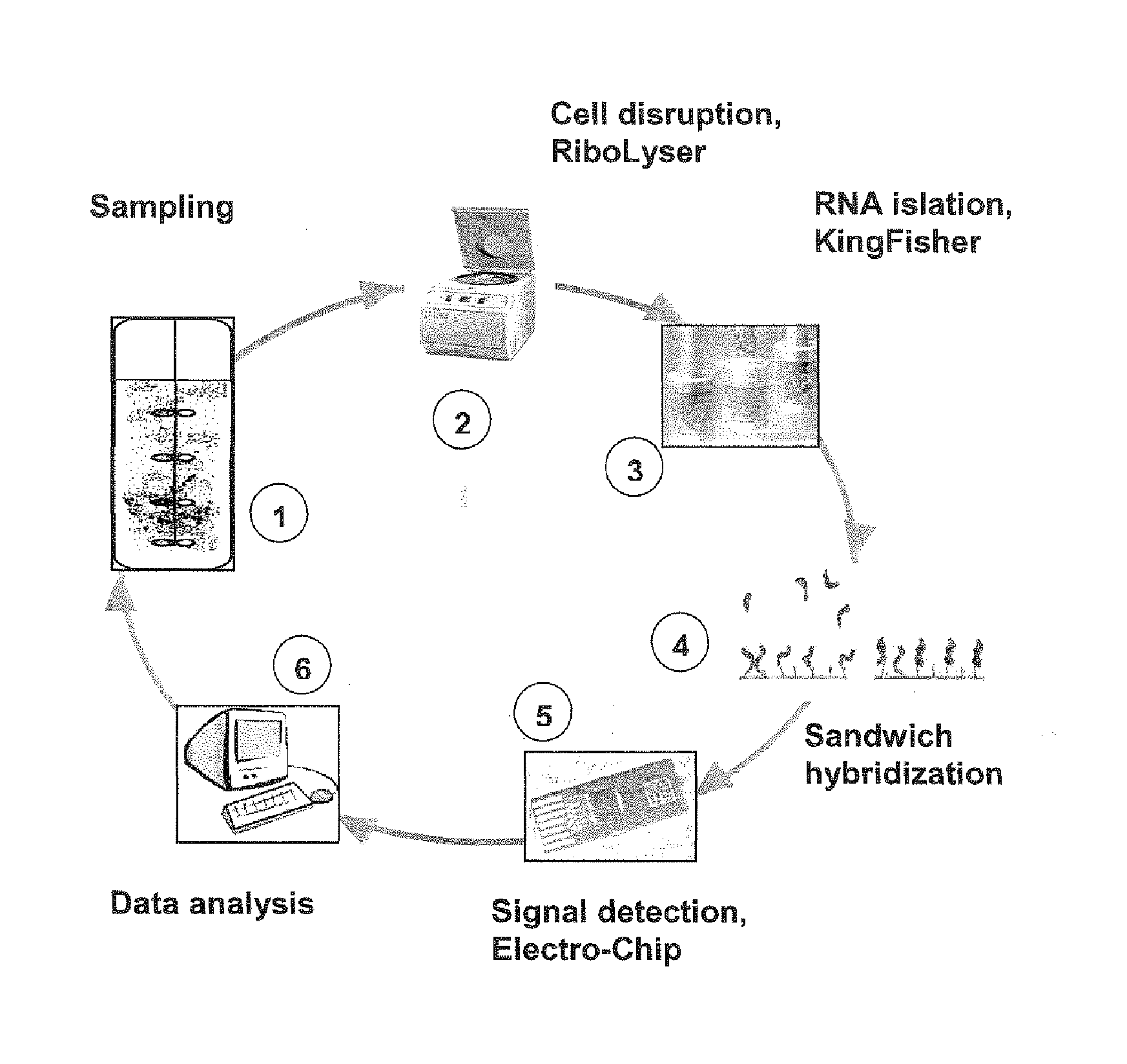
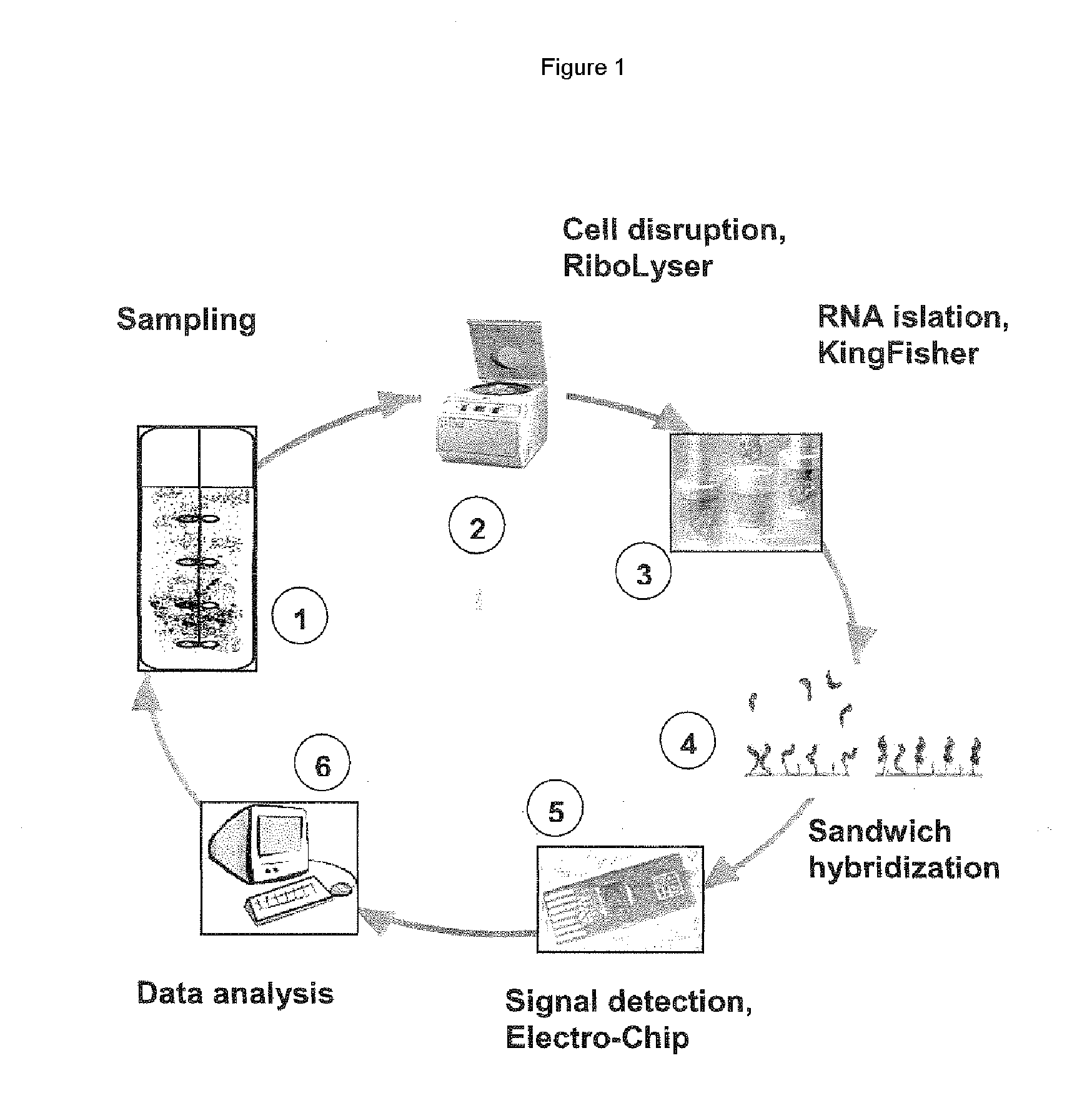
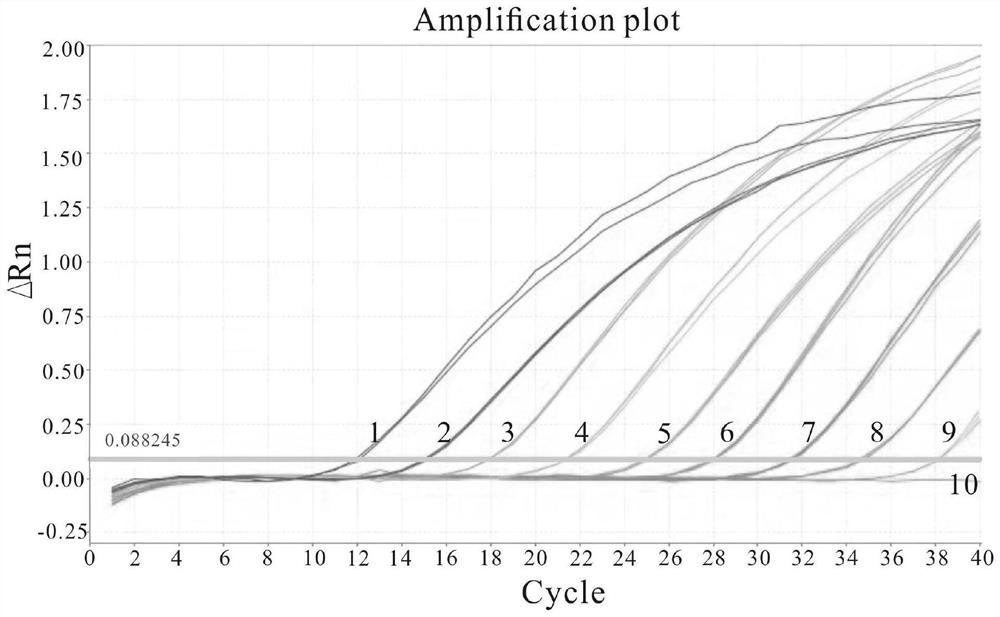
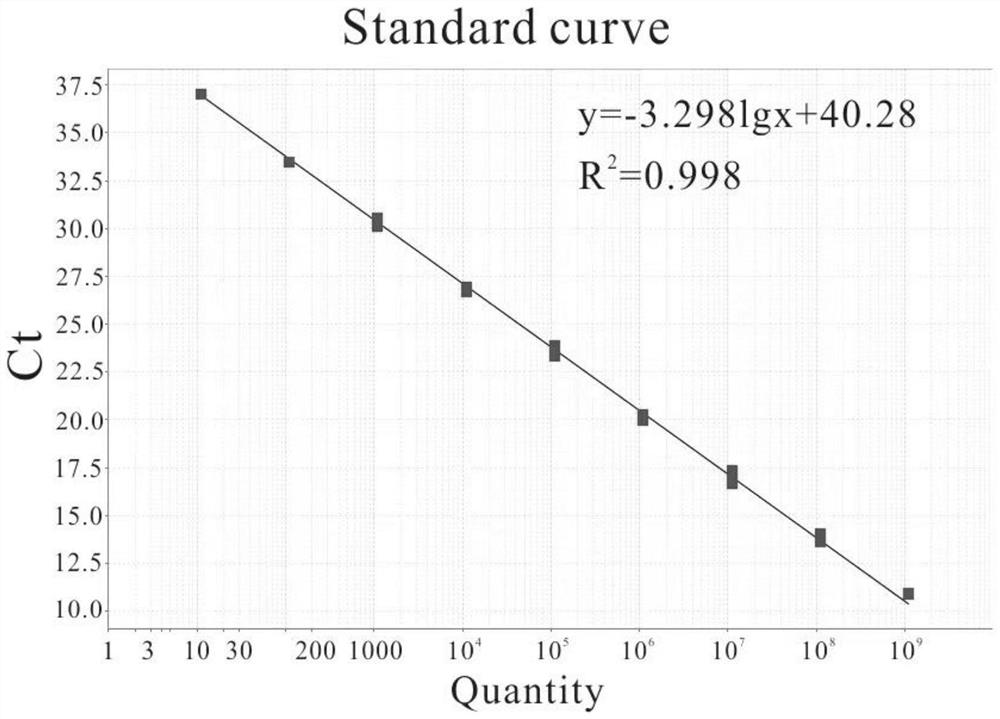
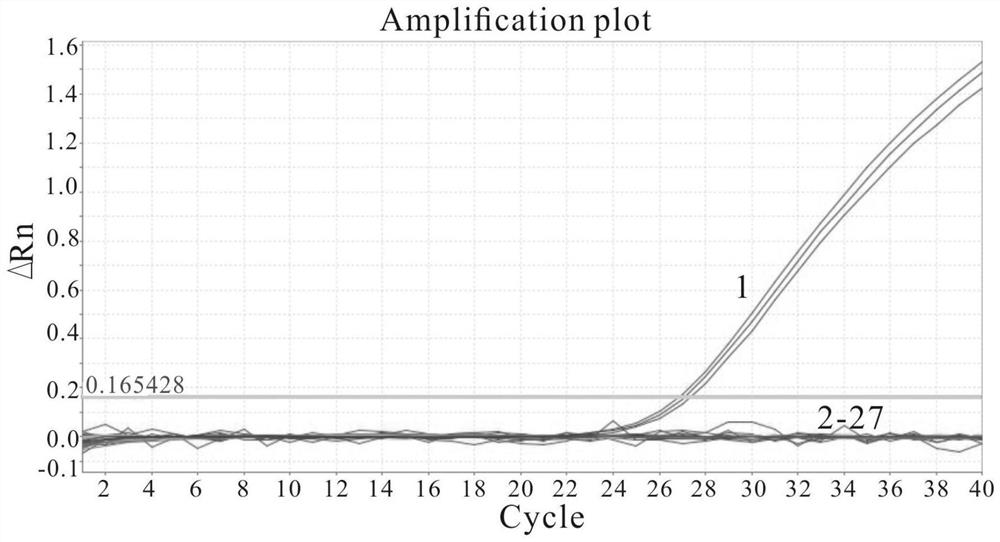
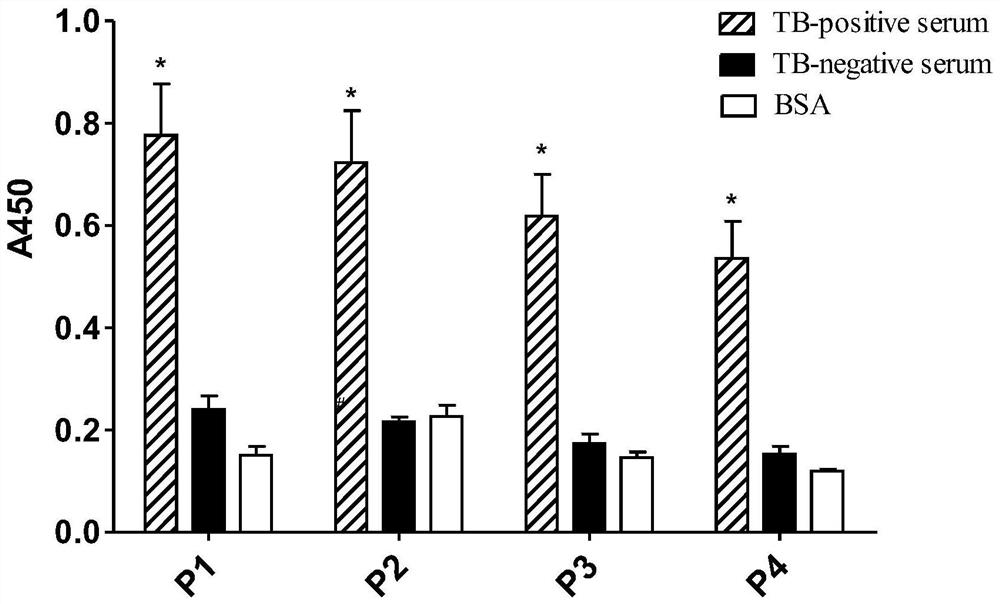
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Hypothetical protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biochemistry, a hypothetical protein is a protein whose existence has been predicted, but for which there is a lack of experimental evidence that it is expressed in vivo. Sequencing of several genomes has resulted in numerous predicted open reading frames to which functions cannot be readily assigned. These proteins, either orphan or conserved hypothetical proteins, make up ~ 20% to 40% of proteins encoded in each newly sequenced genome. Even when there is enough evidence that the product of the gene is expressed, by techniques such as microarray and mass-spectrometry, it is difficult to assign a function to it given its lack of identity to protein sequences with annotated biochemical function. Nowadays, most protein sequences are inferred from computational analysis of genomic DNA sequence. Hypothetical proteins are created by gene prediction software during genome analysis. When the bioinformatic tool used for the gene identification finds a large open reading frame without a characterised homologue in the protein database, it returns "hypothetical protein" as an annotation remark.
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
ActiveUS20060166277A1Diagnosing and effectively treatingSave maternalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPregnancyUdp glycosyltransferase
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1 anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Porphyromonas Gingivalis Polypeptides Useful in the Prevention of Periodontal Disease
The invention is directed to vaccine compositions and methods based on P. gingivalis proteins identified to be regulated by haem availability that can be used in the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease. In particular, two specific internalin-like P. gingivalis proteins, namely PG0350 and PG1374 involved in the internalization of P. gingivalis by host cells, the hypothetical protein, PG1019 purported to be a cell surface lipoprotein and the alkyl hydroperoxide reductase protein, PG0618 have been identified as useful targets for the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease.
Owner:ORAL HEALTH AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Protein of acinetobacter baumannii hypothetical protein A1S_1523 as well as preparation method and application of protein
ActiveCN104877019ADefend against deadly infectionElicit a protective immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantAmino acid
The invention relates to recombinant protein of A1S_1523 as well as a preparation method and application of the recombinant protein. The recombinant protein comprises A1S_1523 mature peptide, and an amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. The recombinant protein disclosed by the invention is high in expression quantity and convenient to separate and purify, is efficient and safe, can be directly matched with adjuvants for use, and can be used for preparing acinetobacter baumannii infection resistant subunit vaccines and related detection kits; proven by animal experiments, gene engineering recombinant monovalent subunit vaccines have good immune protective effects on acinetobacter baumannii infection resistance; and the recombinant protein can be used for laying a foundation for further researching combined vaccines and multi-subunit fusion vaccines, and can also play important roles in the development and application of prevention and treatment vaccines and diagnostic kits.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Malaria Vaccines
InactiveUS20120328645A1ConfidenceEfficient protective immunityProtozoa antigen ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsProtection sexProtective immunity
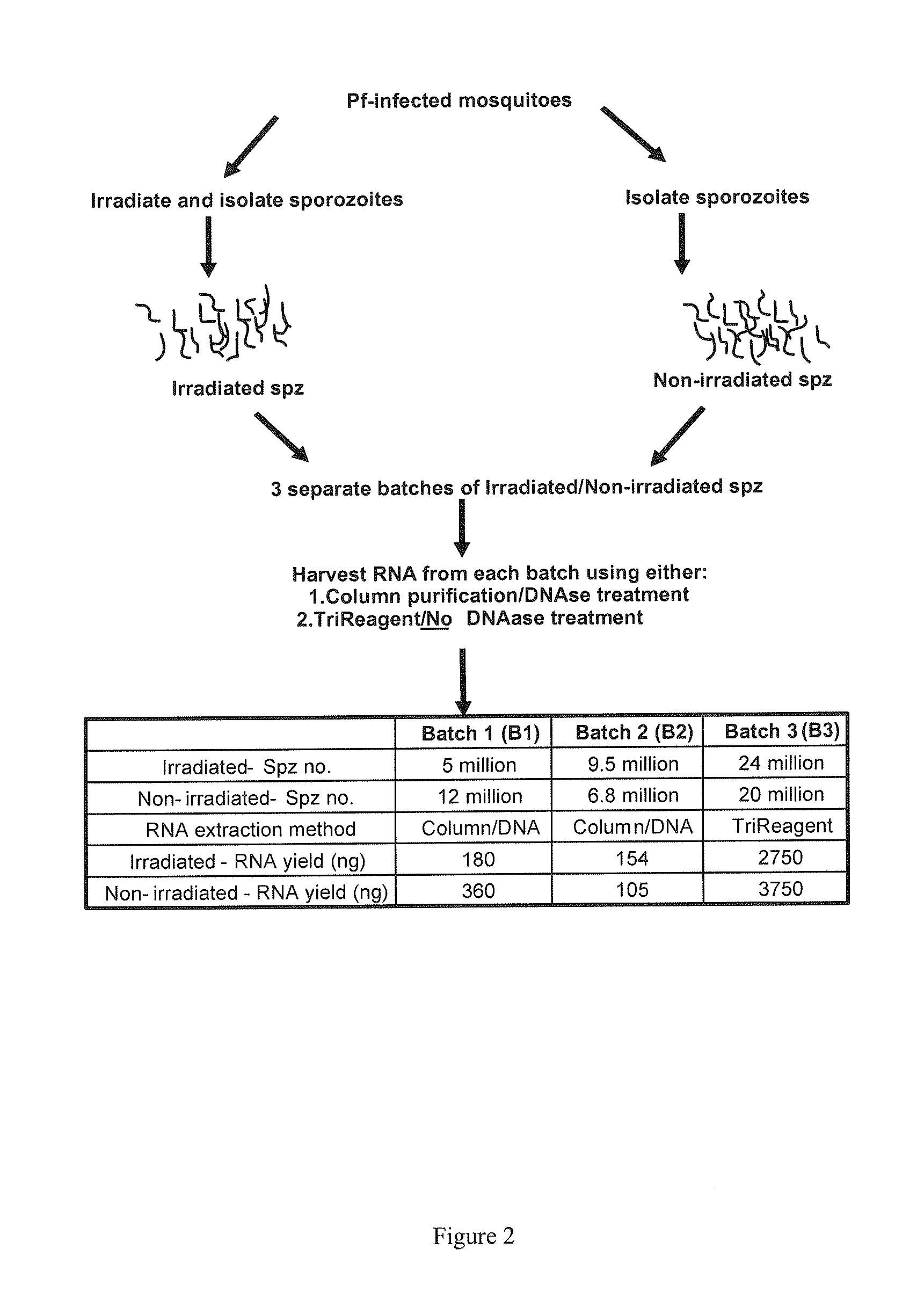
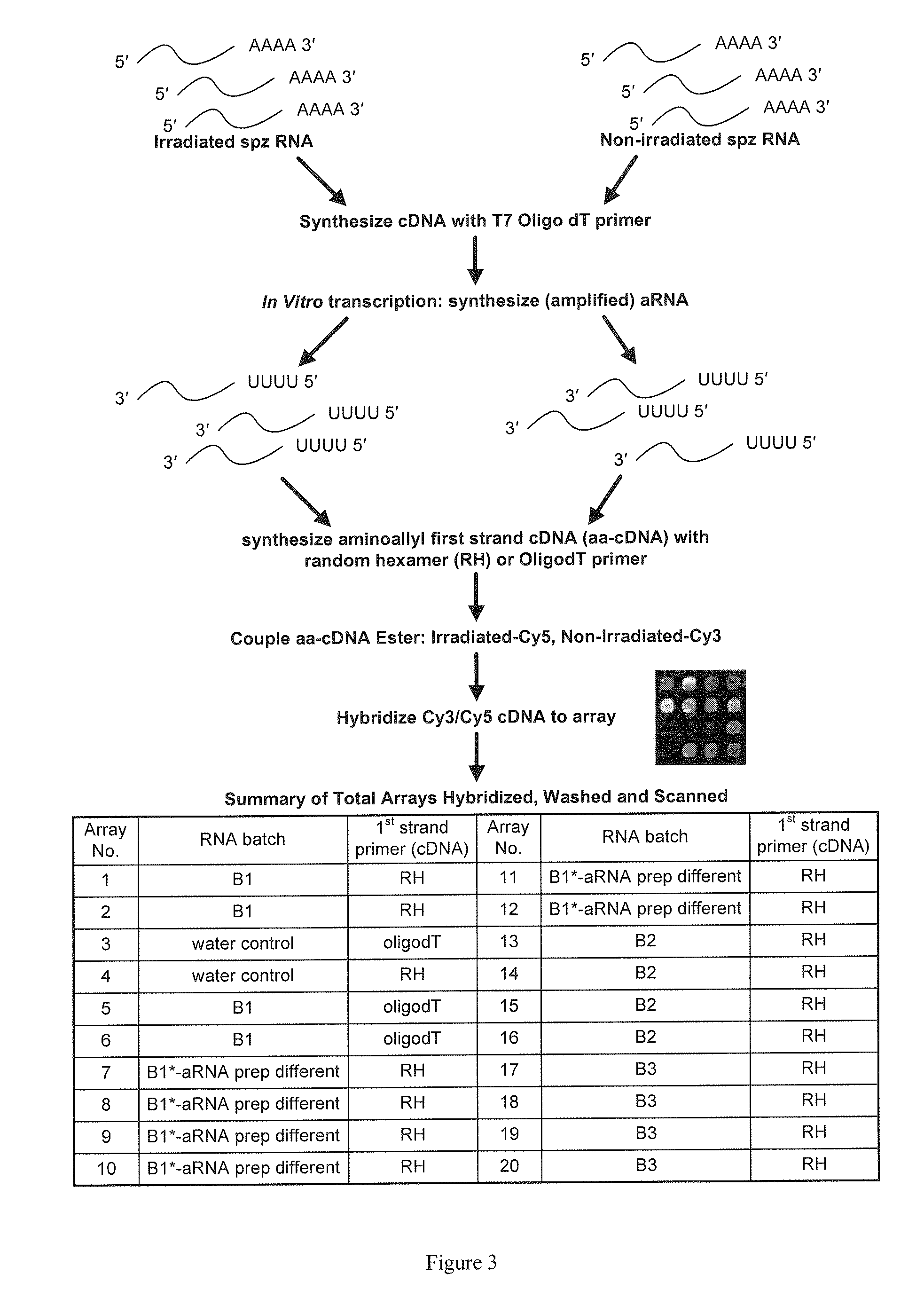
Transcript profiles for irradiated and non-irradiated P. falciparum sporozoites were compared in an attempt to identify transcripts that are reproducibly perturbed by irradiation. Four loci were identified with high confidence. Three of these transcripts were derived from 3 different known gene families, and the fourth from a gene encoding a conserved hypothetical protein of unknown function. All four loci are up-regulated in radiation attenuated sporozoites which have been shown to be very effective in establishing protective immunity against malaria. Up-regulation of these transcripts contributes directly to protective immunity. The polypeptides encoded by the transcripts, individually and / or in combination, are incorporated into subunit vaccines, useful for the prevention of malaria and the establishment of protective immunity against malaria.
Owner:SANARIA INC
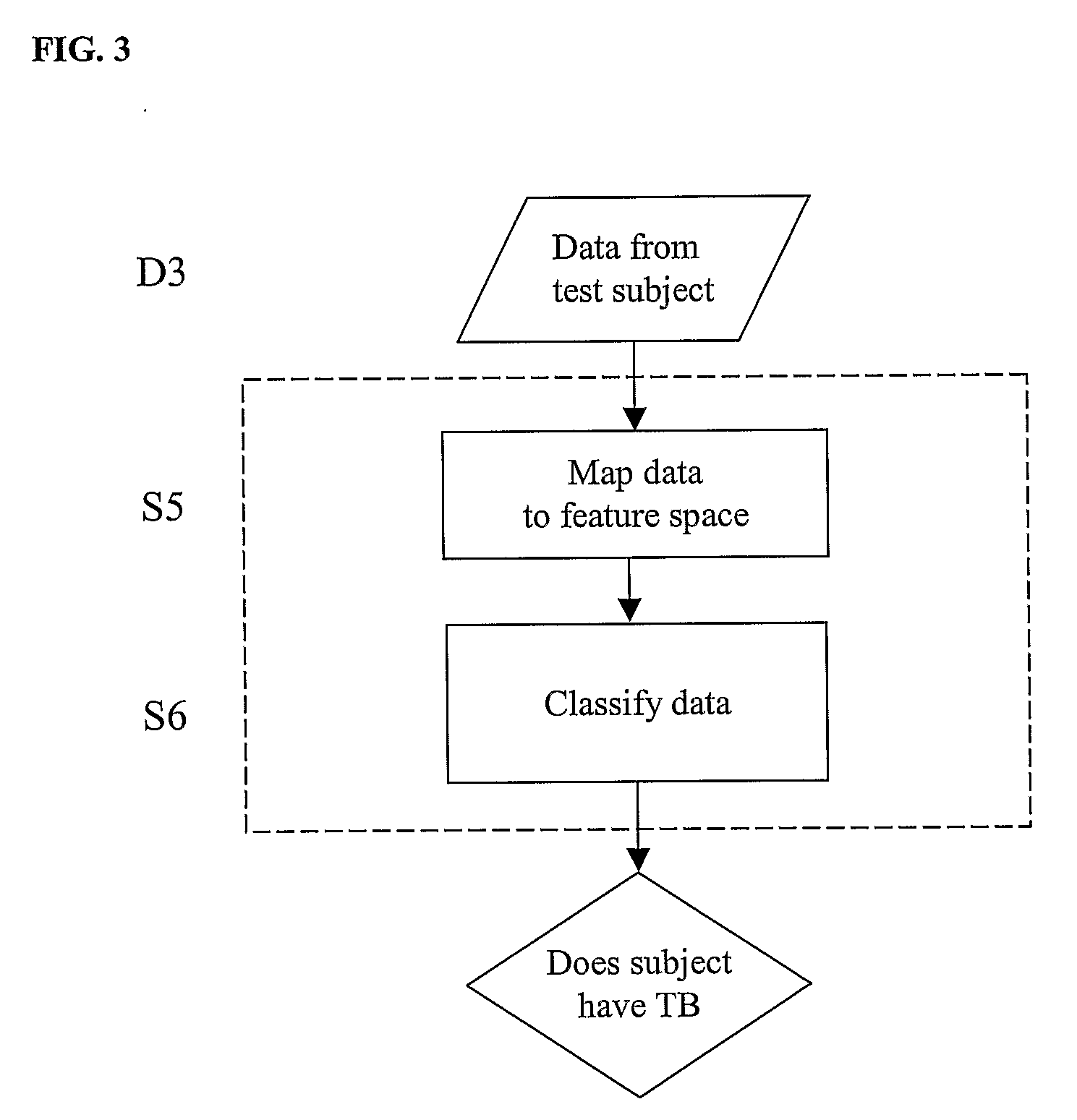
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
InactiveUS20090104602A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSerum protein albuminApolipoproteins E
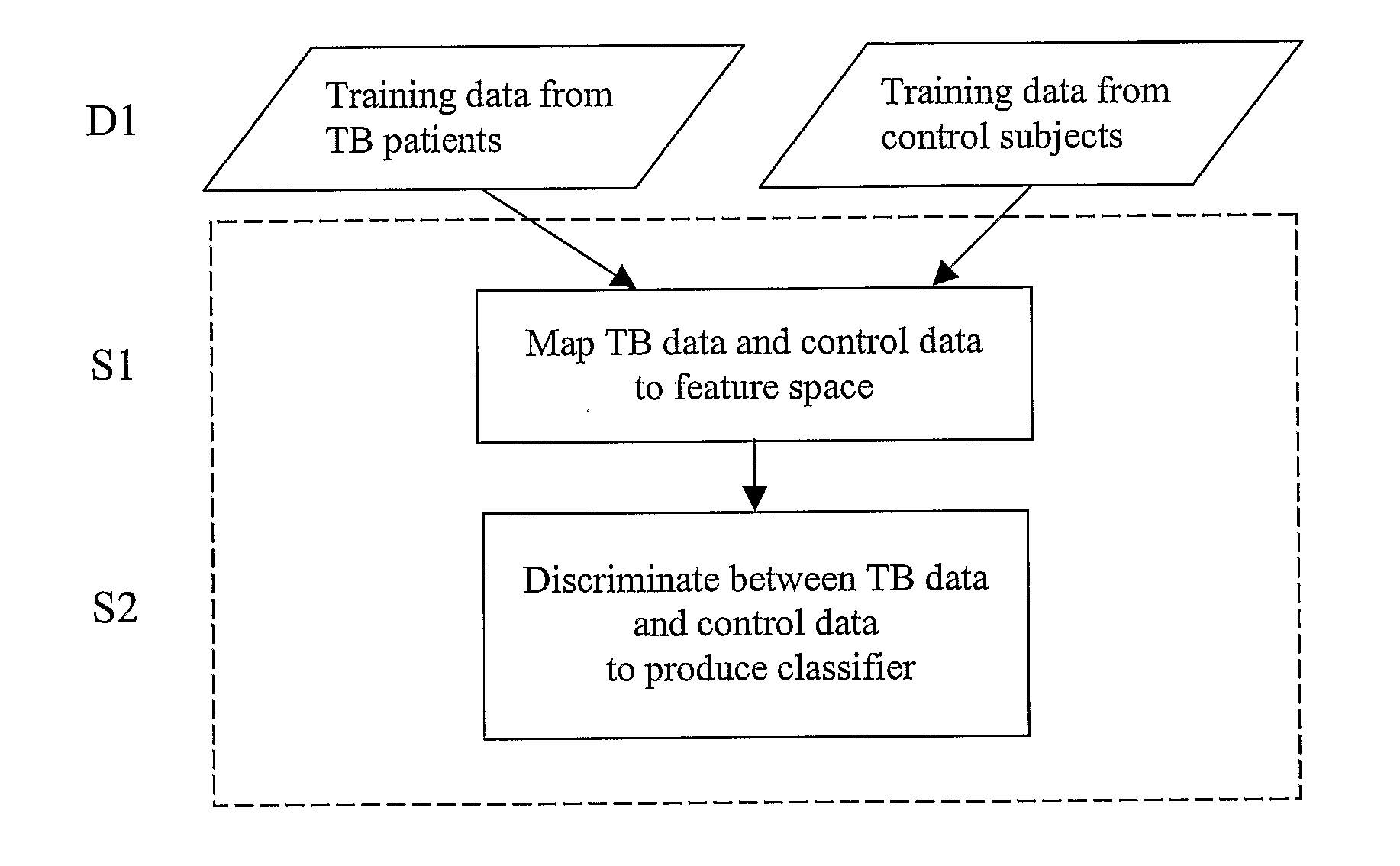
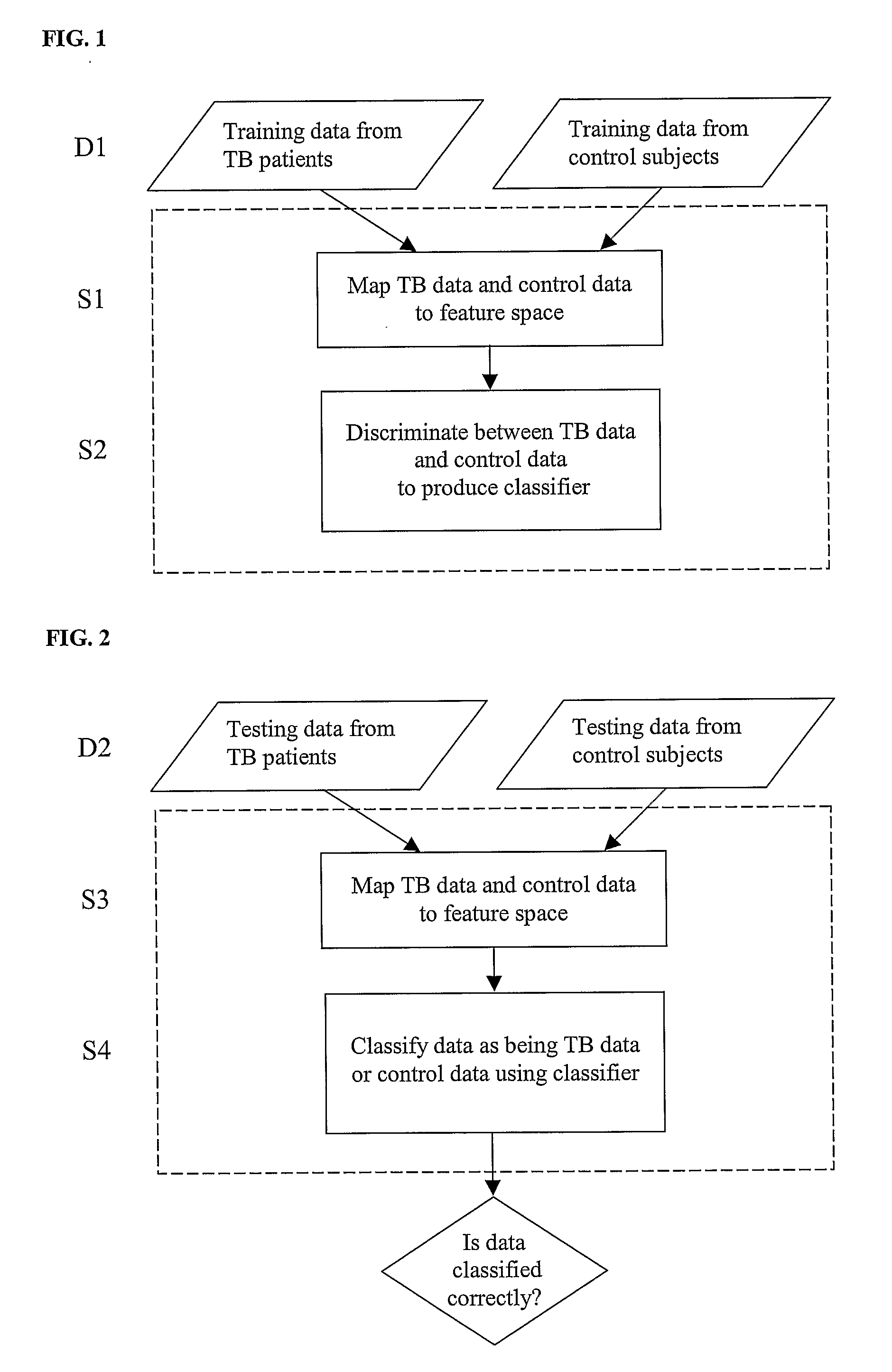
The invention provides a method of diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) in a test subject, said method comprising: (i) providing expression data of two or more markers in a subject, wherein at least two of said markers are selected from transthyretin, neopterin, C-reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid A (SAA), serum albumin, apoliopoprotein-A1 (Apo-A1), apolipoprotein-A2 (Apo-A2), hemoglobin beta, haptoglobin protein, DEP domain protein, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein (A2GL) and hypothetical protein DFKZp667I032; and (ii) comparing said expression data to expression data of said marker from a group of control subjects, wherein said control subjects comprise patients suffering from inflammatory conditions other than TB, thereby determining whether or not said test subject has TB.
Owner:FERNANDEZ REYES DELMIRO +3
Porphyromonas gingivalis polypeptides useful in the prevention of periodontal disease
InactiveUS20130236488A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPorphyromonas gingivalisHeme
The invention is directed to vaccine compositions and methods based on P. gingivalis proteins identified to be regulated by haem availability that can be used in the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease. In particular, two specific internalin-like P. gingivalis proteins, namely PG0350 and PG1374 involved in the internalization of P. gingivalis by host cells, the hypothetical protein, PG1019 purported to be a cell surface lipoprotein and the alkyl hydroperoxide reductase protein, PG0618 have been identified as useful targets for the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease.
Owner:ORAL HEALTH AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
InactiveCN101299962AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAlpha defensinInsulin-like growth factor-binding protein
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1- anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
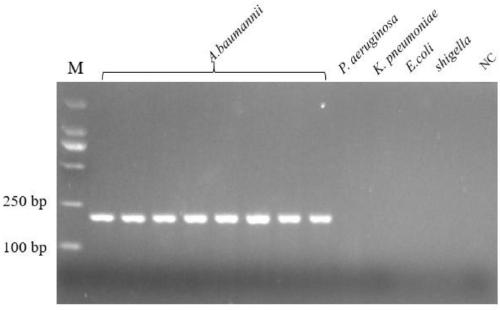
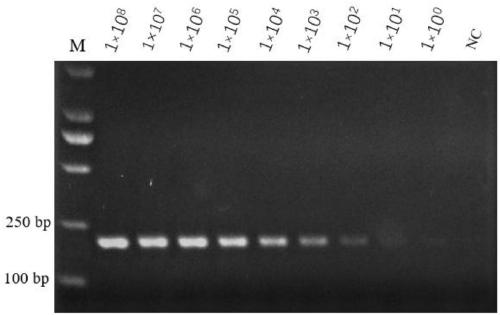
Specific gene of Acinetobacter baumannii and primer and application thereof
ActiveCN109266658AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesLoop-mediated isothermal amplificationAcinetobacter baumannii
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, provided are a specific gene of Acinetobacter baumannii and primers and applications thereof, the specific gene is hypothetical protein, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:5, and the PCR amplification primer pair is designed, the upstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the downstream primer is shown as SEQID NO:2; loop-mediated isothermal amplification primers, outbound primers as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2, and inbound primers as shown in SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4; the primers were used todetect Acinetobacter baumannii by PCR or loop-mediated isothermal amplification. The method has the advantages of accurate detection of environmental samples, convenience, good specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
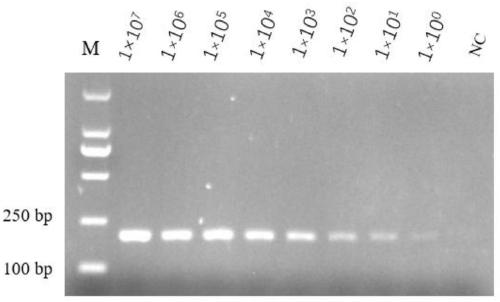
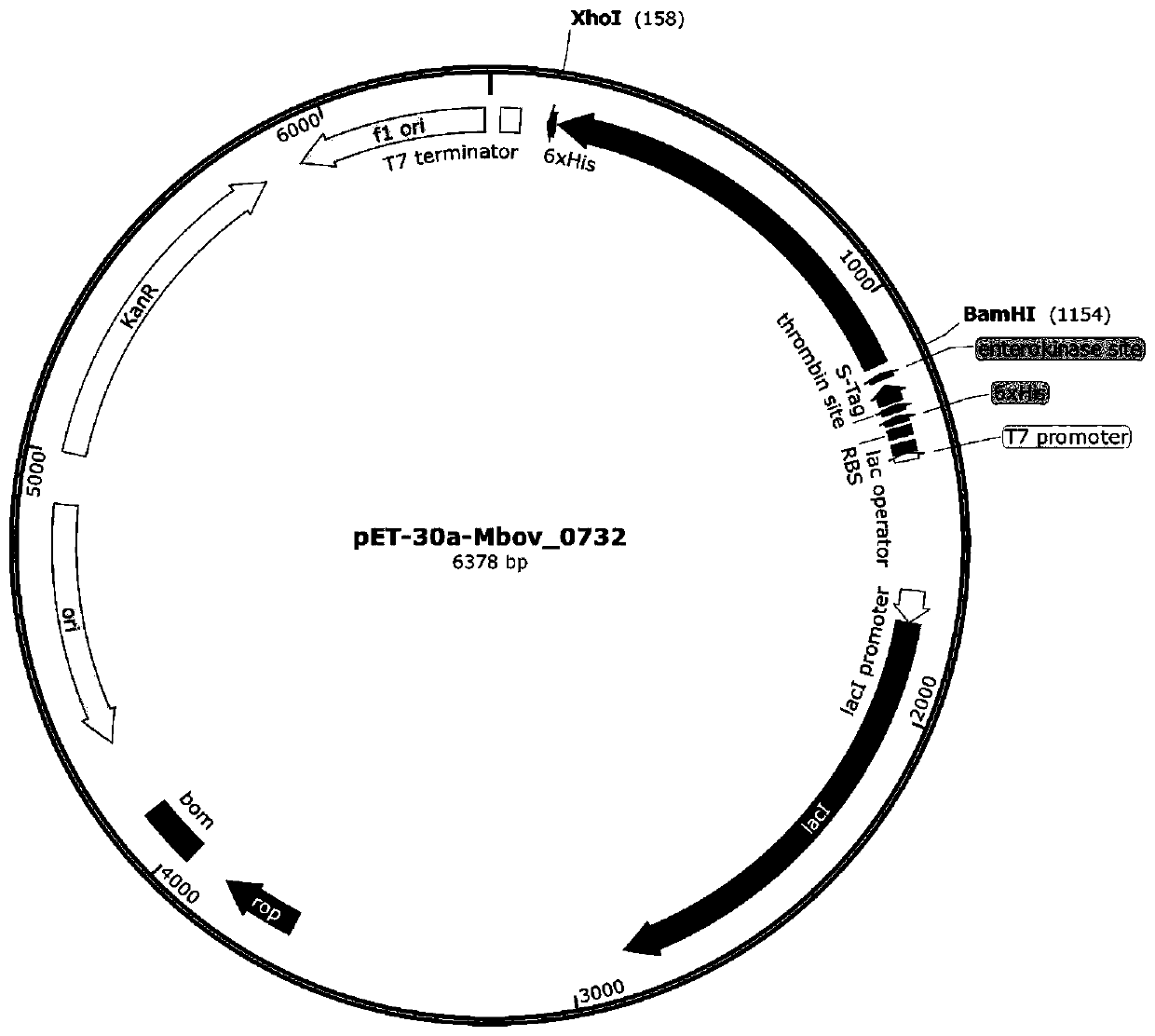
Bovine mycoplasma hypothetical protein MbovP732 and application thereof
InactiveCN110483625AValid differential diagnosisBacteriaImmunoglobulins against bacteriaNucleotide sequencingFhit gene
The invention discloses a bovine mycoplasma hypothetical protein MbovP732 and application thereof. The bovine mycoplasma hypothetical protein MbovP732 has an amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:1, and a gene encoding the protein has a nucleotide sequence as shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:2. The bovine mycoplasma hypothetical protein MbovP732 has reactogenicity and immunogenicity, can specifically react with bovine mycoplasma wild strains, and cannot react with vaccine strains, therefore, the bovine mycoplasma hypothetical protein MbovP732 can be used for distinguishing infection of the bovine mycoplasma wild strains from immunization of the vaccine strains.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Porphyromonas gingivalis polypeptides useful in the prevention of periodontal disease
InactiveUS8916166B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPorphyromonas gingivalisHeme
The invention is directed to vaccine compositions and methods based on P. gingivalis proteins identified to be regulated by haem availability that can be used in the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease. In particular, two specific internalin-like P. gingivalis proteins, namely PG0350 and PG1374 involved in the internalization of P. gingivalis by host cells, the hypothetical protein, PG1019 purported to be a cell surface lipoprotein and the alkyl hydroperoxide reductase protein, PG0618 have been identified as useful targets for the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease.
Owner:ORAL HEALTH AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Primers for specific gene of Escherichia coli and detection method of Escherichia coli
InactiveCN110229916AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention discloses a method for detecting Escherichia coli on basis of a specific gene of Escherichia coli. The specific gene of Escherichia coli is a hypothetical protein gene which has been registered in Genbank under the registration number 13702648; the specific gene widely exists in Escherichia coli, and has no obvious similarity with other species; and the specific gene has the characteristics of intraspecific commonality and interspecific specificity. Four primers, including a pair of external primers B3 and F3 as well as a pair of internal primers BIP and FIP, are designed on basis of the gene; and then, the primers are applied in loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), and the external primers B3 and F3 are further applied in polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The nucleotide sequence of the primers is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4. Identification systems of two kinds of Escherichia coli, namely a PCR reaction system and a LAMP reaction system, are established according to the primers involved; and thus, the identification systems have the characteristics of being good in specificity, high in sensitivity, rapid and reliable indetection result as well as easy to operate. The detection method of Escherichia coli is used for detecting Escherichia coli in water, foods, beverages and cosmetics.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Glycoprotein elicitor of magnaporthe grisea in rice leaves and its purification method
InactiveCN1721433AEasy to trainOvercome expensivePeptide preparation methodsBacteria peptidesPurification methodsOpen reading frame
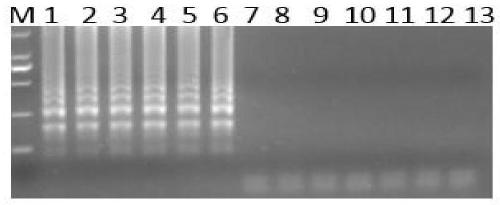
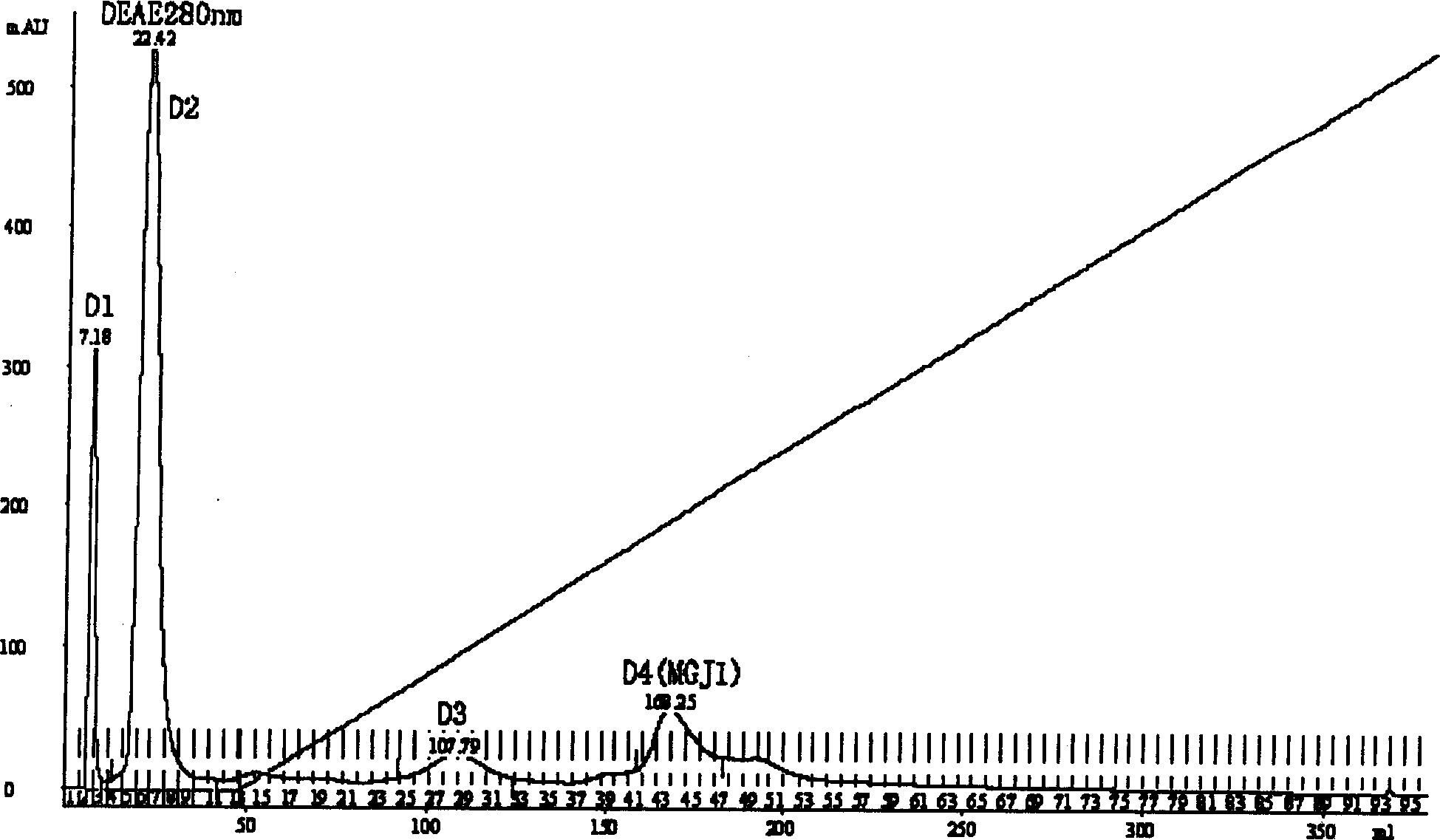
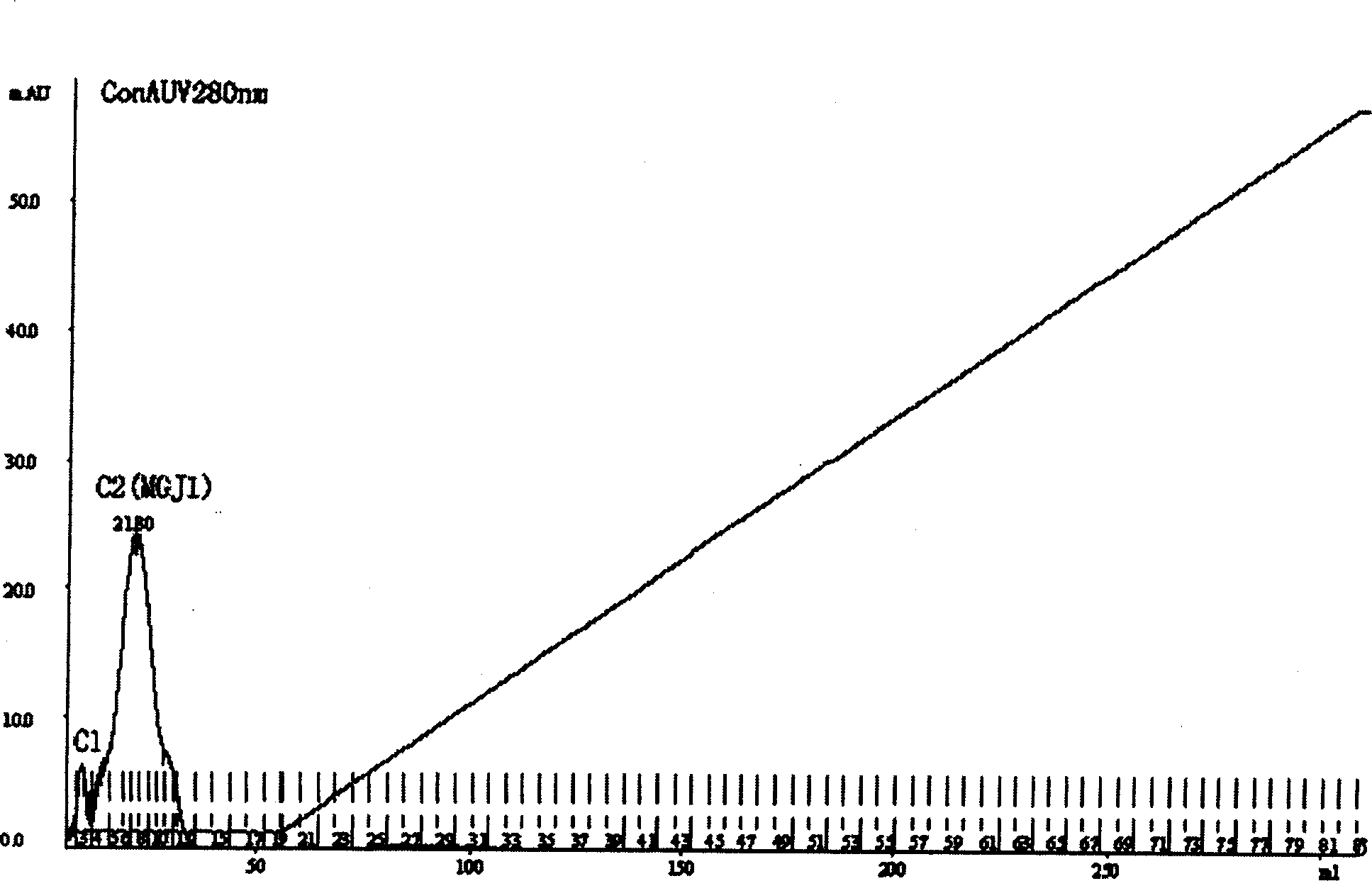
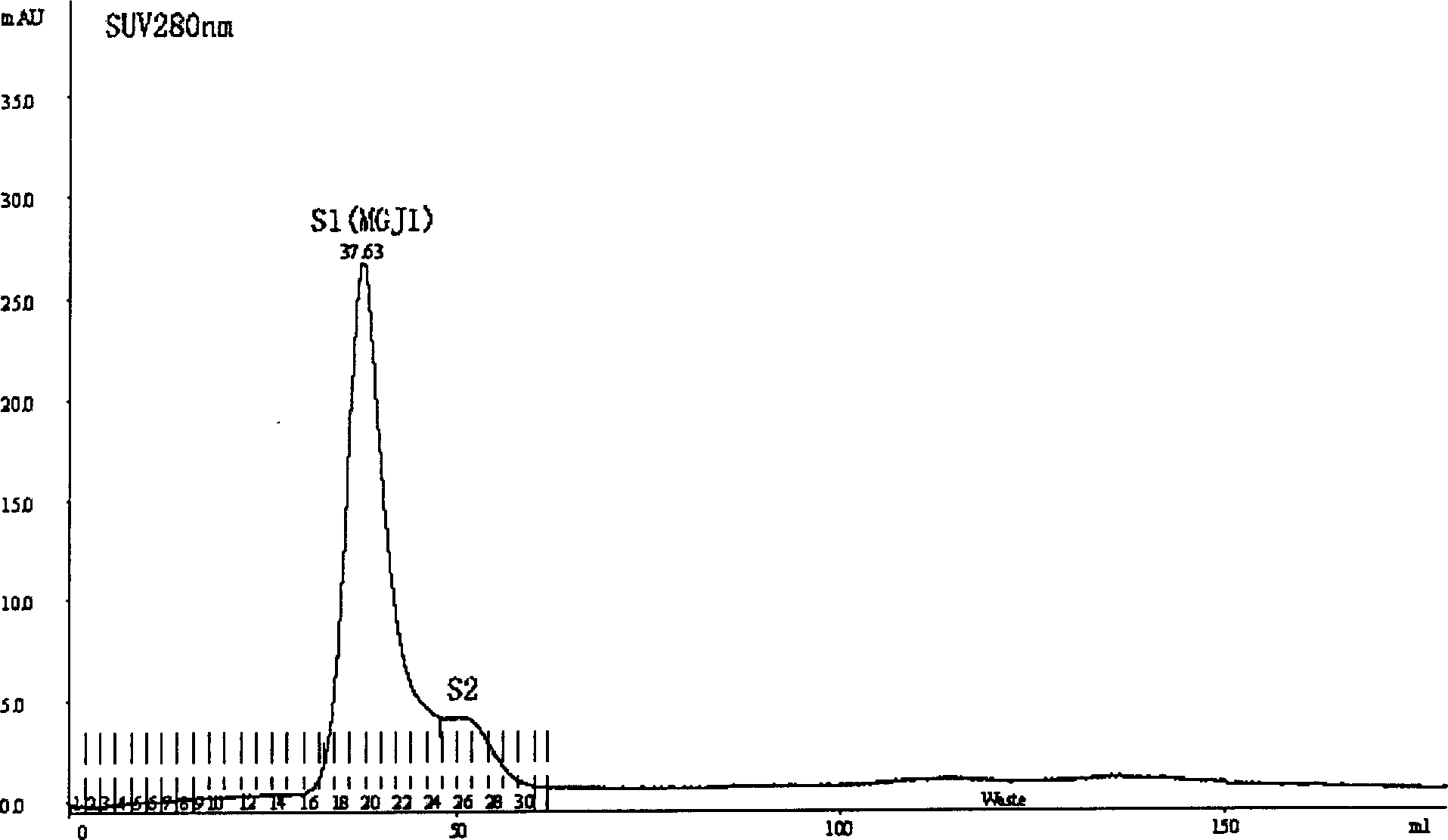
The present invention first obtains coarse exciton with rice blast germ mycelium as material and through culturing, freezing-thawing, homogenating, centrifuging and PM-10 membrance ultrafiltering, and then obtain the new rice blast germ glucoprotein exciton through further freezing-thawing and serial chromatographic purifications. The rice blast germ glucoprotein exciton has molecular weight 49.08 kDa, isoelectric point 6.01 and silver staining electrophoresis purity. Mass spectroscopic identification shows that the exciton is rice blast germ MG05155.4 open reading frame coded hypothetical protein MG05155.4. The exciton has stable property, relatively high induction on Phe deaminase activity in non-compatible interactive rice line and lowest effective concentration of 1.5 nmol / L for inducing rice peroxidase. The present invention has excellent application foreground in the biological prevention and control of rice blast.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nucleic acid-binding chips for the detection of phosphate deficiency conditions in the framework of bioprocess monitoring
InactiveUS20070281312A1Reliable indicationImprove readabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhosphoric acidPhosphatase I
The present application relates to nucleic acid-binding chips for monitoring bioprocesses, especially for detecting phosphate deficiency conditions. Said chips support probes for at least three of the following 47 genes: yhcR, tatCD, ctaC, gene for a putative acetoin reductase, spoIIGa, nasE, pstA, spoIIAA, gene for a hypothetical protein, yhbD, cotE, gene for a conserved hypothetical protein, yurl, spoVID, gene for a putative aromatic-specific dioxygenase, yhbE, gene for a putative benzoate transport protein, pstBB, spoIIIAH, gene for a hypothetical protein, spoIIQ, spoIIIAG, yvmA, gene for a putative ribonuclease, dhaS, yrbE, gene for a putative decarboxylase / dehydratase, htpG, yfkH, spoIIAB, spoIIIAF, alsD, gdh, yfkN, pstC, yfmQ, pstBA, dhaS homolog, gene for a putative phosphatase, phy, cypX, alsS, phoD, pstS, phoB, yvnA, yvmC, the total number of phosphate metabolism-specific different probes on the nucleic acid-binding chips not exceeding 100. The present application further relates to the use of corresponding gene probes, in particular on such chips, and to corresponding methods and possible uses.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
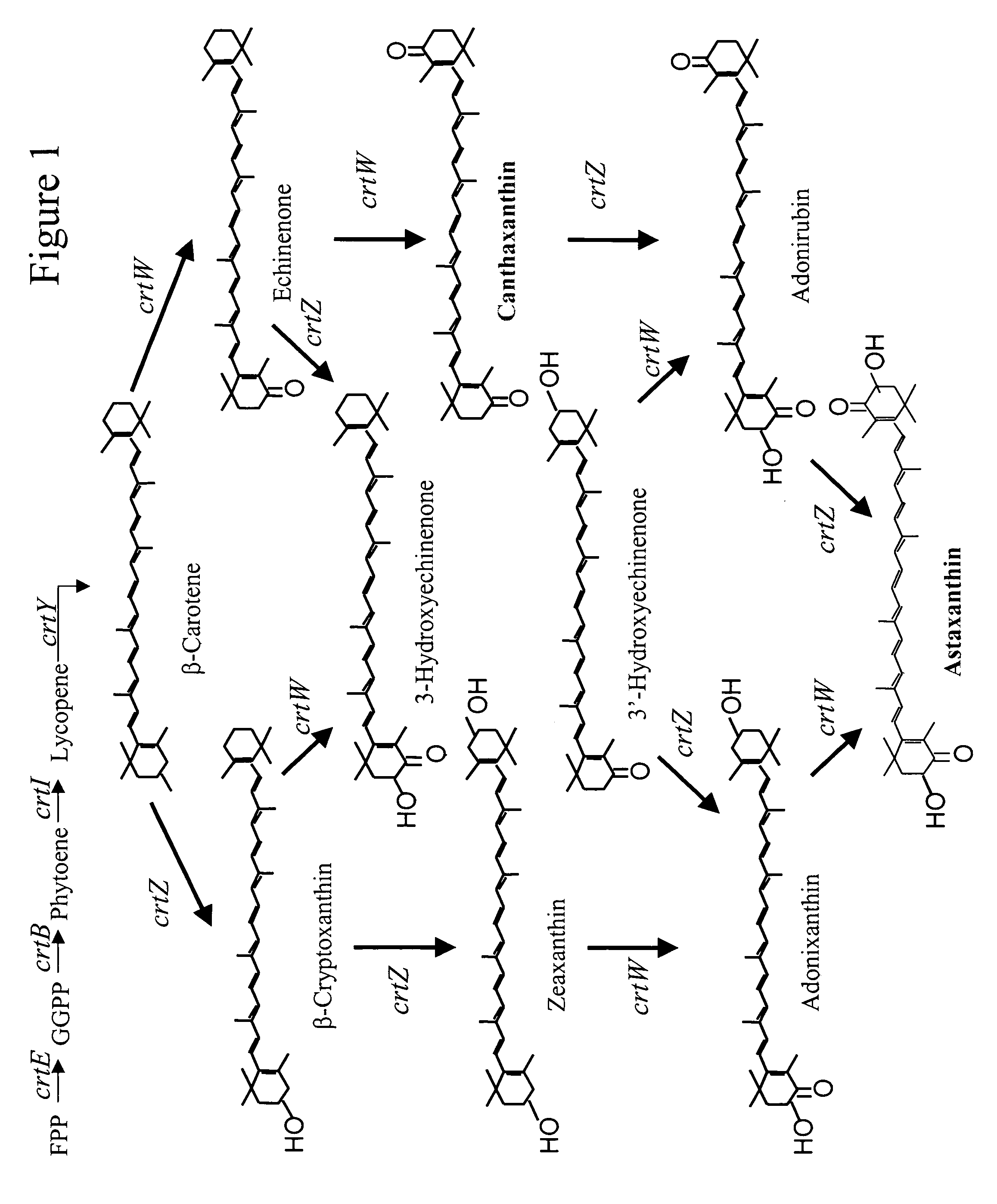
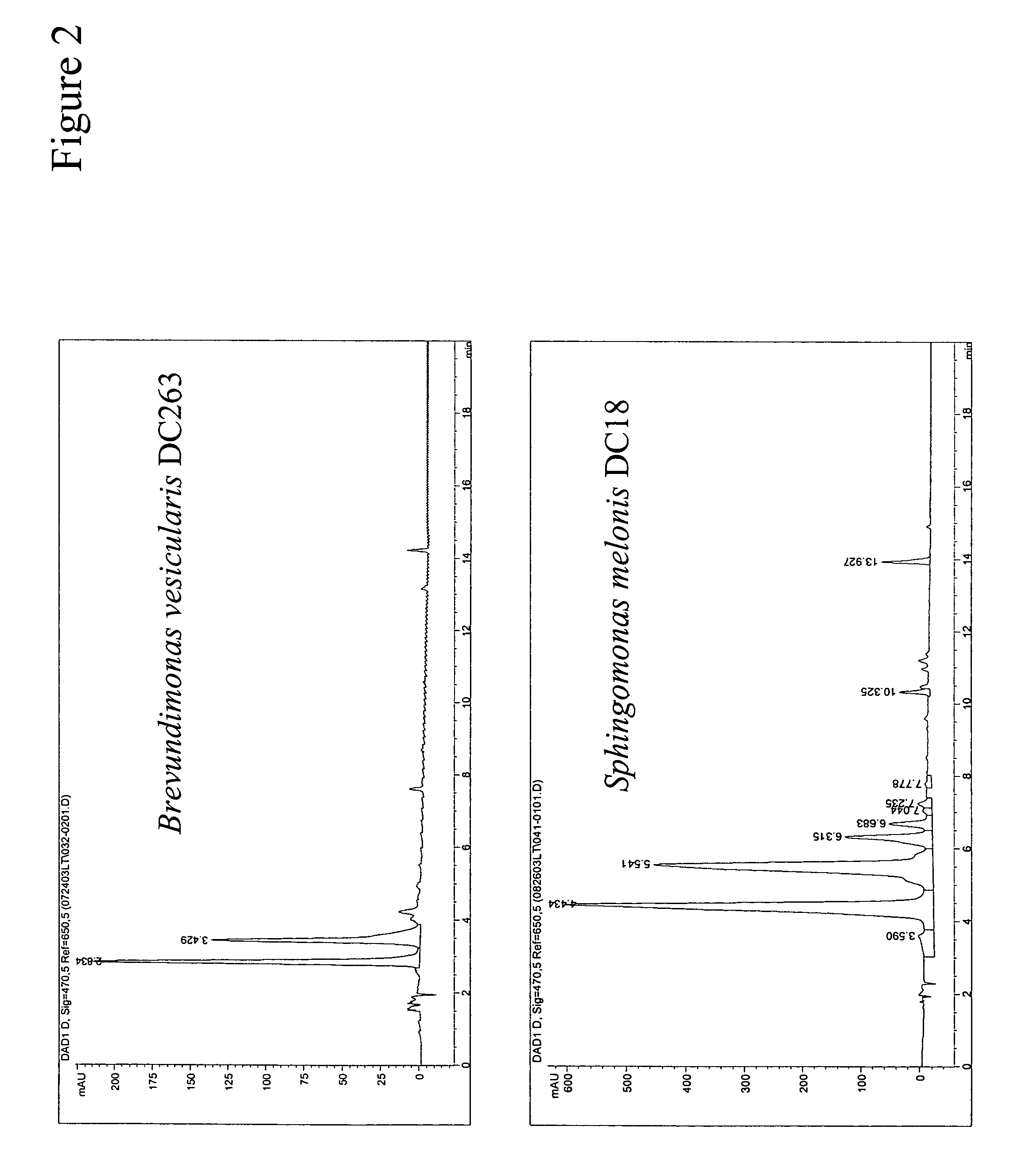
Carotenoid hydroxylase enzymes
A novel CrtZ carotenoid hydroxylase, isolated from Brevundimonas vesicularis DC263, is provided that is useful for the production of hydroxylated carotenoids. Additionally, a previously identified hypothetical protein from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans has found to have carotenoid hydroxylase activity. Both hydroxylase genes exhibit low homology in comparison to other CrtZ hydroxylases previously reported. Expression of the hydroxylases in heterologous host cells enabled production of hydroxylated carotenoids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Fasciola hepatic fasciola hypothetical protein gene and colloidal gold immunochromatography test paper
The invention discloses a hypothetical protein gene of fasciola hepatica. Meanwhile, the invention further provides colloidal gold immunochromatography test paper prepared from the hypothetical protein gene of the fasciola hepatica. A fasciola hepatica infection detection colloidal gold test paper strip prepared by the hypothetical protein gene of the fasciola hepatica, the test paper has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience, easiness in operation, high sensitivity, high specificity, short time and the like and clear and visible result and is suitable for clinical field detection andlarge-scale epidemiological investigation.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for identification of novel virulence associated genes
InactiveUS20070160986A1High proportionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismOpen reading frame
In a method of identifying novel virulence associated genetic information about a pathogenic microorganism including information about open reading frames (ORFs) having (a) assigned functions, (b) no assigned functions, (c) showing similarity with hypothetical proteins from other species is provided. An obligate human parasite evolutionary deprived of a substantial portion of its coding capacity is selected and genetic information about it is provided. By comparing the genetic information at least one open reading frame (ORF) common to the microorganism and the human parasite is identified, which codes for a protein (c) showing similarity with a hypothetical protein from other microorganism species. By introduction of a mutation in the ORF a mutated ORF is produced. The pathogenicity of the mutated pathogenic organism is assessed and compared with that of the corresponding non-mutated pathogenic organism.
Owner:INNATE PHARM AB
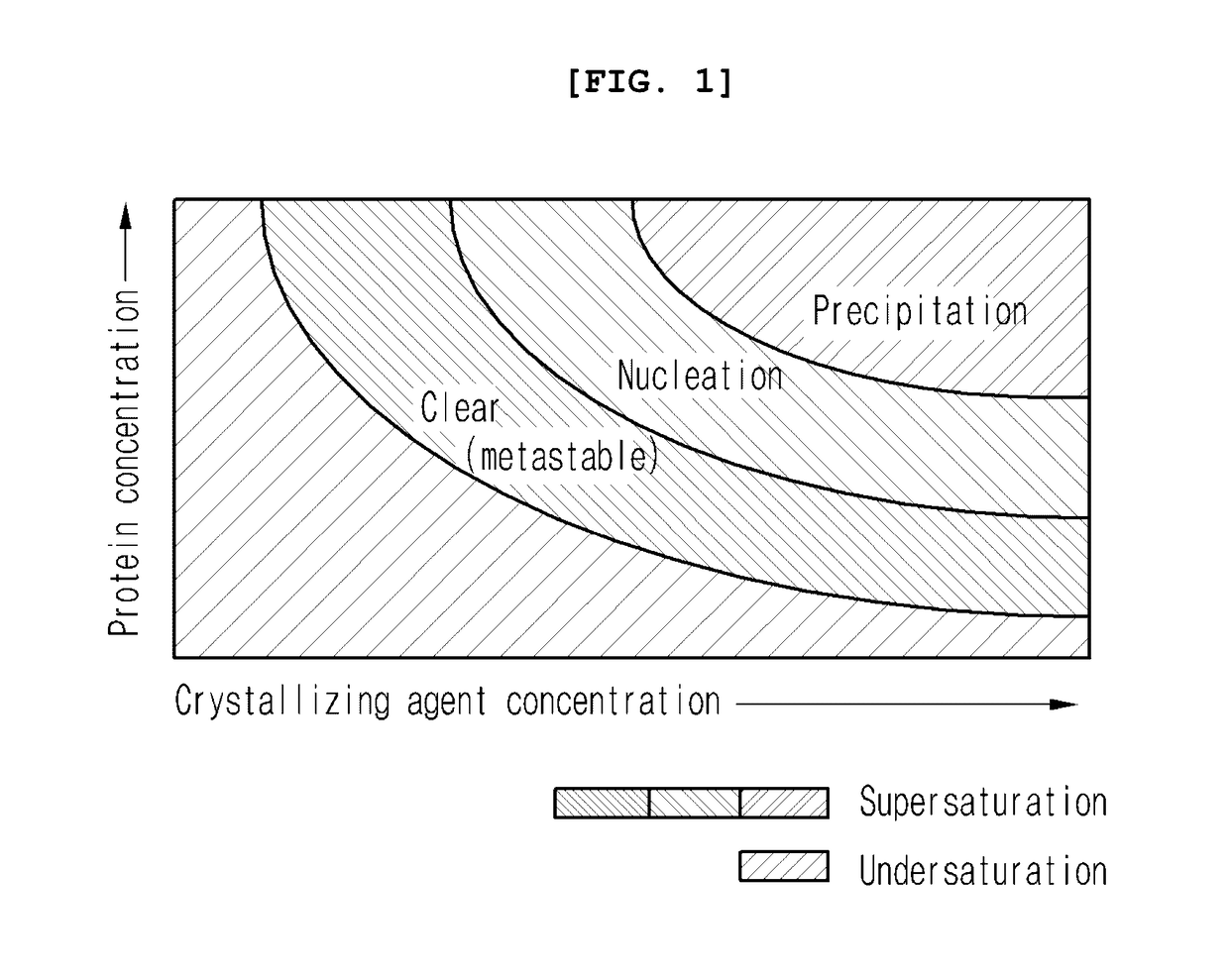
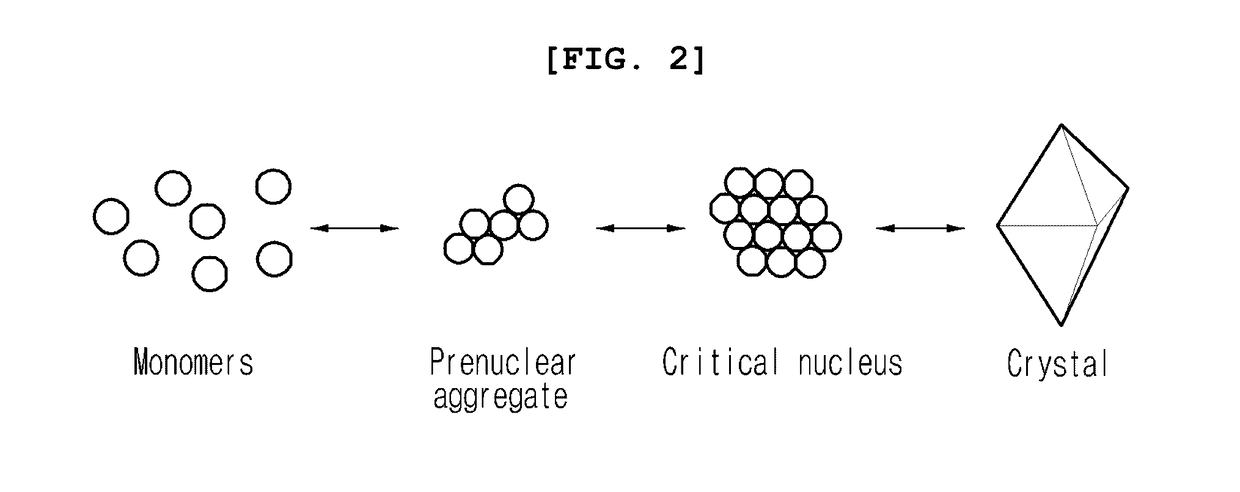
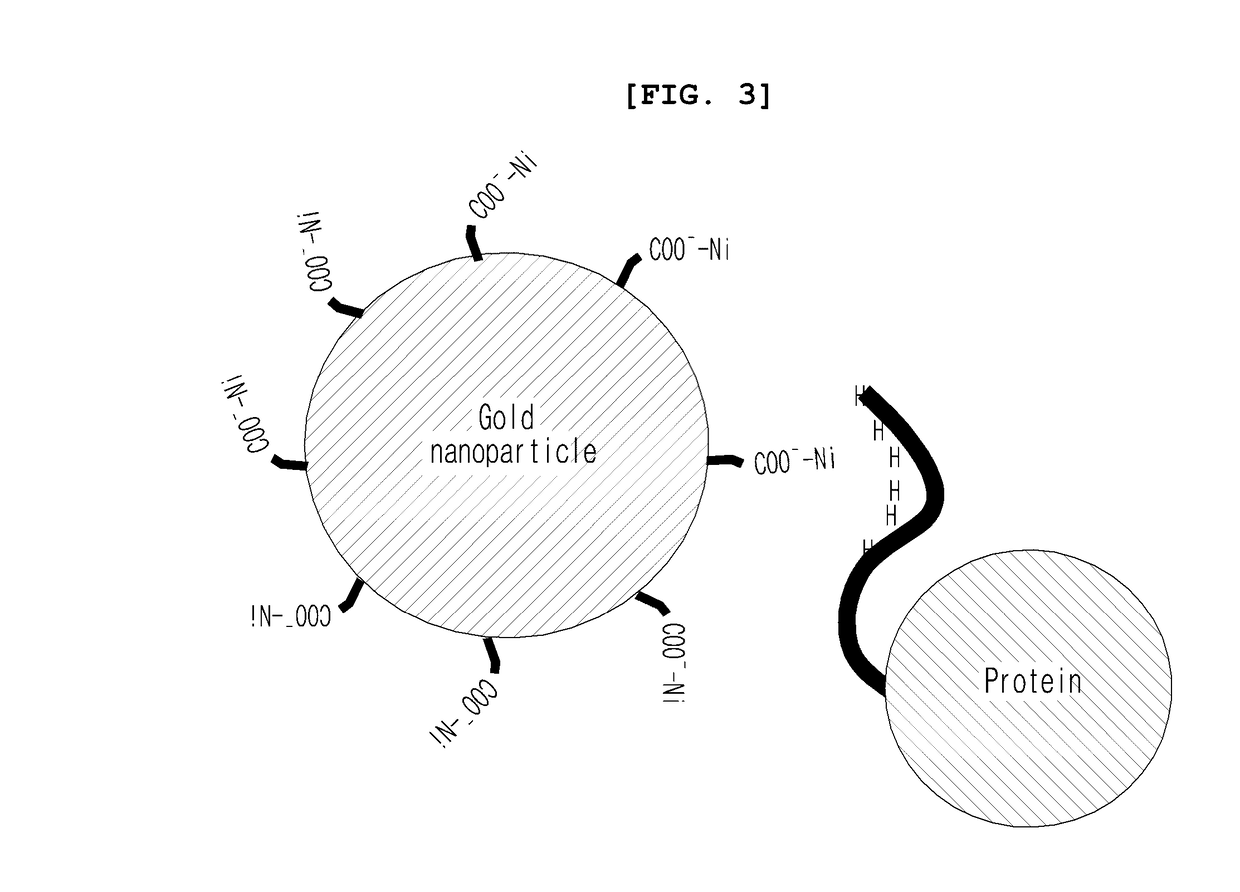
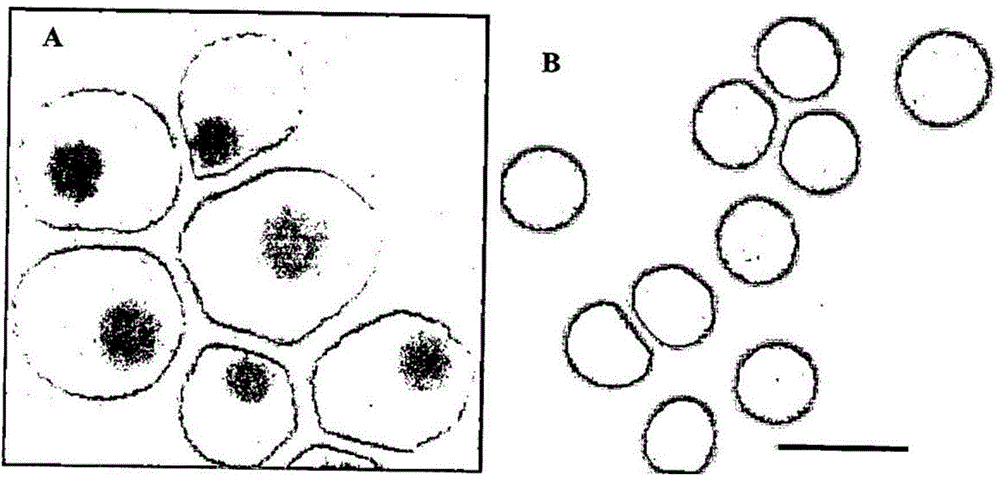
Method for using nanoparticles as nucleation agents for the crystallization of proteins
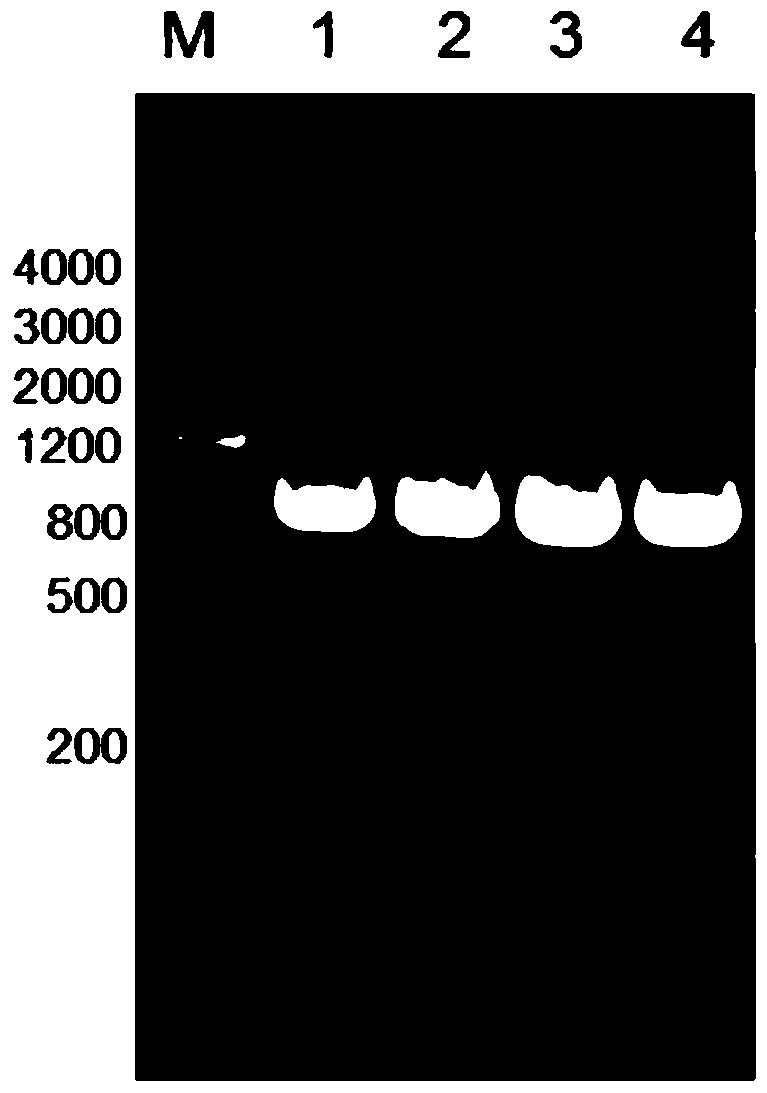
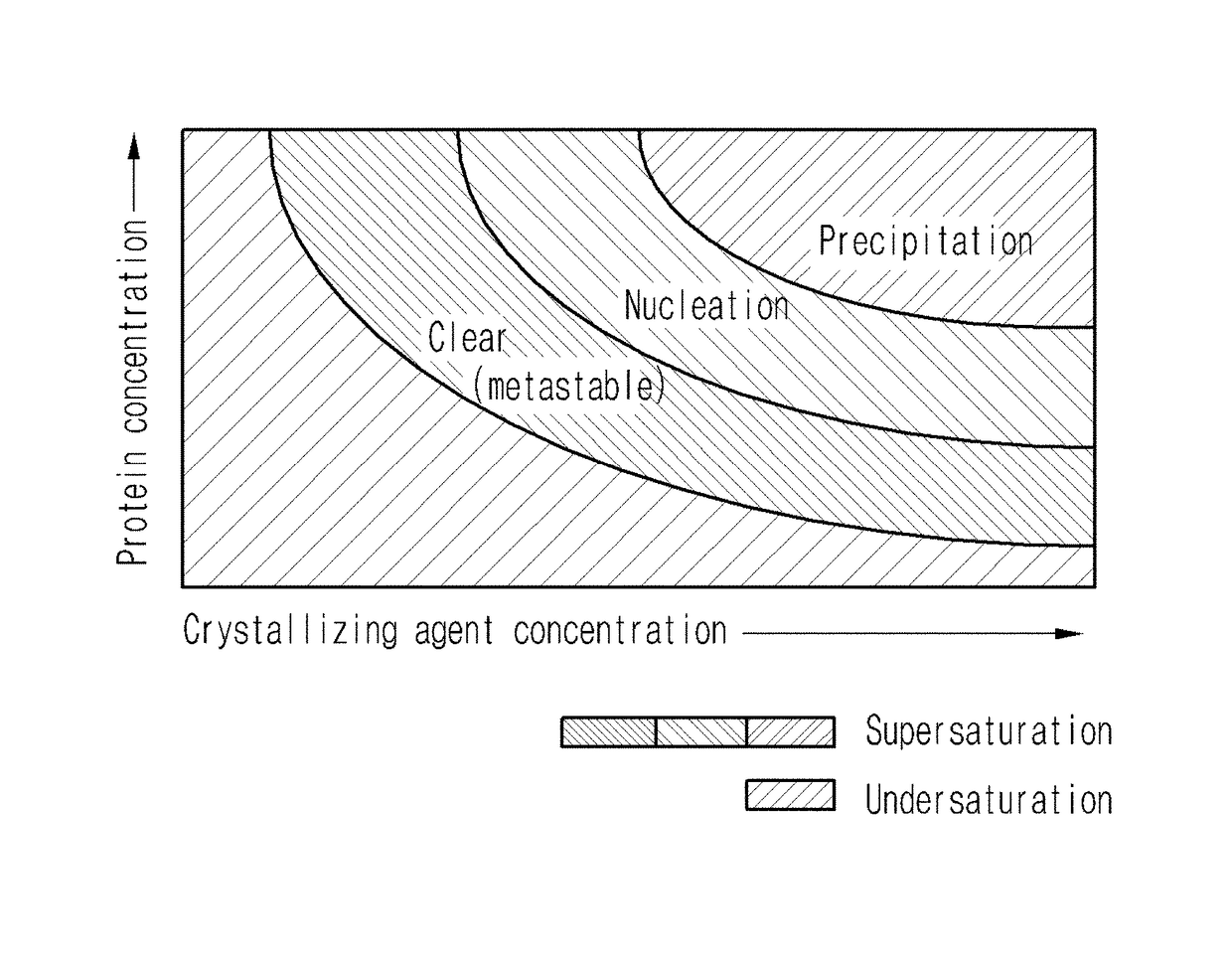
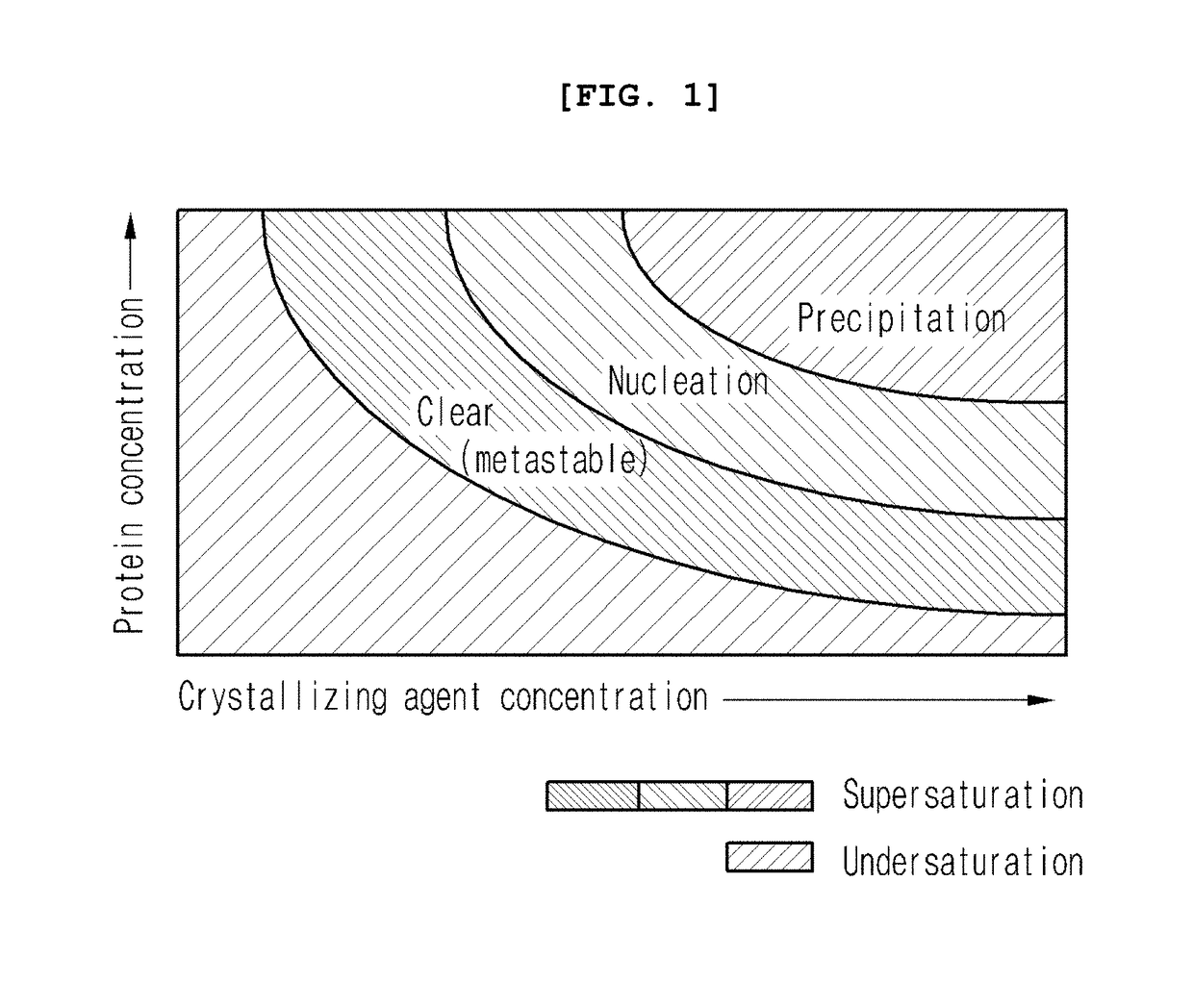
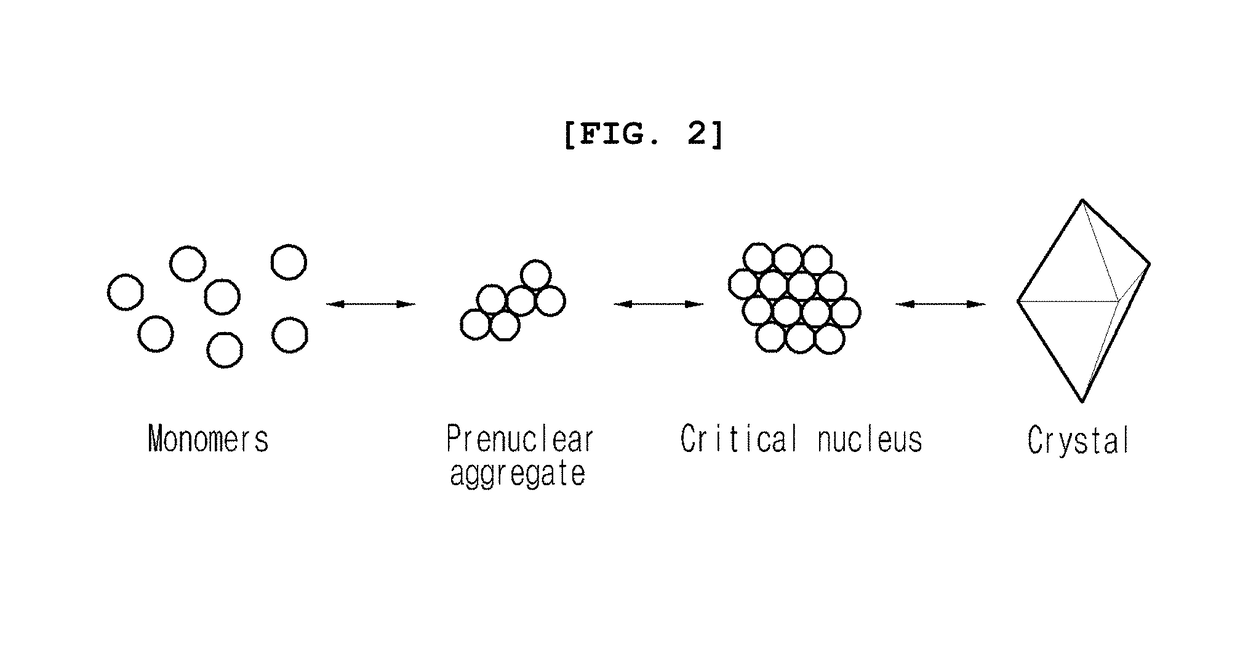
ActiveUS20170101436A1Increase opportunitiesHigh success ratePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein structureBovine serum albumin
The present invention relates to a method for the crystallization of protein using nanoparticles as nucleation agents. Precisely, the inventors performed the crystallization of such proteins as Bacillus subtilis YesR, chicken egg white lysozyme, bovine serum albumin, Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and Listeria monocytogenes hypothetical protein which have his-tag at amino terminal by using gold nanoparticles in diverse sizes and shapes in the presence of Ni2+ ions. As a result, it was confirmed that the chance of successful crystallization was higher with the gold nanoparticles than without the gold nanoparticles and the various crystallization conditions were successfully screened. Therefore, the method for inducing nucleation of the invention can be advantageously used for the disclosure of protein structure by increasing the chance of successful crystallization of protein.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
Method of identifying foetal erythroblast
InactiveCN104603618ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementIon Channel ProteinIntegral membrane protein
There is provided a method for identifying at least one foetal erythroblast the method comprising: (a) detecting the expression of at least one foetal erythroblast specific marker selected from the group consisting of neutral amino acid transporter B (SLC1A5), solute carrier family 3 (activators of dibasic and neutral amino acid transport) member 2 isoform A (SLC3A2), Splice Isoform A of Chloride channel protein 6, Transferrin receptor protein 1, Splice Isoform 3 of Protein GPR107 precursor, Olfactory receptor 11H4, Splice Isoform 1 of Protein C9orf5, Cleft lip and palate transmembrane protein 1, BCG induced integral membrane protein BIGM103, Antibacterial protein FALL-39 precursor, CAAX prenyl protease 1 homolog, Splice Isoform 2 of Synaptophysin-like protein, Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1-like protein 1, Splice Isoform 1 of Protein C20orf22 (ABHD12), Hypothetical protein DKFZp564K247 (Hypoxia induced gene 1 protein) (IPI Accession No. IPI00295621), Hypothetical protein DK-FZp586C1924 (IPI Accession No. IPI00031064), ALEX3 protein variant, Hypothetical protein MGC14288 (IPI Accession No. IPI00176708), protein with IPI Accession No. IPI00639803 and protein with IPI Accession No. IPI00646289, wherein detection of the marker indicates the presence of the foetal erythroblast.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Protein, An Antibody and Measurement of the Protein
ActiveUS20090233316A1Promote conversionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteNeutrophil granulocyte
A novel mammalian protein related to human hypothetical protein FLJ22662 (SEQ ID NO: 1) and homologous hypothetical proteins from mammal species other than Homo sapiens. The protein is expressed in neutrophils and is characterized as a phospholipase B of a novel family (PLB-II). The protein is characterized in comprising one or two single chain polypeptide SU subunits that are different with respect to their amino acid sequences (i.e. at least one SU1 subunit and / or at least one SU2 subunit), where the amino acid sequence of: i) SU1 comprises SEQ ID NO: 2 or a variant thereof ii) SU2 comprises SEQ ID NO: 3 or a variant thereof. There is also described an antibody preparation which is specifically directed against the mammalian protein and a method for determining the occurrence or level of an analyte in a sample. The method is characterized in that analyte is related to the mammalian protein.
Owner:FUTURE MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Application of mycobacterium tuberculosis protein
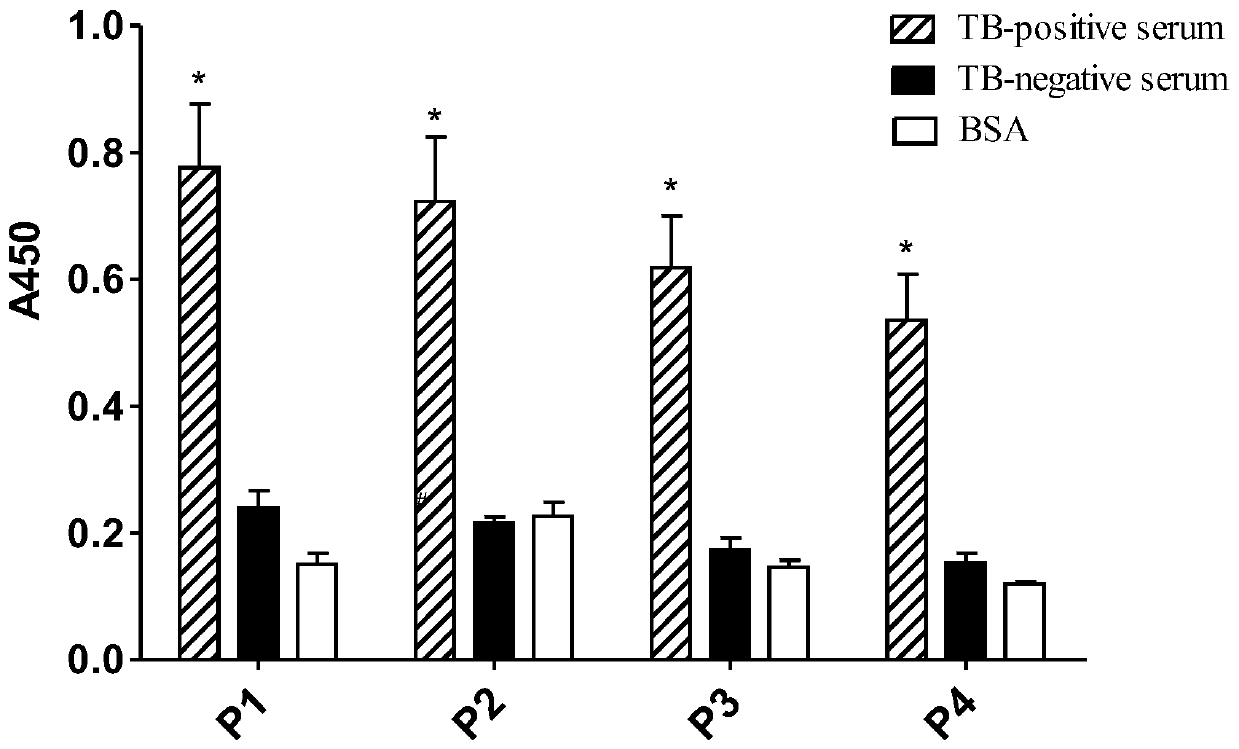
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and discloses application of a mycobacterium tuberculosis protein. According to the application of the mycobacterium tuberculosis protein, ribose kinase, fatty acyl-AMP ligase, cystathionine beta-lyase and hypothetical protein in the mycobacterium tuberculosis protein are used as a diagnostic antigen, a corresponding antibody in a serum to be detected is detected through an indirect ELISA so as to judge whether a person to be detected is infected with mycobacterium tuberculosis or not, whether the a person to be detected is suffered tuberculosis or not is further judged, high reliability, specificity and sensitivity are achieved, and the application of a mycobacterium tuberculosis protein can be applied to the field of serological diagnosis of the tuberculosis.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Acinetobacter baumannii putative protein a1s_1462 protein and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104861048BHigh expressionQuality and safety controllableAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantGenetic engineering
The invention relates to an A1S-1462 recombinant protein and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombinant protein comprises A1S-1462 mature peptide, and the amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is shown as SEQ ID NO. 3. The recombinant protein is high in expression amount, easy to separate and purify, efficient and safe, can be directly used with an adjuvant, and is used for the preparation of an acinetobacter baumannii infection resistant subunit vaccine and a related detection kit. Confirmed by animal experiments, the genetic engineering recombinant subunit vaccine has good acinetobacter baumannii infection resistant immune protection effect, lays a foundation for the further study on combined vaccines and multicomponent fusion vaccines, and plays an important role for development and application of prevention and control vaccines and diagnostic kits.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for using nanoparticles as nucleation agents for the crystallization of proteins
ActiveUS9932366B2Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsTear lysozymeProtein structure
The present invention relates to a method for the crystallization of protein using nanoparticles as nucleation agents. Precisely, the inventors performed the crystallization of such proteins as Bacillus subtilis YesR, chicken egg white lysozyme, bovine serum albumin, Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and Listeria monocytogenes hypothetical protein which have his-tag at amino terminal by using gold nanoparticles in diverse sizes and shapes in the presence of Ni2+ ions. As a result, it was confirmed that the chance of successful crystallization was higher with the gold nanoparticles than without the gold nanoparticles and the various crystallization conditions were successfully screened. Therefore, the method for inducing nucleation of the invention can be advantageously used for the disclosure of protein structure by increasing the chance of successful crystallization of protein.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
Hypothetical protein gene, primer probe group thereof and application of hypothetical protein gene and primer probe group in detection of Meiqi yeast two sharp
InactiveCN114807427AHigh sensitivityImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYeastNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a hypothetical protein gene, a primer probe group thereof and application of the hypothetical protein gene to detection of metschinia dicuspidata, and belongs to the technical field of quantitative detection of the metschinia dicuspidata. The nucleotide sequence of the gene segment used for detecting the metschhia pastoris is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the nucleotide sequence of the hypothetical protein gene containing the gene segment is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the primer probe group used for amplifying the gene segment is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3-5. The gene segment and the primer probe group for detecting the Meiqi yeast two-pointed, provided by the invention, have the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity and high detection accuracy, can be used for quantitatively detecting the quantity of the Meiqi yeast two-pointed carried in river crabs, and have important significance on prevention and control of diseases caused by the Meiqi yeast two-pointed.
Owner:天津市水产研究所
Applications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and discloses the application of mycobacterium tuberculosis protein. In the present invention, ribokinase, fatty acyl-AMP ligase, cystathionine β-lyase and hypothetical protein in Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein are used as diagnostic antigens, and the corresponding antibodies in the serum to be tested are detected by indirect ELISA to determine the Whether the patient is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and further judge whether to suffer from tuberculosis, has high reliability, specificity and sensitivity, and can be used in the field of serological diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Protein, an antibody and measurement of the protein
ActiveUS8288112B2Promote conversionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteNeutrophil granulocyte
A novel mammalian protein related to human hypothetical protein FLJ22662 (SEQ ID NO: 1) and homologous hypothetical proteins from mammal species other than Homo sapiens. The protein is expressed in neutrophils and is characterized as a phospholipase B of a novel family (PLB-II). The protein is characterized in comprising one or two single chain polypeptide SU subunits that are different with respect to their amino acid sequences (i.e. at least one SU1 subunit and / or at least one SU2 subunit), where the amino acid sequence of: i) SU1 comprises SEQ ID NO: 2 or a variant thereof ii) SU2 comprises SEQ ID NO: 3 or a variant thereof. There is also described an antibody preparation which is specifically directed against the mammalian protein and a method for determining the occurrence or level of an analyte in a sample. The method is characterized in that analyte is related to the mammalian protein.
Owner:FUTURE MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Nosema bombycis hypothetical protein NB29, recombinant expression vector containing nosema bombycis hypothetical protein NB29 and application of recombinant expression vector
ActiveCN109536517ASecretoryStable editStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorNucleotideSecretory protein
The invention discloses nosema bombycis hypothetical protein NB29, a recombinant expression vector containing the nosema bombycis hypothetical protein NB29 and an application of the recombinant expression vector. A nucleotide sequence of the nosema bombycis hypothetical protein NB29 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, expressed protein is secretory, a truncation form N3 is screened out according to the nosema bombycis hypothetical protein NB29, fusion Cas9 protein is stably expressed in silkworm cytoplasm, during infection of nosema bombycis, secretory protein NB29-B and NB29-N3 of nosema bombycis interact, Cas9 is dragged in a host cell nucleus, and the purpose of host gene editing is achieved. The Cas9 medicated inducible gene editing vector can stably edit host genes, a new idea is provided for preparing insect nosema bombycis death causing models and nosema bombycis control, reference is provided for control of nosema bombycis and other pathogens capable of infecting humans, and meanwhile, afoundation is laid for functional research of related genes.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Immunogenic antigens of shigella
ActiveUS9636390B2Broad protectionBacteria material medical ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsSerotypeImmunogenicity
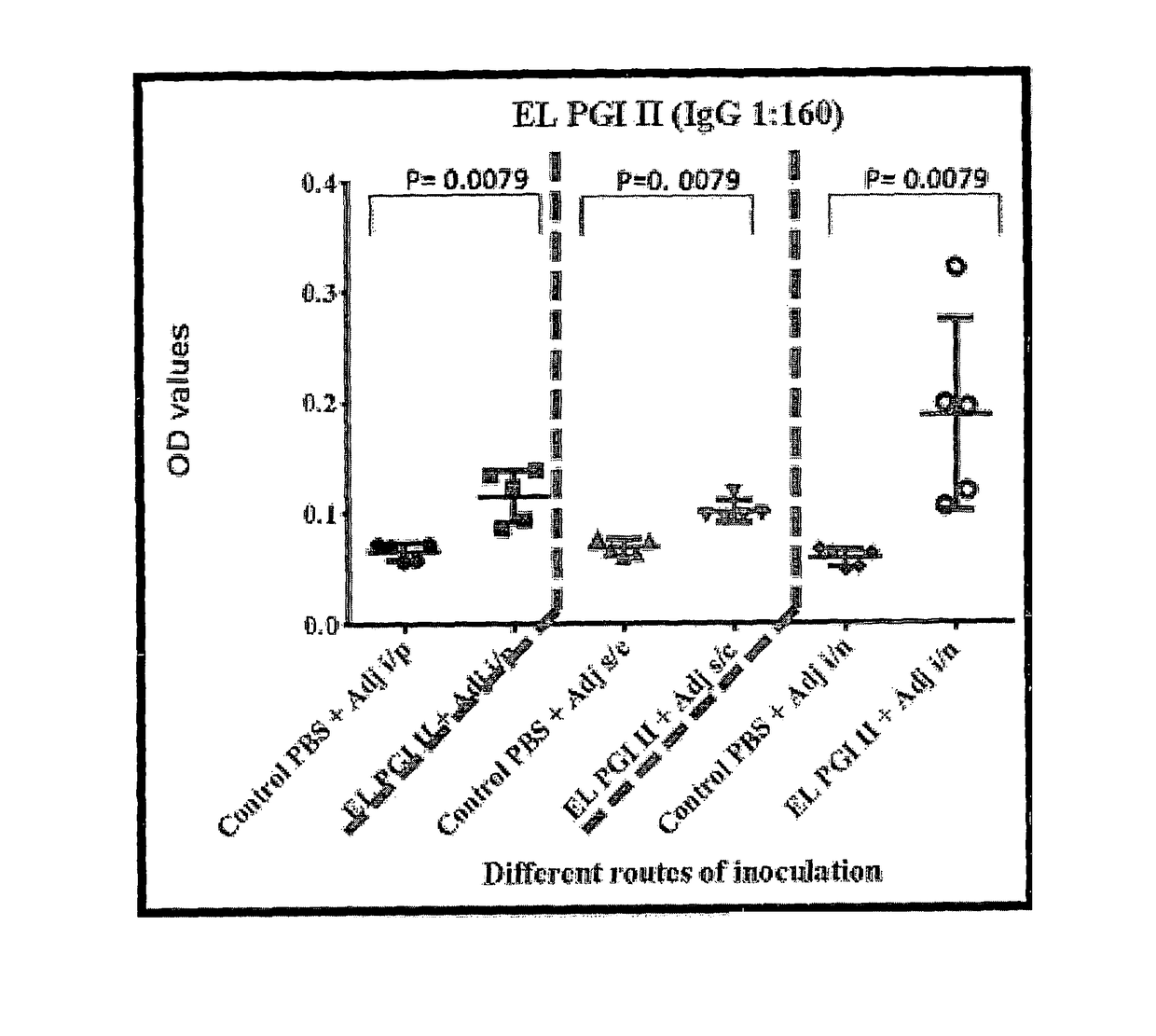
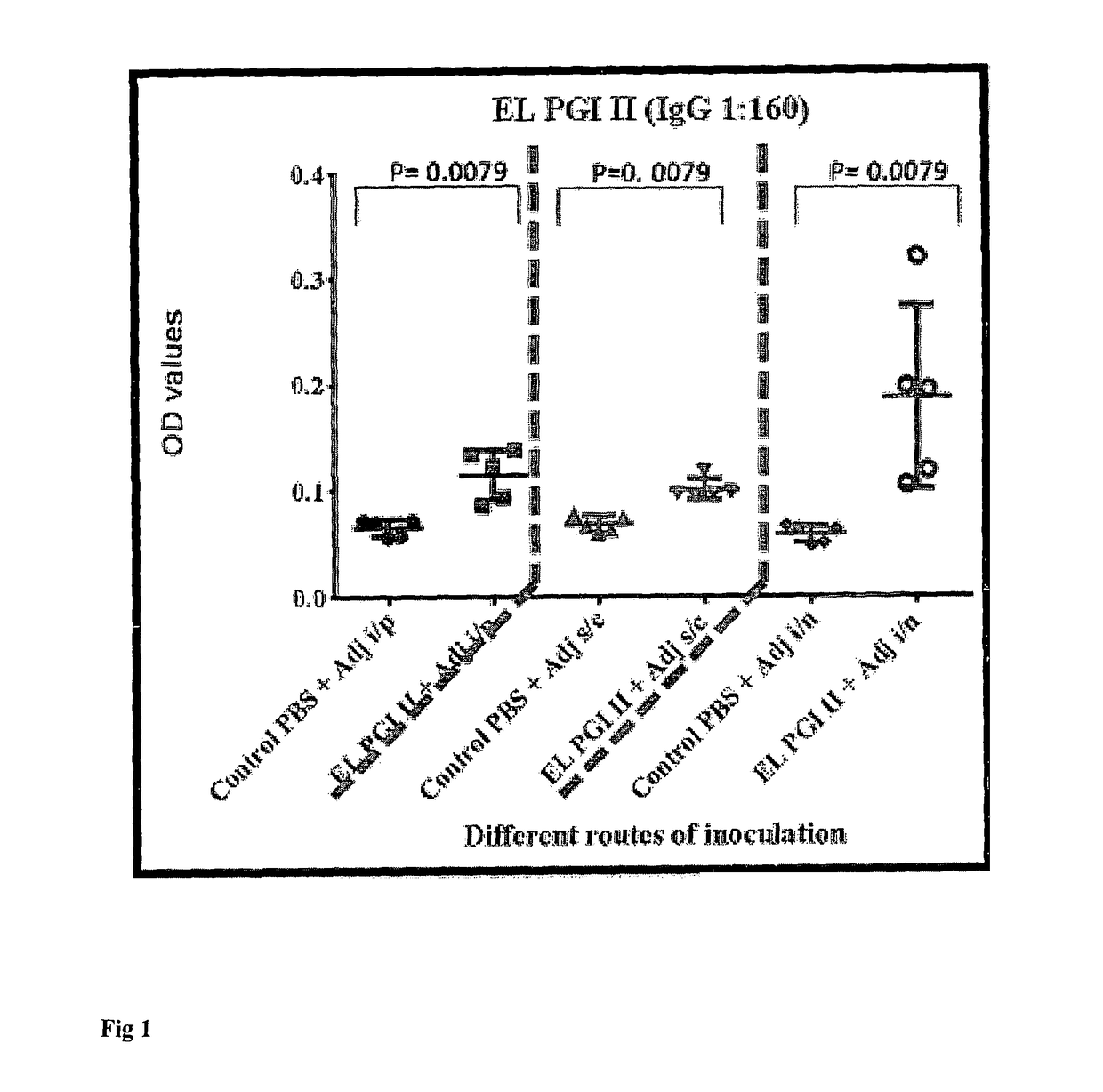
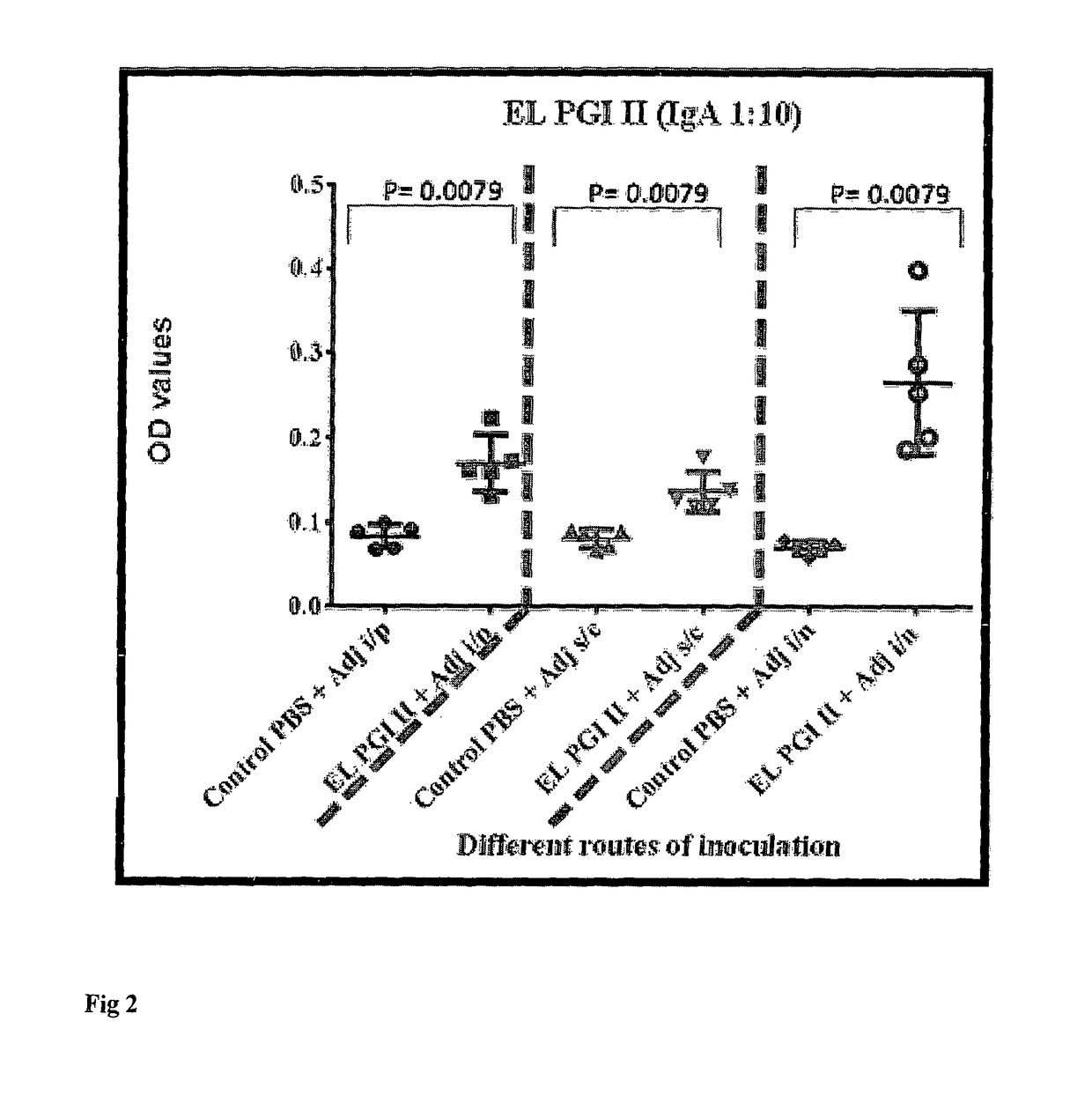
A vaccine for protection against multiple serotypes of Shigella sp., comprising a putative heat shock protein (EL PGI II), and Hypothetical Protein (EL PGIV) is provided.
Owner:INDIAN COUNCIL OF MEDICAL RES +1
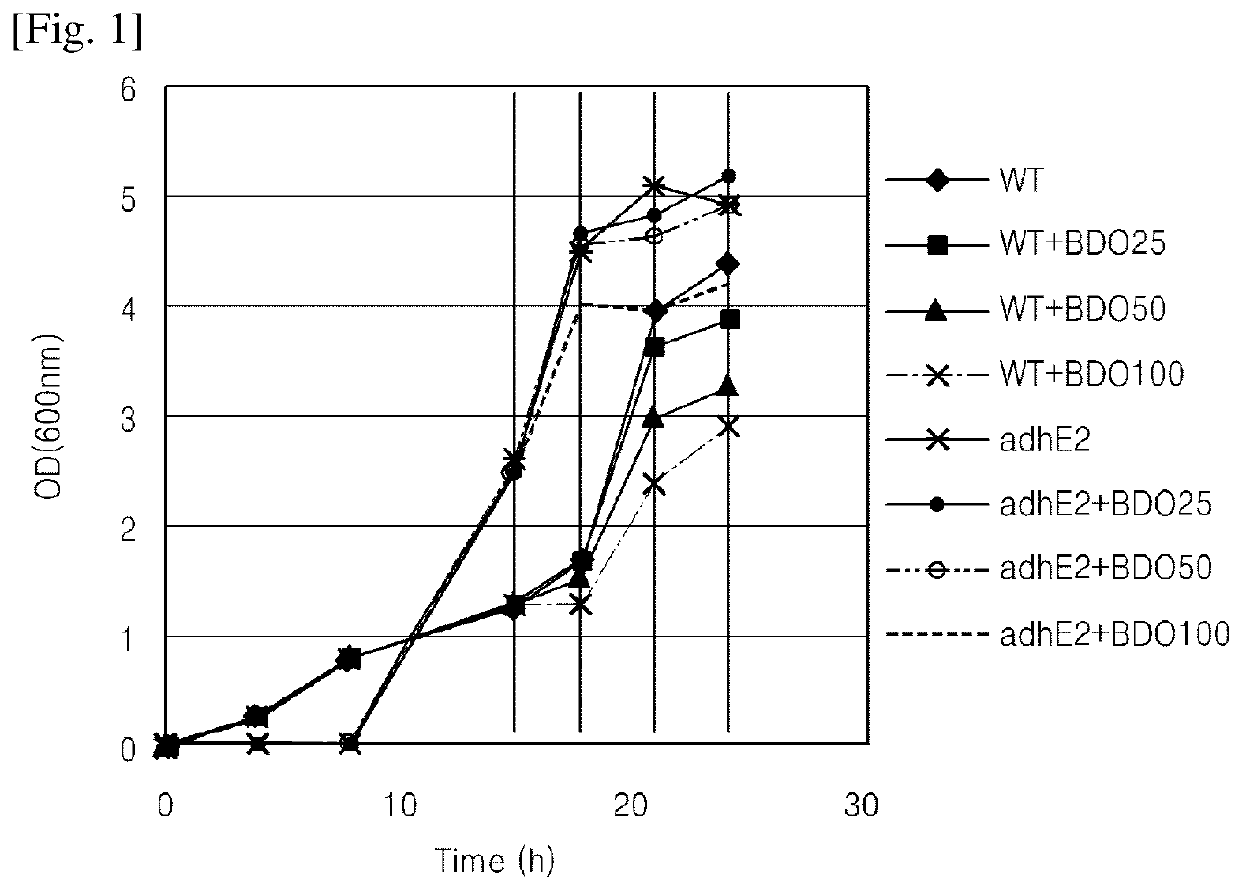
Method of screening gene for 1,4-BDO production
Provided is a screening method of discovering genes capable of increasing 1,4-BDO production on the basis of proteomics data. Over-expression of proteins screened by the method, NCgl0630 (citrate synthase) and NCgl2145 (hypothetical protein), increase 1,4-BDO productivity. The method may lead to screening of a protein associated with 1,4-BDO productivity, thereby increasing 1,4-BDO productivity, and thus, the method may be recognized as being industrially applicable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
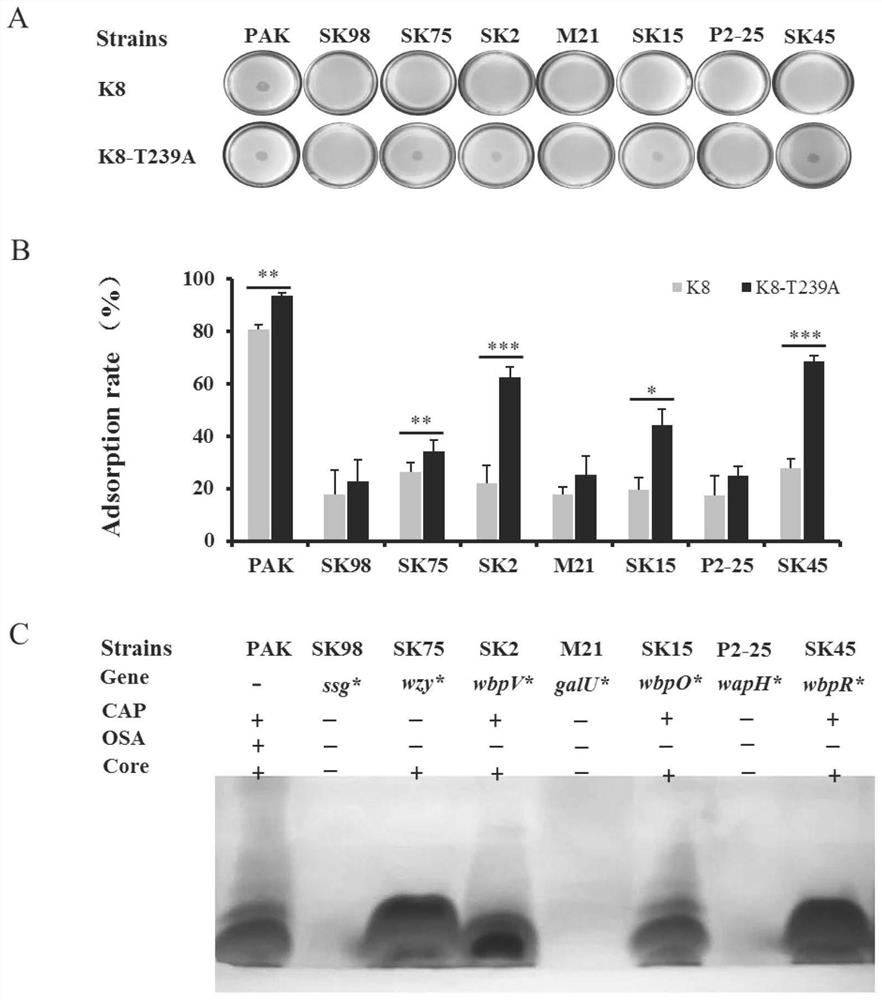
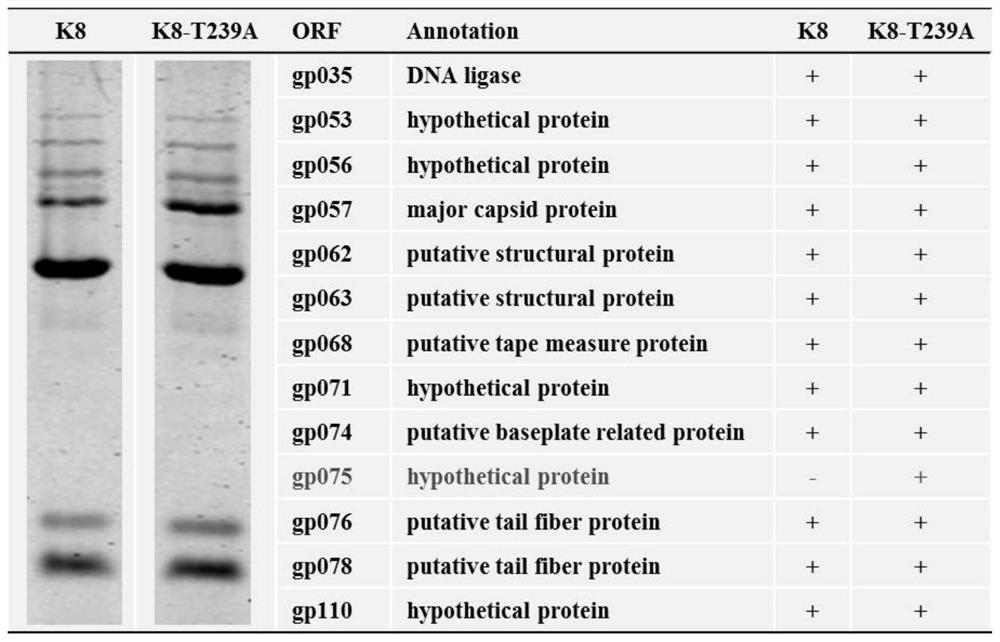
A kind of hypothetical protein gp075 of pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage k8 and its mutant strain, mutant protein and application
ActiveCN110563815BWide host rangeImprove adsorption capacityVirus peptidesMicroorganism based processesAntigenMutated protein
The present invention relates to a hypothetical protein GP075 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage K8, whose nucleotide sequence is SEQ No.1, and whose amino acid sequence is SEQ No.10. The hypothetical protein GP075 is mutated, and the mutated protein has the function of a structural protein. On the basis of the original recognition of lipopolysaccharide, this type of phage mutant strain has added an additional receptor recognition protein, which can recognize lipopolysaccharide O-antigen-deficient host cells Or host cells that only contain core oligosaccharides, and have a wider host range, stronger ability to lyse and adsorb host cells, and are expected to be used in phage preparations to prevent and treat various diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gene related to proteolytic ability and screening method of lactobacillus helveticus with high proteolytic ability based on gene
PendingCN112029784AHigh hydrolytic activityFast screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHypothetical proteinProteolysis
The invention provides a gene related to protein hydrolysis capacity and a screening method for lactobacillus helveticus with high protein hydrolysis capacity based on the gene, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the invention, a whole-genome correlation analysis technology is adopted for rapid screening so as to obtain a coding hypothetical protein gene relatedto lactobacillus helveticus proteolytic activity. The hypothetical protein gene regulates and controls the proteolysis capacity of lactobacillus helveticus in a negative regulation and control mode, and can be used as a molecular marker for detecting the proteolysis activity of lactobacillus helveticus to be applied to screening of lactobacillus helveticus strains. The screening work of lactobacillus helveticus strains with high protein hydrolysis capacity is greatly simplified, and a new thought is provided for the strain screening work.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com