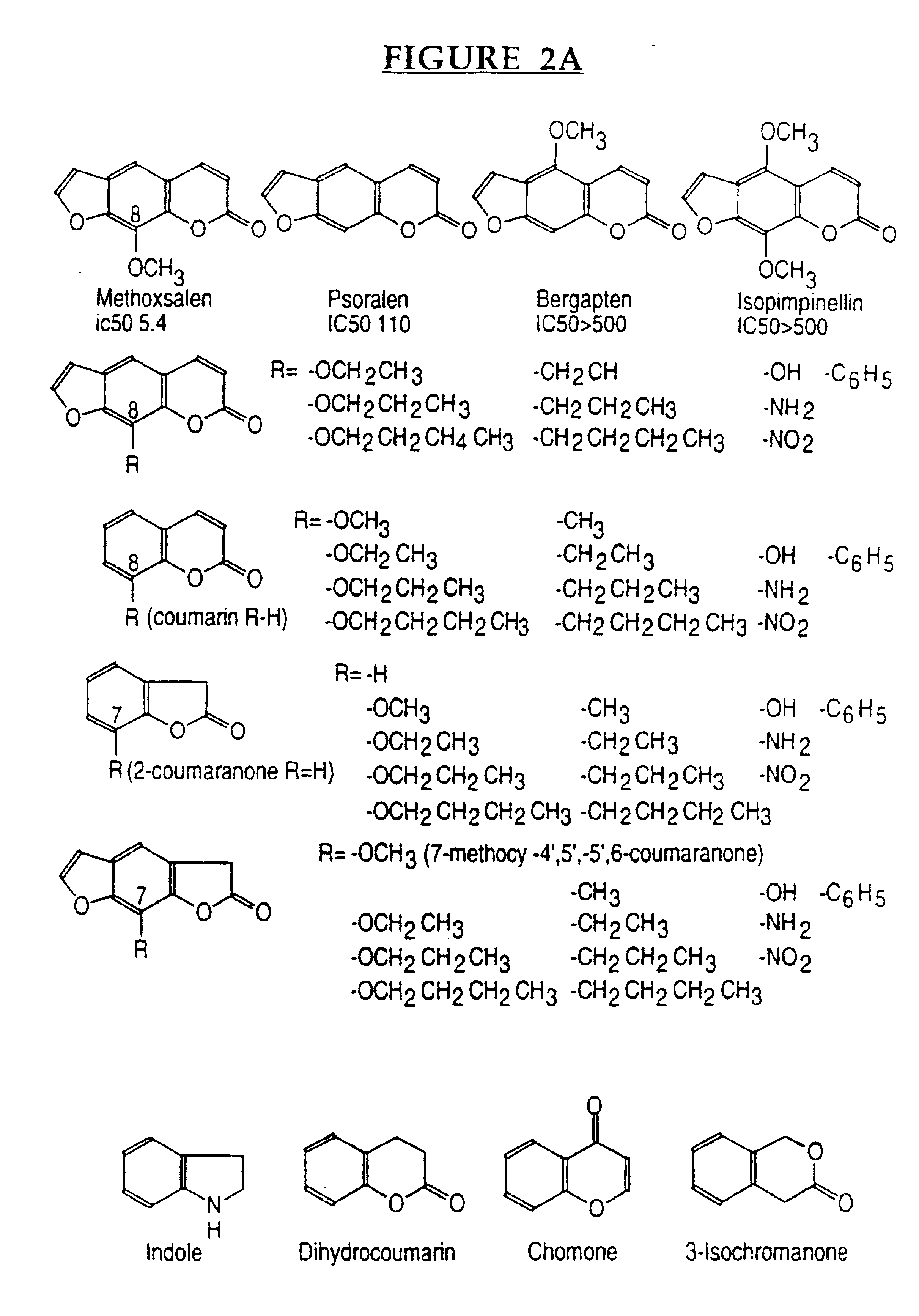
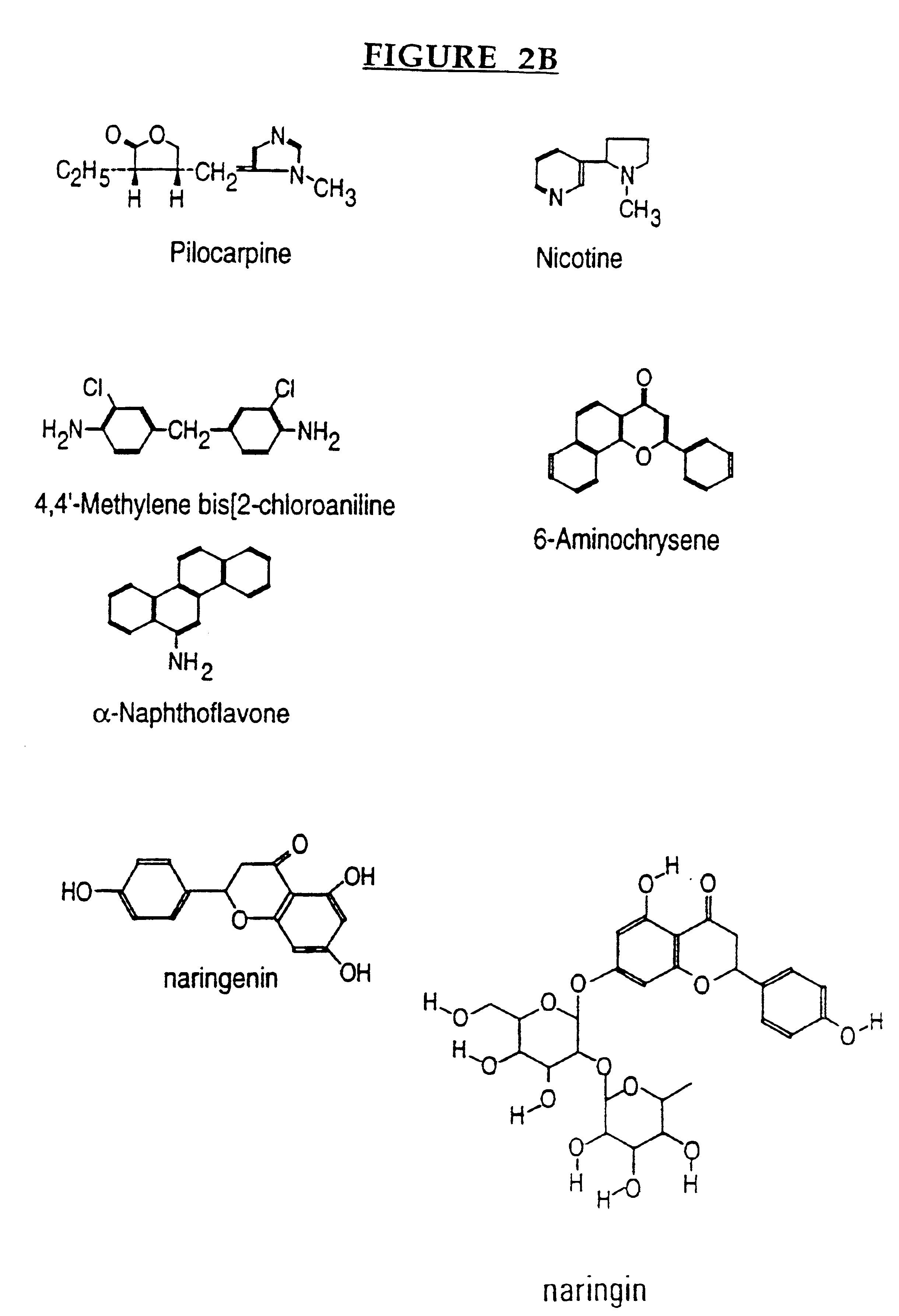
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Human cytochrome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Primer system for detecting genetic polymorphic sites related to human cytochrome P450 and application of primer system
InactiveCN103233068AHigh detection sensitivityOperational securityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceHuman cytochrome
The invention discloses a primer system for detecting genetic polymorphic sites related to human cytochrome P450. Based on a product prepared by adopting the primer system, seven genetic polymorphic sites related to the human cytochrome P450 can be simultaneously detected. By using the product, through detecting the genetic polymorphic sites related to the human cytochrome P450, clinical medication scheme can be guided and regulated, the basis is provided for clinical personalized medicine, and adverse medicine effects are prevented. The primer system is capable of simultaneously detecting the seven genetic polymorphic sites on different genes in a reaction system, and has the advantages of being lower in cost and more convenient to operate, and increasing the accuracy and the sensitivity in comparison with technologies of sequencing and real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction).
Owner:BIOYONG TECH +1
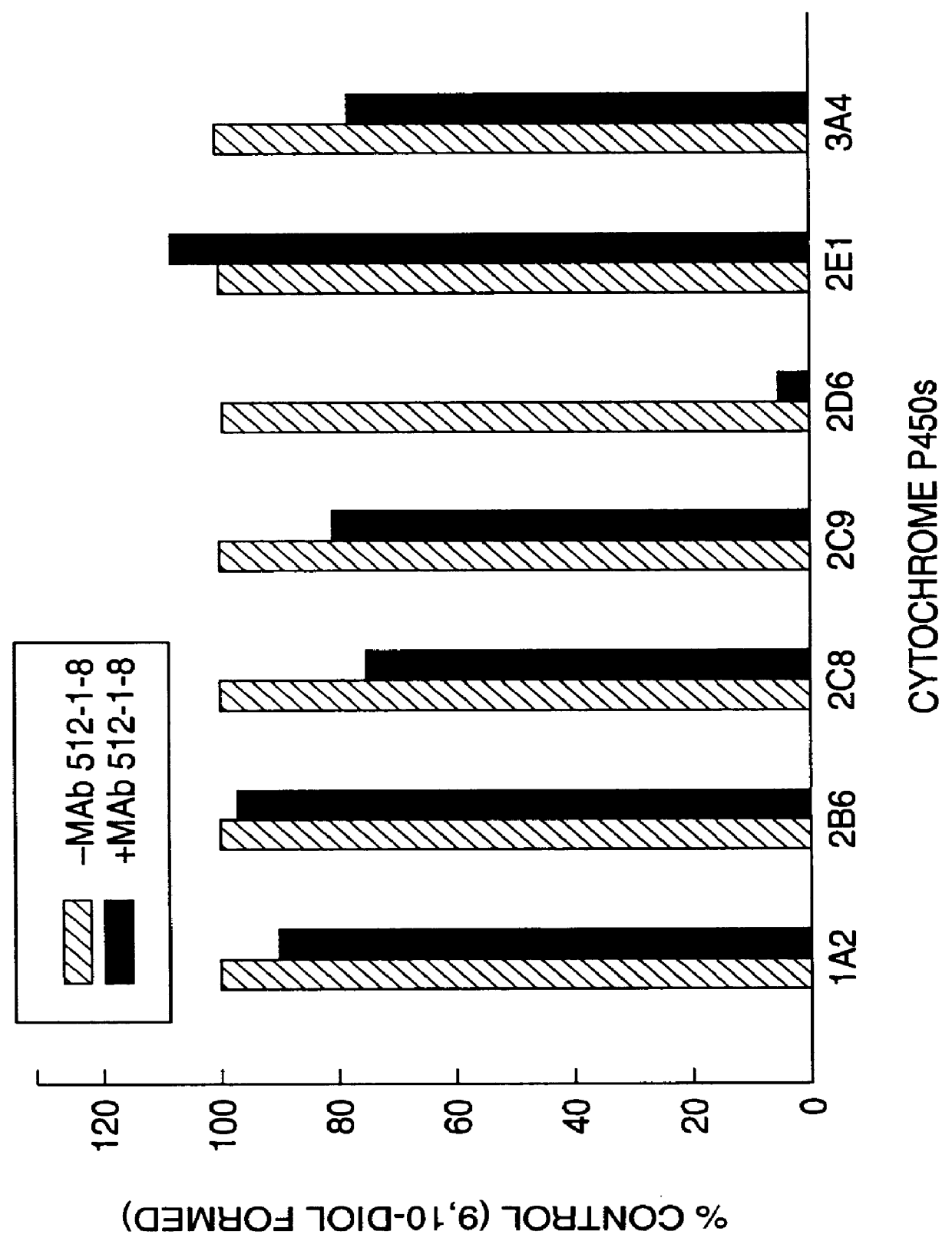
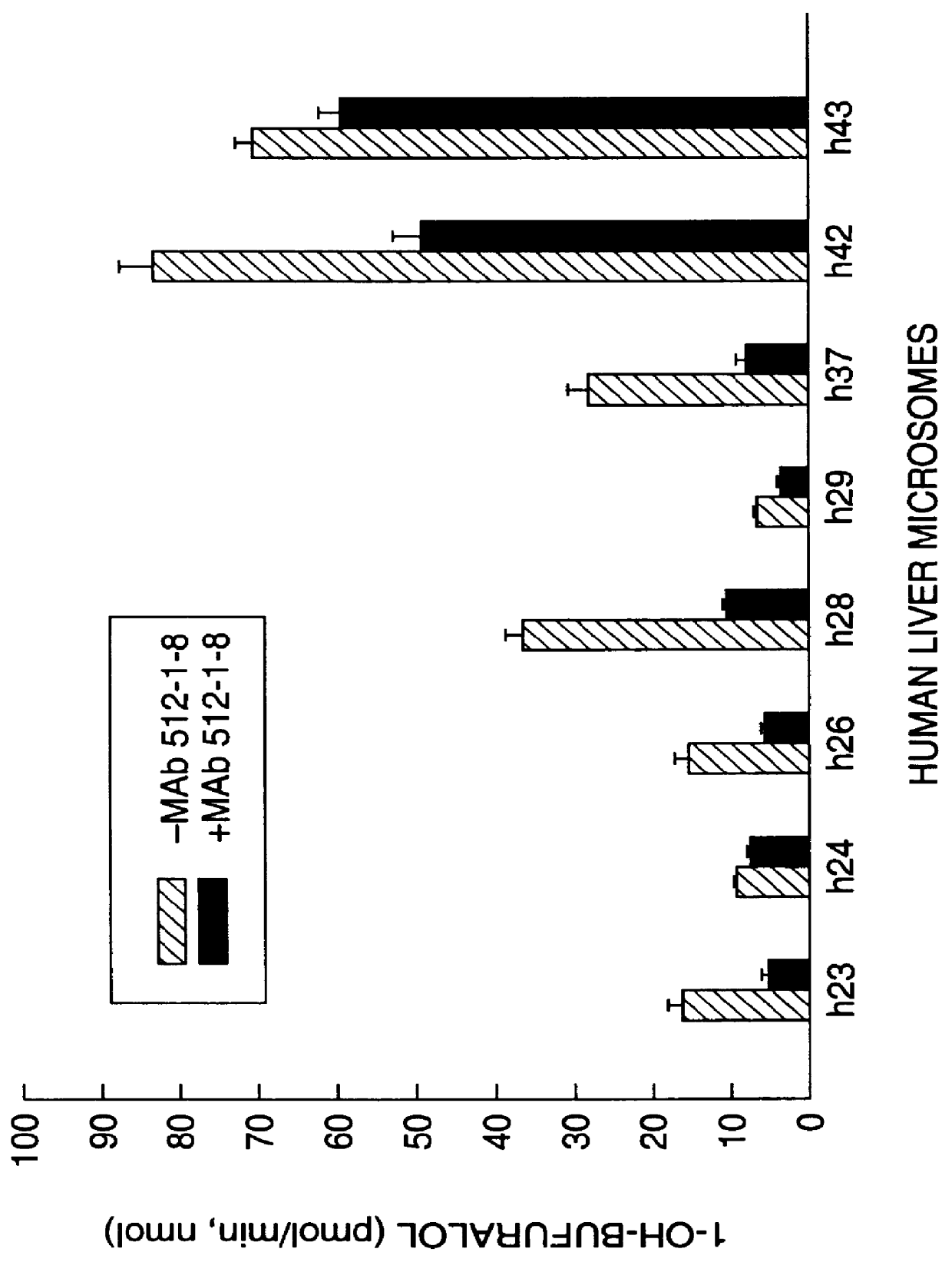
Agents that bind to and inhibit human cytochrome P450 2D6
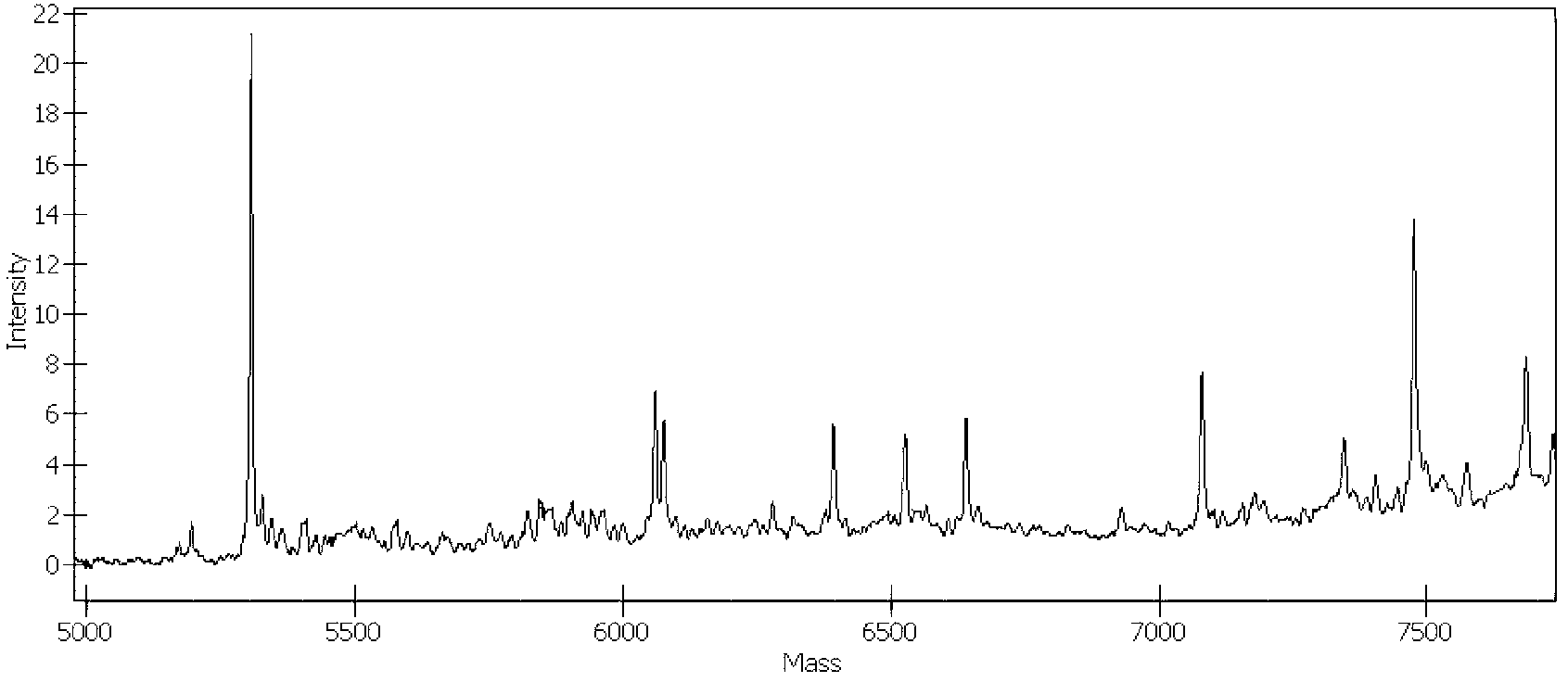
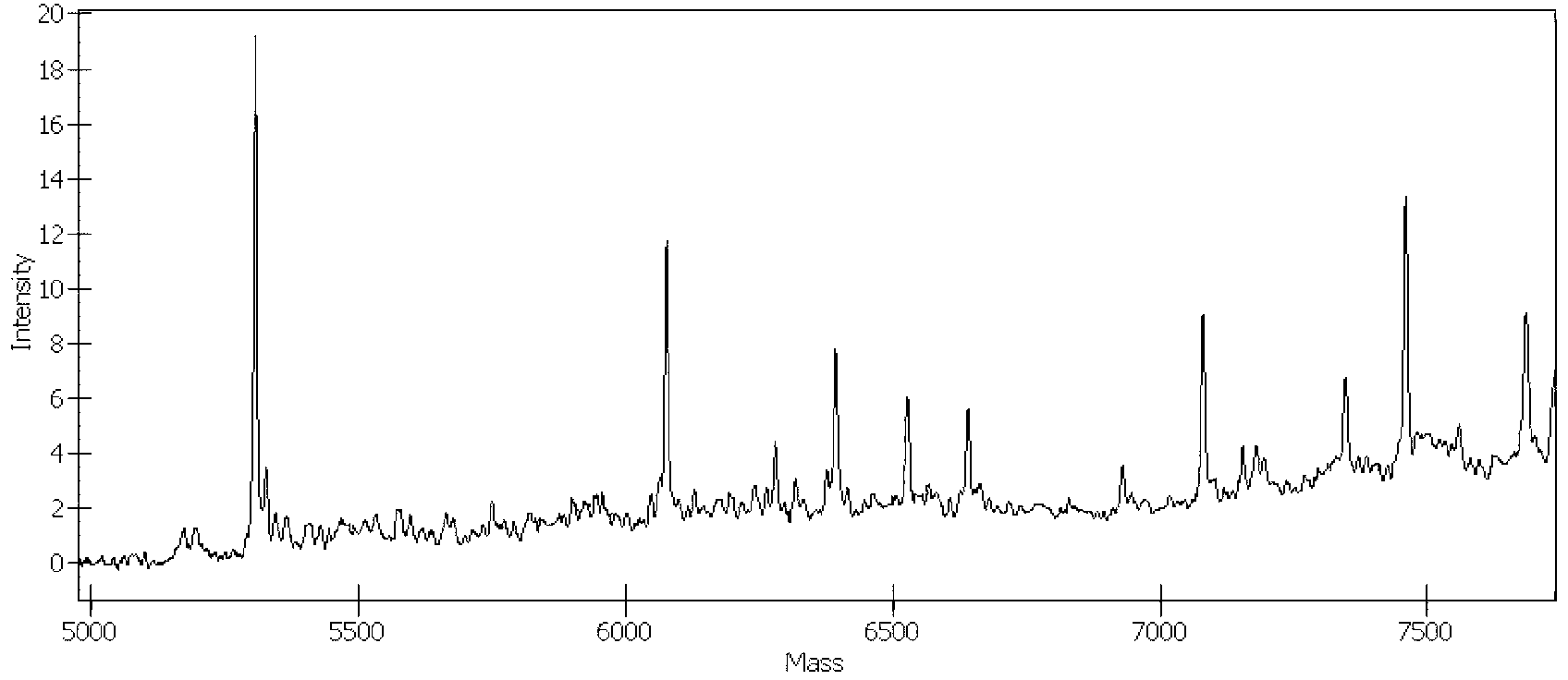
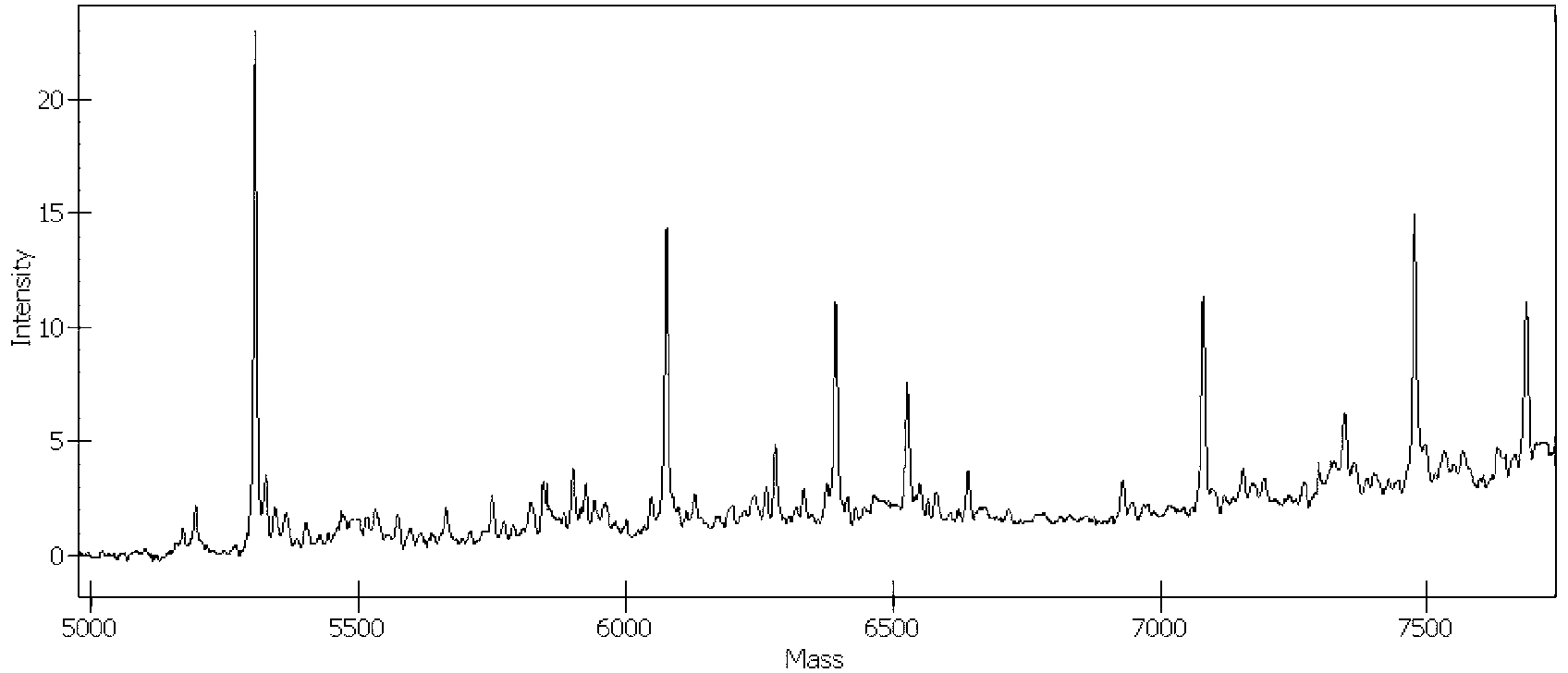
The invention provides monoclonal antibodies and other binding agents to human cytochrome P450 2D6 having advantageous properties, including capacity substantially to inhibit enzyme activity of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and lack of specific binding to other human cytochromes P450. The binding agents of the invention are useful in methods for screening drugs for metabolism by cytochrome P450 2D6, and in methods of screening individuals for a poor metabolizing human P450 2D6 phenotype.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
Method and kit for detecting gene mutation of human cytochrome P450 CYP2C19
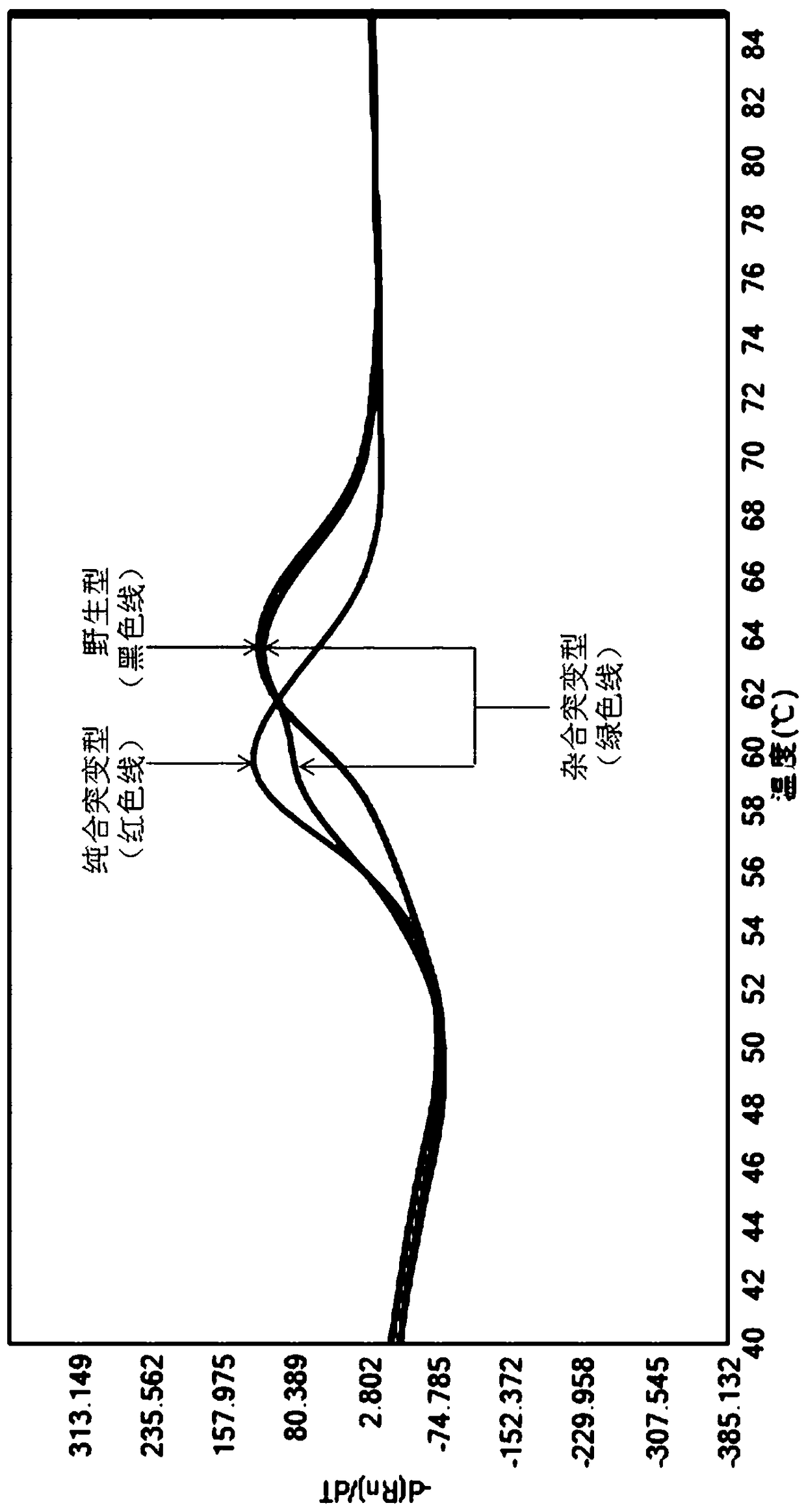
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and discloses a method for detecting gene mutation of human cytochrome P450 CYP2C19, which comprises the following steps of: performing amplification on a sample genome by using primers, wherein the primers comprise upstream and downstream primers for detecting M1 mutation, and upstream and downstream primers for detecting M2 mutation, the nucleotides of the upstream and downstream primers for detecting M1 mutation are shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, and the nucleotides of the upstream and downstream primers for detecting M2 mutation are shown as SEQ ID No.5 and SEQ ID No.6; and setting a reference for quality control, and sequencing an amplification product by using sequencing primers of which the nucleotides are shown as SEQ ID No.9 and SEQ ID No.10. The invention also provides a kit for detecting gene mutation of human cytochrome P450 CYP2C19. According to detection results of the method, guidance and adjustment of clinical medication schemes are carried out, a basis is provided for clinical individualized medication, the treatment effect can be improved and the toxic and side effect risks can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING ADINOVO TECH
Detection gene chip for helicobacter pylori infection individualized treatment and application of gene chip
ActiveCN103060455AStrong specificityConsistent specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyIndividualized treatment
The invention relates to a biological engineering detection product and an application of the gene chip, and in particular relates to a detection gene chip for helicobacter pylori infection individualized treatment. The chip is capable of simultaneously detecting polymorphisms of helicobacter pylori clarithromycin medicine-resistant mutation sites A2142G and A2143G, carbostyril medicine-resistant mutation sites Asn87(N87K) and Asp91(D91G / Y / N), and sites 2C19*2(G6981A) and 2C19*3(G636A) related to metabolism of a proton pump inhibitor on human cytochrome enzyme CYP450. The chip detection method disclosed by the invention is rapid and accurate and is capable of identifying helicobacter pylori etiology, carrying out medicine-resistant analysis of clarithromycin and carbostyril, and analyzing metabolic individual differences of the proton pump inhibitor, so that the detection gene chip is used for guiding individualized administration of helicobacter pylori infection triplex process treatment.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Gene carrier for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy and application of gene carrier
The invention relates to a gene carrier for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy (BCD) and application of the gene carrier. The gene carrier for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy comprises a packaging plasmid and a carrier plasmid. The packaging plasmid is an AAV2 packaging plasmid where a gene sequence of anti-CD59 short-chain-polypeptide C9 is inserted; the carrier plasmid is an AAV carrier plasmid where a gene sequence of human cytochrome P450 superfamily protein CYP4V2, a gene sequence of anti-VEGF short-chain-polypeptide HRH and a starting sub sequenceare inserted. The AAV carrier can conduct fusion expression on C9 anti-CD59 short-chain-polypeptide to virus coat protein; coexpression of CYP4V2 and HRH can be achieved, protein function loss causedby CYP4V2 genic mutation in a RPE cell is compensated for, the normal function of the RPE cell can be effectively repaired, specificity antagonism of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can be achieved, and retinal atrophy caused by choroid hyperplasia is delayed. The invention further application of the gene carrier to preparation of medicine for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy (BCD).
Owner:深圳泓熙生物科技发展有限公司
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on cyp2a enzymes
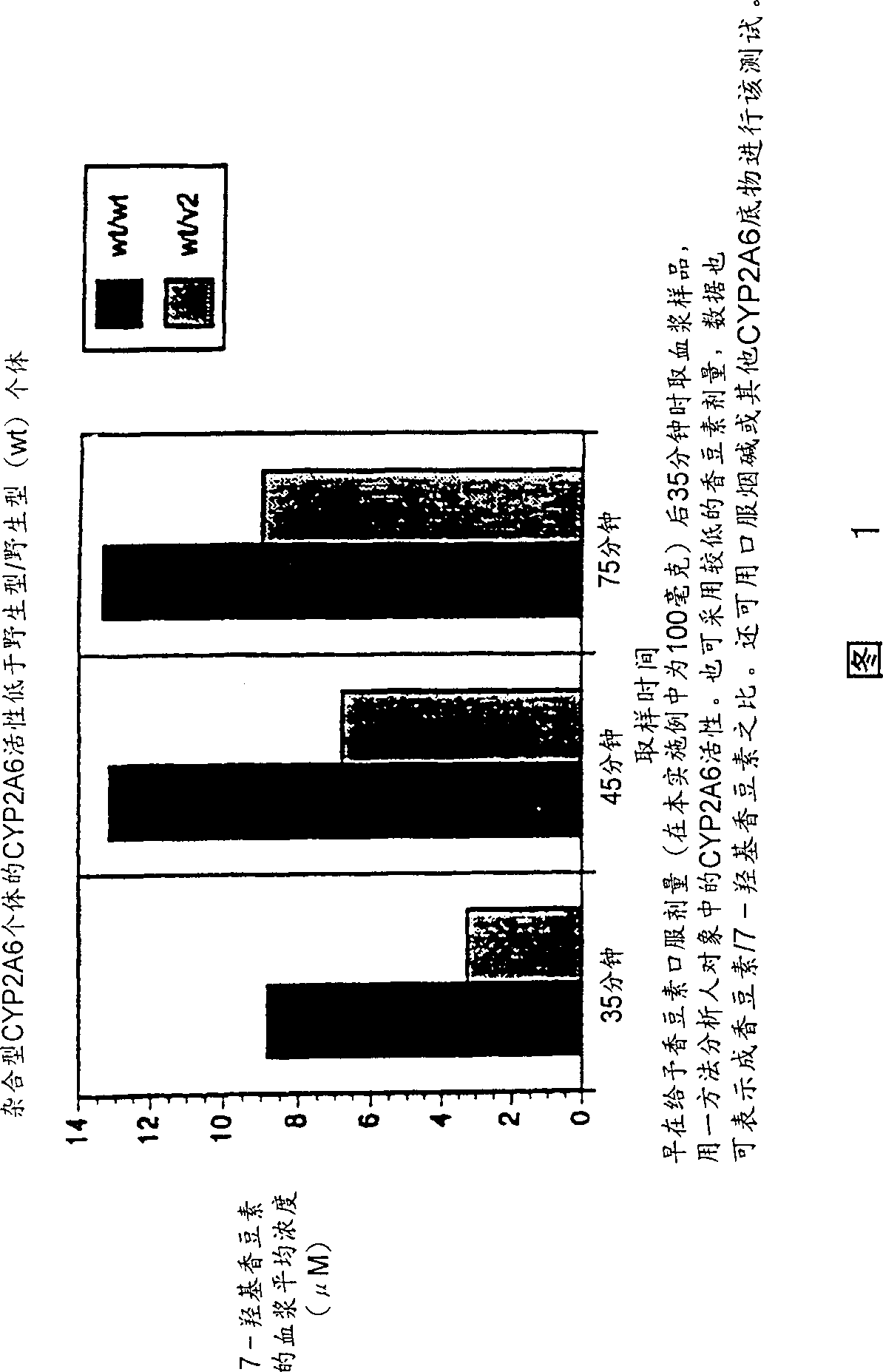
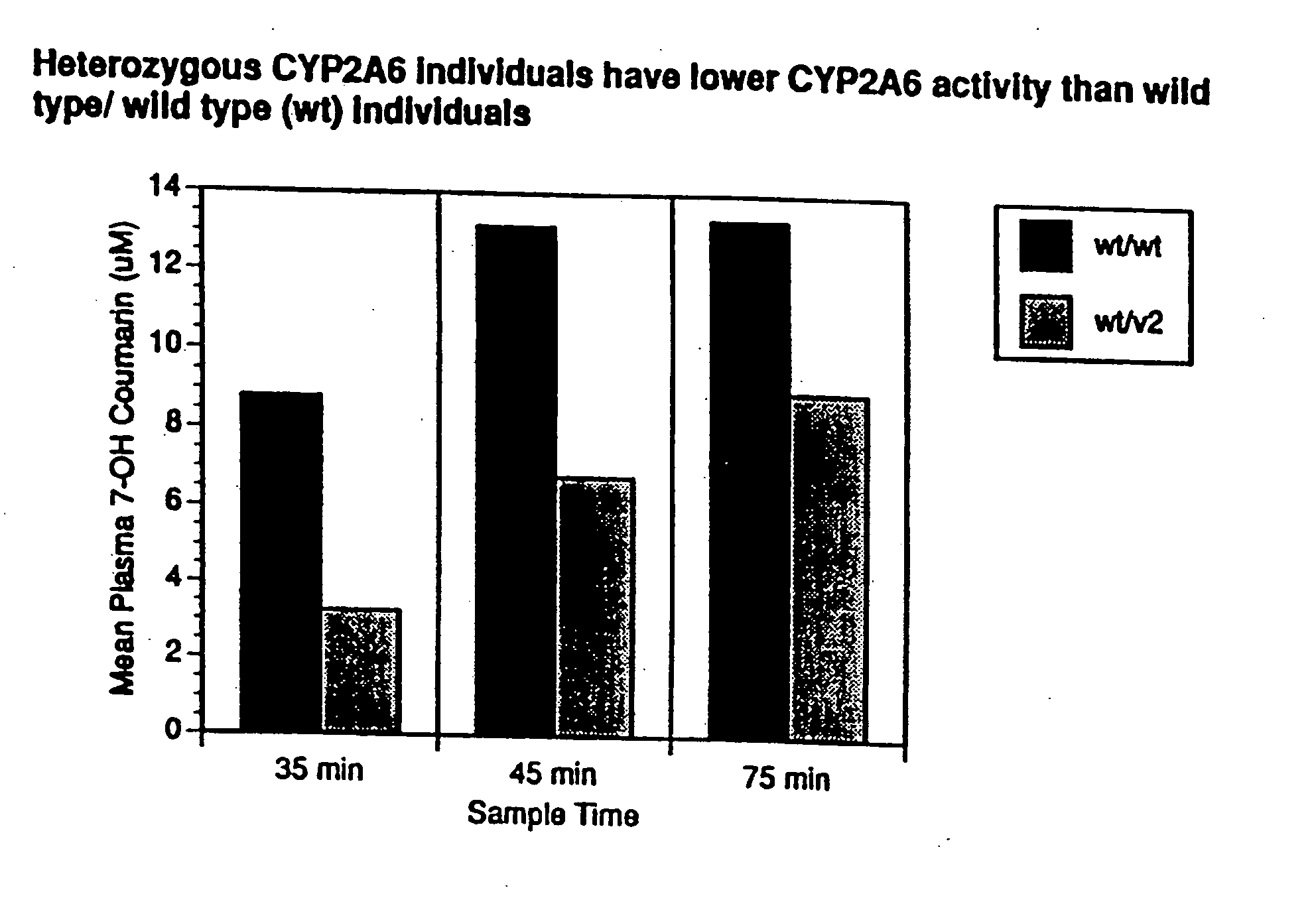
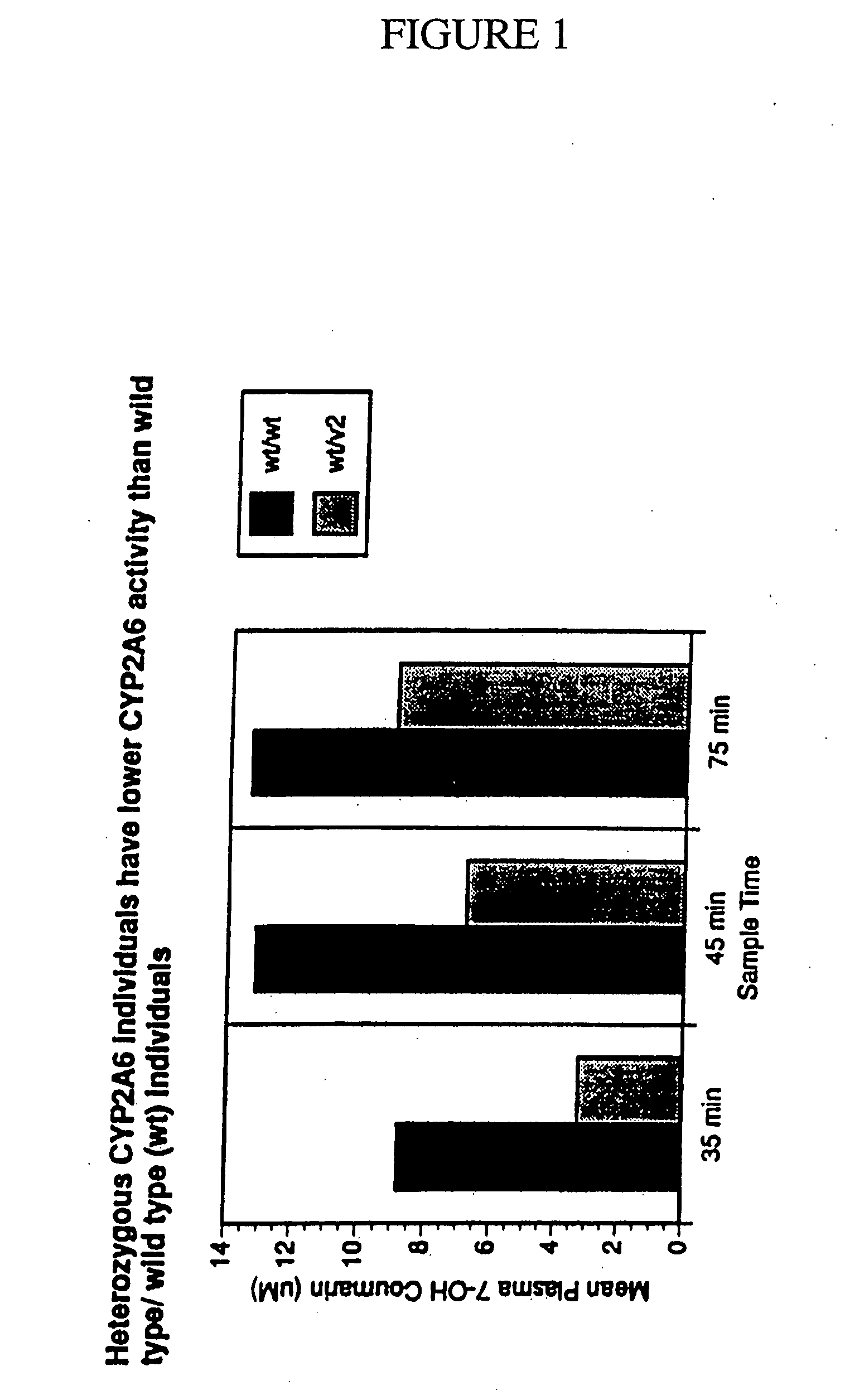
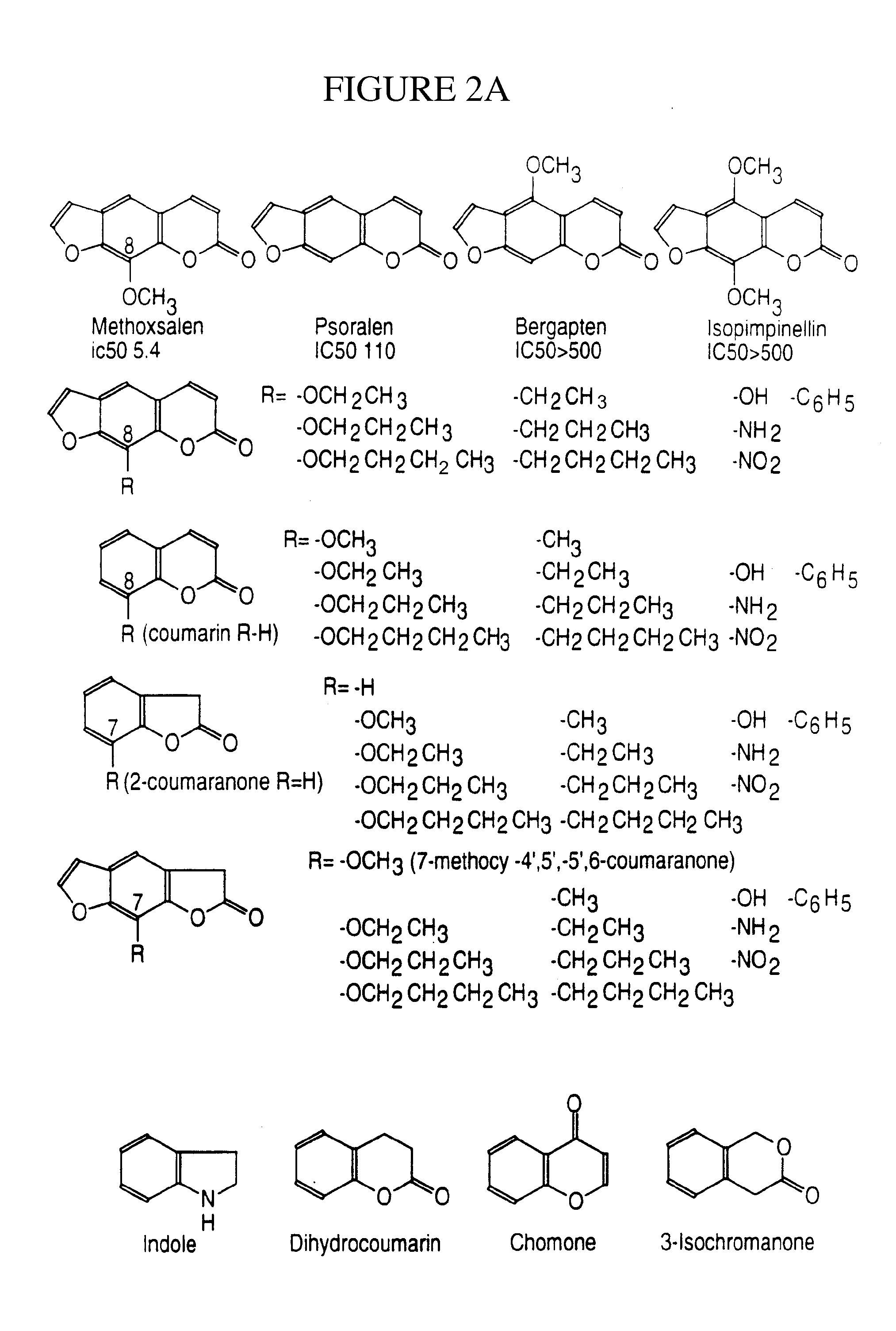
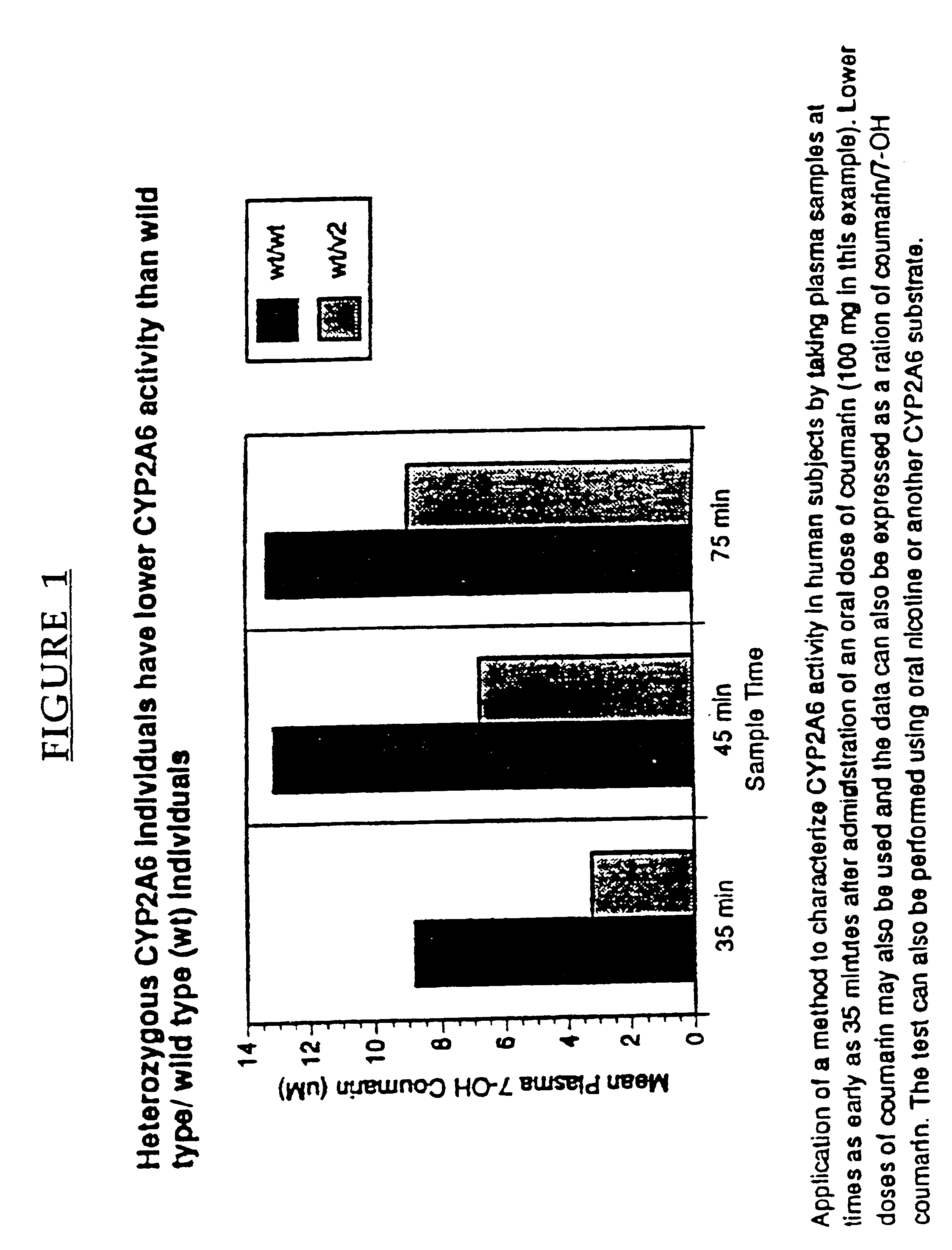
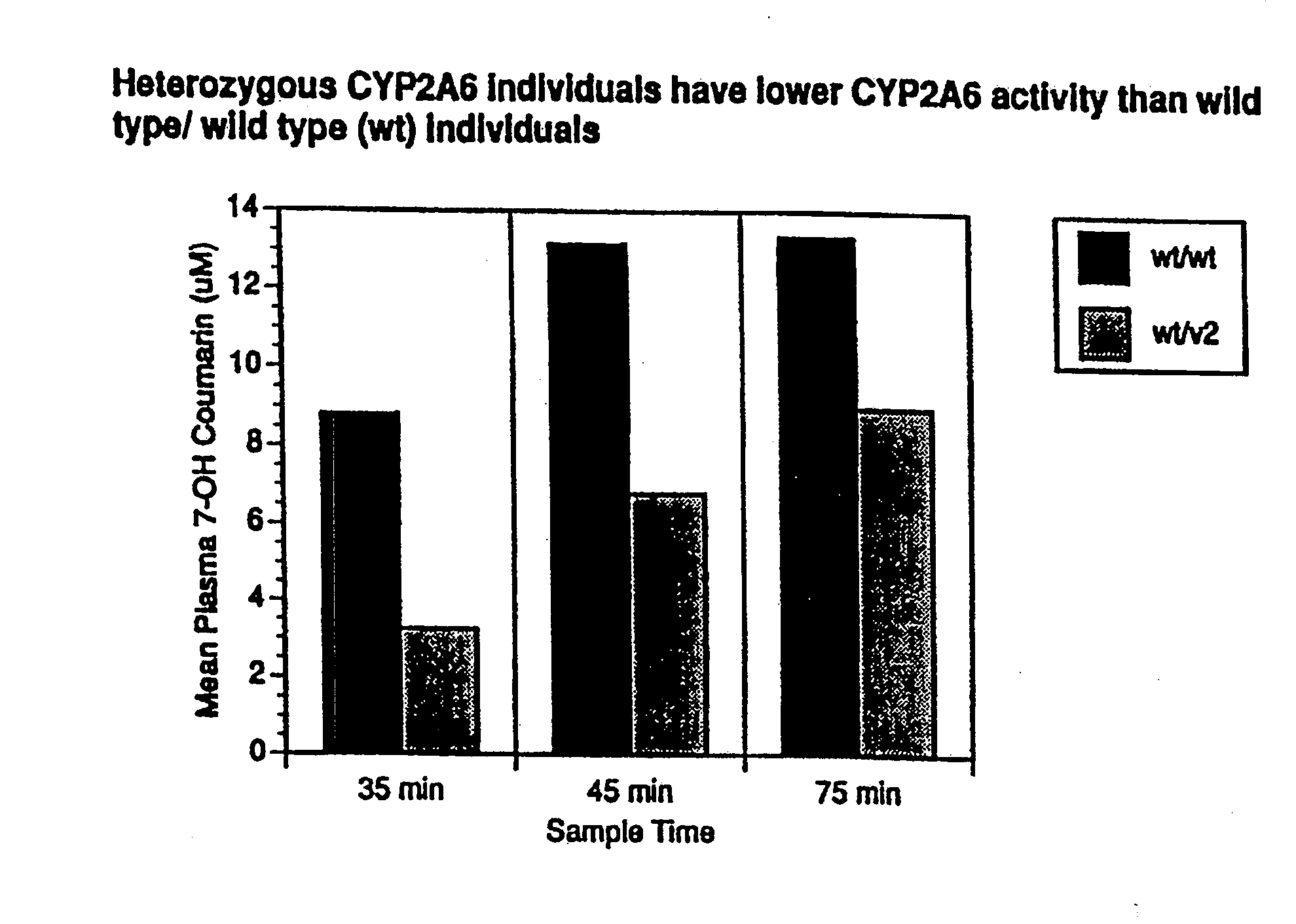
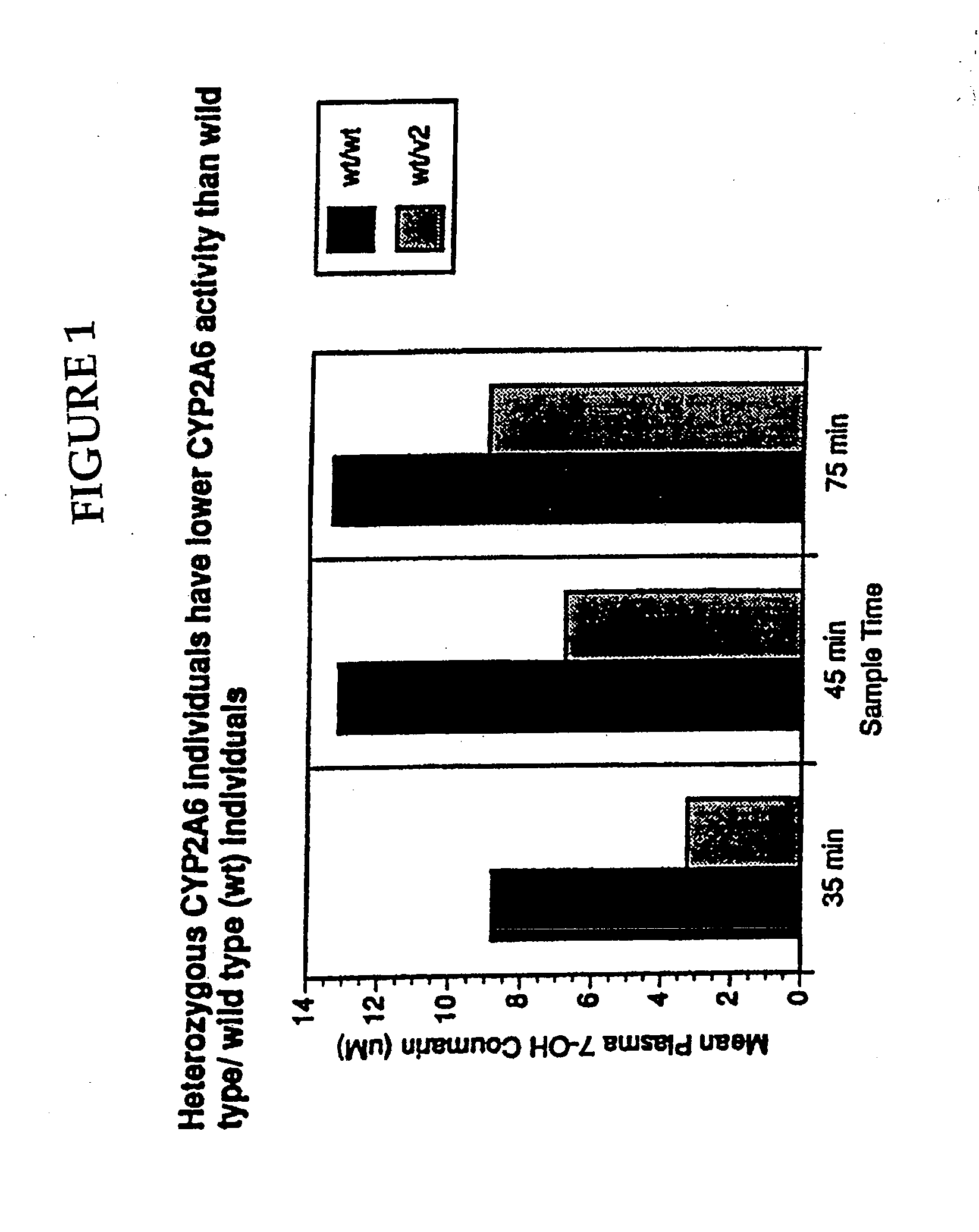
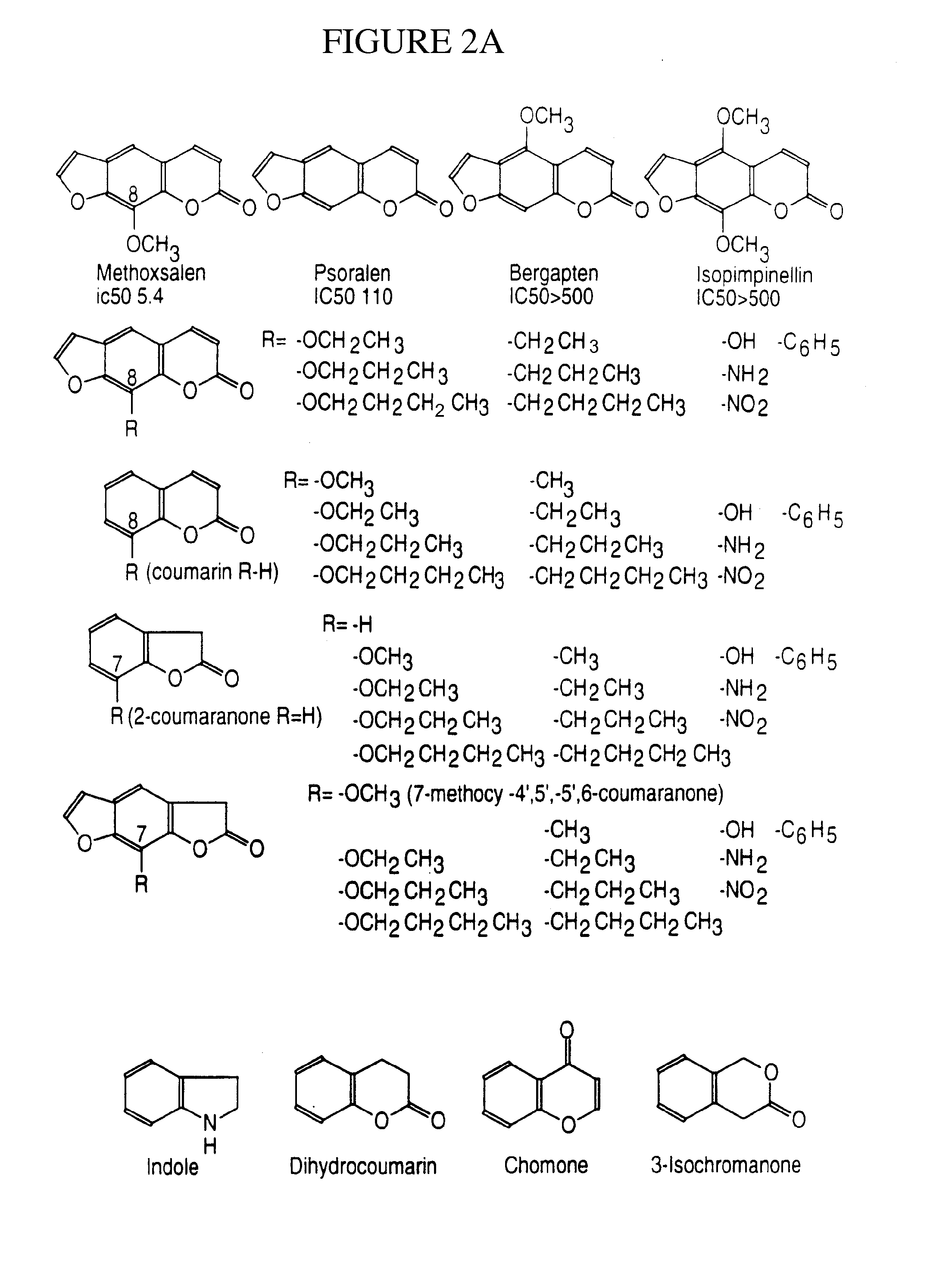
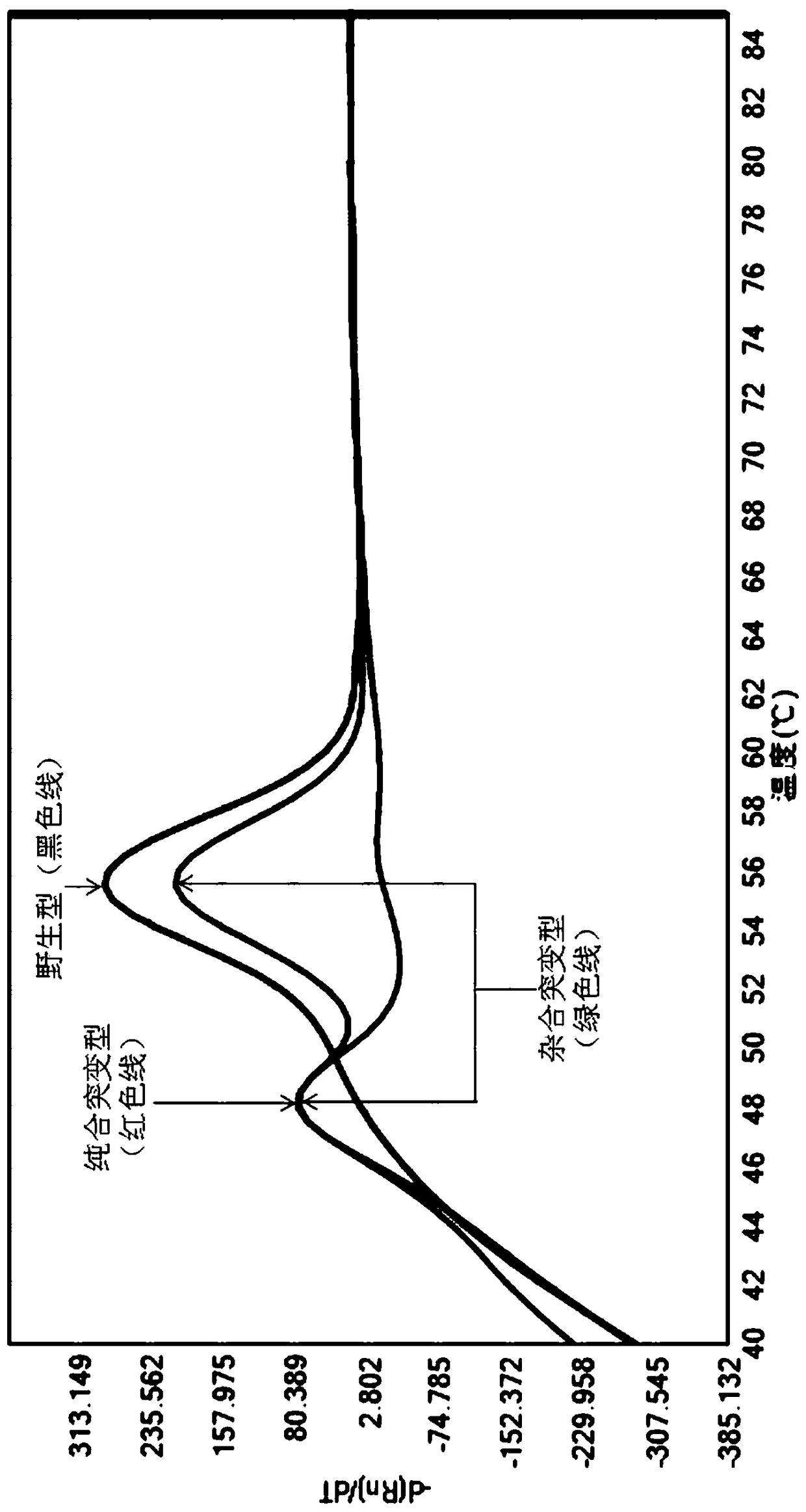
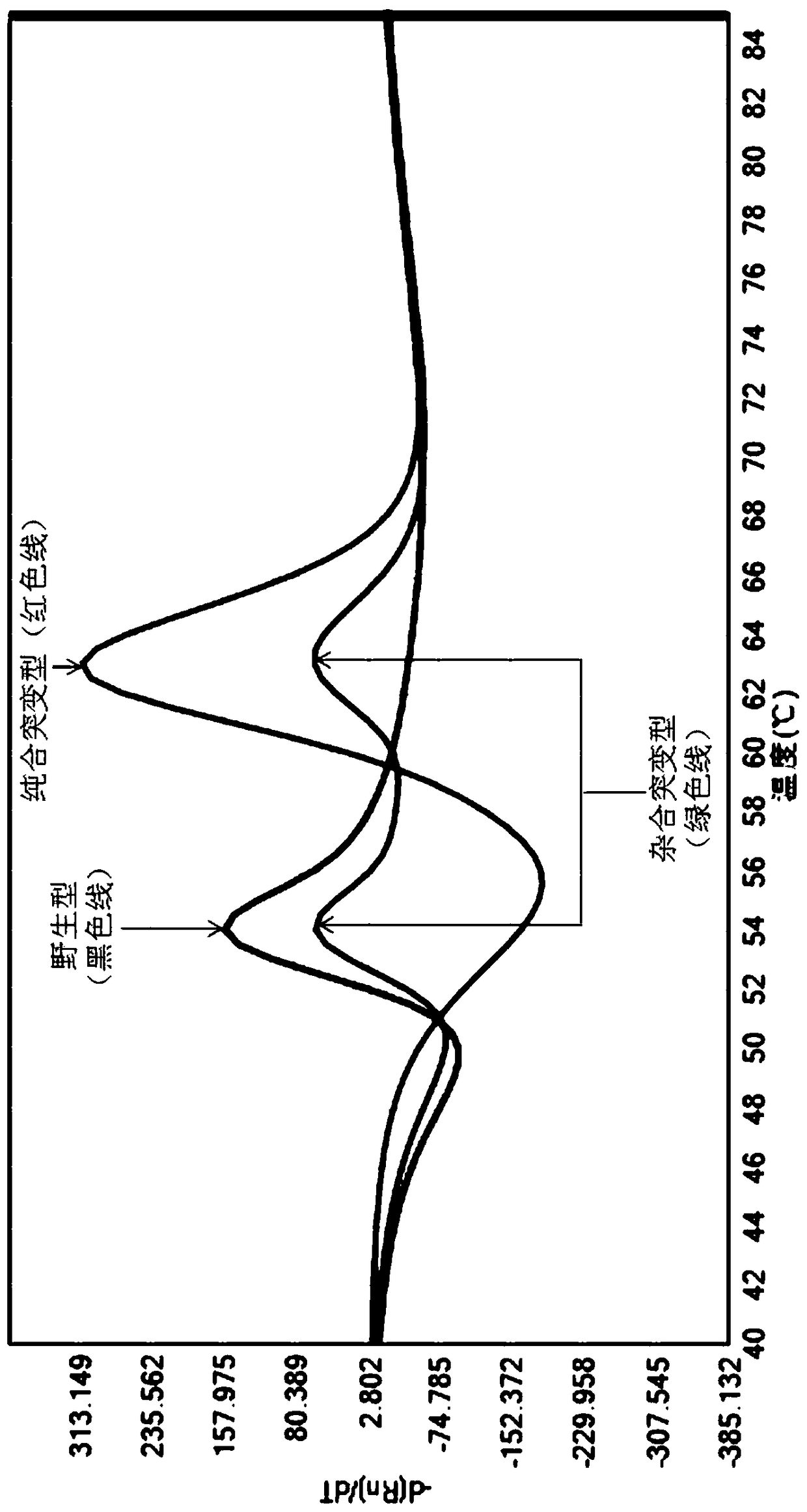
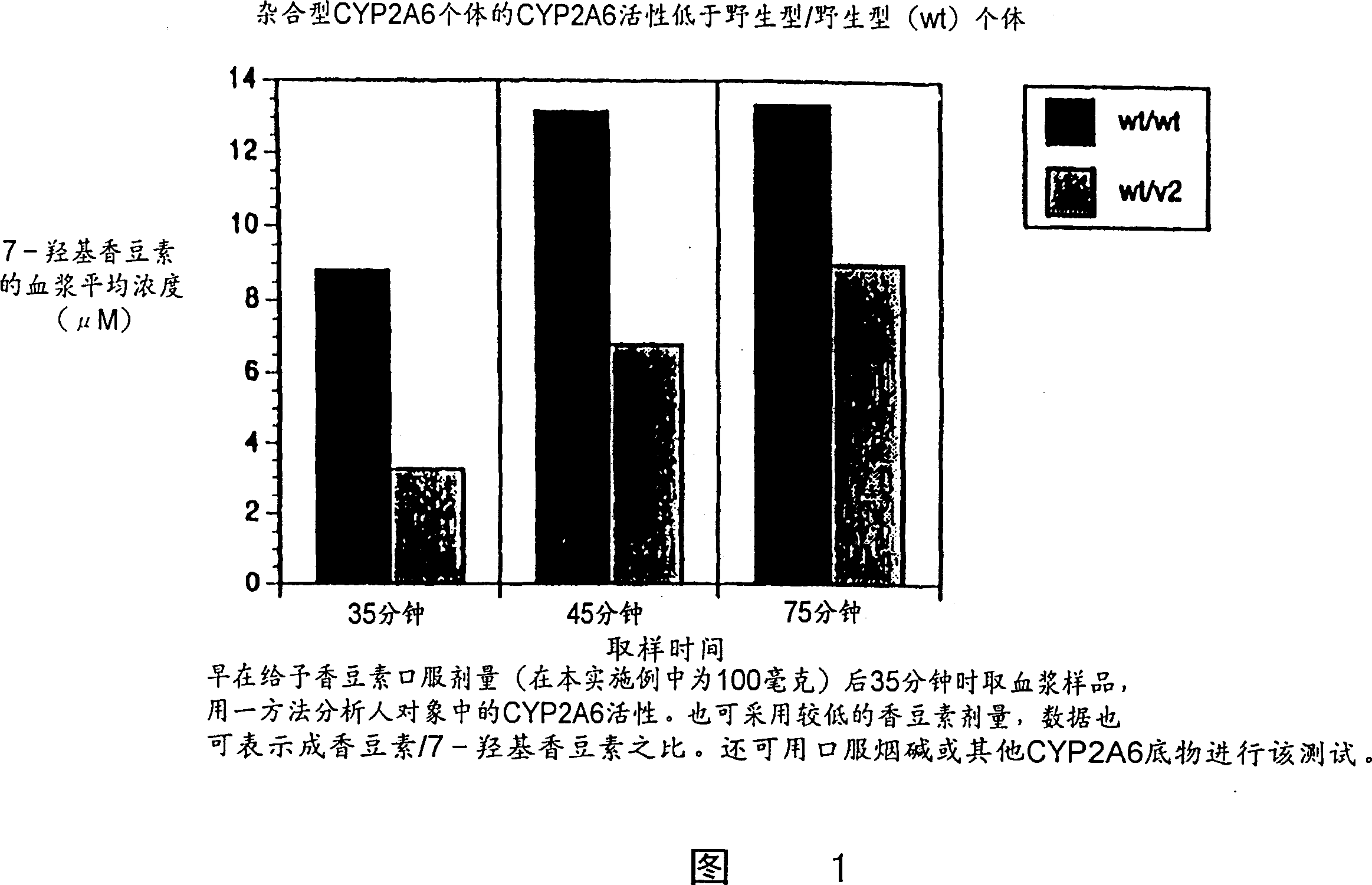
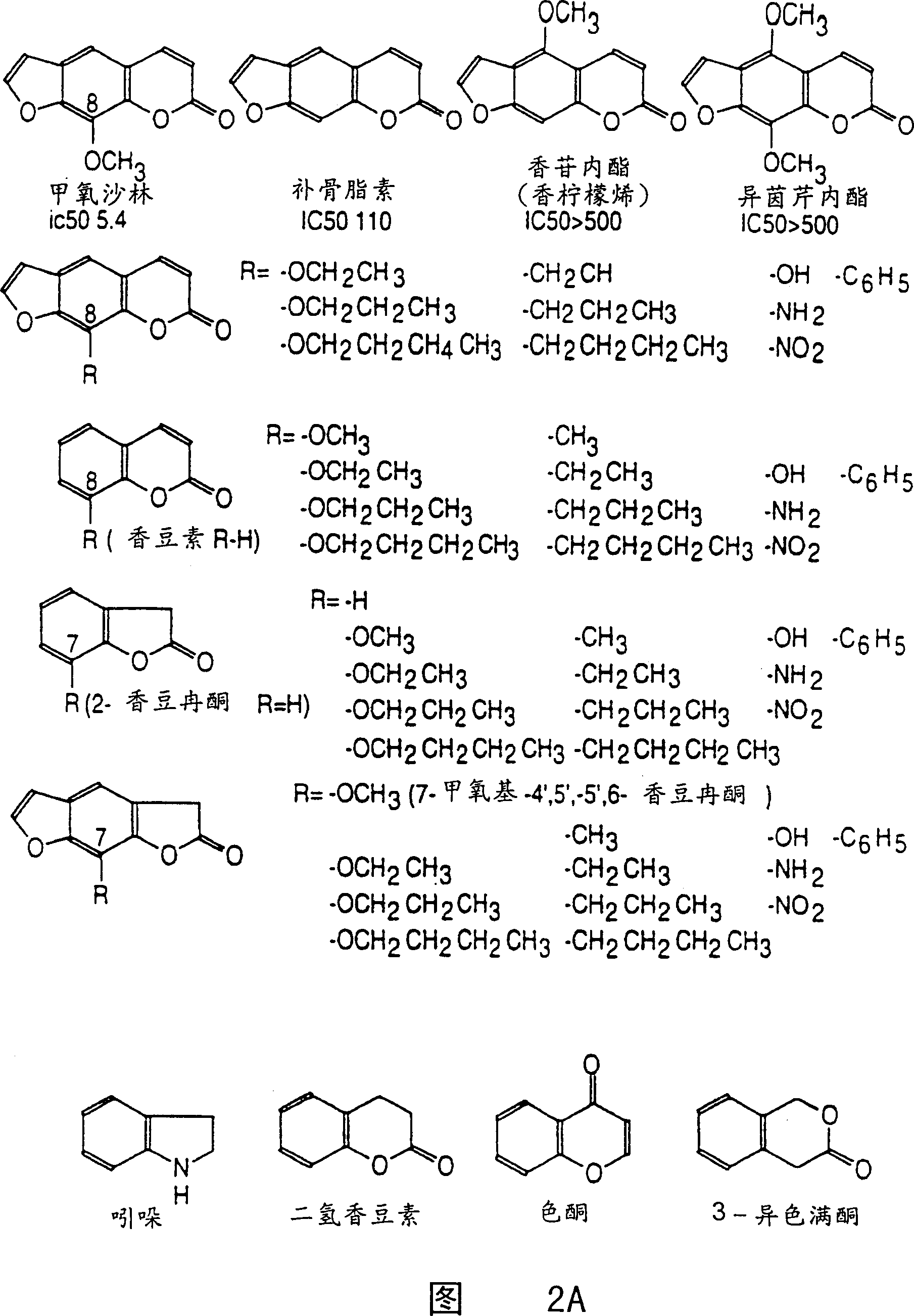
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Expression systems for functional membrane polypeptides
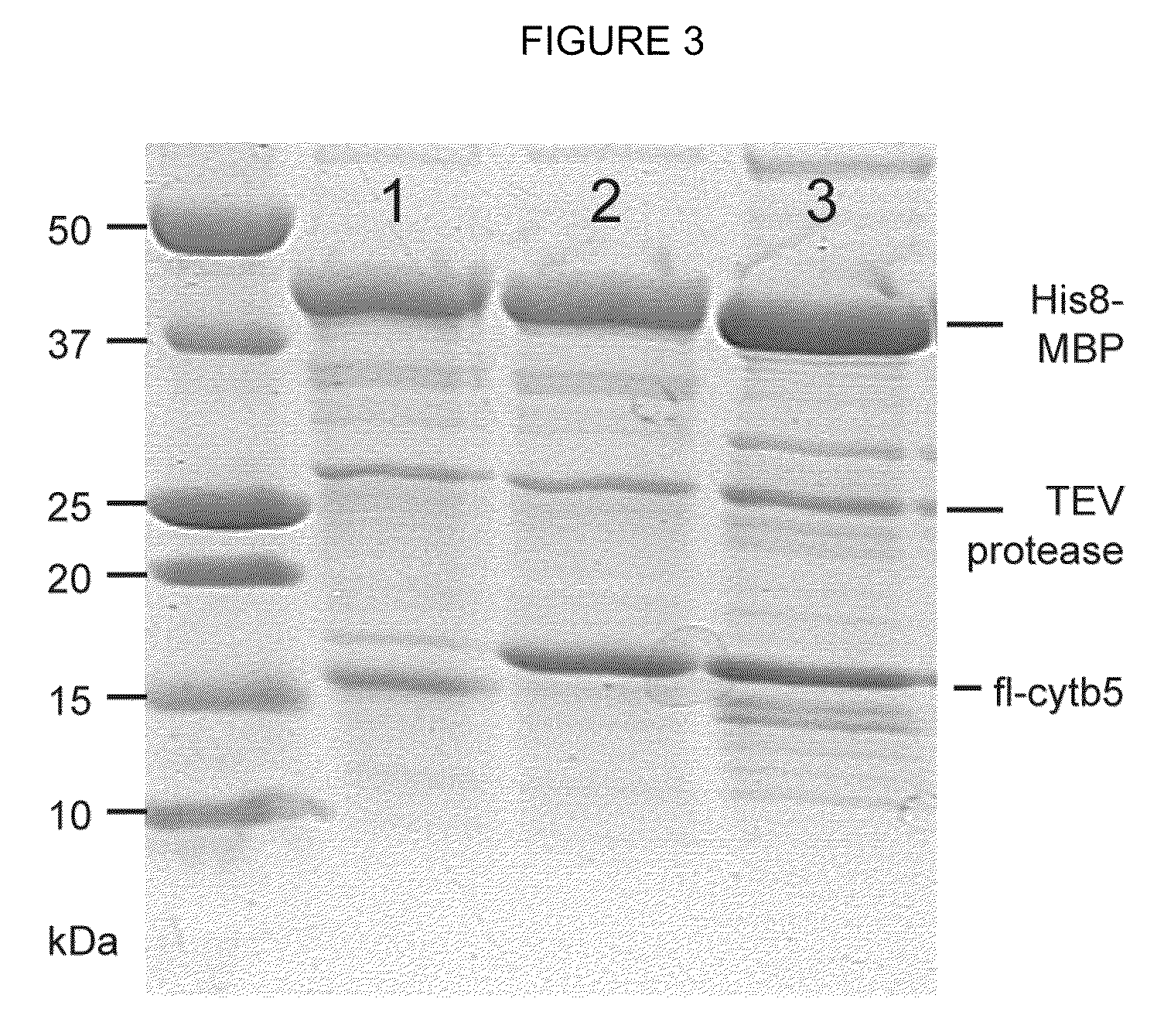
InactiveUS8088601B2Extension of timeUptake and efficient catabolism of maltodextrinsPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesHuman cytochromeProtease
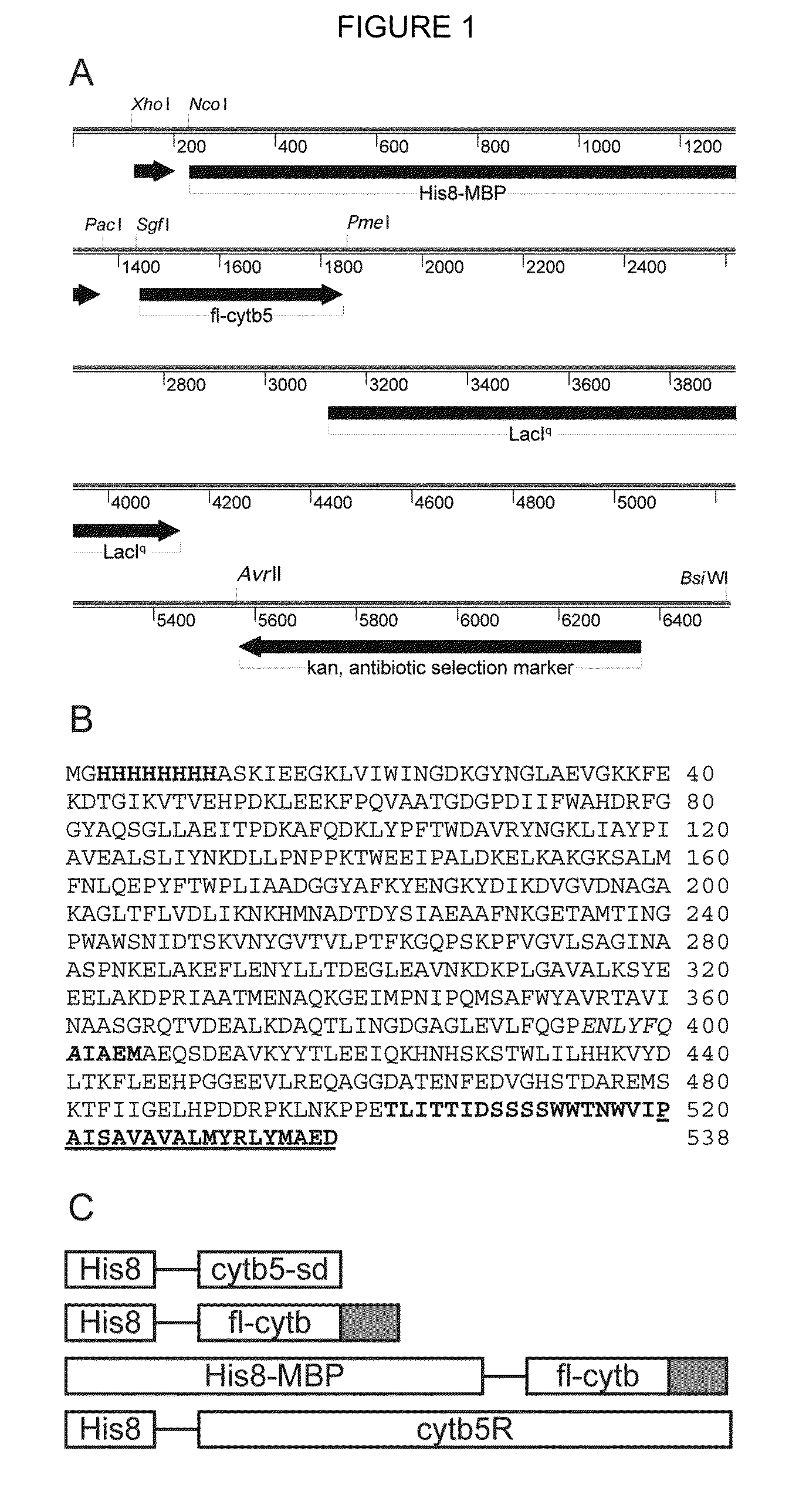
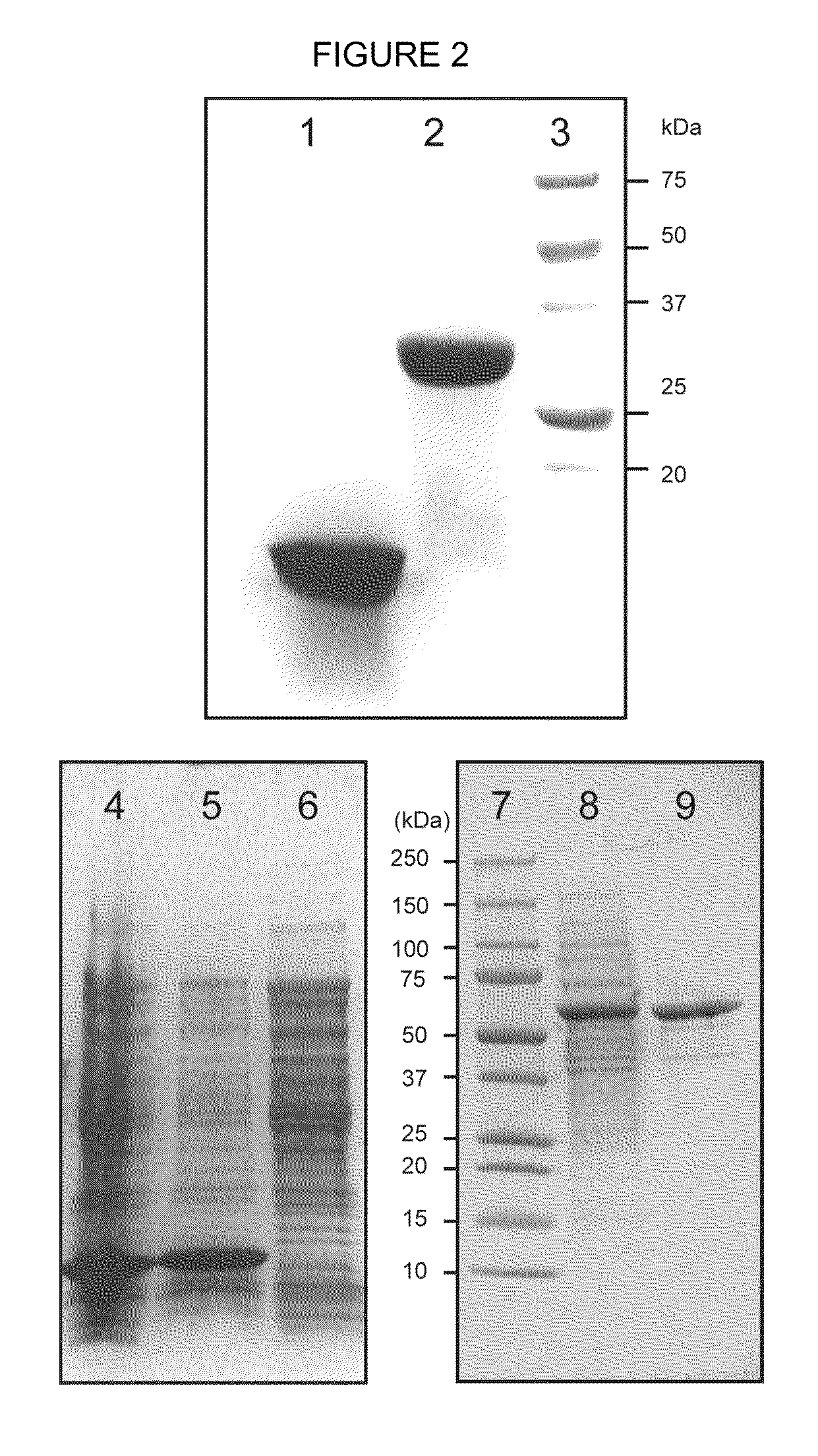
Expression systems and methods for the expression of functional membrane polypeptides such as human cytochrome b5 are provided. The systems include recombinant expression vectors capable of expressing soluble fusion proteins that include a solubilizing agent, a linker, and a membrane polypeptide, as well as one or more cleavers, e.g. proteases, capable of cleaving the linker to release the membrane polypeptide. When the fusion protein is expressed, the linker is cleaved by the cleaver to allow association of the membrane polypeptide with a membrane.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of detecting and quantifying human P450 molecular species and probe and kit for this method
The present invention provides a kit for detecting and quantifying human cytochrome P450 molecular species, comprising one or more oligonucleotide probes each hybridizable with a specific region of the gene encoding a human cytochrome P450 species, for example, the 616 to 641 region of the CYP1A1 gene, and one or more specific primer pairs; and a method of detecting and quantifying one or more human cytochrome P450 molecular species using the kit.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM FAB INC
Human cytochrome P450CYP2C19 and SVIL (Supervillin) gene polymorphic site detection kit and application
PendingCN107523610AEfficiently determine sensitivityDetermine sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenetic correlationNucleotide
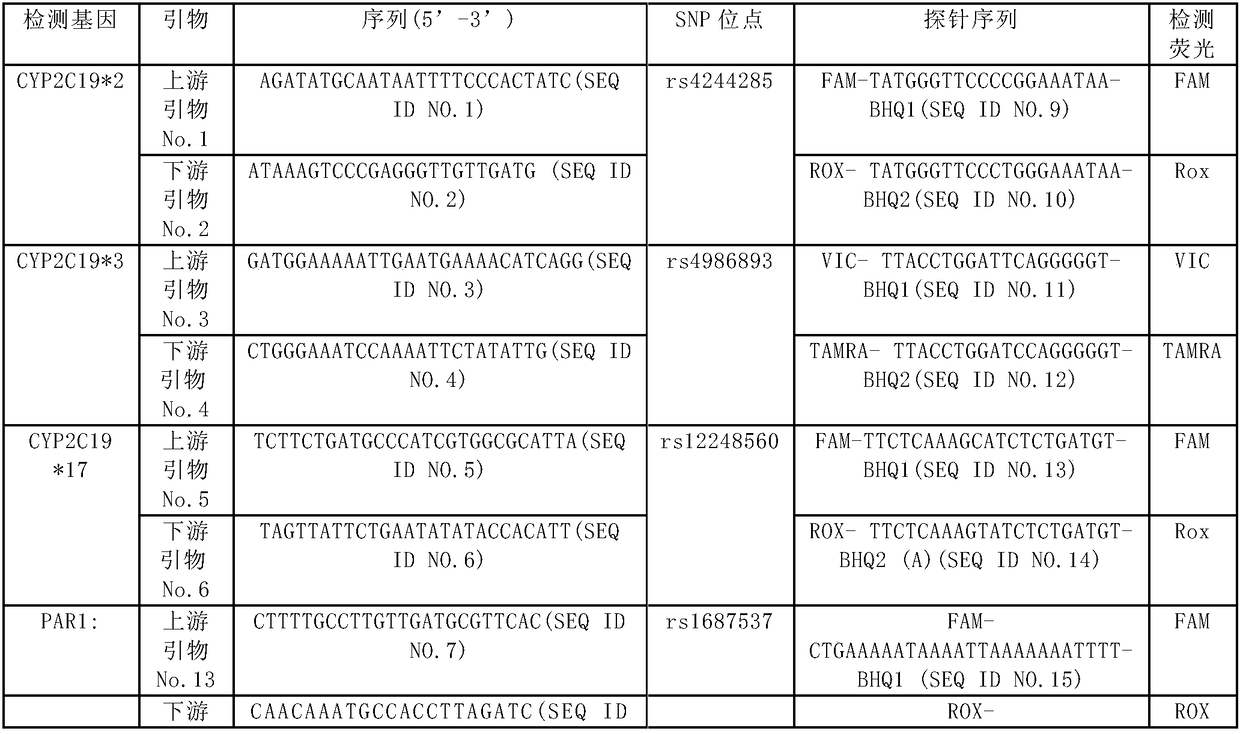
The invention provides a cerebral apoplexy pharmacy and genetic correlation detection method. According to the detection method, primers and probes are synthesized through four polymorphic sites of two genes of cytochrome P450CYP2C19*2: rs4244285, CYP2C19*3: rs4986893, CYP2C19*17: rs12248560, and SVIL: rs17834991, real-time fluorescence quantification allele probe detection is implemented, and whether a target belongs to pharmacy susceptible populations or not can be judged. By adopting the method, clinical pharmacy schemes can be instructed and adjusted, bases can be made for clinical individual treatment, and adverse reactions of medicines are prevented. The method is capable of simultaneously detecting four polymorphic sites and has the advantages of being simple and convenient, accurate, rapid, high in flux and the like.
Owner:龙凌云 +1
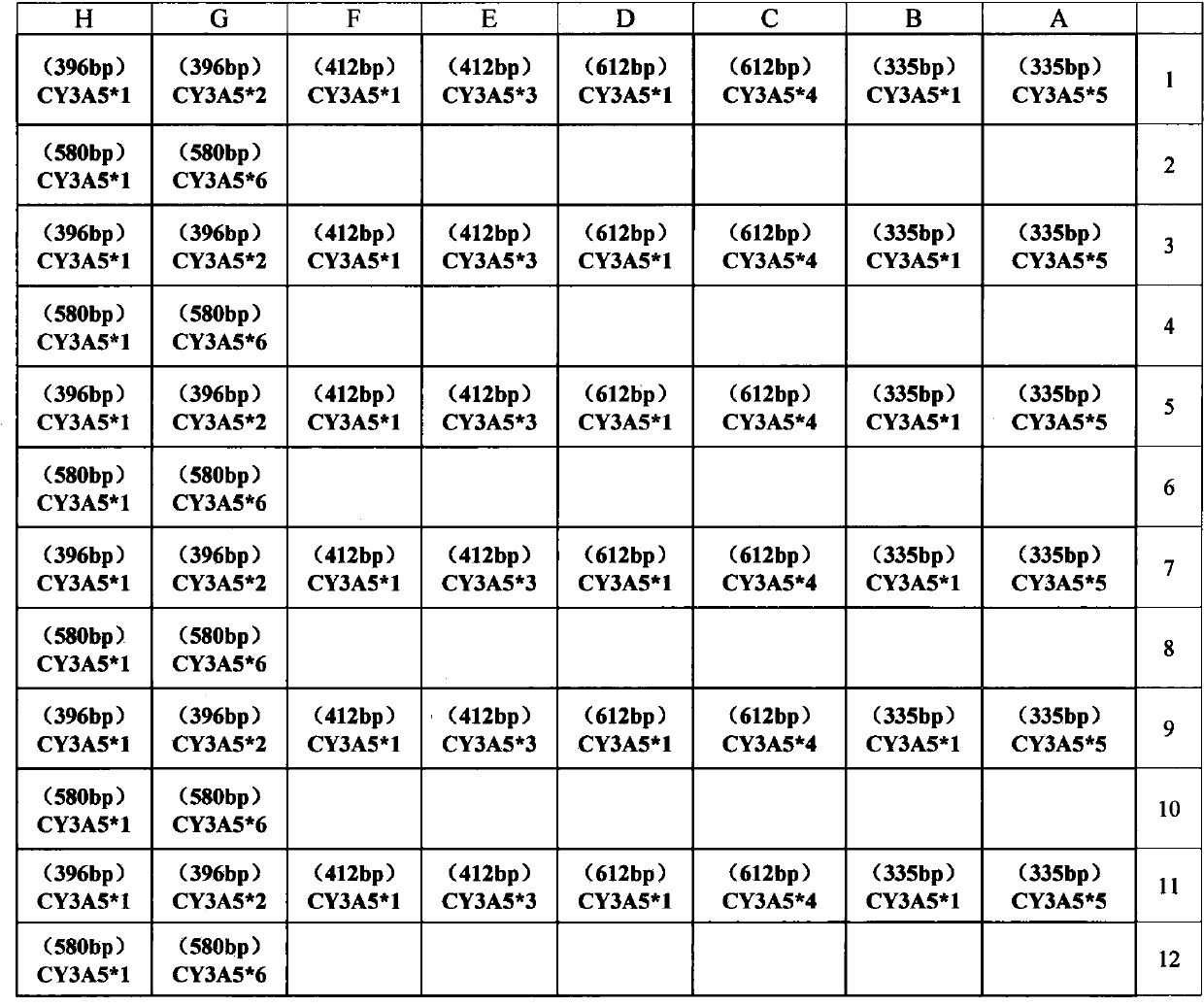
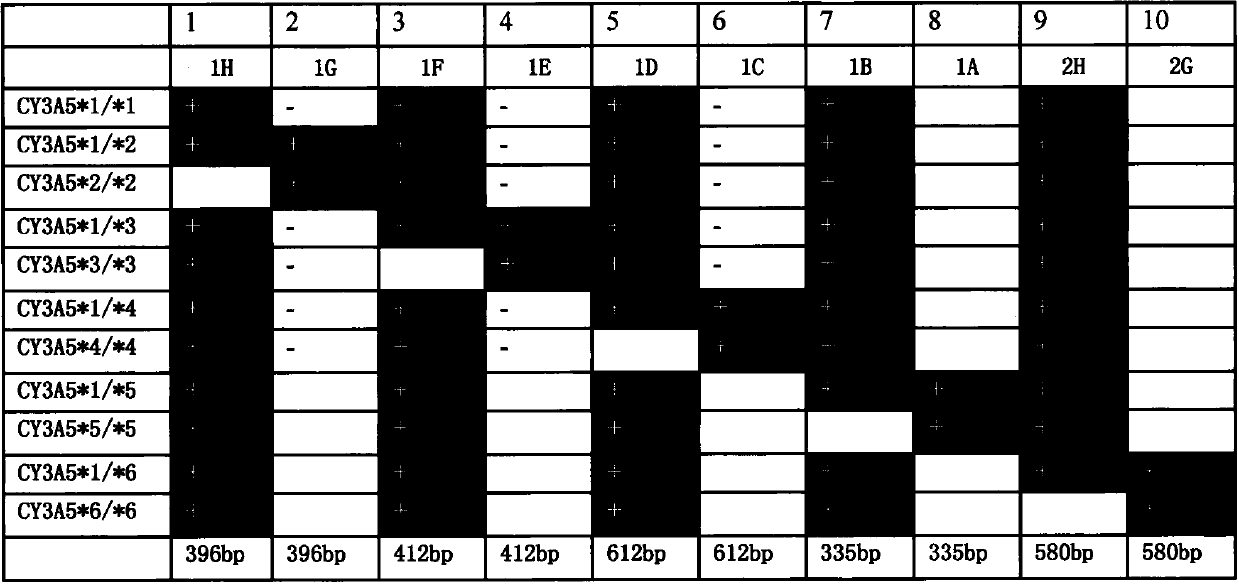
Primer group and kit for detecting genetic typing of human cytochrome P450 enzyme system 3A5(CYP3A5)
InactiveCN103361433AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOrgan transplantationCytochrome p450 enzyme
The invention discloses a primer group and a kit for detecting genetic typing of CYP3A5. The primer group for detecting CYP3A5 gene typing comprises a CY3A5*1 primer pair, a CY3A5*2 primer pair, a CY3A5*3 primer pair, a CY3A5*4 primer pair, a CY3A5*5 primer pair, a CY3A5*6 primer pair and an internal reference primer pair. The application of the kit helps to realize good typing for CYP3A5 gene; and in clinical application of organ transplantation, good guidance effects on individualized use and secure use of immunosuppressant are realized.
Owner:天津市秀鹏生物技术开发有限公司
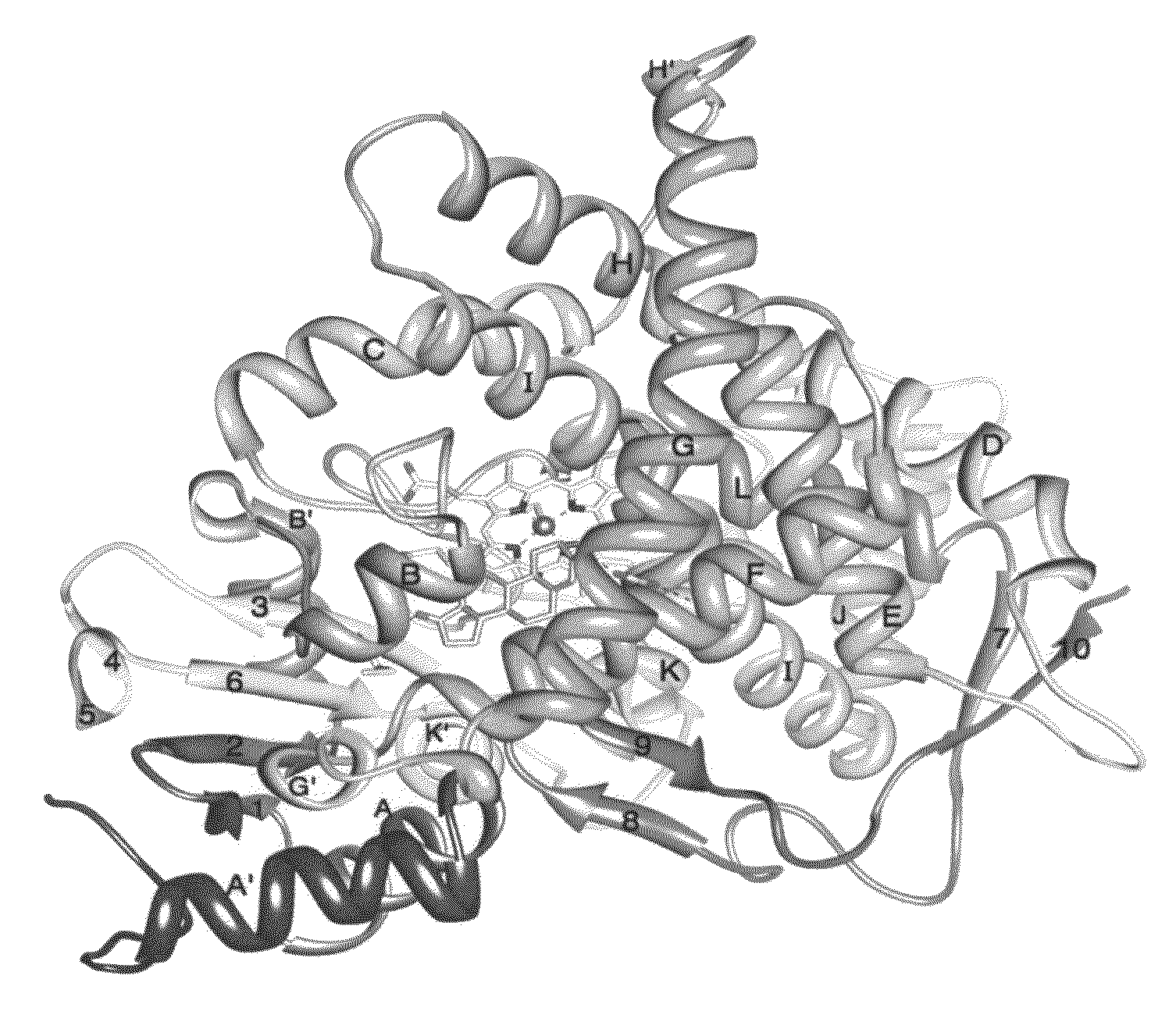
Protein crystal of human cytochrome P450 aromatase and uses thereof
InactiveUS7687252B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesP450 aromataseBinding site
The present invention relates to a protein crystal of at least one binding site of a human aromatase. The present invention also relates to a fully processed human cytochrome P450 aromatase and a protein crystal thereof. The present invention further relates to methods of making and using the aromatase and the protein crystal thereof.
Owner:GHOSH DEBASHIS DR
Mammalian artificial chromosome vector comprising human cytochrome p450 gene (cluster) and non-human mammalian animal retaining the same
InactiveUS20110023138A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsGene clusterMammal
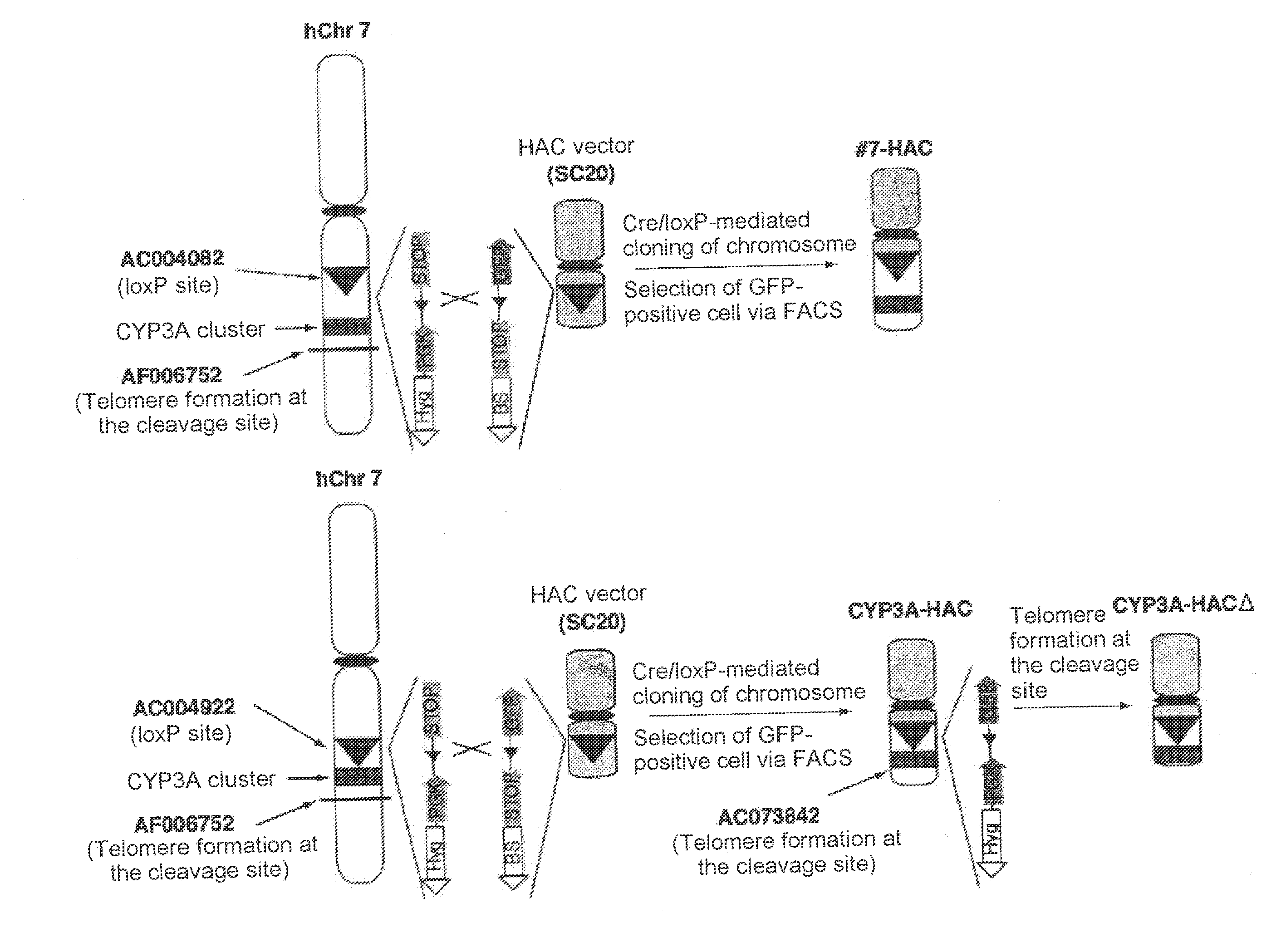
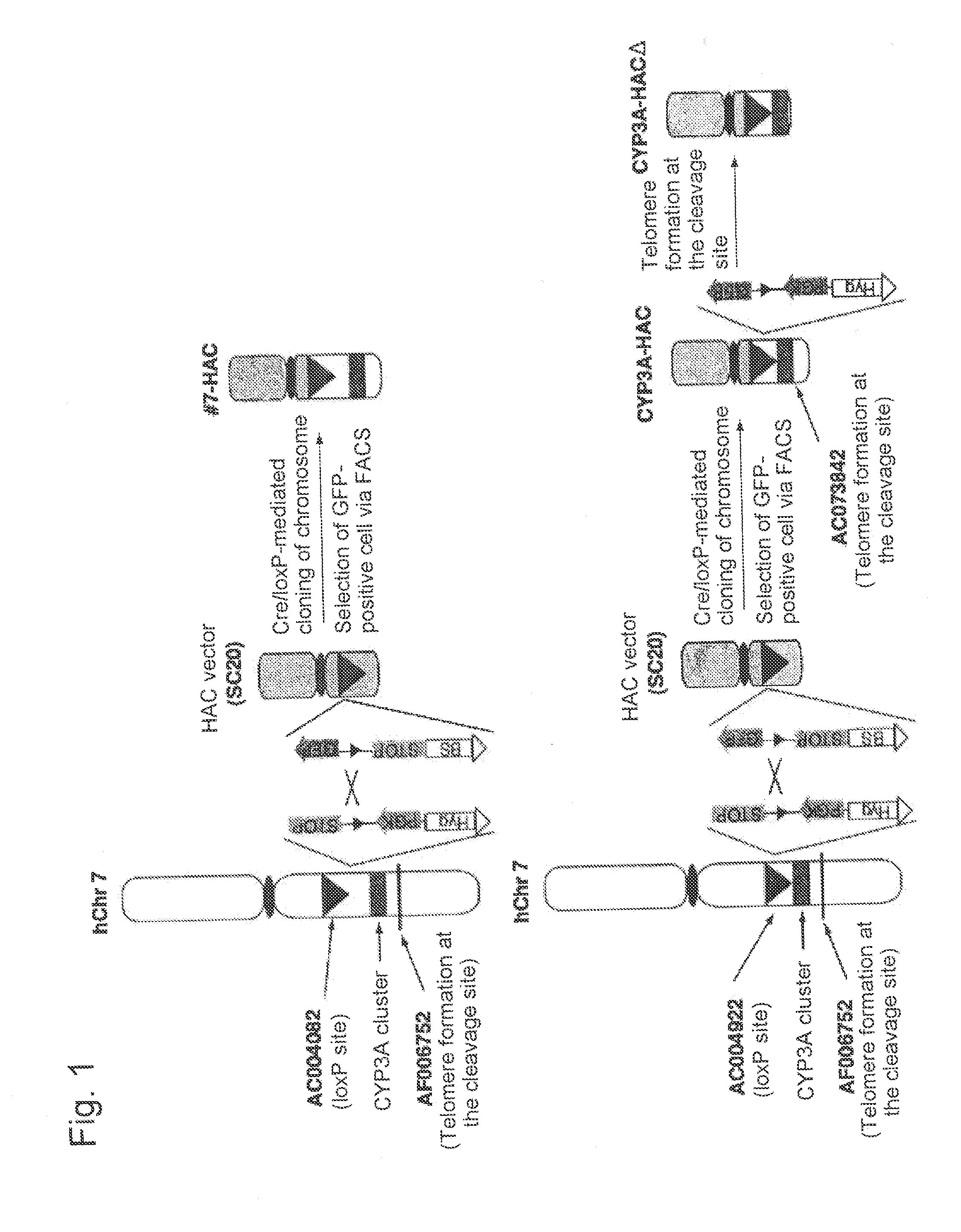
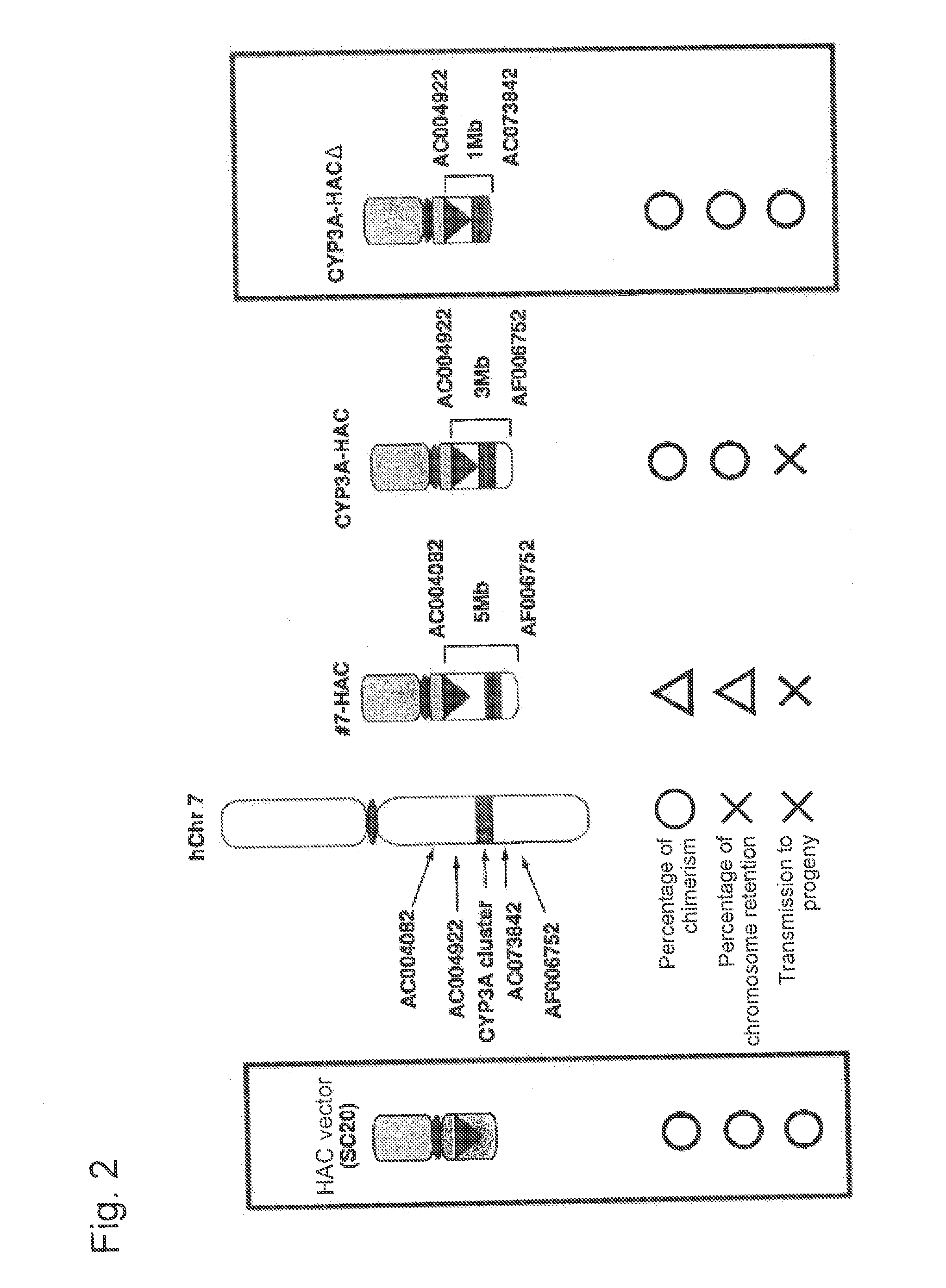
This invention relates to a mammalian artificial chromosome vector, which retains a human chromosome 7 fragment comprising human cytochrome P450 genes and is transmittable to progeny, wherein the human chromosome 7 fragment retains a region of approximately 1 Mb±500 Kb in size comprising at least a human CYP3A gene cluster, which region is located between chromosome markers AC004922 and AC073842, and to a non-human mammalian animal retaining the vector.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY +1
A gene chip for detection of individualized treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection and its application
ActiveCN103060455BStrong specificityConsistent specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyIndividualized treatment
The invention relates to a biological engineering detection product and an application of the gene chip, and in particular relates to a detection gene chip for helicobacter pylori infection individualized treatment. The chip is capable of simultaneously detecting polymorphisms of helicobacter pylori clarithromycin medicine-resistant mutation sites A2142G and A2143G, carbostyril medicine-resistant mutation sites Asn87(N87K) and Asp91(D91G / Y / N), and sites 2C19*2(G6981A) and 2C19*3(G636A) related to metabolism of a proton pump inhibitor on human cytochrome enzyme CYP450. The chip detection method disclosed by the invention is rapid and accurate and is capable of identifying helicobacter pylori etiology, carrying out medicine-resistant analysis of clarithromycin and carbostyril, and analyzing metabolic individual differences of the proton pump inhibitor, so that the detection gene chip is used for guiding individualized administration of helicobacter pylori infection triplex process treatment.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
CYP2A enzymes and their use in therapeutic and diagnostic method
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as 'CYP2A6' for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Helicobacter pylori infected individual treatment gene chip, preparation method and detection method
InactiveCN105969864AFast and correct treatmentImprove featuresNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeGene Microarray
The invention discloses a gene chip for individualized treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection, a manufacturing method and a detection method. The gene chip includes: wild type and mutation corresponding to clarithromycin resistance mutation sites A2142G and A2143G on the Helicobacter pylori 23s rRNA gene Type SNP typing oligonucleotide probe; wild-type and mutant SNP typing oligonucleotide probes corresponding to quinolone resistance mutation sites N87K, D91G, and D91N on the Helicobacter pylori gyrA gene: human cytochrome Wild-type and mutant SNP typing oligonucleotide probes corresponding to two sites of CYP2C19*2 (G681A) and CYP2C19*3 (G636A) related to proton pump inhibitor metabolism on P450. The gene chip and detection method of the invention can simultaneously detect CYP2C19 gene polymorphism and HP's drug resistance to clarithromycin and quinolone, and has good specificity and sensitivity, good reproducibility and rapid detection.
Owner:HUZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on CYP2A enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Human cytochrome CYP2C19 and PAR1 gene polymorphism site detection kit and application thereof
The invention provides a method for detecting cerebral apoplexy drug administration and heredity correlation, according to the method, primers and probes are synthesized according to nucleotide sequences of four polymorphic sites CYP2C19*2: rs4244285; CYP2C19*3: rs4986893; CYP2C19*17: rs12248560 and PAR-1: rs168753 of two genes of cytochrome P450, and by real-time fluorescence quantitative alleleprobe detection, whether a target is a drug susceptible population is determined. Using the method, the guidance and adjustment of a clinical drug regimen can be carried out to provide a basis for clinical personalized treatment and prevent adverse drug reactions. The method can simultaneously detect the four polymorphic sites of the two genes, and has the advantages of simplicity, accuracy, rapidity and high throughput.
Owner:BEIJING TIANTAN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
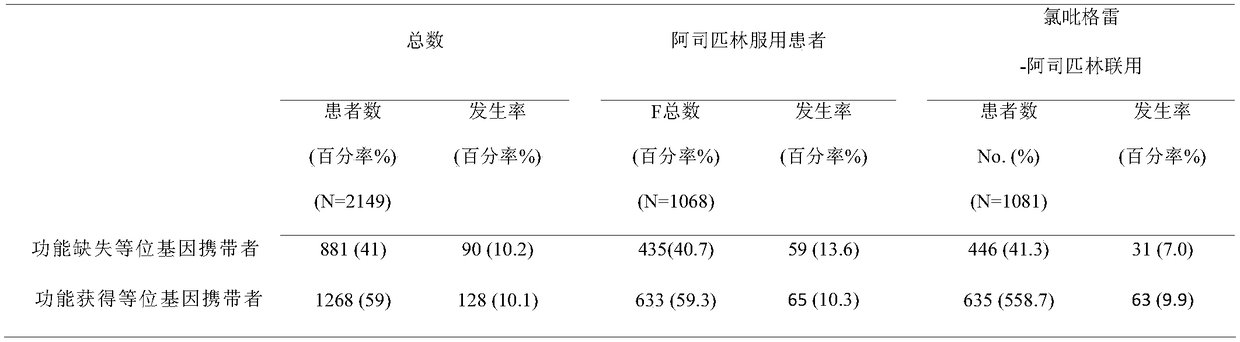
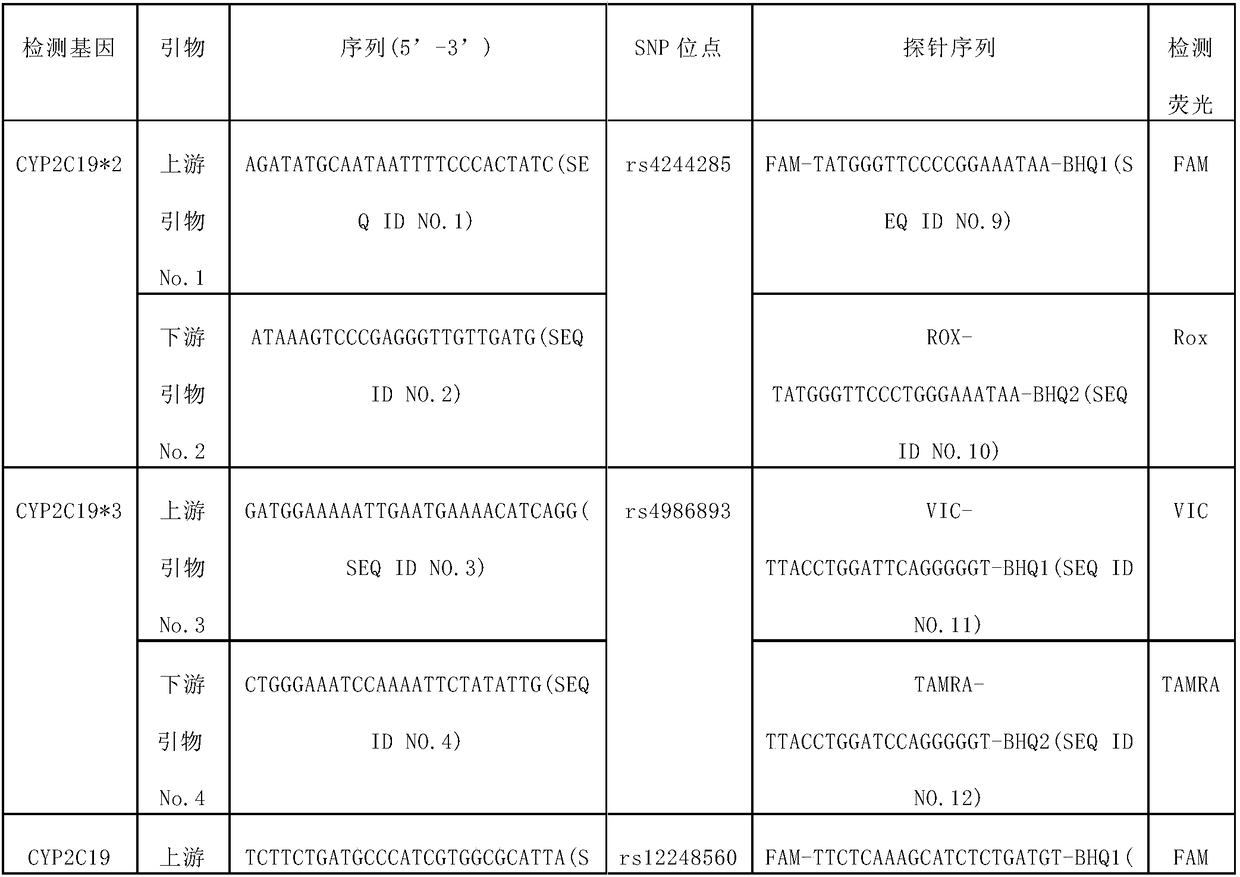
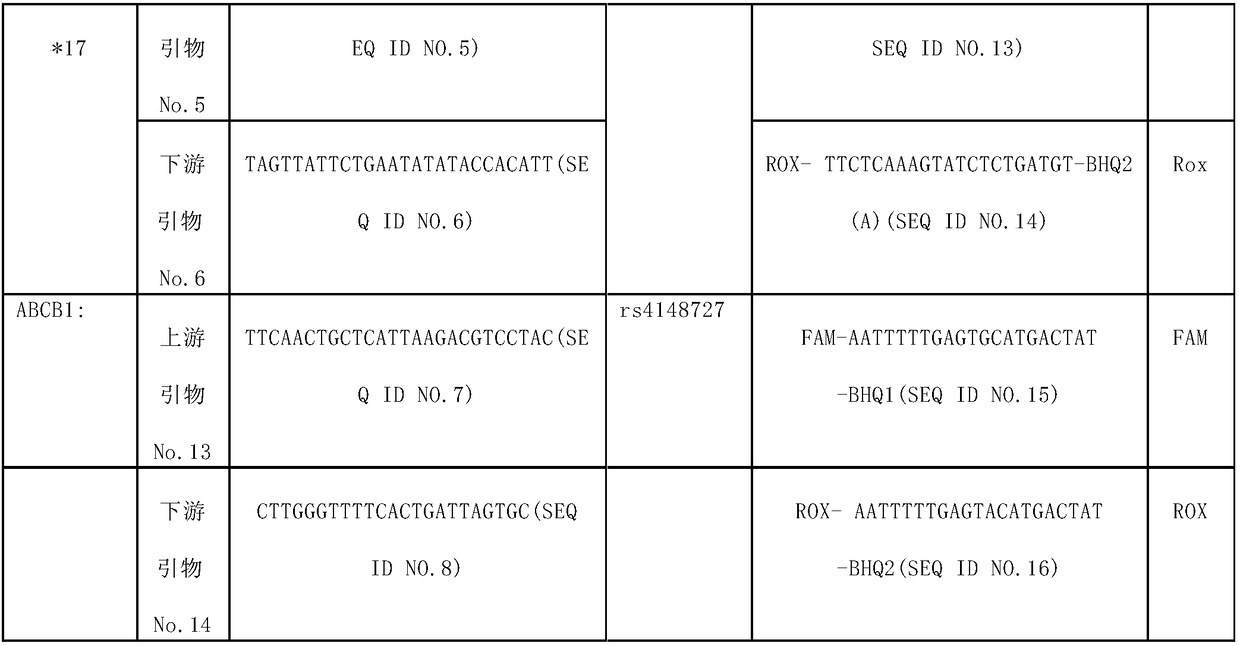
Human cytochrome CYP2C19 and ABCB1 gene polymorphism site detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN109423512AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluorescenceNucleotide
The invention provides a human cytochrome CYP2C19 and ABCB1 gene polymorphism site detection kit and application thereof, primers and probes are synthesized according to nucleotide sequences of four polymorphic sites CYP2C19*2: rs4244285; CYP2C19*3: rs4986893; CYP2C19*17: rs12248560 and ABCB1: rs4148727 of two genes of cytochrome P450, and by real-time fluorescence quantitative allele probe detection, whether a target is a drug susceptible population is determined. Using the method, the guidance and adjustment of a clinical drug regimen can be carried out to provide a basis for clinical personalized treatment and prevent adverse drug reactions. The method can simultaneously detect the four polymorphic sites of the two genes, and has the advantages of simplicity, accuracy, rapidity and highthroughput.
Owner:BEIJING TIANTAN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Protein crystal of human cytochrome p450 aromatase and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090204378A1High selectivityLow sequence homologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesP450 aromataseBinding site
The present invention relates to a protein crystal of at least one binding site of a human aromatase. The present invention also relates to a fully processed human cytochrome P450 aromatase and a protein crystal thereof. The present invention further relates to methods of making and using the aromatase and the protein crystal thereof.
Owner:GHOSH DEBASHIS DR
Method of detecting human cytochrome p450 (CYP) 2d6 gene mutation
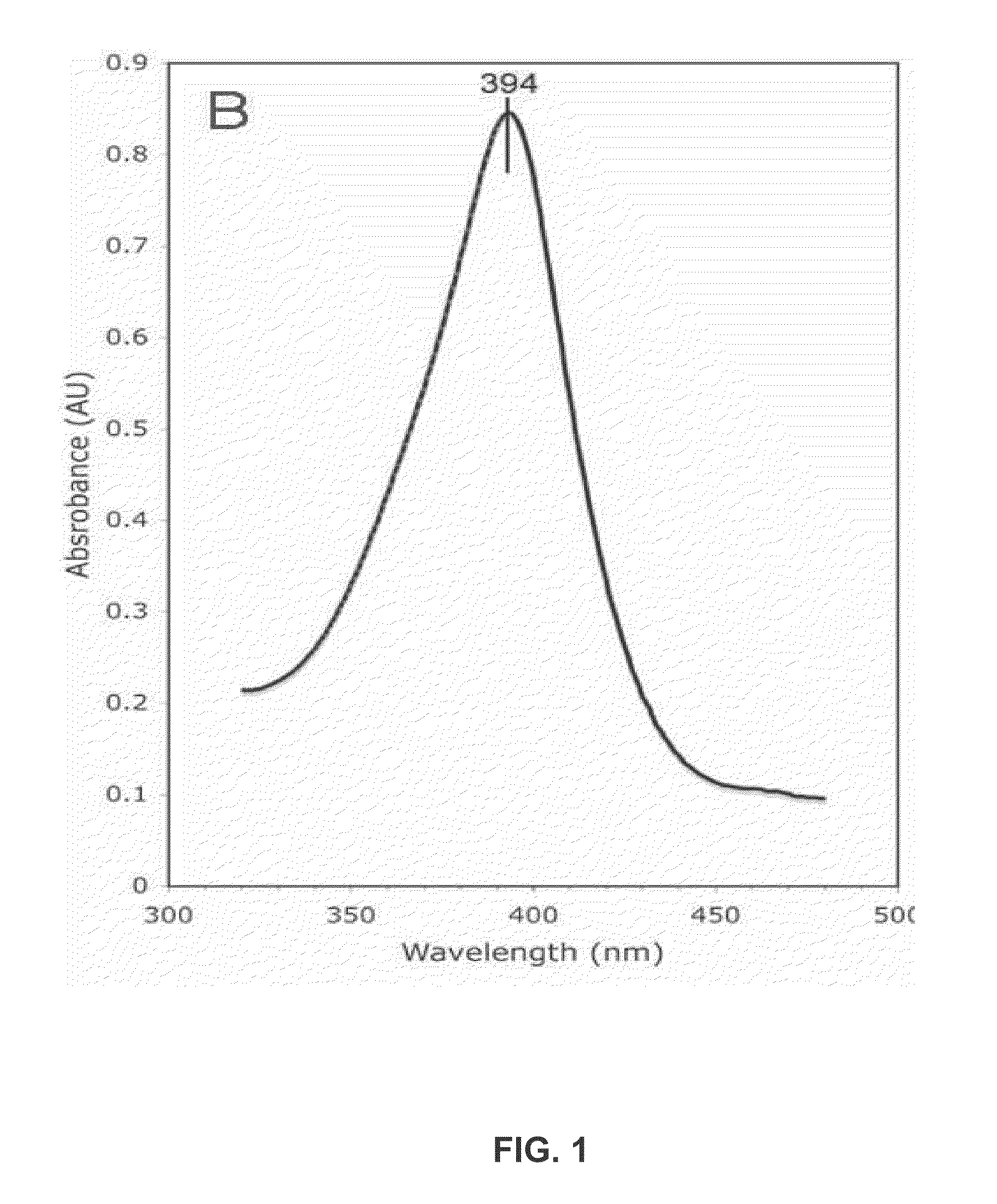
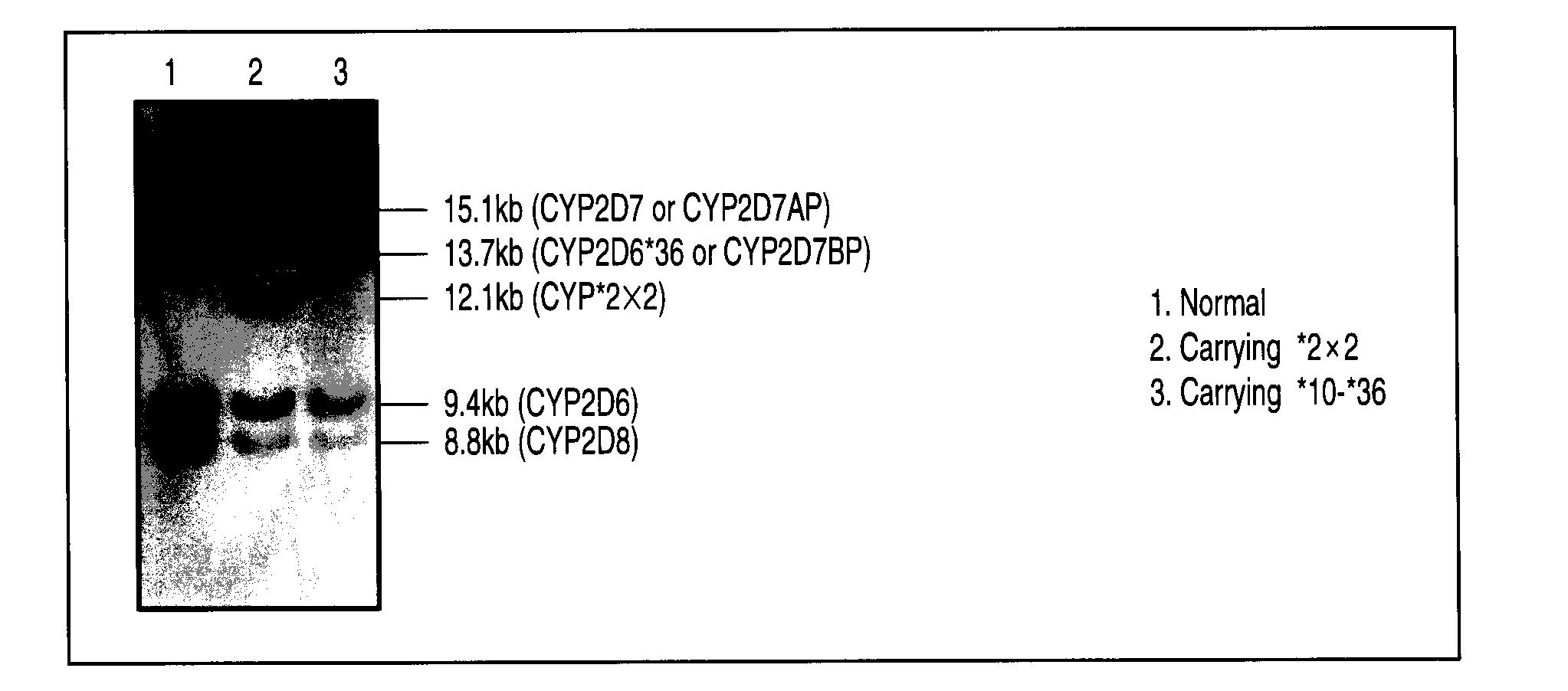
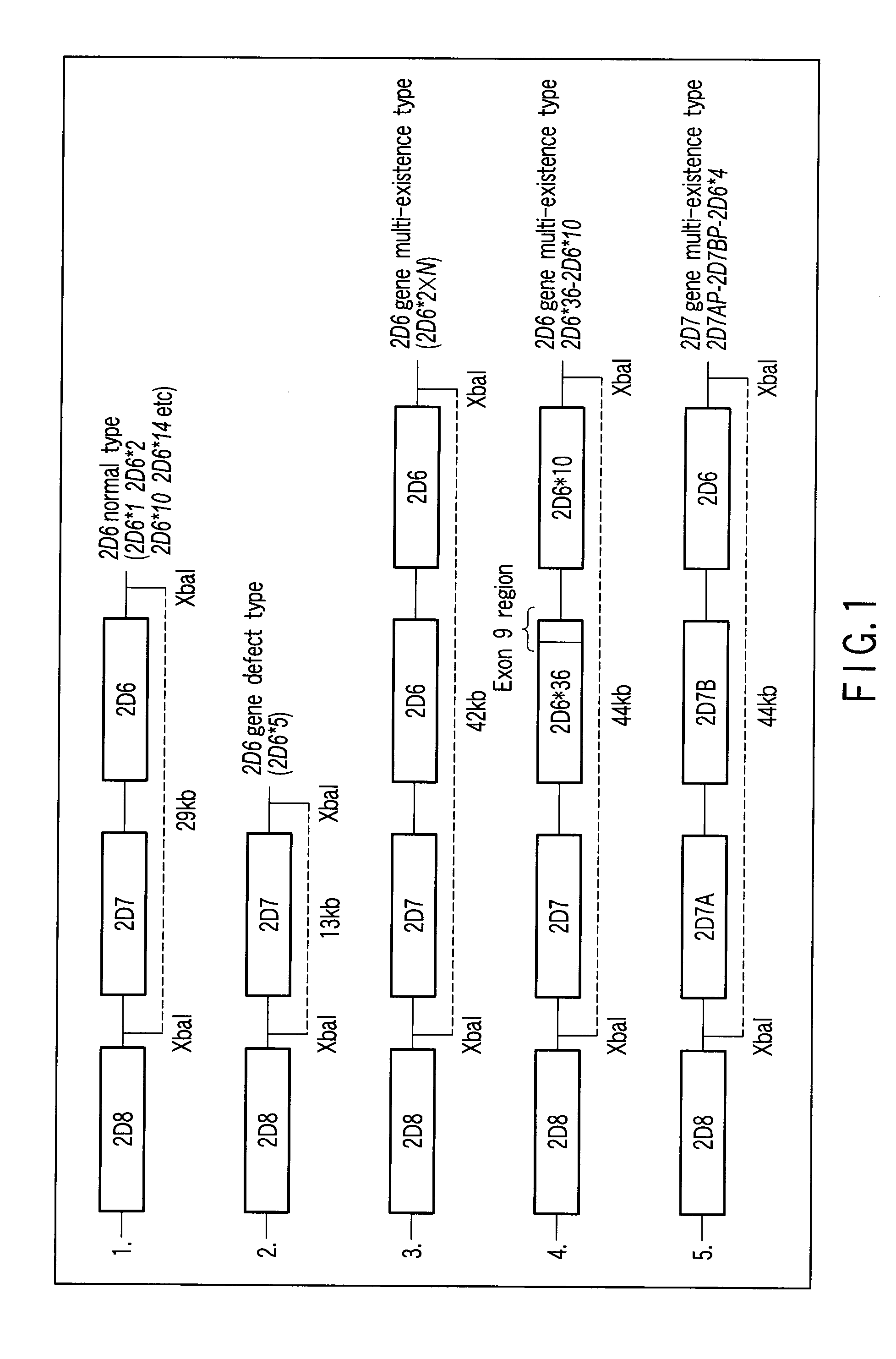
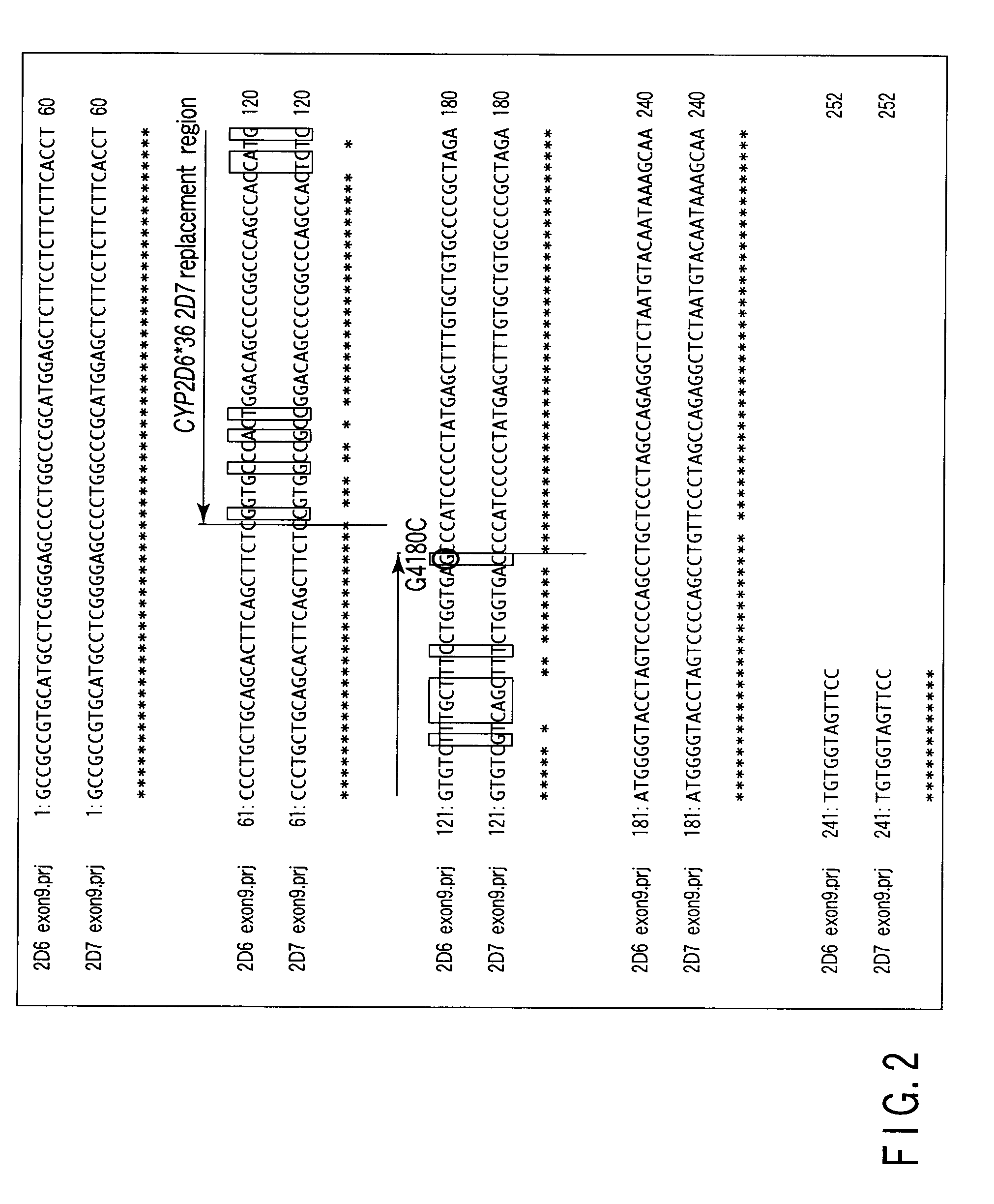
A defect or multi-existence of a CYP2D6 gene is detected with a primer includes a complementary sequence to a sequence which is common between the CYP2D6 gene and a CYP2D8 gene but different from a CYP2D7 gene and which contains one or more of bases at the 86-, 90- and 93-positions in Exon 9 region of the CYP2D6 gene.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Human cytochrome P450 3A5 enzyme and NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase co-expression system
InactiveCN103937829AReduce outputAddresses defects with lower expression levelsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionYeastP450 oxidoreductase
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a human cytochrome P450 3A5 enzyme and an NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase co-expression system. The co-expression system comprises host yeast, and a co-expression vector inserting into a P450 oxidoreductase gene and a human-source P450 3A5 gene in an oriented manner. The human cytochrome P450 3A5 enzyme and the NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase co-expression system can be heterologously expressed in the yeast. In addition, a disadvantage of the low P450 oxidoreductase expression level in yeast cells is overcome. A transfected cell can co-express two proteins simultaneously and a large amount of metabolites can be prepared.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN PHARMASS
Therapeutic and Diagnostic Methods Dependent on CYP2A Enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme.Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
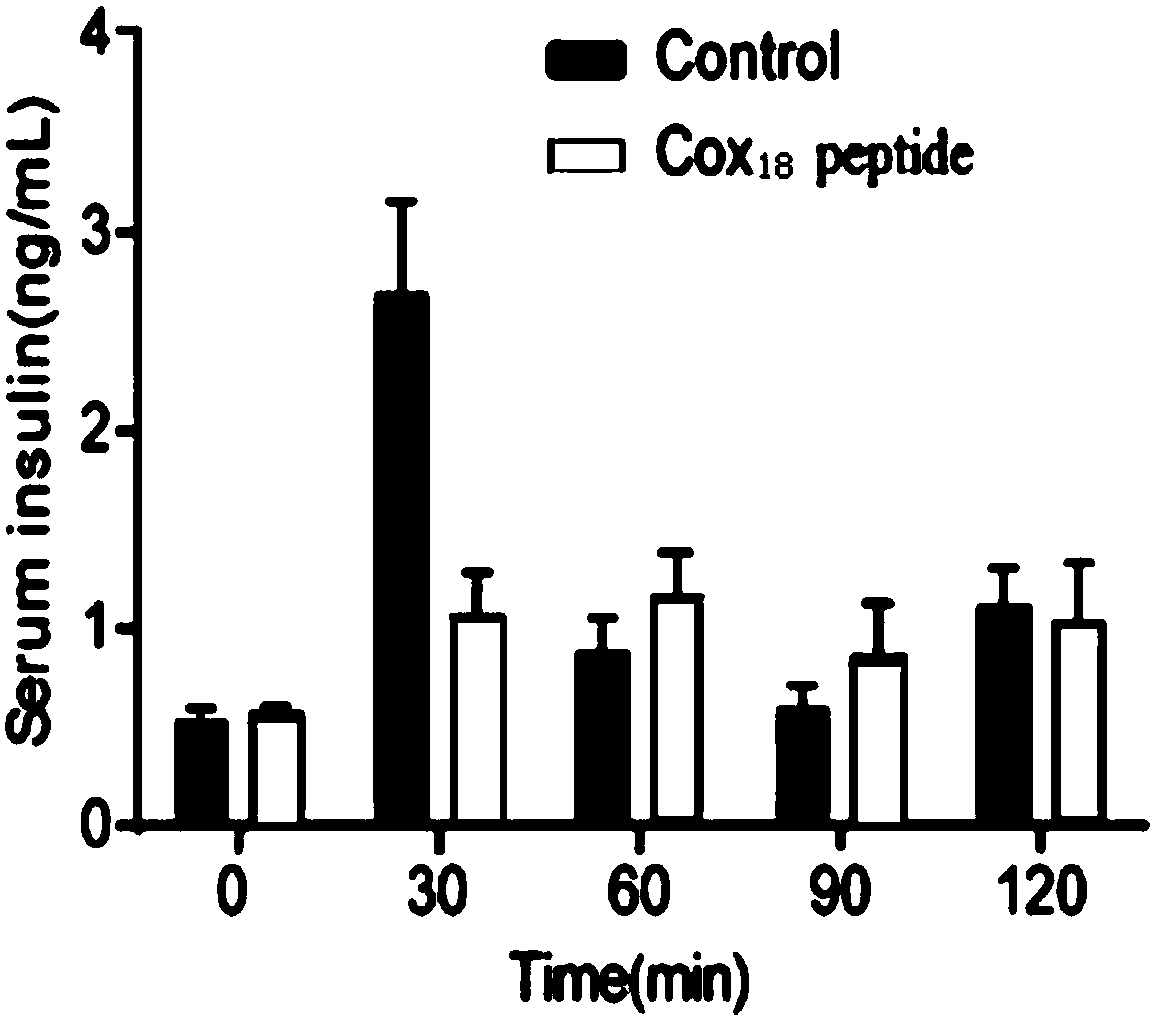
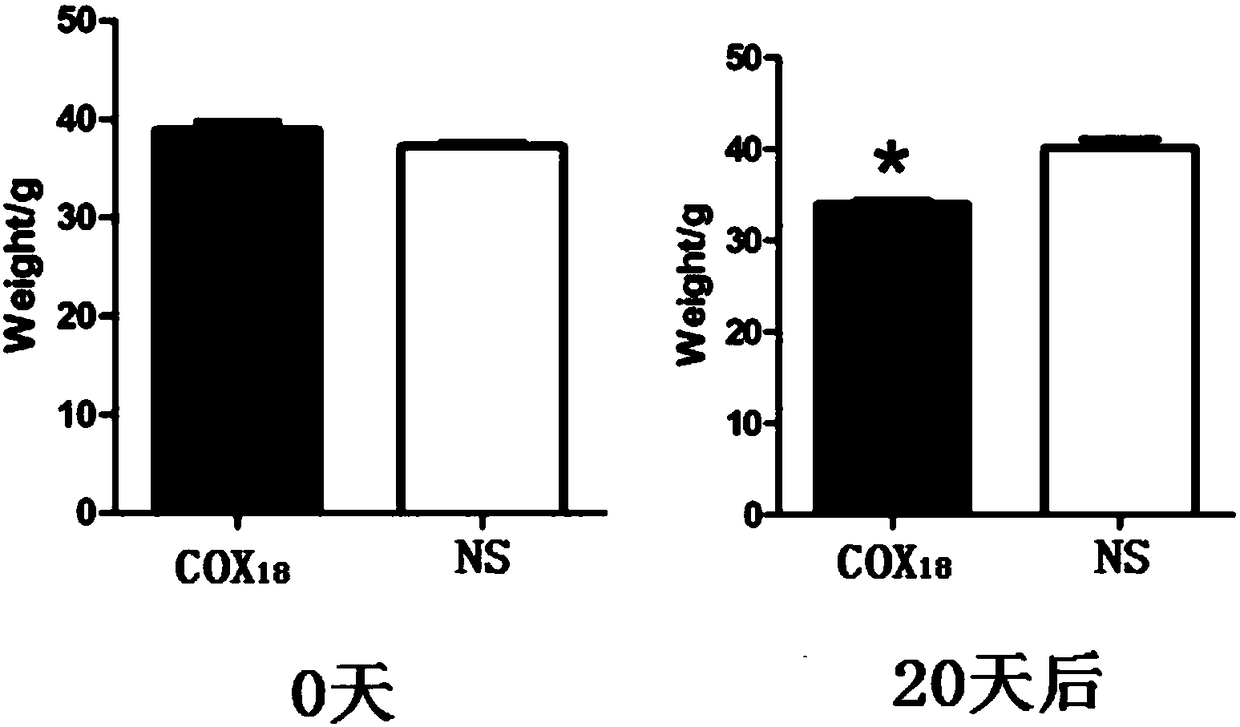
COX18 polypeptide with biological activity as well as synthesis method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN108315308ASimplify biochemical tedious proceduresLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderChemical synthesisSide effect
The invention provides a COX18 polypeptide with biological activity. An amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1: LLPAGWILSH LETYRRPE. The invention further provides a methodfor synthesizing the COX18 polypeptide through a chemical synthesis method, namely an Fmoc method as well as application, and the polypeptide is applicationd for preparing drugs which inhibit sugar induced insulin secretion, resist insulin tolerance, resist hyperinsulinemia and reduce body weight. The invention finds a novel COX18 polypeptide which is 52-69th part of human cytochrome c oxidase 8A, which is different from the precious porcine sequence. Compared with the previous sequence, the sequence has 38.88% of different amino acid. Moreover, the sequence is humanized, and has better homology, fewer immunoreactions and side effects while being applied to a human body.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
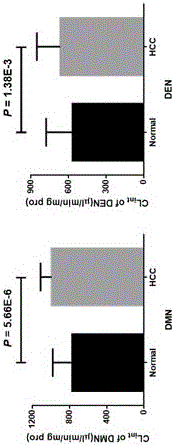
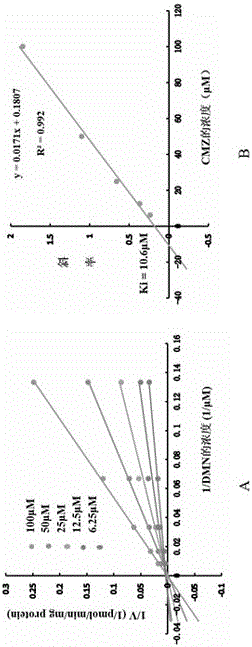
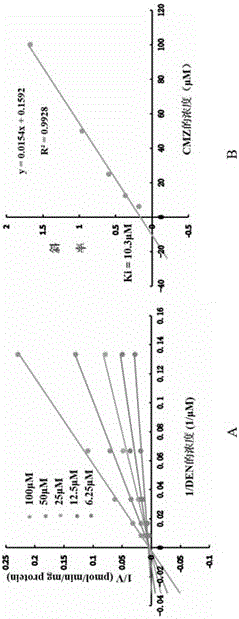
Application of clomethiazole as medicine for preventing and treating liver and esophageal disease
InactiveCN105769860AInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticEsophageal diseaseDisease
The invention discloses novel application of clomethiazole CMZ. Research findings show that the CMZ has the inhibiting effect on human cytochrome P4502E1(CYP2E1) metabolism nitrosamines compounds of dimethylinitrosamine DMN and Diethylinitrosamine DEN, and therefore clomethiazole can be used as a medicine for preventing and treating hepatic diseases such as hepatitis, hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer and esophageal diseases such as ingluveosis phrenospasm, hiatal hernia, esophageal diverticula, esophagus polypus and papilloma and esophagus cancers.
Owner:乔海灵
Microsomal bioreactor for synthesis of drug metabolites
InactiveUS20180044657A1Improve stabilityOxidoreductasesEnzyme production/based bioreactorsMetaboliteNiacinamide
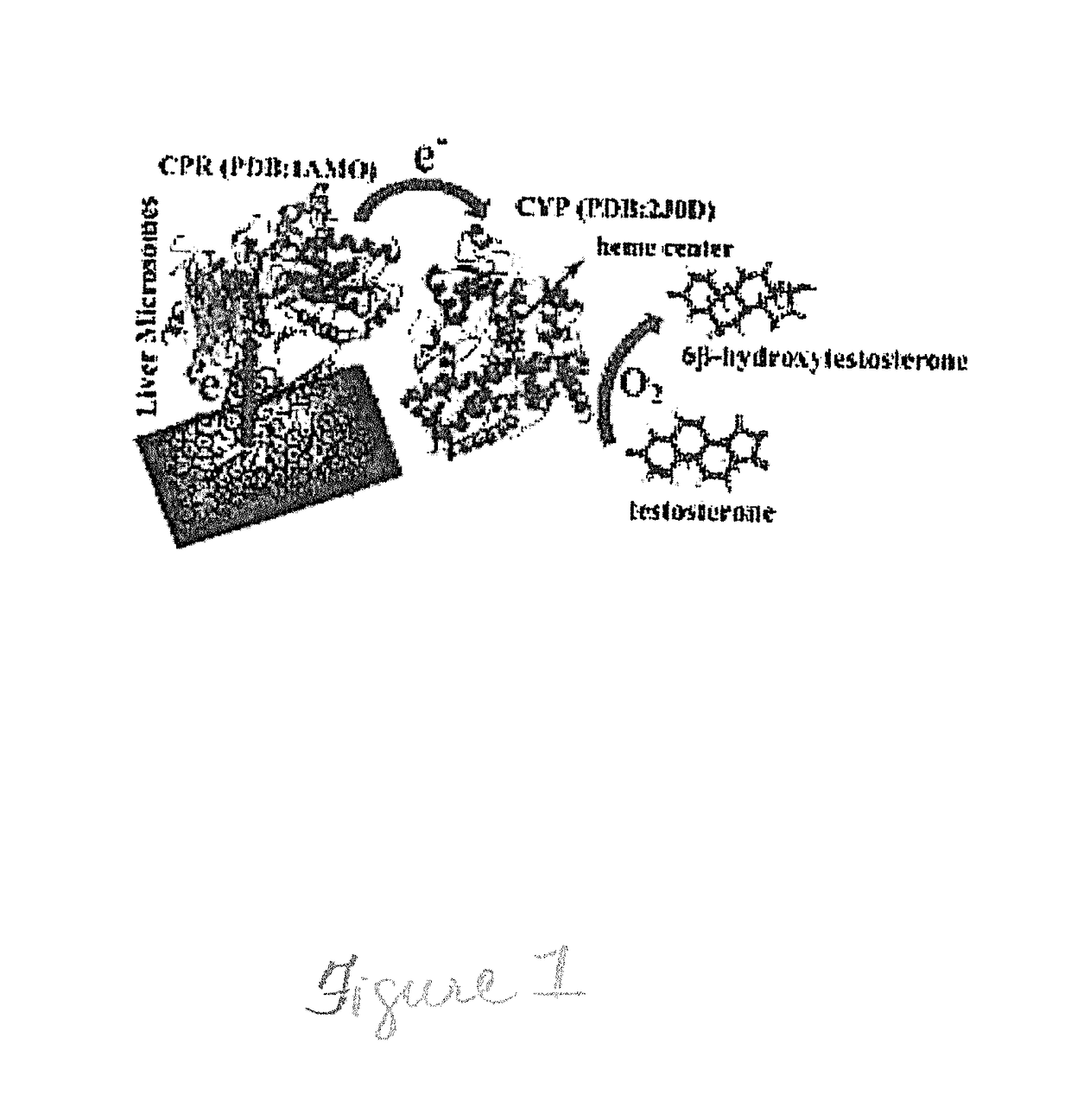
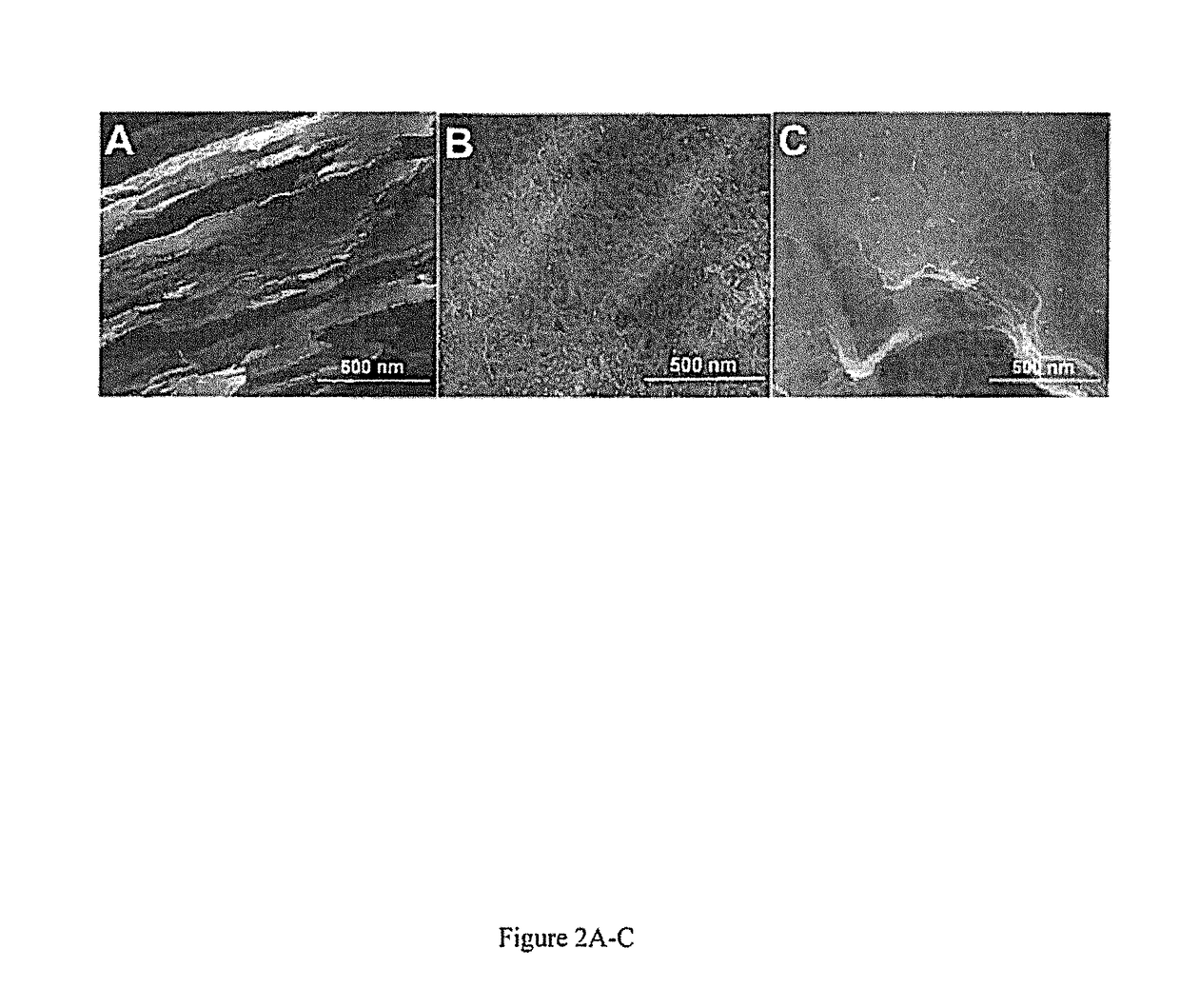
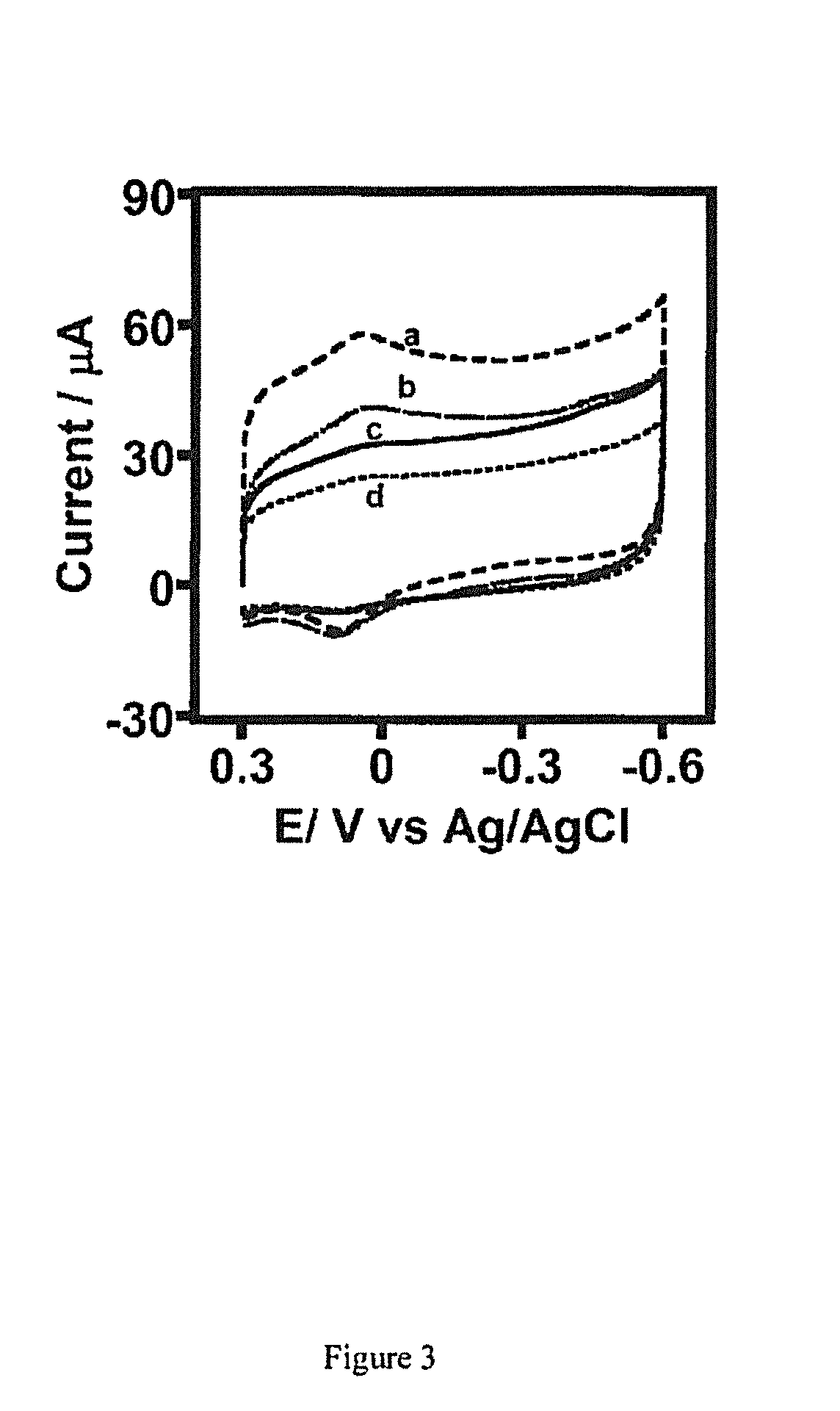
Reusable microsomal biocatalytic systems (bioreactors) constructed on carbon nanostructure modified electrodes are provided. The bioreactors comprise stable, biologically active immobilized enzymes such as human cytochromes P 450 (CYPs) and their redox partner proteins, e.g. CYP-NADPH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) reductases (CPR), on the carbon nanostructure surface. The immobilized enzymes may be present in liver microsomes, such as human liver microsomes (HLM) or as bactosomes, S9 fractions, etc. The bioreactors are used, for example, for synthesizing metabolites of interest from compounds such as drugs that are catabolized by the enzymes.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Primer group for detecting polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 related gene, kit and detection method
InactiveCN108841948AStrong specificityRelieve painMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNACYP3A5
The invention discloses a primer group for detecting polymorphism of a human cytochrome P450 related gene. The primer group comprises specific primers and probes aiming at gene sites of CYP2C19*2, CYP2C19*3, CYP3A4*18, CYP2C9*3, CYP2D6*10 and CYP3A5*3. The invention further relates to a kit for detecting polymorphism sites of the human cytochrome P450 related gene. The kit comprises PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction liquid freeze-dried powder (PCR buffer, dNTPs, MgCl2, UNG enzyme, Taq enzyme and trehalose) with the primers and the probes. The invention further relates to a method for detecting polymorphism sites of the human cytochrome P450 related gene. By adopting the method, a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction procedure is avoided, micro whole-blood amplification is directlyimplemented, a small amount of blood is used, and patients can be relieved from pain; the time and the labor can be saved, and in addition, economic expense can be greatly reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN WIZ BIOTECH CO LTD
CYP2A enzymes and their use in therapeutic and diagnostic method
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as 'CYP2A6' for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
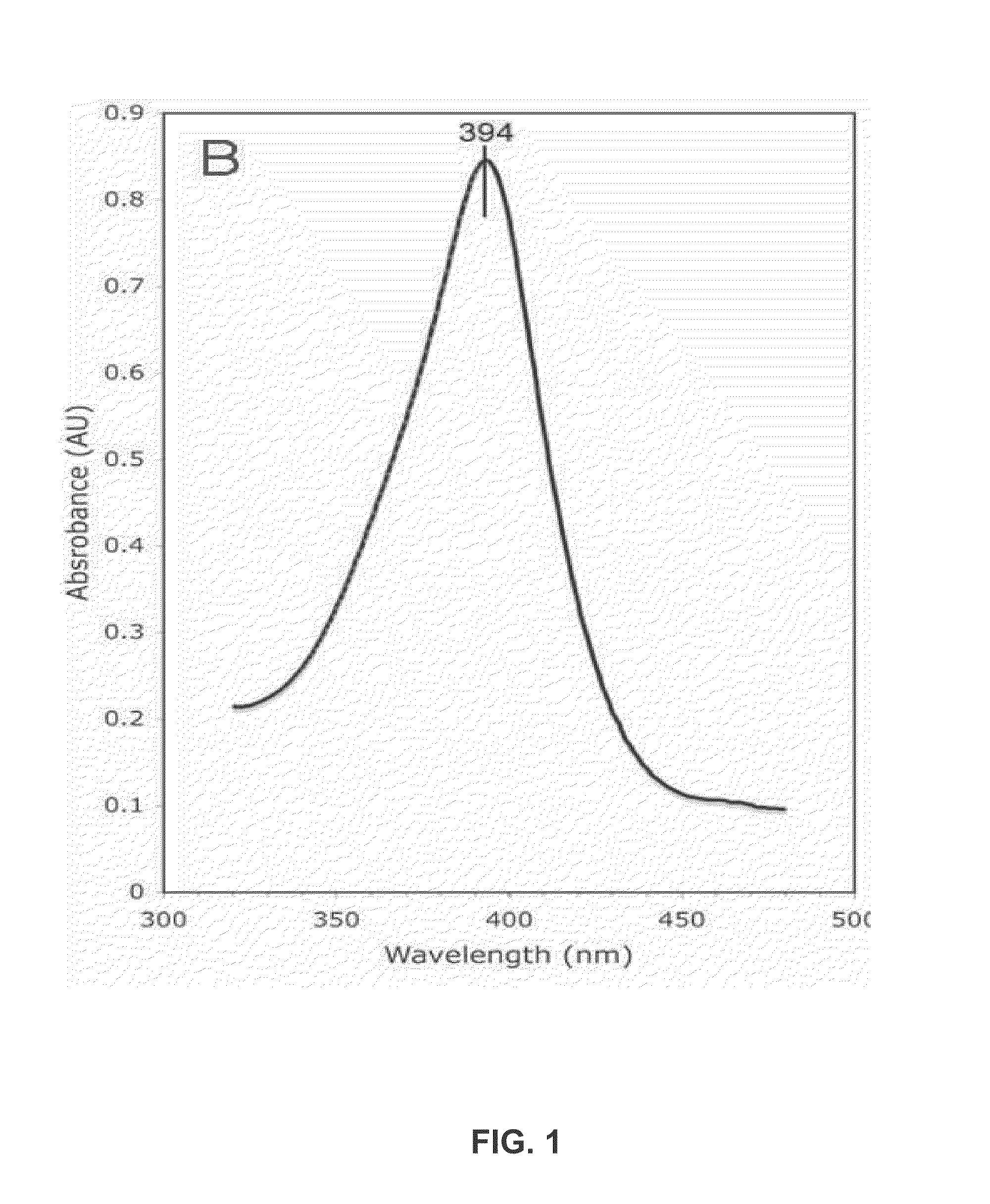
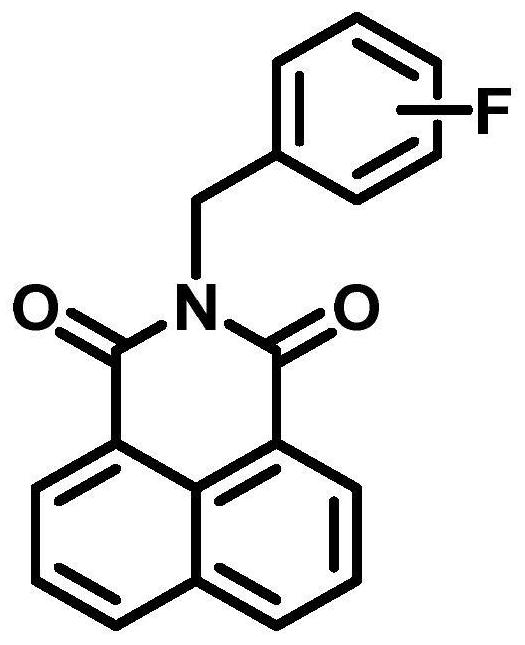
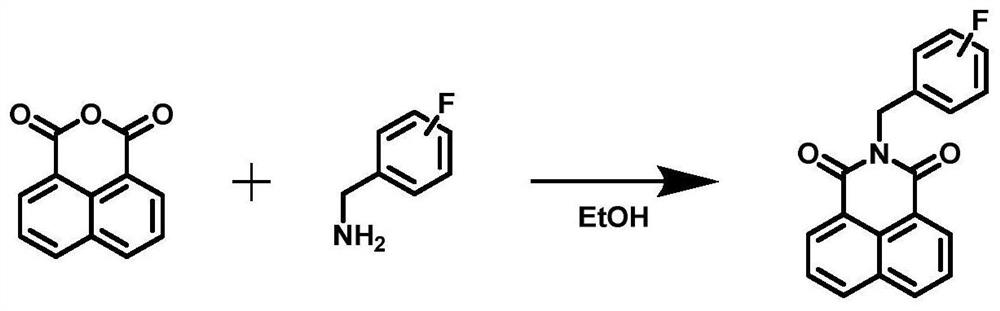
Fluorescent substrate for detecting human cytochrome P450 3A4 as well as preparation method and application of fluorescent substrate
PendingCN114478383ASignificant technological progressAdvantages of detecting CYP3A4 enzyme activityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceRecombinaseFluorogenic Substrate
The fluorescent substrate for detecting the human cytochrome P450 3A4 is an N-fluorobenzyl-1, 8-naphthalimide compound, and the structural general formula of the fluorescent substrate is as shown in the formula (1). The invention also provides a preparation method of the fluorescent substrate. The substrate disclosed by the invention is specifically catalyzed by CYP3A4 to generate C-4 hydroxylation reaction and generate a single 4-hydroxylation product, and the activity or residual activity of CYP3A4 in a biological sample can be quantitatively detected by detecting elimination of the substrate in unit time or the generation amount of the 4-hydroxylation product. A CYP3A4 activity detection method constructed by virtue of the fluorescent substrate can be used for evaluating the activity of CYP3A4 in products such as recombinant CYP enzyme and commercial cell / tissue preparations so as to carry out quality control on the products, and also can be used for screening and evaluating the regulation effect of compounds on CYP3A4.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
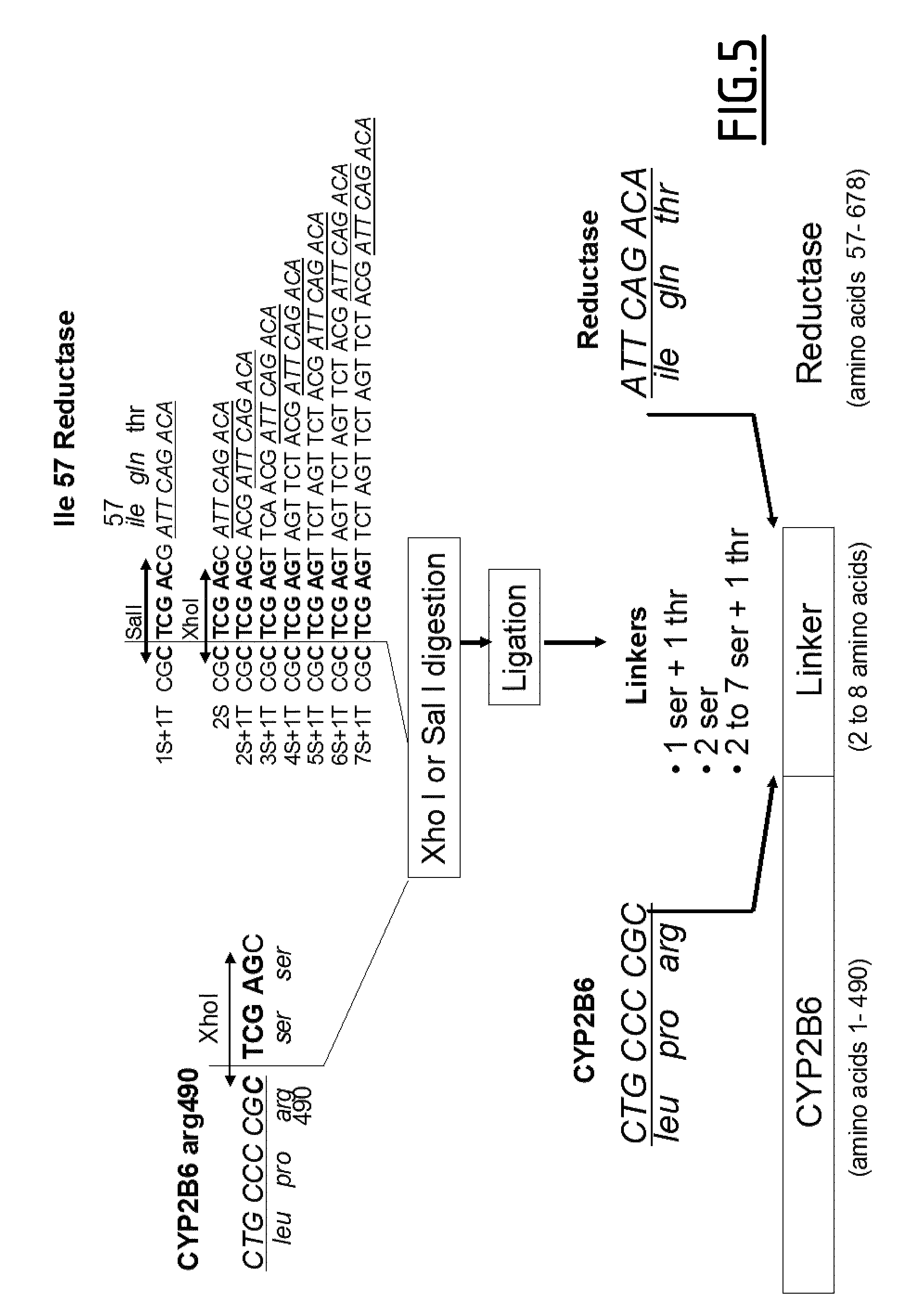
Mutant cytochrome P450 2B6 proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS9243231B2Confer cytotoxic activityImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCytochrome P450 reductaseADAMTS Proteins
The present invention to relates mutant human cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6) proteins, and fusion proteins comprising said mutant CYP2B6 proteins. In particular, fusion proteins comprising mutant CYP2B6 and NAPDH-cytochrome P450 reductase are provided. The invention also relates to methods of treatment of cancer and the use of said proteins and fusion proteins in the treatment of cancer, in particular via virus-directed enzyme prodrug therapy.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
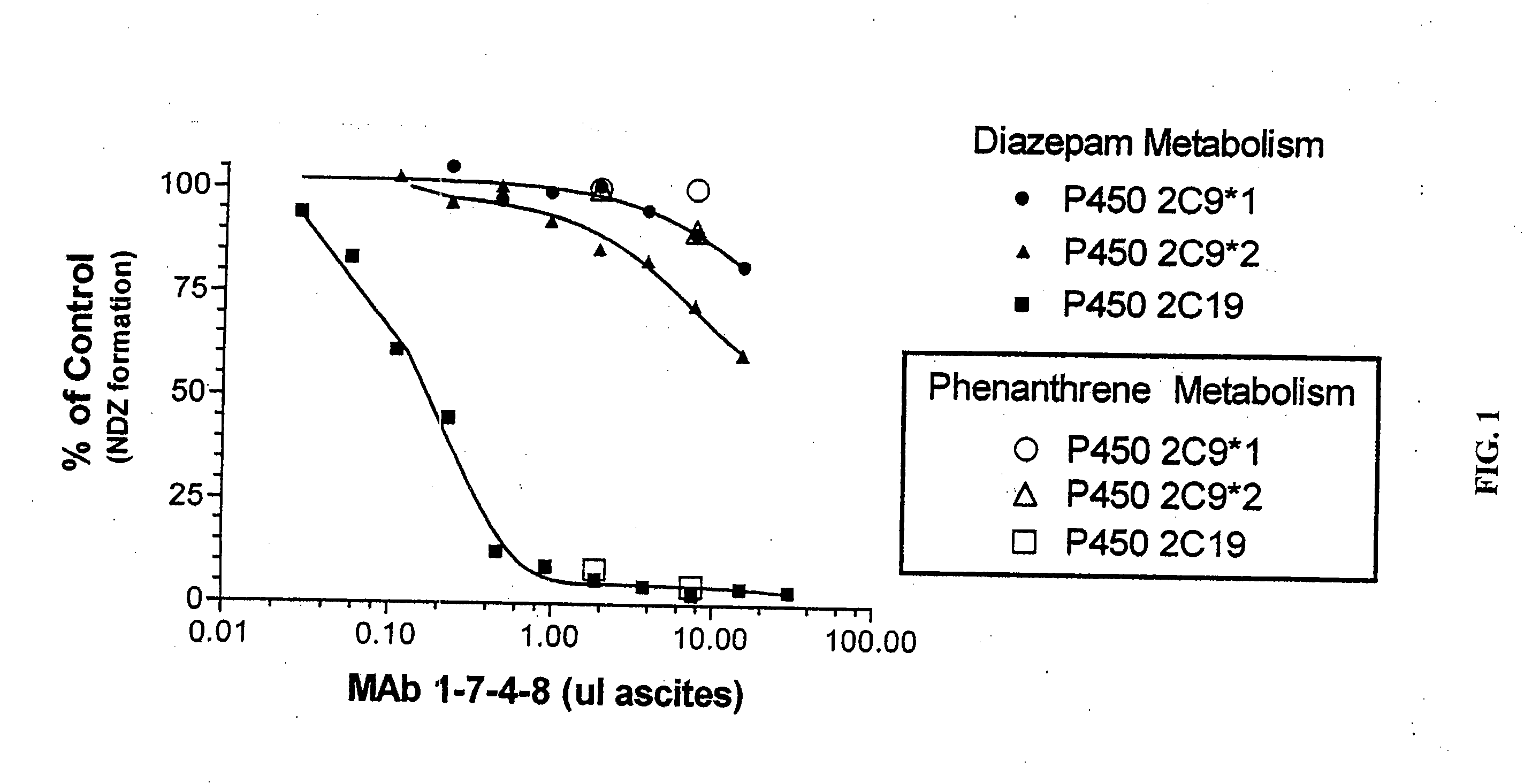
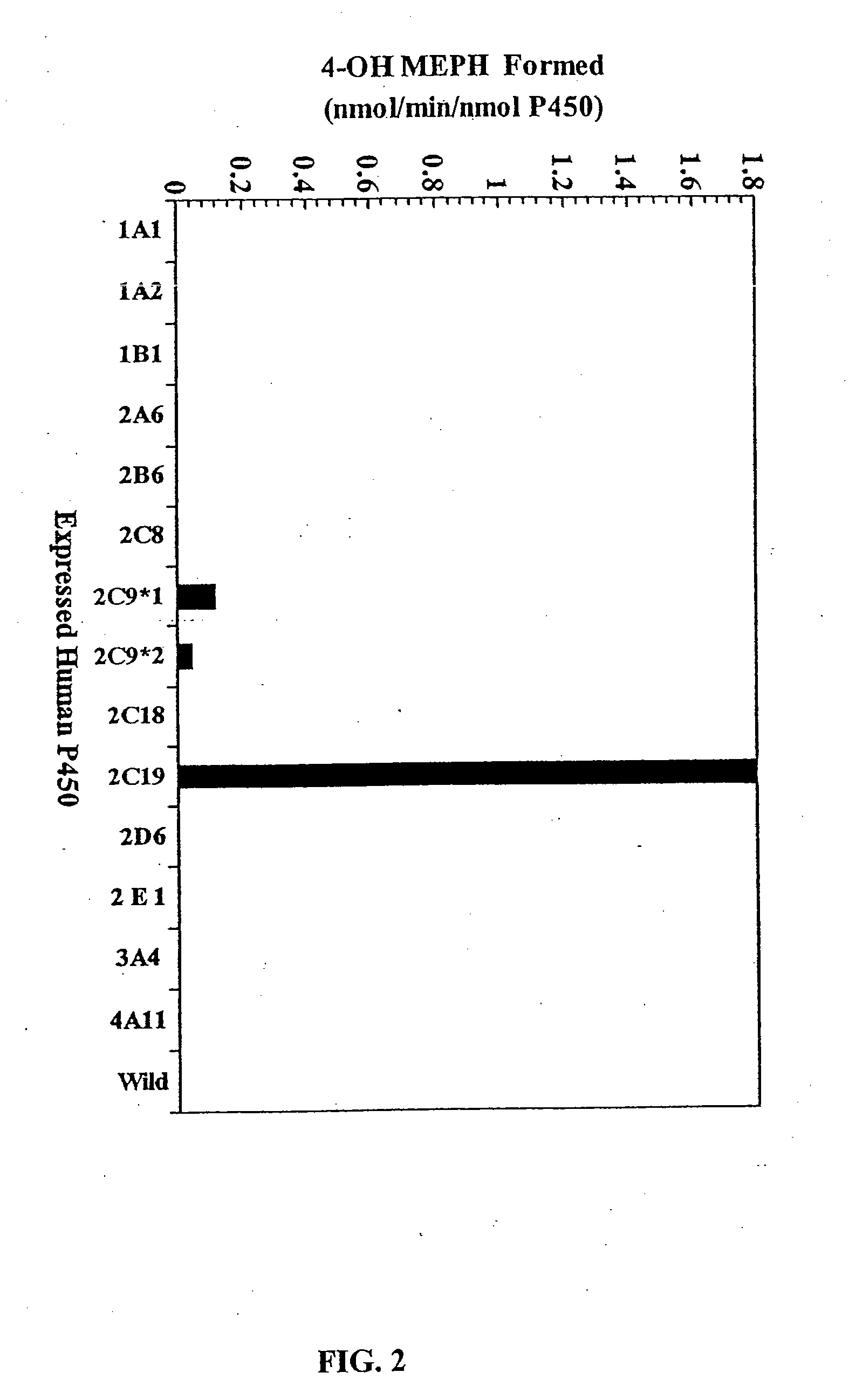
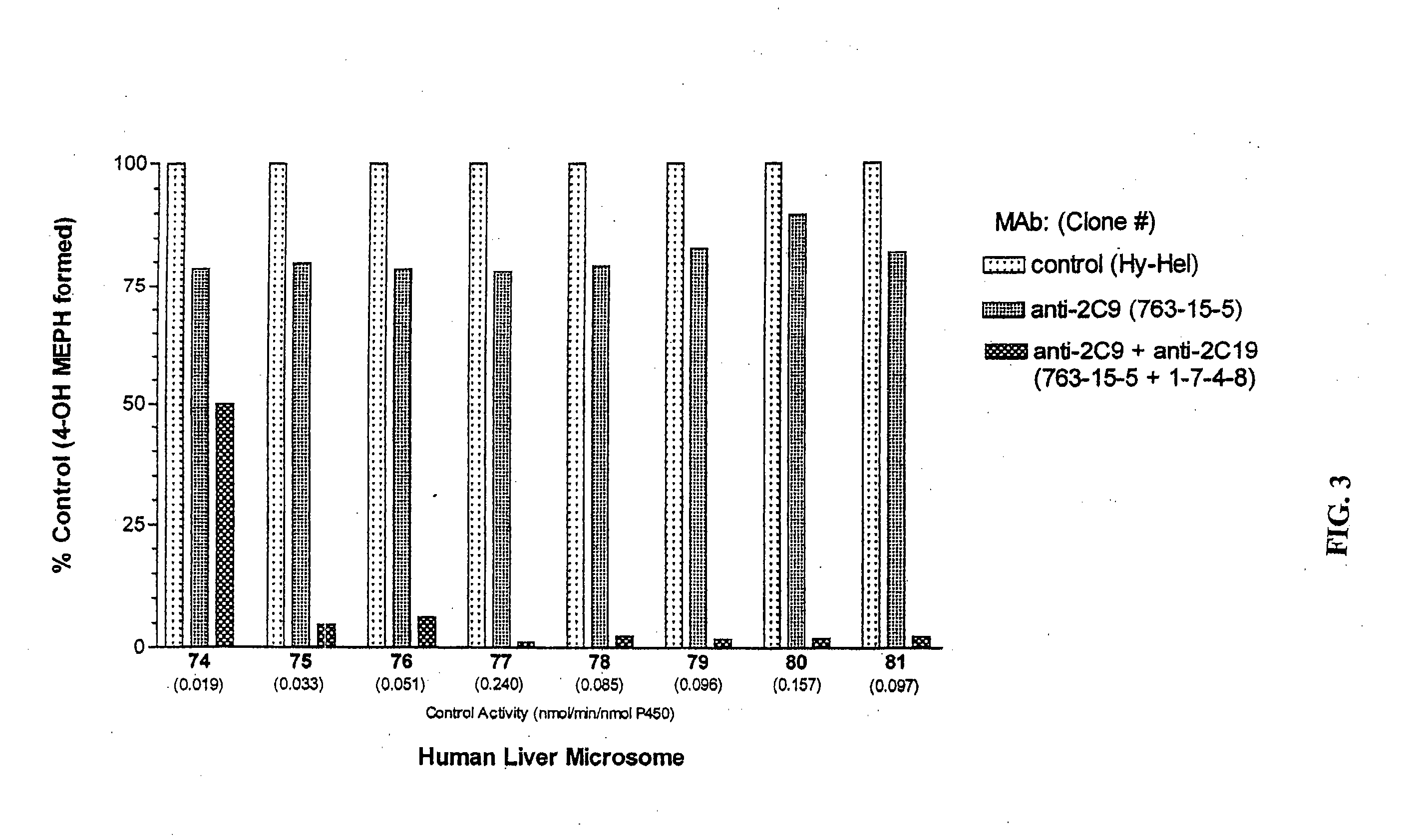
Agents that bind to and inhibit human cytochrome p450 2c19
InactiveUS20070154971A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingDrug metabolismMonoclonal antibody
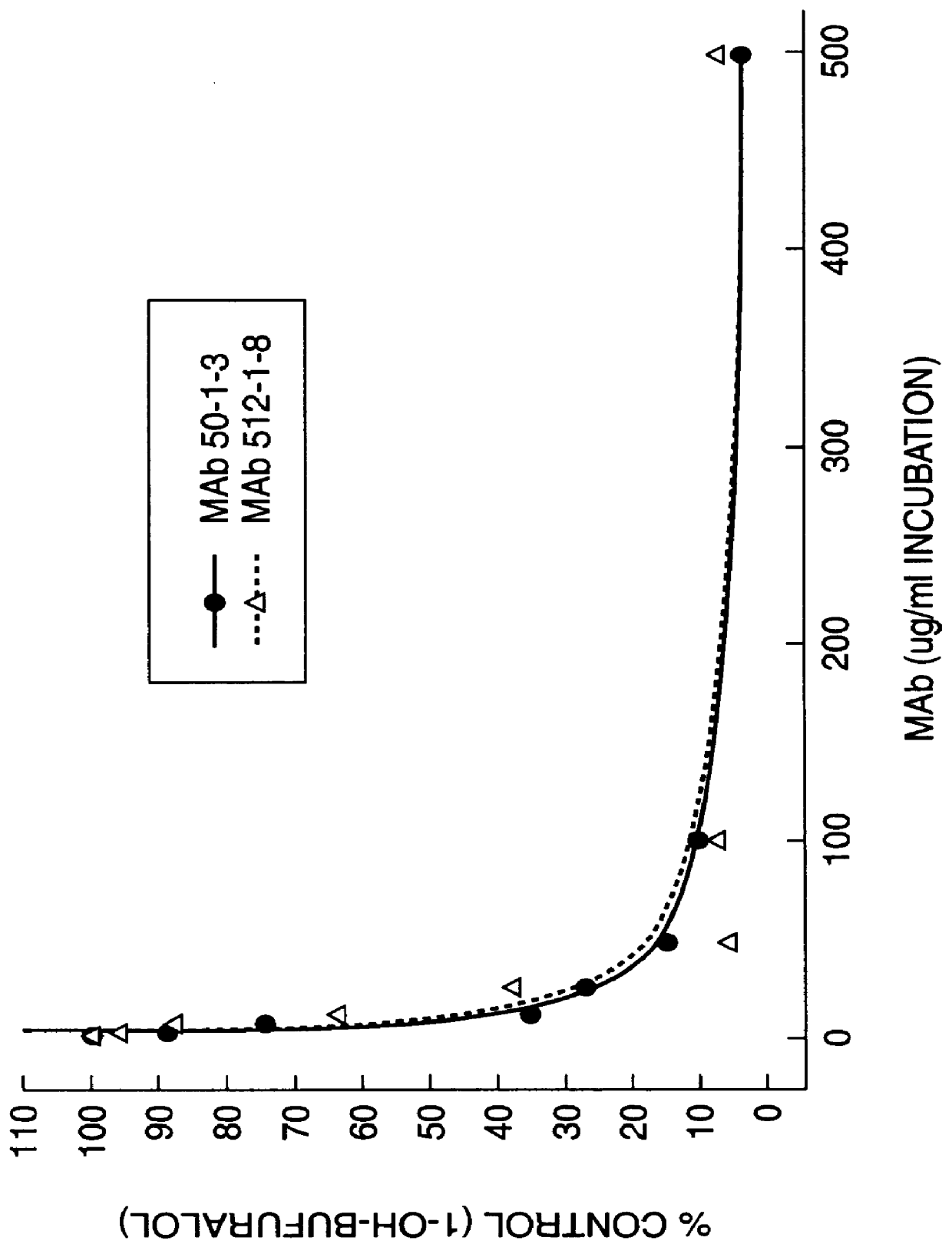
The invention provides monoclonal antibodies and other binding agents to human cytochrome P450 2C19 having advantageous properties, including capacity substantially to inhibit enzyme activity of human cytochrome P450 2C19 and lack of specific binding to other human cytochrome P450s. The binding agents of the invention are useful inter alia in methods for screening drugs for metabolism by cytochrome P450 2C19, and in methods of measuring P450 2C19 levels in individuals relative to P450 2C19 levels in a control population.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com