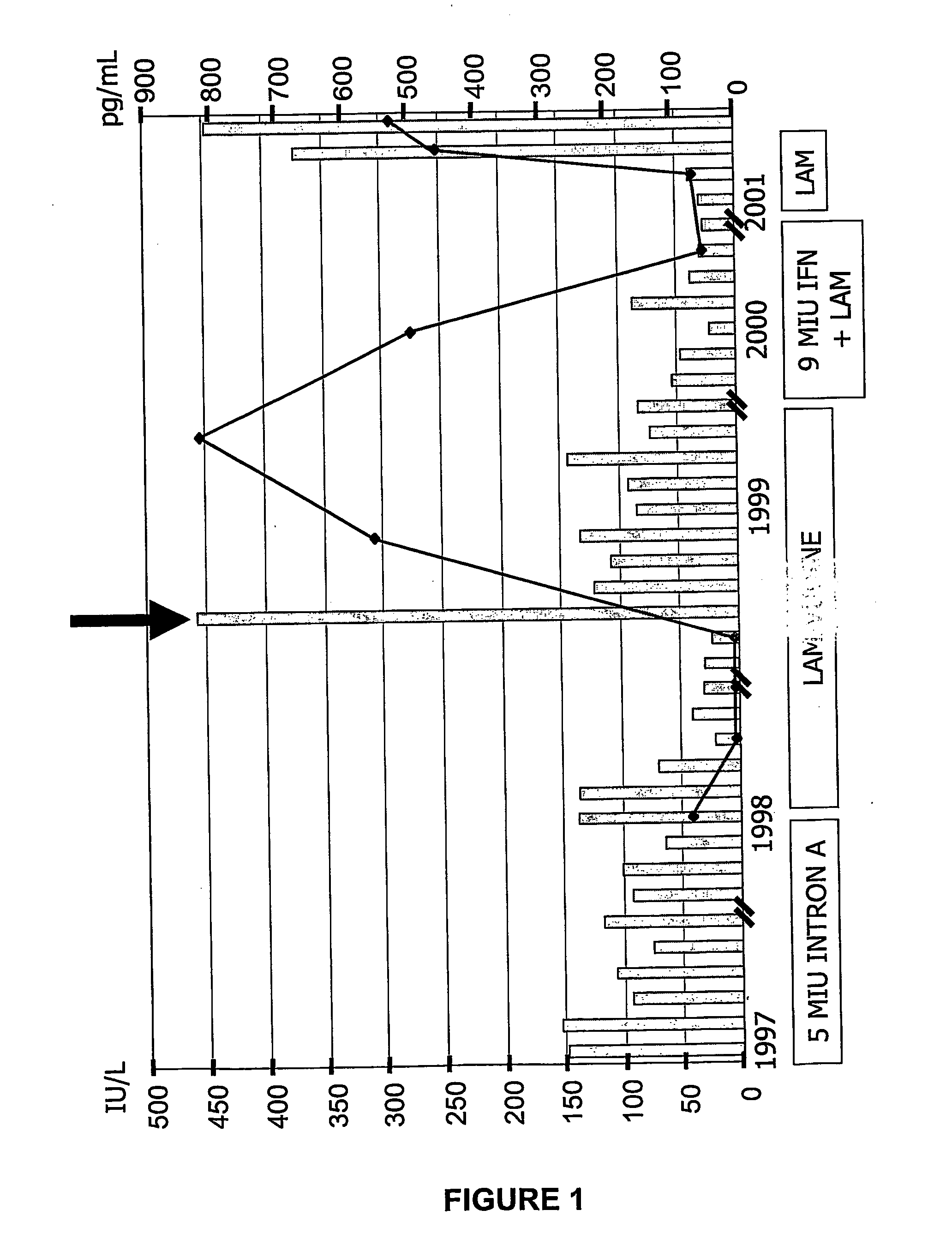
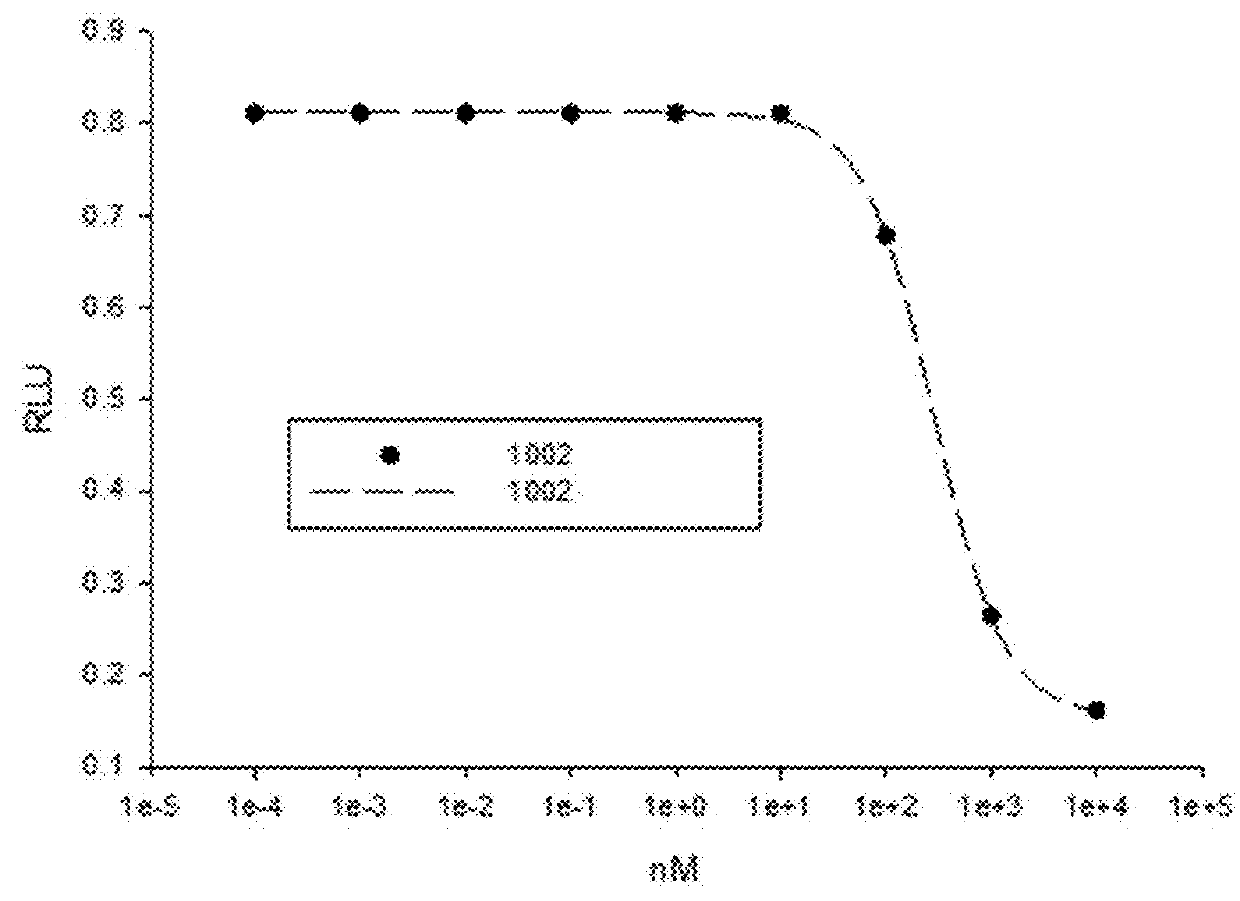
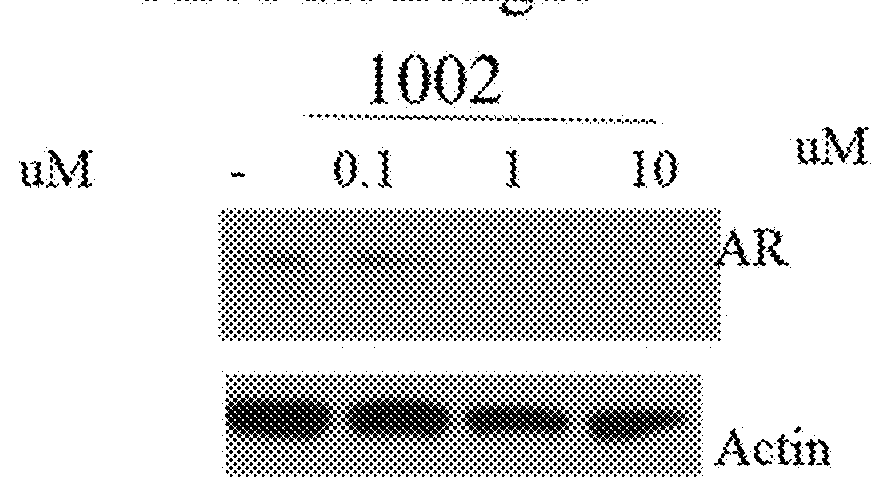
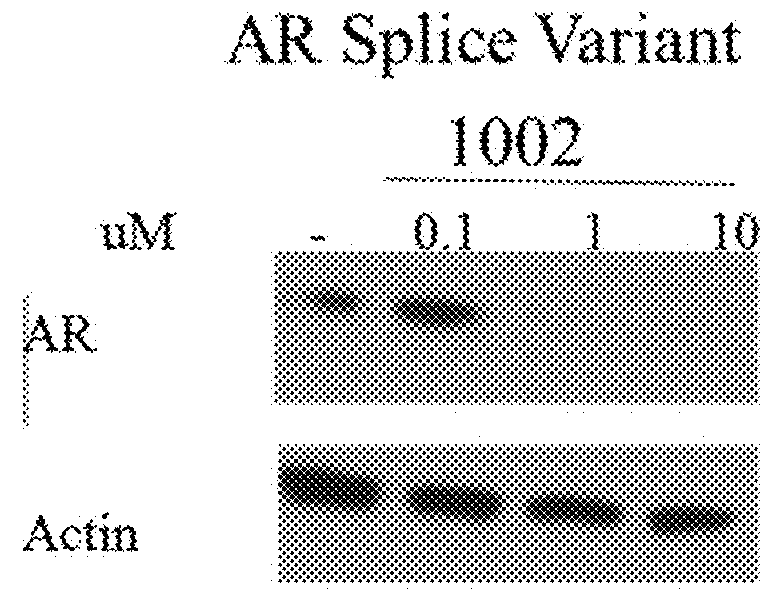
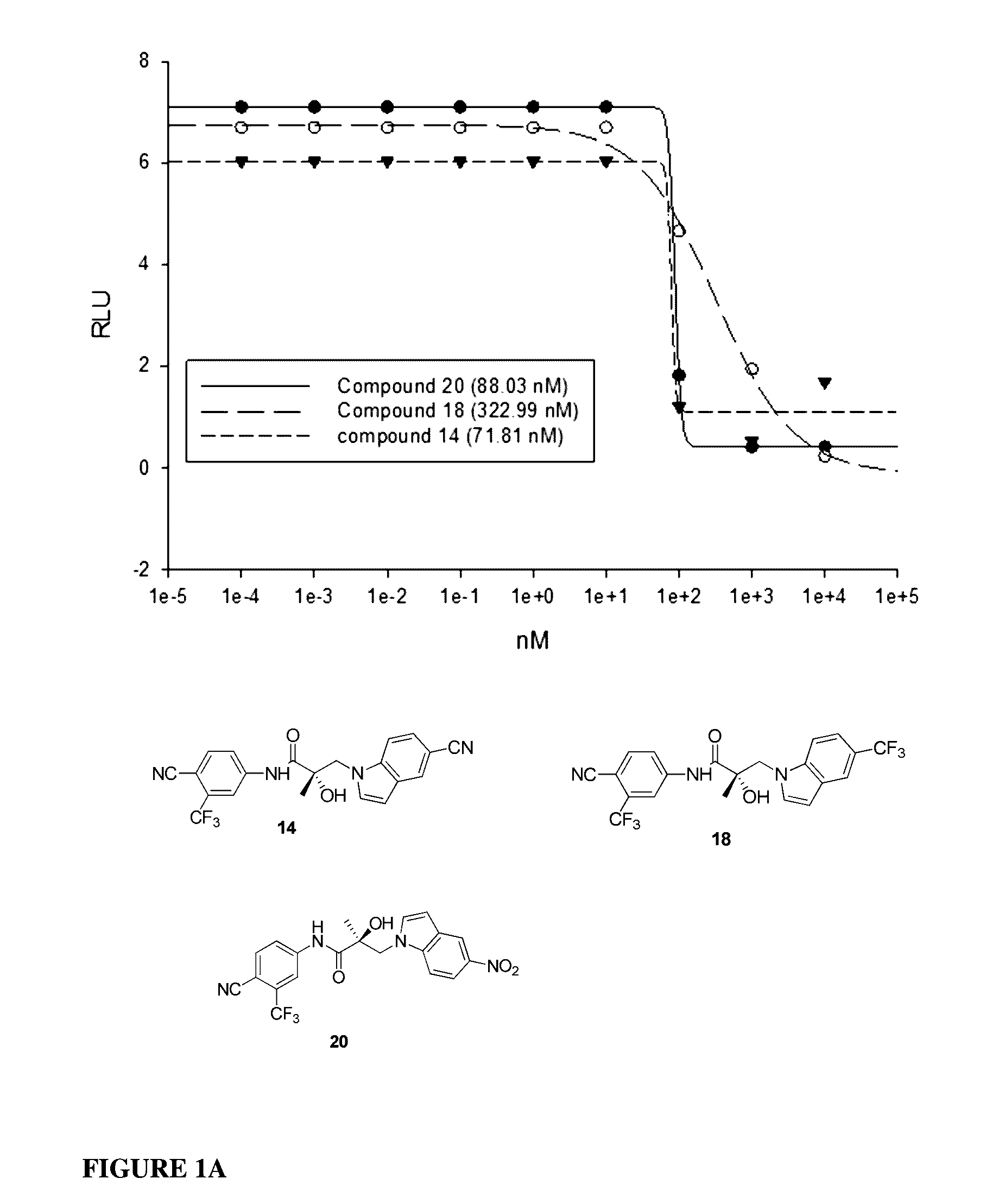
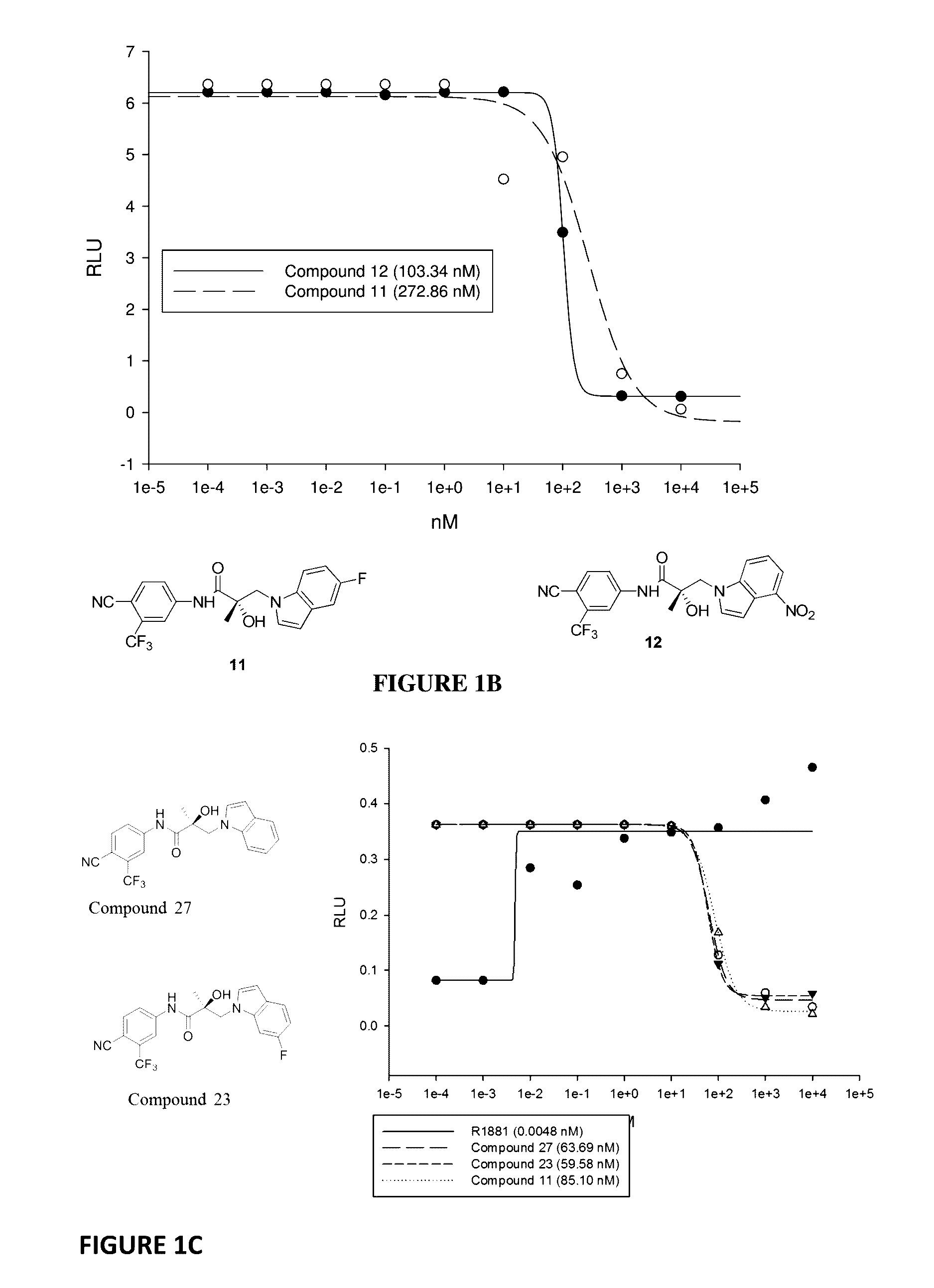
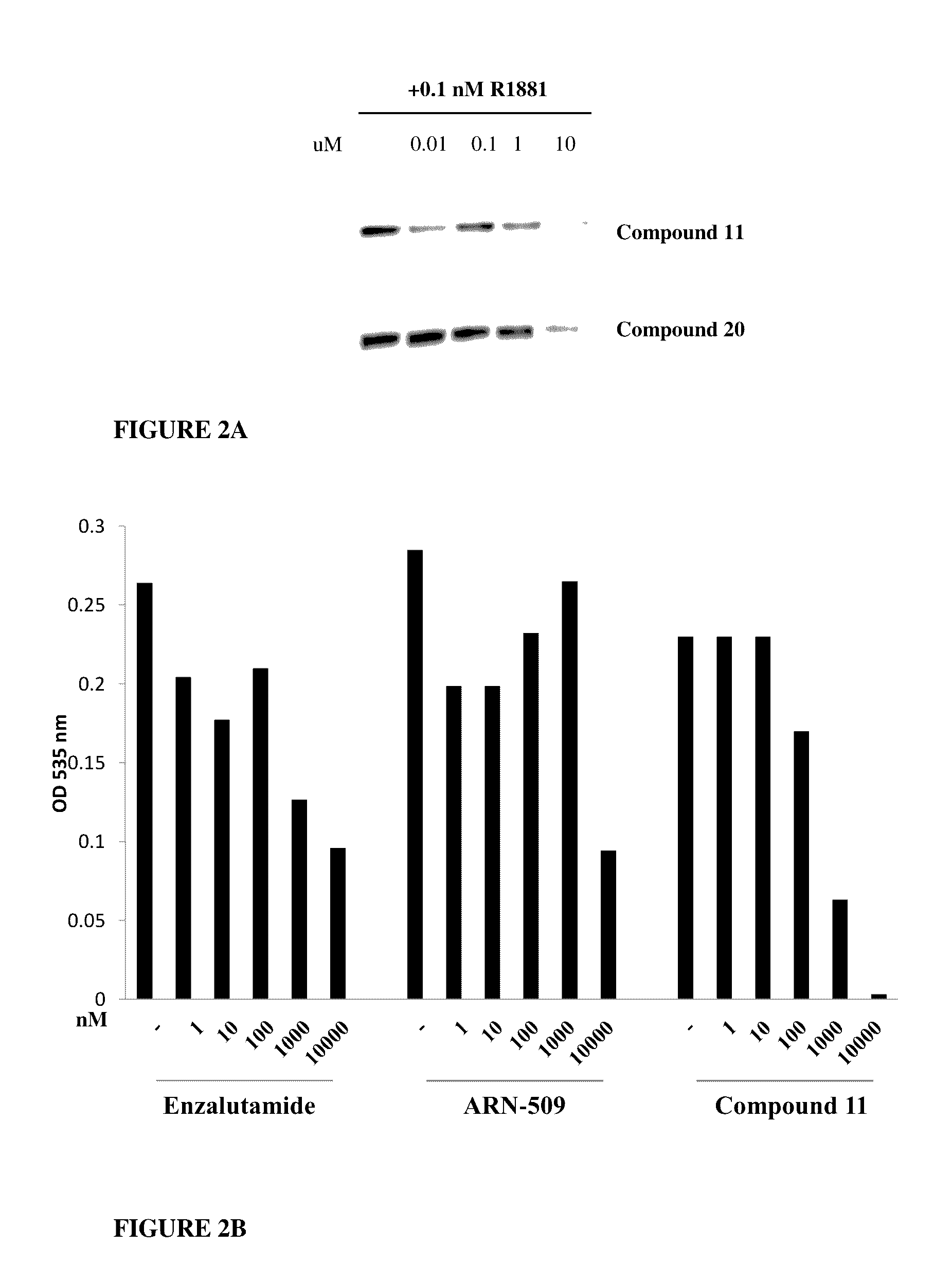
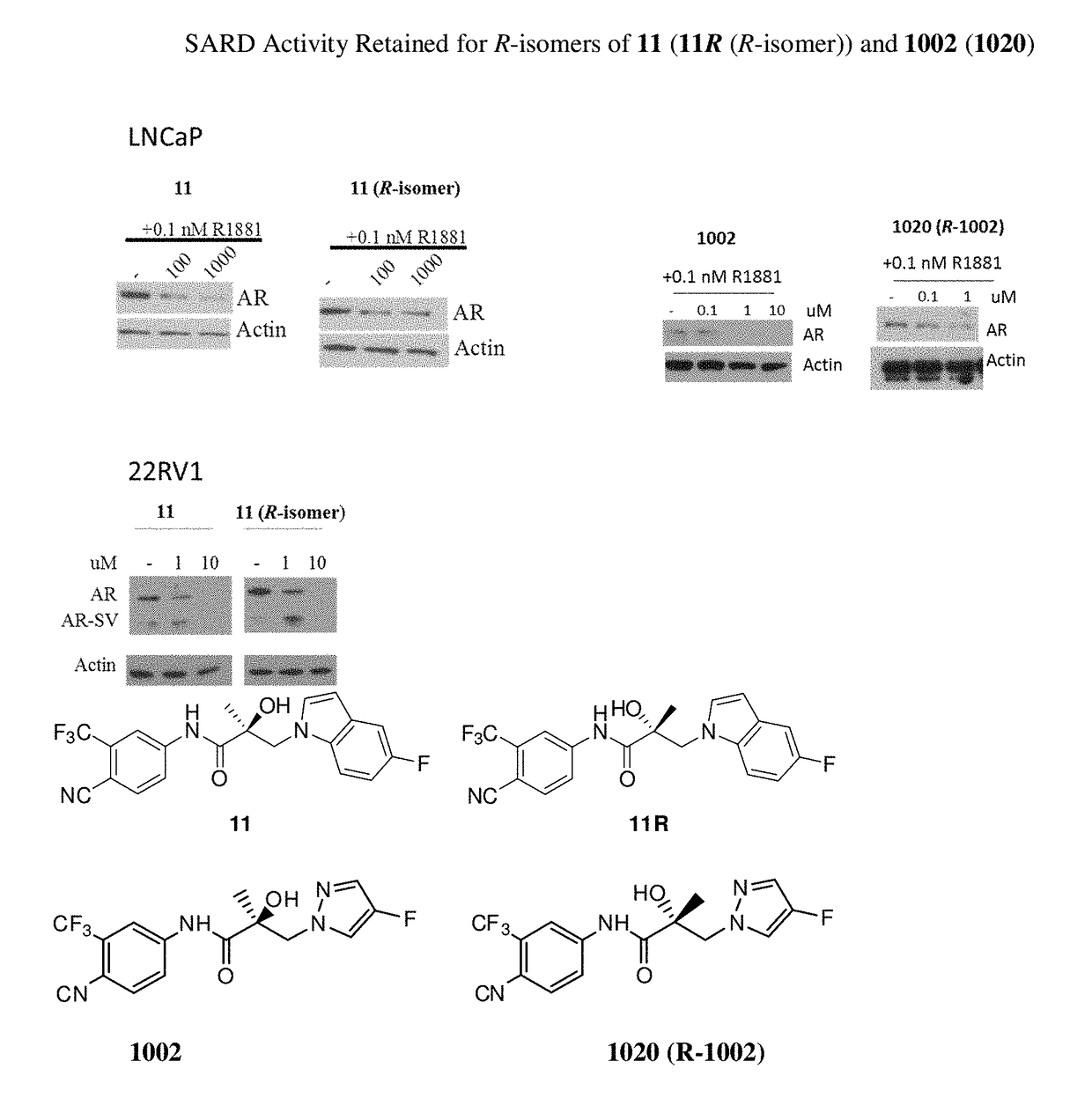
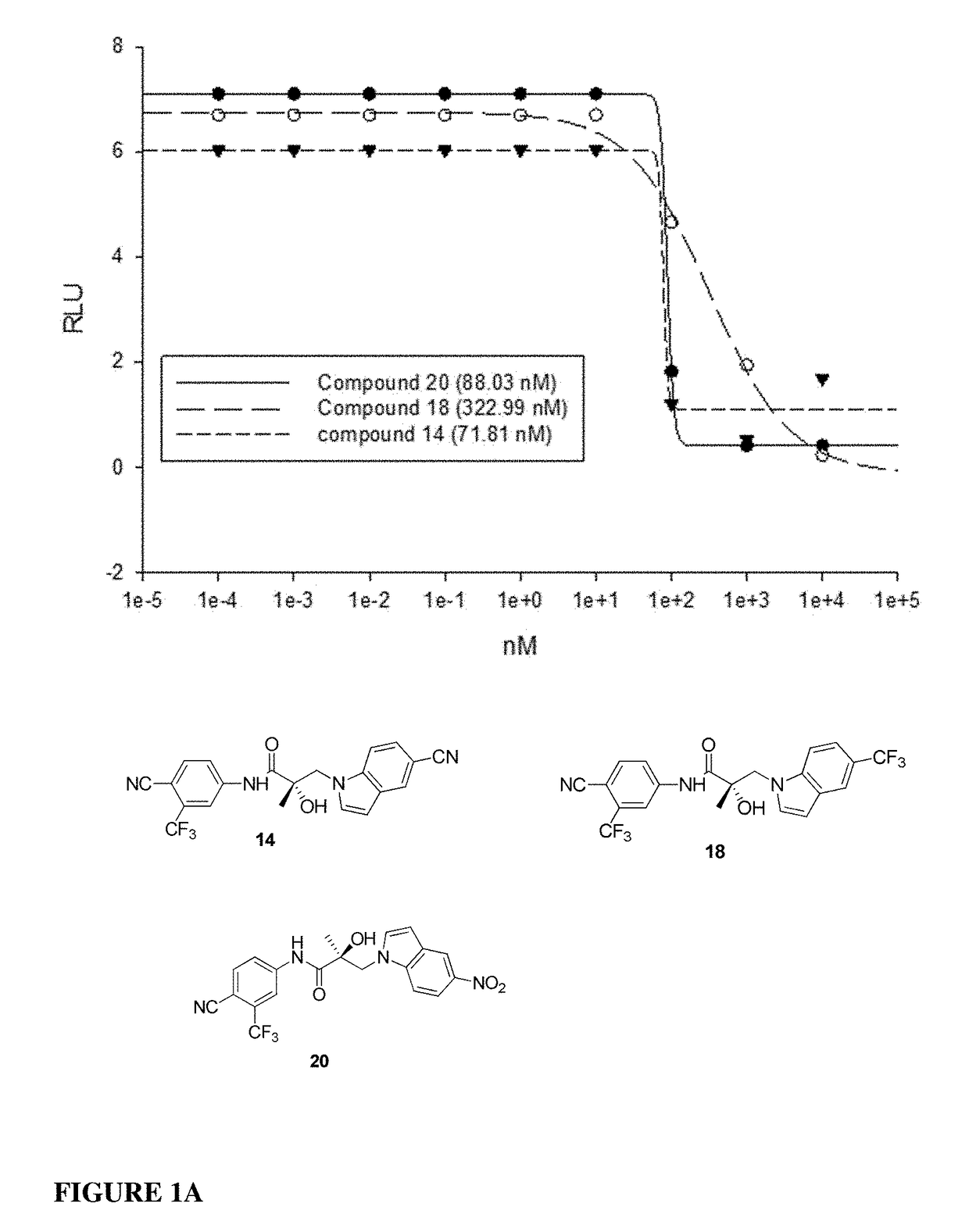
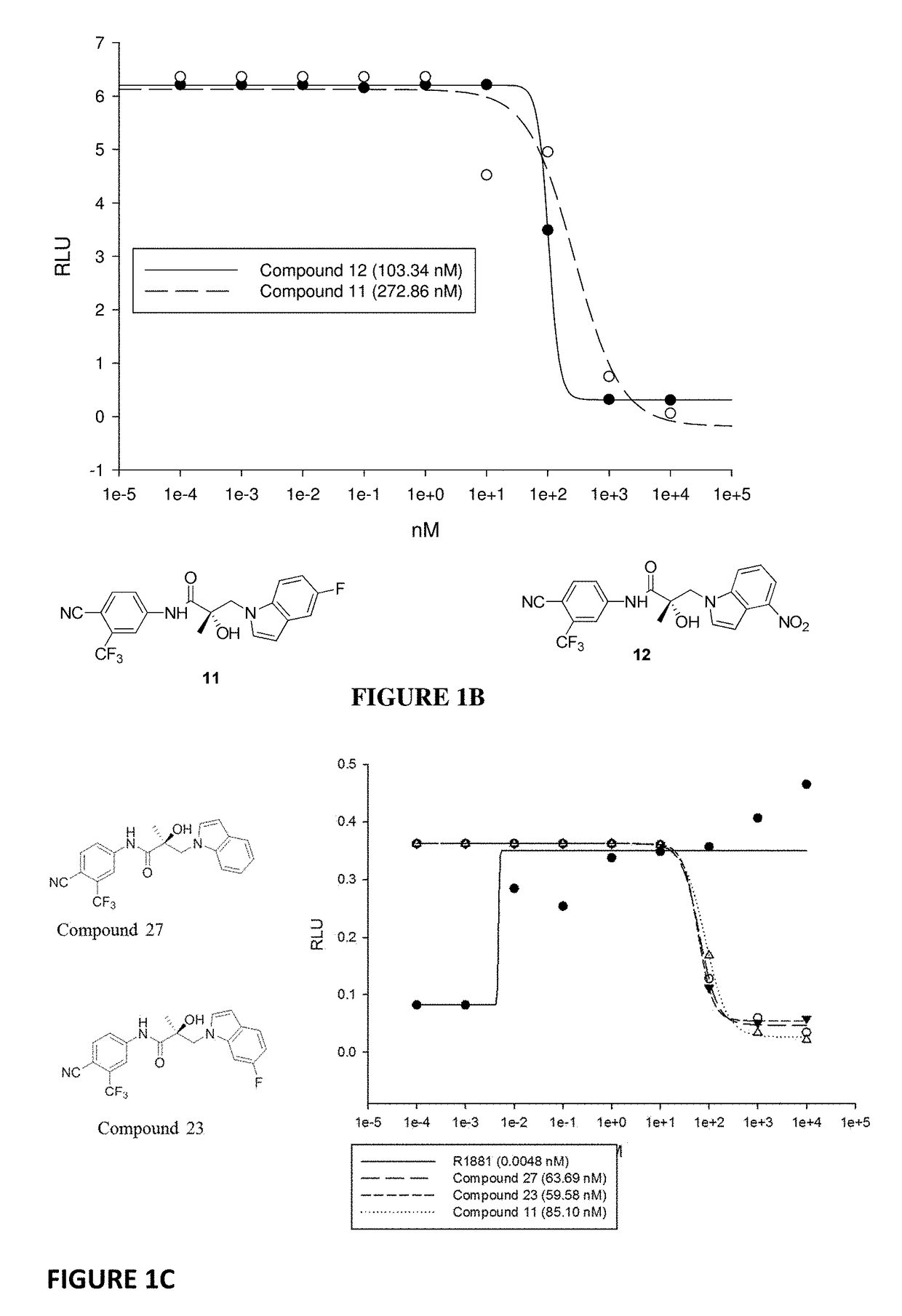
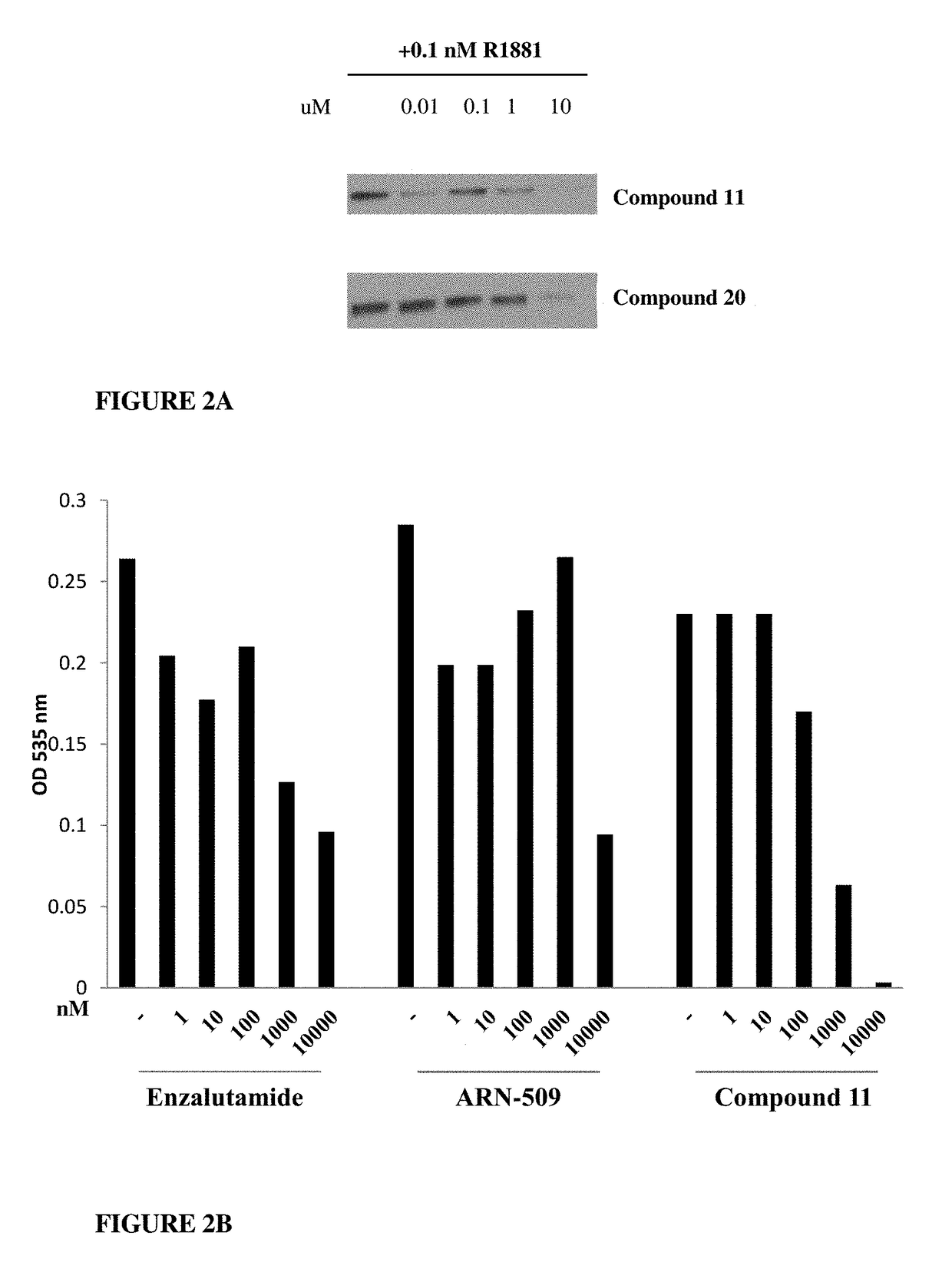
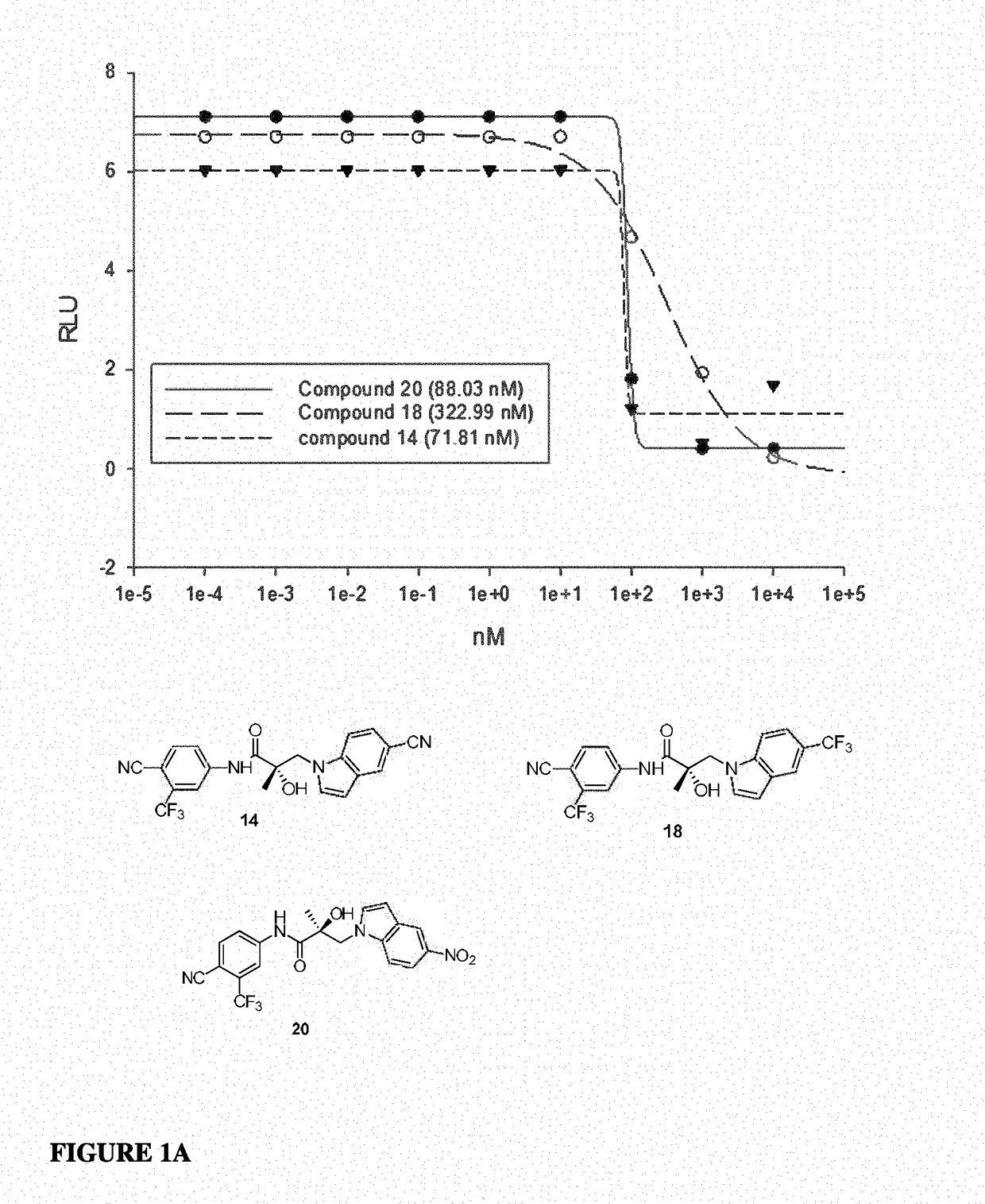
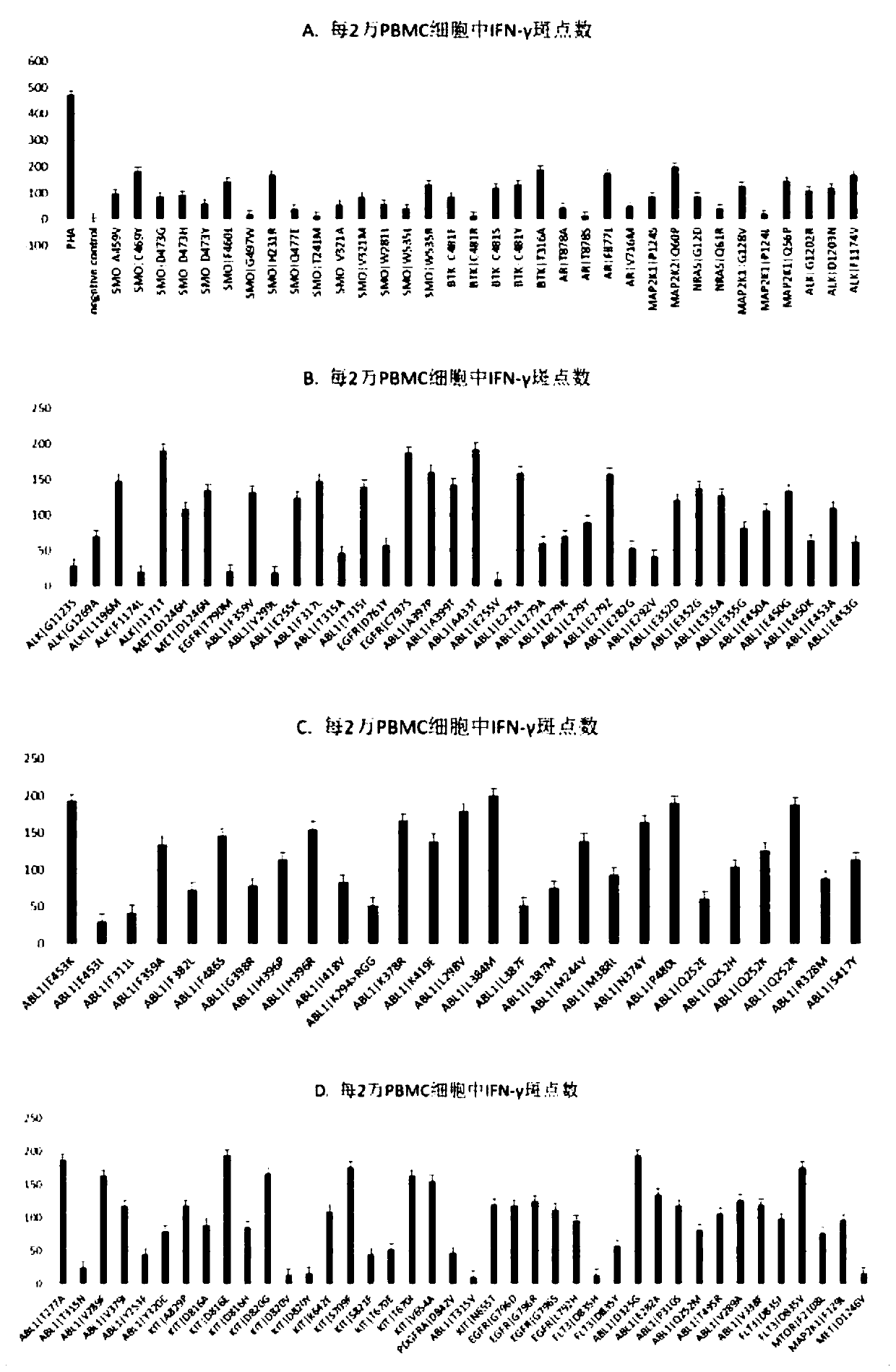
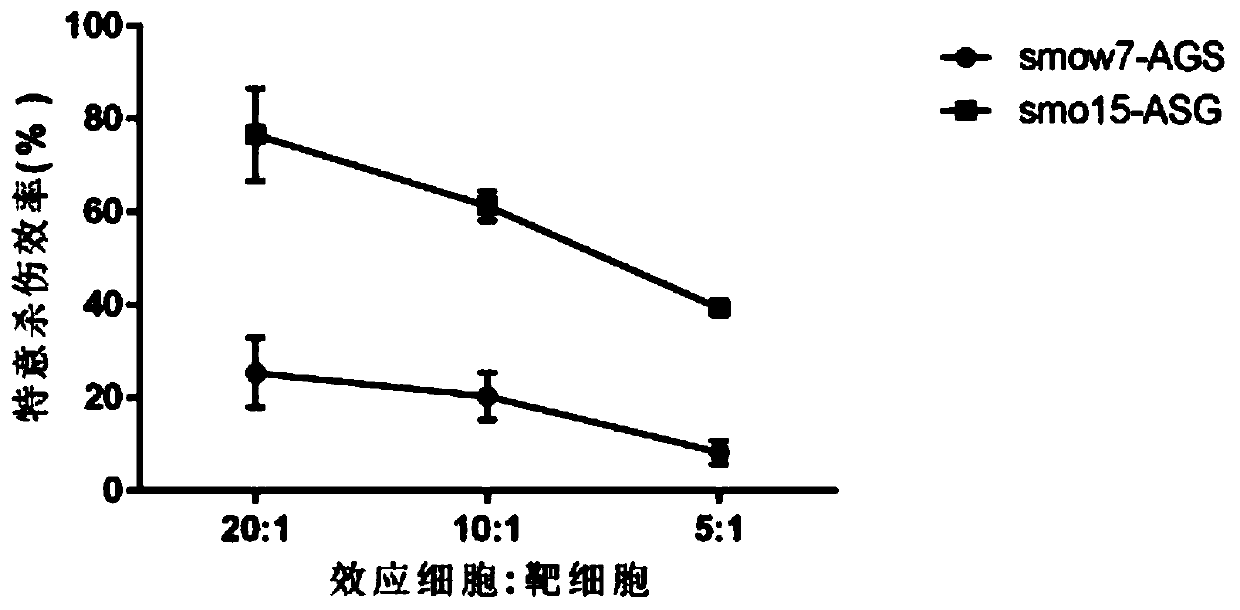
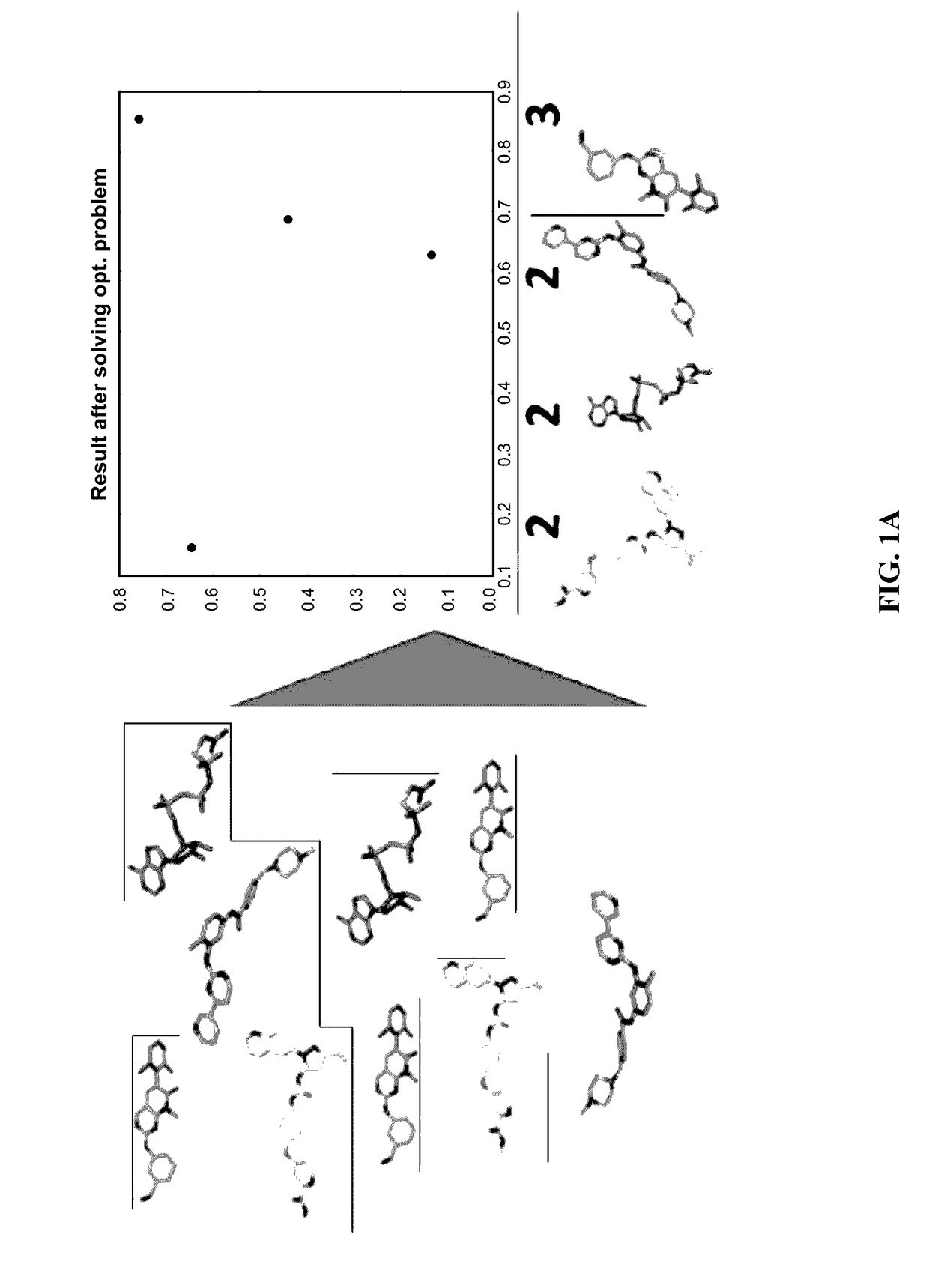
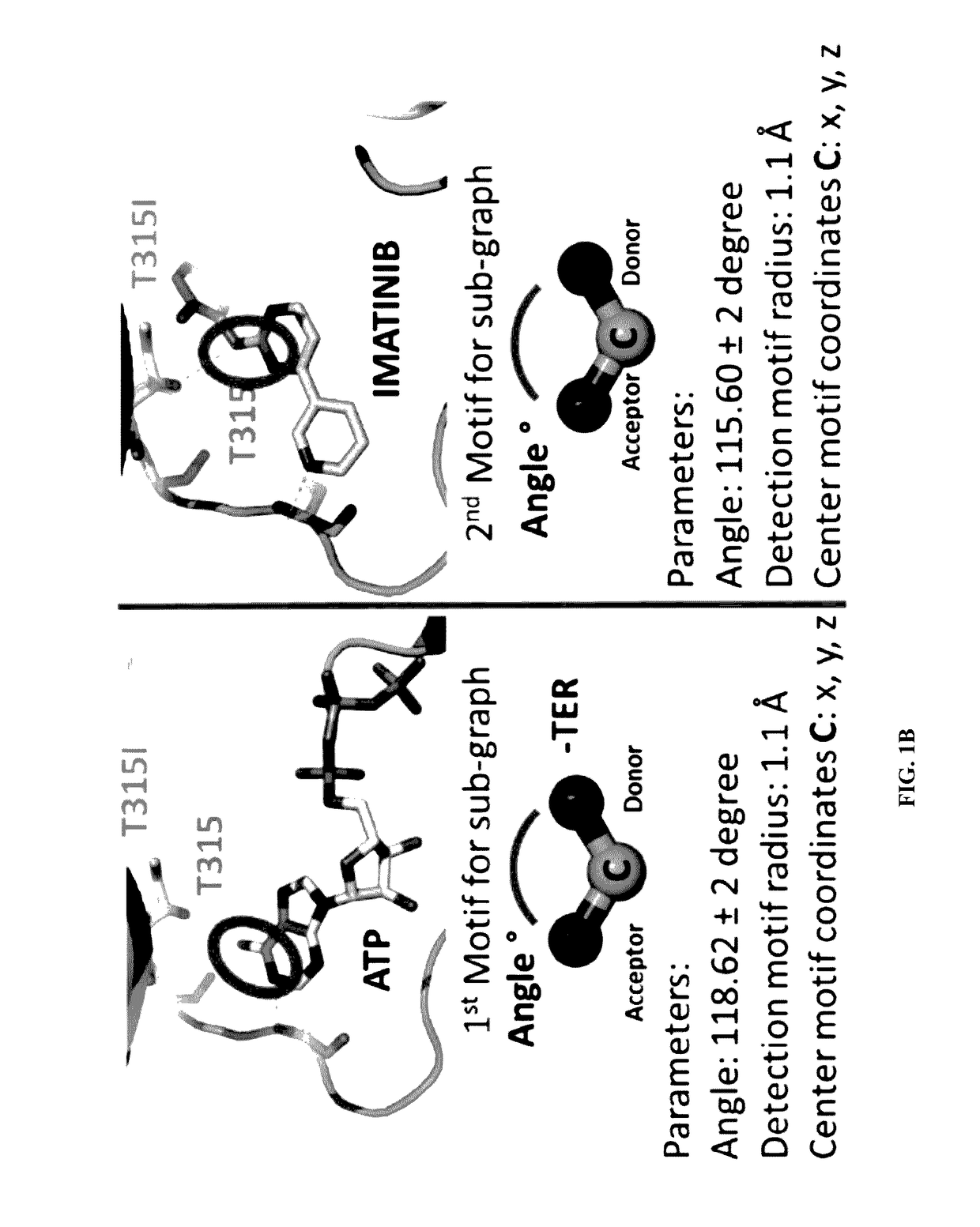
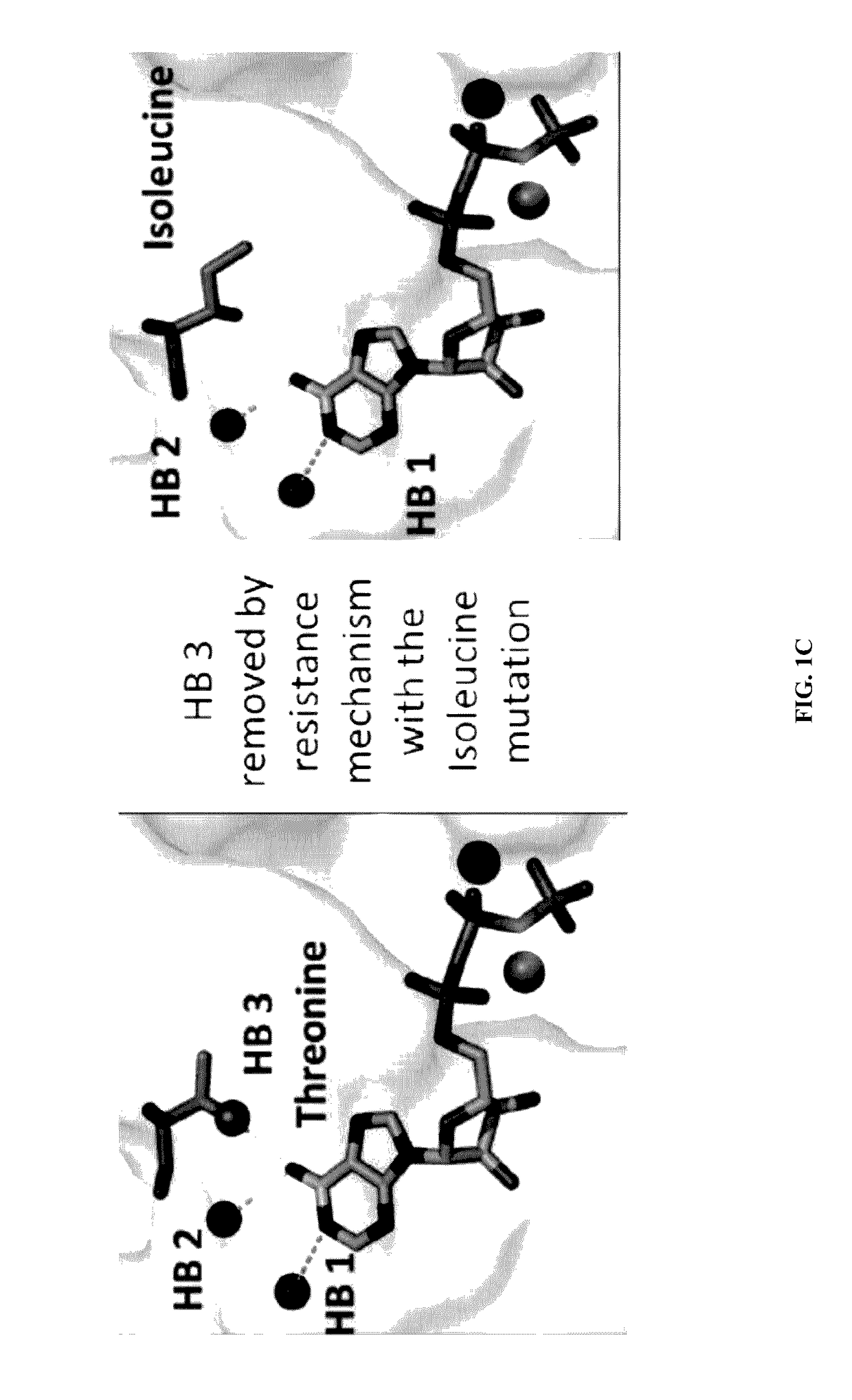
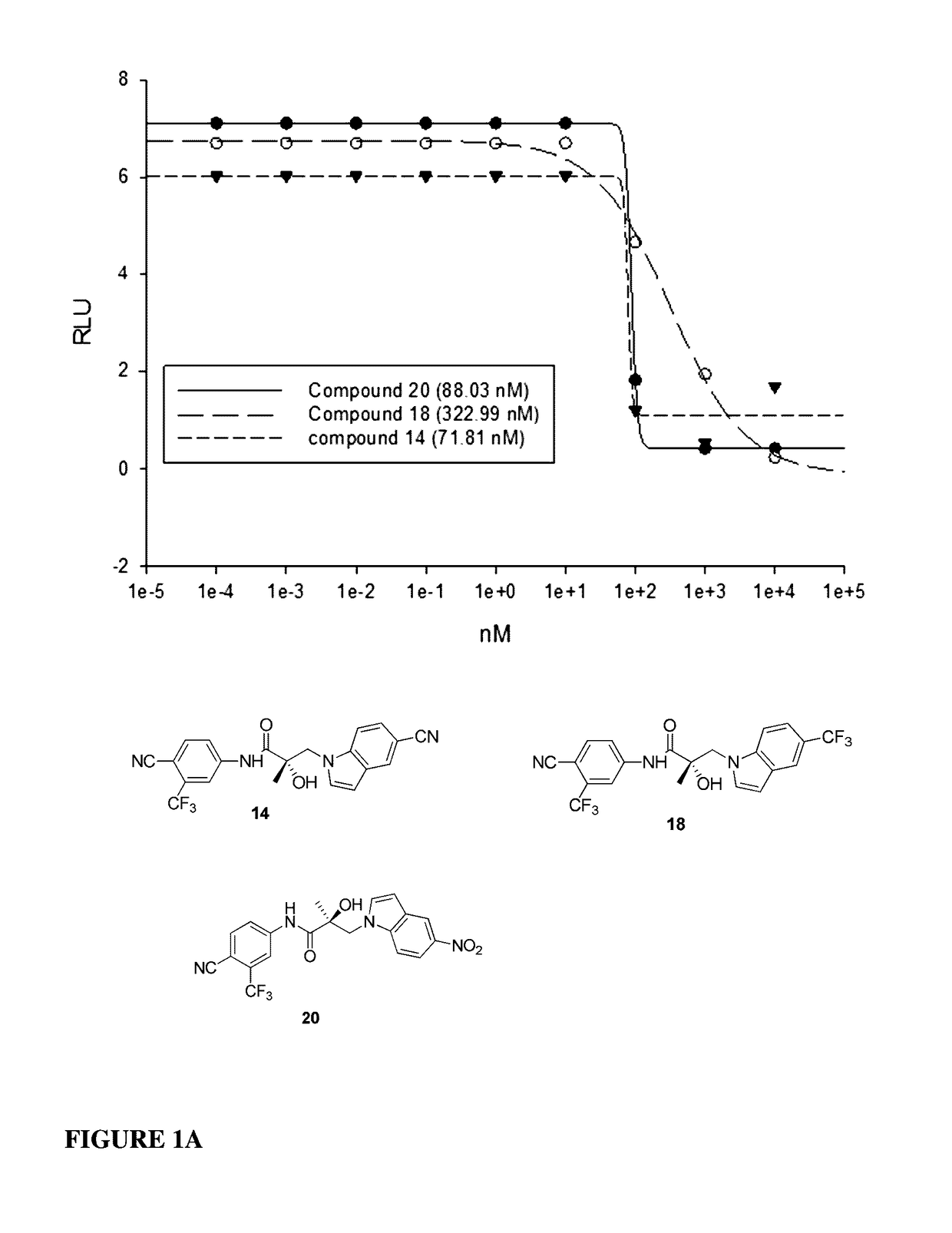
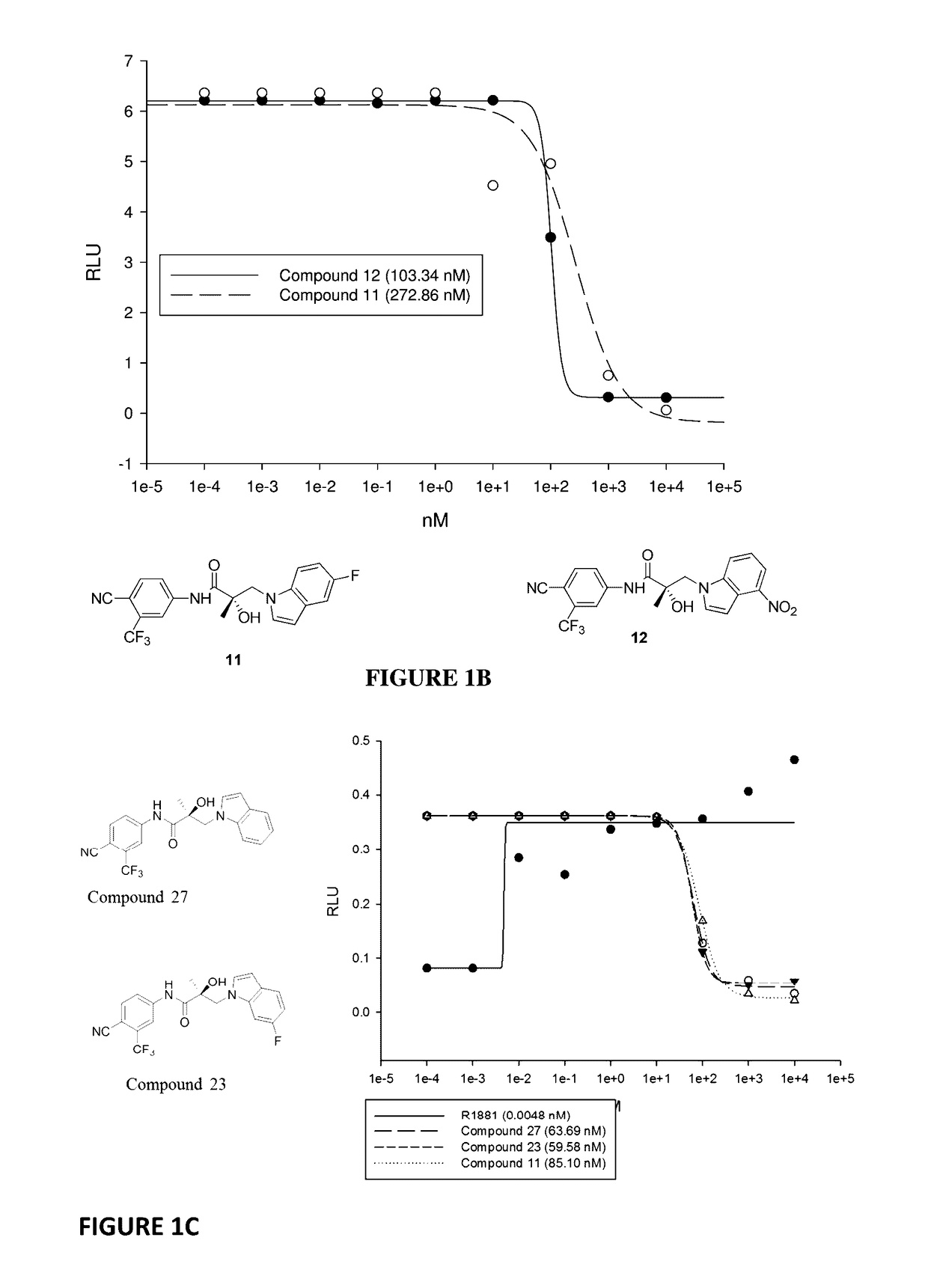
Patents
Literature
94 results about "Resistance mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
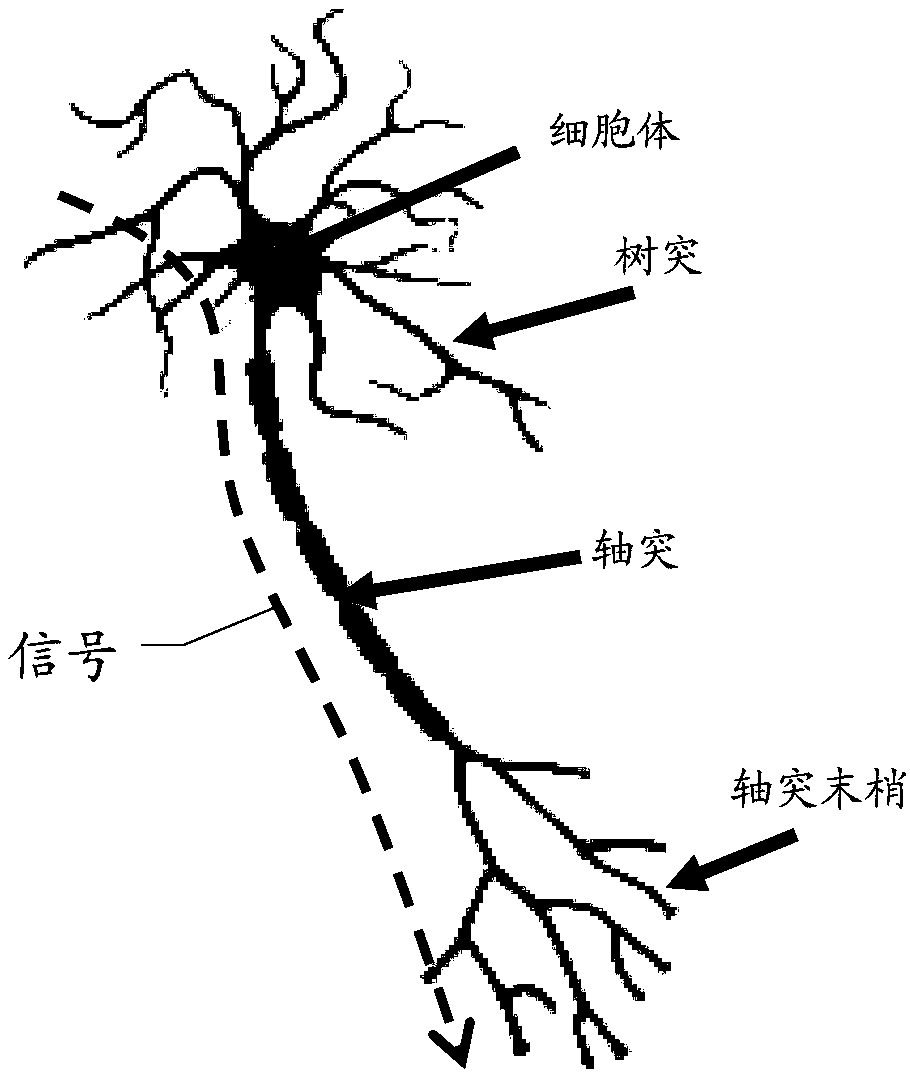
A resistance mutation is a mutation in a virus gene that allows the virus to become resistant to treatment with a particular antiviral drug. The term was first used in the management of HIV, the first virus in which genome sequencing was routinely used to look for drug resistance. At the time of infection, a virus will infect and begin to replicate within a preliminary cell. As subsequent cells are infected, random mutations will occur in the viral genome. When these mutations begin to accumulate, antiviral methods will kill the wild type strain, but will not be able to kill one or many mutated forms of the original virus. At this point a resistance mutation has occurred because the new strain of virus is now resistant to the antiviral treatment that would have killed the original virus. Resistance mutations are evident and widely studied in HIV due to its high rate of mutation and prevalence in the general population. Resistance mutation is now studied in bacteriology and parasitology.
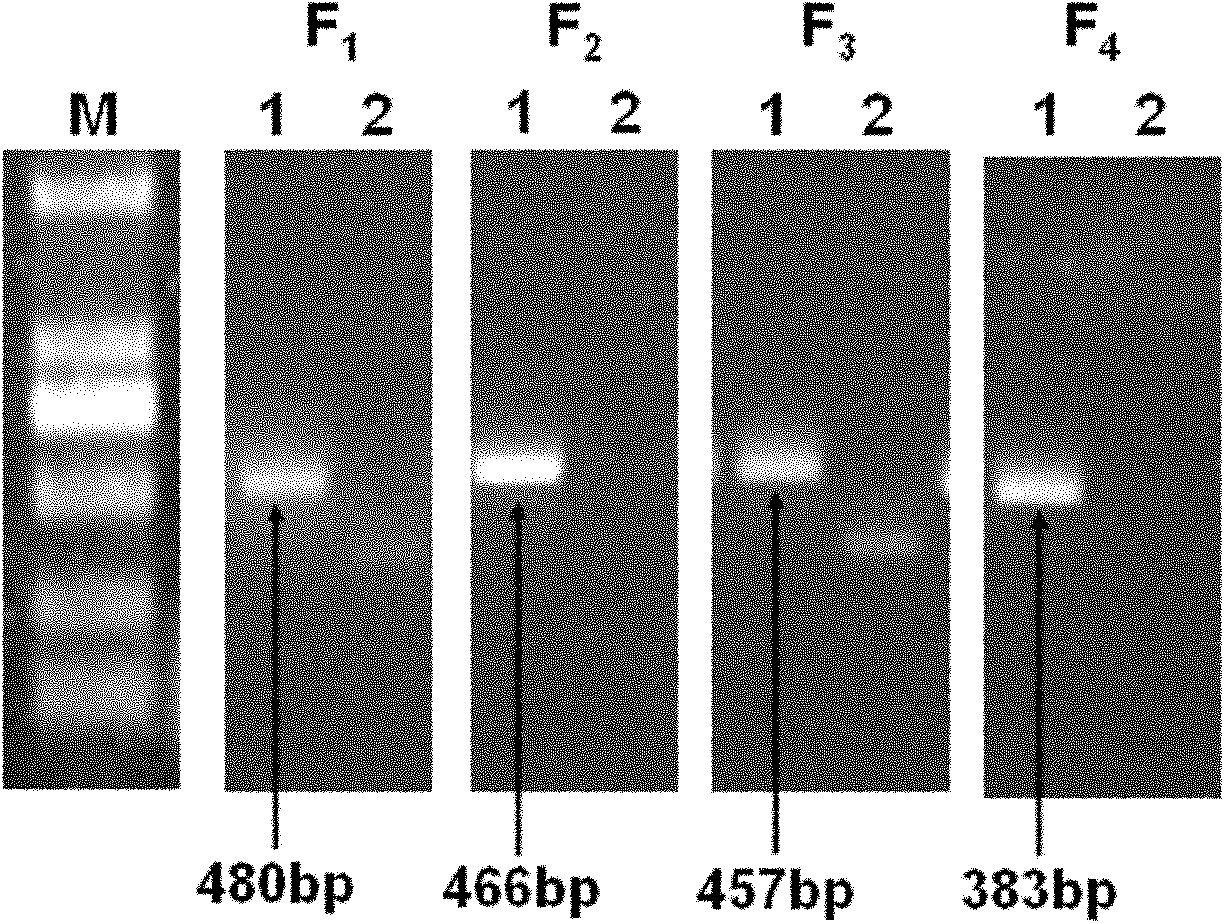
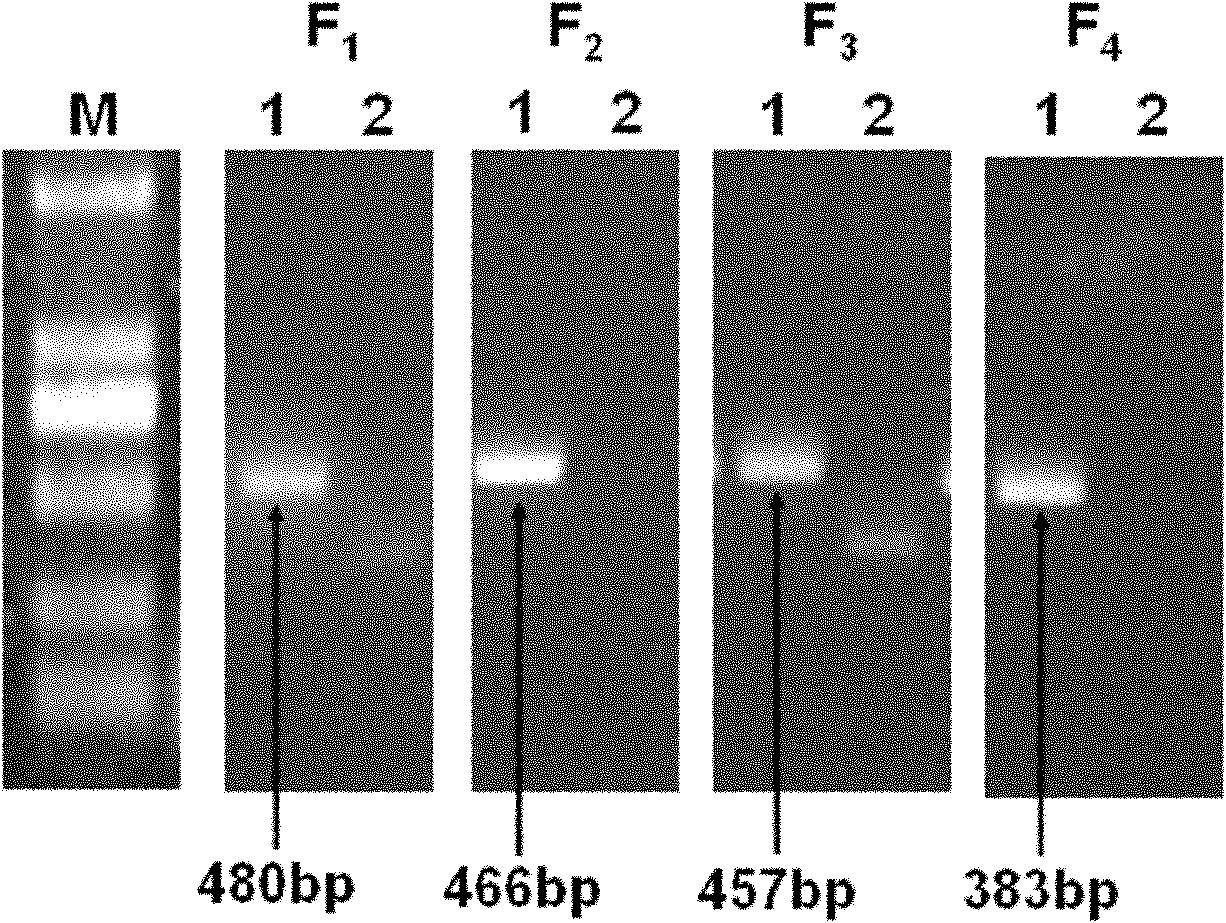
Primers and method for detecting drug resistance mutation site of hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN102181575AEasy to operateImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesResistance mutationHepatitis B virus
The invention discloses primers and a method for detecting a drug resistance mutation site of hepatitis B virus. The invention provides four pairs of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers for detecting the drug resistance mutation site of the hepatitis B virus, the four pairs of the PCR primers are used for amplifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a genome of the hepatitis B virus, and obtained four fragments are covered on the whole reverse transcriptase gene sequence of the hepatitis B virus in the overlapping way. The four PCR fragments are mixed according to the equal molar ratio for preparing a reverse transcriptase gene bank, 454 high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis are performed, and whether the hepatitis B virus in a blood serum sample of a patient with the hepatitis B virus contains the drug resistance mutation site or not can be detected. By adopting the primers and the method, above 1% of drug resistance mutation of the hepatitis B virus in blood serum of the patient can be detected, the method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simpleness in operation, large throughput and the like, and the analysis of the drug resistance mutation site of a plurality of samples can be performed by sequencing once.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
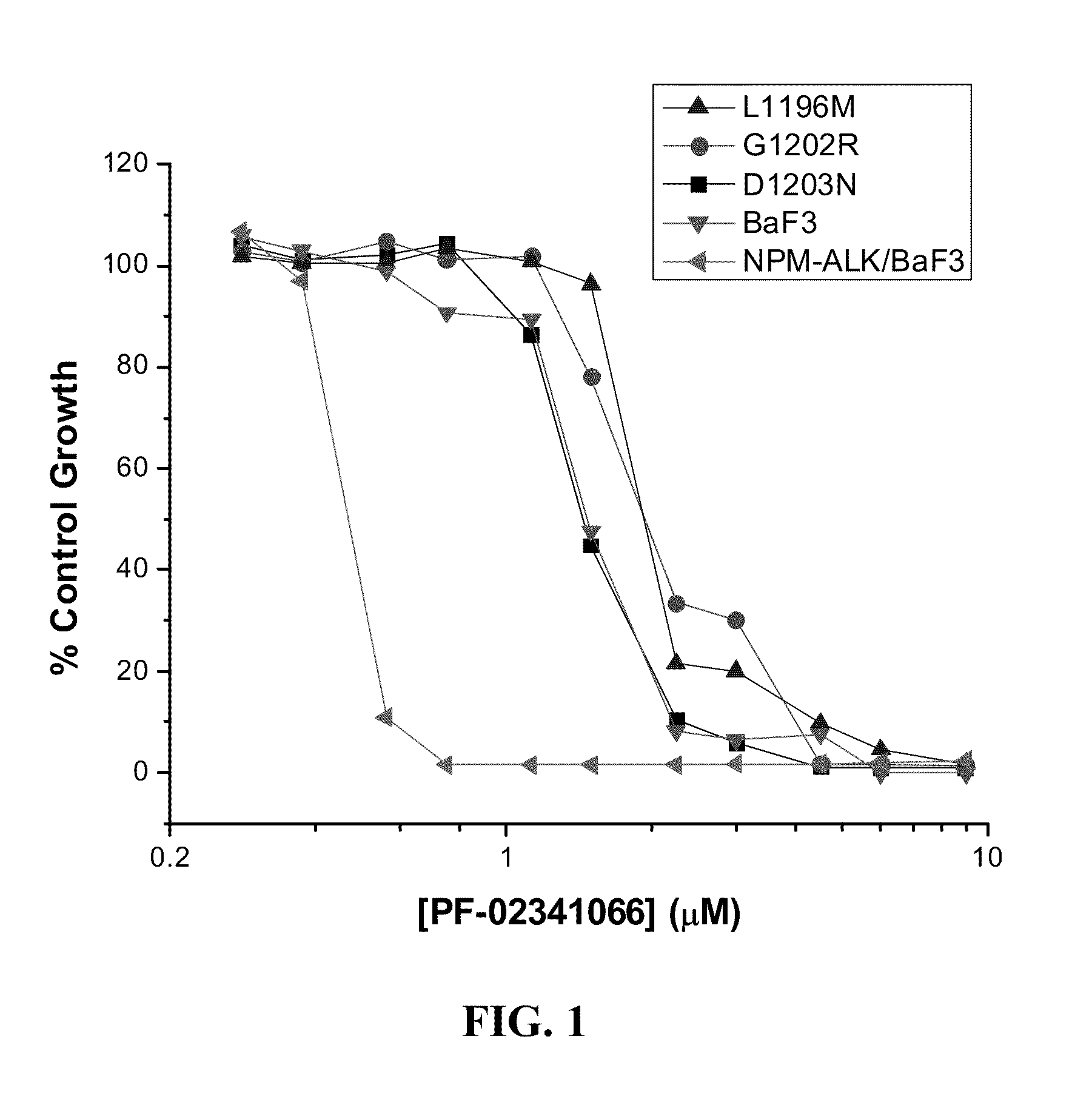
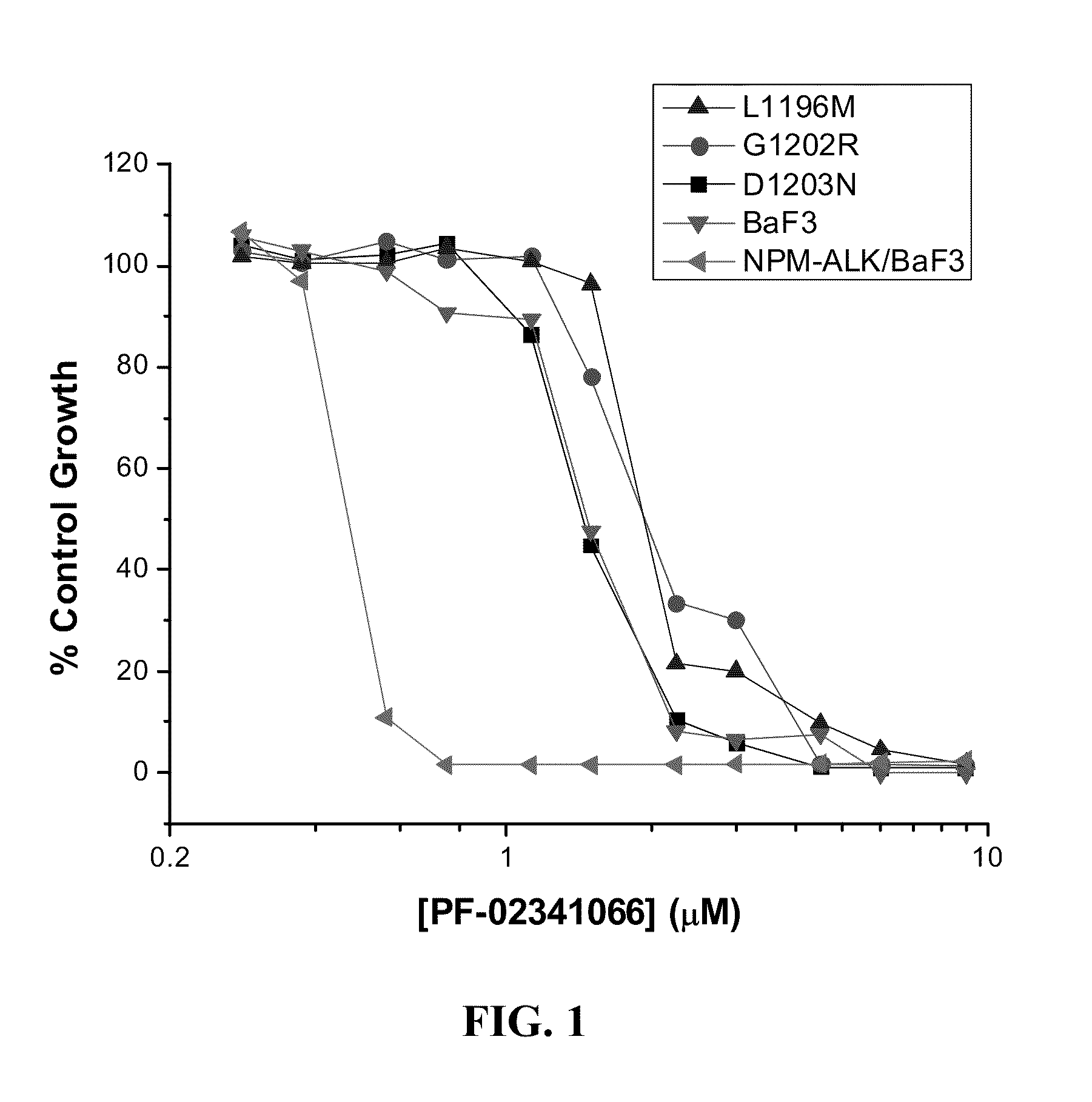
Methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer resistant to anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) kinase inhibitors
Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of a cancer that is resistant to at least one anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) kinase inhibitor are provided herein. The present invention is based on the discovery of mutations within ALK that confer resistance to at least one ALK kinase inhibitor. Polynucleotides and polypeptides having at least one ALK inhibitor resistance mutation are provided and find use in methods and compositions useful in the diagnosis, prognosis, and / or treatment of diseases associated with aberrant ALK activity, more particularly, those that are resistant to at least one ALK kinase inhibitors. Methods and compositions are also provided for the identification of agents that can inhibit the kinase activity and / or reduce the expression level of the ALK resistance mutants.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Unit cell fungus, engineering fungus prepared through motion ferment and application
InactiveCN1600850ALess quantityIncreased conversion efficiency to ethanolBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementResistance mutationBiology
This invention relates to motion fermentation monocell engineering bacterium, its prepn. method and its application in fermentation for producing ethanol. In the prepn. of said engineering bacterium, the resistance gene of tetracycline is inserted into glucose-fructose oxide-erductase gene of motion fermentation monocell baterium XW101, endo zyme being used for digesting said recombination plasmid to form linear plasmid, after the transformation of motion fermentation monocell bacterium XW101, screening the strain having tetracycline resistance mutation. Carbon source is used as substrate, with this inventive engineering bacterium to produce ethanol with high ethanol prodn. yield and less by-produt-sorbicolan.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
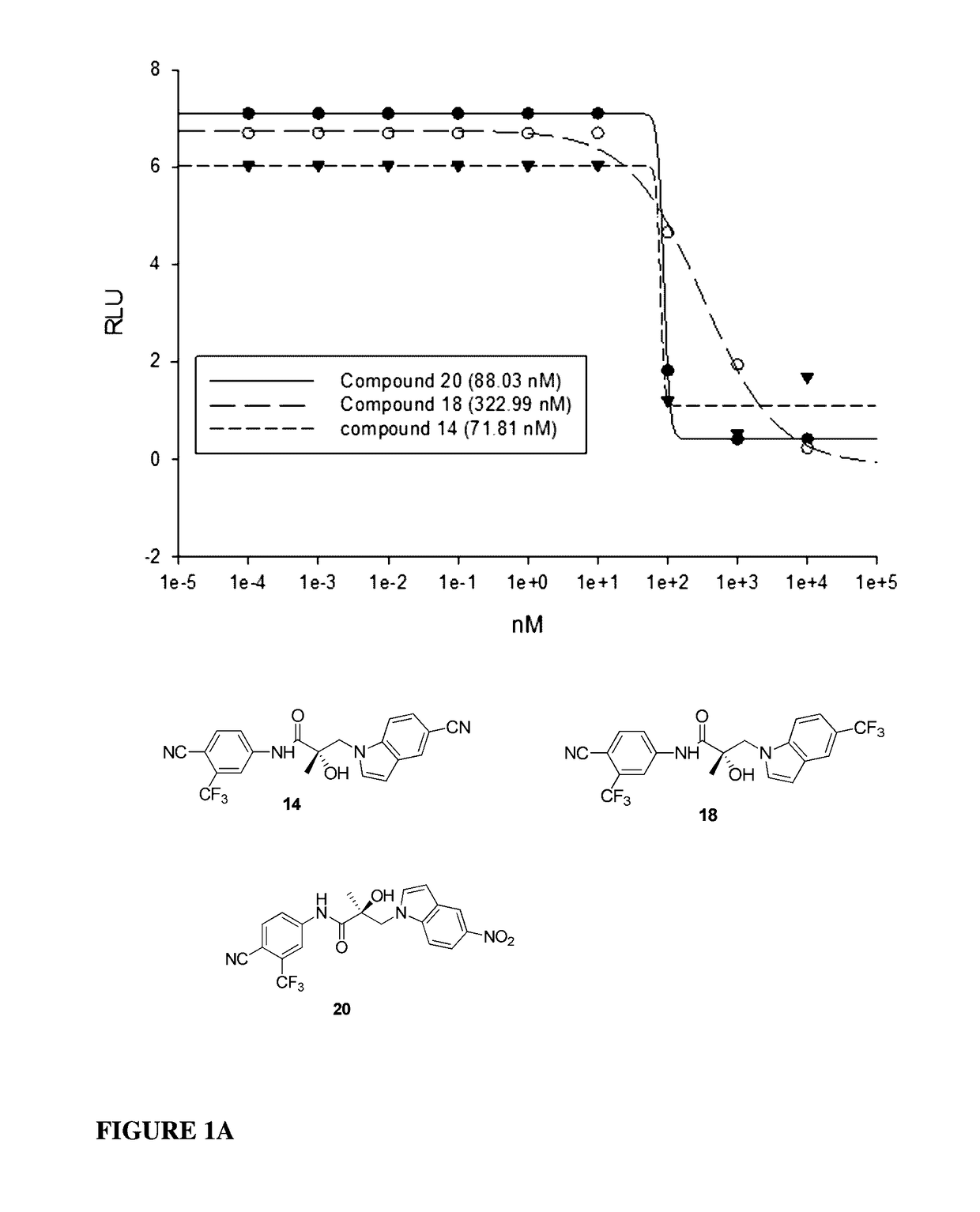
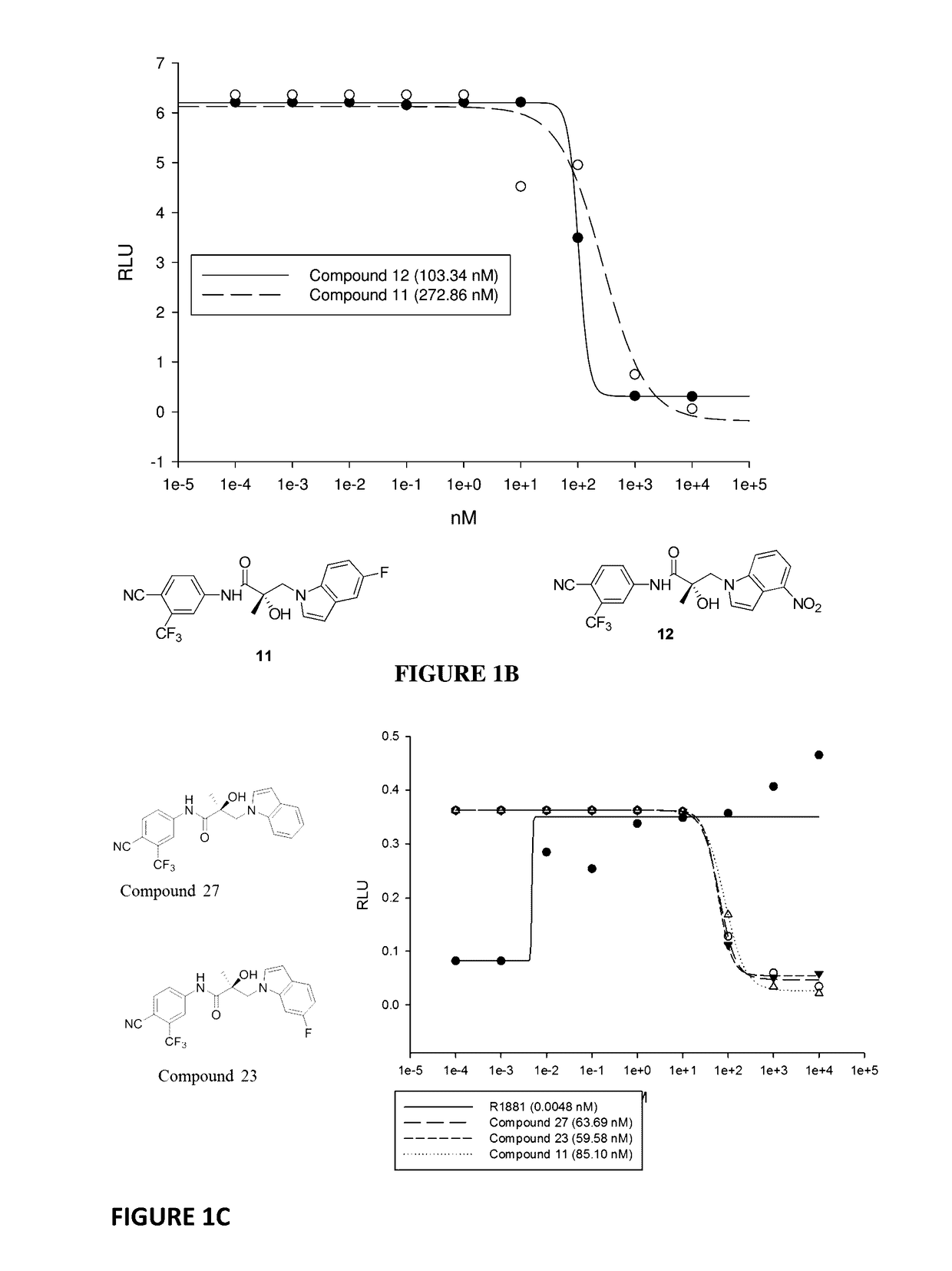
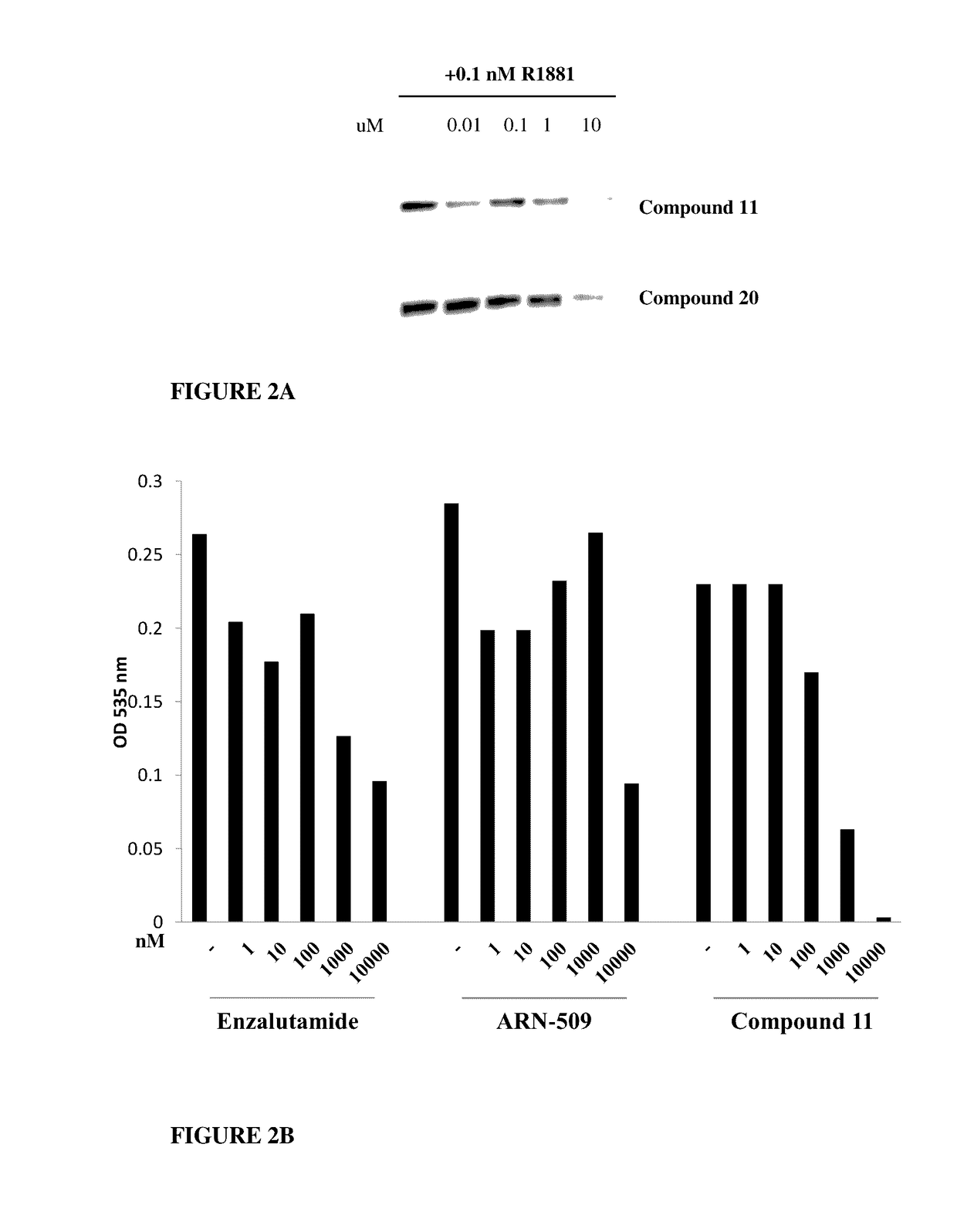
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20170095446A1Improve survivalReduce morbidityOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismResistance mutationGlutamine
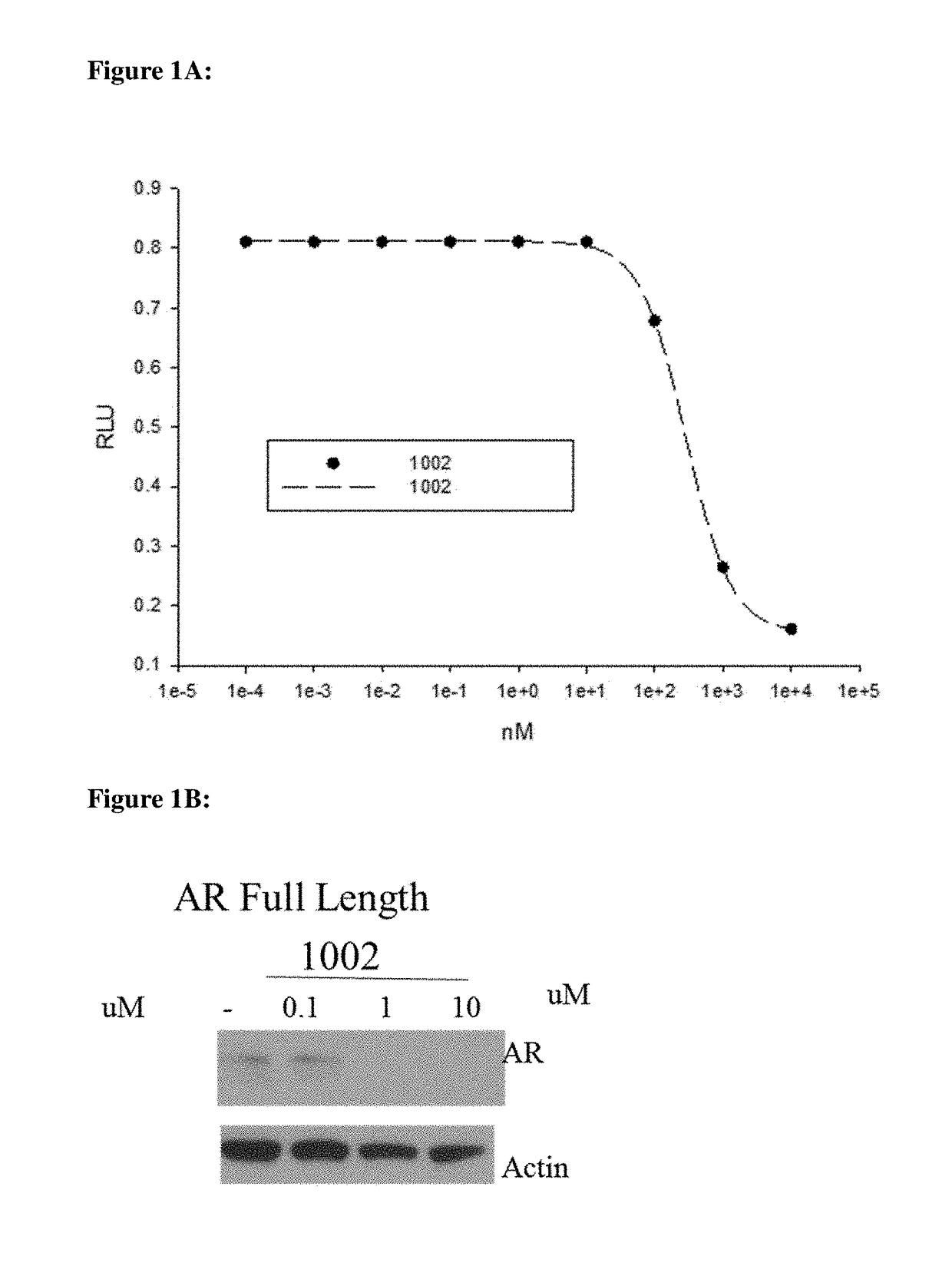
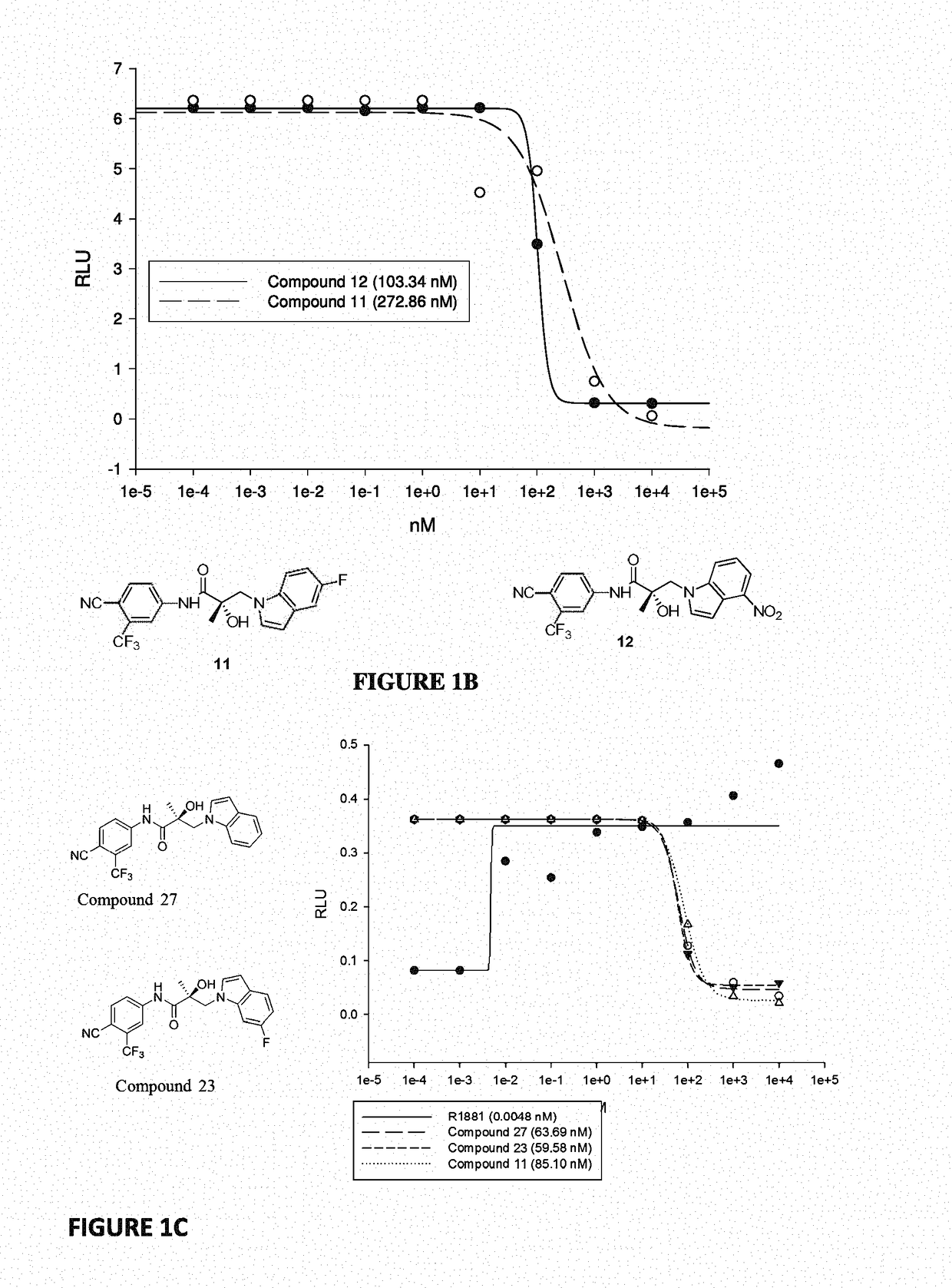
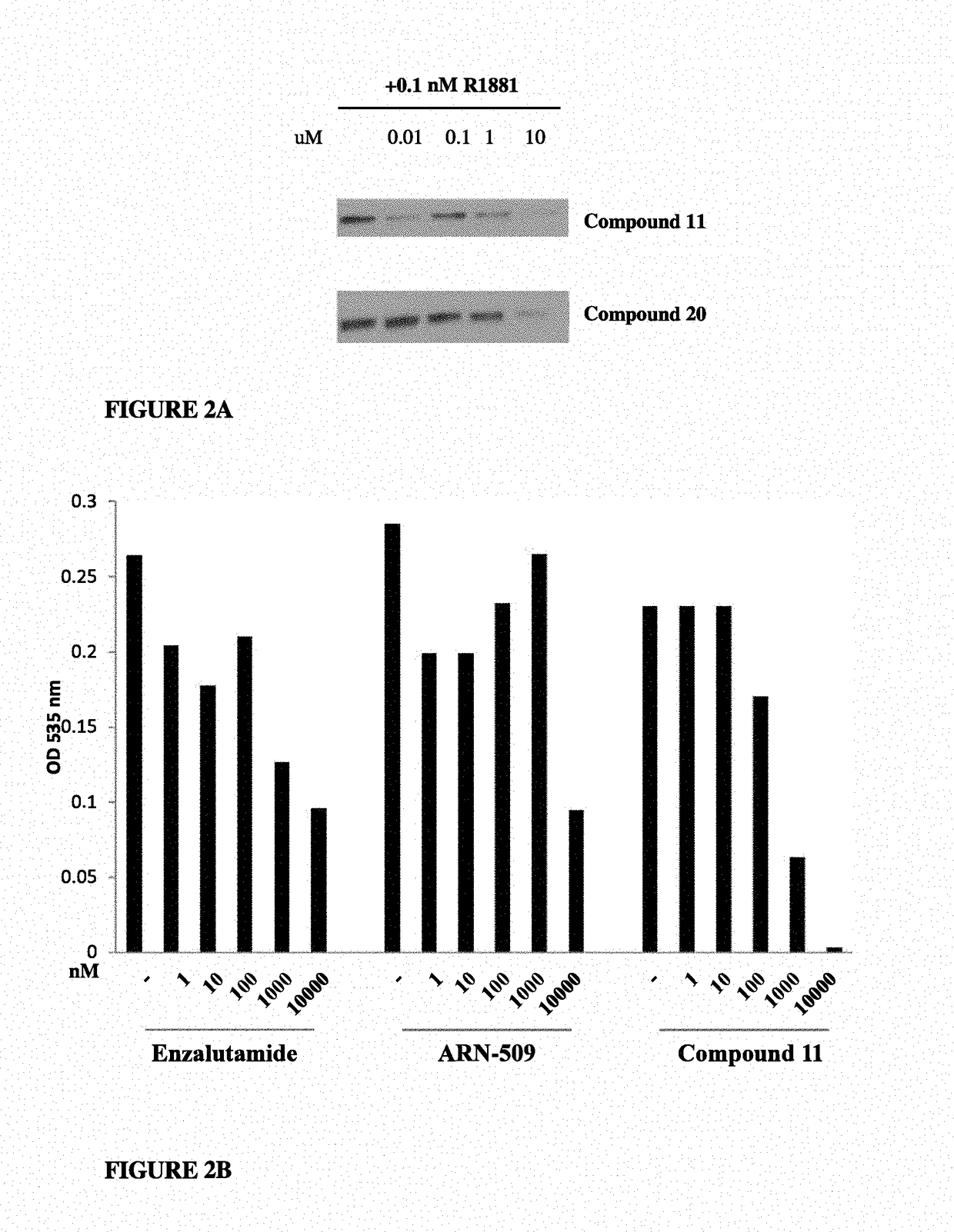
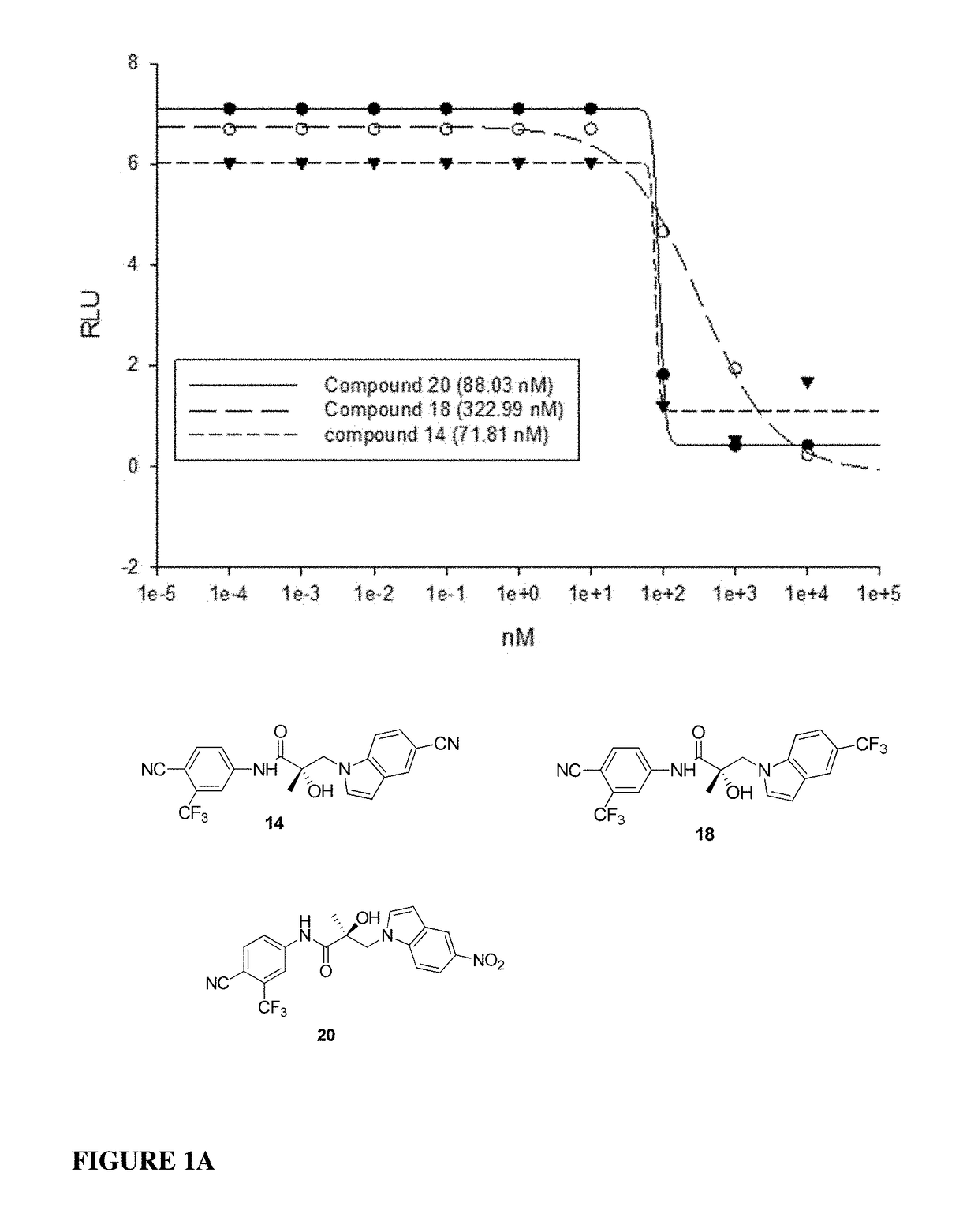
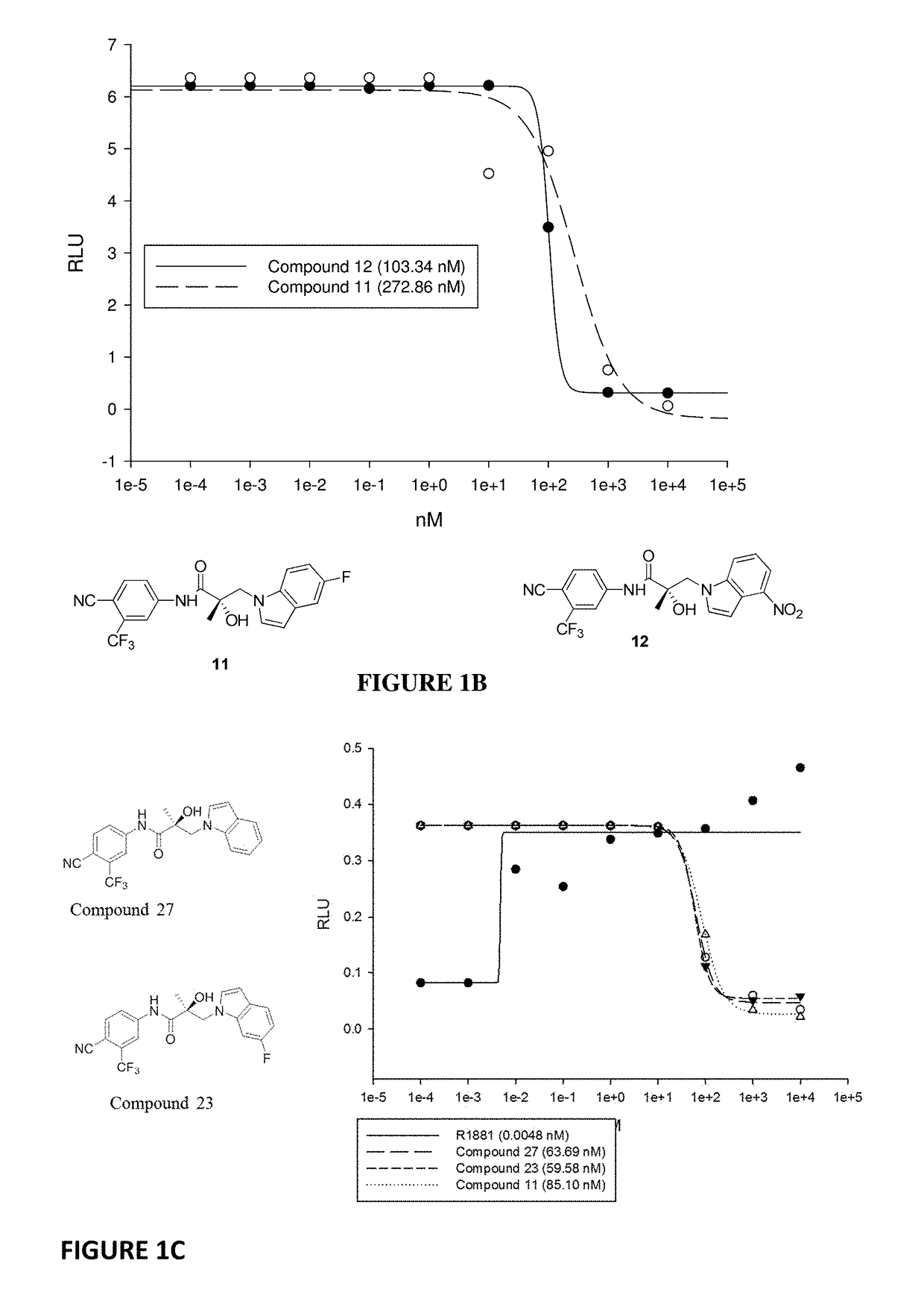
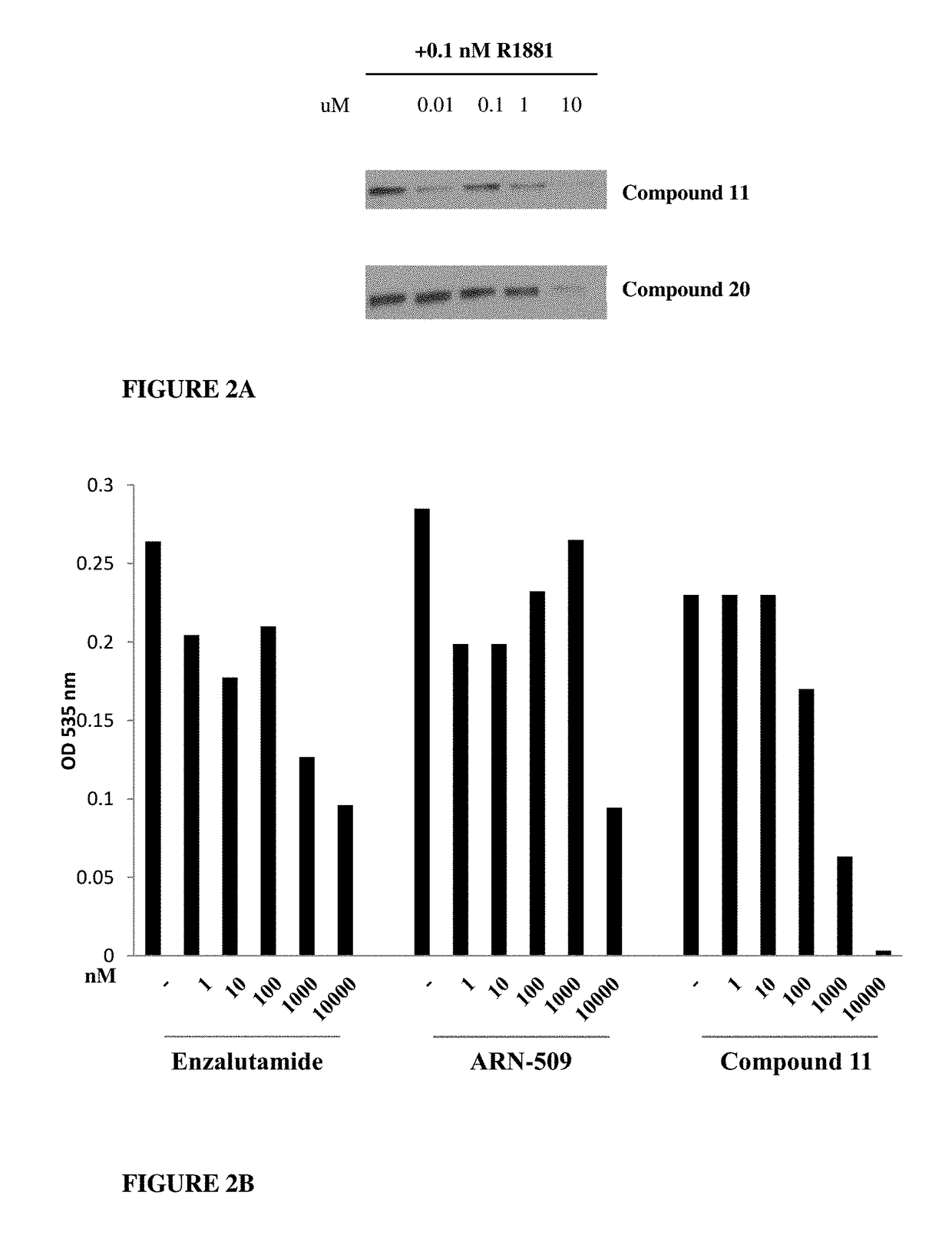
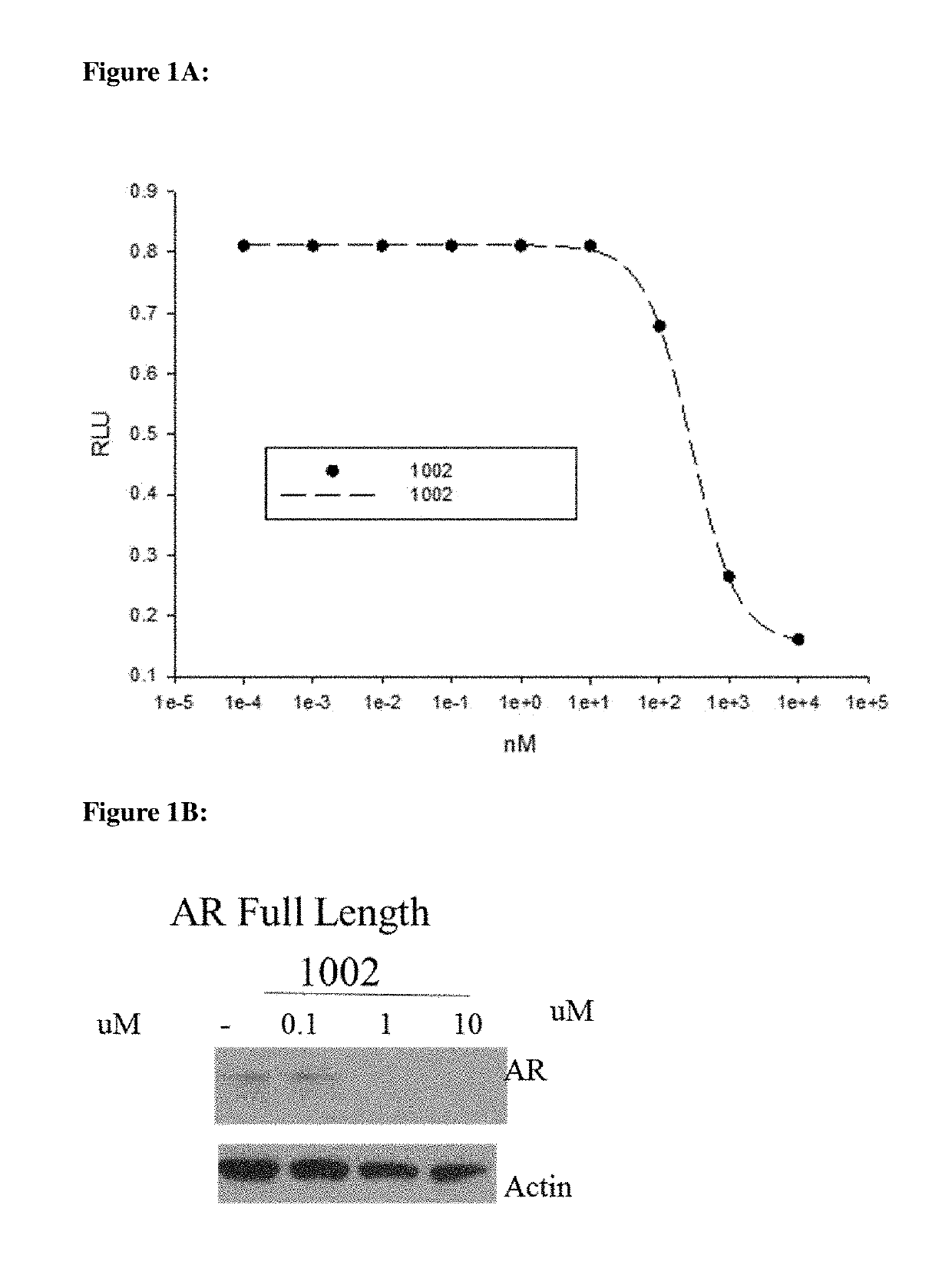
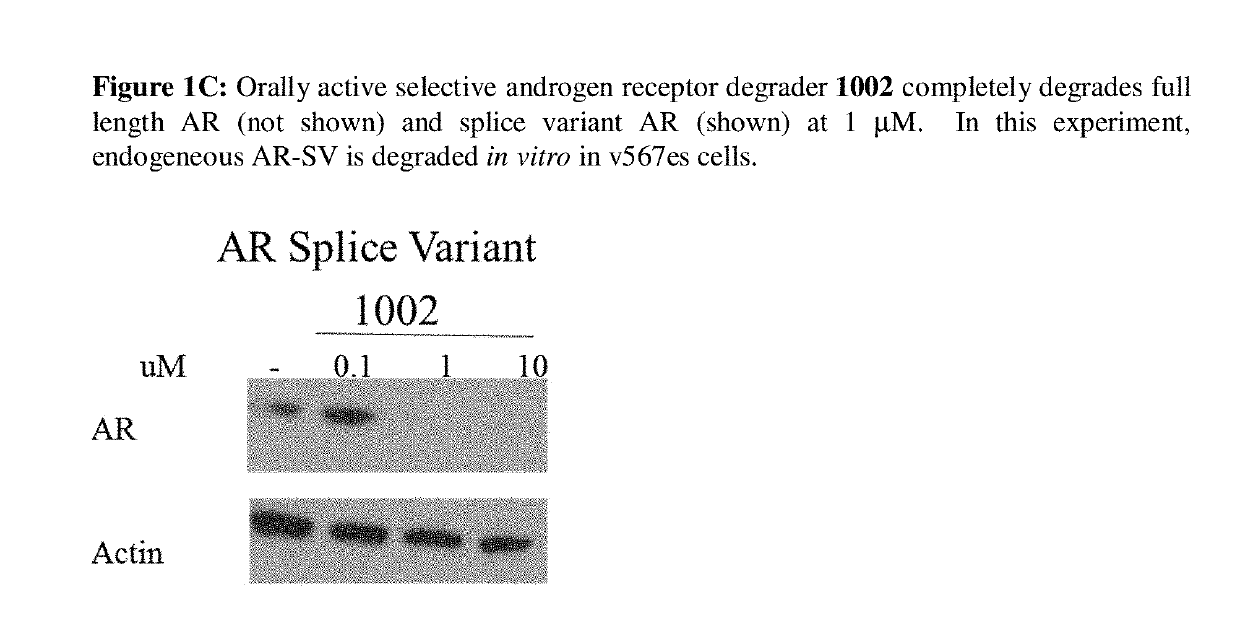
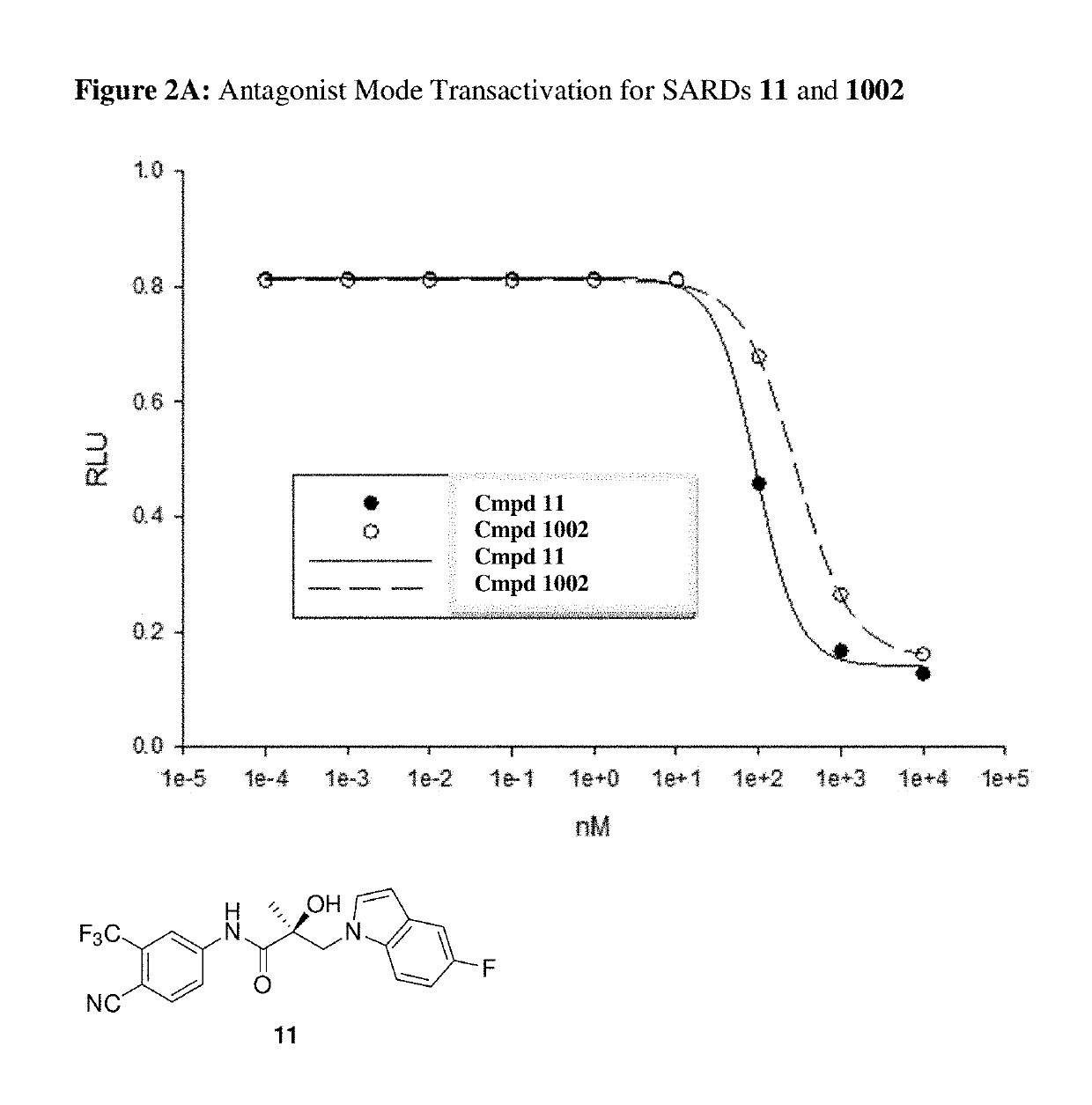
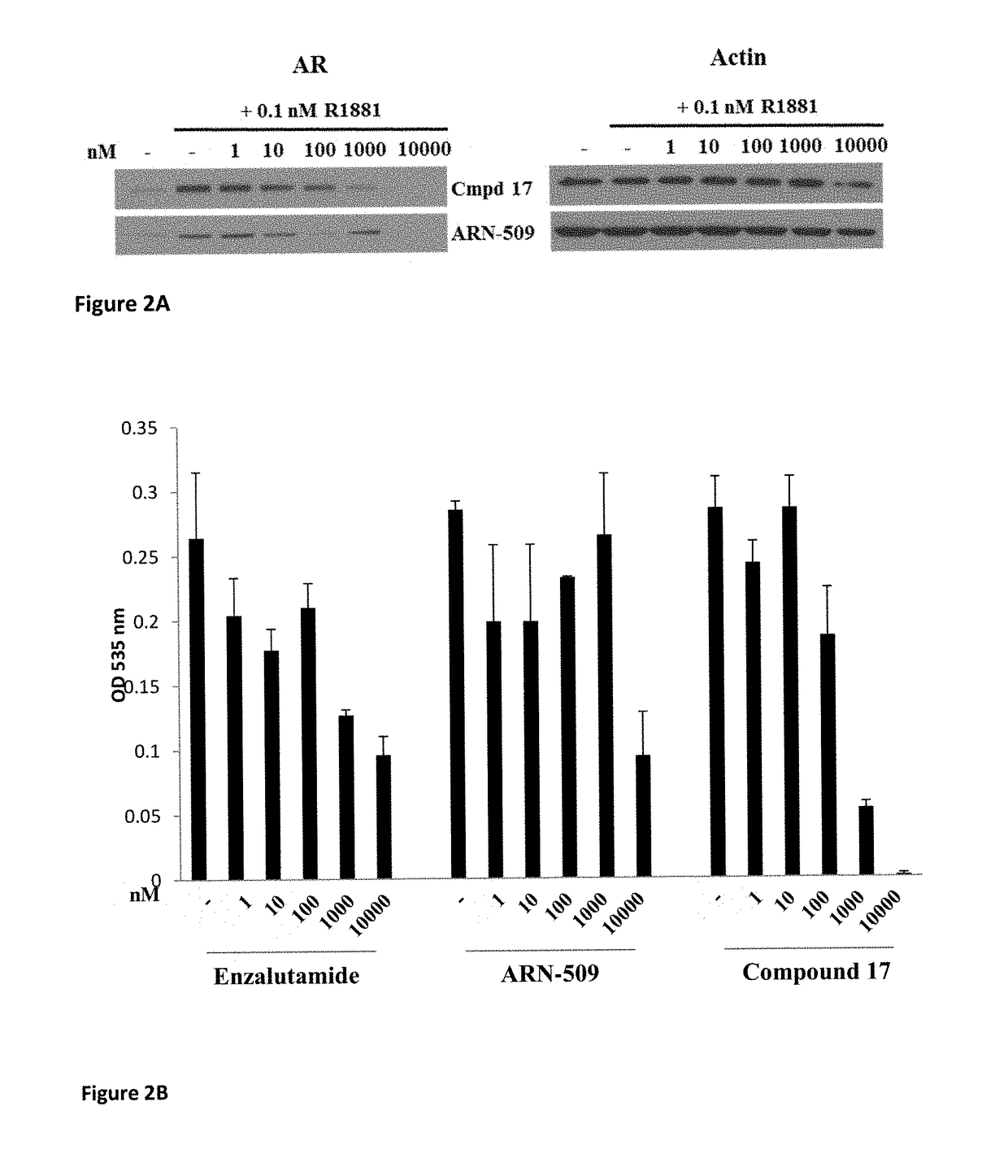
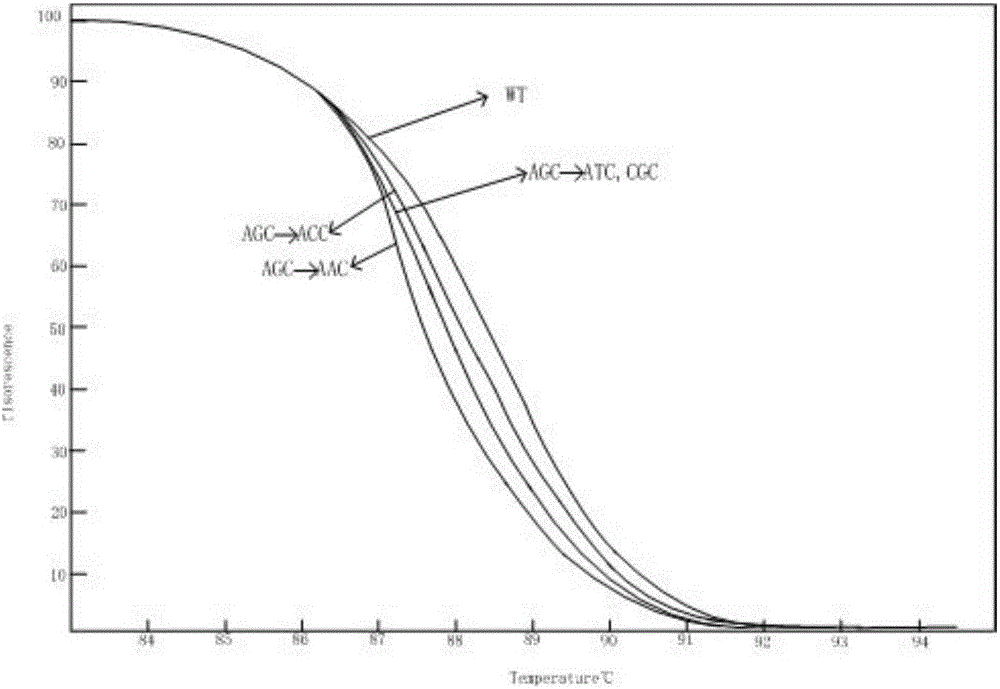
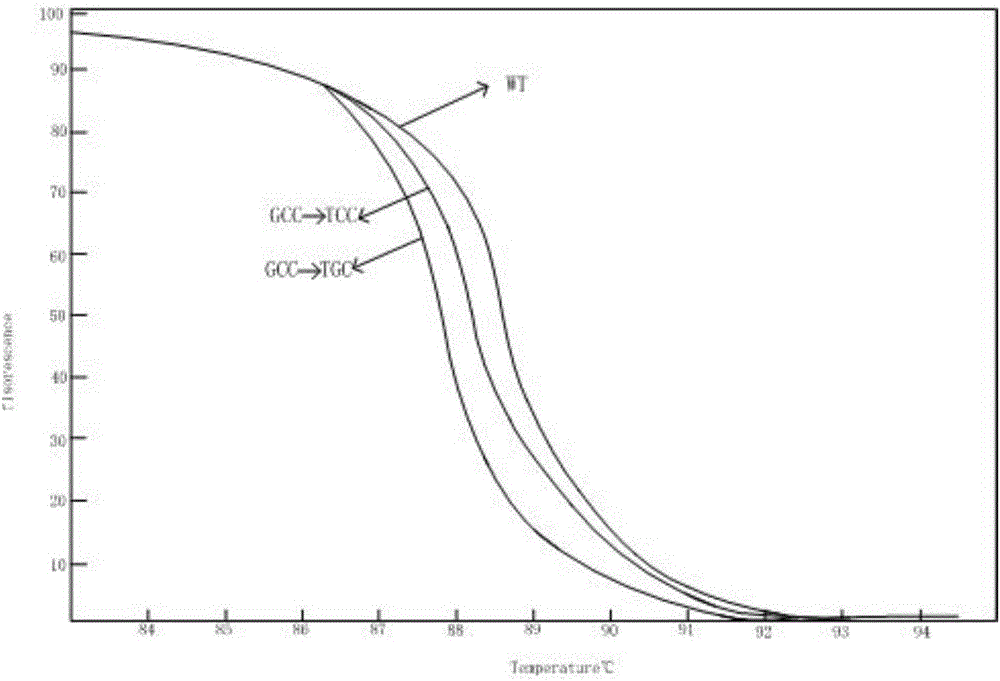
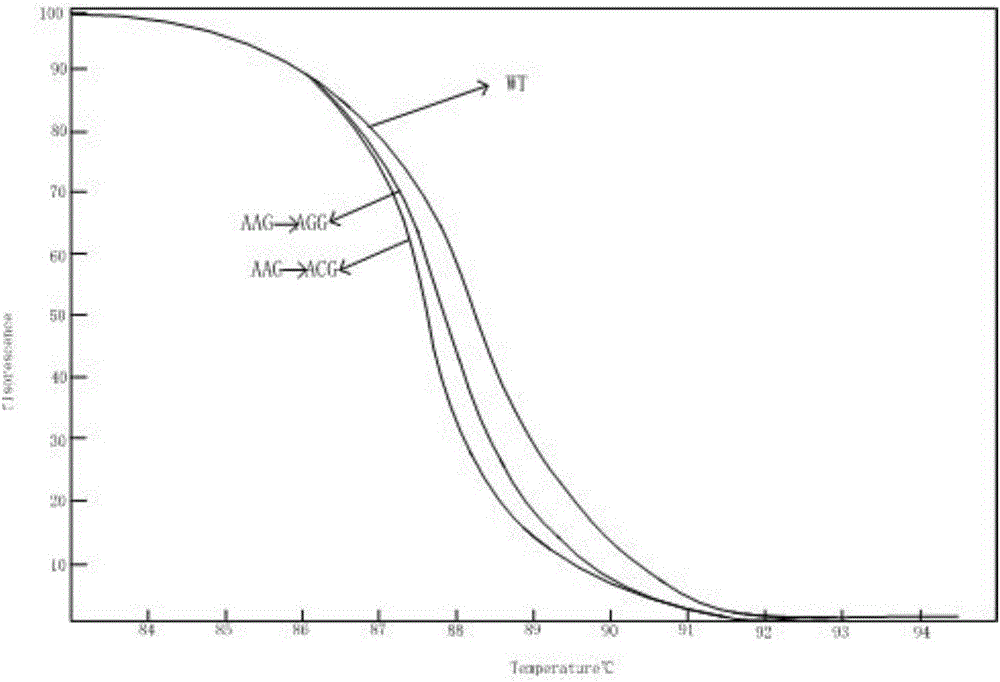
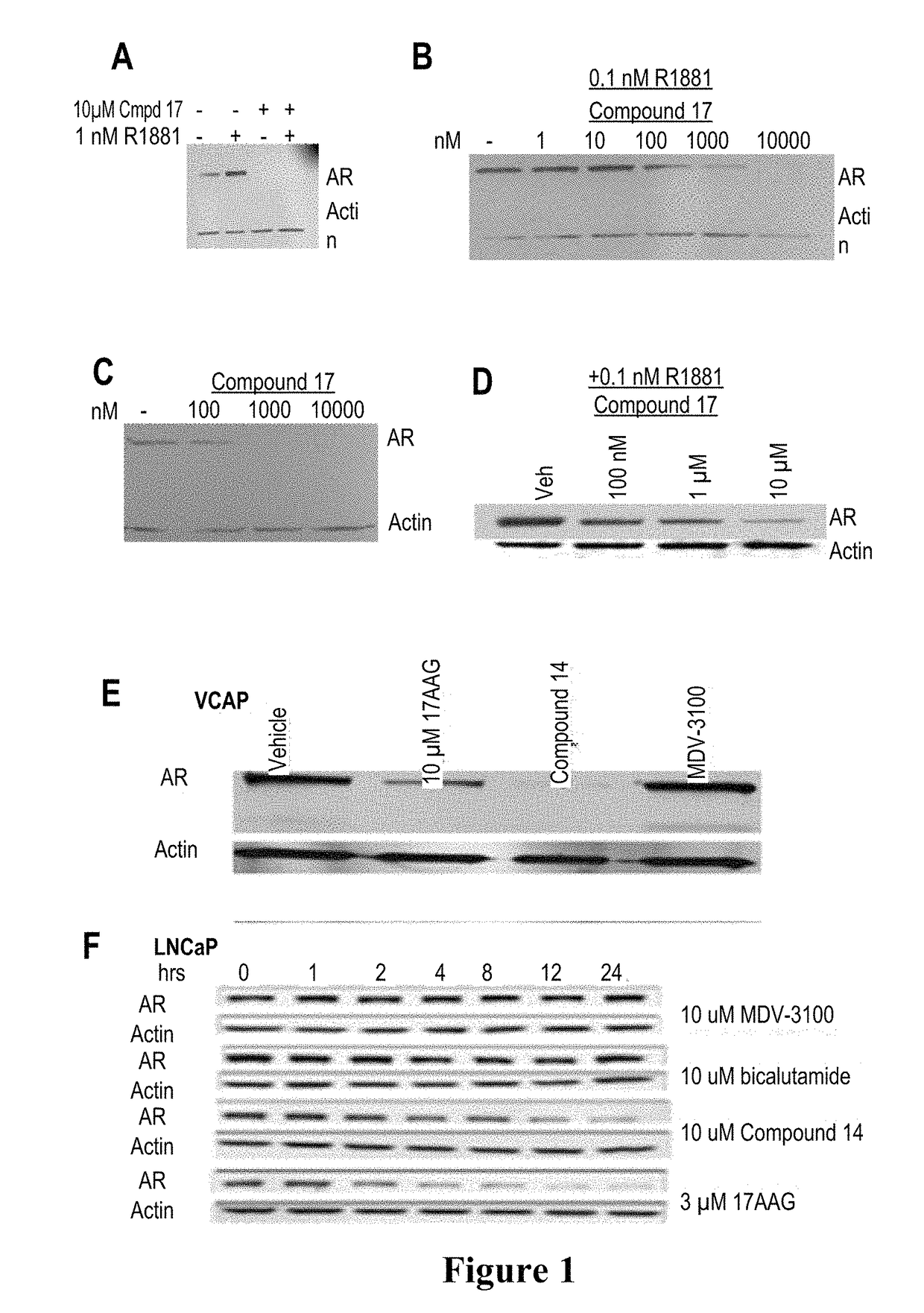
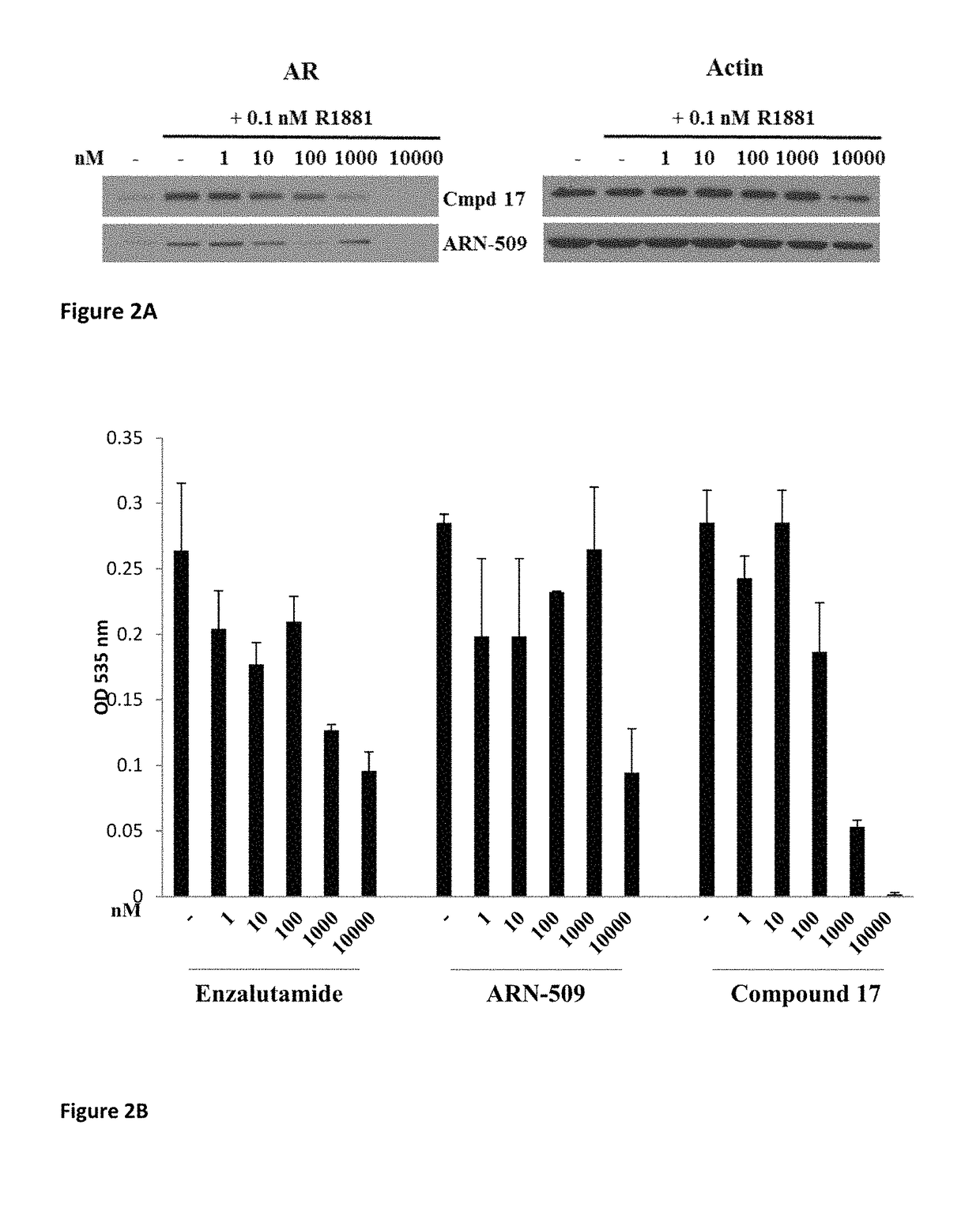
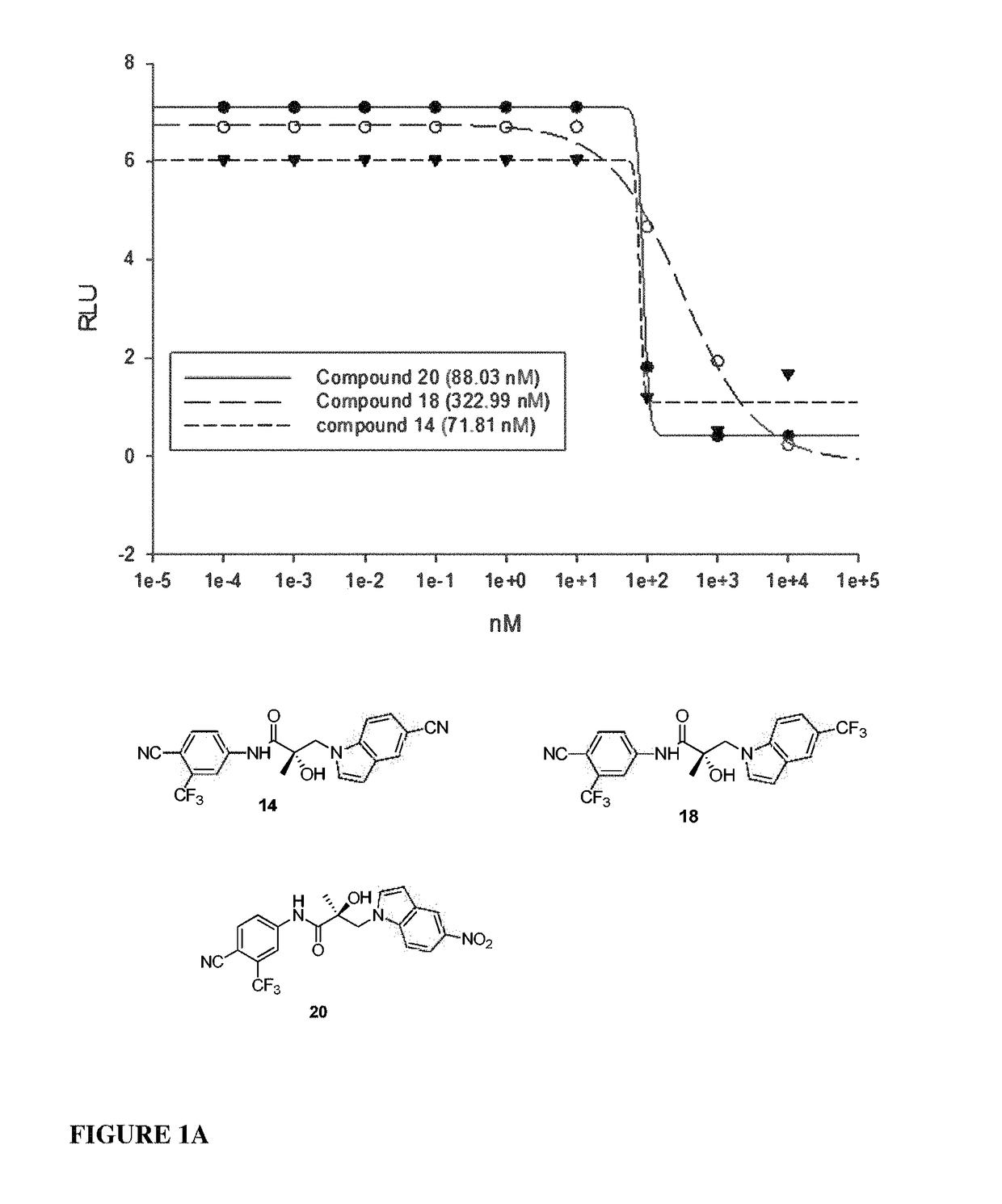
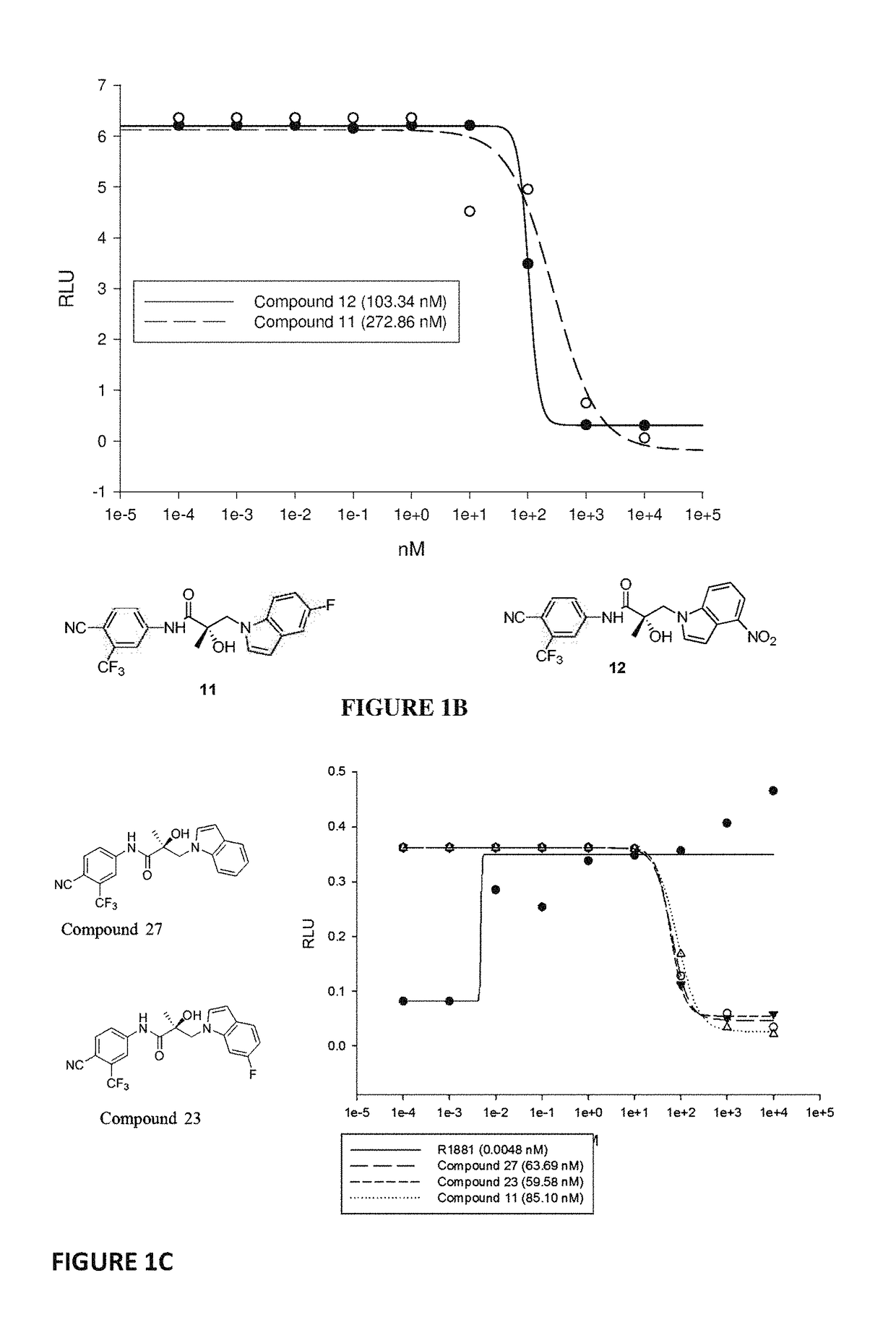
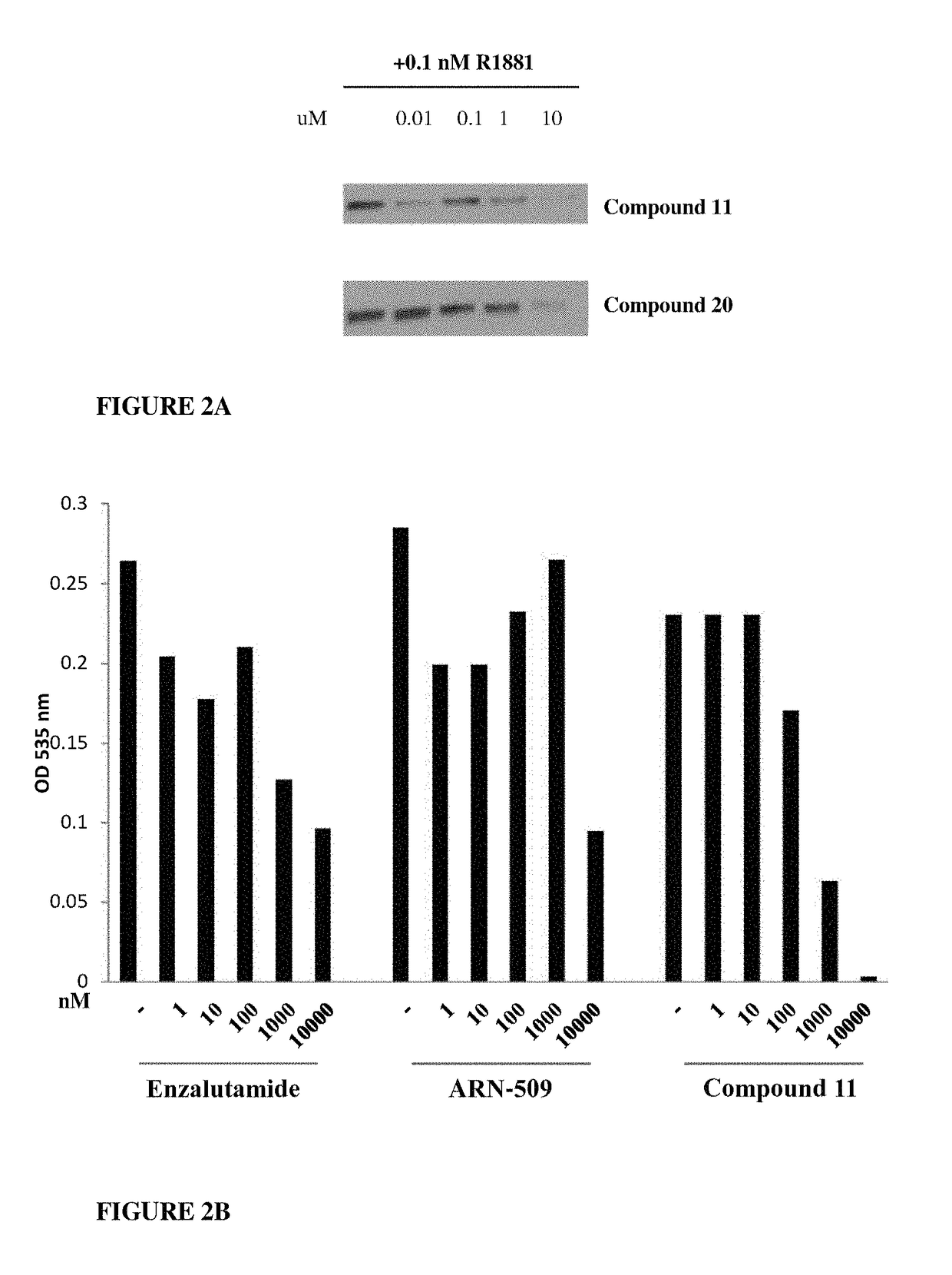
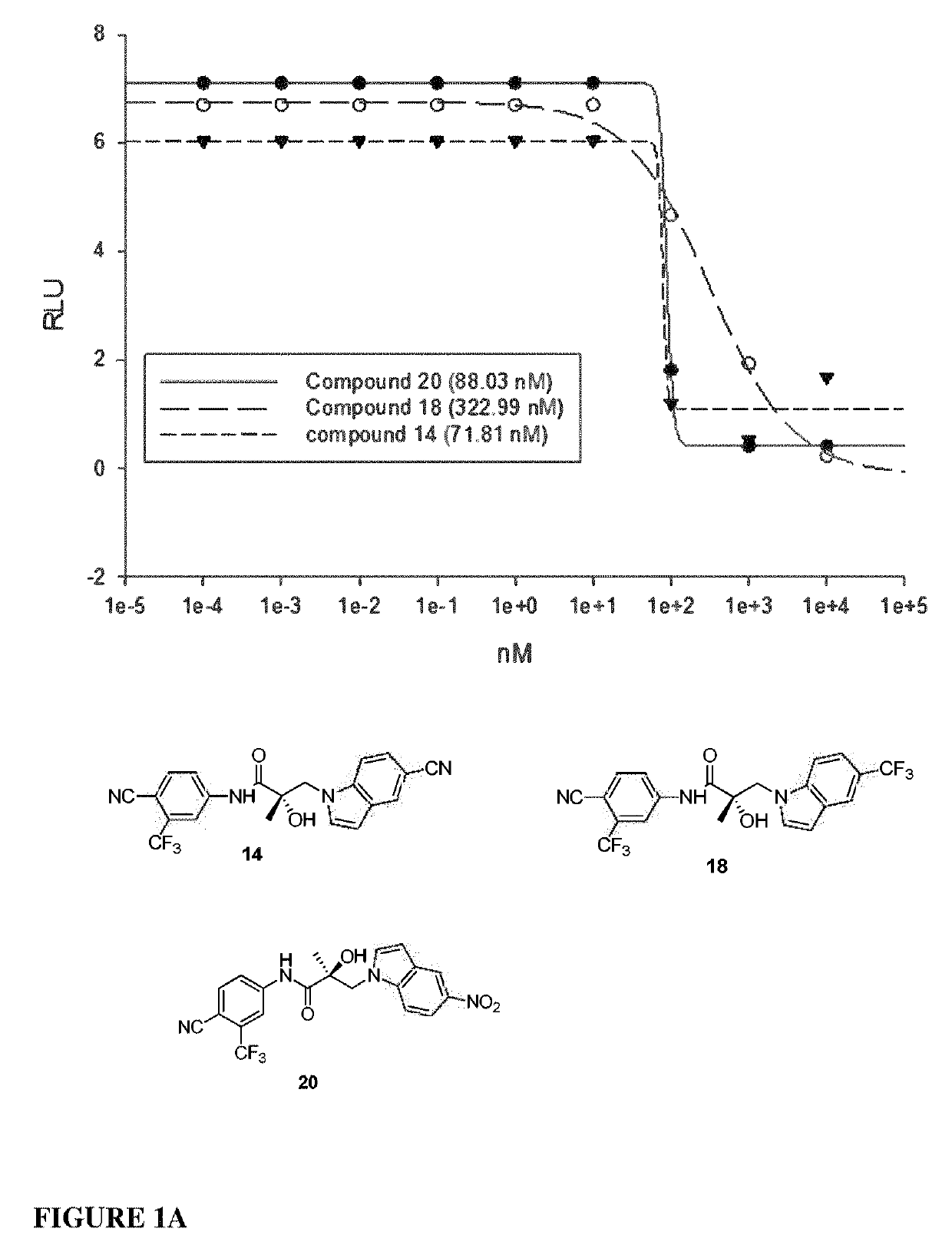
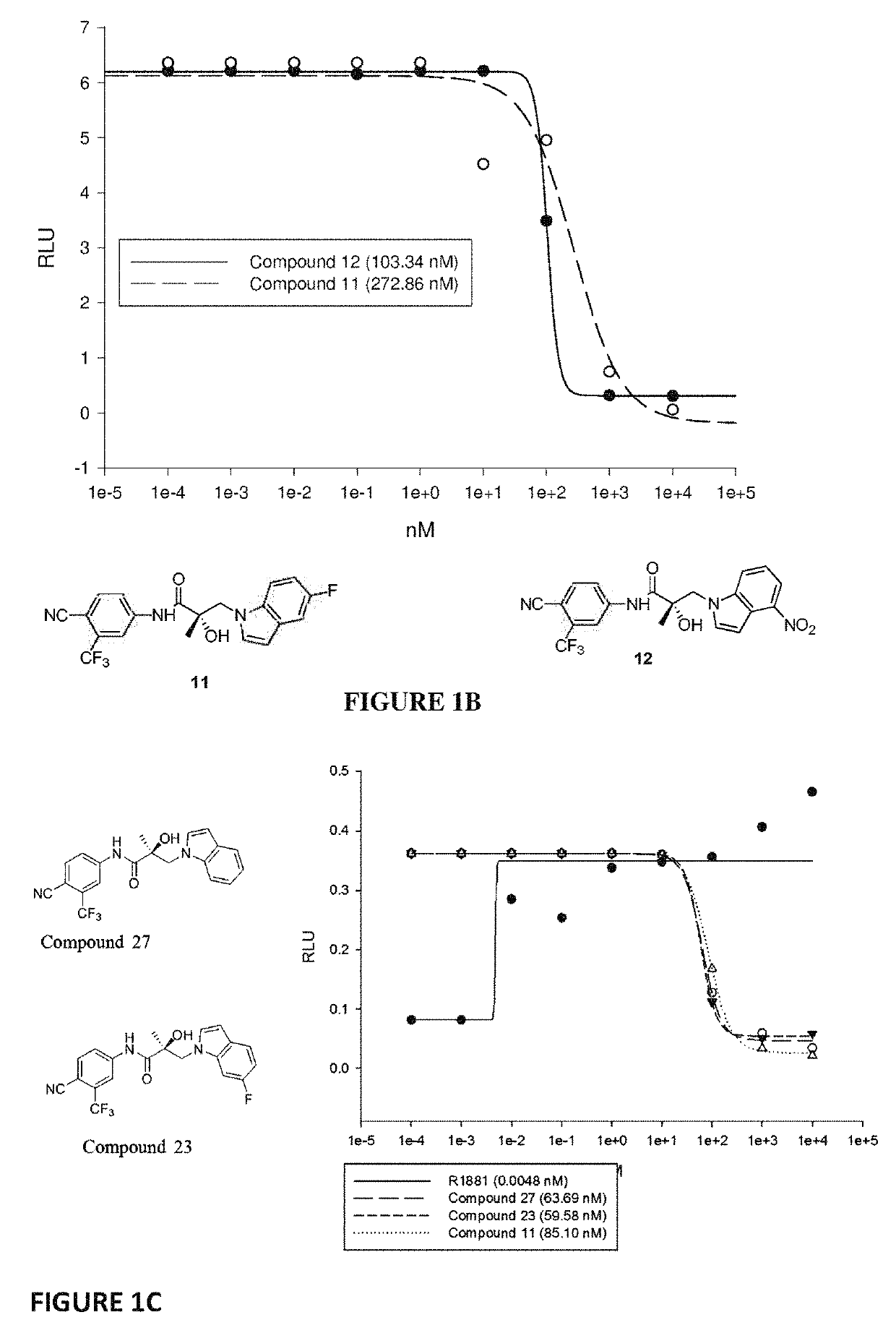
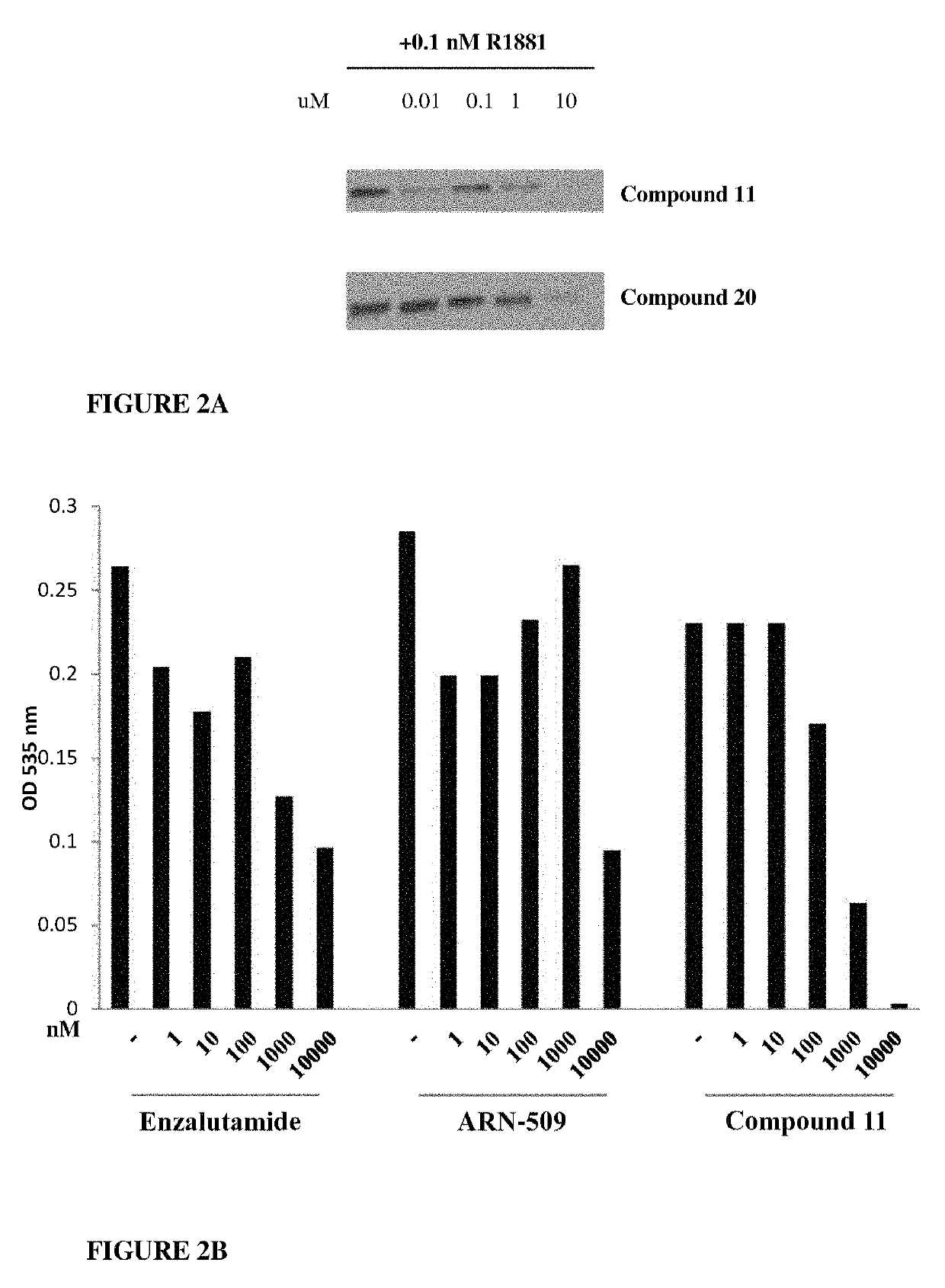
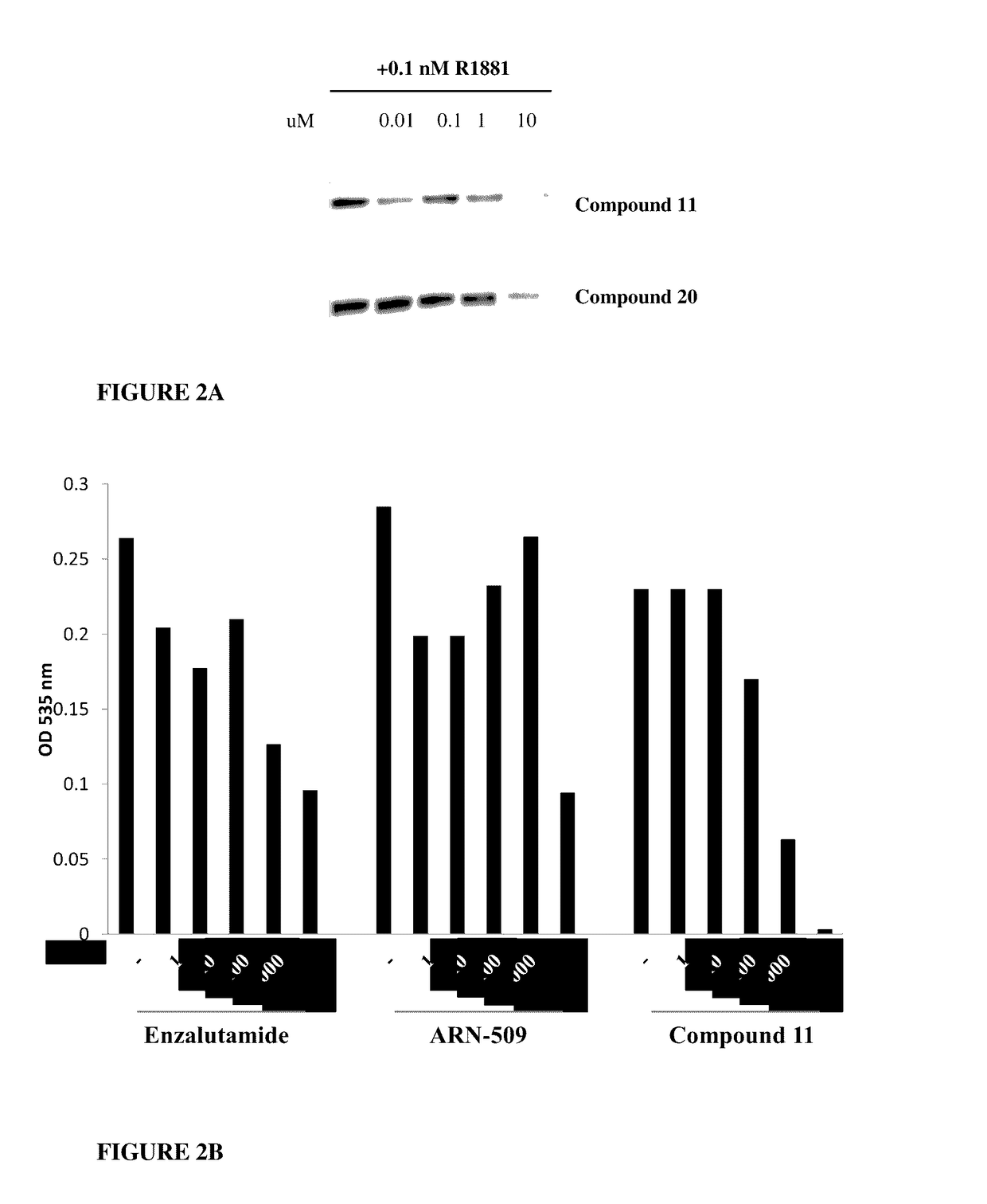
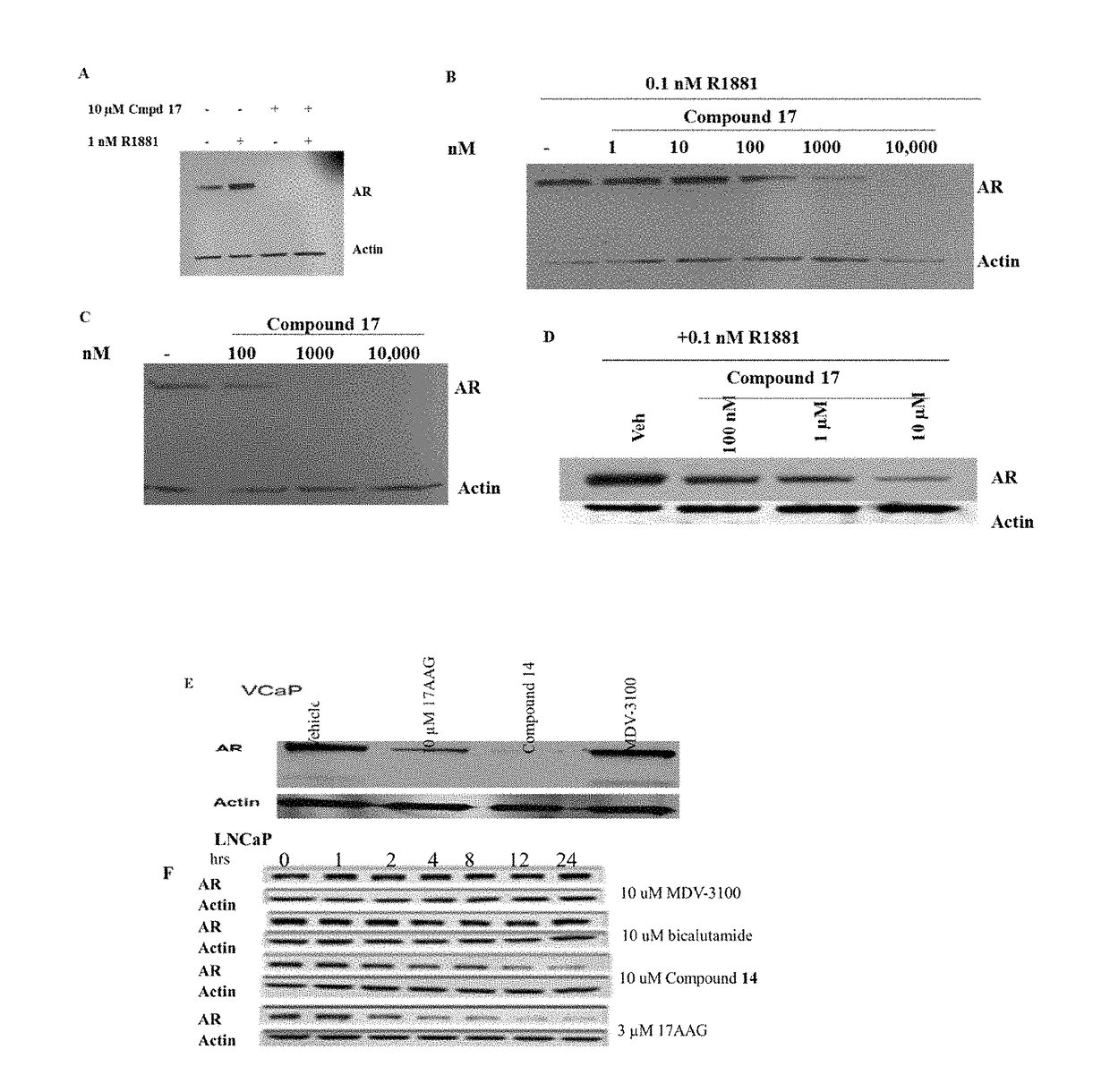
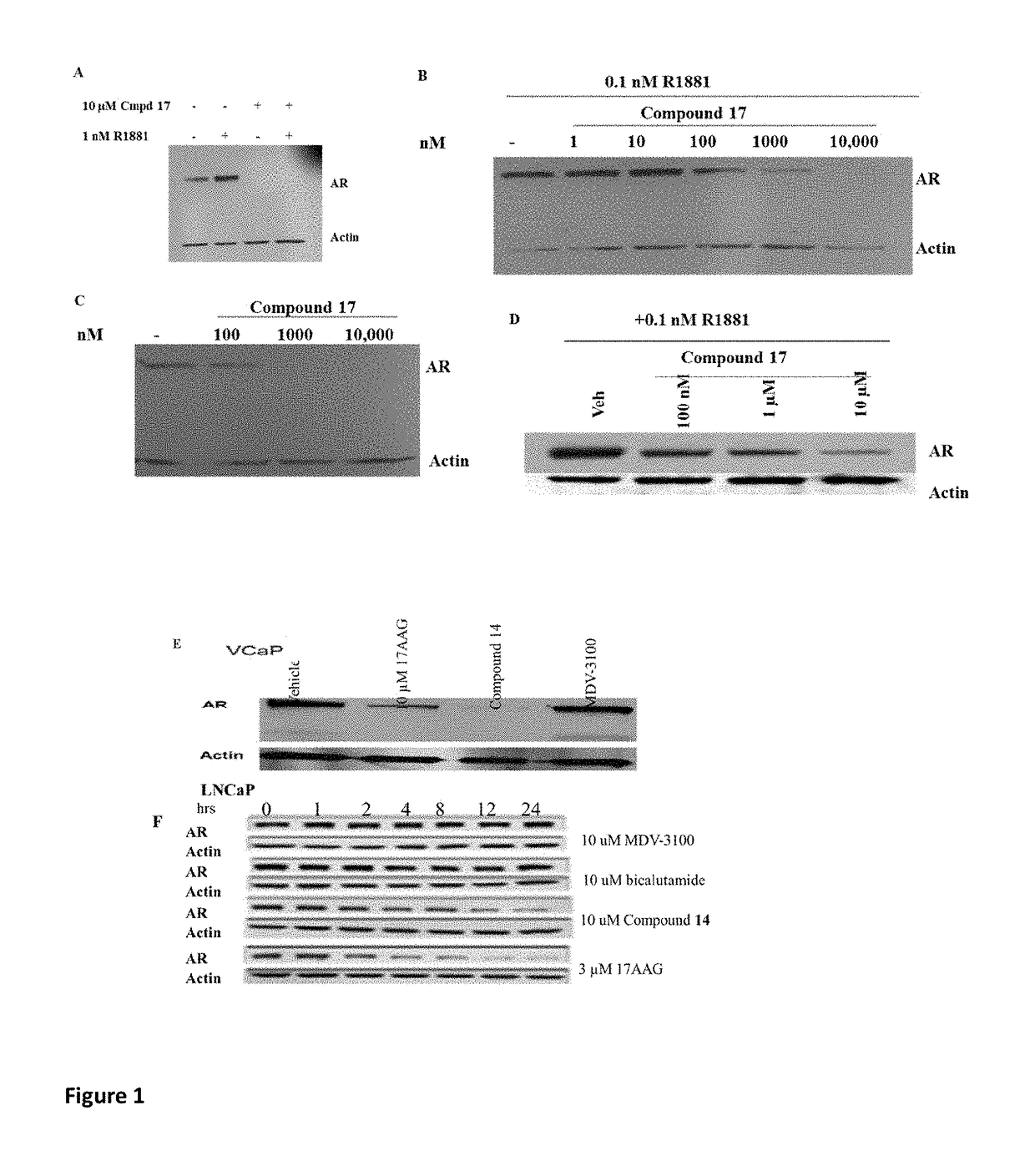
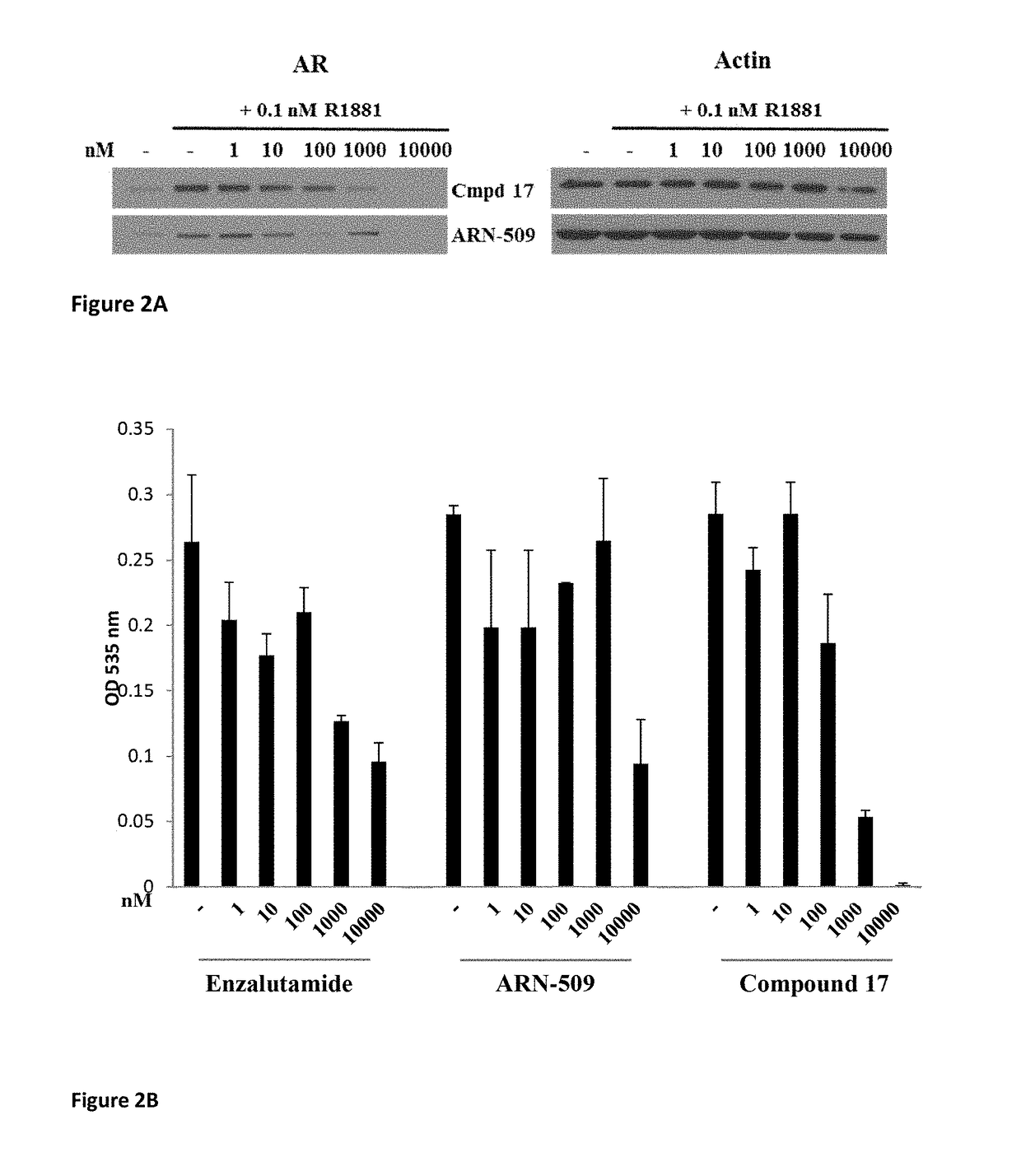
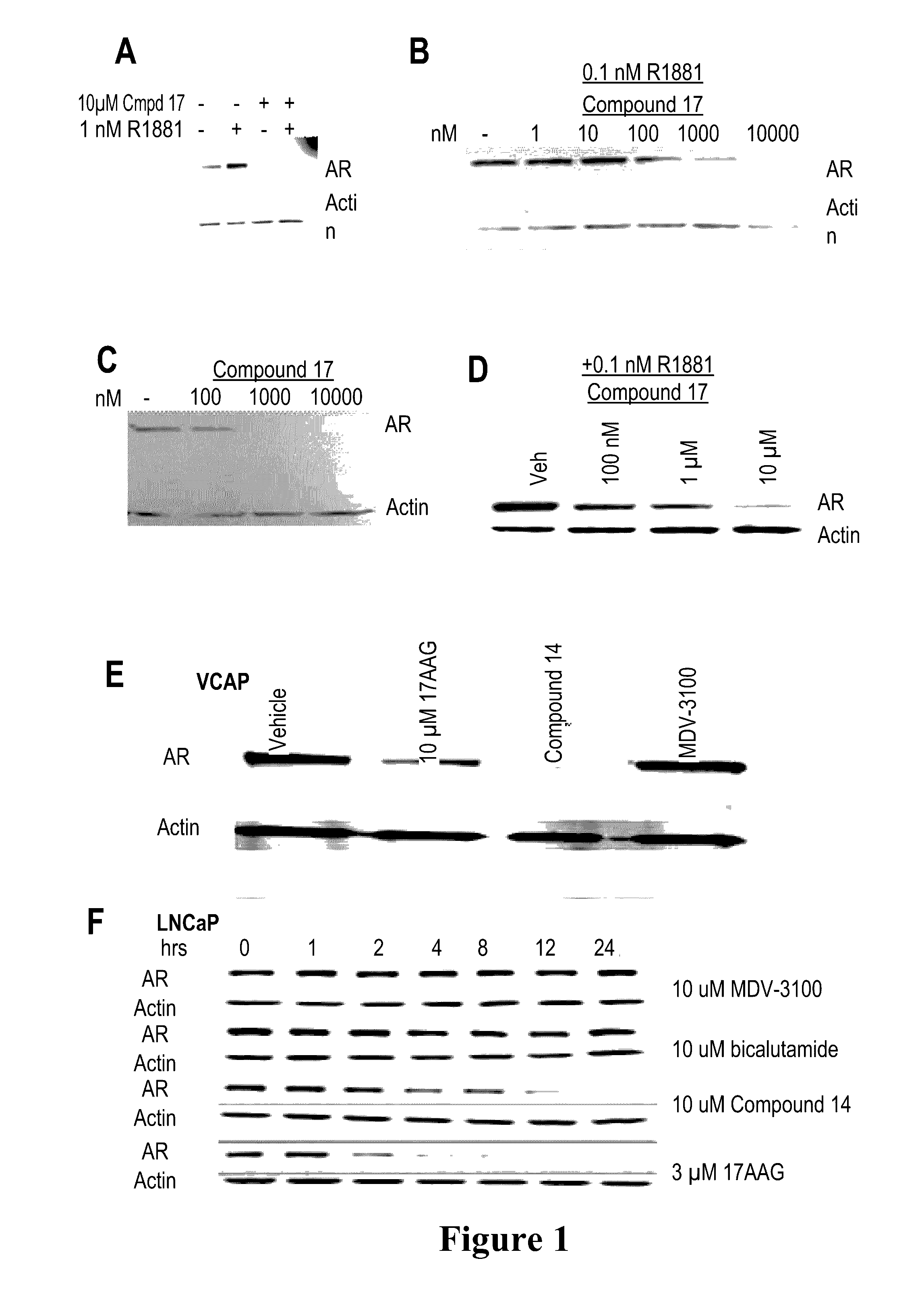
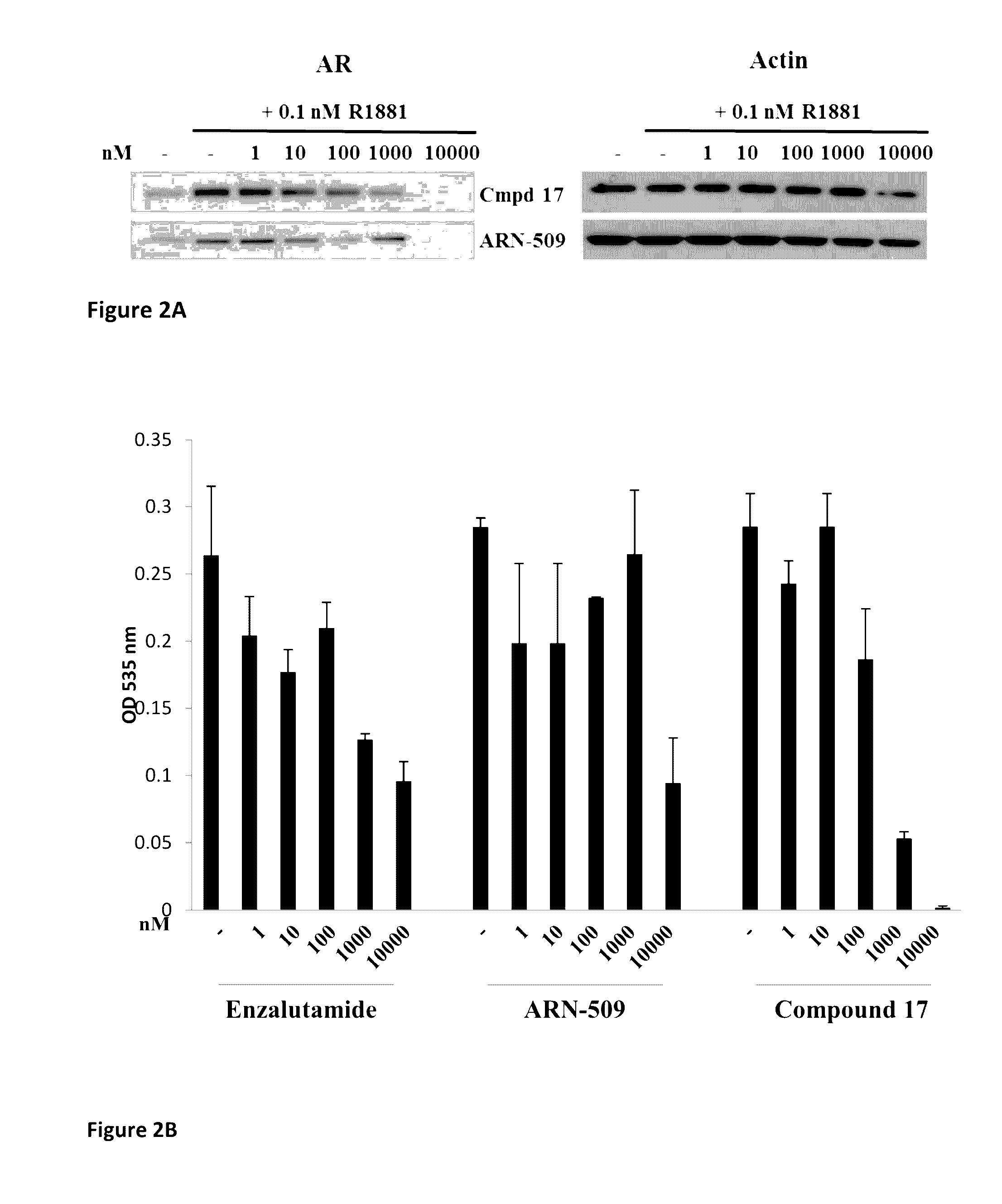
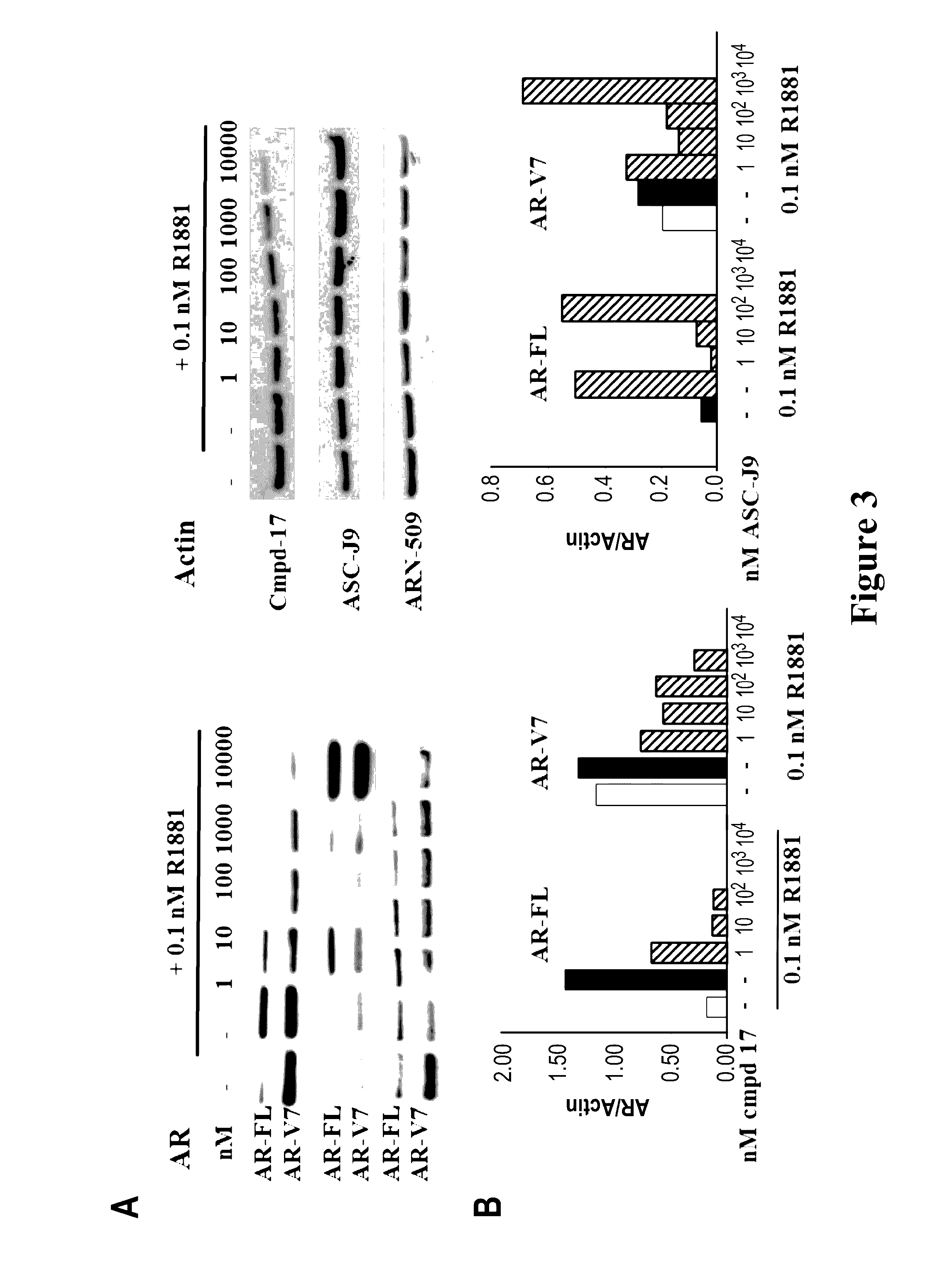
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
HBV drug resistance drug resistance detection methods
New polymorphisms in the nucleic acid sequences of the DNA polymerase / reverse transcriptase open reading frame and viral surface antigen open reading frame of the hepatitis B virus are reported. In particular, the present invention relates to the mutation YMDD YSDD in the HBV reverse transcriptase domain and to the W196V mutation in the small HBV viral surface antigen. Said polymorphisms are affecting the detection of drug resistance mutations by genotypic methods and diagnostic kits based thereon. The present invention relates to methods and diagnostic kits for detection of a HBV virus comprising said nucleic acid polymorphisms. In particular, those methods utilizing oligonucleotides capable of hybridizing to said HBV nucleic acid polymorphisms are envisaged.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20180273487A1Lower Level RequirementsShorten the lengthOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMorpholineResistance mutation
This invention is directed to pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, triazole, and morpholine based selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds including heterocyclic anilide rings and their synthetic precursors, R-isomers, and non-hydroxylated and / or non-chiral propanamides, and pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, triple negative breast cancer, other cancers expressing the androgen receptor, androgenic alopecia or other hyperandrogenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, other AR-expressing cancers, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels (through degradation) and / or activity (through inhibition) of any androgen receptor including androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20170368003A1Lower Level RequirementsShorten the lengthHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsNervous disorderMorpholineResistance mutation
This invention is directed to pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, triazole, and morpholine based selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds including heterocyclic anilide rings and their synthetic precursors, R-isomers, and non-hydroxylated and / or non-chiral propanamides, and pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, triple negative breast cancer, other cancers expressing the androgen receptor, androgenic alopecia or other hyperandrogenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Assay for imidazolinone resistance mutations in Brassica species
ActiveUS7595177B2Improve toleranceReliable and quick to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBrassicaResistance mutation
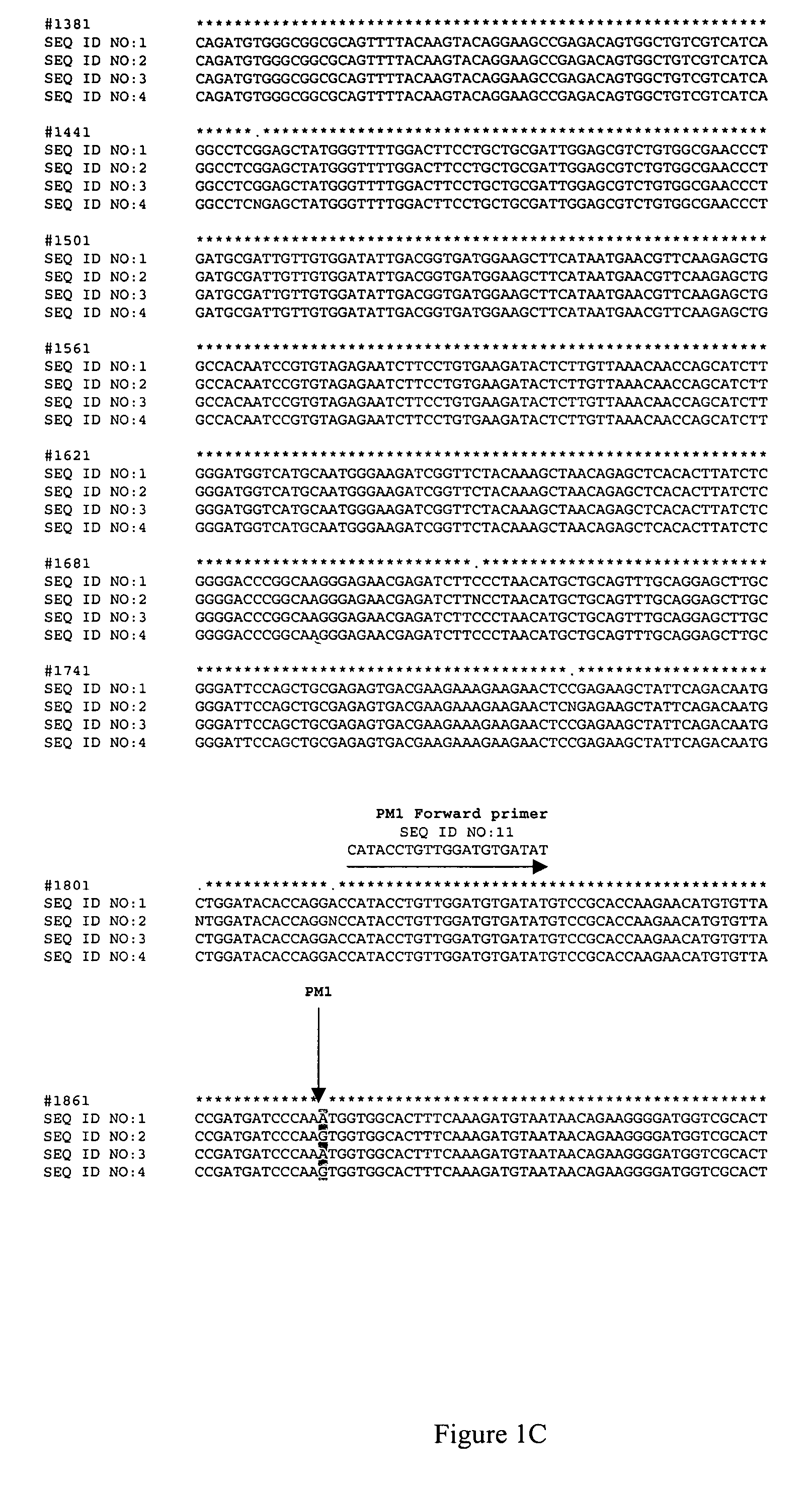
The invention provides methods and oligonucleotide primers for assaying Brassica napus plants for the presence or absence of mutations that confer resistance to imidazolinone herbicides. Specifically, the methods and primers of the invention are useful for detecting the PM1 mutation of the B. napus AHAS1 gene and the PM2 mutation of the B. napus AHAS3 gene.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9814698B2Improve survivalReduce morbidityOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismResistance mutationGlutamine
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10035763B2Improve survivalReduce morbidityOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismResistance mutationGlutamine
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, other AR-expressing cancers, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels (through degradation) and / or activity (through inhibition) of any androgen receptor including androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, other AR-expressing cancers, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels (through degradation) and / or activity (through inhibition) of any androgen receptor including androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Method and kit for detecting streptomycin medicine resistant mutation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveCN102229991AAvoid False Positive ResultsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceNucleotide
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting the streptomycin medicine resistant mutation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The invention relates to medicine resistant mutation detection technique and provides a method for detecting streptomycin medicine resistant mutation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which effectively improves sensitivity and specificity, and is simple and convenient in operation and short in period. The method comprises: designing primers and probes according to the complete sequence of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the gene sequences of the genomes rpsL and rrs of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis; extracting the DNA of a sample of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis; constructing a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction system; and performing PCR amplification and analysis on a fusion curve. In the method, experiments are performed in two tubes respectively by using the specific primers and probes, and the amplification of the nucleic acid fragment of a target nucleotide sequence and subsequent analysis on the fusion curve are realized by using heat-resistance DNA polymerase, four kinds of nucleotide monomers and other components and by using real-time PCR technique. A fluorescent PCR fusion curve method with high specificity can quickly and accurately detects common medicine-resistance mutation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is expected to be directly used for medicine-resistance detection of a clinic Mycobacterium tuberculosis sample.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10314797B2Halogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsNervous disorderMorpholineResistance mutation
This invention is directed to pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, triazole, and morpholine based selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds including heterocyclic anilide rings and their synthetic precursors, R-isomers, and non-hydroxylated and / or non-chiral propanamides, and pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, triple negative breast cancer, other cancers expressing the androgen receptor, androgenic alopecia or other hyperandrogenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Primer pair and probe used for detecting AIDS treatment medicine 3TC and FTC drug-resistance mutation sites and application thereof
ActiveCN104911252AStrong specificityEnrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPatient survivalPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a primer pair and a probe used for detecting AIDS treatment medicine 3TC and FTC drug-resistance mutation sites, which comprise an ARMS primer and a Taqman probe of mutation sites M184V, M184I, Q151M and K65R at 184th site, 151st site and 65th site of pol gene for detecting HIV-1 virus RNA. The invention also provides the application of the primer pair and the probe on detection of 3TC and FTC main drug-resistance mutation sites M184V, M184I, Q151M and K65R. The kit has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, good specificity, and low detection cost, and provides medicine usage guidance for treating clinic AIDS patient, individuation treatment for AIDS patient can be realized, medicine effectiveness can be increased, AIDS patient living time can be prolonged, and the primer pair and the probe have wide application prospect and social benefit.
Owner:江苏亦文生物科技有限公司
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9834507B2Improve survivalReduce morbidityOrganic chemistry methodsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisAndrogen
This invention provides novel 3-amino propanamide selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, androgenic alopecia or other hyperandrogenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:ONCTERNAL THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Kit for detecting drug resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis based on HRM technology and primers thereof
InactiveCN106811530AShort detection cycleIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTest sampleResistance mutation
The invention relates to a kit for detecting the drug resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis based on an HRM technology and primers thereof. The invention discloses the kit for detecting drug resistance genes of the mycobacterium tuberculosis and application thereof. The invention discloses a group of primers for detecting whether each of the genes of the mycobacterium tuberculosis in a to-be-tested sample generates a drug resistance mutation or not, and the sequences of the primers are shown in SEQ NO.1-SEQ NO.10. The kit containing the primers can detect the mutation situations of the four drug resistance indicator genes (embB, rpsL, inhA and katG) in DNA extracted from the to-be-tested sample. The kit provided by the invention detects the mutation situations of the four drug resistance indicator genes of the mycobacterium tuberculosis in the to-be-tested sample within a shorter time through the high resolution melting (HRM) technology and is high in result sensitivity, better in specificity, and simple and convenient in analysis process.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIYUAN GENT CO LTD
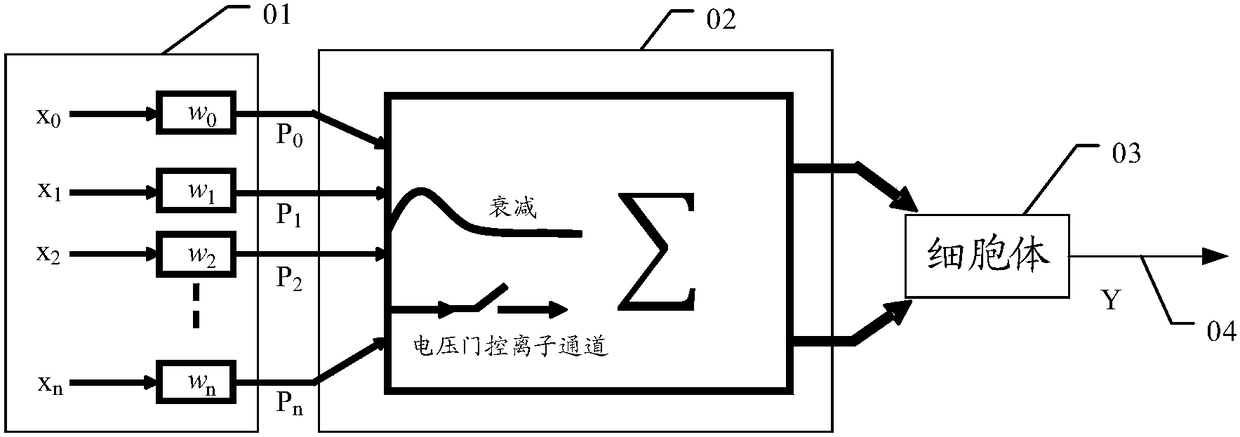
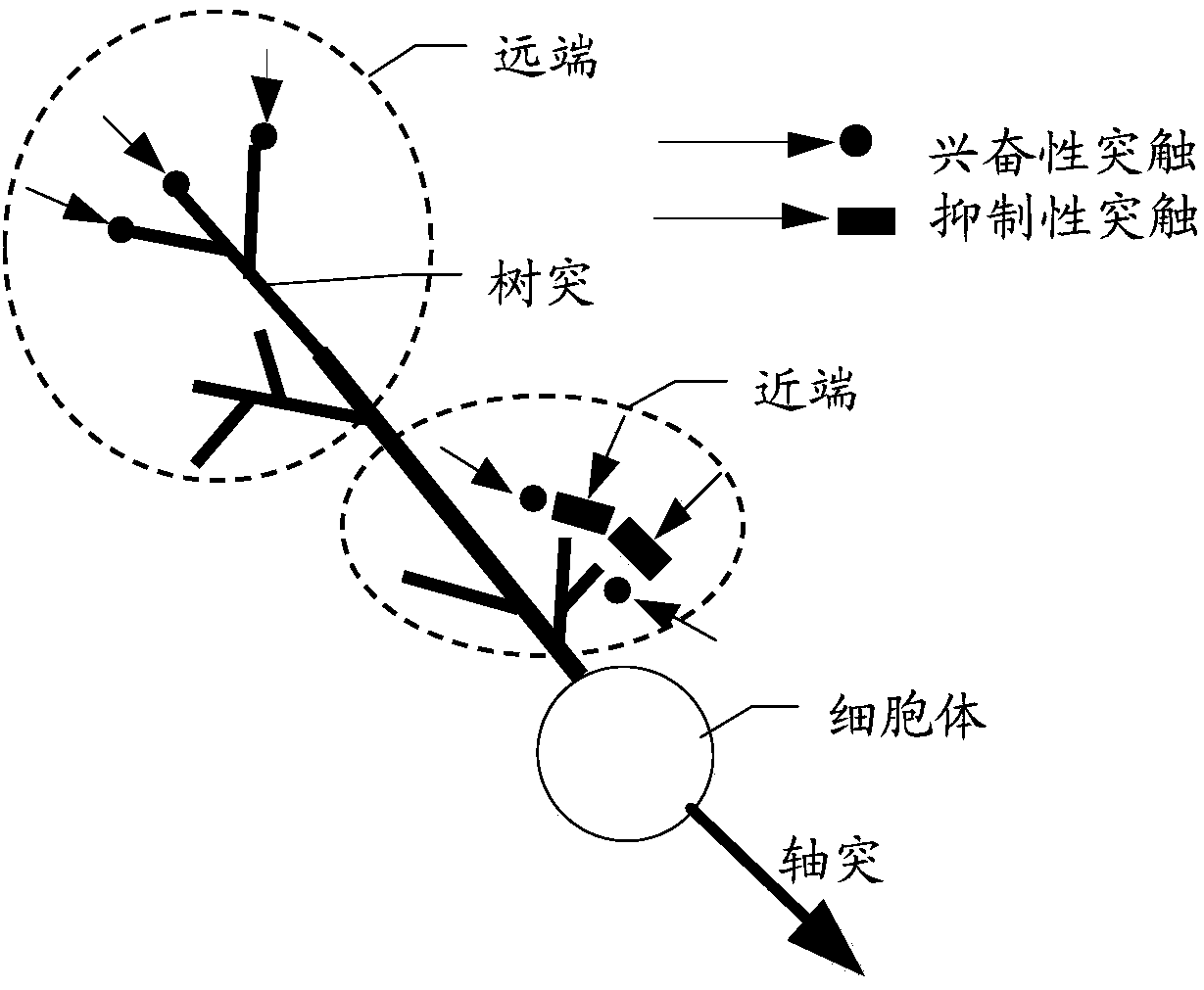
Neural network, information processing method thereof, and information processing system thereof
Disclosed are a neural network, an information processing method thereof, and an information processing system thereof. The neural network includes N neuron layers connected one by one, and except forthe first neuron layer, each neuron of each neuron layer includes m dendritic units and one hippocampal unit. Each dendritic unit includes a resistance gradient device, each hippocampal unit includesa resistance mutation device, and the m dendritic units can be respectively set with different threshold voltages or currents; and the neurons of the n-th neuron layer are respectively connected withthe m dendritic units of the neurons of the n+1-th neuron layer. N is an integer greater than or equal to 3, m is an integer greater than 1, and n is an integer greater than or equal to 1 and less than N. The neural network can filter most non-key information through the dendritic units, thus, the information processing amount of the neural network is reduced, the power consumption of the neuralnetwork operation is reduced, and the processing efficiency of key information by the neural network is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9815776B2Improve survivalReduce morbidityNervous disorderOrganic chemistry methodsResistance mutationGlutamine
Owner:ONCTERNAL THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20180360805A1Antineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsMalignancyResistance mutation
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, benzotriazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating hyperproliferations of the prostate including pre-malignancies and benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, other AR-expressing cancers, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels (through degradation) and / or activity (through inhibition) of any androgen receptor including androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) Ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10441570B2Antineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsResistance mutationMalignancy
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer resistant to anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) kinase inhibitors
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Primers, probe, kit, and method used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis isoniazid resistance mutation
InactiveCN103224984ALow costHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceIsoniazid resistanceFluorescence
The invention discloses primers, a probe, a kit and a method used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis isoniazid resistance mutation. The invention belongs to the technical field of mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance mutations. The primers and probe used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis isoniazid resistance mutation comprises detection-use primers and a fluorescent probe. The kit comprises a nucleic acid extraction reaction solution, a PCR reaction solution, a control reagent, a nucleic acid extraction reaction solution, a PCR reaction solution, and a control reagent. The kit detection method comprises the steps of: (1) reagent preparation; (2) sample collection and processing; (3) sample dosing; (4) PCR amplification; and (5) result analysis and determination. The primers and the probe have high sensitivity and good specificity. The kit has low cost. With the detection method, simultaneous implementation can be carried out without cover opening, pollution is prevented, the result is more reliable, the operation is simple and fast, and quantitation is realized.
Owner:WUHAN BIOTECH GENE ENG
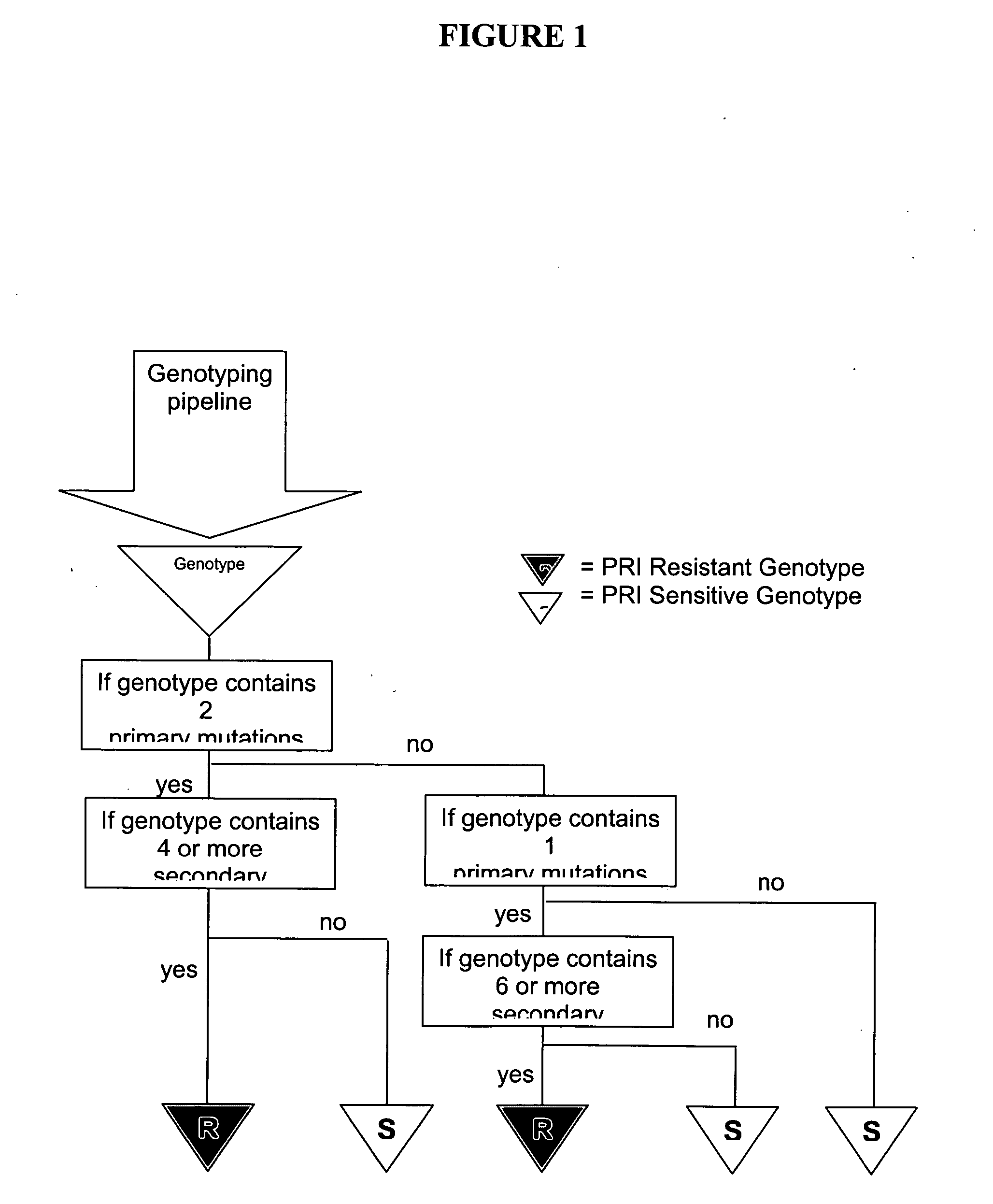
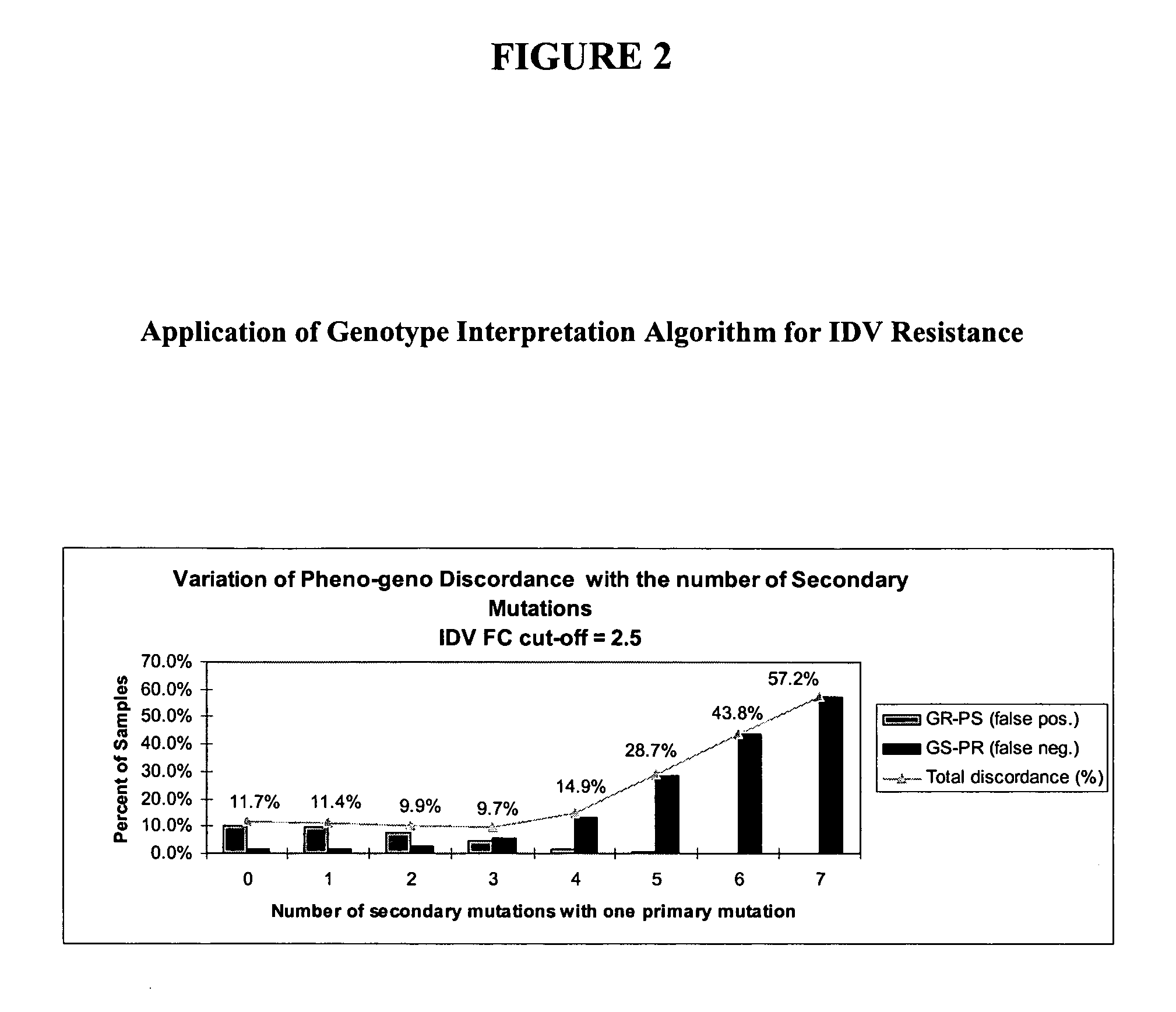
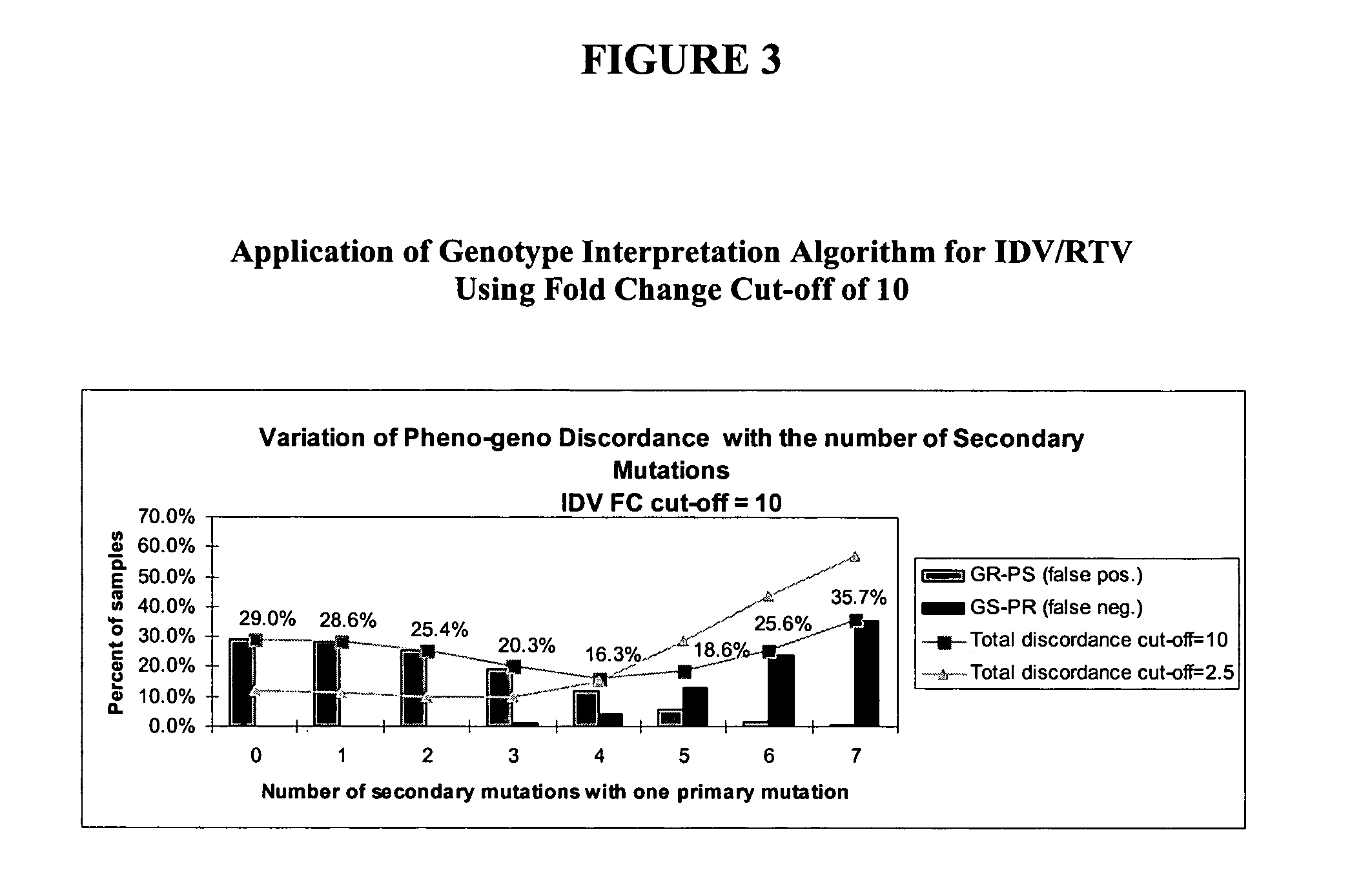
Method for determining reduced susceptibility of HIV to protease inhibitor treatment
InactiveUS20050214749A1Reduce sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisAntiviral drugResistance mutation
The present invention provides methods and devices for predicting whether a HIV variant will be resistant to an antiviral drug based on the variant's genotype. In one aspect, methods are provided comprising determining whether a combination of protease inhibitor resistance mutations meet certain conditions, as disclosed herein, thereby assessing the effectiveness of ritonavir-boosted indinavir therapy in the HIV-infected subject. Computer implemented methods comprising determining HIV resistance are provided.
Owner:VIROLOGIC INCORPORATED
Polypeptide vaccine against tumor-targeted drug resistance sites and design method thereof
ActiveCN109887553AProlong the effective timeIncreased disease response rateMolecular designProteomicsTumor targetDisease
The invention discloses a polypeptide vaccine against tumor-targeted drug resistance sites and a design method thereof. The design method includes the steps: collecting data of targeted drug resistance mutations; intercepting a drug resistance mutant polypeptide sequence and predicting the affinity and immunogenicity of MHC molecules; obtaining the relationship between targeted drugs and drug resistance sites, and performing drug clustering; and artificially designing a corresponding vaccine polypeptide sequence. The targeted drug combination polypeptide vaccine combination obtained by the method can cover common targeted therapeutic drugs, can effectively reduce the probability of tumor drug resistance, can prolong the effective action time of the targeted drugs, can increase the diseaseresponse rate of the patient, has broad-spectrum, can shorten the time from analysis to treatment of individualized peptide vaccines, and can reduce medical costs.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEOANTIGEN THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Methods and systems for determination of an effective therapeutic regimen and drug discovery
ActiveUS20170152570A1Chemical property predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementMatch algorithmsPattern matching
The present invention relates to the discovery of a method for identifying a treatment regimen for a patient diagnosed with cancer, predicting patient resistance to therapeutic agents and identifying new therapeutic agents. Specifically, the present invention relates to the use of an algorithm to identify a mutation in a kinase, determine if the mutation is an activation or resistance mutation and then to suggest an appropriate therapeutic regimen. The invention also relates to the use of a pattern matching algorithm and a crystal structure library to predict the functionality of a gene mutation, predict the specificity of small molecule kinase inhibitors and for the identification of new therapeutic agents.
Owner:DNA SEQ 2 INC
Viral polymerase and modulation thereof
The present invention provides the tertiary structure of a Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) polymerase reverse transcriptase (rt) domain from which a variant HBV polymerase mutations associated with resistance to or having reduced sensitivity to an anti-viral drug have been mapped. The present invention further provides methods of identifying, designing and / or modifying agents capable of modulating the functional activity of the HBV polymerase based on the atomic co-ordinates provided by the tertiary structure. The present invention still further provides a method of modulating HBV polymerase functional activity and agents useful for same. The agents identified in accordance with the method of the present invention are particularly useful inter alia in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of infection by an HBV resistant to or exhibiting reduced sensitivity to an anti-viral drug. The agents may also have utility as diagnostic agents such as to distinguish between resistance mutations. Furthermore, the present invention enables responses of particular potential anti-viral drugs to be predicted. In addition, new targets within the polymerase have been identified.
Owner:MELBOURNE HEALTH
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20170166526A1Improve survivalReduce morbidityOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismResistance mutationGlutamine
This invention provides novel indole, indazole, benzimidazole, indoline, quinolone, isoquinoline, and carbazole selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, other AR-expressing cancers, androgenic alopecia or other hyper androgenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels (through degradation) and / or activity (through inhibition) of any androgen receptor including androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic and / or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20180118663A1Reduce morbidityReduce severityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryResistance mutationGlutamine
This invention provides novel 3-amino propanamide selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, androgenic alopecia or other hyperandrogenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:ONCTERNAL THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20170050921A1Improve survivalReduce morbidityNervous disorderOrganic chemistry methodsAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisAndrogen
This invention provides novel 3-amino propanamide selective androgen receptor degrader (SARD) compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof in treating prostate cancer, advanced prostate cancer, castration resistant prostate cancer, androgenic alopecia or other hyperandrogenic dermal diseases, Kennedy's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and uterine fibroids, and to methods for reducing the levels of androgen receptor-full length (AR-FL) including pathogenic or resistance mutations, AR-splice variants (AR-SV), and pathogenic polyglutamine (polyQ) polymorphisms of AR in a subject.
Owner:ONCTERNAL THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com