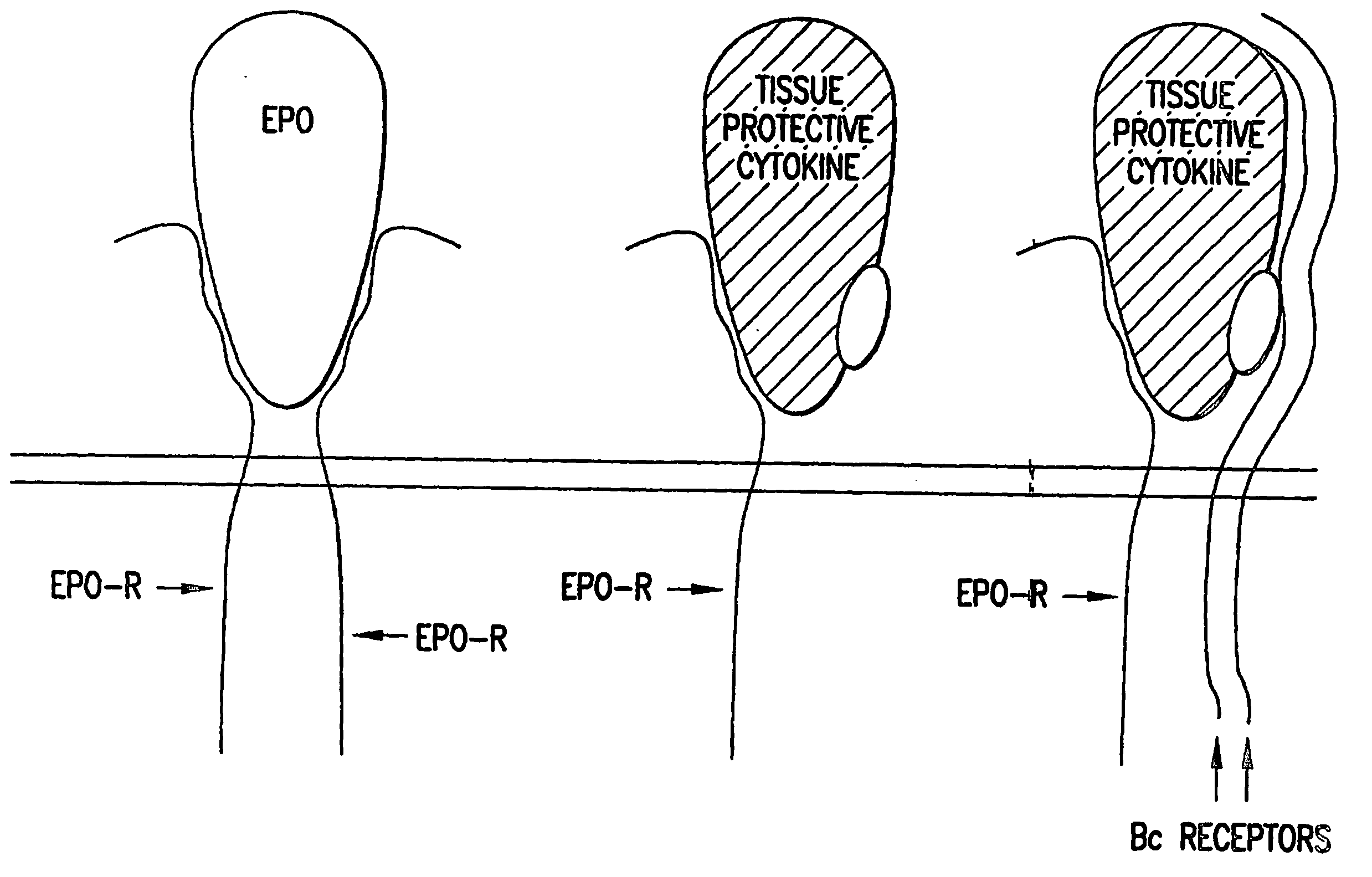
Tissue Protective Cytokine Receptor Complex, Assays for Identifying Tissue Protective Compounds and Uses Thereof
a cytokine receptor and tissue technology, applied in the field of tissue protective cytokine receptor complexes, can solve the problems of not having a physiologically relevant effect, unable to achieve 100% effective flu vaccines, and many flu vaccines not 100% effective at preventing flu, so as to improve the function of excitable tissue, improve recovery, and mitigate apoptosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
6.1 Example 1
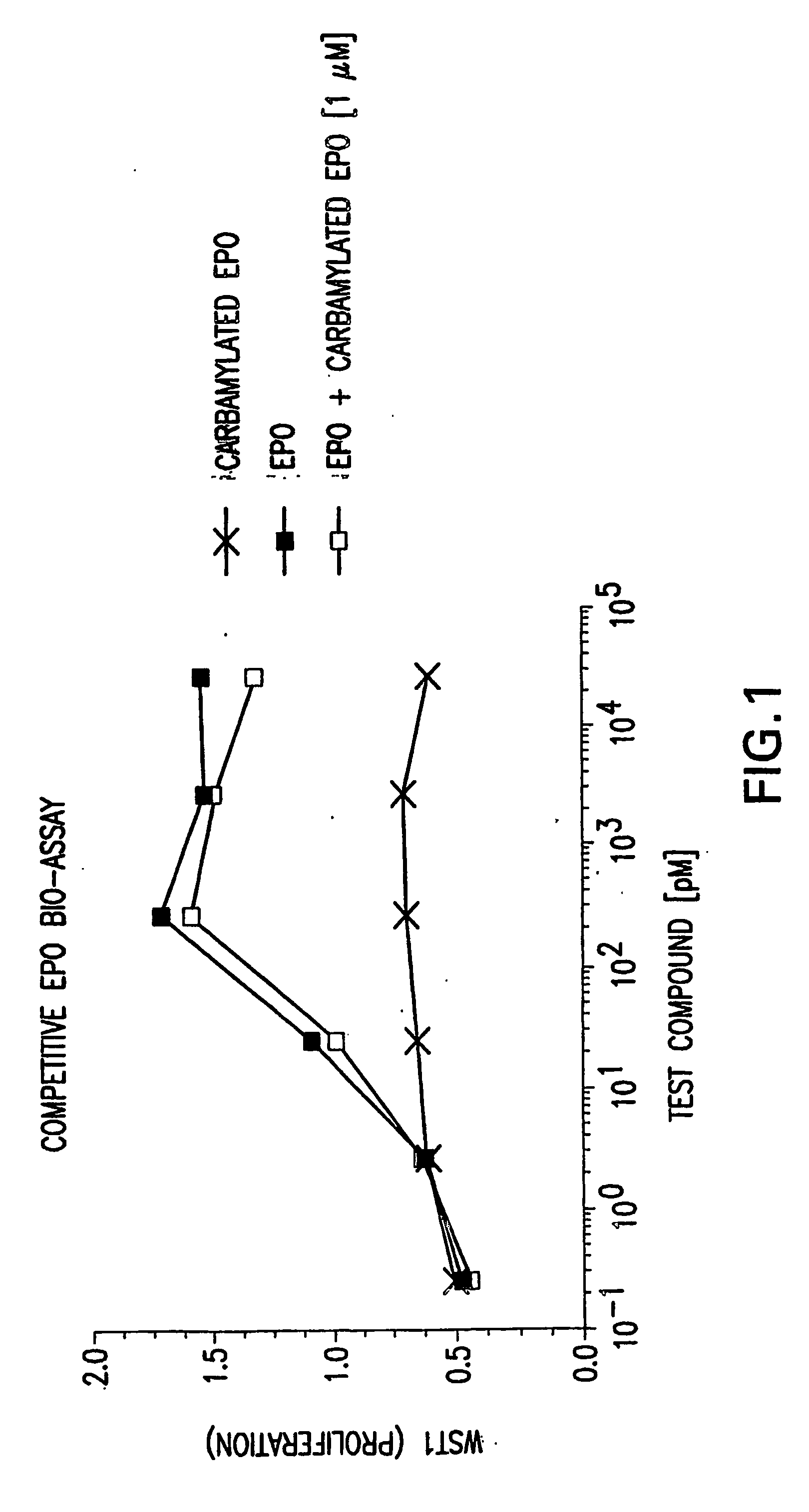
Competitive EPO Bioassay
[0254]The competitive binding assay described below was performed to determine whether carbamylated EPO binds to the EPO-R. UT-7 cells which express EPO-R were utilized to determine whether carbamylated EPO competitively inhibits binding of rhEPO to the EPO-R. With binding of rhEPO to the EPO-R, cells exhibited proliferation. Inhibition of the proliferation is indicative of competitive binding.
Methods
[0255]For the purpose of the competitive binding assay, erythroleukemic UT-7 cells (Komatsu, N. et al., 1991, Cancer Res., 51:341-8) were obtained from DSMZ (Braunschweig, Germany, ACC137). The assays of the carbamylated EPO and rhEPO were performed as described in Leveque et al. (1996, Hematol Oncol 14:137-46) over 48 hours. A WST-1 reduction (Roche #1 644 807) was used to quantitate the living cells. Signal to noise ratio of the assay was 8-15, and the half-maximal effective concentration of carbamylated EPO and rhEPO determined by a four parameter...
example 2
6.2 Example 2
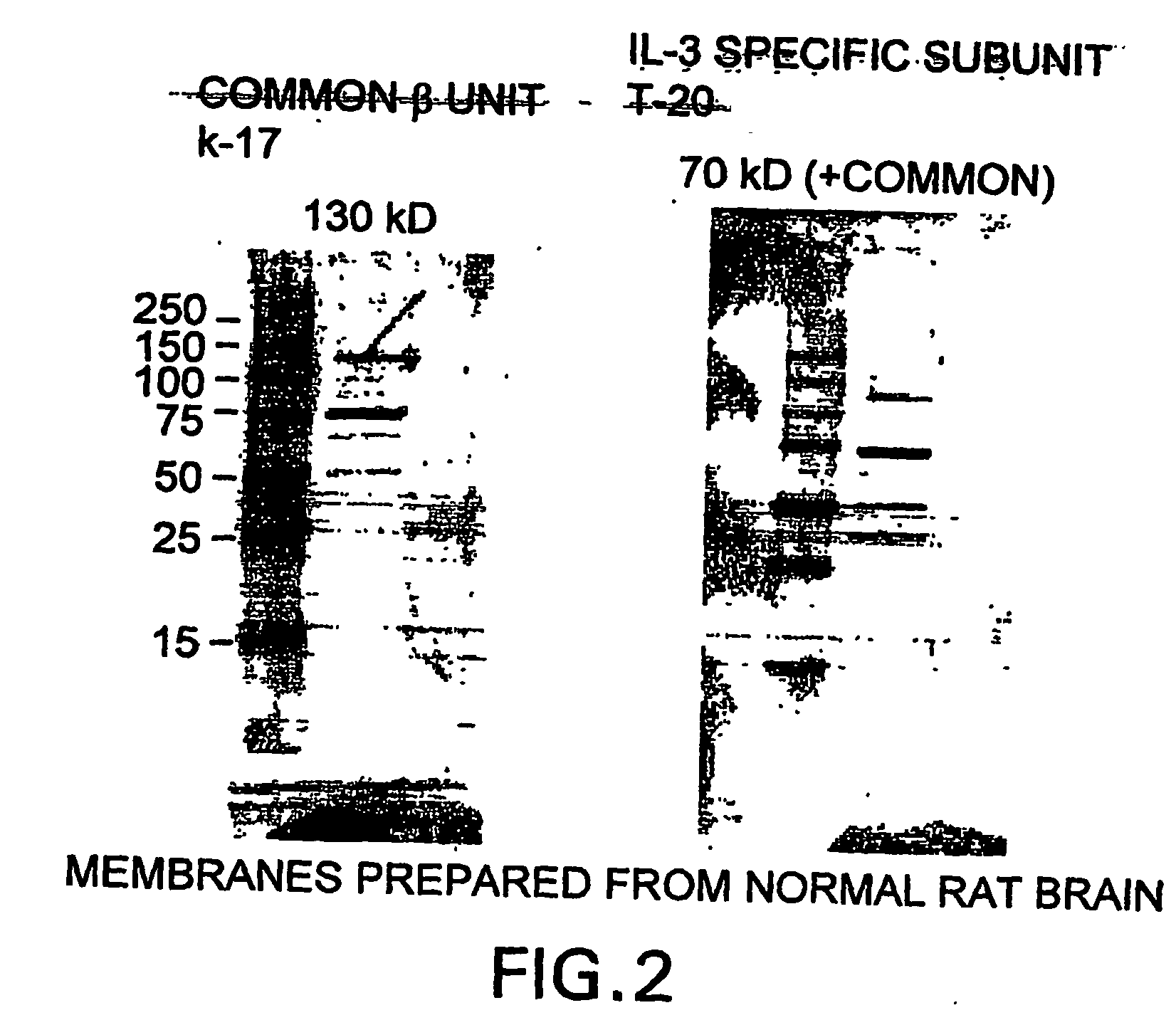
Western Blot of Rat Brain Membrane
[0259]Rat brain cells have been shown to be responsive to EPO. Membrane proteins of rat brain cells were isolated to determine whether these EPO responsive cells express either the βc receptor or the βc receptor associated with IL-3 specific receptor component.
Methods
[0260]Rat membrane proteins were isolated using the following protocol. Rat brain was homogenized in PBS containing protease inhibitors (25 μg / ml Leupeptin (5 mg / ml in stock), 10 μg / ml Aprotin (1 mg / ml in stock), 1 mM PMSF (100 mM in stock) 20×. The homogenized tissue was then centrifuged at 3,800 rpm for 5 minutes at 4° C. The supernatant is then collected and further centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 30 minutes at 4° C. The pellet resulting from is centrifugation is then homogenized in PBS containing the protease inhibitor and 1% Triton X-100. This homogenate is then further centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 30 minutes at 4° C. The resulting supernatant contains the membrane prot...
example 3
6.3 Example 3
Immunohistochemistry for Bc Receptor in Rat Spinal Cord
[0264]A rat spinal cord section was stained in order to test for the presence of βc receptors.
Methods
[0265]The spinal cord of a rat was removed and fixed in paraffin. The embedded tissue was then sectioned (6 um). The section of spinal cord was then stained using anti-βc receptor antibody (K-17, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, Calif.
[0266]FIG. 3 shows a photograph the sectioned spinal cord stained for βc receptor using anti βc receptor antibody. The stain indicates the βc receptor is present within the spinal cord.
[0267]FIG. 4 shows a photograph of a close up of the stained areas of the sectioned spinal cord demonstrating reactivity with the anti-βc receptor antibody.
[0268]This finding suggests the presence of tissue protective cytokine receptor complexes in spinal cord tissue, since βc receptors and EPO receptors are present in these tissues.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mass tolerance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com