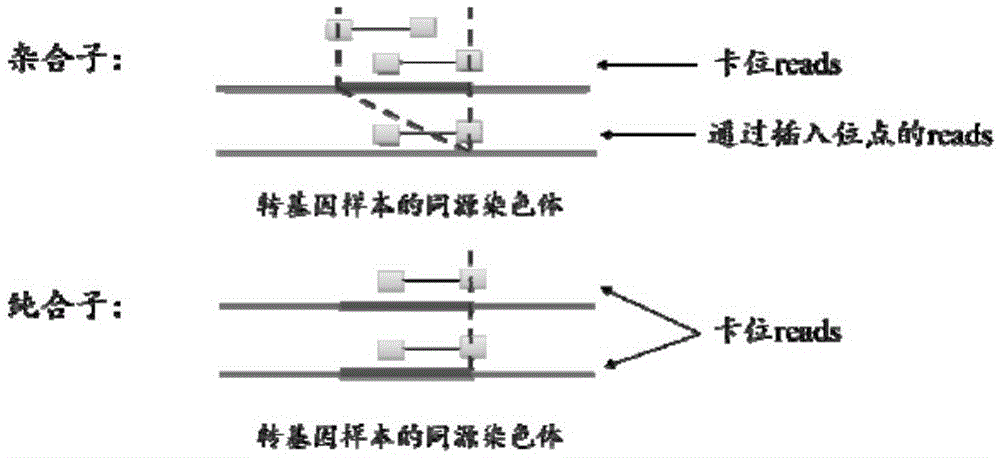
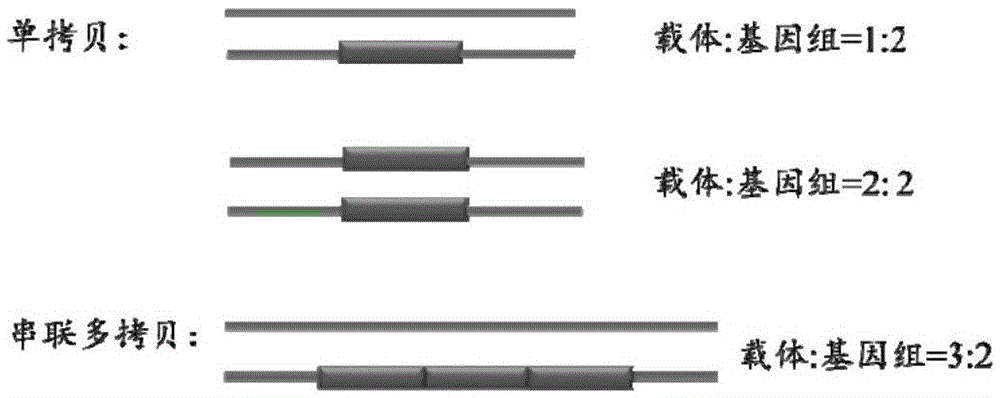
Method for identifying transgenic events through whole genome sequencing data
A technology for whole-genome sequencing and transgenic events, applied in the fields of genomics, electrical digital data processing, and special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of low throughput, long experiment cycle, single identification content, etc., and achieve high repeatability, short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] 1. Experimental materials: pBS-CD46-neo vector sequence (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1), full-length 12864bp, pig reference genome sequence, Ensemble version ssc3, whole genome sequencing data of transgenic pigs, with an average sequencing depth of about 30×.
[0058] 2. Alignment: Merge the vector and reference genome sequences by inputting the vector sequences and reference genome sequences into the comparison software bwa-0.7.10, and using the comparison software bwa-0.7.10 to compare the sequencing data and It compares.
[0059] Use a high-throughput sequencer (illuminaHiseq2000) to perform paired-end sequencing on the transgenic whole genome sample ssc3 containing the carrier pBS-CD46-neo to obtain paired-end sequencing reads, and the read length of each end of the paired-end sequencing reads is The 100bp sequence is called the end read; compare the sequencing data of the end read with the wild-type known reference genome sequence ssc3 of the transgenic sample ssc3 to be...
Embodiment 2
[0113] 1. Experimental materials: HLF-HLYBAC1 carrier sequence (as shown in SEQ ID NO.2), full-length 128496bp; Duroc reference genome sequence, Vega version ssc_v57; whole genome sequencing data of transgenic pigs, with an average sequencing depth of about 12×.
[0114] 2. Alignment: Merge the reference genome sequences of the vector and Duroc, and use the alignment software bwa-0.7.10 to compare the sequencing data with the same method as in Example 1.
[0115] 3. Extract card position readings: use the same method as in Example 1 to screen card position readings, and obtain 21 preliminary card position readings and 138 supplementary card position readings, a total of 159.
[0116] 4. Card position and rough positioning: The boundary of S / H and M in the comparison results of 21 preliminary card position reads is used as the insertion site, and the results are as follows:
[0117]
[0118] In the output results, each row of data represents the alignment output of a prelimi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com