Regulators of type-1 tumor necrosis factor receptor and other cytokine receptor shedding
a type-1 tumor necrosis factor and cytokine receptor technology, applied in the direction of immunoglobulins against animals/humans, peptides, enzymology, etc., can solve the problems of rheumatoid arthritis, tissue injury and chronic inflammatory diseases,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of ARTS-1, a Novel Human Aminopeptidase Regulator of Type-1 Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (TNFR1) Shedding
A) Yeast Two-Hybrid Library Screening
[0319] A yeast two-hybrid library screening was conducted to identify proteins that interact with or are capable of interacting with the extracellular domain of the type I, 55 kDa TNF receptor (TNFR1). A human lung cDNA library (Clontech), cloned into pGADIO (GAL4 DNA-activation domain vector), was screened to detect interactions with a GAL4BD-TNFR1 fusion protein using a Matchmaker System 2 (Clontech) using methods known in the art as well as the manufacturer's recommended protocols. Amino acids 26 to 216 of TNFR1, corresponding to the extracellular domain (i.e., the ectodomain) located between the putative leader domain and the transmembrane domain (Nophar et al, EMBO J., 10:3269-3278 [1990]) were cloned into pAS2-1 (GAL4 DNA-binding domain vector) to generate the bait GAL4 DNA-binding domain fusion protein, GAL4BD-TNFR1....
example 2
Molecular Analysis of the ARTS-1 cDNA and Predicted Polypeptide
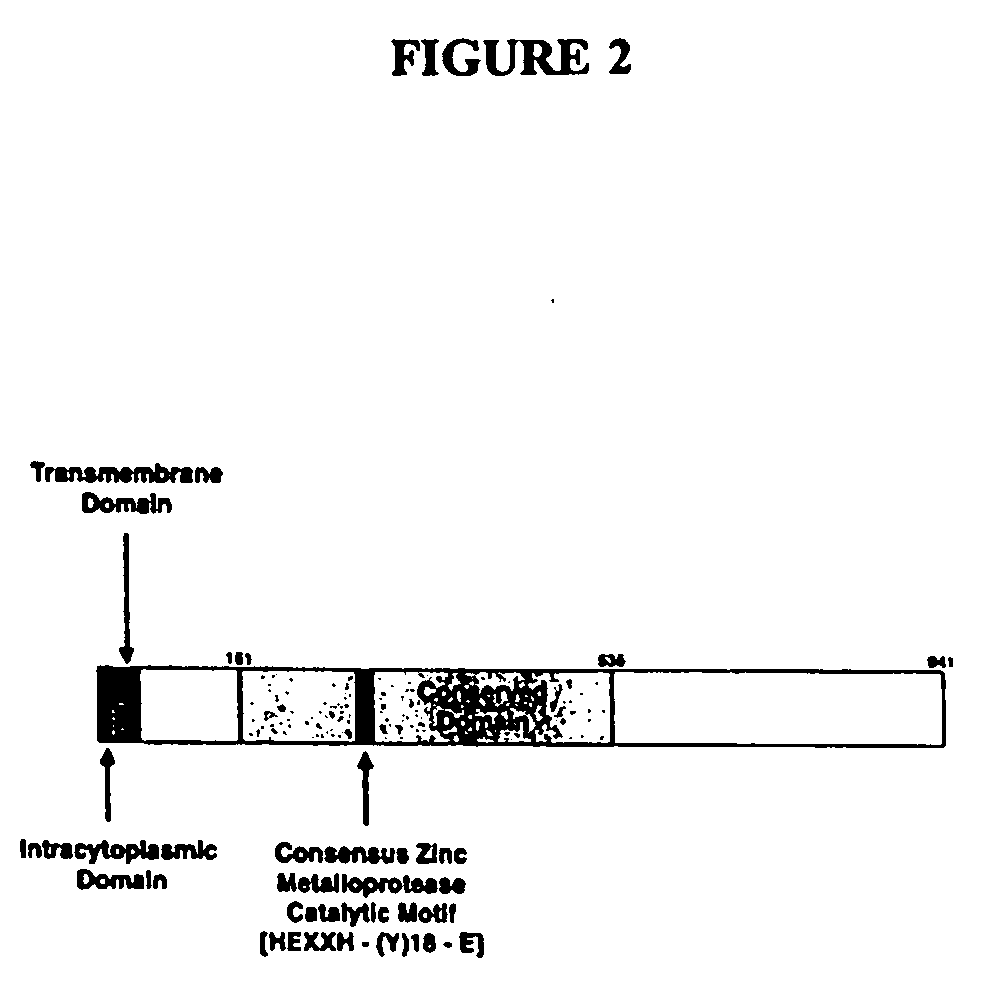
[0323] The complete cDNA corresponding to the human ARTS-1 transcription unit contains 4845 nucleotides and encodes an open reading frame of 2823 bp, as shown in FIG. 1 and set forth in SEQ ID NO:1. The first in-frame ATG codon, located at nucleotide 88, follows an in-frame stop codon, located at nucleotide 76, and matches the −3 and +4 nucleotides of the consensus Kozak sequence consistent with a strong initiator codon (aagatgg) (Kozak, J. Cell Biol, 108:229-241 [1989]). Sequence analysis revealed five potential N-glycosylation sites and a TAA stop codon, located at nucleotide 2911. The putative 3′ untranslated region contained a consensus polyadenylation site (AATAAA), located at nucleotides 4876 to 4800, which is 18 nucleotides upstream of a 27 nucleotide poly(A) tail. The 3′ untranslated region also included two ATTTA sites, located at nucleotides 3929 and 4457; this sites have been identified as an mRNA destabiliza...
example 3
ARTS-1 mRNA Expression Analysis
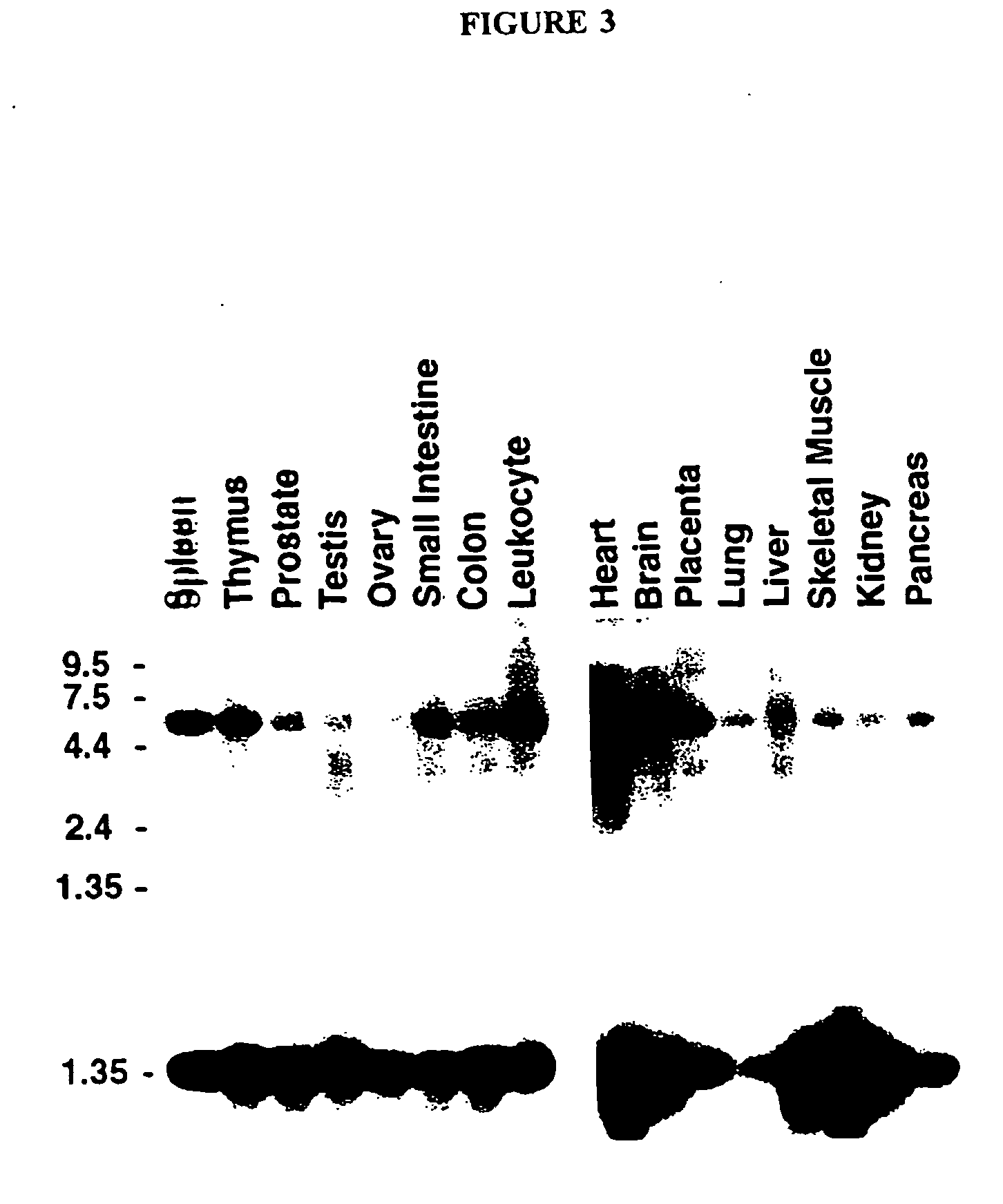
[0327] Following analysis of the ARTS-1 cDNA, the expression pattern of endogenous of ARTS-1 mRNA was investigated using a Northern immunoblotting protocol. RT-PCR was performed on human lung poly(A+) mRNA (Clontech) to generate the human ARTS-1 cDNA coding sequence utilizing the following primers:
(SEQ ID NO:5)5′-GCAAGAAGATGGTGTTTCTGCCCCTC-3′ (80-105)and(SEQ ID NO:6)5′-TTACATACGTTCAAGCTTTTCACT-3′ (2890-2913).
The full length ARTS-1 coding sequence amplified by these primers was cloned into the pTarget mammalian expression vector (Promega). The DNA sequence of this cloned open reading frame was obtained from both strands by automated fluorescent sequencing, as known in the art. There were no discrepancies between the sequence obtained from these two strands, nor from the sequence obtained from the PMA-stimulated NCI-H292 cell line cDNA library. A 32P-labelled cDNA probe, corresponding to the full length ARTS-1 coding sequence, was utilized as a probe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance at a wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com