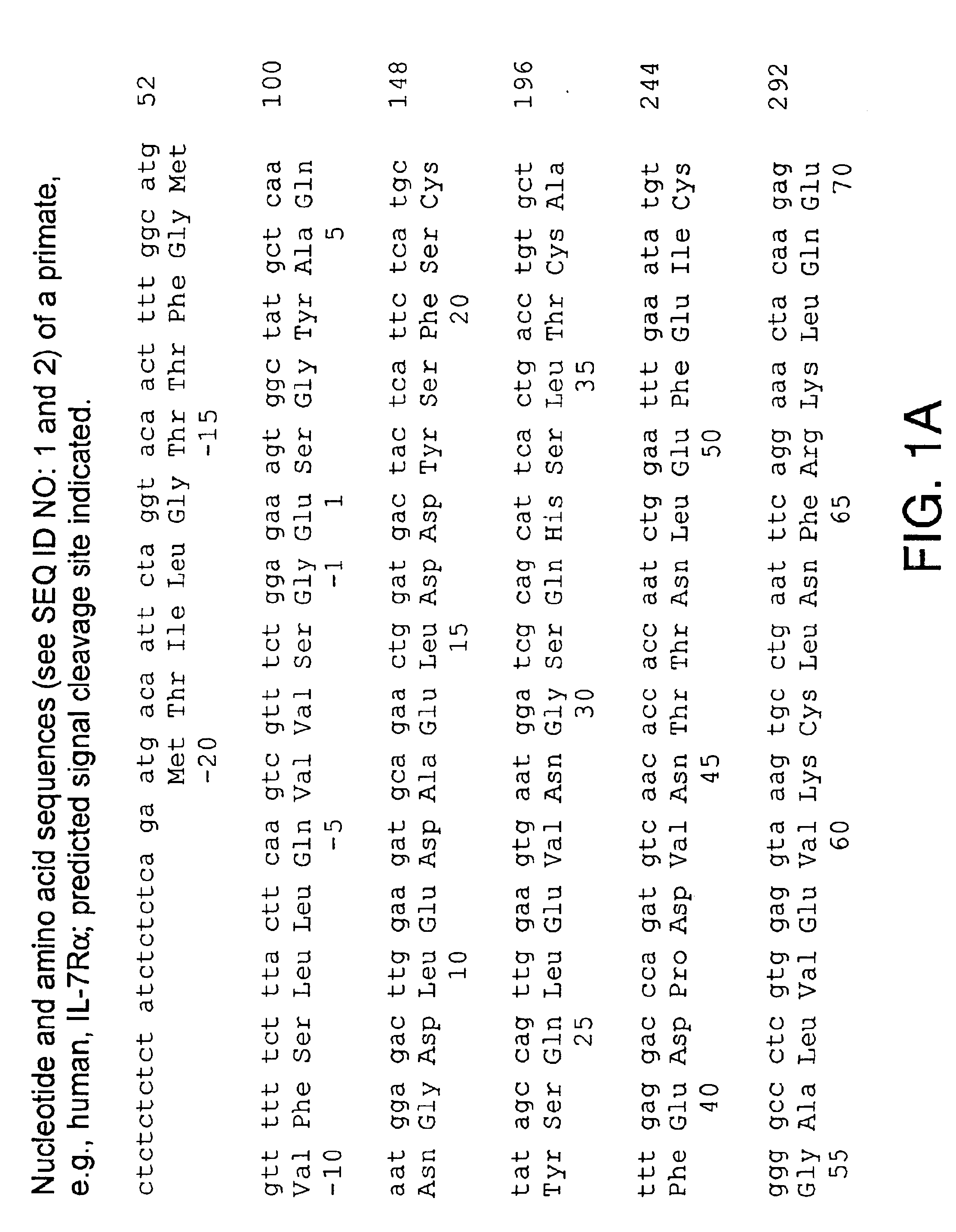
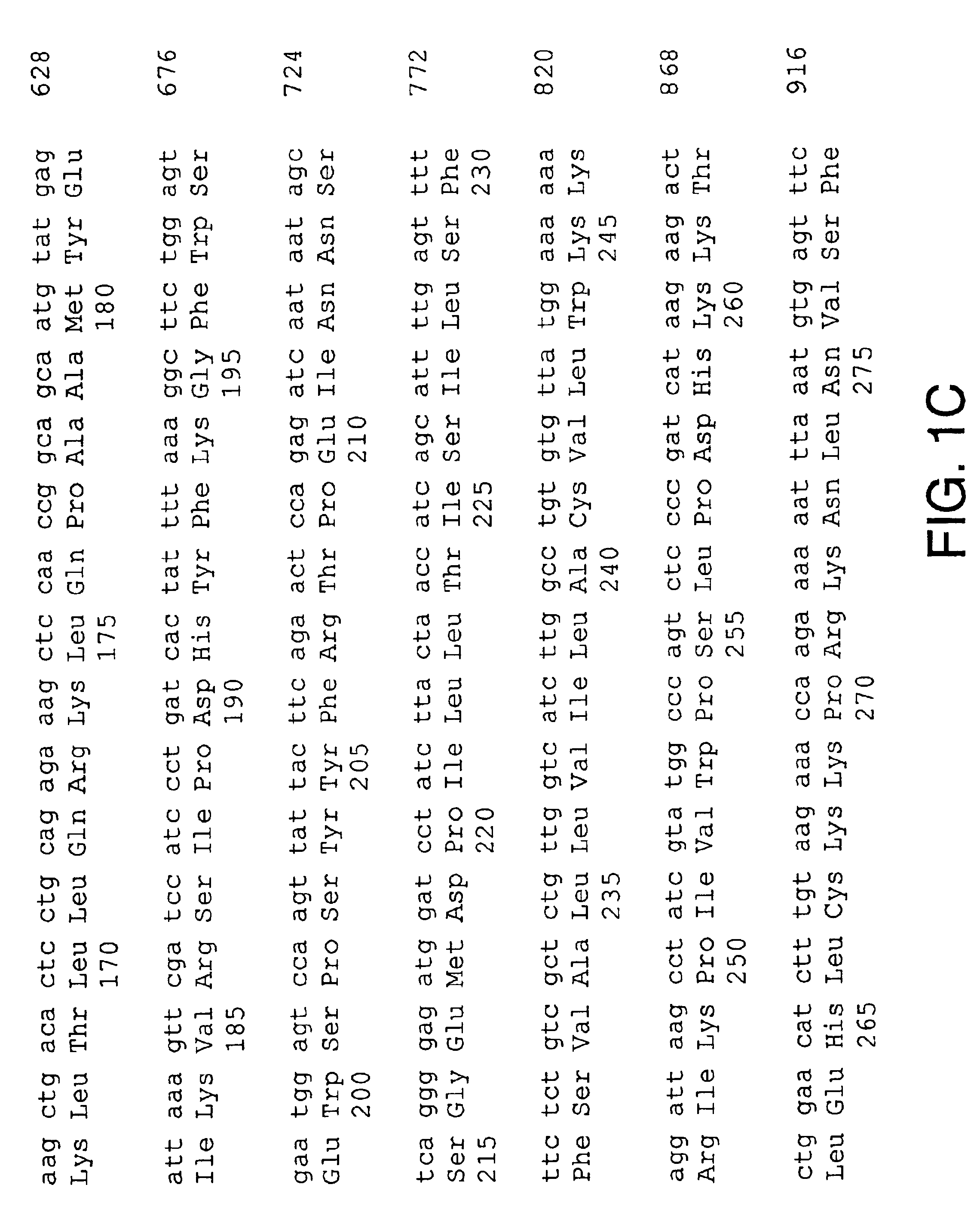
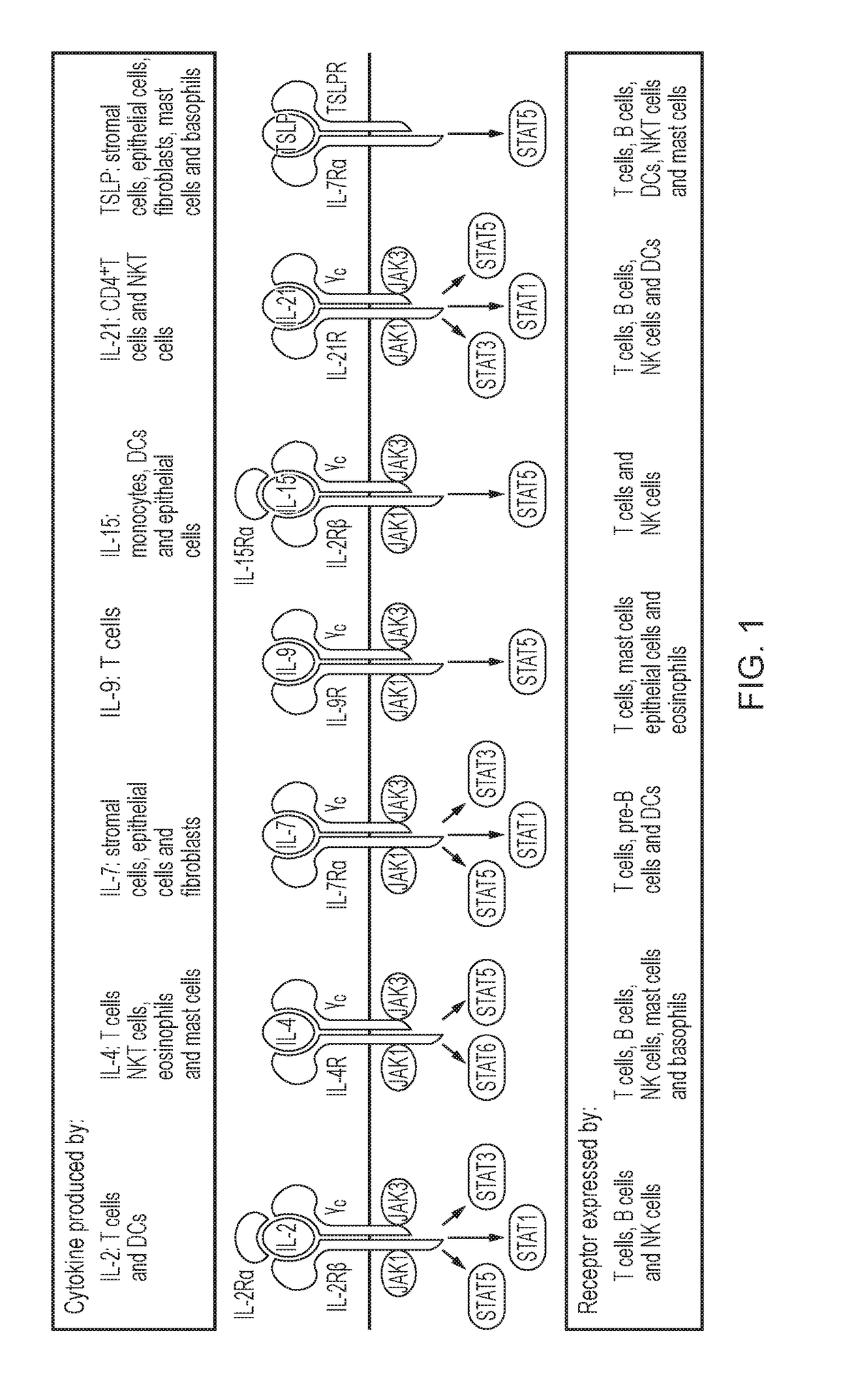
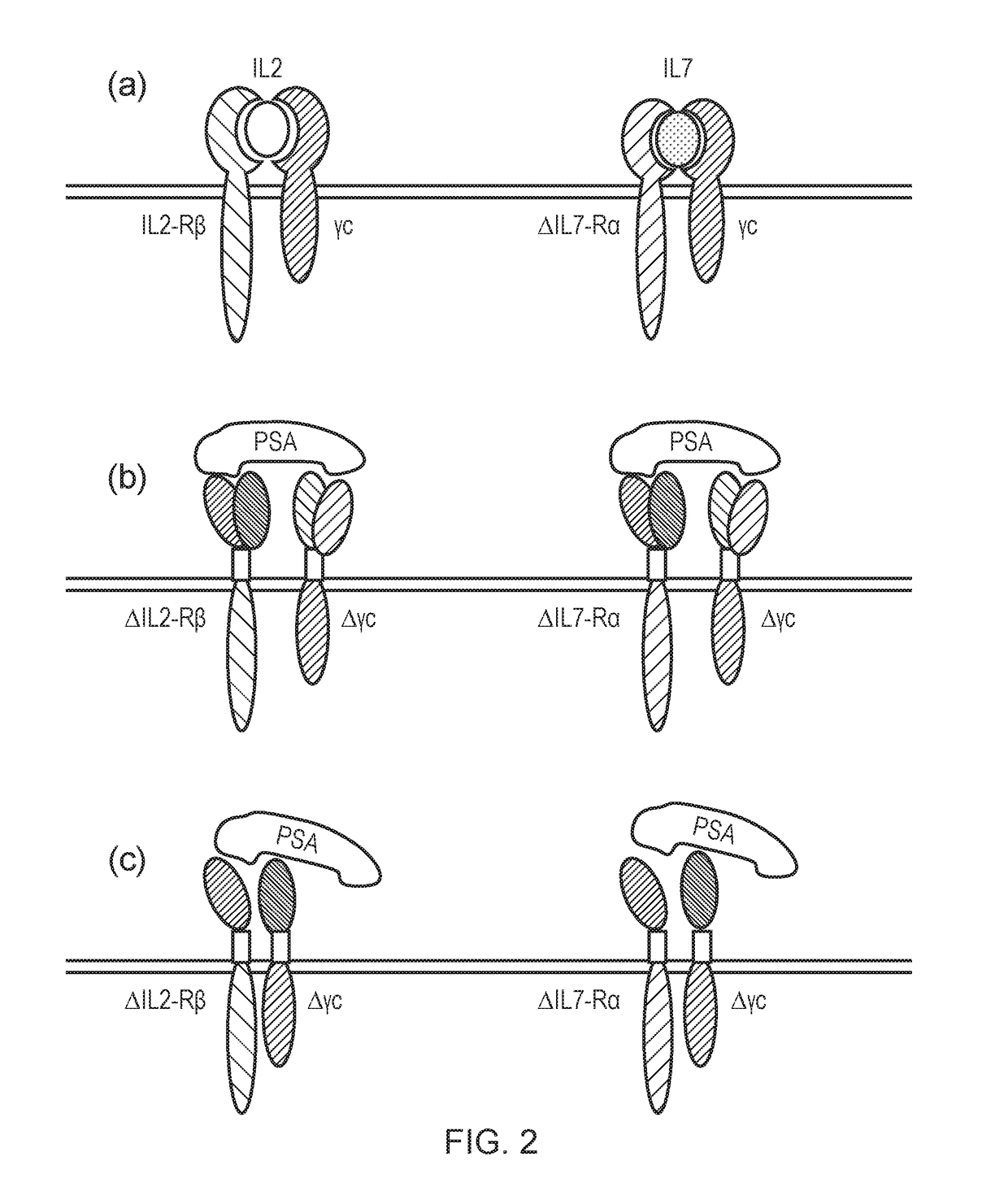
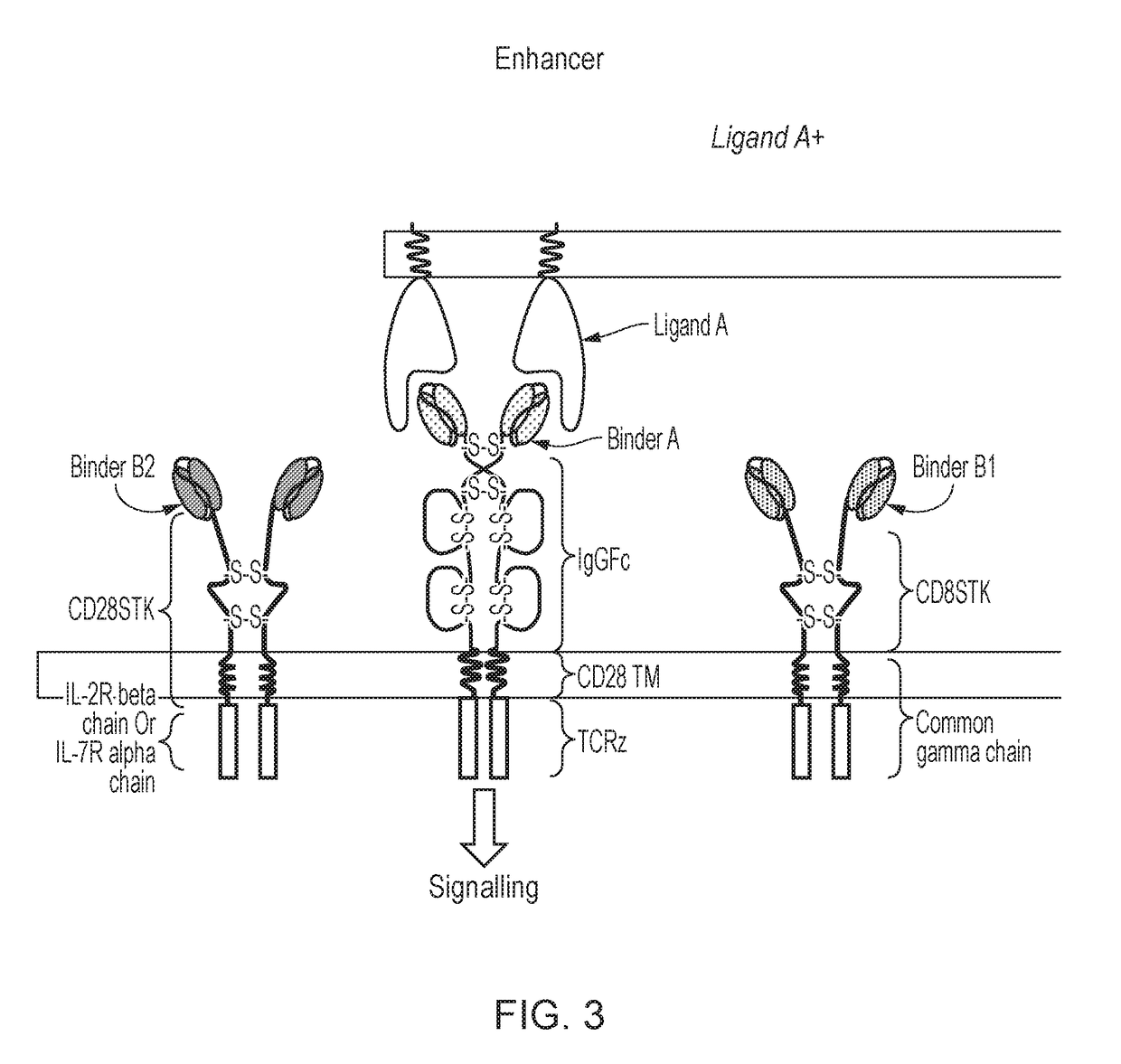
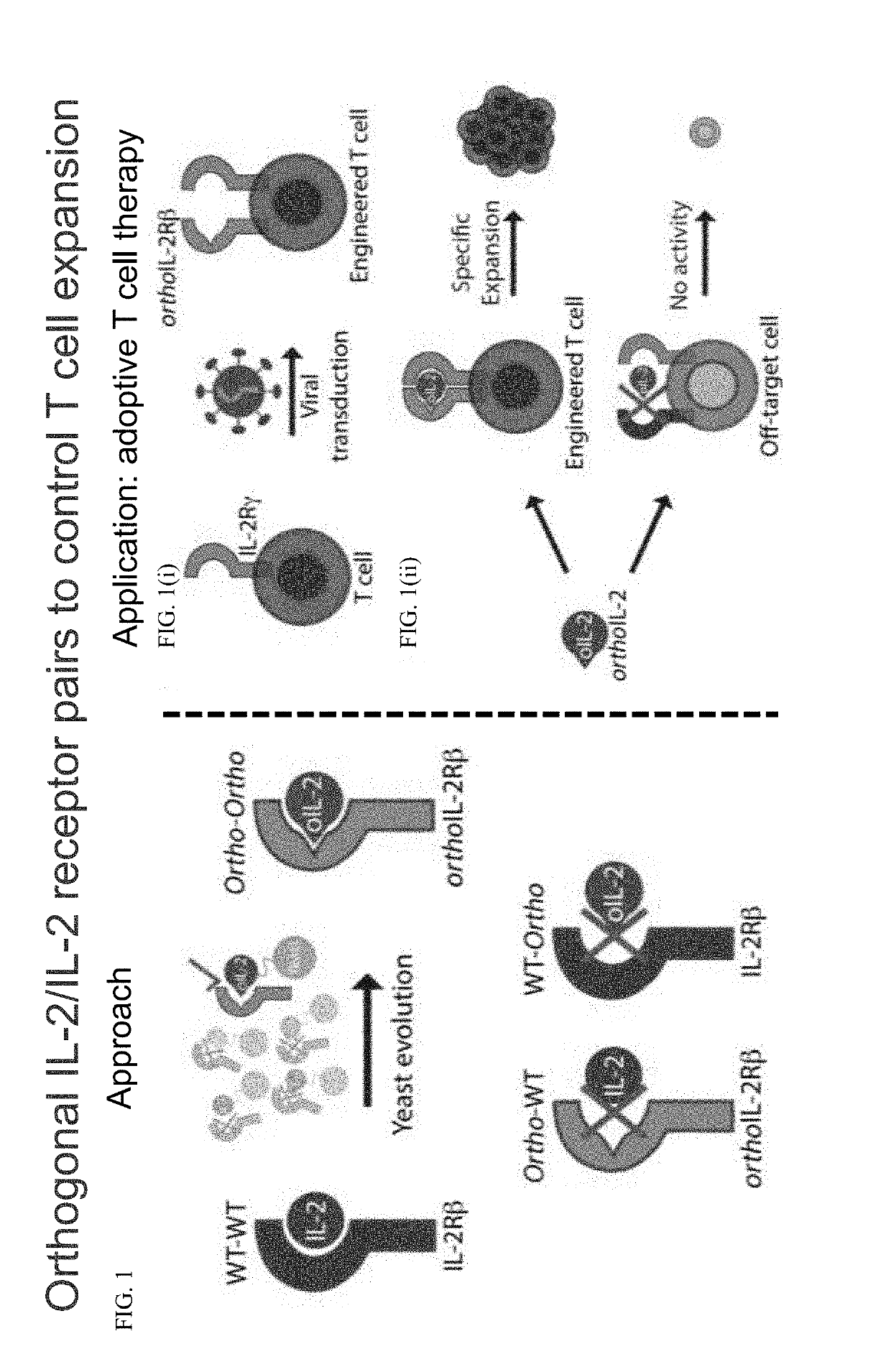
Patents
Literature
123 results about "Cytokine receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cytokine receptors are receptors that bind to cytokines. In recent years, the cytokine receptors have come to demand the attention of more investigators than cytokines themselves, partly because of their remarkable characteristics, and partly because a deficiency of cytokine receptors has now been directly linked to certain debilitating immunodeficiency states. In this regard, and also because the redundancy and pleiotropy of cytokines are a consequence of their homologous receptors, many authorities are now of the opinion that a classification of cytokine receptors would be more clinically and experimentally useful.
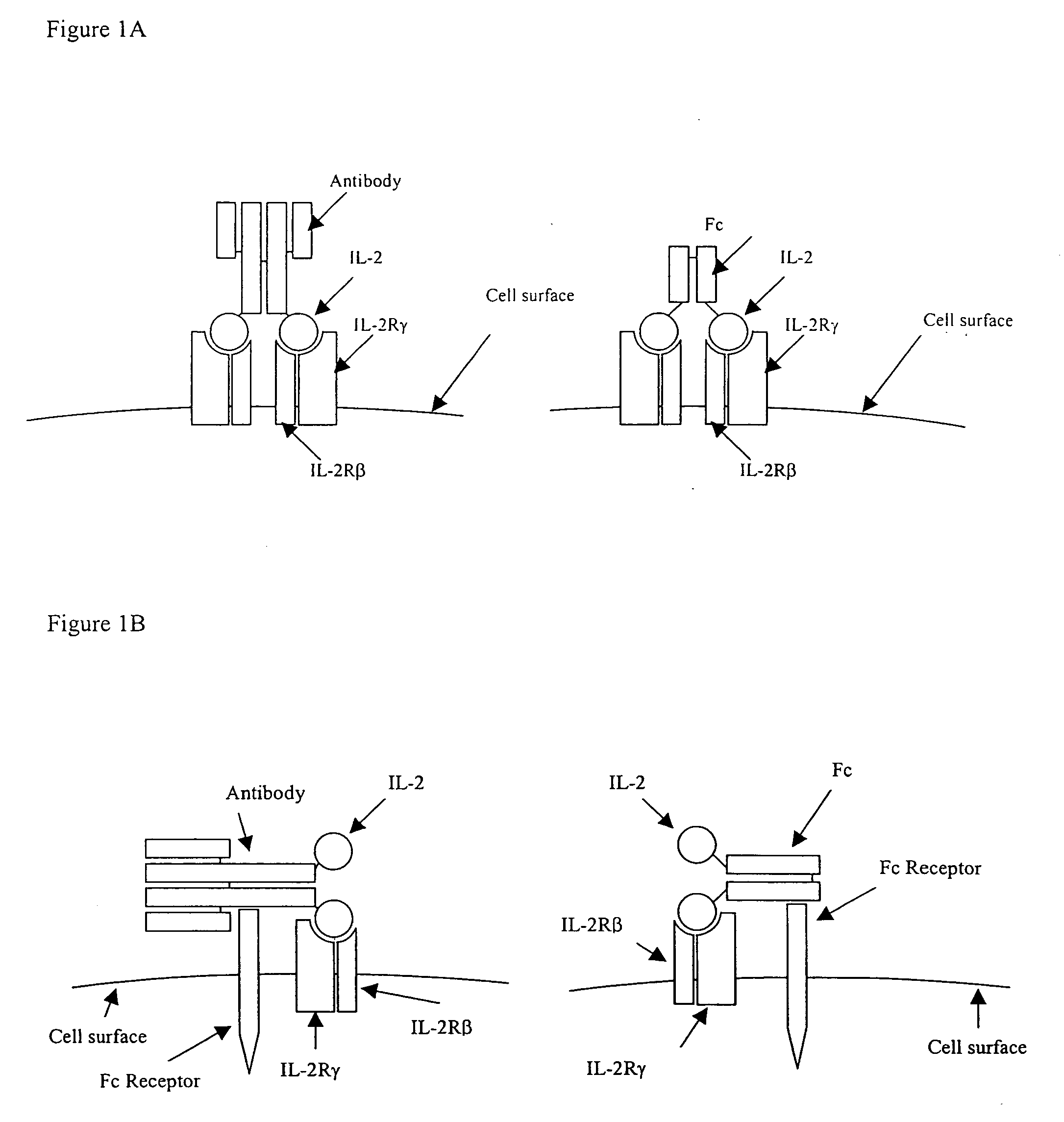
IL-2 fusion proteins with modulated selectivity
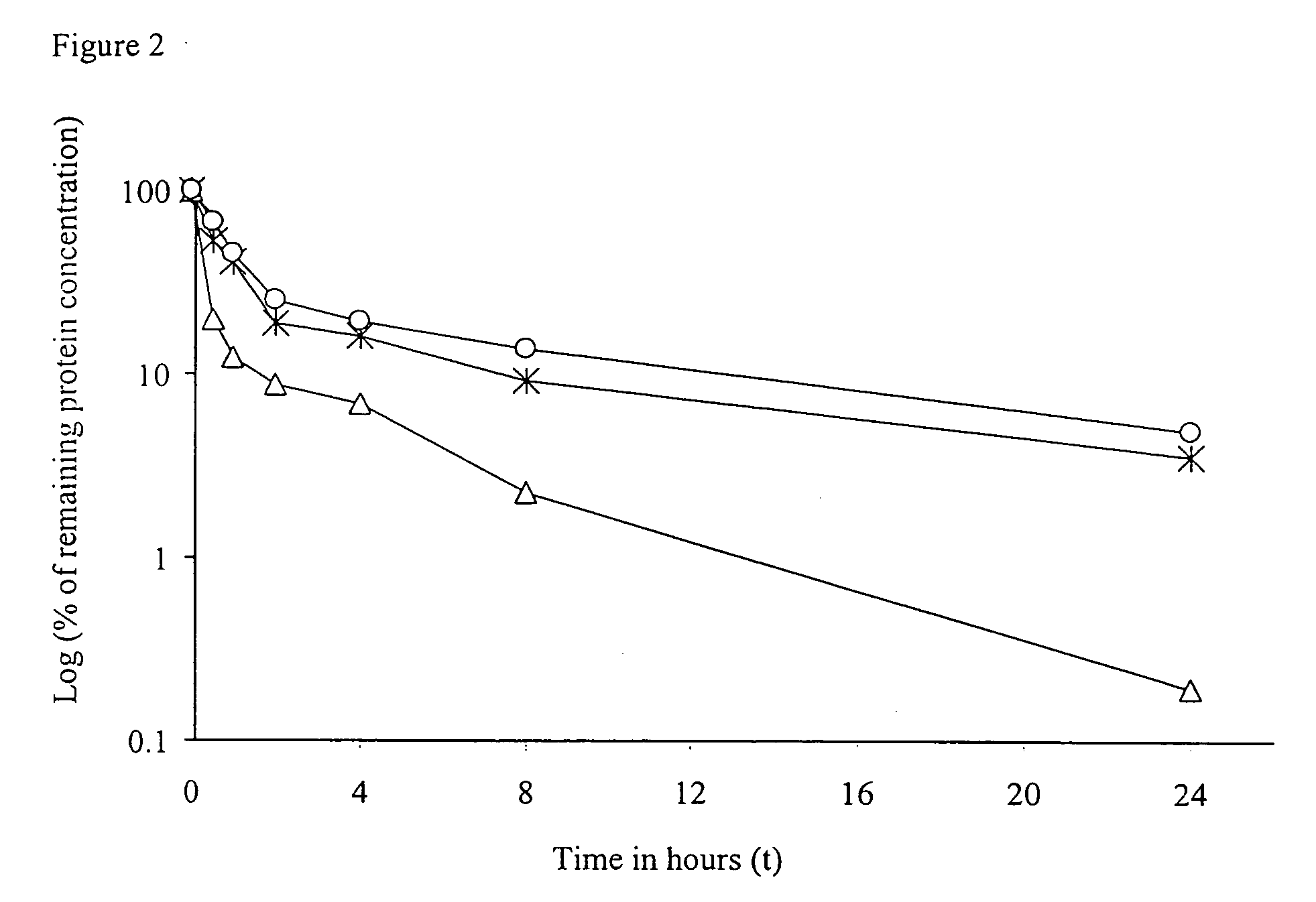
The invention provides cytokine fusion proteins with an increased therapeutic index, and methods to increase the therapeutic index of such fusion proteins. The fusion proteins of the invention are able to bind to more than one type of cytokine receptor expressed on cells and also bind to more than one cell type. In addition, the fusion proteins of the invention exhibit a longer circulating half-life in a patient's body than the corresponding naturally occurring cytokine.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
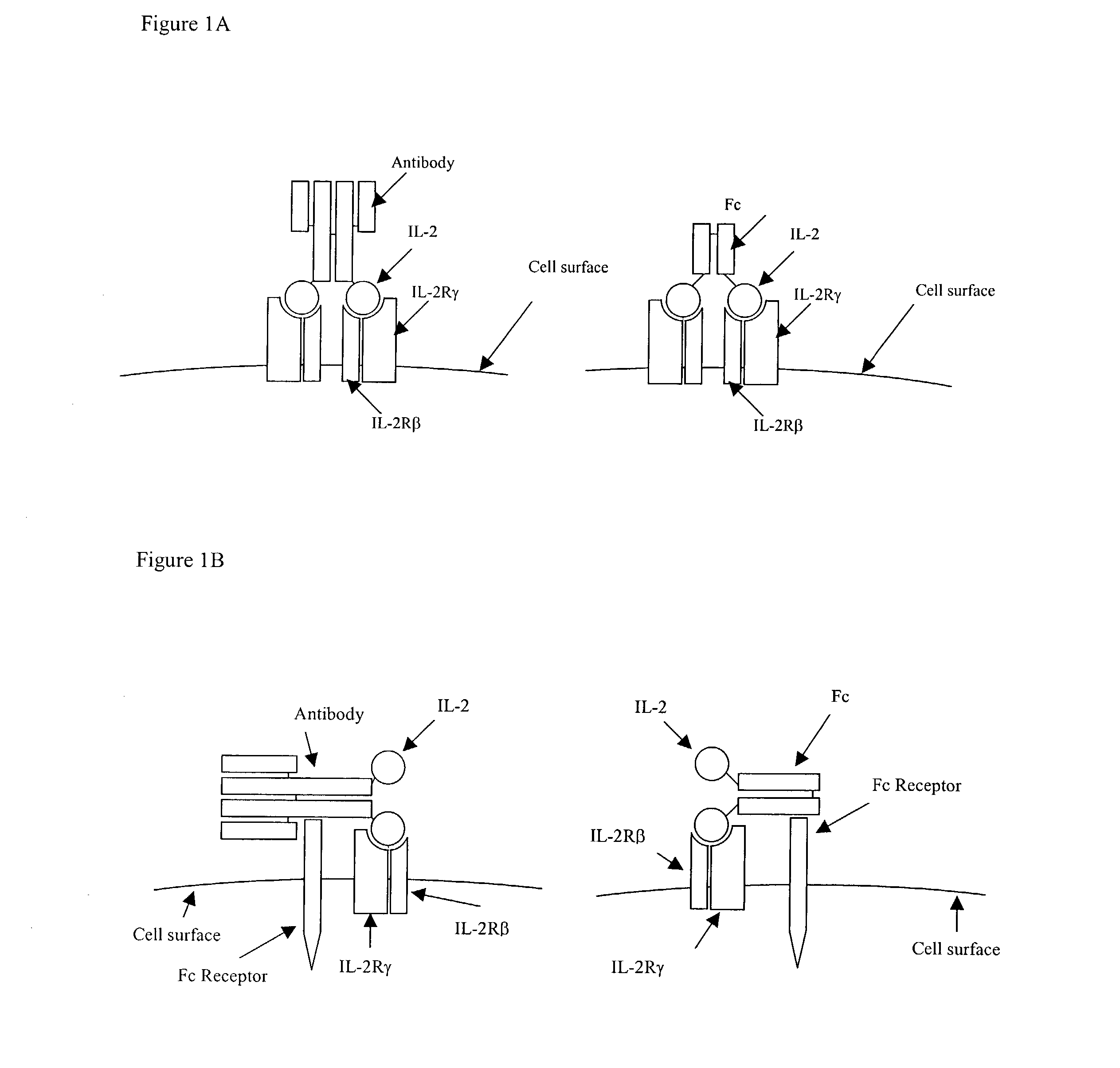
IL-2 fusion proteins with modulated selectivity
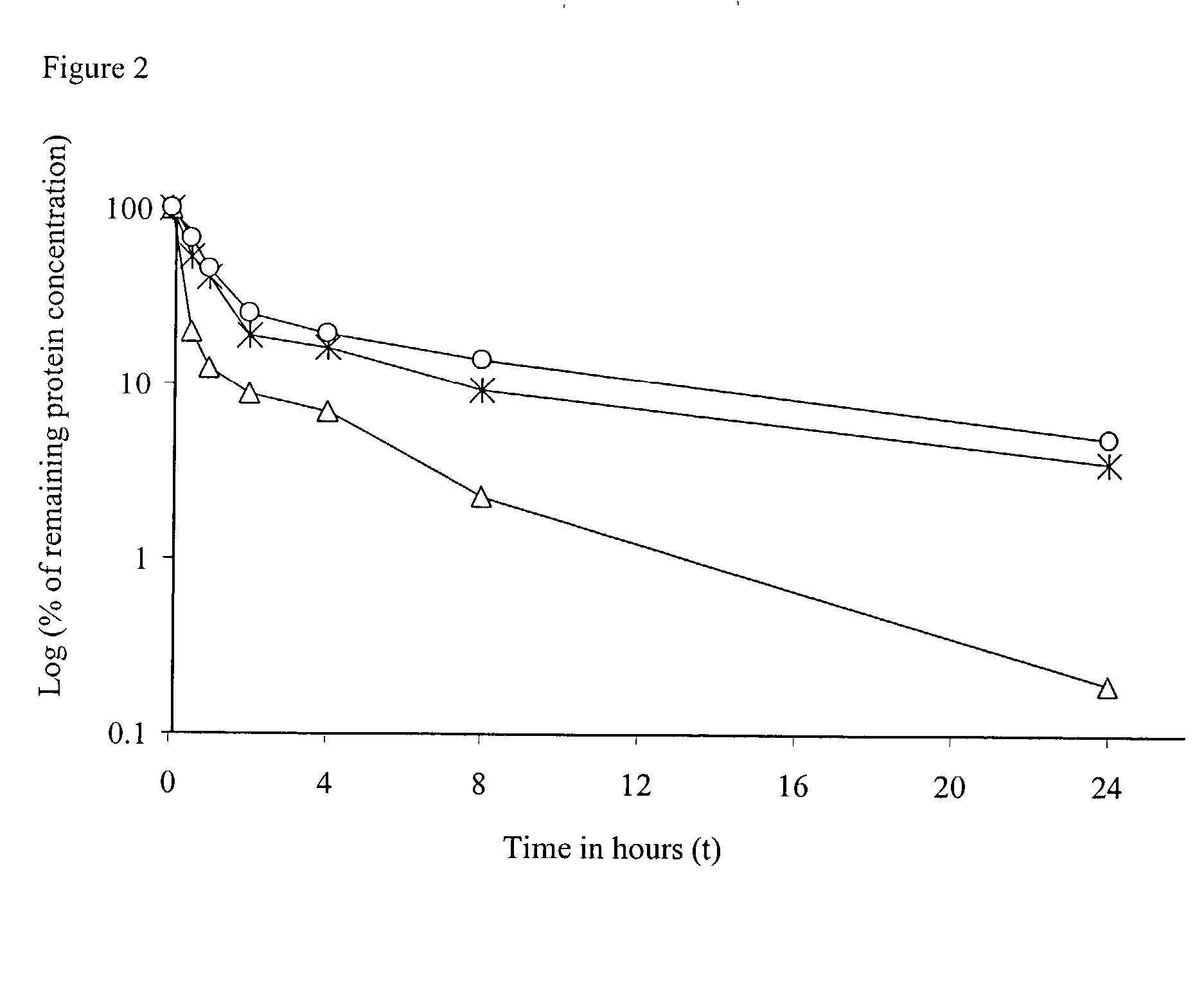
The invention provides cytokine fusion proteins with an increased therapeutic index, and methods to increase the therapeutic index of such fusion proteins. The fusion proteins of the invention are able to bind to more than one type of cytokine receptor expressed on cells and also bind to more than one cell type. In addition, the fusion proteins of the invention exhibit a longer circulating half-life in a patient's body than the corresponding naturally occurring cytokine.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Cytokine receptor
InactiveUS20070032640A1Enhanced interactionEnhanced signalAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineScreening method
A crystalline composition comprising a crystal of the IL-6 receptor I chain is provided. Also provided are methods of using the crystal and related structural information to screen for and design compounds that interact with IL-6R, or variants thereof. Also provided arc methods of modulating an IL-6 receptor comprising contacting the IL-6 receptor with a compound identified by the screening method of the invention.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +2
Method and composition for treatment of renal failure with antibodies and their equivalents as partial or complete replacement for dialysis
InactiveUS7504106B2Lower Level RequirementsSlow onsetBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterleukin 6Creatinine rise
A method for treating patients with renal failure includes administering to them an effective amount of antibody or of a functional equivalent thereof to at least two of urea, creatinine, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 6 and interleukin 1 beta. Soluble cytokine receptors also can be employed. The method can be used as a supplement to or as partial or complete replacement for dialysis. A pharmaceutical composition includes antibody or functional equivalent thereof to urea, creatinine, or both; antibody, functional equivalent or soluble cytokine receptor to tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 6, interleukin 1 beta or any combination thereof The composition can be included in a kit.
Owner:SKURKOVICH BORIS +2
Methods for diagnosis using anti-cytokine receptor antibodies
Labeled antibodies, antibody fragments or peptides binding to soluble cytokines or cytokine receptors are used to diagnose whether a patient has cancer or an autoimmune disease. In a preferred embodiment, a radiolabelled tag that is chemically bound to a peptide, antibody, or antibody fragment specific for sTNFR-1 and / or sTNFR2 is injected into a patient with a tumor, or suspected tumor, or with any disease associated with STNF-1 / STNF-2. The patient is then imaged using standard nuclear imaging equipment to detect areas or sites of concentration of the radiolabel and / or receptor / inhibitor and / or antigen. By screening for cancer by the substances it produces, using an injected antibody to that substance with a tracer attached to it, one can detect cancer at a very early stage, potentially even microscopically.
Owner:EARLY DETECTION
Combination therapy for the prevention or treatment of cancer, inflammatory disorders or infectious diseases in a subject
InactiveUS20030035790A1Good treatment effectReduce dosageVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDendritic cellT cell
The present invention relates to compositions comprising compounds which augment activated immune cells, such as T-cells, dendritic cells and natural killer ("NK") cells, and methods for the treatment or prevention of diseases and disorders, including cancer, inflammatory disorders, and infectious diseases, in a subject comprising the administration of said compositions to said subject. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for the treatment or prevention of diseases and disorders, including cancer, inflammatory disorders, and infectious diseases, in a subject comprising administrating to said subject one or more compounds that activate one or more cytokine receptors and one or more compounds that activate one or more co-stimulatory molecules expressed by activated immune cells. The present invention also relates to compositions and kits comprising a compound that activates one or more cytokine receptors and a compound that activates one or more co-stimulatory molecules expressed by activated immune cells.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for diagnosis using anti-cytokine receptor antibodies
Labeled antibodies, antibody fragments or peptides binding to soluble cytokines or cytokine receptors are used to diagnose whether a patient has cancer or an autoimmune disease. In a preferred embodiment, a radiolabelled tag that is chemically bound to a peptide, antibody, or antibody fragment specific for sTNFR-1 and / or sTNFR2 is injected into a patient with a tumor, or suspected tumor, or with any disease associated with STNF-1 / STNF-2. The patient is then imaged using standard nuclear imaging equipment to detect areas or sites of concentration of the radiolabel and / or receptor / inhibitor and / or antigen. By screening for cancer by the substances it produces, using an injected antibody to that substance with a tracer attached to it, one can detect cancer at a very early stage, potentially even microscopically.
Owner:EARLY DETECTION
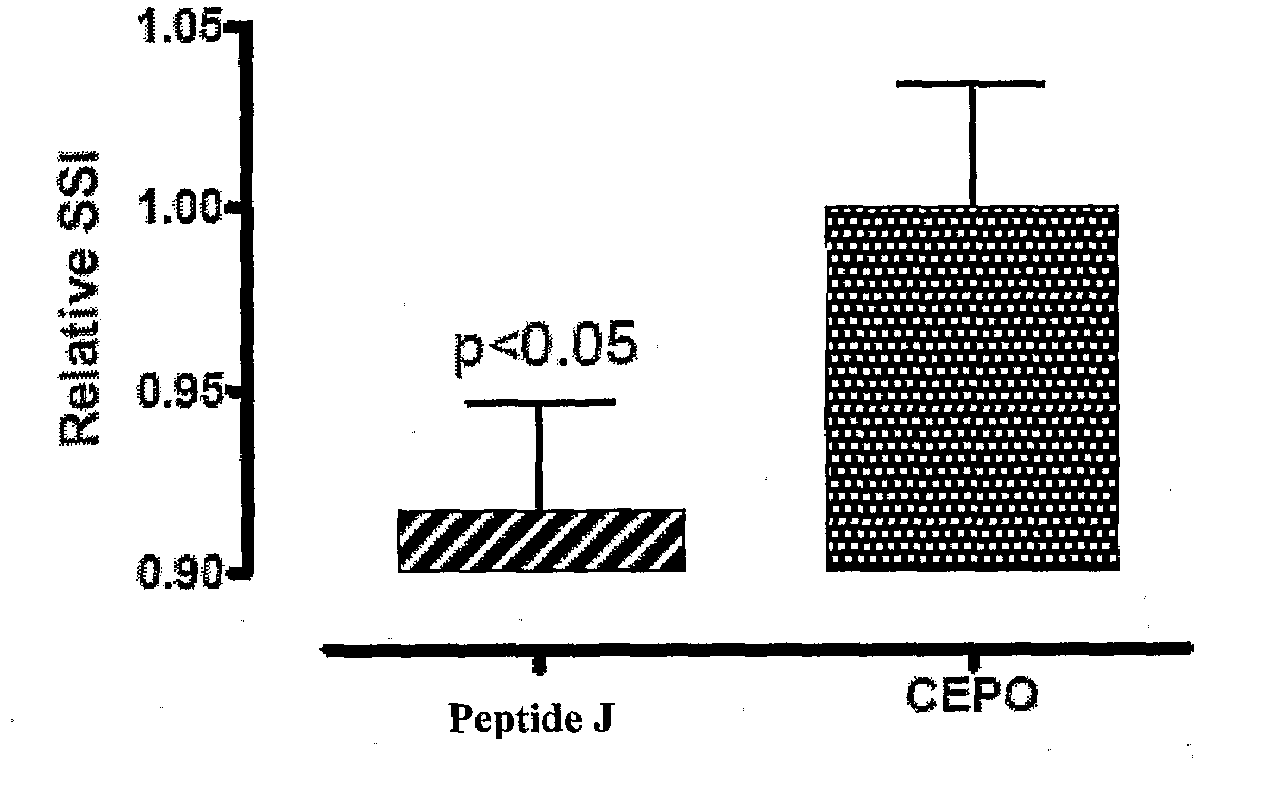
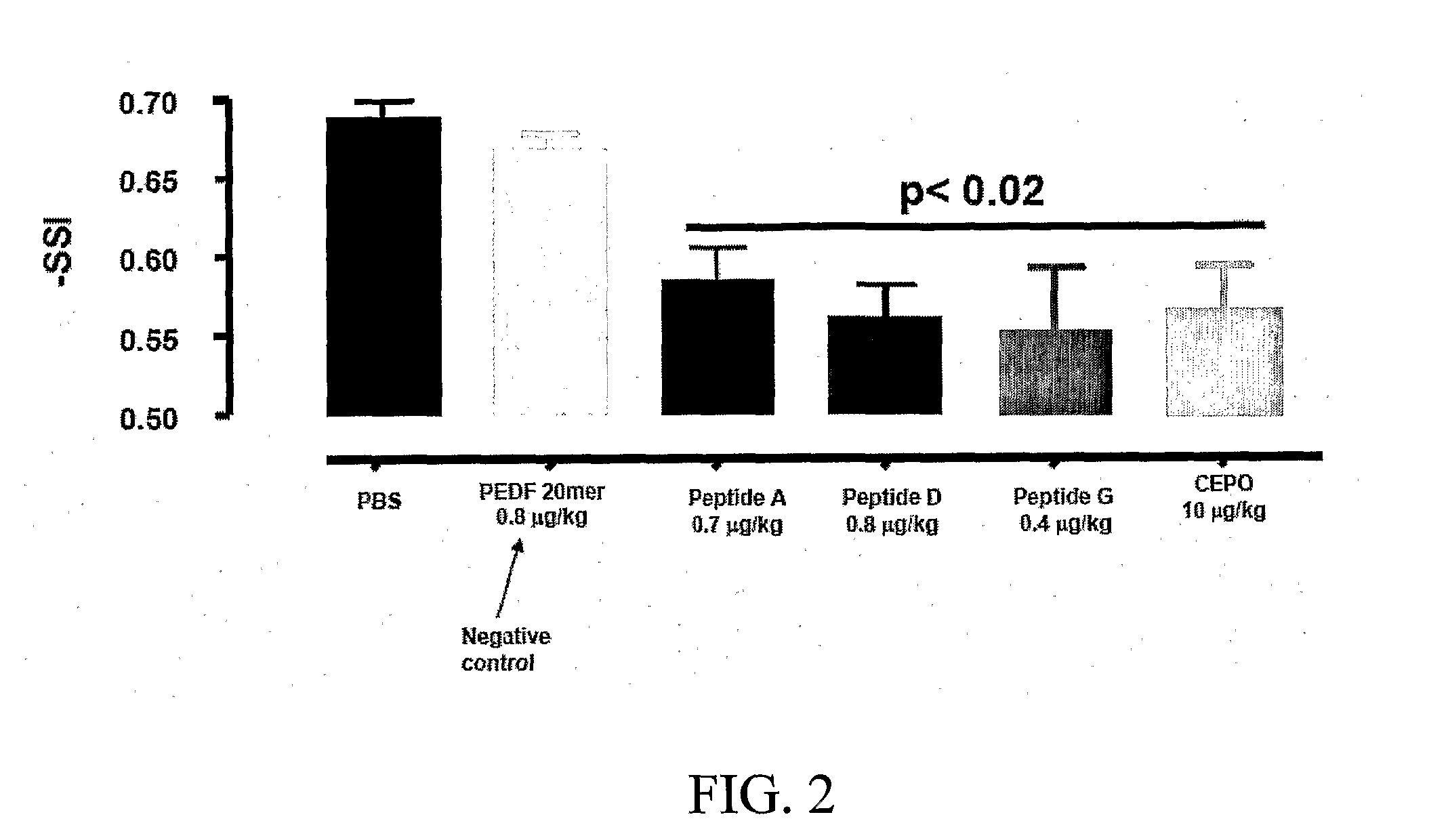
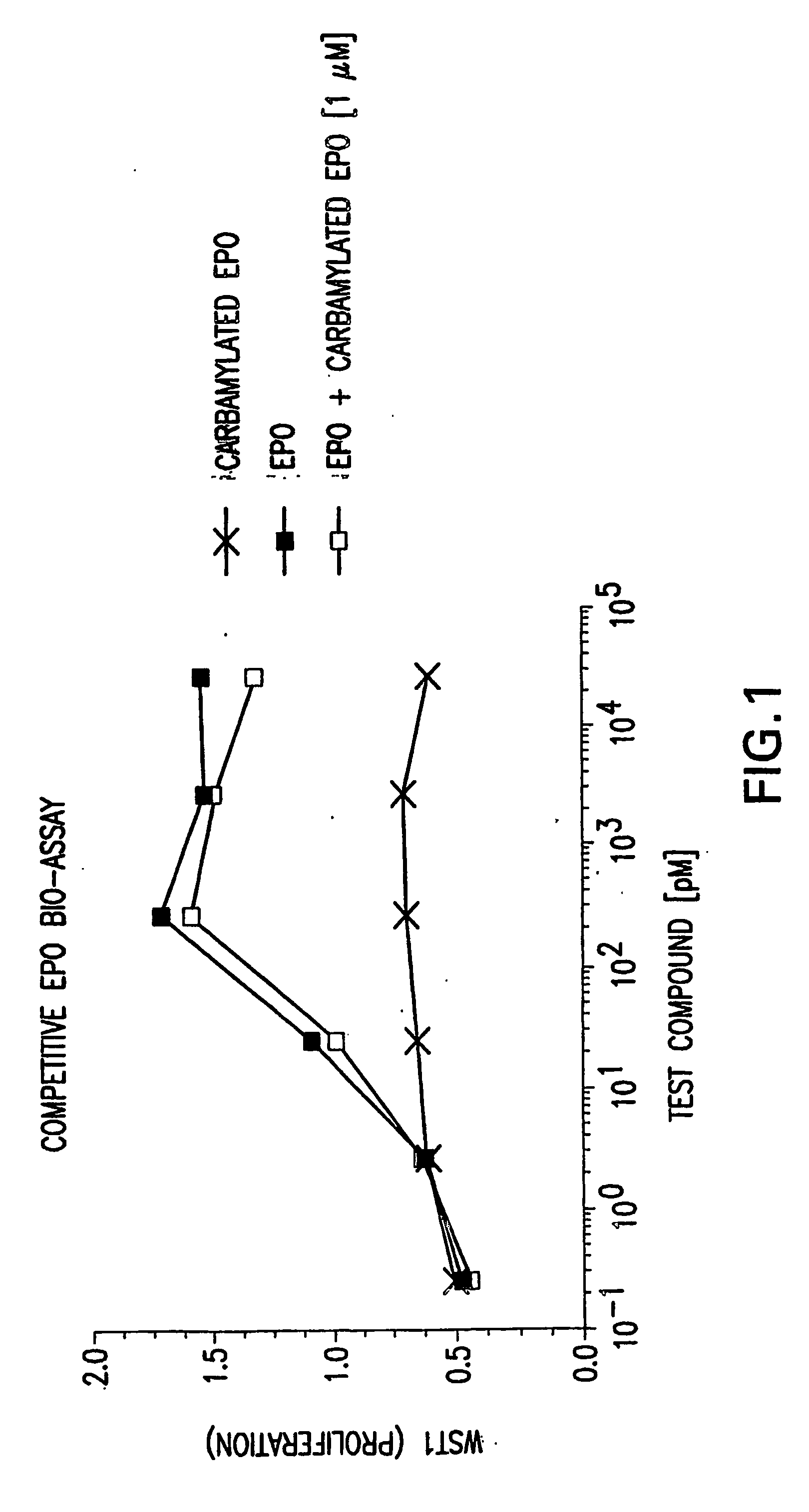
Tissue protective peptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090221482A1Avoid damageFacilitate optimal expressionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTissue protection
The present invention is directed to novel tissue protective peptides. The tissue protective peptides of the invention may bind to a tissue protective receptor complex. In particular, the present invention is drawn to tissue protective peptides derived from or sharing consensus sequences with portions of cytokine receptor ligands, including Erythropoietin (EPO), that are not involved in the binding of the ligand to the receptor complex, e.g., to the EPO receptor homodimer. Accordingly, the tissue protective peptides of the invention are derived from the amino acid sequences of regions of cytokine receptor ligands that are generally located on or within the region of the ligand protein that is opposite of the receptor complex, i.e., are generally derived from amino acid sequences of regions of the ligand protein that face away from the receptor complex while the ligand is bound to the receptor. The invention is further directed to the consensus sequences for use in engineering a synthetic tissue protective peptide. These tissue protective peptides also include fragments, chimeras, as well as peptides designed to mimic the spatial localization of key amino acid residues within the tissue protective receptor ligands, e.g., EPO. The invention further encompasses methods for treating or preventing a disease or disorder using tissue protective peptides of the current invention. The invention also encompasses methods for enhancing excitable tissue function using tissue protective peptides of the current invention.
Owner:ARAIM PHARMA INC
Nucleic acid encoding novel type-1 cytokine receptor GLM-R
Owner:GENENTECH INC
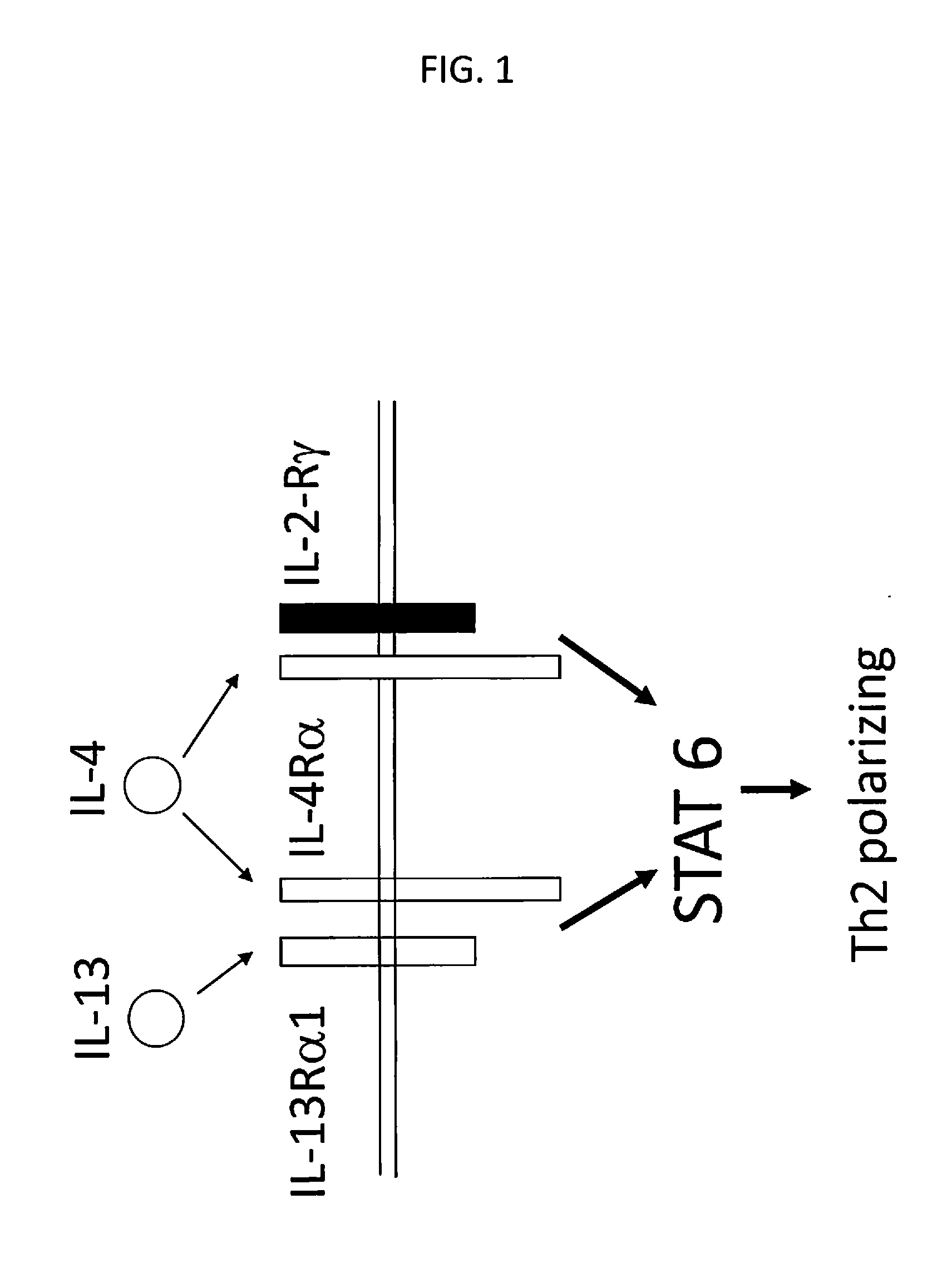
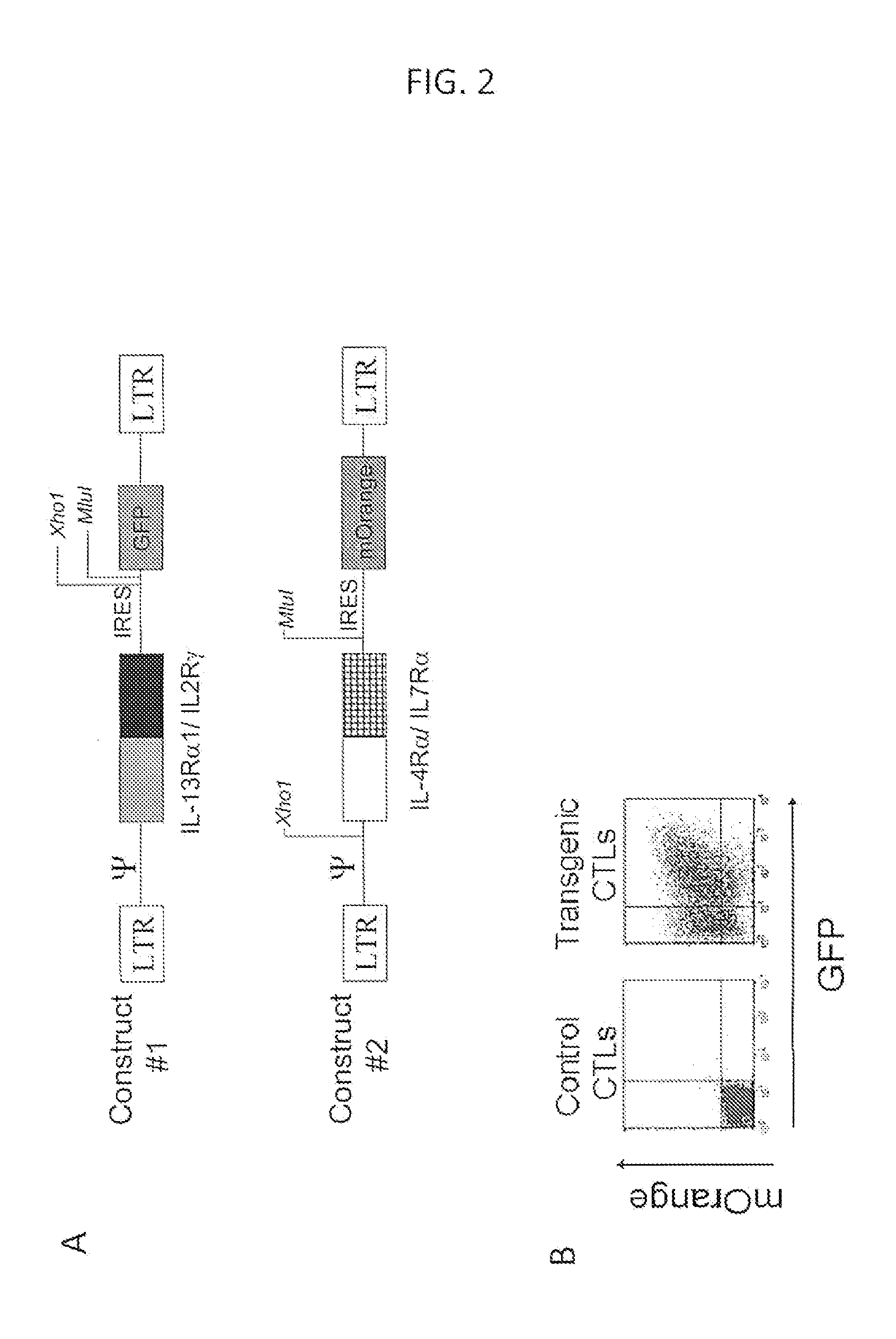
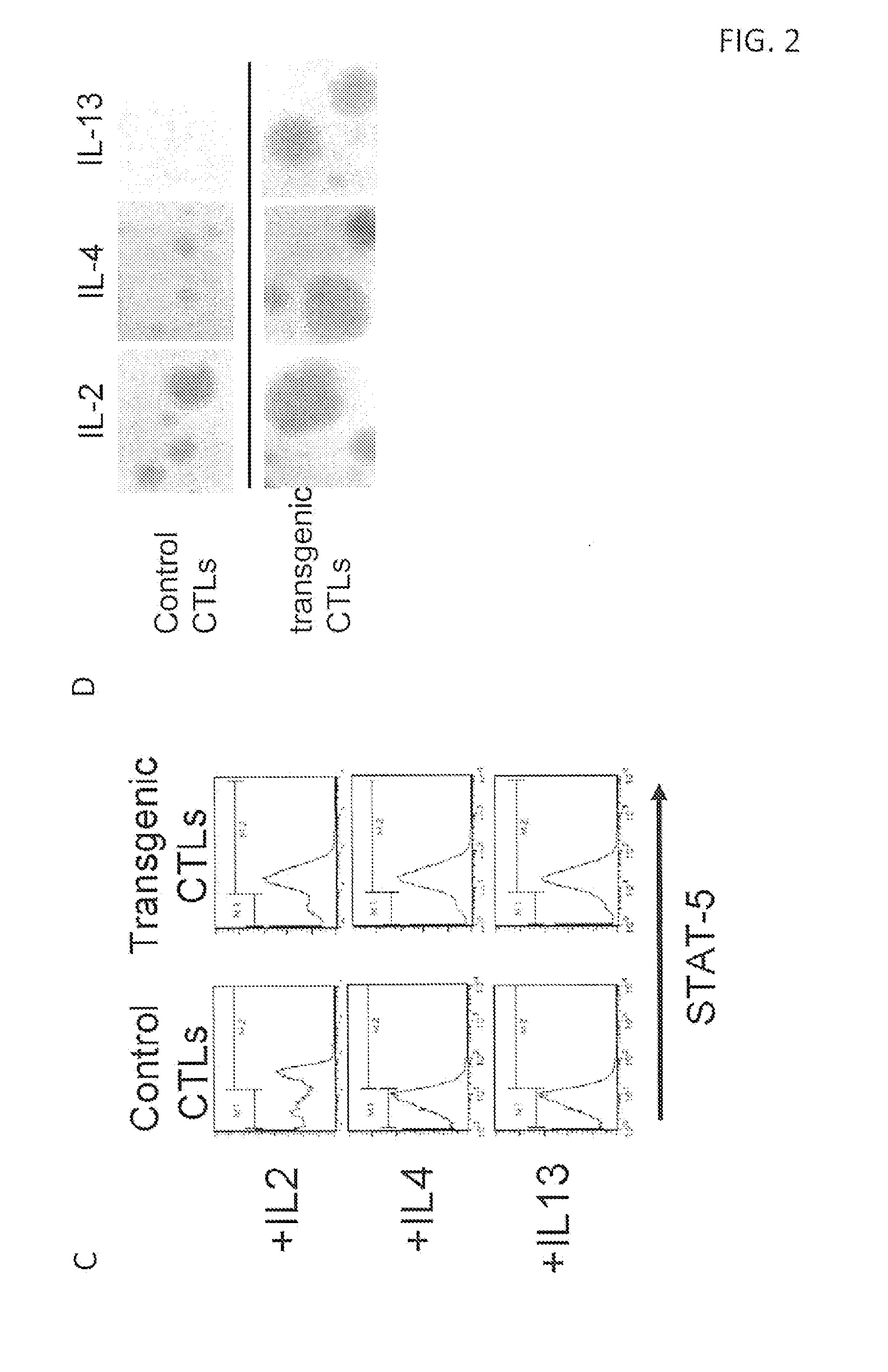
Reversing the effects of the tumor microenvironment using chimeric cytokine receptors
ActiveUS20140050709A1High activityIncrease expansionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigen receptorCytokine milieu
Disclosed are compositions and methods related to rendering ineffective Th1 T cells resistant to the inhibitory cytokine milieu present in a cancer microenvironment. Tumor-specific T cells are modified to employ a chimeric receptor that binds inhibitory / suppressive cytokines and converts their intracellular consequences to a Th1 immunostimulatory / activating signal. The T cells employ a chimeric antigen receptor having exodomains for IL10, IL13 and / or IL4 fused with the signal transducing endodomains for IL2 and / or IL7.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Nucleic acids encoding a cytokine receptor complex
Nucleic acids encoding mammalian cytokine receptor, e.g., for cytokine IL-B50, purified proteins and fragments thereof. Antibodies, both polyclonal and monoclonal, are also provided. Methods of using the compositions for both diagnostic and therapeutic utilities are described.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Method for Expanding Monocytes
ActiveUS20100003272A1Extended half-lifeImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDendritic cellAgonist
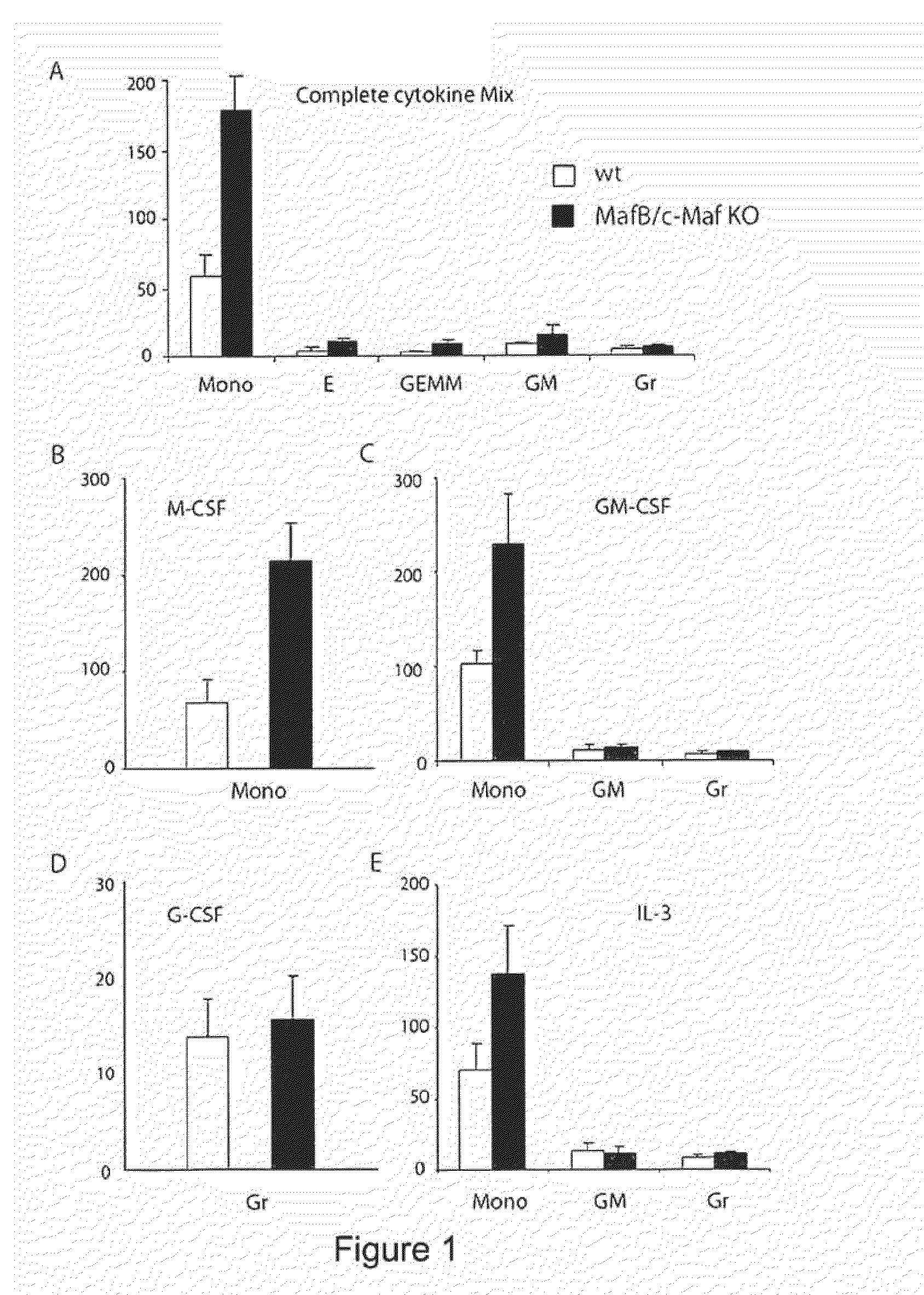
The invention relates to an ex vivo method for expanding monocytes, macrophages or dendritic cells, which method comprises inhibiting the expression or the activity of MafB and c-Maf in monocytes, macrophages or dendritic cells; and expanding the cells in the presence of at least one cytokine or an agonist of cytokine receptor signaling.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
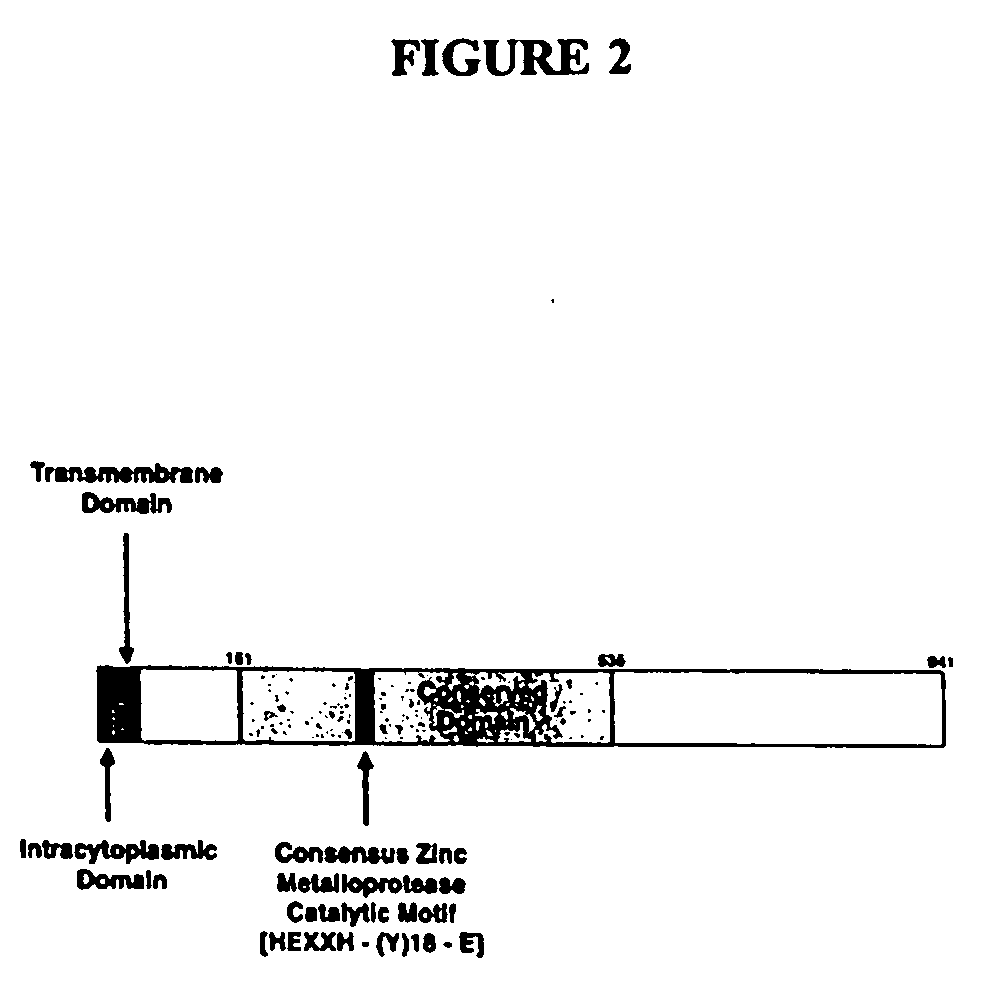
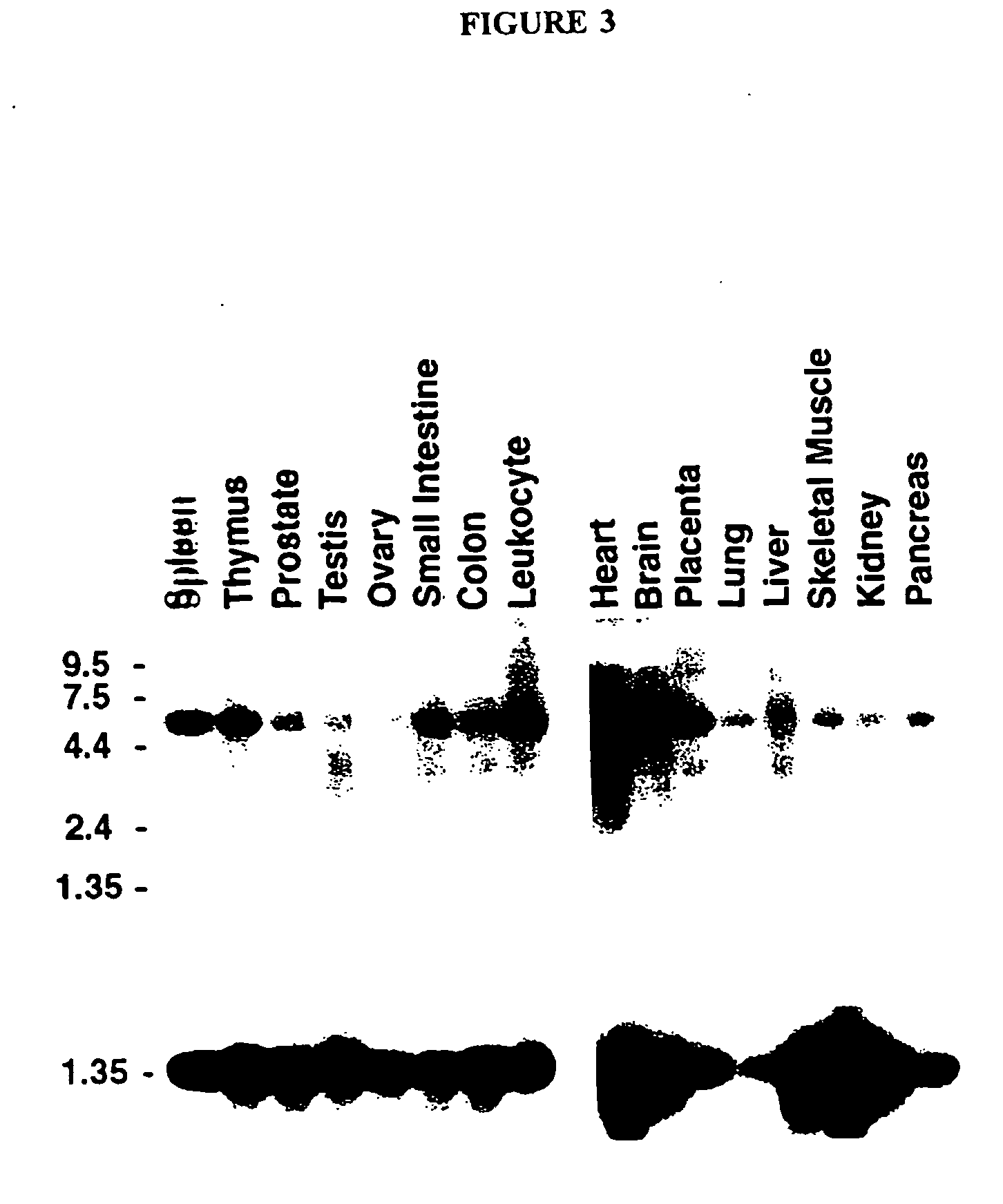
Regulators of type-1 tumor necrosis factor receptor and other cytokine receptor shedding
InactiveUS20070059758A1Peptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesTumor necrosis factor receptorNovel gene
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the regulation of cytokine signaling through the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) pathway. Specifically, the invention provides a novel gene, polypeptide and related compositions and methods for the regulation of ectodomain shedding. In preferred embodiments, methods and compositions for the regulation of TNF Type-1 Receptor ectodomain shedding are provided. The present invention finds use in therapeutics, diagnostics, and drug screening applications.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE USA OF AMERICA REP BY THE SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
ActiveUS20060166277A1Diagnosing and effectively treatingSave maternalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPregnancyUdp glycosyltransferase
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1 anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Multi-target chimeric antigen receptor
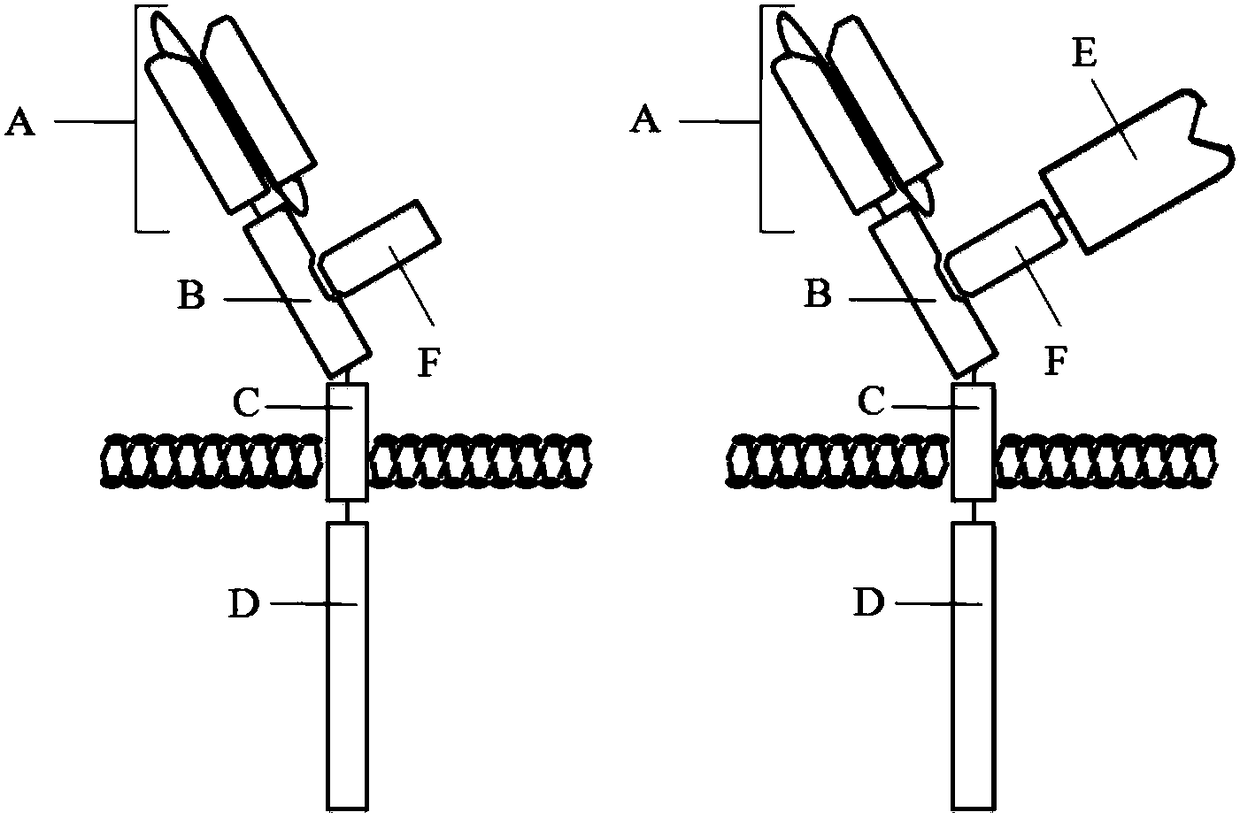
InactiveCN108250301AEliminate dependenciesReduced activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTransmembrane domainChimeric antigen receptor
The invention discloses a multi-target chimeric antigen receptor. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention consists of a main peptide chain and an assistant peptide chain.The main peptide chain includes an antigen binding domain A, an assistant peptide chain connection domain B, a transmembrane domain C and an intracellular signal conduction domain D. The assistant peptide chain includes a main peptide chain connection domain F. The antigen binding domain A is a polypeptide with antigen-bonding function. The assistant peptide chain connection domain B and the mainpeptide chain connection domain F are mutually combined. The transmembrane domain C is the transmembrane domain of arbitrary membrane binding protein or the transmembrane domain of transmembrane protein. The intracellular signal conduction domain D includes a primary signal conduction region. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention can mediate specific cell killing bycombining two antigen binding domains with different antigens. Also a cytokine and cytokine receptor compound are introduced into the multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention and can play the role of cytokines.
Owner:TIMMUNE BIOTECH INC
3,3'-Diindolylmethane immune activating compositions
The invention provides immune response activating compositions and methods of use. The general methods deliver an immune response activator to a patient determined to be in need thereof, comprising the steps of: (a) administering to the patient a predetermined amount of an immune response activating, optionally substituted DIM; and (b) detecting in the patient a resultant immune response activation, such as an increase in T-cell proliferation, NO production, cytokine production, cytokine receptor expression, or cytokine signaling.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
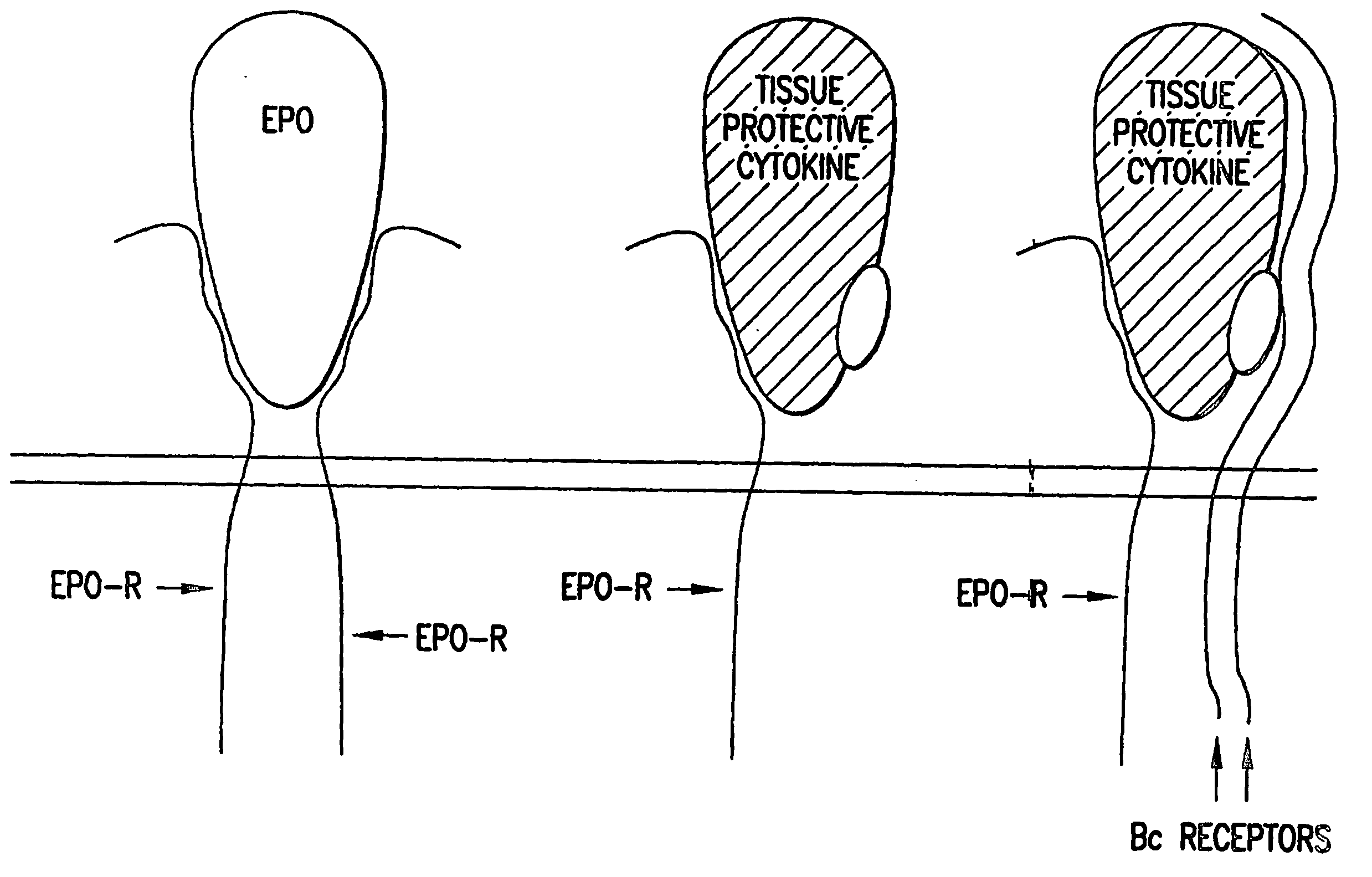
Tissue protective cytokine receptor complex and assays for identifying tissue protective compounds
InactiveUS20040214236A1High activityEnhanced interactionSenses disorderNervous disorderNervous systemExcitable cell
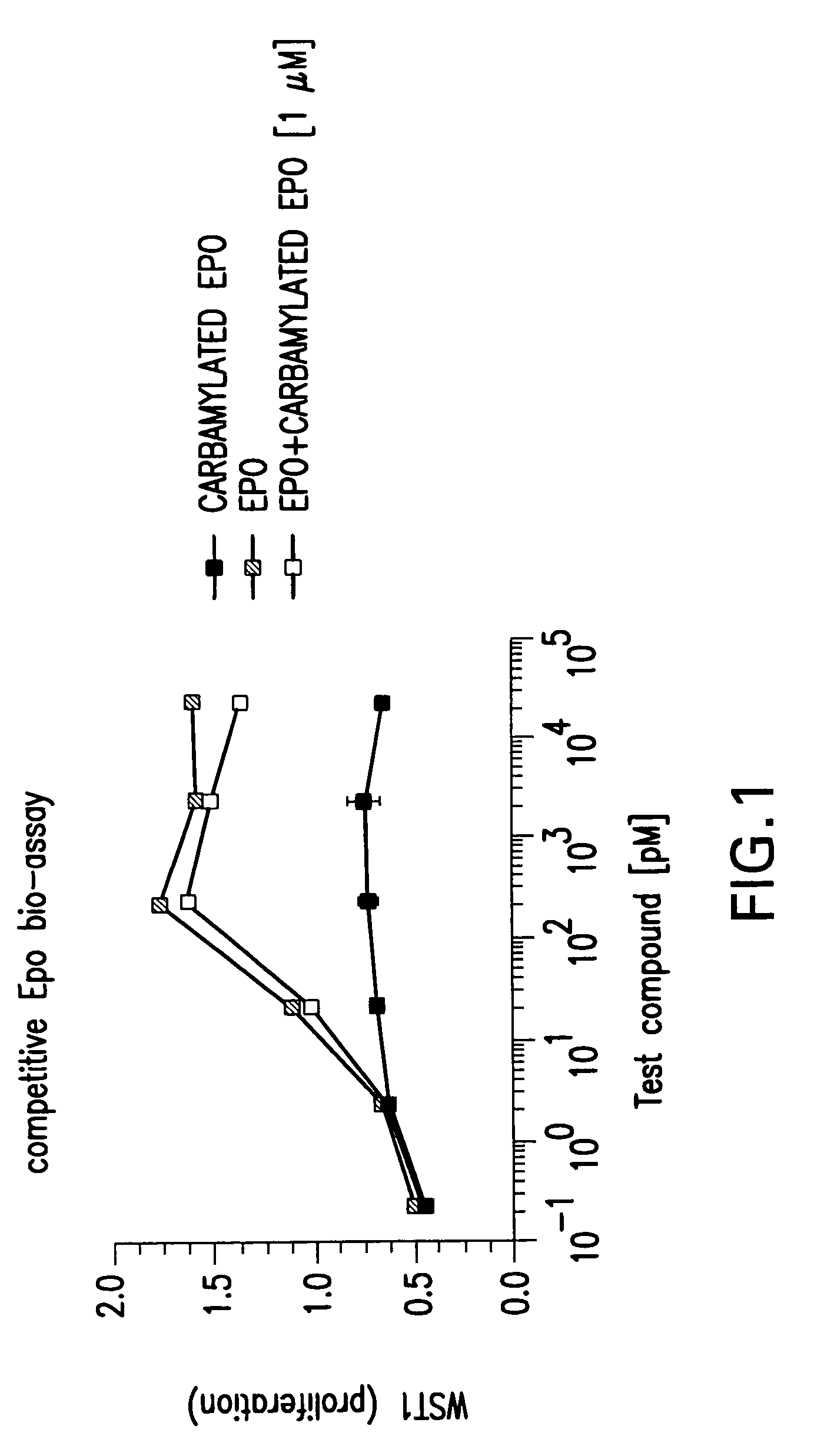
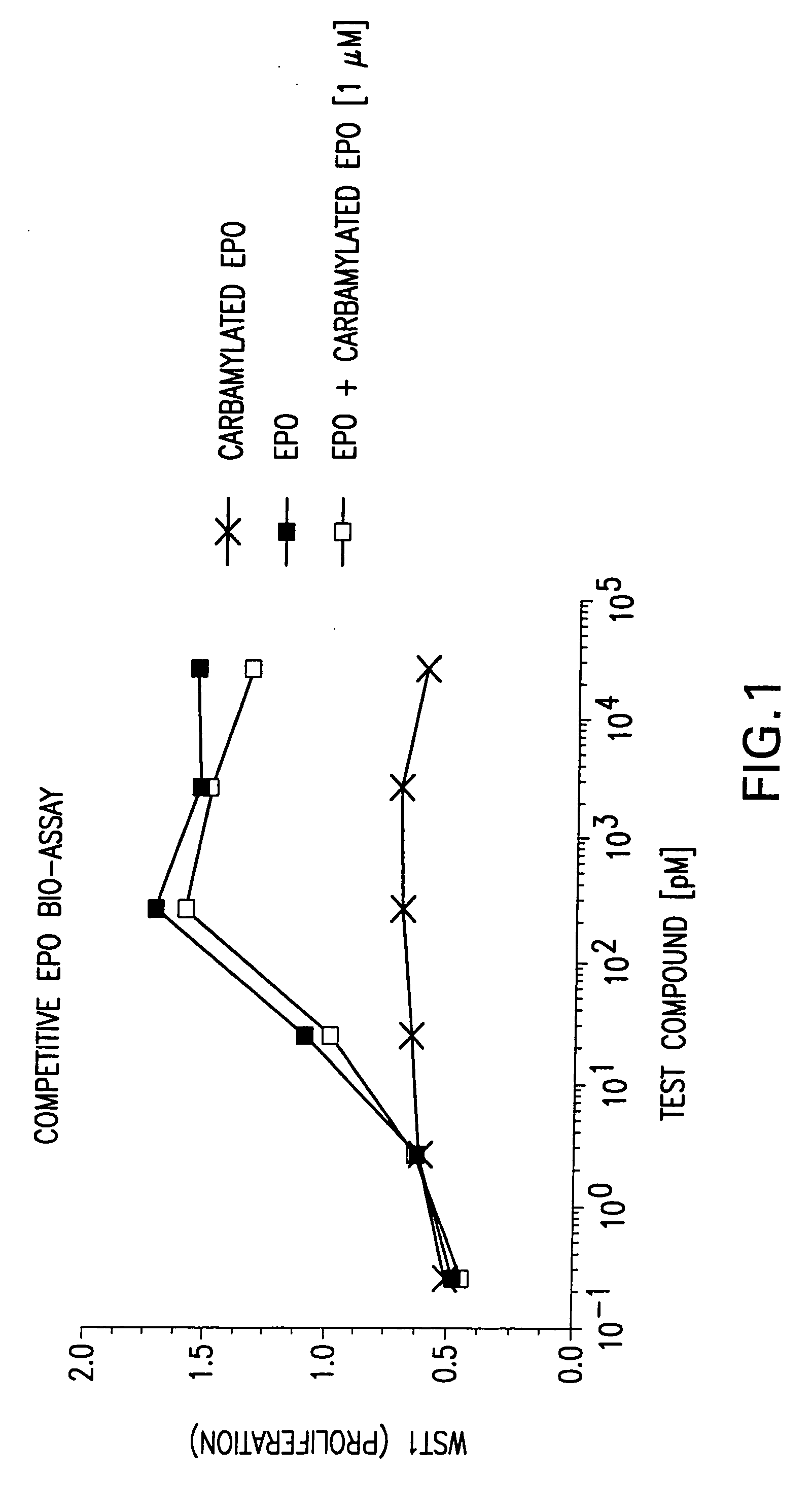
The present invention is directed methods for identifying compounds that have a tissue protective activity using a heteromultimer receptor complex that mediates the tissue protective activities. The complex consists of at least one EPO-R in complex with at least one betac Receptor. These compounds used in the assays to identify tissue protective compounds include, but are not limited to, small molecules and biologics. The compounds identified using these assays can be used to treat various conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as those of other erythropoietin-responsive or excitable cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS +2
Chimeric Protein
InactiveUS20080292628A1Extended half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseChimera Protein
A fusion protein containing a first segment that is located at the amino terminus of the fusion protein and specifically binds to and neutralizes a first cytokine or growth factor; and a second segment that is located at the carboxyl terminus of the fusion protein and specifically binds to a second cytokine receptor which is often rich at disease sites such as IL-1 receptor-rich inflammatory site. In addition, the said second segment is usually the receptor antagonist such as IL-1 receptor antagonist and its functional equivalent analogues. Also disclosed are nucleic acids encoding the fusion protein, vectors and host cells having the nucleic acids, and related composition and methods to target inflammatory diseases and indications co-existed with inflammation.
Owner:AMPROTEIN CORP
CC chemokine receptor 5 DNA, new animal models and therapeutic agents for HIV infection
InactiveUS7151087B2Effective in regulating monocyte accumulationEffective in regulating activationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsChemokine receptor D6Mammal
The susceptibility of human macrophages to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection depends on cell surface expression of the human CD4 molecule and CC cytokine receptor 5. CCR5 is a member of the 7-transmembrane segment superfamily of G-protein-coupled cell surface molecules. CCR5 plays an essential role in the membrane fusion step of infection by some HIV isolates. The establishment of stable, nonhuman cell lines and transgenic mammals having cells that coexpress human CD4 and CCR5 provides valuable tools for the continuing research of HIV infection. In addition, antibodies which bind to CCR5, CCR5 variants, and CCR5-binding agents, capable of blocking membrane fusion between HIV and target cells represent potential anti-HIV therapeutics for macrophage-tropic strains of HIV.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Tissue protective cytokine receptor complex, assays for identifying tissue protective compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060216757A1Reduce apoptosisPromote recoveryCompound screeningPeptide librariesNervous systemExcitable cell
The present invention is directed methods for identifying compounds that have a tissue protective activity using a heteromultimer receptor complex that mediates the tissue protective activities. The complex consists of at least one EPO-R in complex with at least one βc Receptor. These compounds used in the assays to identify tissue protective compounds include, but are not limited to, small molecules and biologics. The compounds identified using these assays can be used to treat or prevent various diseases, disorders, or conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as those of other erythropoietin-responsive or excitable cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:THE KENNETH S WARREN INST
Method and composition for treatment of renal disease with antibodies and their equivalents
InactiveUS20070218063A1Improve the quality of lifeMore pathogenetic treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansInterleukin 6Interleukin 10
A method for treating renal disease includes administering to a patient suffering from renal disease an effective amount of antibody or of a functional equivalent thereof to at least two of urea, creatinine, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 6 and interleukin 1 beta. Soluble cytokine receptors also can be employed. Antibody, functional equivalent thereof or soluble cytokine receptor to interleukin 10 or interleukin 13 also can be administered. The method can be used as a supplement to or as partial or complete replacement for dialysis. A pharmaceutical composition includes antibody or functional equivalent thereof to urea, creatinine, or both; antibody, functional equivalent or soluble cytokine receptor to tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 6, interleukin 1 beta or any combination thereof; and, optionally, antibody, functional equivalent or soluble cytokine receptor to interleukin 10, interleukin 13 or both. The composition can be included in a kit.
Owner:SKURKOVICH BORIS +2
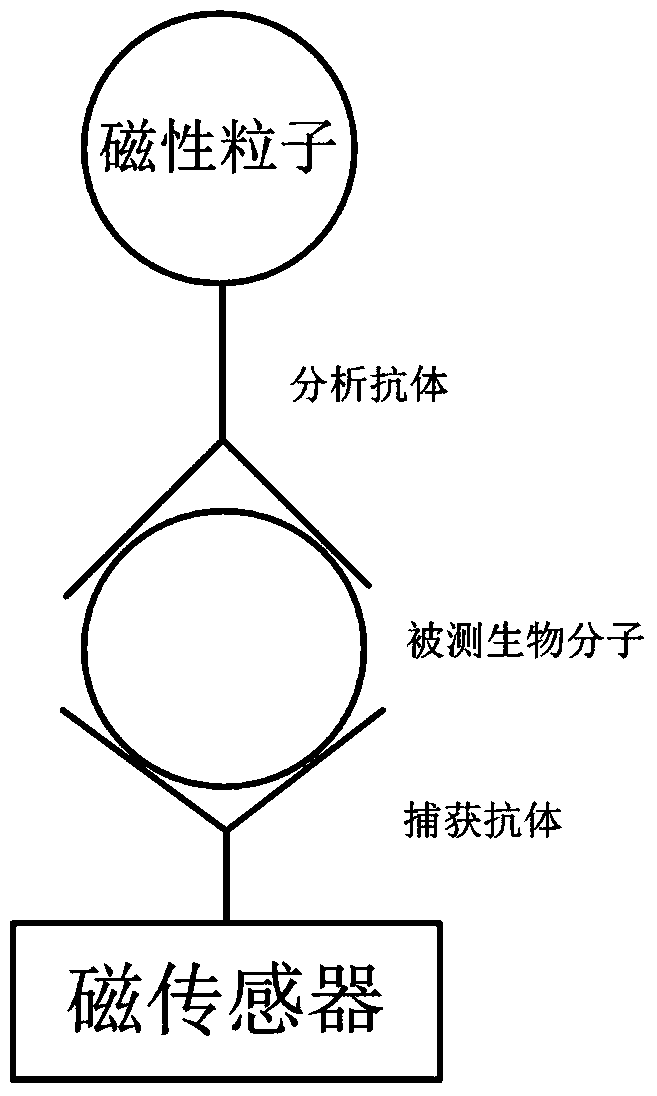
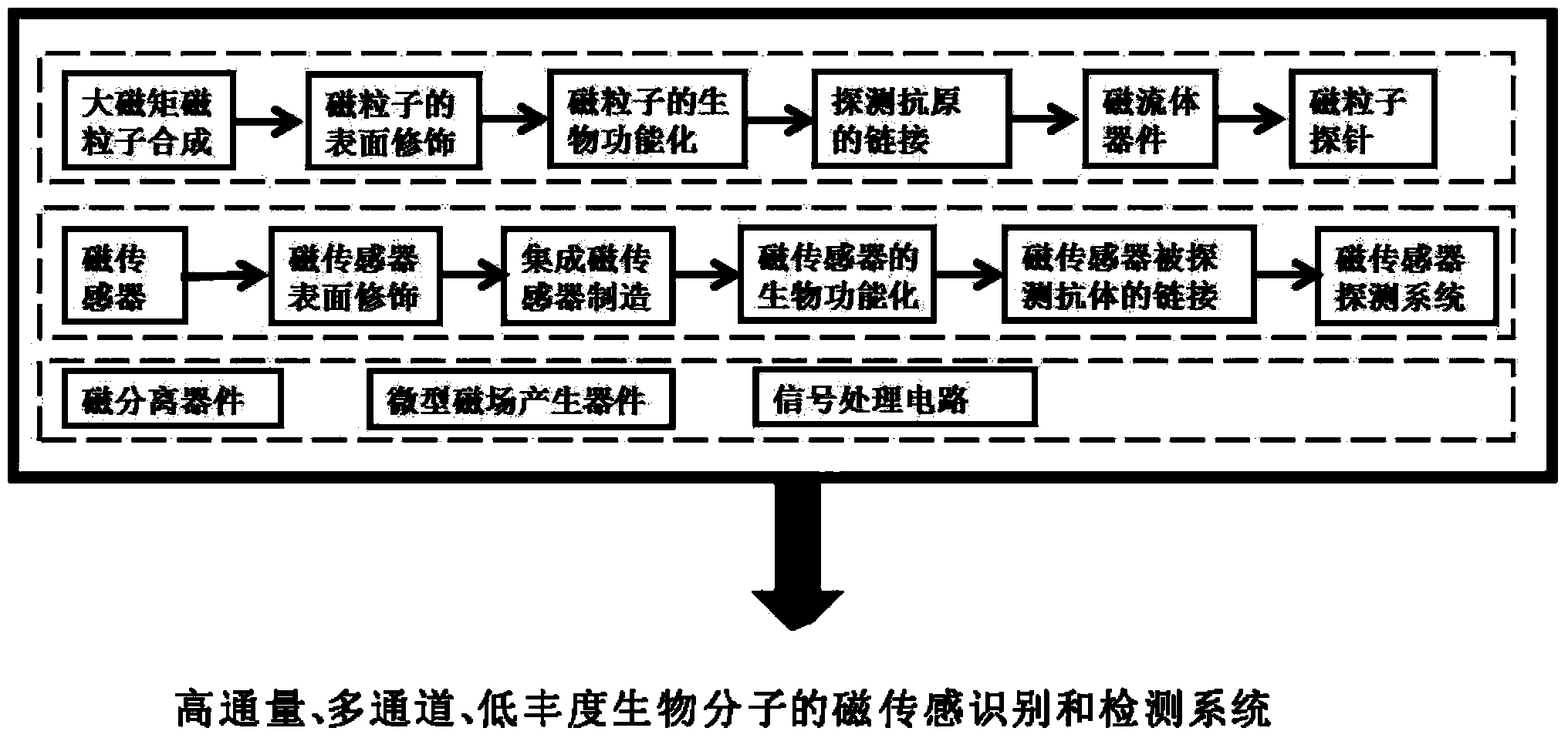
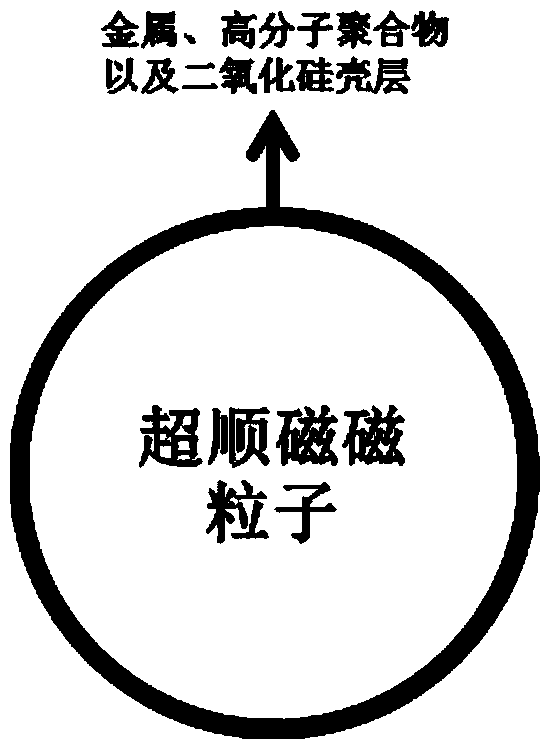
Magnetic sensing identification method for high-flux multi-channel low-abundance biomolecules
ActiveCN104034881AHigh sensitivityImprove throughputBiological testingMaterial magnetic variablesAntigenSomatic cell
The invention relates to a magnetic sensing identification method for high-flux multi-channel low-abundance biomolecules, and belongs to the technical field of biomolecule identification. The invention mainly aims at an immunolabelling biomolecule detection, monitoring and identification method based on systems such as antigens-antibodies, cell factors-cell factor acceptors, bioactive peptides-acceptors, biotin-avidin and chiral molecules. A biomolecule probe and detection system consists of superparamagnetic particles and high-performance magnetic sensors. The magnetic sensing identification method can be applied to the application fields of biology, medicines, food safety and the like, and can be used for biomolecule identification, detection and monitoring, clinical disease diagnose, food safety detection and virus and germ detection.
Owner:NANJING YIDEGUAN ELECTRONICS TECH
Tissue Protective Cytokine Receptor Complex, Assays for Identifying Tissue Protective Compounds and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090136519A1Easy to measureFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNervous systemExcitable cell
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS +1
Cytokine receptor
Nucleic acids encoding mammalian cytokine receptor, e.g., for cytokine IL-B50, purified proteins and fragments thereof. Antibodies, both polyclonal and monoclonal, are also provided. Methods of using the compositions for both diagnostic and therapeutic utilities are described.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Cytokines and cytokine receptors with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS20050220800A1Low immunogenicityReduced immunogenic responsePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureTumor necrosis factor receptorBiology
The present invention provides methods for the identification of CD4+ T-cell epitopes in the sequences of various proteins, namely, human cytokines and cytokine receptors, as well as the production of peptides which when incorporated into the protein sequence, are no longer capable of initiating the CD4+ T-cell response. In some embodiments, the present invention provides means and compositions suitable for reducing the immunogenicity of cytokines and cytokines receptors such as interferon-β, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor-1, erythropoietin, and thrombopoietin.
Owner:SCOTT POWER D +1
Chimeric cytokine receptor
ActiveUS20180244797A1Easy to implantAvoid toxicityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsCell Surface AntigensWilms' tumor
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
Biologically relevant orthogonal cytokine/receptor pairs
ActiveUS20190183933A1Sufficient solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetically modified cellsBiologic DMARDA-Factor Receptor
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
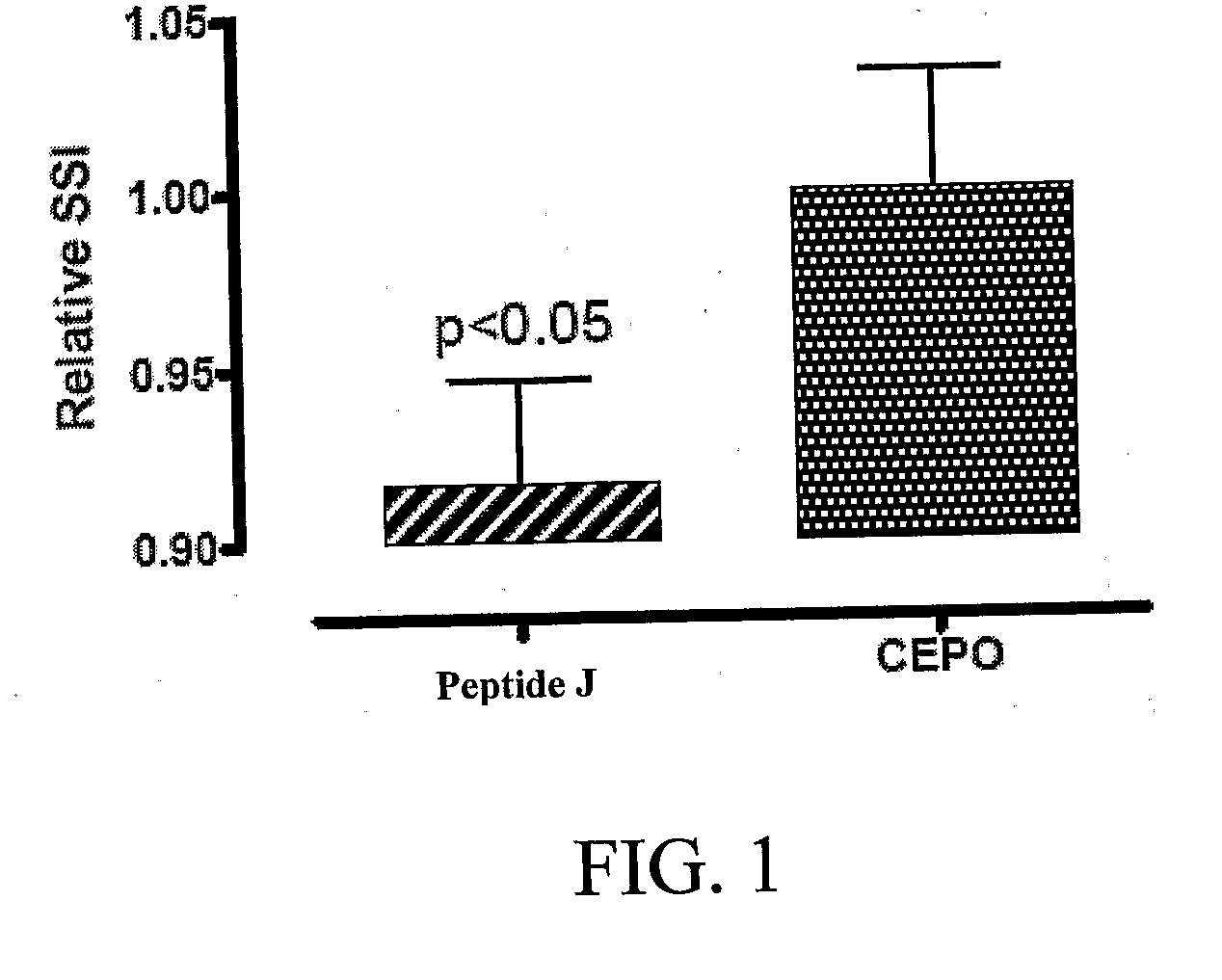
Tissue protective peptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS8071554B2Facilitate optimal expressionHigh expressionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBiology
The present invention is directed to novel tissue protective peptides. The tissue protective peptides of the invention may bind to a tissue protective receptor complex. In particular, the present invention is drawn to tissue protective peptides derived from or sharing consensus sequences with portions of cytokine receptor ligands, including Erythropoietin (EPO), that are not involved in the binding of the ligand to the receptor complex, e.g., to the EPO receptor homodimer. Accordingly, the tissue protective peptides of the invention are derived from the amino acid sequences of regions of cytokine receptor ligands that are generally located on or within the region of the ligand protein that is opposite of the receptor complex, i.e., are generally derived from amino acid sequences of regions of the ligand protein that face away from the receptor complex while the ligand is bound to the receptor. The invention is further directed to the consensus sequences for use in engineering a synthetic tissue protective peptide. These tissue protective peptides also include fragments, chimeras, as well as peptides designed to mimic the spatial localization of key amino acid residues within the tissue protective receptor ligands, e.g., EPO. The invention further encompasses methods for treating or preventing a disease or disorder using tissue protective peptides of the current invention. The invention also encompasses methods for enhancing excitable tissue function using tissue protective peptides of the current invention.
Owner:ARAIM PHARMA INC
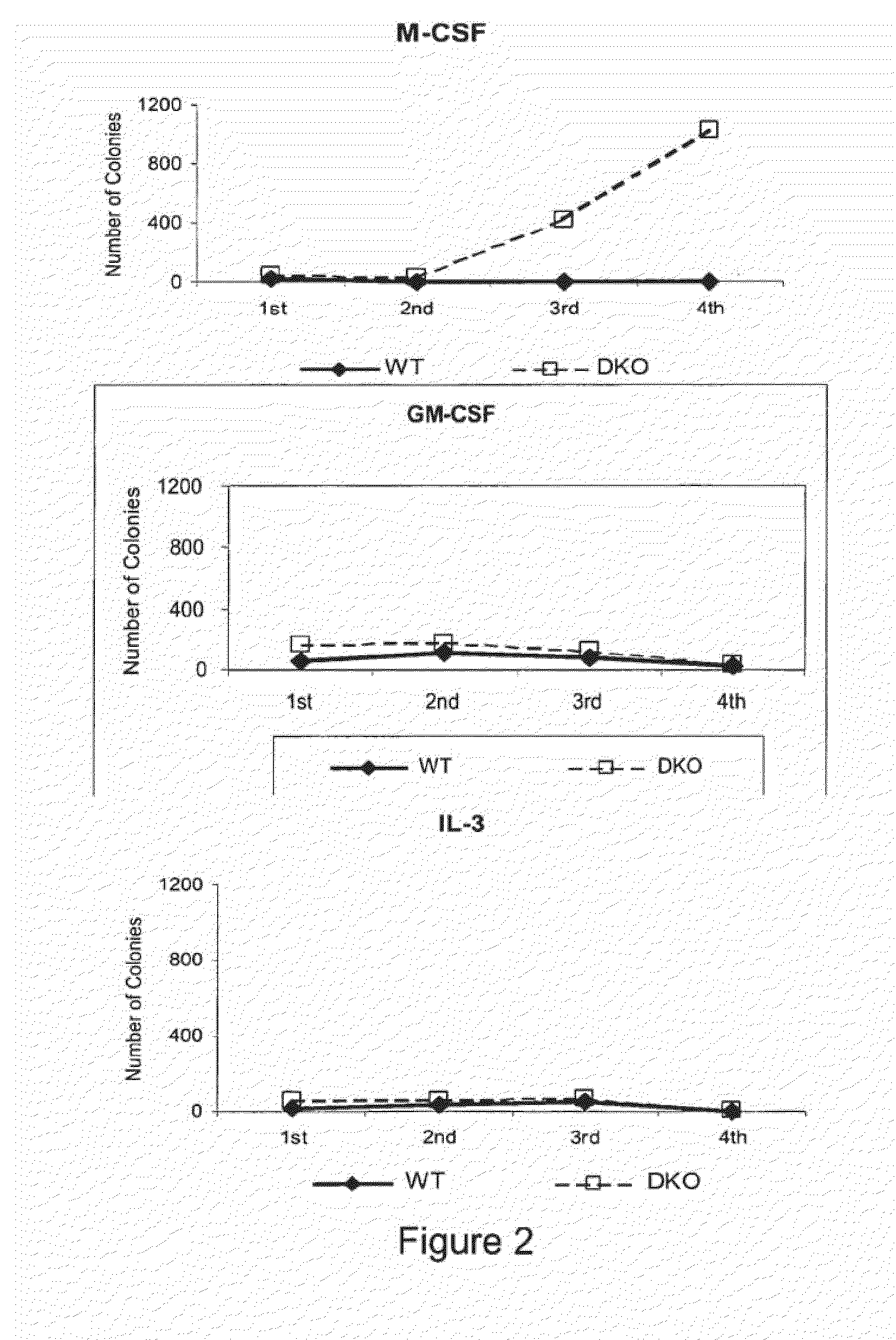
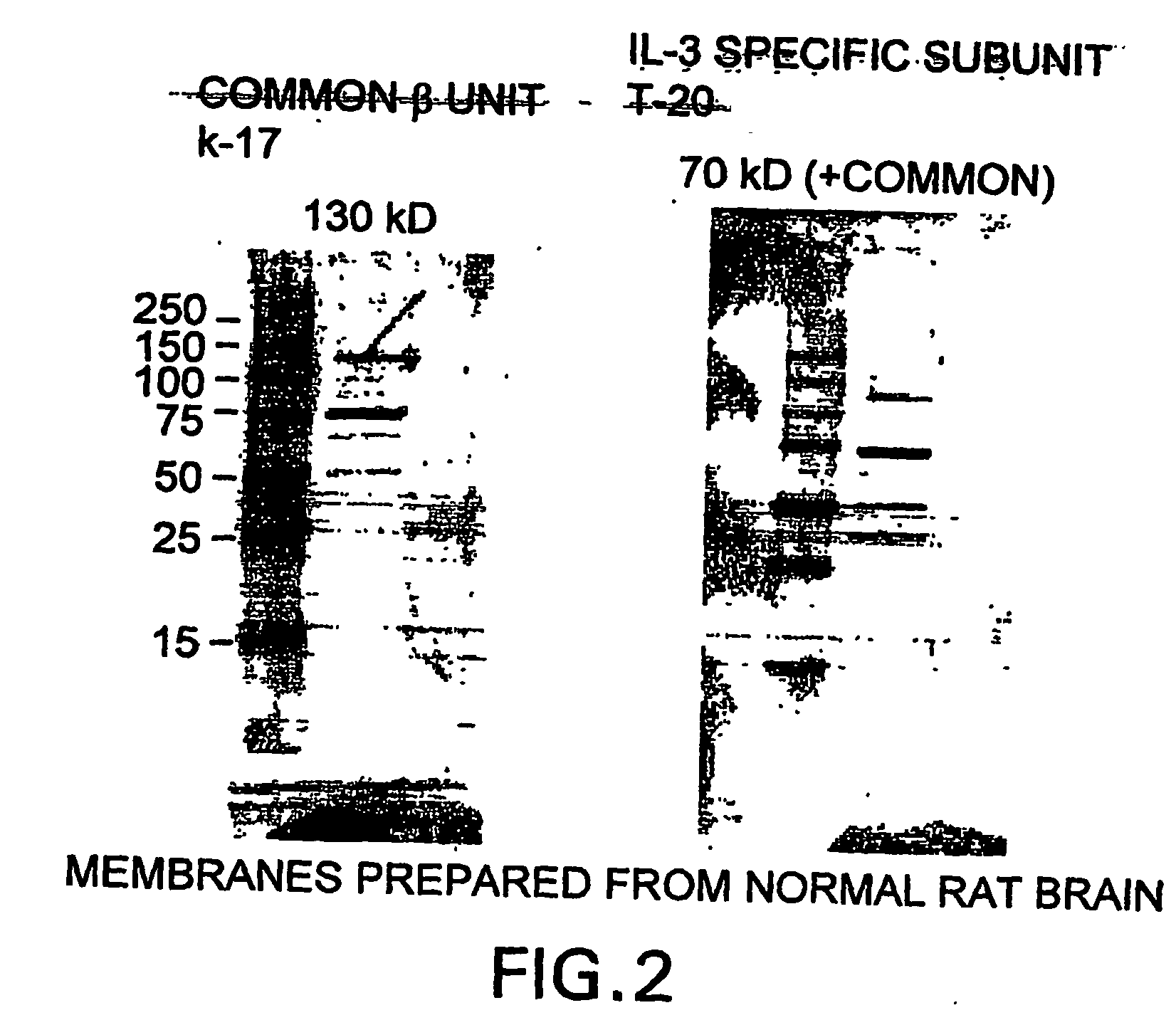
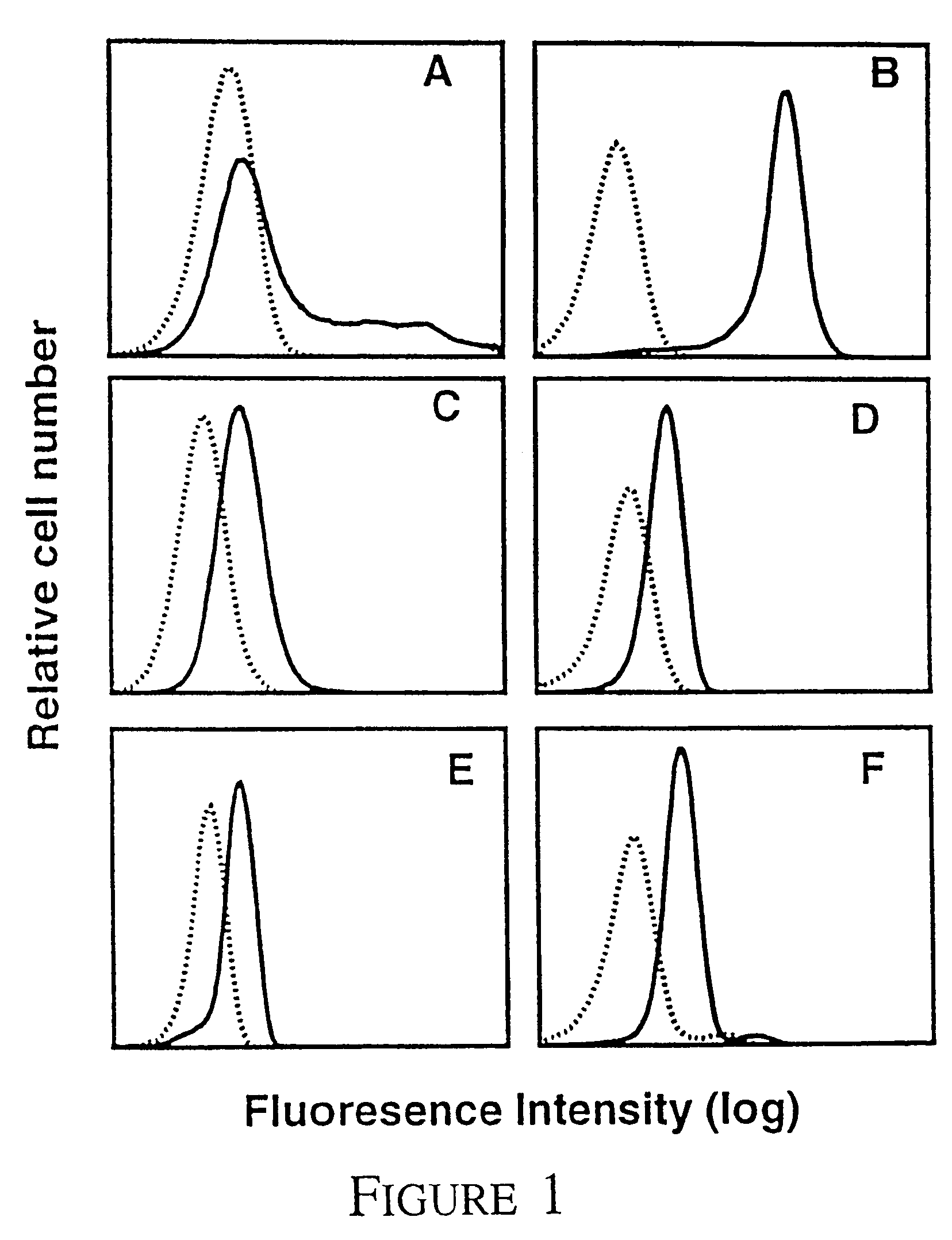
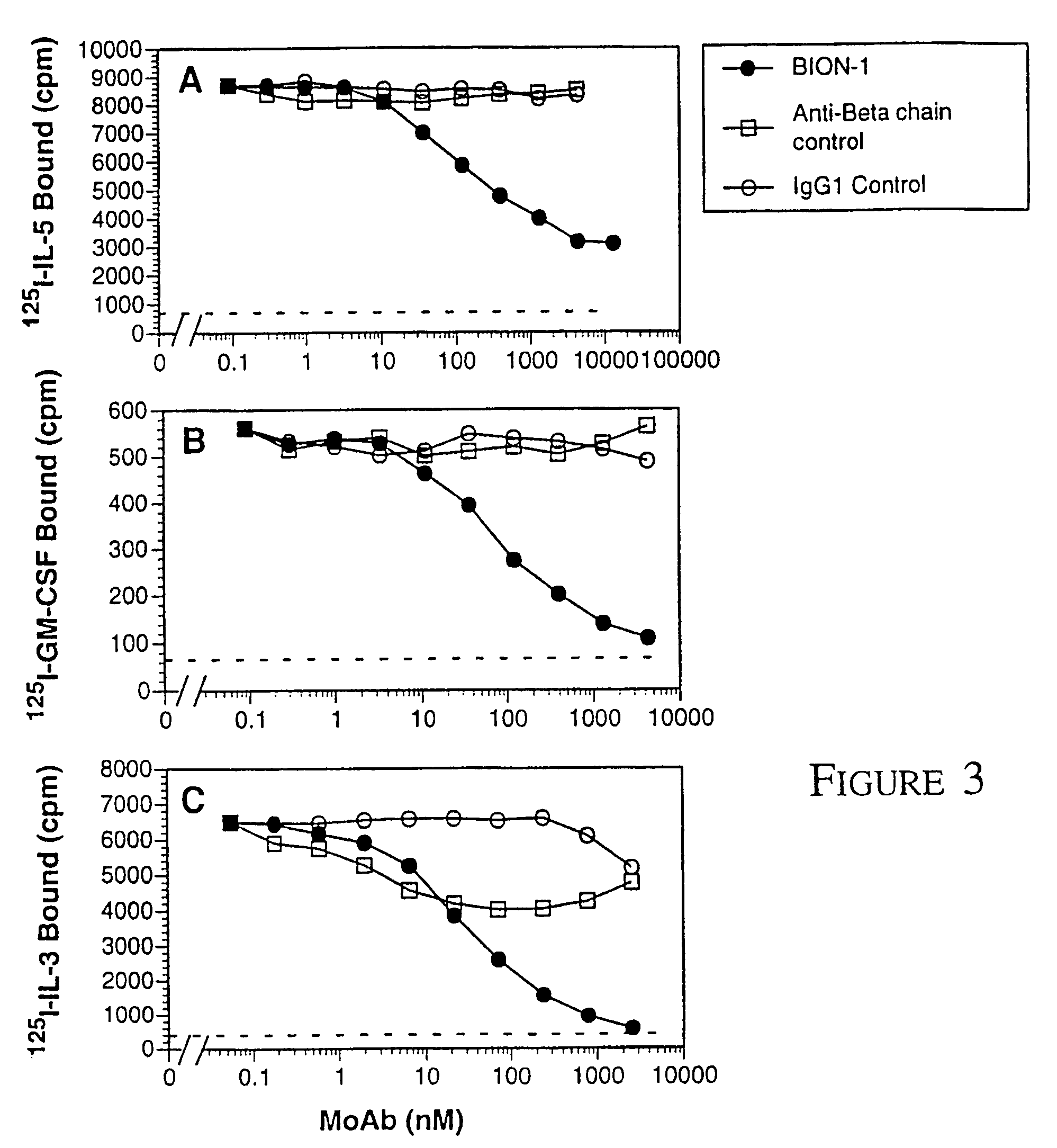
Method of modulating leukemic cell and eosinphil activity with monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS7427401B2Block high affinity bindingInhibition of activationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsBinding siteEosinophil
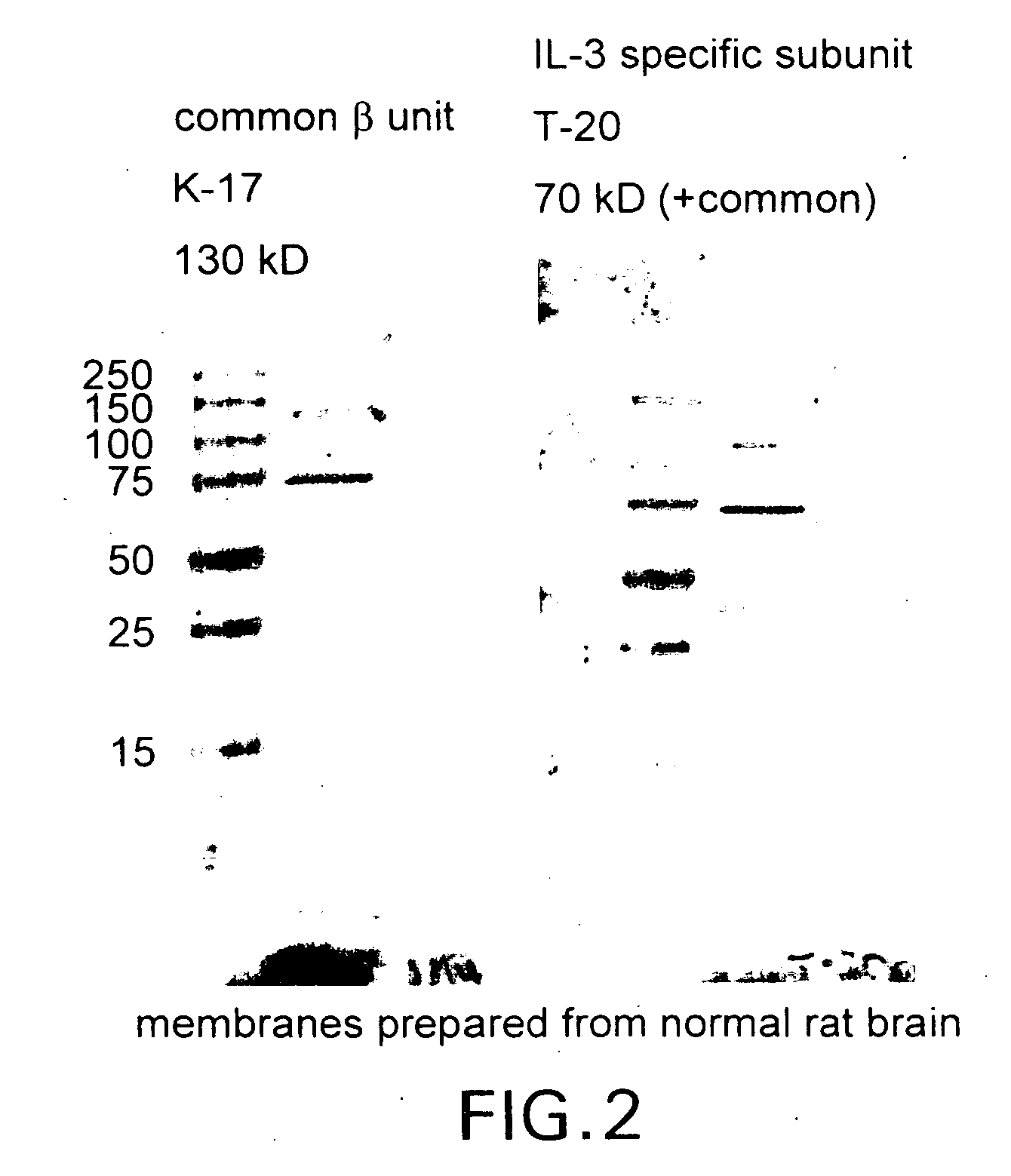
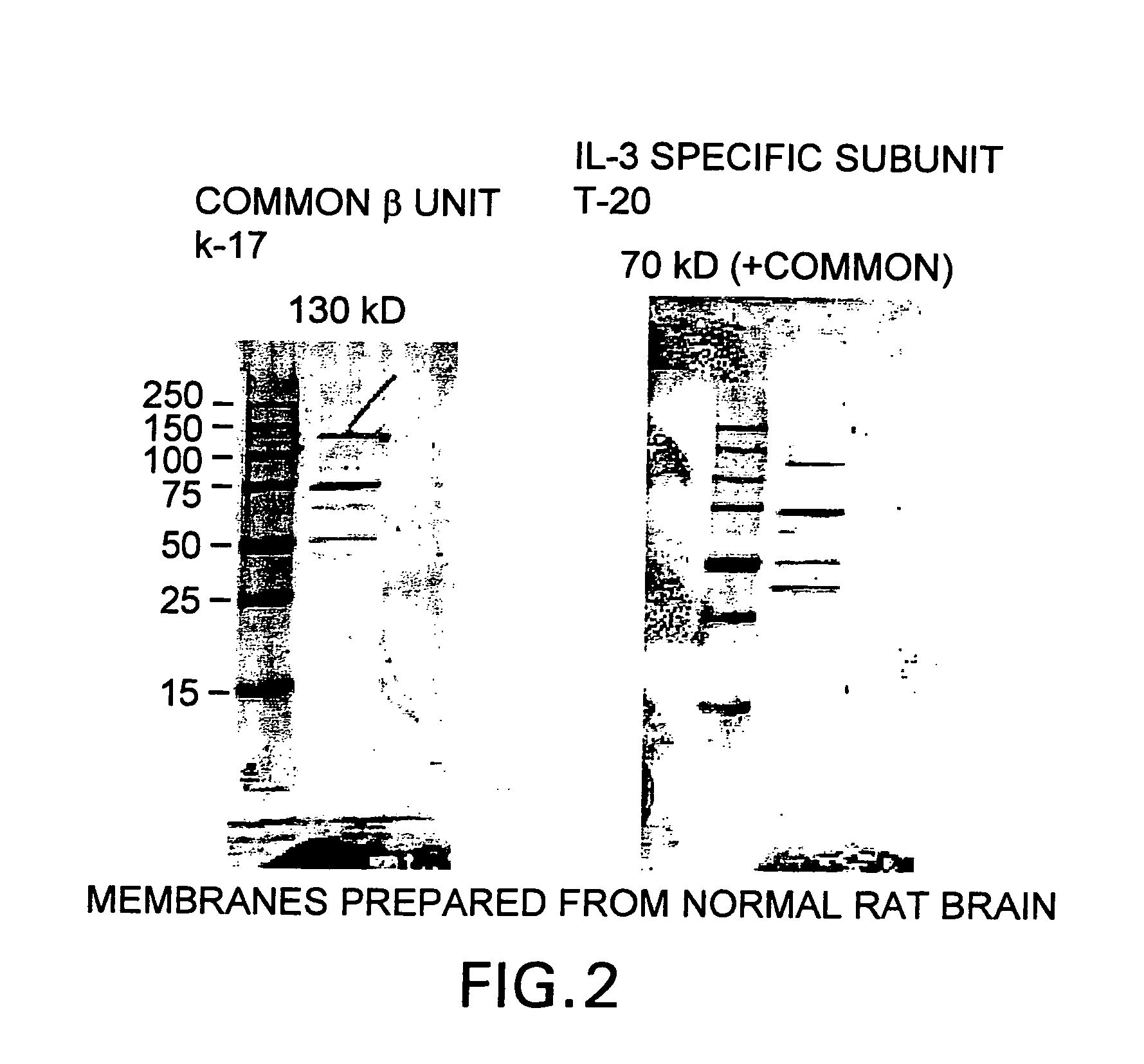
A method of isolating a monoclonal antibody capable of inhibiting any one of IL-3, GM-CSF and IL-5 binding to the common receptor βc, or a monoclonal antibody capable of inhibiting the cytokines binding to a receptor analogous to βc. The method includes the steps of immunizing an animal with a cytokine receptor or portion of a cytokine containing the critical binding site which portion includes the extracellular domain 4 or analogous domain in the analogous common receptor or part thereof. Antibodies producing cells from the animal are then isolated and fused with a myeloma cell line and then screened for a cell line that produces an antibody of the desired type. A monoclonal antibody, or fragments thereof capable of inhibiting the binding of the cytokines IL-3, GM-CSF and IL-5 to the βc receptor, and a hybridoma cell line producing the antibody are also claimed.
Owner:MEDVET SCI
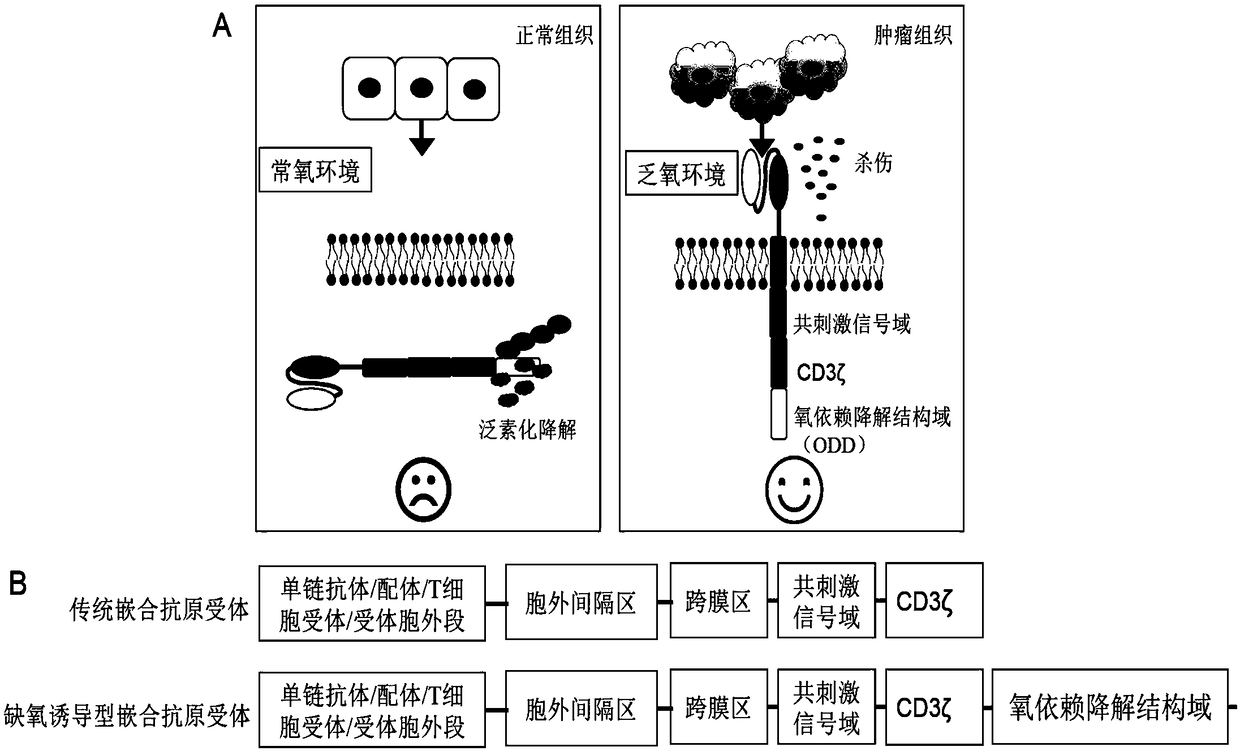
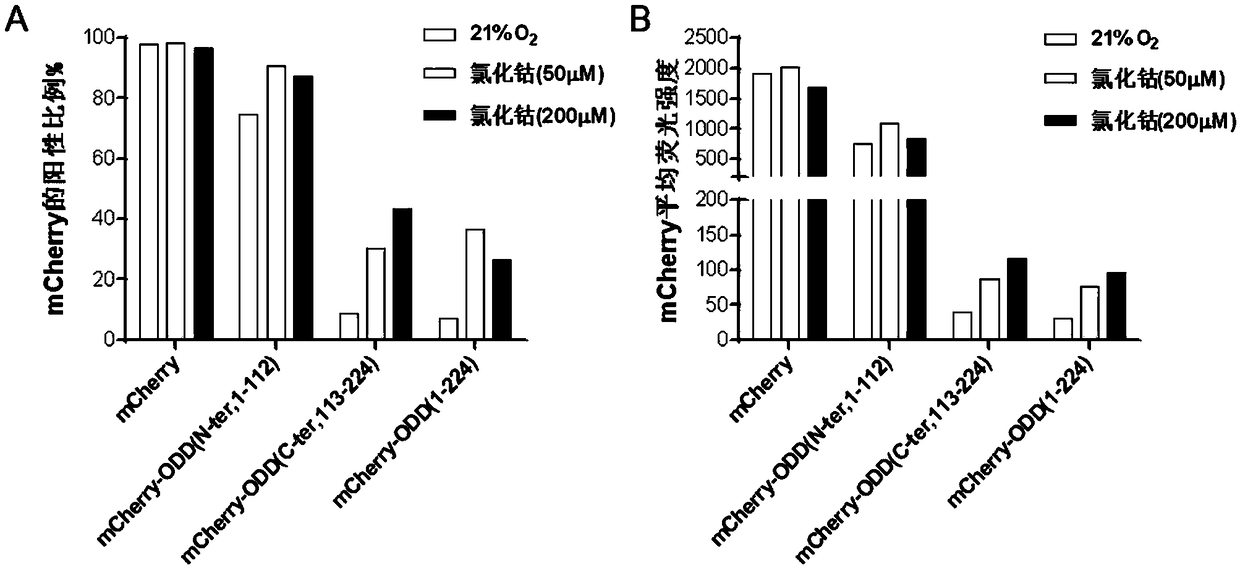
Hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor capable of achieving specific activation of tumor microenvironment
ActiveCN109280086AStay targetedStay lethalPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingCell membrane
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical science, and relates to a hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor capable of achieving specific activation of a tumor microenvironment. The structural domain of the hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor comprises: (1) one or more structural domains with specific combination of target antigens; (2) a structural domain in an extracellular spacer region; (3) a transmembrane structural domain; (4) one or more costimulatory signal structural domain and a cytokine receptor signal-transduction structural domain; (5) an intracellularsignal-transduction structural domain; and (6) an oxygen-dependent degradation structural domain. Once the hypoxia-inducible chimeric antigen receptor is exposed to an anoxic environment, efficient expression of the Hi-CAR on effect cell membranes is achieved, and specific recognition of target antigens is achieved, so that the specific activation property of the anoxic microenvironment is achieved; and since the anoxic situation of the tumor microenvironment is more significant than that of normal tissue, damage to the normal tissue can be reduced significantly, and meanwhile the activity ofspecific killing of tumors is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com