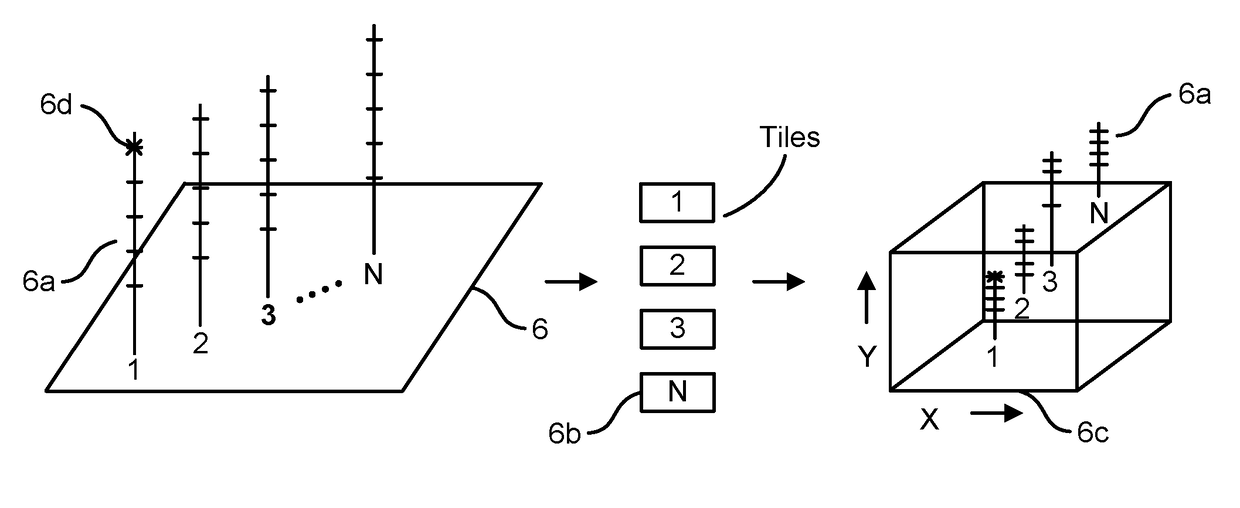
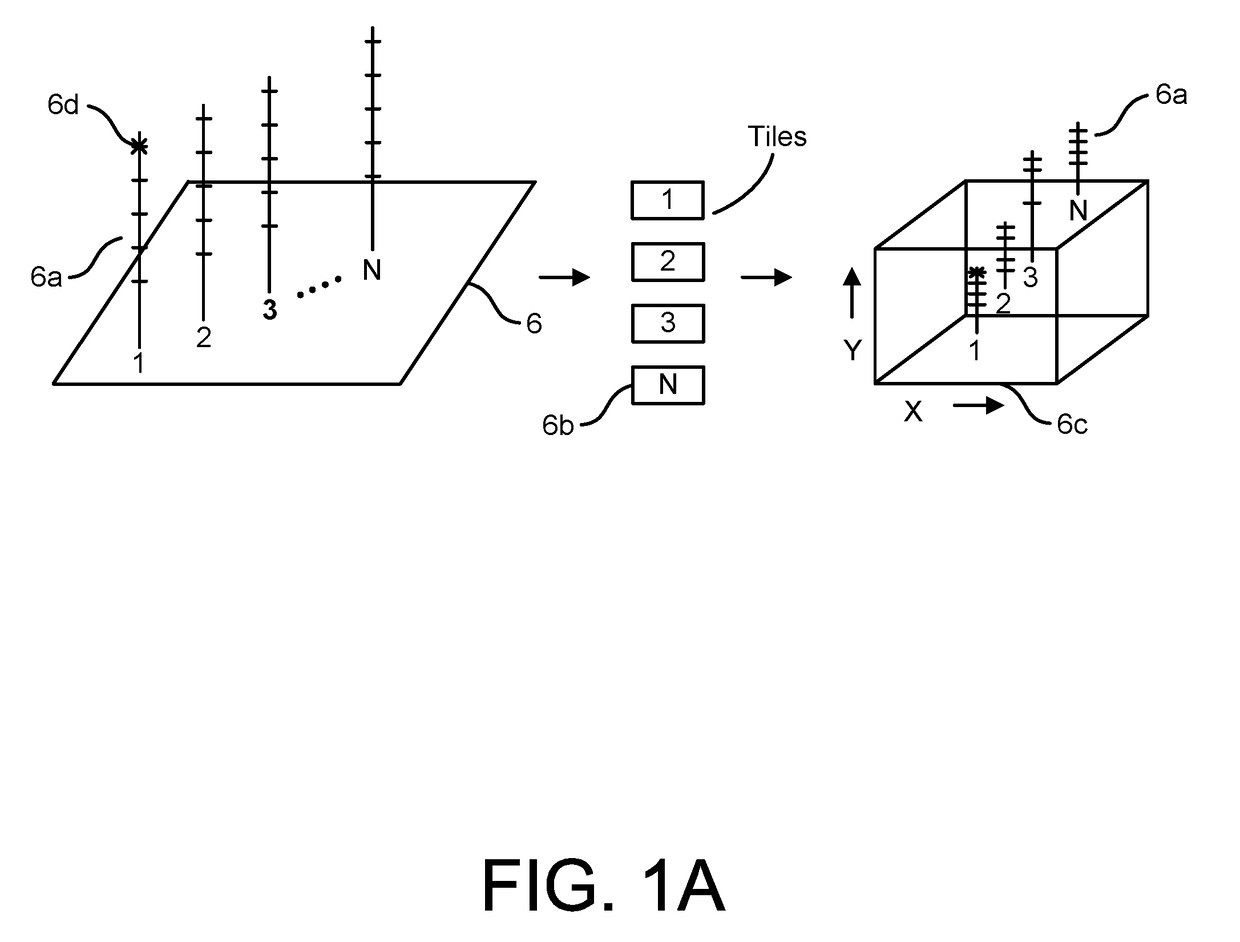
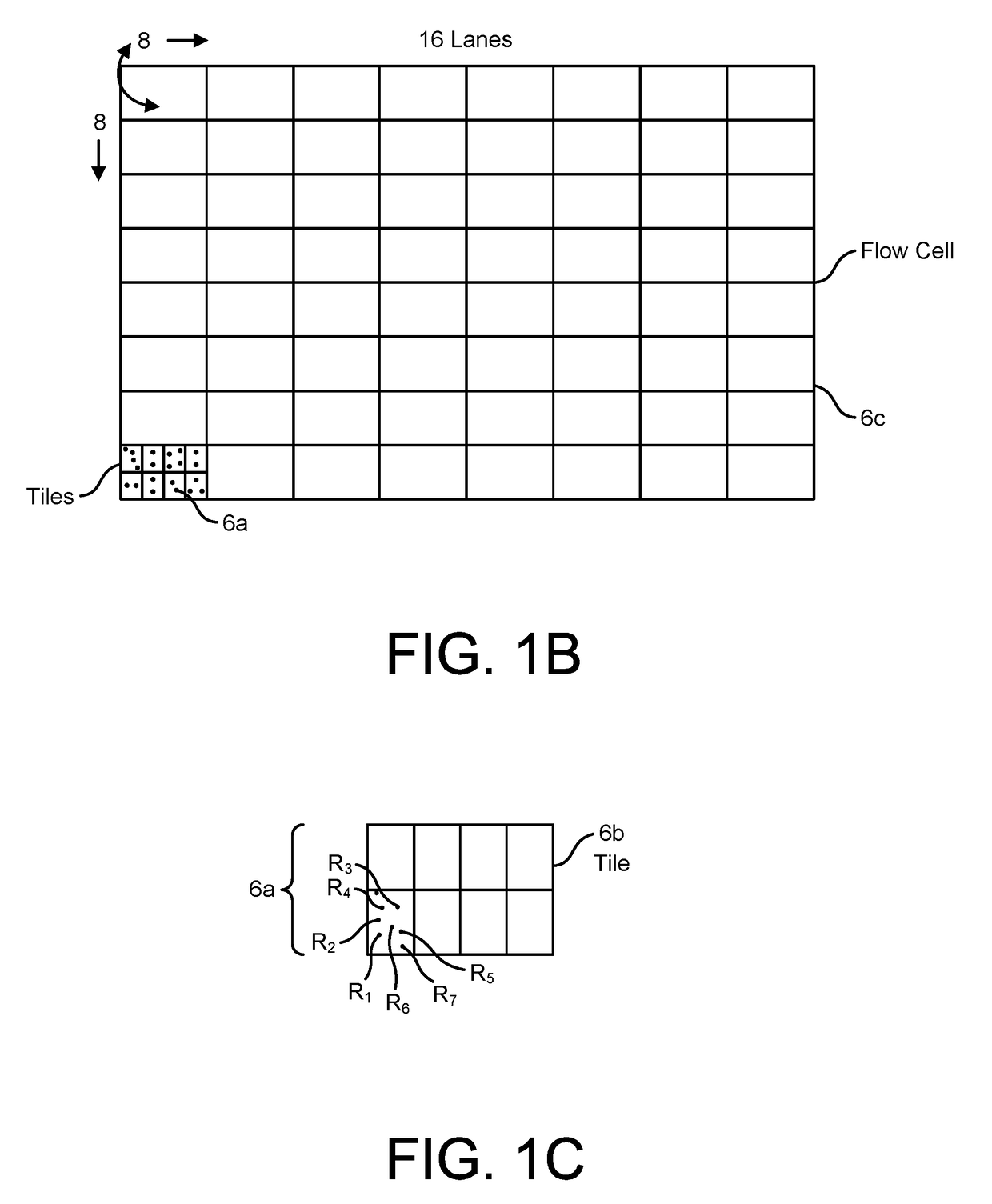
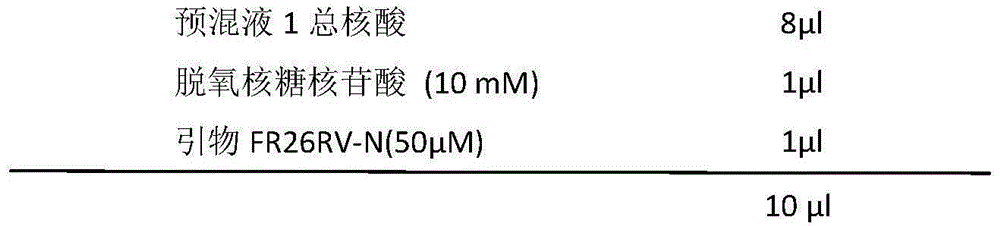
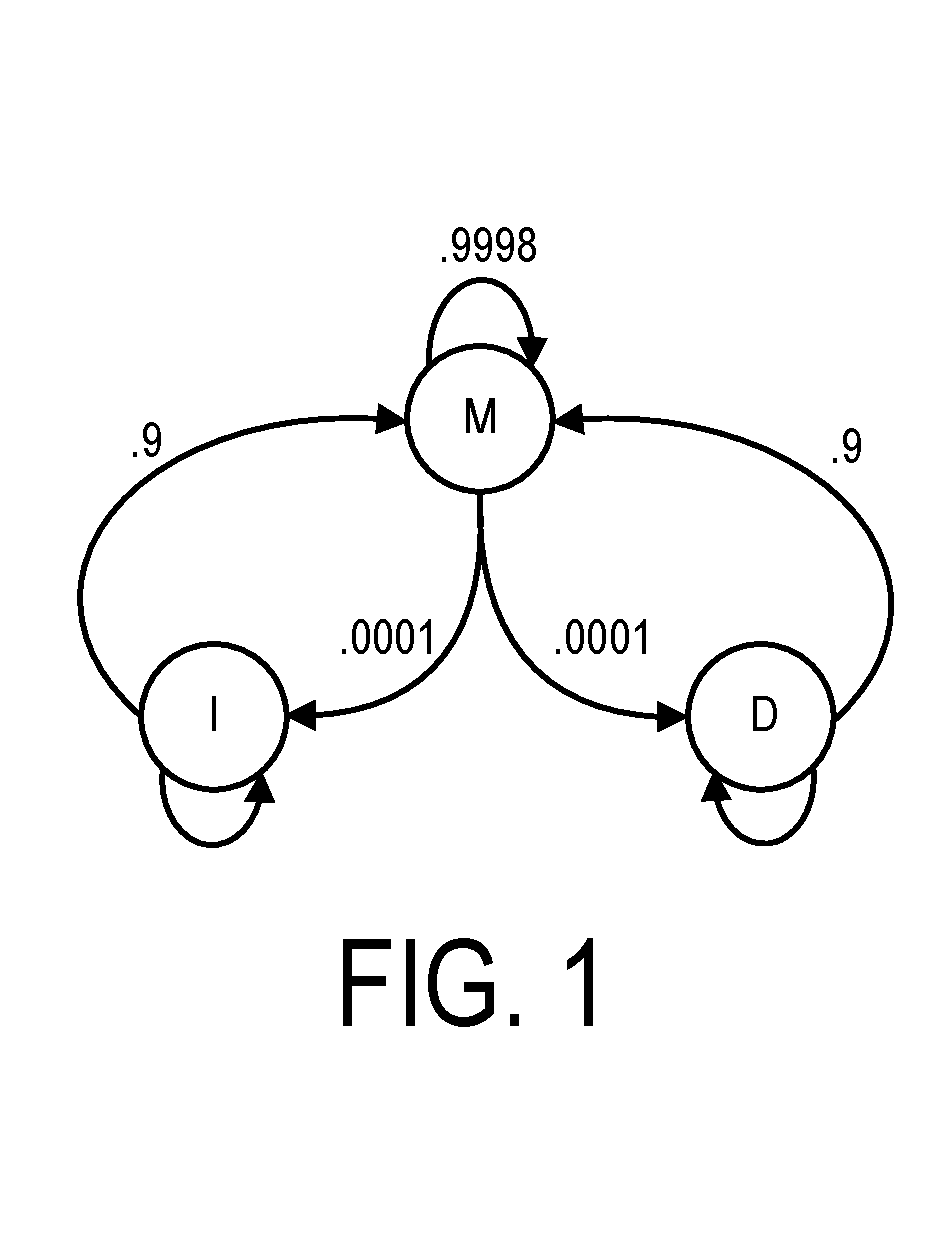
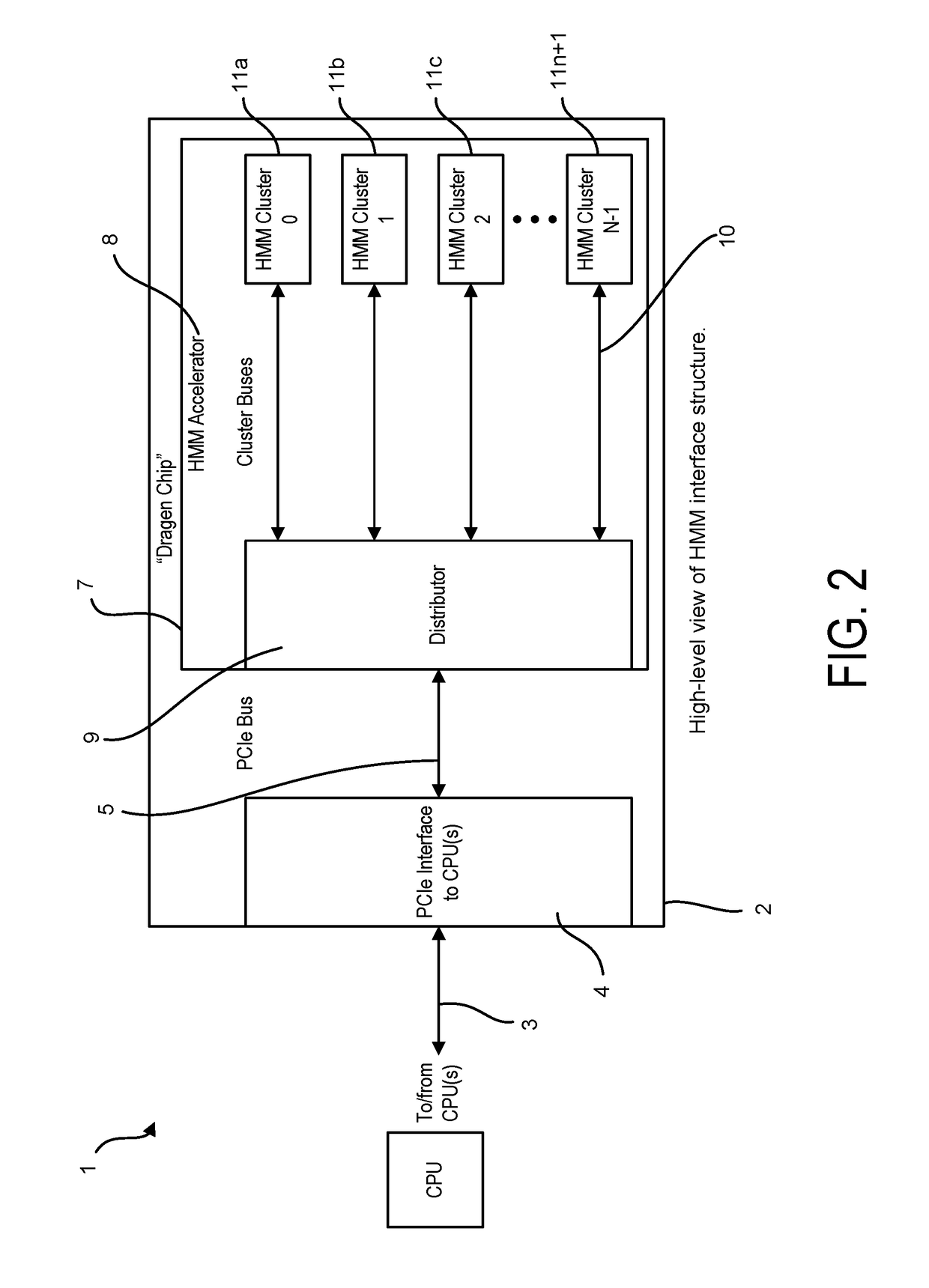
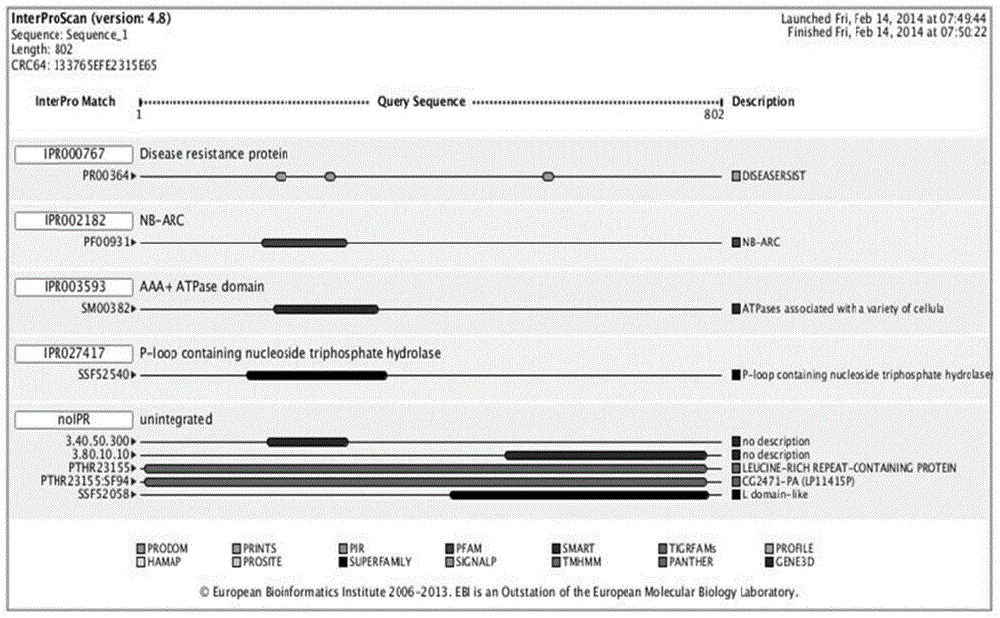
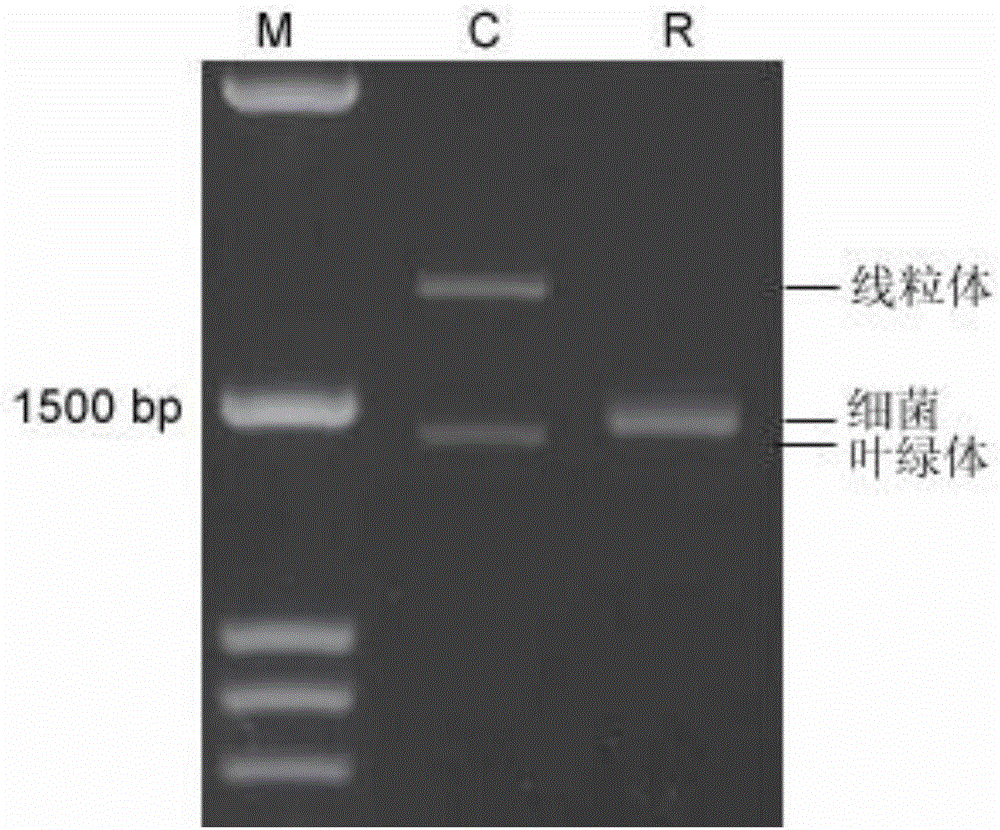
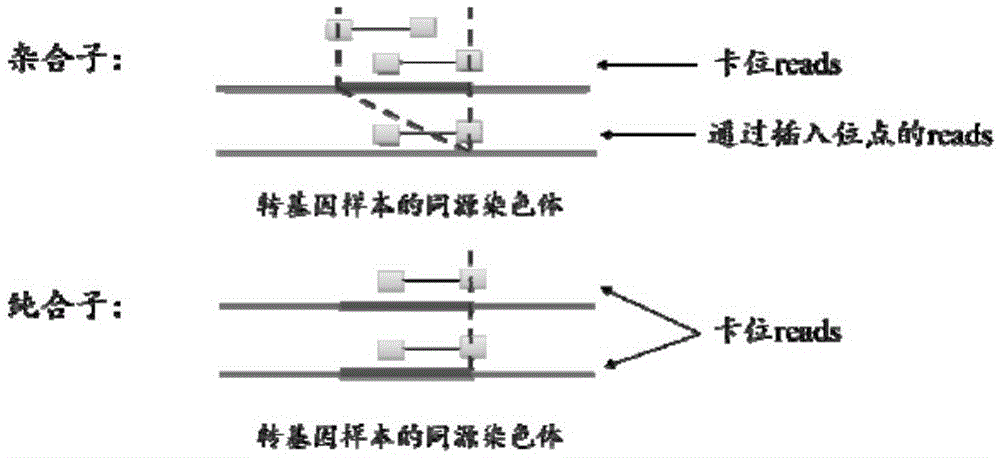
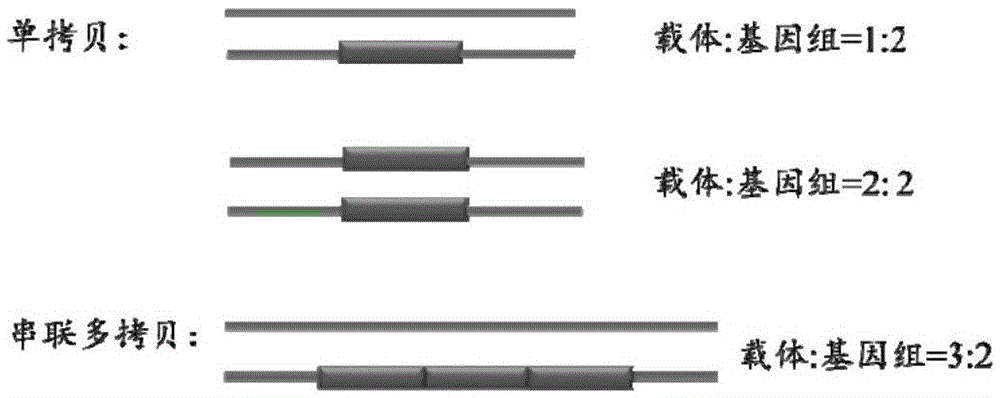
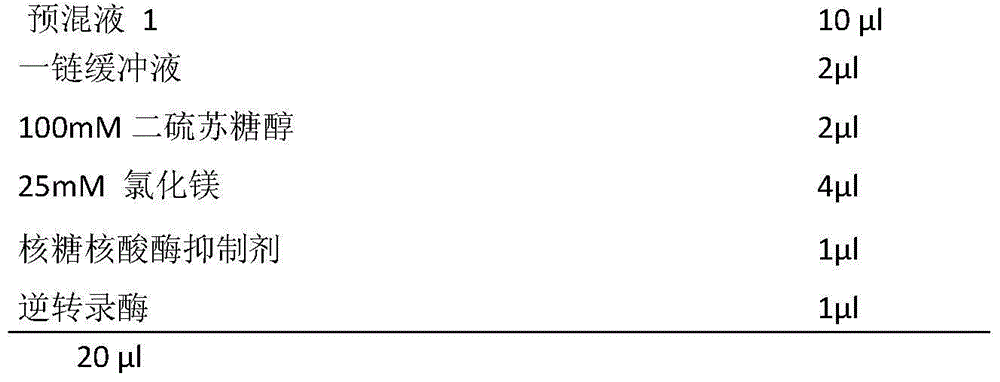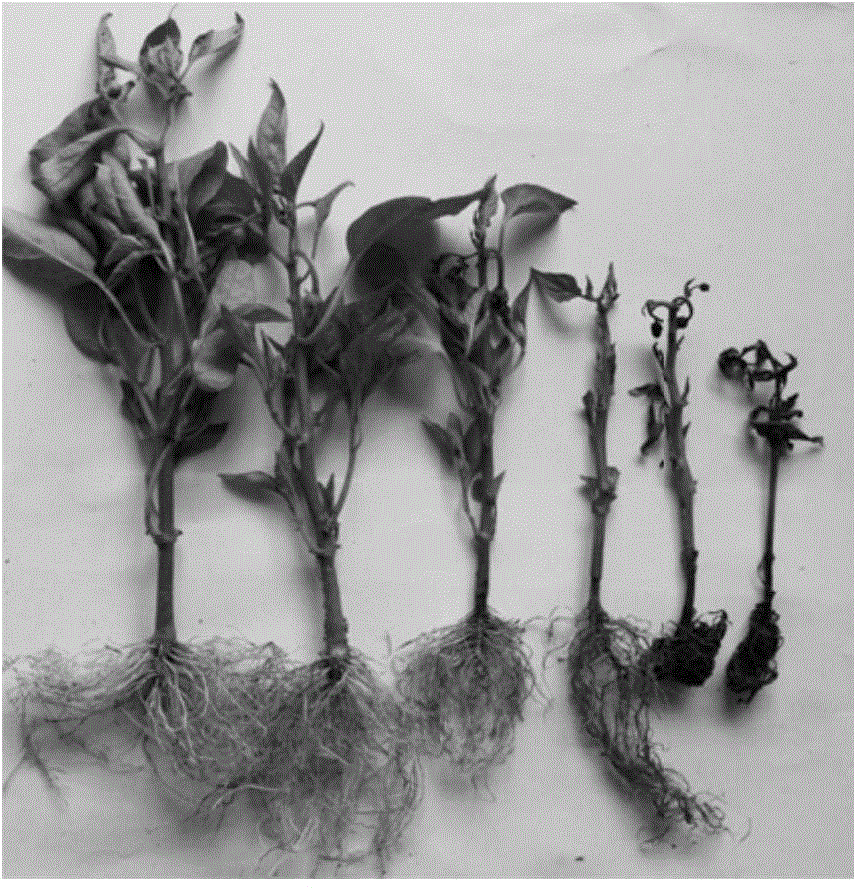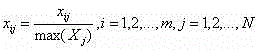Patents
Literature
667 results about "Bioinformatics analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioinformatics analysis can be used to analyze the information so that the researchers can spend their time generating more data. The ability to analyze more data can result in more accurate, compelling, and significant information.
Response element
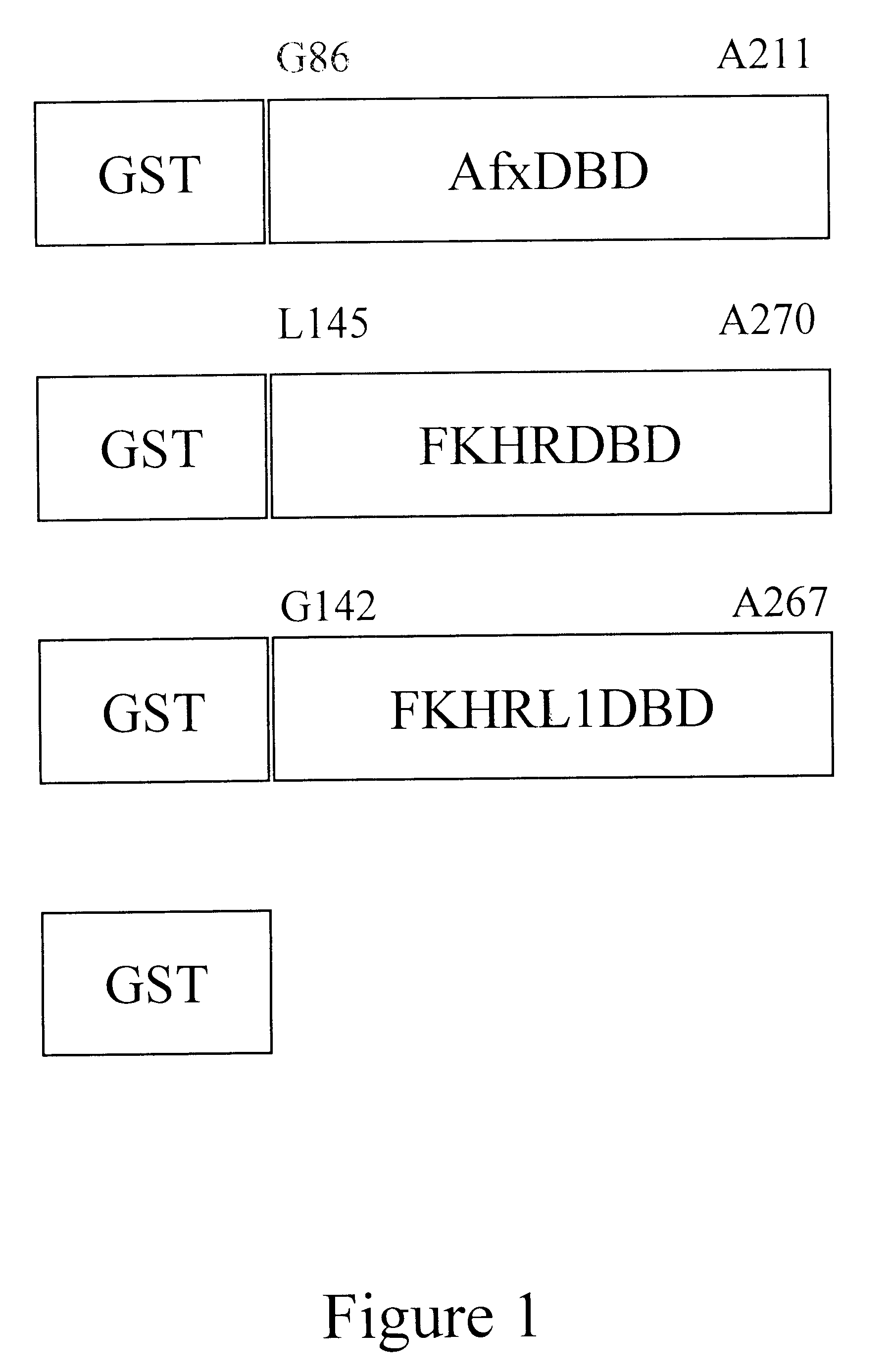
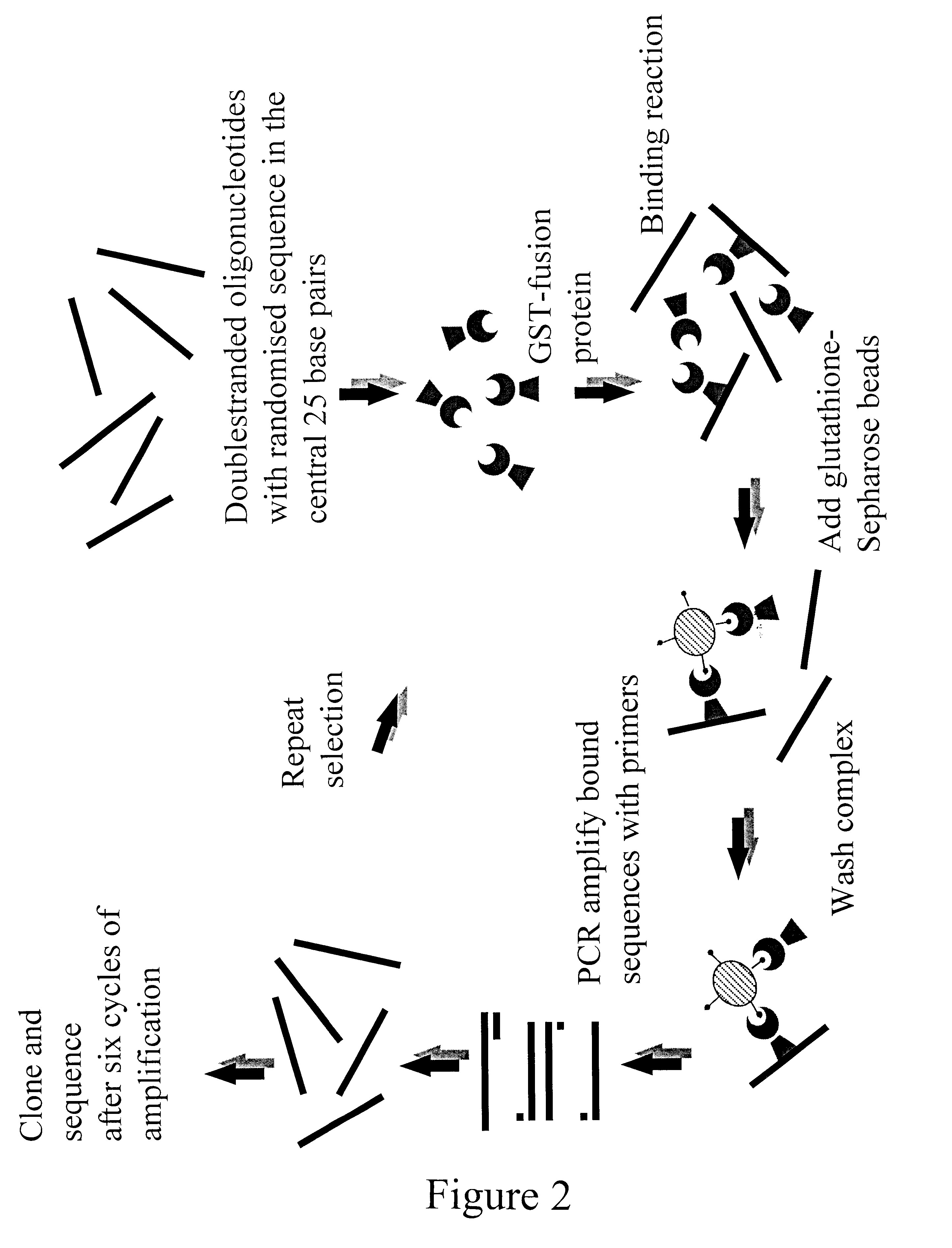
The present invention is directed to a novel Afx response element comprising the nucleotide sequence AACATGTT, said nucleotide sequence having a DNA binding site for the human fork head transkription factor Afx. The invention also relates to the use of the Afx response element in the screening for genes as diabetes drug targets and in the bioinformatic analysis of the human genome, said genes in turn being useful in other screening methods for compounds modifying the insulin receptor signaling pathway. A further aspect of the invention is a vector construct comprising the novel nucleotide sequence, a host cell transformed with said vector construct as well as the fusion protein expressed by said host cell.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL) +1
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods executed on an integrated circuit processing platform
ActiveUS20160306922A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyHealth-index calculationTelemedicineElectricityData source
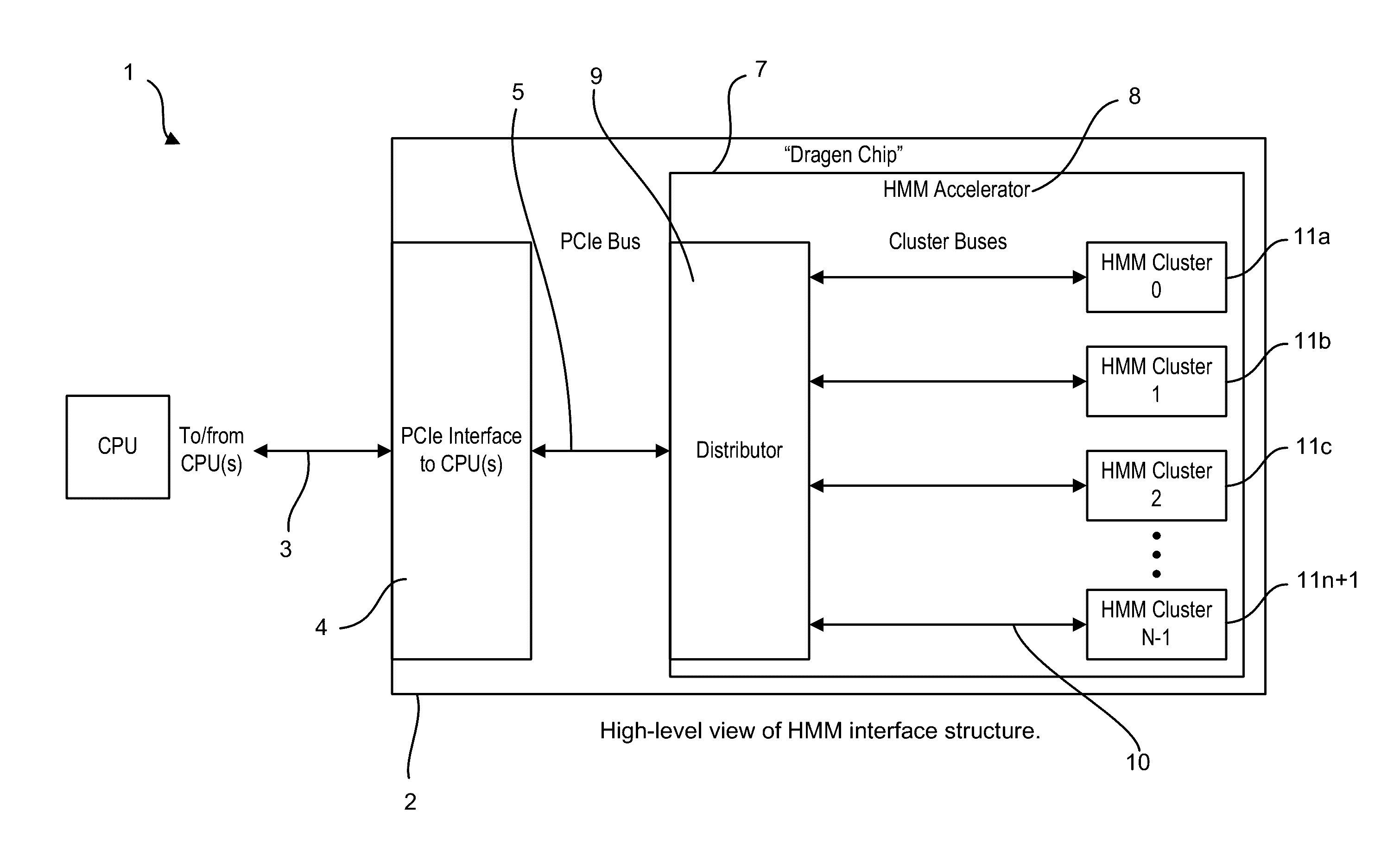
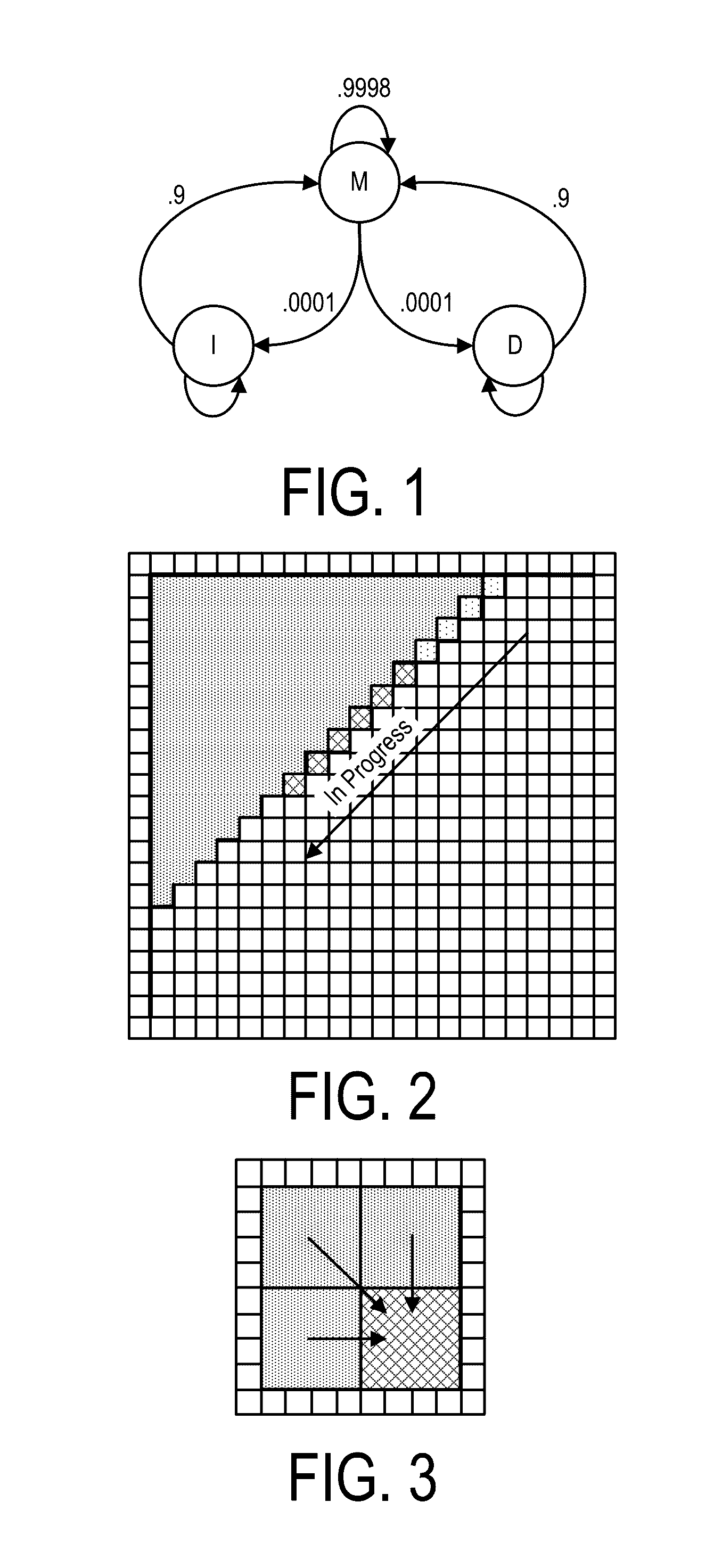
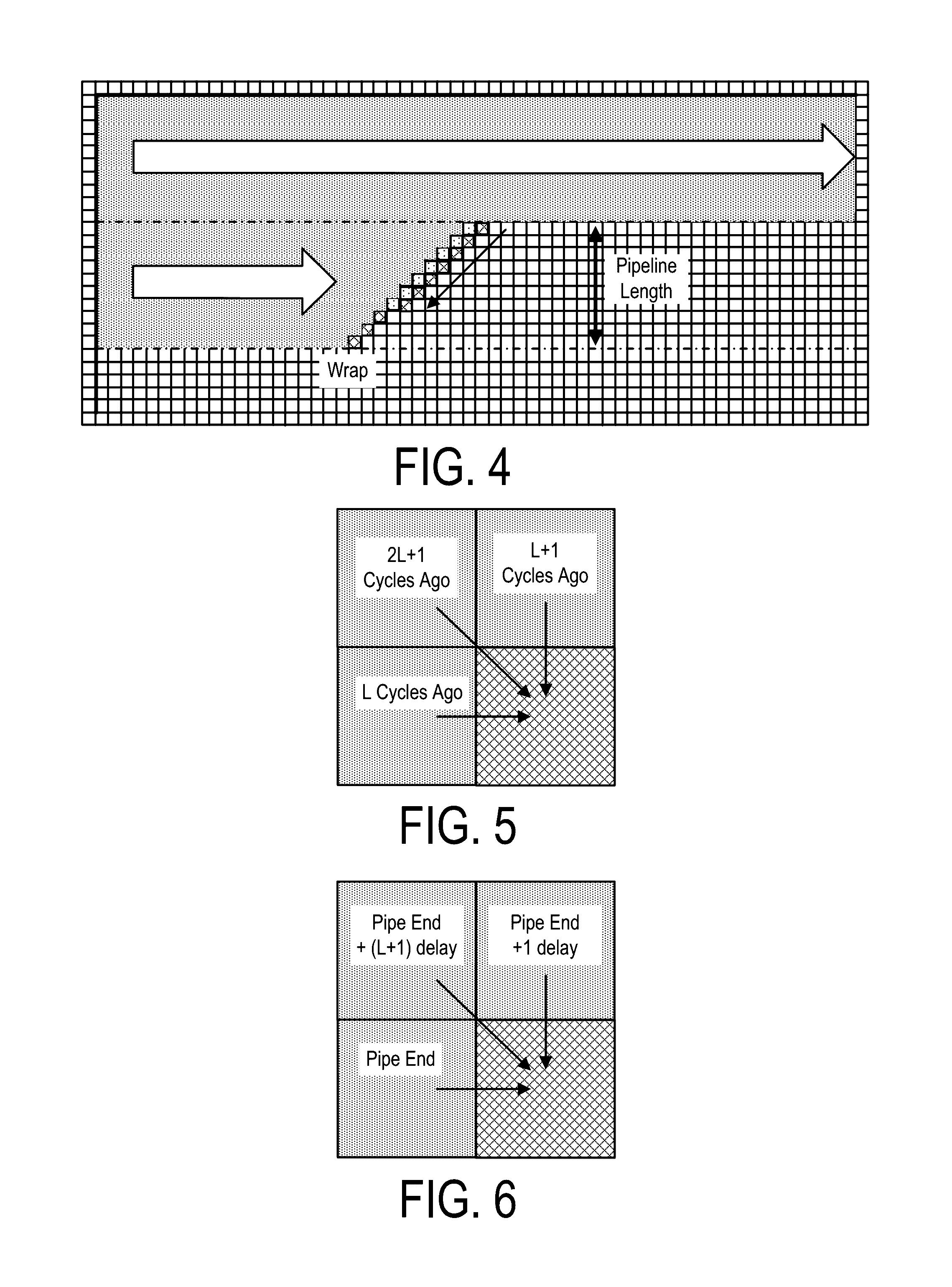
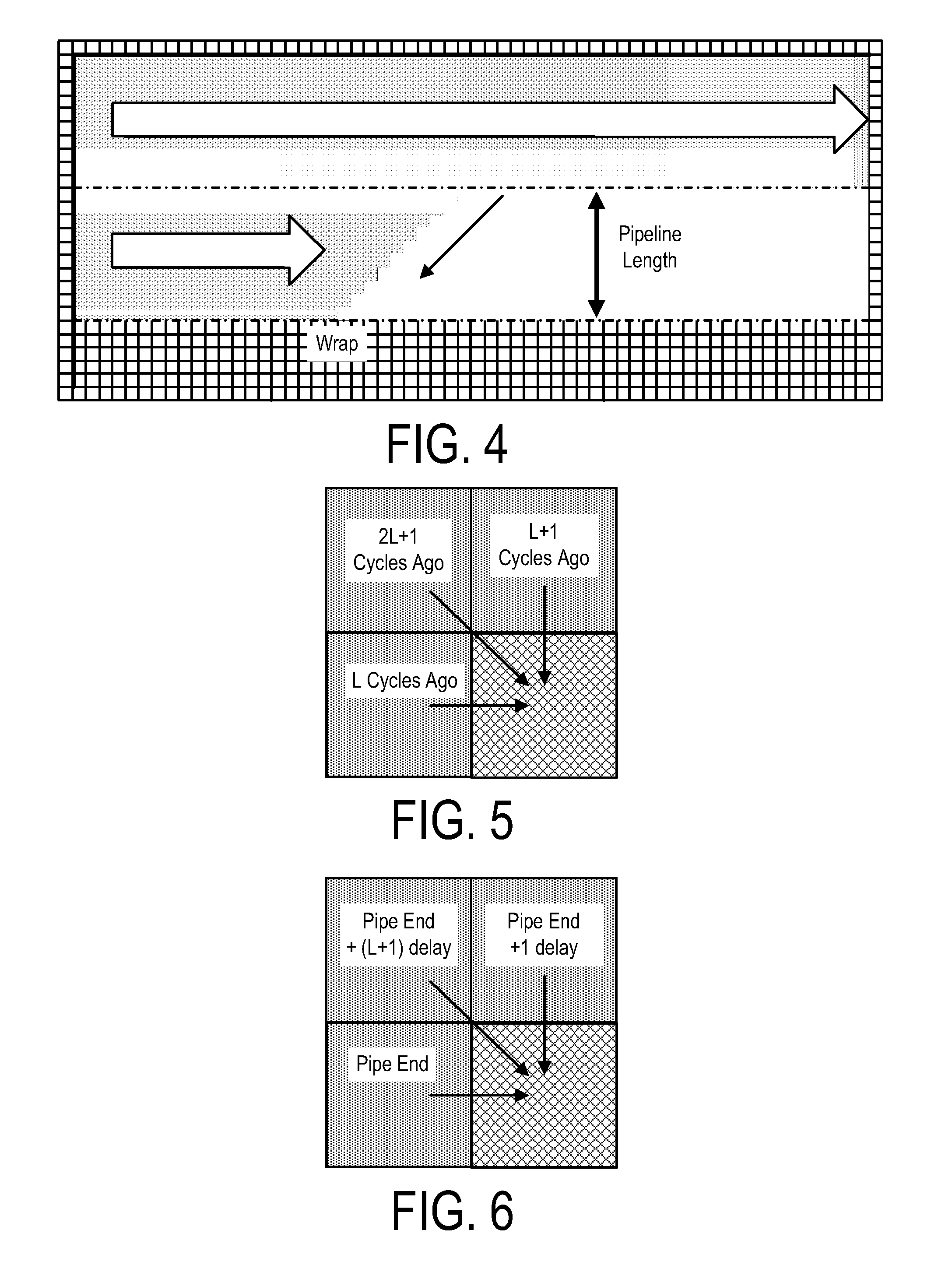
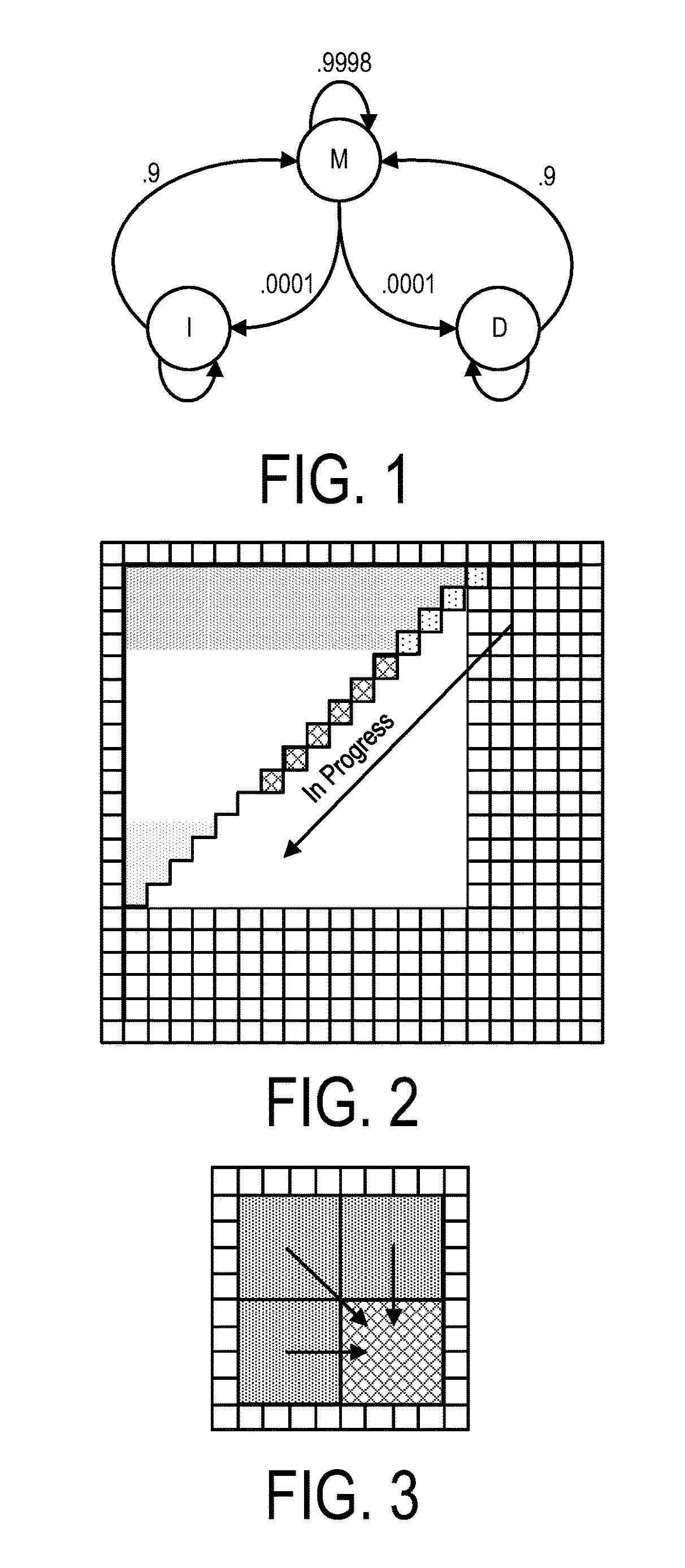
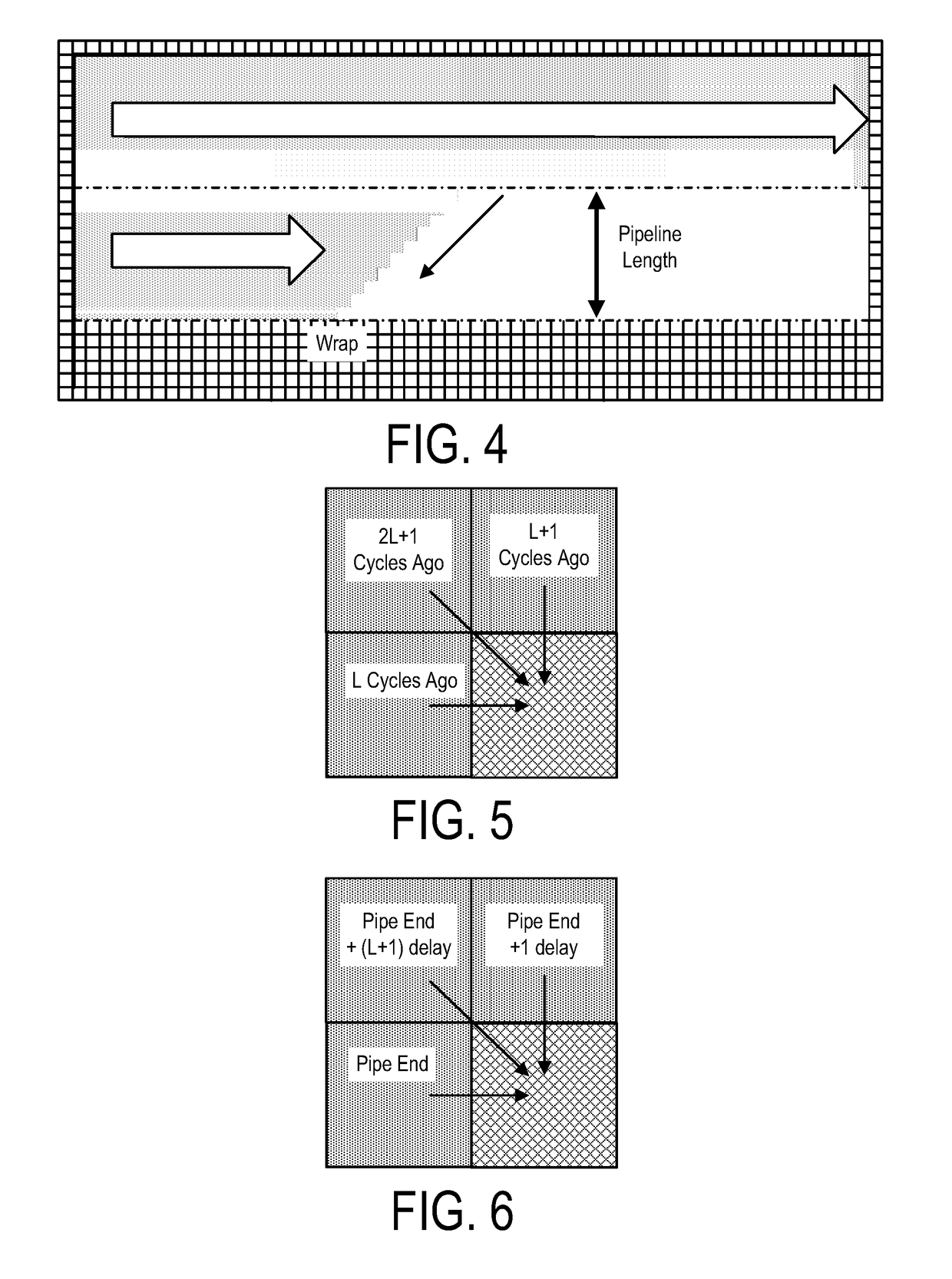
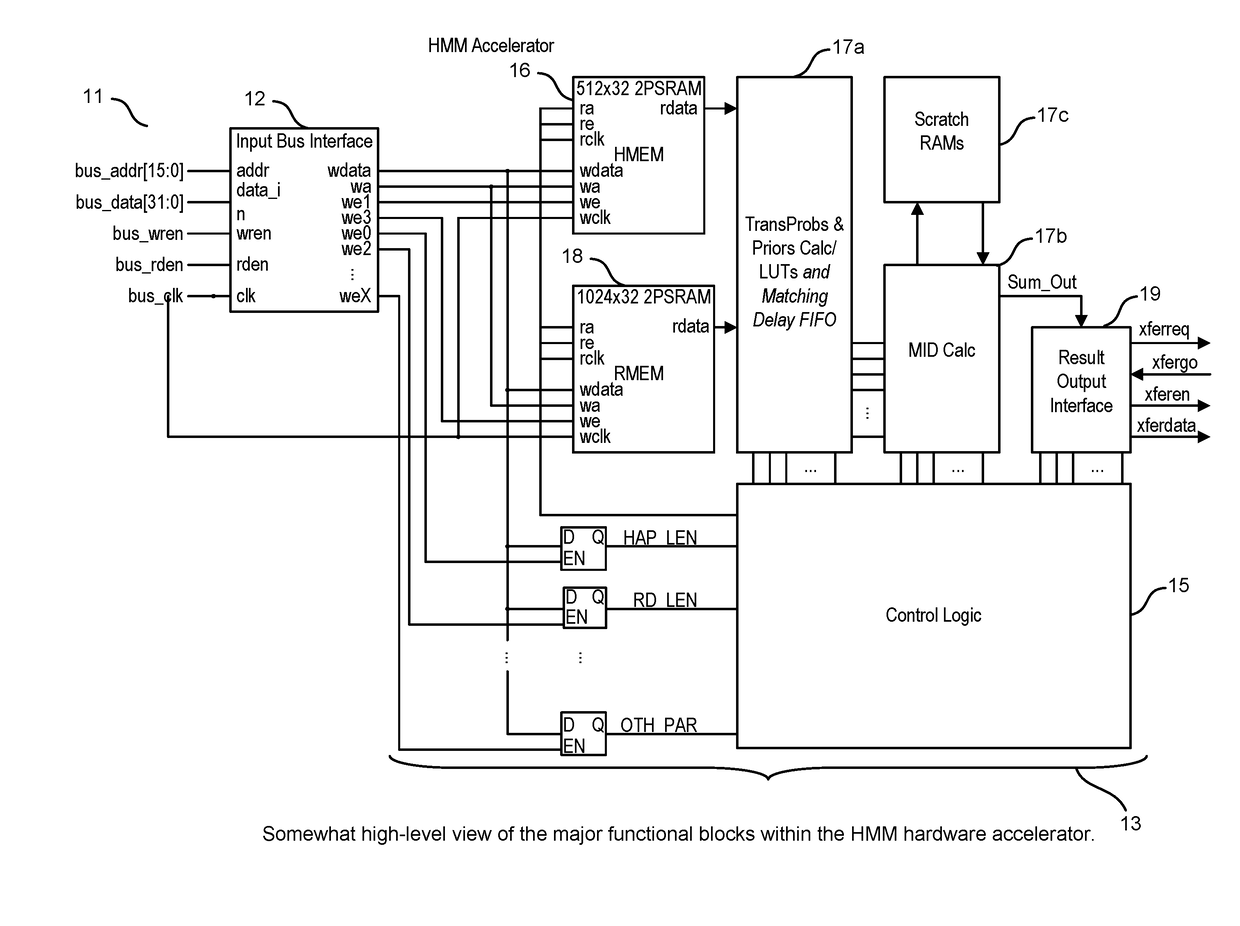
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data includes an integrated circuit formed of a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by physical electrical interconnects. One of the physical electrical interconnects forms an input to the integrated circuit that may be connected with an electronic data source for receiving reads of genomic data. The hardwired digital logic circuits may be arranged as a set of processing engines, each processing engine being formed of a subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits to perform one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis on the reads of genomic data. Each subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits may be formed in a wired configuration to perform the one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods executed on an integrated circuit processing platform
ActiveUS20160306923A1Processing speedProcessed result accuracyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMathematical modelsData sourceGenomic data
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data includes an integrated circuit formed of a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by physical electrical interconnects. One of the physical electrical interconnects forms an input to the integrated circuit that may be connected with an electronic data source for receiving reads of genomic data. The hardwired digital logic circuits may be arranged as a set of processing engines, each processing engine being formed of a subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits to perform one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis on the reads of genomic data. Each subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits may be formed in a wired configuration to perform the one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Virus infection detection and identification method based on metagenomics
ActiveCN105112569AHigh detection sensitivityLow initial sample size requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementViral nucleic acidNucleic acid sequence
The invention provides a virus infection detection and identification technology based on metagenomics. The virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics comprises the four portions of sample preparation, high-throughput sequencing, bioinformatic analysis and result re-checking. In the sample preparation portion, viral nucleic acid is effectively extracted or enriched from detection samples according to the requirements of the virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics and characteristics of different types of detection samples, and a nucleic acid library which can be used for a next-generation sequencing instrument is established. In the high-throughput sequencing portion, the nucleic acid library established in the sample preparation step is sequenced so to obtain sufficient high-quality nucleic acid sequence information. In the bioinformatic analysis portion, a large number of high-quality nucleic acid sequences obtained in the high-throughput sequencing step is analyzed to further obtain viral component information prompted by the nucleic acid of the samples. In the result re-checking portion, a bioinformatic analysis result and other information, such as technical contrast, are integrated to perform comprehensive study and judgment, finally alternative infection virus is determined, and other technologies, such as PCR, are utilized to perform re-checking.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
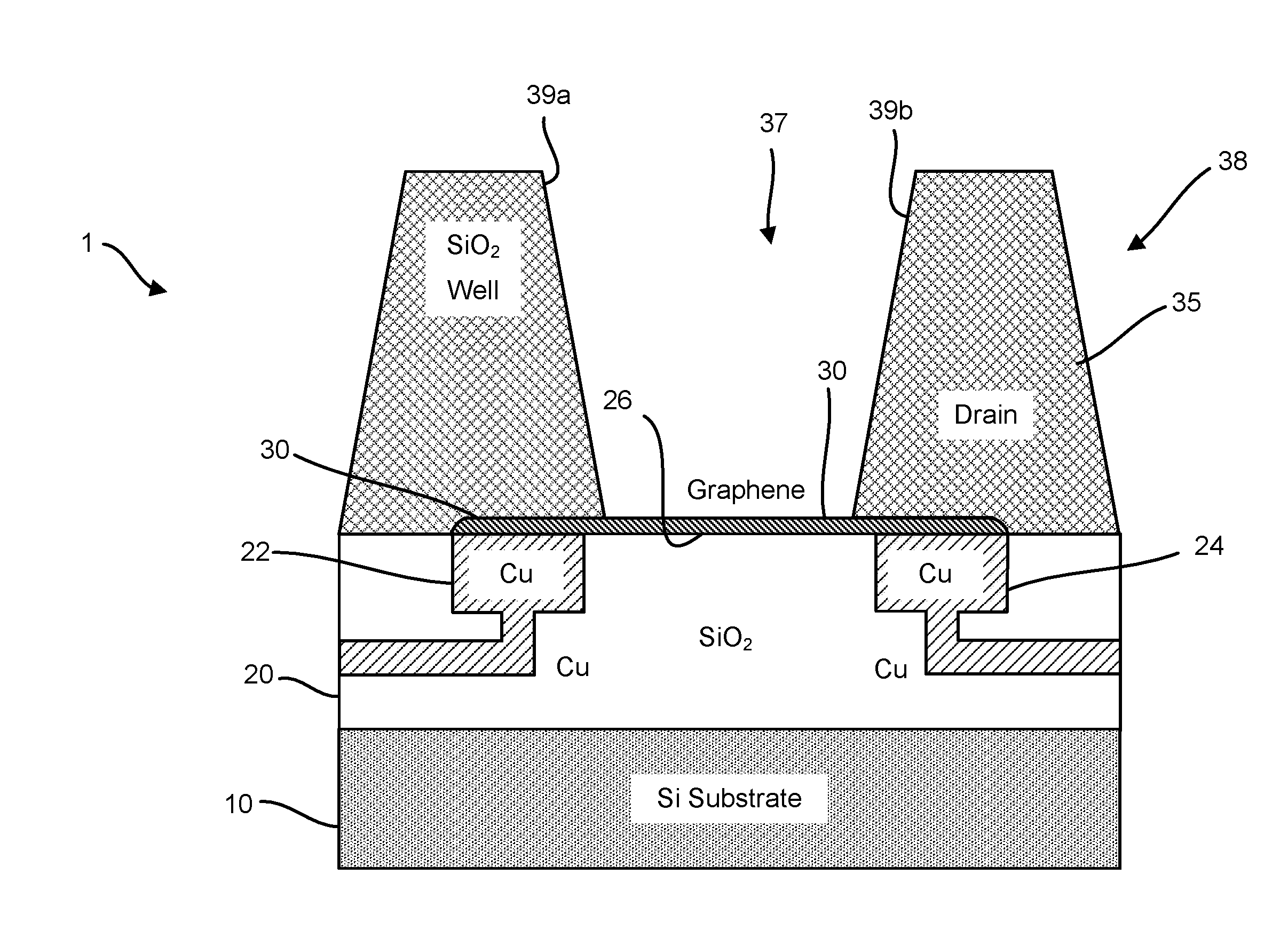
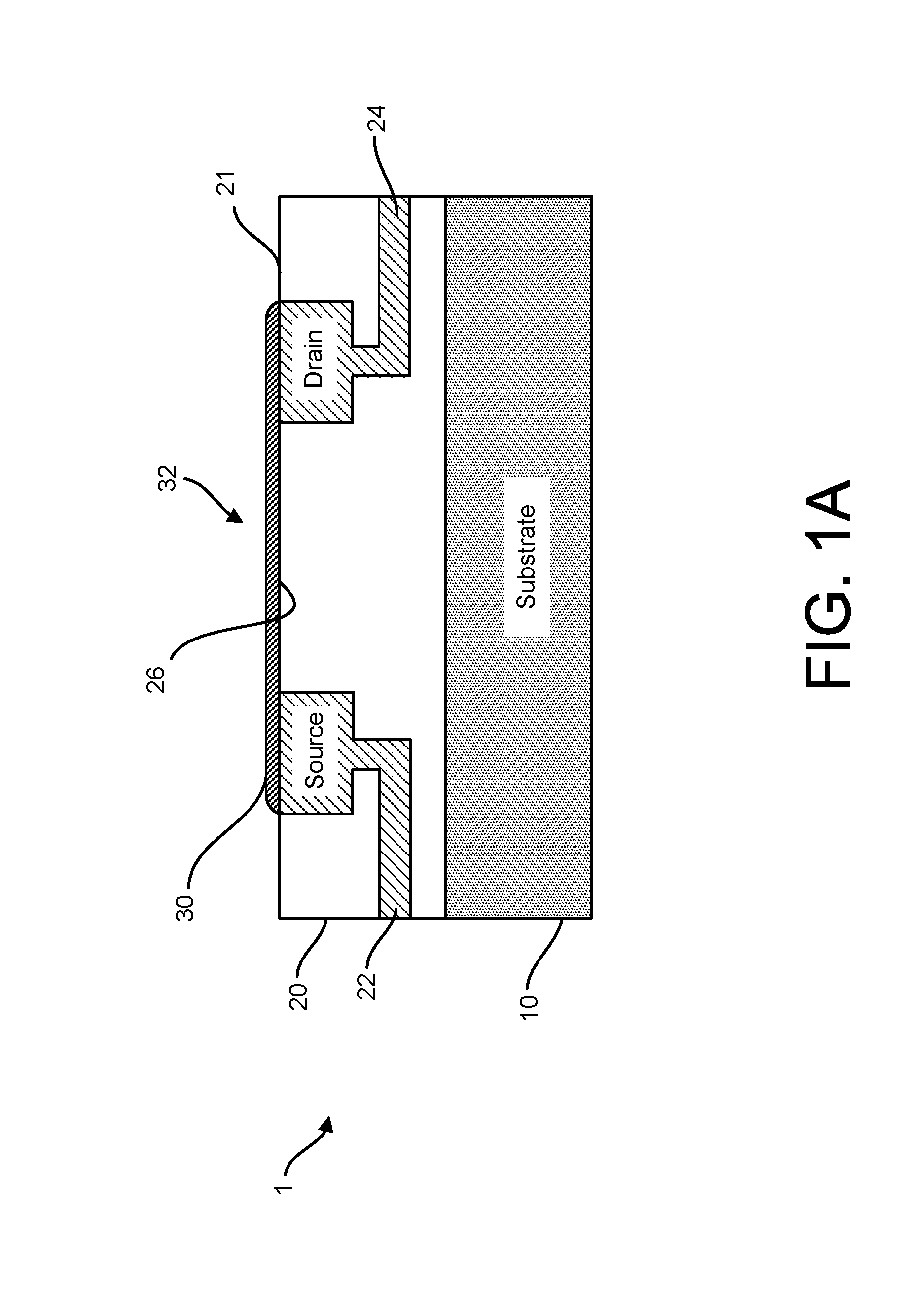
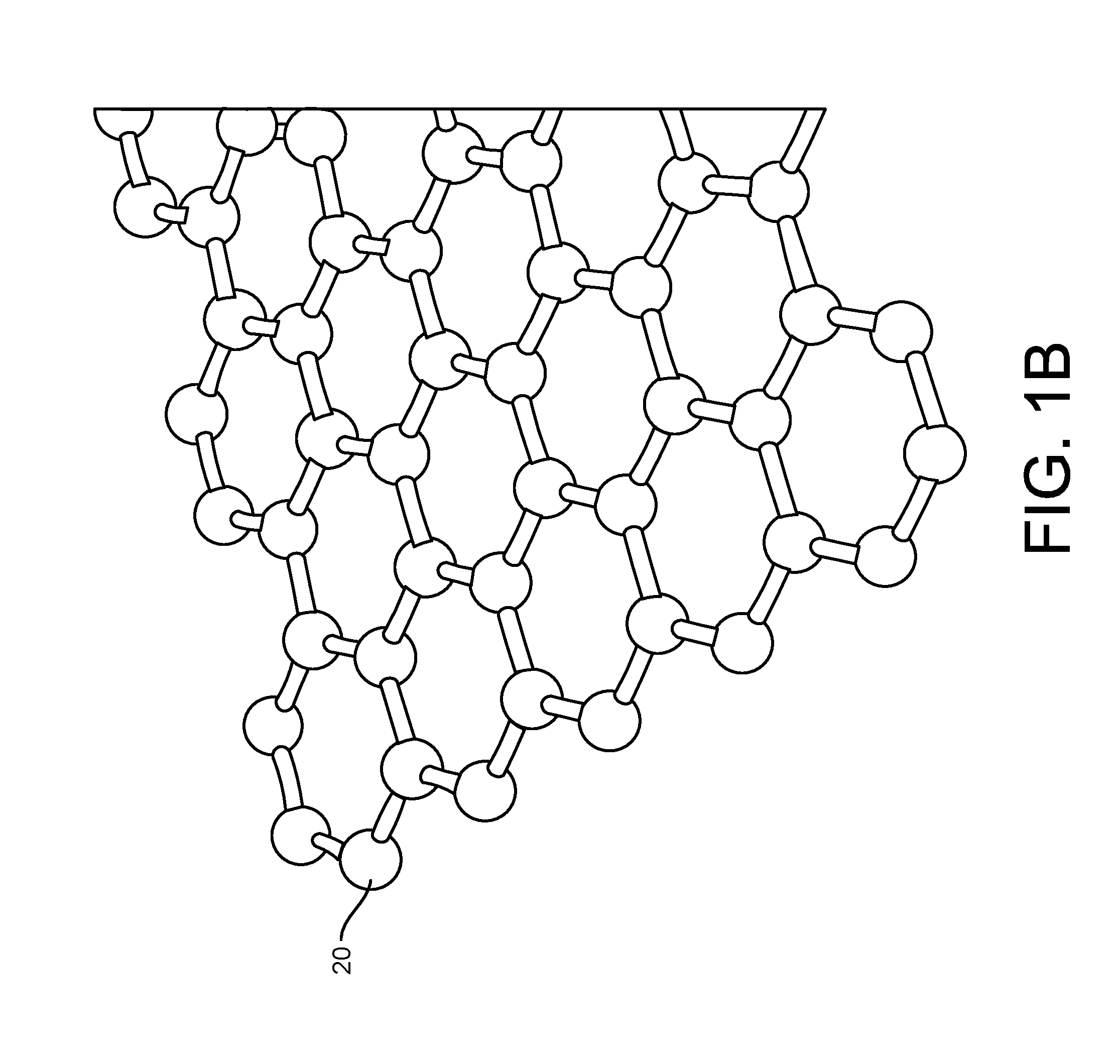
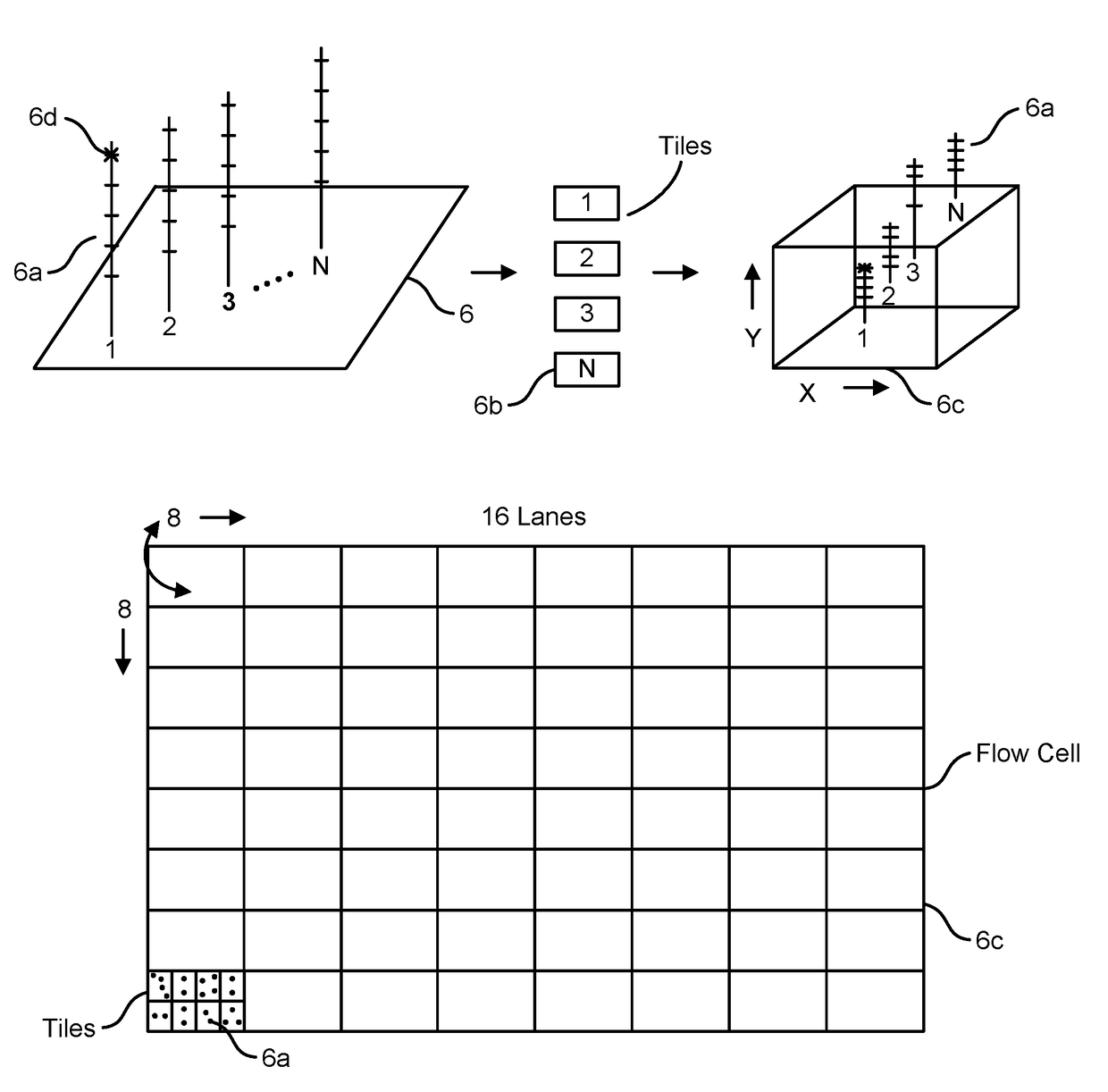
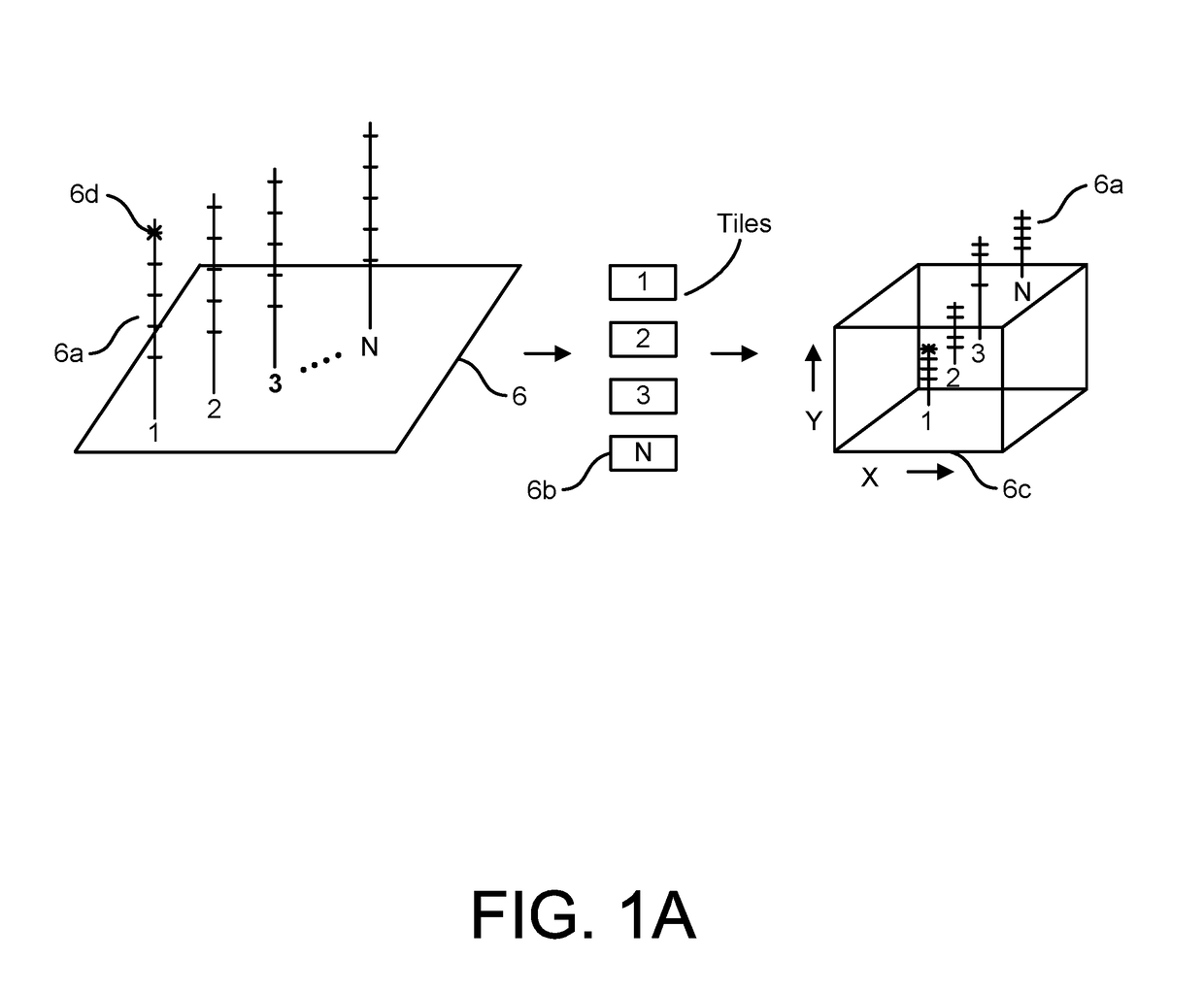
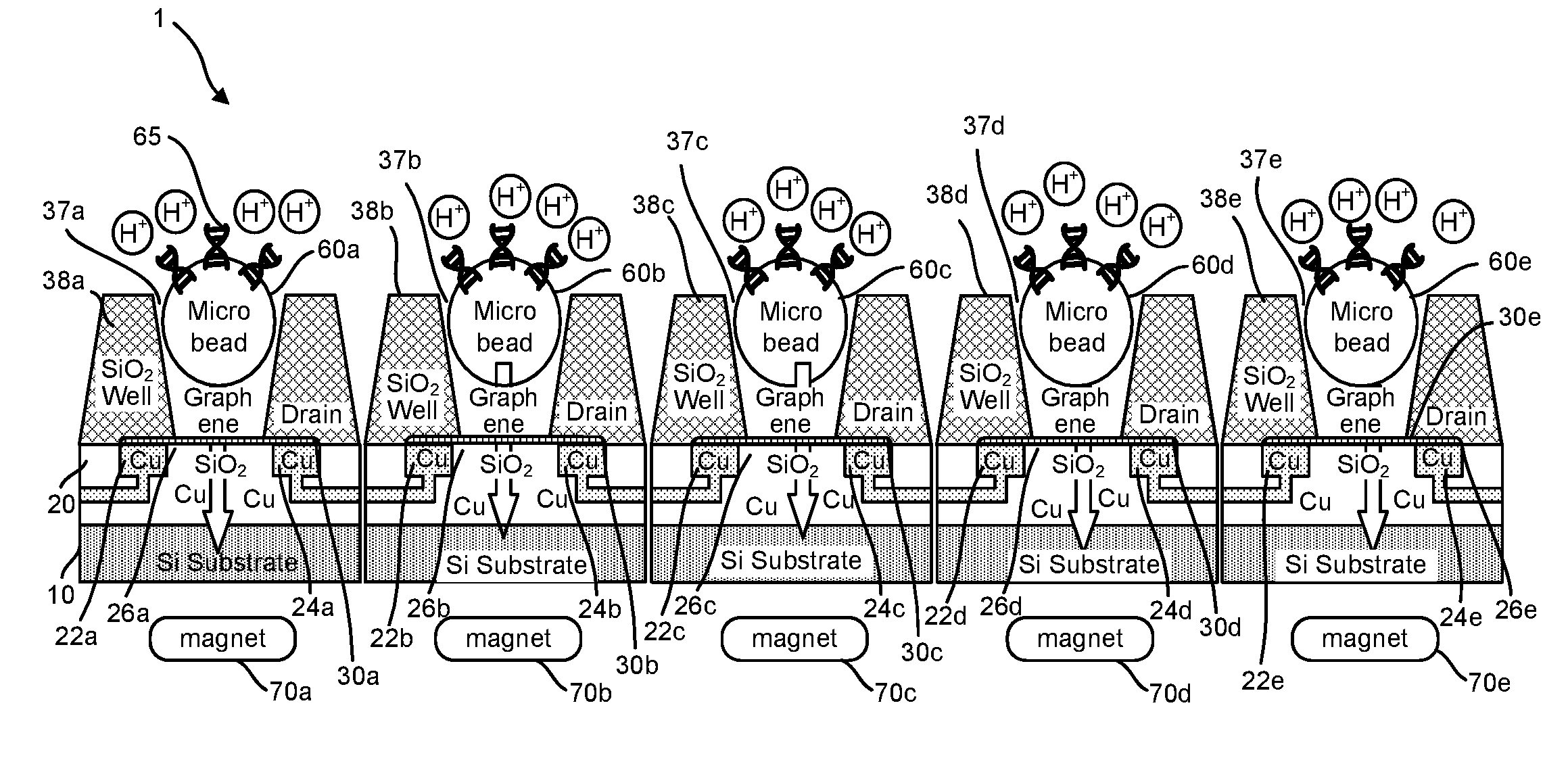
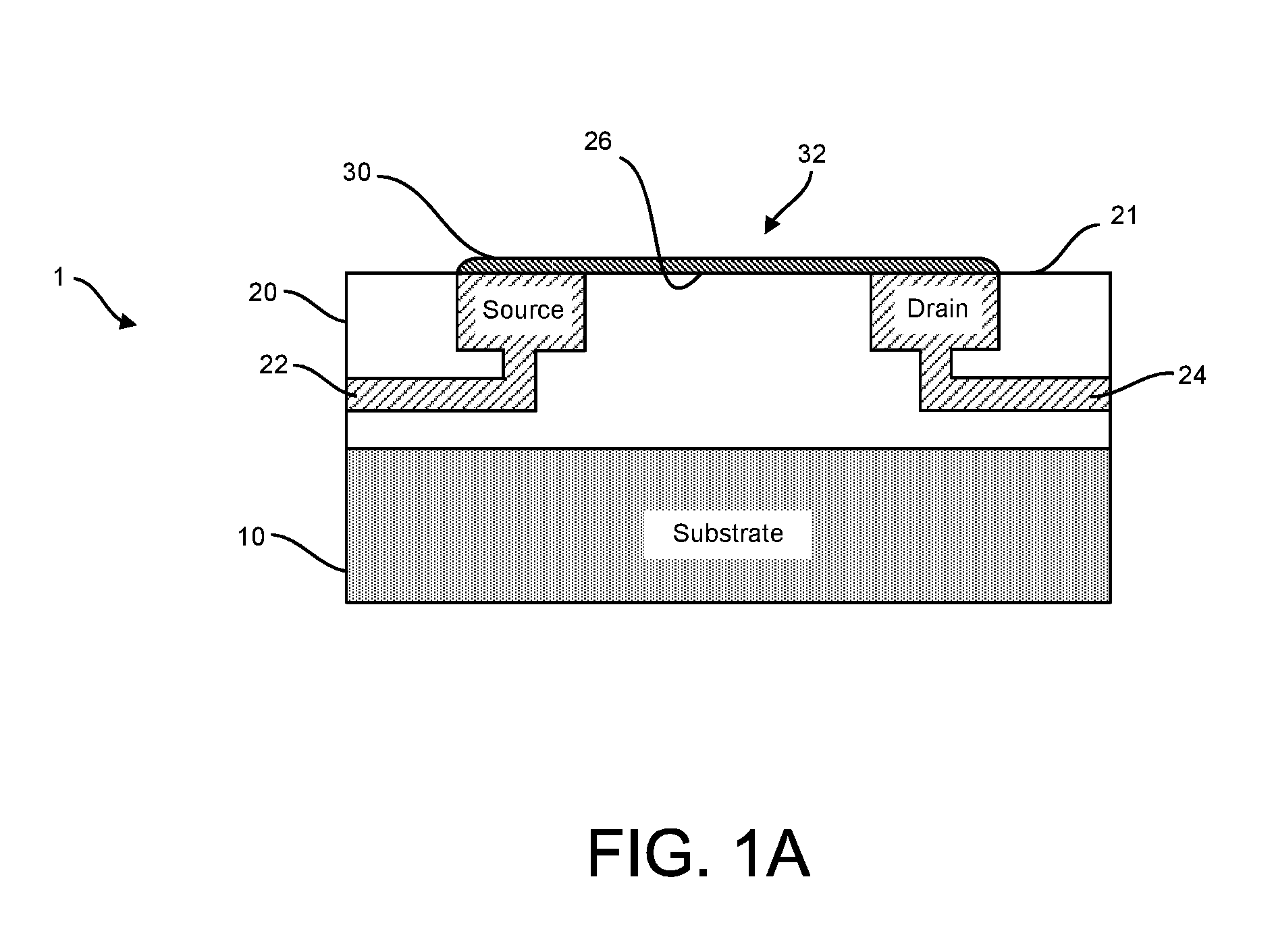
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
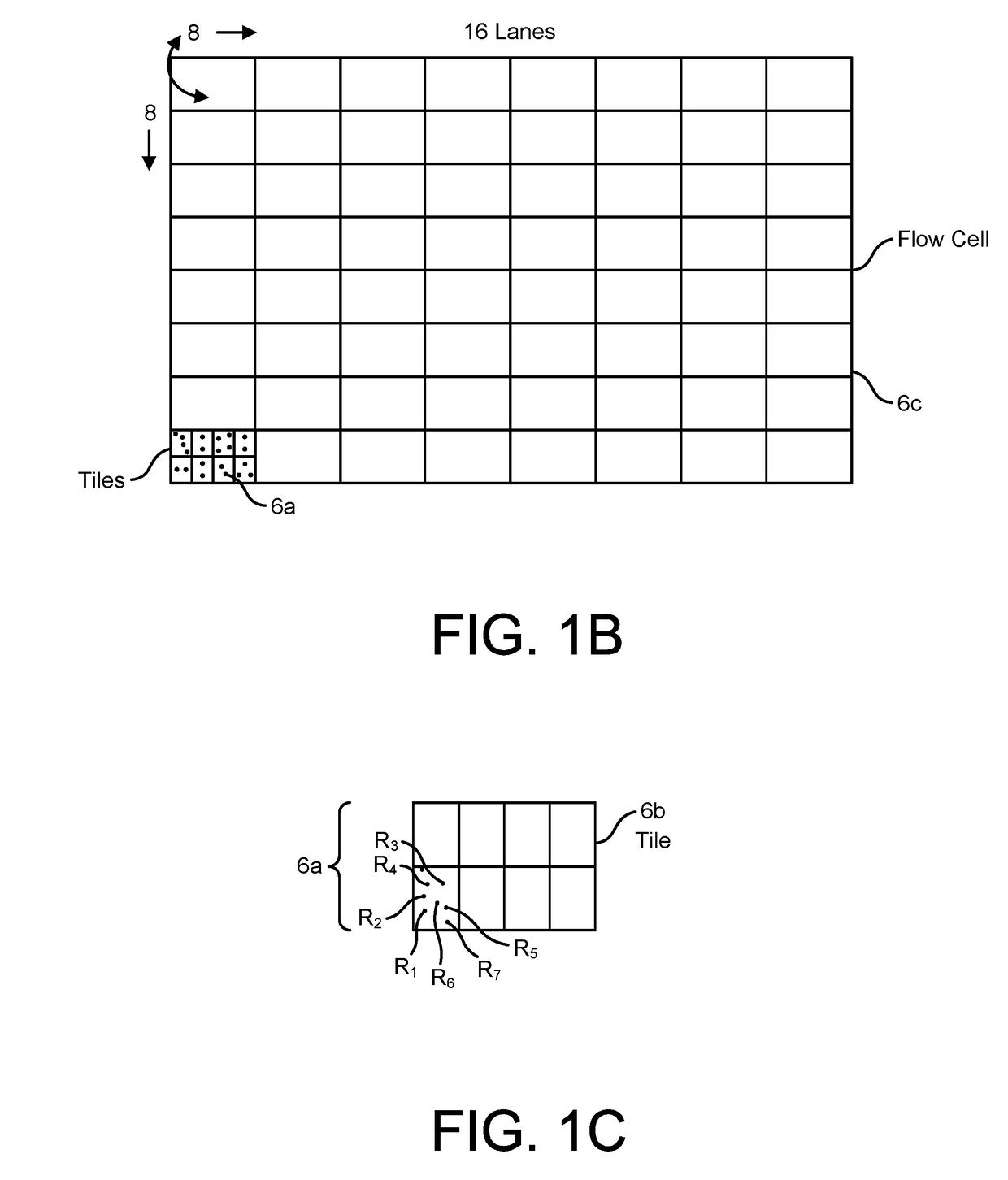
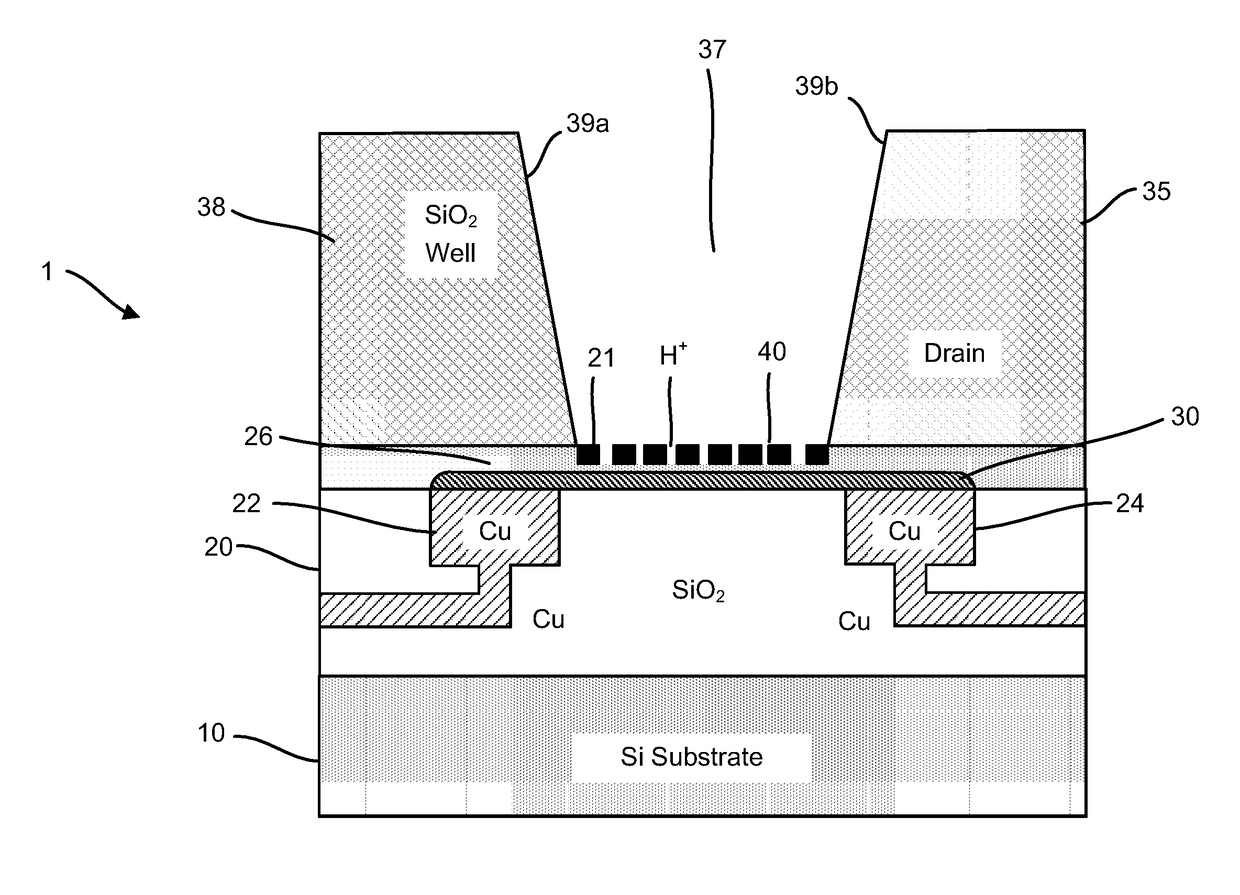
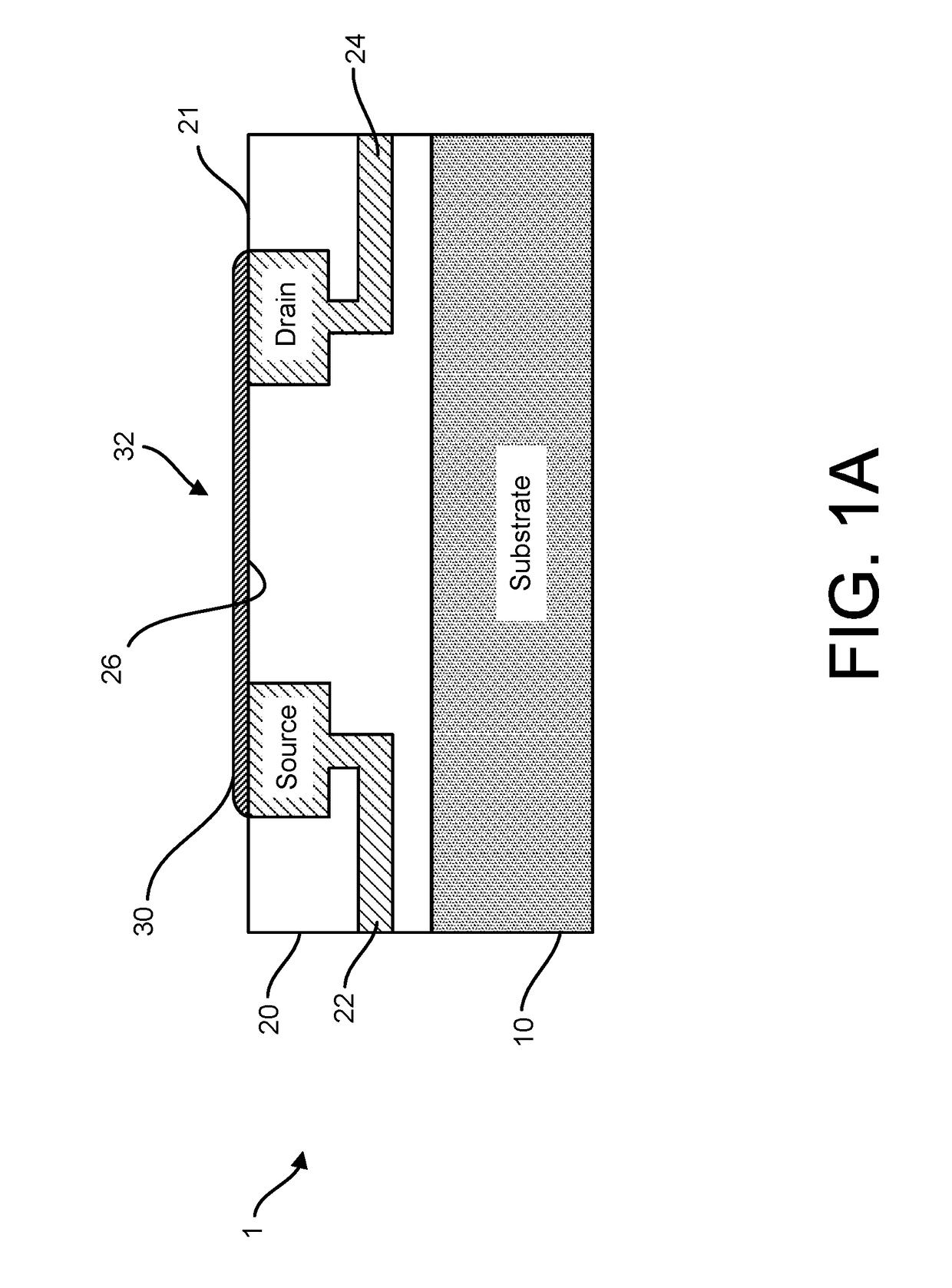
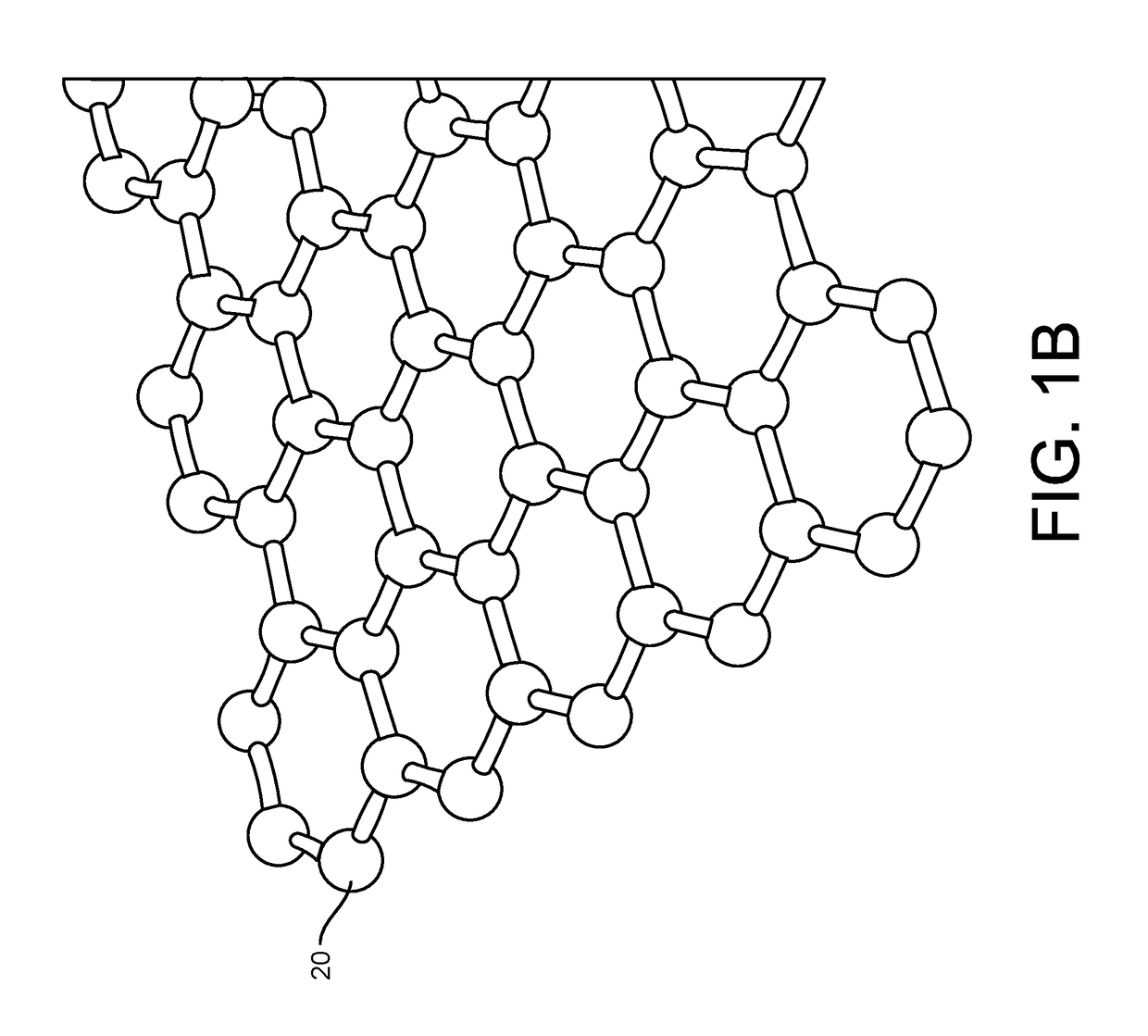
ActiveUS20160265047A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayReaction layer
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
InactiveUS20180121601A1Improve processing speedImprove accuracyInternal/peripheral component protectionProteomicsSequence analysisGenomics
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
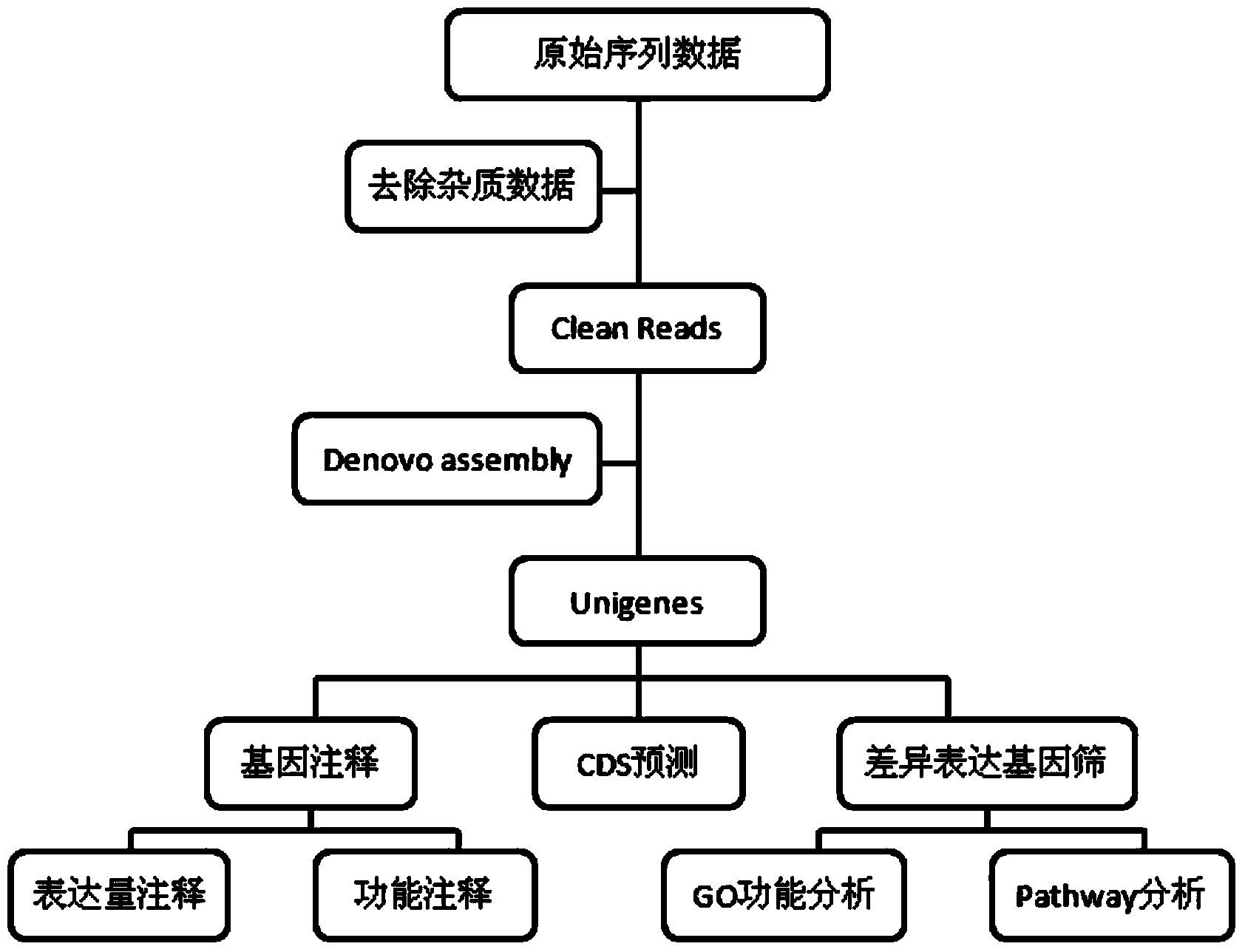
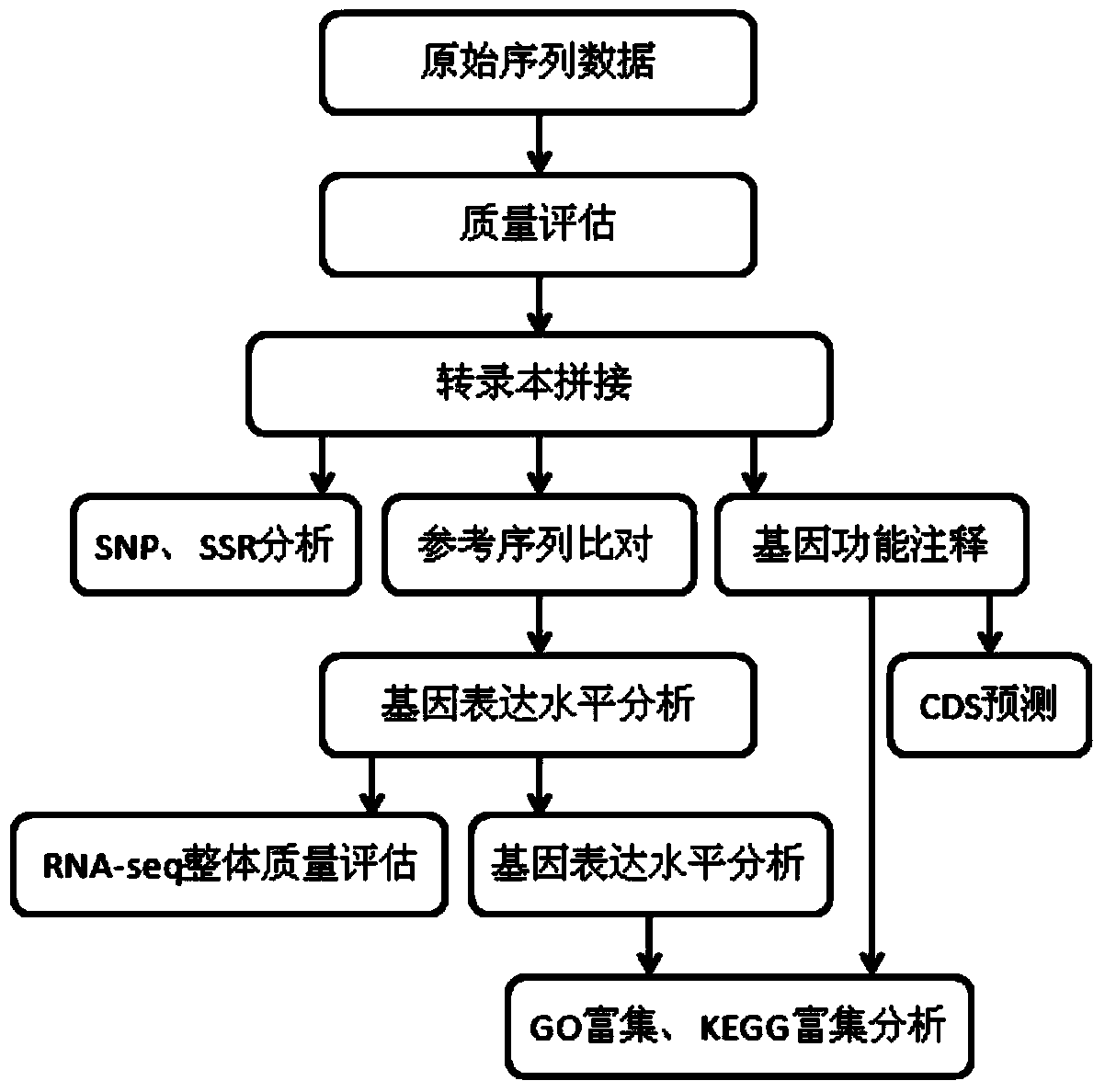
Method for developing mung bean simple sequence repeat (SSR) primer based on transcriptome sequencing
InactiveCN103642912AImprove design success rateSimple designMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence databaseTranscriptome Sequencing
The invention provides a method for developing a mung bean simple sequence repeat (SSR) primer based on transcriptome sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a set of mung bean genome-wide transcription, and forming a sequence database; splicing sequencing sequences into a transcriptome by Trinity; taking the longest transcript in each gene as Unigene; carrying out bioinformatics analysis of a Unigene sequence; carrying out SSR detection on the Unigene by adopting MISA1.0; carrying out SSR primer design by using a Primer 3, and carrying out SSR primer polymorphism identification. 13134 pairs of SSR primers are successfully designed by application of the method; 50 pairs of primers are randomly selected to verify 8 parts of mung bean deoxyribonucleic acids (DNAs) from different countries, wherein 32 pairs of polymorphic primers are formed in all; the mung bean materials with different geographical origins can be distinguished by using the 32 pairs of SSR primers. The method disclosed by the invention is convenient, fast and accurate, and low in cost, and a new thought is provided for development of the mung bean SSR primer.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Graphene FET devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS9618474B2Faster data acquisitionImprove accuracyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20170018626A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
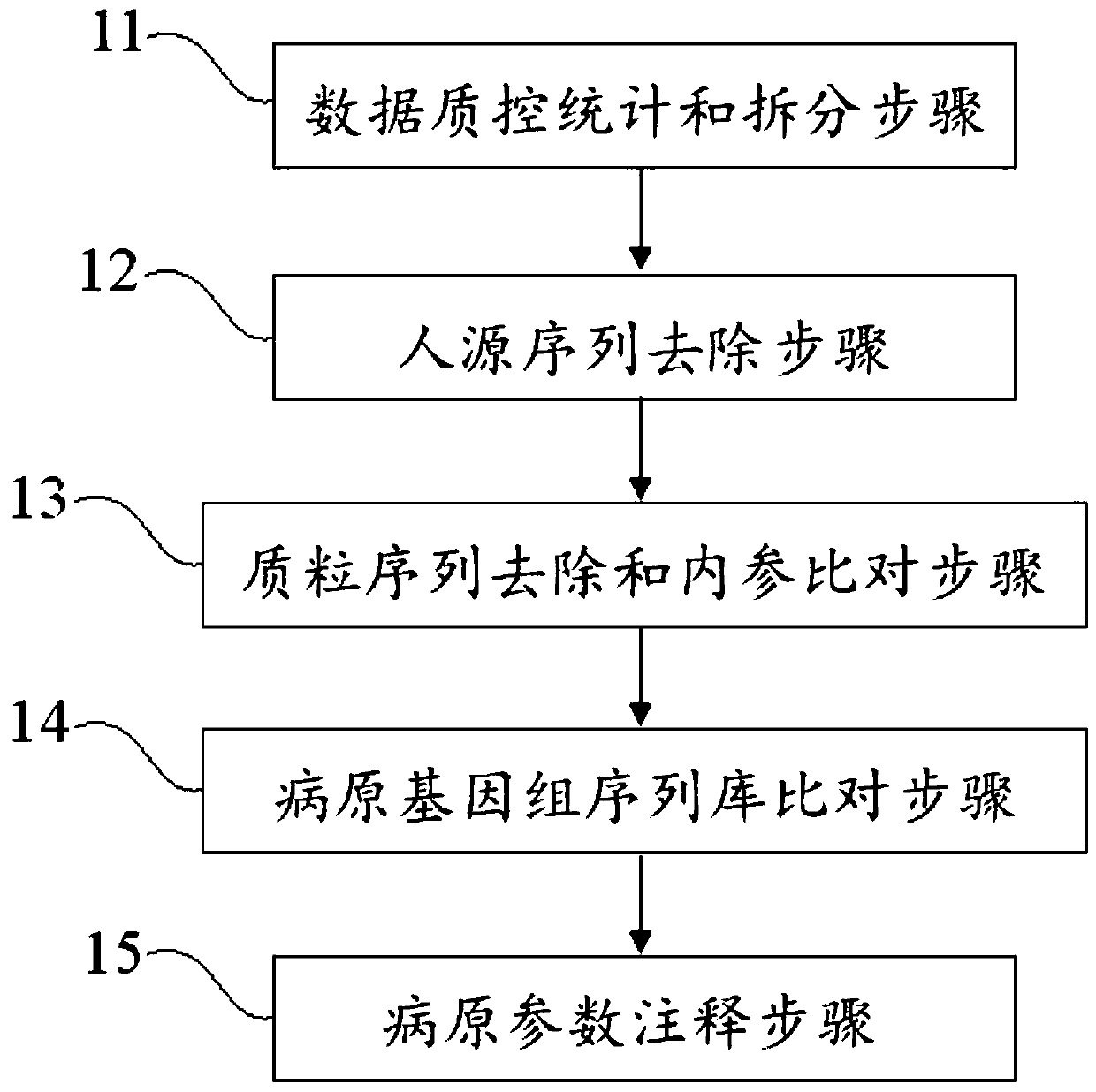
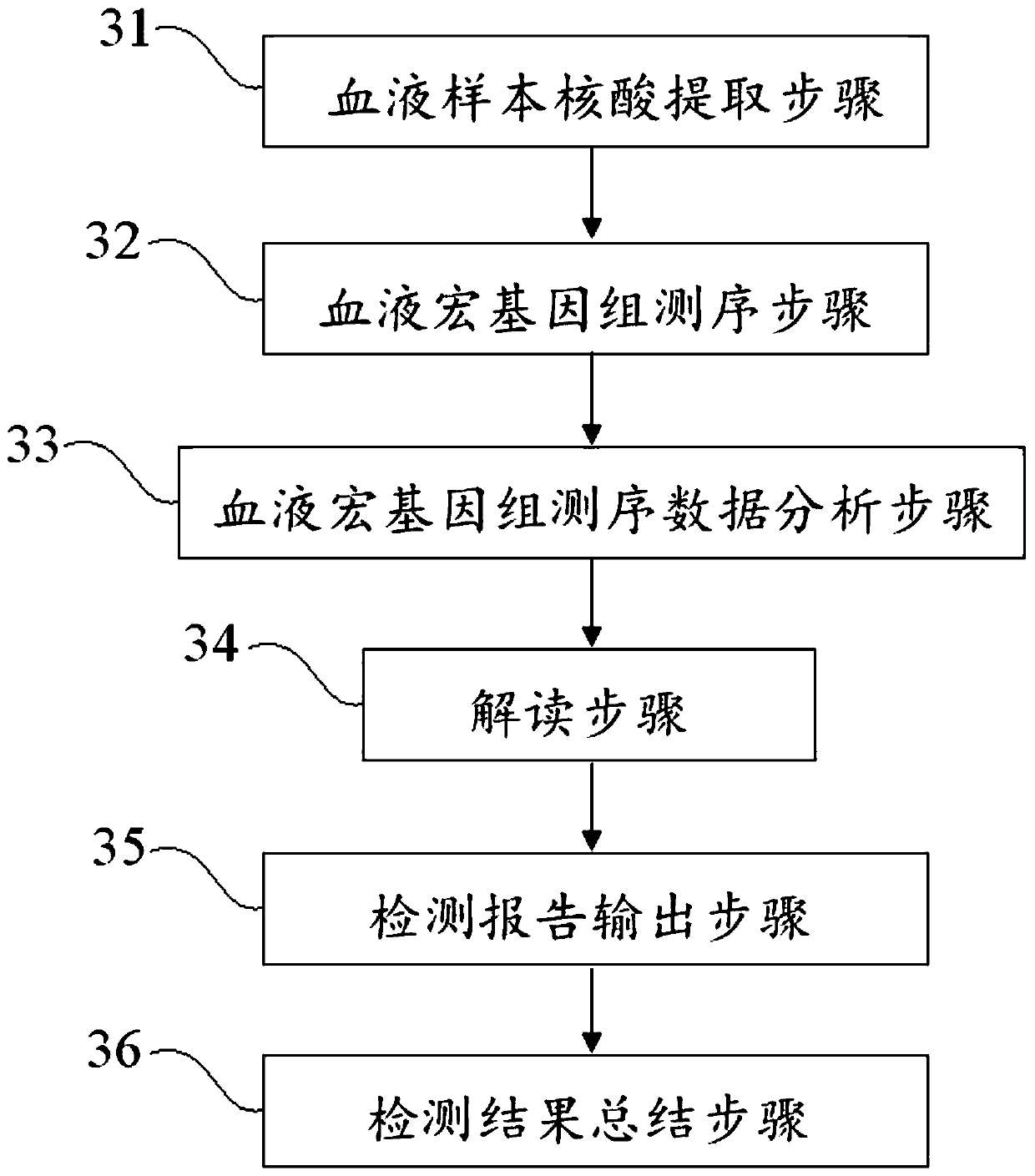
Blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method and device and application thereof
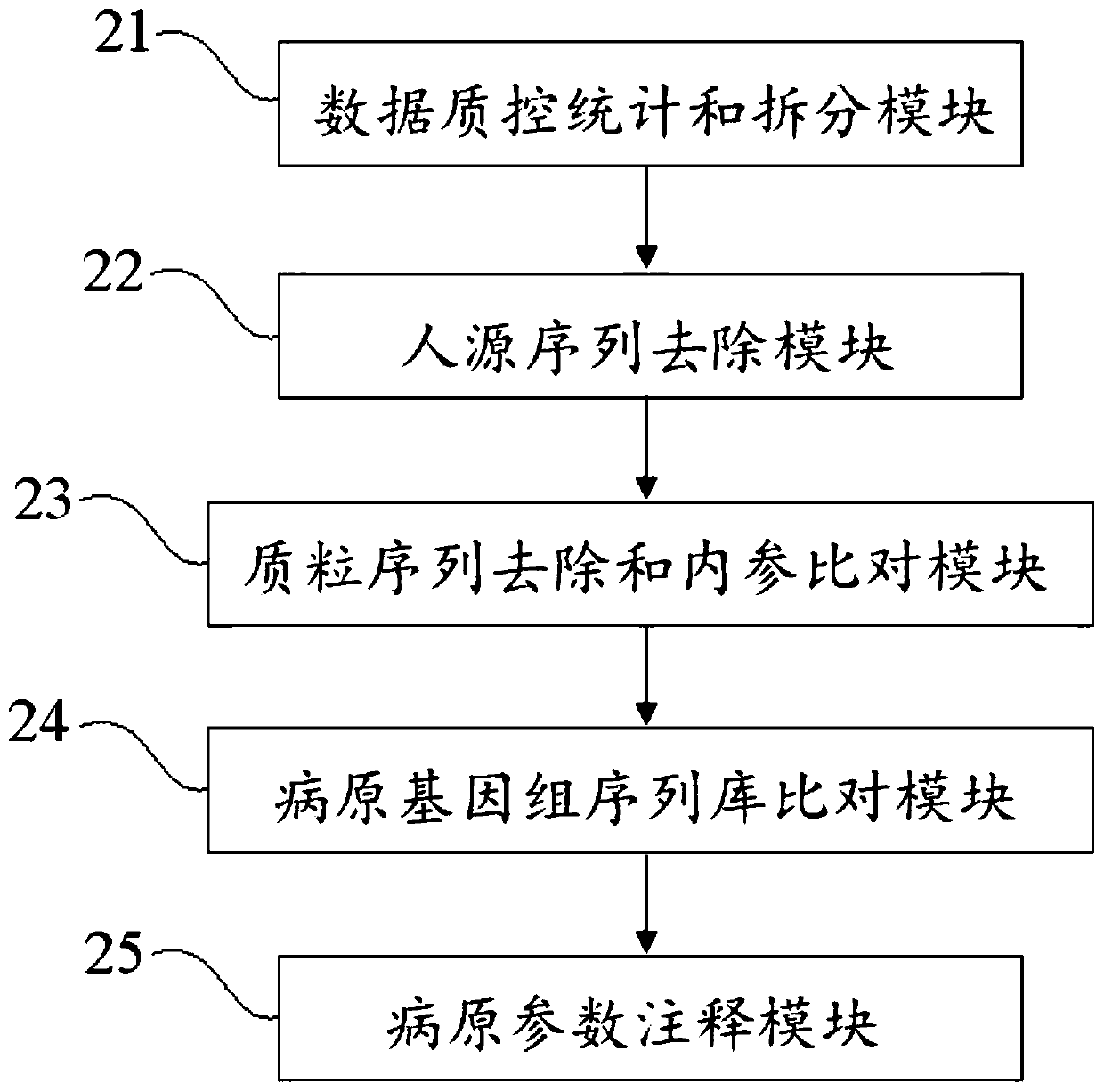
ActiveCN110349630AEffective deep diggingRealize Interpretation AnalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic sequencingData quality
The invention discloses a blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method and device and an application thereof. The blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method comprises a data quality controlstatistics and splitting step, a humanized sequence removal step, a plasmid sequence removal and internal reference comparison step, a pathogen genome sequence library comparison step and a pathogen parameter annotation step. The invention provides a blood flow infection detection device based on a blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method. According to the method and device provided by theinvention, the free nucleic acid sequences in blood are detected through a metagenome sequencing method, a bioinformatics analysis method is combined, more than 8,000 pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites possibly existing in a blood flow infection patient body are detected at a time, and a detection result can be obtained within 24 hours at the soonest. The speed, the sensitivity, the accuracy and the efficiency of blood flow infection detection are greatly improved.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +1
Database-building method for amplicon sequencing
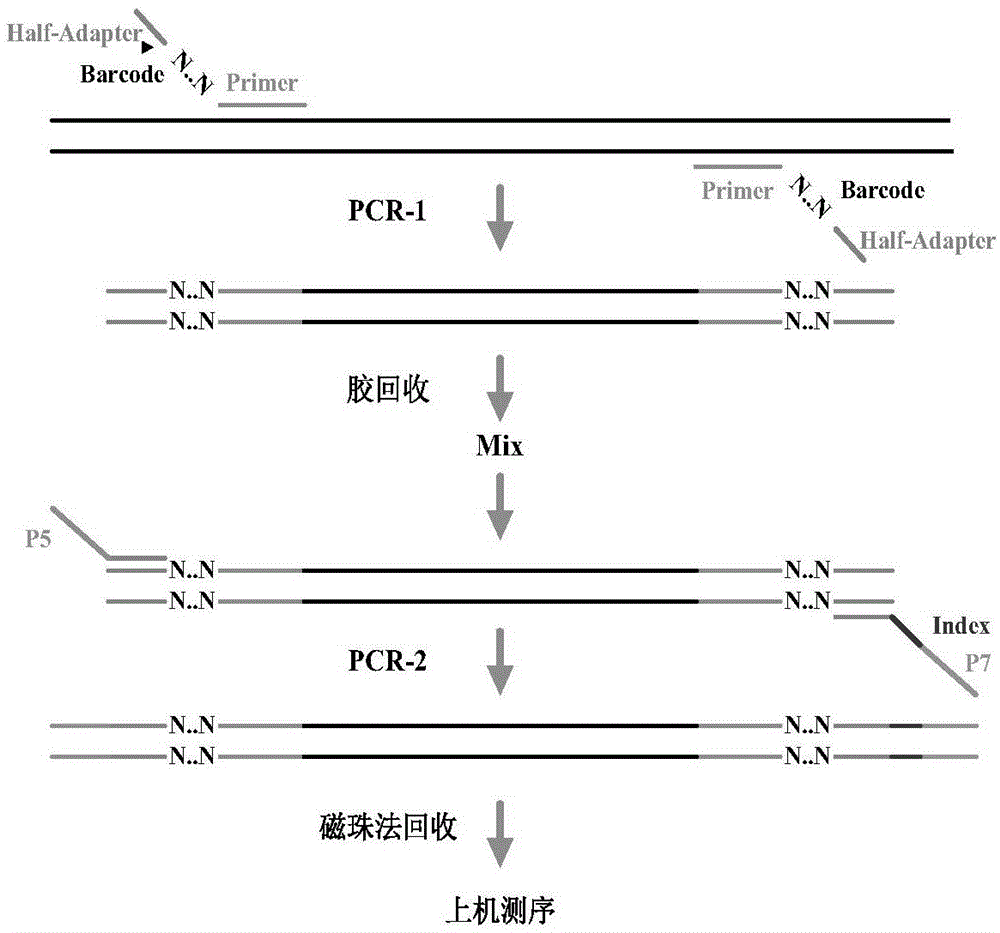
The invention relates to the technical field of high-flux sequencing and discloses a database-building method for amplicon sequencing. The database-building method comprises the following steps of 1, object region enrichment based on PCR amplification: designing primer sequences aiming at an object region of genome DNA of a sample to be detected, wherein ends 5' of a forward primer and a reverse primer in the primer sequences are provided with random base sequences and linking sequences, carrying out PCR amplification and recovering the PCR product, and 2, sequencing linker introduction based in PCR amplification: carrying out mixing on the PCR product obtained by the step 1, designing primer sequences comprising sequences complementary with the linking sequences obtained by the step 1, carrying out PCR amplification on the mixture, and recovering the PCR product so that a DNA database for amplicon sequencing is obtained. The database-building method reduces building time and cost of the DNA database for amplicon sequencing, reduces error of bioinformatics analysis of the sequencing result and improves accuracy and authenticity of the analysis result.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Primers and method for detecting drug resistance mutation site of hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN102181575AEasy to operateImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesResistance mutationHepatitis B virus
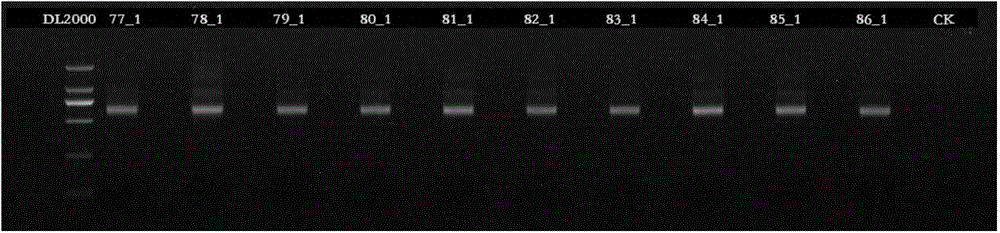
The invention discloses primers and a method for detecting a drug resistance mutation site of hepatitis B virus. The invention provides four pairs of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers for detecting the drug resistance mutation site of the hepatitis B virus, the four pairs of the PCR primers are used for amplifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a genome of the hepatitis B virus, and obtained four fragments are covered on the whole reverse transcriptase gene sequence of the hepatitis B virus in the overlapping way. The four PCR fragments are mixed according to the equal molar ratio for preparing a reverse transcriptase gene bank, 454 high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis are performed, and whether the hepatitis B virus in a blood serum sample of a patient with the hepatitis B virus contains the drug resistance mutation site or not can be detected. By adopting the primers and the method, above 1% of drug resistance mutation of the hepatitis B virus in blood serum of the patient can be detected, the method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simpleness in operation, large throughput and the like, and the analysis of the drug resistance mutation site of a plurality of samples can be performed by sequencing once.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
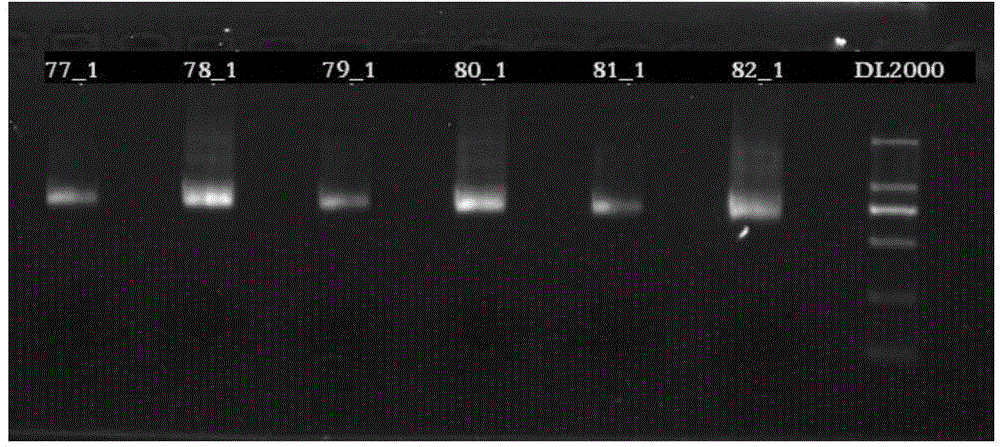
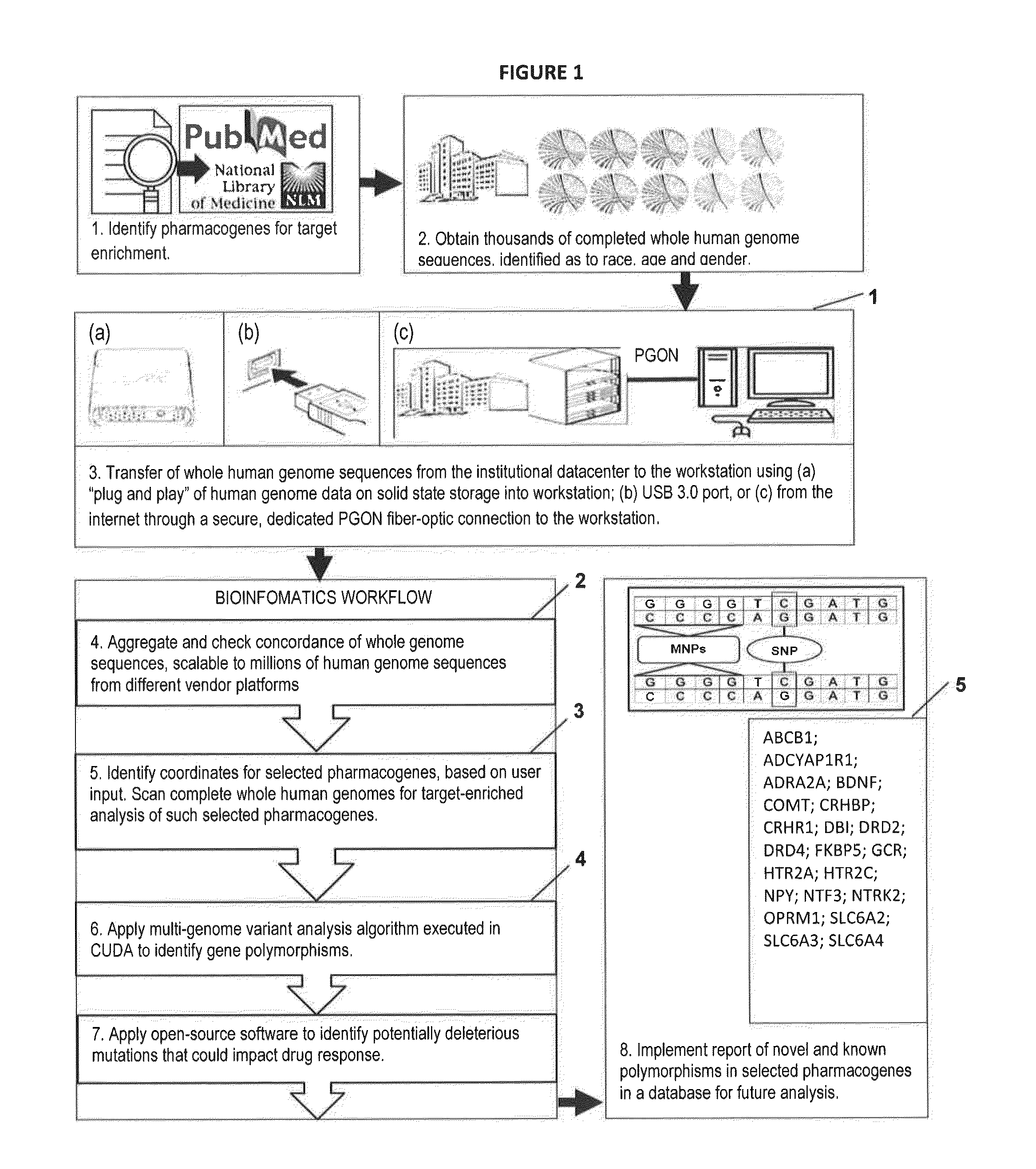
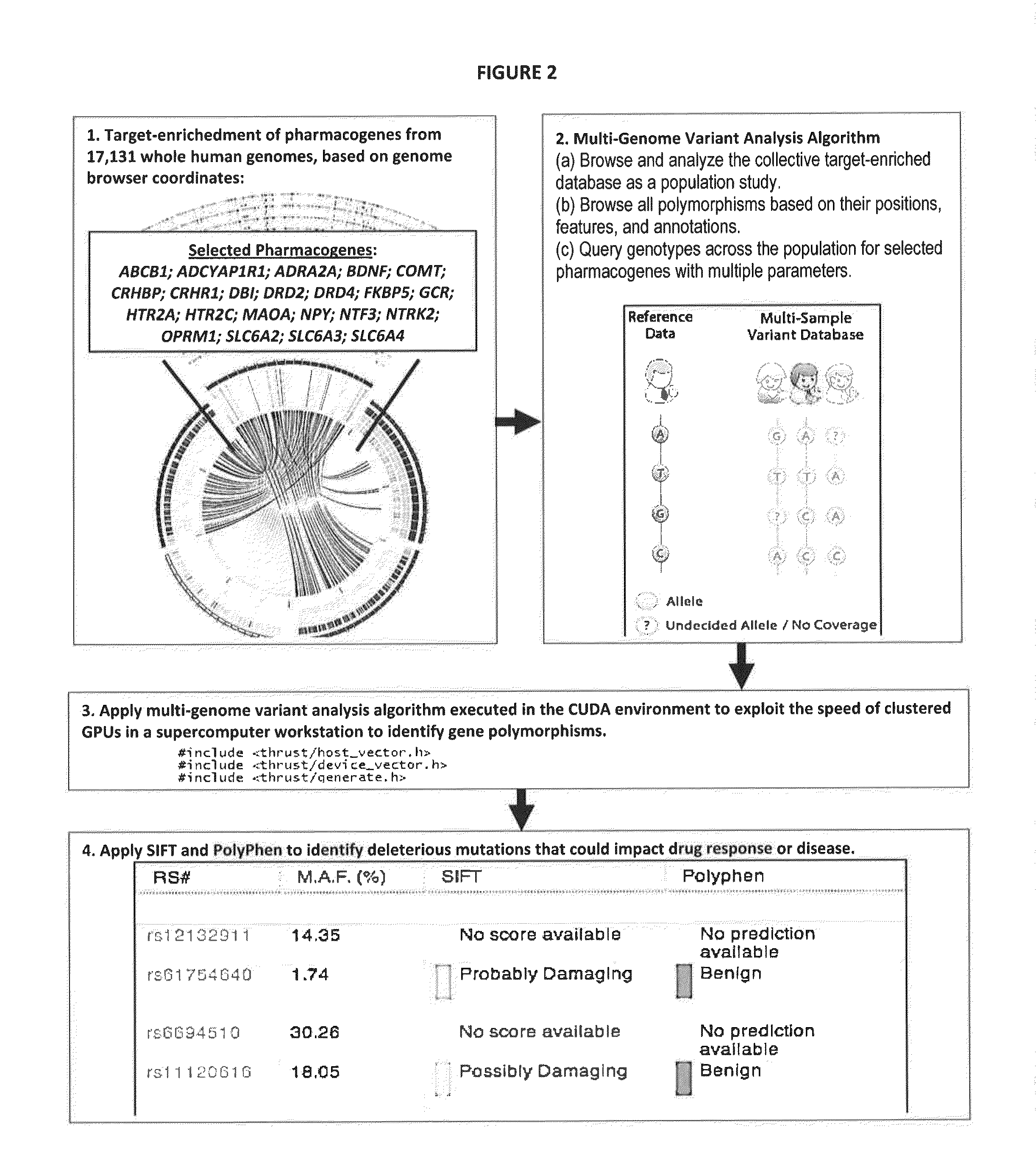
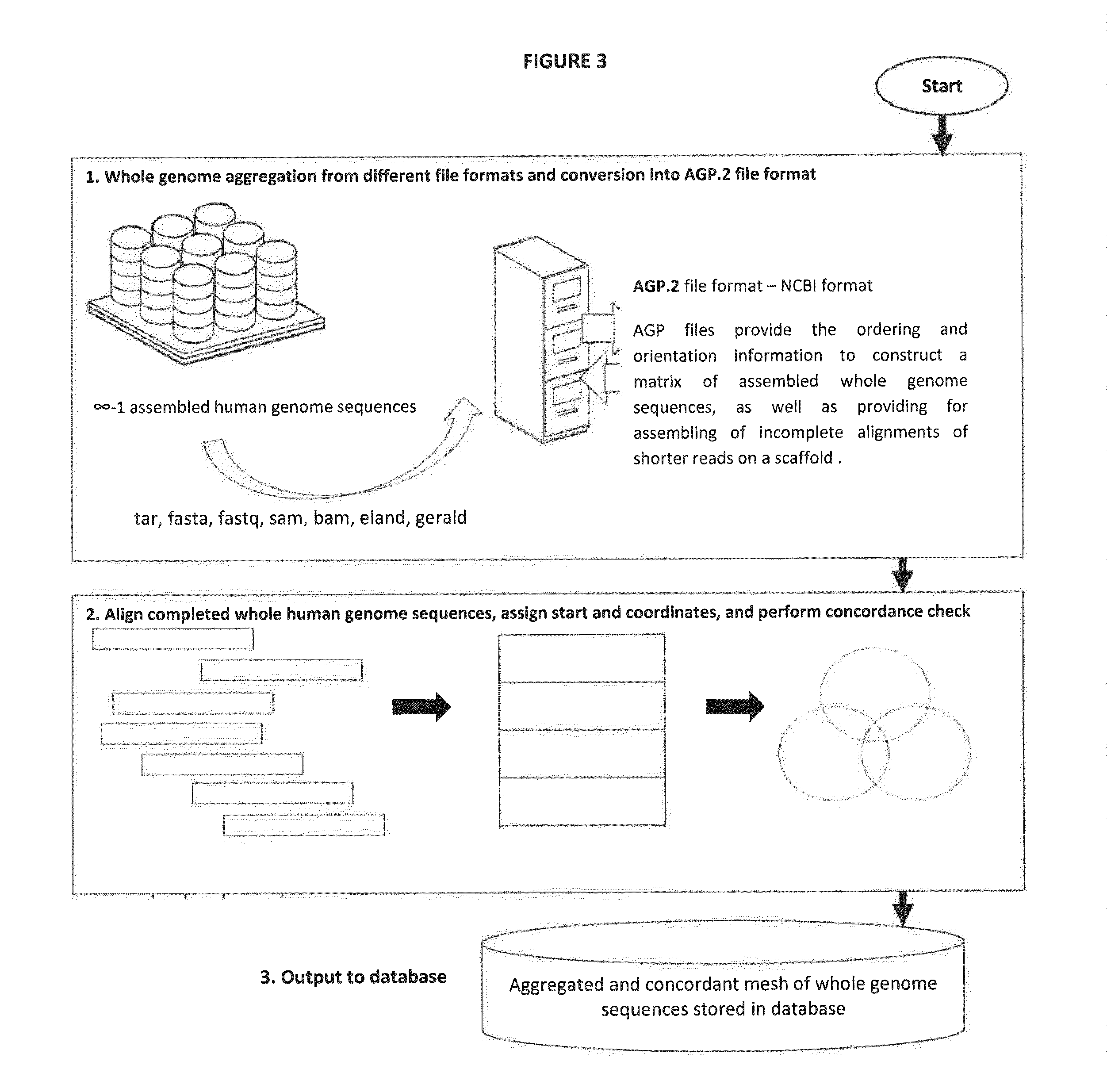
Novel Pharmacogene Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Methods of Detecting Same
InactiveUS20140038836A1Energy efficiencyInexpensive, energy-efficientSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingNucleotide
The present invention provides pharmacogene polymorphisms and their use in predicting therapeutic effectiveness. The present invention also provides methods comprising targeted analysis of selected pharmacogenes in thousands of compiled whole human genome sequences for identifying polymorphic sequences associated with drug response are described. The methods also provide confirmation and validation of these pharmacogene polymorphisms, based on concordance between different sequencing technologies, and statistical error-checking. Imputation of the deleterious consequences of novel variants is predicted by bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:ASSUREX HEALTH INC
Nervous system genetic disease gene united screening method, kit and preparation method thereof
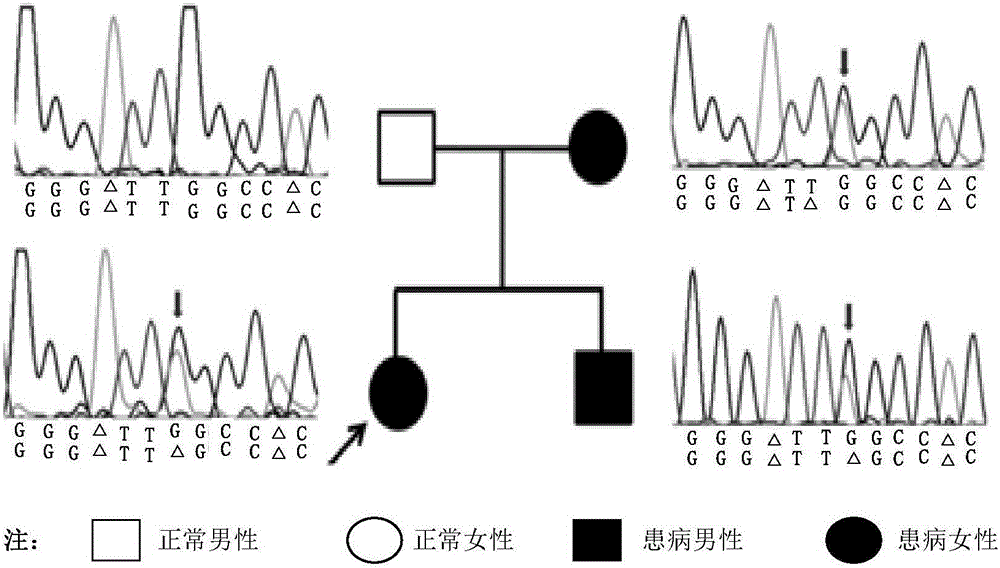
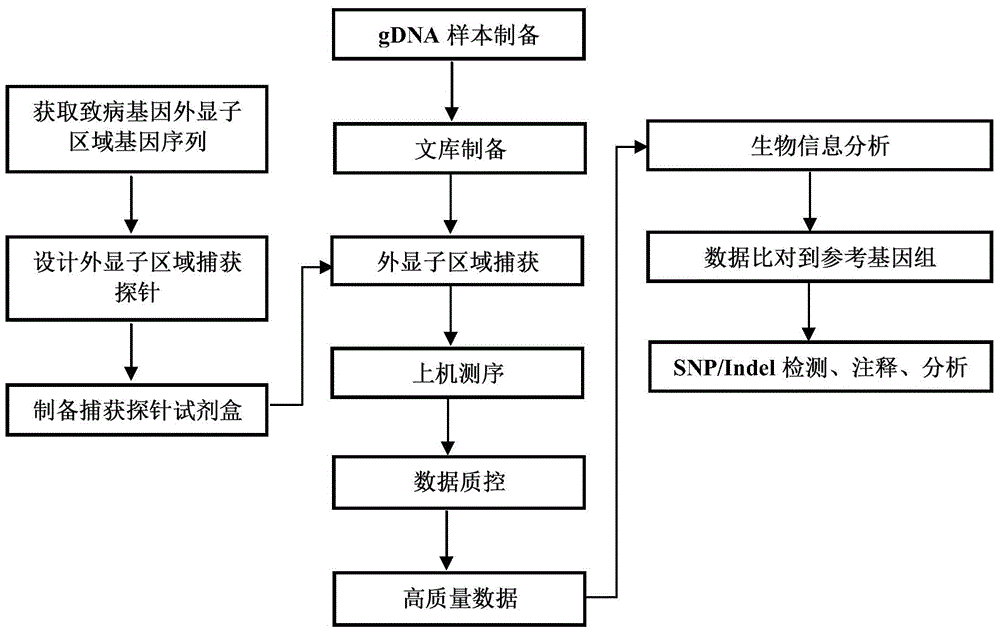
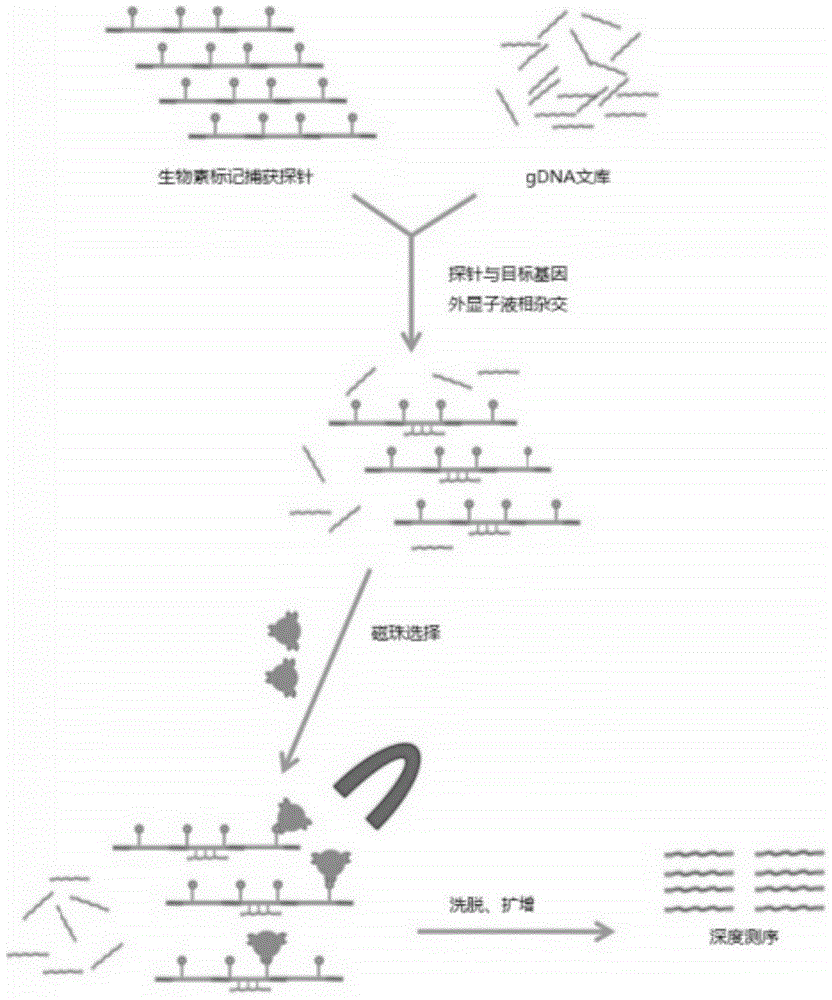
The invention provides a nervous system genetic disease gene united screening method, a kit and a preparation method thereof. The gene screening method includes: firstly constructing a whole-genome DNA library construction of a subject, then capturing a target gene sequence with the prepared nervous system genetic disease gene screening kit, then detecting the sample through a double-end 150bp sequencing mode of a high-throughput sequencing platform (Illumina HiSeq 3000), performing bioinformatic analysis of the data result, and finding out mutation information sites of genes related to nervous system genetic diseases so as to reach the genetic diagnosis purpose. The method provided by the invention can rapidly and accurately cover the exon regions of all nervous system genetic disease genes known at present.
Owner:GENERGY BIO TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
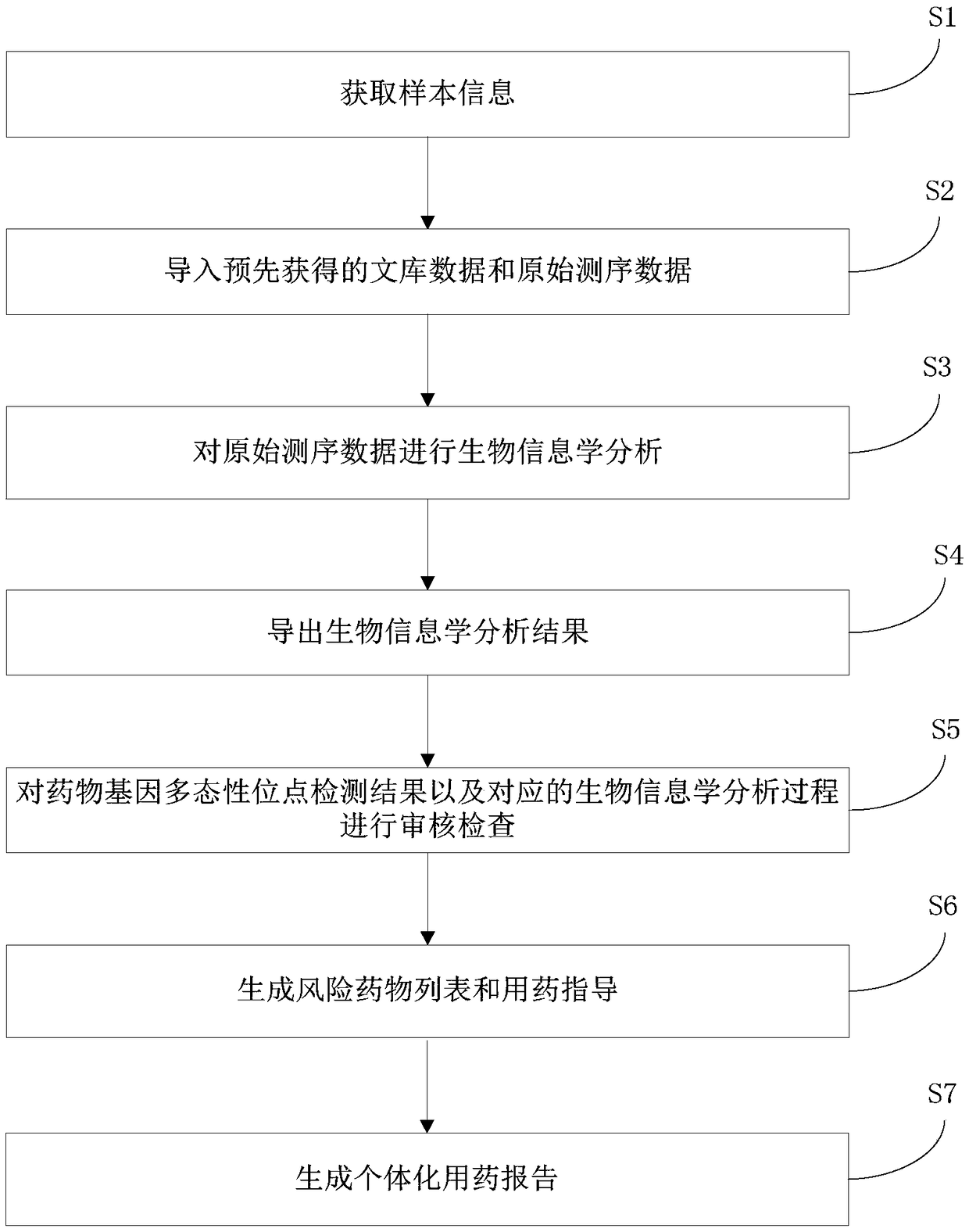
Individualized pharmacy report generation method and system
InactiveCN109378044AImprove user experienceReduce participationProteomicsMedical practises/guidelinesBiologySimple computation
The invention discloses an individualized pharmacy report generation method and system. The method comprises the steps: acquiring sample information; inputting library data and original sequencing data obtained by genetic testing in advance; performing bioinformatics analysis on the original sequencing data; outputting a bioinformatics analysis result, carrying out examination and checking on a drug gene polymorphic site detection result and a corresponding bioinformatics analysis process, generating a risk drug list and a pharmacy guidance, and generating an individualized pharmacy report andthe like. According to the invention, the method is convenient to implement based on the computer program. Related data can be invoked automatically and conveniently as long as a checked person or another user inputs sample information at the user terminal; the individualized pharmacy report is generated and is outputted by the user terminal, so that the error caused by the manual operation is reduced. The user does not need to master the relevant medical and computer professional knowledge and only needs to make the simple compute operation, so that the user experience is improved. The individualized pharmacy report generation method and system can be widely applied to the technical field of the medical information engineering.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Method for screening HRDs disease-causing mutation and gene chip hybridization probe designing method involved in same
ActiveCN103667438AClear relationshipScreening benefits are highMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseHybridization probe
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines, and relates to a method for screening HRDs disease-causing mutation and a gene chip hybridization probe designing method involved in the same. The method for screening the HRDs disease-causing mutation comprises the steps of (1) establishing an HRDs genetic resource repository; (2) designing and synthesizing a gene chip hybridization probe of an HRDs disease-causing gene, and integrating the gene chip hybridization probe onto a gene chip; (3) capturing a target area by utilizing the prepared gene chip and executing the depth sequencing; (4) analyzing the sequencing data on the aspect of bioinformatics, and screening the candidate disease-causing gene; (5) functionally predicting a newly-discovered splicing gene mutation site. By establishing the high-efficient HRDs target gene capturing technology, adopting the depth sequencing as a means and confirming the efficiency of the HRDs capturing chip, a high-efficient credible biological information analysis model is established.
Owner:赵晨
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods executed on an integrated circuit processing platform
ActiveUS9792405B2High sensitivityImprove accuracyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMathematical modelsElectricityData source
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data includes an integrated circuit formed of a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by physical electrical interconnects. One of the physical electrical interconnects forms an input to the integrated circuit that may be connected with an electronic data source for receiving reads of genomic data. The hardwired digital logic circuits may be arranged as a set of processing engines, each processing engine being formed of a subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits to perform one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis on the reads of genomic data. Each subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits may be formed in a wired configuration to perform the one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods executed on a quantum processing platform
ActiveUS20180240032A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyQuantum computersDigital data information retrievalDevice formGenomic data
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data includes a quantum computing device formed of a set of hardwired quantum logic circuits interconnected by a plurality of superconducting connections to process information represented as a quantum state that is configured as a set of one or more qubits. The hardwired quantum logic circuits may be arranged as a set of processing engines, each processing engine being formed of a subset of the hardwired quantum logic circuits to perform one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis on the reads of genomic data. Each subset of the hardwired quantum logic circuits may be formed in a wired configuration to perform the one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
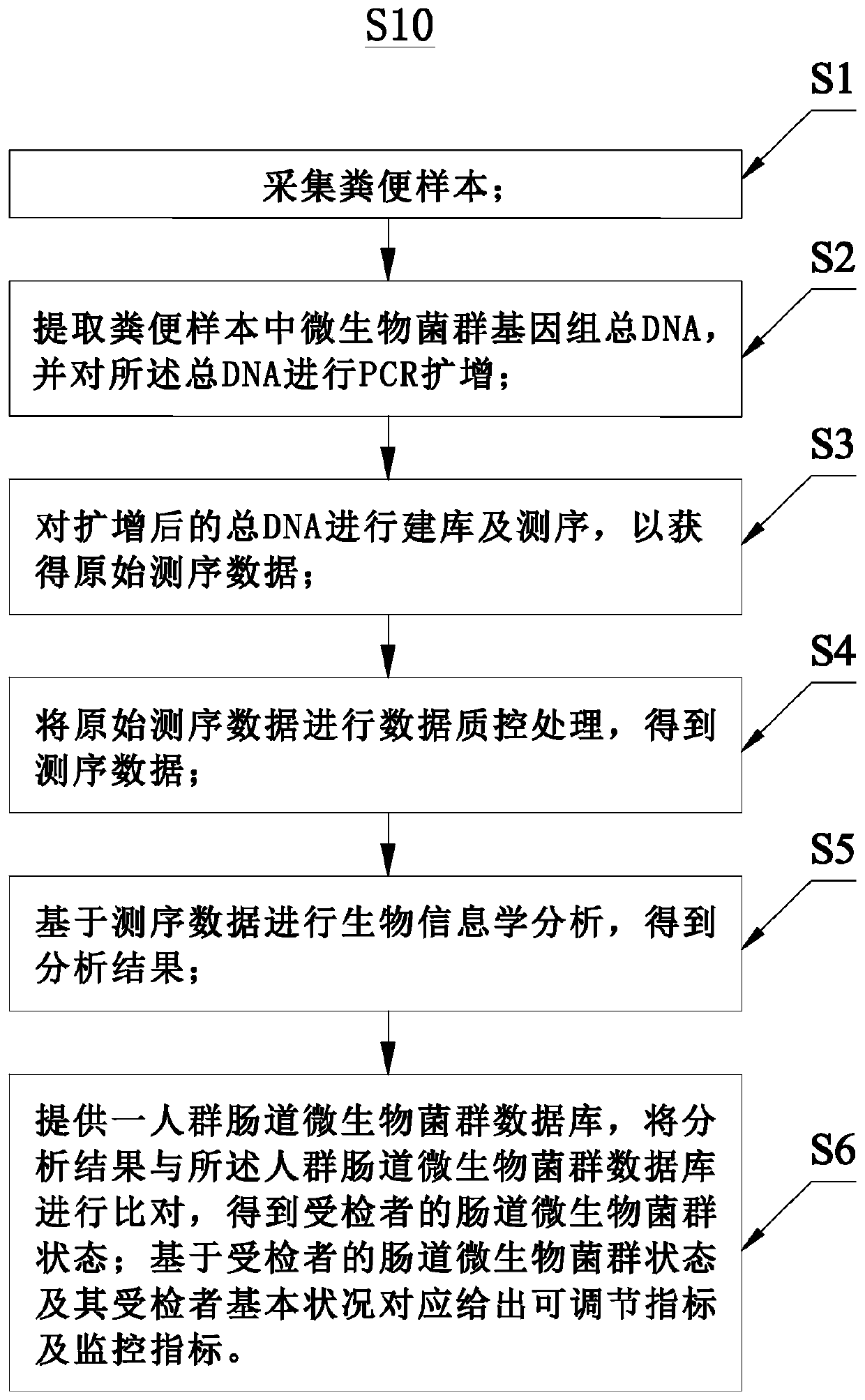
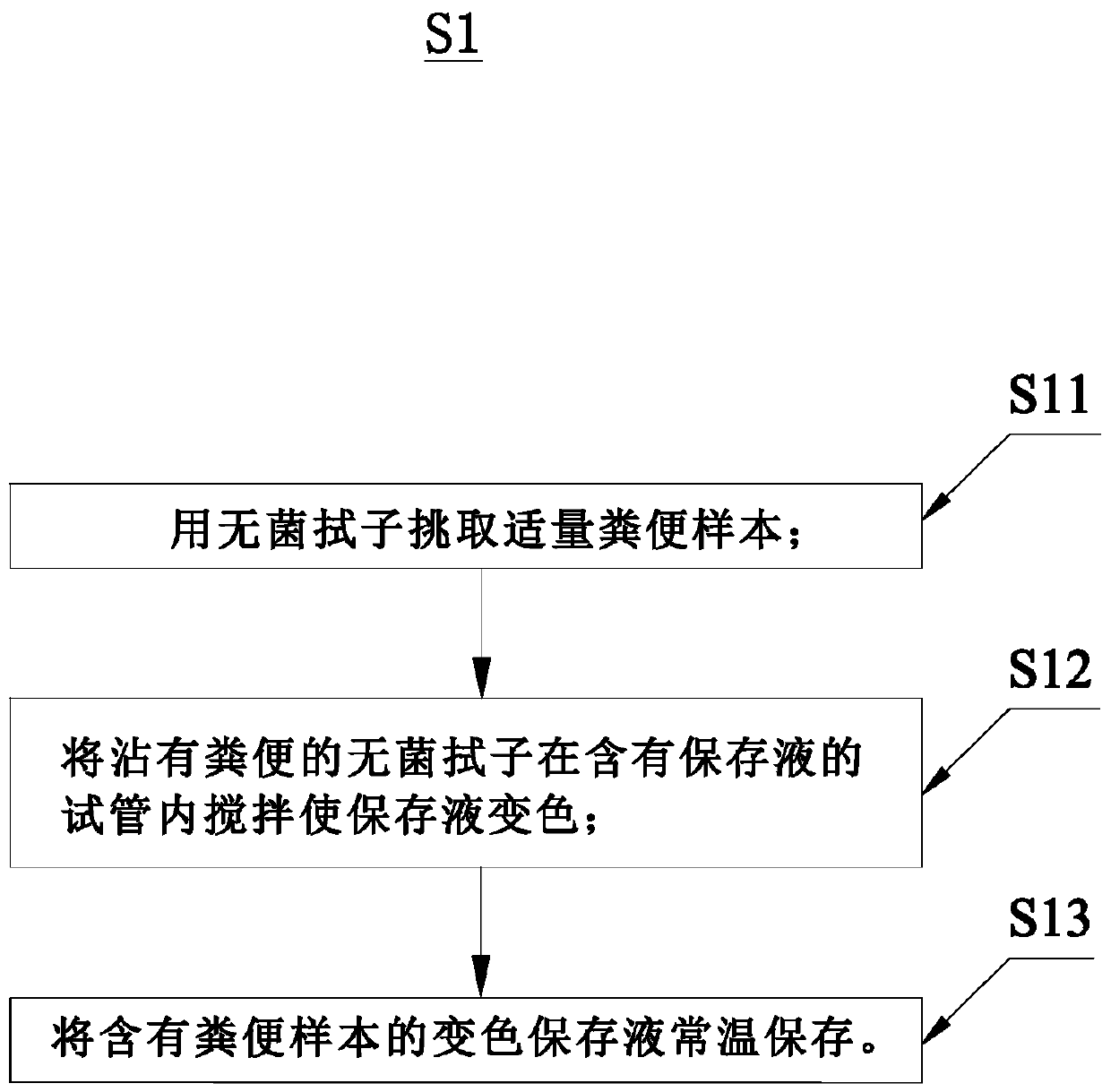
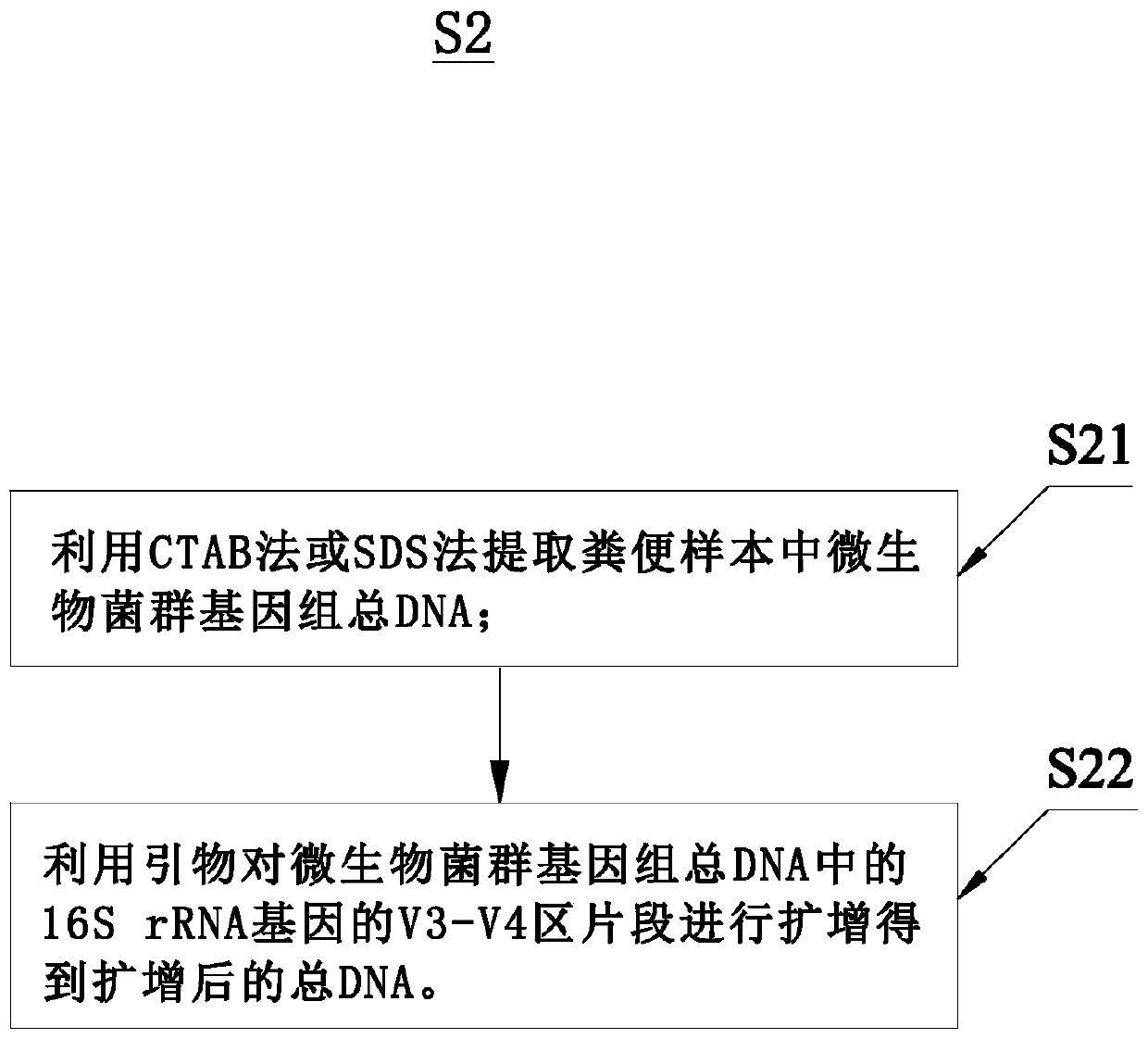
Detection and analysis method and system for intestinal microbial florae
InactiveCN109706235AAvoid embarrassmentDetect humanizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFecesHealth index
The invention relates to the field of biological detection, in particular to a detection and analysis method and system for intestinal microbial florae. The detection and analysis method for the intestinal microbial florae comprises the steps as follows: acquiring an excrement sample; extracting total DNA of microbial flora genome in the excrement sample and performing PCR amplification on the total DNA; performing bioinformatic analysis based on sequencing data to obtain an analysis result; comparing the analysis result with a crowd intestinal microbial flora database to obtain an intestinalmicrobial flora state of a subject; and giving an adjustable index and a monitoring index correspondingly on the basis of the intestinal microbial flora state and the basic condition of the subject. Acorresponding intestinal nutrition structure adjustment suggestion is given on the basis of the detection result obtained by the detection and analysis method for the intestinal microbial florae, andthe internal health index of the subject is increased.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGXINRUI GENE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
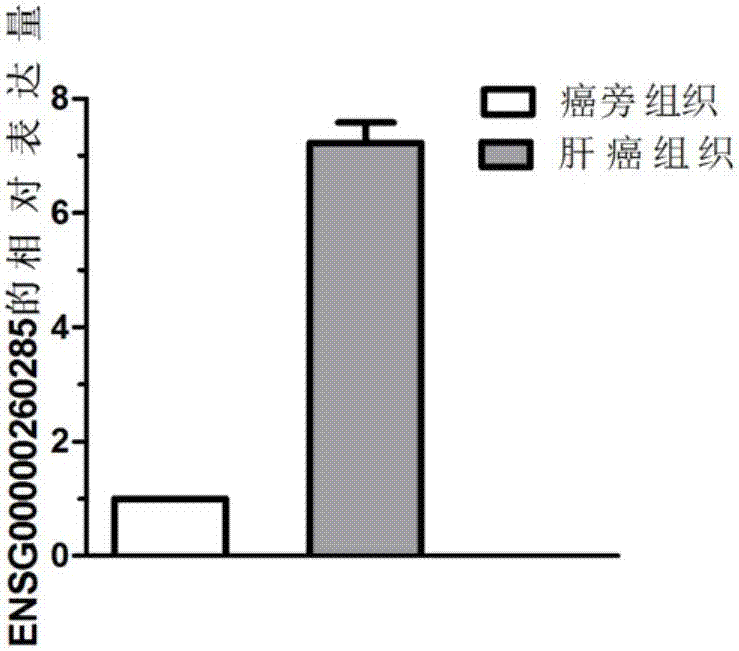
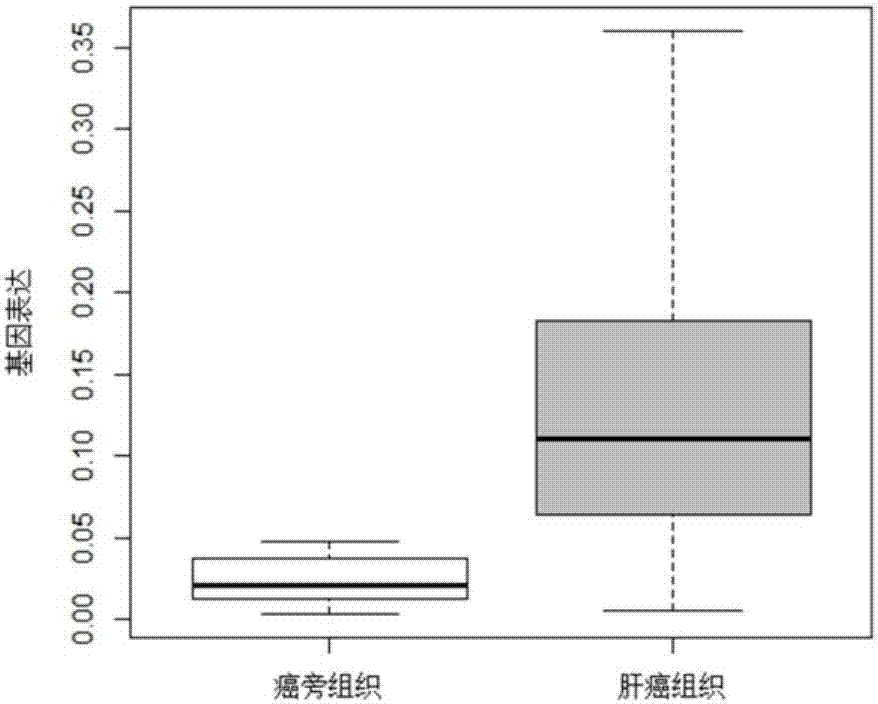
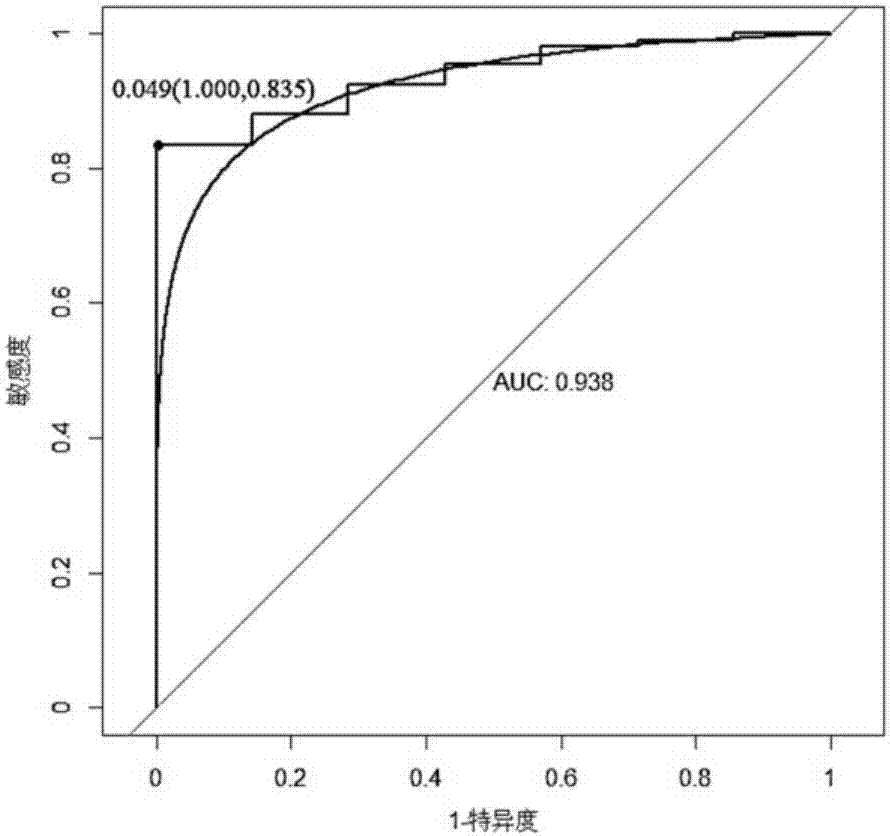
Gene related to liver cancer and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene related to liver cancer and application thereof. Specifically, the gene is ENSG00000260285. According to the gene disclosed by the invention, up-regulated expression of the ENSG00000260285 in a liver cancer patient is found for the first time through high-throughput sequencing, and differential expression of the gene in the liver cancer patient is further verified by qPCR. Bioinformatic analysis finds that the ENSG00000260285 has higher accuracy when serving as a diagnosing marker of the liver cancer. According to the gene disclosed by the invention, in-vitro experiments find that restraining expression of the ENSG00000260285 can affect physiological characteristics of liver cancer cells, so that the gene can serve as a potential target to be applied to treating liver cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
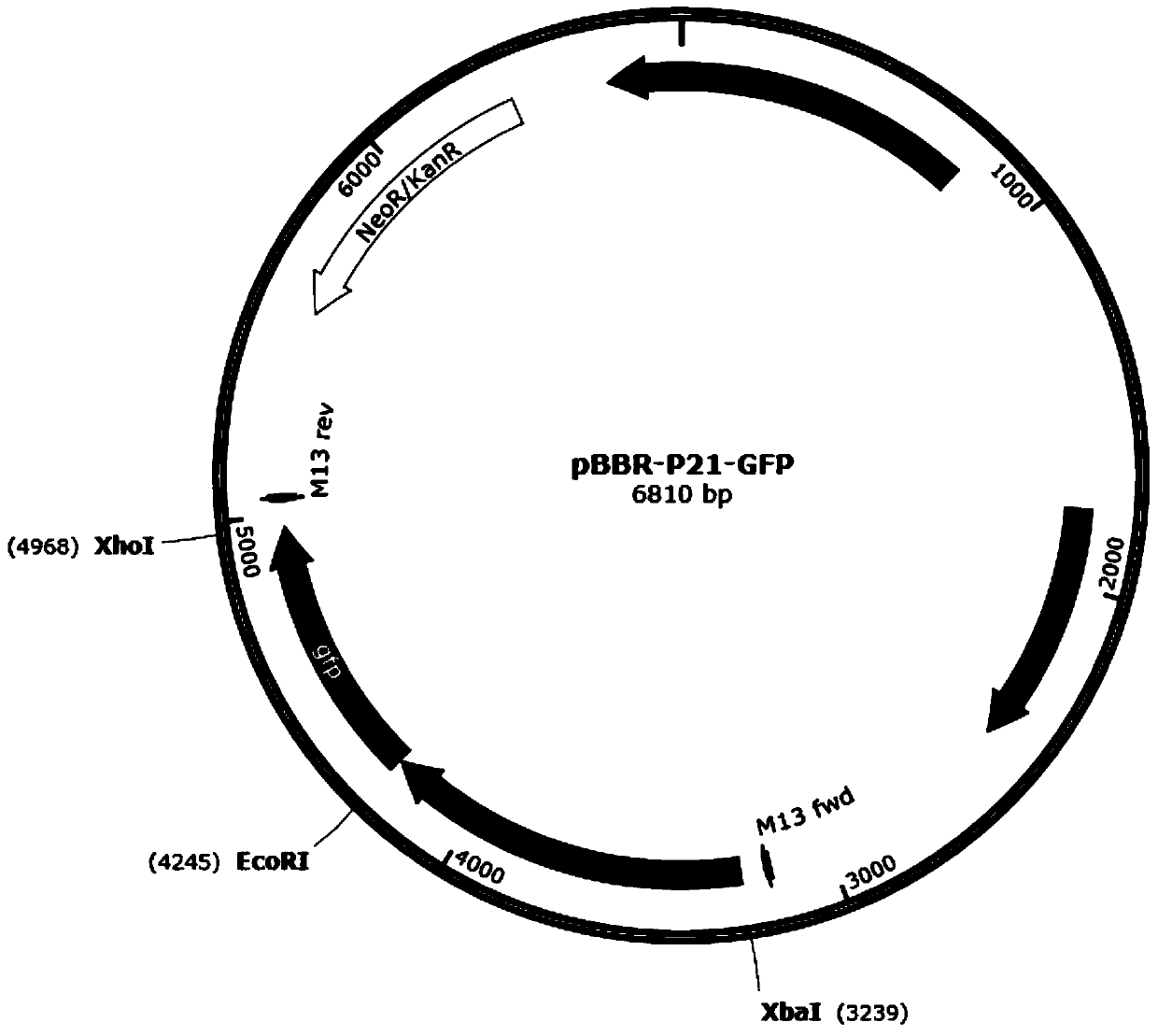
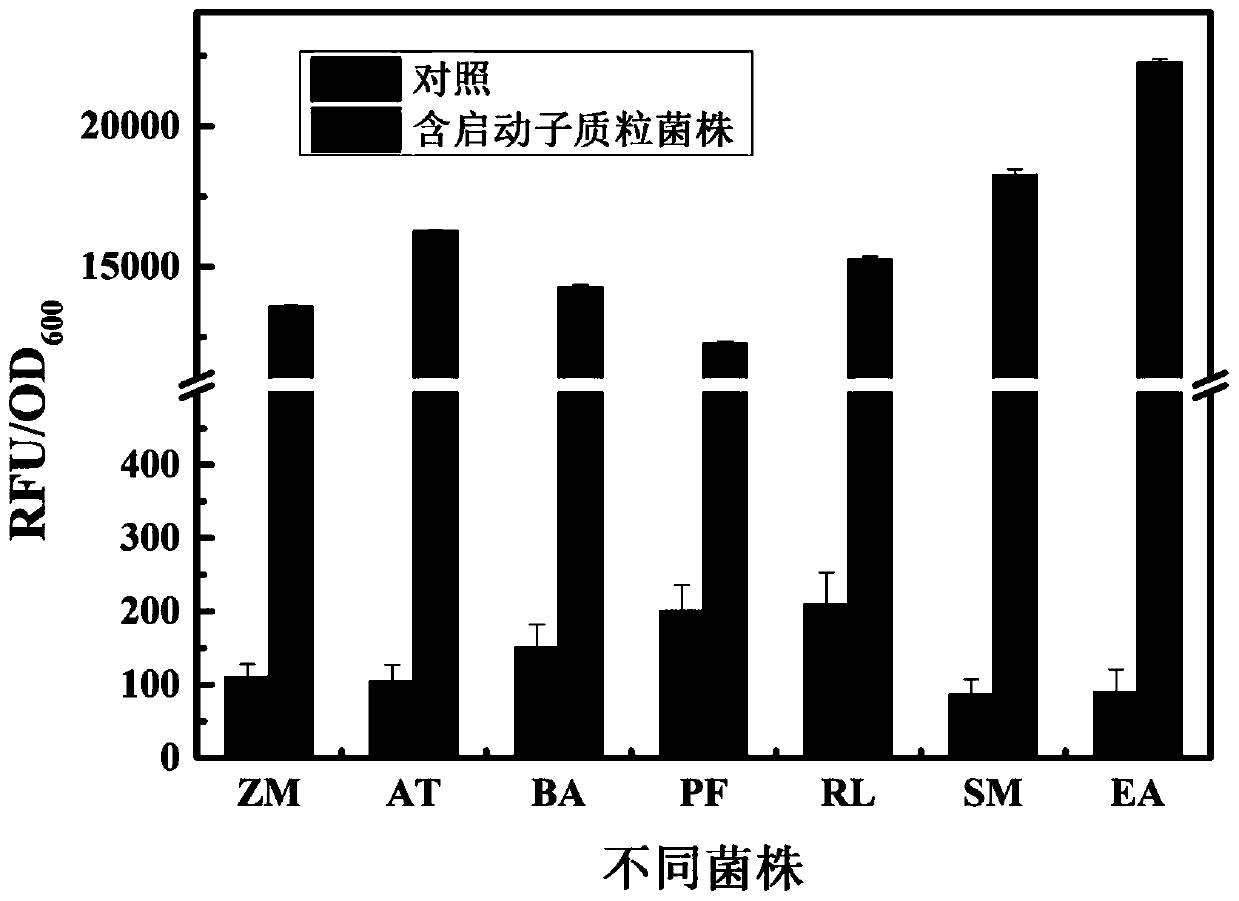
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
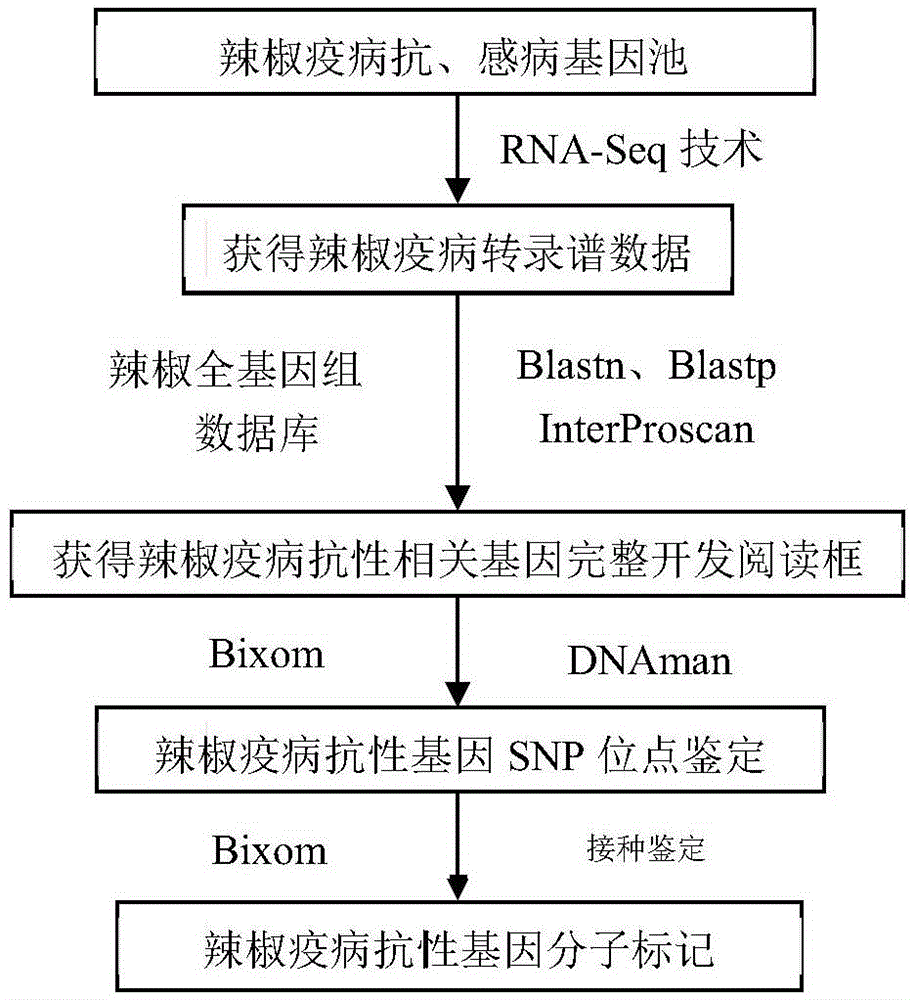
Method for obtaining capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and molecular marker, and application
InactiveCN104560973AAccurate identificationLarge amount of data informationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyData information
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and a molecular marker, and application. The method is used for obtaining the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene by utilizing capsicum phytophthora transcriptome and whole-genome sequencing data information, differentially-expressed gene identification, bioinformatics analysis, molecular marker development and phytophthora inoculation identification and belongs to the technical field of capsicum biology. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing a phytophthora resistant and susceptible gene pool transcriptome obtained after phytophthora inoculation of an F2 population constructed by capsicum highly-resistant and highly-susceptible phytophthora materials, performing expression analysis and functional annotation on differential genes, extracting DNAs (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of a capsicum phytophthora highly-resistant and highly-susceptible phytophthora material genome, performing primer design and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, performing sequence difference analysis and SNP site identification, performing SNP specific primer design and validity verification, and performing other steps to efficiently obtain the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and the molecular marker. According to the method, the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene can be accurately identified, and the effective molecular marker can be developed.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Plant endophyte 16S rRNA gene amplification method and application
ActiveCN106282165ABig amount of dataThe test result is completeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSequence analysisAmplicon sequencing
The invention discloses a plant endophyte 16S rRNA gene amplification method and application. The amplification method includes the following steps of plant pretreating; plant-sample total DNA extracting; sample 16S rRNA gene amplifying, wherein sample 16S rRNA gene amplifying comprises 16S rRNA gene total-length emulsion PCR amplifying and 16S rRNA gene hypervariable-region / conserved-region amplifying sub-amplifying; high-throughput sequencing and biological information analyzing based on a Illumina platform, wherein high-throughput sequencing and biological information analyzing based on the Illumina platform comprises plant endophyte 16S rRNA gene amplicon purifying and recycling, amplicon sequencing library establishing, Illumina HiSeq sequencing and sequencing data bioinformatics analysis. The gene amplification method is used for high-throughput-sequencing plant disease detection and phytophagous animal enteric microorganism detection. Sequencing analysis of plant endophytic bacteria is carried out with the high-throughput sequencing technology, the data size is larger, the detection result is more complete, pollution of plant hosts is reduced to the maximum degree, the result multiformity is higher, and the cost is low.
Owner:成都罗宁生物科技有限公司
Method for identifying transgenic events through whole genome sequencing data
ActiveCN105631242AAccurate analysisValid identificationProteomicsGenomicsBiological bodyWhole genome sequencing
The invention provides a method for identifying transgenic events through whole genome sequencing data. The method comprises the steps that transgenic events are identified through a bioinformatics means, and the position, direction, copying number and flanking sequence information of foreign fragments inserted into genomes and the homozygous and heterozygous state of transgenic samples can be rapidly and effectively identified. Compared with traditional Genome walking, real-time quantitative PCR and other experiments methods, the method has the advantages that time is short, repeatability is high, the result is stable, and explaining is easier. The method is the most comprehensive in existing transgenic event detection methods, can accurately analyze influences of transgenic events on the living body within a short time, carries out safety evaluation on transgenic animals and plants, and pushes the transgenic technology to be applied in agriculture.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
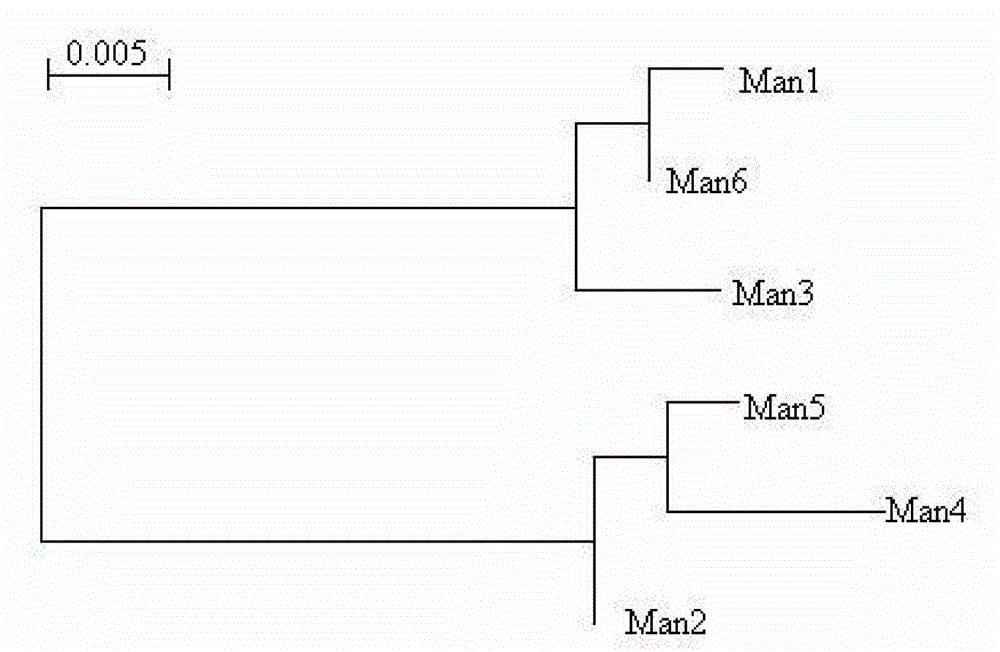
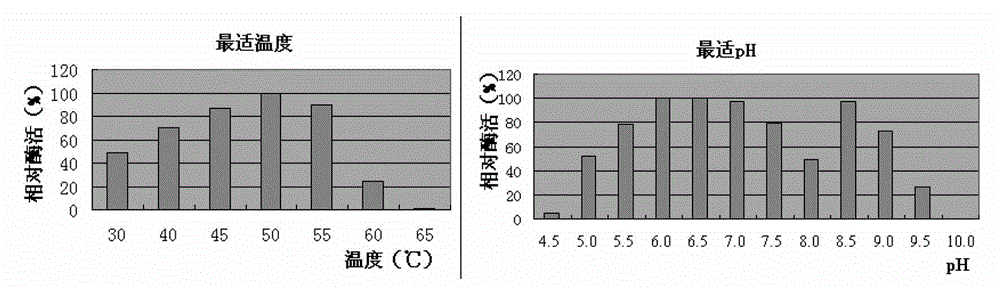
Mannase and mutants thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering and provides mannase with a high enzyme activity and mutants thereof. According to the mannase and the mutants thereof, six mannase genes obtained by cloning different strains of Bacillus licheniformis and encoded mannase of the mannase genes, difference and genetic relationships among the six mutants are analyzed by bioinformatics. The mannose has the high enzyme activity in a neutral pH condition, and can be used as a feed enzyme preparation in an optimum temperature.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Method for efficiently and rapidly separating T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and uses thereof
InactiveCN107190003AQuick analysisEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadSeparation technology
The invention provides a method for efficiently and rapidly separating a T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence. The method comprises: extracting the genomic DNA of an Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic plant; fragmenting the genomic DNA, carrying out DNA repairing, adding A, linking, carrying out fragment selection by using magnetic beads, carrying out library construction, carrying out hybridization capture on the constructed library and a T-DNA boundary sequence, and carrying out PCR enrichment; and carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the library, and carrying out bioinformatics analysis on the sequenced data so as to obtain the T-DNA insertion site. According to the present invention, the capture is performed with the target DNA, and the low-throughput sequencing is specially performed on the T-DNA boundary sequence; the disadvantages of low throughput, low efficiency and low success rate of the existing flanking sequence separation technology are overcome with the method of the present invention; and with the method of the present invention, the DNA capture and the second-generation sequencing technology are combined, the T-DNA boundary sequence is specially sequenced and the simple analysis is performed to obtain the T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and the method has characteristics of high efficiency, economy, and simple analysis.
Owner:武汉天问生物科技有限公司
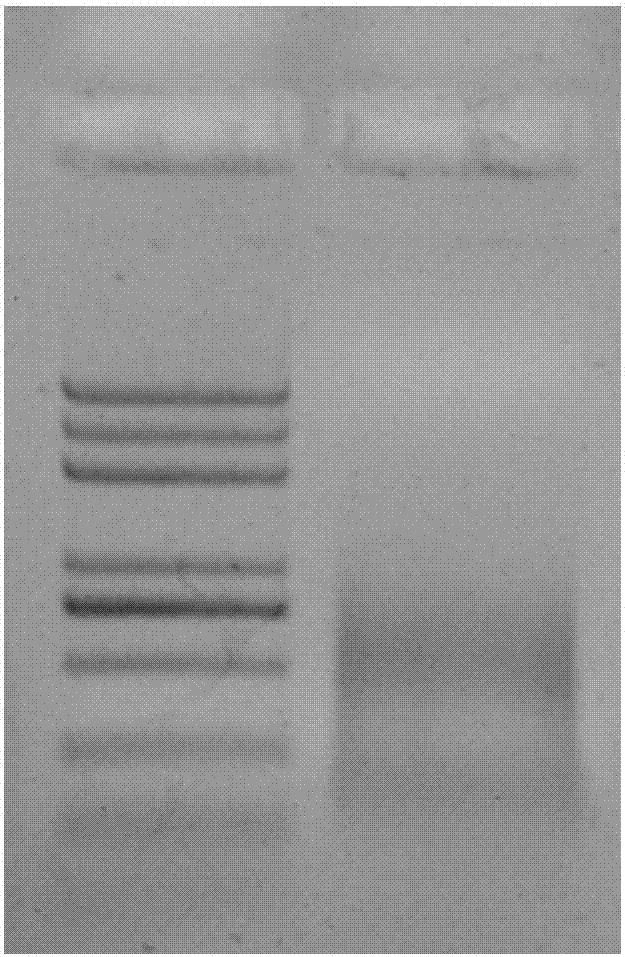
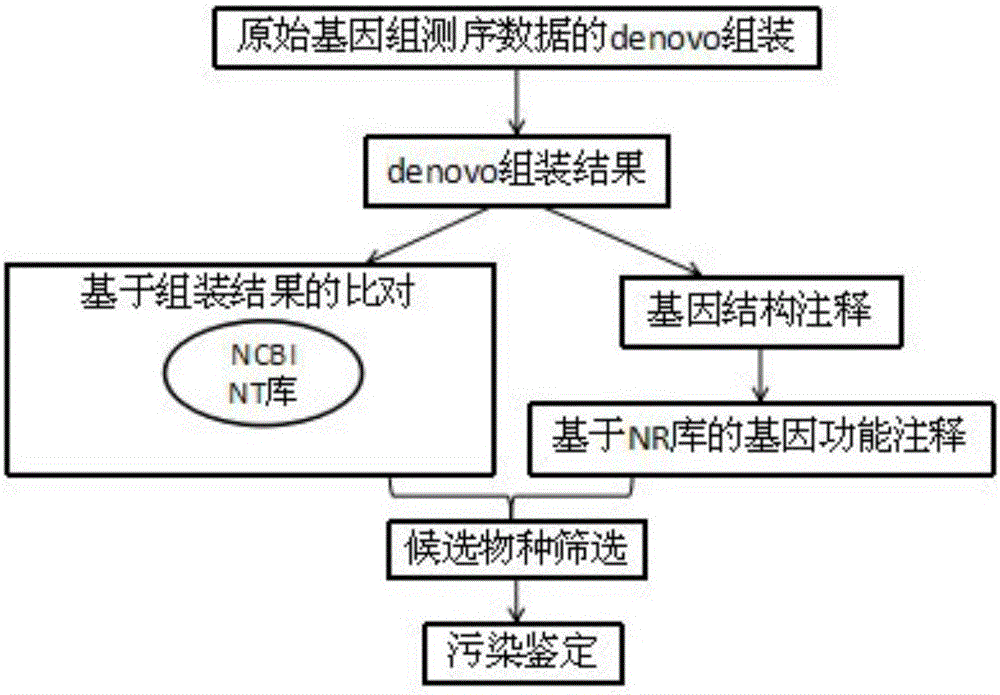
Method for rapidly and accurately identifying high-throughput genome data pollution sources
ActiveCN105740650AOvercome the disadvantage of taking too longFully reflectProteomicsGenomicsInformaticsHomologous Sequences
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and accurately identifying high-throughput genome data pollution sources. The method comprises the steps that original genome sequencing data for denovo sequencing are firstly assembled to obtain assembly results, gene prediction is conducted on the assembly results, amino acid sequences of proteins corresponding to genes are obtained through translation, and blast comparison is conducted on assembled genomic sequences and the amino acid sequences respectively with an NT database and an NR database of the NCBI to obtain homologous sequences serving as original comparison databases; species information corresponding to the sequences is extracted from the original comparison databases and is sequenced, the species corresponding to the sequences are sequenced from most to least, and whether exogenous pollution exists or not is comprehensively judged by combining with gene data results and amino acid data results. The method can reduce high-throughput genome sequencing data pollution and subsequent bioinformatics analysis influence of exogenous pollution sources in a genome denovo project to the most degree and improve pollution source identifying speed and efficiency.
Owner:广西作物遗传改良生物技术重点开放实验室
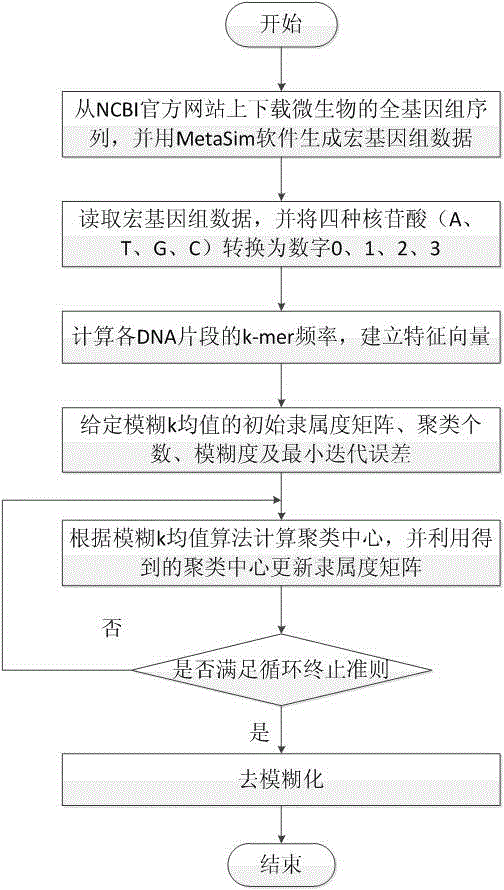
Micro genome segment clustering method based on fuzzy k-mean
The invention relates to a micro genome segment clustering method based on fuzzy k-mean, and belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics analysis. The micro genome segment clustering method based on the fuzzy k-mean aims at utilizing the self features of micro genome segments under the condition of no assembly of the micro genome segments, and then the micro genome segments are clustered, so the number of contained species and the abundance ratio of species are obtained. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining the micro genome segments, establishing the feature vectors, utilizing the fuzzy k-mean method to cluster, and calculating the number of the contained species and the abundance ratio of the species according to the clustering results. The method has the advantages of directness and convenience.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com