deliveryDiseaseNanocarriers
The disclosure provides methods for preparation of carbohydrate replacement therapies (CRT) that include nanocarriers of carbohydrates and glycolipids for pharmaceutical delivery to cell interior, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi for treating CDG type I and CDG type II diseases as well as other metabolic disorders.
Owner:GLYCOMINE INC
A targeted antitumor complex based on ricin, a preparing method thereof and applications of the complex
InactiveCN107693800AReduce the impact of enzymatic hydrolysisImprove targeted anti-tumor effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectLysosome
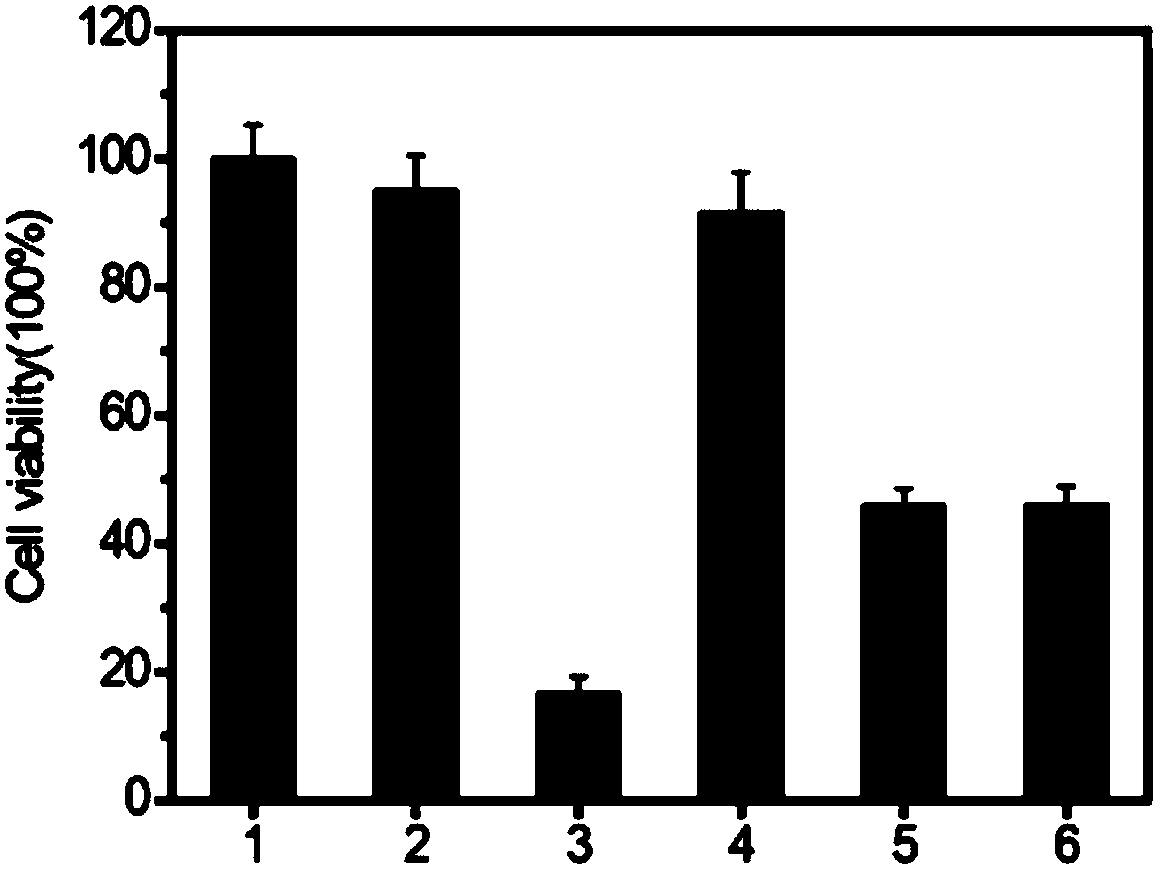
The invention relates to a targeted antitumor complex based on ricin, a preparing method thereof and applications of the complex. The complex is prepared by compositing carbon quantum dots and a ricinA chain to form a carbon quantum dot-ricin A chain complex, then encapsulating the complex with the lipidosome, and modifying the lipidosome with a nucleolin nucleic acid aptamer. The prepared complex can enter cells more easily, acts on ribosome through a Golgi apparatus path, has higher cytotoxicity, can effectively protect the A chain from being enzymatically decomposed by lysosome, utilizes specificity of the nucleolin nucleic acid aptamer, can be targeted on a tumor cell, reduces toxic and side effects on normal cells, and is of great importance for targeted treatment on tumor cells.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Cell lines for high level production of protein-based pharmaceuticals
ActiveUS10329594B1High densityStably inheritableHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsCulture fluidReticulum cell
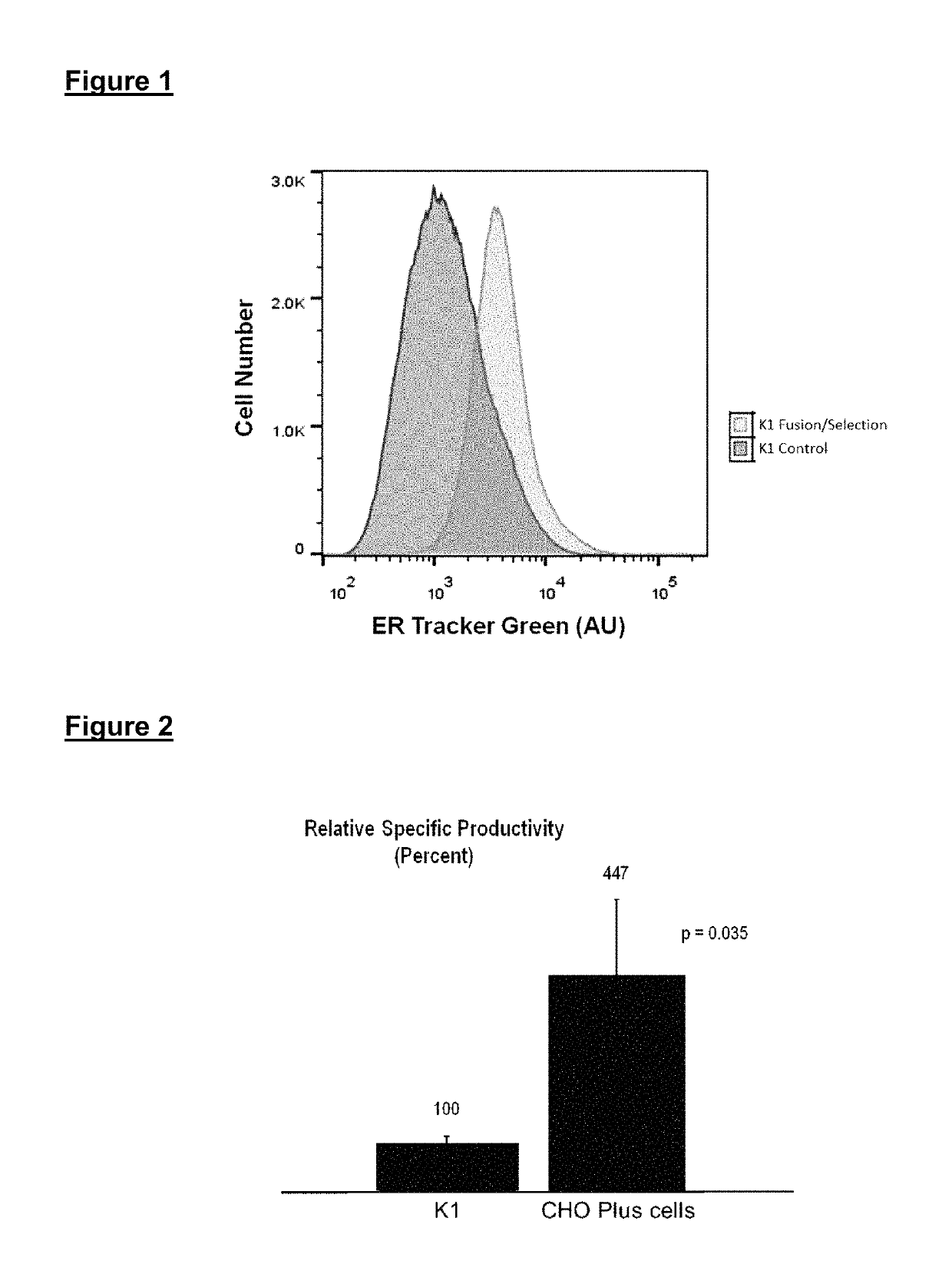
This invention provides improved cell lines for manufacture of protein-based pharmaceutical agents, considerably reducing the cost of commercial production. The cell lines are obtained by fusing cells from one or more parental cell populations. The hybrid cells are then selected for one or more characteristics that support protein production on a non-specific basis, such as the level of endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and / or other desired phenotypic features, compared with other hybrids or parental cells in the starting mixture. A gene encoding a therapeutic protein is transfected into the cells before or after one or more cycles of fusion and selection. Depending on the protein product being expressed, cell lines may be obtained that produce as much as eight grams or more of protein per liter of culture fluid.
Owner:CHO PLUS INC
Orange-light carbon quantum dots as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN113583670AHas the ability to targetGood water solubilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsAqueous ethanolSolvothermal reaction
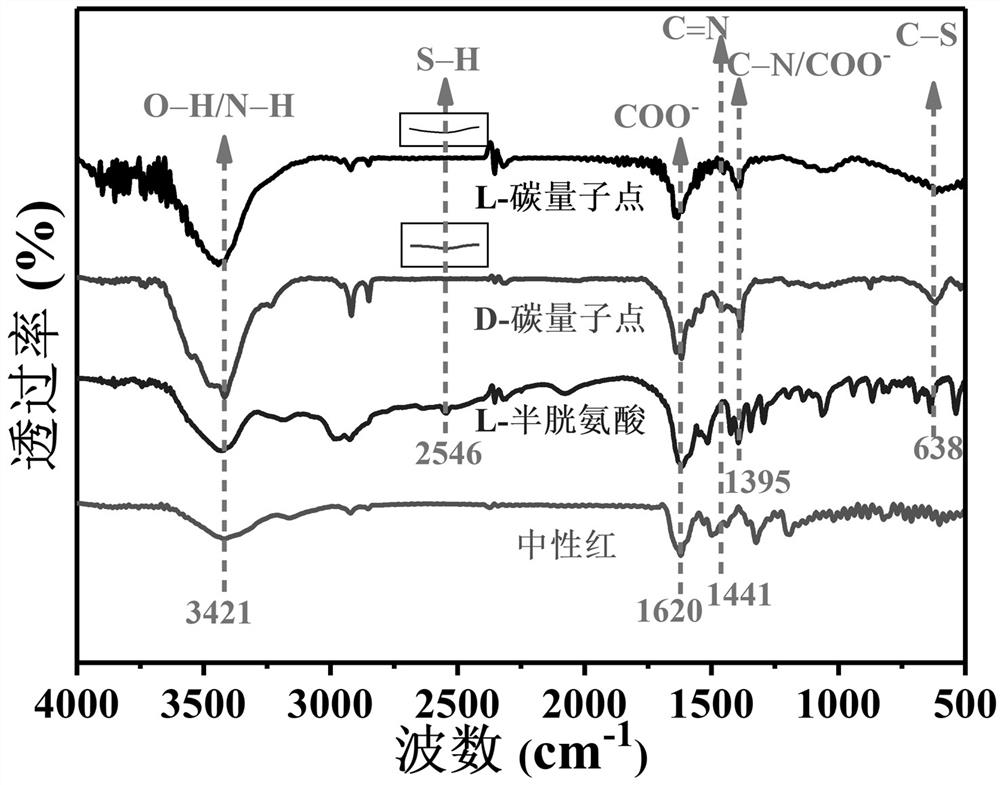
The invention relates to orange-light carbon quantum dots, which are carbon quantum dot solid powder obtained by dissolving neutral red as a carbon source and cysteine as a targeting source in water or an ethanol water solution, performing a solvothermal reaction for 6-14 hours at 120-160 DEG C under a closed condition, and purifying a reaction product. The carbon quantum dots prepared by the invention not only have good water solubility, but also have excellent fluorescence characteristics, and can emit orange light. When the carbon quantum dots are applied to cell imaging, target imaging of a Golgi body can be realized. The carbon quantum dots have an application prospect in the field of Golgi body target imaging.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV +1
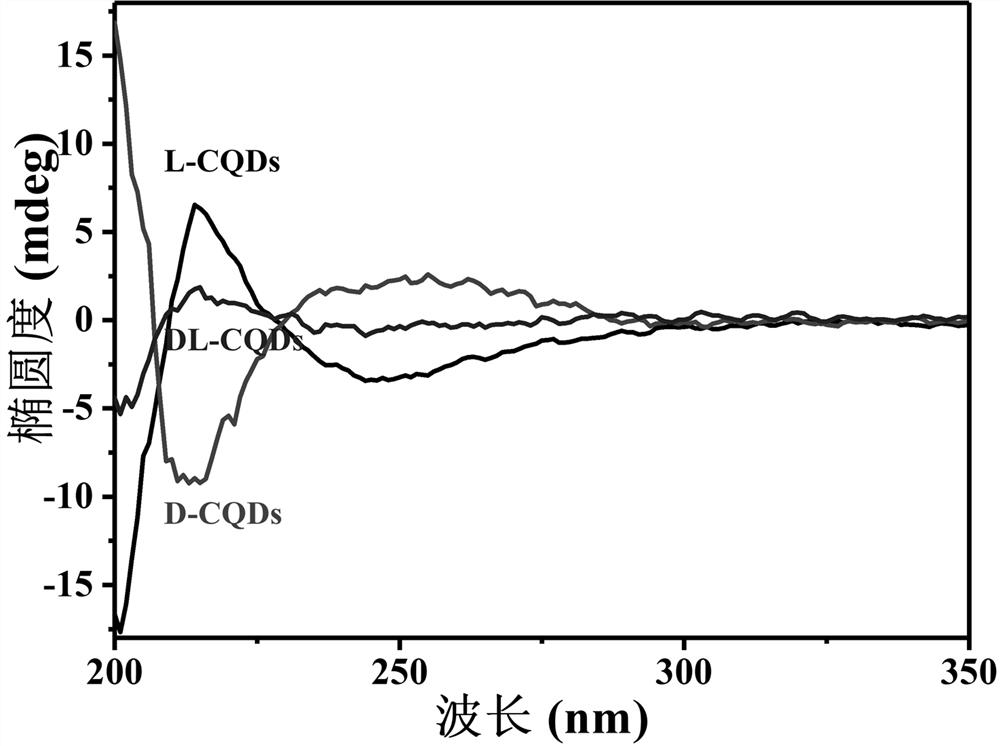
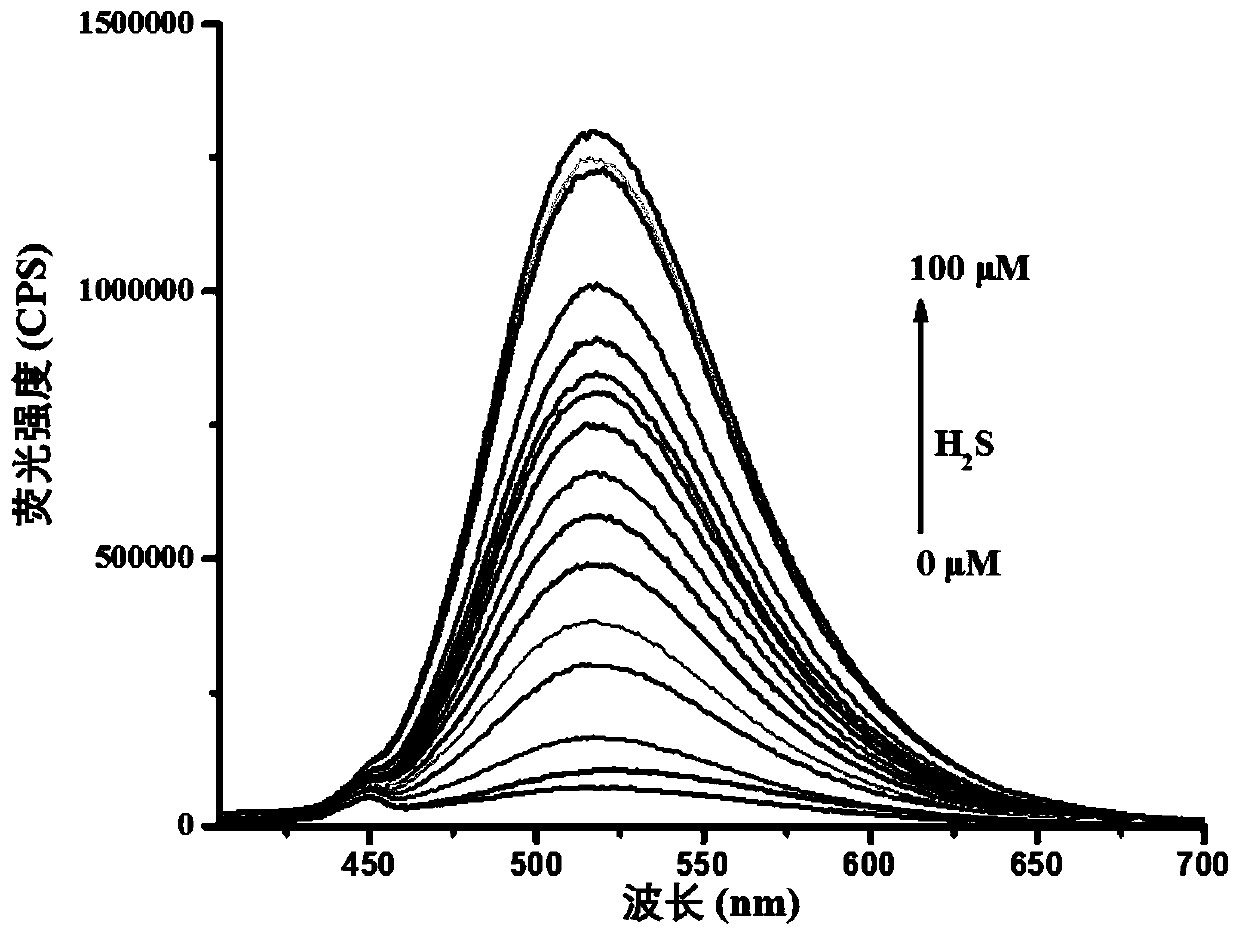
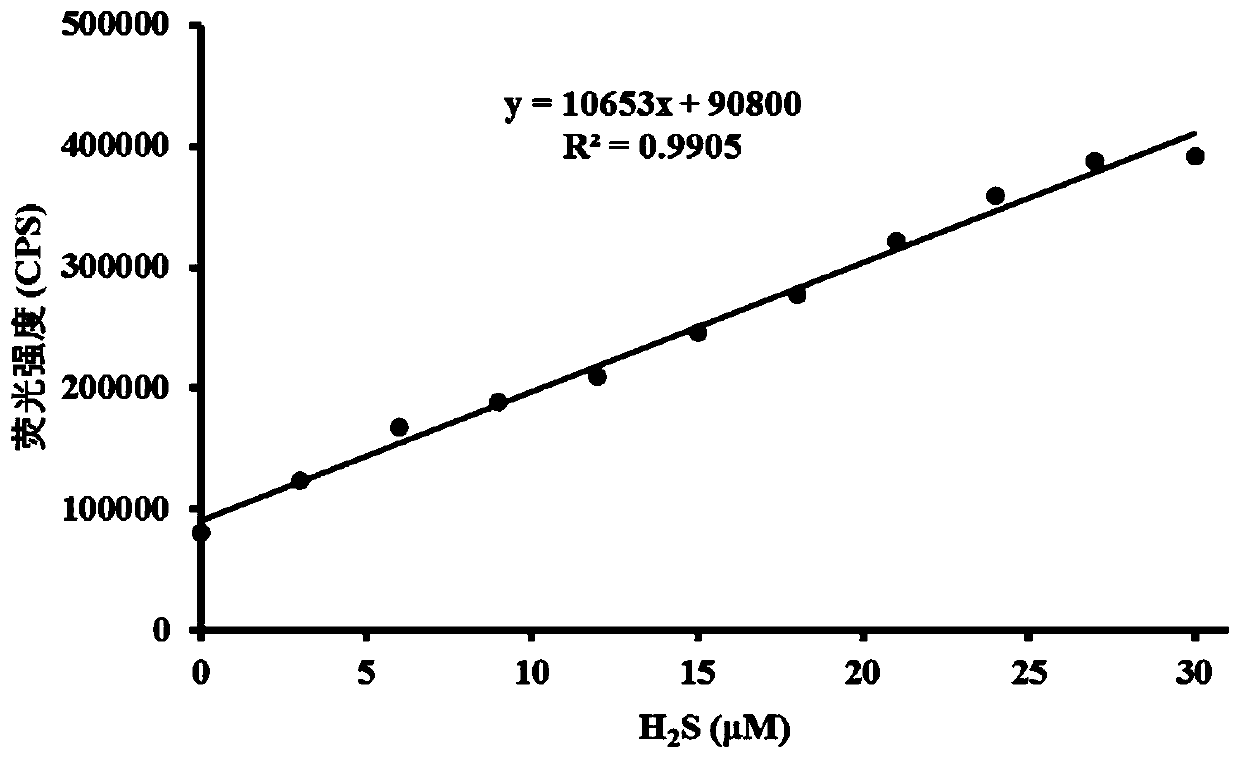
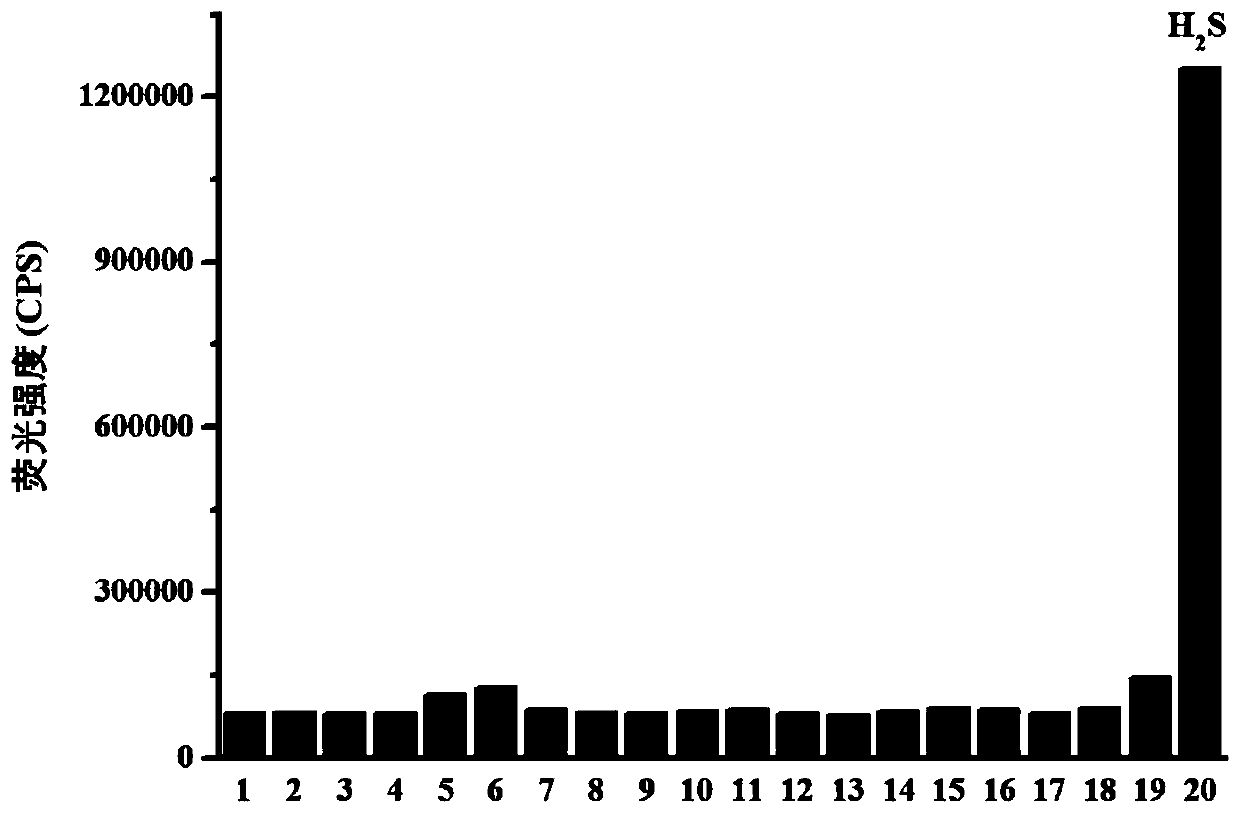
Hydrogen sulfide fluorescent probe targeting Golgi apparatus, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111039866AHigh selectivityImprove anti-interference abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesFluorescence
The invention relates to a hydrogen sulfide fluorescent probe targeting Golgi apparauts, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The probe is a quinoline compound fluorescent probe concretely, and can be used as the hydrogen sulfide fluorescent probe of the targeting Golgi apparauts to measure, detect or screen hydrogen sulfide and perform living cell fluorescence imaging. The probe can achieve at least one of the following technical effects: good targeted positioning effect of the Golgi apparauts, identification of hydrogen sulfide in a high-selectivity manner, quick response tohydrogen sulfide, ultra-sensitive analysis on hydrogen sulfide, strong anti-interference capability, simplicity in synthesis and stable properties.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Cholestosome vesicles for incorporation of molecules into chylomicrons
ActiveUS20160030361A1Increase milk productionSimple structureAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChylomicronNanoparticle
The present invention is directed to a cargo-loaded cholesteryl ester nanoparticle with a hollow compartment (“cholestosome”) consisting essentially of at least one non-ionic cholesteryl ester and one or more encapsulated active molecules which cannot appreciably pass through an enterocyte membrane in the absence of said molecule being loaded into said cholestosome, the cholestosome having a neutral surface and having the ability to pass into enterocytes in the manner of orally absorbed nutrient lipids using cell pathways to reach the golgi apparatus. Pursuant to the present invention, the novel cargo loaded cholestosomes according to the present invention are capable of depositing active molecules within cells of a patient or subject and effecting therapy or diagnosis of the patient or subject.
Owner:THERASYN SENSORS
Identification of novel post-translational protein modifications
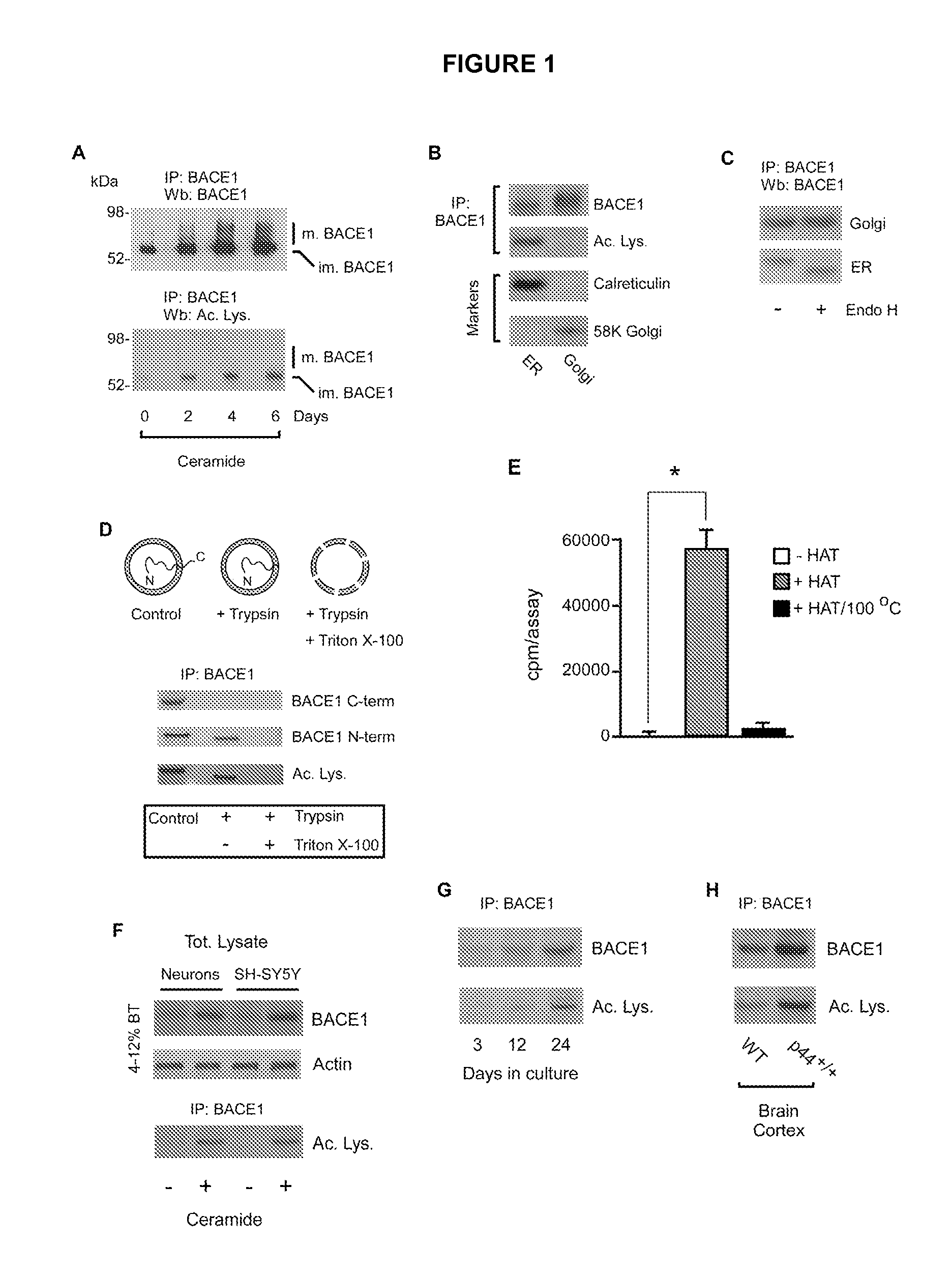
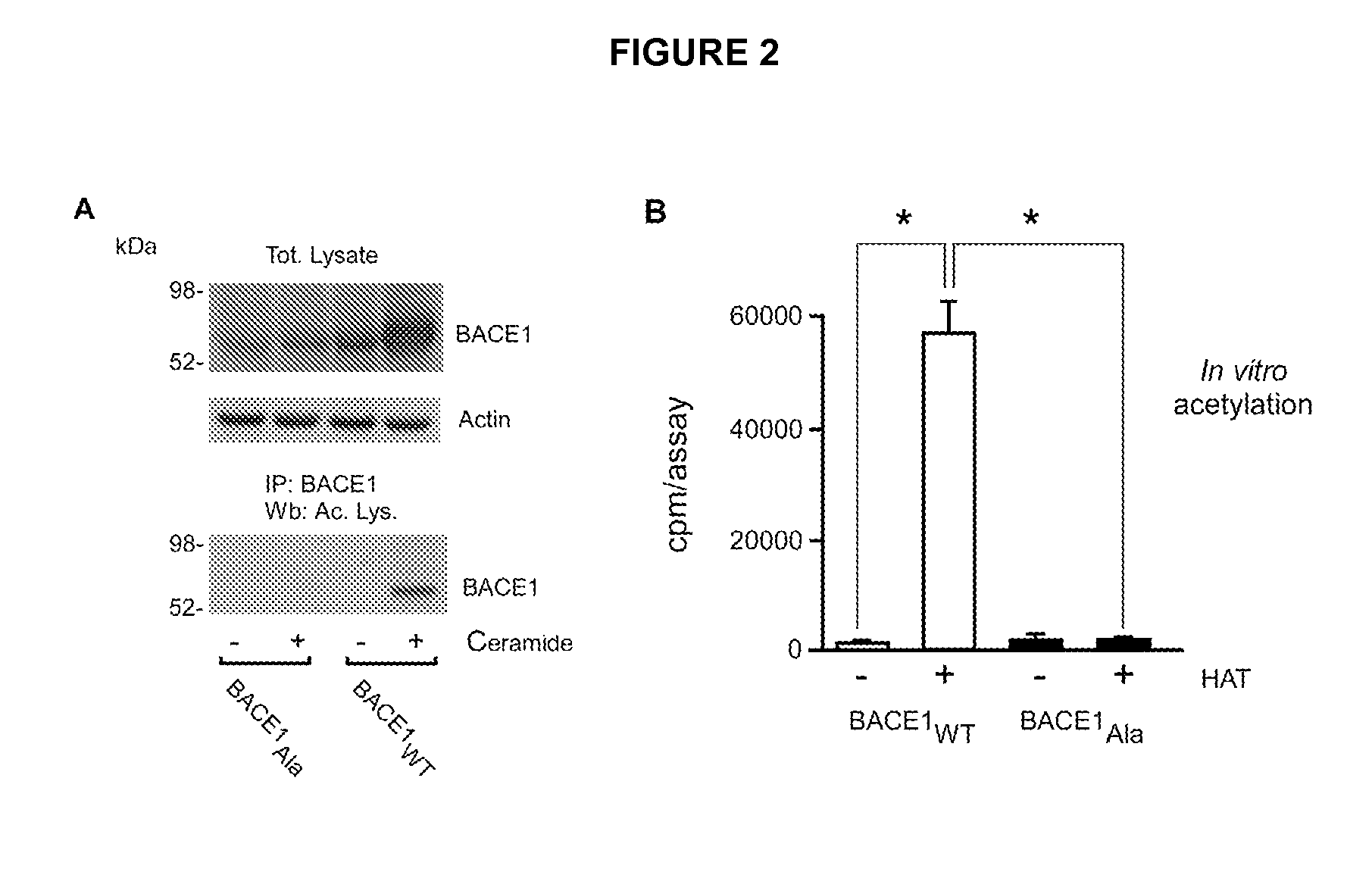
InactiveUS20090042993A1Reducing the acetyl-CoA transport activityReduce or eliminate the acetyl-CoA transport activityBiocideNervous disorderPost translationalProtein Acetylation
Compositions and methods for post-translational modifications that include protein acetylation in the ER lumen and deacetylation in the Golgi apparatus are provided. The disclosed methods are especially suited for the identification of compounds useful for the prevention or treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
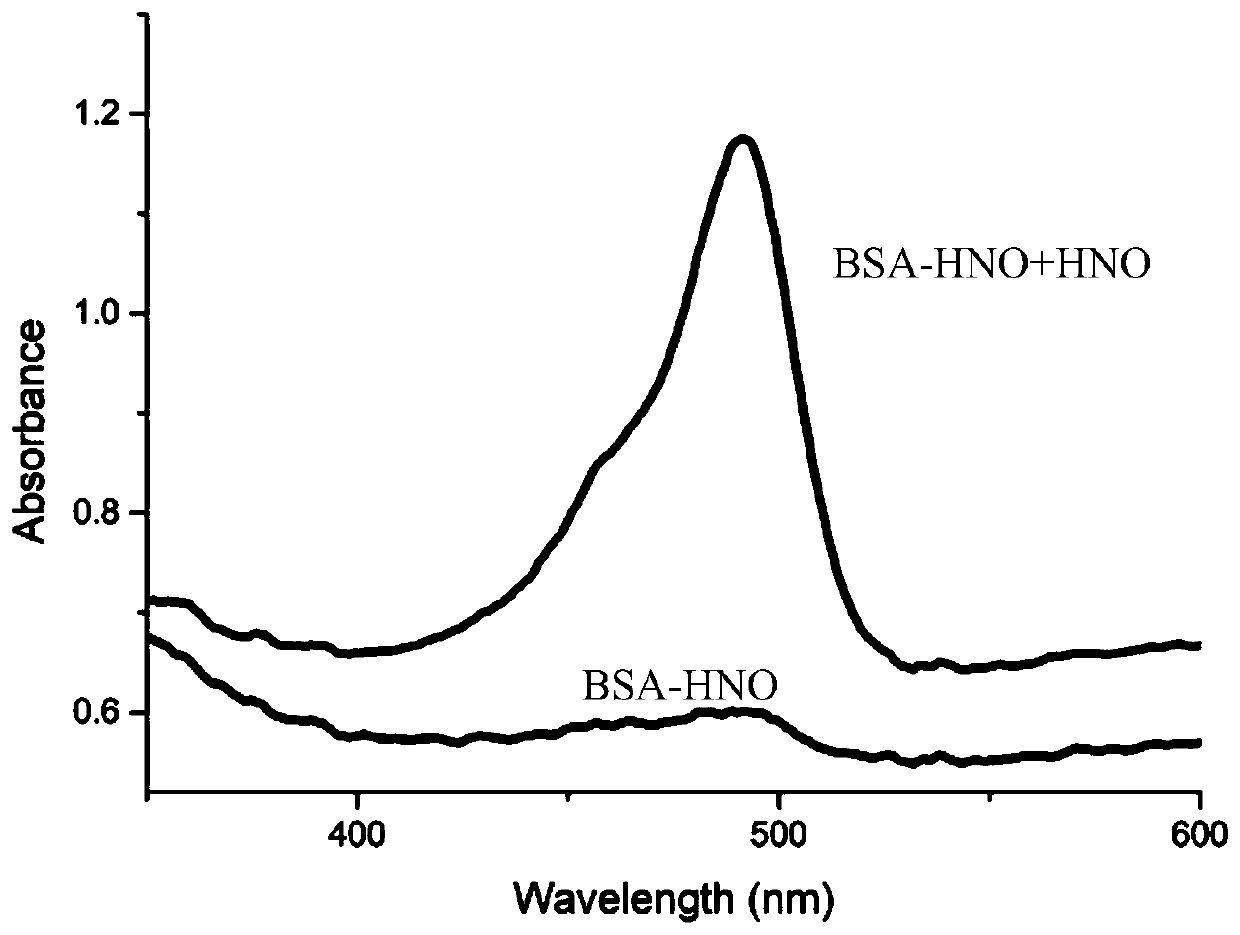
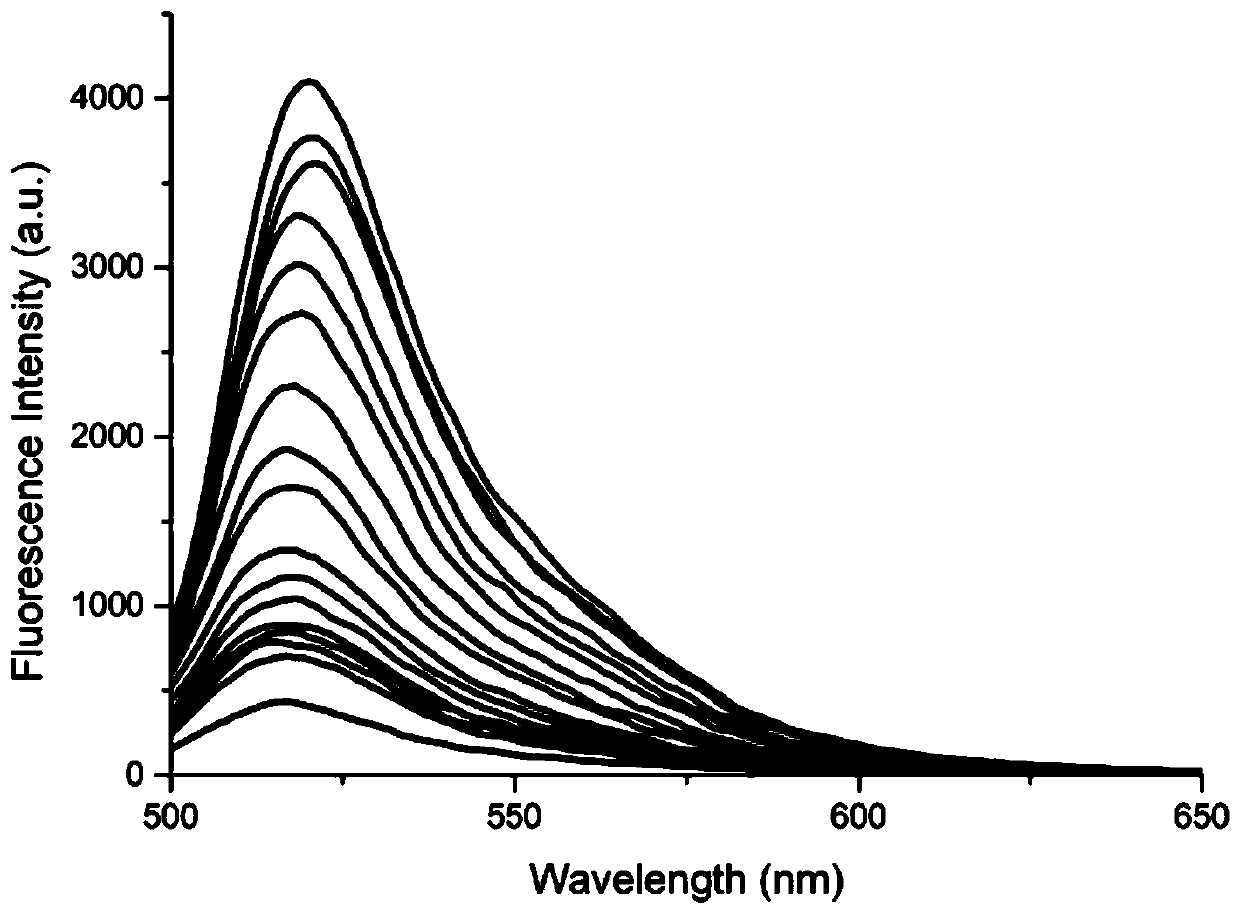
Nano fluorescent probe, and preparation method and application thereof in detection of HNO in Golgi apparatus
ActiveCN110885675AHas a targeting effectReduce phototoxicityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureFluoProbes
The invention provides a nano fluorescent probe, and a preparation method and an application thereof in detection of HNO in a Golgi apparatus. The nano fluorescent probe comprises a probe molecule C-HNO and bovine serum albumin (BSA), the bovine serum albumin coats the probe molecule C-HNO, and the chemical structural formula of the probe molecule C-HNO is shown in the specification. The nano fluorescent probe shows an excellent Golgi apparatus targeting positioning effect, can be used for imaging HNO, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, high selectivity and simplicity and conveniencein synthesis.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
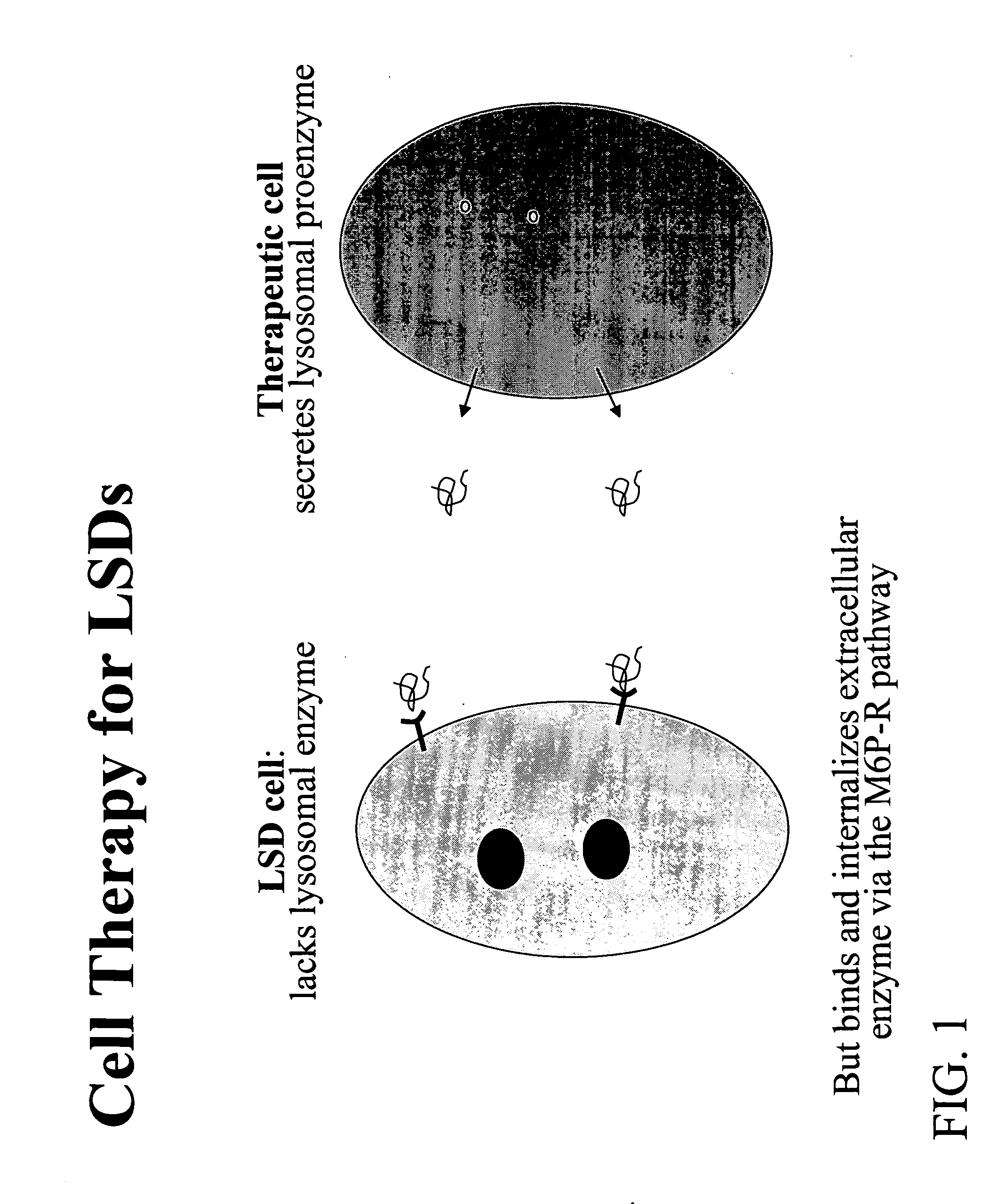
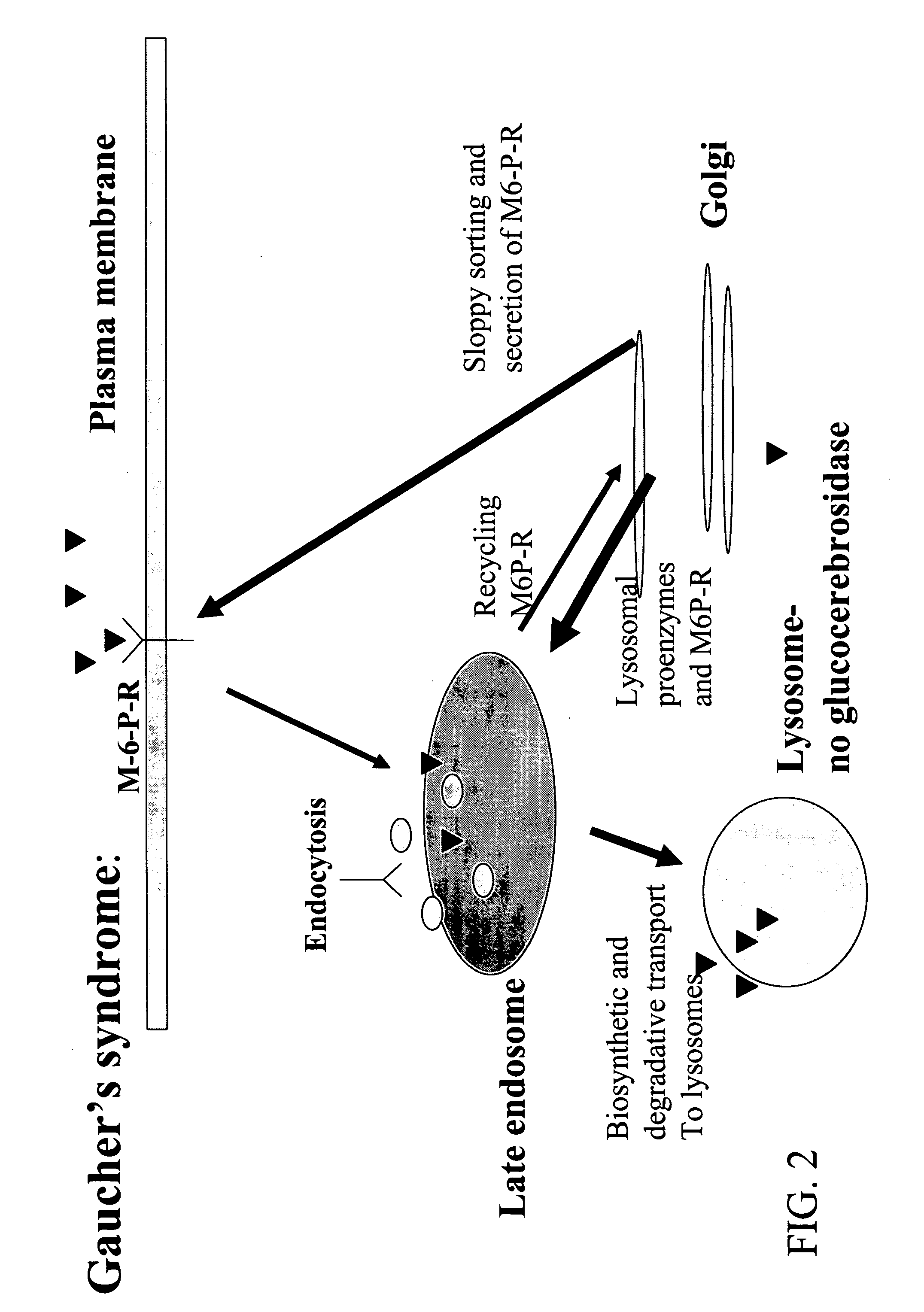
Genetically modified somatic cells for sustained secretion of lysosomal proenzymes deficient in lysosomal storage disorders
InactiveUS20060188975A1Avoids adverse immunological side effectAvoids renal clearance problemNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsProgenitorZymogen
The invention relates to various methods of treating lysosomal storage disorders using somatic cells and methods of delivering therapeutic enzymes. More particularly, gain-of-function or loss-of-function mutations in components of the intracellular Golgi to lysosome sorting pathway are used to enhance secretion of one or more lysosomal enzymes in somatic cells, thereby providing treatment for lysosomal storage disorders, particularly in neuronal cells. In addition, homologous recombination may be used to engineer therapeutically useful cells, for example, somatic cells, such as, glial progenitor cells, mesenchymal stem cells and astrocyte precursor cells, to enhance secretion of one or more lysosomal enzymes.
Owner:Q THERAPEUTICS
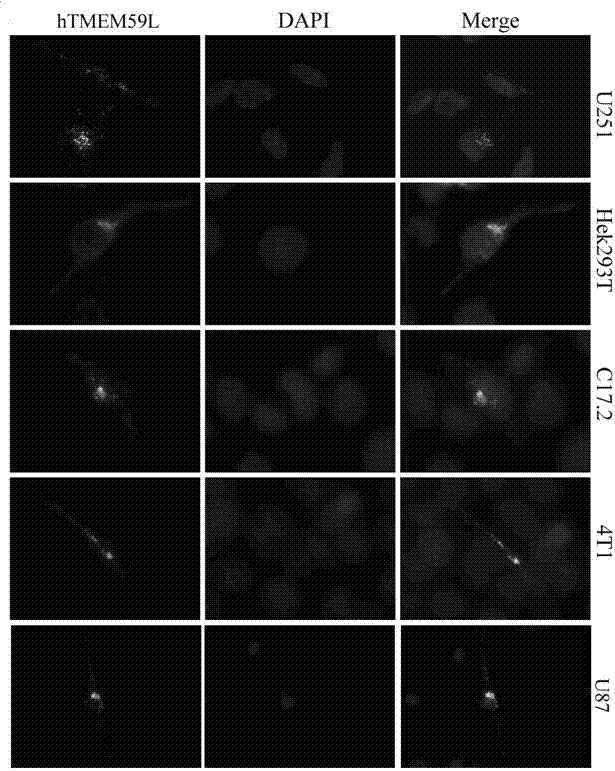
Specific interaction of dentritic cell factor 1 (DCF1) genes and transmembrane protein 59 like (TMEM 59 L) genes
InactiveCN102776236APrevent disengagementNo inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseasePharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to specific interaction of a dentritic cell factor 1 (DCF1) genes and transmembrane protein 59 like (TMEM 59 L) genes. Under the overexpression condition of the DCF1 and the TMEM 59 L, amyloid precursor protein (APP) can be highly and specifically inhibited from separating from golgi apparatus, the transportation of GDP dissociation inhibitor 1 (GDI1) and GDP dissociation inhibitor 2 (GDI2) are partially inhibited, the transportation of beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 2 (BACE2) protein is not inhibited, and a new drug target is provided for diagnosing and treating the Alzheimer disease.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
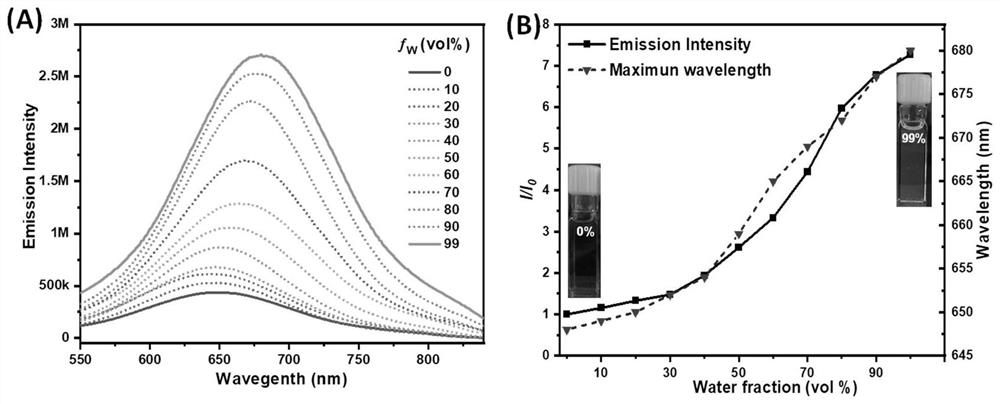
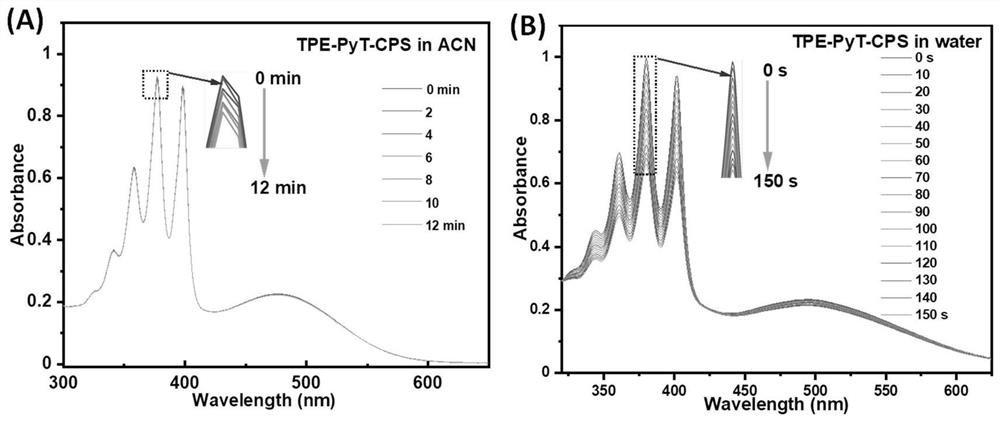
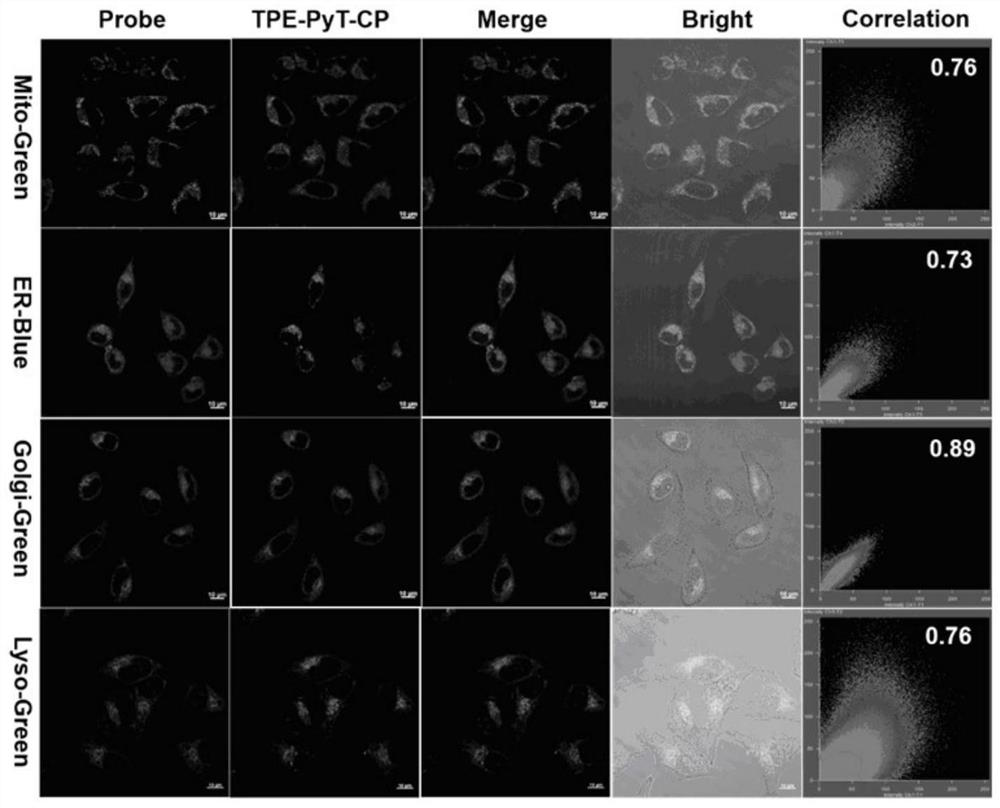
High-efficiency Golgi apparatus targeting compound and biological application thereof
ActiveCN113683605AImprove targetingEffective imagingOrganic chemistryPhotodynamic therapyTumor therapyCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a high-efficiency Golgi apparatus targeting compound and biological application thereof, and the compound has the following general formula structure, wherein R1 represents an electron withdrawing group selected from one or more of electron withdrawing groups, R2 represents a substituted / substituted electron donating group in which one or multiple sites of one or more benzene rings is / are substituted by H or R3, R3 represents C1-C12 alkyl, C1-C12 alkoxy or C1-C12 fluoroalkoxy, and when the the sites are substituted by a plurality of R3 , the substituent groups are the same or different. The compound based on aggregation-induced emission can effectively target Golgi apparatus, is used for tumor treatment or cell imaging, and is especially used for cell / tissue / living tumor treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
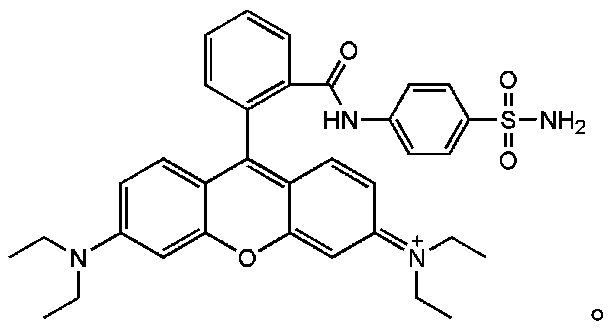
Compound represented by formula (I), and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110386913ASolve the problem of targetingUniversalOrganic chemistryPreparing sample for investigationCombinatorial chemistryStructural formula
The invention discloses a compound represented by a formula (I), and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound represented by formula (I) has the following structural formula. The compound has an excellent Golgi apparatus targeting positioning effect when being used as a dye.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Application of tetracera asiatica and extract thereof to preparation of medicine for treating and/or preventing alcoholic liver injury
ActiveCN110787196AImprove indexing performanceGood effectDigestive systemPlant ingredientsReticulum cellEthyl acetate
The invention relates to the field of medicine application, in particular to application of tetracera asiatica and an extract thereof to preparation of a medicine for treating and / or preventing alcoholic liver injury. The tetracera asiatica extract is selected from any one of a mixture of more than one of the following components: a tetracera asiatica water extract, a tetracera asiatica alcohol extract, a tetracera asiatica ethyl acetate extract and a tetracera asiatica normal butanol extract. The tetracera asiatica extract provided by the invention can obviously increase the albumin content of serum of mice suffering from alcoholic liver injury and can improve the albumin synthesis ability of the liver by repairing endoplasmic reticulum, golgiosome, ribosome and the like of injured cellsso as to provide protection for the liver.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com