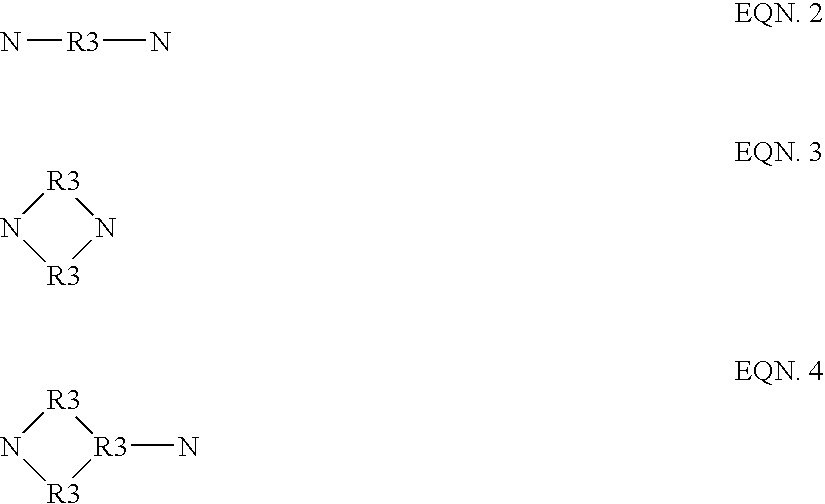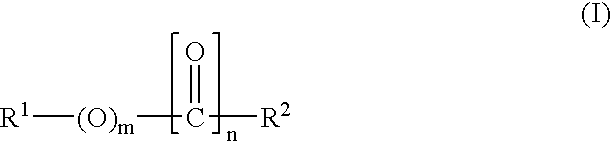Patents
Literature
1782 results about "Dolichol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dolichol refers to any of a group of long-chain mostly unsaturated organic compounds that are made up of varying numbers of isoprene units terminating in an α-saturated isoprenoid group, containing an alcohol functional group.
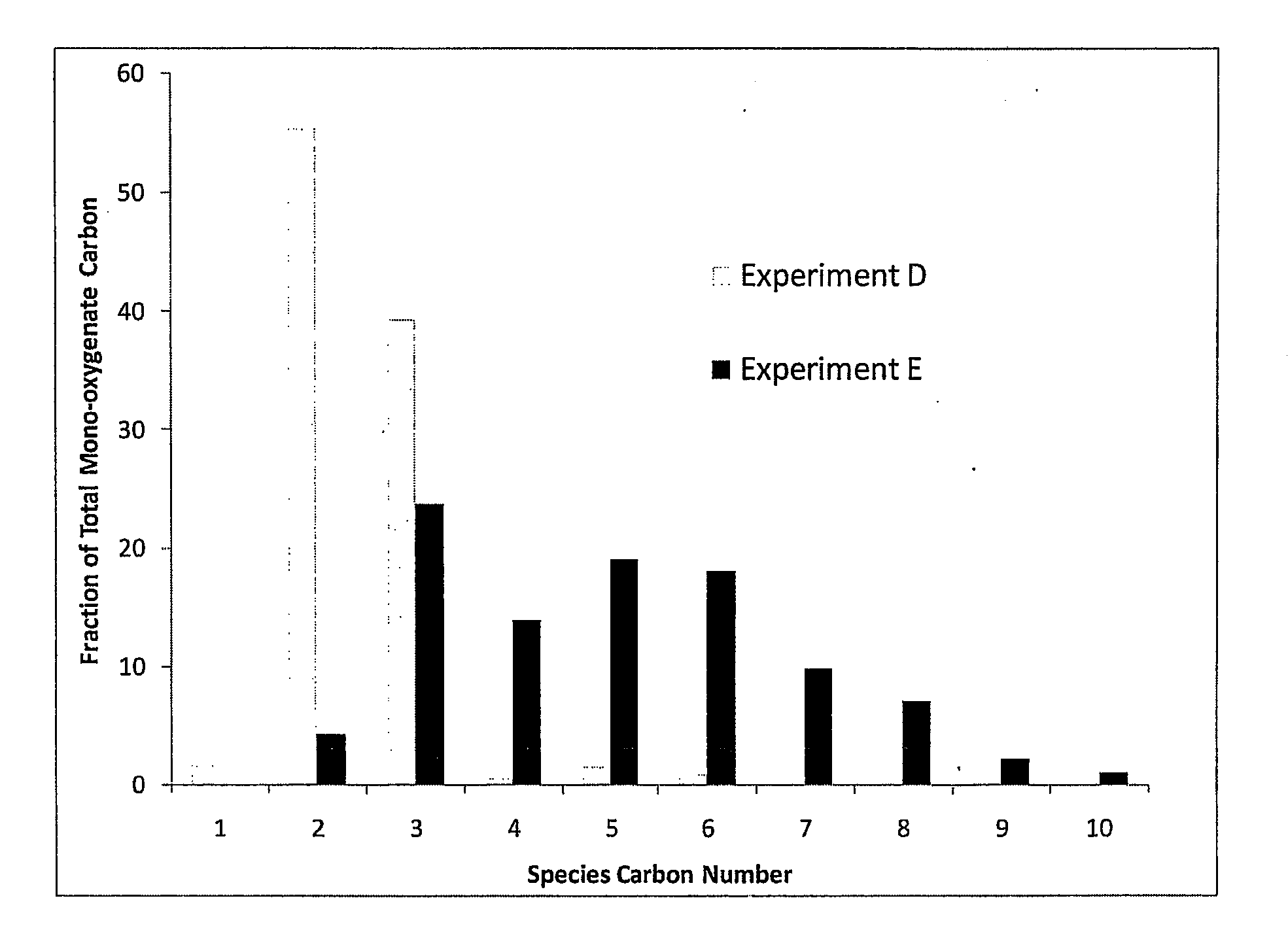
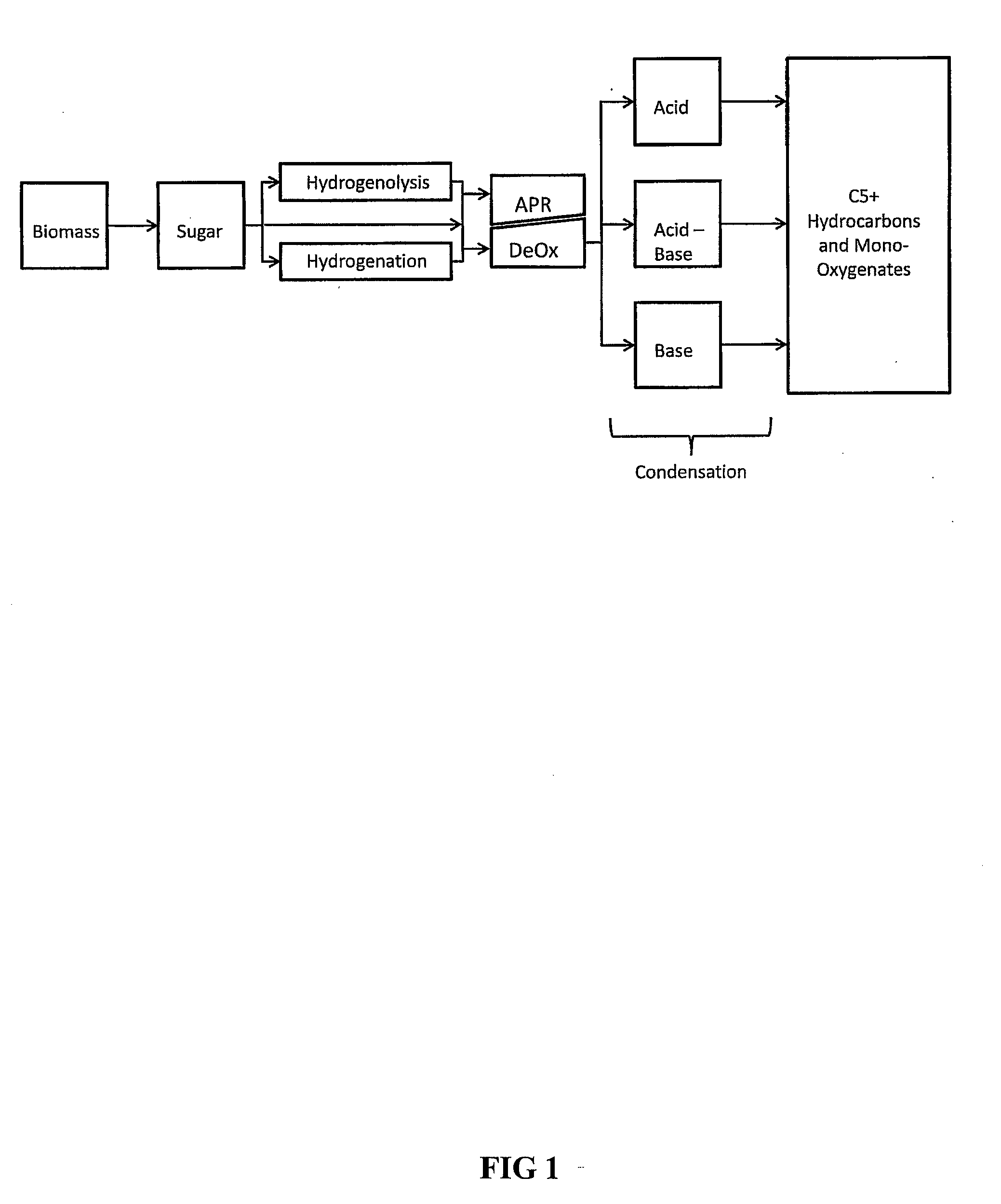
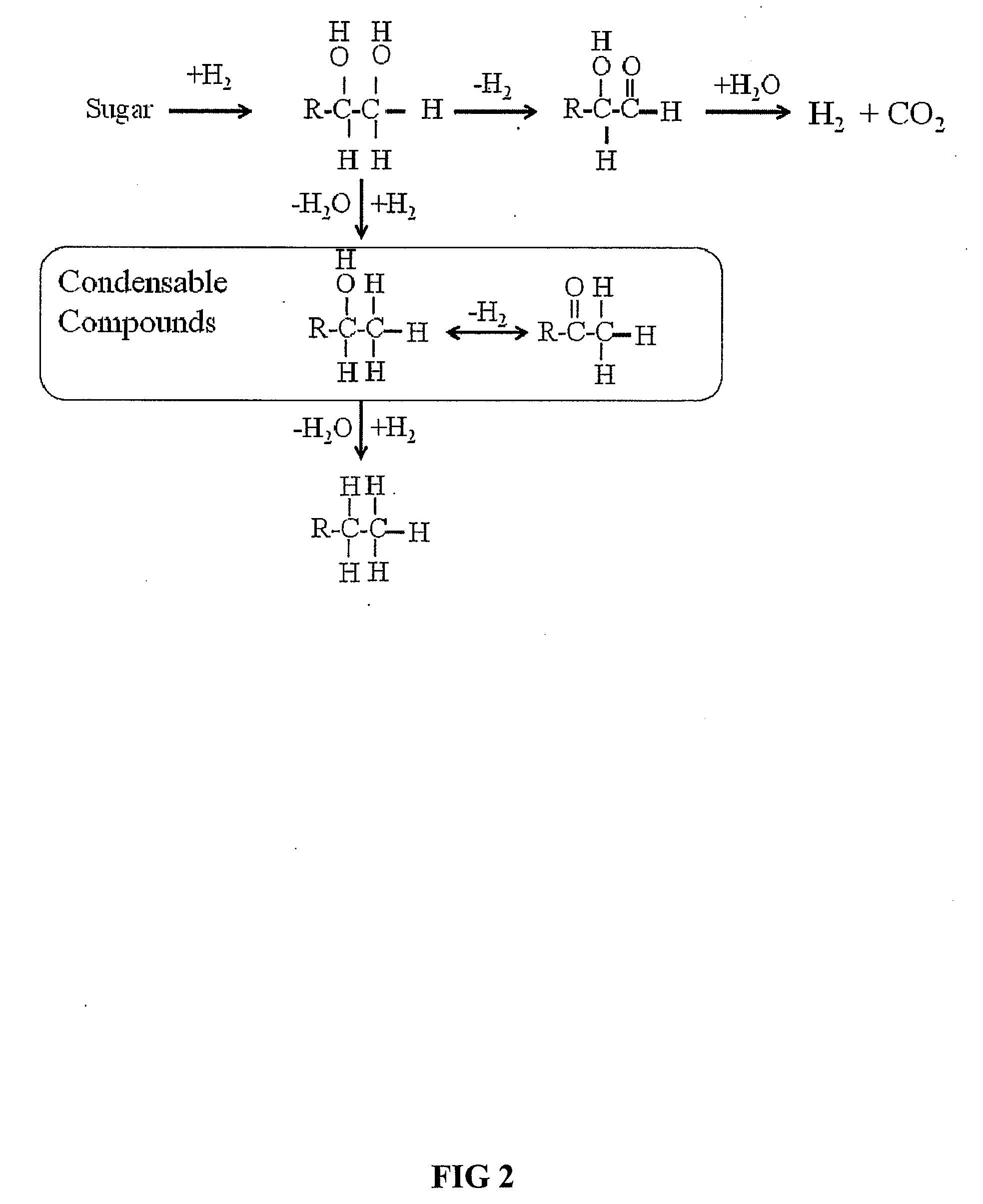
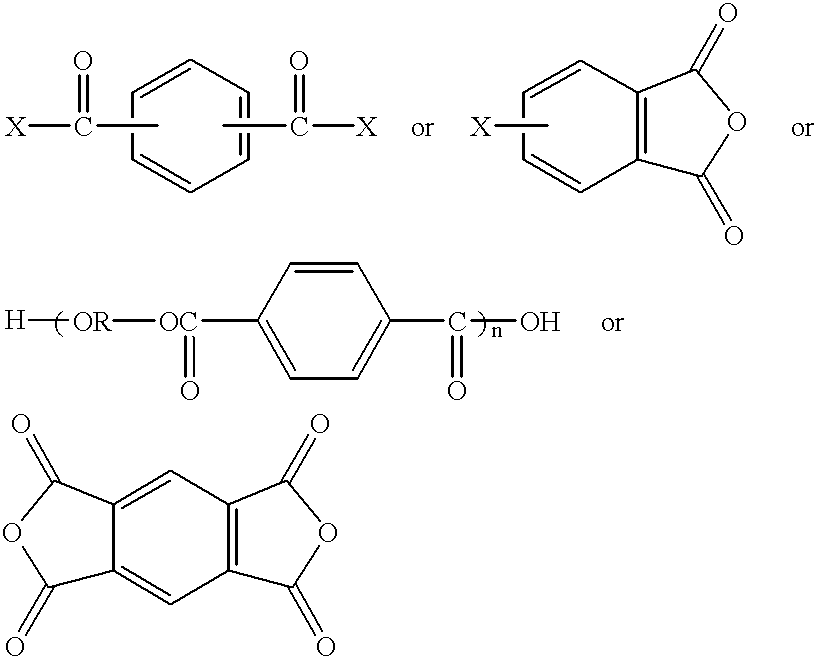
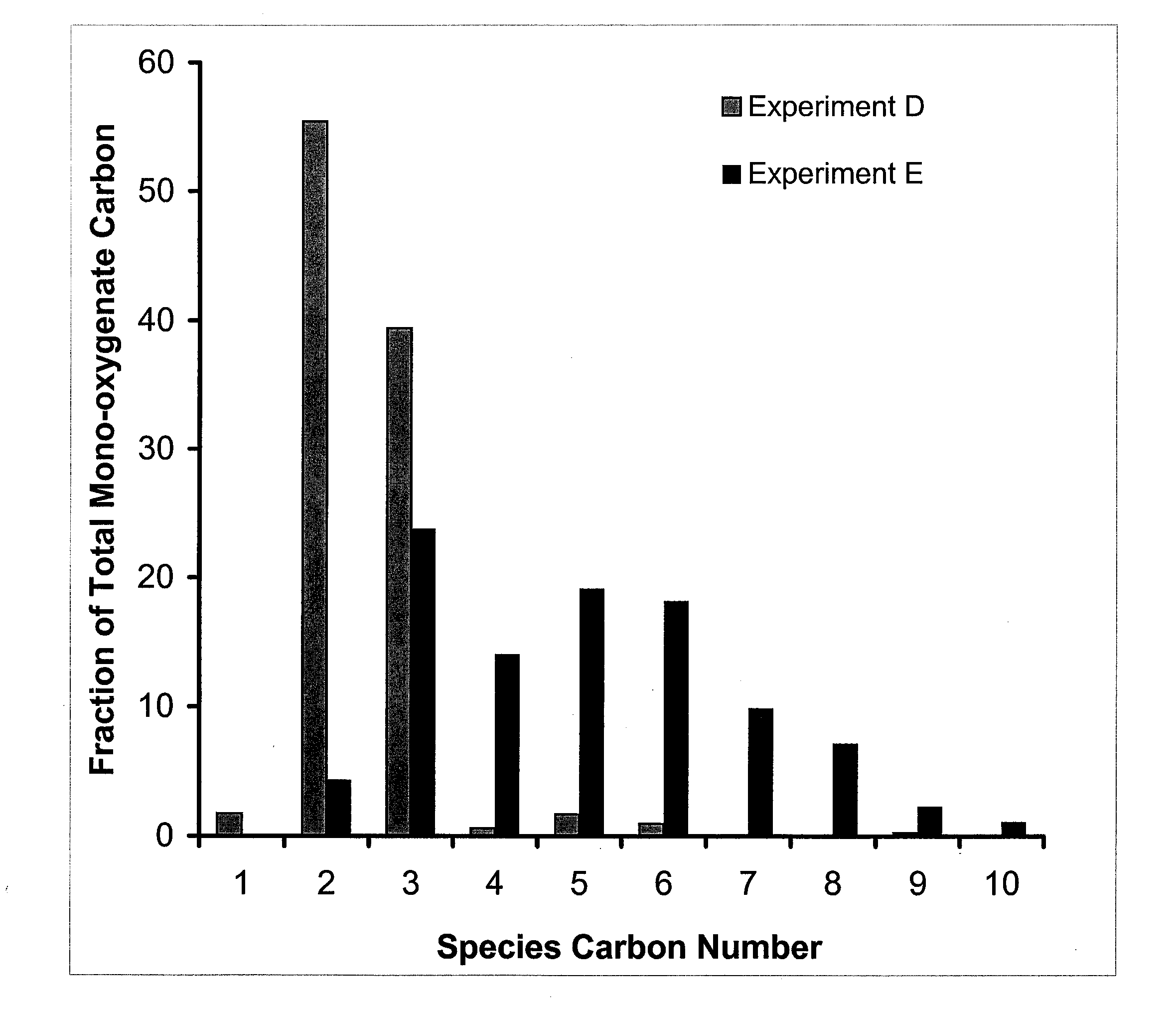
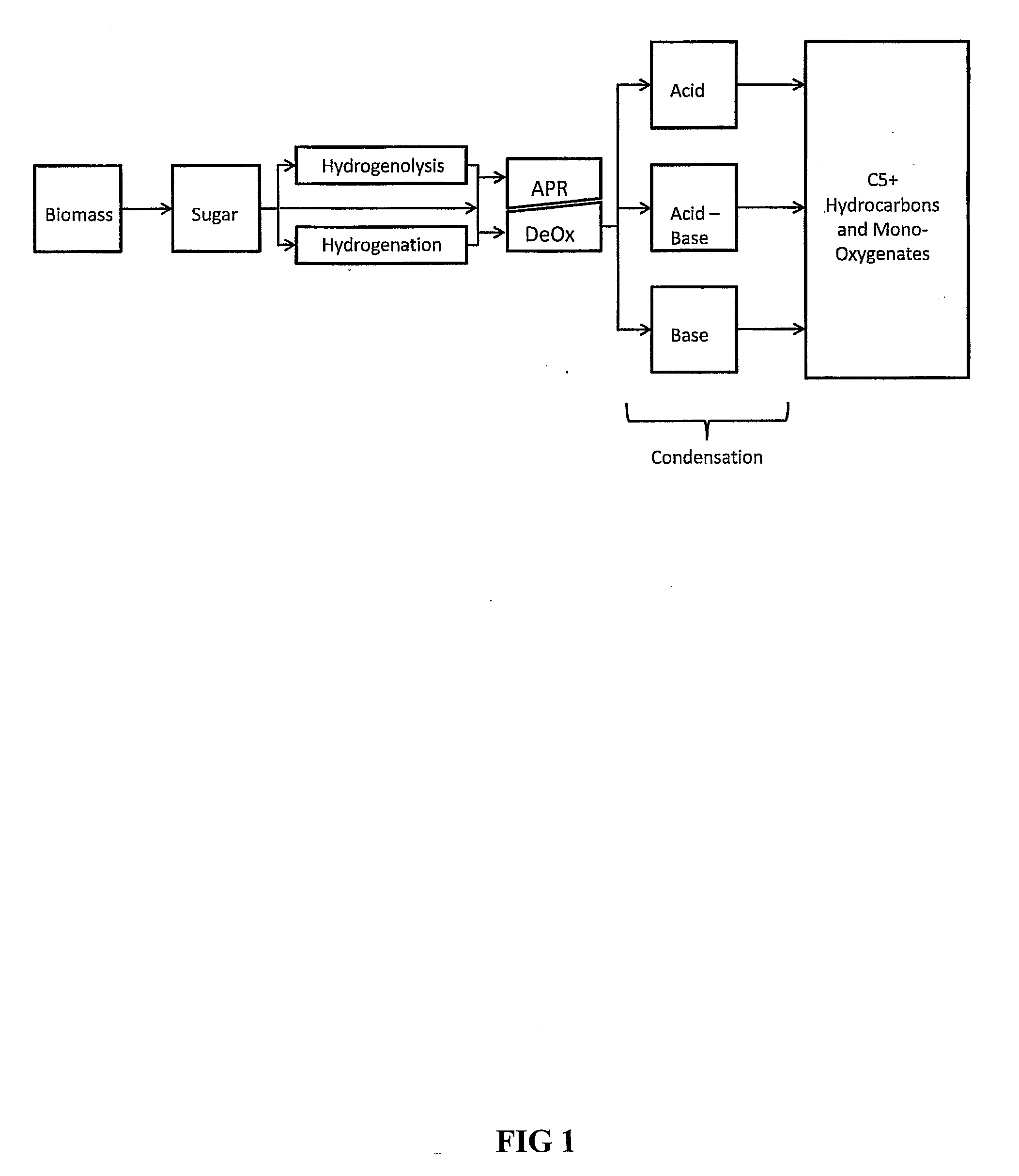
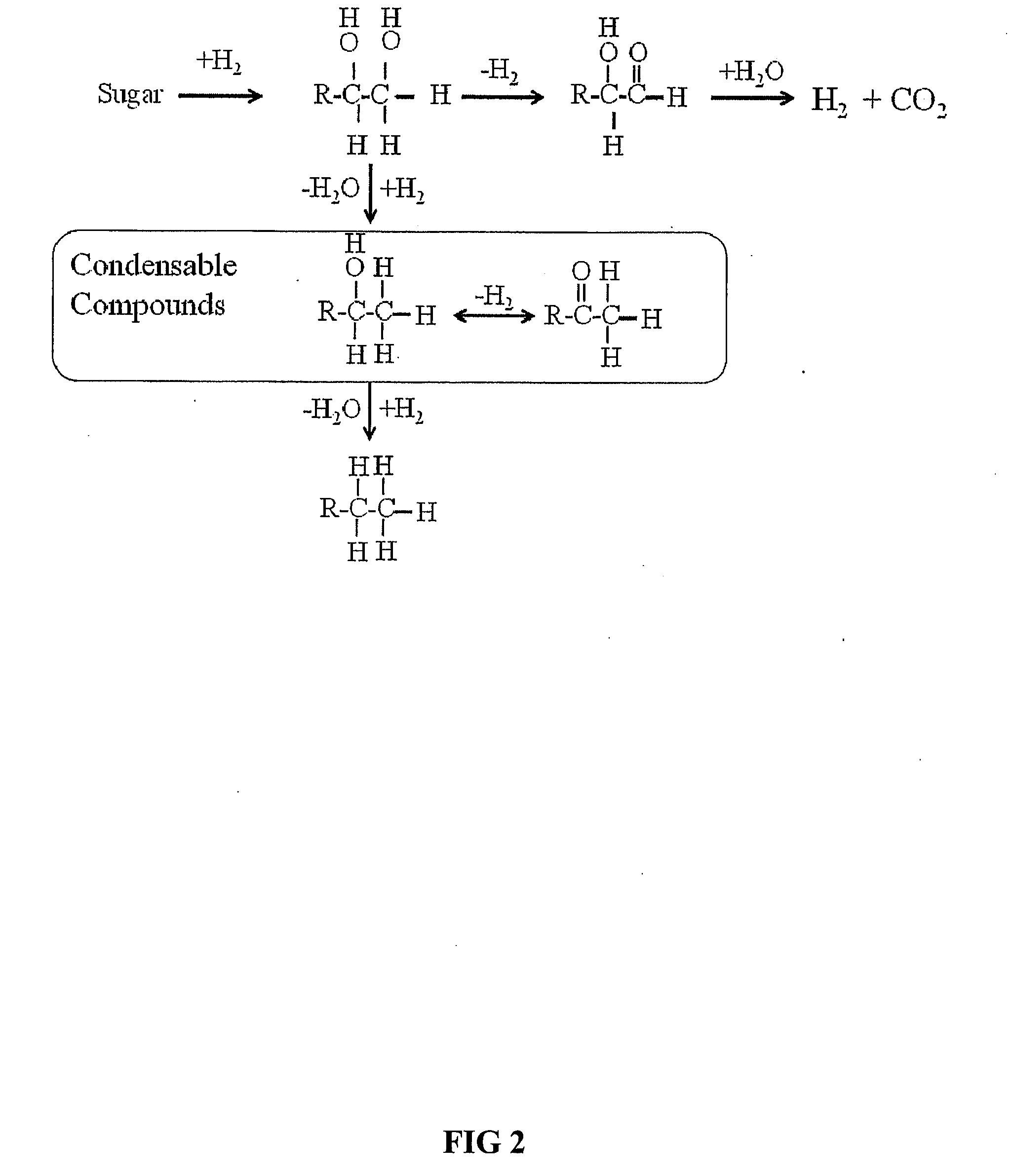
Synthesis of liquid fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300435A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFuranLiquid fuel
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Pentane compatible polyester polyols
InactiveUS6359022B1Increase valueImprove flame retardant performanceOther chemical processesPolyesterDolichol
Disclosed are aromatic polyester polyols, polyol based resin blends, and rigid closed-cell polyisocyanate-based foams made using the polyol based resin blends. The resin blends generally comprise:(a) an aromatic polyester polyol reaction product formed by inter-esterification of a phthalic acid based material; a hydroxylated material having a functionality of at least 2; and a hydrophobic material; and(b) a C4-C7 hydrocarbon blowing agent. Also disclosed is a method for preparing rigid closed-cell polyisocyanate-based foams comprising reacting a polyisocyanate and a polyol based resin blend.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
Synthesis of liqiud fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300434A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationHydrocarbon purification/separationFuranCarboxylic acid
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Polycarboxy/polyol fiberglass binder
InactiveUS7067579B2Excellent recovery and rigidity propertyMany solutionsNon-fibrous pulp additionNon-woven fabricsGlass fiberPolyol
Provided is a novel fiberglass binder comprising a polycarboxy polymer and a polyol. The amount of polycarboxy polymer and polyol contained in the binder is such that the ratio of equivalents of hydroxyl groups to carboxy groups is preferably in the range from from about 0.6 / 1 to 0.8 / 1. It is further preferred that the molecular weight of the polycarboxy polymer is less than 10,000, and more preferably less than 5000.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Polyoxyalkylene polyols, derivatives thereof, and process for producing the polyoxyalkylene polyols
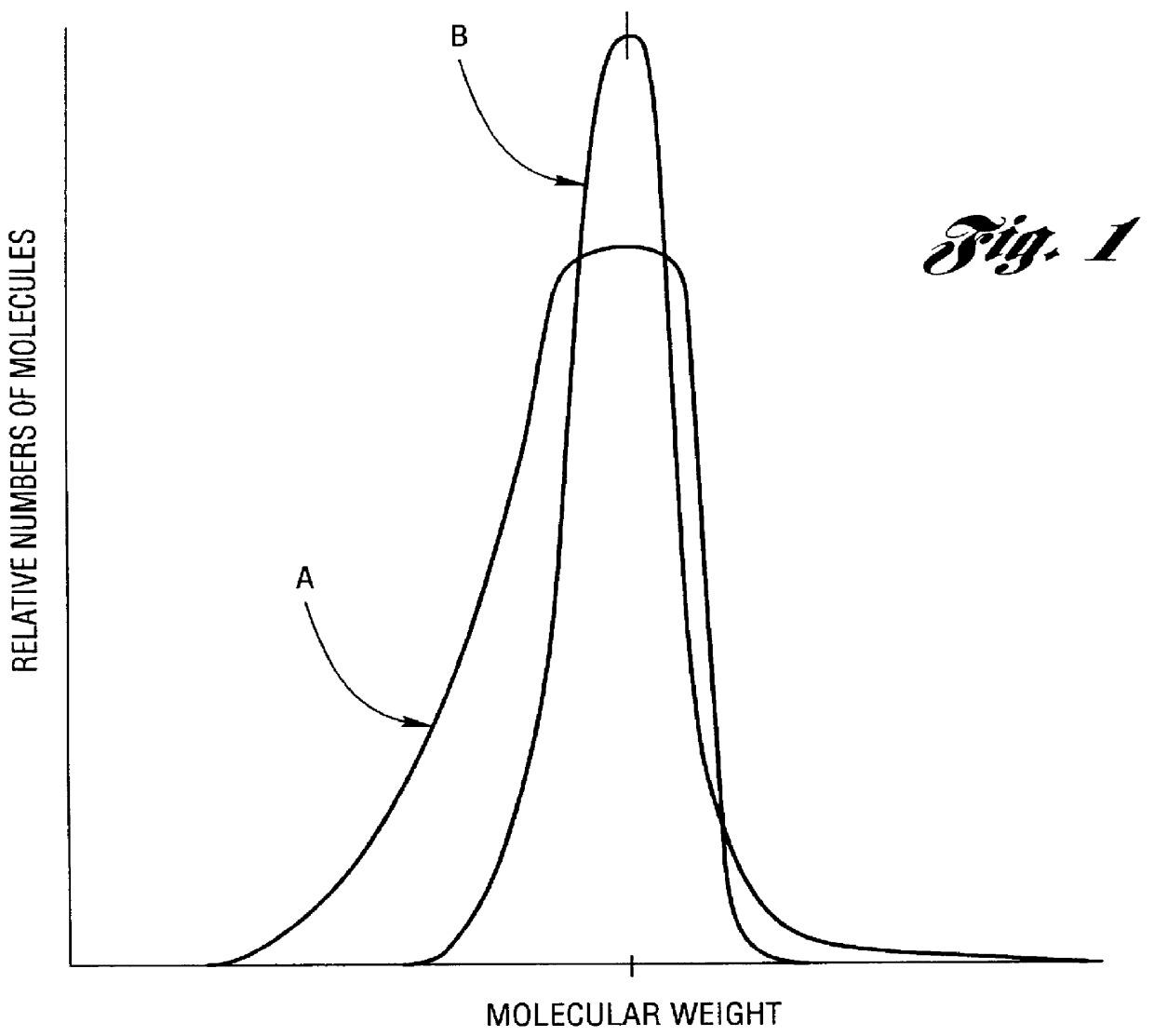
The present invention is a polyoxyalkylene polyol, its manufacture method, and derivatives, wherein: it is obtained using a phosphazenium compound as a catalyst; the hydroxyl value is 2~200 mgKOH / g; total degree of unsaturation is 0.0001~0.07 meq. / g; the head-to-tail bond selectivity of the polyoxyalkylene polyol is 95 mole %; and when the maximum height of the peak of GPC elution curve is set to be 100%, W20 is defined as the peak width at the 20% peak height, and W80 is defined as the peak width at 80% peak height, the ratio of W20 / W80 is 1.5 or greater, and less than 3.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM & SKC POLYURETHANES INC
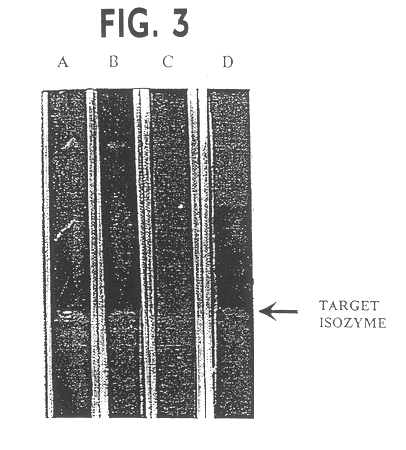
Isozyme of autoclavable superoxide dismutase (SOD), a process for the identification and extraction of the SOD in cosmetic, food and pharmaceutical compositions
The invention relates to a novel purified isozyme of an autoclavable superoxide dismutase extracted from the plant Potentilla atrosanguinea Lodd. Var. orgyrophylla, said isozyme having the following characteristics, O2- scavenging activity remains same before and after autoclaving; scavenges O2- from sub-zero temperature of -20° C. to high temperature of +80° C.; O2- scavenging activity at 25° C. for 30 days without adding any stabilizing agent such as polyols or sugars; O2- scavenging activity in the presence of saline (0.9% sodium chloride) to 61.8% of the control (without 0.9% sodium chloride), stable at 4° C. for at least 8 months; contamination free and infection free from any living micro- and / or macro-organism after autoclaving; possesses temperature optima at 0° C.; possesses a molecular weight of 33 kD under non-denaturating conditions; possesses a molecular weight of 36 kD under denaturating conditions; has clear peaks in UV range at 268 and 275 nm; has an enzyme turnover number of 19.53x104% per nmol per min at 0° C.; and requires Cu / Zn as a co-factor, method for the preparation of the purified isozyme of autoclavable superoxide dismutase and formulations containing the said autoclavable superoxide dismutase.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
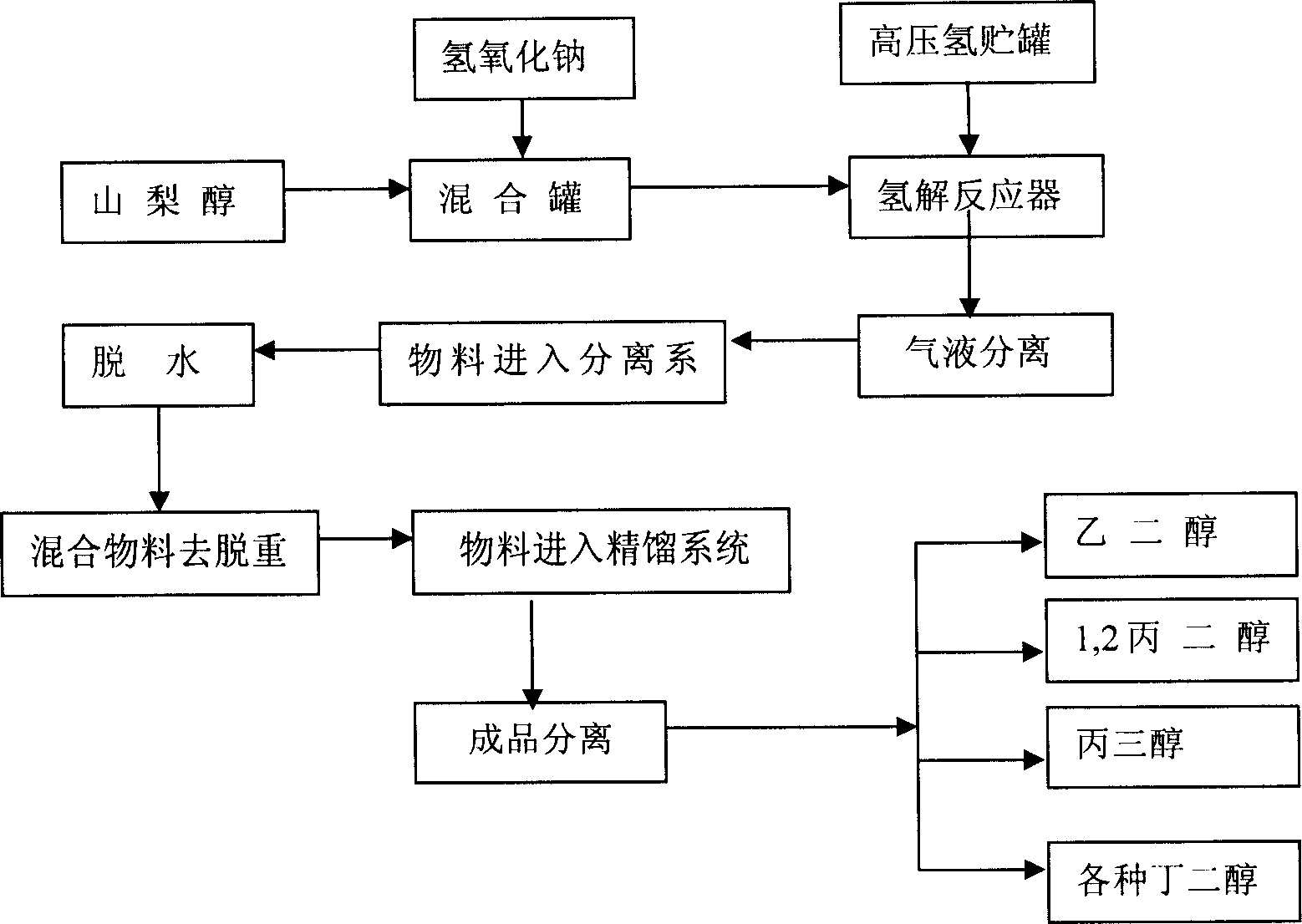
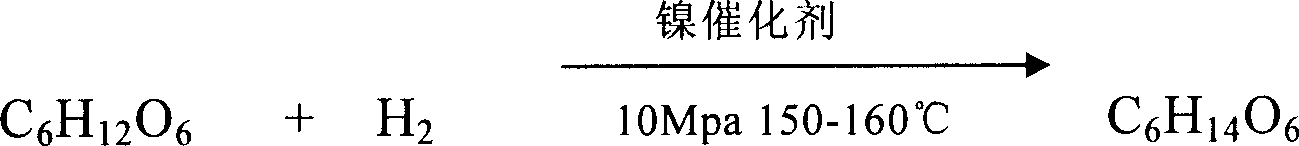
Process for producing diatomic alcohol and polyol from cracking sorbierite
InactiveCN1683293AQuality improvementIncreased production flexibilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPolyolAlcohol
The present invention relates to sorbierite cracking process to prepare C2-C4 diatomic alcohol and polyol, and is especially the process of preparing sorbierite with corn material and hydrocracking sorbierite to prepare C2-C4 diatomic alcohol and polyol. The process includes hydrocracking sorbierite to prepare the mixture of C2-C4 diatomic alcohol and polyol at high temperature and high pressure in the presence of cracking sodium hydroxide and nickel / ruthenium catalyst, separation and refining to obtain single product. The production process of the present invention has the advantages of novel production path, unique technological condition, simultaneous production of several kinds of alcohol and high product quality. In addition, using grains, such as corn, as material to replace non-regenerable resource is significant.
Owner:王宗国
Polyamide polyols and polyurethanes, methods for making and using, and products made therefrom
InactiveUS20080223519A1Polyureas/polyurethane adhesivesOrganic non-macromolecular adhesivePolyolPolyamide
A polyamide diol is prepared by the reaction of a diamine comprising a polymeric diamine and a non-polymeric diamine, dicarboxyic acid, and a hydroxy substituted carboxylic acid. A polyurethane is prepared by the reaction of the polyamide polyol with a diisocyanate.
Owner:ARIZONA CHEM CO
Process for the production of five-membered or six-membered cyclic ethers, in particular of anhydropolyols
InactiveUS6013812AImprove stabilityCost of processSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationPolyolCyclic ether
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
InactiveUS20050239179A1Promote recoveryProduct can be usedBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
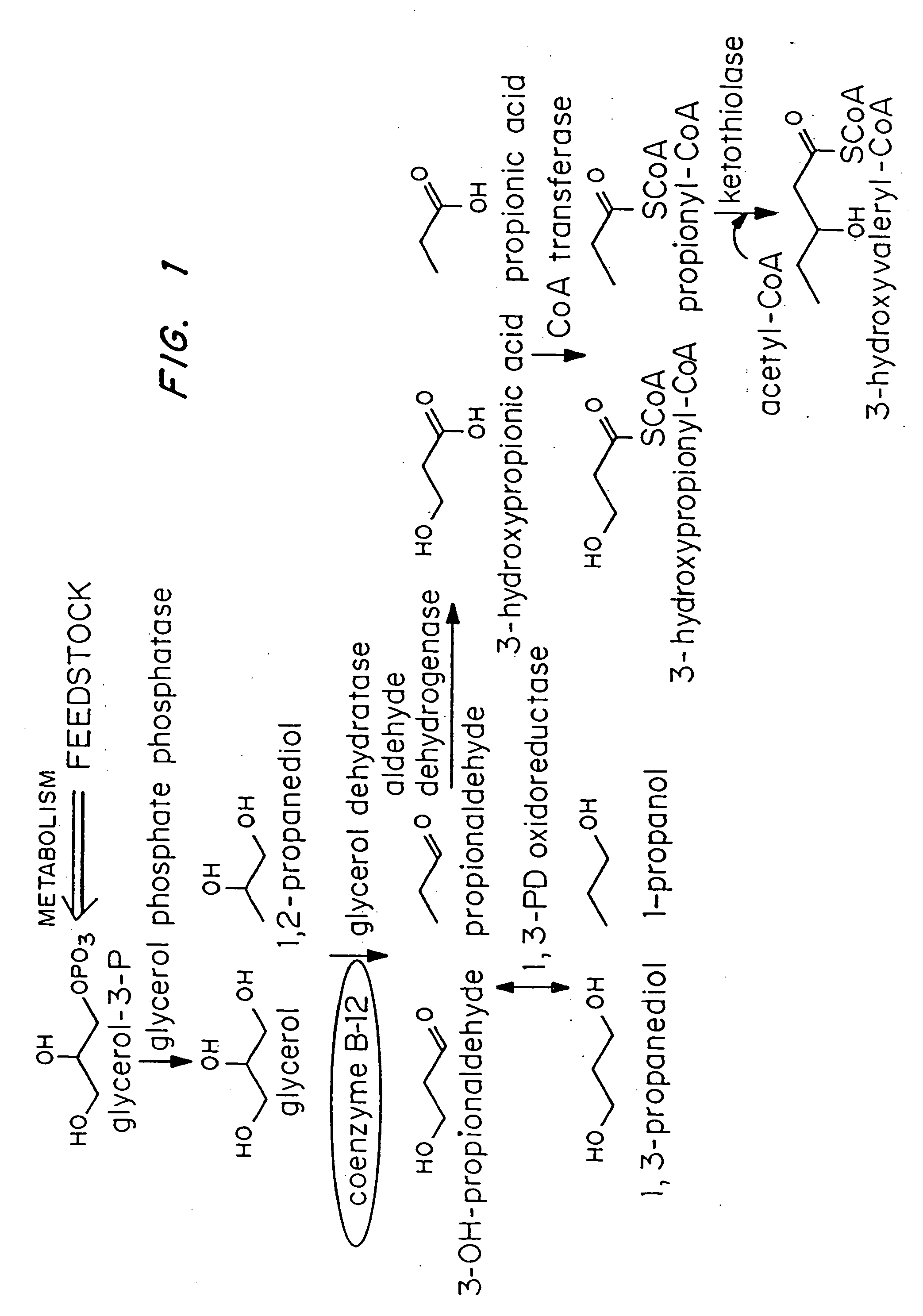
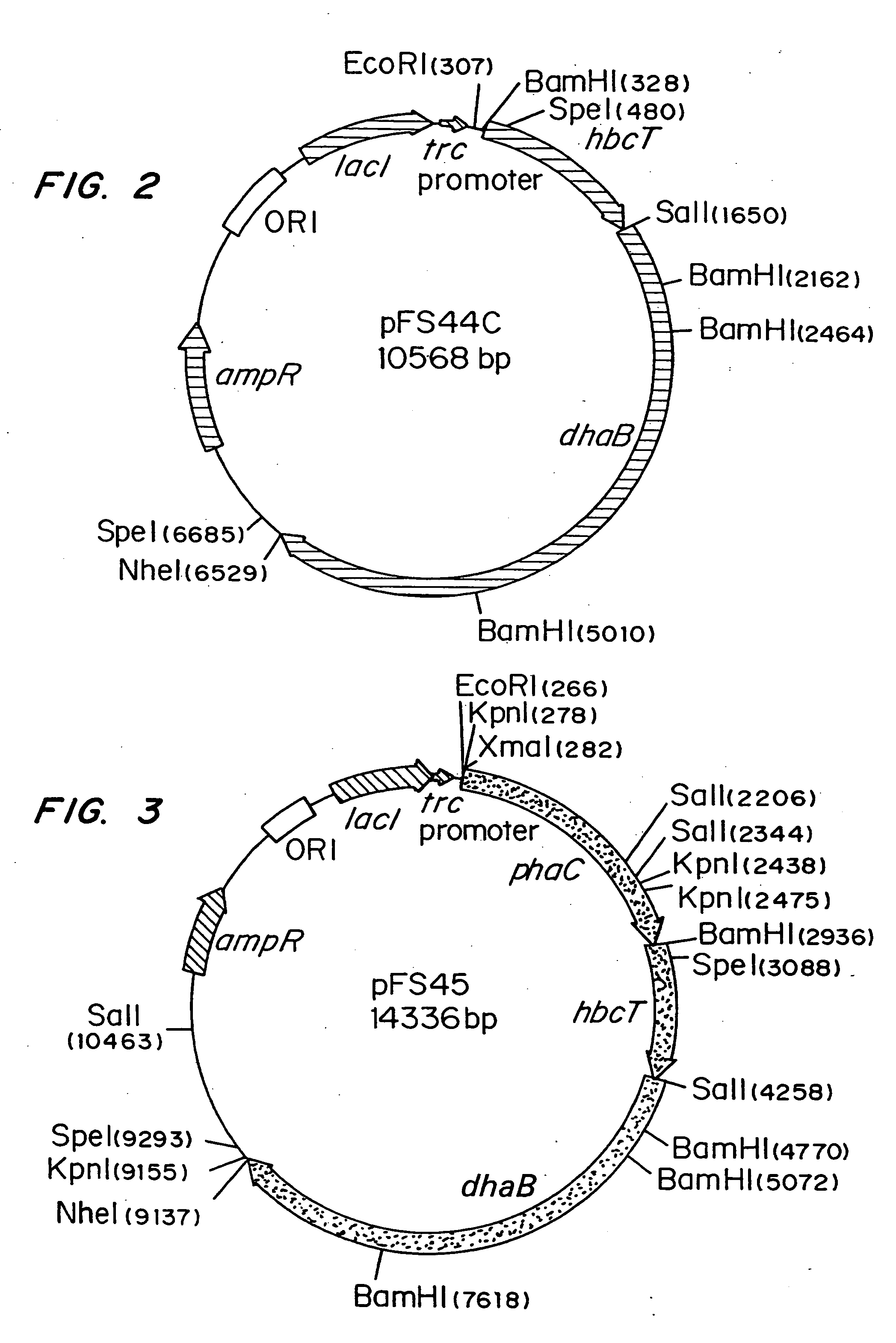
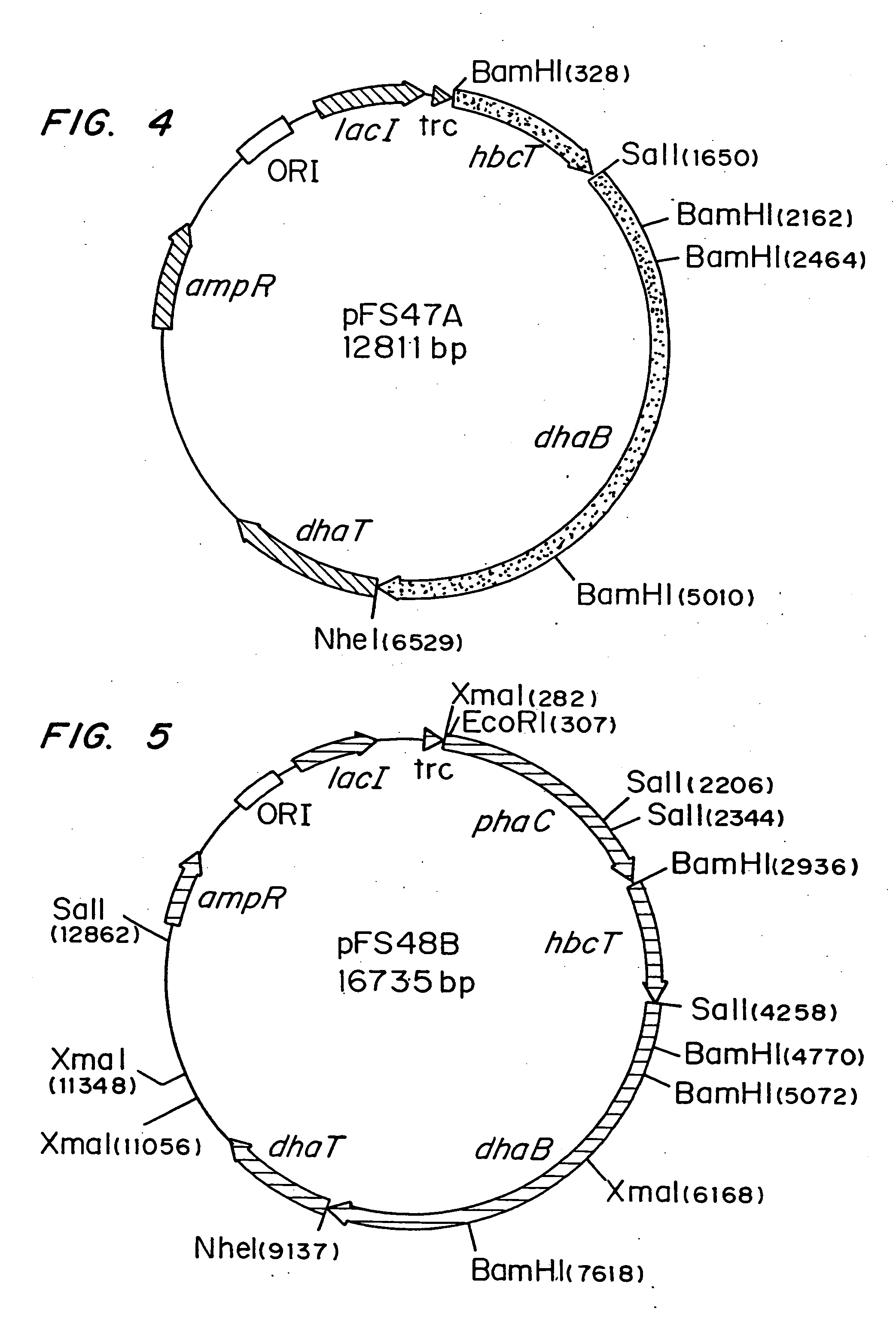
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalreate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for preparing ethanediol from polyhydroxy compounds
ActiveCN101735014ARaw material resources are renewableMeet the requirements of sustainable developmentOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogen pressureCobalt
The invention provides a method for preparing ethanediol from polyhydroxy compounds comprising starch, hemicellulose, cane sugar, glucose, fructose and fructosan. The method comprises the following steps of: taking the polyhydroxy compounds as reaction raw materials, and taking metals, carbides, nitrides, and phosphides of transition metals in families VIII, IX and X, such as ferrum, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, iridium, platinum, molybdenum and tungsten as catalytic active components to form a polymetallic catalyst; and performing further catalytic conversion under a hydrothermal condition that the temperature is 120 to 300 DEG C and the hydrogen pressure is 1 to 13 MPa to prepare the ethanediol from the polyhydroxy compounds with high efficiency, high selectivity and high yield. The method for preparing the ethanediol from the polyhydroxy compounds has the outstanding advantages of renewable raw materials, environment-friendly reaction process, and atom economical efficiency. Simultaneously, compared with other techniques taking biomasses as the raw materials, the method has the advantages of simple process and high yield.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stable high protein concentration formulations of human Anti-tnf-alpha-antibodies
InactiveUS20140141007A1High concentrationIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationPolyol
The invention provides a liquid pharmaceutical formulation which does not include NaCl and comprises more than 20 mg of a polyol and at least about 100 mg / mL of a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof. The invention provides a high concentration antibody formulation having long-term stability and advantageous characteristics for subcutaneous administration.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC +1
Preparing method of poly (carbonic ester-ether) polyalcohol
ActiveCN102617844AIncreased content of carbonate unitsSuppression of continuous insertionCyanidePolyol
The invention discloses a preparing method of poly (carbonic ester-ether) polyalcohol. Rare-earth doped bi-metal cyanides based on Zn3[Co(CN)6]2 serve as catalysts, carboxylic acids serve as chain transfer agents, and carbon dioxide and epoxy compounds are performed with a copolymerization reaction to obtain the poly (carbonic ester-ether) polyalcohol. Compared with the prior art, the carboxylic acids serve as chain transfer agents, and due to the fact that the carboxylic acids are strong in coordination capability, faster in chain transfer, capable of restraining continuous inserting of epoxy monomers and free of ether structure, unit content of carbonic ester is improved, and the prepared poly (carbonic ester-ether) polyalcohol has higher carbonic ester unit content. Experimental results indicate that molecular weight of the prepared poly (carbonic ester-ether) polyalcohol is 1500g / mol-5000g / mol, molecular weight distribution is 1.11-1.50, unit content of the carbonic ester is 40%-80%, catalytic activity is larger than 1.0kg / gLn-DMC, and cyclic carbonic ester content is less than 10wt%.
Owner:南通华盛高聚物科技股份有限公司
Method for producing polyether polyol
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a polyether polyol which is little colored and has a high degree of polymerization in high yield by a dehydration-condensation of a polyol. In the present invention, a dehydration-condensation reaction is carried out in the presence of a catalyst composed of an acid and a base.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Stable polypeptide formulations
ActiveUS20080124326A1Inorganic non-active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPolyolSugar
The invention provides a formulation including a buffer having a pH less than 6.0, a divalent cation between about 5-200 mM, an excipient comprising a sugar or polyol and an effective amount of a therapeutic polypeptide. Also provided is a method of stabilizing a polypeptide. The method includes contacting a therapeutic polypeptide with a concentration of divalent cation between about 5-150 150 mM in a buffer having a pH less than 6.0 and an excipient comprising a sugar or polyol.
Owner:AMGEN INC
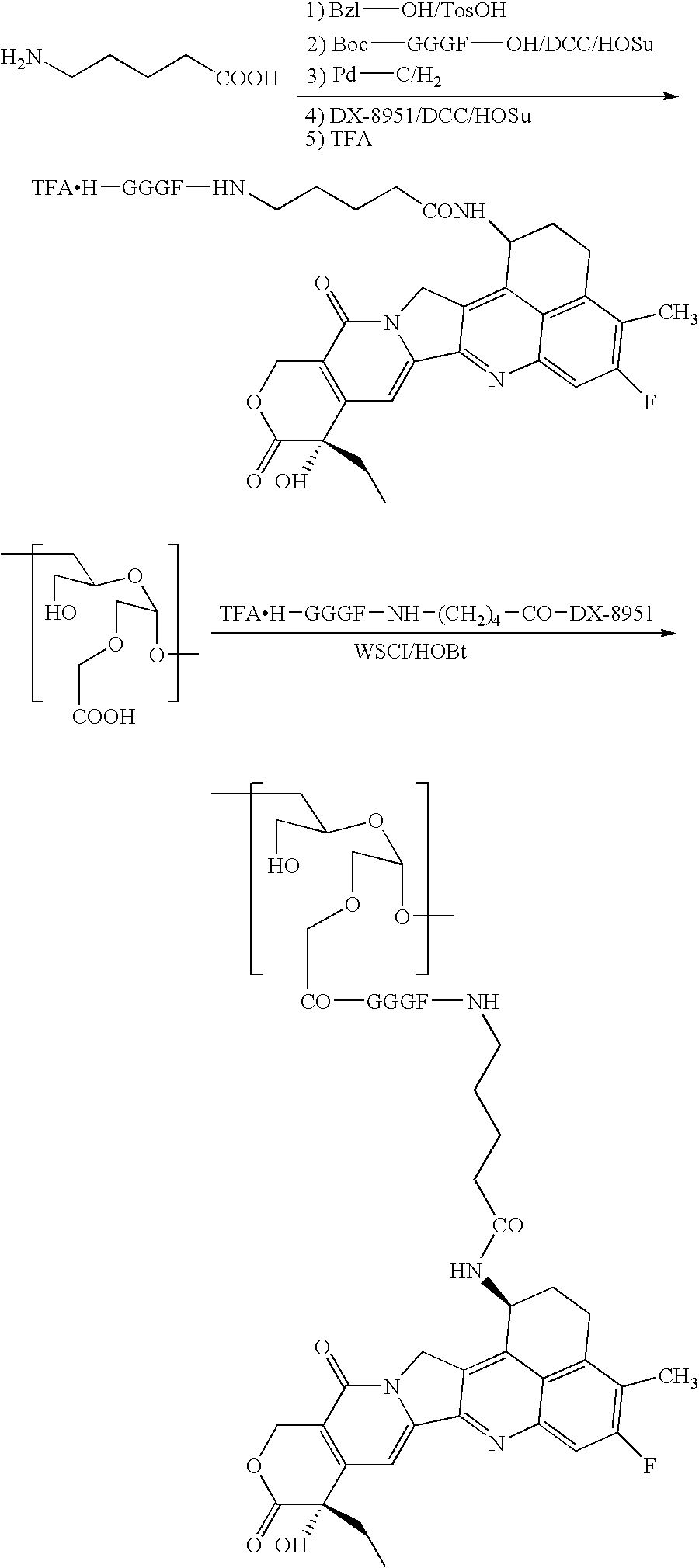
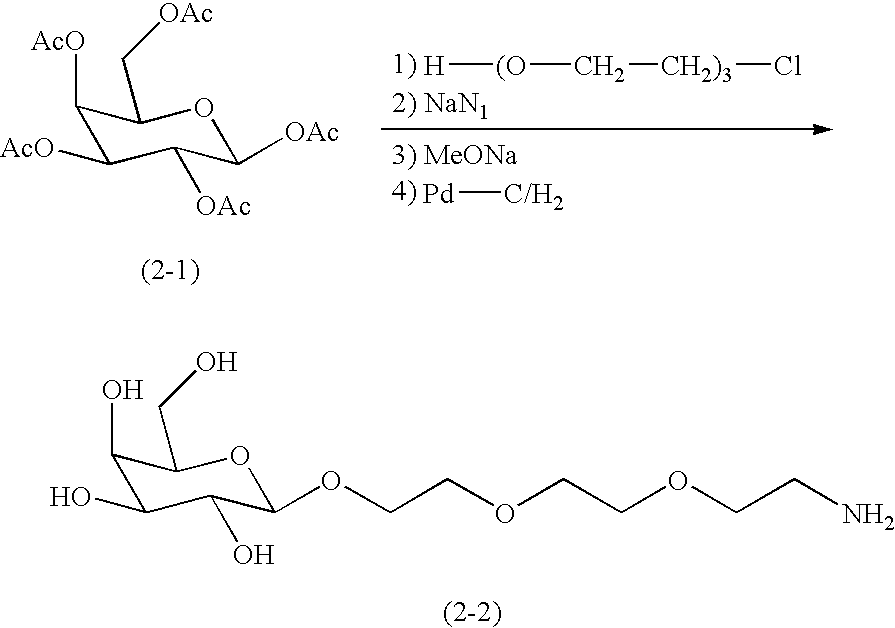
DDS compound and method for measurement thereof
InactiveUS7041818B2High organ selectivityExcellent liver selectivityBiocidePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyolHydrolysate
A DDS compound comprising a carboxy(C1-4)alkyldextran polyalcohol modified with a saccharide compound and a residue of drug compound bound to the carboxy(C1-4)alkyldextran polyalcohol, and a method for measuring a DDS compound in which a polymer carrier and a residue of drug compound are bound to each other by means of a spacer comprising 2 to 8 amino acids linked by peptide bond(s), which comprises the steps of treating the DDS compound with a peptidase, and measuring the resulting hydrolysate.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
Polyurethane Resin and a Process for the Production Thereof
InactiveUS20080281013A1Reduce the amount requiredDomestic articlesLignocellulosic moulding material treatmentHydrogenPolyol
Reduced aldehyde emissions during heated storage of a polyurethane resin are obtained by including at least one sulfurous compound selected from the group consisting of hydrogen sulfites and disulfites in the polyol component from which that polyurethane is produced. The amount of the sulfurous compound added is generally from 0.02 to 2.0 parts by weight for every 100 parts by weight of the polyol component.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Preparation of a double metal cyanide catalyst
InactiveUS6977236B2High activityIncrease the molar ratioOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSaline waterPolyol
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of a double metal cyanide (DMC) catalyst, which process involves:(a) combining an aqueous solution of metal salt with an aqueous solution of a metal cyanide salt and reacting these solutions; and(b) recovering the DMC catalyst from the reaction mixture,in which process the DMC catalyst is prepared in the presence of from 0.03 to 0.4 mole of alkaline metal compound, based on amount of metal salt. Further, the present invention relates to DMC catalyst obtainable by such process, to DMC catalyst prepared from a metal salt and a metal cyanide salt in which the molar ratio of metal derived from the metal salt to metal derived from the metal cyanide salt is at least 2.25 and to a process for polymerization of alkylene oxides which process involves reacting initiator with alkylene oxide in the presence of at most 15 ppm of DMC catalyst. It also relates to a process for the polymerization of alkylene oxides in which the resulting polyol contains less than 60 ppm of ultra-high molecular weight compounds.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Adhesive compositions containing blocked polyurethane prepolymers
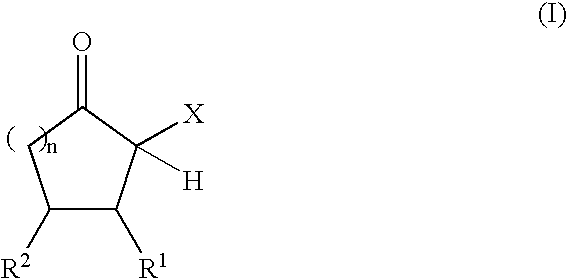
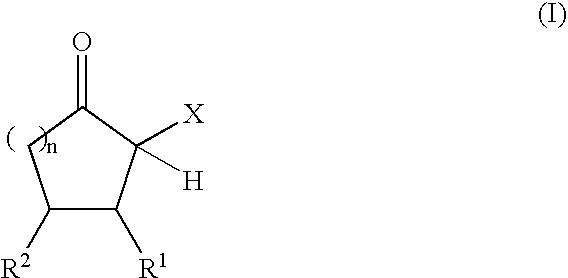
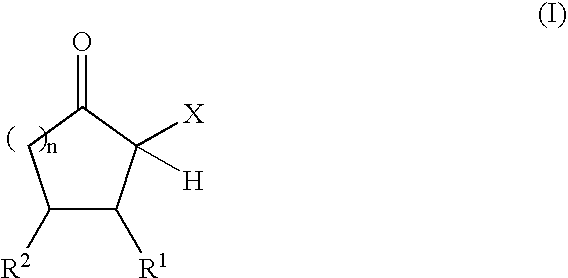
The present invention relates to reactive compositions containing A) one or more blocked polyurethane prepolymers which have a content of blocked isocyanate groups (calculated as NCO) of 0.1 to 20 wt. % and are prepared from i) at least one aromatic, aliphatic, araliphatic and / or cycloaliphatic diisocyanate having a content of free NCO groups of 5 to 60 wt. %, ii) a polyol component containing at least one polyester polyol, and / or at least one polyether polyol and / or at least one polycarbonate polyol, iii) CH-acidic cyclic ketones corresponding to formula (I) as blocking agents wherein X represents an electron-attracting group, R1 and R2 independently of one another represent the radicals H, C1-C20 (cyclo)alkyl, C6-C24 aryl, C1-C20 (cyclo)alkyl ester or amide, C6-C24 aryl ester or amide, mixed aliphatic / aromatic radicals with 1 to 24 carbon atoms that can also be part of a 4- to 8-membered ring, n is an integer from 0 to 5, and B) one or more OH-functional compounds in which the OH component undergoes activation by a deposition amine component. The present invention also relates to a composite system containing two adherends bonded together with the reactive composition according to the invention.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
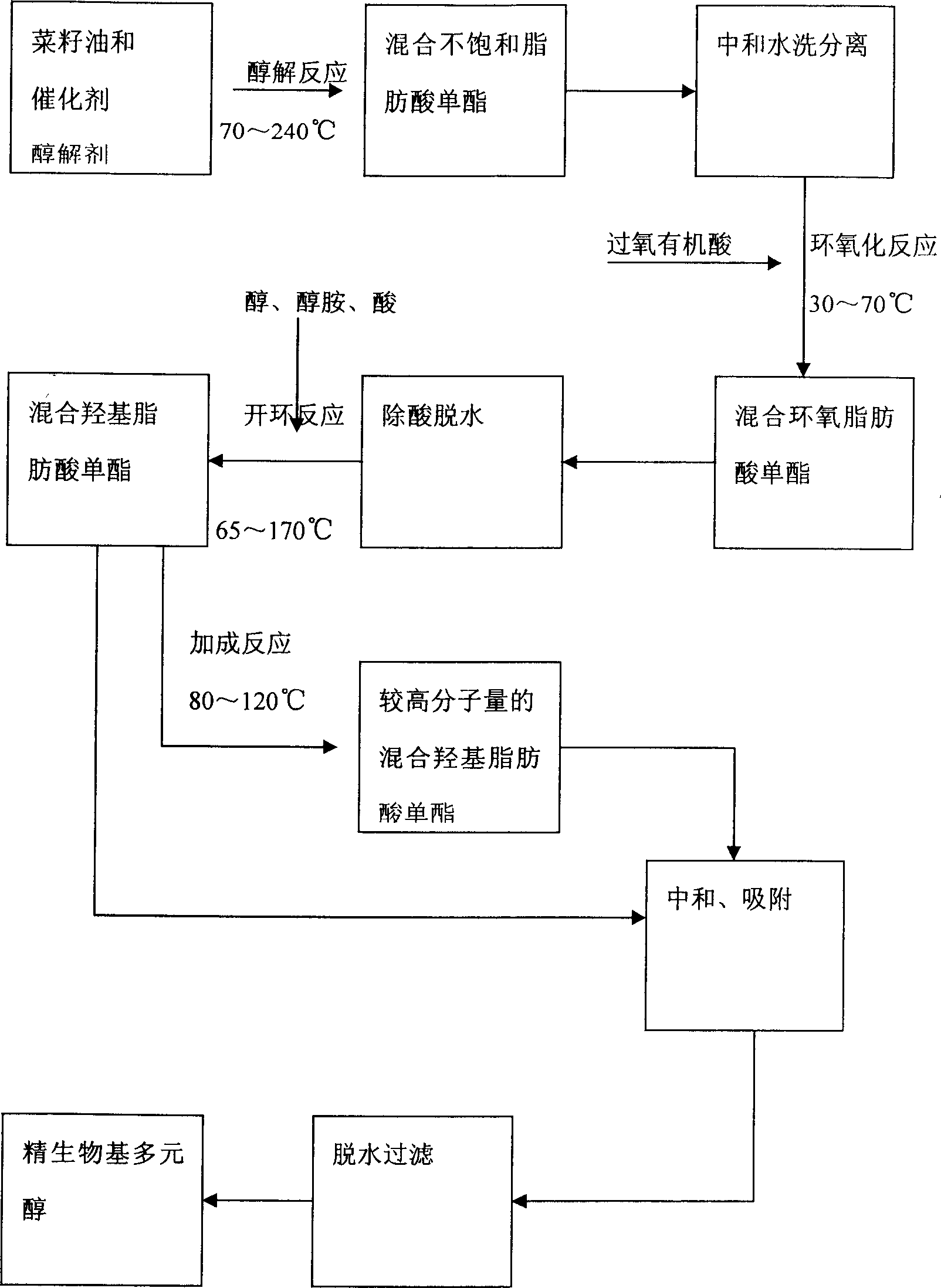
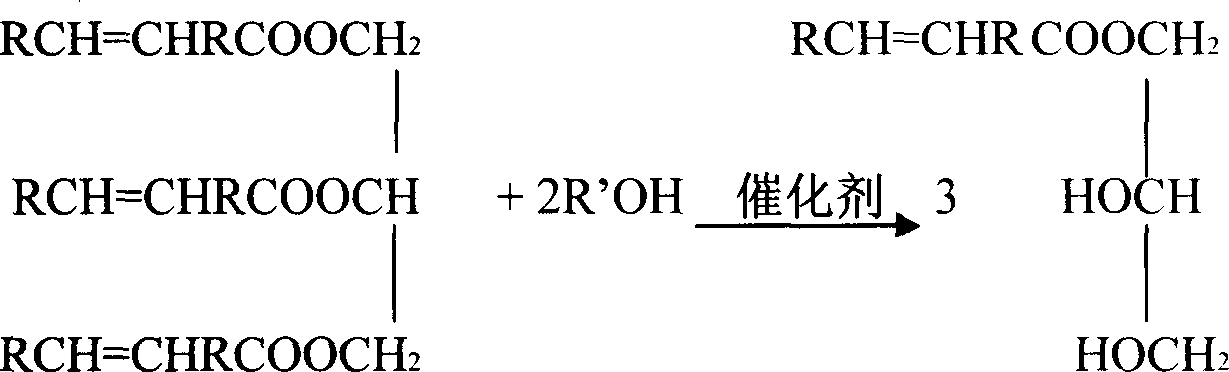
Bio-based polyhydric alcohol prepared by using rape seed oil
The invention discloses a rape oil preparing biological radical polyatomic alcohol, which comprises the following steps: carrying on alcoholysis reaction with rape oil alcohol and accelerant; generating mixed unsaturated fatty acid monoesters; adding in epoxidation agent to proceed epoxidation reaction; getting mixed epoxy aliphatic acid monoesters-biological radical polyatomic alcohol. The invention has high reaction active, which is convenience to prepare high-functionality product.
Owner:HONGBAOLI GRP CO LTD
Lower alkyl ester recycling in polyol fatty acid polyester synthesis
InactiveUS6465642B1Quality improvementReduce side effectsEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesPolyesterPolyol
Process for synthesizing polyol fatty acid polyesters which includes the steps of reacting an excess of lower alkyl ester with polyol to esterify hydroxyl groups thereof and form polyol fatty acid polyester, separating at least a portion of the unreacted lower alkyl ester from the polyol fatty acid polyester, and recycling the separated unreacted lower alkyl ester for further reaction with polyol or partially esterified polyol. The recycled lower alkyl ester is substantially free of lower alkyl ester degradation reaction products, such as carbonyls and free fatty acids.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Polymerized thylene carbonate urethane elastomer and its preparation method
ActiveCN1865311AMolecular chain softRoom temperature and good flexibilityCross-linkMedical equipment
The invention discloses a polyethylene carbonate polyurethane elastomer and making method, which produces polycarbonate polyhydric alcohol through carbon dioxide and oxirane with 20-60 percent diisocyanate, 0.05-2 percent polymerization inhibitor, 2.4-17 percent chain-extending agent and or cross linking agent and 0-0.4 percent catalyst. The method possesses better mechanic property, plasticity, anti-oxidizing property and water weakened-durability, which can be applied in the liner, screen, sealing ring and medical equipments.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGKE JINLONG CHEM
Polyurethane foams made with vegetable oil hydroxylate, polymer polyol and aliphatic polyhydroxy alcohol
The present invention provides polyurethane foams made from a polyisocyanate and a polyol component containing a polymer polyol (PMPO), a vegetable oil hydroxylate and an aliphatic polyhydroxy alcohol, and optionally a non-vegetable oil-based polyol. The vegetable oil hydroxylates are environmentally-friendly, bio-based polyols. The inclusion of low amounts of a polymer polyol unexpectedly results in a foam having significantly improved tear strength. The combination of polymer polyol and aliphatic polyhydroxy alcohol provides improved foam processing while maintaining or improving tear strength of the foam.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Organosilicon modified aqueous polyurethane resin and preparation thereof
An organosilicon modified aqueous polyurethane resin comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 10 to 20 percent of isocyanate, 20 to 40 percent of polyester polyol, 0.1 to 5 percent of organic silicon oil, 2 to 5 percent of a hydrophilic chain extender, 2 to 5 percent of a polyol chain extender, 1 to 3 percent of a polybasic amine chain extender, 0.01 to 1 percent of a catalyst, 1 to 4 percent of a salifying agent, 5 to 8 percent of a solvent and the rest of water. The emulsion made by the organosilicon modified aqueous polyurethane resin is obviously better than the emulsion made by a non-modified aqueous polyurethane resin regarding adhesion force, abrasion resistance, heat tolerance, smoothness, etc. The polyurethane emulsion made by the organosilicon modified aqueous polyurethane resin can be applied to the surface of a product through spray coating, brush coating, roller coating and dip coating. At present, the polyurethane emulsion is mainly used for the coating of the surfaces of gloves, condoms, medical ducts, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG INOV POLYURETHANE
Polyglycerol based polyols and polyurethanes and methods for producing polyols and polyurethanes
InactiveUS20090082483A1Function increaseImprove performanceFatty acid esterificationOrganic compound preparationVegetable oilPolyol
A new class of polyols derived from renewable resources, including polyglycerol and vegetable oils, the use of such polyols in polyurethane foams and cast resins, and methods for making the polyols and polyurethanes are provided.
Owner:PITTSBURG STATE UNIVERSITY
Mannich polyols for rigid spray foams
Provided herein are polyurethane foams which may be prepared by spray techniques. The foams of the invention are prepared using conventional isocyanates and a novel Mannich condensate polyol having a hydroxy number in the range of 250-340 and a viscosity of 3500 cps or less, and wherein the Mannich condensate polyol is derived from nonylphenol, formaldehyde, an alkanolamine, and propylene oxide as the sole alkoxylating agent. Polyurethane foams prepared according to the invention possess superior physical properties over sprayed polyurethane foams prepared using Mannich condensate polyols which are made using mixtures of propylene oxide and ethylene oxide.
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC
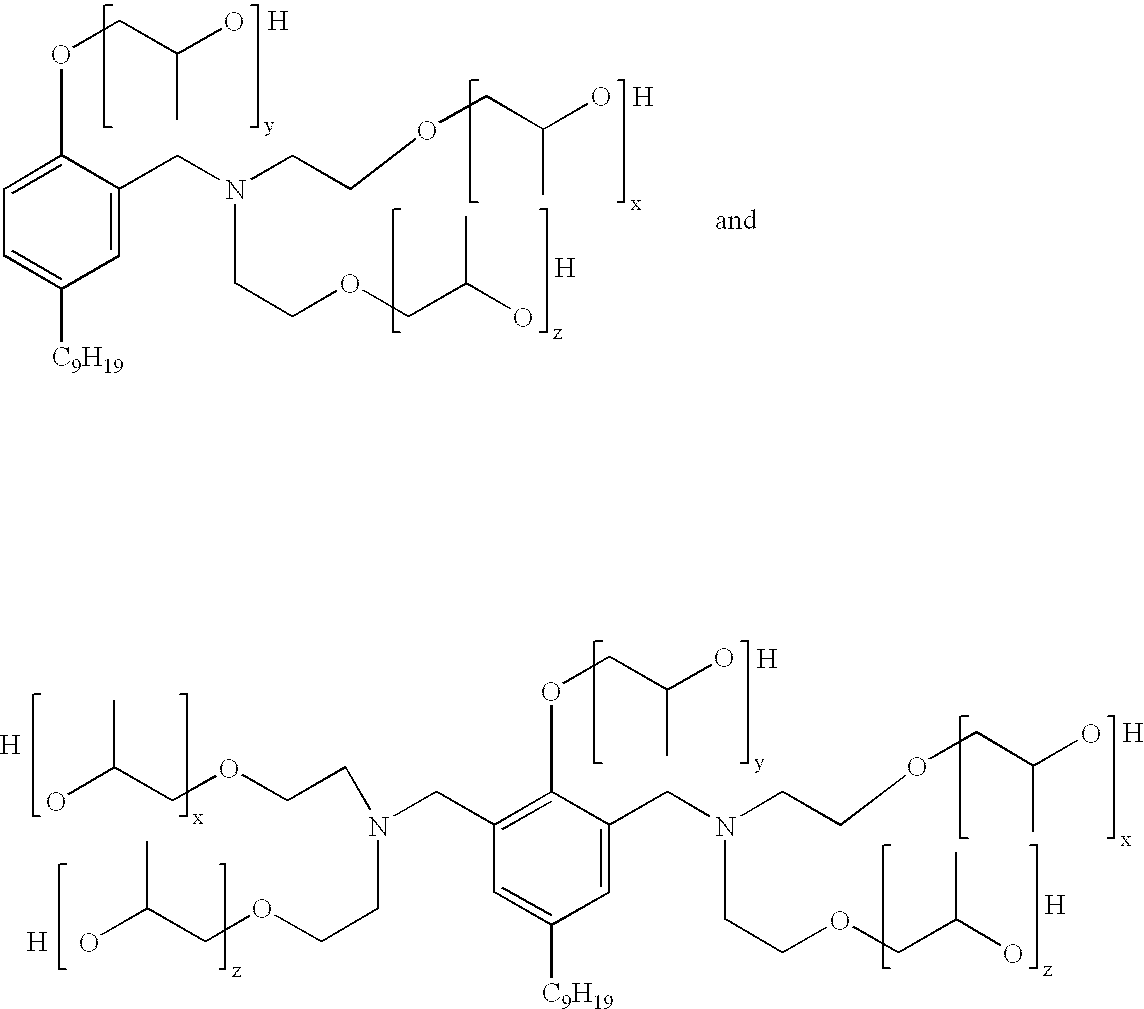
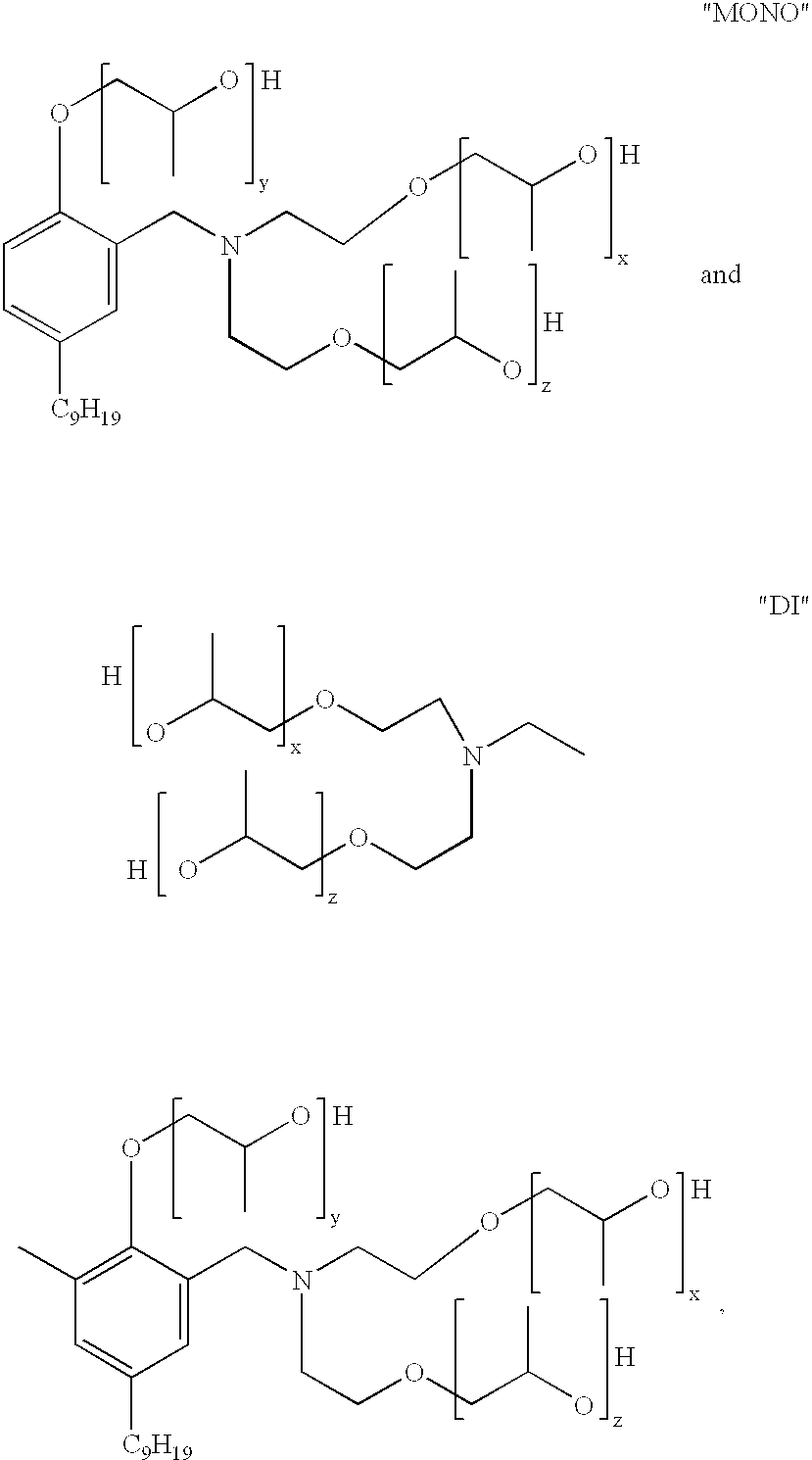
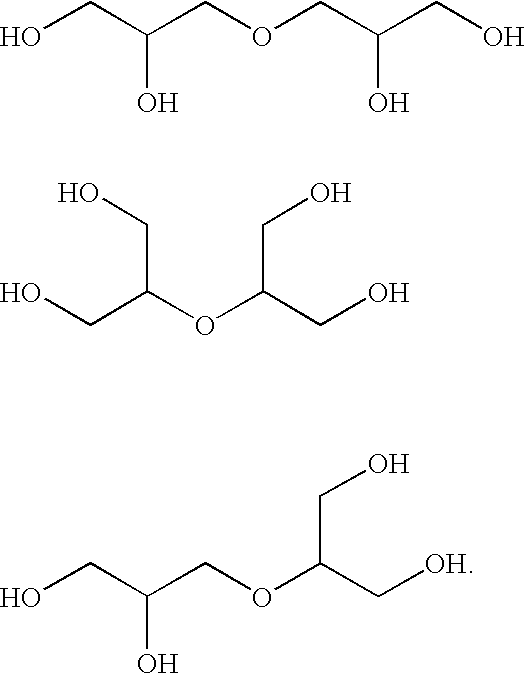
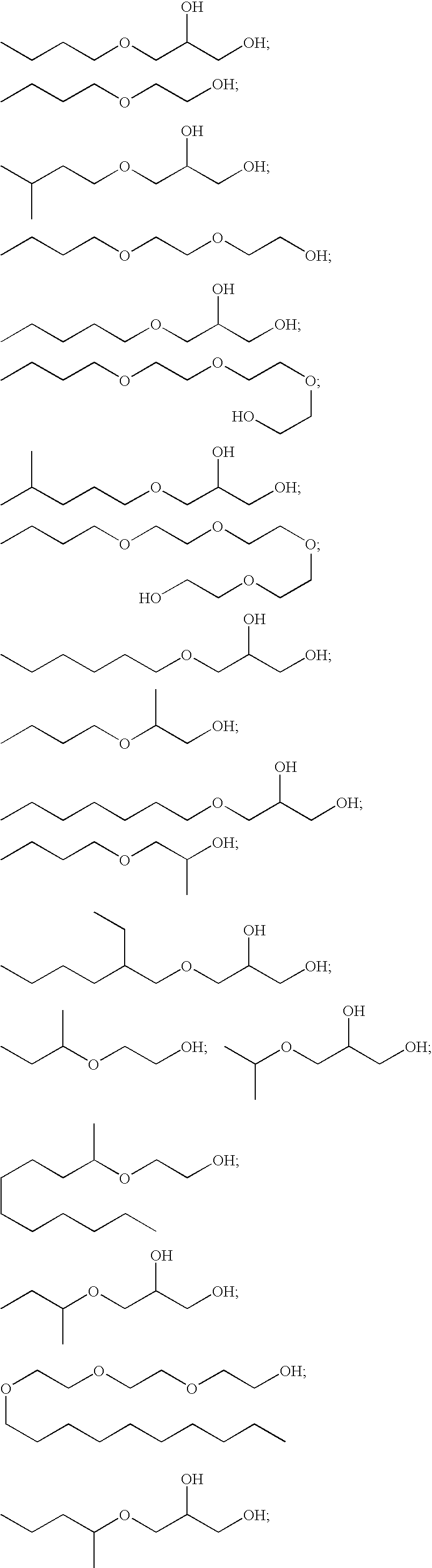
Polyol ethers and process for making them
ActiveUS20100048940A1High selectivityImprove reaction speedOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolyolHydrogen
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Novel polyether polyols based on cashew nutshell liquid, a process for the production of these polyether polyols, flexible foams produced from these polyether polyols, and a process for the production of these foams
This invention relates to novel polyether polyols which are prepared by alkoxylation of renewable resource materials, and particularly cashew nutshell liquid (CNSL), and to a process for the preparation of these novel polyether polyols. This invention also relates to flexible polyurethane foams prepared from these long chain polyether polyols, and to a process for the production of these flexible polyurethane foams.
Owner:COVESTRO LLC
Methods for preparing ethylene glycol from polyhydroxy compounds
ActiveUS20120172633A1High yieldHigh selectivityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrogen pressureHeteropoly acid
This invention provides methods for producing ethylene glycol from polyhydroxy compounds such as cellulose, starch, hemicellulose, glucose, sucrose, fructose, fructan, xylose and soluble xylooligosaccharides. The methods uses polyhydroxy compounds as the reactant, a composite catalyst having active components comprising one or more transition metals of Groups 8, 9, or 10, including iron, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, iridium, and platinum, as well as tungsten oxide, tungsten sulfide, tungsten hydroxide, tungsten chloride, tungsten bronze oxide, tungsten acid, tungstate, metatungstate acid, metatungstate, paratungstate acid, paratungstate, peroxotungstic acid, pertungstate, heteropoly acid containing tungsten. Reacting at a temperature of 120-300° C. and a hydrogen pressure of 1-13 MPa under hydrothermal conditions to accomplish one-step catalytic conversion. It realizes efficient, highly selective, high yield preparation of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol from polyhydroxy compounds. The advantage of processes disclosed in this invention include renewable raw material and high atom economy. At the same time, compared with other technologies that converts biomass raw materials into polyols, methods disclosed herein enjoy advantages including simple reaction process, high yield of targeted products, as well as easy preparation and low cost for the catalysts.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com