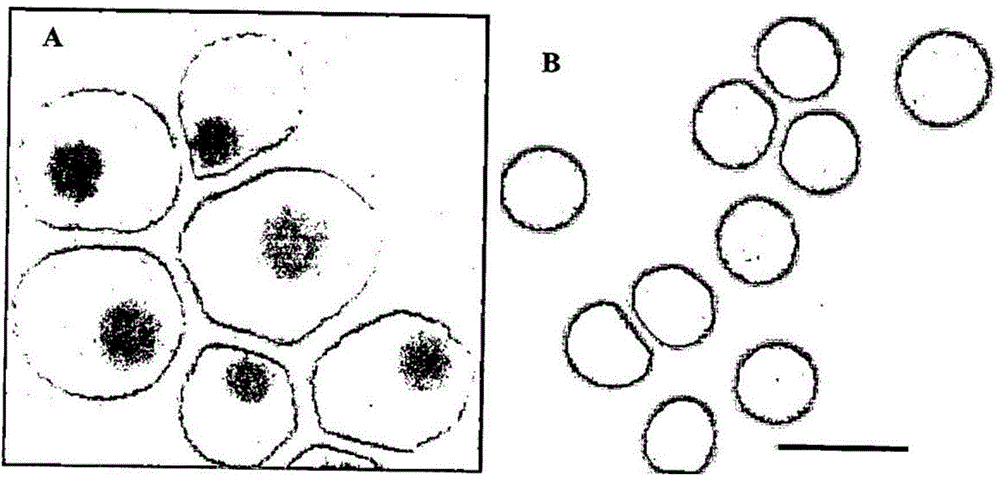
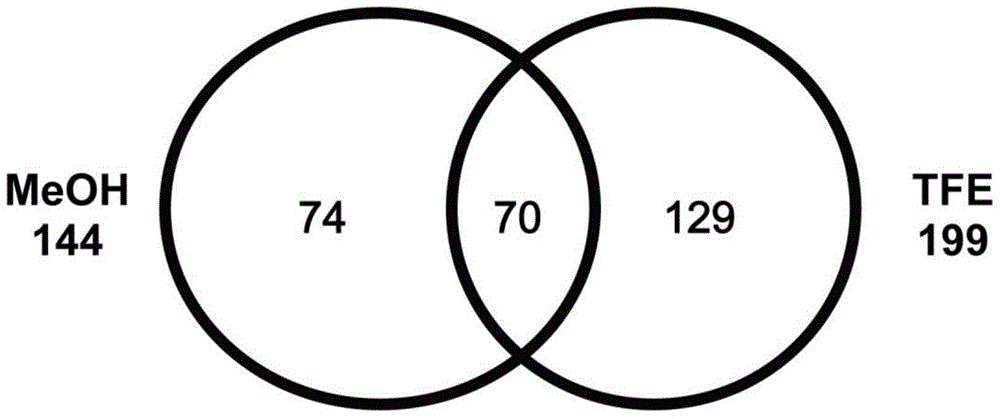
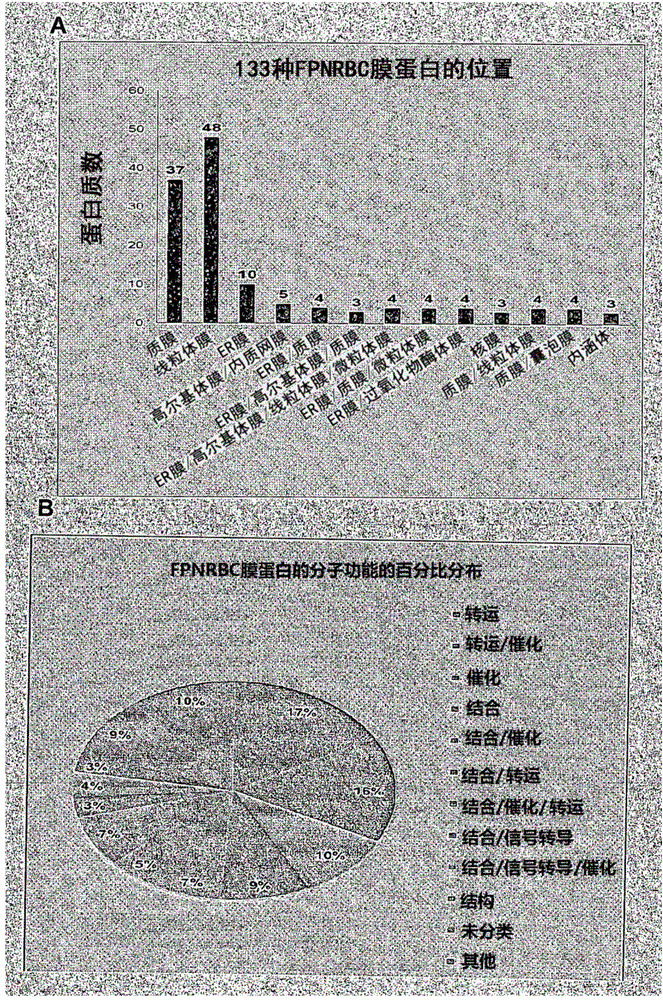
Method of identifying foetal erythroblast
An erythroblastic, fetal technique applied in the field of identifying and/or isolating at least one fetal nucleated primitive red blood cell, identifying at least one fetal nucleated primitive red blood cell in a sample
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Materials and methods
[0084] Intensive literature studies have been conducted on the presence and functional role of plasma membrane proteins characteristic of FPNRBCs in various human tissues and cells, including the fetus (trophoblast / placenta). A brief description of the location of these proteins, their physiological roles (including those associated with human fetal development), and diseases associated with their mutations has been provided above, along with available data on similar functions of AARBCs.
[0085] FPNRBCs can be isolated from WBCs in maternal blood by negative depletion of CD45-positive cells, and these ideal cells for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis can be enriched by AARBCs if known suitable surface antigens for FPNRBCs are available. Membrane proteins of FPNRBCs were graphically represented by mass spectrometry data, and the data graphs were compared with data graphs of AARBCs membrane proteomes known in the art to identify specific surface me...
Embodiment 2
[0211] Enrichment of FPNRBCs from post-termination of pregnancy (TOP) maternal blood using anti-ASCT2 antibody following a three-step enrichment protocol
[0212] Maternal blood after 10 mls TOP was collected from two patients. Blood samples were processed using our laboratory's three-step enrichment protocol. Briefly, diluted blood samples were layered on Percoll 1118 density medium and centrifuged. The interface was collected and all leukocytes were depleted by magnetic active cell sorting (MACS) using anti-CD45 magnetic beads. Cells from the negative fraction were incubated with anti-ASCT2 antibody for 30 minutes, washed, and then incubated with anti-rabbit IgG-magnetic beads for indirect MACS (positive) selection of FPNRBCs. 20 FPNRBCs were able to be recovered from each sample (Table 11).
[0213] Table 11 - Enrichment of FPNRBCs from maternal blood after TOP using anti-ASCT2 antibody
[0214] Maternal blood after TOP
gestational age of the fetus
Volu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com