Patents
Literature
62 results about "Functional role" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
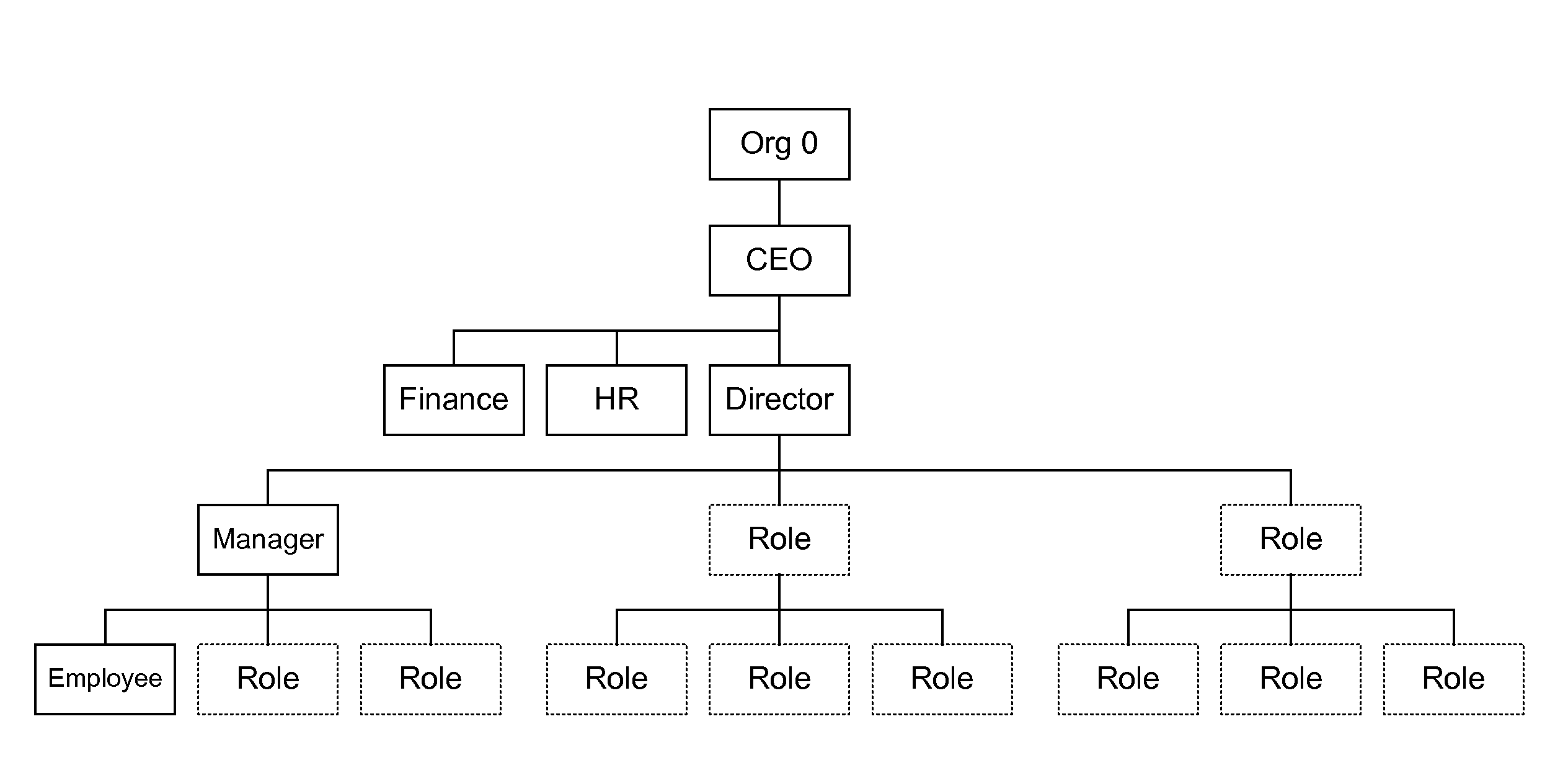
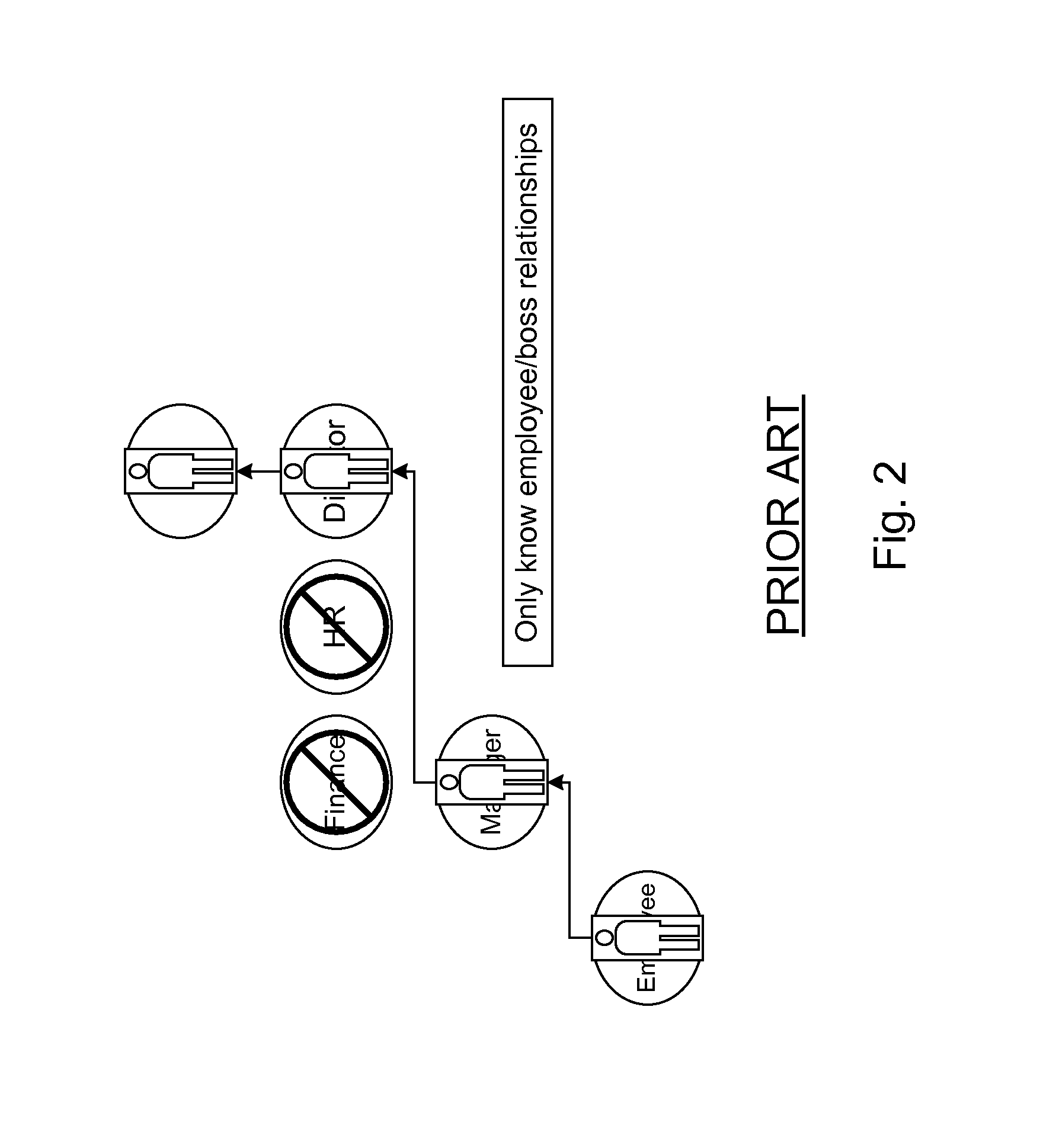
Functional roles. A functional role describes a set of skills and activities that are typically performed by a department within an organization, for example, a manager, director, or vice president. Functional roles are defined by the organizational structure of a company. Resources are assigned to these roles within that department.
System and method for setting user-right, and recording medium
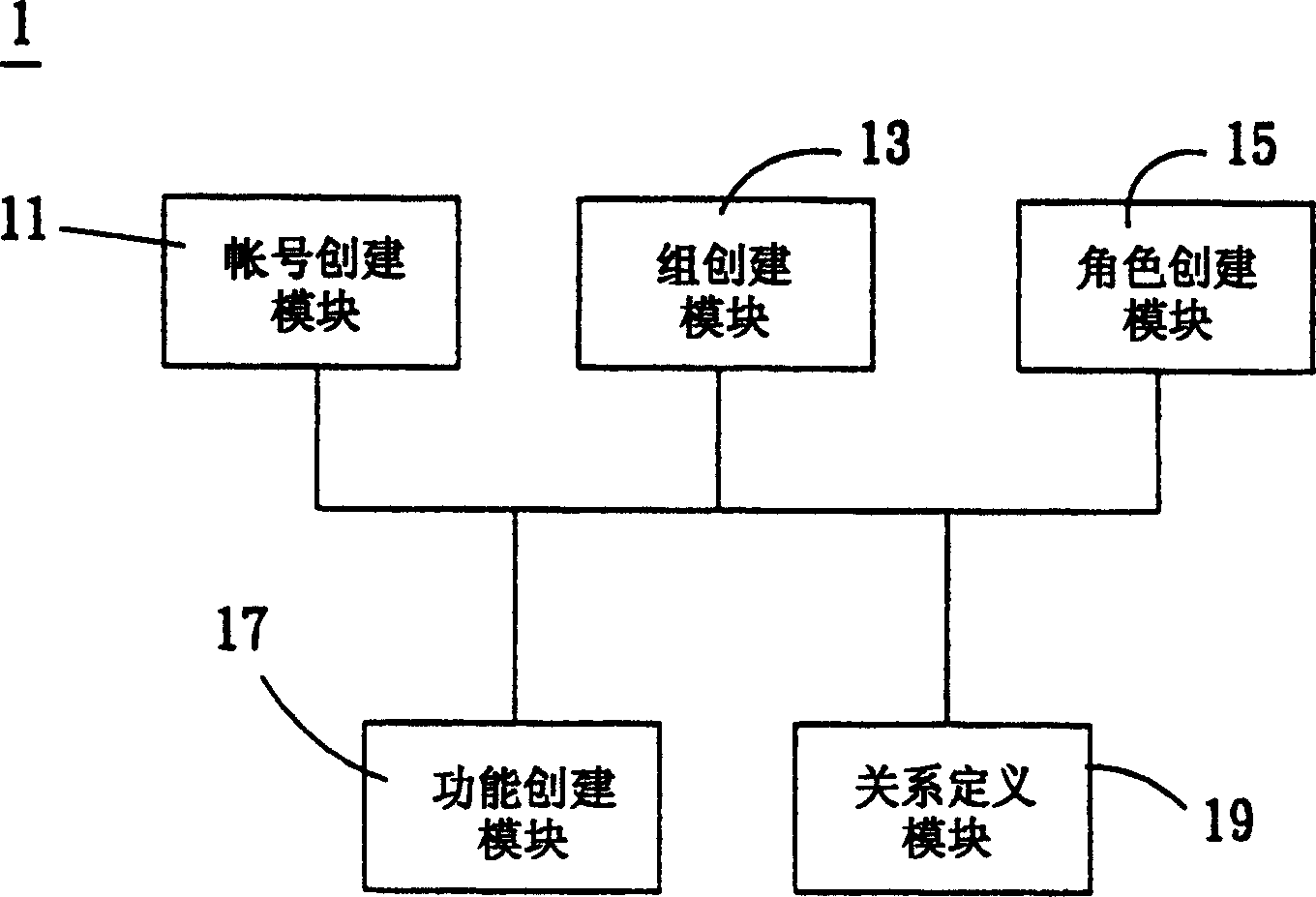
InactiveUS20050144060A1Create efficientlyEstablishing connectionOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsWorld Wide WebRecording media
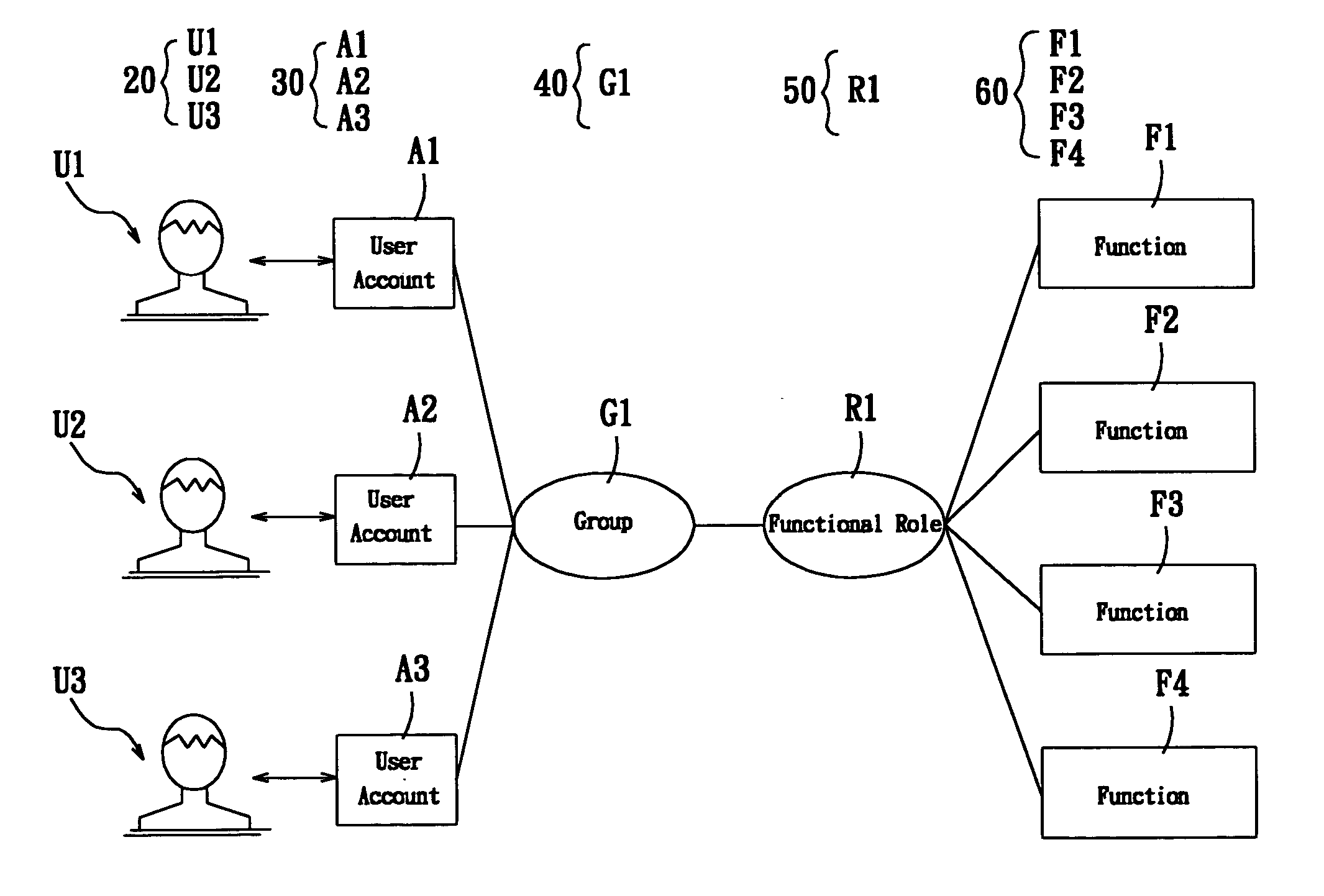
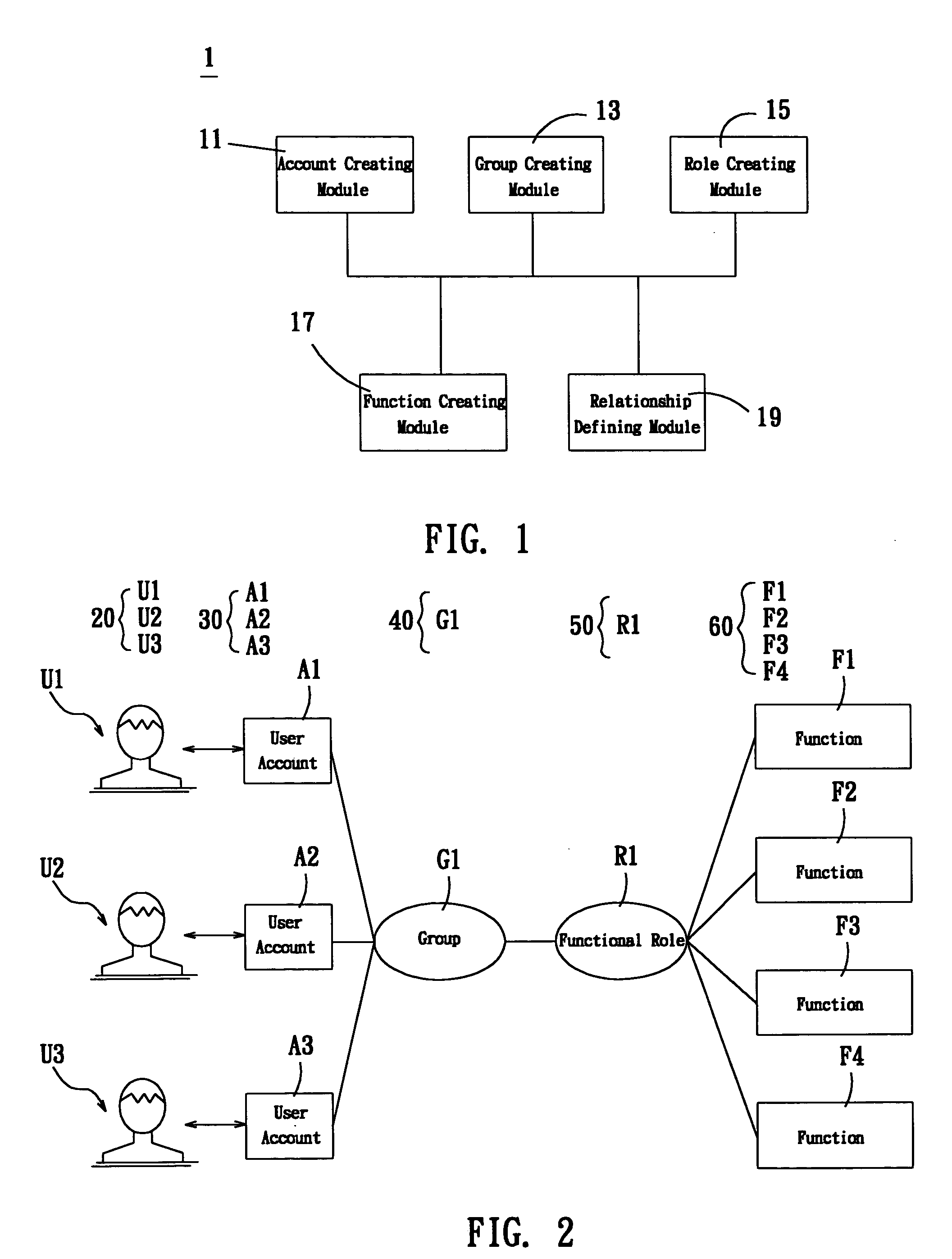
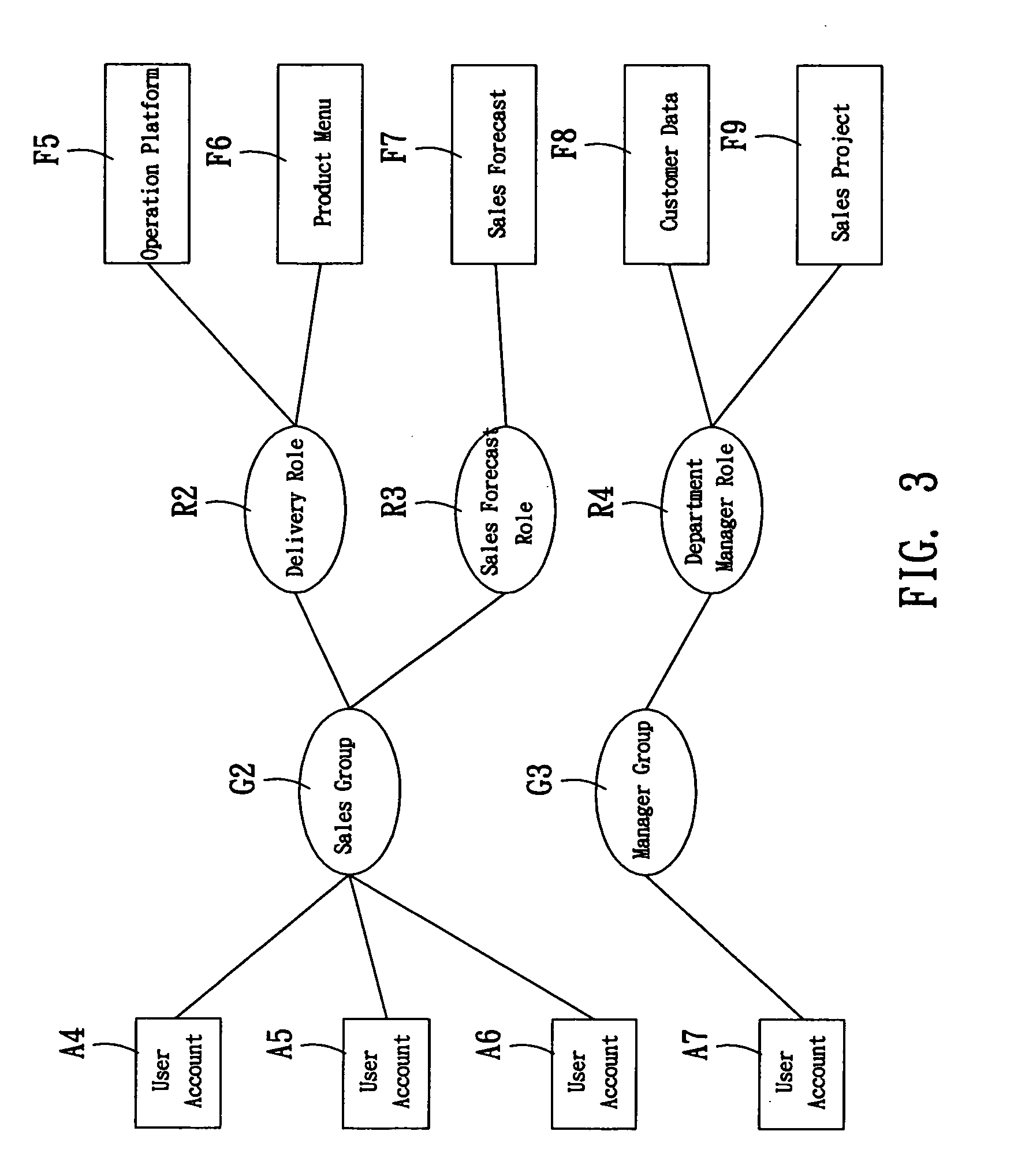
A system for setting user-right is used to set user rights of a plurality of users. The system comprises an account creating module, a group creating module, a role creating module, a function creating module, and a relationship defining module. The account creating module creates a plurality of user accounts corresponding to the users. The group creating module creates at least one group according to the user's organization. The role creating module creates at least one functional role according to jobs or projects of the users. The function creating module creates a plurality of functions corresponding to execution items of the users. The relationship defining module defines that at least one user account is subordinate to the group, and the functional role has the right to execute at least one of the functions. The relationship defining module further creates the relationship between the group and the function role. Furthermore, a method for setting user-right and a recording medium, having a computer executable program for performing the method, are provided.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
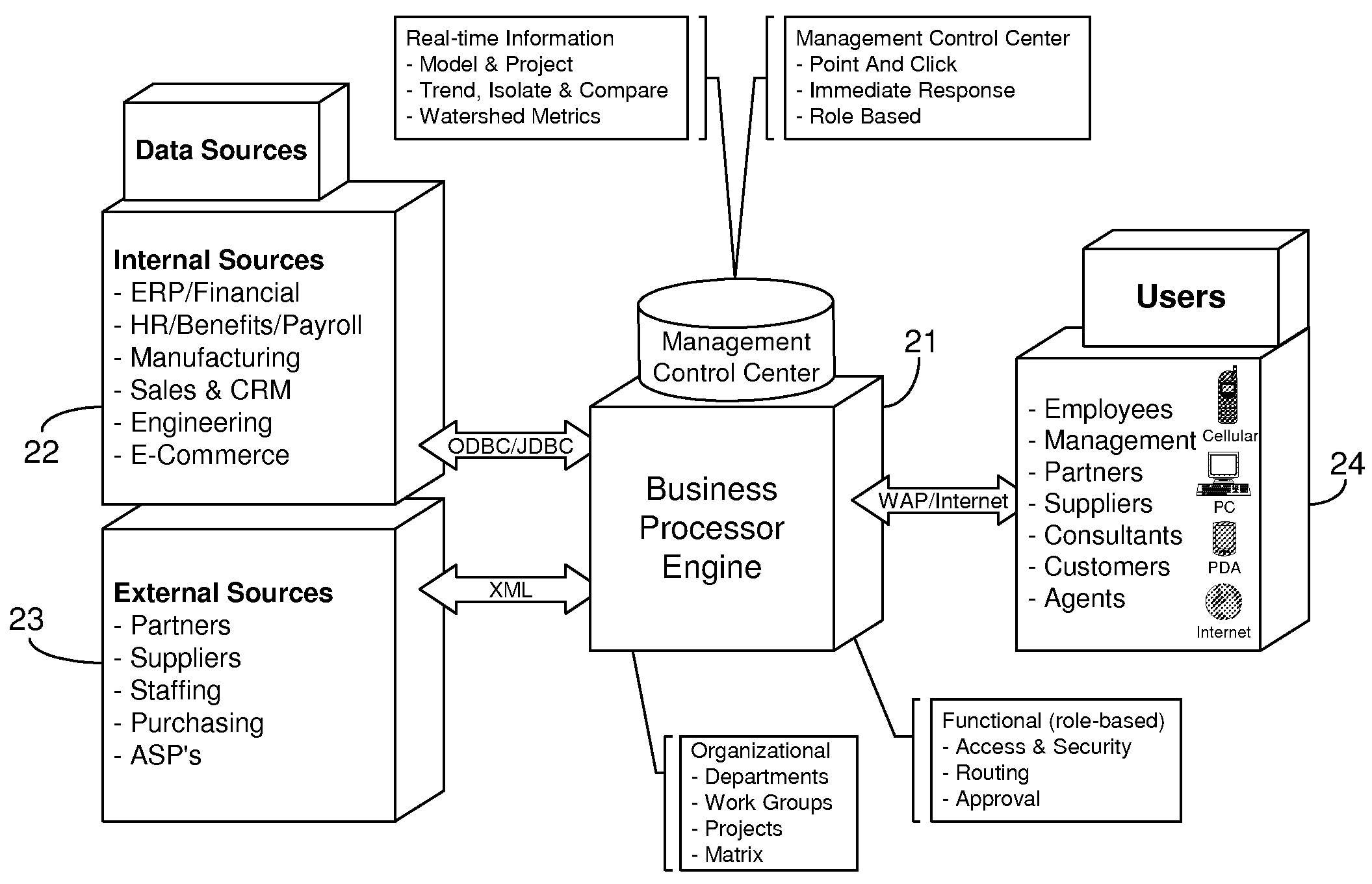
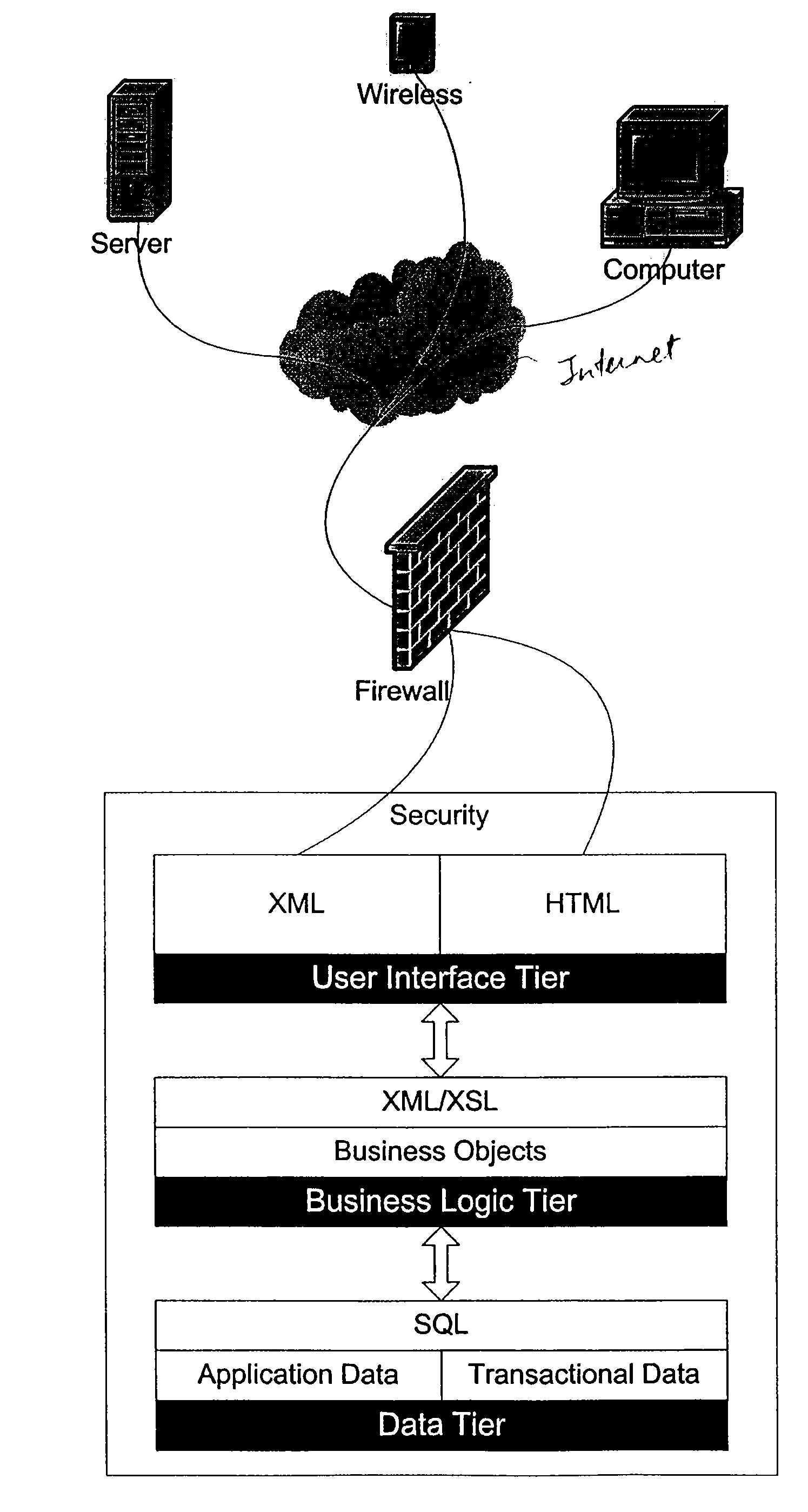
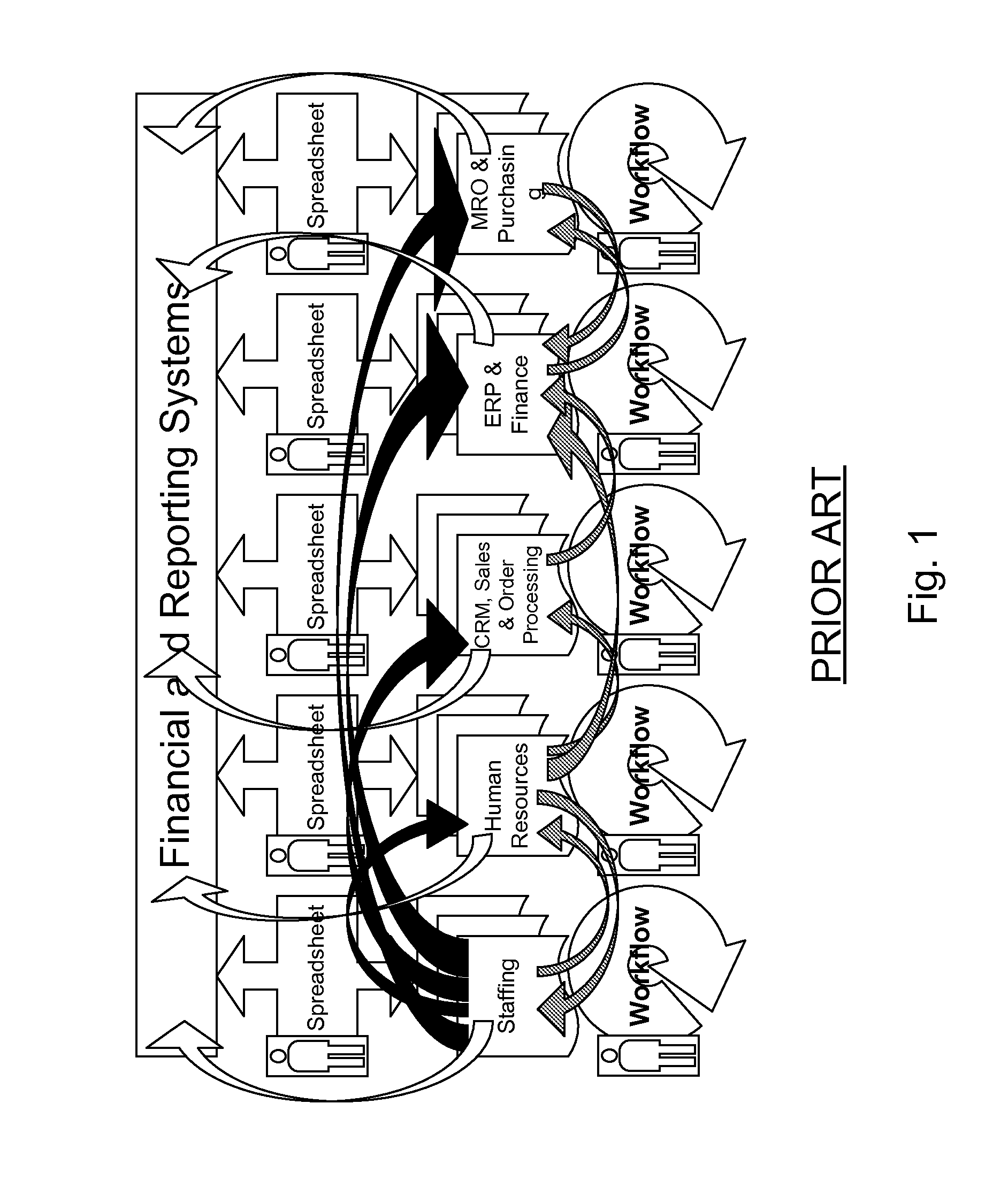
Installation of a data processing solution
Provided are methods and computer programs for managing installation of a set of data processing components. An installation manager program allows users to specify which of a set of predefined functional roles are to be implemented on which of their data processing systems and then the installation program automates installation of the set of data processing components which correspond to the specified roles.
Owner:LINKEDIN
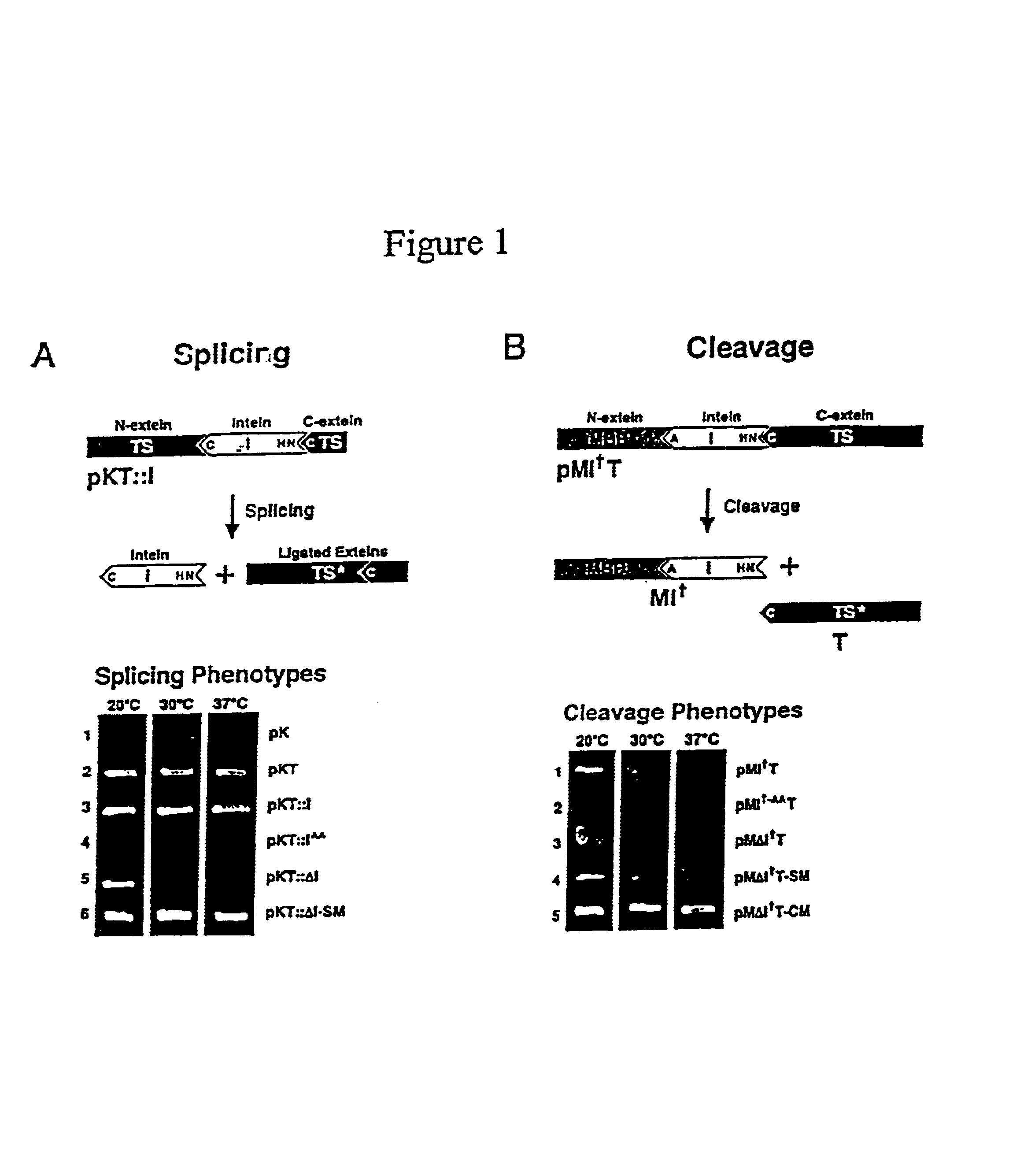
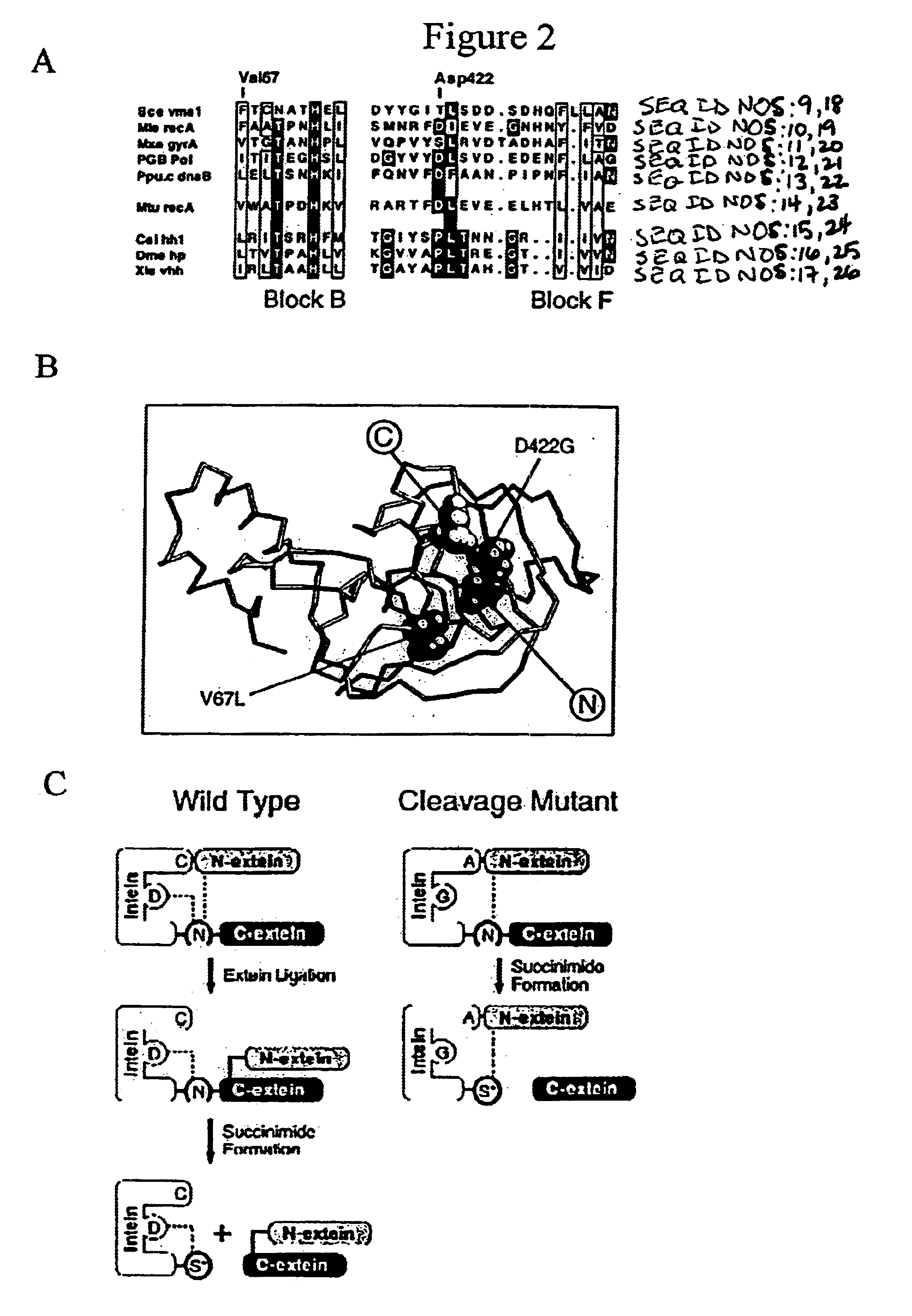
Genetic system and self-cleaving inteins derived therefrom, bioseparations and protein purification employing same, and methods for determining critical, generalizable amino acid residues for varying intein activity
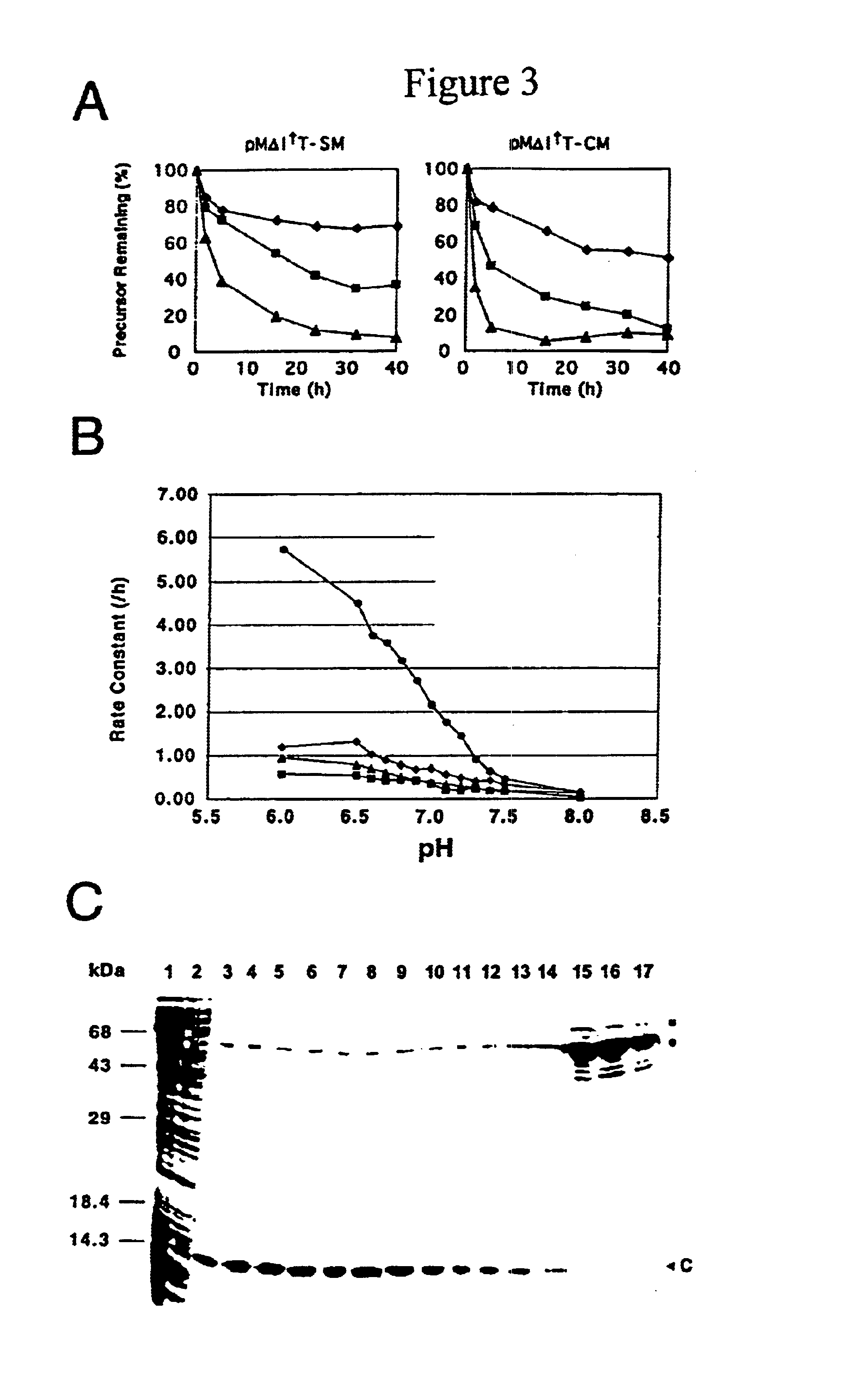
A self-cleaving element for use in bioseparations has been derived from a naturally occurring, 43 kDa protein splicing element (intein) through a combination of protein engineering and random mutagenesis. A mini-intein (18 kDa) previously engineered for reduced size had compromised activity and was therefore subjected to random mutagenesis and genetic selection. In one selection a mini-intein was isolated with restored splicing activity, while in another, a mutant was isolated with enhanced, pH-sensitive C-terminal cleavage activity. The enhanced cleavage mutant has utility in affinity fusion-based protein purification. The enhanced splicing mutant has utility in purification of proteins such as toxic proteins, for example, by inactivation with the intein in a specific region and controllable splicing. These mutants also provide new insights into the structural and functional roles of some conserved residues in protein splicing. Thus, disclosed and claimed are: a genetic system and self-cleaving inteins therefrom; bioseparations employing same; protein purification by inactivation with inteins in specific regions and controllable intein splicing; methods for determining critical, generalizable residues for varying intein activity; and products.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Nucleolar targeting of therapeutics against HIV
InactiveUS6995258B1Improve the immunityImprove the level ofSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHiv 1 rnaT cell
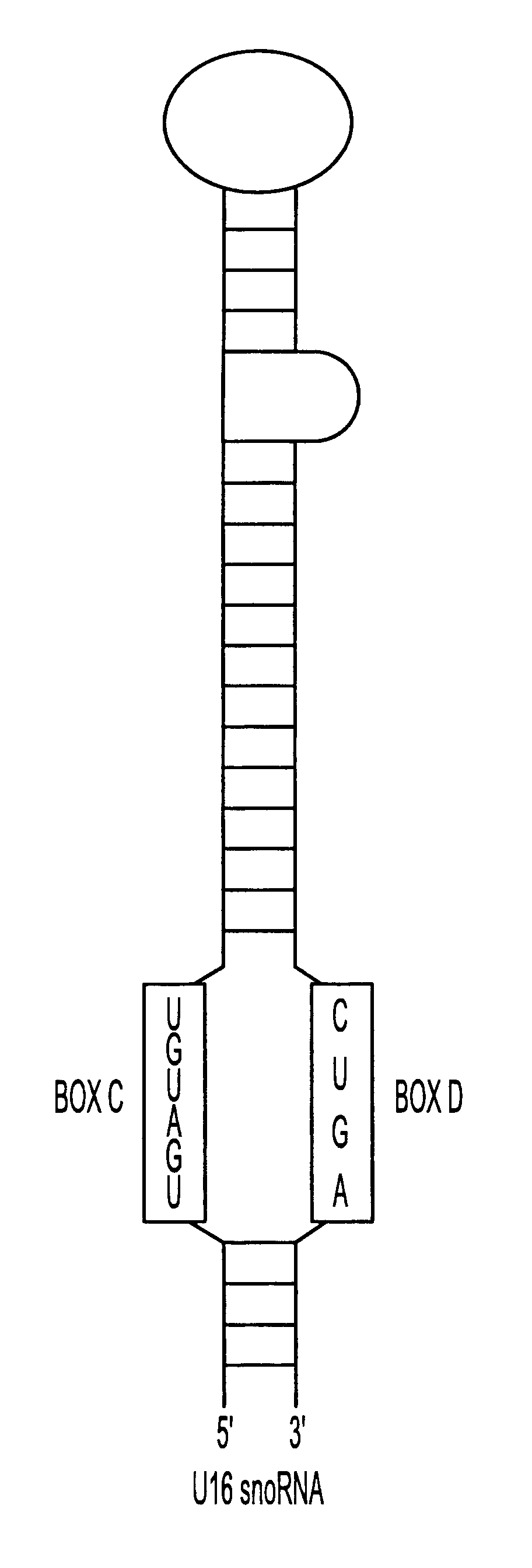
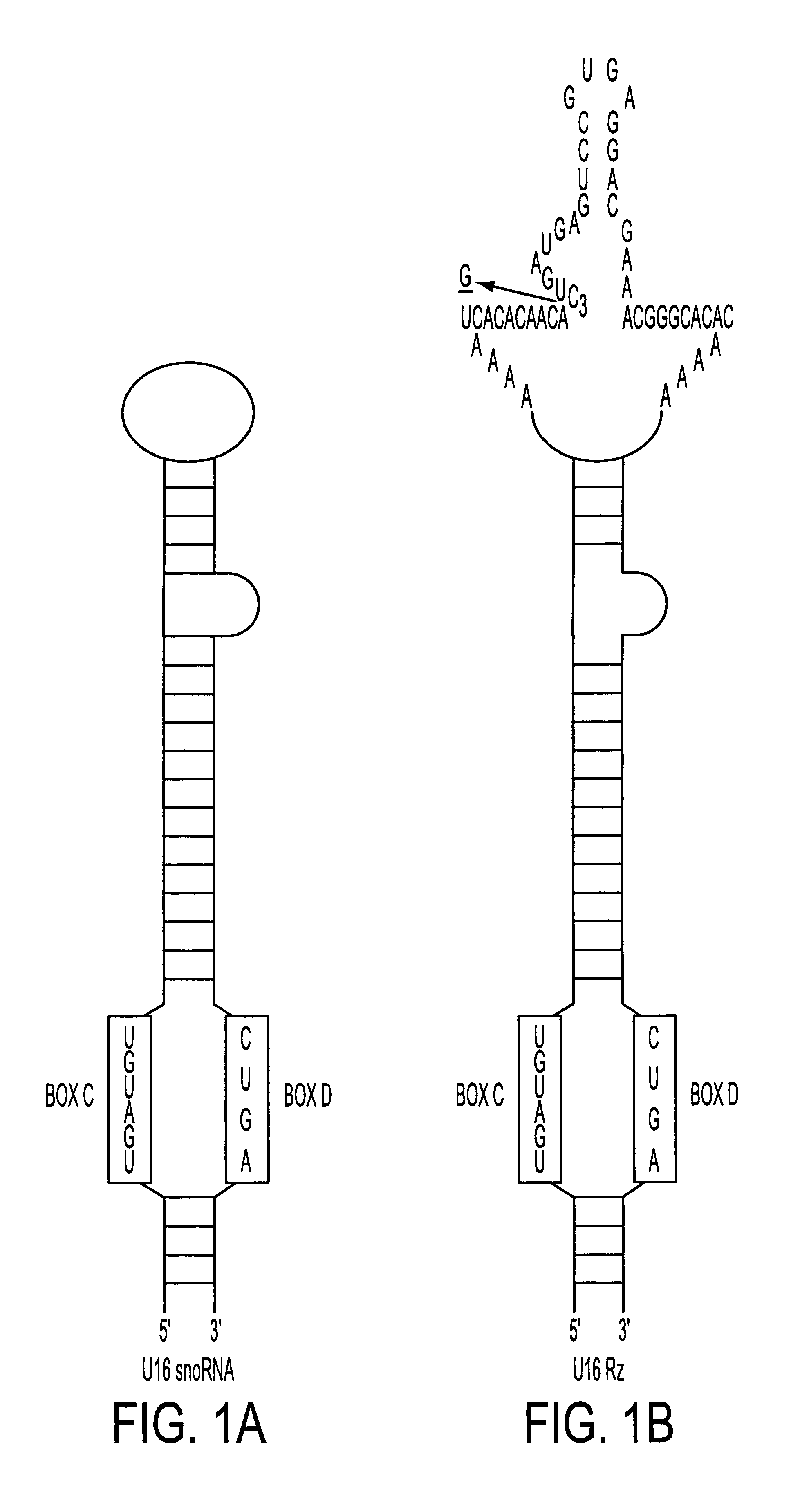
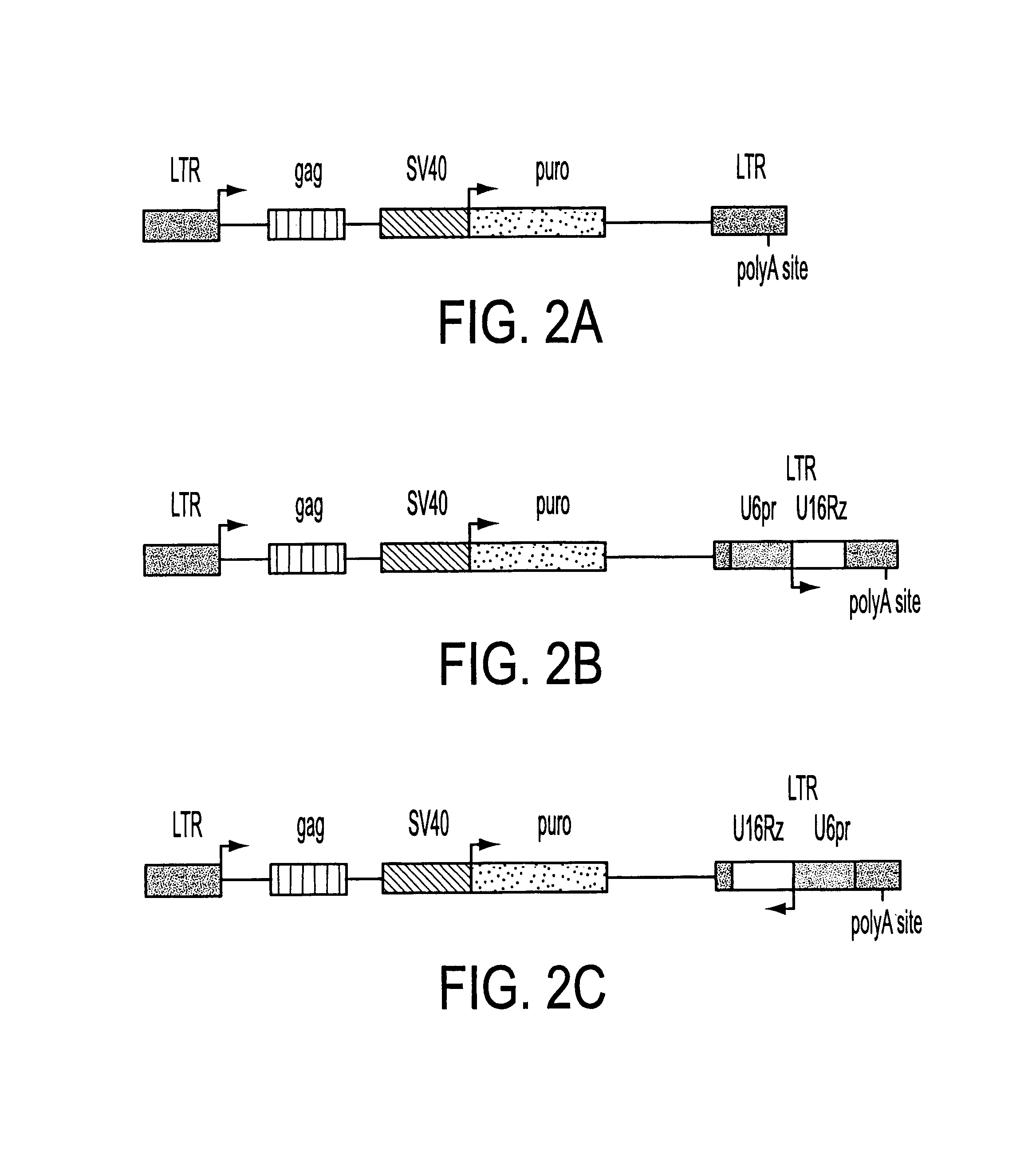
The HIV regulatory proteins Tat and Rev accumulate in nucleoli of human cells. No functional role has been attributed to this localization. Recently it was demonstrated that expression of Rev induces nucleolar re-localization of some nuclear factors involved in Rev export. Thus, it is likely that the nucleolus plays a critical role in Rev-mediated export of singly spliced and unspliced HIV-1 RNAs. As a test for trafficking of HIV-1 RNAs into the nucleolus, a hammerhead ribozyme which specifically cleaves HIV-1 RNA was joined to the U16 snoRNA resulting in accumulation of the ribozyme within nucleoli of human cells. Stably transduced human T-cells expressing this nucleolar localized ribozyme dramatically suppressed HIV-1 replication, confirming a possible trafficking of the HIV RNA through the nucleoli of human cells. In addition, a TAR element which binds Tat was joined to the U16 snoRNA, also resulting in localization in the nucleoli and inhibiting HIV replication.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Methods for enhancing engraftment of purified hematopoietic stem cells in allogenic recipients
InactiveUS20070098693A1Facilitate HSC engraftmentEnhance engraftmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDendritic cellGraft versus host disease induction
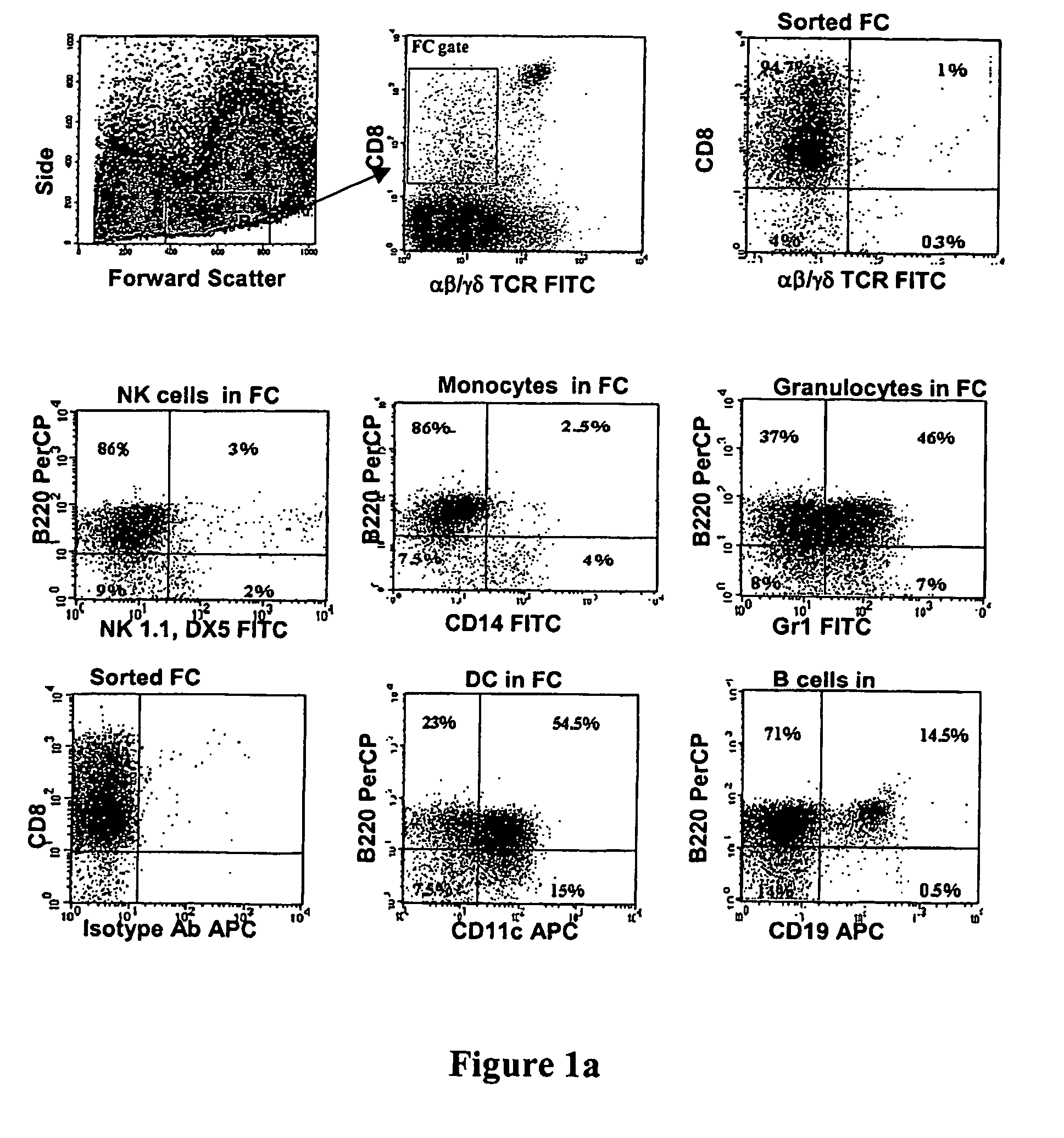
CD8+ / TCR− bone marrow cells facilitate engraftment of hemapoietic stem cells (HSQ in allogeneic recipients without causing graft versus host disease. The present invention identifies the main subpopulation (55-65%) of CD8+ / TCR− facilitating cells (FQ as plasmacytoid precursor dendritic cells (p-preDC). The present invention notably demonstrates that FC and p-preDC share many phenotypic, morphological, functional features, including IFN-α production, activation and survival after stimulation, and expansion and maturation after FIO-Ligand (FL) treatment. FL mobilized FC, the majority of which express a pre-DC phenotype, facilitate HSC engraftment. Although p-preDC significantly enhance HSC engraftment, they do so with less efficiency than FC. The present invention for the first time defines a direct functional role for p-preDC in HSC engraftment and will have a significant impact on strategies to design effective facilitating cell-based therapies for transplantation.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
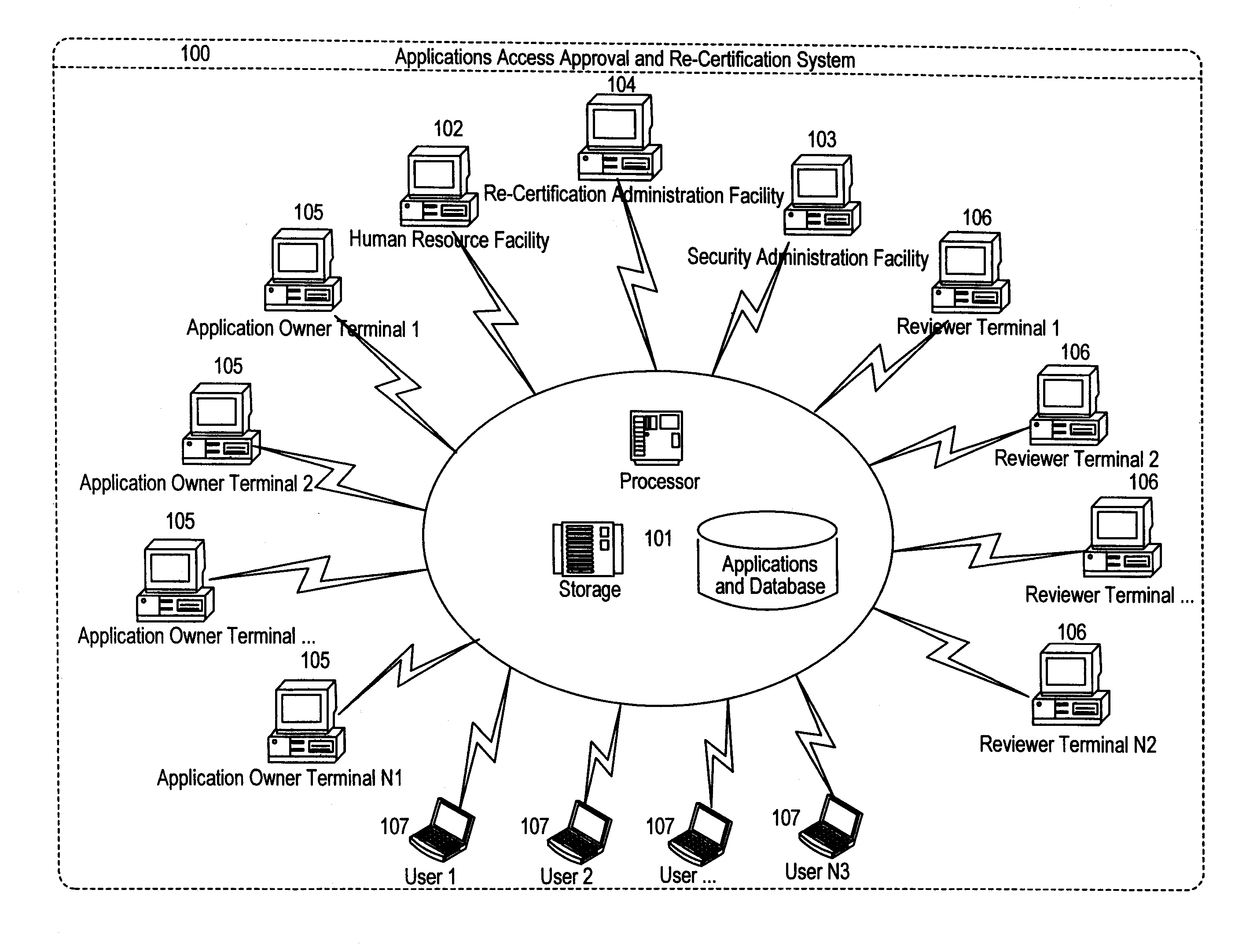
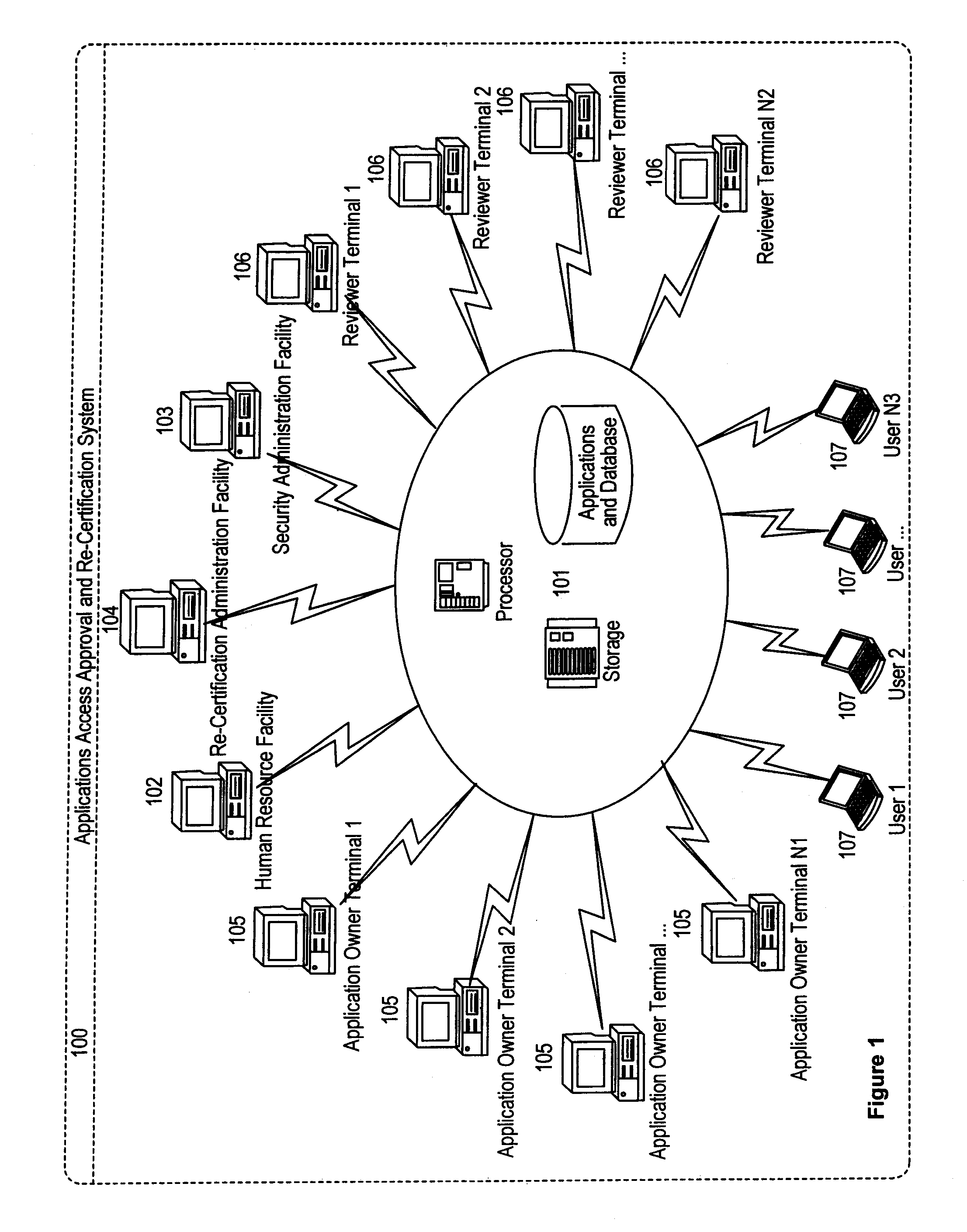
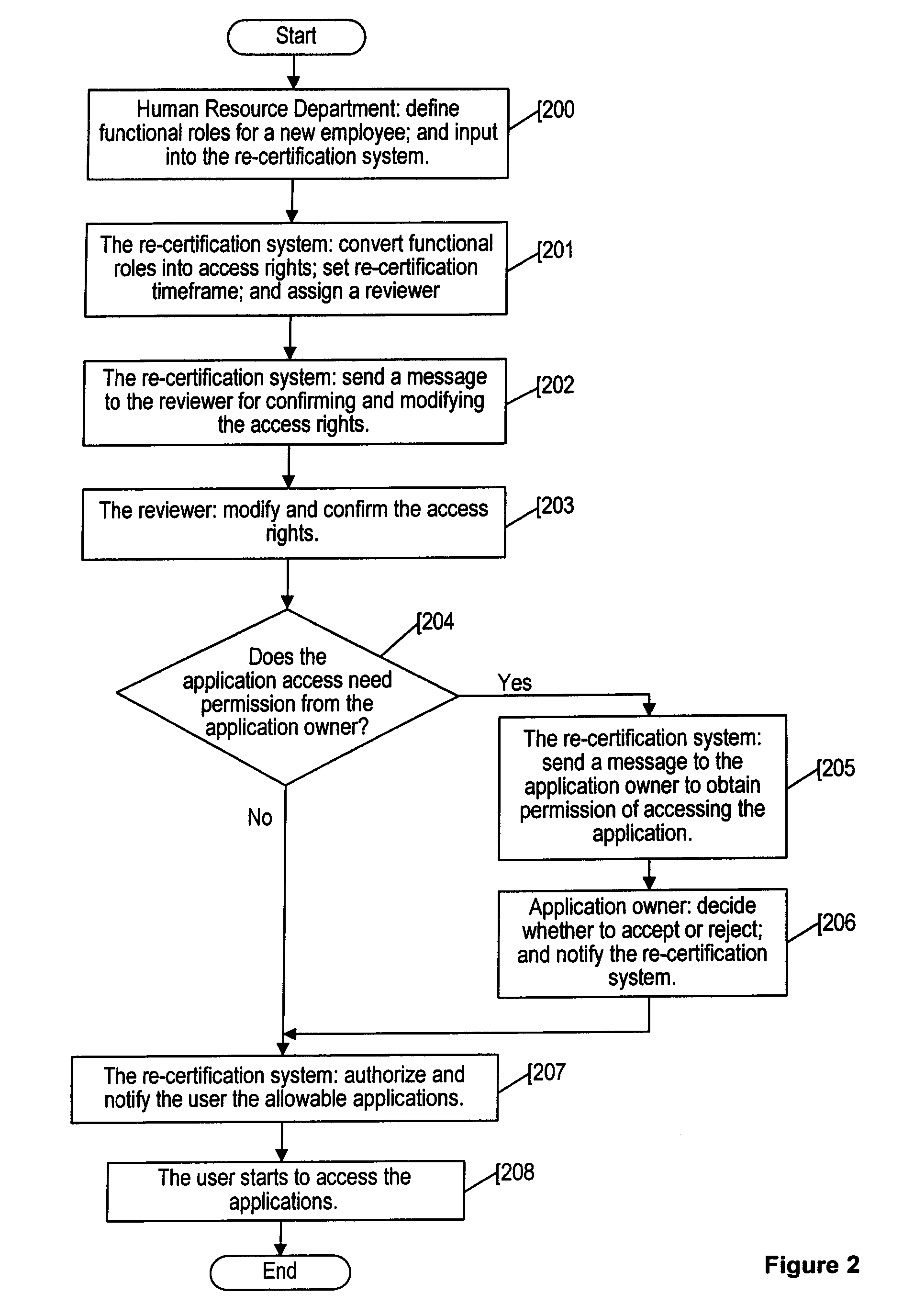
Applications access re-certification system
ActiveUS8181016B1Ensure safetyDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsComputerized systemApplication software
An applications access re-certification system is disclosed. The system is used for approving and re-certifying a user's access rights to applications stored or existing in an institution's computer system based on reviewing in a configurable timeframe the user's functional roles by designated reviewers. The system is used to ensure security of the applications by means of a reviewing process. The system is used to automate the re-certification process by means of a computer-controlled re-certification system which automatically operates in a defined methodology under control of re-certification administrators. The system could perform a management summary of access rights to the applications, and a automated scorecard to monitor the re-certification progress. The system could carry out a control process to ensure the changes to existing permissions are effectively managed at source destinations. The system has a capability of initiating multiple approvers for re-certifying a user's access rights.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
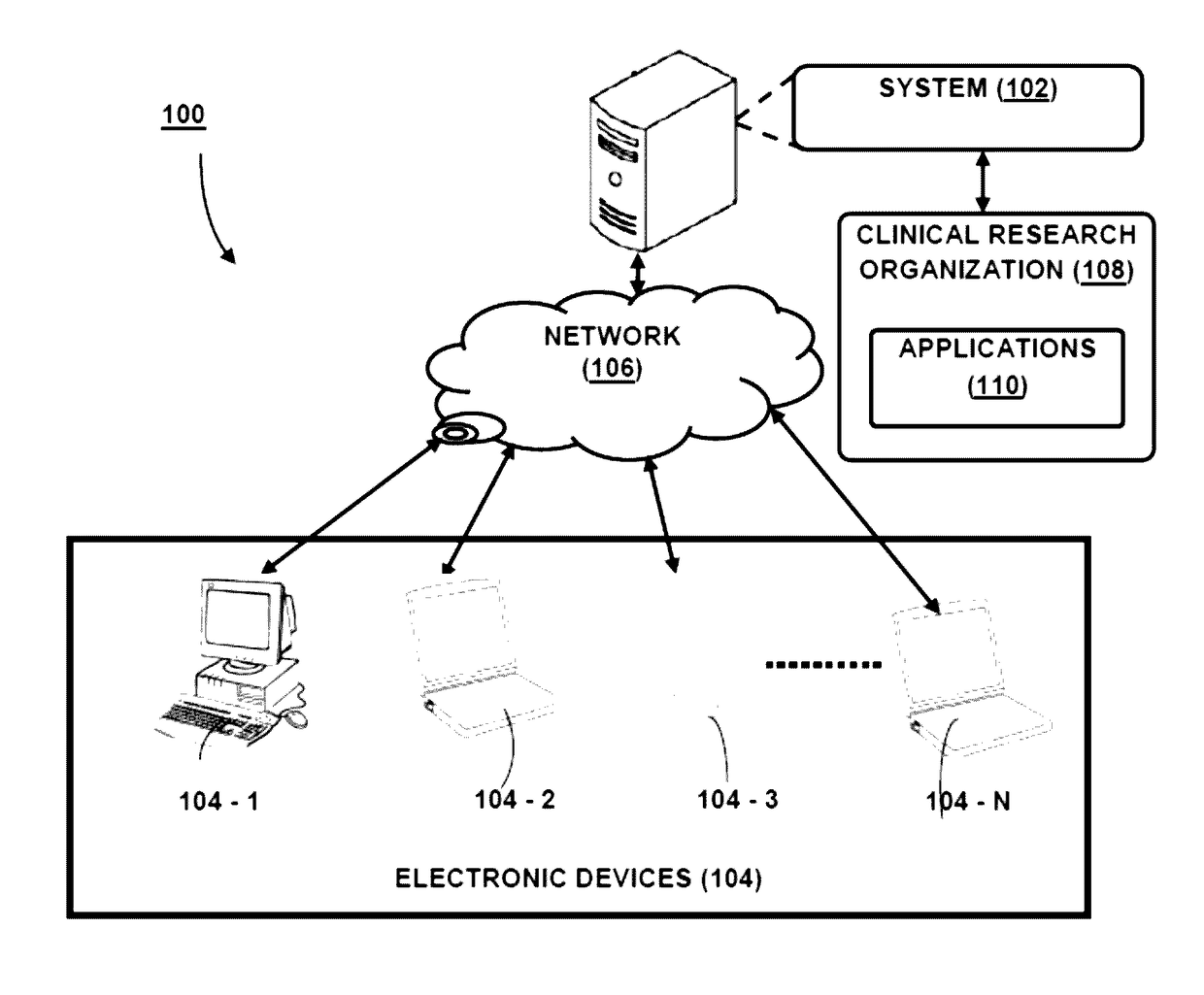
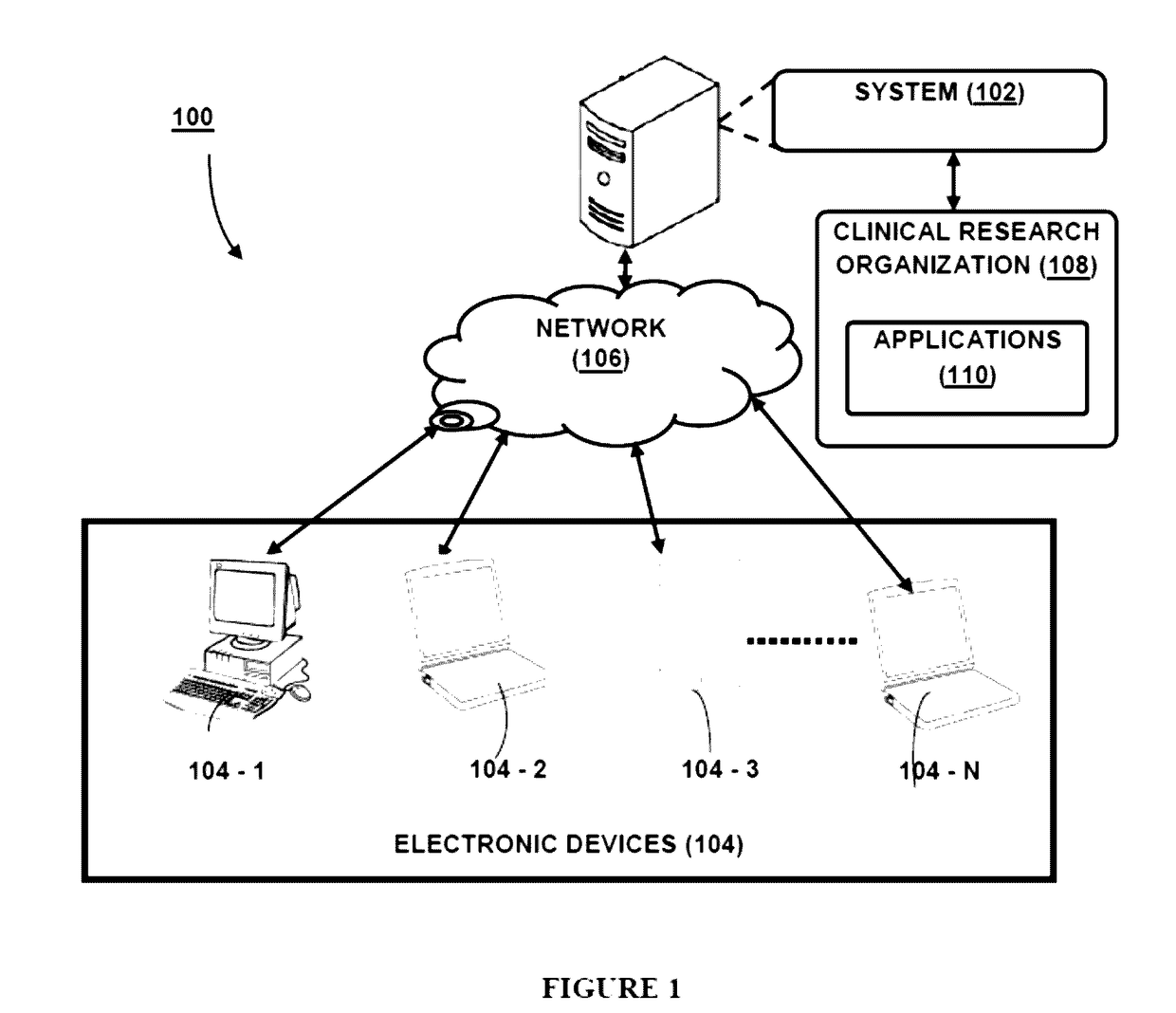
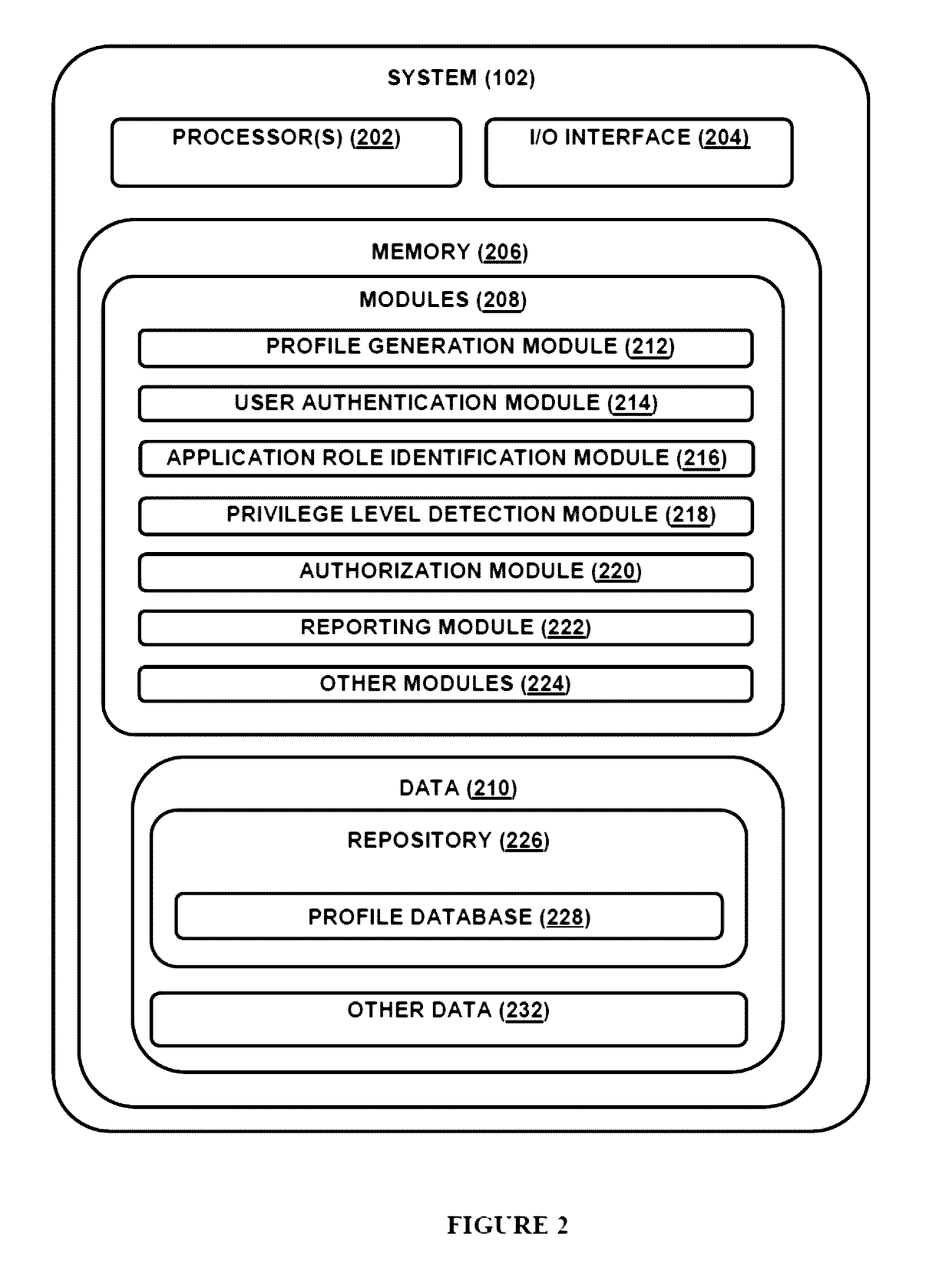
System and Method for Identity and Role Base Access Management
InactiveUS20170147790A1Computer-assisted medical data acquisitionTransmissionClinical trialSystem configuration
The present disclosure relates to system(s) and method(s) for enabling role based privileged access to a user for accessing a plurality of applications. The system is configured to maintain a user profile in a profile database. The user profile stores authentication details and a functional role as well as application role and privilege level corresponding to each application from a plurality of applications, wherein the plurality of applications are configured for conducting clinical trials. Further, the system is configured to provide the user a privileged access to the plurality of application based on the application role of the user and the privileged level associated with the application role.
Owner:HCL TECH LTD
Lightning arrester operation analog simulation system
InactiveCN103207336AAchieving dual output characteristicsFirmly connectedElectrical testingHuman–machine interfaceElectric power system
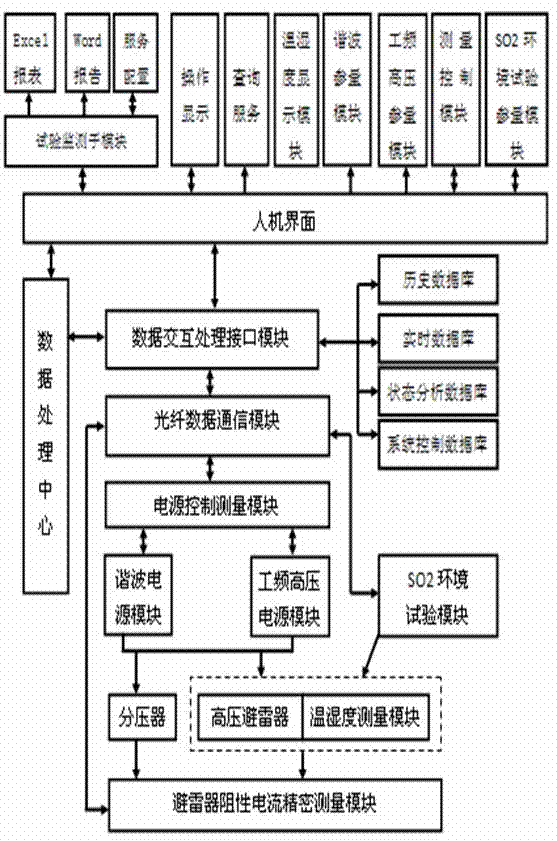
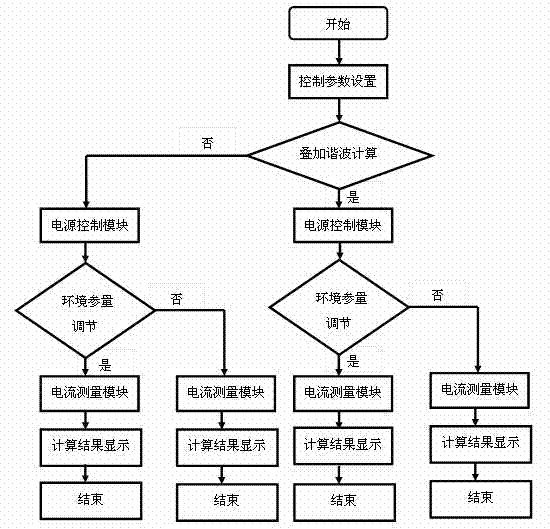
The invention provides a lightning arrester operation analog simulation system. The lightning arrester operation analog simulation system mainly comprises a data processing center, a data interactive processing interface module, a human-computer interface, an optical fiber data communication module, a power supply control measurement module, a harmonic wave power module, a power frequency high-voltage power module, a voltage divider, a high-voltage lightning arrester, a temperature and humidity measuring module, a lightning arrester resistive current precision measurement module and a SO2 environmental testing module. The data processing center, the human-computer interface and the data interactive processing interface module perform operation through a computing control platform, a host machine of the computing control platform is an industrial control computer and is provided with an optical fiber conversion module, and the host machine of the computing control platform is respectively connected with the power supply control measurement module, the lightning arrester resistive current precision measurement module and the SO2 environmental testing module through the optical fiber conversion module. In functional roles, the system can simulate joint effects of double factors including an electrical characteristic and a natural environment to simulate operation condition of an actual electric power system lightning arrester.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Method and device for deploying OpenStack
InactiveCN104754032AImprove the efficiency of deploying OpenStackProgram loading/initiatingTransmissionOperating systemFunctional role
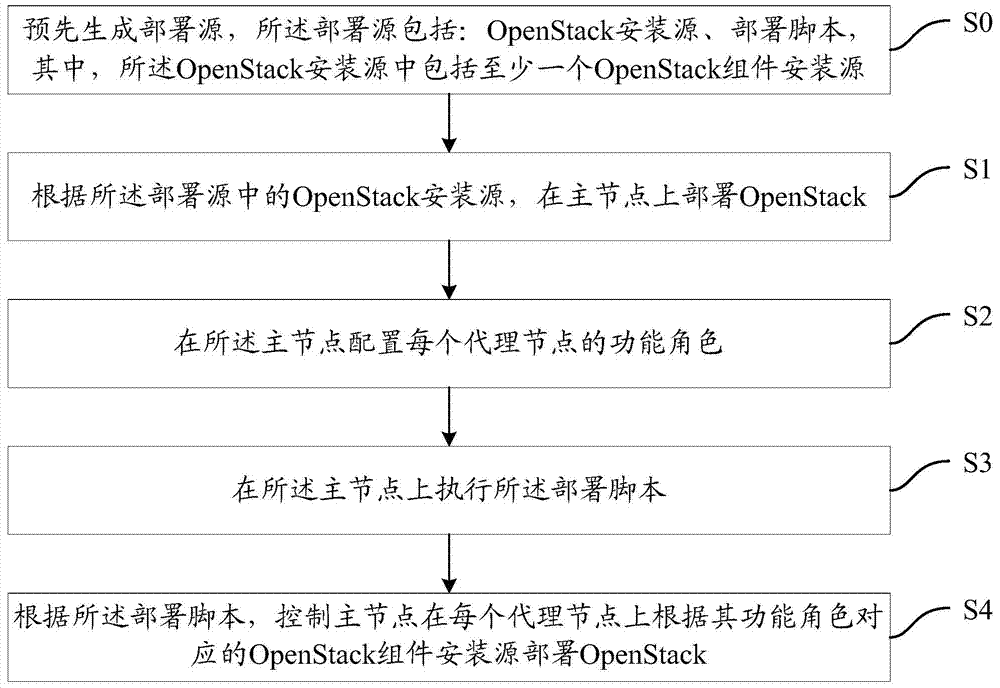
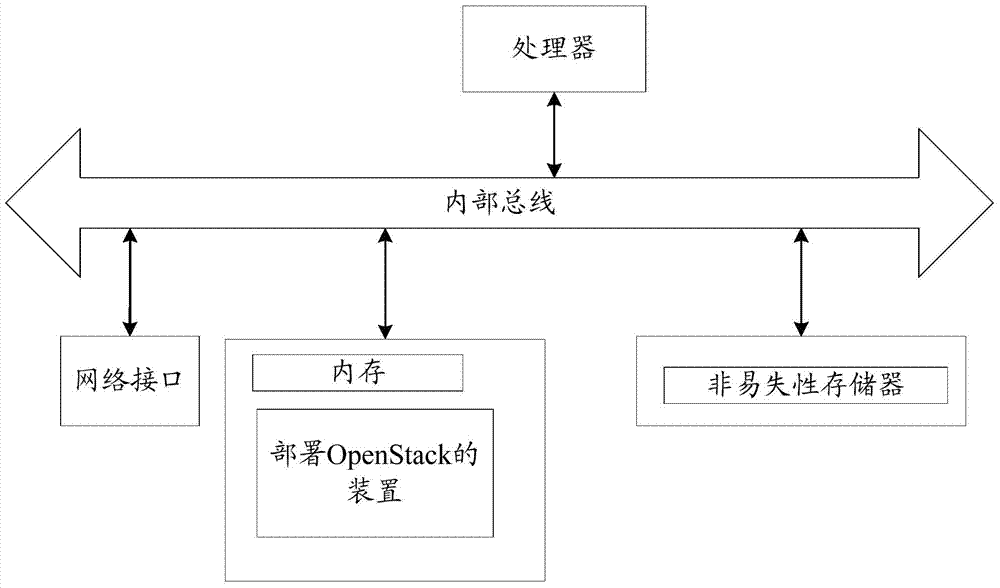
The invention provides a method and a device for deploying OpenStack. The method comprises the steps of pre-generating a deployment source, deploying the OpenStack on a main node according to an OpenStack mounting source in the deployment source, configuring the functional role of each agent node on the main node, executing a deployment script on the main node, and controlling the main node to deploy the OpenStack on each agent node according to the OpenStack component mounting source corresponding to the functional role according to the deployment script, wherein the deployment source comprises the OpenStack mounting source and the deployment script, and wherein the OpenStack mounting source comprises at least one OpenStack component mounting source. The method and the device for deploying the OpenStack are capable of improving the OpenStack deploying efficiency.
Owner:INSPUR GROUP CO LTD
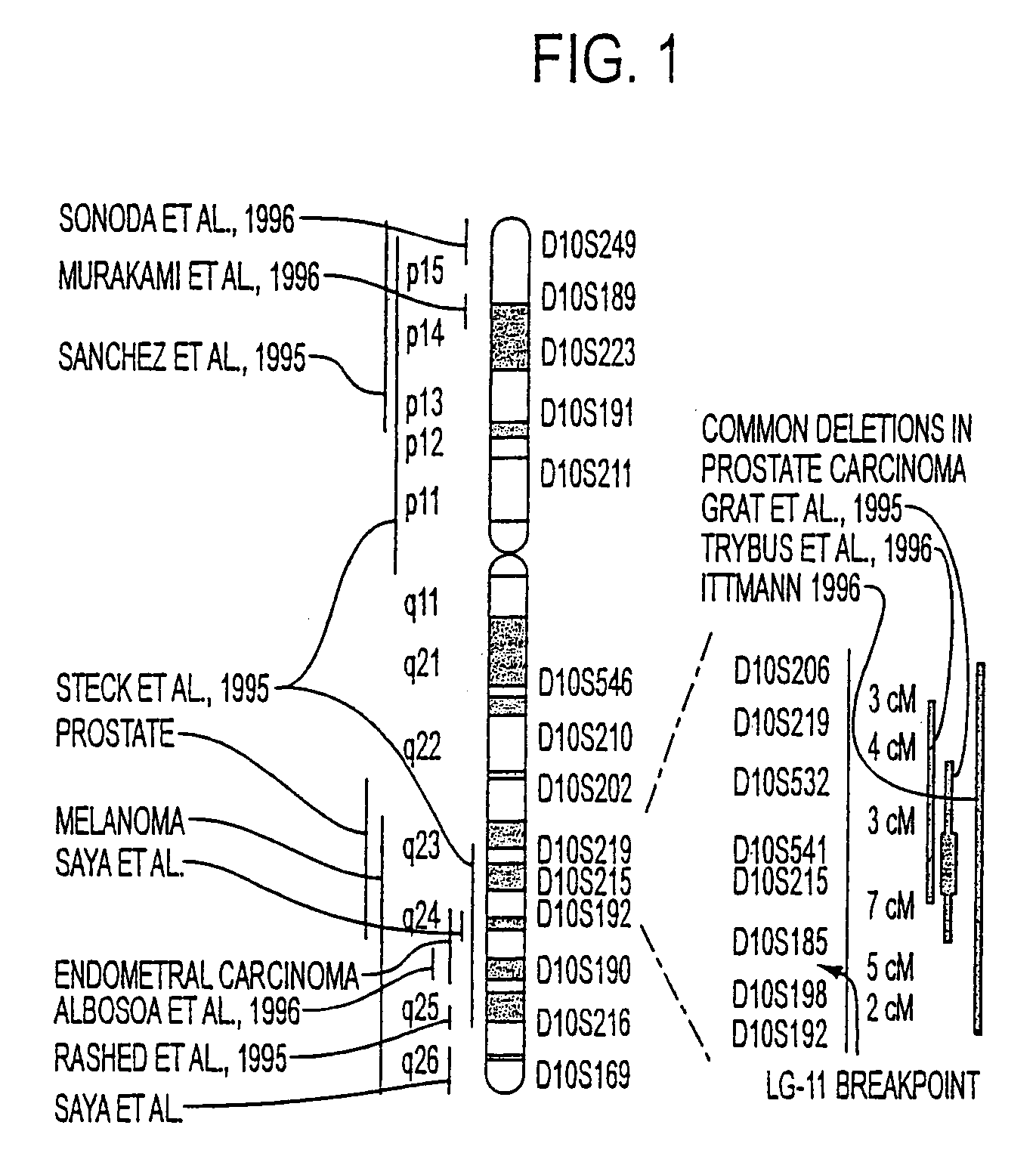
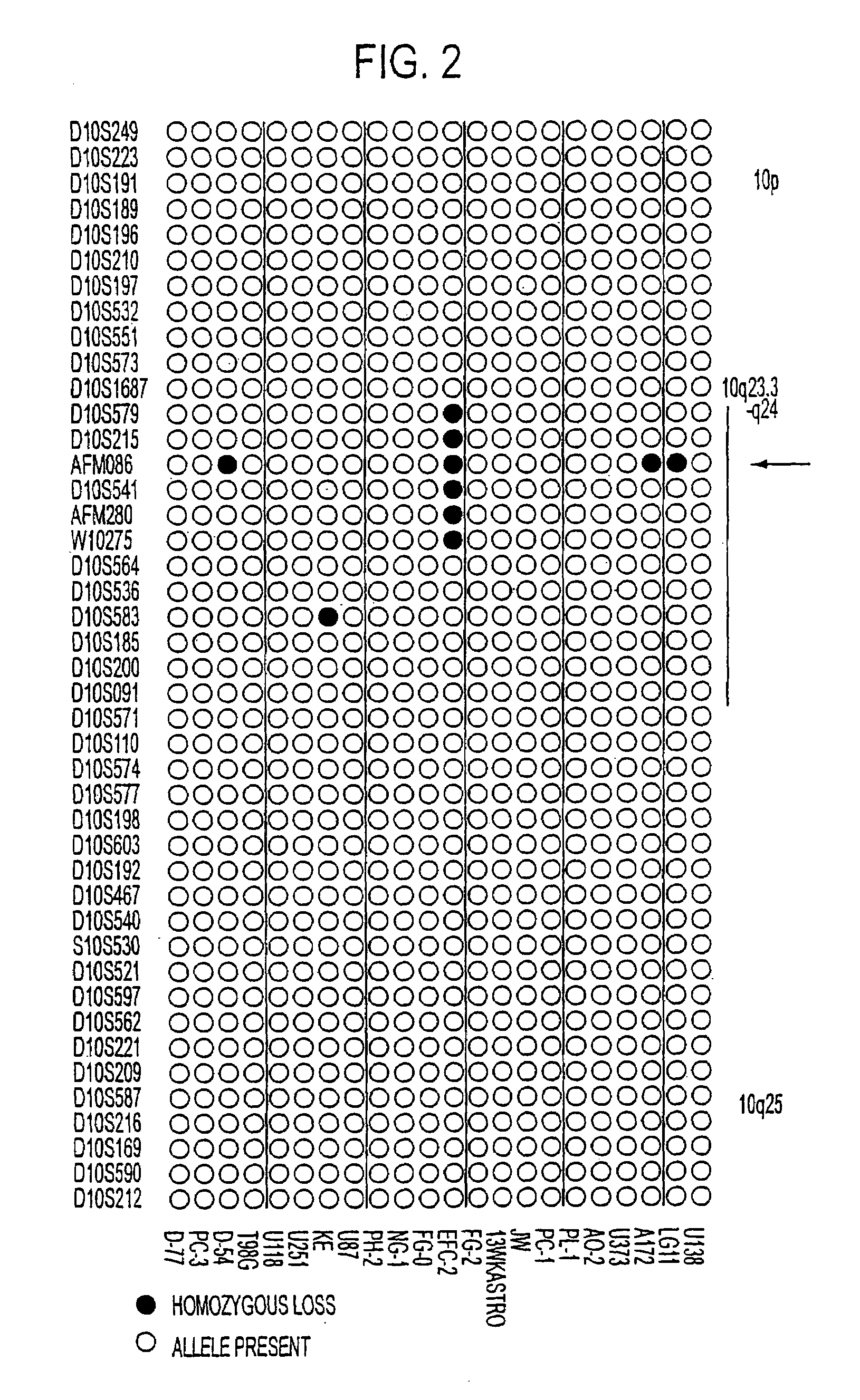
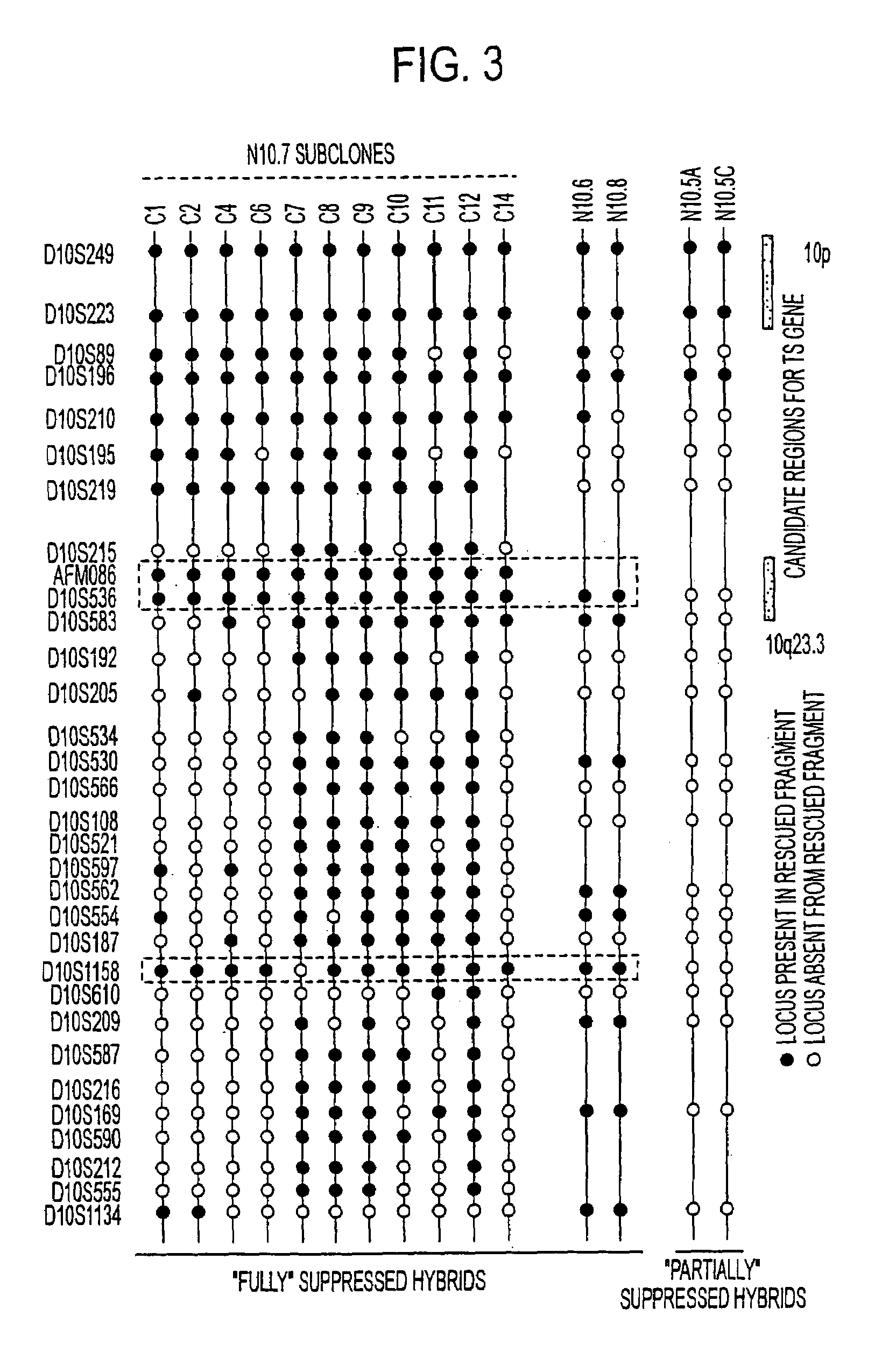
Tumor suppressor designated TS10q23.3
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
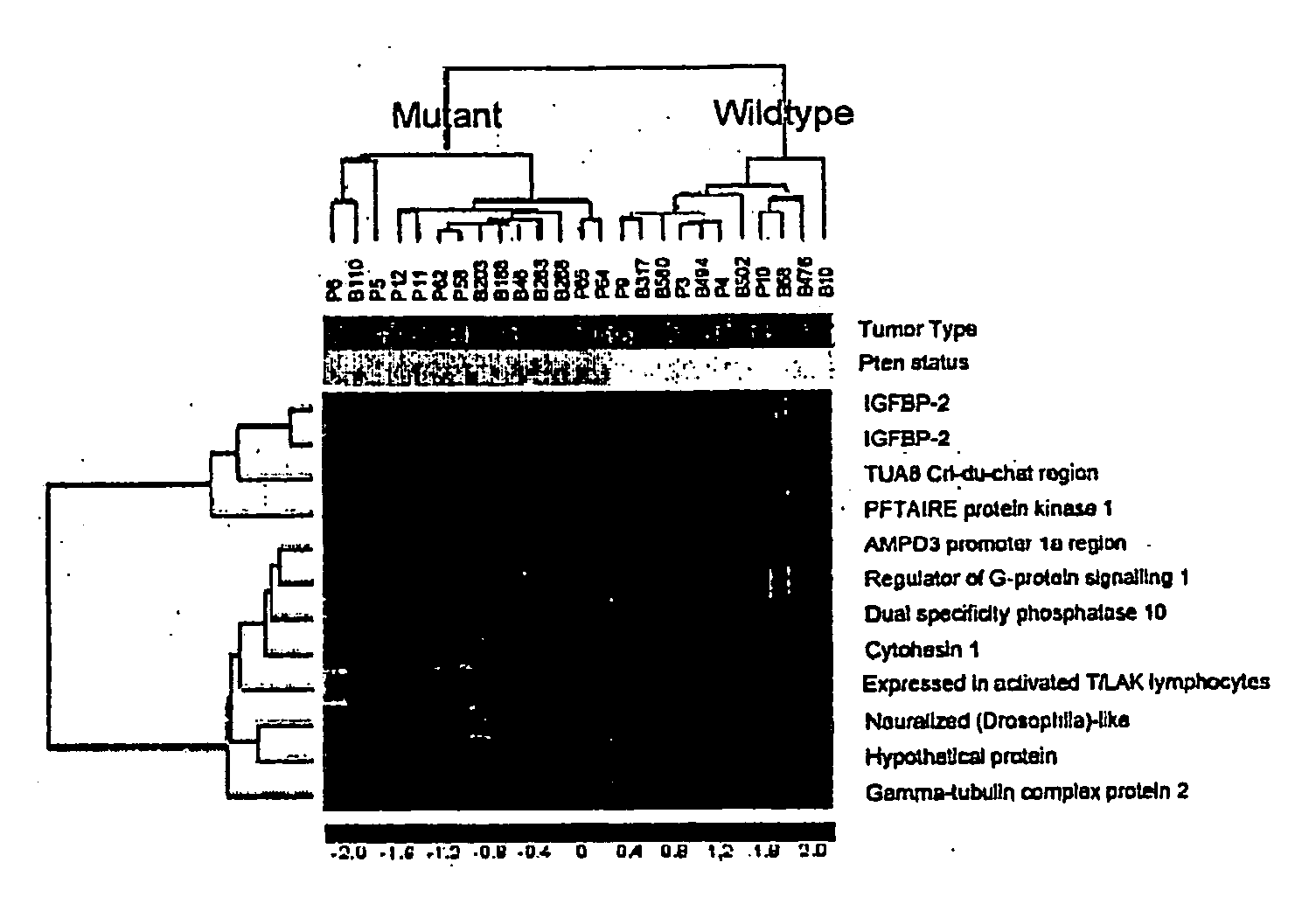
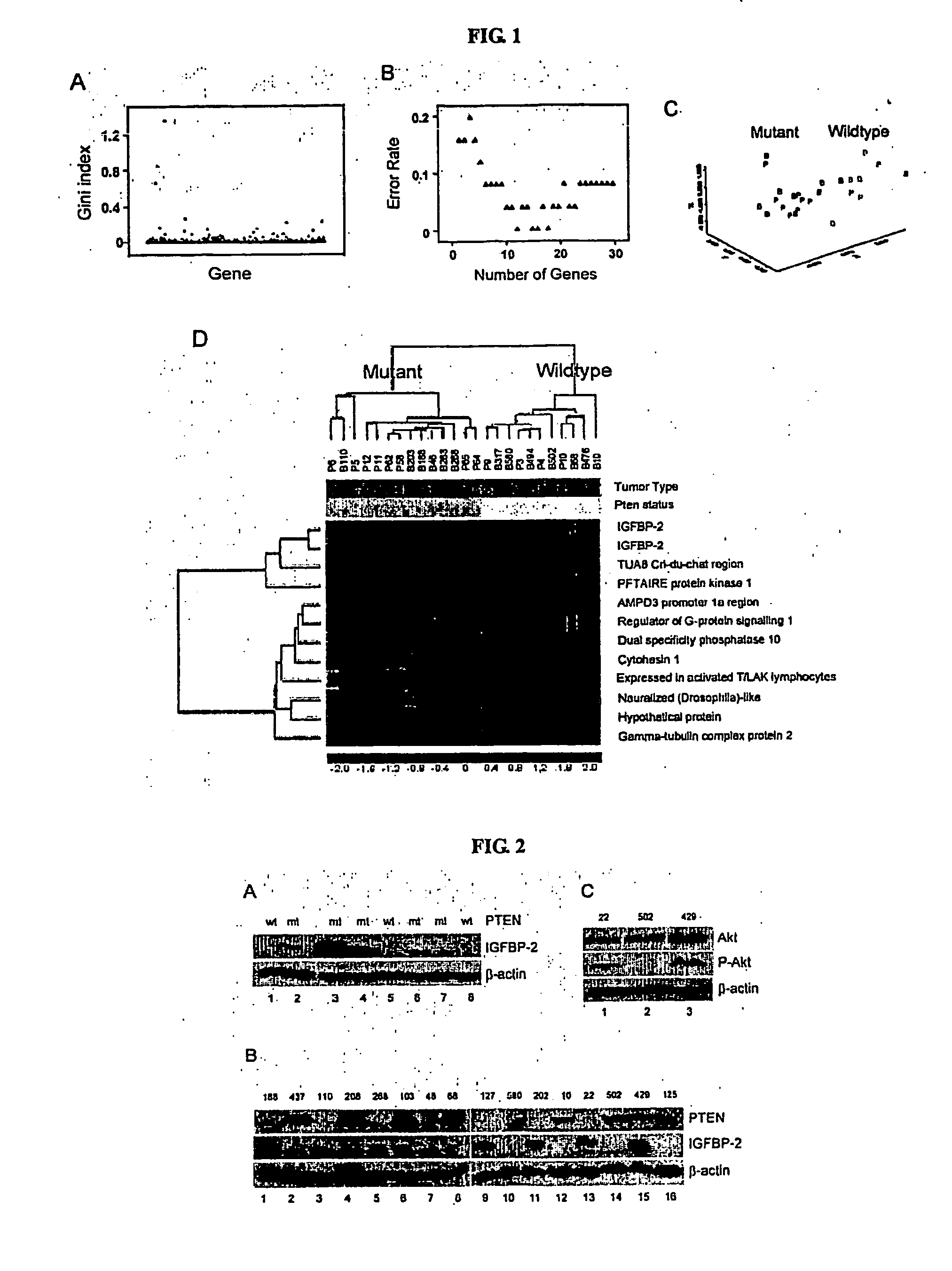
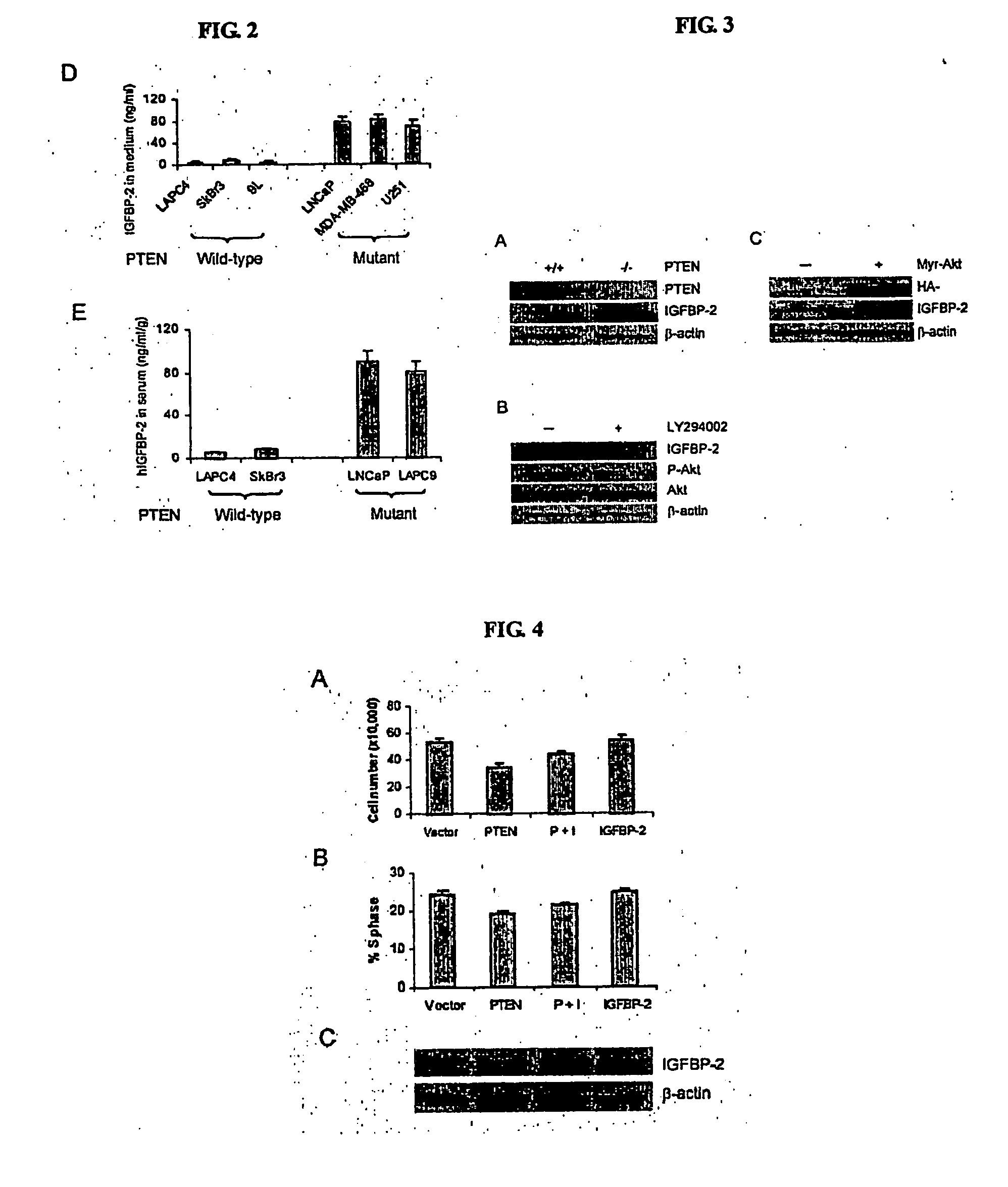
Molecular Signature of the Pten Tumor Suppressor
InactiveUS20070253953A1Predicting effectivenessPredicting responsivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthDrug study
The present invention relates to the identification a molecular signature for PTEN tumor suppressor. The molecular signature comprising a gene or genes that are of use for diagnosis, prognosis, drug research and development and therapeutics. Specifically, the present invention relates to identification of IGFBP2 gene, its mRNA and / or protein products that closely associate with PTEN mutations. The present invention further demonstrates that IGFBP2 expression is negatively regulated by PTEN, positively regulated by PI3K and Akt activation, that IGFBP2 plays a functional role in the PTEN signaling and is required for Akt transformation. The use of IGFBP2 gene, its gene product such as its RNA transcript, protein and molecular probes in diagnosis, prognosis, drug discovery and validation and therapeutic target and therapeutics is also contemplated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
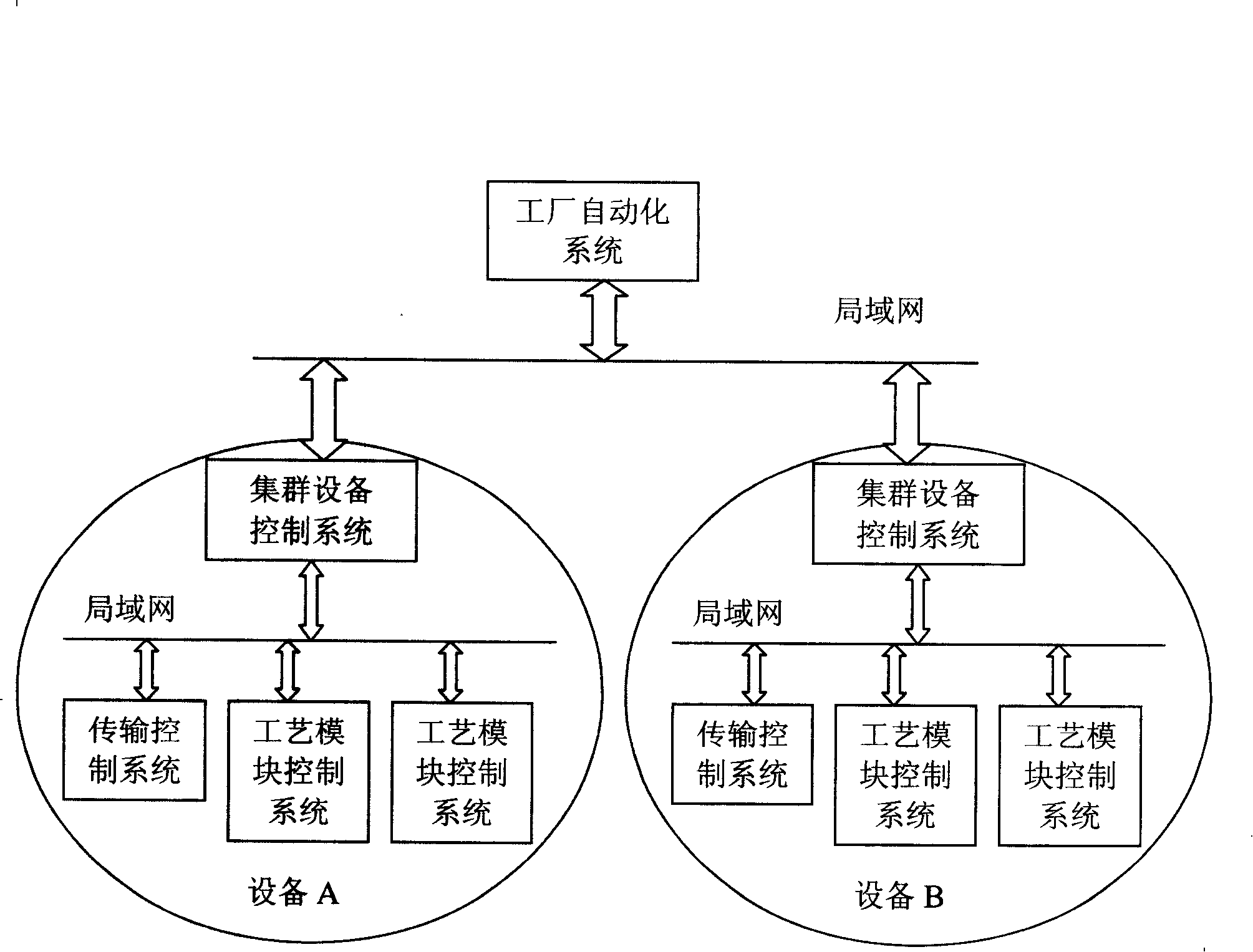
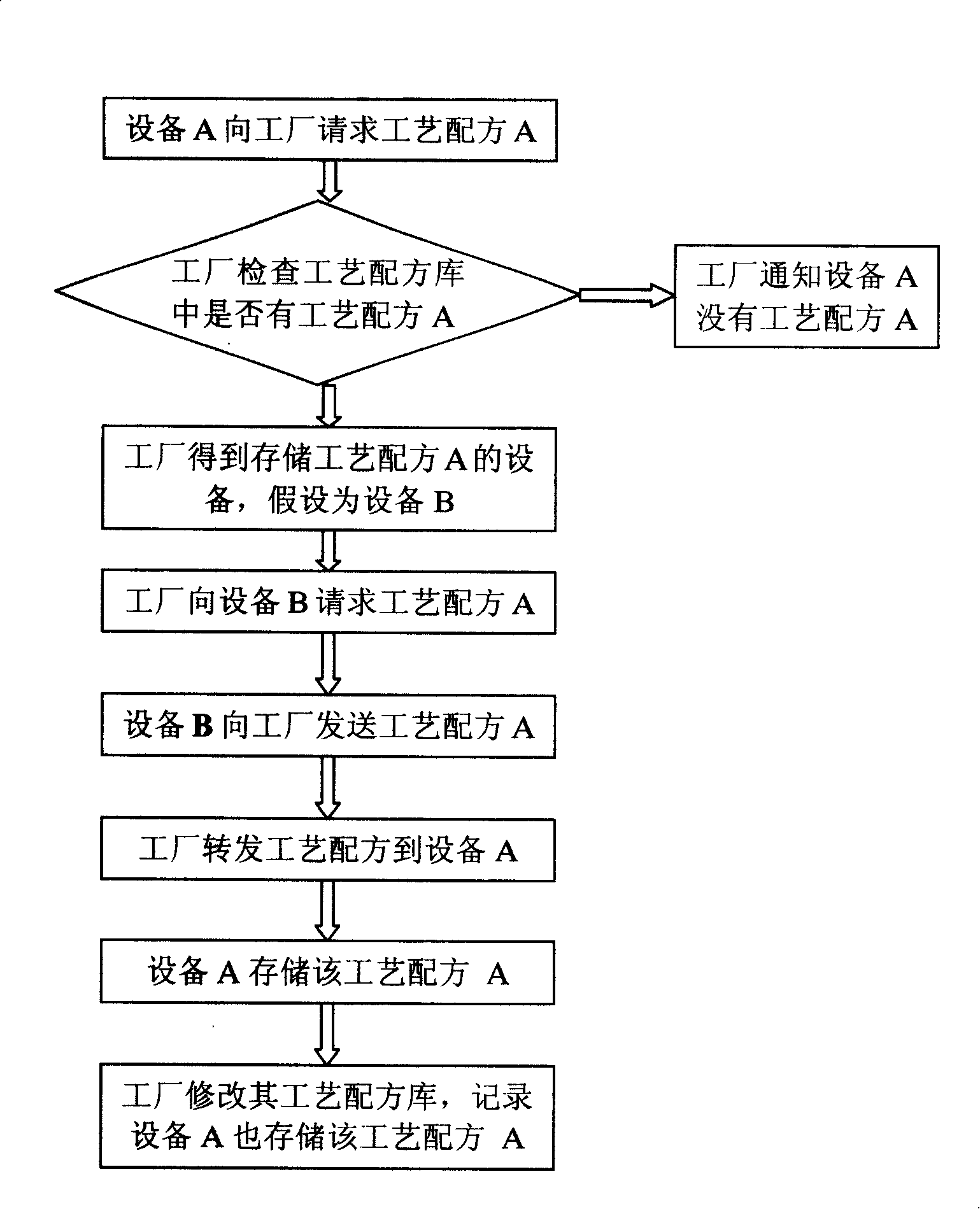
Semiconductor fabrication process formula management process
InactiveCN101216698AResolve synchronizationRealize automatic disseminationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersManagement processSemiconductor factory
The invention relates to the automation technical field of a semiconductor factory, in particular to a management method for semiconductor manufacturing process formulation. On the basis of dividing specific functional roles between a factory automation system and a device, the management method for the semiconductor manufacturing process formulation provided by the invention realizes the management on the process formulation in accordance with a plurality of strategies between the system and the device such as connection, disconnection and management. Through specifically dividing roles between the factory automation system and the device, two systems manage the process formulation coordinately, thereby decreasing the complexity of management and improving the efficiency of management.
Owner:BEIJING NAURA MICROELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
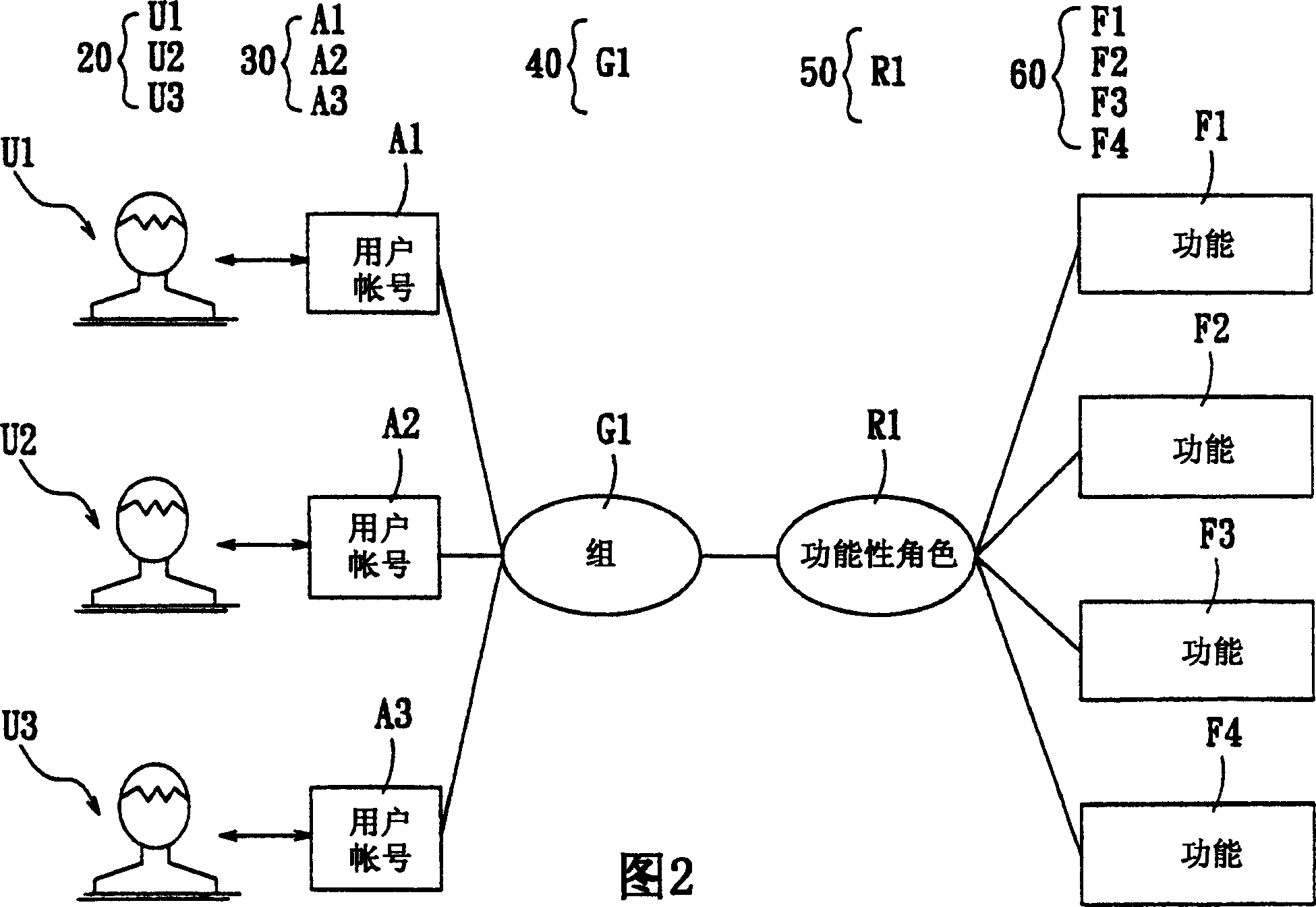
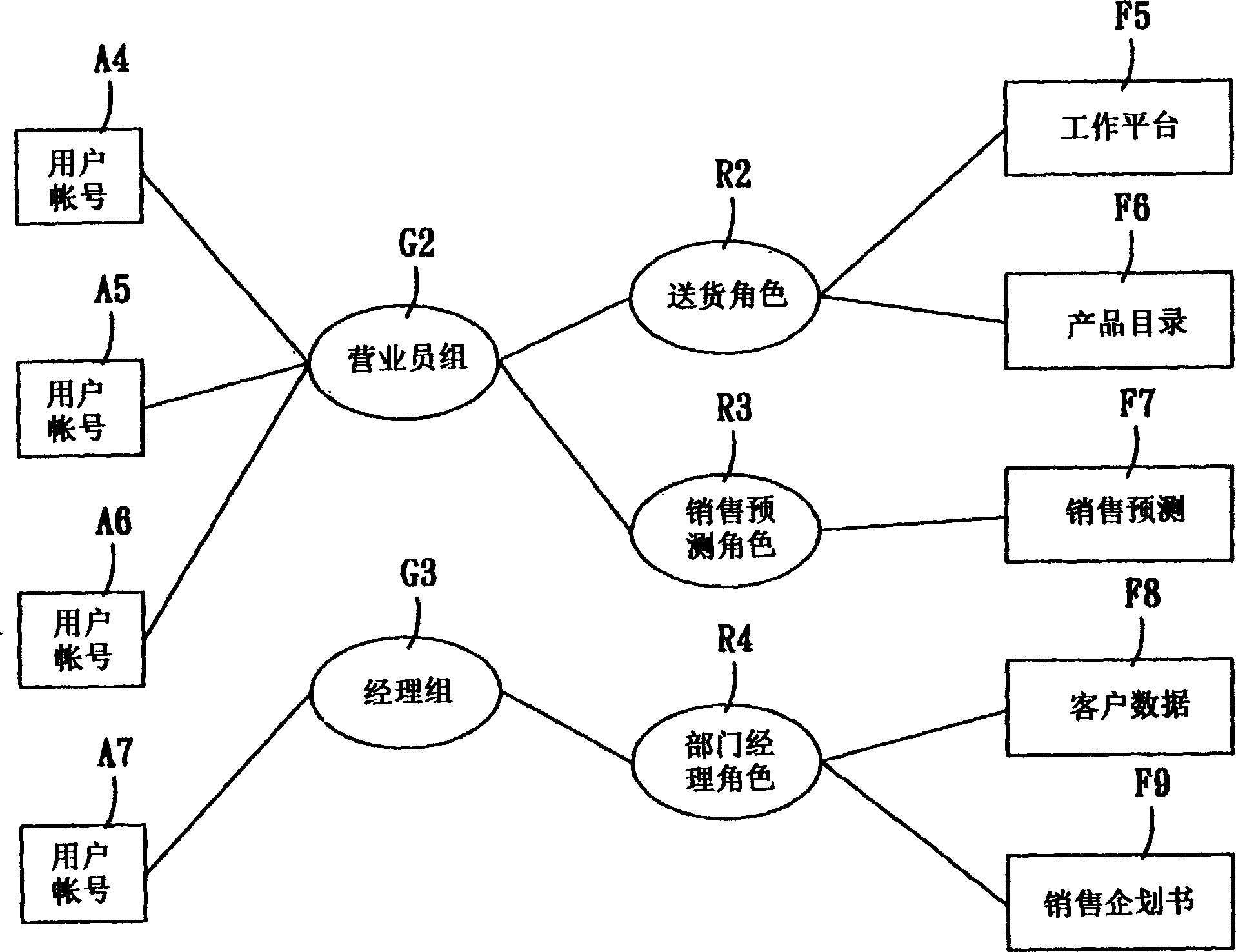
User authority setting system, setting method and recording medium thereof
ActiveCN1558354AEffective masteryCreate validResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsWork contentWorld Wide Web
The user authority setting system includes account number creating module, group creating module, role creating module, function creating module and relation defining module. The account number creating module creates users' account numbers, the group creating module creates at least one group based on the user organism mechanism, the role creating module creates at least one functional role based on the users' work content, the function creating module creates several functions based on users' executed items, and the relation defining module defines the relations among the account numbers, the groups, the functional roles and function using authority. In addition, the present invention also discloses user authority setting method and corresponding record medium for computer to execute.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Approver Identification Using Multiple Hierarchical Role Structures
Systems and methods for automating and increasing the efficiency of business processes using multiple hierarchical role structures. In one embodiment, a method comprises defining two or more hierarchies, defining an approver for a business process where the approver is associated with at least a first role in a first one of the hierarchies and a second role in a second one of the hierarchies, and identifying an approver position within an organization where the approver position is associated with the first and second roles. The hierarchies may, for example, be selected from a hierarchy of functional roles, a hierarchy of legal roles and a hierarchy of level roles.
Owner:MORINVILLE PAUL V
Methods of Modulating Inflammatory Reactions by Modulating Xanthine Oxidoreductase Activity
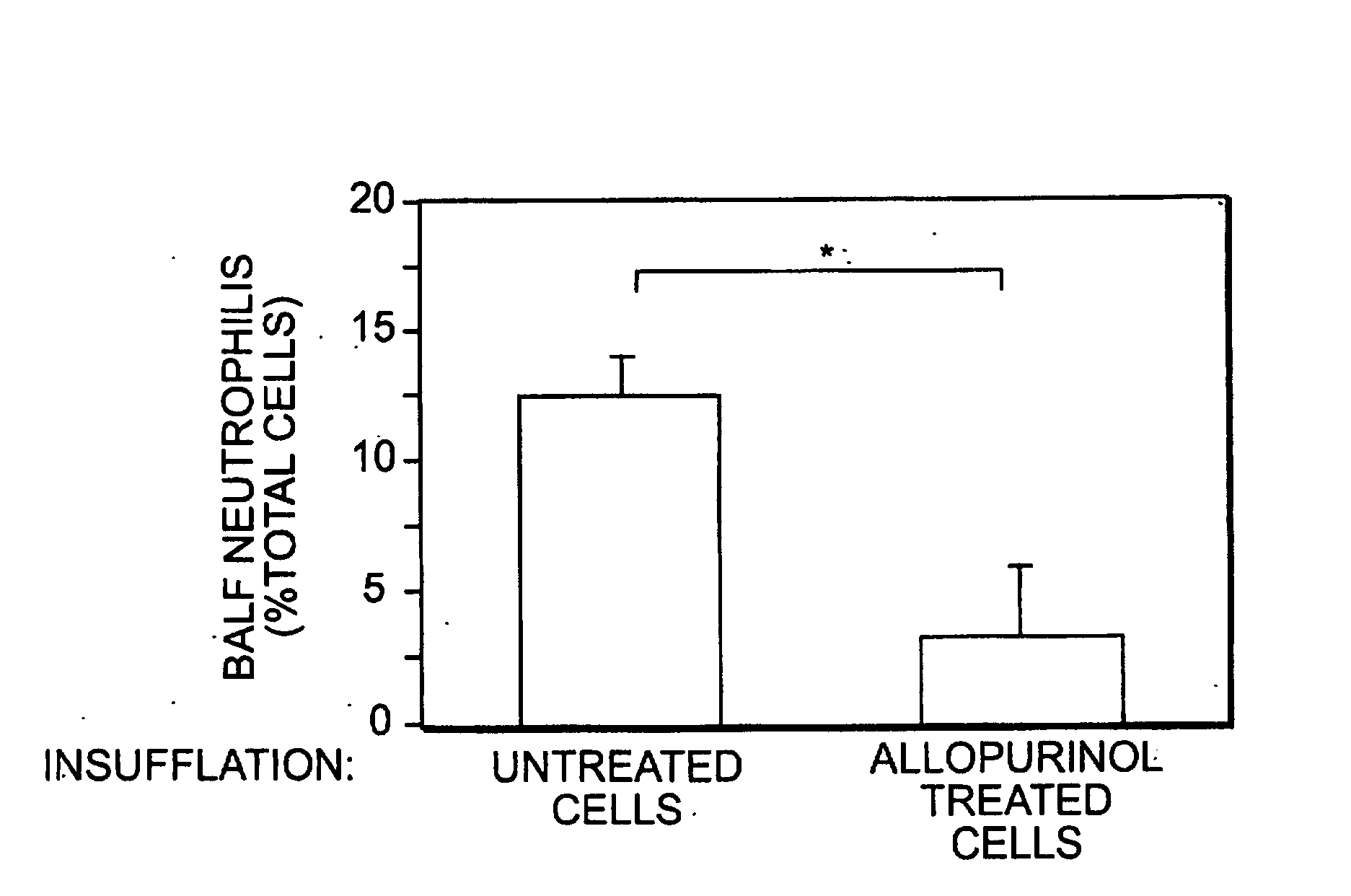
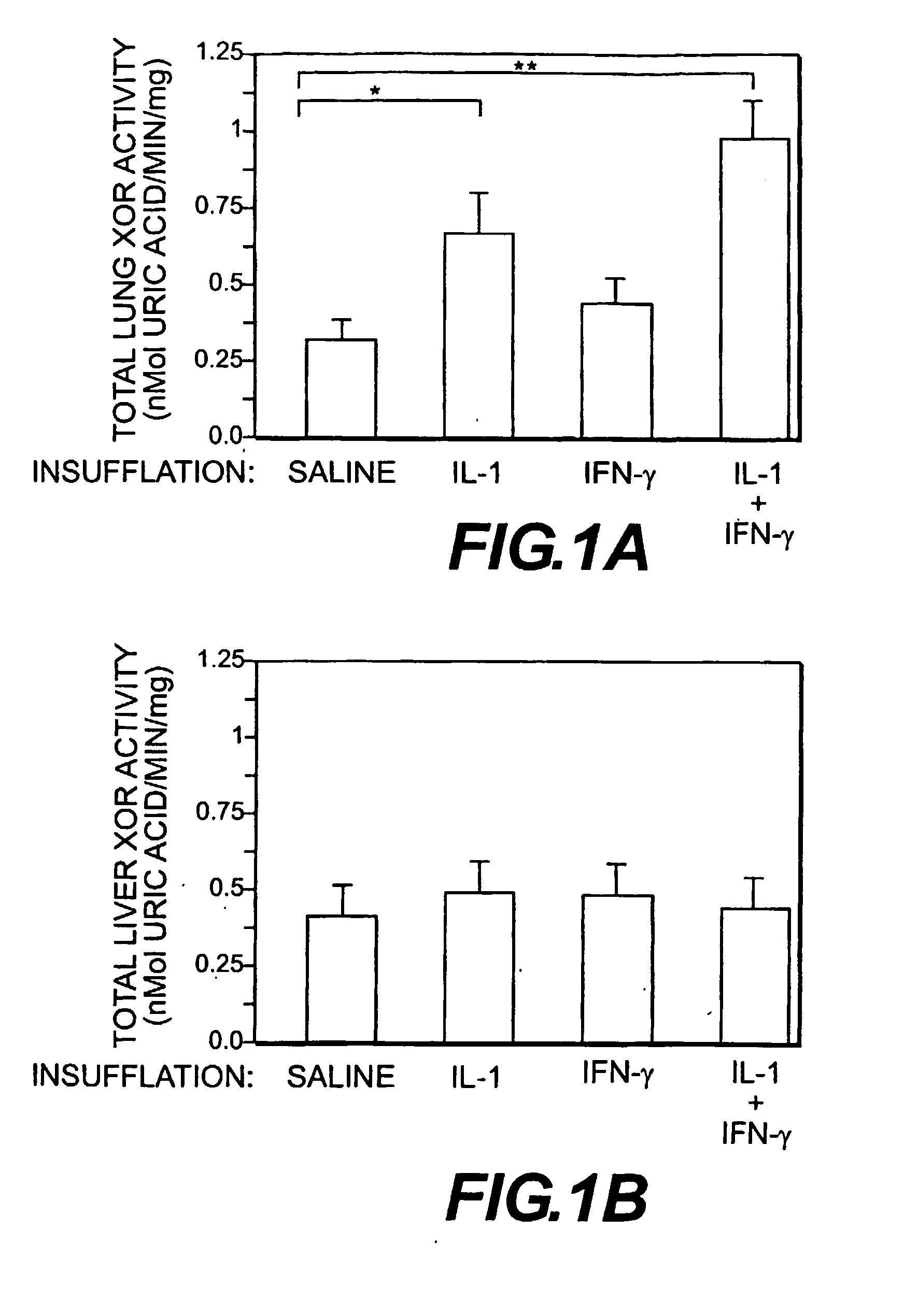
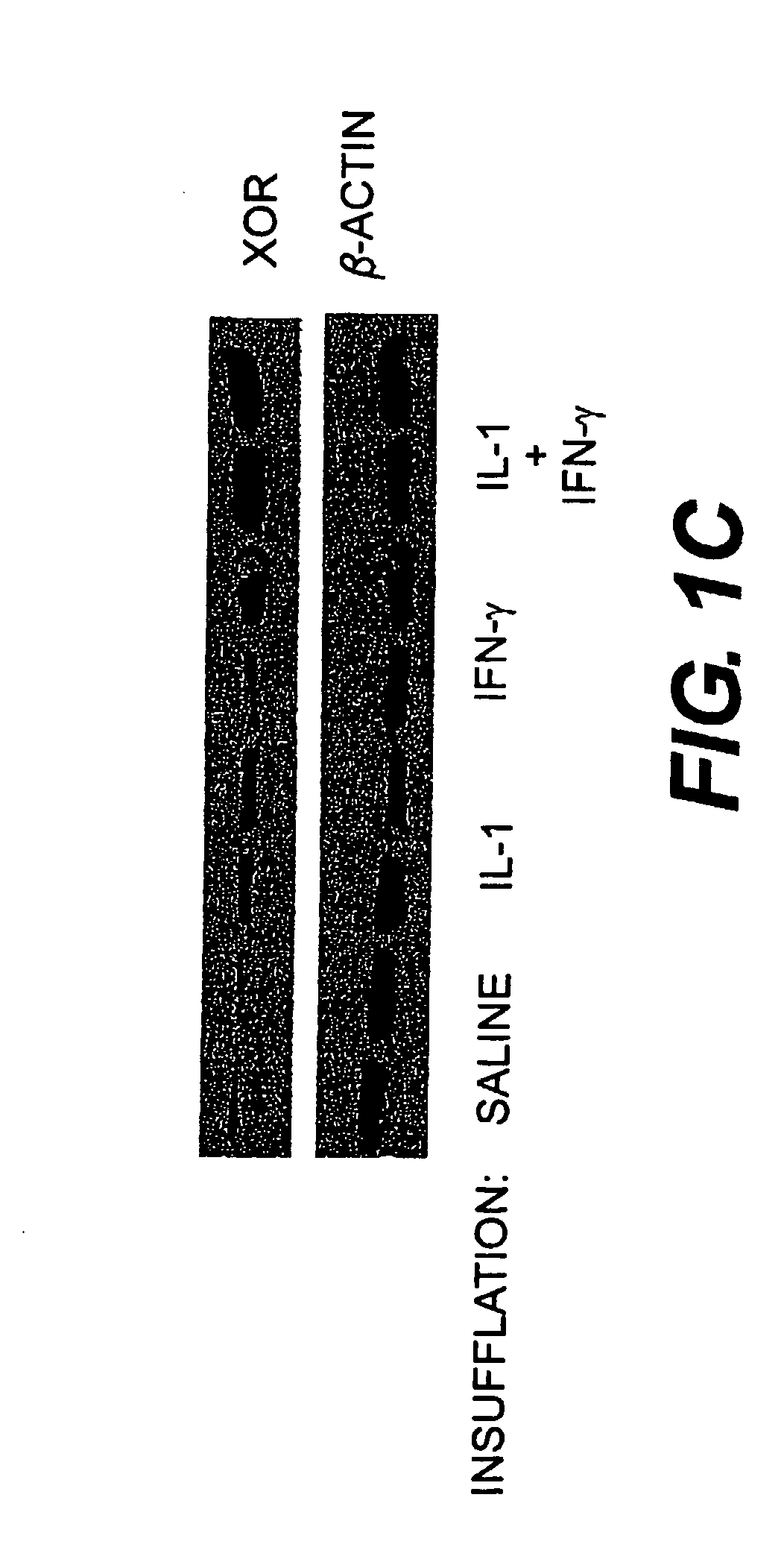
Evidence is presented that inflammation and injury involves activation of xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) in the newly recruited mononuclear phagocytes (MNP). XOR has been shown to be increased predominantly in the MNP that increase rapidly in the lungs of rats that develop acute lung injury (ALI) following intratracheal cytokine insufflation. XOR was recovered from the MNP largely converted to its oxygen radical generating, reversible O-form, and alveolar MNP exhibited increased oxidative stress as evidenced by increased nitrotyrosine staining. Cytokine insufflation also increased alveolar cell apoptosis. A functional role for XOR in cytokine induced inflammation was demonstrated. Tungsten and allopurinol decreased MNP XOR induction, nitrotyrosine staining, inflammatory cell infiltration, and alveolar cell apoptosis. Transfer of control or allopurinol treated MNP into rat lungs and confirmed a specific role for MNP XOR in promoting lung inflammation. These data indicate that XOR can contribute to lung inflammation by its expression and conversion in a highly mobile inflammatory cell population.
Owner:WEBB WARING INST
Lectin protein prepared from maackia fauriei, process for preparing the same and the use thereof
InactiveUS20050084903A1Return to normal activitiesSaccharide peptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesMelanomaCancer cell
The present invention relates to a lectin protein, designated MFA isolated and purified from the bark of the Korean legume Maackia fauriei, process for preparing the same and the use thereof. This protein can be used as reagents in the study of carbohydrate binding proteins as well as to examine the distribution of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cancer cells owing to its capability that specifically recognizes N-acetylneuraminic acid which plays important structural and functional roles in the expressions of various cells or oligosaccharide terminal residue of glycoconjugates, and, in addition, used as an anti-cancer drug in view of its anti-proliferation effect against various cancers such as breast cancer, melanoma, hepatoma, etc.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Methods for promoting t cells response
ActiveUS20190309075A1Inhibits degree qualityResistant to tumor growthOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoBiological activation
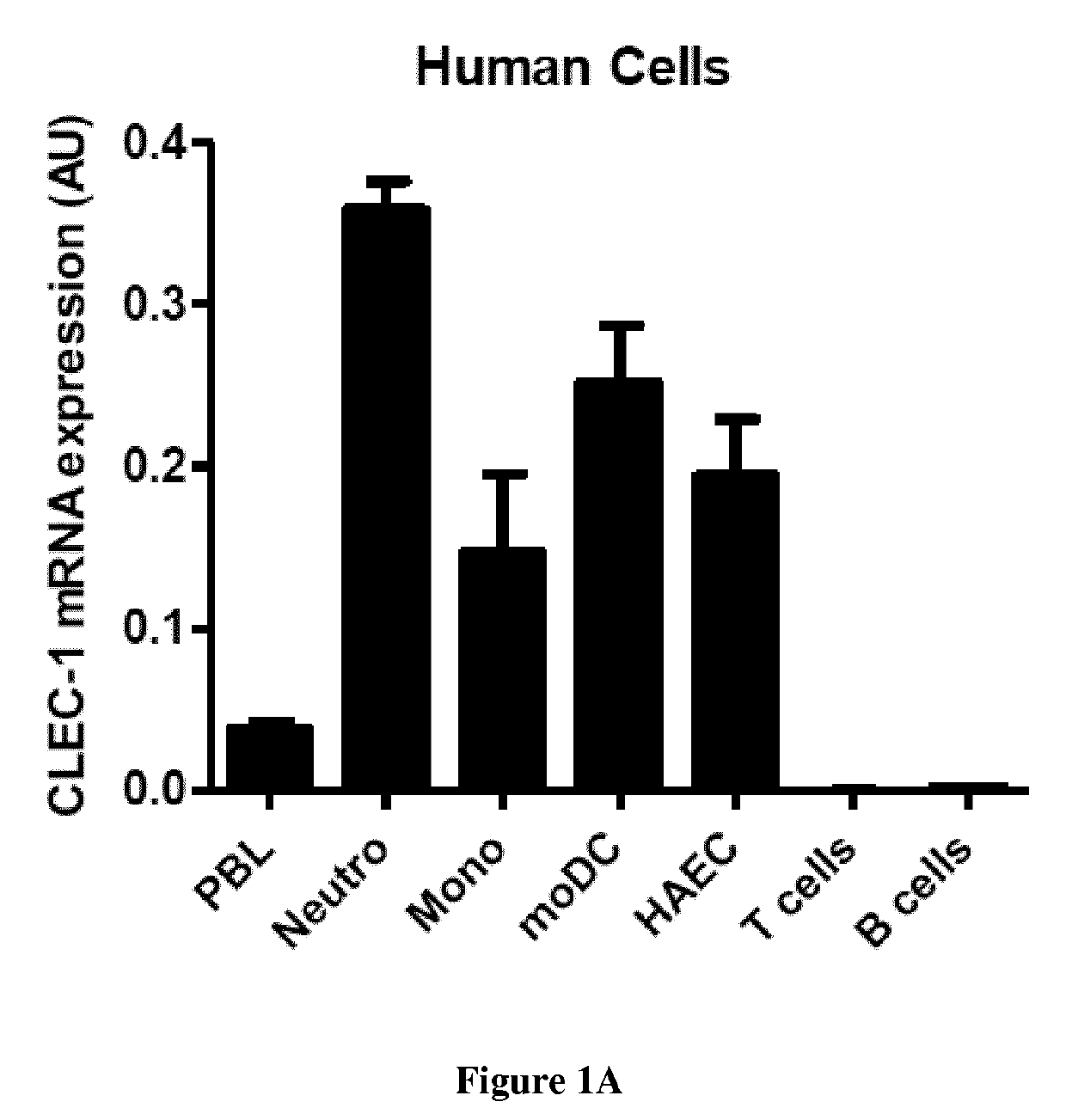
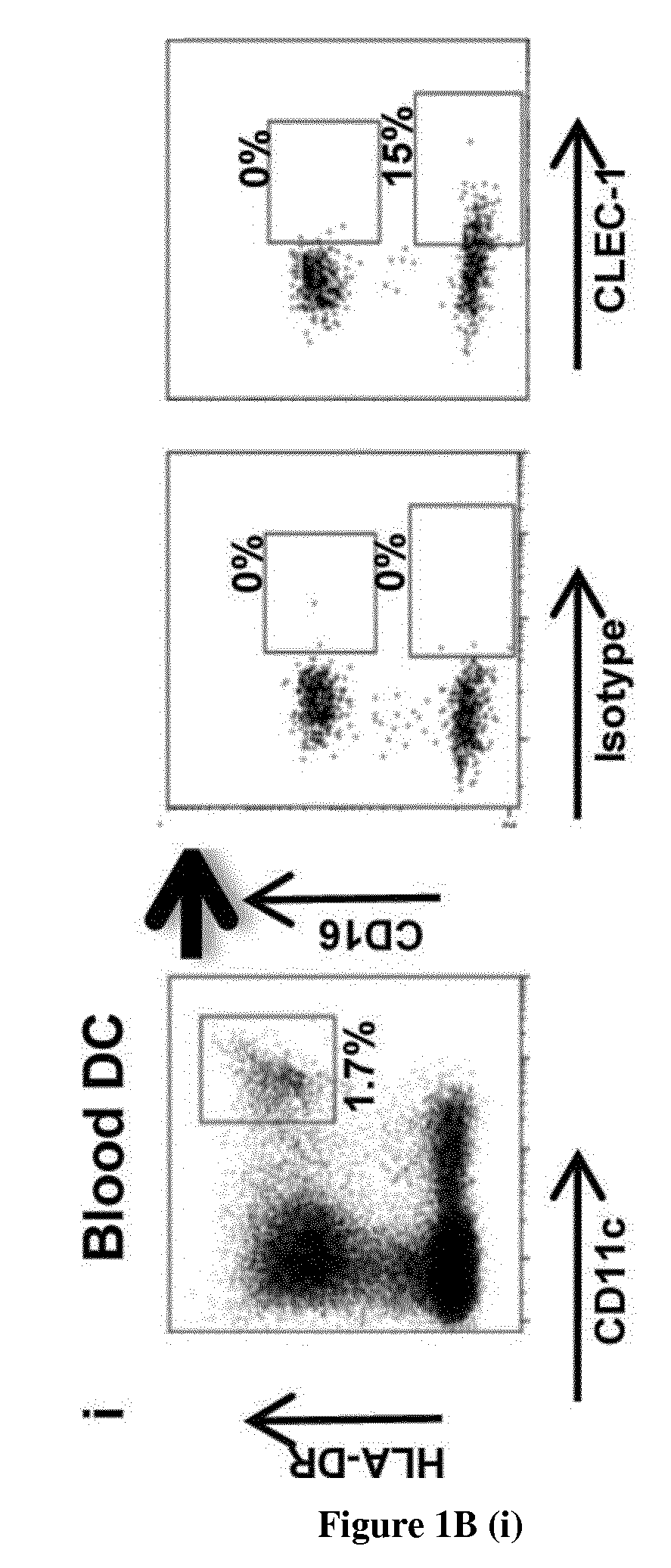
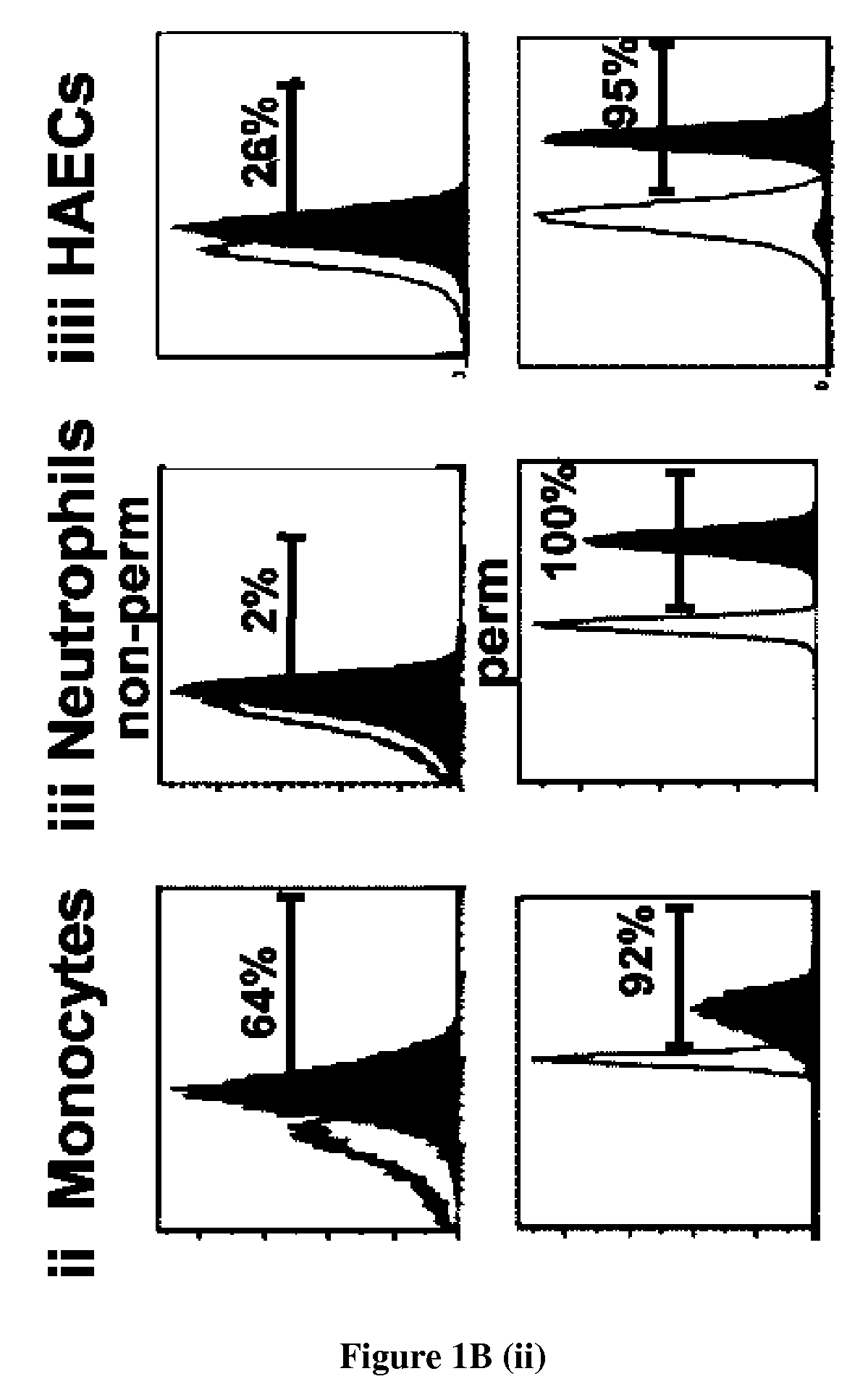
The present invention relates to methods for promoting T cells response. The inventors examined the expression and function of CLEC-1 in human DCs and demonstrated for the first time a cell-surface expression. They investigated its functional role following triggering on orchestration of T-cell responses. The inventors showed in vitro and in vivo with CLEC-1 deficient rats and rat CLEC-1 Fc fusion protein that disruption of CLEC-1 signalling enhances in vitro Th17 activation and in vivo enhances T cell priming and Th17 and Th1 activation. In particular, the present invention relates to CLEC-1 antagonists for promoting T cells response in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV DE NANTES +2
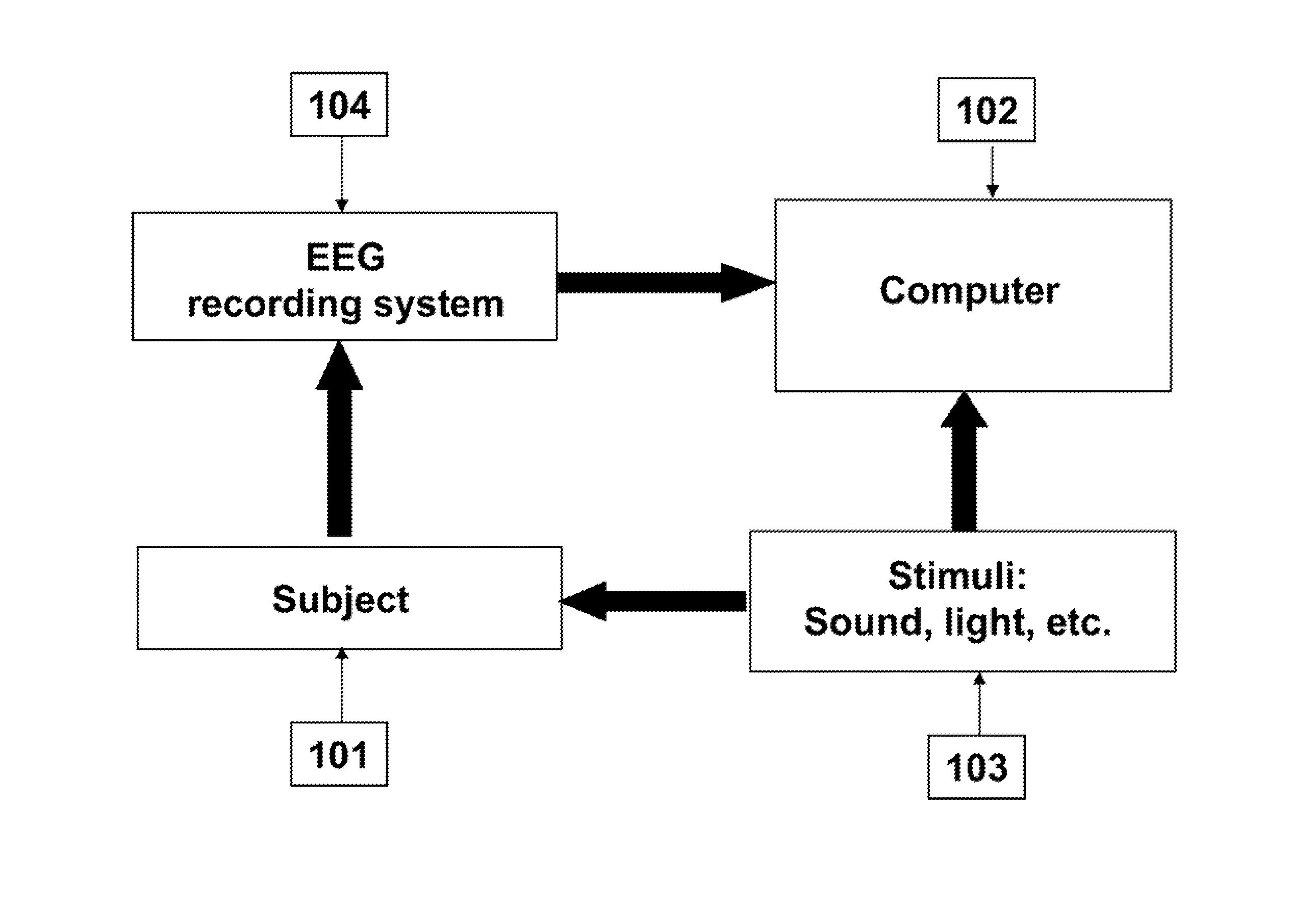
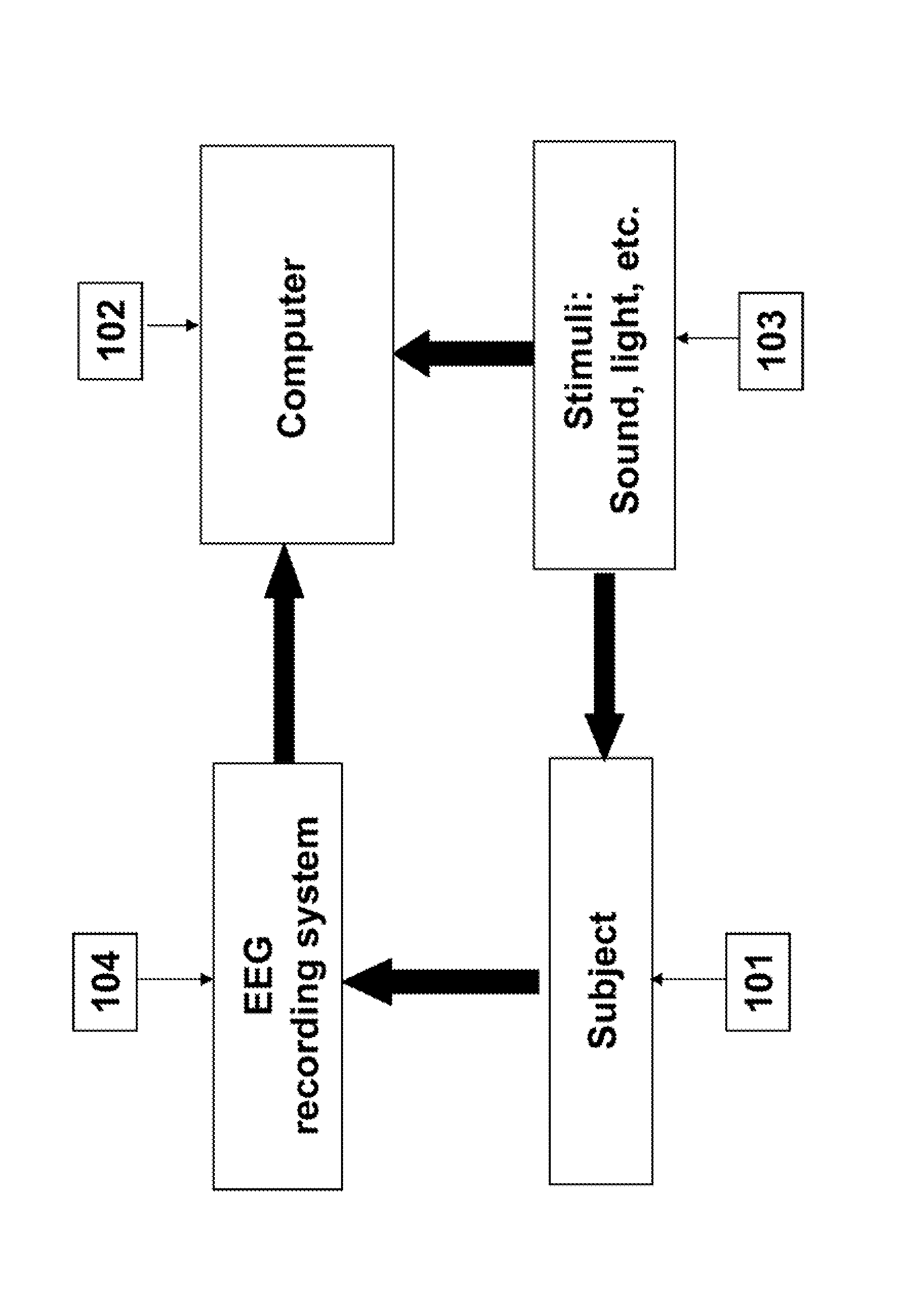
Functional eeg imager
A system for identifying the connectivity between different brain regions to determine the functional role of brain regions in various human and animal actions.
Owner:NORCONNECT
Lectin protein prepared from Maackia fauriei, process for preparing the same and the use thereof
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
CCN1 compositions and methods
InactiveCN1835763AEasy to synthesizePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCysteineAlanine
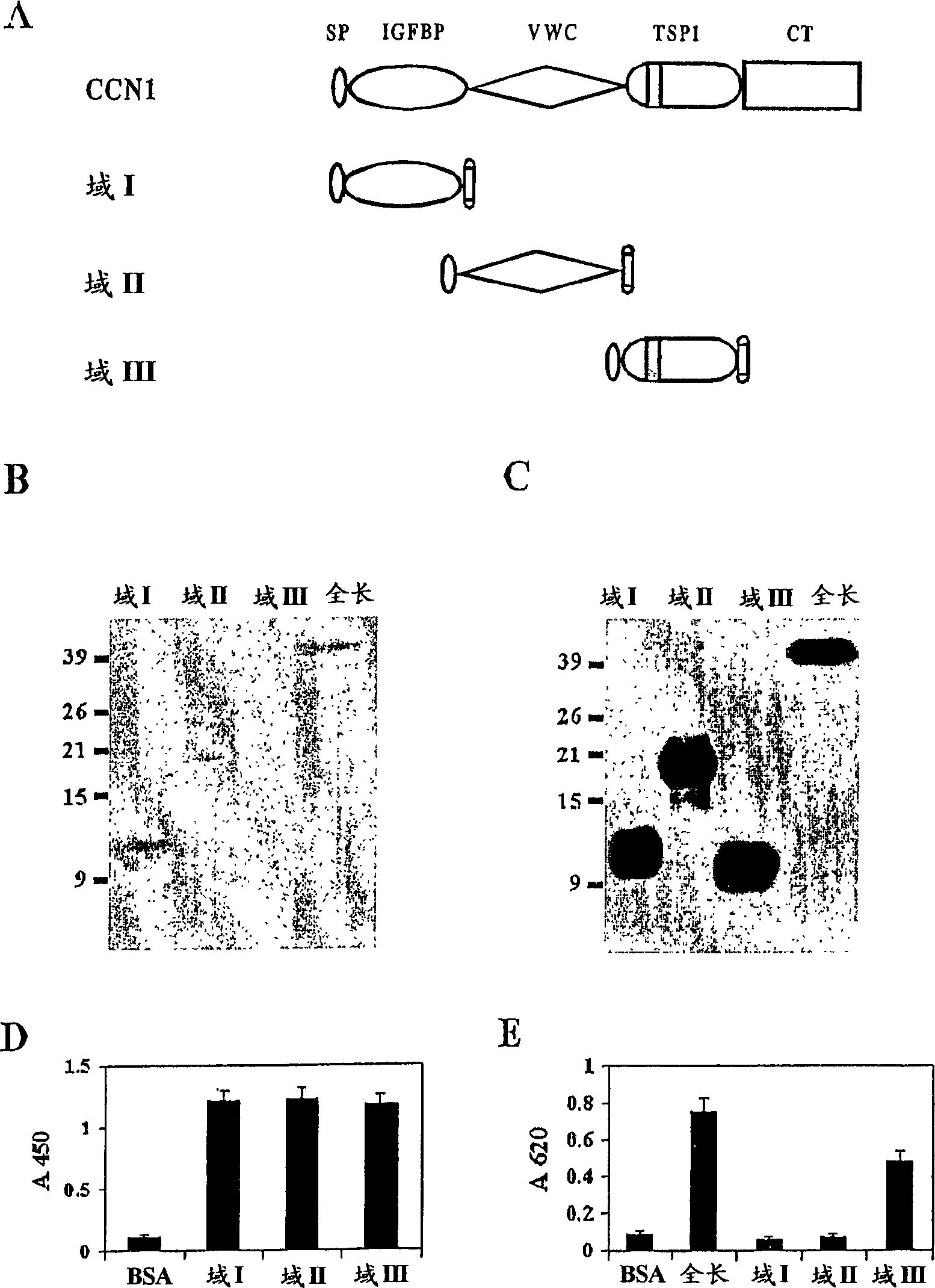
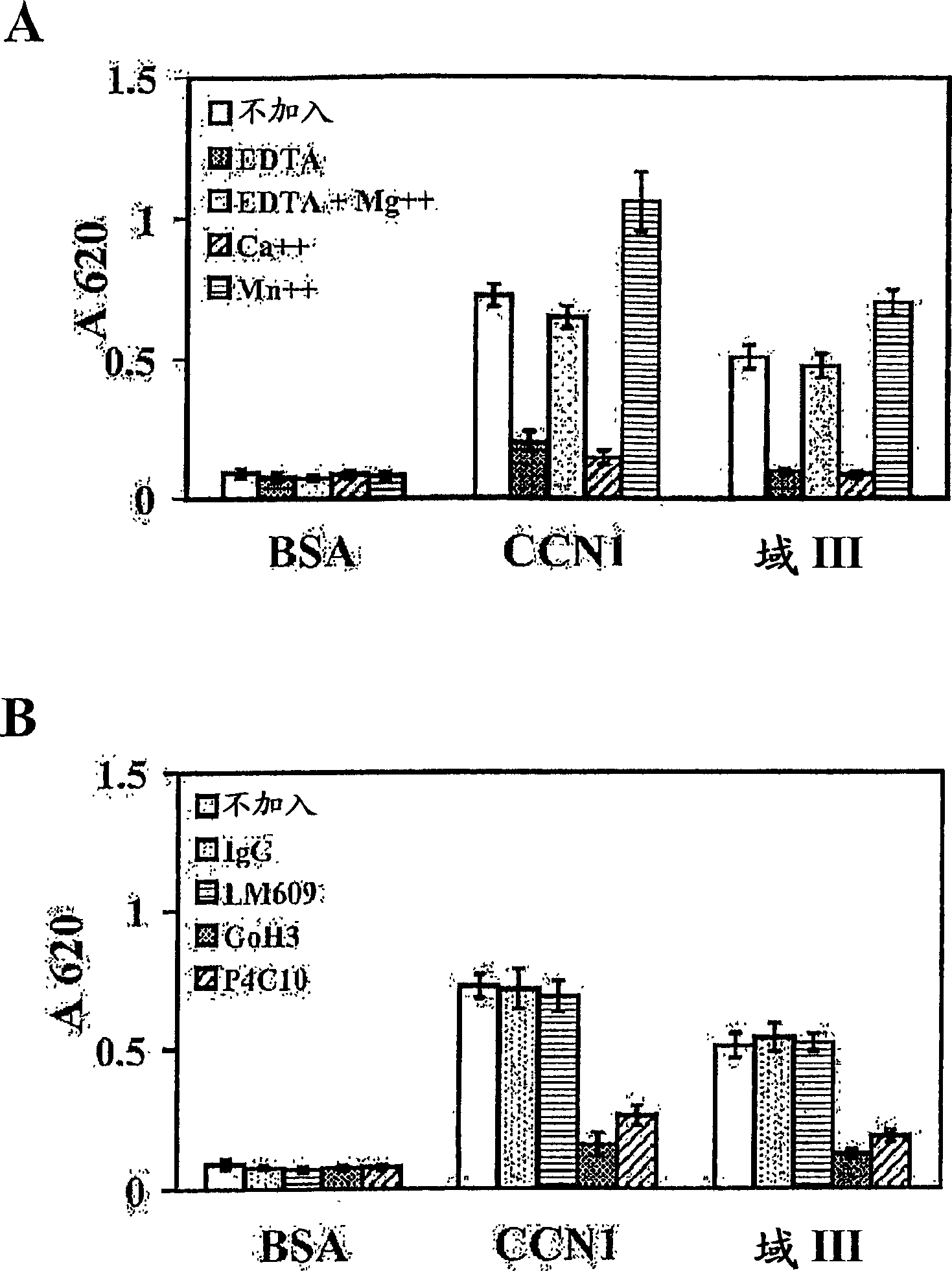
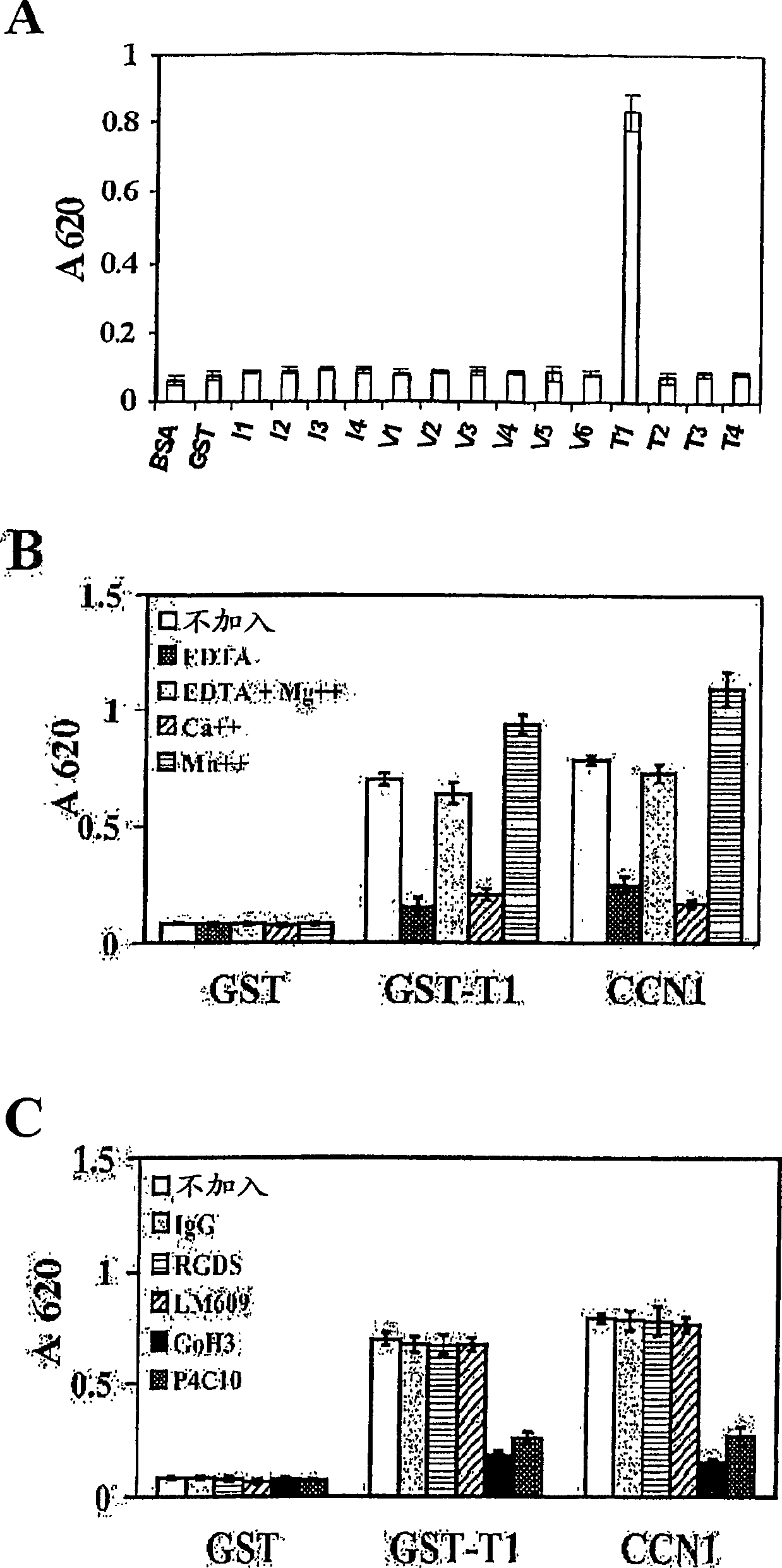
The angiogenesis inducer CCN1 (cysteine-rich 61, CYR61) is a secreted stromal cell protein of the CCN family, including α 6 beta 1 Ligands for various integrins. Previous studies have shown that CCN1 interacts with integrin α 6 beta 1 The interaction mediates cell adhesion of fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, as well as migration of smooth muscle cells. Recently, we reported that CCN1-induced tubule formation in unactivated endothelial cells is also mediated by integrin α 6 beta 1 mediate. In this study, we demonstrate that human dermal fibroblasts specifically adhere to the T1 sequence (GQKCIVQTTSWSQCSKS) in domain III of CCN1, and that this process is inhibited by a 6 and anti-b 1 blocked by monoclonal antibodies. Alanine substitution mutagenesis of the T1 sequence further identified the sequence TTSWSQCSKS as mediator of α 6 beta 1 Key determinants of dependent adhesion. Soluble T1 peptide specifically inhibits fibroblast adhesion to CCN1 in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, T1 also inhibits cell adhesion to other α 6 beta 1 Ligands, including CCN2 (CTGF), CCN3 (NOV) and laminin, but not ligands that inhibit other integrins. Furthermore, in a collagen gel matrix containing CCN1, T1 specifically inhibited the α 6 beta 1 Dependent tubule formation. To confirm that T1 directly binds integrin α 6 beta 1 , we performed affinity chromatography showing that integrin α was isolated from octyl glucoside extracts of fibroblasts on T1-conjugated Affi-gel 6 beta 1 . Taken together, these findings identify the T1 sequence in CCN1 as a novel integrin α 6 beta 1 Binding motifs for developing peptidomimetics form a detection alpha 6 beta 1 Basis for a functional role in angiogenesis.
Owner:MUNIN
Research and Application of Functional Artificial Pit Mud
The research and application of functional artificial pit mud mainly includes: separating and purifying beneficial and functional microorganisms from high-quality old pit mud, and expanding them through a series of methods such as artificial cultivation, as strains; According to the living habits of functional bacteria, nutritional components, adaptation to the environment and other factors, scientifically match the cultivation conditions such as the composition content, pH, and temperature of the pit mud to prepare high-quality pit mud suitable for the growth of functional bacteria. Inoculate functional bacteria into high-quality pit mud to make functional pit mud.
Owner:李绍亮 +1
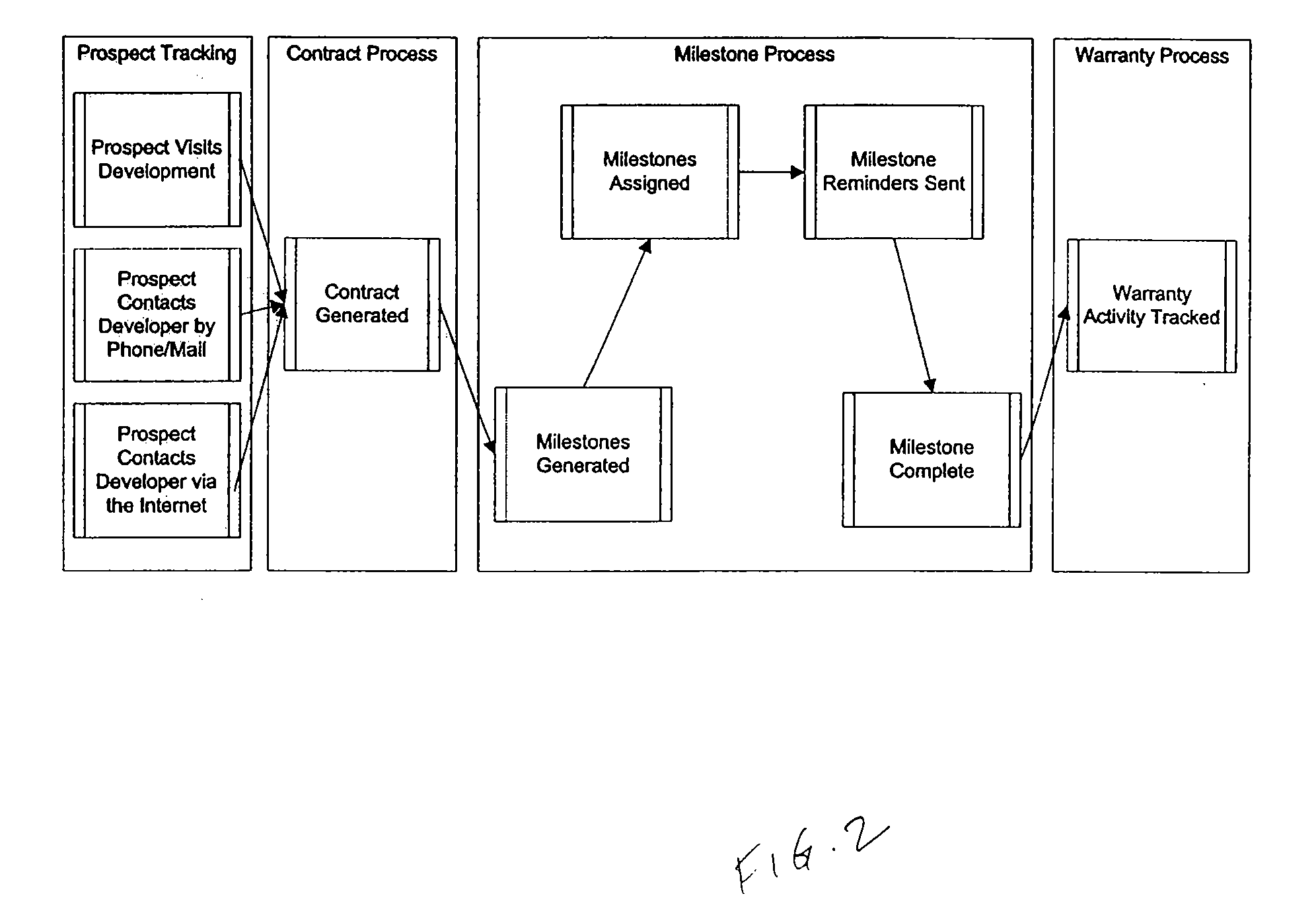
Method and system for managing real estate transactions
A system for managing real estate purchase transactions is provided. The system collects various types of information relating to real estate purchase transactions. The system then tracks various milestones under a real estate purchase contract and provides automated alerts to one or more users. The system further allows different users with varying functional roles to monitor their respective real estate purchase contracts.
Owner:SCHELLINGER SCOTT +1
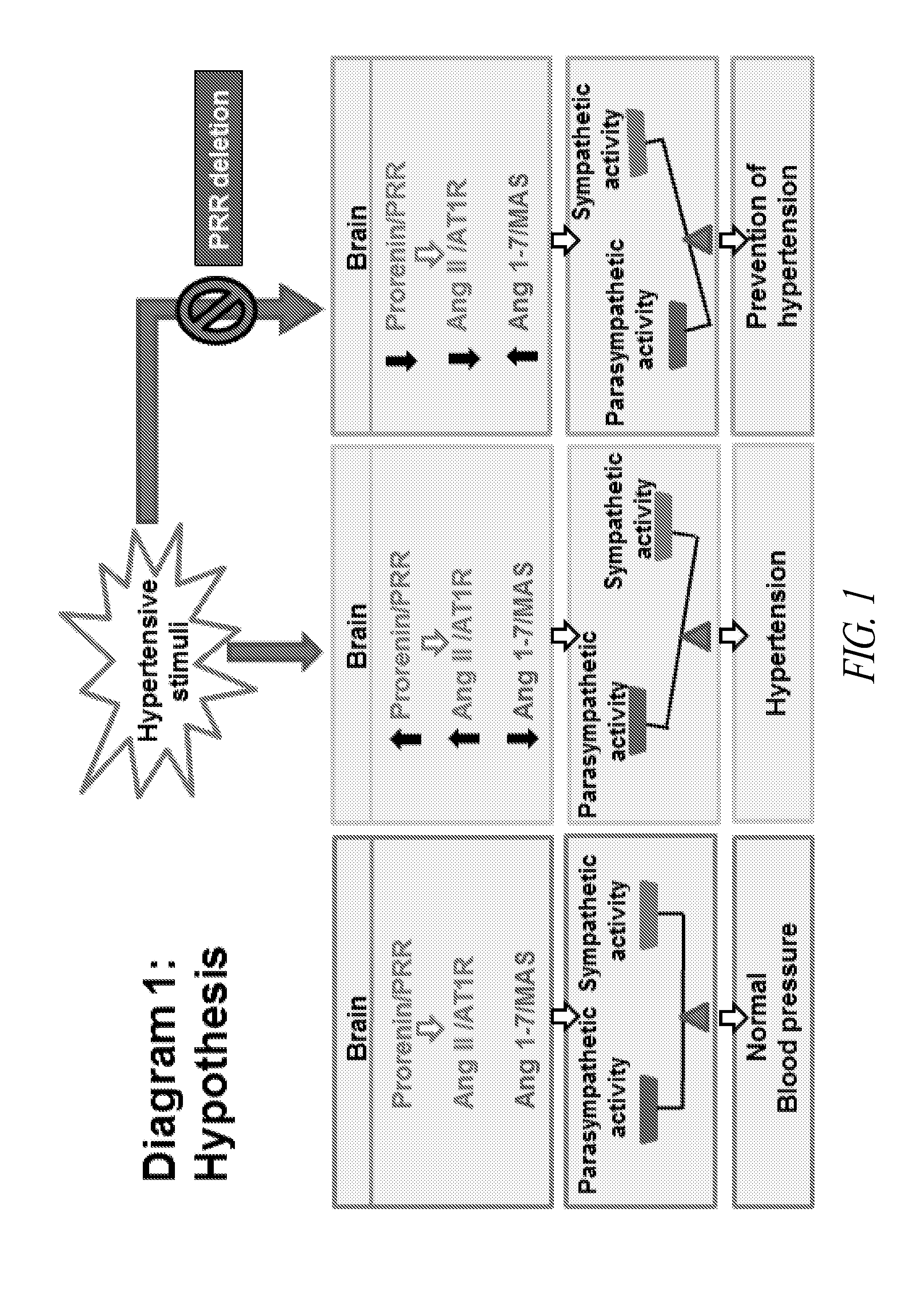
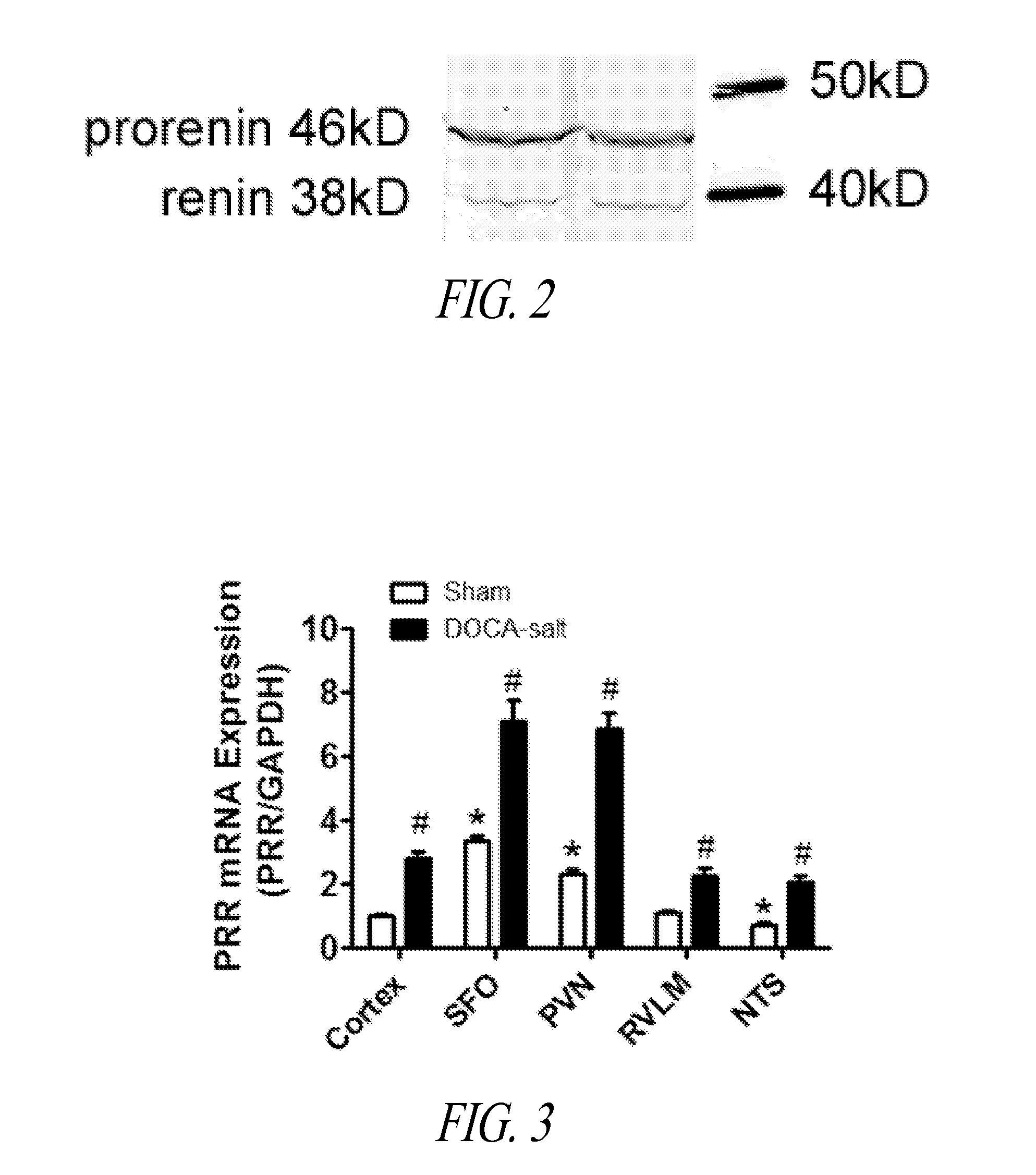
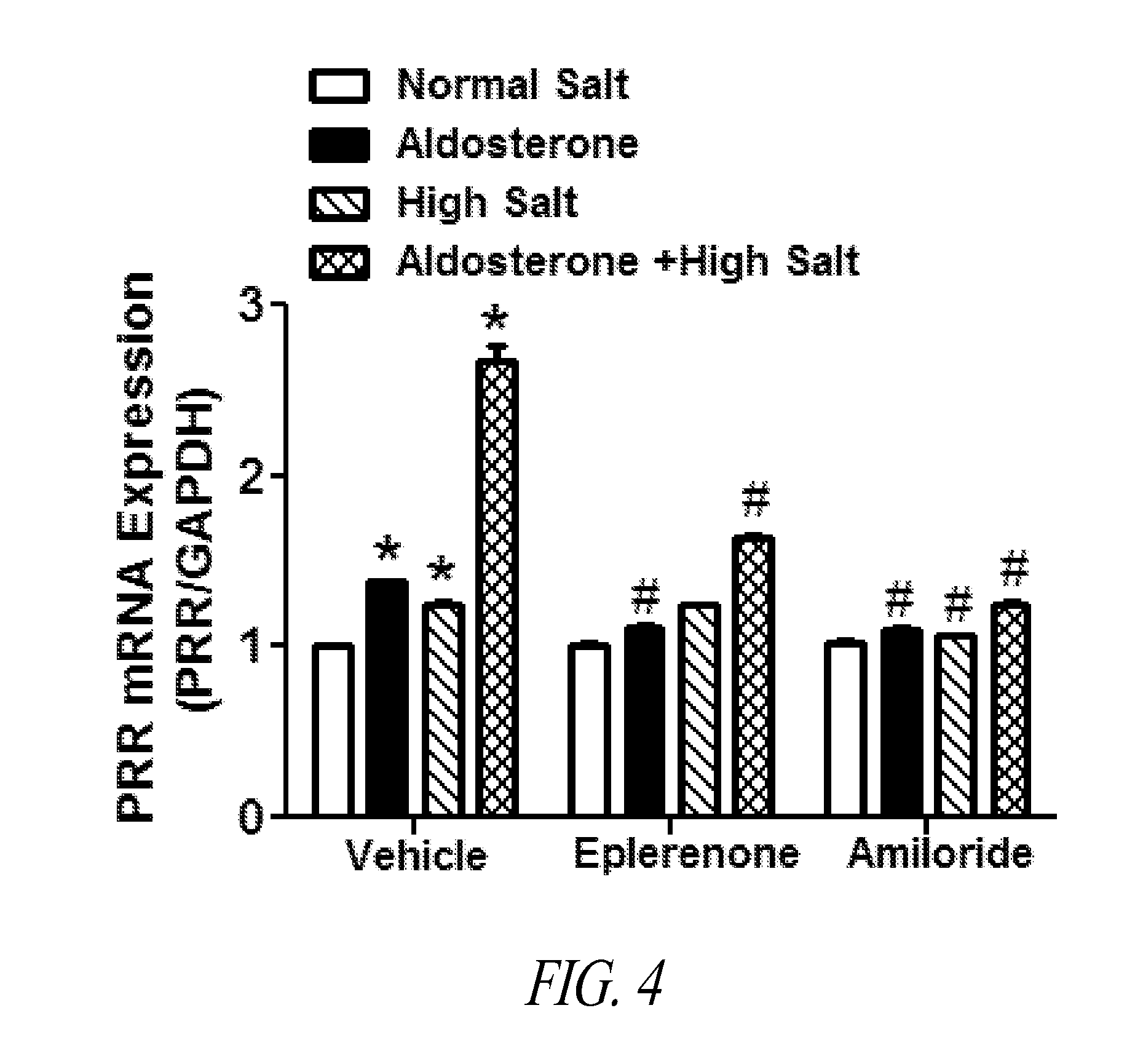
Antagonist for (PRO)renin receptor for the treatment of hypertension and diabetes
InactiveUS20140094409A1Peptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiabetes mellitusTreatment hypertension
Brain prorenin and the (pro)renin receptor (PRR) have a functional role in the development of hypertension. The present disclosure presents functional PRR antagonistic peptides (e.g., PR10, PR20, PR30, and PR40). In addition, modified peptides comprising one or more thioether-bridges that are stable and strong PRR antagonists are also provided. Methods for treating and preventing hypertension, including neurogenic hypertension, and diabetes with a PRR antagonist are also provided.
Owner:FENG YUMEI
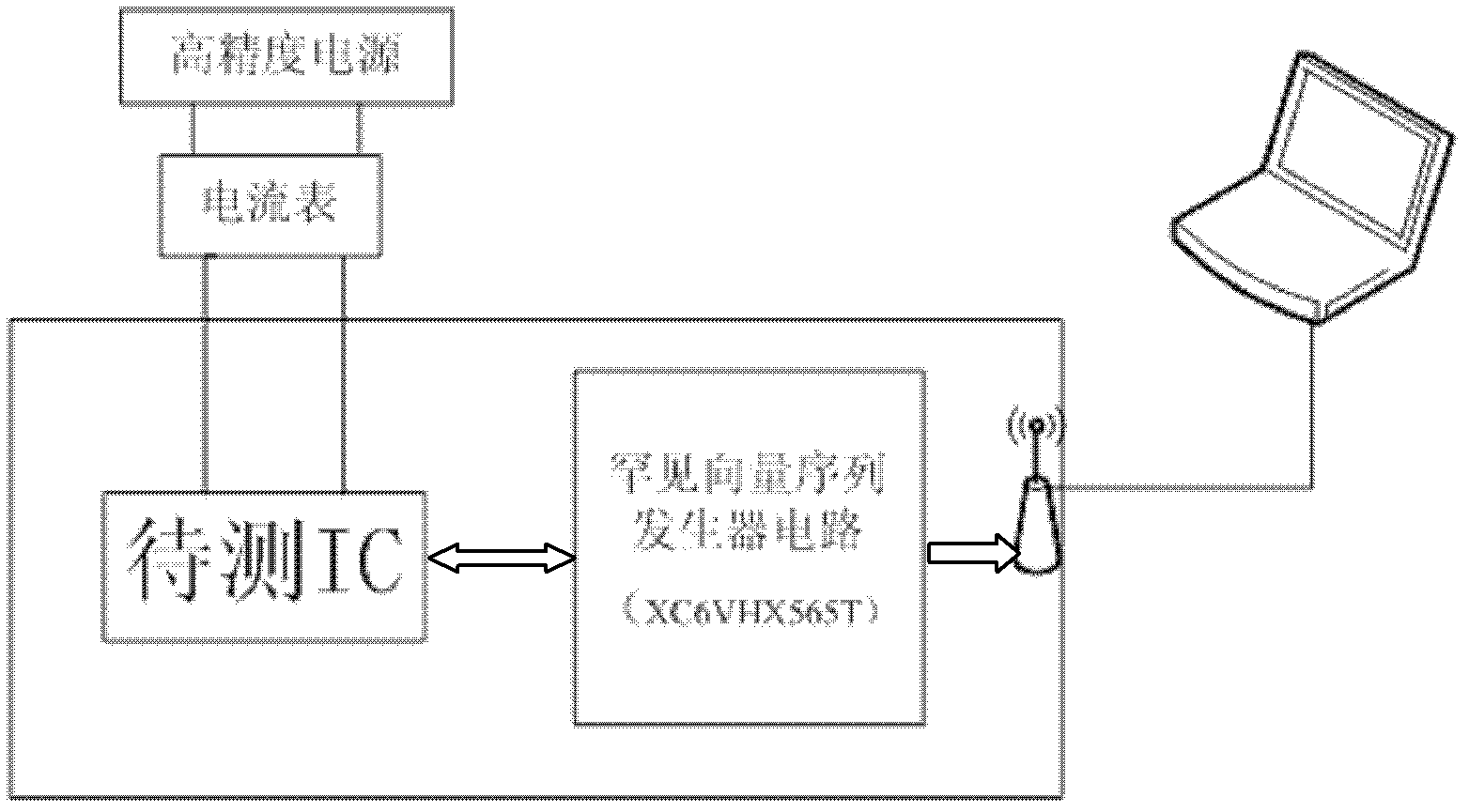
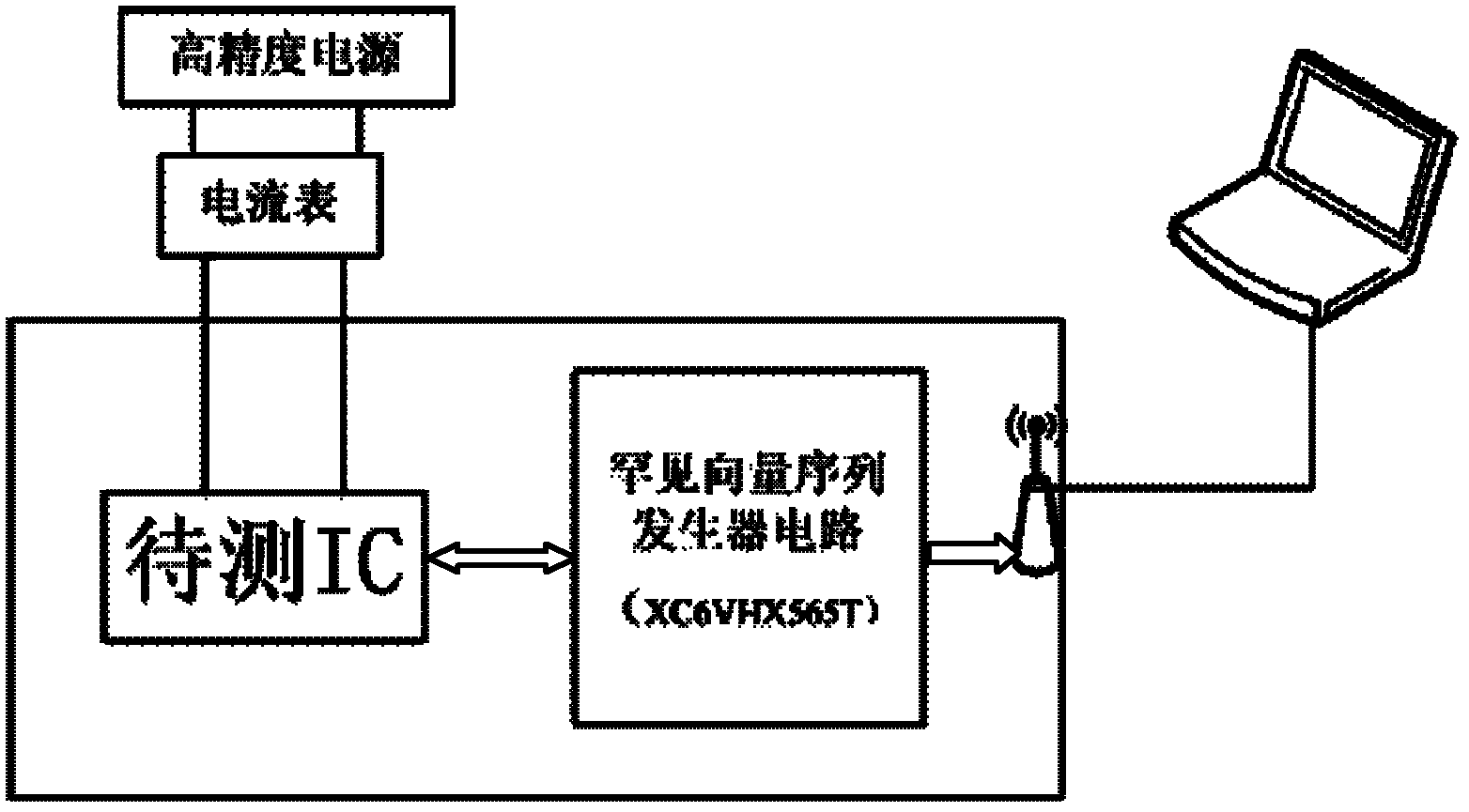
Rare-vector-sequence-activated lossless detection method for hardware Trojans in integrated circuits
InactiveCN102636743AAvoid threatsEnsure safetyDigital circuit testingHardware TrojanIntegrated circuit layout
The invention relates to a rare-vector-sequence-activated lossless detection method for hardware Trojans in integrated circuits. The method comprises the following steps of: providing corresponding testing environments for integrated circuits to be tested; producing rare vector sequences for the integrated circuits to be tested; and exciting the integrated circuits to be tested by using the rare vector sequences, testing whether the characteristic parameters and functional roles of the integrated circuits to be tested are abnormal or not, and detecting the integrated circuits implanted with the hardware Trojans and recording breaking manners if the characteristic parameters and functional roles of the integrated circuits to be tested are abnormal. Based on the rare-vector-sequence-activated lossless detection method for the hardware Trojans in the integrated circuits, the integrated circuits implanted with the hardware Trojans can be detected before entering an application system, so that the application system is prevented from being threatened by the hardware Trojans, and the safety of key equipment in important systems is guaranteed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Financial collection management system
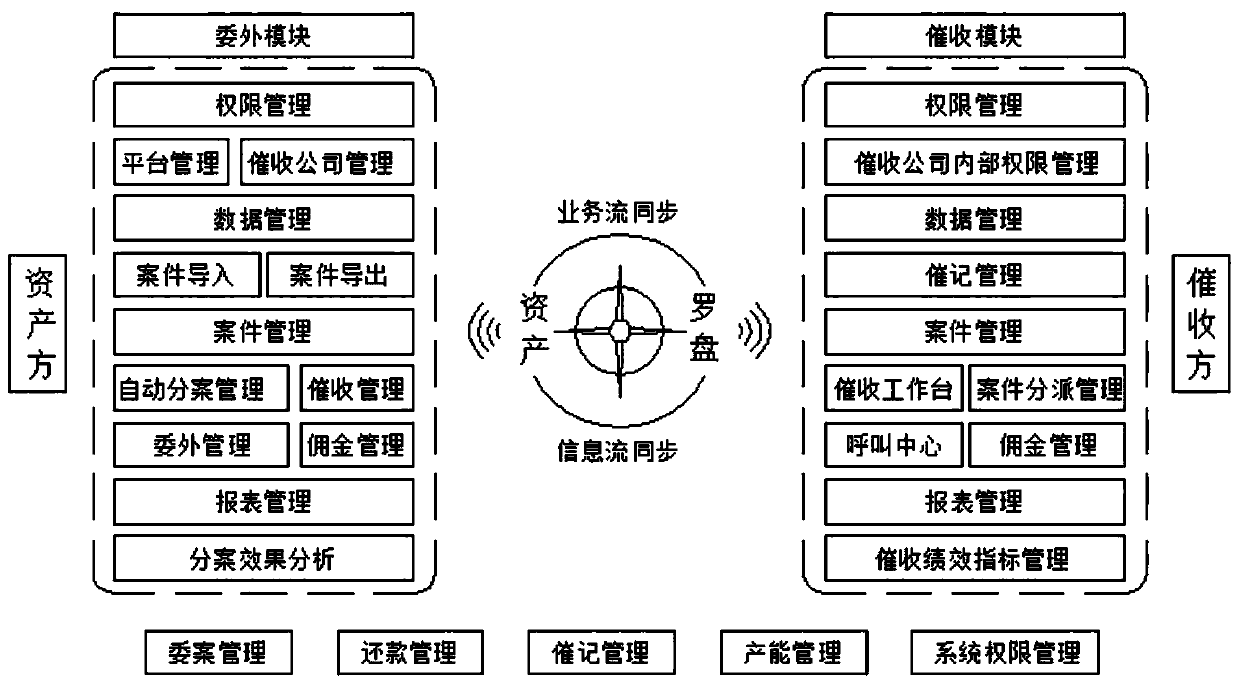
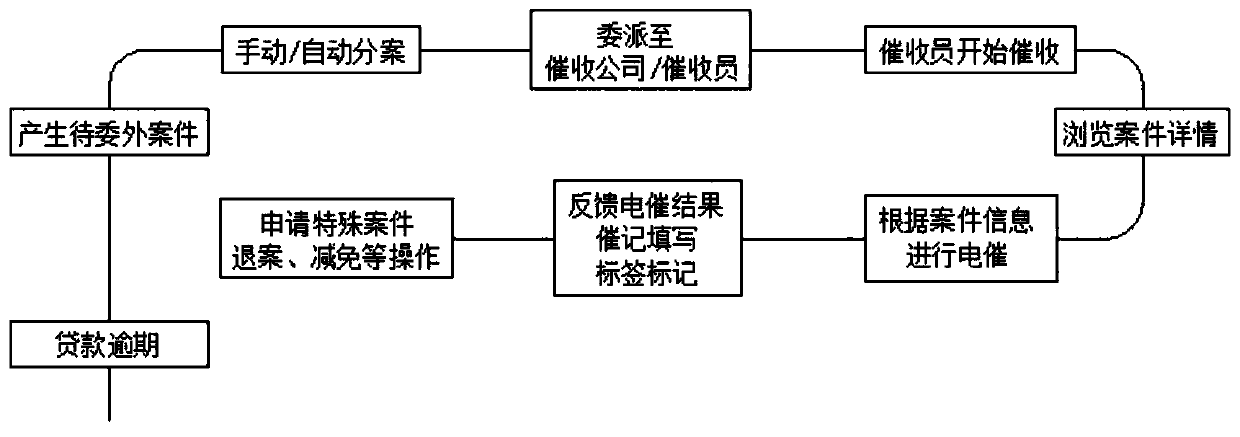
InactiveCN110363657AImprove analysisComprehensive process-based post-loan management servicesFinanceSystems managementOnline and offline
The invention discloses a financial collection management system. The system can be divided into system management, automatic case division management, platform management, collection company management, case management, cancel-after-verification management, commission management, repayment management, data management, external access management, homepage management, report management, intelligentcollection, interface management, content management, workbench basic general situation and case information according to functional roles. According to authority roles, the system can be divided into an asset company management platform, a collection company management platform, a collector workbench and a collection company external visit APP. The system is convenient and fast to use, can provide comprehensive process post-loan management service for asset parties, improves the post-loan management efficiency, supports the online and offline work of related business personnel, improves thecollection efficiency, and enhances the analysis and application of historical data in the collection process.
Owner:何彬
Reflecting plate
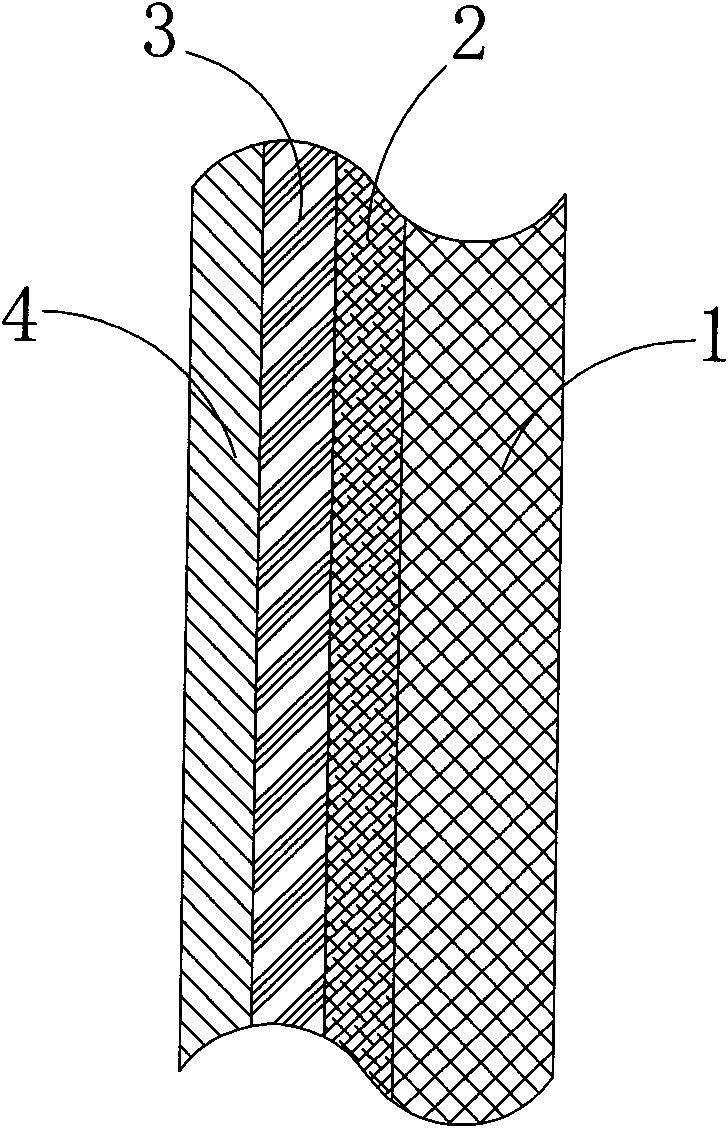
InactiveCN102213781AGood light reflection performanceExtended service lifeMirrorsLight reflectionLight penetration
The invention discloses a reflecting plate which comprises a substrate layer, a bottom color layer used for preventing light rays from penetrating, a metal light reflection layer for reflecting the light rays and a protection layer for preventing the metal light reflection layer from being oxidized and damaged; by taking the transmission direction of the light rays as a reference, the bottom color color layer is fixed on the rear surface of the metal light reflection layer; the substrate layer is fixed on the rear surface of the bottom color layer; the protection layer is fixed on the front surface of the metal light reflection layer; the metal light reflection layer is a main material layer which plays a functional role; when the light rays irradiate to the metal light reflection layer, the light rays can be reflected back; more particularly, due to the existence of the bottom color layer, the light rays can be prevented from penetrating the metal light reflection layer so that the light rays can be completely reflected by the metal light reflection layer; and the protection layer covers the metal light reflection layer and can prevent the metal light reflection layer from being damaged or oxidized. The reflecting plate disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good light reflection property, long service life, simple structure and easiness in implementation and can be widely applied to various products having light reflection requirements.
Owner:盛玉林
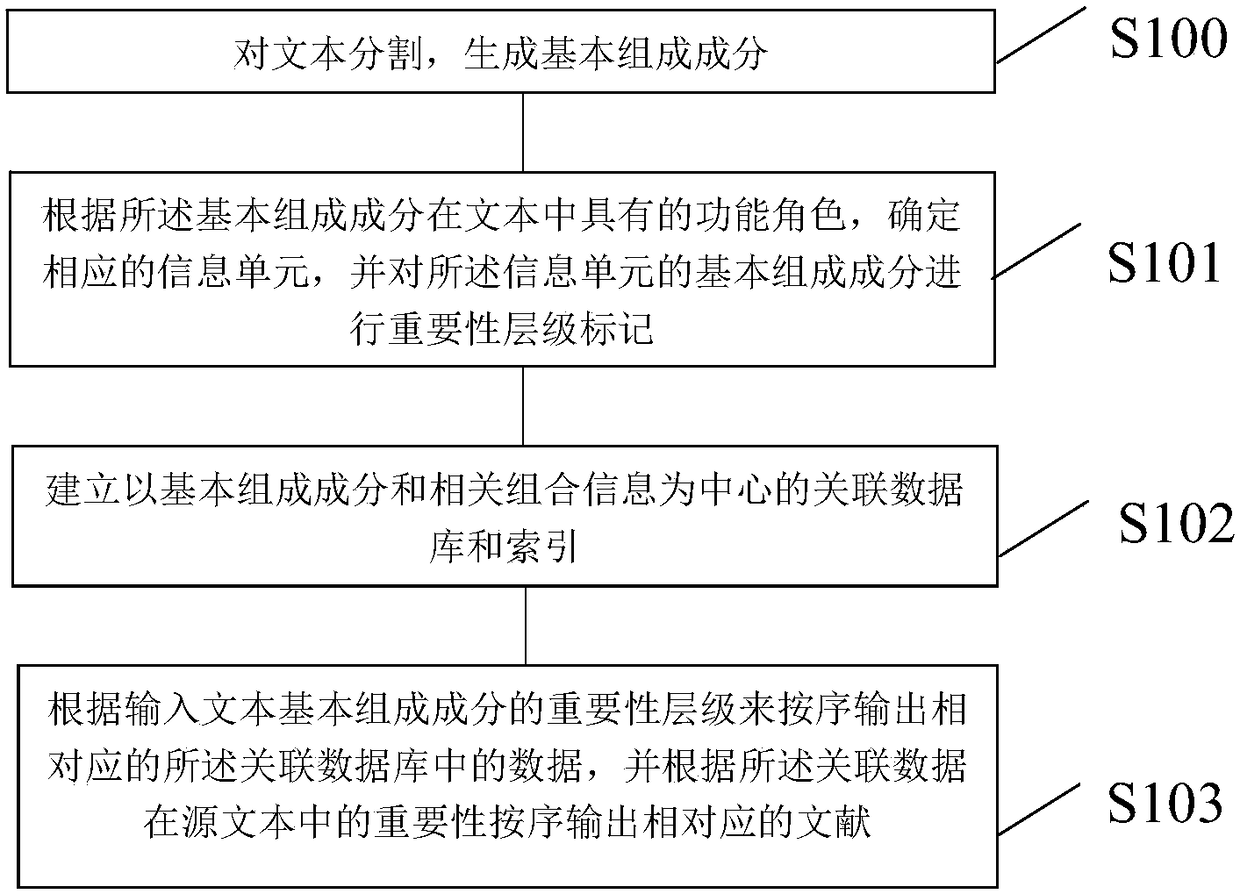
Method and device for processing text information
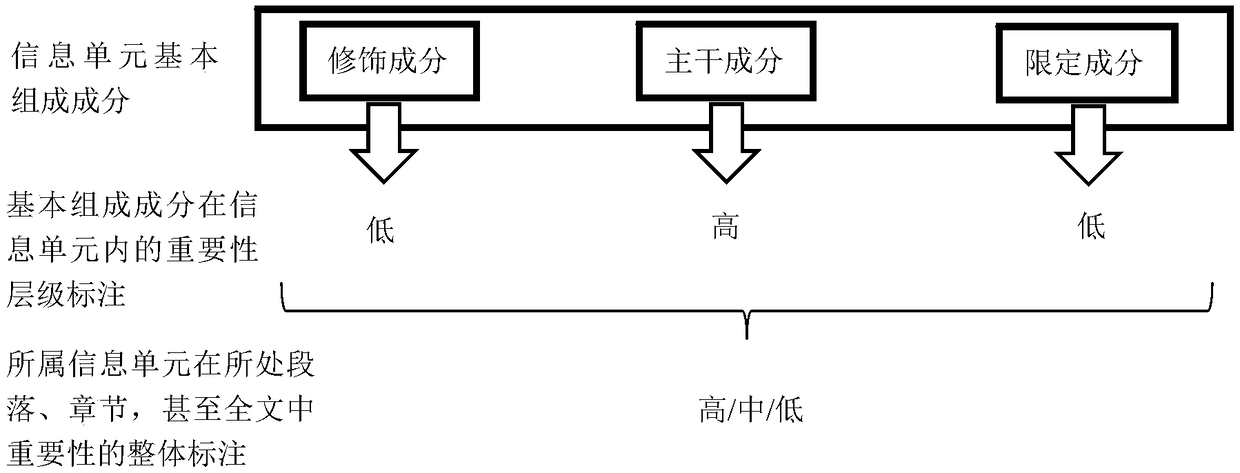
InactiveCN108363696ASolve odds and endsOne-sided solutionDatabase queryingNatural language data processingData miningSource text
The invention discloses a method and device for processing text information. The method comprises the steps that a basic component is generated by segmenting a text; according to the functional role of the basic component in the text, a corresponding information unit is determined, and importance level marking is conducted on the basic component of the information unit; an association database andan index with the basic component and relevant combination information as the center are established; data in the corresponding association database is sequentially output according to the importancelevel of the basic component of the input text, and corresponding documents are sequentially output according to the importance of the associated data in the source text. According to the method andthe device for processing the text information, partial and impurity information in information retrieval can be effectively filtered away, the integration and the output efficiency of the text information are improved, and a user can fully and efficiently utilize existing text data.
Owner:李小明
Capsules for improving memory and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104547264AImprove memory lossAnti agingNervous disorderCapsule deliveryMemory lapsesFunctional role
The invention discloses capsules for improving memory and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following step: by taking three medicinal materials namely Chinese magnoliavine fruit, mulberry fruit and barbary wolfberry fruit as main medicines, adding raw materials with functional roles such as DHA dry powder, lecithin, taurine and vitamin E to prepare the capsules. By adopting the capsules disclosed by the invention, situations of memory lapse caused by the factors including brain aging, body function drops or malnutrition and the like of old people can be improved; and meanwhile, the capsules have multiple effects of enhancing cerebral functions, delaying brain aging, improving memory and the like, and are suitable for patients suffering Alzheimer's disease and other persons suffering memory lapse.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANDIJIAN BIOLOGICAL ENG COMPANY
Prefabricated fabricated type anti-collision wall structure with pulley device
InactiveCN107905156AReduce impact damageReasonable structural designTraffic signalsAlarmsReinforced concreteCarriageway
The invention discloses a prefabricated fabricated type anti-collision wall structure with a pulley device. The prefabricated fabricated type anti-collision wall structure with the pulley device is suitable for strengthening structural design of protective handrails on the two sides of a motor vehicle road. The prefabricated fabricated type anti-collision wall structure comprises a carriageway, steel stand columns, steel guardrail plates, steel track grooves, a reinforced concrete prefabricated plate wall, a pulley, a damper, I-shaped steel, a steel track groove, a plate wall facing and an alarming device. The steel stand columns and the steel guardrail plates are arranged on the two sides of the carriageway. The steel track grooves are formed in the steel guardrail plates. The reinforcedconcrete prefabricated plate wall is connected with the steel track grooves through the pulley and the damper. The I-shaped steel is arranged at the lower part of the reinforced concrete prefabricatedplate wall. Sliding and moving are achieved through the steel track grooves in the carriageway. The plate wall facing has multi-functional roles, the alarming device can transmit an accident signal in real time and performs positioning. The prefabricated fabricated type anti-collision wall structure with the pulley device is reasonable in structural design, the reinforced concrete prefabricated plate wall is used as an anti-collision wall, and by combining the pulley device, the damage degree of impact of a vehicle is reduced.
Owner:IANGSU COLLEGE OF ENG & TECH
Approver Identification Using Multiple Hierarchical Role Structures
InactiveUS20120016682A1Improve efficiencyConsistently appliedComputer security arrangementsOffice automationProcess efficiencyData mining
Systems and methods for automating and increasing the efficiency of business processes using multiple hierarchical role structures. In one embodiment, a method comprises defining two or more hierarchies, defining an approver for a business process where the approver is associated with at least a first role in a first one of the hierarchies and a second role in a second one of the hierarchies, and identifying an approver position within an organization where the approver position is associated with the first and second roles. The hierarchies may, for example, be selected from a hierarchy of functional roles, a hierarchy of legal roles and a hierarchy of level roles.
Owner:MORINVILLE PAUL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com