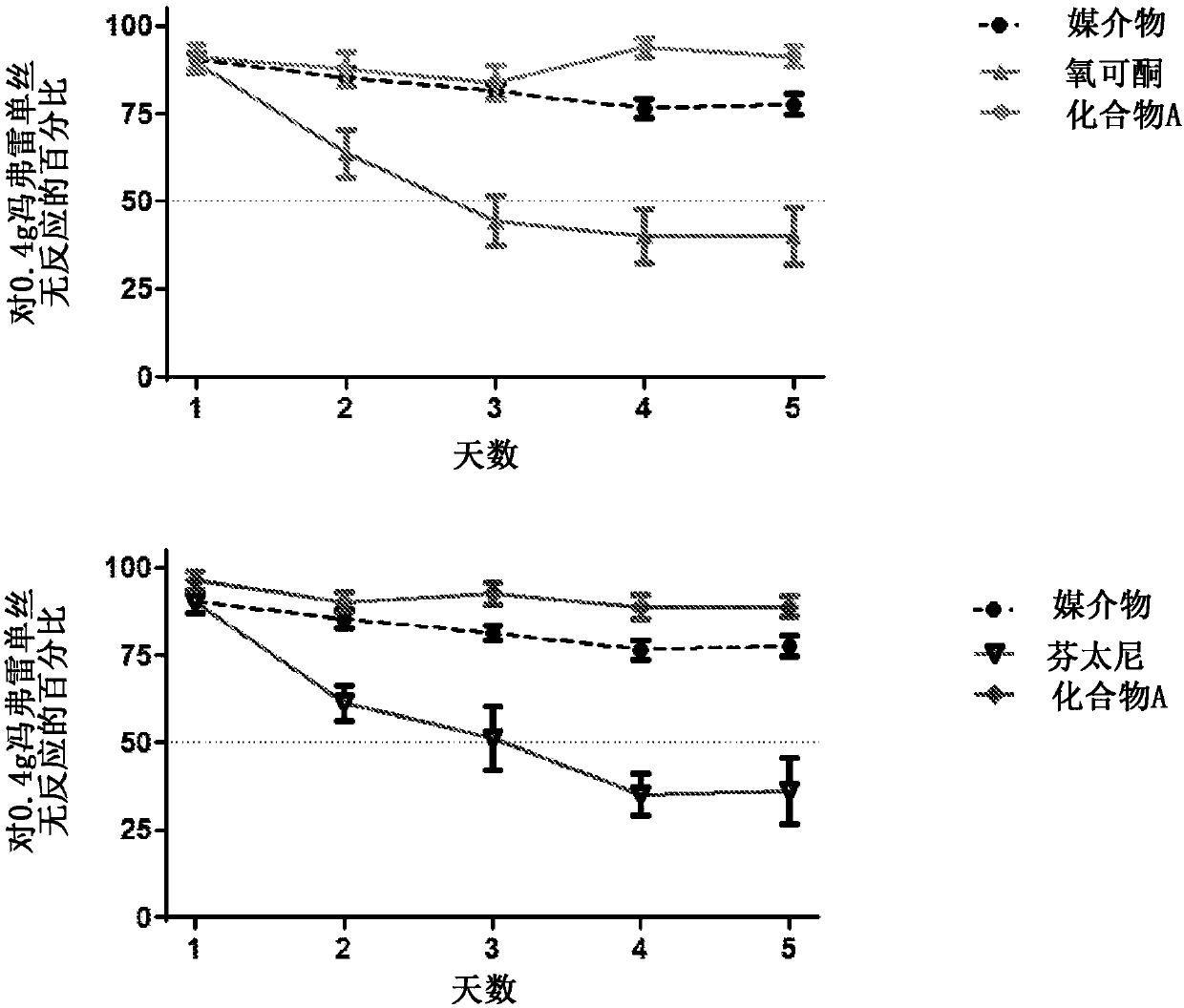
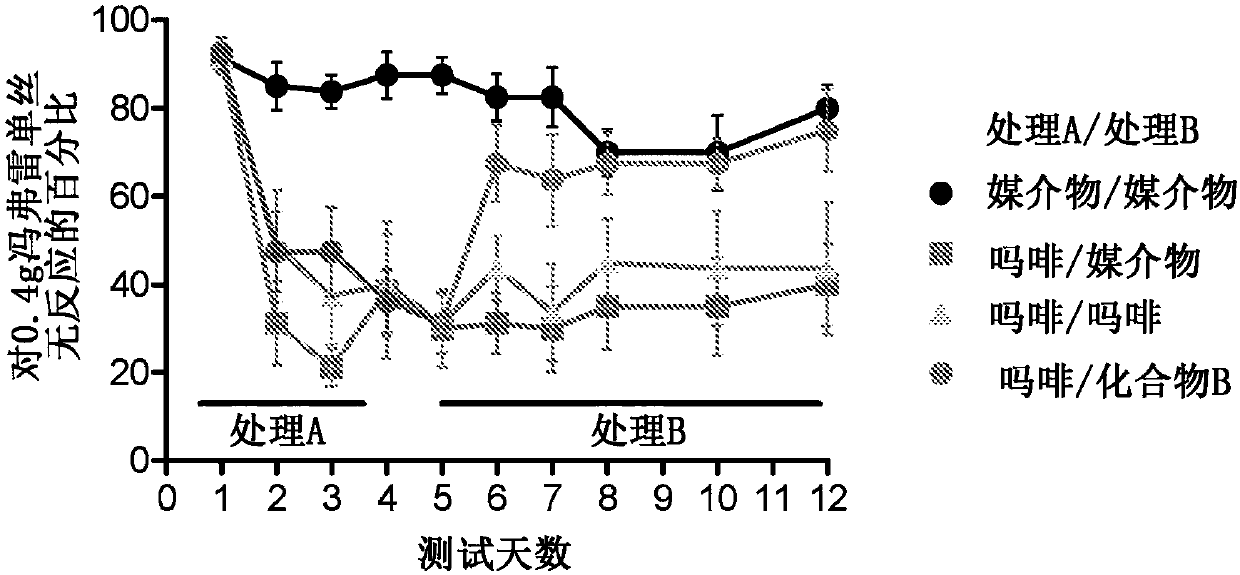
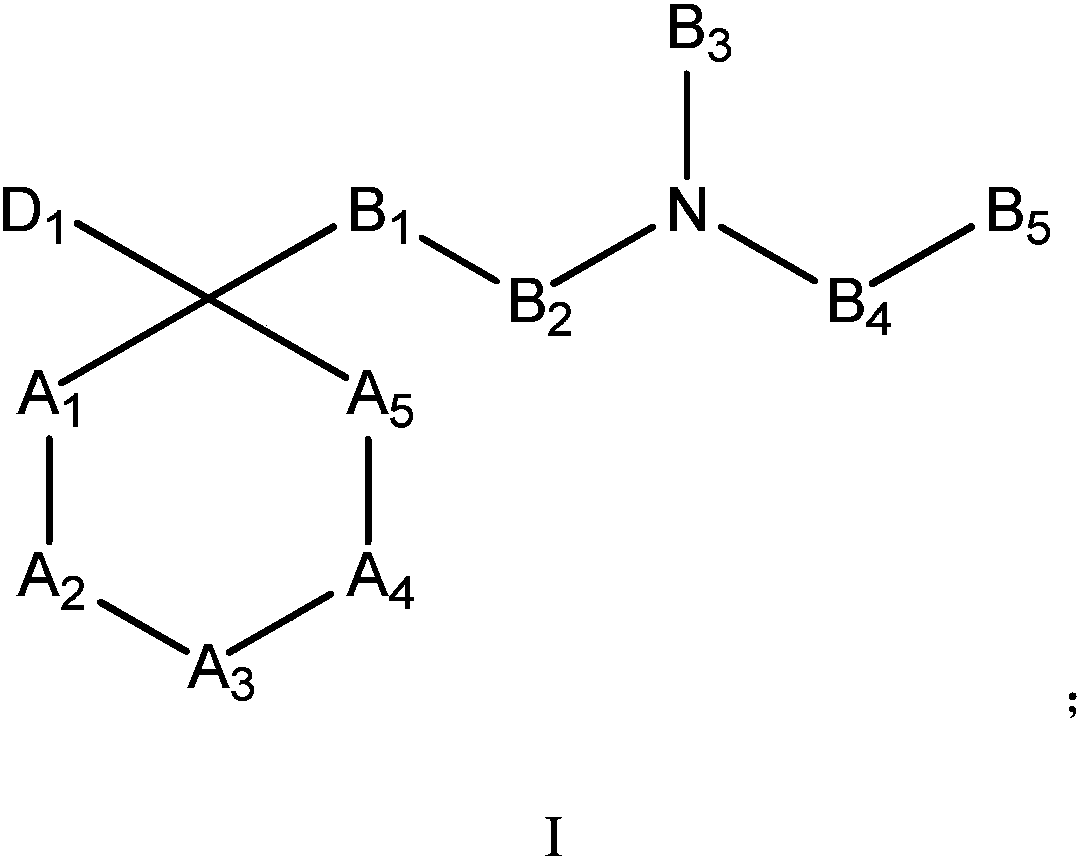
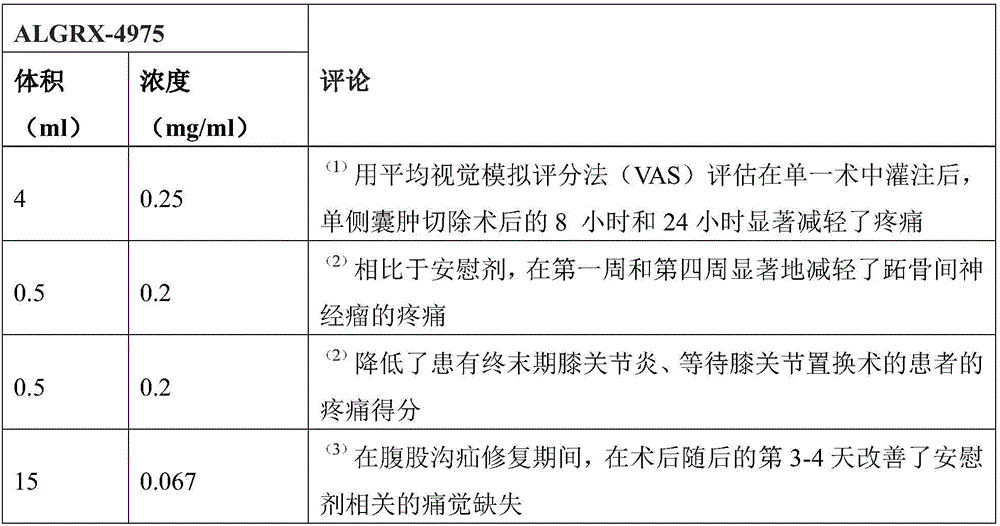
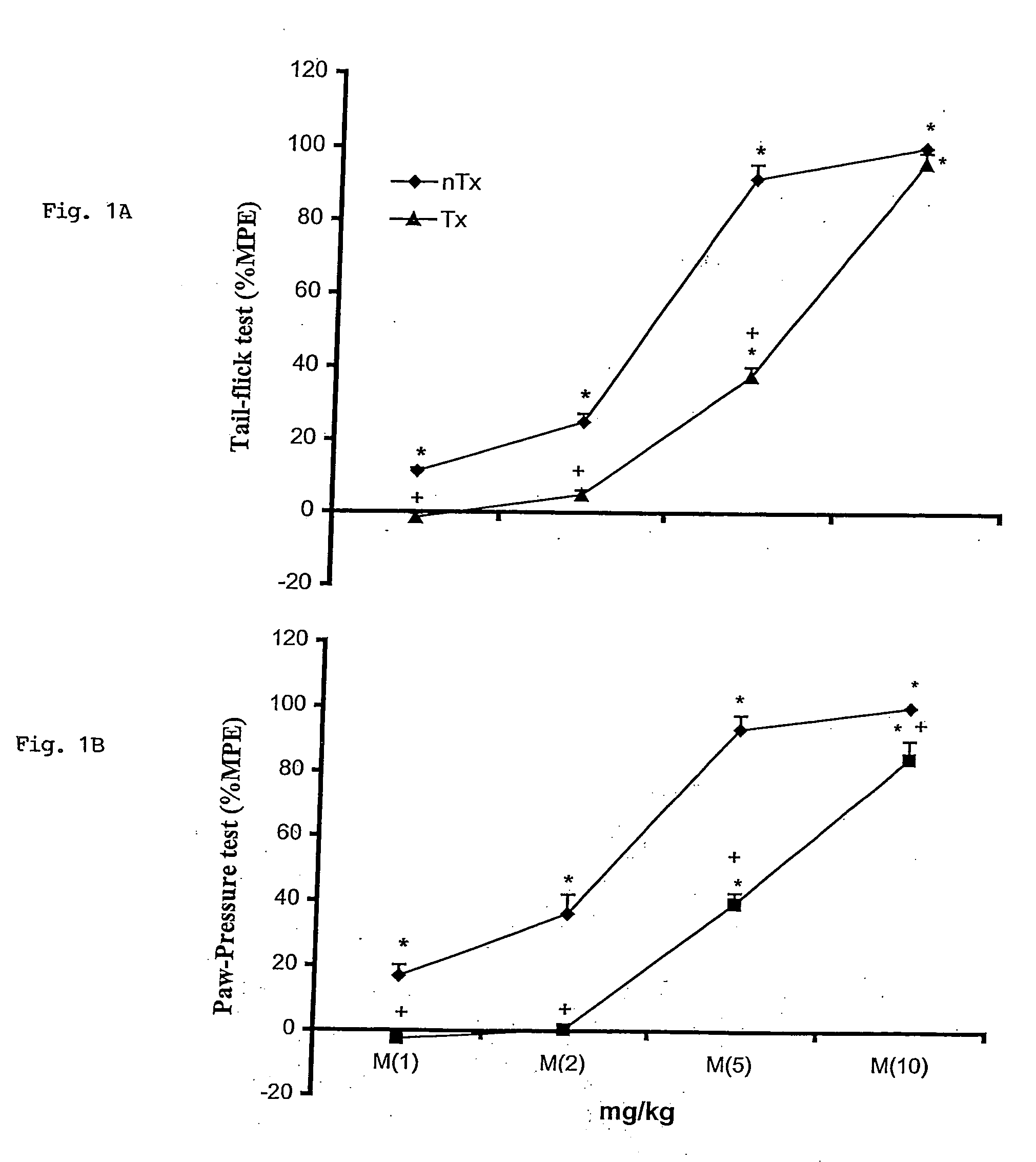
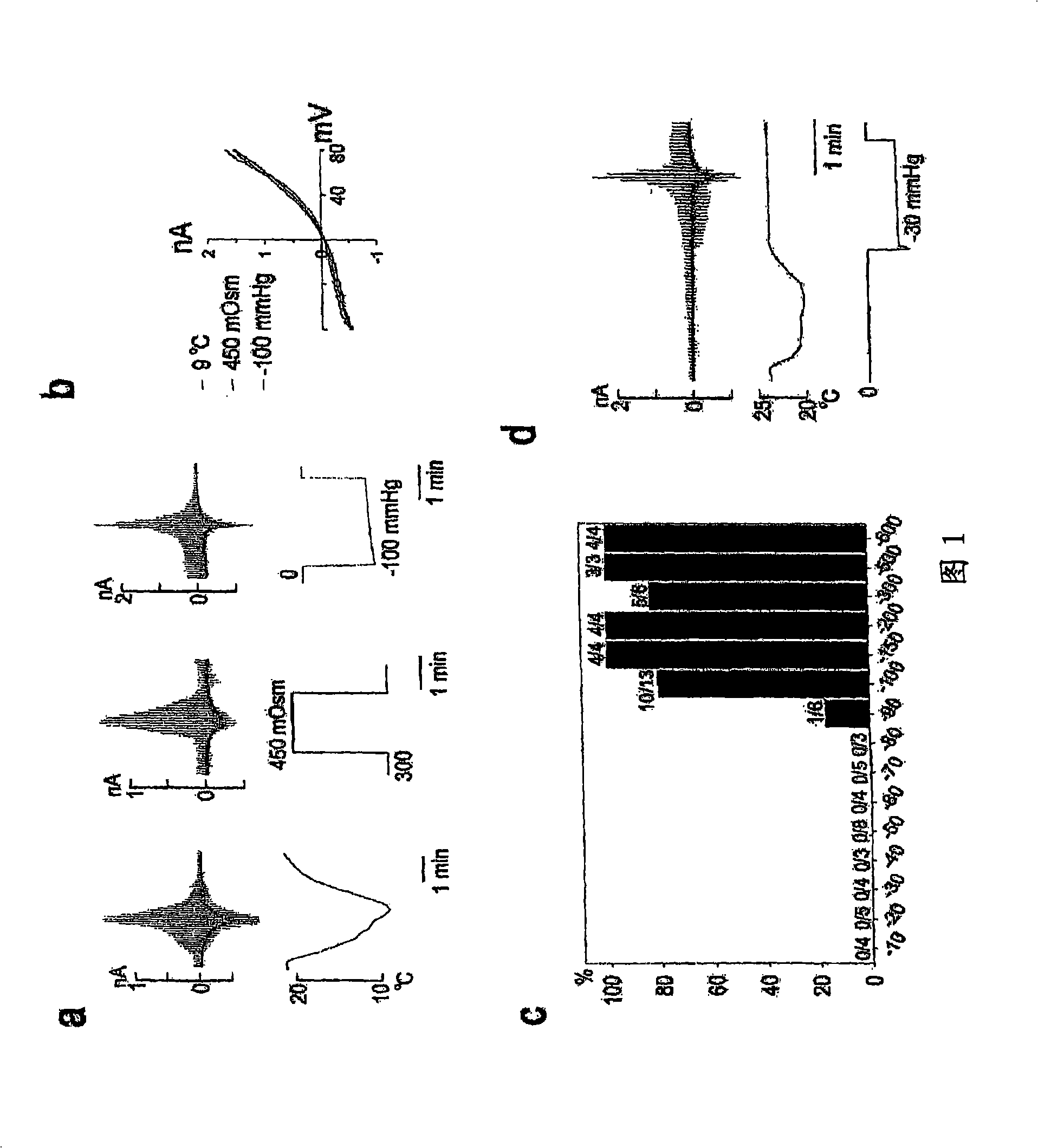
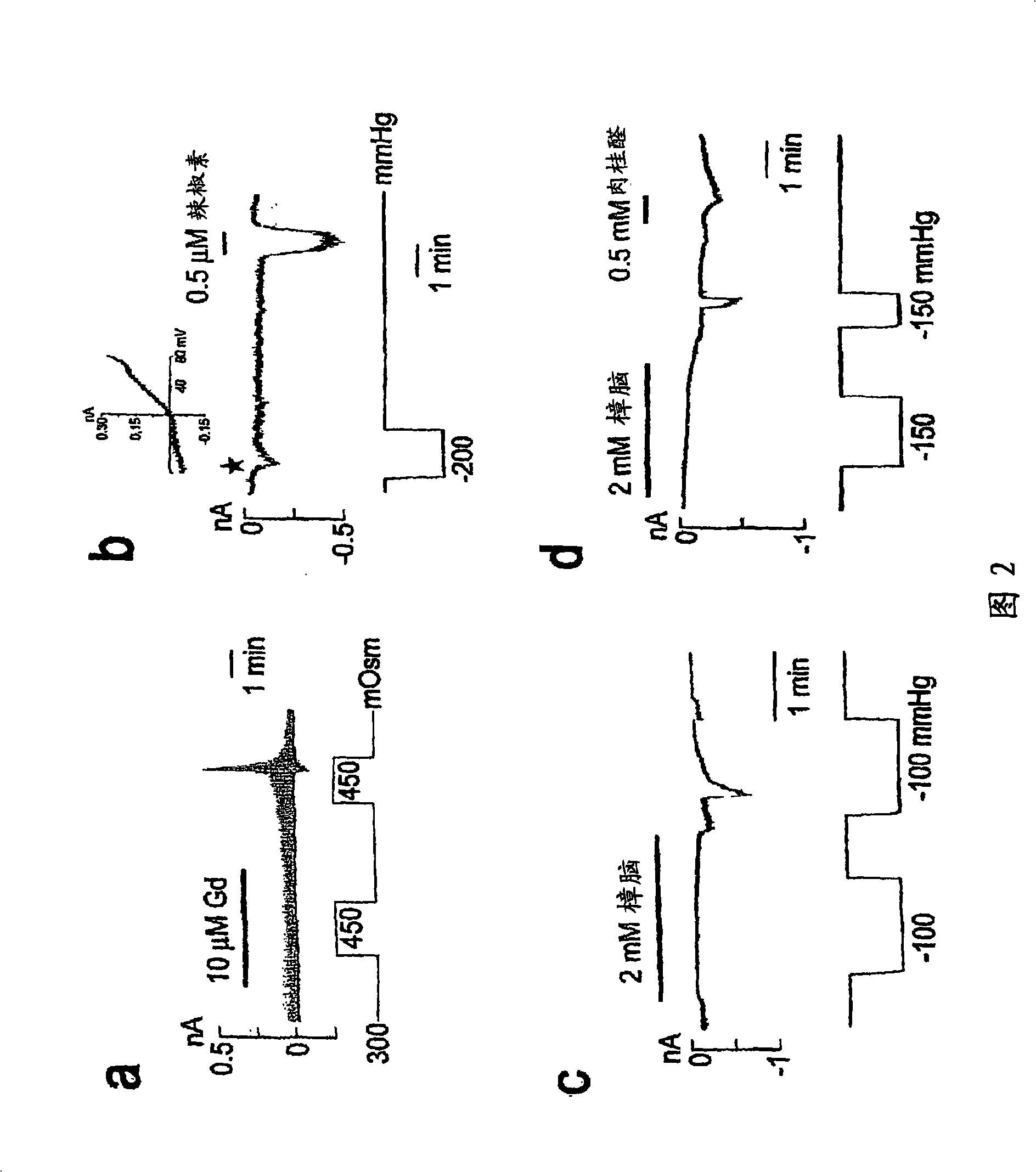
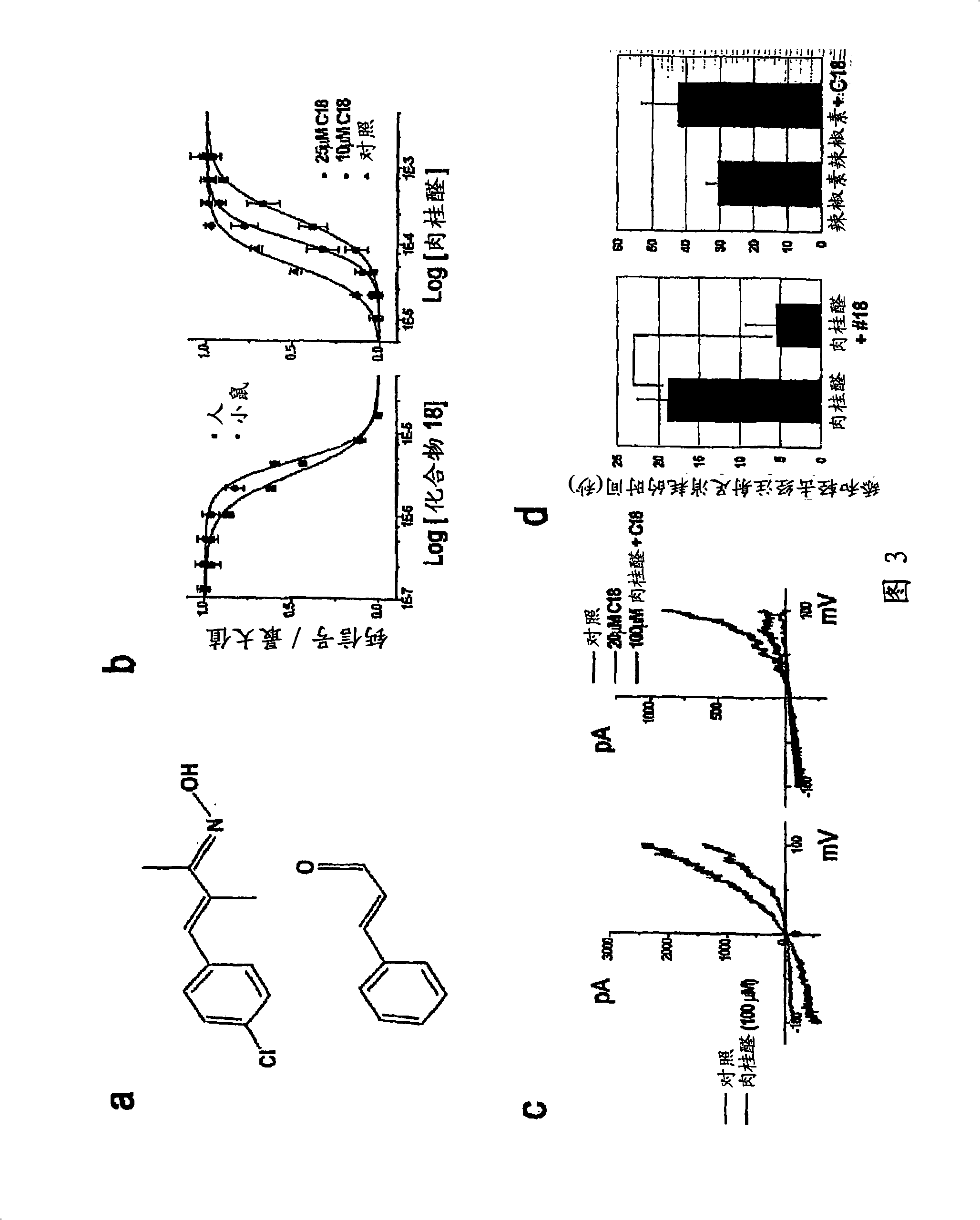
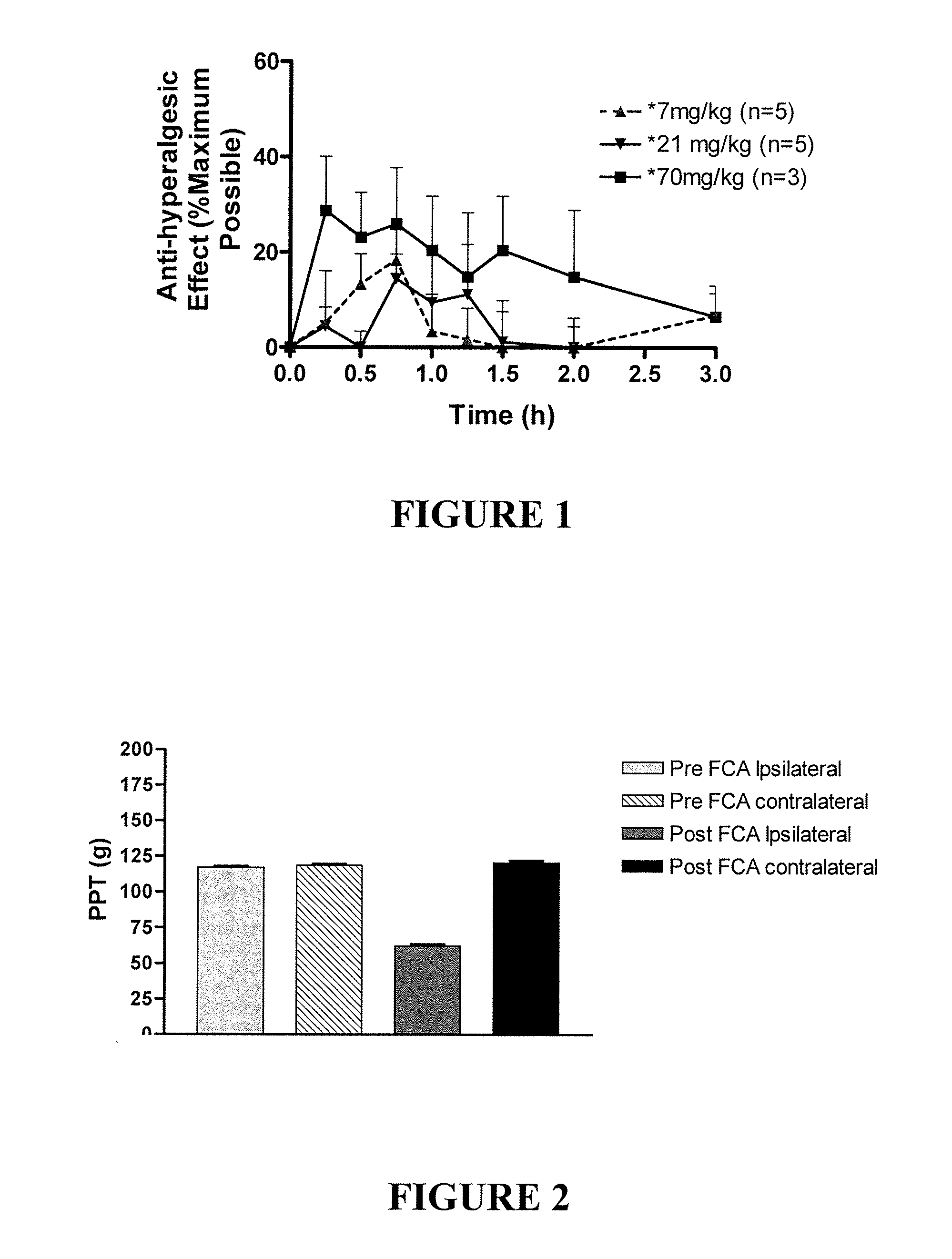
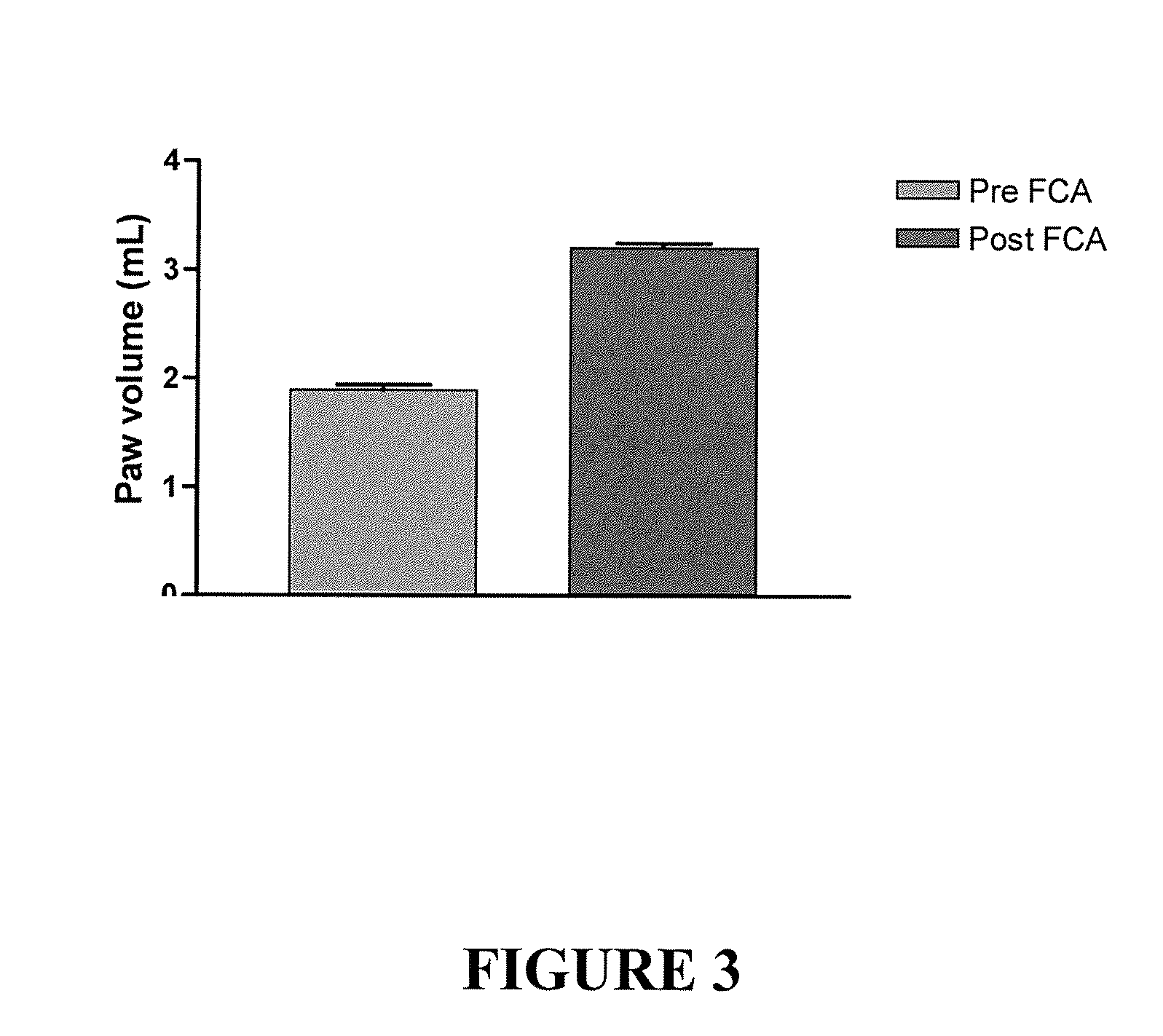
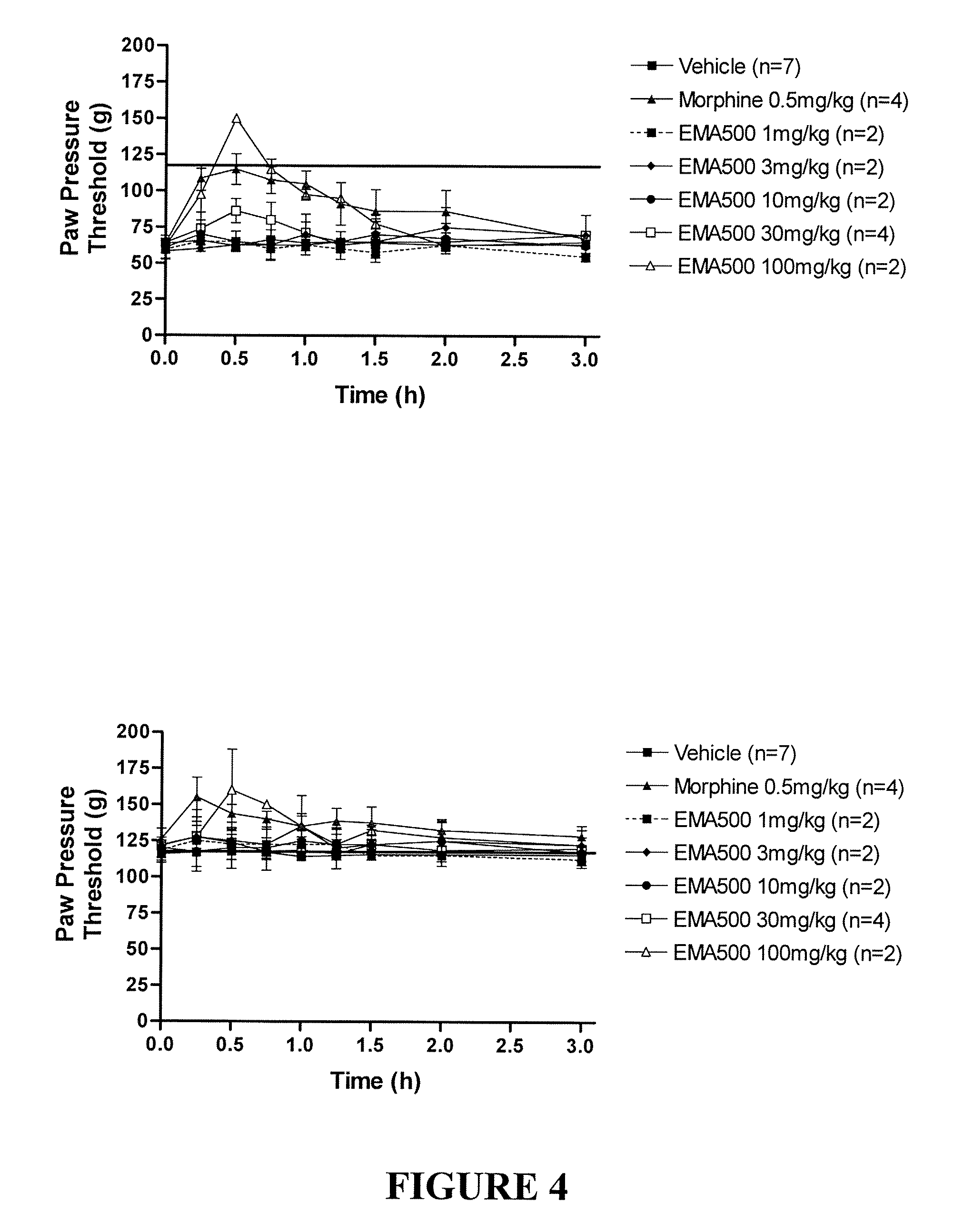
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Hyperalgesia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hyperalgesia (/ˌhaɪpərælˈdʒiːziə/ or /-siə/; 'hyper' from Greek ὑπέρ (huper, “over”), '-algesia' from Greek algos, ἄλγος (pain)) is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can cause hypersensitivity to stimulus. Prostaglandins E and F are largely responsible for sensitizing the nociceptors. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of sickness behavior, the evolved response to infection.
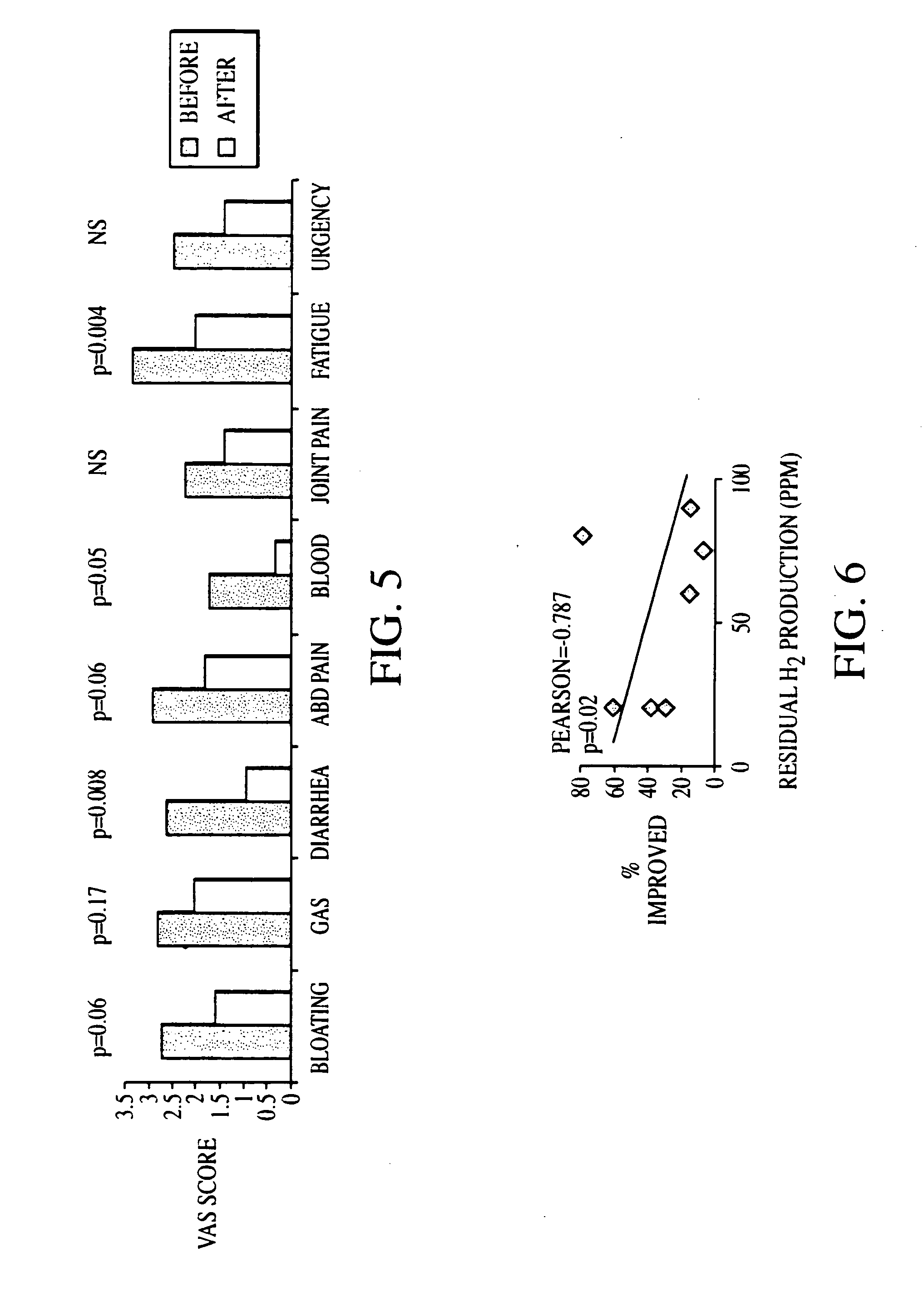
Methods of diagnosing or treating irritable bowel syndrome and other disorders caused by small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
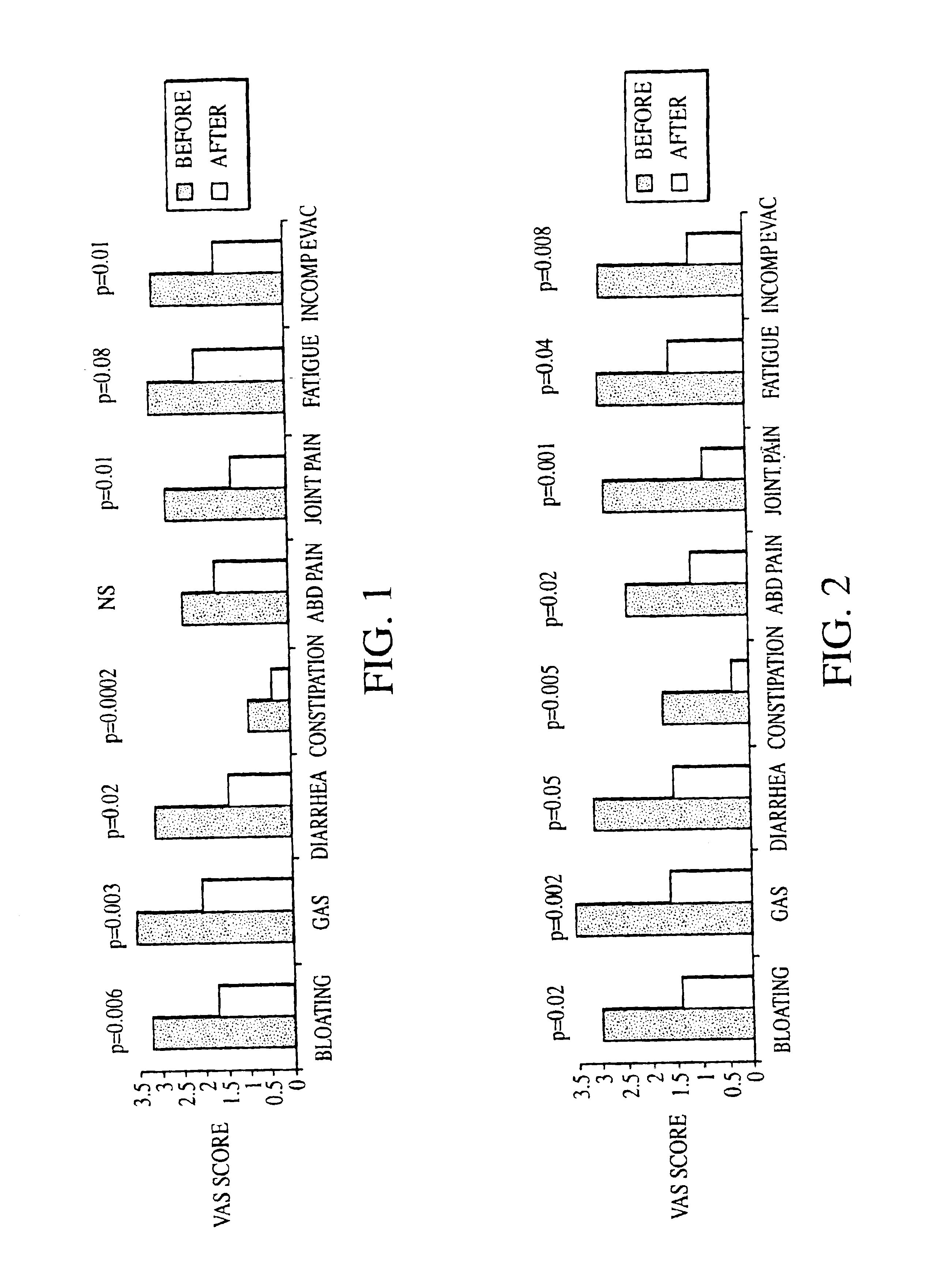
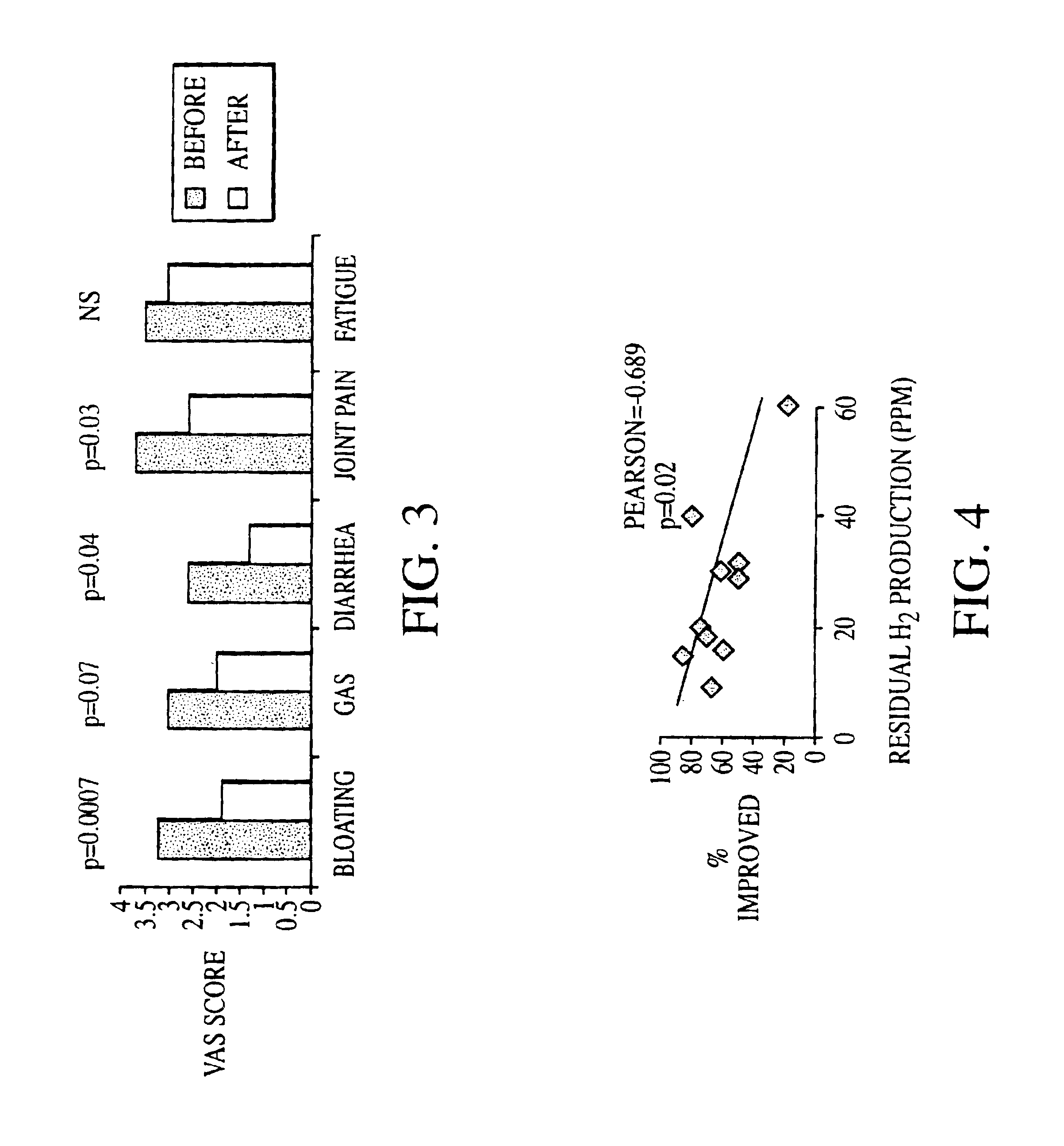
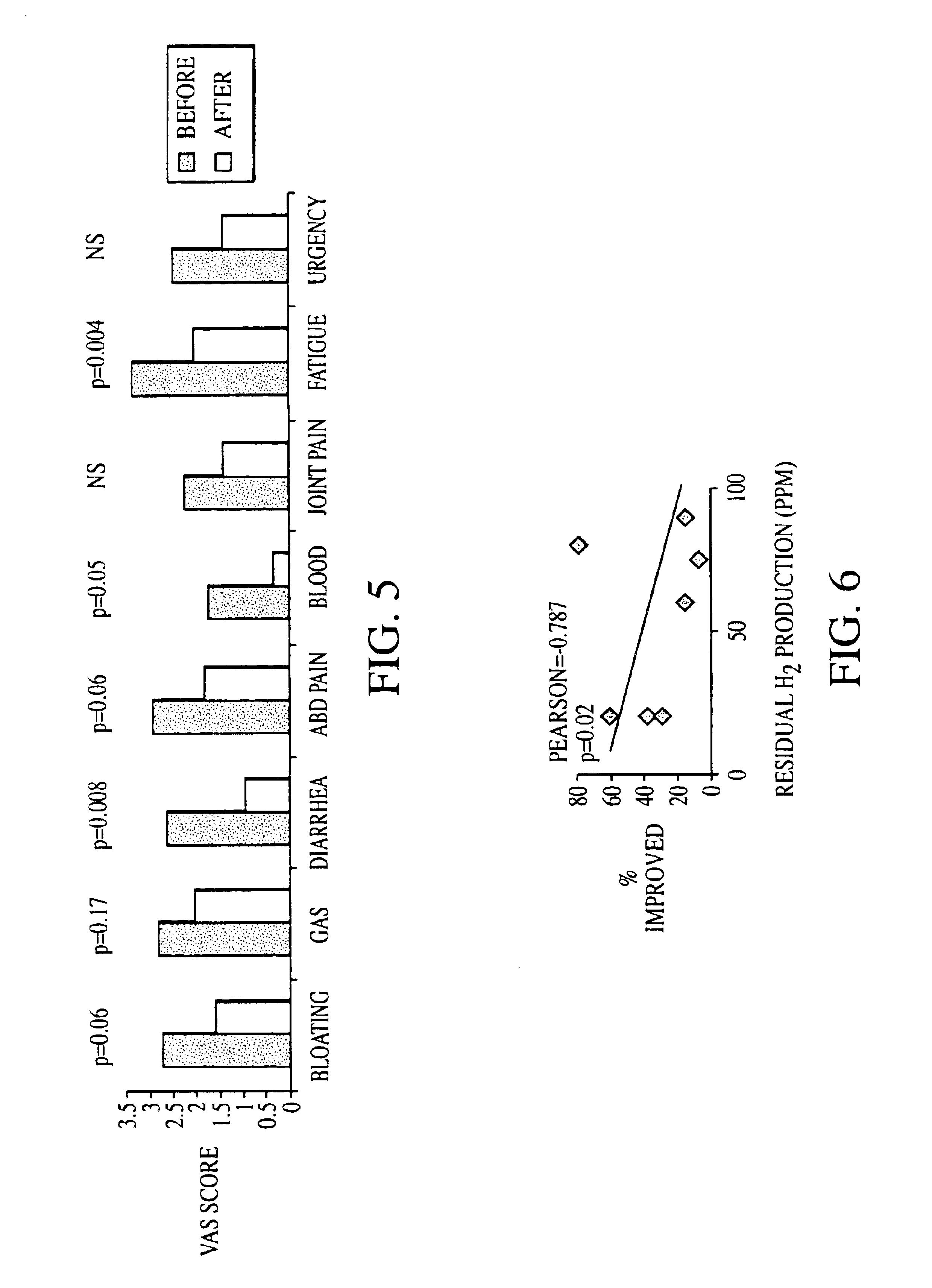
InactiveUS6861053B1Eradicate small intestinal bacterial overgrowthSymptoms improvedAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesAutoimmune responses
Disclosed is a method of diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder, autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus, or Crohn's disease, which involves detecting the presence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in a human subject having at least one symptom associated with a suspected diagnosis of any of those diagnostic categories. Also disclosed is a method of treating these disorders, and other disorders caused by SIBO, that involves at least partially eradicating a SIBO condition in the human subject. The method includes administration of anti-microbial or probiotic agents, or normalizing intestinal motility by employing a prokinetic agent. The method improves symptoms, including hyperalgesia related to SIBO and disorders caused by SIBO. Also disclosed is a kit for the diagnosis or treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder, autoimmune diseases, or Crohn's disease.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
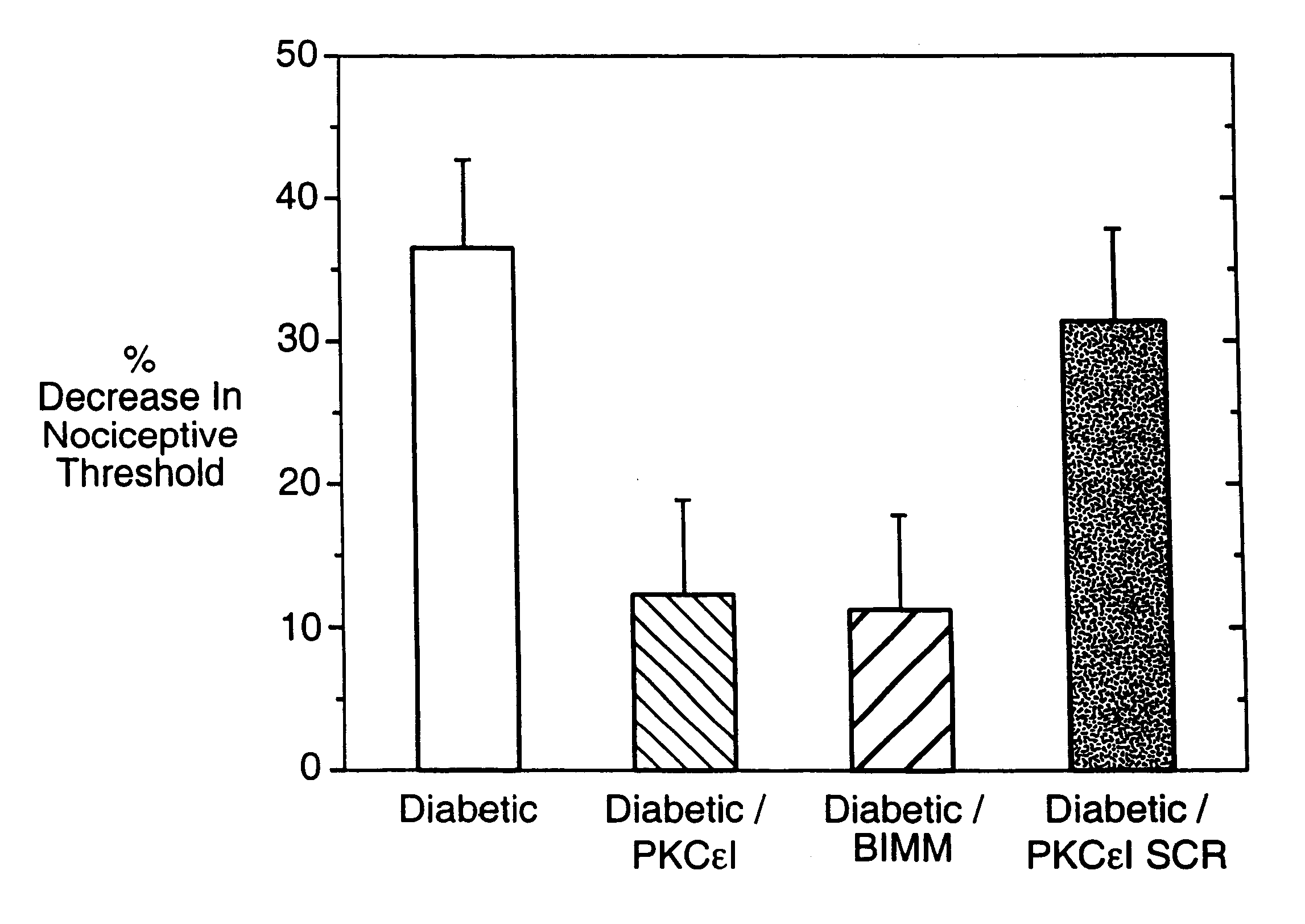
Use of inhibitors of protein kinase C epsilon to treat pain
The role of the epsilon isozyme of protein kinase C ("PKCepsilon") in pain perception, particularly hyperalgesia, methods of lessening pain through administration of inhibitors of PKCepsilon, methods of identifying compounds that modulate pain, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of PKCepsilon and PKCepsilon-independent analgesic agent are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome and other disorders caused by small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
InactiveUS20050008652A1Eradicate small intestinal bacterial overgrowthSymptoms improvedBiocideAntipyreticAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
Disclosed is a method of diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder, autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus, or Crohn's disease, which involves detecting the presence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in a human subject having at least one symptom associated with a suspected diagnosis of any of those diagnostic categories. Also disclosed is a method of treating these disorders, and other disorders caused by SIBO, that involves at least partially eradicating a SIBO condition in the human subject. The method includes administration of anti-microbial or probiotic agents, or normalizing intestinal motility by employing a prokinetic agent. The method improves symptoms, including hyperalgesia related to SIBO and disorders caused by SIBO. Also disclosed is a kit for the diagnosis or treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder, autoimmune diseases, or Crohn's disease.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Methods of Reducing Side Effects of Analgesics
InactiveUS20100227876A1Decreased gastrointestinal motilityReduce resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsMu-Opioid Receptor AgonistsSide effect
The invention provides for compositions and methods of reducing pain in a subject by administering a combination of mu-opioid receptor agonist, kappa1-opioid receptor agonist and a nonselective opioid receptor antagonist in amounts effective to reduce pain and ameliorate an adverse side effect of treatment combining opioid-receptor agonists. The invention also provides for methods of enhancing an analgesic effect of treatment with an opioid-receptor agonist in a subject suffering from pain while reducing an adverse side effect of the treatment. The invention also provides for methods of reducing the hyperalgesic effect of treatment with an opioid-receptor agonist in a subject suffering from pain while reducing an adverse side effect of the treatment. The invention further provides for methods of promoting the additive analgesia of pain treatment with an opioid-receptor agonist in a subject in need while reducing an adverse side effect of the treatment.
Owner:RECHFENSEN
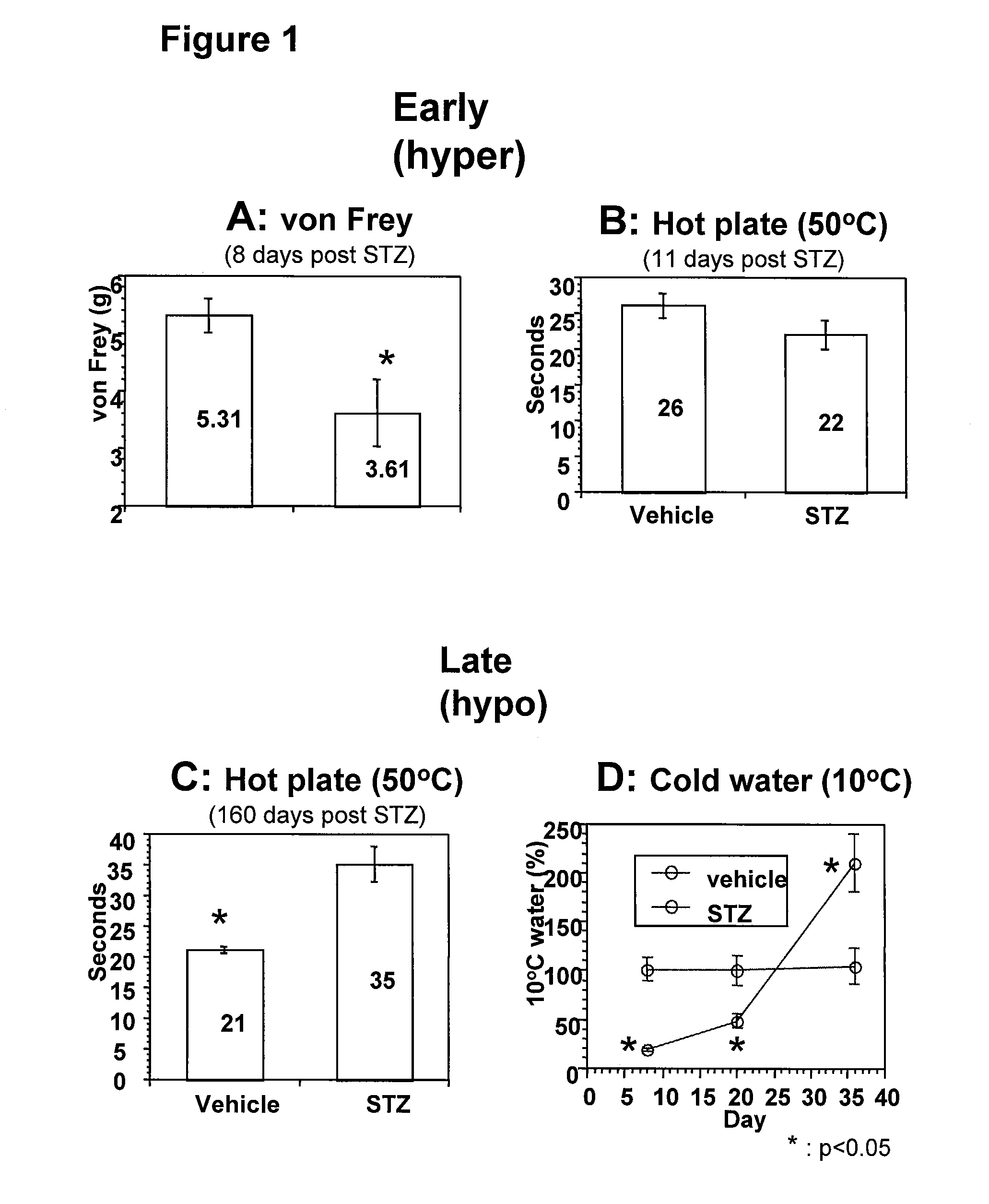
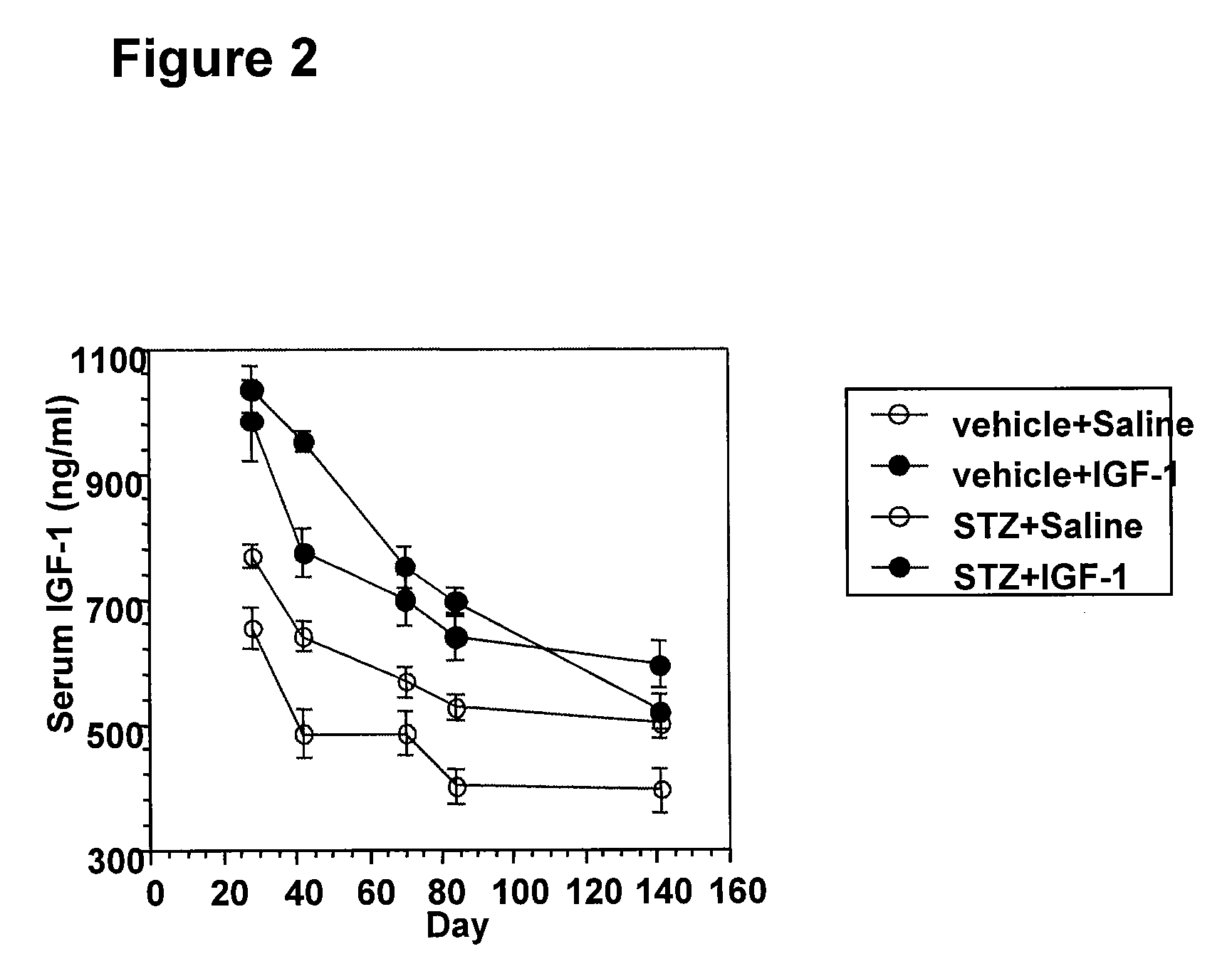
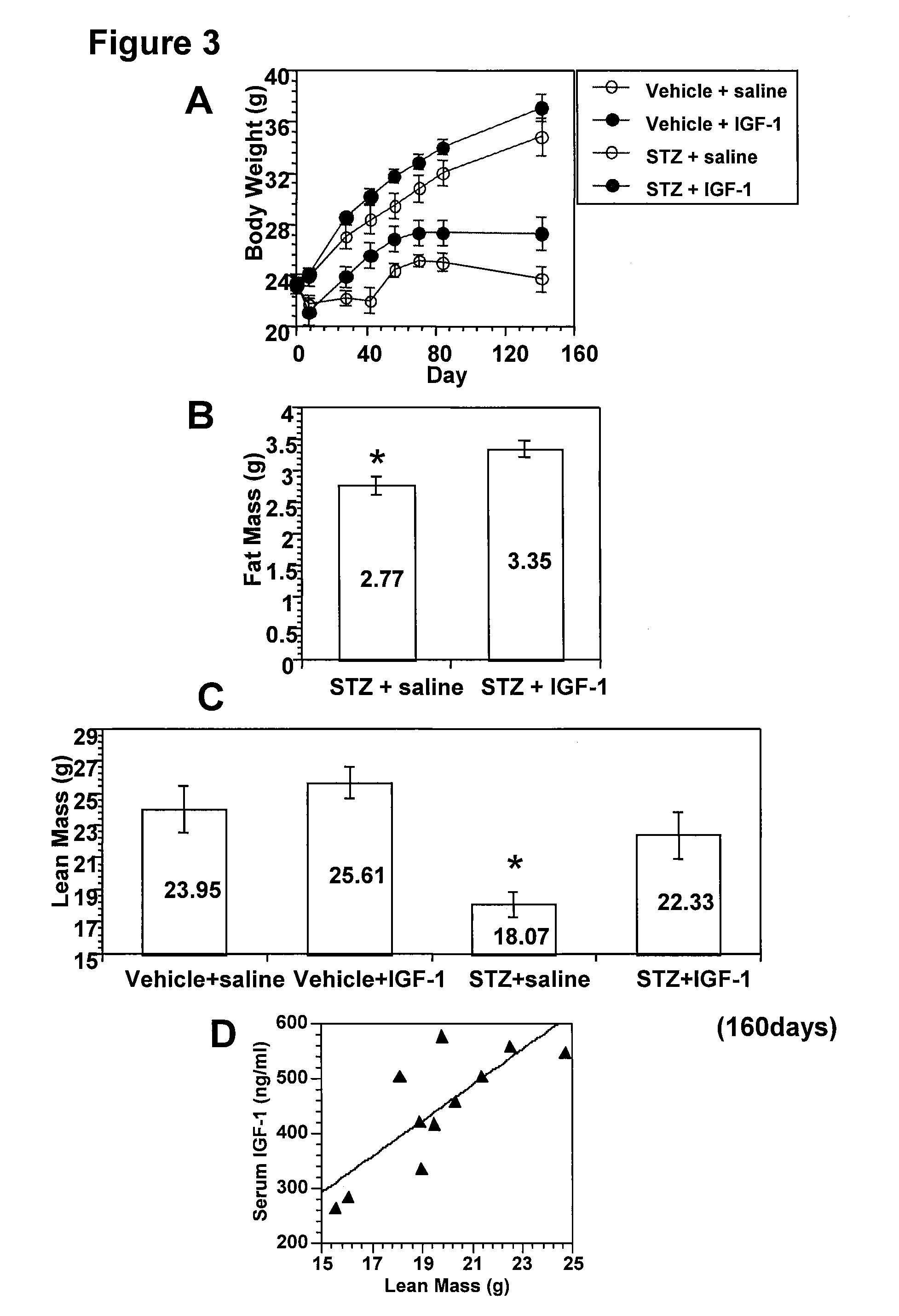
Systemic insulin-like growth factor-1 therapy reduces diabetic peripheral neuropathy and improves renal function in diabetic nephropathy
InactiveUS20100216709A1Prevents subsequent hyposensitivityEasy maintenanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderInsulin-like growth factorHyperglycemic disorder
The present invention provides methods of treatment of patients suffering from the complications of blood sugar disorders: diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetic nephropathy by administration of IGF-1 via protein therapy or gene therapy. It relates to methods of treating an individual having a diabetic disorder or a hyperglycemic disorder, comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a DNA vector expressing IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec in vivo or an effective amount of at the IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec protein in the early hyperalgesia stage or in patients that have advanced to the hyposensitivity stage. Treatment at the early hyperalgesia stage prevents subsequent hyposensitivity with increases or maintenance of sensory nerve function. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec treatment also increases muscle mass and improves overall mobility, which indicates a treatment-related improvement in motor function. Treatment with IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec at the hyposensitivity stage reverses hyposensitivity and improves muscle mass and overall health. Systemic IGF-1 provides a therapeutic modality for treating hyposensitivity associated with DPN. In addition, IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec provides a therapeutic modality for treating diabetic nephropathy. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec improves renal function as evidenced by a modulation in serum albumin concentration and a reduction in urine volume and protein levels. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec also reduces diabetic glomerulosclerosis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Compositions and methods for enhancing analgesic potency of covalently bound-compounds, attenuating its adverse side effects, and preventing their abuse
InactiveUS20100144645A1Lower potentialAmenable to synthesizing conjugatesBiocideNervous disorderChemical MoietyOpioid antagonist
The invention generally relates to compositions and methods with covalently bound compounds, such as controlled substances covalently attached to a chemical moiety, and opioid antagonists or covalently bound opioid antagonists to enhance analgesic potency and / or attenuate one or more adverse effects of covalently bound compounds, including adverse side effect(s) in humans such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, sedation (somnolence), physical dependence or pruritis. This invention relates to compositions and methods for selectively enhancing the analgesic potency of a covalently bound compound and simultaneously attenuating anti-analgesia, hyperalgesia, hyperexcitability, physical dependence and / or tolerance effects associated with the administration of a covalently bound compound. The methods of the invention comprise administering to a subject an analgesic or sub-analgesic amount of a covalently bound compound and an amount of excitatory opioid receptor antagonist such as naltrexone or nalmefene effective to enhance the analgesic potency of a covalently bound compound and attenuate the anti-analgesia, hyperalgesia, hyperexcitability, physical dependence and / or tolerance effects of covalently bound compound. The invention also relates to the addition of covalently-bound opioid antagonists to the compositions containing covalently bound compounds such that if the compositions are subjected to manipulation by illicit chemists, the opioid antagonist is released effectively reducing or eliminating the euphoric effect of the covalently bound compounds.
Owner:SHIRE PLC
Pharmaceutical combinations of cox-2 inhibitors and opiates
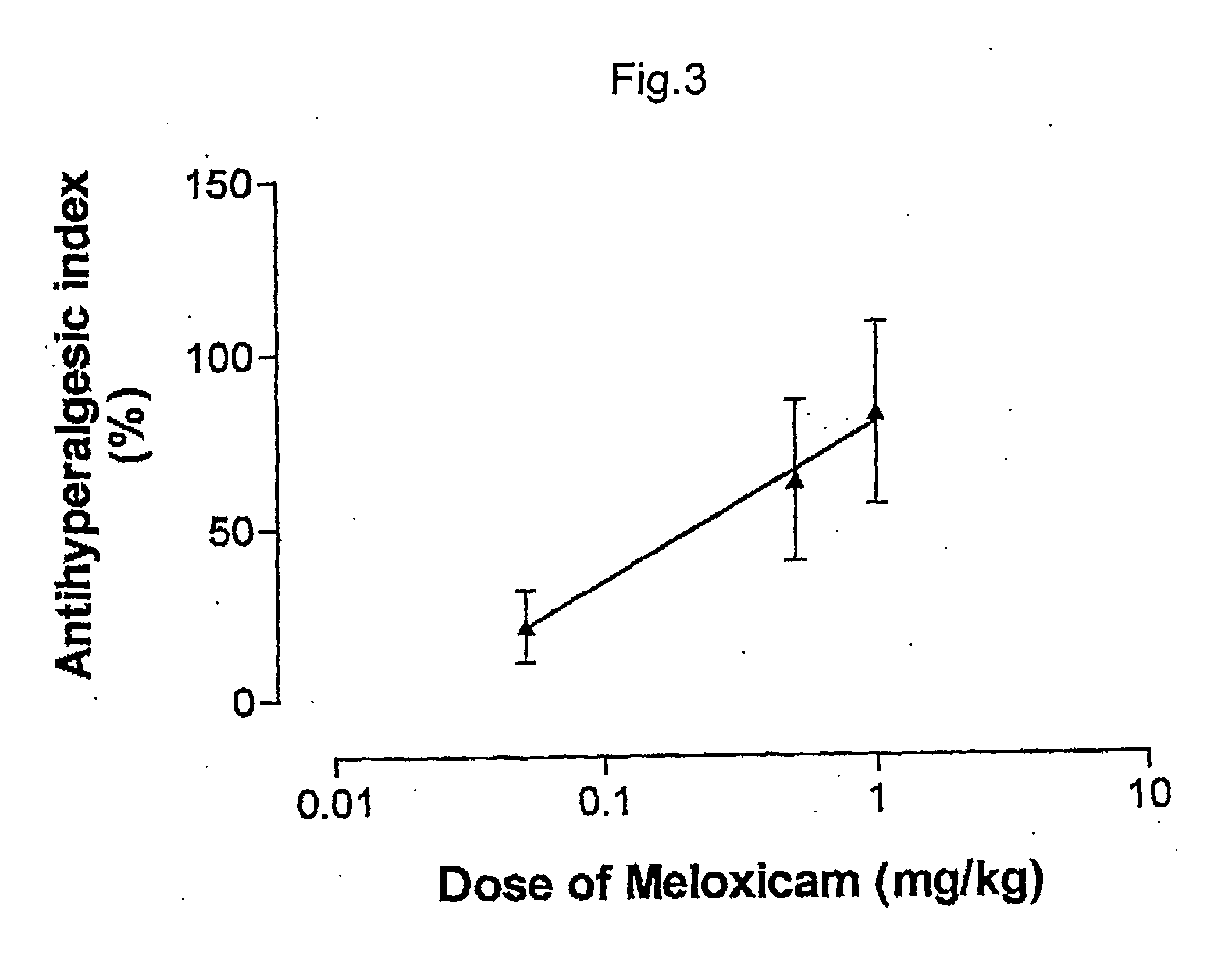
ABSTRACTA pharmaceutical composition comprises a combination of a selective or specific COX 2 inhibitor or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof and an opiate or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof, for example a combination of meloxicam and codeine, as active ingredients, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. It may include a centrally-acting cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor such as paracetamol or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts or derivatives. The pharmaceutical compositions are used in methods of providing symptomatic relief or treatment of pain, in an algesic and / or hyperalgesic state, with or without fever, in particular that associated with inflammation such as that associated with trauma, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, non-inflammatory myalgia or dysmenorrhoea
Owner:ADCOCK INGRAM LTD
Antagonists to the vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR1) and uses thereof
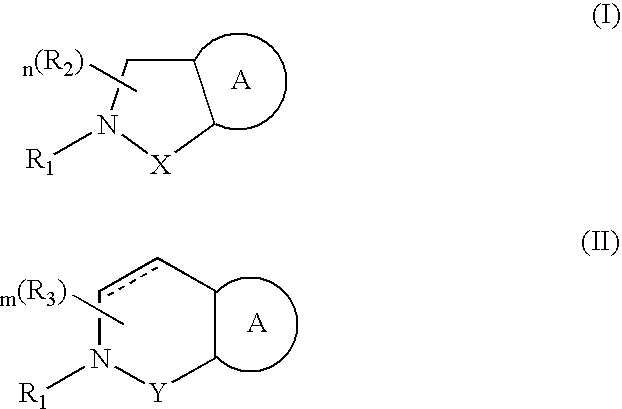
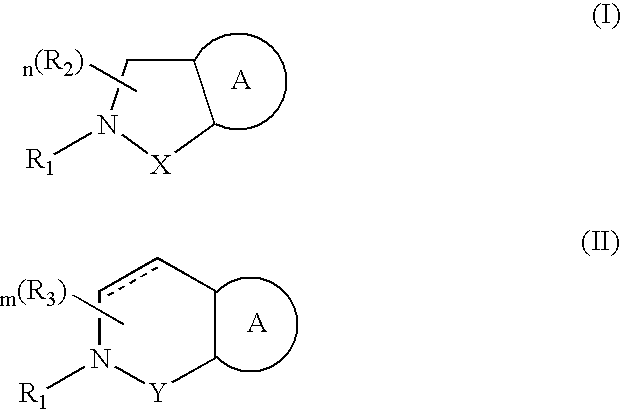
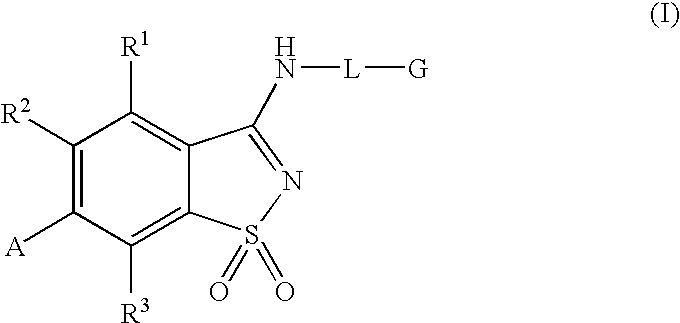
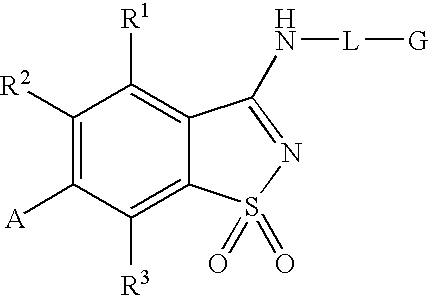
Compounds having formula (I) or formula (II) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, or salt of a prodrug thereof, wherein A, N, X, Y, R1, R2 and R3 are as defined in the specification. These compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of pain, inflammatory hyperalgesia, and urinary dysfunctions, such as bladder overactivity and urinary incontinence.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
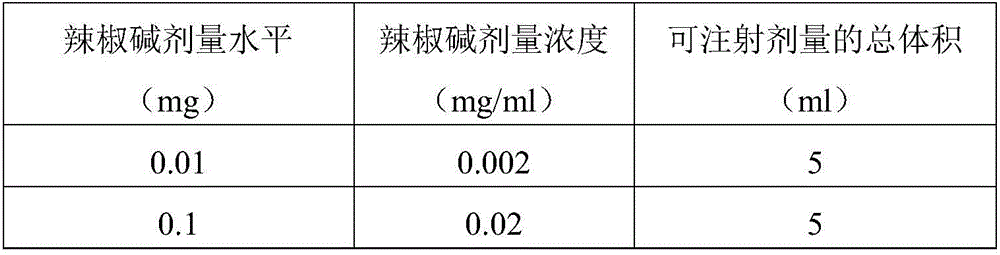
Aqueous based capsaicinoid formulations and methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20150133561A1Reduces and eliminates burning and stingingBiocideNervous disorderTreatment painMedicinal chemistry
Capsaicinoid formulations and methods of treatment are disclosed herein which can be utilized to treat / attenuate pain in mammals. Typically, administration is via injection at a discrete site to provide pain relief for an extended period of time. The formulations are administered in a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle. The formulations include an analgesic agent in an amount sufficient to attenuate the burning and hyperalgesic effects of capsaicinoid administration. The invention also includes a method of treating pain by administering a corticosteroid followed by administration of a capsaicinoid.
Owner:PROPELLA THERAPEUTICS INC
Combinations of Superoxide Dismutase Mimetics and Nonsteroidal Analgesic/Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
InactiveUS20090131377A1Inhibit inflammationAvoid painBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsSuperoxide dismutase mimeticsSuperoxide
Combinations of synthetic low molecular weight catalysts for the dismutation of superoxide and Nonsteroidal Analgesic / Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are potent analgesics that are effective in elevating the pain threshold in hyperalgesic conditions.
Owner:METAPHORE PHARMA
Antagonists to the vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR1) and uses thereof
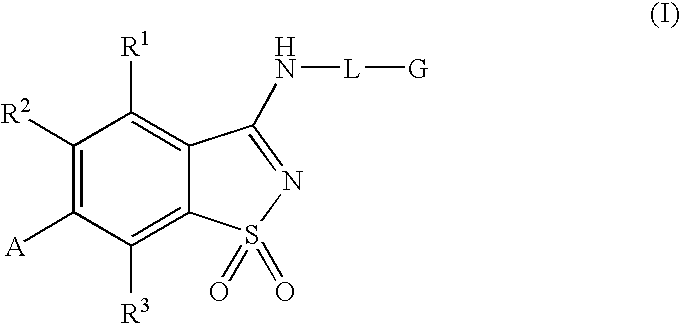
Compounds having formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, or salt of a prodrug thereof, wherein L, A, G, R1, R2 and R3 are as defined herein. These compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of pain, inflammatory hyperalgesia, and urinary dysfunctions, such as bladder overactivity and urinary incontinence.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Use of inhibitors of protein kinase C epsilon to treat pain
The role of the epsi isozyme of protein kinase C ("PKCepsi") in pain perception, particularly hyperalgesia, methods of lessening pain through administration of inhibitors of PKCepsi, methods of identifying compounds that modulate pain, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of PKCepsi and PKCepsi-independent analgesic agent are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
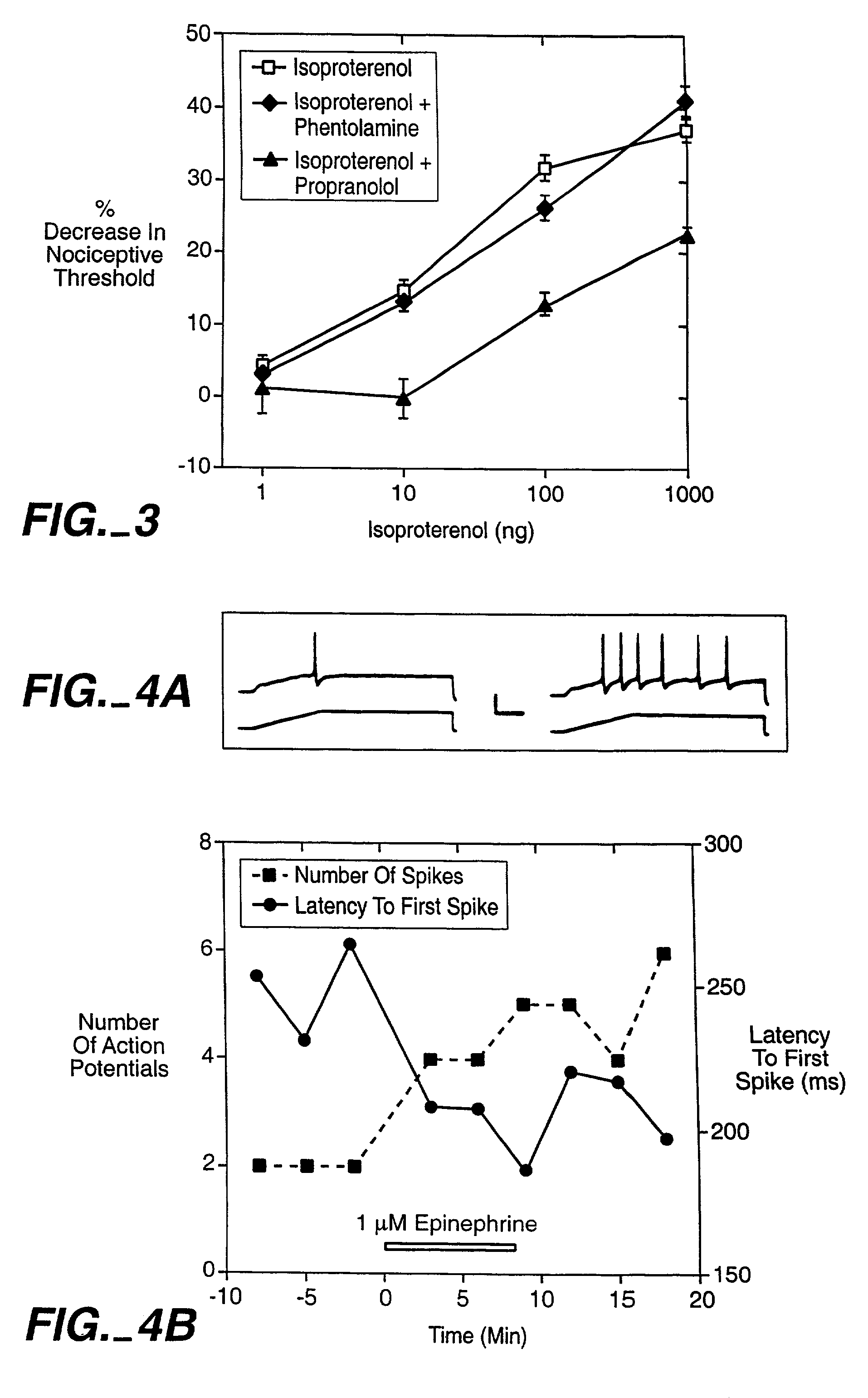
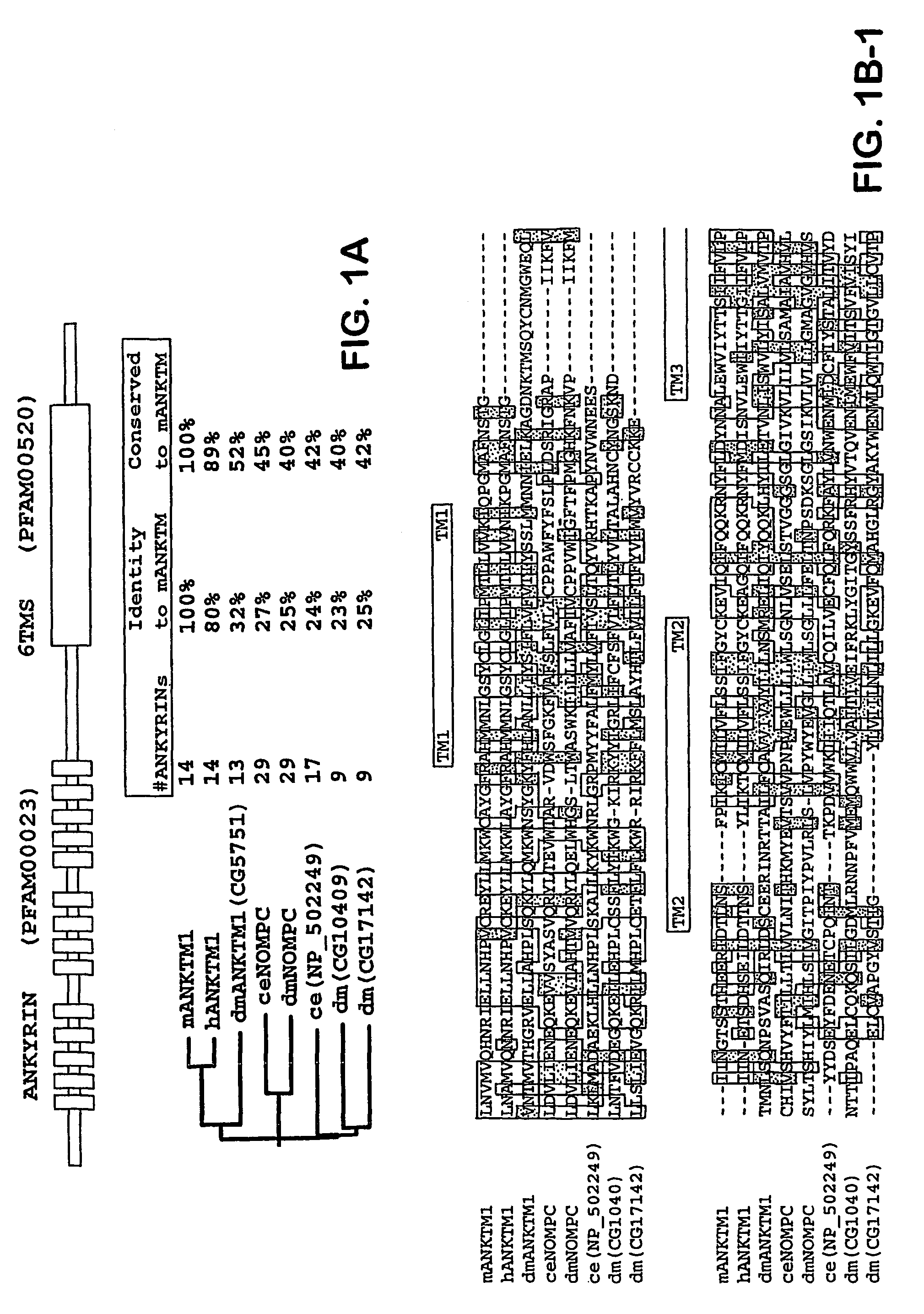
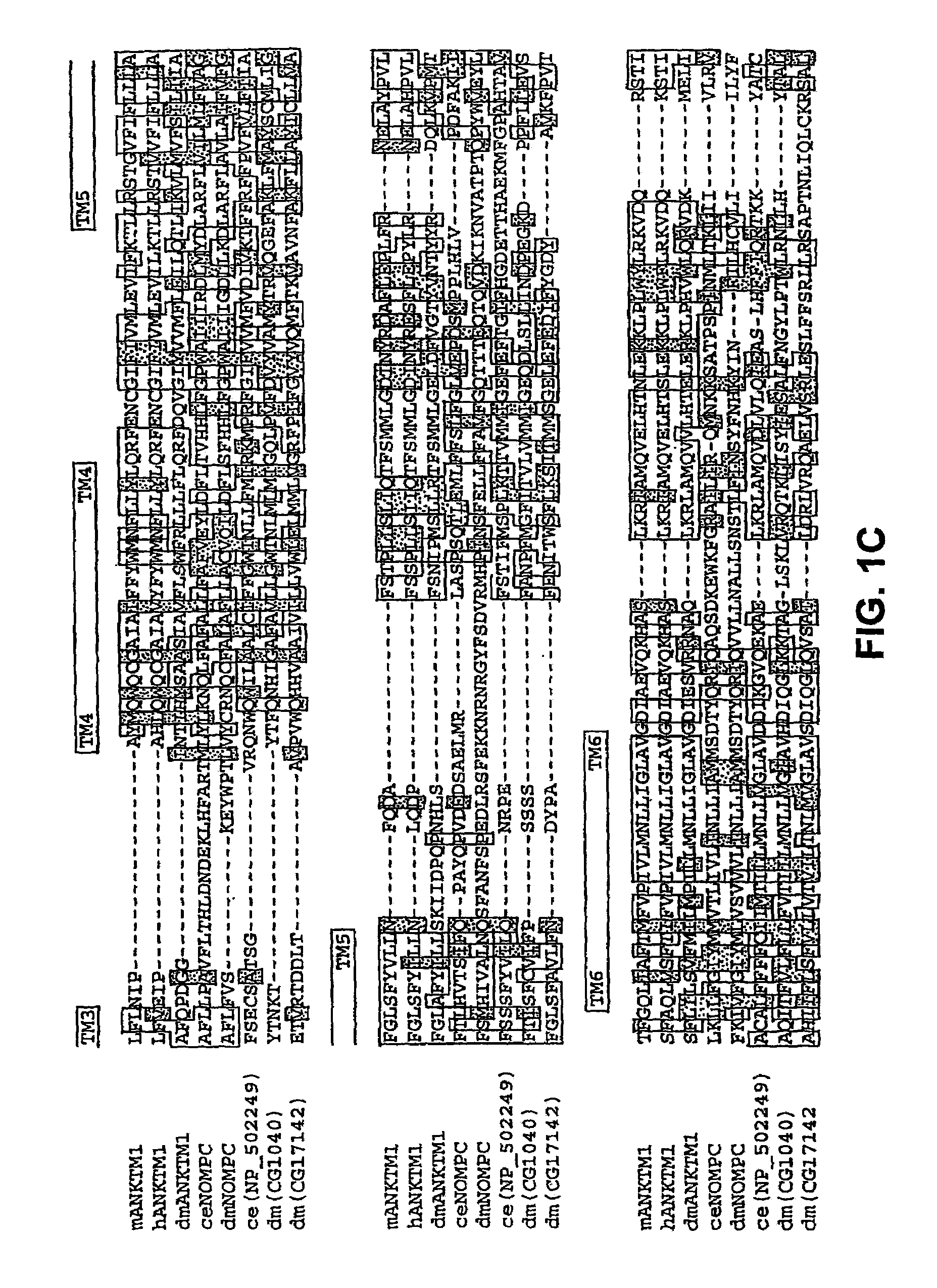
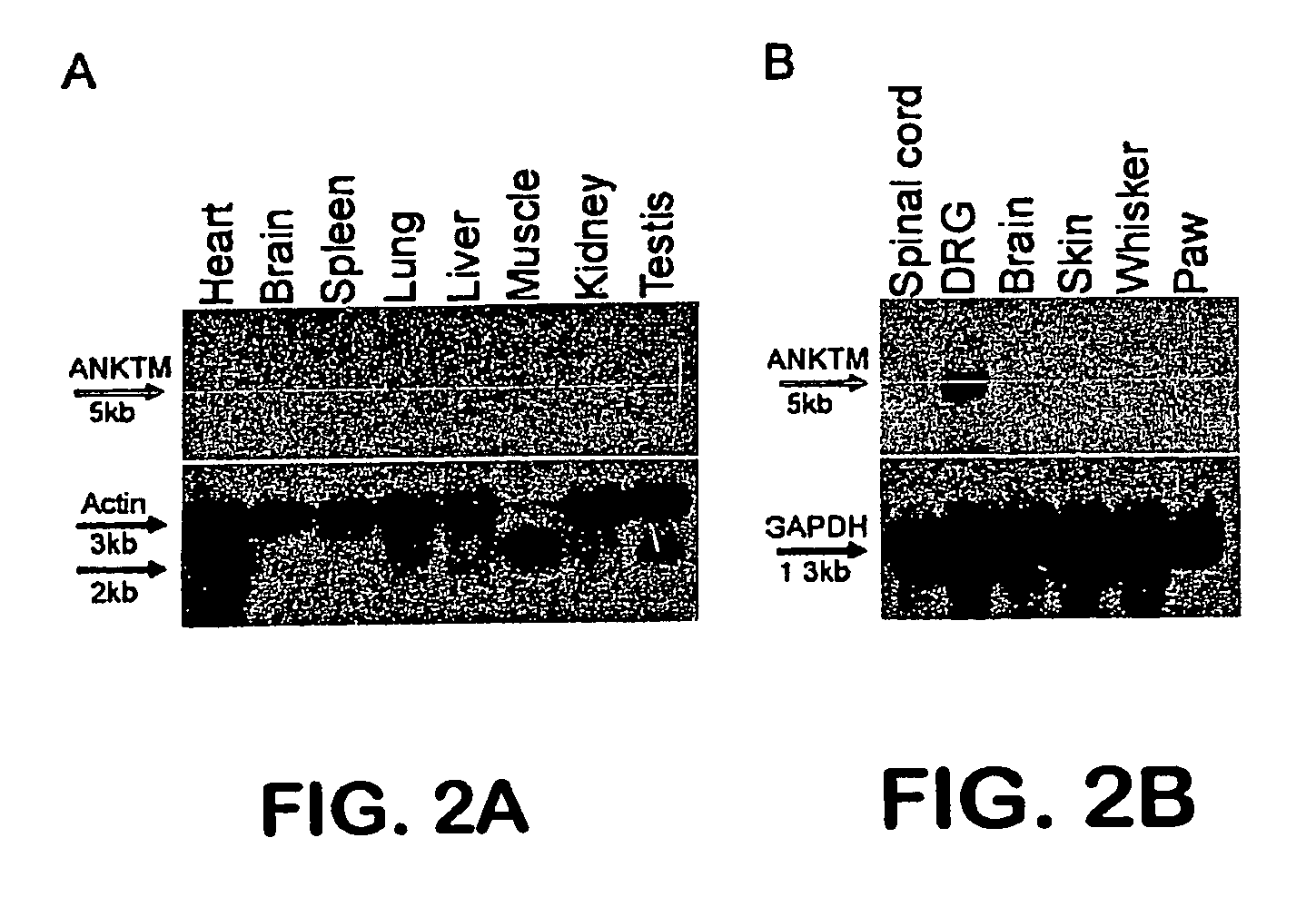
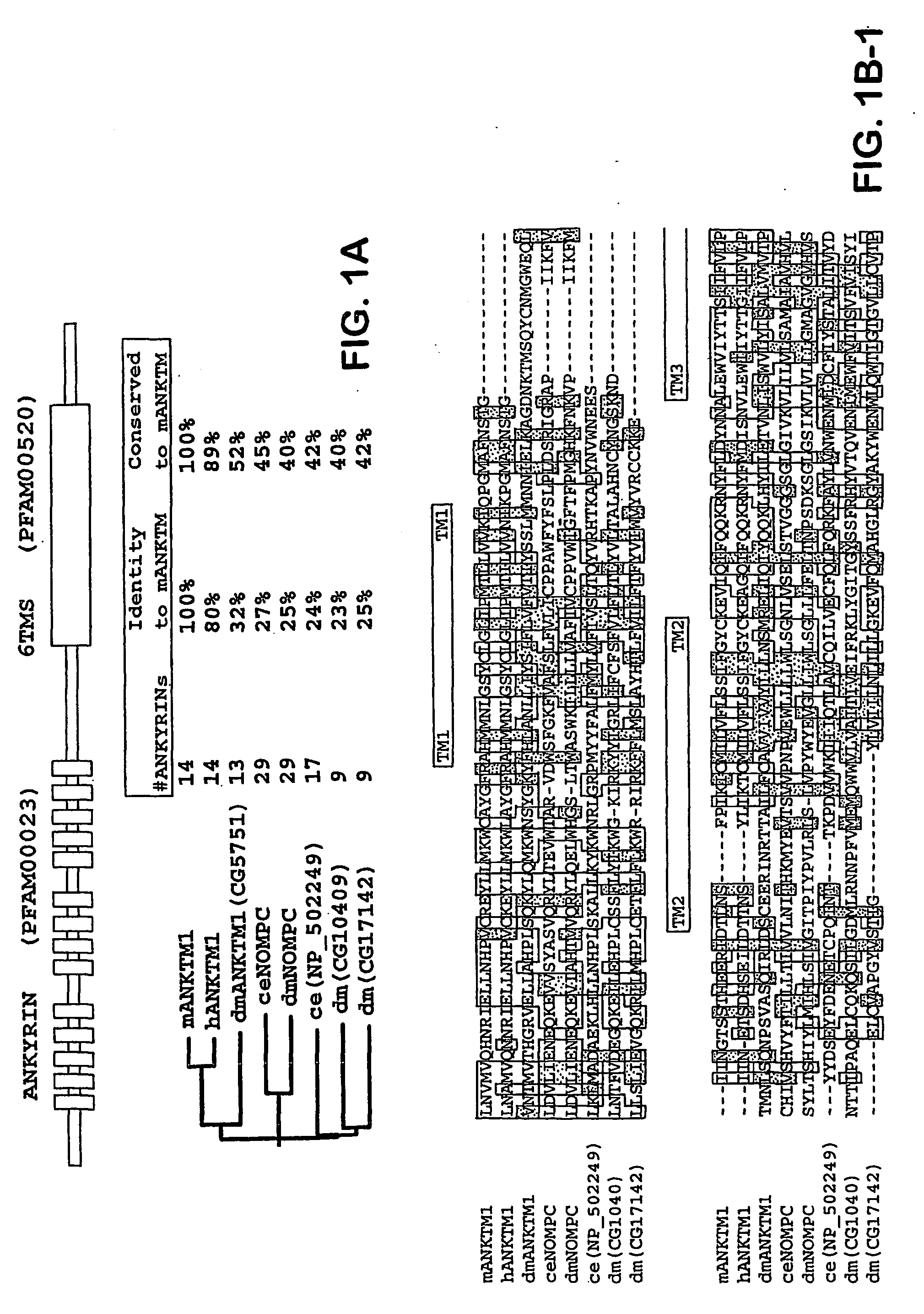
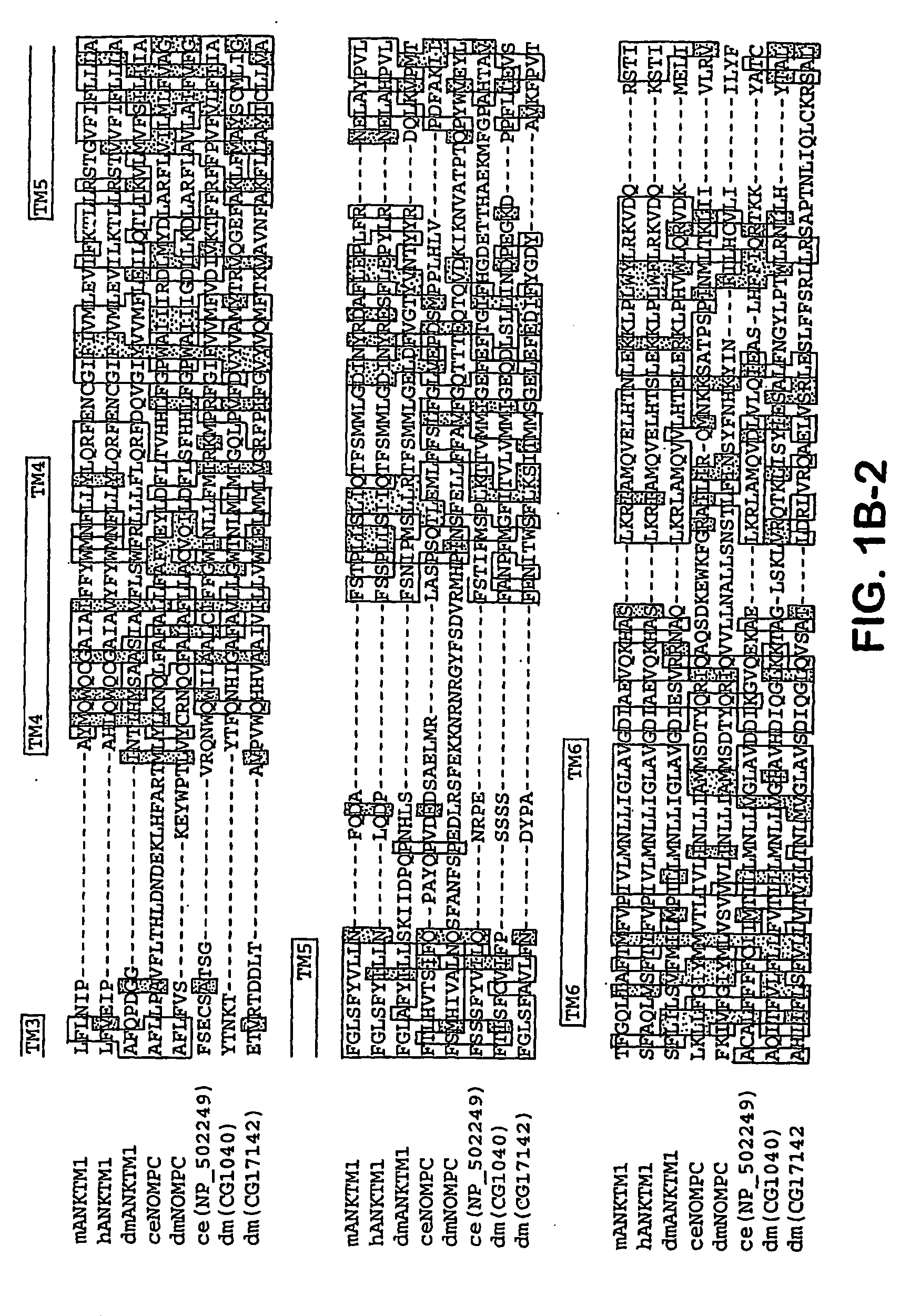
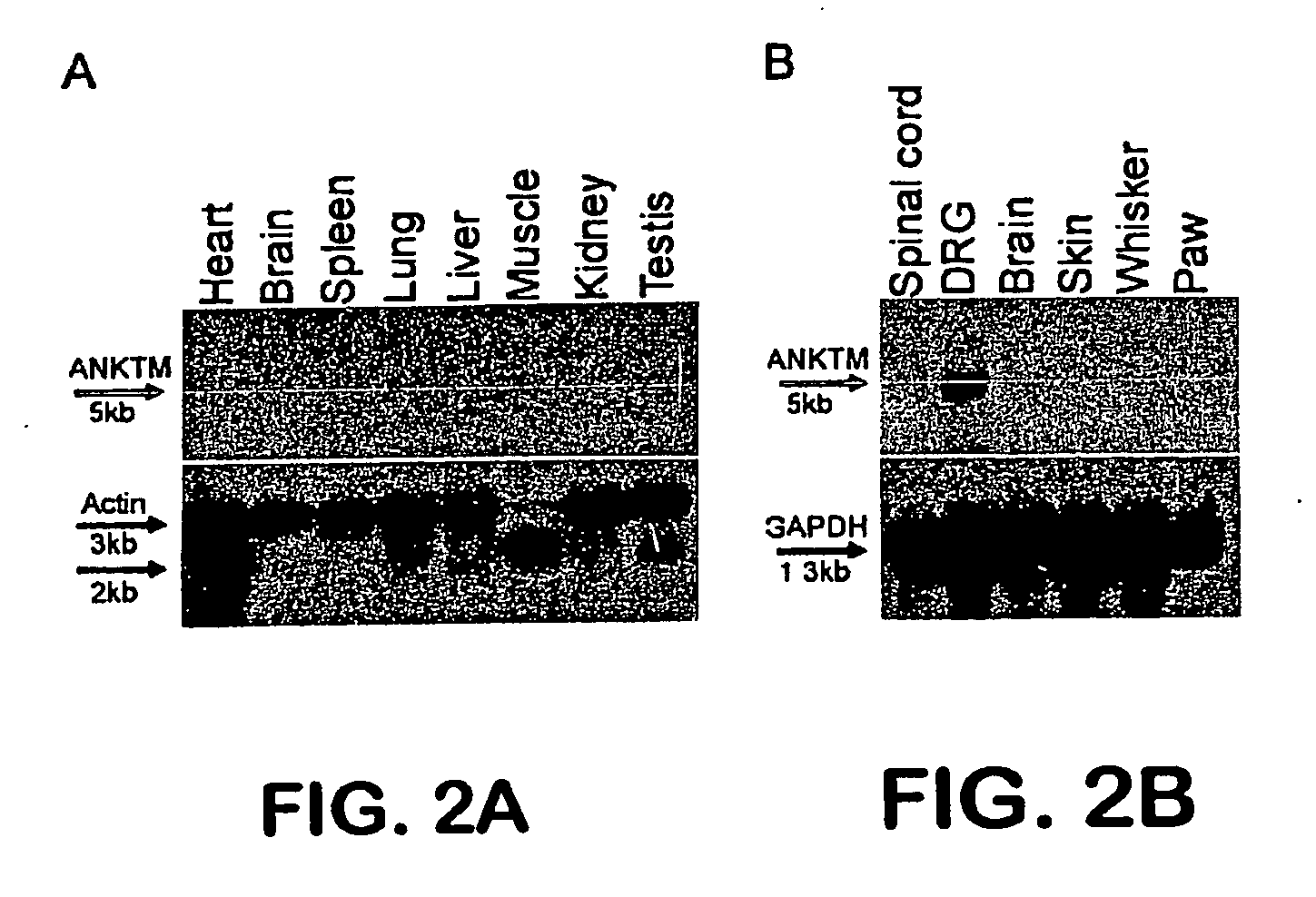
ANKTM1, a cold-activated TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons
The methods and compositions of the invention are based on a method for measuring nociceptive responses in vertebrates, including humans and other mammals utilizing a newly discovered thermoreceptor belonging to the Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) family of non-selective cation channels that participates in thermosensation and pain. This receptor, designated ANKTMI, is associated with nociceptive pain, such as hyperalgesia. Accordingly, the invention provides isolated polypeptides and polynucleotides associated with nociception as well as methods for identifying or screening agents that modulate nociception.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Thermo-electric device
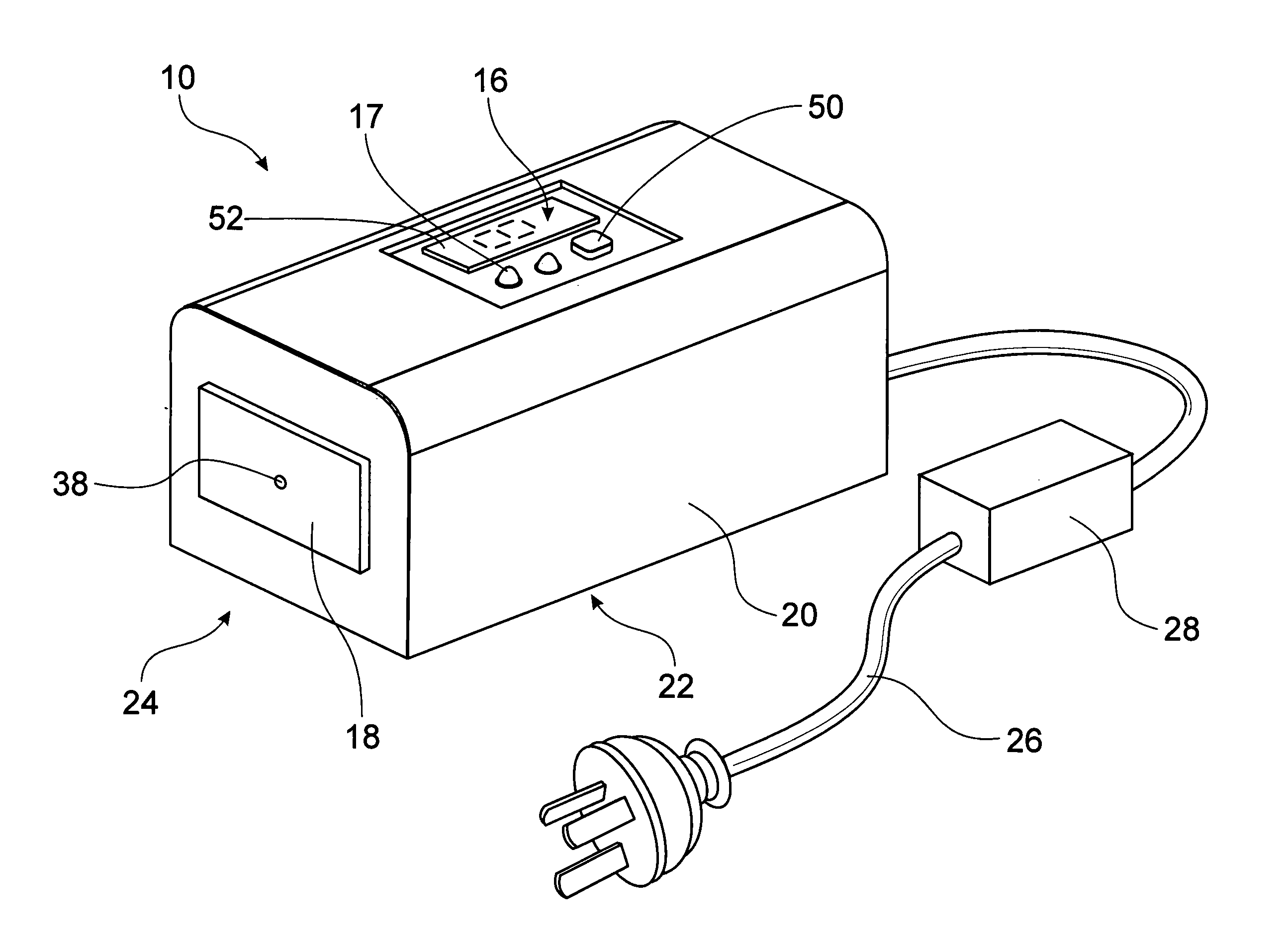
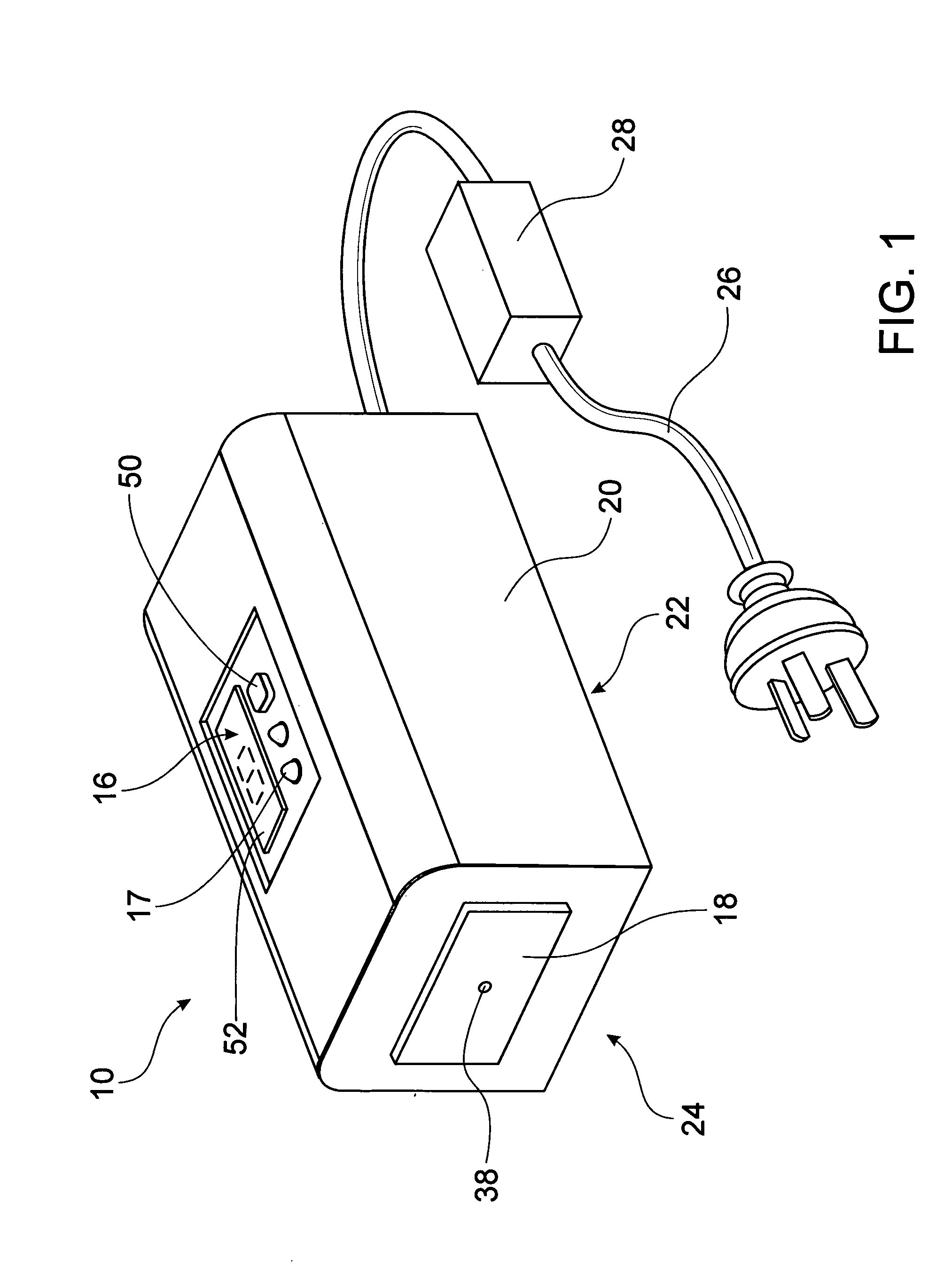
A portable handheld thermo-electric device (10) is used to test for decreased cold pain thresholds or increased sensitivity to cold stimulation (cold hyperalgesia) in a patient. The thermo-electric device (10) comprises a probe (18), a Peltier module (12) and a control unit (16) operable to energize the Peltier module (12) so that the temperature of the probe 18 is variable in a range between a predetermined upper temperature limit and a predetermined lower temperature limit during a test cycle of the thermo-electric device (10). A thermal mass (14) is adapted for thermal contact with an interface side (34) of the Peltier module (12). The Peltier module (12) has thermal properties which enables it to be cooled to a temperature below the predetermined upper temperature limit and thereafter maintain the interface side (34) of the Peltier module (12) at a temperature below the predetermined upper temperature limit for the duration of the test cycle.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Anktm1, a cold-activated trp-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons
InactiveUS20060142547A1Reducing nociceptive painReduce painNervous disorderBacteriaThermoreceptorMammal
The methods and compositions of the invention are based on a method for measuring nociceptive responses in vertebrates, including humans and other mammals utilizing a newly discovered thermoreceptor belonging to the Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) family of non-selective cation channels that participates in thermosensation and pain. This receptor, designated ANKTMI, is associated with nociceptive pain, such as hyperalgesia. Accordingly, the invention provides isolated polypeptides and polynucleotides associated with nociception as well as methods for identifying or screening agents that modulate nociception.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
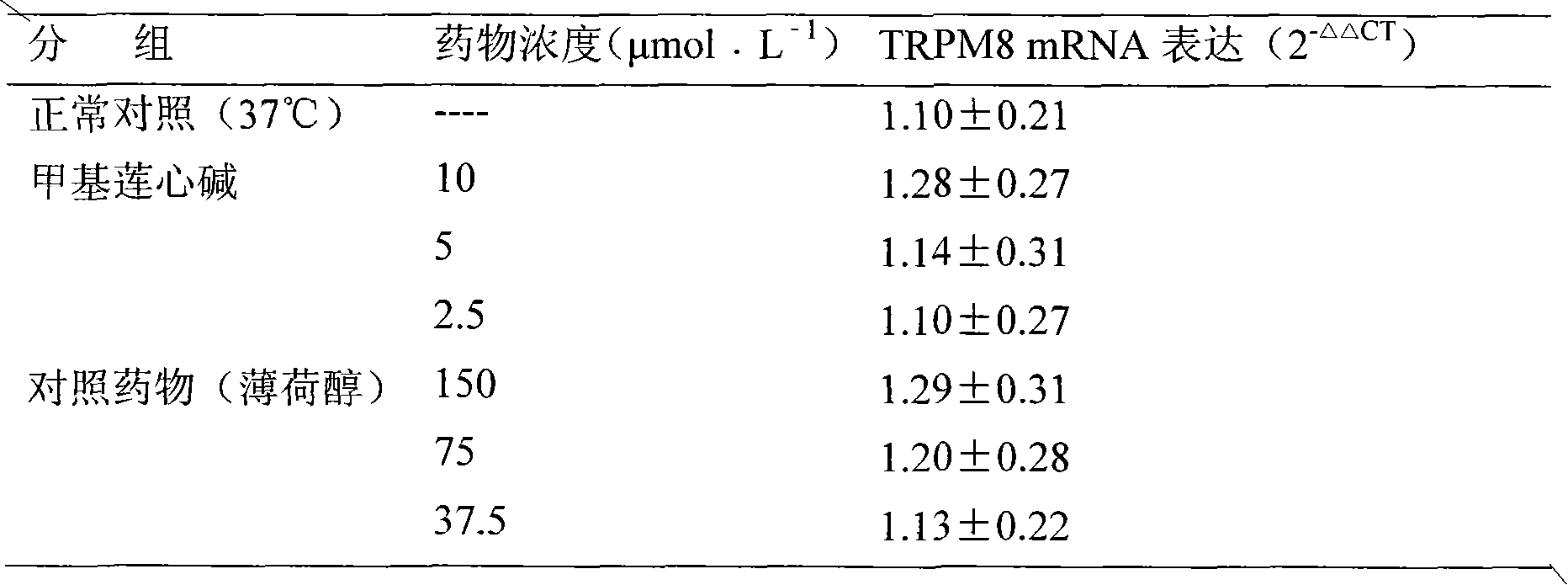
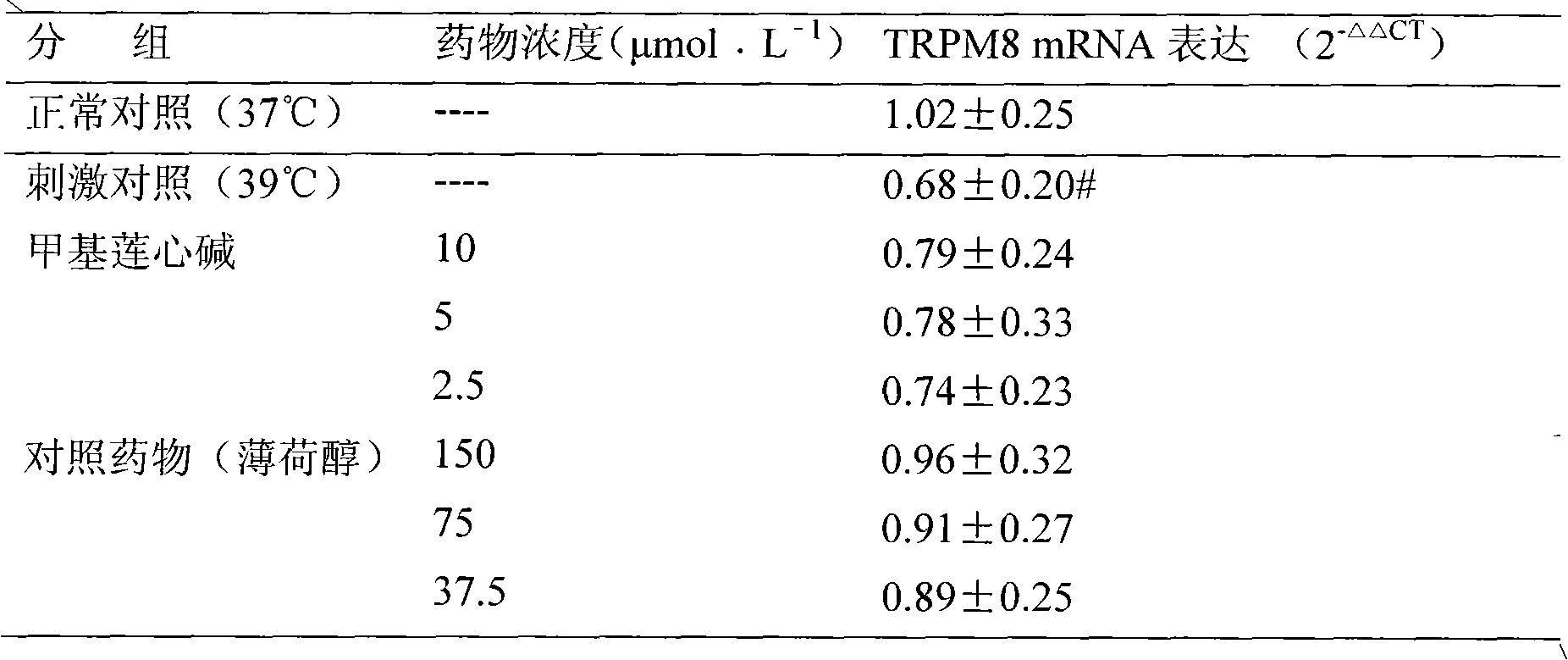
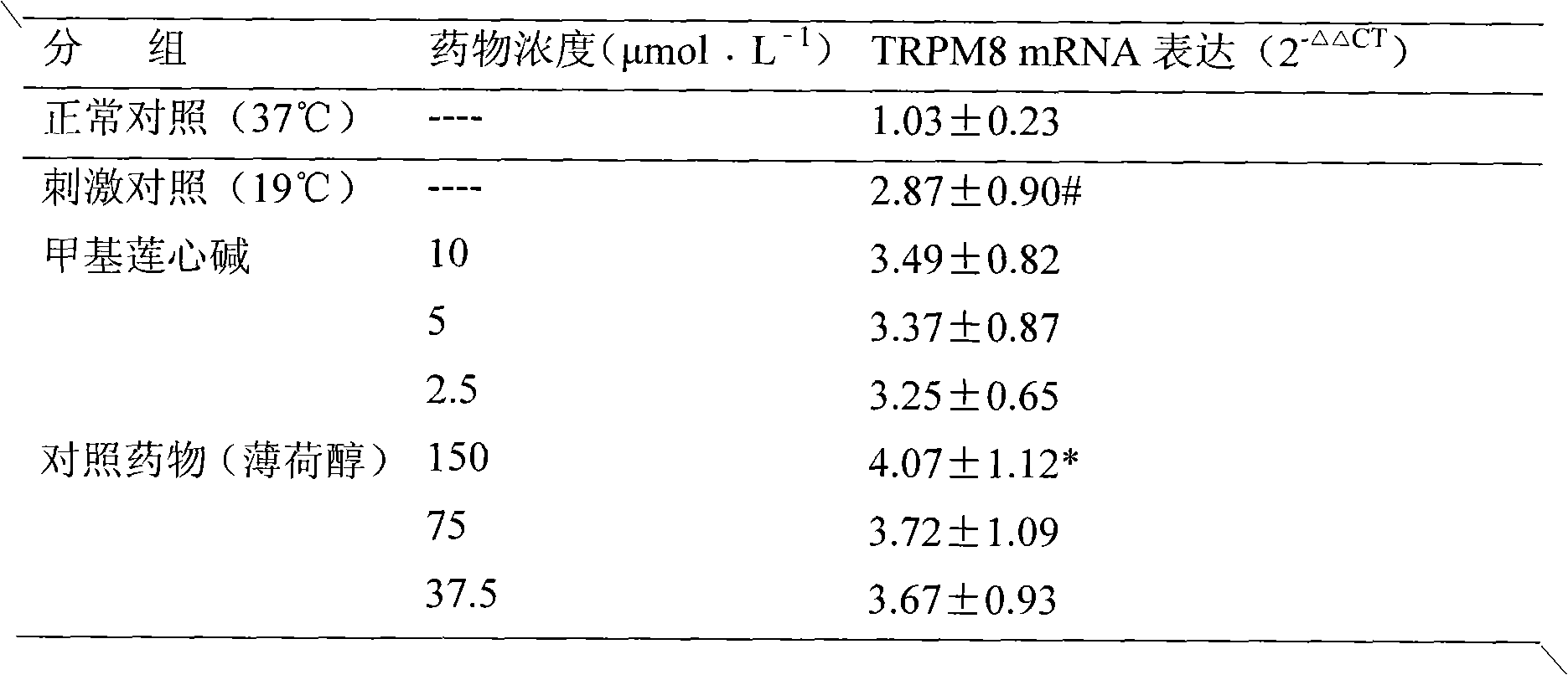
New use of methyl liensinine
ActiveCN101862331AIncrease the strength of actionStrong creativityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderWilms' tumorHyperalgesia
The invention discloses a new use of methyl liensinine. Methyl liensinine respectively regulates M8 and V1 subtype transient receptor potential ion channels (TRPM8 and TRPV1 for short) of mammal including human, so as to prepare medicine for treating related diseases joined by the ion channels (such as cold hyperalgesia, parkinsonism, nociceptive bladder syndrome, chronic obstructive lung diseaseand tumours of skin, prostate, breast, lung and colon). The action strength of methyl liensinine of the invention is higher than that of menthol.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
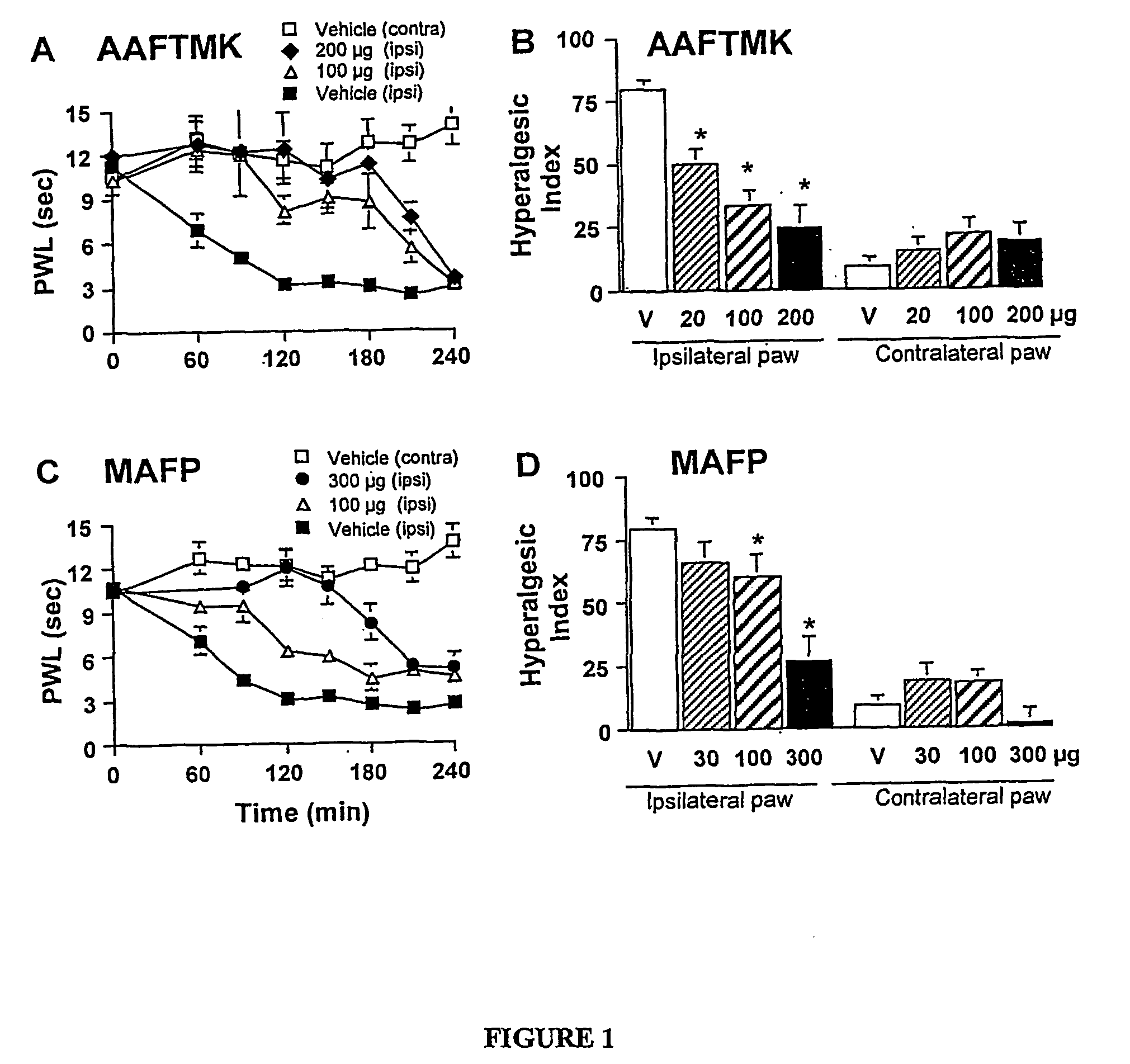
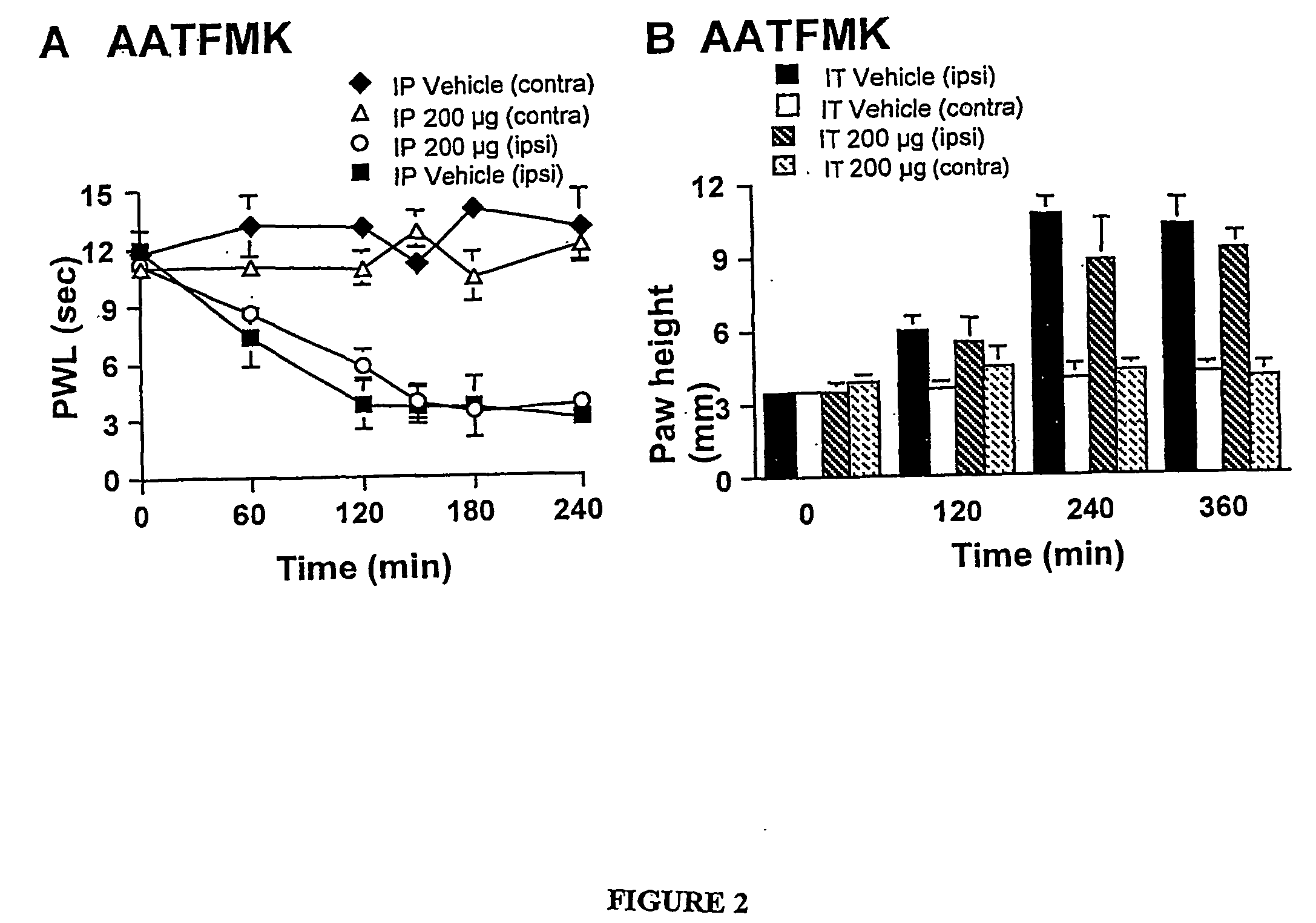
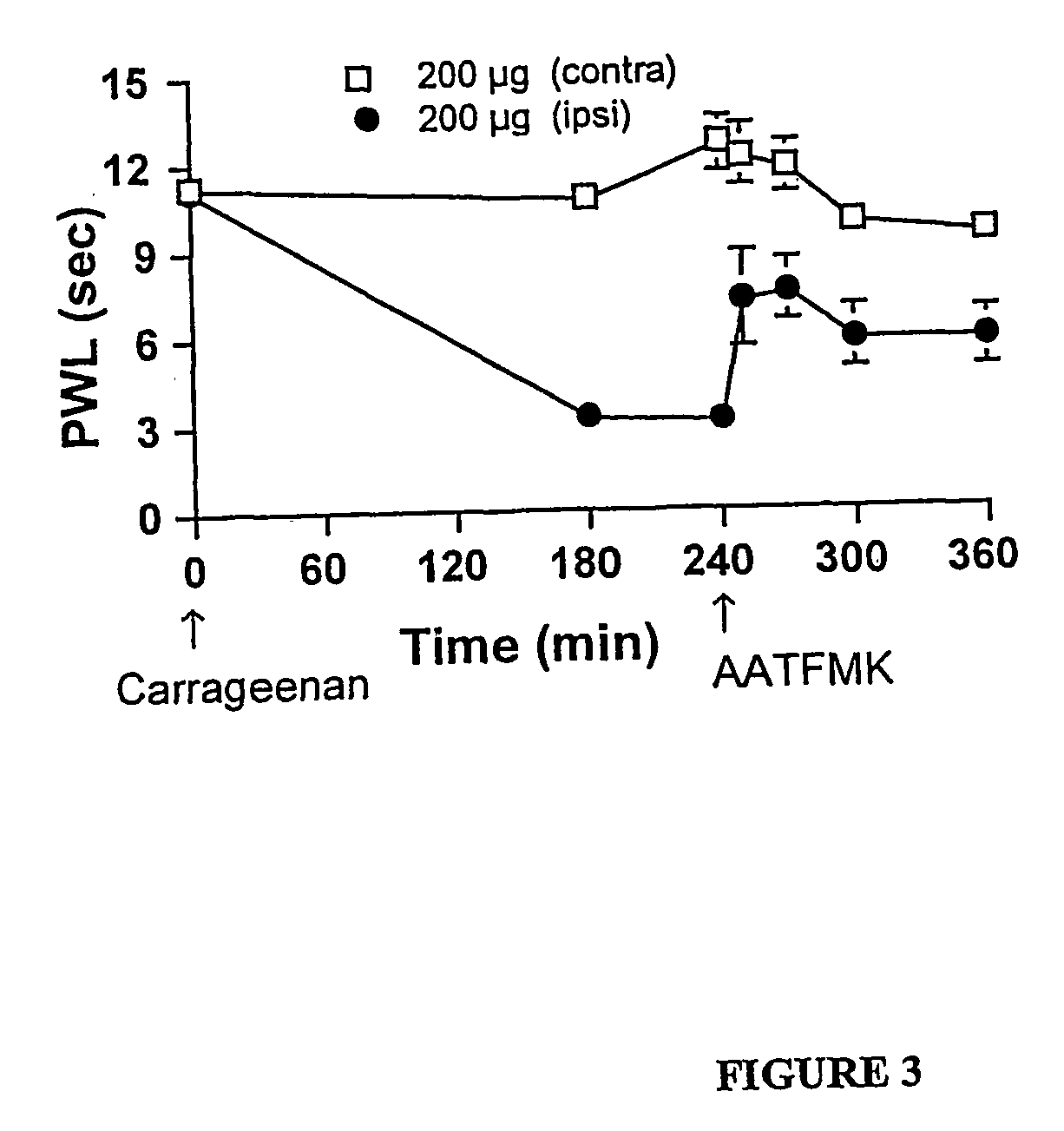
Compositions and methods for inhibition of phospholipase a2 mediated inflammation
Specific, highly potent 2-oxo-amide based inhibitors of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity are provided. A role for PLA2 activity in spinally mediated inflammatory processes is established, and a method for treating hyperalgesia and other inflammatory conditions associated with PLA2 activity is provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of treating hyperalgesia
This invention describes compounds and methods that can be used to treat, reverse, or avoid hyperalgesia.
Owner:特维娜SPV2有限责任公司
Aqueous based capsaicinoid formulations and methods of manufacture and use
The invention discloses capsaicinoid formulations and methods of treatment are disclosed herein which can be utilized to treat / attenuate pain in mammals. Typically, administration is via injection at a discrete site to provide pain relief for an extended period of time. The formulations are administered in a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle. The formulations include an analgesic agent in an amount sufficient to attenuate the burning and hyperalgesic effects of capsaicinoid administration. The invention also includes a method of treating pain by administering a corticosteroid followed by administration of a capsaicinoid.
Owner:PREPA THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Short-chain peptides as Kappa (κ) opioid receptors (KOR) agonist
The present invention relates to novel short-chain peptides of the general formula (I), which are selective and peripherally acting KOR agonist, their tautomeric forms, their enantiomers, their diastereoisomers, their stereoisomers, their pharmaceutically accepted salts, or prodrugs thereof which are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which the Kappa (κ) opioid receptors (KOR) are involved, such as treatment or prevention of visceral pain, hyperalgesia, rheumatoid arthritic inflammation, osteoarthritic inflammation, IBD inflammation, IBS inflammation, ocular inflammation, otitic inflammation or autoimmune inflammation. The invention also relates to process for the manufacture of said short-chain peptides, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use.
Owner:CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD
Compositions and method for enhancing the therapeutic activity of opioids in treatment of pain
Compositions and methods for inhibiting opioid tolerance and opioid withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia are provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Antagonists to the vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR1) and uses thereof
Compounds having formula (I)or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, or salt of a prodrug thereof, wherein L, A, G, R1, R2 and R3 are as defined herein. These compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of pain, inflammatory hyperalgesia, and urinary dysfunctions, such as bladder overactivity and urinary incontinence.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
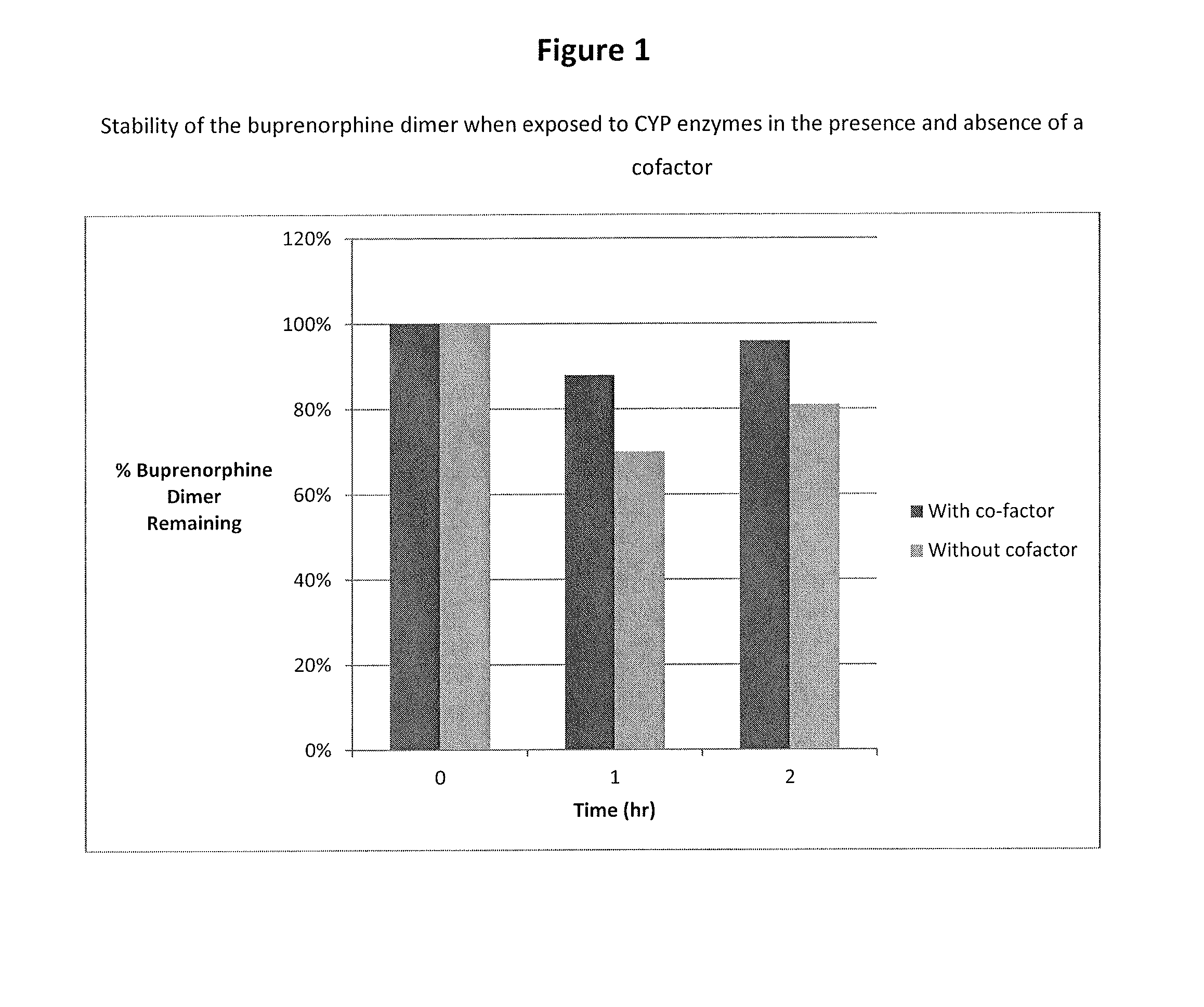
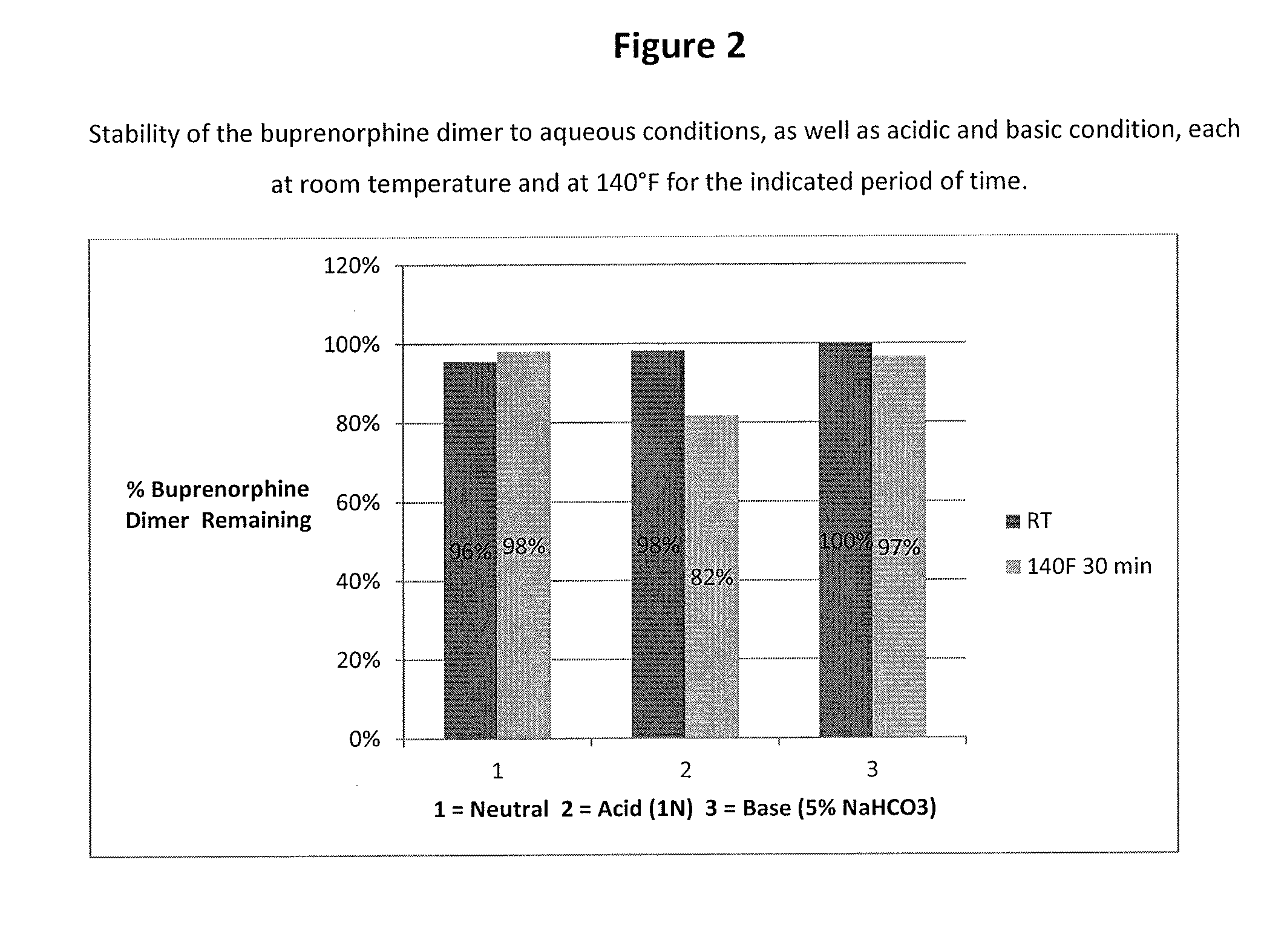
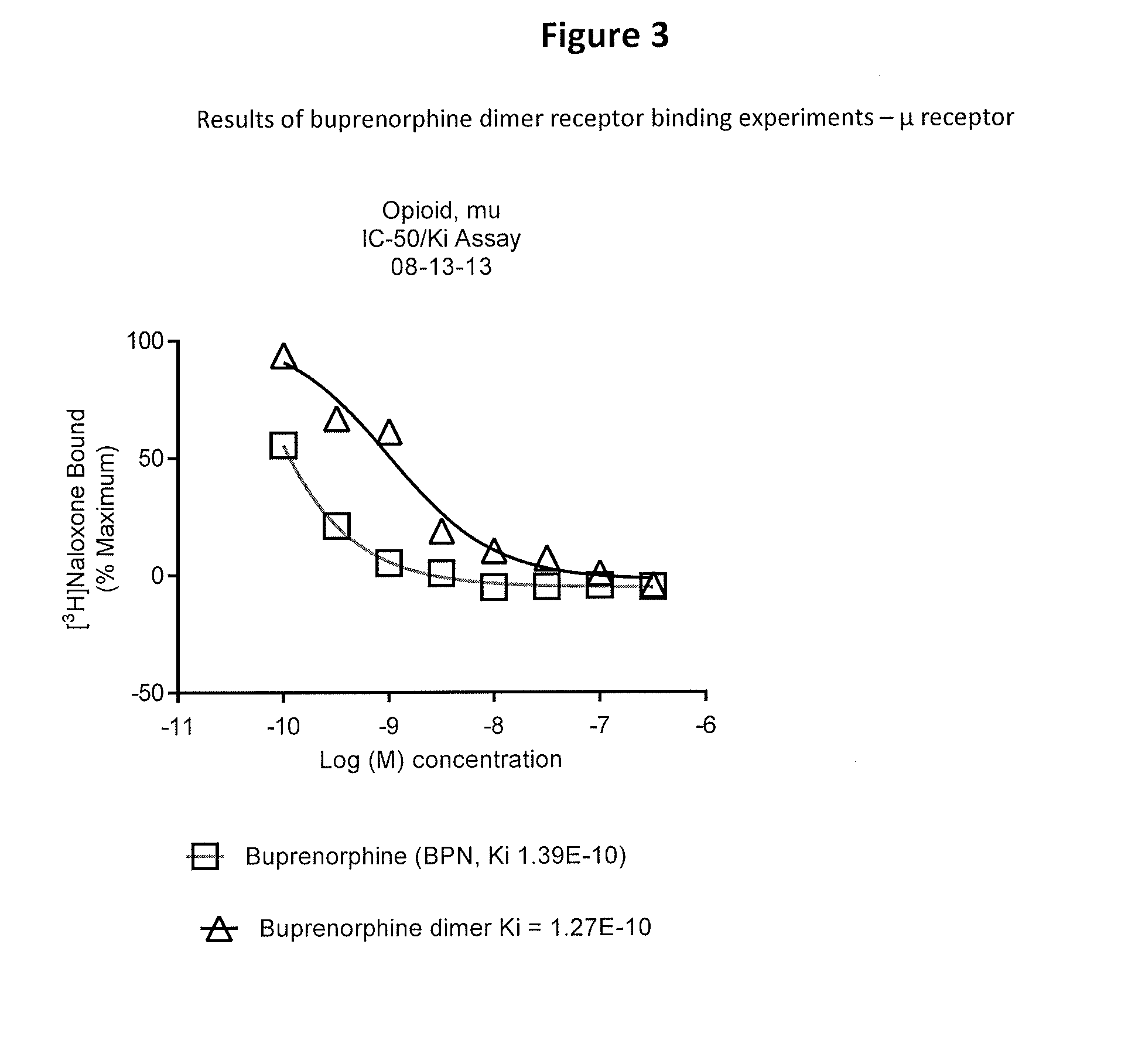
Buprenorphine dimer and its use in treatment of gastrointestinal disorders
ActiveUS20150307504A1Reduces visceral (colonic) hypersensitivityEffective treatmentBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides a buprenorphine dimer compound, wherein the two buprenorphine portions are linked via an ethylene spacer, wherein the spacer is bonded to the two opioid molecules via an ether bond. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such a buprenorphine dimer drug are also disclosed, and the use of such compounds in the treatment of gastrointestinal hyperalgesia generally and in particular diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.
Owner:DIMERX INC
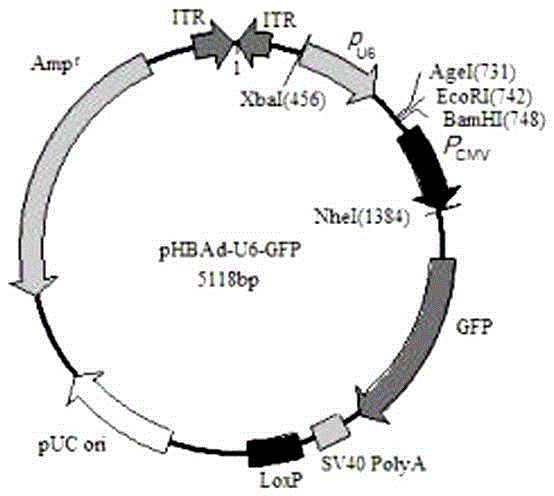
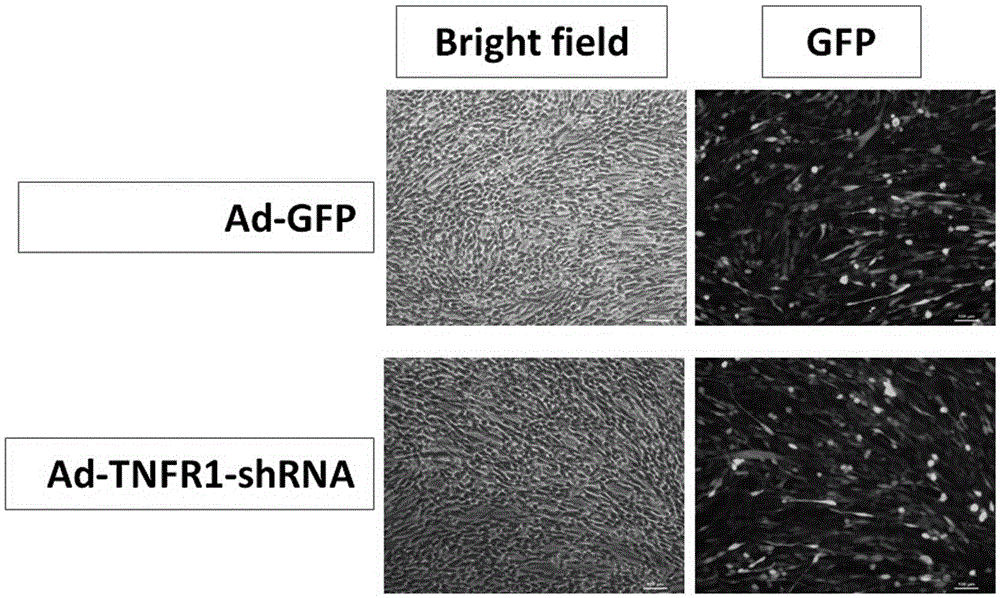
TNFR1 gene recombinant adenovirus and construction thereof
PendingCN105349502AReduce hyperalgesiaOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderInflammatory factorsNucleotide
The invention discloses a TNFR1 gene recombinant adenovirus. The adenovirus contains siRNA expressed by an interference TNFR1 gene of a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1, the siRNA is connected to the place below a U6 promoter of shuttle plasmid pHBAd-U6-GFP to prepare an adenovirus shuttle plasmid, and then the adenovirus shuttle plasmid and a skeleton plasmid pHBAd-BHG are subjected to cotransfection 293 cells to obtain adenovirus Ad-TNFR1 shRNA. The TNFR1 gene recombinant adenoviru is used for blocking or reducing TNFR1 expression and blocking a biological effect produced through TNF in a new way, so that tool medicine is designed to explore the effect of TNFR1 in hyperalgesia generation and the intracellular action mechanism, and medicine for preventing inflammatory factors from activating a receptor is designed to weaken the hyperalgesia effect caused after receptor activation.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
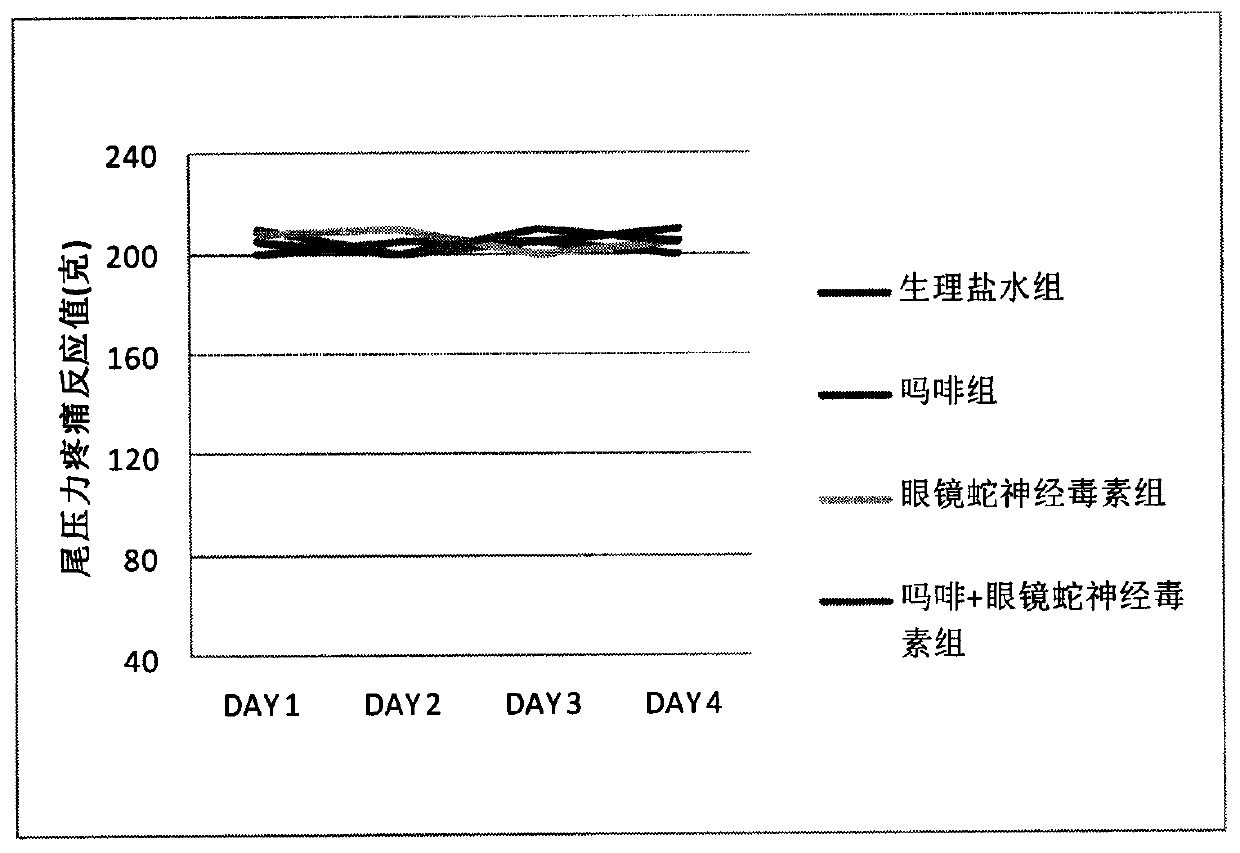
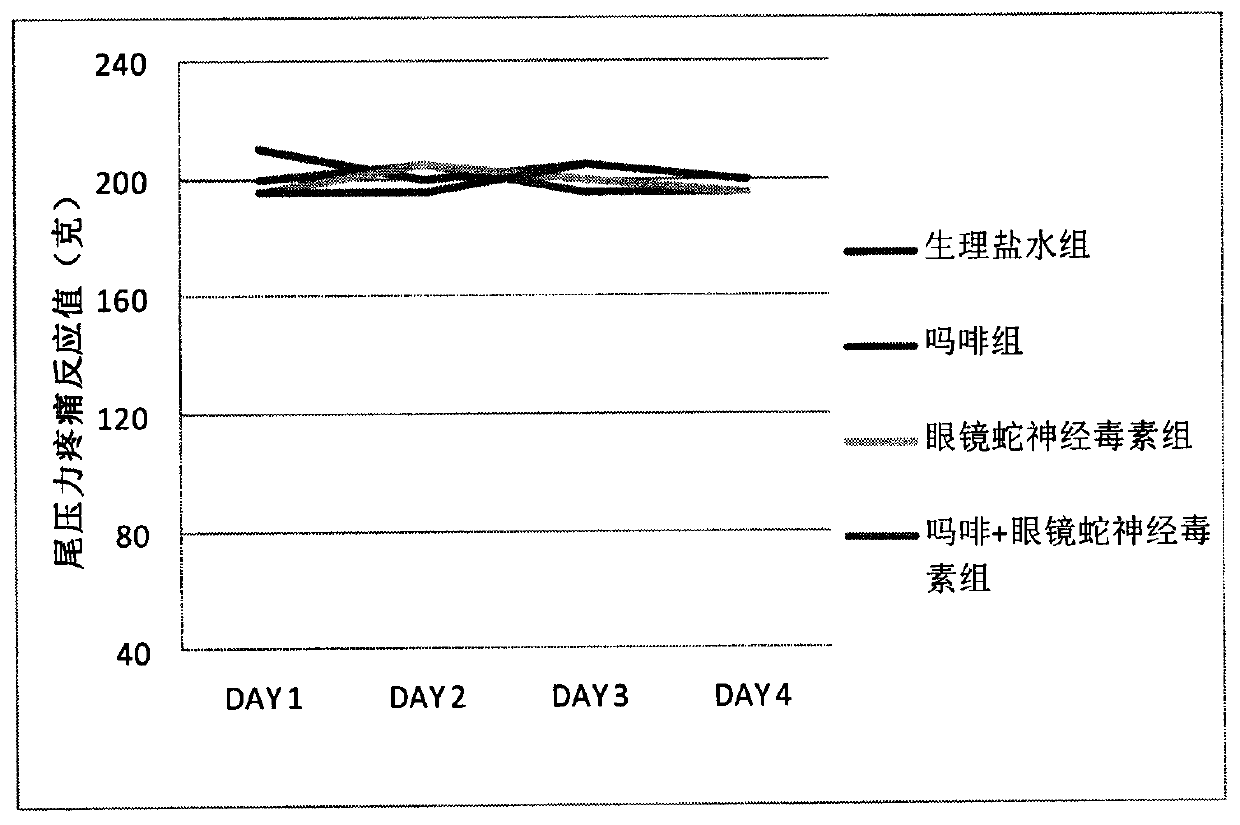
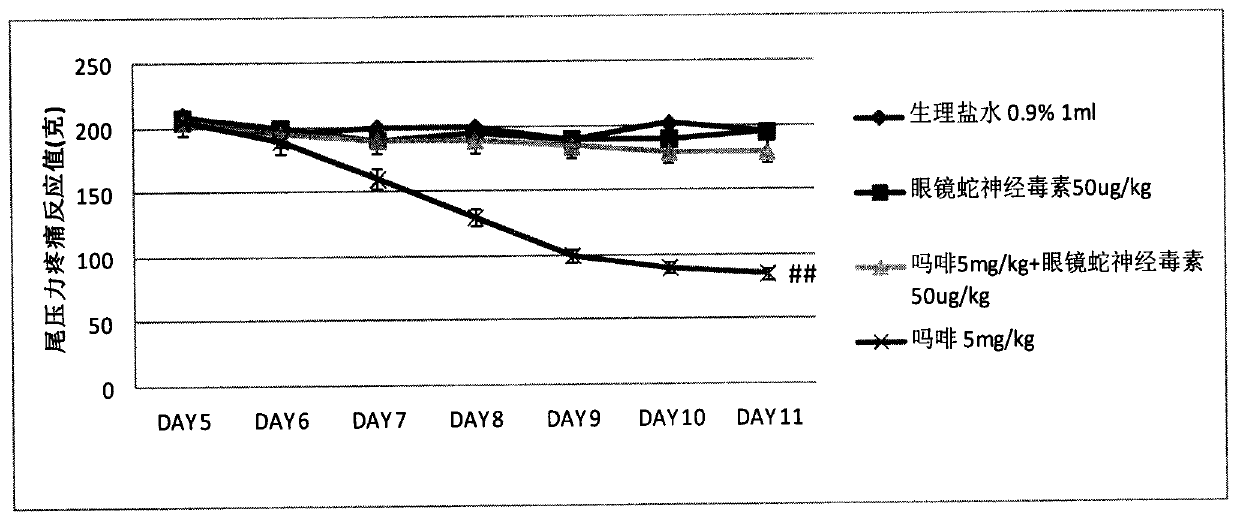
Synergy effect of cobra neurotoxin polypeptide on hyperalgesia and tolerance and alleviating pain of opioids
An opioid receptor agonist is a powerful effect analgesic medicine which is clinically and widely used, morphine is representative, and the medicine can effectively relieve pain of patients, particularly for pain of people after an operation and in the terminal cancer. However, opioids are easy to cause tolerance and hyperalgesia of patients, and the tolerance and the hyperalgesia can be easily formed within one week. Once the tolerance and the hyperalgesia are formed, dosage is continuously increased to continue to maintain the effect of alleviating pain, namely that organisms need a massivedose of medicines to achieve the effect of alleviating pain as the initial dose, but the higher dose can cause serious hyperalgesia, tolerance, constipation, addiction and respiratory depression. Cobra neurotoxin polypeptide can restrain the hyperalgesia and the tolerance of the opioids, and can also improve the treatment effects of opioids, and when the cobra neurotoxin polypeptide and the opioids are combined together for use, the opioids can alleviate pain at the lower dose and does not generate tolerance and hyperalgesia, so that the clinical technical problem that the opiods cannot be used for a long term can be solved.
Owner:江苏毫末医药生物科技有限公司
Method of treatment or prophylaxis of inflammatory pain
InactiveUS8551950B2Good curative effectAvoid painAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsVertebrate AnimalsMechanical Allodynia
A method of treatment, reversal and / or symptomatic relief of inflammatory pain, including hyperalgesia, thermal or mechanical allodynia, in vertebrate animals, particularly in human subjects, comprising administering angiotensin II receptor 2 (AT2 receptor) antagonists is disclosed. The AT2 receptor antagonist may be provided alone or in combination with other compounds such as those that are useful in the control of inflammatory pain.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
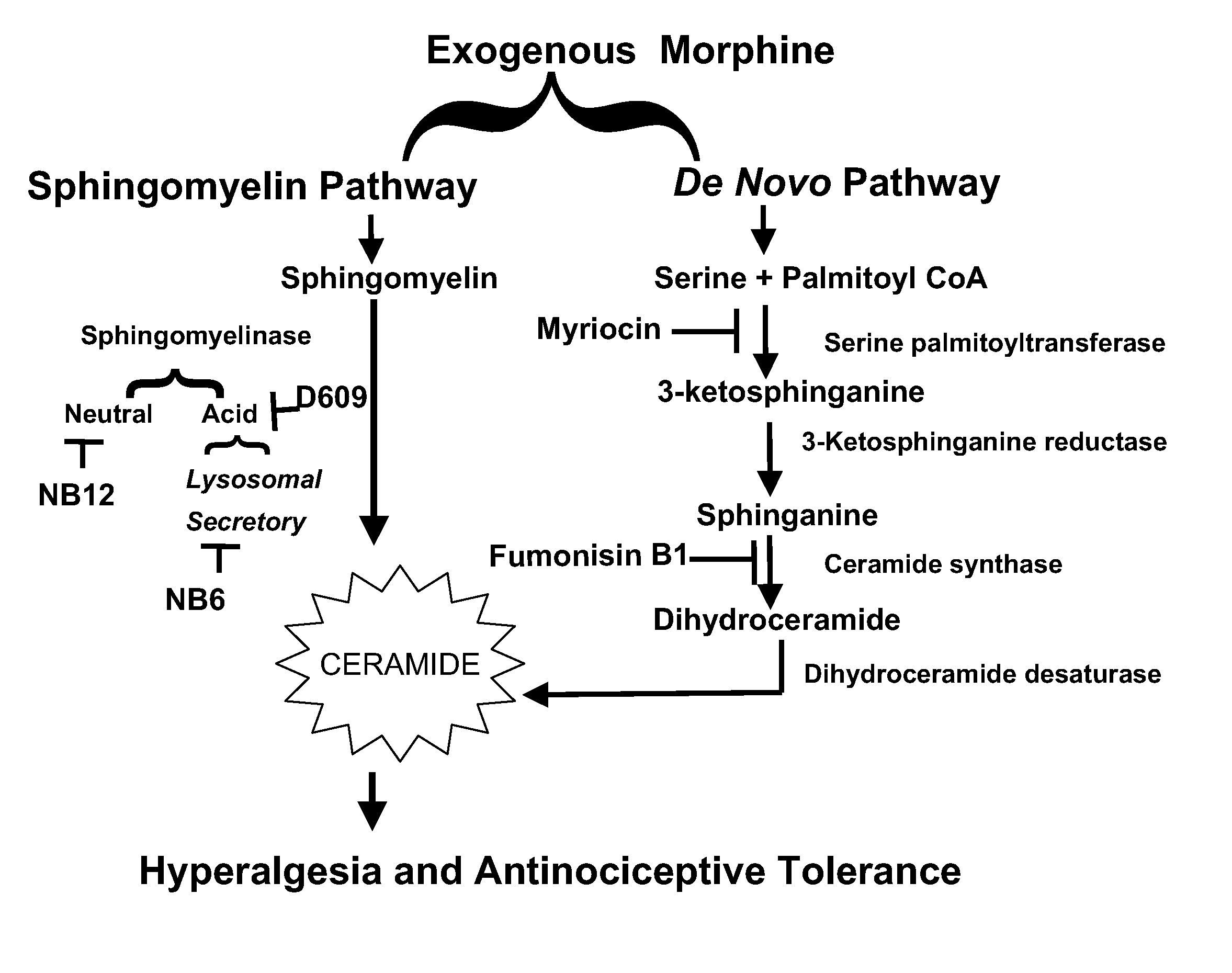
Inhibitors of the ceramide metabolic pathway as adjuncts to opiates for pain
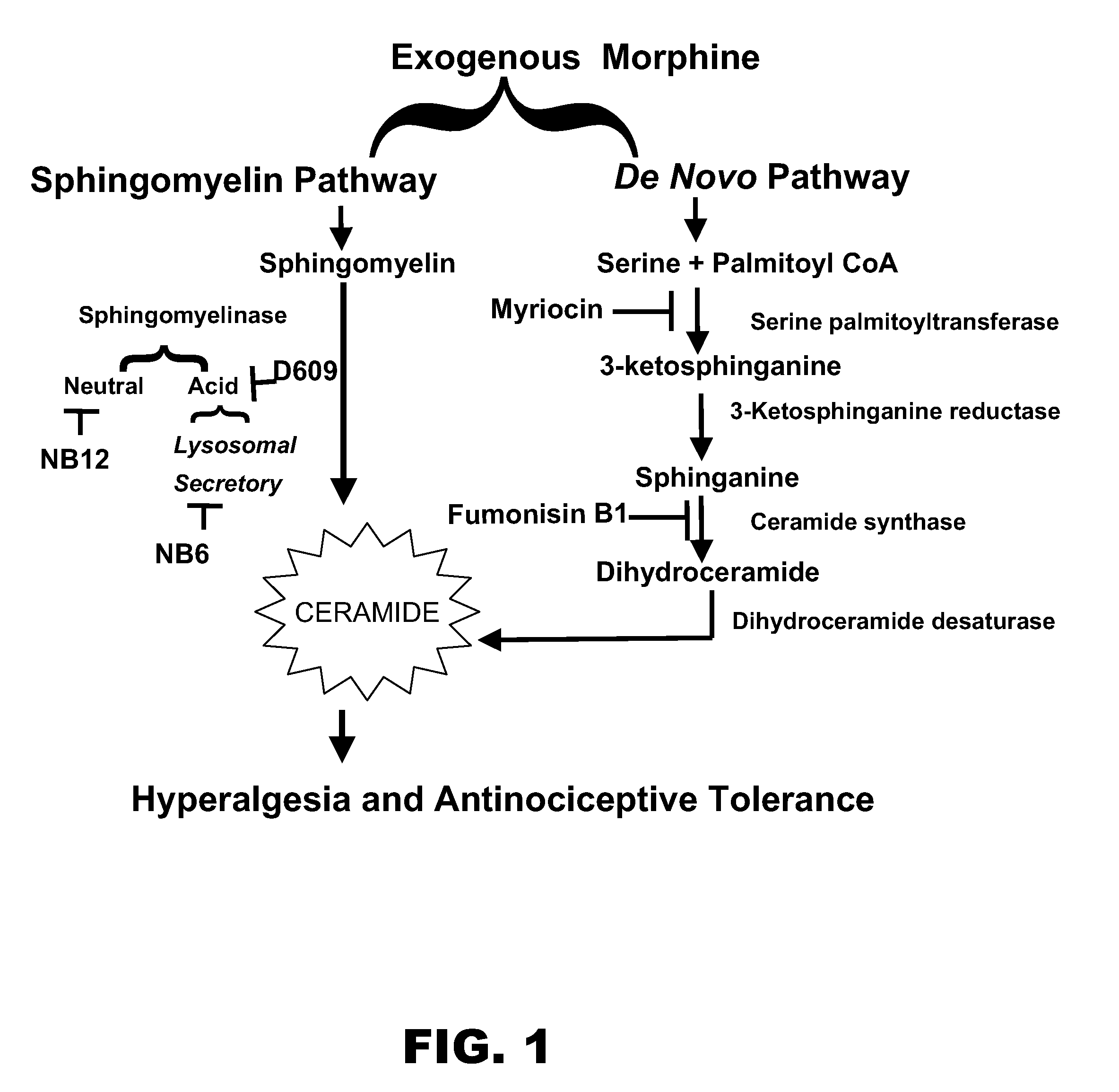
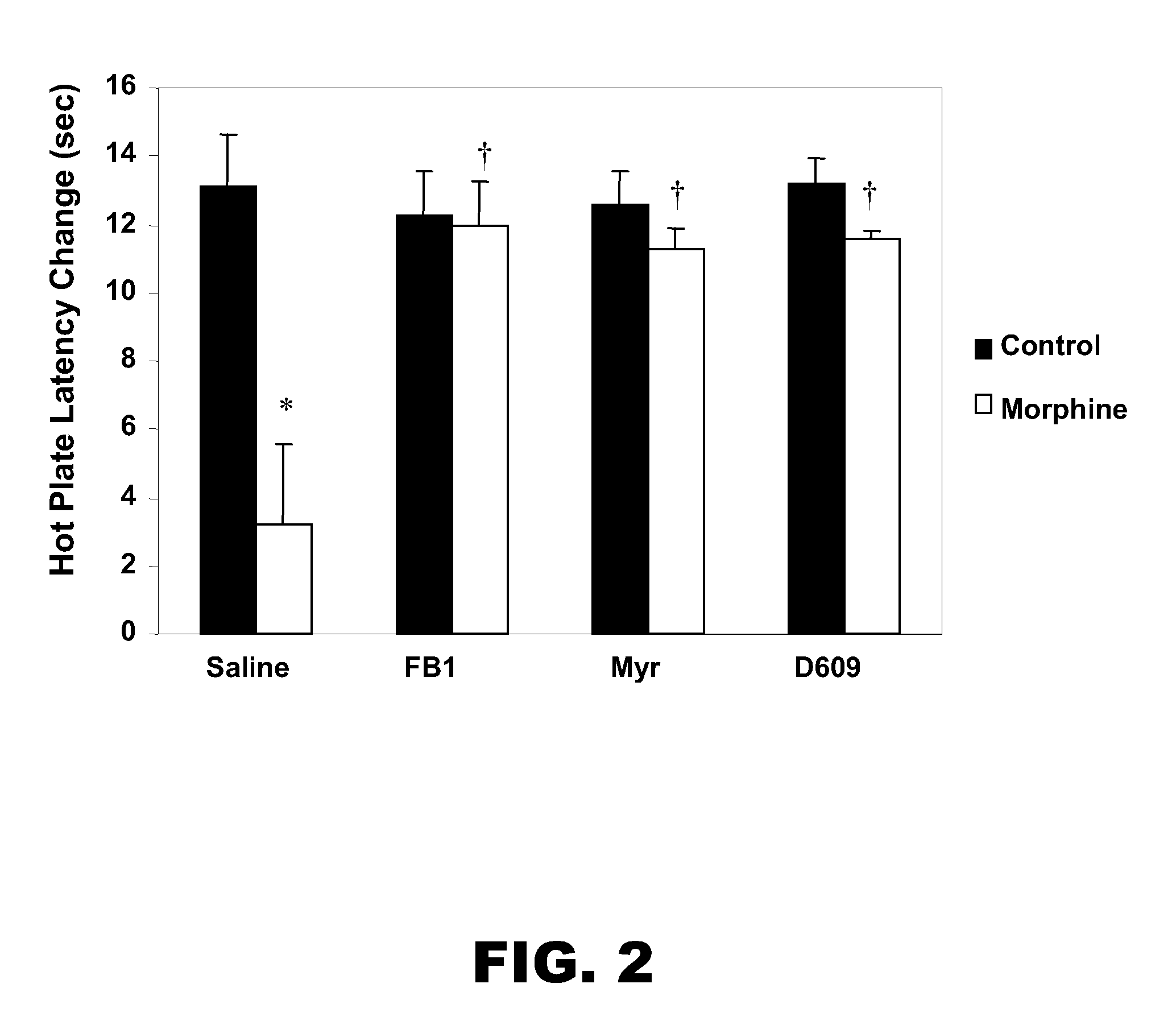
InactiveUS20080241121A1Reduce ceramideOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTolerabilityOpiate
A method for treating opiate induced tolerance or opiate induced hyperalgesia in a subject is closed. More specifically, the method provides for reducing ceramide levels with an agent thereby treating opiate induced antinociceptive / analgesic tolerance or hyperalgesia in a human or non-human subject. The method further allows for improved pain management in subjects suffering from chronic pain as well as treatment for opiate induced disorders.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Agent for neuropathic pain
ActiveUS20130230509A1Increase painFunction increaseNervous disorderOrganic chemistryMechanism of actionMedicine
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
Use of koumine and its homologues in preparation of medicament for treatment of autoimmune diseases of involved bones and joints
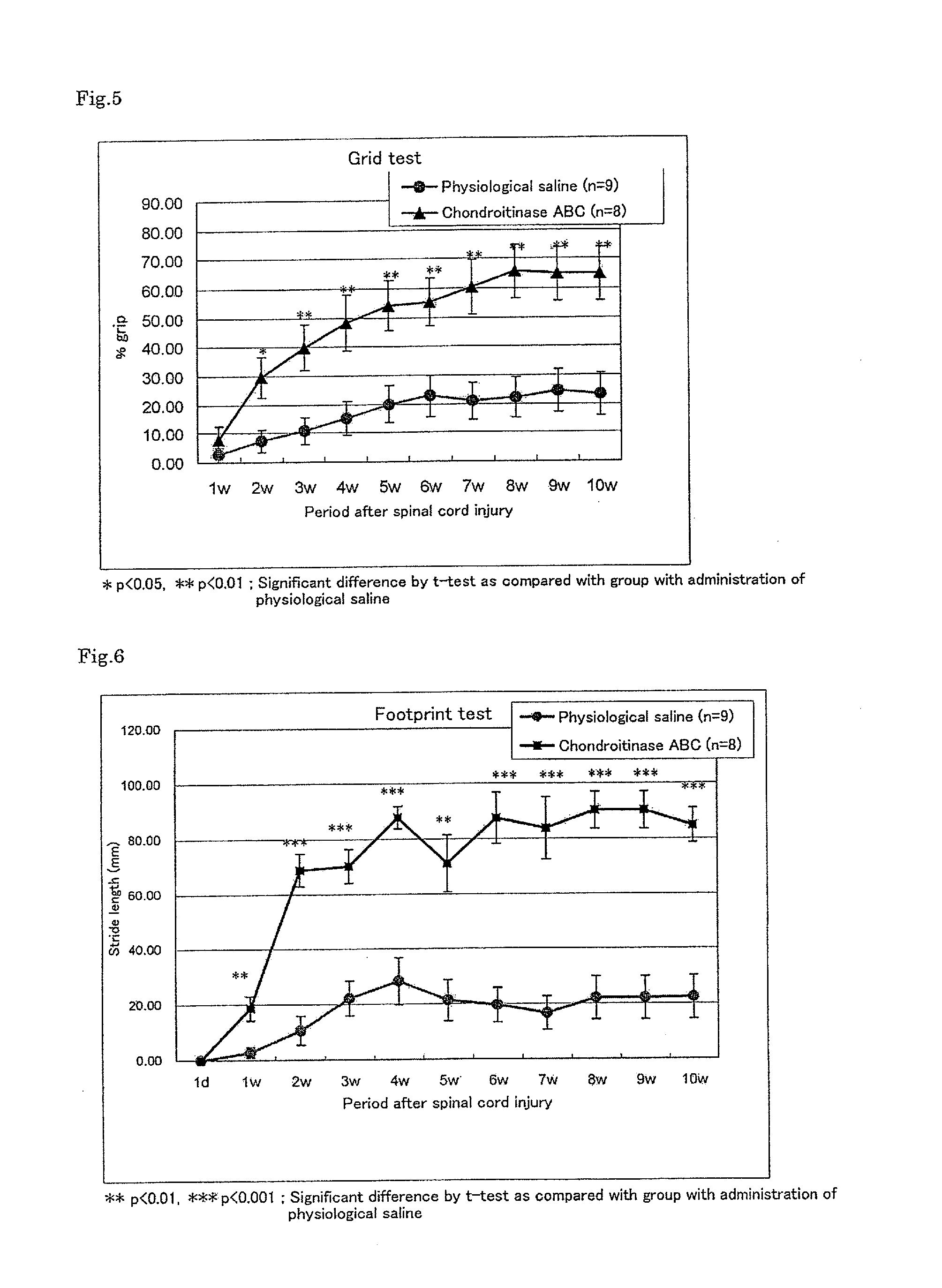
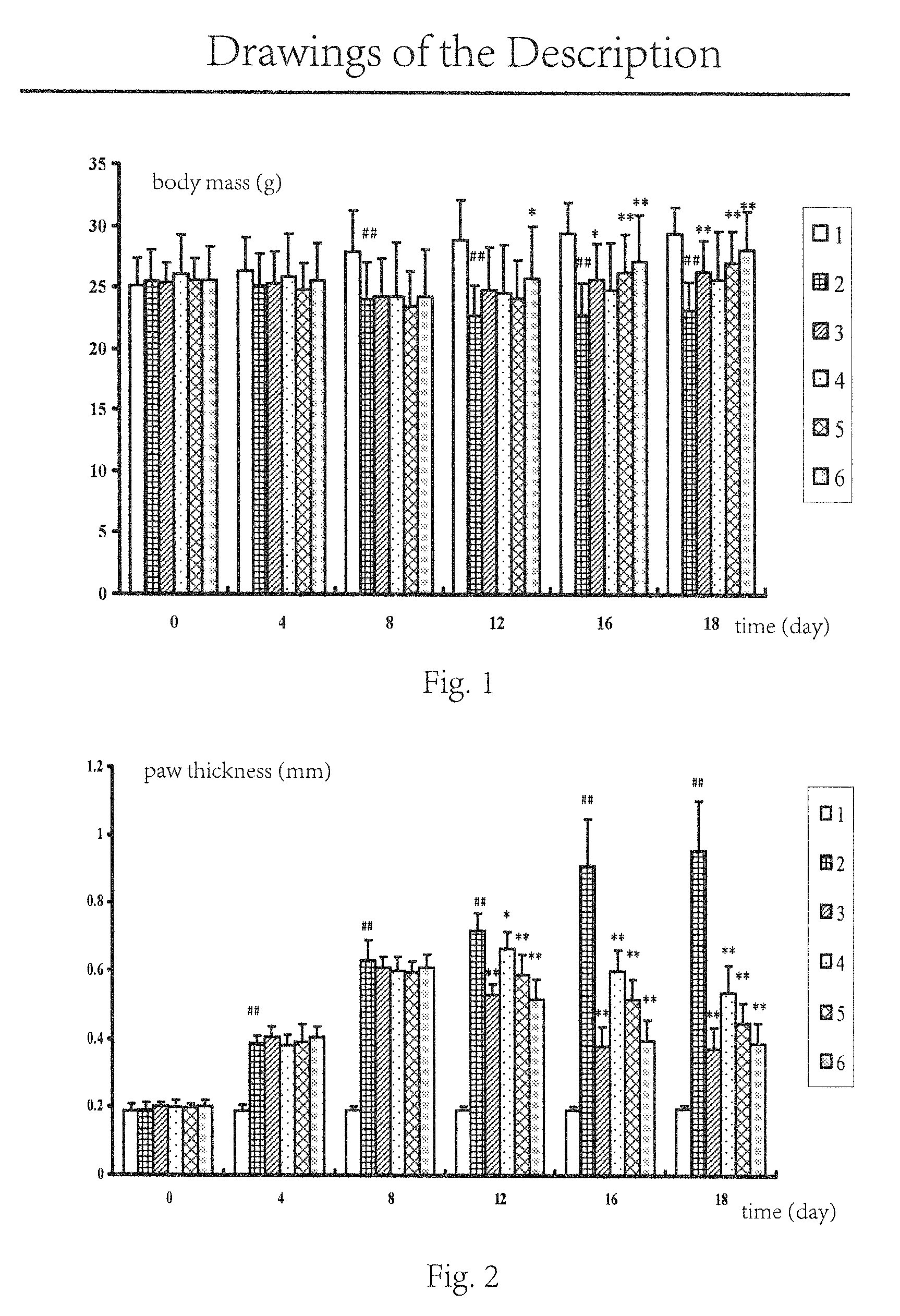
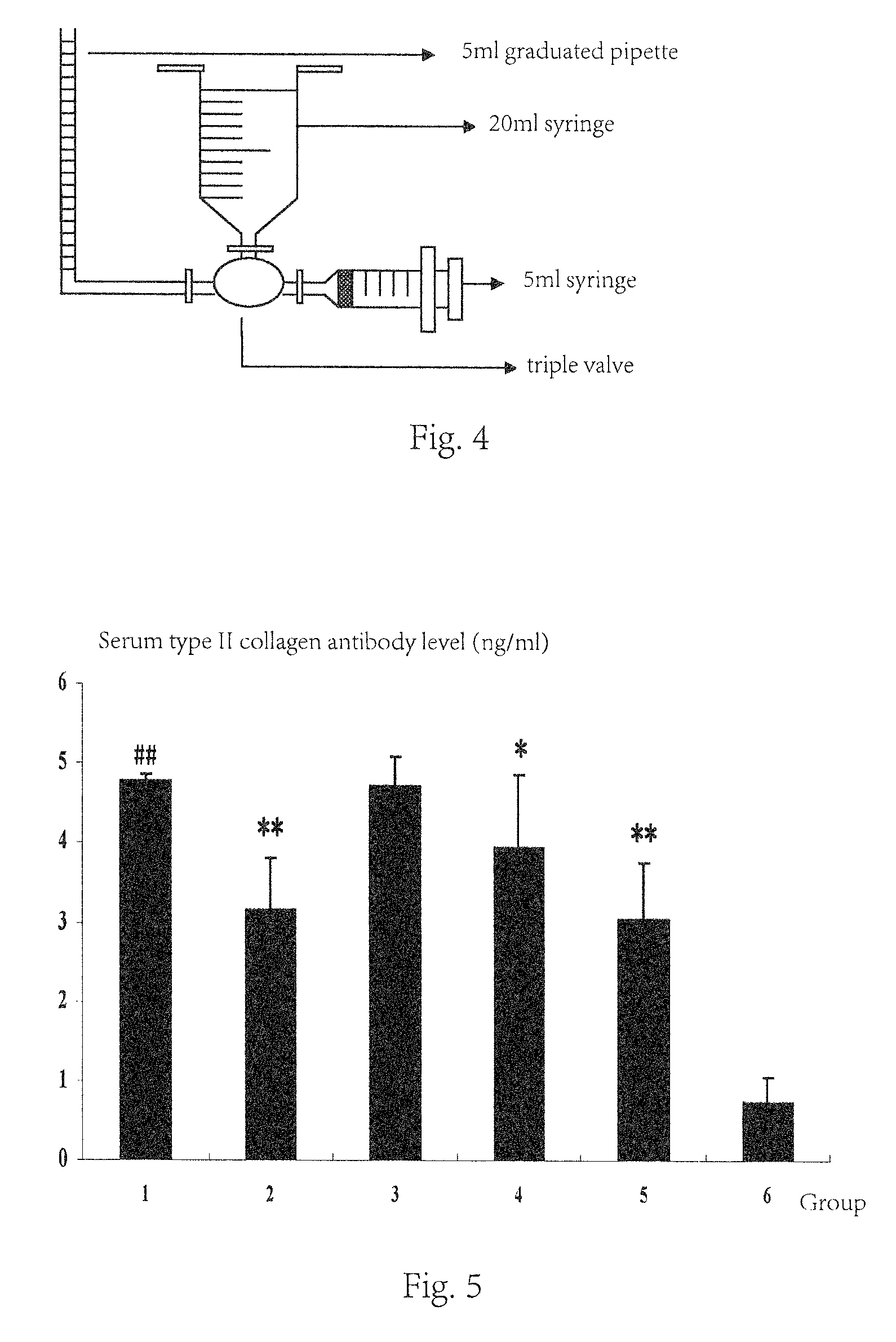
ActiveUS9078890B2Improve efficiencyLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticImmunologic disordersDisease
The present invention discloses an application of koumine and homologue thereof in preparation of drugs for treating autoimmune diseases involving bones and joints including rheumatoid arthritis, spondylitis ankylopoietica or the like, in particular an application of Gelsemium alkaloid monomer koumine and homologue thereof or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as active ingredient in preparation of drugs for treating autoimmune diseases involving bones and joints including rheumatoid arthritis, spondylitis ankylopoietica or the like. The result of pharmacology experiment shows that koumine can decrease the generation of organism antibody against autoimmune diseases involving bones and joints in a dose dependent manner, improve symptoms of swelling and hyperalgesia, reduce arthritis index, reverse joint pathological changes, and has no serious shortage of commonly used clinical drugs; thus koumine has an effect against autoimmune diseases involving bones and joints including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis etc. with strong potency and low toxicity. Koumine can be developed into a new drug for treating autoimmune disease involving bones and joints including rheumatoid arthritis, spondylitis ankylopoietica etc., which has a clear industrial prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com