Pharmaceutical preparation of carbohydrates for therapeutic use
a technology of pharmaceutical preparation and carbohydrates, applied in the direction of medical preparations, liposomal delivery, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of limited treatment options, delivery and maintenance of such a systemic supply of man-1-p, and the ineffective treatment of cdg-ia patients, so as to enhance the retention of lipid particles, enhance circulation and retention, and minimize the degradation of lipid particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Mannose-1-Phosphate Liposomes
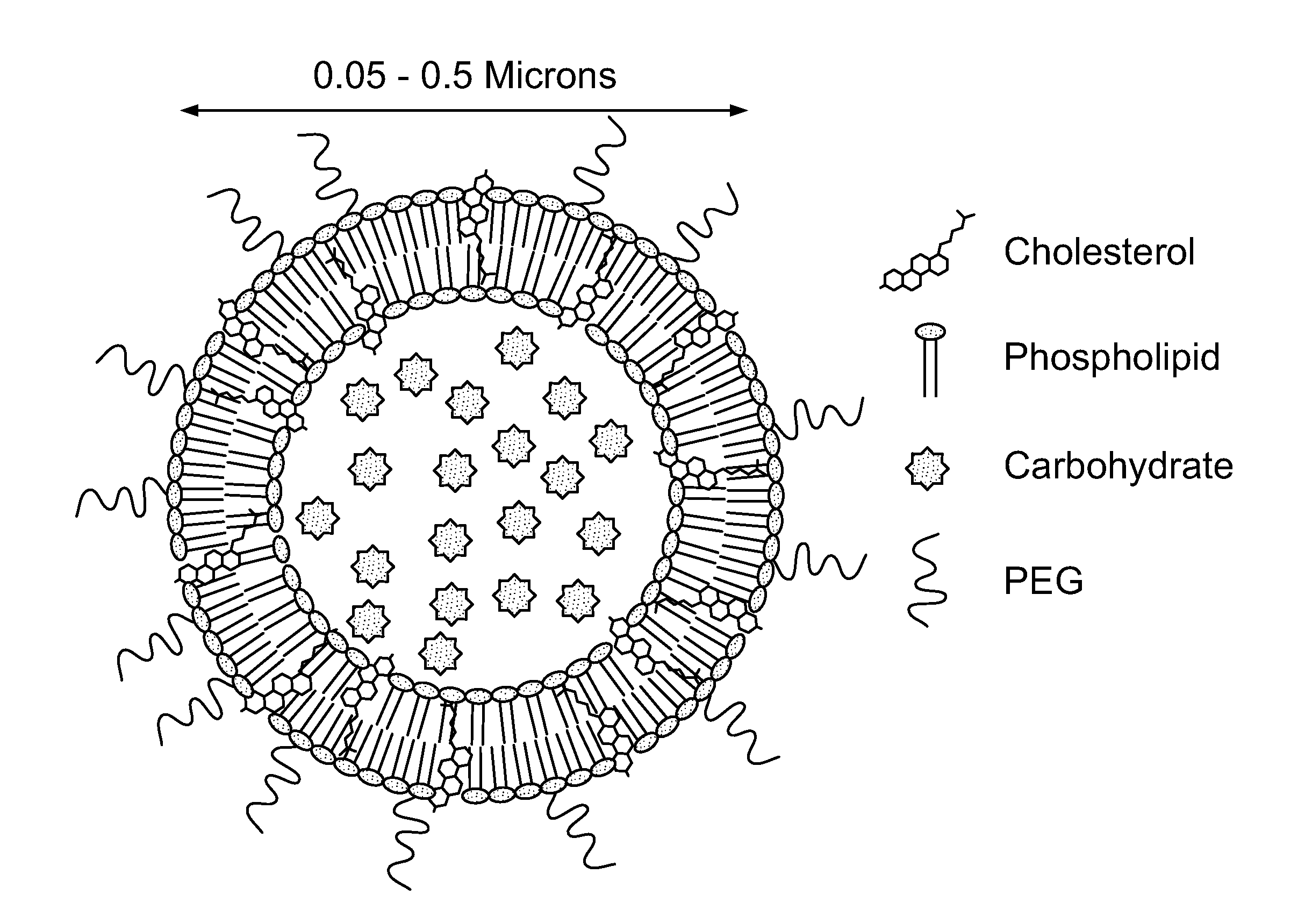
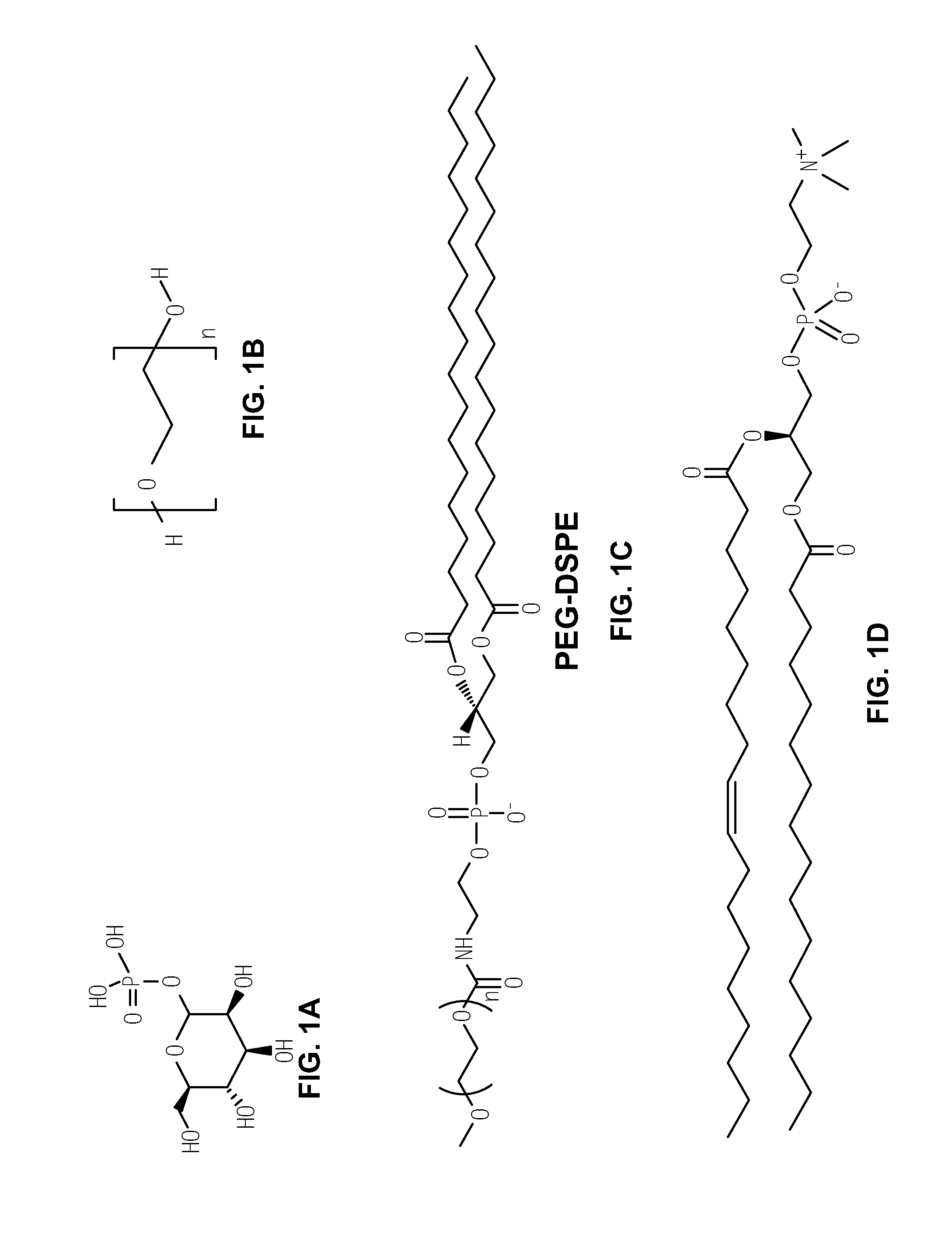
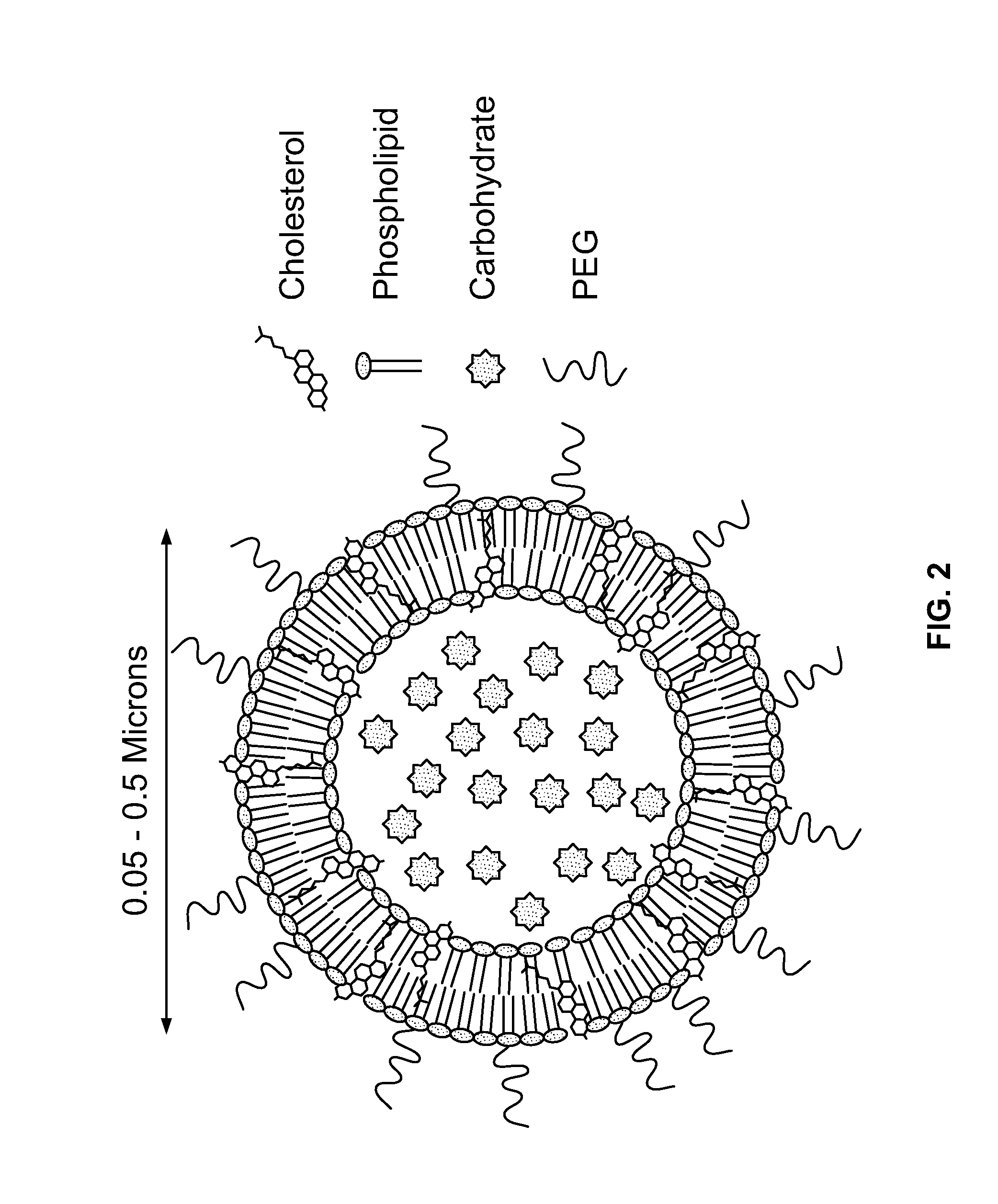
[0309]The following Example demonstrates the preparation of liposomes containing mannose-1-phosphate (M1P-liposomes). The structure of mannose-1-phosphate (M1P) is depicted in FIG. 1A. While a specific isomer is depicted in FIG. 1A, it should be understood that the carbohydates used in the compositions and methods provided herein may be any isomeric form, provided that such carbohydrates are endogenous carbohydrates for a given subject.
Liposome Preparation Method
[0310]Liposomes were prepared by thin-film hydration from phosphatidylcholine (PC), cholesterol, and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) conjugated topoly-ethylene-glycol (PEG). The structure of PEG is depicted in FIG. 1B. In FIG. 1B, in one variation, n may be in the range of 800-5000. In other variations, the value of n may be 2000. In yet other variations, PEG may be modified either with meleimide or NHS-ester depending on what the PEG will be conjugated to. The structure of phosphati...
example 2
Measurement of M1P Content in Liposomes
[0314]CDG-Ia disorder is a gycosylation disorder characterized by the deficiency or abnormalities associated with the enzyme phosphomannomutase (PMM). This disorder is diagnosed by testing the serum glycoproteins of hepatic origin (transferrin is the clinically tested protein), which are commonly underglycosylated. Typically transferrin is assessed using isoelectric focusing, which would underscore a dramatic decrease in PMM activity (PMM activity in CDG-Ia patients is approximately 0.29 nM / min / mg, as compared to normal PMM activity of approximately 2.97 nM / min / mg). PMM enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the conversion of mannose-6-phosphate to mannose-1-phosphate, which is in turn a precursor for the ultimate synthesis of G3M9Gn2-P-P-Dolichol, which in turn is a precursor to lipid-linked-oligosaccharide (LLO). This is represented by the following schematic representation of the metabolic glycosylation pathway is: glucose→glucose-6-phosphate→...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com