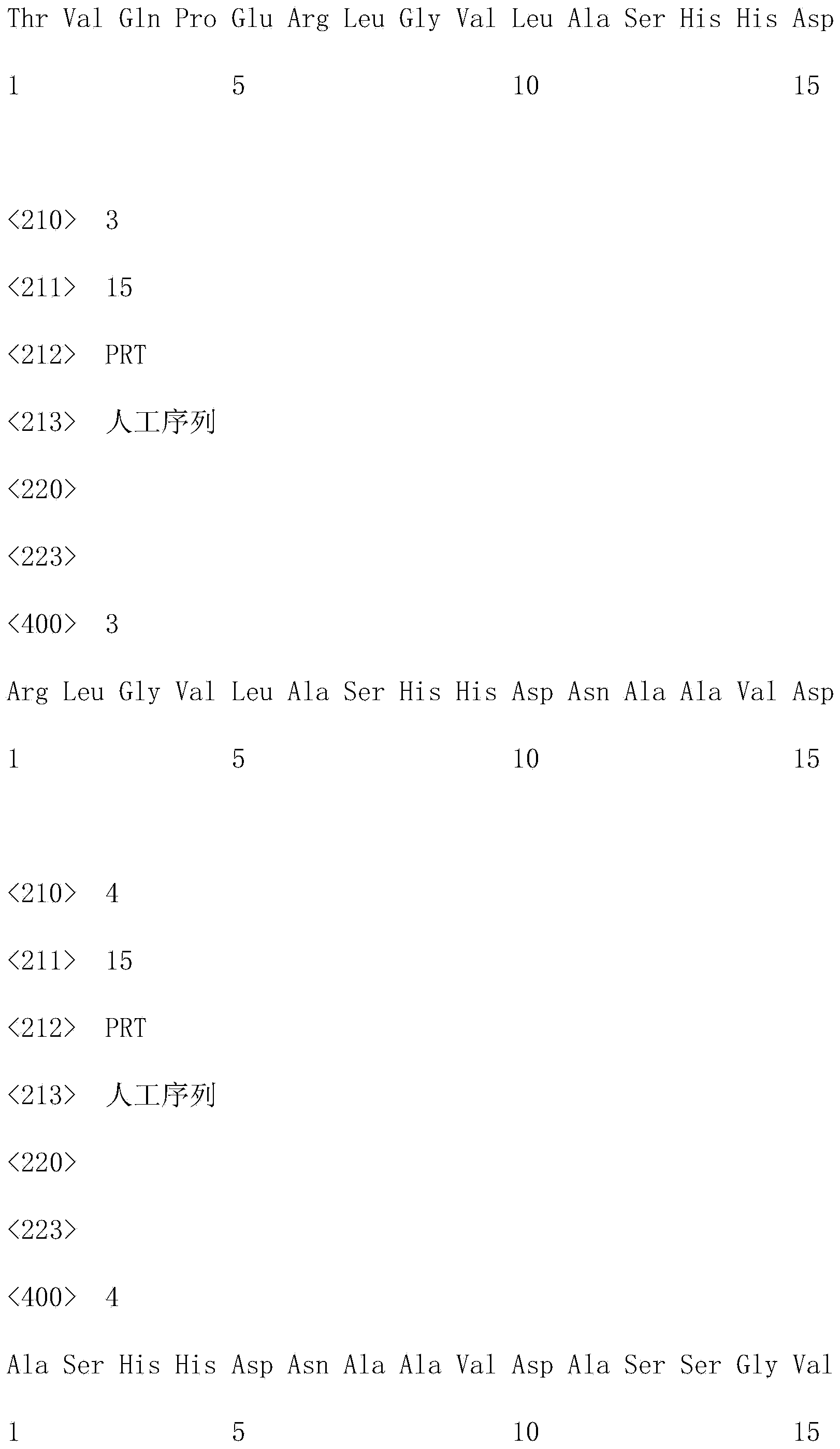Patents
Literature
51 results about "Antigenic stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An antigen is something foriegn to the body that is able to cause an immune resopnse. Therefore, antigenic stimulation I think is a way of saying something (in the air, food, contact etc...) is stimulating his immune response.
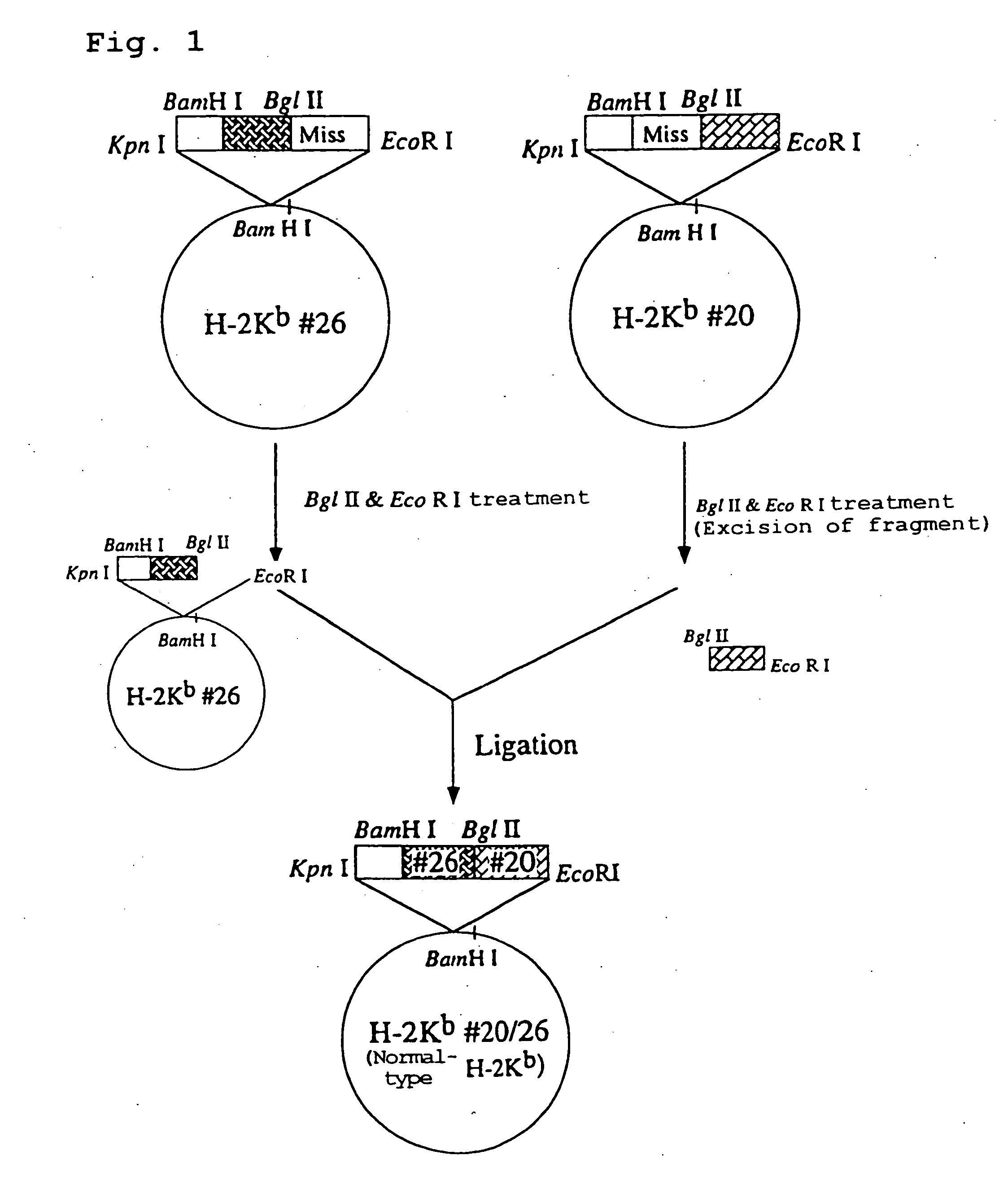
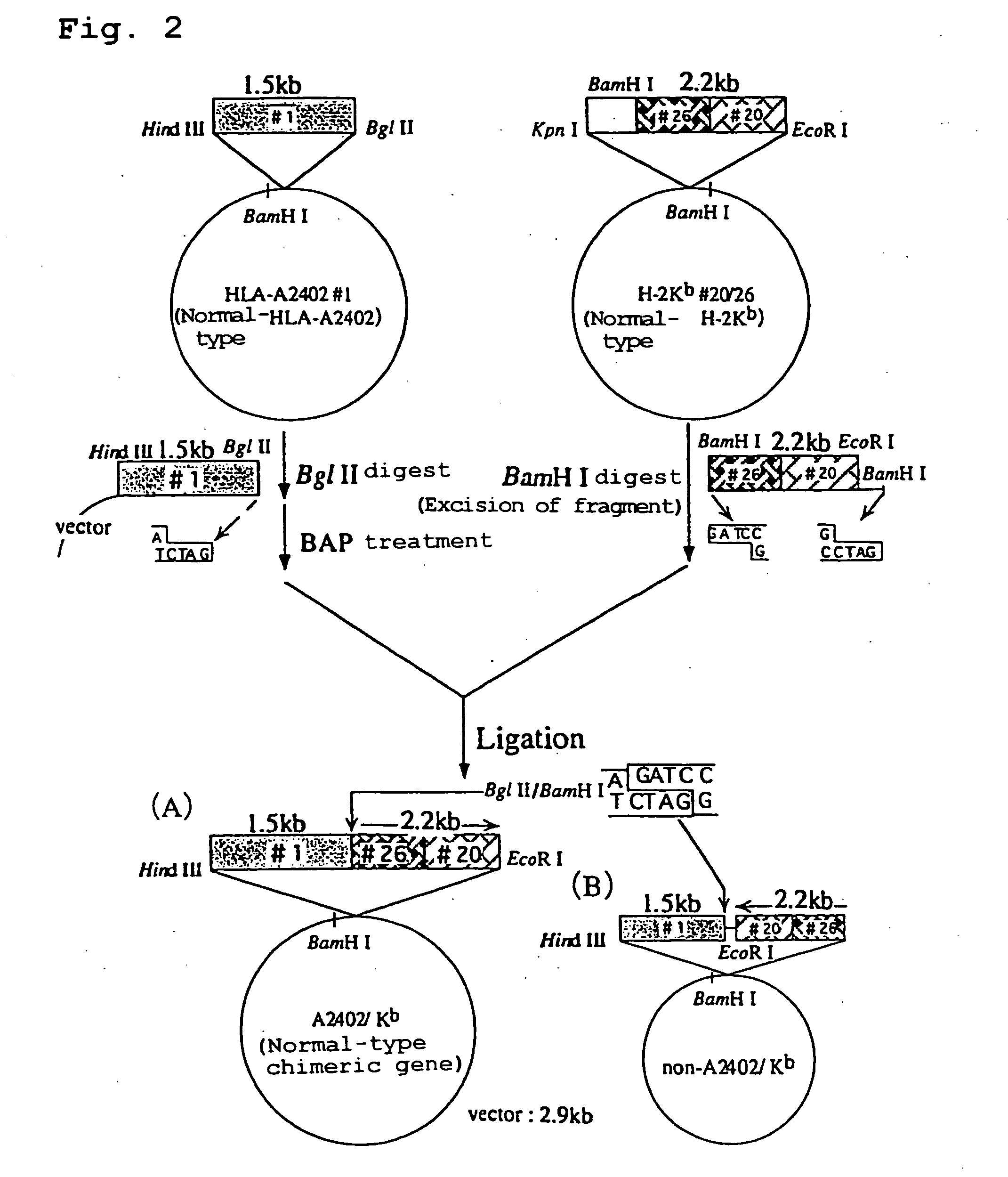
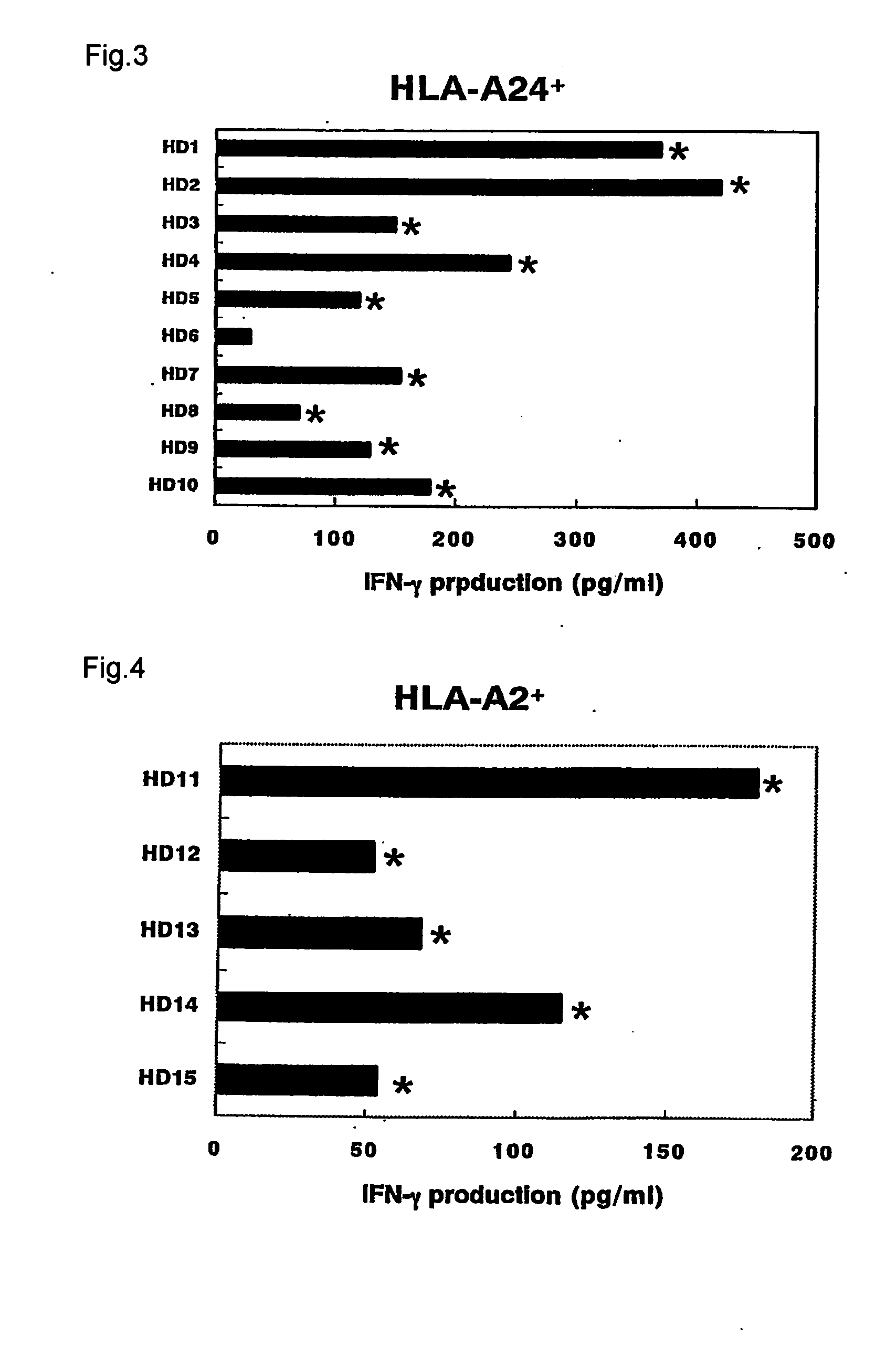
Transgenic animal expressing HLA-A24 and utilization thereof
The present invention relates to a non-human transgenic mammal which has had an HLA-A24 gene introduced and in which CTLs are induced when stimulated by an HLA-A24-binding antigen, a method of screening therapeutic or preventive agents for tumors or virus infections comprising administering a test substance to said transgenic non-human mammal and assaying and evaluating whether CTLs specific for the test substance are induced, an HLA-A24-binding tumor antigen peptide of PSA origin selected by said screening method, a chimera DNA (DNA construct) useful in the generation of said non-human transgenic mammal, and a host cell transformed by said chimera gene and use thereof.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
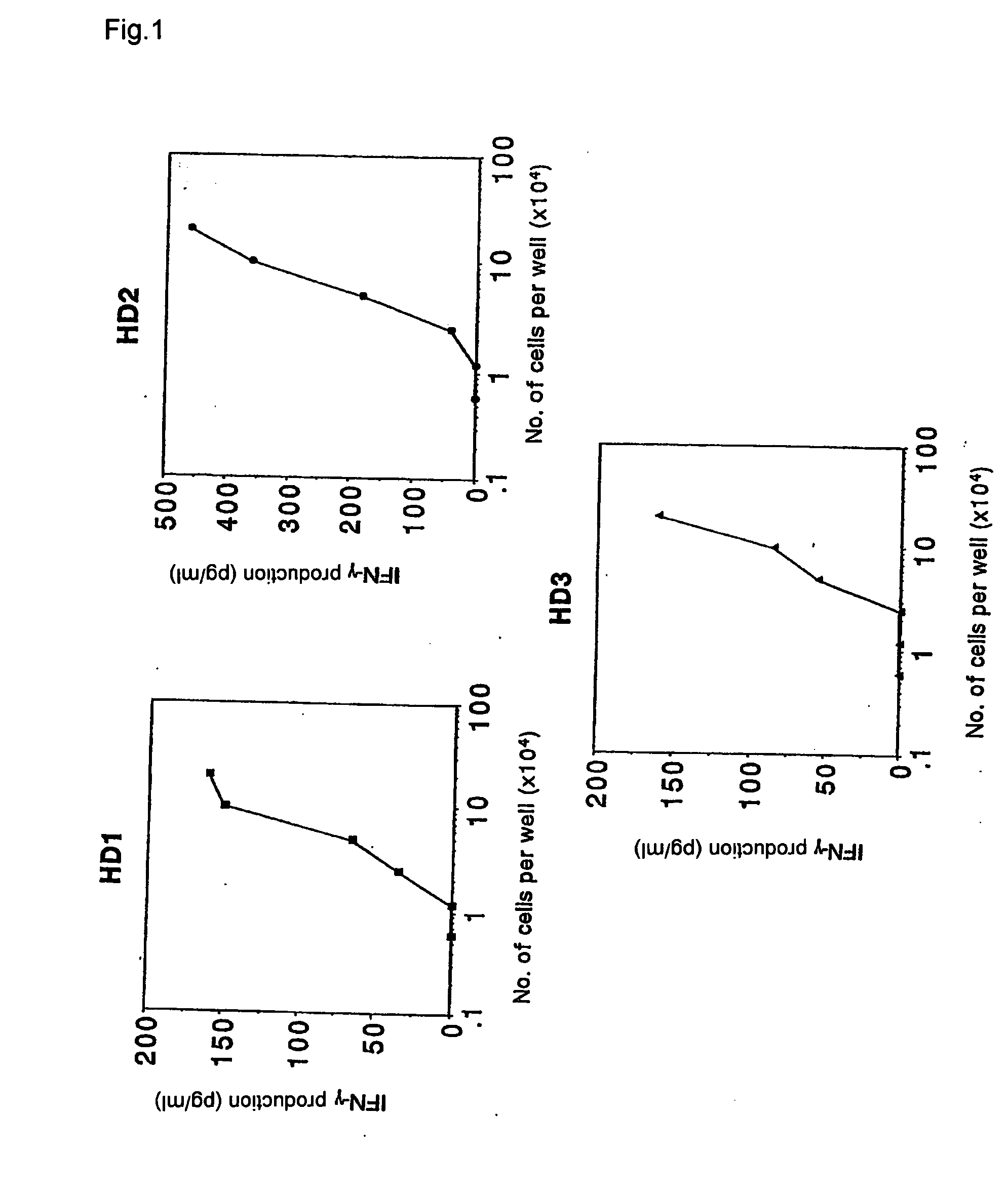
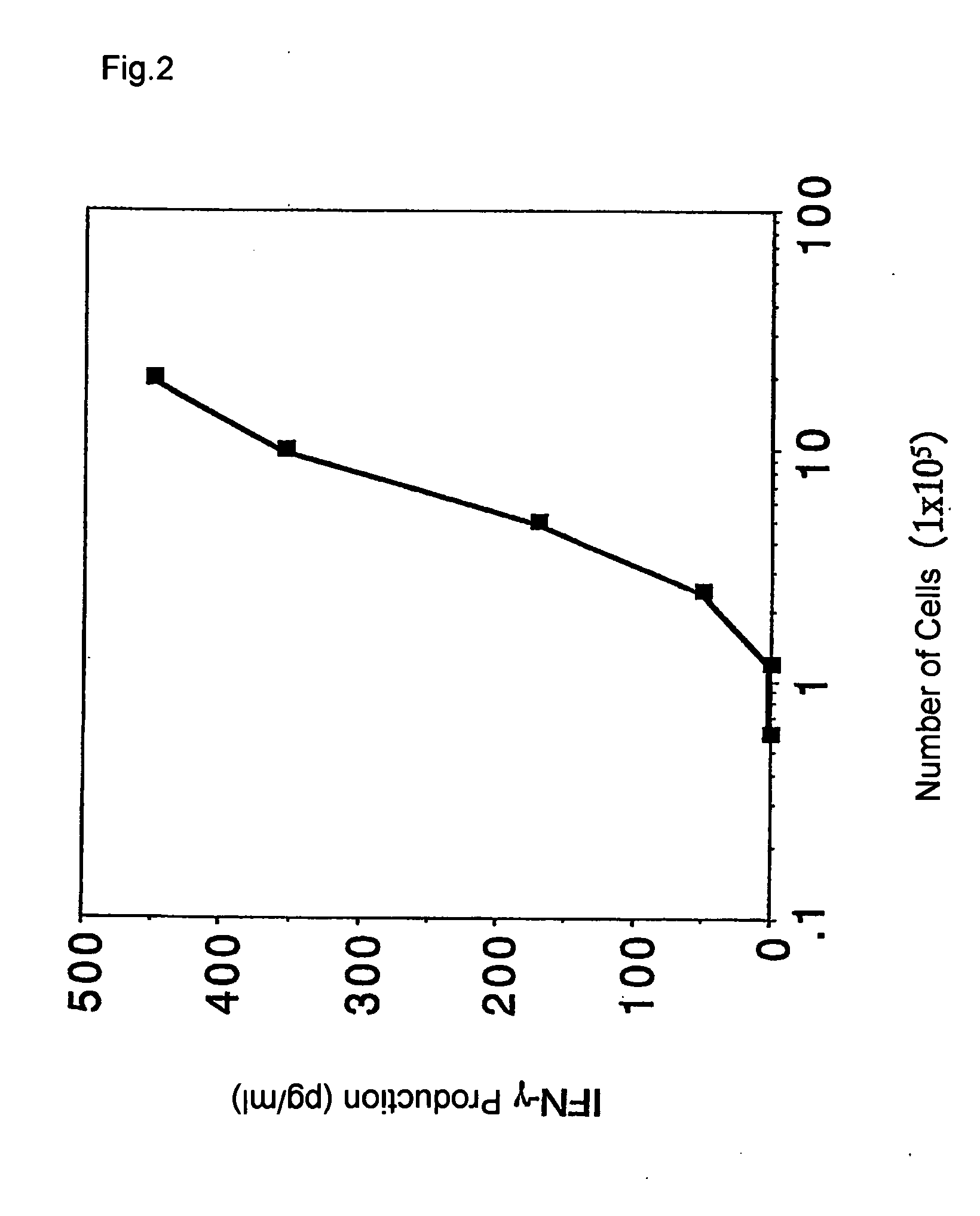
Method of detecting cellular immunity and application thereof to drugs
InactiveUS20060035291A1Reduce needAllergen ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsDiseaseImmune monitoring
It is intended to provide a convenient immunity monitoring system whereby T cell frequencies specific to a plural number of antigen peptides can be assayed by using a relatively small amount of blood. Peripheral monocytes are collected and frequently stimulated with an antigen without directly using any antigen presenting cells. Then T cells specific to the antigen in the thus stimulated peripheral monocytes are detected to thereby detect antigen-specific T cells. thus, diseases such as cancer can be prevented or treated with the use of a peptide having such a function, in particular, cancer tumor-rejection antigen peptide.
Owner:GREEN PEPTIDE CO LTD +1
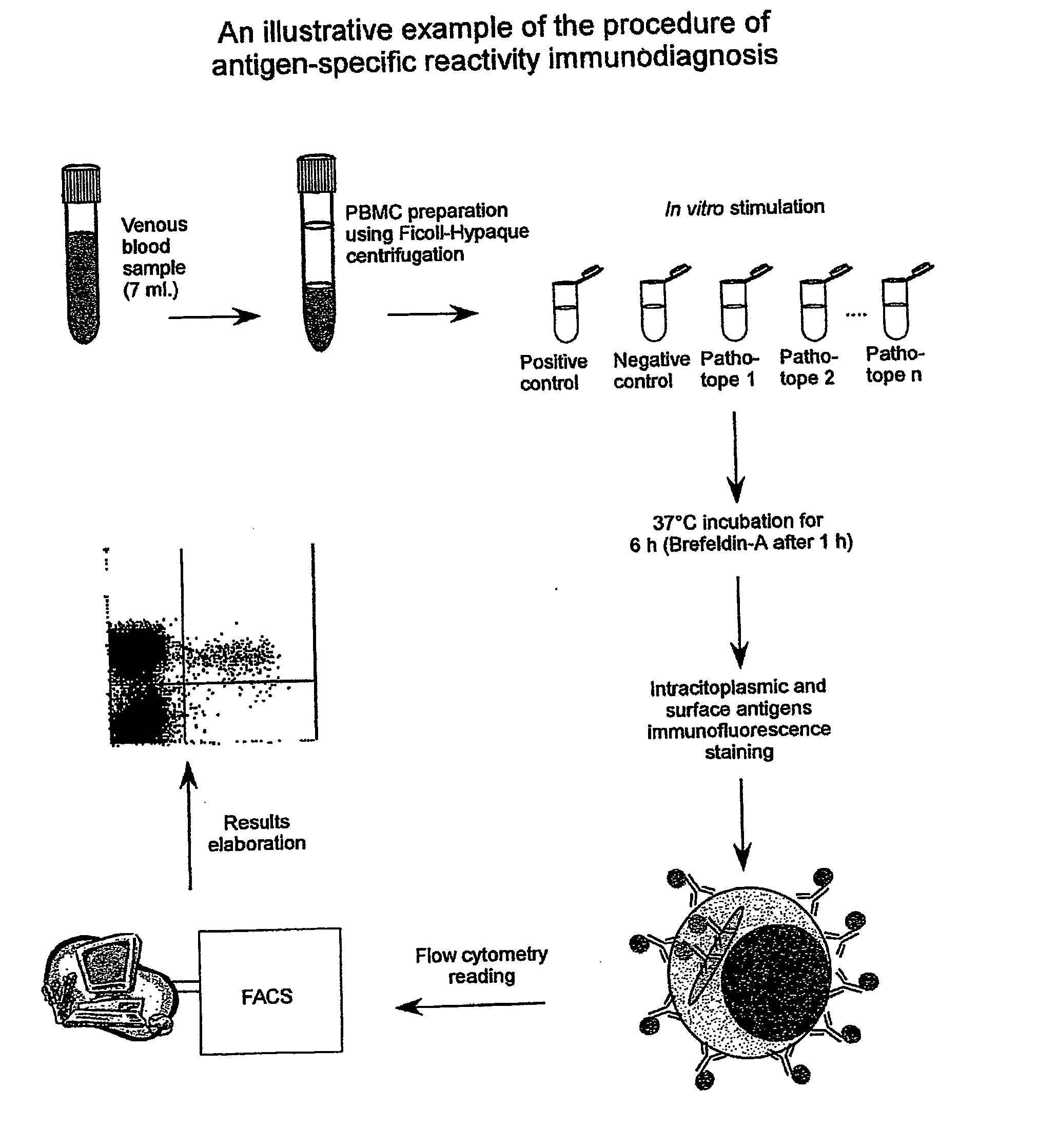
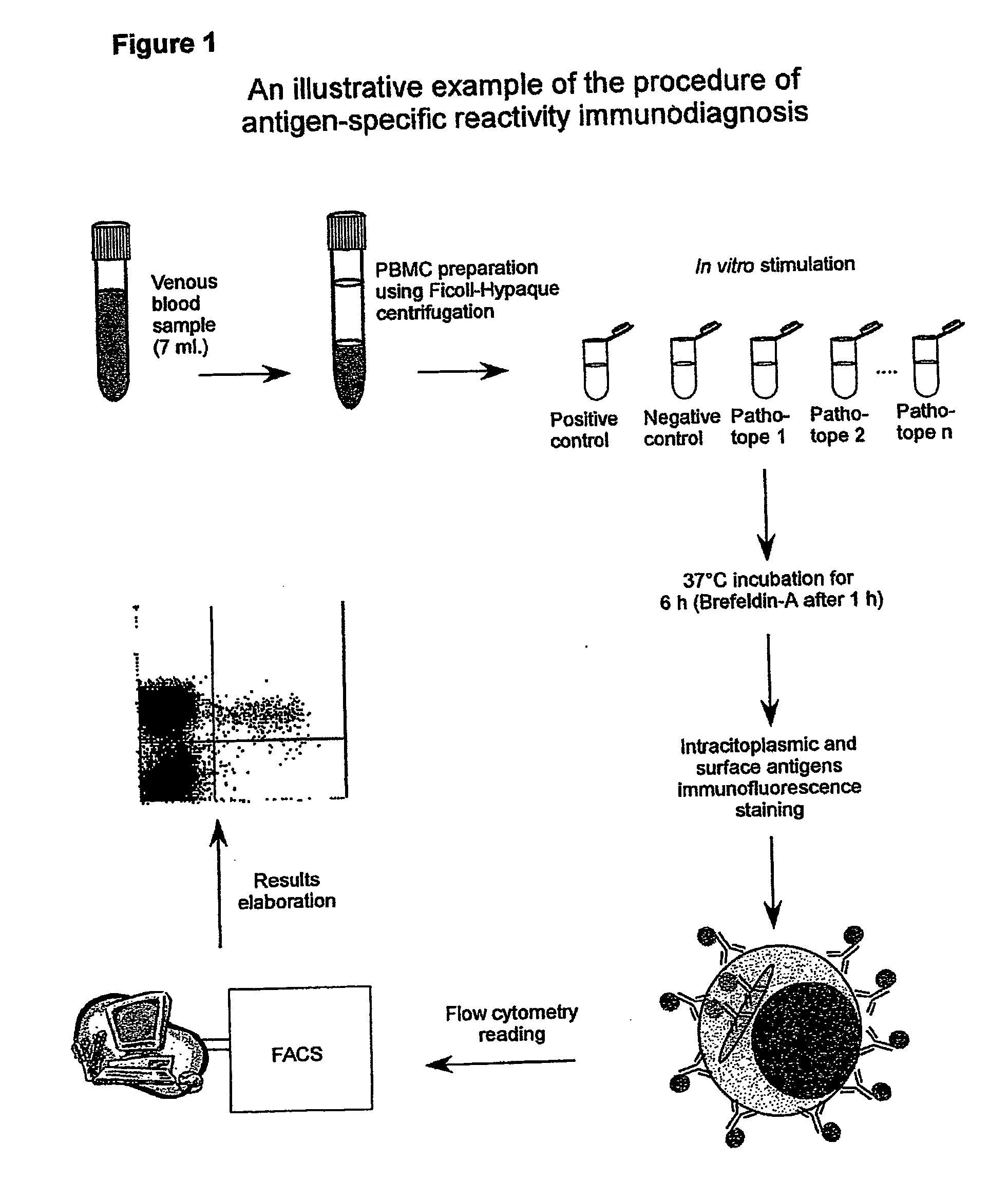
Method and diagnostic tests based on flow cytometric analysis of antigen-specific t lymphocytes
The present invention provides a method for the immuno-diagnosis of diseases with different aetiology (infectious diseases, tumors etc) by measurement of the T cell response J, B and NK lymphocytes) induced by a set of diseasespecific antigens. The method is based on the quantitative determination of antigenspecific T lymphocytes (referred as Ag-Sp), stimulated by using a newly devised pathology-specific antigen or epitope compositions which represent further embodiments of the invention. After stimulation, the selective measurement of the Ag-Sp T lymphocytes is performed by: A) monoclonal antibodies recognizing membrane structures of T lymphocytes and of their sub-populations; B) monoclonal antibodies binding to cytokines accumulating at intracellular level after the stimulation with the antigen; or C) mixtures of A) and B). The flow cytometric detection of the presence of markers of differentiation on T lymphocytes and of intracytoplasmic cytokines allows the acquisition of both qualitative and quantitative results. The invention also provides diagnostic kits for performing the method of the invention.
Owner:INST NAT PER LE MALATTIE INFETTIVE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI IRCCS
Beta-1,3-glucan recognition protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of a biological medicine, and relates to a beta-1,3-glucan recognition protein which is obtained from a lepidoptera insect body in manners of extraction, separation and purification, and a structure thereof, a preparation method of the obtained beta-1,3-glucan recognition protein in manners of separation and purification, a recombinant beta-1,3-glucan recognition protein which is obtained by using a genetic engineering technology, and structures of a derivative, an analogue, and an active fragment thereof, and a preparation method in manners of separation and purification. In addition, the invention also relates to an antibody which is generated by the process of utilizing natural and recombinant beta-1,3-glucan recognition proteins, and derivatives, analogues and active fragments thereof as antigens to stimulate an organism, and an antibody obtaining method. Meanwhile, the invention also relates to the natural and recombinant beta-1,3-glucan recognition proteins, and the derivatives, the analogues and the active fragments, and the antibodies thereof. The beta-1,3-glucan recognition protein can be widely applied to the fields of prevention and treatment drugs aiming at microorganisms, corresponding detection and diagnosis, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Paper based sensor capable of detecting allergic reactions as well as preparation and application of paper based sensor
InactiveCN108957010AAchieving Specific DetectionHigh sensitivityBiological testingMast cellBasophilic Granulocyte
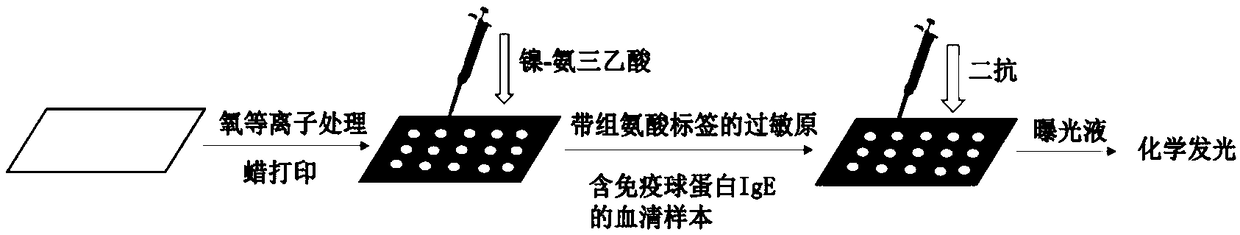
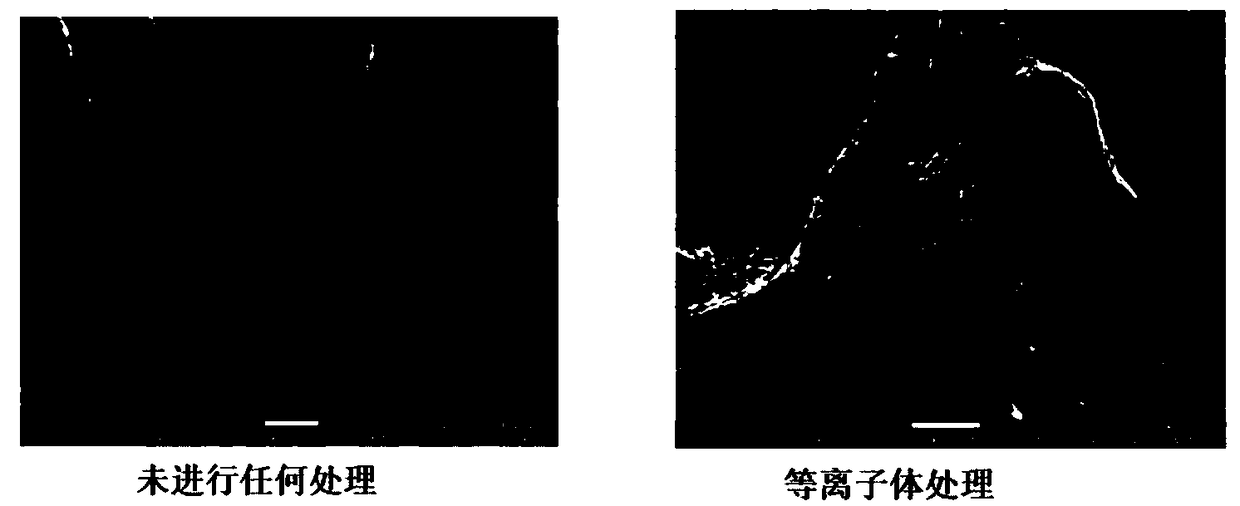
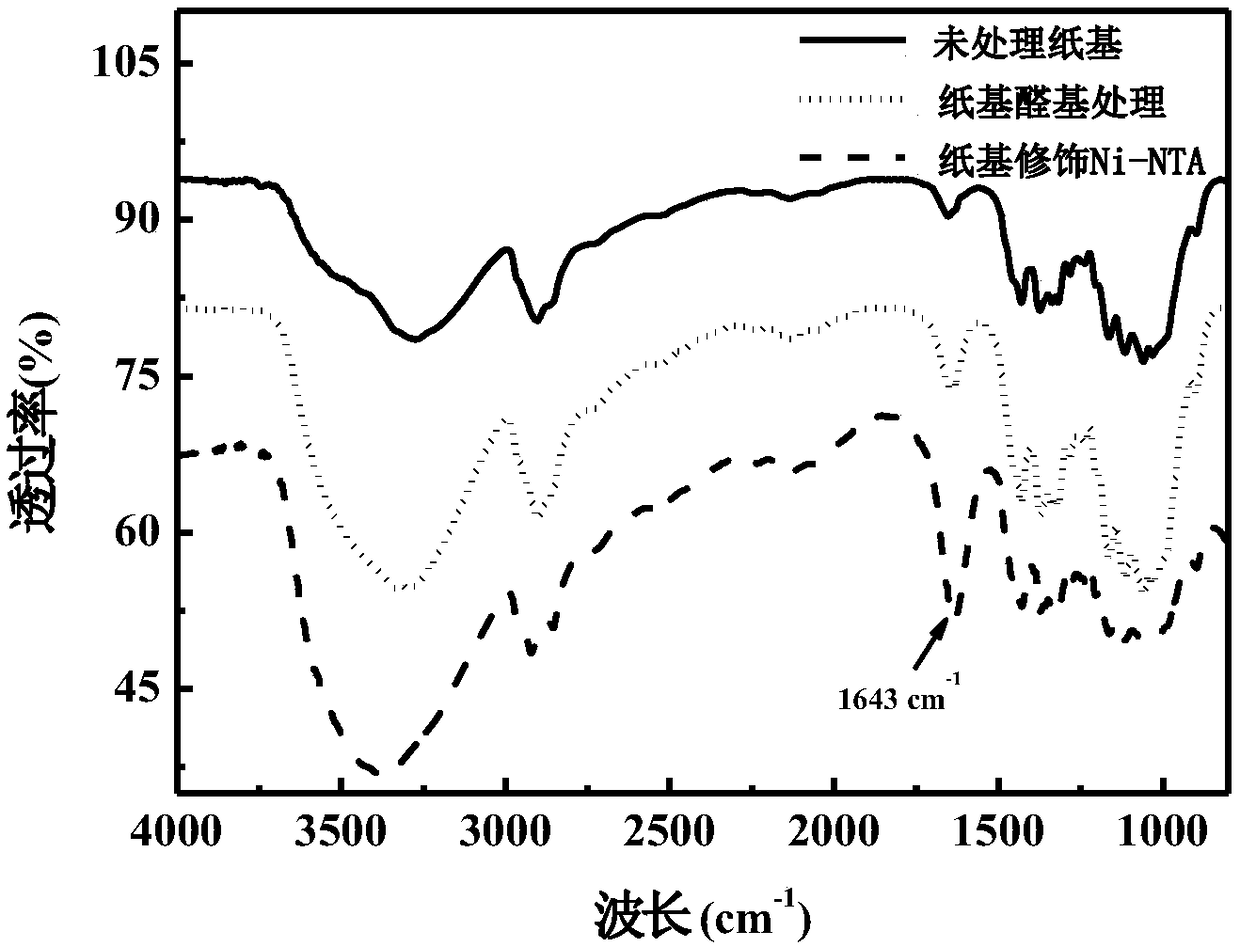
The invention relates to a paper based sensor capable of detecting allergic reactions as well as preparation and application of the paper based sensor and belongs to the field of paper based sensors.The allergic reaction refers to abnormal and excessive immune response caused by the reasons that a specific immunoglobulin (IgE) antibody is produced when the body is stimulated by a certain antigenand the IgE can be bound to an IgE specific receptor on the surface of mast cells and basophilic granulocyte. Therefore, the IgE in serum is an important marker for detecting the allergic reaction. Ni-NTA can be specifically bound with a His label, thereby realizing affinity purification of proteins. The paper based material has the advantages of being cheap, portable, high in selectivity and biocompatibility and the like, so the paper based sensor containing the Ni-NTA is prepared and can be firmly bound to an allergen containing the His label, and qualitative detection of the immune globulinis realized. The paper based sensor has important significance for rapidly and sensitively detecting the allergic reactions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
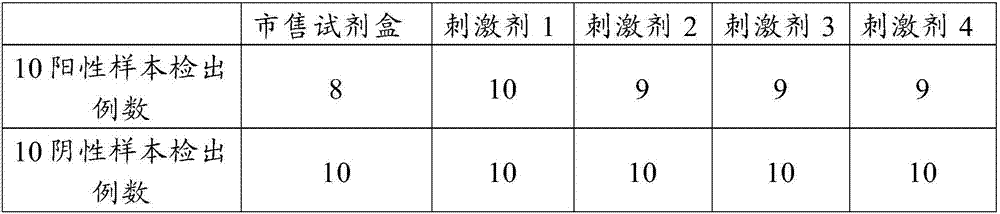
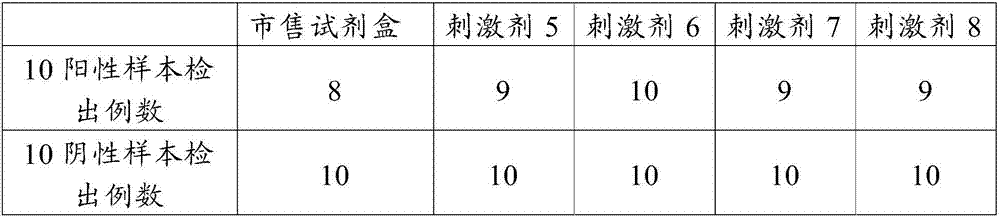
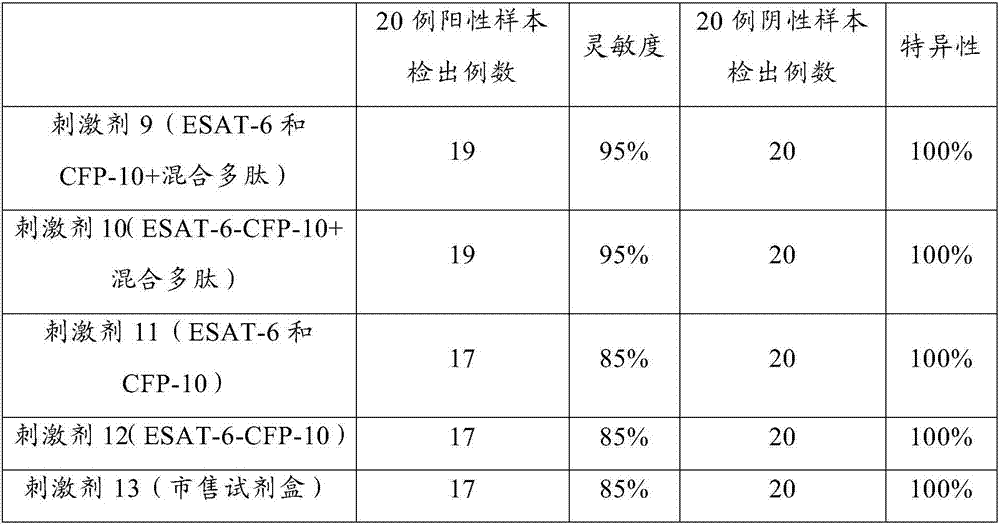
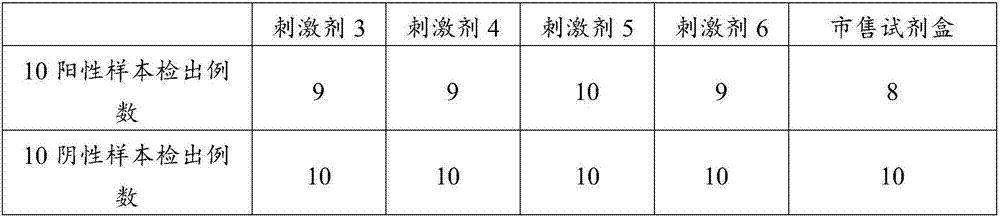
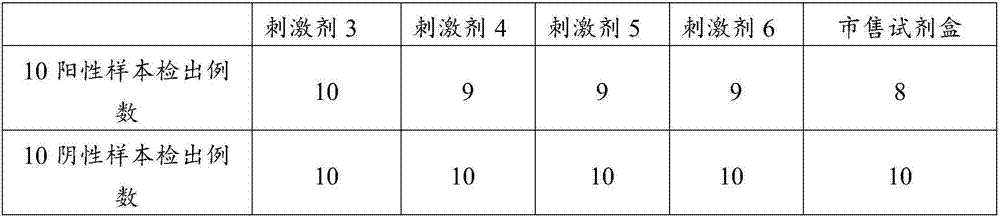
Antigen stimulant and kit for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, and application of antigen stimulant
ActiveCN104597239AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMycobacterium InfectionsStimulant
The invention provides an antigen stimulant for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, and a kit comprising the antigen stimulant. The invention also provides an application of the antigen stimulant in reagents for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. The antigen stimulant comprises at least one polypeptide or analogues thereof in polypeptides shown as the sequences 1-11 in a sequence table, wherein the polypeptides respectively come from tuberculosis specific antigen polypeptides ESAT-6 and tuberculosis specific antigen polypeptides CFP-10. According to the antigen stimulant provided by the invention, peripheral blood T lymphocytes of tuberculosis infection patients can be effectively stimulated to generate IFN-gamma, so that the tuberculosis infection can be diagnosed at high sensitivity and high specificity, and the influence on BCC inoculation or other underlying diseases can be avoided.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
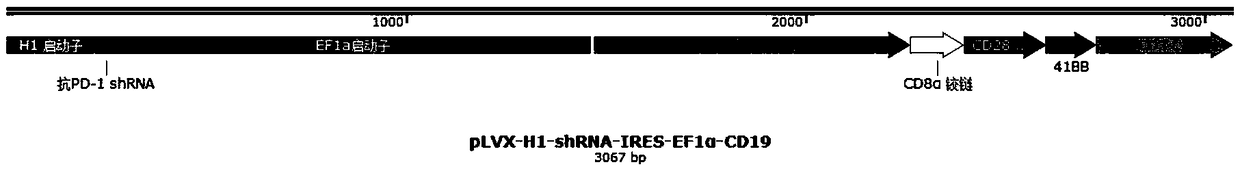
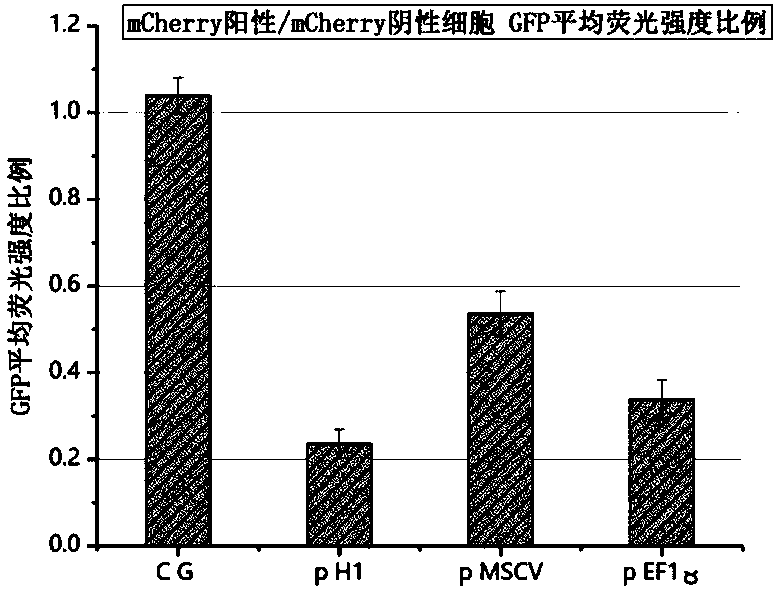
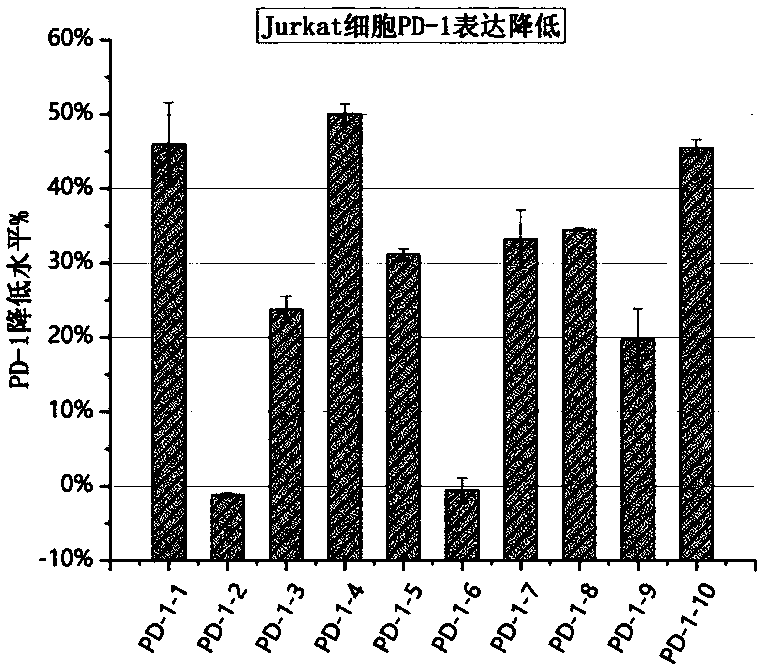
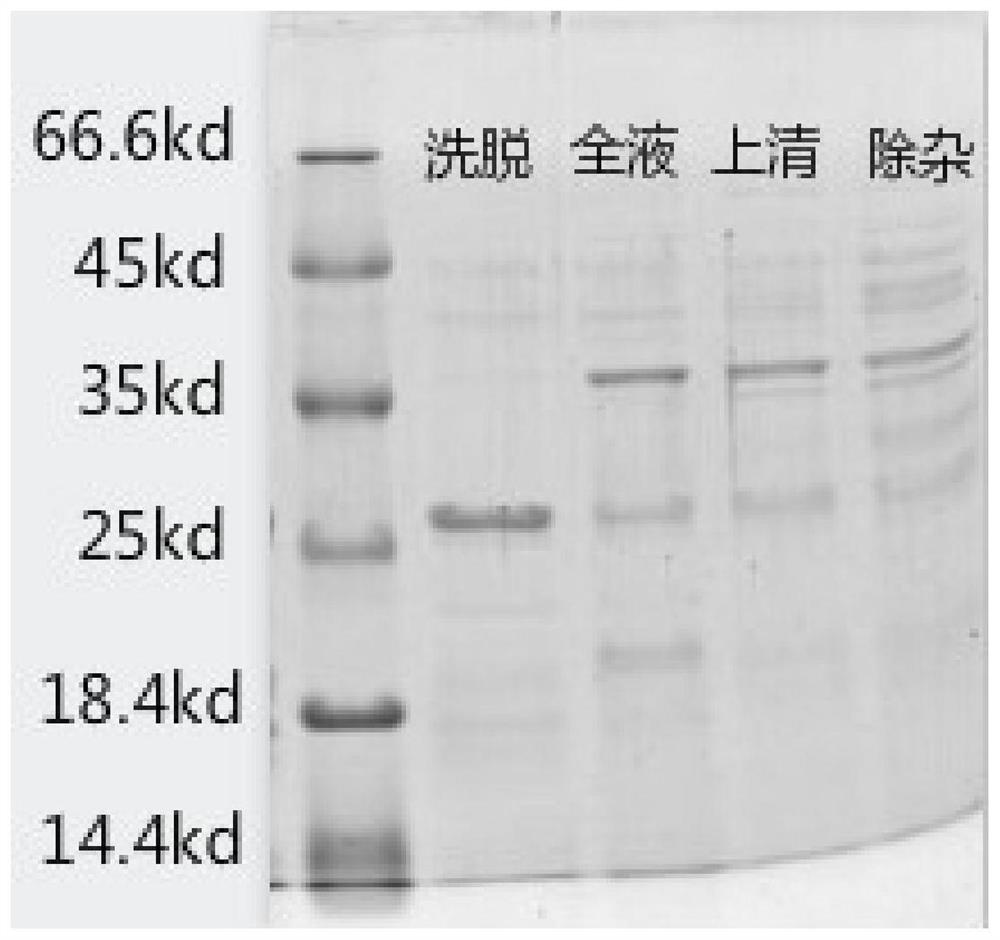
Plasmid structure for expressing CD19CAR and knocking down T cell surface PD-1 expression simultaneously and construction method thereof
InactiveCN108424927ALow efficiencyEnhanced killing effect in vitroVector-based foreign material introductionHinge regionWilms' tumor
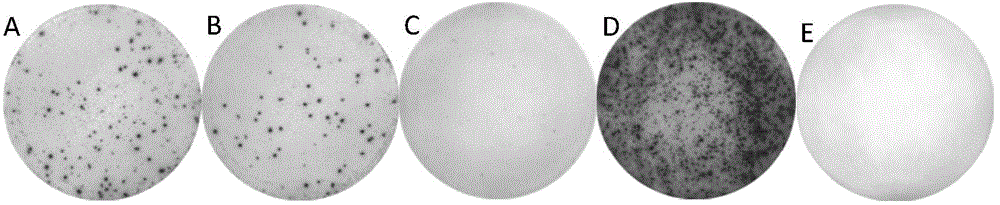
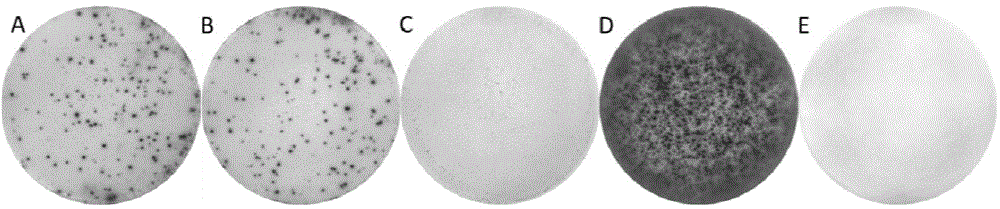
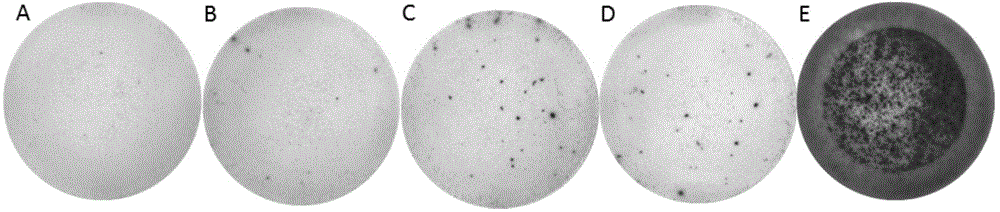
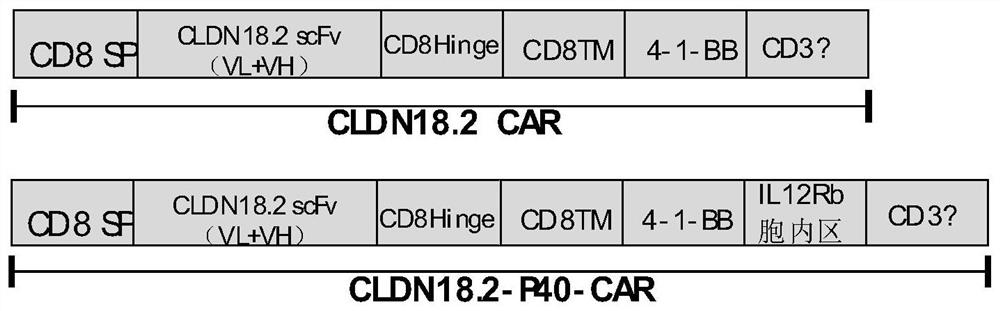
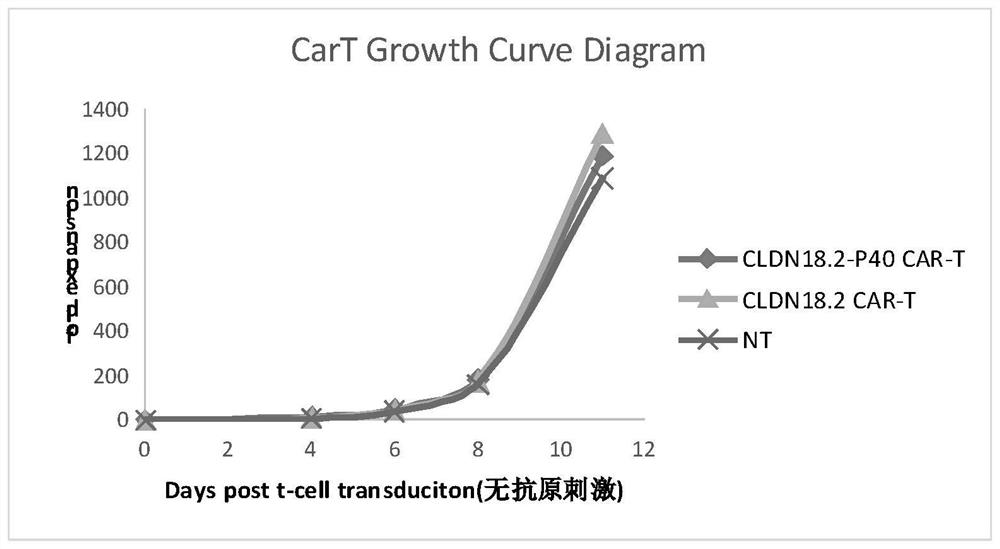
The invention relates to a plasmid structure for expressing CD19CAR and knocking down T cell surface PD-1 expression simultaneously. The plasmid structure comprises an H1 promoter, an anti-PD-1shRNA sequence started by the H1 promoter, an EF1alpha promoter and a three-generation CD19CAR sequence started by the EF1alpha promoter that are connected in series in order. The three-generation CD19CAR sequence consists of a CD19 single chain variable region, a human CD8alpha hinge region, a human CD28 transmembrane region and an intracellular region, a human 41BB intracellular region and a human CD3zeta intracellular region that are connected in series. The plasmid structure provided by the invention is transduced into T cells by a lentivirus, and the CART cell production process is significantlysimplified than using CRISPR / Cas9 for knockout of PD-1. Moreover, the CART cells show enhanced tumor cytotoxicity killing ability and increased persistent cell repair and cytokine secretion ability after antigenic stimulation in vitro.
Owner:WUHAN BIO RAID BIOTECH CO LTD
Kit for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by using peripheral blood and application of kit
The invention discloses a kit for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by using peripheral blood. The kit provided by the invention comprises the following substances: (1) a mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3615c mixed polypeptide library which consists of all or a part of 19 polypeptides consisting of amino acid sequences shown as sequences 1 to 19 in a sequence table, (2) an anti-CD3 antibody labeled with a fluorescent dye A, (3) an anti-gamma-interferon antibody labeled with a fluorescent dye B, and (4) a Golgi apparatus blocking agent, wherein the fluorescent dye A and the fluorescent dye B emit different fluorescent colors. A novel method which can be used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection is provided. As proved by experiments, antigenic stimulation can be performed by directly using the peripheral blood without separating single karyocytes of the peripheral blood. As indicated by experimental data, the kit has high sensitivity and high specificity when being used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Moreover, the kit is easy and convenient to operate and low in cost, and has high clinical application value.
Owner:北京同生时代生物技术有限公司
2019-nCoV double-target antibody detection microsphere complex combination, preparation method, kit and use method of kit
PendingCN111896734AReduce dosageEfficient detectionBiological material analysisViral testSpecific antibody
Owner:湖北新纵科病毒疾病工程技术有限公司
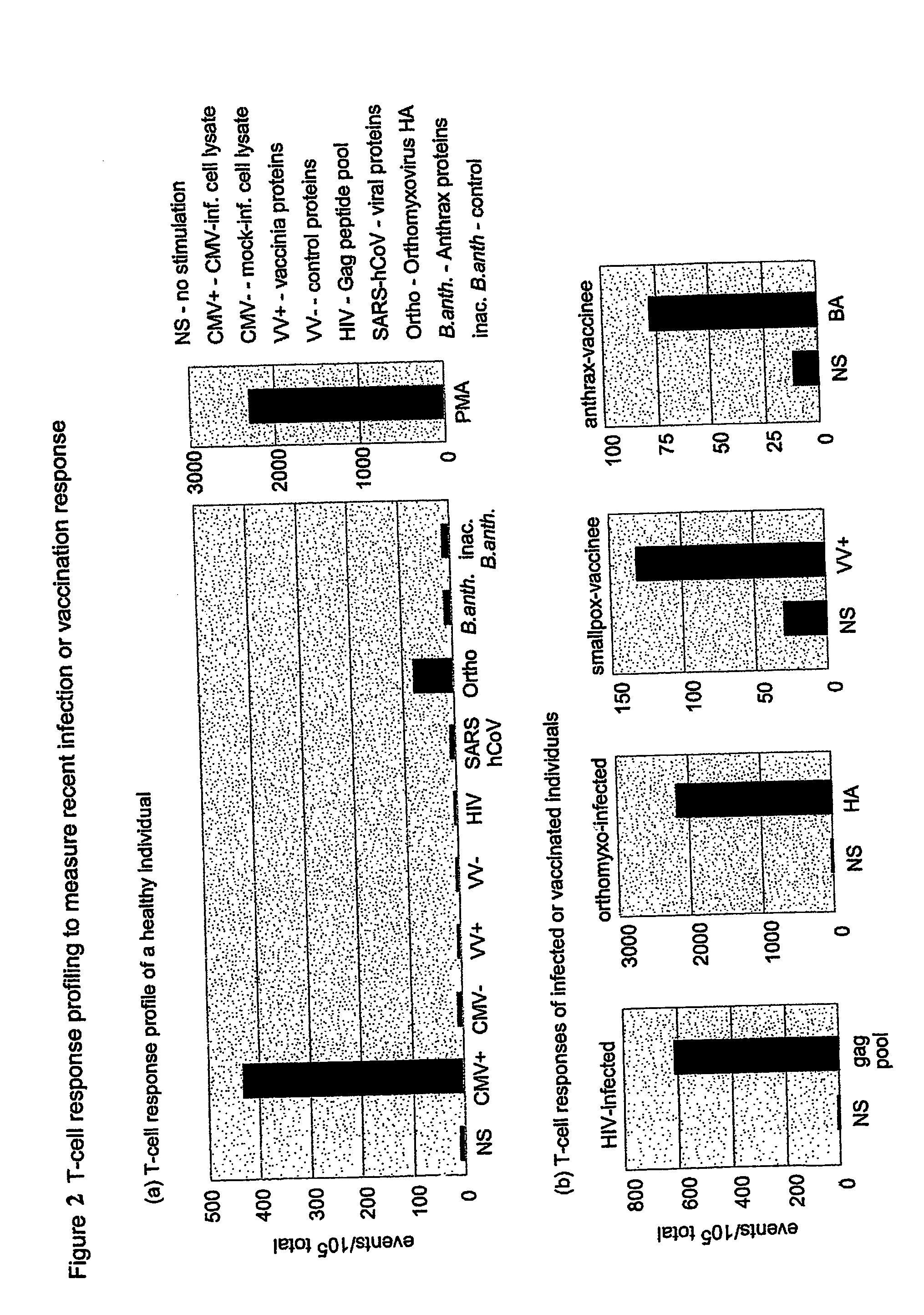
Method for Diagnosing Tuberculosis Disease by Detecting Induced Markers After Stimulation of T-Cells With Antigens
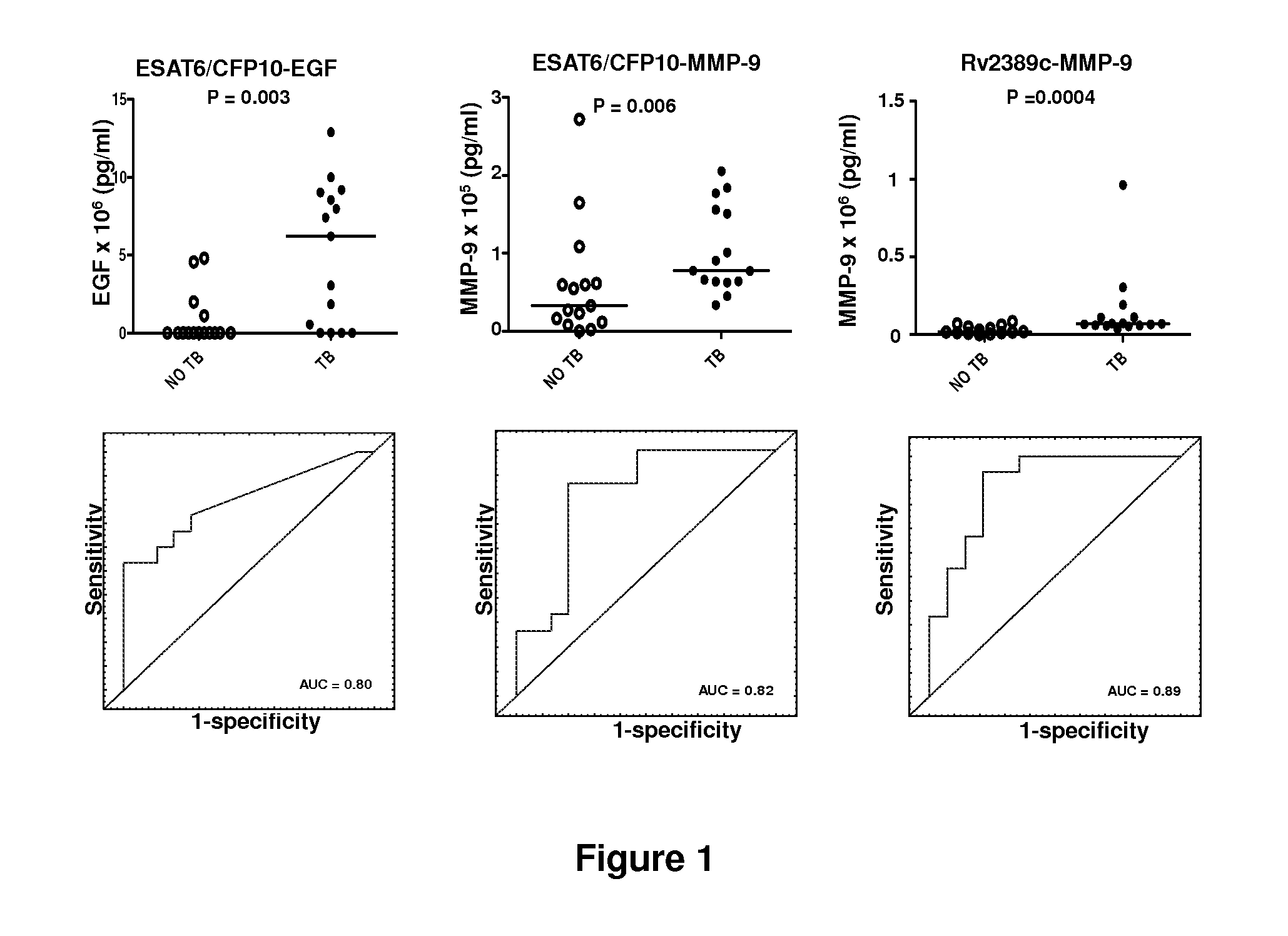
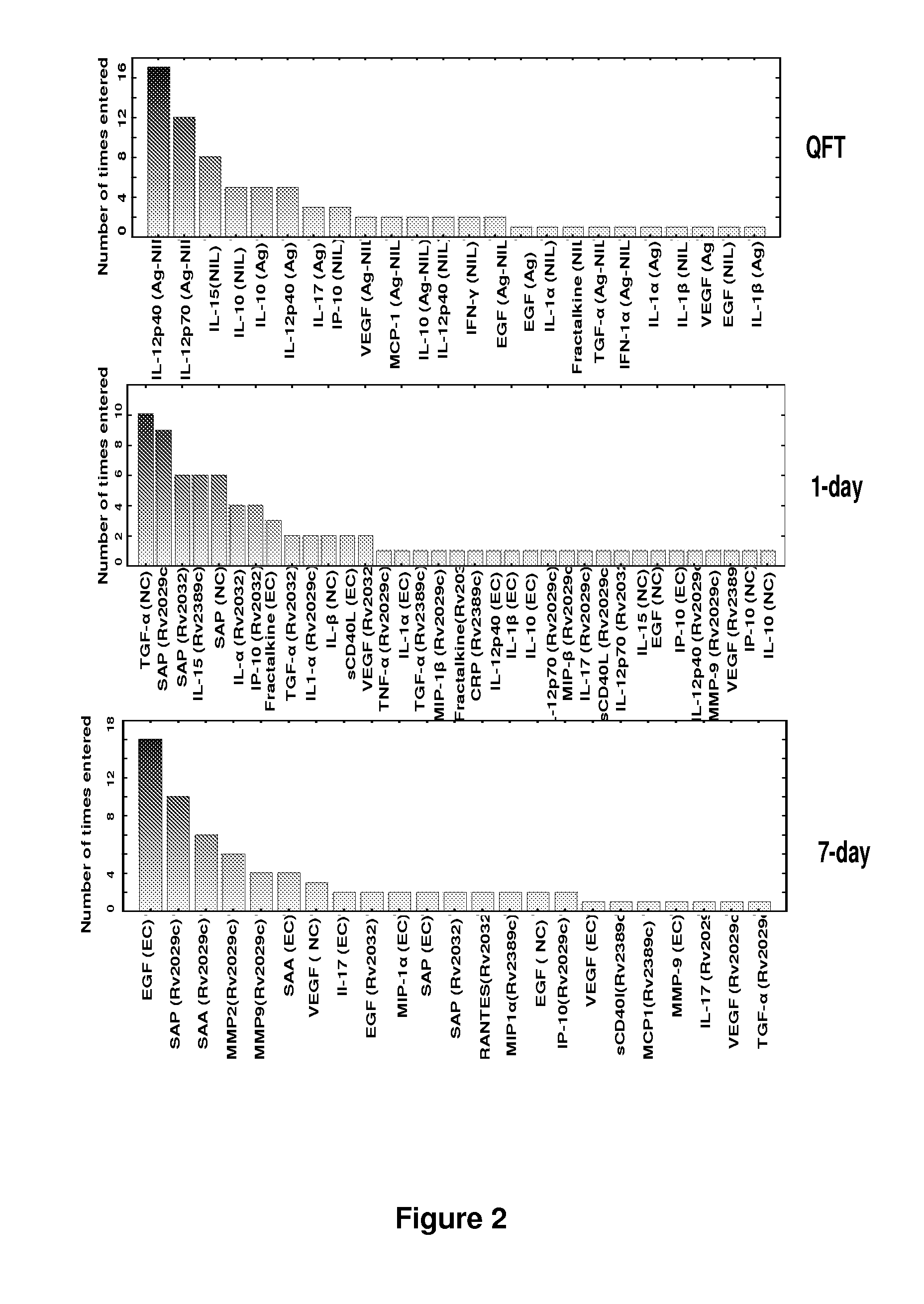
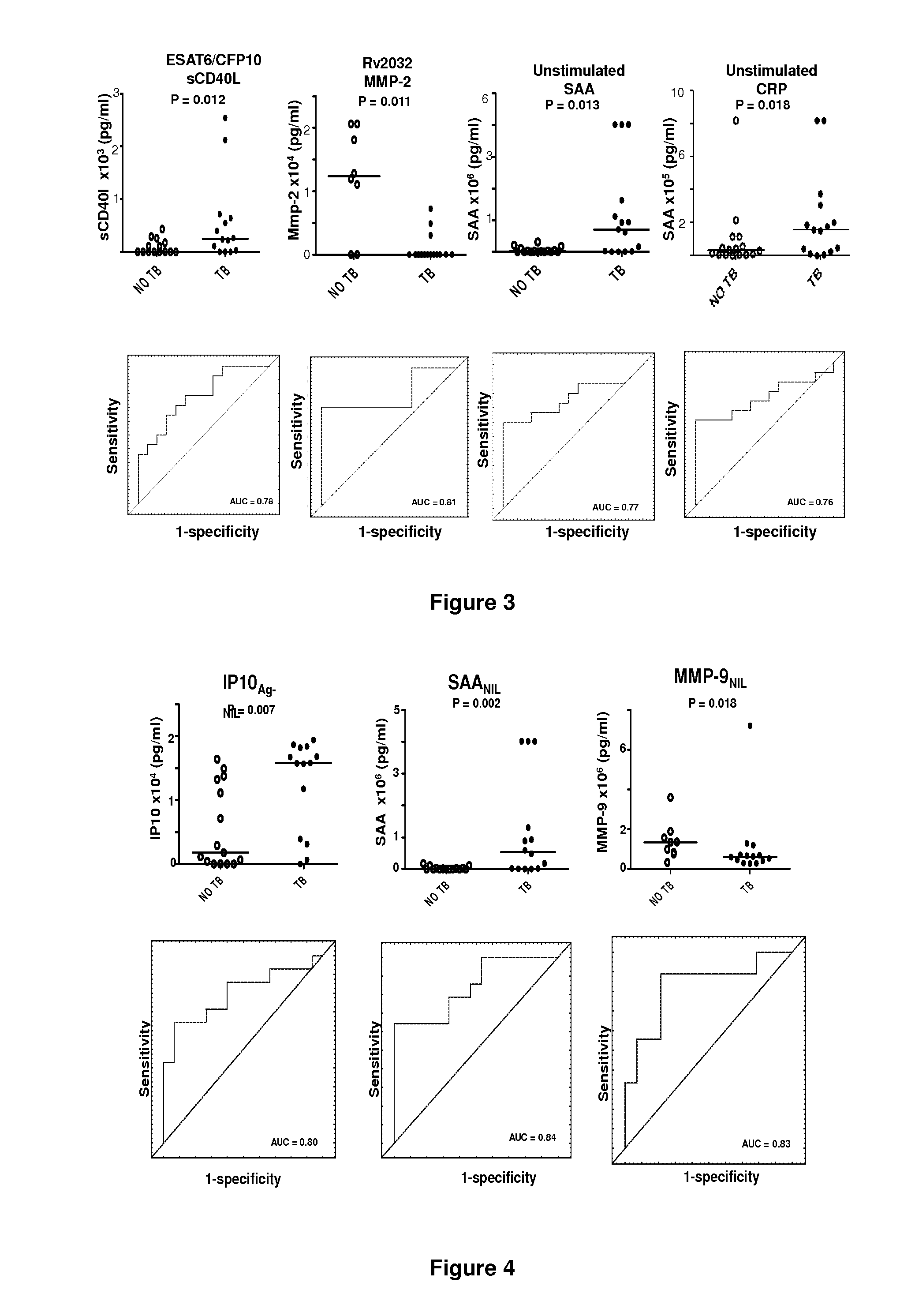
A method of diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) disease and distinguishing between active TB and latent TB infection in a subject is described herein. A sample from the subject is stimulated with at least one Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) infection phase-dependent antigen selected from Rv0081, Rv2032, Rv1737c, Rv2389c, Rv0867c, TB18.2, Rv2099c, Rv1733c, M.tb PPD, PHA and ESAT-6 / CFP-10 and the presence of at least one host marker in the sample is detected, the host marker being selected from EGF, TGF-α, TNF-α, VEGF, RANTES, IL-12(p40), IL-12(p70), IL-10, IP-10, IFN-α2, fractalkine, IFN-γ, IL-13, IL-1Ra, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, MIP-1α, ENA-78, BCA-1, TARC, X6-Ckine, eotaxin, eotaxin-2, SCF, APOA-1, APOE, HPALBN, HCF, Serum amyloid protein A (SAA), C-reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid protein P (SAP), TIMP-1, MIP-1β, IL-6, GM-CSF, IL-1α, MMP-9, MMP-2, MCP-1, TRAIL, IL-15, IL-17F, IL-22, TNF-β, MCP-2 and MCP-4. Additional host markers may also be detected in an unstimulated sample from the subject.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
HCV (hepatitis C virus) poly-epitope peptide vaccine and application thereof
ActiveCN102757484AImproving immunogenicityImprove immunityVirus peptidesAntiviralsChronic viral hepatitis CPeptide vaccine
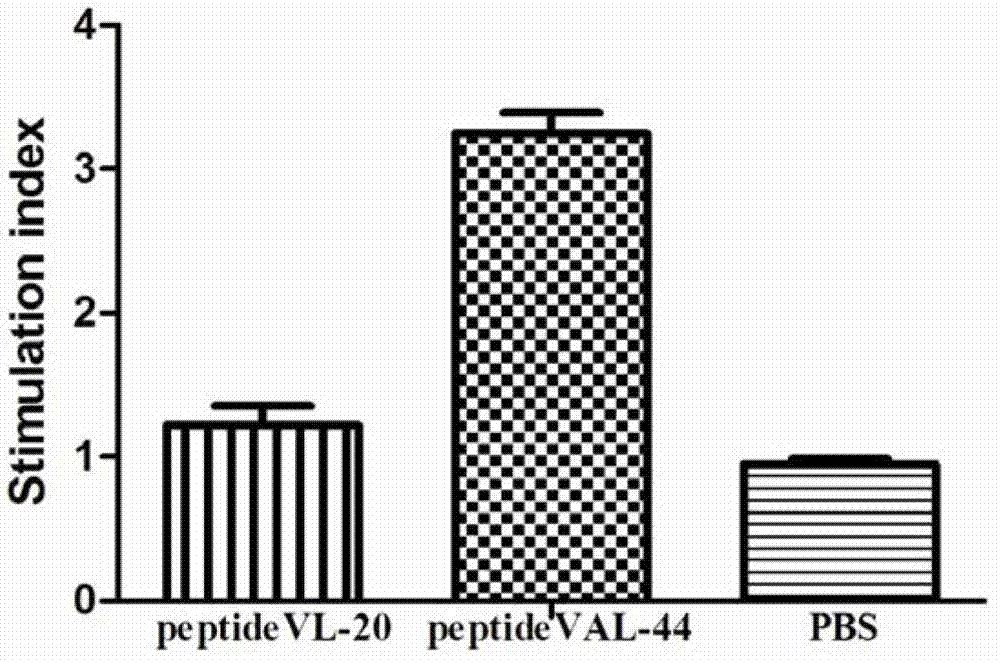
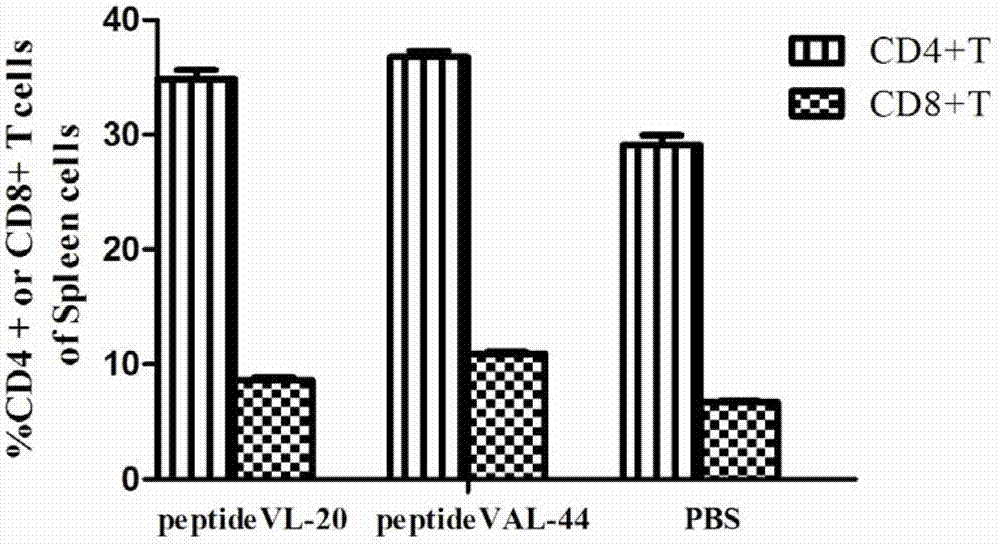
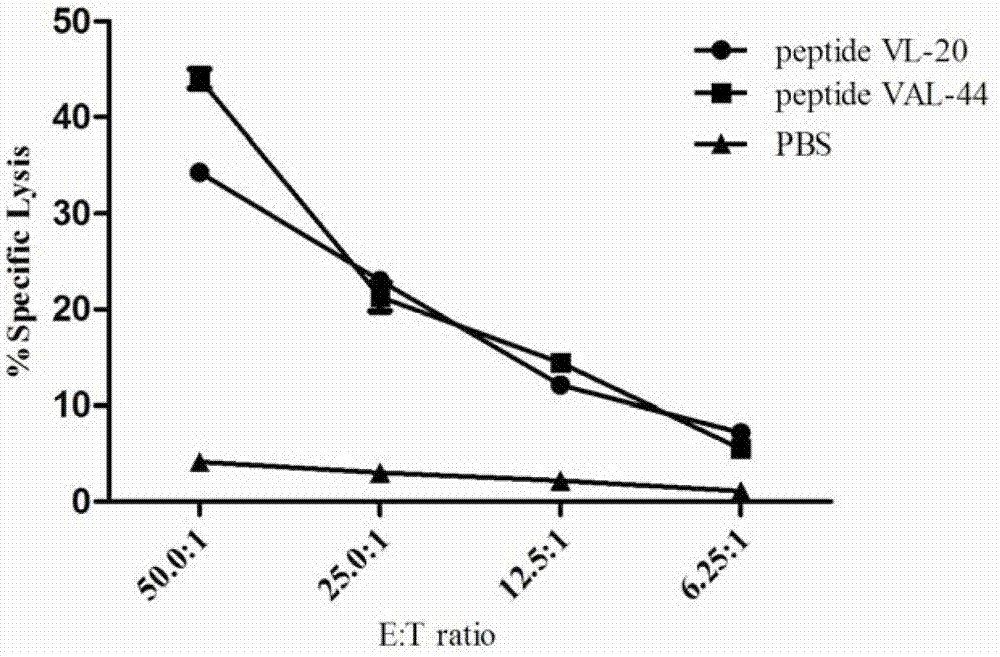
The invention discloses an HCV (hepatitis C virus) poly-epitope peptide vaccine and application thereof. The HCV poly-epitope peptide vaccine comprises the following poly-epitope polypeptides: poly-epitope polypeptide of which the amino acid residue sequence is disclosed as SEQ.ID.NO.1, or poly-epitope polypeptide of which the amino acid residue sequence is disclosed as SEQ.ID.NO.2. The polypeptide VAL-44 HCV can induce the specific T cell immune response, including CD4 cells and CD8 cells; and the T cells can quickly generate IFN-gamma and IL-2 after being subjected to specific antigenic stimulation. The HCV polypeptide vaccine can stimulate 3 of 10 chronic HCV infected persons PBMC to secrete IFN-gamma. The HCV poly-epitope polypeptide can be an ideal HCV preventive / curative candidate vaccine.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Antigenic polypeptide pool for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and application
ActiveCN107141341AStop transmissionStop the epidemicBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesMycobacterium InfectionsTrue positive rate
The invention discloses an antigenic polypeptide pool for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. The specific antigenic polypeptide pool can specifically secrete IFN-gamma by specifically stimulates fresh whole blood infected by the mycobacterium tuberculosis to improve the detection sensitivity. The invention provides a new detection kit applied to detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Experiments prove that antigenic stimulation can be conducted by directly using peripheral blood, single karyocyte of the peripheral blood does not need to be separated, experiment data shows that the antigenic polypeptide pool has high sensitivity and specificity when being used for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, is simple and convenient to operate, and low in cost, and has high clinical application value.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
Antigen and kit for detecting tuberculosis-infected T cells and application of kit
ActiveCN107144694AStop transmissionStop the epidemicChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDisease diagnosisTrue positive rateT cell
The invention discloses an antigen for detecting tuberculosis-infected T cells. The amino acid sequence of the antigen is shown as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.26; eight polypeptides are randomly selected from the SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.26 and are collaborated with ESAT-6 and CFP-10 polypeptides and derivatives thereof, and specifically-stimulated mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected T cells can specifically secrete IFN-gamma, so that the detection sensitivity is increased. The invention provides a novel kit applicable to detection of the tuberculosis-infected T cells. The kit is used for directly performing antigenic stimulation on peripheral blood, without needing separating mononuclear cells from the peripheral blood; the kit is relatively high in detection sensitivity and detection specificity, easy and convenient to operate, low in detection cost and relatively high in clinical application value.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
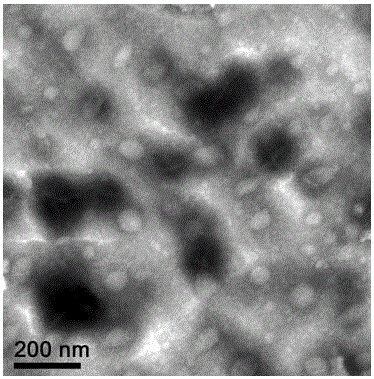
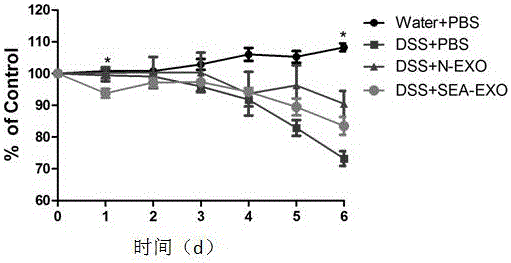
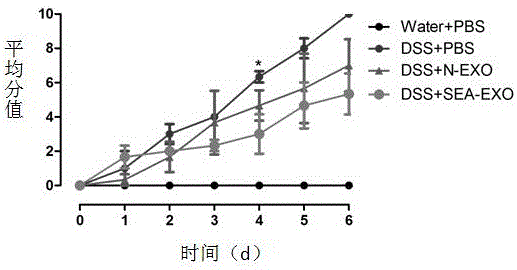
Exosome of Schistosoma japonicum egg antigen (SEA) bone marrow dendritic cell origin and application thereof
ActiveCN105907715AAvoid side effectsLow toxicity and high efficiencyAntipyreticAnalgesicsSchistosoma japonicum eggDendritic cell
Schistosoma japonicum egg antigen (SEA) bone marrow dendritic cells produce an exosome, an exosome is obtained by isolating and purifying and is used to treat a mouse with immune diseases, and then various indexes of this mouse such as body weight change, disease activity index, colon length, tissue lesions and pathological tissue score show that the disease of the experimental mouse is clearly better; it is noted that the exosome produced by japonicum egg antigen (SEA) bone marrow dendritic cells (BMDC) has clear therapeutic effect on immune diseases. The invention belongs to biological therapy, toxic and side effects of existing anti-inflammatory drugs are avoided maximally, the exosome has low toxicity and high efficiency, and a new method for treating immune diseases is provided.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A method for enhancing t cell response
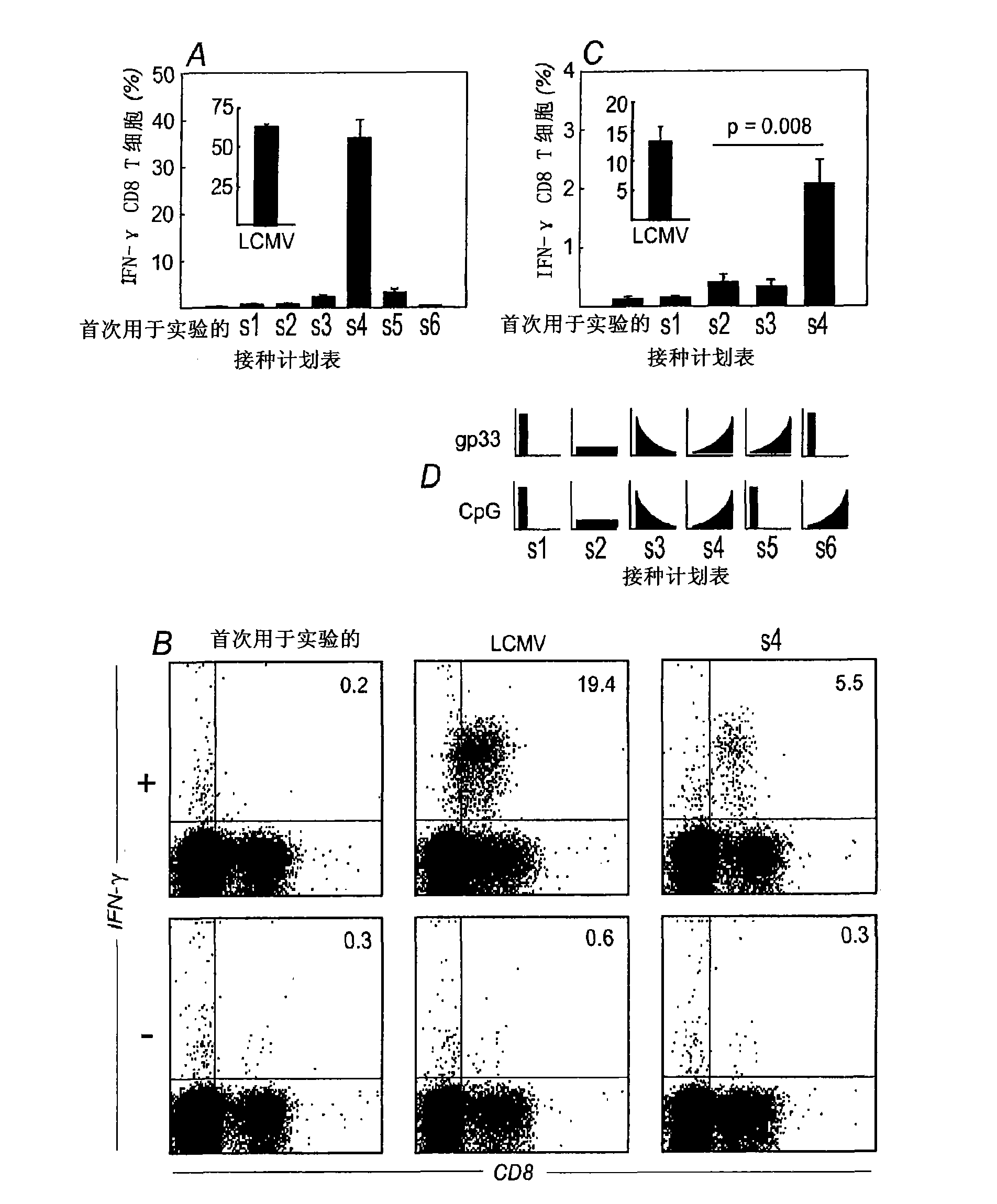
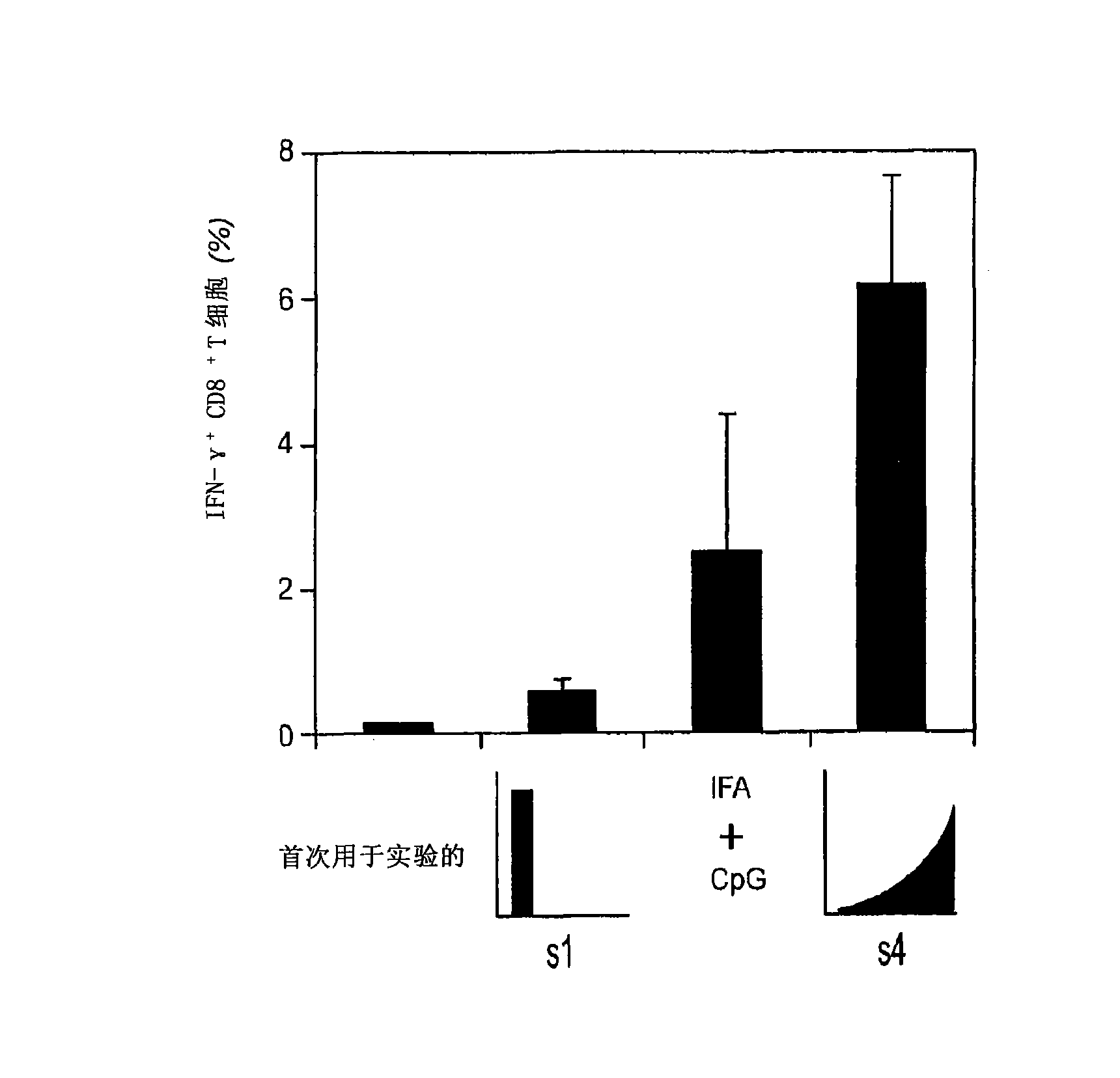
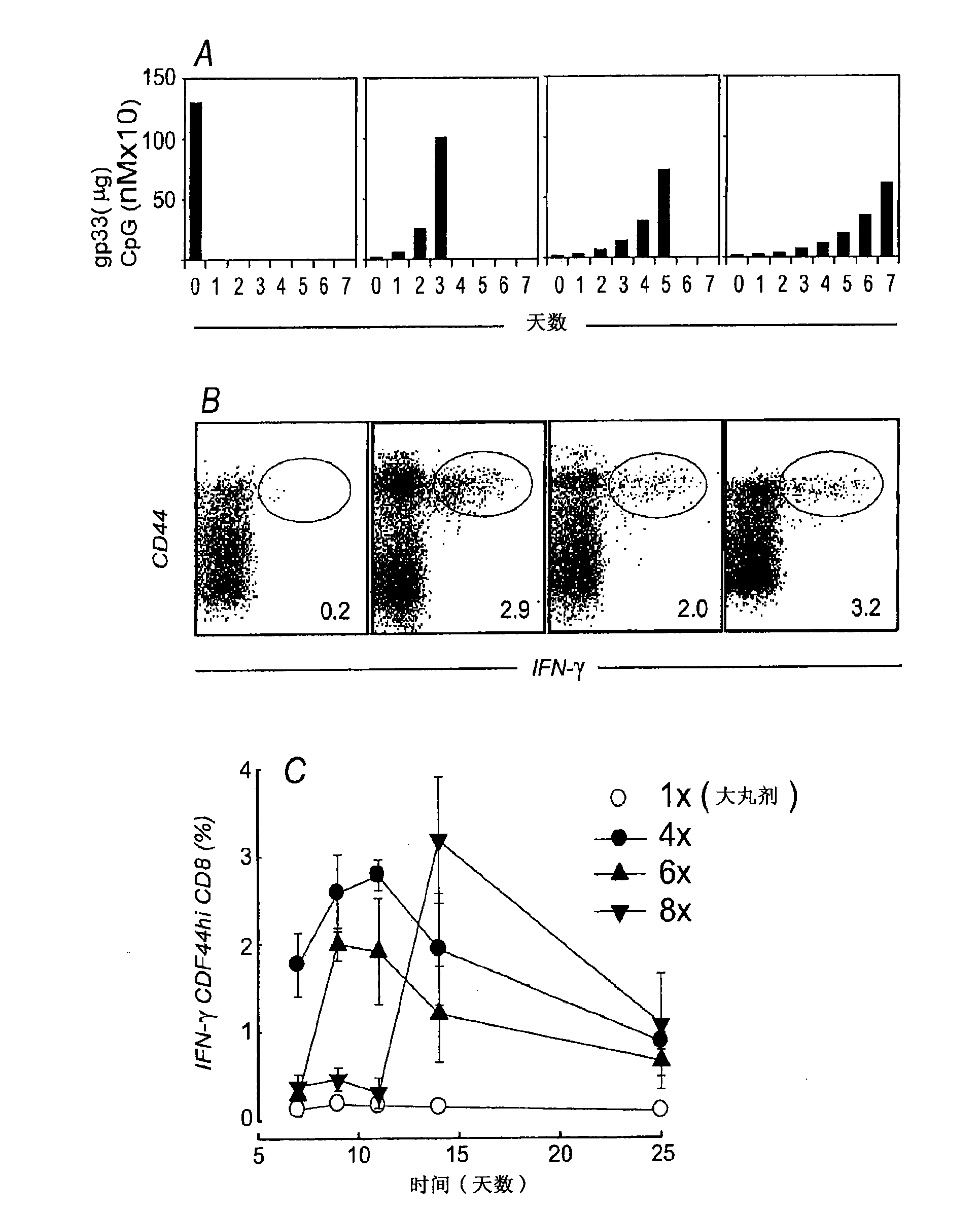
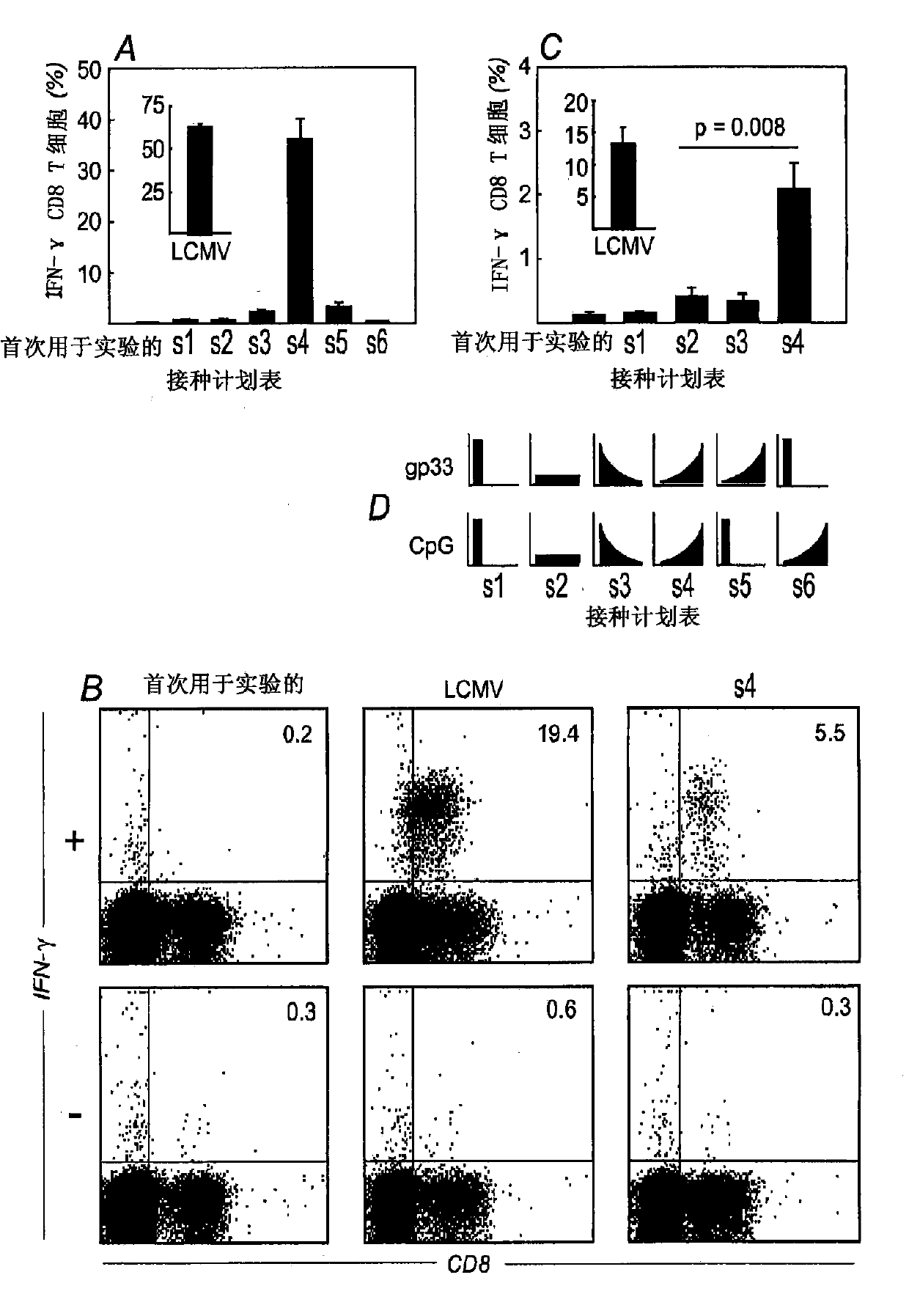
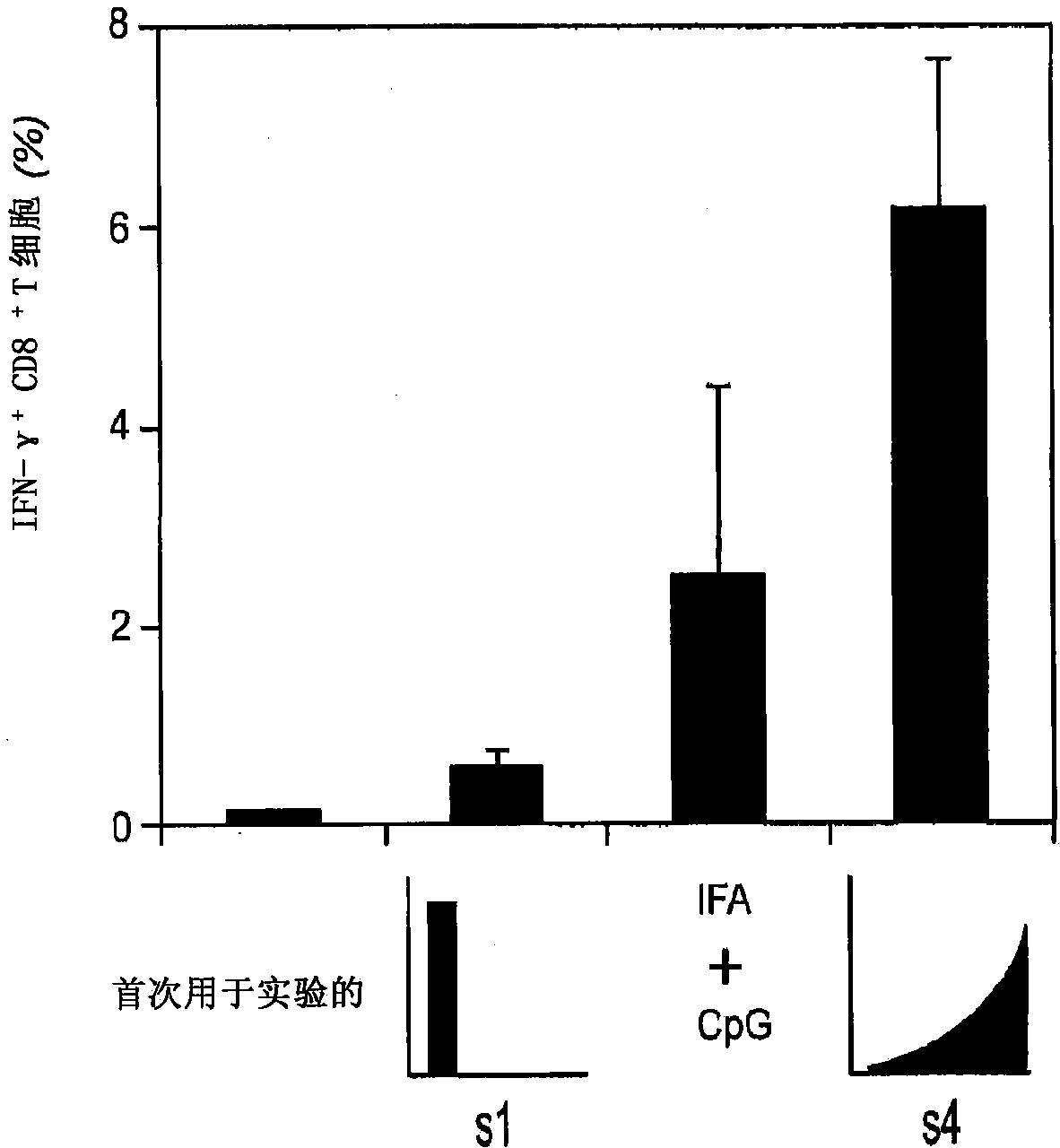
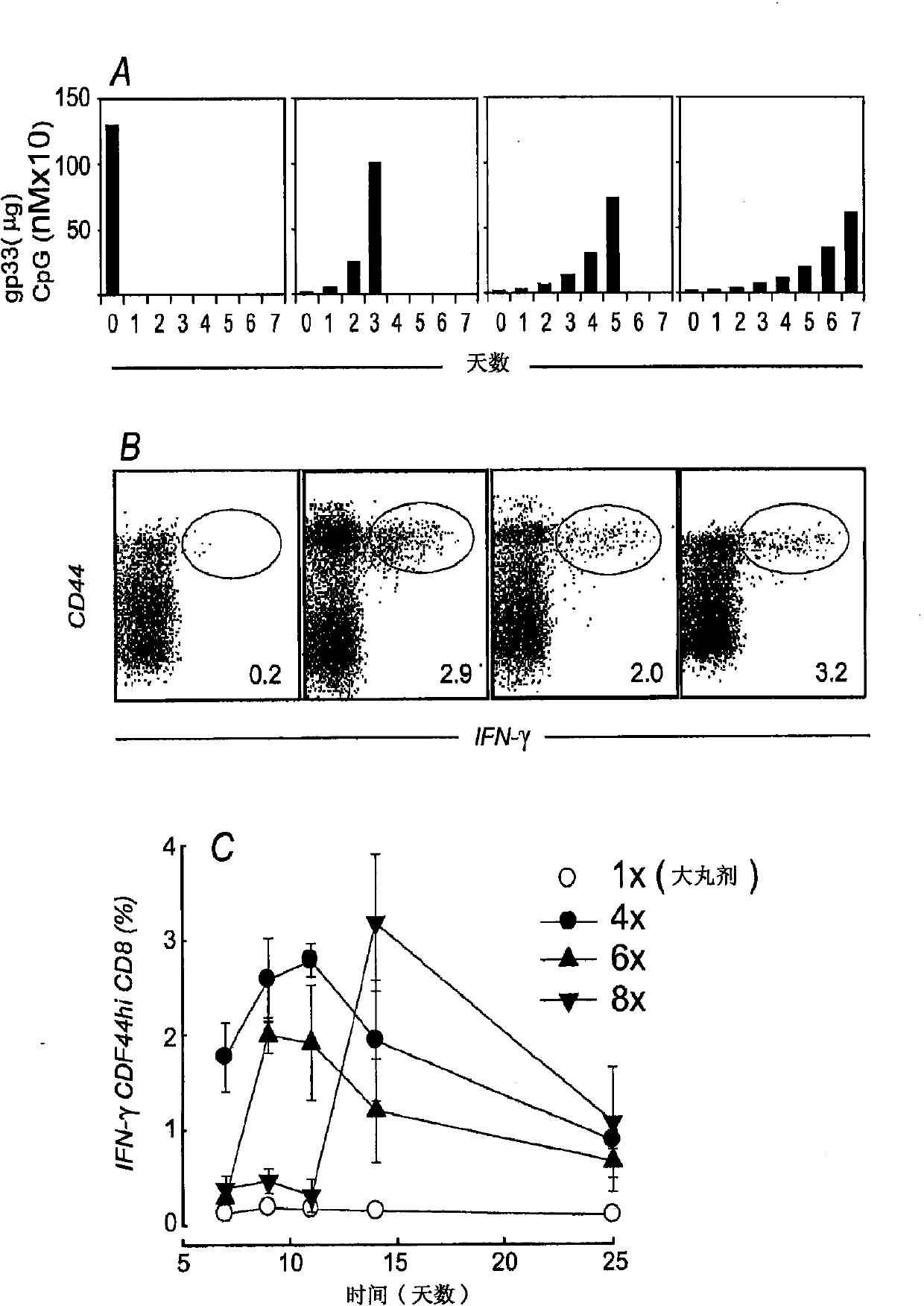
Embodiments of the invention disclosed herein relate to methods and compositions for exponentially increasing antigenic stimulation of class I MHC CD8<+> T cell responses over that based in the art. Some embodiments relate to an immunogenic composition that enhances an immune response in a subject. In some embodiments, the immunogenic composition comprises an antigen in combination with an immunopotentiator or a biological response modifier (BRM). Overall, the invention disclosed herein demonstrates that increasing antigenic stimulation in a manner independent of the dose of the antigen enhances immunogenicity.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Recombinant IgG4 monovalent antibodies
ActiveUS9322035B2High affinityGenerate efficientlySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainTransgene
The invention relates to novel non-human transgenic animals, which upon antigenic stimulation are capable of producing monovalent antibodies binding to a selected antigen, modified heavy chain transgenes, methods for producing the non-human transgenic animals, methods for immunizing the non-human transgenic animals for as well as monovalent antibodies obtainable by such immunization methods.
Owner:GENMAB AS
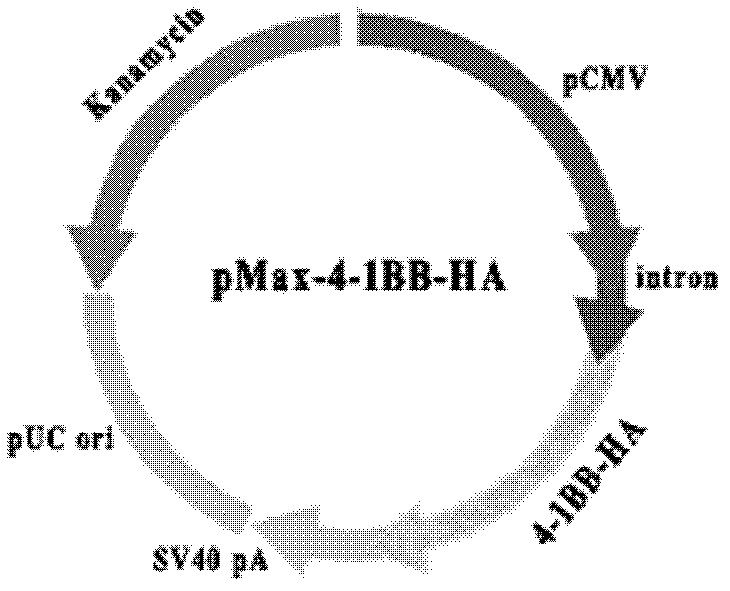
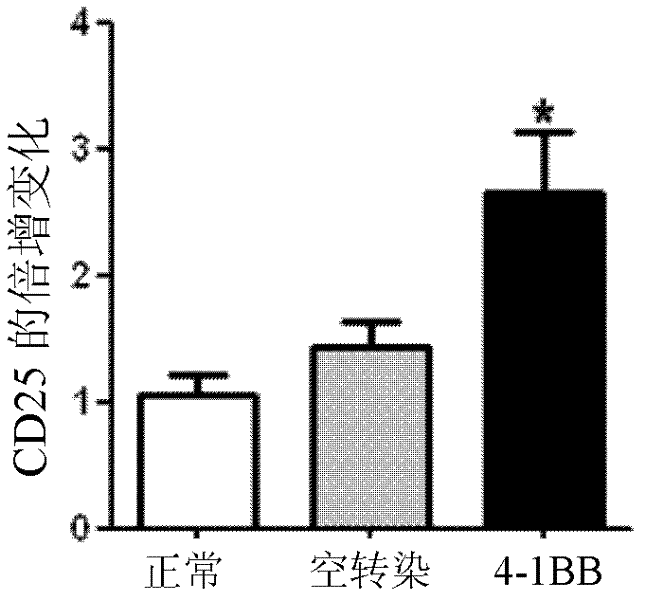
Pig 4-1BB receptor, gene for encoding pig 4-1BB receptor and application thereof
The invention provides a pig 4-1BB receptor molecule, which is the flowing protein (1) or (2): the protein (1) is composed of amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO. 3 or 4, and the protein (2) is derived from the protein (1) by substitution, deletion or insertion of one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO. 3 or 4, and has the same activity. . The invention also provides a gene for encoding the pig 4-1BB receptor, which has nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 or 2. The costimulatory receptor 4-1BB provided by the invention is specifically and highly expressed in peripheral blood T cells of pig, can enhance activation, proliferation and secretion activity of cell factor when transgenic T cells are suffered from antigenic stimulation, thus enhance acquired immunity response of host and immunity effect of vaccine.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Transgenic animals producing monovalent human antibodies and antibodies obtainable from these animals
ActiveUS20100306867A1High affinityGenerate efficientlySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHeavy chainTransgene
The invention relates to novel non-human transgenic animals, which upon antigenic stimulation are capable of producing monovalent antibodies binding to a selected antigen, modified heavy chain transgenes, methods for producing the non-human transgenic animals, methods for immunizing the non-human transgenic animals for as well as monovalent antibodies obtainable by such immunization methods.
Owner:GENMAB AS
Porcine CD28 receptor and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102558341APromote activationEnhanced secretory activityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNucleotideBiological activation
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Immune cell for expressing cytokine receptor fusion type chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
InactiveCN113416708AImprove proliferative abilityEnhance tumor killing activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTumor reductionCytokine Receptor Binding
The invention discloses an immune cell for expressing a cytokine receptor fusion type chimeric antigen receptor and application of the immune cell. A cytokine receptor fusion type chimeric antigen receptor is expressed on a cell membrane of the immune cell, and a cytokine receptor intracellular domain is fused in an intracellular domain structure of the cytokine receptor fusion type chimeric antigen receptor. The immune cell can enhance the proliferation capacity of the cell, reduce the influence of a tumor microenvironment and enhance the tumor killing activity of the immune cell under the condition of receiving antigen stimulation, so that the negative regulation of the tumor microenvironment on the immune cell is weakened, the exhaustion of the immune cell is reduced, and corresponding JAK and STAT signal channels are activated by combining with a cytokine receptor, the cells are induced to secrete various active substances such as IFN-gamma, perforin and granzyme, so that the growth of tumor cells is inhibited, the anti-tumor capability is enhanced, and the inhibition of a tumor microenvironment on immune cells is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN FIRST CONDOR BIOSCIENCE CO LTD
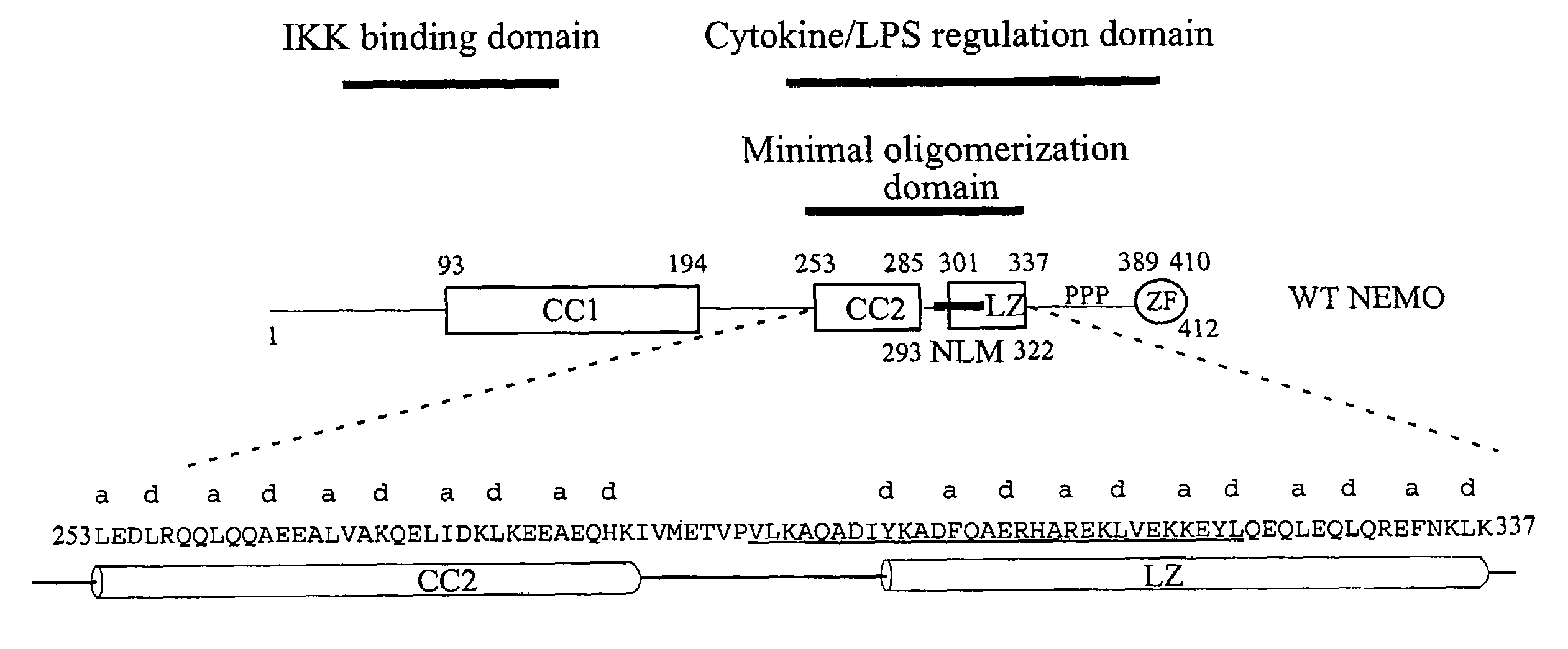
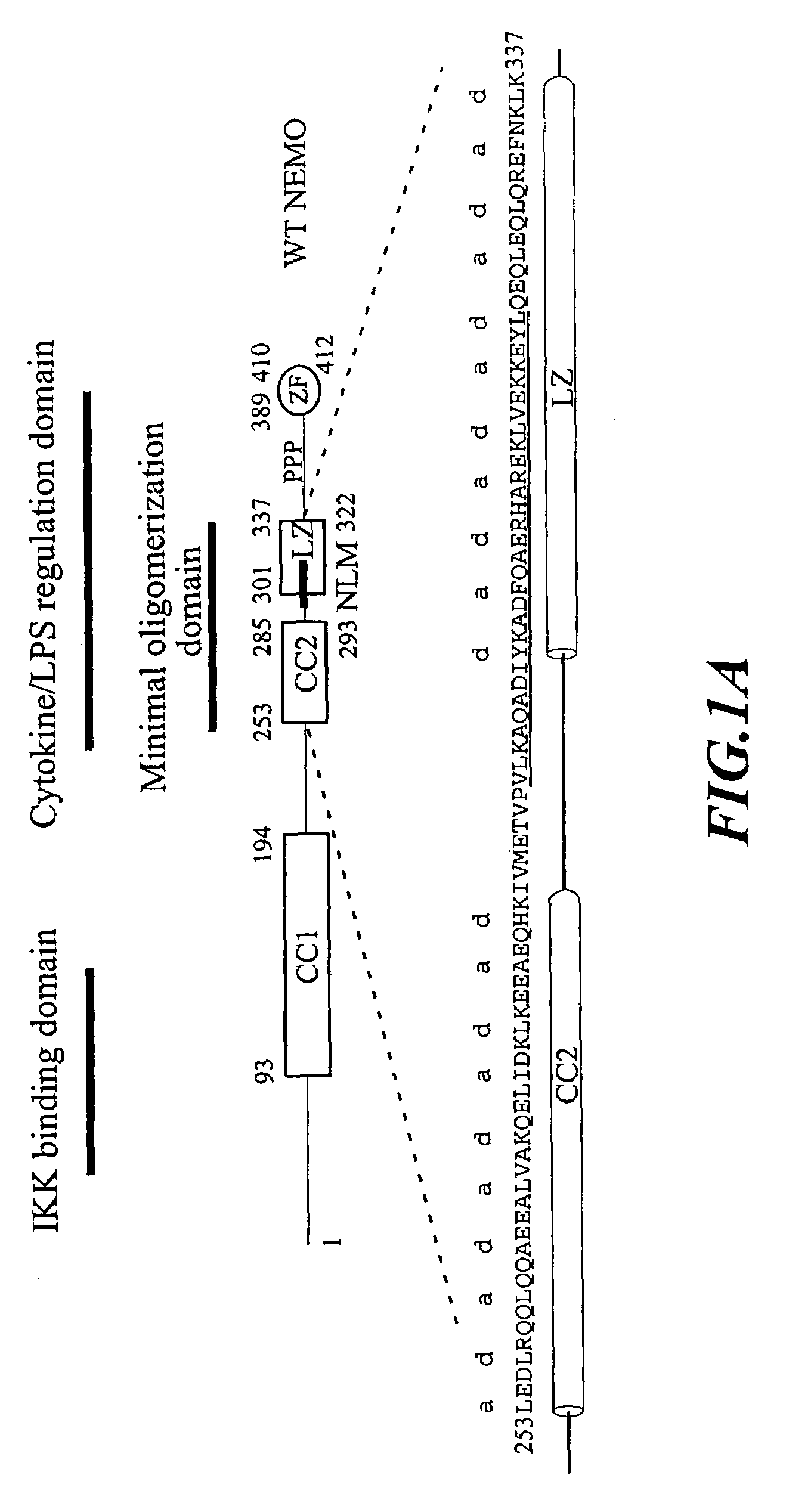
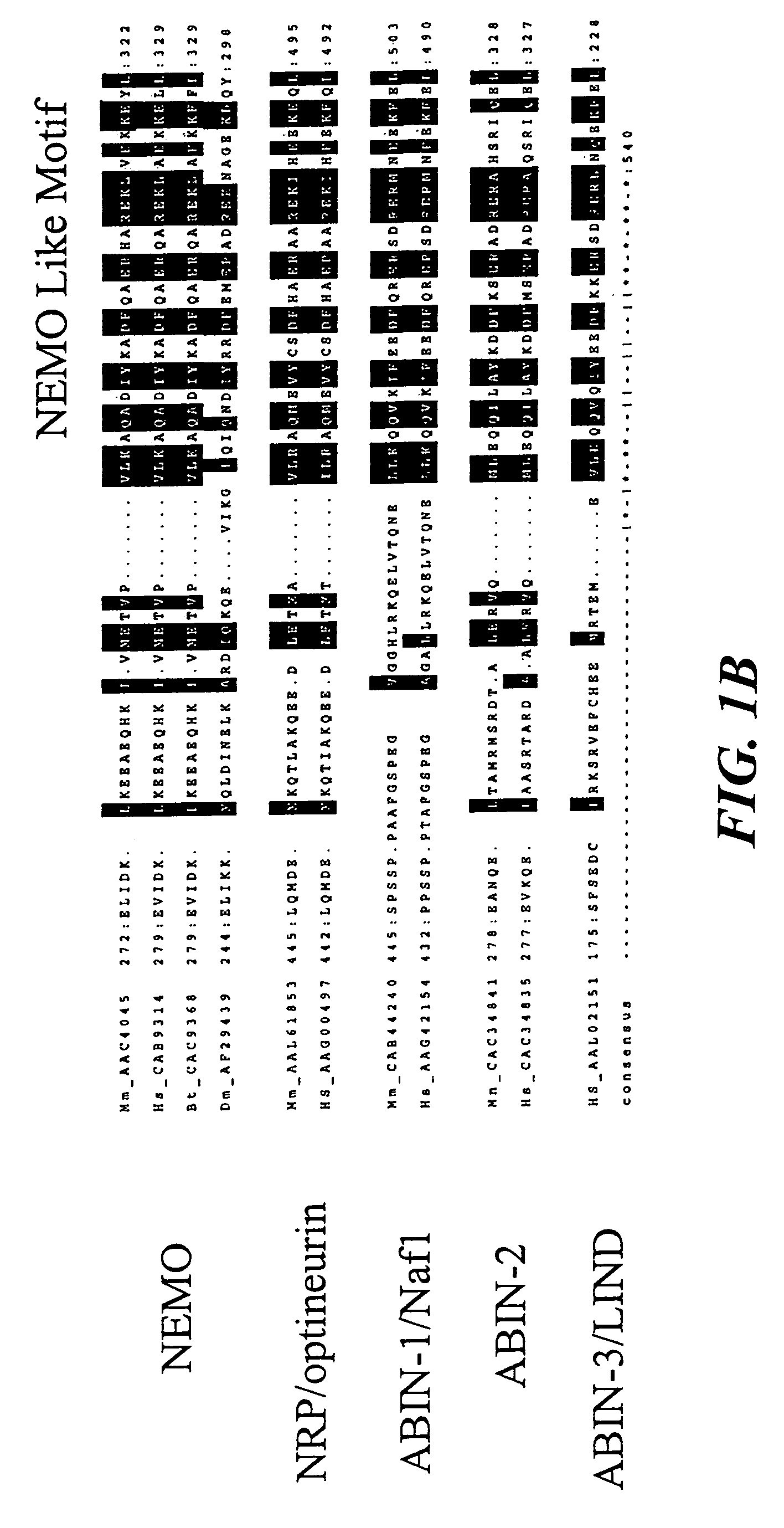
NF-kappaB peptides designed to disrupt NEMO oligomerization
Owner:INST PASTEUR
A method for enhancing t cell response
Embodiments of the invention disclosed herein relate to methods and compositions for exponentially increasing antigenic stimulation of class I MHC CD8<+> T cell responses over that based in the art. Some embodiments relate to an immunogenic composition that enhances an immune response in a subject. In some embodiments, the immunogenic composition comprises an antigen in combination with an immunopotentiator or a biological response modifier (BRM). Overall, the invention disclosed herein demonstrates that increasing antigenic stimulation in a manner independent of the dose of the antigen enhances immunogenicity.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Tuberculous infection diagnostic kit, screening system and application of kit
ActiveCN108872610AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityBiological testingInfection diagnosisBCG vaccine
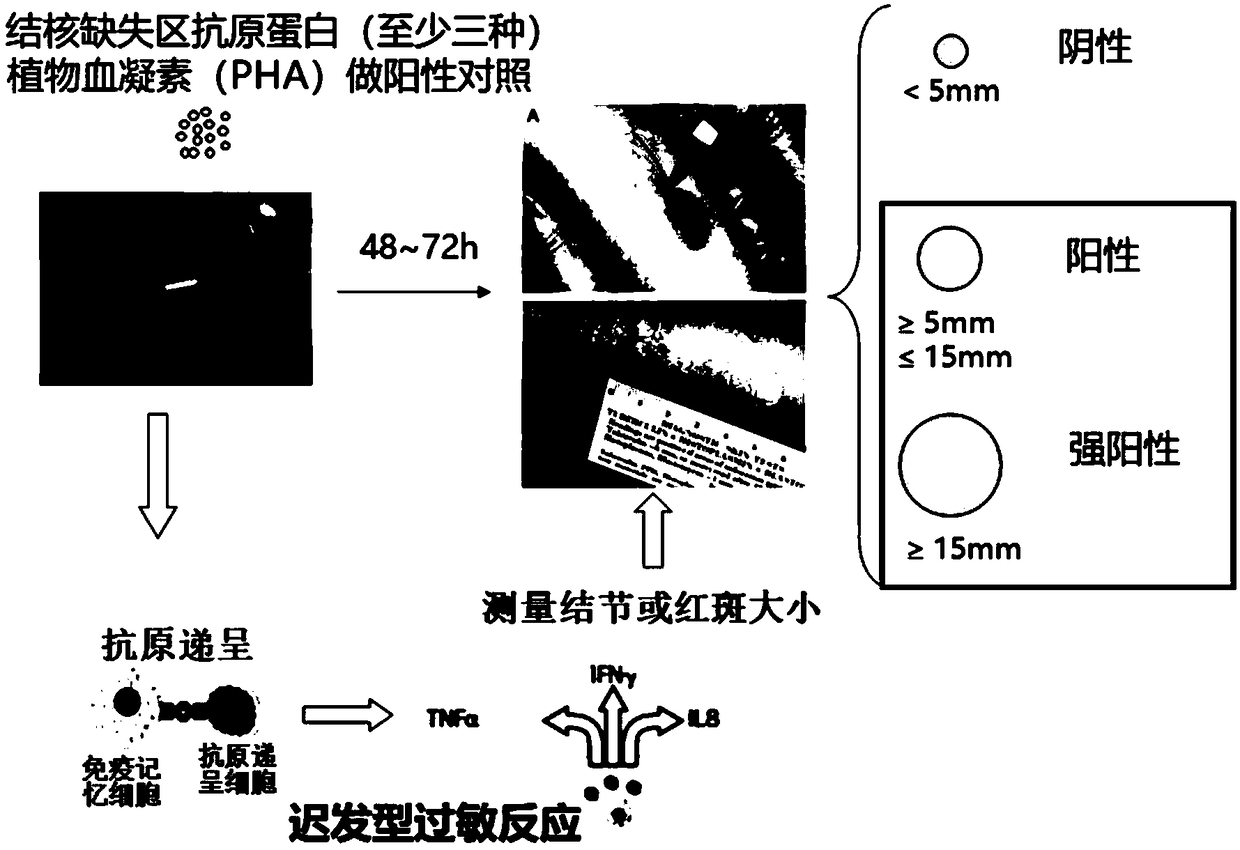
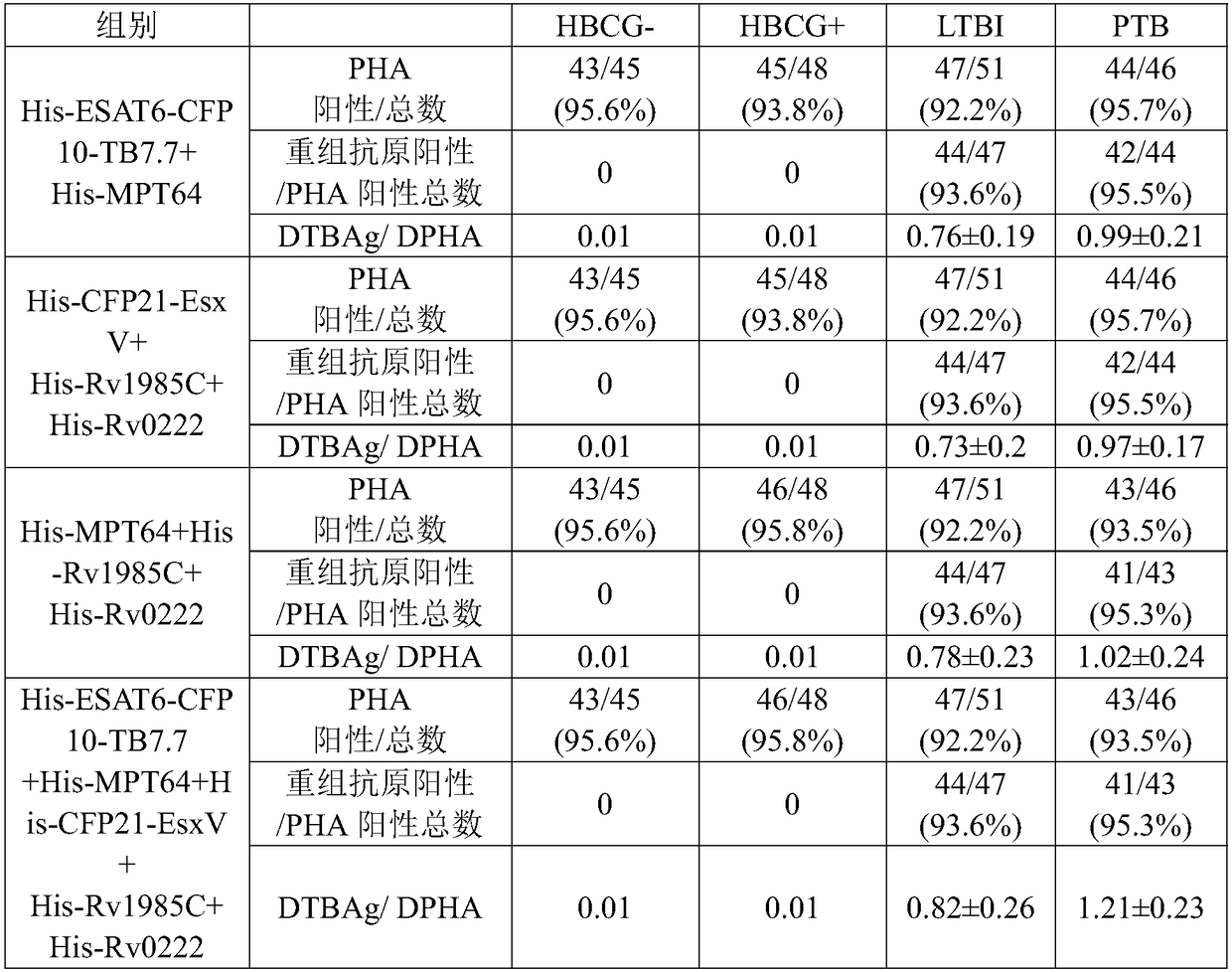
The invention relates to the field of medical test, in particular to a tuberculous infection diagnostic kit, a screening system and application of the kit. The kit contains mitogen and an antigen irritant. The antigen irritant is selected from the following tuberculin pure protein or three or more kinds of derivatives thereof, such as ESAT6, CFP10, TB7.7, MPT64, CFP21, EsxV, Rv1985C and Rv0222. The novel skin experiment for screening latent tuberculosis infection and active tuberculosis, provided by the invention, has the advantages of high specificity (identification of BCG vaccination and tuberculosis infection), high sensitivity (limited multiple antigen protein costimulation), small influence from individual basic immune differences and the like.
Owner:BEIJING CHEST HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Cancer vaccines and methods of using the same
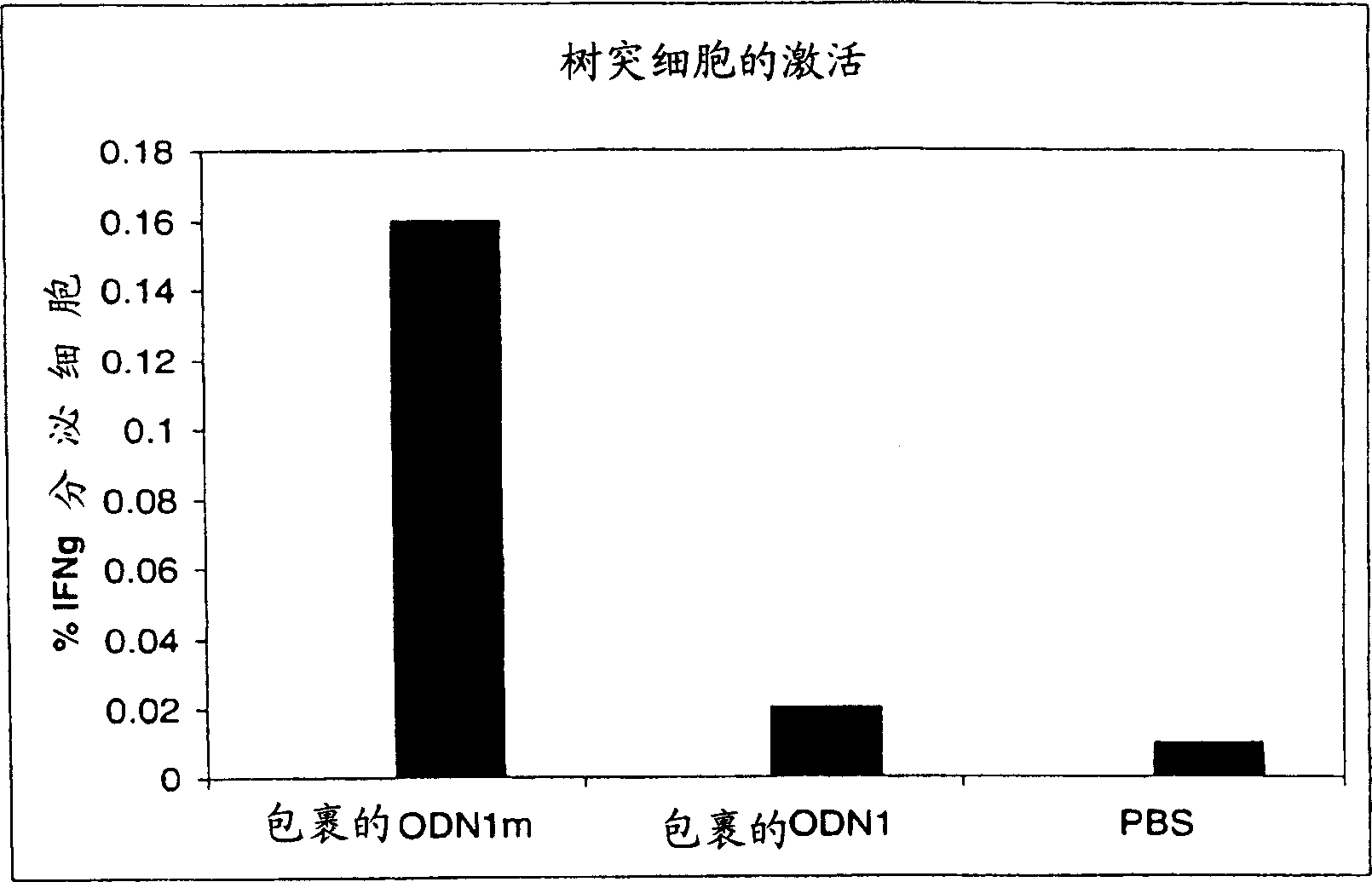
The present invention has found that by encapsulating nucleotides in lipid particles, methylated nucleic acids, especially methylated oligonucleotides, and more particularly methylated nucleic acids containing methylated cytosine CPG dinucleotide motifs can be made Methylated oligonucleotides possess immunostimulatory activity in vivo. The present inventors also discovered that encapsulated methylated nucleic acids, which are generally not immunostimulatory in vivo, are as effective as or more effective than their encapsulated unmethylated counterparts. The present invention also discovers methods of activating and / or expanding dendritic cells in response to antigenic stimulation using the compositions and methods disclosed herein.
Owner:INEX PHARMA CORP
A kind of hcv multi-epitope peptide and truncated ns3, dc activation molecule eda recombinant protein vaccine and its application
ActiveCN103601809BImproving immunogenicityImprove immunityAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsNucleotideT cell
The invention discloses a recombinant protein of HCV multi-epitope peptide, truncated NS3 and DC activation molecule EDA and application thereof. The recombinant protein vaccine includes the following EDA, ΔNS3 and three HCV multi-epitopes: the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ .ID. NO.1. HCV EDA‑ΔNS3‑VAL‑44 protein can induce specific humoral immune responses and T cell immune responses. T cells can rapidly produce IFN‑γ and produce highly efficient CTLs after being stimulated by specific antigens. This HCV polyepitope The peptide and its recombinant protein vaccine with truncated NS3 and DC activating molecule EDA may be ideal HCV prophylactic / therapeutic candidates.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
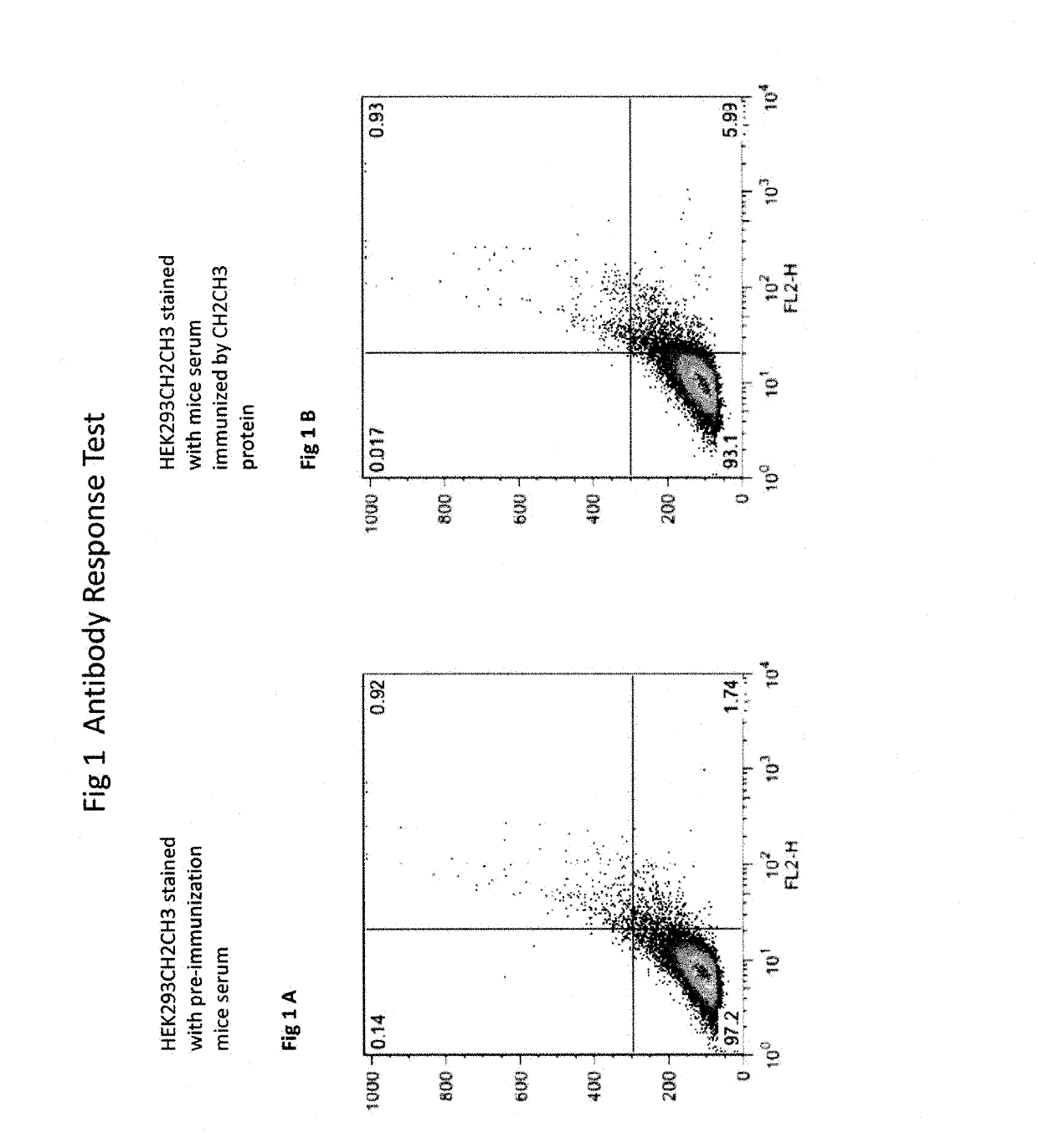
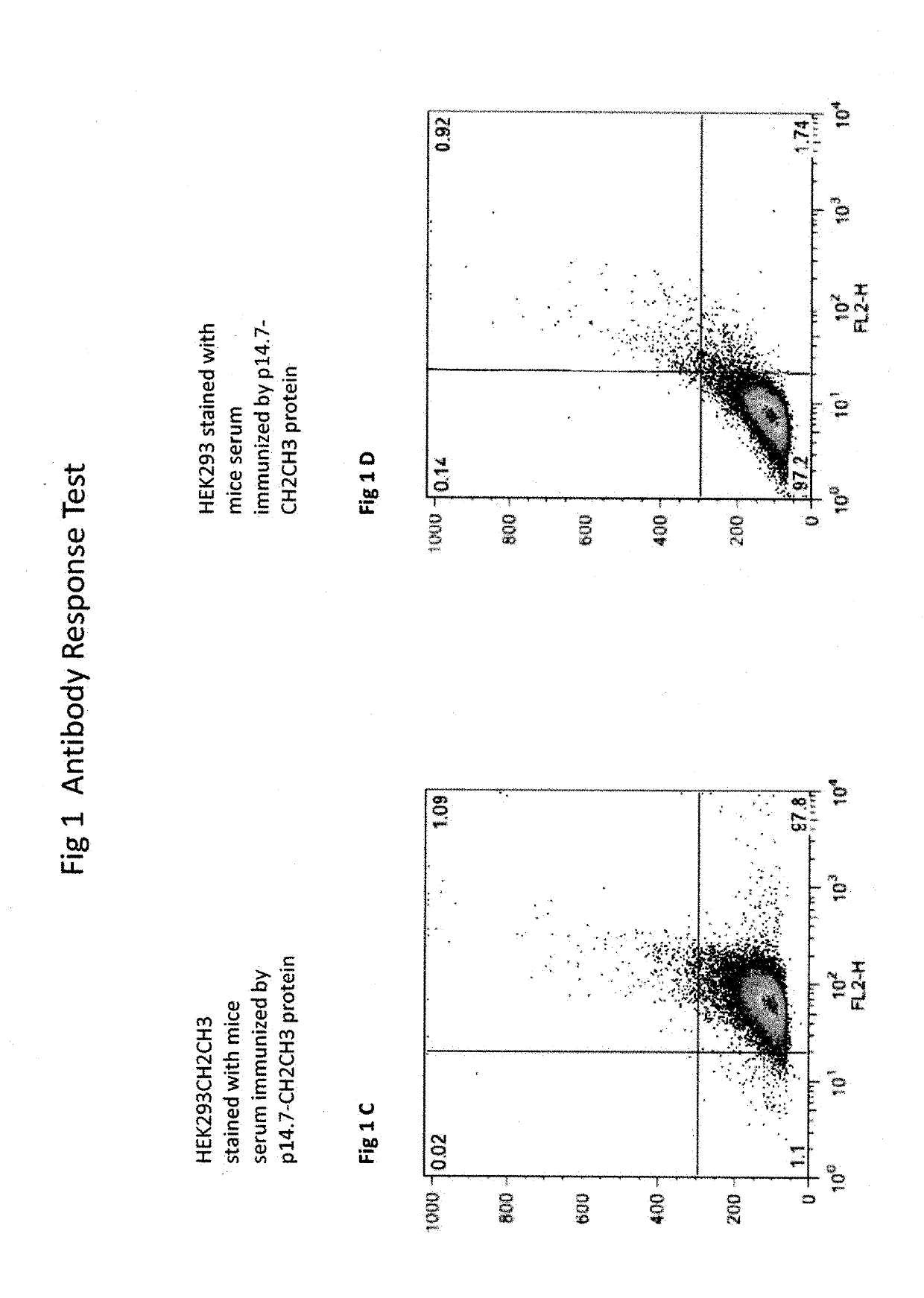
P14.7 protein and uses thereof as vaccine adjuvant
ActiveUS20190298823A1Viral antigen ingredientsVertebrate antigen ingredientsAgonistImmunity response
The present invention Provides composition and method for stimulating immune responses against antigens without using conventional adjuvants (such as aluminum salt adjuvants, oil-in-water emulsion adjuvants, toll-like receptor agonist adjuvants, and the like). The composition contains p14.7 protein and an antigen to which the stimulated illumine responses are desired. The p14.7 protein functions as an adjuvant so that the immune responses to the antigen stimulated by the composition comprising p14.7 protein and the antigen are greater than the immune responses stimulated by the antigen alone. The current invention also provides a method for producing thermostable vaccines and a simple strategy for avoiding vaccine cold-chain maintenance by lyophilization.
Owner:FEMTOMAB
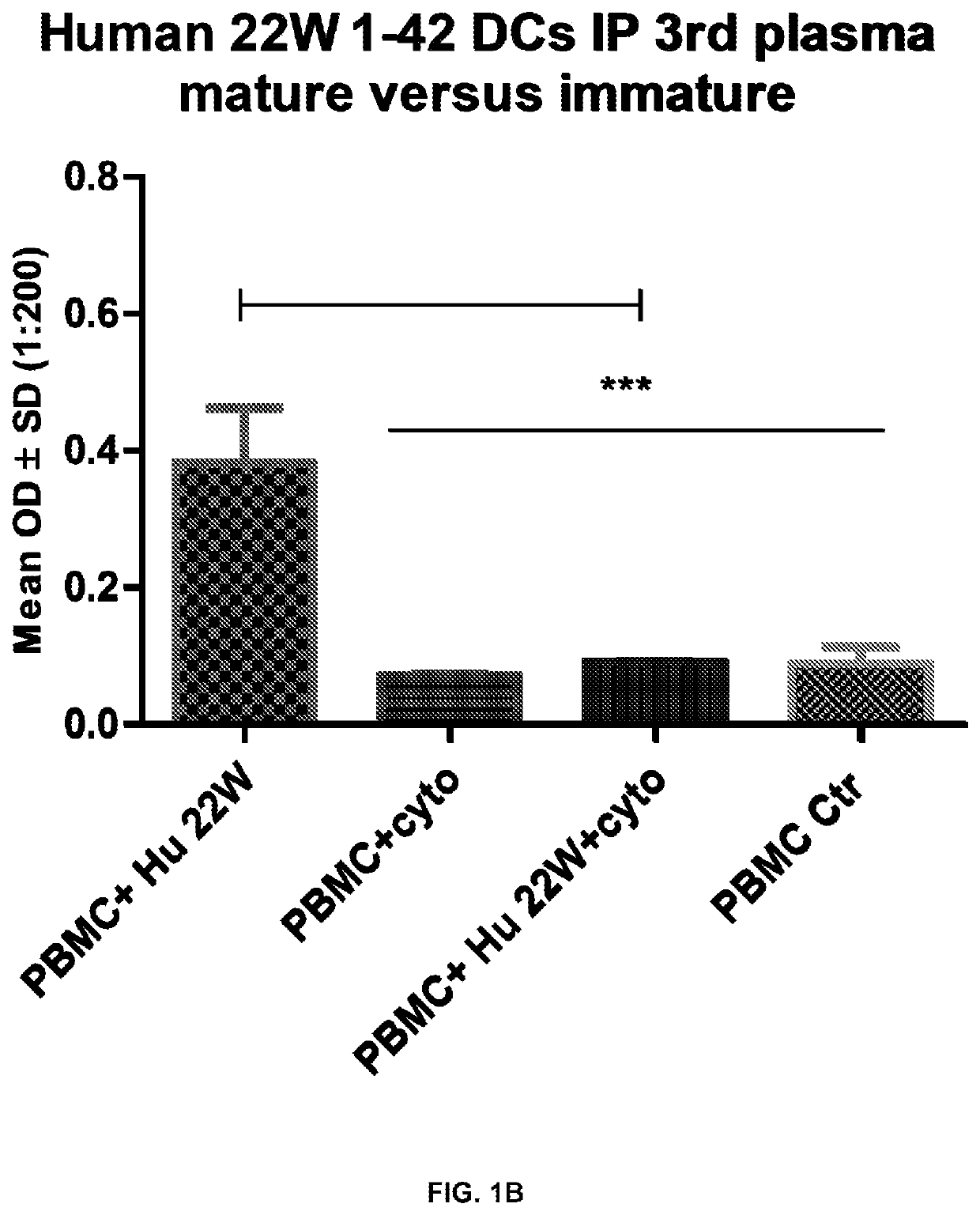
Dead antigen stimulated immature heterogenous dendritic cells as therapeutics for diseases
PendingUS20200338173A1Enhance immune responseNervous disorderNervous system antigen ingredientsDiseaseDendritic cell
Owner:MEGANANO DIAGNOSTICS INC
HCV multi-epitope peptide, truncated NS3, and DC activating molecule EDA recombinant protein vaccine and applications thereof
ActiveCN103601809AImproving immunogenicityImprove immunityAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsPeptideIfn gamma
The invention discloses a HCV multi-epitope peptide, truncated NS3, and DC activating molecule EDA recombinant protein vaccine and applications thereof. The recombinant protein vaccine comprises the following components: EDA, deltaNS3 and three HCV multi-epitopes, whose nucleic acid sequence is represented by the SEQ. ID. No.1. The HCVEDA-deltaNS3-VAL-44 protein can induce a specific humoral immune response and T cell immune response, the T cell can rapidly generate IFN-gamma and generate high efficient CTL after being stimulated by a specific antigen, and the HCV multi-epitope peptide, truncated NS3, and DC activating molecule EDA recombinant protein vaccine is probably an ideal HCV preventive / therapeutic candidate vaccine.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Porcine CD28 receptor and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102558341BPromote activationEnhanced secretory activityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNucleotideTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a porcine CD28 receptor molecule. The molecule is 1) protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, or 2) protein which is obtained by substituting, deleting or adding one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, has the same activity as the protein 1) and is derived from the protein 1). The invention also provides a coding gene of the molecule. The coding gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. The co-stimulation receptor CD28 is specifically and highly expressed in a T cell, the activation, proliferation and cell factor secretion activity of the T cell when the T cell is subjected to antigenic stimulation can be enhanced, the acquired immune response of a host is enhanced, and the immune effect of a vaccine is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for predicting effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor
PendingUS20220011297A1The way is simple and fastAppropriate treatmentOrganic active ingredientsDisease diagnosisPeripheral blood mononuclear cellInterstitial pneumonias
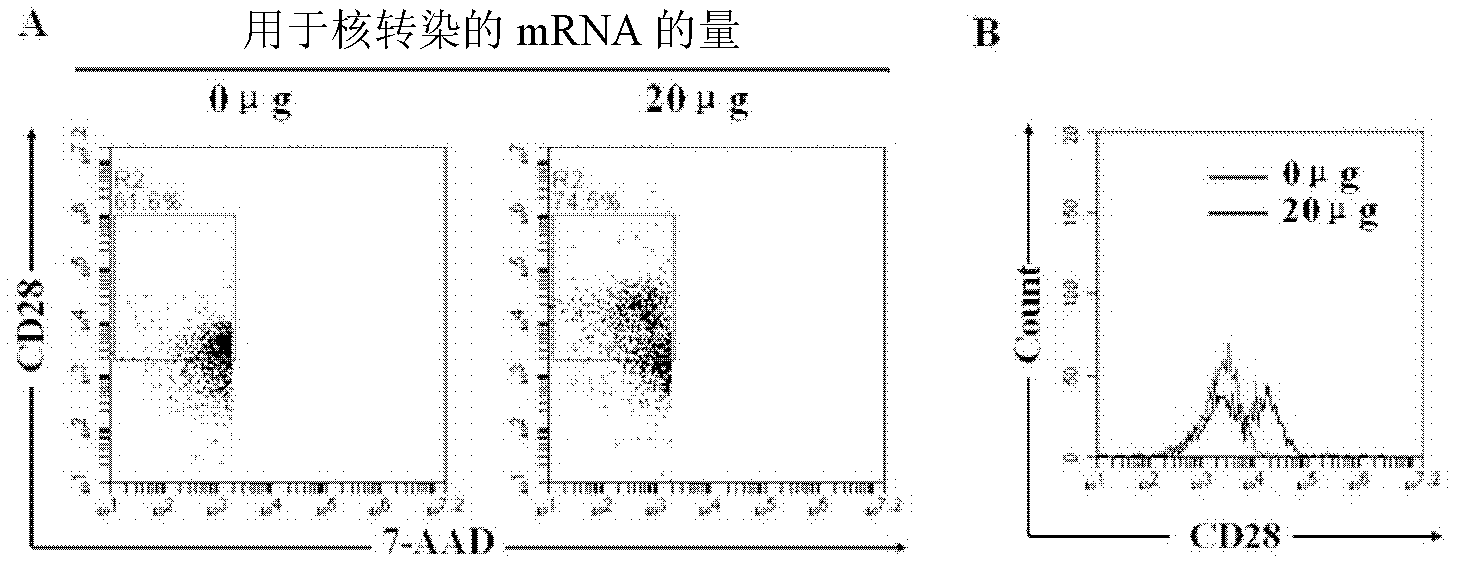
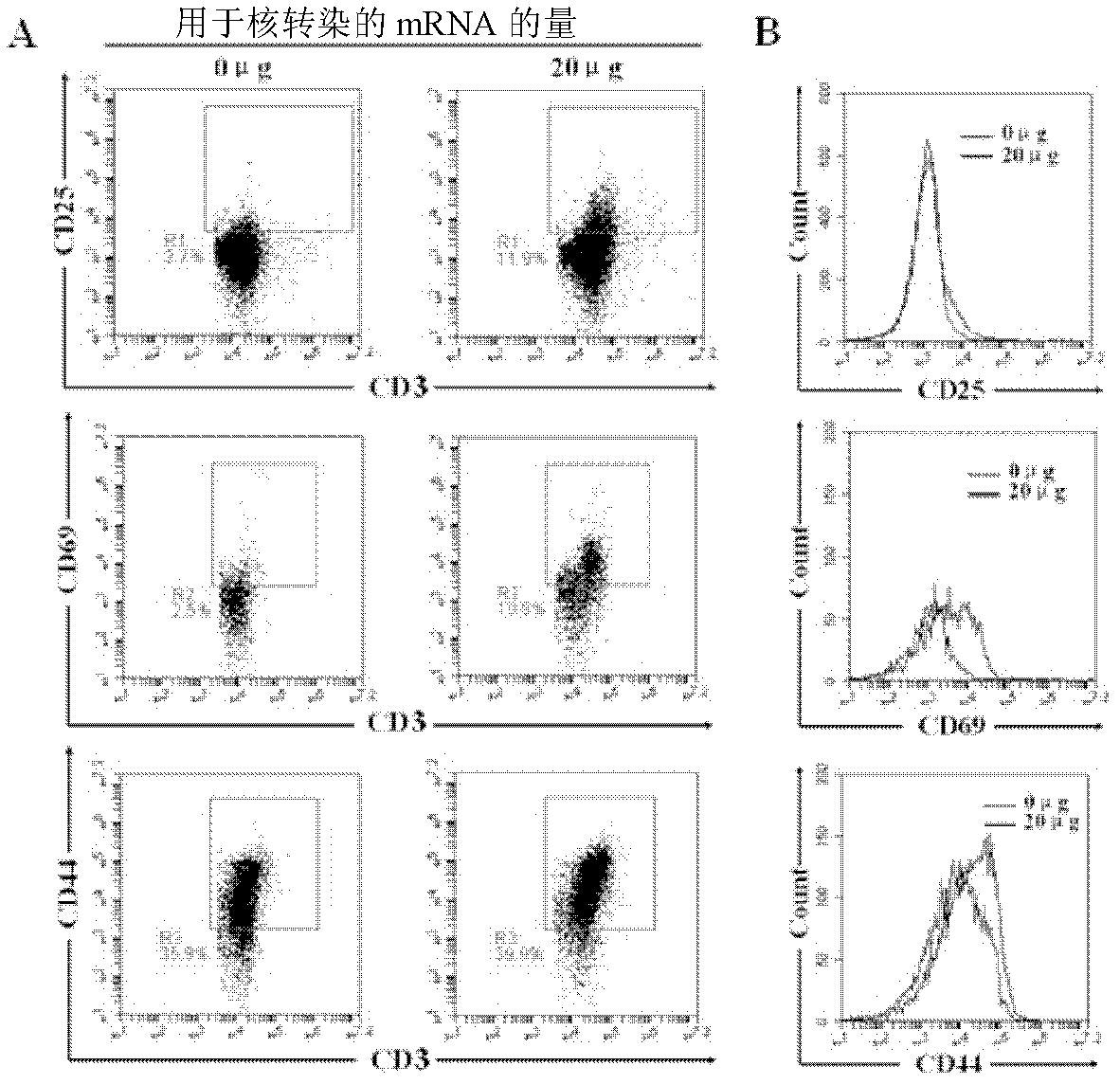
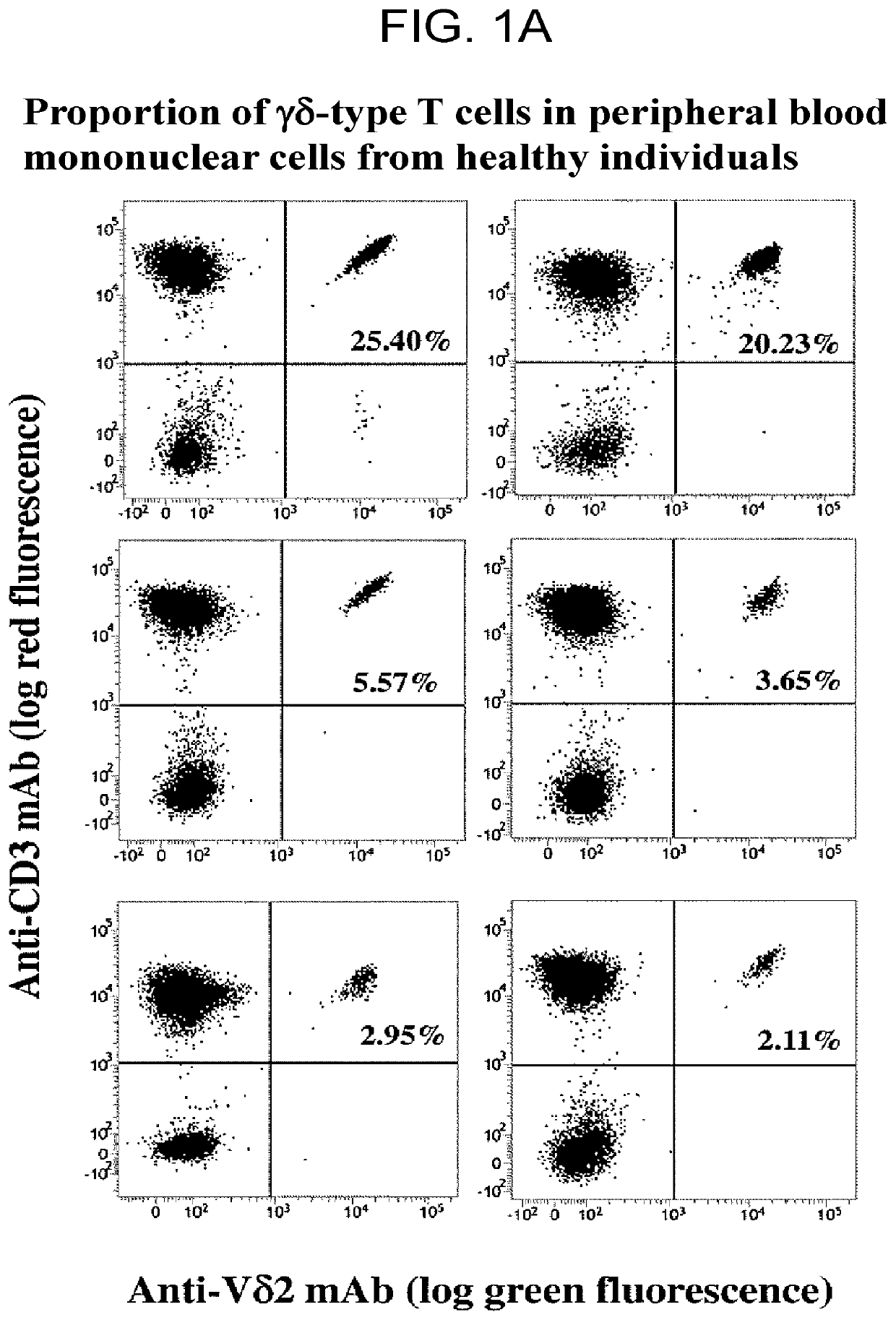
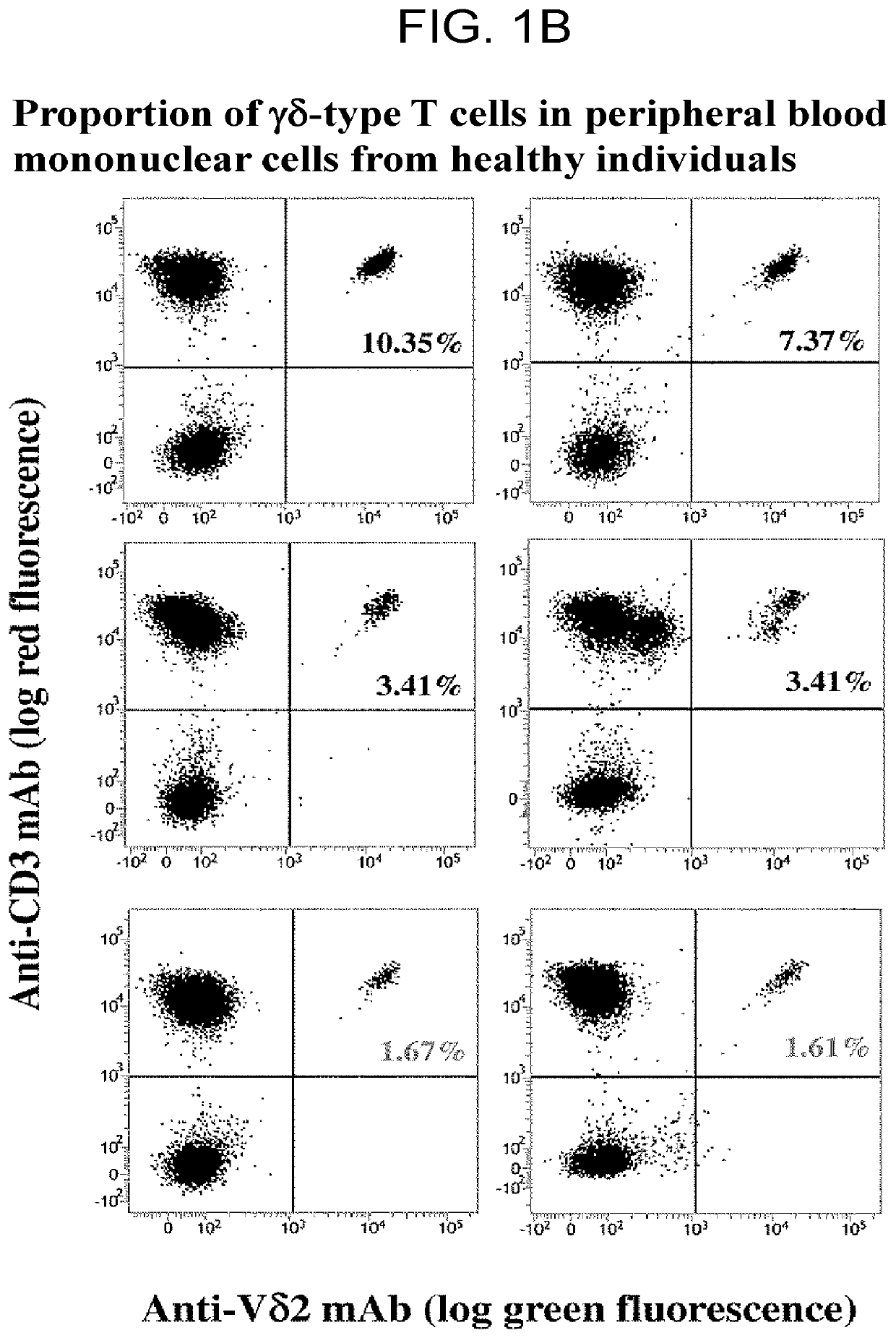
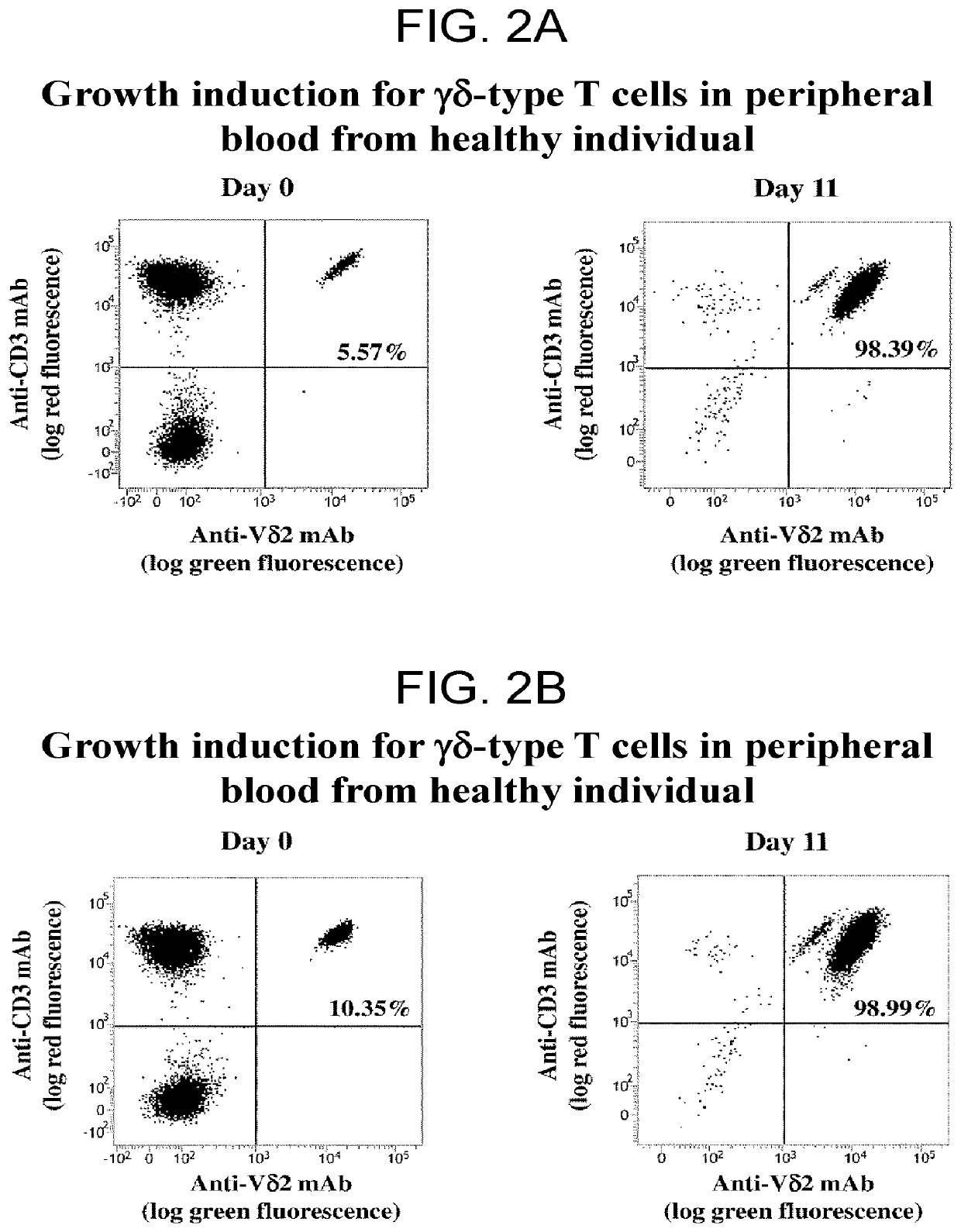
A method may predict risk of onset of severe interstitial pneumonia caused by an immune checkpoint inhibitor to achieve a safe and highly effective cancer immunotherapy. Any one or more selected from: (a) cell count or proportion of Vδ2+γδ T cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from a subject; (b) cell count or proportion of Vδ2+γδ T cells after antigenic stimulation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from a subject; (c) cell count or proportion of Vδ2+γδ T cells in peripheral blood T cells isolated from a subject; and (d) cell count or proportion of Vδ2+γδ T cells after antigenic stimulation in peripheral blood T cells isolated from a subject are measured, and the risk of onset of severe interstitial pneumonia is predicted by using the cell count or proportion as an index.
Owner:NAGASAKI UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com