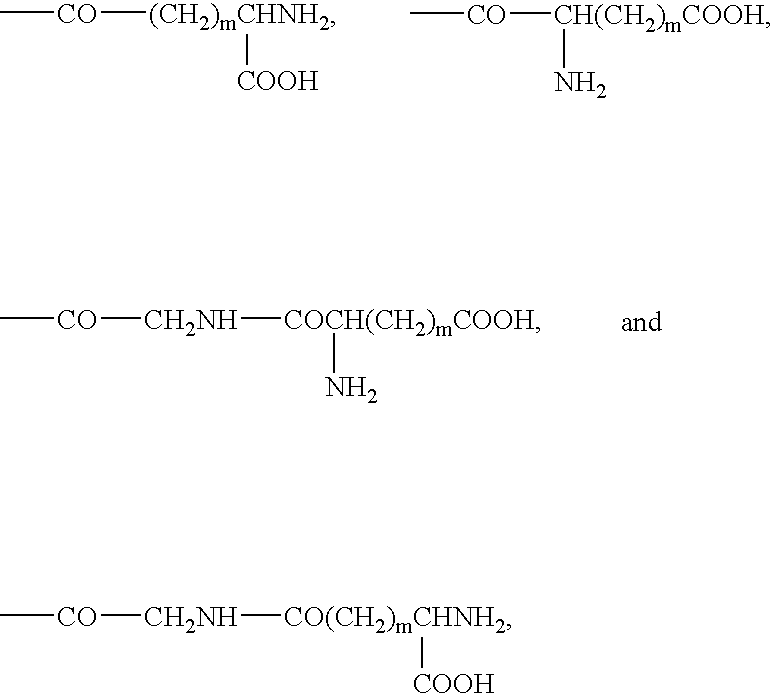Patents
Literature
215 results about "Isozyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes usually display different kinetic parameters (e.g. different KM values), or different regulatory properties. The existence of isozymes permits the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage. In biochemistry, isozymes (or isoenzymes) are isoforms (closely related variants) of enzymes. In many cases, they are coded for by homologous genes that have diverged over time. Although, strictly speaking, allozymes represent enzymes from different alleles of the same gene, and isozymes represent enzymes from different genes that process or catalyse the same reaction, the two words are usually used interchangeably.
Plants and seeds of corn variety I325350
ActiveUS7157625B1Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationIsoenzyme typingTissue culture
According to the invention, there is provided seed and plants of the corn variety designated I325350. This invention thus relates to the plants, seeds and tissue cultures of the variety I325350, and to methods for producing a corn plant produced by crossing a corn plant of variety I325350 with itself or with another corn plant, such as a plant of another variety. This invention further relates to corn seeds and plants produced by crossing plants of variety I325350 with plants of another variety, such as another inbred line, and to crosses with related species. This invention further relates to the inbred and hybrid genetic complements of plants of variety I325350, and also to the SSR and isozyme typing profiles of corn variety I325350.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
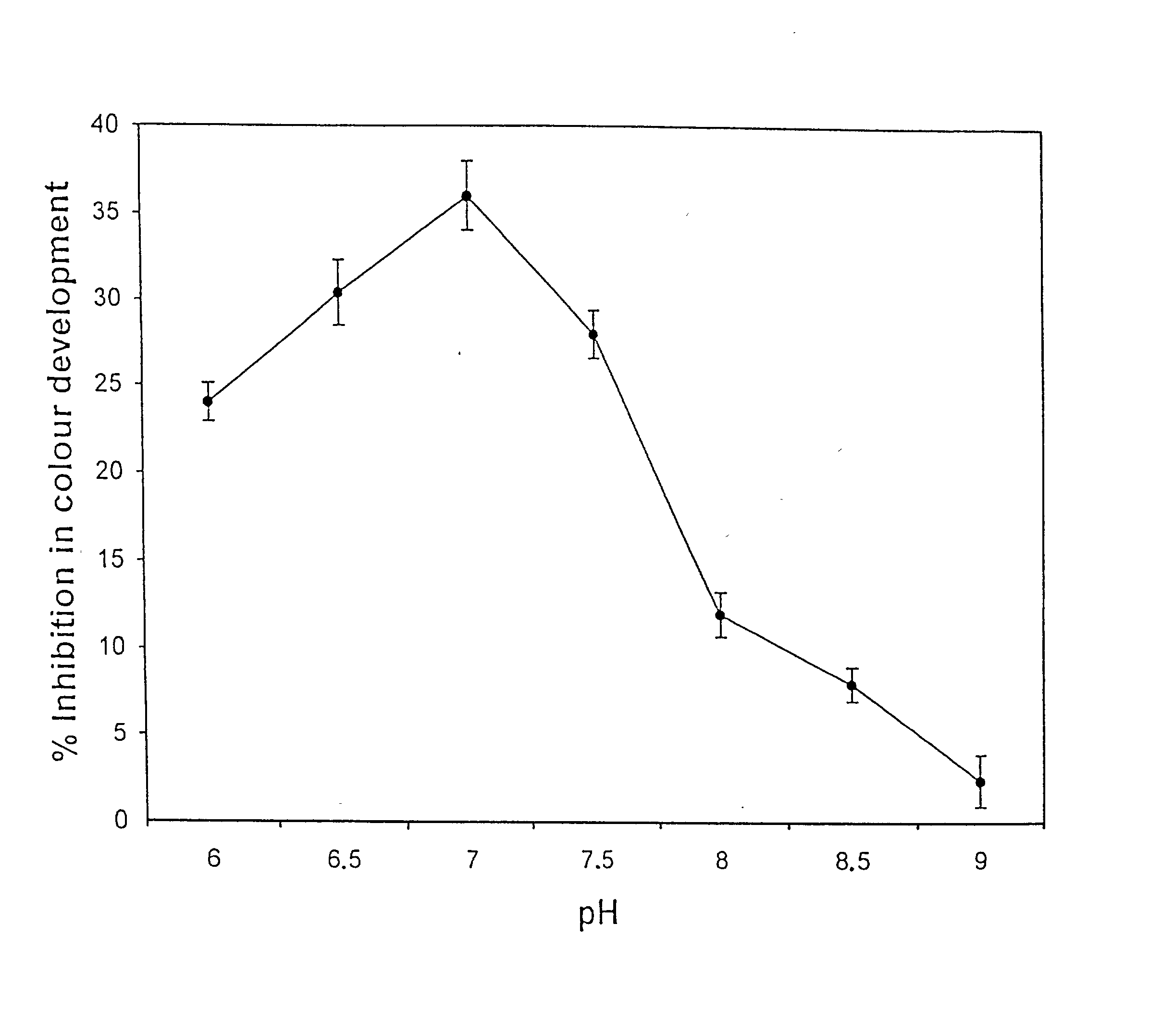
Isozyme of autoclavable superoxide dismutase (SOD), a process for the identification and extraction of the SOD in cosmetic, food and pharmaceutical compositions
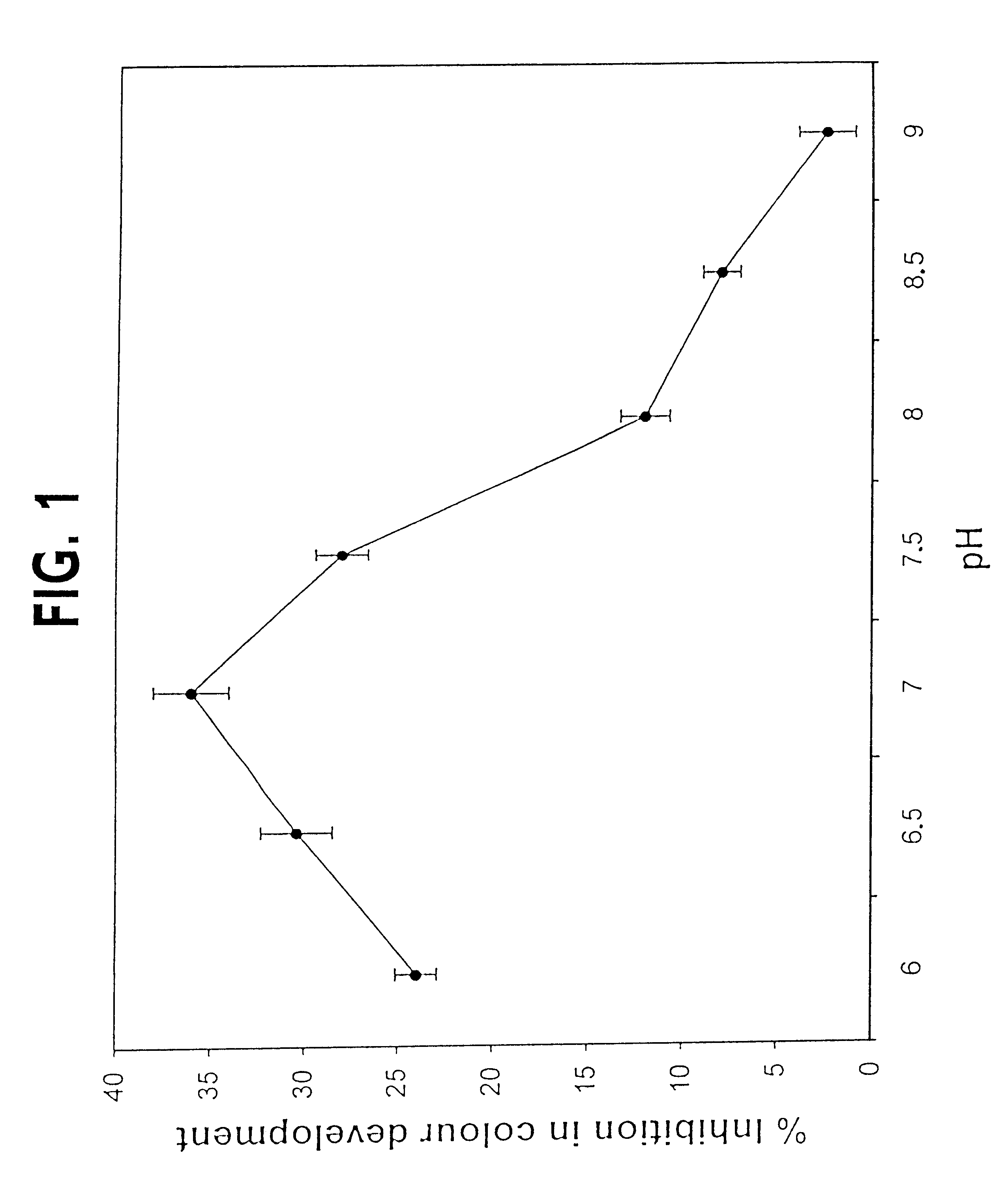
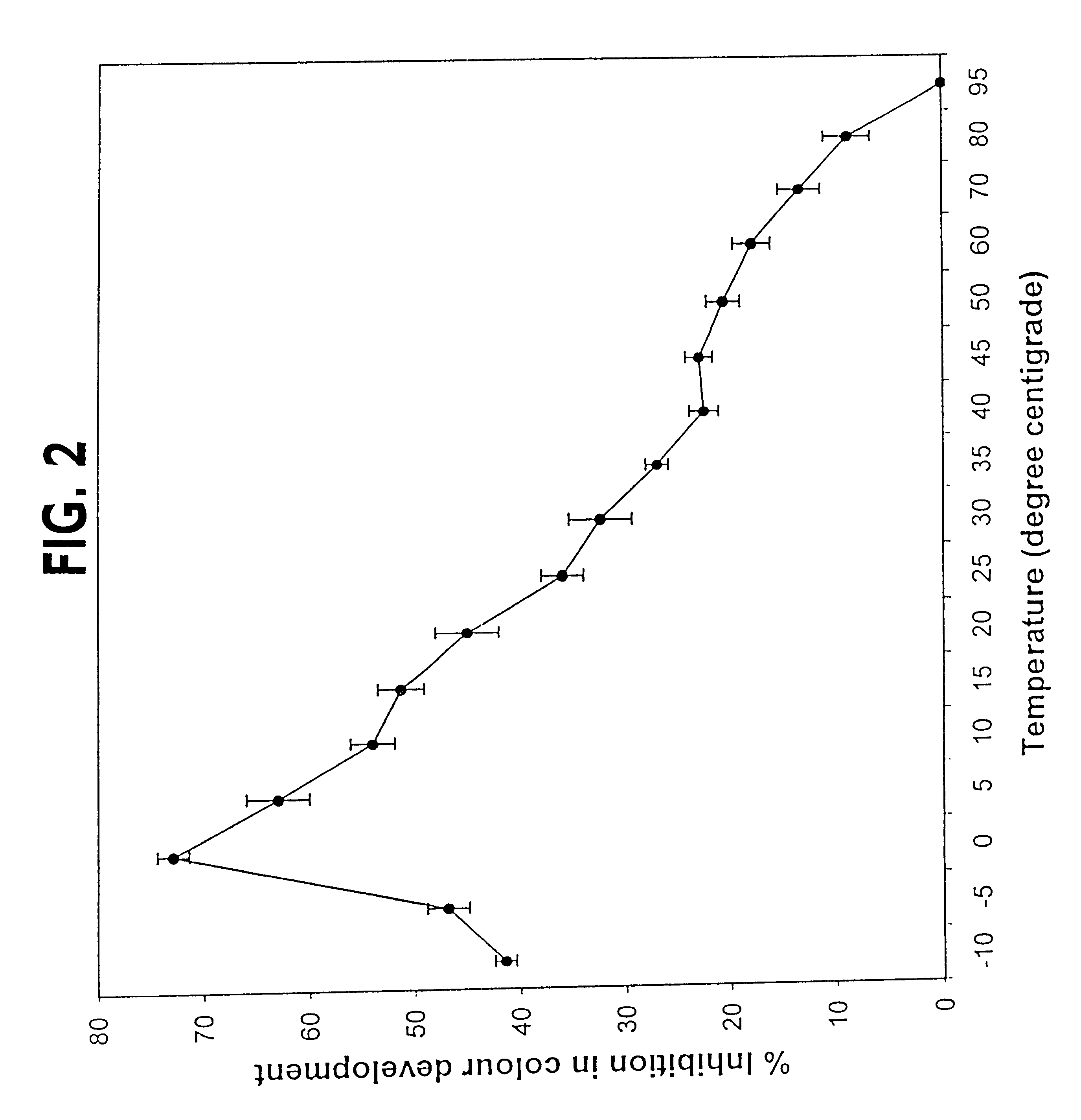
The invention relates to a novel purified isozyme of an autoclavable superoxide dismutase extracted from the plant Potentilla atrosanguinea Lodd. Var. orgyrophylla, said isozyme having the following characteristics, O2- scavenging activity remains same before and after autoclaving; scavenges O2- from sub-zero temperature of -20° C. to high temperature of +80° C.; O2- scavenging activity at 25° C. for 30 days without adding any stabilizing agent such as polyols or sugars; O2- scavenging activity in the presence of saline (0.9% sodium chloride) to 61.8% of the control (without 0.9% sodium chloride), stable at 4° C. for at least 8 months; contamination free and infection free from any living micro- and / or macro-organism after autoclaving; possesses temperature optima at 0° C.; possesses a molecular weight of 33 kD under non-denaturating conditions; possesses a molecular weight of 36 kD under denaturating conditions; has clear peaks in UV range at 268 and 275 nm; has an enzyme turnover number of 19.53x104% per nmol per min at 0° C.; and requires Cu / Zn as a co-factor, method for the preparation of the purified isozyme of autoclavable superoxide dismutase and formulations containing the said autoclavable superoxide dismutase.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
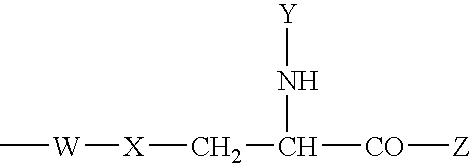
Nicotinamide acids, amides, and their mimetics active as inhibitors of PDE4 isozymes
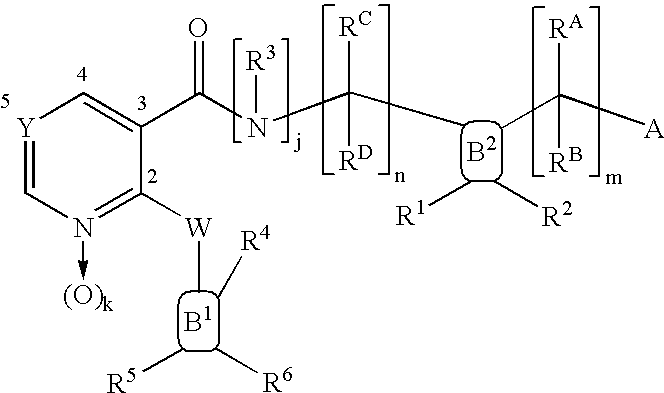
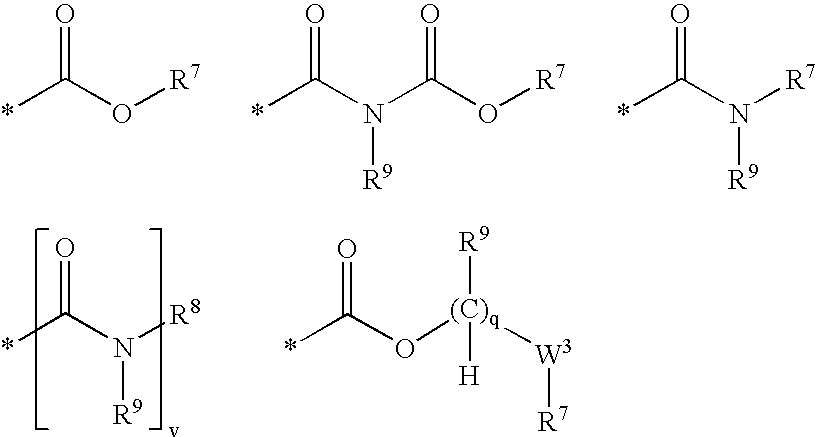
Compounds useful as inhibitors of PDE4 in the treatment of diseases regulated by the activation and degranulation of eosinophils, especially asthma, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructuive pulmonary disease, of the formula: wherein j is 0 or 1, k is 0 or 1, m is 0, 1, or 2; n is 1 or 2; A is selected from the partial Formulas: where q is 1, 2, or 3, W3 is -O-; -N(R9)-; or -OC(=O)-; R7 is selected from -H; -(C1-C6) alkyl, -(C2-C6) alkenyl, or -(C2-C6) alkynyl substituted by 0 to 3 substituents R10; -(CH2)u-(C3-C7) cycloalkyl where u is 0, 1 or 2, substituted by 0 to 3 R10; and phenyl or benzyl substituted by 0 to 3 R14; R8 is tetrazol-5-yl; 1,2,4-triazol-3-yl; 1,2,4-triazol-3-on-5-yl; 1,2,3-triazol-5-yl; imidazol-2-yl; imidazol-4-yl; imidazolidin-2-on-4-yl; 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl; 1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-on-5-yl; 1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl; 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-on-3-yl; 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl; 1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-on-5-yl; 1,2,5-thiadiazolyl; 1,3,4-thiadiazolyl; morpholinyl; parathiazinyl; oxazolyl; isoxazolyl; thiazolyl; isothiazolyl; pyrrolyl; pyrazolyl; succinimidyl; glutarimidyl; pyrrolidonyl; 2-piperidonyl; 2-pyridonyl; 4-pyridonyl; pyridazin-3-onyl; pyridyl; pyrimidinyl; pyrazinyl; pyridazinyl; indolyl; indolinyl; isoindolinyl; benzo[b]furanyl; 2,3-dihydrobenzofuranyl; 1,3-dihydroisobenzofuranyl; 2H-1-benzopyranyl; 2-H-chromenyl; chromanyl; benzothienyl; 1H-indazolyl; benzimidazolyl; benzoxazolyl; benzisoxazolyl; benzothiazolyl; benzotriazolyl; benzotriazinyl; phthalazinyl; 1,8-naphthyridinyl; quinolinyl; isoquinolinyl; quinazolinyl; quinoxalinyl; pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidinyl; pyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidinyl; imidazo[1,2-a]pyridinyl; pyridopyridinyl; pteridinyl; or 1H-purinyl; or A is selected from phosphorous and sulfur acid groups; W is -O-; -S(=O)t-, where t is 0, 1, or 2; or -N(R3)-; Y is =C(R1a)-, or -[N<custom-character file="US20020111495A1-20020815-P00900.TIF" wi="20" he="20" id="custom-character-00001" / >(O)k] where k is 0 or 1; R4, R5 and R6 are (1) -H; provided that R5 and R6 are not both -H at the same time, -F; -Cl; -(C2-C4) alkynyl; -R16; -OR16; -S(=O)pR16; -C(=O)R16, -C(=O)OR16, -C(=O)OR<highlight><sup
Owner:PFIZER INC
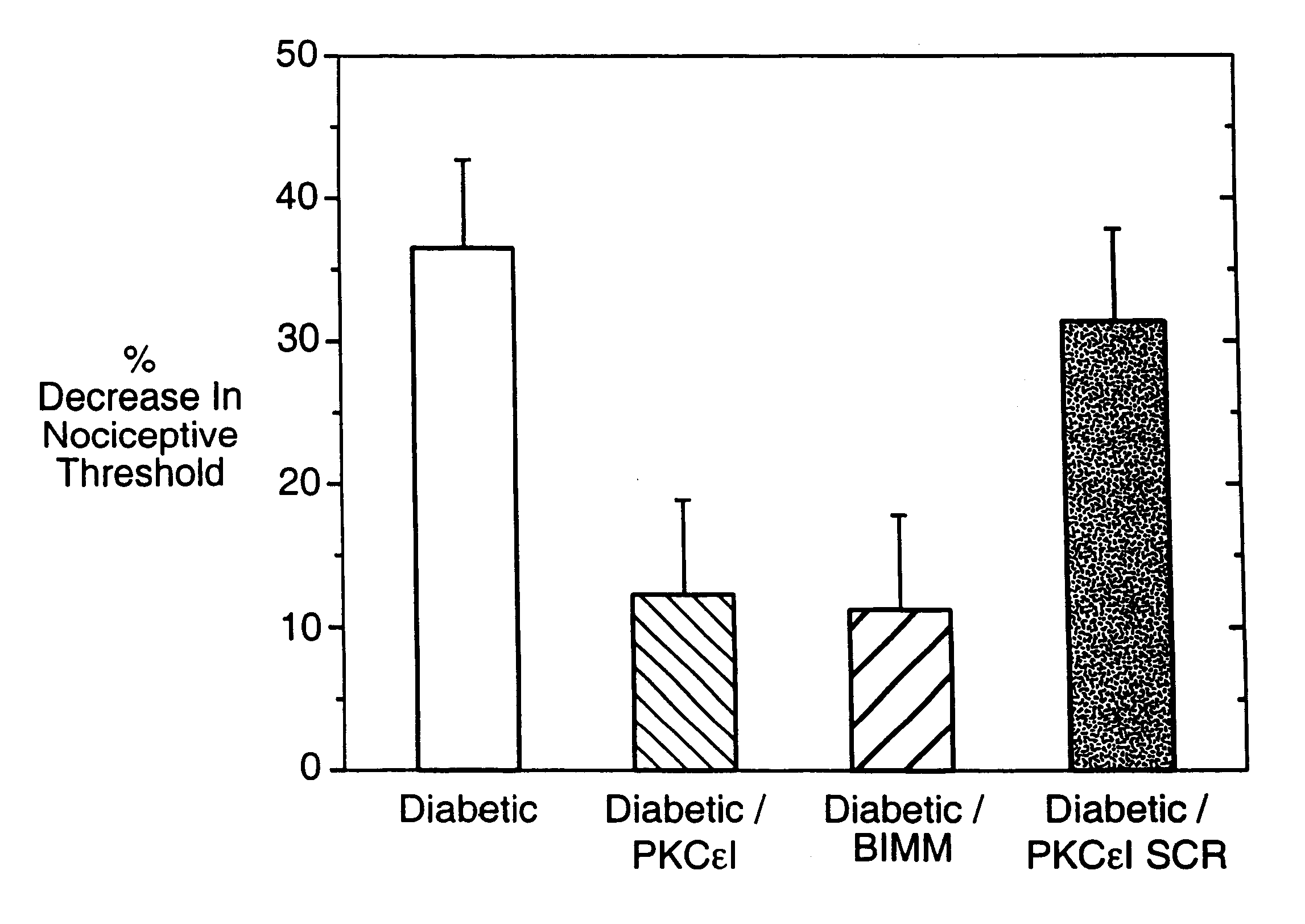
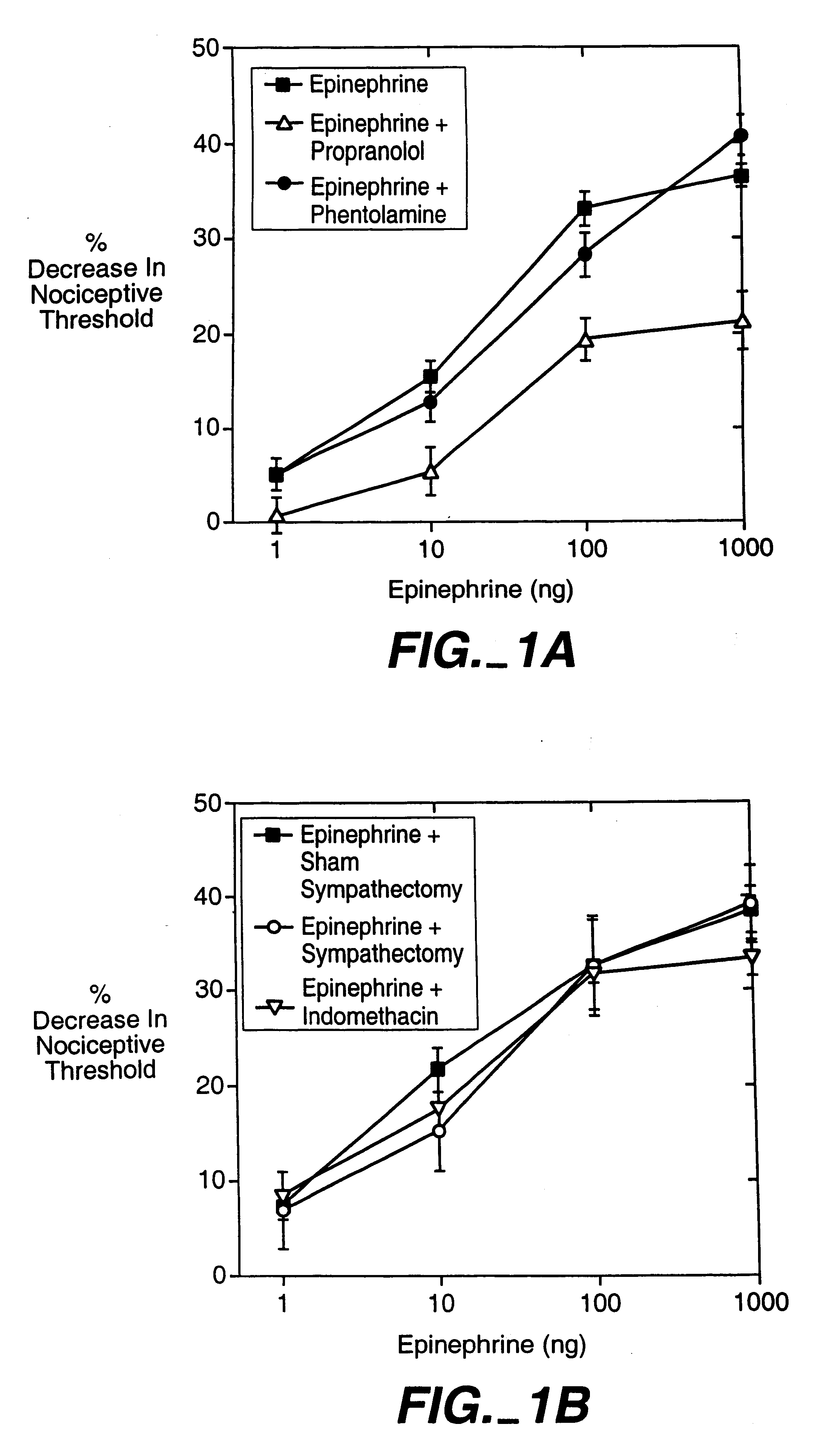
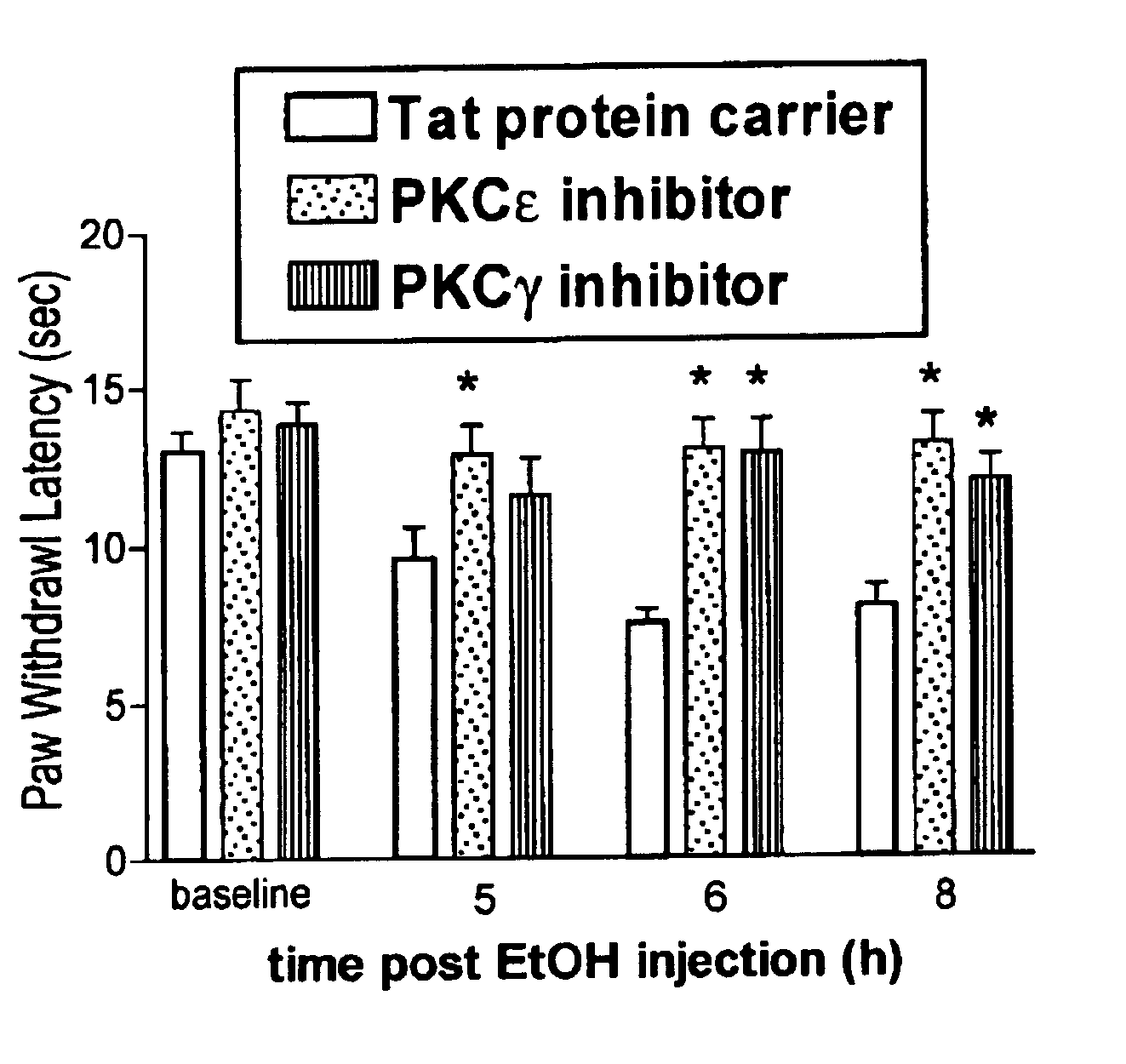
Use of inhibitors of protein kinase C epsilon to treat pain
The role of the epsilon isozyme of protein kinase C ("PKCepsilon") in pain perception, particularly hyperalgesia, methods of lessening pain through administration of inhibitors of PKCepsilon, methods of identifying compounds that modulate pain, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of PKCepsilon and PKCepsilon-independent analgesic agent are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
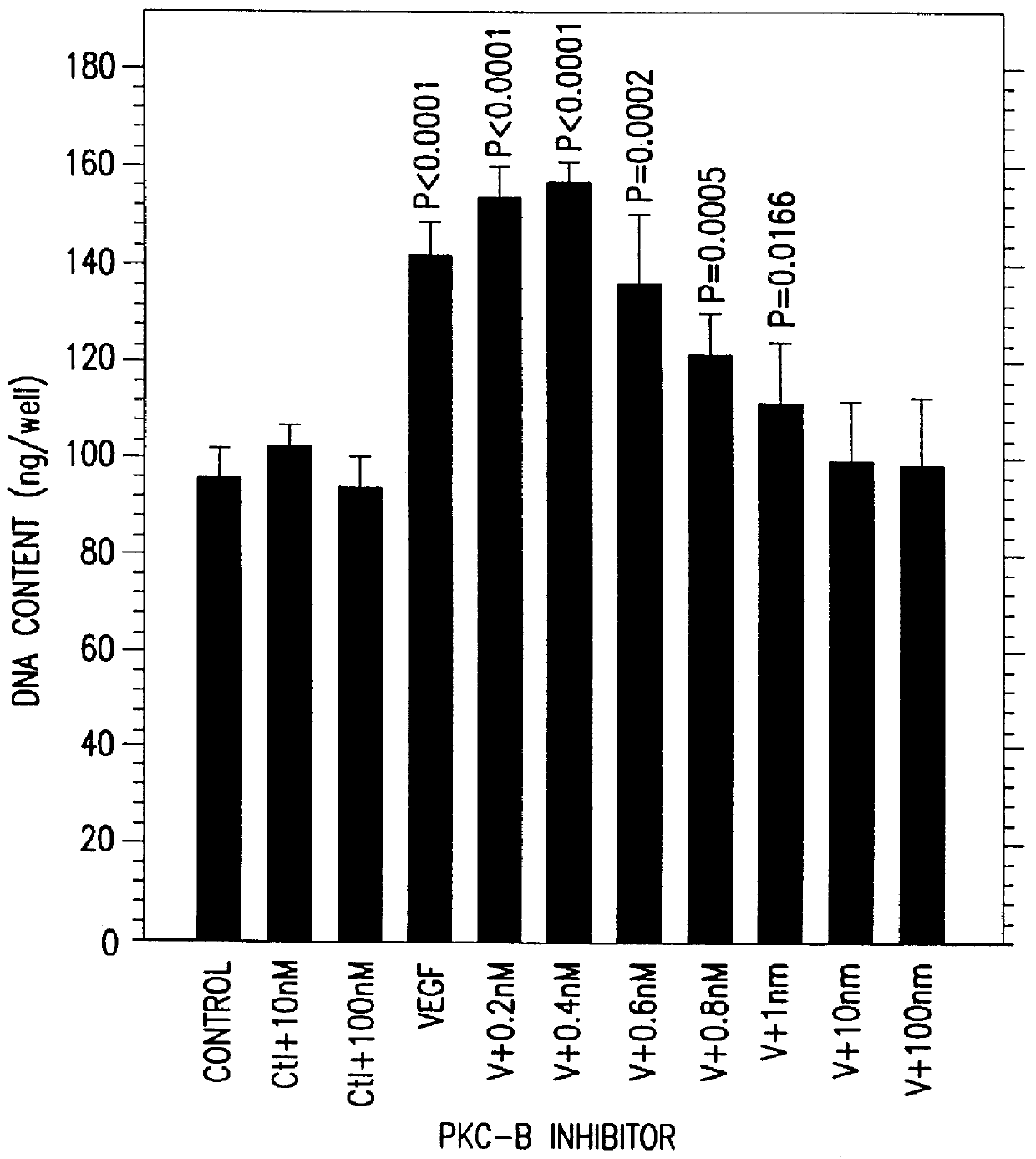
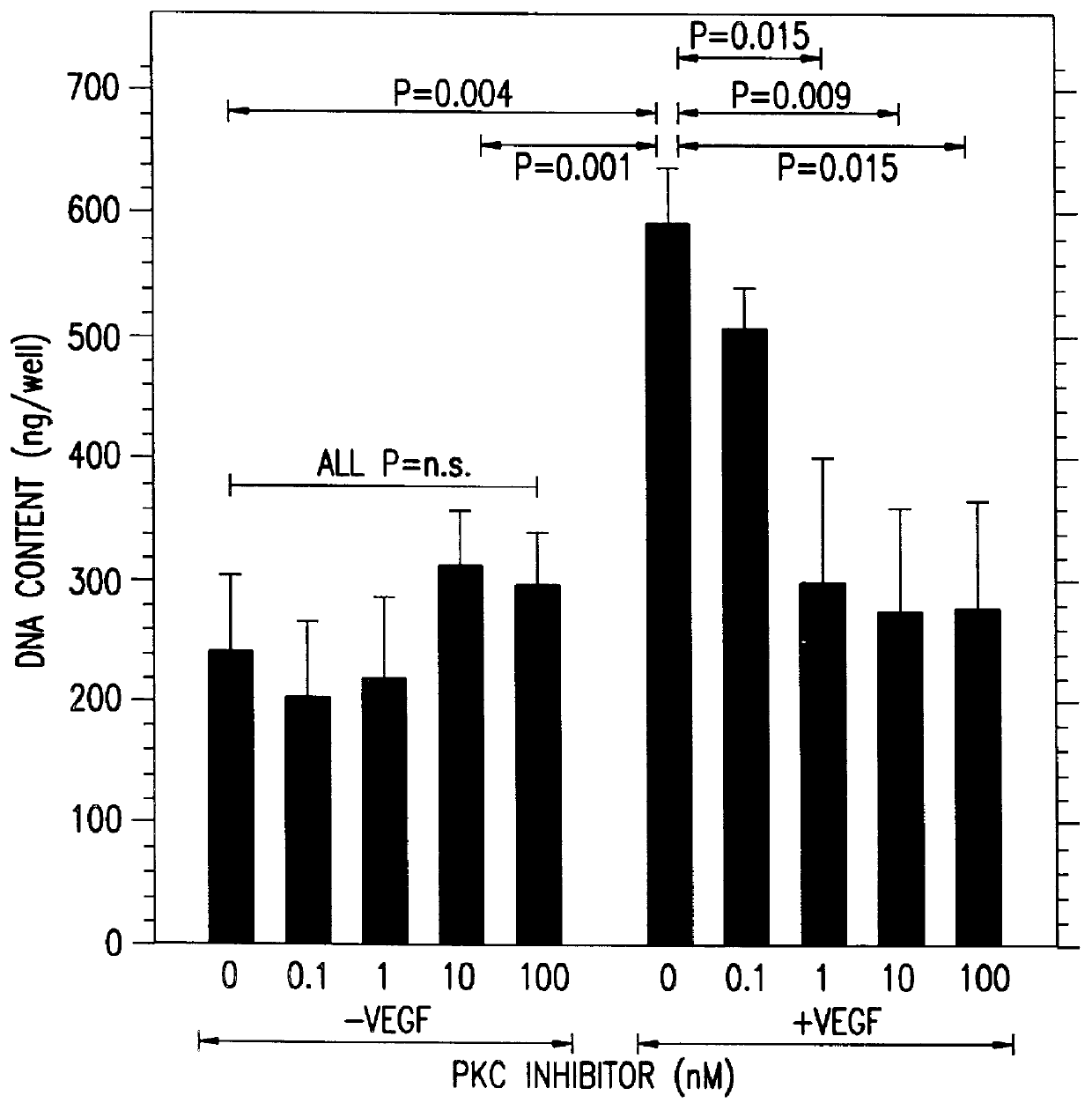
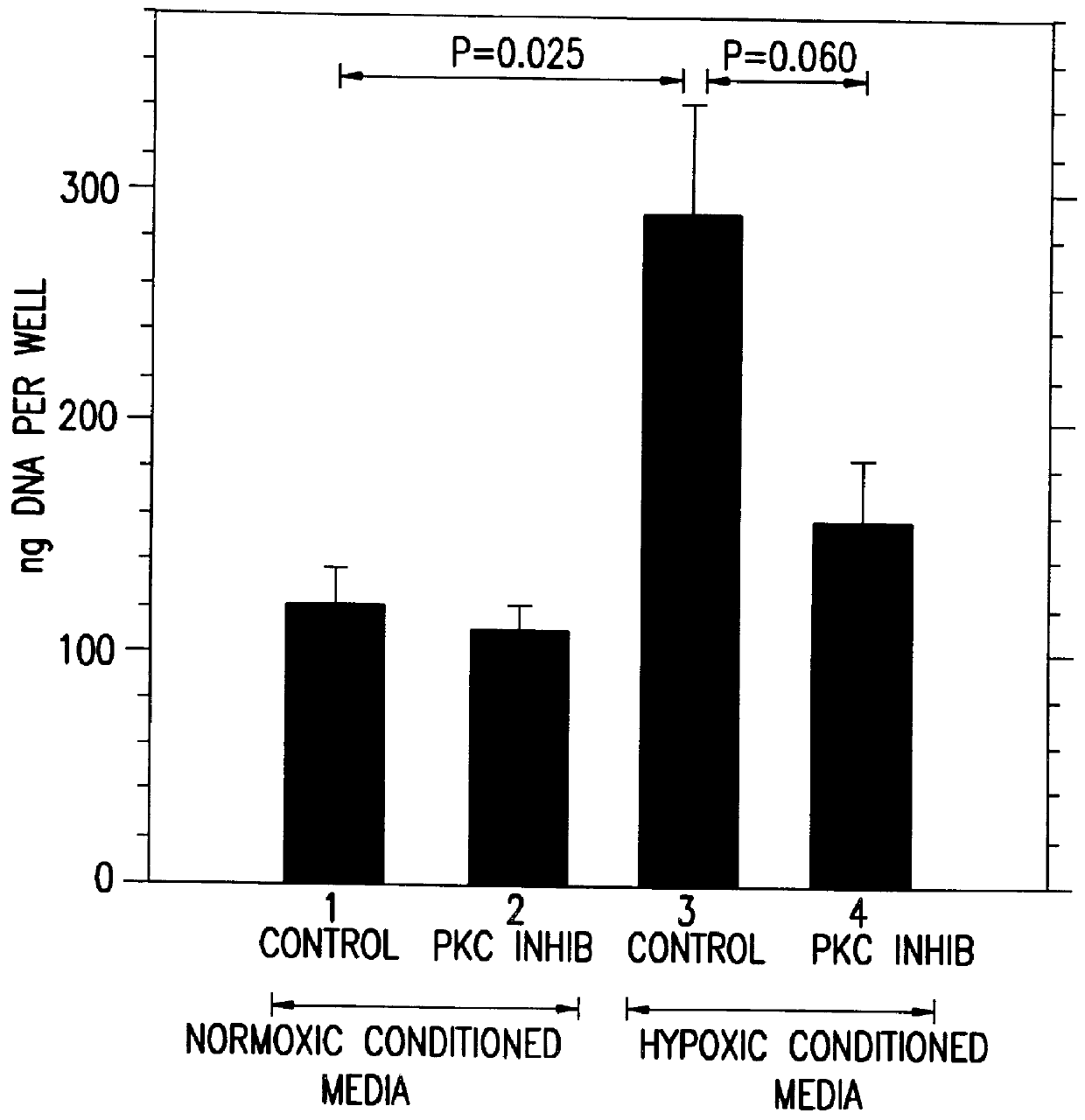
Therapeutic treatment for VEGF related diseases
InactiveUS6284751B1Promote growthPromote absorptionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseCapillary hyperpermeability
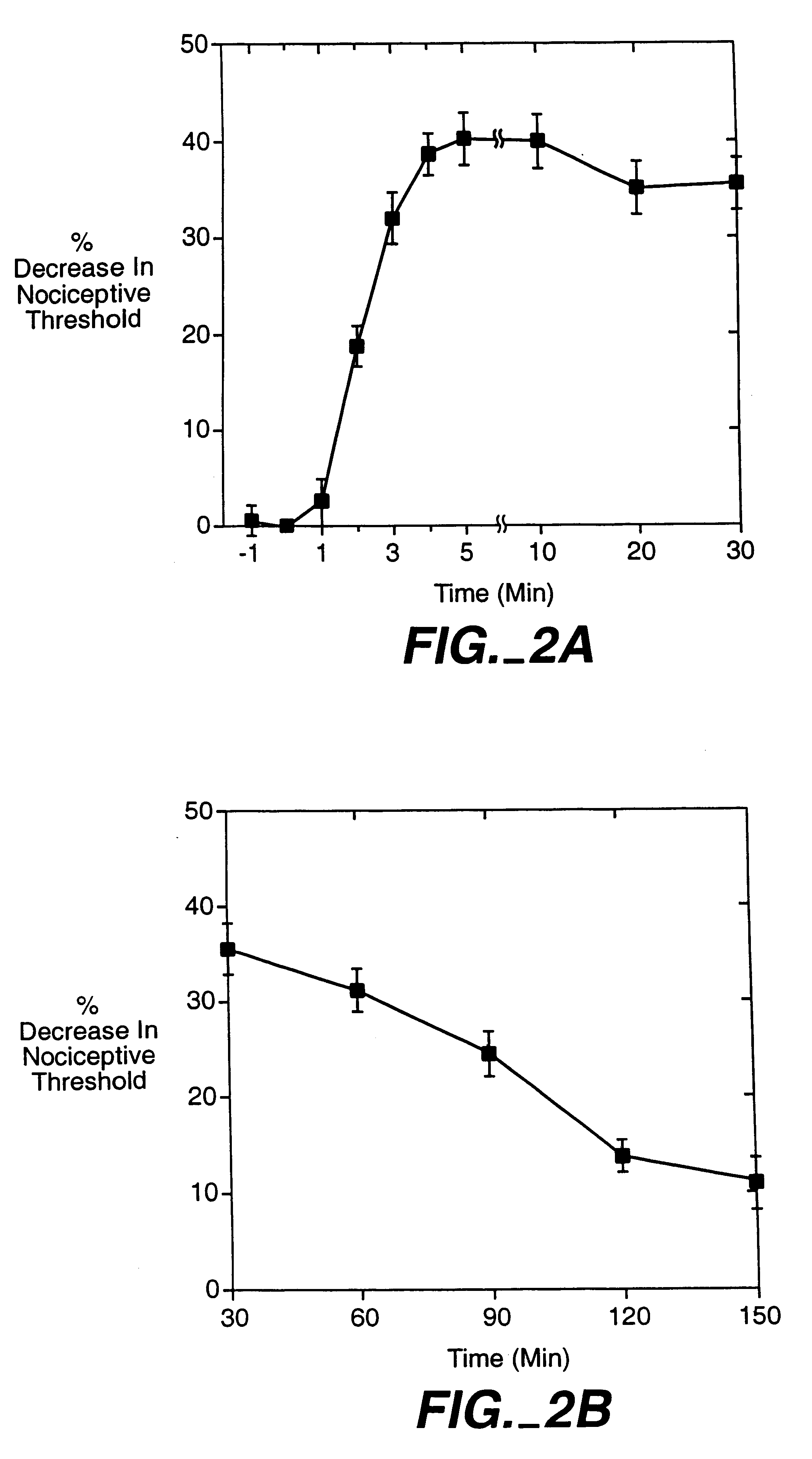
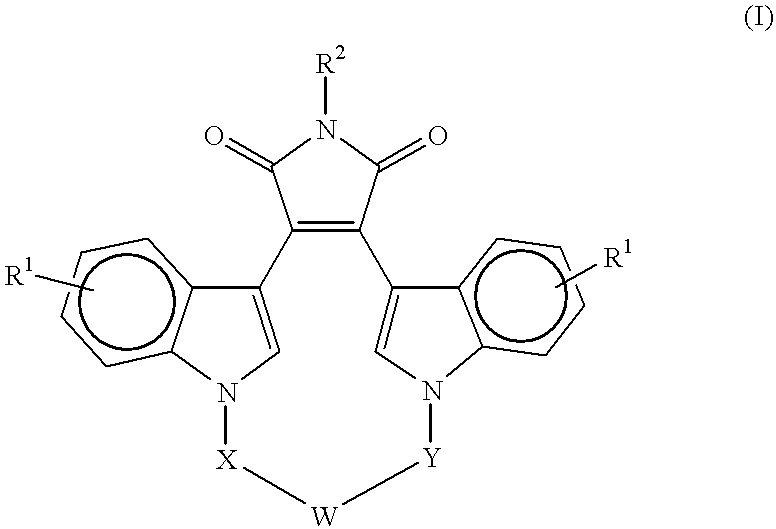
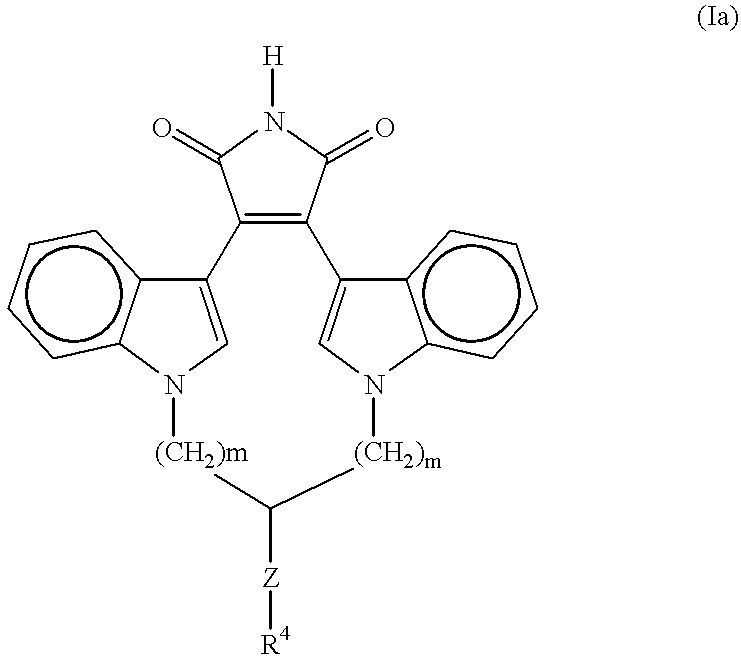
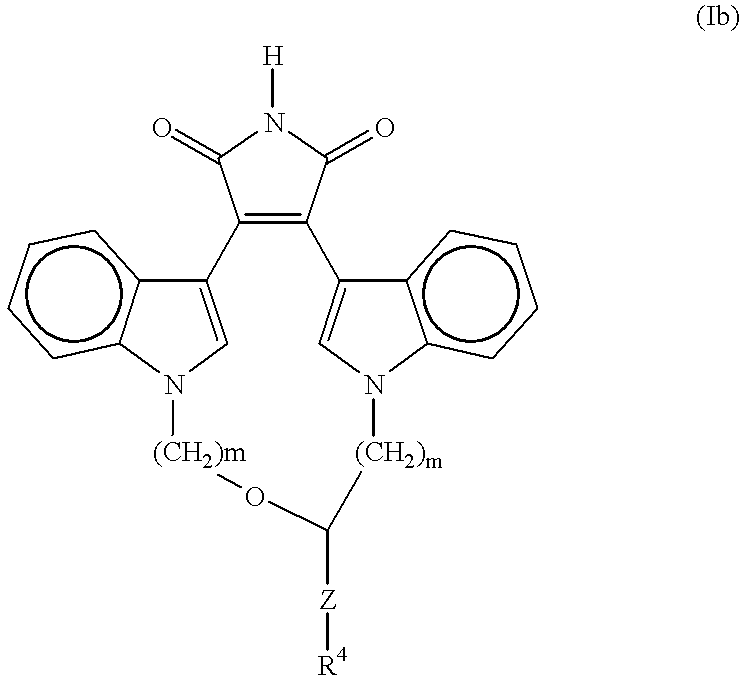
A method for inhibiting VEGF stimulated endothelial cell growth, such as associated with neoplasia, and VEGF stimulated capillary permeability, such as associated with pulmonary edema are disclosed, particularly using the beta-isozyme selective PKC inhibitor, (S)-3,4-[N,N'-1,1'-((2''-ethoxy)-3'''(O)-4'''-(N,N-dimethylamino)-butane)-bis-(3,3'-indolyl)]-1(H)-pyrrole-2,5-dionehydrochloridesalt.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
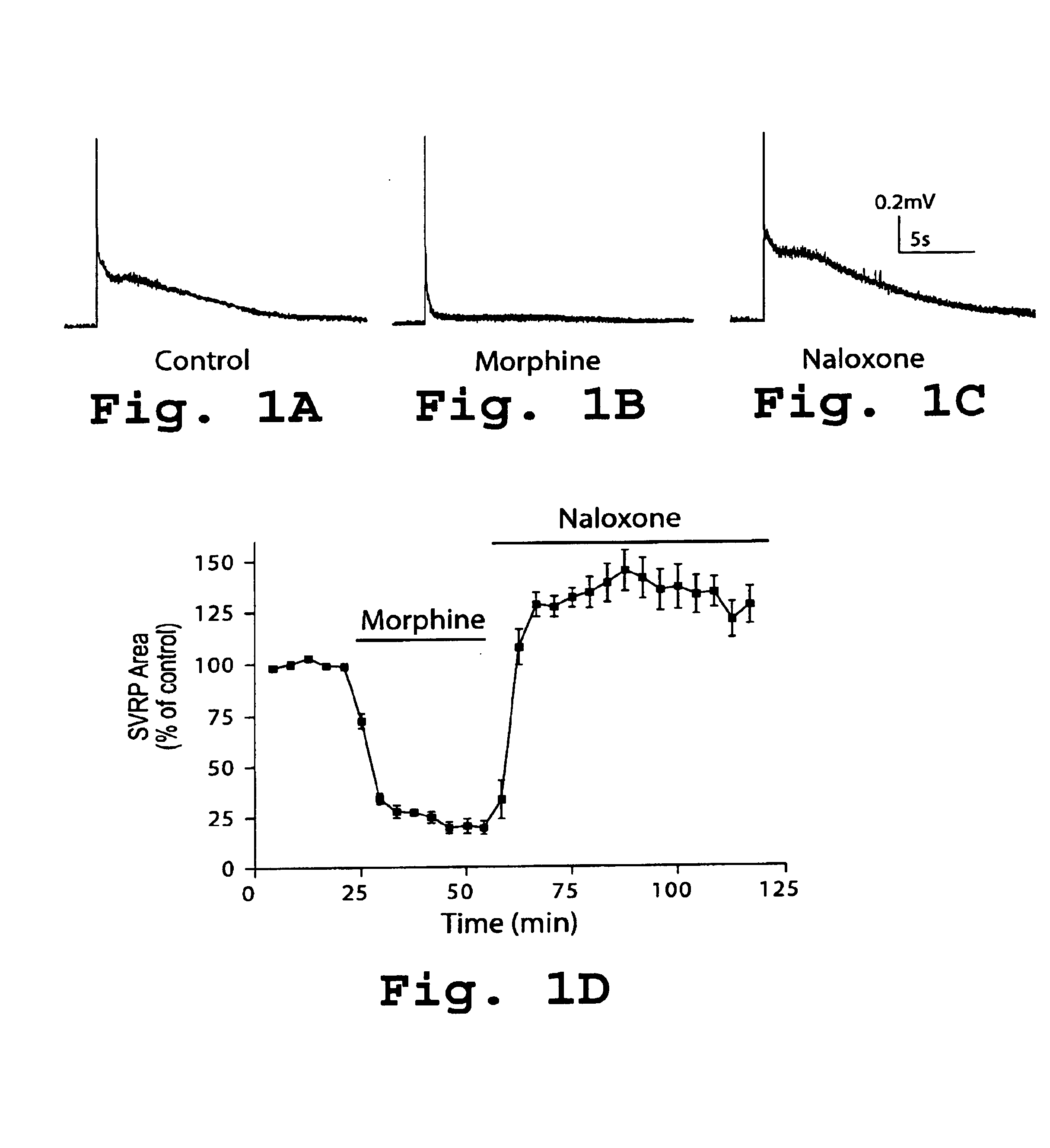
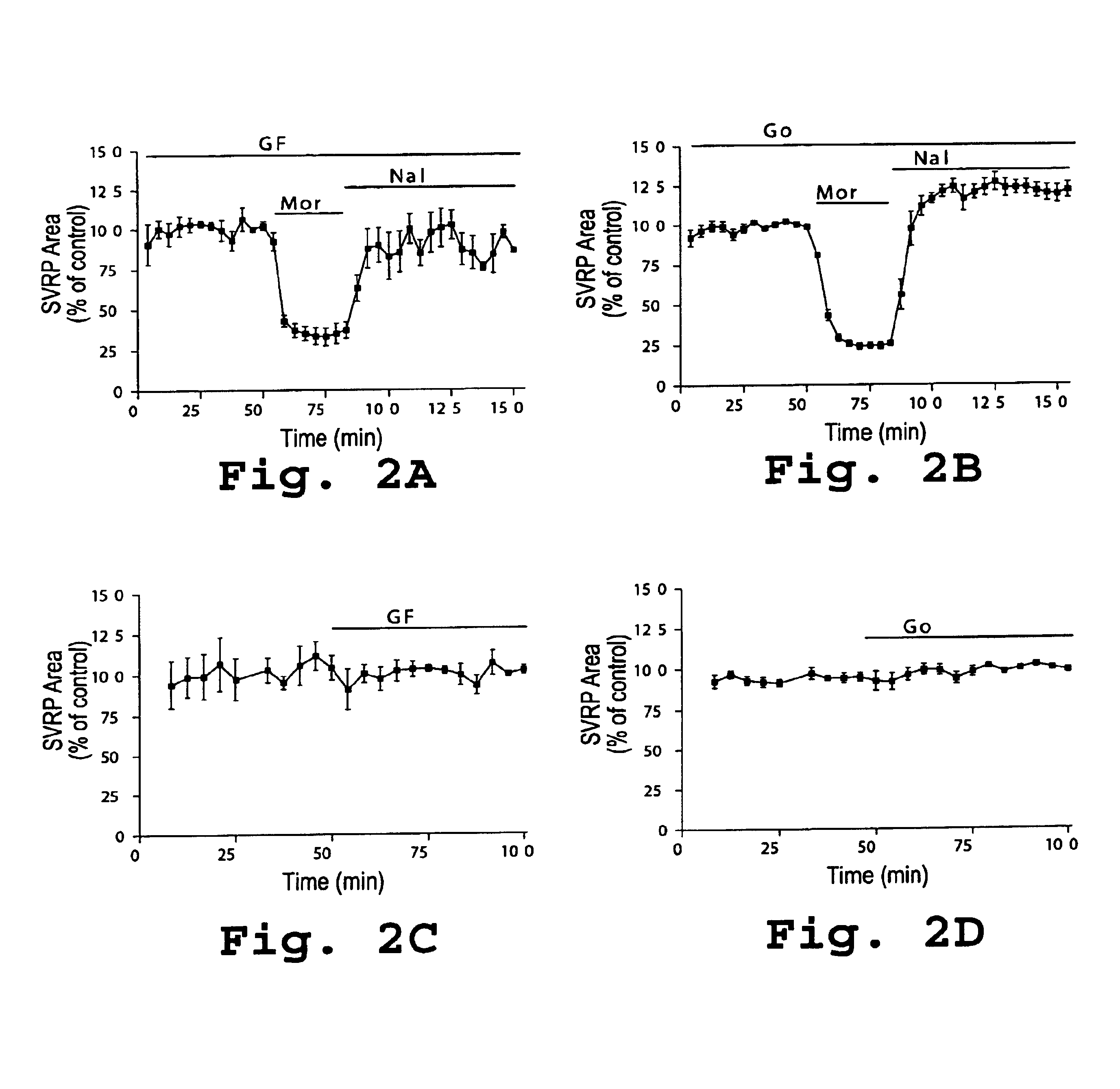
Protein kinase C peptides for use in withdrawal
A method for managing withdrawal from an addictive substance is described. The method involves administering one or more peptides having specific activity for the ε and / or γ isozyme of protein kinase C (PKC). The peptide(s) can be administered prior to, concurrent with, or subsequent to administration of the addictive substance. Also described is a kit having at least one container containing a peptide having isozyme-specific activity for εPKC or γPKC and instructions for use.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Novel isozyme of autoclavable superoxide dismutase (SOD), a process for the identification and extraction of the SOD and use of the said SOD in cosmetic, food, and pharmaceutical compositions
The invention relates to a novel purified isozyme of an autoclavable superoxide dismutase extracted from the plant Potentilla astrisanguinea Lodd. Var. orgyrophylla, said isozyme having the following characteristics, O2-. scavenging activity remains same before and after autoclaving; scavenges O2-. from sub-zero temperature of -20° C. to high temperature of +80° C.; O2-. scavenging activity at 25° C. for 30 days without adding any stabilizing agent such as polyols or sugars; O2-. scavenging activity in the presence of saline (0.9% sodium chloride) to 61.8% of the control (without 0.9% sodium chloride), stable at 4° C. for at least 8 months; contamination free and infection free from any living micro- and / or macro-organism after autoclaving; possesses temperature optima at 0° C.; possesses a molecular weight of 33 kD under non-denaturating conditions; possesses a molecular weight of 36 kD under denaturating conditions; has clear peaks in UV range at 268 and 275 nm; has an enzyme turnover number of 19.53x104% per nmol per min at 0° C.; and requires Cu / Zn as a co-factor, method for the preparation of the purified isozyme of autoclavable superoxide dismutase and formulations containing the said autoclavable superoxide dismutase.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
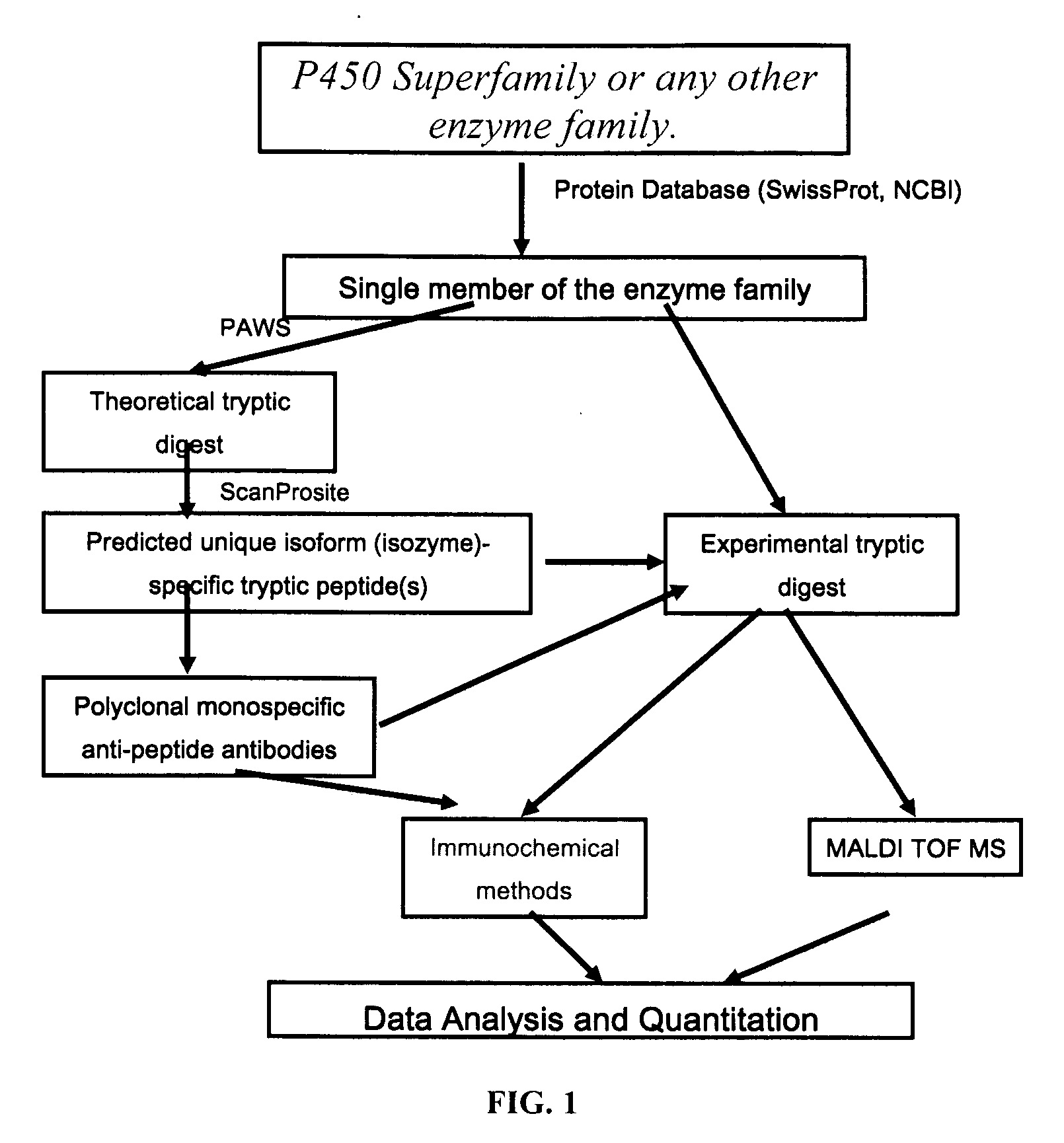
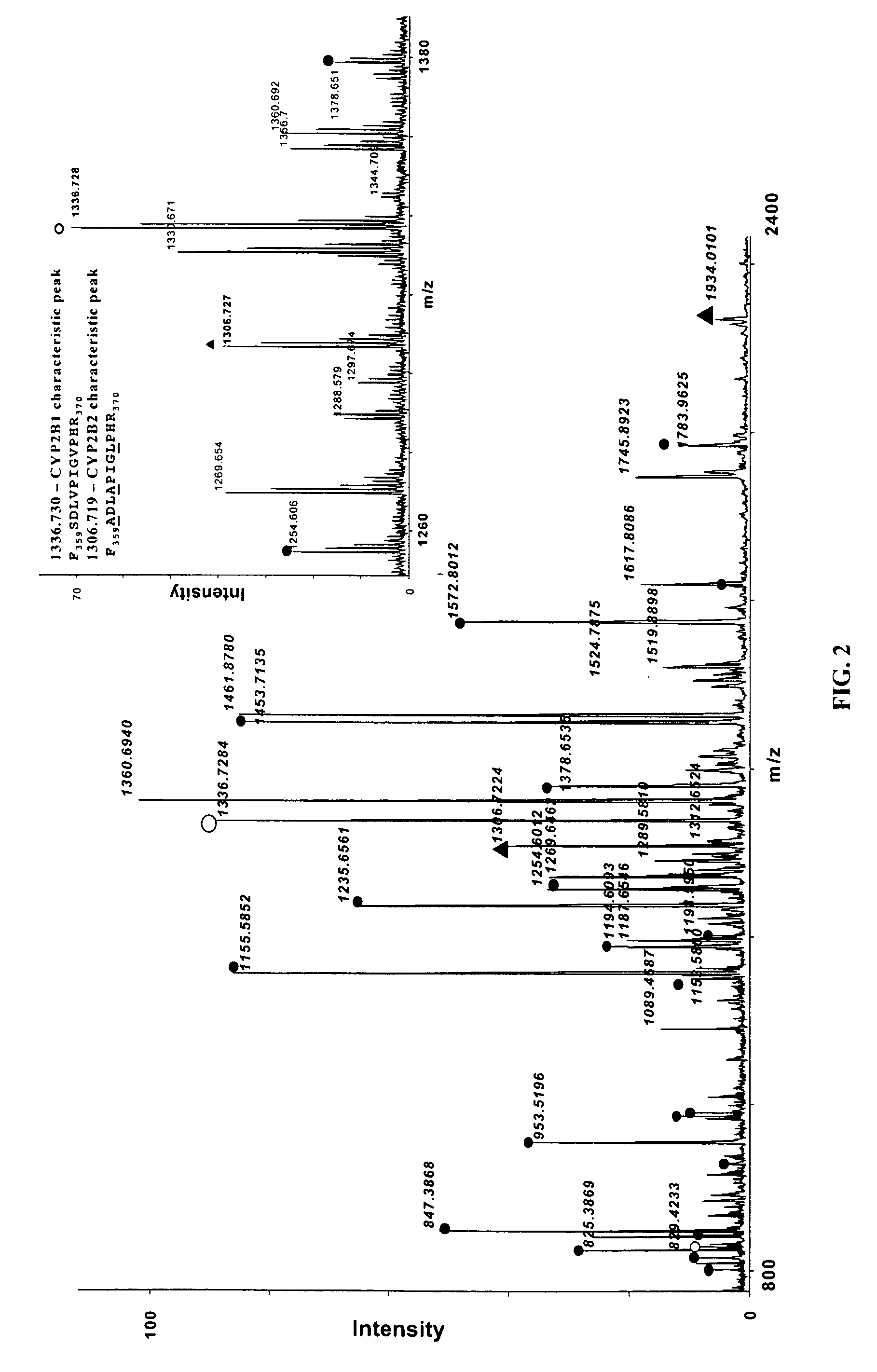
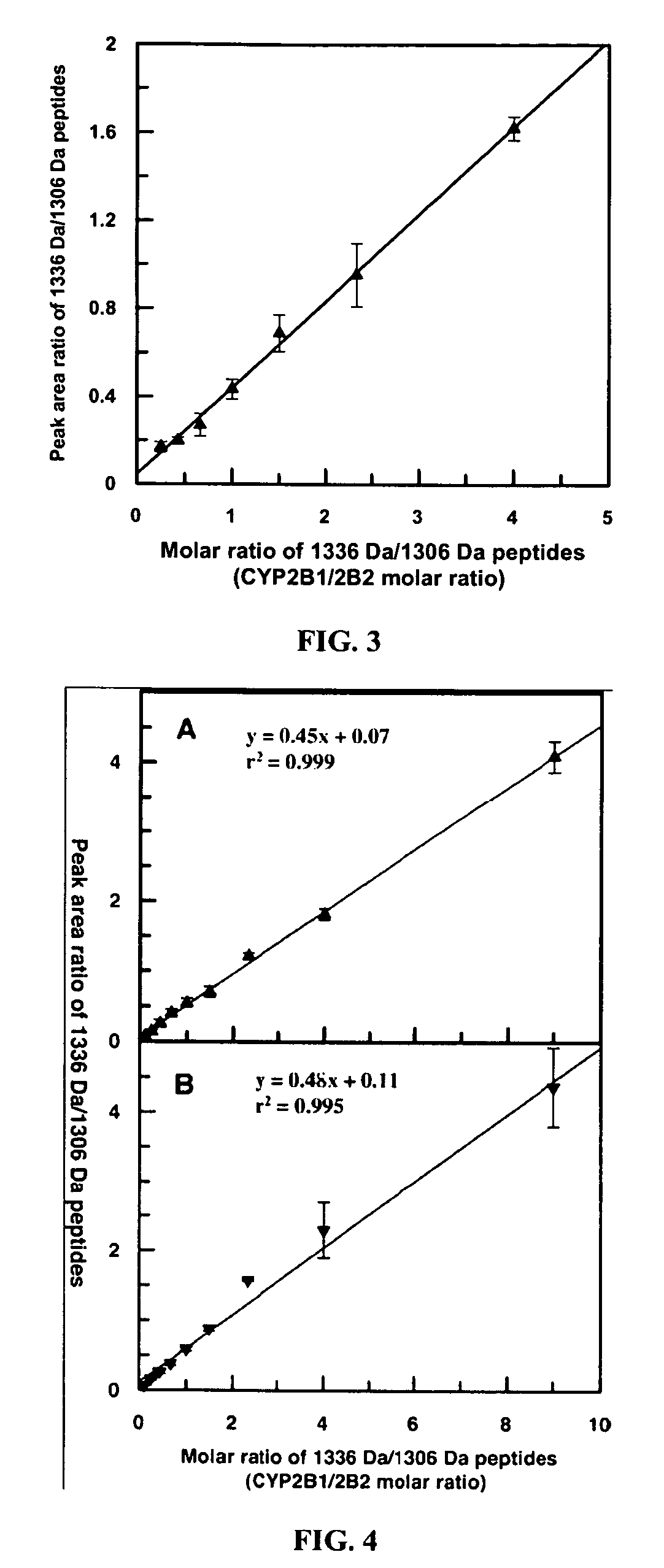
Analysis of protein isoforms using unique tryptic peptides by mass spectrometry and immunochemistry
InactiveUS20070092926A1Accurate measurementReliable detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisIsozymeMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
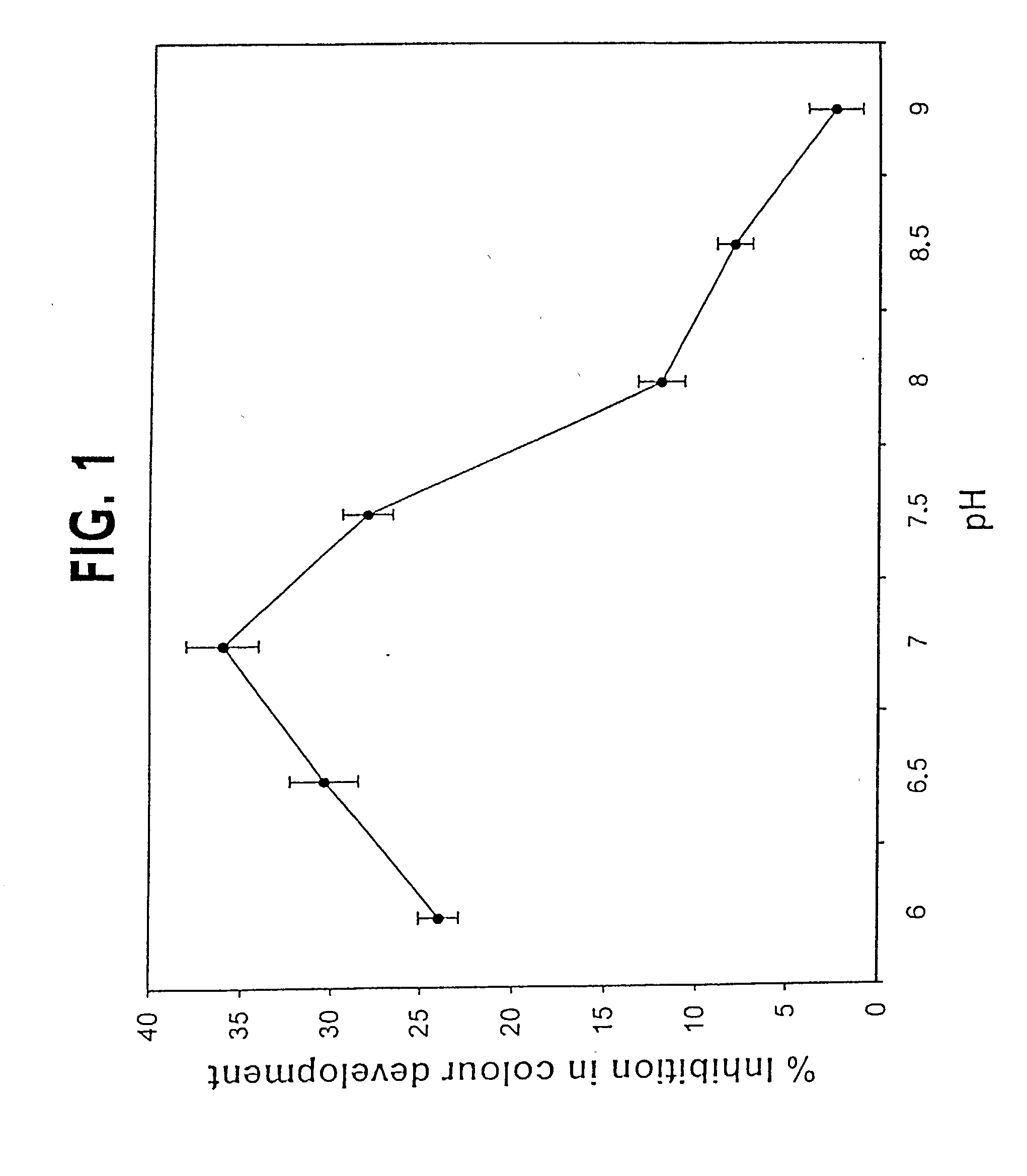
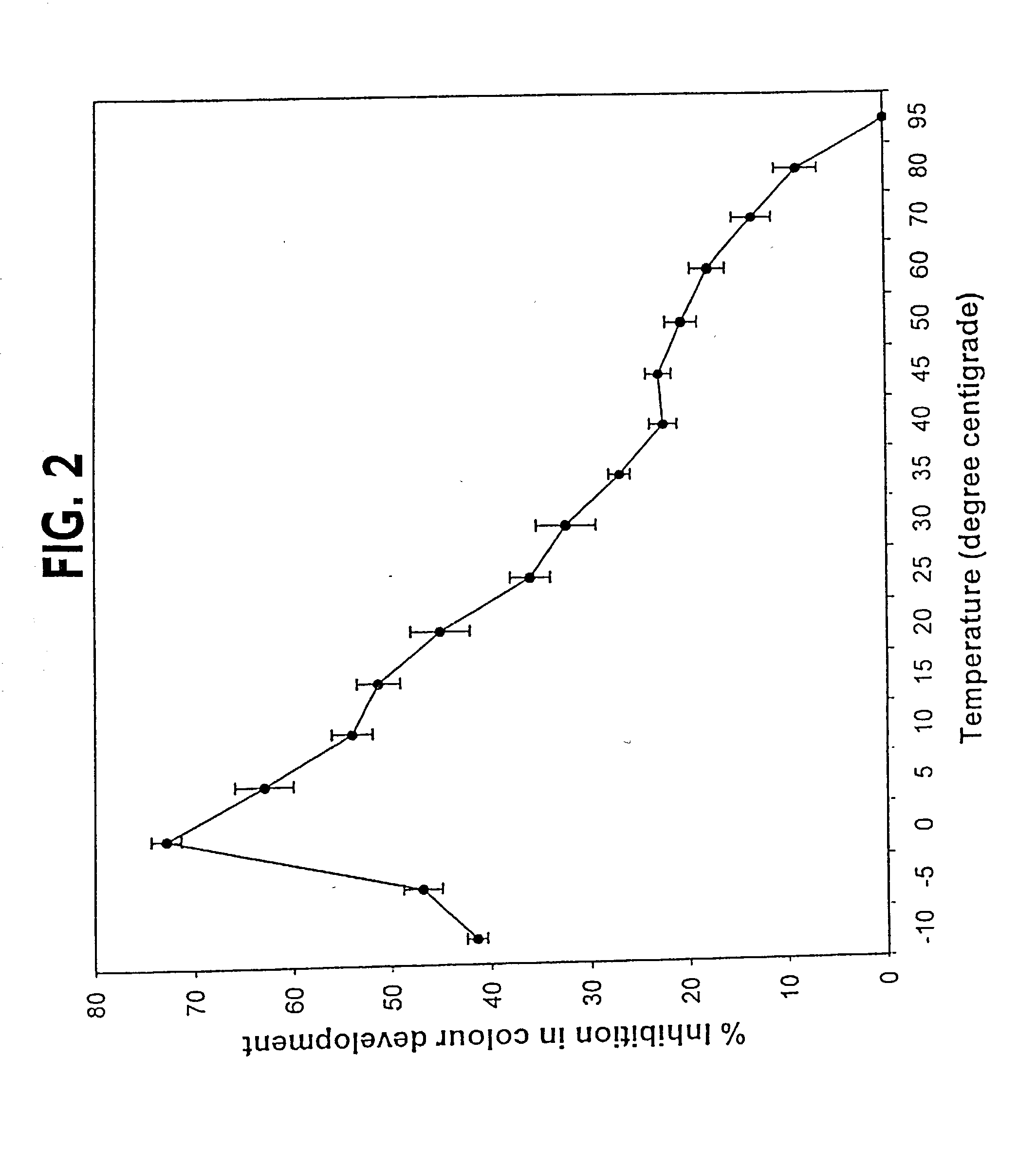
A method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting a protein isoform (p450 isozyme) in a sample using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry or immunochemistry using a unique proteolytic peptide for the isoform. Relative and absolute quantitation can be performed using calibration curves with P450 isozyme-specific peptide standards.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
Peptide inhibitors of protein kinase C gamma for pain management
Peptide sequences derived from the V5 domain of isozymes of protein kinase C for use in pain management are described. Also described are compositions comprising the peptides for treating pain and / or inducing analgesia. Methods of pain treatment and methods of identifying compounds that mimic the activity of the peptides are also described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Therapeutic treatment for VEGF related ocular diseases
InactiveUS6114320APromote growthPromote cell growthBiocideSenses disorderIsozymeTherapeutic treatment
A method for inhibiting VEGF stimulated endothelial cell growth, such as associated with macular degeneration, and VEGF stimulated capillary permeability, such as associated with macular edema are disclosed, particularly using the isozyme selective PKC inhibitor, (S)-3,4-[N,N'-1,1'-((2''-ethoxy)-3'''(O)-4'''-(N,N-dimethylamino)-butane)-bis-(3,3'-indoly 1)]-1(H)-pyrrole-2,5-dionehydrochloridesalt.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO +1
Bivalent inhibitors of Glutathione-S-Transferases
InactiveUS20050004038A1High affinityHigh selectivityBiocideTetrapeptide ingredientsCrystallographyIsozyme
Bivalent inhibitors having affinity for one or more dimeric GST isozymes are provided. The bivalent inhibitors comprise two ligand domains connected by a molecular linker, wherein the ligand domains have affinity for one or more monomers in the one or more dimeric GST isozymes. The ligand domains are separated by a distance ranging from about 5 to about 100 Å. The bivalent inhibitors of the invention demonstrate greatly improved affinity for GST isozymes. In a specific embodiment, the bivalent inhibitors of the invention further provide affinity for substantially one GST isozyme and for substantially one GST class. The bivalent inhibitors of the invention have numerous uses that include the treatment of drug-resistant cancer, malaria, and stimulation of hematopoiesis.
Owner:LYON ROBERT P +3
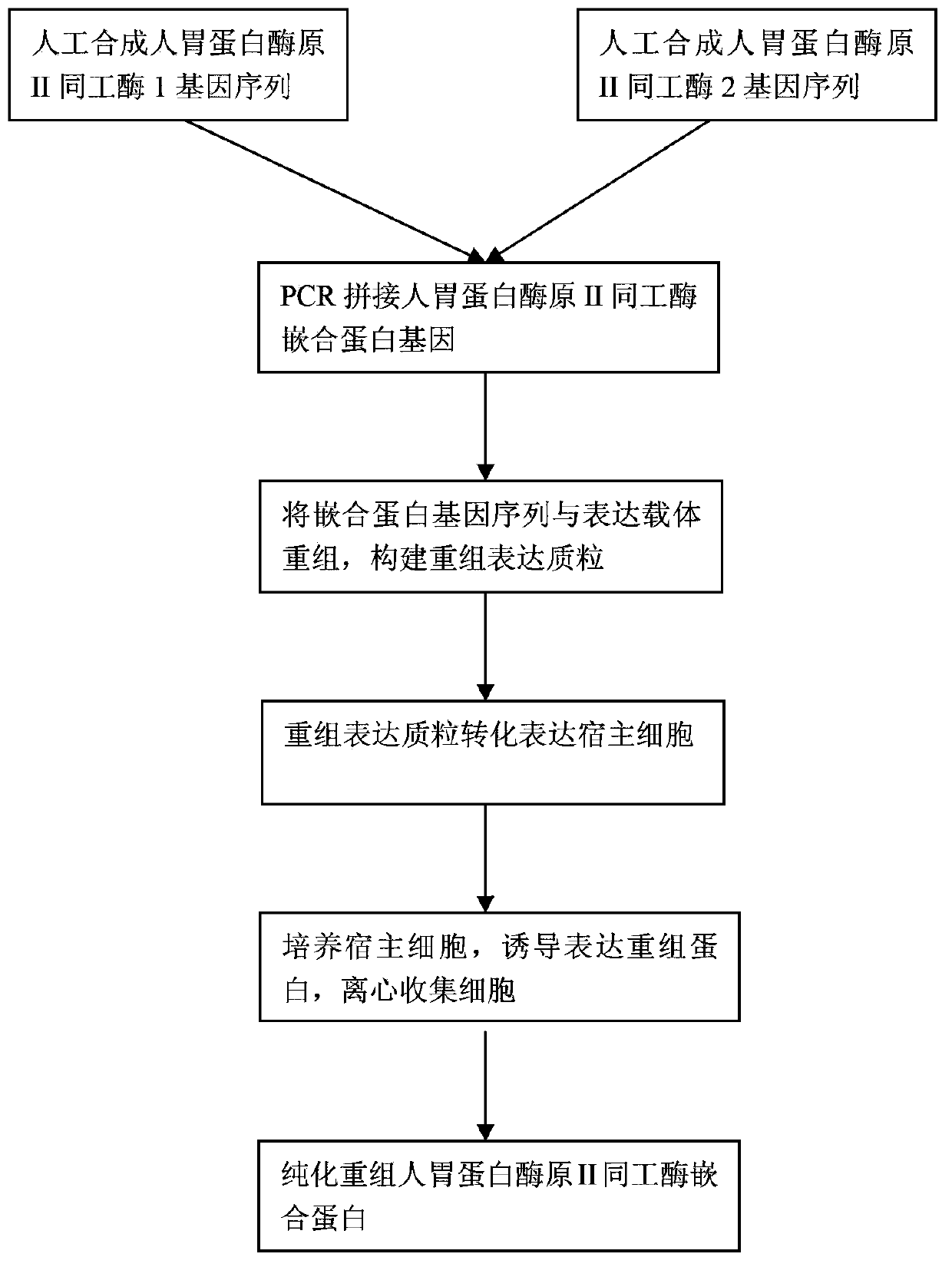
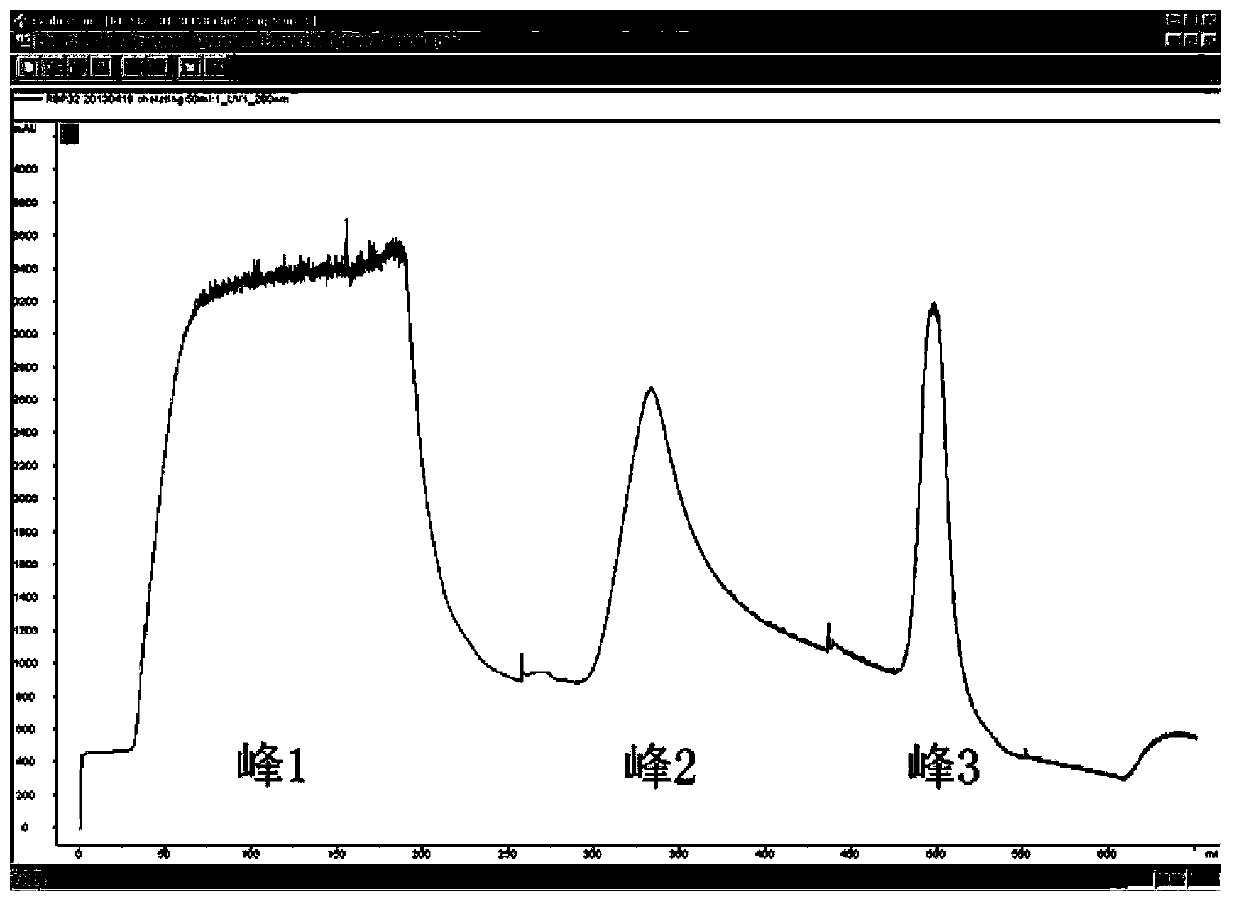
Recombinant human pepsinogen II isozyme chimeric protein, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103387971AHigh sensitivityIncrease catch rateHydrolasesSerum immunoglobulinsPepsinogen IIIsozyme
The invention discloses a recombinant human pepsinogen II isozyme chimeric protein, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: by taking gene sequences of two isozymes of recombinant human pepsinogen II as a template, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) splicing to obtain a chimeric protein coding gene sequence, constructing recombinant expression plasmids, transforming the screened positive clone plasmids into expression host cells, screening an efficiently-expressed recombinant chimeric protein strain, carrying out enlargement culture on the cells and inducing expression chimeric protein, and purifying to obtain the recombinant human pepsinogen II isozyme chimeric protein. The invention further discloses the applications of the recombinant human pepsinogen II isozyme chimeric protein in preparing monoclonal antibodies and multiresistant serums or pepsinogen II kit calibration products. A great amount of stably expressed recombinant human pepsinogen II isozyme chimeric protein can be produced by utilizing a genetic engineering technology, and one protein has two chimeric protein sequences of the human pepsinogen II.
Owner:常州爱复康生物科技有限公司
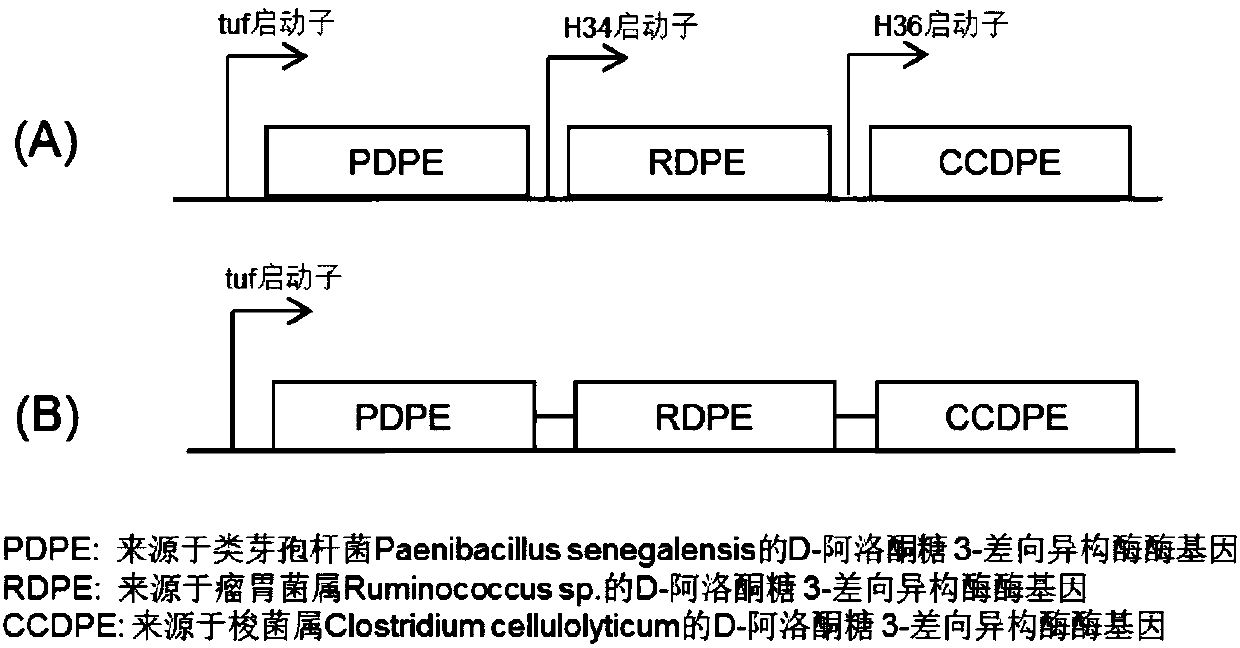
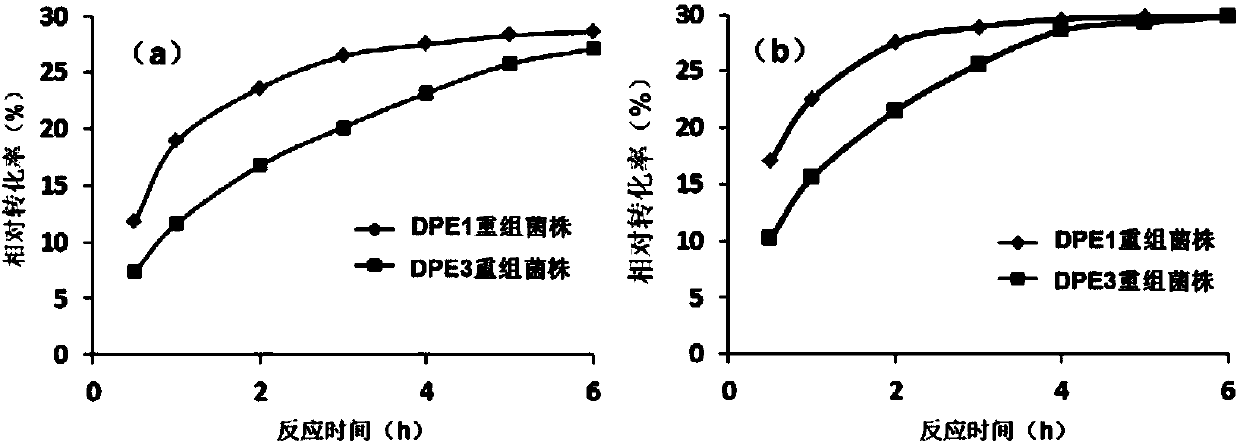
Method for efficiently preparing D-psicose 3-epimerase and use of D-psicose 3-epimerase
InactiveCN107723307ALow costHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymePsicose
The invention discloses a method for efficiently preparing D-psicose 3-epimerase and a use of the D-psicose 3-epimerase and provides a method for efficiently preparing an enzyme catalyst for catalyzing the same reaction through isozyme combined expression. The method utilizes corynebacterium glutamicum as a host cell to construct a recombinant strain expressed by plasmid dissociation and chromosomal integration, measures D-fructose catalytic efficiency, improves enzyme catalytic efficiency by 2-4 times than that of single expression of D-psicose 3-epimerase through combined expression and hasa conversion ratio of 29% when 70% of fructose is a substrate. The method improves D-psicose production efficiency and is suitable for industrial production of D-psicose. The invention also disclosesa novel use of the D-psicose 3-epimerase in psicose synthesis. The enzyme is derived from Paenibacillus senegalensis, has catalytic activity of about 25 U / mg and can be used to convert D-fructose intoD-psicose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of fish protein biological peptide fertilizer
ActiveCN1597626AIncrease contentImprove disease resistanceAnimal corpse fertilisersClimate change adaptationIsozymeFresh fish
A fish protein-biologic peptides fertilizer is prepared from the leftover of fresh fish, fish skin or fish bone through pulverizing, regulating pH=1-6.5, adding trypsase or pepsin, degradating, filtering concentrating and sterilizing. It is rich in biologic peptide, amino acids, Ca, P, Zn, Cu, Se, Fe, trace element, vitamines, etc.
Owner:WEIHAI WENXI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Protein kinase c epsilon as modulator of anxiety, alcohol consumption and self-administration of drugs of abuse
InactiveUS20020124272A1Nervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawal syndromeAlcoholisms
The present invention is directed to the production of PKC isozyme epsi (PKCepsi)-deficient cells and non-human animals. The present invention is further directed to the identification of PKCepsi as a target for drugs that reduce anxiety. According to the present invention, PKCepsi-inhibiting compounds act in synergy with drugs acting at the GABAA receptor. The present invention is also directed to the use of modulators of PKCepsi to modulate alcohol consumption, self-administration of other drugs of abuse, and the effects of alcohol consumption as well as the use of inhibitors of PKCepsi, either alone or in conjunction with allosteric agonists of GABAA receptors, to treat conditions, such as addiction, withdrawal syndrome, skeletal muscle spasms, convulsive seizures, and epilepsy, that are amenable to treatment by allosteric agonists of GABAA receptors. Additional aspects of the present invention are diagnostic methods for identifying individuals at risk for becoming alcoholics or abusers of other drugs and kits for performing such diagnostic methods. The present invention relates to: cells and non-human animals deficient for the PKC isozyme epsi (PKCepsi); the use of PKCepsi as a target for drugs; the use of inhibitors of PKCepsi in methods of reducing anxiety and treating conditions associated with insufficient activity of the GABAA receptor; the use of modulators of PKCepsi in methods of modulating alcohol consumption, modulating self-administration of other drugs of abuse, and altering the effects of alcohol; pharmaceutical compositions comprising inhibitors of PKCepsi and allosteric agonists of GABAA receptors; and the identification of individuals with enhanced susceptibility to alcoholism or other forms of addiction.
Owner:GALLO CLINIC & RES CENT +1
Method for detecting the polymorphism of ADH2 genes
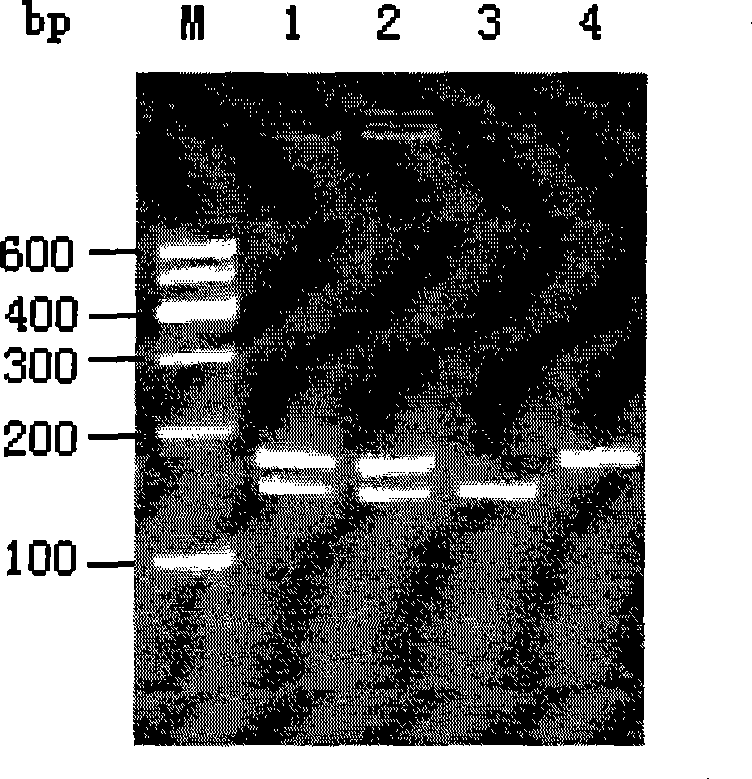
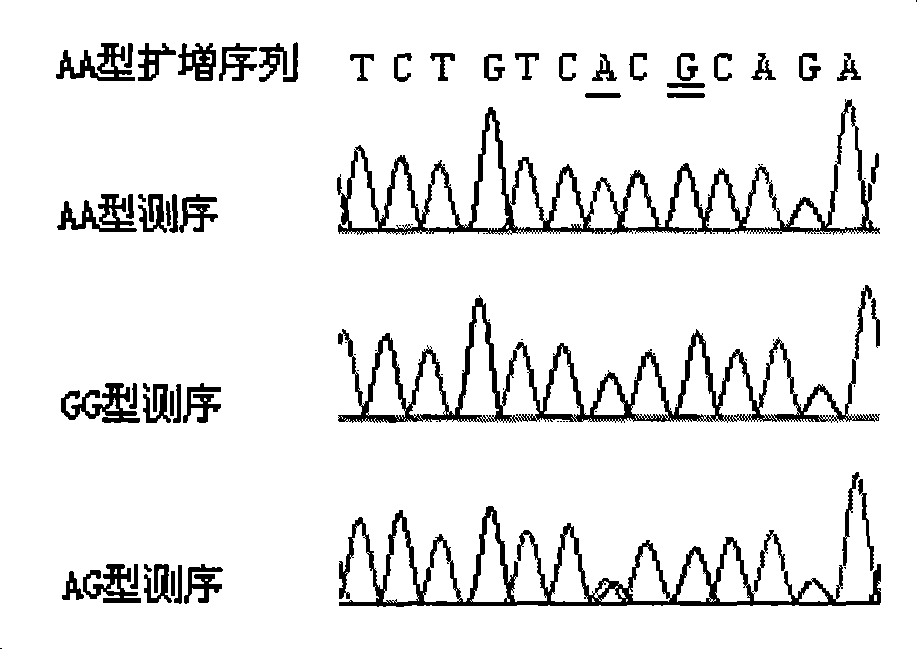
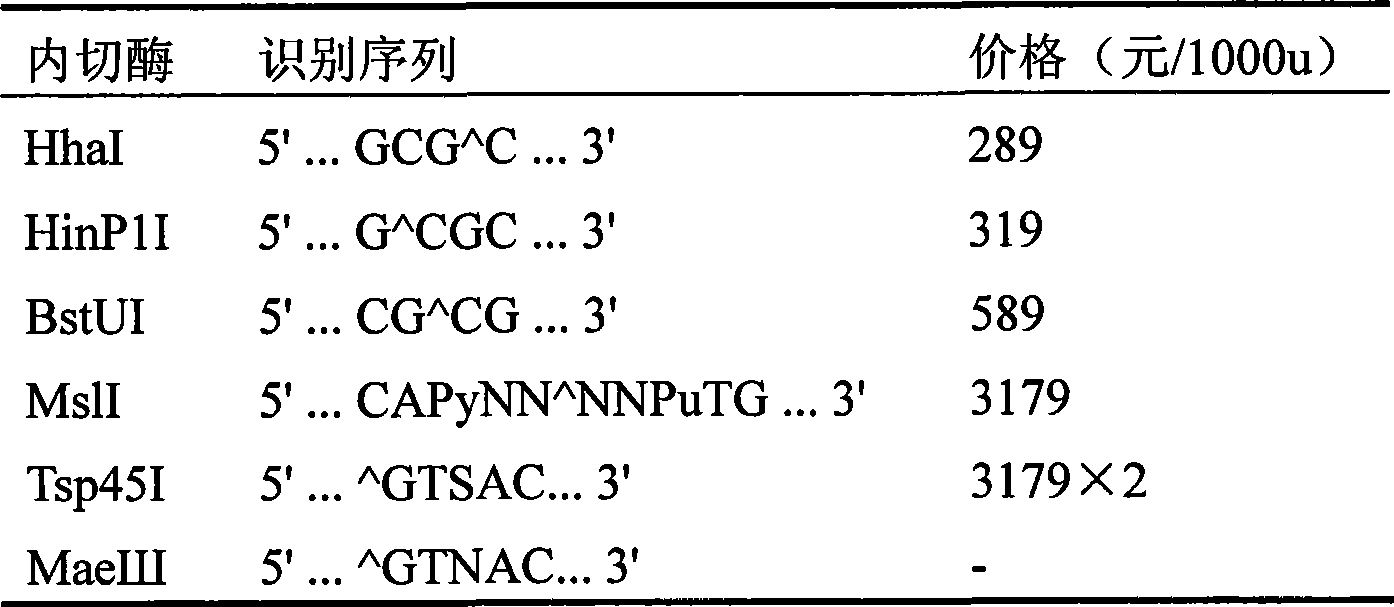
The invention pertains to the field of biotechnology and relates to a method for detecting the polymorphism of ADH2 genes. Based on the feature analysis of ADH2 genes and relevant polymorphic base sequences thereof, primers are designed according to the principle that mismatched basic groups create enzyme cutting sites; one of the primers is designed according to the neighboring sequence of a mutant site; mismatched basic groups are introduced to cause the end of a primer 3' and a mutant of the monobasic mutation to form an enzyme cutting site after the amplification of polymerase chain reaction (PCR); and then, incision enzymes are used for enzyme cutting identification. By experimental verification, the design of primers is reasonable and the amplification of PCR is successful, the polymorphism of amplified DNA fragments can be identified by incision enzymes including HhaI, HinP1I, BstUI and isoenzymes thereof. The electrophotogram of BstUI after enzyme cutting has clear straps and is easy to identify. The used incision enzymes are low in price and easy to obtain. According to sequencing verification, the features of sequences with different genotypes are consistent with the expected results. According to the results of verification on population-based samples, the method is stable and reliable.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and composition to evaluate cytochrome P450 2D6 isoenzyme activity using a breath test
InactiveUS20070026480A1Organic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMetaboliteOral medication
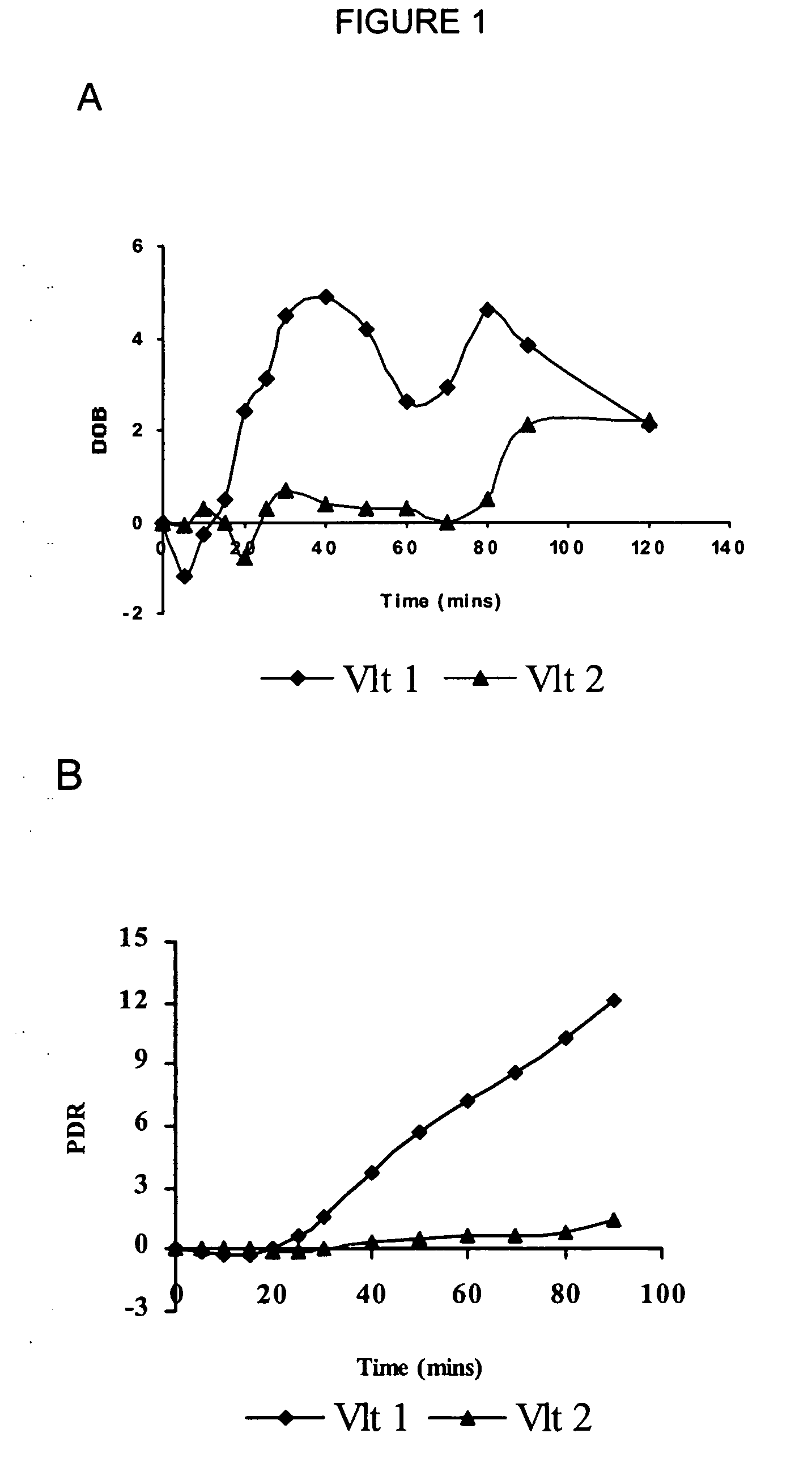
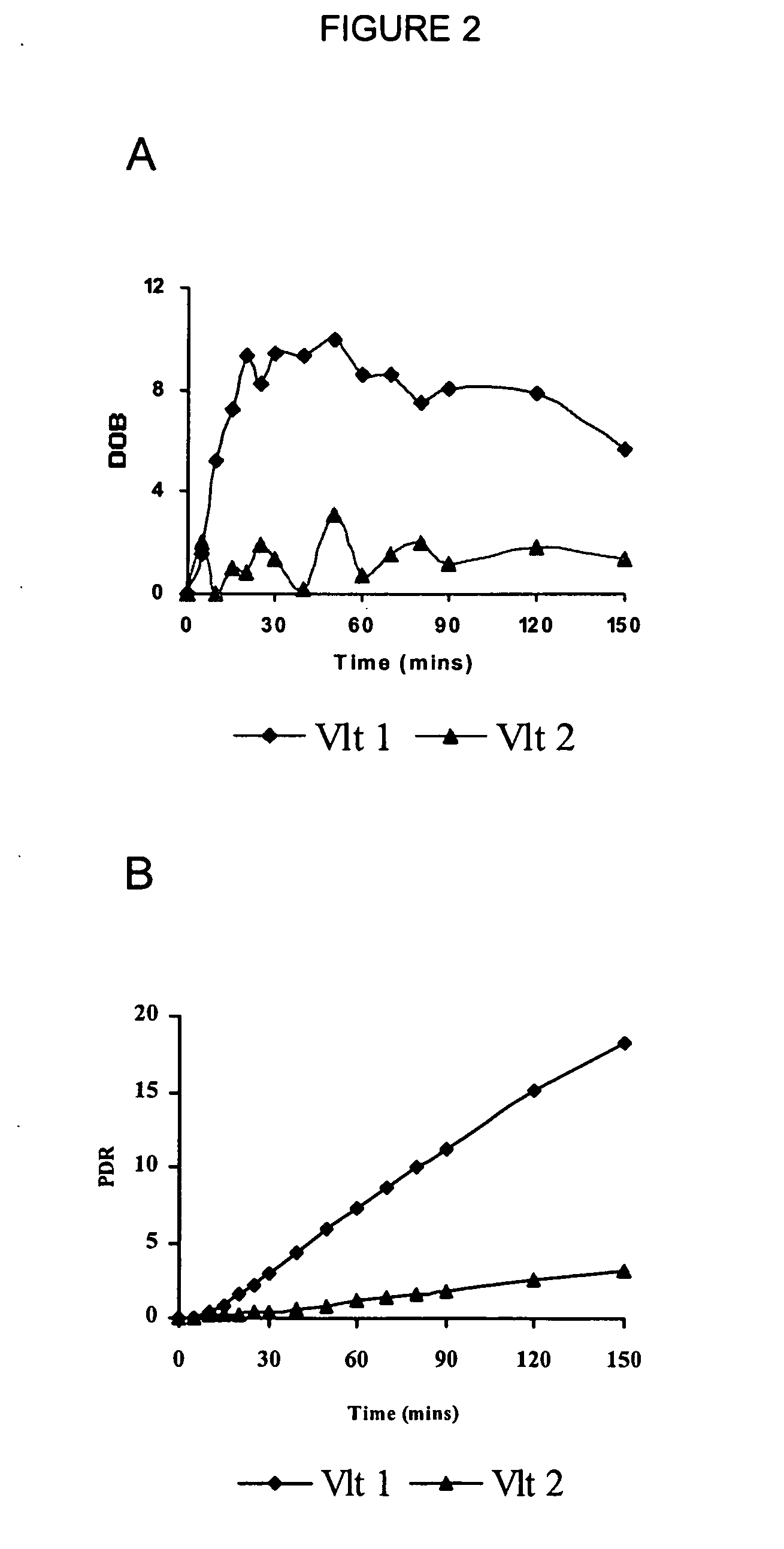
The present invention relates, generally to a method of determining and assessing cytochrome P450 2D6 isoenzyme (CYP2D6)-related metabolic capacity in an individual mammalian subject via a breath assay, by determining the relative amount of 13CO2 exhaled by a the subject upon intravenous or oral administration of a 13C-labeled CYP2D6 substrate compound. The present invention is useful as an in vivo phenotype assay for evaluating CYP2D6-related activity using the metabolite 13CO2 in expired breath and to determine the optimal dosage and timing of administration of CYP2D6 substrate compound.
Owner:OTSUKA AMERICA PHARMA INC
Gene engineering bacterium for producing 1,3-propanediol and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101260379AImprove stabilityHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymeGlycerol
The invention belongs to the biochemical field and discloses a 1, 3-propylene glycol genetic engineering bacterium and a preparation method and application thereof. The strain is classified and named as Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955-pUC18-yqhD-Tet<R>, and is obtained by connection of a 3-propylene redoxase isozyme gene yqhD from Escherichia coli and a tetracycline resistant gene Tet<R> from a plasmid pHY300PLK, insertion of a carrier pUC18 and conversion of Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955. The bacterium can obviously improve the capacity for conversion of glycerol into 1, 3-propylene glycol, improve the utilization ability and the conversion rate of the substrate glycerol and the final concentration of the final offspring 1, 3-propylene glycol, simultaneously shorten the fermentation time, and is convenient for industrial production of the 1, 3-propylene glycol through the microbial fermentation method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
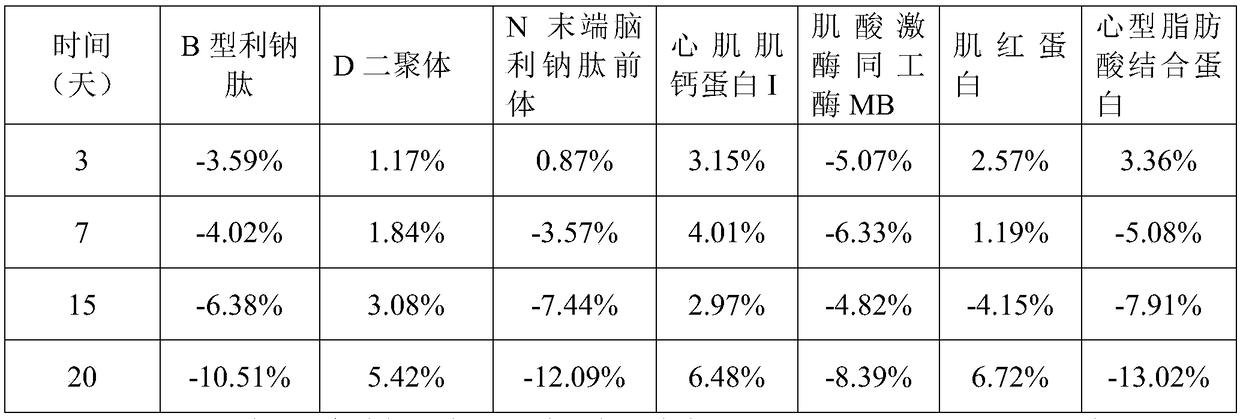
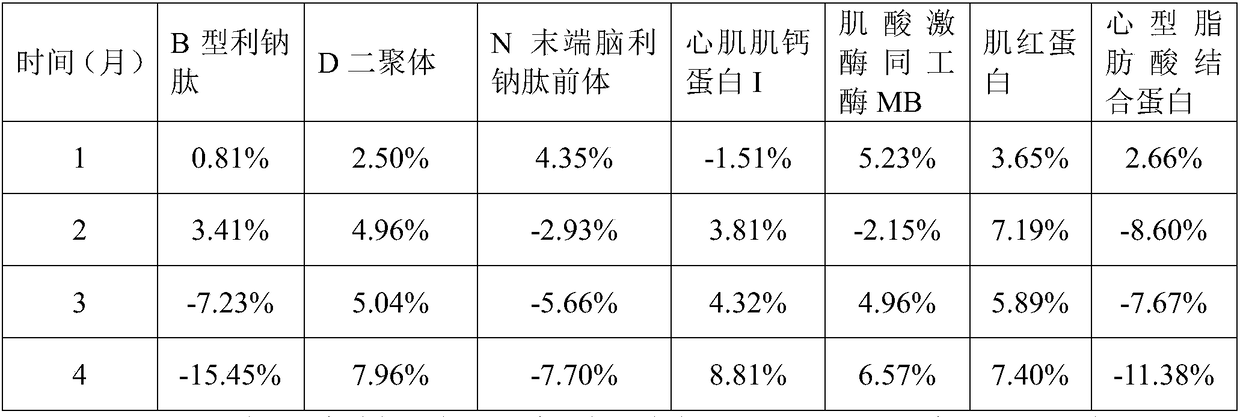
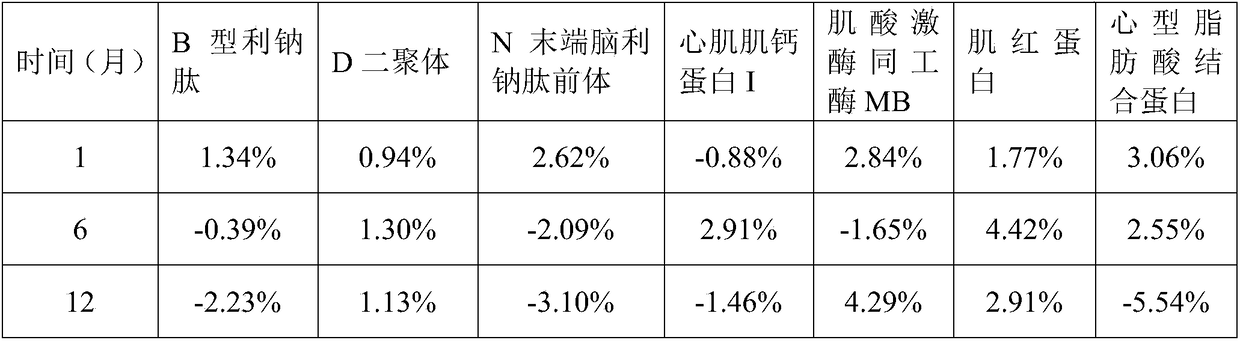
Cardiac muscle control material, preparation method therefor, detection kit and detection device for cardiac muscle
The invention relates to a cardiac muscle control material, a preparation method therefor, a detection kit and a detection device for cardiac muscle. The cardiac muscle control material comprises quality control component and protection component, the quality control component comprises at least one of B-type natriuretic peptide, D-dimer, NT-proBNP, cardiac troponin I, myoglobin, creatine kinase isozyme and cardioid fatty acid binding protein and heart fatty acid binding protein. The protective component comprises 5 mM to 100 mM of a buffer agent, 0.5 % to 5% by weight of an excipient, 0.05 mMto 5 mM of an antioxidant, 0.05 mM to 15 mM of a protease inhibitor, 0.5% to 10% by weight of a stabilizer and 0.01% to 2% by weight of a surfactant. The cardiac muscle control material disclosed bythe invention is good in stability.
Owner:深圳天深医疗器械有限公司
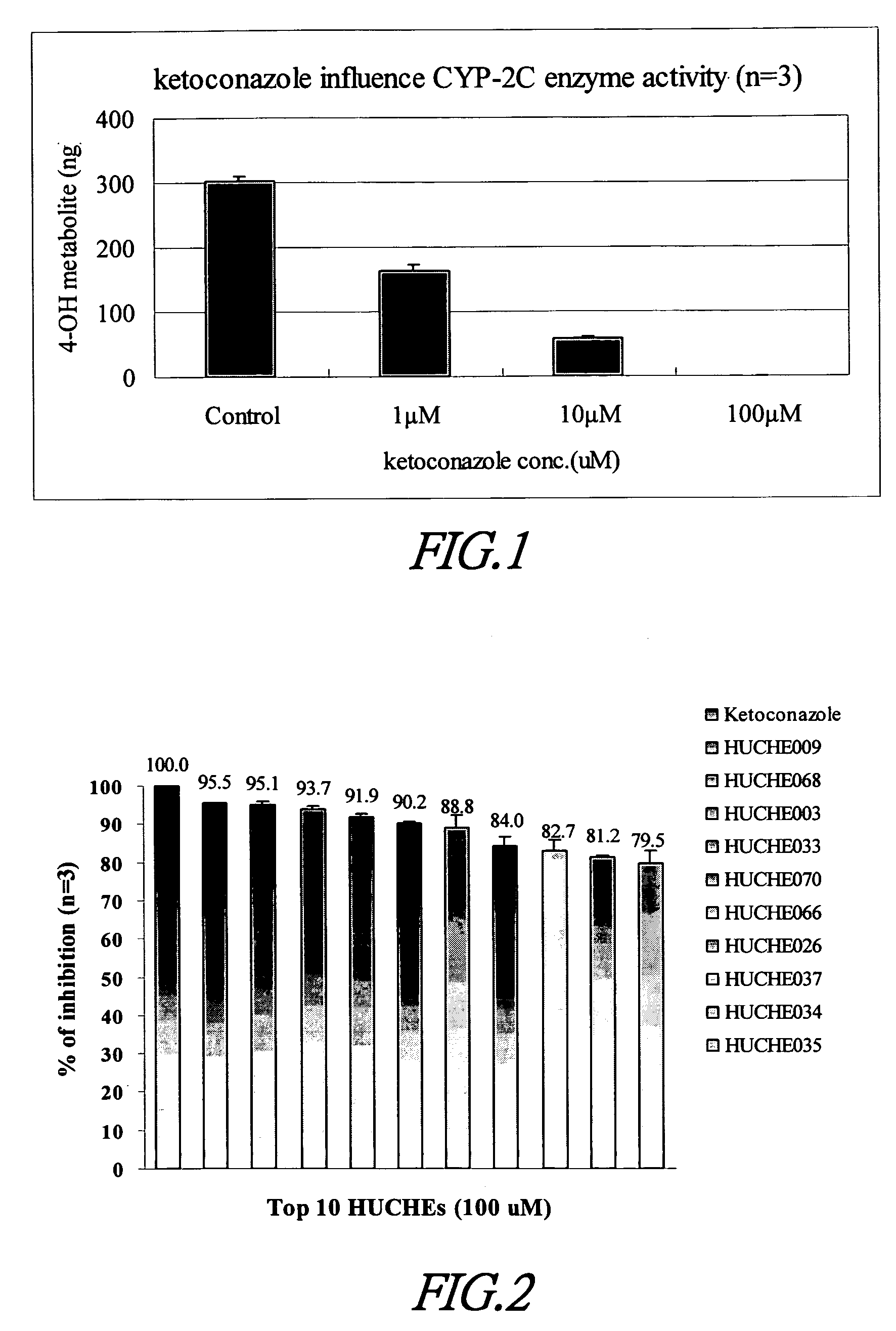
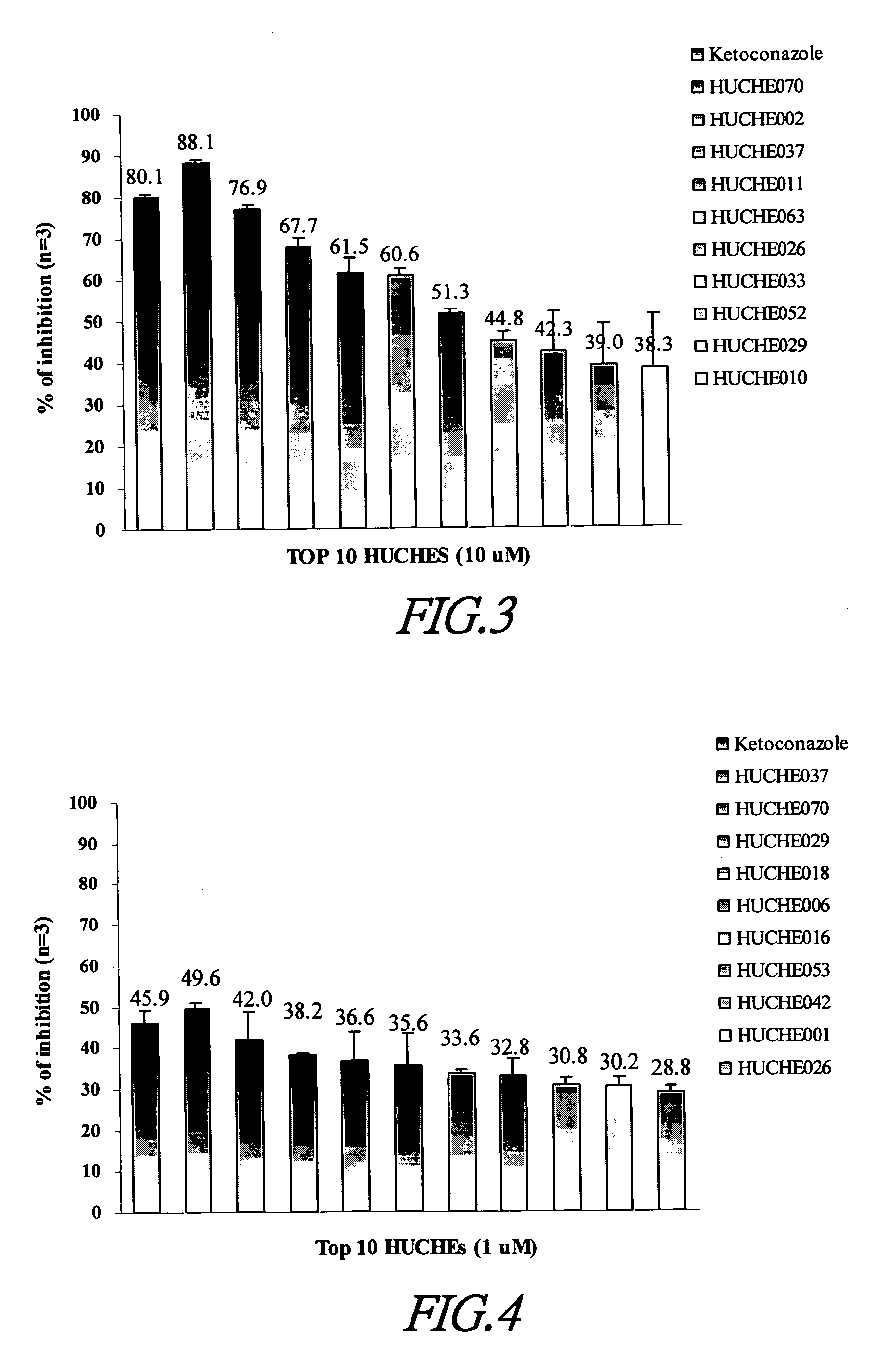
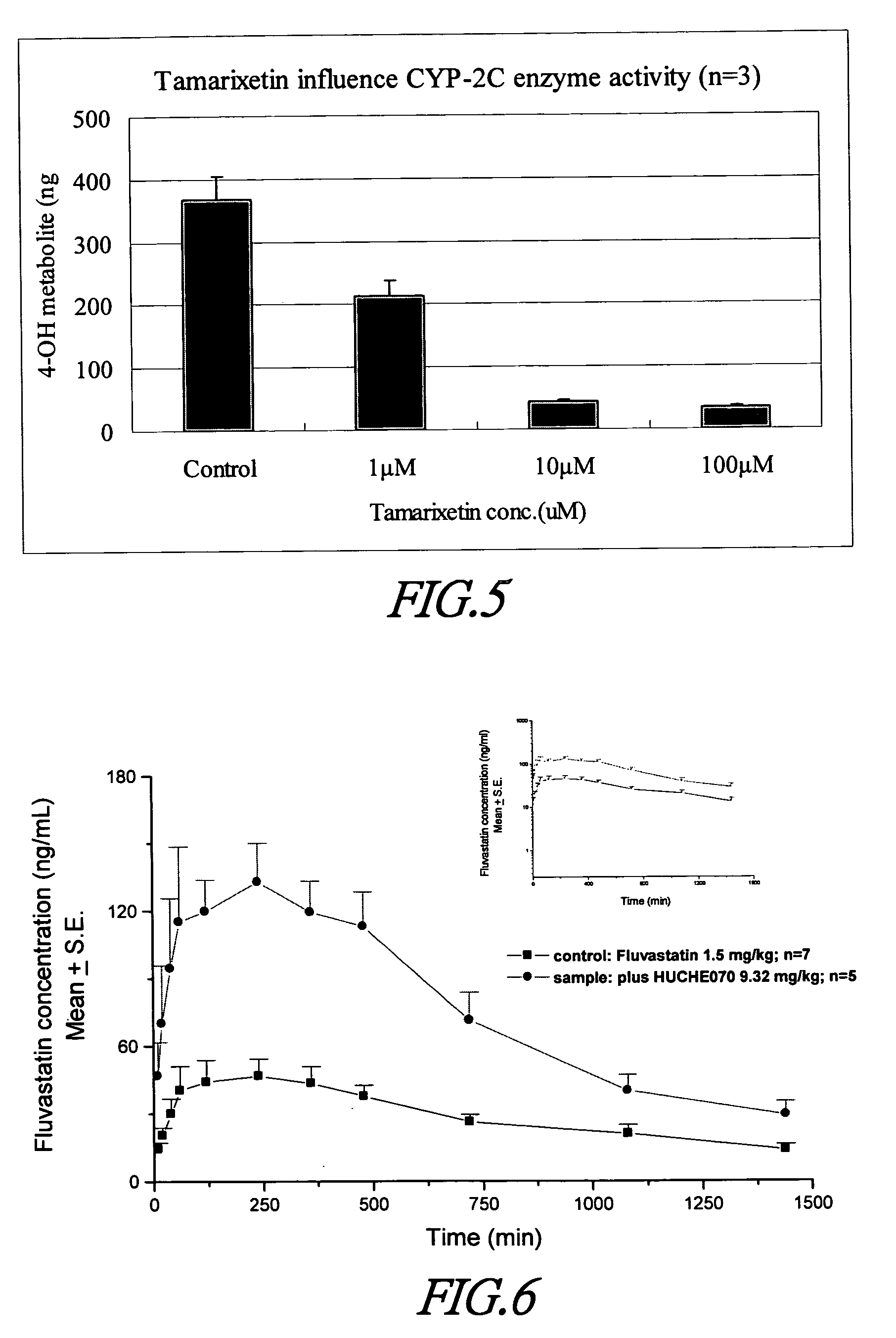
Cytochrome P450 2C9 inhibitors
InactiveUS20060069042A1Improve bioavailabilityBiocideKetone active ingredientsEriodictyolTamarixetin
This invention is to provide multiple specific inhibitors of cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2C9. These inhibitors can be derived from any combinations with the following compounds including: Tamarixetin, Formononetin, isoliquritigenin, Phloretin, luteolin, Quercitrin, quercetin, myricetin, Wongonin, Puerarin, Genistein, Nordihydroguaiaretic acid, Narigenin, Capillarisin, Chrysin, Fisefin, eriodictyol, 6-Gingerol, Isorhamneti, isoquercitrin, Morin, (+)-Taxifolin, isovitexin, 3-Phenylpropyl Acetate, Oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, β-Myrcene, cinnamic acid, Luteolin-7-Glucoside, Liquiritin, (+)Limonene, Homoorientin, Swertiamarin, Embelin, Daidzein, Poncirin, (−)-Epicatechin, ergosterol. These natural products can be used to enhance the bioavailability of therapeutic agents (drugs).
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
Use of inhibitors of protein kinase C epsilon to treat pain
The role of the epsi isozyme of protein kinase C ("PKCepsi") in pain perception, particularly hyperalgesia, methods of lessening pain through administration of inhibitors of PKCepsi, methods of identifying compounds that modulate pain, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of PKCepsi and PKCepsi-independent analgesic agent are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Creatine kinase isozyme detection kit and preparation thereof
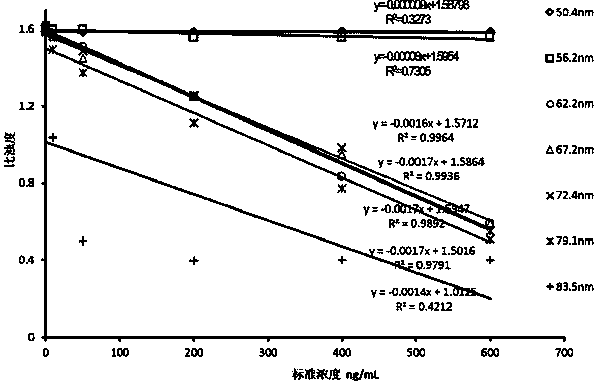
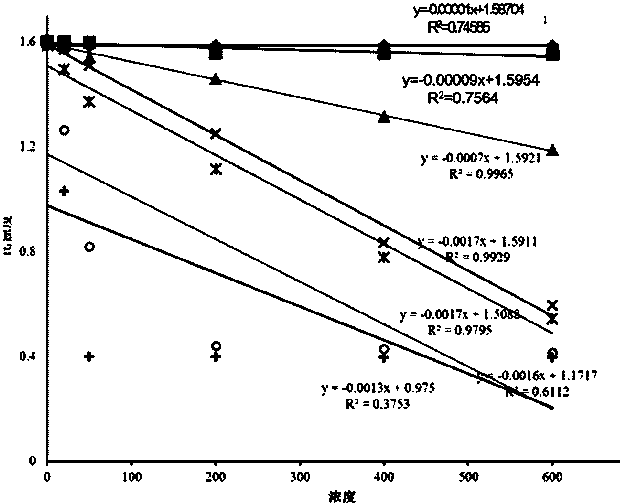
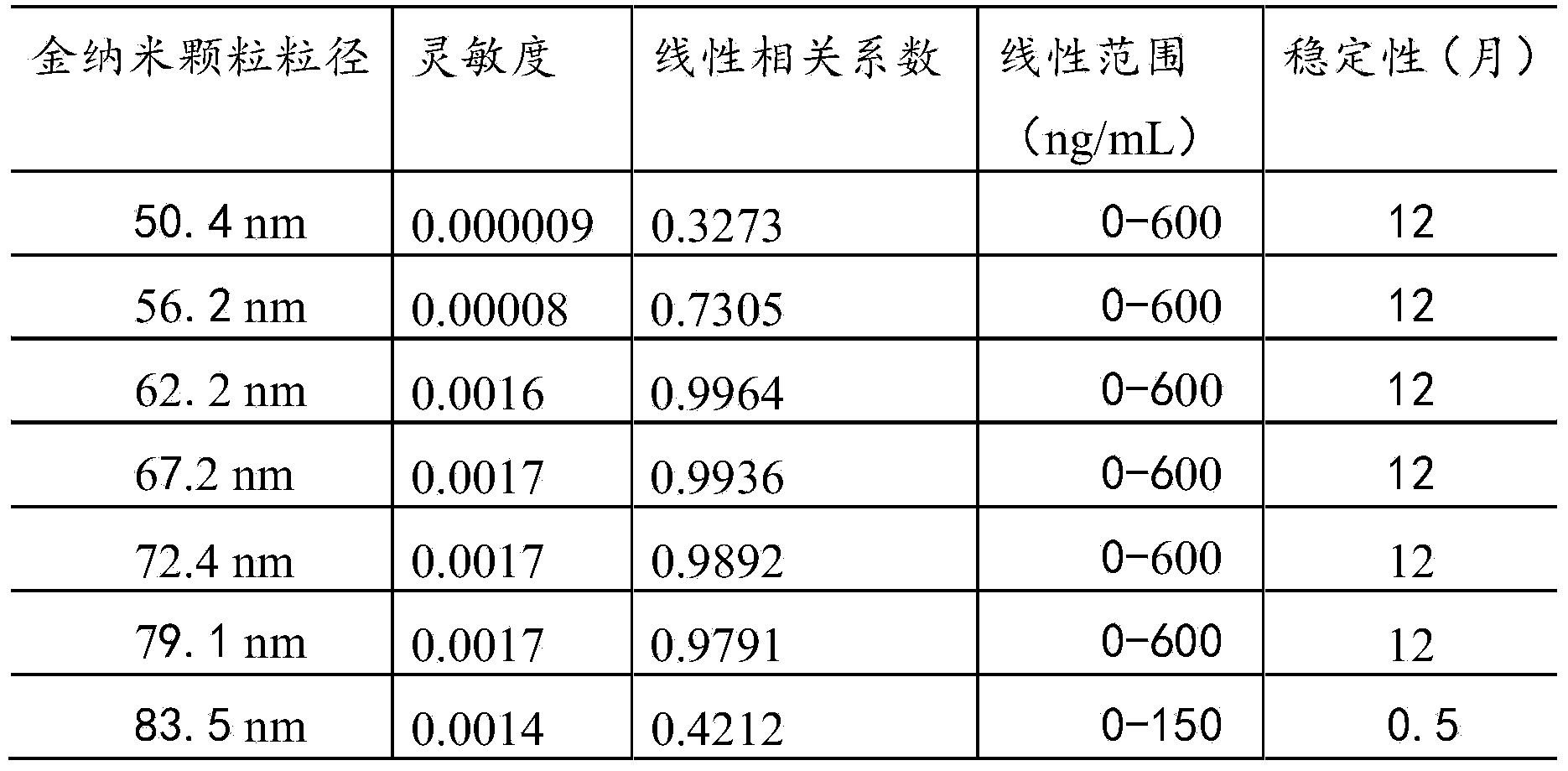
The invention provides a creatine kinase isozyme detection kit. The kit is based on colloidal gold immunoturbidimetry, and comprises reagents R2, and the reagents R2 are solutions of gold nanoparticles marked with creatine kinase isozyme antibodies. The kit is characterized in that the particle diameter of the gold nanoparticles is 62.2 nm to 79.1 nm, and the mass ratio of the gold nanoparticles and the antibodies is 50:20-60. The invention further provides a preparation method of the kit. The kit has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, fast in response and good in stability, no sediment is generated after a reaction, a biochemical analyzer is convenient to clean, and the service life of the biochemical analyzer is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING JIUJIAYI TECH
Creatine phosphokinase isozyme chemiluminescence immune quantitative detection kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102809651AStrong specificityImprove performanceMaterial analysisIsozymeAntibody Coated Plate
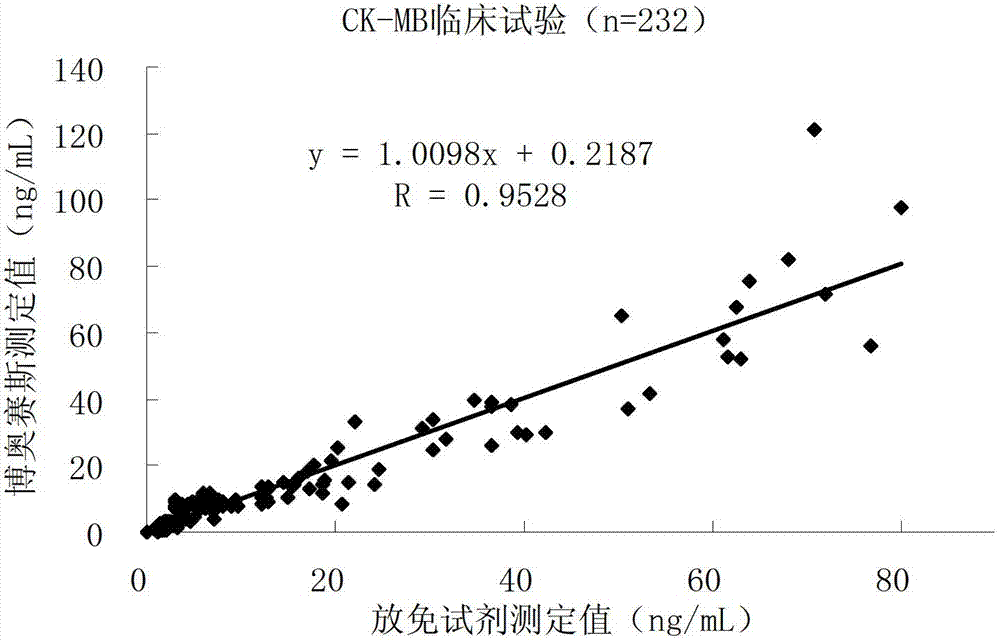
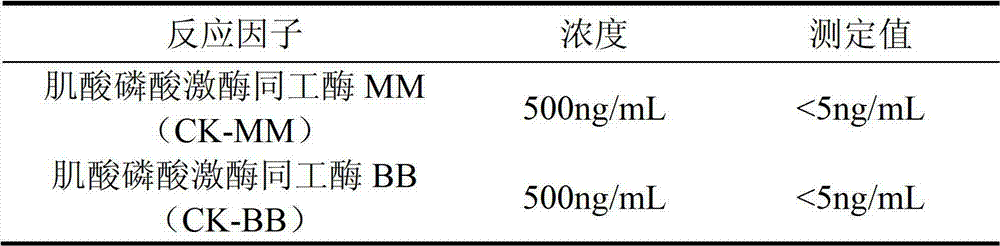
The invention discloses a creatine phosphokinase isozyme chemiluminescence immune quantitative detection kit and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) antibody coated plate, a CK-MB antibody enzyme conjugate, a CK-MB calibrator, a CK-MB quality control product, a 20-times concentrated lotion, a light-emitting solution A and a light-emitting solution B. In addition, the invention also discloses the preparation method for the creatine phosphokinase isozyme chemiluminescence immune quantitative detection kit. Compared with the conventional kit, the kit provided by the invention is operated conveniently and safely, and does not pollute environment. Moreover, the kit also has the advantages that the concentration range of a detection sample is wide, the validity period of a reagent is long, the stability is high and the like.
Owner:BIOSCIENCE (TIANJIN) DIAGNOSTIC TECH CO LTD
Method for degrading octyl phenol by utilizing laccase
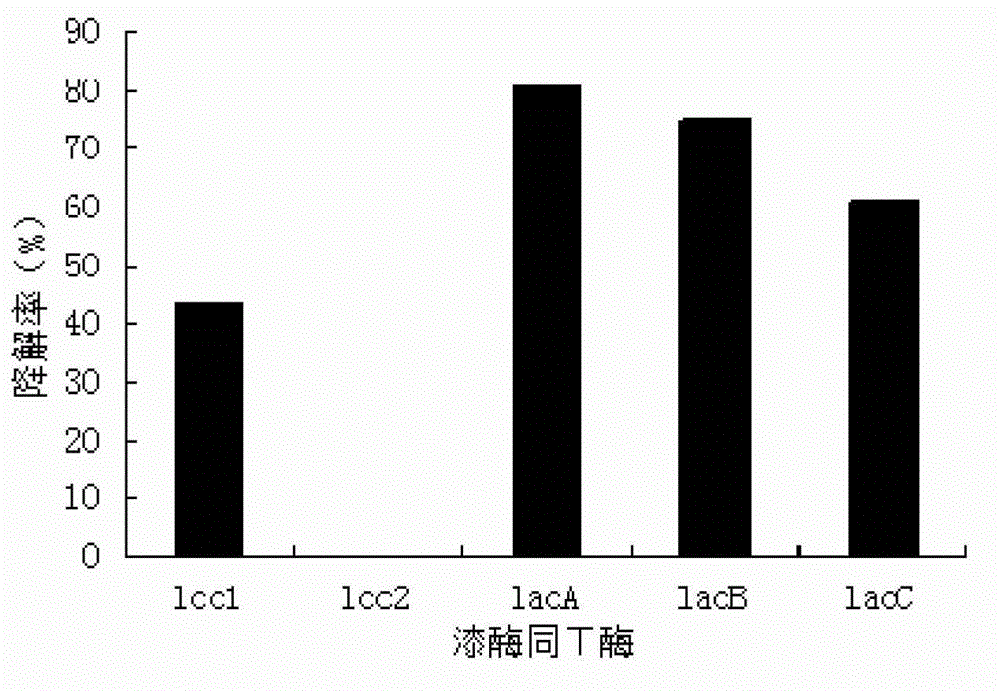
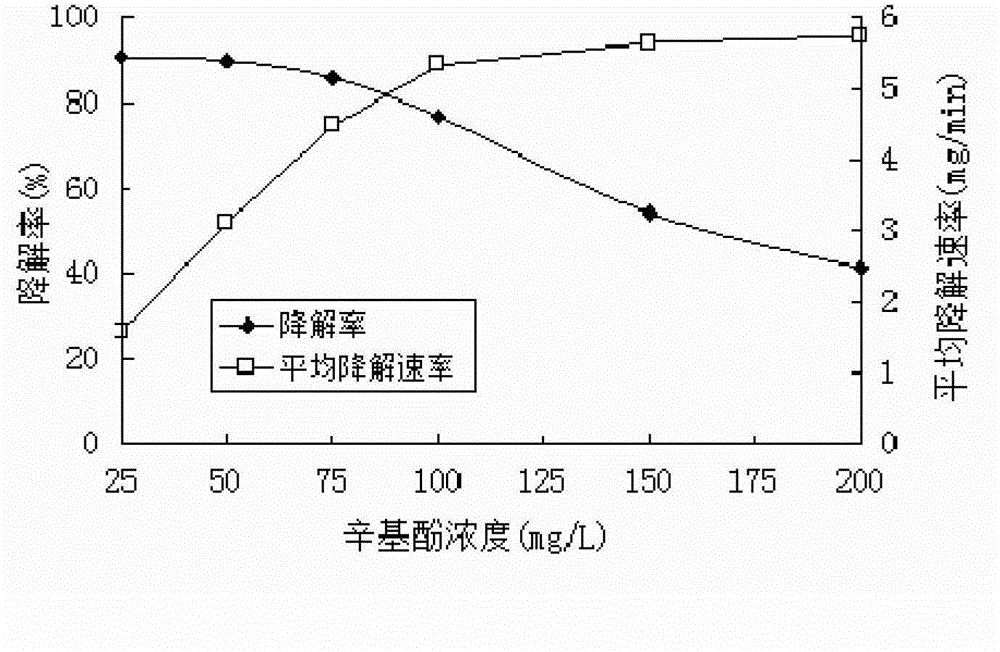
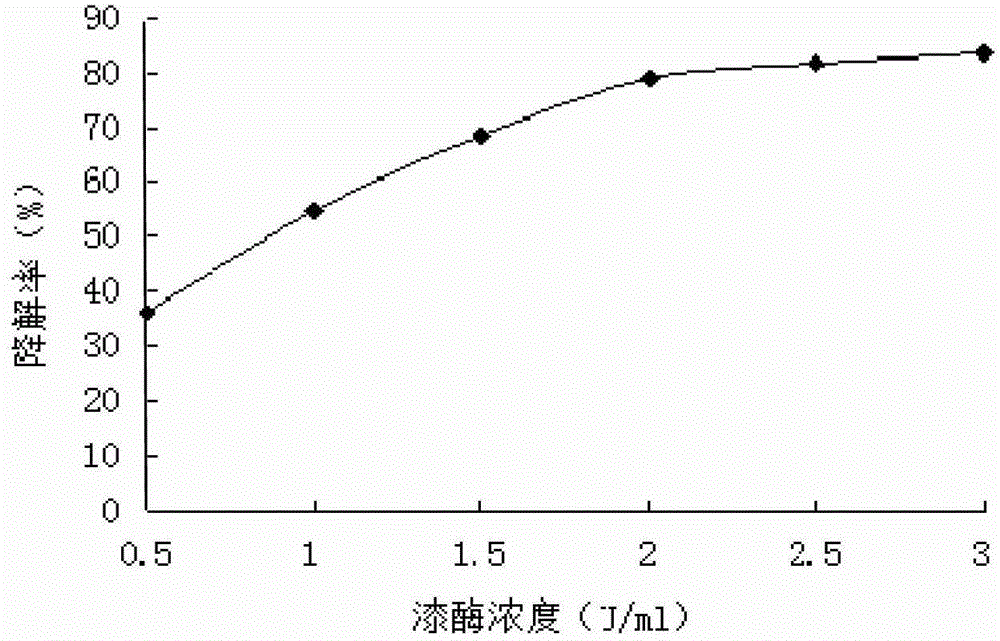
ActiveCN103055464AImprove removal efficiencyNo pollution in the processMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesIsozymeEnzyme catalysis
The invention discloses a method for degrading octyl phenol by utilizing laccase. The method comprises the steps of: preparing a LacA enzyme solution; adjusting the concentration of the octyl phenol within 25-200 mg / L; adding the laccase having a concentration of 0.5-3 U / mL in the LacA enzyme solution; controlling the pH of a reaction system to 3.5-6; and degrading under the condition of keeping the temperature at 25-50 DEG C. As a bio-enzyme catalysis technology is adopted, the method for degrading the octyl phenol by utilizing the accase has outstanding characteristics of high removal efficiency, good convenience and safety, no pollution and the like. By comparing specifity of different isozymes to the octyl phenol, selecting the laccase having the strongest specifity to the octyl phenol and adding a medium substance, the method for degrading thhe octyl phenol by utilizing the laccase increases the reaction efficiency of the laccas, redudes reaction time, therefore reduces usage amount of the laccase, and lowers operating cost. The method for degrading the octyl phenol by utilizing the laccase can degrade octyl phenol efficiently and can obtain the degradation rate up to 97.2% after 12-hour reaction under a suitable catalysis condition when the concentration of the octyl phenol is 100 mg / L.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Methods for maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity in hypertensive subjects using a delta-PKC inhibitor
InactiveUS20090062208A1Avoid disruptionEasy to transportPeptide/protein ingredientsEndocrine system disorderIsozymeRisk stroke
Methods for maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier are described. Compounds that act to inhibit the action of the delta isozyme of protein kinase C (PKC) to prevent disruption of the blood-brain barrier in hypertensive subjects are described, to, in one embodiment, decrease the likelihood of hypertension-induced stroke or hypertension-induced encephalopathy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Genetically modified reduced-browning fruit-producing plant and produced fruit thereof, and method of obtaining such
ActiveUS20110004957A1Reduced activityReduce browning in the fruitSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesWild typePolyphenol oxidase
A genetically modified fruit-producing plant, said plant having sufficiently reduced total Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO) activity relative to a wild type of said plant to reduce browning in the fruit of said plant relative to said wild type, wherein the reduced total PPO activity results from a reduction in activity of at least two PPO isoenzymes in said plant relative to said wild type, or a cell, seed, seedling, part, tissue, cell, fruit or progeny of said plant.
Owner:OKANAGAN SPECIALTY FRUITS
Detecting method for fusarium oxysporum pathogenicless strain
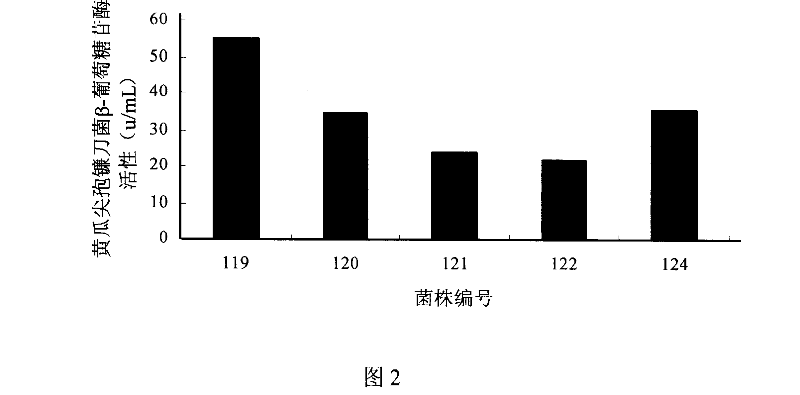
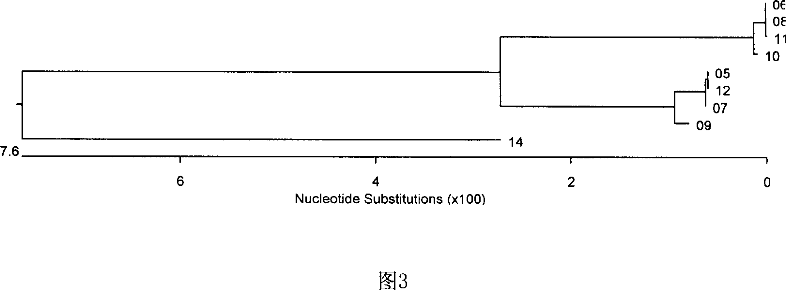
The invention discloses a detecting method of avirulent strains of fusarium, which is characterized in including following steps: (a) detecting isozyme of fusarium; (2) detecting beta-glucosaccharase of fusarium; (c) sequence detecting ITS of fusarium; (d) detecting liquid culture of fusarium, the detecting method can discriminate avirulent strains of fusarium effectively to use thereof as immuno inoculation dose for curepreventing fusarium wilt.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chemiluminescent quantitative detection kit for detection of creatine kinase MB in serum/plasma and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109490549ALow costHigh detection sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexCreatine kinase
The invention belongs to the technical field of immunoassay and particularly relates to a chemiluminescent quantitative detection kit for detection of creatine kinase MB in serum / plasma and a preparation method thereof. The chemiluminescent quantitative detection kit for detection of creatine kinase MB in serum / plasma comprises: 1) magnetic particles coated with streptavidin; 2) biotin-labeled creatine kinase MB antibody; 3) acridinium ester-labeled creatine kinase MB antibody; 4) calibrator and quality control material. The calibrator and the quality control material contain high and low concentration points respectively. The chemiluminescent quantitative detection kit for detection of creatine kinase MB in serum / plasma provided herein employs the principle of double-antibody sandwich process as well as an avidin-biotin system and employs acridinium ester to chemically illuminate; detection sensitivity of the kit herein is greatly improved, reaction time is shortened, and agent cost is reduced.
Owner:DIRUI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
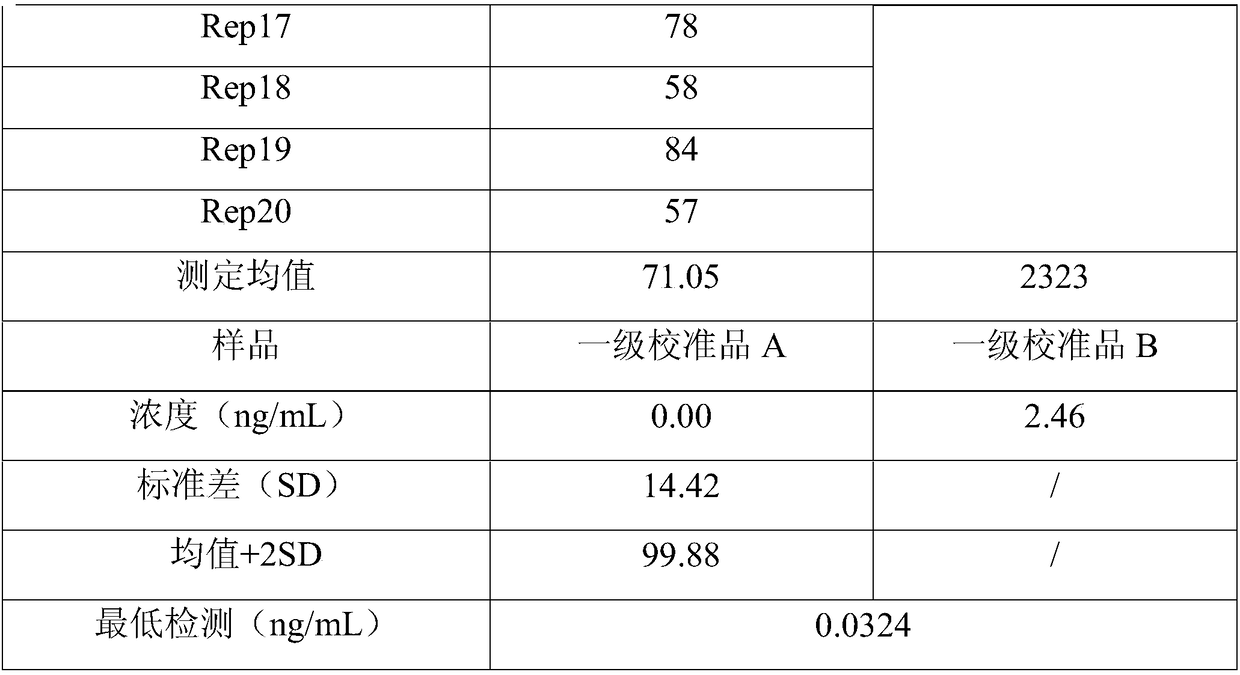
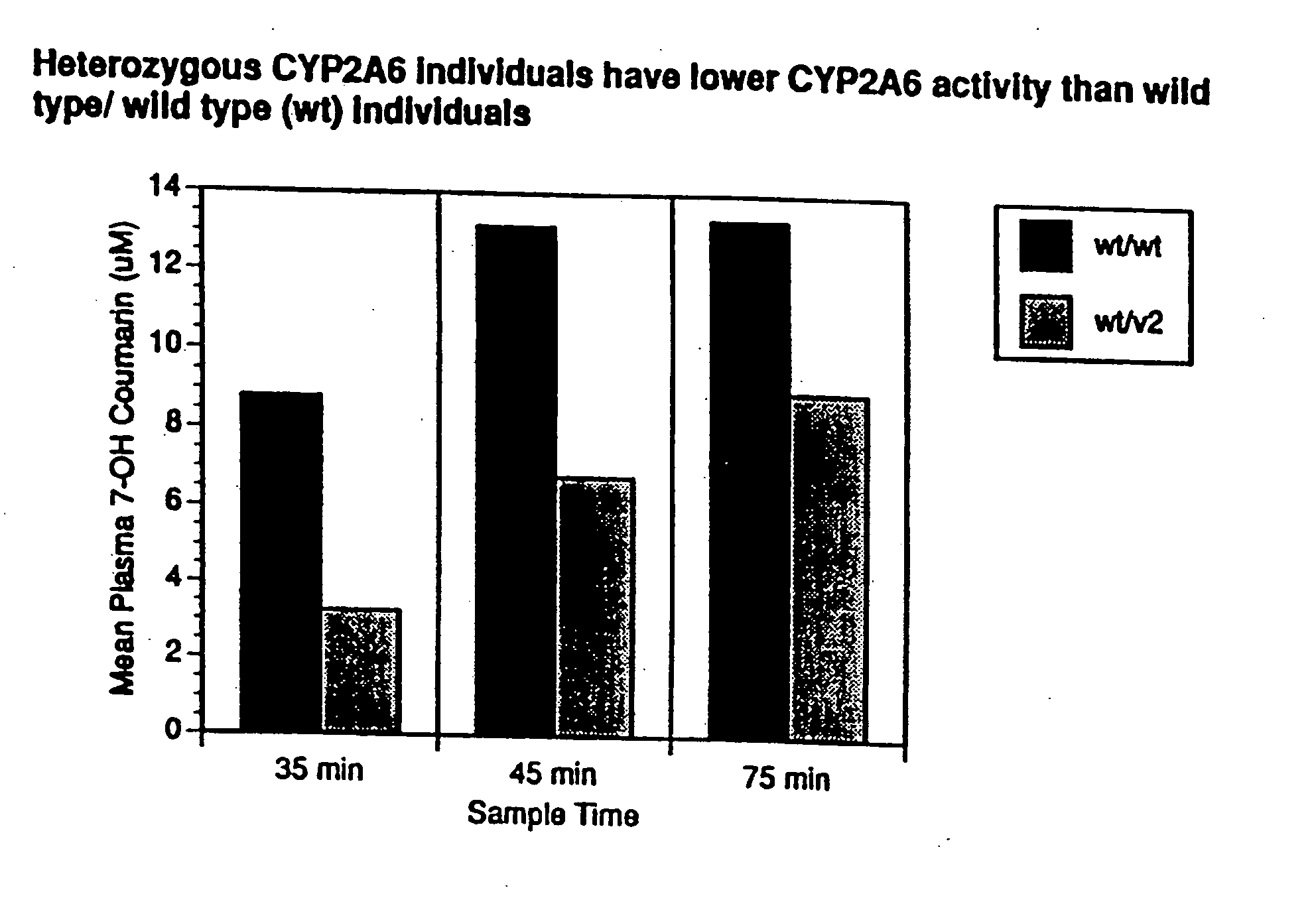
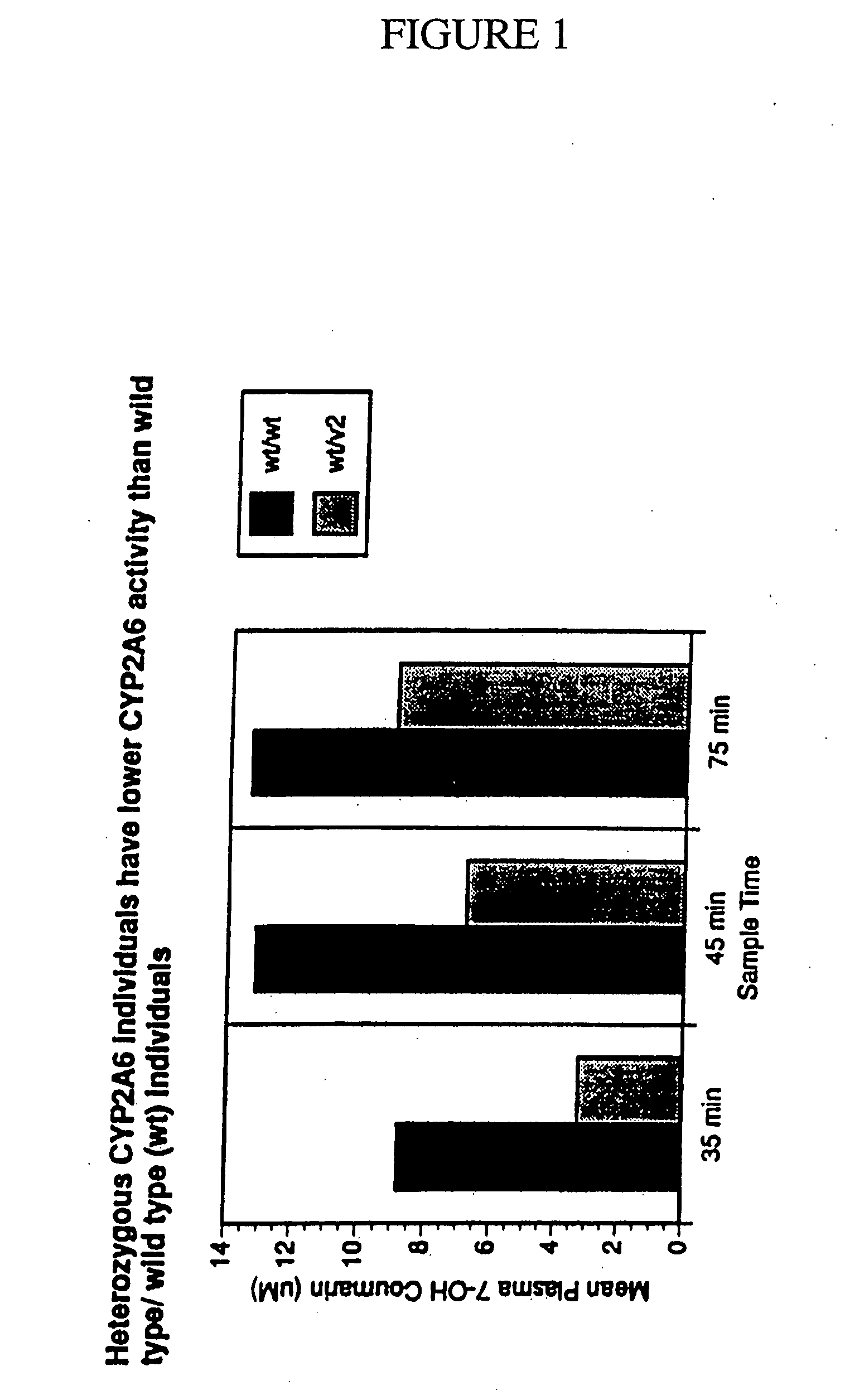
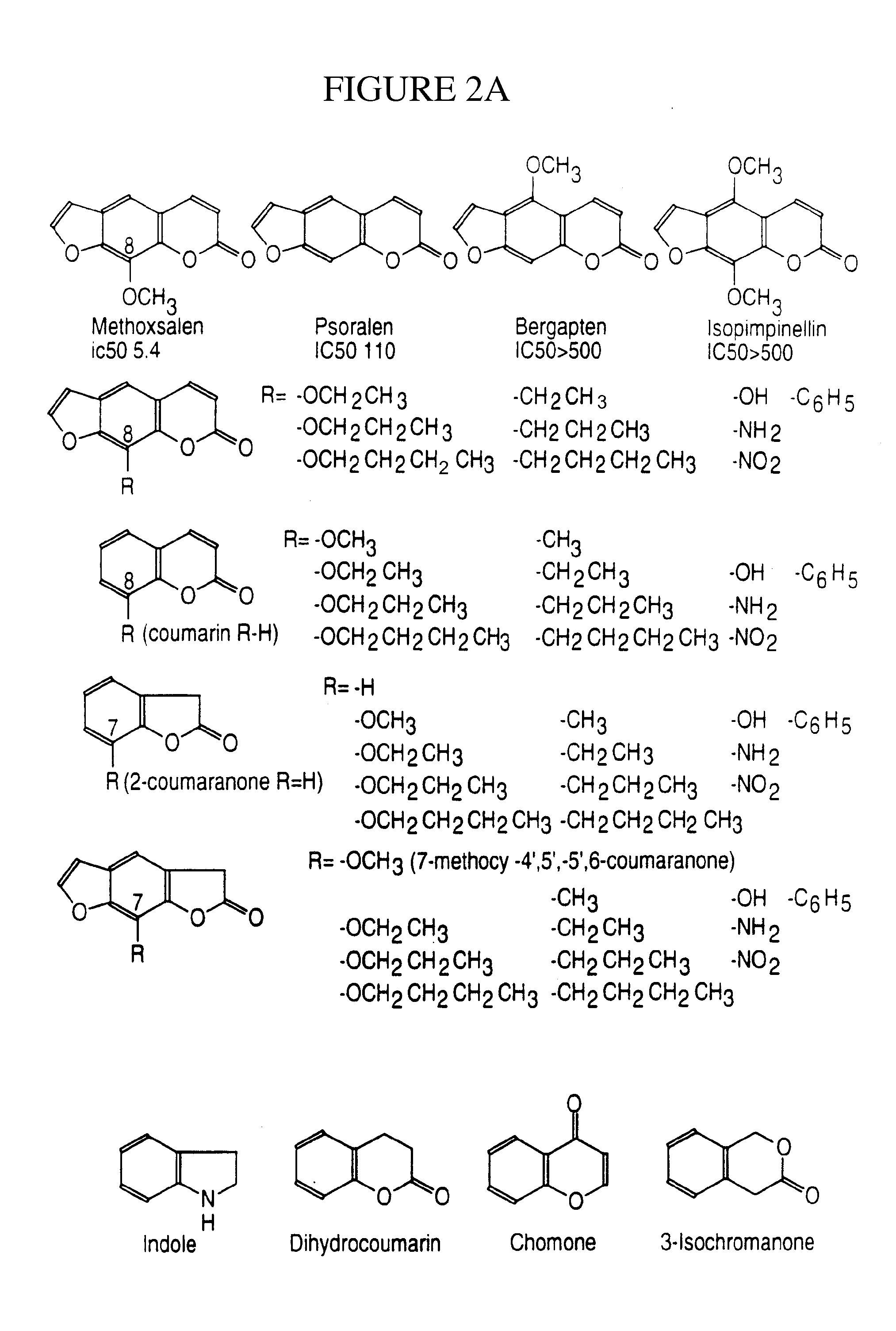
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on cyp2a enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com